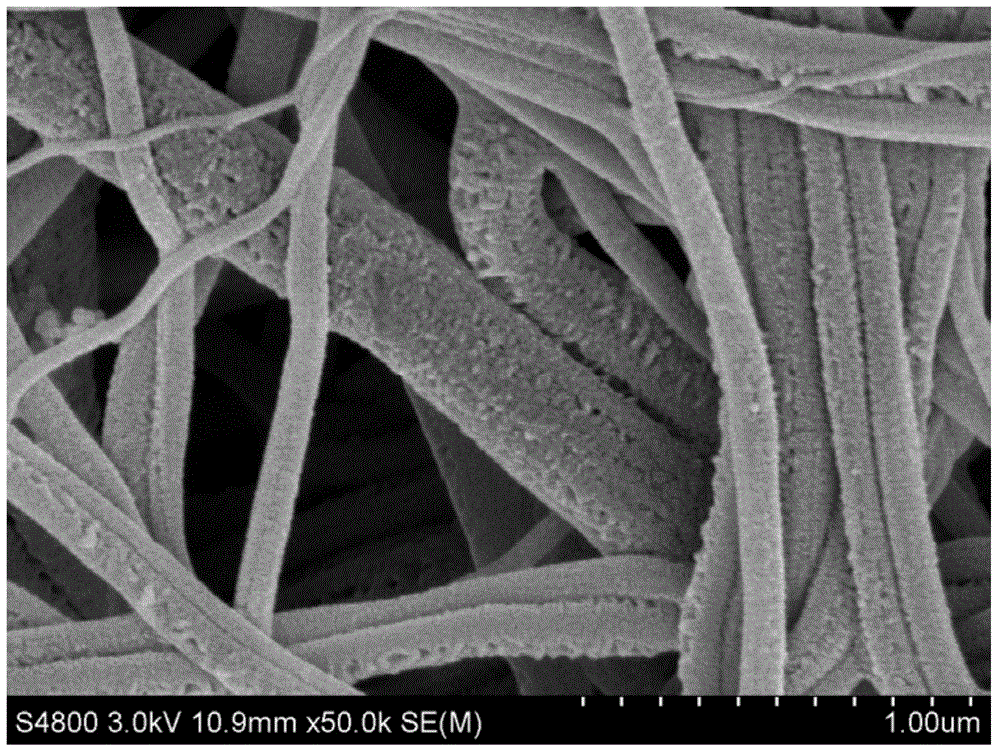
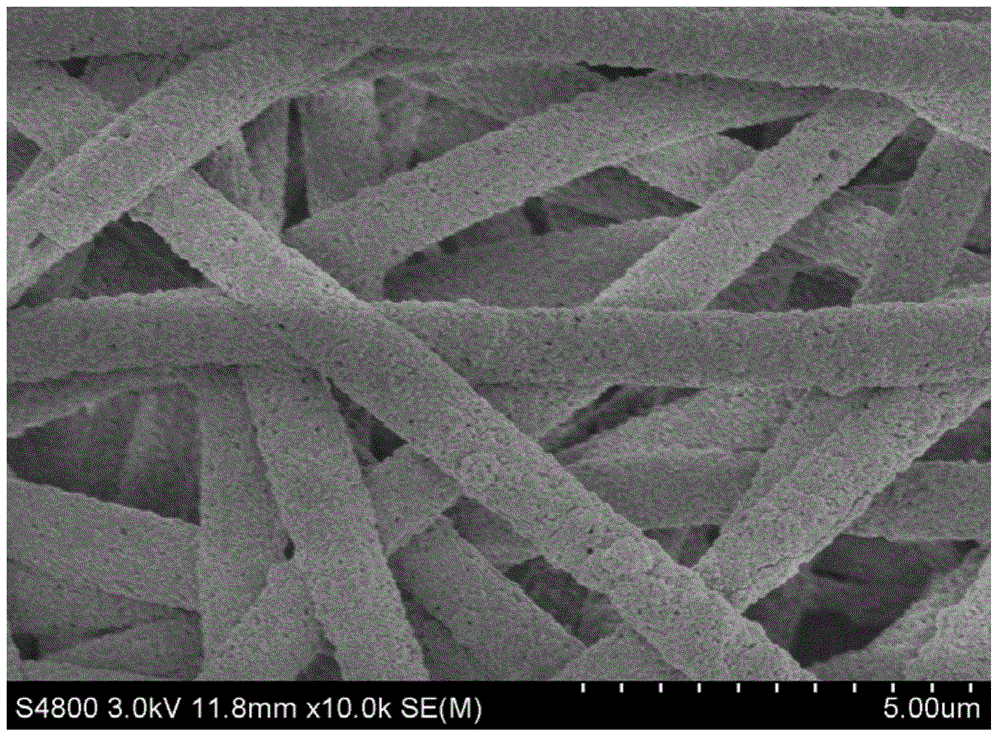
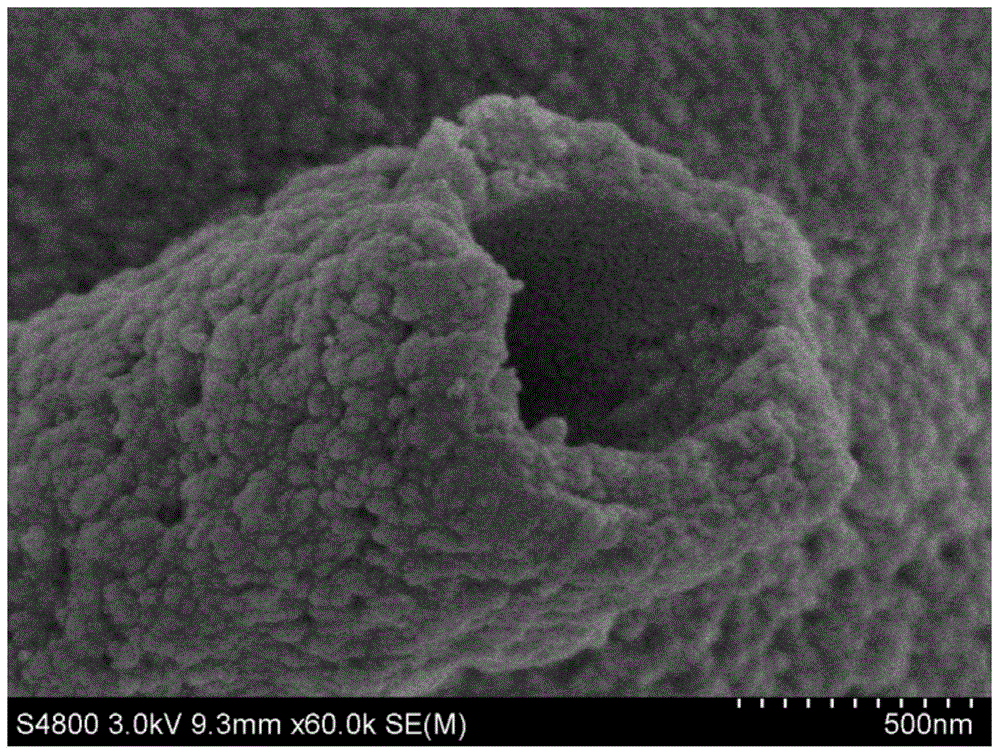
Preparation method of porous nanofiber non-woven fabric
A nanofiber, non-woven technology, applied in fiber processing, separation methods, chemical instruments and methods, etc., can solve the problems of decreased mechanical properties of fibers, incomplete dissolution, high viscosity of pure melt, etc., and can reduce the dissolution temperature and The effect of phase separation temperature, whipping time extension, and stability improvement
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] Example 1 Polyvinylidene fluoride / dimethylacetamide / n-butyl phthalate thermally induced solvent volatile phase separation system
[0031] The polymer raw material is polyvinylidene fluoride 6010 produced by Solvay, the good solvent in the composite diluent is dimethylacetamide, the latent solvent is n-butyl phthalate, and the extractant is ethanol. The mass percentage concentration of polyvinylidene fluoride is 20%, the mass percentage concentration of dimethylacetamide is 64%, and the mass percentage concentration of n-butyl phthalate is 16%; it is stirred and dissolved in a reactor at a temperature of 85°C to completely produce into a homogeneous solution that is stable at room temperature. The homogeneous solution is melt-blown. The process parameters are slit nozzle, spinneret diameter 0.25mm, air groove angle 30°, slit width 0.42mm, die temperature 40°C, hot air temperature 50°C, gas pressure 0.09 Mpa, the receiving distance is 25cm, the spinning speed is 100kg / h,...
Embodiment 2
[0032] Example 2 Polyvinylidene fluoride / dimethylacetamide / n-butyl phthalate thermally induced solvent volatile phase separation system
