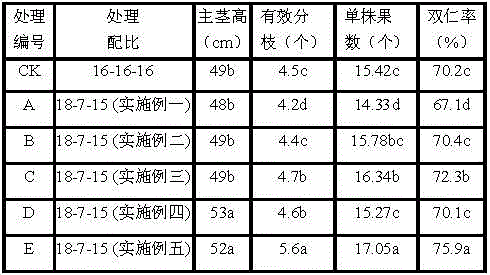
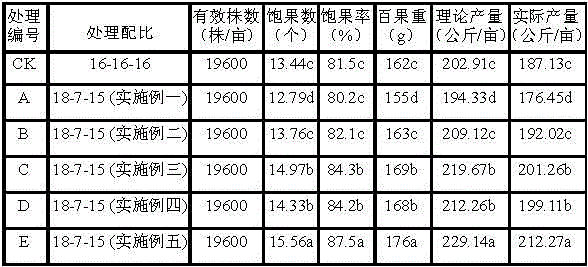
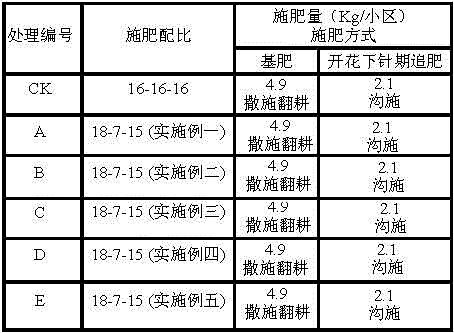
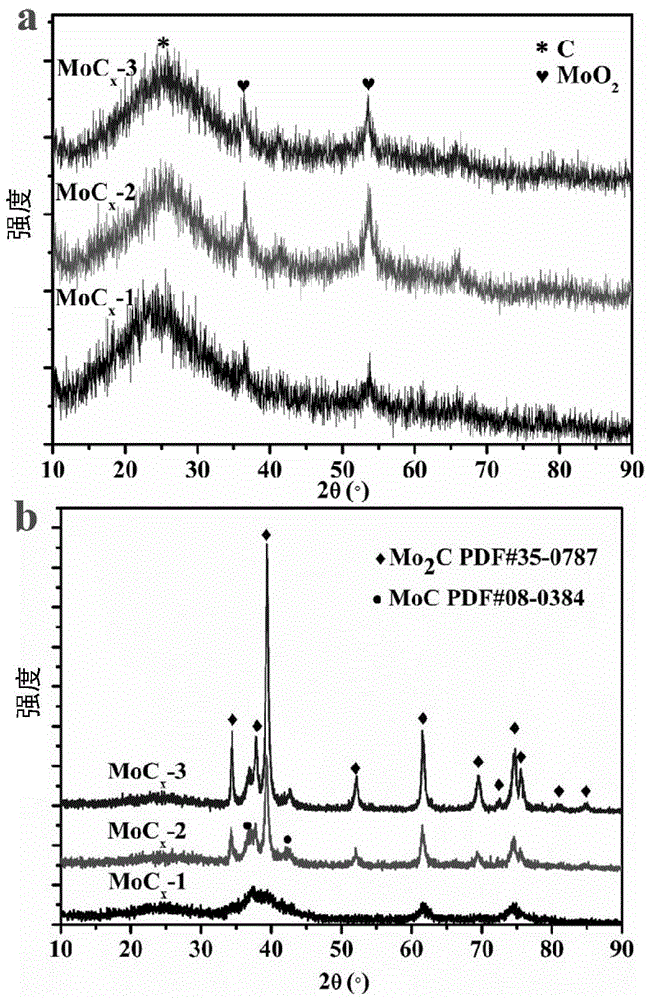
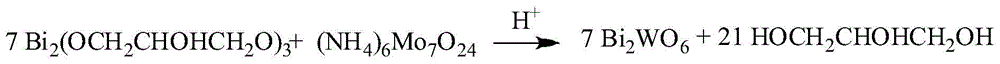Patents
Literature
238 results about "Ammonium heptamolybdate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Ammonium heptamolybdate is the inorganic compound whose chemical formula is (NH₄)₆Mo₇O₂₄, normally encountered as the tetrahydrate. A dihydrate is also known. It is a colorless solid, often referred to as ammonium paramolybdate or simply as ammonium molybdate, although "ammonium molybdate" can also refer to ammonium orthomolybdate, (NH₄)₂MoO₄, and several other compounds. It is one of the more common molybdenum compounds.
Functional granular major-element water soluble fertilizer and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104003783AFormulation ScienceNutritional diversityFertilizer mixturesChelated zincPhosphate
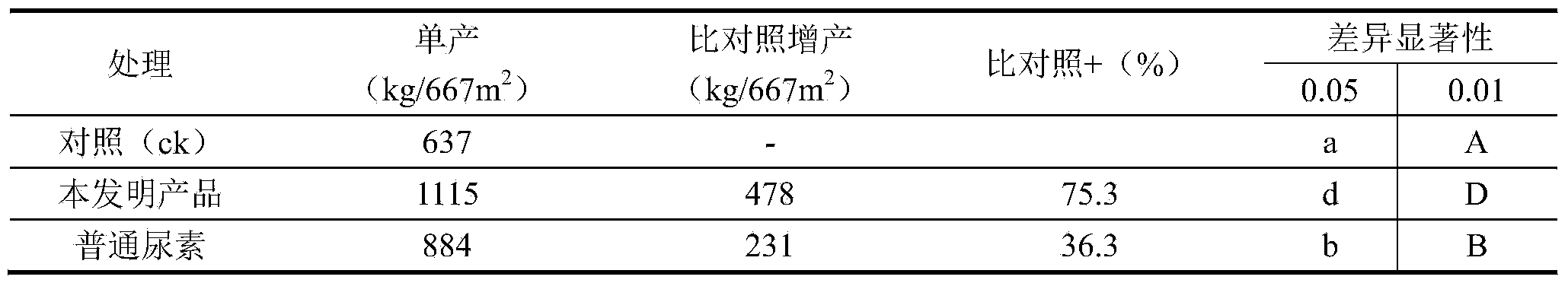
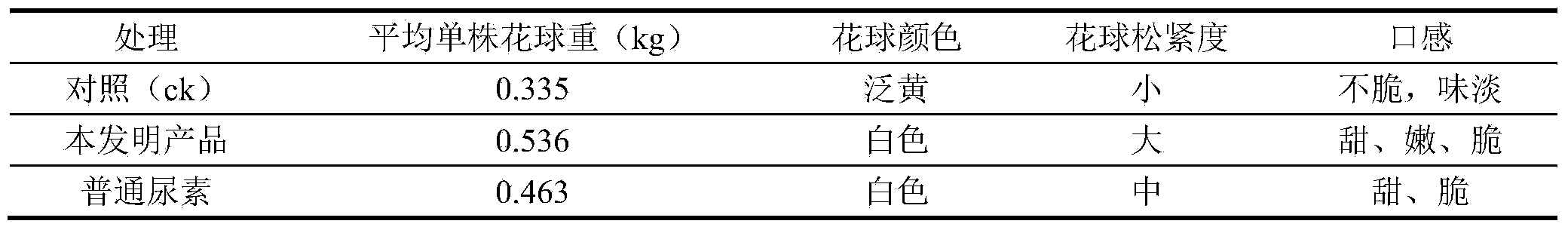
The invention discloses functional granular major-element water soluble fertilizer. The fertilizer comprises, by weight, 345-350 parts of urea, 210-220 parts of potassium nitrate, 240-250 parts of monopotassium phosphate, 20-30 parts of potassium sulphate, 110-115 parts of monoammonium phosphate, 11-11.6 parts of boric acid, 6-6.6 parts of EDTA chelated zinc, 7-7.7 parts of EDTA chelated iron, 3-3.9 parts of EDTA chelated manganese, 0.1-0.2 part of ammonium heptamolybdate and 5-10 parts of polyglutamic acid. Compared with the prior art, the functional granular major-element water soluble fertilizer is scientific in formula, complete in nutrition, balanced and stabilized in nutrient, capable of moisture retention and drought resistance and high in utilization rate and has the functions such as improving and restoring soil.
