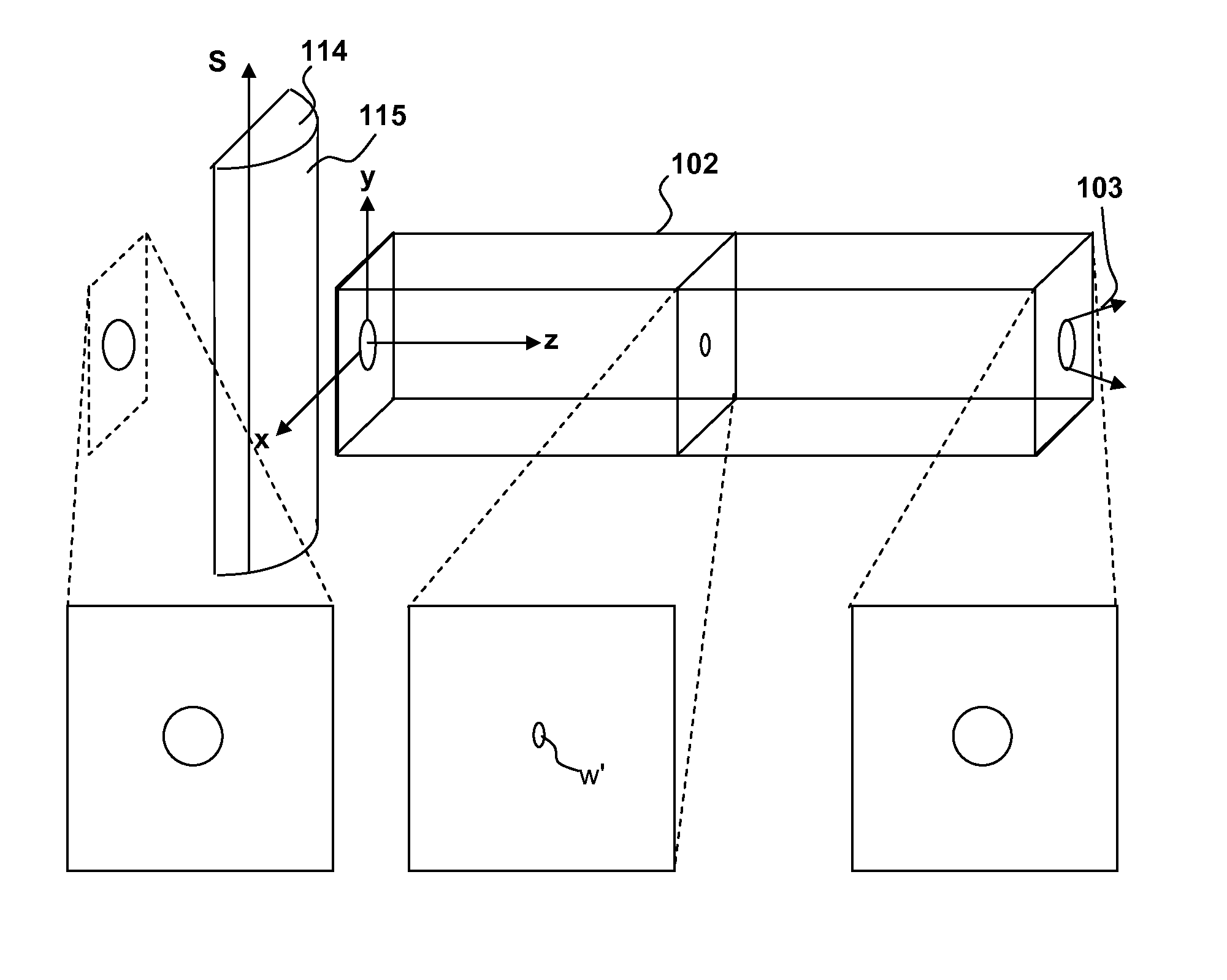
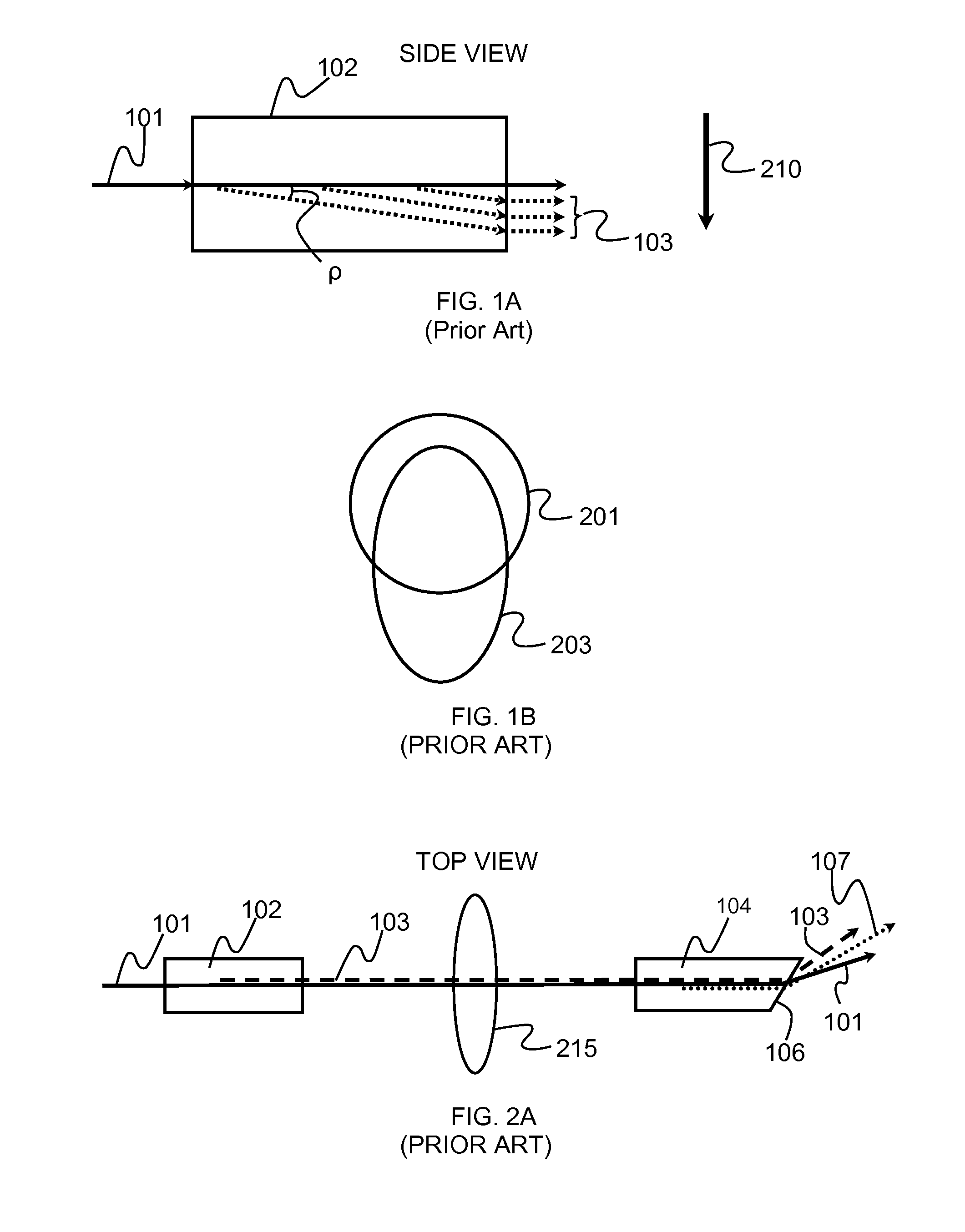
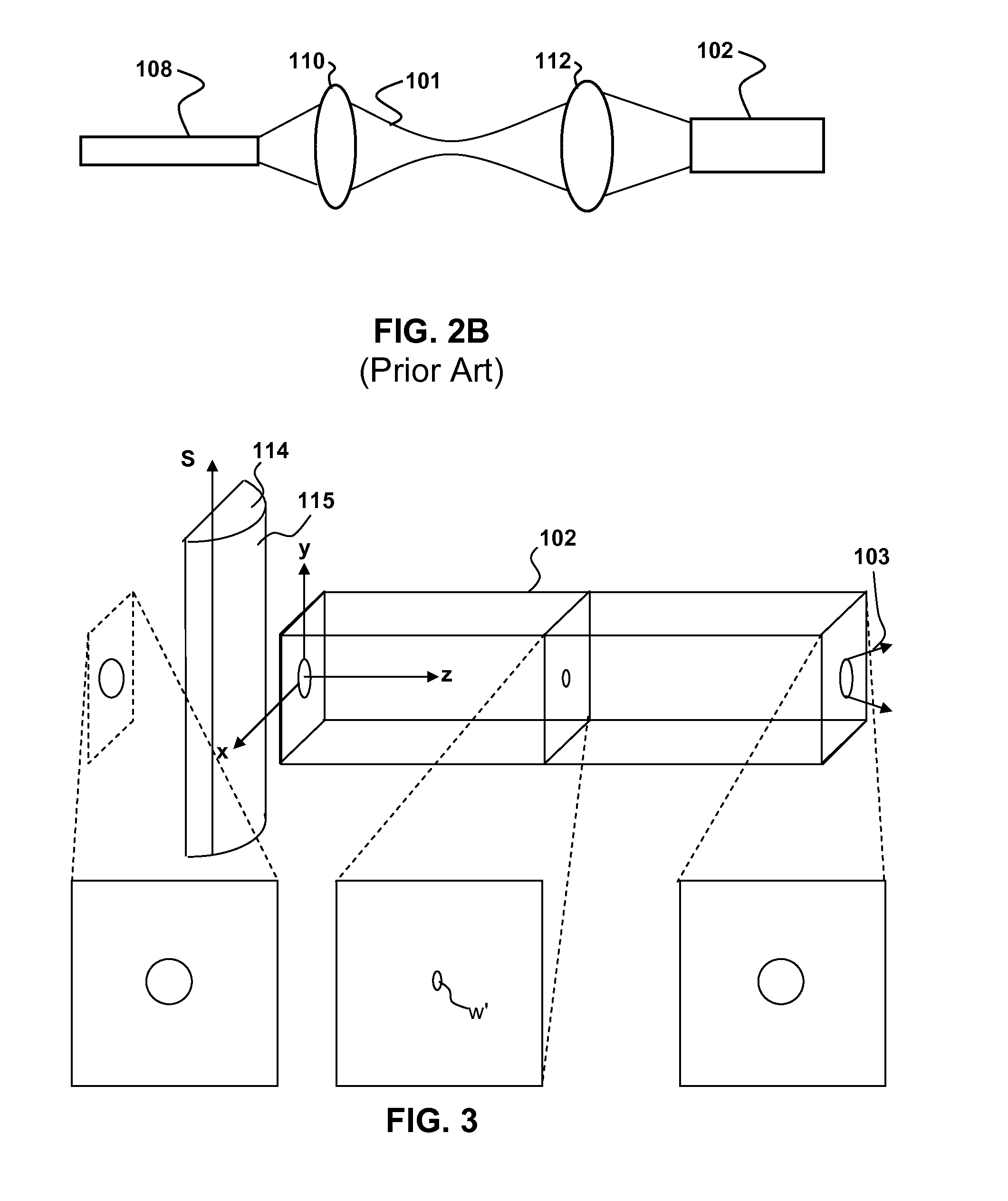
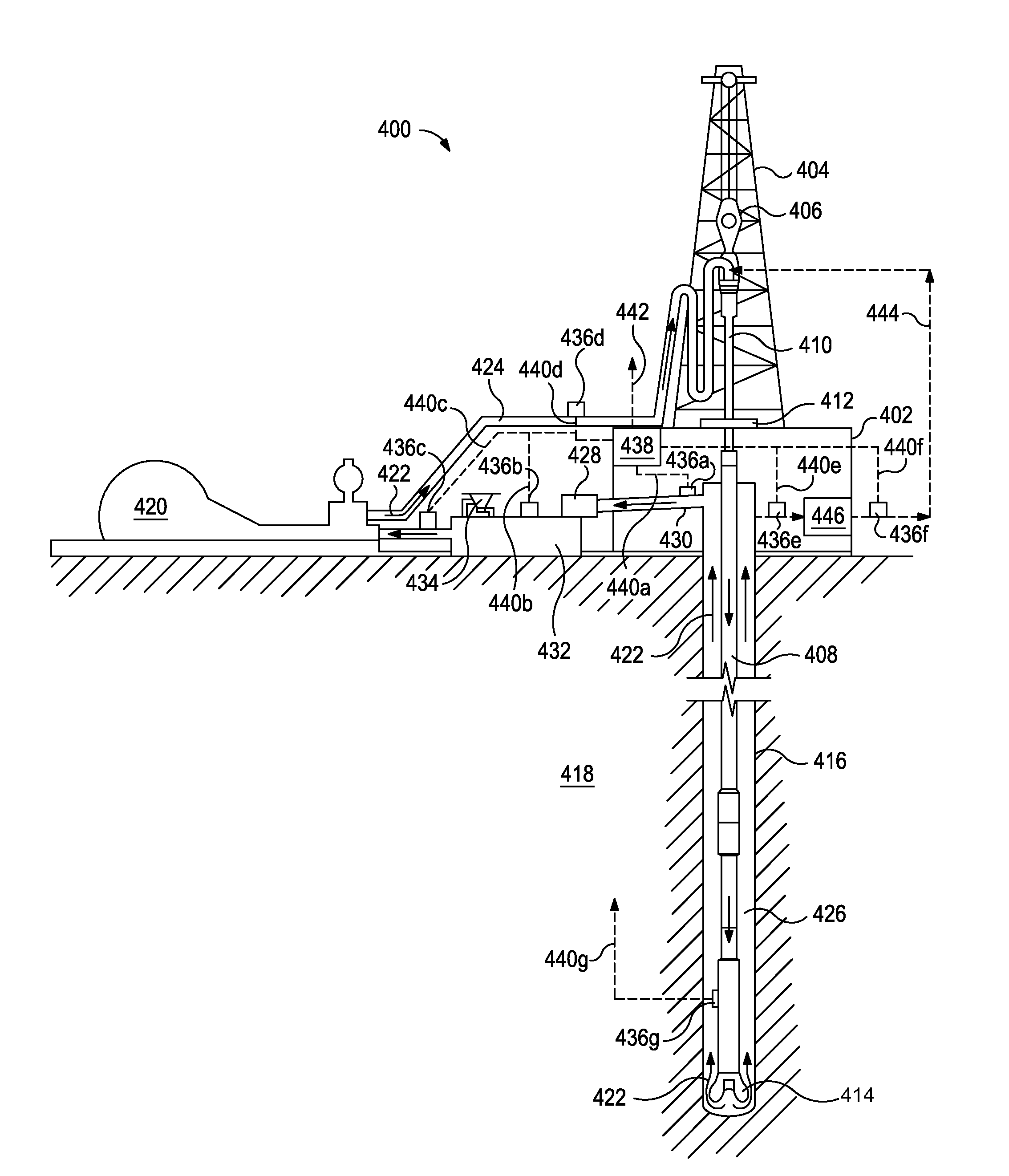
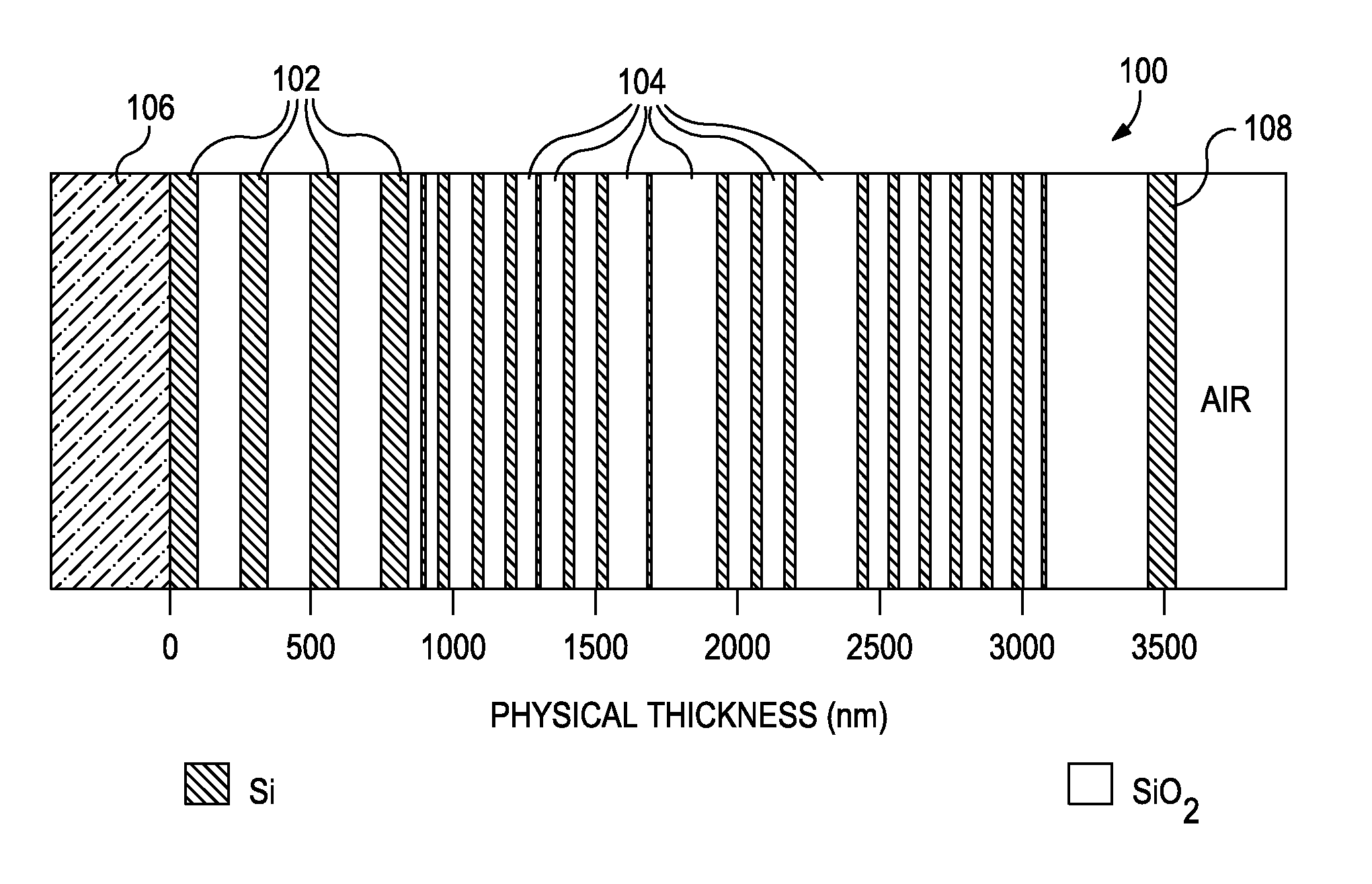
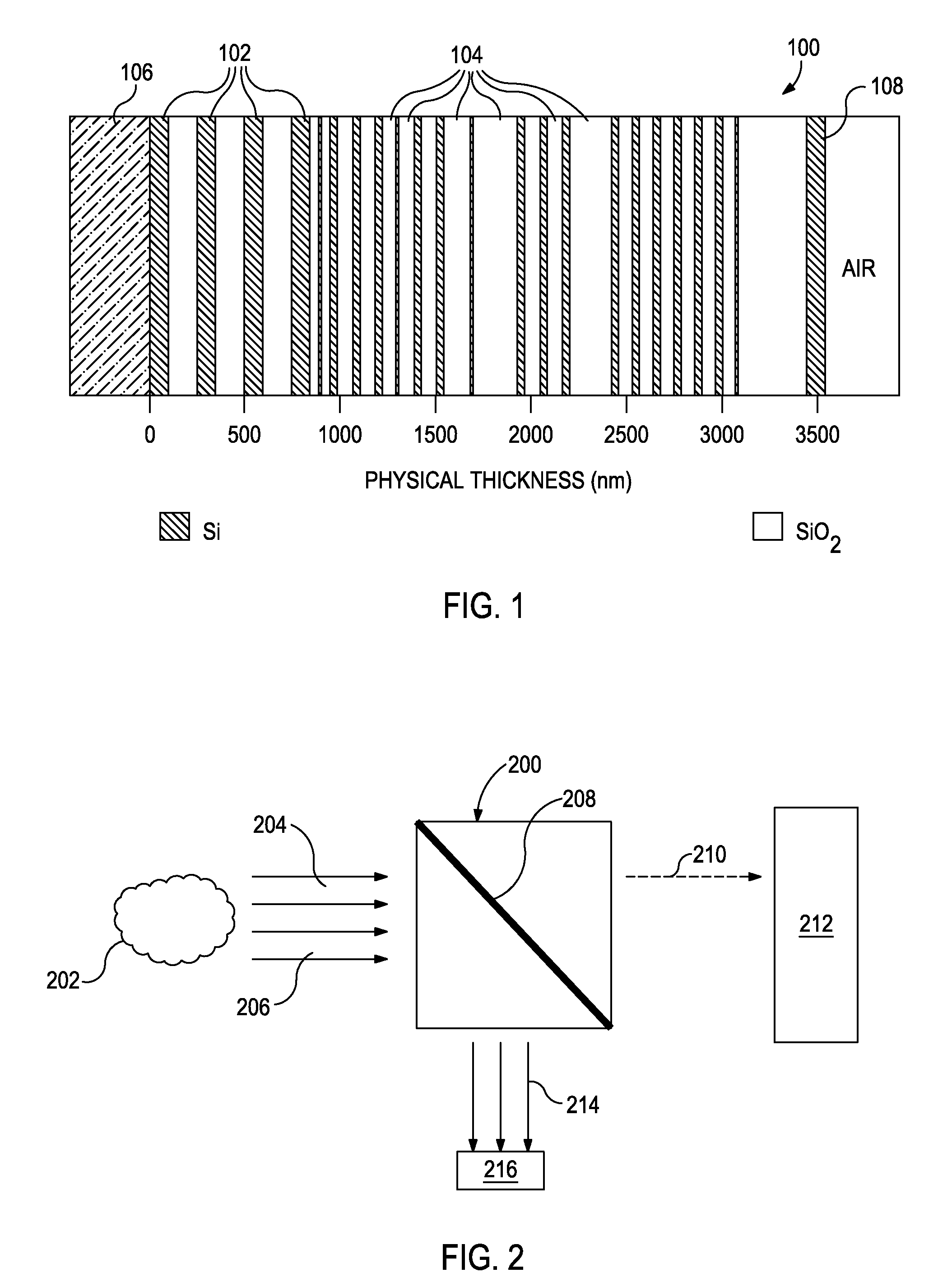
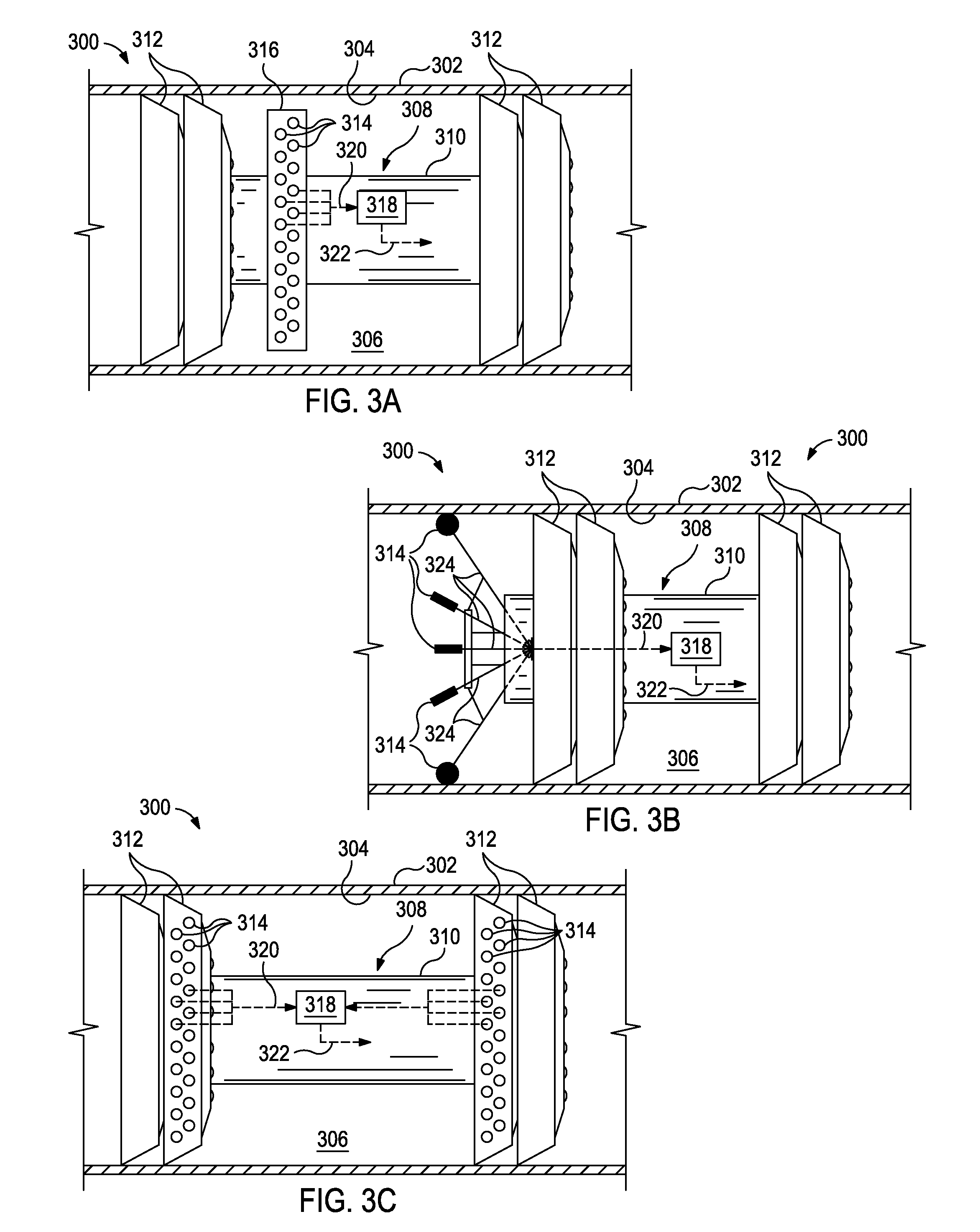
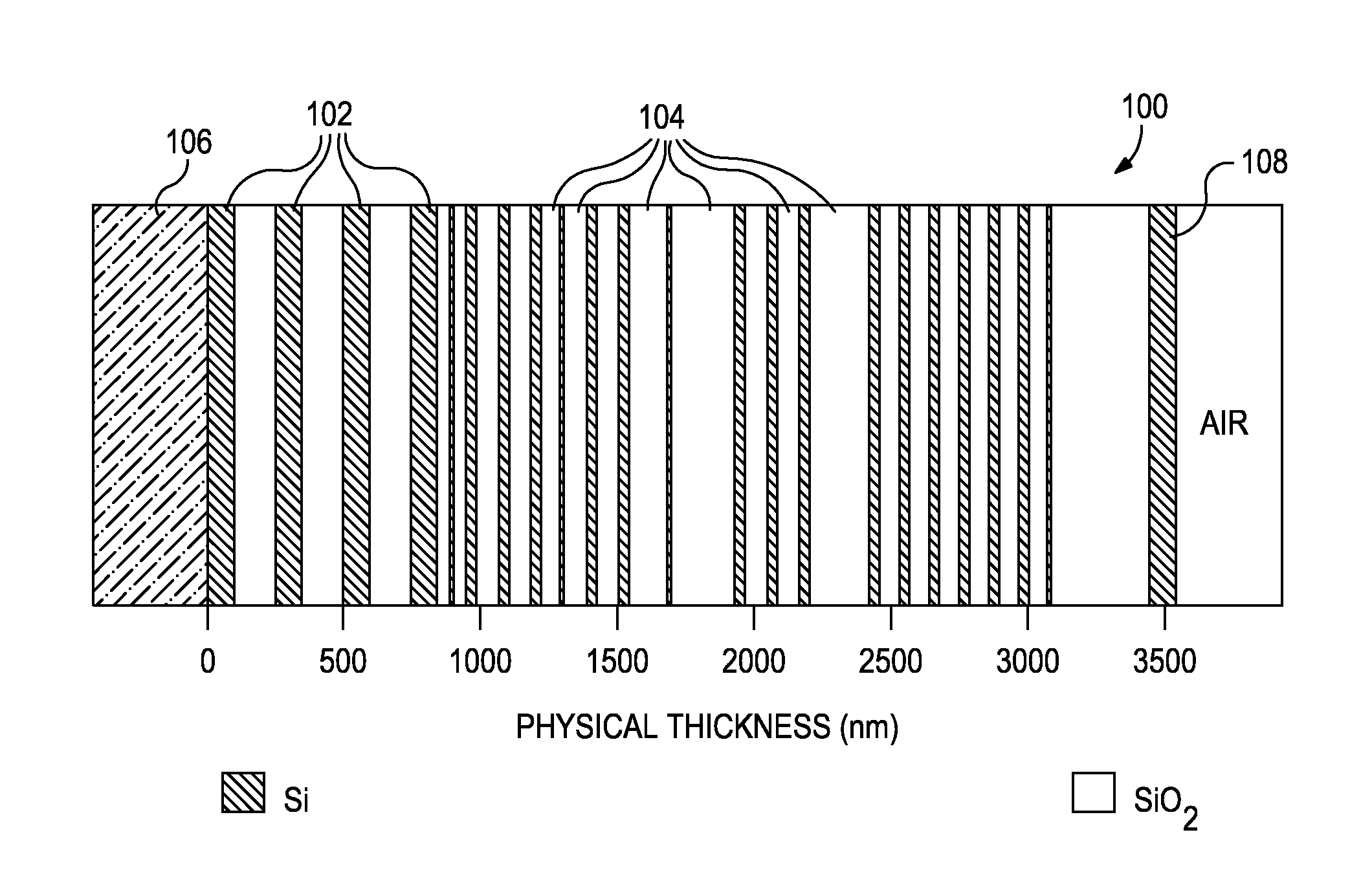
Patents
Literature
120 results about "Optical interaction" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
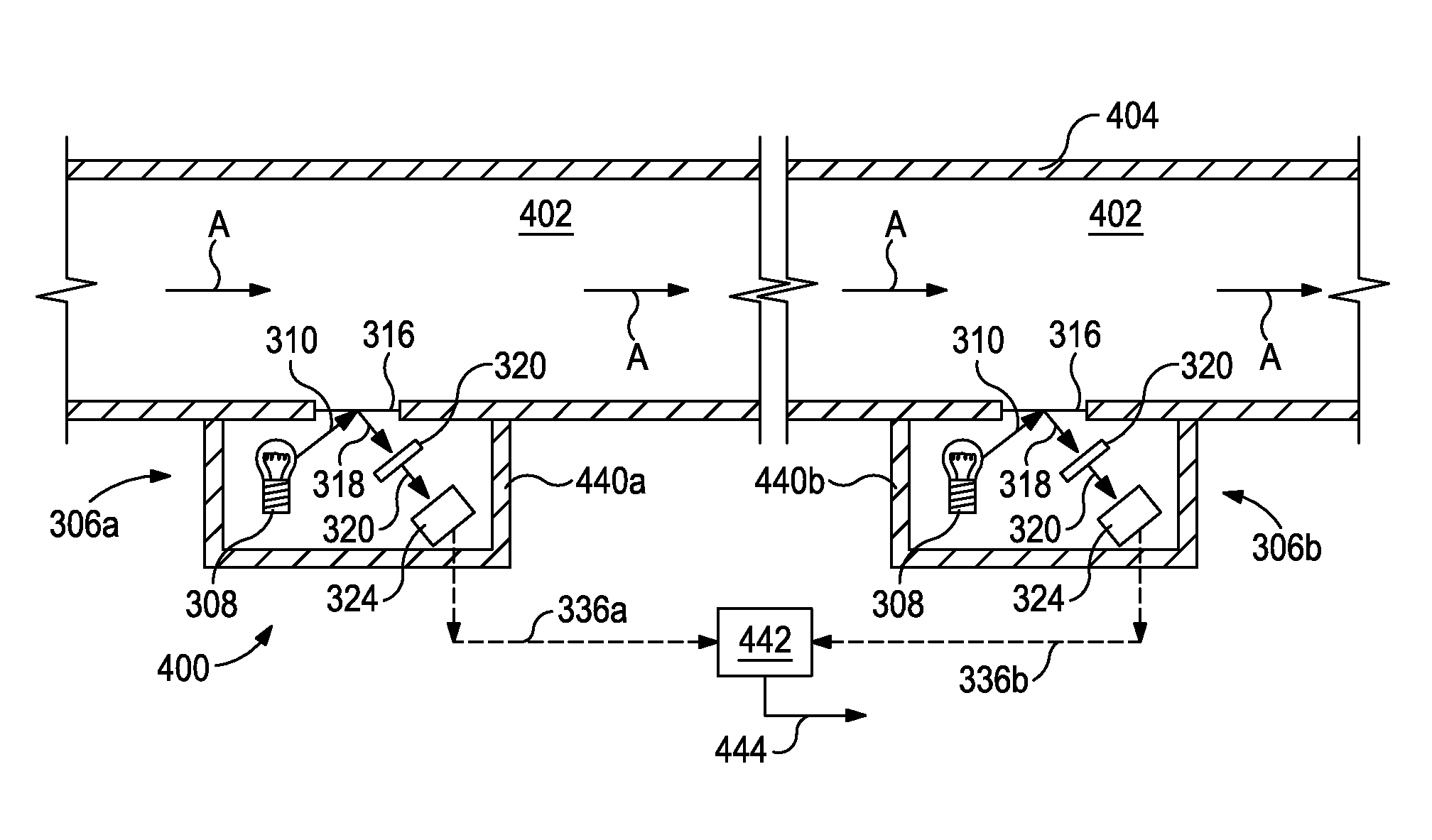
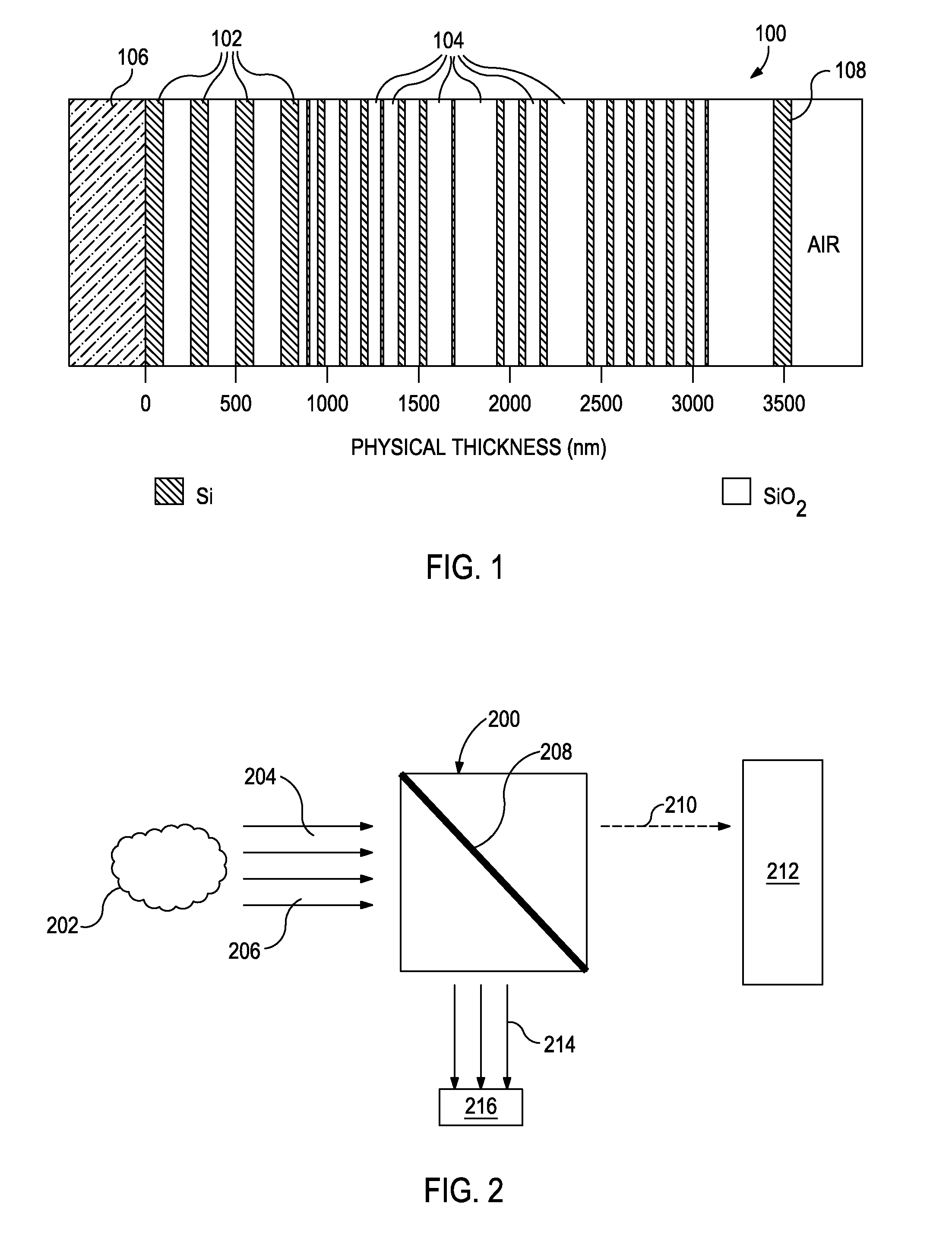
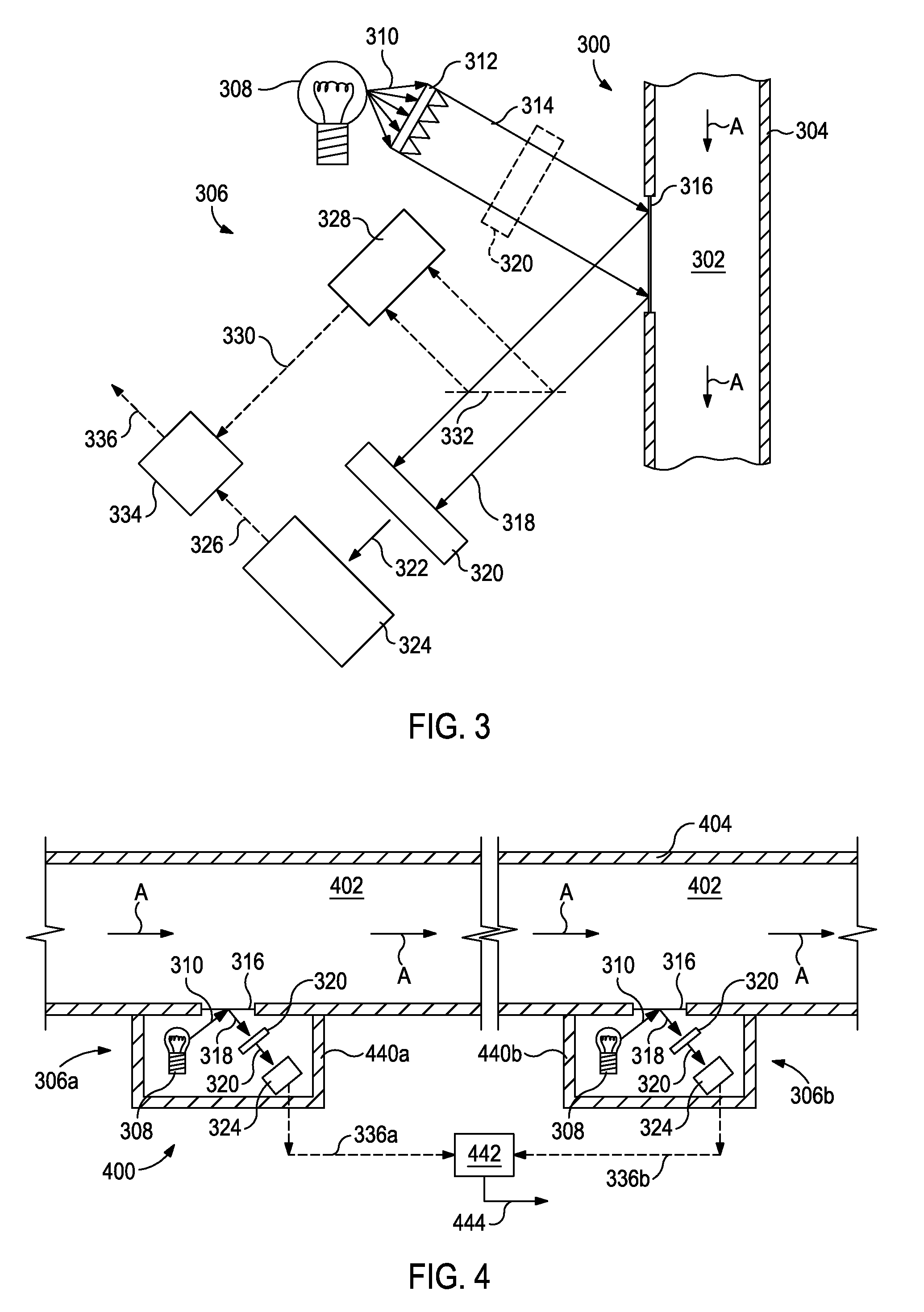
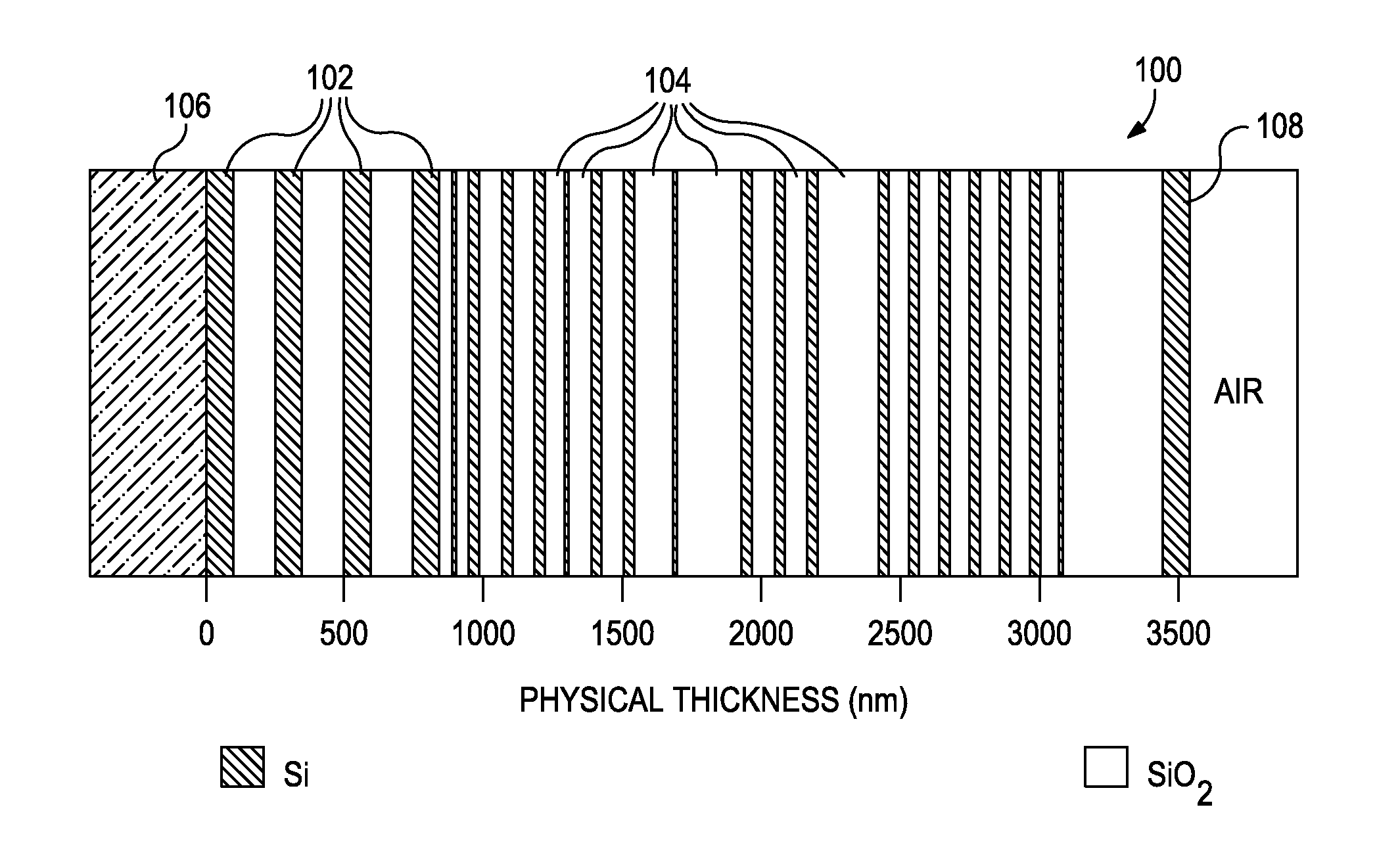
