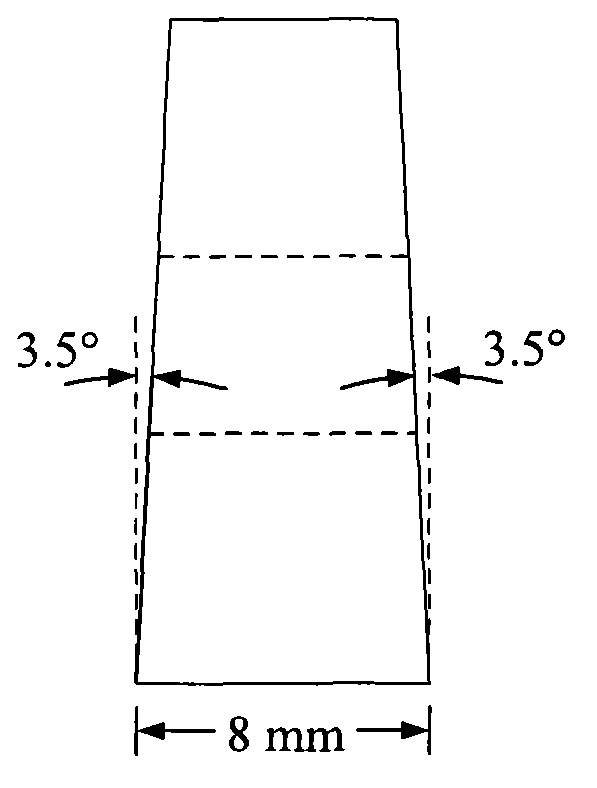
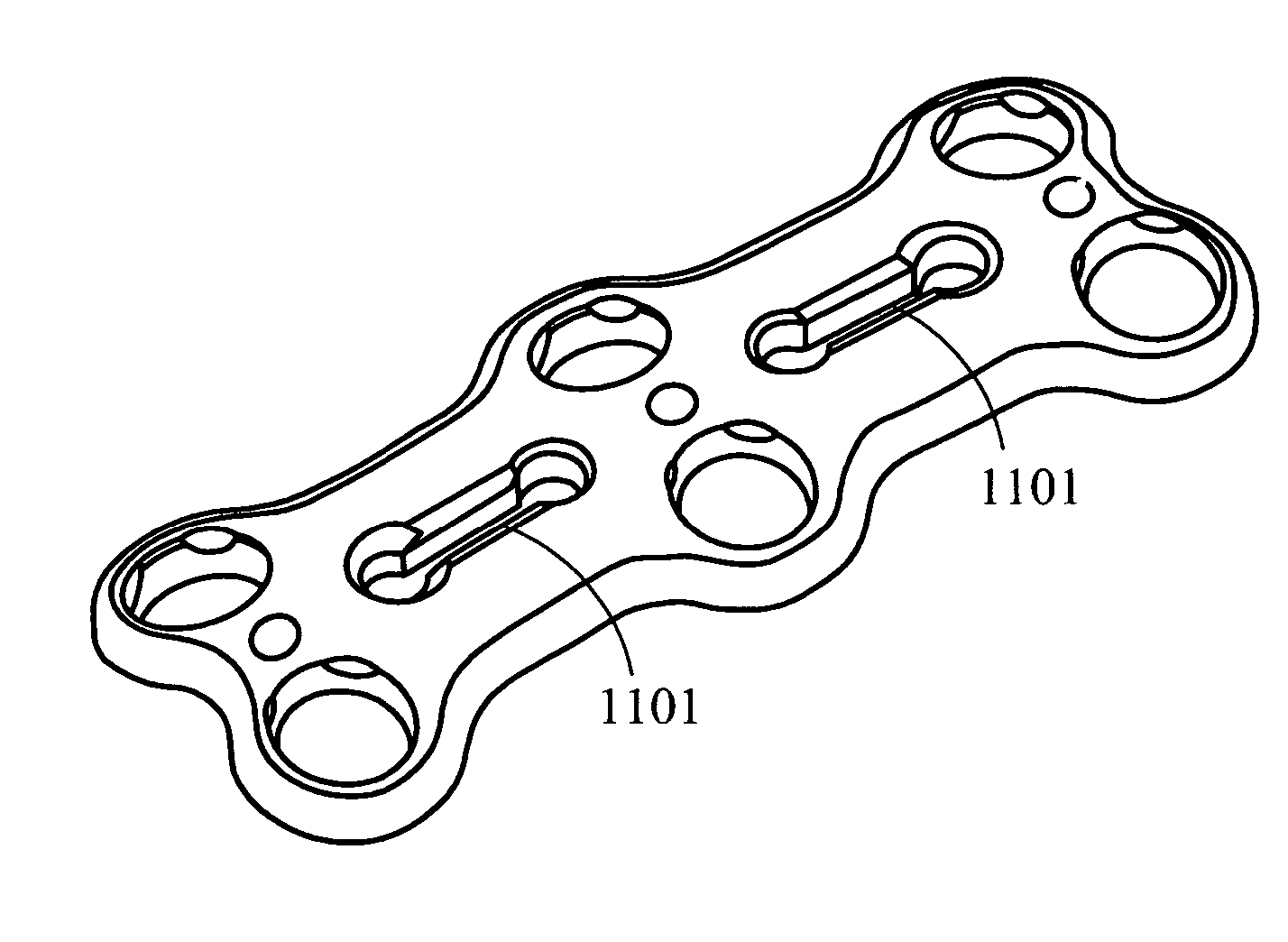
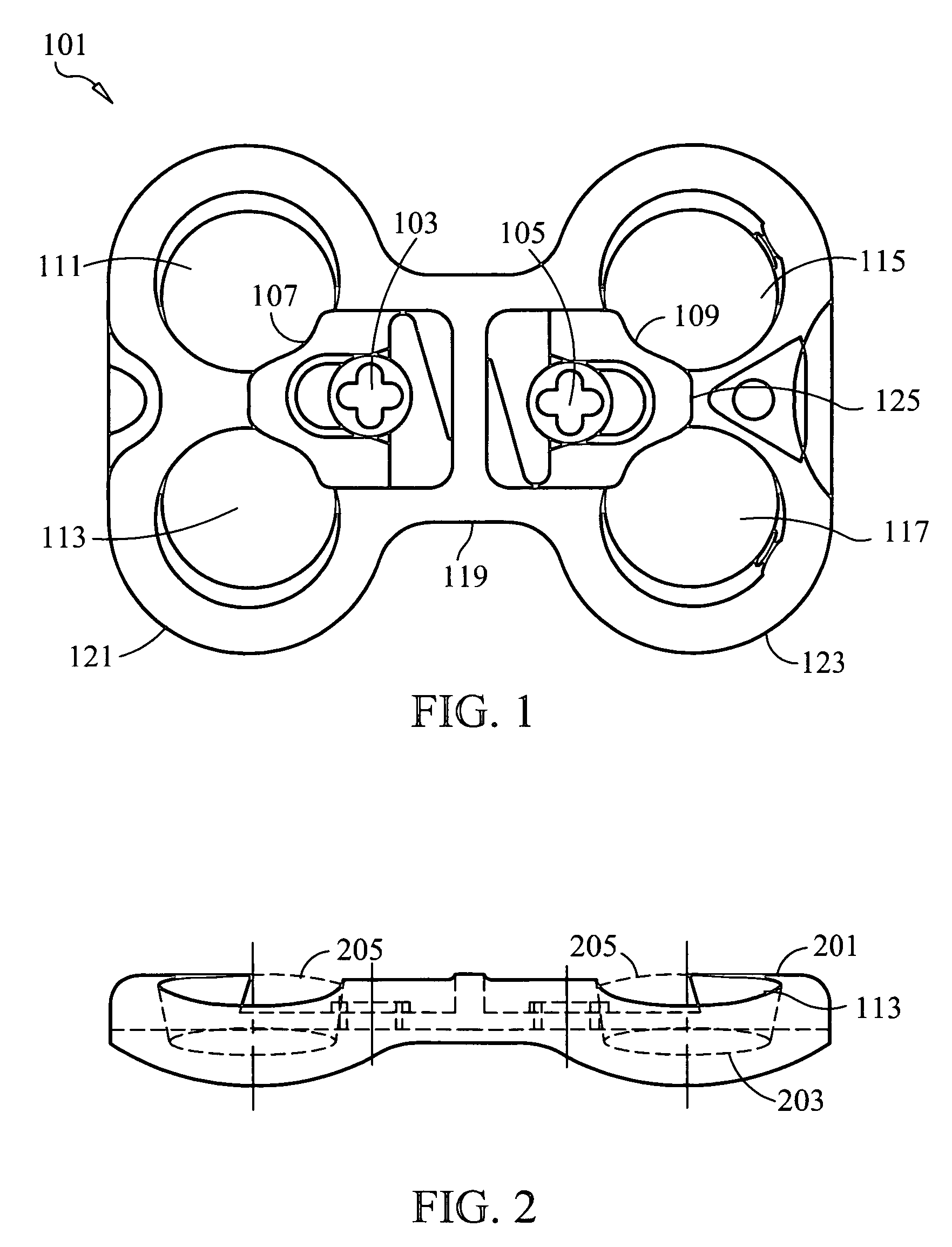
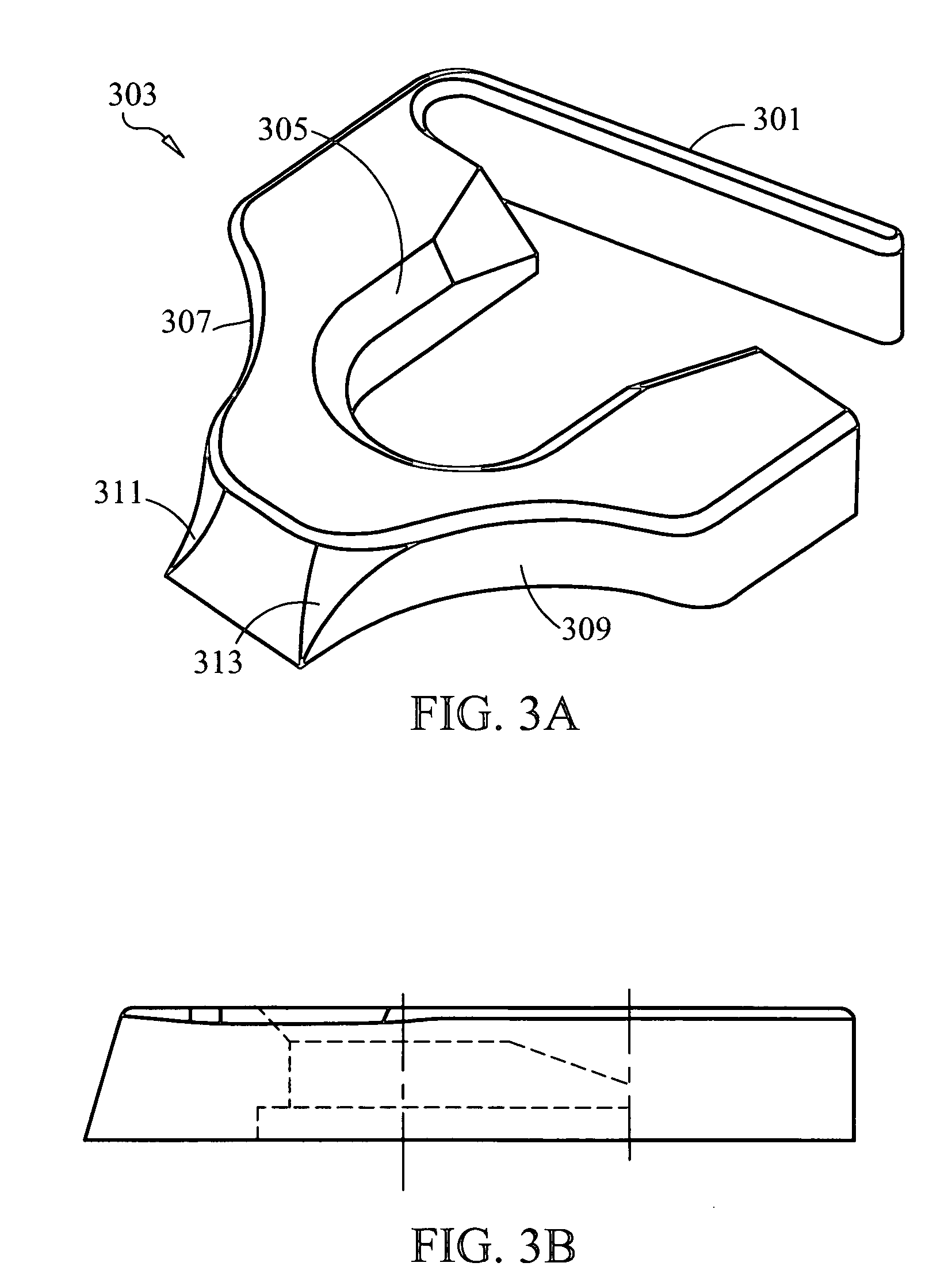
Patents
Literature
208 results about "Bony Tissues" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Bone tissue (osseous tissue) is a hard tissue, a type of dense connective tissue. It has a honeycomb-like matrix internally, which helps to give the bone rigidity.
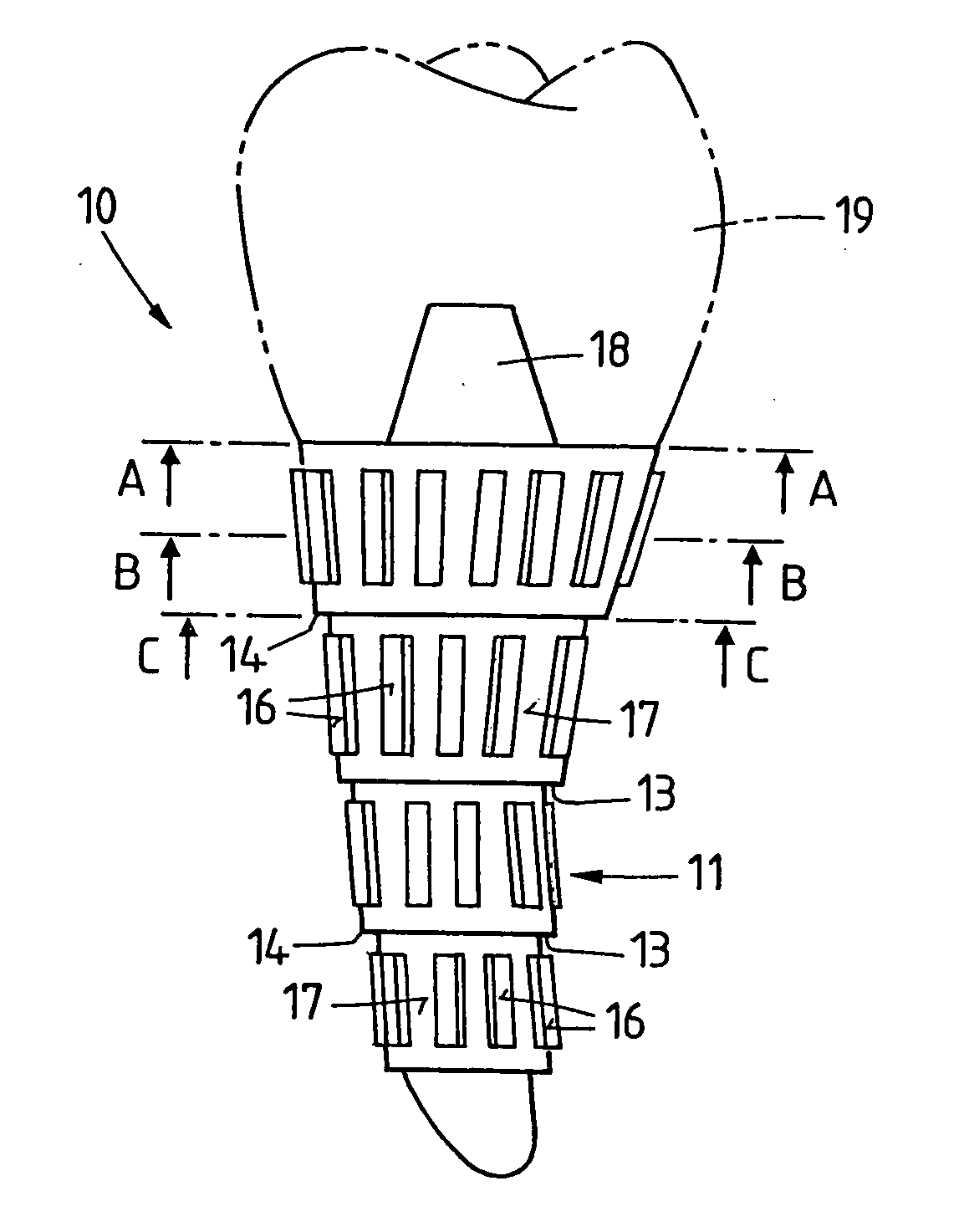
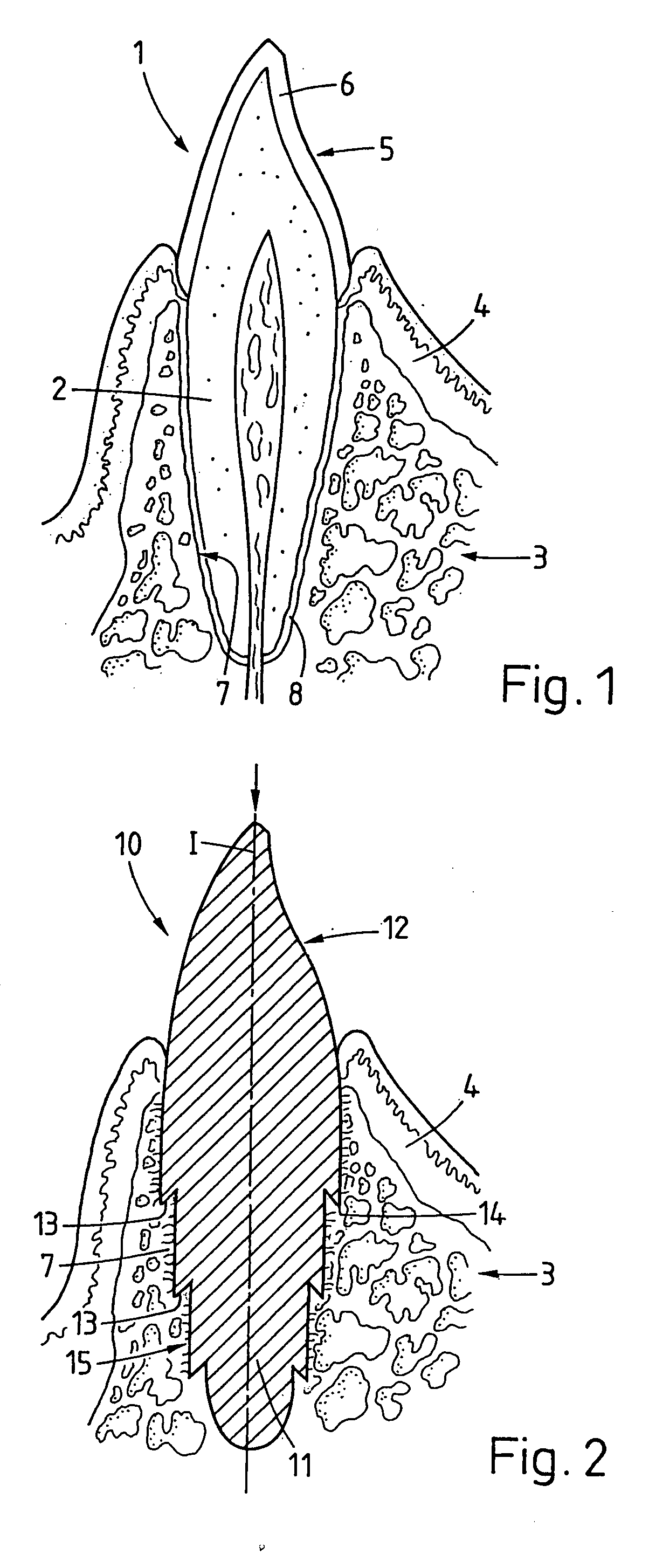
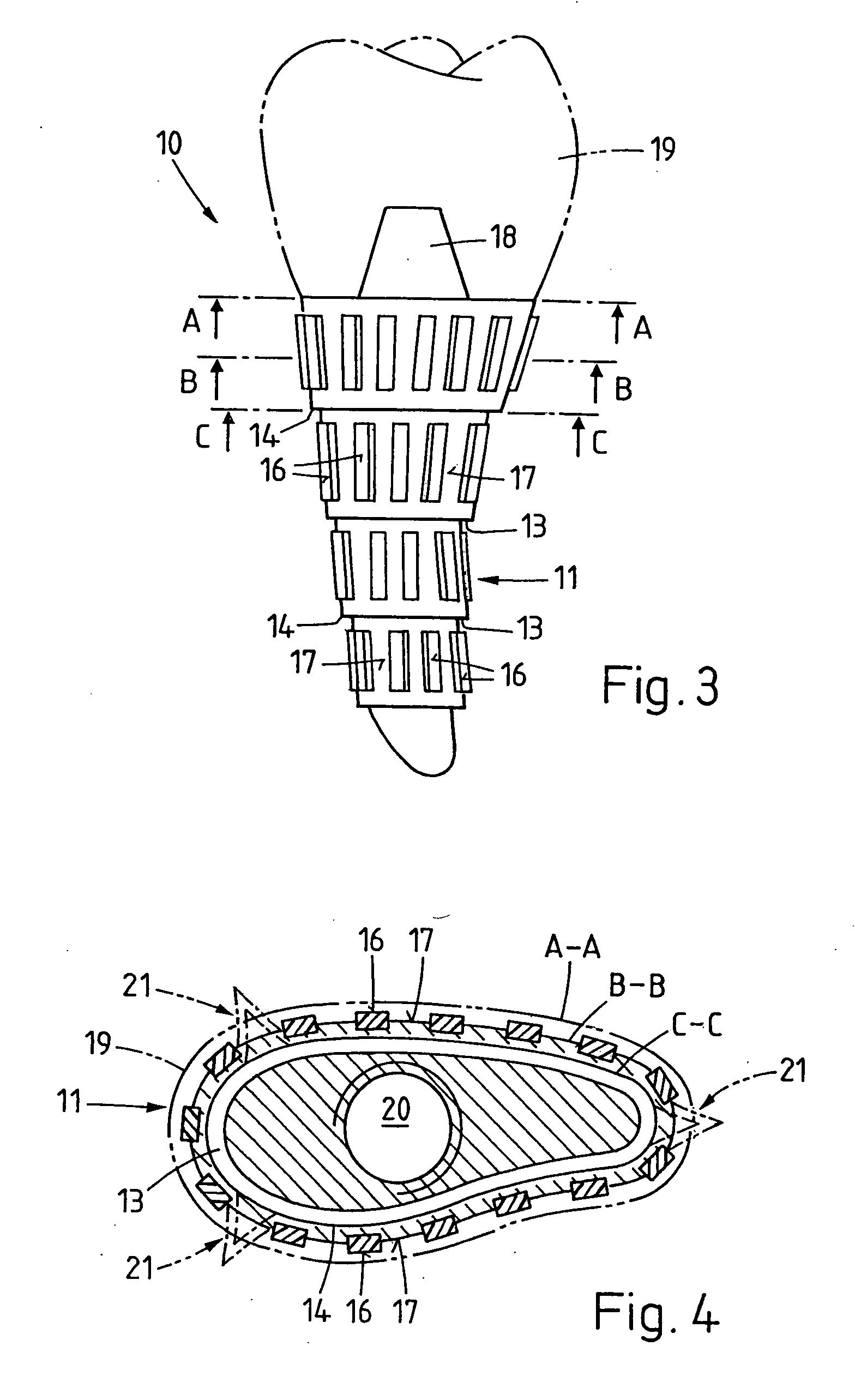
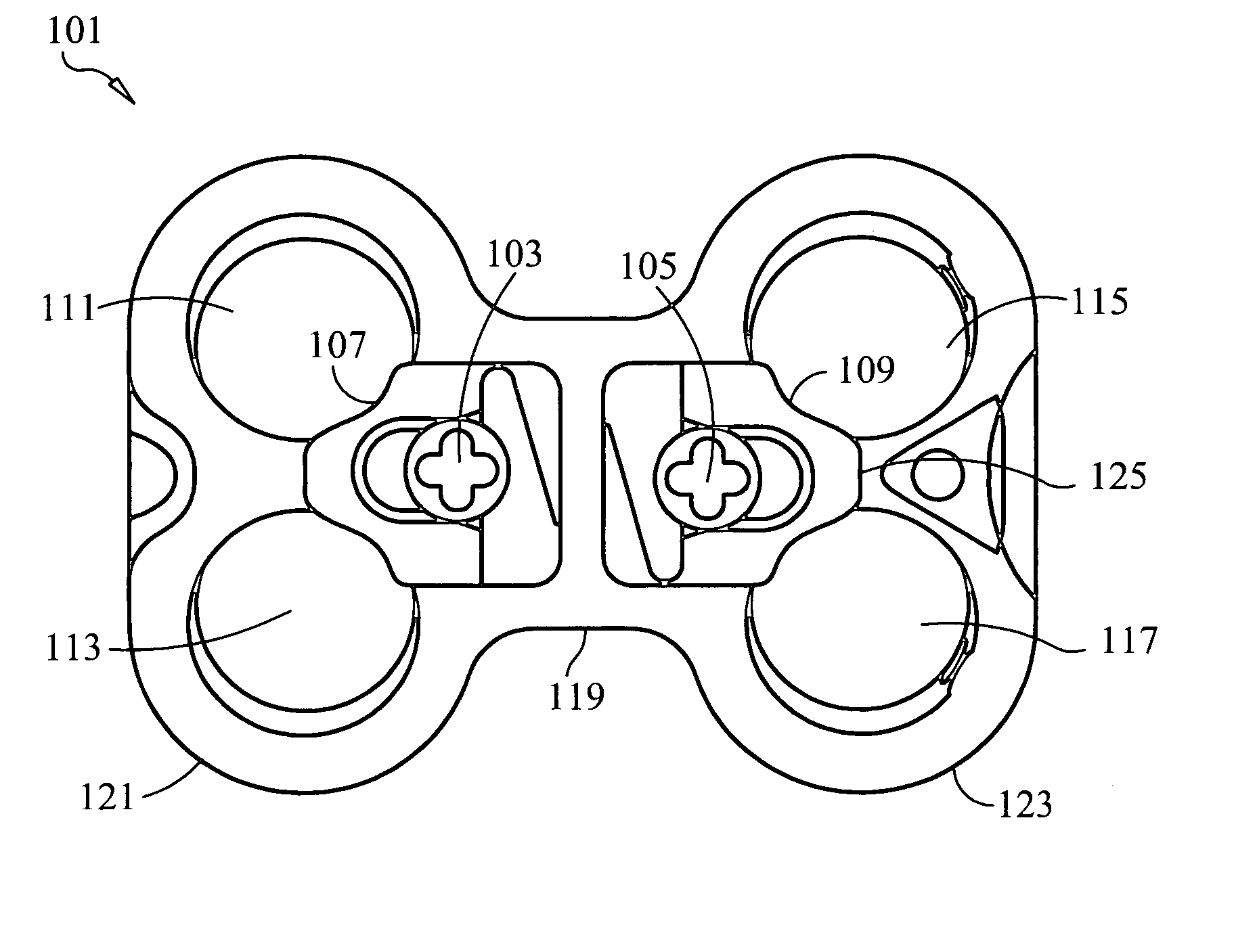
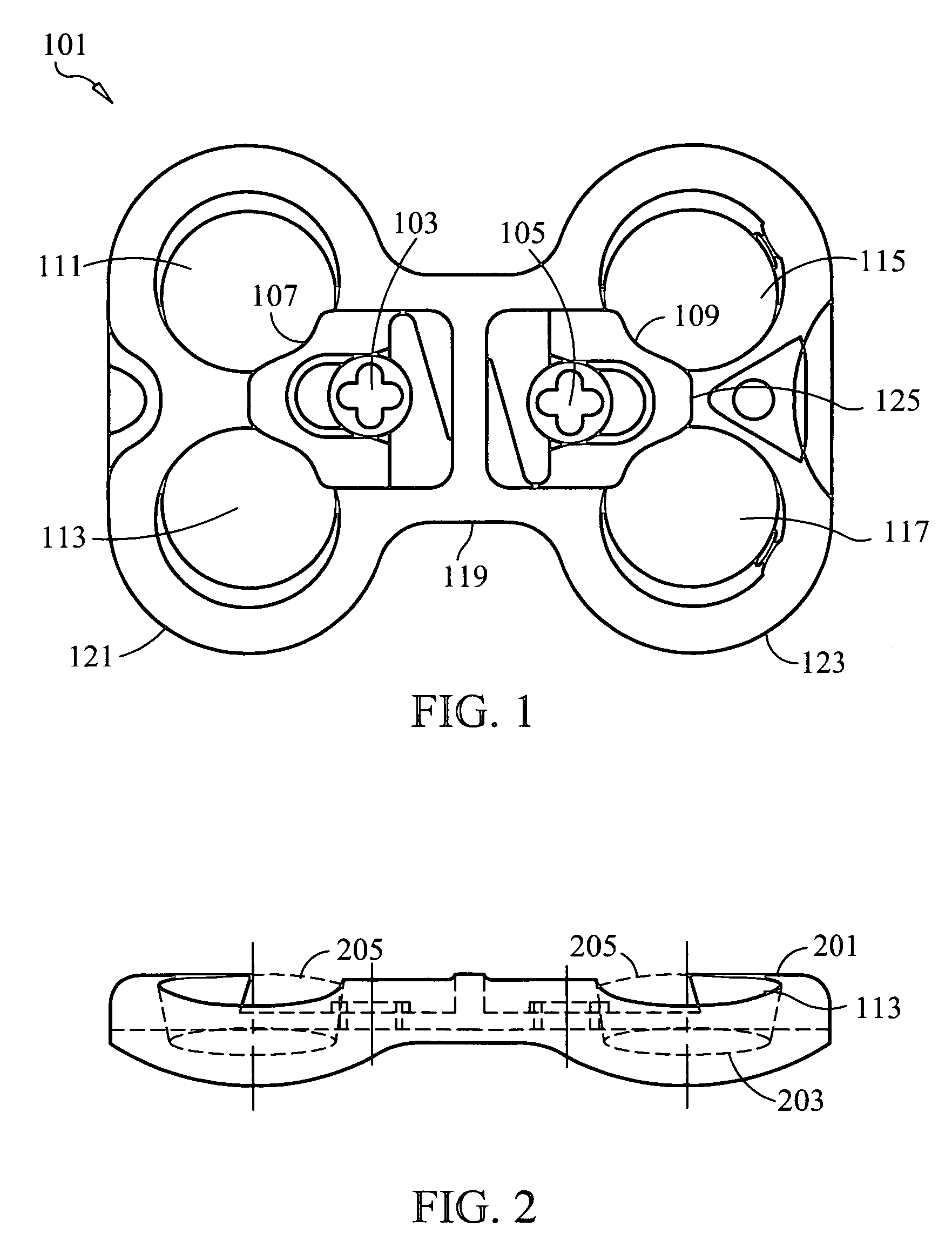
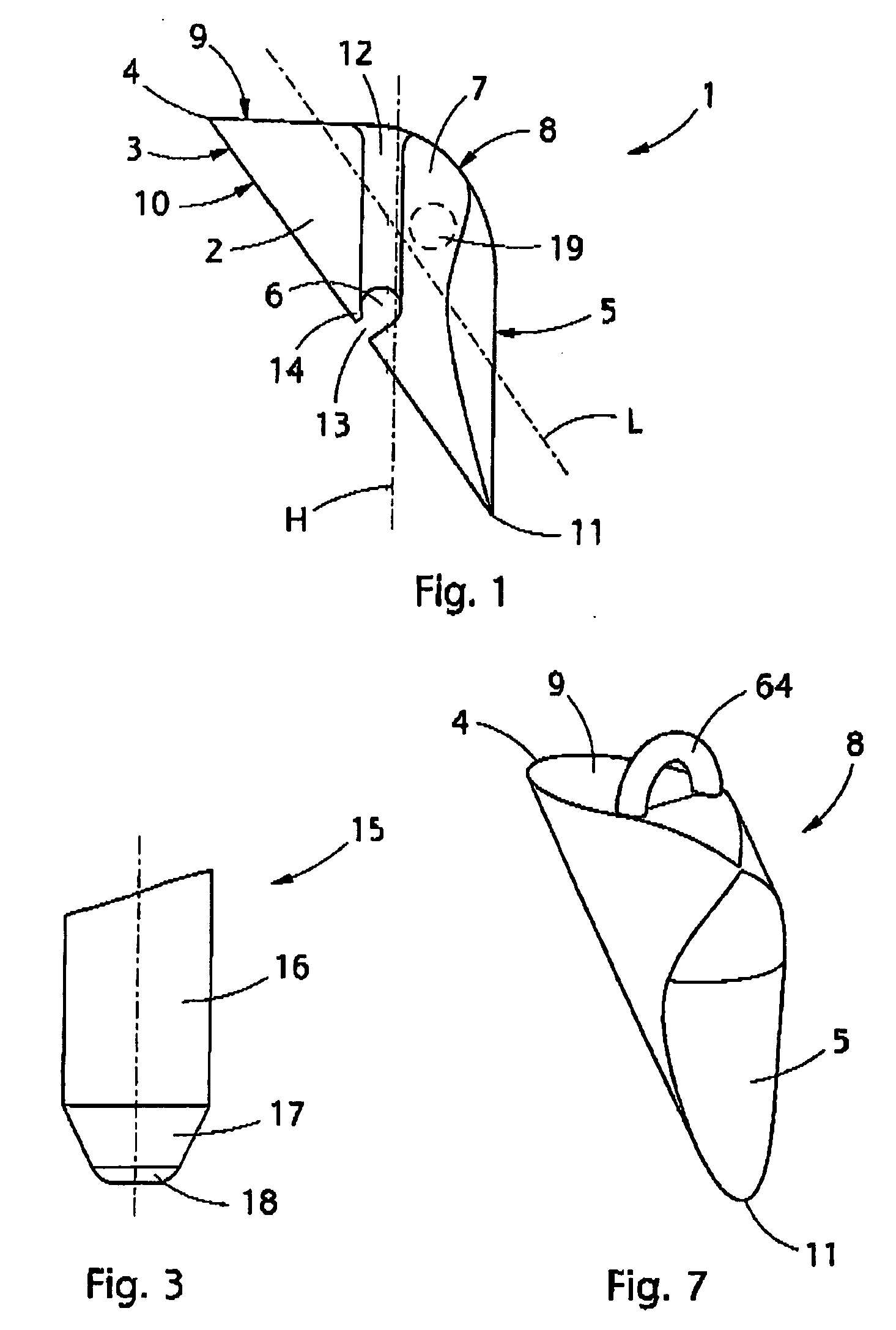
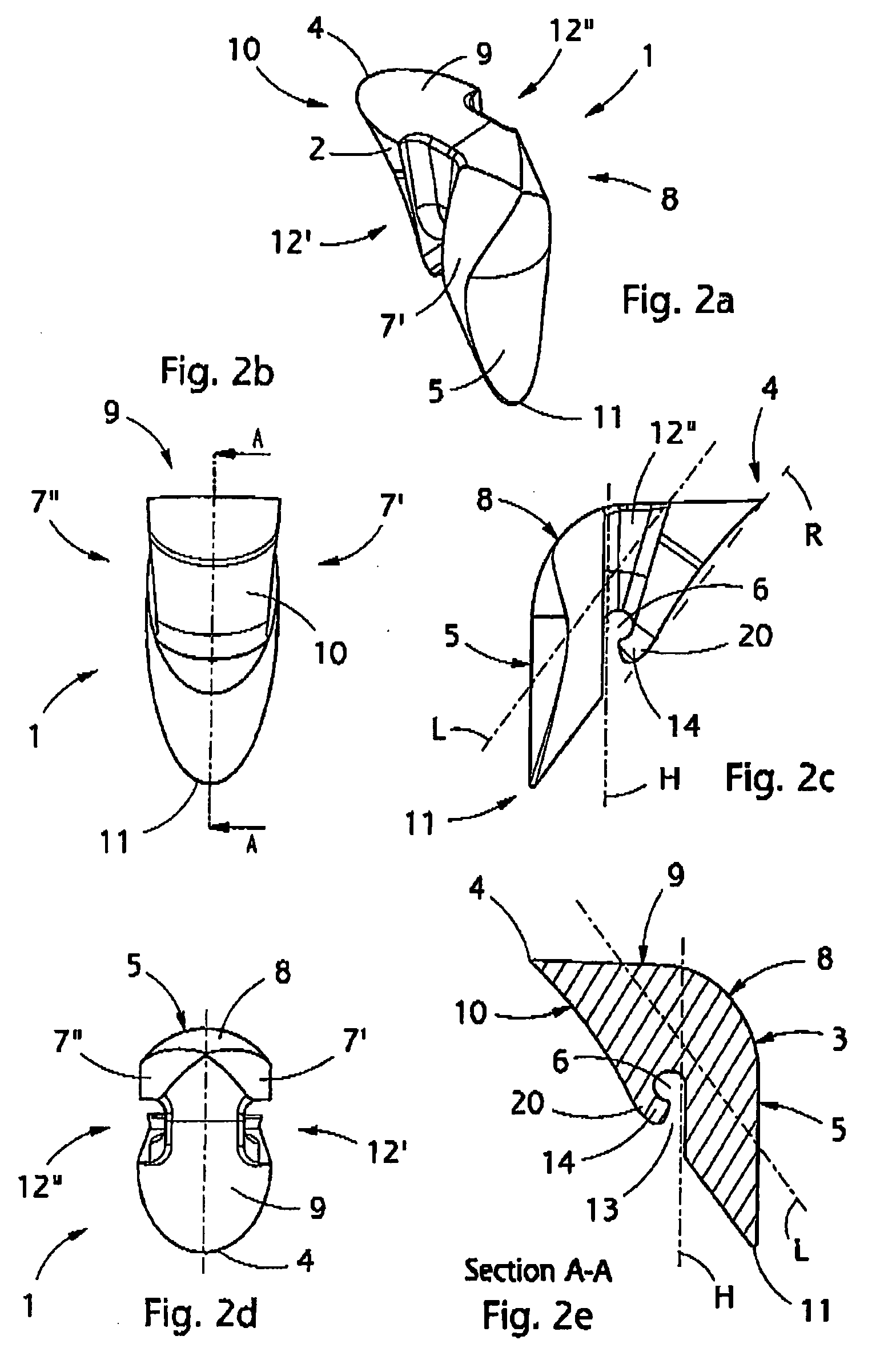
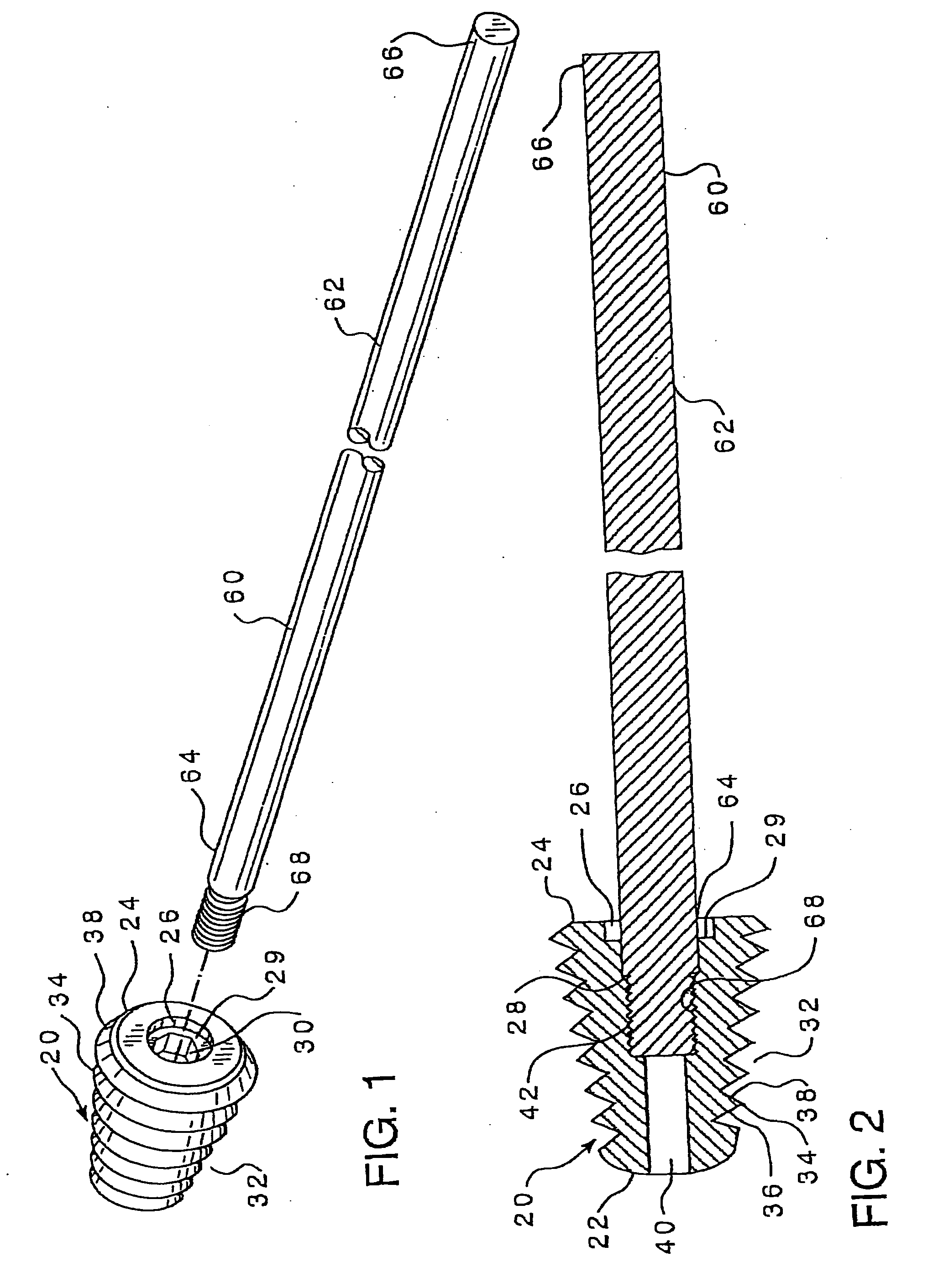
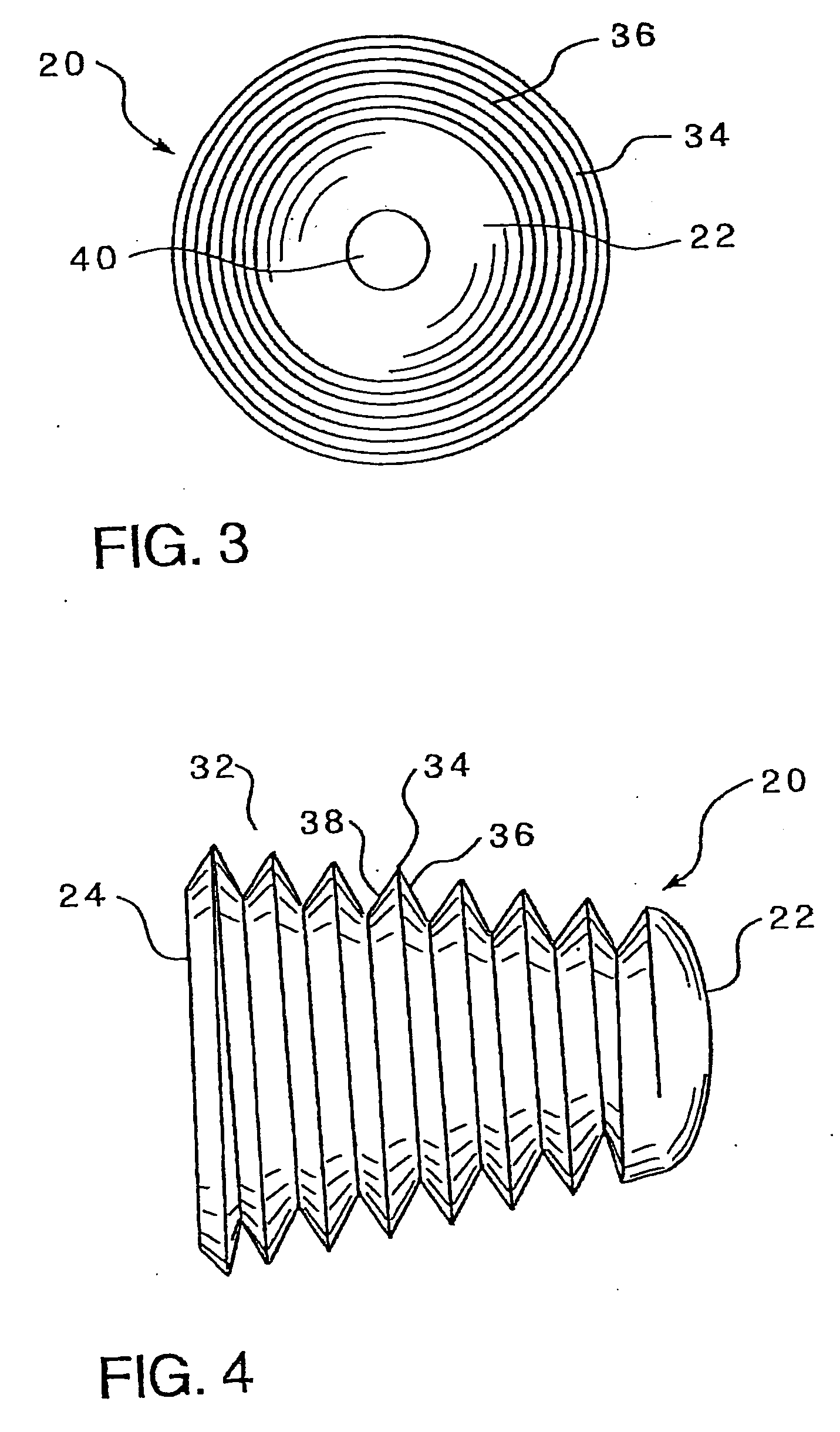
