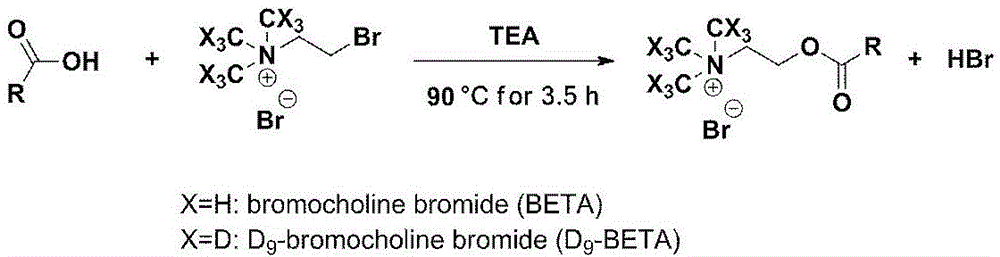
Patents
Literature
42 results about "Heavy isotope" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Heavy isotope. a stable atom in which there are more neutrons than in the normal isotope of the element, giving it a greater mass. For example, 15N is the heavy isotope, 14N the common form.
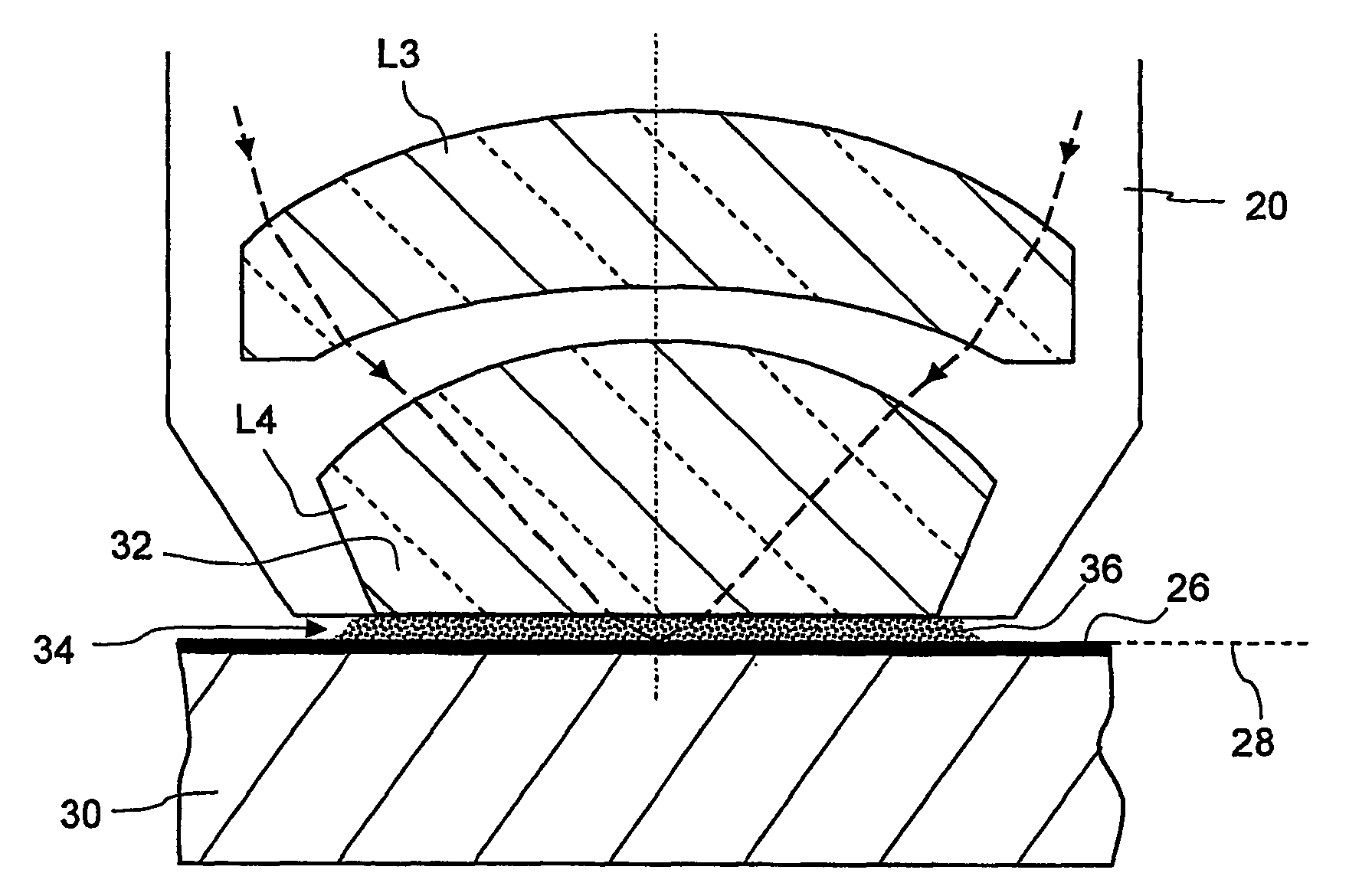
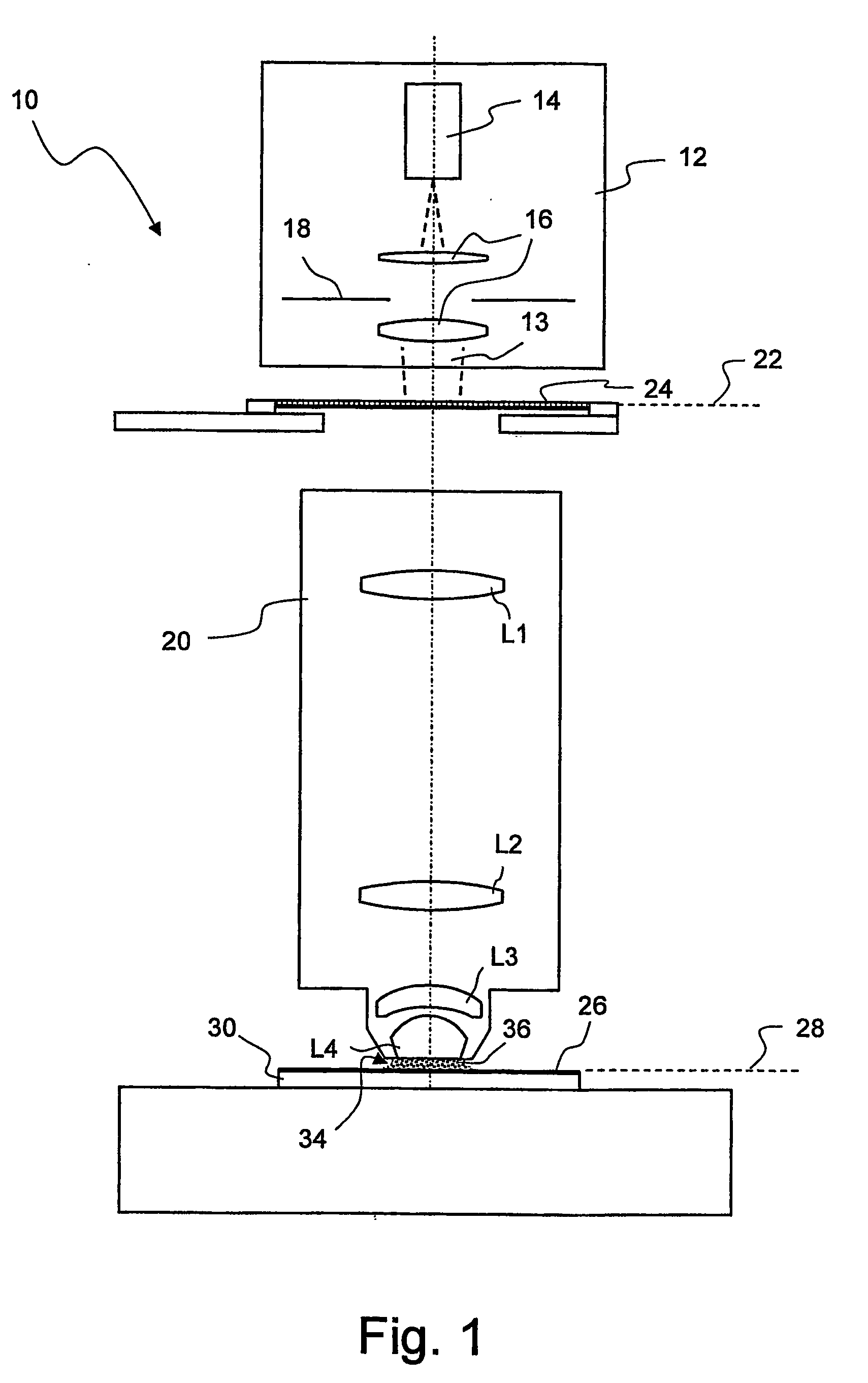
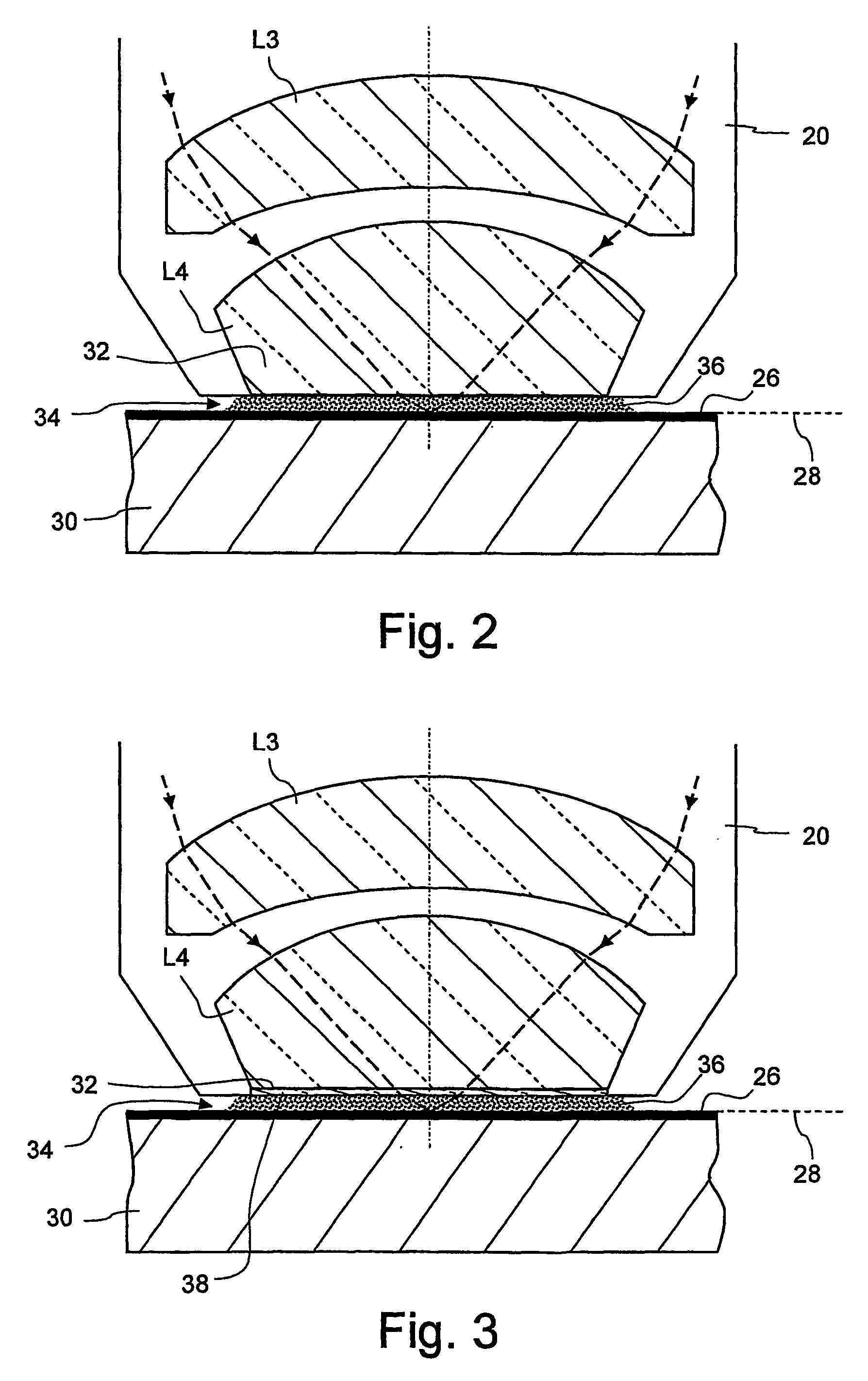
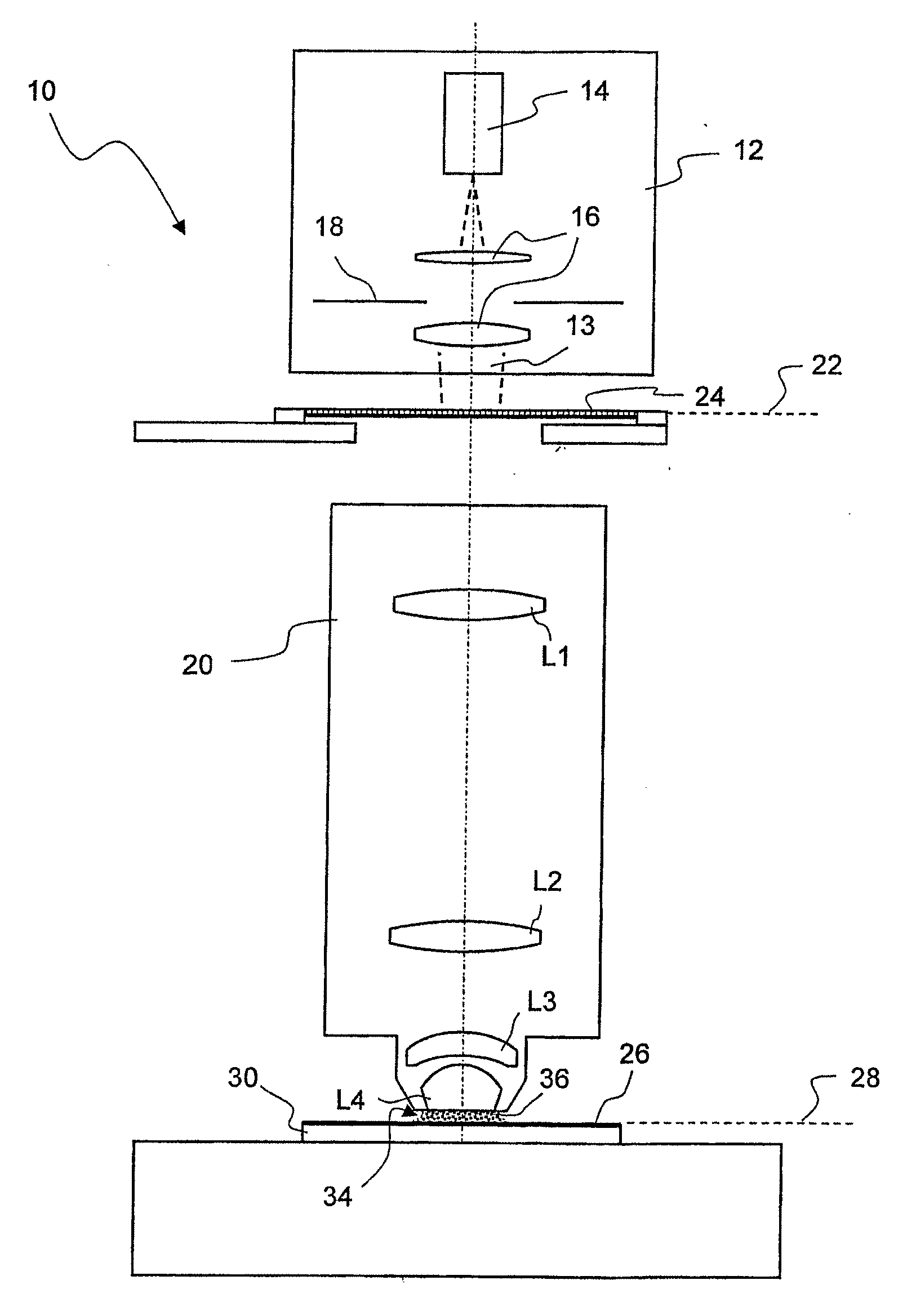
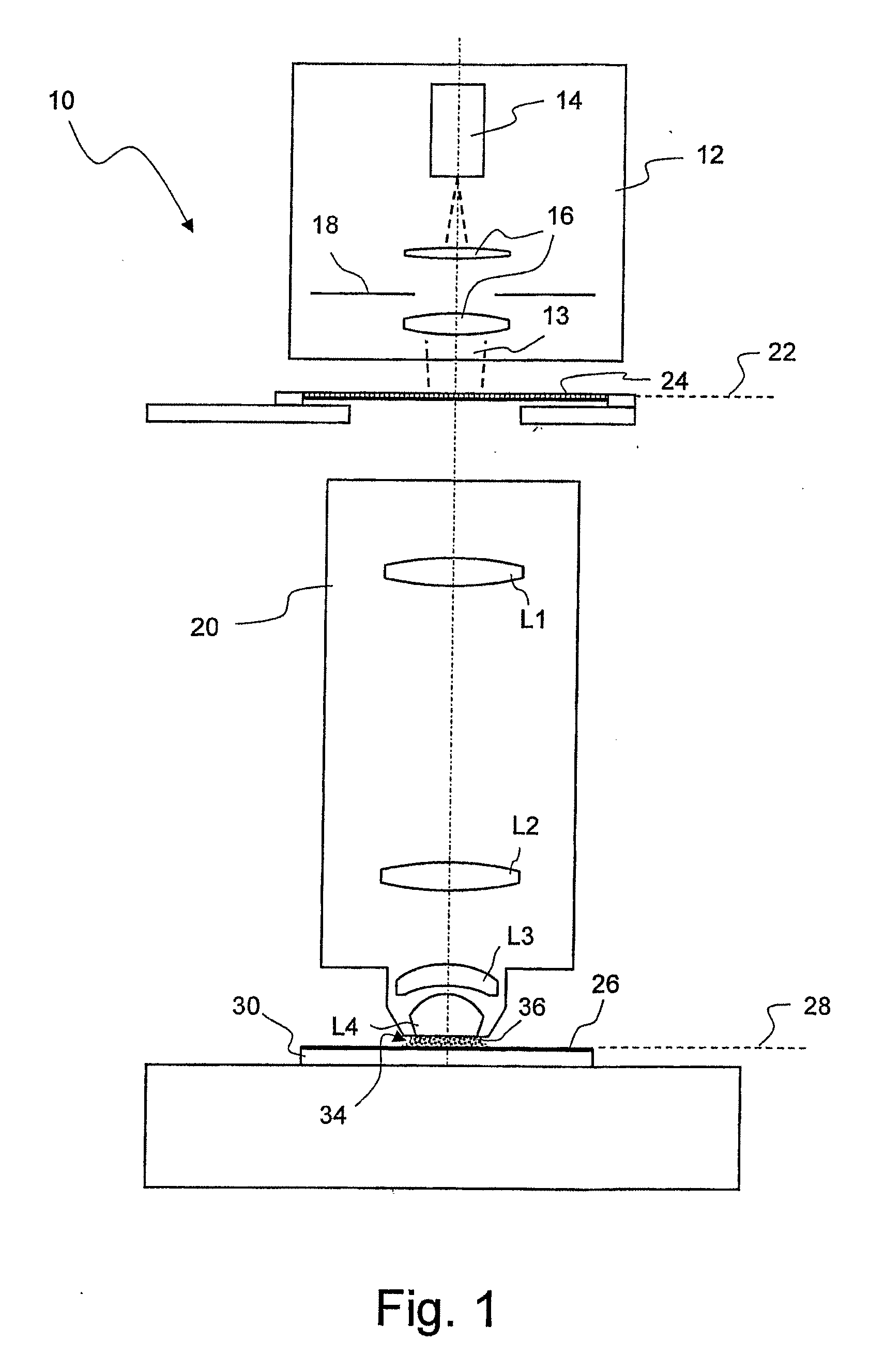
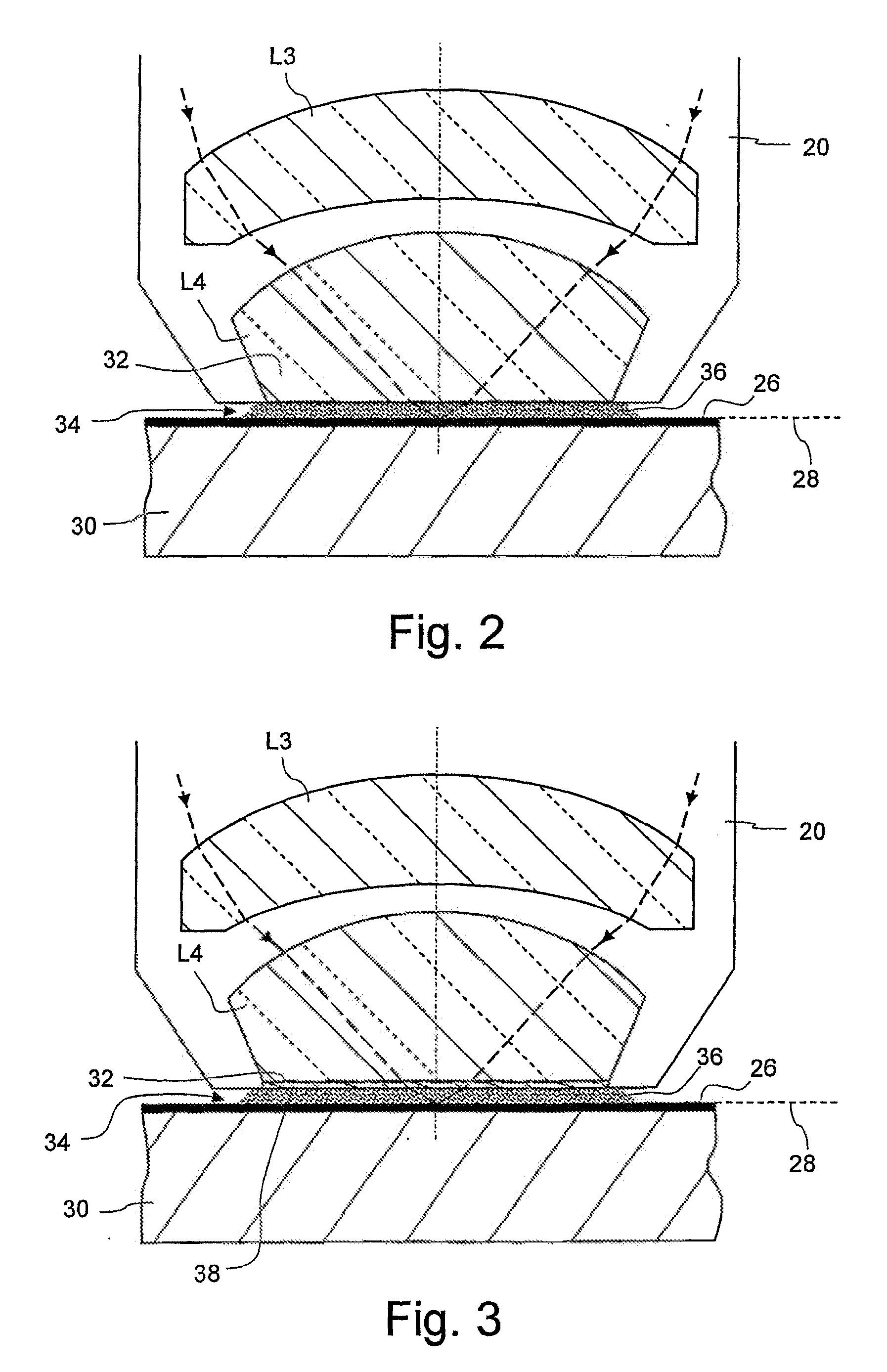
Microlitographic projection exposure apparatus and immersion liquid therefore
InactiveUS20060244938A1Transparent highLittle chemical effectMicroscopesPhotomechanical exposure apparatusSimple Organic CompoundsO-Phosphoric Acid
An immersion liquid for a microlithographic projection exposure apparatus is enriched with heavy isotopes. This reduces the chemical reactivity, which leads to an extension of the lifetime of optical elements which come in contact with the immersion liquid. For example, heavy water (D2O), deuterated sulfuric acid, (D2SO4) or deuterated phosphoric acid D3P16O4 may be used. Organic compounds such as perfluoro polyethers, which have been deuterated or enriched with heavy oxygen (18O), are furthermore suitable.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
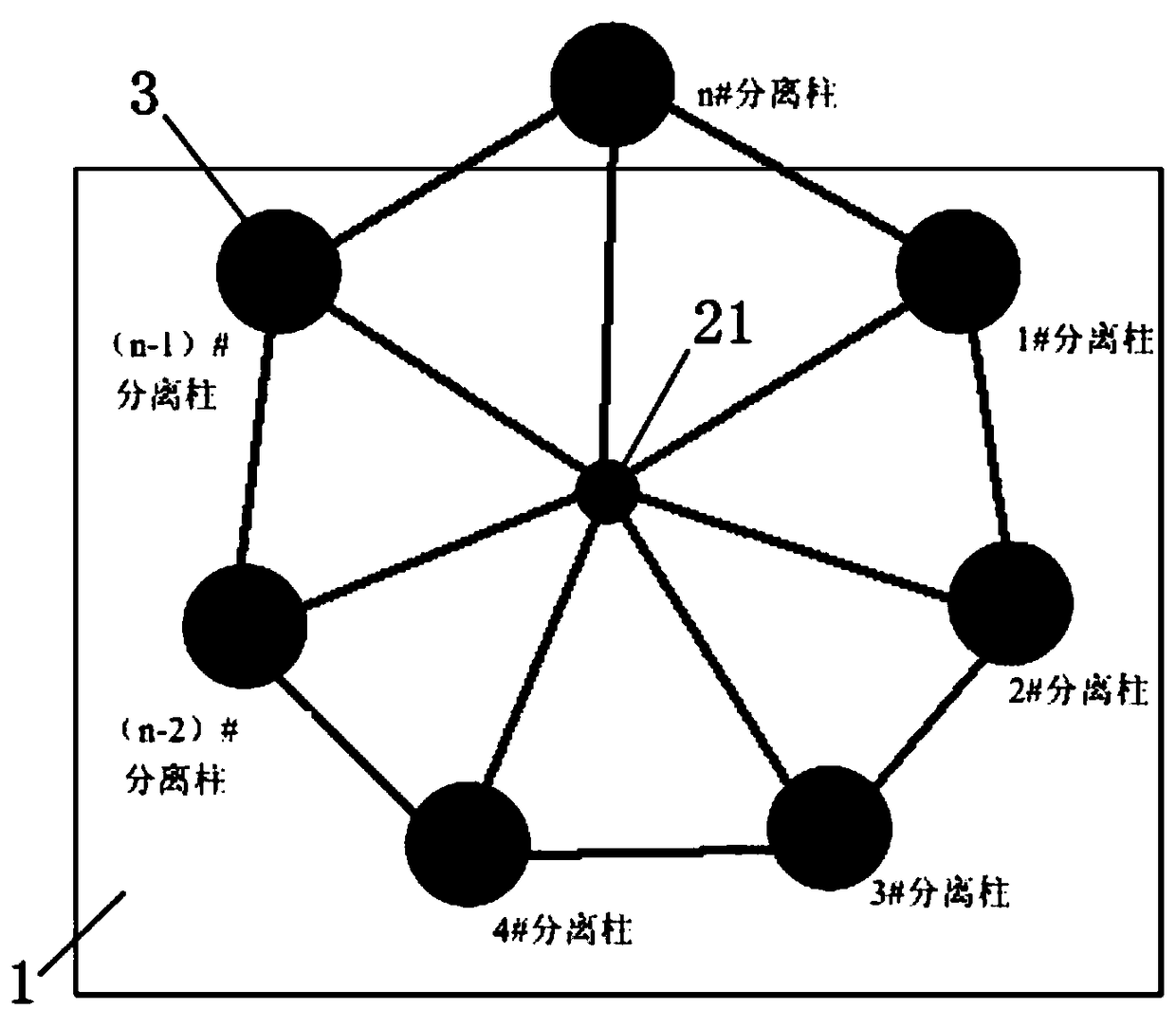
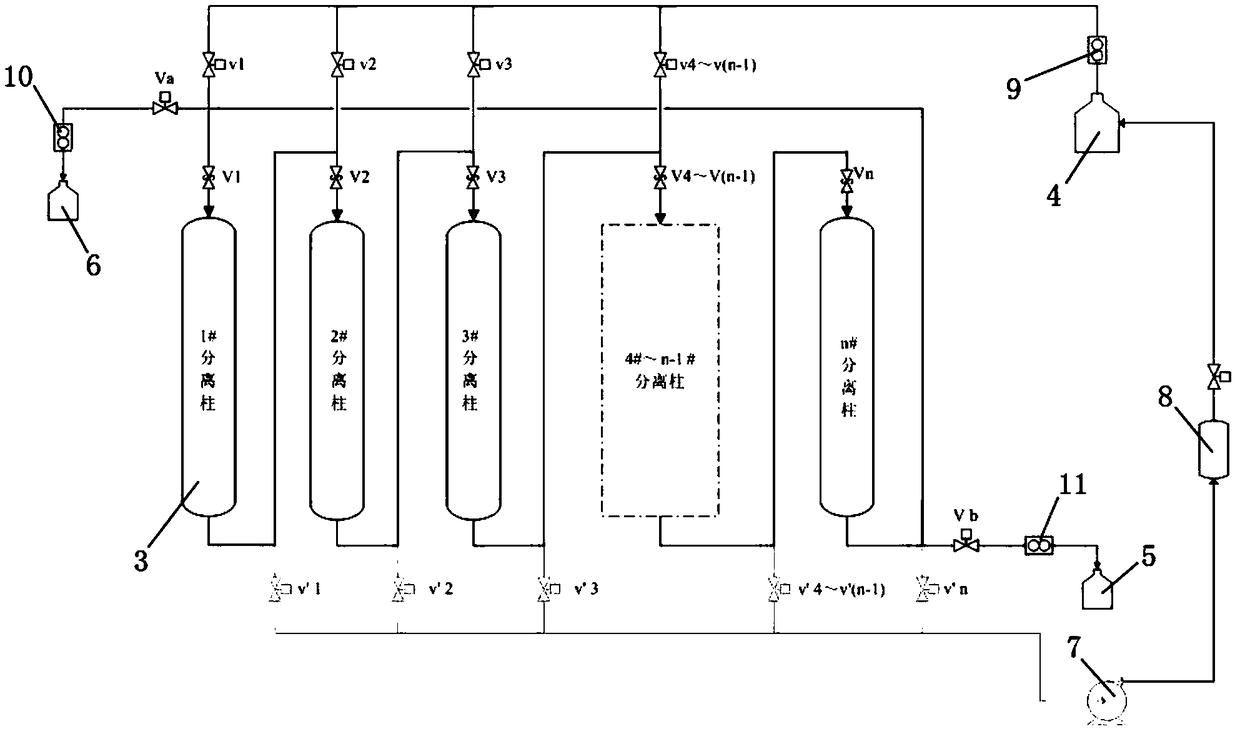
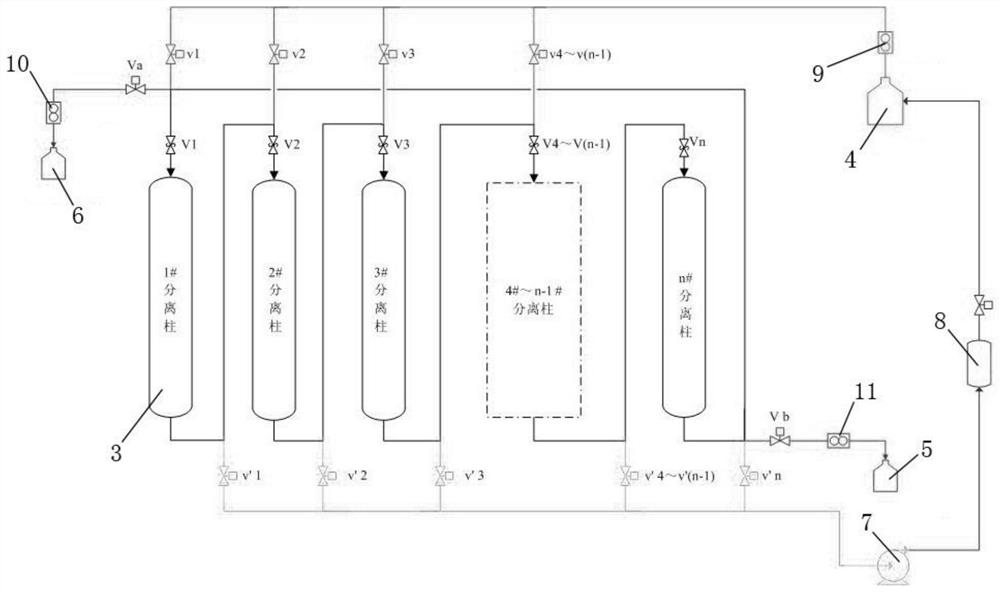
Low-temperature displacement chromatography hydrogen isotope separation device and method
ActiveCN101850215AAchieving Self-Displacement ChromatographyOvercome the disadvantage of low separation coefficientCation exchanger materialsOrganic anion exchangersSeparation factorGas release
The invention provides a low-temperature displacement chromatography hydrogen isotope separation device and a method. The invention makes the mixed gas of hydrogen isotope gas and helium after being cooled sequentially pass through a cooled main separation column and a cooled product gas collecting column which are filled with granulate palladium-loaded aluminum trioxide (Al2O3 / Pd) to obtain the product gas rich in heavy isotope components of deuterium and tritium; a hot helium flow passes through and heats the main separation column so as to make the released gas sequentially pass through the cooled secondary separation column and the product gas collecting column which are filled with granulate palladium-loaded aluminum trioxide (Al2O3 / Pd) to obtain the product gas rich in heavy isotopecomponents of deuterium and tritium; after the product gas is collected, middle rich gas flowing out from the secondary separation column is directly fed back into a raw material gas tank; and after the middle rich gas feedback process is accomplished, the main separation column and the secondary separation column are heated, and the gas released by heating is collected via a tail gas collecting column. The separation device has simple structure, reasonable separation process, and low cost for the construction and operation of the device. The invention has higher separation factor for hydrogen isotope separation.
