Patents
Literature
297 results about "Body conduit" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
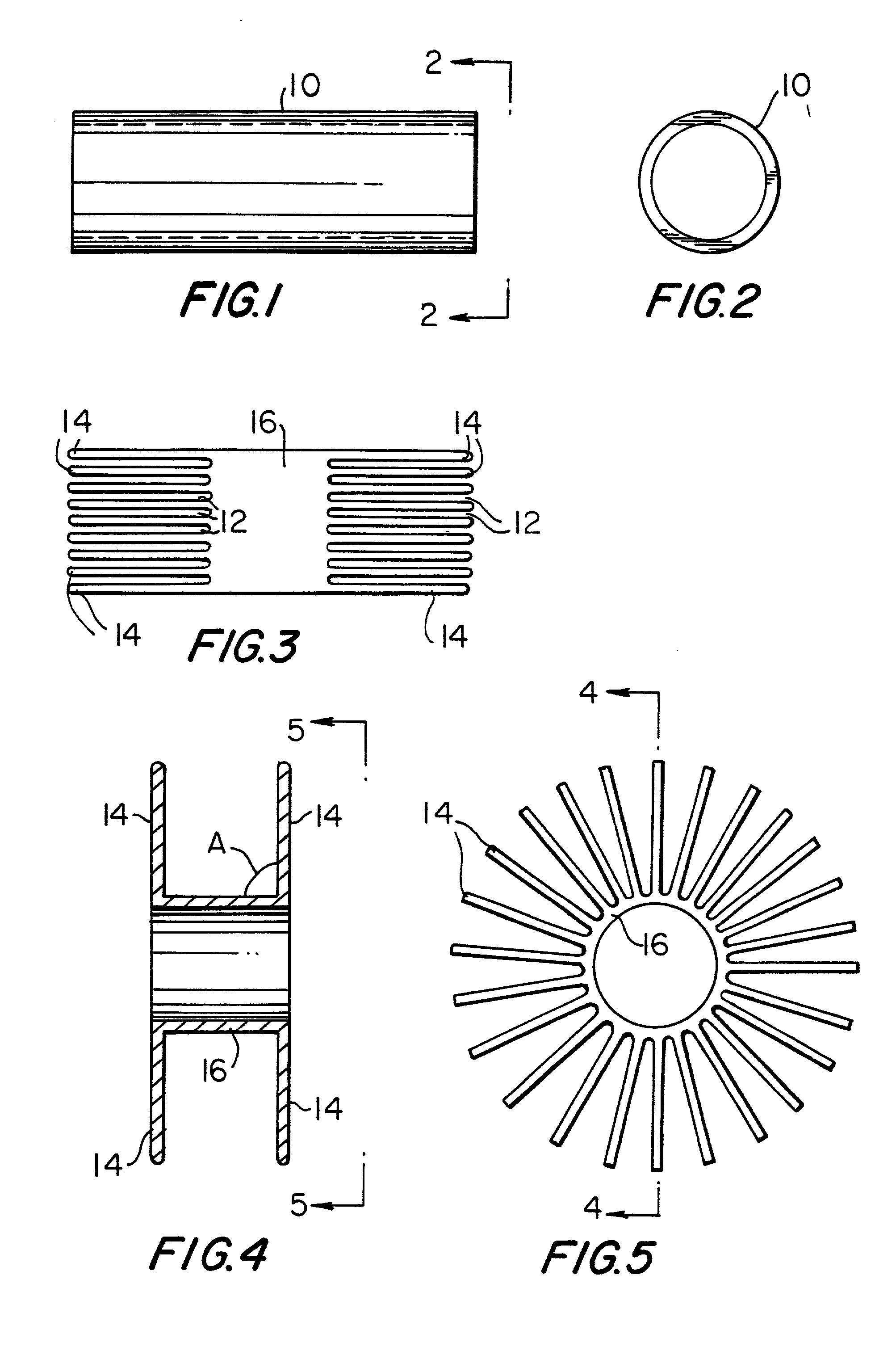
Conduit bodies. A conduit body can be used to provide pulling access in a run of conduit, to allow more bends to be made in a particular section of conduit, to conserve space where a full size bend radius would be impractical or impossible, or to split a conduit path into multiple directions.
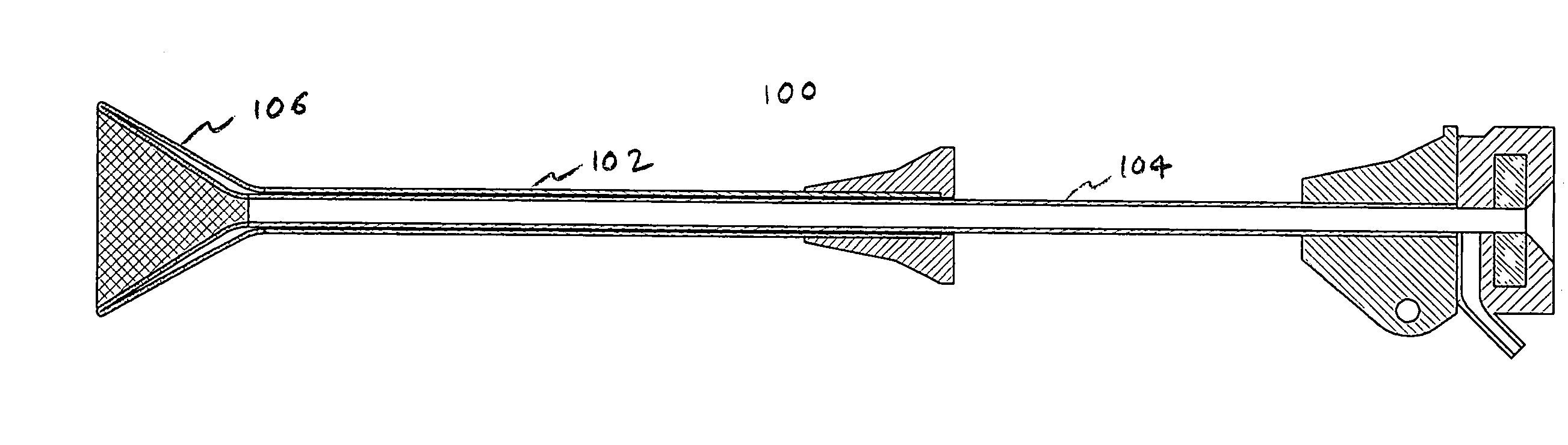
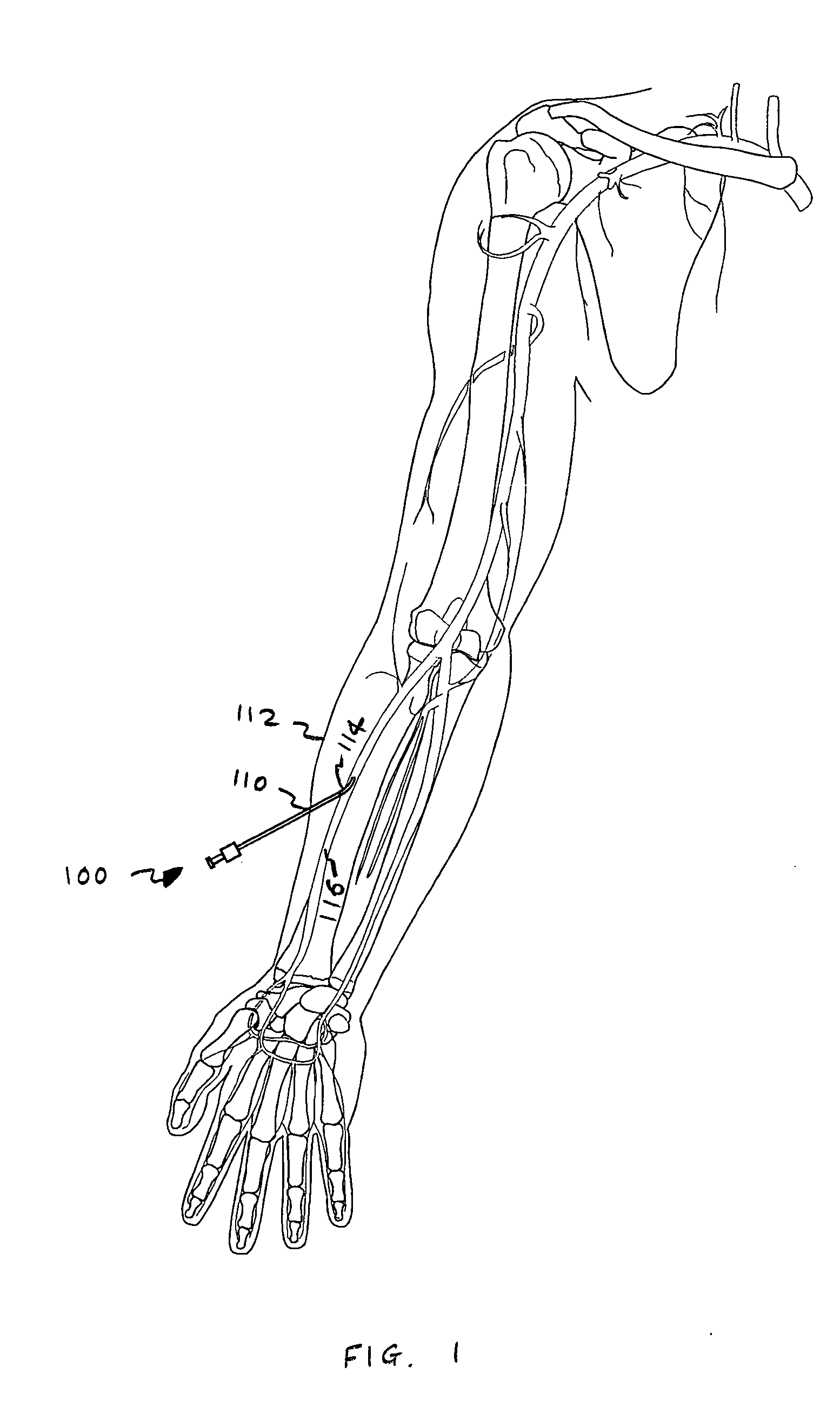
Indwelling heat exchange catheter and method of using same
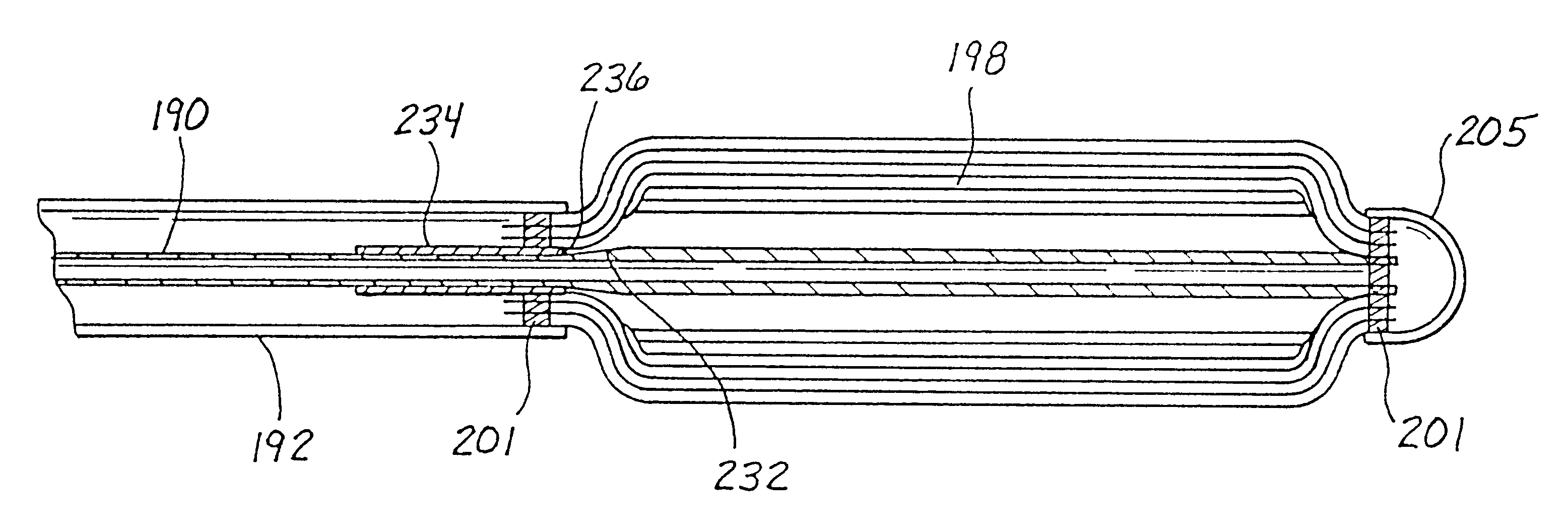
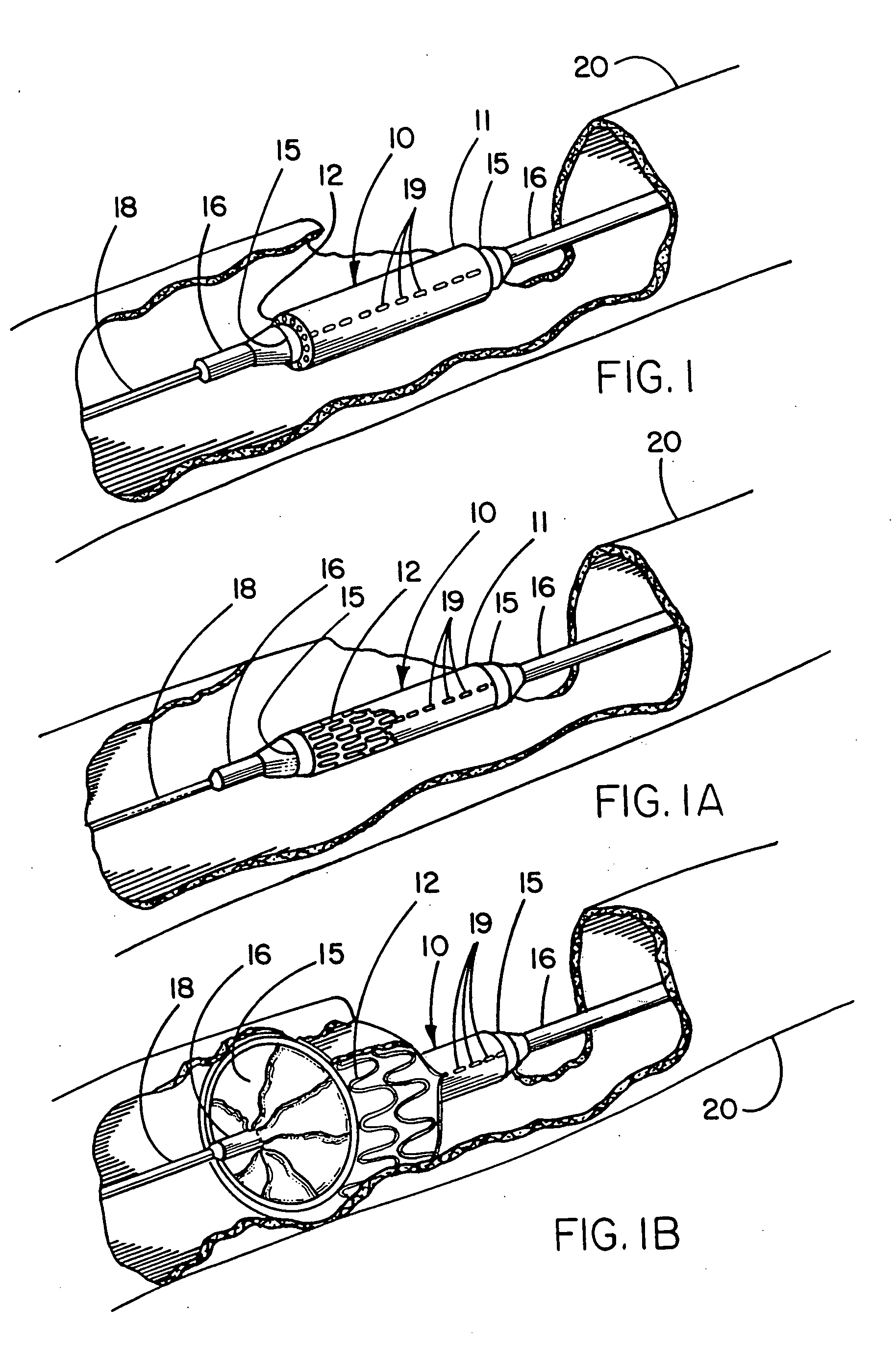
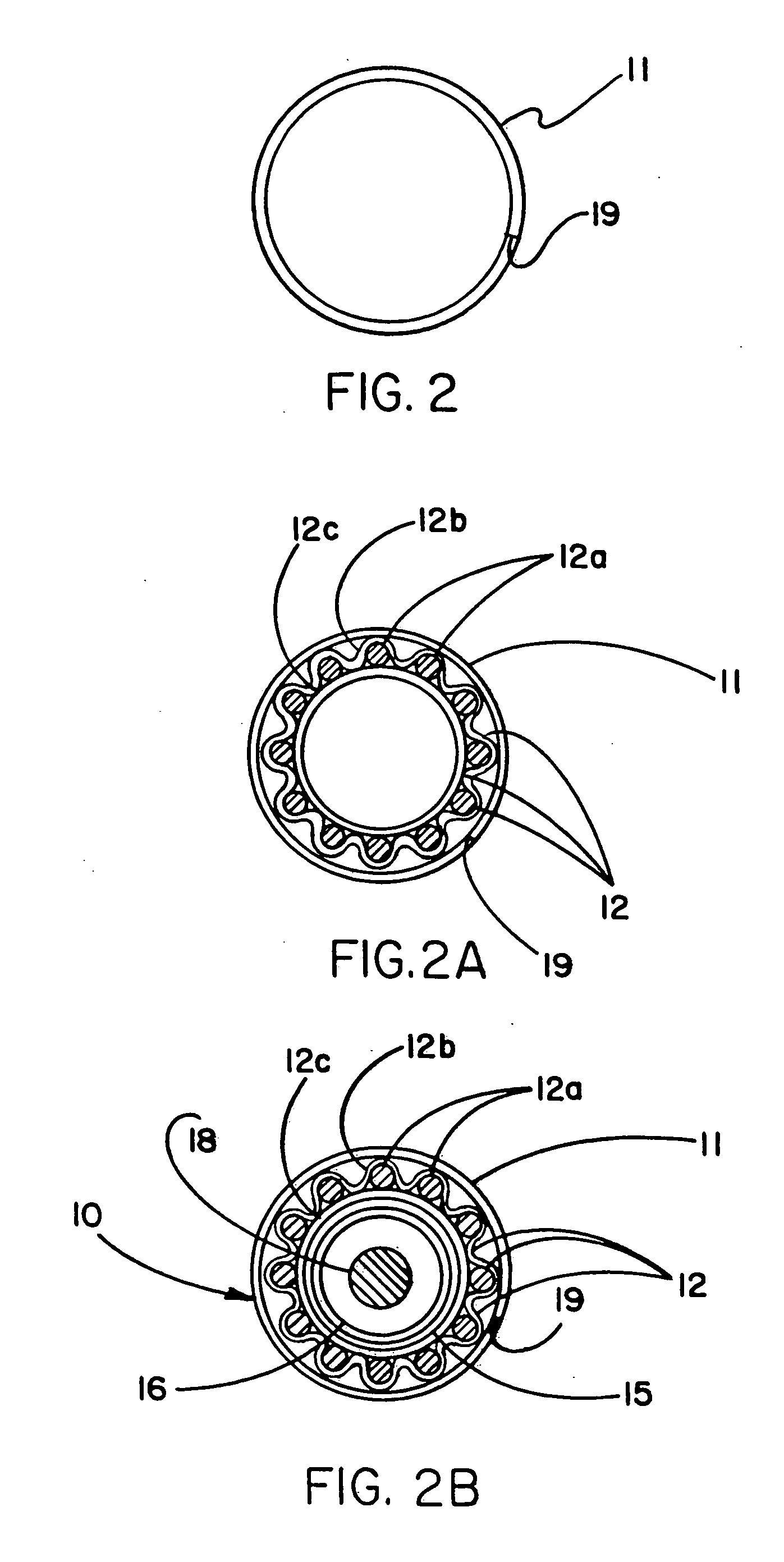
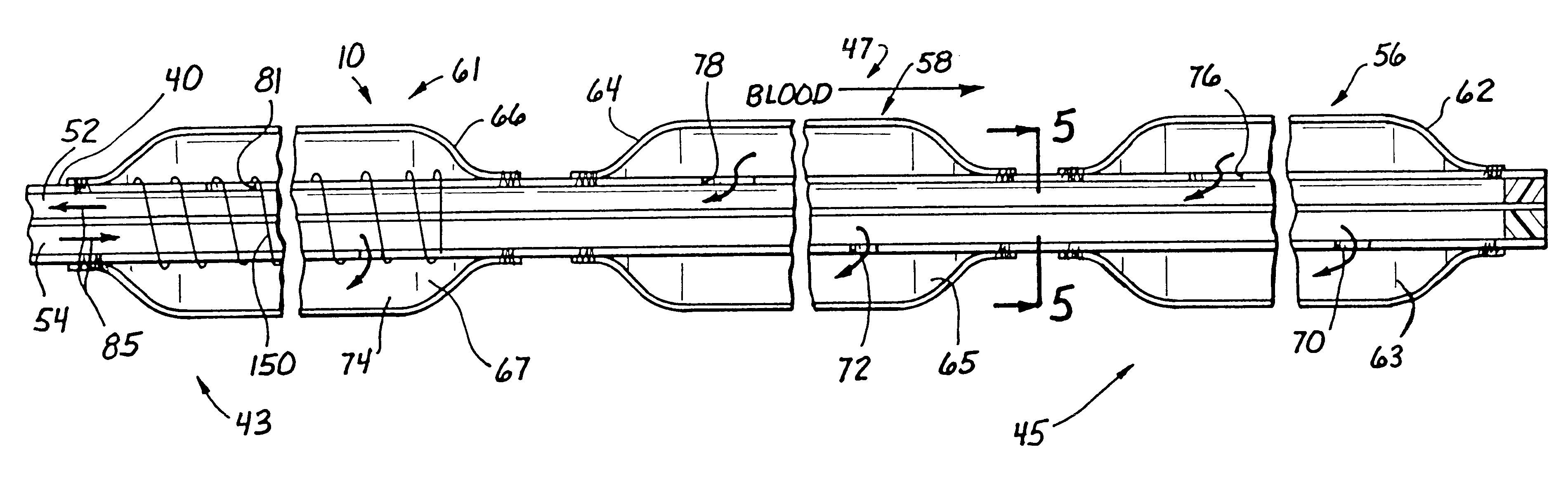
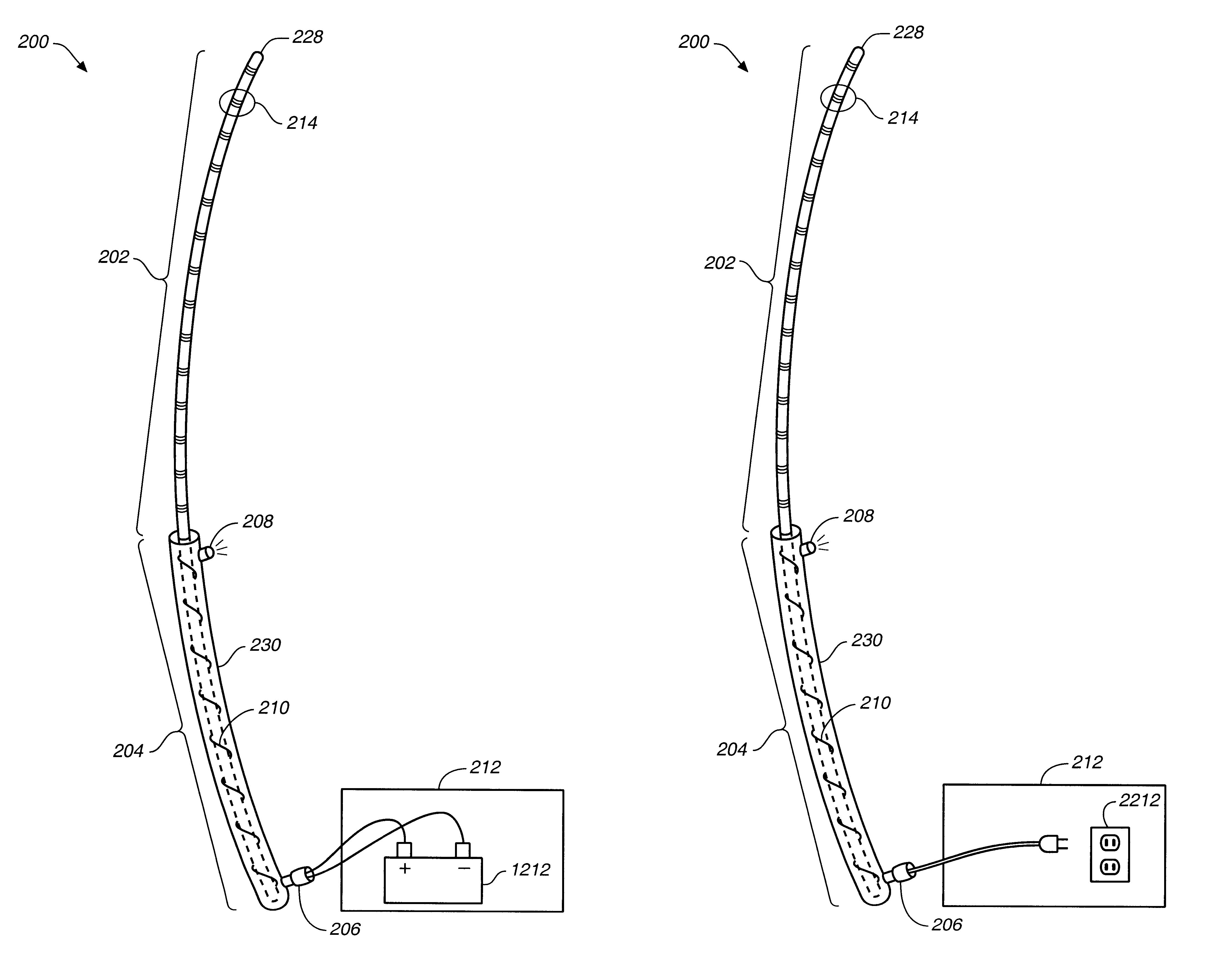
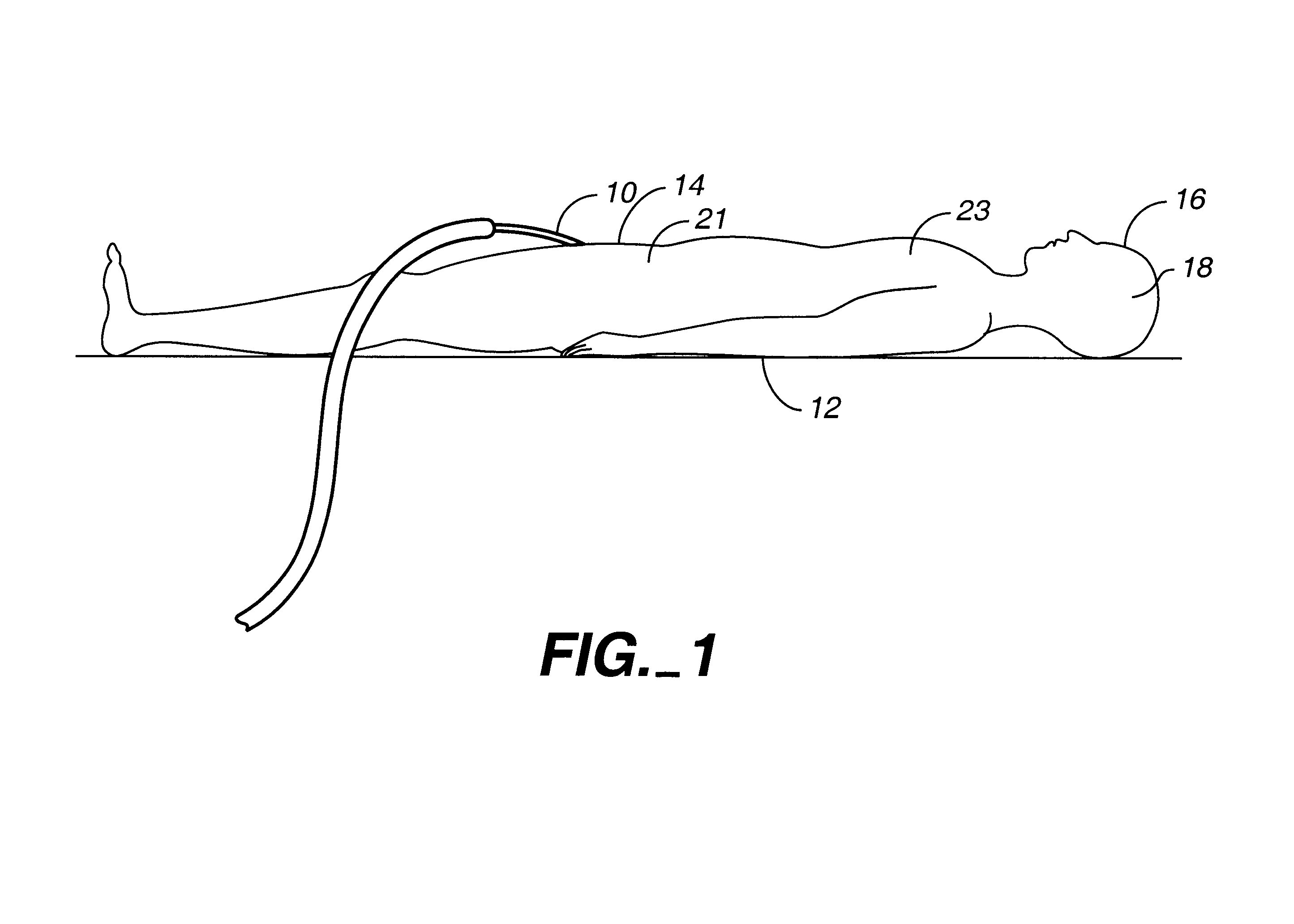
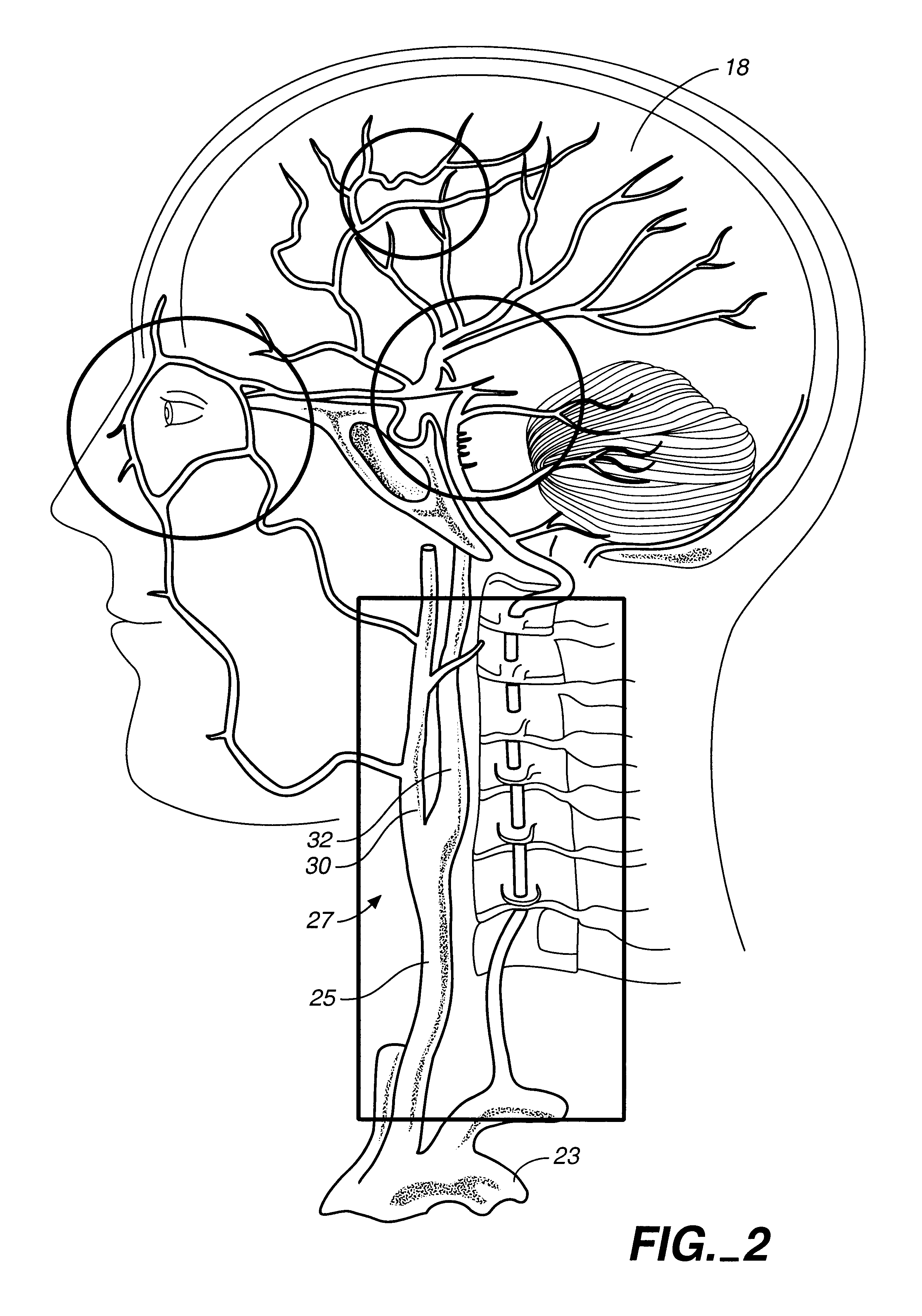
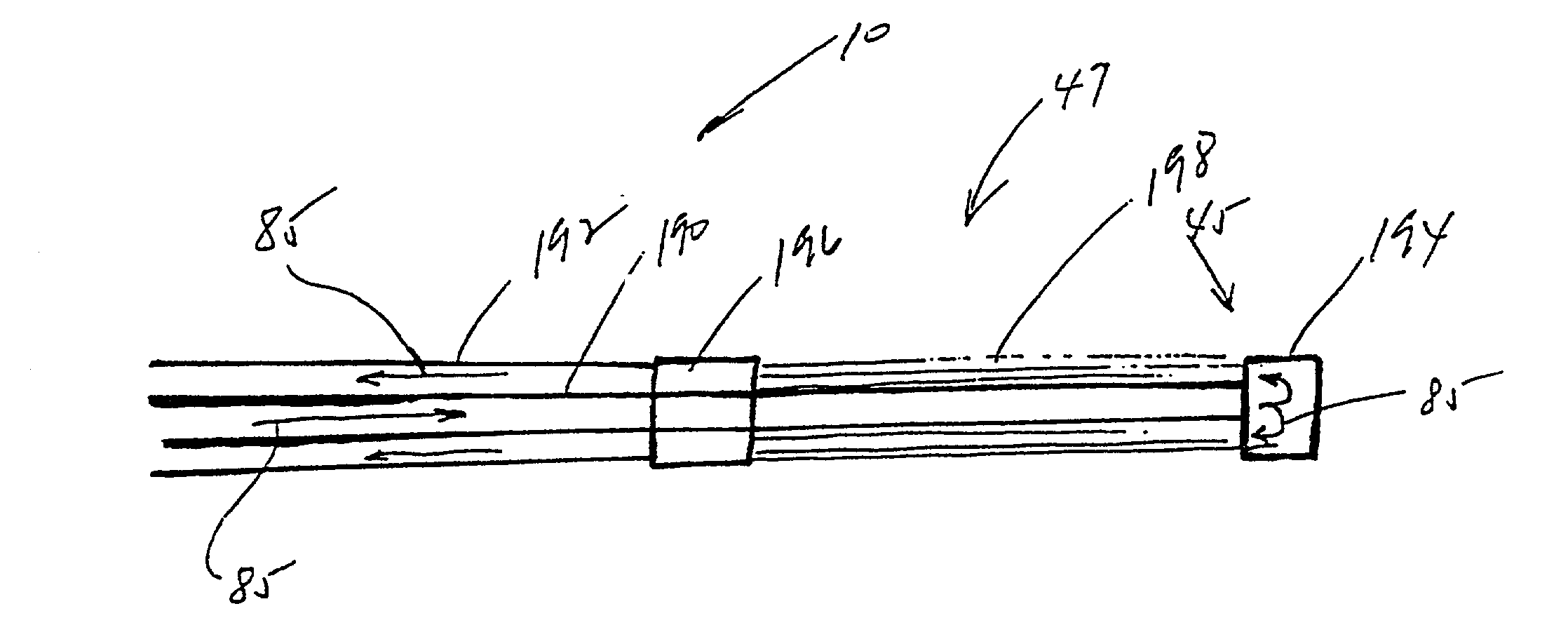
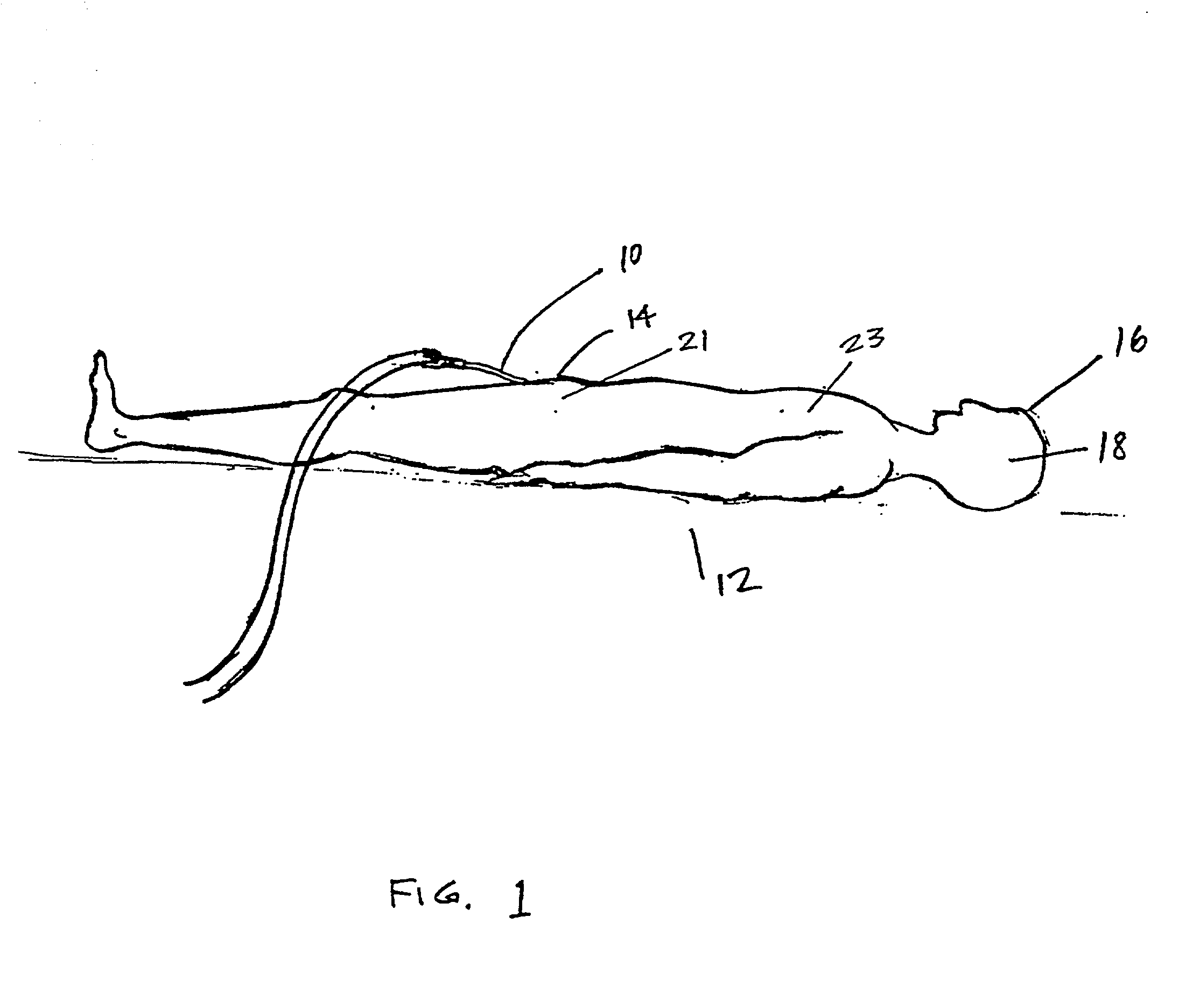
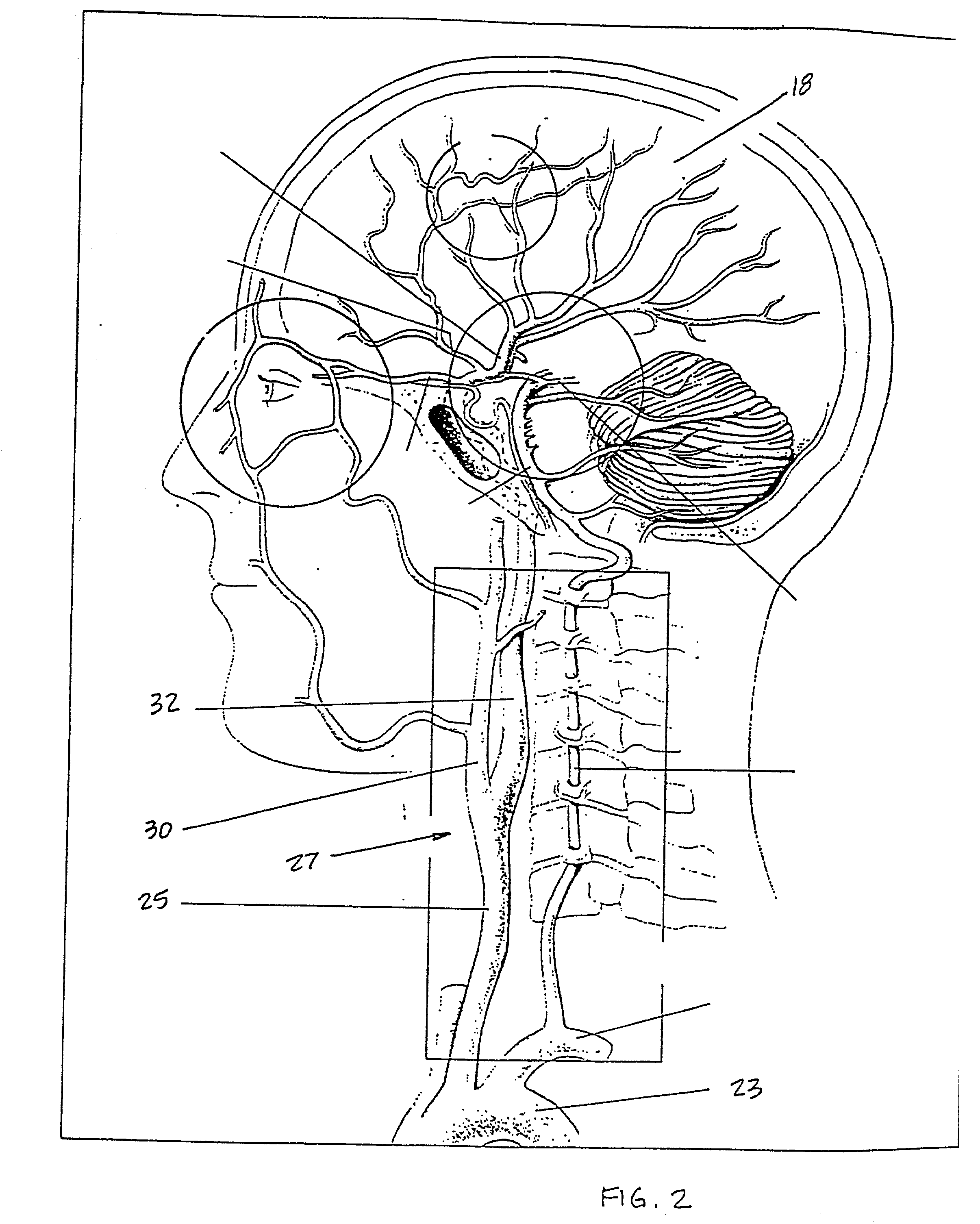
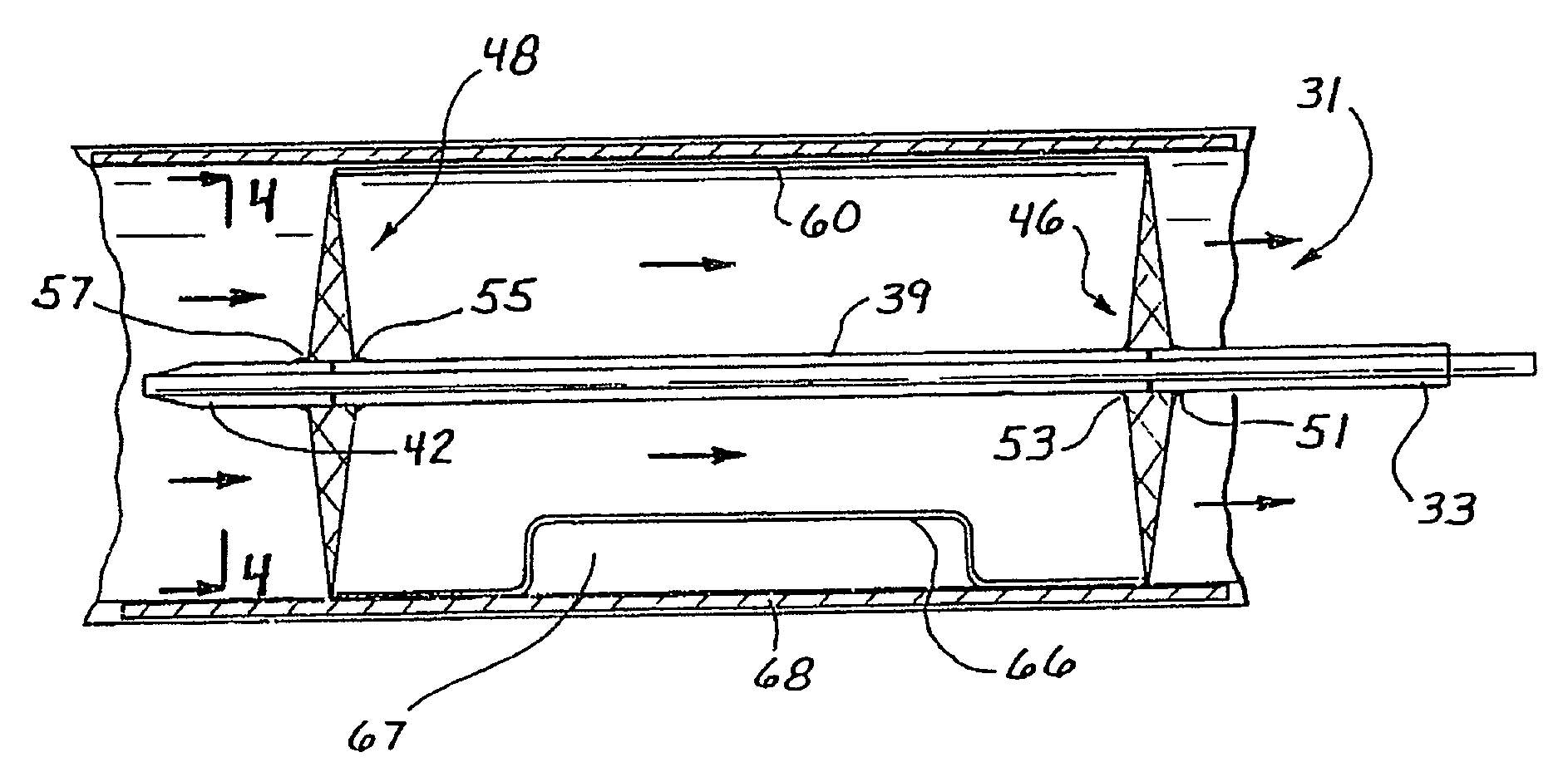
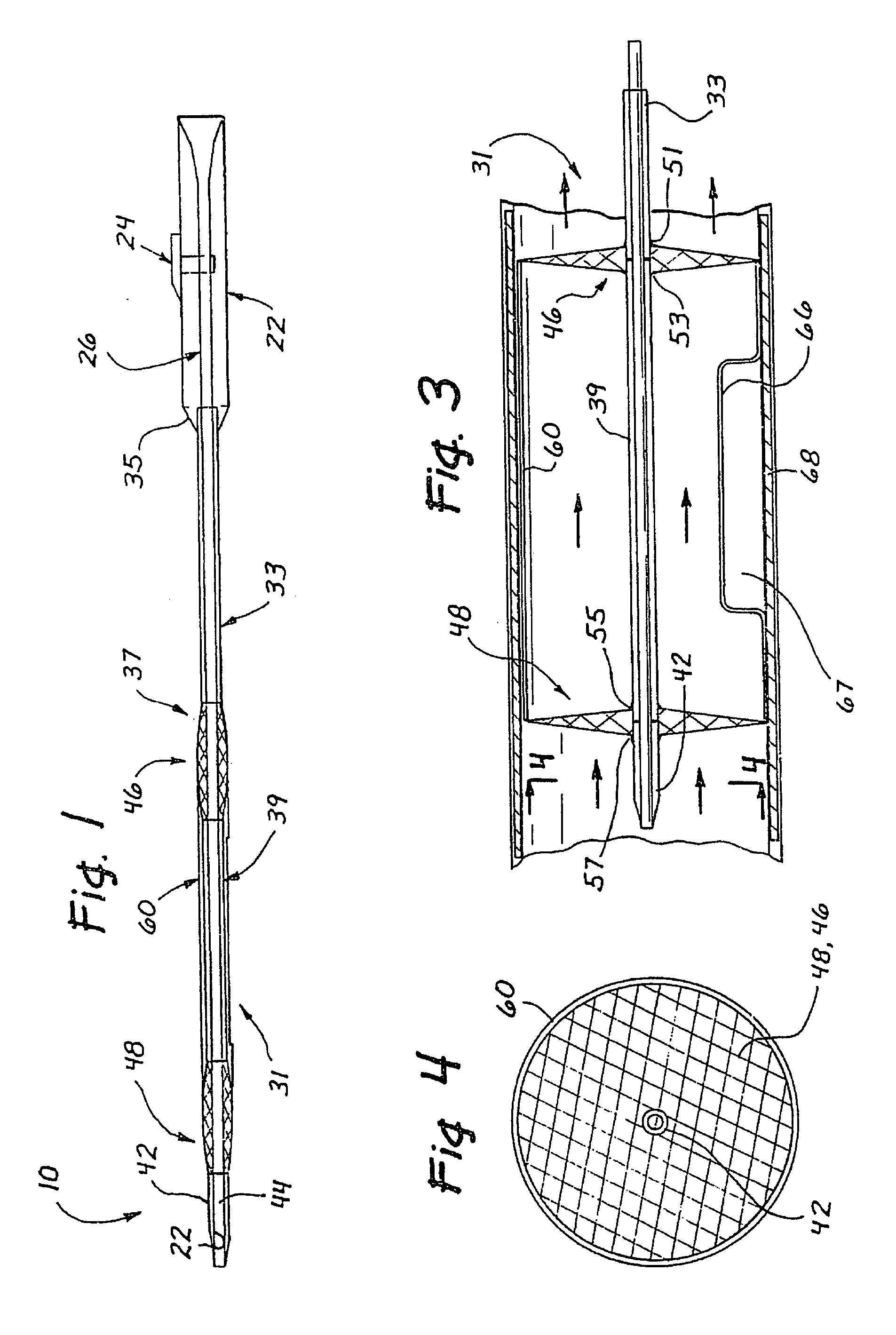
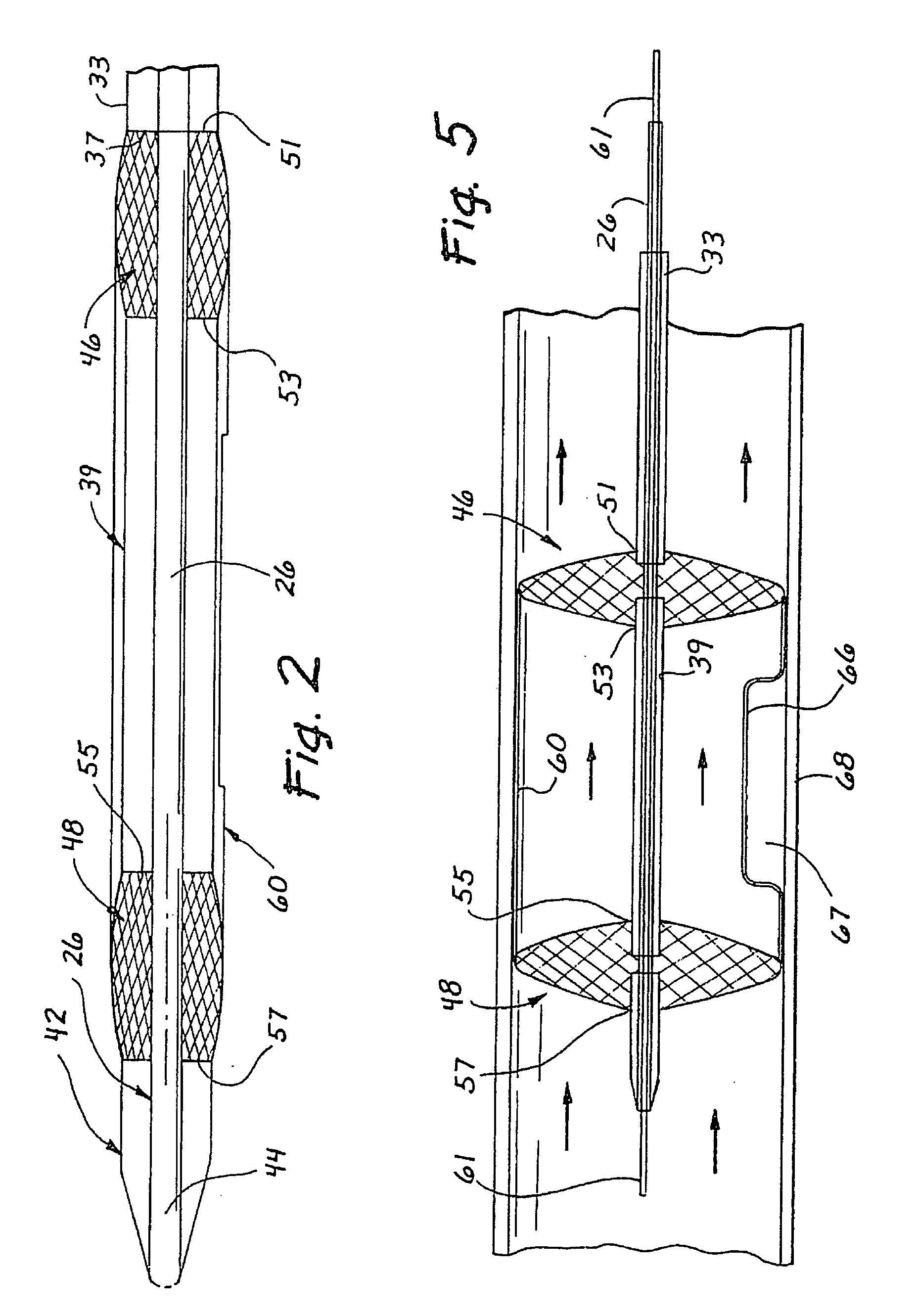
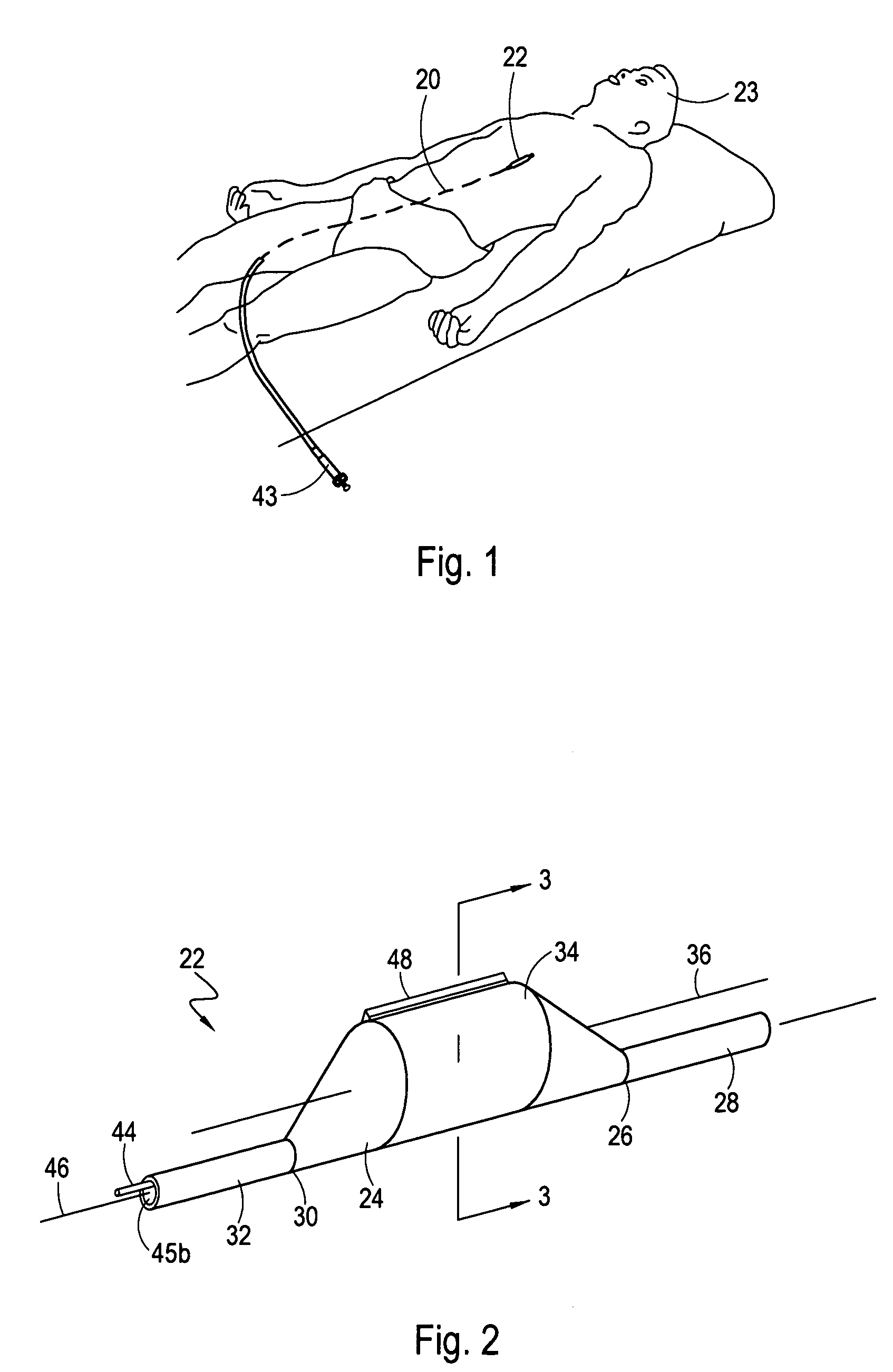
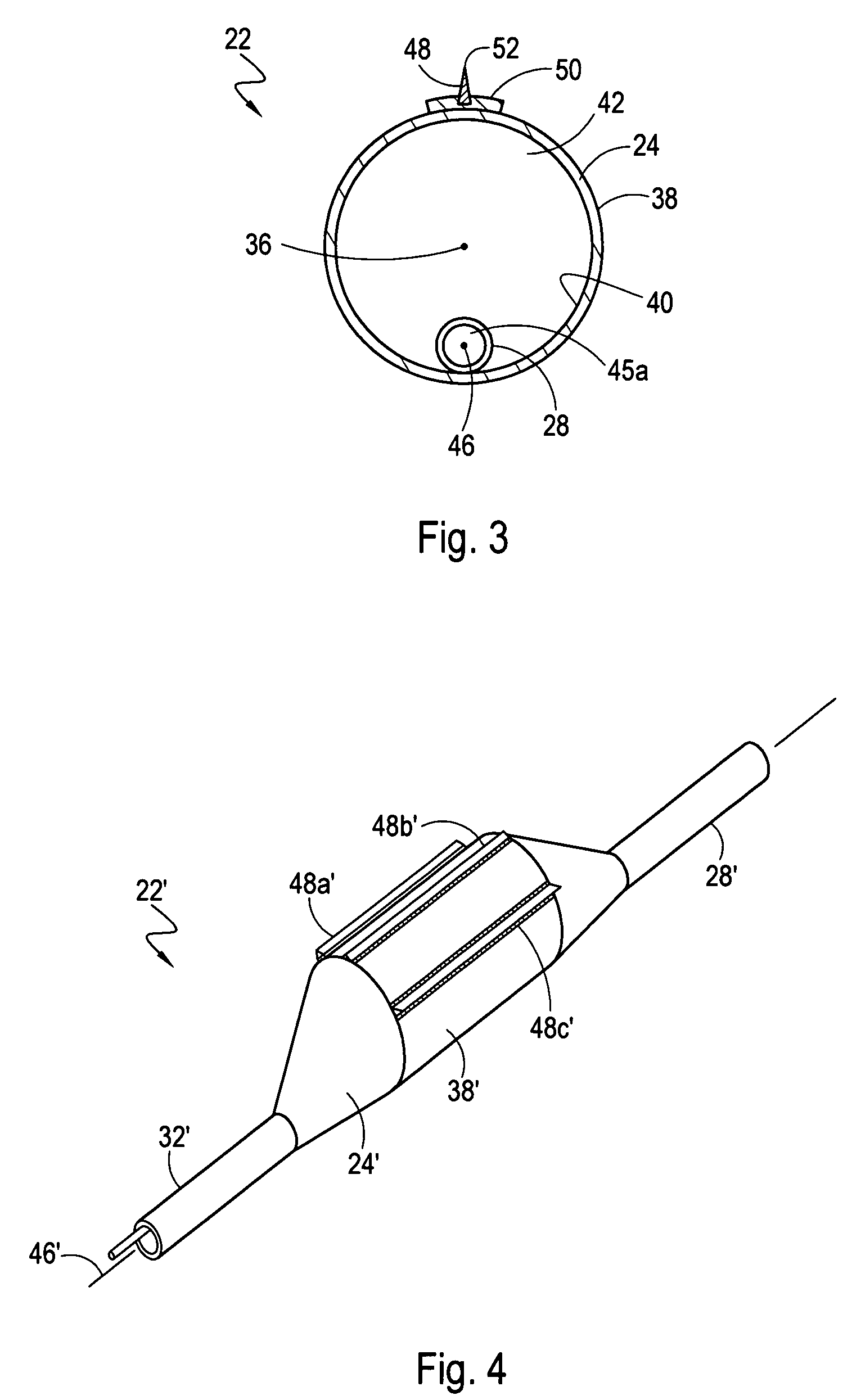
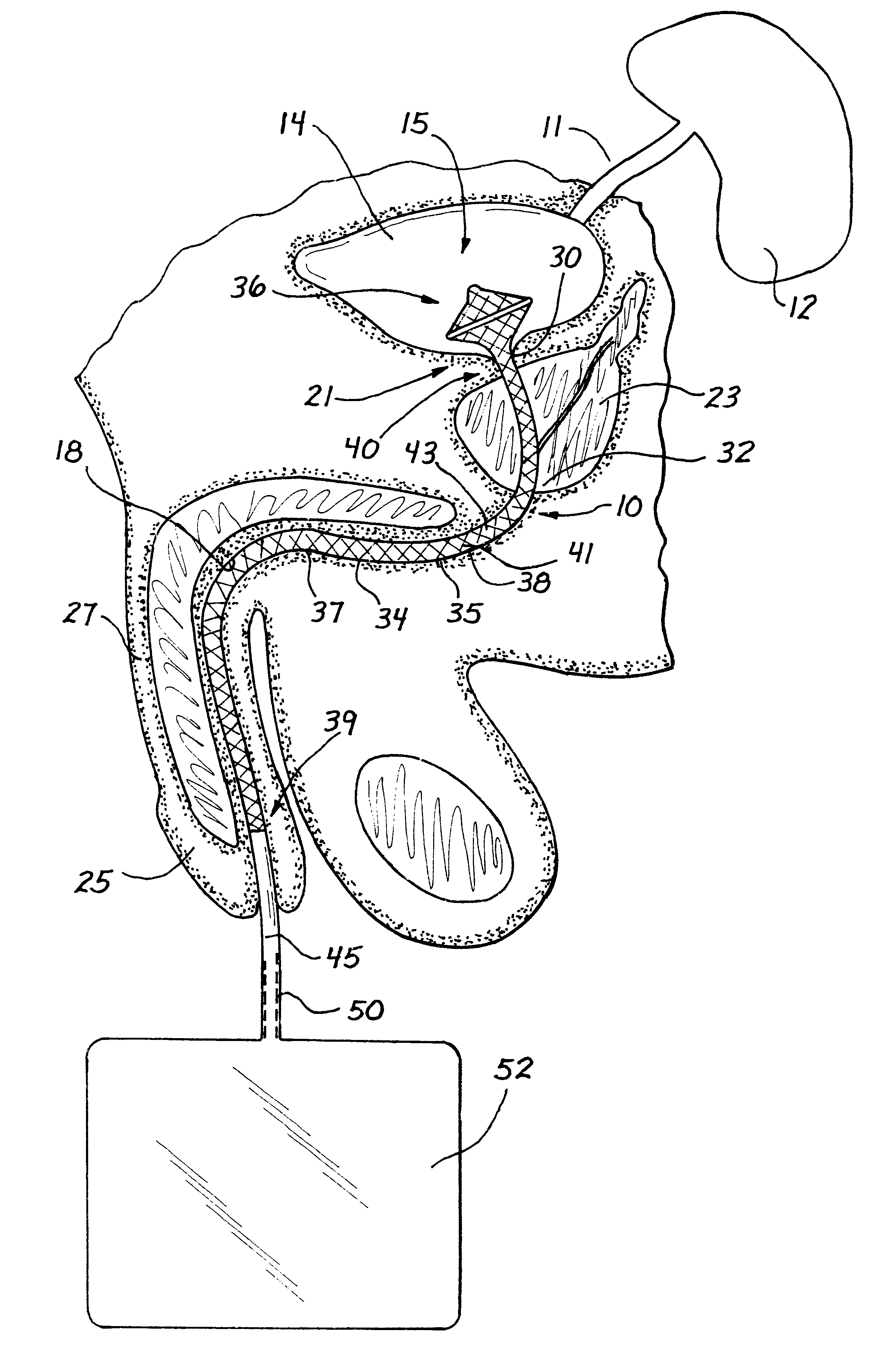
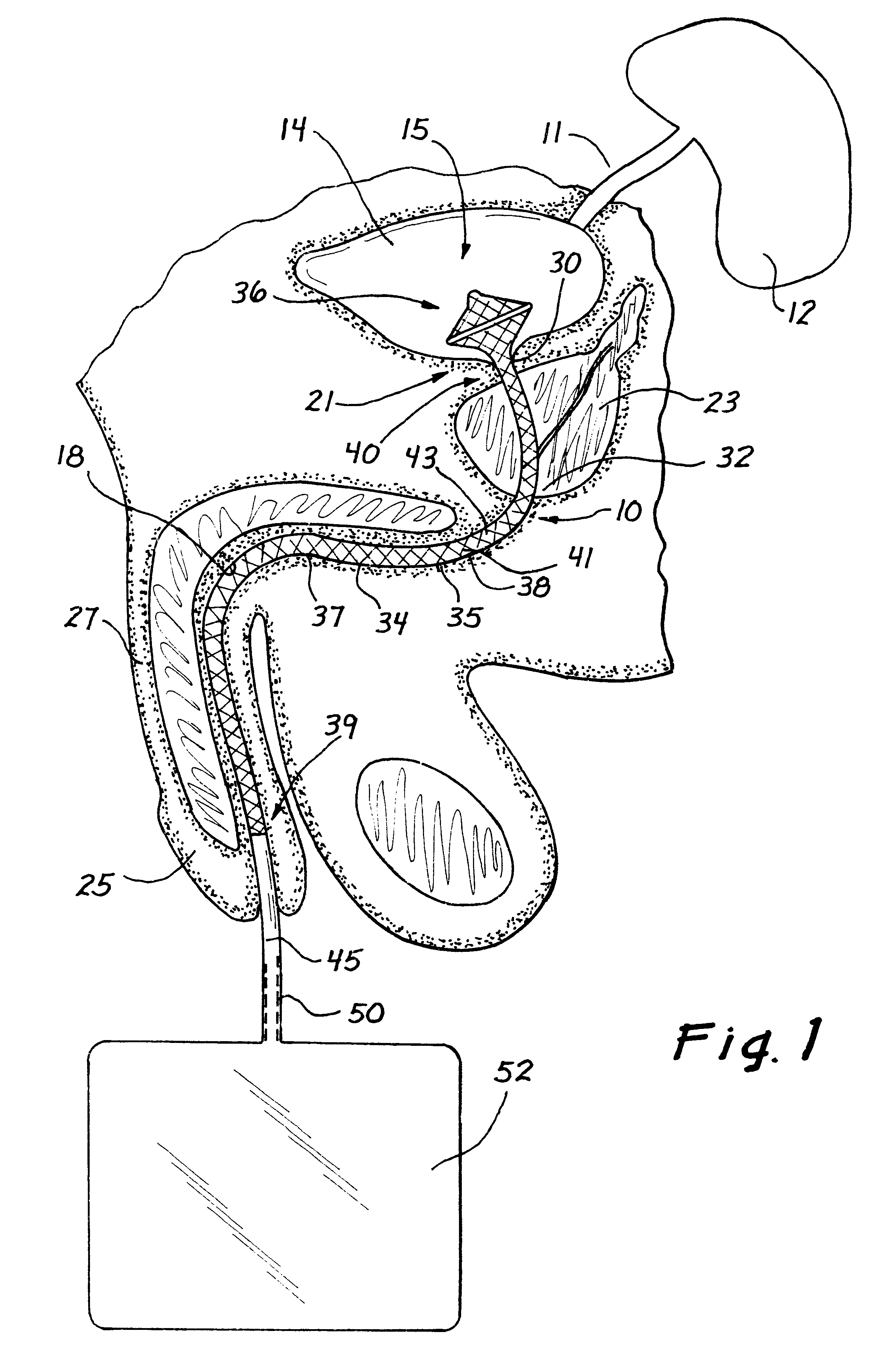
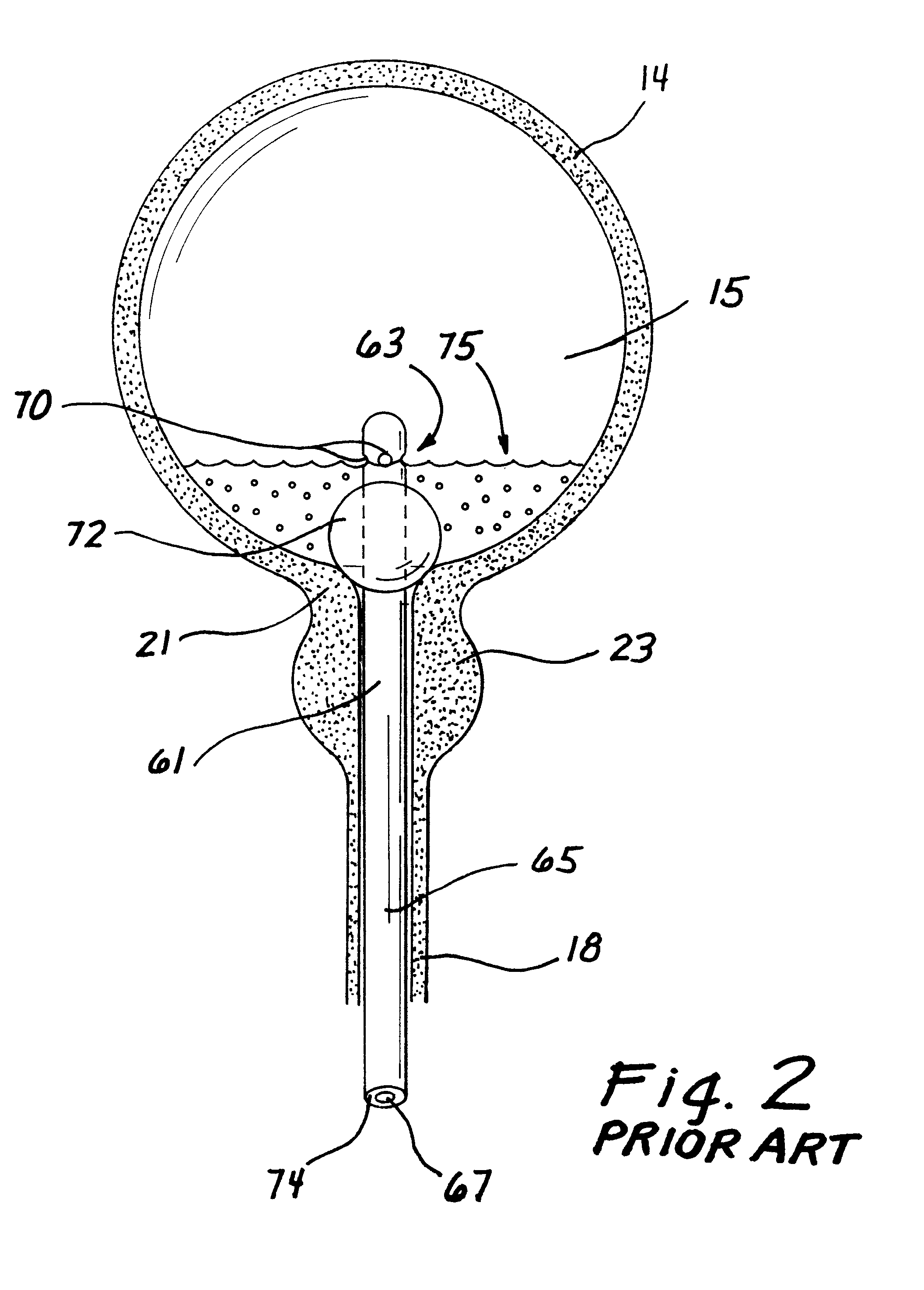
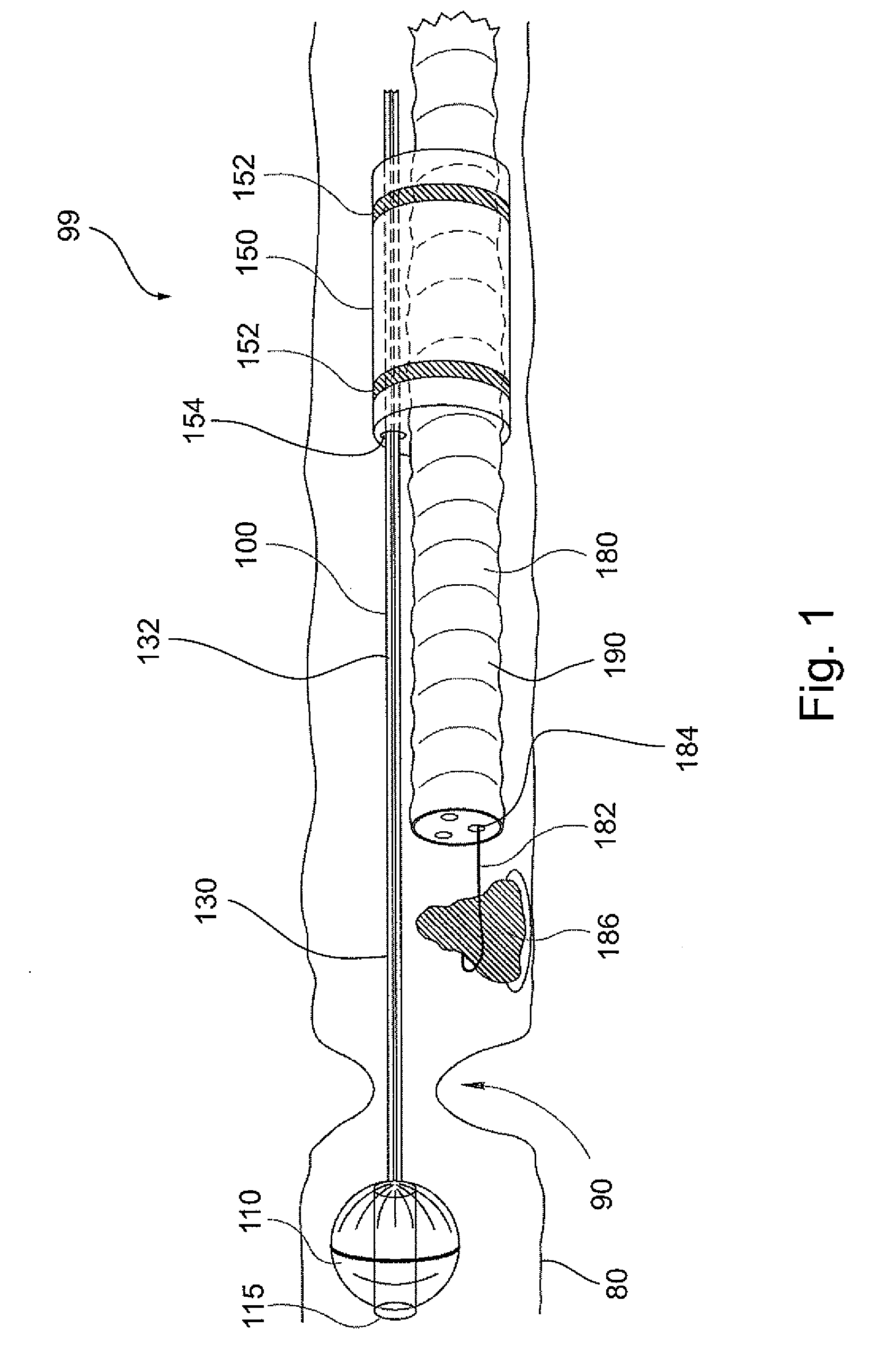
A catheter is adapted to exchange heat with a body fluid, such as blood, flowing in a body conduit, such as a blood vessel. The catheter includes a shaft with a heat exchange region disposed at its distal end. This region may include hollow fibers which are adapted to receive a remotely cooled heat exchange fluid preferably flowing in a direction counter to that