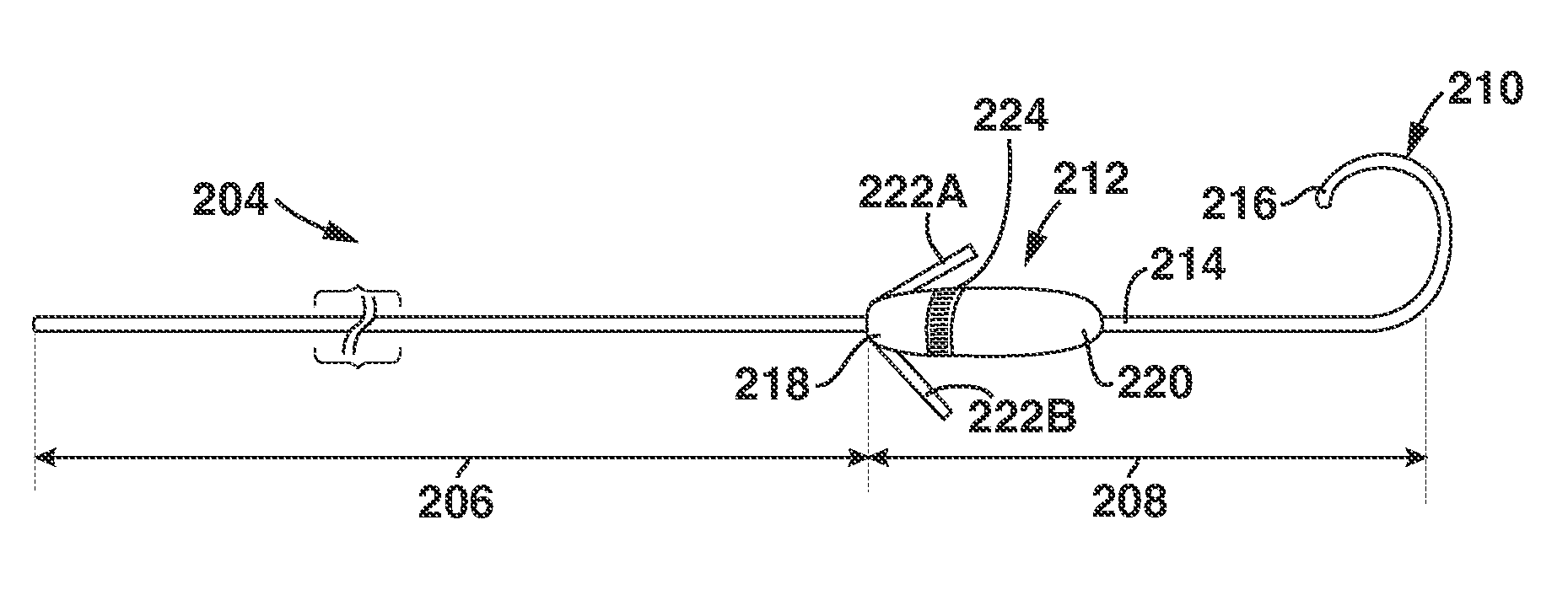
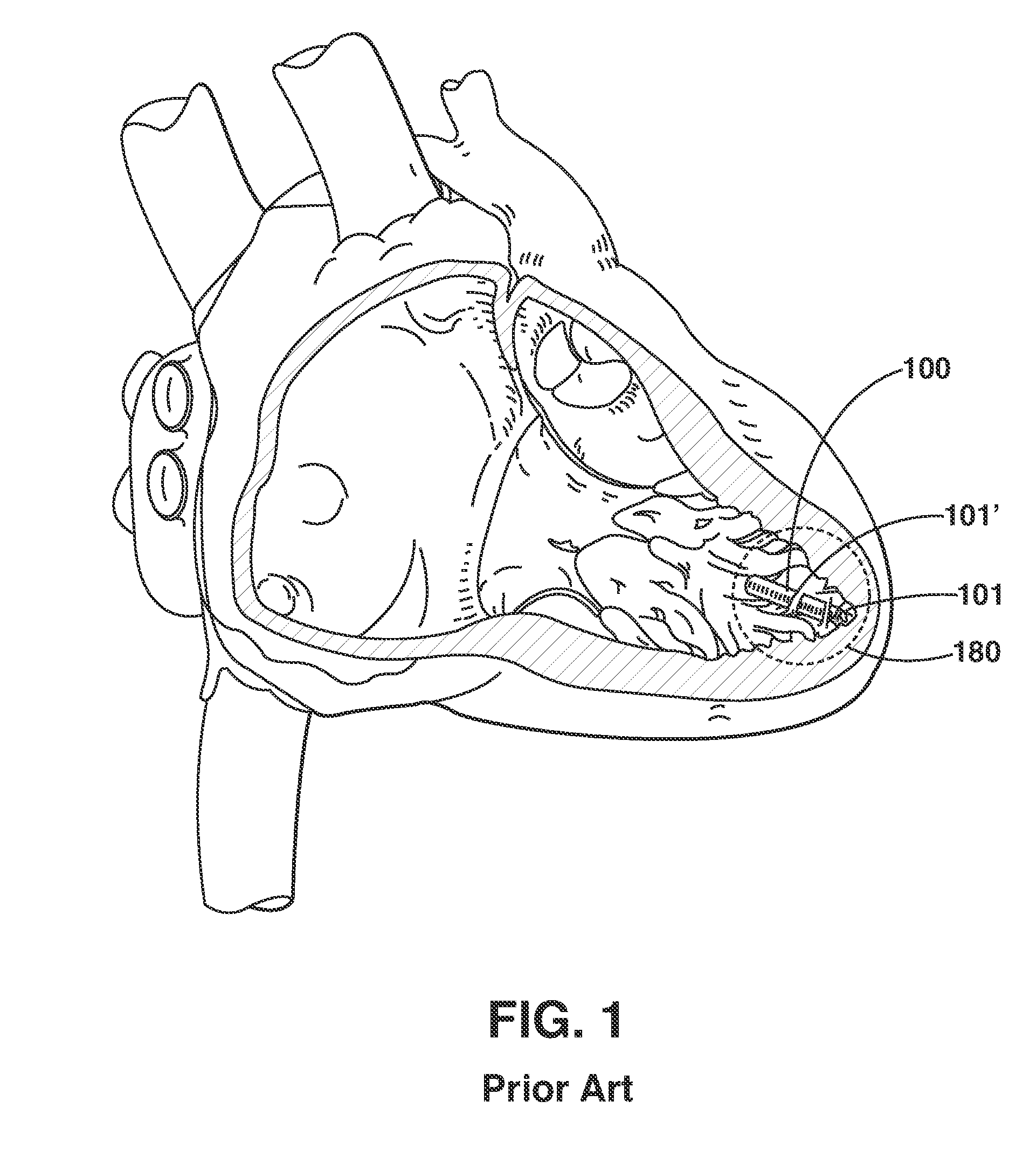
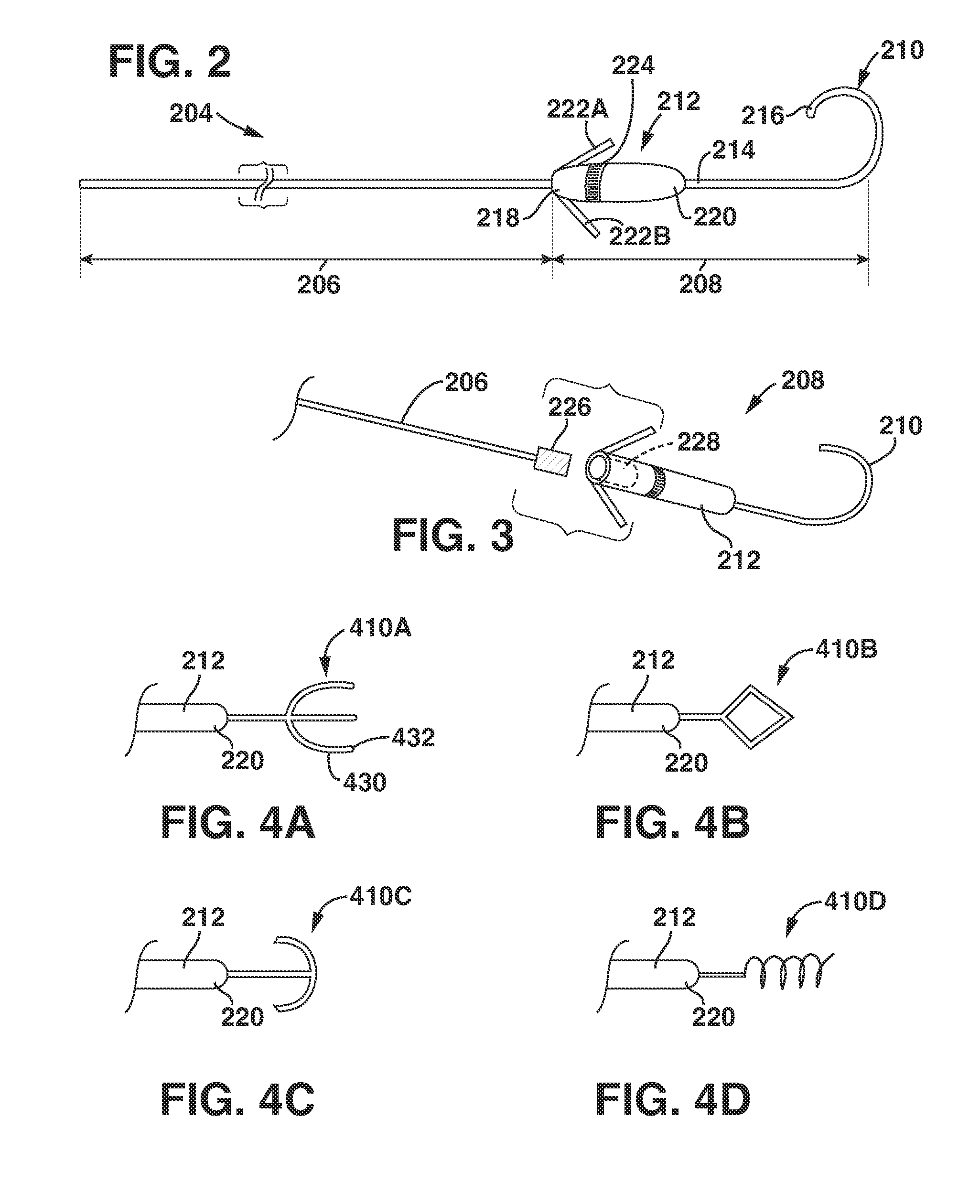
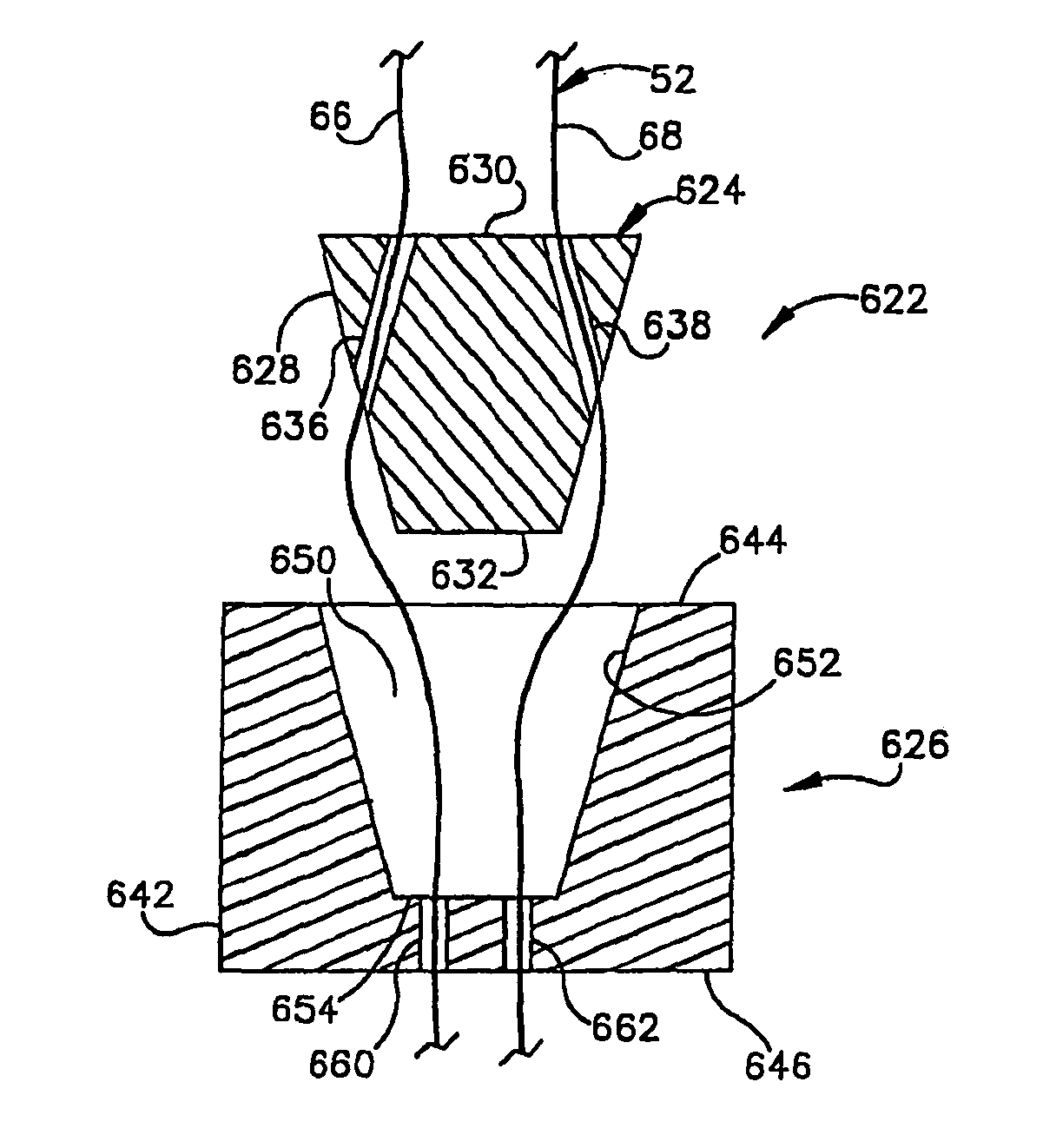
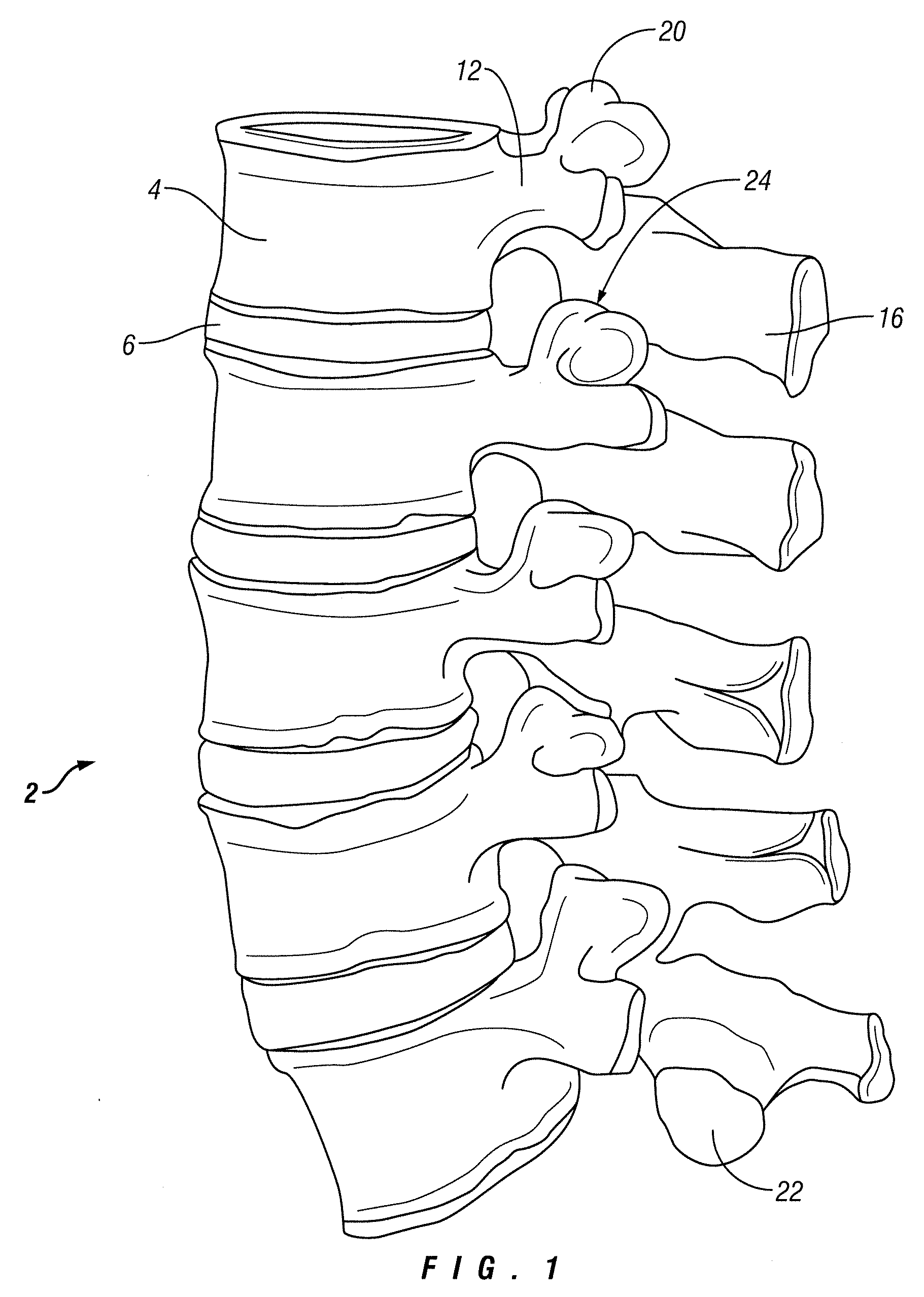Patents
Literature
364 results about "Implant fixation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Implant fixation. In essence there are two basic principles by which orthopaedic hip implants are secured to the bone, ‘cemented’ and ‘uncemented’. Traditionally acrylic bone cement is used, functionally as a grout, to lock the acetabular and/or femoral component into the patient’s bone.