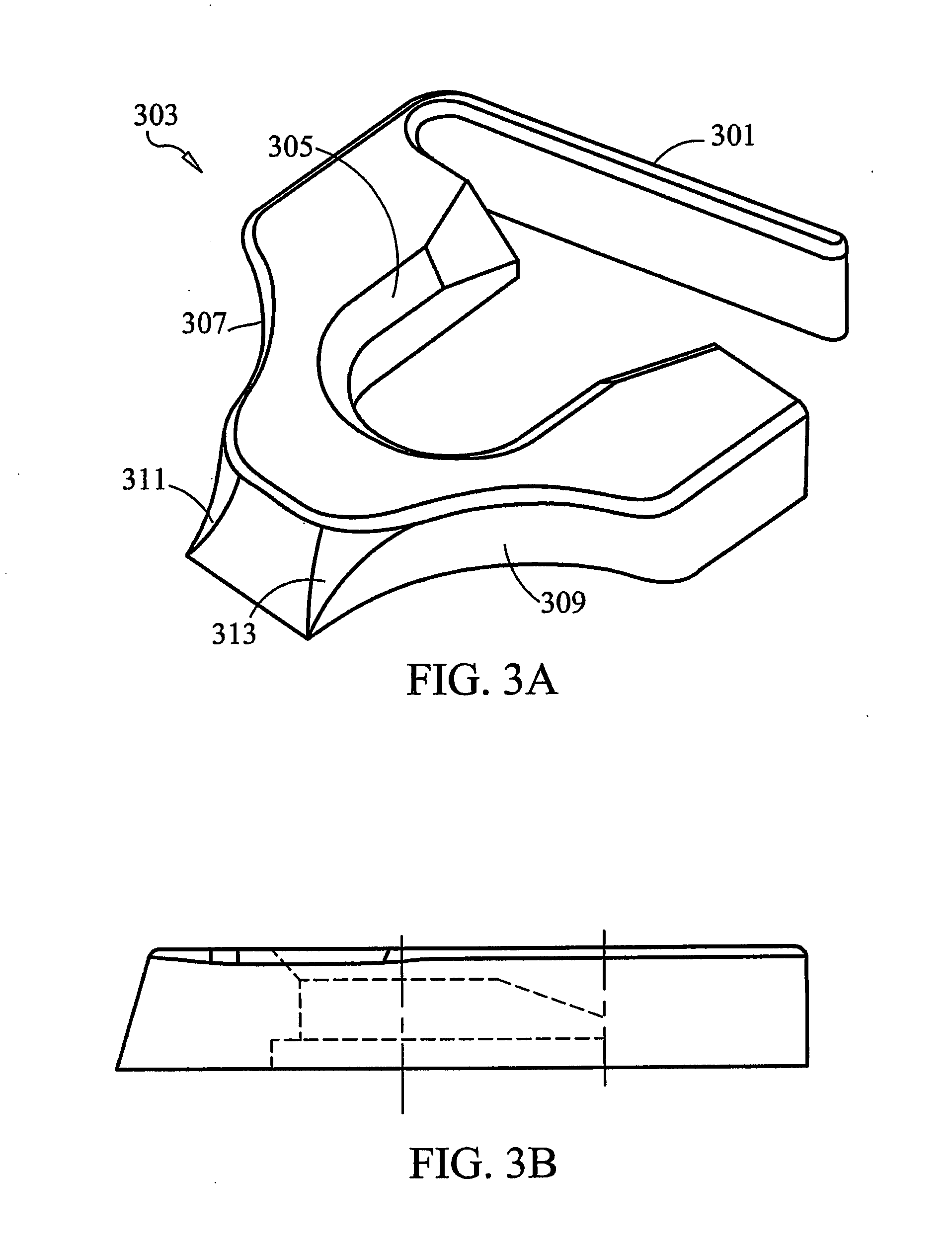
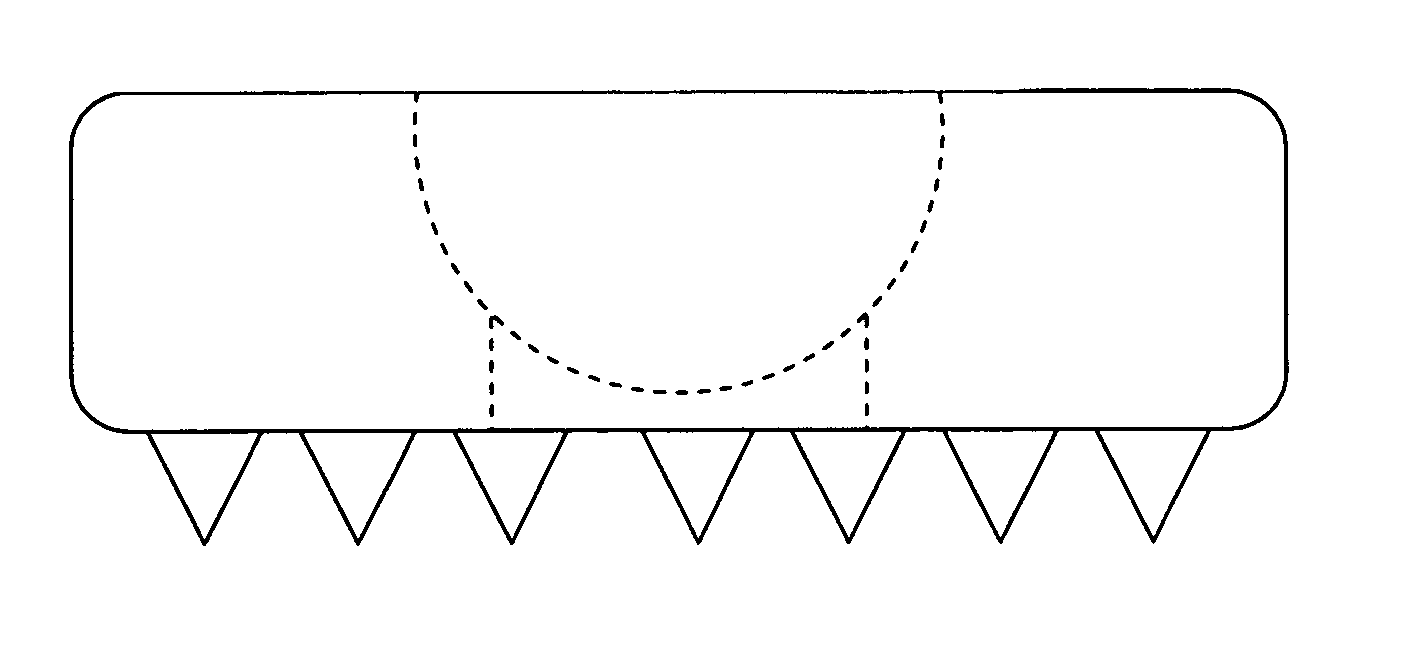
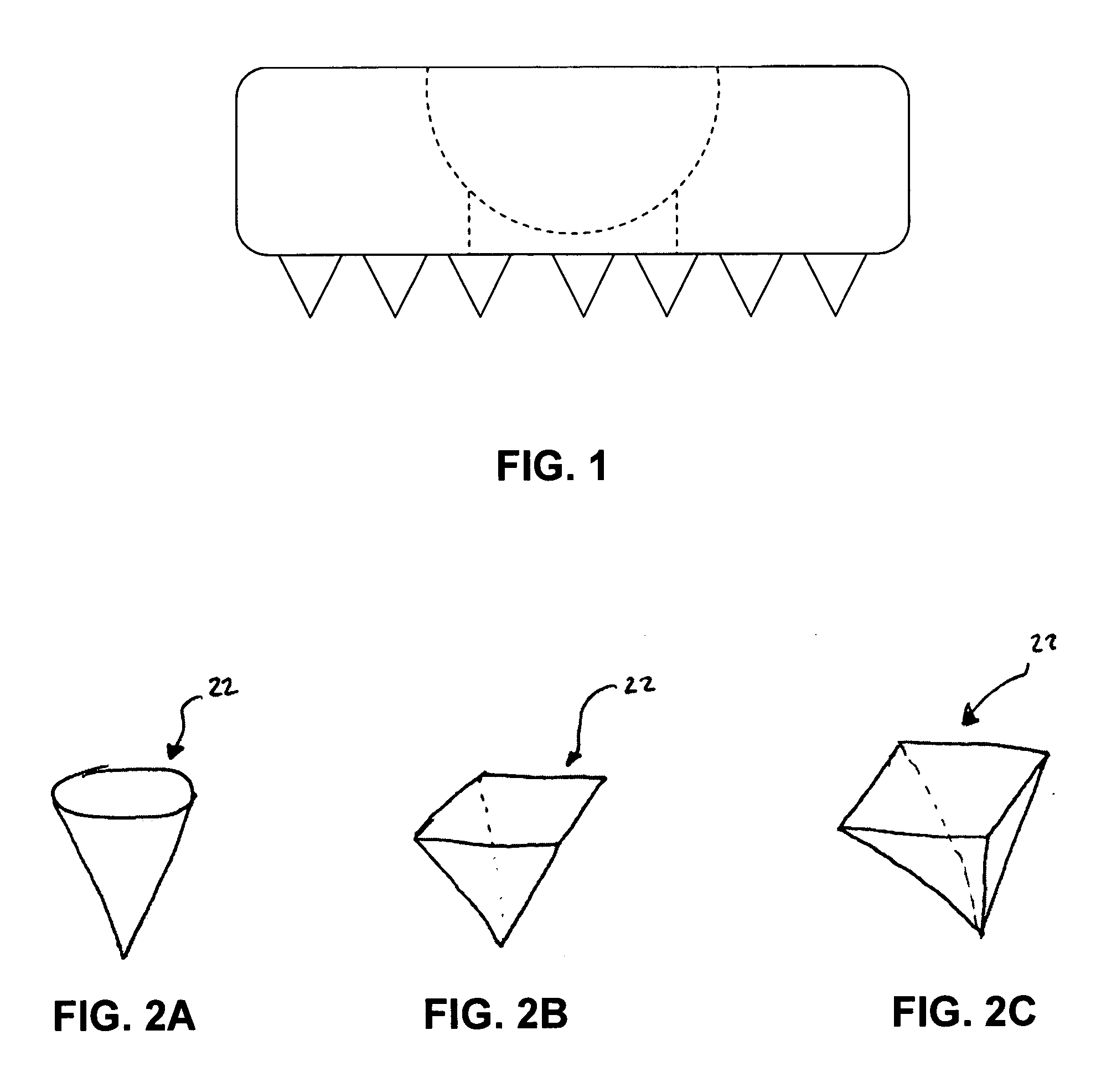
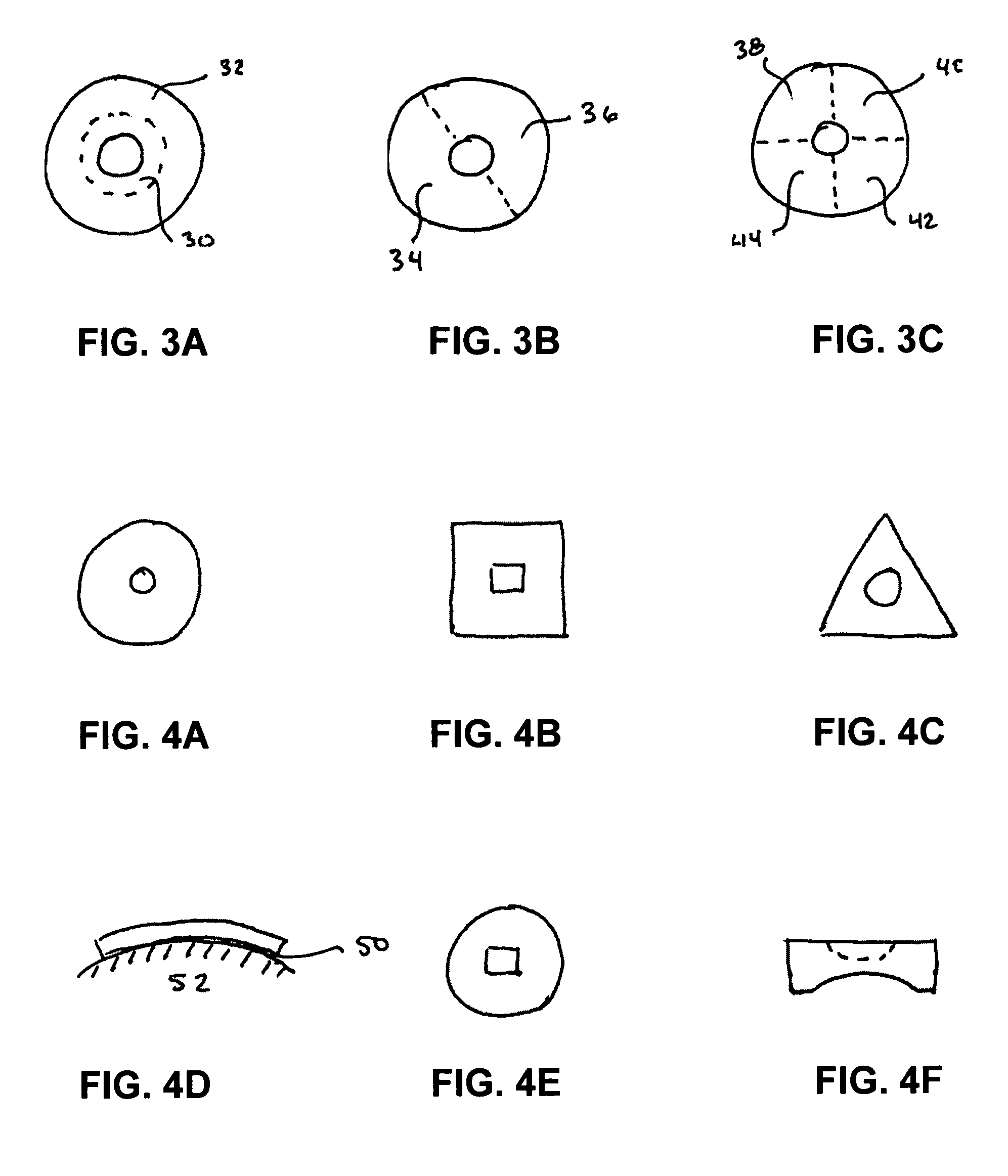
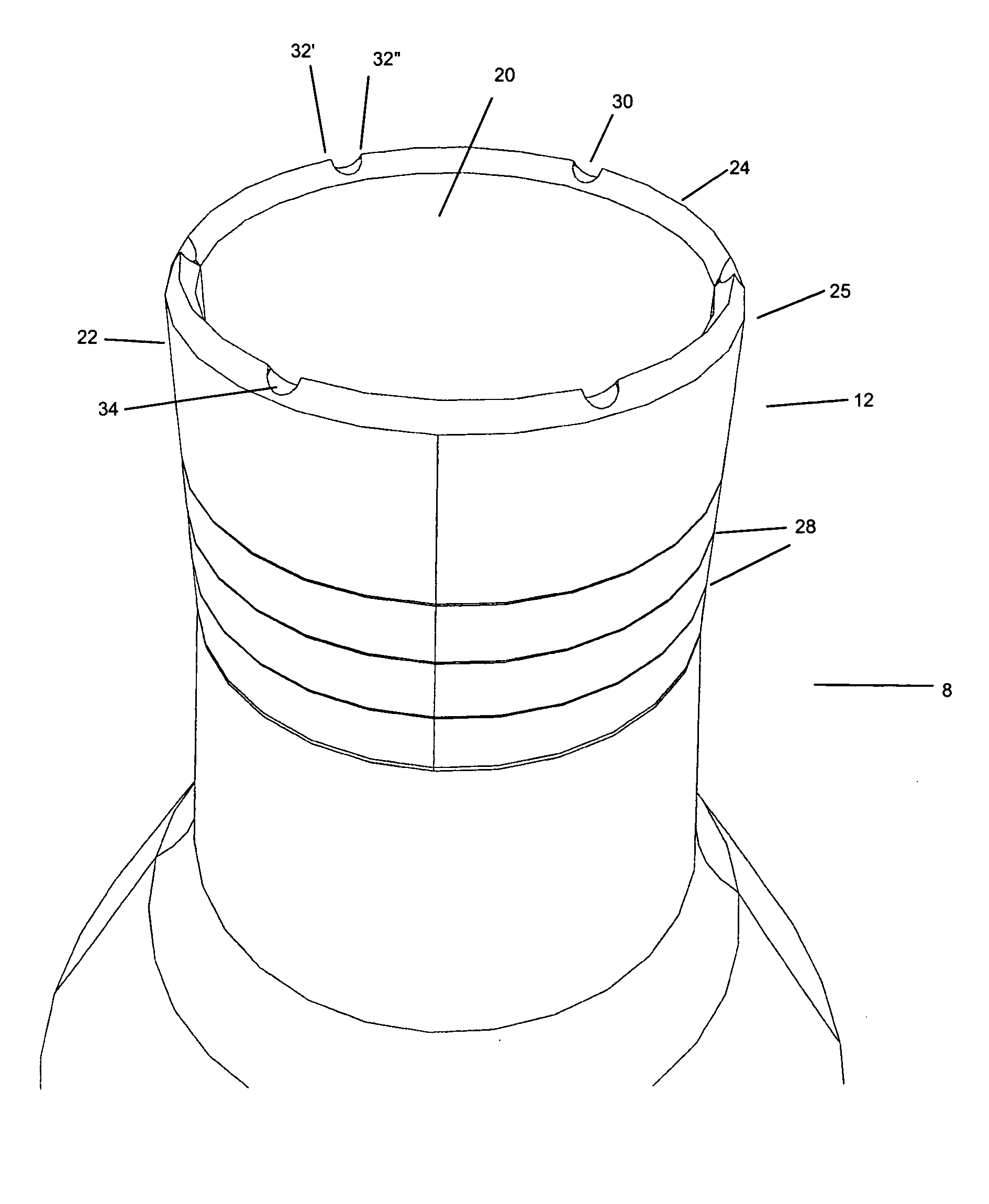
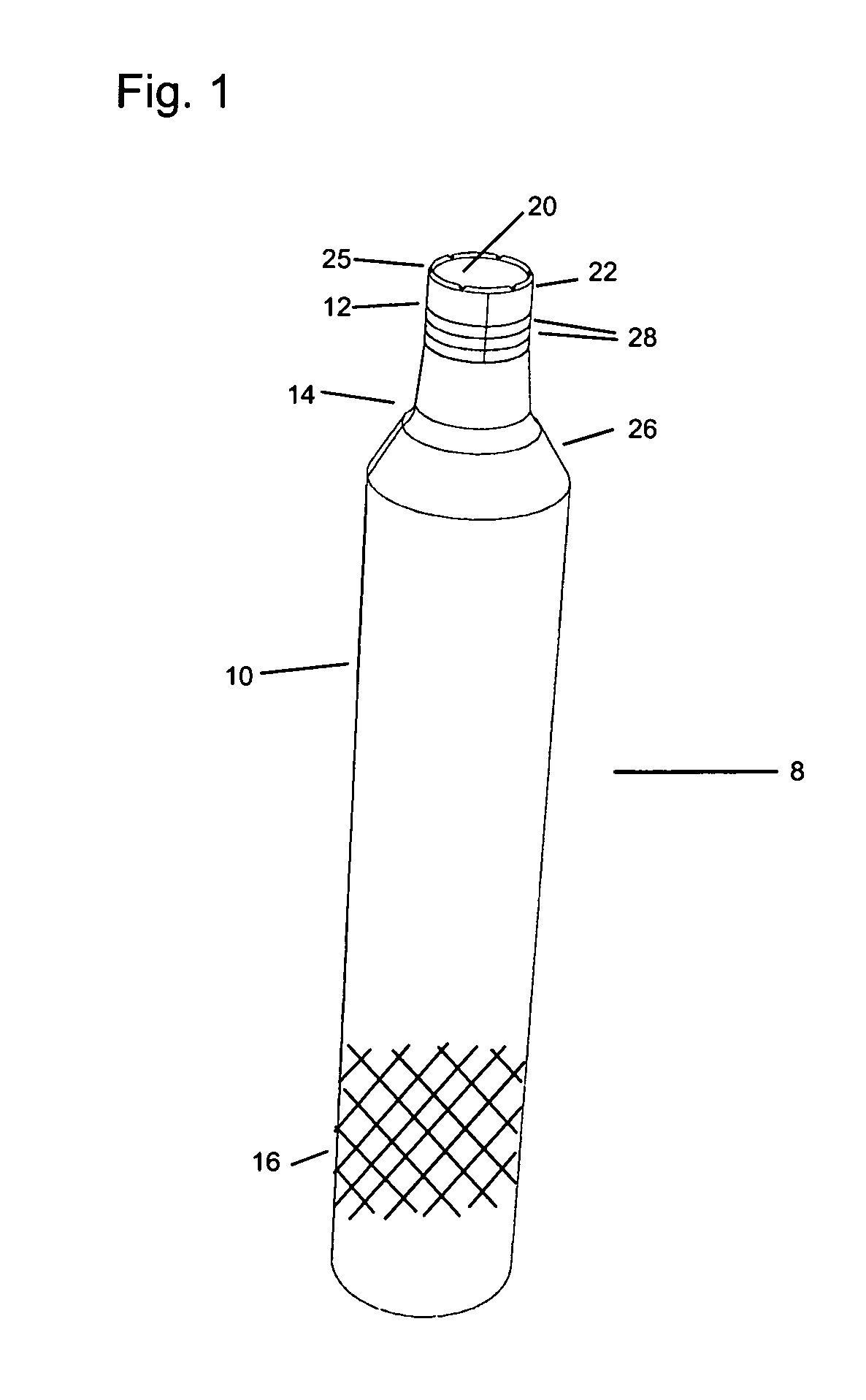
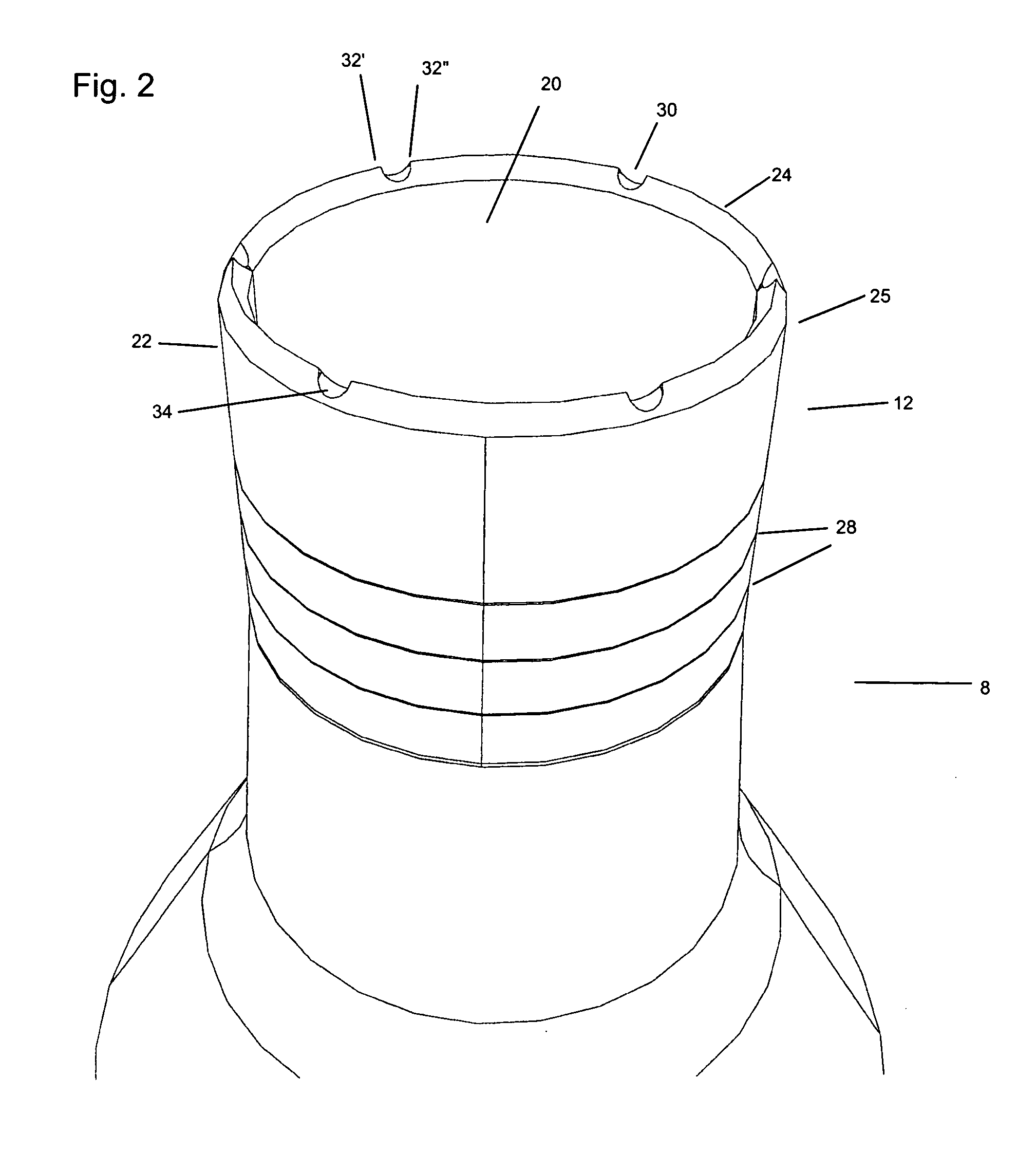
Implant that can be implanted in osseous tissue and method for producing said implant corresponding implant
ActiveUS20060105295A1Strong long-term anchoringProcess stabilityDental implantsInternal osteosythesisBone implantCavity wall
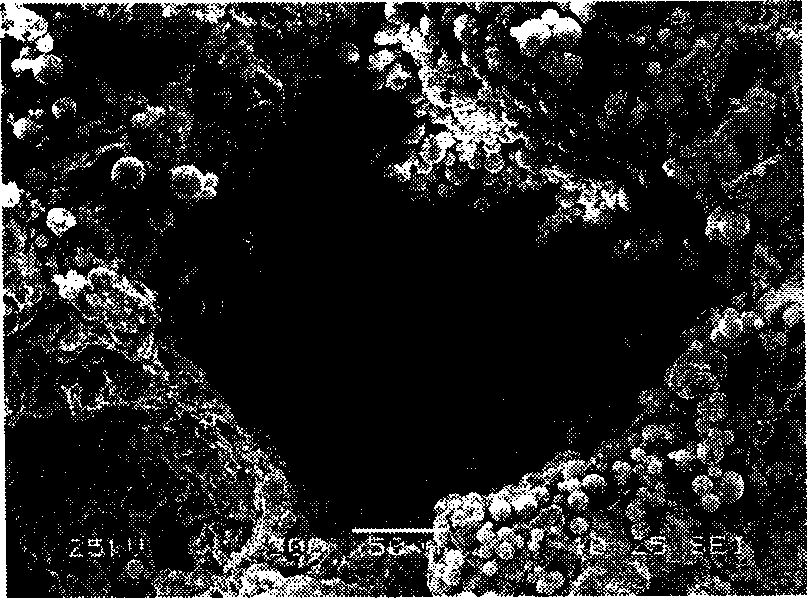
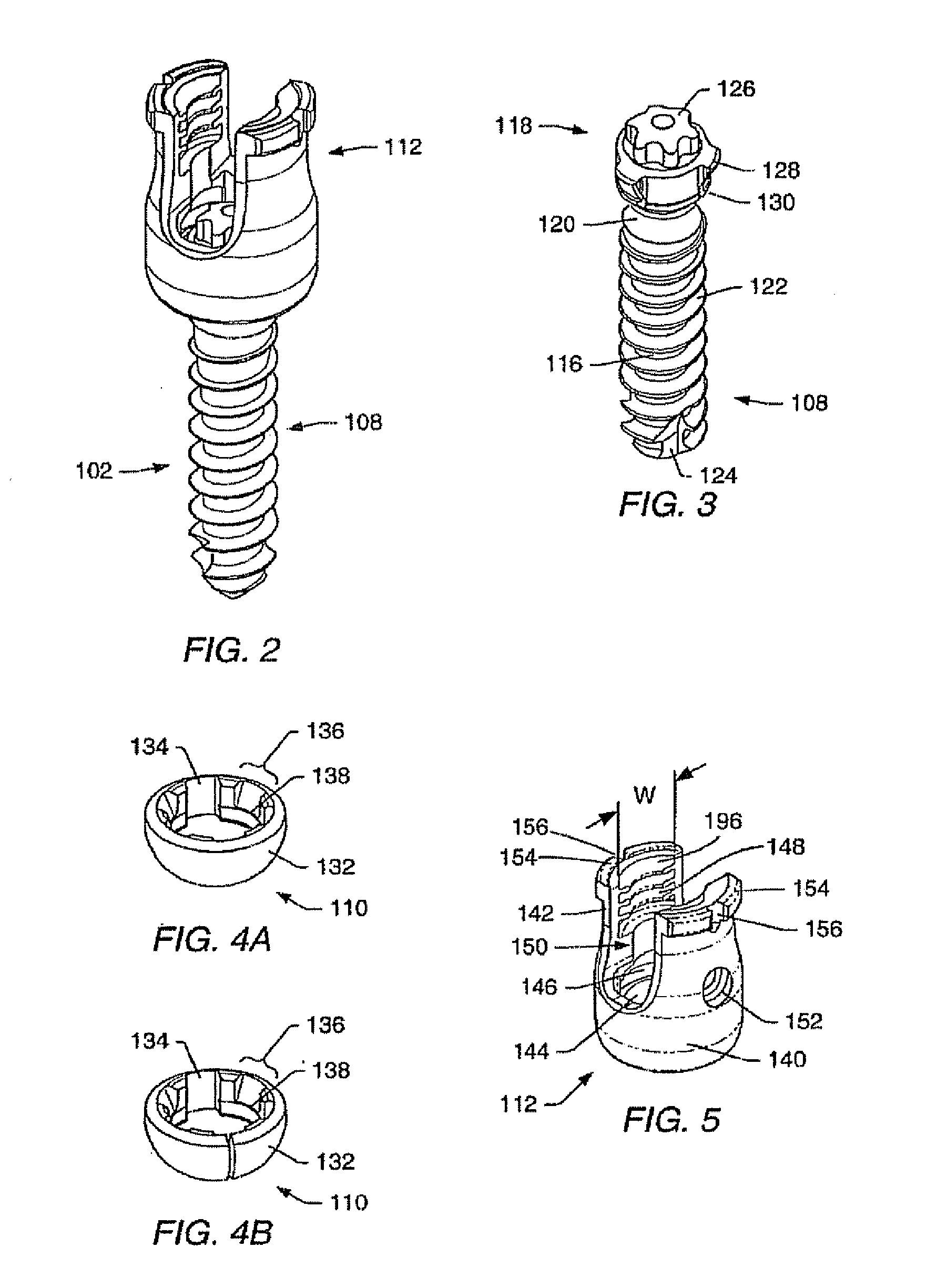
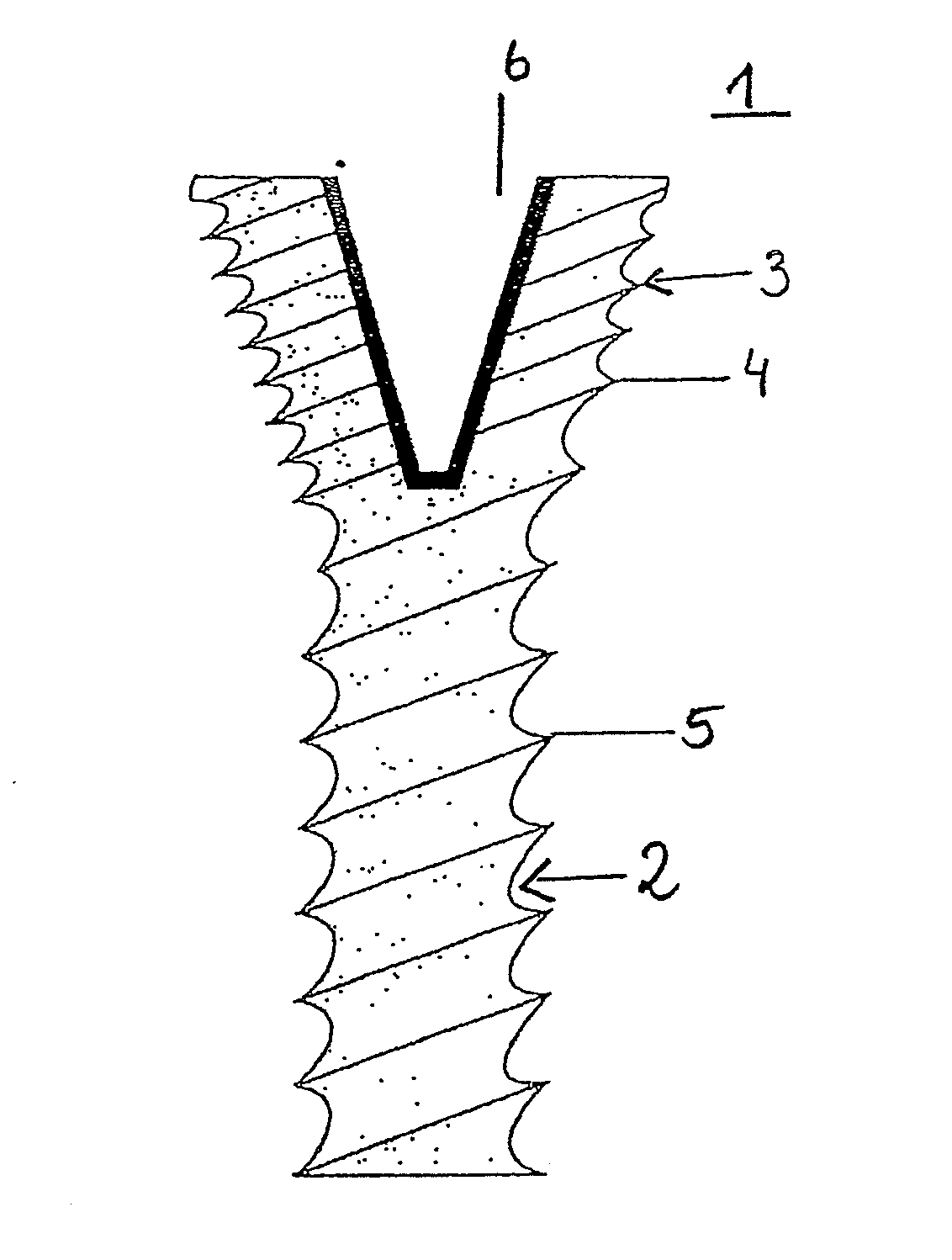
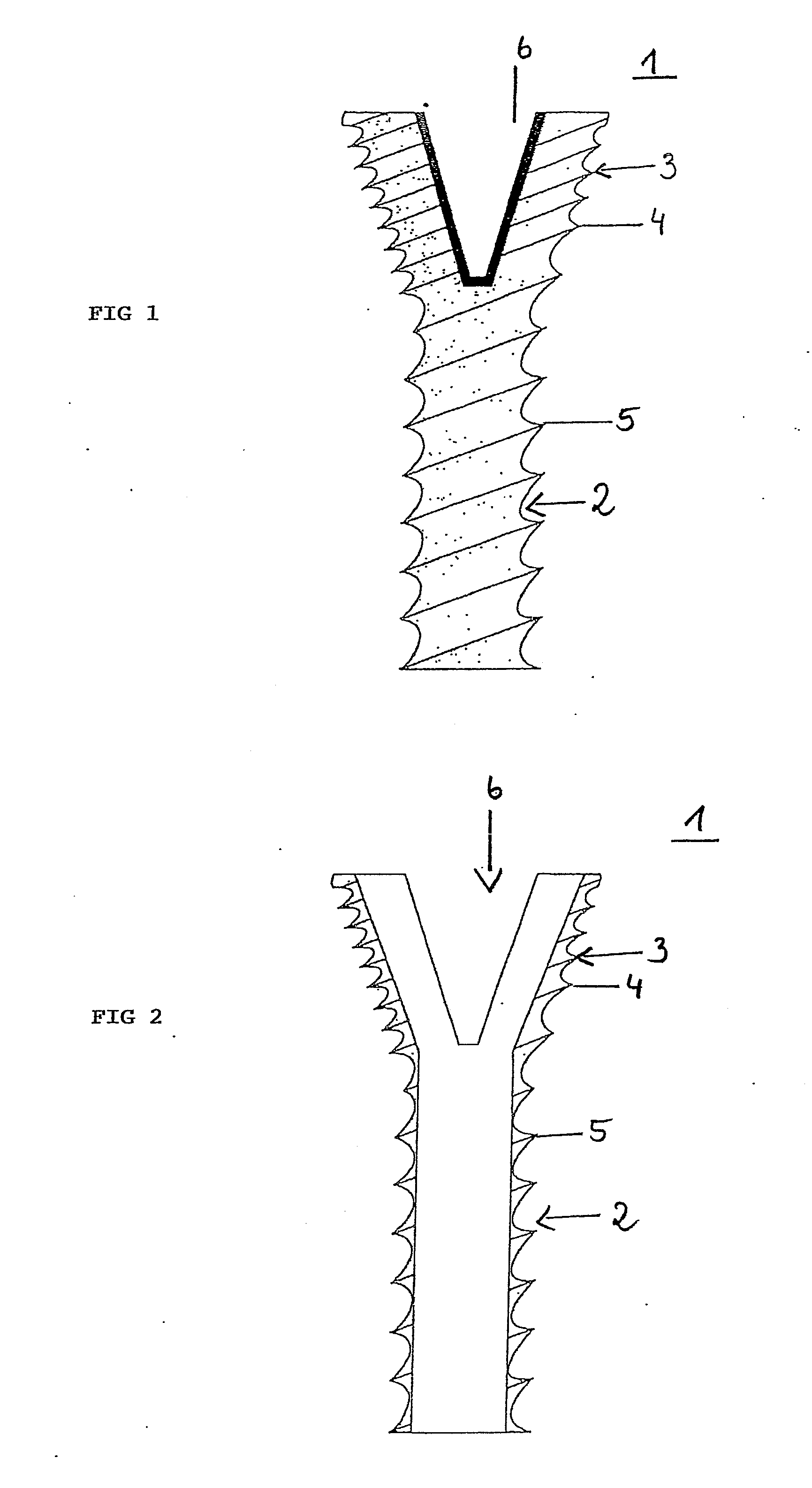
A bone implant (10) is implanted in a cavity parallel to an implant axis (I) and without substantial rotation. The implant includes, on an implant portion to be implanted, cutting edges (14), which do not extend in a common plane with the implant axis and are facing toward the distal end of the implant. The implant also includes surface ranges (16) of a material that is liquefiable by mechanical oscillations. The cutting edges (14) are dimensioned such that they are lodged in the cavity wall after implantation. For implantation, the implant is impinged with mechanical oscillations, resulting in the thermoplastic material being at least partially liquefied and pressed into unevennesses and pores of the cavity wall to form a form-fit and / or material-fit connection between implant (10) and cavity wall, when re-solidified. The cutting edges (14) anchor the implant in the cavity wall.