of the body fluid. The hollow fibers enhance the surface area of contact, as well as the mixing of both the heat exchange fluid and the body fluid. The catheter can be positioned to produce hypothermia in a selective area of the body or alternatively positioned to systemically cool the entire body system.
Owner:ZOLL CIRCULATION +1
Indwelling heat exchange catheter and method of using same
A catheter is adapted to exchange heat with a body fluid, such as blood, flowing in a body conduit, such as a blood vessel. The catheter includes a shaft with a heat exchange region disposed at its distal end. This region may include at least one balloon which is adapted to receive a remotely cooled heat exchange fluid preferably flowing in a direction counter to that of the body fluid. Embodiments including multiple balloons enhance the surface area of contact, and the mixing of both the heat exchange and the body fluid. The catheter can be positioned to produce hypothermia in a selective area of the body without cooling the entire body system. It is of particular advantage in brain surgeries where stroke, trauma or cryogenic tumors can best be addressed under hypothermic conditions.
Owner:ZOLL CIRCULATION +1
Deployment system for intraluminal devices
ActiveUS20060015171A1Short working lengthRisk minimizationStentsDiagnosticsProsthesisBiomedical engineering
A constraining sheath for use around an endoprosthesis (e.g., a stent device, with or without a graft covering), which may be a balloon expandable endoprosthesis but more preferably is a self-expanding prosthesis. The endoprosthesis is coaxially enclosed within and substantially covered by the constraining sheath, which is an outer, removable tubular