Patents
Literature
58 results about "Fused filament fabrication" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
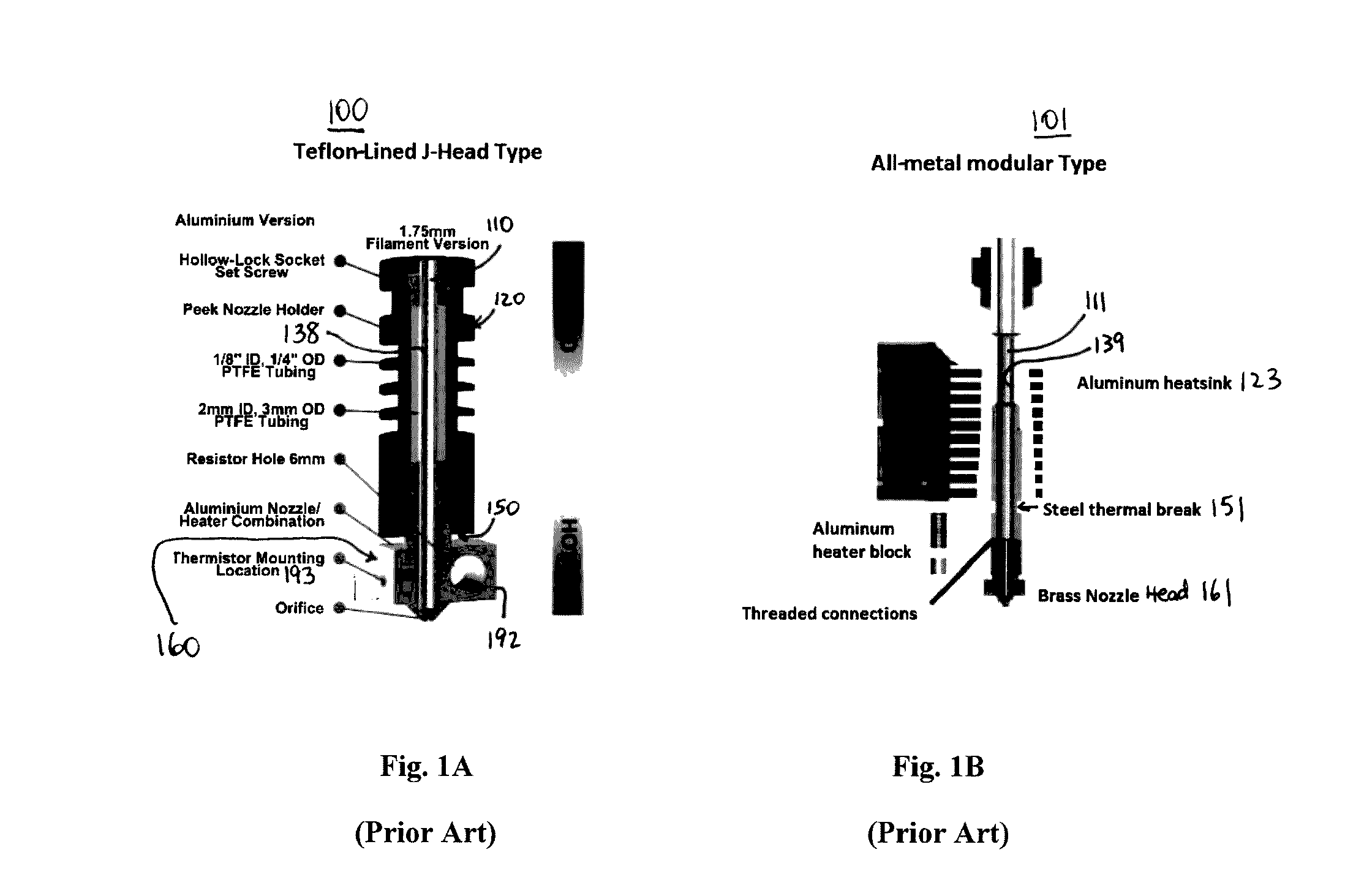
Fused filament fabrication (FFF), also known under the trademarked term fused deposition modeling (FDM), sometimes also called filament freeform fabrication, is a 3D printing process that uses a continuous filament of a thermoplastic material. Filament is fed from a large coil through a moving, heated printer extruder head, and is deposited on the growing work. The print head is moved under computer control to define the printed shape. Usually the head moves in two dimensions to deposit one horizontal plane, or layer, at a time; the work or the print head is then moved vertically by a small amount to begin a new layer. The speed of the extruder head may also be controlled to stop and start deposition and form an interrupted plane without stringing or dribbling between sections. "Fused filament fabrication" was coined by the members of the RepRap project to give a phrase that would be legally unconstrained in its use, given trademarks covering "fused deposition modeling".
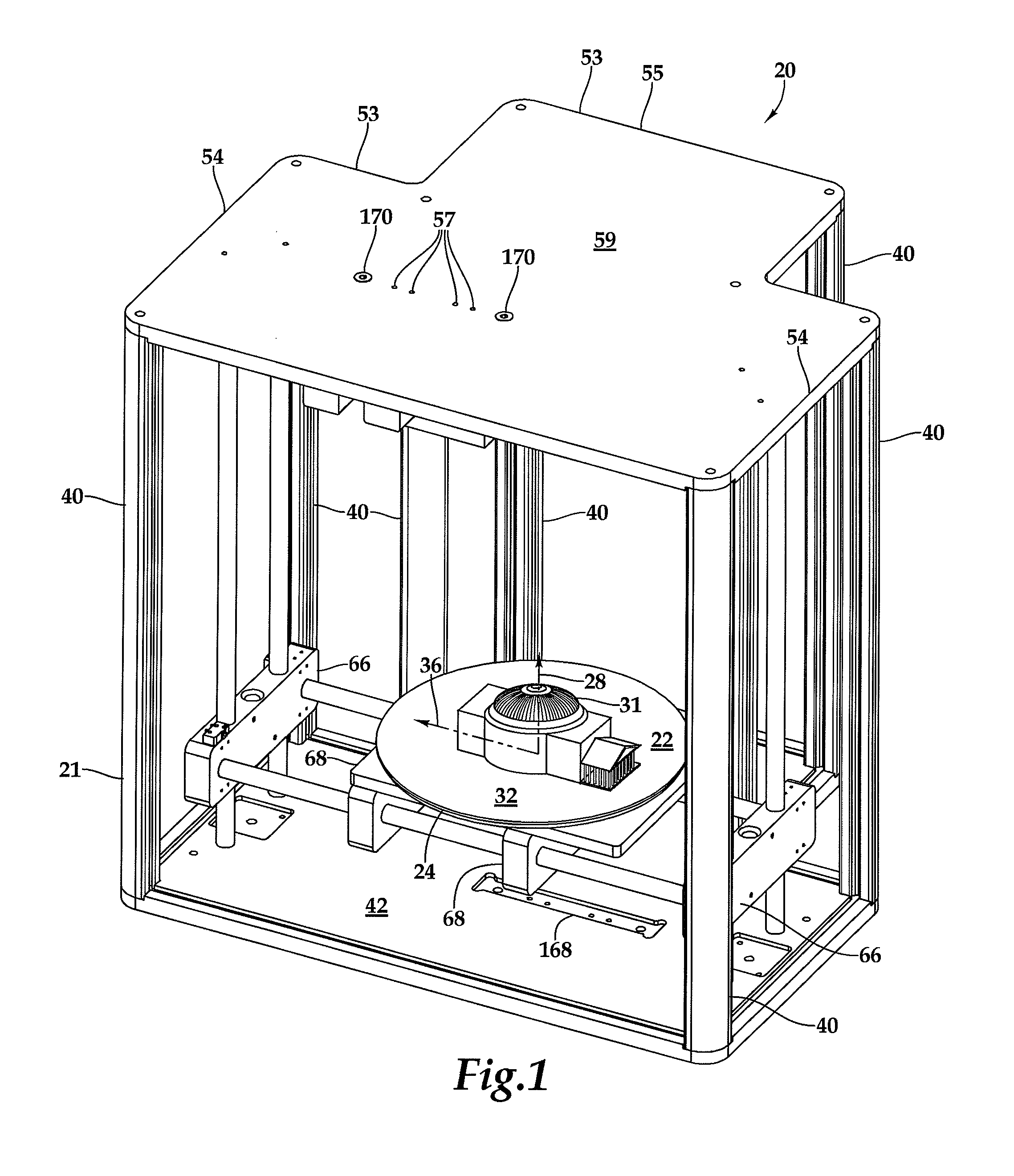
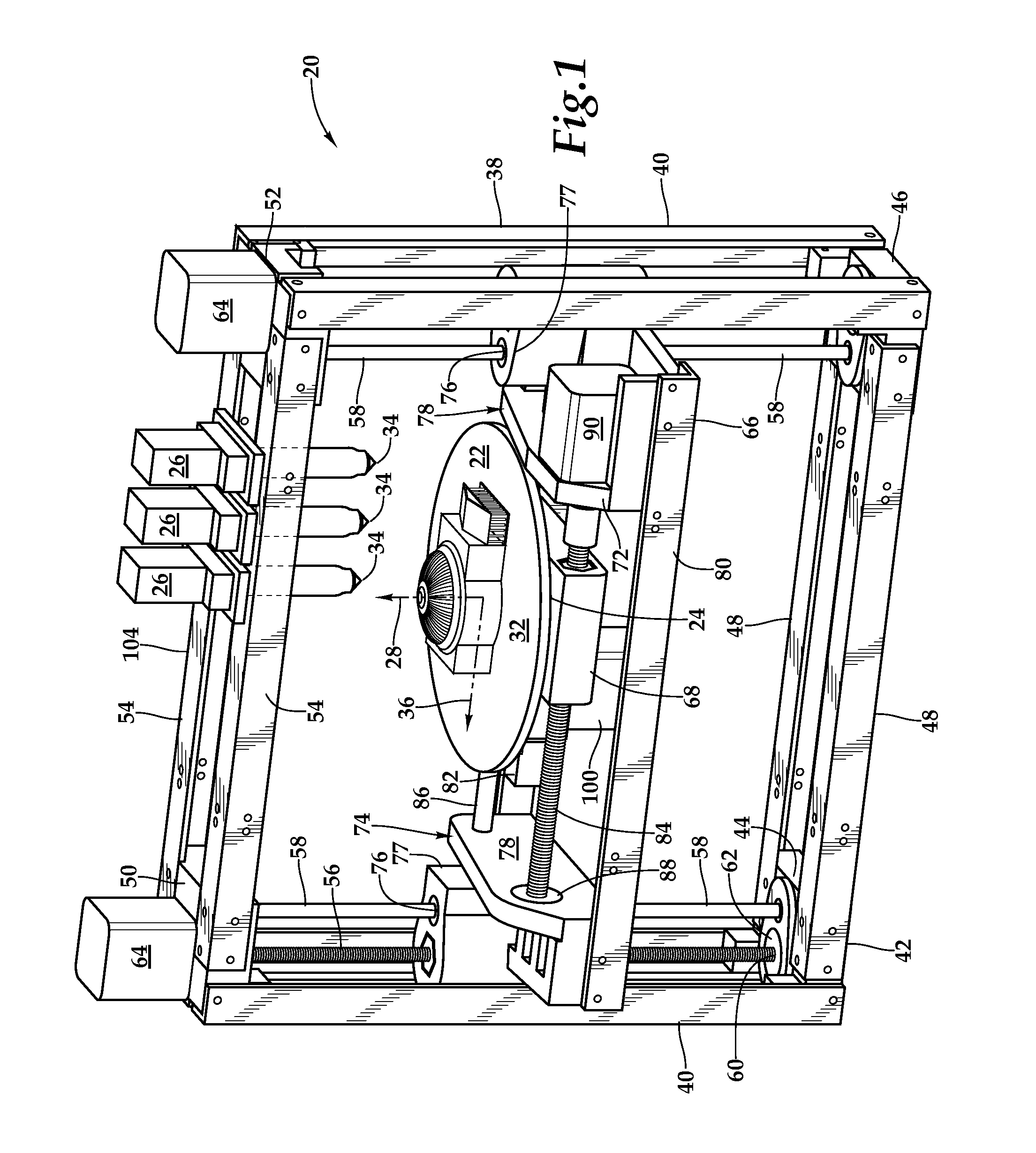
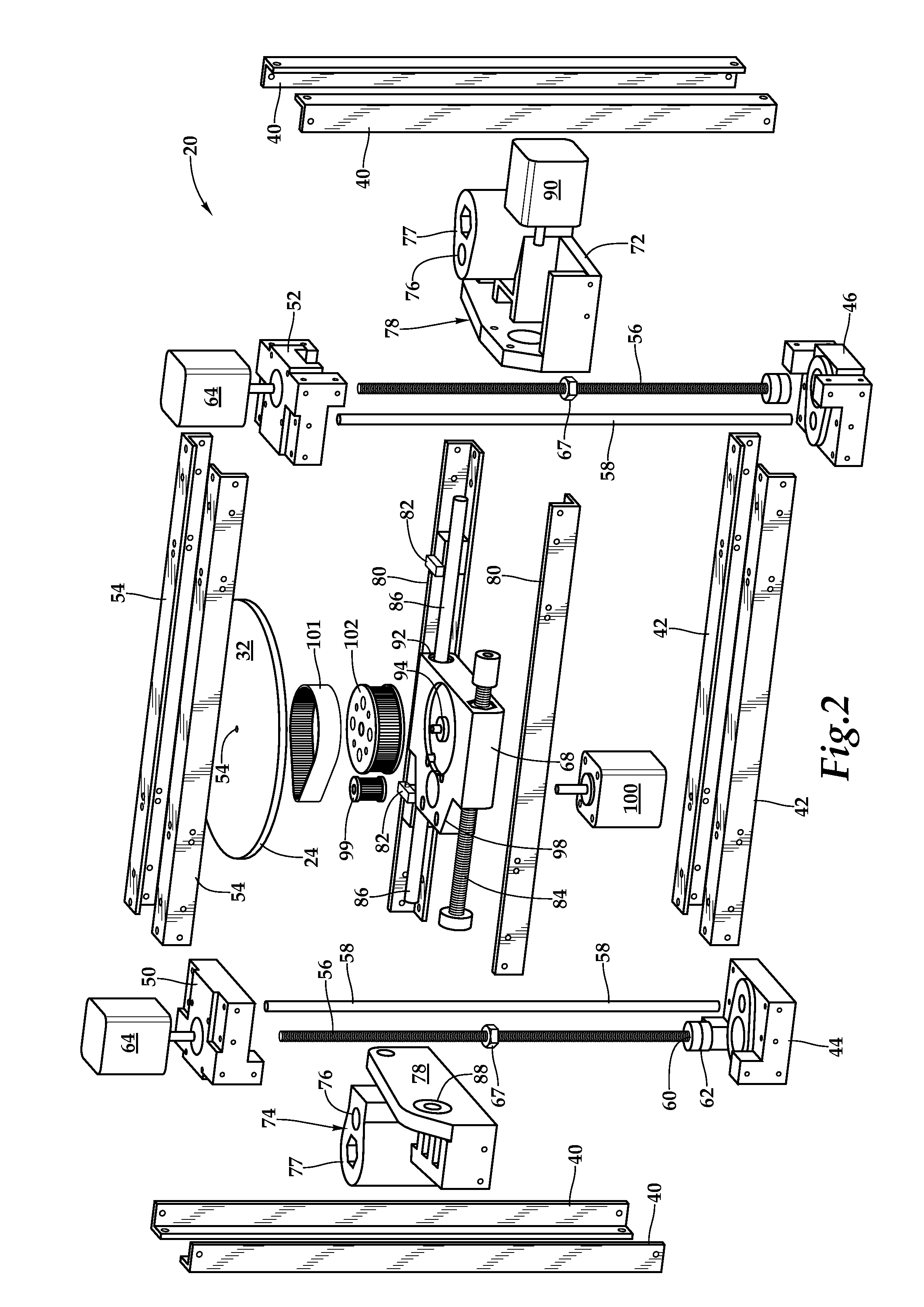
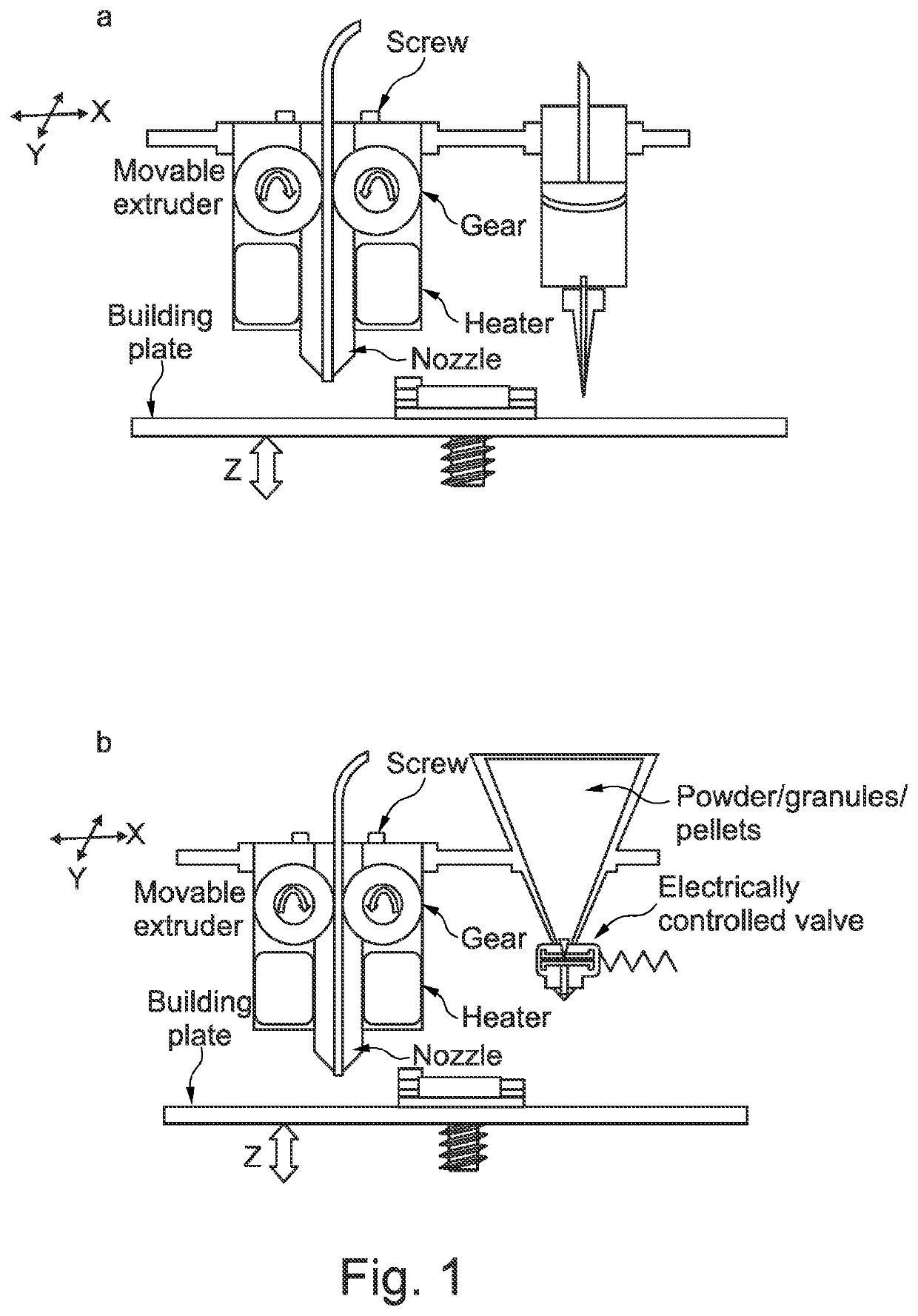
3D printer and printhead unit with multiple filaments
InactiveUS8827684B1Reduce complexityIncrease speedConfectionerySweetmeatsFused filament fabricationMetal filament
A fused filament fabrication printer has a fixed extrusion module having multiple printheads having print tips. The fixed arrangement of the printing heads allows the close spacing of multiple print tips in a printhead unit, and the simple routing of multiple plastic or metal filaments to the individual printing heads. The closely spaced print tips in the printhead unit share common components. An exemplary printhead unit has four printing heads which share a common heating block and heating block temperature sensor. The heating block incorporates a group of four print tips evenly spaced along a line. Each printing head has a separate filament which is controlled and driven by its own stepper motor through the heating block to one of the print tips. Printing of a part is by control of individual stepper motors which drive filaments through the heating block and through one of the printing tips.