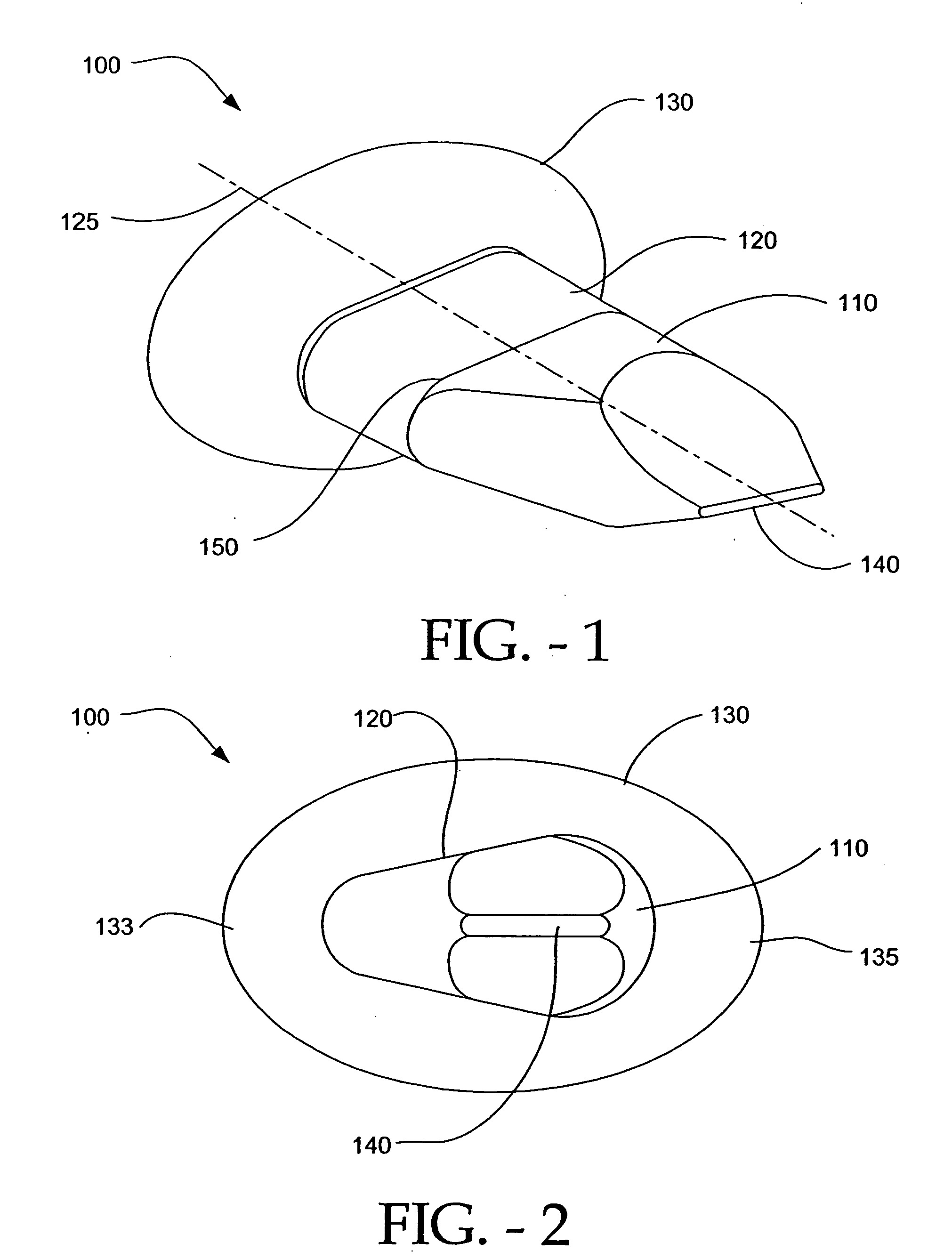
Cartilage repair implant with soft bearing surface and flexible anchoring device
InactiveUS9050192B2Strong and more permanent fixationSoft and bendableJoint implantsHip jointsCartilage repairSurgical implant
A surgical implant for replacing hyaline cartilage in a knee or other articulating synovial joint has an anchoring side on one side of the implant adapted for fixing the implant to one of the bones in the joint, and a bearing surface on the opposite side of the implant for lubricious rubbing and sliding contact with another bone in the joint. The anchoring side can be configured with an irregular surface for tissue ingrowth. The bearing side can include hydrogel. The implant can be rolled up from an original shape and surgically inserted by arthroscopic means, and opens into its original shape when released inside the joint.
Owner:FORMAE
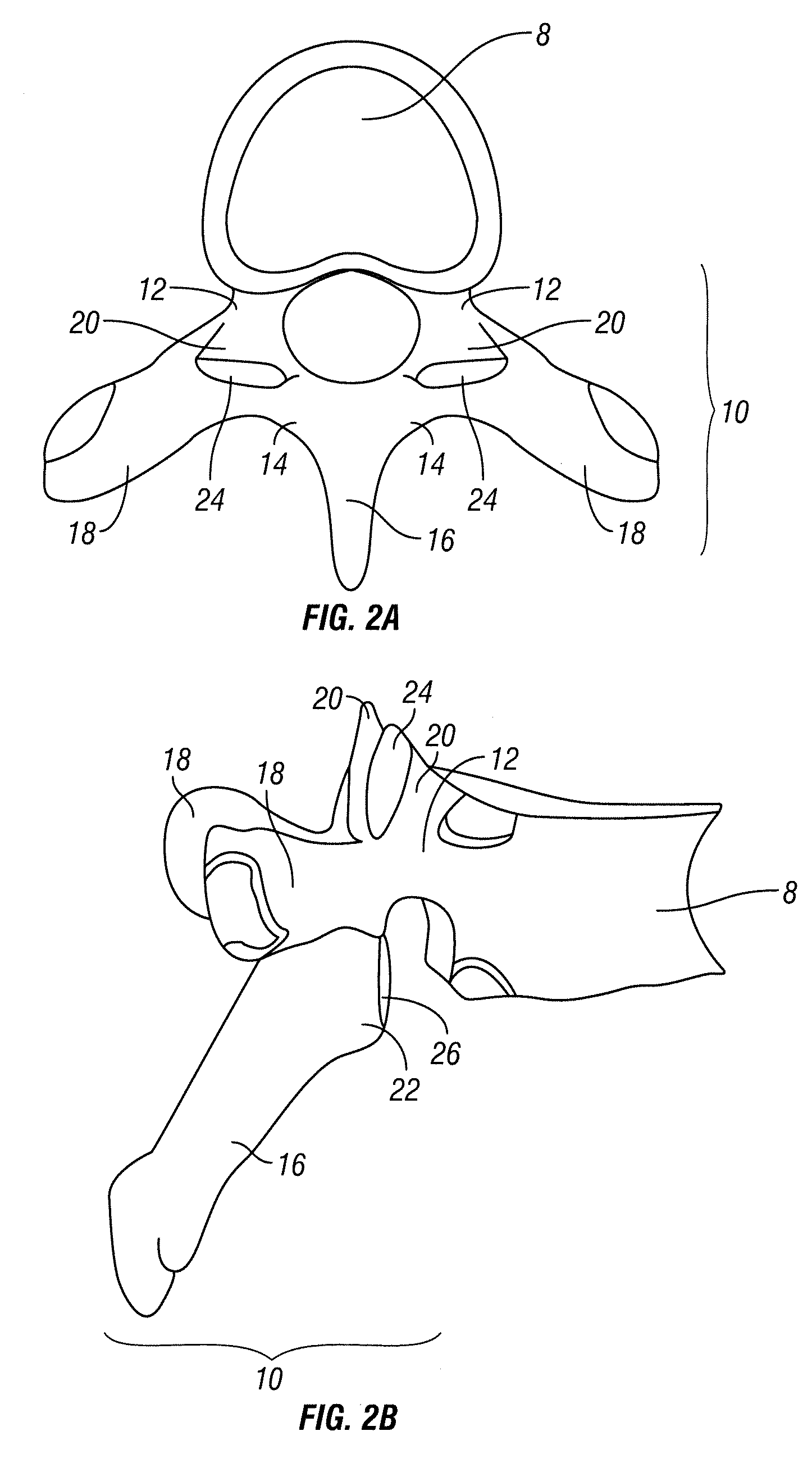
Device for Securing an Implant to Tissue
An implant device is provided for implantation within an intervertebral space between adjacent vertebrae comprising an implant body, a rotatable portion and a piercing portion configured to pierce the adjacent vertebra.
Owner:PIONEER SURGICAL TECH INC
Interspinous process implant having deployable wings and method of implantation
An embodiment of a system in accordance with the present invention can include an implant having a spacer with a thickness and a wing, wherein a first configuration of the wing has a first height substantially similar to the thickness and wherein the wing is adapted to be selectably arranged in a second configuration such that the wing has a second height greater than the first height. A periphery of the implant has a shape generally conformal with a shape of an inner surface of a cannula and a cross-sectional diameter smaller than an inner diameter of the cannula. The cannula is inserted such that a proximal end of the cannula is arranged between the adjacent spinous processes. The implant is then urged into position between the adjacent spinous processes by way of the cannula, and subsequently arranged in a second configuration to fix the implant in position.
Owner:MEDTRONIC EURO SARL
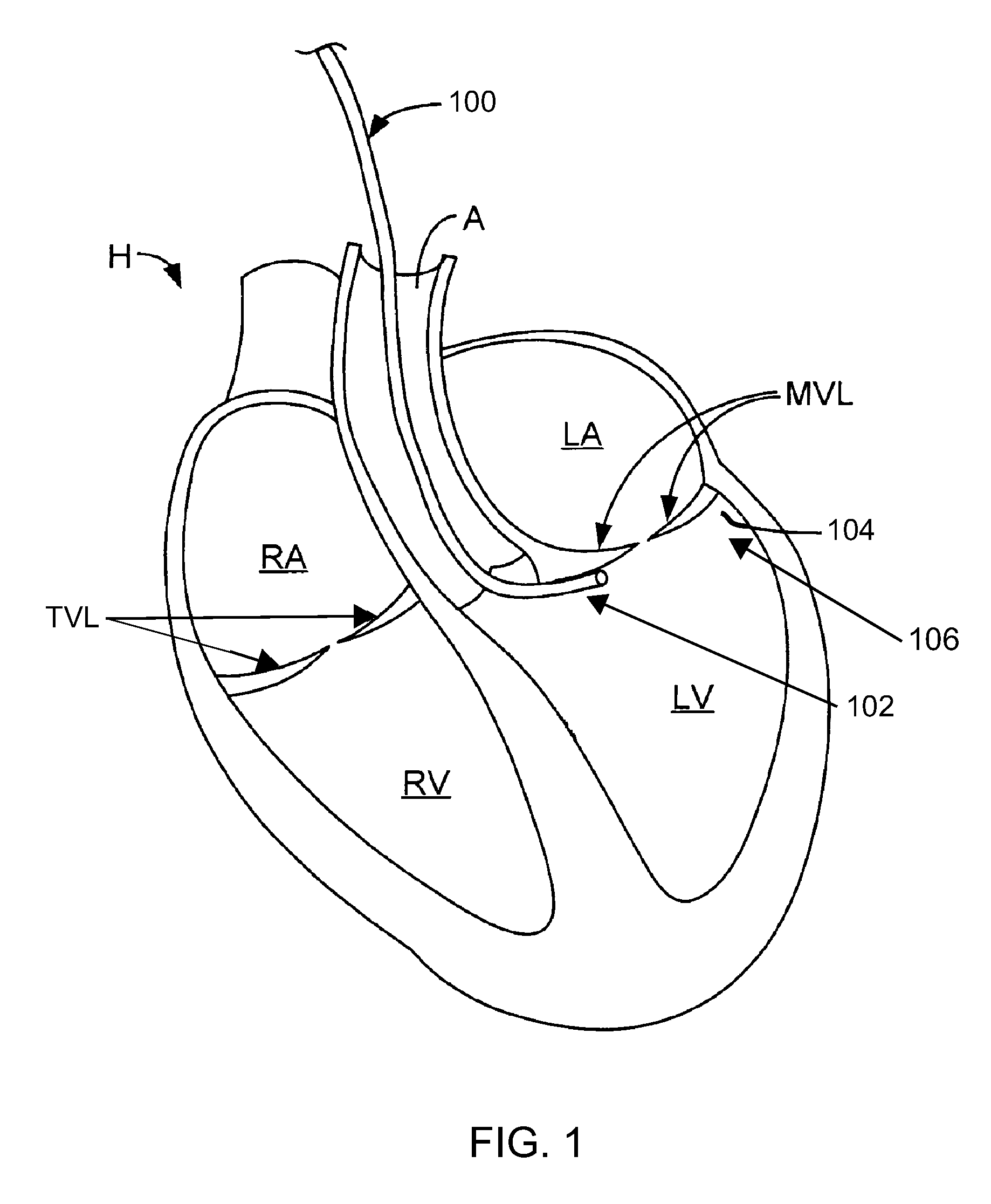
Cardiovascular anchoring device and method of deploying same
InactiveUS7149587B2Efficient deploymentElectrocardiographyTransvascular endocardial electrodesMeasurement deviceOrgan wall
An anchoring device and a delivery method thereof can effectively provide a means for securing an implant to a wall of an internal organ within a patient in a variety of clinical applications. In one embodiment, an anchoring device used to retain a cardiac pressure measurement device is provided. The device is implanted in the body by deforming it to a small cross section profile, sliding it through a low profile delivery device and ejecting from the delivery device at a targeted site. The anchoring mechanism, when ejected from the delivery device, reverts back to pre-formed configuration and engages opposite sides of an organ wall, thereby anchoring the implant in the organ wall.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Tissue integration design for seamless implant fixation
The present invention relates to orthopaedic implants having a fenestrated hollow shell and a biologic core. These design features provide an improved interface between the implant and the surrounding tissue, aiding fixation, and provide a vehicle for applying new bone healing and enhancing modalities, such as gene therapy, tissue engineering, and growth factors.
Owner:BIEDERMANN TECH GMBH & CO KG
Interspinous process implant having a fixed wing and a deployable wing and method of implantation
An embodiment of a system in accordance with the present invention can include an implant having a first wing, a spacer with a thickness and a second wing, wherein a first configuration of the second wing has a first height substantially similar to the thickness and wherein the second wing is adapted to be selectably arranged in a second configuration such that the second wing has a second height greater than the first height. The implant is then urged into position between adjacent spinous processes and subsequently arranged in a second configuration to fix the implant in position.
Owner:KYPHON
Two-Stage Delivery Systems and Methods for Fixing a Leadless Implant to Tissue
Systems and methods of delivering and retaining a leadless medical implant to tissue, wherein a docking base and the implant are sequentially delivered to an implantation site. In a first stage, the docking base is delivered and deployed into tissue at an implantation site. In a second stage, the implant is navigated through the vasculature and coupled to the docking base. Various mechanisms for navigating the implant to the previously implanted docking base and coupling the implant thereto are described. Navigational mechanisms include advancing the implant over a proximally extending wire portion that is releasably attached to the previously implanted docking base, utilizing fluoroscopic visualization to guide the implant to a previously implanted docking base that is at least partially radiopaque and utilizing electromagnetism to guide the implant to a previously implanted docking base that is electro-magnetizable.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
Two-Stage Delivery Systems and Methods for Fixing a Leadless Implant to Tissue
InactiveUS20110270339A1Transvascular endocardial electrodesExternal electrodesMedicineImplantation Site
Systems and methods of delivering and retaining a leadless medical implant to tissue, wherein a docking base and the implant are sequentially delivered to an implantation site. In a first stage, the docking base is delivered and deployed into tissue at an implantation site. In a second stage, the implant is navigated through the vasculature and coupled to the docking base. Various mechanisms for navigating the implant to the previously implanted docking base and coupling the implant thereto are described. Navigational mechanisms include advancing the implant over a proximally extending wire portion that is releasably attached to the previously implanted docking base, utilizing fluoroscopic visualization to guide the implant to a previously implanted docking base that is at least partially radiopaque and utilizing electromagnetism to guide the implant to a previously implanted docking base that is electro-magnetizable.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
Method for implanting a flowable fastener
The present invention provides a method for securing an implant in the human body. The method includes providing a fastener having a substantially smooth outer surface and a conical shaped portion having a first end and a tapered end. The fastener is made of a polymeric material. The method also includes inserting the fastener in the body with the tapered end of the conical shaped portion leading the first end, heating the polymeric material of the fastener in the body, and applying pressure to the polymeric material of the fastener while heating to cause the polymeric material to flow in the body. Furthermore, the method includes collapsing the fastener with the heat and pressure to thereby secure the fastener relative to tissue in the body.
