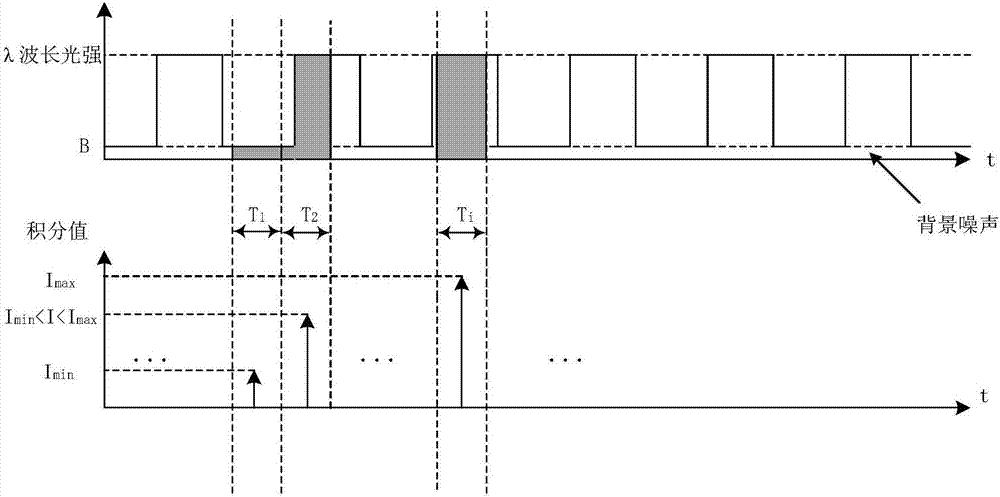
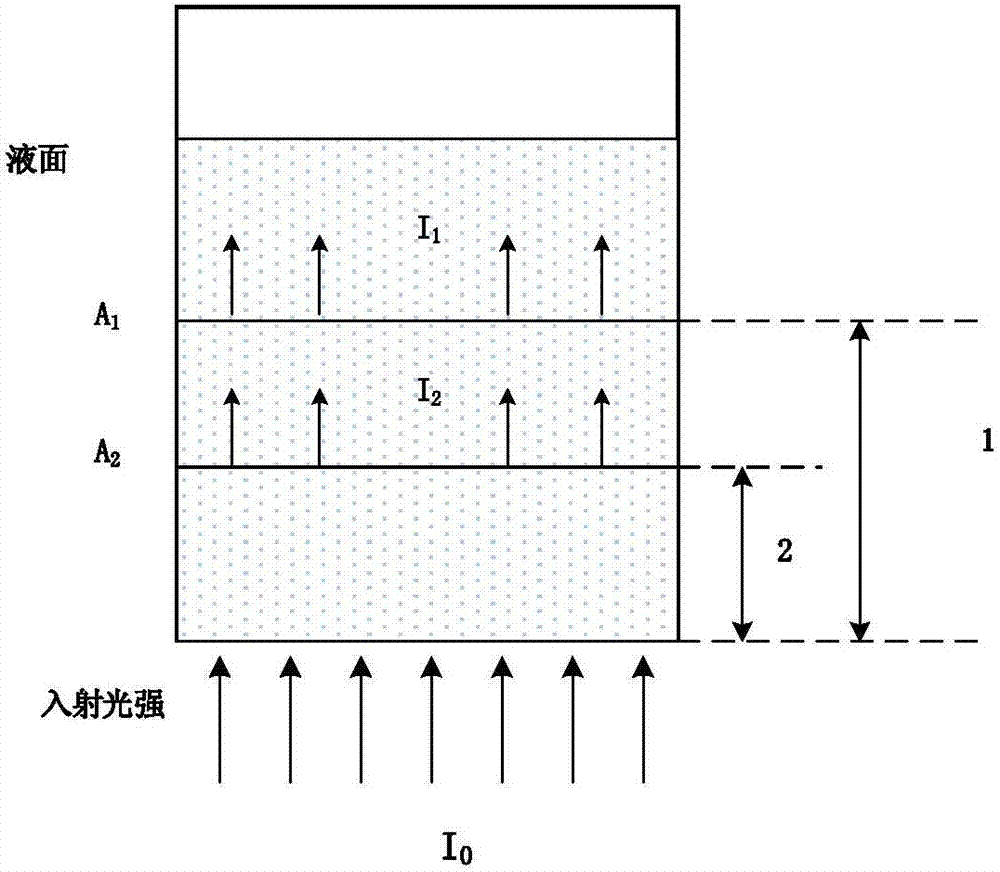
Method for measuring content of free hemoglobin in blood bag by dual-light path modulated light source
A technology for modulating light source and hemoglobin, which is applied in color/spectral characteristic measurement, measuring device, material analysis through optical means, etc. It can solve the problem that it is difficult to ensure that the position of the sample and the neutral attenuator are consistent, and it is difficult to find the neutral attenuator and other problems, to achieve the effect of solving non-destructive testing problems, eliminating the influence of spectral background noise, and strong operability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
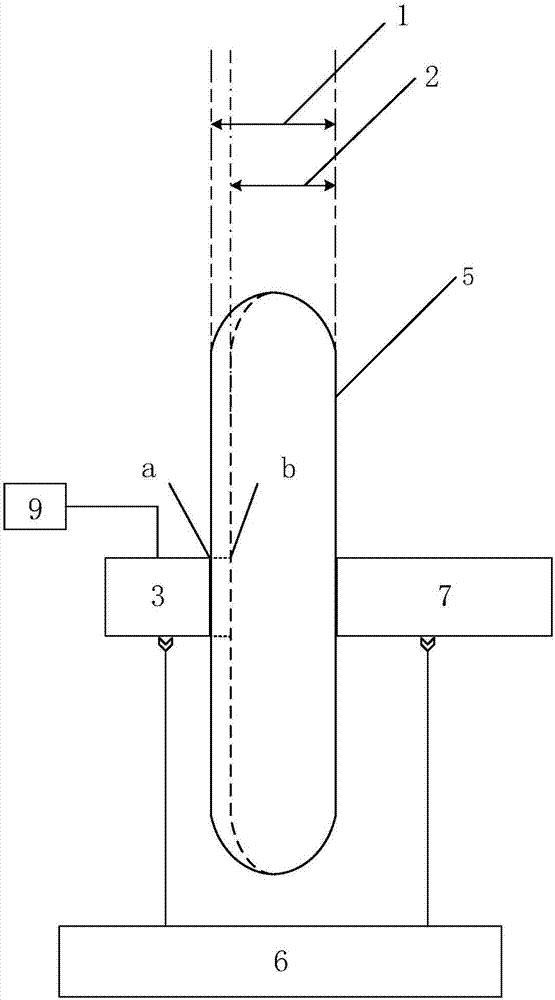
[0072] The embodiment of the present invention provides a method for measuring the content of free hemoglobin in a blood bag with a dual optical path modulation light source. The devices used are such as image 3 As shown, it includes: a light source 3 , a blood bag 5 , a displacement platform 6 , a spectrum receiving device 7 and a modulation device 9 .
[0073] Wherein, ensure that the light output port of the light source 3 and the incident slit of the spectrum receiving device 7 are close to the blood bag 5 and coaxial, the modulation device 9 modulates the light source 3 so that it sends out a square wave light signal, and the light source 3 is at the first position a (corresponding to the first light Process 1) transmits the blood sample in the blood bag 5, and the transmission spectrum is collected by the spectrum receiving device 7. Then, the displacement platform 6 controls the light source to move to the second position b (corresponding to the second optical path 2) ...
Embodiment 2
[0082] The difference between the embodiment of the present invention and embodiment 1 is only that the light source 3 and the movement mode of the spectrum receiving device 7 are different, see the following description for details:
[0083] see Figure 4 To ensure that the light outlet of the light source 3 and the incident slit of the spectrum receiving device 7 are close to the blood bag 5 and coaxial, the modulation device 9 modulates the light source 3 so that it sends out a square wave light signal, and the light source 3 transmits the blood sample in the blood bag 5, The transmission spectrum is acquired by the spectral receiving device 7 at the first position a. Then, under the premise of ensuring that the light outlet of the light source 3 is coaxial with the incident slit of the spectrum receiving device 7, the displacement platform 6 controls the spectrum receiving device 7 to move to the second position b, and collects the transmission spectrum at the second posit...
Embodiment 3
[0088] The difference between the embodiment of the present invention and embodiment 1 is only that the light source 3 and the moving direction of the spectrum receiving device 7 are different, see the following description for details:
[0089] see Figure 5 , ensure that the light source 3 and the spectrum receiving device 7 are close to the blood bag 5 and ensure that the light outlet of the light source 3 is coaxial with the incident slit of the spectrum receiving device 7, and the modulating device 9 modulates the light source 3 so that it sends out a square wave optical signal, at the first position a The blood sample in the blood bag 5 is transmitted by the light source 3, and the transmission spectrum is collected by the spectrum receiving device 7 at the first position a', and then the displacement platform 6 is used to ensure that the light output port of the light source 3 and the light spectrum receiving device 7 incident narrow On the premise that the slits are co...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com