Anionic displacer molecules for hydrophobic displacement chromatography
A technique of displacement chromatography, hydrophobicity, applied in the field of anion displacer molecules for hydrophobic displacement chromatography, which can solve the problem that the displacer compound does not work well
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0198] If the first DC experiment with loaded samples resulted in an overloaded condition (>100% loading), the experiment was rerun at half the sample concentration. From the results of the first successful DC experiment using the sample, the actual loading concentration and actual column loading capacity were easily calculated, and these values were then used to adjust the sample concentration and loading for the second DC experiment.
[0199] Sample Preparation - Prepare loading sample solutions at the concentrations and amounts described above. A sufficient excess of solution is required to overfill the loop or to fill the dead volume of the sample loading pump and delivery line. The pH, the amount of pH buffer and the amount of organic solvent are the same as the carrier and displacer buffers. Dissolving the sample in the carrier changes its pH, so the pH of the sample solution must be adjusted again after dissolution. However, the amount of ion-pairing reagent can v...
Embodiment 2
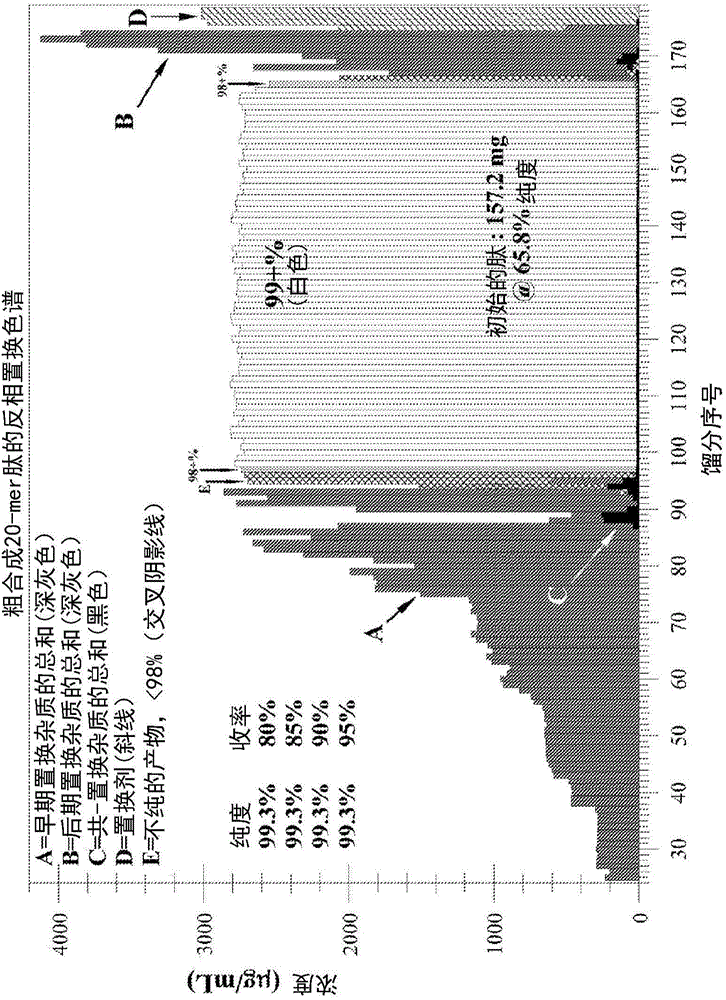
[0252] Example 2: Displacement Protocol for Purification of Crude Synthetic Oligonucleotides
[0253] Instrument configuration : Main pump (1) with 4 buffer lines, sample loading pump (2) with 1 solvent line, pump selector valve, column bypass valve
[0254] Pump selector valve: 6-way valve controlled by single-channel toggle logic (S3=0, pump 1 to column-pump 2 to waste; S3=1, pump 1 to waste- pump 2 to column)
[0255] Column valve: 6-way valve, which is controlled by a single channel switching logic (S6 = 0, liquid flows through the column; S6 = 1, liquid flow bypasses the column)
[0256] A UV photodiode array detector (flow cell: 0.5 mm flow, 9 μL volume) after the column, followed by a conductivity detector (flow cell: 170 μL volume); the conductivity flow cell was removed when fractions were collected for analysis.
[0257] Loading buffer = A-line on pump 1 (S1 = 1 - flow on, S1 = 0 - flow off); Displacer buffer = B-line on pump 1 (S2 = 1 - flow on, S2 = 0 - flow o...