Owner:WOODWELDING
Low profile bioactive agent delivery device
InactiveUS20080057106A1Low external profileMinimize damageEye implantsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismDevice implantDistal portion
Disclosed are implantable devices that are configured for implantation through tissue or membrane and into an implantation site comprising viscoelastic fluid or non-osseous tissue. In embodiments of the invention, the implantable devices comprise: (a) a nonlinear body member having a direction of extension, a longitudinal axis along the direction of extension, and a proximal portion and a distal portion, wherein at least a portion of the body member deviates from the direction of extension, (b) a retention element at the proximal portion of the body member, the retention element configured to retain the implantable device at the implantation site, the retention element presenting an external profile of no greater than 0.5 mm when the device is implanted in a patient; and (c) a bioactive agent delivery system at the distal portion of the body member, the bioactive agent delivery system comprising one or more bioactive agents. Also disclosed are methods of delivering a bioactive agent to a patient using the devices.
Owner:SURMODICS INC
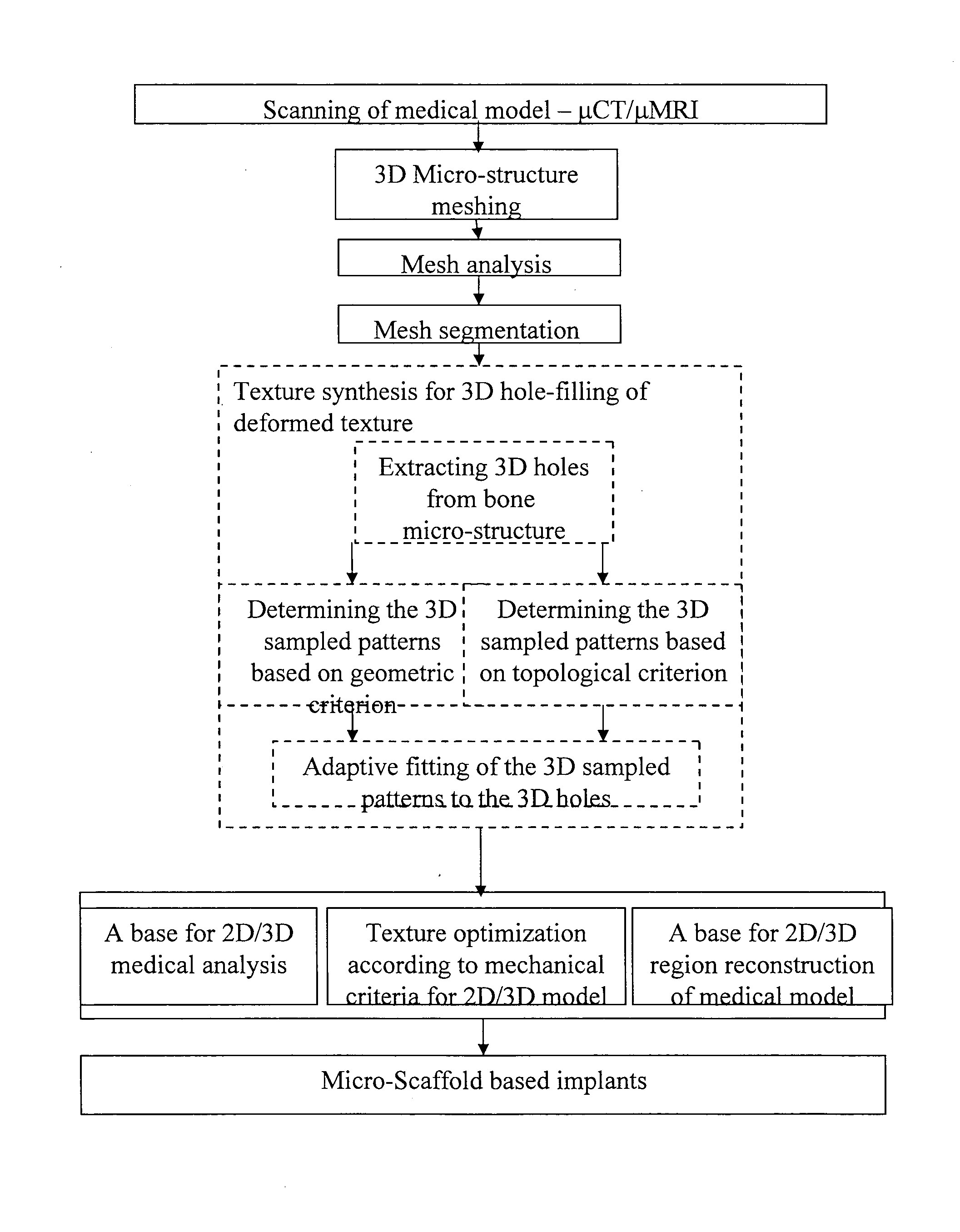
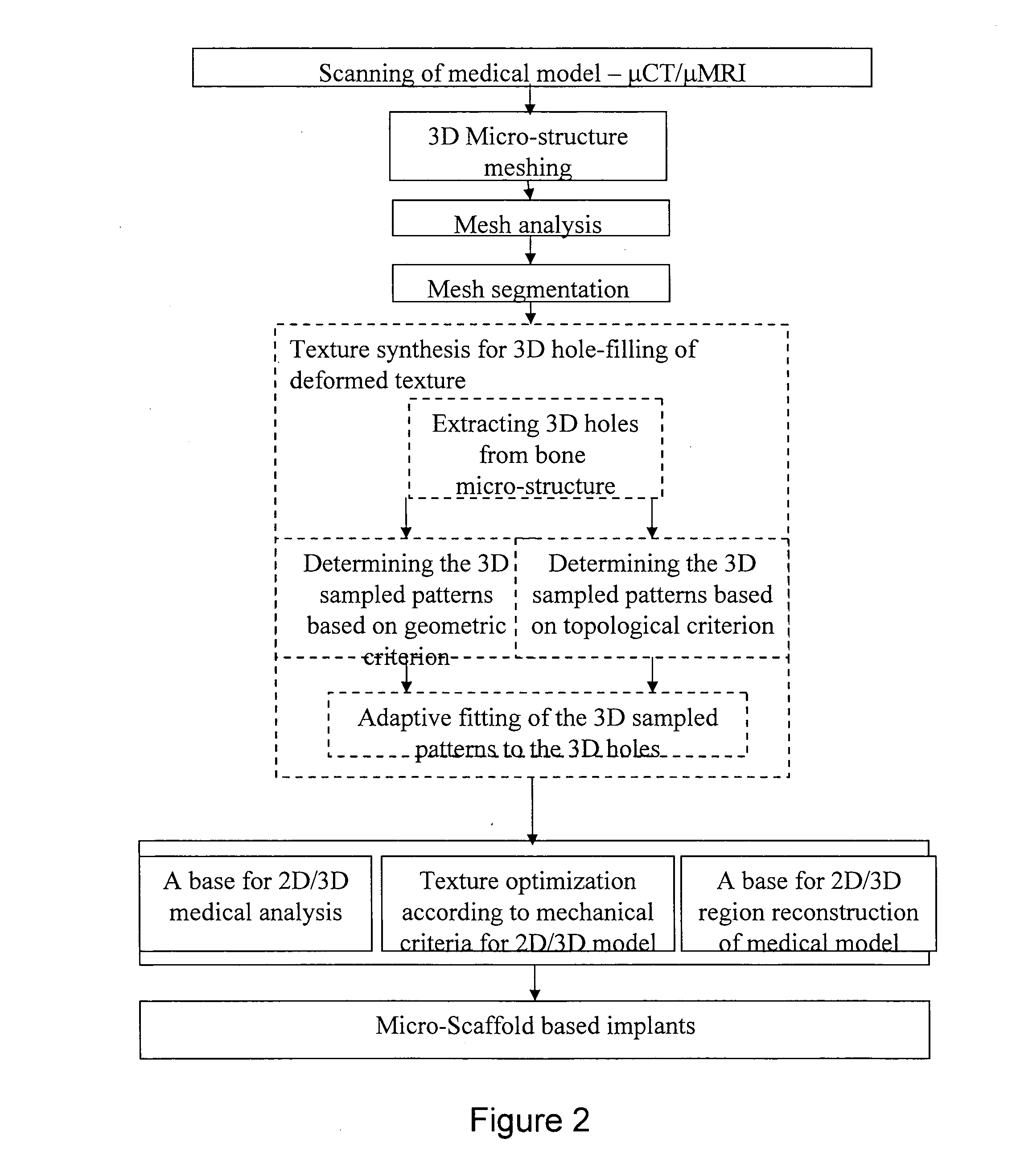
Modeling micro-scaffold-based implants for bone tissue engineering
InactiveUS20110022174A1Easy to integrateSimple processBone implantCharacter and pattern recognitionMicro structureNatural bone
A new conceptual biomedical method is presented for designing scaffold-based bone implants and using these implants in treating deteriorated bones. These implants have micro-architectural bone structures that are capable of mimicking the stochastic micro-structure as in natural bone bio-mineral structures. Moreover, they can be adapted as specific tailor-made compatible bone-repair mediator implants to be used as effective substitutes for natural damaged bone fracture structures.
Owner:TECHNION RES & DEV FOUND LTD
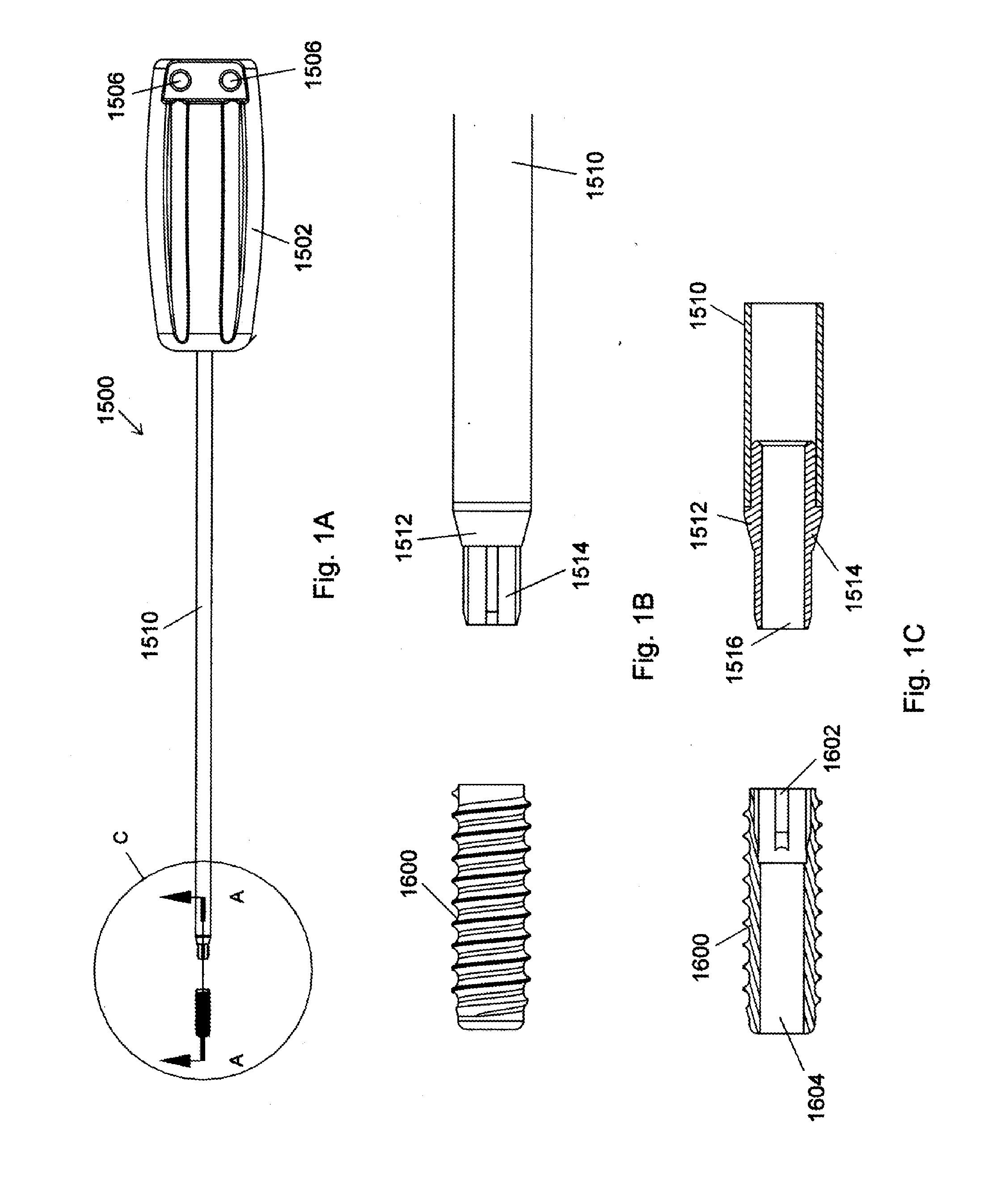
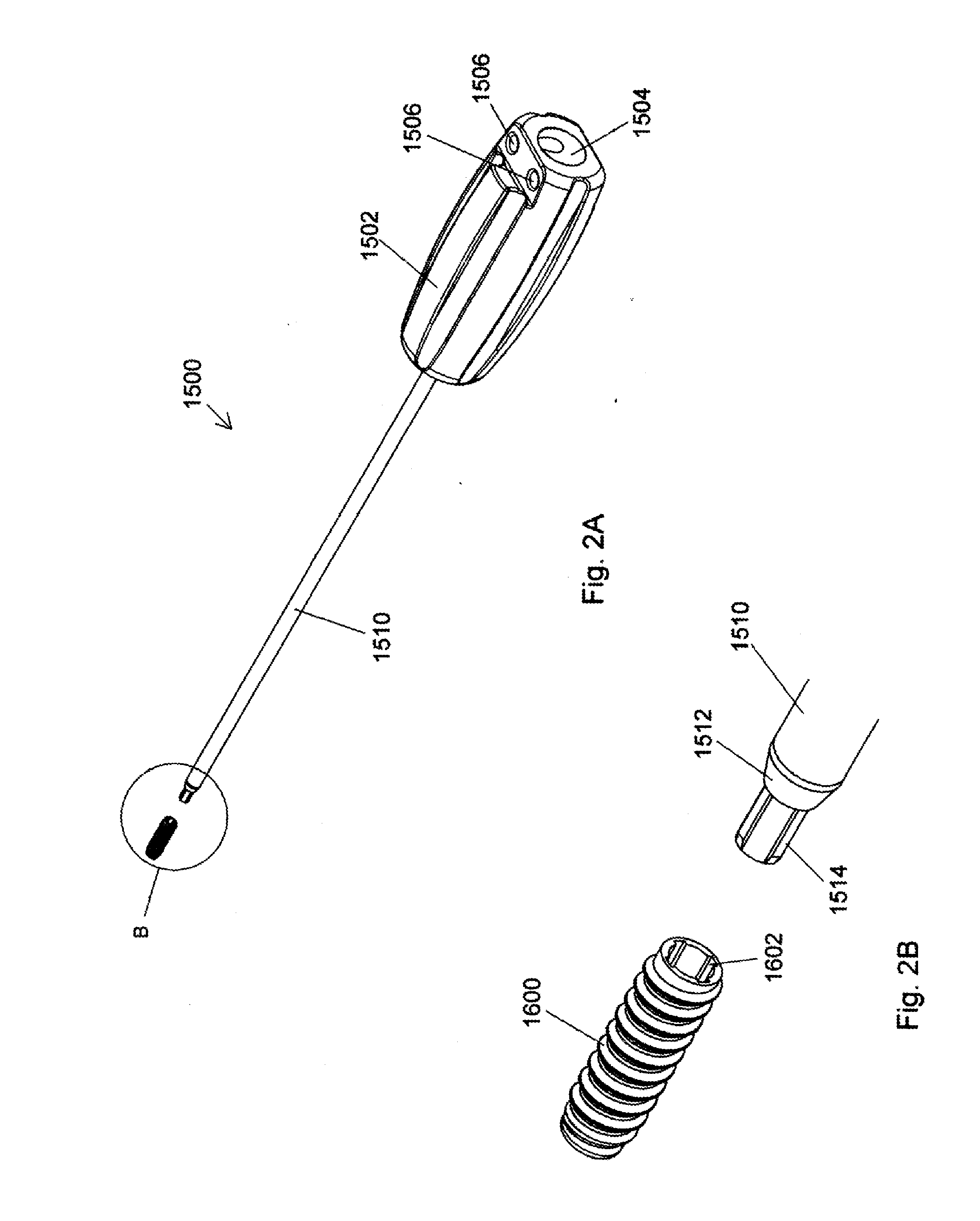
Rotational securing of a suture
A suture fixation apparatus having a first body portion having a bone engaging feature to fixedly engage a bony tissue and a second body portion defining an eyelet for receipt of a suture. The second body portion is rotatable with respect to the first body portion. Rotating the second body portion causes the suture to form a twist to frictionally secure the suture.
Owner:BIOMET MFG CORP
Bone fixation plate
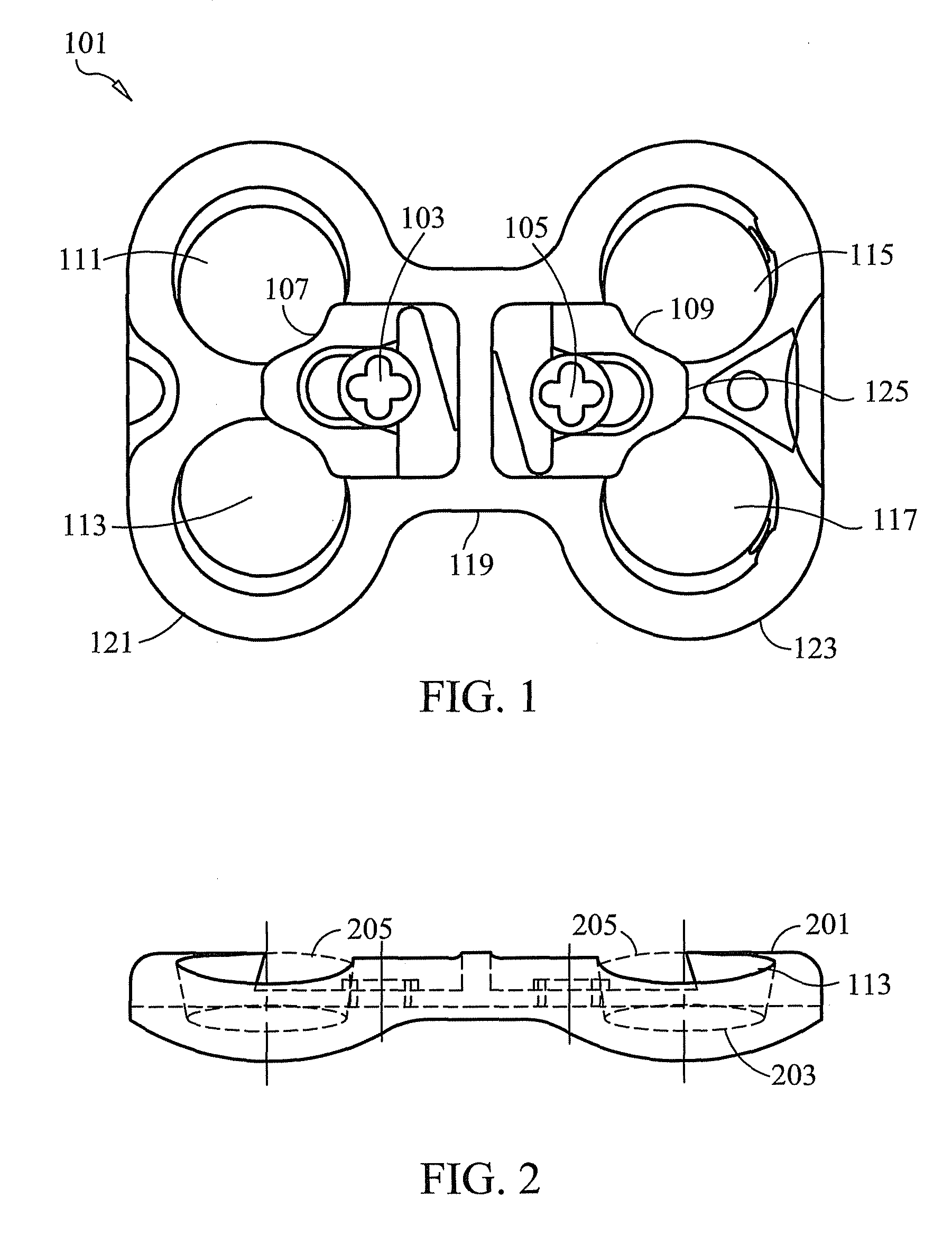
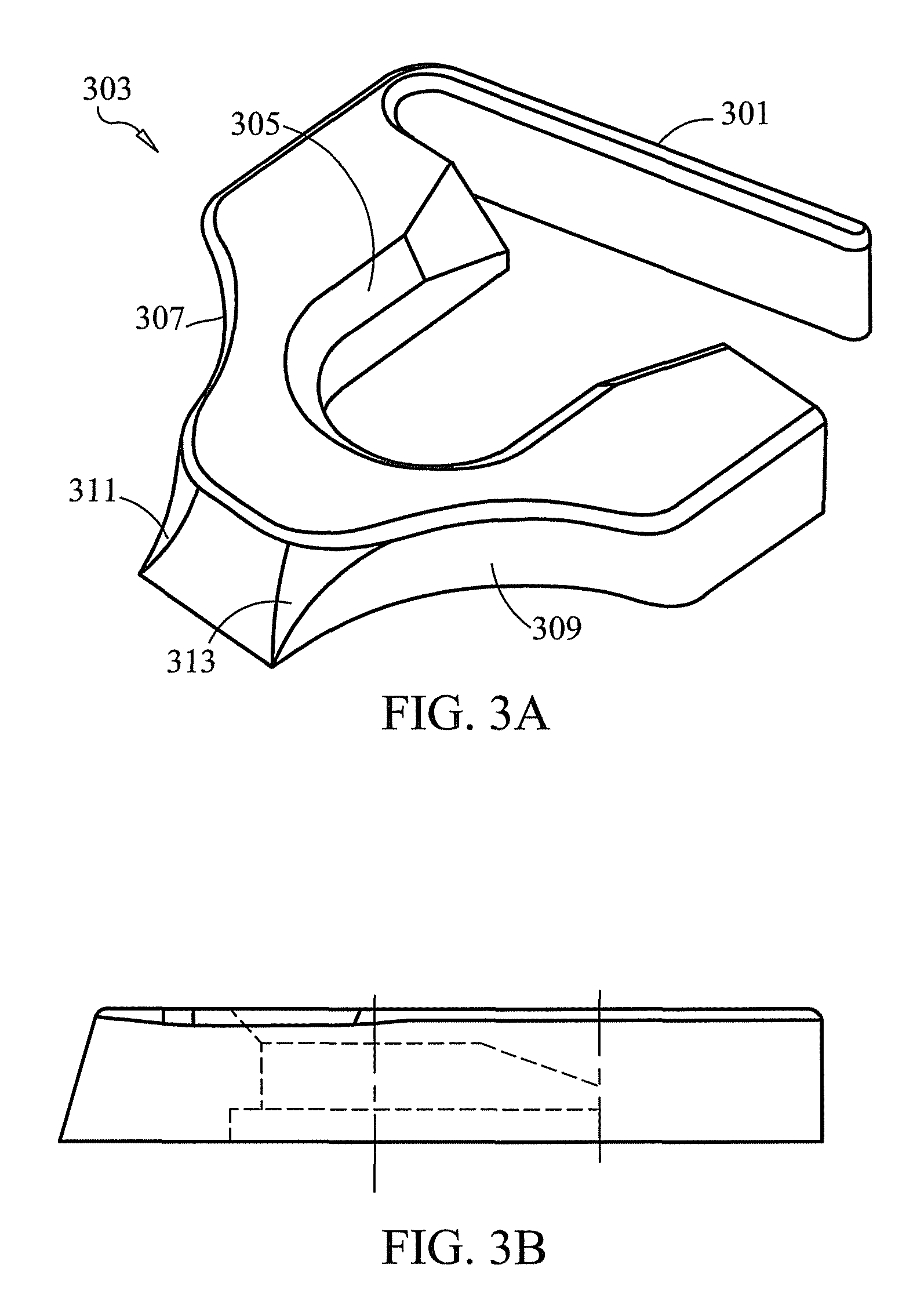
ActiveUS20050261690A1Increases magnitudeSmall resistance forceInternal osteosythesisFastenersSet screwSmall patellae
An apparatus for reducing the profile of a bone fixation plate while preventing backing out of screws is disclosed. The plate has at least two openings though which two screws can pass through bony tissue. The apparatus includes at least one section of relief and sections of engagement. As the screw is tightened, it will begin to lag the plate to the bone. When the screw head interferes with the plate at the interference point, there is a slight resistance that insertion forces can overcome. When the screw is advanced further, it snaps into the sliding fit area and is allowed to move freely. The forces that cause the screw to back out from the plate are preferably not strong enough to pass the screw head back past the interference section. At least one of the two openings is configured as an elongated slot to allow the screw to translate in the slot. It may be desirable to include a set screw to help prevent backout.