Owner:STANLEY AGRI GRP CO LTD
Graphene/silver molybdenum oxide compound visible-light catalyst and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102580739AUniform sizeHigh purityMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsPtru catalystAmmonium heptamolybdate
The invention relates to a graphene / silver molybdenum oxide compound visible-light catalyst and a preparation method thereof, in particular to a method for preparing the graphene / silver molybdenum oxide-combined visible-light catalyst by water and heat, belonging to the technical field of compound materials and photocatalysis. The preparation method comprises the following steps: taking graphene oxide, silver nitrate and ammonium heptamolybdate as raw materials according to certain proportion, mechanically stirring and mixing the raw materials uniformly in sequence, adjusting the pH value of solution, and then utilizing hydro-thermal reaction to prepare the graphene / silver molybdenum oxide compound visible-light catalyst. The photocatalytic degradation experiment shows that the graphene / silver molybdenum oxide compound visible-light catalyst prepared by the method has a good phtocatalytic degradation effect on rhodamine B due to the irradiation of the visible light and is ideal.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Synthesis method for molybdenum disulfide nanosheet catalyst
ActiveCN104689837AHigh yieldReaction conditions are easy to controlPhysical/chemical process catalystsSynthesis methodsSulfur
The invention relates to a synthesis method for a molybdenum disulfide nanosheet. The method employs ammonium heptamolybdate and sulfur powder as the raw materials and hydrazine hydrate as the reducing agent to prepare the molybdenum disulfide nanosheet catalyst by a hydrothermal process in one step. By controlling the concentration of a hydro-thermal synthesis precursor, the size and stacking layers of the molybdenum disulfide nanosheet can be controlled, thus obtaining molybdenum disulfide nanosheets of different sizes. The molybdenum disulfide nanosheet prepared by the method provided by the invention has the characteristics of high yield, easily controllable reaction condition, good stability and regular shape, is expected to realize mass production, and has very high application value.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Nano-molybdenum sulfide antibacterial material and synthetic method thereof and application thereof
InactiveCN105948124AHigh yieldGood biocompatibilityAntibacterial agentsMaterial nanotechnologyThioureaPolyethylene glycol
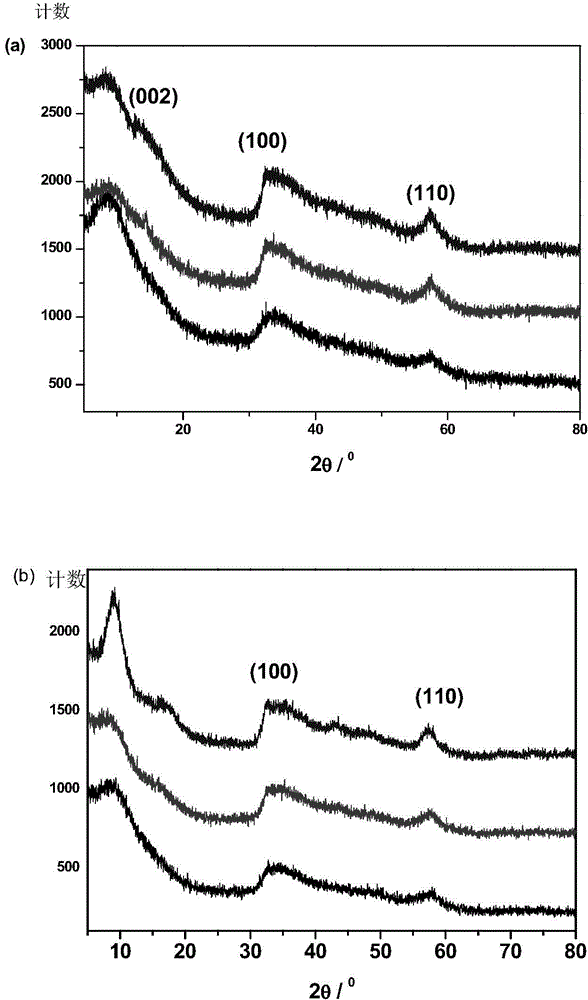
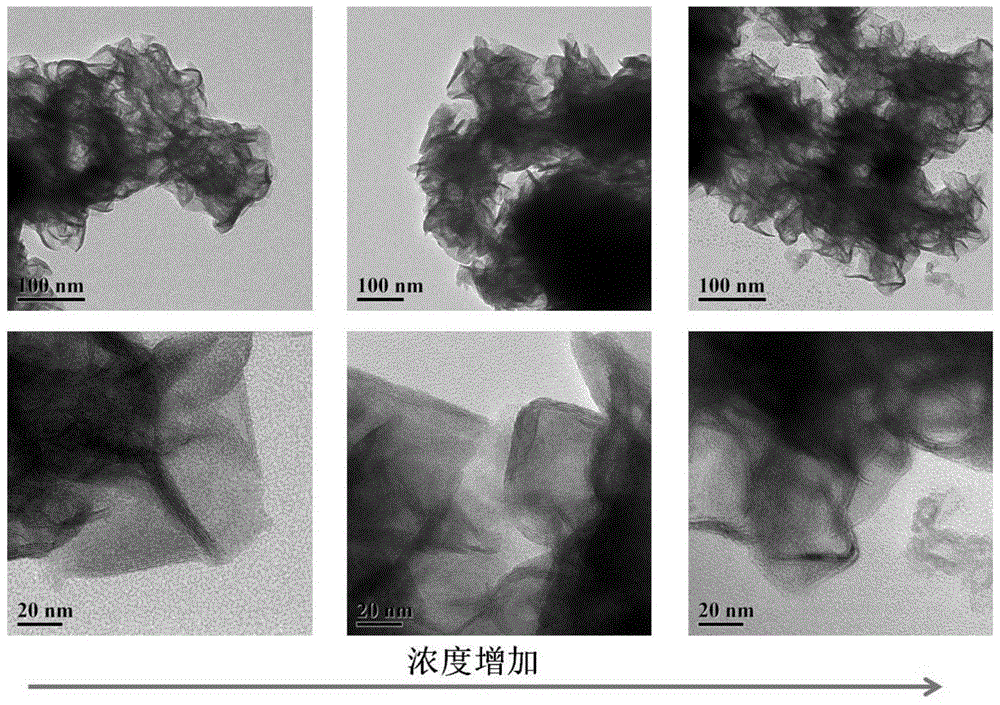
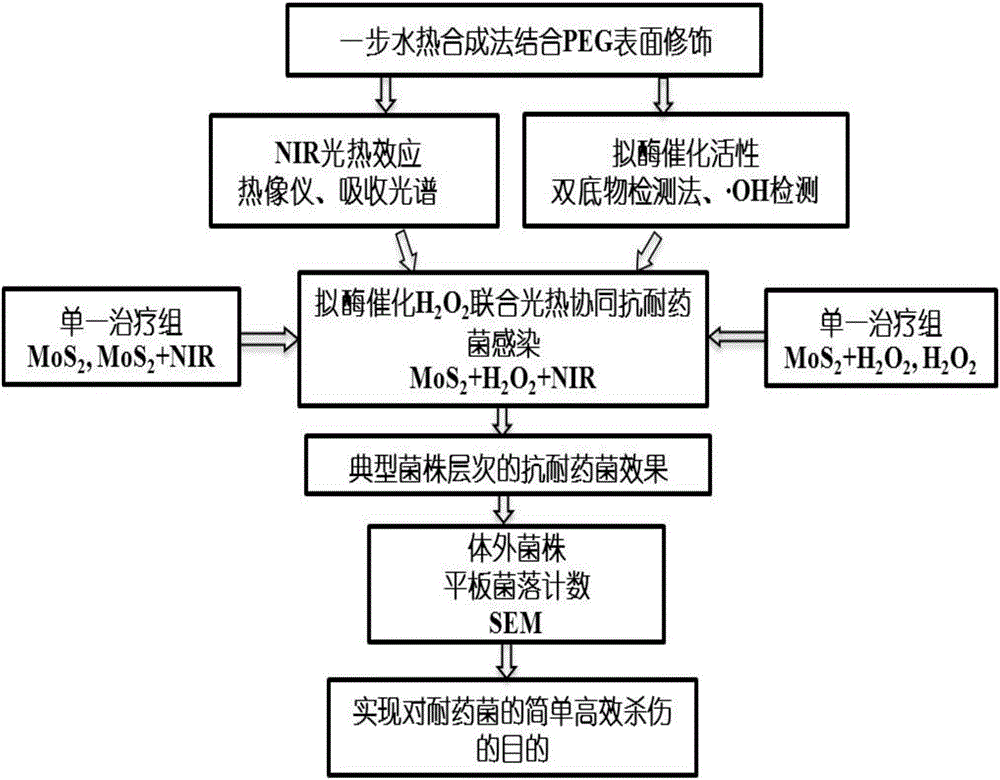
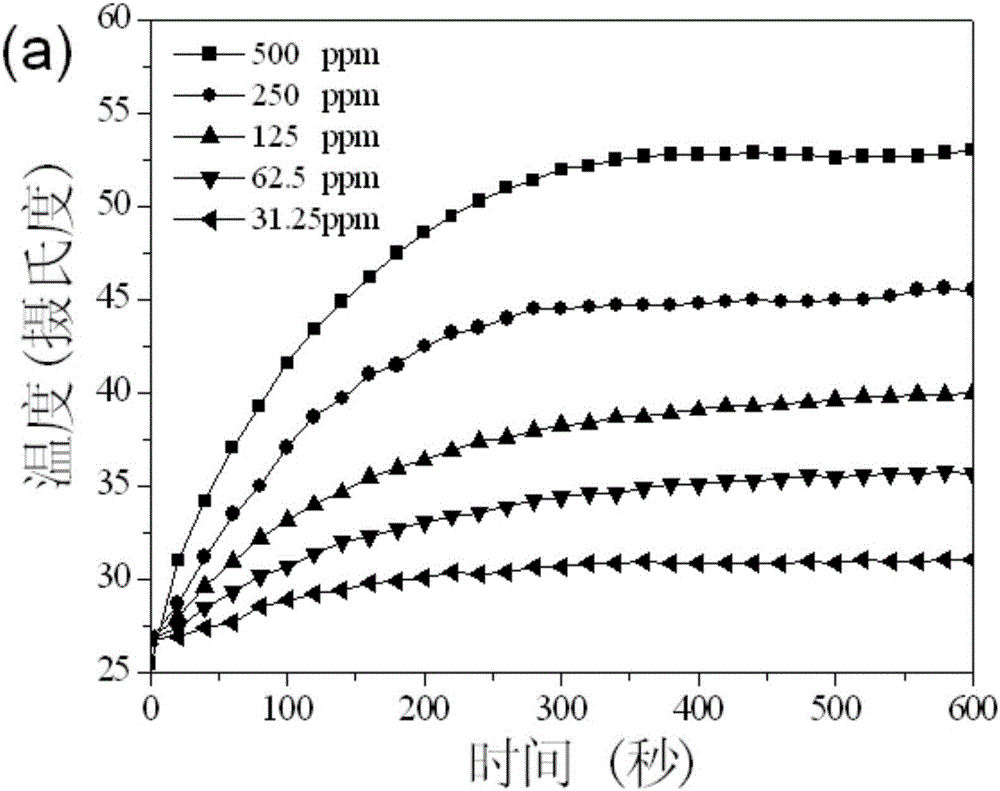
The invention discloses a nano-molybdenum sulfide antibacterial material and a synthetic method thereof and application thereof. The synthetic method comprises the following steps: (1) dissolving polyethylene glycol solid in water, performing ultrasonic processing in an ultrasonic pool until the polyethylene glycol is dissolved completely, adding ammonium heptamolybdate solid, and performing ultrasonic processing until the ammonium heptamolybdate is dissolved completely to obtain a mixed solution; and (2) dissolving thiourea solid in water, dissolving the thiourea with stirring, adding the dissolved thiourea into the mixed solution, stirring the mixture, putting the mixture into a hydrothermal reactor having a polytetrafluoroethylene inner container, sealing the reactor, and performing heating reaction to obtain a black precipitate which is the nano-molybdenum sulfide antibacterial material. The invention also provides the nano-molybdenum sulfide antibacterial material which is prepared by the synthetic method. The invention also provides application of the nano-molybdenum sulfide antibacterial material on synergistic anti-microbial combining biomimetic catalysis hydrogen peroxide and near-infrared optothermal. The nano-molybdenum sulfide antibacterial material prepared by the synthetic method in the invention has high yield, and can be captured easily by bacteria. Moreover, the antibacterial effect of the material is obviously better than that of single biomimetic catalysis anti-microbial or single near-infrared optothermal anti-microbial.
Owner:INST OF HIGH ENERGY PHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Biological-organic fertilizer special for corn and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105085111AMeet nutrient needsEven distribution of nutrientsFertilizer mixturesChelated zincNutrition
