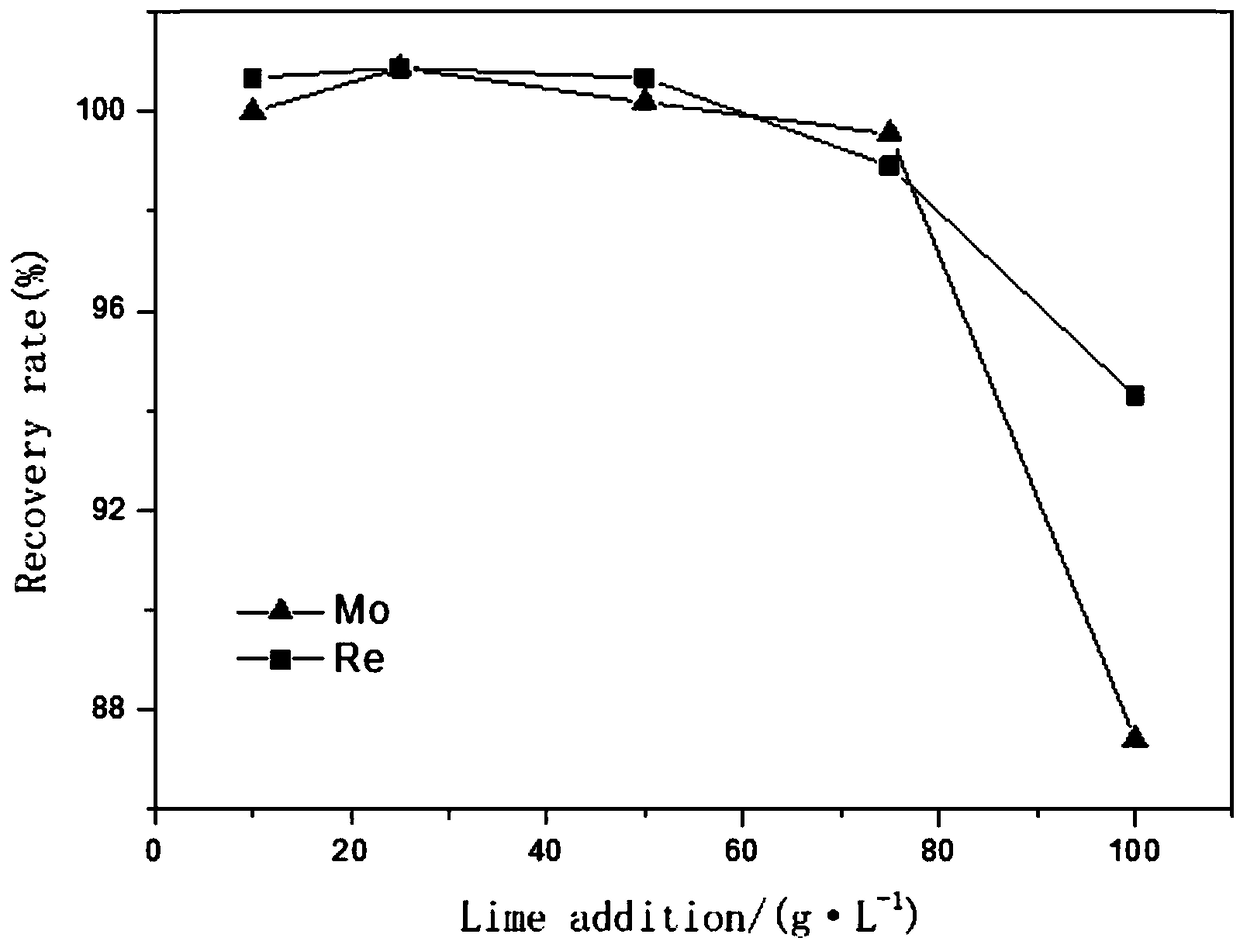
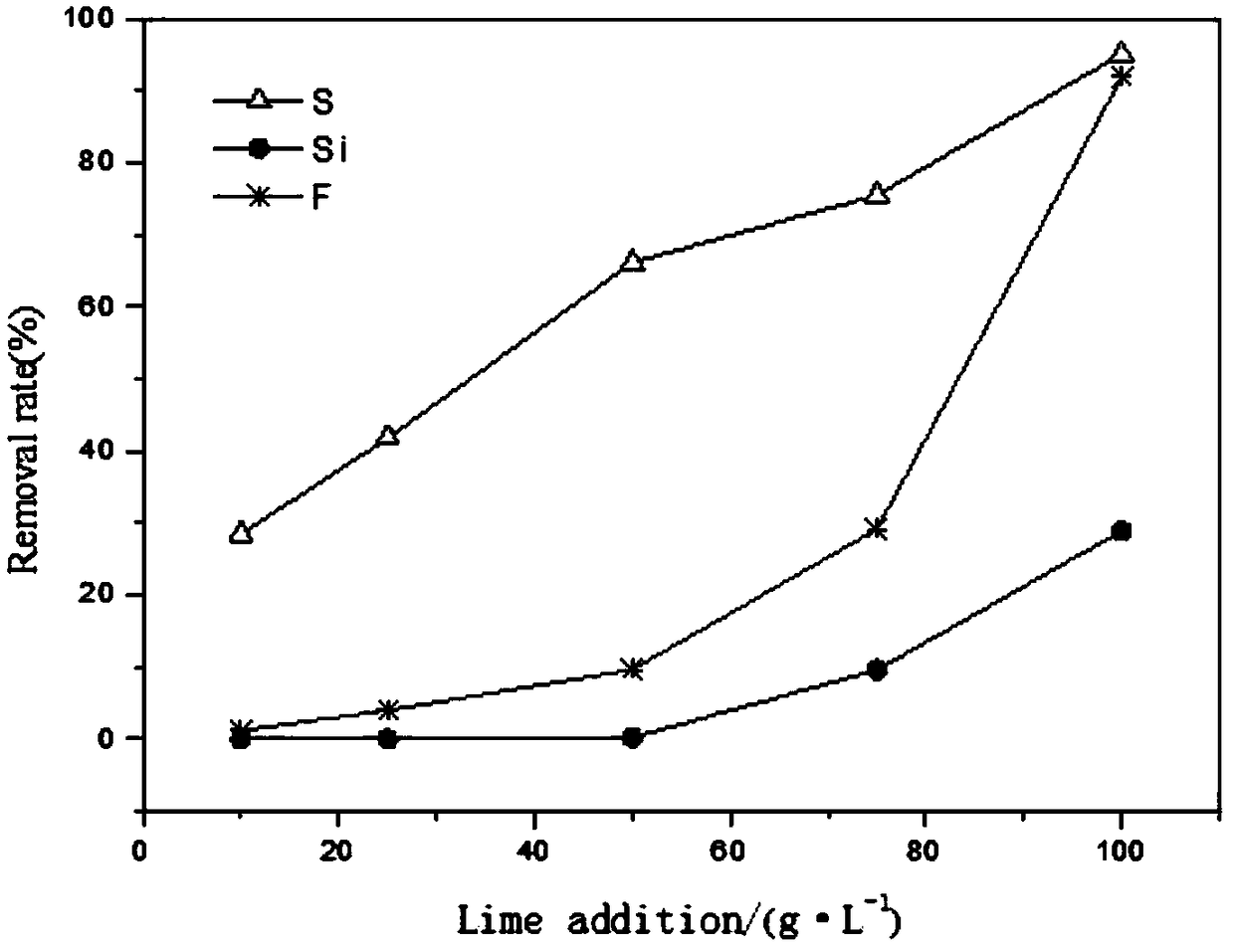
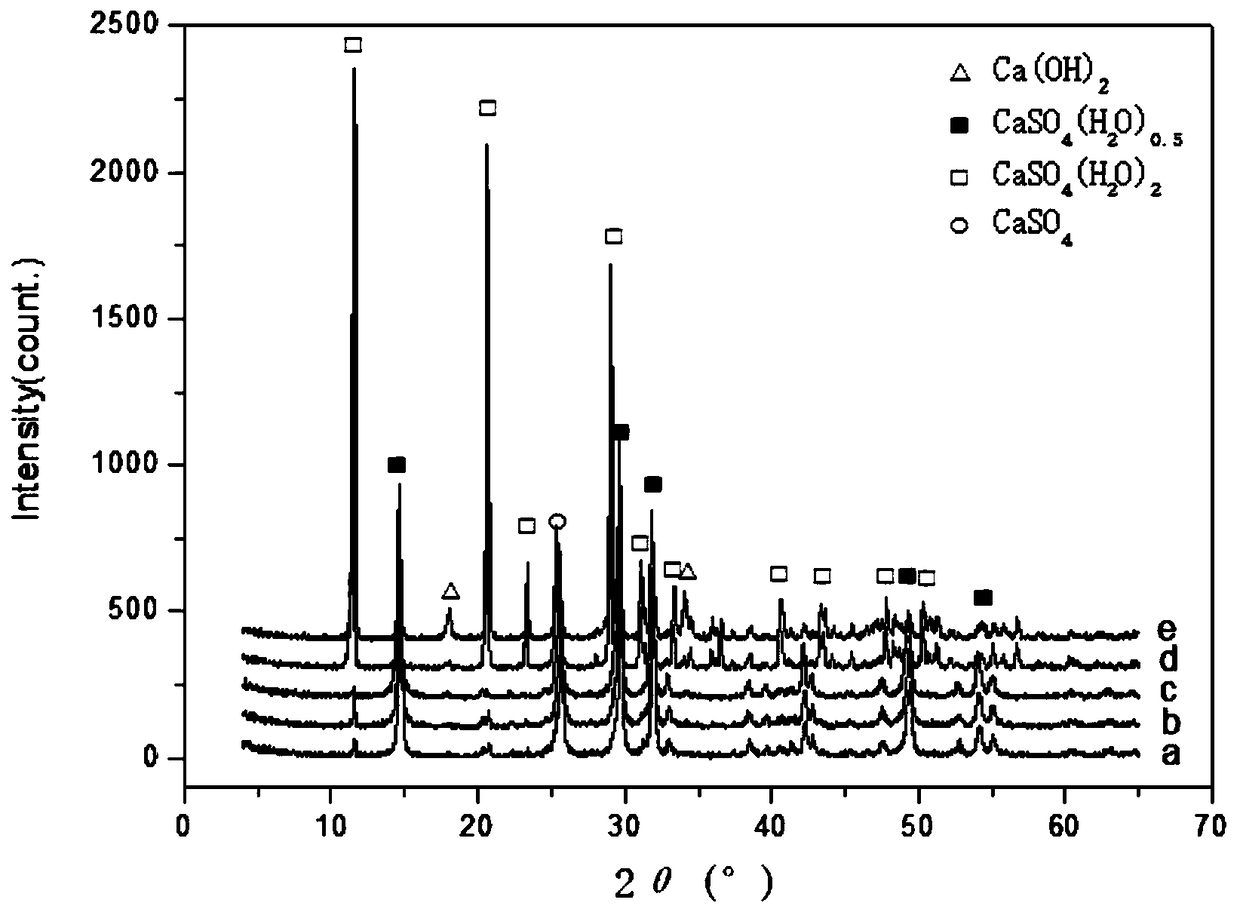
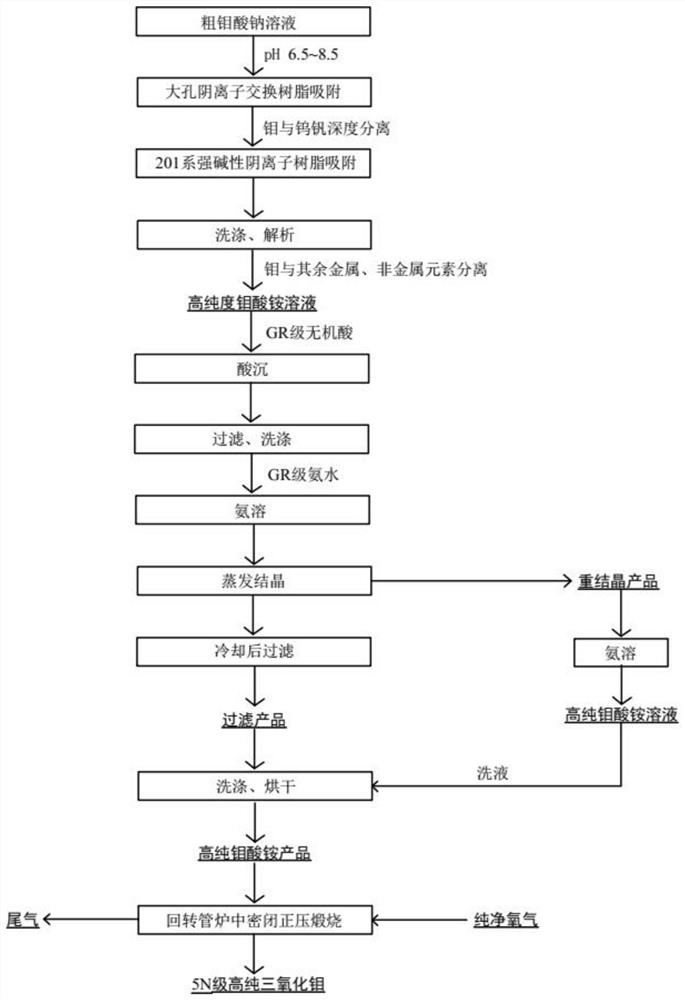
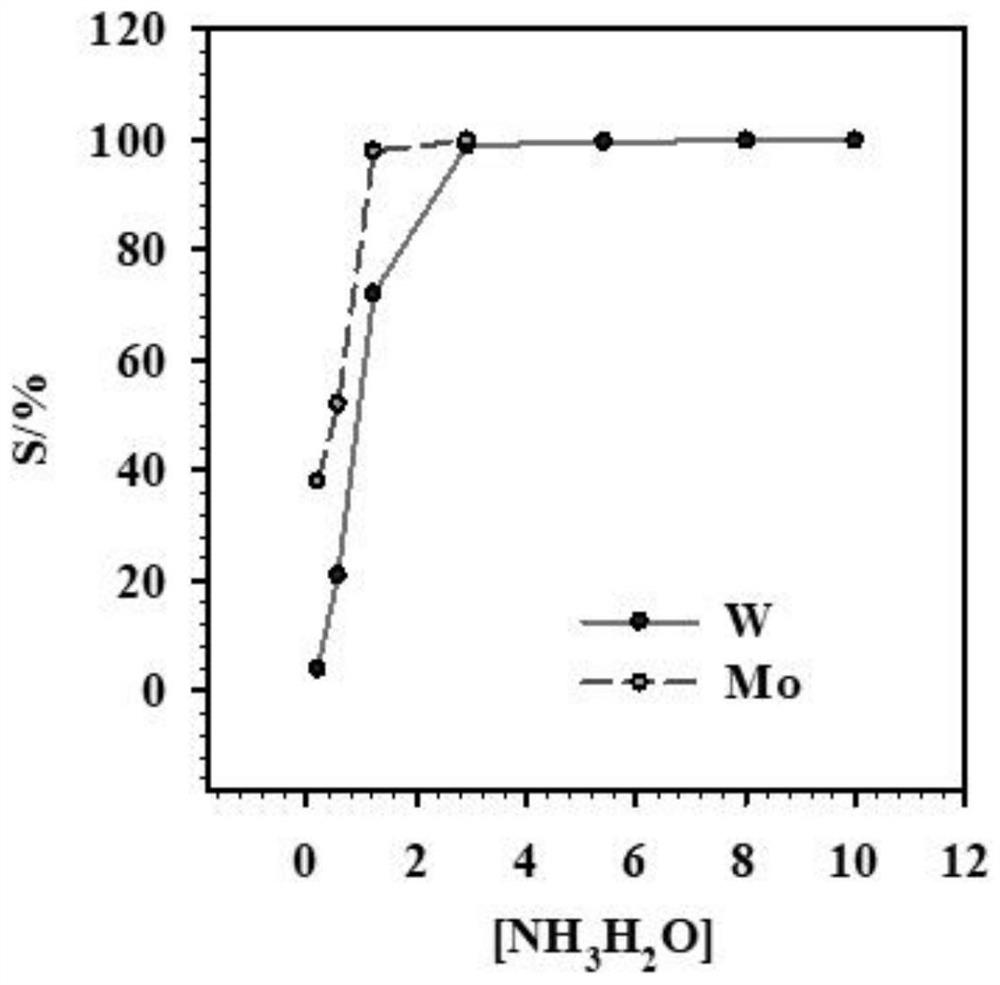
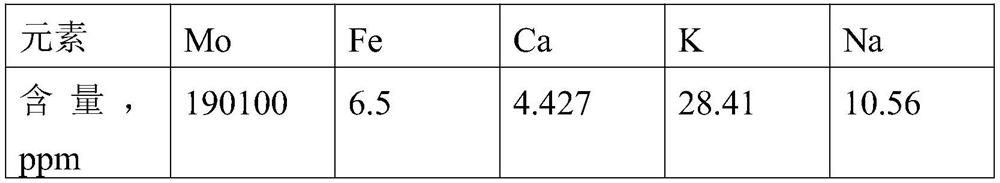
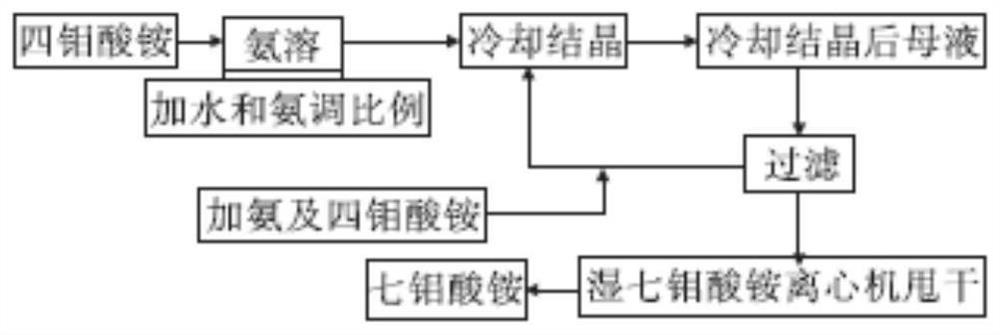
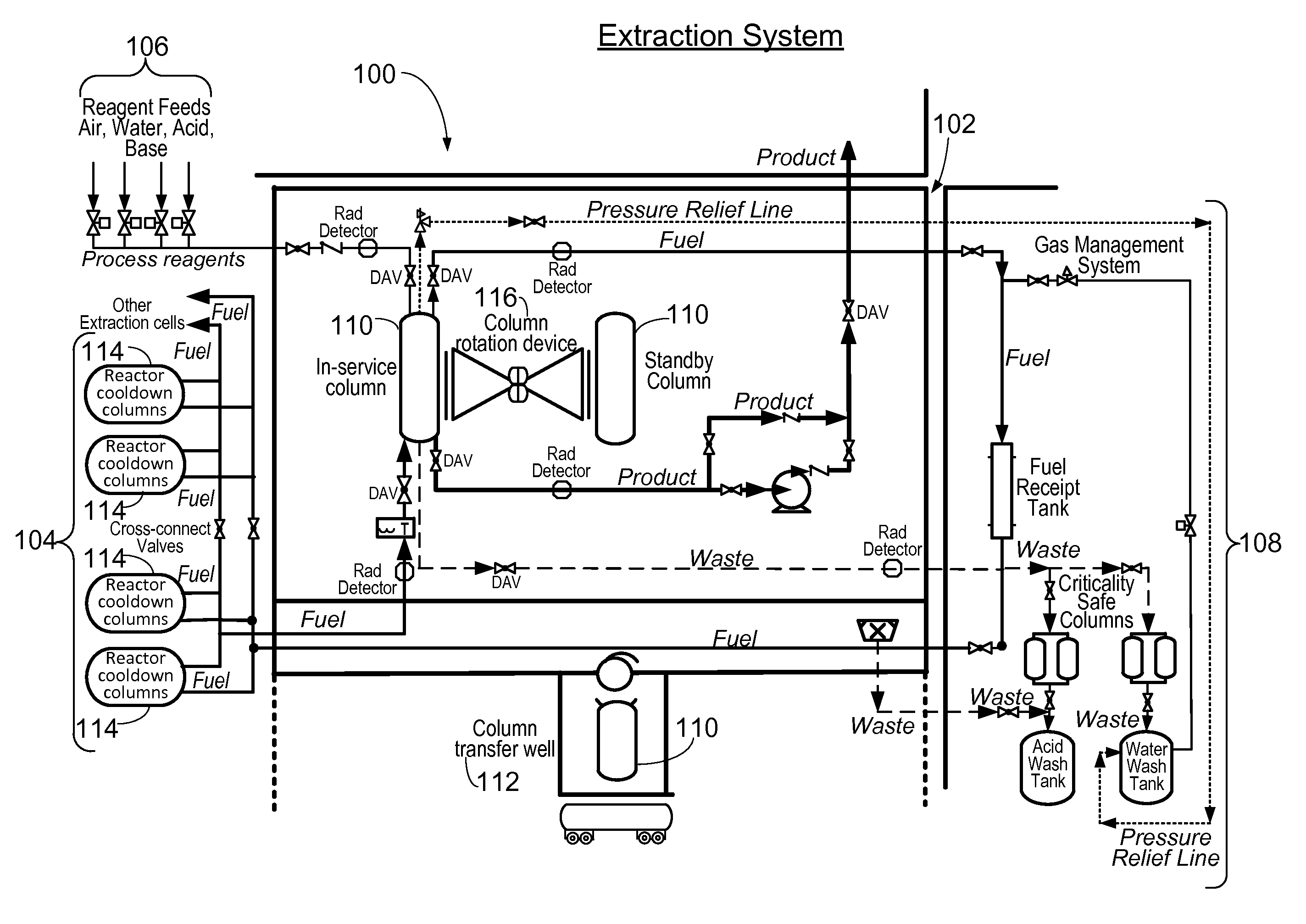
Patents
Literature
48results about "Molybdeum compounds preparation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
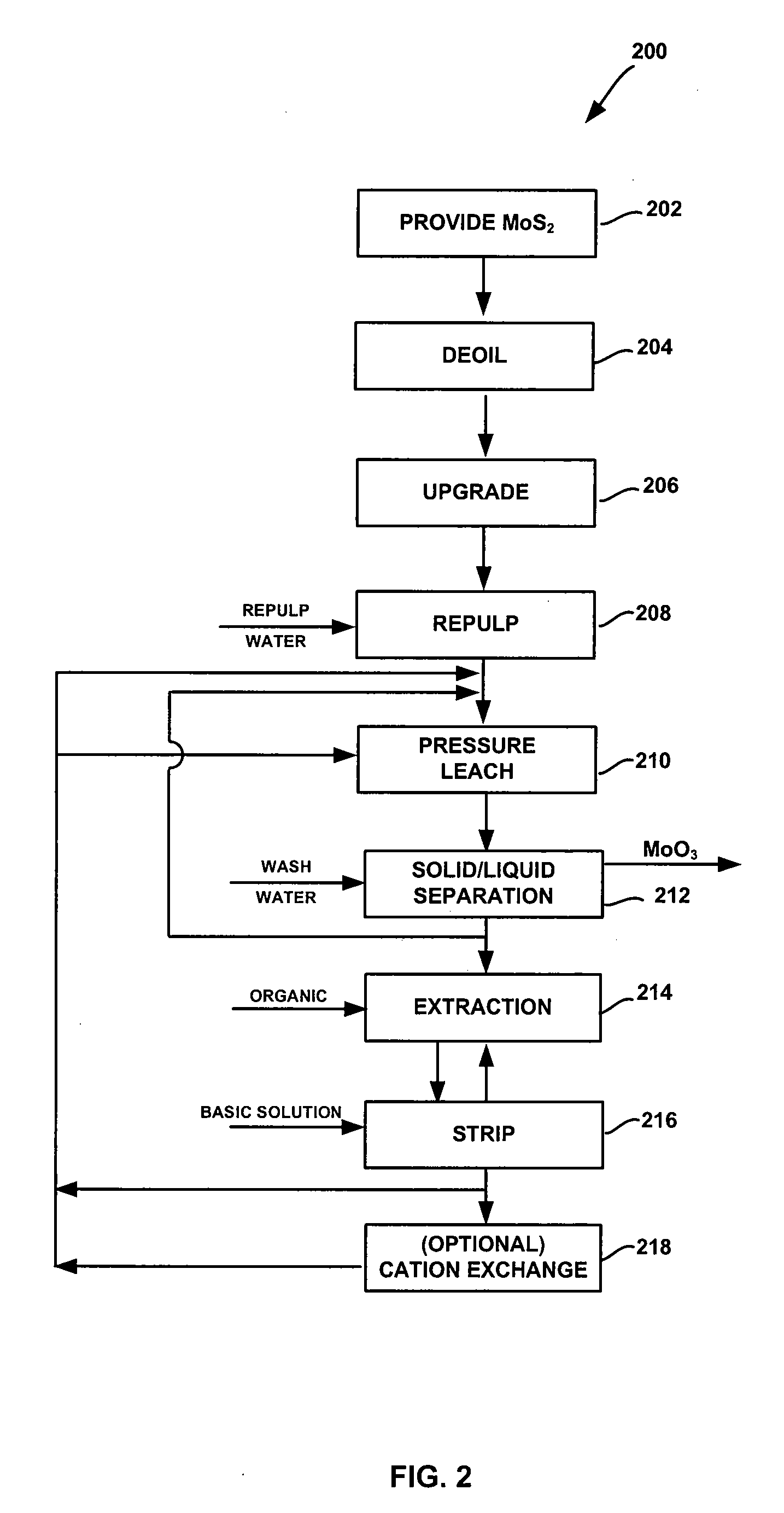
Production of pure molybdenum oxide from low grade molybdenite concentrates
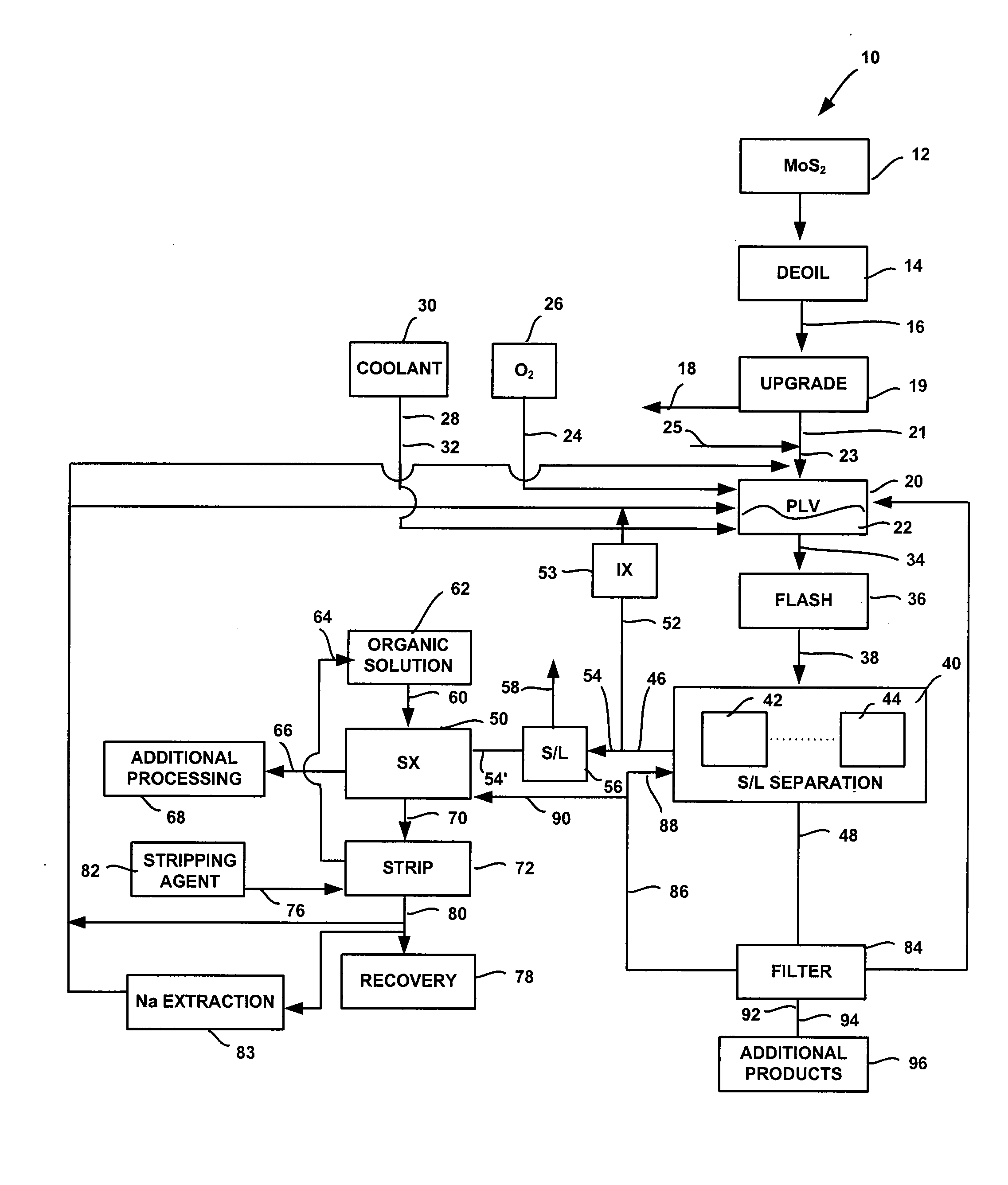
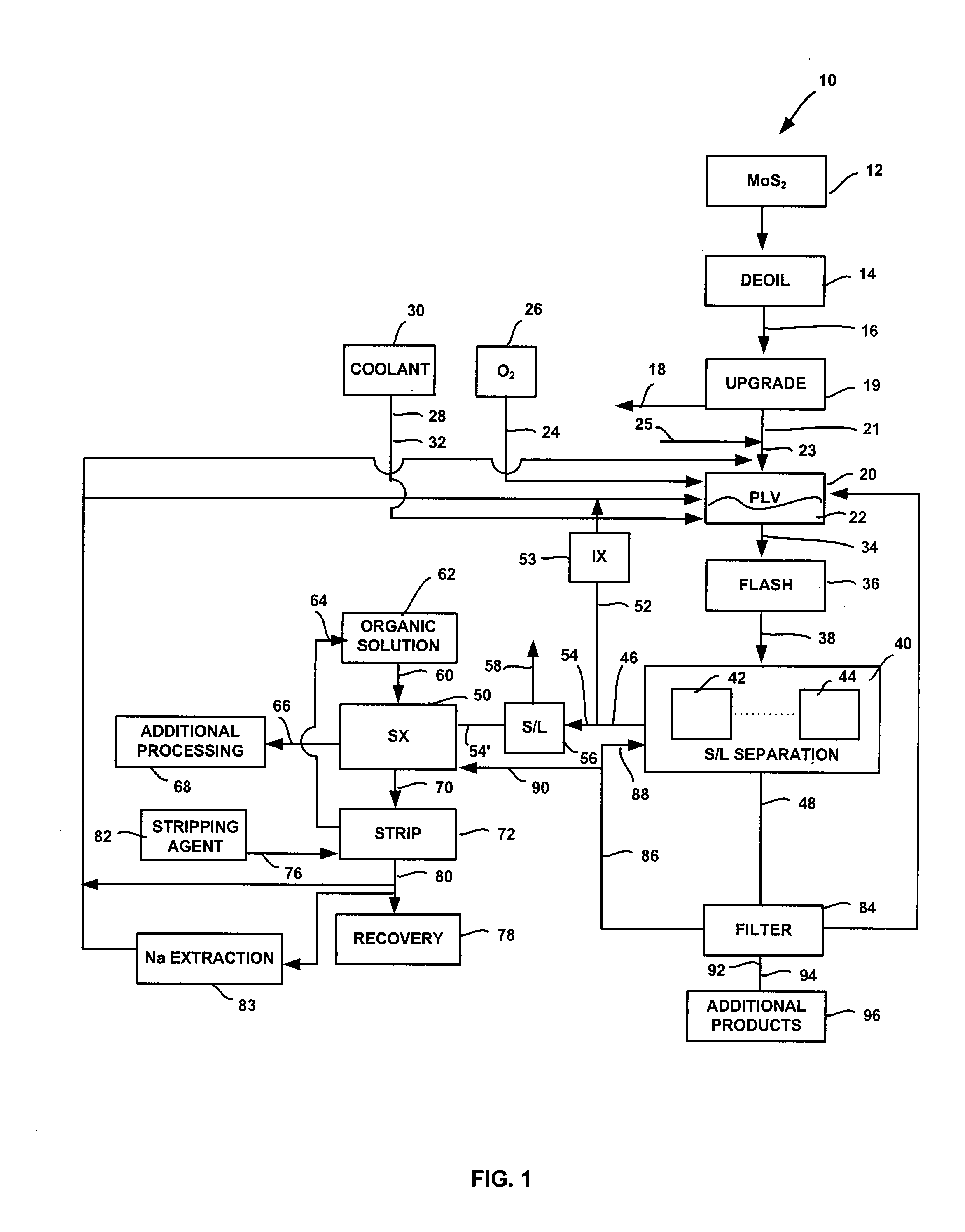
InactiveUS20050019247A1High purityValue maximizationOxide/hydroxide preparationMolybdeum compounds preparationProcess chemistryFiltration
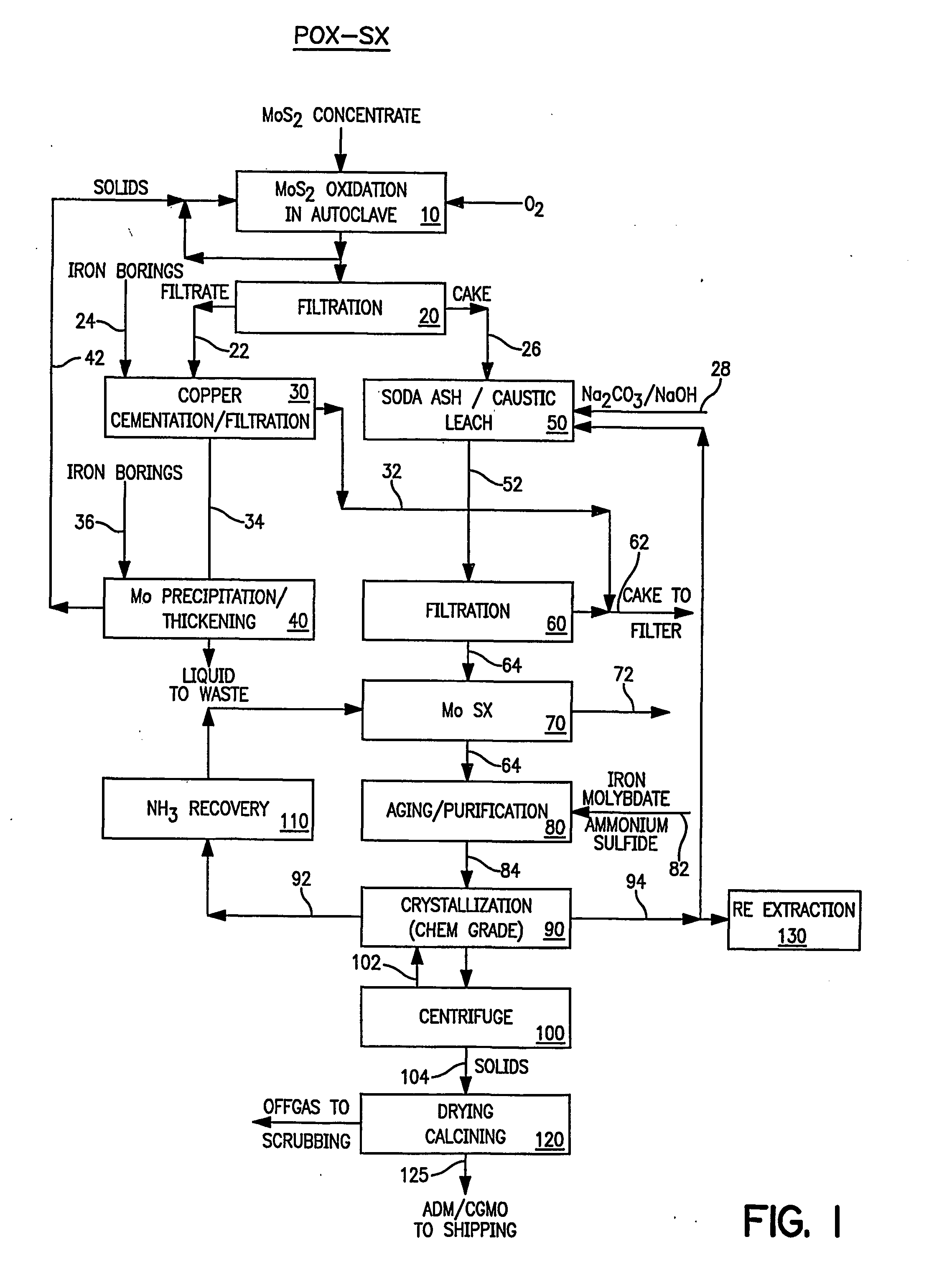
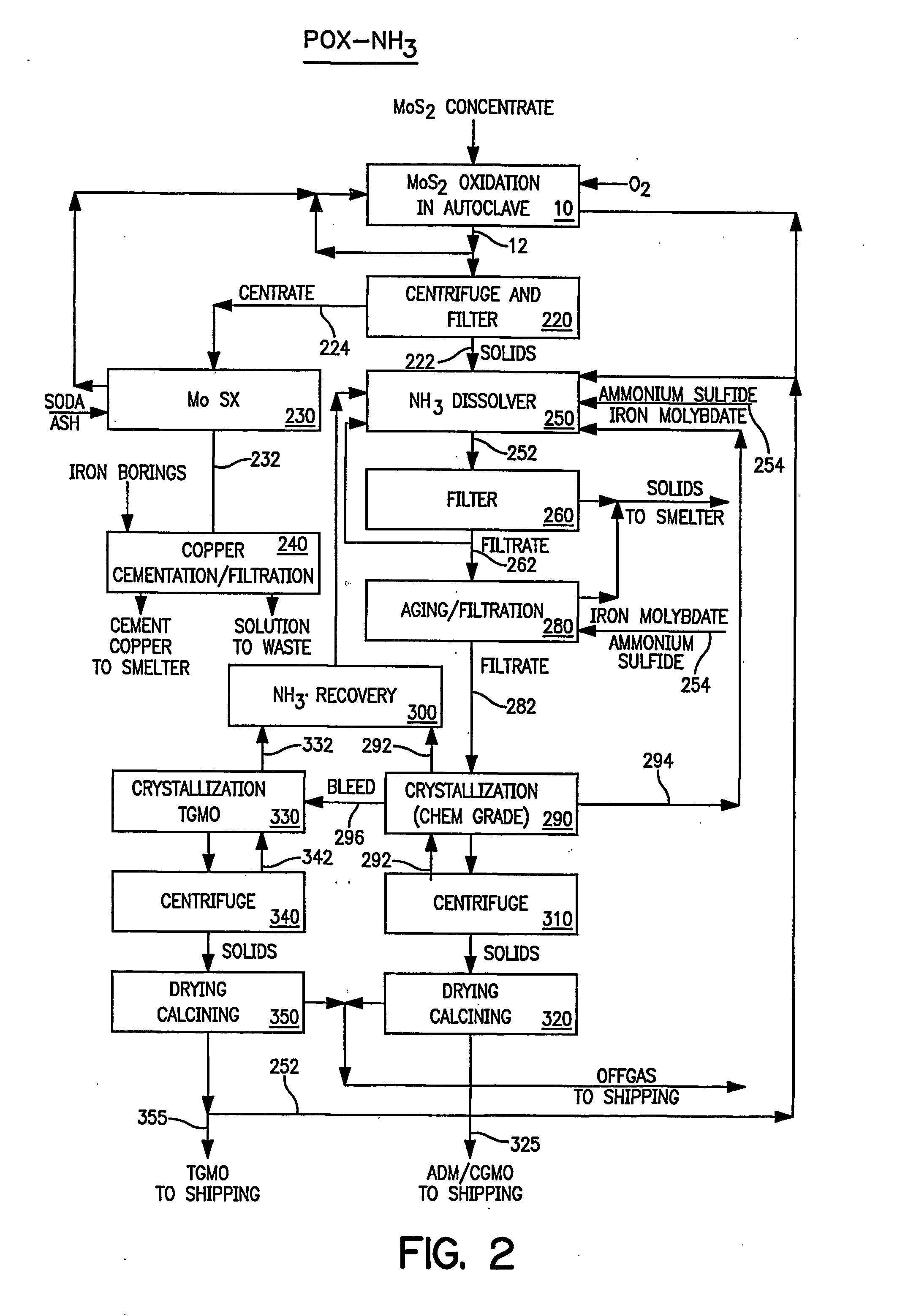
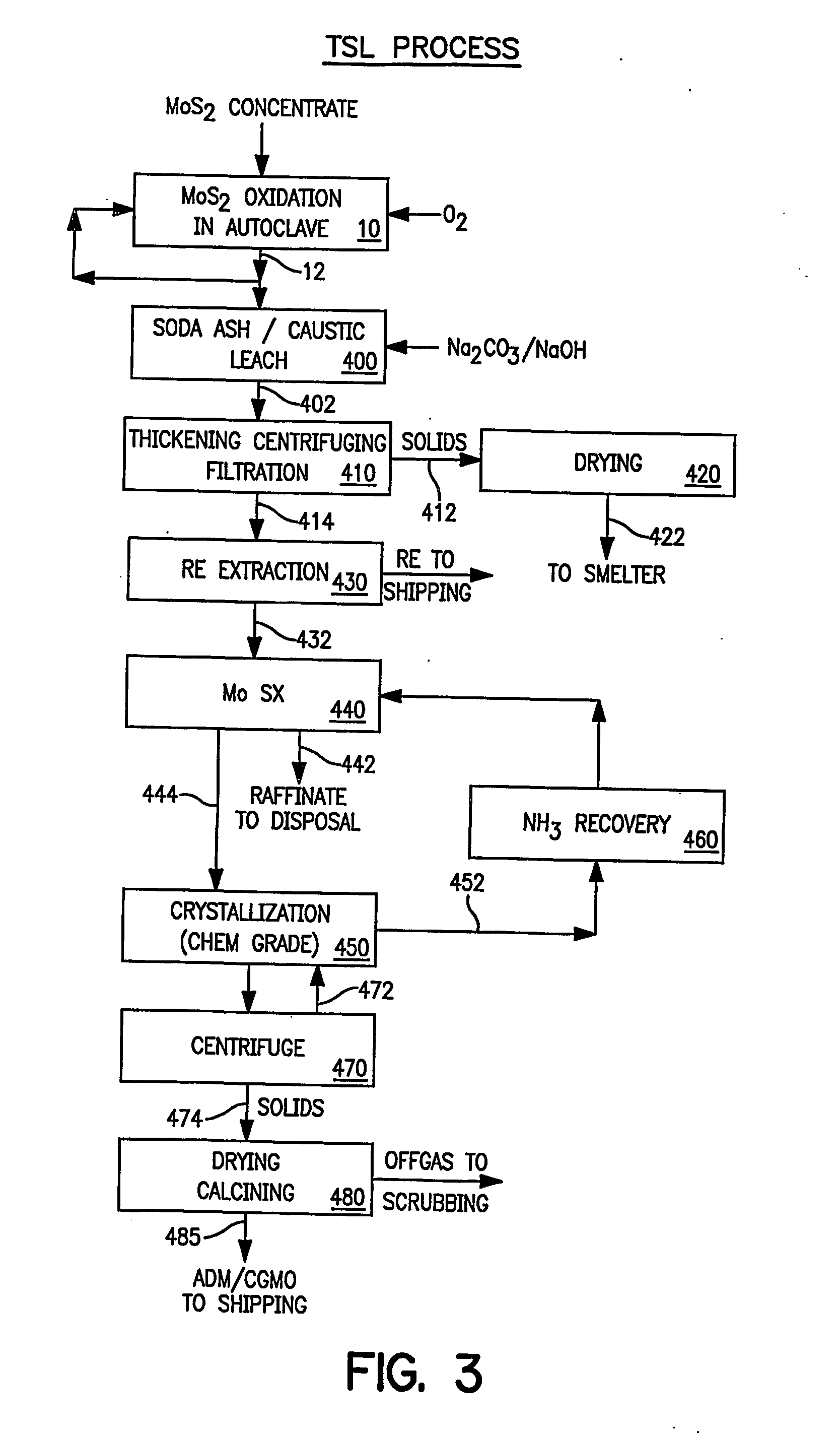
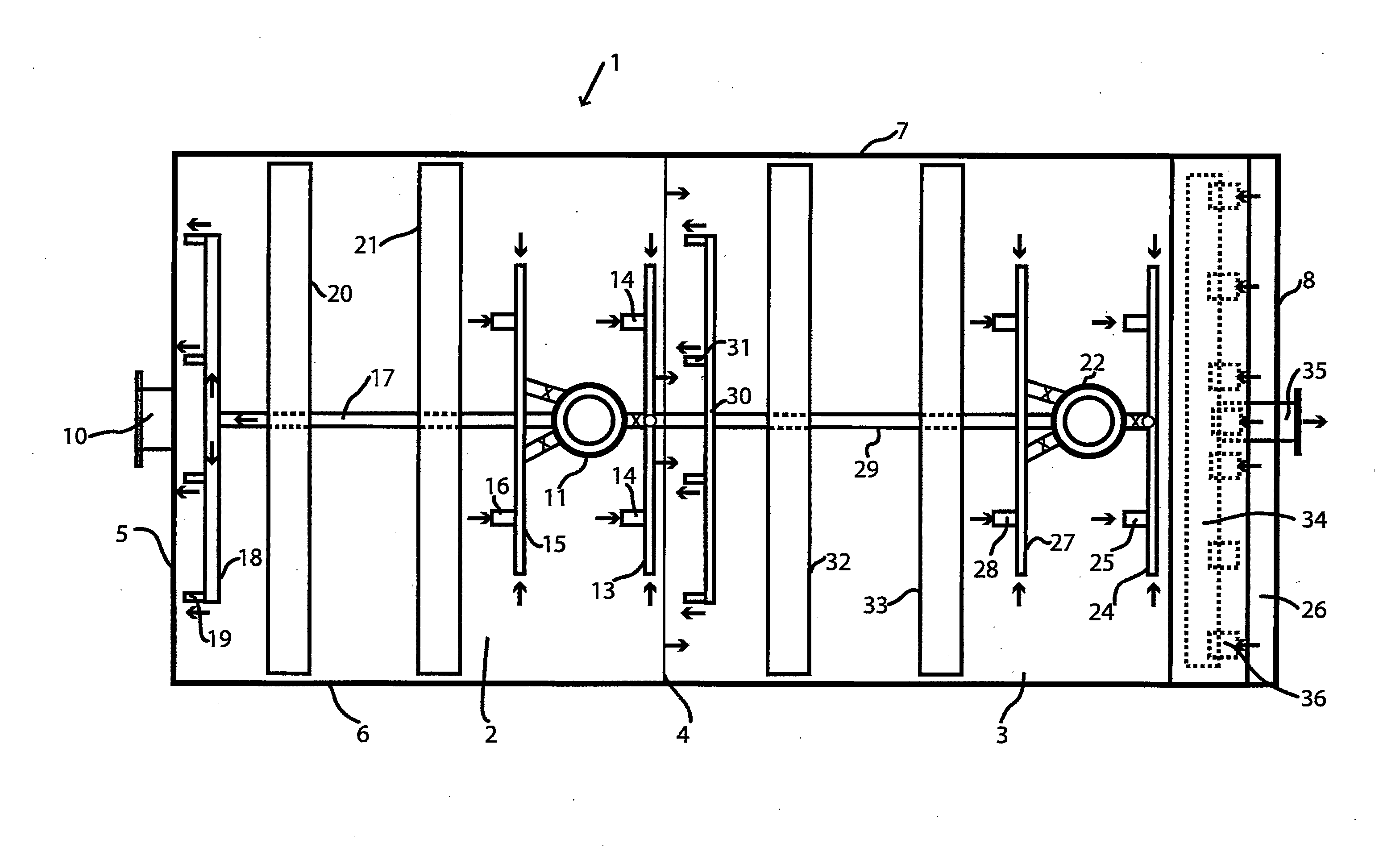
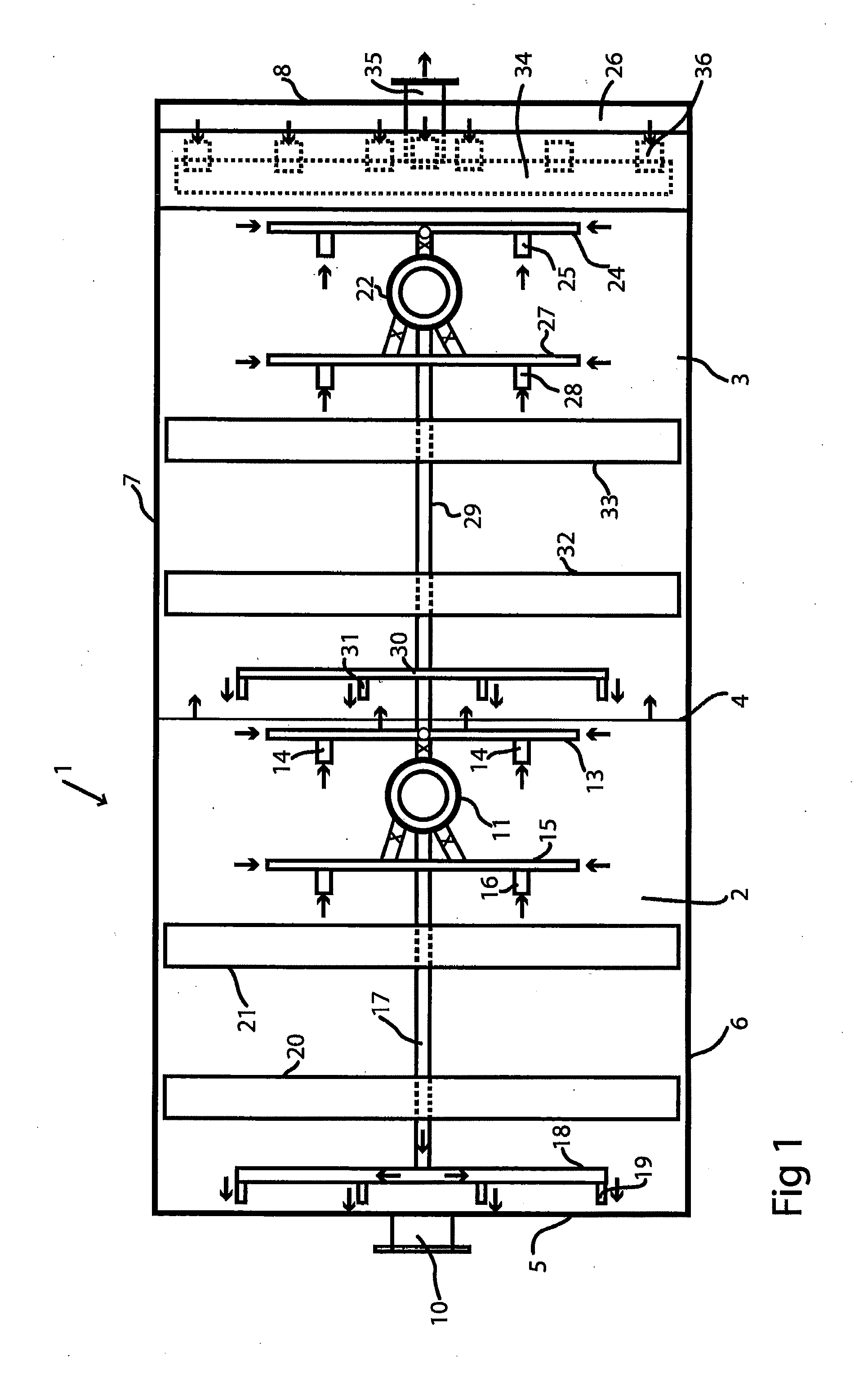
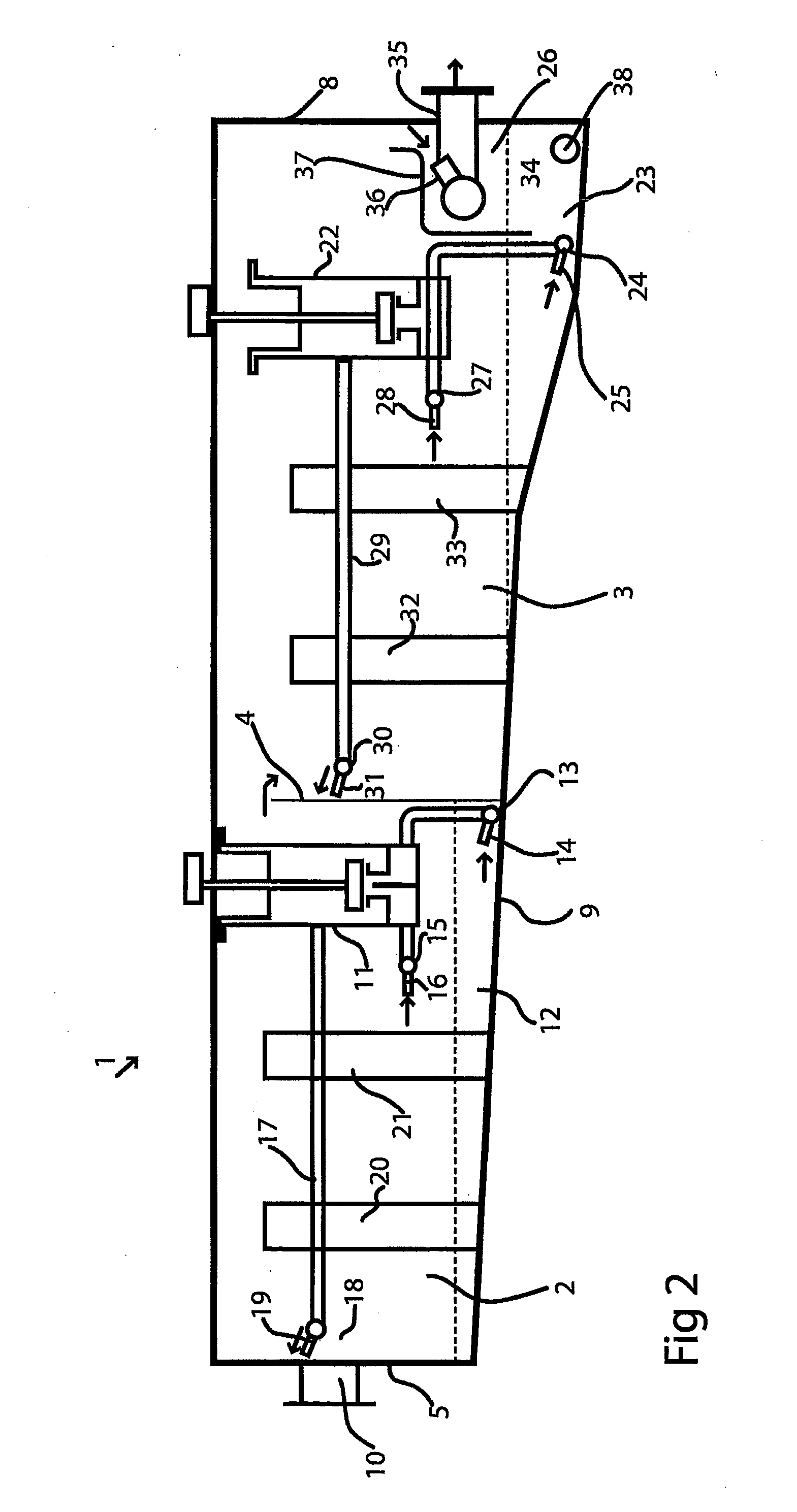