Uniform illumination system
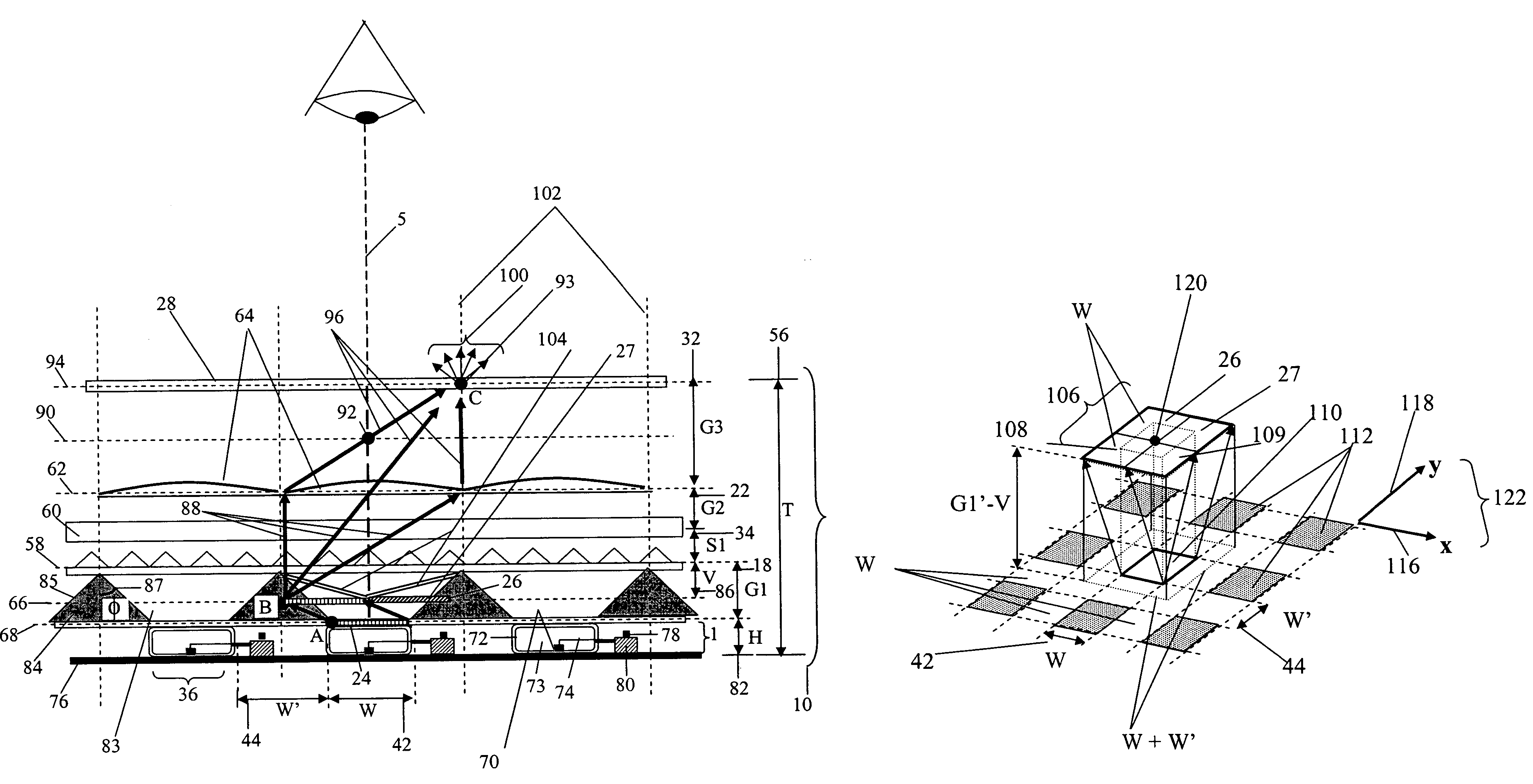
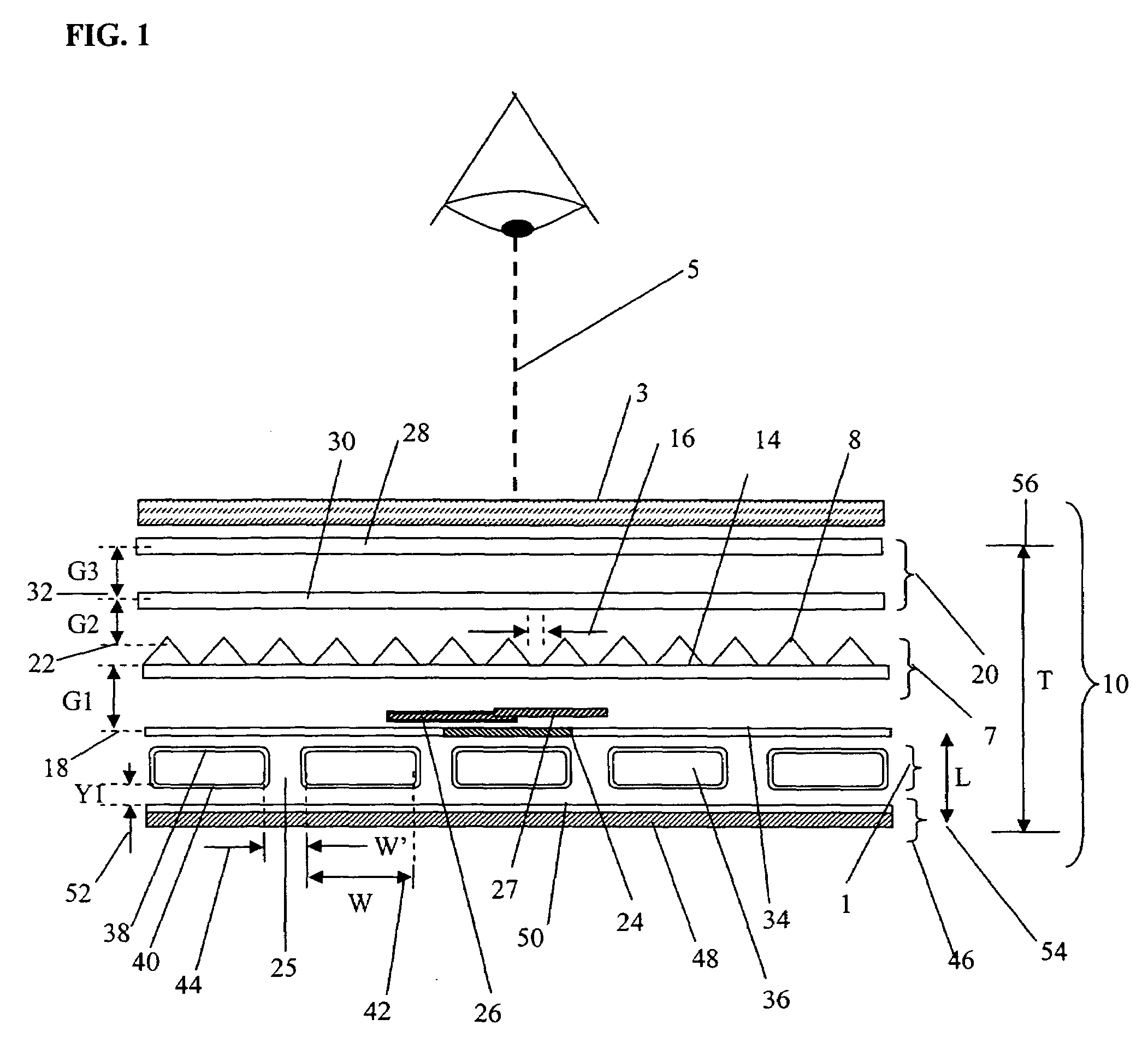
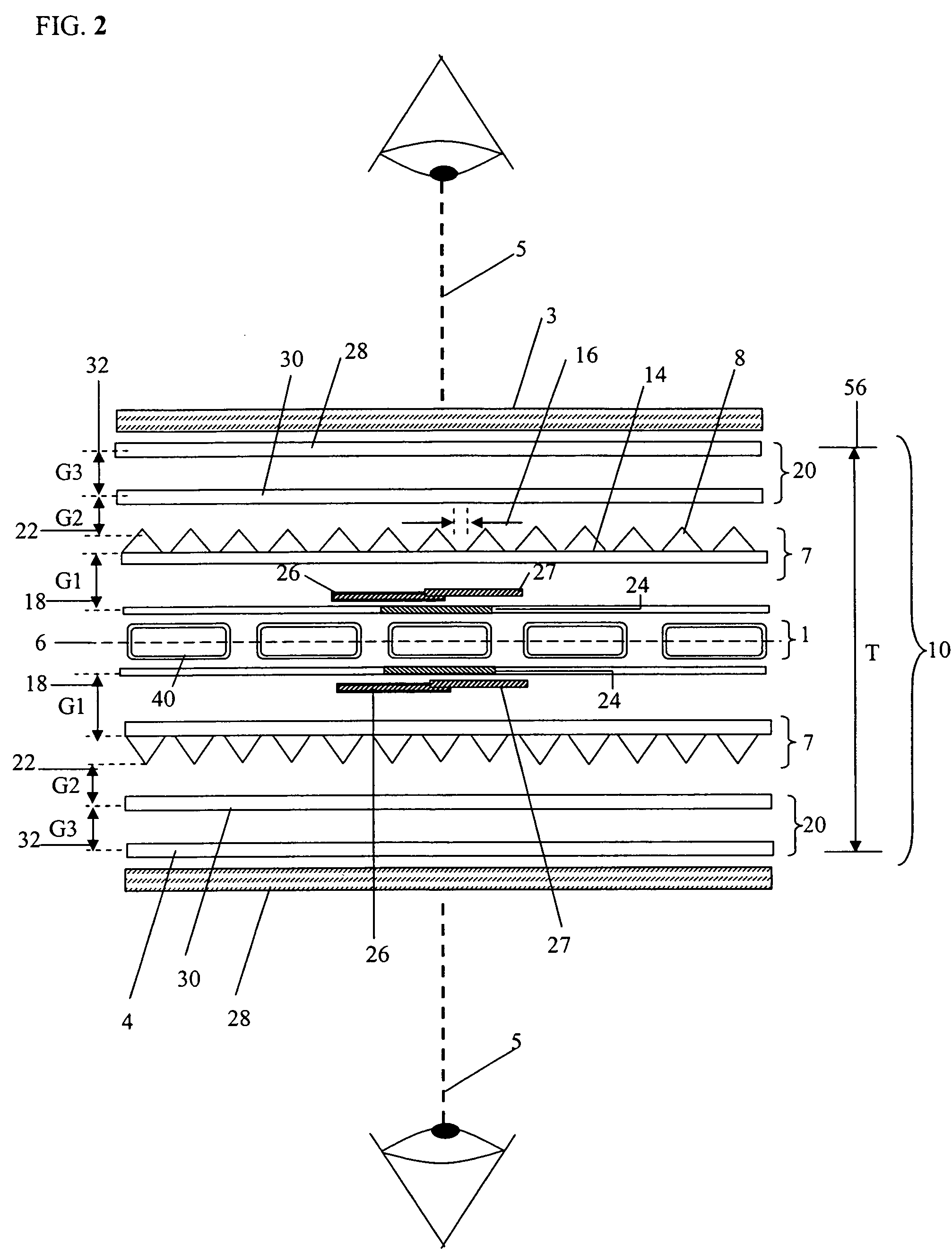
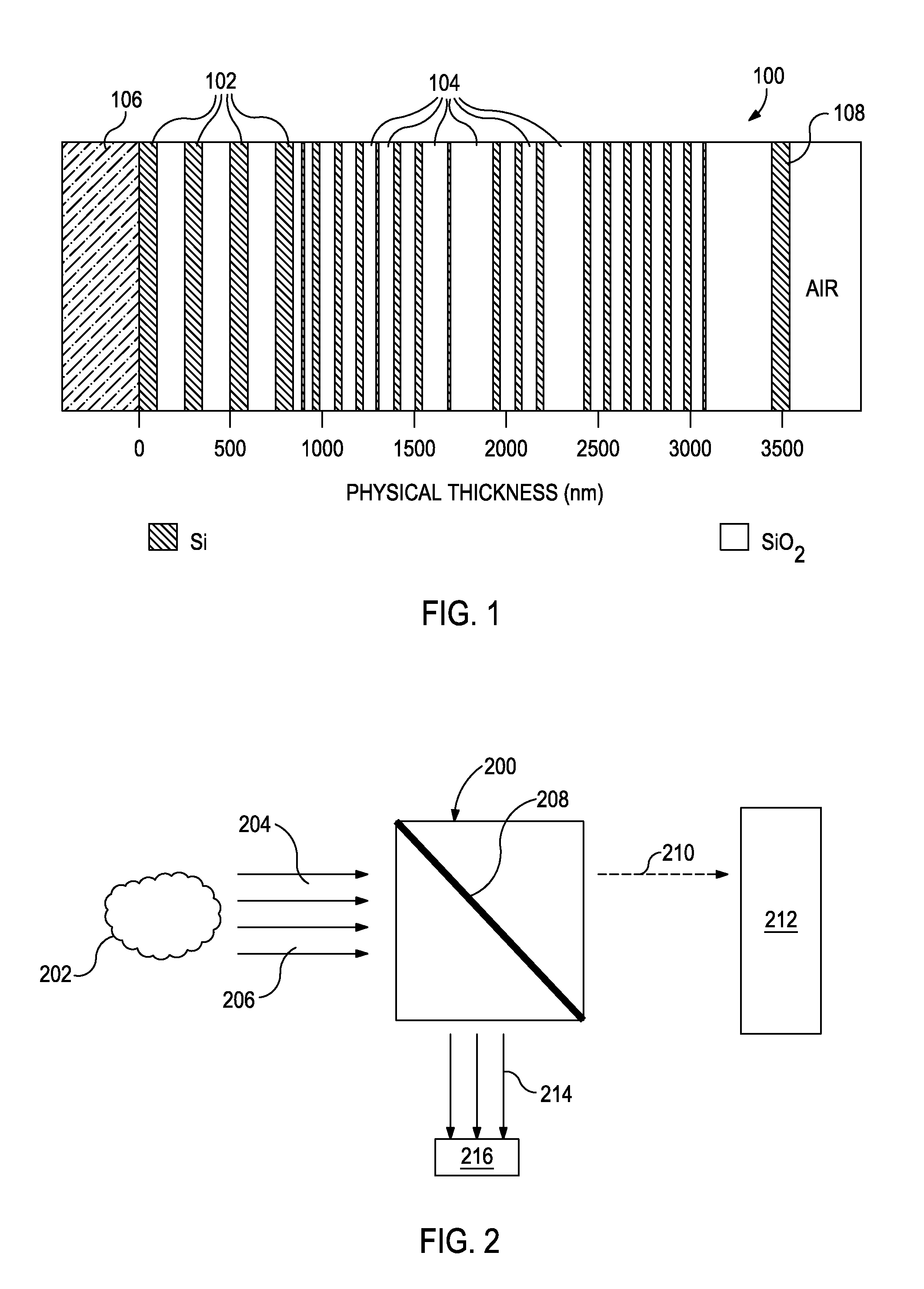
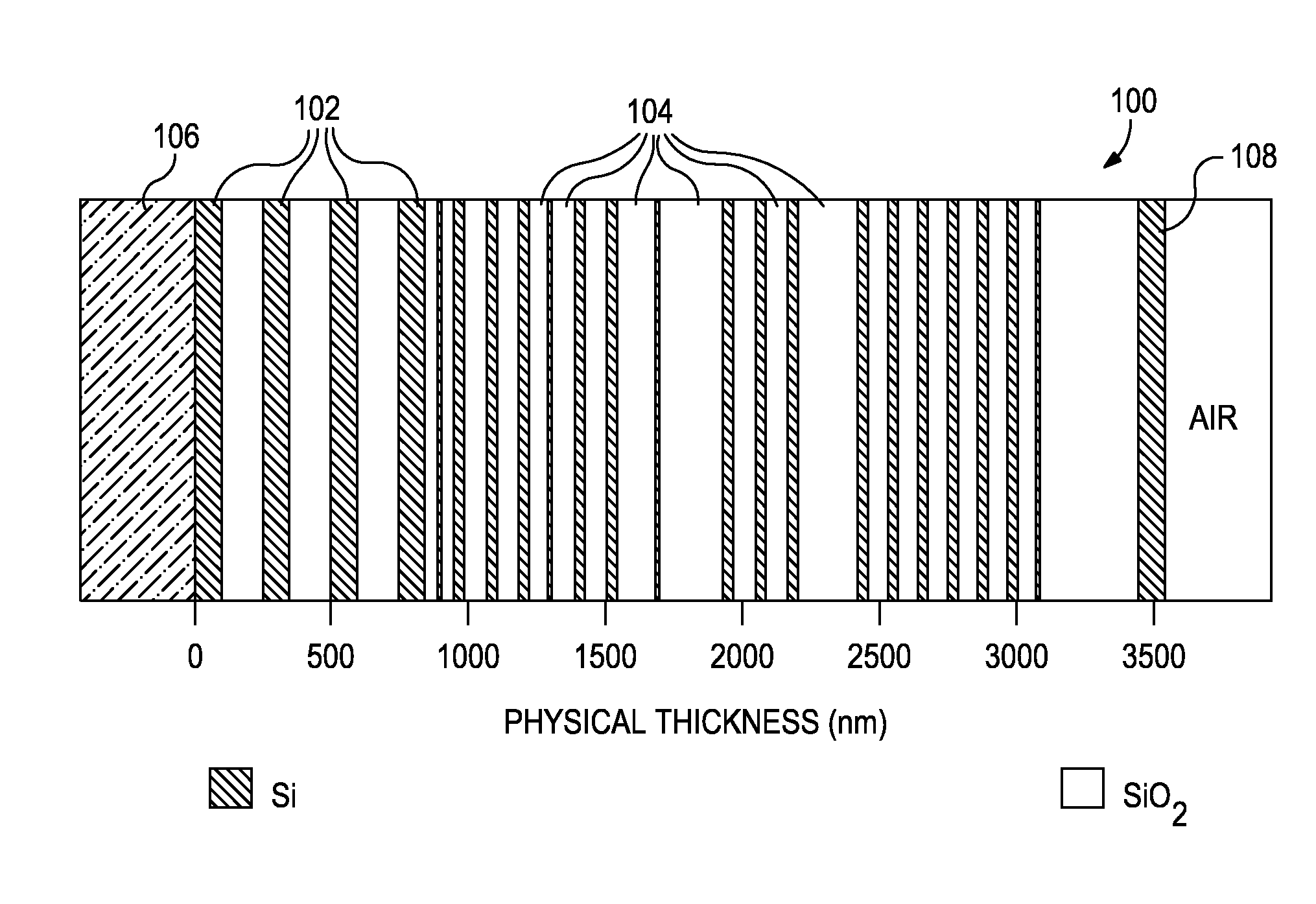
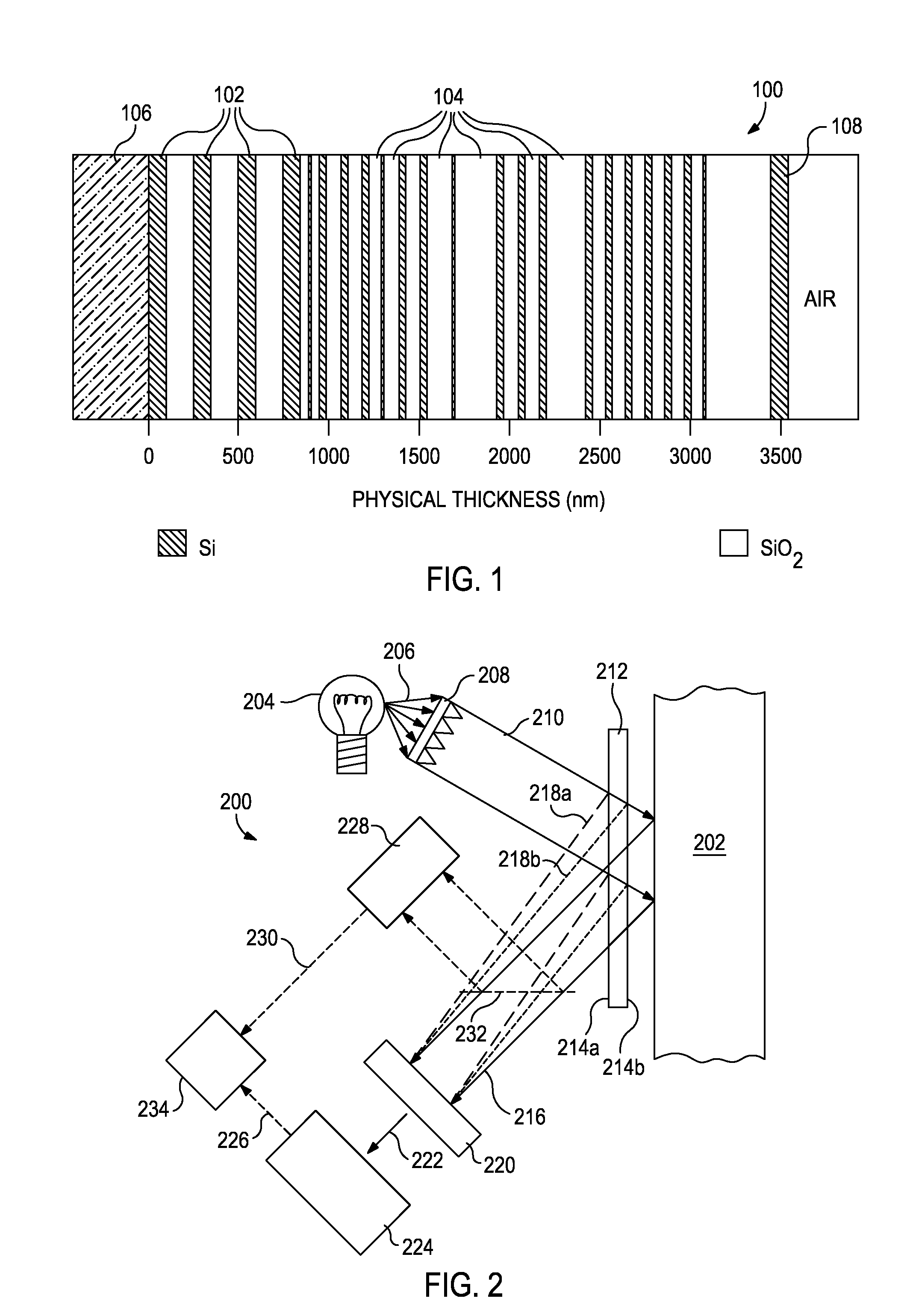
A compact and efficient optical illumination system featuring planar multi-layered LED light source arrays concentrating their polarized or un-polarized output within a limited angular range. The optical system manipulates light emitted by a planar light emitters such as electrically-interconnected LED chips. Each light emitting region in the array is surrounded by reflecting sidewalls whose output is processed by elevated prismatic films, polarization converting films, or both. The optical interaction between light emitters, reflecting sidewalls, and the elevated prismatic films create overlapping virtual images between emitting regions that contribute to the greater optical uniformity. Practical illumination applications of such uniform light source arrays include compact LCD or DMD video image projectors, as well as general lighting, automotive lighting, and LCD backlighting.