Owner:SICHUAN INST OF MATERIALS & TECH
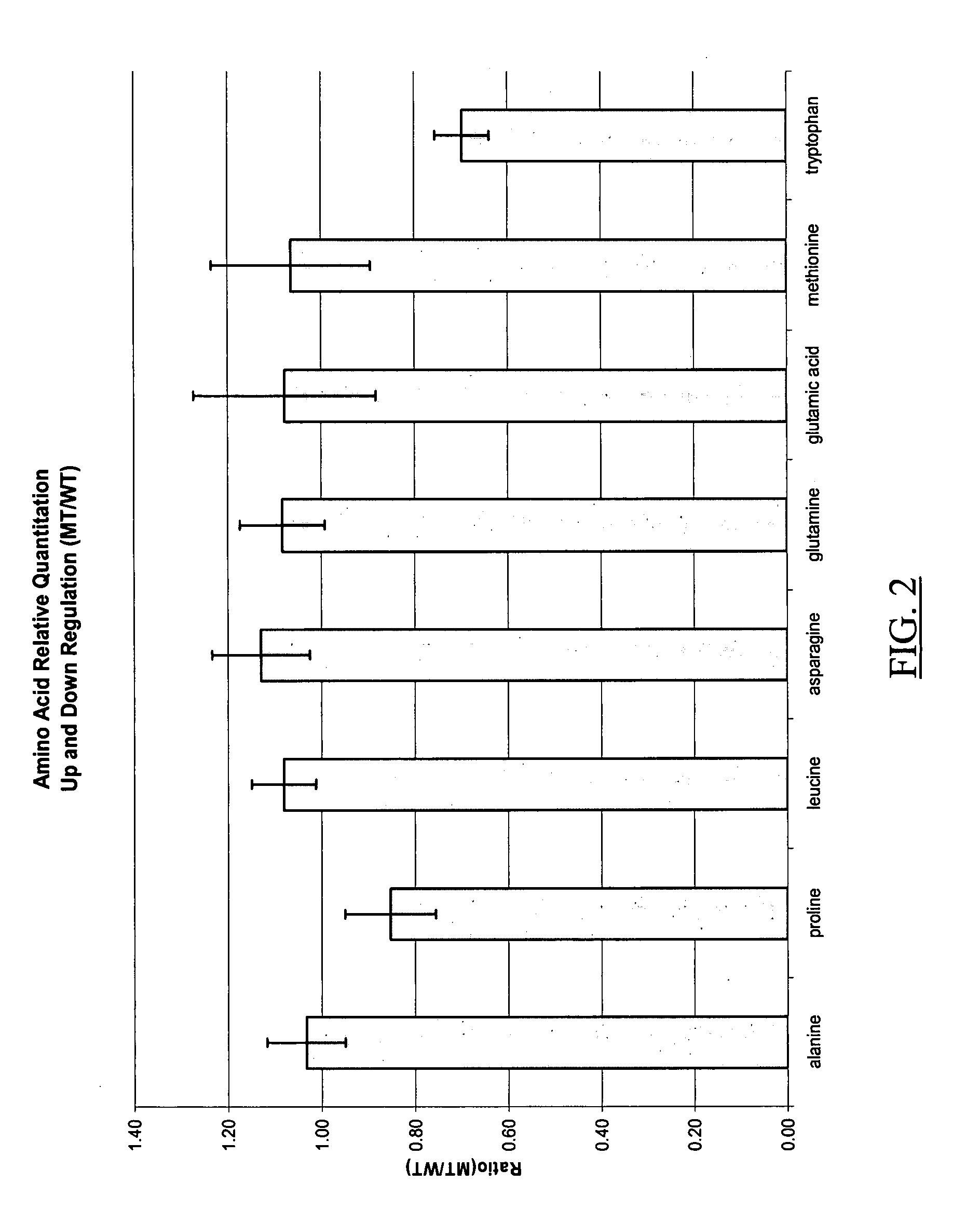
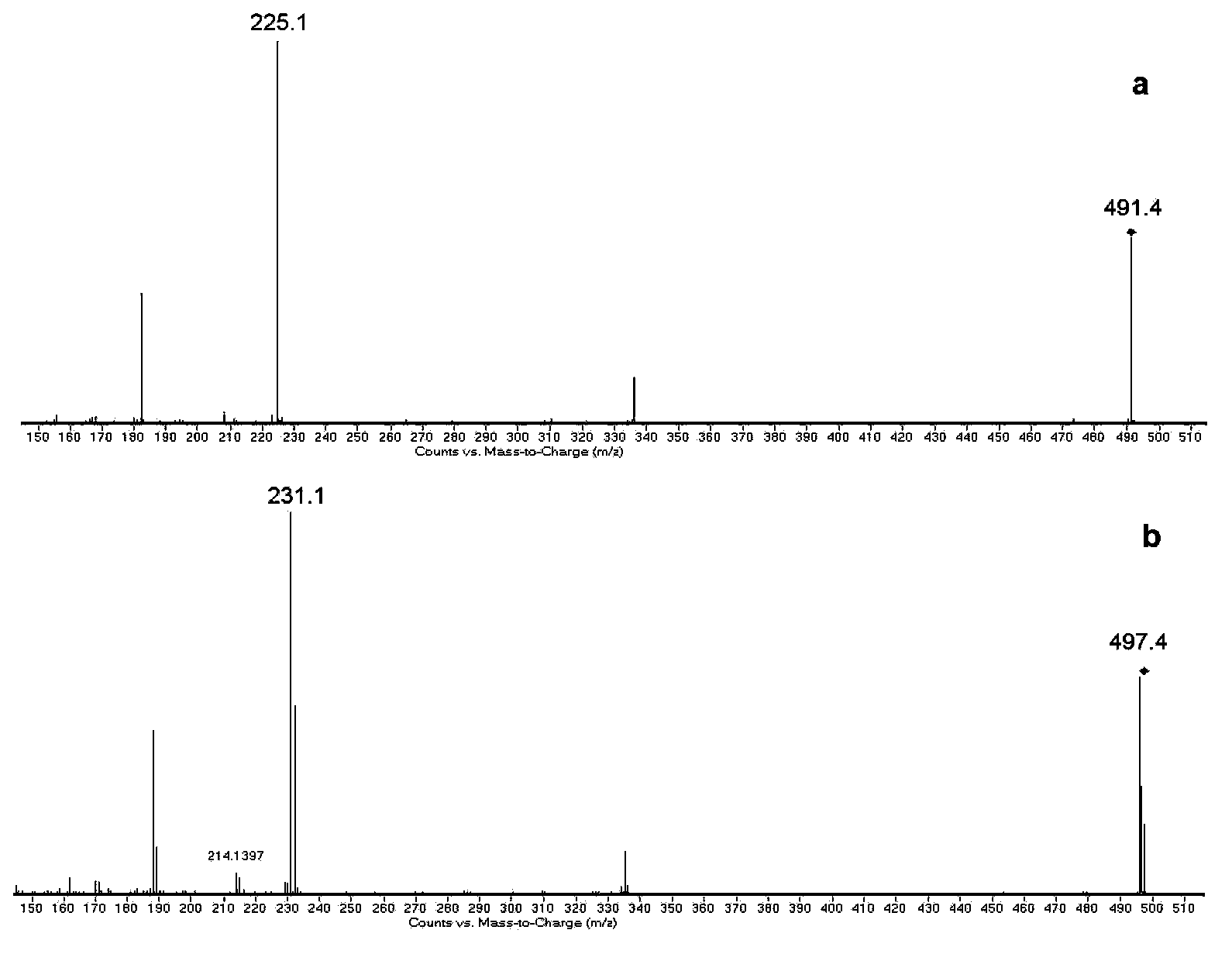
Ionizable isotopic labeling reagents for relative quantification by mass spectrometry
ActiveUS20080050833A1Improve ETD analysisConvenient charging statusOrganic compound preparationComponent separationMetaboliteIsotopic labeling
Relative quantification of metabolites by Electrospray Ionization Mass Spectrometry (ESI-MS) requiring a mechanism for simultaneous analysis of multiple analytes in two or more samples. Labeling reagents that are reactive to particular compound classes and differ only in their isotopic kit facilitating relative quantification and providing tangible evidence for the existence of specific functional groups. Heavy and light isotopic forms of methylacetimidate were synthesized and used as labeling reagents for quantification of amine-containing molecules, such as biological samples. Heavy and light isotopic forms of formaldehyde and cholamine were also synthesized and used independently as labeling reagents for quantification of amine-containing and carboxylic acid-containing molecules, such as found in biological samples. Advantageously, the labeled end-products are positively charged under normal acidic conditions involving conventional Liquid Chromatography Mass Spectrometry (LC / MS) applications. Labeled primary and secondary amine and carboxylic acid end-products also generated higher signals concerning mass-spectra than pre-cursor molecules and improved sensitivity. Improved accuracy concerning relative quantification was achieved by mixing heavy and light labeled Arabidopsis extracts in different ratios. Labeling strategy was further employed to ascertain differences in the amounts of amine-containing metabolites for two strains of Arabidopsis seeds.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS +1
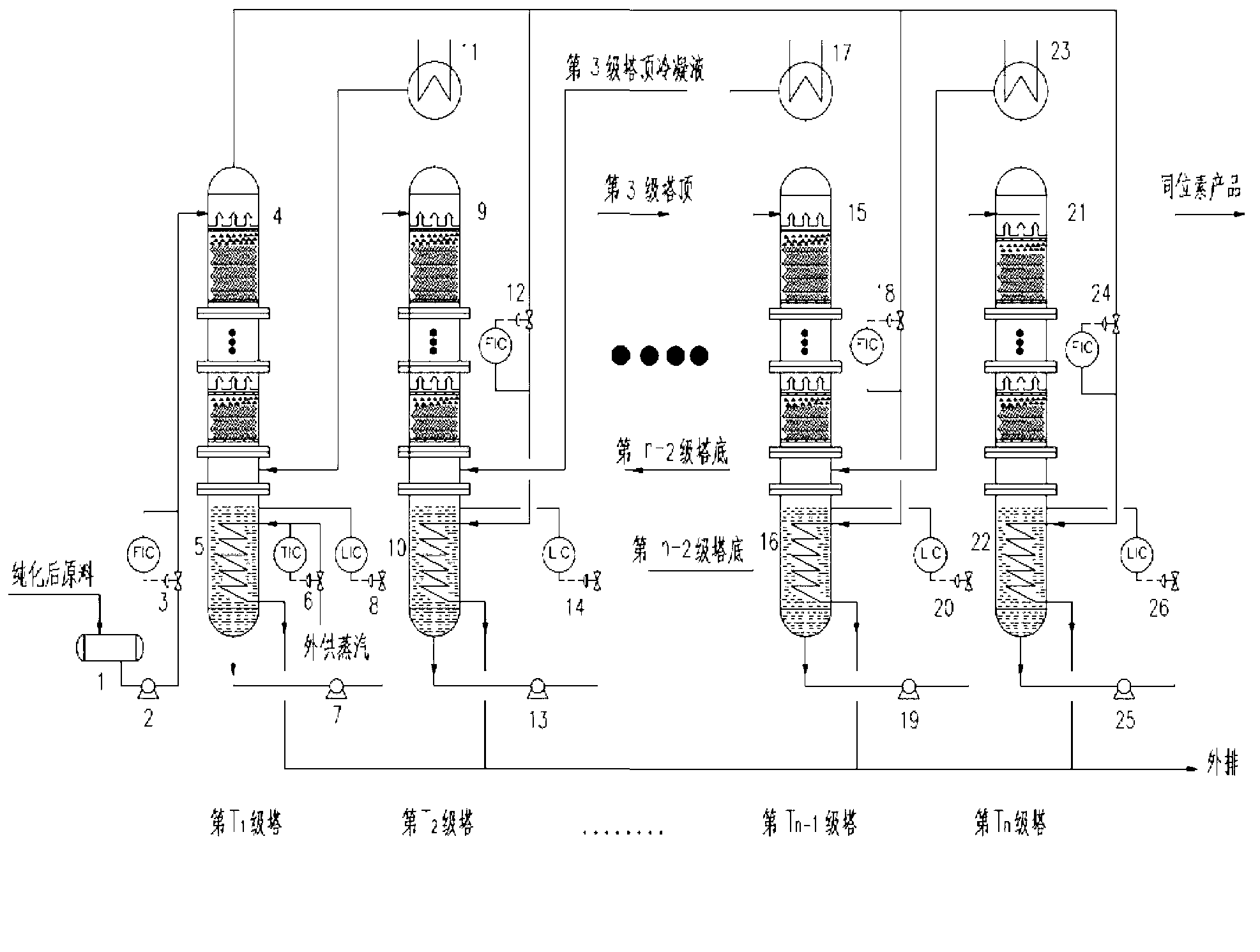
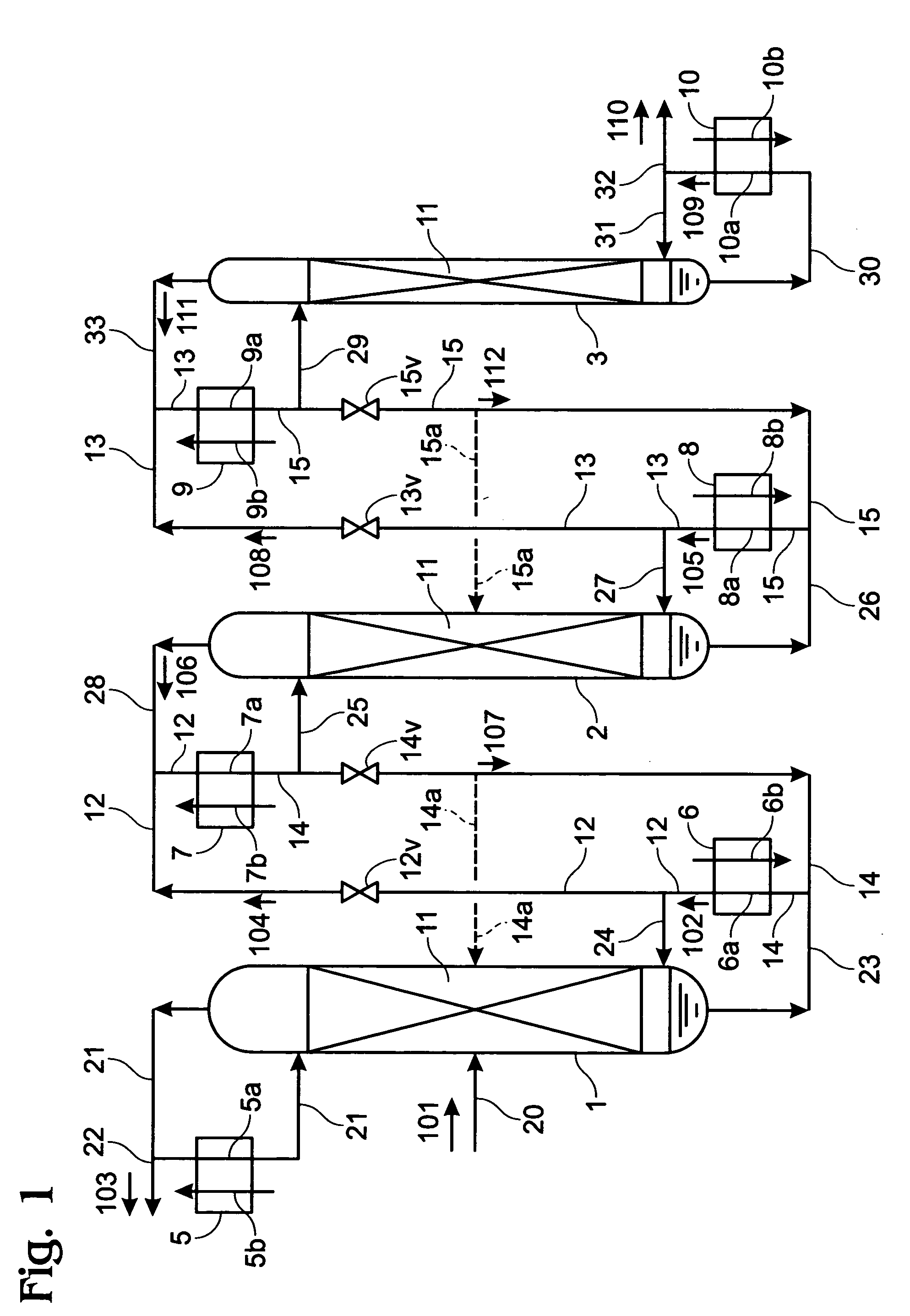
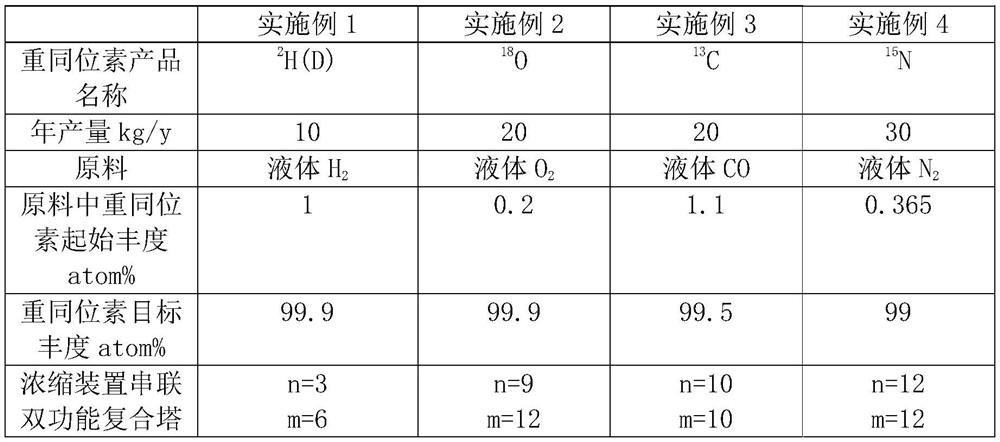
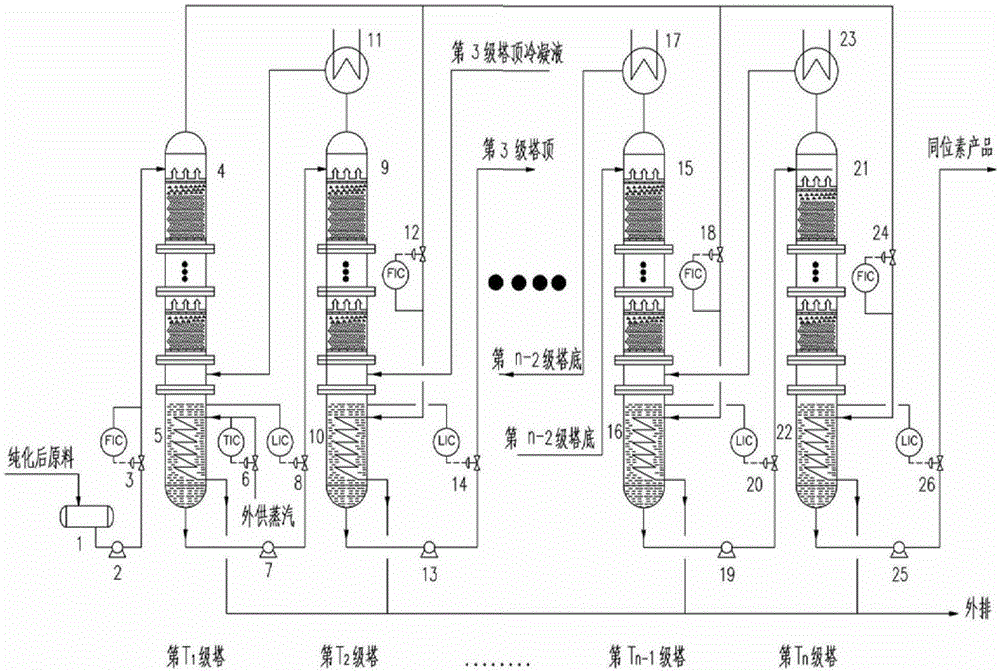
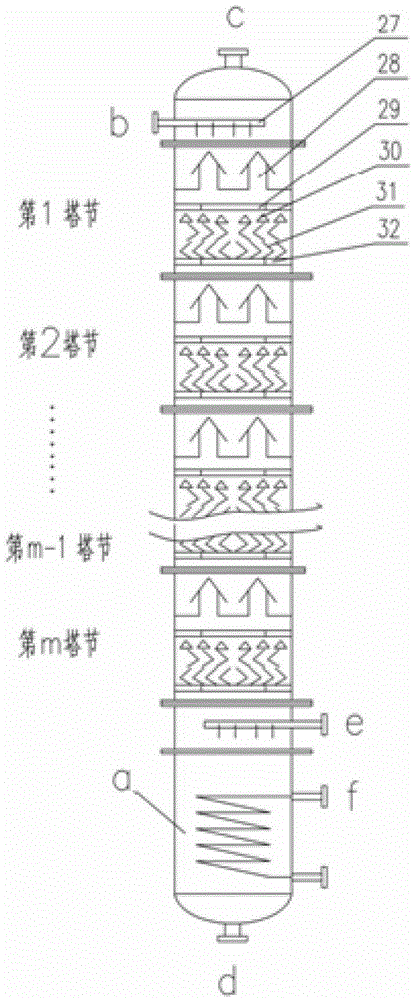
Method and device for concentrating and enriching stable isotopes 2H, 18O and 13C
The invention relates to a method and a device for concentrating and enriching stable isotopes 2H, 18O and 13C. The method comprises the steps of: by taking compounds respectively containing stable isotopes 2H, 18O and 13C as materials, carrying out purification treatment, adding to a heavy isotope concentration tower group formed by a plurality stages of gas-liquid mass transfer towers connected in series; continuously and partially vaporizing and partially condensing in the gas-liquid mass transfer towers connected in series by weak vapor pressure difference between light and heavy isotopes of hydrogen, oxygen, and carbon elements, and gradually concentrating and purifying corresponding heavy isotope. Each tower disclosed by the invention adopts different operation pressures and coupling utilization of heat between the towers; over 30-40% of energy consumption can be saved; a composite structure mass transfer component composed of a liquid collecting distributer, a Dixon mass transfer component, a corrugated mass transfer component and the like is adopted inside the tower; the device is easy to amplify; the device of producing heavy 2H, 18O or 13C isotope at a large scale just needs to be connected with 2-8 gas-liquid mass transfer towers in series; over 50% of investment is saved in comparison with the same scale of device, and the towers adopt a single tandem cascade technology; and the method is simple in flow and easy to control and operate.
