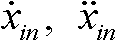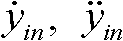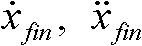Intelligent vehicle lane change path planning method based on polynomial and radial basis function (RBF) neural network
A neural network and intelligent vehicle technology, applied in the field of computer applications, can solve problems such as inability to directly apply the vehicle system, increase the amount of calculation, and the path is difficult to meet the design requirements.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0049] Next, the embodiment of the present invention will be described in detail in conjunction with specific drawings:
[0050] Step 1: Obtain the state information of lane-changing vehicles and obstacles in the lane and determine the lane-changing mode.
[0051] Determine the position, velocity, acceleration information, and external contour information of the lane-changing vehicle and obstacles in the lane according to the measurement results of the vehicle environment perception system. On this basis, the lane-changing mode of the vehicle is determined. The ultimate goal of this step is to use the data collected by the vehicle environment perception system to make a decision and determine which way to complete the lane change maneuver. Such as figure 2 As shown, the figure shows four common lane-changing modes, where C 0 Indicates lane-changing vehicles, O 1 with O 2 Indicates an obstacle vehicle. Different lane-changing modes correspond to different known and unkno...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com