The invention discloses a biological-organic fertilizer special for corn and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of crop formula fertilizers. The biological-organic fertilizer special for the corn is prepared form, seaweed extracts, urea, ammonium polyphosphate, potassium nitrate, magnesium sulfate monohydrate, EDTA chelate ferrum, EDTA chelate manganese, EDTA chelate zinc, EDTA chelate cuprum, boric acid, ammonium molybdae and fulvic acid potassium. The raw materials all adopts commercially available materials except that the seaweed extracts are produced by Stanley Fertilizer Limited Company. The prepared fertilizer is comprehensive in nutrition, scientific and reasonable in formula, water-soluble, easy to apply and capable of improving soil and effectively promoting the growth of crops by combining quick acting and long acting.
Owner:生之道生态农业科技股份有限公司
Fulvic acid potassium-containing total-nutrient fertilizer for special purpose of potatoes and production method thereof
InactiveCN104496705ANutrient balanceNutrient stabilityMagnesium fertilisersAlkali orthophosphate fertiliserChelated zincPhosphate
The invention discloses a fulvic acid potassium-containing total-nutrient fertilizer for special purpose of potatoes and a production method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of crop formula special fertilizers. The fertilizer is prepared from the following raw materials: urea, monoammonium phosphate, monopotassium phosphate, potassium sulfate, boric acid, EDTA chelated zinc, EDTA chelated iron, EDTA chelated manganese, ammonium heptamolybdate, anhydrous magnesium sulfate, inhibitor NAM and fulvic acid potassium. The fertilizer has the advantages of balanced and comprehensive nutrition, smooth appearance, hardening prevention, long fertilizer efficiency, high utilization, labor output reduction, soil improvement and environmental pollution reduction.
Owner:STANLEY AGRI GRP CO LTD
Method for preparing nano molybdenum carbide (Mo2C) flake powder with regular-hexagon structure
ActiveCN105217633AAchieve synthesisWell mixedMaterial nanotechnologyTungsten/molybdenum carbideSucroseMetallurgy
The invention relates to a method for preparing nano molybdenum carbide (Mo2C) flake powder with a regular-hexagon structure. According to the method, water-soluble ammonium dimolybdate (or ammonium heptamolybdate) and glucose (or saccharose) are respectively adopted as a molybdenum source raw material and a carbon source raw material; and through precursor solution drying, molecular-level uniform mixing of all elements in a reactant system is realized, the temperature for carbothermal reduction reaction is lowered, the reaction time for the carbothermal reduction reaction is shortened, and the synthesis of nano Mo2C is realized. In addition, during the reaction, a molten halogenating agent provides a uniformly-heated stable-state system for a reaction system, so that the homogeneous growth of regular-hexagonal nano flaky Mo2C is promoted.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING
High-activity seaweed fertilizer specially used for peanut and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104151114APromote vegetative growthPromote reproductive growthAlkali orthophosphate fertiliserAmmonium orthophosphate fertilisersBiotechnologyNutrition
The invention discloses a high-activity seaweed fertilizer specially used for peanuts and a preparation method thereof and belongs to the technical field of production of crop specially-used fertilizers. The high-activity seaweed fertilizer is prepared from following raw materials comprising: urea, monoammonium phosphate, a calcium magnesium phosphate fertilizer, potassium sulfate, borax, EDTA chelating iron, EDTA chelating manganese, EDTA chelating zinc, ammonium heptamolybdate, a seaweed extraction liquid and seaweed residues. Compared with a fertilizer in the prior art, the high-activity seaweed fertilizer specially used for the peanuts is reasonable in formula, is complete in nutrition, can achieve an effect of increasing yield of the peanuts and improving quality of the peanuts.
Owner:STANLEY FERTILIZER GUIGANG
Preparation of highly dispersed molybdenum carbide/carbon composite electro-catalyst by adopting oxidation, reduction and fixation method
ActiveCN106694006AGood dispersionEasy to synthesizePhysical/chemical process catalystsElectrodesCarbon compositesMass ratio
The invention relates to a preparation method of a highly dispersed molybdenum carbide / carbon composite electro-catalyst by adopting an oxidation, reduction and fixation method. The preparation method comprises the following steps that 1, reducing organic matter and ammonium heptamolybdate are dissolved in water to prepare a mixed solution, wherein the mass ratio of the reducing organic matter to the ammonium heptamolybdate is 1: (0.1-2); 2, the mixed solution is subjected to hydrothermal treatment at the temperature of 120-200 DEG C for 4-24 hours, solid is separated out, and washing and drying are performed; 3, the dried solid is calcined in a protective atmosphere at the temperature of 600-1000 DEG C for 2-10 hours to obtain the highly dispersed molybdenum carbide / carbon composite electro-catalyst. The used raw materials are safe, non-toxic, simple to obtain and convenient to prepare and can be synthesized into molybdenum carbide nanomaterials in a large-scale mode.