Owner:P TECH
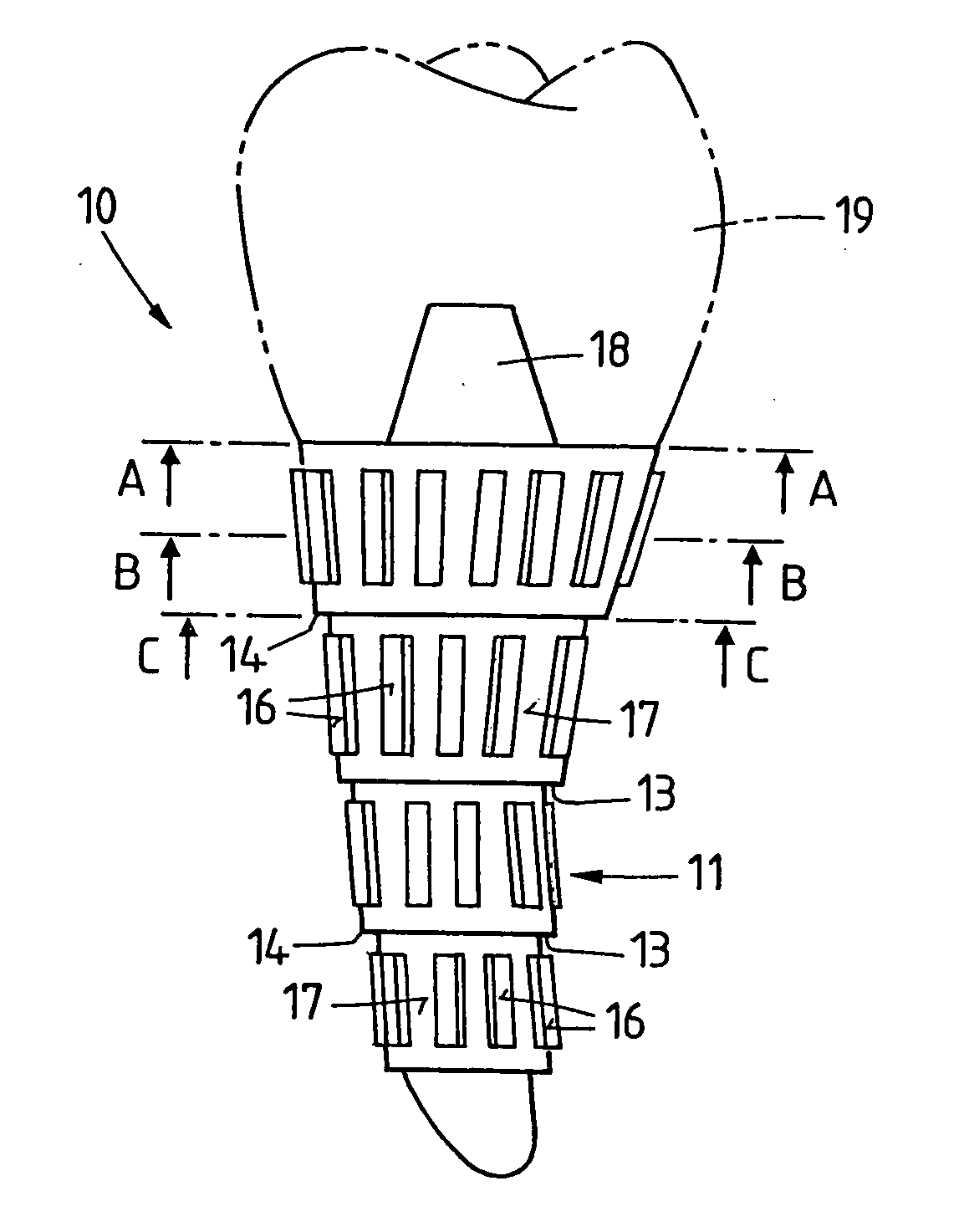
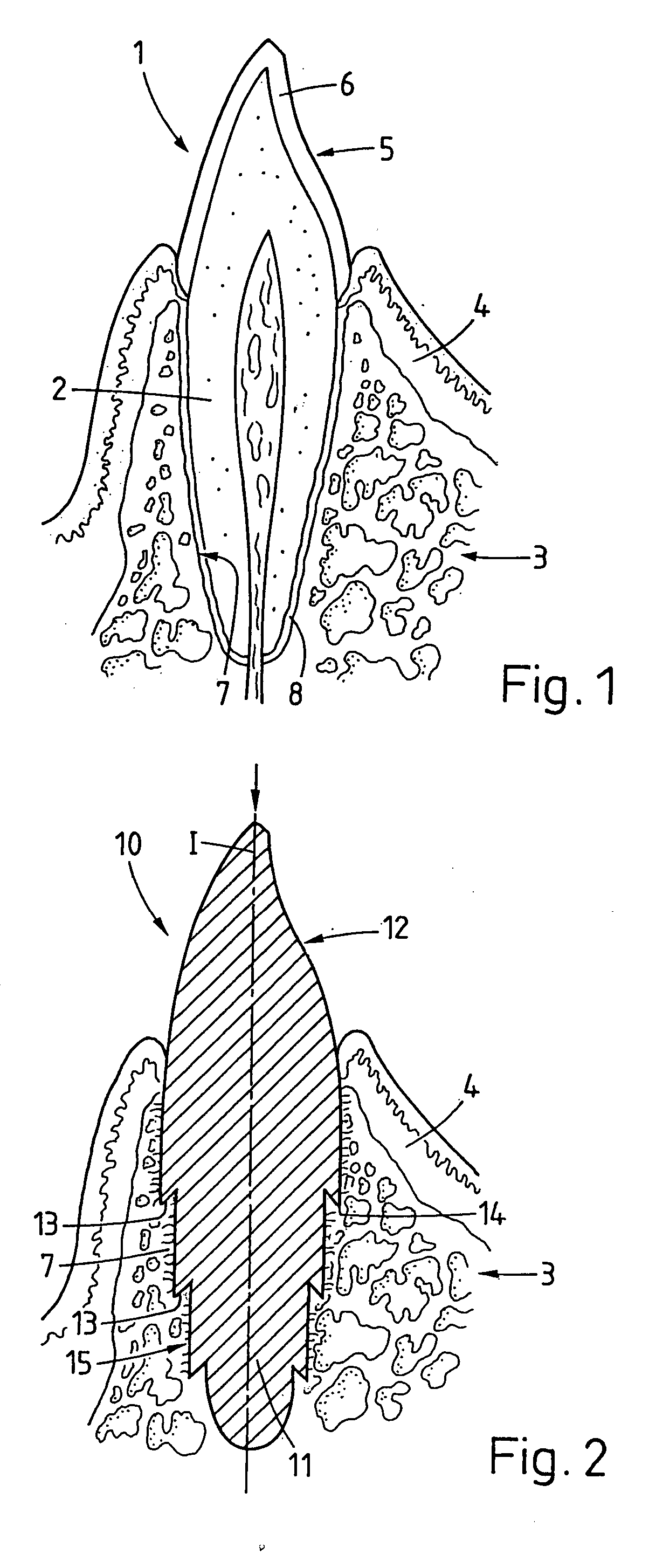
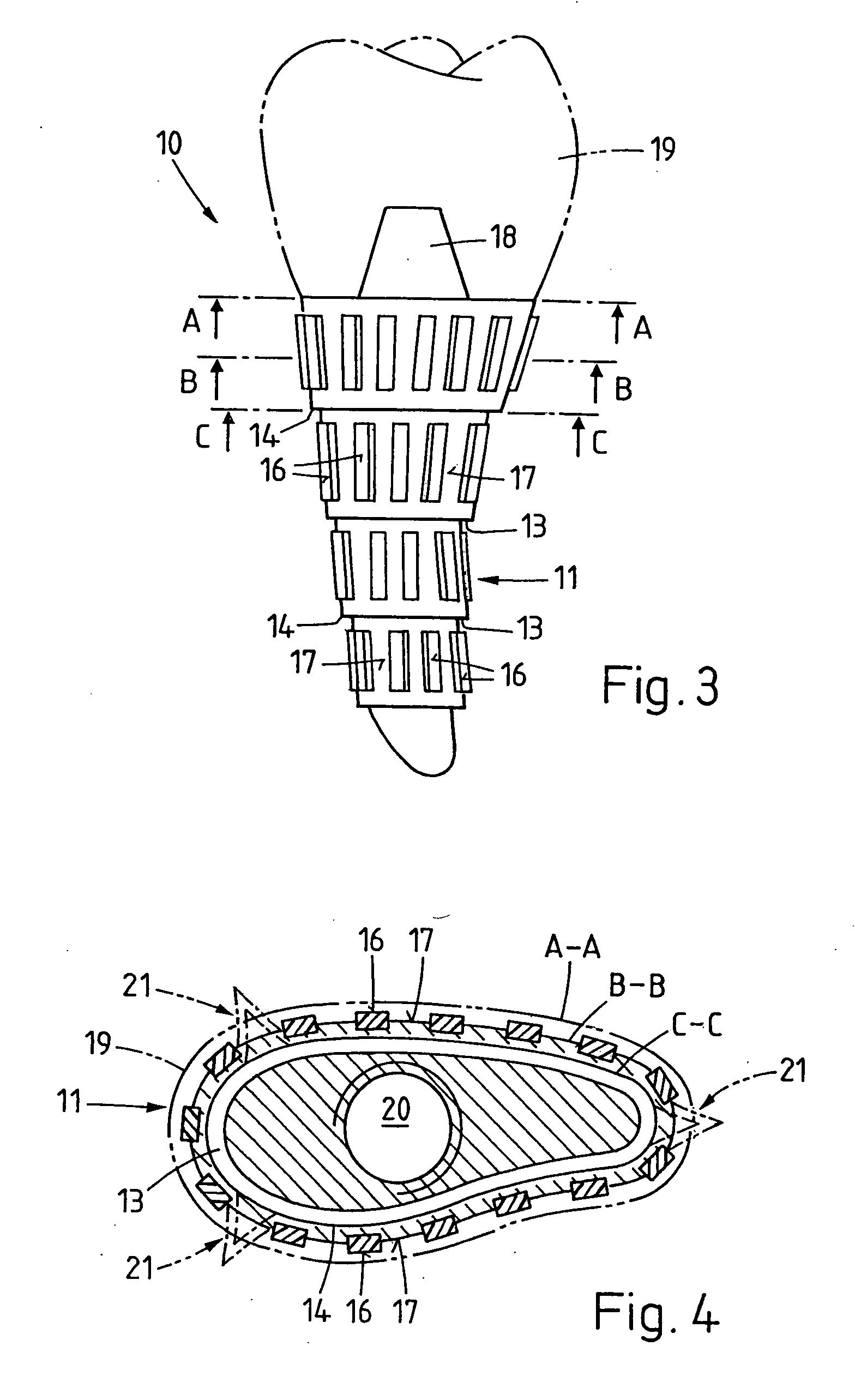
Implant that can be implanted in osseous tissue and method for producing said implant corresponding implant
ActiveUS20060105295A1Strong long-term anchoringProcess stabilityDental implantsInternal osteosythesisBone implantCavity wall
A bone implant (10) is implanted in a cavity parallel to an implant axis (I) and without substantial rotation. The implant includes, on an implant portion to be implanted, cutting edges (14), which do not extend in a common plane with the implant axis and are facing toward the distal end of the implant. The implant also includes surface ranges (16) of a material that is liquefiable by mechanical oscillations. The cutting edges (14) are dimensioned such that they are lodged in the cavity wall after implantation. For implantation, the implant is impinged with mechanical oscillations, resulting in the thermoplastic material being at least partially liquefied and pressed into unevennesses and pores of the cavity wall to form a form-fit and / or material-fit connection between implant (10) and cavity wall, when re-solidified. The cutting edges (14) anchor the implant in the cavity wall.
Owner:WOODWELDING
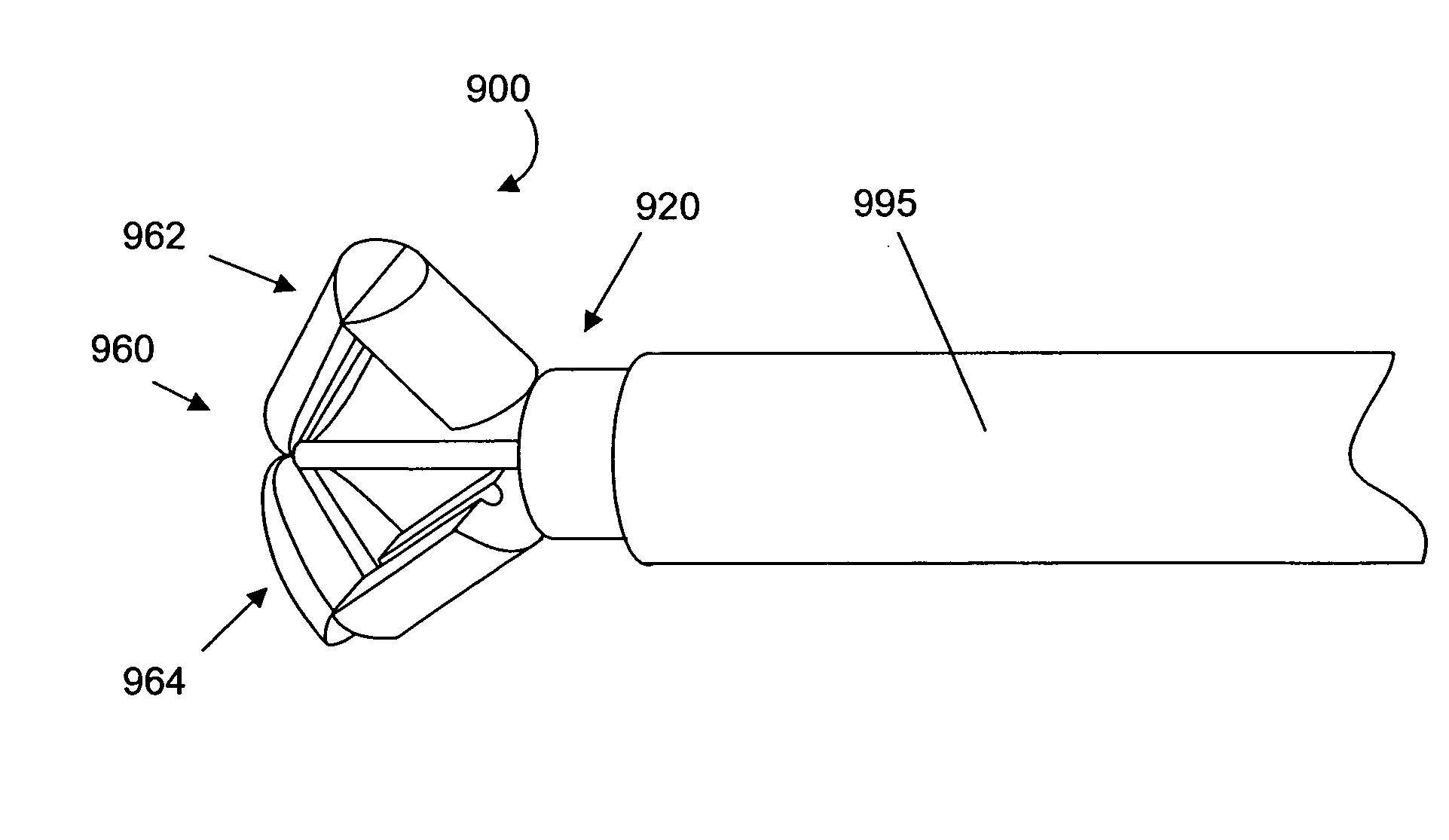
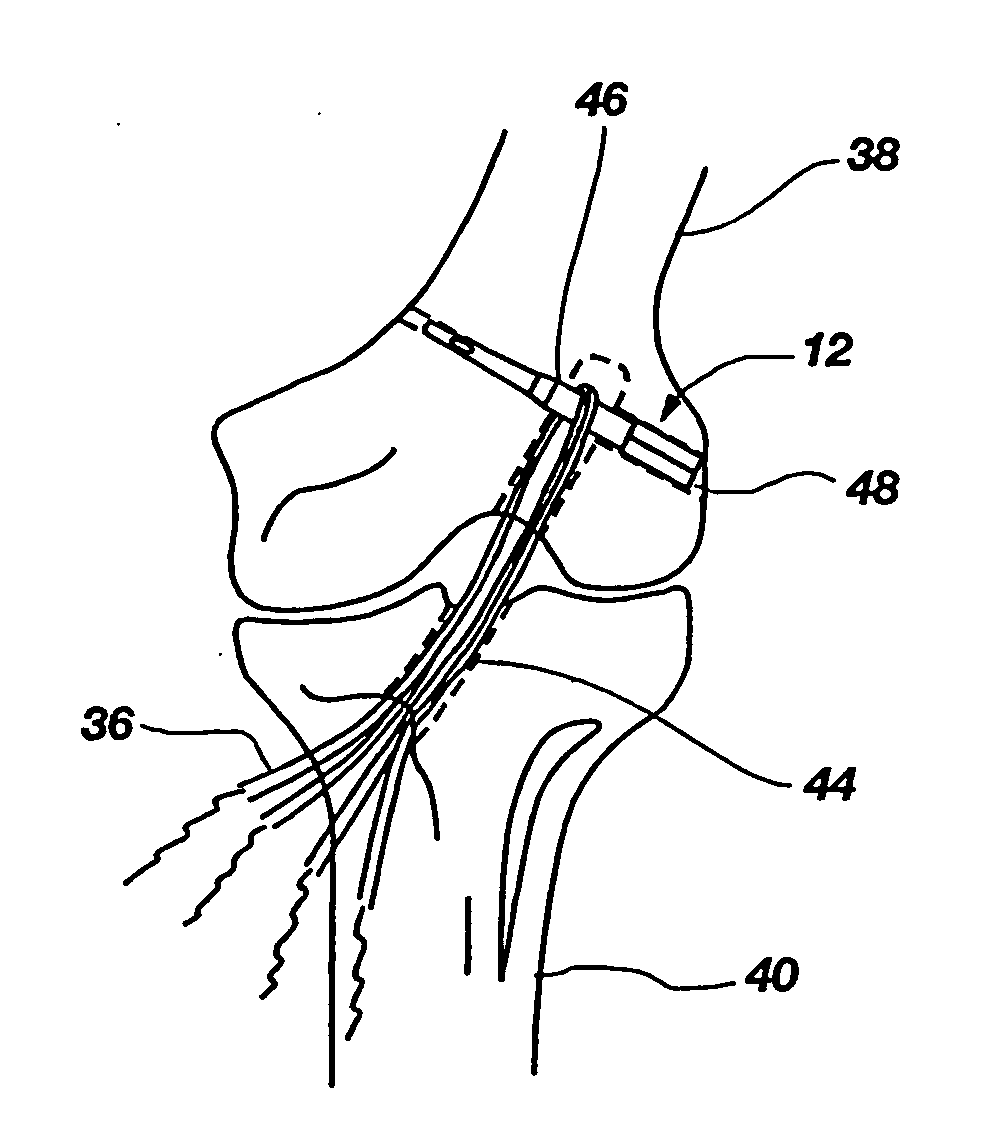
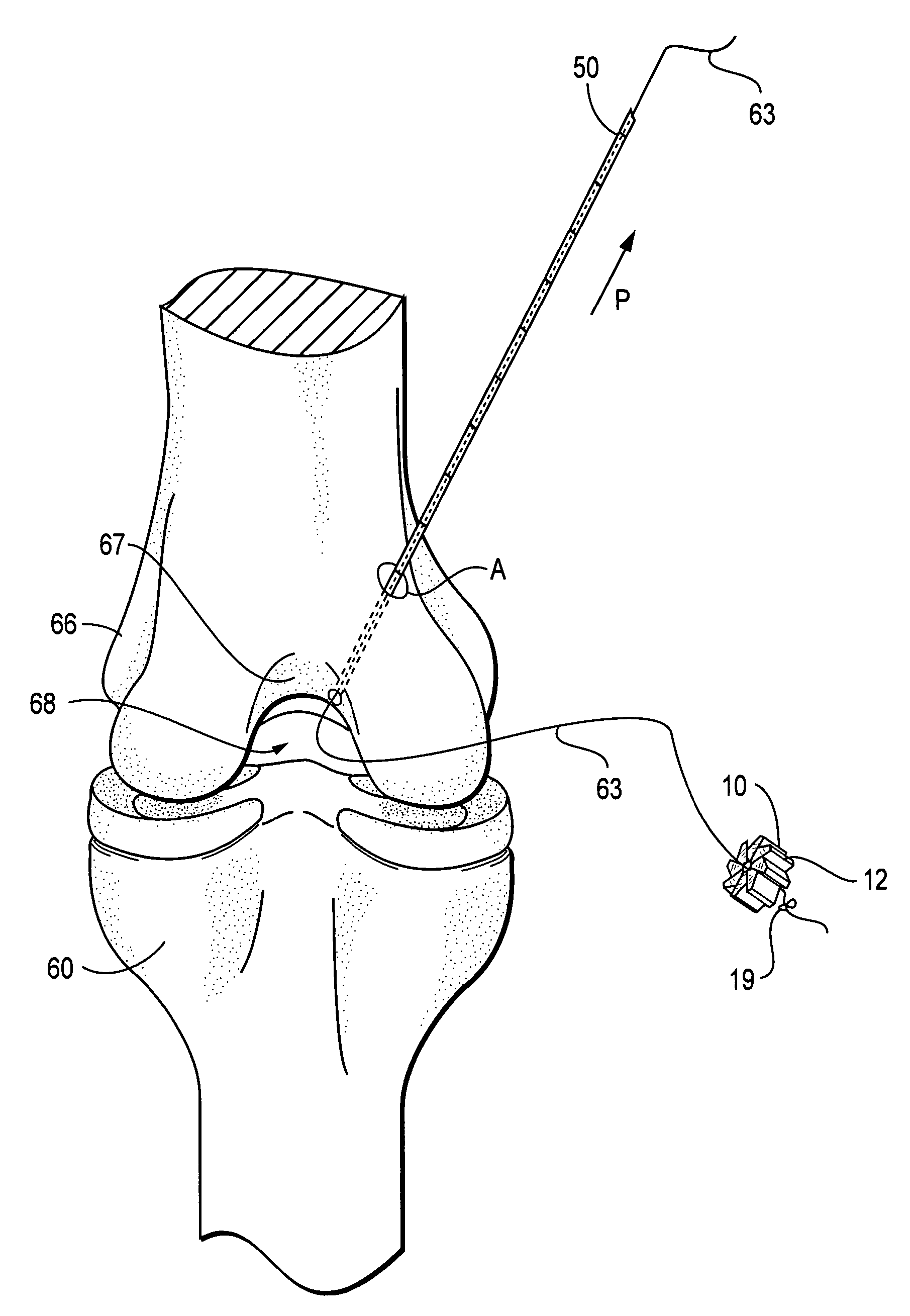
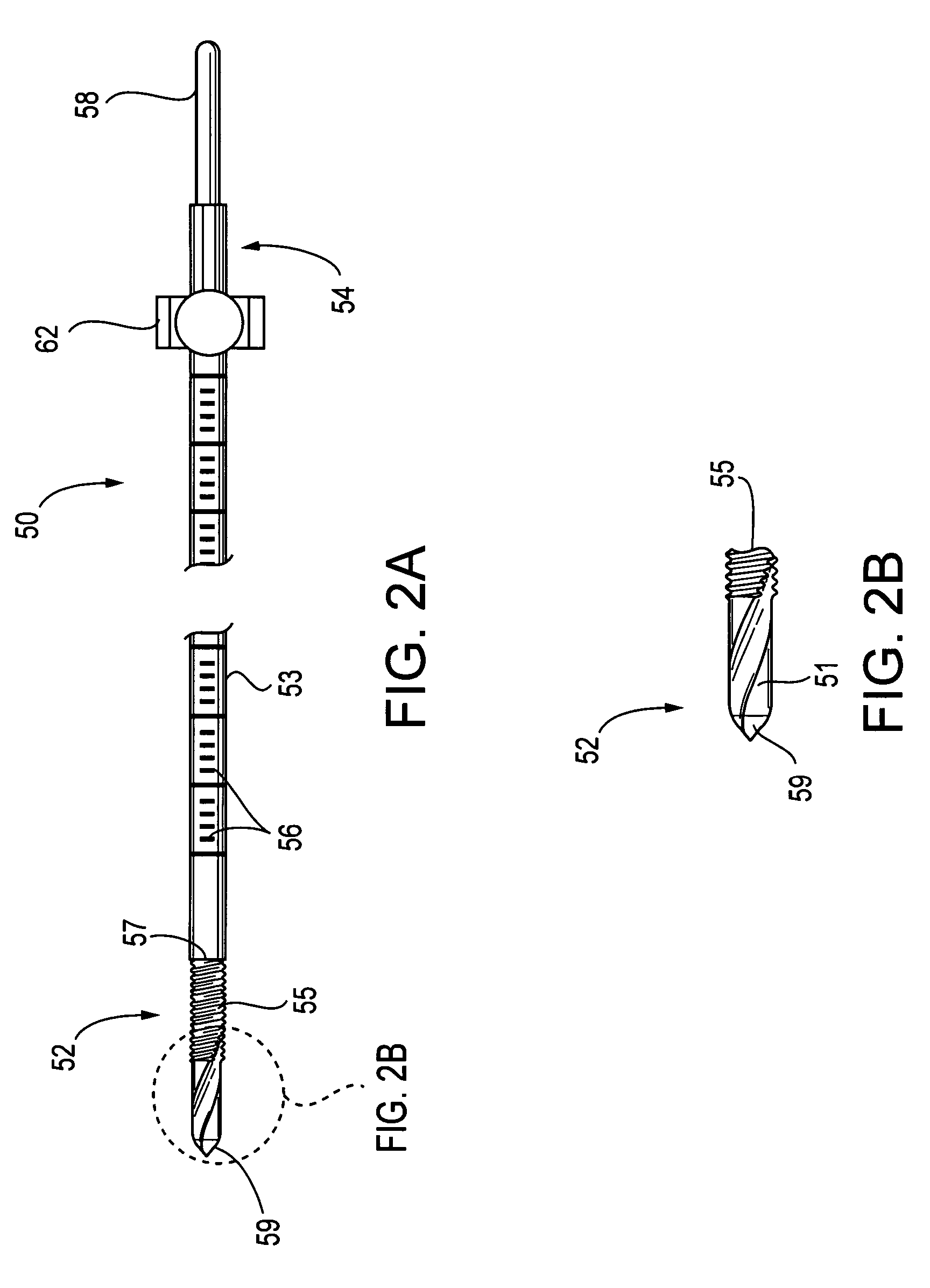
Method and implant for securing ligament replacement into the knee
A surgical method and implant for directing and securing a replacement ligament into the femur or tibia of the knee. A transverse tunnel may be formed in the femur approximately perpendicular to a femoral tunnel. A flexible strand passing through the transverse tunnel may be used to draw the replacement ligament into the femoral tunnel. The implant may then be placed into the transverse tunnel and through the replacement ligament to secure the replacement ligament in place. The implant may include an eyelet to receive the flexible strand and a tapered portion forming a shoulder to prevent the implant from being inserted too far into the transverse tunnel. The implant may also have a multi-angular configured portion to secure the implant within the transverse tunnel through an interference fit.
