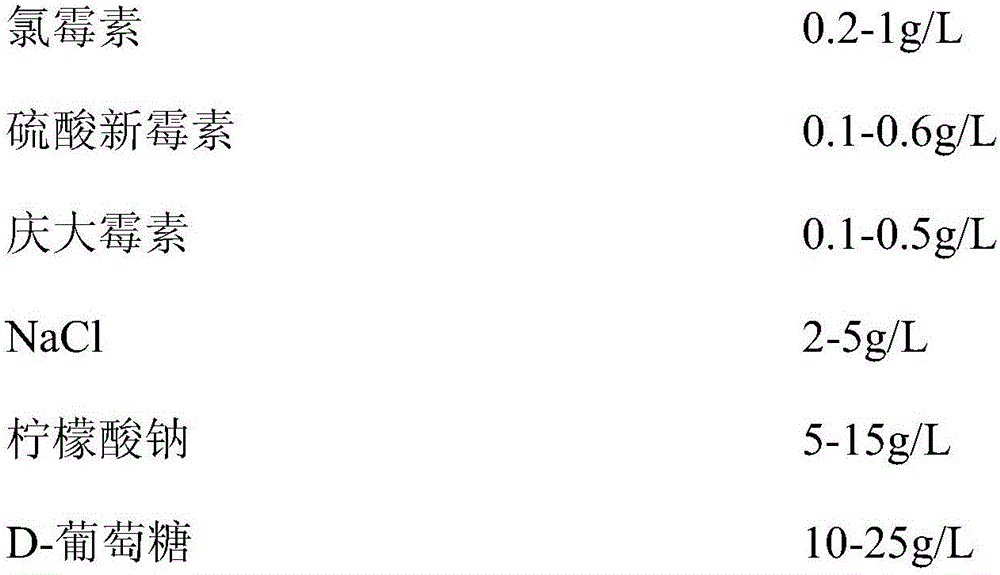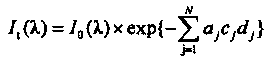Patents
Literature
65 results about "Free hemoglobin" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
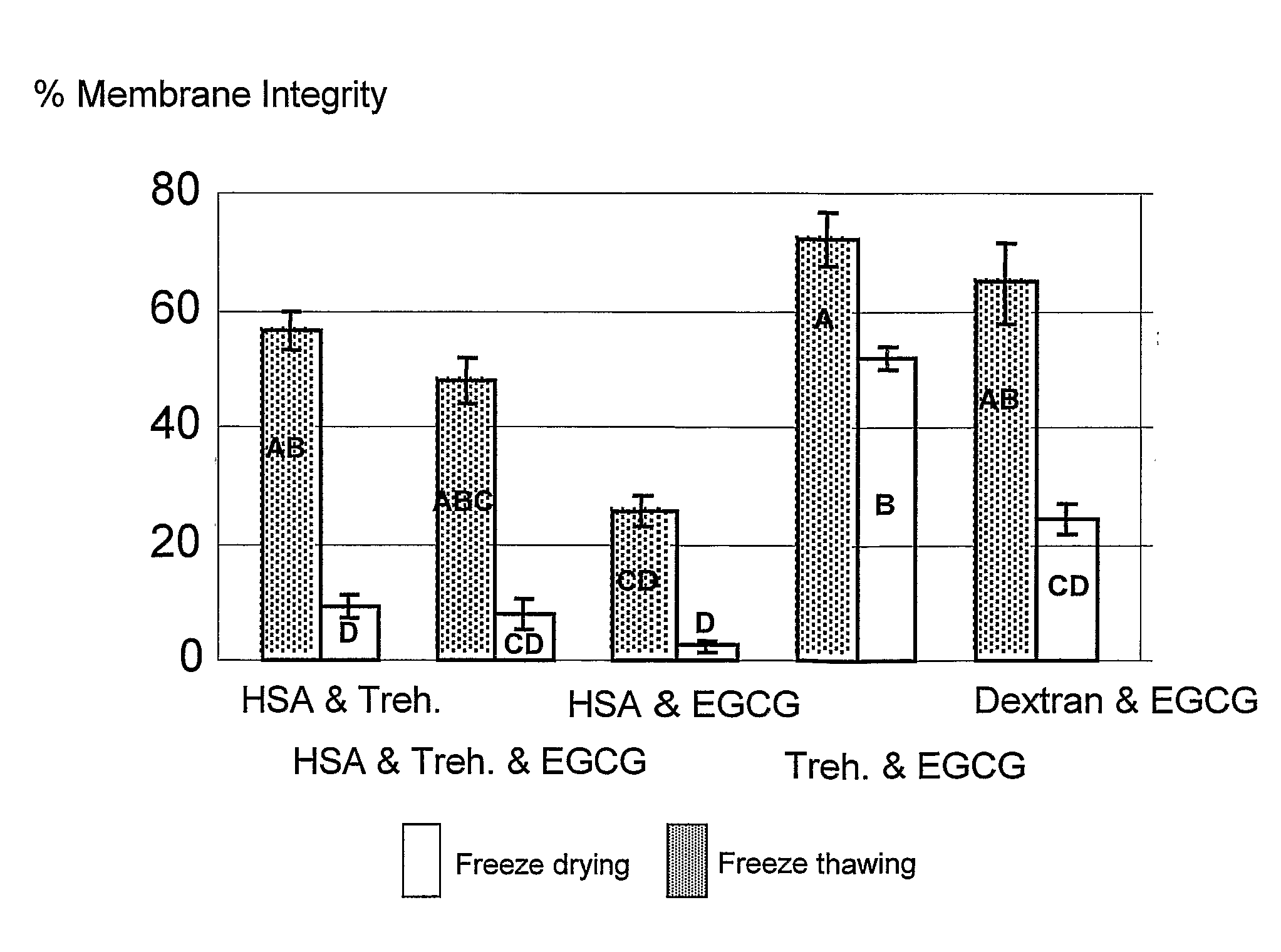
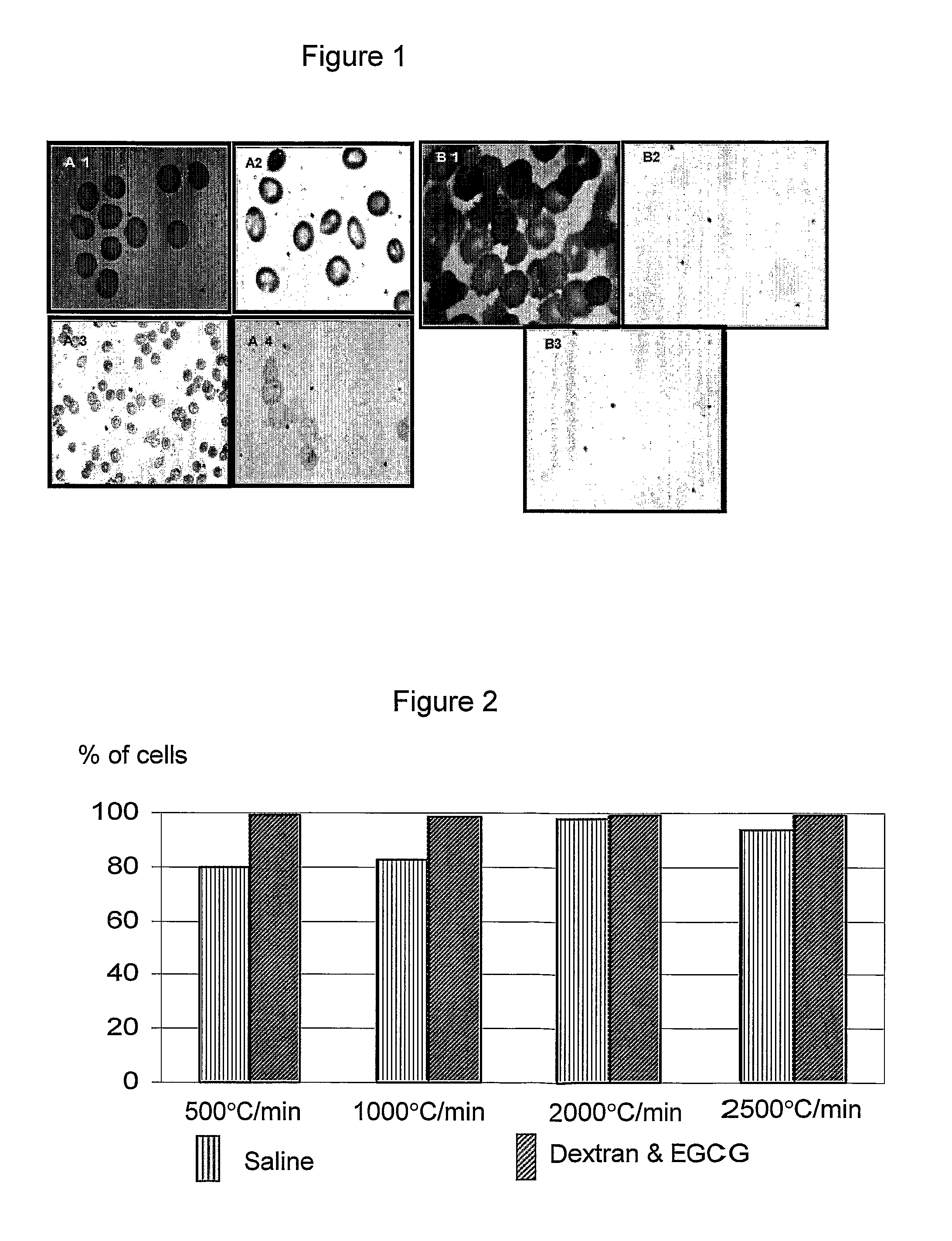
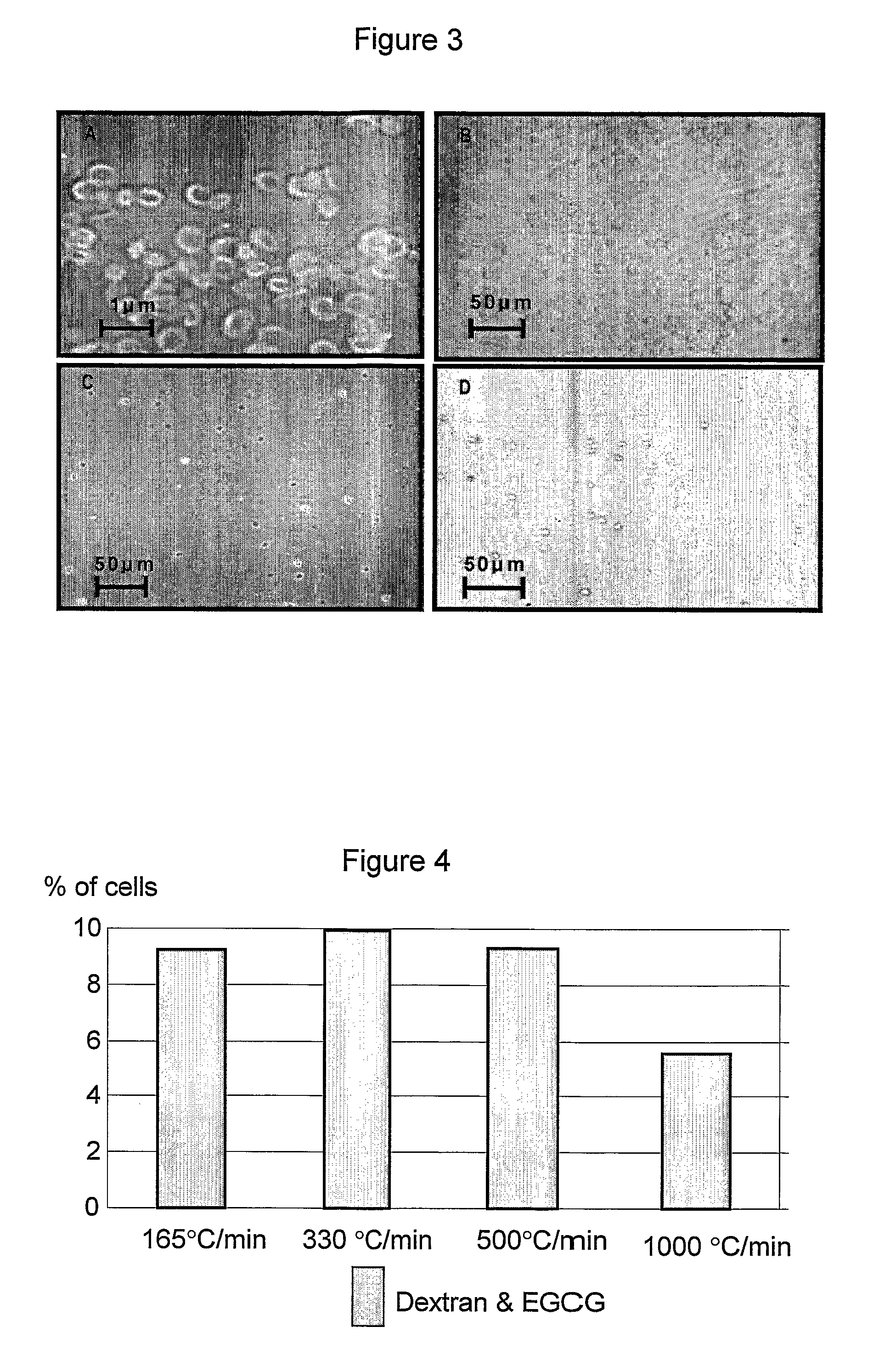
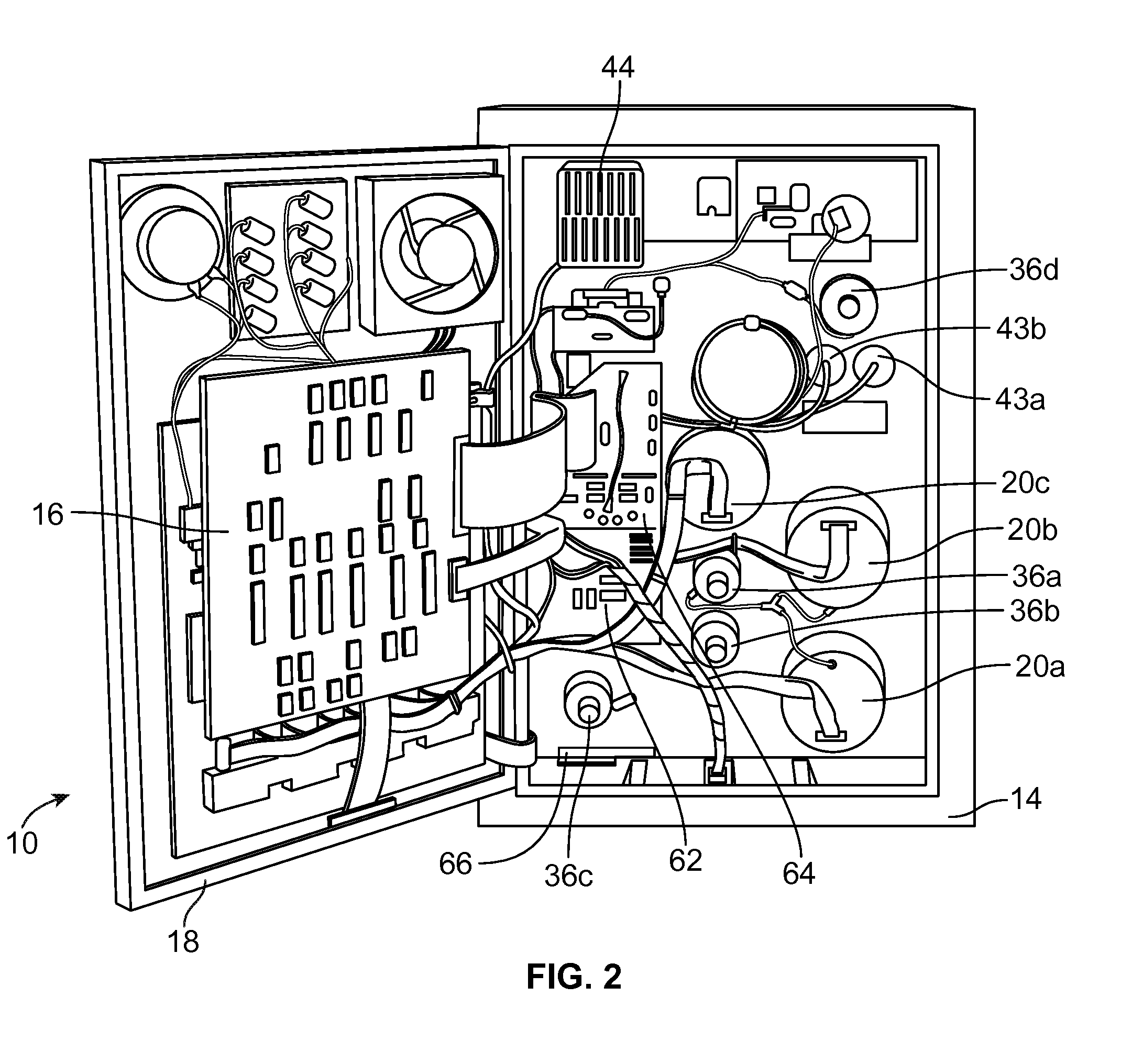
Biological material and methods and solutions for preservation thereof
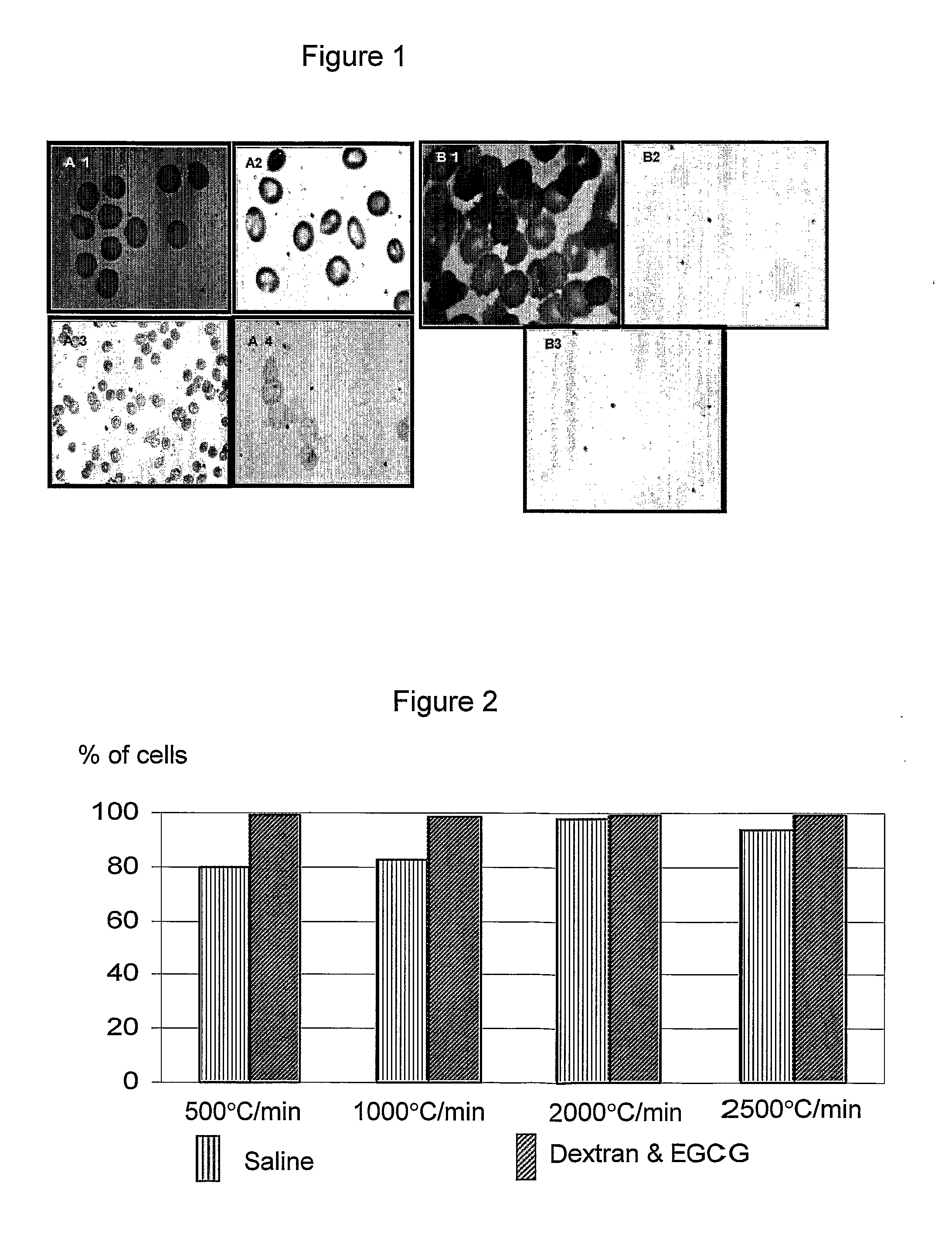
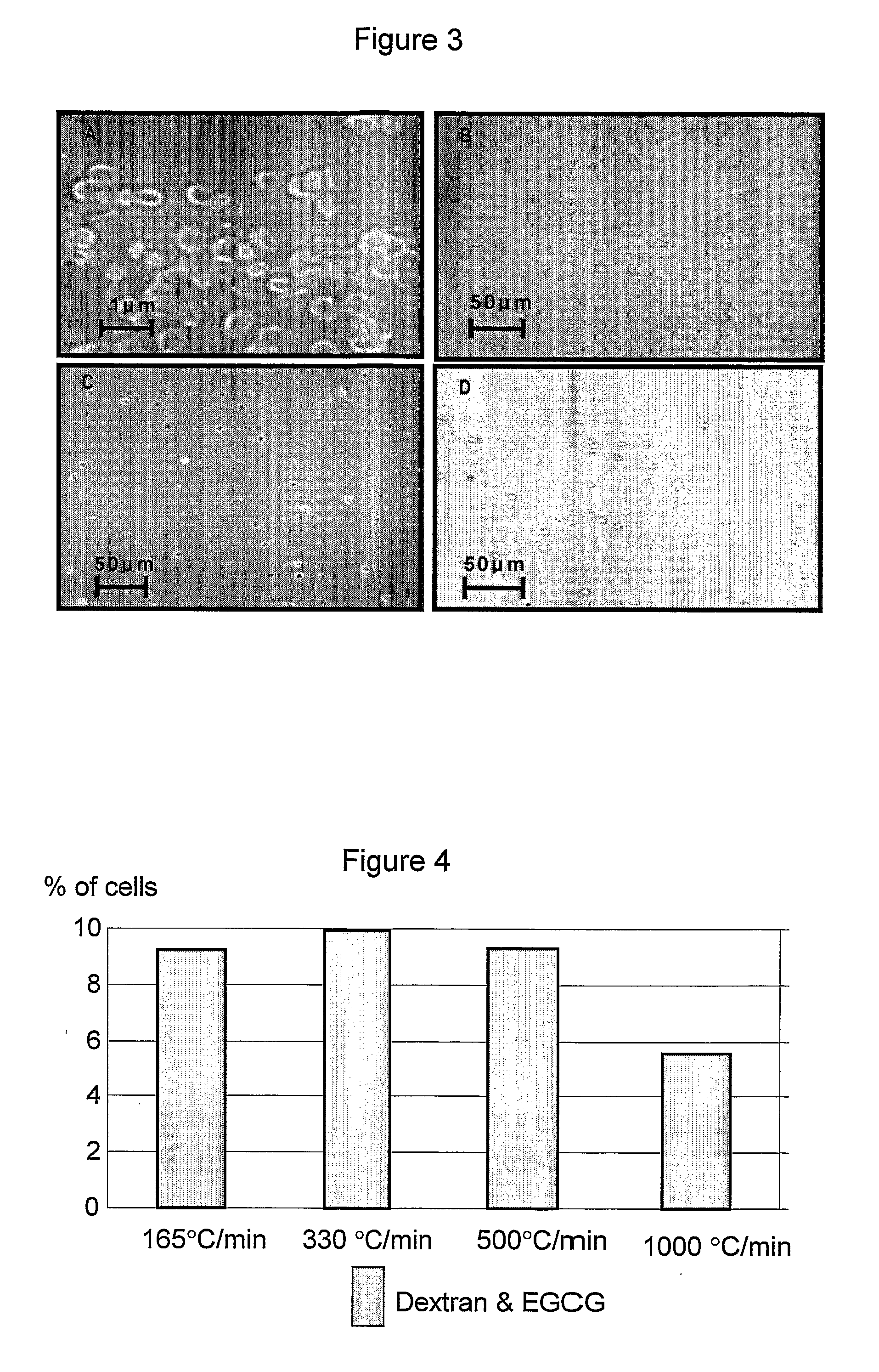
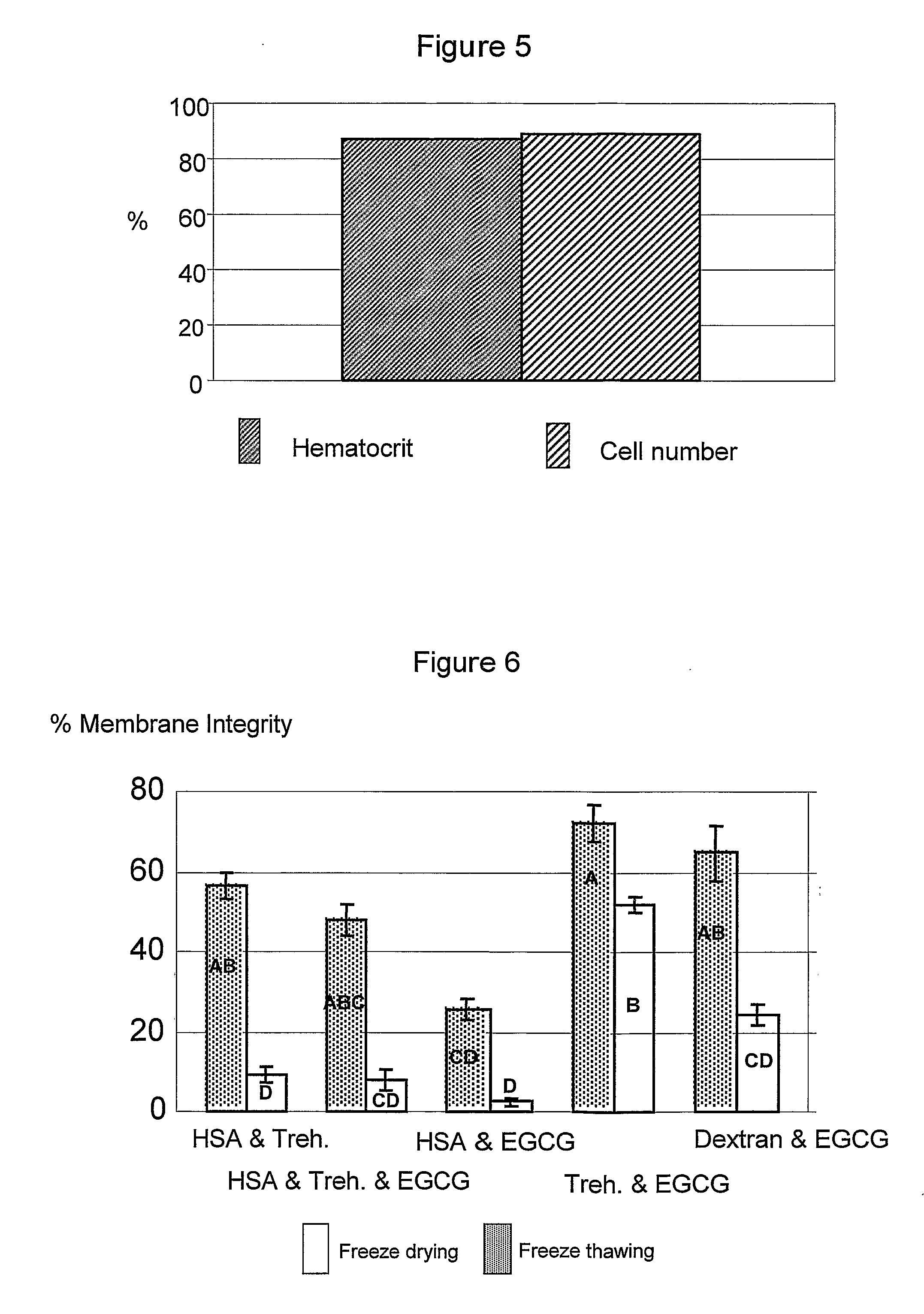
InactiveUS20070178434A1Improve viabilityStabilize membraneDead animal preservationBlood/immune system cellsFree hemoglobinCryopreservation
A preservation solution for preserving a biological material at a low temperature including one or more polyphenols, and a method for preserving a biological material are provided. The method includes adding the preservation solution to a biological material, cooling the biological material and storing it under appropriate storing conditions. The method can be used for hypothermic preservation or for cryopreservation, including freezing and lyophilization, of any biological material, including cells selected from RBC, WBC, MNC, UCB, MNC, and bacteria. A method is also provided for freezing RBCs such that upon thawing, the RBCs include less than 2% free hemoglobin.