Owner:江苏先进无机材料研究院
Preparation method of nitrogen-doped carbon nanofiber aerogel with inlaid molybdenum carbide particles
ActiveCN105413729AIncrease the areaHigh porosityMaterial nanotechnologyPhysical/chemical process catalystsCarbon nanofiberAmmonium heptamolybdate
The invention discloses a preparation method of nitrogen-doped carbon nanofiber aerogel with inlaid molybdenum carbide particles. The preparation method comprises the following steps of immersing bacterial cellulose in deionized water for removing acid, then immersing the bacterial cellulose in an ammonium heptamolybdate aqueous solution, conducting absorption till saturation, and obtaining ammonium heptamolybdate / bacterial cellulose; freezing the ammonium heptamolybdate / bacterial cellulose with liquid nitrogen, then conducting drying in a freeze dryer, and obtaining bacterial cellulose aerogel hybridized with ammonium heptamolybdate; finally, placing the hydridized bacterial cellulose aerogel in a tube furnace, conducting high temperature pyrolysis, and obtaining the nitrogen-doped carbon nanofiber aerogel with the inlaid molybdenum carbide particles. According to the method, the ammonium heptamolybdate and the bacterial cellulose are combined for being applied to preparation of functional carbon nano-materials, the method has the advantages of being simple, low in price, green, environmentally friendly, easy to produce on a large-scale and the like, and the prepared nitrogen-doped carbon nanofiber aerogel with the inlaid molybdenum carbide particles can serve as a catalyst for electric hydrogen production.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Novel activated carbon fiber adsorbing substance as well as preparation method and use thereof
InactiveCN101480605AHigh mercury removal efficiencyStrong adsorption capacityOther chemical processesAlkali metal oxides/hydroxidesSolventIon
The invention discloses a novel activated carbon fiber adsorbent a preparation method and the application thereof. The activated carbon fiber adsorbent is characterized by carrying MoS2 on the surface of activated carbon fiber. The preparation method comprises the following steps: the activated carbon fiber is used as a carrier, ammonium molybdate is used as a precursor, and deionized water is used as a solvent to be prepared into steeping liquor, wherein the mass ratio of the activated carbon fiber to the ammonium molybdate is 1 : 0.25 to 0.3; the ammonium molybdate is carried in the activated carbon fiber by a wet immersion method, and then, the activated carbon fiber immersed with the ammonium molybdate is heated to 450 to 500 DEG C in inert atmosphere to be oxidized and decomposed to obtain MoO3-activated carbon fiber; and then, the MoO3-activated carbon fiber is heated to 800 to 825 DEG C in Ar / H2S to be sulfurized, and finally, the activated carbon fiber with the surface carried with MoS2 is prepared, i.e. the activated carbon fiber adsorbent is prepared. When the activated carbon fiber adsorbent is used for removing mercury in fume, the effect is good, and the activated carbon fiber adsorbent also has the advantages of simple preparation and easy process control.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Preparation method of high-purity phase spherical molybdenum disulfide
ActiveCN105776335AFavorable to replaceGood for sulfur reductionMaterial nanotechnologyMolybdenum sulfidesSpherical shapedAmmonium heptamolybdate
The invention relates to a preparation method of high purity phase spherical molybdenum disulfide. The method comprises the following steps: ammonium heptamolybdate, thioacetamide, and a surfactant are dissolved in a solvent with uniformly mixing; a reducing agent is added, the prepared solution is transferred into a high pressure reaction vessel, the high pressure reaction vessel is sealed, the sealed high pressure reaction vessel is placed into a thermotank at 120-250 DEG C for 3-72 hours; temperature is cooled to room temperature, after filtering, washing and drying processes, spherical nanometer molybdenum disulfide is obtained. The prepared high purity phase nanometer molybdenum disulfide has the advantages of structured morphology, uniform and adjustable size, high sphericility, good dispersibility, simple synthesis process, mild condition, low cost, and simple synthesizer. The high purity phase nanometer molybdenum disulfide has wide applications to electrode materials, lubrication materials and catalysis fields, and is hopeful to be used in industrial production.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD +1
Fruit swelling type seaweed organic liquid water soluble fertilizer and production method thereof
PendingCN105060986AThe formula is scientific and reasonableNutritional diversityFertilizer mixturesChelated zincNutrition
The invention discloses a fruit swelling type seaweed organic liquid water soluble fertilizer, and belongs to the technical field of formula fertilizers of crops. The fruit swelling type seaweed organic liquid water soluble fertilizer is prepared from the following raw materials: a seaweed extracting solution, urea, ammonium polyphosphate, potassium nitrate, magnesium sulfate monohydrate, EDTA chelated iron, EDTA chelated manganese, EDTA chelated zinc, EDTA chelated copper, boric acid, ammonium heptamolybdate and potassium fulvic. The fruit swelling type seaweed organic liquid water soluble fertilizer is comprehensive in nutrition, scientific and reasonable in formula, fully water-soluble and easy to apply, improves soil, integrates fast acting and long acting, and effectively promotes the crop growth.
Owner:STANLEY AGRI GRP CO LTD
Special cotton fertilizer produced by using biochemical fulvic acid through melt granulation and production method of special fertilizer
ActiveCN103073365AUnique preparation processNutrient balanceFertilizer mixturesChelated zincPhosphate
The invention discloses special cotton fertilizer produced by using biochemical fulvic acid through melt granulation, relating to the technical field of special fertilizer of crop formula. The special fertilizer is obtained by taking 450-650 parts of nitramine phosphorus, 50-160 parts of potassium chloride, 80-300 parts of potassium sulfate, 50-150 parts of monoammonium phosphate, 1-100 parts of biochemical fulvic acid, 1-15 parts of EDTA (Ethylene Diamine Tetraacetic Acid) chelating zinc, 1-15 parts of EDTA chelating manganese, 1-20 parts of EDTA chelating iron, 1-20 parts of borax and 0.1-0.5 part of ammonium heptamolybdate as raw materials, mixing, stirring, heating, granulating, cooling and screening. The special fertilizer disclosed by the invention has the advantages of comprehensive nutrients, favorable water solubility, greenness, no pollution, high utilization rate, improvement on soil, increase of crop yield and improvement on quality.
Owner:STANLEY AGRI GRP CO LTD
Acrolein catalyst and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103934000AReduce performanceAchieve optimized resultsOrganic compound preparationCarbonyl compound preparationPtru catalystAcrolein
The present invention relates to an acrolein catalyst and a preparation method thereof, mainly solves the long-term operation performance degradation problem of a catalyst in the prior art. The acrolein catalyst is prepared by mixing a powder catalyst precursor with a binder and a molybdenum additive for molding, and finally roasting to obtain the catalyst; wherein the powder catalyst precursor uses at least one substance selected from SiO2 or Al2O3 as a carrier, and the molybdenum additive comprises, by molar, 50-100% of ammonium heptamolybdate and 0-50% of molybdenum trioxide. The technical solution better solve the long-term operation performance degradation problem of the catalyst in the prior art. The acrolein catalyst can be used in industrial production of preparation of the acrolein catalyst by oxidization of propene.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Method for nickel-assisted low-temperature synthesis of molybdenum carbide electrocatalyst
ActiveCN106925314ASimple processSynthesis temperature is lowElectrolysis componentsPhysical/chemical process catalystsNano structuringSynthesis methods
The invention relates to a method for nickel-assisted low-temperature synthesis of a molybdenum carbide electrocatalyst. The method comprises the steps that a carbon source, a nickel source and a molybdenum source are added into water, and ultrasonic dissolution is performed to obtain a mixed solution; then the obtained mixed solution reacts at the temperature of 15-30 DEG C for 4-48 hours, and centrifugal washing and drying are performed to obtain a light green product; the obtained light green product is arranged in a protective atmosphere and is calcined at the temperature of 500-750 DEG C for 2-10 hours, and then acid pickling is performed to obtain the molybdenum carbide electrocatalyst. The carbon source is selected from imidazole group organic matter or / and organic matter providing nitrogen-atom coordination, and the molybdenum source is selected from at least one of ammonium heptamolybdate, sodium molybdate and potassium molybdate. The molybdenum carbide nano-structure synthesis method is simple in process, economic, reasonable, environmentally friendly and low in synthesis temperature and makes large-scale production easy.