High purity ammonium dimolybdate or molybdenum oxide is produced by the pressure oxidation of low grade molybdenite concentrates or molybdenum intermediates. The process entails nearly complete oxidation of the sulfide minerals while optimizing the process chemistry and autoclave conditions to solubilize as little of the molybdenum values as possible. The autoclave discharge 12 is then subjected to a leaching step, either an alkaline leach 50, 400 or ammonium leach 250 process, before or after a liquid / solid separation step 20, 220, 410. The solution is then subjected to (a) filtration 60, 410, solvent extraction 70, 440, crystallization 90, 450, and calcination 120, 480 or (b) filtration 260, 280, crystallization 290, and calcination 320 to produce a product suitable for chemical-grade molybdenum oxide 125, 325, 485.
Owner:BALLIETT ROBERT W +6
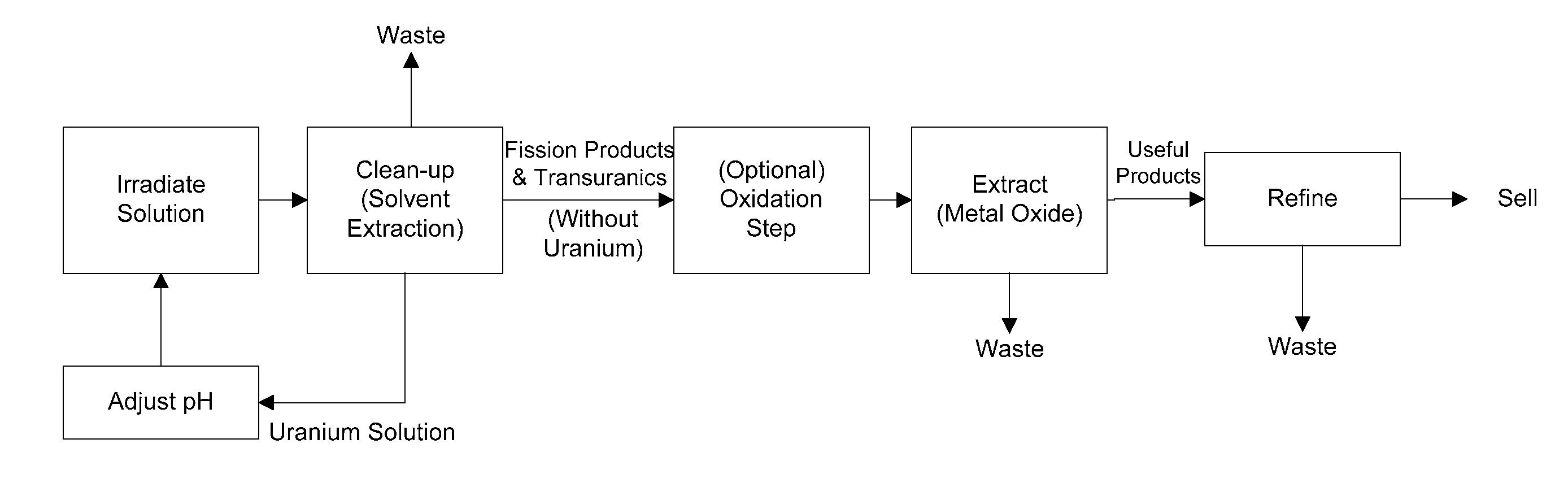
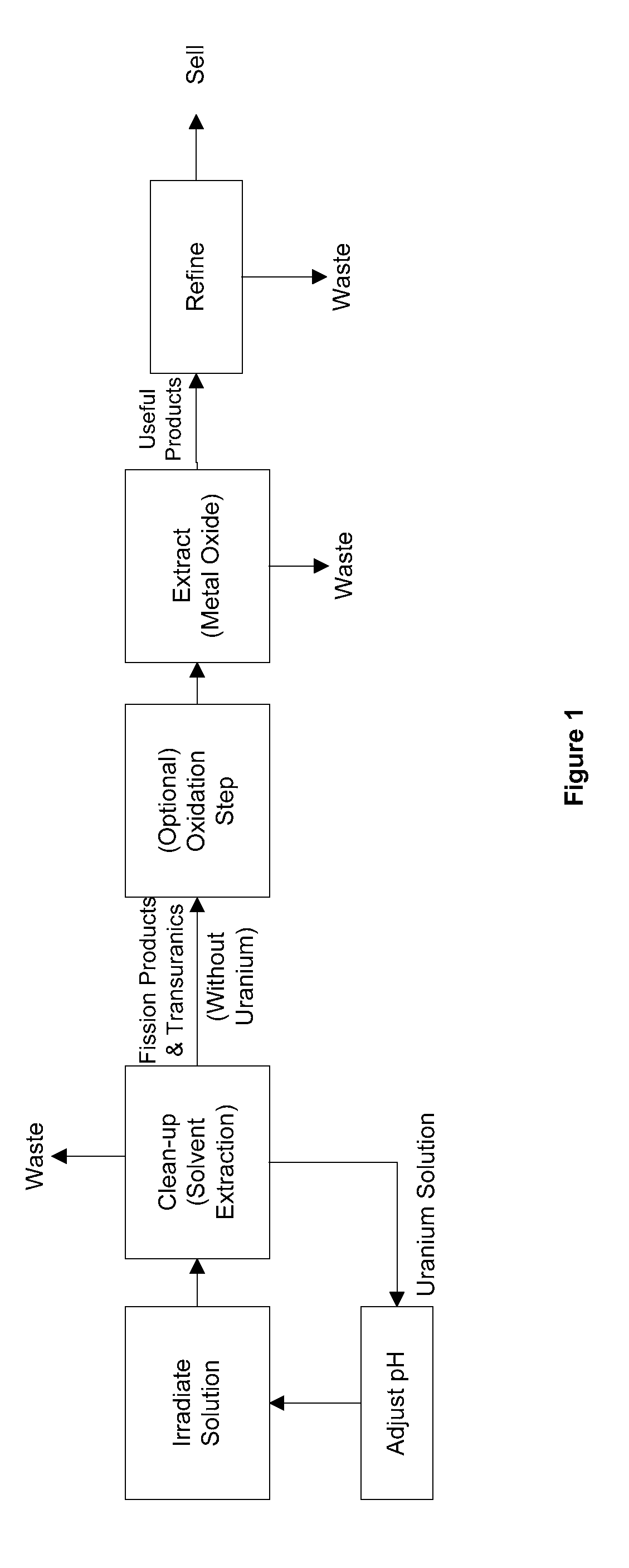
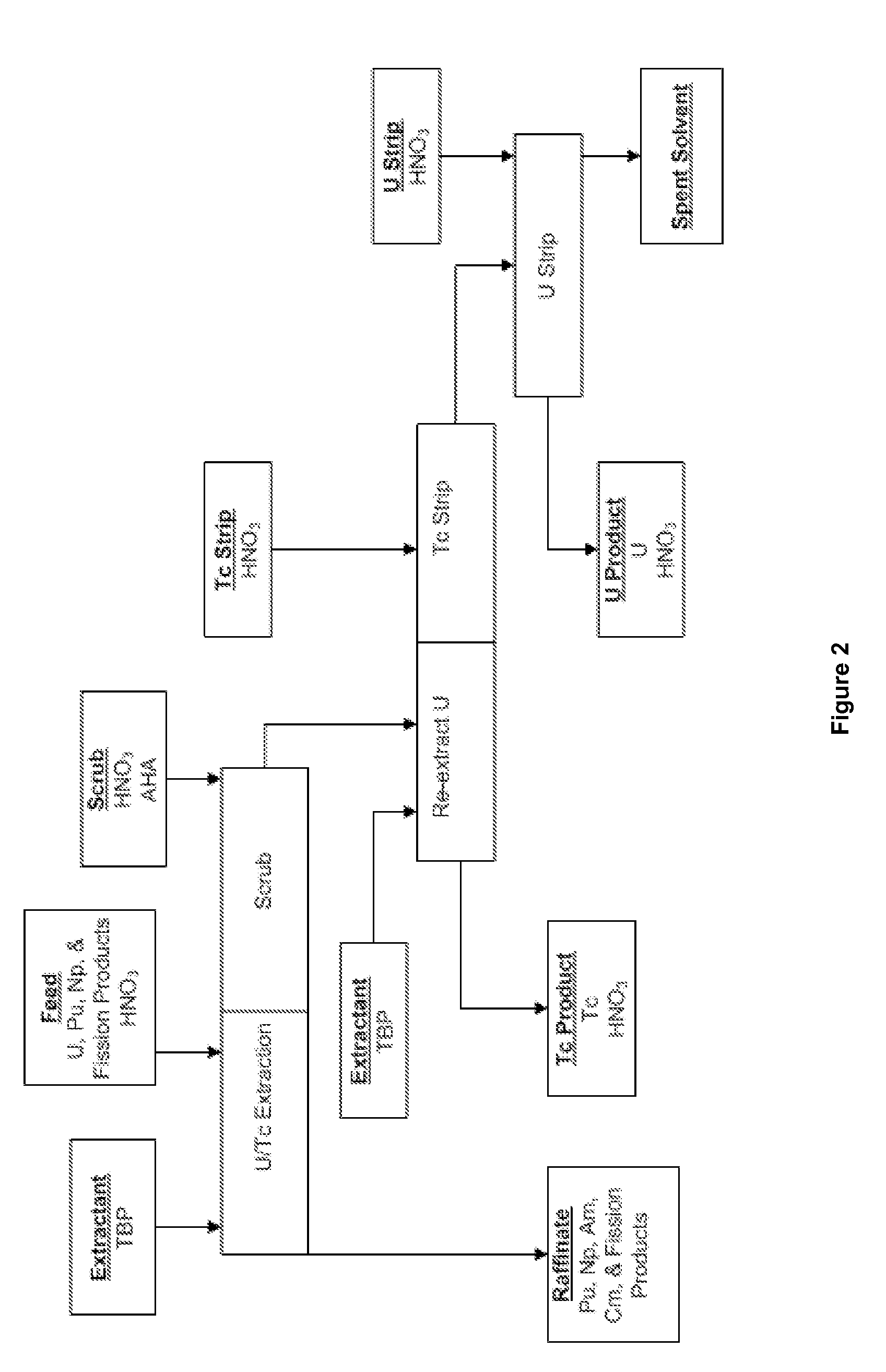
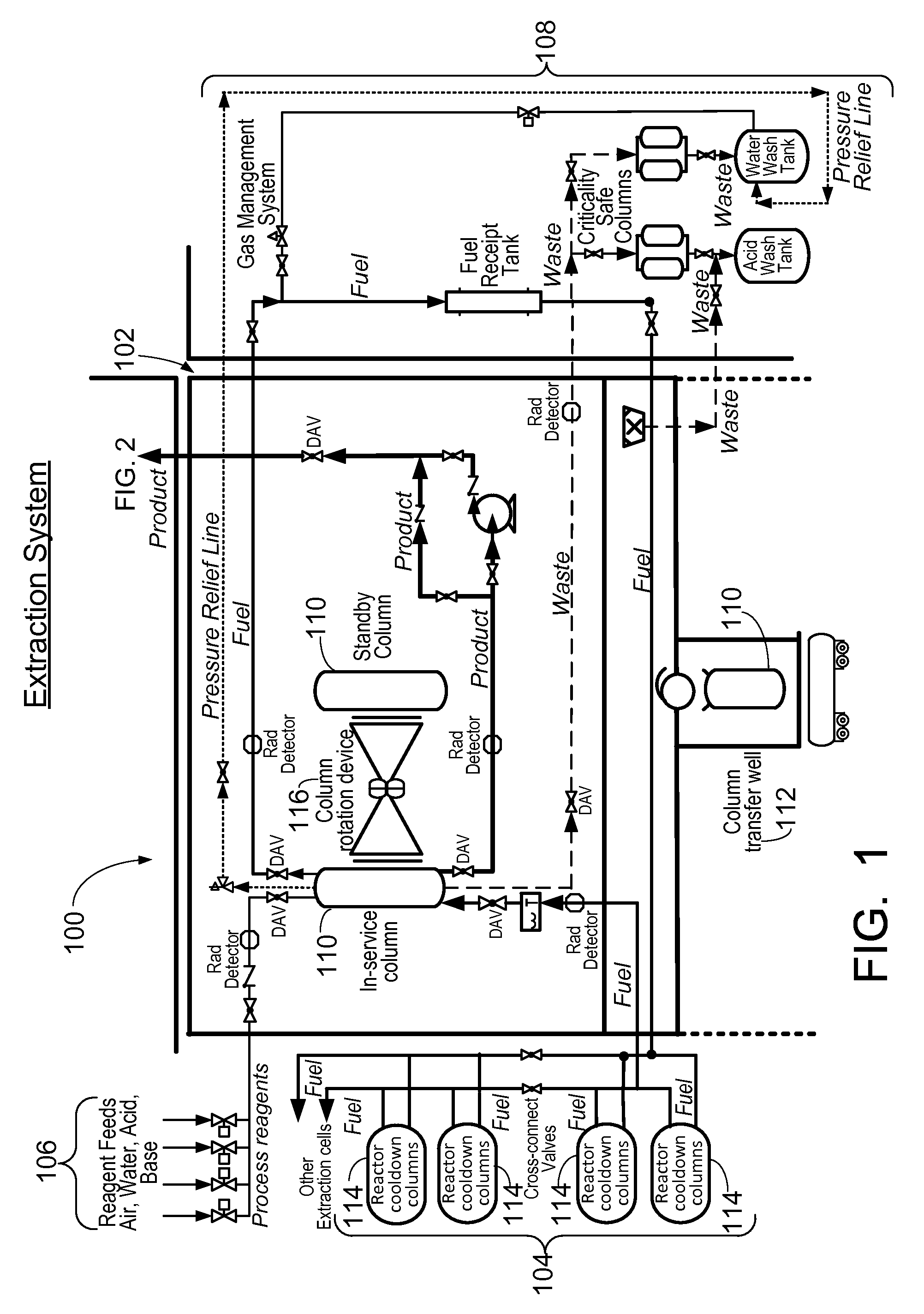
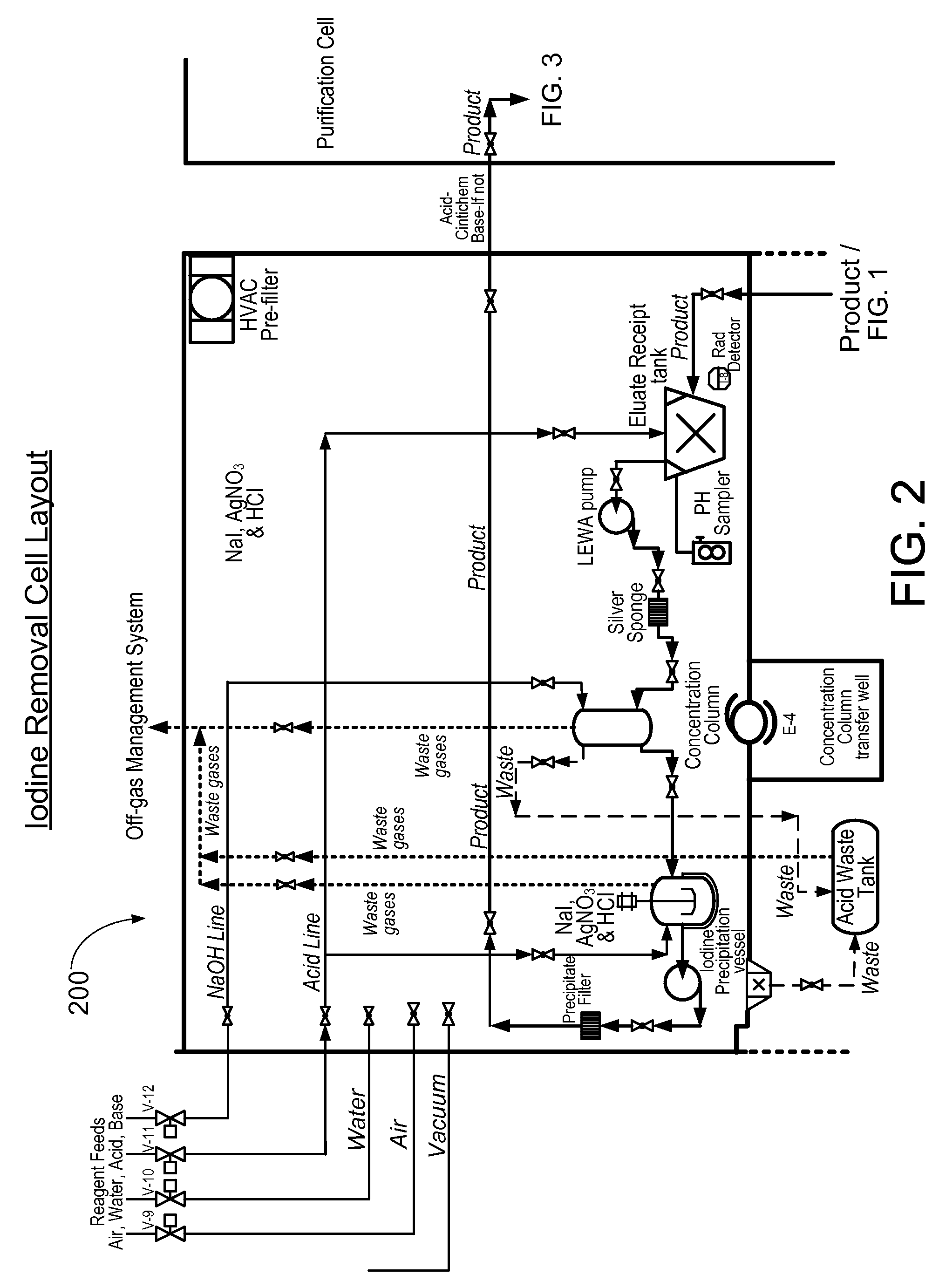
Method and apparatus for the extraction and processing of molybdenum-99