Owner:RADIANT FABTION
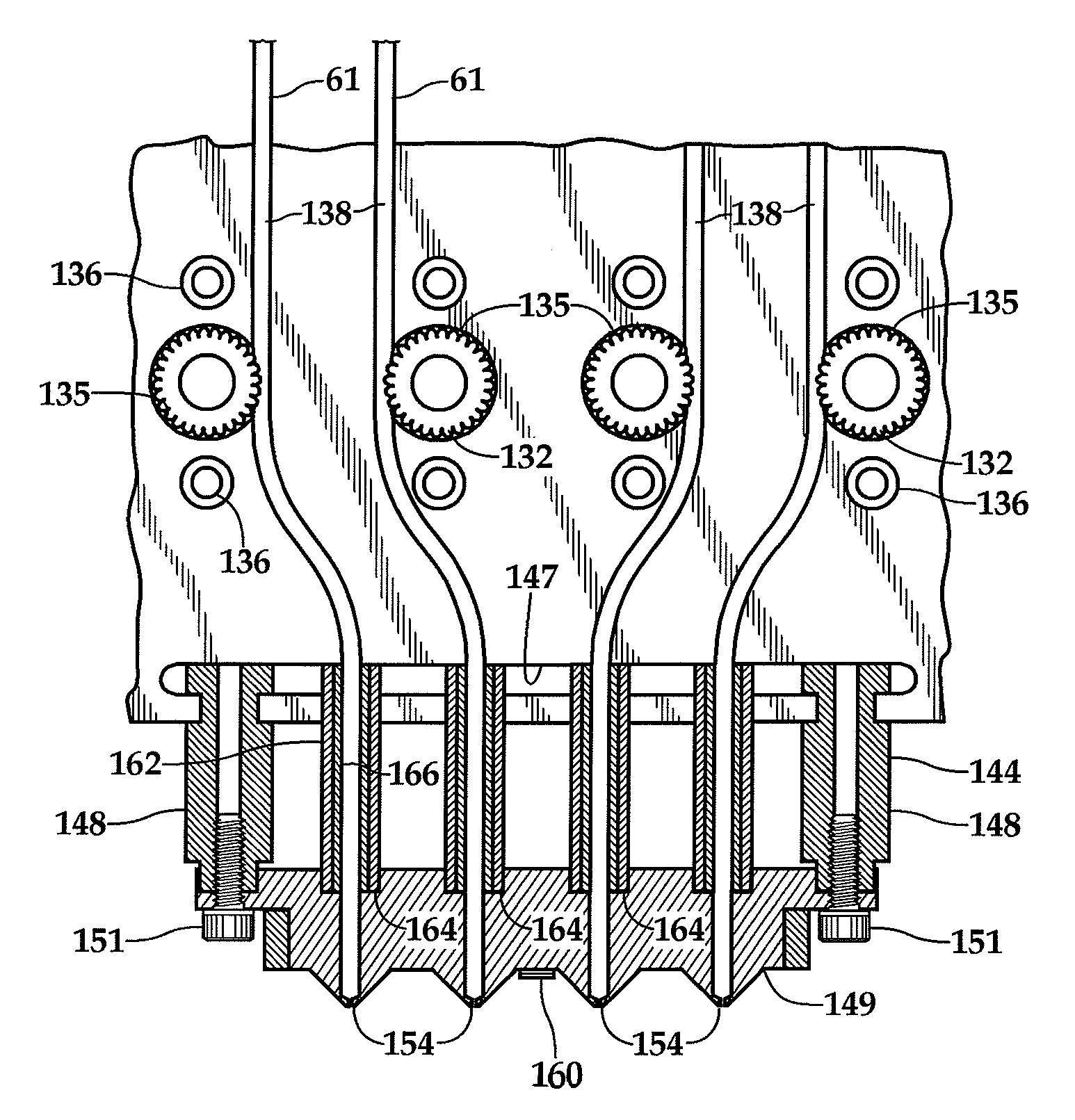
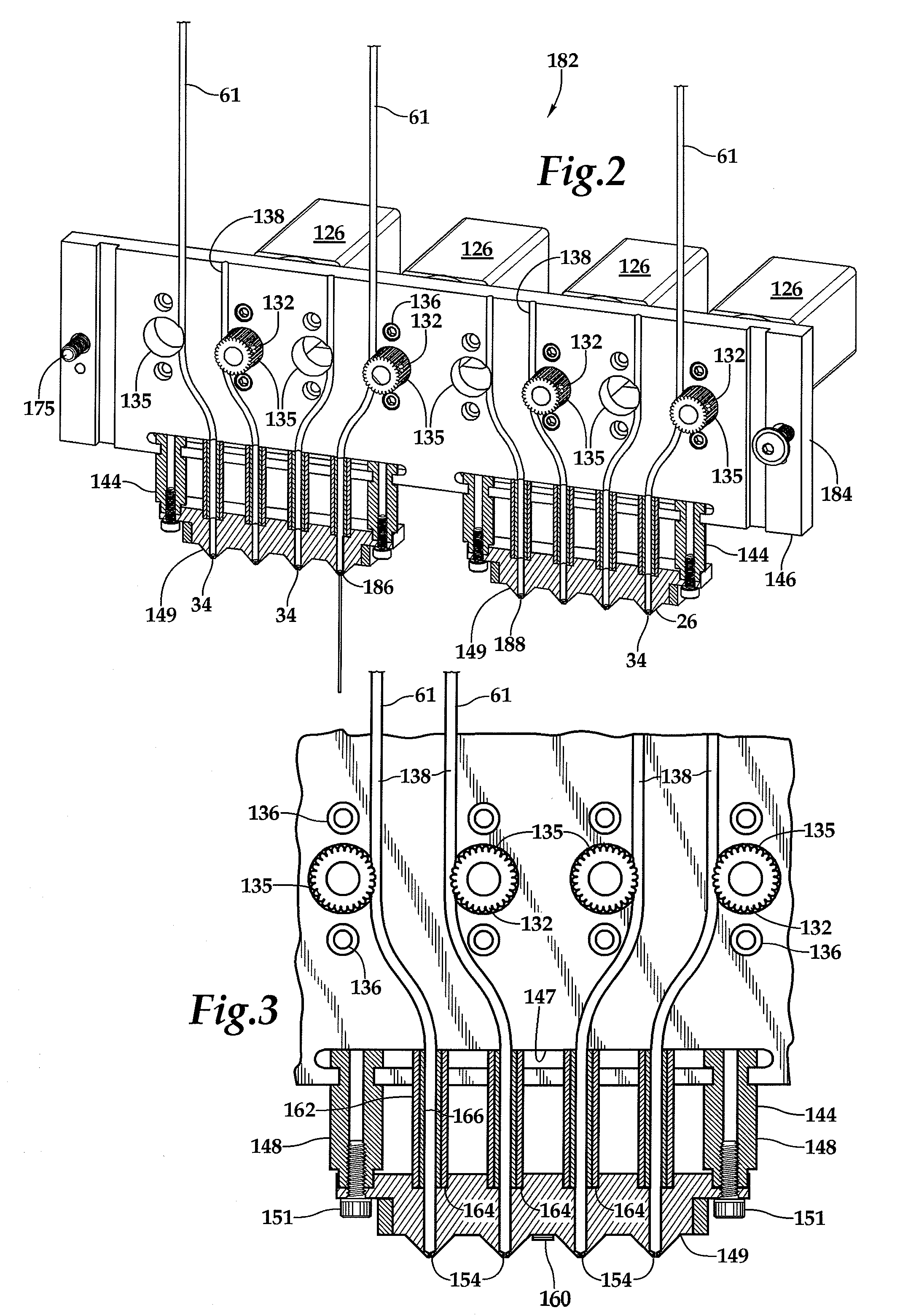
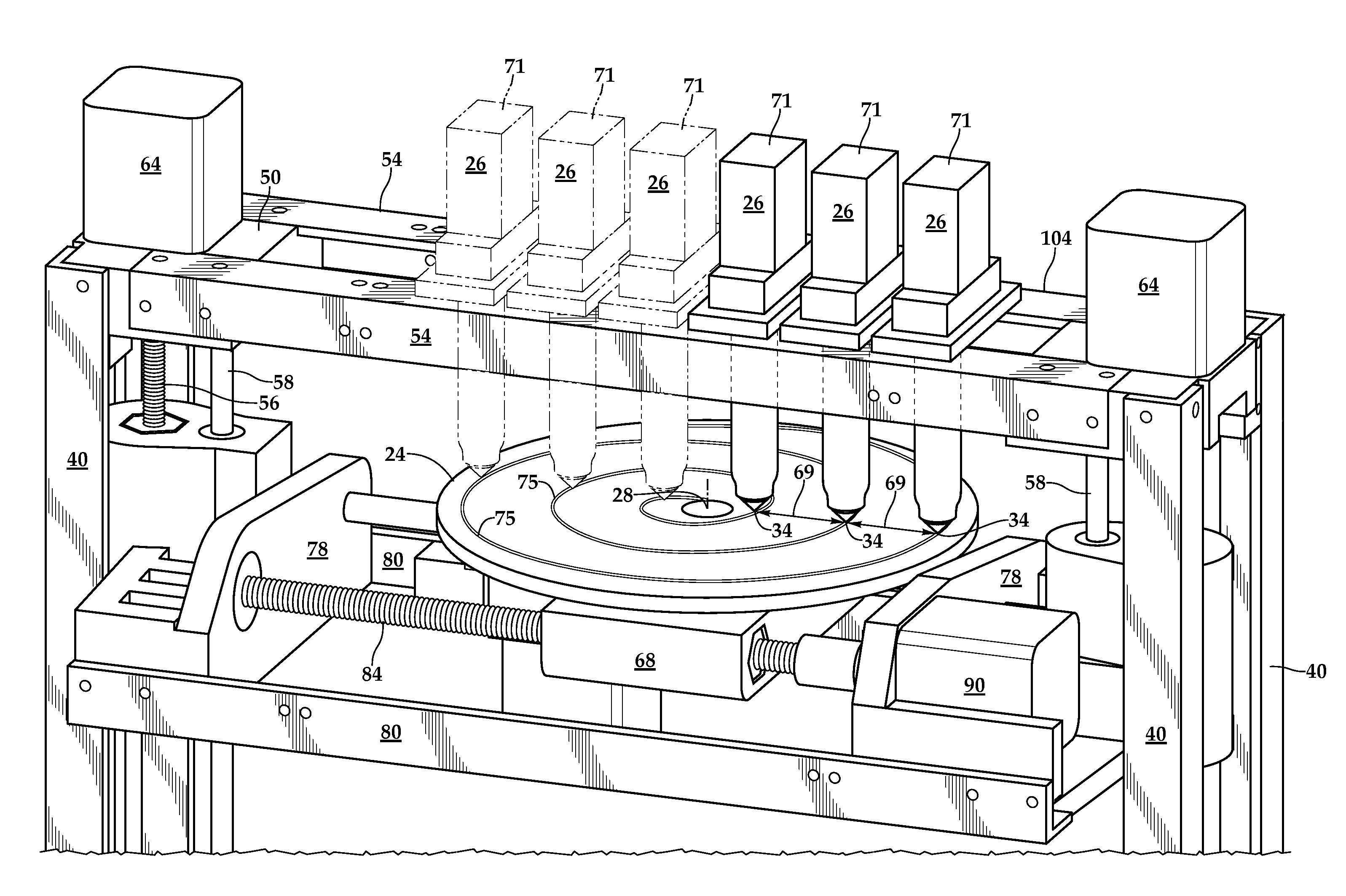
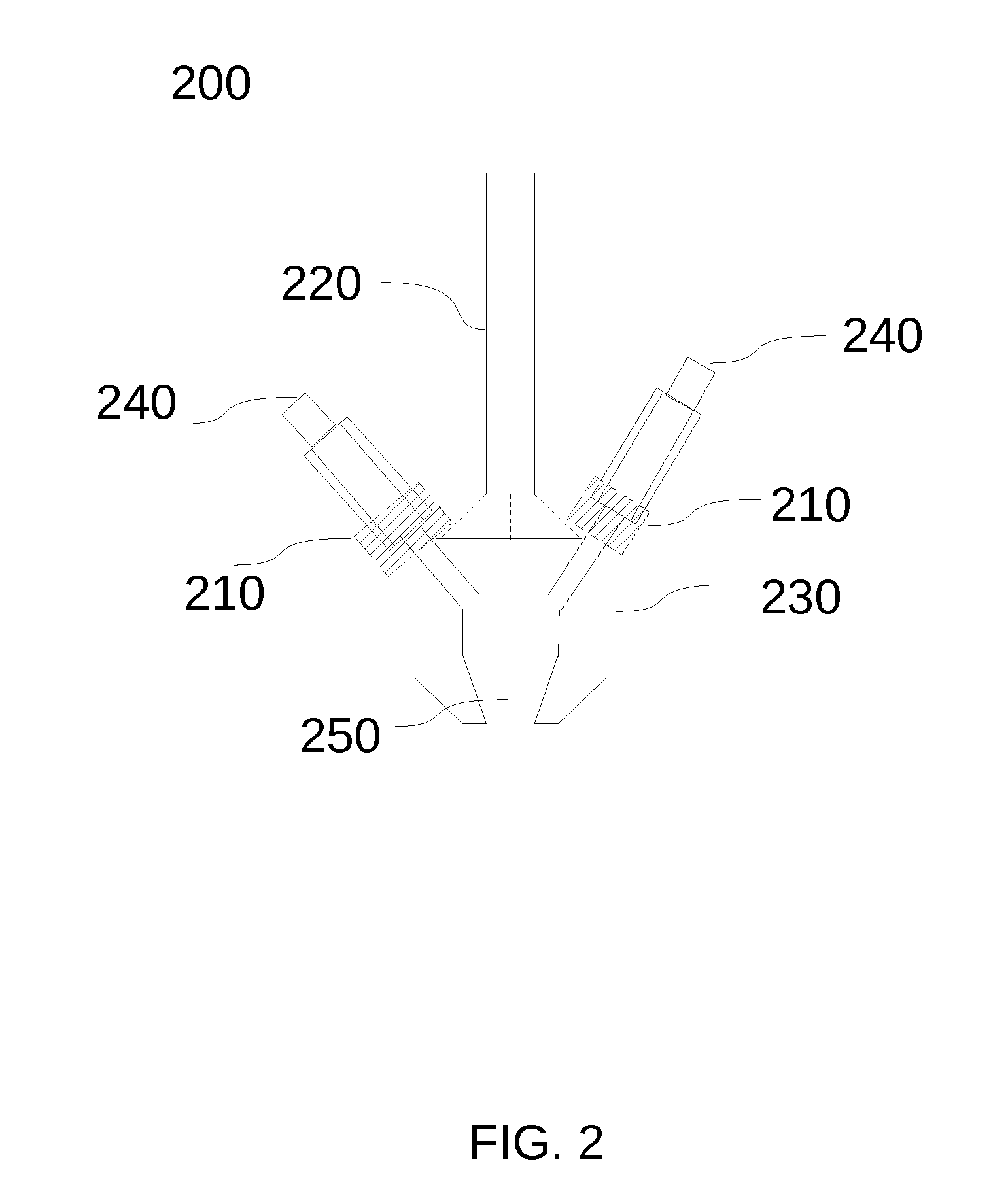
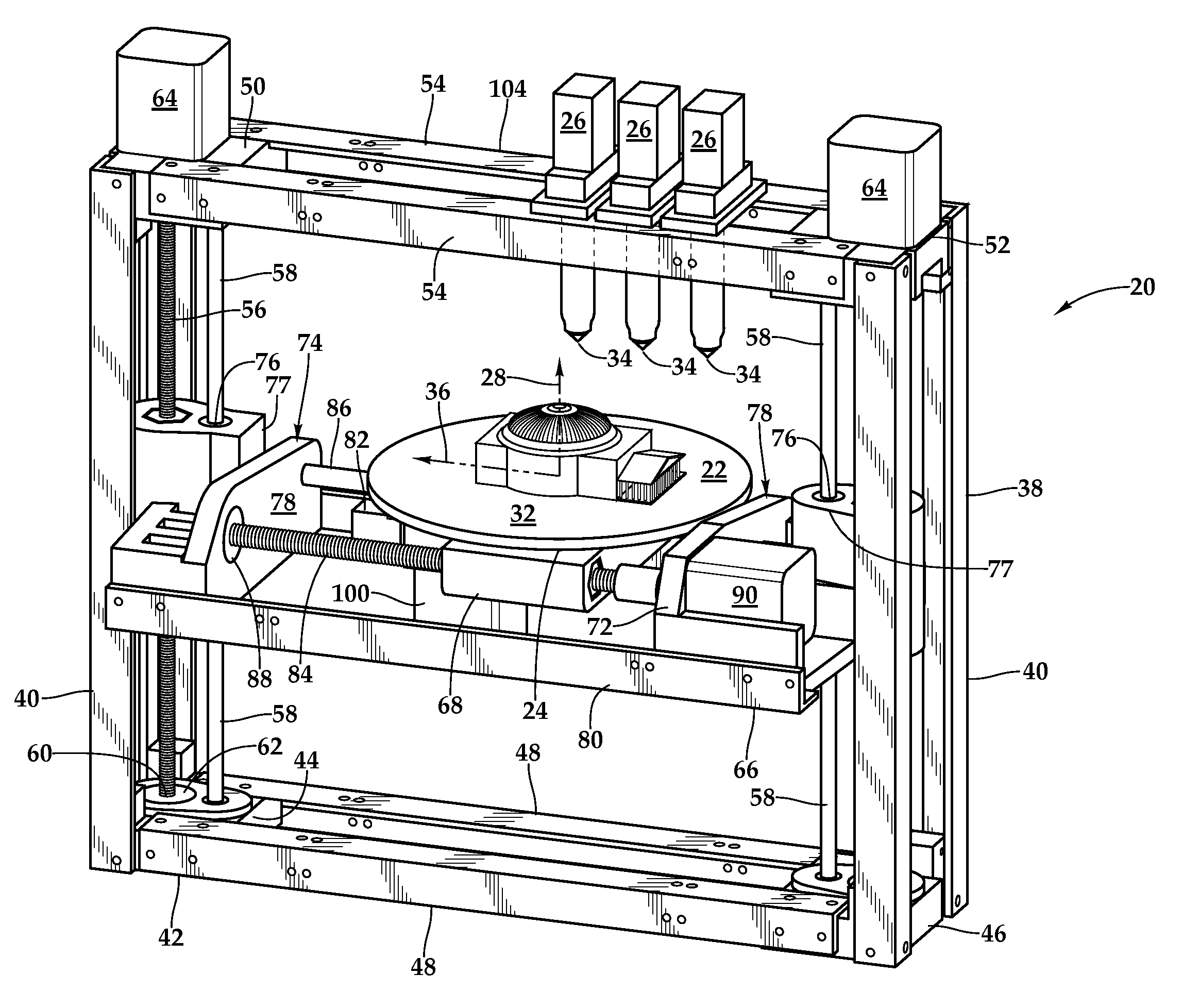
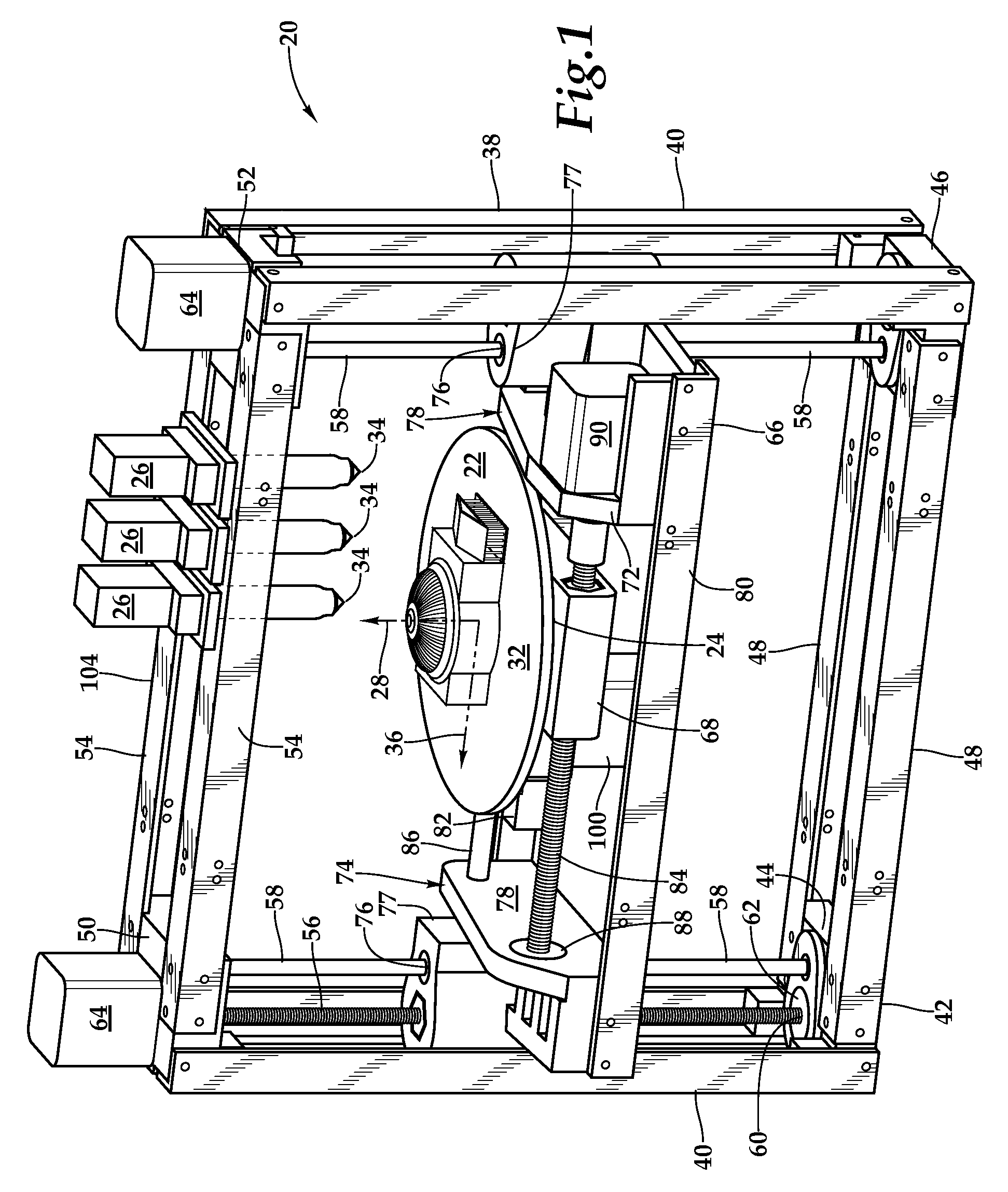
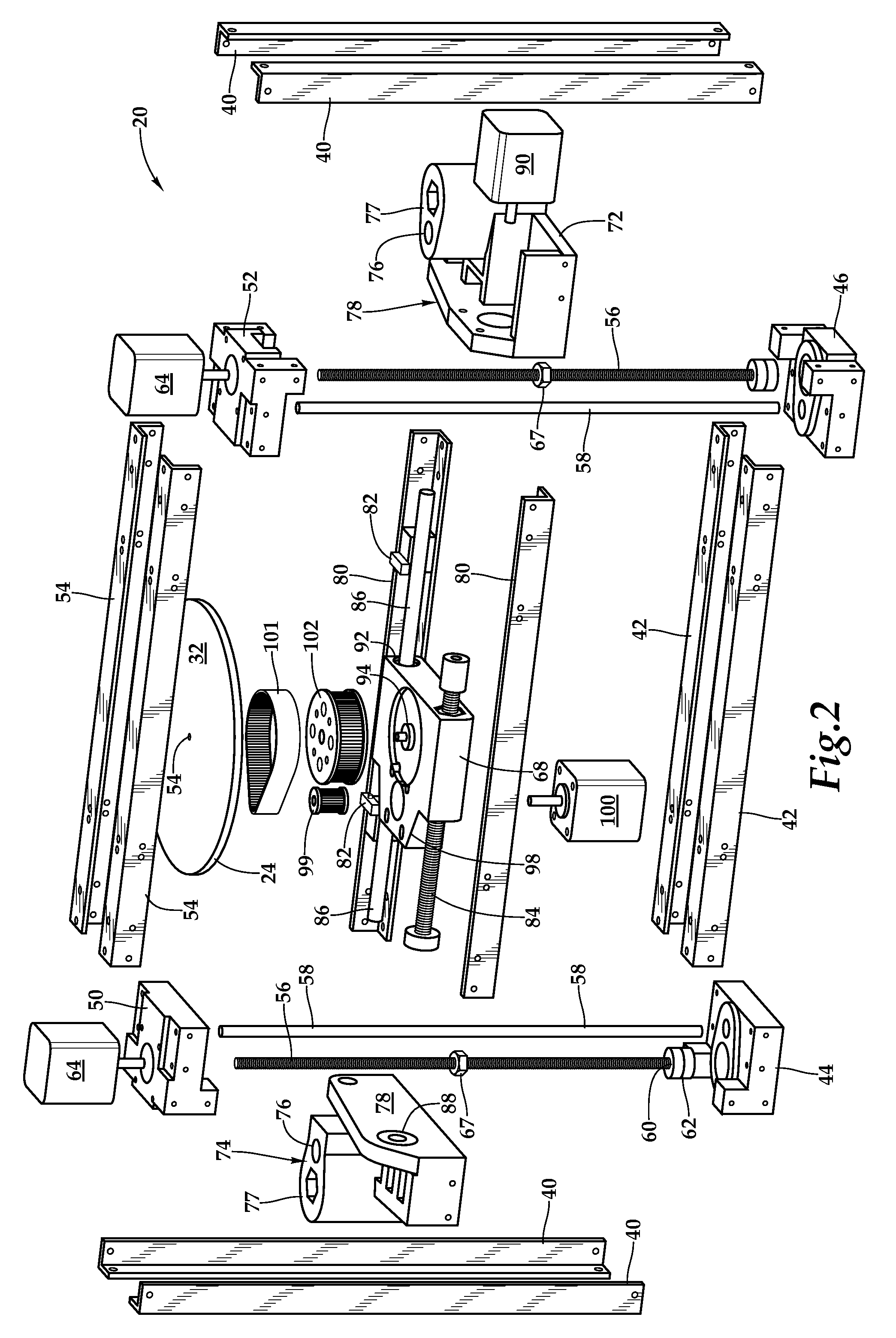
Fixed Printhead Fused Filament Fabrication Printer and Method
InactiveUS20140210137A1Increase printing speedEasily affixedConfectionerySweetmeatsCircular discLinear motion
A fused filament fabrication printer uses a plurality of fixed printing heads mounted to a structure over a build platform on which the model is built by constructing each layer of the model as the build platform is indexed through a multiplicity of successive print planes. The build platform may be in the form of a circular disk mounted for rotation about a z-axis and for linear motion along the z-axis between successive print planes, and for linear motion along a y-axis which is a selected radial direction perpendicular to the z-axis. Because the printheads are fixed, multiple printheads are easily affixed with respect to the build platform along the same radial line defining the y-axis transverse to the selected radial direction along which the build platform moves.
Owner:RADIANT FABTION
Compositions for use in fused filament 3D fabrication and method for manufacturing same
InactiveUS20170198104A1Good chemical resistanceHigh mechanical strengthAdditive manufacturing apparatus3D object support structuresFused filament fabrication3d fabrication
A method for forming a blended material for use as a deposition material in a fused filament fabrication (FFF) printer is provided. A semi-crystalline material and an amorphous material are physically mixed at an appropriate ratio. The mixed material is then heated to a temperature that is above the melting point of the semi-crystalline material and above the glass transition temperature of the amorphous material to form a blended material. The blended material is then extruded through an extruder die for use in the FFF printer.
Owner:AREVO INC
Extruder for fused filament fabrication 3D printer
InactiveUS20170157826A1Increase extrusion speedIncrease feed rateAdditive manufacturing with liquids3D object support structuresFused filament fabricationHigh acceleration
Disclosed is an improved extruder head for a fused filament fabrication 3D printer. It would be beneficial with a thinner nozzle diameter and higher extrusion speed without slippage in the feeding mechanism. The proposed improved extruder head enables extrusion of thinner extruded material at a higher extrusion speed without any slippage in filament feeding mechanism, thereby allowing higher overall building speed of the 3D printer with high quality build. Higher feed-rate of the filament material is achieved by increased usable friction between pinch wheel and filament by increasing the grippable area of the filament. This is done by feeding the filament into the feeding mechanism at an angle different to the outlet angle and routing it around the pinch wheel, back supported by a plurality of support rollers, so that the filament is in frictional contact with the pinch wheel along a greater part of its circumference, thereby increasing the surface contact area between the pinch wheel and the filament. Owing to non-slippage of the filament feeder, nominal volume of extruded material is exactly the same as desired volume with high filament feeding rate. Due to compact feeding mechanism, total mass of extruder kept small enough to enable higher acceleration of the printing nozzle resulting higher printing speed. Owing to horizontal loading of the filament material, feed roll can be mounted just above the extruder for smooth filament supply and compact size of 3D printer.