Owner:中国科学院上海硅酸盐研究所苏州研究院
Small molecule alginic acid microbial fertilizer
InactiveCN110183266AKeep active ingredientsAvoid decompositionBio-organic fraction processingMicroorganism based treatmentSpecific functionDecomposition
The invention discloses a small molecule alginic acid microbial fertilizer, which comprises, by weight, 7-15 parts of a biological enzymolysis small molecule alginic acid solution, 15-25 parts of a compound microbial agent, 5-15 parts of humic acid, 5-10 parts of urea, 1-5 parts of boric acid, 0.2-0.5 part of EDTA-Cu, 0.3-0.6 part of EDTA-Fe, 1-3 parts of EDTA-Zn, 0.1-0.2 part of EDTA-Mn, and 0.06-0.1 part of ammonium heptamolybdate. According to the present invention, the small molecule alginic acid microbial fertilizer can avoid the destruction caused by strong alkalis, high temperature andhigh pressure, avoid the decomposition of active substances such as alginic acid, plant growth promoting factors and the like under mild process conditions, and maintain the effective active components in seaweed at a maximum; after alginic acid is released, the alginic acid is further subjected to enzymolysis to form the low molecular weight alginic acid so as to be easily absorbed and used by plants; and the liquid rich in the small molecule alginic acid is prepared, and is compounded with the special forma, and the agricultural microbial bacteria with specific functions are added, such thatthe nutrient requirements and the stress resistance of crops can be completely met.
Owner:青岛明月蓝海生物科技有限公司
Molybdenum sulfide-based catalyst for preparing low-carbon alcohol from synthesis gas and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN108325548ASimple preparation processMild conditionsOrganic compound preparationHydroxy compound preparationAlcoholThiourea
The invention relates to a preparation method of a molybdenum sulfide-based catalyst for preparing low-carbon alcohol from synthesis gas. The method comprises the following steps that (1) ammonium molybdate tetrahydrate and thiourea are added into water according to the mole ratio of Mo:S being 1:(2 to 4); after dissolution, a solution A is prepared; (2) the solution A is added into a hydrothermalreaction kettle; reaction is performed at 220 DEG C; products are washed and dried to obtain a precipitate A, i.e., petaloid MoS2; (3) the precipitate A and potassium carbonate are subjected to mechanical grinding according to a mole ratio of Mo:K being 1:(0.5 to 1) to obtain the catalyst for preparing low-carbon alcohol from the synthesis gas. The catalyst has the advantages that the preparationmethod is simple; the sulfur-resistant performance is good; the product total alcohol and C<2+> alcohol selectivity is high, and the like. Good industrial application prospects are realized.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA UNIVERSITY
Microelement-rich liquid urea ammonium nitrate solution fertilizer and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104262064AImprove securityAvoid corrosionMagnesium fertilisersAmmonium nitrate fertilisersPolyethylene glycolManganese
The invention discloses a microelement-rich liquid urea ammonium nitrate solution fertilizer, which comprises 20-25 parts of urea, 20-30 parts of ammonium nitrate, 0.1-2 parts of liquid ammonia, 0.01-0.1 part of magnesium nitrate, 1-3 parts of sodium polyaspartate, 0.01-0.1 part of any one or a mixture of any more than two of ammonium carbonate, ammonium thiocyanate and ammonium bicarbonate, 0.02-0.08 part of an urease inhibitor, 1-2 parts of edta-2nacu tetrahydrate, 1-3 parts of ferric-sodium edentate, 1-3 parts of magnesium-disodium edetate, 1-3 parts of manganese-disodium edetate, 1-3 parts of zinc-disodium edentate, 1-3 parts of disodium octaborate tetrahydrate, 0.01-0.1 part of ammonium heptamolybdate, 1-3 parts of citric acid, 1-3 parts of an antifreezing agent PX-60 or polyethylene glycol PEG-200, and 16.5-41 parts of water. A product disclosed by the invention is high in safety, and pH value is 6-7; and due to the addition of an anticorrosive antiscale agent, the corrosion of products on production, storage, transportation and application facilities is effectively prevented.
Owner:中化(临沂)作物营养有限公司
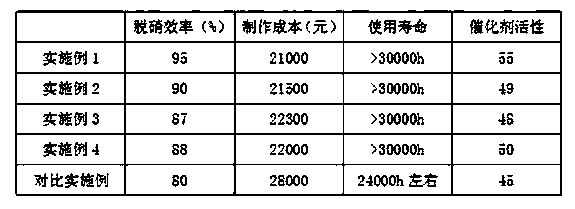
A preparing method of a catalyst for low-temperature denitrification
InactiveCN105521777AHigh activityHigh selectivityGas treatmentOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsOXALIC ACID DIHYDRATECellulose
The invention relates to a preparing method of a catalyst for low-temperature denitrification, and belongs to the field of flue gas denitrification. The denitrification efficiency of the catalyst for flue gas at 150-420 DEG C is 95% or above. Raw materials for preparing the catalyst comprise 55-91 parts of superfine titanium dioxide, 1-10 parts of lanthanum nitrate, 1-5 parts of polyoxyethylene, 1-10 parts of cerous nitrate, 1-10 parts of zirconium nitrate, 0.05-10 parts of ammonium metavanadate, 0.05-15 parts of ammonium heptamolybdate, 0.05-10 parts of ammonium paratungstate, 1-5 parts of carboxymethylcellulose, 10-30 parts of deionized water, 1-15 parts of monoetanolamine and 1-5 parts of oxalic acid. The catalyst is characterized by high selectivity, high activity and strong poison resistance.
Owner:ANHUI YUANCHEN ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION SCI & TECH