sheath, preferably made of ePTFE. The sheath is preferably corrugated circumferentially along at least a portion of the length of the endoprosthesis. The constraining sheath and endoprosthesis are preferably mounted together as an assembly at the distal end of a delivery means such as a catheter shaft, for delivery of the endoprosthesis to a desired location within a body conduit such as an artery. The constraining sheath is removed by the application of tension to a tensile member such as a tether to cause sequential pulling out of the corrugations followed by release and deployment of the endoprosthesis. The use of a corrugated constraining sheath in comparison to a non-corrugated sheath results in a more smoothly applied tensile force to effect the endoprosthesis release as well as requiring less maximum force.
Owner:WL GORE & ASSOC INC
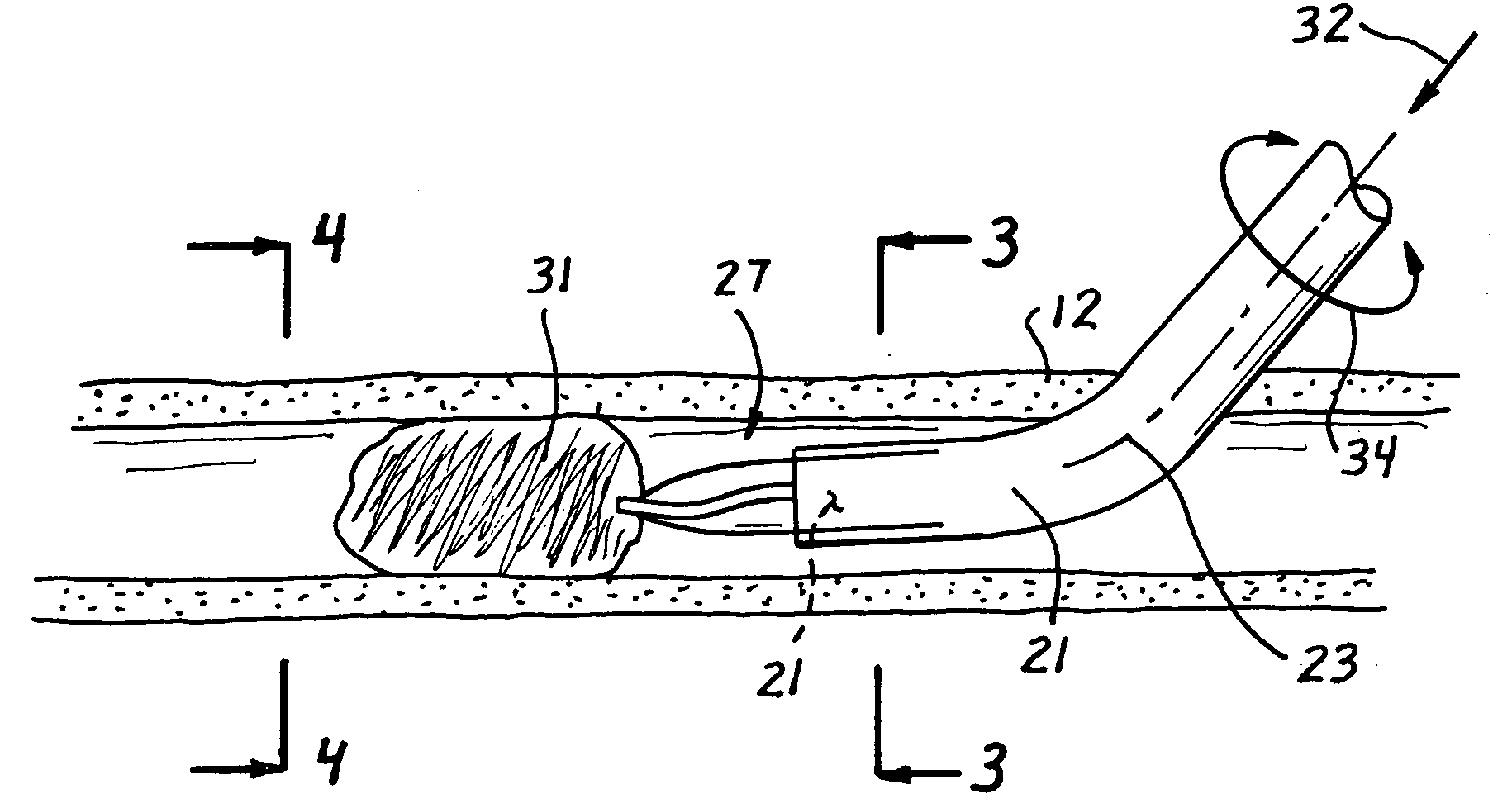
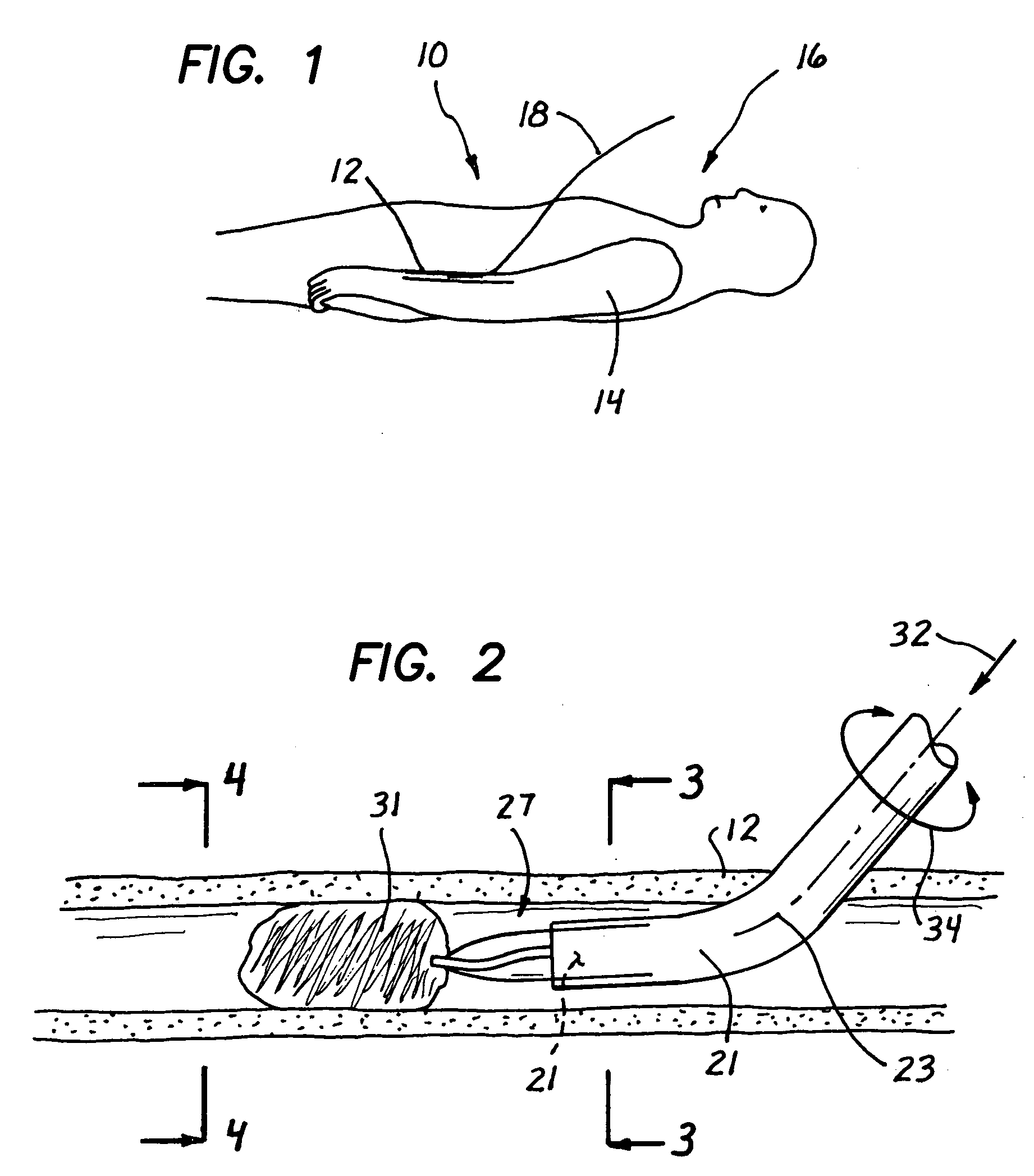
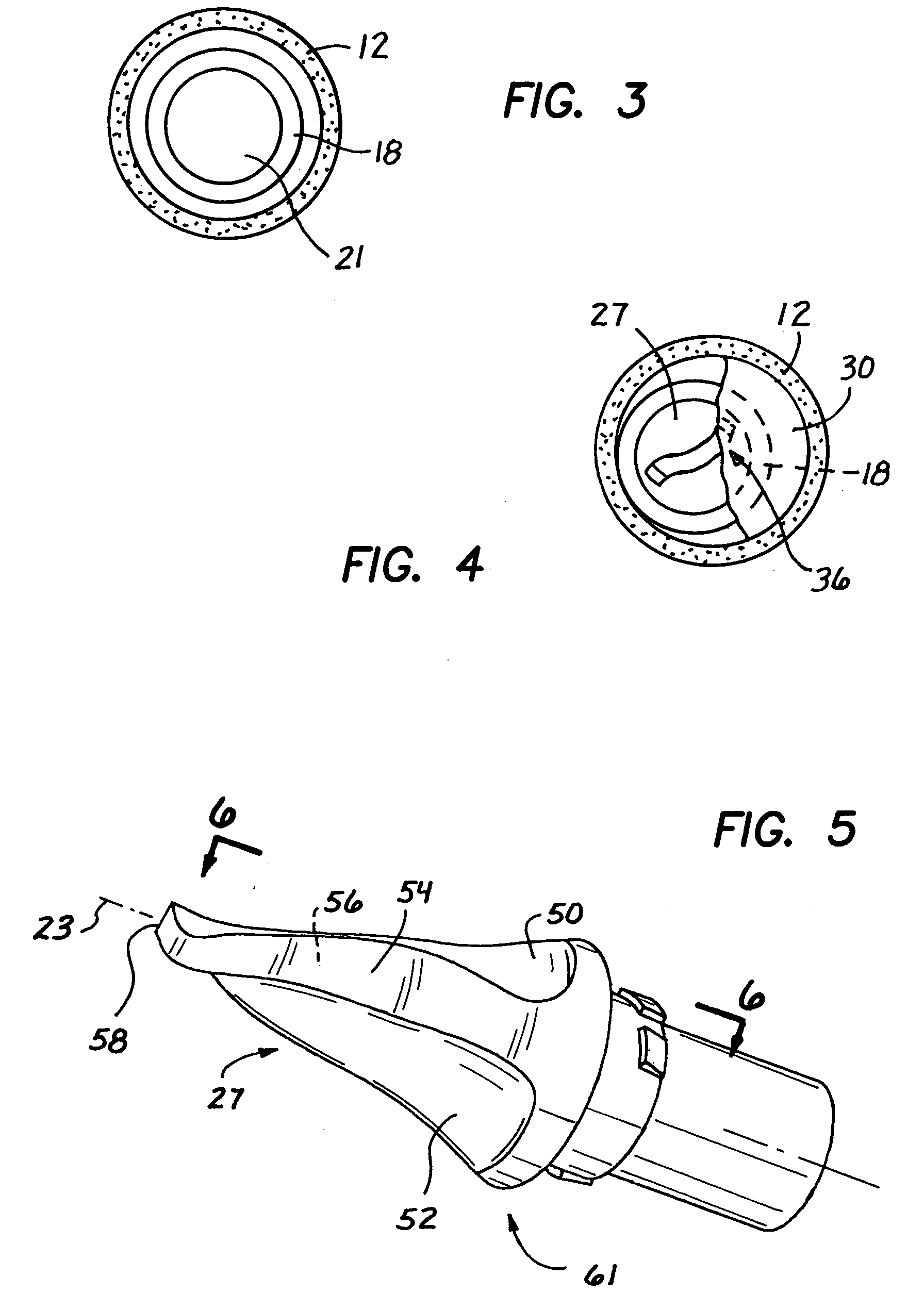
Surgical clamp with improved traction
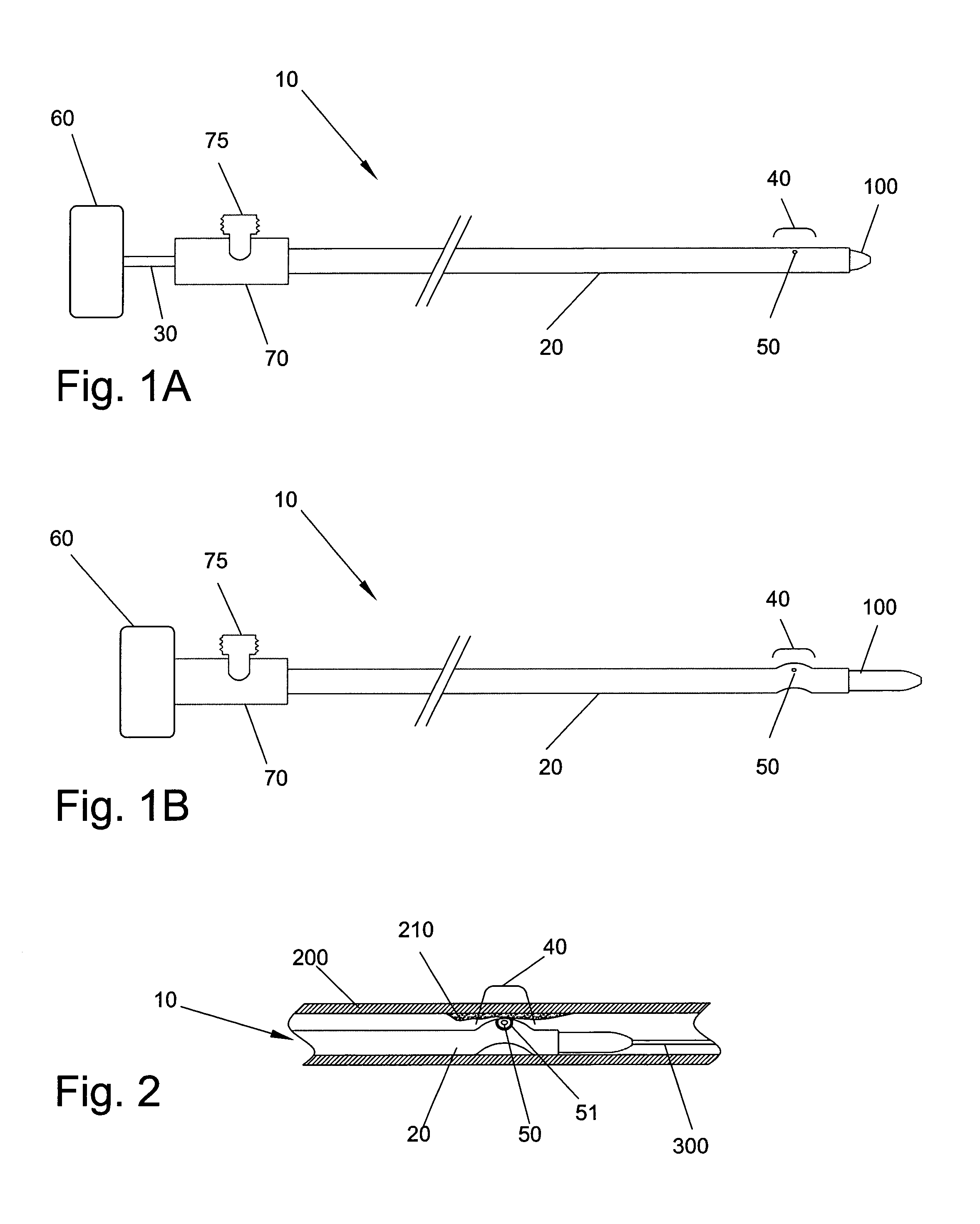
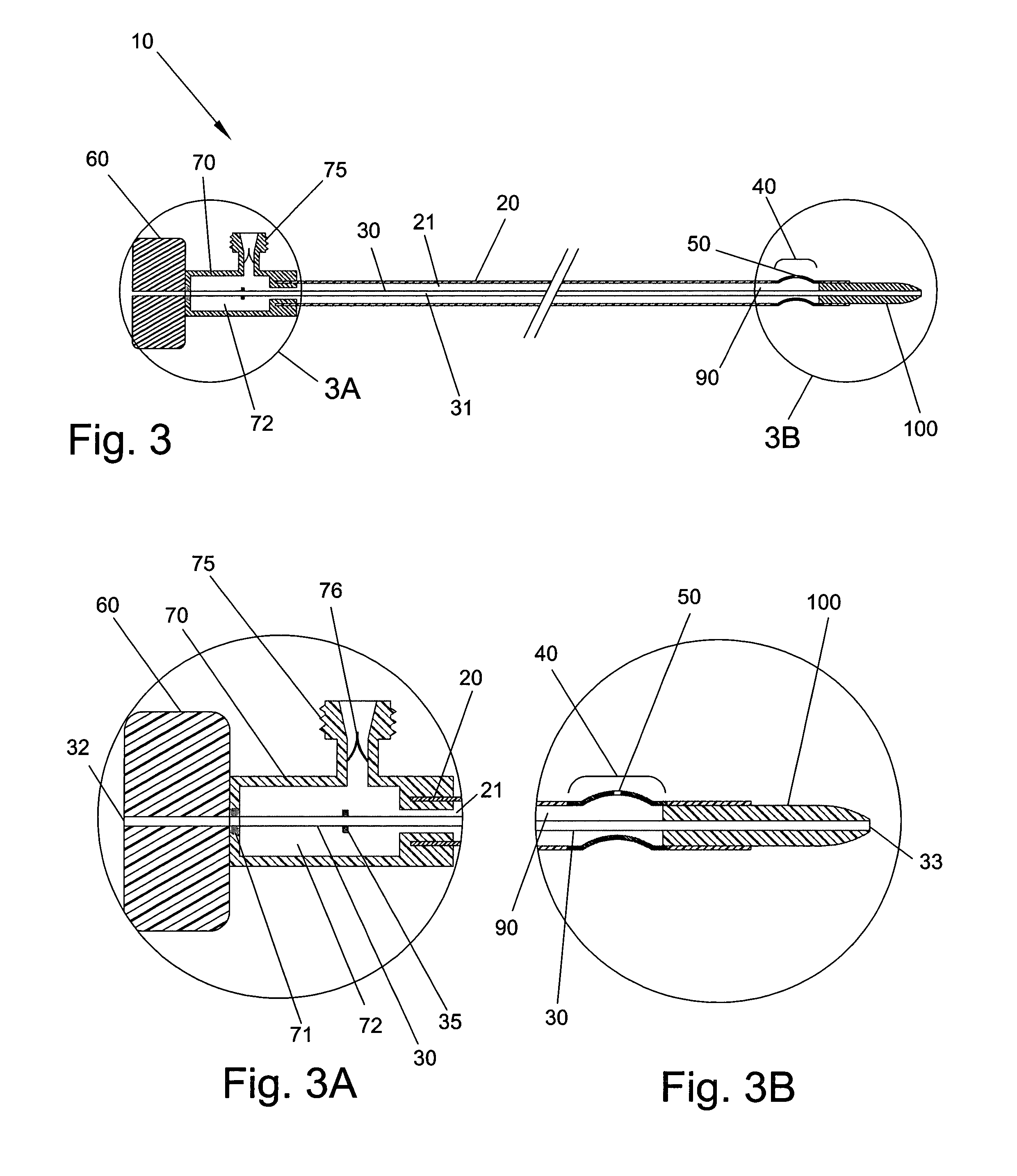
A surgical clamp includes opposing jaws and a covering enhancing traction between the jaws and a body conduit. A multiplicity of fibers oriented to extend longitudinally between the clamp and conduit may be composed of filaments and either woven or non-woven to form a fabric. A variety of weaves are contemplated to provide different textures, each having its own traction characteristics. The nature of the weave can control characteristics such as smoothness, absorption, and texture. The fibers or filaments may be formed from any solid or semi-solid material, adding its own characteristics to the resulting fabric insert or clamp.