Owner:SNAPTRACK
Method of authenticating articles, authenticatable polymers, and authenticatable articles
Disclosed is a method for authenticating that an article is an authenticatable article. The method uses an optical tester, the optical tester comprising an electromagnetic radiation source and a detector. The authenticatable article comprises a heat responsive compound having a temperature dependent optical interaction with the electromagnetic radiation source in the presence of a heat stimulus to produce a heat induced electromagnetic radiation signature. The method comprises placing a test portion of the article in interaction with the electromagnetic radiation source of the optical tester, creating a heated portion by exposing the test portion of the article to a heat stimulus sufficient to raise the temperature of the test portion from a temperature T1 to a temperature T2, measuring the heat induced electromagnetic radiation signature of the heated portion with the detector, and authenticating that the article is an authenticatable article if the heat induced electromagnetic radiation signature is present.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Optical display device having prismatic film for enhanced viewing
InactiveUS6166787AImprove visibilityImprove legibilityPrismsLaser detailsOptical propertyOptical interaction
The display device includes an optical cell having a cell front with at least one cell region being capable of an optically transmissive mode and an optically nontransmissive mode with reference to the cell front. The optical cell contains an optically active material responsive to an applied electrical field such that optical properties of the material are controllably changeable. A reflector may be optically coupled to the cell. A prismatic film including a prismatic surface is optically coupled to the optical cell. The prismatic surface preferably comprises a series of prisms. The prisms have first faces and second faces intersecting the first faces. The first faces are oriented to refract light obliquely intercepting the first faces and the second faces are oriented to minimize refractive, reflective, and optical interactions of the light with the second faces. The prismatic film, the cell, and the reflector optically cooperate such that light entering a display at an incident angle is emitted from the display at an exiting angle distinct from the incident angle for viewing of the display.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
Methods and Devices for Optically Determining A Characteristic of a Substance
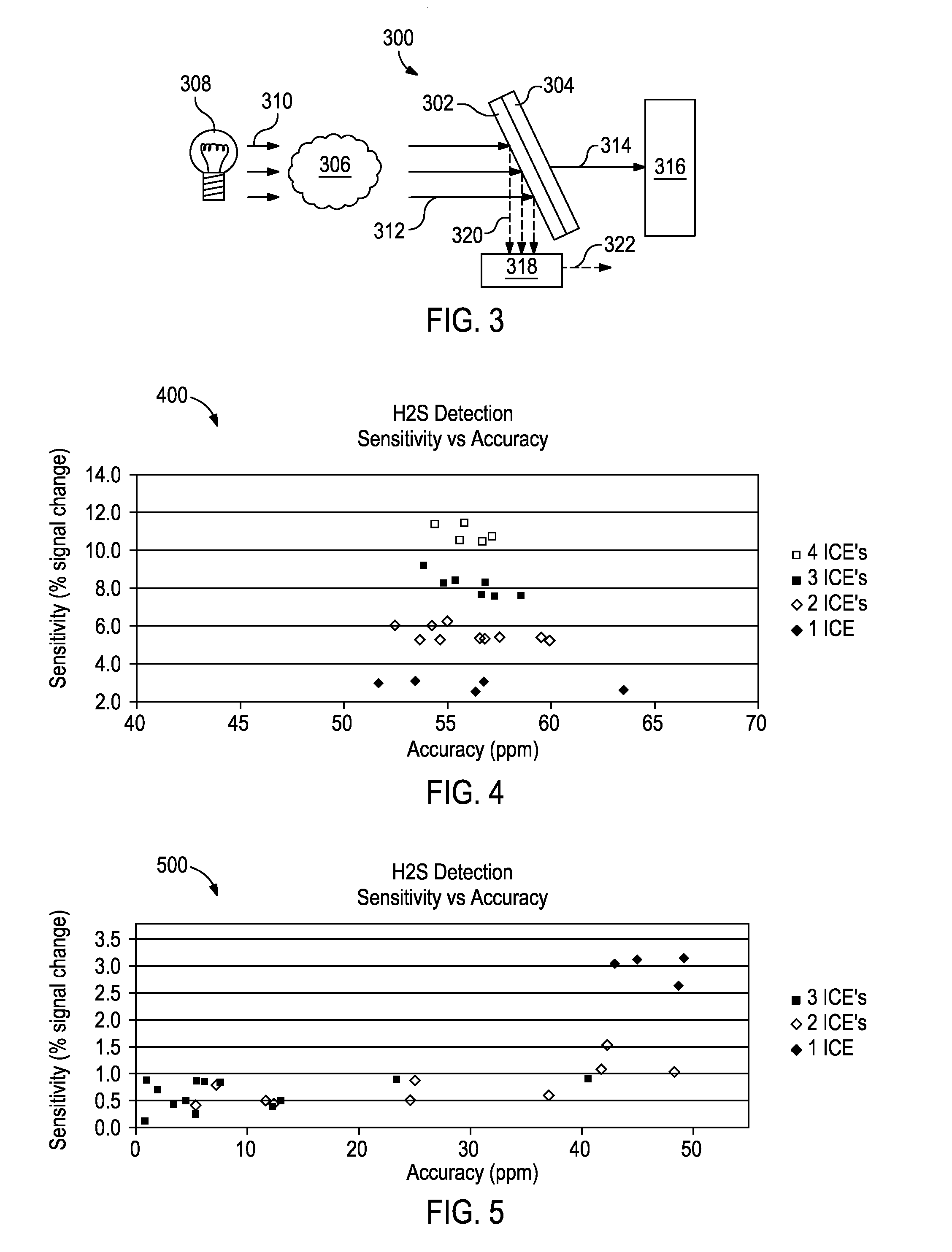
ActiveUS20130284895A1Photoelectric discharge tubesColor/spectral properties measurementsOptical interactionElectromagnetic radiation
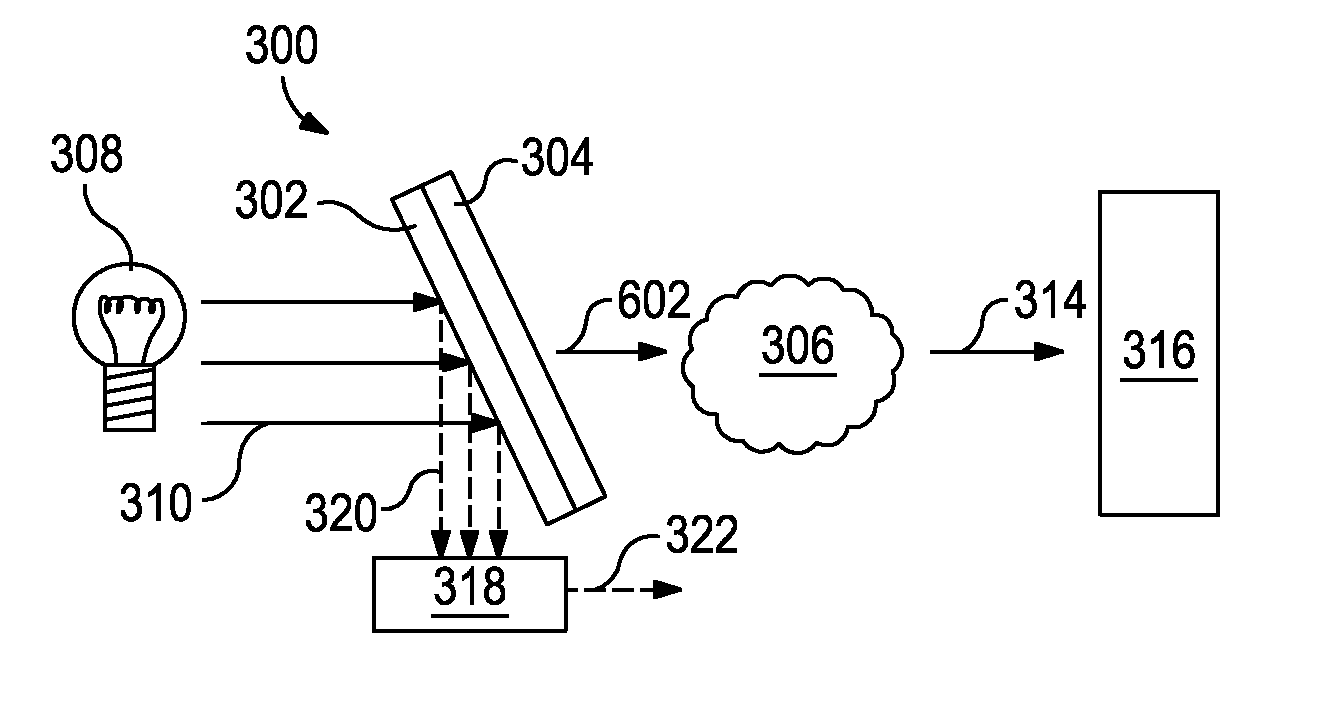
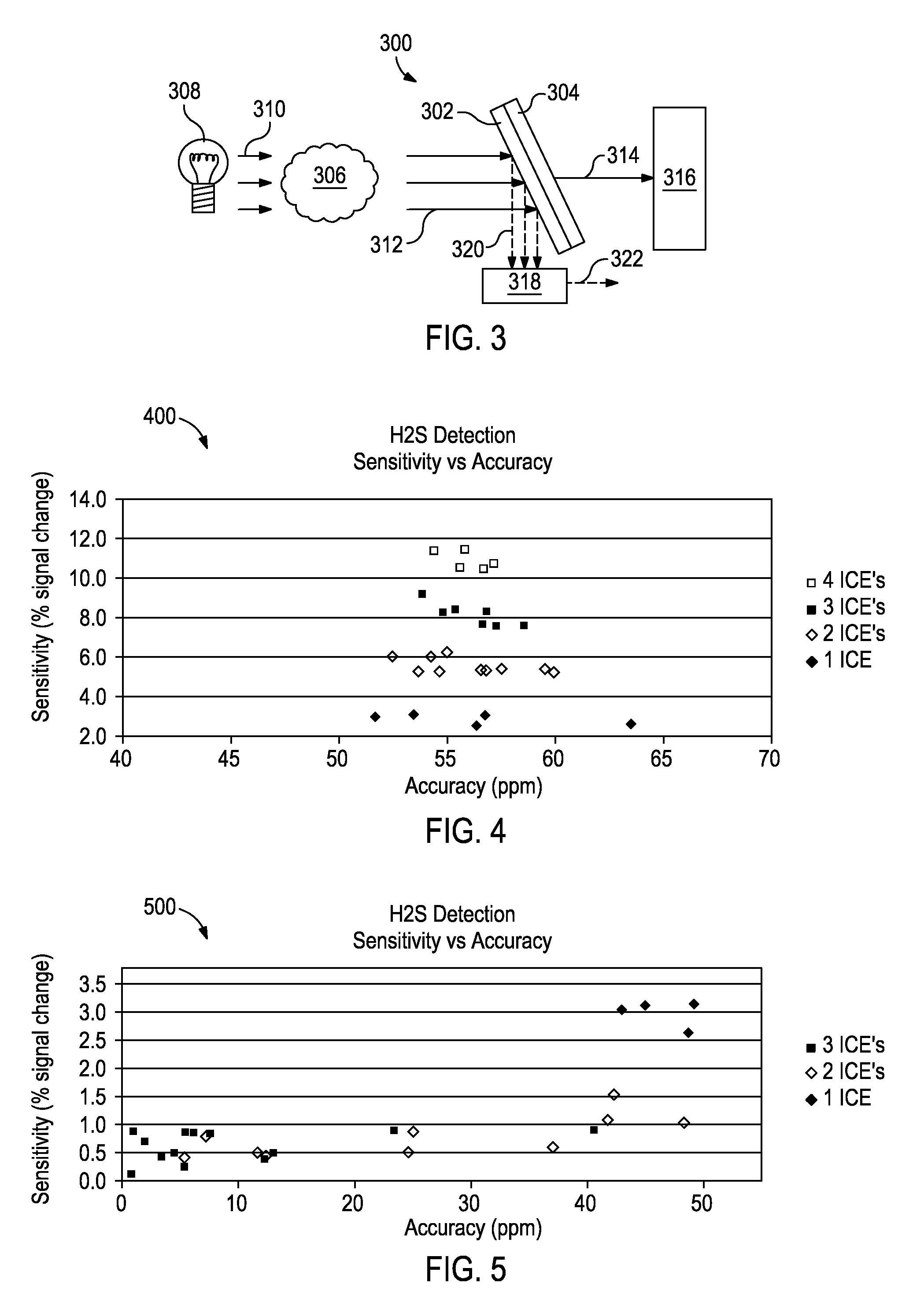
Optical computing devices are disclosed. One exemplary optical computing device includes an electromagnetic radiation source configured to optically interact with a sample and at least two integrated computational elements. The at least two integrated computational elements are configured to produce optically interacted light and further configured to be associated with a characteristic of the sample. The optical computing device further includes a first detector arranged to receive the optically interacted light from the at least two integrated computational elements and thereby generate a first signal corresponding to the characteristic of the sample.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Compensation of beam walkoff in nonlinear crystal using cylindrical lens
ActiveUS8422119B1Optical resonator shape and constructionLight demodulationNonlinear optical crystalOptical interaction
Owner:DISCO CORP
Systems and methods for real time monitoring and management of wellbore servicing fluids
InactiveUS8575541B1Withdrawing sample devicesInvestigating moving fluids/granular solidsChemical reactionOptical interaction
Disclosed are systems and methods for monitoring wellbore servicing fluids. One system includes a flow path fluidly coupled to a borehole and containing a wellbore servicing fluid that is exiting the borehole, the wellbore servicing fluid being configured to chemically react with and remove filter cake from the borehole, an optical computing device arranged in the flow path and having at least one integrated computational element configured to optically interact with the wellbore servicing fluid and thereby generate optically interacted light, and at least one detector arranged to receive the optically interacted light and generate an output signal corresponding to a characteristic of the wellbore servicing fluid, the characteristic of the wellbore servicing fluid corresponding to a concentration of a filter cake chemical constituent.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Methods and Devices for Optically Determining A Characteristic of a Substance
ActiveUS20130284898A1Absorption/flicker/reflection spectroscopyPhotoelectric discharge tubesOptical interactionElectromagnetic radiation
Optical computing devices are disclosed. One exemplary optical computing device includes an electromagnetic radiation source configured to optically interact with a sample and at least two integrated computational elements. The at least two integrated computational elements may be configured to produce optically interacted light, and at least one of the at least two integrated computational elements may be configured to be disassociated with a characteristic of the sample. The optical computing device further includes a first detector arranged to receive the optically interacted light from the at least two integrated computational elements and thereby generate a first signal corresponding to the characteristic of the sample.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Systems and Methods for Analyzing Microbiological Substances
ActiveUS20130034842A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsOptical interactionElectromagnetic radiation
Disclosed are systems and methods for monitoring a fluid for the purpose of identifying microbiological content and / or microorganisms and determining the effectiveness of a microbiological treatment. One method of monitoring a fluid includes containing the fluid within a flow path, the fluid including at least one microorganism present therein, optically interacting electromagnetic radiation from the fluid with at least one integrated computational element, thereby generating optically interacted light, receiving with at least one detector the optically interacted light, and generating with the at least one detector an output signal corresponding to a characteristic of the fluid, the characteristic of the fluid being a concentration of the at least one microorganism within the fluid.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Systems and Methods for Monitoring the Quality of a Fluid