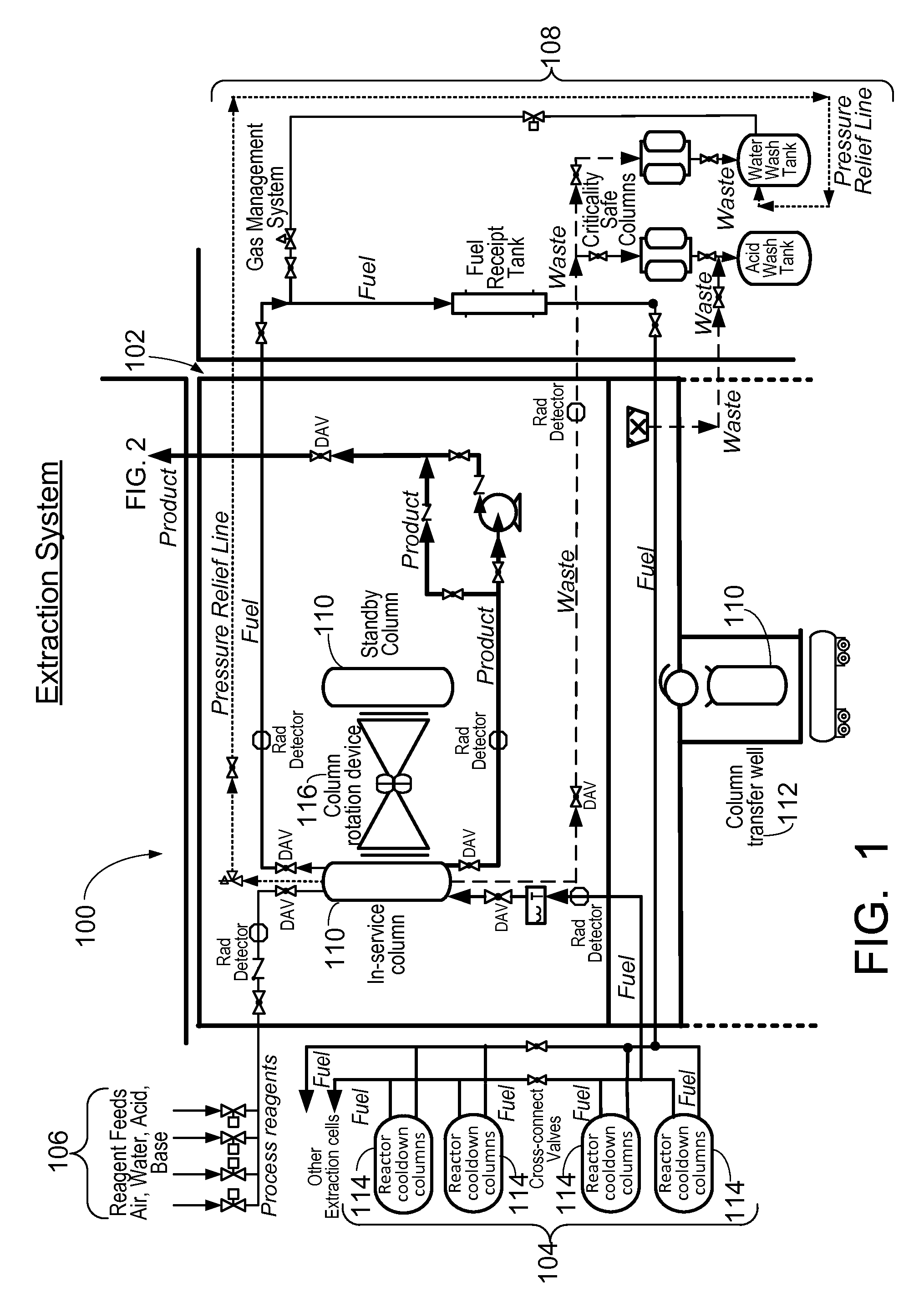
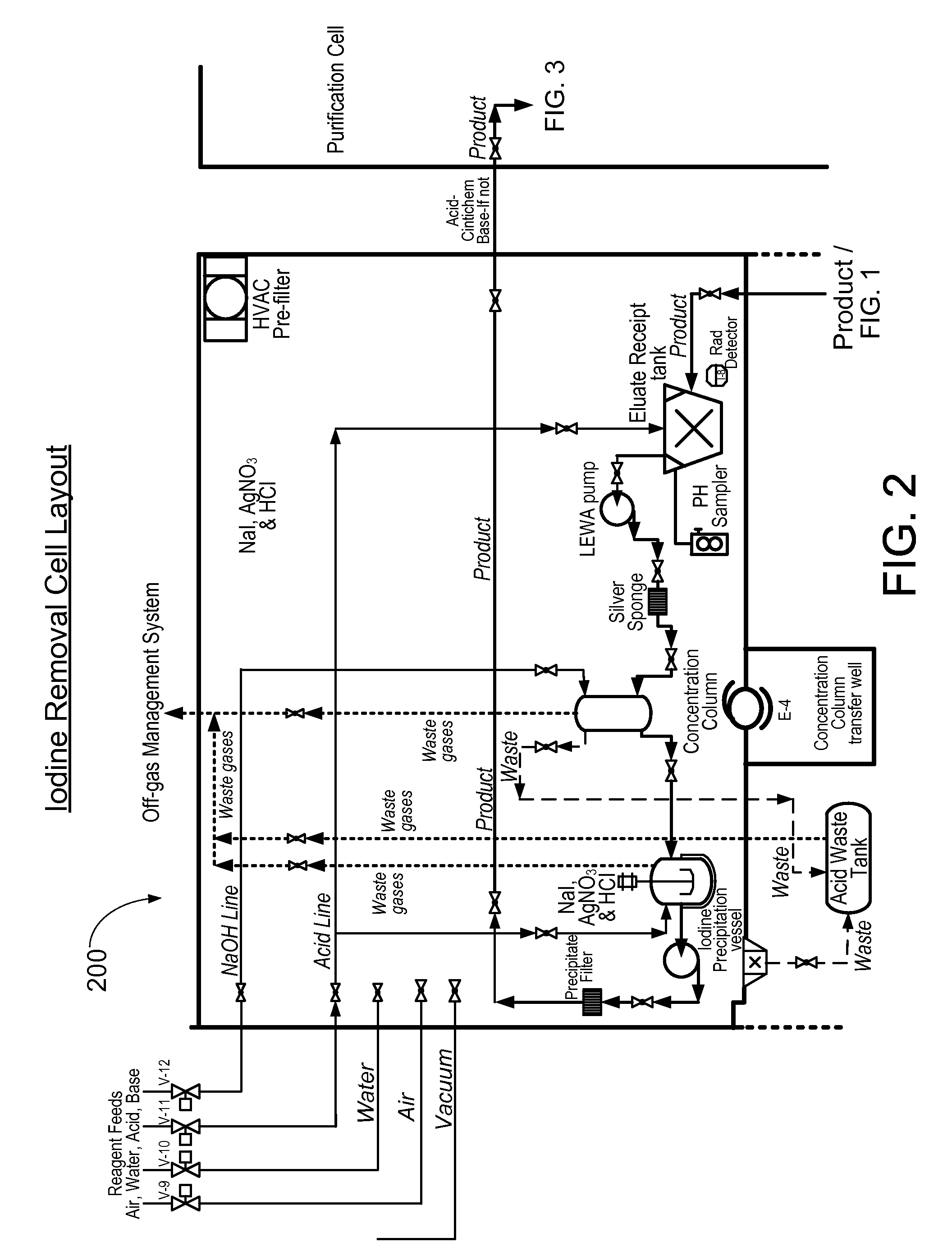
ActiveUS20110206579A1Reduce the amount requiredTransuranic element compoundsSolid sorbent liquid separationSorbentIodine
A method for the extraction and purification of molybdenum, the method comprising the steps of: transferring an irradiated fuel solution to an extraction system, the irradiated fuel solution comprising iodine and molybdenum and other fission products, the extraction system comprising at least one sorbent column; passing the irradiated fuel solution upwards through the at least one sorbent-containing extraction column; directing the irradiated fuel solution towards a fuel management system by means of at least one discharge alignment valve; directing the extraction column eluate towards an iodine removal system; removing the iodine from the extraction column eluate; purifying the extraction column eluate; and collecting the purified eluate. Also disclosed is an apparatus for accomplishing the aforementioned method.