Owner:JIANGSU ZHENGNENG ISOTOPE
Phospholipid classification detection and quantification method based on stable isotope labeling
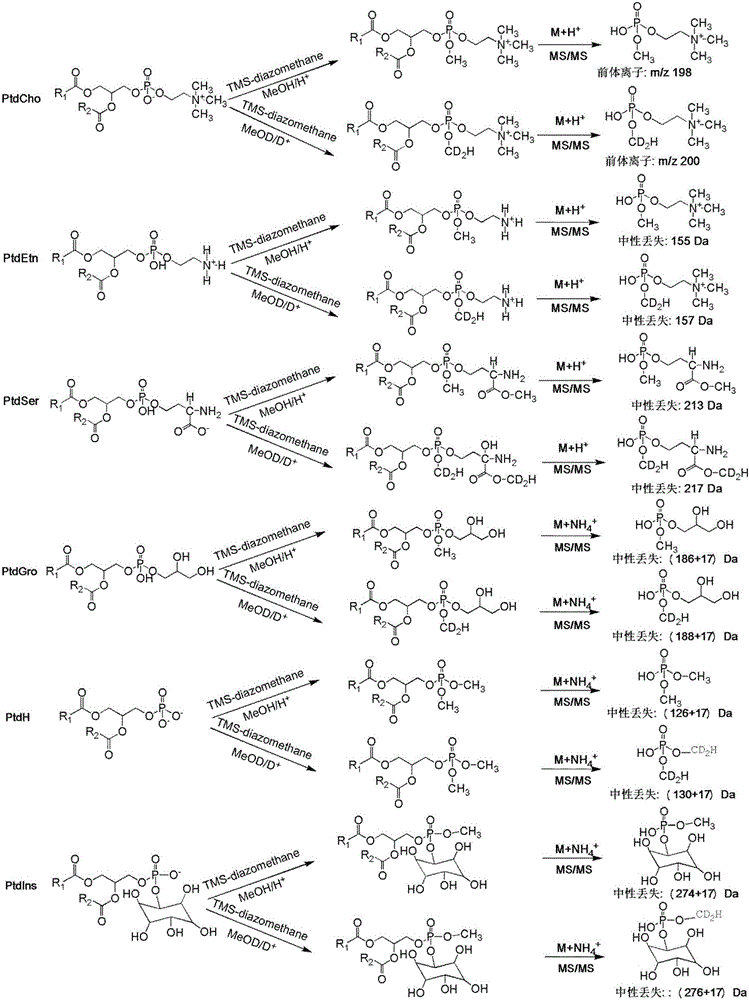
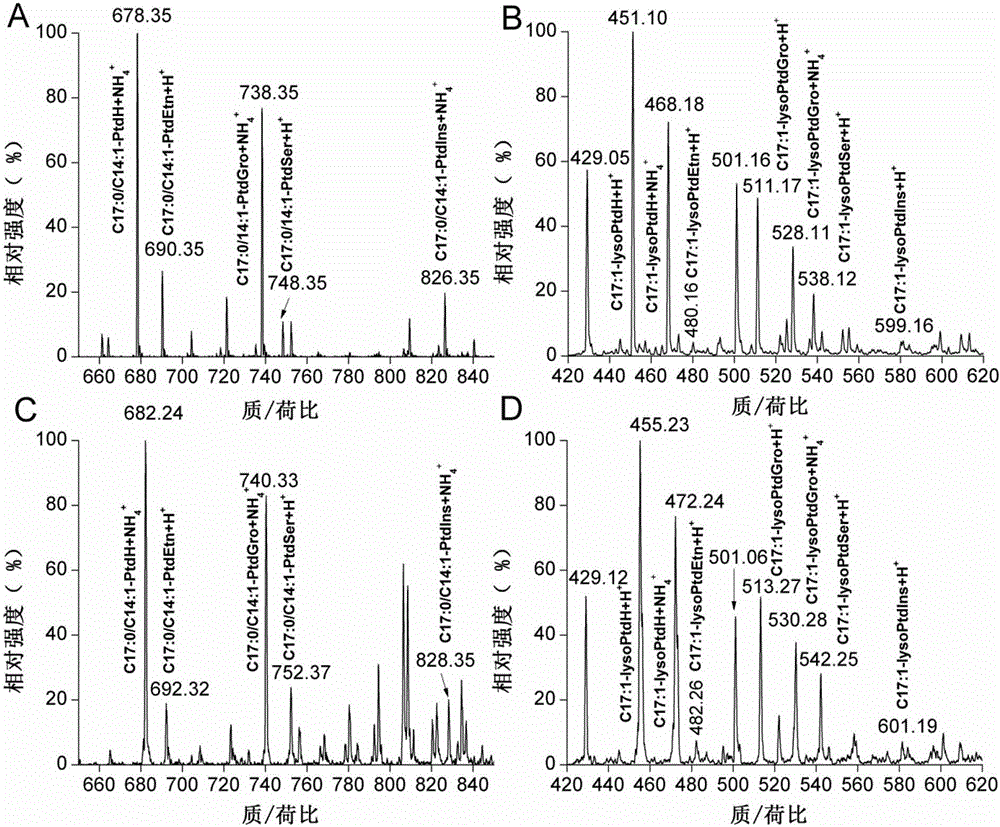
ActiveCN105067697AHigh sensitivityComponent separationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansStable Isotope LabelingPhosphoric acid
The present invention discloses a phospholipid classification detection and quantification method based on stable isotope labeling, and belongs to the technical field of phospholipid quantification detection methods. According to the method, mainly trimethylsilyl diazomethane is used to respectively generate diazomethane and deuterium-labeled diazomethane in a methyl tert-butyl ether / methanol / 1N hydrochloric acid solution system and a methyl tert-butyl ether / deuteromethanol / 1N deuterium chloride solution system in an in-situ manner so as to further respectively carry out methyl esterification on the phosphoric acid group or carboxylic acid group in the phospholipid molecule to generate the light isotope labeled-phospholipid methyl esterification derivative and the heavy isotope labeled-phospholipid methyl esterification derivative, wherein the light isotope labeled-phospholipid methyl esterification derivative and the heavy isotope labeled-phospholipid methyl esterification derivative have the same physical and chemical properties and different molecular weights; and the relative intensity of the light isotope labeled-mass spectrum peak signal and the heavy isotope labeled-mass spectrum peak signal are compared to associate with the phospholipid molecule amount in the sample so as to achieve the relative quantification on the phospholipid. The method of the present invention has characteristics of enhanced sensitivity and completion within a shor time.
Owner:INSITUTE OF BIOPHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCIENCES
Materials and methods for controlling isotope effects during fractionation of analytes
ActiveUS7449170B2Improve accuracyError is reduced and eliminatedBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAnalyteMass Spectrometry-Mass Spectrometry
Compositions and methods for controlling or eliminating isotope effects during fractionation of chemically equivalent but isotopically distinct compounds. Isotope coding agents contain heavy isotopes other than deuterium. The invention facilitates intelligent data acquisiton. After sample fractionation, isotope abundance ratios are calculated using mass spectrometry, and analytes of interest are identified in real time.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
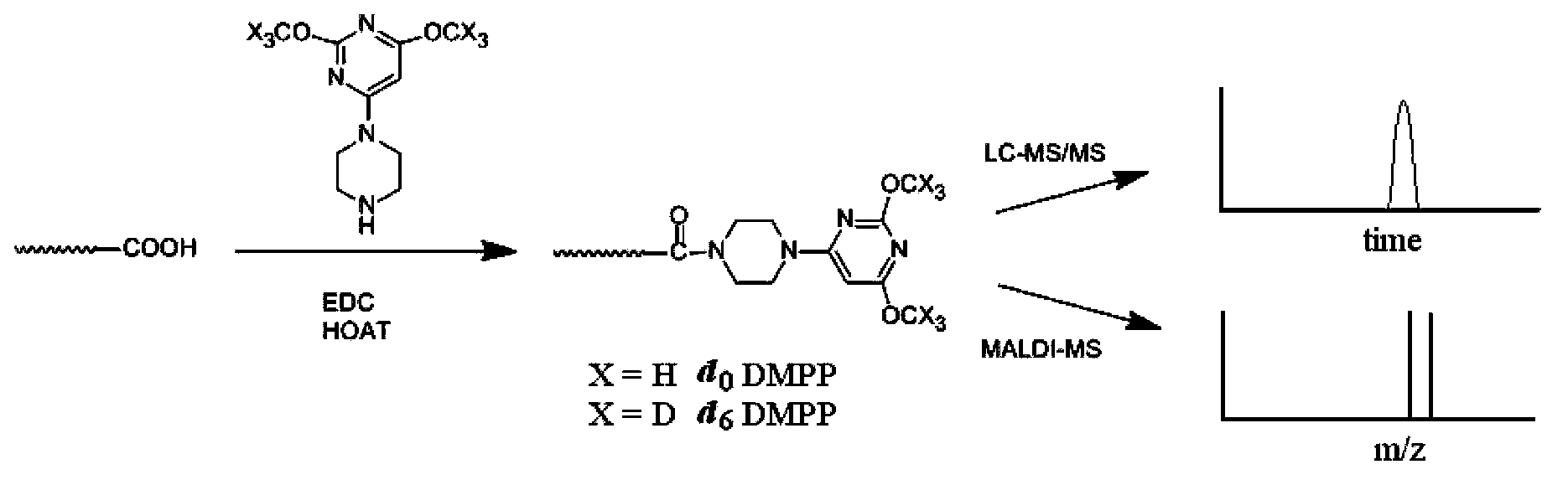
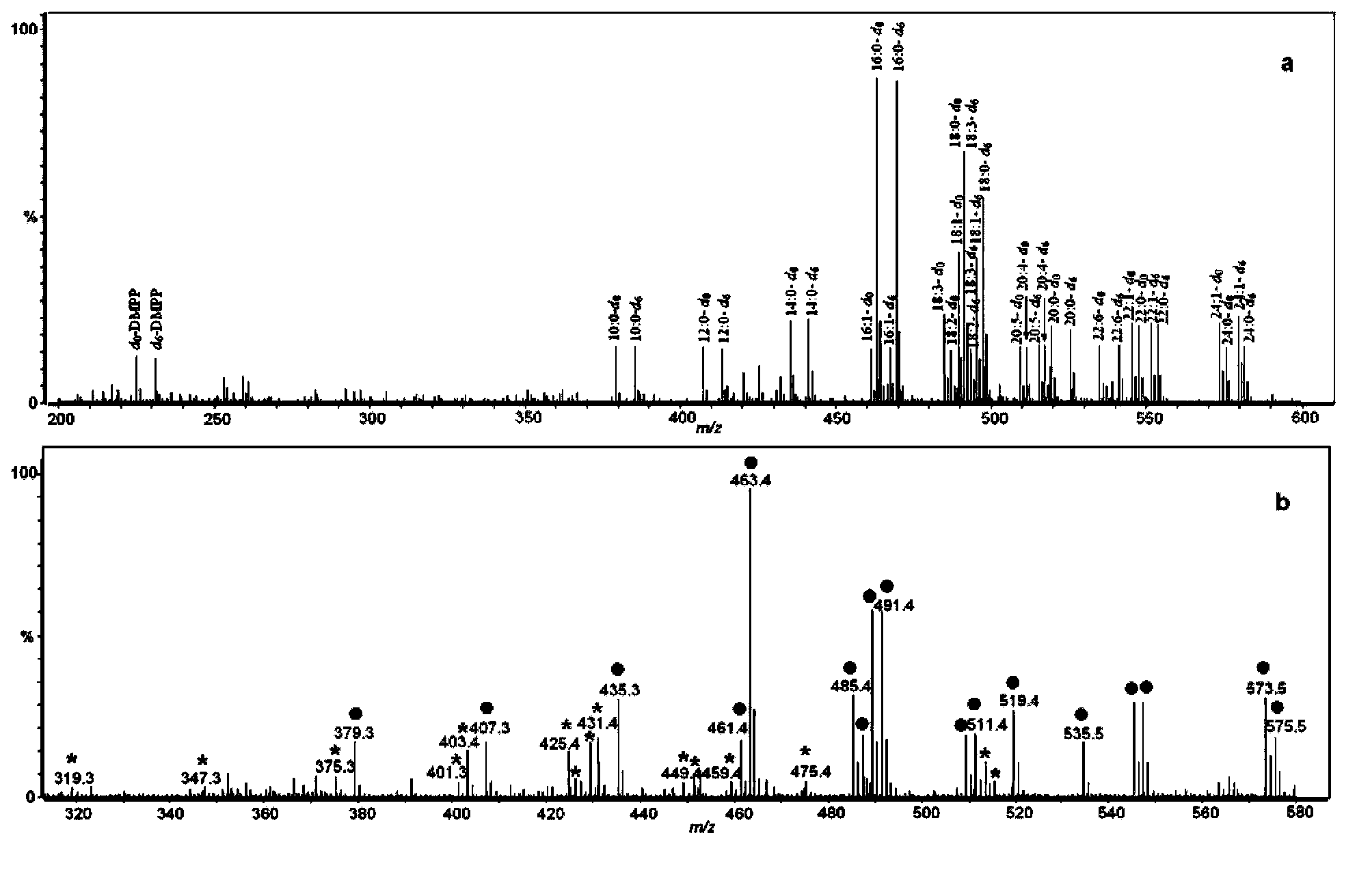
Methylsulfonyl miazines isotope labelling reagent, synthesis method and uses thereof
InactiveCN101339187AReflect concentration ratioReduce complexityMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansBiological testingTarget analysisCysteine thiolate
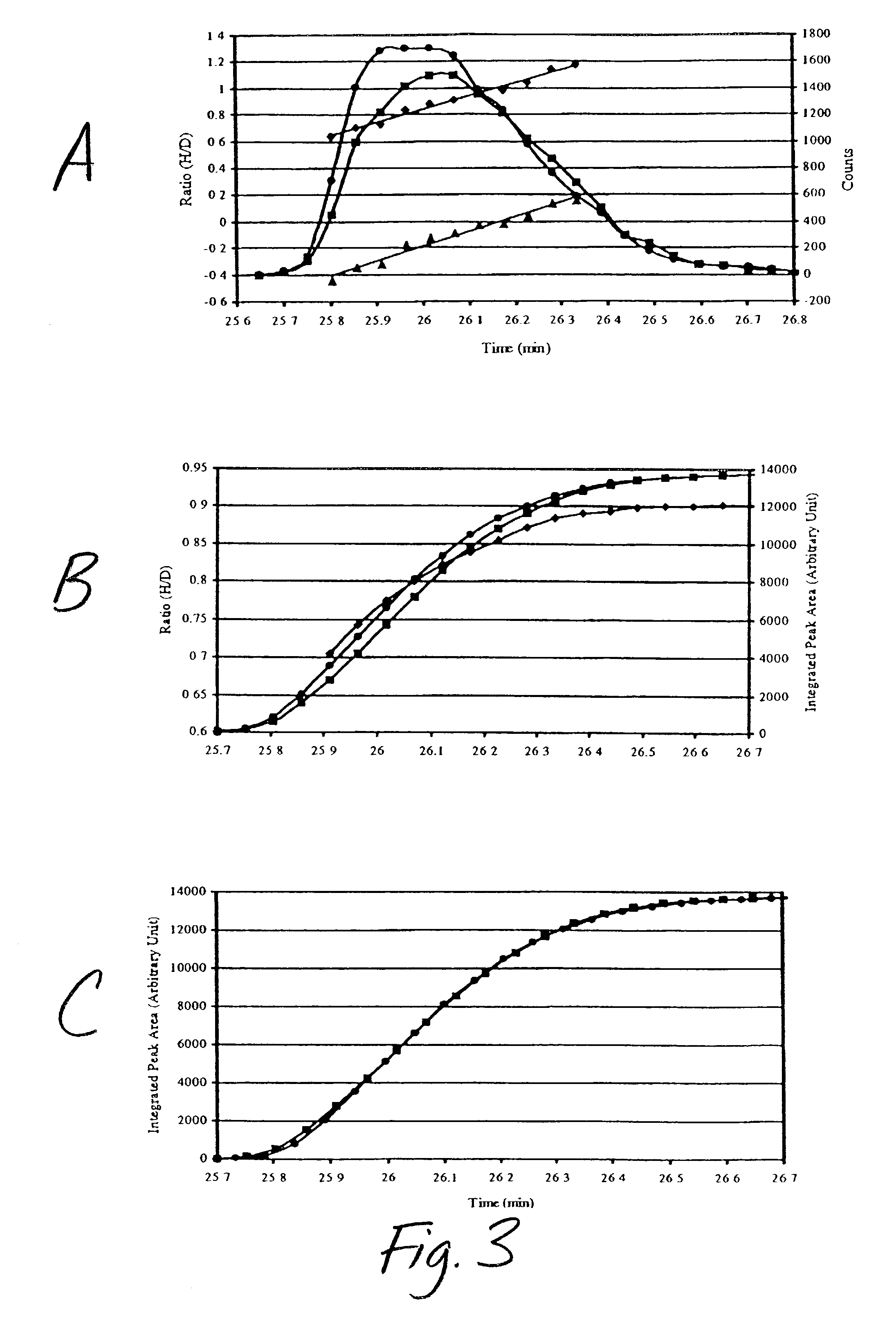
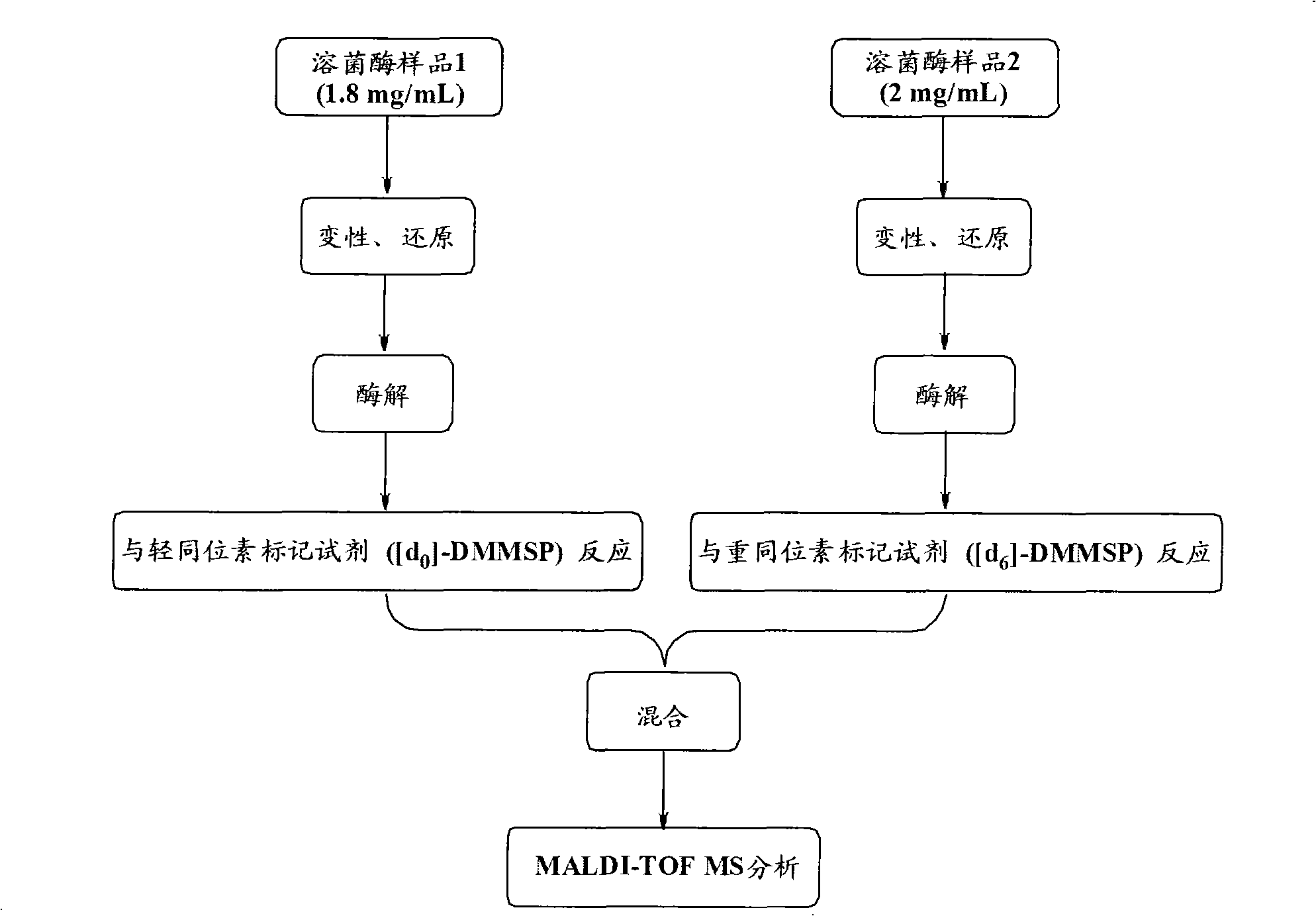
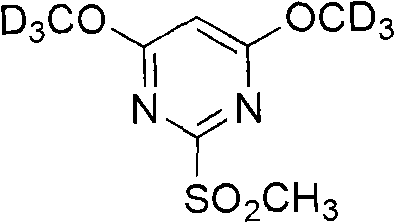
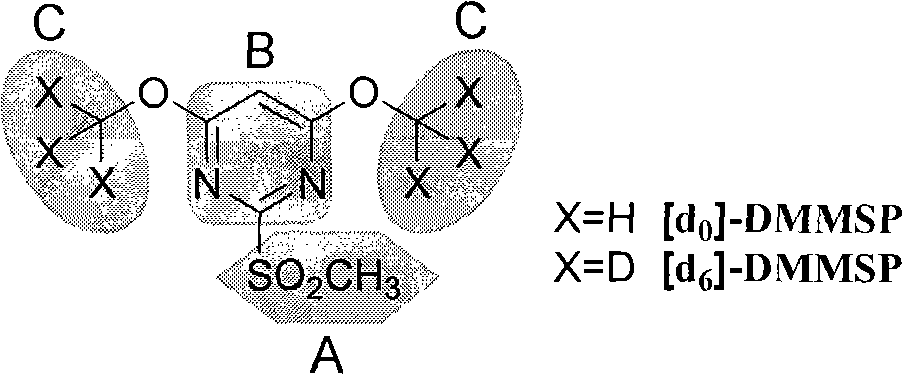
The invention relates to a method for designing and synthesizing a stable isotope labelling reagent for methylsulphonyl miazines and the application in protein comparative analysis. The isotope labelling reagent of the invention has a chemical name of (d6)-4, 6 dimethoxy-2 methylsulphonyl metadiazine. The reagent can be applied to qualitative and relatively quantitative analysis of cysteine, polypeptide containing cysteine, and protein. The method includes the following methods: a) denaturation and reduction as well as zymohydrolysis of target analyte; b) reaction of the target analyte and the light or heavy isotope labelling reagent; c) direct MALDI-TOF MS analysis of sample solution labeled.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF ORGANIC CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
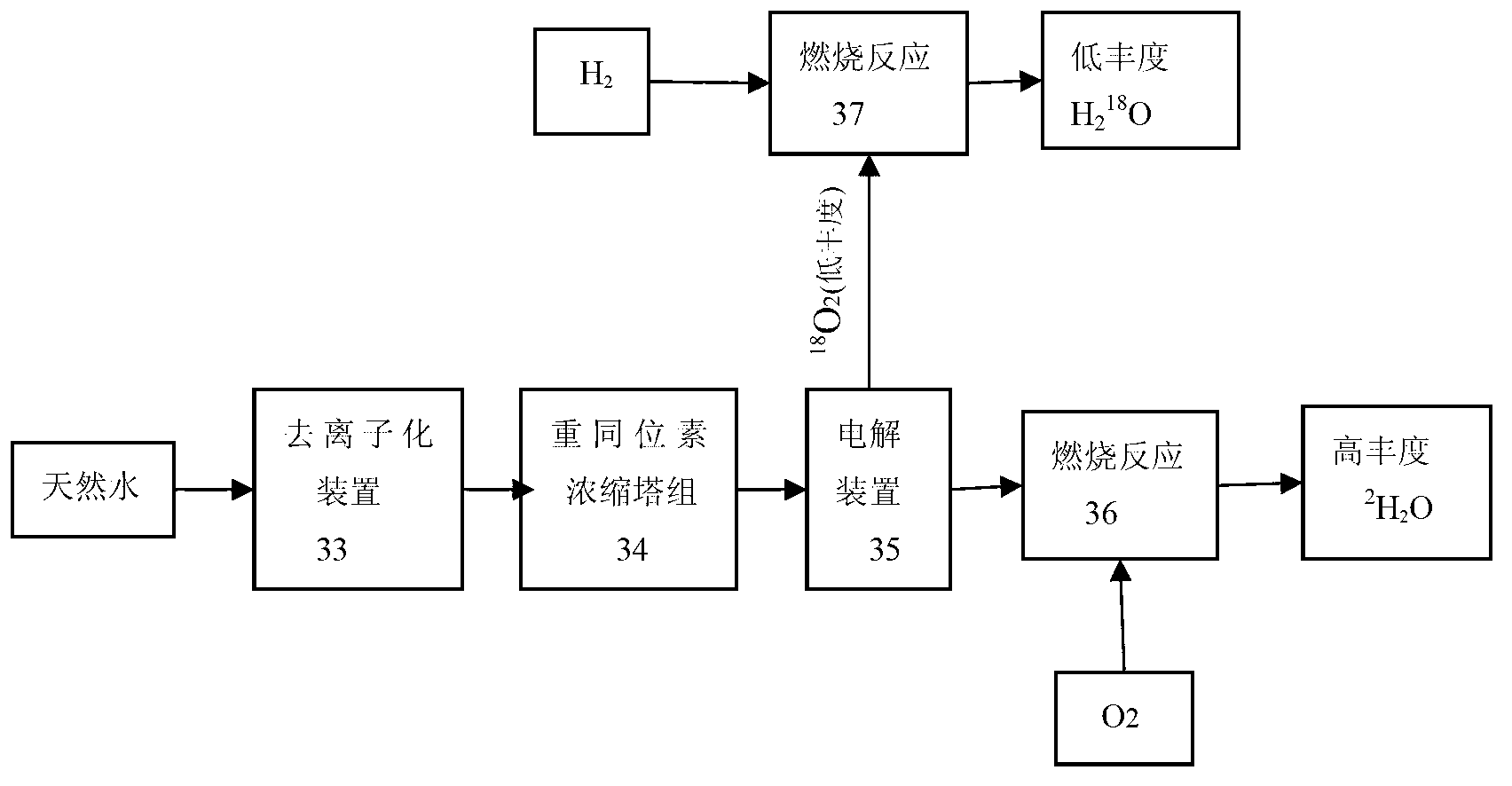
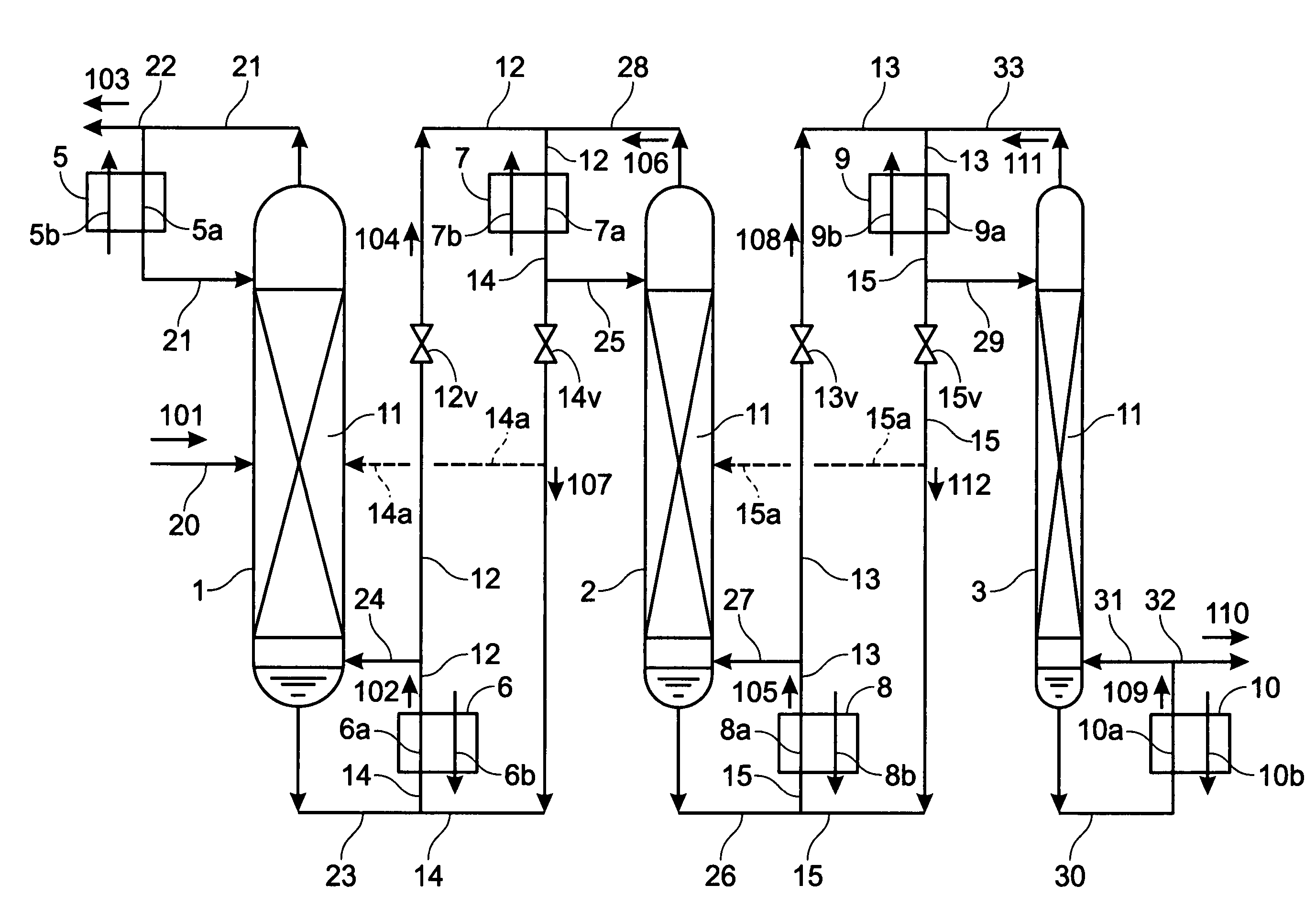
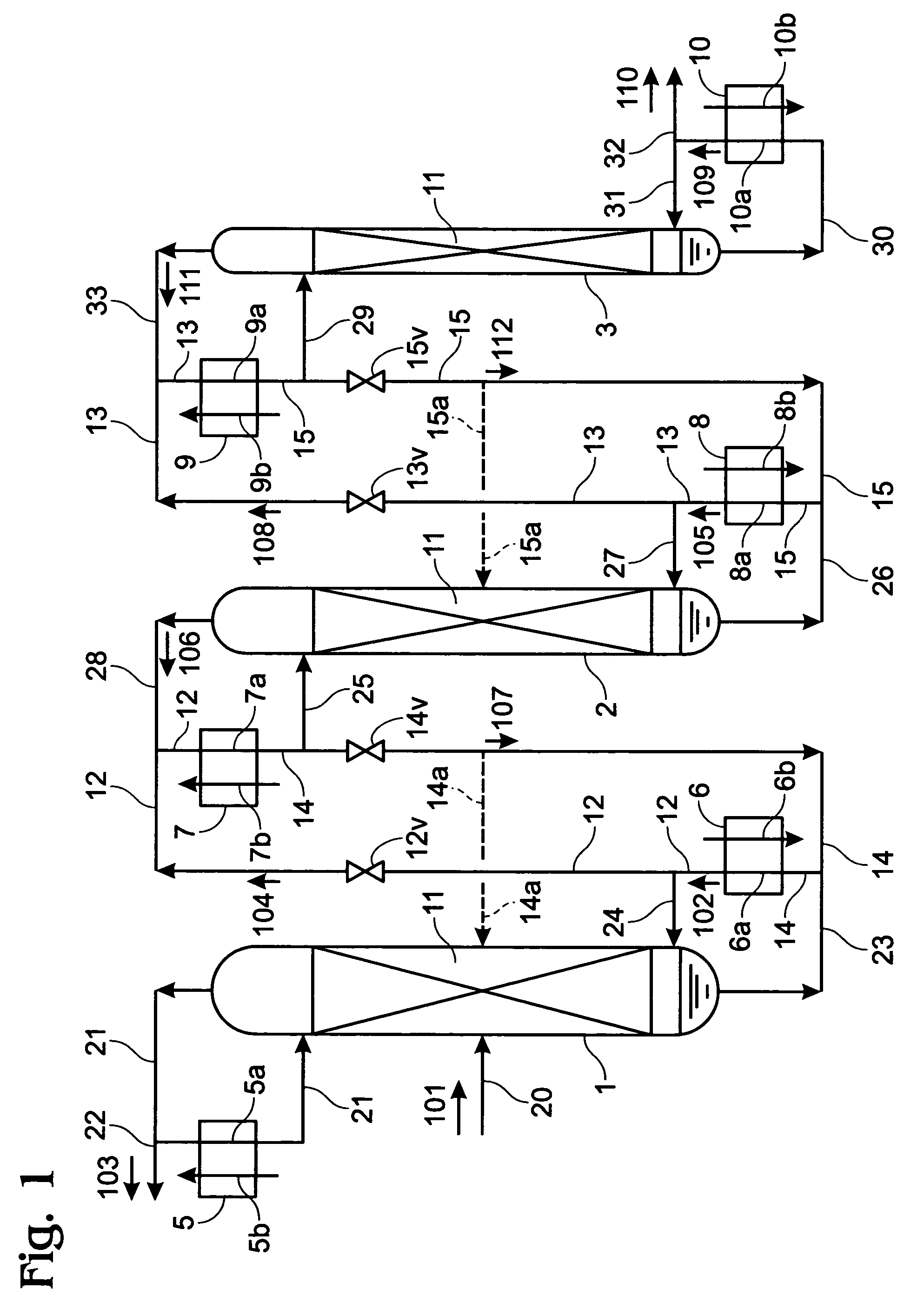
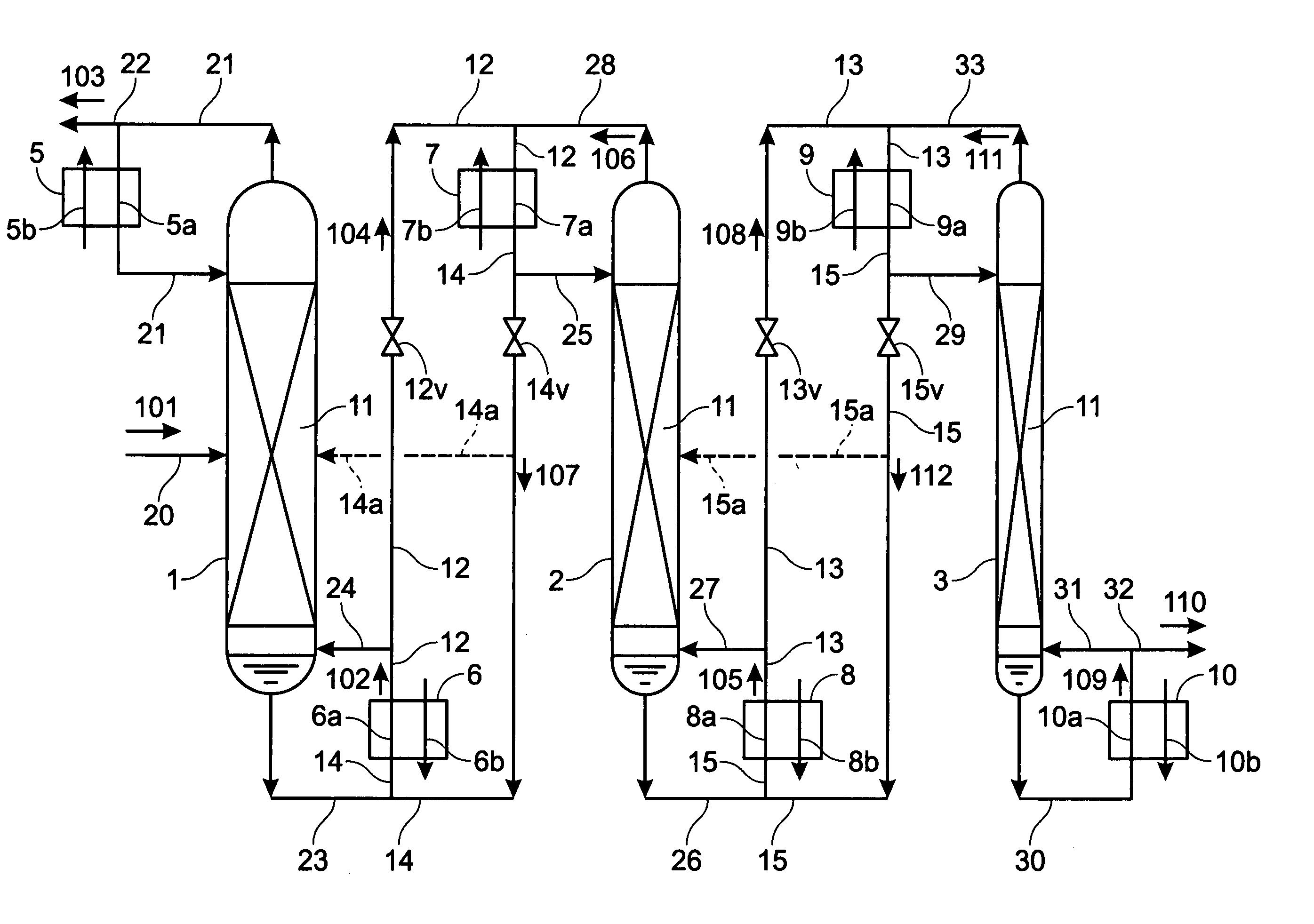
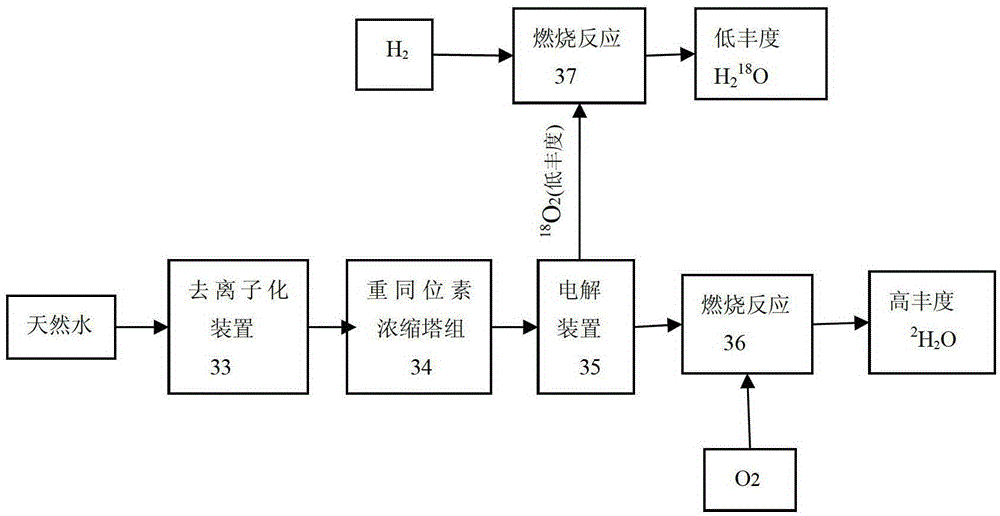
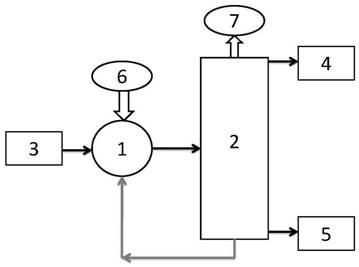
Apparatus, method for enrichment of the heavy isotopes of oxygen and production method for heavy oxygen water
InactiveUS7393447B2Increase vapor pressureImprove distillation efficiencySolidificationLiquefactionReboilerOxygen