Owner:CORE DYNAMICS
Method and device for measuring blood information
InactiveCN104136911ADiagnostic recording/measuringColor/spectral properties measurementsFlow cellThrombus
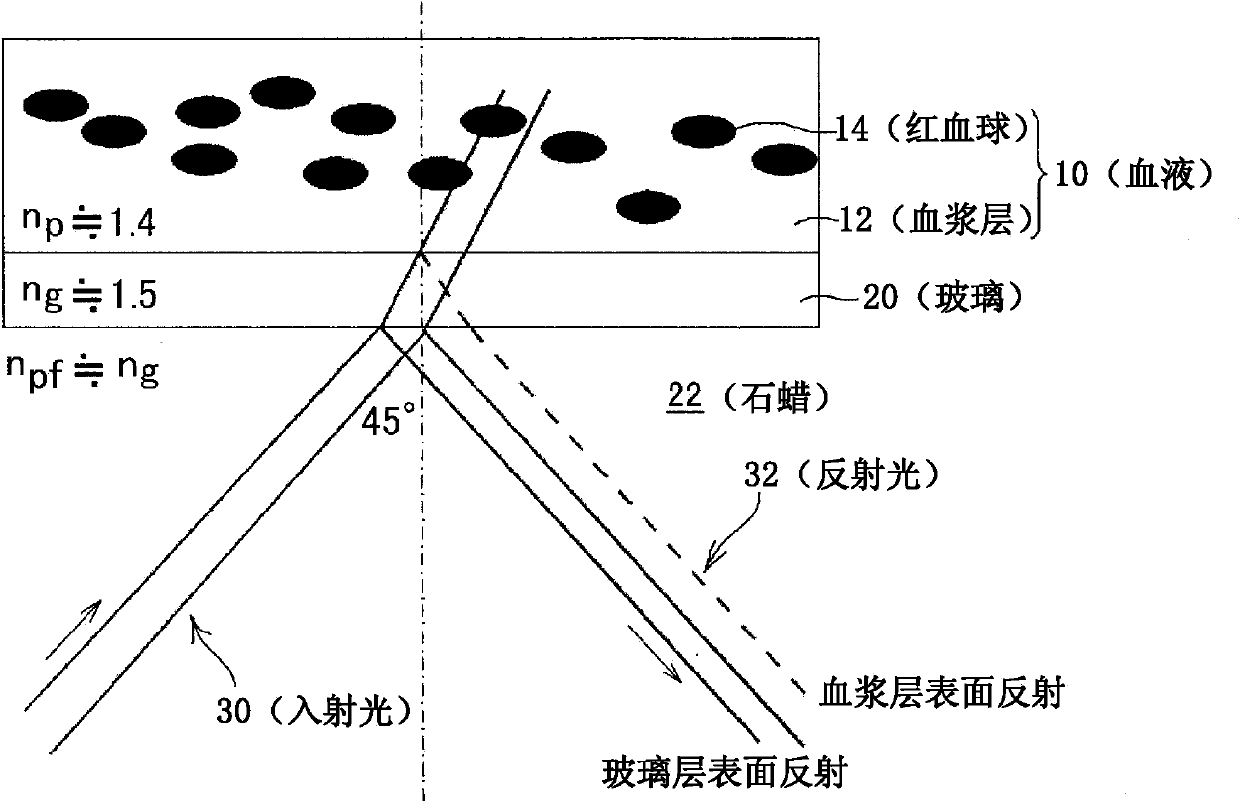
Blood information such as hemolysis (a plasma-free hemoglobin concentration) and a blood coagulation level (thrombus) can be obtained by extracting only reflected light in a plasma layer, and non-invasively and continuously obtaining information only on a plasma component independently of a hematocrit without separating blood components by a mechanical or chemical process. First measurement light 30 is caused to be incident on a boundary surface between blood 10 flowing through a flow cell 40 formed of a transparent material having a different refractive index from plasma (layer) 12 in the blood 10 and the flow cell 40, from an oblique direction at an angle smaller than 90 degrees. Reflected light 32 regularly reflected at the boundary surface between the flow cell 40 and the blood 10 is subjected to spectrometry. Information on a plasma component (a refractive index Np of plasma) is obtained from an absorption spectrum measured.