Owner:BABCOCK & WILCOX TECHNICALSERVICES GRP INC
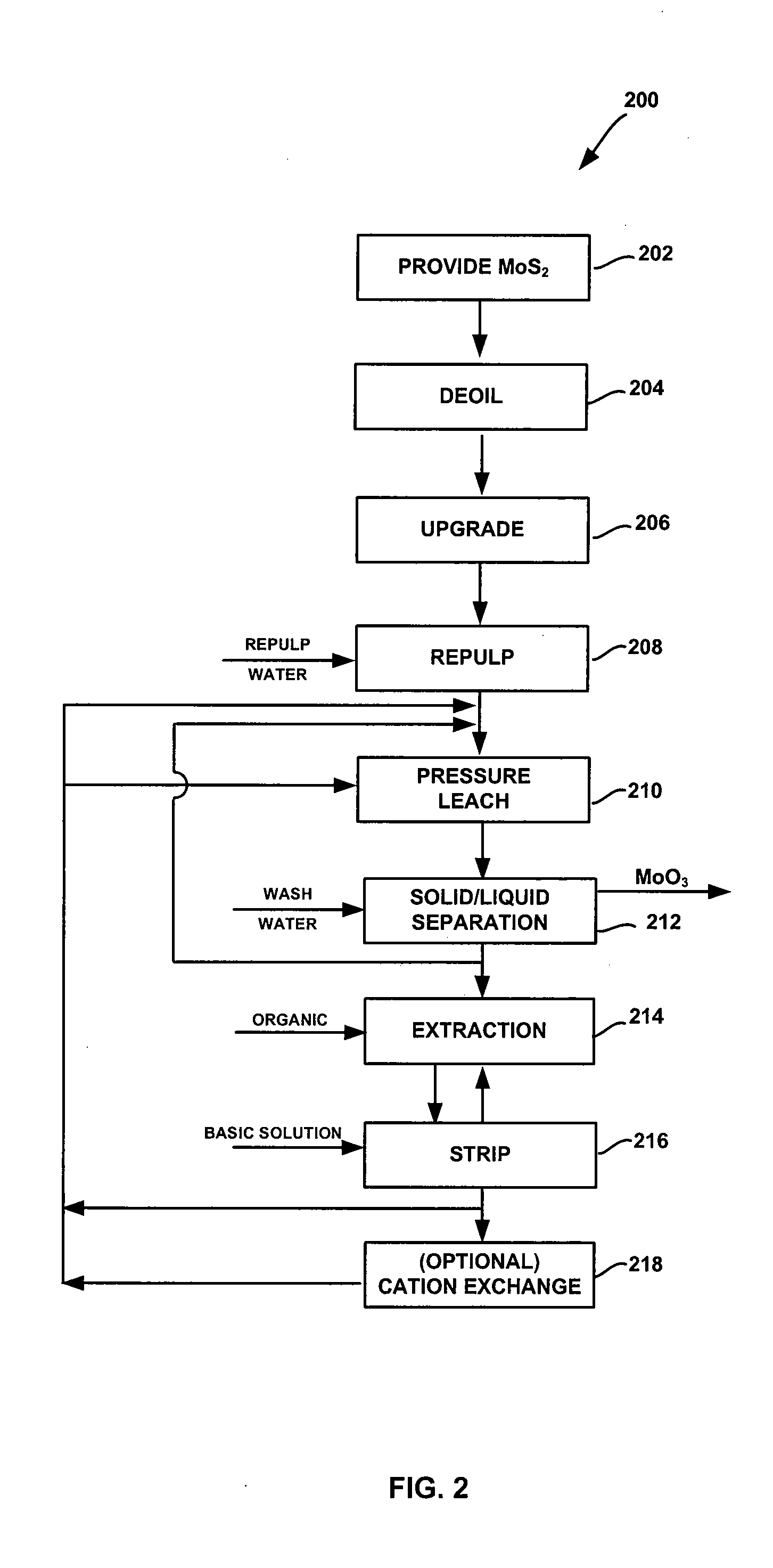
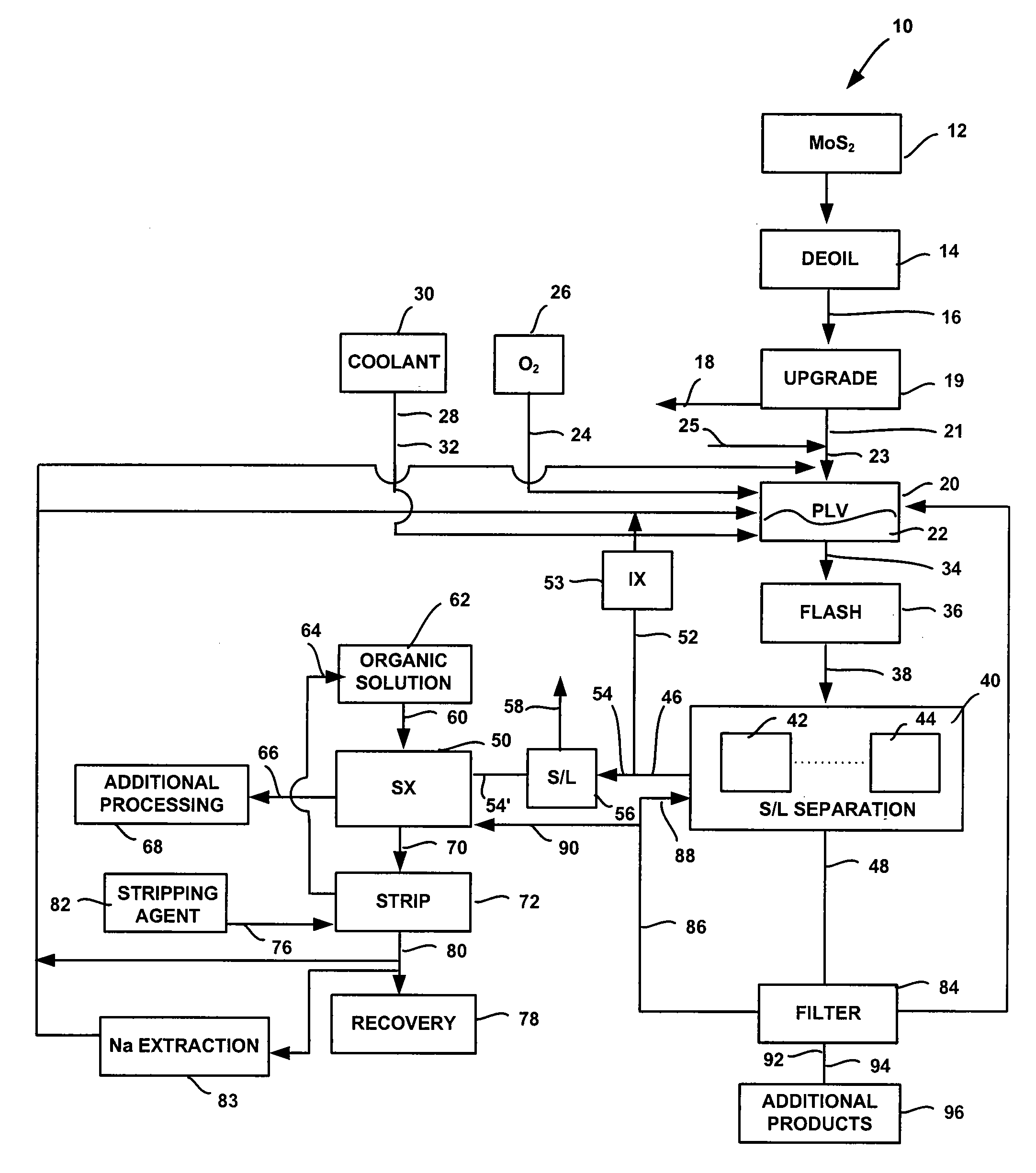
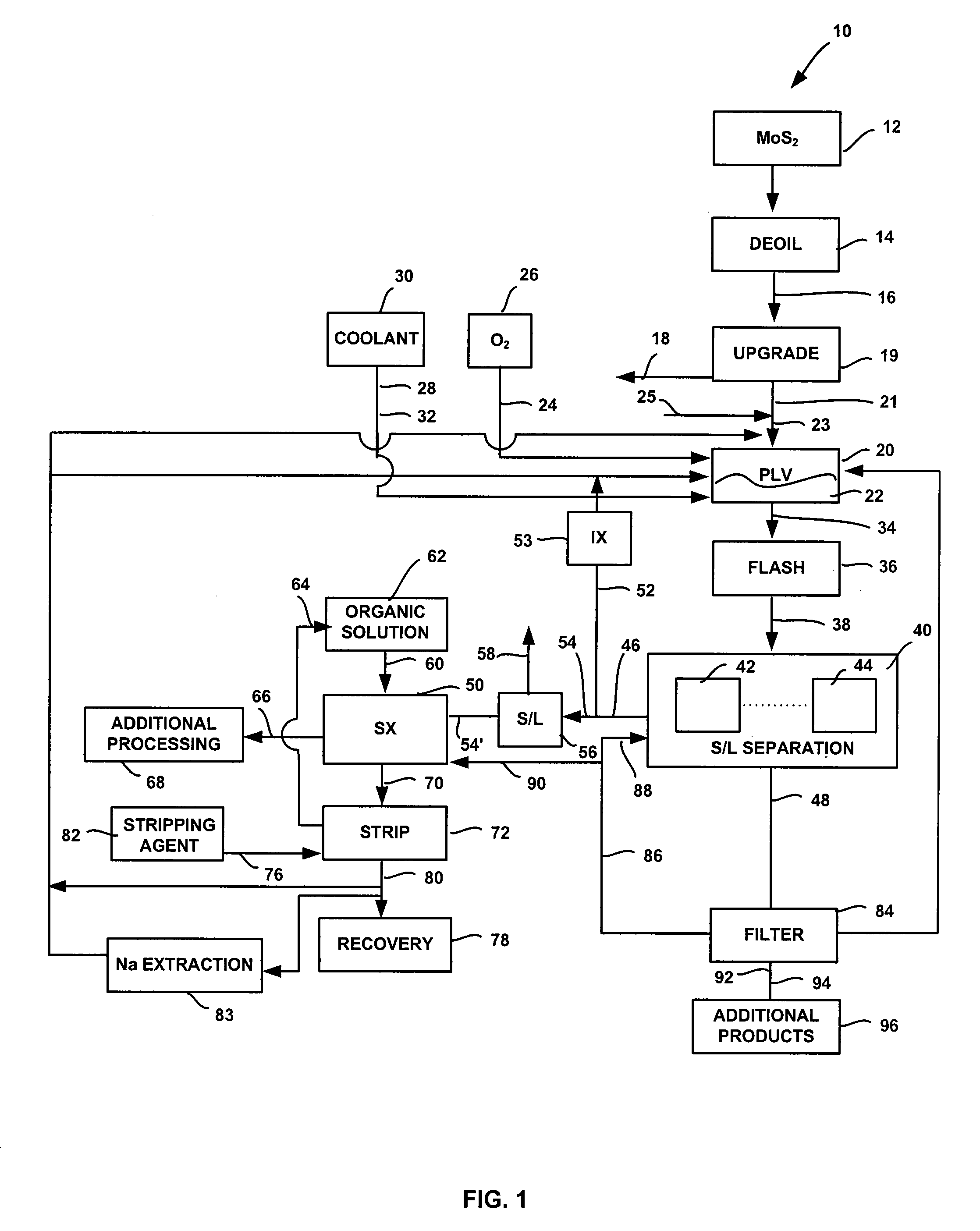
System and method for conversion of molybdenite to one or more molybdenum oxides
InactiveUS20080118422A1Promote oxidationMaintain pressurePressurized chemical processOxygen/ozone/oxide/hydroxideSolventSolvent extraction
A system and method for producing molybdenum oxide(s) from molybdenum sulfide are disclosed. The system includes a pressure leach vessel, a solid-liquid separation stage coupled to the pressure leach vessel, a solvent-extraction stage coupled to the solid-liquid separation stage, and a base stripping stage coupled to the solvent-extraction stage. The method includes providing a molybdenum sulfide feed, subjecting the feed to a pressure leach process, subjecting pressure leach process discharge to a solid-liquid separation process to produce a discharge liquid stream and a discharge solids stream, and subjecting the discharge liquid stream to a solvent extraction and a base strip process.