Disclosed are systems and methods for monitoring a fluid having one or more adulterants therein. One method of monitoring the fluid includes containing the fluid within a flow path, the fluid including at least one adulterant present therein, optically interacting at least one integrated computational element with the fluid, thereby generating optically interacted light, receiving with at least one detector the optically interacted light, and generating with the at least one detector an output signal corresponding to a characteristic of the at least one adulterant in the fluid.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
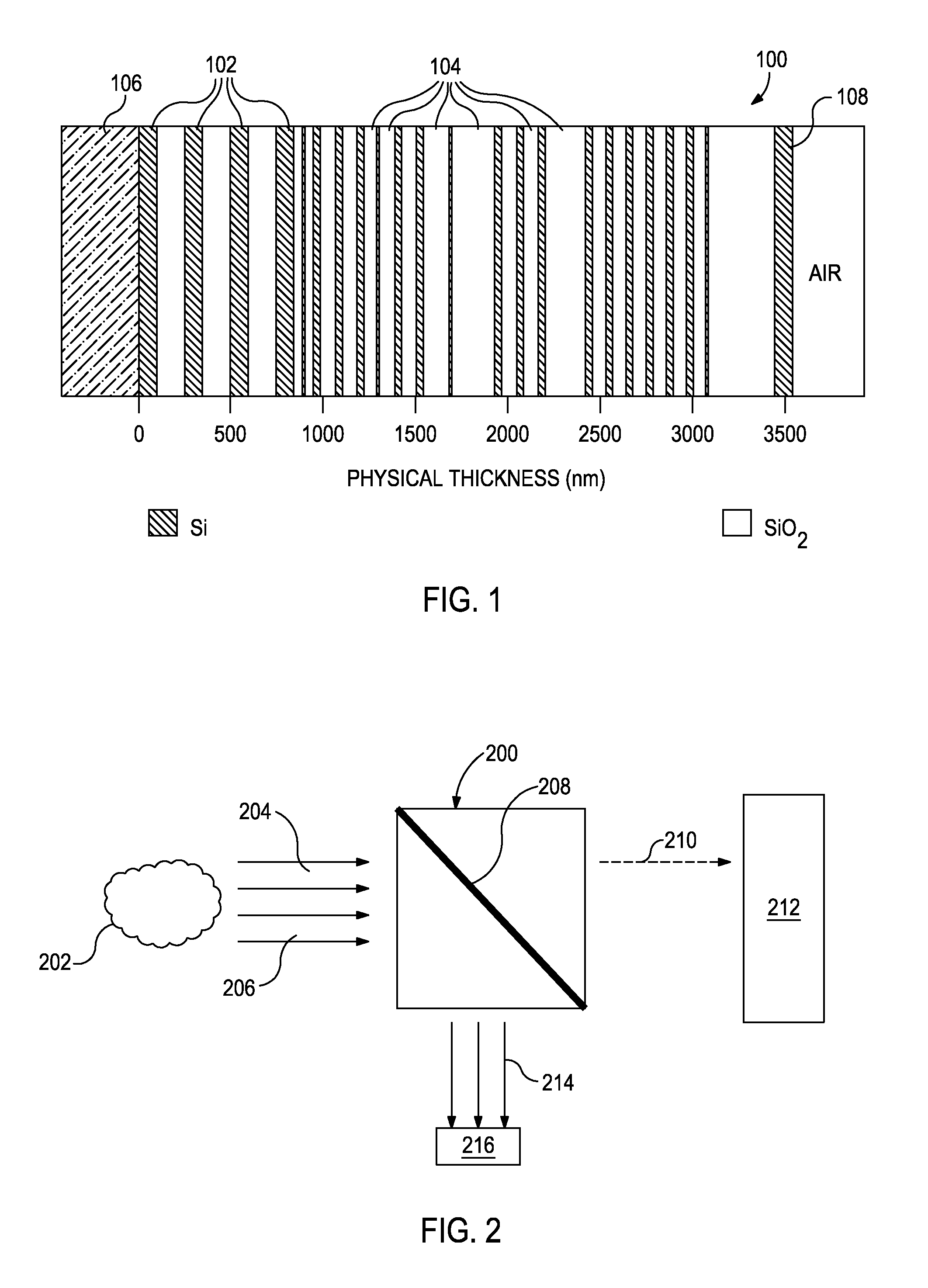
Porous microsphere resonators
InactiveUS20050078731A1Increase volumeEnhanced interactionMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorActive medium shape and constructionWhispering galleryOptical interaction
There are several different applications where it is desirable to increase the amount of material that can be introduced to the surface of a microresonator that has whispering gallery modes. The use of a porous surface on the microresonator permits greater amounts of the material to be captured on or near the surface of the microresonator, resulting in an increased optical interaction between the material and the light propagating in the whispering gallery mode(s) of the microresonator.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Methods and Devices for Optically Determining A Characteristic of a Substance
ActiveUS20130284897A1Absorption/flicker/reflection spectroscopyPhotoelectric discharge tubesOptical interactionElectromagnetic radiation
Optical computing devices are disclosed. One exemplary optical computing device includes an electromagnetic radiation source configured to optically interact with a sample and at least two integrated computational elements. The at least two integrated computational elements are configured to produce optically interacted light and further configured to be associated with a characteristic of the sample. The optical computing device further includes a first detector arranged to receive the optically interacted light from the at least two integrated computational elements and thereby generate a first signal corresponding to the characteristic of the sample.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
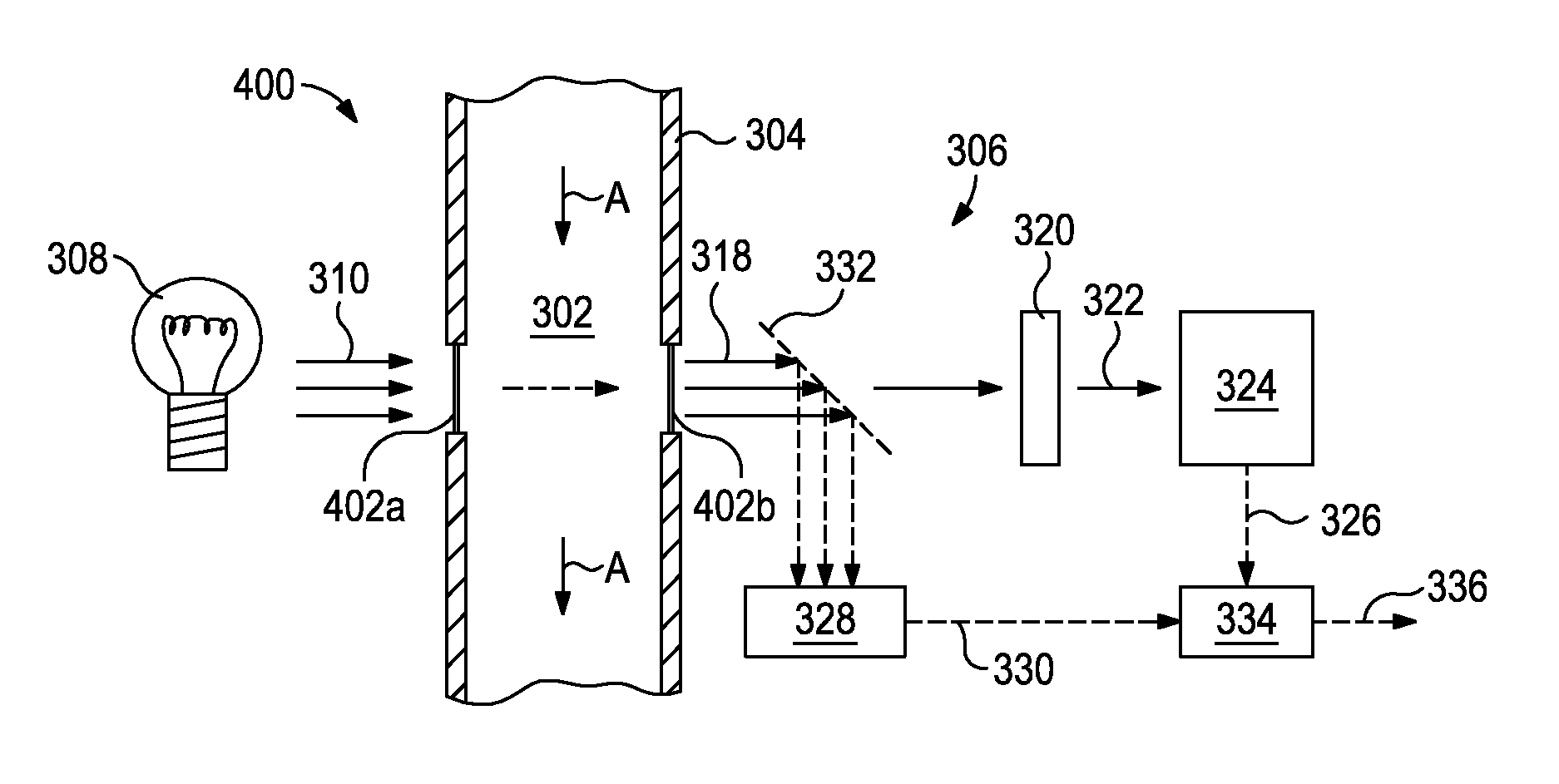
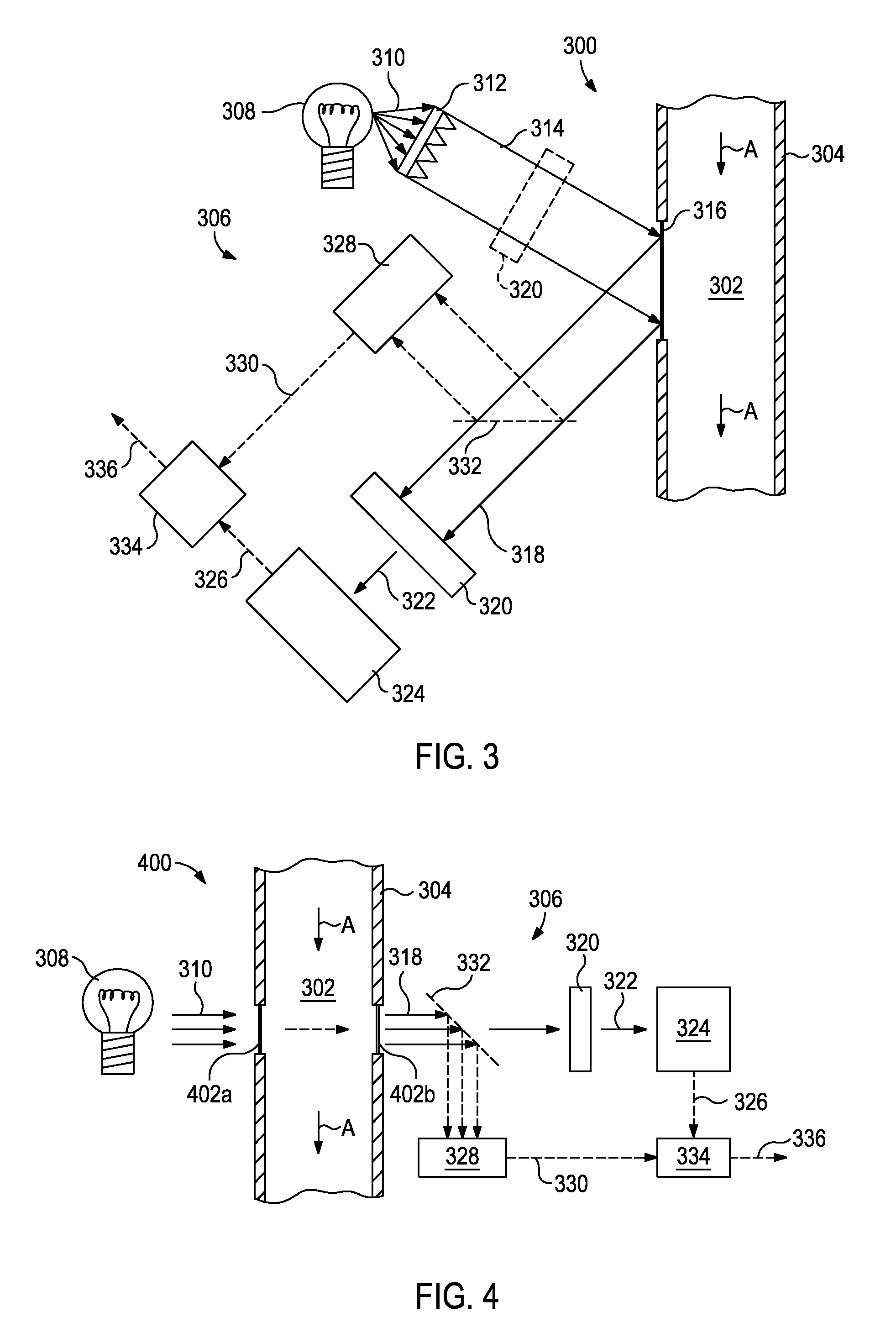
Imaging Systems for Optical Computing Devices
ActiveUS20130286399A1Investigating moving fluids/granular solidsTransmissivity measurementsOptical interactionElectromagnetic radiation
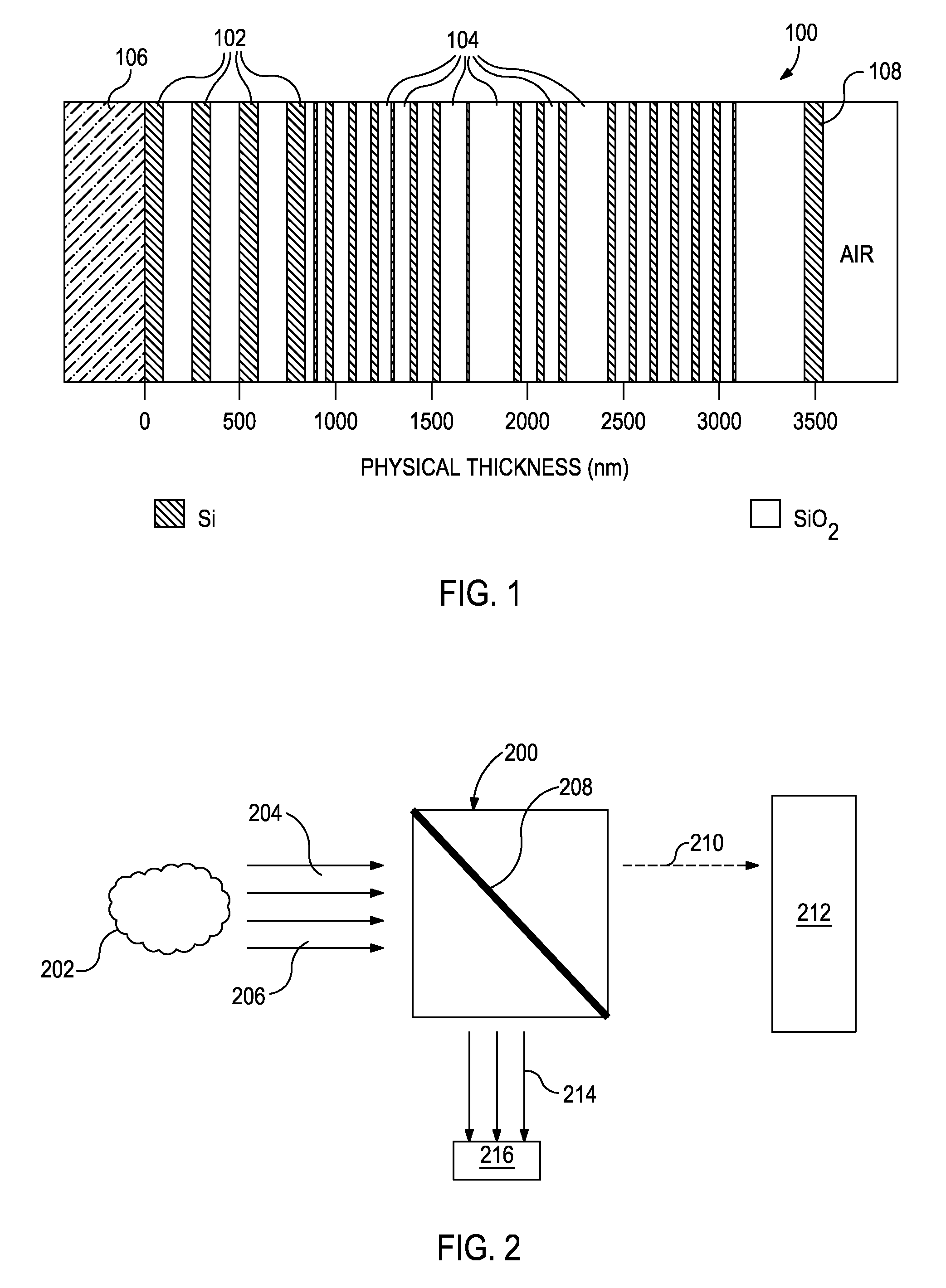
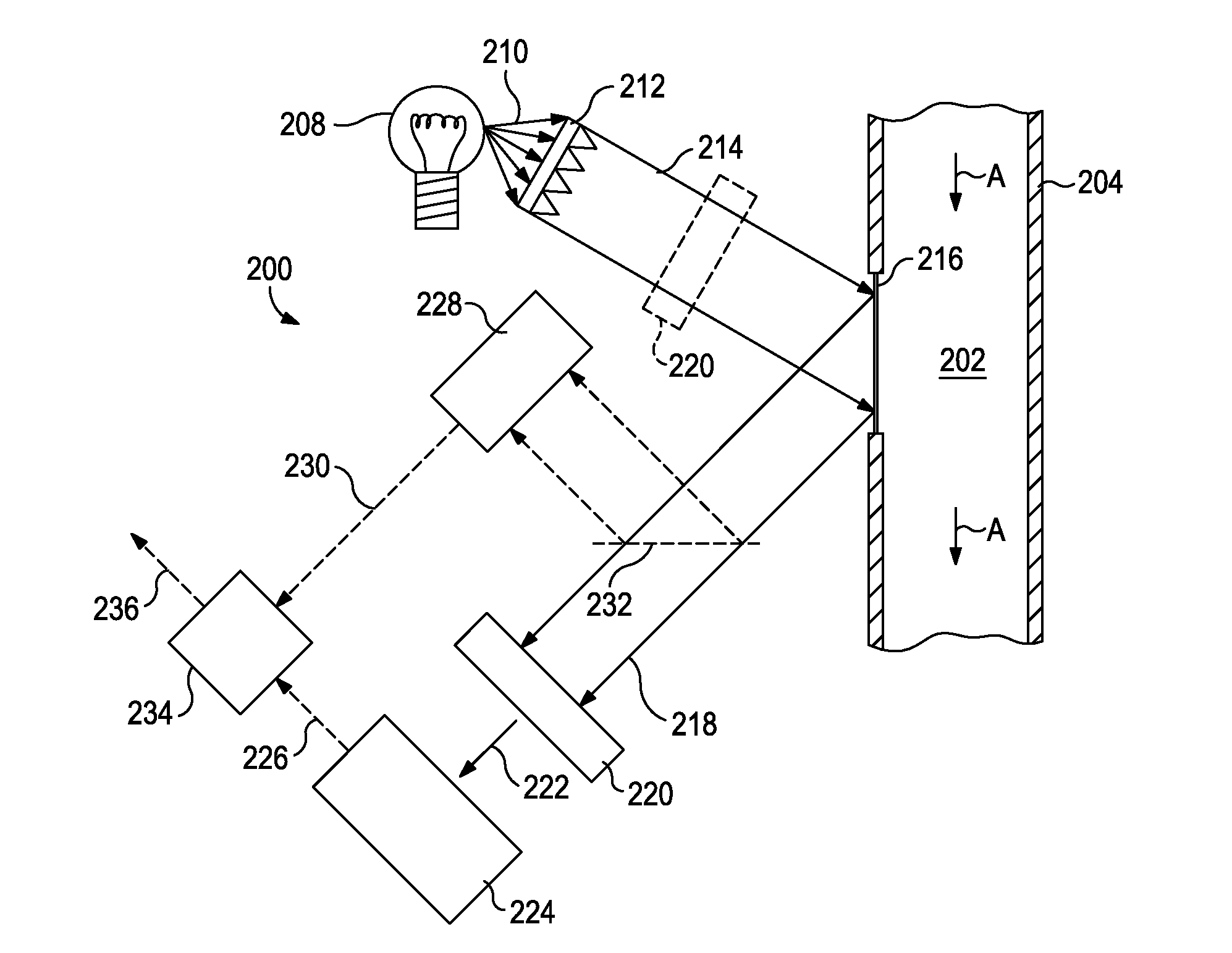
Optical computing devices are disclosed. One optical computing device includes an electromagnetic radiation source that emits electromagnetic radiation into an optical train to optically interact with a sample and at least one integrated computational element, the sample being configured to generate optically interacted radiation. A sampling window is arranged adjacent the sample and configured to allow transmission of the electromagnetic radiation therethrough and has one or more surfaces that generate one or more stray signals. A first focal lens is arranged to receive the optically interacted radiation and the one or more stray signals and generate a primary focal point from the optically interacted radiation. A structural element defines a spatial aperture aligned with the primary focal point such that the optically interacted radiation is able to pass therethrough while transmission of the one or more stray signals is substantially blocked by the structural element.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Systems and methods for monitoring the properties of a fluid cement composition in a flow path
ActiveUS8619256B1ConstructionsInvestigating moving fluids/granular solidsOptical interactionEngineering
Optical analysis systems may be useful in systems and methods for various properties of fluid cement compositions. For example, a method may include generating with an optical computing device a plurality of output signals corresponding to a plurality of time points and a characteristic of a fluid cement composition at a monitoring location within a flow path, the optical computing device having an electromagnetic radiation source configured to optically interact with the fluid cement composition and an integrated computational element, wherein the integrated computational element is configured to produce and convey optically interacted light to a detector which generates a plurality of output signals corresponding to the characteristic at a plurality of time points; receiving the plurality of output signals with a signal processor communicably coupled to the detector; and determining a difference between at least two of the output signals with the signal processor.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
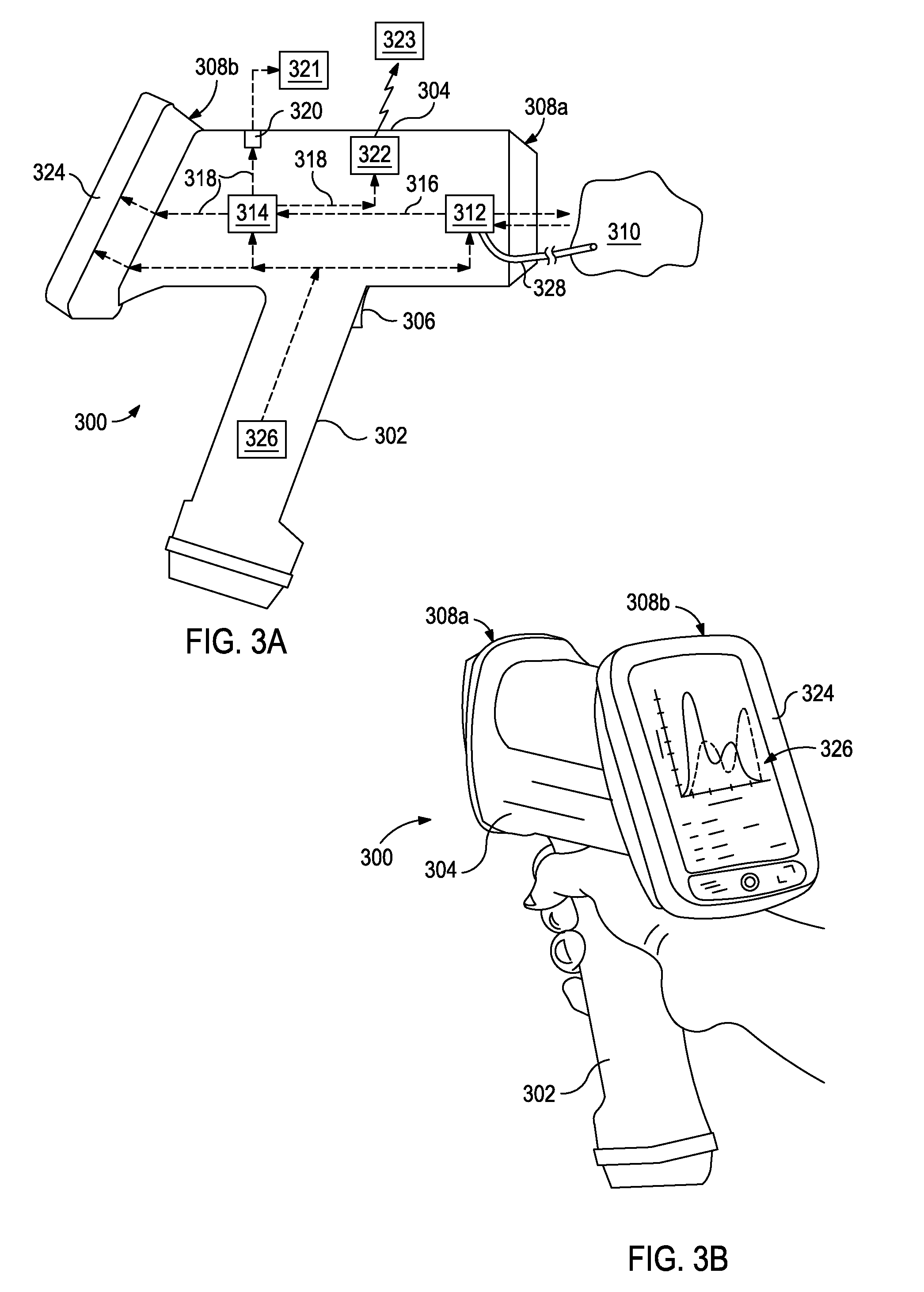
Handheld Characteristic Analyzer and Methods of Using the Same
ActiveUS20140061449A1Radiation pyrometryInvestigating moving fluids/granular solidsChemical compositionOptical interaction
Disclosed is a portable handheld characteristic analyzer used to analyze chemical compositions in or near real-time. One method of using the analyzer to determine a characteristic of a sample includes directing the handheld characteristic analyzer at the sample, the handheld characteristic analyzer having at least one integrated computational element arranged therein, activating the handheld characteristic analyzer, thereby optically interacting the at least one integrated computational element with the sample and generating optically interacted light, receiving the optically interacted light with at least one detector arranged within the handheld characteristic analyzer, generating an output signal corresponding to the characteristic of the sample with the at least one detector, receiving the output signal with a signal processor communicably coupled to the at least one detector, and determining the characteristic of the sample with the signal processor.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Imaging Systems for Optical Computing Devices
