Preparation method of chiral ligand exchange chromatographic stationary phase
A technology of exchange chromatography and chiral ligands, which is applied in the field of preparation of chiral ligand exchange chromatography stationary phases, can solve the problems of long analysis time, complicated operation, long time required, etc., and achieves wide application range and short analysis time. , the effect of a large amount of bonding
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
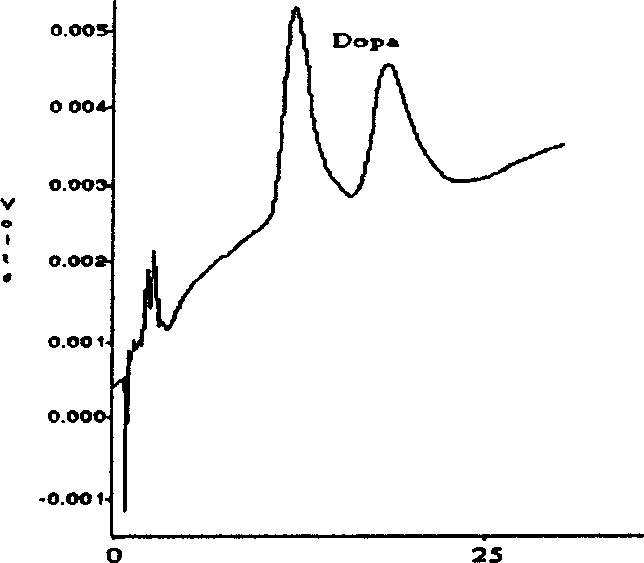
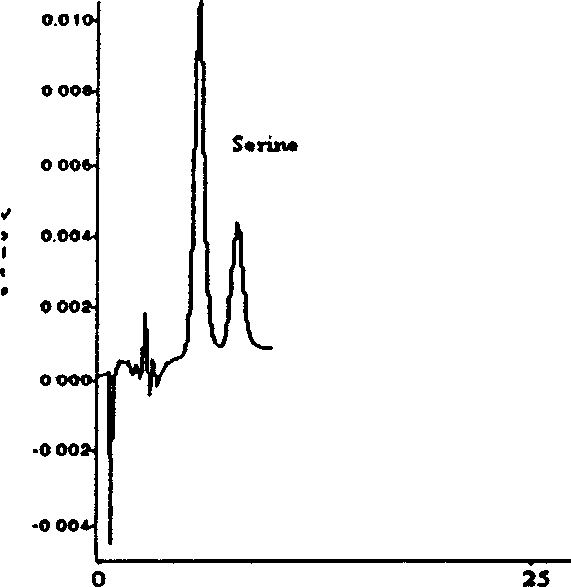
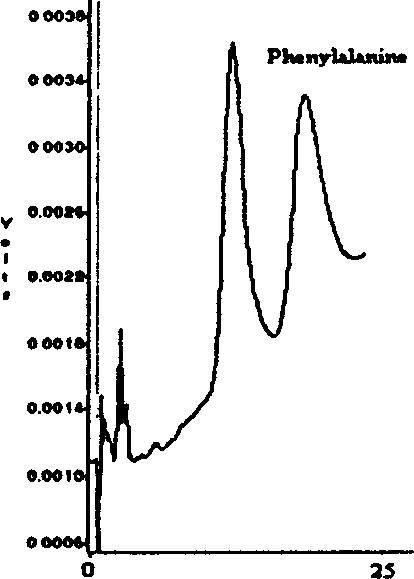
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029] Preparation of chiral ligand exchange chromatography stationary phase with L-isoleucine as chiral selector:
[0030] Kromasil spherical silica gel: Sweden Eka Nobel company, particle size 5μm, specific surface 340m 2 / g, pore size 10nm; L-isoleucine: purchased from Sigma (USA)
[0031] Take 4.0g of acid-treated silicon spheres, dry them in vacuum at 150°C for 4-6 hours, cool them down, place them in a 250mL round-bottomed three-necked flask, add 2mL of 3-glycidylpropyltrimethoxysilane and 40ml of toluene, and put them in Stir and reflux at 110°C for 6-7 hours, cool, filter, wash several times with toluene, methanol, and acetone in sequence, and dry in vacuum at 50°C for 2 hours to obtain 3-glycidylpropyl silica gel;
[0032] Take 3.93g L-isoleucine, add a considerable amount of sodium carbonate (for example: 0.03mol isoleucine is treated with 0.015mol sodium carbonate) and an appropriate amount of water, stir to dissolve, evaporate to nearly dryness, add 40ml methanol,...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com