An apparatus comprising first to third columns, wherein the outlet of a first column reboiler and the inlet of a second column condenser are connected by a first introduction conduit, and the outlet of a second distillation column reboiler and the inlet of a third column condenser are connected by a second introduction conduit, and additionally the outlet of the second column condenser and the inlet of the first column reboiler are connected by a first return conduit, and the outlet of the third column condenser and the inlet of the second column reboiler are connected by a second return conduit.
Owner:NIPPON SANSO CORP
Apparatus, method for enrichment of the heavy isotopes of oxygen and production method for heavy oxygen water
InactiveUS20050129592A1Increase vapor pressureImprove distillation efficiencySolidificationLiquefactionReboilerOxygen
An apparatus comprising first to third columns, wherein the outlet of a first column reboiler and the inlet of a second column condenser are connected by a first introduction conduit, and the outlet of a second distillation column reboiler and the inlet of a third column condenser are connected by a second introduction conduit, and additionally the outlet of the second column condenser and the inlet of the first column reboiler are connected by a first return conduit, and the outlet of the third column condenser and the inlet of the second column reboiler are connected by a second return conduit.
Owner:NIPPON SANSO CORP
Ovarian-cancer marker detection kit based on PRM (Parallel Reaction Monitoring) detection and detection method
InactiveCN108152430AImprove consistencyHigh selectivityComponent separationProtein markersPeptide fragment
The invention provides an ovarian-cancer marker detection kit based on PRM (Parallel Reaction Monitoring) detection and a detection method thereof and belongs to the technical field of ovarian-cancermarker detection. The ovarian-cancer marker detection kit is used for rapidly and accurately detecting the contents of 5 types of markers and comprises a reagent for conventional mass-spectrometric detection, a heavy-isotope-labeled standard peptide fragment test tube and a special chromatographic analysis column; 10 artificially-synthesized heavy-labeled isotope peptide fragments of 5 ovarian-cancer protein markers are doped into serum, and a PRM technology is used for carrying out absolute quantitative analysis on the 5 ovarian-cancer protein markers which are endogenous in the serum so as to achieve the purpose of helping diagnosis of the ovarian cancer. The ovarian-cancer marker detection kit provided by the invention has the advantages of simple operation, short consumed time, short experimental period, strong specificity and high sensitivity.
Owner:上海中科新生命生物科技有限公司
Rotary low-temperature hydrogen isotope separation system and separation method thereof
The invention discloses a rotary low-temperature hydrogen isotope separation system and a separation method thereof, which solve the complicated construction, complicated parameter control, and high operation cost, or helium gas supply requirement, hydrogen and helium separation, and complex separation column regeneration treatment, or high cost of palladium displacement chromatogram filling material and easy failure in the prior art. The separation system includes a cryogenic tank, a reversing frame, a separation column, a raw material hydrogen-storage tank, a light isotope storage tank, a heavy isotope storage tank, a vacuum pump, and an exhaust gas storage tank. The separation method is characterized in that a separation column absorbing the raw material hydrogen to gradually separate the liquid nitrogen liquid level to desorb the hydrogen isotope to complete rearrangement of hydrogen isotope in other separation columns; and the light and heavy isotopes can be finally collected respectively from the far and near ends of the loop. The system creatively utilizes the technical principle of a simulated moving bed, the hydrogen isotope can continuously circulate in the closed loop separation loop, the heavy isotope concentration gradually decreases from the near end to the far end where the desorption occurs in the separation loop, and the concentration gradient of the heavy isotope is continuously increased with the adsorption / desorption frequency.
Owner:MATERIAL INST OF CHINA ACADEMY OF ENG PHYSICS
Materials and methods for controlling isotope effects during fractionation of analytes
Compositions and methods for controlling or eliminating isotope effects during fractionation of chemically equivalent but isotopically distinct compounds. Isotope coding agents contain heavy isotopes other than deuterium. The invention facilitates intelligent data acquisition. After sample fractionation, isotope abundance ratios are calculated using mass spectrometry, and analytes of interest are identified in real time.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