Owner:APPL MEDICAL RESOURCES CORP
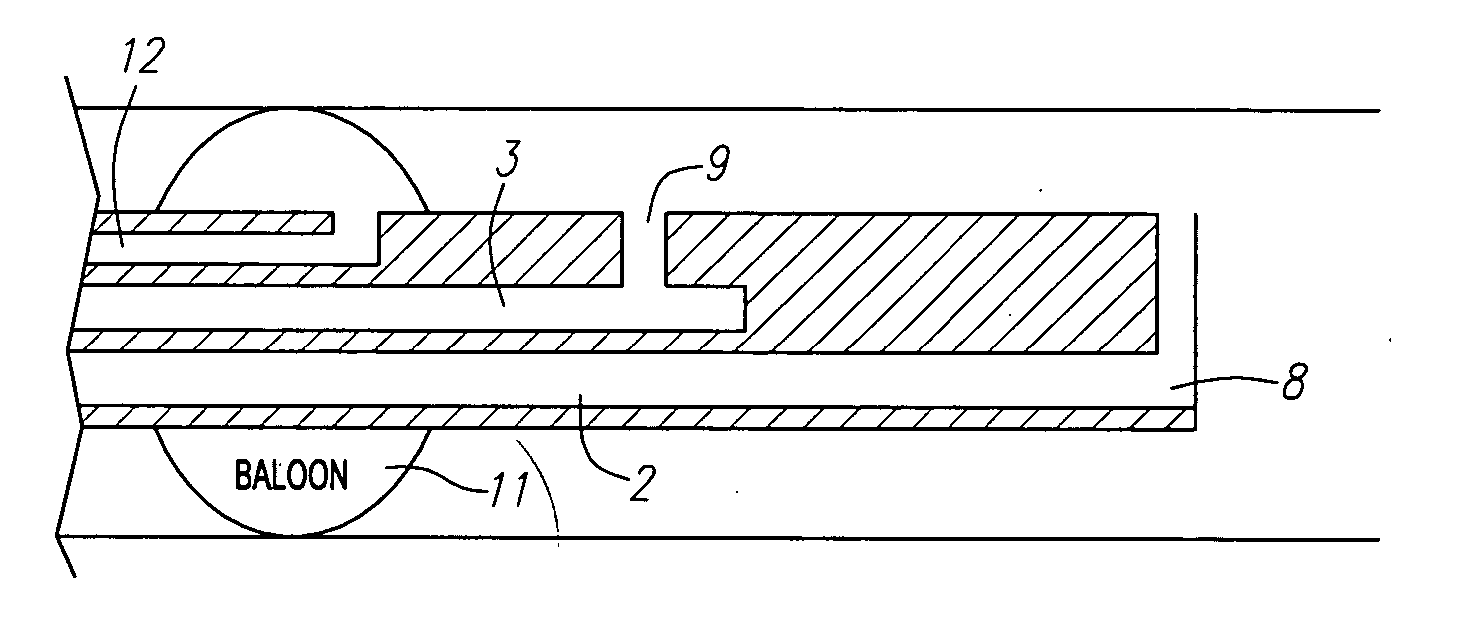
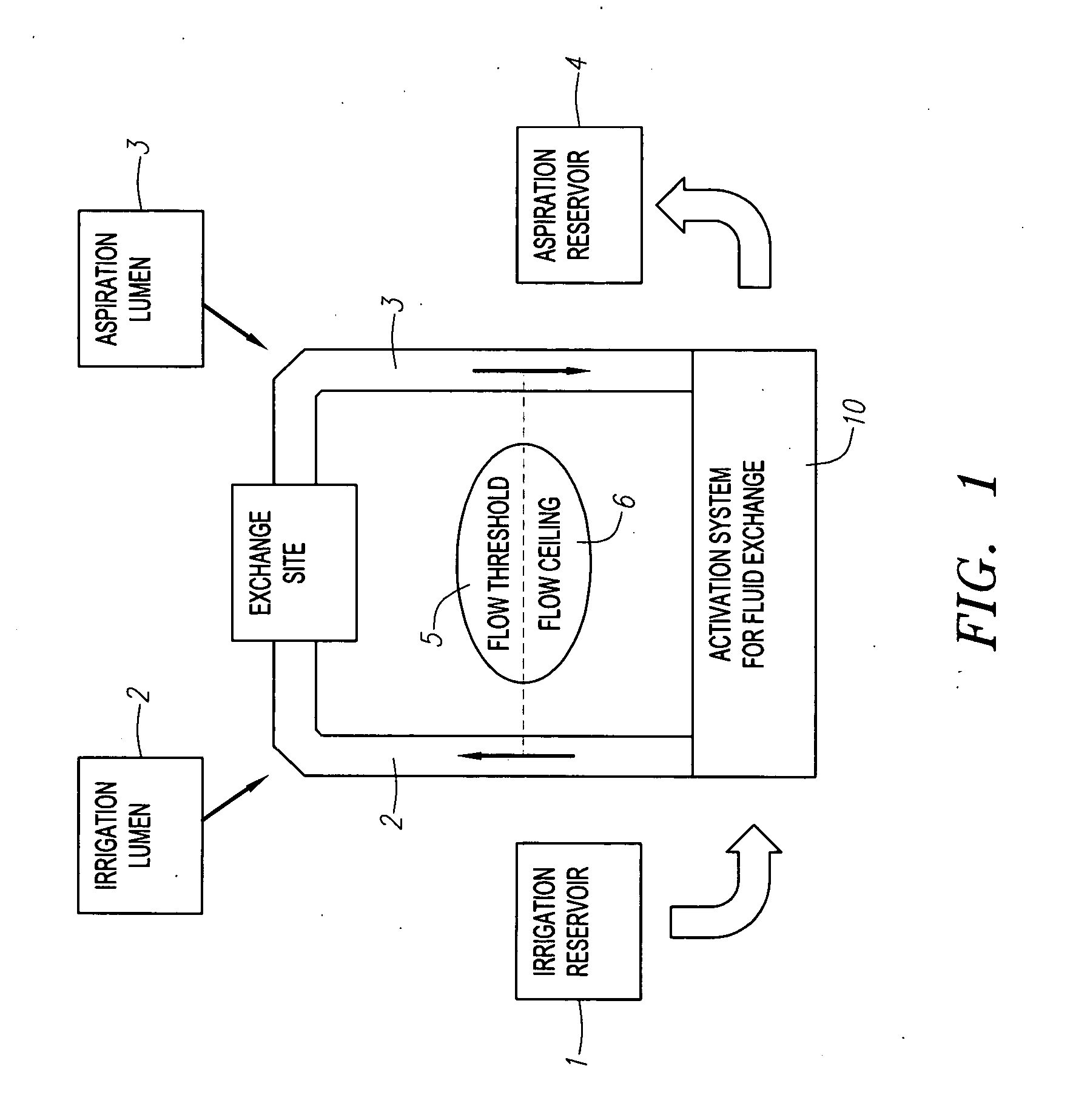
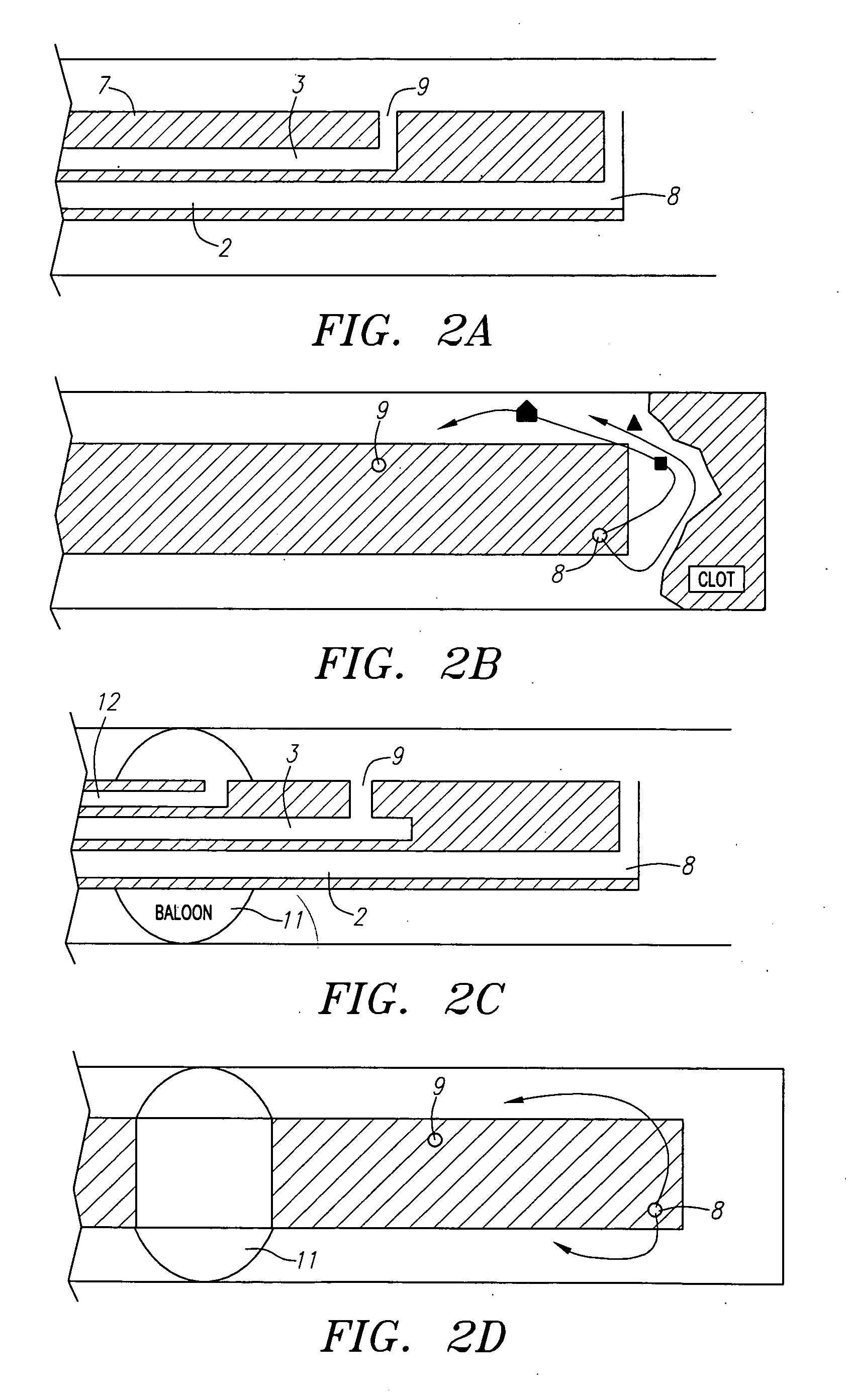
Fluid exchange system for controlled and localized irrigation and aspiration
InactiveUS20050085769A1Improved exchangeSpeed up the flowInfusion syringesSurgeryElectricityFluid management
The control of fluid introduction into and out of body conduits such as vessels, is of great concern in medicine. As the development of more particular treatments to vessels and organs continues it is apparent that controlled introduction and removal of fluids is necessary. Fluid delivery and removal from such sites, usually referred to as irrigation and aspiration, using fluid exchange devices that control also need to be considerate of potential volume and / or pressure in the vessel or organ are described together with catheter and lumen configurations to achieve the fluid exchange. The devices include several electrically or mechanically controlled embodiments and produce both controlled and localized flow with defined volume exchange ratios for fluid management. The applications in medicine include diagnostic, therapeutic, imaging, and uses for the introduction or removal of concentrations of emboli within body cavities.
Owner:FOX HOLLOW TECH
Indwelling heat exchange catheter and method of using same
Owner:ZOLL CIRCULATION +1
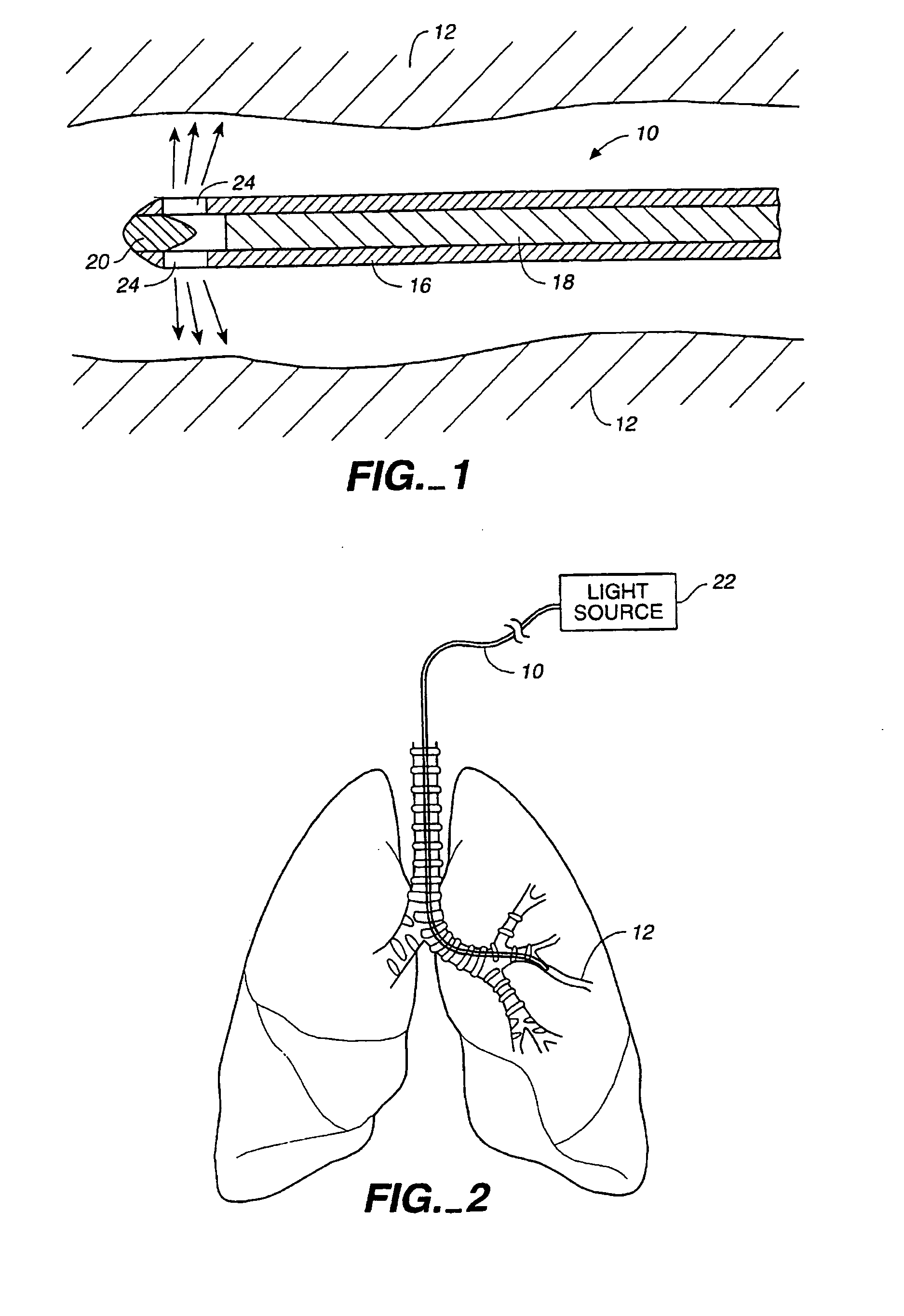
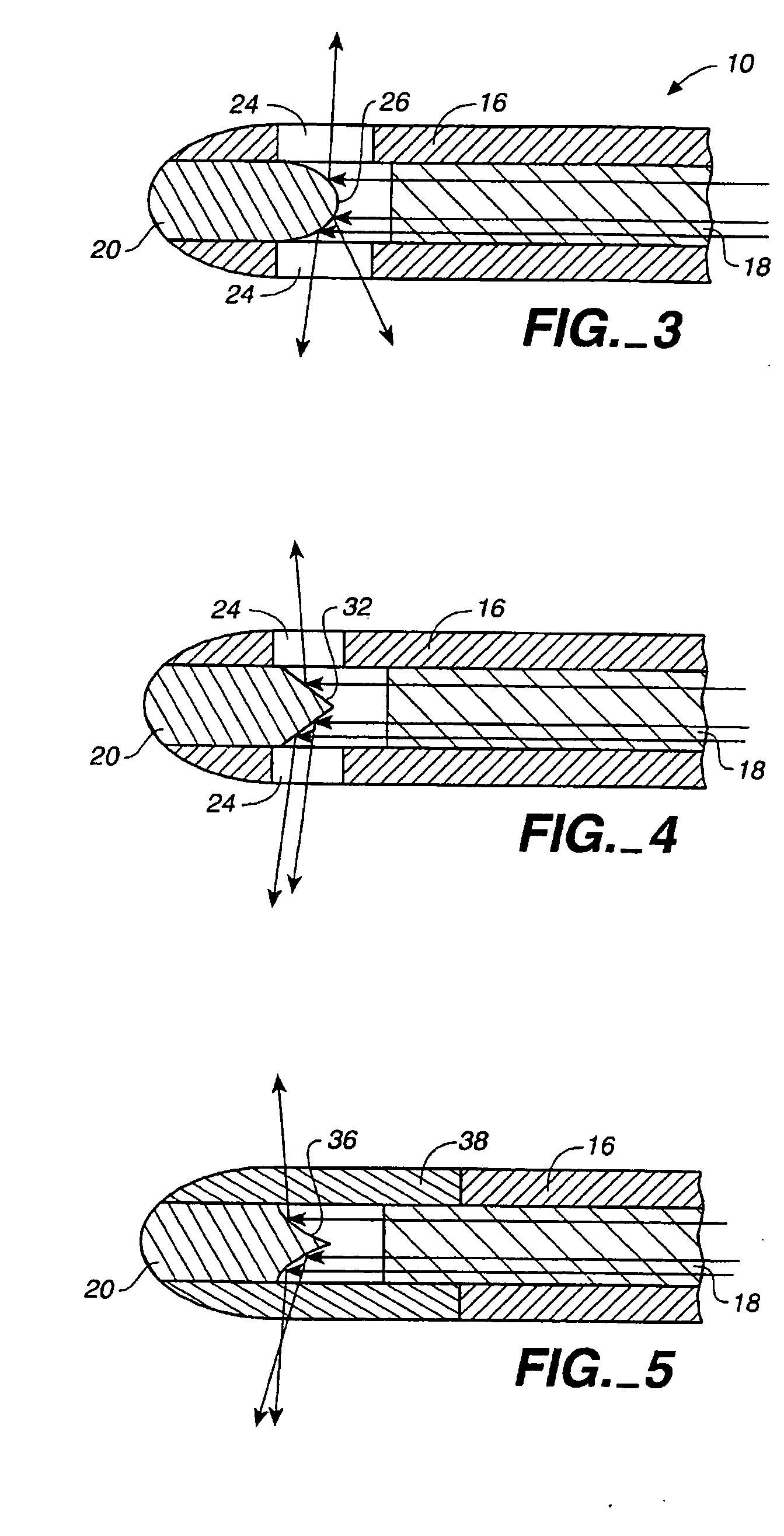
Method of treating airways in the lung
InactiveUS20050010270A1Reduce the amount requiredIncrease inner diameterSurgical instrument detailsLight therapyBronchospasmSmooth muscle spasm
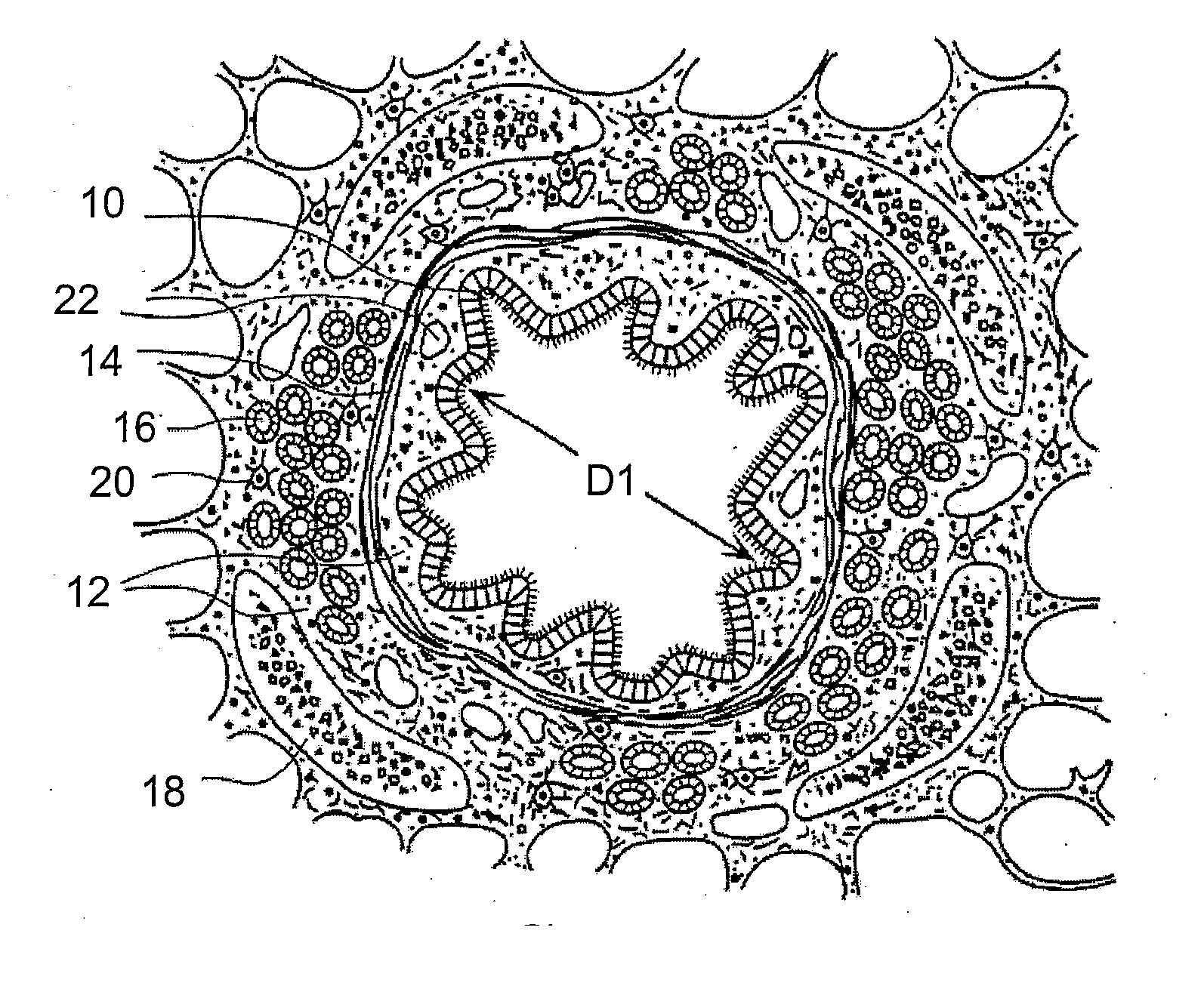
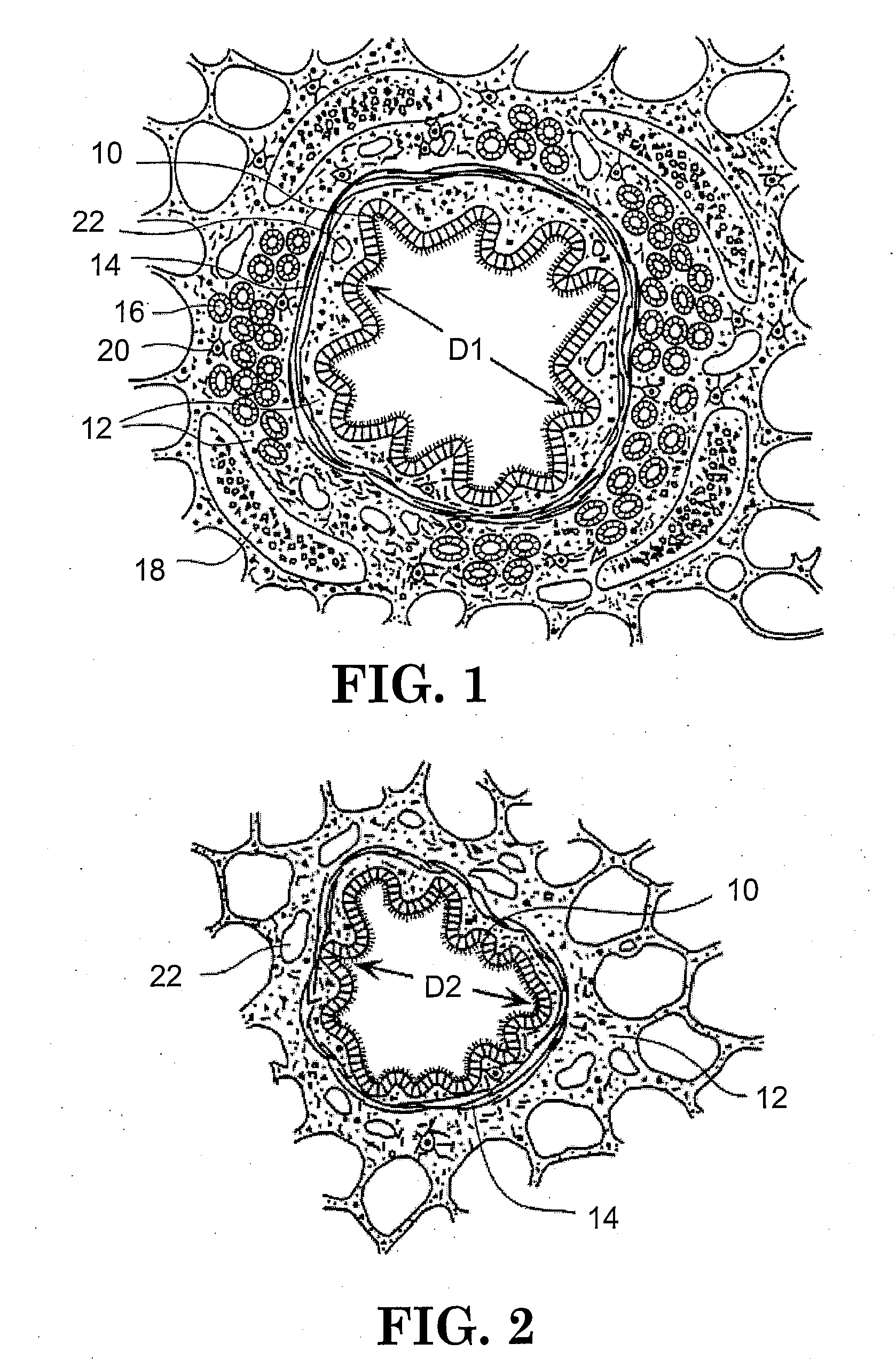
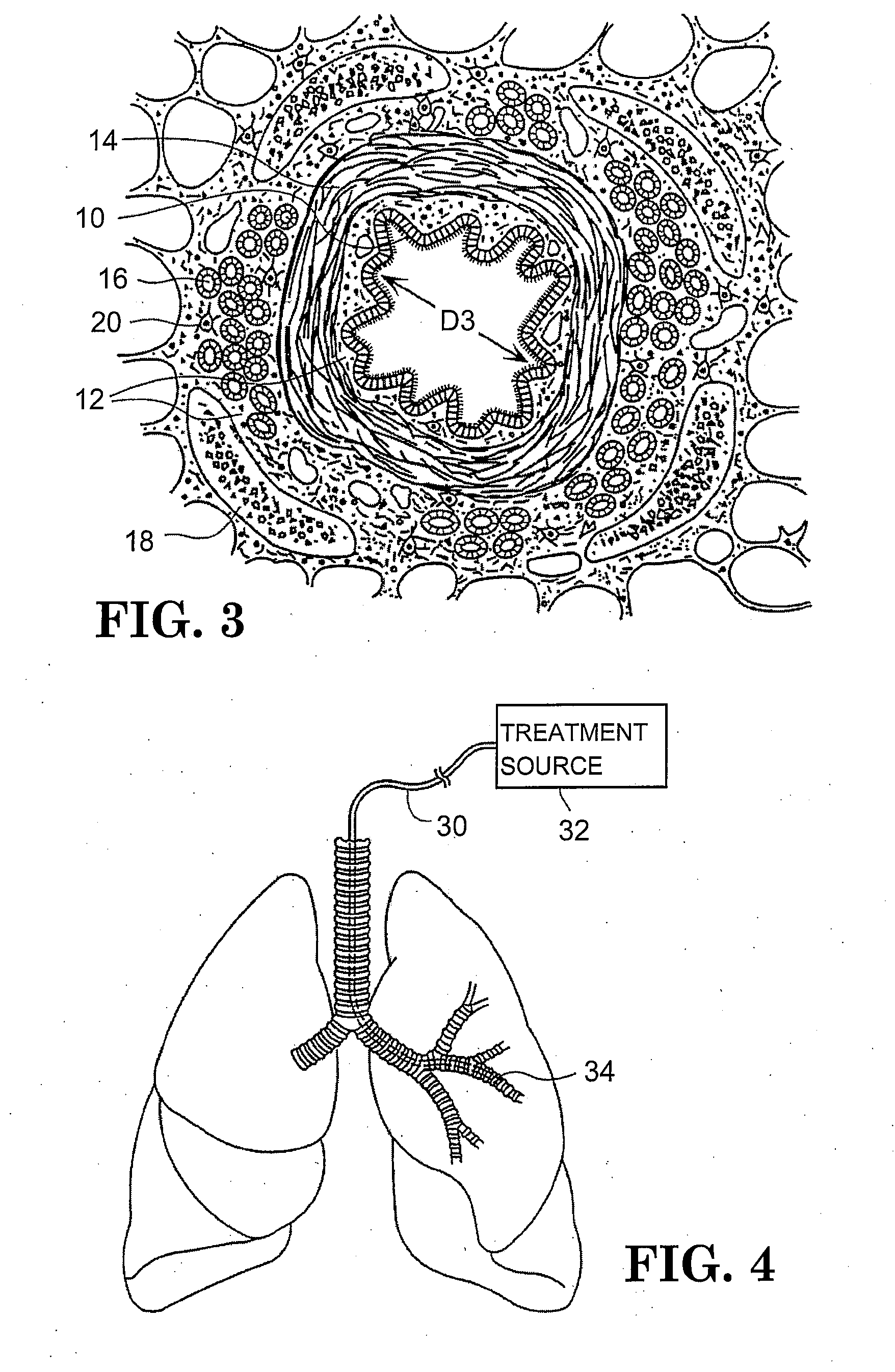