Composition containing various microelements, preparation and preparation method thereof
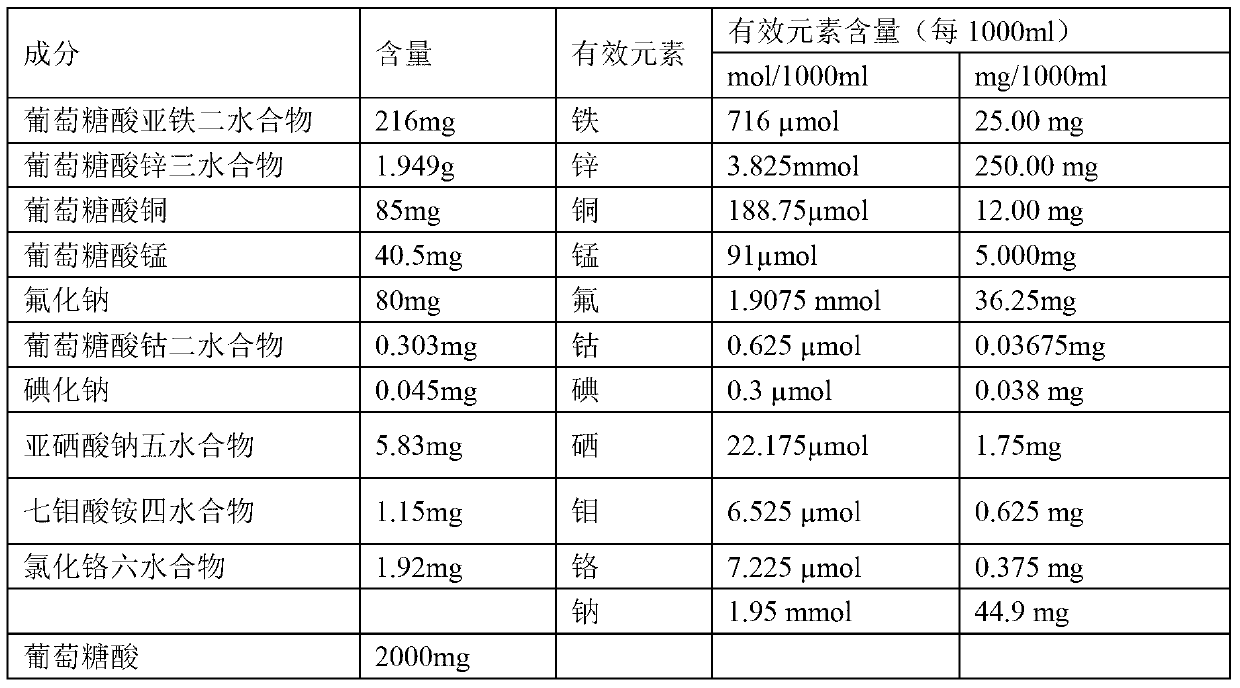
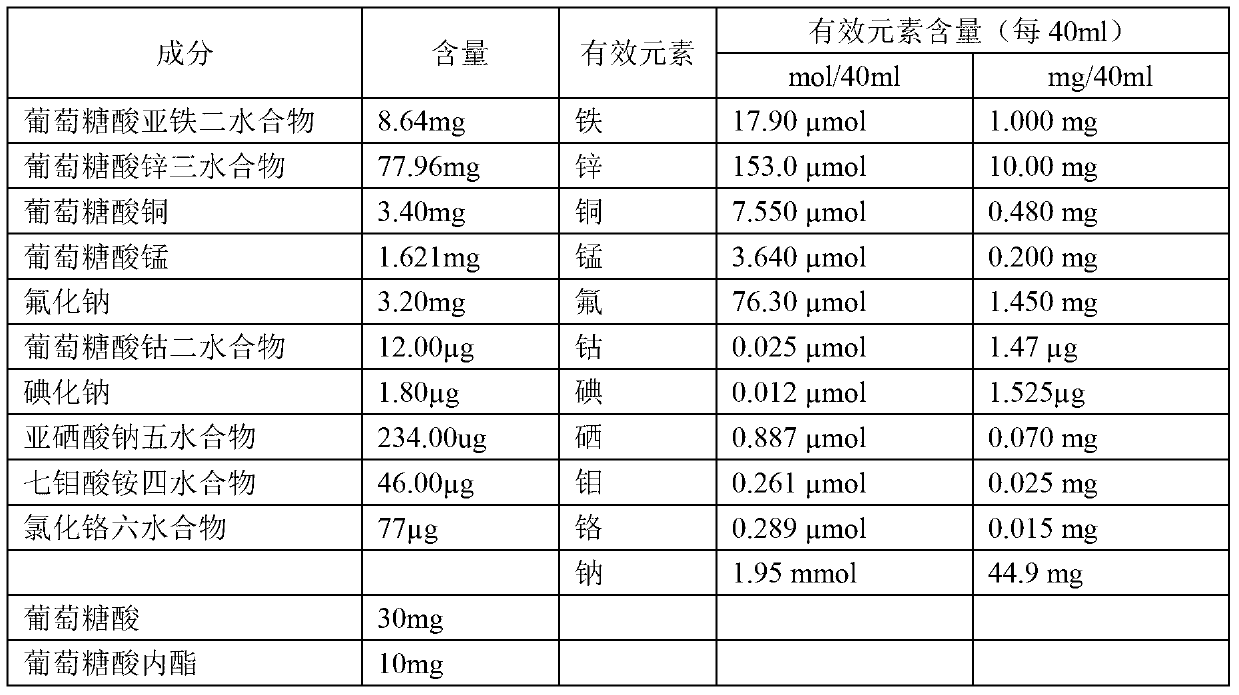
InactiveCN103340895AImprove stabilitySuitable for clinical applicationHeavy metal active ingredientsMetabolism disorderSodium iodideFreeze-drying
The invention relates to a pharmaceutical composition, and in particular relates to a composition containing various microelements, a preparation and a preparation method thereof. The composition comprises ferrous gluconate dihydrate, a zinc gluconate trihydrate compound, copper gluconate, manganese gluconate, sodium fluoride, cobalt gluconate dihydrate, sodium iodide, sodium iodide pentahydrate, ammonium heptamolybdate tetrahydrate, chromic chloride hexahydrate and a medicine auxiliary material. The form of the pharmaceutical composition can be injection or freeze-dried powder injection. According to the invention, organic iron, organic zinc, organic copper, organic manganese and organic cobalt are adopted to replace chloride, so that not only is the property of the composition more stable, but also the adverse reaction is reduced, and the bioavailability of the medicine is increased. Therefore, the preparation provided by the invention is better in safety and more suitable for clinical application.
Owner:江西博意特科技有限公司
Plate-type SCR denitration catalyst, and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN103349981AWell mixedEvenly distributedDispersed particle separationCatalyst activation/preparationPolyethylene oxideAmmonium metavanadate
The invention discloses a plate-type SCR (Selective Catalytic Reduction) denitration catalyst, and a preparation method and the application thereof. The method comprises the following steps: kneading, aging, stretching production of a steel mesh, coating and baking, wherein in the kneading step, mixing step by step is adopted, that is TiO2-W-1, TiO2-D-2, deionized water, ammonia water, ammonium heptamolybdate, clay, an ammonium metavanadate solution, hydroxyethyl cellulose and polyethylene oxide are added into a mixer for kneading; the coating step is that the ageing material is uniformly coated on the stainless steel wire mesh. The invention further discloses the application of the catalyst in the field of gas denitration. The plate-type SCR denitration catalyst prepared by the method has higher mechanical strength and efficient denitration efficiency.
Owner:江苏万德环保科技有限公司
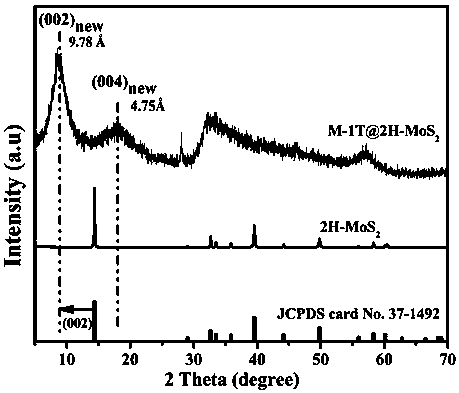
Method for microwave hydrothermal preparation of 1T@2H-MoS2
InactiveCN107651708AEasy to operateSuitable for large-scale industrial productionEnergy based chemical/physical/physico-chemical processesMolybdenum sulfidesMicrowaveAlcohol
The invention discloses a microwave hydrothermal preparation method of 1T@2H‑MoS2. The preparation method comprises: firstly, using deionized water as a solvent, stirring ammonium heptamolybdate and thiourea for 30 minutes, adjusting the temperature to 200 ° C for 10 minutes, Secondly, using alcohol as a solvent, the product obtained in the first step was reacted at 220 °C for 4-10 min to obtain 1T@2H‑MoS2 nanospheres. The method of the invention uses a microwave hydrothermal instrument, which is simple, safe and fast, has good repeatability and low cost, and the obtained sample has uniform morphology and two phase structures of 1T and 2H.
Owner:XINJIANG UNIVERSITY
Acrolein catalyst and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103769161AReduce performanceAchieve optimized resultsOrganic compound preparationCarbonyl compound preparationPtru catalystAcrolein
The invention relates to an acrolein catalyst and a preparation method thereof, which mainly solve the problem of performance reduction of the catalyst after long-time running in the prior art. With the adoption of the technical scheme that the method comprises the following steps of mixing a powdered catalyst precursor selected from at least one of SiO2 or Al2O3 as a carrier, with an adhesive agent and a molybdenum additive, forming, and finally roasting to obtain the catalyst, wherein the molybdenum additive comprises 50-100 mol% of ammonium heptamolybdate and 0-50 mol% of molybdenum trioxide, the technical problem is better solved, and the method can be used for industrial production of the propylene oxidation to acrolein catalyst.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Plate-type denitration catalyst
ActiveCN103706409AHigh strengthFlat surfaceDispersed particle separationMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsGlass fiberAmmonium heptamolybdate
The invention relates to a plate-type denitration catalyst, and belongs to the technical field of a selective catalytic reduction (SCR) catalyst. The catalyst is prepared from a base material, titanium dioxide, vanadium pentoxide, ammonium heptamolybdate, lactic acid, a glass fiber and silicon dioxide, wherein the base material is coated with the titanium dioxide, the vanadium pentoxide, the ammonium heptamolybdate, the lactic acid, the glass fiber and the silicon dioxide and then is sintered to form the plate-type denitration catalyst. The plate-type denitration catalyst is applied to a denitration treatment process, so that the plate-type denitration catalyst has the advantages of being high in mechanical strength, durable and high in denitration efficiency, can be recycled, and the like.