Owner:NAT UNIV CORP TOKYO MEDICAL & DENTAL UNIV
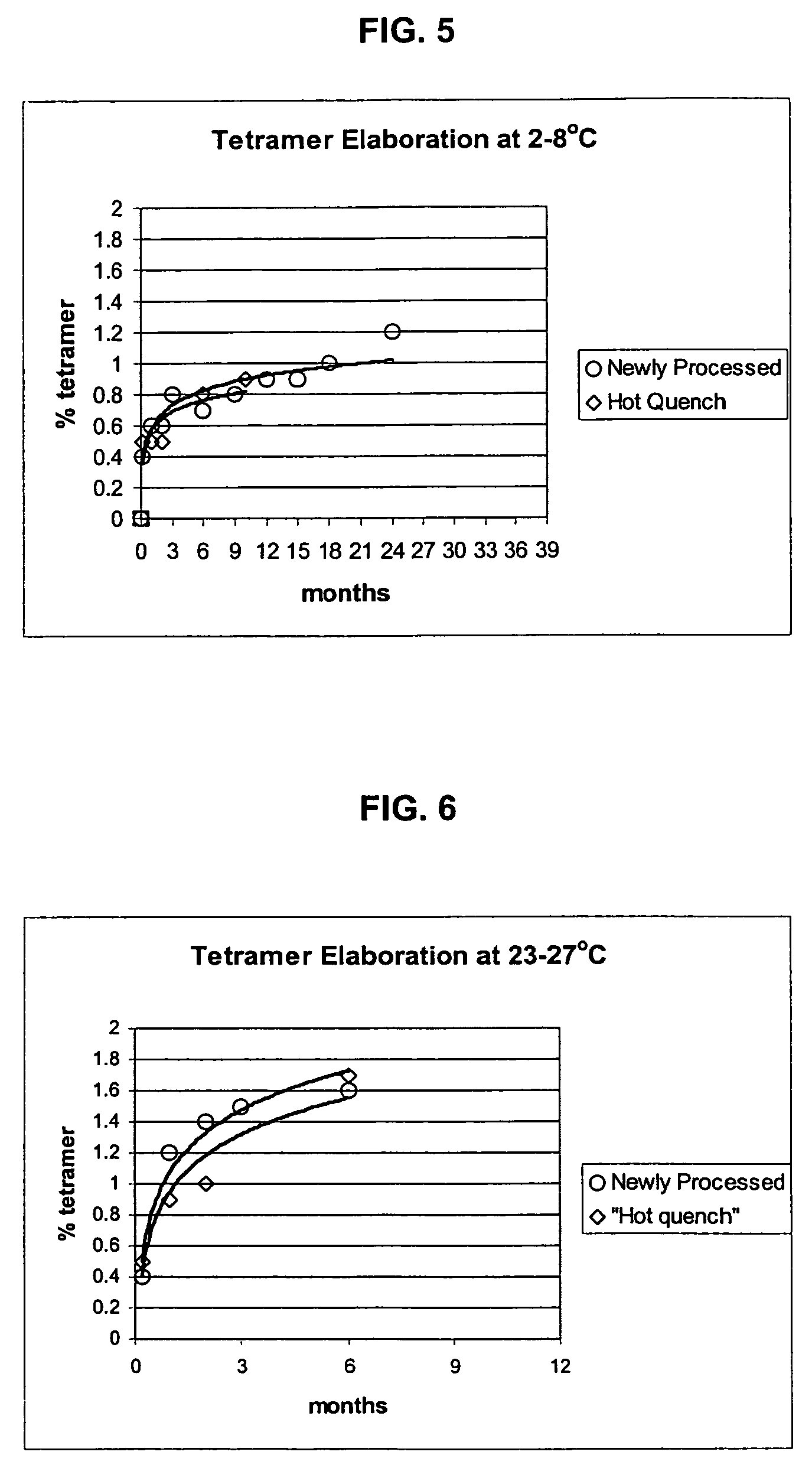
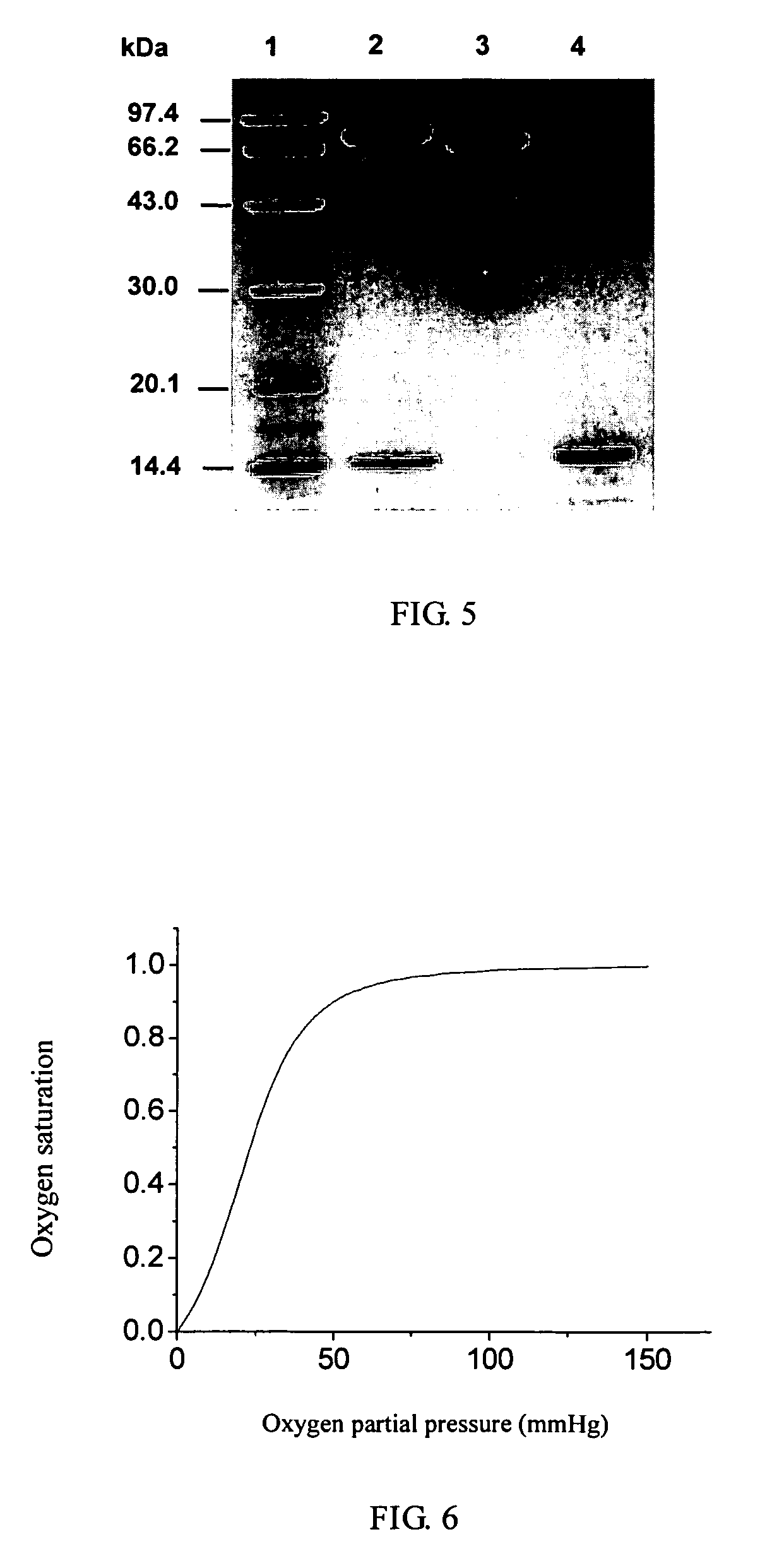
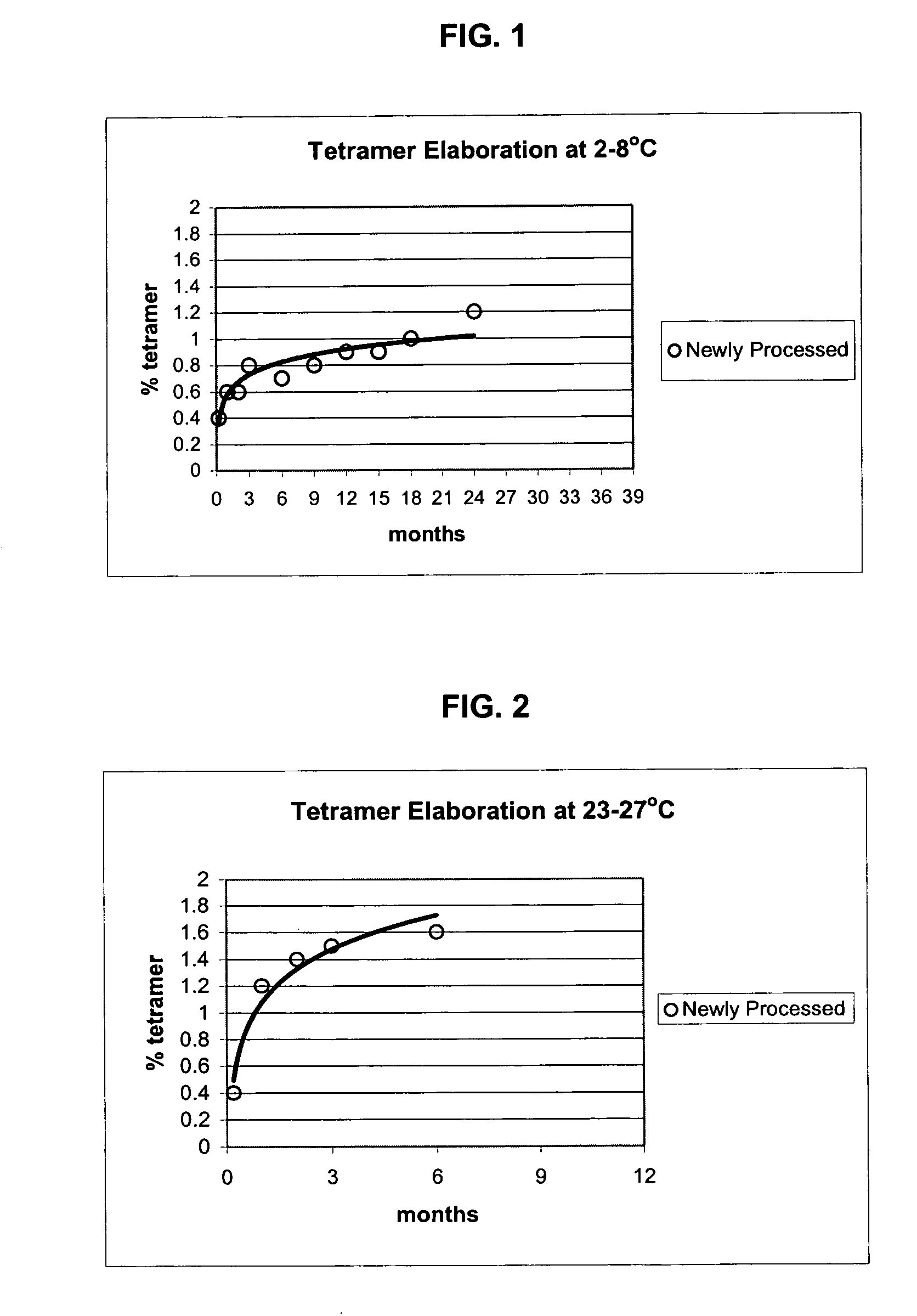
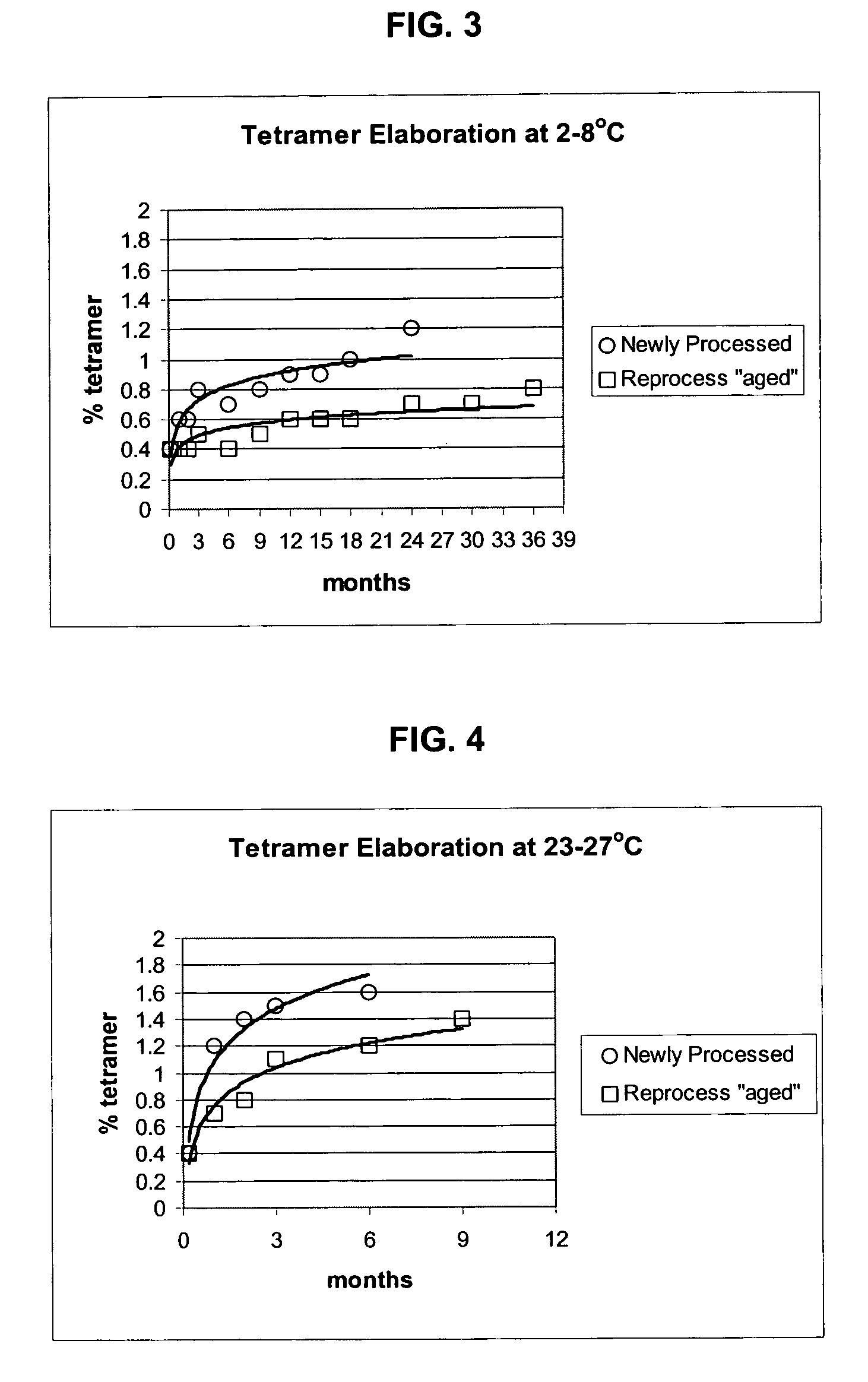
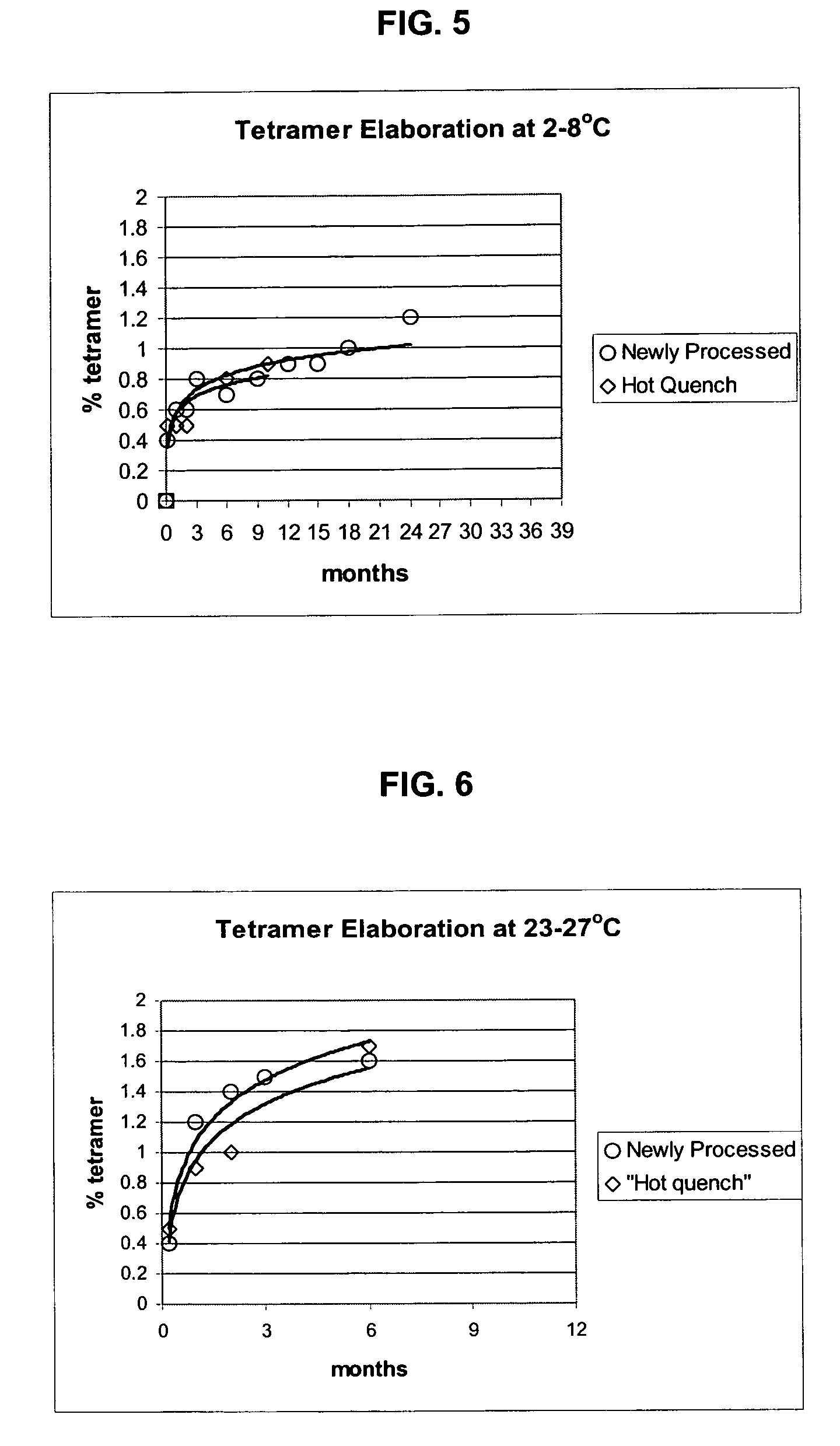
Polymerized hemoglobin solutions having reduced amounts of tetramer and method for preparing
InactiveUS7411044B2Peptide/protein ingredientsHaemoglobins/myoglobinsFree hemoglobinPhysical chemistry
A substantially tetramer free hemoglobin solution and a method for producing a substantially tetramer free hemoglobin solution. The method includes polymerizing a solution of hemoglobin, treating the polymerized hemoglobin solution to partially degrade the polymer to tetramer and removing tetramer from the hemoglobin solution.
Owner:HEMOGLOBIN OXYGEN THERAPEUTICS
Hemoglobin conjugate and the preparation method and its use
InactiveUS20060247423A1Maintain osmotic pressureFunction is performedPeptide/protein ingredientsHaemoglobins/myoglobinsAnion-exchange chromatographyAlbumin
The present invention relates to conjugates of hemoglobin and human serum albumin and the preparation process thereof. The conjugates have molecular weight in the range of 100-300 kD, comprising 1-3 intermolecularly or intramolecularly cross-linked hemoglobin molecules and 1-3 human serum albumin molecules. The conjugates are obtained by the following steps: preparing stroma-free hemoglobin, then coupling hemoglobin to human serum albumin and purifying the products using anion exchange chromatography. The hemoglobin and human serum albumin conjugates have characteristics suitable for being used as blood substitutes.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Red cell storage solution and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106561634AInhibition of reproductive growthProtect normal metabolismDead animal preservationFree hemoglobinNeomycin Sulfate
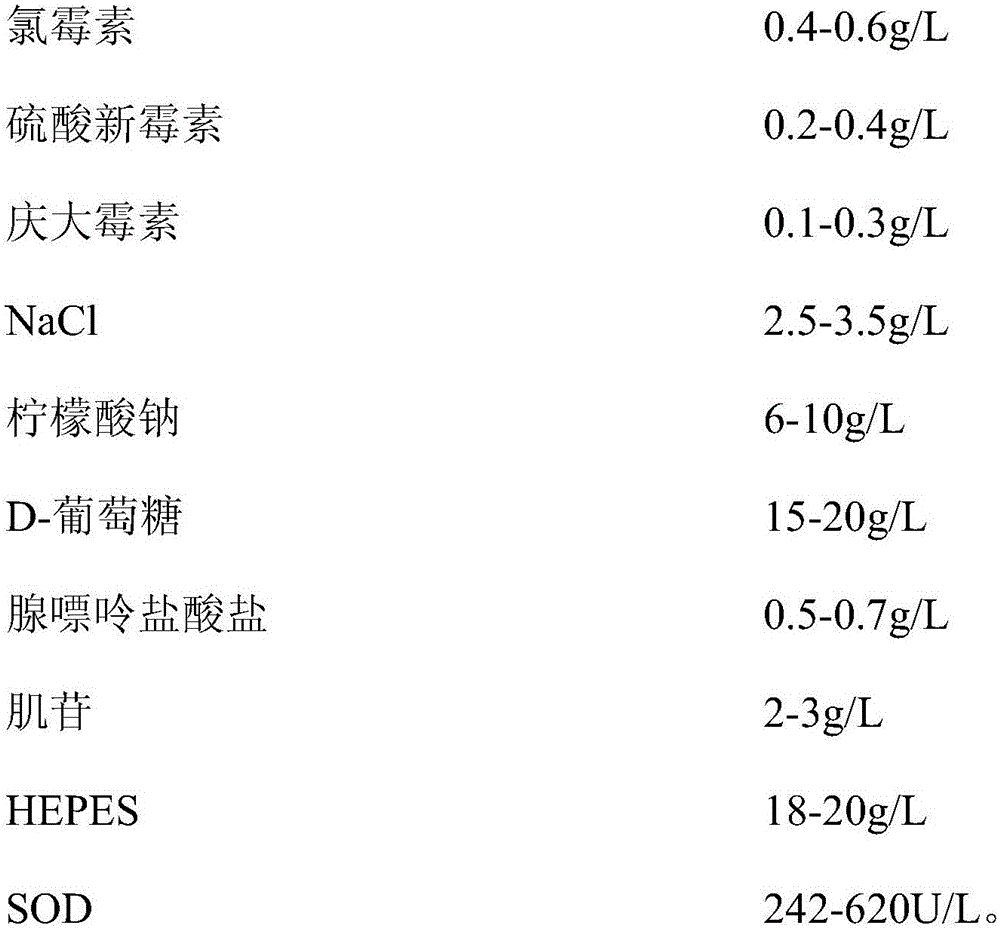
The invention relates to a red cell storage solution and a preparation method thereof. The storage solution comprises a buffering system, a nutritional system, an osmotic pressure system and an anticorrosion system, wherein the anticorrosion system comprises the following components according to mass concentration: 0.2-1g / L of chloramphenicol, 0.1-0.6g / L of neomycin sulfate, and 0.1-0.5g / L of gentamicin. Through mutual concurrent effects of the buffering system, the nutritional system, the anticorrosion system and the osmotic pressure system of the red cell storage solution provided by the invention, long storage cycle of the red cell storage solution is ensured, at the end of the sixth month of the storage, that red cell suspension free hemoglobin concentration still conforms to national standard is detected, and the hemolysis ratio at the end of the storage is smaller than 0.8 percent of the total of red cells; the red cell storage solution provided by the invention can ensure relatively strong antigenic activity and stability of the red cells.
Owner:北京乐普诊断科技股份有限公司
Polymerized hemoglobin solutions having reduced amounts of tetramer and method for preparing
InactiveUS7135553B2Peptide/protein ingredientsHaemoglobins/myoglobinsFree hemoglobinPhysical chemistry
A substantially tetramer free hemoglobin solution and a method for producing a substantially tetramer free hemoglobin solution. The method includes polymerizing a solution of hemoglobin, treating the polymerized hemoglobin solution to partially degrade the polymer to tetramer and removing tetramer from the hemoglobin solution.
Owner:OPK BIOTECH
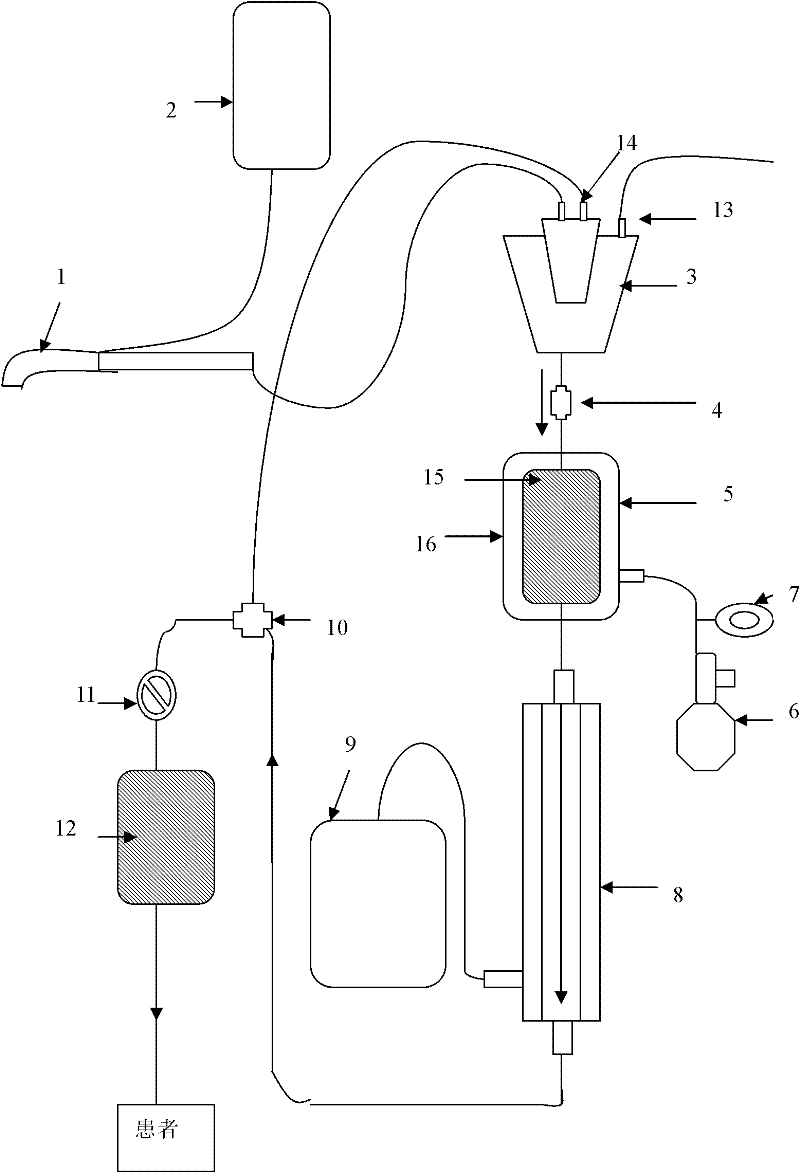
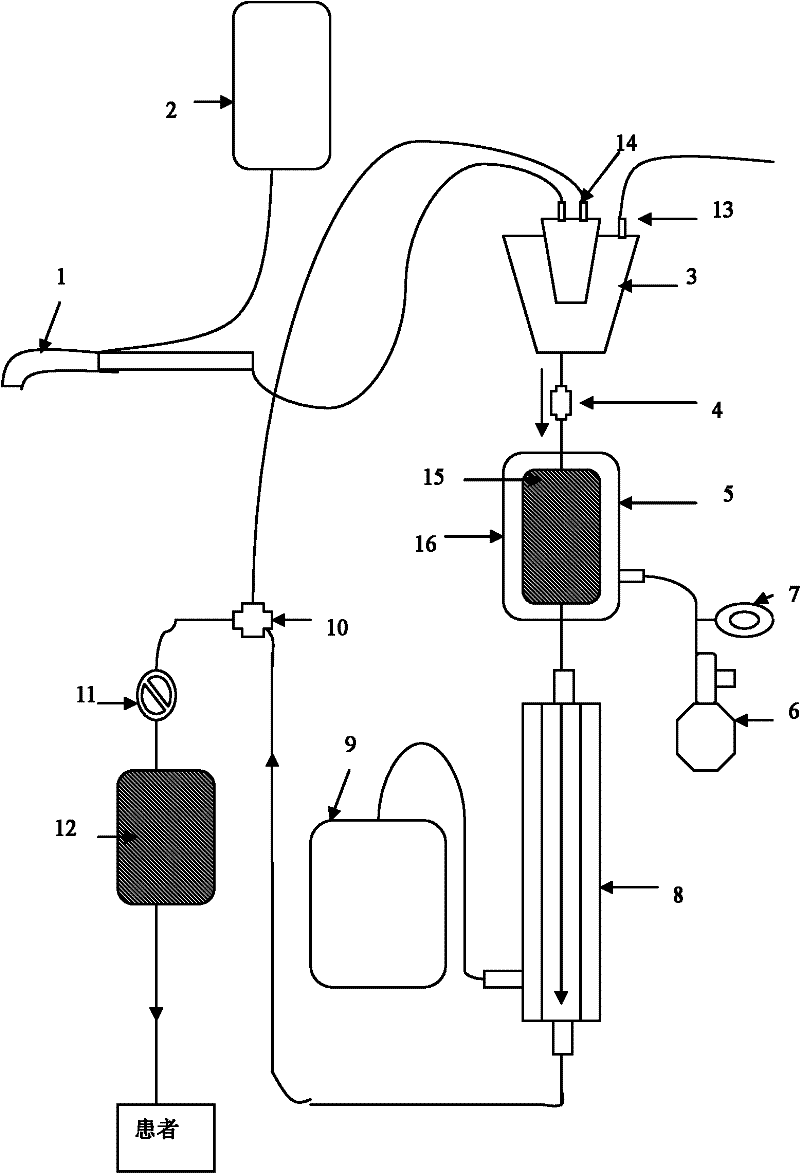
Blood transfusion system for autologous blood recovery, filtration and purification
InactiveCN102500005ARetain plasma componentsReduce tensionOther blood circulation devicesFiltrationUltrafiltration