Owner:GLOBUS MEDICAL INC
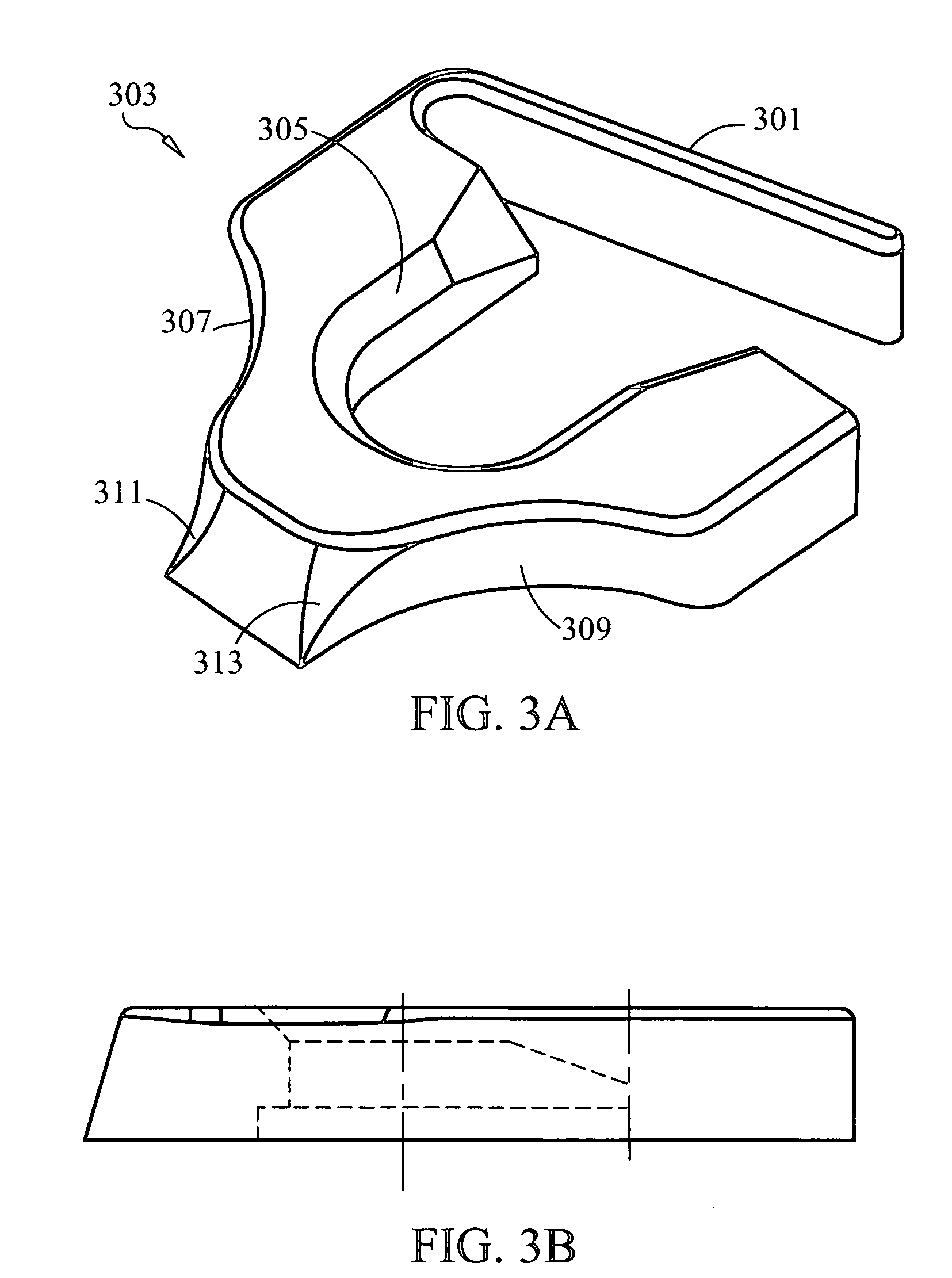
Apparatus for attaching sutures
A suture anchor, an insertion tool for inserting a suture anchor, and a device for internal working of hole in bony tissue. The anchor comprises an anchor body having a longitudinal cross-section defined by a perimeter. The perimeter comprises at least one tissue-intruding edge formed between the first side and the second side of the perimeter. The intruding edge is arranged to penetrate the tissue during a rotating motion of the anchor in said opening. The anchor further comprises an abutment surface, arranged substantially on the opposite side of the anchor body in relation to said intruding edge. The first side of the intruding edge is arranged to connect with the abutment surface by a connecting part of the perimeter having the shape of a substantially curved piece in said longitudinal cross-section.
Owner:INION
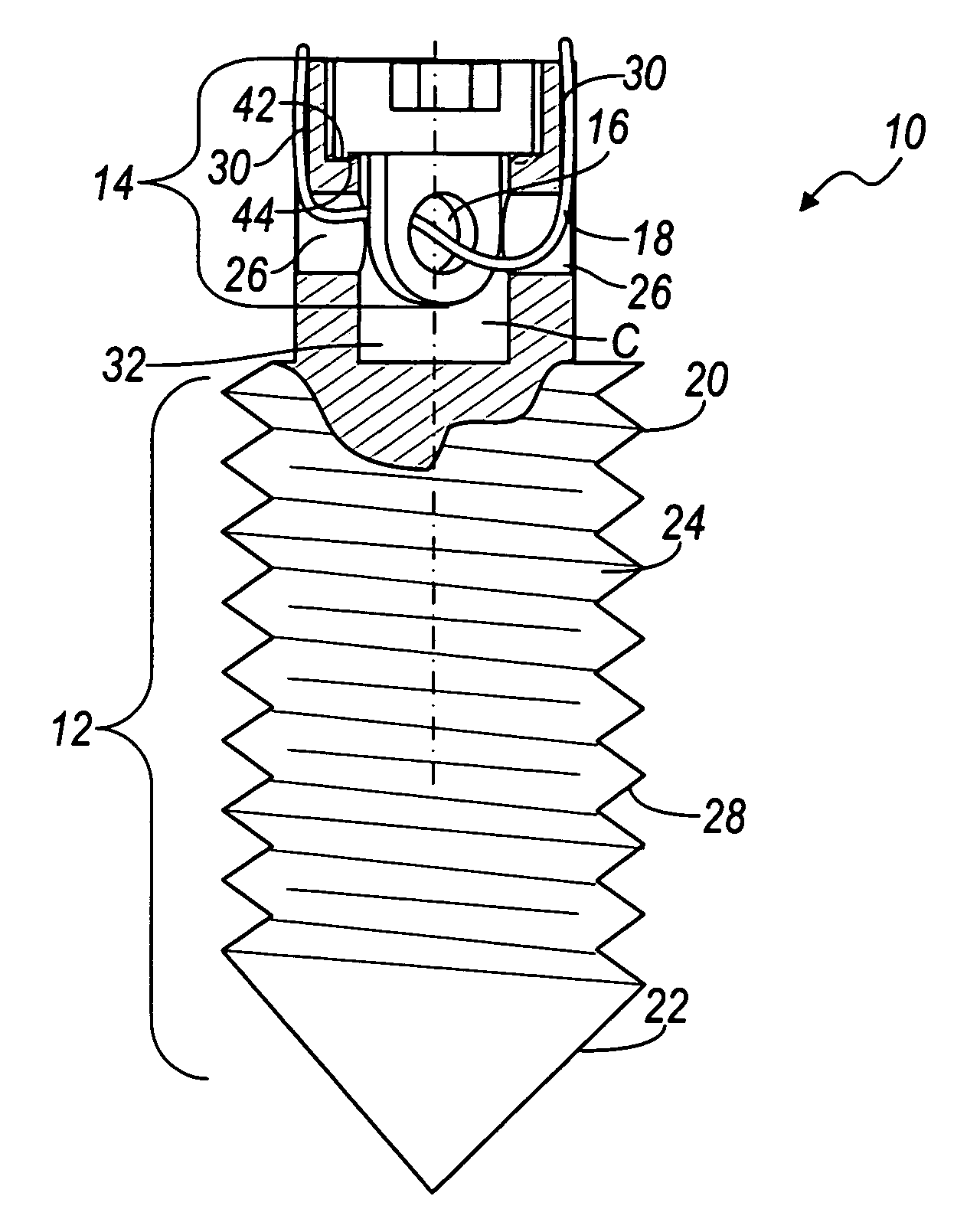
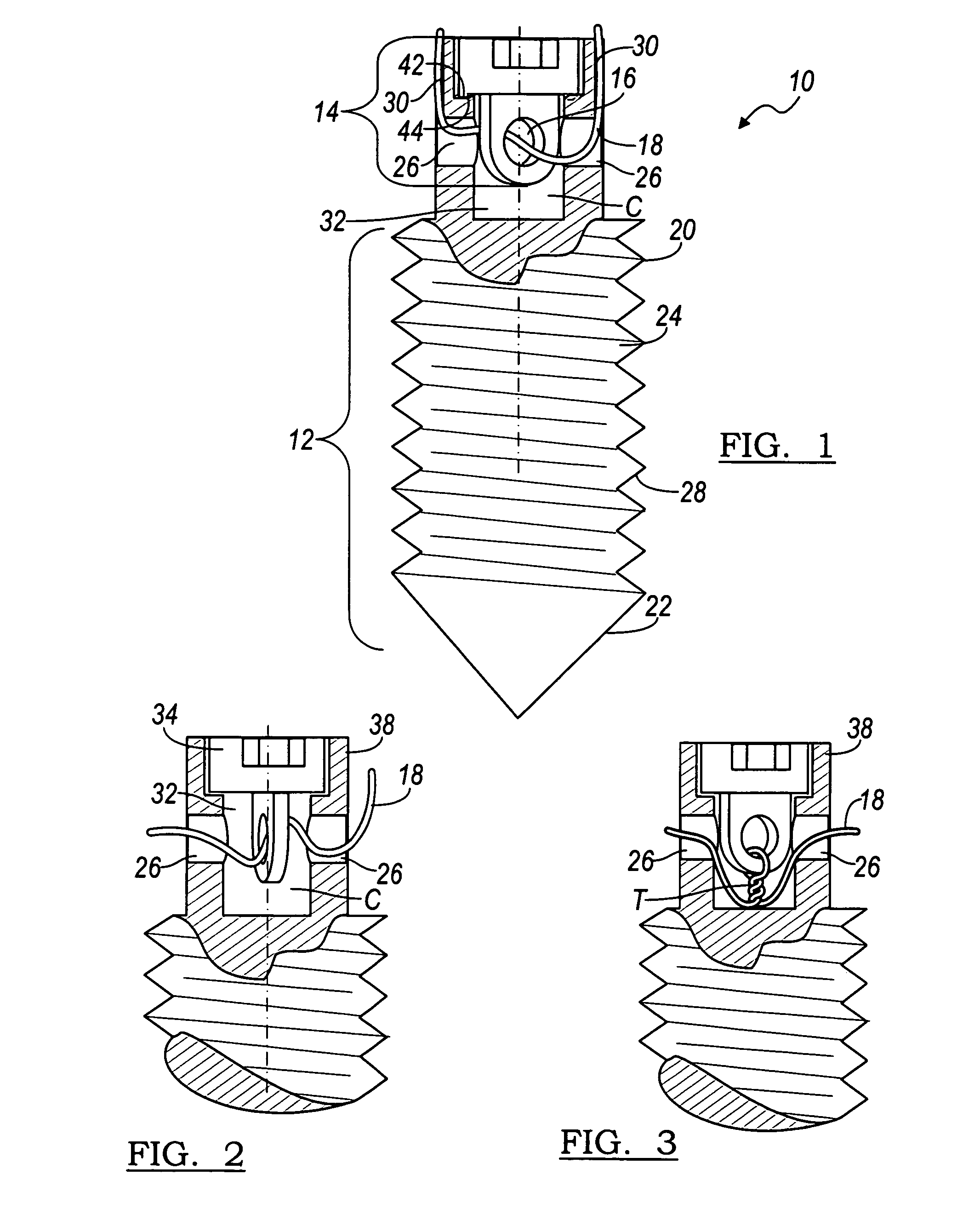
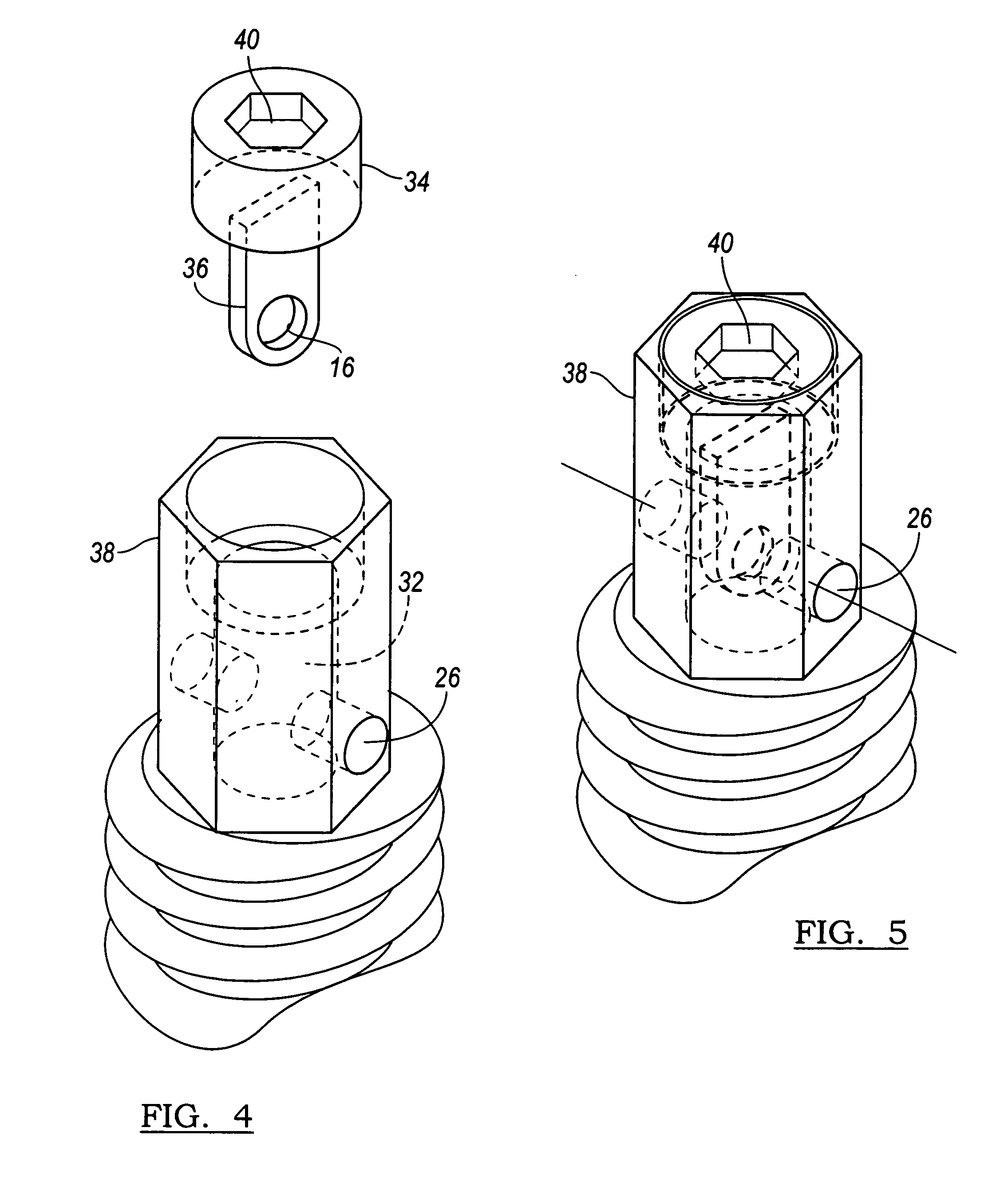
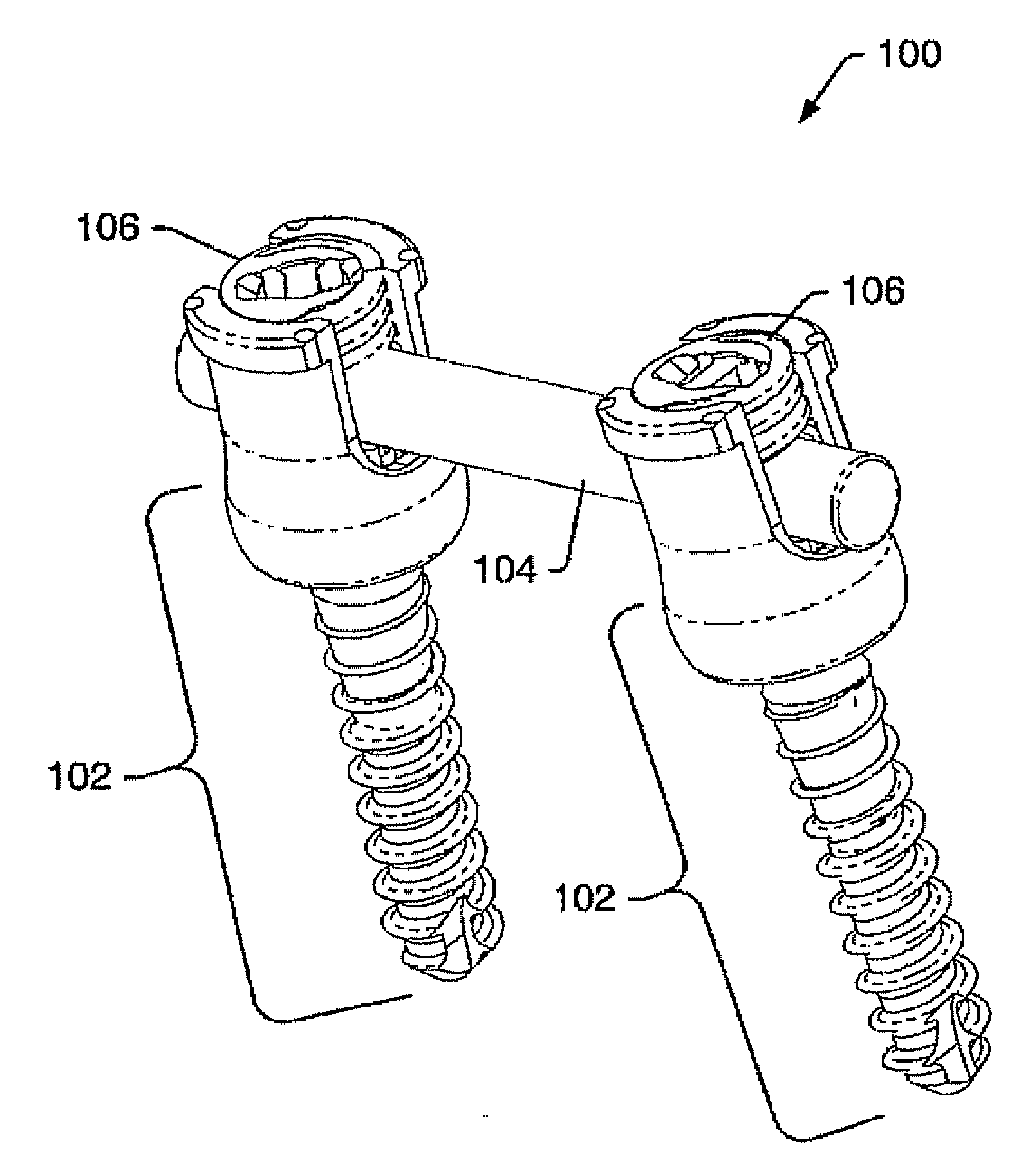
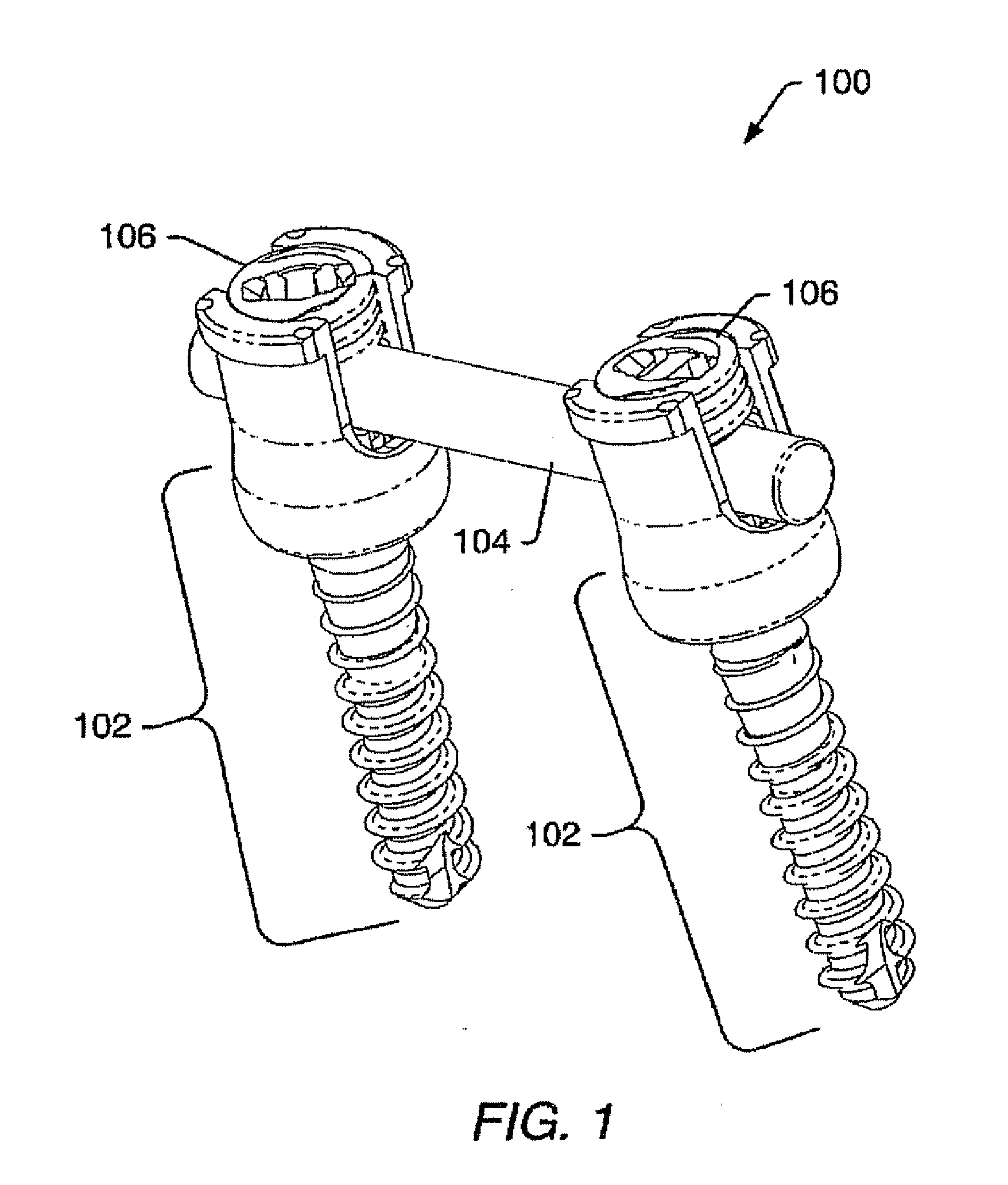
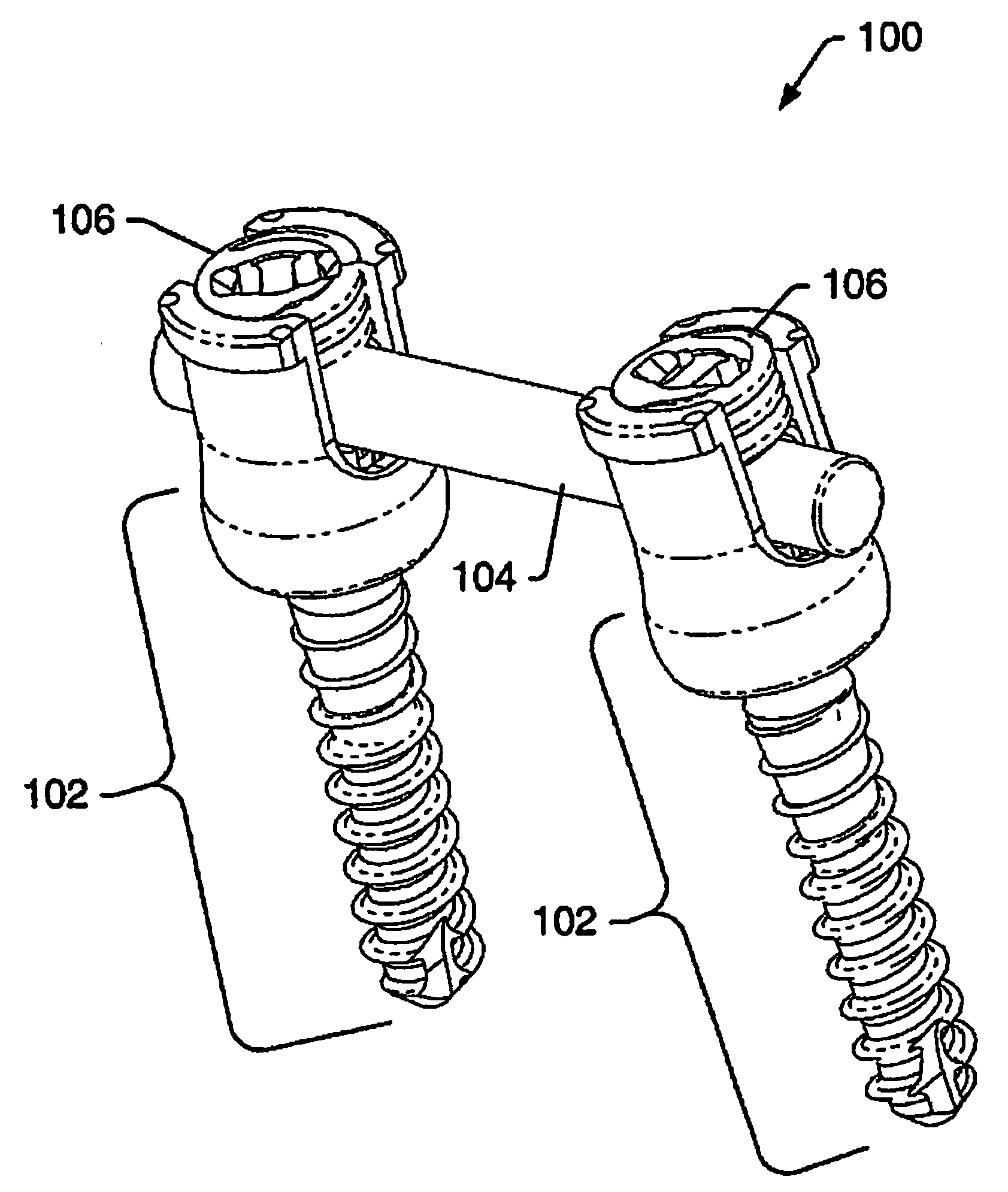
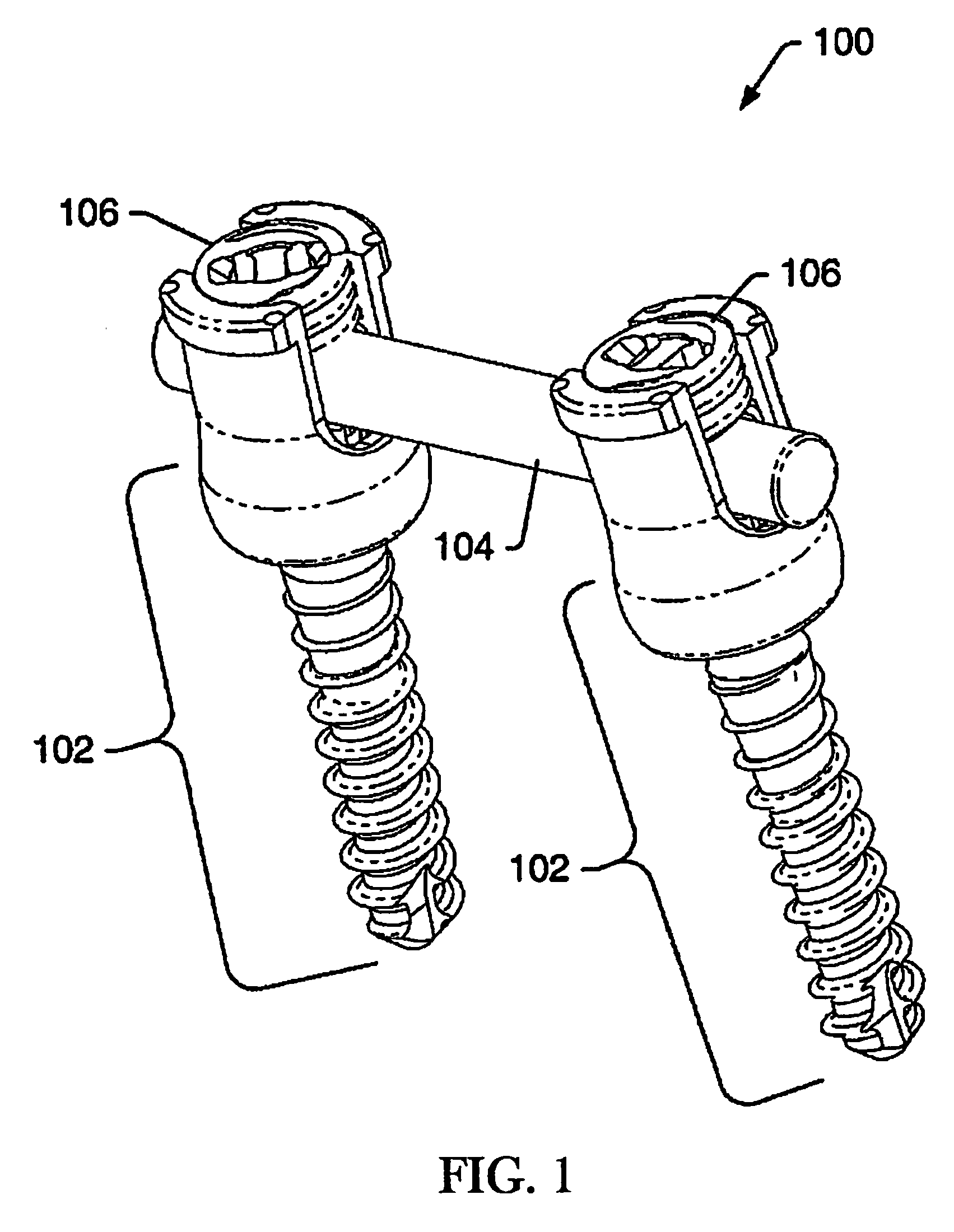
Device and system for implanting polyaxial bone fasteners
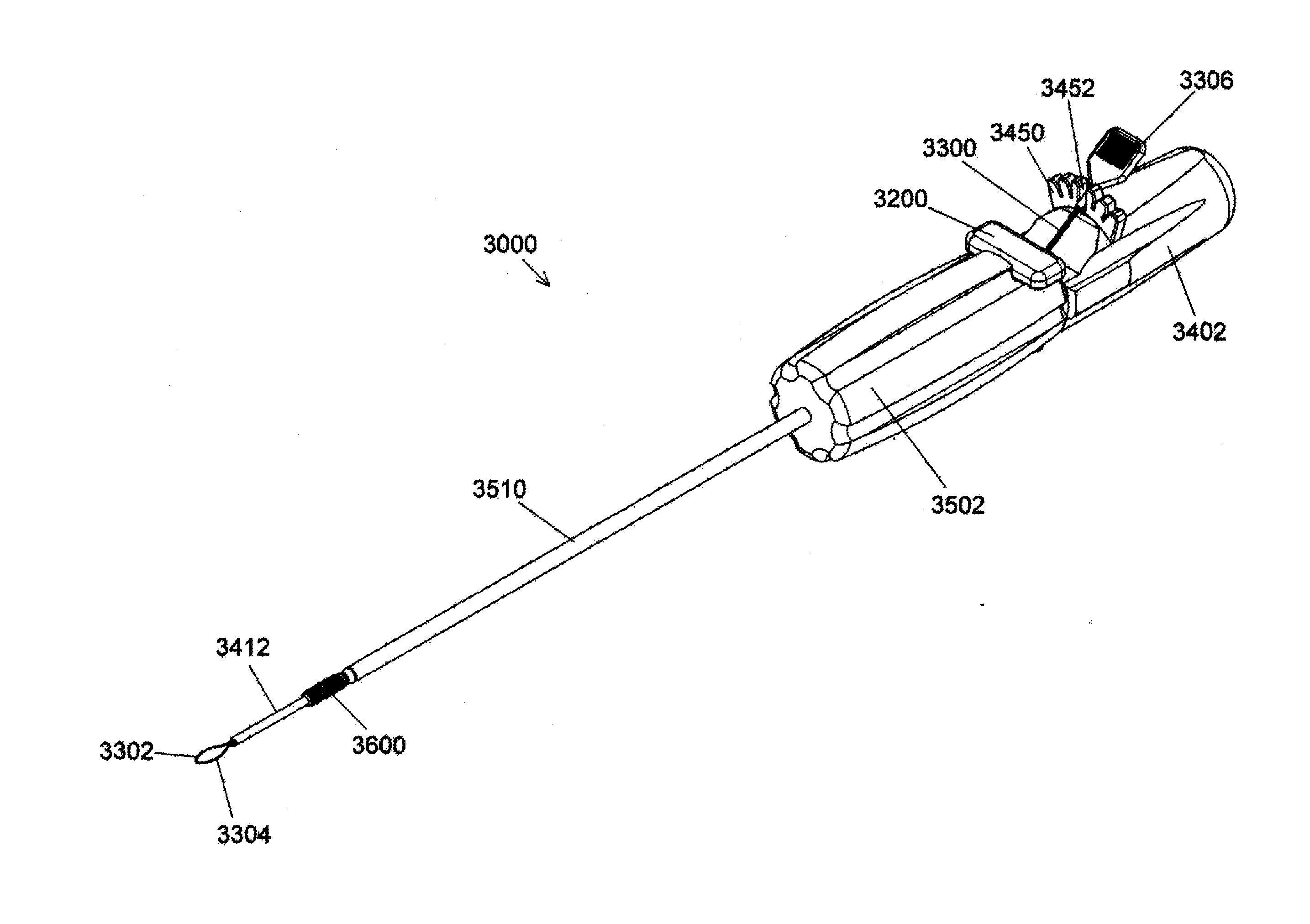
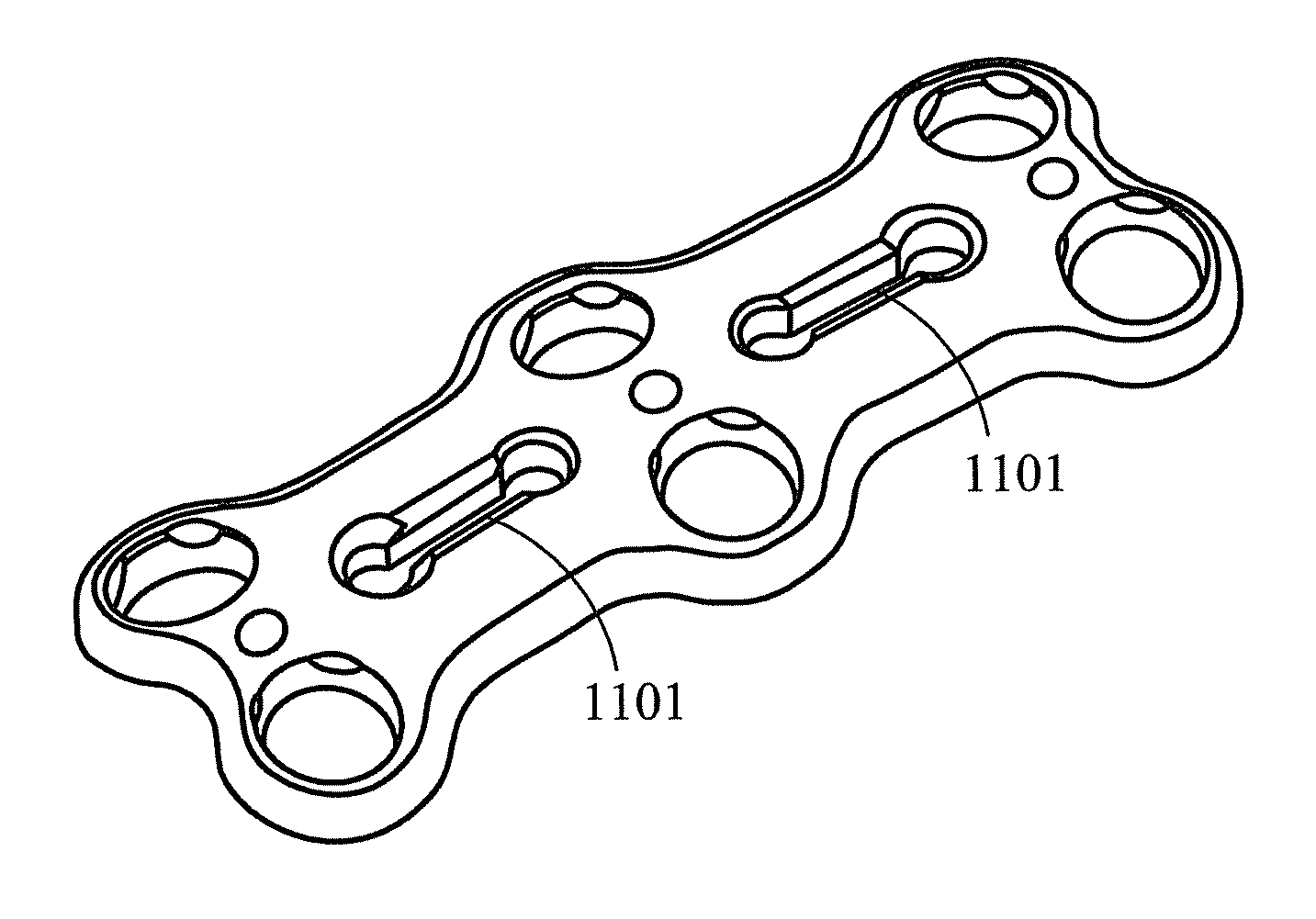
InactiveUS20090005787A1Extension of timeMinimize damageSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisFastenerBony Tissues
A device, is provided for implanting in bony tissue a bone fastener rotatably connected to a collar. The sleeve is configured for threaded connection to the collar and has a central bore aligned with the longitudinal axis of the sleeve for receiving an inner shaft. The inner shaft inserts in the sleeve and has a distal end configured for connection to a portion of the bone fastener, such as an internal hex feature. In some embodiments a movable member may be inserted in an opening transverse the central bore and positionable to either rotatably or fixedly connect the inner shaft to the sleeve. In other embodiments, a collet nut threads onto a collet thread to radially compress sleeve tangs to frictionally engage inner shaft to sleeve.
Owner:ZIMMER SPINE INC
Method for using acoustic shock waves in the treatment of an ischemic condition
This invention relates to methods for medical treatment of a variety of pathological conditions associated with bone environments and musculoskeletal environments, including the treatment of ischemic conditions such as bursitis. The method involves applying a sufficient number of acoustic shock waves to the site of a pathological condition including micro-disruptions, non-osseous tissue stimulation, increased vascularization, and circulation and induction of growth factors to induce or accelerate the body's natural healing processes and responses.
Owner:SANUWAVE INC
Bone screw
InactiveUS20100137919A1Avoid problemsConvenient ArrangementSuture equipmentsLigamentsEngineeringScrew thread
Owner:WOLTER DIETMAR
Implants comprising biodegradable metals and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20100075162A1High strengthImprove interface strengthDental implantsInternal osteosythesisUltimate tensile strengthBiodegradable magnesium
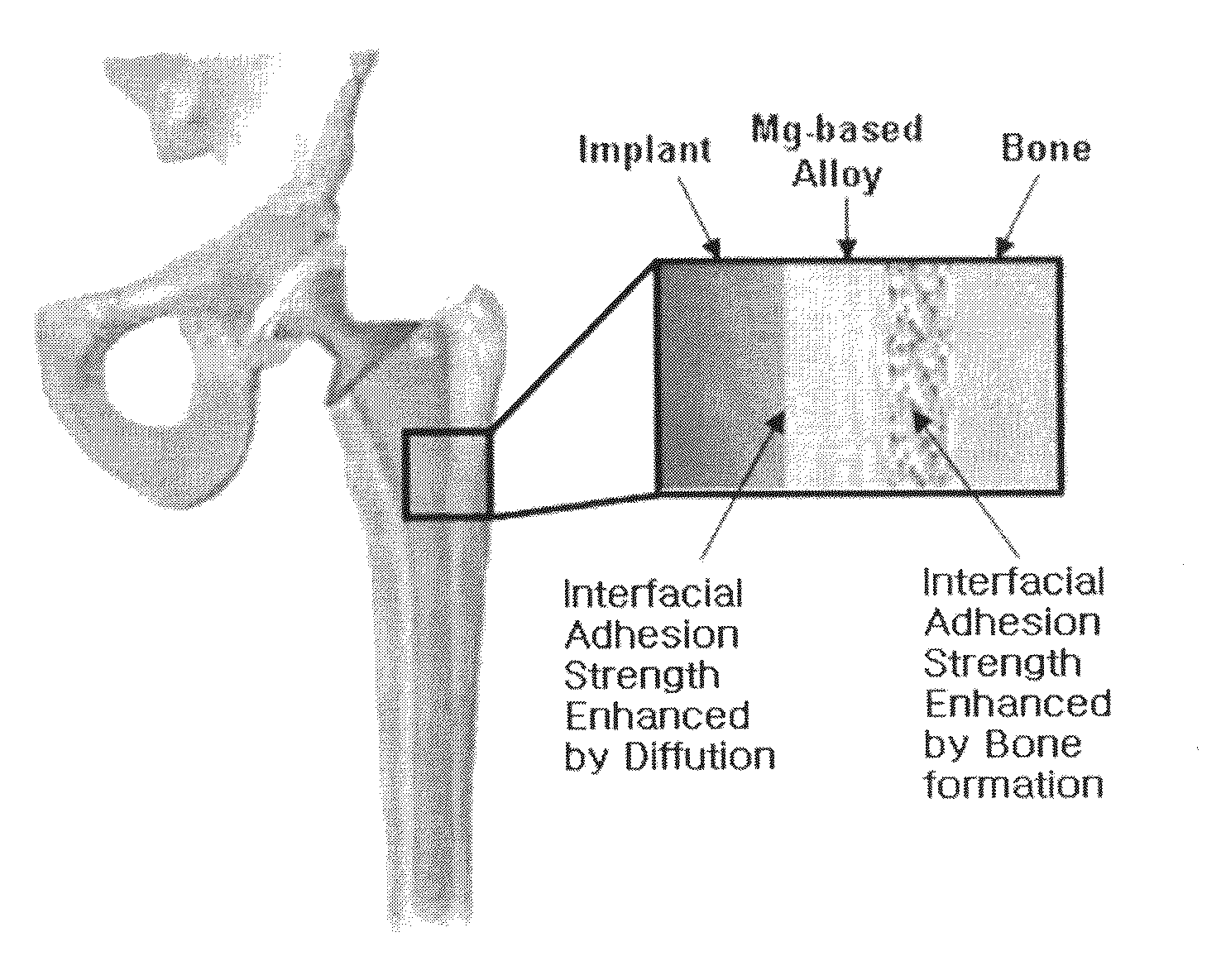
The present invention provides an implant consisting of a biodegradable magnesium-based alloy or partially applied with the magnesium-based alloy, and a method for manufacturing the same. The implant according to the present invention is biodegradable, in which its biodegradation rate can be easily controlled, and the implant has excellent strength and interfacial strength to an osseous tissue.
Owner:U & I INC
Material for bone tissue engineering scaffold and making method thereof
InactiveCN101032632AImprove mechanical propertiesGood biocompatibilityBone implantBiocompatibility TestingBiological materials
The present invention relates to biological material technology, and is especially porous magnesium, magnesium alloy and composite magnesium material used as high strength biomedicine rack material for human body hard tissue defection and its preparation process. The porous magnesium, magnesium alloy and composite magnesium material used in bone tissue engineering rack has porosity of 5-99 % and pore diameter of 50-900 microns. Owing to easy degradation and absorption of magnesium inside body, the bone tissue engineering rack of porous magnesium, magnesium alloy and composite magnesium material has excellent mechanical performance and excellent biocompatibility and can provide 3D space for cell to grow.
Owner:INST OF METAL RESEARCH - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Apparatus and methods for correcting nasal valve collapse
The present invention relates to apparatus ad methods for correcting nasal valve collapse comprising a device configured for suspending a nasal valve, the device comprising a body portion comprising a proximal end, a distal end, and a plurality of barbs, wherein the body portion is configured to be inserted through or underneath the upper lateral cartilage of a patient and wherein the plurality of barbs are configured to engage a soft tissue overlying a bony tissue proximal to the upper lateral cartilage, and a head portion coupled to the proximal end of the body portion wherein the head portion is configured to engage the upper lateral cartilage of the patient when the plurality of barbs are engaged with the soft tissue overlying the bony tissue proximal to the upper lateral cartilage
Owner:SPIROX INC
Medicinal porous titanium implant and method for preparing same