Owner:ZHEJIANG TUNA ENVIRONMENTAL SCI & TECH
Special fertilizer for pasture rich of selenium
InactiveCN101597188AIncrease selenium contentIncrease grass yieldOrganic fertilisersAmmonium salt fertilisersMonopotassium phosphateChalcanthite
The invention relates to a special fertilizer for pasture rich of selenium, which basically comprises the following components: monopotassium phosphate, ammonium heptamolybdate tetrahydrate, ascorbic acid, heptahydrate zinc sulphate, chalcanthite, ferrous sulfate heptahydrate, anhydrous boric acid, humic acid, calcium nitrate and sodium selenite. A method for producing the special fertilizer comprises the following steps: respectively crushing the components into powder and then uniformly the powder according to a certain proportion. The special fertilizer for pasture rich of selenium can increase the yield of pasture by 15 percent-30 percent, improve the selenium content in a body by 5 times-30 times, improve the contents of mineral elements including calcium, phosphorus, zinc, ferrum, copper, molybdenum, and the like by more than 15 percent and improve the crude protein content by more than 10 percent; and the produced pasture rich of selenium is safe to utilize and has complete nutrition and high additional value.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU COLLEGE OF ANIMAL HUSBANDRY ENG
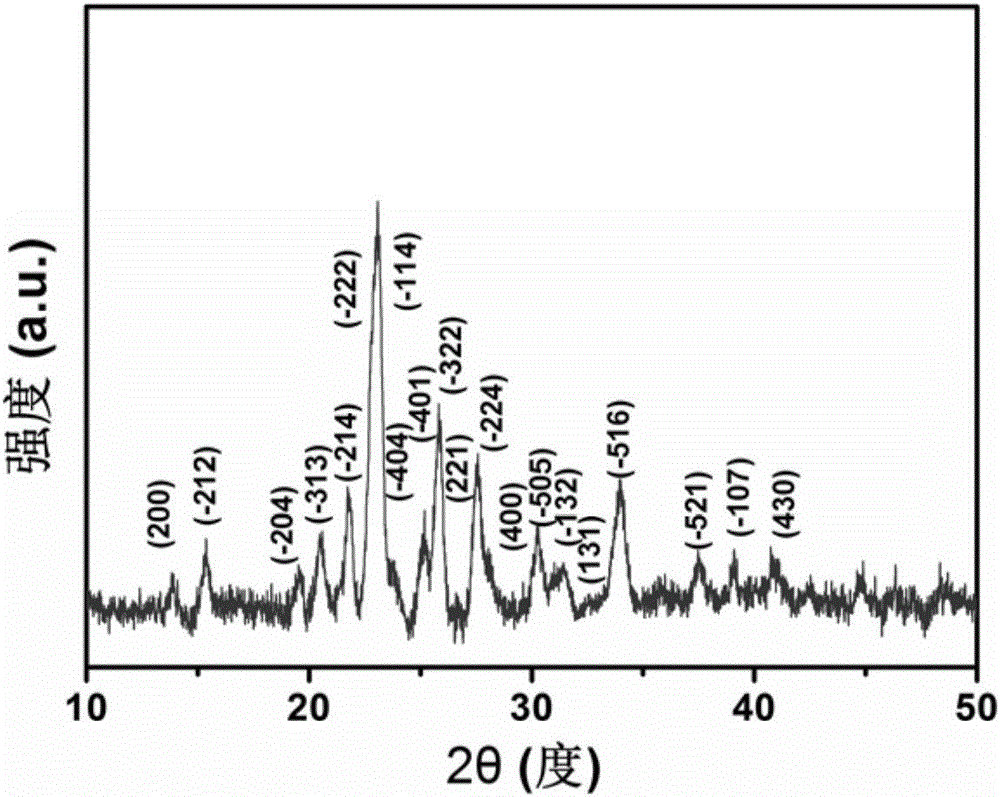
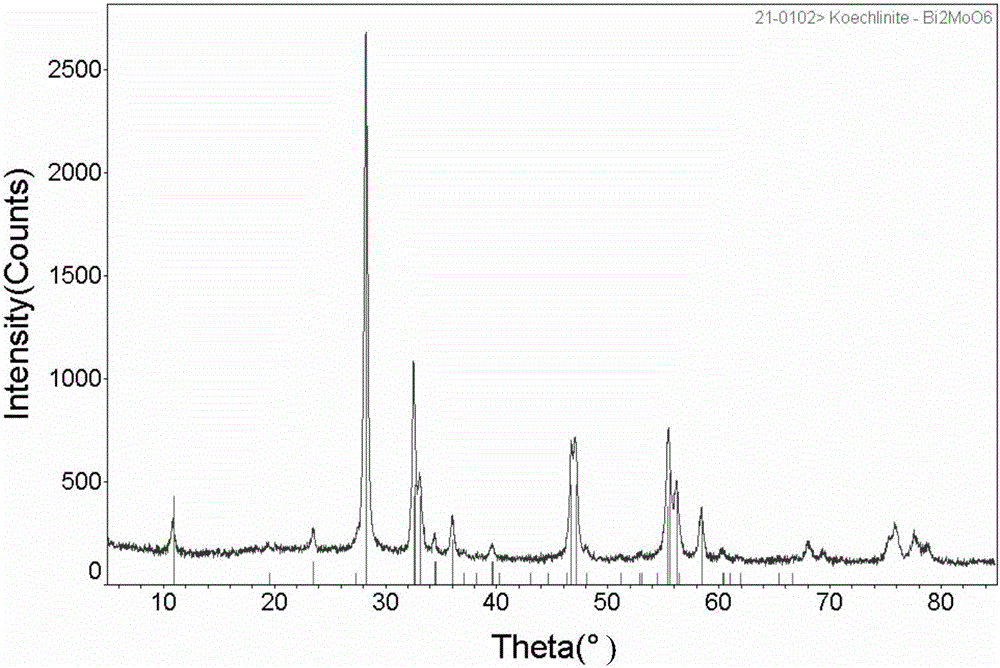
Bismuth molybdate composite photocatalytic material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105562056APromote migrationImprove migration efficiencyPhysical/chemical process catalystsBoron nitrideElectronegativity
The invention discloses a bismuth molybdate composite photocatalytic material. A boron nitride nanosheet serves as a catalyst carrier, and the boron nitride nanosheet is loaded with bismuth molybdate, wherein the molar ratio of the boron nitride nanosheet to bismuth molybdate is 1: (0.01-0.6). The invention further discloses a preparation method of the bismuth molybdate composite photocatalytic material. Bismuth nitrate pentahydrate is dissolved in a nitric acid solution with the concentration being 10%, then the boron nitride nanosheet and ammonium heptamolybdate are added, a mixed solution is obtained, the mixed solution is evenly stirred in an ultrasonic mode, transferred into a hydrothermal reaction kettle and placed in an oven to be subjected to a hydrothermal reaction, then the product is naturally cooled to room temperature, finally, centrifugal separating, washing and dying are performed, and the bismuth molybdate composite photocatalytic material is obtained. The composite photocatalytic material has certain electronegativity because of nitrogen vacancy on the surface of the boron nitride nanosheet, photogenerated holes, formed after illumination stimulation, of a bismuth molybdate valence band are absorbed so that migration of the holes can be promoted, and therefore the migration efficiency of photon-generated carriers is improved; besides, the large specific surface area of the boron nitride nanosheet is favorable for improvement of the adsorption performance of a composite system.