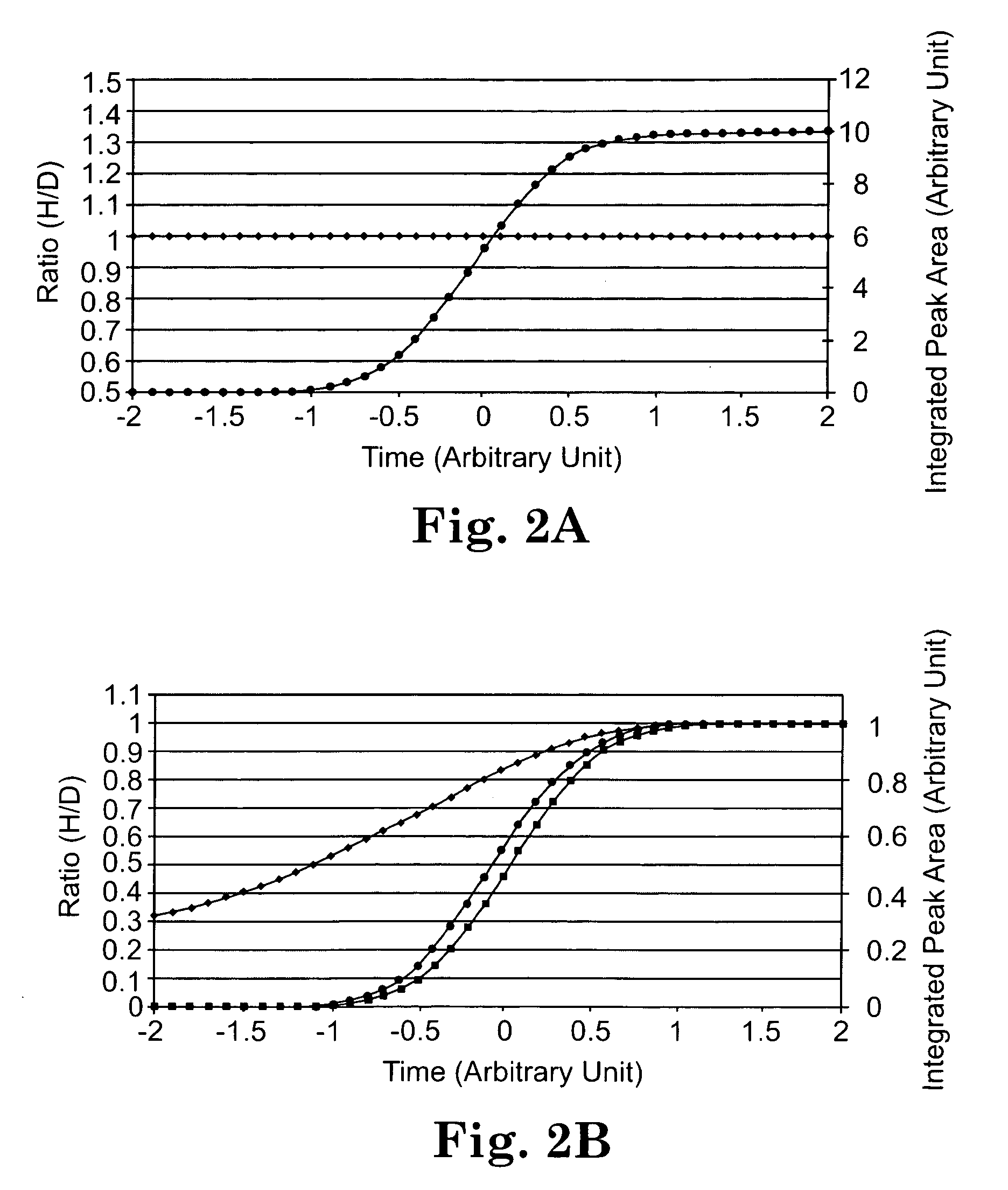
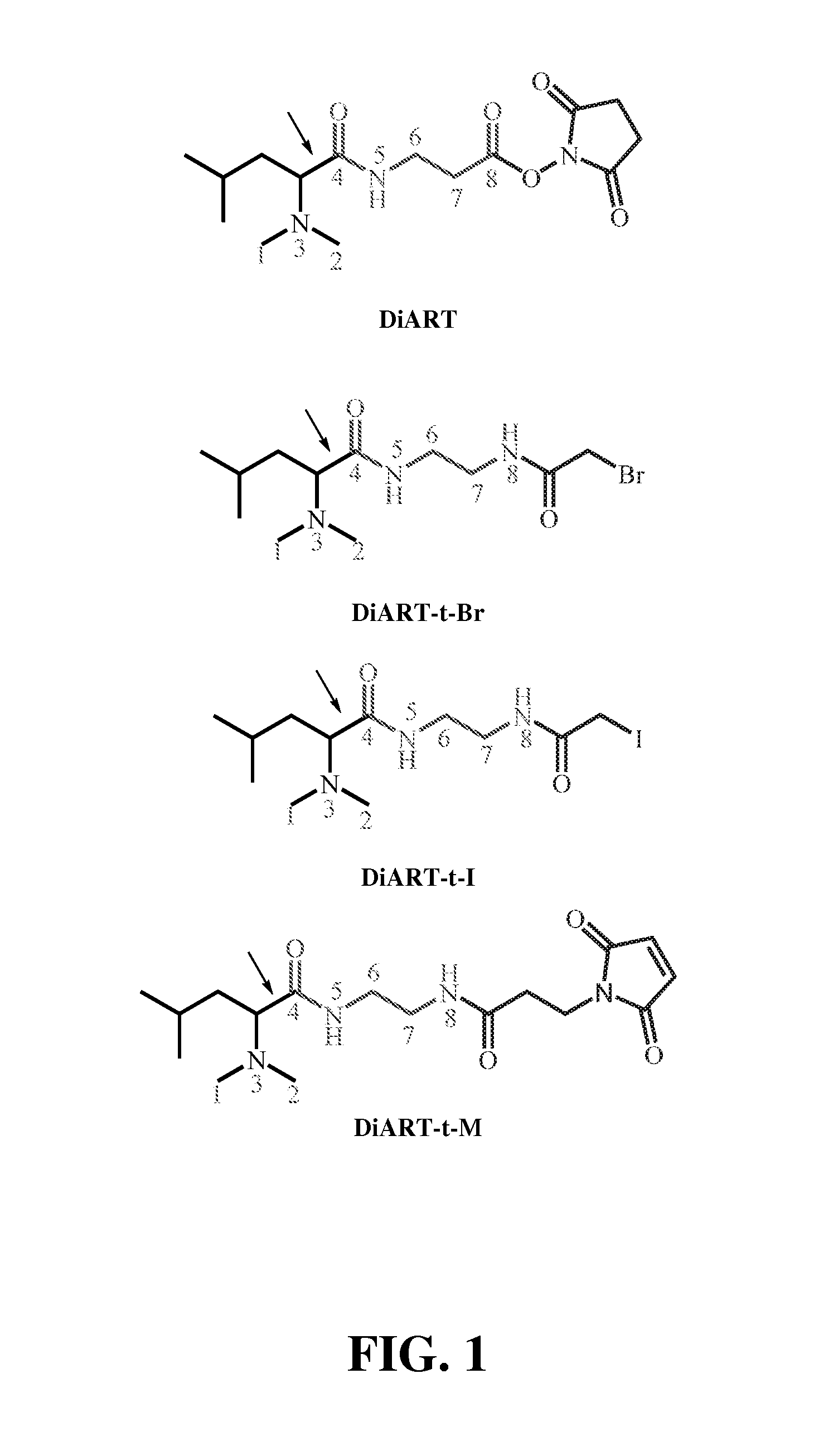
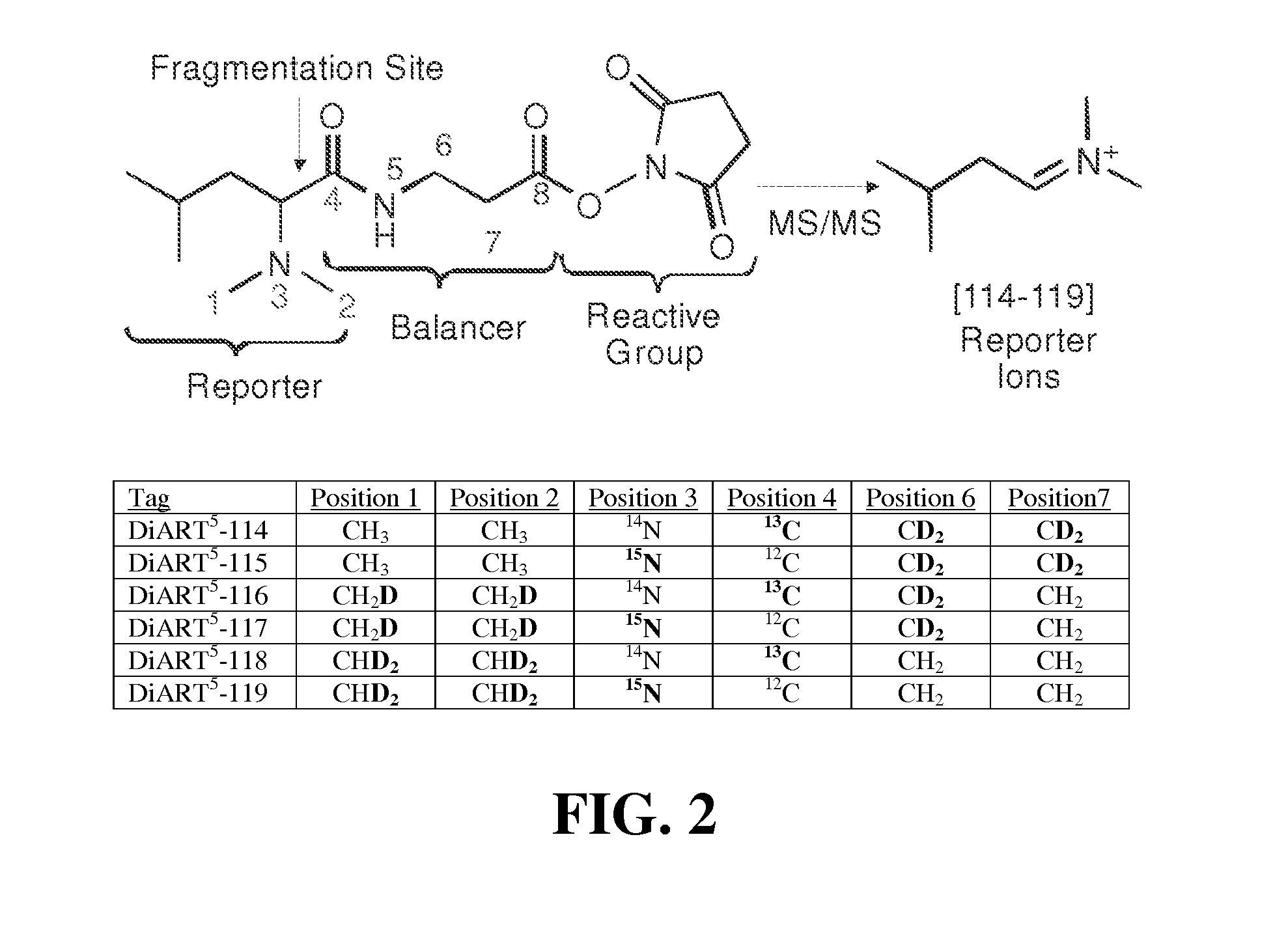
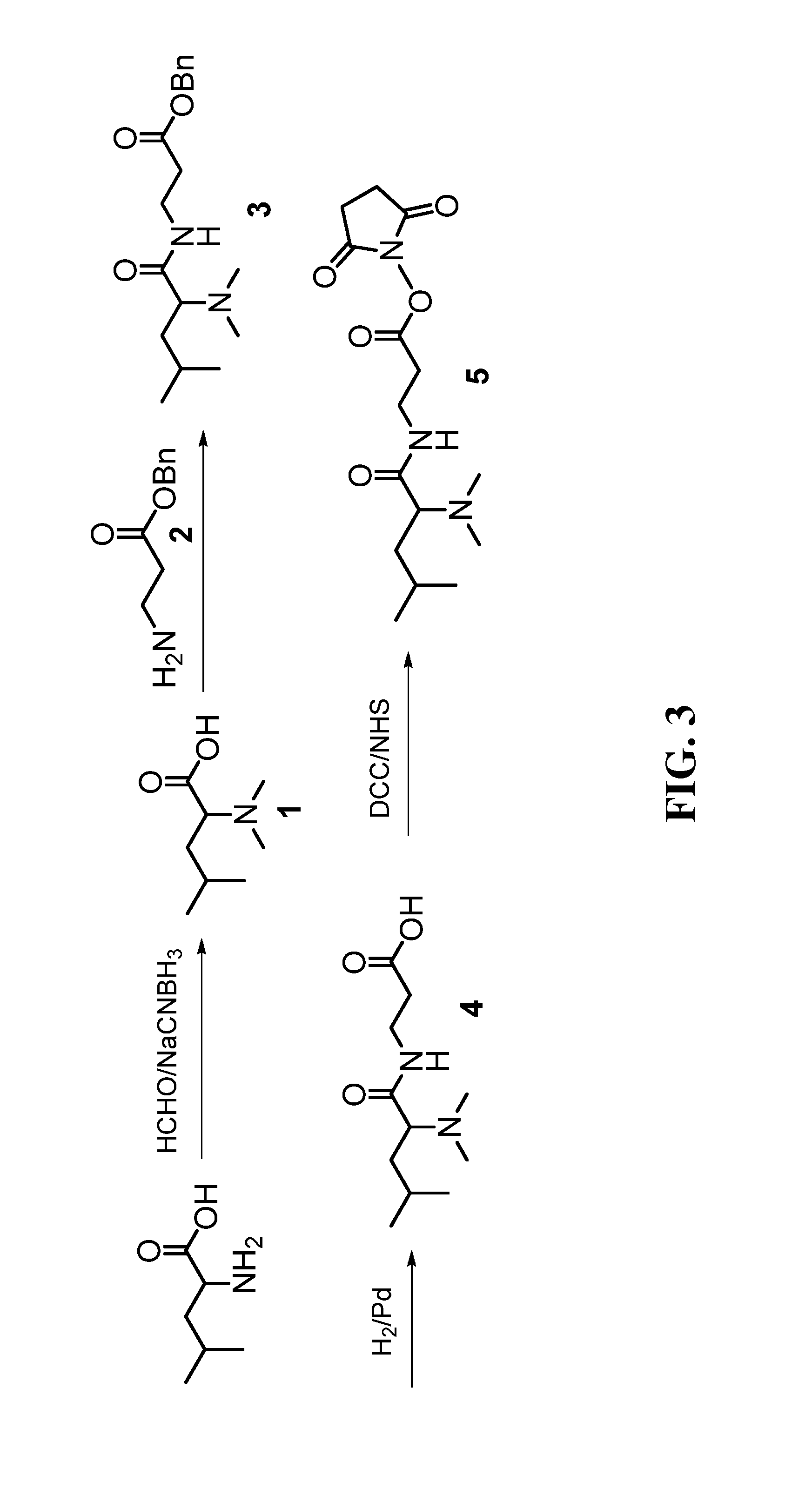
Deuterium isobaric tag reagents for quantitative analysis
InactiveUS20110318771A1Easy to analyze and useOrganic chemistryMicrobiological testing/measurementCombinatorial chemistryReagent
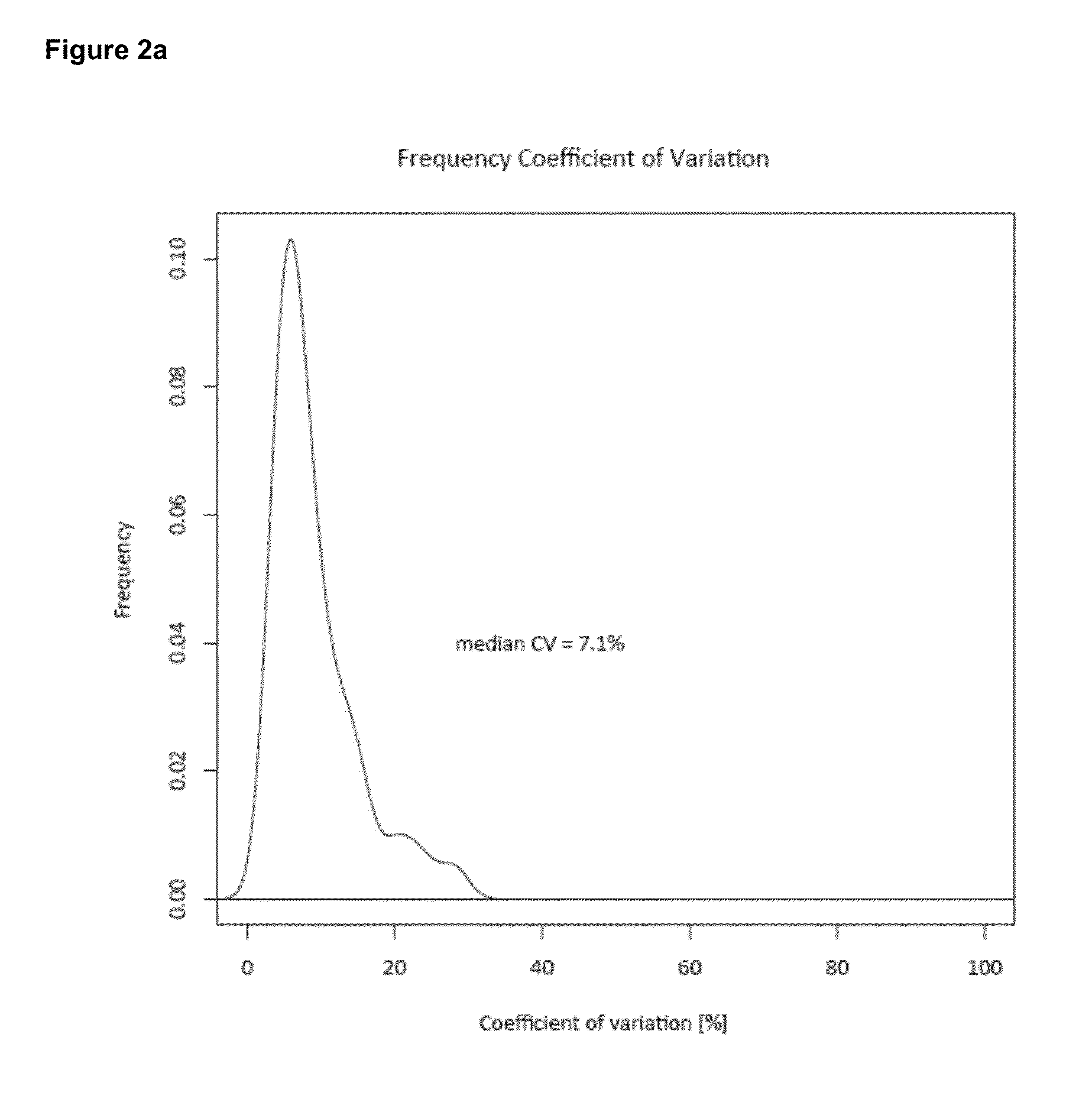
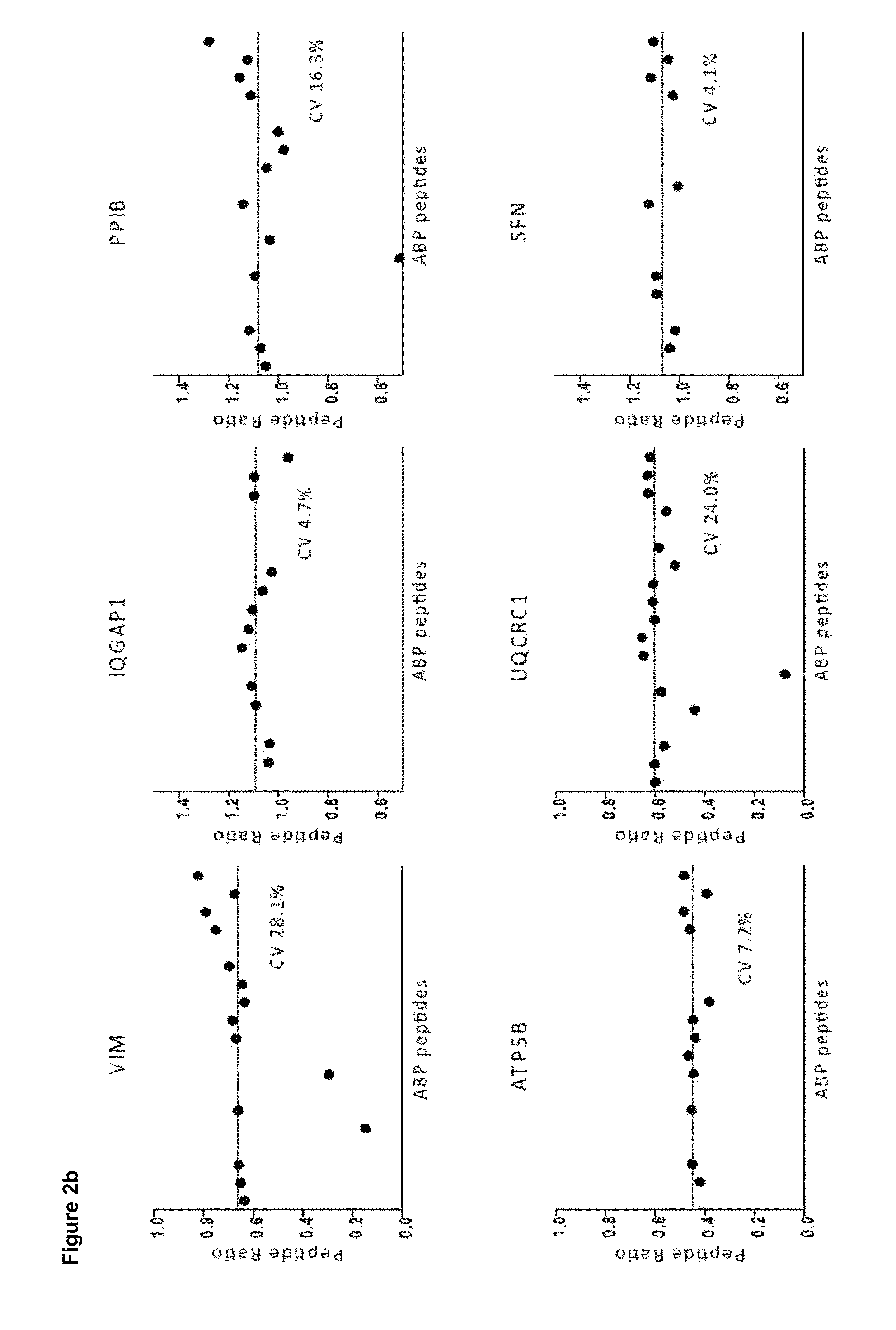
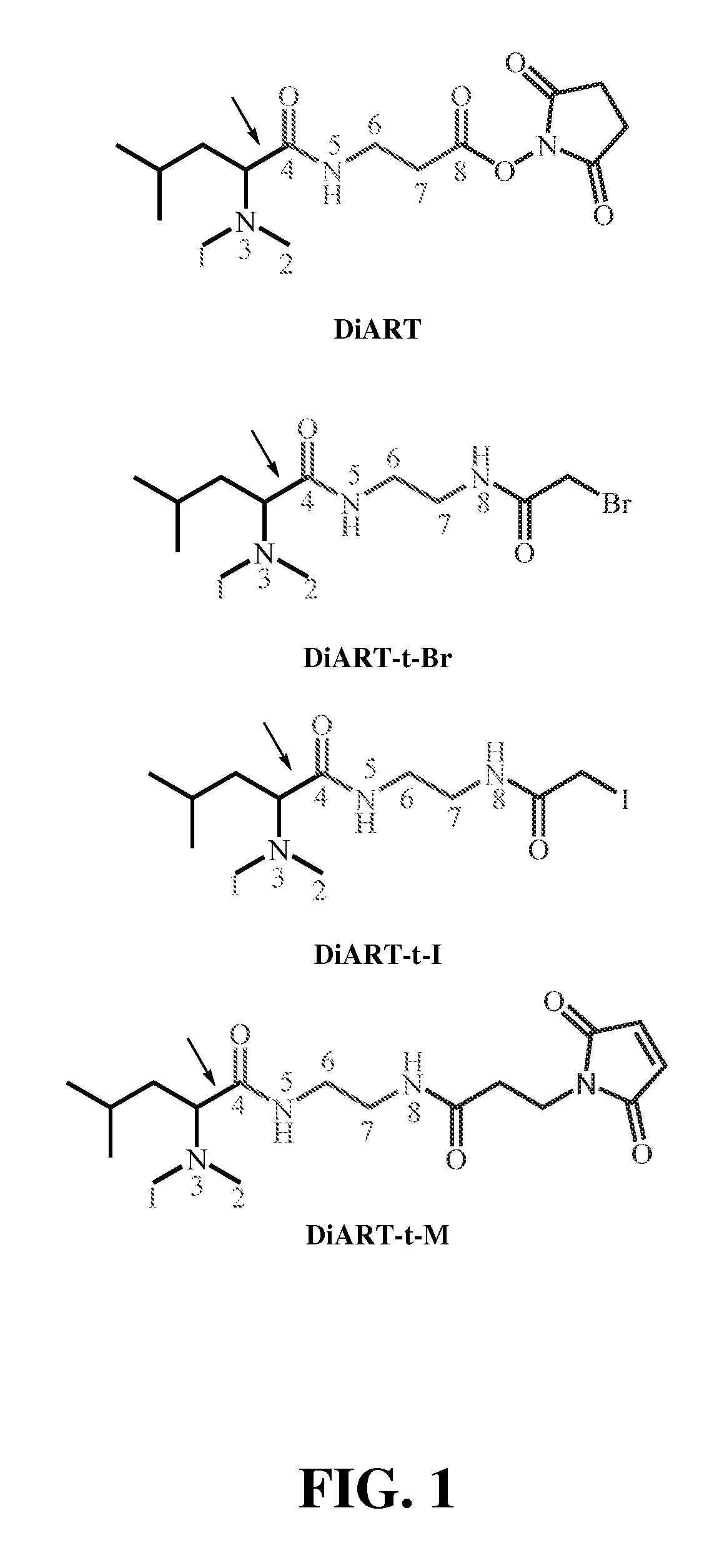
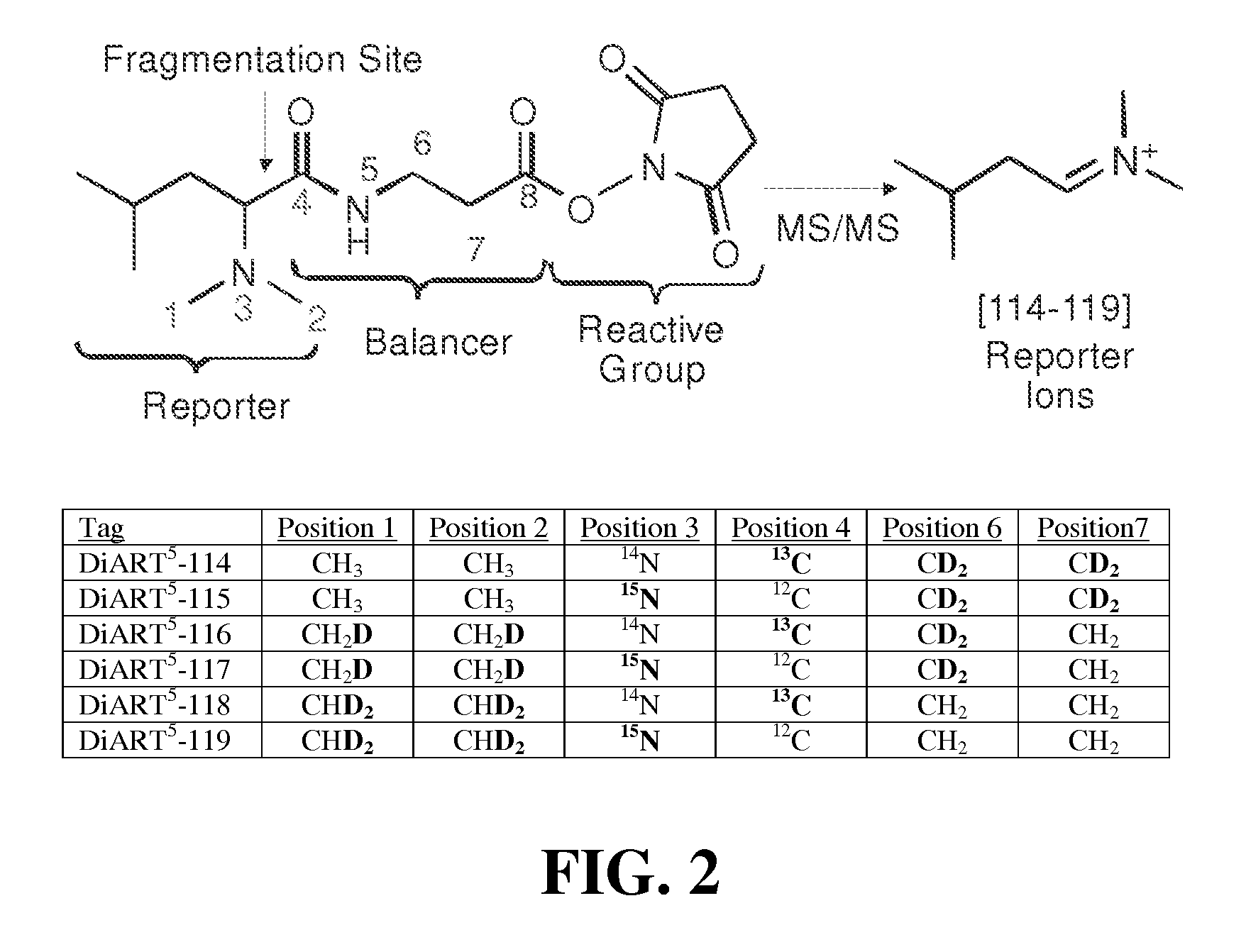
Deuterium isobaric tag reagents are provided for the quantitation of biomolecules, where the reagents contain heavy isotope atoms, including one or more 2H in each reagent. Generally, the reagents are described by the formula: reporter group—balancer group—reactive group, wherein the reporter group and the balancer group are linked by an MS / MS scissionable bond. Each of the reporter group and balancer groups independently contain 0 to 9 heavy isotope atoms selected from 13C, 15N and 2H and the total number of 2H atoms in each reagent is 1 to 6. The mass of the reporter group is from 114-123 Daltons. Exemplary deuterium isobaric tag reagents include Di-ART, DiART-t-I, DiART-t-Br and DiART-t-M. Also provided are compositions containing more than one deuterium isobaric tag reagent and methods for making and using deuterium isobaric tag reagents.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
Microlitographic projection exposure apparatus and immersion liquid therefore
InactiveUS20080304032A1Reduced responseProlonged down-timesMicroscopesPhotomechanical exposure apparatusChemical reactionPerfluoropolyether
An immersion liquid for a microlithographic projection exposure apparatus is enriched with heavy isotopes. This reduces the chemical reactivity, which leads to an extension of the lifetime of optical elements which come in contact with the immersion liquid. For example, heavy water (D2O), deuterated sulfuric acid, (D2SO4) or deuterated phosphoric acid D3P16O4 may be used. Organic compounds such as perfluoro polyethers, which have been deuterated or enriched with heavy oxygen (18O), are furthermore suitable.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
Quantitative standard for mass spectrometry of proteins
ActiveUS20140072991A1Easy to handleAvoidance of biasPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsSpectroscopyMass spectrometry imaging
The present invention provides a method of determining the absolute amount of a target polypeptide in a sample, said method comprising the following steps: (a) adding (aa) a fusion polypeptide to said sample, said fusion polypeptide comprising (i) at least one tag sequence and (ii) a subsequence of the target polypeptide; and (ab) a known absolute amount of a tag polypeptide comprising or consisting of said tag sequence according to (aa) to said sample, wherein said fusion polypeptide on the one hand is mass-altered as compared to said target polypeptide and said tag polypeptide on the other hand, for example, said fusion polypeptide on the one hand and said target polypeptide and said tag polypeptide on the other hand are differently isotope labeled; (b) performing proteolytic digestion of the mixture obtained in step (a); (c) subjecting the result of proteolytic digestion of step (b), optionally after chromatography, to mass spectrometric analysis; and (d) determining the absolute amount of said target polypeptide from (i) the peak intensities in the mass spectrum acquired in step (c) of said fusion polypeptide, said tag polypeptide and said target polypeptide and (ii) said known absolute amount of said tag polypeptide.Furthermore provided is a fusion polypeptide for the quantification of a target polypeptide by mass spectroscopy, wherein: said fusion polypeptide consists of 35 to 455 amino acid residues and comprises (i) a target region, which is a fragment of the target polypeptide, and (ii) a tag region, which is not a fragment of the target polypeptide, said target region consists of 15 to 205 amino acid residues and comprises at least two signature regions; said tag region consists of 20 to 250 amino acid residues and comprises at least two signature regions; and each signature region has the structure Y-Z-X4-28-Y-Z, wherein all Y:s are selected from one of (i)-(iv), wherein (i) is R or K, (ii) is Y, F, W or L, (iii) is E and (iv) is D and each X and each Z are independently any amino acid residue, provided that the Z:s are not P if the Y:s are selected from (i)-(iii); and each signature region comprises at least one amino acid residue comprising a heavy isotope.