The invention discloses a blood transfusion system for autologous blood recovery, filtration and purification, which comprises a suction head, a blood storage and filtration tank, a blood storage pressurizing bag, a blood ultrafiltration purifier and a blood bag which are sequentially connected through a pipeline. The blood transfusion system has the advantages that by the aid of the complete system which is simple in structure, convenient in use and low in cost, outflow blood is effectively recovered, filtered and purified, impurity particles such as harmful free hemoglobin, inflammatory mediators, cell activation products, small tissue dross, micro-polymers and the like in blood are removed, the blood is concentrated, and adverse transfusion reaction caused by prior filtration-type blood recovery is eliminated. Besides, the system is capable of effectively retaining plasma components and blood platelet components in the blood, and avoiding the influence of cleaning out blood coagulation factors and blood platelets in the blood on a blood coagulation function during cleaning blood recovery. In addition, by the aid of the system, infectious diseases caused by homologous blood transfusion are avoided, shortage of blood sources is relieved, and the economic burden of a patient is reduced.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Method for determining red blood cell penetration fragility
InactiveCN1588062AEasy to operateShorten the timeMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorTransmissivity measurementsTurbidityFragility
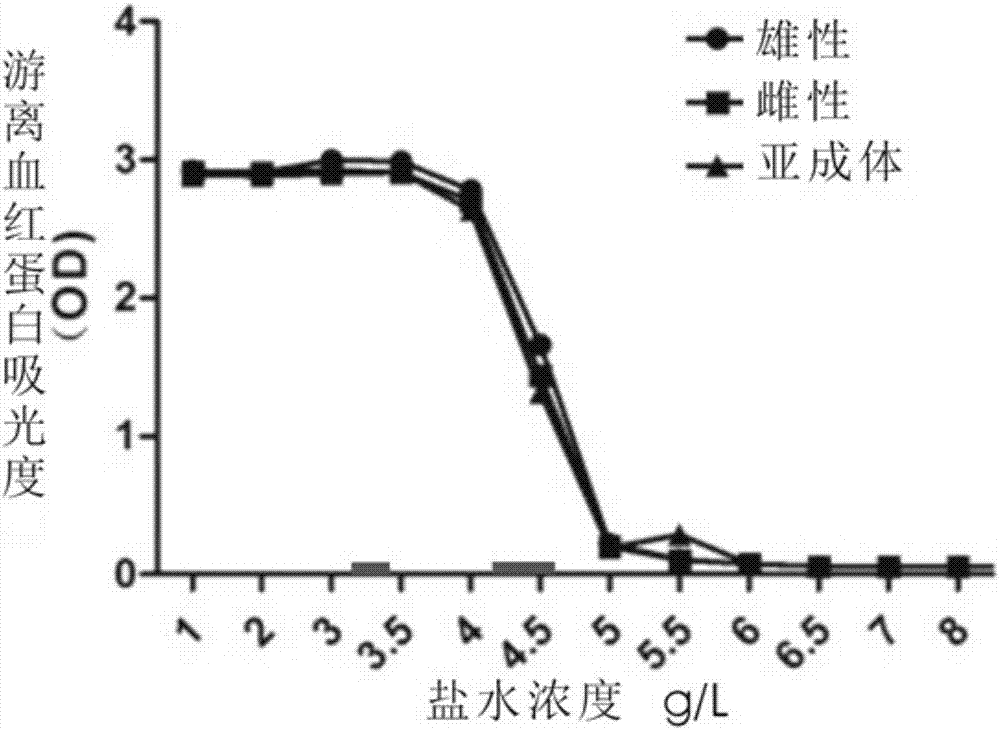
The invention relates to a determining method for the erythrocyte osmotic brittleness. It adopts turbidimetric analytic method as below: mixing the blood sample with the hypotonic solution with specific osmotic pressure, taking the undissolved erythrocyte as the main particle forming the turbidity of the mixed solution., selecting a undissolved erythrocyte which has higher absorbency to it, taking the specific wave length that the soluble coloured substance such as the free hemoglobin which is dissolved from erythrocyte have a weaker absorbency to it as the determining wave length, making turbidimetric analysis on the spectrophotometer: calculating the value of the haemolytic rate which is in direct ratio with the erythrocyte osmotic brittleness by comparing the different absorbency of erythrocyte in different duration of time and on the same determining condition within the hypotonic solution with the said specific osmotic pressure, or by comparing the different absorbency of erythrocyte between in the isotonic solution and in the above said hypotonic solution with specific osmotic pressure. The invention has the advantages of high accuracy, good repeatability of measurement, simple procedure, high velocity of determination, capability of realizing the dynamic determination and the full automatic analysis easily.
Owner:潘干华
Systems and methods for determining free plasma hemoglobin
ActiveUS9833557B2Other blood circulation devicesHaemofiltrationFree hemoglobinFree plasma hemoglobin
Owner:FENWAL
Methods of improving fluid delivery
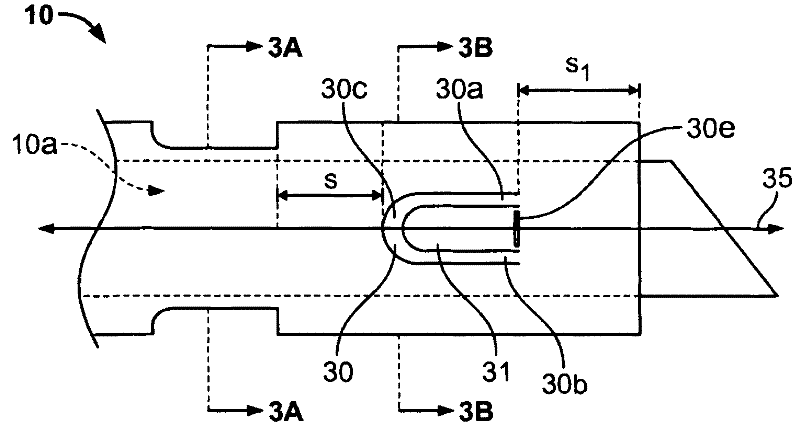
A method of reducing cell damage can include inserting device into a blood vessel, wherein the device includes a hollow shaft, a lumen, a fluid directing portion comprising a U-shaped lateral orifice extending between the exterior and interior surfaces and a corresponding U-shaped diverter adjacent to the U-shaped lateral orifice, wherein the diverter is disposed within the lumen and transverse to the central axis, and decreasing free plasma hemoglobin levels, thereby reducing damage to circulating blood cells or endothelium during dialysis.
Owner:阿尔佛雷德·R·扎拉特
Hemoglobin-based oxygen carrier and preparation method thereof
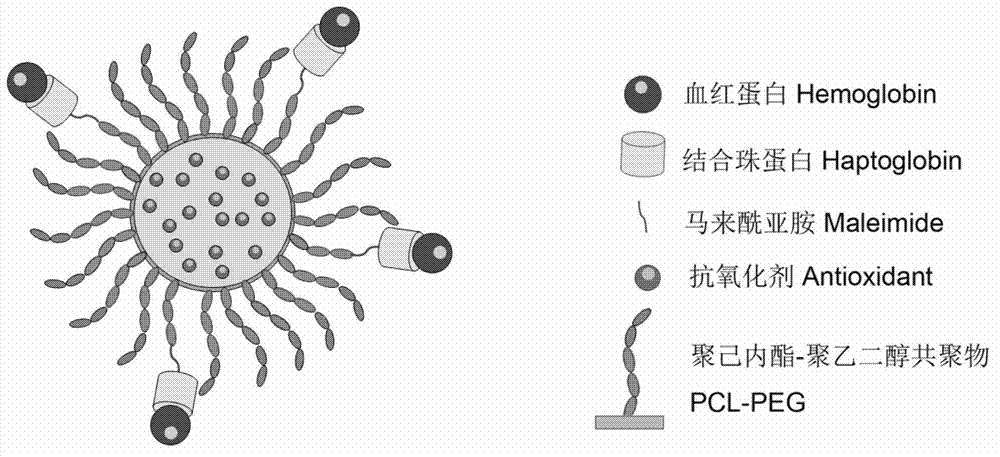
InactiveCN102861322ARealize fixed-point quantitative combinationQuality improvementPeptide/protein ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsFree hemoglobinPolyester
The invention discloses a hemoglobin-based oxygen carrier, which comprises hemoglobin, haptoglobin and polyethyleneglycol-polyester nanoparticles. Hemoglobin is connected on the surfaces of the polyethyleneglycol-polyester nanoparticles by haptoglobin. The hemoglobin-based oxygen carrier provided by the invention has no obvious toxicity on the cells, the blood plasma does not have obvious free hemoglobin in the blood plasma after the hemoglobin-based oxygen carrier is infused, and no hypertension reaction is produced, so that the defect that the traditional hemoglobin-based oxygen carrier is high in side effects is overcome. The hemoglobin-based oxygen carrier has a good application prospect and a economic benefit.