Owner:RHOMBUS INT TECH
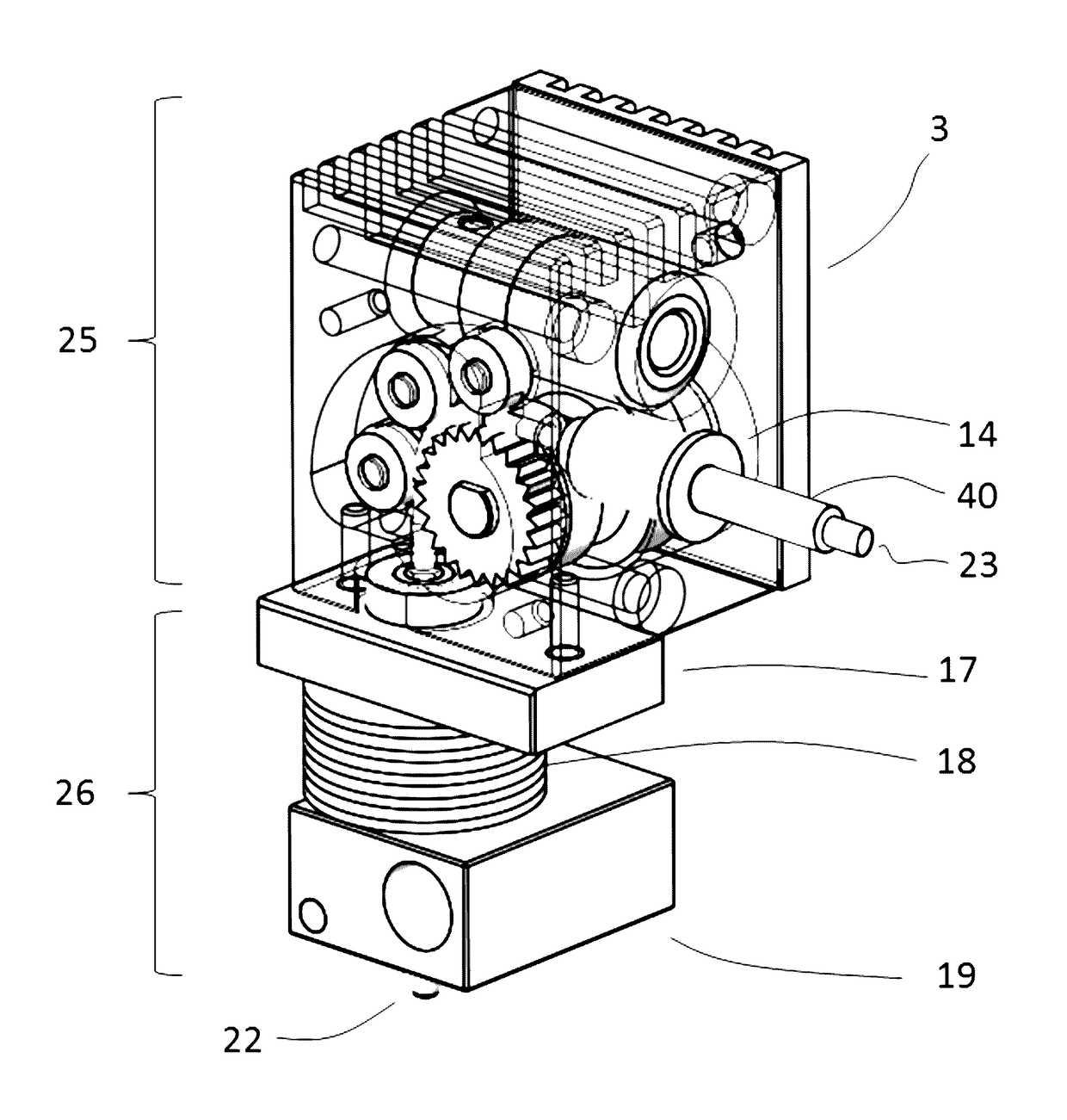
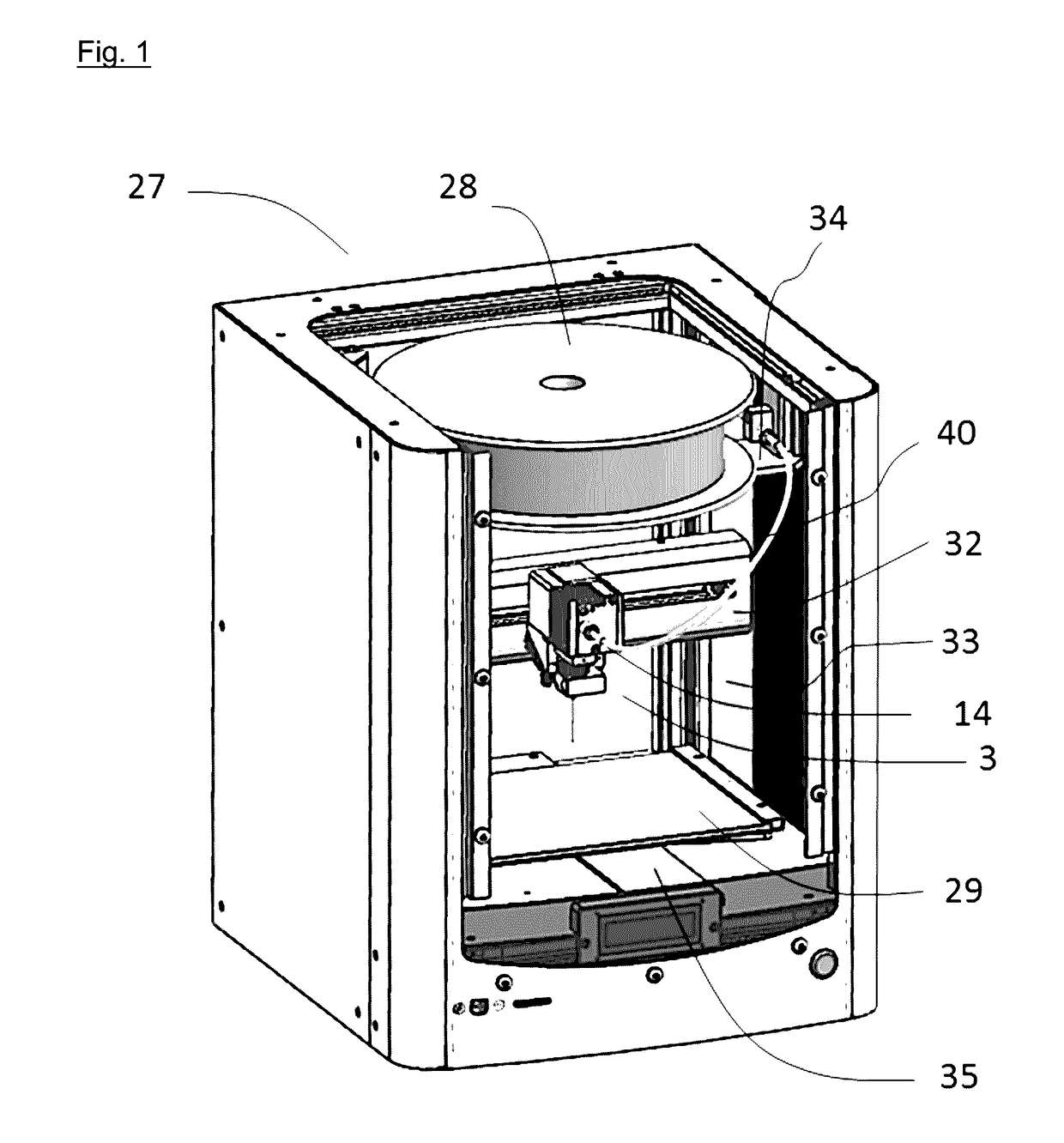
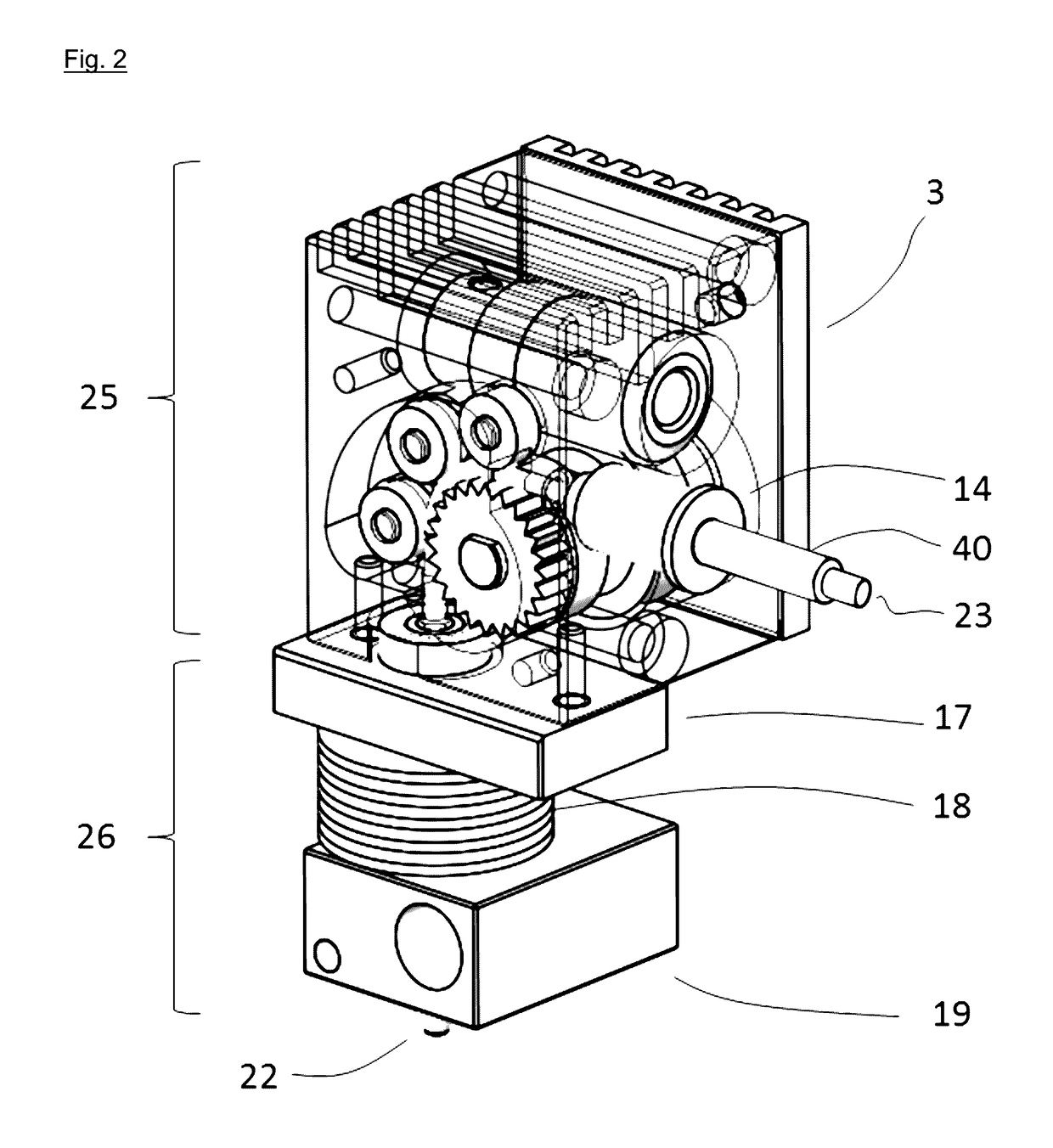
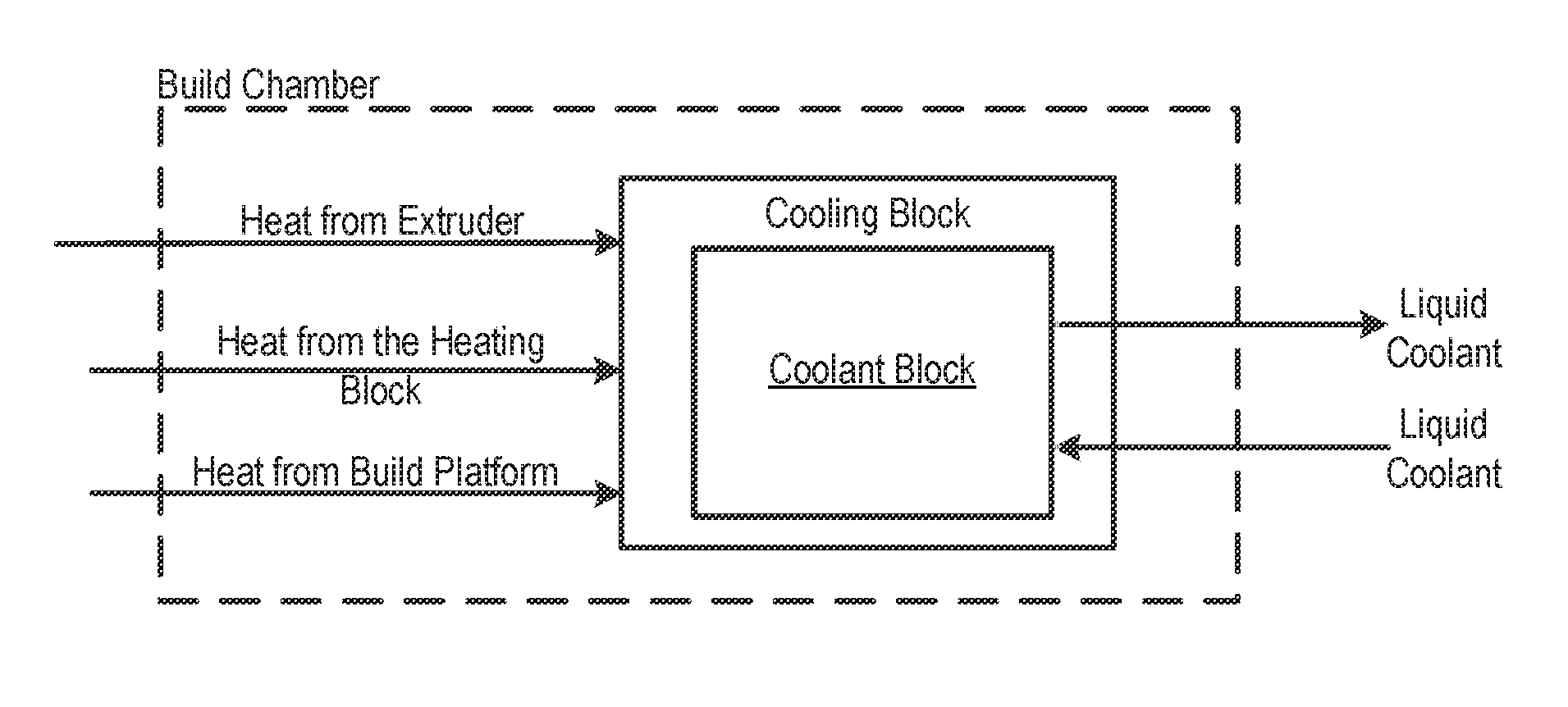
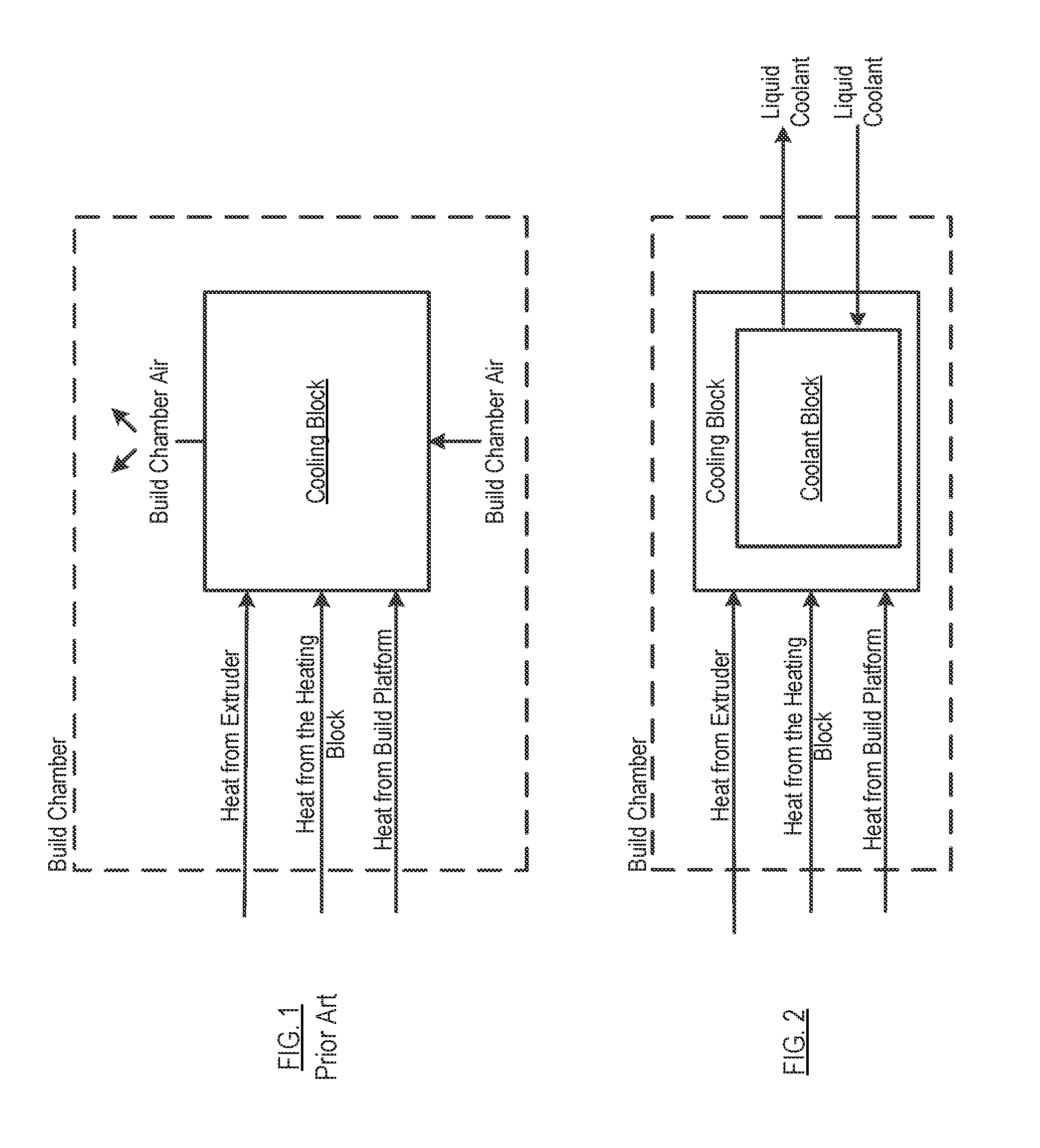
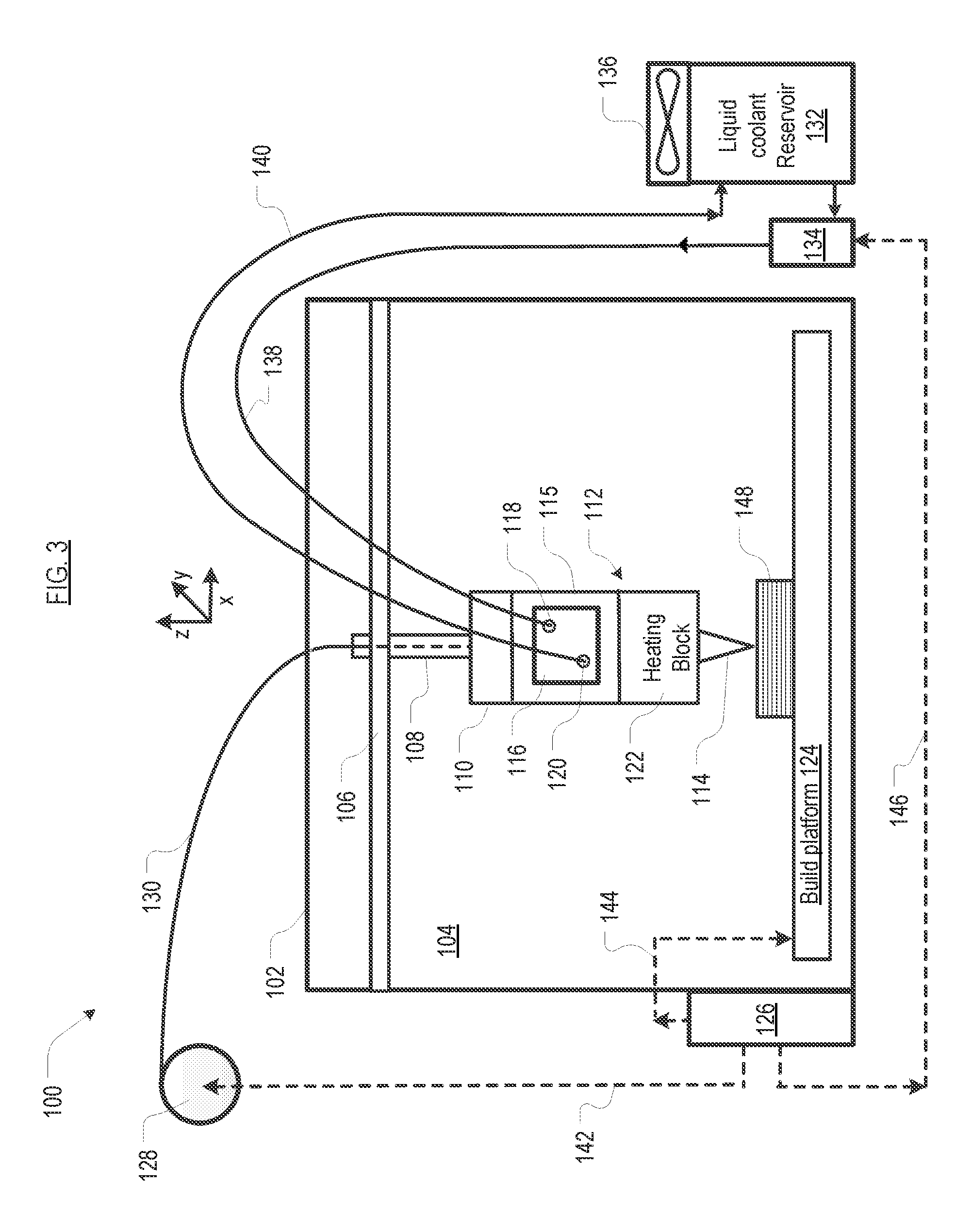
Fused filament fabrication using liquid cooling
InactiveUS20160271880A1Reduce incidenceReduce of of materialApplying layer meansFused filament fabricationNuclear engineering
A FFF-based 3D printer includes a thermal management system that incorporates liquid cooling for the cooling block. In the illustrative embodiment, the thermal management system includes a coolant block that couples to the surface of the existing cooling block, a liquid-coolant reservoir, a fan for cooling the reservoir, a pump for pumping the coolant, and conduits for conducting the coolant to and from the coolant block. Embodiments of the invention provide a way to prevent or substantially reduce the incidence of clogging as otherwise occurs when attempting to print high-temperature, high-viscosity materials using FFF-based 3d printers.