A device and method for treating bodily conduits involves the application of energy to the smooth muscle tissue of the conduit walls to reduce the bulk of smooth muscle tissue and mucus glands. The irradiation treatment of the smooth muscle tissue causes a reduction in the amount of smooth muscle tissue over time which increases the inner diameter of the body conduit for improved fluid flow and prevents smooth muscle spasms. The treatment is particularly useful in the lungs for treatment of asthma to prevent bronchospasms, increase the airway diameter for improved air exchange, and reduce mucus secretions in the lungs.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
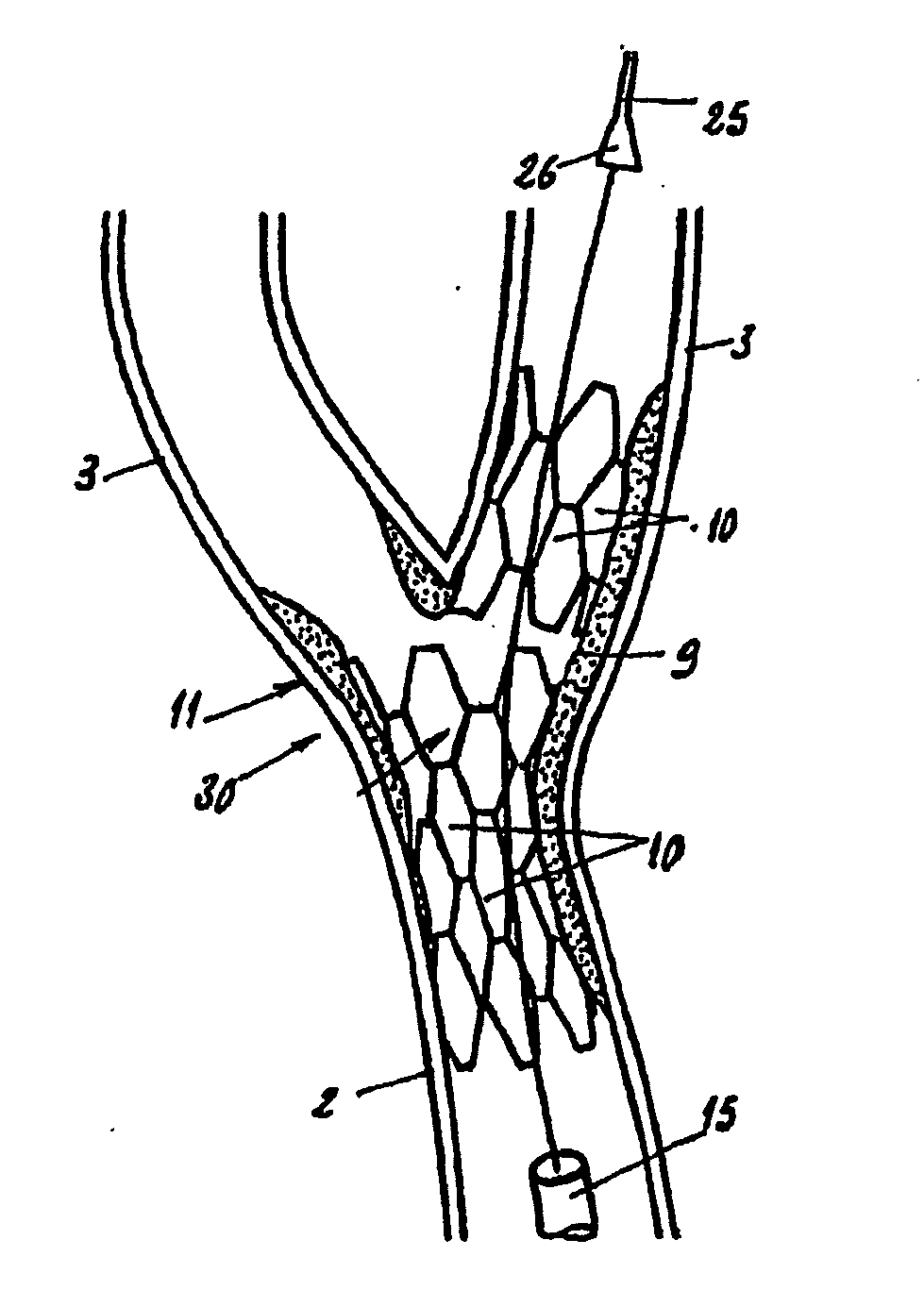
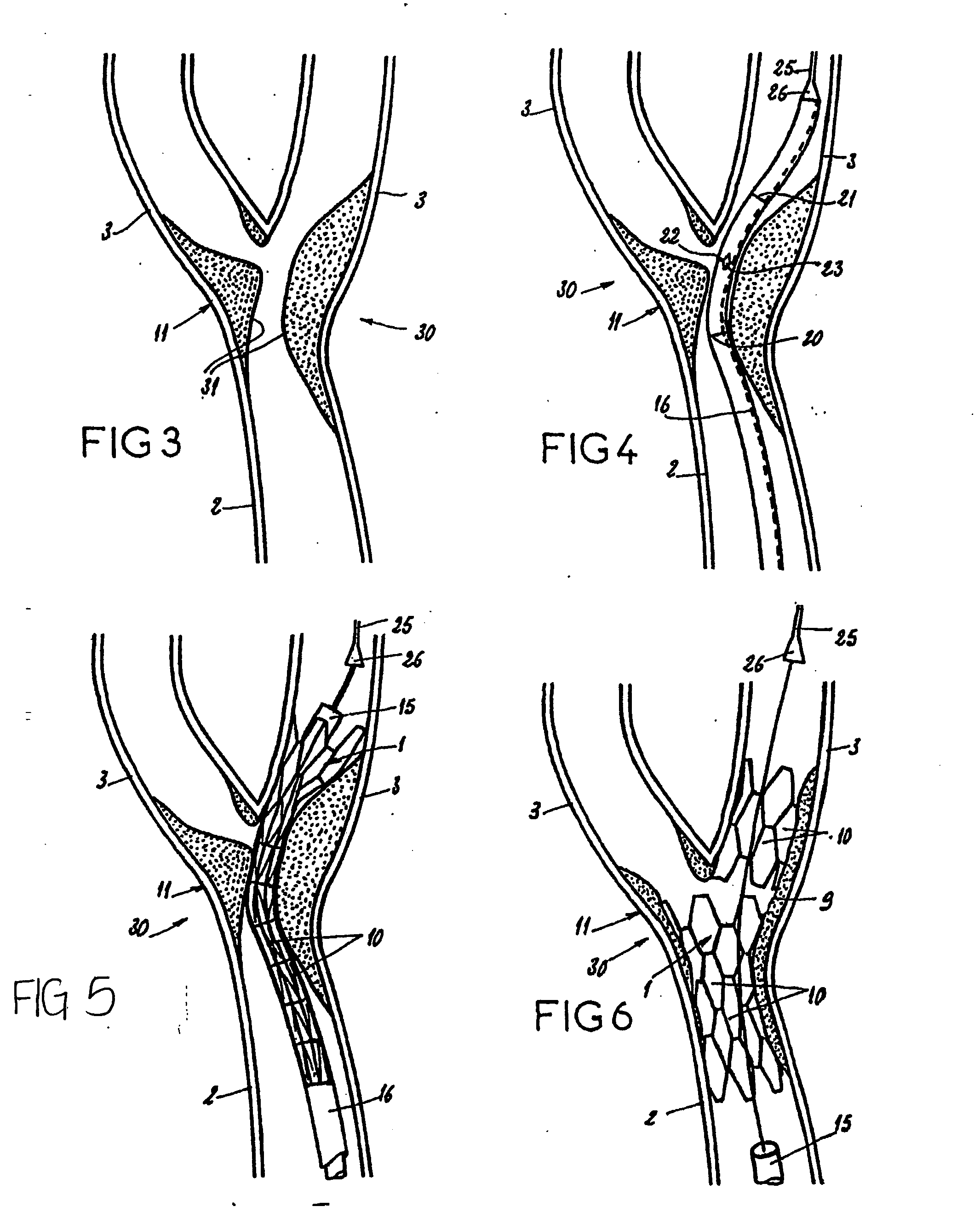
Endoprosthesis for vascular bifurcation
An apparatus for treating an area of bifurcation where a principal body conduit separates into at least two secondary conduits comprises a radially expandable first stent body. The first stent body has a substantially conical shape and a first end having a greater diameter than a second end when fully expanded. The first stent body is preferably shaped to be independent of any other stent bodies, and is free of any means for connecting to any other stent bodies when fully expanded.
Owner:SEGUIN JACQUES +1
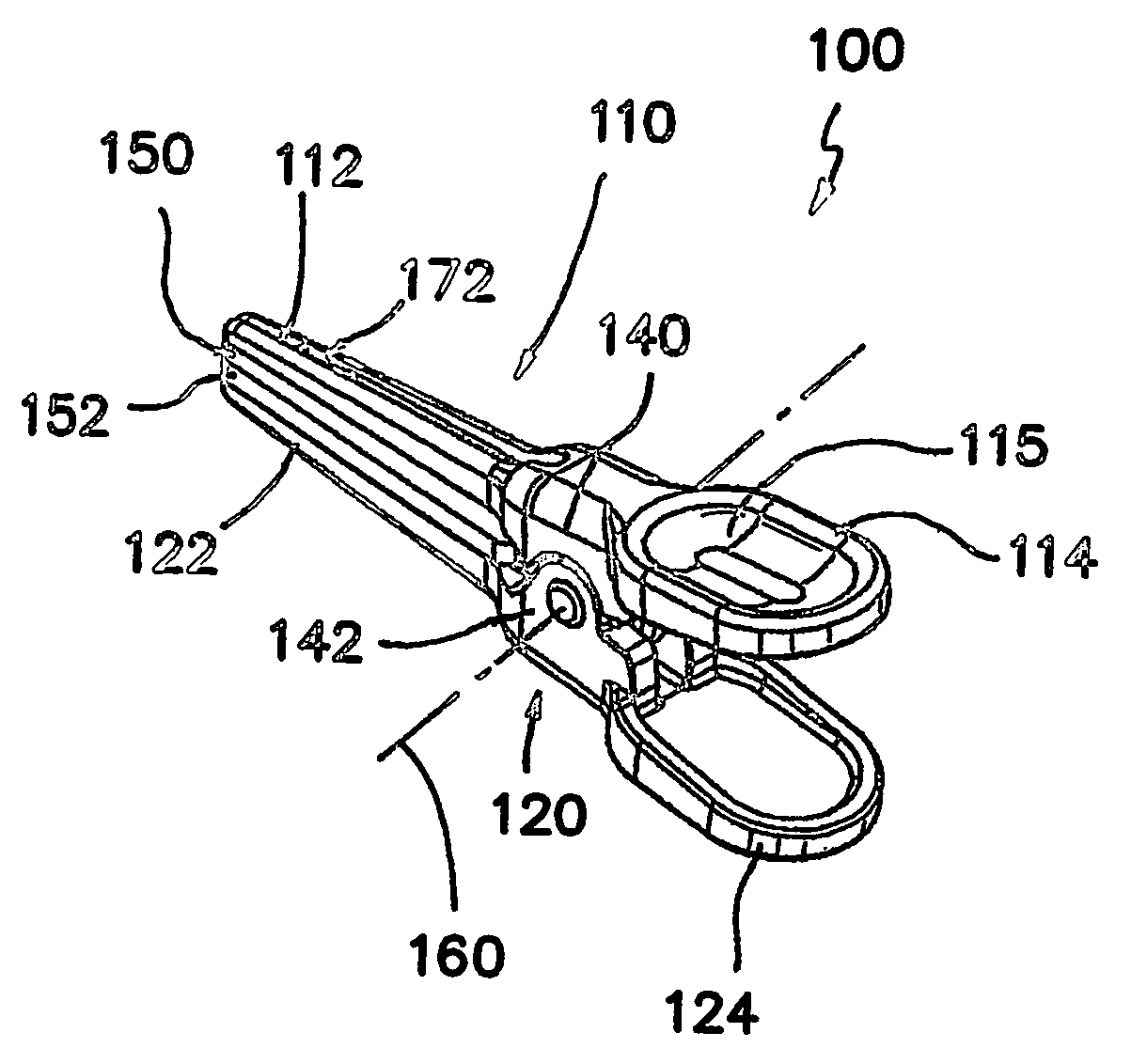
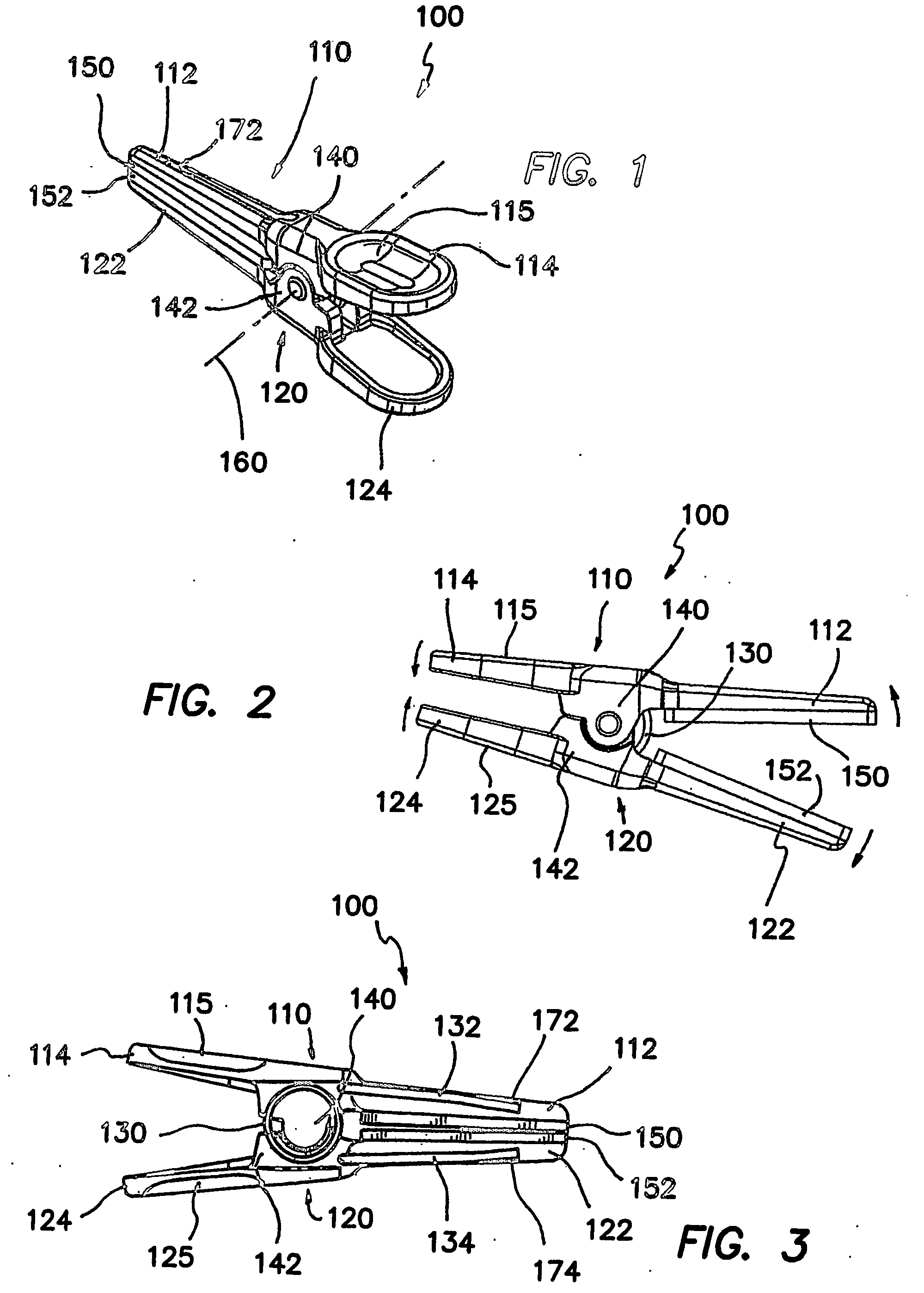
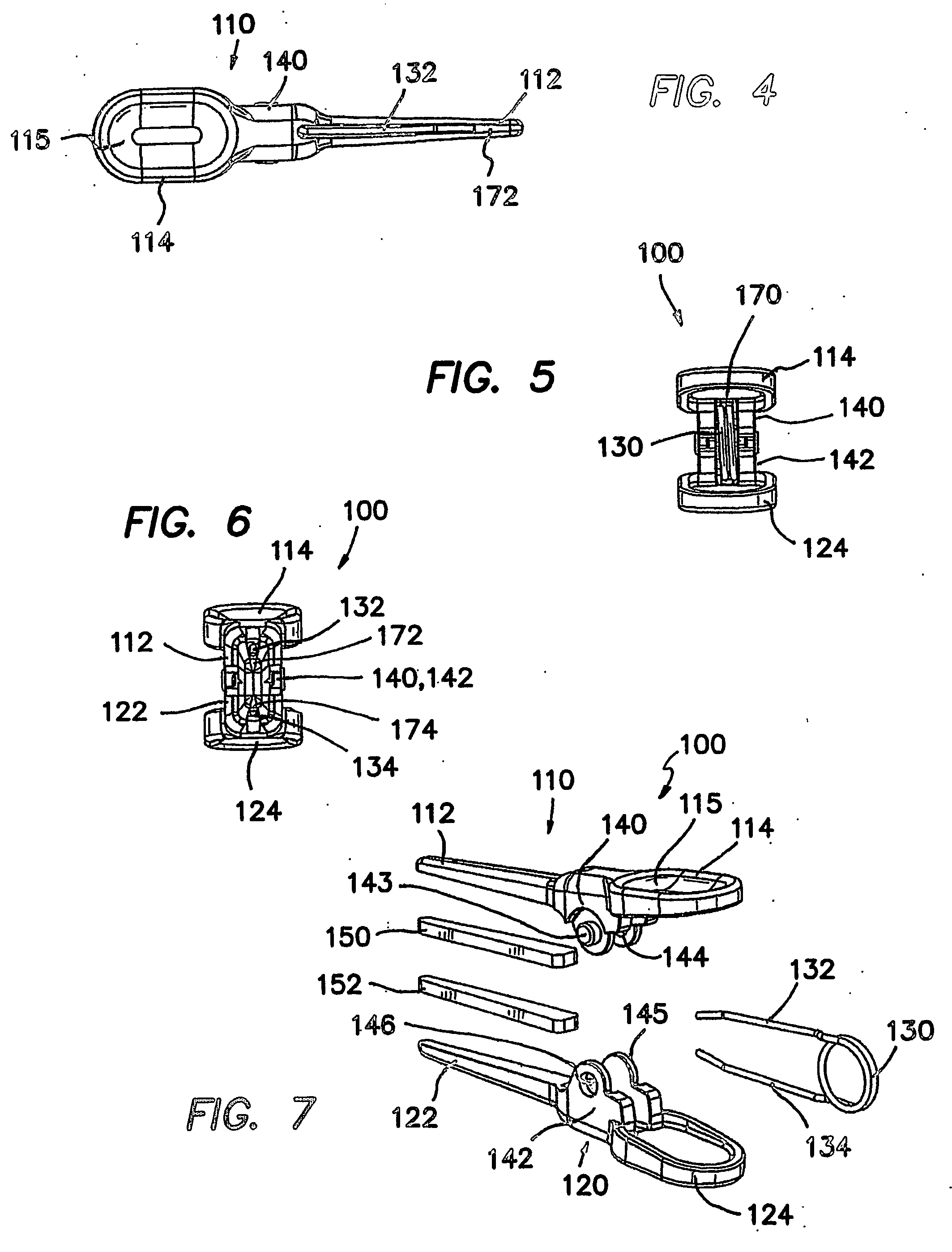
Spring clip and method for assembling same
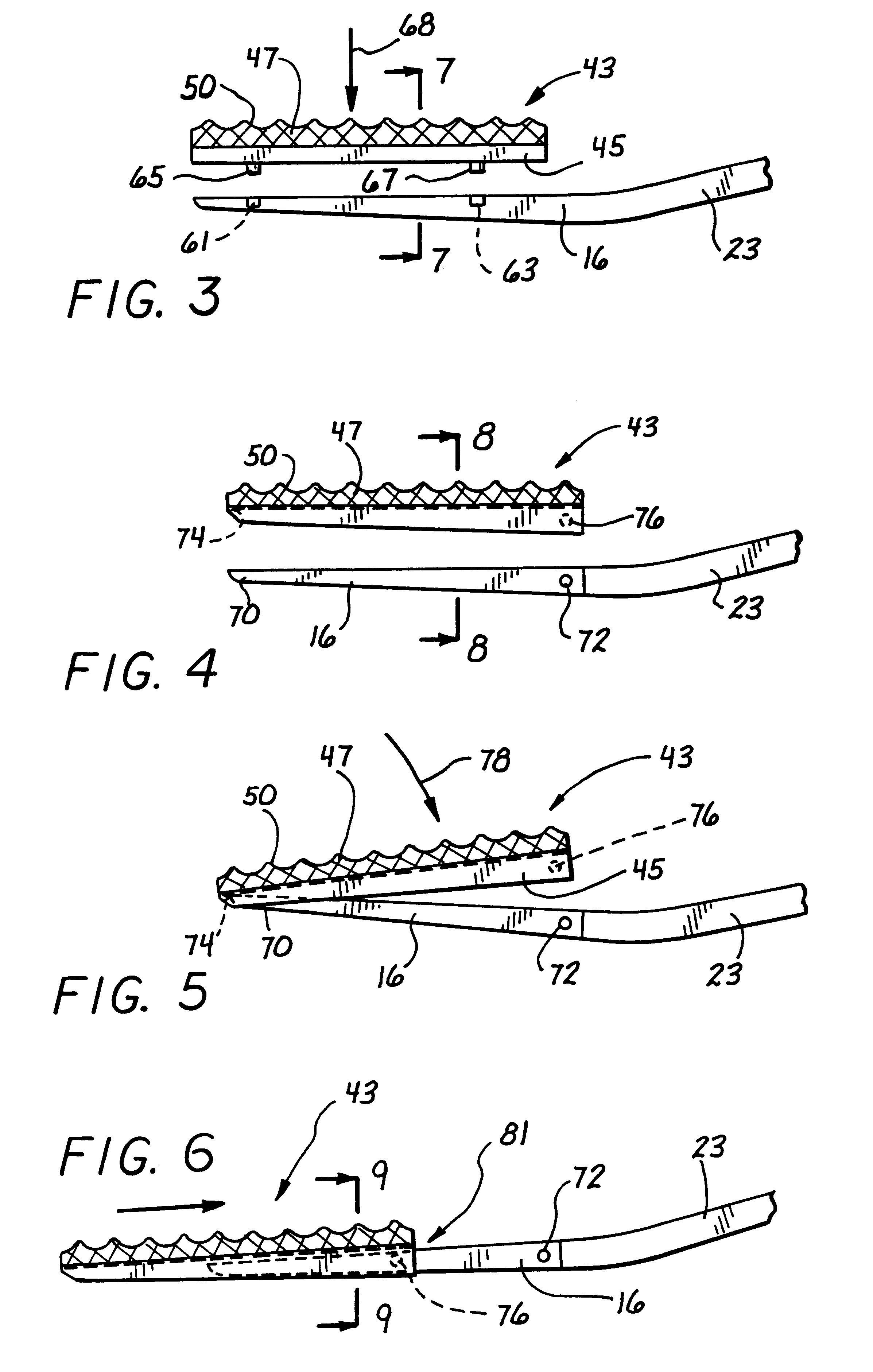
ActiveUS20060195125A1Easy to participateReduce traumaWound clampsEngineeringUltimate tensile strength
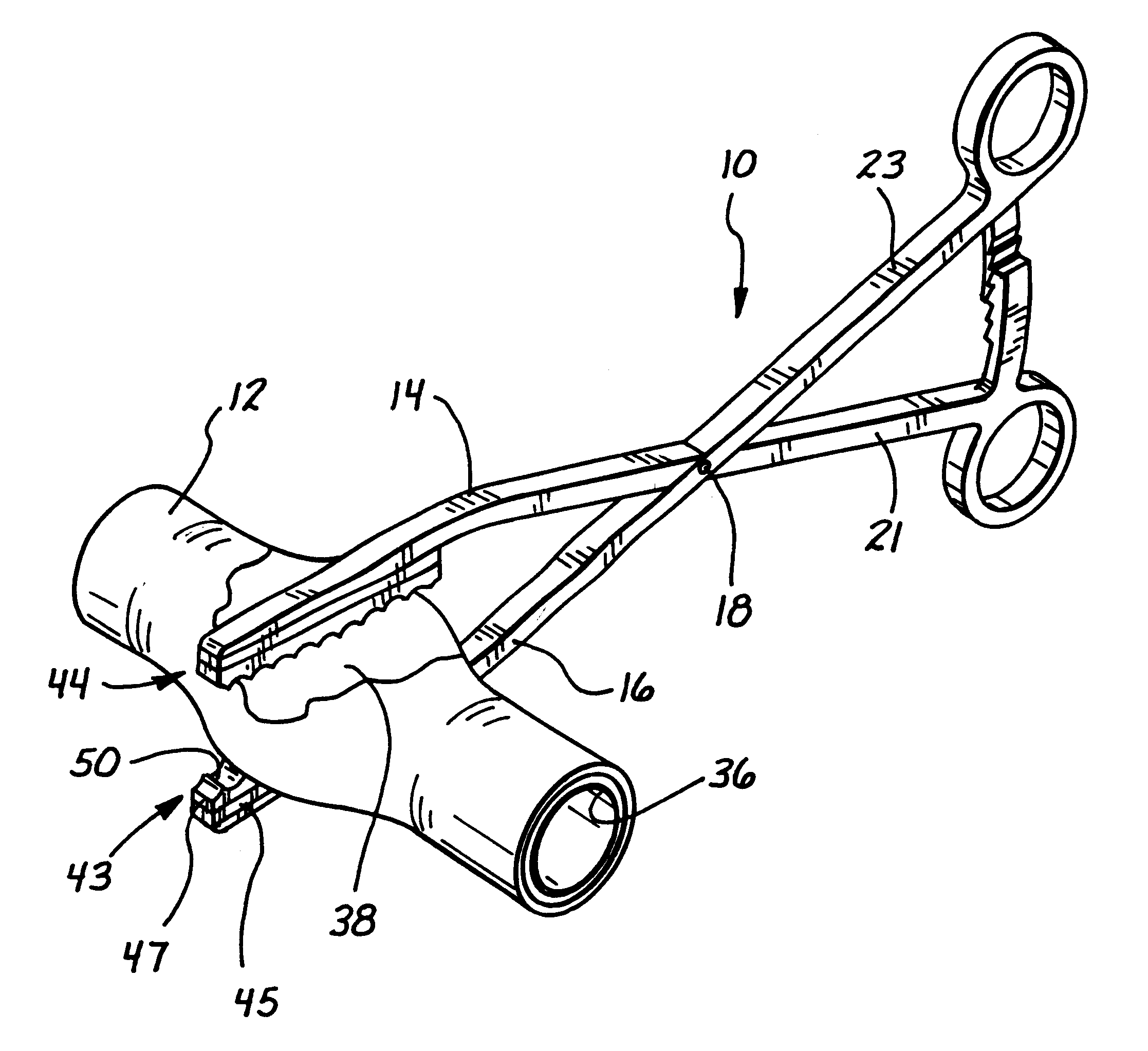
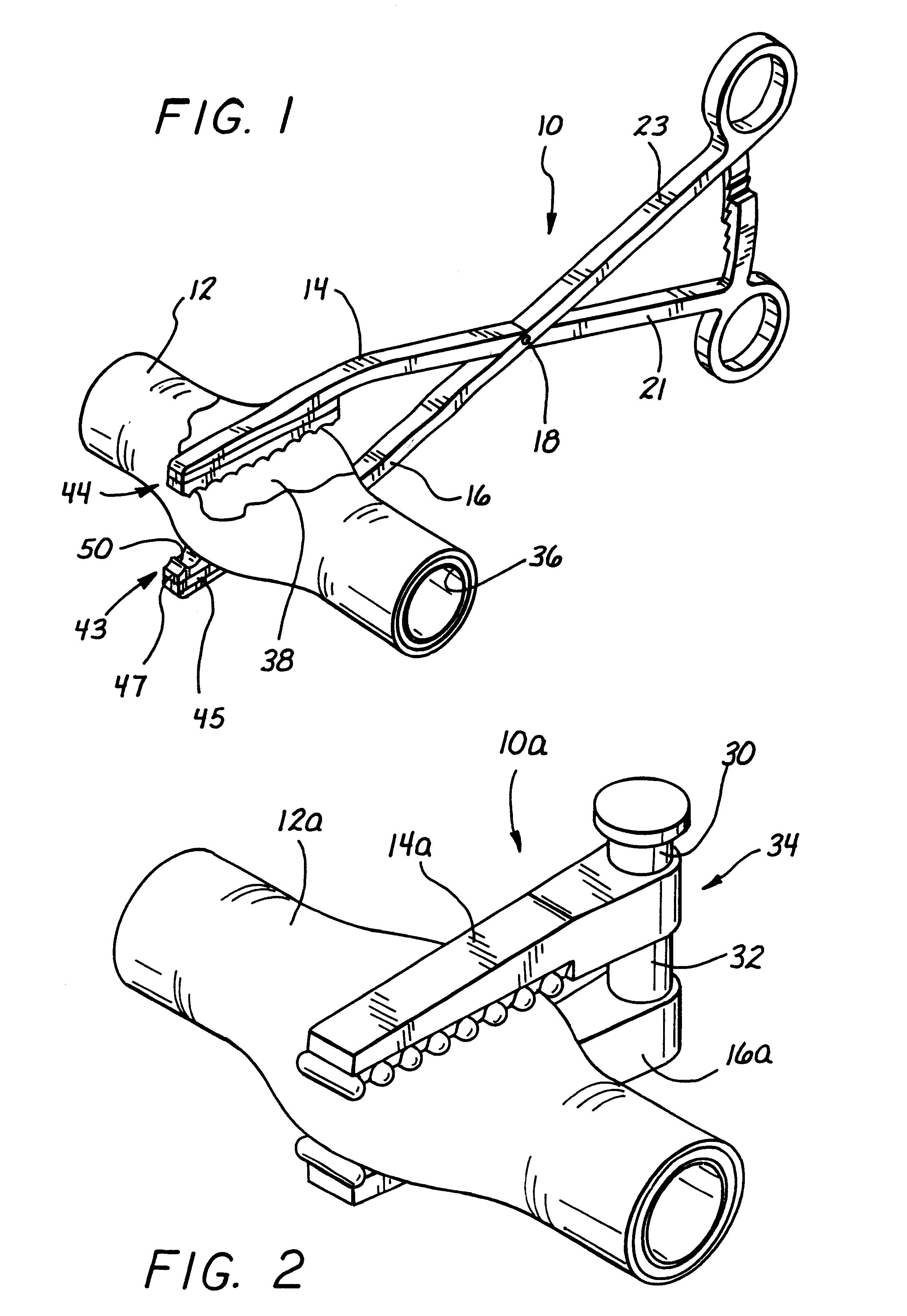
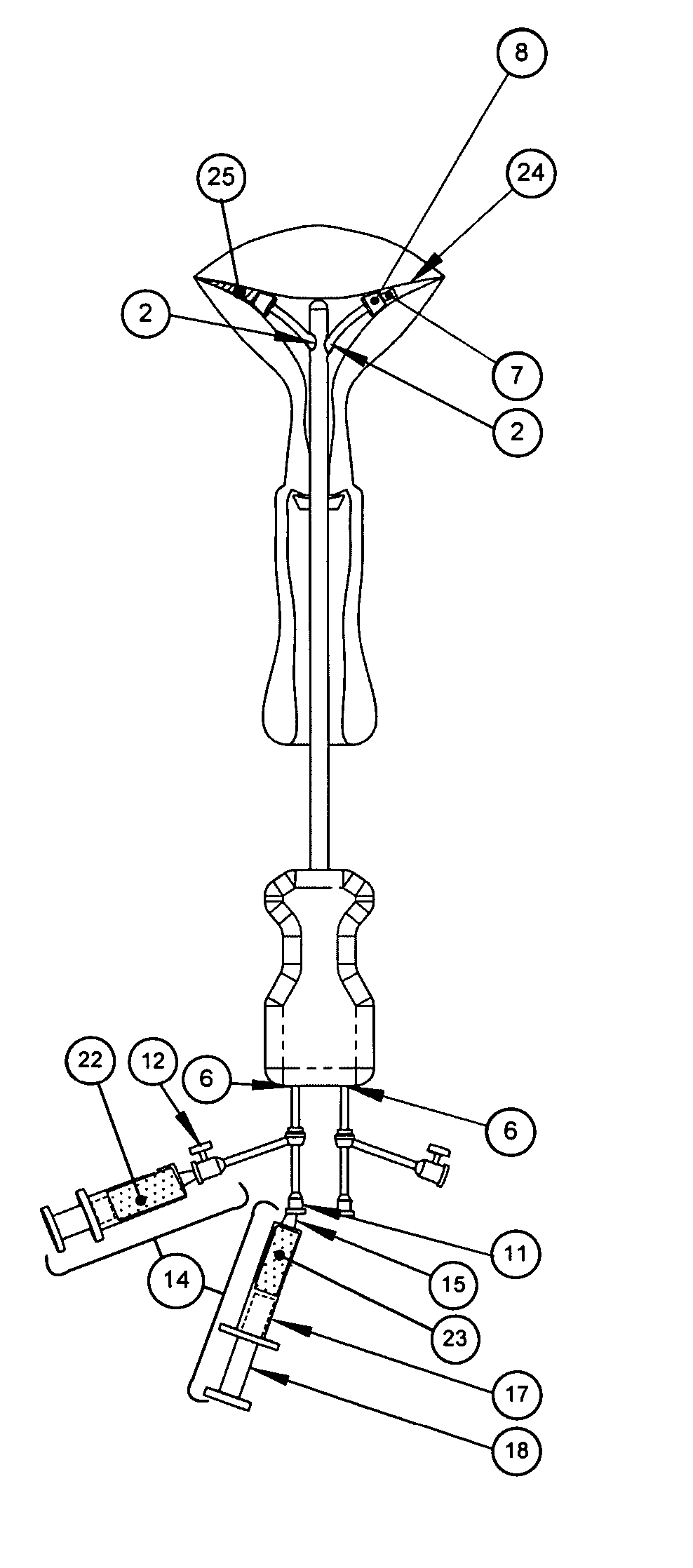
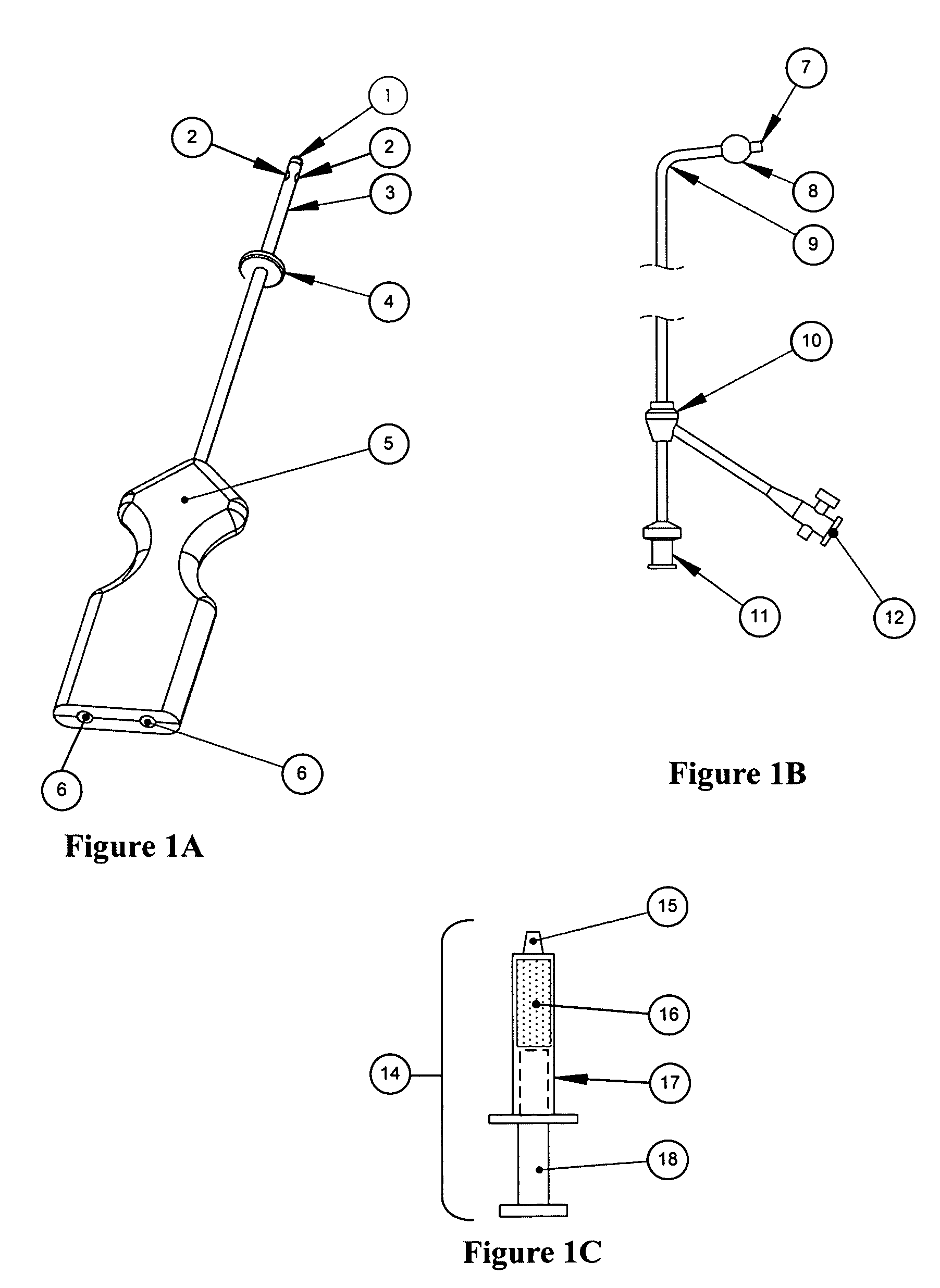
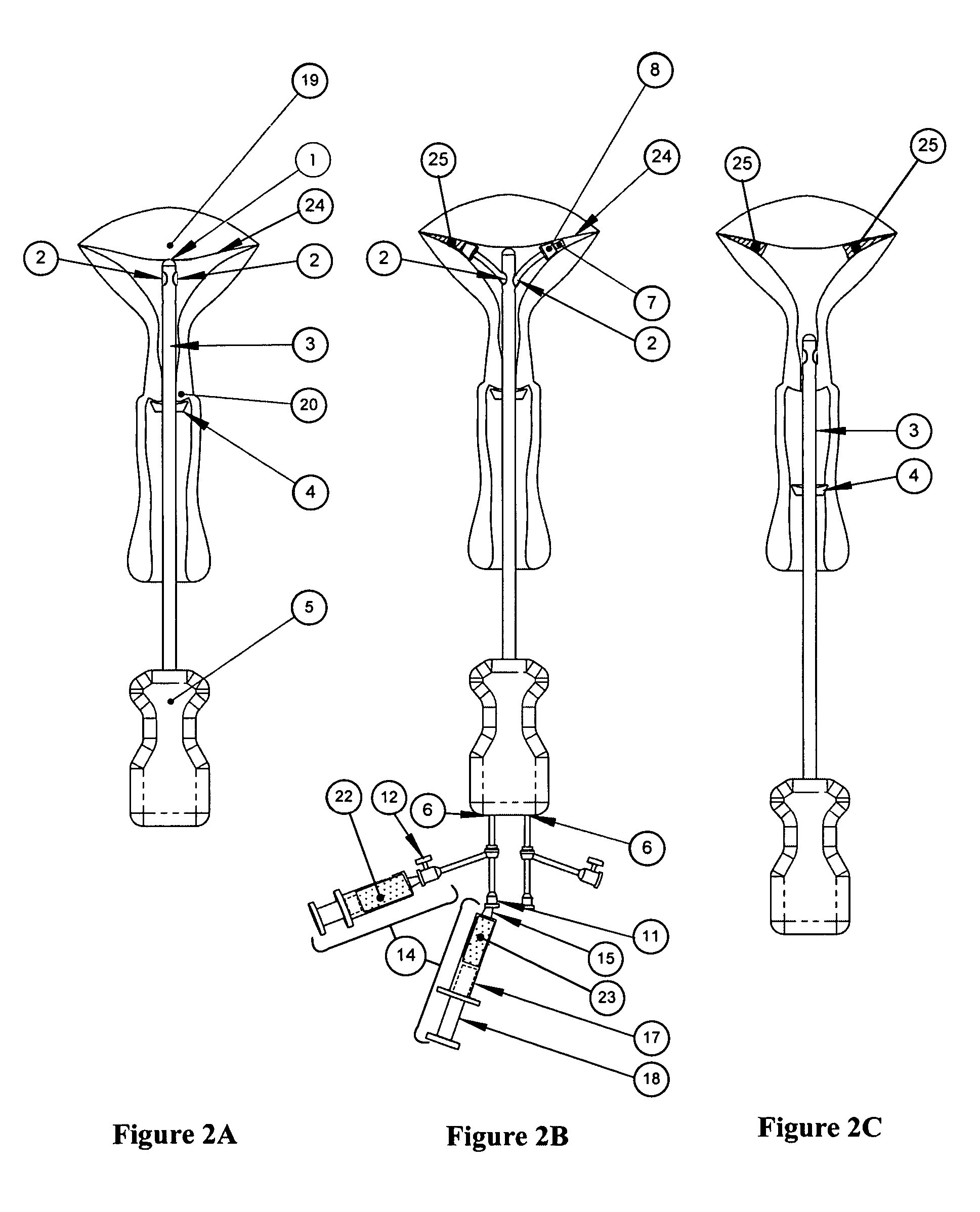