Owner:WEST CHINA HOSPITAL SICHUAN UNIV
Biological material and methods and solutions for preservation thereof
InactiveUS7935478B2Improve viabilityStabilize membraneDead animal preservationPeptide preparation methodsFree hemoglobinCryopreservation
A preservation solution for preserving a biological material at a low temperature including one or more polyphenols, and a method for preserving a biological material are provided. The method includes adding the preservation solution to a biological material, cooling the biological material and storing it under appropriate storing conditions. The method can be used for hypothermic preservation or for cryopreservation, including freezing and lyophilization, of any biological material, including cells selected from RBC, WBC, MNC, UCB, HSC and bacteria. A method is also provided for freezing RBCs such that upon thawing, the RBCs include less than 2% free hemoglobin.
Owner:CORE DYNAMICS
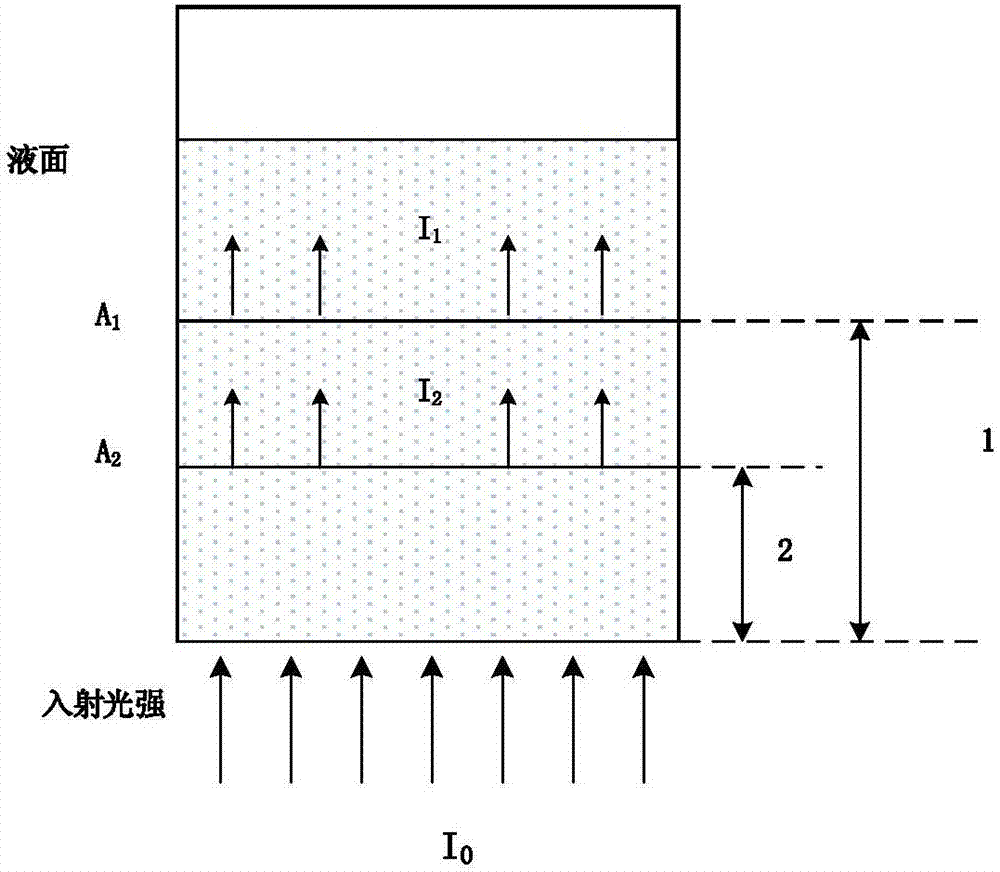
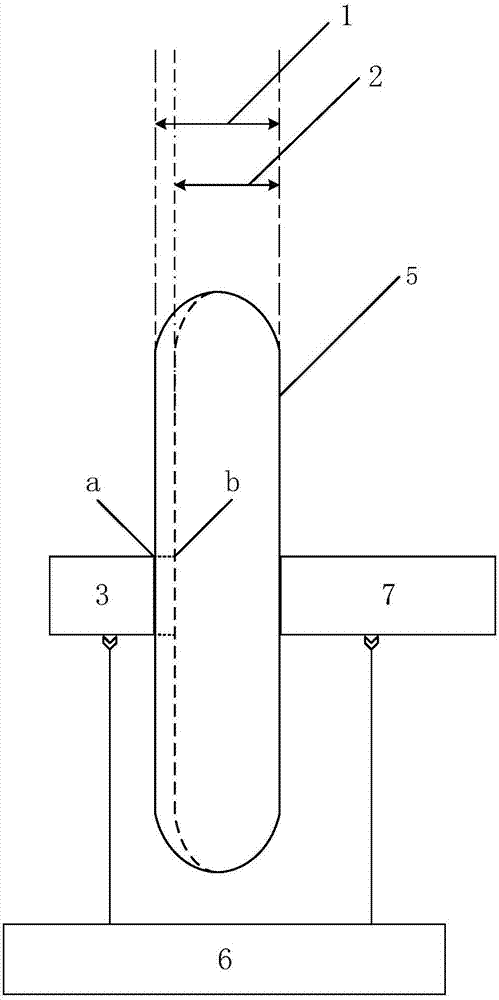
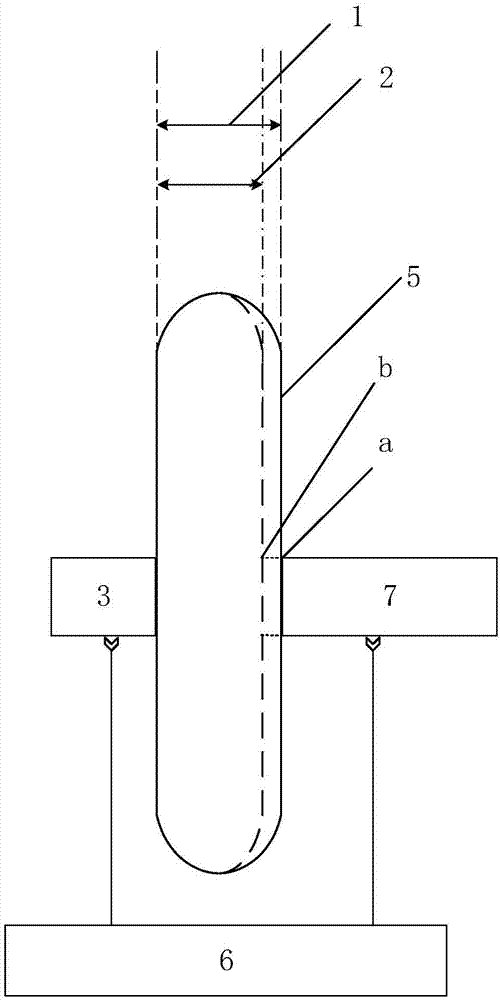
Method for nondestructive measurement of content of free hemoglobin in blood bag
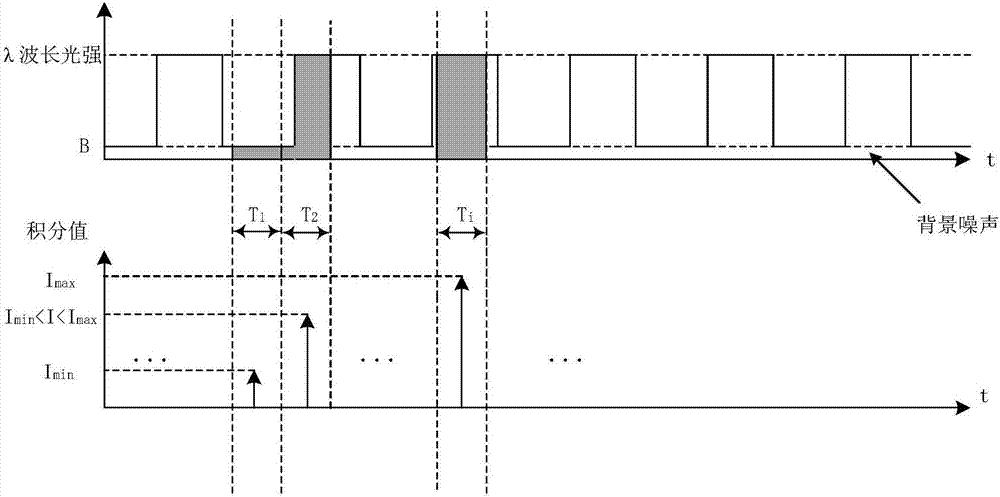
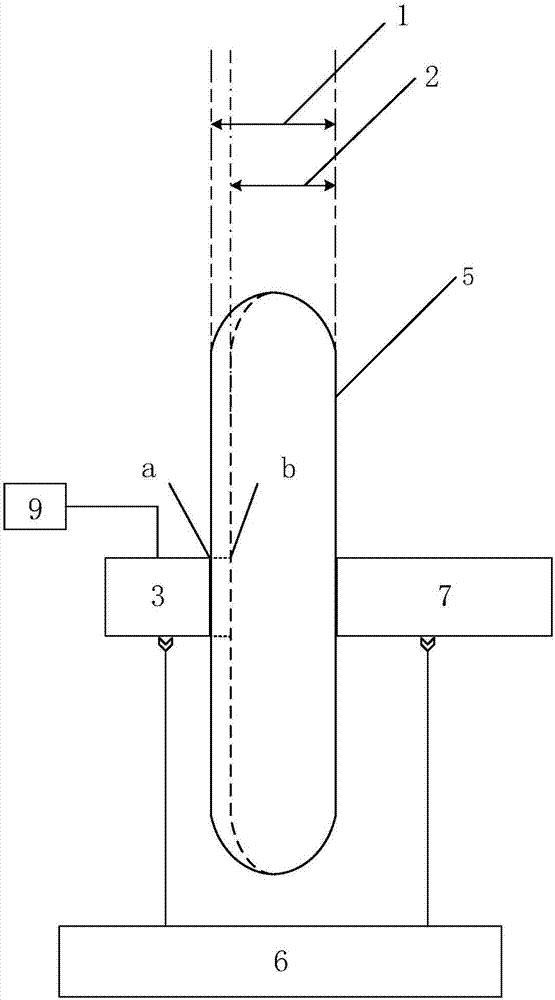
InactiveCN107367484AHigh precisionSolving NDT ProblemsColor/spectral properties measurementsFluorescence/phosphorescenceFree hemoglobinMathematical model
The invention discloses a method for nondestructive measurement of the content of free hemoglobin in a blood bag. The method comprises the following steps that a modulation apparatus modulates a light source; a displacement platform controls the light source to move to dual-light-path locations of a plurality of positions for transmission and excitation of blood separately; a spectrum receiving apparatus acquires the dual-light-path transmission and fluorescence spectra of each position; the dual-light-path transmission and fluorescence spectra are converted to frequency domains for construction of within-frequency-domain transmission spectra and within-frequency-domain fluorescence spectra; the logarithm of a ratio of transmission spectra in two frequency domains at each position is calculated so as to obtain the absorption spectrum of the blood at the position, the absorption spectra at the plurality of positions and the fluorescence spectra of the plurality of positions in dual-light-path frequency domains are subjected to normalization together, and then a mathematic model is established on the basis of the normalization and chemical examination data; and the absorption spectra and within-frequency-domain of an unknown complex solution at a plurality of positions are acquired by using same methods mentioned above, then subjected to normalization and finally substituted into the mathematic model so as to obtain the content of free hemoglobin.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Determination Of Cause Of Redness In Biological Fluid
An optical sensor device includes a light source configured to emit a light including a wavelength in a range of 650 to 900 nm that is exposed to a biological fluid at first and second times. At least a portion of the light is reflected off of the fluid and received by a light detector. The light detector analyzes at least a portion of the received light to determine a first intensity of the light at the wavelength at the first time and a second intensity of the light at the wavelength at the second time. A controller compares the first and second intensities and generates an output indicative of the presence of red blood cells or free hemoglobin in the biological fluid depending on which intensity is greater and whether there is more redness in the biological fluid at the first time or at the second time.
Owner:FENWAL
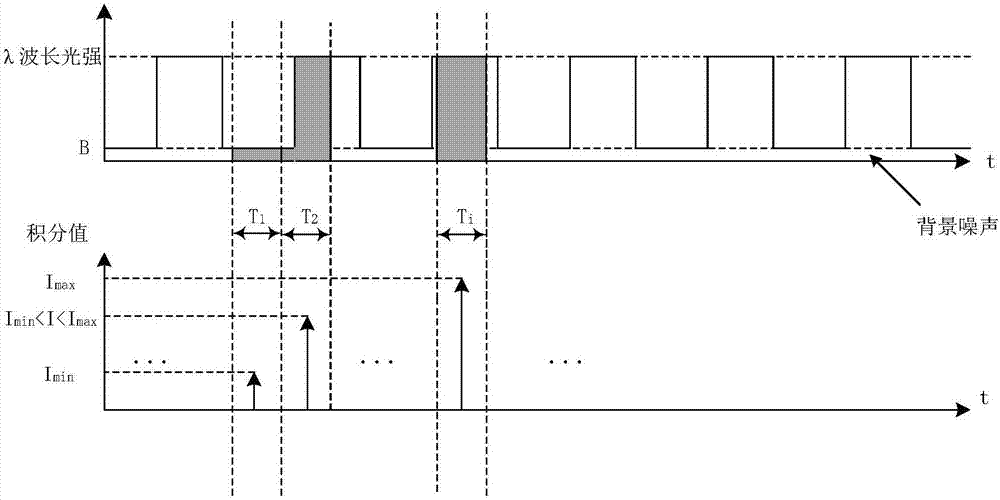
Method for measuring content of free hemoglobin in blood bag by multiple-position modulated light source
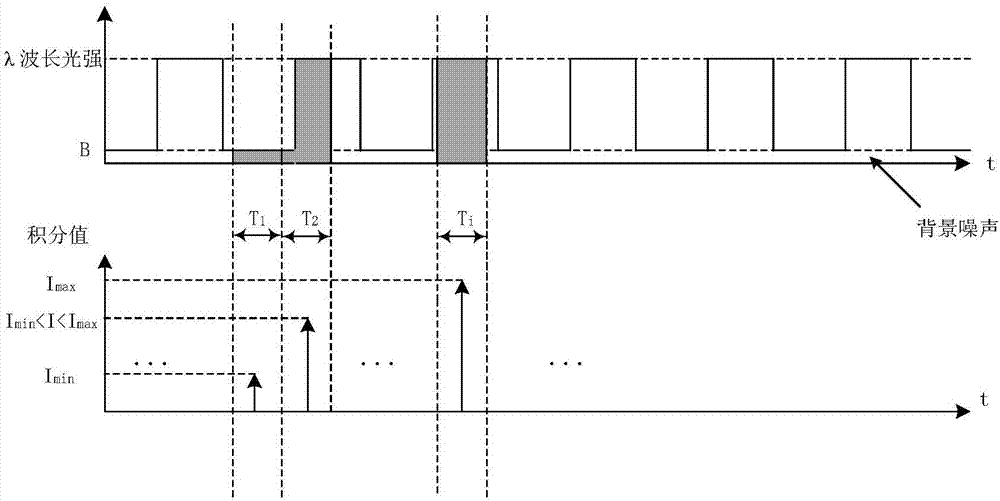
InactiveCN107356533ARemove background noiseLarge amount of informationColor/spectral properties measurementsFree hemoglobinMathematical model