ActiveUS20130286398A1Investigating moving fluids/granular solidsTransmissivity measurementsOptical interactionElectromagnetic radiation
Optical computing devices are disclosed. One optical computing device includes an electromagnetic radiation source that emits electromagnetic radiation into an optical train to optically interact with a sample and at least one integrated computational element, the sample being configured to generate optically interacted radiation. A sampling window is arranged adjacent the sample and configured to allow transmission of the electromagnetic radiation therethrough and has one or more surfaces that generate one or more stray signals. A first focal lens is arranged to receive the optically interacted radiation and the one or more stray signals and generate a primary focal point from the optically interacted radiation. A structural element defines a spatial aperture aligned with the primary focal point such that the optically interacted radiation is able to pass therethrough while transmission of the one or more stray signals is substantially blocked by the structural element.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Methods and Devices for Optically Determining A Characteristic of a Substance
ActiveUS20130284896A1Spectrum investigationPhotoelectric discharge tubesOptical interactionElectromagnetic radiation
Optical computing devices are disclosed. One exemplary optical computing device includes an electromagnetic radiation source configured to optically interact with a sample and at least two integrated computational elements. The at least two integrated computational elements may be configured to produce optically interacted light, and at least one of the at least two integrated computational elements may be configured to be disassociated with a characteristic of the sample. The optical computing device further includes a first detector arranged to receive the optically interacted light from the at least two integrated computational elements and thereby generate a first signal corresponding to the characteristic of the sample.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Systems and Methods of Monitoring a Multiphase Fluid
InactiveUS20140110105A1Flow propertiesVolume/mass flow measurementOptical interactionSignal processing
Disclosed are systems and methods for monitoring a multiphase fluid and determining a characteristic of the multiphase fluid. One system includes a flow path containing a fluid, at least one integrated computational element configured to optically interact with the fluid and thereby generate optically interacted light, at least one detector arranged to receive the optically interacted light from the at least one integrated computational element and generate an output signal corresponding to at least one characteristic of a phase of the fluid, and a signal processor communicably coupled to the at least one detector and configured to determine the at least one characteristic of the phase of the fluid.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
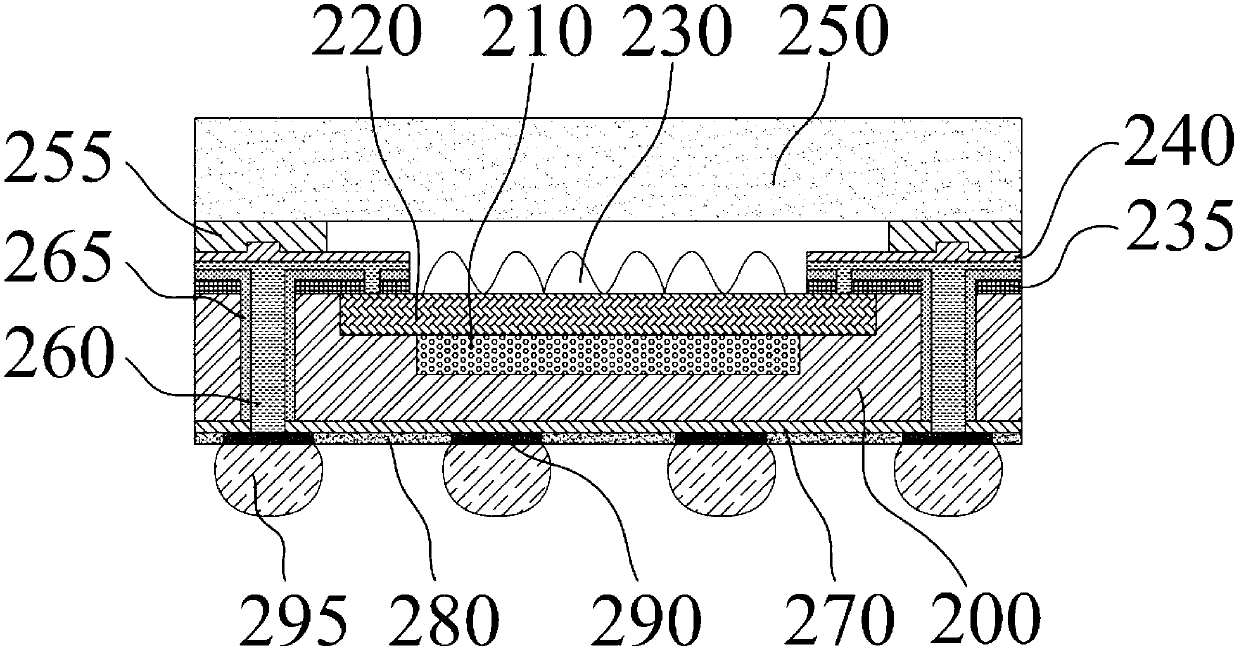
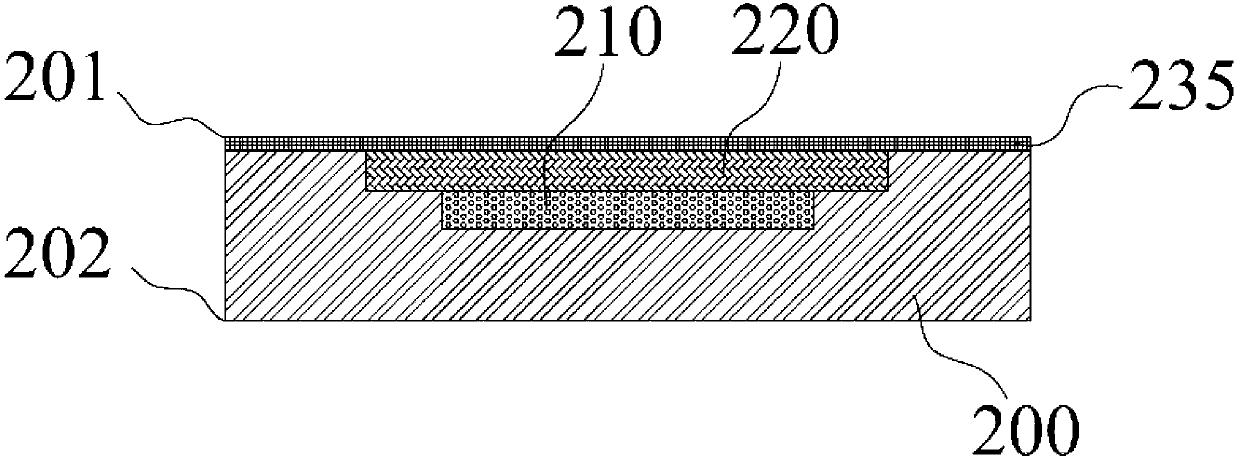
Packaging structure and manufacture method for complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor transistor (CMOS) image sensors
InactiveCN103000649AHigh bonding strengthImprove warpageRadiation controlled devicesMetal interconnectRedistribution layer
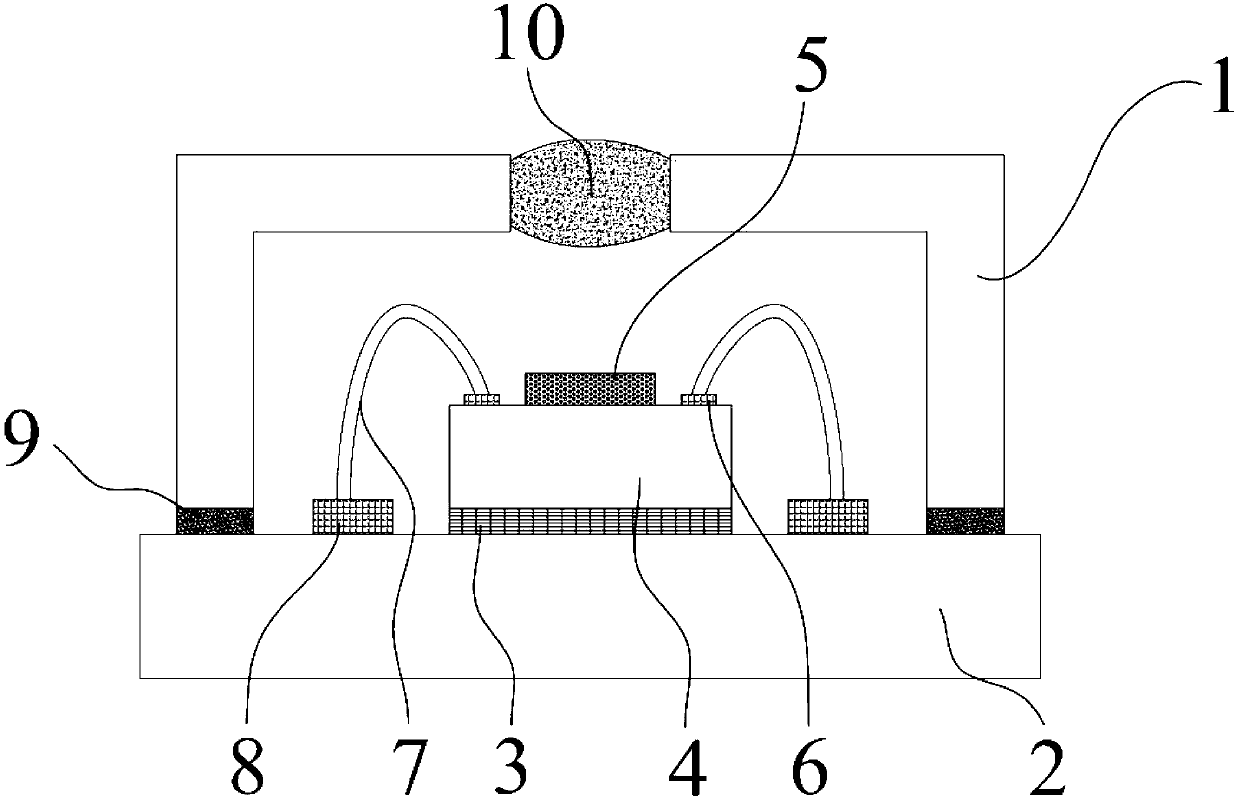
The invention discloses a packaging structure and a manufacture method for CMOS image sensors, and belongs to the sensor field. An optical interaction area is placed at a center on a first surface on the front surface of a silicon substrate, a metal interconnection layer is formed on the optical interaction area, a micro lens array is placed on the metal interconnection layer, and a first protection layer is arranged on the outer side of the metal interconnection layer; silicon through holes not penetrating through the silicon substrate and a redistribution layer are manufactured on the first surface, and an input / output (I / N) around the optical interaction area is connected with the silicon through holes through the redistribution layer; passivation layers are manufactured on the silicon through hole walls, and the silicon through holes are filled; a second protection layer is arranged on the redistribution layer; the silicon substrate is bonded with a glass sheet, and a cavity is arranged between the glass sheet and the silicon substrate; the second surface of the silicon substrate is thinned to expose the silicon through holes; a line layer is manufactured on the second surface of the silicon substrate to connect the silicon through holes to pads, and a solder mask layer is manufactured on the line layer and exposes the pads; and solder balls are arranged on the pads. According to the packaging structure and the manufacture method for CMOS image sensors, the layering problem between the glass and the silicon substrate in the packaging structure is solved, the reliability is improved, and the packaging structure is suitable for chips with large sizes.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
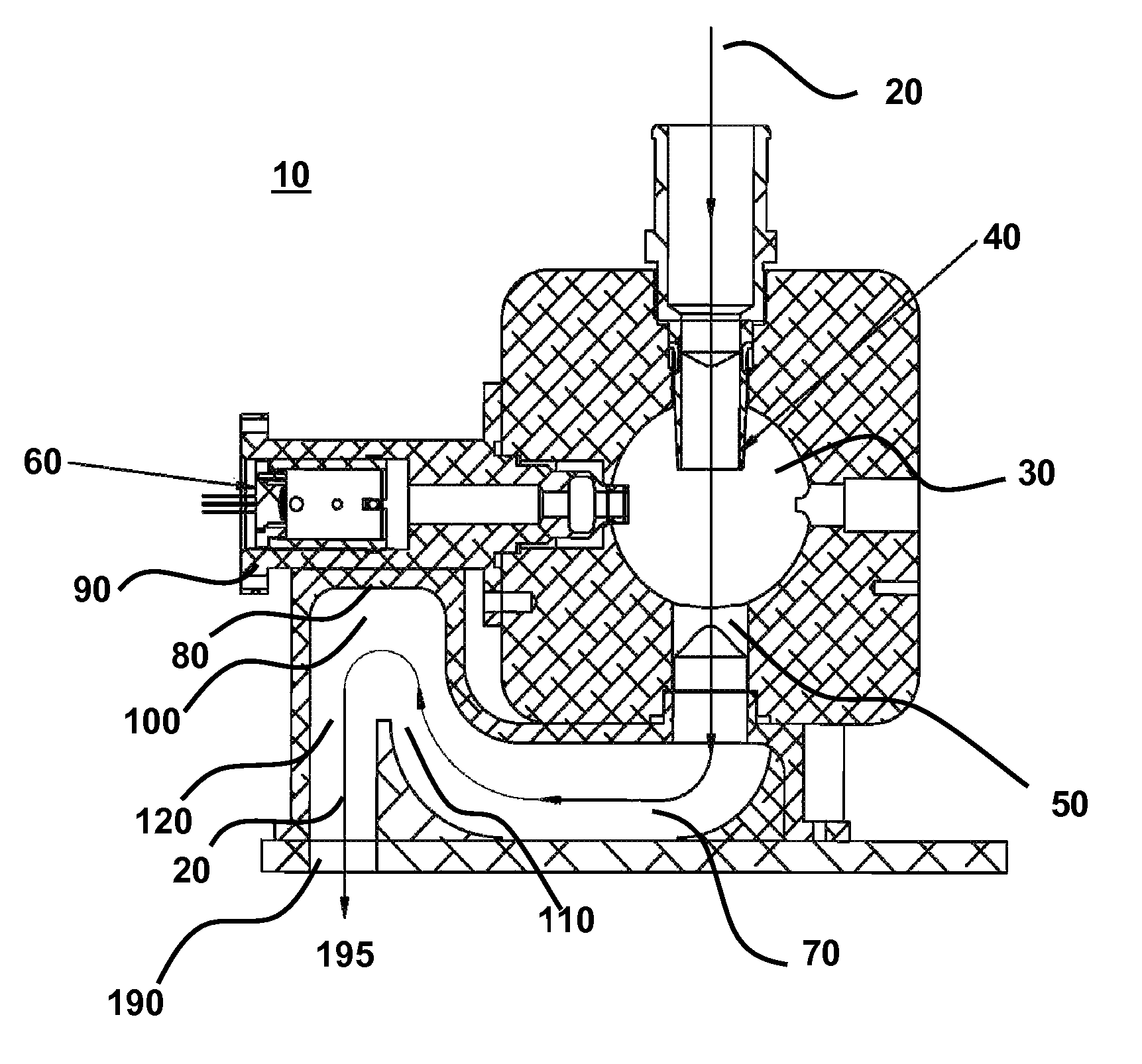
Optical particle sensor with exhaust-cooled optical source
ActiveUS7796255B2Efficient thermal managementImprove performanceWithdrawing sample devicesMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansOptical interactionThermal contact
The invention relates to particle sensors that are capable of passively cooling high-powered optical sources within the sensor, thereby extending the optical source lifetime without requiring additional power. The sensor detects particles within a sample fluid by optical interaction of the optical source with flowing sample fluid in the sample chamber. Sample fluid that exits the sample chamber is directed into thermal contact with the optical source, thereby cooling the optical source. Sample fluid that has come into thermal contact with the optical source is continuously removed from the sensor to ensure the optical source is adequately cooled. A variety of elements are used to facilitate thermal contact between the optical source and sample fluid including plenums, heat sinks, and airflow cavities. Provided are related methods for cooling a one or more heat-producing device within a particle sensor.