[0033] The polymer raw material is polyvinylidene fluoride 1010 produced by Solvay, the good solvent in the compound diluent is dimethylacetamide, the latent solvent is n-butyl phthalate, and the extractant is n-hexane. The mass percentage concentration of polyvinylidene fluoride is 20%, the mass percentage concentration of dimethylacetamide is 25%, and the mass percentage concentration of n-butyl phthalate is 55%. Stir and dissolve in a reactor at a temperature of 120°C to completely form a homogeneous solution, which can only exist stably at 100°C. The homogeneous solution is melt-blown, and the process parameters are slit nozzle, spinneret diameter 0.35mm, air groove angle 40°, slit width 0.55mm, die temperature 110°C, hot air temperature 120°C, gas pressure 0.2 Mpa, the receiving distance is 30cm, the spinning speed is 80kg / h, and the w...
Embodiment 3
[0034] Example 3 Polyacrylonitrile / dimethylformamide / n-tetradecyl alcohol dry solvent volatile phase inversion system
[0035] The polymer raw material is polyacrylonitrile with a number average molecular weight of 160,000, the good solvent in the composite diluent is dimethylformamide, the non-solvent is n-tetradecyl alcohol, and the extractant is acetone. The mass percent concentration of polyacrylonitrile is 15%, the mass percent concentration of dimethylformamide is 65%, and the mass percent concentration of n-tetradecyl alcohol is 20%. Stir and dissolve in the reactor at 60°C to make a homogeneous solution, which can exist stably at room temperature. The homogeneous solution is melt-blown, and the process parameters are slit nozzle, spinneret diameter 0.42mm, air groove angle 30°, slit width 0.55mm, die temperature 25°C, hot air temperature 30°C, gas pressure 0.15 Mpa, the receiving distance is 15cm, the spinning speed is 120kg / h, and the weight of the primary non-woven ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| The inside diameter of | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Outer diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Outer diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com