Owner:FREEPORT MCMORAN COPPER & GOLD INC
Methods of separating medical isotopes from uranium solutions
Provided are methods to separate an isotope from a first solution including uranium. The methods may include (a) cleaning the first solution to form a second solution including the uranium and a third solution including the isotope; (b) oxidizing the third solution to form an oxidized isotope; and (c) separating the oxidized isotope.
Owner:SHINE TECH LLC
Process for Recovering Molybdate or Tungstate from Aqueous Solutions
InactiveUS20090274598A1Reduce consumptionReduce the ratioWater treatment parameter controlSolvent extractionMolybdateTungstate
Process for recovering molybdate or tungstate from an aqueous solution, in which molybdate or tungstate is bound to a water-insoluble, cationized inorganic carrier material from the aqueous solution at a pH in the range from 2 to 6, the laden carrier material is separated off and the bound molybdate or tungstate is liberated once again into aqueous solution at a pH in the range from 6 to 14. The process is suitable for recovering molybdate or tungstate in the delignification of pulp with hydrogen peroxide in the presence of molybdate or tungstate as catalyst. The recovered molybdate or tungstate can be recycled to the delignification.
Owner:EVONIK DEGUSSA GMBH
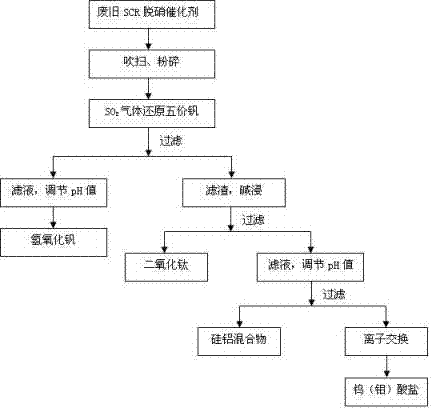
Recovery method of waste SCR denitration catalyst
ActiveCN110817944AGood removal effectImprove permeabilityAlkaline earth titanatesTungsten compounds preparationPtru catalystTungstate
The invention belongs to the field of non-ferrous metal recovery, and particularly relates to a recovery method of a waste SCR denitration catalyst. The recovery method comprises the steps of pretreatment, TiO2 separation, extraction and purification, titanium recovery, vanadium recovery, tungsten / molybdenum recovery and the like. The recovery method is capable of recycling a several precious recovery products such as V2O5, ammonium tungstate / ammonium molybdate and BaTiO3 from the waste SCR denitration catalyst. The invention provides an effective technical scheme, and efficient resource utilization of the waste SCR denitration catalyst can be realized.
Owner:北京华电光大环境股份有限公司
Method for recycling ammonium molybdate from waste molybdenum catalysts
ActiveCN108017089ANo pollution in the processReduce consumptionMolybdeum compounds preparationSulfideAmmonium hydroxide
The invention relates to a method for recycling ammonium molybdate from waste molybdenum catalysts. The method includes the following steps of 1, conducting sampling and measuring the mass content ofmolybdenum sulfide in the waste molybdenum catalysts; 2, preparing waste molybdenum catalyst powder; 3, adding an appropriate quantity of ionic liquids into a reaction still to serve as a reaction medium, turning on a stirring device of the reaction still, sequentially putting the catalyst powder, ammonium hydroxide and hydrogen peroxide into the reaction still, and closing the reaction still forcarrying out a reaction to obtain a reaction product; 4, filtering and separating the reaction product to obtain a filter cake and a filtrate; 5, conducting extraction separation on the filtrate, thenadding deionized water into the filtrate, extracting ammonium molybdate from the ionic liquids into water to obtain an ammonium molybdate aqueous solution and an ionic solution; 6, placing the ammonium molybdate aqueous solution in a crystallizer for crystallization to obtain ammonium molybdate crystals. The method for recycling ammonium molybdate from the waste molybdenum catalysts has the advantages that the craft process is environmentally friendly and free of pollution, the consumption is low, and the recycling rate of molybdenum is high.
Owner:宁夏共宣环保科技有限责任公司
Method of recycling component substances in a waste SCR denitration catalyst
InactiveCN107416904AEfficient separationHigh purityTungsten compounds preparationTitanium dioxideTungstateIon-exchange resin
The invention discloses a method of recycling component substances in a waste SCR denitration catalyst. The method includes the following steps: 1) performing pretreatment to remove impurities on the surface of the waste SCR denitration catalyst and crushing the catalyst; 2) adding the crushed catalyst to a sulfuric acid solution to reduce vanadium (V) with SO2 gas, filtering and separating the solution, and regulating the pH value of the filtrate to precipitate vanadium hydroxide; 3) adding an alkali solution to filter residues to dissolve tungsten (molybdenum) trioxide, silicon dioxide and aluminum oxide, and filtering and separating the solution to obtain TiO2 and an alkaline filtrate; 4) regulating the pH value of the alkaline filtrate to precipitate silicon and aluminum, filtering and separating the filtrate, and adsorbing tungsten (molybdenum) ions from the filtrate by ion exchange resin; 5) eluting the tungsten (molybdenum) ions from the resin to obtain tungstate (molybdate). The method achieves high-effective separation of the component substances in a SCR denitration catalyst, reaches more than 96% in recycling rate and more than 98% in purity. The method is low in energy consumption and cost and has wide industrial application prospect.
Owner:北京清树科技发展有限公司
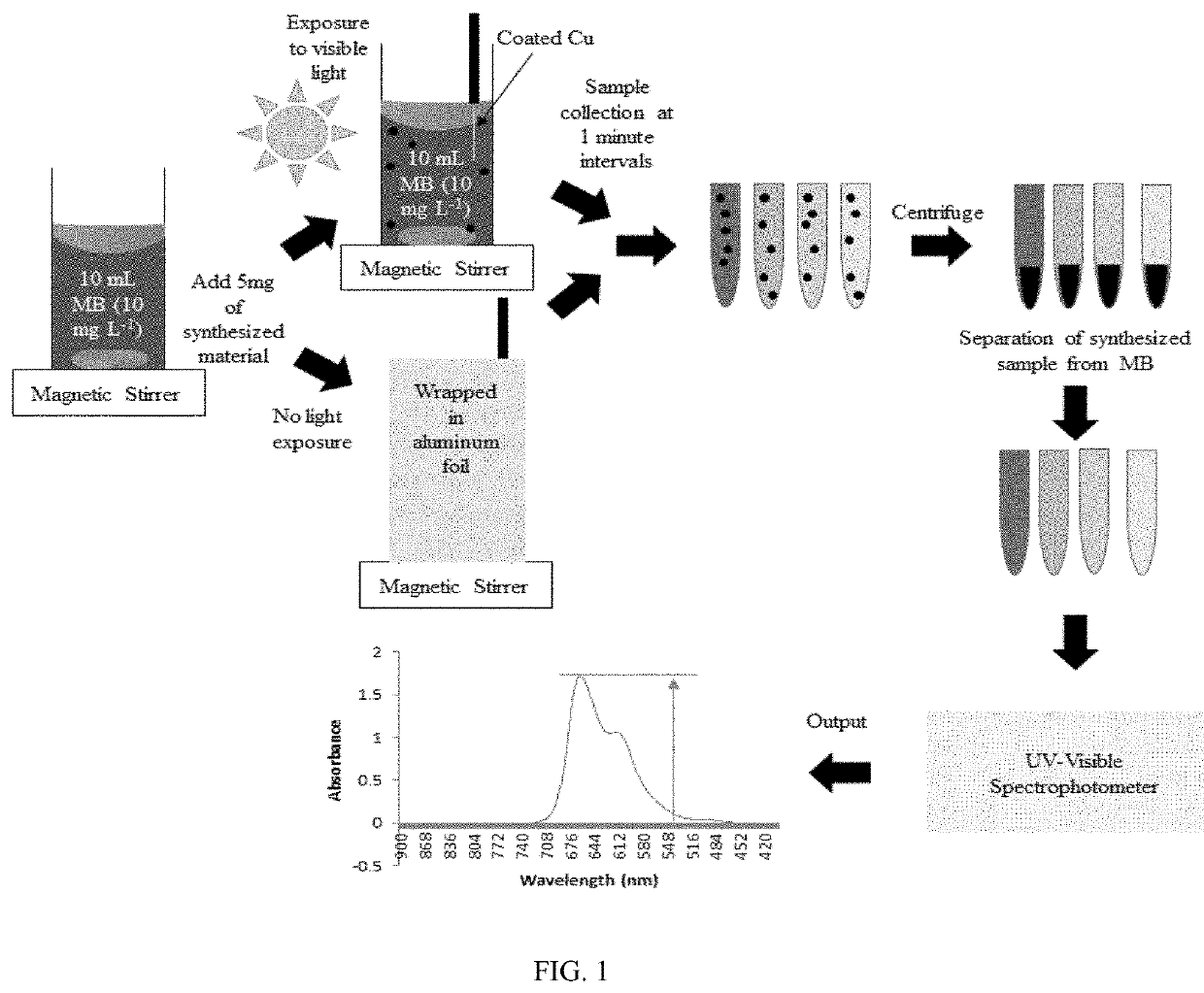
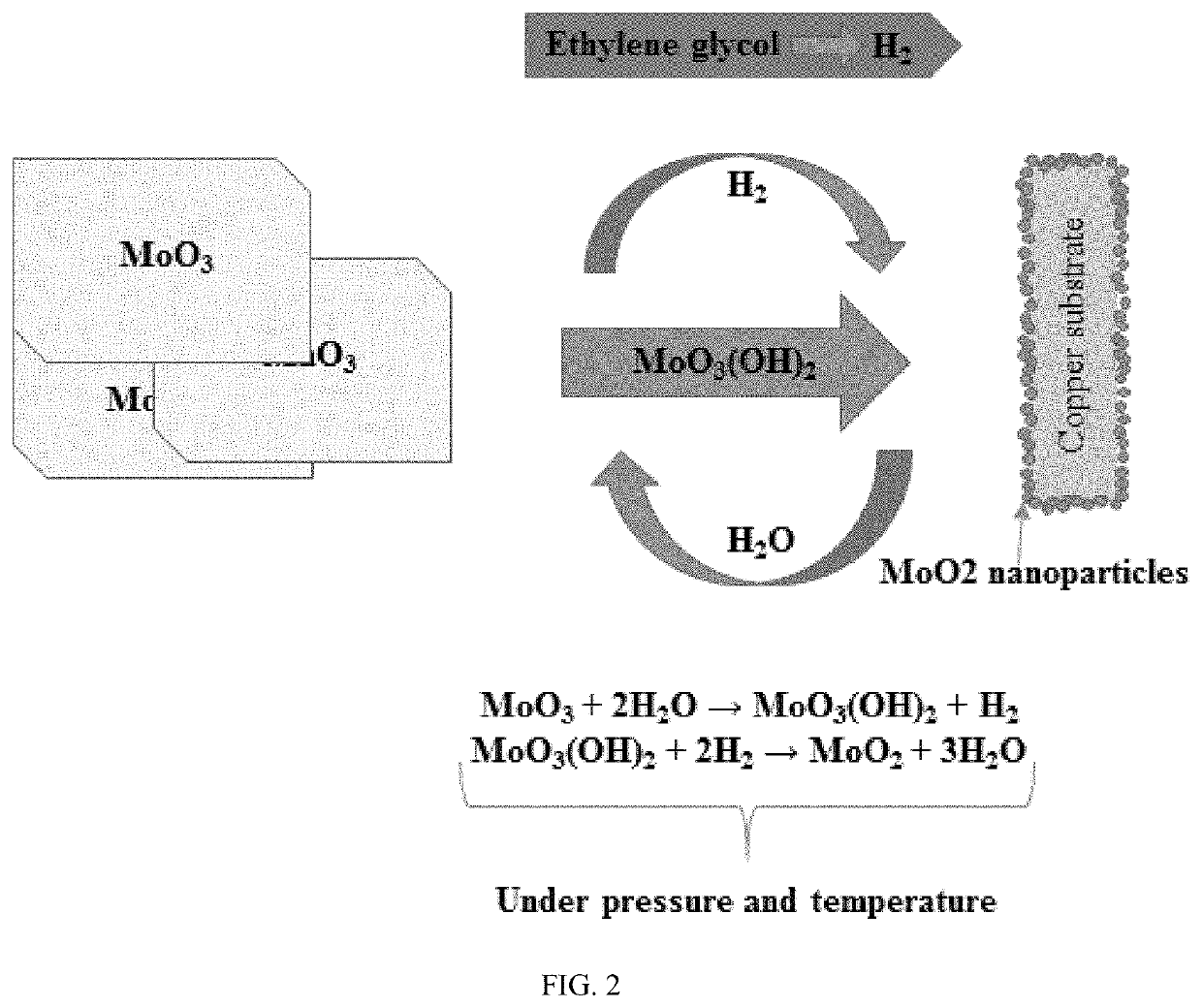
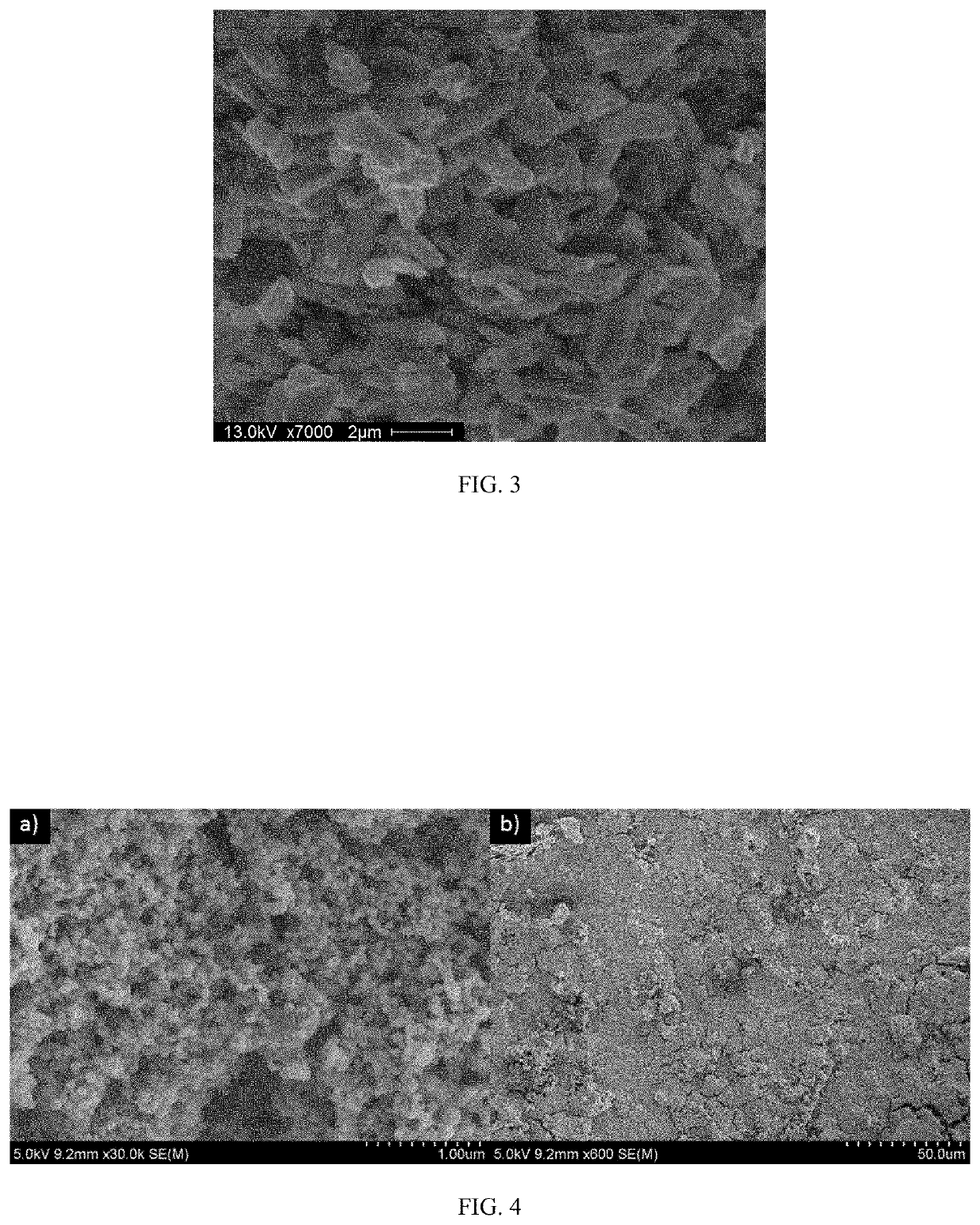
Hydrothermal synthesis of the molybdenum dioxide nanoparticles directly onto a metal substrate
PendingUS20200354229A1Promote conversionElectrode carriers/collectorsWater/sewage treatment by oxidationNanoparticlePhysical chemistry
Provided are a method of synthesizing molybdenum dioxide (MoO2) directly onto a metal substrate to form a coating on the surface of the substrate, products having a coated metal surface produced by the disclosed method, and their uses to decontaminate water and / or air. The coated metal surface disclosed herein also may be used as a structural component of a Li-ion battery, a supercapacitor, or a sensor for detecting a molecule.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA
Method for preparing high-purity molybdate from rough sodium molybdate solution
InactiveCN107298462AEfficient separationMolybdeum compounds preparationProcess efficiency improvementSodium molybdateMolybdate
The invention discloses a method for preparing high-purity molybdate from a rough sodium molybdate solution. The method mainly comprises the following steps: adding a proper amount of inorganic acid into the rough sodium molybdate solution to perform primary acid regulation until the pH value of the solution is regulated to be 4-5, and stirring the solution for 5 minutes; adding a proper amount of transition additive, and stirring and mixing for 10 minutes; adding a proper amount of inorganic acid to perform secondary acid regulation, regulating the pH value of the solution to be 1-2, and uniformly stirring the solution for 20-30 minutes; performing centrifugal filtration, washing a obtained washing solution for solid, filtering again, and drying to obtain solid, namely high-purity molybdate; and adsorbing centrifugal filtered solution and washing solution with weakly basic macro porous anion resin, and recycling valuable metal molybdenum. The method can realize effective separation of molybdenum, calcium and magnesium in the rough sodium molybdate solution, so that the high-purity molybdate is prepared.
Owner:XINYANG HUARUI MOLYBRENUM NEW MATERIALS CO LTD
Method for synergistic recovery of molybdenum and rhenium from molybdenum concentrate roasting eluent
ActiveCN109179506AImprove adsorption speedImprove adsorption capacityRhenium compounds preparationMolybdeum compounds preparationLoss rateDesorption
The invention discloses a method for synergistic recovery of molybdenum and rhenium from a molybdenum concentrate roasting eluent, which belongs to the technical field of comprehensive recycling of metal rhenium and molybdenum. The method comprises the following steps: mixing the molybdenum smelting waste acid and a pretreatment agent, stirring a mixture, and then performing solid-liquid separation; introducing a filtrate to an exchange column containing weakly basic anion exchange resin A to adsorb rhenium, and introducing the adsorbed liquid in an exchange column filled with the weakly basicanion exchange resin B to adsorb molybdenum; performing desorption with the adsorbed saturated A column, collecting a desorption solution, and performing evaporation crystallization to obtain an ammonium perrhenate product; performing desorption with the adsorbed saturated B column, collecting the desorption solution, and performing evaporation crystallization to obtain an ammonium molybdate product. In a pretreatment step in the process, no rhenium loss is generated, the molybdenum loss rate is less than 8%, after treatment, the liquid is introduced into ion exchange, compared with the direct adsorption process, the method can increase the adsorption capacity of the resin A to the rhenium, and by changing the acidity of the solution and the impurity ion content, the high-efficiency adsorption of the resin B to the molybdenum is achieved.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU MINERALS COMPOSITIVE UTILIZATION RES INST CHINESE GEOLOGICAL ACAD
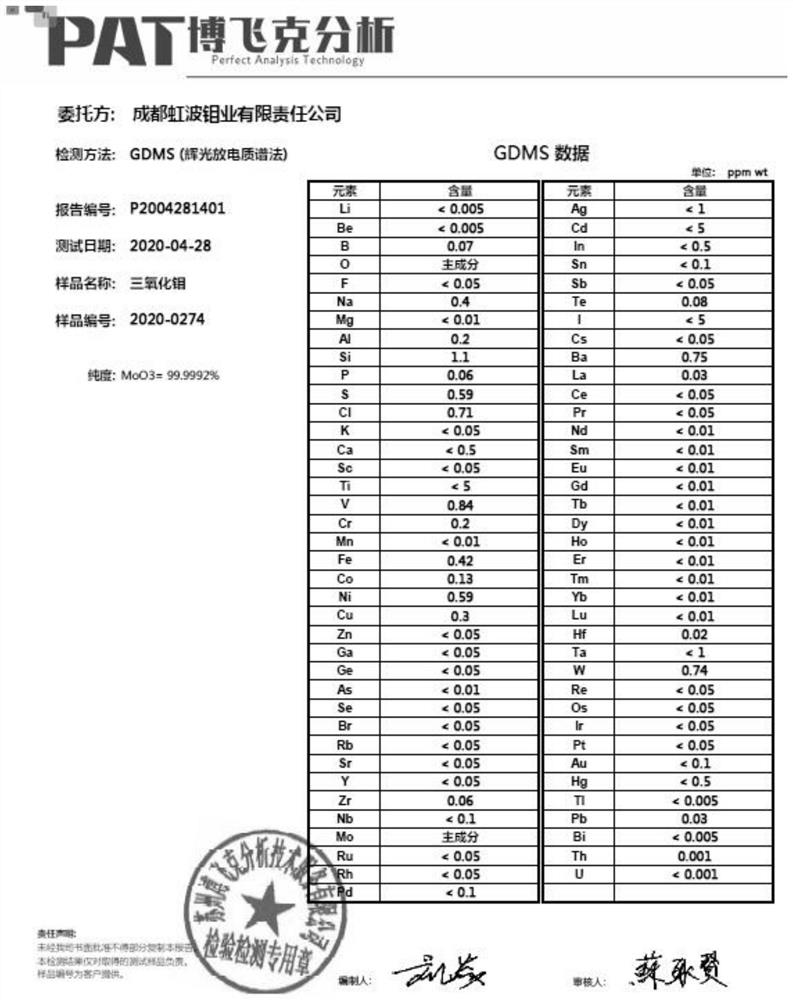
Production process of 5N-grade high-purity molybdenum trioxide
ActiveCN112744864AHigh purityProcess parameters are precisely controlledMolybdeum compounds preparationMolybdenum oxides/hydroxidesIon exchangeMolybdic acid
The invention provides a production process of 5N-grade high-purity molybdenum trioxide. The production process comprises the following steps: by taking crude sodium molybdate containing impurity elements such as tungsten, vanadium and the like as a raw material, deeply separating molybdenum from metal impurities and deeply separating molybdenum from non-metal impurities through multi-stage ion exchange, transforming the obtained high-purity sodium molybdate solution to obtain a high-purity ammonium molybdate solution, after the high-purity ammonium molybdate solution is subjected to acid precipitation to form a solid product, finally obtaining the 5N-grade high-purity molybdenum trioxide with the total impurity content smaller than or equal to 10 ppm through full-process closed conveying and operation. The technological parameters in the production process are precisely controlled, and equipment and environment pollution is strictly prevented and controlled.