InactiveCN101518467AAchieve long-term stabilityIncrease initiativeDental implantsImpression capsStress concentrationMicrosphere
The invention discloses a medicinal porous titanium implant and a method for preparing the same. The porous titanium implant is prepared by a powder coinjection molding method; and a nano HA and TGF loaded sustained-release gelatin microsphere compound coating is deposited on the porous outer layer of the product. The outer layer of the implant has a communicated porous structure, the thickness of the porous layer is 0.4 to 1.1 millimeters, the porosity of the porous layer is 50 to 70 percent, and the aperture of the porous layer is 50 to 400 mum; the surface of the porous layer is deposited; and the binding strength of the outer layer and an inner core is 150 to 300MPa. Compared with the prior medicinal titanium implant material, the material of the medicinal porous titanium implant has higher mechanical strength, is in accordance with the mechanical performance of osseous tissue, avoids stress concentration and stress shielding, promotes stress transmission and growth of new bones, reduces time for osseointegration, and ensures the long-term stability of the implant. The method adopts once-for-all molding without post machining, thereby considerably reducing the cost.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Implant placement systems, devices, and methods
Described herein is a simplified placement system and method for a tissue graft anchor by which a surgeon may introduce one or more sutures into a hole in a boney tissue, apply tension to the sutures to advance a soft tissue graft to a desired location, and then advance the anchor into the bone while maintaining suture tension and without introducing spin to the suture.
Owner:TENJIN
Subtalar implant and methods of use thereof
ActiveUS20070173954A1Facilitate proper positioningAnkle jointsJoint implantsAnatomical structuresSacroiliac joint
The present invention provides a subtalar implant as well as methods of use thereof for the purpose of correcting podiatric disorders such as various types of flat foot conditions relating to the subtalar joint. The subtalar implant is capable of threaded engagement with a positioning element used to position and manipulate the implant during surgical implantation in the sinus tarsi of the foot. The implant is cannulated to receive a guide rod to facilitate final positioning of the implant. Once implanted, the subtalar implant provides anatomical fit with the subtalar joint anatomical structure without the need for indentations to receive osseous tissue growth to anchor the subtalar implant.
Owner:VILEX LLC
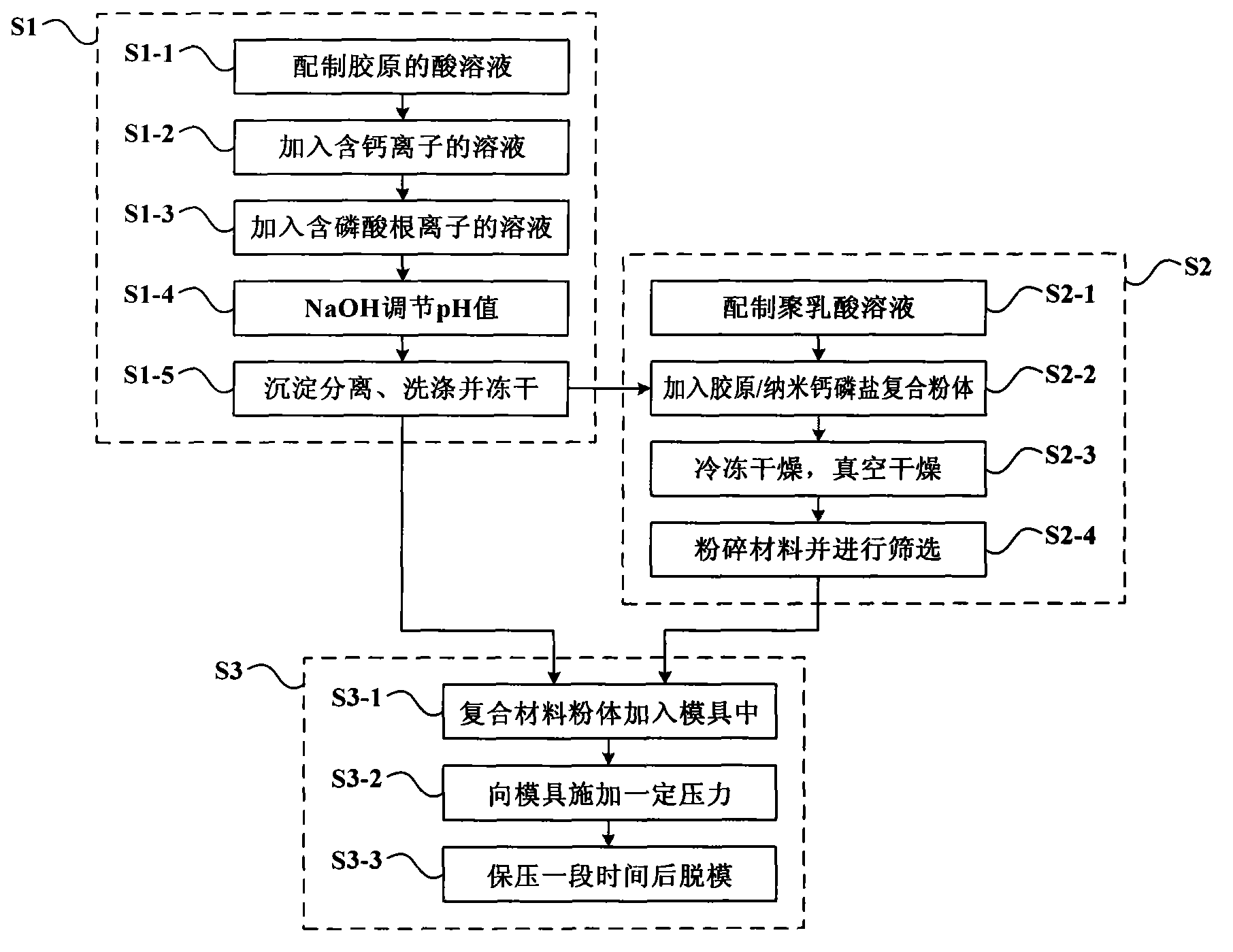
High-strength collagen base artificial bone repair material
ActiveCN103830775AImprove mechanical propertiesImprove biological activityProsthesisHuman bodyBone Cortex
The invention provides a high-strength collagen base artificial bone repair material which can be used for repairing the bone defect of bearing parts of a human body. The high-strength collagen base artificial bone repair material has chemical composition and structure formed by self-assembly of nanometer calcium phosphate and collagen molecules, so that the high-strength collagen base artificial bone repair material has a biomimetic mineralization structure similar to the natural bone tissue of the human body. In terms of mechanical properties, the material has the mechanical strength similar to that of the cortical bone of the human body and can be used for repairing the bone defect of the bearing parts of the human body. The invention also provides a preparation method of the high-strength collagen base artificial bone repair material.
Owner:BEIJING ALLGENS MEDICAL SCI & TECH
Bone fixation plate
ActiveUS8236034B2Small resistance forcePrevent exitInternal osteosythesisFastenersEngineeringIliac screw
An apparatus for reducing the profile of a bone fixation plate while preventing backing out of screws is disclosed. The plate has at least two openings though which two screws can pass through bony tissue. The apparatus includes at least one section of relief and sections of engagement. As the screw is tightened, it will begin to lag the plate to the bone. When the screw head interferes with the plate at the interference point, there is a slight resistance that insertion forces can overcome. When the screw is advanced further, it snaps into the sliding fit area and is allowed to move freely. The forces that cause the screw to back out from the plate are preferably not strong enough to pass the screw head back past the interference section. At least one of the two openings is configured as an elongated slot to allow the screw to translate in the slot. It may be desirable to include a set screw to help prevent backout.
Owner:GLOBUS MEDICAL INC
Bone fixation plate
An apparatus for reducing the profile of a bone fixation plate while preventing backing out of screws is disclosed. The apparatus includes at least one section of relief and sections of engagement. The plate has at least two openings though which two screws can pass through bony tissue. As the screw is tightened, it will begin to lag the plate to the bone. When the screw head interferes with the plate at the interference point, there is a slight resistance that insertion forces can overcome. When the screw is advanced further, it snaps into the sliding fit area and is allowed to move freely. The forces that cause the screw to back out from the plate are preferably not strong enough to pass the screw head back past the interference section. It may be desirable to include a set screw to help prevent backout.