Owner:MAX PLANCK GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER WISSENSCHAFTEN EV +1
Deuterium isobaric tag reagents for quantitative analysis
InactiveUS8486712B2Organic chemistryMicrobiological testing/measurementCombinatorial chemistryReagent
Deuterium isobaric tag reagents are provided for the quantitation of biomolecules, where the reagents contain heavy isotope atoms, including one or more 2H in each reagent. Generally, the reagents are described by the formula: reporter group—balancer group—reactive group, wherein the reporter group and the balancer group are linked by an MS / MS scissionable bond. Each of the reporter group and balancer groups independently contain 0 to 9 heavy isotope atoms selected from 13C, 15N and 2H and the total number of 2H atoms in each reagent is 1 to 6. The mass of the reporter group is from 114-123 Daltons. Exemplary deuterium isobaric tag reagents include Di-ART, DiART-t-I, DiART-t-Br and DiART-t-M. Also provided are compositions containing more than one deuterium isobaric tag reagent and methods for making and using deuterium isobaric tag reagents.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
Materials and methods for controlling isotope effects during fractionation of analytes
Compositions and methods for controlling or eliminating isotope effects during fractionation of chemically equivalent but isotopically distinct compounds. Isotope coding agents contain heavy isotopes other than deuterium. The invention facilitates intelligent data acquisition. After sample fractionation, isotope abundance ratios are calculated using mass spectrometry, and analytes of interest are identified in real time.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
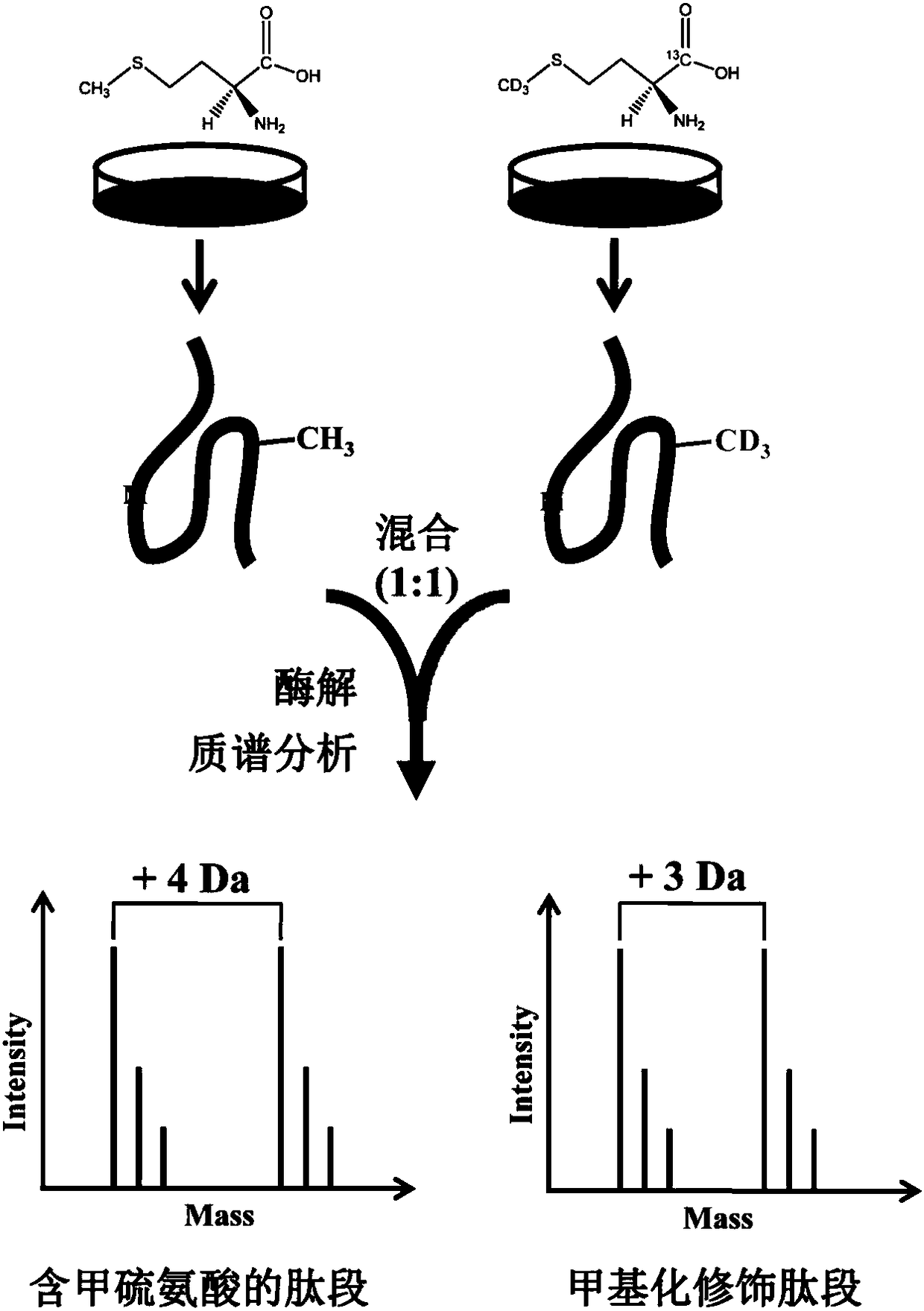
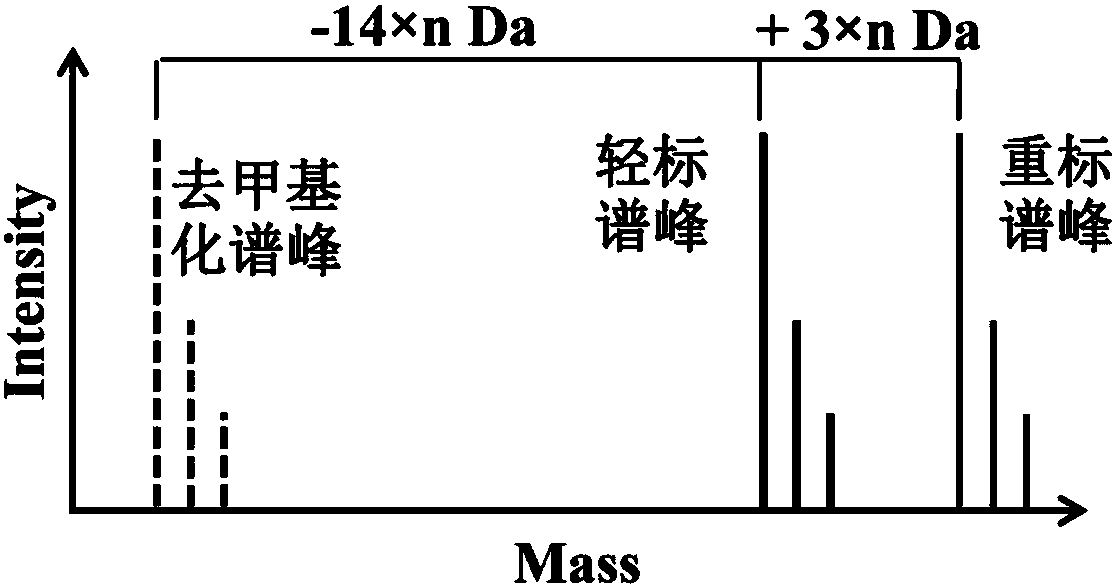
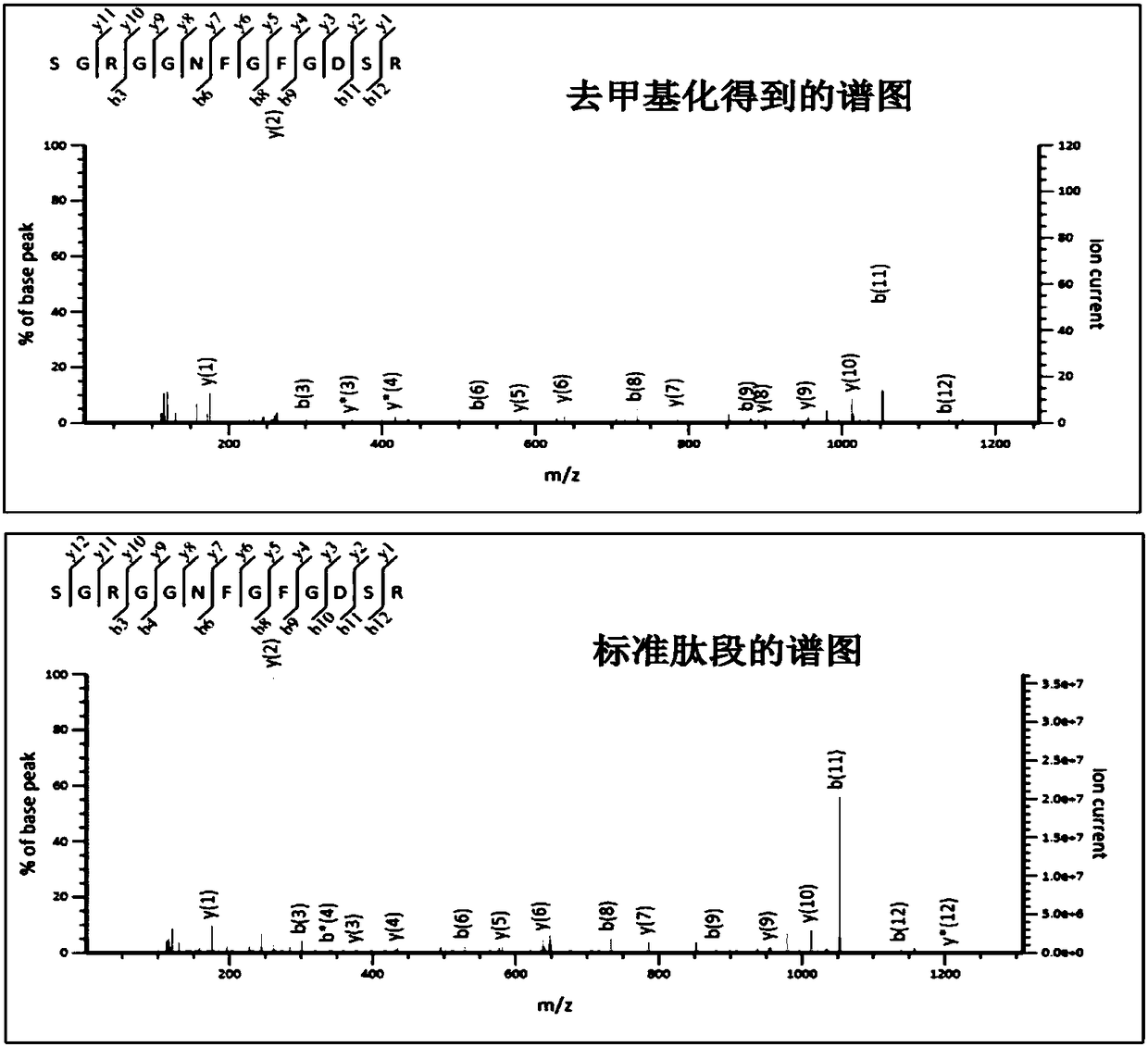
Protein methylation identification method
The invention relates to a new protein methylation identification method. According to the present invention, the methylation site is labeled by using the novel heavy isotope labeled methionine, and the methylation peptide fragment analysis method integrating the methionine cell culture amino acid stable isotope labeling, the identification and extraction of the fragmentation spectrum of the methylation peptide fragment, and the spectrum peak demethylation treatment is developed, and is used in the large-scale analysis of methylated proteome; the amino acid labeling method can distinguish themethylated peptide fragment from the peptide fragment containing methionine, can identify and extract the fragmentation spectrum derived from the methylated peptide fragment, and can demethylate the fragmentation spectrum so as to obtain the spectrum of the unmethylated peptide fragment, and the peptide fragment sequence is determined by searching in a database so as to determine the modificationsite by binding to the spectrum of the methylated peptide fragment; and the method does not require the preset of the modification type so as to simultaneously analyze all the known methylation types.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
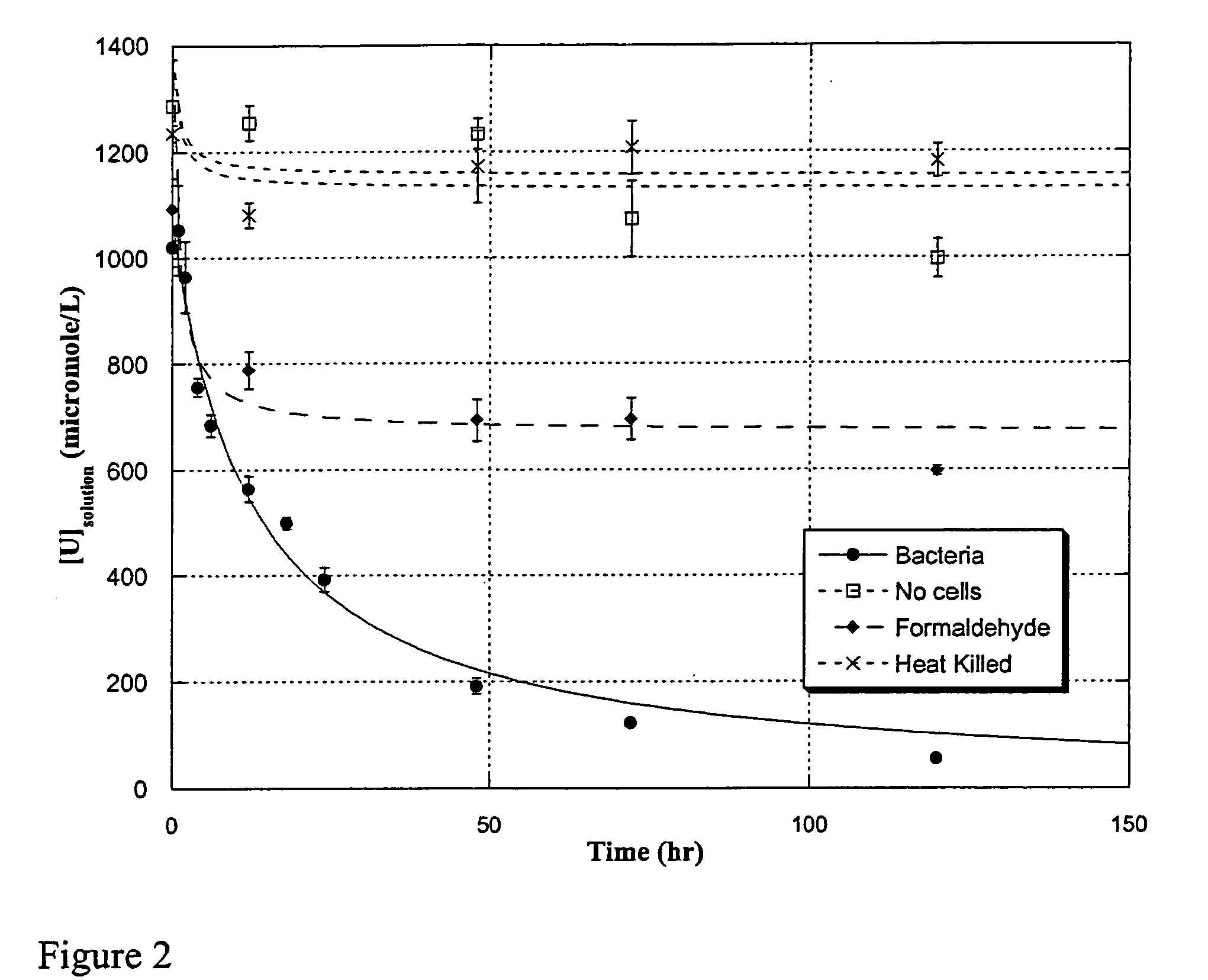
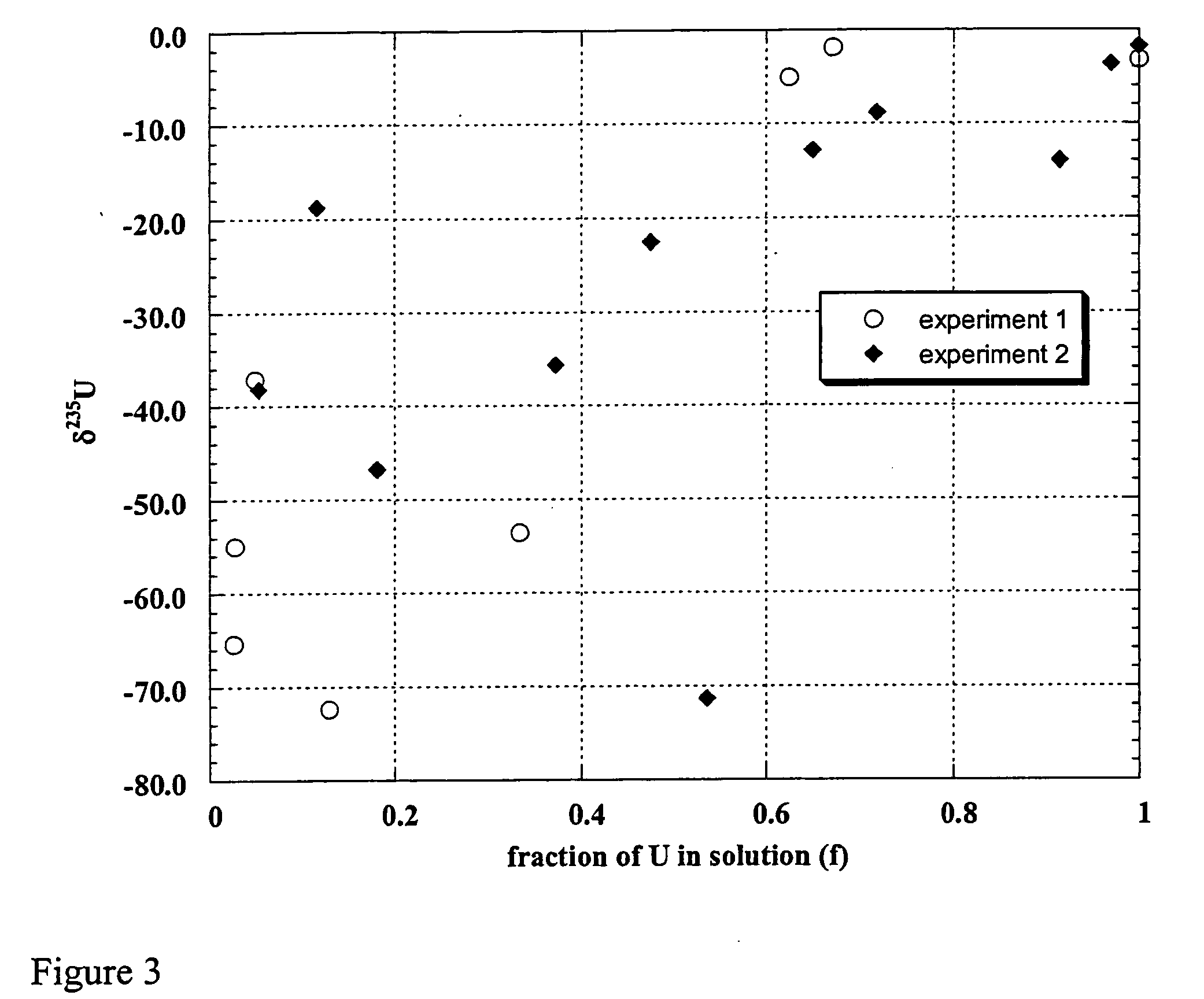
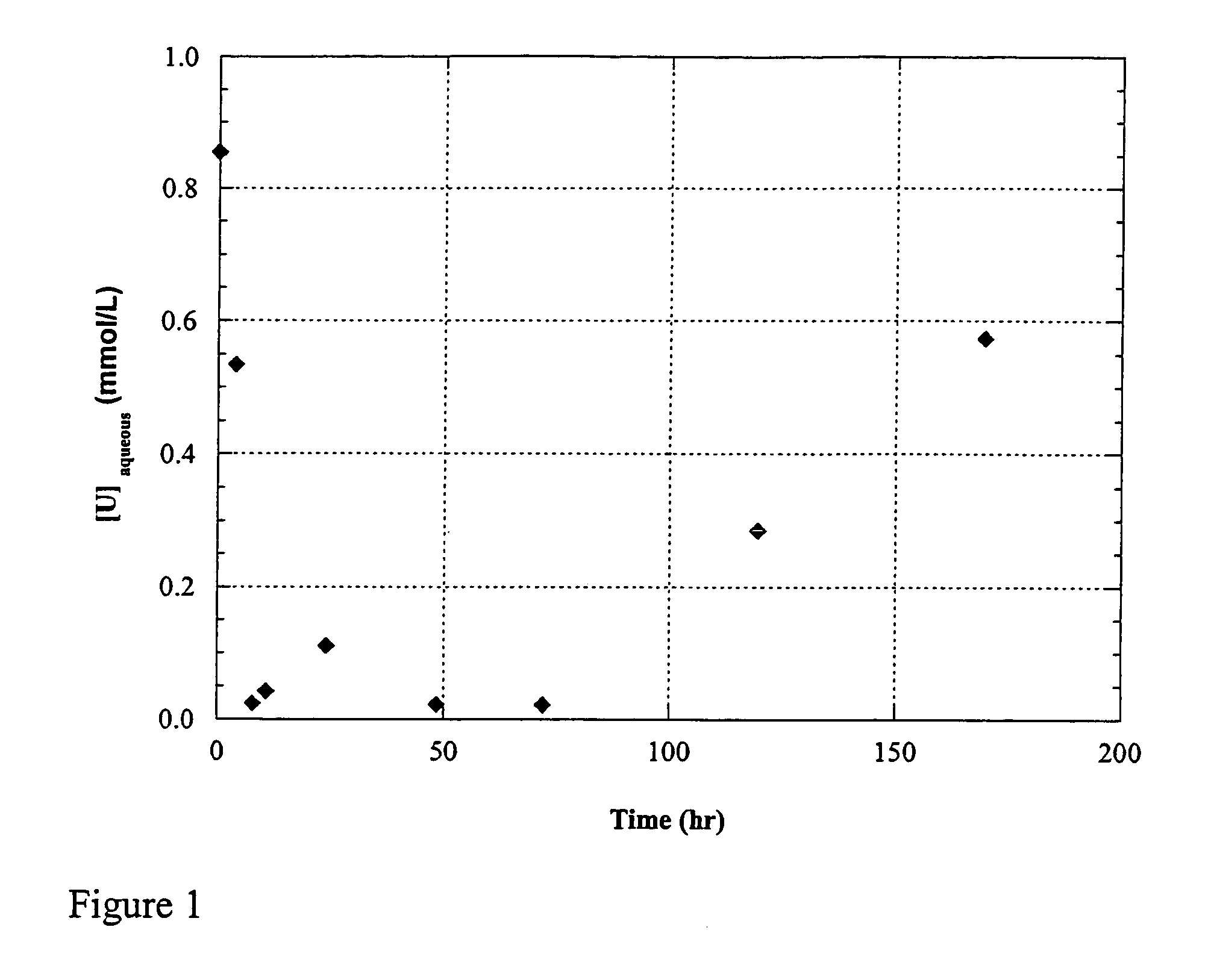
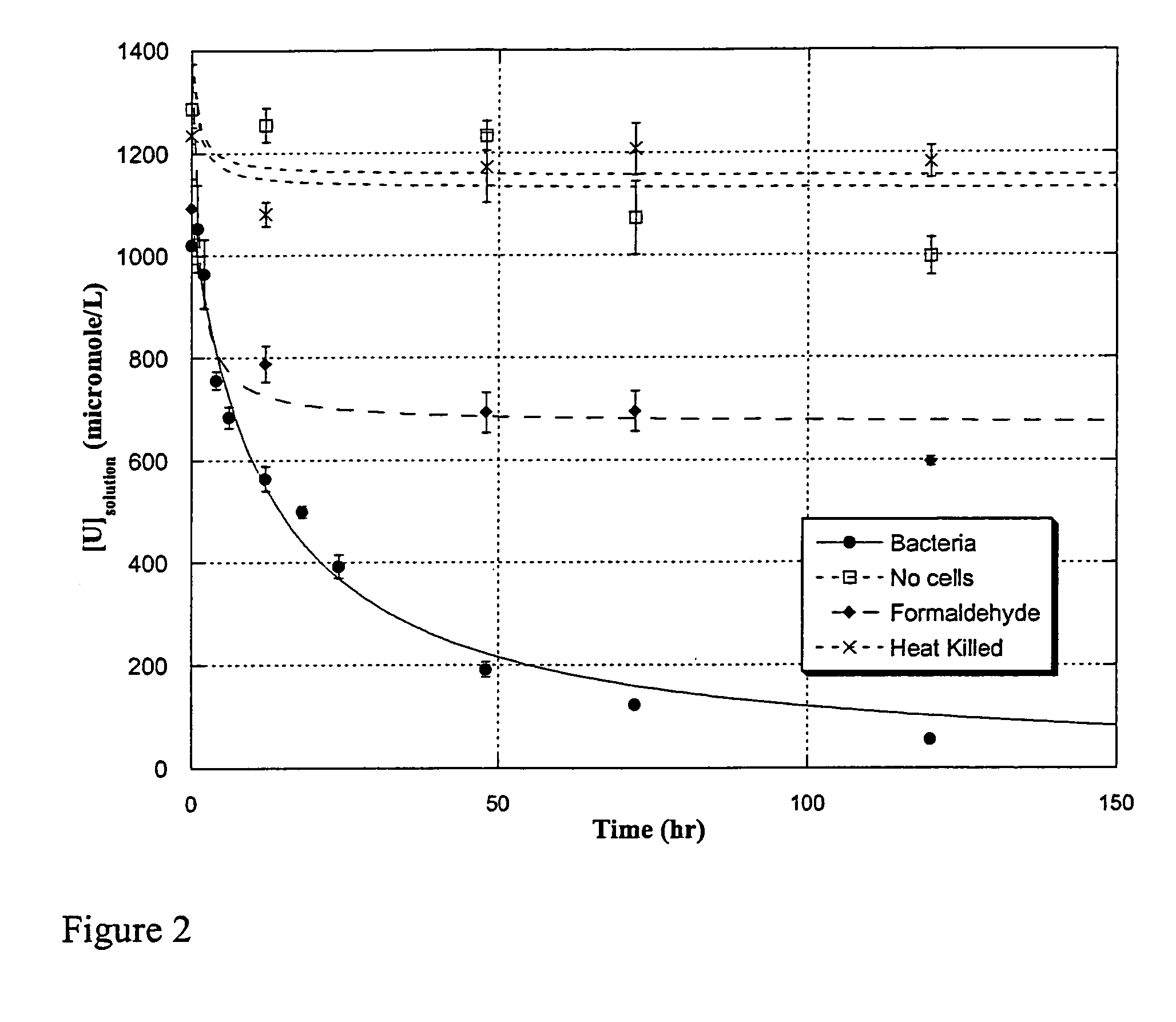
Uranium enrichment using microorganisms
InactiveUS20080268513A1Reduced activityEasy to separateBacteriaIsotope separationCell freeSulfate-reducing bacteria
The present invention provides methods for separating isotopes of actinide elements such as uranium using microorganisms, e.g., metal or sulfate reducing bacteria. The microorganisms reduce the actinide element to form a precipitate, which contains a greater proportion of the lighter isotope relative to the heavier isotope than the starting material. The precipitate may be collected, re-oxidized, and subjected to multiple rounds of enrichment. Alternately, separation processes not requiring formation of a precipitate may be used. The invention also features cell-free systems for isotope separation. The invention further provides compositions produced according
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Uranium enrichment using microorganisms
The present invention provides methods for separating isotopes of actinide elements such as uranium using microorganisms, e.g., metal or sulfate reducing bacteria. The microorganisms reduce the actinide element to form a precipitate, which contains a greater proportion of the lighter isotope relative to the heavier isotope than the starting material. The precipitate may be collected, re-oxidized, and subjected to multiple rounds of enrichment. Alternately, separation processes not requiring formation of a precipitate may be used. The invention also features cell-free systems for isotope separation. The invention further provides compositions produced according to the foregoing methods, including compositions comprising enriched uraninite.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
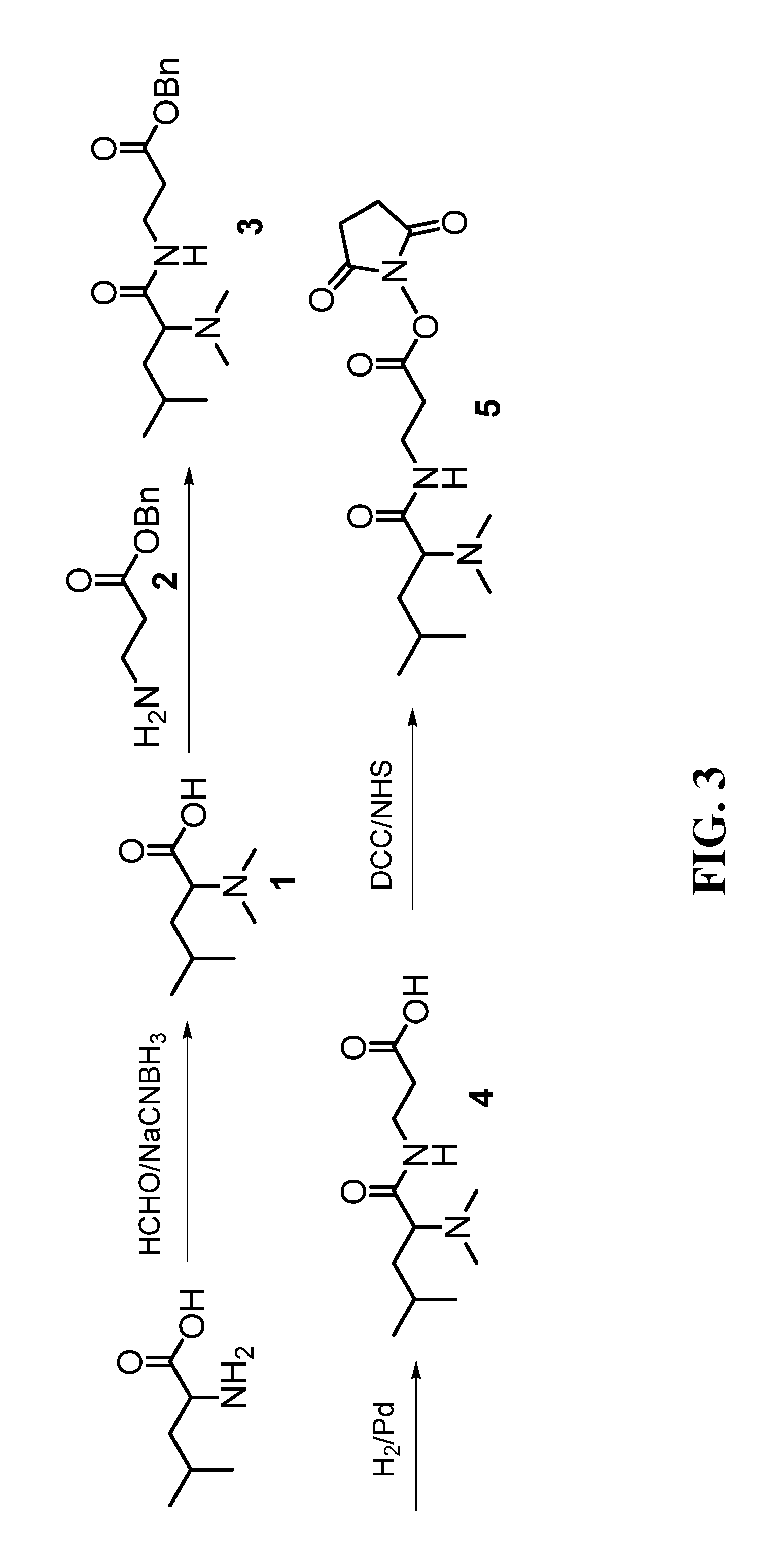
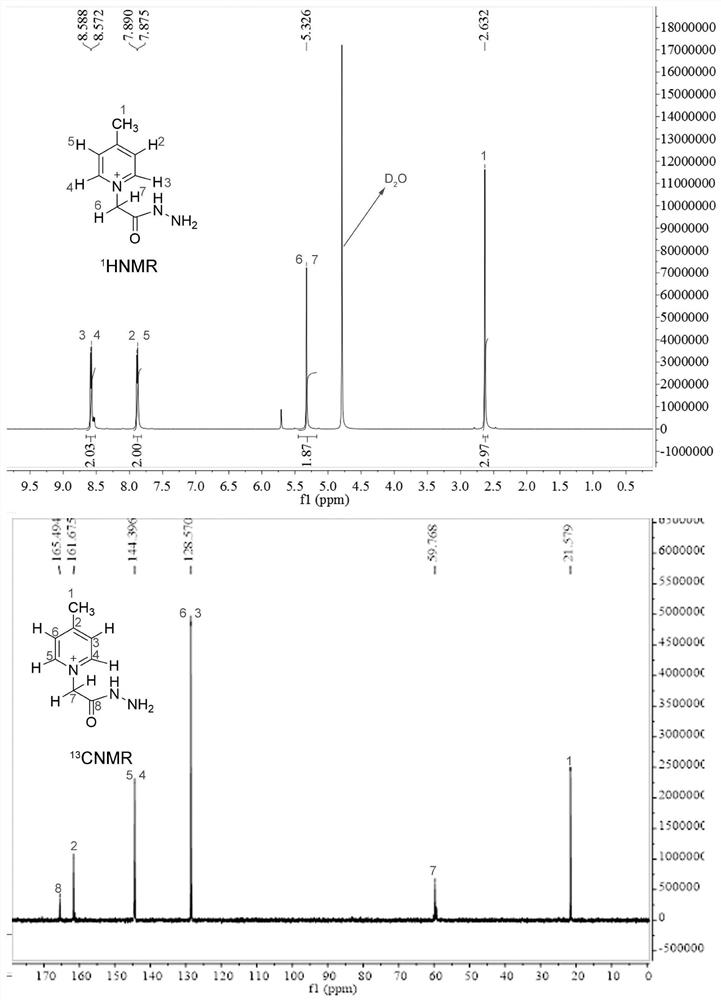
Compound containing amide functional group of stable heavy isotope and application thereof
The invention provides a compound containing a stable heavy isotope-enriched amide functional group. The compound is as shown in a formula (I) and is used for adjusting the pharmacokinetic characteristics, metabolic characteristics and / or delivery efficiency and treatment and prevention effects of a drug or a prodrug. The invention also relates to the application of the drug or prodrug containingisotope-enriched amide in the treatment or prevention of illness and symptoms of diseases.