Owner:PARTICLE MEASURING SYST
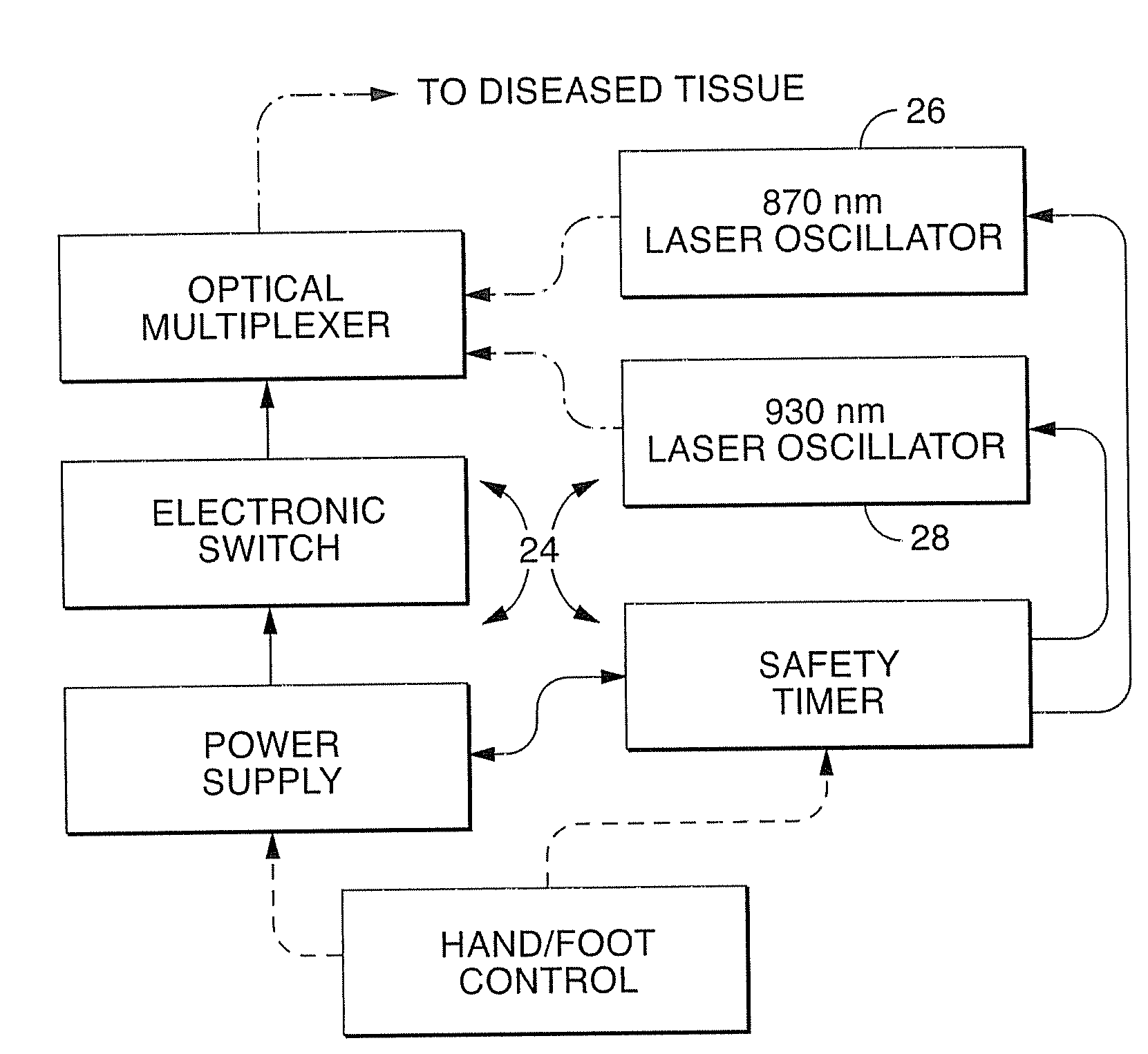
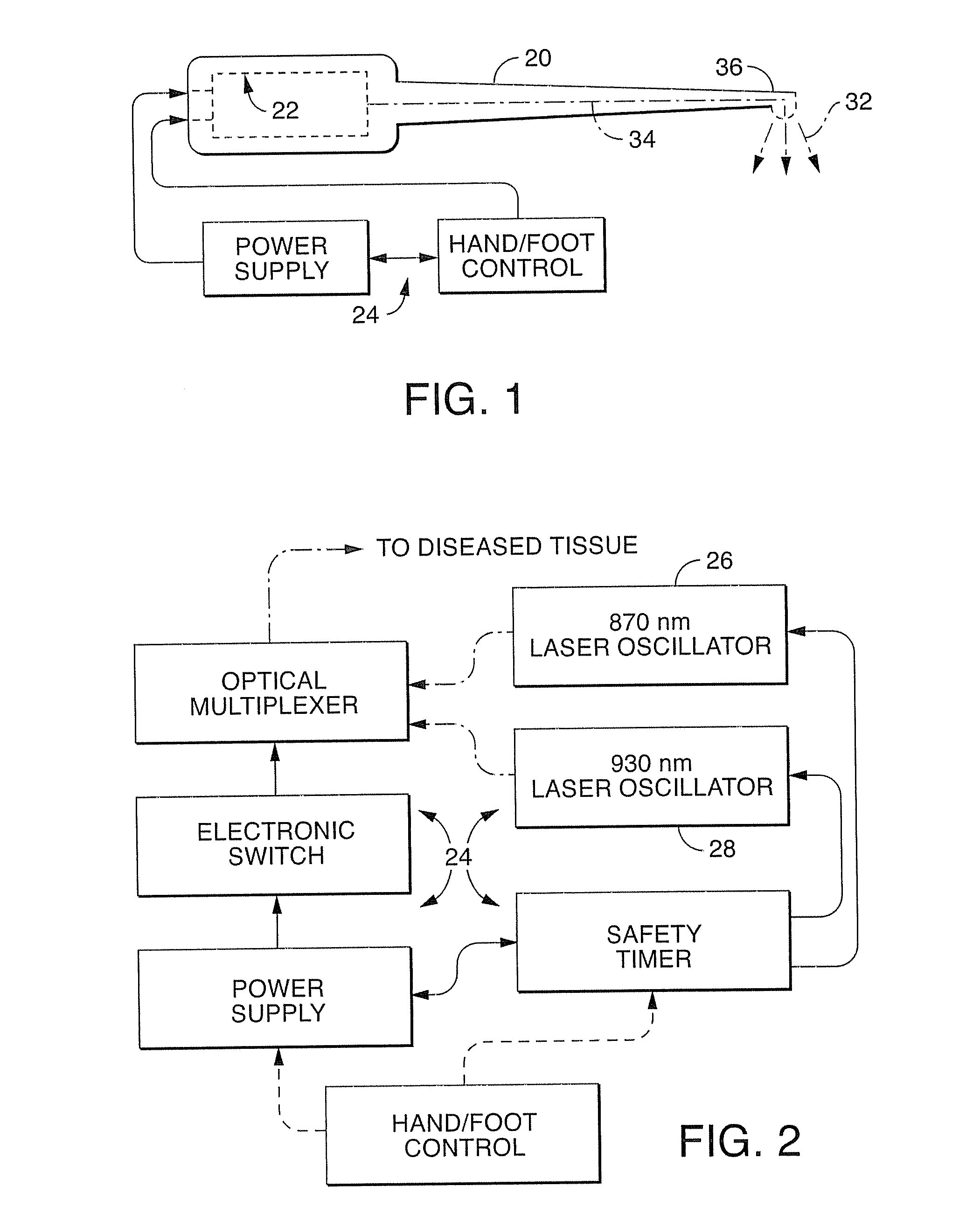
Near infrared microbial elimination laser system
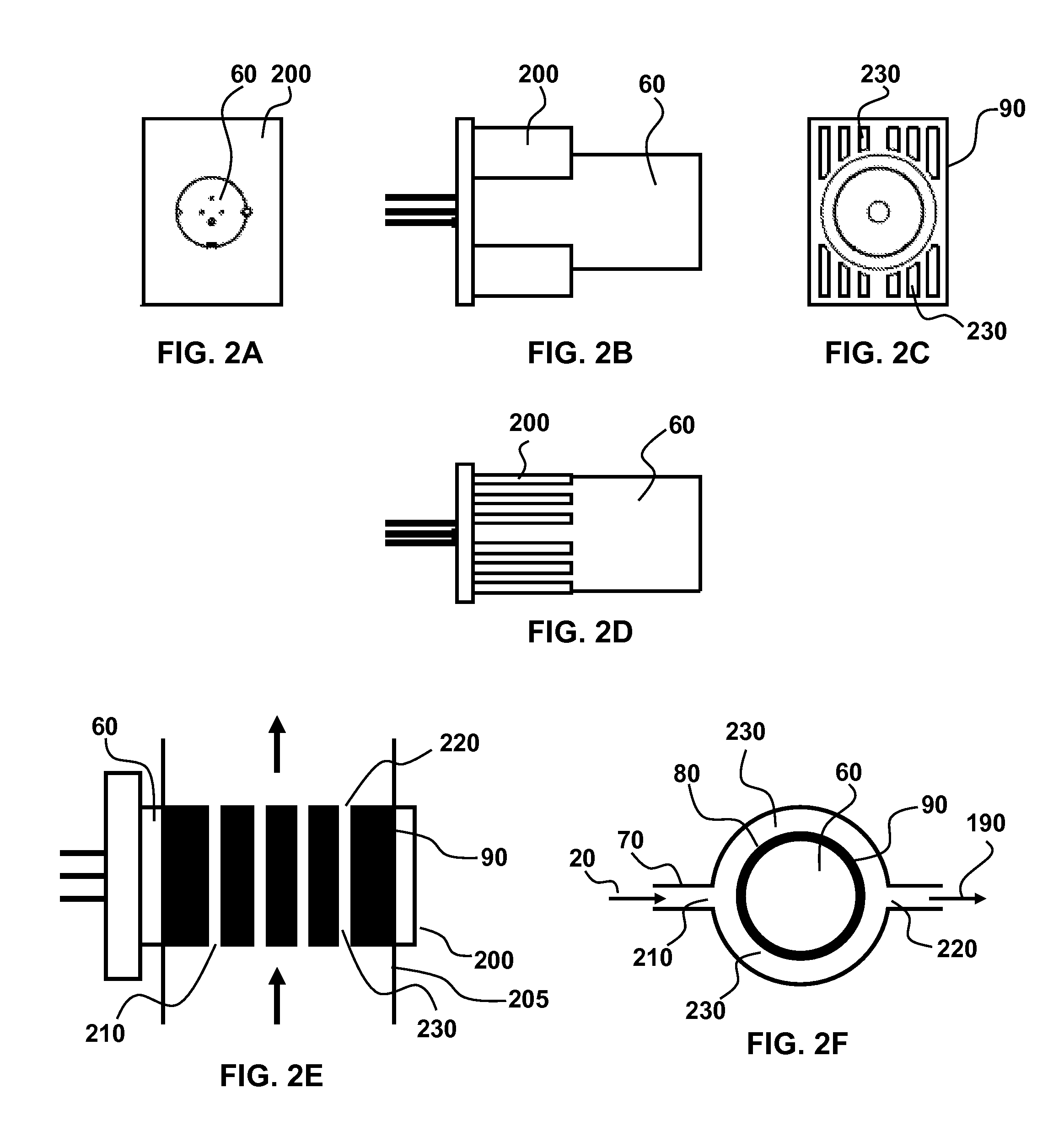
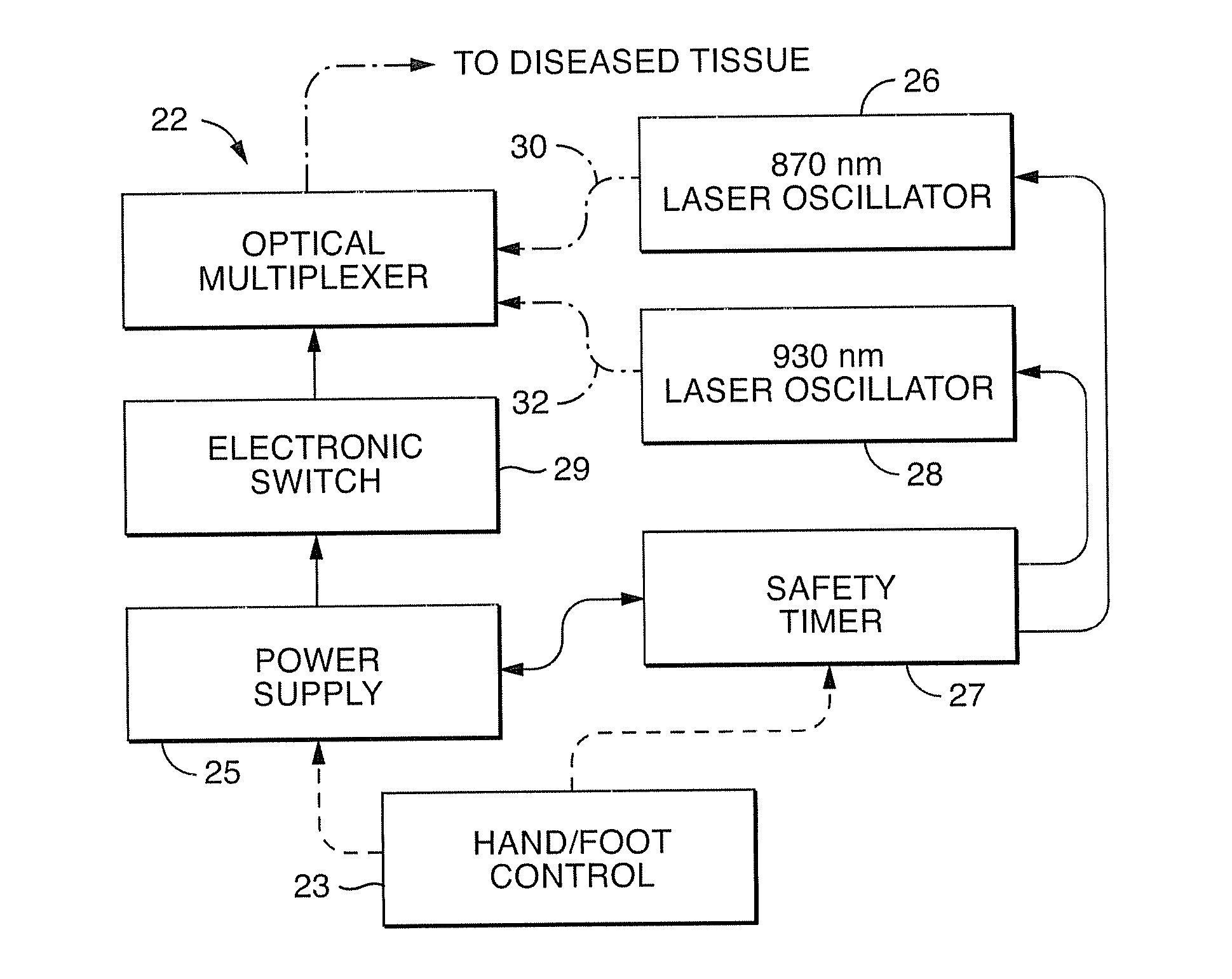
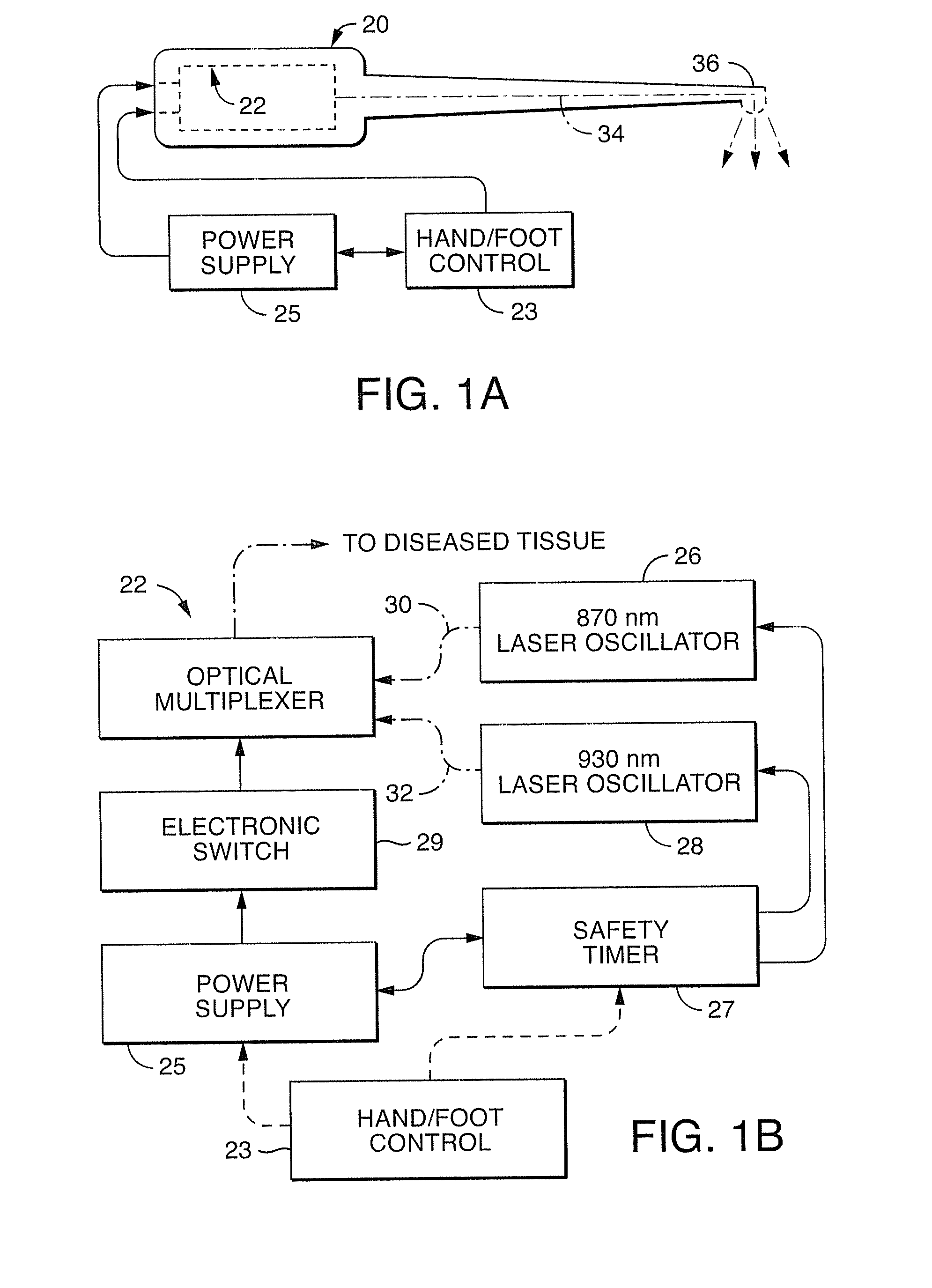
InactiveUS20080021370A1Minimal heat depositionElectrotherapyGum massageOptical interactionHeat deposition
Dual wavelength laser energy in the near infrared electromagnetic spectrum is described as destroying bacteria via photo-damage optical interactions through direct selective absorption of optical energy by intracellular bacterial chromophores. Use of various dual wave length laser systems include use of optical assembly including two distinct diode laser ranges (including 870 nm and 930 nm) that can be emitted to achieve maximal bacterial elimination without intolerable heat deposition. Related processes for medical procedures are also described.
Owner:NOMIR MEDICAL TECH
Near infrared microbial elimination laser system
InactiveUS20080159345A1Minimal heat depositionWide applicabilityLaser detailsWater/sewage treatment by irradiationOptical interactionDual wavelength laser
A dual wavelength laser in the low infrared electromagnetic spectrum is disclosed for destruction of bacteria via photo-damage optical interactions through direct selective absorption of optical energy by intracellular bacterial chromophores. The dual wavelength (NIMELS) laser includes an optical assembly and all associated components necessary for the housing of two distinct diode laser arrays (870 nm diode array and 930 nm diode array) that can be emitted through an output connector and wavelength multiplexer as necessary. With this preferred design, the dual wavelengths (870 nm and 930 nm) can be emitted singly, or multiplexed together to be conducted along a common optical pathway, or multiple optical pathways, to achieve maximal bacterial elimination.