The invention discloses a method for measuring the content of free hemoglobin in a blood bag by a multiple-position modulated light source. The method comprises the following steps: modulating a light source by a modulation device, allowing the light exit port of the light source and the entrance slit of a spectrum receiving device to cling to the blood bag, controlling the light source to move to multiple positions by a displacement platform in order to transmit a blood sample, and acquiring the transmission spectrum by the spectrum receiving device; transforming the time sequence of every wavelength in the acquired transmission spectrum into a frequency domain, constructing a transmission spectrum in the frequency domain based on the fundamental wave component of every wavelength, carrying out normalization processing, comparing the obtained result with existing chemical analysis results, and establishing a mathematical model; and acquiring the transmission spectrum in the frequency domain of an unknown blood sample through using above steps, normalizing the obtained transmission spectrum, and substituting the normalization result into the mathematical model in order to obtain the content of the free hemoglobin. The method eliminates the influences brought by spectral background noises and scattering, increases the information content of all components in the blood, and improves the precision of the free hemoglobin content analysis.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Method for determining red blood cell penetration fragility
InactiveCN1268928CEasy to operateShorten the timeMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorTransmissivity measurementsTurbidityFragility
The invention relates to a determining method for the erythrocyte osmotic brittleness. It adopts turbidimetric analytic method as below: mixing the blood sample with the hypotonic solution with specific osmotic pressure, taking the undissolved erythrocyte as the main particle forming the turbidity of the mixed solution., selecting a undissolved erythrocyte which has higher absorbency to it, taking the specific wave length that the soluble coloured substance such as the free hemoglobin which is dissolved from erythrocyte have a weaker absorbency to it as the determining wave length, making turbidimetric analysis on the spectrophotometer: calculating the value of the haemolytic rate which is in direct ratio with the erythrocyte osmotic brittleness by comparing the different absorbency of erythrocyte in different duration of time and on the same determining condition within the hypotonic solution with the said specific osmotic pressure, or by comparing the different absorbency of erythrocyte between in the isotonic solution and in the above said hypotonic solution with specific osmotic pressure. The invention has the advantages of high accuracy, good repeatability of measurement, simple procedure, high velocity of determination, capability of realizing the dynamic determination and the full automatic analysis easily.
Owner:潘干华
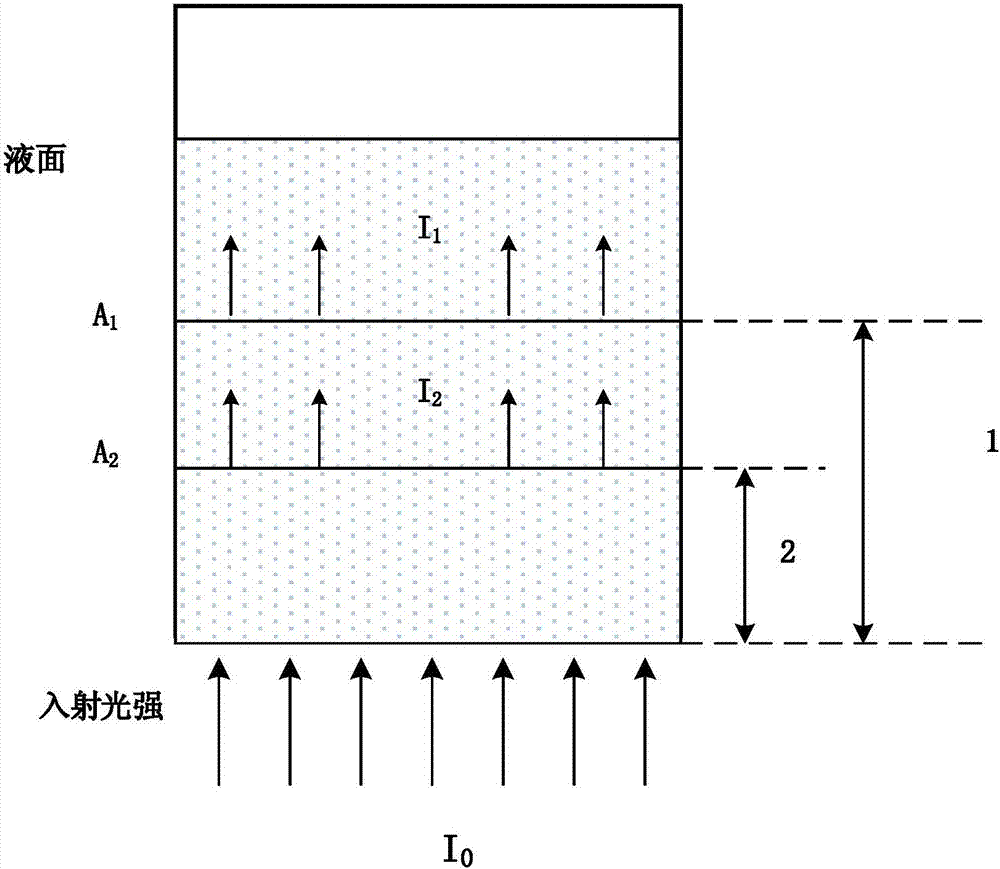
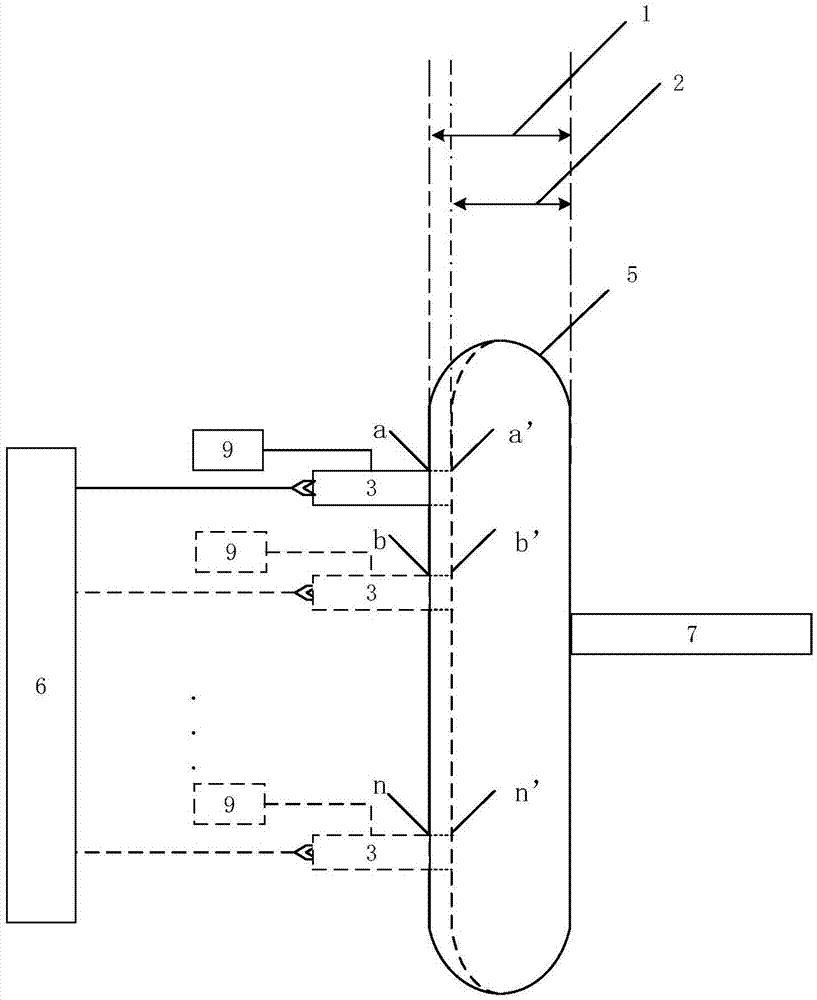
Optical Detection And Measurement Of Hematocrit And Free Hemoglobin Concentration
ActiveUS20190313953A1Other blood circulation devicesScattering properties measurementsFree hemoglobinOptical spectrometer
A colorimetric optical sensor device includes a broadband light source configured to emit a light that is exposed to a fluid in a vessel. At least a portion of the light is reflected off of the fluid and received by an optical spectrometer. The optical spectrometer analyzes at least a portion of the received light to determine a main wavelength of the light. A controller correlates the main wavelength to a corresponding hematocrit or free hemoglobin concentration and generates an output indicative of the hematocrit or the free hemoglobin concentration of the fluid. The hematocrit or free hemoglobin concentration information may be used by a separation assembly in which the colorimetric optical sensor device may be incorporated to modify a separation procedure in which the monitored fluid is to be separated or is a component or constituent of a previously separated biological fluid.