Owner:GLOBUS MEDICAL INC
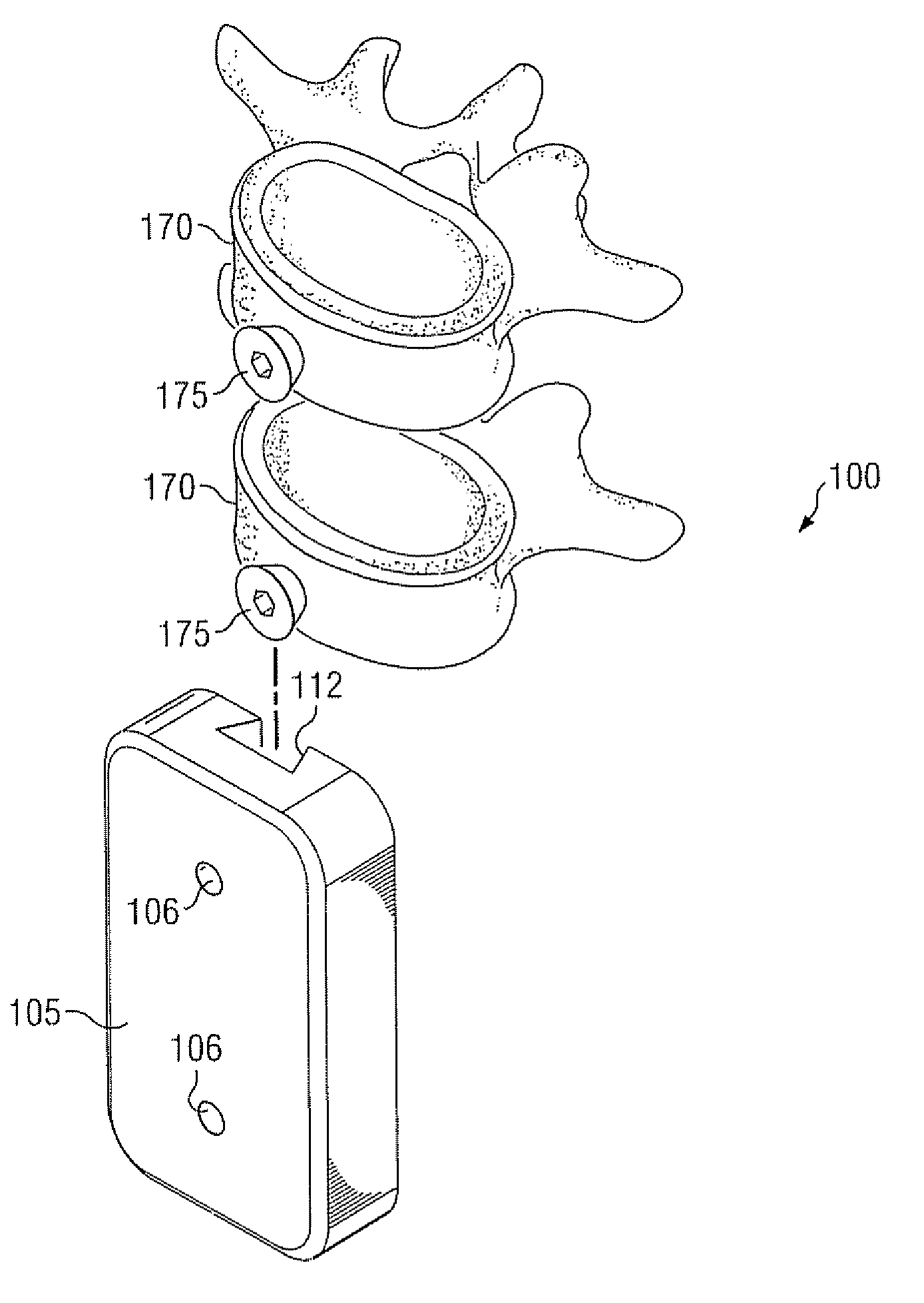
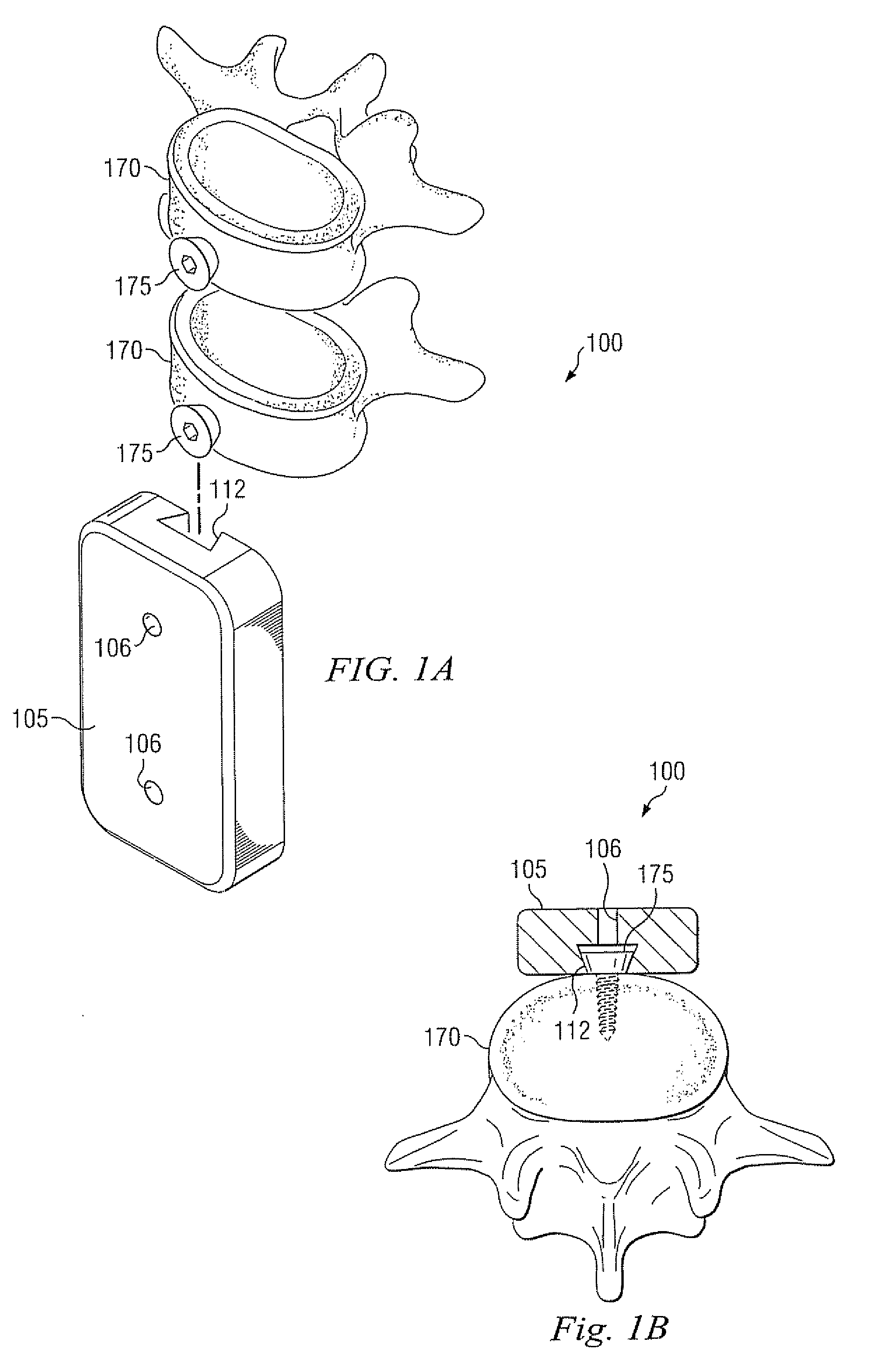
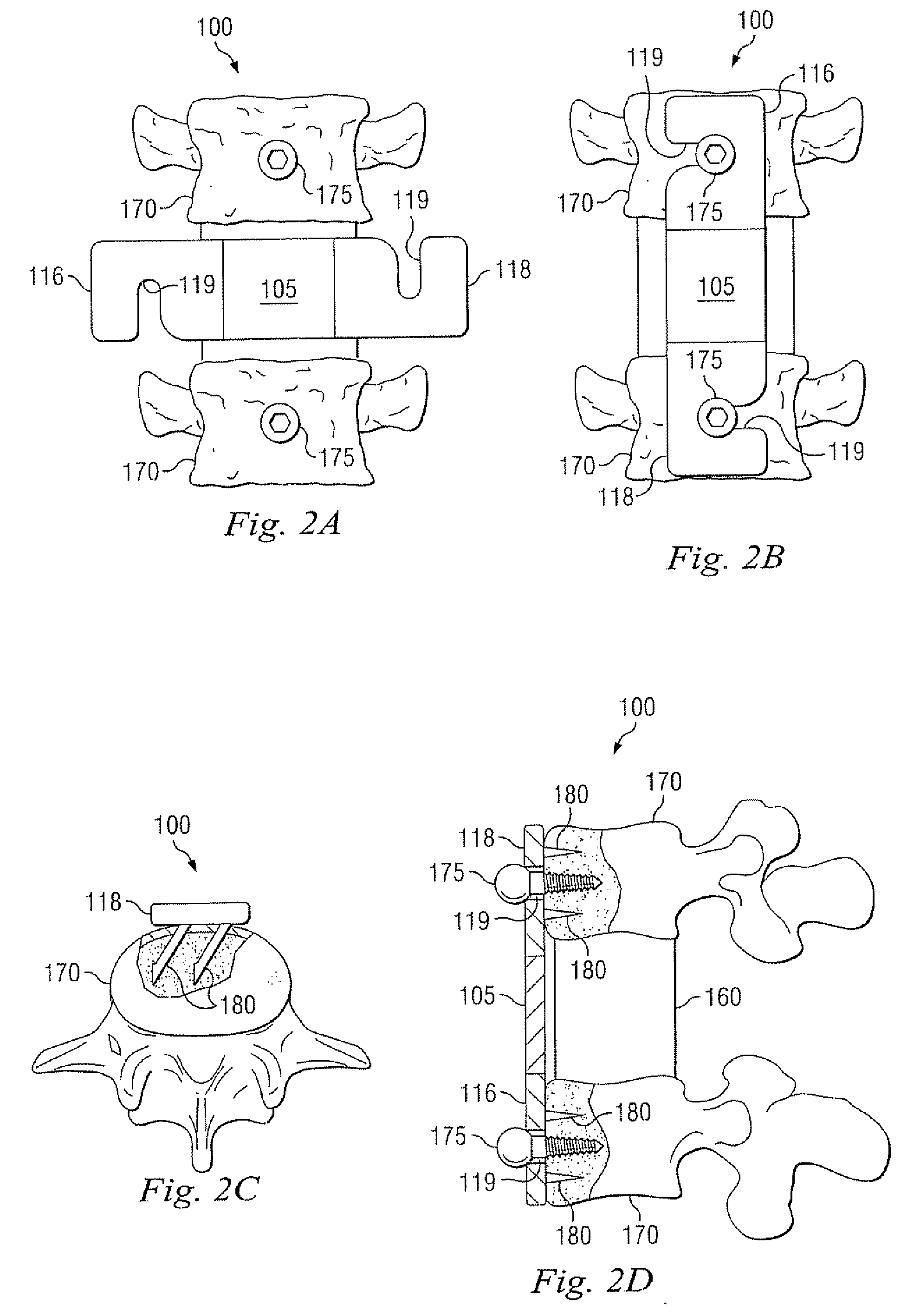
Device and system for stabilizing movement between bony tissue and method for implanting
InactiveUS20080312698A1Avoid damageLess stressSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisPhysical medicine and rehabilitationMedical treatment
A device and system for stabilizing movement between two or more vertebral bodies and methods for implanting. Specifically, embodiments of the present disclosure may provide medical professionals the ability to selectively position and orient anchors in bony tissue and then attach a plate to the pre-positioned anchors. The plate assembly, once positioned on the anchors, prevents the anchors from backing out of the bony tissue.
Owner:ZIMMER SPINE INC
Bone Fixation Plate
Owner:GLOBUS MEDICAL INC
Shape changing bone implant and method of use for enhancing healing
ActiveUS20140257420A1Block soft tissue infiltrationStores recoverable mechanical energyInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsShape changeBone apposition
Described is a new bone healing method and class of bone fixation implants that change shape once implanted so as to minimize non-healing and speed the bone healing process. The bone fixation method involves shape changing implants that continuously hold the bones in apposition so that a gap does not form. Gaps in time allow non-bony tissue to infiltrate and stop healing. Furthermore, the implants actively compress bone to increase bone mass and strength. Bone cell pressure due to compression and electrical current flow due to bone deformation act to stimulate healing. The new implant designs also provide a scaffolding to conduct bone through the implant and across the healing bone interface. The methods and designs are applicable to but not limited to use for bone screws, plates, staples, rods, cylinders and external fixation devices.
Owner:FOX WILLIAM CASEY
Dynamic stabilization system
InactiveUS20090005815A1Promote recoveryMore natural movementSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisBiomedical engineeringBony Tissues
Embodiments of the disclosure provide a device and system for dynamic spinal stabilization. A collar has an opening for connection to a bone fastener implanted in bony tissue and a slot for receiving a portion of an elongated member. When the elongated member is seated in the slot and a closure member is securely connected to the collar, the collar is capable of selected rotation about the bone fastener to provide dampened motion of the stabilization system.
Owner:ZIMMER SPINE INC
Implants comprising biodegradable metals and method for manufacturing the same
ActiveCN101516292AExcellent interface strengthSuitable for maintaining initial stabilityDental implantsInternal osteosythesisUltimate tensile strengthBiodegradable polymer
The present invention provides an implant consisting of a biodegradable magnesium-based alloy or partially applied with the magnesium-based alloy, and a method for manufacturing the same. The implant according to the present invention is biodegradable, in which its biodegradation rate can be easily controlled, and the implant has excellent strength and interfacial strength to an osseous tissue.
Owner:U & I INC
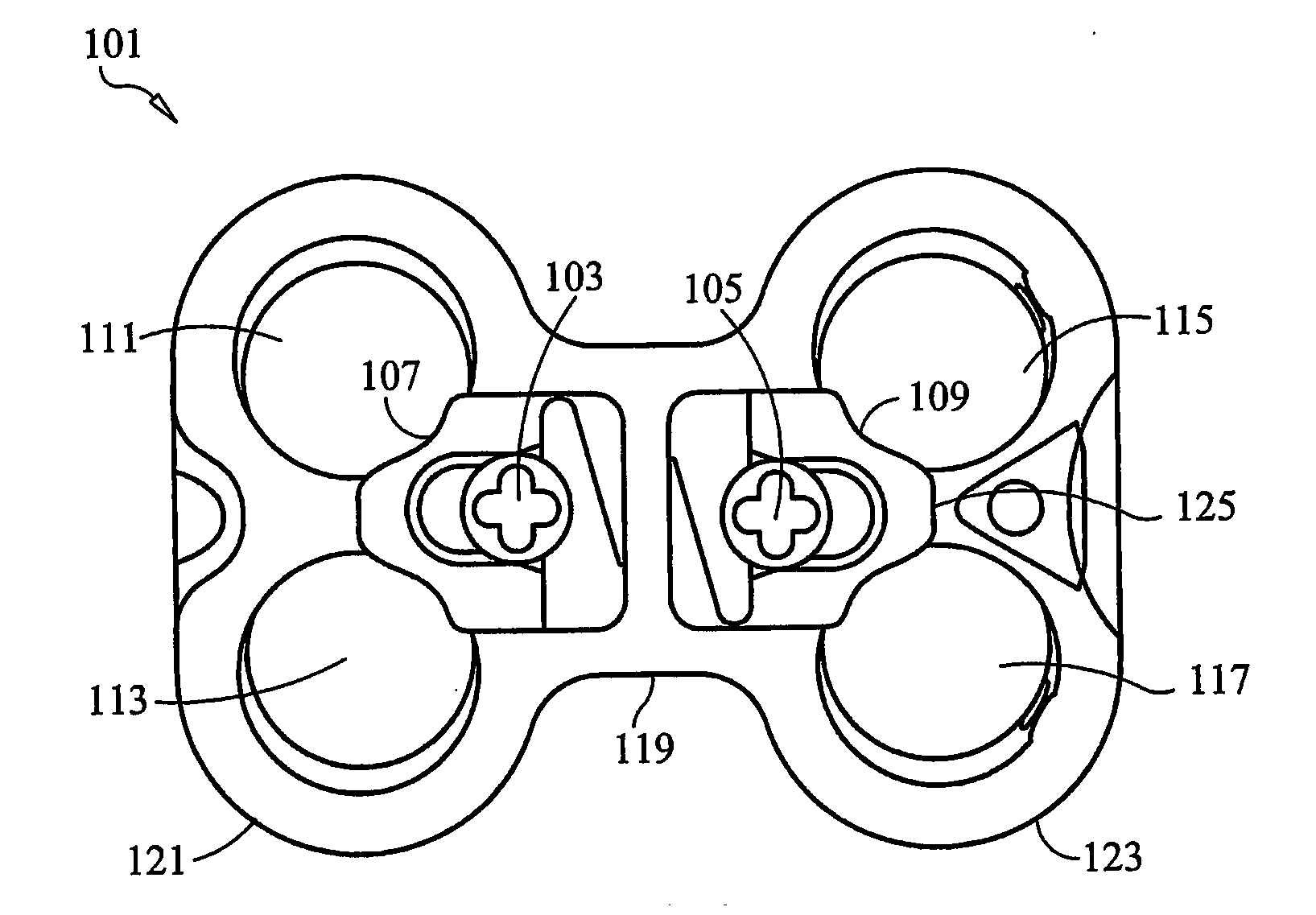
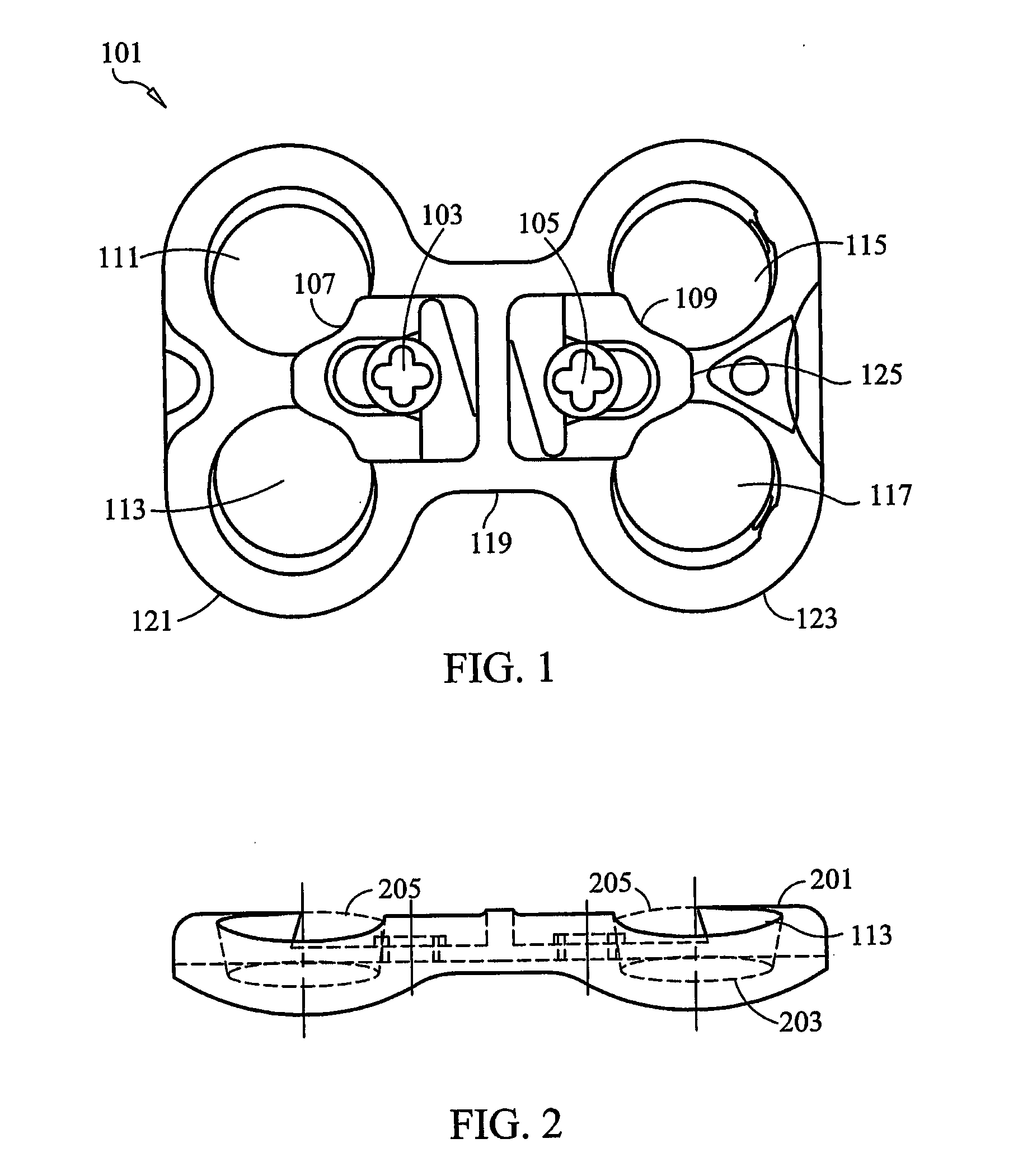
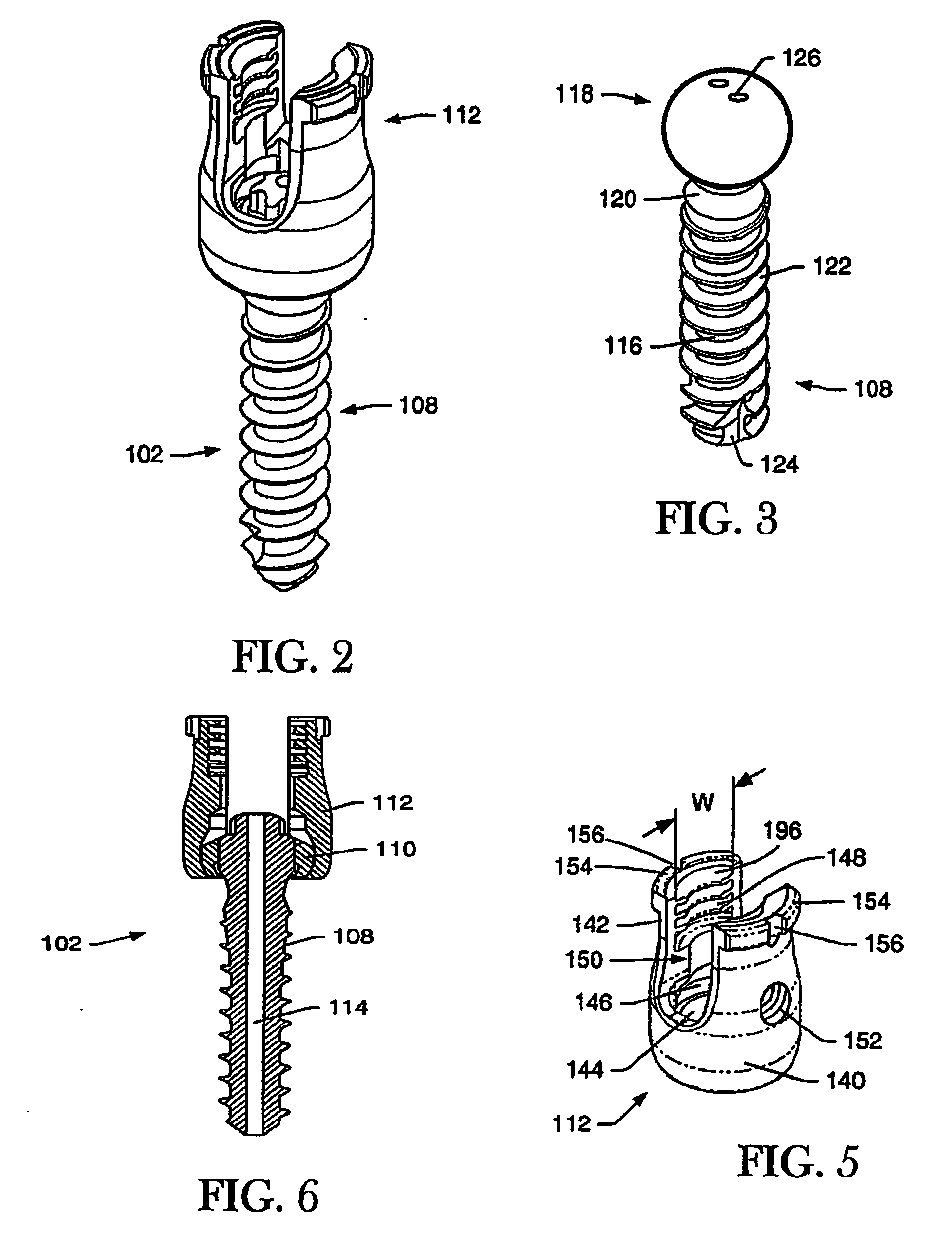
Load distribution crown
ActiveUS20050228387A1Reduce chanceEqually distributedSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisLoad distributionNon orthogonal
An apparatus for distributing the load caused by the insertion of a fastening device into bony tissue is disclosed. In one embodiment, the apparatus comprises a crown having a plurality of protrusions. The protrusions may have any desired physical properties, and function to obtain purchase in the bony tissue. Preferably, the crown includes an opening that is selectively engageable with a spherical head of the fastening device. The opening preferably comprises a spherical curvature that allows the surfaces of the spherical head and the opening to maintain flush contact, even when the fastening device is inserted into the bony tissue at a non-orthogonal angle. When the fastening device is inserted into the bony tissue, the crown distributes the load over a wider section of the bone, allowing the bone to maintain its structural integrity.
Owner:GLOBUS MEDICAL INC
Coring device for preserving living tissue
ActiveUS20060173476A1Easy to cutAffect cellular viabilityExcision instrumentsEndoscopic cutting instrumentsCoringSacroiliac joint
Improved coring devices suitable for articular cartilage and bone, wherein the cutting device is capable of slicing through a tough protective tangential zone, delicately separating the shock absorbing columns of cells in the radial zone of the cartilage, and finally cutting into the hard underlying bone in a manner that preserves the viability of osteochondral cells. The coring device features an annulus having a flat annular cutting edge interrupted by at least one serration having neutral cutting angles. A method for concurrently removing cartilaginous and bony tissue using an improved coring device that preserves the viability of osteochondral cells.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
Orthopedic prosthetic devices containing compositions for repair of defects in osseous tissues
Implantable orthopedic prosthetic devices containing tissue repair compositions that contain demineralized bone fragments and homogenized connective tissue.
Owner:LIFENET HEALTH
Composition for repair of defects in osseous tissues
ActiveUS20070082058A1Pharmaceutical delivery mechanismUnknown materialsTissue repairConnective tissue fiber
Tissue repair compositions, particularly bone repair compositions, containing demineralized bone fragments and homogenized connective tissues. The compositions can be used in the form of an injectable gel, an injectable paste, a paste, a putty, or a rehydratable freeze-dried form.
