Method for synergistic recovery of molybdenum and rhenium from molybdenum concentrate roasting eluent
A technology of eluent and molybdenum concentrate, which is applied in the preparation of molybdenum compounds, chemical instruments and methods, and the preparation of rhenium compounds, etc., which can solve the problems of slow adsorption speed, small saturated adsorption capacity of rhenium, and no consideration of synergistic recovery of molybdenum, etc. problems, to achieve the effect of improving the adsorption speed and adsorption capacity, realizing synergistic utilization, and improving the level of comprehensive utilization
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0046] Example 1: Comparison experiment of molybdenum-rhenium static adsorption before and after waste acid pretreatment
[0047] Add different amounts of CaO to the eluate, react for 100 minutes, filter and wash a small amount (quantitative washing), mix the filtrate and washing water, measure the pH value of the filtrate, analyze the content of molybdenum and rhenium in the solution, and then according to the test results , add a small amount of ammonium perrhenate and ammonium molybdate, and adjust the molybdenum-rhenium content in the solution to be consistent with the molybdenum-rhenium content in the untreated eluate.
[0048] Measure 250ml each of the solution obtained after the pretreatment of waste acid and different lime additions, put them into 500ml conical flasks respectively, put 1ml D314 resin under stirring conditions, take samples after adsorption for different times, and measure the molybdenum content in the solution; Test conditions, put 1ml ZS70 resin to ad...
Embodiment 2
[0061] Embodiment 2: Molybdenum dynamic adsorption test
[0062] Take 10ml of the pretreated D314 resin, put it into the ion exchange column for the test, use a constant flow pump to send the eluent into the ion exchange column at a flow rate of 1BV, take a sample of the effluent at a certain time point, and detect the molybdenum content.
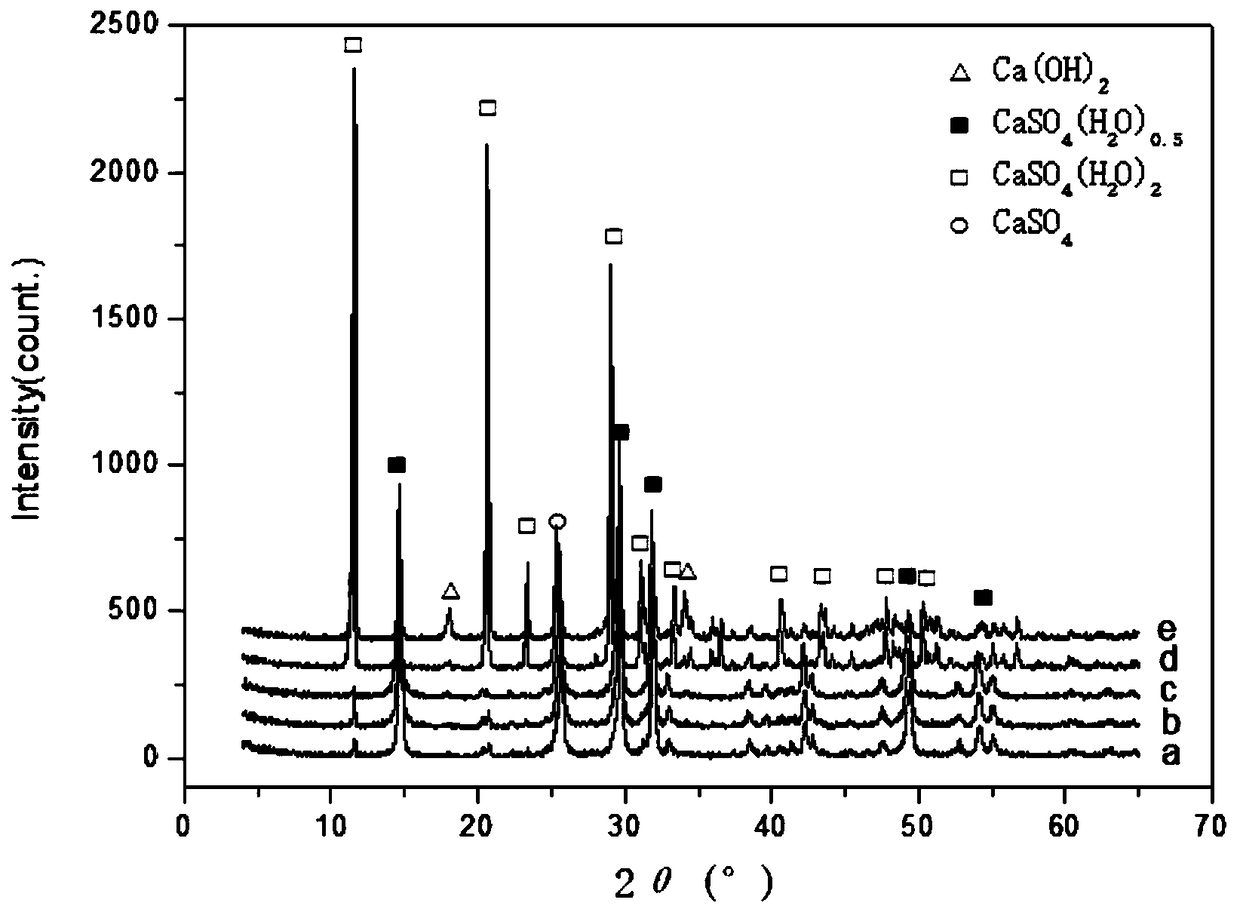
[0063] X-ray diffraction adopts PhilipsX.PertMPD X-ray diffractometer in the Netherlands, CuKα ray, tube voltage 40kV, tube current 30mA, scan rate 0.12° s -1 , the step width is 0.02°.