Owner:BIOMET MFG CORP
Retrieval devices for anchored cardiovascular sensors
ActiveUS20070106328A1Efficient deploymentPharmaceutical delivery mechanismStaplesOrgan wallMeasurement device
An anchoring device and a delivery method thereof can effectively provide a means for securing an implant to a wall of an internal organ within a patient in a variety of clinical applications. In one embodiment, an anchoring device used to retain a cardiac pressure measurement device is provided. The device is implanted in the body by deforming it to a small cross section profile, sliding it through a low profile delivery device and ejecting from the delivery device at a targeted site. The anchoring mechanism, when ejected from the delivery device, reverts back to pre-formed configuration and engages opposite sides of an organ wall, thereby anchoring the implant in the organ wall.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Implant and method for facet immobilization
ActiveUS20090264928A1Reduce relative motionRestores motionSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisAdhesiveSacroiliac joint
Devices and methods are provided for immobilizing facet joints of the vertebral column. Embodiments of the invention provide an implant that is inserted in a facet joint from which cartilage has been removed, and which retains the approximate original spacing of the facets in the joint. A retaining arrangement, such as an adhesive, a threaded fastener, or a screw is then used to secure the implant in the joint.
Owner:SPINAL ELEMENTS INC
Method and apparatus for performing an open wedge, high tibial osteotomy
Apparatus for performing an open wedge, high tibial osteotomy, the apparatus comprising: a wedge-shaped implant for disposition in a wedge-shaped opening created in the tibia, wherein the wedge-shaped implant comprises a hole extending therethrough; a fixation screw for extending through the hole and securing the wedge-shaped