Owner:成都虹波钼业有限责任公司 +1
Process for recovering molybdate or tungstate from aqueous solutions
InactiveUS8277765B2Reduce consumptionReduce the ratioWater treatment parameter controlSolvent extractionMolybdateTungstate
Process for recovering molybdate or tungstate from an aqueous solution, in which molybdate or tungstate is bound to a water-insoluble, cationized inorganic carrier material from the aqueous solution at a pH in the range from 2 to 6, the laden carrier material is separated off and the bound molybdate or tungstate is liberated once again into aqueous solution at a pH in the range from 6 to 14. The process is suitable for recovering molybdate or tungstate in the delignification of pulp with hydrogen peroxide in the presence of molybdate or tungstate as catalyst. The recovered molybdate or tungstate can be recycled to the delignification.
Owner:EVONIK DEGUSSA GMBH
Method for recovery of molybdate in a molybdate-catalysed delignification of pulp with hydrogen peroxide
In a delignification of pulp with hydrogen peroxide catalysed with molybdate, molybdate can be recovered by bringing the aqueous solution containing molybdate into contact with a carrier material that comprises a layered silicate ion-exchanged with a quaternary ammonium salt at a pH value ranging between 2 and 7 and subsequent flotation, without the need to add a tenside for the flotation.
Owner:EVONIK DEGUSSA GMBH
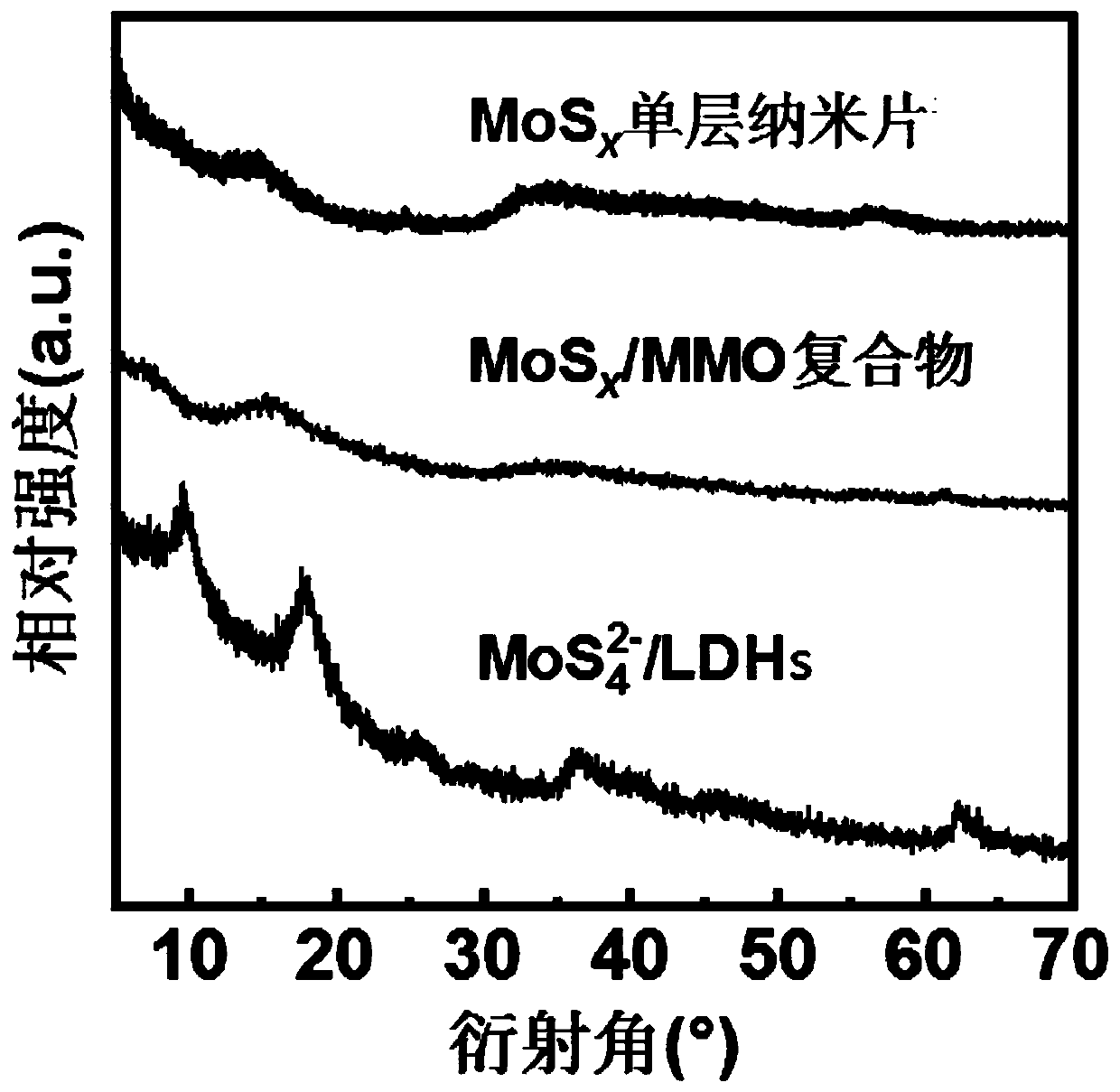
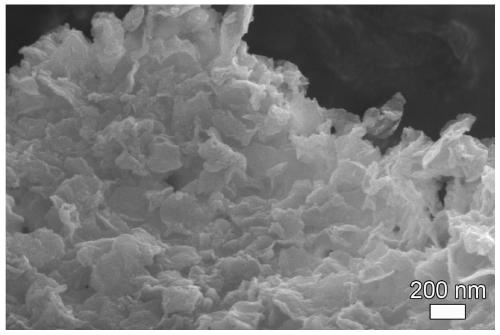
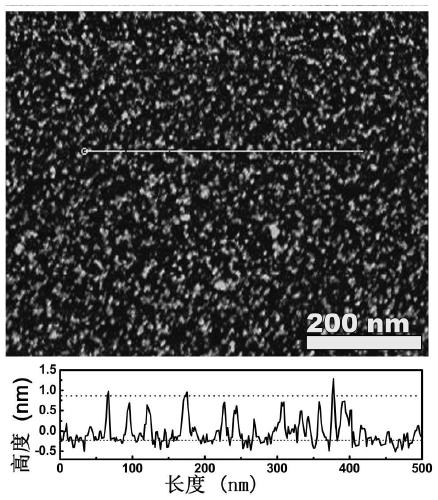
Preparation method of amorphous MoSx monolayer nanosheet
InactiveCN110194486AAchieving controllable synthesisEasy to synthesizePhysical/chemical process catalystsNanotechnologyDecompositionAcid dissolution
The invention provides a preparation method of an amorphous MoSx (x=2-4) monolayer nanosheet. The method includes: taking the interlayer of layered double hydroxides (LDHs) as the microreactor, and firstly preparing an MoS4<2-> intercalated LDHs compound; then performing low temperature calcination to enable low temperature decomposition of MoS4<2-> into Mo3S13 nanoclusters, then conducting arrangement at the interlayer to form MoSx monolayer nanosheet, and then carrying out acid dissolution to remove mixed metal oxides (MMO), thus obtaining the amorphous MoSx monolayer nanosheet. The preparation method is simple, has mild reaction conditions, and is easy to realize, does not use organic reagents, is safe, green and environment-friendly. The obtained amorphous MoSx is a monolayer and porous nanosheet structure, has large specific surface area, also has a large number of active sites and defects on the surface, and has excellent electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution performance.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
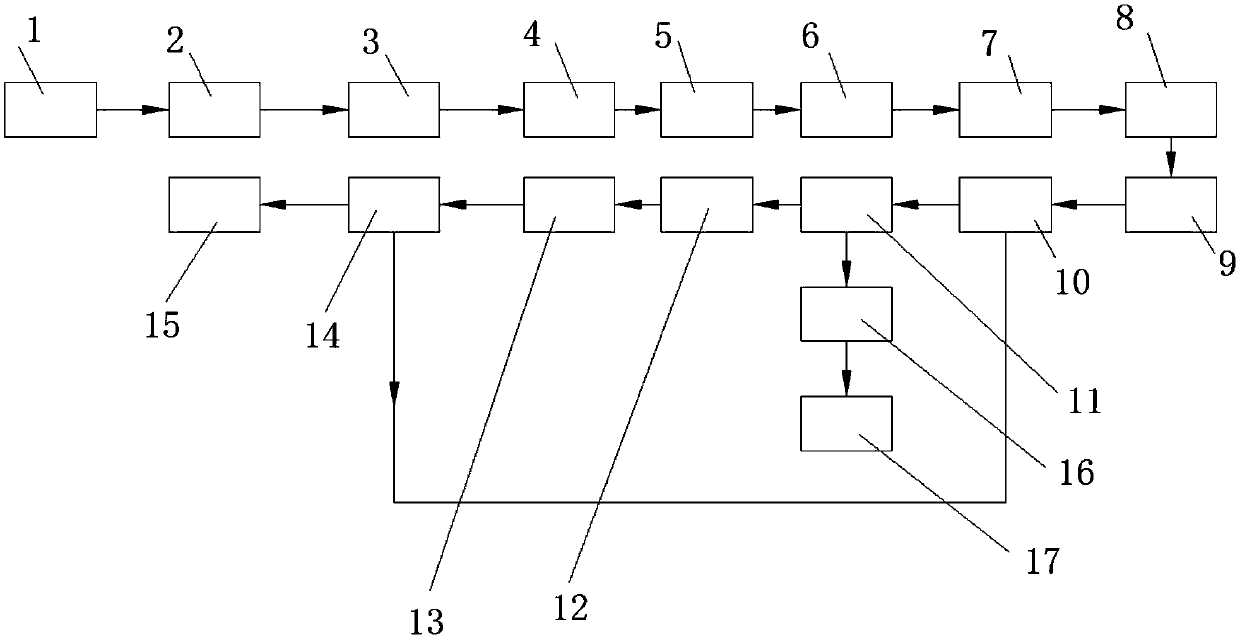
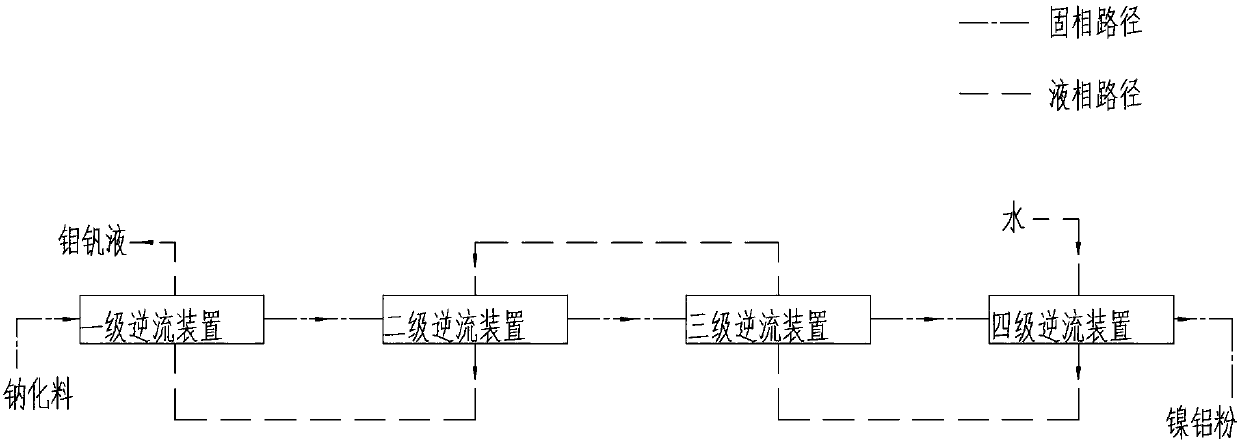
Comprehensive utilization system of spent catalyst
PendingCN107723468AReduce processing costsMolybdeum compounds preparationVanadium compoundsAmmonium metavanadateEngineering
The invention discloses a comprehensive utilization system of a spent catalyst. The comprehensive utilization system of the spent catalyst is characterized by comprising a deoiling furnace, a rotary kiln, a four-stage countercurrent device, a stirring tank I, a plate-and-frame filter I, a precipitation tank I, a plate-and-frame filter II, a stirring tank II, a centrifuge I, ion exchange resin, anextraction device, a back extraction device, a precipitation tank II, a centrifuge II and a washing tank. The comprehensive utilization system of the spent catalyst is low in process cost, green and environment-friendly, and capable of effectively recycling useful components in the residual oil hydrotreating spent catalyst to obtain industrial steam, nickel-aluminum powder, ammonium metavanadate,high-purity molybdic acid, anhydrous sodium sulfate, distilled water and the like, wherein the high-purity molybdic acid can be obtained without repeated separation processes, and the purity of the high-purity molybdic acid can reach 99. 9%.
Owner:DALIAN DONGTAI RESOURCE RENEWABLE
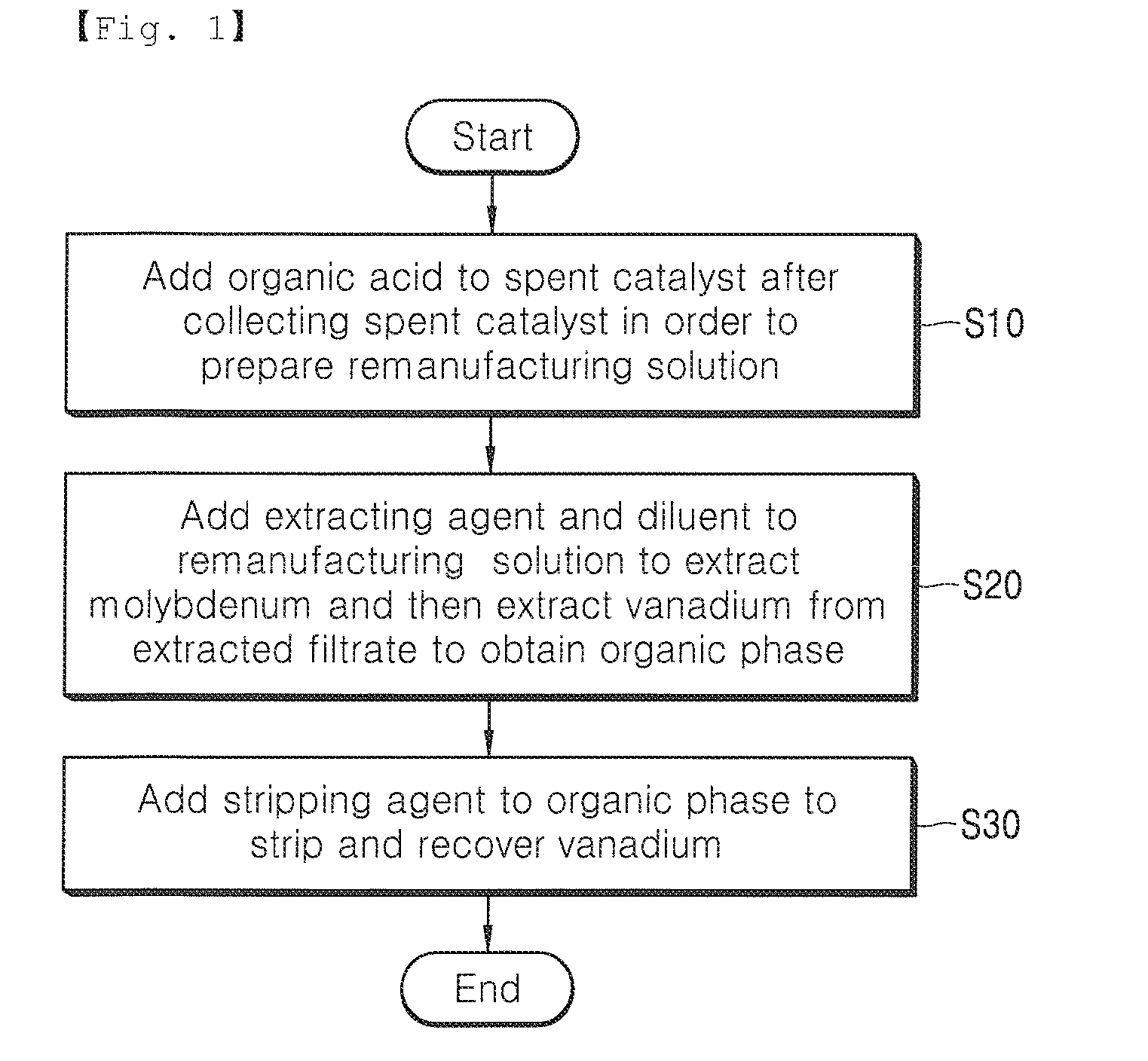
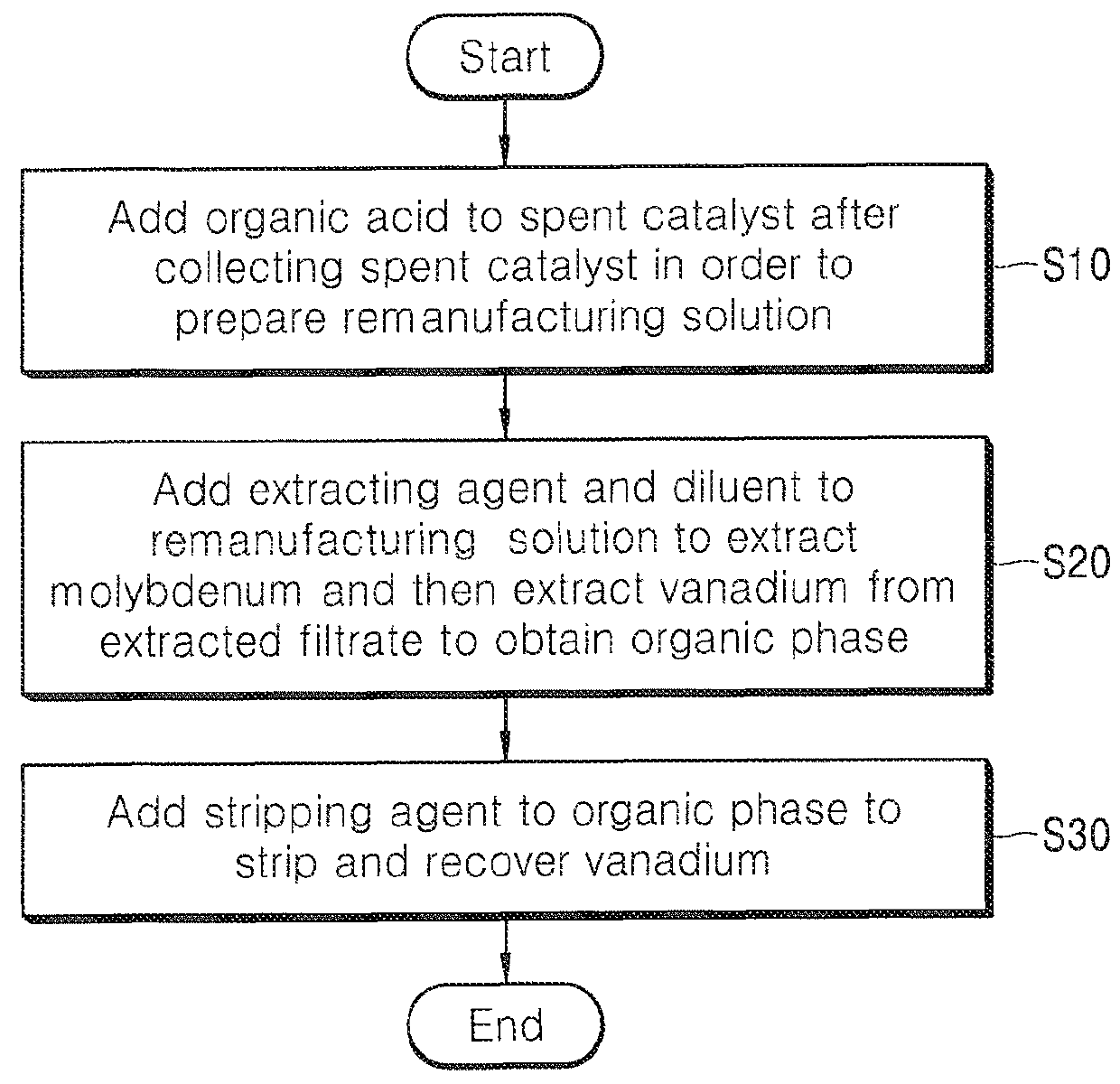
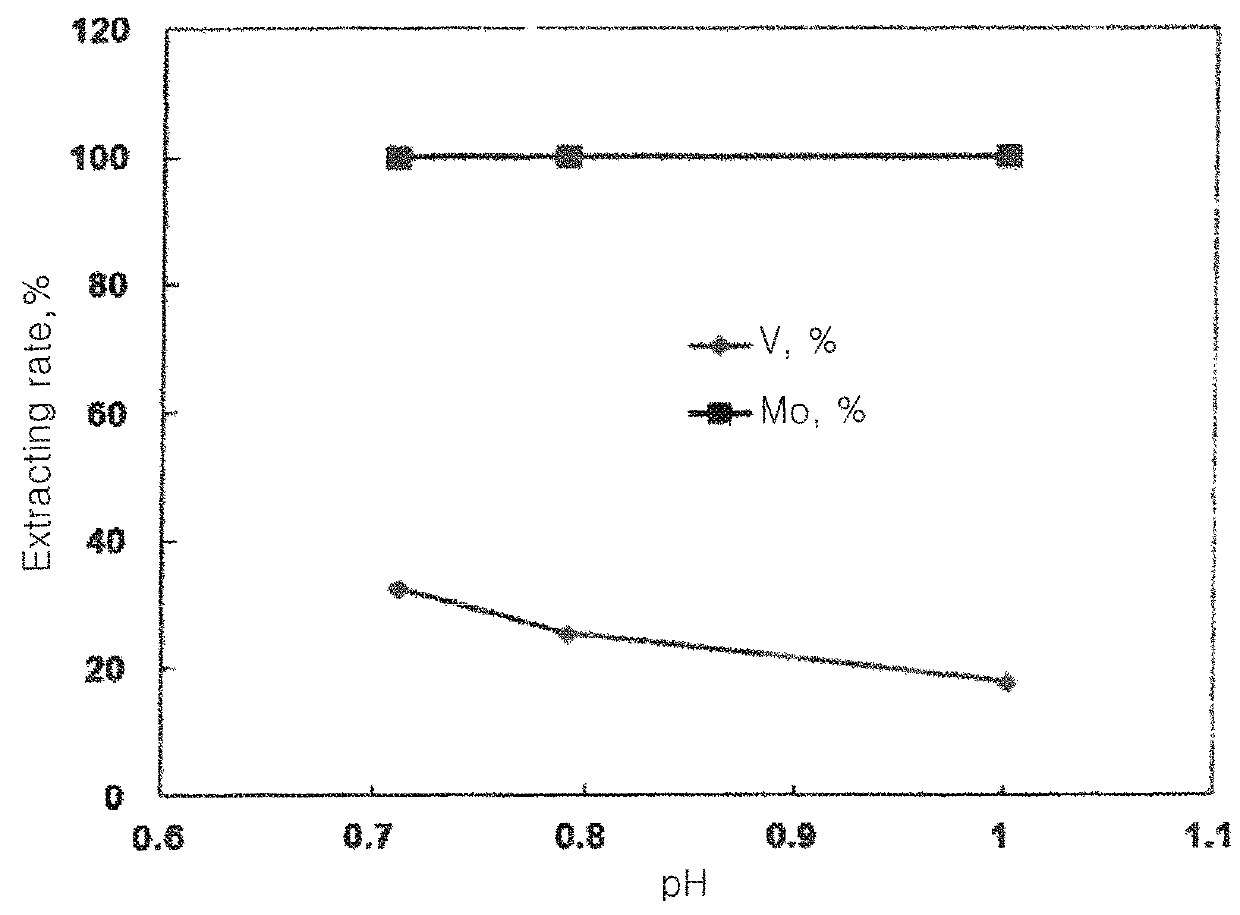
Method of separating and recovering valuable metal from remanufacturing solution of spent desulfurization catalyst containing vanadium
ActiveUS20160138131A1Increase chanceLow costSolvent extractionTantalum compoundsHydrodesulfurizationDiluent
The disclosure describes a method of separating and recovering valuable metals from remanufacturing solution of a spent desulfurization catalyst containing vanadium, and more particularly, to a method of separating and recovering a valuable metal from remanufacturing solution of a spent desulfurization catalyst containing vanadium, which includes: adding organic acid to a spent hydrodesulfurization catalyst after collecting the spent hydrodesulfurization catalyst in order to prepare the remanufacturing solution of the spent hydrodesulfurization catalyst; adding an extracting agent and a diluent to the remanufacturing solution to extract molybdenum and extracting vanadium from an extracted filtrate to obtain an organic phase; and adding a stripping agent to the organic phase to strip and recover vanadium.