Owner:AREVO INC
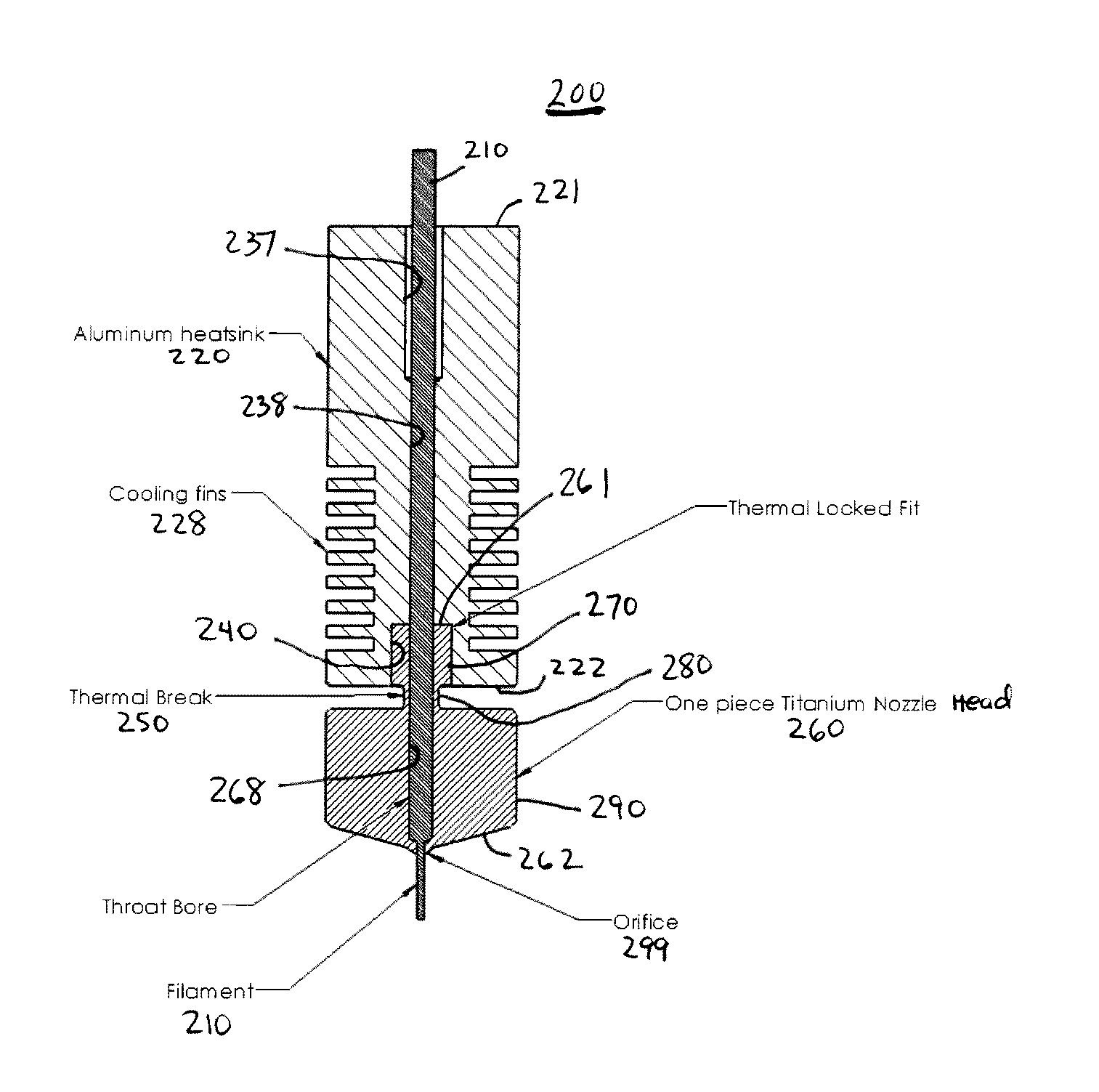
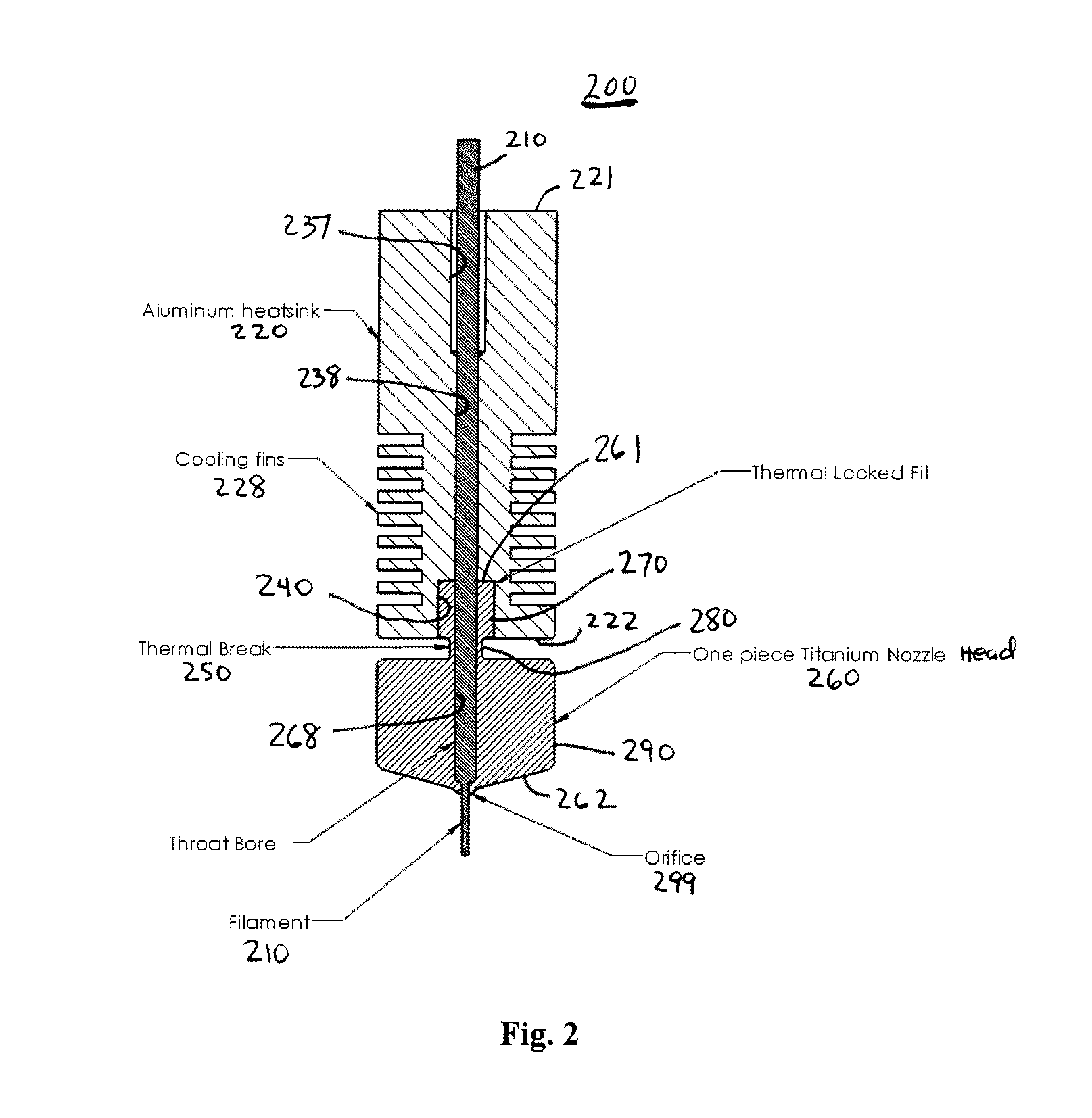
Nozzle system with monolithic nozzle head for fused filament fabrication additive manufacturing and method of manufacturing same
ActiveUS20170057168A1Additive manufacturing with liquids3D object support structuresFused filament fabricationSystems design
A nozzle system and method of manufacturing a nozzle system for use in an additive manufacturing system for fabricating an object is disclosed. The nozzle system includes a monolithic nozzle head designed such that the thermal locking member, neck member, and nozzle member of the nozzle head are manufactured into one component. The nozzle head is made of a material that has a high specific heat capacity but low thermal heat conductivity. The result is a nozzle system design that virtually eliminates heat migration from the nozzle head to the heat sink, and thereby improves the overall quality of polymer filament deposition during printing.
Owner:COSINE ADDITIVE INC
Amorphous polyaryletherketone and blends thereof for use in additive manufacturing
ActiveUS20170096576A1High melt flowHigh viscosityAdditive manufacturing apparatusAdditive manufacturing with liquidsFused filament fabricationAdditive layer manufacturing
A material for use in a fused filament fabrication (FFF) printer comprises a polyaryletherketone (PAEK) having an amorphous morphology. In some embodiments, the material also includes a PAEK having a semi-crystalline morphology.
Owner:AREVO INC
Methods for 3D printing of poly-4-hydroxybutyrate and copolymers
ActiveUS20190375149A1Reduce molecular weightImprove printing qualityManufacturing driving meansManufacturing enclosuresSelective laser meltingFused filament fabrication
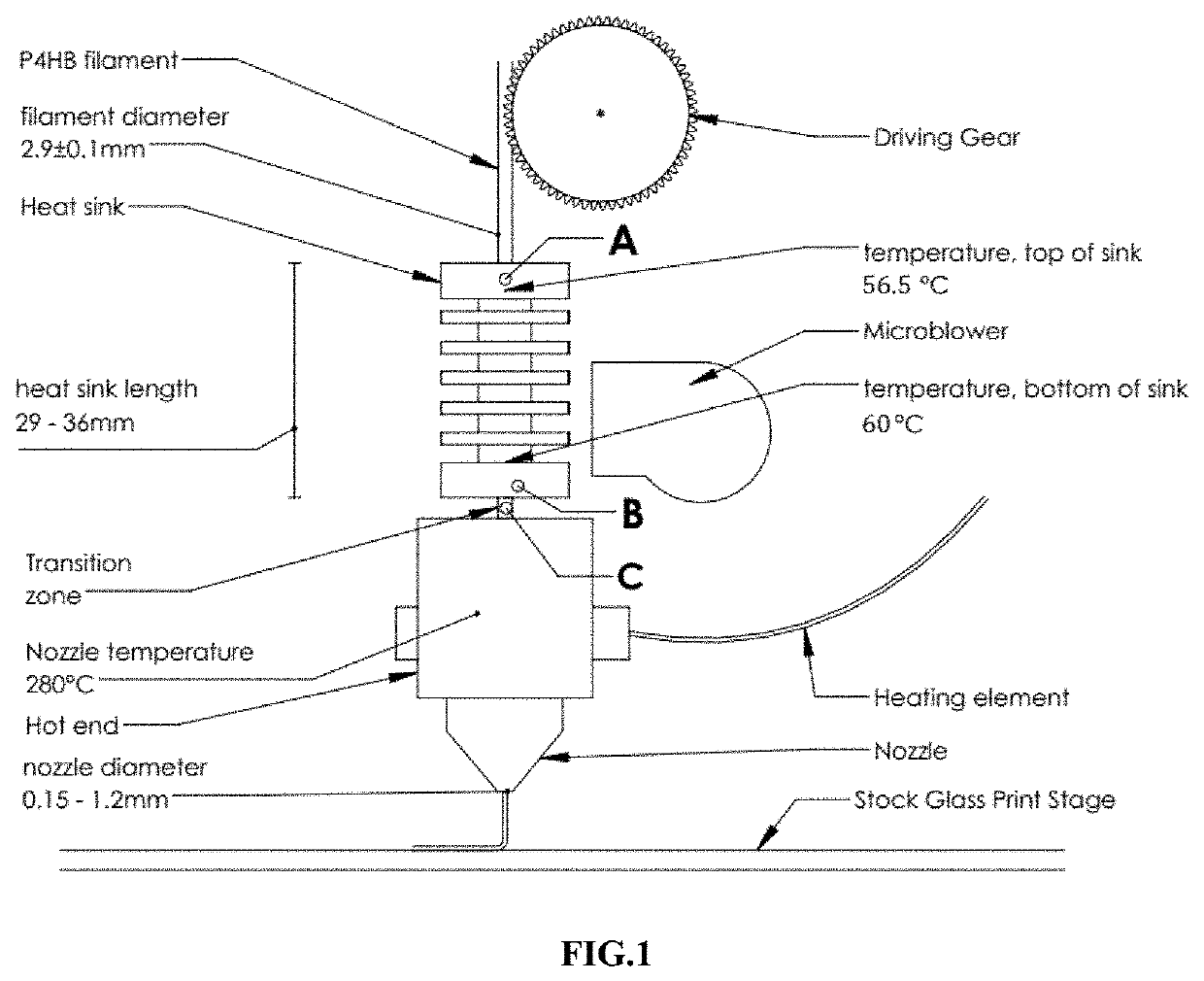
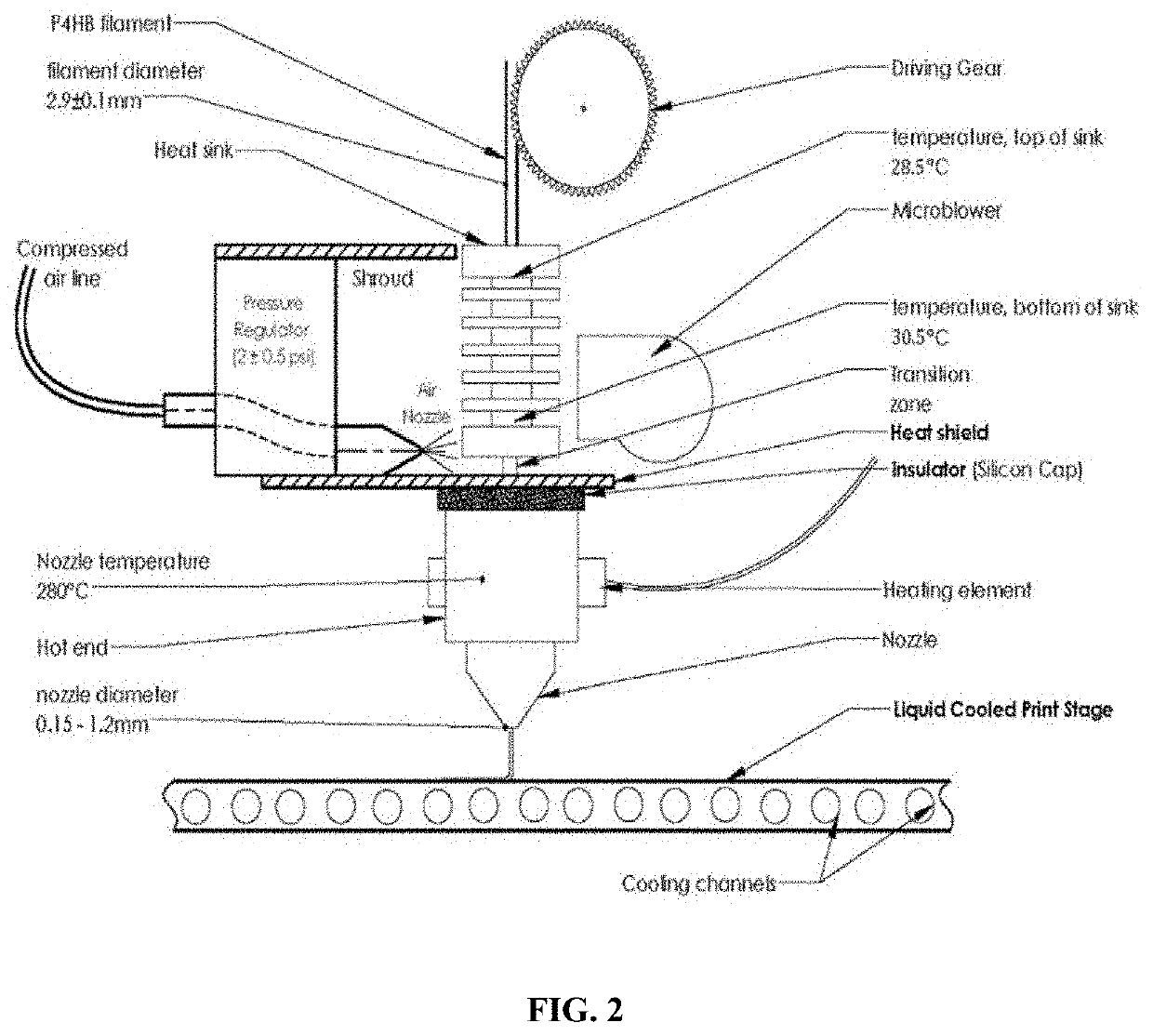
Methods to fabricate objects by 3D printing of poly-4-hydroxybutyrate (P4HB) and copolymers thereof have been developed. In one method, these objects are produced by continuous fused filament fabrication using an apparatus and conditions that overcome the problems of poor feeding of the filament resulting from the low softening temperature of the filament and heat creep along the fed filament. Methods using an apparatus including a heat sink, a melt tube, a heating block and nozzle, and a transition zone between the heat sink and heating block, with the melt tube extending through the heat sink, transition zone, and heat block to the nozzle are disclosed. 3D objects are also printed by fused pellet deposition (FPD), melt extrusion deposition (MED), selective laser melting (SLM), printing of slurries and solutions using a coagulation bath, and printing using a binding solution and polymer granules.
Owner:TEPHA INC
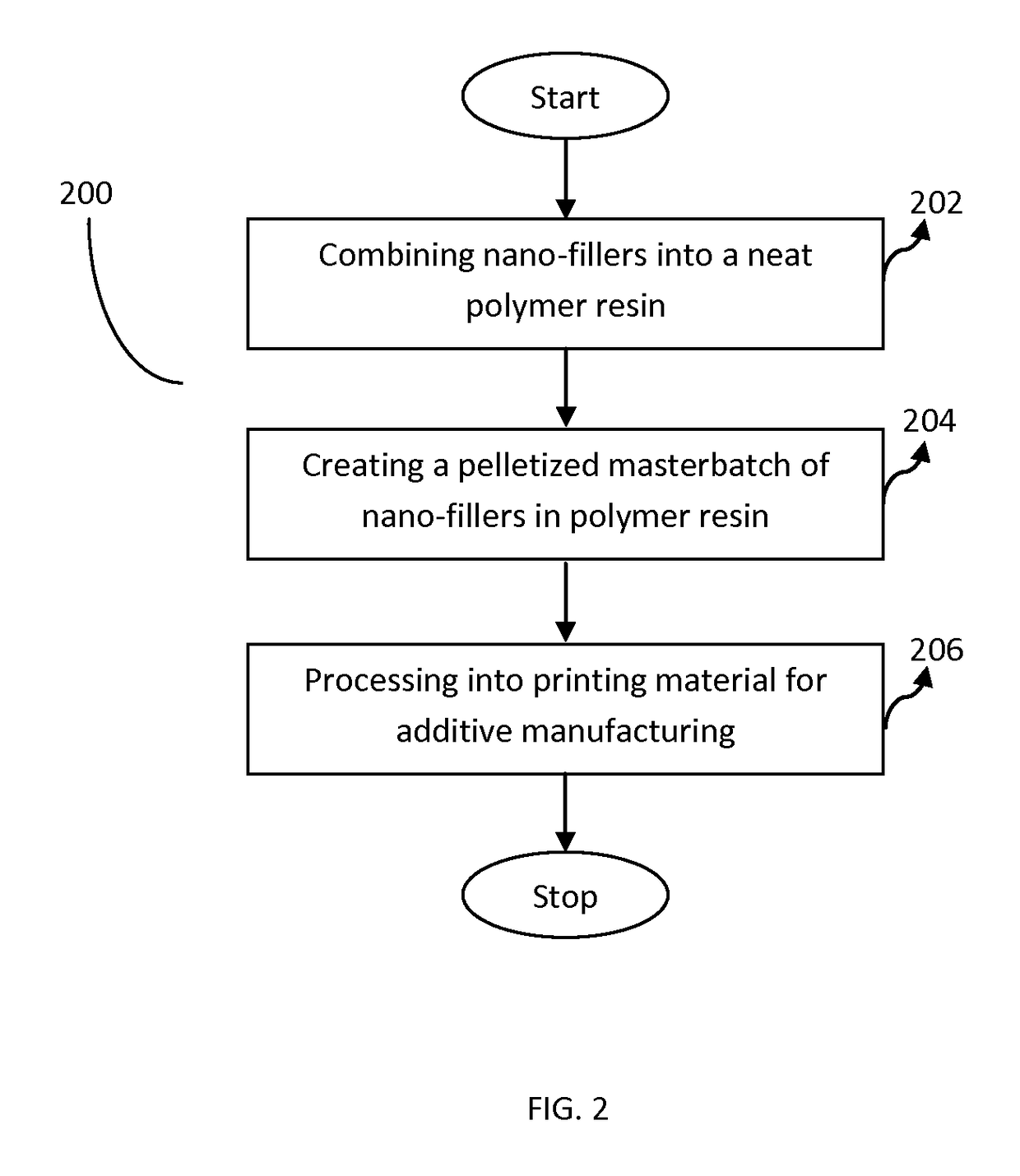
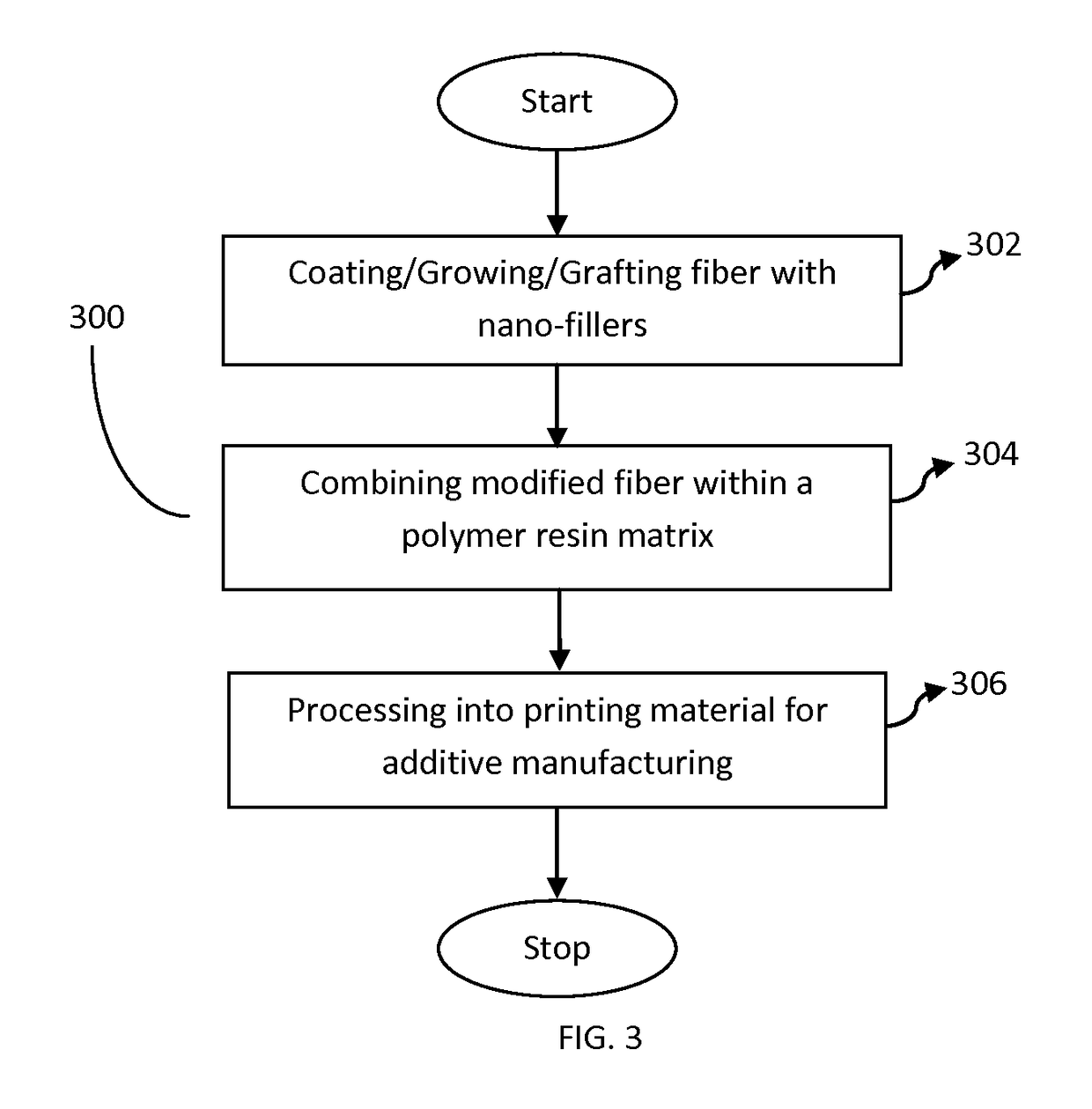
Method to manufacture polymer composite materials with nano-fillers for use in additive manufacturing to improve material properties
ActiveUS9908978B2Improved propertyImprove material performanceAdditive manufacturing apparatusFiberCarbon nanotube
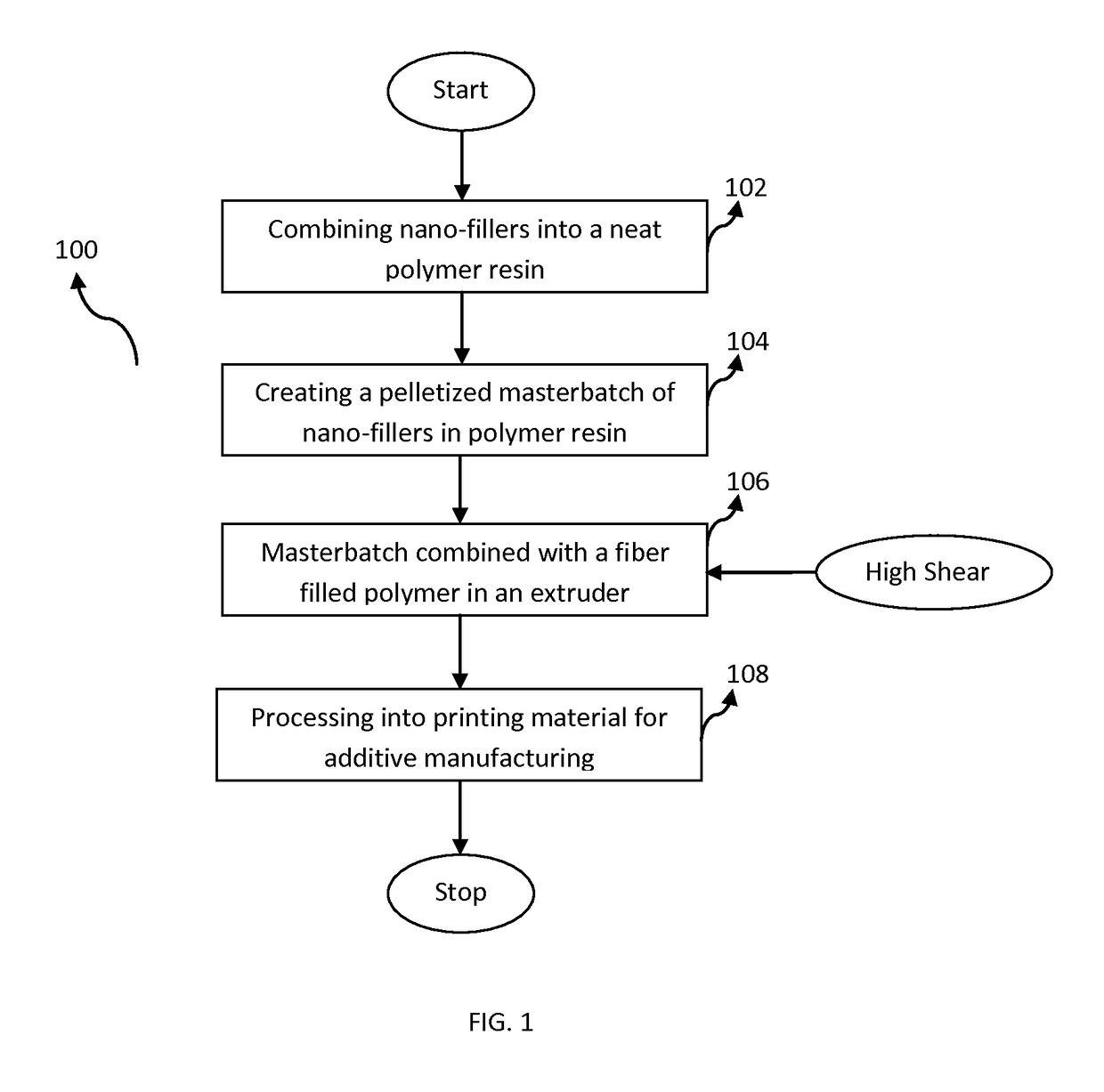
Methods for producing 3D printing composite polymer materials for use in additive manufacturing processes are provided. The methods result in enhancing the material properties of the printing material by providing a uniform and smooth surface finish of the printing material and the nozzle extrudate for additive manufacturing processes, such as Fused Filament Fabrication. The method includes implementing impregnation techniques for combining carbon nanotubes or other nano-fillers, a polymer resin and a fiber material to produce a polymer material that can be processed into a printing material. Further, the method may include combining the carbon nanotubes or other nano-fillers and the polymer resin to form a masterbatch that may be further combined with the fiber material through an extrusion process. The method results in a printing material with enhanced material properties and smooth surface finish for the printing material and resulting nozzle extrudate for Fused Filament Fabrication.