Owner:LIFENET HEALTH
Biodegradable unsaturated polyphosphate, preparation and use method thereof
InactiveCN101402736AGood drug sustained release performanceNo side effectsMetabolism disorderAntiinfectivesCross-linkTissue repair
The invention relates to a biodegradable unsaturated polyphosphate ester containing phosphate ester and fumarate ester bonds and discloses a preparation method of the polyphosphate ester and a method for the application of the polyphosphate ester as a medical sustained release preparation for injecting into a treated part and as a hard tissue repair and filling material. The mixture composed of the polyphosphate ester, a cross-linking vinyl monomer, a free radical thermal initiator or photo initiator being capable of initiating or assist in initiating covalent cross-linking reaction and biologically active drugs has excellent medical sustained release effect and no toxic side effects. As a material for repairing the defects of osseous tissue, the biodegradable unsaturated polyphosphate ester can stimulate the formation of new bones; and the material can also be degraded gradually and finally be substituted by a new bone completely. The biodegradable unsaturated polyphosphate ester has outstanding biocompatibility and no obvious inflammation reactions and teratogenesis.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
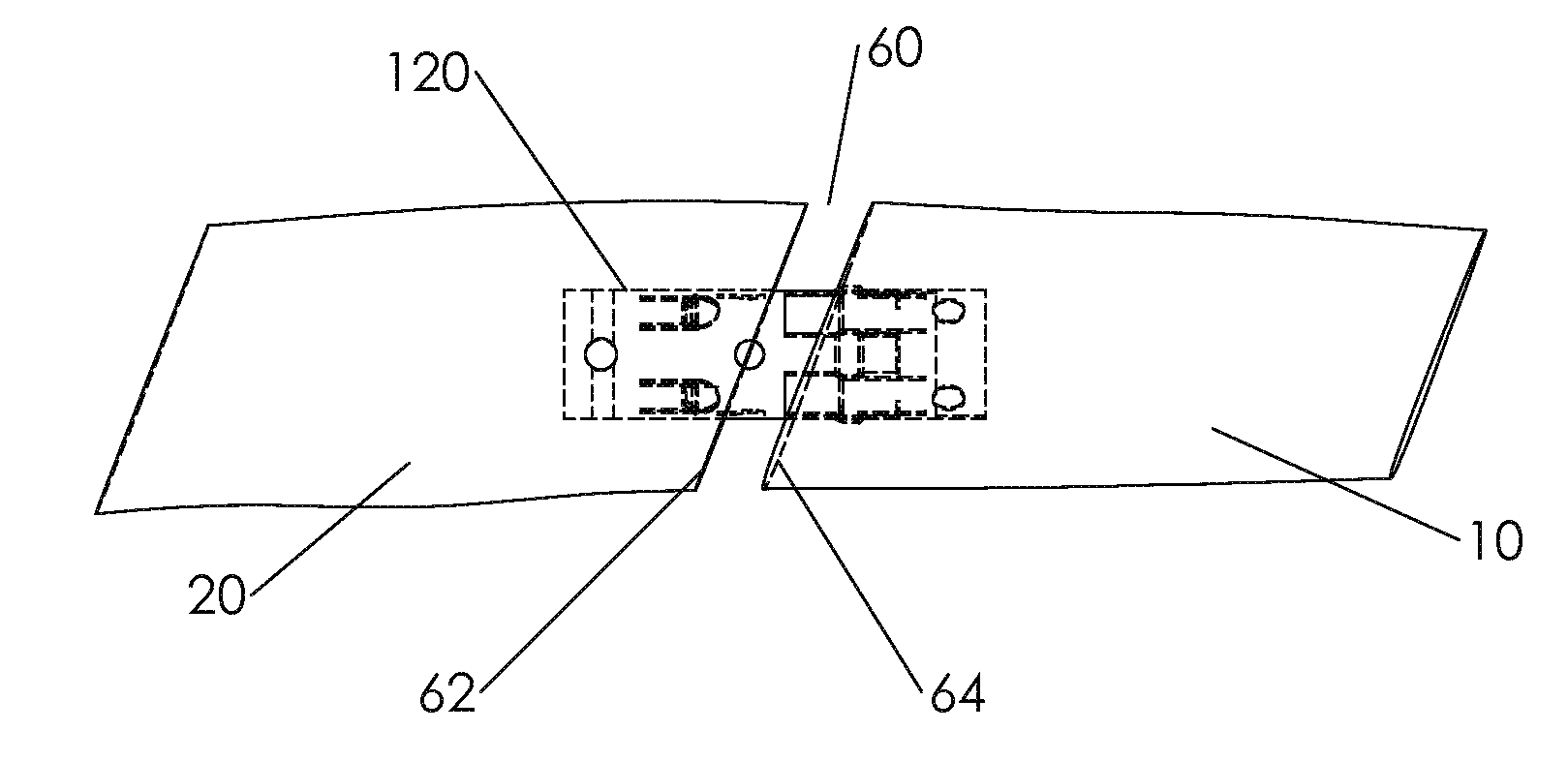
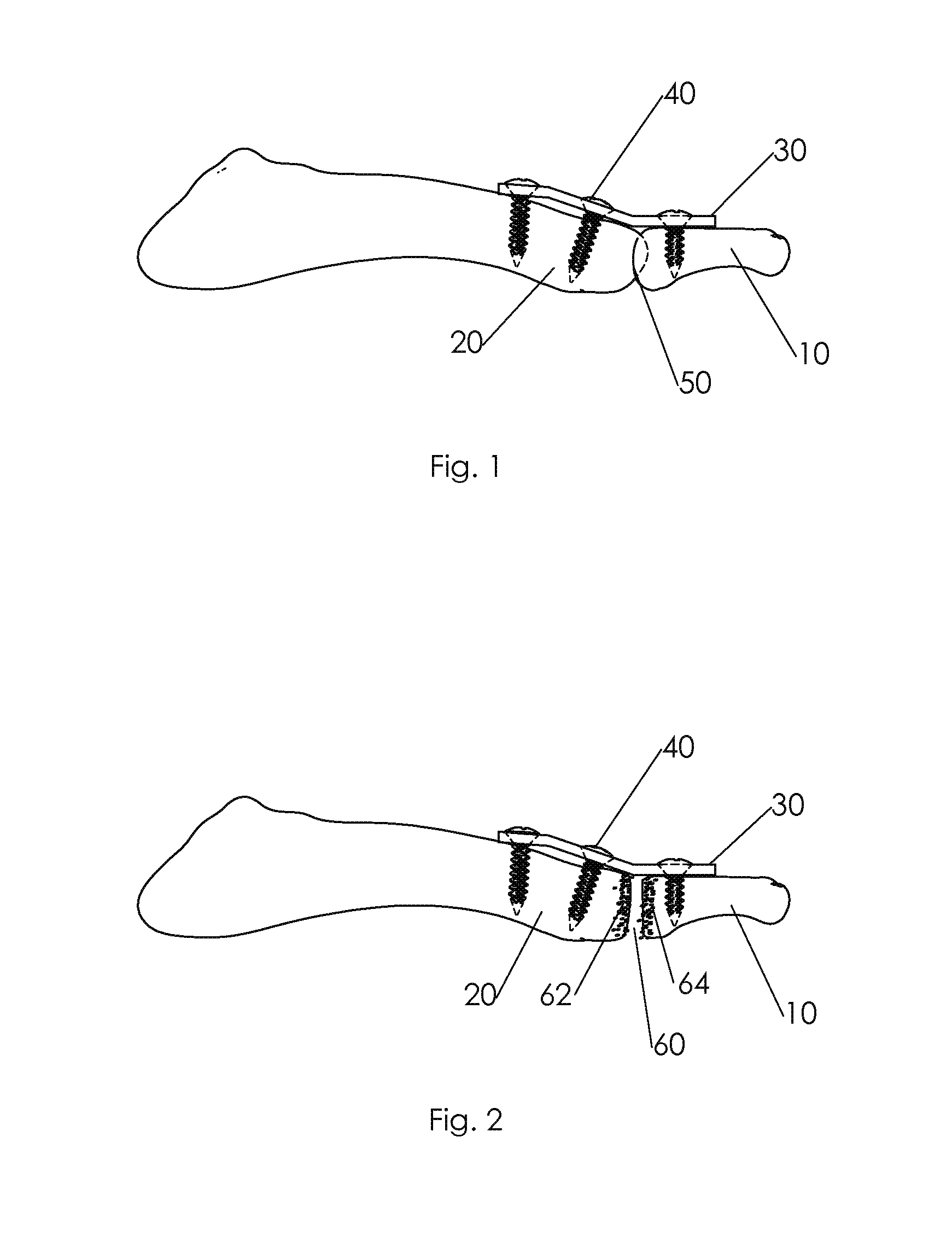
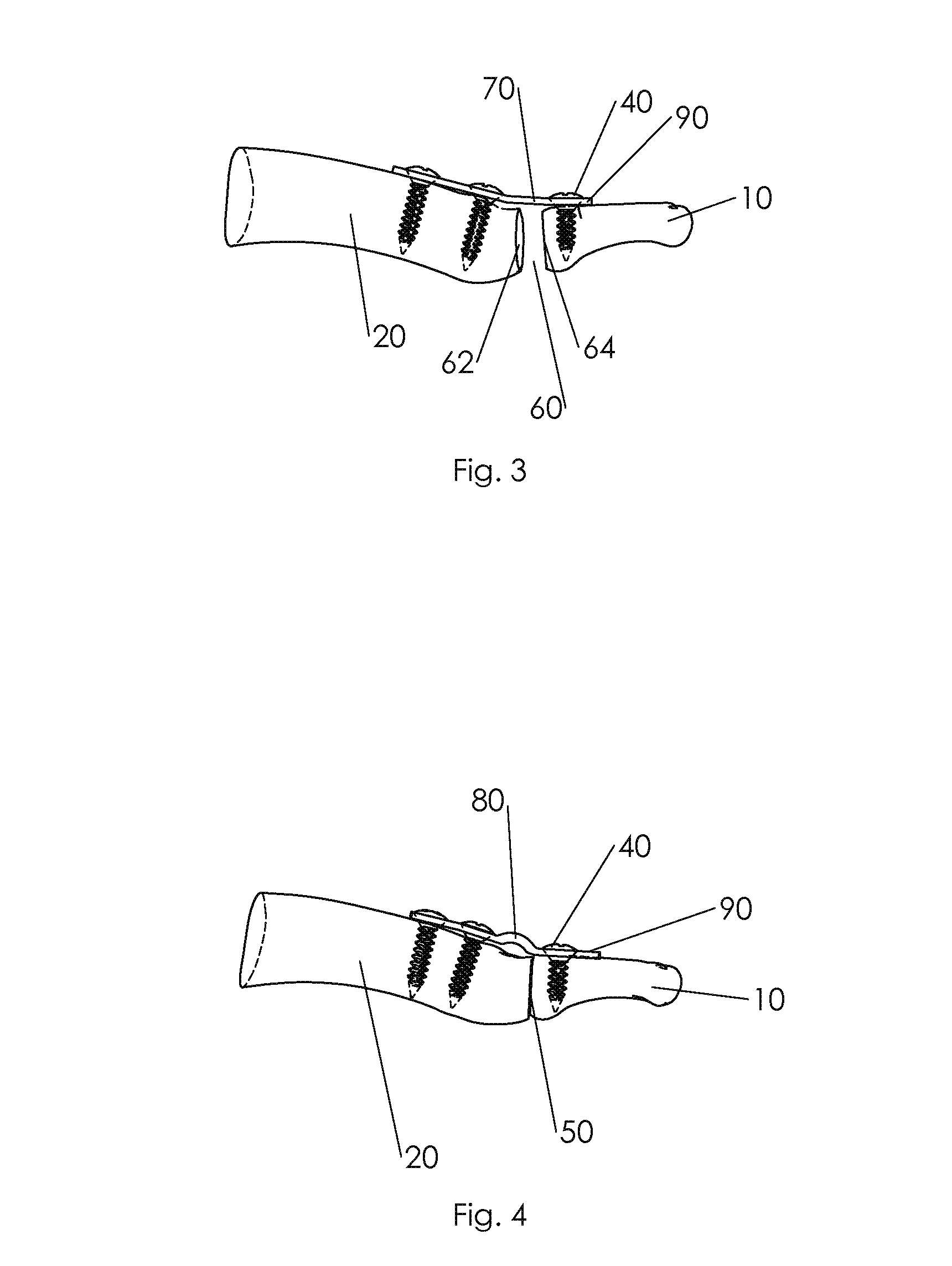
Orthopedic Prosthesis
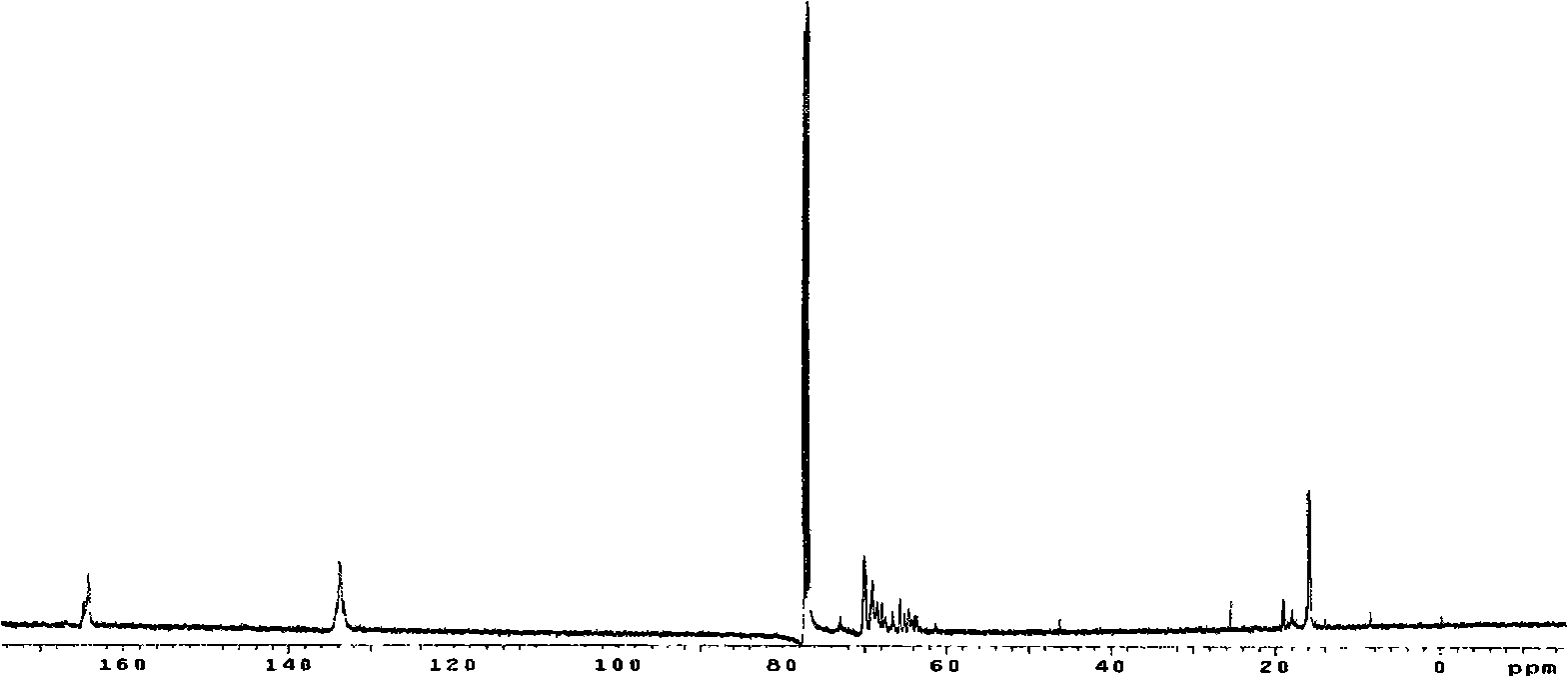
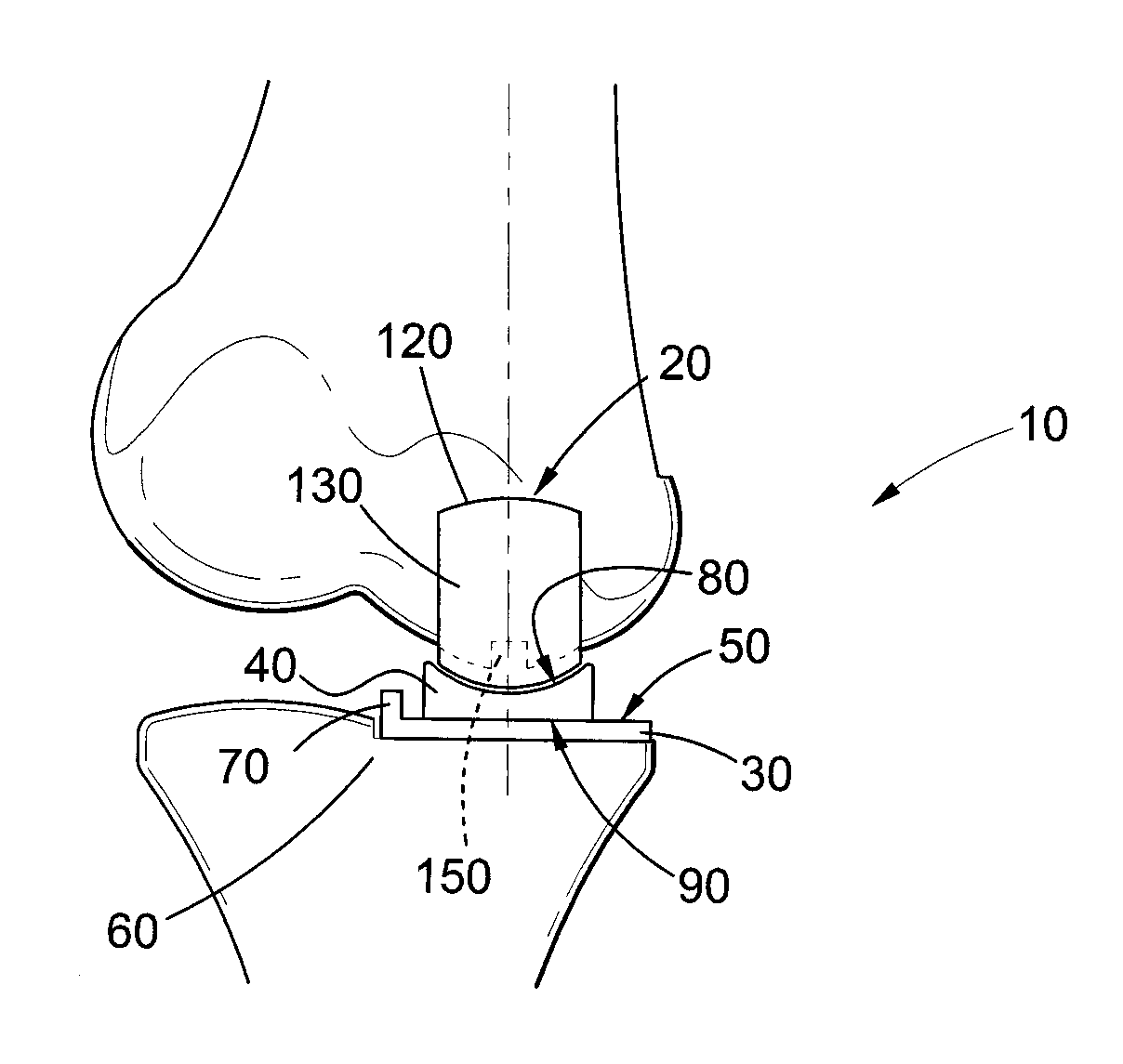
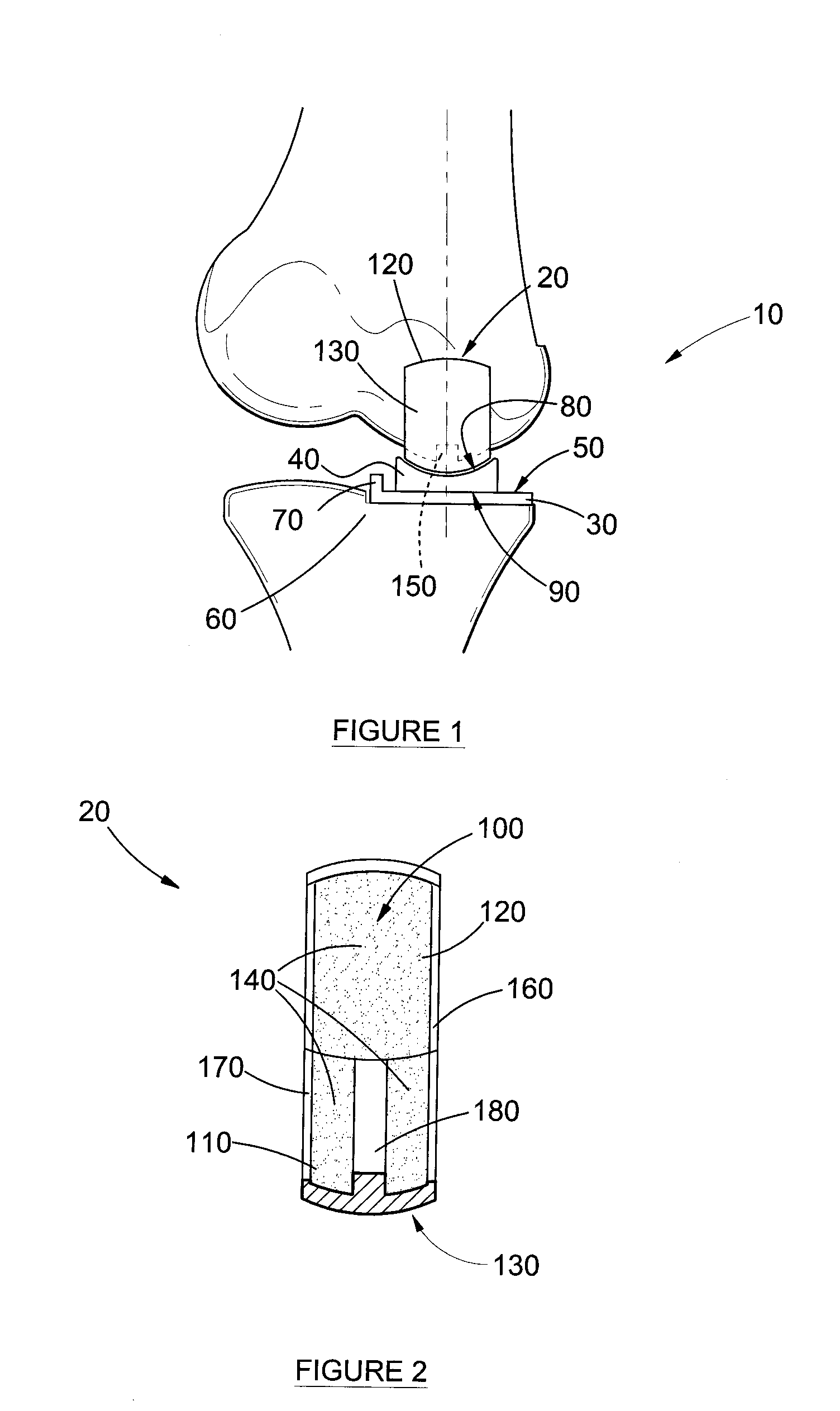
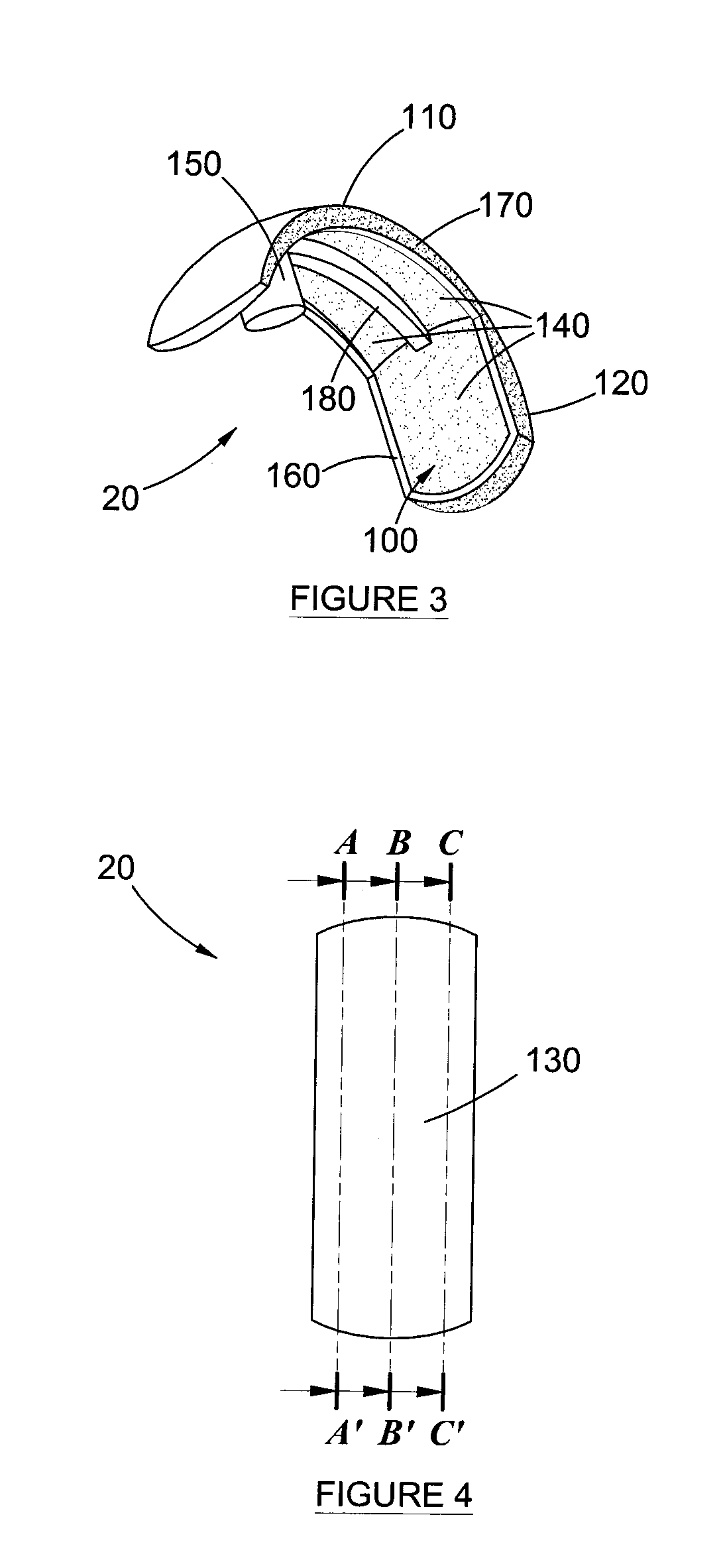
InactiveUS20110178607A1Increase the attachment surfaceIncrease the sectionJoint implantsCoatingsTibiaKnee Joint
According to one aspect of the present invention, there is provided an orthopedic prosthesis (10) suitable for resurfacing chondral deficient surface areas in knee joints, including a tibial component (30) defining a tibial articular bearing surface (50), a femoral component (20) defining a femoral articular bearing surface (130) and a spacer bearing (40) disposed therebetween, the femoral component further including an elliptical body having an anterior member (110) and a posterior member (120), and an internal femoral attachment surface (140), the femoral articular bearing surface and the internal femoral attachment surface having a substantially uniform cross-sectional curvature at any point along the length of the anterior member, thereby providing an increased radius of the internal femoral attachment surface and an increased cross sectional line of fixation to bony tissue.
Owner:OOSTHUIZEN CHRISTIAAN RUDOLF
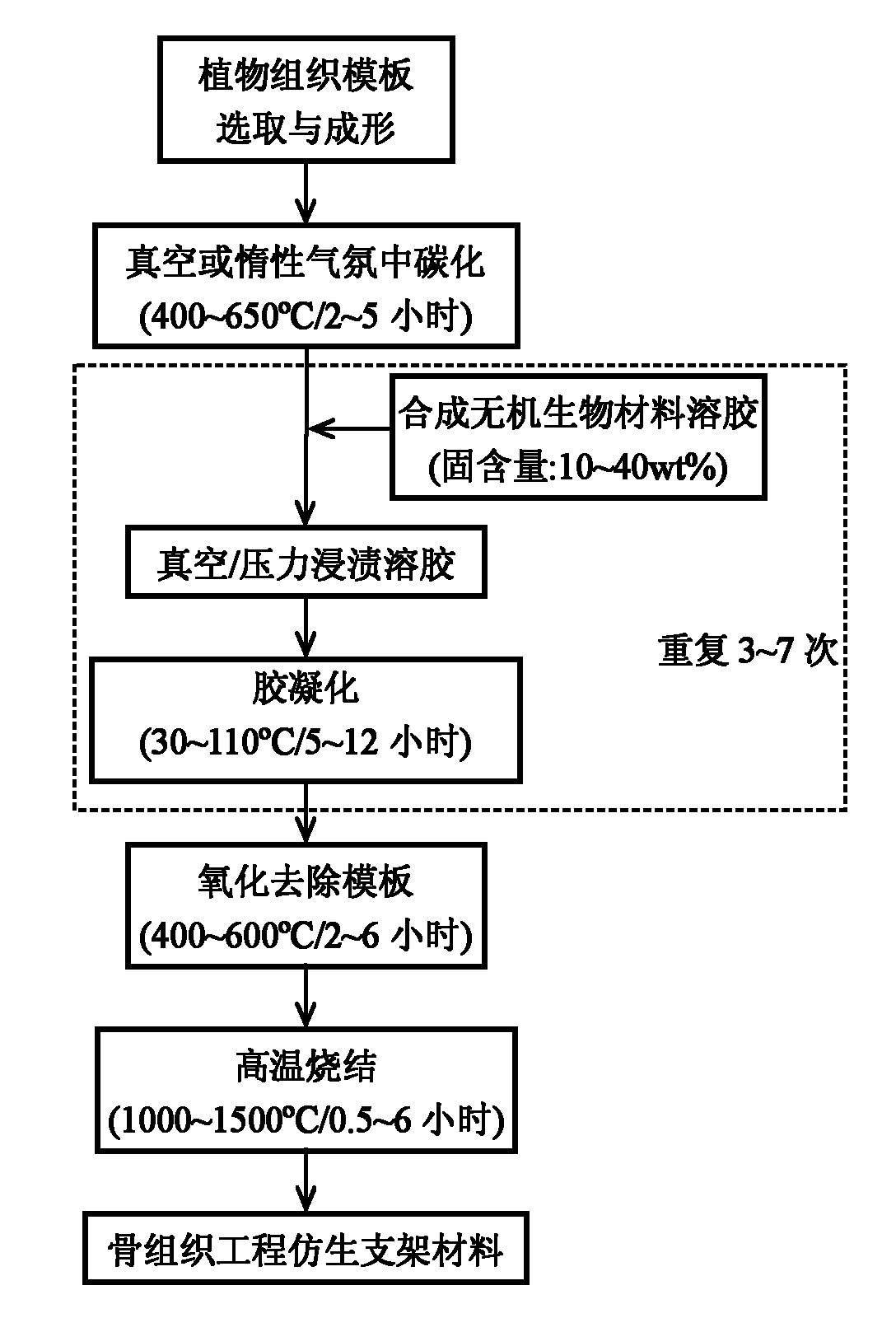
Preparation method of bionic bracket material in bone tissue engineering
InactiveCN101829363AHave structural propertiesWith mechanical propertiesProsthesisPorosityCarbonization
The invention discloses a preparation method of a novel bionic supporting material in bone tissue engineering, belonging to the field of the bone tissue engineering. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: using a natural plant tissue as a template and preparing a bioceramic or bioactive glass porous bracket material with a bionic structure through processes of carbonization, vacuum / pressure impregnation of an inorganic sol, template removal by oxidation in the air, high temperature sintering and the like. The porous bracket material prepared by the invention has favorable physicochemical and biological properties, particularly has a plant tissue porous structure obviously characterized by tubular holes, wherein the structure is extremely similar to a cancellous bone and has a porosity of 70-95% and aperture range of 10-28 mu m. The unique porous structure of the porous bracket material can quicken the substance exchange speed outside and inside the bracket, is in favor of controlling the degradation speed of the bracket material and promoting the growth of new bones. The preparation method of the bionic bracket material of the bone tissue engineering has wide application potential in the generation and repair fields of hard tissues of the orthopaedics, the dentistry, the maxillofacial surgery and the like.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com