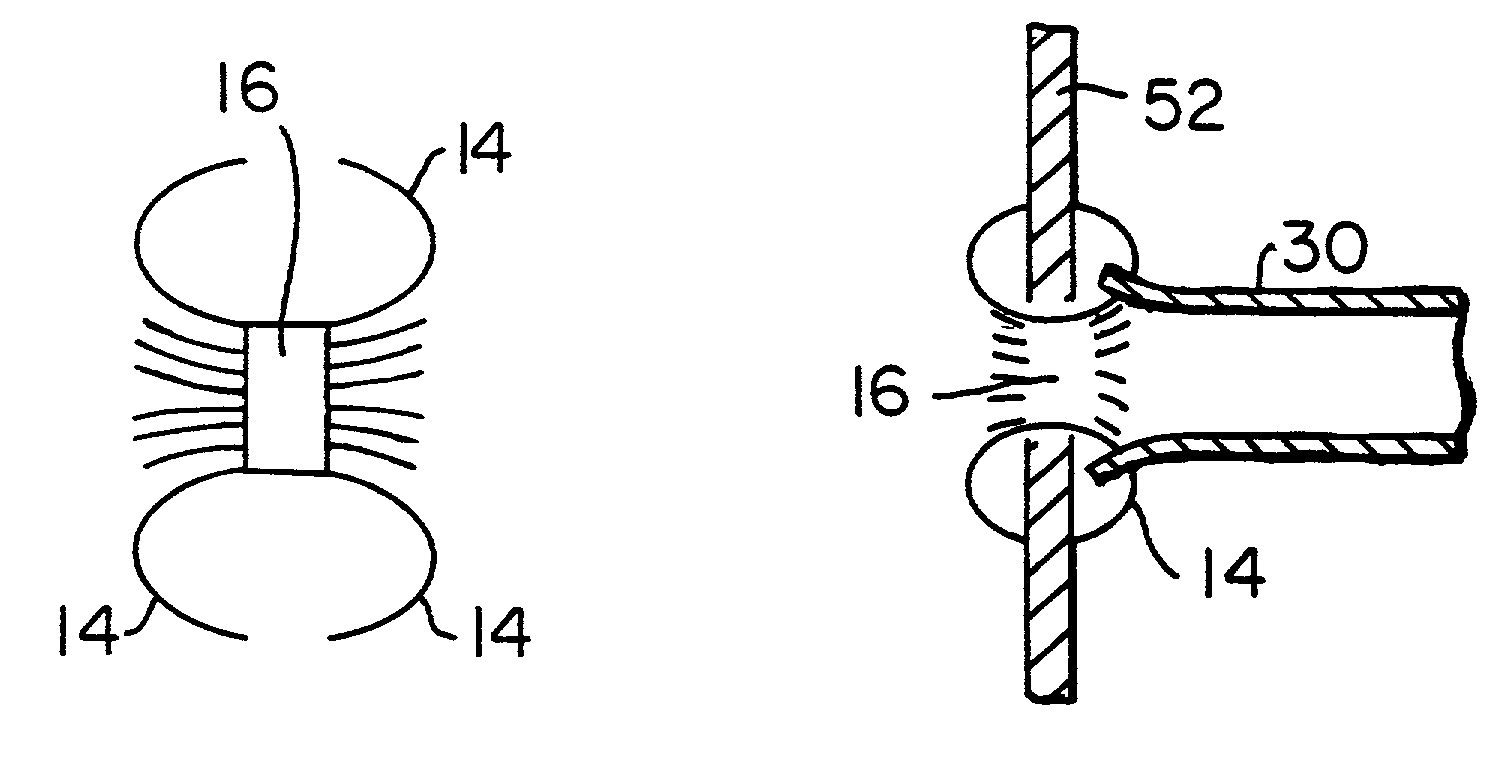
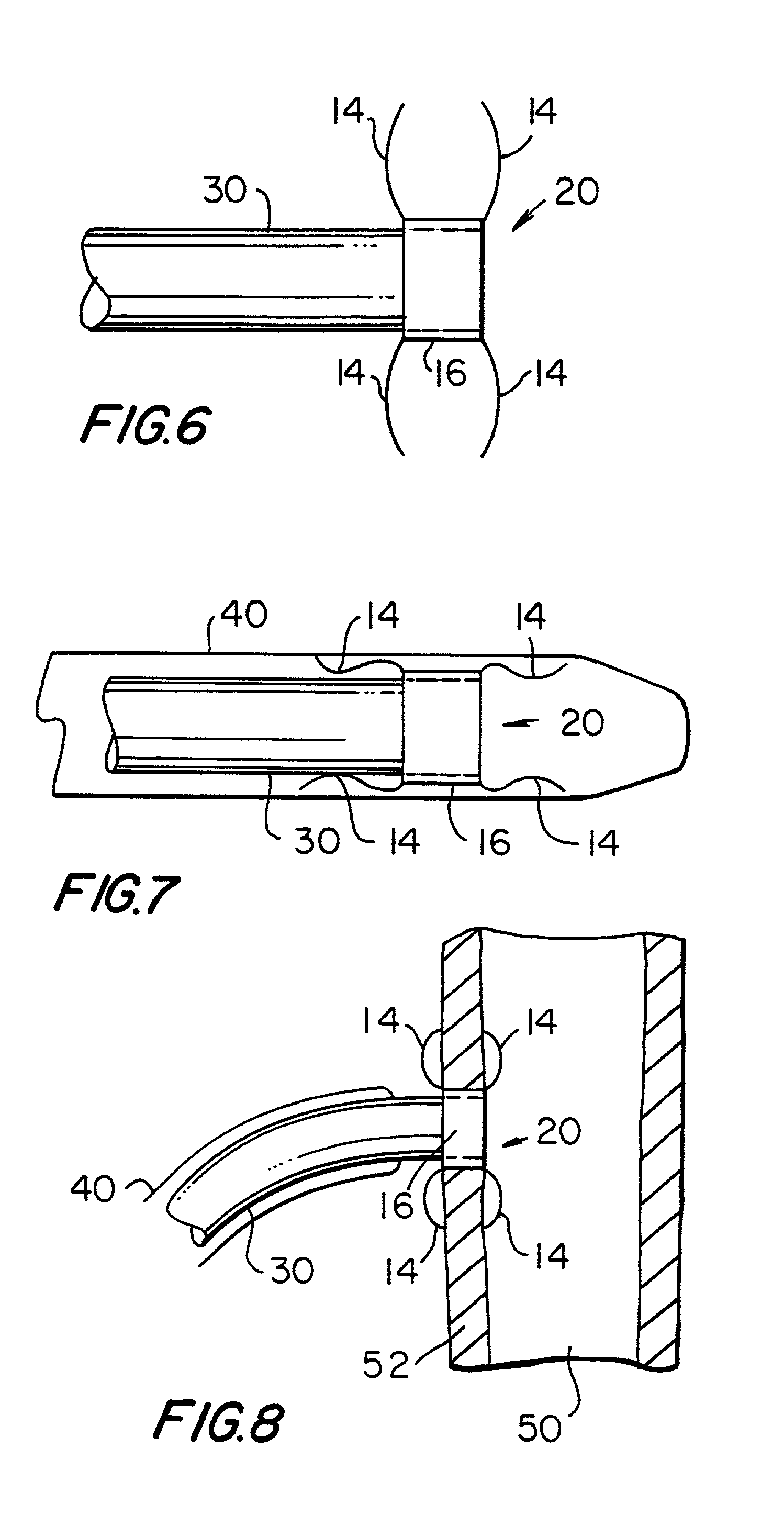
A surgical clip assembly is provided having two molded components and a tension spring. In one aspect of the invention, the spring clip includes a first molded portion having a first jaw and a first finger tab, a second molded portion coupled to the first molded portion and having a second jaw and a second finger tab, and a tension spring coupled to both the first and second molded portions. The first and second molded portions may be identical components and are moveable by operation of the first and second finger tabs between a generally closed position and a generally open position. The finger tabs may include cavities or grooves to facilitate engagement with a user or the jaws of a clip applier. The jaws may be shaped, curved or bent to provide access to specific areas of a procedure. Each of the jaws can be provided with an insert to further reduce trauma and increase traction with a target body conduit In a preferred process of assembling the clip, the tension spring is wound at least one turn forming a central coil and two extensions, and each of the molded portions is formed with a hinge area. Each of the hinge areas includes a hinge stud and a hinge cavity. The hinge areas operate to align and snap-fit with one another to form the clip assembly. With the assembly process of the invention, the extensions of the tension spring may be mounted into guide slots or ribs of either the jaws or finger tabs of the molded portions. A feature of the present invention is different tension springs having various strength and tension properties may be used in accordance with the needs and requirements of each surgical procedure without changing the construction of the molded portions.