Owner:STRATSYS INC
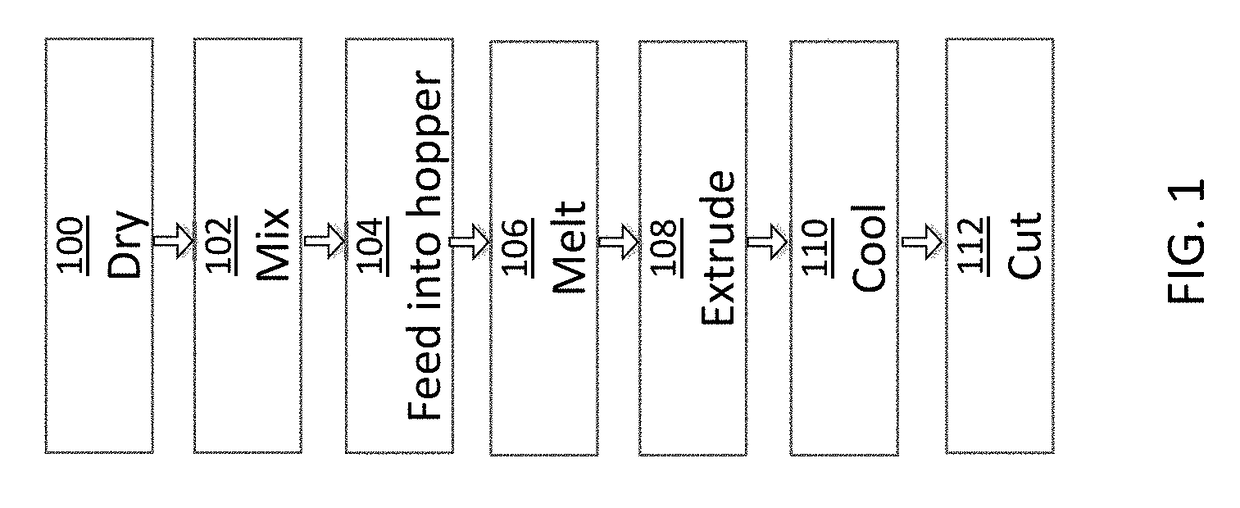
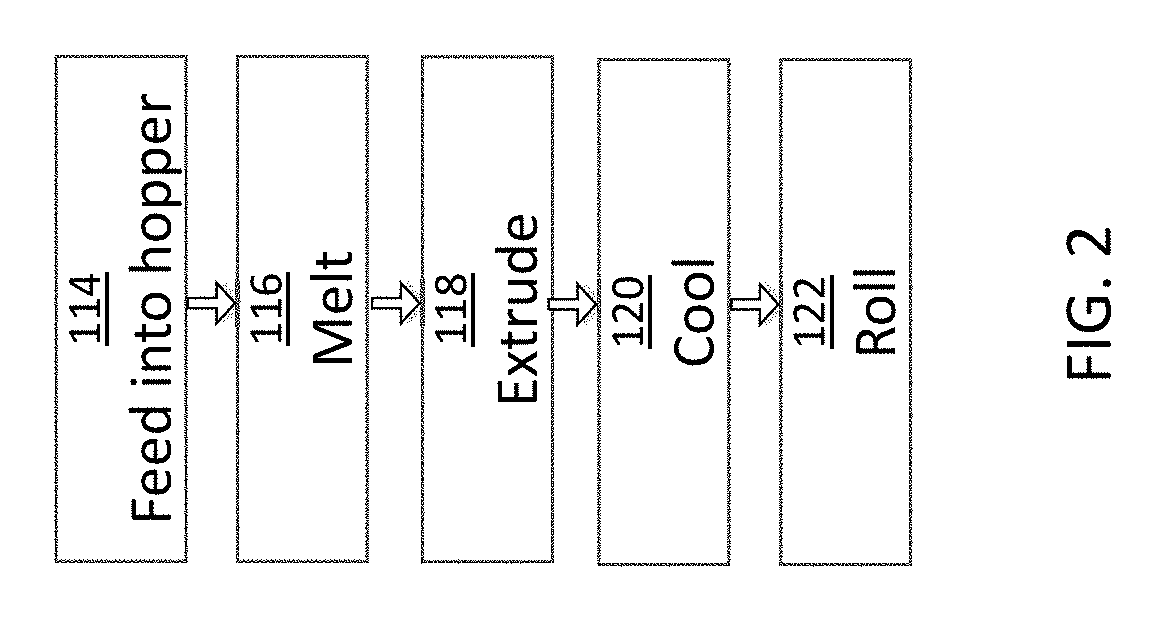
Method for producing a supply obtained from the recycling of plastic material of industrial and post-consumer residues, to be used by 3D printers
A process uses a starting material including recycled post-consumer and industrial “scrap” thermoplastics based on polyester and polyamide, where a supply is obtained suitable for 3D printing / additive manufacturing / rapid prototyping with “Fused Deposition Model” (FDM), “Fused Filament Fabrication” (FFF) and similar technologies. The supply can have the form of a solid filament suitable to be used by “3D” printers, or it can form a pulverulent material to be used in more sophisticated printers, such as those with SLS technology. This method includes a series of first stages that consist of: a) Selecting the starting material which was originally produced by one of the processes of transformation; b) starting material is duly cleaned; c) once it is cleaned, the material is dried at temperatures greater than 100° C. but less than 240° C.; d) the material obtained thereof is driven into an extruder machine where it is subject to temperatures between 200° C. and 350° C. from the head to the dosing zone to be pelletized; e) the addition of additives to the material may occur in the feed zone in order to grant distinctive physicochemical properties to the end product, such as color, hardness, erosion strength, etc. f) from the material resulting from the previous stage either a plastic filament is created by using a single screw extruder and is placed in a spool, or a pulverulent material is created. The supply obtained from the previous stages is subject to an additional heat treatment by varying the process temperature between 100° C. and 240° C., during a processing time varying between 1 minute and 24 hours. The starting material consists of plastic post-consumer items or industrial scrap made of polyethylene-terephthalate (PET) and polyamide (PA). The additional heat treatment varies the process temperature between 100° C. and 180° C. in the case of polyamides (PA) and between 100° C. and 240° C. in the case of polyethylene-terephthalate (PET).
Owner:ENYE TECH SA
Fused filament fabrication extruder
InactiveUS20160354977A1Additive manufacturing with liquids3D object support structuresFused filament fabricationTemperature control
3D Fused Filament Fabrication (FFF) is improved by heating the deposition nozzle with one or more non-contact heat sources. 3D FFF is also improved by cooling the deposition nozzle with one or more active cooling elements. Temperature control of the deposition nozzle is improved due to the reduction in mass of the nozzle by eliminating conductive heat elements and their associated devices, such as thermal transfer blocks. Responsiveness of the nozzle is improved by using lasers as non-contact heating sources, allow for rapid changes in temperature when necessary.
Owner:GORDON MARK CHRISTOPHER
Fixed printhead fused filament fabrication printer and method
InactiveUS8944802B2Increase printing speedEasily affixedConfectionerySweetmeatsLinear motionCircular disc
A fused filament fabrication printer uses a plurality of fixed printing heads mounted to a structure over a build platform on which the model is built by constructing each layer of the model as the build platform is indexed through a multiplicity of successive print planes. The build platform may be in the form of a circular disk mounted for rotation about a z-axis and for linear motion along the z-axis between successive print planes, and for linear motion along a y-axis which is a selected radial direction perpendicular to the z-axis. Because the printheads are fixed, multiple printheads are easily affixed with respect to the build platform along the same radial line defining the y-axis transverse to the selected radial direction along which the build platform moves.
Owner:RADIANT FABTION
Adaptable high-performance extrusion head for fused filament fabrication systems
ActiveUS20180333915A1Reduce heat transferAdditive manufacturing with liquids3D object support structuresFused filament fabricationEngineering
An extrusion head for a three-dimensional printer is disclosed including a feed tube, a heater, a cooler, and a bridge. The feed tube can be made of metal and has an inlet for receiving a forwardly driven filament of solid deposition material, an outlet, a downstream portion adjacent to the outlet, an upstream portion upstream from the downstream portion, and an internal passage extending from the inlet to the outlet. The heater is thermally coupled with the downstream portion of the feed tube for heating a filament to provide softened fluid deposition material. The cooler is thermally coupled with the upstream portion and spaced generally axially from the heater to define a generally axially extending gap traversed by the feed tube. The bridge traverses the gap and provides a rigid mechanical connection between the heater and the cooler.
Owner:SLICE ENG LLC
Feedstock for an additive manufacturing method, additive manufacturing method using the same, and article obtained therefrom
ActiveUS20190308241A1Increase loadLow shrinkageAdditive manufacturing apparatusTransportation and packagingFused filament fabricationPolymer alloy
A feedstock for a 3D manufacturing process, in particular a Fused Filament Fabrication process. The feedstock includes (P) sinterable particles made of a metal, metal alloy, glass, ceramic material, or a mixture thereof; and (B) a binder composition including (b1) 5-15% by weight, relative to the total weight of the binder composition, of a polymeric compatibilizer, and (b2) 85-95% by weight, relative to the total weight of the binder composition, of a polymeric binder component, the polymeric binder component being selected from the group consisting of (b2-1) a polymer mixture or polymer alloy, the mixture or alloy including at least a first and a second polymer; (b2-2) one, two or more block copolymers, including at least a first polymer block and second polymer block; and (b2-3) mixtures of (b2-1) and (b2-2), wherein the amount of sinterable particles P is 40 Vol % or more of the composition.
Owner:HOGANAS AB
Compositions for use in fused filament 3D fabrication and method for manufacturing same
InactiveUS20180201737A1Good chemical resistanceHigh mechanical strengthAdditive manufacturing apparatus3D object support structuresVitrificationFused filament fabrication
A method for forming a blended material for use as a deposition material in a fused filament fabrication (FFF) printer is provided. A semi-crystalline material and an amorphous material are physically mixed at an appropriate ratio. The mixed material is then heated to a temperature that is above the melting point of the semi-crystalline material and above the glass transition temperature of the amorphous material to form a blended material. The blended material is then extruded through an extruder die for use in the FFF printer.
Owner:AREVO INC
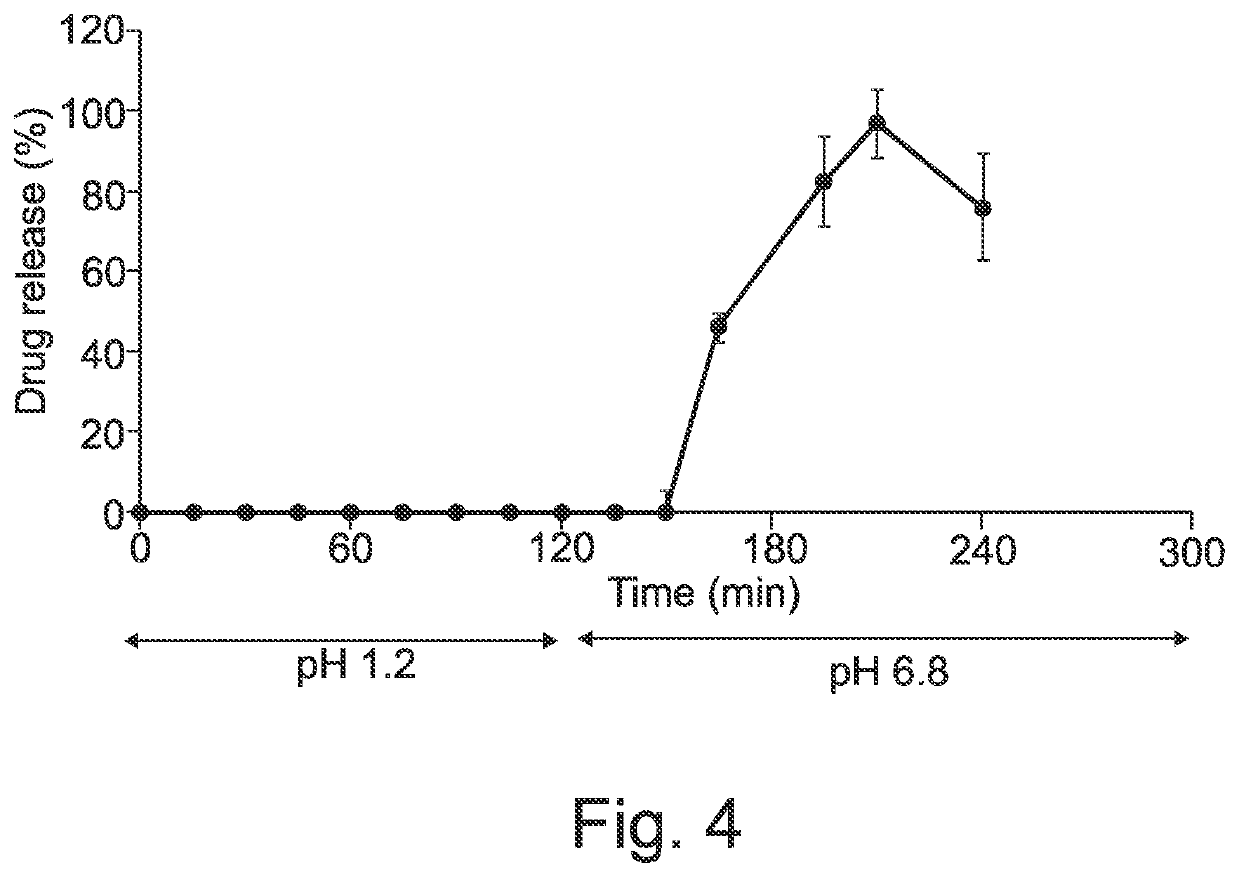
Solid dosage form production
ActiveUS20200146994A1Organic active ingredientsAdditive manufacturing apparatusFused filament fabricationDrug capsule
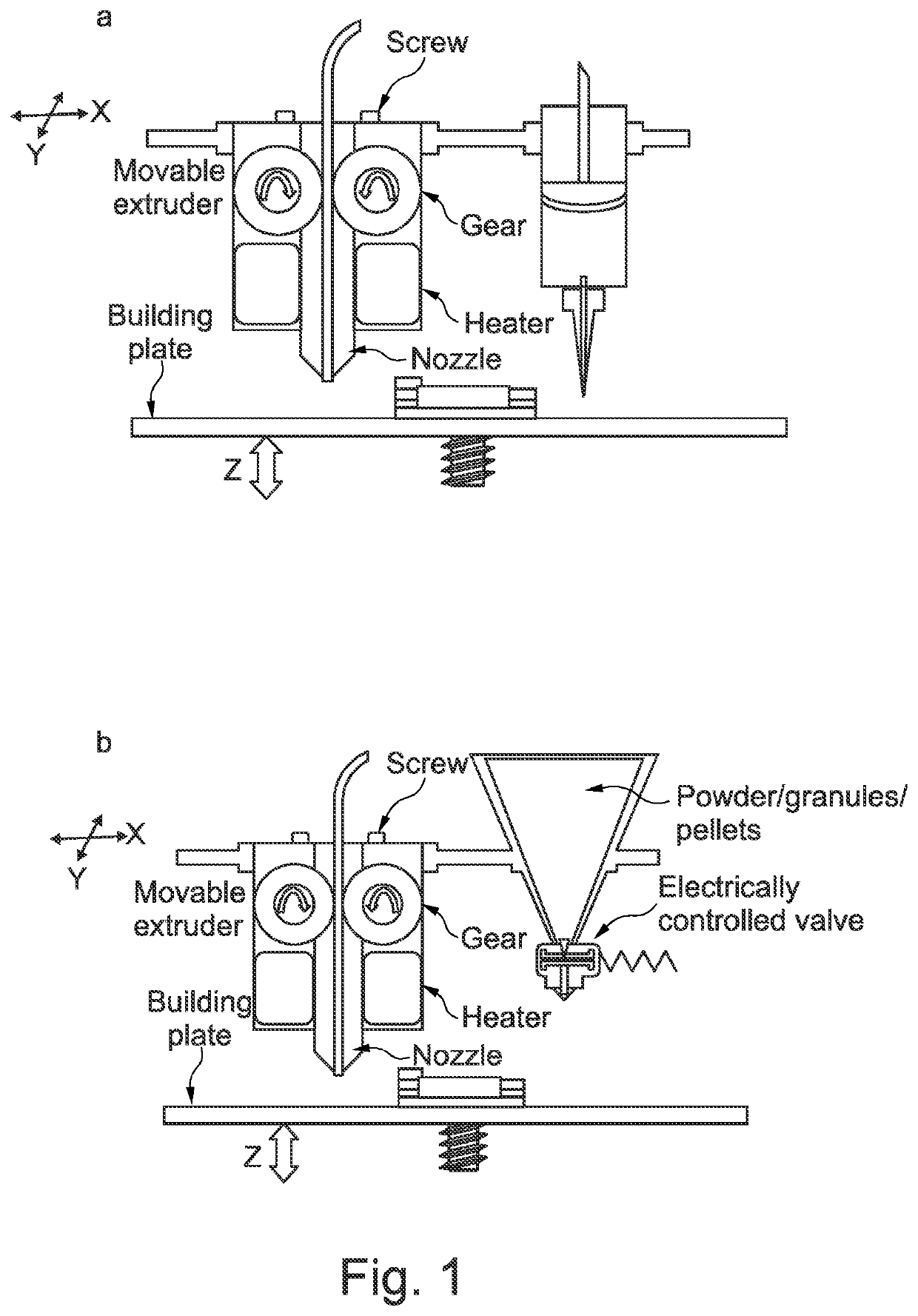
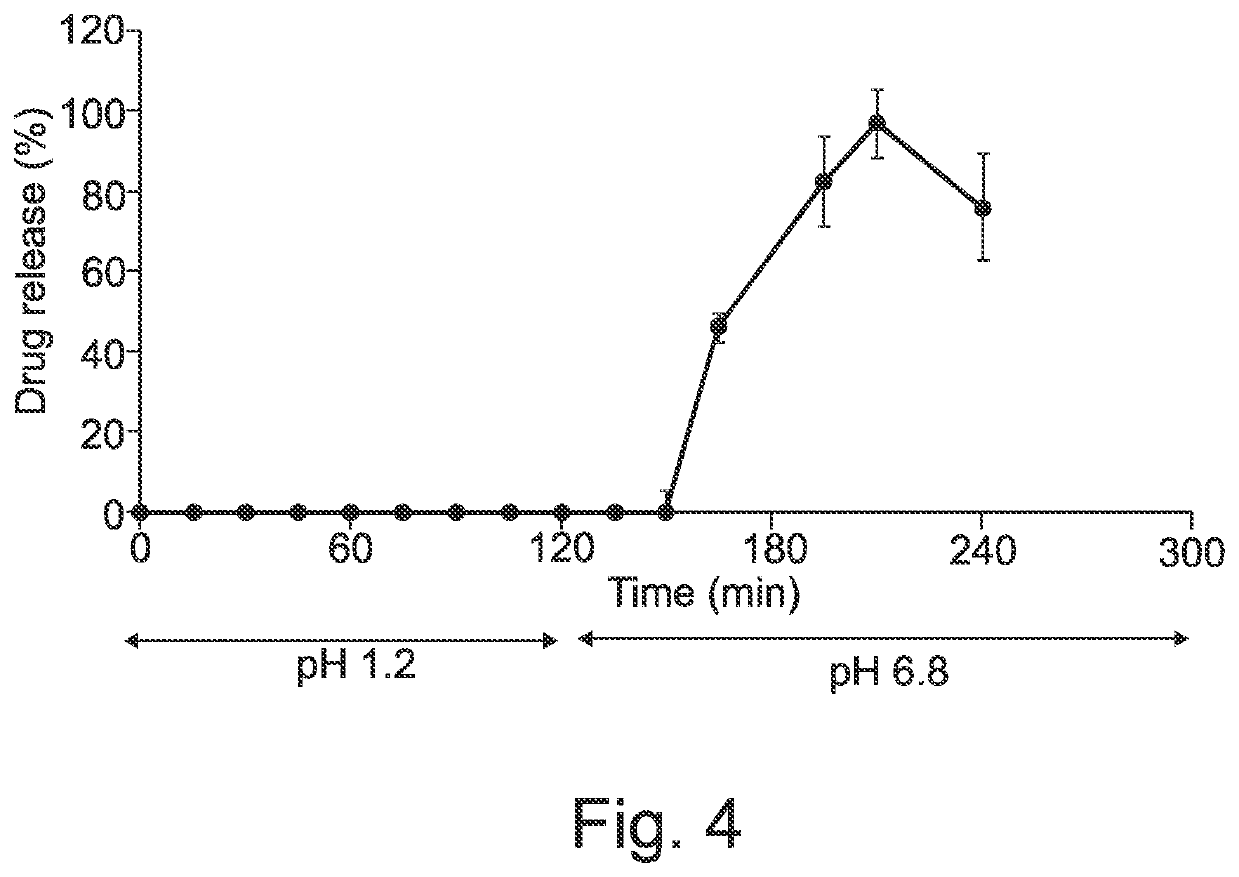
The present disclosure utilises 3D printing technology, particularly fused filament fabrication, FFF, 3D printing, in conjunction with solid and / or liquid dispensers to produce solid dosage forms, such as pharmaceutical capsules. Such solid dosage forms have a shell, which is 3D printed, and a core, which is dispensed.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CENTRAL LANCASHIRE
Methods and systems for additive manufacturing
InactiveCN108698297AProgramme controlAdditive manufacturing apparatusFused filament fabricationComputer printing
In an aspect, a printer fabricates an object from a computerized model using a fused filament fabrication process and a metallic build material. An ultrasonic vibrator is incorporated into the printerto improve the printing process, e.g., by disrupting a passivation layer on the deposited material to improve interlayer bonding, and to prevent adhesion of the metallic build material to a nozzle and other printer components.