implant to the tibia; and a locking mechanism for releasably locking the fixation screw to the wedge-shaped implant.Apparatus for performing an open wedge, high tibial osteotomy, the apparatus comprising: a fixation screw for securing an implant to the tibia, the fixation screw comprising: a shaft having a distal threaded portion and a proximal threaded portion, wherein the distal threaded portion and the proximal threaded portion are characterized by different thread pitches.
Owner:ARTHREX
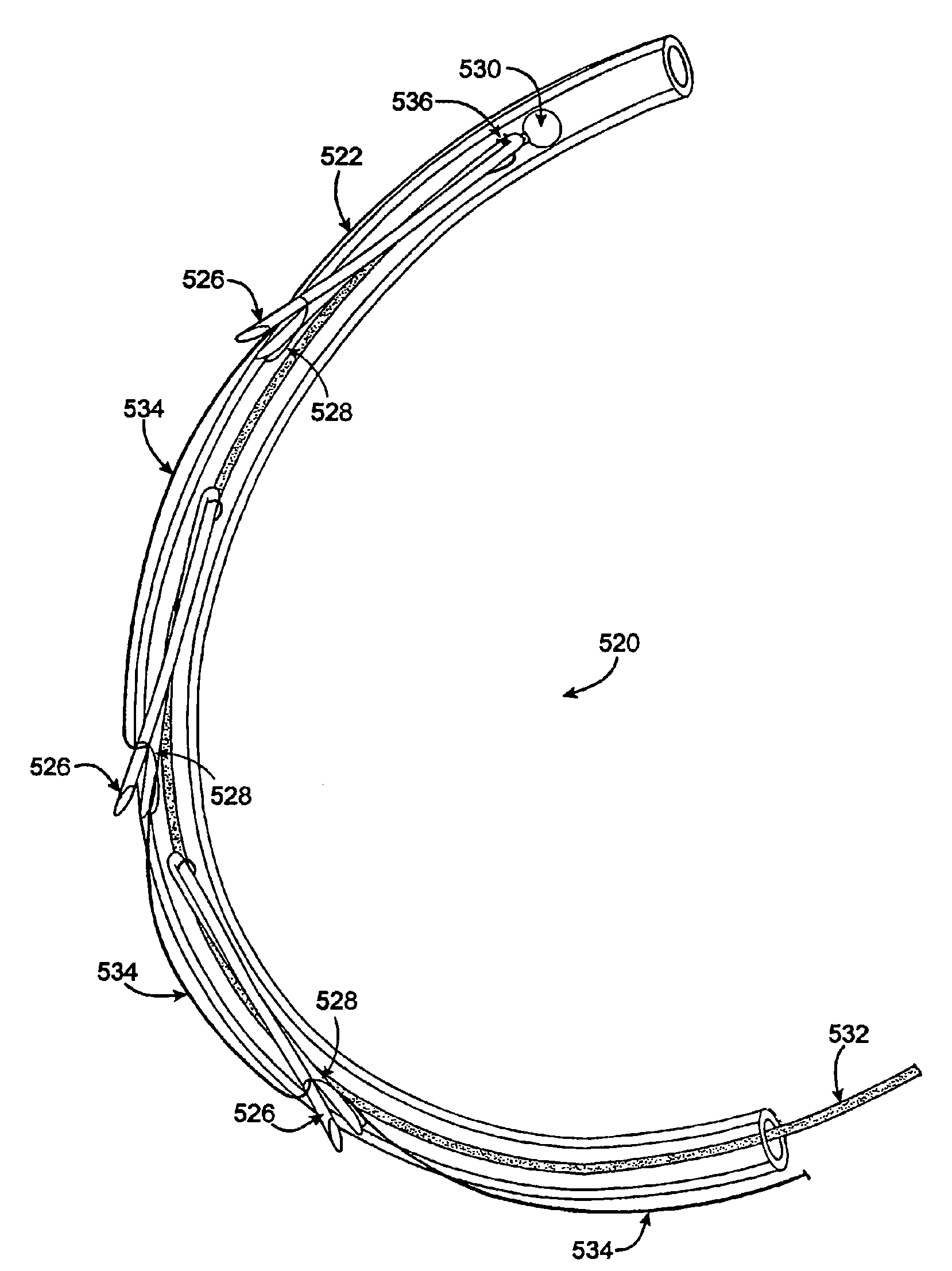
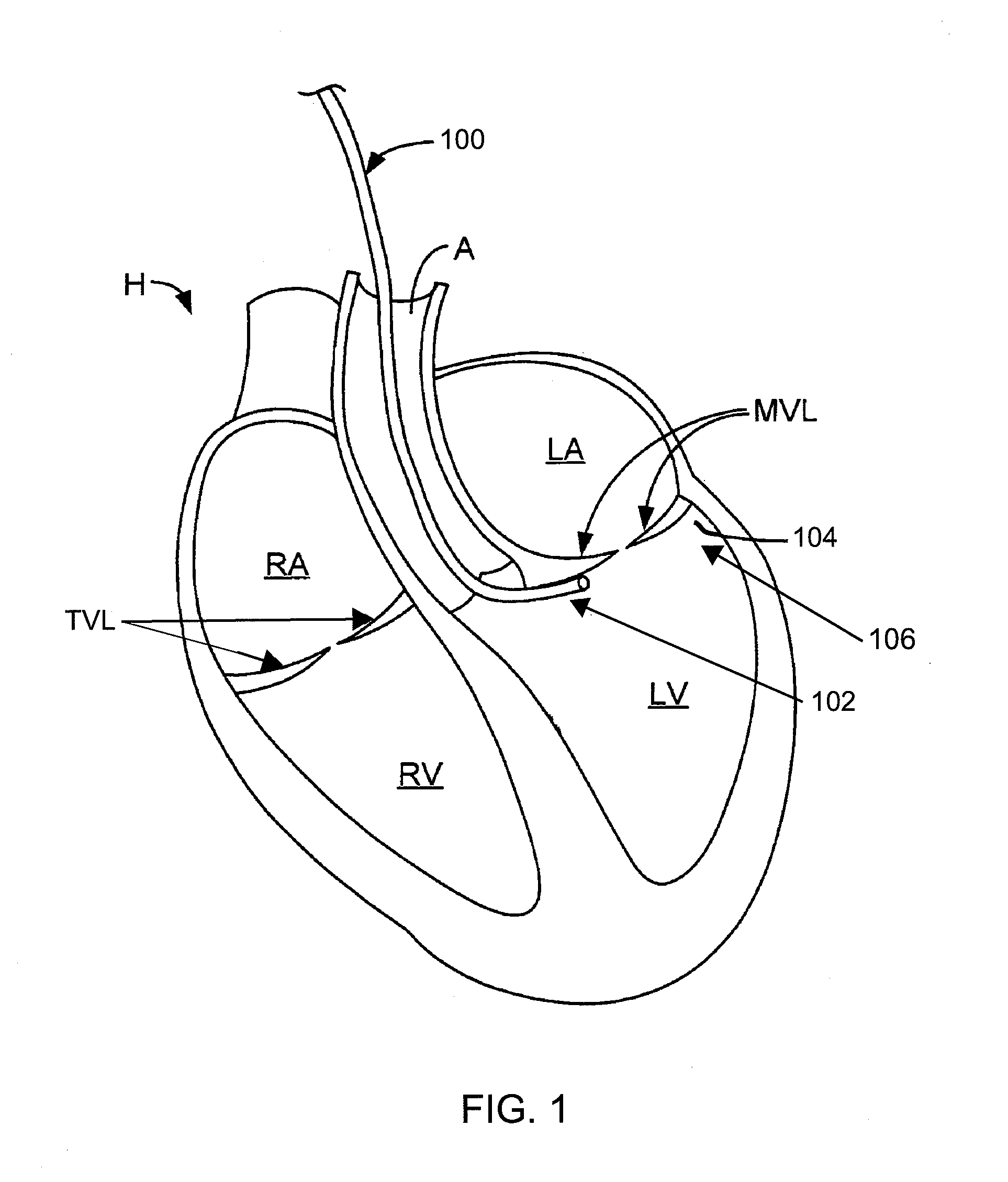
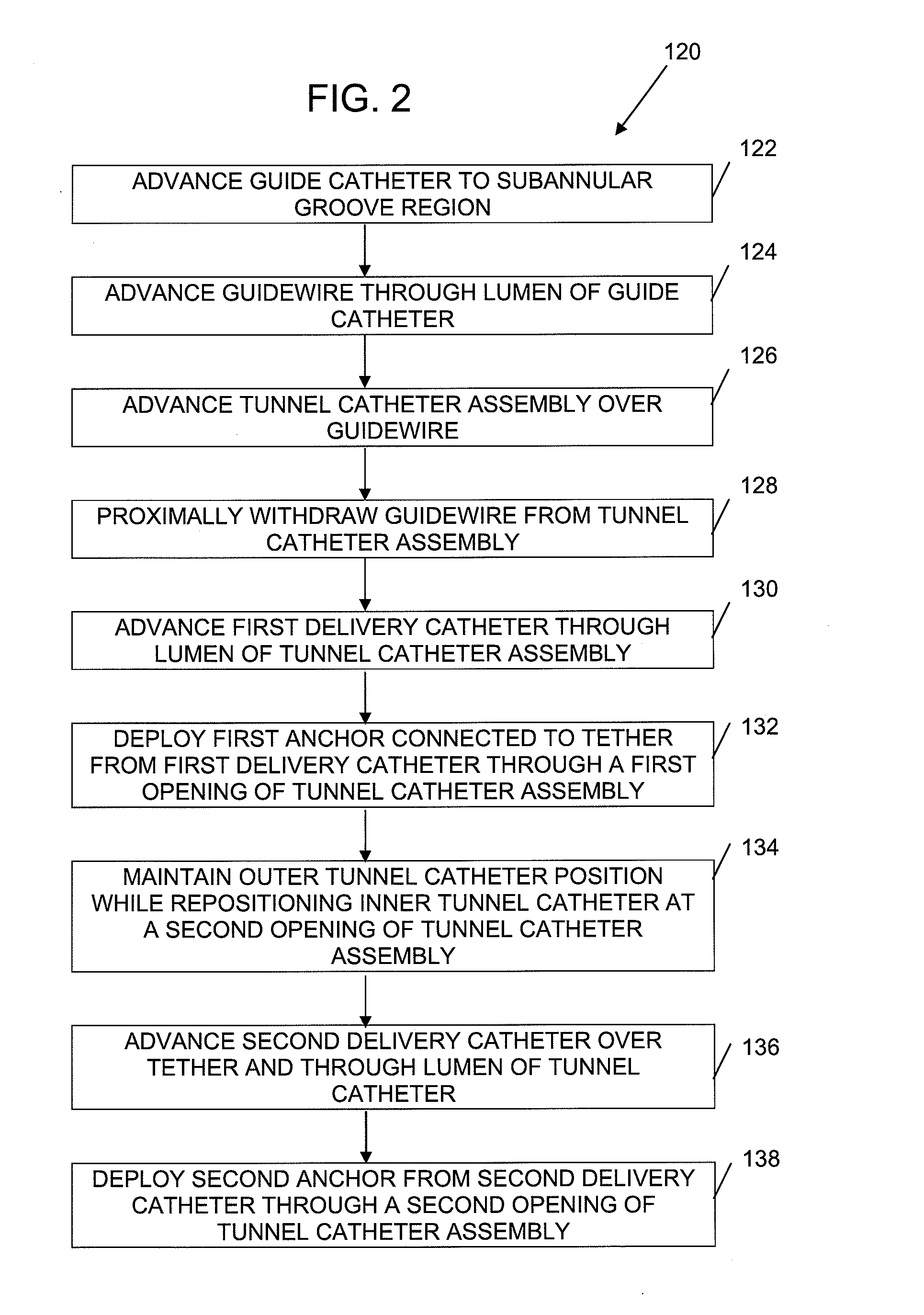
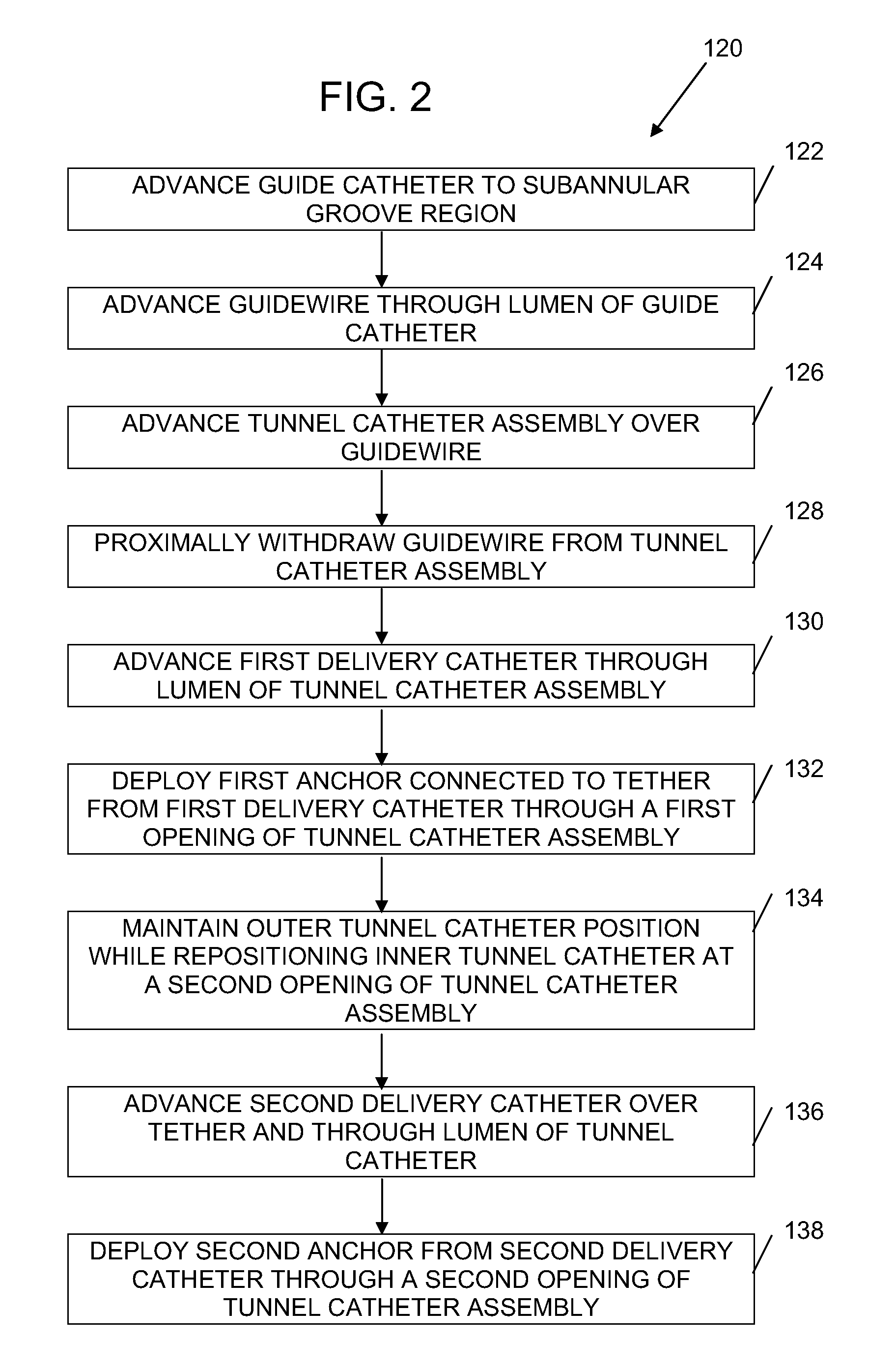
Multi-window guide tunnel
ActiveUS20090222083A1Improve stabilitySuture equipmentsAnnuloplasty ringsMedicineBiomedical engineering
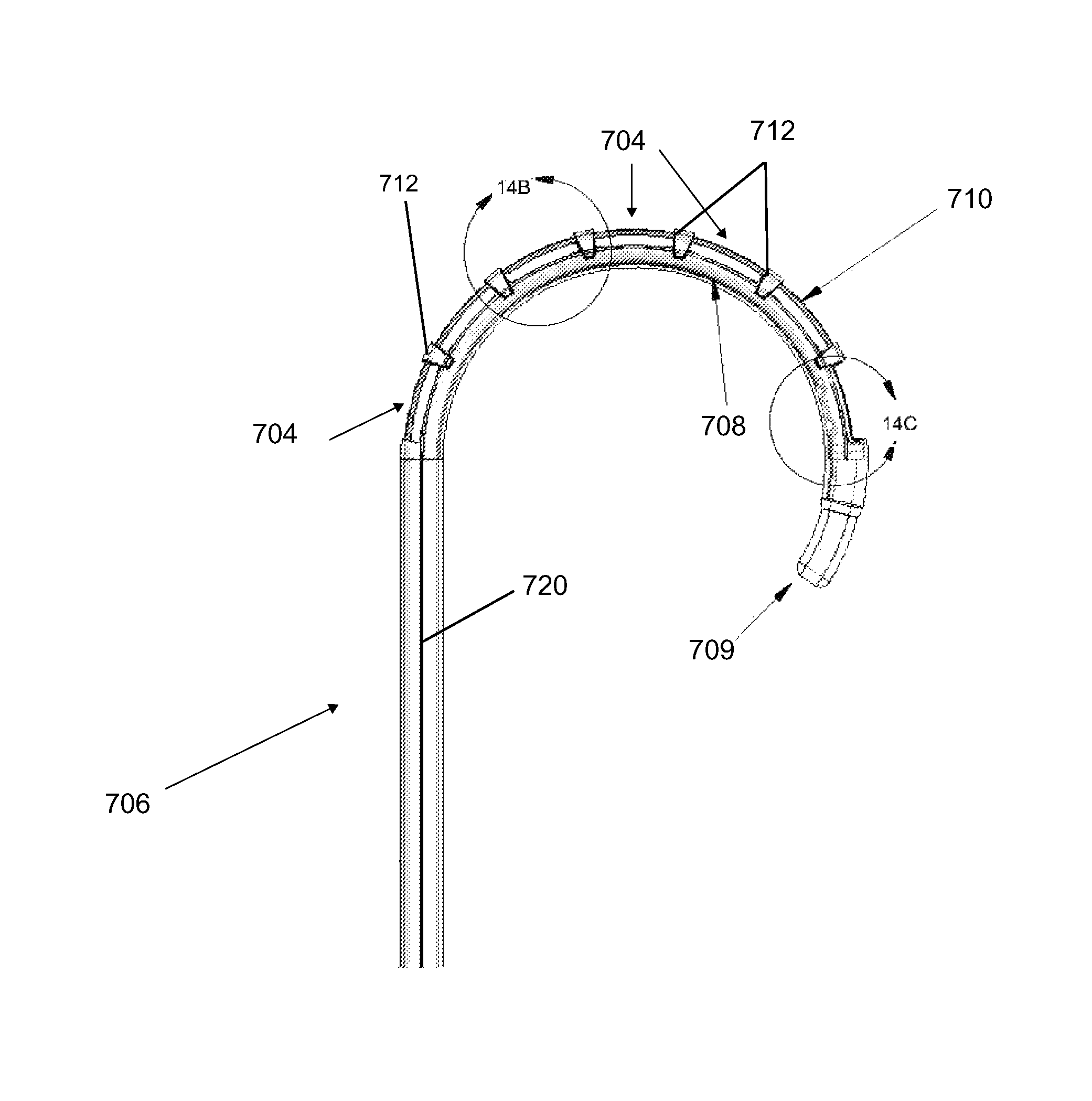
Described herein are devices and methods for delivering implants that comprise multiple coupled anchors. The anchors are secured to tissue using a multi-opening guide tunnel that is configured to releasably retain one or more portions of the implant located between two of the anchors. The releasable retention of one or more intervening portions of the implant maintains the position of the implant and the guide tunnel until the implant is secured to the tissue. The multi-opening guide tunnel permits securement of the multiple anchors without requiring repositioning of the guide tunnel for each anchor.
Owner:ANCORA HEART INC
Medical foot implant and system
InactiveUS20090082770A1Easy to introduceMinimizes strainJoint implantsArtificial legsFirst tarsometatarsal jointSacroiliac joint
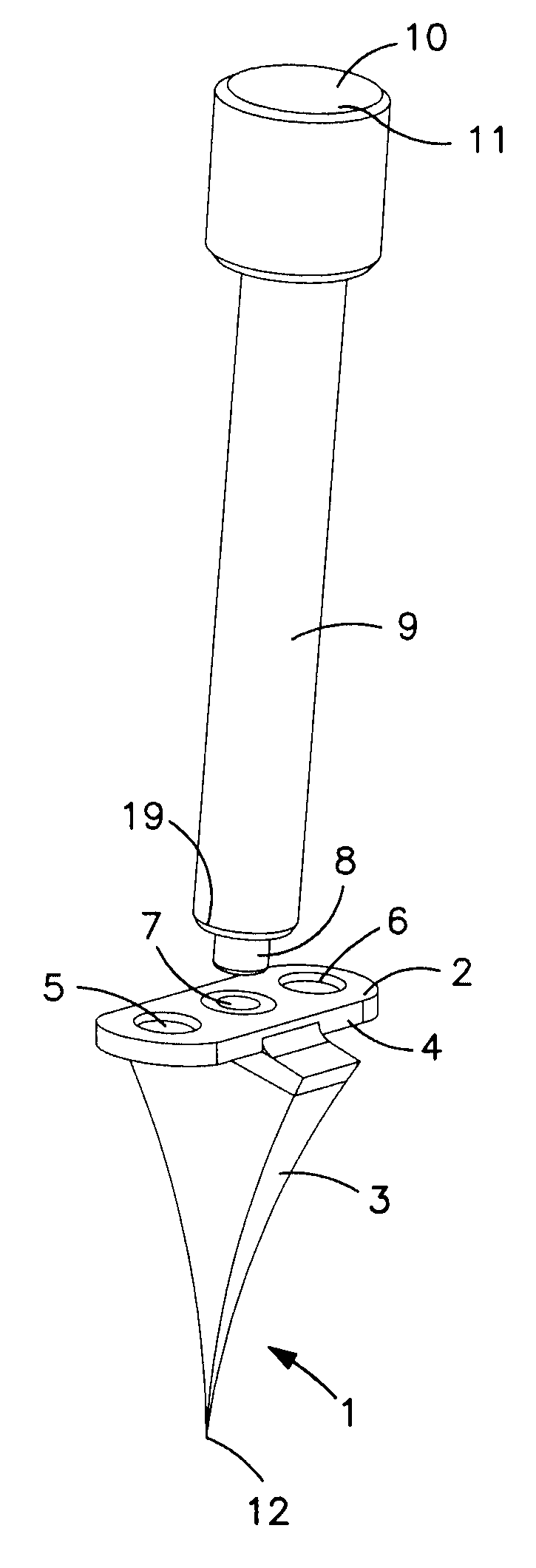
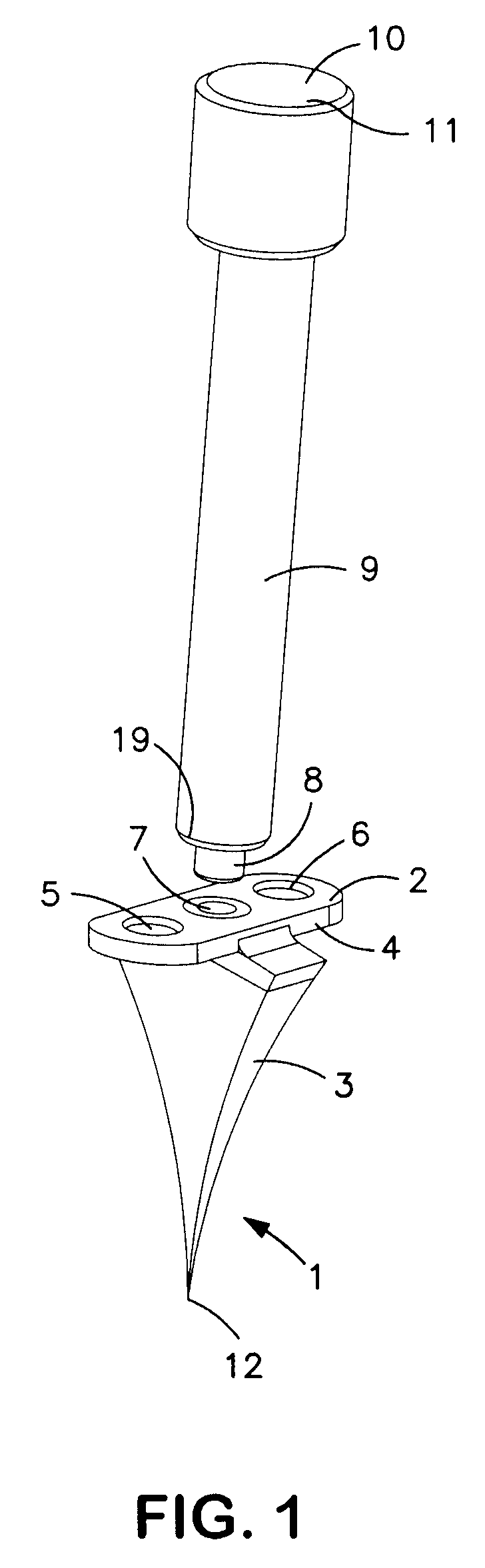
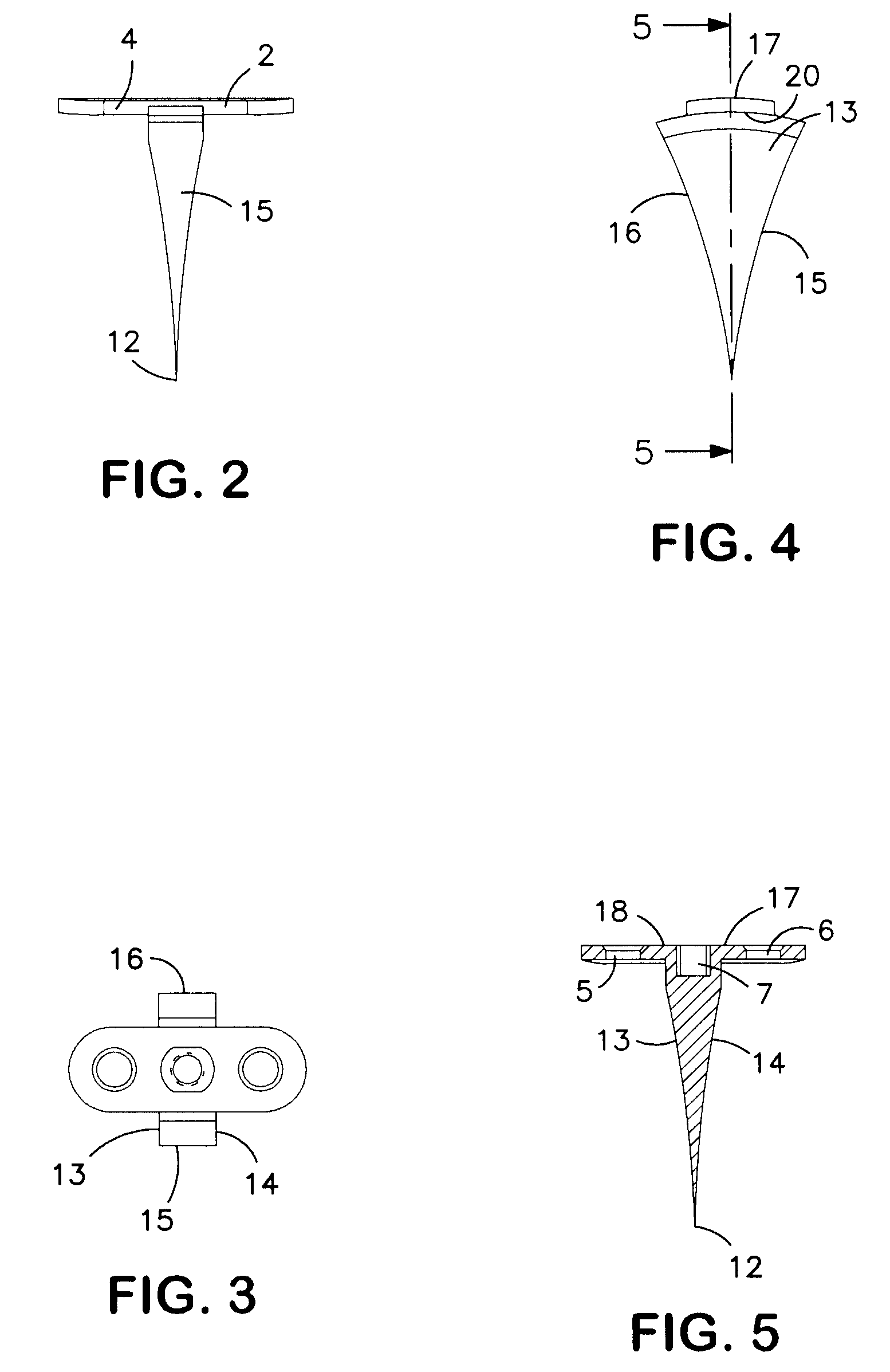
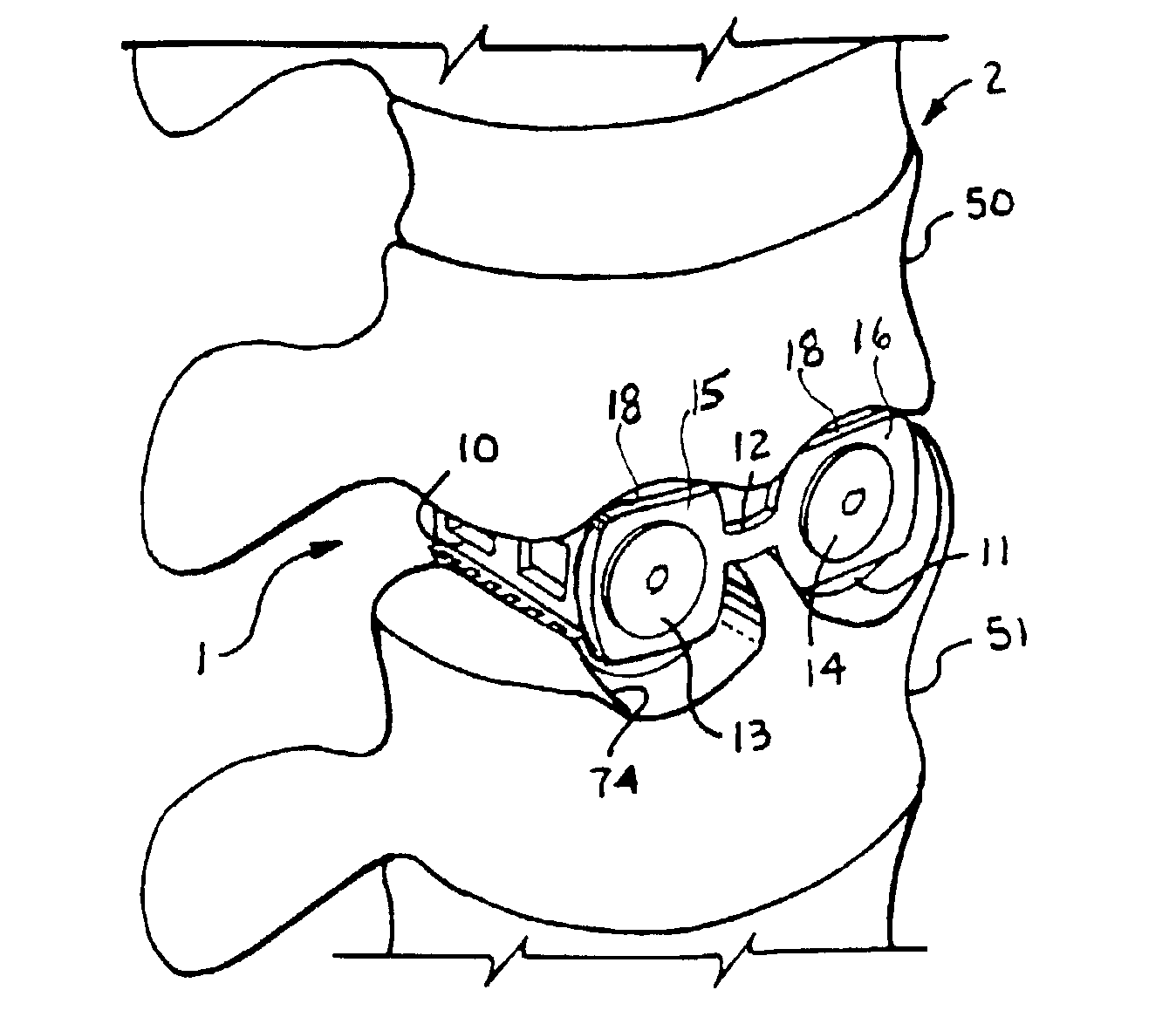
A medical foot implant (1) with a fastening section (2) for fixing the foot implant (1) to two adjacent bones or bone segments and with a wedge section (3). The wedge section (3) has an end-side tip (12), in a plan view at least approximately punctiform, for easier introduction of the foot implant (1) into bone or into tarsometatarsal joint.