Owner:FENWAL
Liquid for preserving red cells of ursid and application of liquid for preserving red cells of ursid
ActiveCN107873696AImprove maintenance effectThe save effect is validDead animal preservationFree hemoglobinMANNITOL/SORBITOL
The invention relates to a liquid for preserving red cells of a ursid. The liquid for preserving the red cells of the ursid comprises NaCl, NaH2PO4, ATP, glucose, mannitol and glutathione. According to the blood physiological characteristics of pandas, four liquids for preserving the red cells are prepared, and tests of free hemoglobins in supernatant of the liquids for preserving the red cells atdifferent time points indicate that: the B3 liquid has significant differences from other liquids on the tenth day, the B2 and B3 liquids have significant differences from the other two liquids on the 20th day, and the B2, B3 liquids have significant differences from the other two liquids on the 30th day. The results show that the B3 liquid is the best system for preserving the red cells; the preservation effect of the B3 liquid is verified by using ATP tests and 2,3-DPG tests, and results show that: the content of ATP and 2,3-DPG in the B3 liquid is significantly different from that in the B1 liquid, and it is indicated that the B3 liquid has a better effect on the preservation of the red cells of the pandas. The liquid for preserving the red cells can preserve the red cells of the ursideffectively for 30 days, and can be applied to clinical red cell transfusion of the ursid.
Owner:SHANGHAI BLOOD CENT
Systems And Methods For Determining Free Plasma Hemoglobin
A system is provided for separating a plasma-containing fluid into separated plasma and a concentrated fluid. The system cooperates with a fluid flow circuit including a fluid separation chamber and a plasma outlet line associated therewith for removing separated plasma from the fluid separation chamber. The system includes an optical sensor assembly to monitor the contents of the plasma outlet line and produce an output indicative of the concentration of free plasma hemoglobin in the plasma outlet line. A controller of the system calculates the amount of free plasma hemoglobin in at least a portion of the concentrated fluid based at least in part on the output of the optical sensor assembly. The controller may periodically calibrate the optical sensor assembly by determining an instrument-specific correlation between optic output and free hemoglobin concentration and comparing it to experimentally determined data to ensure continued reliability of the optical sensor assembly.
Owner:FENWAL
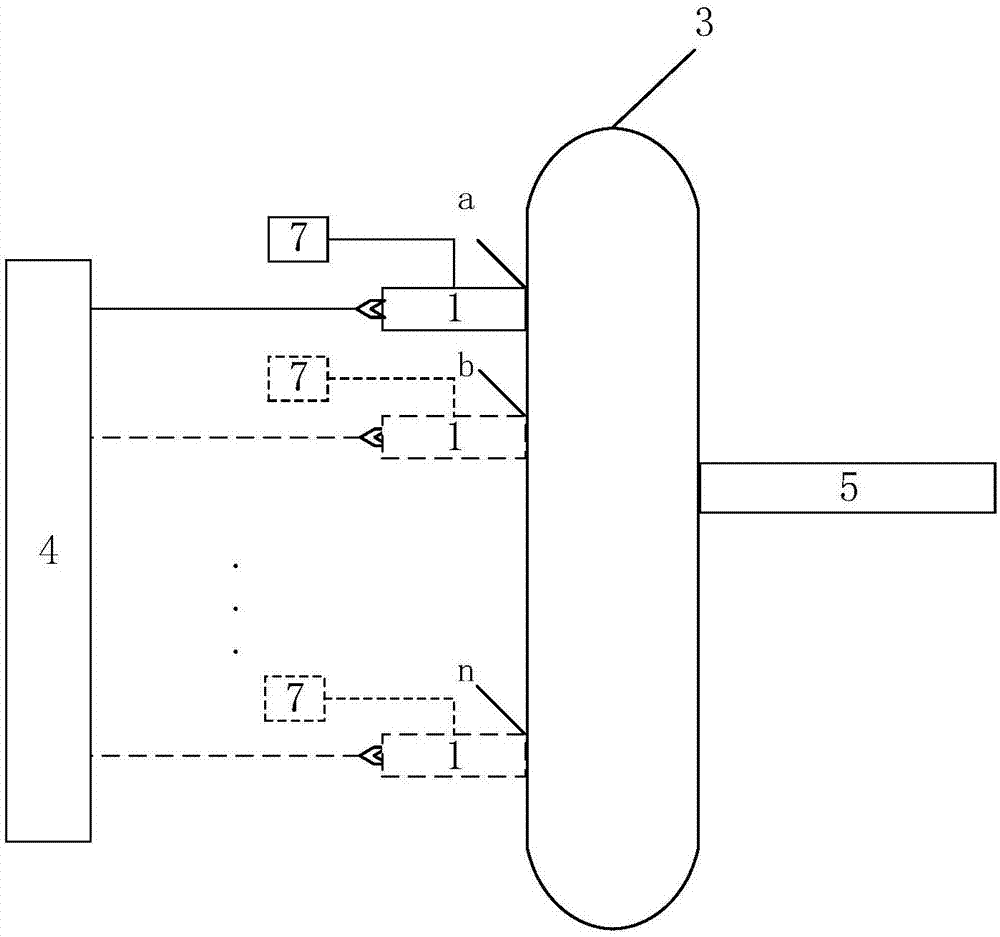
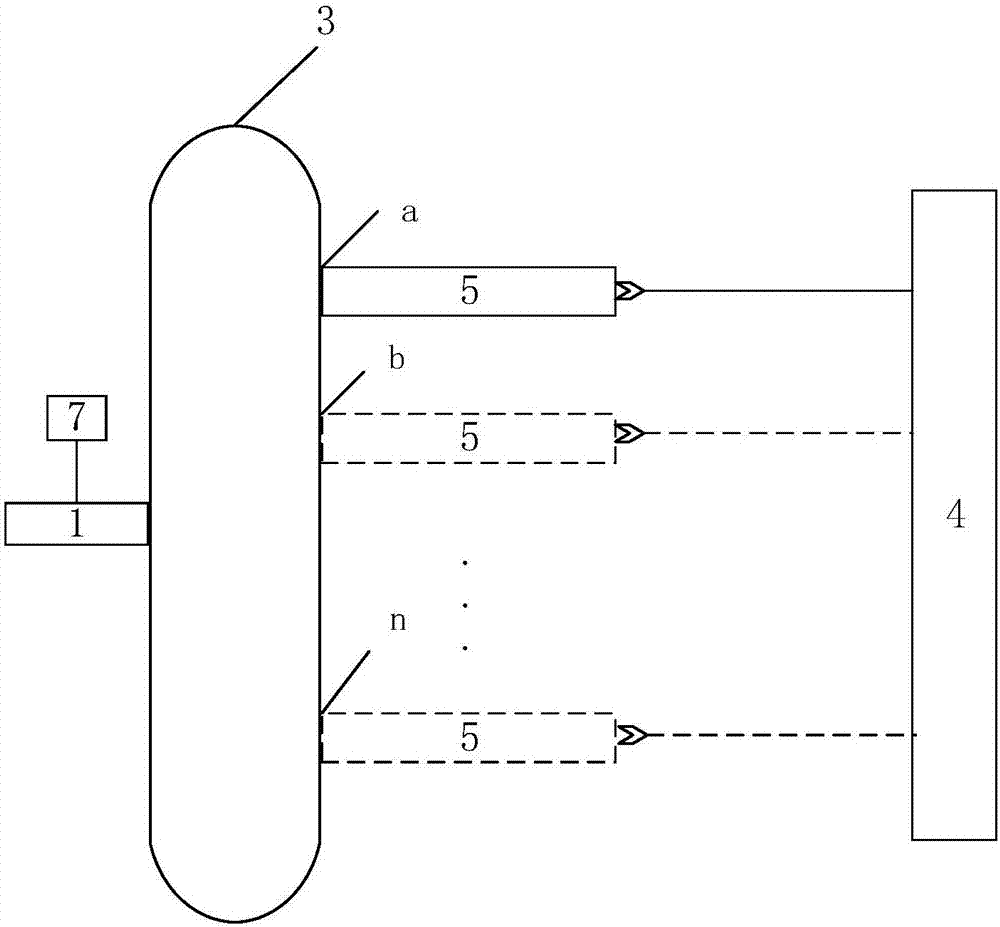
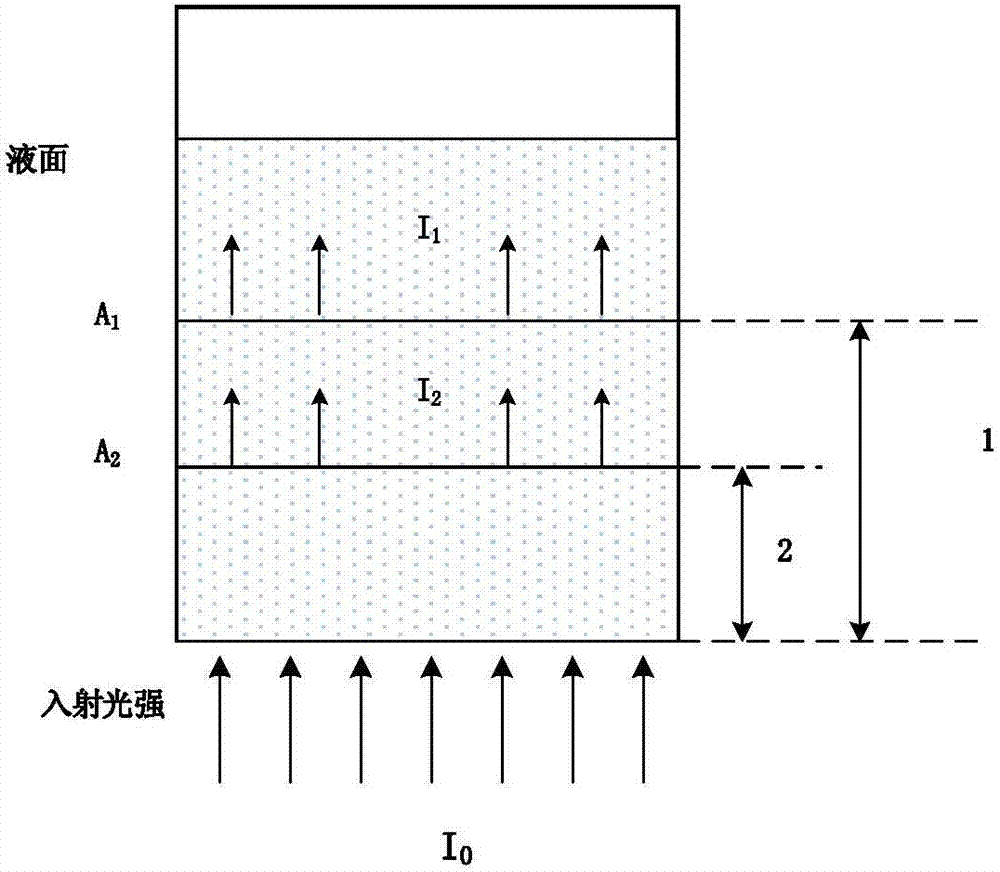
Method for measuring content of free hemoglobin in blood bag based on multi-position transmission spectra
InactiveCN107421901ALarge amount of informationInhibition effectColor/spectral properties measurementsFree hemoglobinMathematical model
The invention discloses a method for measuring the content of free hemoglobin in a blood bag based on multi-position transmission spectra. The method comprises the steps that the emergent light outlet of a light source and the incident slit of a spectrum receiving device both cling to the blood bag, the light source carries out transmission on a blood sample, a displacement platform controls the light source to move to a plurality of positions for transmission of the blood sample, and the spectrum receiving device acquires transmission spectra; and the transmission spectra acquired at the plurality of positions are subjected to normalization, and a mathematical model is constructed on the basis of the normalized transmission spectra and chemical examination data; the transmission spectra of an unknown blood sample at a plurality of positions are acquired and are separately normalized and then substituted into the mathematical model for calculation so as to obtain the content of free hemoglobin. The method provided by the invention improves the information amounts of all the components in blood, suppresses influence caused by the scattering of blood, and improves the analysis precision of the free hemoglobin content.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Method for measuring content of free hemoglobin by double-optical-path transmittance and fluorescence spectra
InactiveCN107421922ASuppression of non-linear effectsQuick measurementColor/spectral properties measurementsFluorescence/phosphorescenceMathematical modelOptical path length
The invention discloses a method for measuring the content of free hemoglobin by double-optical-path transmittance and fluorescence spectra. The method includes transmitting a blood sample in a blood bag by a transmittance light source, and exciting the blood sample in the blood bag by the fluorescence excitation light source, wherein light sources include the transmittance light source and the fluorescence excitation light source; controlling the light sources to move by a displacement platform on the premise that the light outlets of the light sources are coaxial with a entrance slit of a spectrum receiving device, and collecting the transmittance spectra and the fluorescence spectra by the spectrum receiving device; solving the logarithm of the light intensity ratio of the double-optical-path transmittance spectra under each wavelength to acquire absorption spectra, combining and normalizing the absorption spectra and the two fluorescence spectra, combining with chemical testing data, and creating a mathematical model; collecting transmittance spectra and fluorescence spectra of an unknown blood sample under two optical paths, and after normalization, inputting the absorption spectra, acquired by solving the logarithm of the ratio of the two transmittance spectra, and the two fluorescence spectra into the mathematical model for calculation to acquire the content of the free hemoglobin.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
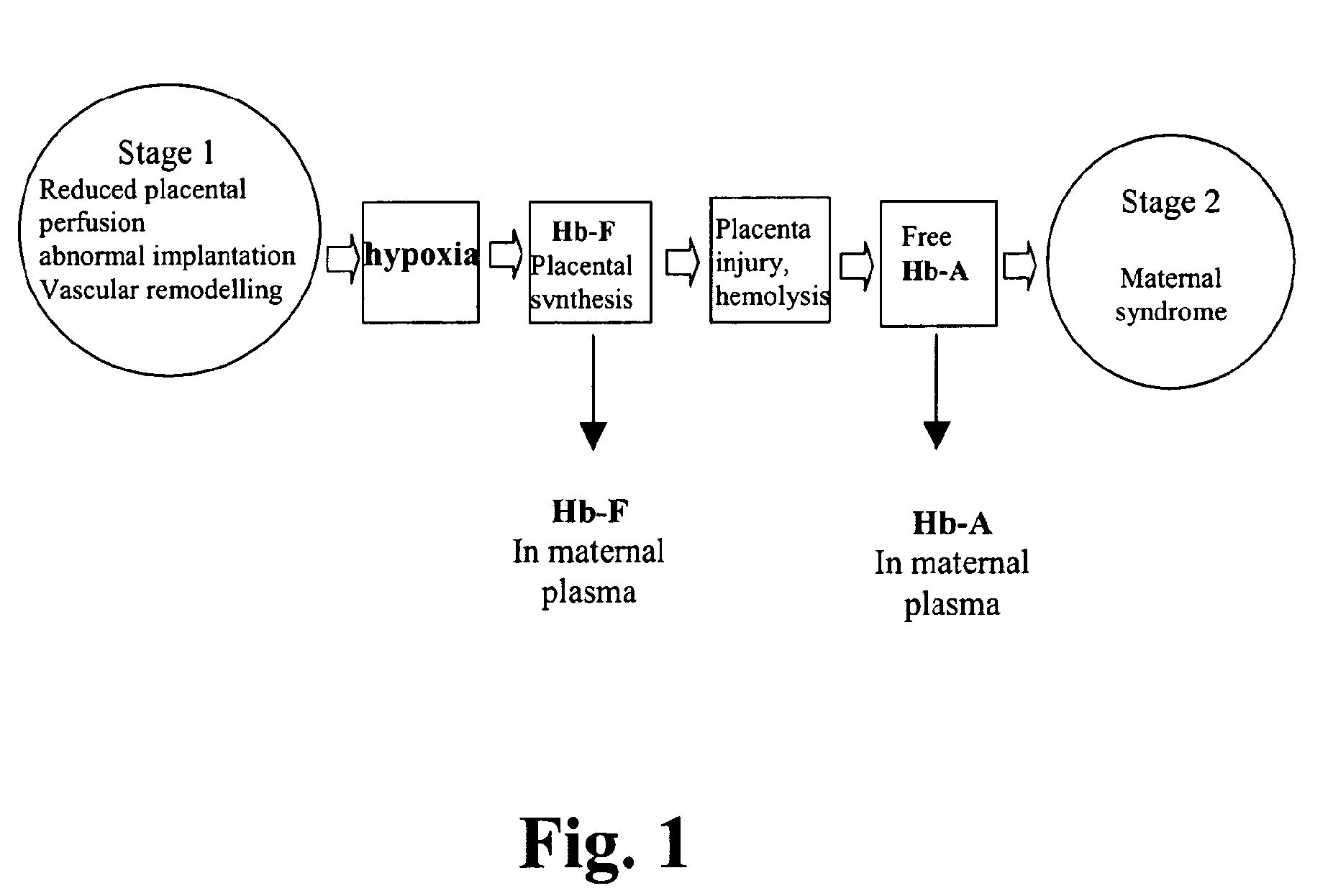
Diagnosis and treatment of preeclampsia
InactiveUS20100105070A1Avoid unnecessary hospitalisationReduce riskPeptide/protein ingredientsDisease diagnosisDiagnosis earlyFree haemoglobin
The present invention relates to biomarkers for preeclampsia as well as treatment of this disease. In particular, the invention relates to methods for diagnosis or aiding in the diagnosis of preeclampsia of a pregnant female mammal to detect elevated levels of free haemoglobin, particularly free fetal haemoglobin. This facilitates and makes possible early diagnosis and clinical intervention when a preeclamptic condition is found. In addition, the invention relates to a method to treat female mammals with preeclampsia with the purpose to reverse the pathological conditions associated with this disease.