Owner:DESKTOP METAL INC
Low printing temperature filaments for 3D printing
ActiveUS20180187000A1Reduce the temperatureAdditive manufacturing apparatusAdditive manufacturing with liquidsFused filament fabrication3d printer
A low printing temperature thermoplastic filament composition for fused filament fabrication 3D printing is described. The filament includes polycaprolactone in an amount from 70 to 90 wt %, at least one thermoplastic polymer having a melting temperature between approximately 60° C. and approximately 90° C. in an amount from approximately 10 to 30 wt %, at least one antioxidant, and at least one plasticizing agent. This 3D printing filament can be printed out at temperatures below 100° C. and no heated print bed is needed, which saves energy and minimizes the complexity of 3D printer. Besides the low printing temperature, this 3D printing material is bio-friendly which makes it safe for household use.
Owner:NANO & ADVANCED MATERIALS INST
Multifilament feedstocks for fused deposition modeling
InactiveUS20210187825A1Additive manufacturing apparatusIncreasing energy efficiencyFused filament fabricationComputer printing
A substantially continuous, entwined filamentary feedstock for additive manufacturing processes and fused filament fabrication (“FFF”) equipment is provided. Generally, the entwined filamentary feedstocks may contain a plurality of filaments and comprise a diameter suited for use in FFF and three-dimensional printers. Typically, the entwined feedstocks may comprise at least one filament forming a core and one or more filaments entwined around this core.
Owner:UNIVERSAL FIBERS INC
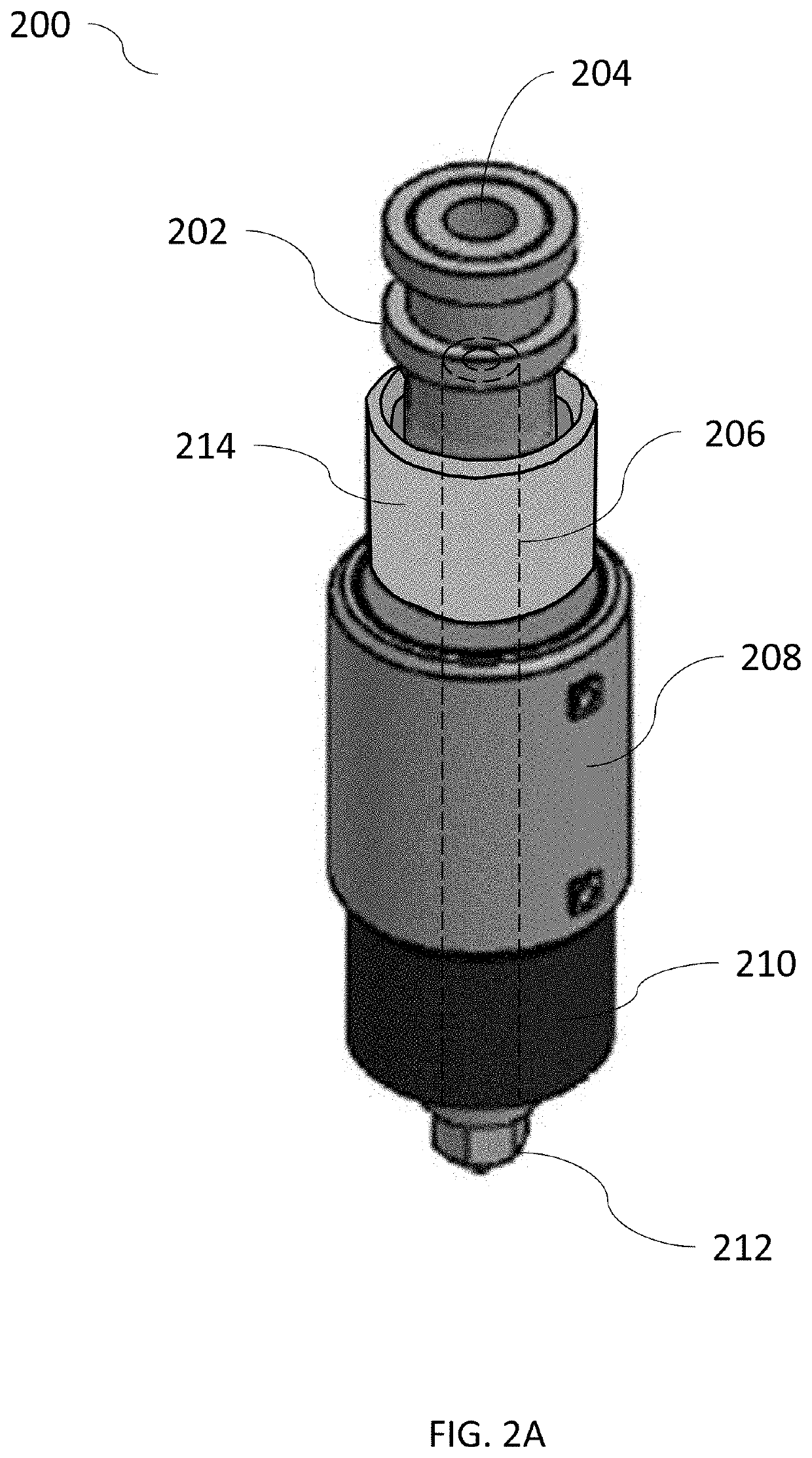
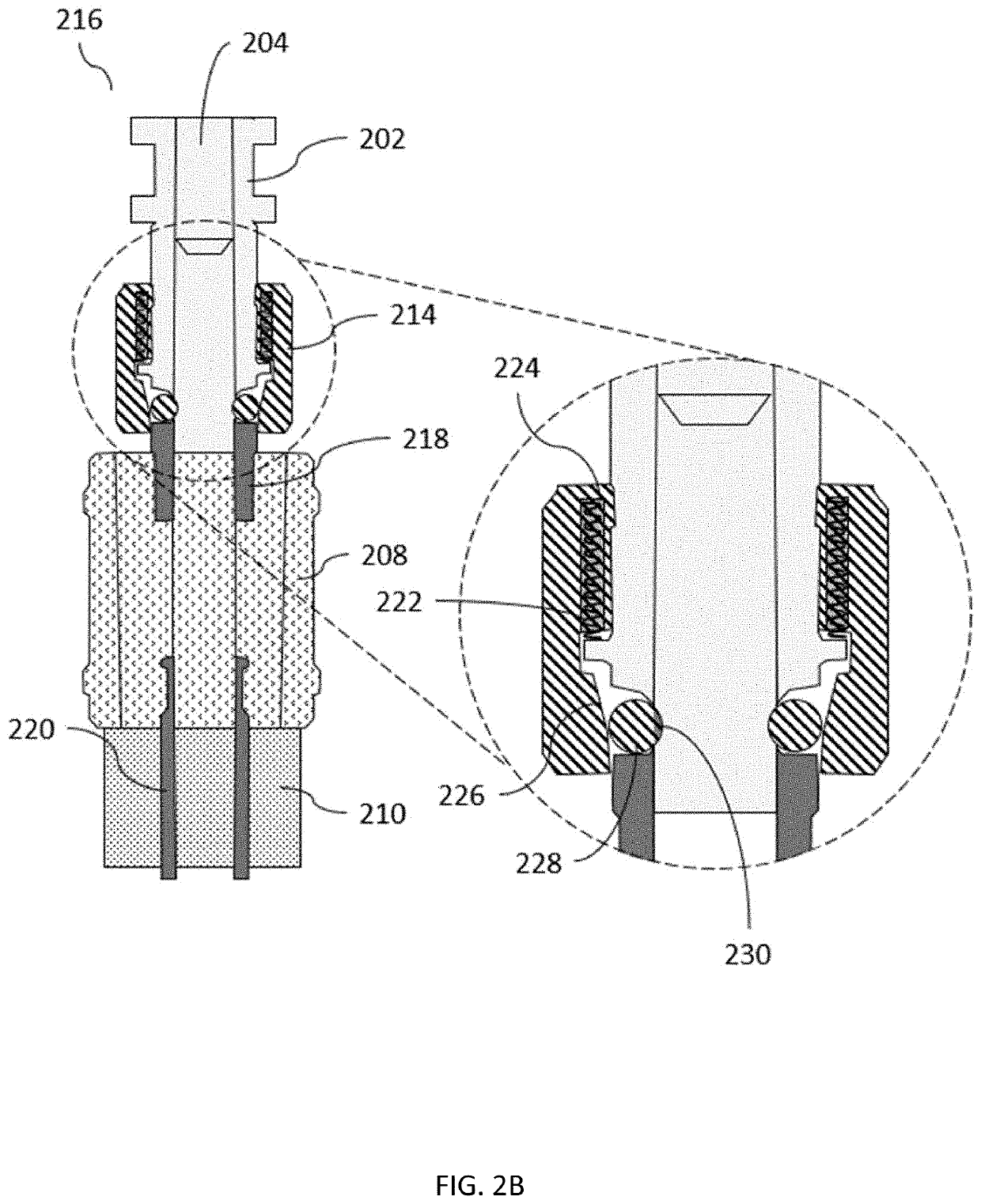
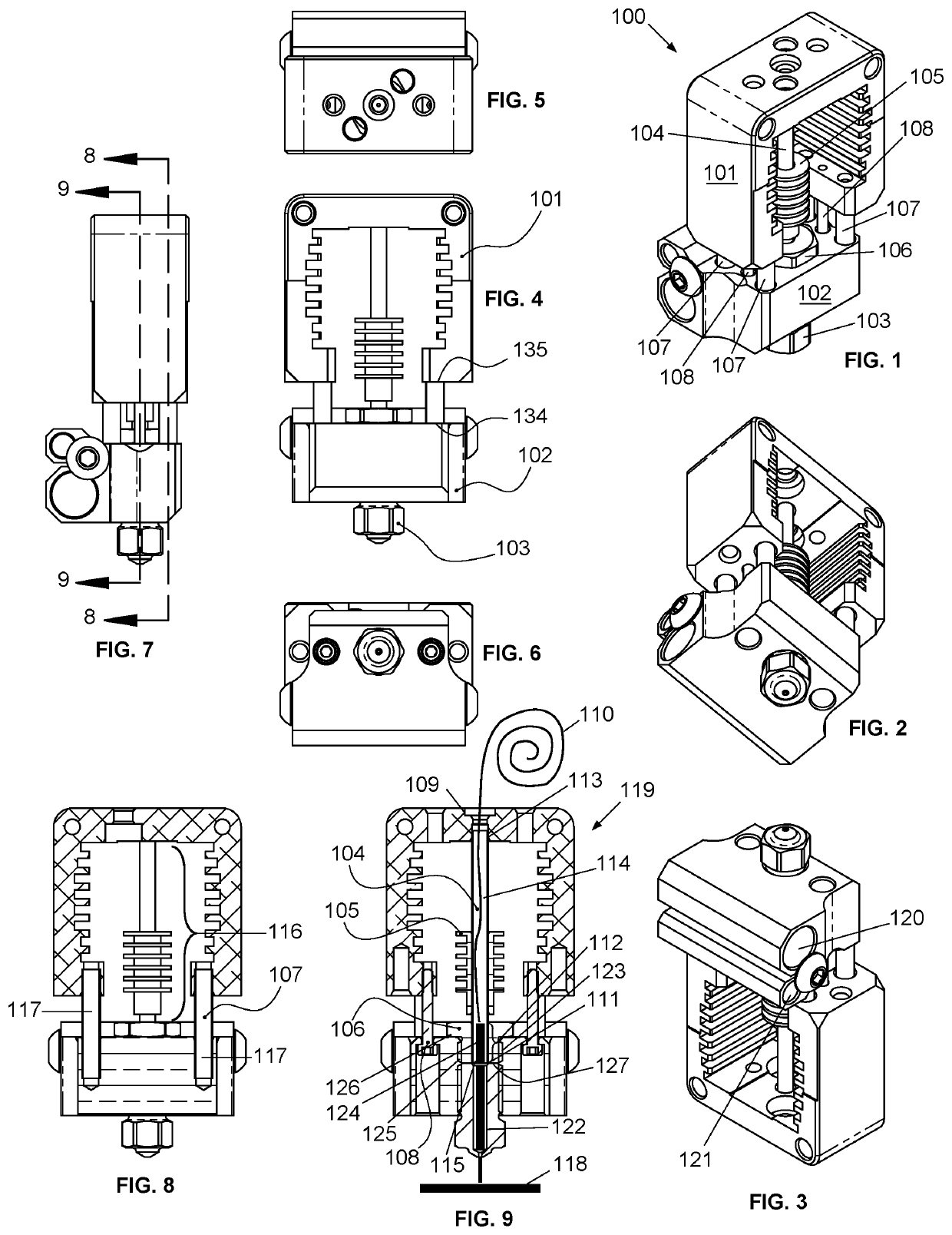
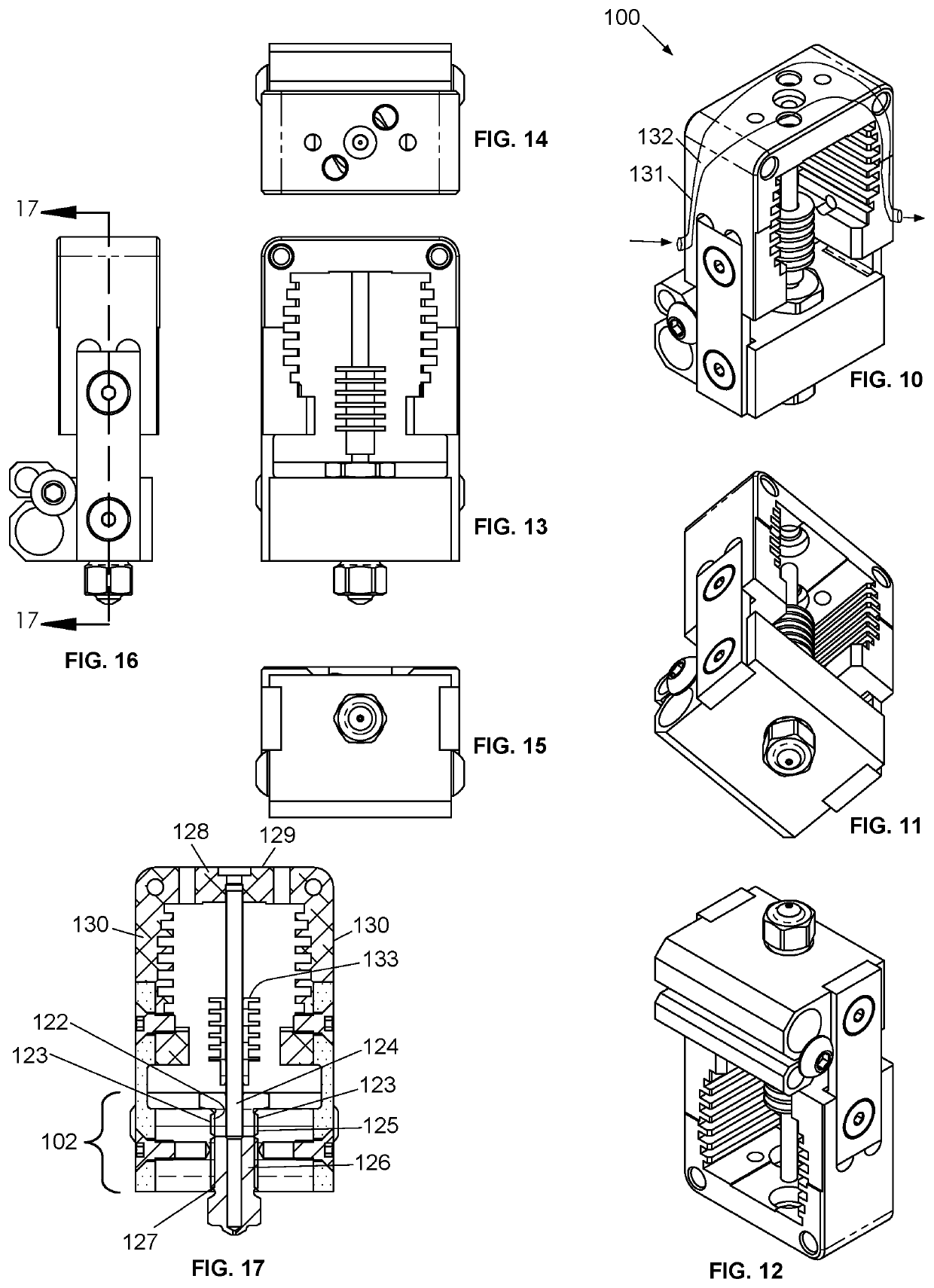
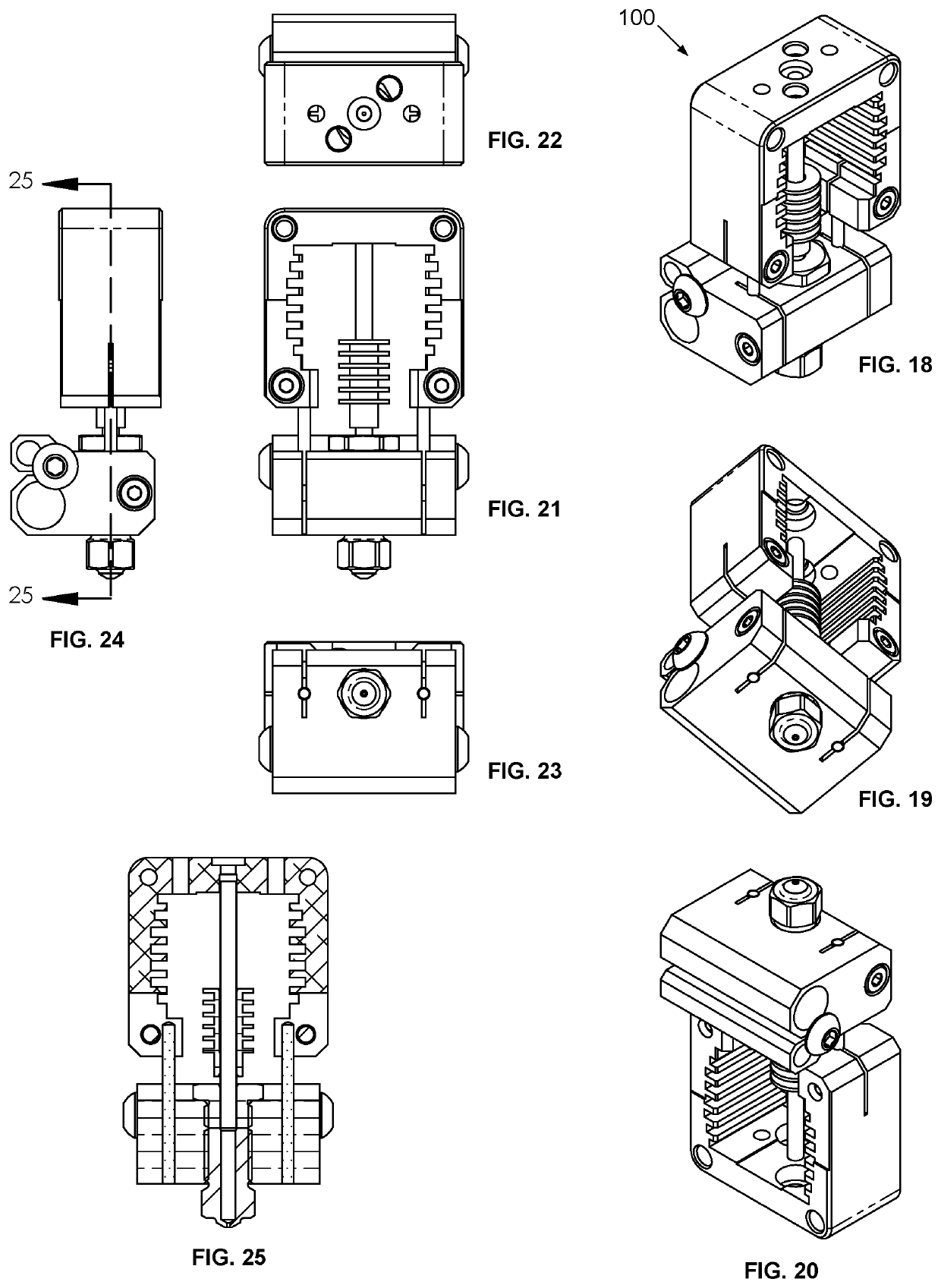
Quick-change fused filament fabrication nozzle assembly
ActiveUS20190375141A1Easy to removeQuick delete3D object support structuresDomestic articlesFused filament fabricationExtrusion
The present invention provides a system and method for quickly removing and installing a filament tube and nozzle in an FFF extrusion system. The system utilizes a primary manifold that includes a cooling block, a heating block and a quick-change mechanism. This primary manifold is adapted to mate a filament tube / nozzle assembly. The quick-change mechanism, which in a particular embodiment utilizes a recessed biased-bearing arrangement, enables the filament / nozzle assembly to be removed and inserted without the use of any tools, and without causing any significant downtime for the FFF extrusion system. Once removed, the filament tube / nozzle assembly can be refurbished by a technician, trained so as not to over torque the tube / nozzle threaded interface. This refurbishment (typically consisting of a cleaning and the installation of a new nozzle) could be accomplished “off-line”, without any impact on the continued use of FFF extrusion system.
Owner:STRATSYS INC
Improving inter-road adhesion and coalescence in plastic parts fabricated in 3D printing
InactiveCN110520273AAdditive manufacturing apparatusAdditive manufacturing with liquidsFused filament fabricationPolymer chemistry
This disclosure describes a composition for additive manufacturing, which contains a thermoplastic polymer and a mineral additive capable of reducing a specific heat of the composition relative to a specific heat of the thermoplastic polymer, A proportion of the mineral additive in the composition may be set such that the specific heat of the composition is equal to or less than 95% of the specific heat of the thermoplastic polymer, and the composition may be in the form of a filament, rod, pellet or granule. Compositions disclosed herein may be adapted to function as compositions suitable forperforming additive manufacturing by material extrusion. Also disclosed herein are additive manufacturing processes and methods for producing the compositions for fused filament fabrication.
Owner:IMERYS TALC AMERICA INC
Adaptable high-performance extrusion head for fused filament fabrication systems
ActiveUS10875244B2Reduce heat transferAdditive manufacturing with liquids3D object support structuresFused filament fabricationComputer printing
An extrusion head for a three-dimensional printer is disclosed including a feed tube, a heater, a cooler, and a bridge. The feed tube can be made of metal and has an inlet for receiving a forwardly driven filament of solid deposition material, an outlet, a downstream portion adjacent to the outlet, an upstream portion upstream from the downstream portion, and an internal passage extending from the inlet to the outlet. The heater is thermally coupled with the downstream portion of the feed tube for heating a filament to provide softened fluid deposition material. The cooler is thermally coupled with the upstream portion and spaced generally axially from the heater to define a generally axially extending gap traversed by the feed tube. The bridge traverses the gap and provides a rigid mechanical connection between the heater and the cooler.
