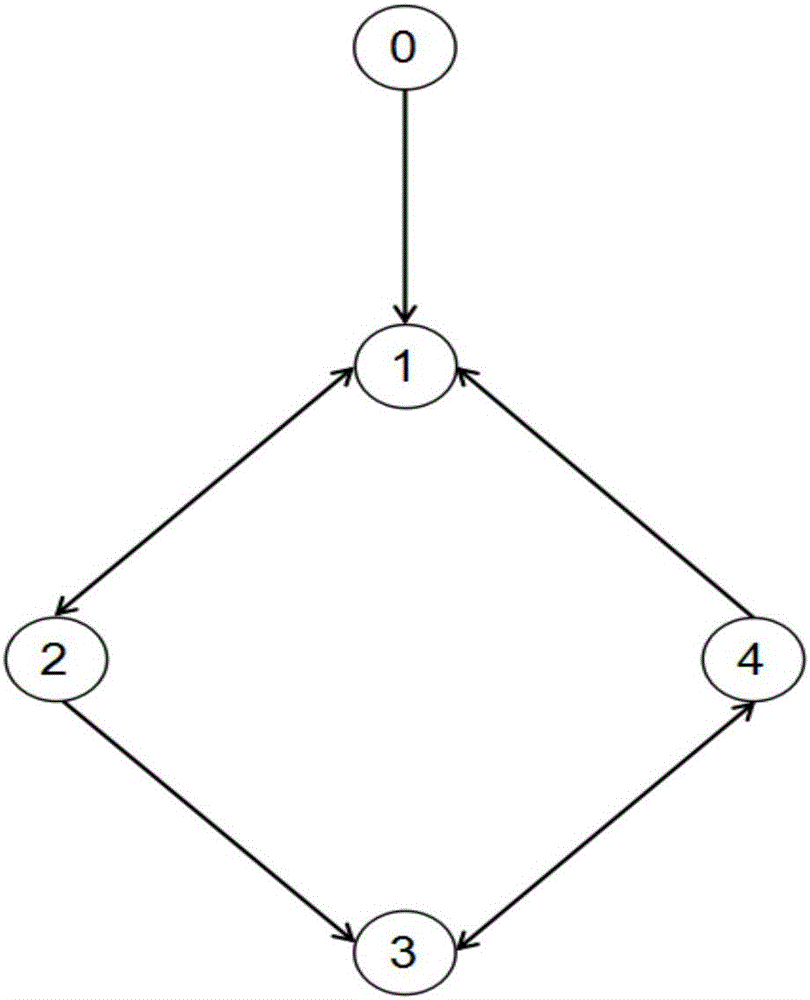
Finite time robust fault diagnosis design method for leader-follower multi-agent system
A multi-agent system, limited time technology, applied in the field of multi-agent systems, can solve problems such as unusable, poor transient performance, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0150] Suppose the first and fourth follower nodes fail at the same time:
[0151] Failure of the first follower node
[0152]
[0153] Failure of the 4th follower node
[0154]
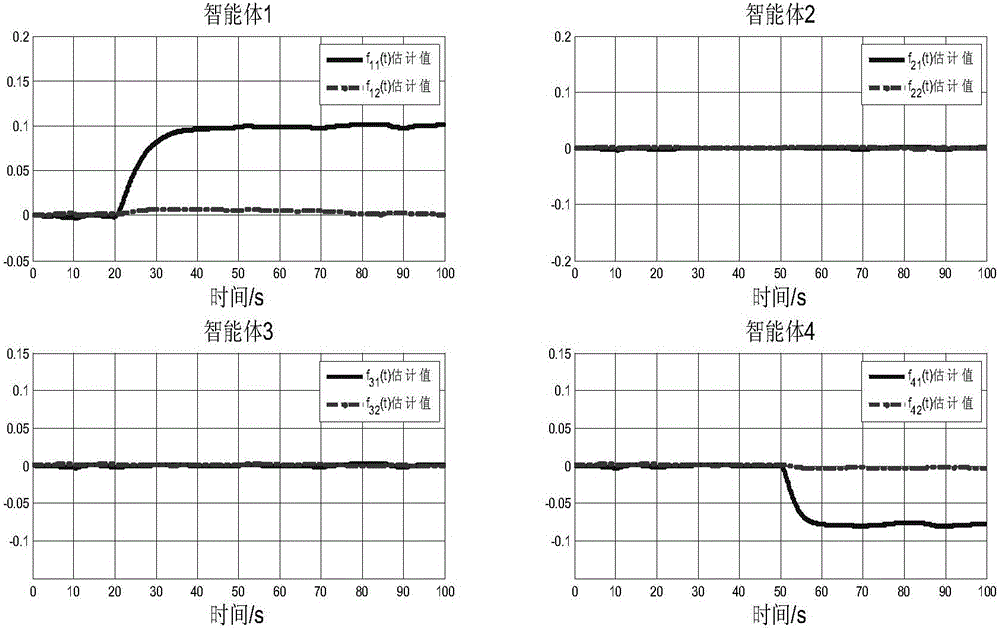
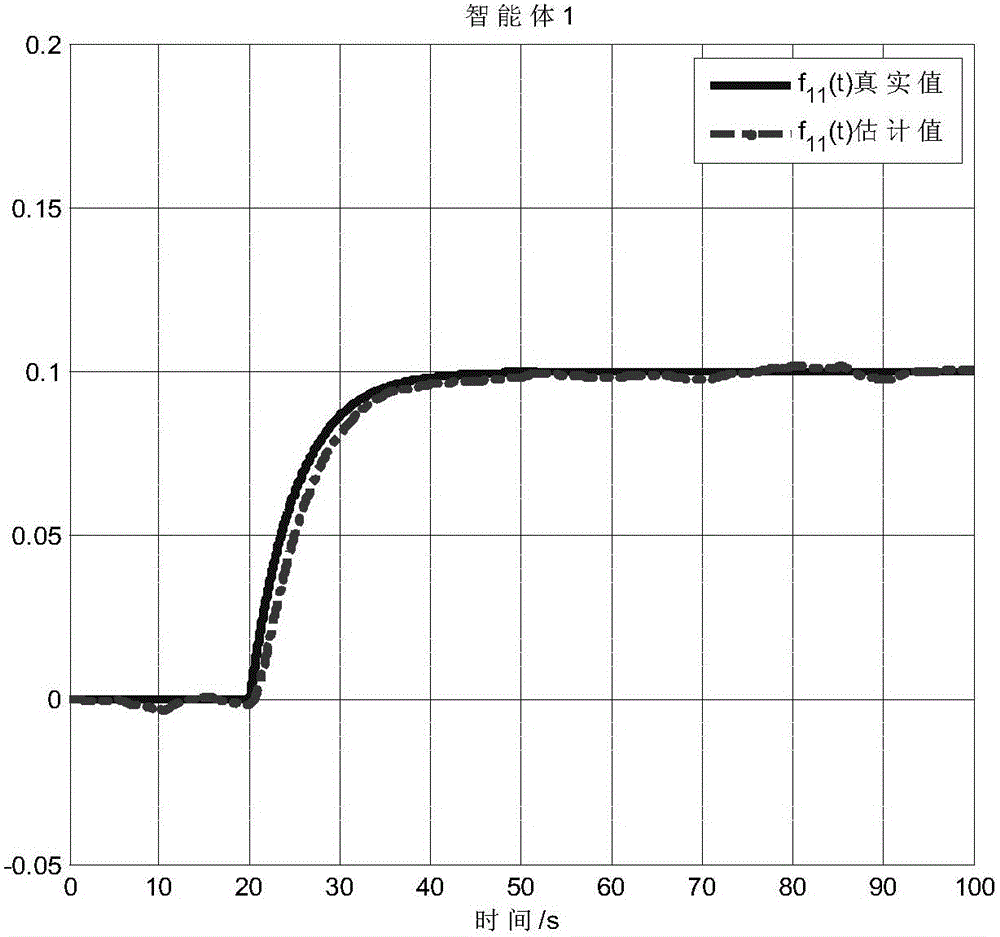
[0155] That is, the first follower node has an actuator failure in 20s, and the fourth follower node has a failure in 50s. The experimental simulation results are shown in Figure 2. diagram 2-1 This is the failure of the four follower nodes 2 (agent 1, 2, 3, and 4) when the first and fourth follower nodes (agent 1 and agent 4) fail at the same time as measured in embodiment 1 of the present invention Schematic diagram of the fault estimation curve of the diagnostic observer; Figure 2-2 This is the fault detected by the fault diagnosis observer of the follower node 1 (agent 1) when the first and fourth follower nodes (agent 1 and agent 4) all have faults measured in the first embodiment of the present invention Schematic diagram of the comparison curve between the estimated value and the true value of ...
Embodiment 2
[0157] Suppose the second and third follower nodes fail at the same time:
[0158] Failure of the second follower node
[0159]
[0160] Failure of the third follower node
[0161]
[0162] That is, the second follower node has an actuator failure at 10s, and the third follower node has an actuator failure at the aggregate distance at 40s. The experimental simulation results are shown in Figure 3 and Figure 4.
[0163] Figure 3-1 This is the failure of the four follower nodes 2 (agent 1, 2, 3, and 4) when the second and third follower nodes (agent 2 and agent 3) fail at the same time as measured in embodiment 2 of the present invention Schematic diagram of the fault estimation curve of the diagnostic observer; Figure 3-2 This is the fault measured by the fault diagnosis observer of the follower node 2 (agent 2) when the second and third follower nodes (agent 2 and agent 3) are both faulty measured in the second embodiment of the present invention Schematic diagram of the compari...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com