Owner:APPL MEDICAL RESOURCES CORP
Coaxial cable connector with replaceable compression ring
ActiveUS7252546B1Small diameterElectrically conductive connectionsTwo pole connectionsCoaxial cableEngineering
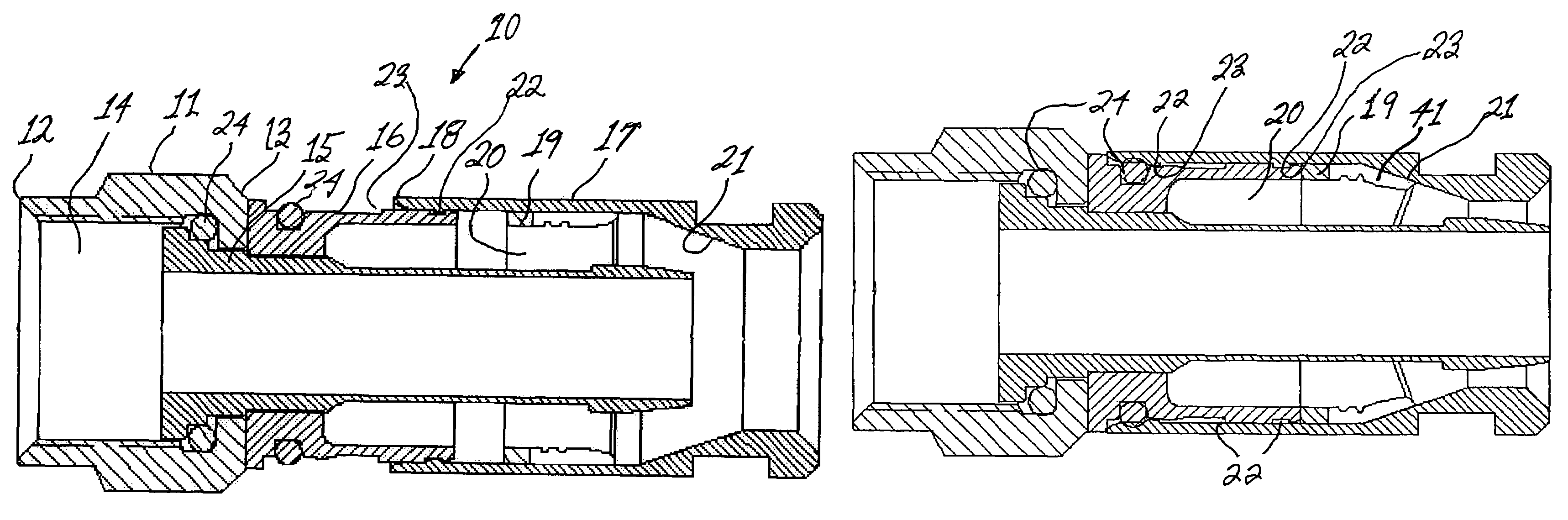
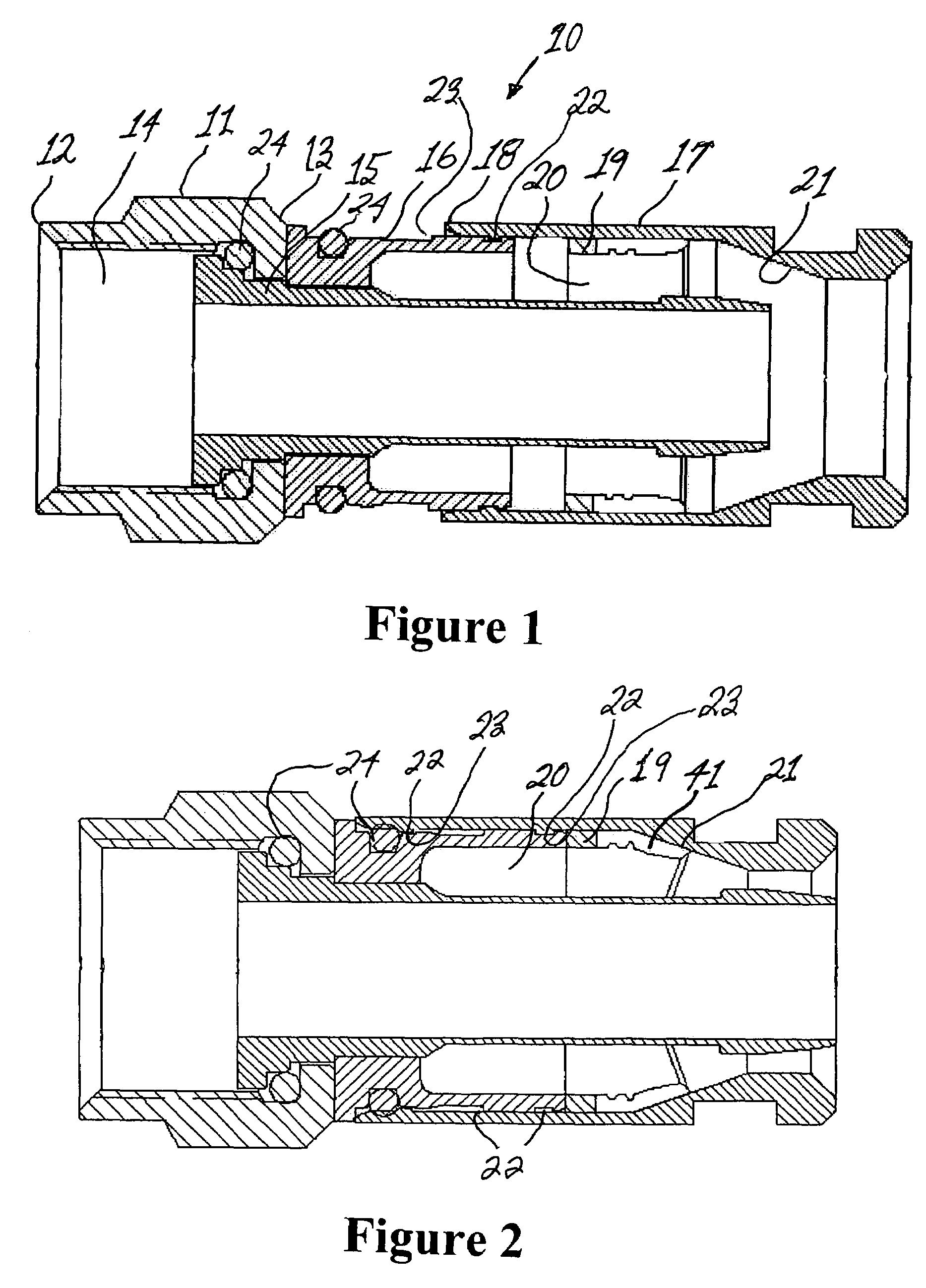
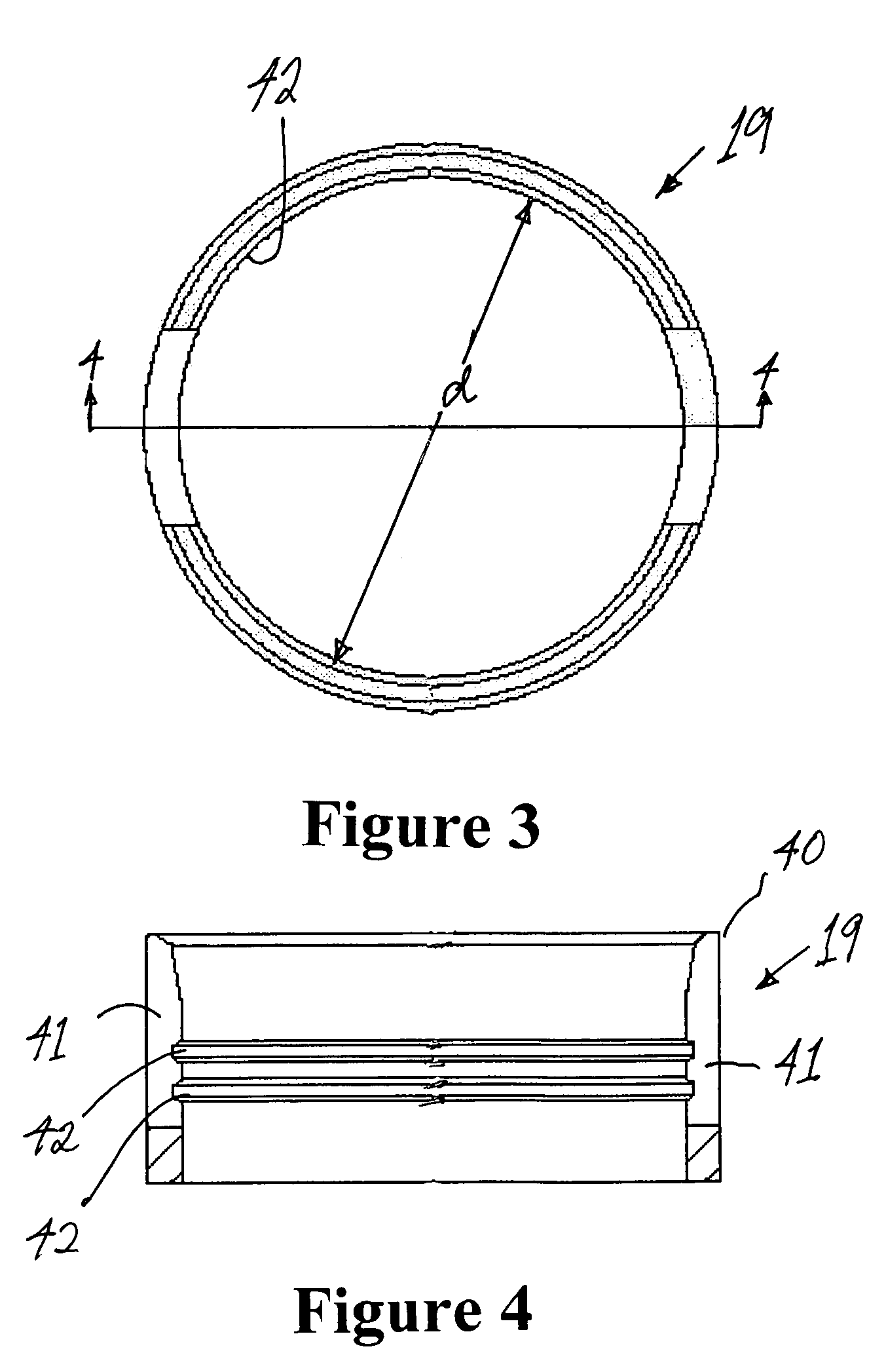
A male compression-type coaxial cable connector having an adapter nut attached to a leading end of a tubular connector body portion. The connector body portion has a first axial conduit with a barbed ferrule coaxially mounted therein. The connector further comprises a compression sleeve having a second axial conduit slidingly disposed over a trailing end of the tubular connector body portion. A deformable compression ring is removably disposed within the second axial conduit. In use, the prepared end of the coaxial cable is inserted through the compression sleeve and compression ring and advanced into the connector body conduit until it can be advanced no further. Subsequent advancement of the compression sleeve over the connector body portion, with the assistance of a compression tool, forces the deformable trailing end of the compression ring radially inward to compress the cable jacket and braid thereby providing secure attachment of the connector to the cable. The compression ring is removable and can be replaced with another compression ring having a different inner diameter to accommodate a variety of coaxial cables. The construction permits the compression sleeve to be easily removed for replacing the compression ring and easily reinstalled over the connector body after ring replacement.
Owner:HOLLAND ELECTRONICS
Bioabsorbable self-expanding endolumenal devices
InactiveUS20060025852A1Enhance tissue complianceReliable deploymentStentsOcculdersThermal transitionMedical device
The present invention is directed to bioabsorbable self-expanding medical devices for use inside or outside body conduits that self-expand at, or below, normal human body temperature without requisite for a polymeric thermal transition
Owner:WL GORE & ASSOC INC
Embolectomy capture sheath
InactiveUS20050187570A1Variable flexibilityVariable kink-resistanceGuide needlesCannulasPlastic materialsActuator
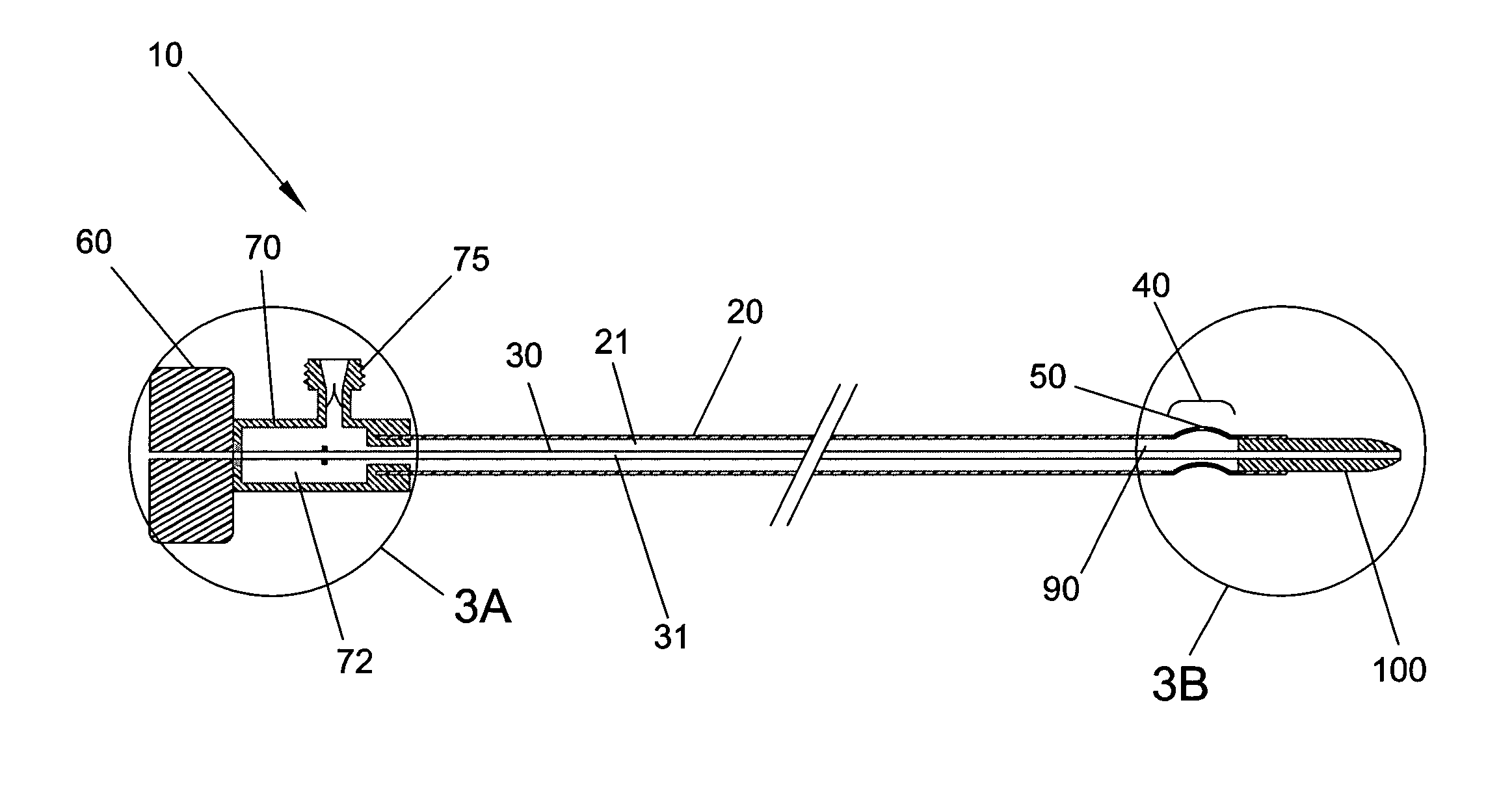
An access device adapted for use in a body conduit is provided comprising an outer tube having a proximal end and a distal end, an inner tube disposed coaxially with the outer tube having a proximal end and a distal end, and an expandable portion having a first end coupled to the distal end of the outer tube and a second end coupled to the distal end of the inner tube. The outer tube and the inner tube are movable relative to each other to transform the expandable portion between a low-profile state and a high-profile state, and at least one of the outer and inner tubes comprises a wire-reinforced tube or is formed from a plurality of individual, discrete, generally ring-shaped elements arranged in series and fused or bonded together to form a continuous tubular structure. The access device may further comprise an actuator coupled to one of the outer and inner tubes and being movable relative to the other of the outer and inner tubes to transform the expandable portion between the low- and high-profile states. The expandable portion may be formed with a braid material and has the shape of a cone. The ring-shaped elements may be formed of a thermoplastic or a thermoset material, and they may include at least one of plastic rings, metallic rings, un-reinforced plastic rings and metal reinforced plastic rings assembled along the length of at least one of the tubes to provide variable flexibility and kink-resistance. The wire-reinforced tube is formed by coating a wire with a plastic material, wrapping the coated wire around a mandrel forming a plurality of windings, and heating the wound coated wire until the plastic material melts and bonds the windings forming the wire-reinforced tube.
Owner:APPL MEDICAL RESOURCES CORP
Catheter with conduit traversing tip
InactiveUS20050149096A1Improve scalabilityHigh pressureSurgical needlesDilatorsDistal portionEndoscope
A catheter facilitating traversal of restrictions in body conduits includes a shaft having a distal tip with a shape that is non-conical, radially twisted, and rectangular in radial cross section. An outer surface of the tip includes at least one side section extending from a blunt point radially outwardly with progressive positions proximally along an axis of the tip. The side section includes a proximal portion in proximity to the shaft, and a distal portion twisted radially with respect to the proximal portion. The catheter can be adapted for placement over a guidewire and can be made transparent thereby facilitating visualization through an endoscope in the catheter.
Owner:APPL MEDICAL RESOURCES CORP
Methods and devices for conduit occlusion
The present invention comprises systems, methods and devices for the delivery of compositions for occluding or of means for opening conduits. The implantable occlusive material may be delivered pre-formed or in situ cured and, may be a resorbable material that supports tissue ingrowth that eventually replaces the material leaving little or no original material in place. The delivery system is positioned to allow for placement of the occlusive material into the body conduit. Use of delivery systems, methods and devices for re-opening an occluded body conduit are also included.
Owner:FEMASYS INC
Dual reservoir implantable access port
InactiveUS20090118683A1Small sizeReducing geometric footprintMedical devicesBlood componentGuide tube
An implantable access port for use in transferring fluid transdermally between an external fluid storage or dispensing device and a site within a patient is disclosed. The access port includes a body, at least two reservoirs defined within the access port body, and at least one septum secured to the body and enclosing the reservoirs within the body. The access port also includes reservoir outlets defined within the reservoirs. The access port also has body conduits defined within the body and in fluid communication with the reservoir outlets and external openings defined in the exterior of the body. An implantable access port and system for use in apheresis is also provided that includes an implantable access port, at least one needle, and a catheter that is fluidly connected to the access port.
Owner:ANGIODYNAMICS INC
Removable stent-graft
A removable device such as a stent-graft, intended for applications where it may be desirable to remove the device at some time following implantation. The stent-graft of the present invention includes a helically-wound stent component provided with a covering of graft material. It is removable by gripping an end of the helically-wound stent component with a retrieval device and applying tension to the stent component in the direction in which it is intended to be withdrawn from the site of implantation. The use of such a retrieval device allows the stent-graft to be removed remotely, such as via a catheter inserted into the body at a different location from the implantation site. The design of the stent-graft is such that the stent component is extended axially while the adjacent portion of the graft separates between windings of the stent component. The axial extension of the stent component, with portions of the graft still joined to the stent component, allows the device to be “unraveled” (or “unwound”) and removed through a catheter of diameter adequately small to be inserted into the body cavity that contained the stent-graft. It is removed atraumatically, without incurring significant trauma to the body conduit in which it had been deployed.
Owner:WL GORE & ASSOC INC
Indwelling heat exchange heat pipe catheter and method of using same
A catheter is adapted to exchange heat with a body fluid, such as blood, flowing in a body conduit, such as a blood vessel. The catheter includes a shaft with a heat exchange region disposed at its distal end. This region may include at least one balloon which is adapted to receive a remotely cooled heat exchange fluid preferably flowing in a direction counter to that of the body fluid. Embodiments including multiple balloons enhance the surface area of contact, and the mixing of both the heat exchange and the body fluid. The catheter can be positioned to produce hypothermia in a selective area of the body without cooling the entire body system. It is of particular advantage in brain surgeries where stroke, trauma or cryogenic tumors can best be addressed under hypothermic conditions. Heat pipe technology can be used to form a heat pipe heat exchange catheter. The heat pipe heat exchange catheter includes metallic bellows which allow for flexibility. The temperature control source can be portable to enable the heat pipe heat exchange catheter to be used in the ambulatory environment.
Owner:ZOLL CIRCULATION
Indwelling heat exchange catheter and method of using same
A catheter is adapted to exchange heat with a body fluid, such as blood, flowing in a body conduit, such as a blood vessel. The catheter includes a shaft with a heat exchange region disposed at its distal end. This region may include hollow fibers which are adapted to receive a remotely cooled heat exchange fluid preferably flowing in a direction counter to that of the body fluid. The hollow fibers enhance the surface area of contact, as well as the mixing of both the heat exchange fluid and the body fluid. The catheter can be positioned to produce hypothermia in a selective area of the body or alternatively positioned to systemically cool the entire body system.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
Material removal catheter and method
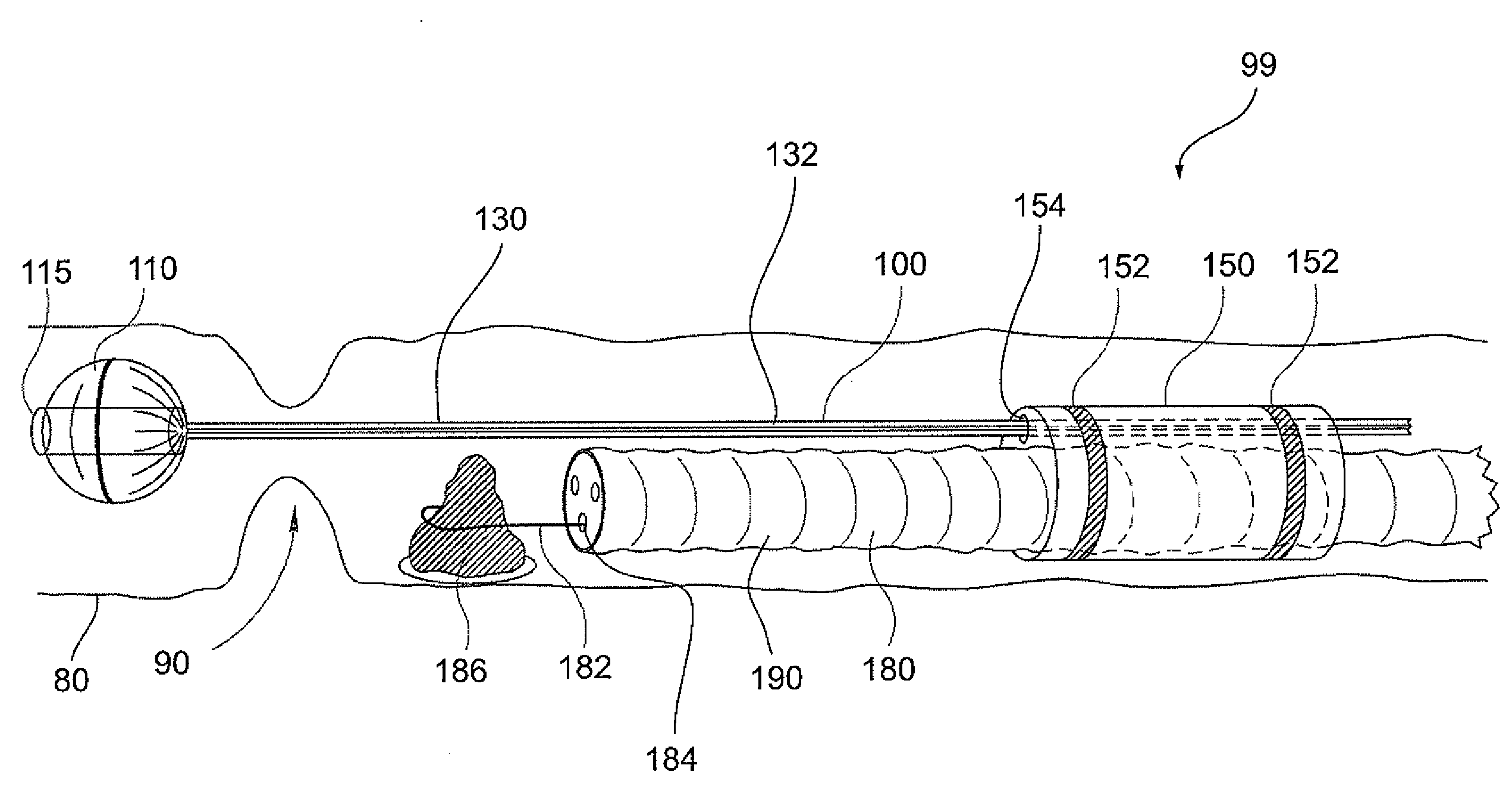
InactiveUS7449010B1Efficient use ofEasy to change shapeSurgeryMedical devicesMaterial removalGuide tube
A catheter device that is useable to extract material from a body conduit, such as a blood vessel, comprises a flexible catheter advanceable into the body conduit, an opening in the wall of the catheter that is in fluid communication with a material collection chamber, and a controllably arcuate segment along the catheter shaft, near the distal tip of the catheter and including the opening. Further said catheter may include a sliding member, located within a lumen of the catheter, that is used to move the material entering the catheter through the arcuate segment opening, into the material collection chamber and away from said opening. The catheter may include a single mechanism utilized to both generate a vacuum to cause material to enter the catheter at the arcuate segment opening and also cause the sliding member to travel, inside the catheter, moving material away from the opening and into the material collection chamber. Methods of utilizing such a catheter device to remove material from a body conduit are also disclosed.
Owner:HAYASE MOTOYA +1
Vascular exclusion catheter
A fluid controlled device is adapted for disposition in a body conduit where it controls the flow of body fluids within the conduit. A sleeve is provided with a wall of separation having a first surface which defines a flow passage facilitating the flow of body fluids, and a second surface which defines an exclusion chamber sealed from the flow passage. Various dilators have properties for moving the seal between a low-profile state facilitating insertion of the device, any high-profile state defining the flow passage and exclusion chamber. The dilator may be skeletal, inflatable, and / or porous. An associated method includes the step of dilating a dilation assembly to move a wall from a low profile, insertible state, to a high-profile wherein the wall defines a flow passage and an exclusion cavity.
Owner:NGUYEN ERIC +5
Medical graft connector or plug structures, and methods of making and installing same
A medical graft connector or plug is made, for example, by cutting end portions of a tube of highly elastic material axially at numerous locations spaced circumferentially around the tube to produce a plurality of fingers which extend axially from each end of an uncut medial portion of the tube. The fingers are deflected radially outwardly from the medial portion and set in that condition. For a graft connector, the medial portion is coaxially connected to an end portion of a tubular graft. The connector is then installed through an aperture in the side wall of a patient's tubular body conduit, for example, by using a delivery tube in which the fingers are elastically deflected back to approximately their initial positions. When the delivery conduit is withdrawn from the connector, the fingers spring out to engage the inner and outer surfaces of the body conduit wall. For a plug, the medial portion is occluded and then the structure is installed through the aperture to be plugged in a manner similar to installation of the connector.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATG
Method for treating airways in the lung
InactiveUS20070106348A1Reduce the amount requiredIncrease inner diameterDiagnosticsMedical devicesBronchospasmSmooth muscle spasm
A device and method for treating bodily conduits involves the application of energy to the smooth muscle tissue of the conduit walls to reduce the bulk of smooth muscle tissue and mucus glands. The irradiation treatment of the smooth muscle tissue causes a reduction in the amount of smooth muscle tissue over time which increases the inner diameter of the body conduit for improved fluid flow and prevents smooth muscle spasms. The treatment is particularly useful in the lungs for treatment of asthma to prevent bronchospasms, increase the airway diameter for improved air exchange, and reduce mucus secretions in the lungs.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Directional cutting balloon
A directional cutting balloon for incising an eccentric lesion in a body conduit includes an inflatable balloon having a distal end and a proximal end. The distal balloon end is attached to a distal tube and the proximal balloon end is attached to a proximal tube. The distal tube is formed with a guidewire lumen and substantially centered along a guidewire axis. The balloon, which is typically formed with a cylindrical working section that defines a balloon axis, is offset from the guidewire axis. Specifically, when the balloon is inflated, the balloon axis is aligned parallel to and offset from the guidewire axis. One or more elongated incising elements are mounted longitudinally on the balloon. During a balloon inflation, the balloon expands eccentrically relative to the guidewire axis to thereby advance the incising element in a pre-selected direction and into an eccentric lesion.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Thin-wall polytetrafluoroethylene tube
A thin-wall PTFE (polytetrafluoroethylene) tube in the form of a tube of porous expanded PTFE film wherein the porous PTFE film has a microstructure containing a multiplicity of fibrils. The thin-wall tube is used in a non-porous embodiment as the balloon portion of a balloon catheter. The thin-wall tube is not elastomeric; however, because of the thinness, strength and flexibility of the tube, it may be inserted into a body conduit in a collapsed state and then deployed from a catheter and inflated up to the maximum diameter of the thin-wall tube. The porous PTFE film is provided with a continuous layer of adhesive to provide the non-porous tube; the adhesive is preferably a thermoplastic and more preferably a thermoplastic fluoropolymer such as fluorinated ethylene propylene.
Owner:GORE ENTERPRISE HLDG INC
Electrosurgical catheter apparatus and method
InactiveUS6231572B1High trafficFacilitates operative dispositionCannulasDilatorsElectrical conductorCatheter device
A catheter adapted to increase the patency of a body conduit includes an elongate tube having an axis extending between a proximal end and a distal end, and a balloon disposed at the distal end of the tube and having properties for being expanded to a high-profile state and for being contracted to a low-profile state. A sleeve disposed over the balloon has a pair of ends disposed on opposing sides of a central section, the ends having a floating relationship relative to the tube with the central section disposed circumferentially of the balloon. An electrode disposed outwardly of the sleeve has properties for being electrosurgically energized to incise materials defining the body conduit when the balloon is in the high-profile state. The electrode can be formed of a plurality of elements stranded to increase the surface area of the electrode. The catheter can be inserted relative to a guide member having a conductor which carries the electrosurgical energy from the proximal end of the tube to the electrode at the distal end of the tube. An associated method includes the step of introducing electrosurgical energy into the conductor of the guide member to energize the electrode of the catheter.
Owner:APPL MEDICAL RESOURCES CORP
Drainage catheter
A drainage catheter is adapted to drain fluid from the body cavity through a body conduit and includes an elongate tube having a distal end and a retention member disposed at the distal end and adapted for movement between the low-profile state facilitating insertion of the catheter and a high-profile state facilitating the tension of the catheter in its operative position. A woven mesh forms at least a portion of one of the tube and the retention member, and can be made permeable or impermeable in various regions of the catheter. The woven mesh can be formed of filaments heat-settable so that the catheter automatically moves to the high-profile state. Insertion of the catheter can be facilitated using an obturator and a guidewire in an associated method, an obturator facilitating insertion of the catheter can be removed to permit the catheter to automatically return to a normal, high-profile state.
Owner:APPL MEDICAL RESOURCES CORP
System and method for navigating a tool within a body conduit
InactiveUS20100105983A1Simple and rapid navigationFast displacementSurgeryEndoscopesBalloon catheterSurgical department
Apparatus and method for navigating surgical tools within a body cavity. Embodiments of the invention are particularly useful for displacing a surgical tool within a body conduit such as an intestine. Embodiments comprise a balloon catheter having a shaft, and a surgical tool operable to slide along that shaft. In some embodiments the surgical tool comprises a second balloon catheter.