Owner:NORMED MEDIZIN TECHN VERTRIEBS
Spinal fusion apparatus and method
InactiveUS6926737B2Relieve stressPhysical recoveryInternal osteosythesisBone implantCushioningVertebral bone
An apparatus for stabilizing and promoting fusion between adjacent vertebrae includes at least a pair of implants to promote bone growth and to fuse with vertebral bone. The implants are joined by a connector. Preferably the implants are inserted into receiving bores in a non-parallel configuration and / or the connector joins the implants so as to bias the implants to a non-parallel configuration. A pair of connecting members also preferably secure the implants to each of the adjacent vertebrae. A method of using the apparatus provides for stabilizing between vertebrae where the original cushioning disc has deteriorated or become damaged. The implants are connected together. Also in the method, the implant receiving bores are non-parallel and / or the implants are biased to non-parallel configurations by joining the implants to the connecting element so as to reduce the inadvertent disturbance of the implants from the receiving bores and to further stabilize the implants overall during the fusion process.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Intervertebral implant with blades for connecting to adjacent vertebral bodies
An intervertebral implant (300) for insertion into an intervertebral disc space between adjacent vertebral bodies or between two bone portions. The implant includes a spacer portion (310), a plate portion (330) operatively coupled to the spacer portion and one or more blades (350) for securing the implant to the adjacent vertebral bodies. The blades preferably include superior and inferior cylindrical pins (360) for engaging the adjacent vertebral bodies. The implant may be configured to be inserted via a direct lateral transposals approach. Alternatively, the implant may be configured for insertion via an anterior approach.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
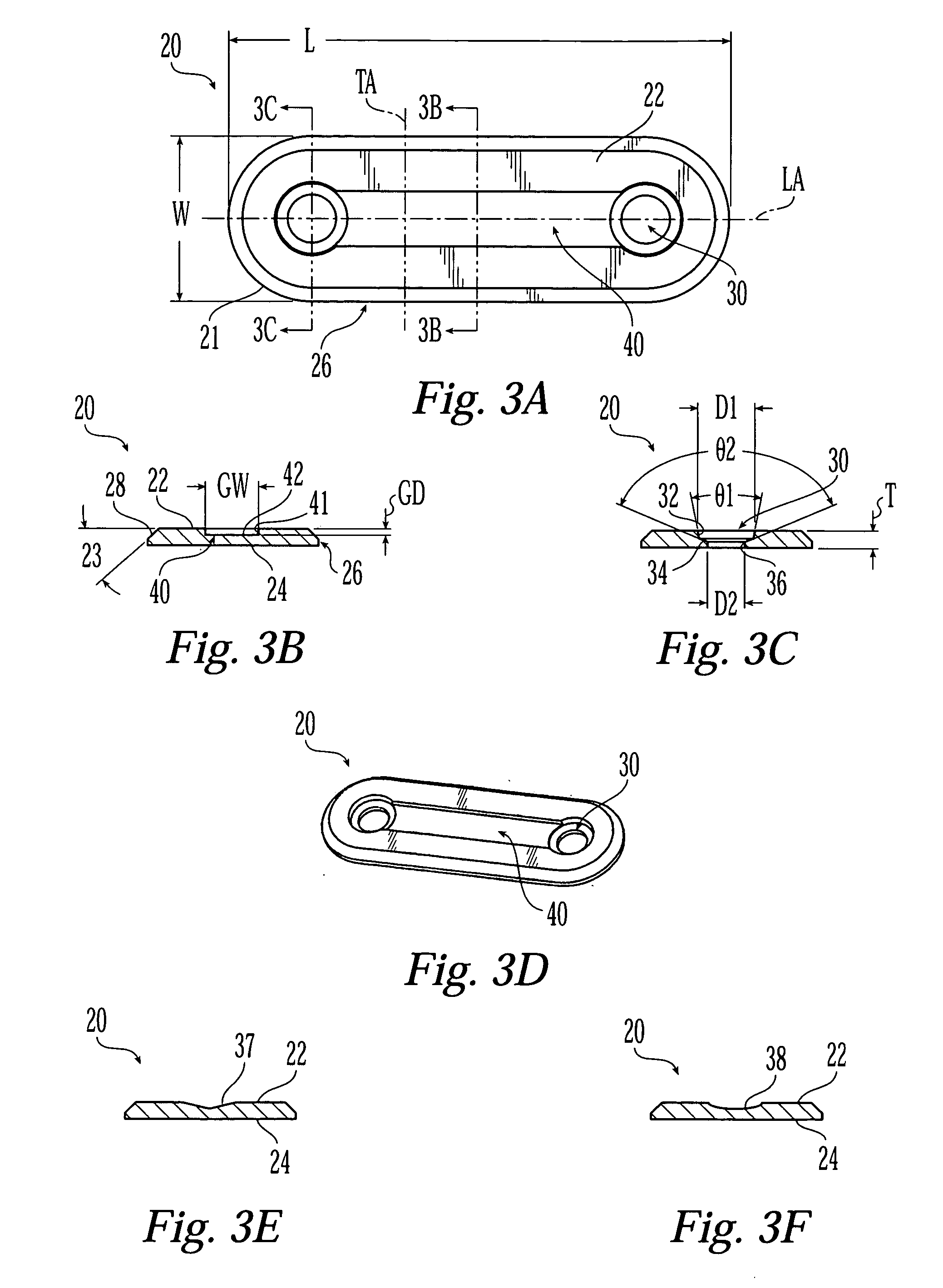
Interspinous implants and methods for implanting same
A spinal implant for treating lumbar spinal stenosis or as an adjunct to spinal fusion. The implant includes a body portion having an interior cavity. A plurality of locking wings are adapted and configured to move between a stowed position retracted within the interior cavity of the body portion and a deployed position extended from the interior cavity of the body portion. In the deployed position, the wings fix the implant in a selected interspinous space. A cable and wheel arrangement moves the plurality of locking wings from the stowed position to the deployed position and a ratchet / pawl assembly prevents backward movement of the wings.
Owner:SPINAL SIMPLICITY
Devices and method for treating pelvic dysfunctions
ActiveUS20090171143A1Prevent movementSuture equipmentsSurgical furnitureFunctional disturbanceUterus
In one embodiment, a method includes securing an implant that includes a pre-formed loop to a vaginal apex. An end of the suture is inserted through a selected portion of a pelvic tissue to dispose at least a portion of the implant within a pelvic region of the patient. The end of the suture is drawn through the loop while simultaneously advancing a uterus to approximate the vaginal apex to the selected portion of pelvic tissue. An apparatus includes an implant and a suture coupled to the implant having a pre-formed loop. configured to receive a portion of a delivery device therethrough. A trocar is coupled to an end of the suture that can be releasably coupled to an end of the delivery device. The trocar can be inserted through a pelvic tissue and drawn through the loop forming a knot to secure the implant to the pelvic tissue.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Multi-window guide tunnel
InactiveUS20100094248A1Improve stabilitySuture equipmentsAnnuloplasty ringsBiomedical engineeringImplant fixation
Described herein are devices and methods for delivering implants that comprise multiple coupled anchors. The anchors are secured to tissue using a multi-opening guide tunnel that is configured to releasably retain one or more portions of the implant located between two of the anchors. The releasable retention of one or more intervening portions of the implant maintains the position of the implant and the guide tunnel until the implant is secured to the tissue. The multi-opening guide tunnel permits securement of the multiple anchors without requiring repositioning of the guide tunnel for each anchor.
Owner:GUIDED DELIVERY SYST INC
Spinal Implant with expandable fixation
ActiveUS20090216331A1Easy to installIncreased pull-out strengthBone implantSpinal implantsIntervertebral spaceSpinal implant
A spinal implant which is configured to be deployed between adjacent vertebral bodies. The implant has at least one fixation element with a retracted configuration to facilitate deployment of the implant and an extended configuration so as to engage a surface of an adjacent vertebral body and secure the implant between two vertebral bodies. Preferably, the implant is expandable and has a minimal dimension in its unexpanded state that is smaller than the dimensions of the neuroforamen through which it must pass to be deployed within the intervertebral space. Once within the space between vertebral bodies, the implant can be expanded so as to engage the endplates of the adjacent vertebrae to effectively distract the anterior disc space, stabilize the motion segments and eliminate pathologic spine motion. Angular deformities can be corrected, and natural curvatures restored and maintained.
Owner:HOWMEDICA OSTEONICS CORP
Method and apparatus for minimally invasive delivery, tensioned deployment and fixation of secondary material prosthetic devices in patient body tissue, including hernia repair within the patient's herniation site
InactiveUS20100069930A1Reduce the possibilityRaise the possibilityProsthesisWound clampsProsthesisAbdominal wall
Apparatus and methods enable insertion and tensioned deployment of a secondary material prosthetic device into a body cavity or other tissue of a patient, such as for example hernia repair mesh into the abdominopelvic cavity of a patient through the hernia site. The present invention establishes fixation sites for the prosthetic device and tensions it against the body tissue. It may also be used implant fixation devices within the body tissue so that the prosthetic device is tensioned into firm abutting contact with the body tissue. Instrument deployment and fixation struts may be advanced in retrograde fashion in order to reduce needed deployment volume within the patient's body cavity. The prosthetic device advantageously may be flexibly coupled to the instrument via fixation devices such as sutures, so as to increase orientation flexibility.
Owner:VENTRALFIX
Flexible fastening system
ActiveUS20140257397A1Reduce the applied forceImprove rigidityInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsIliac screwBiomedical engineering
A flexible implant system includes a flexible implant, an implant housing, and an implant set screw. The flexible implant is configured to loop around a portion of a bony element. The implant housing includes a housing body defining a rod passage configured to receive an rod. The housing body also defines an implant passage that receives a portion of the flexible implant. The implant set screw engages the flexible implant within the implant passage to fix the flexible implant to the implant housing.
Owner:K2M
Multi-window guide tunnel
Described herein are devices and methods for delivering implants that include multiple coupled anchors. The anchors are secured to tissue using a multi-opening guide tunnel that is configured to releasably retain one or more portions of the implant located between two of the anchors. The releasable retention of one or more intervening portions of the implant maintains the position of the implant and the guide tunnel until the implant is secured to the tissue. The multi-opening guide tunnel permits securement of the multiple anchors without requiring repositioning of the guide tunnel for each anchor.
Owner:ANCORA HEART INC
ACL reconstruction technique using retrodrill
Methods and apparatus for arthroscopic tenodesis using sockets in bone created by retrograde cutting. A cannulated pin is drilled through bone and into a joint space in the normal, antegrade direction, guided by a drill guide. A strand provided through the cannulated pin is used to draw a retrodrill cutter into the joint space. The retrodrill cutter is threaded onto the cannulated pin, which is turned for retrograde cutting of a socket into the bone. The method is used to form a pair of sockets in the joint, which accept the respective ends of a replacement graft. The graft is brought into position in the joint space using loops formed in the strands, in a manner similar to introduction of the retrodrill cutter. The reconstruction is completed by securing suture attached to the graft ends with a button implant installed at the bone surface.
Owner:ARTHREX
Spine distraction implant
InactiveUS20080086212A1Increase volumeReduce restrictionsInternal osteosythesisSpinal implantsDistractionDevice implant
A spine distraction implant alleviates pain associated with spinal stenosis and facet arthropathy by expanding the volume in the spine canal and / or neural foramen. The implant provides a spinal extension stop while allowing freedom of spinal flexion. An interspinous process implant with a selectably expandable spacer can be placed between adjacent spinous processes. a device implanted between the spinous processes of adjacent vertebrae of the spine can be used for relieving pain associated with the vertebrae and surrounding tissues and structures by maintaining and / or adding distraction between adjacent vertebrae. A tissue expander can be adapted to move from a first insertion position, for ease of implantation between spinous processes, to a second retention position that prevents displacement of the implant. An embodiment of a system can include an implant having a spacer with a thickness and a wing, wherein a first configuration of the wing has a first height substantially similar to the thickness and wherein the wing is adapted to be selectably arranged in a second configuration such that the wing has a second height greater than the first height. A periphery of the implant has a shape generally conformal with a shape of an inner surface of a cannula and a cross-sectional diameter smaller than an inner diameter of the cannula. The cannula is inserted such that a proximal end of the cannula is arranged between the adjacent spinous processes. The implant is then urged into position between the adjacent spinous processes by way of the cannula, and subsequently arranged in a second configuration to fix the implant in position.
