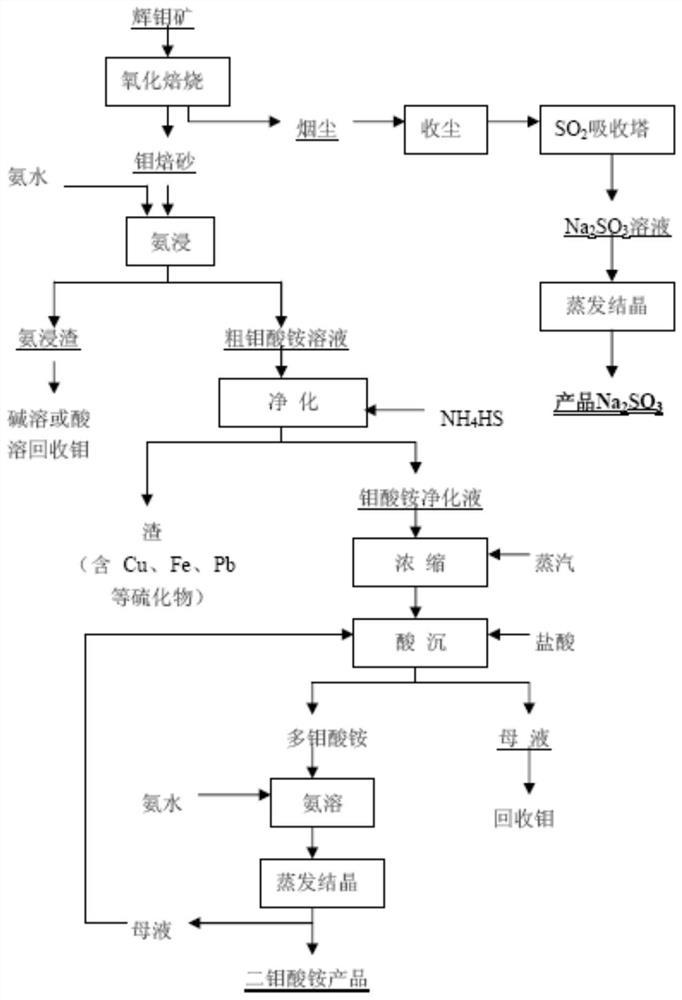
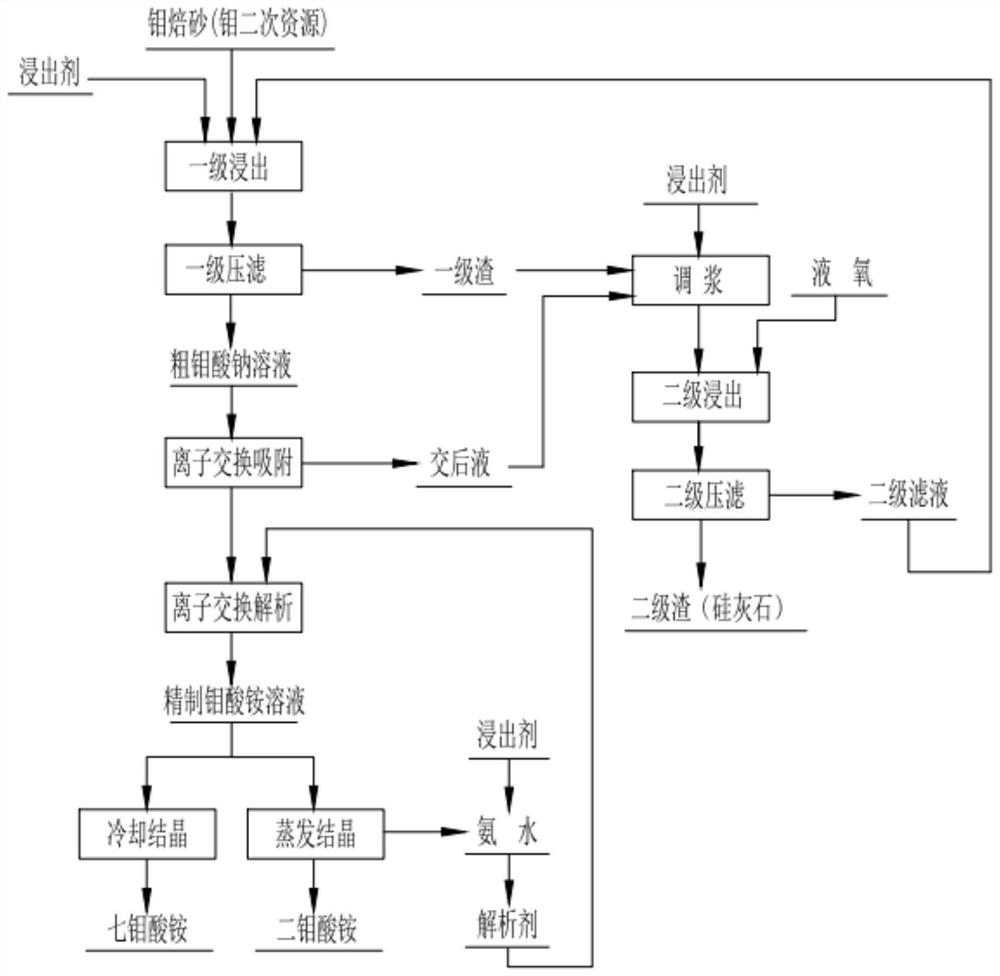
Green molybdenum smelting ion exchange process
An ion exchange and green technology, applied in the chemical industry, can solve problems such as low recovery rate, easy corrosion of equipment, poor adaptability of raw materials, etc., and achieve the effect of reducing alkali consumption and meeting process requirements
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0054] The specific implementation steps of this embodiment are as follows:
[0055] 1. Molybdenum calcined sand with a molybdenum grade of 31.4%, according to the molar ratio of the leaching agent required by Mo, 1:1, processing water and sodium carbonate, at a temperature of 90 ° C, compressed air (pressure 0.3 MPa) stirring reaction for 5 hours, carried out The primary filter press, the primary leaching residue contains 14.8% molybdenum, the molybdenum concentration of the filtrate crude sodium molybdate solution is 25.2g / l, P: 0.43g / l, As: 0.34g / l, Si: 0.28g / l. In the following examples, after the initiation of the secondary leaching, this step can use the secondary filtrate (additional leaching agent) to perform primary leaching of the molybdenum raw material.
[0056] 2. The crude sodium molybdate solution is adsorbed by a strong basic anion exchange resin (201 series can be used), the adsorption flow rate is controlled within 3m / h, and the post-transaction liquid contai...
Embodiment 2
[0061] The specific implementation steps of this embodiment are as follows:
[0062] 1. Molybdenum calcine with a molybdenum grade of 31.4% is mixed with the secondary leaching filtrate at a solid-to-liquid ratio of 1:6, and sodium carbonate is added according to the molar ratio of the leaching agent required for Mo at 1:1. At a temperature of 90°C, compressed air (Pressure 0.3MPa) stirring and reacting for 5 hours, performing primary pressure filtration (temperature before pressure filtration is lower than 60° C.), and the primary leaching residue contains 14.8% molybdenum.
[0063] 2. Mix the primary leaching slag obtained in step 1 with the post-transaction liquid obtained by ion exchange adsorption according to the solid-to-liquid ratio of 1:10, and the molar ratio of Mo to leaching agent of 1:4, and add sodium carbonate and sodium hydroxide to make pulp, and react The conditions are: temperature 200°C, oxygen partial pressure 2.0MPa, reaction time 6 hours, secondary leach...
Embodiment 3
[0072] The specific implementation steps of this embodiment are as follows:
[0073] 1. Molybdenum calcined sand with a molybdenum grade of 51.8% is mixed with the secondary leaching filtrate according to the solid-to-liquid ratio of 1:5, and sodium carbonate is added according to the molar ratio of the leaching agent required by Mo at 1:1. At a temperature of 60°C, compressed air (Pressure 0.15MPa) stirring and reacting for 2.5 hours, and carrying out primary pressure filtration, the primary leaching residue contains 5.7% molybdenum.
[0074] 2. The primary leaching slag obtained in step 1 is mixed with sodium carbonate and sodium hydroxide to make pulp according to the solid-to-liquid ratio of 1:5 and the molar ratio of Mo to leaching agent of 1:2 with the ion-exchange adsorption post-transaction liquid, and the reaction The conditions are: temperature 150°C, oxygen partial pressure 1.5MPa, reaction time 3 hours, secondary leaching slag containing 0.18% molybdenum, molybdenu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com