Owner:COGENTIX MEDICAL
Pressure attenuation device
InactiveUS20070156167A1Reduce peak pressureLower systolic blood pressureStentsDiagnosticsUltrasound attenuationBlood pressure
An implantable blood pressure regulator is provided. The blood pressure regulator includes at least one connection zone and an attenuation zone. The connection zone is suitable for connection to a body conduit, such as a blood vessel. The attenuation zone is movable from a first state to a second state in response to a physiological pressure spikes. The movement from the first state to the second state lowers a level of pressure or dampens a pressure spike in the body conduit.
Owner:ATTENUEX TECH
Cyanoacrylate-capped heterochain polymers and tissue adhesives and sealants therefrom
The present invention is directed toward cyanoacrylate-based tissue adhesive or sealant compositions comprising cyanoacrylate-capped heterochain polymers, such as those comprising one or more oxyalkylene, alkylene carbonate, and ester-units derived from cyclic lactones. Such compositions can be radiochemically sterilized and used in repairing internal organs or tissue blocking body conduits.
Owner:POLY MED
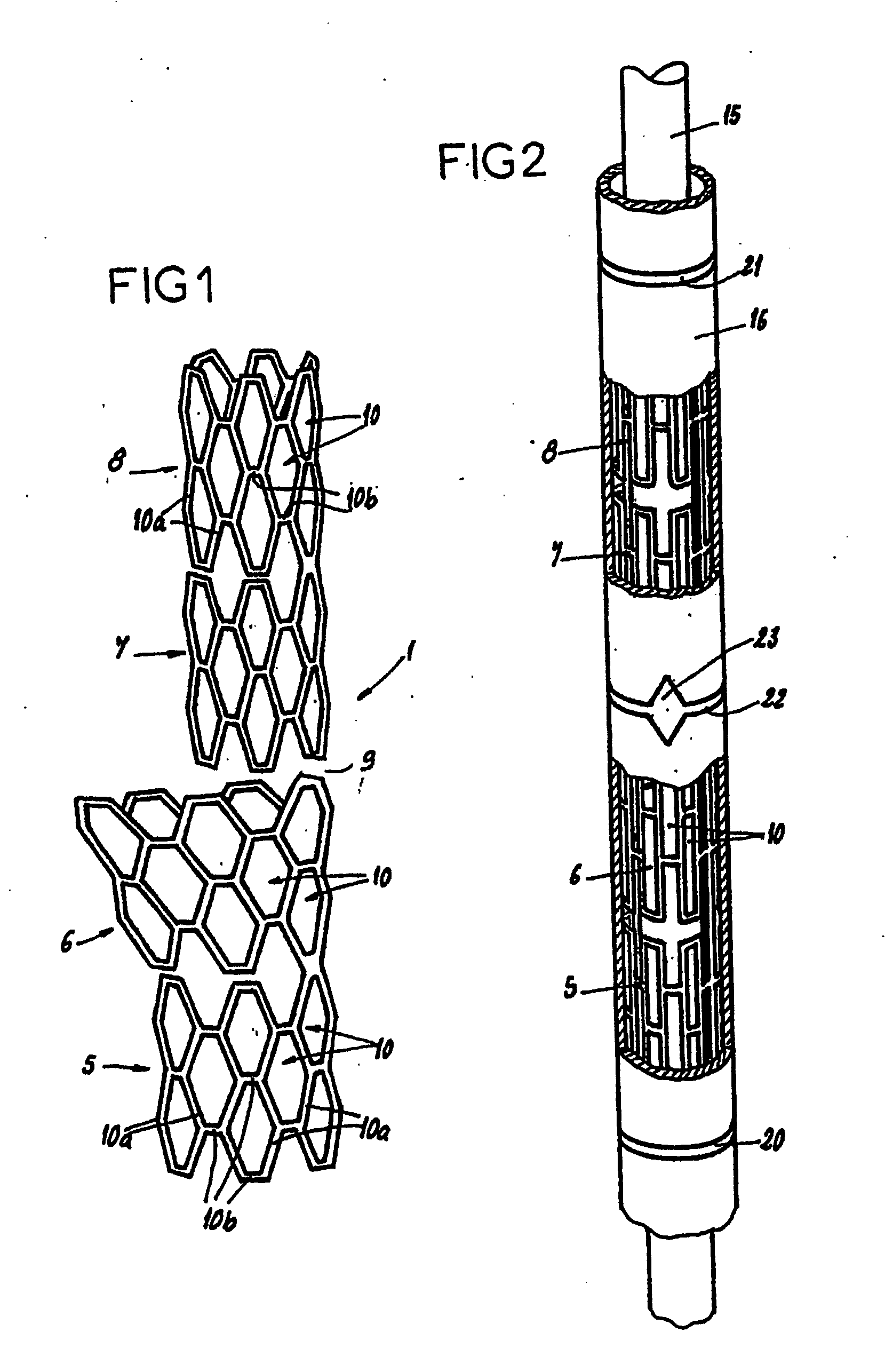
Mesh stent with variable hoop strength
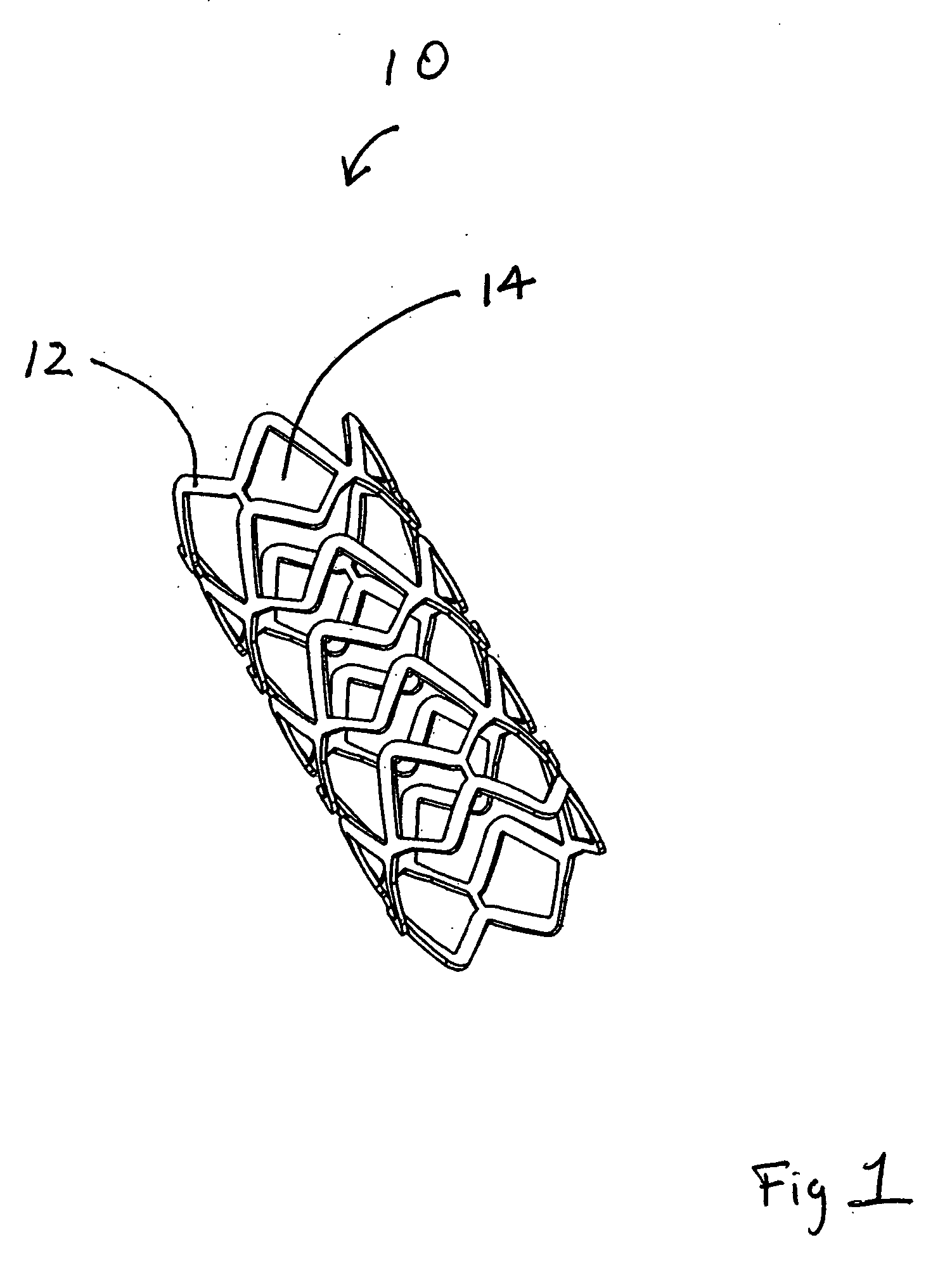
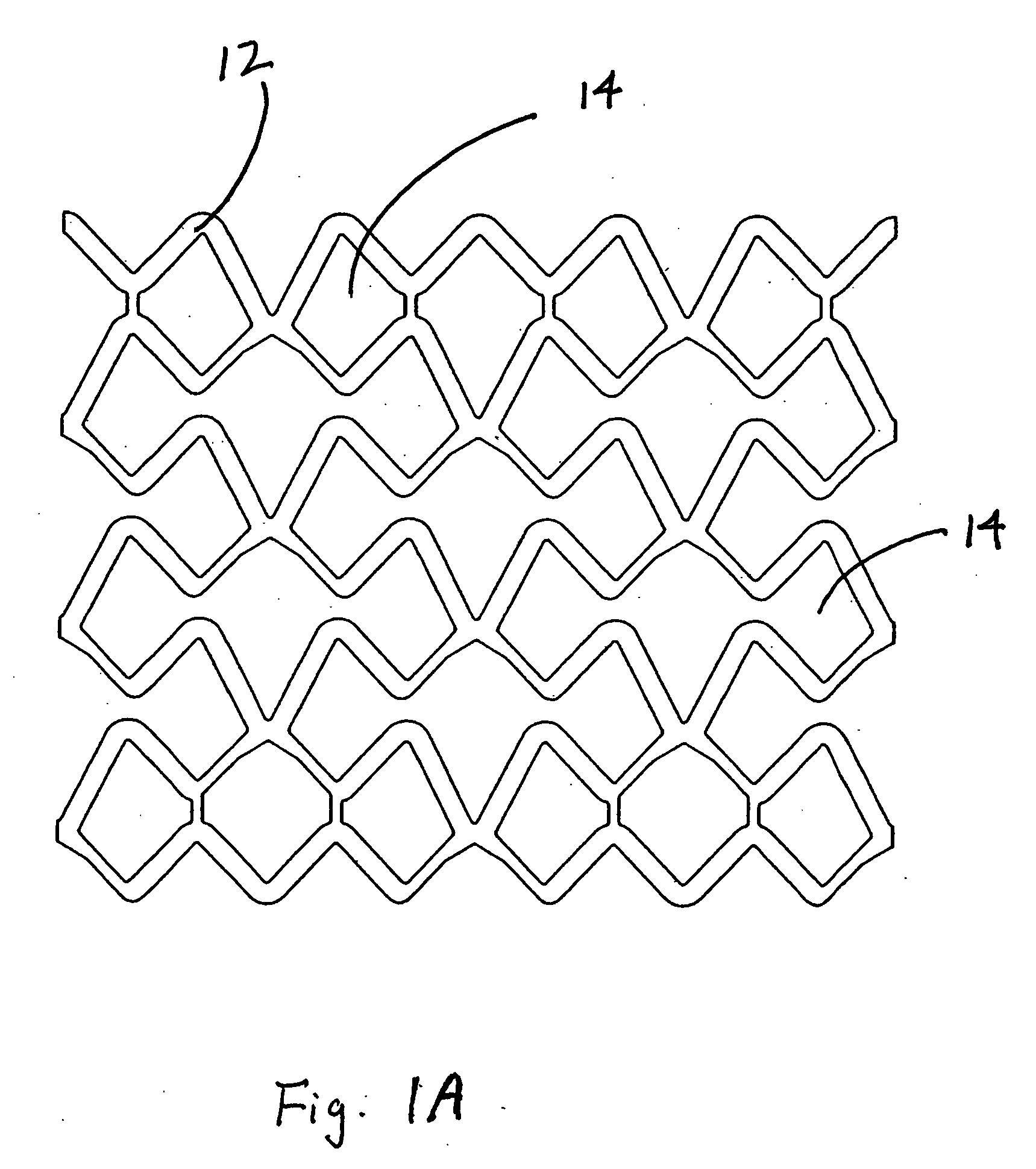
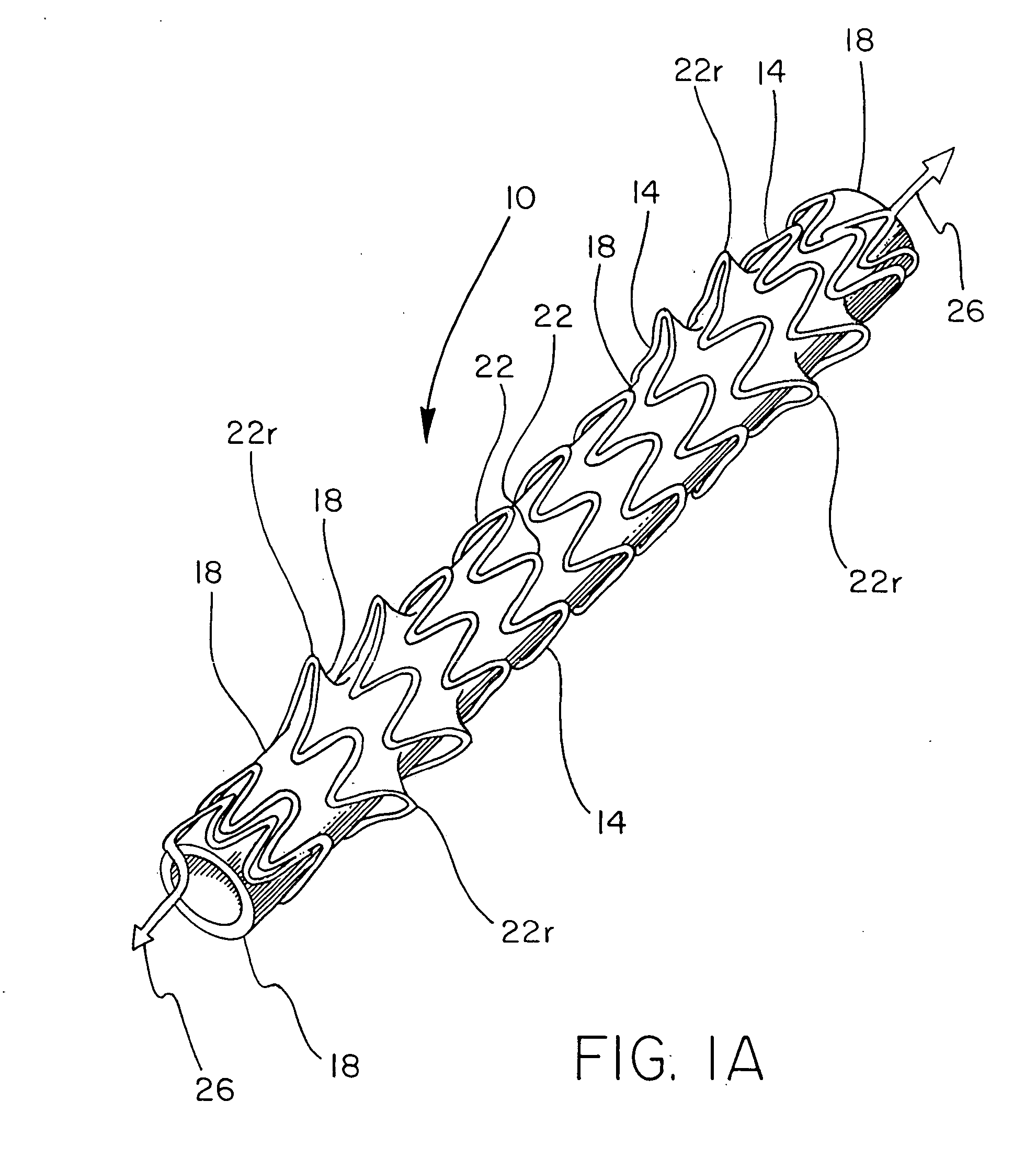
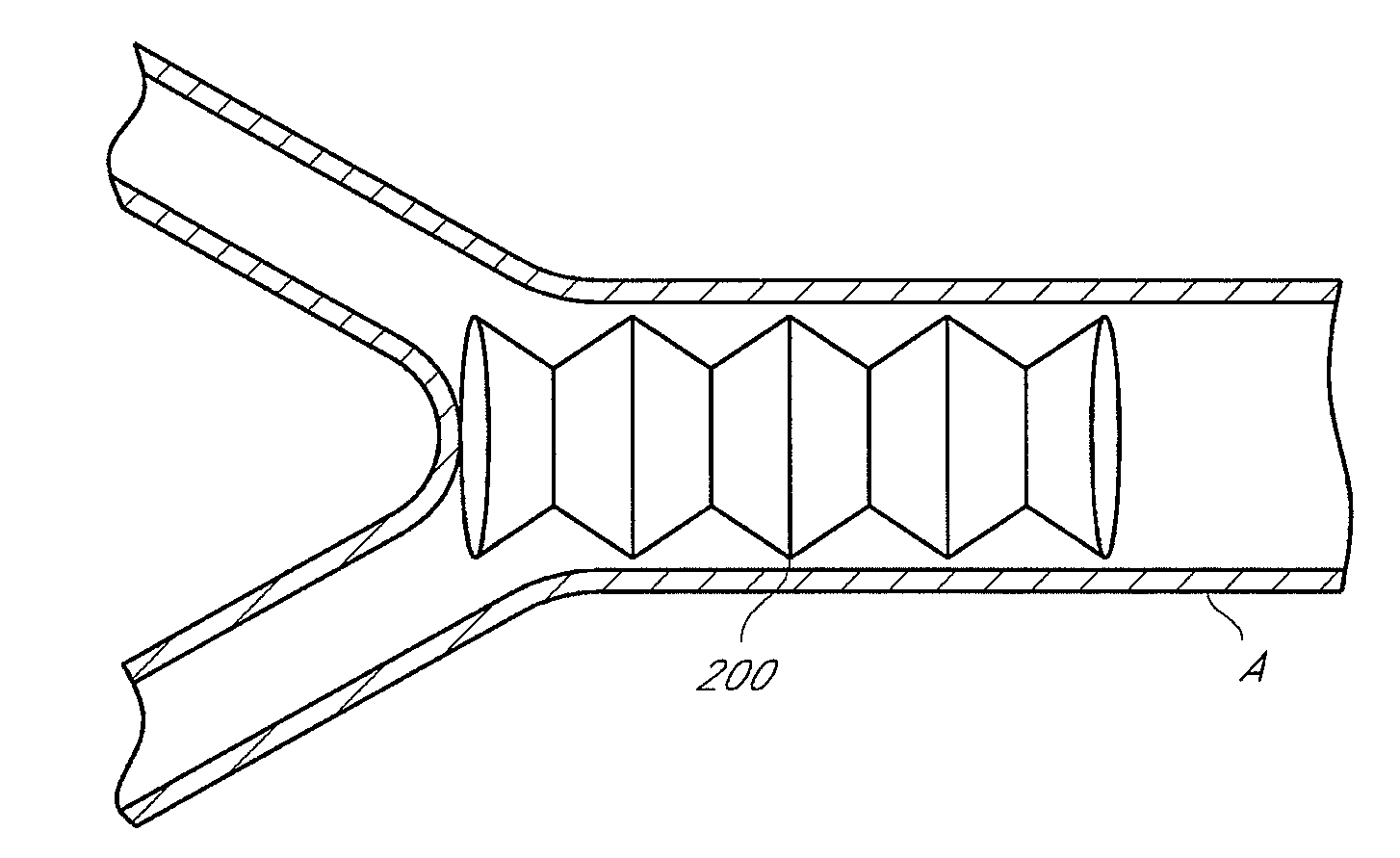
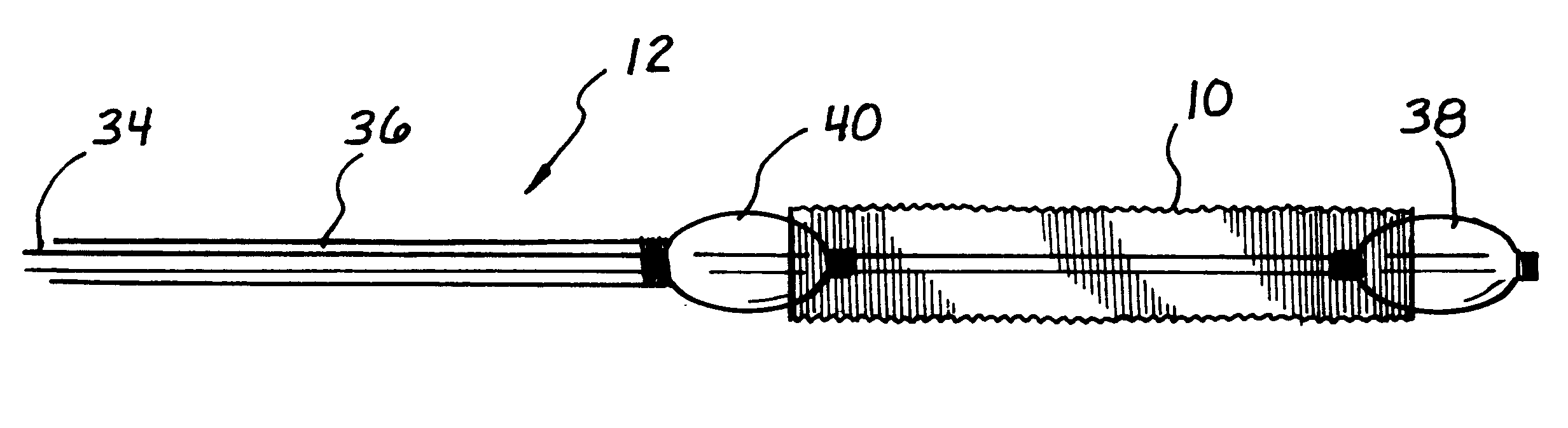
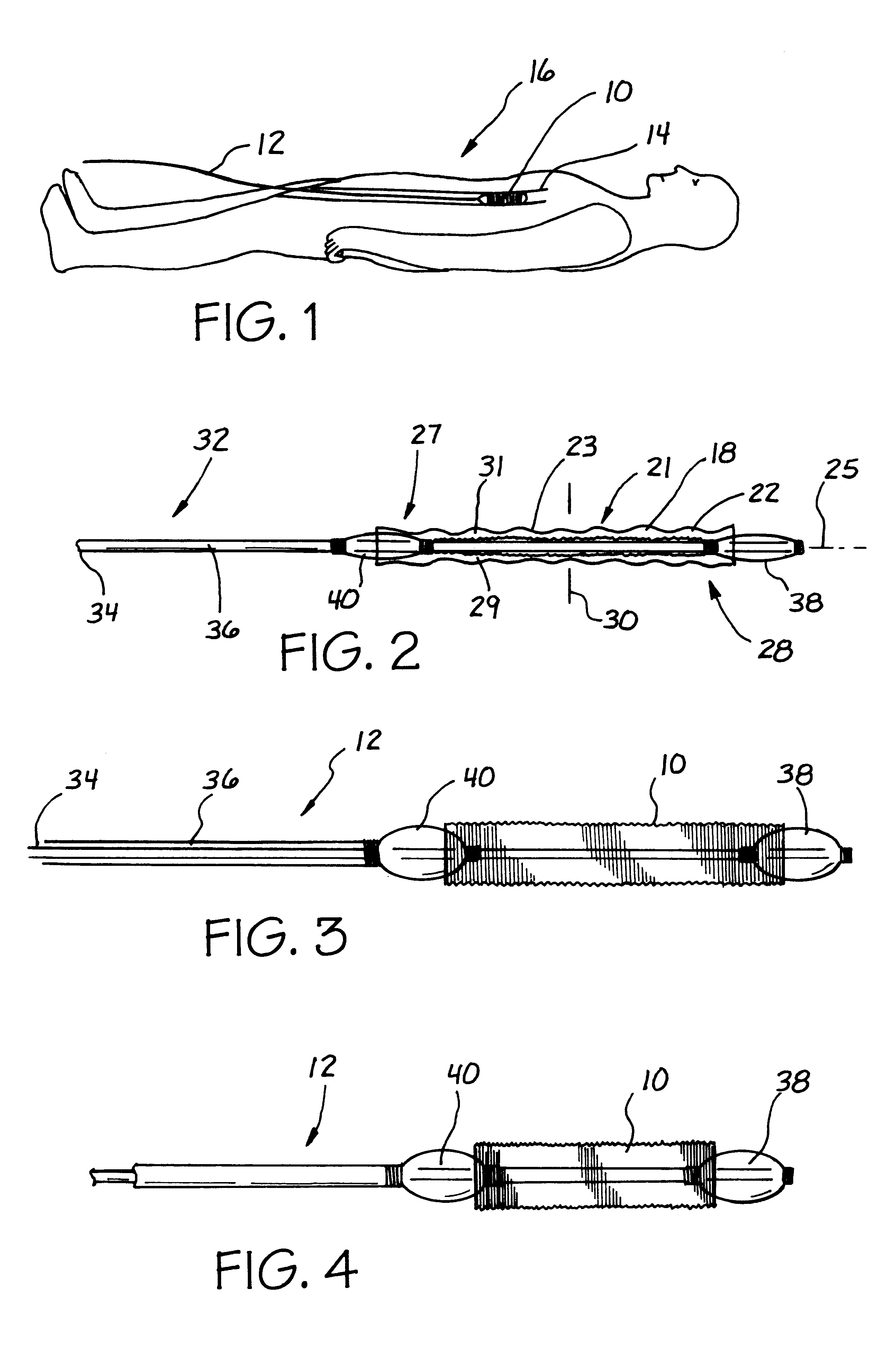
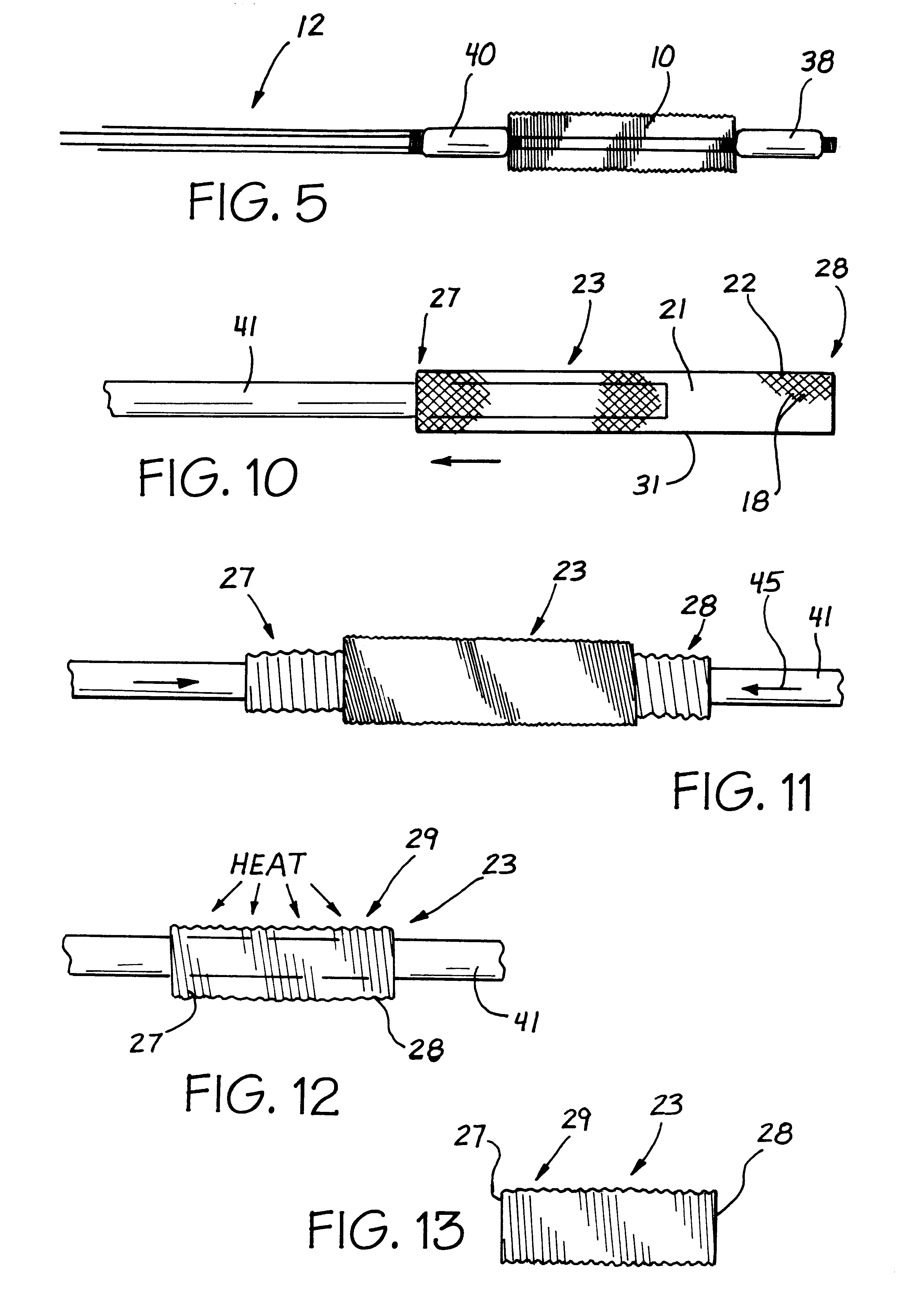
A stent is adapted for disposition in a body conduit of a patient and comprises a mesh formed in the configuration of a tube and having an axis and axial convolutions, which facilitate movement between a low-profile state and a high-profile state. The tube in the low-profile state has an elongate configuration and a wall with a first thickness and first tube strength. The tube in the high-profile state has a compressed configuration and a wall with a second thickness greater than the first thickness and a second hoop strength greater than the first hoop strength. An associated method of use includes the steps of mounting the step on a catheter between first and second enlargement members, increasing the size of the enlargement members, and moving the enlargement members to axially compress the stent to the high-profile state. An associated method of manufacture includes the steps of corrugating the mesh on a mandrel by moving the ends of the mesh toward each other. The mesh can then be heat-set in the high-profile state.
Owner:APPL MEDICAL RESOURCES CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com