Owner:SLICE ENG LLC
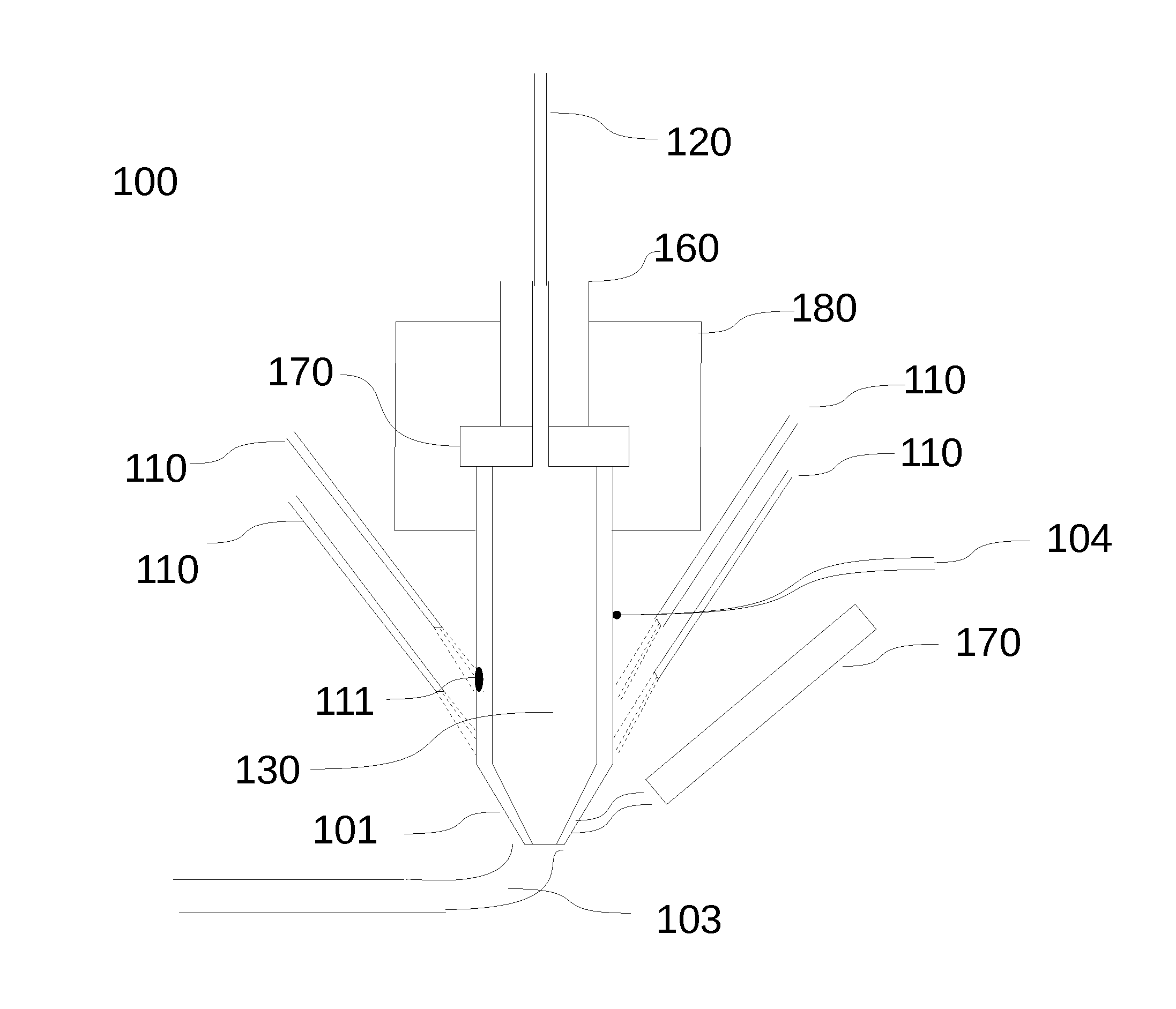
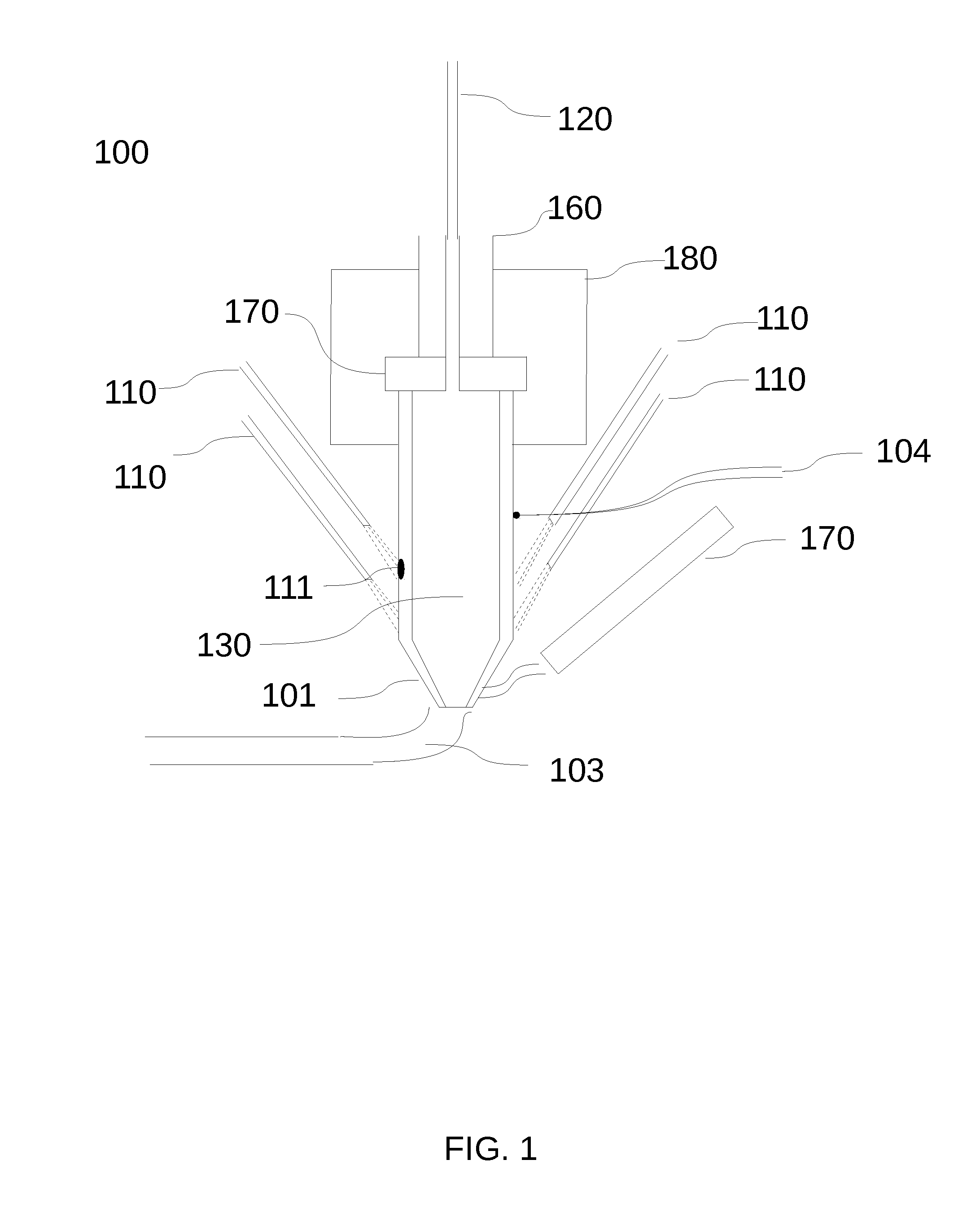
Methods For Making And Enhancing Properties Of Polymer Composite Materials Used In Fused Filament Fabrication
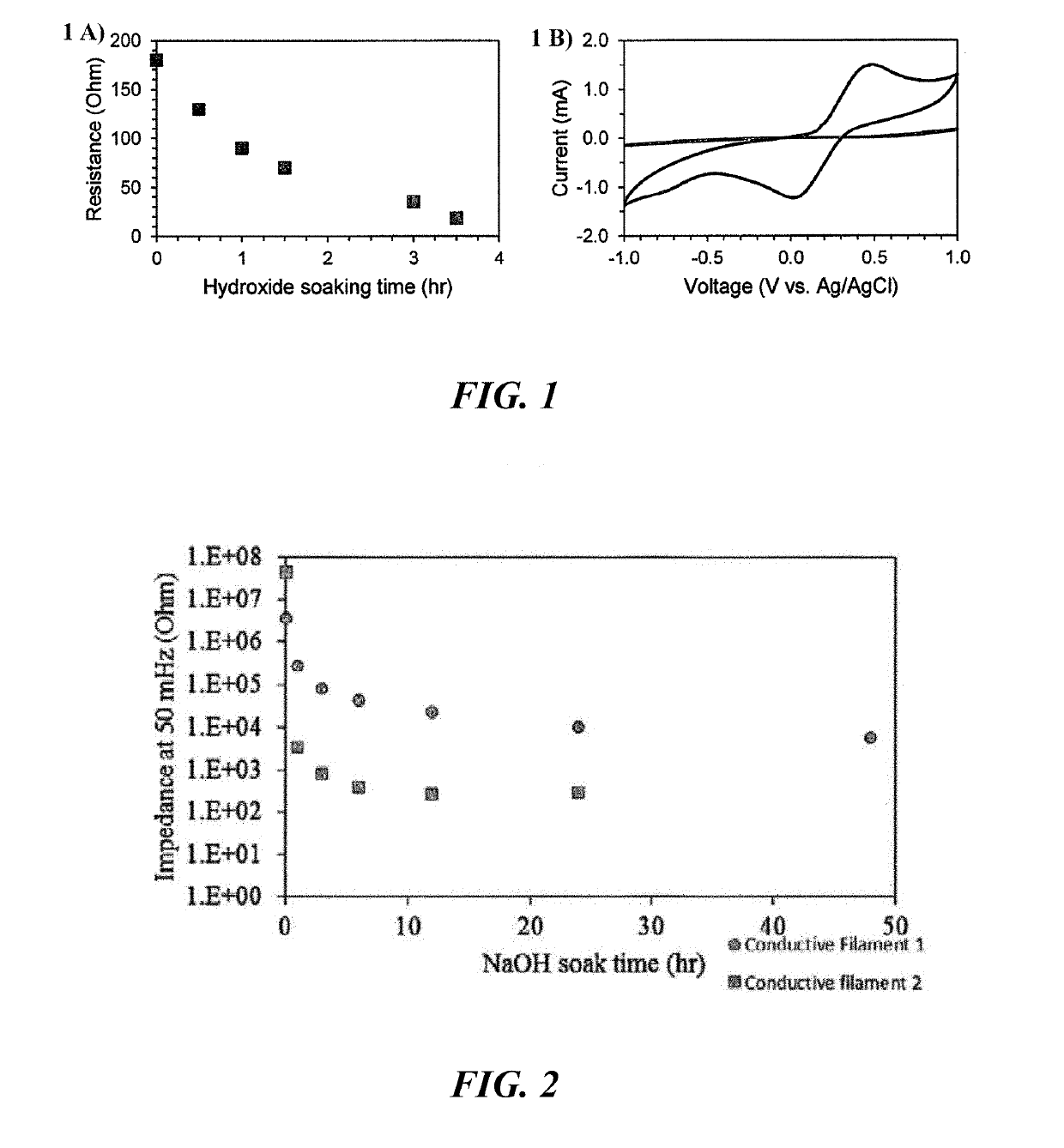
PendingUS20190284424A1Good physical propertiesImprove conductivityAdditive manufacturing apparatusInksFused filament fabricationPolymer science
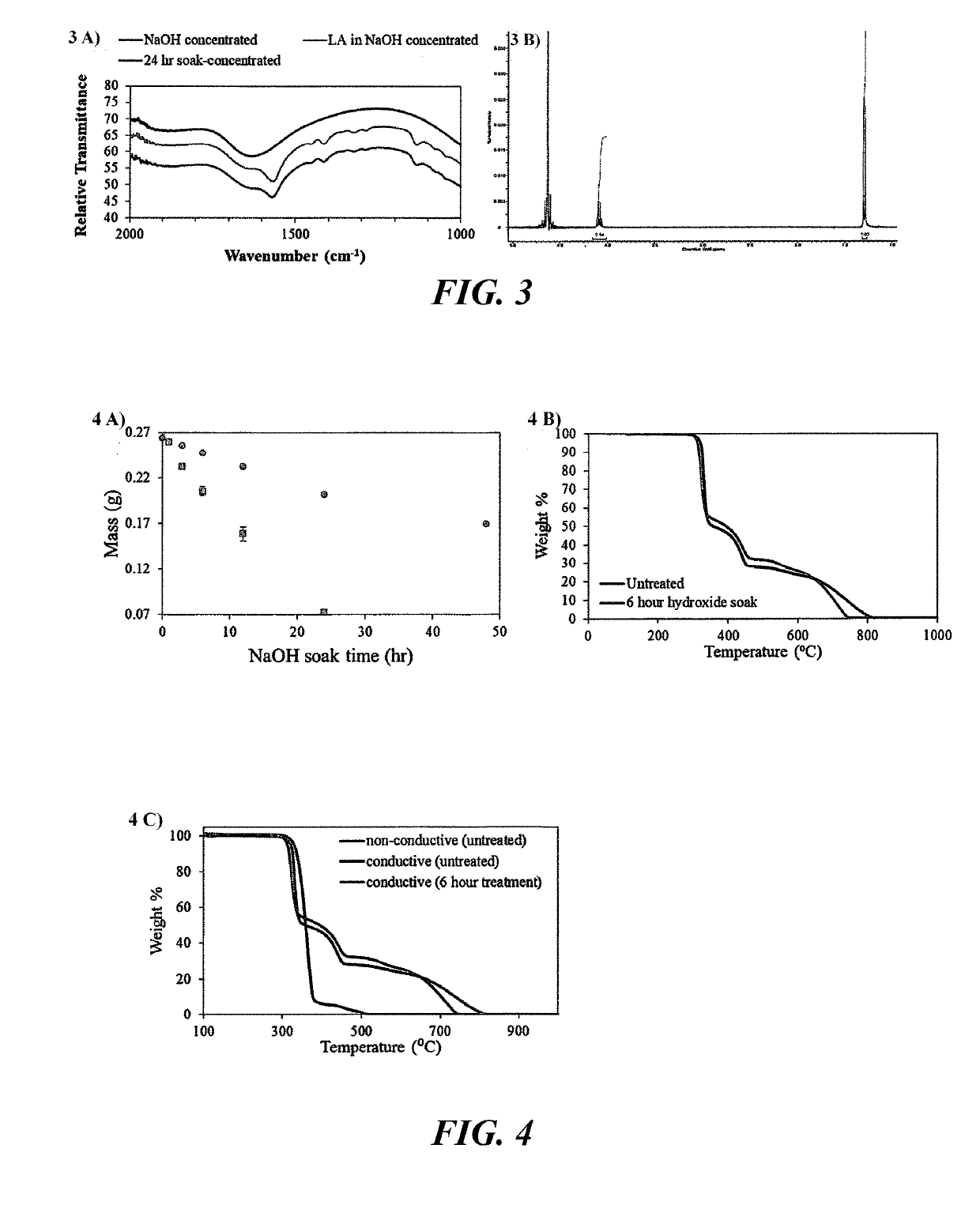
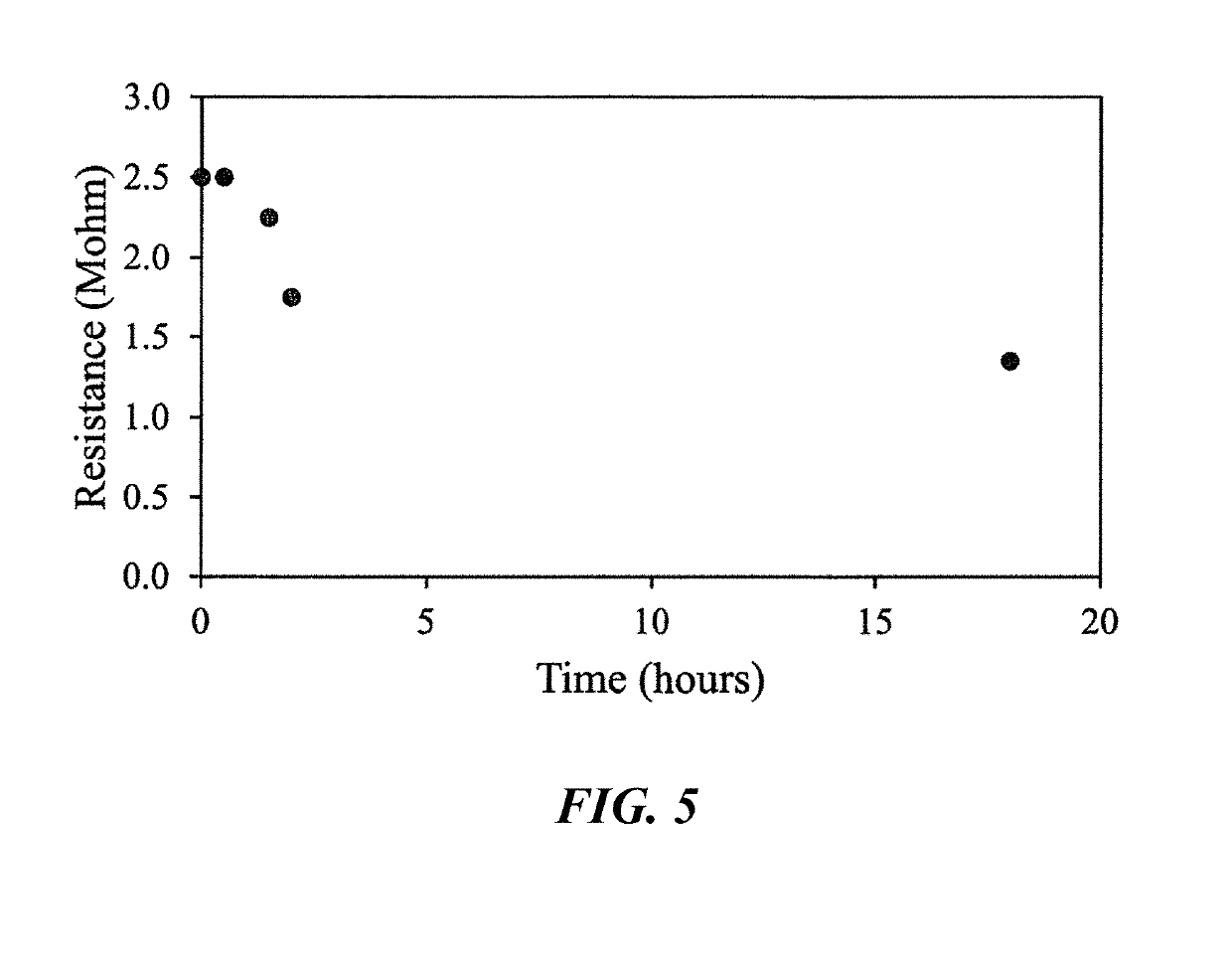
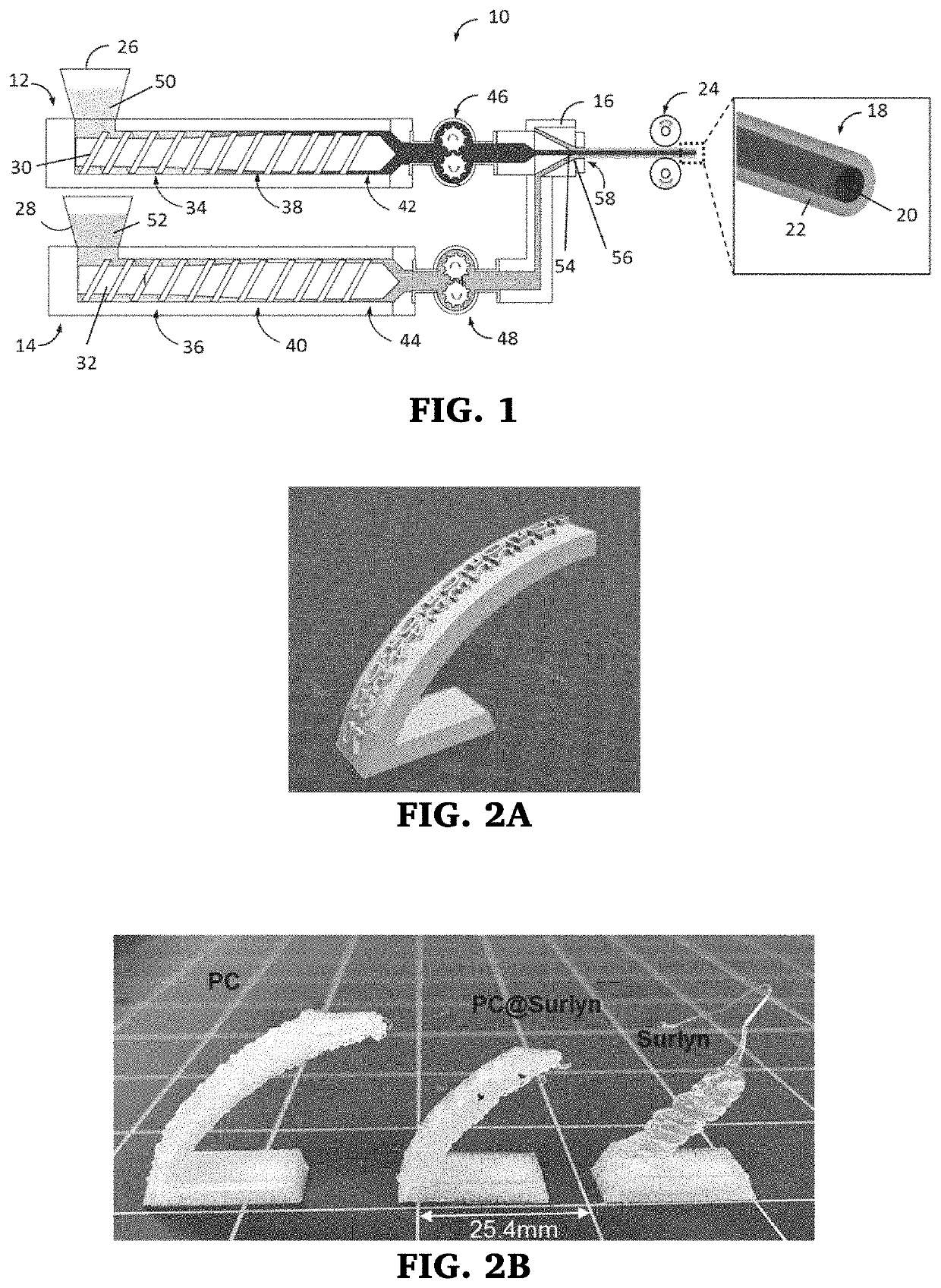
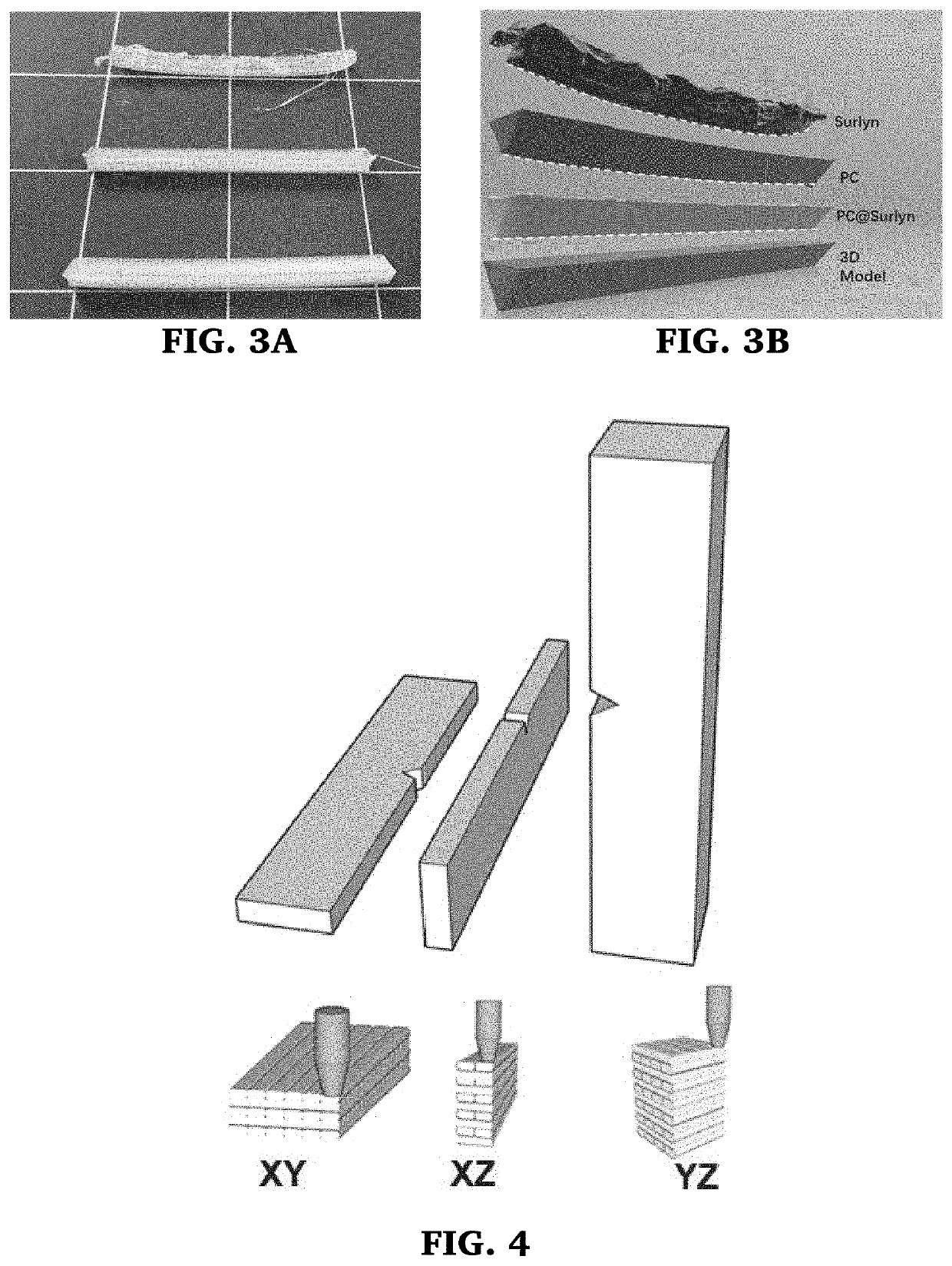
3D printing is an increasingly popular production method to quickly and inexpensively produce specialized components. Designs can be easily shared online and customized to the needs of the end user. One exciting aspect of 3D printing is the potential for printing with electrically conductive materials. Conductive filaments for fused filament fabrication are typically a mixture of polymer and conductive carbon powder. Printing with these should allow for development of unique electrochemical devices. However, commercial conductive filaments are difficult to print with and are not conductive enough for some electrochemical applications. Here we present several post print procedures to increase the conductivity of these filaments. By using and understanding how these strategies enhance the conductivity, the possibilities for performing complicated electrochemical experiments increases, opening up new paths of discovery in electrochemistry and material science.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF TULSA
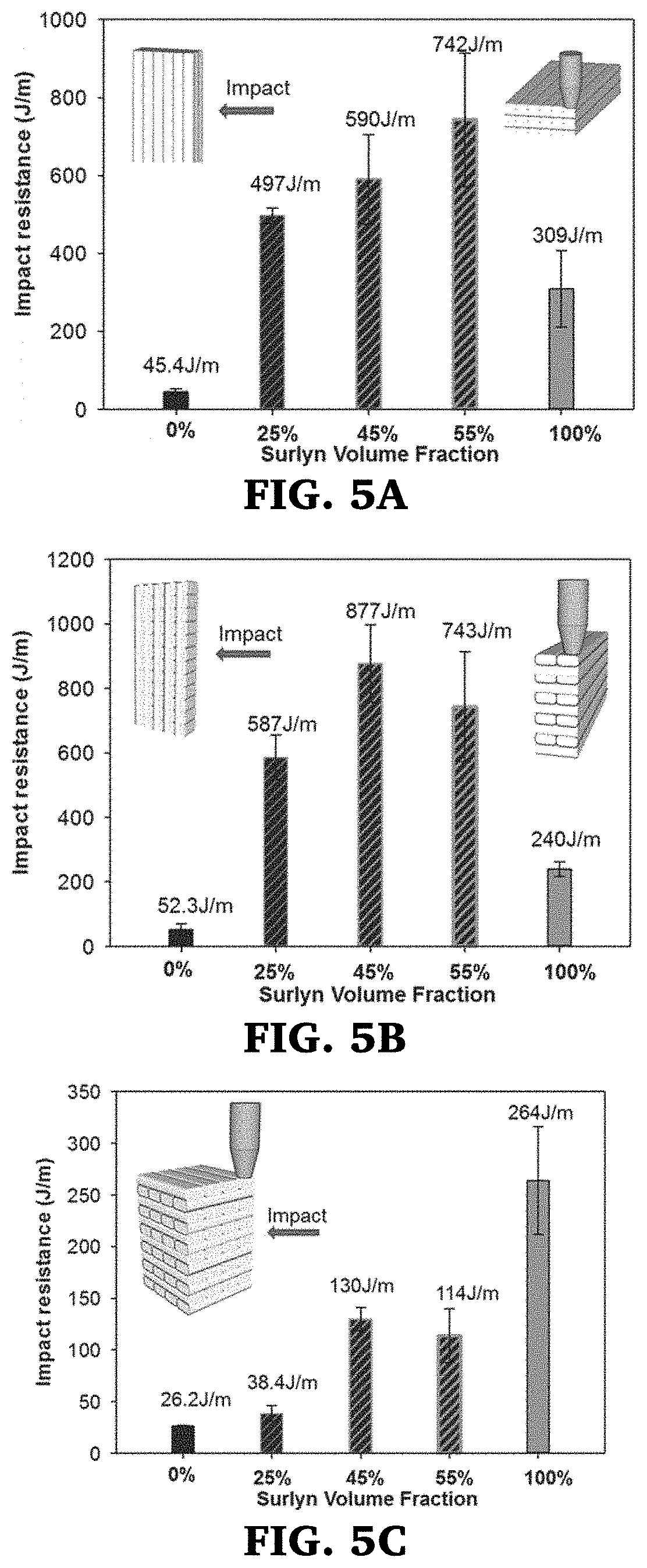
Tough, high impact resistant 3D printed objects from structured filaments
InactiveUS20200080237A1Reinforce printed shapeLow Tg shellAdditive manufacturing apparatus3D object support structuresFused filament fabricationPolymer science
In various embodiments the invention is directed to a structured filament for use in fused filament fabrication comprising an inner core comprising an first polymer or polymer blend; and an outer shell surrounding said inner core comprising a second polymer or polymer blend having ionic or crystalline functionality; wherein said first polymer or polymer blend has a higher solidification temperature than said second polymer or polymer blend. The ionic or crystalline functionality of the outer shell material strengthen the interface between the printed layers. This structured filament leads to printed 3D structures having improved dimensional fidelity and impact resistance in comparison to the individual components. The impact resistance of structures printed from these is greatly increased as energy is dissipated by delamination of the shell from the core near the crack tip, while the core remains intact to provide stability to the part after impact.