Owner:君实润佳(上海)医药科技有限公司
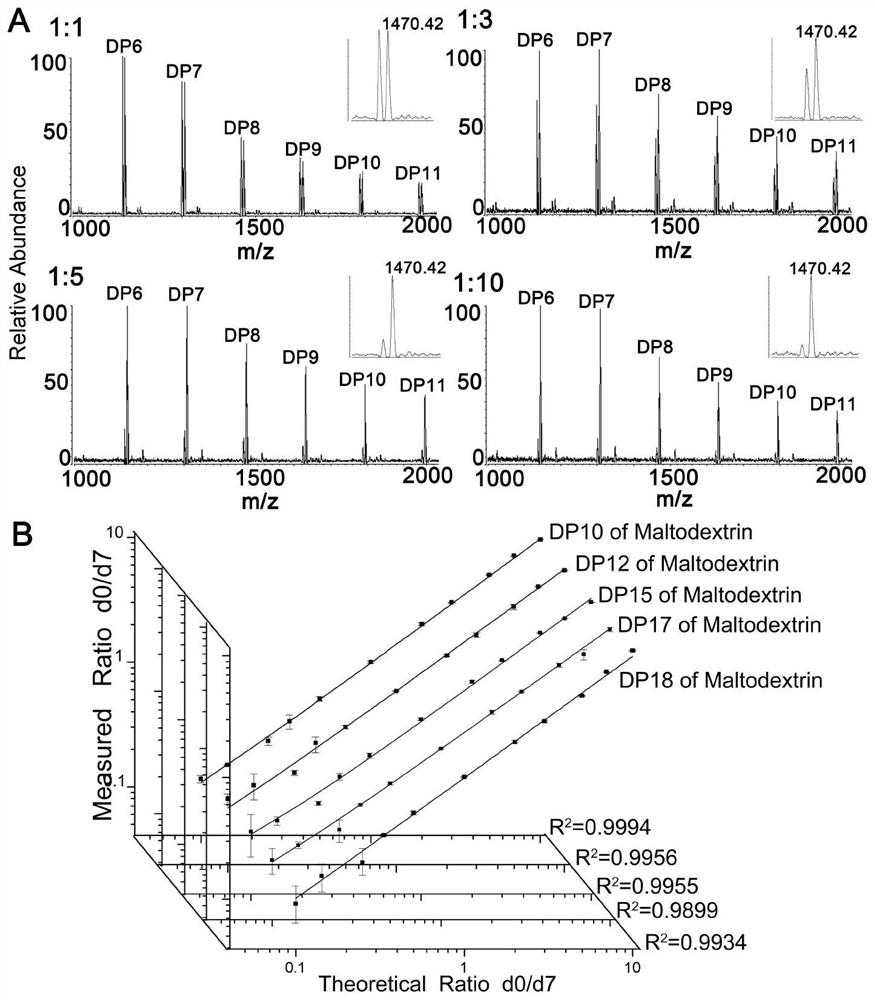
Relative quantification method based on novel mass discrepancy labels for carboxylic acid type signal molecules in biological system
InactiveCN103936598AImprove throughputSave human effortOrganic compound preparationComponent separationSignalling moleculesSynthesis methods
The invention provides a quantification method based on novel mass discrepancy labels for relative concentrations of carboxylic acid type signal molecules in a biological sample system, and provides a mass discrepancy label molecule pair labeled by a light / heavy isotope pair and a synthetic method thereof. The mass discrepancy label molecule pair comprises a light isotope label molecule and a heavy isotope label molecule. The formula of the two label molecules is shown as the formula (I). The light / heavy heavy isotope pair exists in one or two of a structure part A and a structure part B in the structure, wherein the light / heavy heavy isotope pair in the structure part A is selected from one or more of a group comprising H / D, 12C / 13C and 14N / 15N, or the light / heavy heavy isotope pair in the structure part B is one or more selected from a group comprising H / D, 12C / 13C and 16O / 18O.
Owner:INST OF GENETICS & DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
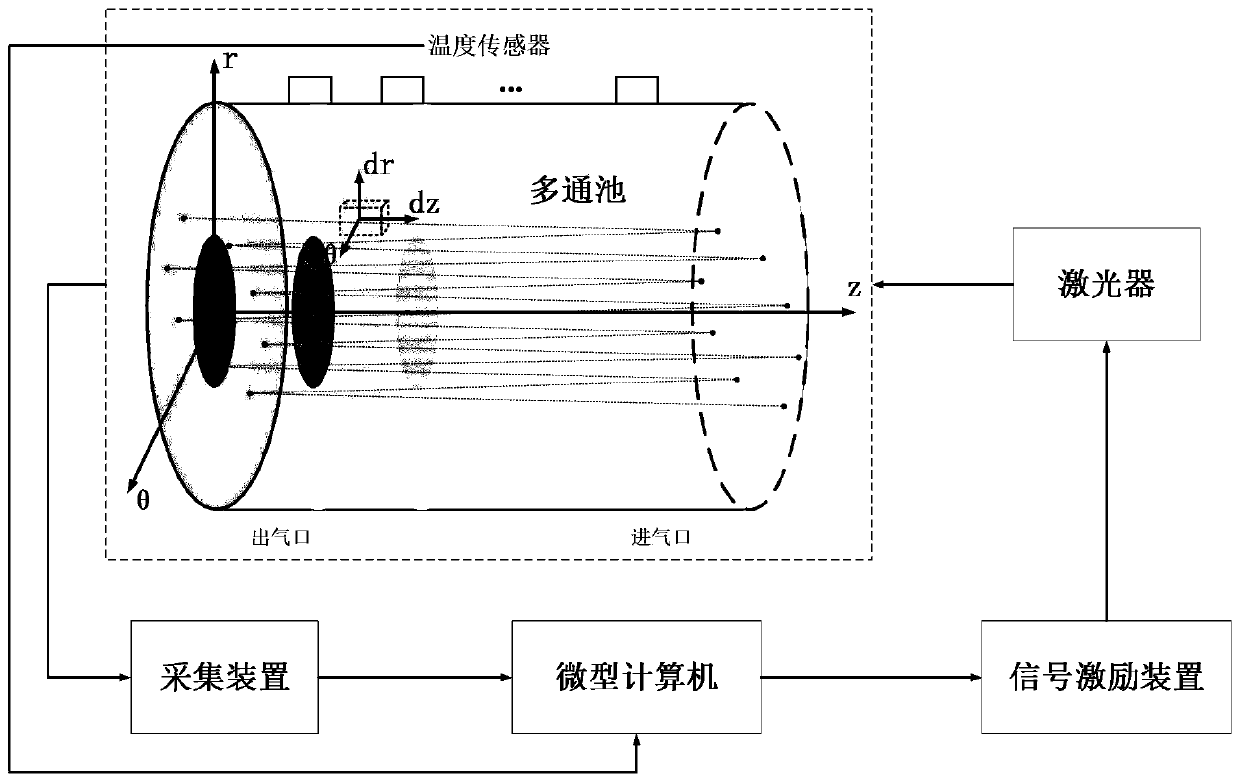
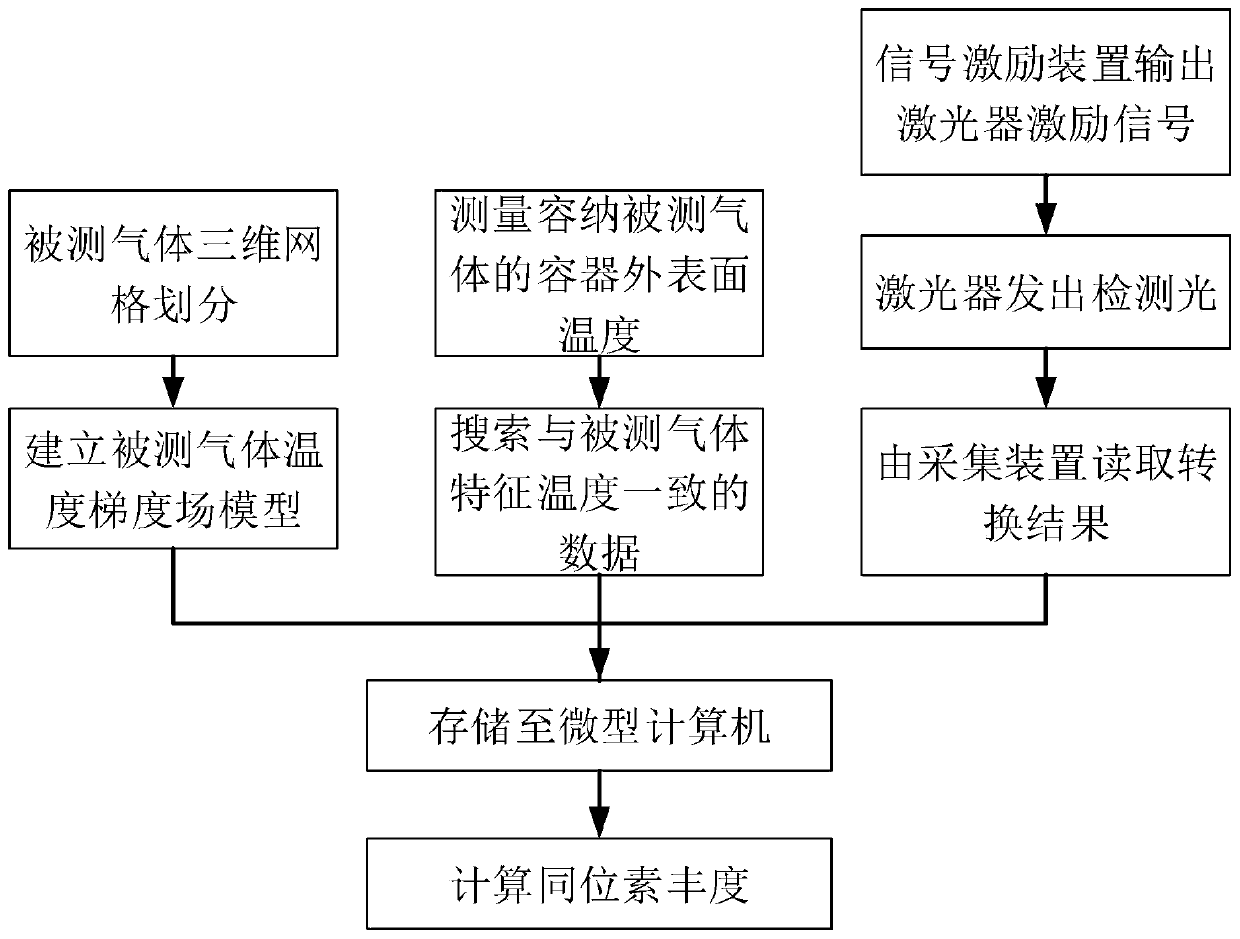
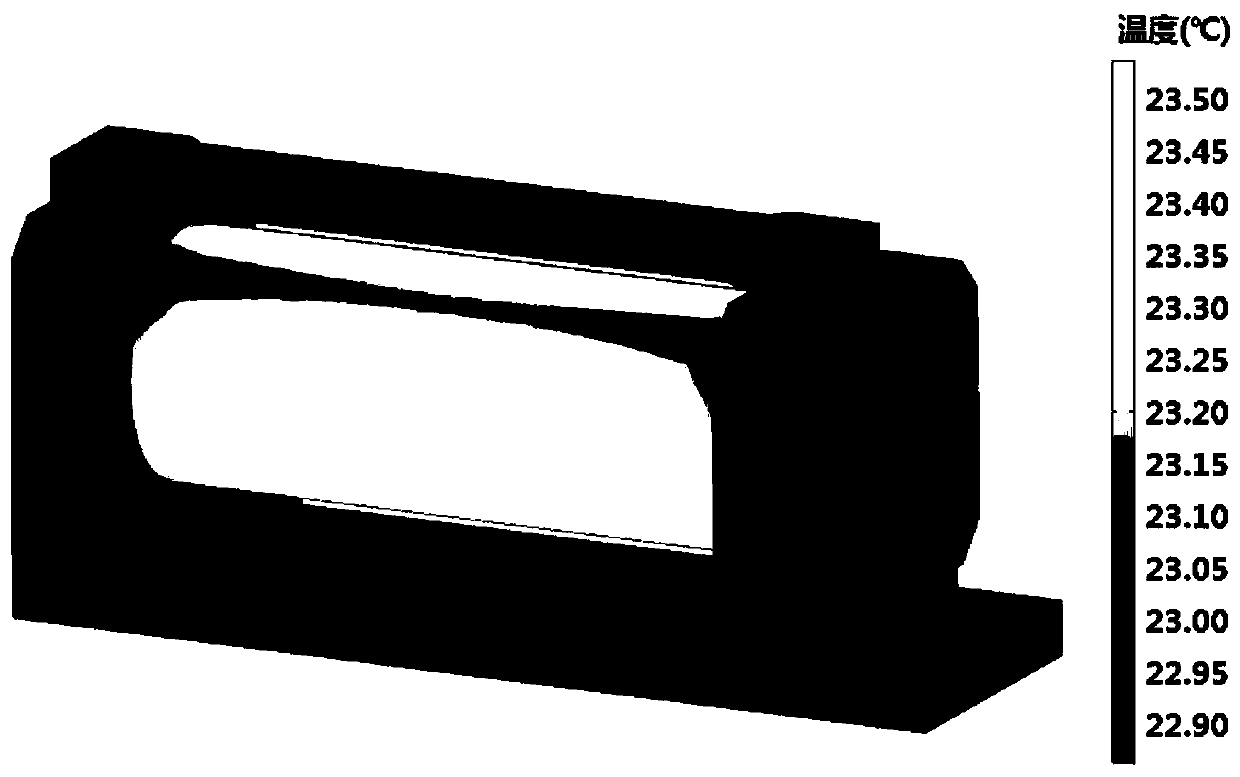
Infrared absorption spectrum isotope abundance detection method based on temperature gradient field compensation
An infrared absorption spectrum isotope abundance detection method based on temperature gradient field compensation belongs to the field of infrared laser absorption spectrums, and comprises the following steps: firstly, according to the distribution and optical path of a measurement light path, carrying out three-dimensional grid division on a measured gas, so that only one beam of measurement light source passes through each grid; establishing a measured gas temperature gradient field model, and obtaining a measured gas temperature gradient field theoretical database; measuring the temperature of the outer surface of the measured gas container by using a high-precision temperature sensor to obtain the characteristic temperature of the measured gas, and fitting a temperature gradient field by using a fitting algorithm according to the characteristic temperature of the measured gas to obtain the temperature gradient field of the measured gas; and finally, controlling the signal excitation device and the excitation laser through the microcomputer to emit light isotope detection light and heavy isotope detection light respectively, a detection result is obtained through the acquisition device, and the isotope abundance is obtained in combination with the temperature gradient field of the measured gas, so that the influence of the temperature gradient on measurement is overcome, and the measurement accuracy is improved.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
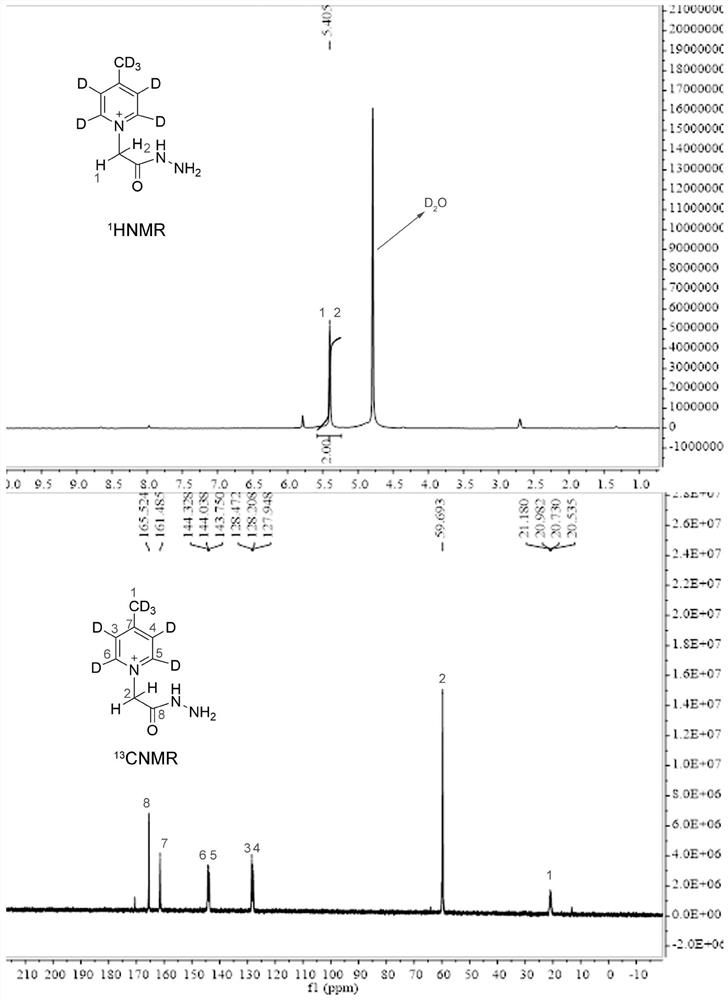
General low-cost quaternary ammonium salt sugar chain isotope labeling reagent and synthesis method
ActiveCN112778194ASimplified peak formImproving MS Detection SensitivityOrganic chemistry methodsMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansStable Isotope LabelingQuinoline
The invention relates to the technical field of bioglycomics analysis, and discloses a general low-cost quaternary ammonium salt sugar chain isotope labeling reagent and a synthesis method thereof. The reagent comprises a labeling reagent deuterated 7-4-methyl-1-(2-hydrazino-2-oxoethyl)-pyridinium bromide in a heavy isotope form and a labeling reagent 4-methyl-1-(2-hydrazino-2-oxoethyl)-pyridinium bromide corresponding to the labeling reagent deuterated 7-4-methyl-1-(2-hydrazino-2-oxoethyl)-pyridinium bromide in a light isotope form. The reagent can be used for mass spectrum high-sensitivity and high-accuracy relative quantitative analysis of biological reducing sugar chains of different molecular weight segments; according to the reagent provided by the invention, the mass spectrometric detection sensitivity of the sugar chain can be greatly improved; meanwhile, the method is suitable for mass spectrum relative quantitative analysis of reducing sugar chains with relatively small and large molecular weights; the synthesis raw materials are low in cost, and the defect that hydrazide quaternary ammonium salt stable isotope labeling reagents synthesized based on deuterated isoquinoline are high in cost is overcome.