Owner:SHAANXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Graphene clad Fe2(MoO4)3 nanoparticle and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN105742598AImprove conductivitySimple processCell electrodesSecondary cellsHigh rateSodium-ion battery
The invention relates to a preparation method of graphene clad Fe2(MoO4)3 nanoparticle. The preparation method comprises the following steps of 1) mixing cyclohexane and cyclohexanol / n-pentyl alcohol, and then adding a surfactant to obtain a mixed liquid; 2) dissolving ferric nitrate in deionized water to obtain a solution A, dissolving ammonium molybdate in the deionized water to obtain a solution B, sequentially adding the solutions A and B into the mixed liquid obtained in the step 1), and stirring the liquid; 3) centrifugally filtering the liquid, and washing the liquid to obtain a precipitant, and drying the precipitant; 4) heating the precipitant in the air, and carrying out heat preservation to obtain molybdic acid nanoparticles; 5) adding a solution containing graphene and stirring the solution to obtain a precipitant; and 6) centrifugally filtering the precipitant, washing the precipitant with the deionized water and alcohol, and drying the product to obtain the graphene clad Fe2(MoO4)3 nanoparticle. The preparation method has the advantages that the graphene clad Fe2(MoO4)3 nanoparticle is endowed with excellent rate performance, relatively high specific capacity and improved cycle performance when the graphene clad Fe2(MoO4)3 nanoparticle is taken as a positive active material of a sodium ion battery, and is a high-rate and long-lifetime potential application material of the sodium ion battery.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
Preparation method of bismuth molybdate nano-wafer
ActiveCN105709718ALarge specific surface areaEasy to makeMaterial nanotechnologyMolybdeum compoundsMicro nanoGlycerol
The invention relates to a preparation method of a bismuth molybdate nano-wafer and belongs to the field of new environment-friendly materials. The preparation method comprises the following steps: S1, in isopropanol solution, thermally reacting bismuth nitrate and glycerol mixed liquid solvent to produce glycerol bismuth; S2, evenly dispersing the glycerol bismuth in ammonium heptamolybdate ((NH4)6Mo7O24.4H2O) solution, and hydrothermally reacting to obtain the bismuth molybdate nano-wafer. Compared with the prior art, the preparation method has the advantages that the prepared bismuth molybdate is a micro-nano structural material 3-10 micrometers in micro-nano size, having large specific surface area, is filterable and recyclable in a solution system, is simple to prepare, has low temperature, needs low energy consumption and is directly useful as a visible light catalyst.
Owner:TIANJIN RES INST FOR ADVANCED EQUIP TSINGHUA UNIV
Fertilizer formula capable of improving growth quality of dragon fruit and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN106810374AImprove growth qualityRealize integrationMagnesium fertilisersAlkali orthophosphate fertiliserRipeningMonopotassium phosphate
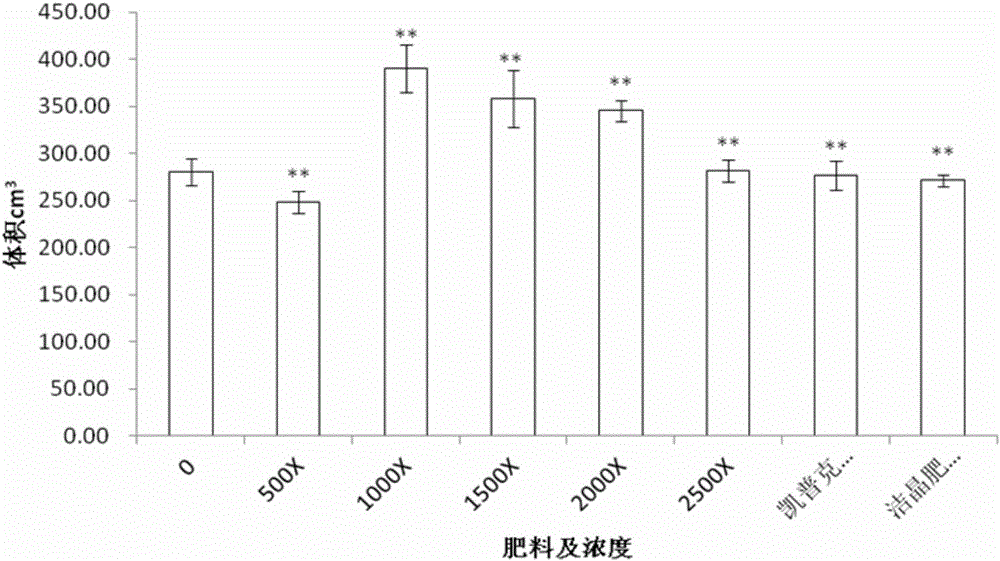
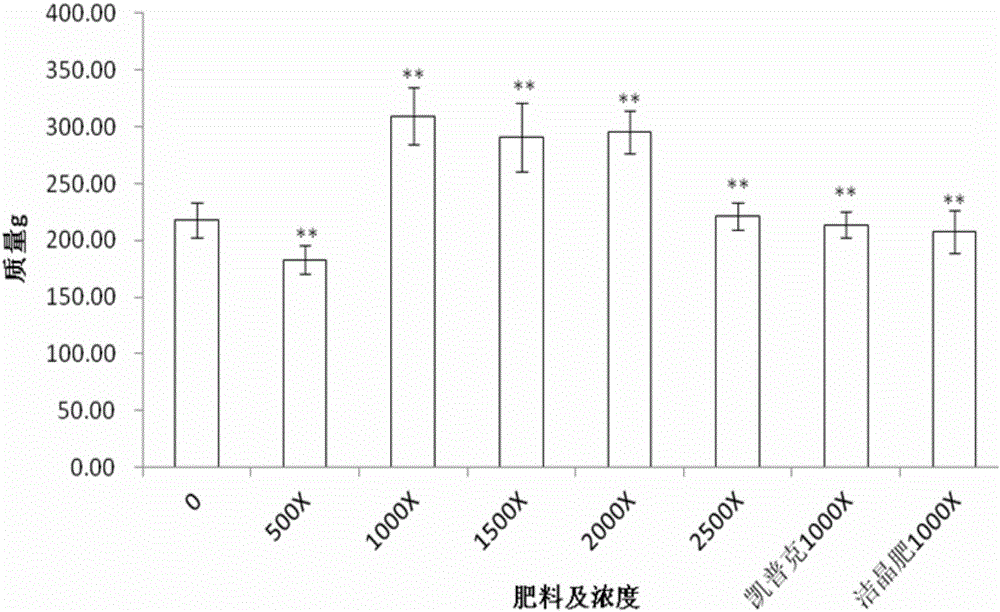
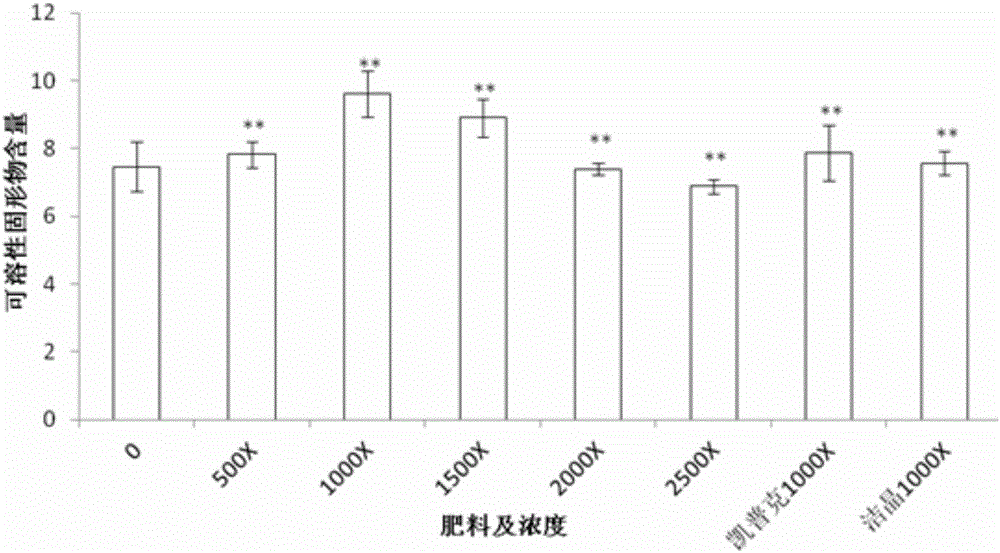
The invention discloses a fertilizer formula capable of improving the growth quality of dragon fruit and a preparation method and application thereof. The fertilizer formula is characterized in that the fertilizer formula is mainly prepared from the following raw materials with concentrations thereof: 11.18 g / kg of urea, 11.4 g / kg of potassium nitrate, 1.66 g / kg of monopotassium phosphate, 475.25 g / kg of tetrahydrated calcium nitrate, 2.28 g / kg of magnesium sulfate heptahydrate, 144.14 mg / kg of boric acid, 117.5 mg / kg of chelated iron, 9.36 mg / kg of copper sulfate pentahydrate, 3.36 mg / kg of heptahydrate, 1.42 mg / kg of manganese sulfate tetrahydrate and 0.13 mg / kg of ammonium heptamolybdate tetrahydrate, wherein the solvent is water, and the fertilizer formula can also comprise a seaweed bio-fertilizer. The fertilizer formula has the advantages that the flowering phase and fruit ripening time can be reduced through application as a leaf fertilizer of the dragon fruit, the blooming fruiting rate is improved, the fruit sugar accumulation is promoted, the fruit quality is optimized, and the volume, quality, sweetness and Vc content of the dragon fruit are improved.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com