Owner:SUNGEEL HIMETAL +1
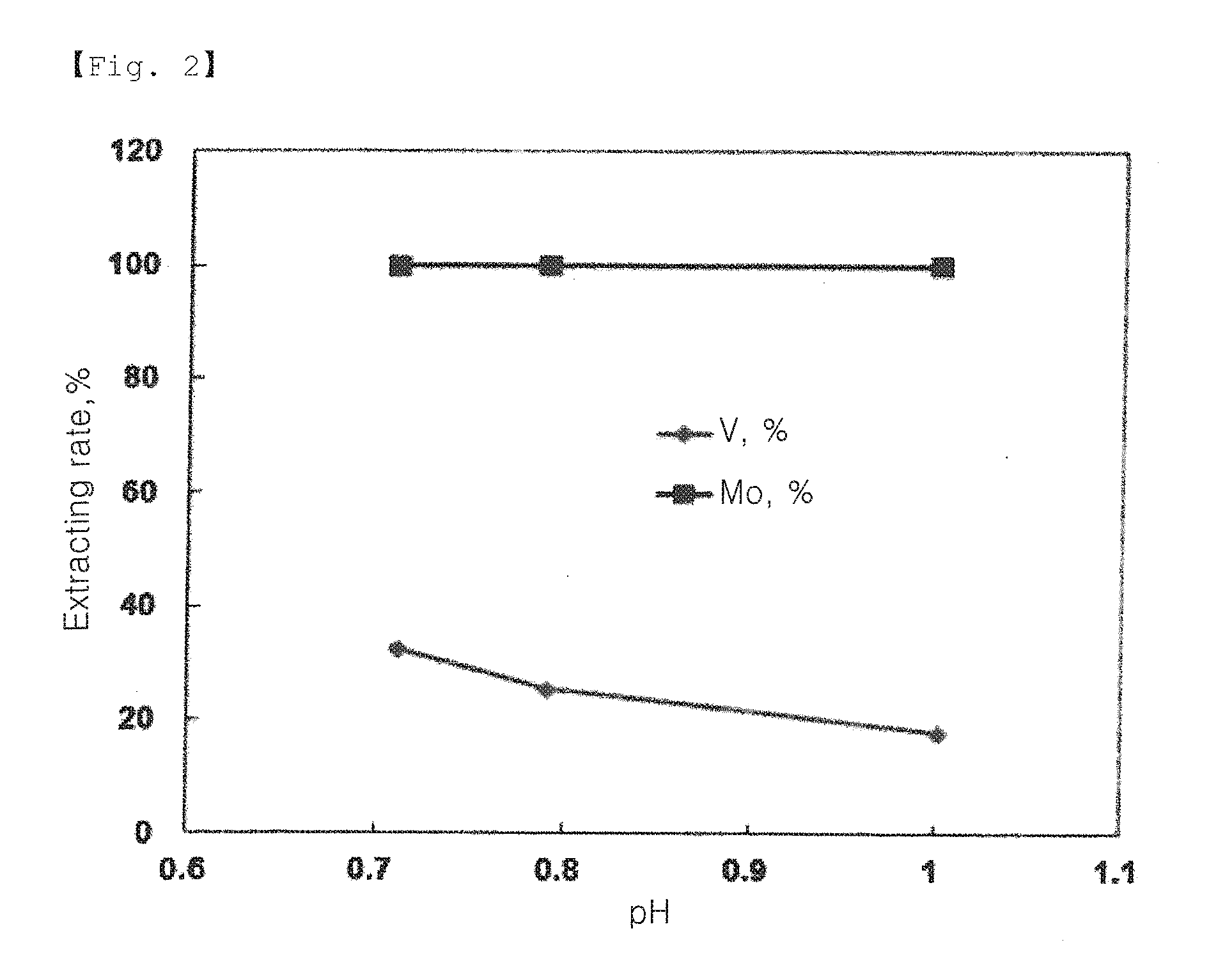
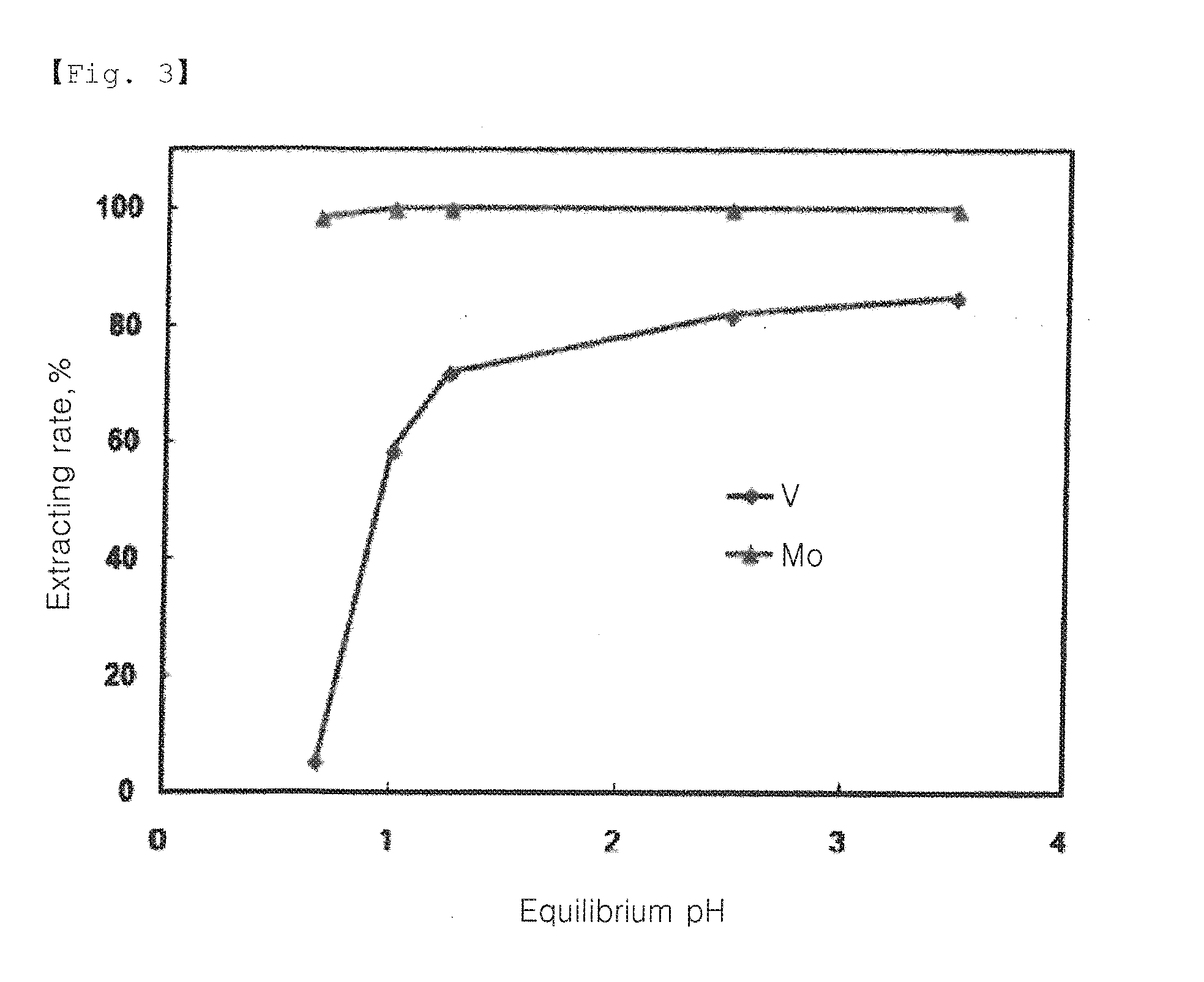
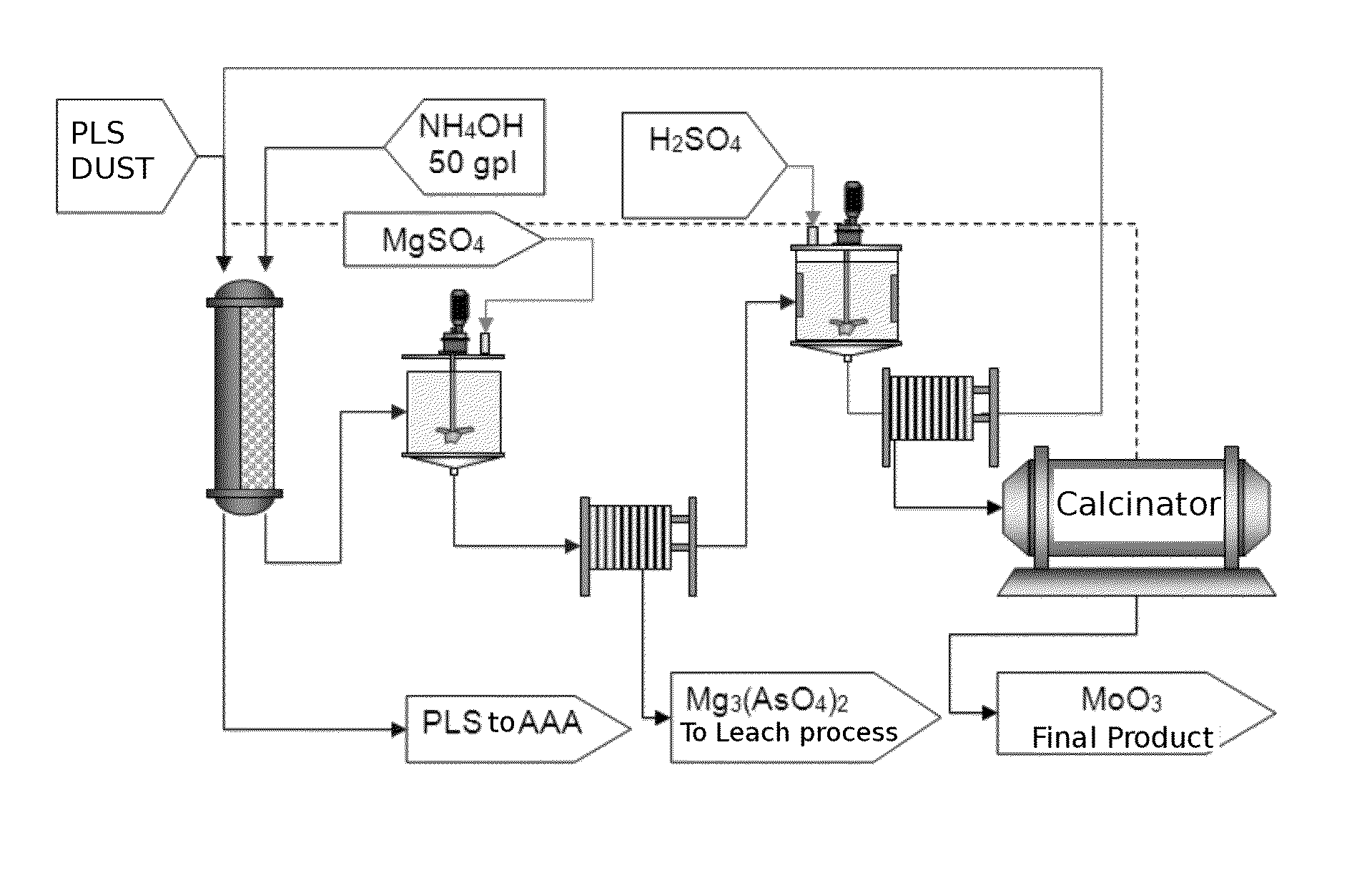
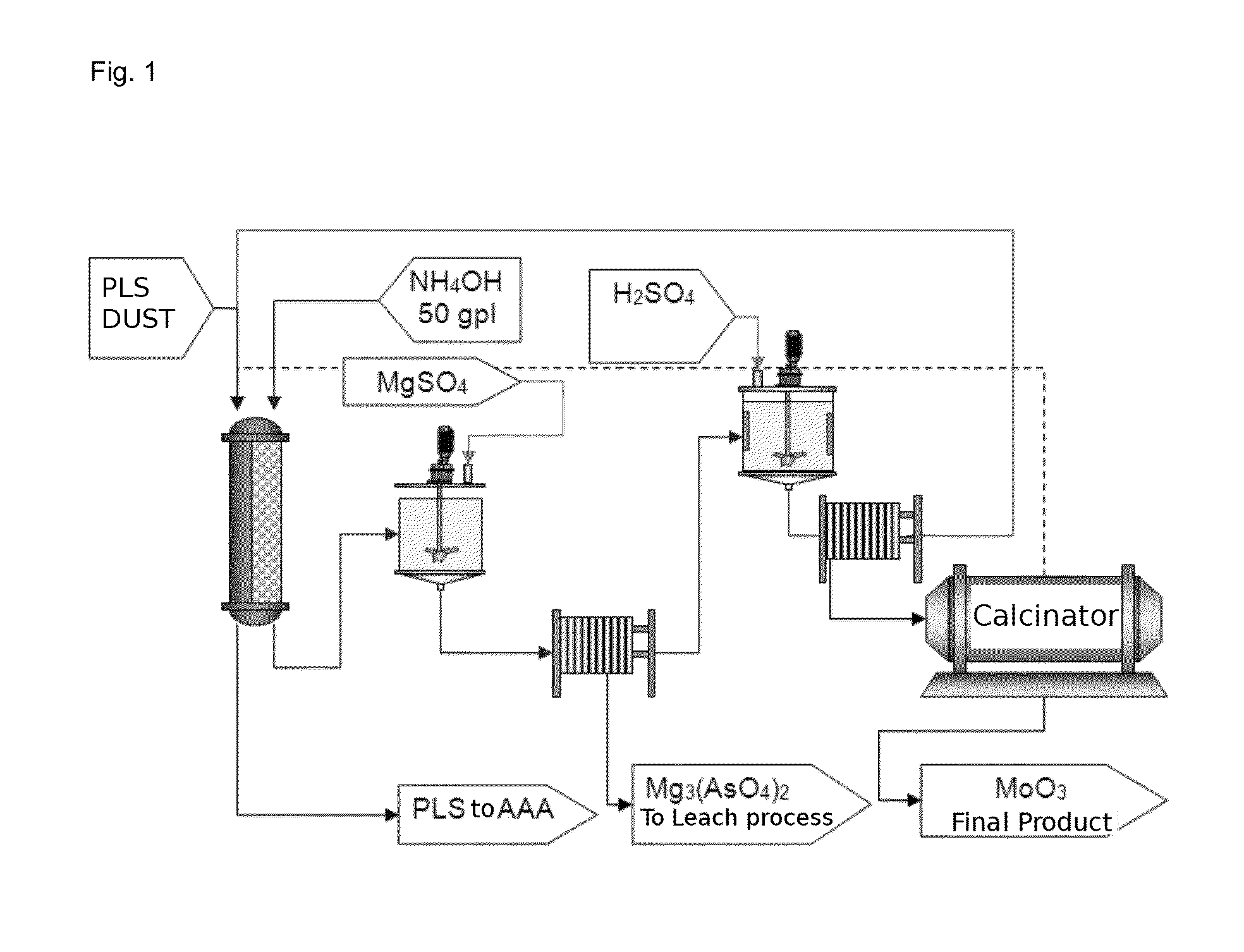
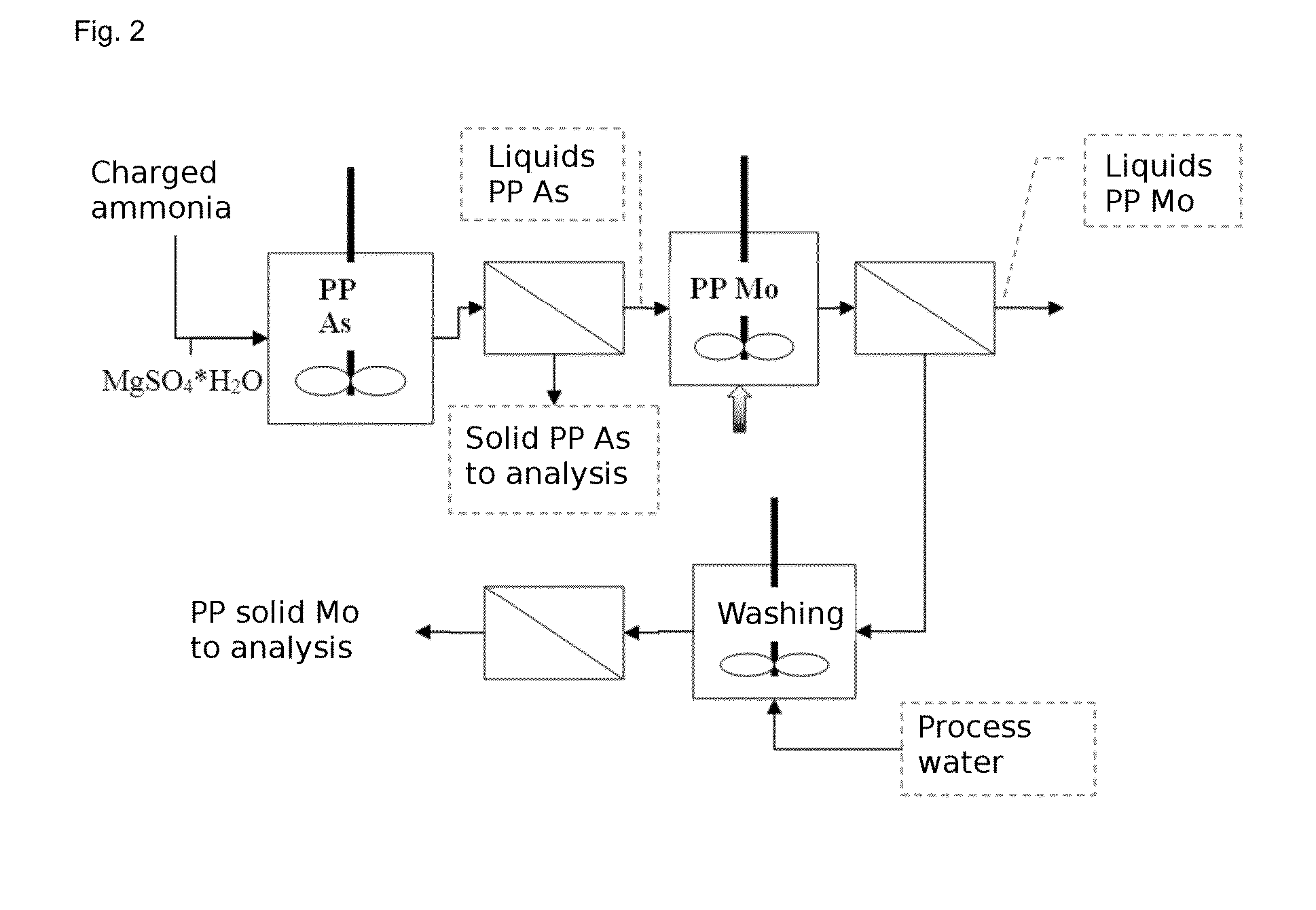
Process for recovery of technical grade molybdenum from diluted leaching acid solutions (PLS), with highly concentrated arsenic, from metallurgical residues
ActiveUS20140301918A1Solvent extractionRecycling and recovery technologiesMagnesium saltTechnical grade
A method for recovering technical-grade molybdenum from diluted acid leaching solutions (PLS) that have a high arsenic concentration is disclosed. The method includes: (a) bringing a pre-filtered acid leaching solution (PLS), originating from the leaching of smelter dust, into contact with an anionic ion-exchange resin; (b) washing the loaded resin with water; (c) extracting molybdenum from the ion-exchange resin with an alkaline ammonium regenerant solution to form ammonium molybdenum in solution; (d) washing the unloaded resin with water; (e) adding iron and / or magnesium salts to the recovered ammoniacal solution to obtain a precipitate which is transferred to the arsenic abatement step and a solution containing ammonium molybdate in solution; (f) adding sulphuric acid to the arsenic-free ammoniacal solution in order to precipitate the moylbdenum in the form of ammonium molybdate; (g) separating the precipitate by filtering the molybdate and re-circulating the solution obtained with the initial PLS solution; (h) calcining the separated precipitate to obtain ammonia and molybdenum trioxide; and (i) recovering the released ammonia for its subsequent use in the method as a recirculated regenerant solution.