Owner:GUARD THERAPEUTICS INT AB
Method for measuring free hemoglobin in blood bag based on double-light-path within-frequency-domain fluorescence intensities
InactiveCN107367493AEliminate background noise effectsLarge amount of informationFluorescence/phosphorescenceFree hemoglobinMathematical model
The invention discloses a method for measuring free hemoglobin in a blood bag based on double-light-path within-frequency-domain fluorescence intensities. The method comprises the following steps that a square signal drives a fluorescent excitation light source, the emergent light outlet of the fluorescent excitation light source and the incident slit of a light intensity receiving device both cling to the blood bag and are coaxial, the fluorescent excitation light source excites a blood sample to generate fluorescent light, and the light intensity receiving device receives a fluorescence intensity; a displacement platform controls the fluorescent excitation light source to move on the premise that the emergent light outlet of the fluorescent excitation light source and the incident slit of the light intensity receiving device are ensured to be coaxial, and the light intensity receiving device receives another fluorescence intensity; the two acquired fluorescence intensities are respectively converted to a frequency domain for construction of within-frequency-domain fluorescence intensities, then normalization is carried out, and a mathematical model is constructed after normalization on the basis of chemical examination data; the fluorescence intensities of an unknown blood sample at two positions are collected and respectively converted to the frequency domain for construction of within-frequency-domain fluorescence intensities, then normalization is carried out, and the normalized fluorescence intensities are substituted into the mathematical model for calculation of the content of free hemoglobin. The method provided by the invention greatly inhibits non-linear influence caused by self absorption of fluorescent light.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Discerning between the presence of red blood cells and free hemoglobin in a biological fluid
Owner:FENWAL
Method for measuring content of free hemoglobin in blood bag by dual-light path modulated light source
InactiveCN107167440AEliminate the effects ofImprove analysis accuracyColor/spectral properties measurementsFree hemoglobinMathematical model
The invention discloses a method for measuring the content of free hemoglobin in a blood bag by a dual-light path modulated light source. The method comprises the following steps: modulating a light source by a modulation device, allowing the light exit port of the light source and the entrance slit of a spectrum receiving device to be close to and coaxial with a packaging bag, allowing the light source to transmit a blood sample, and acquiring the transmission spectrum by the spectrum receiving device; controlling the light source to move by a displacement platform on the premise of guaranteeing that the light exit port of the light source is coaxial with the entrance slit of the spectrum receiving device, and acquiring the transmission spectrum by the spectrum receiving device; transforming the time sequence of every wavelength in the acquired transmission spectrum into a frequency domain, constructing a transmission spectrum in the frequency domains based on the fundamental wave component of every wavelength, carrying out logarithm calculation on the light intensity ratio at every wavelength of the transmission spectrum in the constructed two frequency domains to obtain absorption spectra, carrying out normalization processing, comparing the obtained result with existing chemical analysis results, and establishing a mathematical model; and acquiring the absorption spectrum of unknown blood through using above steps, normalizing the absorption spectrum, and substituting the obtained normalization result into the to the mathematical model in order to obtain the content of the free hemoglobin.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Detection of hemolysis using a chromatographic detection pad
In one aspect, the inventive concepts disclosed herein are directed to a chromatographic assay device for detecting the presence of free hemoglobin in a whole blood sample. The device comprising a chromatographic detection pad with a sample application site and a detection side. The chromatographic detection pad defines a path for capillary fluid flow. The chromatographic detection pad has a pore size. The sample application site on the chromatographic detection pad is for application of a portion of the whole blood sample. The detection site on the chromatographic detection pad is spaced apart from the application site and is downstream of the sample application site. The chromatographic detection pad is devoid of a compound located downstream of the application site that is reactive to the whole blood sample.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE DIAGNOSTICS INC
Optical detection and measurement of hematocrit and free hemoglobin concentration
ActiveUS10893829B2Other blood circulation devicesScattering properties measurementsOptical transducersPhotochemistry
Owner:FENWAL
A detection device for detecting free hemoglobin in sputum
ActiveCN103175828BLow costQuick screeningMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorFree hemoglobinHeme
The invention relates to a detection device for detecting free hemoglobin in sputum. The detection device includes a sample tube, a reagent tube and a pointed dropper, and the reagent tube includes a first reagent tube at the upper part and a second reagent tube at the lower part , the tube bottom of the first reagent tube is funnel-shaped, the bottom of the tube bottom is provided with a nozzle, the nozzle is sealed with tin foil, the tube wall of the first reagent tube extends downwards with a connecting ring, the tube of the second reagent tube The mouth is sealed and connected with the connecting ring, and the detection device provided by the invention is simple, practical, and low in cost, and can quickly screen out whether the sputum contains free hemoglobin.
Owner:崔子伦
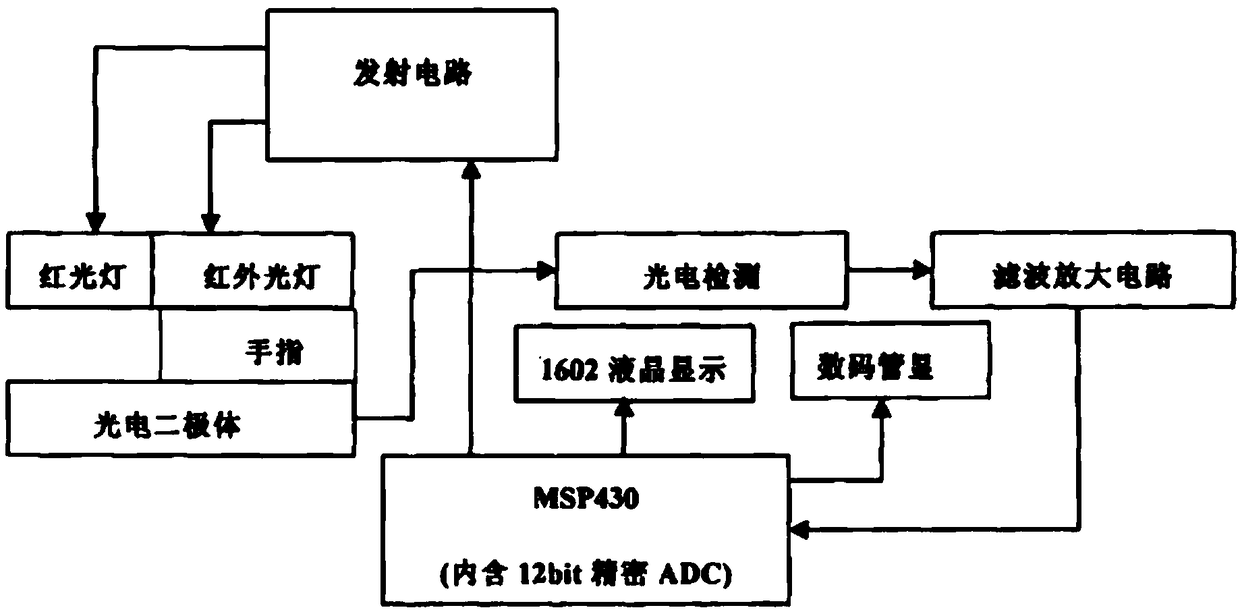
Embedded family medical blood oxygen degree-of-saturation collecting terminal and collecting method thereof
InactiveCN108836355ARealize seekingSmart Medical ConvenienceDiagnostic signal processingSensorsFree hemoglobinInfrared lamp
The invention discloses an embedded family medical blood oxygen degree-of-saturation collecting terminal and a collecting method thereof. The collecting terminal comprises a finger clamp type blood oxygen probe which is in network connection to a central host computer; the finger clamp type blood oxygen probe comprises an embedded microprocessor which is connected to an emitting circuit. The emitting circuit comprises a red lamp and an infrared lamp; red light and infrared light sent by the red lamp and the infrared lamp penetrate the finger and radiate a photoelectric diode below the finger,the photoelectric diode is connected to a filter amplifying circuit through a photoelectric detection circuit, and the filter amplifying circuit is connected to the embedded microprocessor. Accordingto the collecting method, by means of absorbing difference of oxygen-containing hemoglobin and oxygen-free hemoglobin to red light and infrared light and I-V conversion through the photoelectric detection circuit, a blood oxygen degree-of-saturation calculating formula is deduced according to Beer-Lambert law to solve the blood oxygen saturation, so that people can measure the blood oxygen degree-of-saturation in person.
Owner:莫毓昌
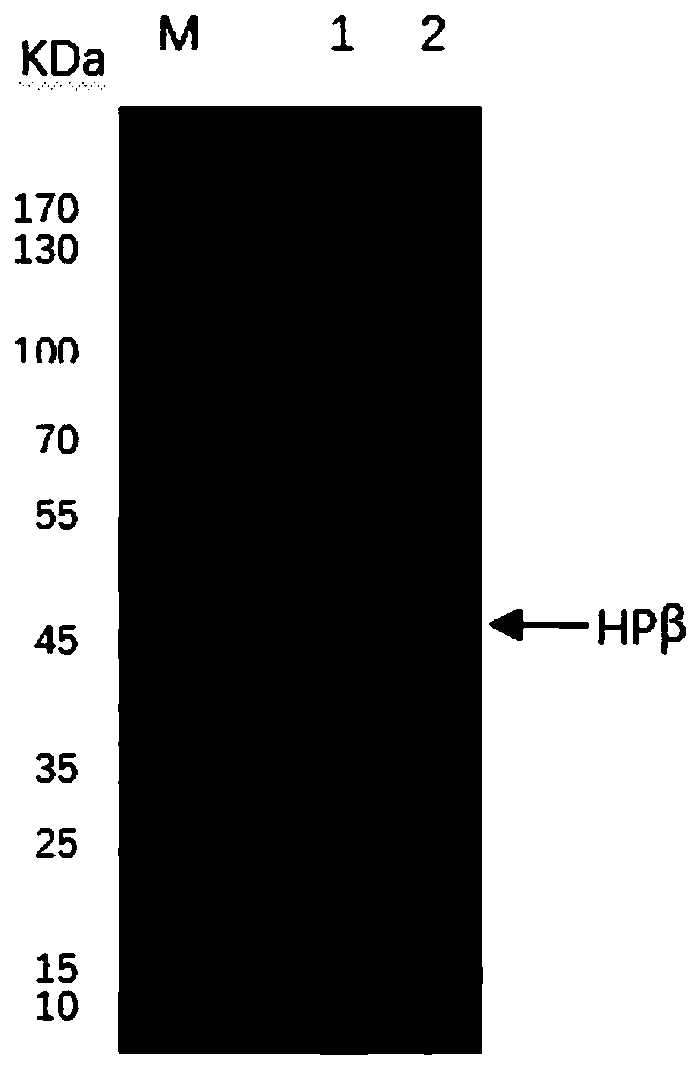
Expression and purification method of recombinant human haptoglobin beta subunit protein
InactiveCN110724185AImprove solubilityEasy to purifyMicroorganism based processesPeptide preparation methodsEscherichia coliFree hemoglobin
The invention discloses an expression and purification method of recombinant human haptoglobin beta subunit protein. According to the invention, a human haptoglobin full-length gene is artificially synthesized, and the human haptoglobin beta subunit gene is amplified by the PCR technology; then, the gene is expressed in Escherichia coli Shuffle T7-B using a prokaryotic expression system. Afterwards, protein purification is performed using a His-tagged soluble protein purification kit to obtain the recombinant human haptoglobin beta subunit recombinant protein. The recombinant human haptoglobinbeta subunit protein prepared according to the method of the invention has the characteristics of high yield of soluble protein and simple operation, and can be used to further study the function ofthe protein to bind hemoglobin in vitro and to remove free hemoglobin from plasma.
Owner:INST OF ENVIRONMENTAL MEDICINE & OCCUPATIONAL MEDICINE ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICINE ACAD OF MILITARY SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com