[0064] Possible chemical reactions during lime neutralization:
[0065] CaO+H 2 SO 4 =CaSO 4 +H 2 O (1)
[0066] CaO+H 2 SO 3 =CaSO 3 +H 2 O (2)
[0067] CaO+H 2 SiF 6 =CaSiF 2 +H 2 O (3)
[0068] CaO+H 2 MoO 4 =CaMoO 4 +H 2 O (4)
[0069] CaO+2HF=CaF 2 +H 2 O (5)
[0070] Put the waste acid before pretreatment and after pretreatment at a temperature of 25°C and a flow rate of 1BV·h -1 Under the conditions, D314 resin was used for ...
Embodiment 3
[0072] Embodiment 3: lime addition
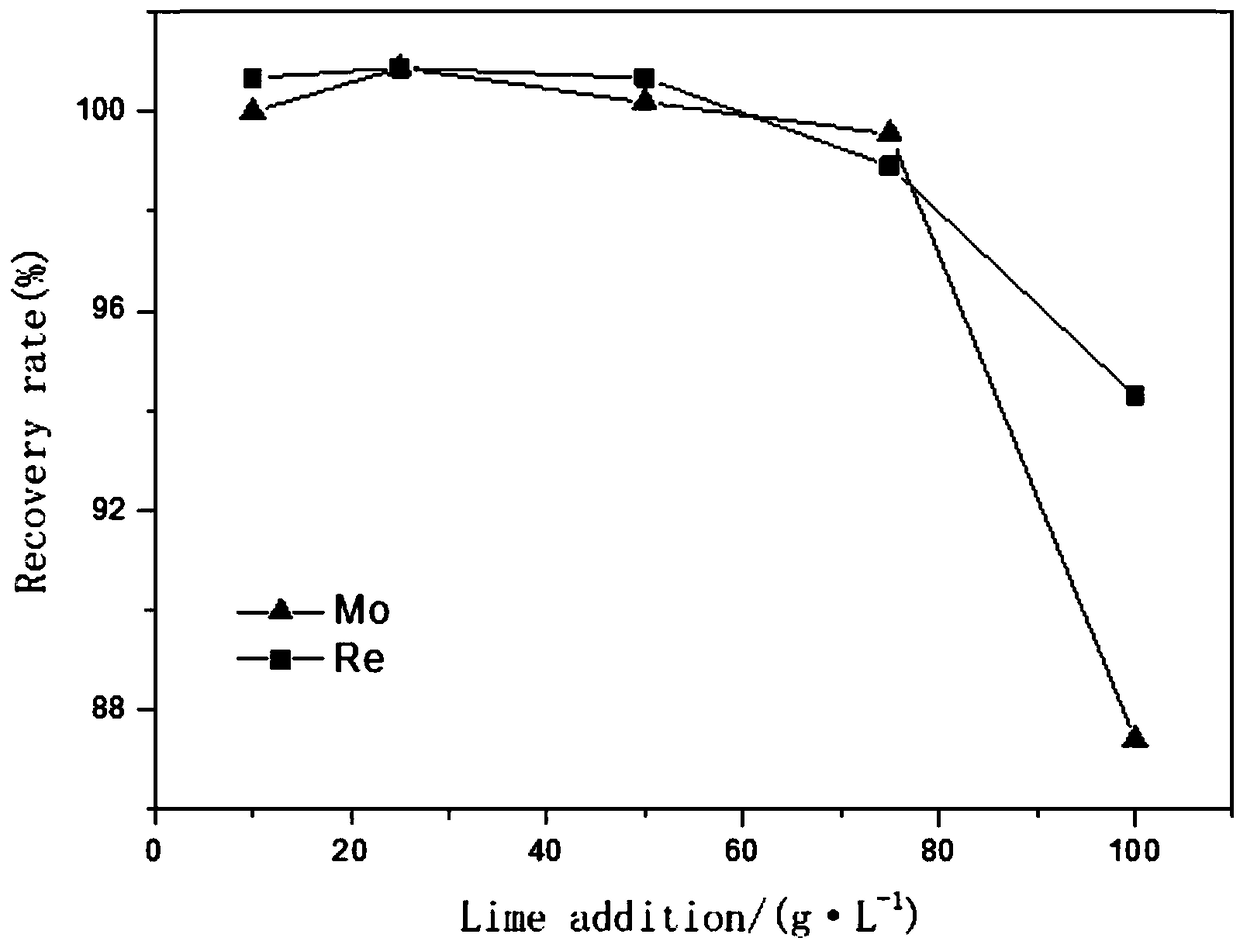
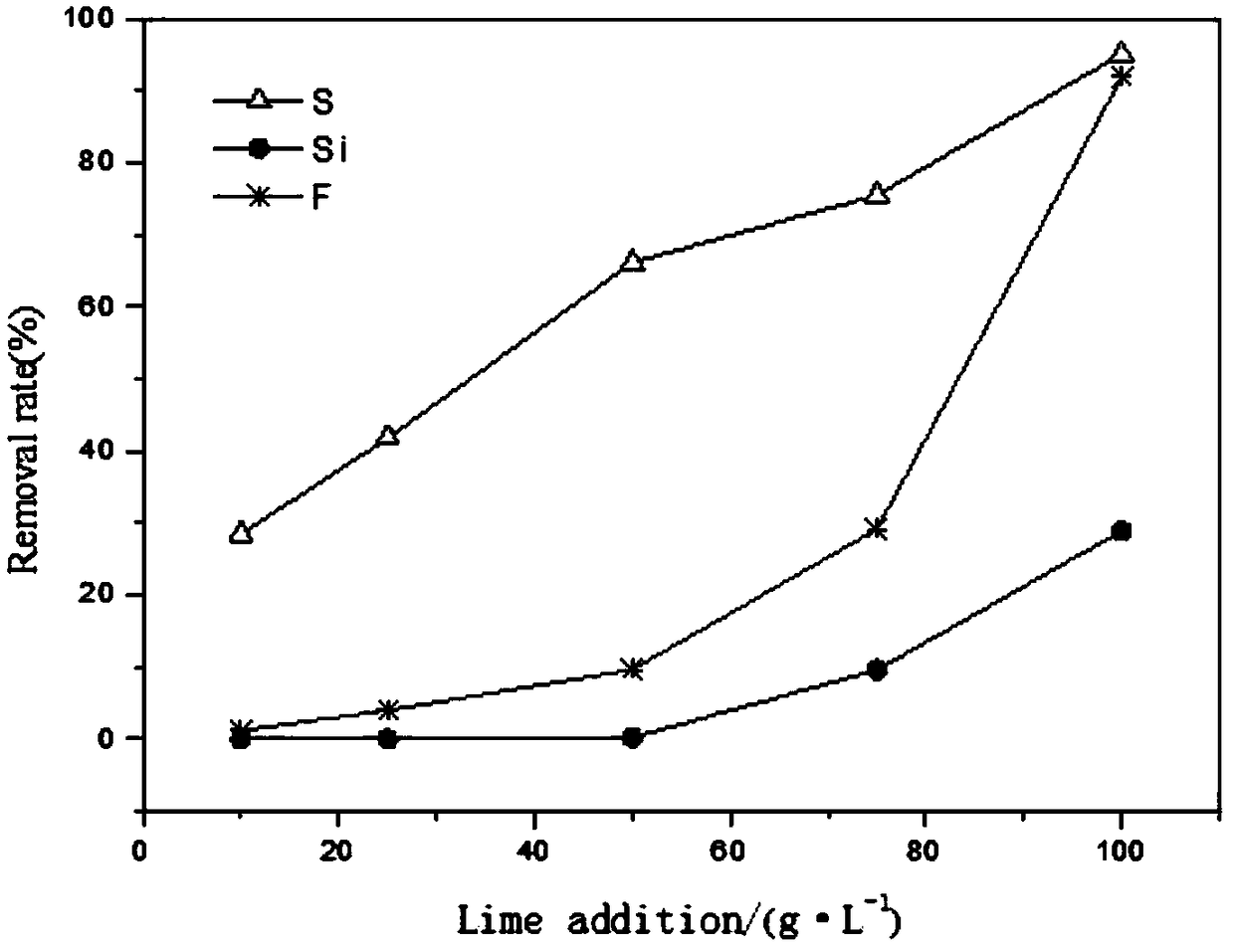
[0073] At 25°C, take 200ml of the eluent into a beaker, add different amounts of CaO under stirring, react for 100 minutes, filter, measure the filtrate and washing water, and conduct multi-element analysis. The relationship between the recovery rate is as figure 1 As shown, the relationship between the amount of CaO added and the removal rate of impurity ions such as sulfur, fluorine, and silicon is as follows: figure 2 shown.
[0074] figure 1 It can be seen that with the addition of CaO at 25g·L -1 ~75g·L -1 When between, the recoveries of molybdenum and rhenium are relatively high, and the addition amount is increased to 100g L -1 , the recovery rate of molybdenum-rhenium is greatly reduced. The amount of CaO added is 75g·L -1 When 15g CaO is added to 200ml waste acid, the recovery rate of molybdenum is 99.56%, and the recovery rate of rhenium is 98.91%; the amount of CaO added is 100g L -1 , the molybdenum yield was 87.40%, an...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com