Owner:KYPHON
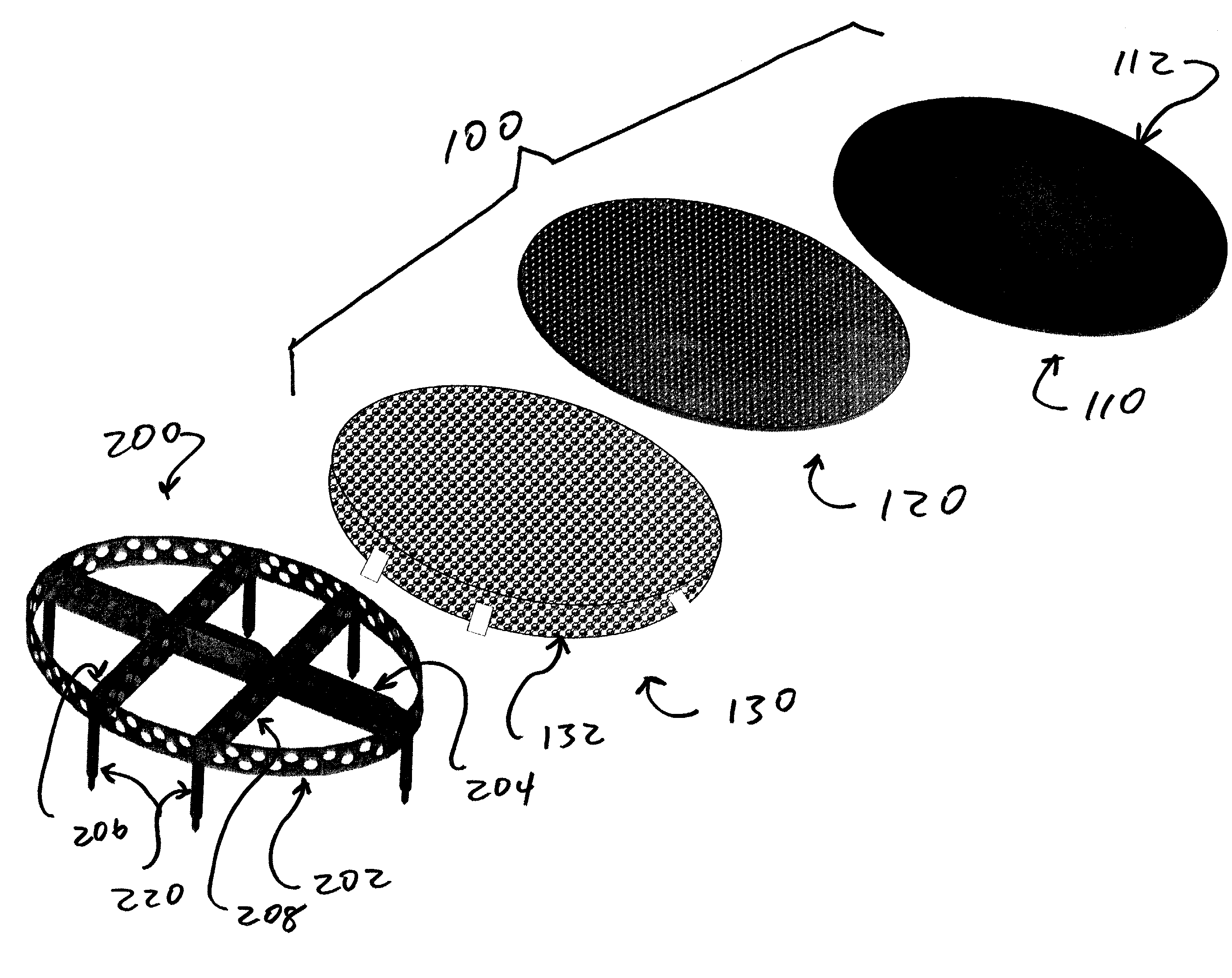
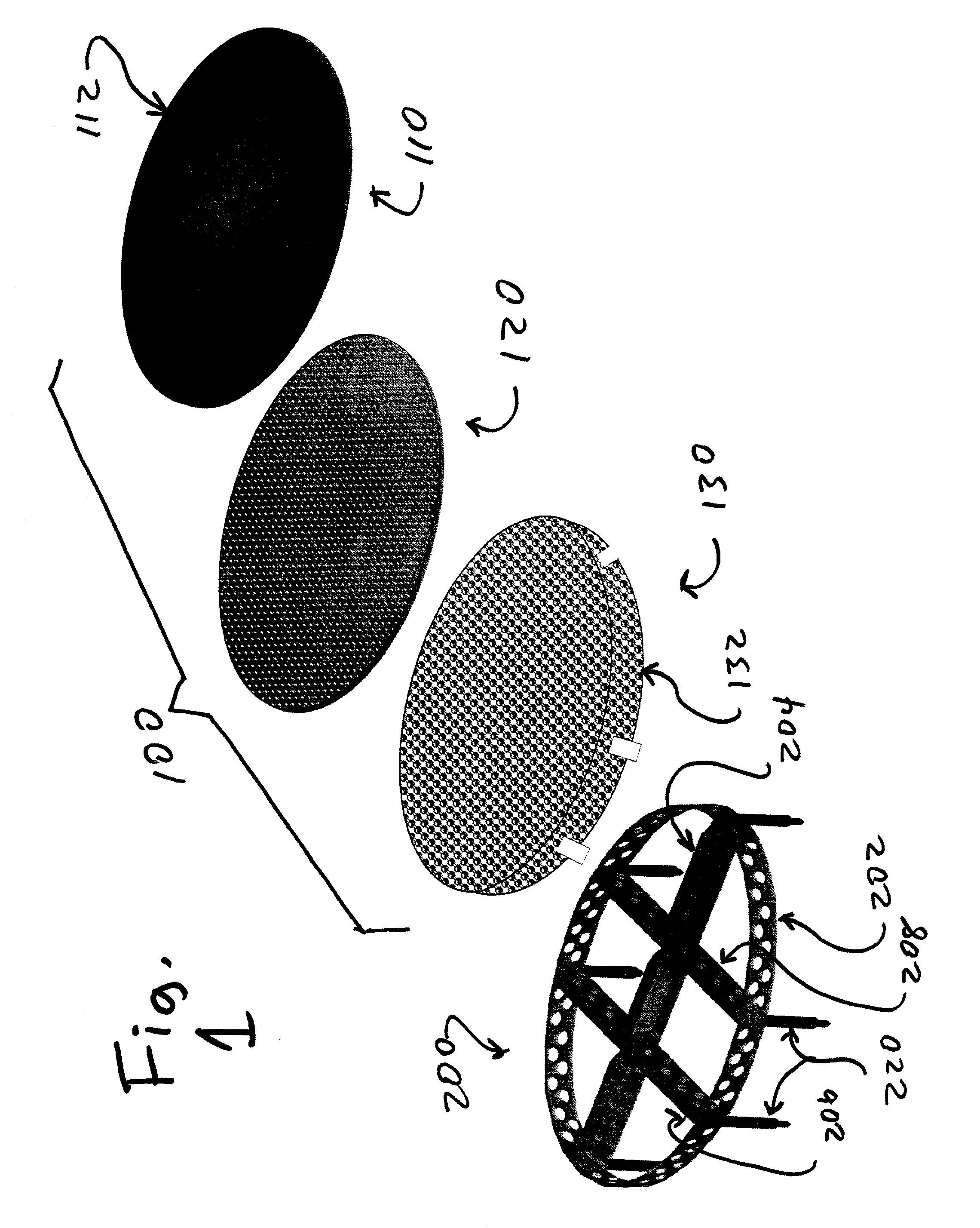
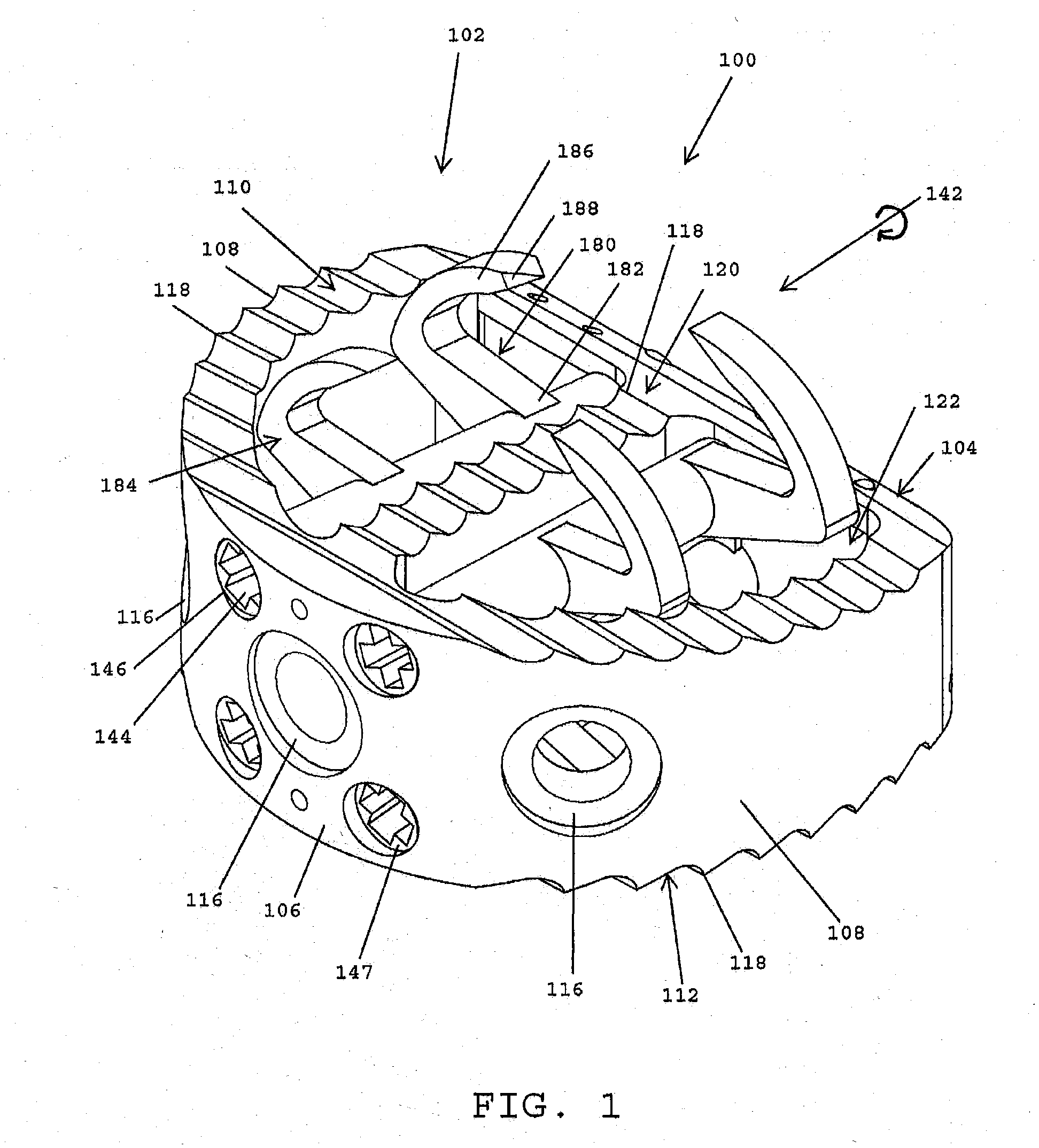
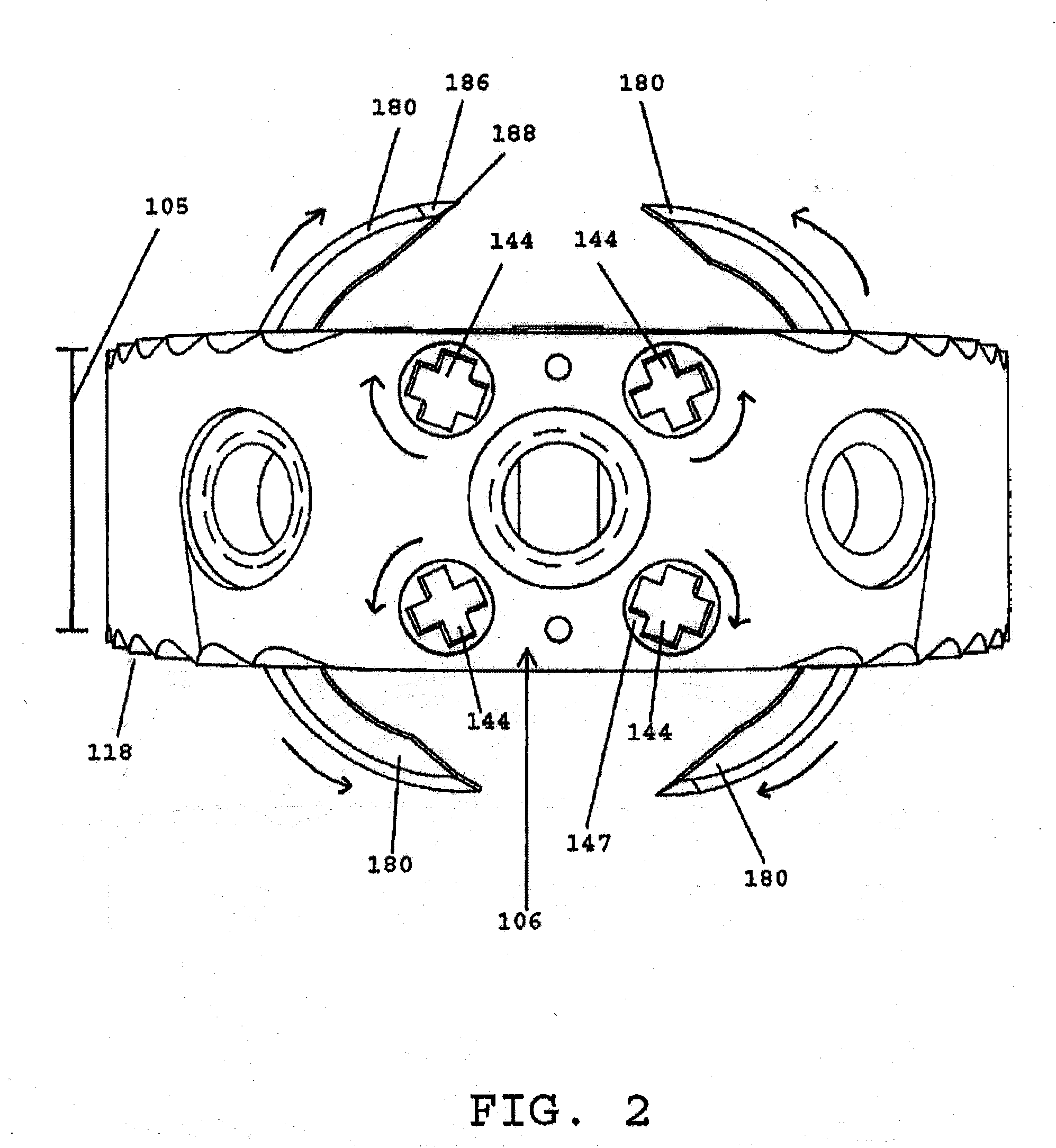
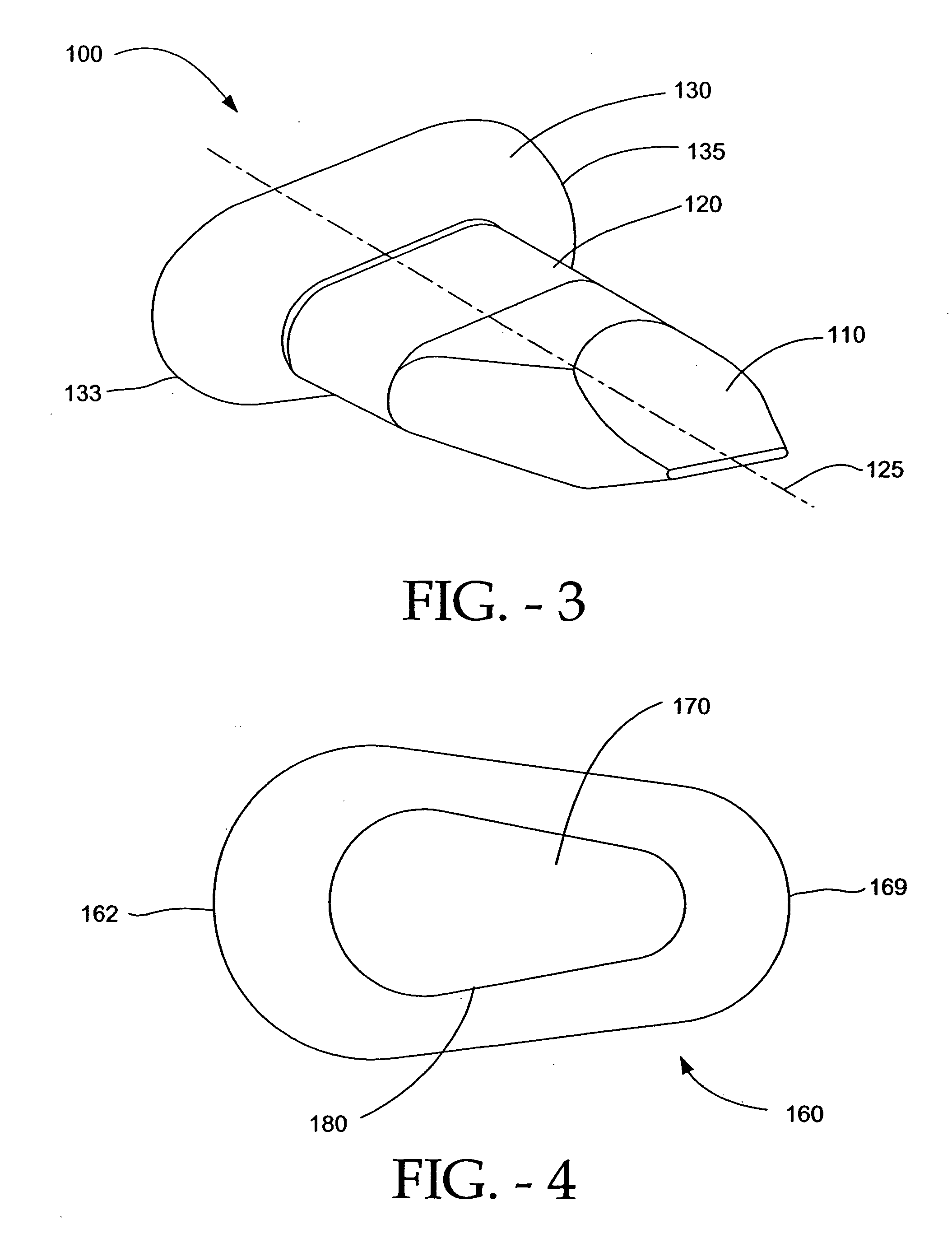