Owner:NORTHWEST UNIV
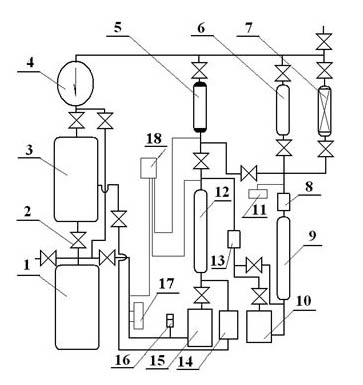
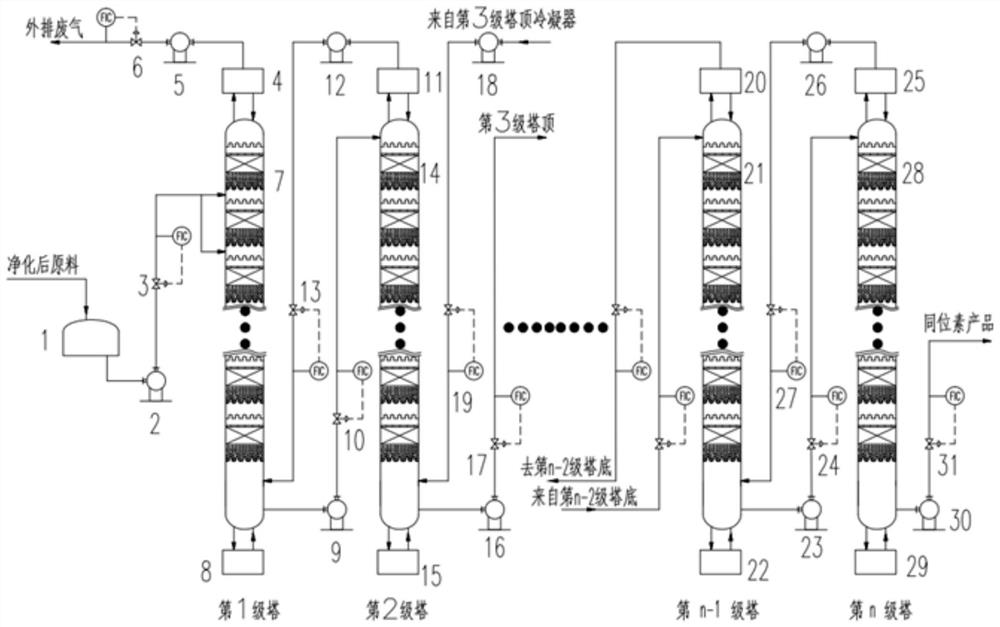
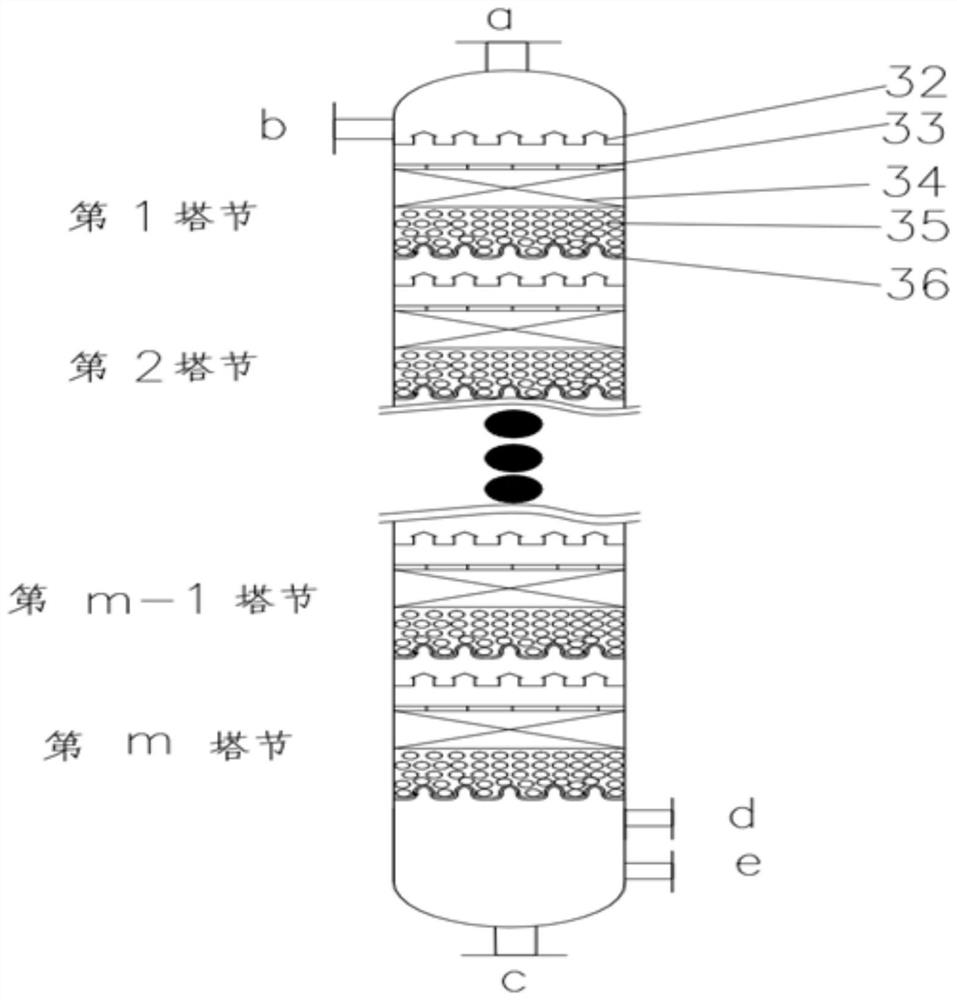
Stable isotope low-temperature separation and concentration device and technology
PendingCN112156653AOvercome the disadvantages of single rectification functionReduce the number of cascade towersIsotope separationThermodynamicsReboiler
The invention relates to a stable isotope low-temperature separation and concentration device and technology. The technology comprises the following steps that purified high-purity feed gas enters a low-temperature separation and concentration device formed by the series connection of n difunctional composite separation towers from a buffer tank through pump metering, and each tower top provides an initial liquid phase of the tower corresponding to a condenser; and each tower bottom provides an initial vapor phase of the tower corresponding to a reboiler, vapor and liquid are in countercurrentcontact in each tower, two processes of isotope exchange reforming and vapor-liquid rectification are continuously and alternately carried out, a heavy isotope product is continuously produced at thelast nth-stage tower bottom through pump metering, and waste gas subjected to heavy isotope separation is continuously produced at the first-stage tower top condenser through pump metering. The device is a cascade system formed by connecting n bifunctional composite separation towers which are horizontally arranged in series, and each bifunctional composite separation tower is composed of m towersections; and the device and the technology effectively overcome the defects of single function and the like of the separation tower in the traditional low-temperature rectification process, reduce the number of cascaded towers, simplify the process and save the energy consumption.
Owner:湖北楚儒同位素科技有限公司
Use of piperazinopyrimidine isotope labeling reagent
InactiveCN102944604BEnhanced signalReduce complexityComponent separationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansThermal denaturationTarget analysis
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF ORGANIC CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
A method and device for enriching and enriching stable isotopes 2h, 18o, 13c
The invention relates to a method and a device for concentrating and enriching stable isotopes 2H, 18O and 13C. The method comprises the steps of: by taking compounds respectively containing stable isotopes 2H, 18O and 13C as materials, carrying out purification treatment, adding to a heavy isotope concentration tower group formed by a plurality stages of gas-liquid mass transfer towers connected in series; continuously and partially vaporizing and partially condensing in the gas-liquid mass transfer towers connected in series by weak vapor pressure difference between light and heavy isotopes of hydrogen, oxygen, and carbon elements, and gradually concentrating and purifying corresponding heavy isotope. Each tower disclosed by the invention adopts different operation pressures and coupling utilization of heat between the towers; over 30-40% of energy consumption can be saved; a composite structure mass transfer component composed of a liquid collecting distributer, a Dixon mass transfer component, a corrugated mass transfer component and the like is adopted inside the tower; the device is easy to amplify; the device of producing heavy 2H, 18O or 13C isotope at a large scale just needs to be connected with 2-8 gas-liquid mass transfer towers in series; over 50% of investment is saved in comparison with the same scale of device, and the towers adopt a single tandem cascade technology; and the method is simple in flow and easy to control and operate.
Owner:JIANGSU ZHENGNENG ISOTOPE
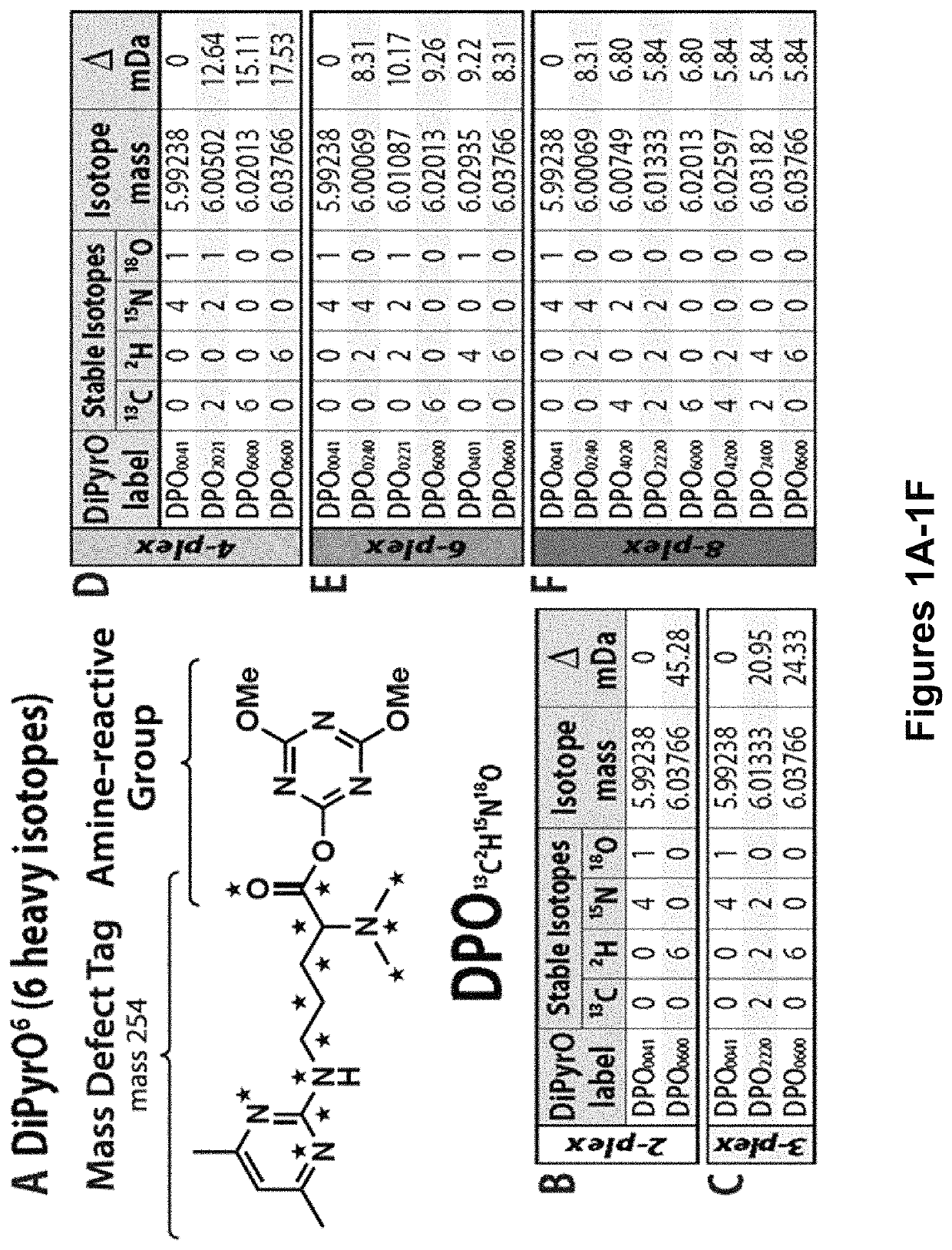
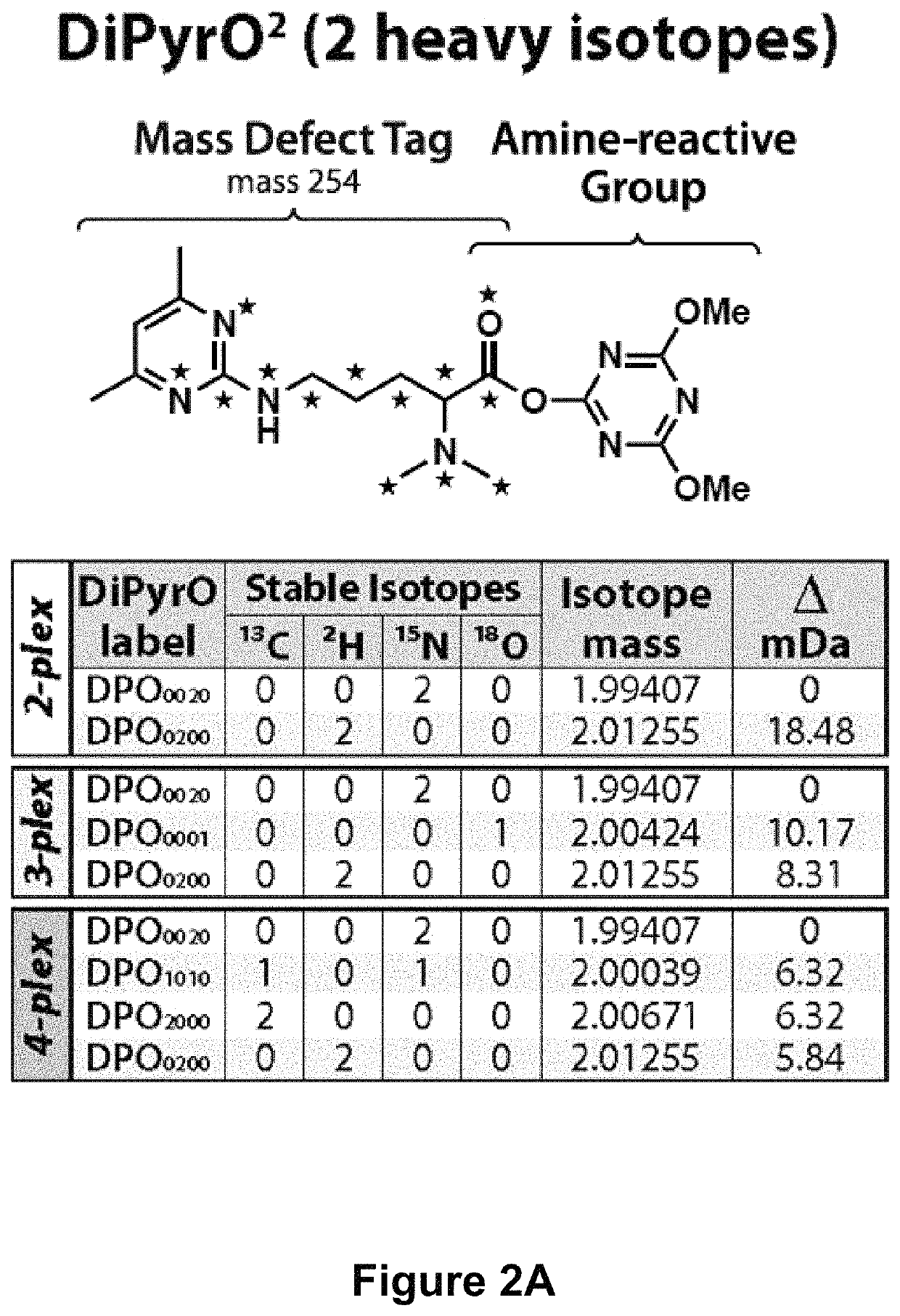
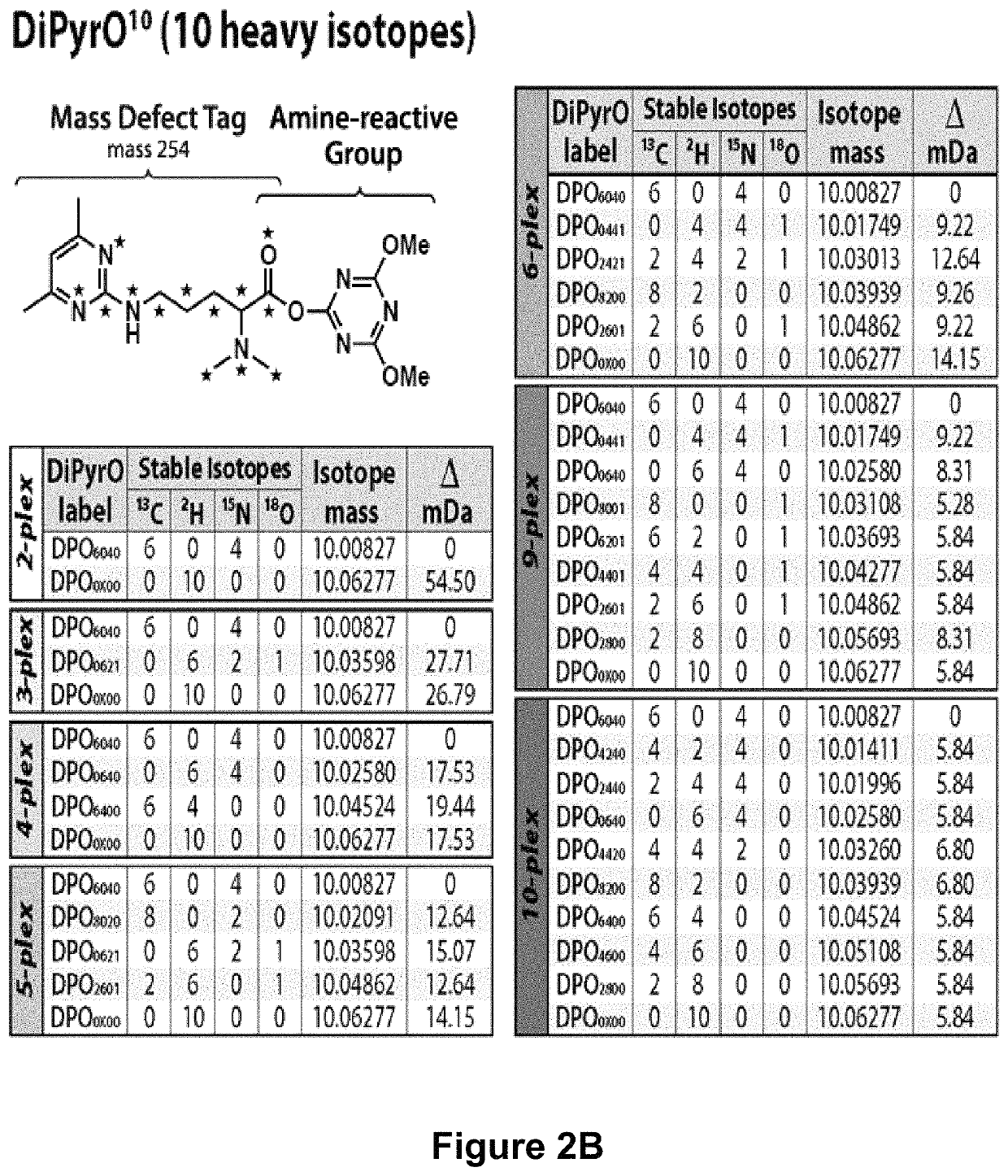
Mass defect-based multiplex dimethyl pyrimidinyl ornithine (DiPyrO) tags for high-throughput quantitative proteomics and peptidomics
ActiveUS11408897B2Promote fragmentationEasy to synthesizeOrganic chemistryBiological testingMultiplexMetabolite
The use of mass defect signatures to impart milliDalton mass differences between isotopically labeled peptides at the MS1-level allows multiplex quantification without the increased mass spectral complexity that occurs with mass difference approaches. Provided herein is a mass defect-based chemical tag, dimethyl pyrimidinyl ornithine (DiPyrO), that is compact and easy to synthesize at high purity in few steps using commercially available starting materials. The multiplex DiPyrO tags are amine-reactive and can impart a mass difference onto labeled peptides and through calculated substitution of heavy isotopes. DiPyrO offers up to 10-plex quantification on current Orbitrap or FT-ICR platforms without increasing mass spectral complexity. The synthesis of the DiPyrO tag is provided along with viability of the DiPyrO tag for labeling complex proteomics samples using yeast extract digests and its effect on labeled peptides during LC-MS2 analysis. Labeling and quantification of glycans and metabolites using the DiPyrO tag is also demonstrated.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
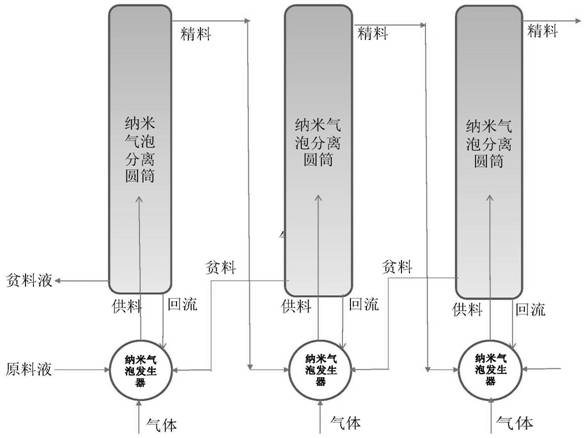
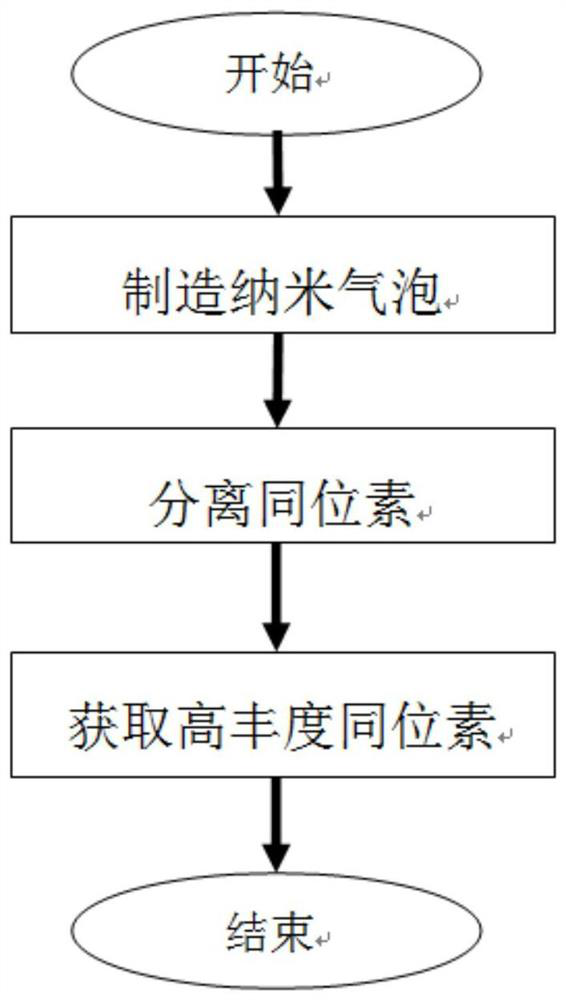
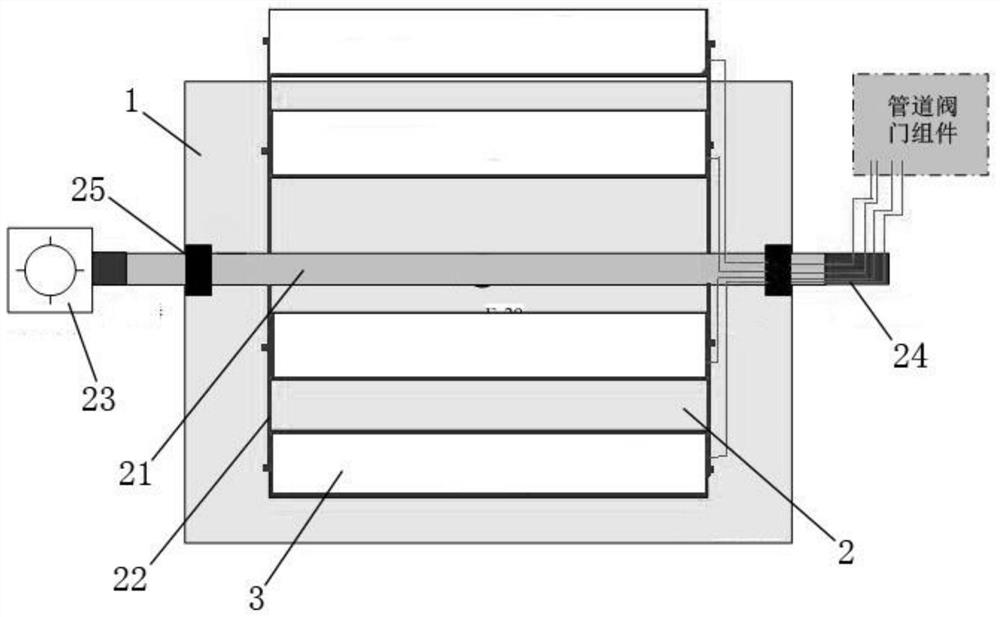
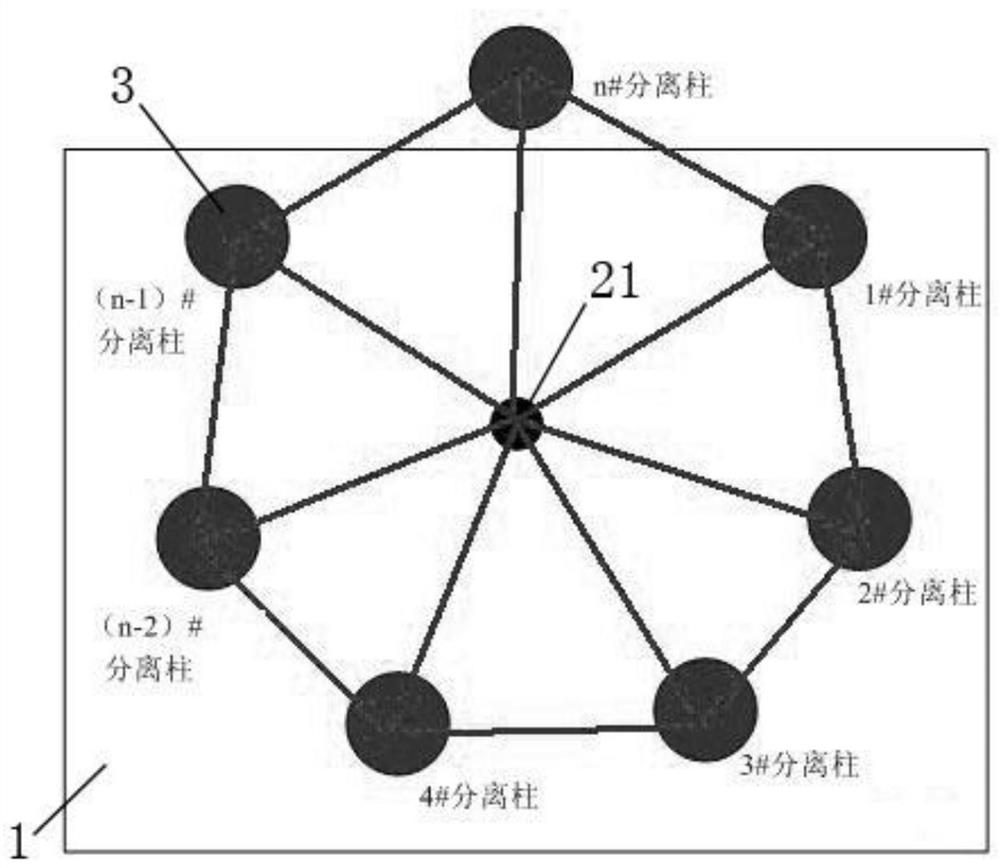
A kind of nanobubble isotope separation method and separation device and cascade
ActiveCN112473368BSolution to short lifeAchieve separationIsotope separationChemical physicsFluid phase
The invention relates to a nano-bubble isotope separation method, a separation device and a cascade. The method firstly prepares a liquid containing nano-bubbles, and then the nano-bubble contacts the liquid during the rising process. When the nano-bubble rises to a certain height, the The heavier isotope enrichment products can be obtained, while the lighter isotope enrichment products are in the liquid phase of the separation cylinder, thereby realizing isotope separation. The separation device of the present invention comprises a nano-bubble generator, a cylindrical separator and a material feeding and reclaiming device, and the cascade is a series-parallel combination of a plurality of separation devices. The invention can be applied to the isotope separation of various elements, and is especially suitable for the separation of light isotopes, especially the separation of lithium isotopes. The invention also has the advantages of less investment, low energy consumption, cheap raw materials, rapid production, flexible scale and no pollution.
Owner:陈邦林 +1
A rotary low temperature hydrogen isotope separation system and separation method
The invention discloses a rotary low-temperature hydrogen isotope separation system and separation method, which solves the problem of complex construction, complex parameter control, high operating cost, or complex helium supply, hydrogen-helium separation, and separation column regeneration in the prior art, or palladium Replacement chromatographic media are expensive and prone to failure, among other issues. The separation system includes cryogenic tank, rotary frame, separation column, raw material hydrogen storage tank, light isotope storage tank, heavy isotope storage tank, vacuum pump and tail gas storage tank. The separation method is to desorb the hydrogen isotopes from the liquid nitrogen liquid surface one by one to complete the rearrangement of the hydrogen isotopes in the remaining separation columns; finally collect the light and heavy isotopes from the far and near ends of the loop respectively. The present invention creatively uses the principle of simulated moving bed technology, hydrogen isotopes can circulate continuously in the closed-loop separation circuit, the concentration of heavy isotopes gradually decreases from the near end to the far end where desorption occurs in the separation circuit, and the concentration gradient of heavy isotopes increases with the adsorption / The desorption times increase continuously.
Owner:MATERIAL INST OF CHINA ACADEMY OF ENG PHYSICS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com