Owner:ECOMETALES LTD
Production process of ammonium molybdate
InactiveCN112607777AHigh yieldEmission reductionMolybdeum compounds preparationSodium molybdateMolybdic acid
The invention discloses a production process of ammonium molybdate, which relates to the technical field of ammonium molybdate production, and comprises the following steps: (1) washing and filter-pressing molybdenum calcine, mixing the filter-pressed molybdenum calcine with a leaching agent, adjusting the pH value to 10-11.5, and keeping the temperature for 2-3 hours under the conditions of oxygen partial pressure of 20 atm and temperature of 150-170 DEG C to obtain a sodium molybdate solution; (2) adding quaternary ammonium salt into the ammonium molybdate solution, extracting molybdenum under an alkaline condition, and adding ammonium bicarbonate into the extracting solution to obtain an ammonium molybdate solution; (3) adding calcium oxide into the extracting solution; (4) evaporating and crystallizing the ammonium molybdate solution to obtain ammonium dimolybdate; and (5) adding acid into the crystallization mother liquor after the ammonium dimolybdate is prepared for precipitation to obtain ammonium tetramolybdate, adjusting the pH value of the ammonium tetramolybdate solution to 1.5-2.0 by using nitric acid, and separating out ammonium tetramolybdate crystals. The method has the beneficial effects that the method has the advantages of short process flow, low consumption of chemical reagents and high resource adaptability.
Owner:安庆市月铜钼业有限公司
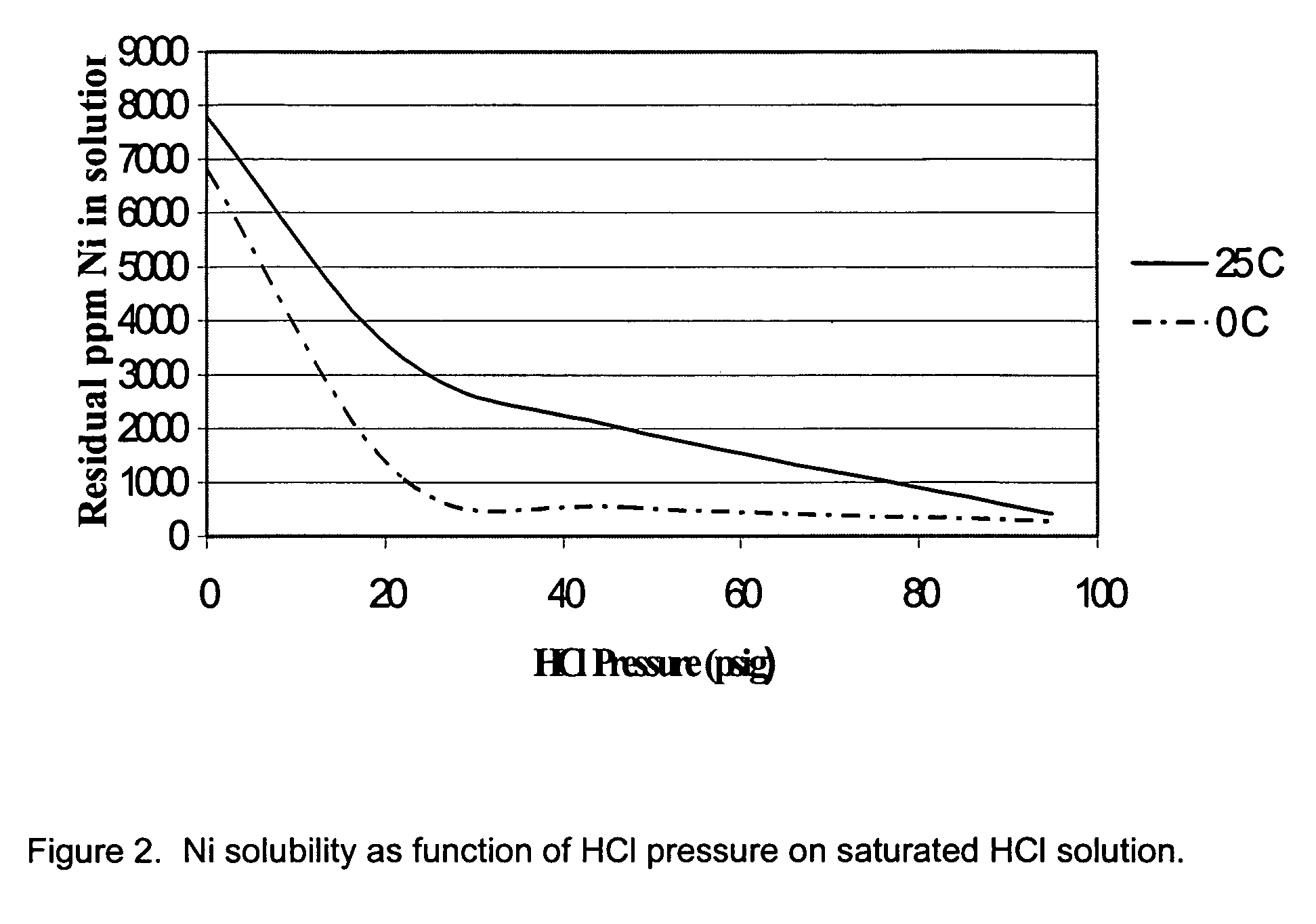
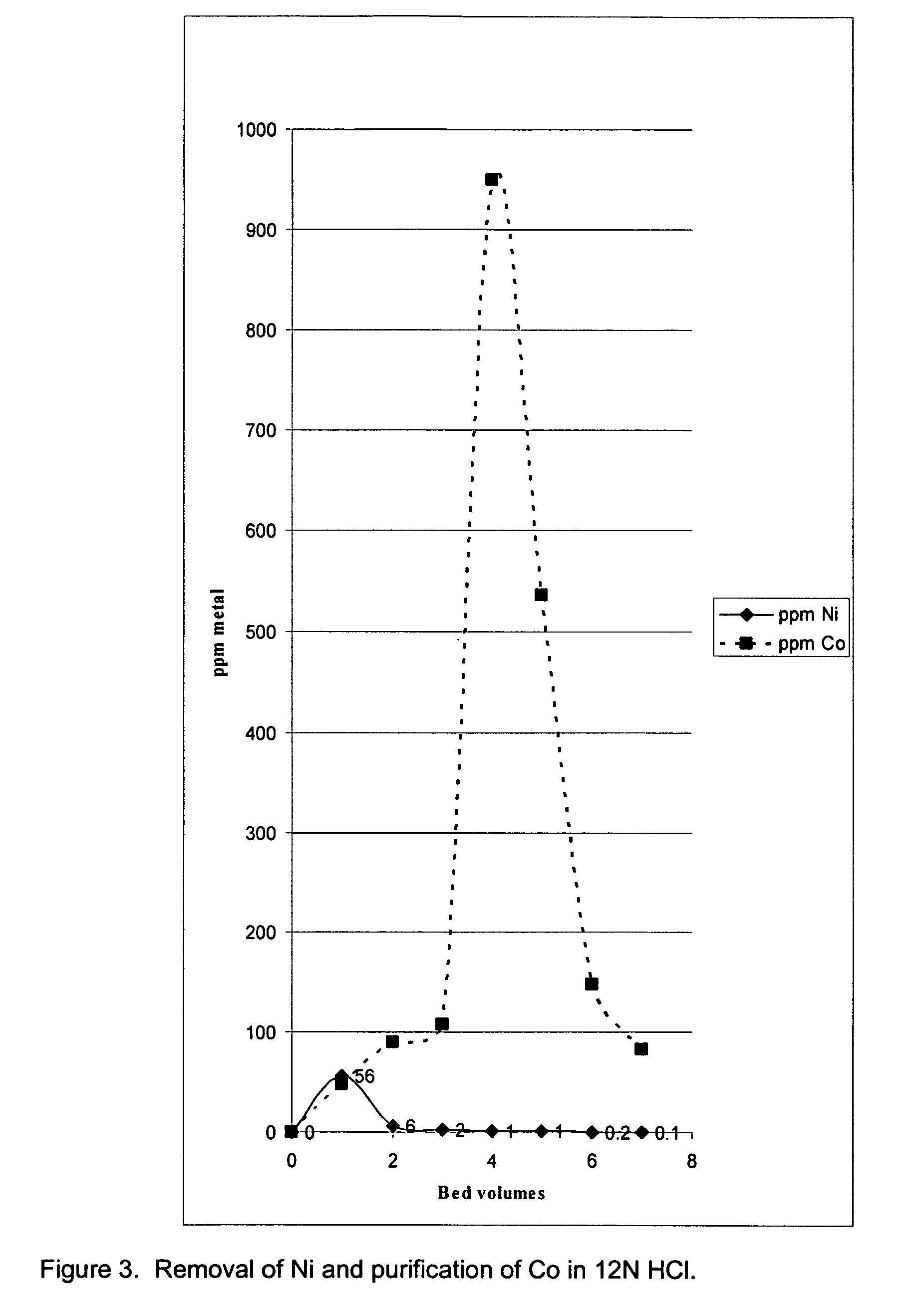
Process for the extraction of specific transition metals with gaseous HCL
A process is disclosed for separation and recovery of vanadium, molybdenum, iron, tungsten, cobalt and nickel from alumina-based materials, mattes, ores, manufacturing by-products and waste. These elements are oxidized. The oxides are reacted with gaseous HCl to form volatile chloride-bearing compounds that subsequently sublimate. The volatile compounds are condensed in a downward-stepped thermal gradient that allows collection of moderate to high purity compounds of individual elements with exception of a nickel-cobalt co-condensate. Nickel is separated from cobalt by precipitation of nickel chloride from concentrated HCl pressurized with gaseous HCl.
Owner:METALS RECOVERY TECH
Apparatus and method for removing impurities in connection with liquid-liquid extraction of copper
The invention relates to an apparatus and method for removing molybdenum and other possible impurities from an organic copper-containing extraction solution in connection with the liquid-liquid extraction related to copper recovery. The removal of impurities occurs in one or several removal units built into the organic extraction solution storage tank.
Owner:METSO OUTOTEC (FINLAND) OY
Method for preparing ammonium tetramolybdate product through reverse extraction and impurity removal
PendingCN113979476AAchieve enrichmentAchieve purification effectChemical industryMolybdeum compounds preparationSodium hydrogencarbonateBuffer solution
The invention relates to a method for preparing an ammonium tetramolybdate product through reverse extraction and impurity removal, and belongs to the technical field of chemical impurity removal. The method specifically comprises the steps that tungsten in molybdenum is removed by adjusting the concentration of a reverse extraction reagent, and silicon and other impurities in reverse extraction liquid are removed through a precipitation method. The preparation and purification integration of the molybdenum product can be realized. According to the method, a molybdenum-loaded organic phase is subjected to reverse extraction, an alkaline solution with the pH value of 6-10 is adopted for reverse extraction, and the alkaline solution comprises ammonia water, sodium hydroxide, sodium bicarbonate or ammonium chloride and sodium hydroxide buffer solution and other alkaline solutions. The phase ratio of the reverse extraction is 10 / 1-1 / 10, the number of the reverse extraction stages is 1-10, and the reverse extraction stages are adjusted according to different compositions of the loaded organic phase. The application range on molybdenum raw materials is wide, and industrialization is easy to achieve. According to changes of raw materials and fluctuation of element content, preparation of molybdenum products can be achieved by adjusting process parameters, and the method is a universal integrated process and has practical application value.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF APPLIED CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for preparing high-purity molybdic acid from waste catalyst
InactiveCN107915256AEfficient separationReduce processing costsMolybdeum compounds preparationProcess efficiency improvementSodium molybdateAqueous solution
The invention discloses a method for preparing high-purity molybdic acid from a waste catalyst. A waste residue oil hydrogenation catalyst undergoes deoiling treatment, the obtained deoiled material undergoes sodiumization roasting, the obtained sodiumized material undergoes leaching reaction, the impurities of separated molybdenum-vanadium liquid are removed, vanadium is separated from obtained pure liquid, obtained molybdenum-containing liquid undergoes extraction and reverse extraction, the obtained sodium molybdate aqueous solution is added with concentrated sulfuric acid for precipitation, obtained molybdic acid is washed, and thereby high-purity molybdic acid is obtained. The process of the method is low in cost and environment-friendly, molybdenum in the waste residue oil hydrogenation catalyst can be effectively separated out, high-purity molybdic acid can be obtained without multiple times of separation processes, and the purity can reach 99.9 percent.
Owner:DALIAN DONGTAI RESOURCE RENEWABLE
Preparation method of ammonium heptamolybdate
PendingCN112758983AEmission reductionSimple processMolybdeum compounds preparationSodium molybdateAmmonium heptamolybdate
The invention discloses a preparation method of ammonium heptamolybdate, and relates to the technical field of ammonium heptamolybdate. The preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) mixing molybdenum calcine with a leaching agent, adjusting the pH value to 10-11.5, and keeping the temperature for 2-3 hours under the conditions that the oxygen partial pressure is 0.5-2 MPa and the temperature is 100-220 DEG C to obtain a sodium molybdate solution; (2) adding quaternary ammonium salt into the ammonium molybdate solution obtained in the step (1), extracting molybdenum under an alkaline condition, and then adding ammonium bicarbonate into an extracting solution to obtain an ammonium molybdate solution; (3) carrying out intermittent negative pressure evaporative crystallization on the ammonium molybdate solution under the conditions that the negative pressure is -0.08 to-0.1 MPa and the temperature is 60-75 DEG C to obtain wet ammonium heptamolybdate, and then performing drying to obtain the ammonium heptamolybdate. The method has the beneficial effects that the process is simple, and the recovery rate is high; the whole process is free of acidification, ammonia-nitrogen wastewater discharge is reduced, the process flow is obviously shortened, the cost is reduced, and industrial production is easy to realize.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Method and apparatus for the extraction and processing of molybdenum-99
ActiveUS8449850B2Reduce the amount requiredTransuranic element compoundsSolid sorbent liquid separationSorbentIodine
A method for the extraction and purification of molybdenum, the method comprising the steps of: transferring an irradiated fuel solution to an extraction system, the irradiated fuel solution comprising iodine and molybdenum and other fission products, the extraction system comprising at least one sorbent column; passing the irradiated fuel solution upwards through the at least one sorbent-containing extraction column; directing the irradiated fuel solution towards a fuel management system by means of at least one discharge alignment valve; directing the extraction column eluate towards an iodine removal system; removing the iodine from the extraction column eluate; purifying the extraction column eluate; and collecting the purified eluate. Also disclosed is an apparatus for accomplishing the aforementioned method.
Owner:BABCOCK & WILCOX TECHNICALSERVICES GRP INC
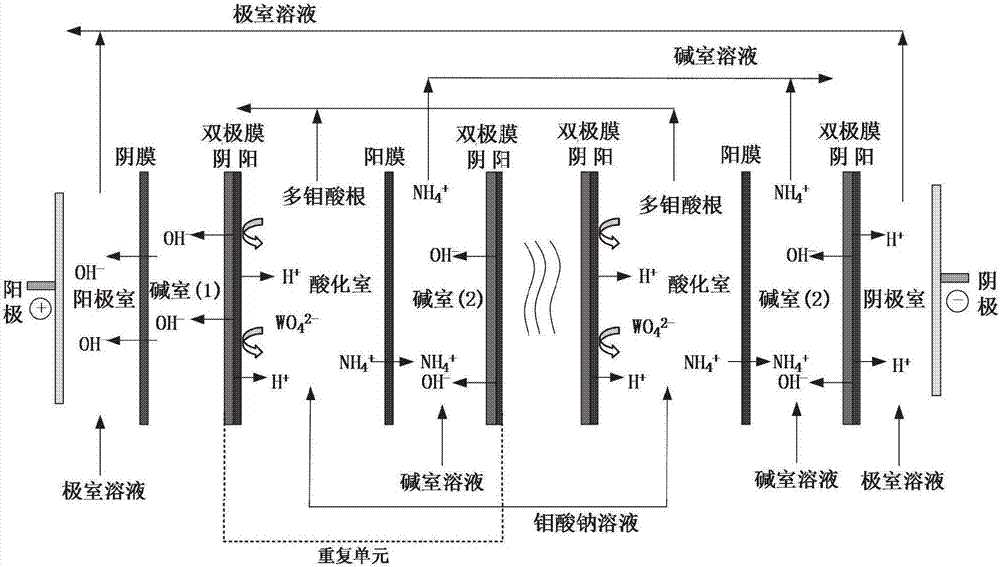
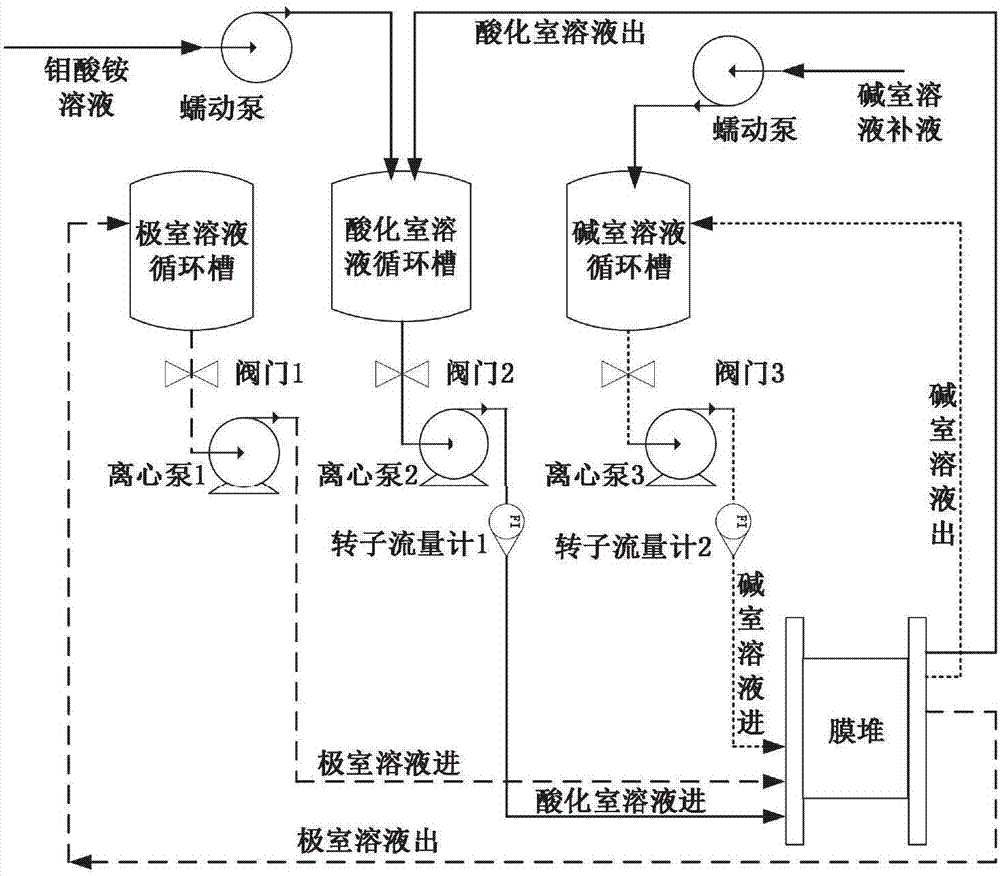
Method for preparing ammonium polymolybdate solution based on bipolar membrane electrodialysis
InactiveCN107020018AAchieve discontinuityIncrease production capacityMolybdeum compounds preparationElectrodialysisOrganic acidElectricity
The invention discloses a method for preparing an ammonium polymolybdate solution based on bipolar membrane electrodialysis. The method comprises the following steps: taking an ammonium molybdate solution as a raw material and adopting a bipolar-membrane electrodialysis system with a two-chamber bipolar membrane electrodialysis membrane stack to remove one part of ammonium ions in the ammonium molybdate solution and reducing the pH (Potential of Hydrogen) value in a bipolar-membrane electrodialysis process under the action of a direct-current electric field force; directly obtaining the ammonium polymolybdate solution in an acidifying chamber of the bipolar-membrane electrodialysis system. According to the method disclosed by the invention, organic acid does not need to be consumed and impurity anions are not introduced; the method has the advantages of short flow, high direct recovery rate, low power consumption, environment friendliness and easiness of realizing industrialization.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Opportunities for recovery augmentation process as applied to molybdenum production
ActiveUS20180274060A1Eliminate entrainmentSedimentation separationMolybdeum compounds preparationSodium hydrosulfideSlurry
A copper / molybdenum separation processor is provided featuring a slurry / media mixture stage configured to receive a conditioned pulp containing hydrophobic molybdenite and hydrophilic copper, iron and other minerals that is conditioned with sodium hydrosulfide together with an engineered polymeric hydrophobic media, and provide a slurry / media mixture; and a slurry / media separation stage configured to receive the slurry / media mixture, and provide a slurry product having a copper concentrate and a polymerized hydrophobic media product having a molybdenum concentrate that are separately directed for further processing. The slurry / media mixture stage include a molybdenum loading stage configured to contact the conditioned pulp with the engineered polymeric hydrophobic media in an agitated reaction chamber, and load the hydrophobic molybdenite on the engineered polymeric hydrophobic media.
Owner:CIDRA CORP SERVICES
Green molybdenum smelting ion exchange process
ActiveCN112174209AWide adaptabilityHigh recovery rateMolybdeum compounds preparationIon exchangeWastewater
The invention discloses a green molybdenum smelting ion exchange process, which adopts mixed alkali two-stage countercurrent leaching to achieve high-level molybdenum metal recovery rate. Zero wastewater is realized through a leaching ion exchange water circulation closed process; post-exchange solution sodium salt extraction is realized through iron exchange, alkali liquor recycling is realized through returning leaching step, and alkali consumption is greatly reduced; the purification and transformation of molybdenum can be synchronously realized by ion exchange adsorption and desorption ofpre-exchange solutions with different Mo concentrations, and various indexes of the obtained ammonium molybdate product meet the highest standard of the national standard.
Owner:成都虹波钼业有限责任公司 +1
System and method for conversion of molybdenite to one or more molybdenum oxides
InactiveUS7824633B2Promote oxidationMaintain pressurePressurized chemical processOxygen/ozone/oxide/hydroxideSolventSolvent extraction
A system and method for producing molybdenum oxide(s) from molybdenum sulfide are disclosed. The system includes a pressure leach vessel, a solid-liquid separation stage coupled to the pressure leach vessel, a solvent-extraction stage coupled to the solid-liquid separation stage, and a base stripping stage coupled to the solvent-extraction stage. The method includes providing a molybdenum sulfide feed, subjecting the feed to a pressure leach process, subjecting pressure leach process discharge to a solid-liquid separation process to produce a discharge liquid stream and a discharge solids stream, and subjecting the discharge liquid stream to a solvent extraction and a base strip process.
Owner:FREEPORT MCMORAN COPPER & GOLD INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com