Owner:NOMIR MEDICAL TECH
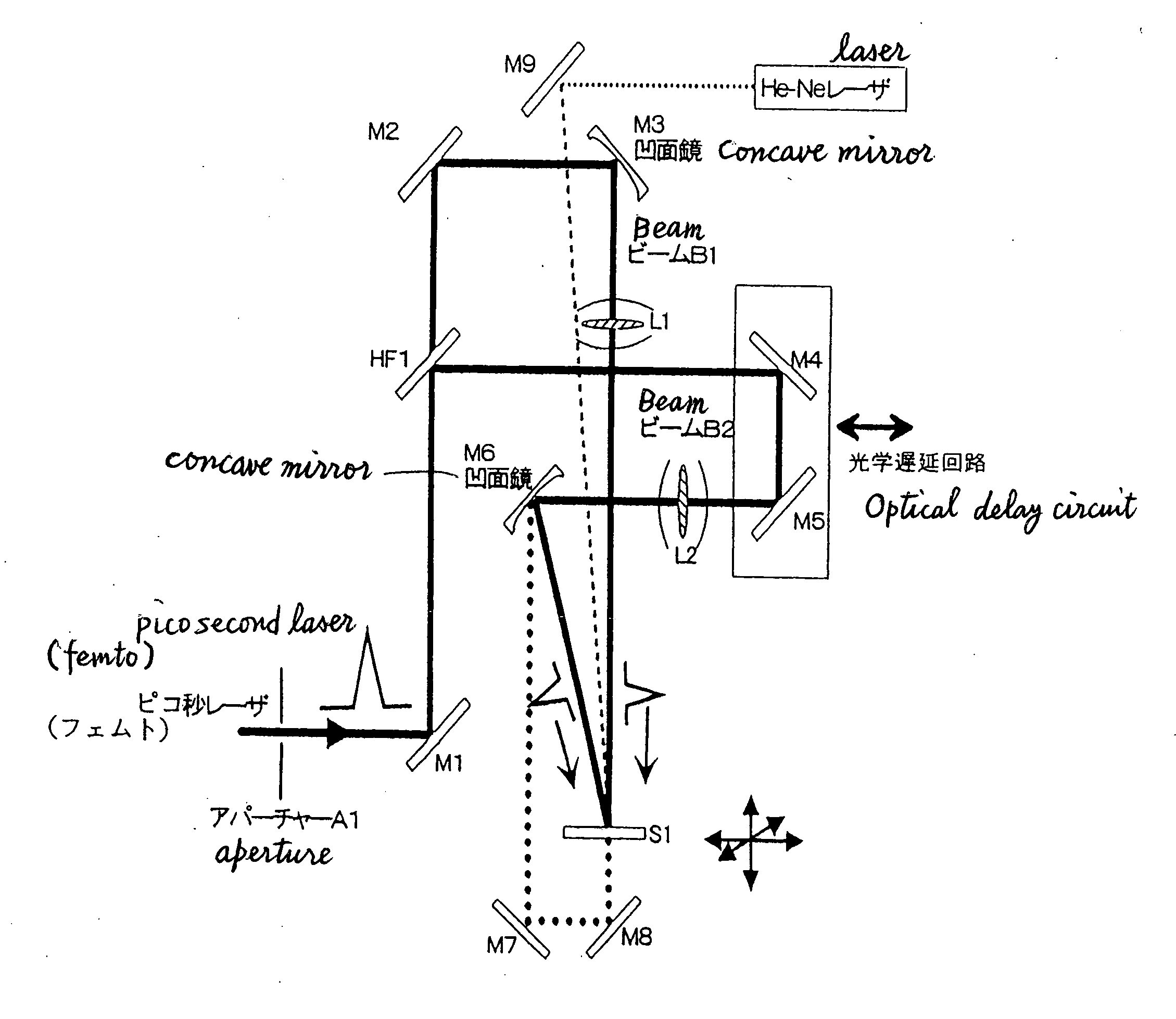
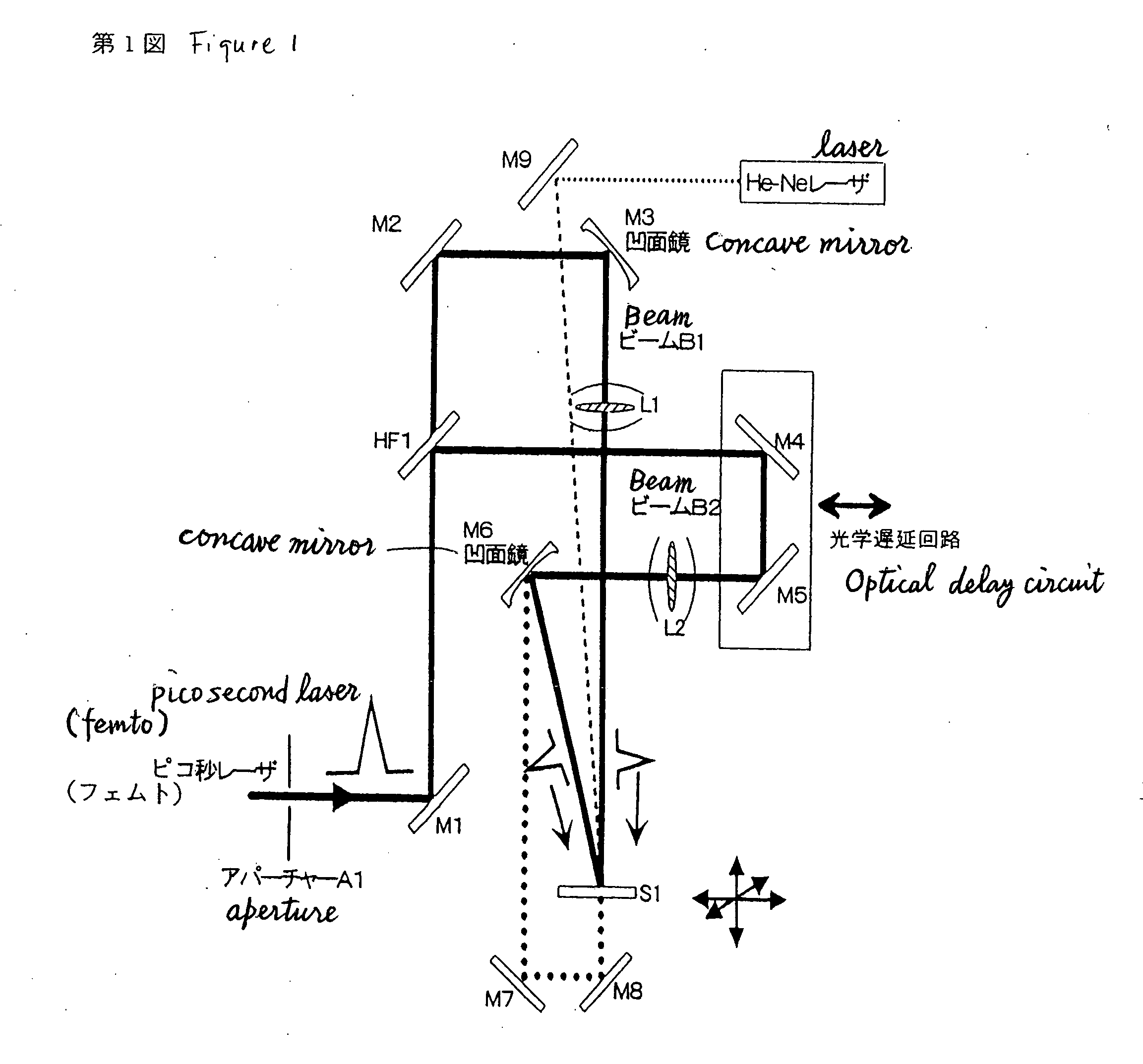
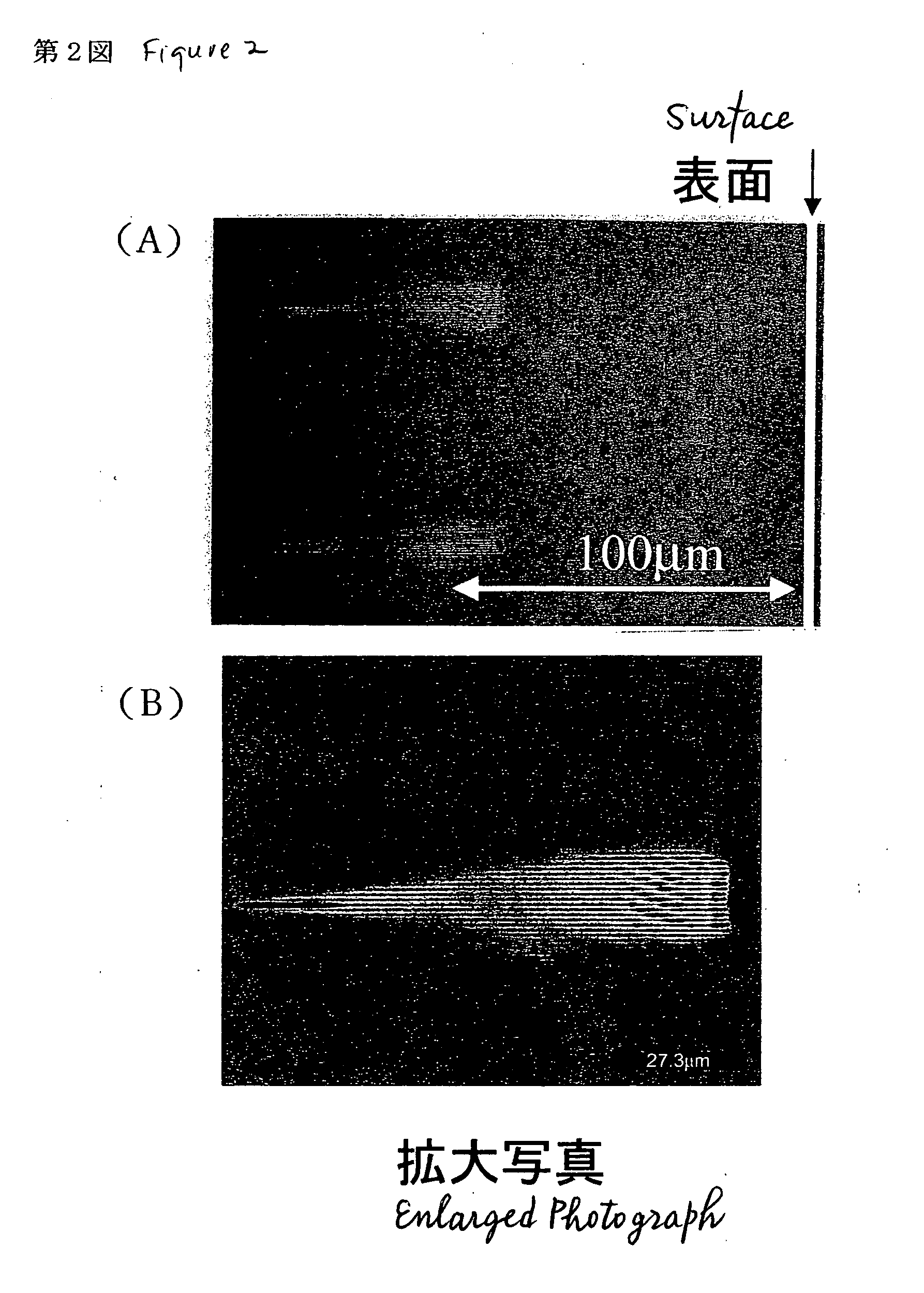
Method for producing hologram by pico-second laser
InactiveUS20060019171A1Reduce waveform distortionStable recordHolographic light sources/light beam propertiesPhotomechanical apparatusPicosecond laserOptical interaction
Disclosed is a method of producing a hologram through a two-beam laser interfering exposure process, which comprises emitting a coherent laser light with a pulse width (τ) ranging from greater than 900 femtoseconds to 100 picoseconds and a laser power of 10 μJ / pulse or more using a solid-state laser as a light source, dividing the pulses light from the laser into two beams, controlling the two beams temporally and spatially in such a manner that the two beam are converged on a surface of or inside a workpiece for recording a hologram while matching the respective converged spots of the two beams with one another temporally and spatially to create the interference therebetween so as to record a surface-relief hologram on the surface of the workpiece or an embedded hologram inside the workpiece in an irreversible manner. The present invention can solve a problem with a conventional process of recording a hologram in a non-photosensitive material in an irreversible manner using interfering femtosecond laser pulses, specifically, distortion in the waveforms of pulsed laser beams and resulting instability in recording of an embedded hologram due to a non-linear optical interaction between the femtosecond laser pulses and air / the material.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
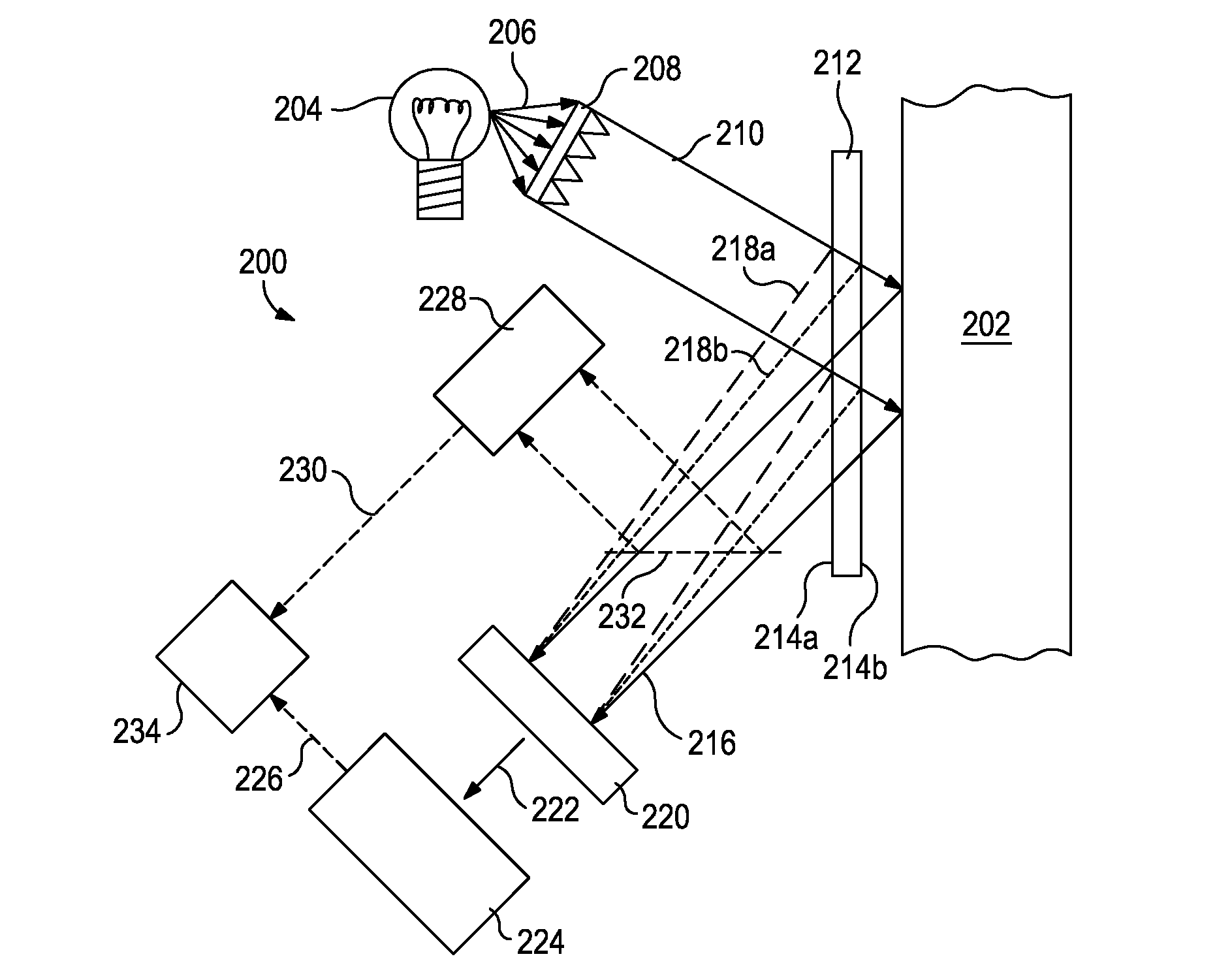
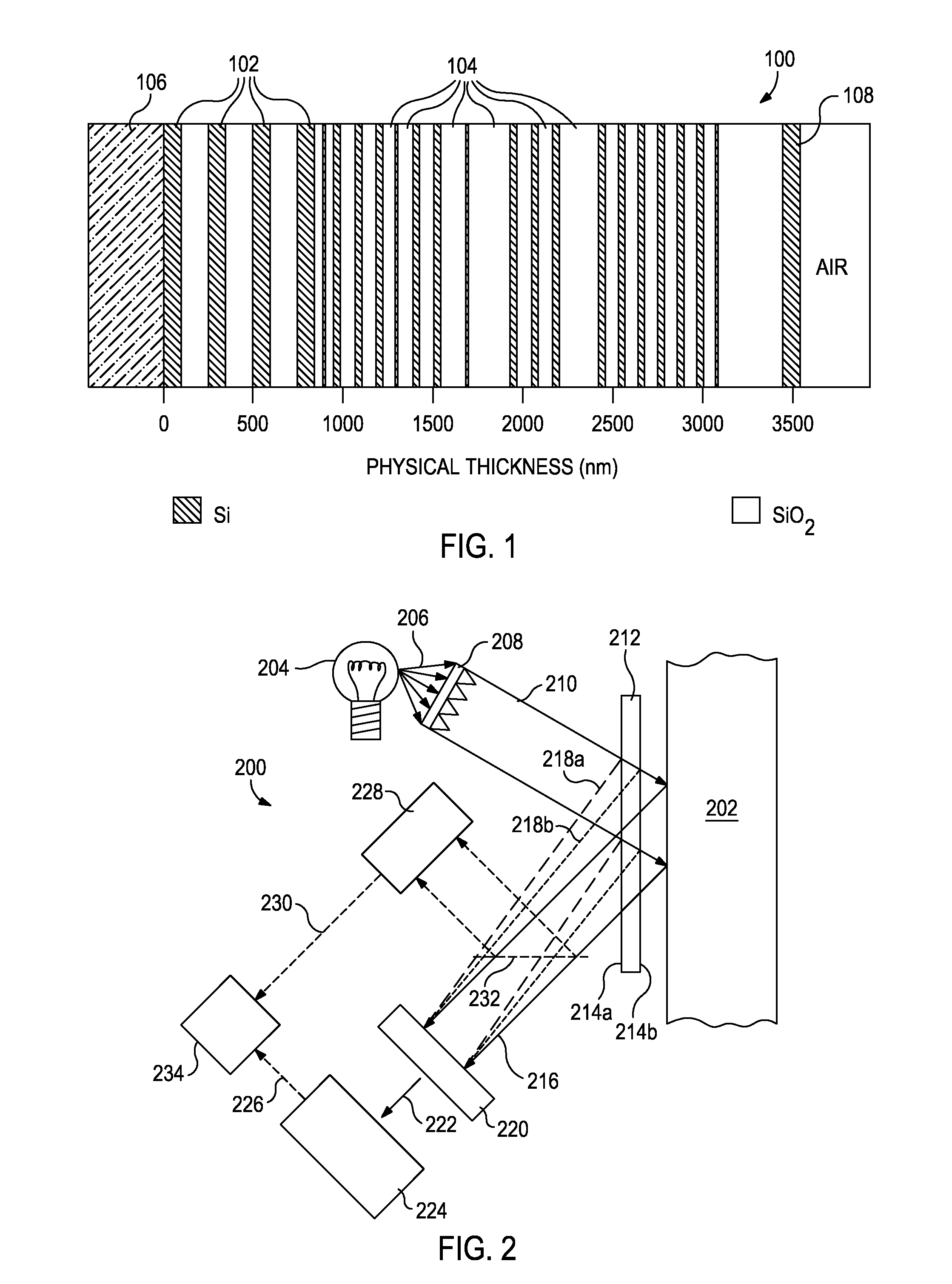
Imaging systems for optical computing devices
ActiveUS9013702B2Investigating moving fluids/granular solidsTransmissivity measurementsOptical interactionElectromagnetic radiation
Optical computing devices are disclosed. One optical computing device includes an electromagnetic radiation source that emits electromagnetic radiation into an optical train to optically interact with a sample and at least one integrated computational element, the sample being configured to generate optically interacted radiation. A sampling window is arranged adjacent the sample and configured to allow transmission of the electromagnetic radiation therethrough and has one or more surfaces that generate one or more stray signals. A first focal lens is arranged to receive the optically interacted radiation and the one or more stray signals and generate a primary focal point from the optically interacted radiation. A structural element defines a spatial aperture aligned with the primary focal point such that the optically interacted radiation is able to pass therethrough while transmission of the one or more stray signals is substantially blocked by the structural element.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Porous microsphere resonators
InactiveUS7259855B2Enhanced interactionIncrease volumeRadiation pyrometryMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorWhispering galleryOptical interaction
There are several different applications where it is desirable to increase the amount of material that can be introduced to the surface of a microresonator that has whispering gallery modes. The use of a porous surface on the microresonator permits greater amounts of the material to be captured on or near the surface of the microresonator, resulting in an increased optical interaction between the material and the light propagating in the whispering gallery mode(s) of the microresonator.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Methods and devices for optically determining a characteristic of a substance
ActiveUS8912477B2Radiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationOptical interactionElectromagnetic radiation
Optical computing devices are disclosed. One exemplary optical computing device includes an electromagnetic radiation source configured to optically interact with a sample and at least two integrated computational elements. The at least two integrated computational elements may be configured to produce optically interacted light, and at least one of the at least two integrated computational elements may be configured to be disassociated with a characteristic of the sample. The optical computing device further includes a first detector arranged to receive the optically interacted light from the at least two integrated computational elements and thereby generate a first signal corresponding to the characteristic of the sample.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Systems and Methods for Real Time Monitoring of Gas Hydrate Formation
ActiveUS20140172177A1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingLevel controlOptical interactionOptical computing
Disclosed are systems and methods for monitoring a drilling fluid for the formation of gas hydrates. One system includes a borehole containing a drilling fluid being circulated therethrough, a first optical computing device arranged in the borehole and having at least one integrated computational element configured to optically interact with the drilling fluid and detect one or more gas hydrates present therein, and at least one detector arranged to receive optically interacted light generated from optical interaction between the at least one integrated computational element and the drilling fluid, the at least one detector being configured to generate a first output signal corresponding to a characteristic of the one or more gas hydrates.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Environmentally Isolated Waveguide Display
Owner:DIGILENS
Systems and Methods for Inspecting and Monitoring a Pipeline
ActiveUS20140080224A1Investigating moving fluids/granular solidsScattering properties measurementsOptical interactionEngineering
Disclosed are systems and methods for inspecting and monitoring an inner surface of a pipeline. One system includes a pig arranged within the pipeline and having a housing that defines a conduit therein for providing fluid communication through the pig, one or more optical computing devices arranged on the conduit for monitoring a bypass fluid flowing through the conduit. The one or more optical computing devices including at least one integrated computational element configured to optically interact with the bypass fluid and generate optically interacted light, and at least one detector arranged to receive the optically interacted light and generate an output signal corresponding to a characteristic of the bypass fluid. A signal processor is communicably coupled to the at least one detector of each optical computing device for receiving the corresponding output signals and determining the characteristic of the fluid.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Systems and methods for inspecting and monitoring a pipeline
ActiveUS9176052B2Material analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesOptically investigating flaws/contaminationOptical interactionEngineering
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Imaging systems for optical computing devices
ActiveUS9013698B2Radiation pyrometryInvestigating moving fluids/granular solidsOptical interactionElectromagnetic radiation
Optical computing devices are disclosed. One optical computing device includes an electromagnetic radiation source that emits electromagnetic radiation into an optical train to optically interact with a sample and at least one integrated computational element, the sample being configured to generate optically interacted radiation. A sampling window is arranged adjacent the sample and configured to allow transmission of the electromagnetic radiation therethrough and has one or more surfaces that generate one or more stray signals. A first focal lens is arranged to receive the optically interacted radiation and the one or more stray signals and generate a primary focal point from the optically interacted radiation. A structural element defines a spatial aperture aligned with the primary focal point such that the optically interacted radiation is able to pass therethrough while transmission of the one or more stray signals is substantially blocked by the structural element.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com