Owner:THE UNIVERSITY OF AKRON
Nozzle system with monolithic nozzle head for fused filament fabrication additive manufacturing and method of manufacturing same
ActiveUS10611138B2Additive manufacturing with liquids3D object support structuresFused filament fabricationAdditive layer manufacturing
A nozzle system and method of manufacturing a nozzle system for use in an additive manufacturing system for fabricating an object is disclosed. The nozzle system includes a monolithic nozzle head designed such that the thermal locking member, neck member, and nozzle member of the nozzle head are manufactured into one component. The nozzle head is made of a material that has a high specific heat capacity but low thermal heat conductivity. The result is a nozzle system design that virtually eliminates heat migration from the nozzle head to the heat sink, and thereby improves the overall quality of polymer filament deposition during printing.
Owner:COSINE ADDITIVE INC
Liquid-cooled fused filament fabrication nozzle
ActiveUS10415898B1Consistent and controlled operationImprove heat transfer performanceIncreasing energy efficiencyStationary tubular conduit assembliesFused filament fabricationCooling chamber
The present invention provides an integral cooling system within an FFF nozzle manifold. The system includes a cooling reservoir formed within the body of the nozzle manifold, adapted to circulate a cooling liquid around the filament chamber and nozzle orifice. The coolant channel is situated to be in close physical proximity to the chamber and orifice, and to be thermally coupled to both via the body of the nozzle manifold. In addition, the interior of the cooling chamber is constructed so as to maximize the available surface area within a given cross-sectional geometry, thereby promoting increase heat transfer between the nozzle manifold and the cooling liquid.
Owner:AREVO INC
Filaments comprising ionomers and use in fused filament fabrication
ActiveUS20210371692A1Excellent surface appearanceDesirable propertyAdditive manufacturing apparatus3D object support structuresFused filament fabricationIonomer
The disclosure generally relates to 3D printed articles prepared from filaments comprising an ionomer (A) prepared from a base resin (B); wherein: base resin (B) is prepared from ethylene and at least one C3 to C8 α,β ethylenically unsaturated carboxylic acid monomer; the carboxylic acid moieties of base resin (B) are 10 to 99.5 percent neutralized by zinc or lithium; the at least one C3 to C8 α,β ethylenically unsaturated carboxylic acid is present from about 2 weight percent to about 30 weight percent, based on the weight of base resin (B).
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
Solid dosage form production
ActiveUS11045426B2Additive manufacturing apparatusCapsule deliveryFused filament fabricationDrug capsule
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CENTRAL LANCASHIRE
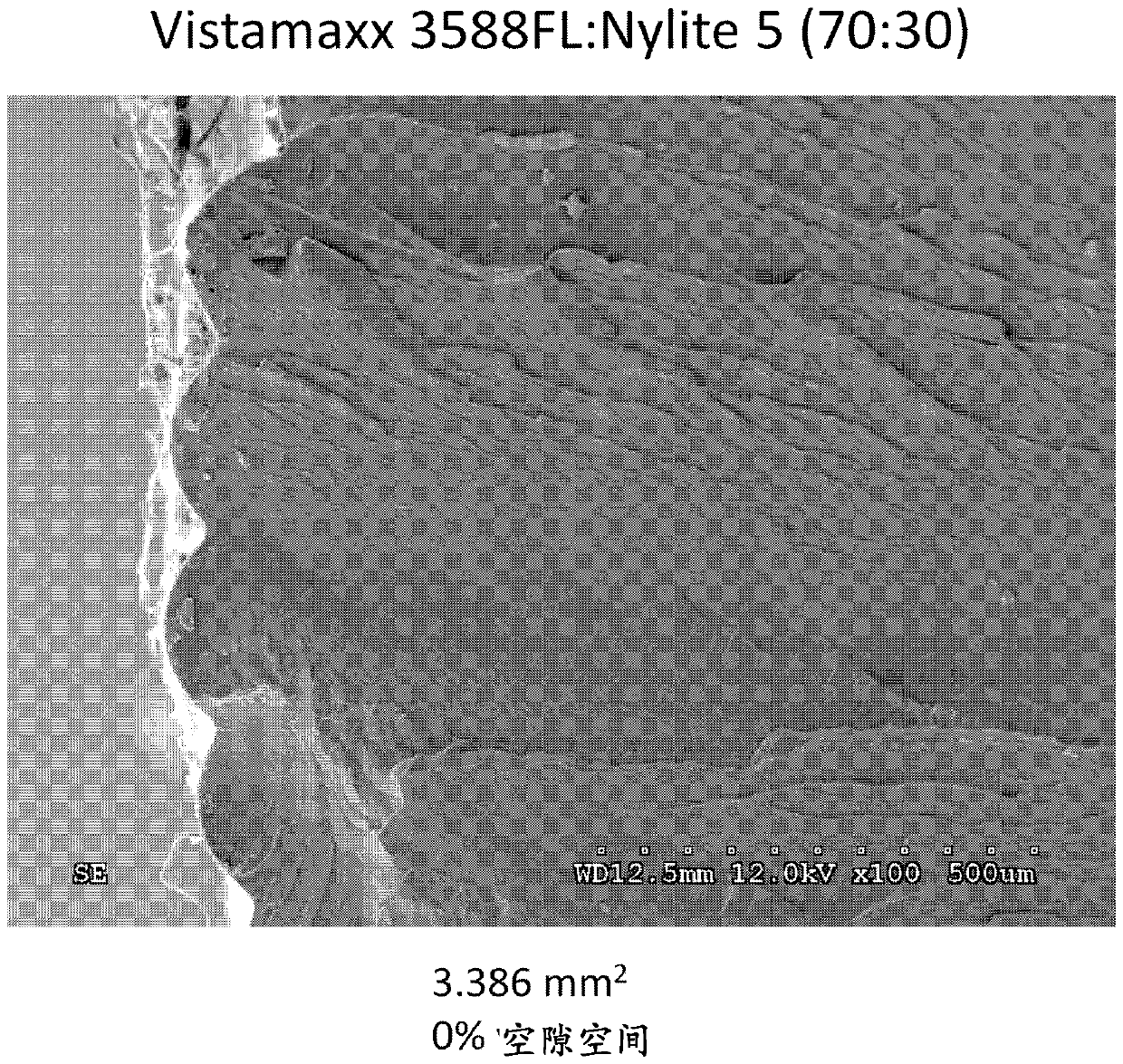
Additive manufacturing with an olefin block copolymer and articles made therefrom
PendingUS20210252774A1Avoid problemsAdditive manufacturing apparatusAdditive manufacturing with liquidsFused filament fabricationPolymer science
A method of fused filament fabrication (FFF) additive manufacturing comprises employing an olefin block copolymer. The method allows for the additive manufacturing article that retains the desirable mechanical properties of polyolefins such as polyethylene or polypropylene without experiencing the problems inherent in FFF printing of polyethylene or polypropylene particularly in the absence of solid fillers. In a particular embodiment, the additive manufactured article is comprised of the olefin block copolymer is comprised of block composite or crystalline block composite polymer or mixture thereof comprising the olefin block copolymer, wherein the olefin block copolymer is comprised of an isotactic propylene block and a polyethylene rich block.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
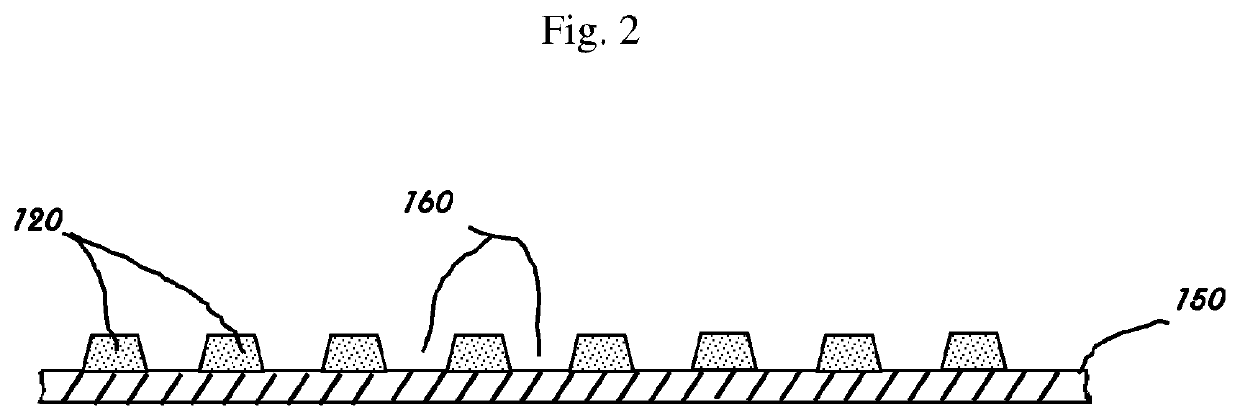
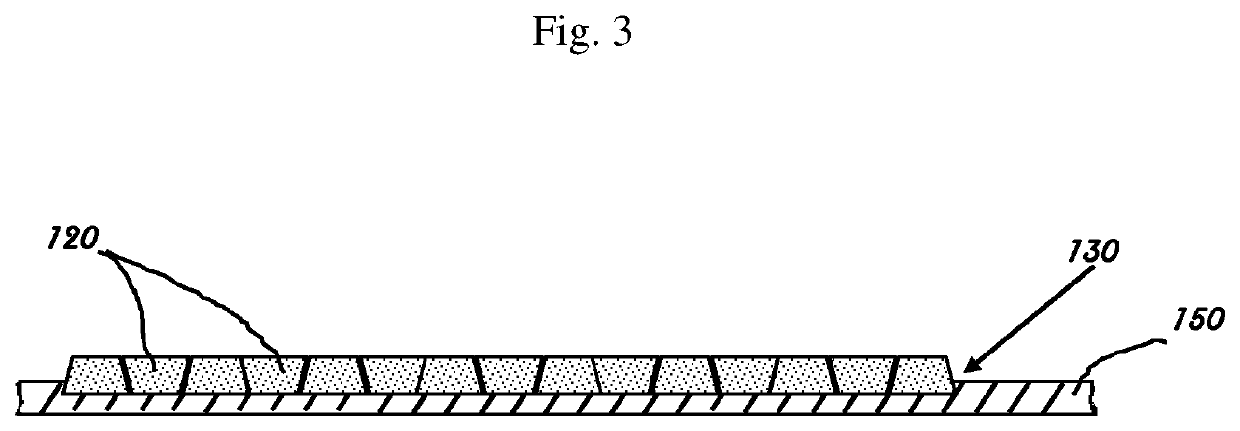
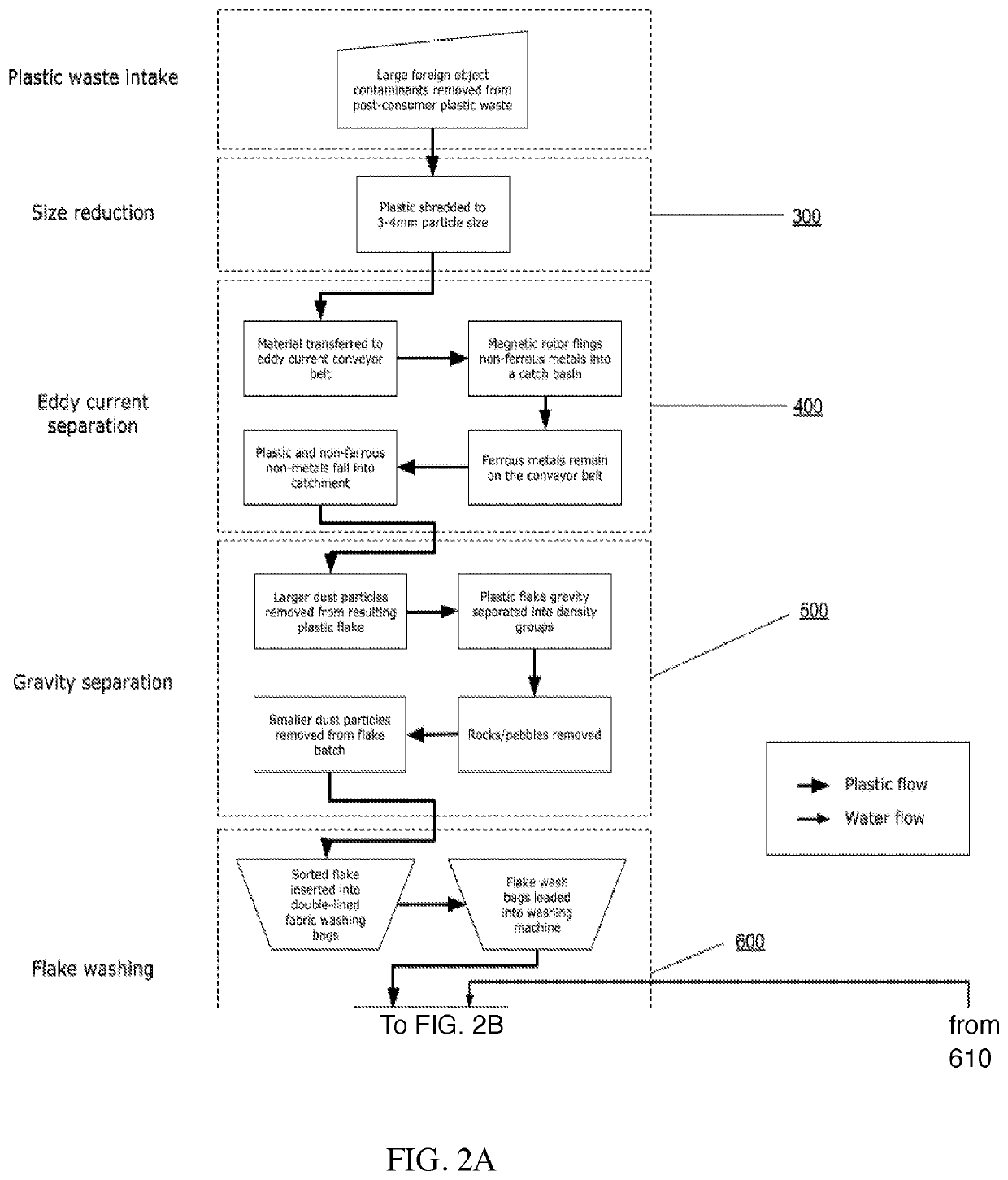
Method and Apparatus for Recycling Post-Consumer Plastic Waste
PendingUS20210323198A1Reduce water consumptionEliminateAdditive manufacturing apparatusPlastic recyclingFused filament fabricationMolten state
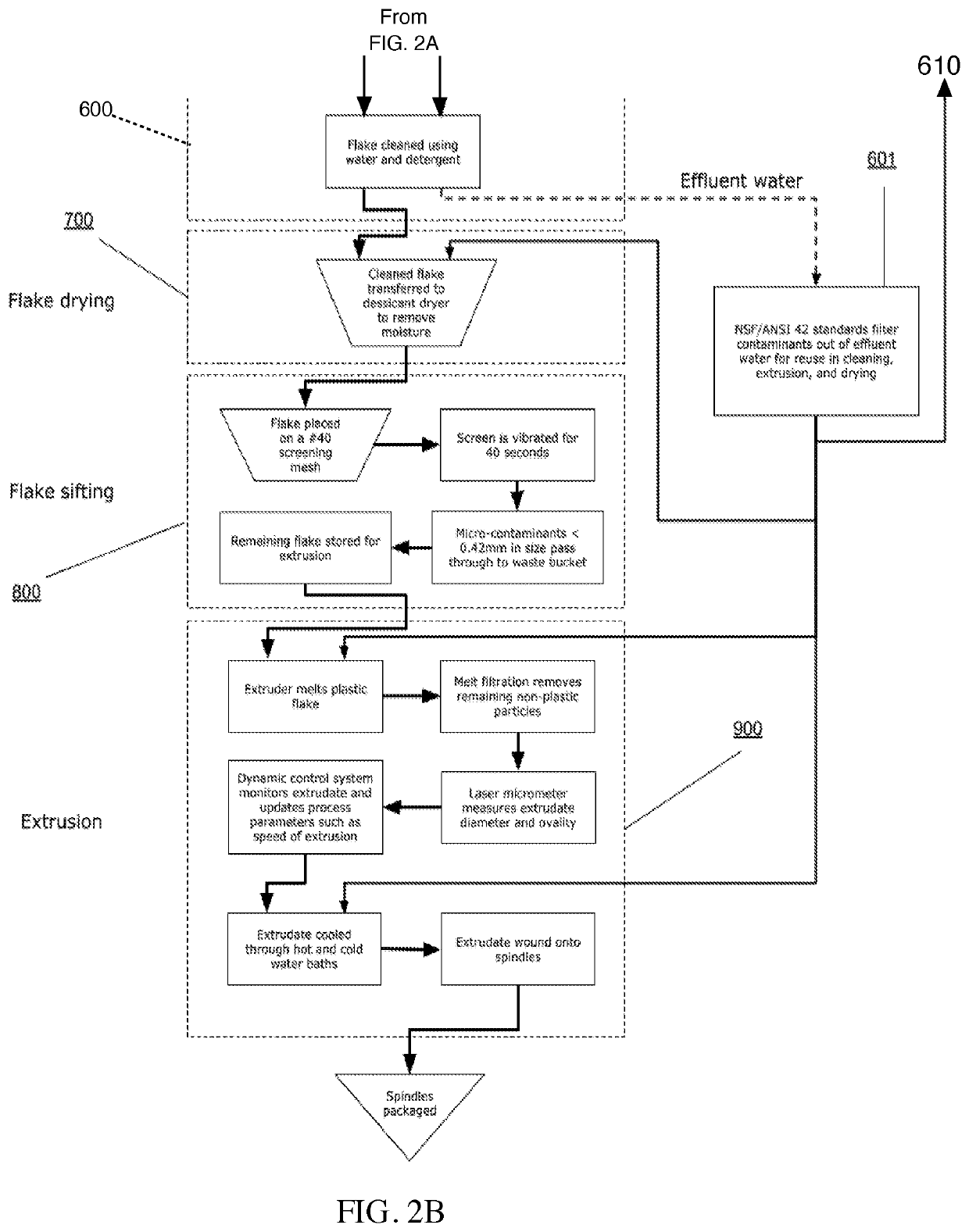
A method of recycling post-consumer plastic waste into mono filament for use in fused filament fabrication, injection molding, or other plastic manufacturing processes. Contaminated curbside plastic waste is sorted and granulated to uniform sized flakes. The plastic regrind is cleaned in a closed-loop wash cycle and dried at 160° F. and −70 dew point to reduce the moisture content to less than 0.03%. The effluent water is purified to be reused in the system. The flake plastic is extruded to a molten state and passes through additional melt filtration. A laser micrometer measures extrudate metrics like diameter and ovality to dynamically control feed and flow rates of the extruder to maintain diameter uniformity within 0.018 mm of target diameter.
Owner:LUPISAN ALDRIN +2
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com