Embodiment 3
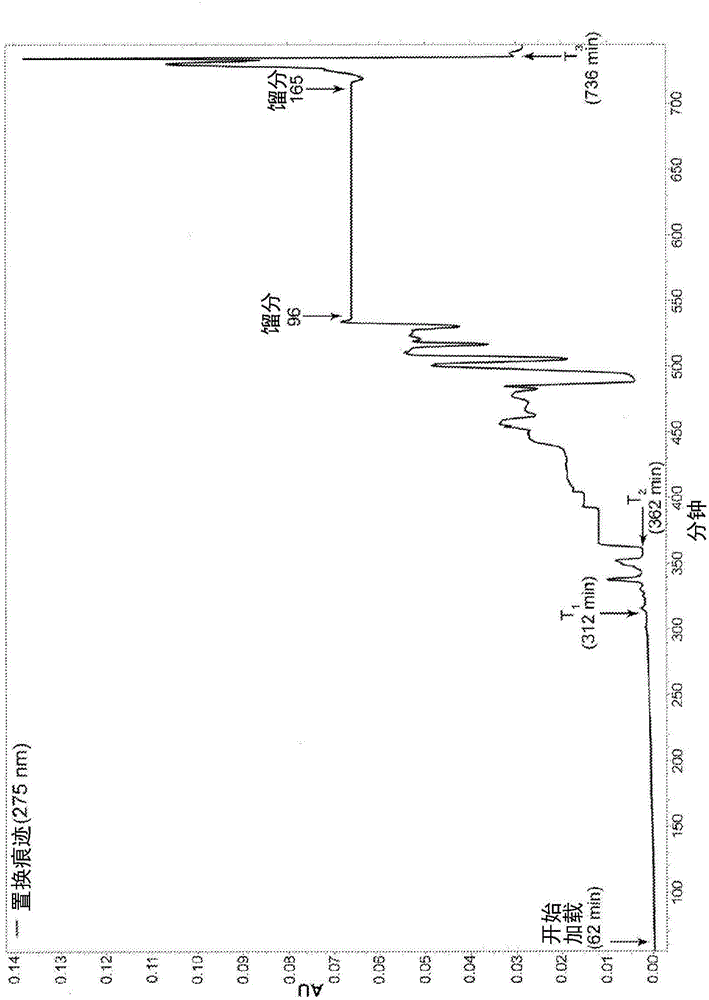
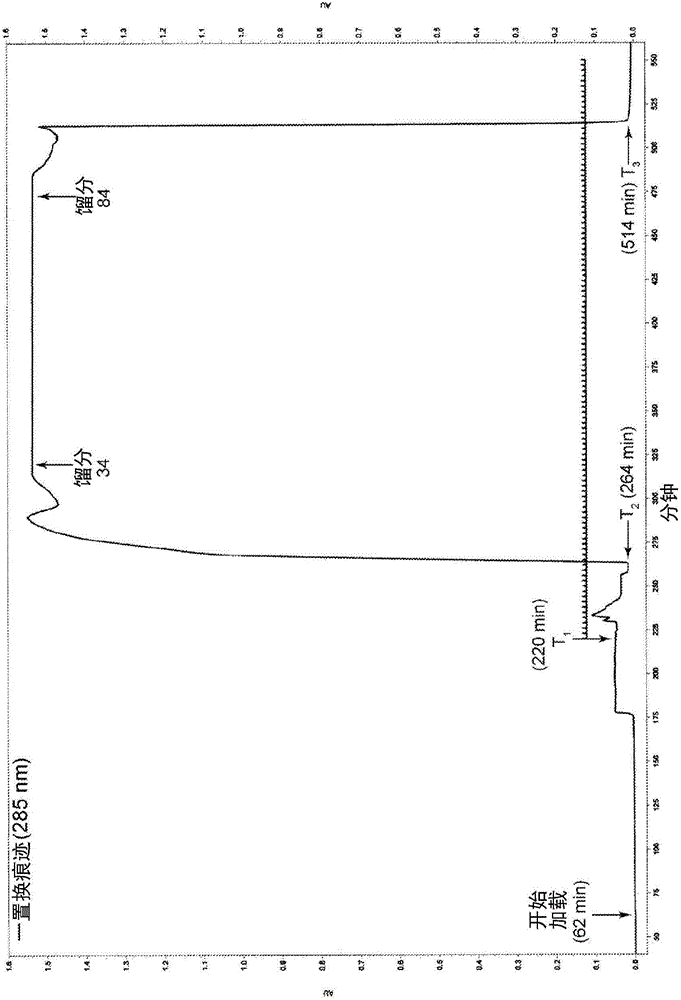
[0263] Example 3: Displacement Chromatographic Purification of Crude Oligonucleotides (20-mer) Using Displacer 607b (5-n-Hexyl-2-Hydroxybenzenesulfonate) - Anionic Displacer at Near Neutral pH (See Figure Show 2A)
[0264] Operating conditions:
[0265] Starting peptide: Crude synthetic oligonucleotide (20-mer, A 2 G 6 T 8 C 4 , ammonium salt, monothiophosphate backbone), 82.2% purity, FW=6.7397 mg / μmole, charge=-19.
[0266] Column: Waters Xbridge BEH130, 5 μm, 4.6x250mm SS, -C on silicone 18 .
[0267] Flow Rate: Load = 208 μL / min; Displacement = 208 μL / min
[0268] Ion-pairing reagent: n-butylammonium ( n NH 3 + )
[0269] Temperature = 23°C
[0270] pH=7.0
[0271] Displacer buffer: 15.0 mM Displacer 607b+20 mM H 3 PO 4 (HPLC grade) + 50 mM purified n-butylamine in DI water containing 5% (v / v) MeOH, pH = 7.0 containing 50% HCO 2 H (HPLC grade).
[0272] Loading buffer: 20mM H 3 PO 4 (HPLC grade) + 50 mM purified n-butylamine in water containing 5% (v...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com