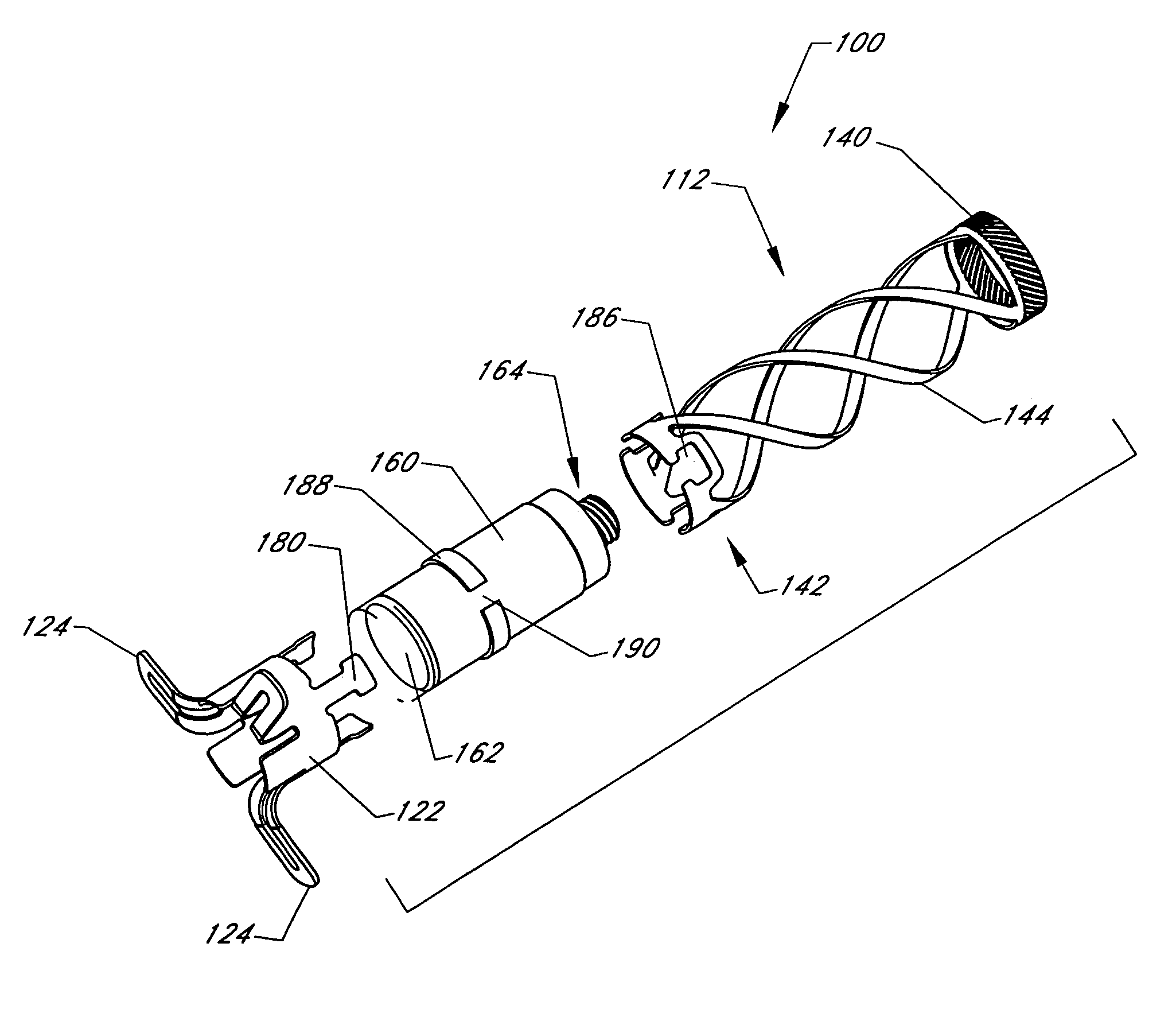
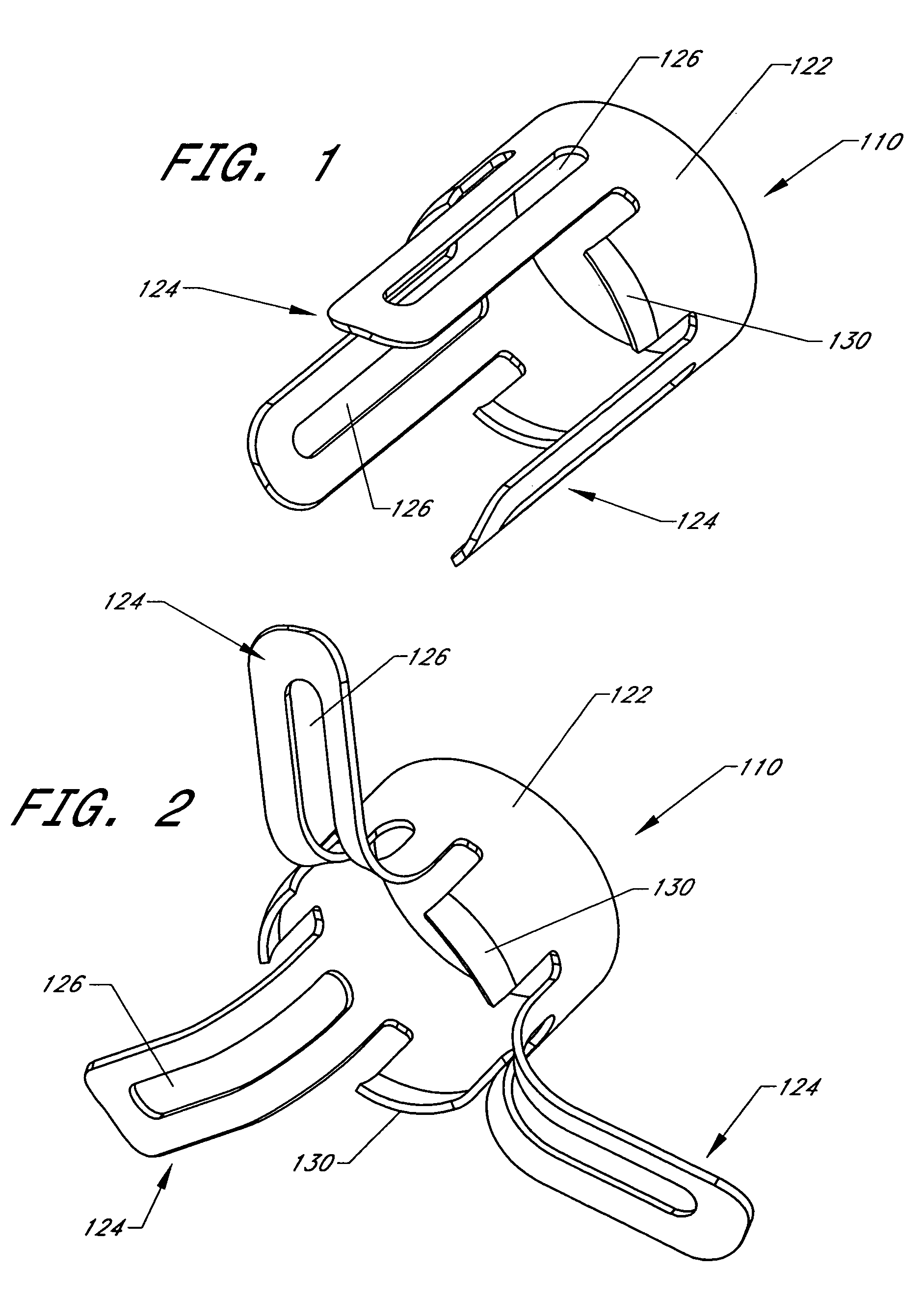
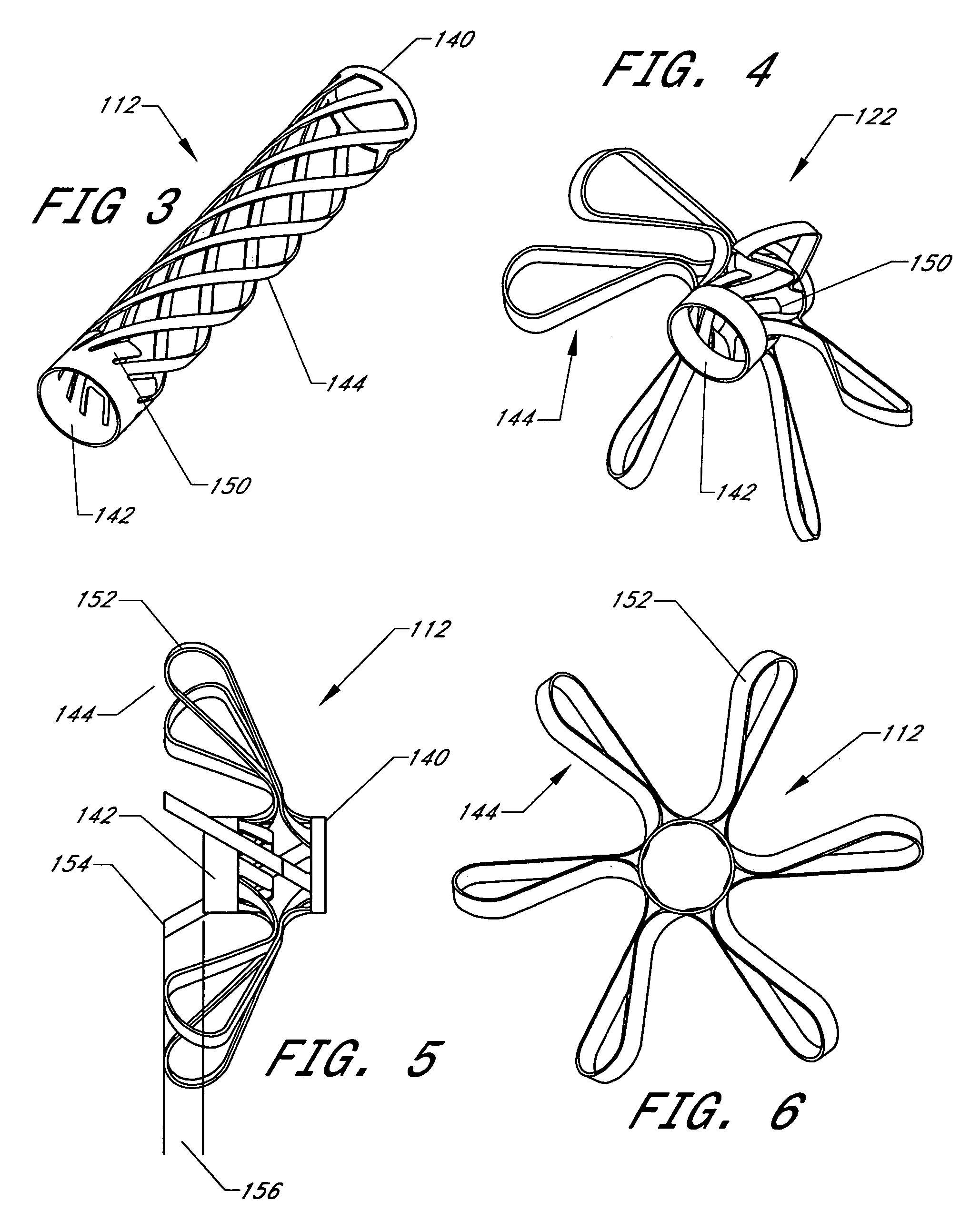
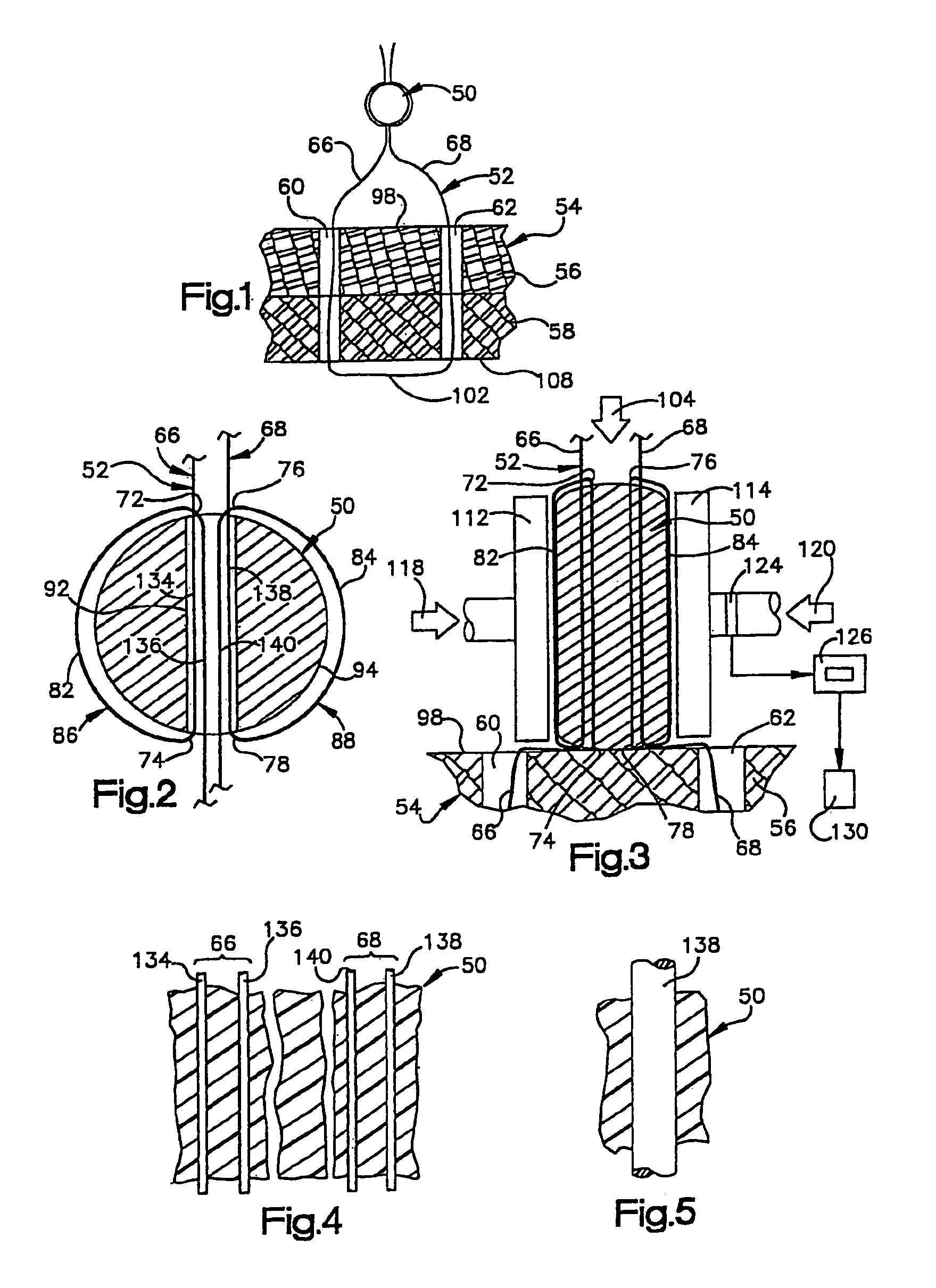
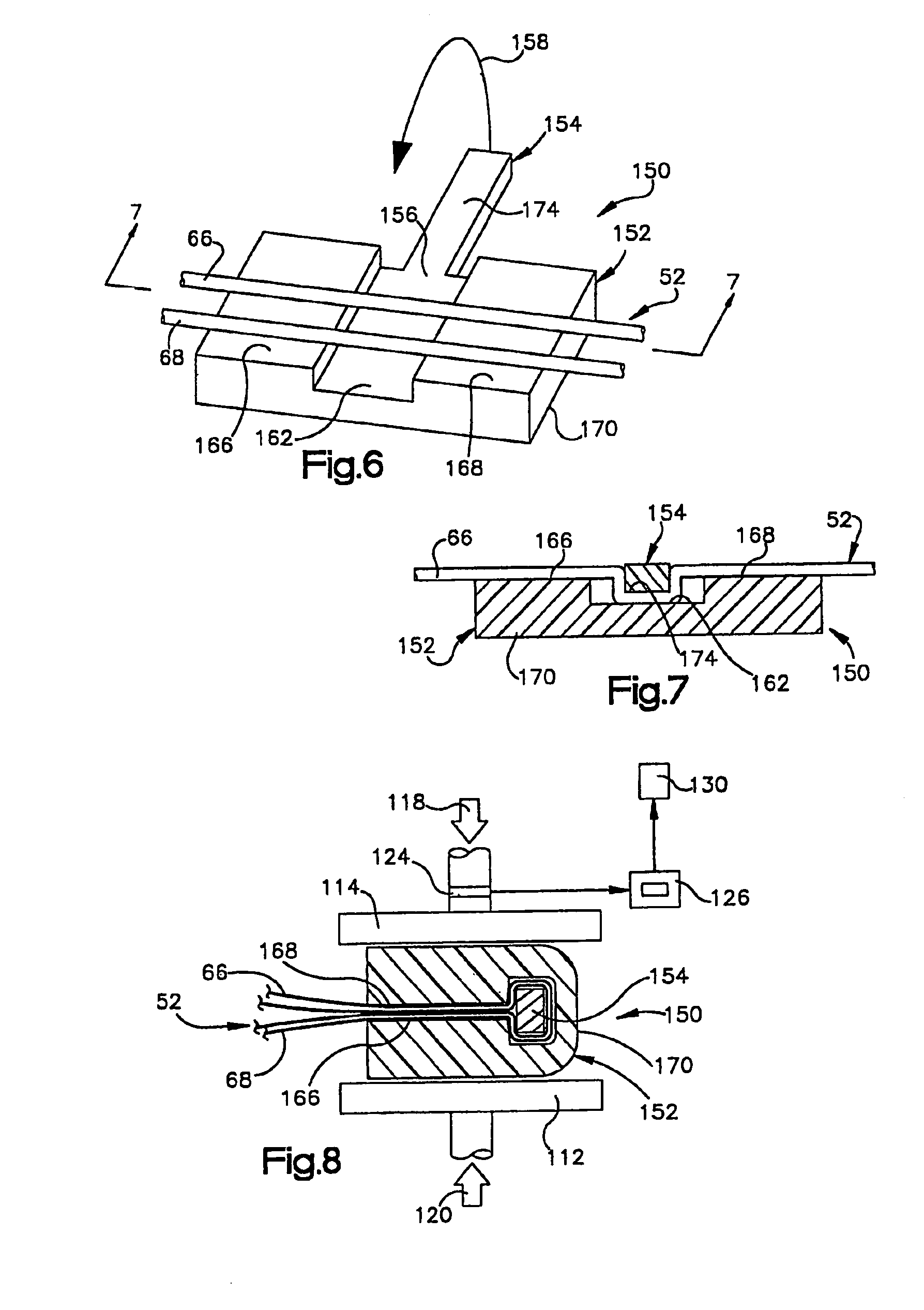
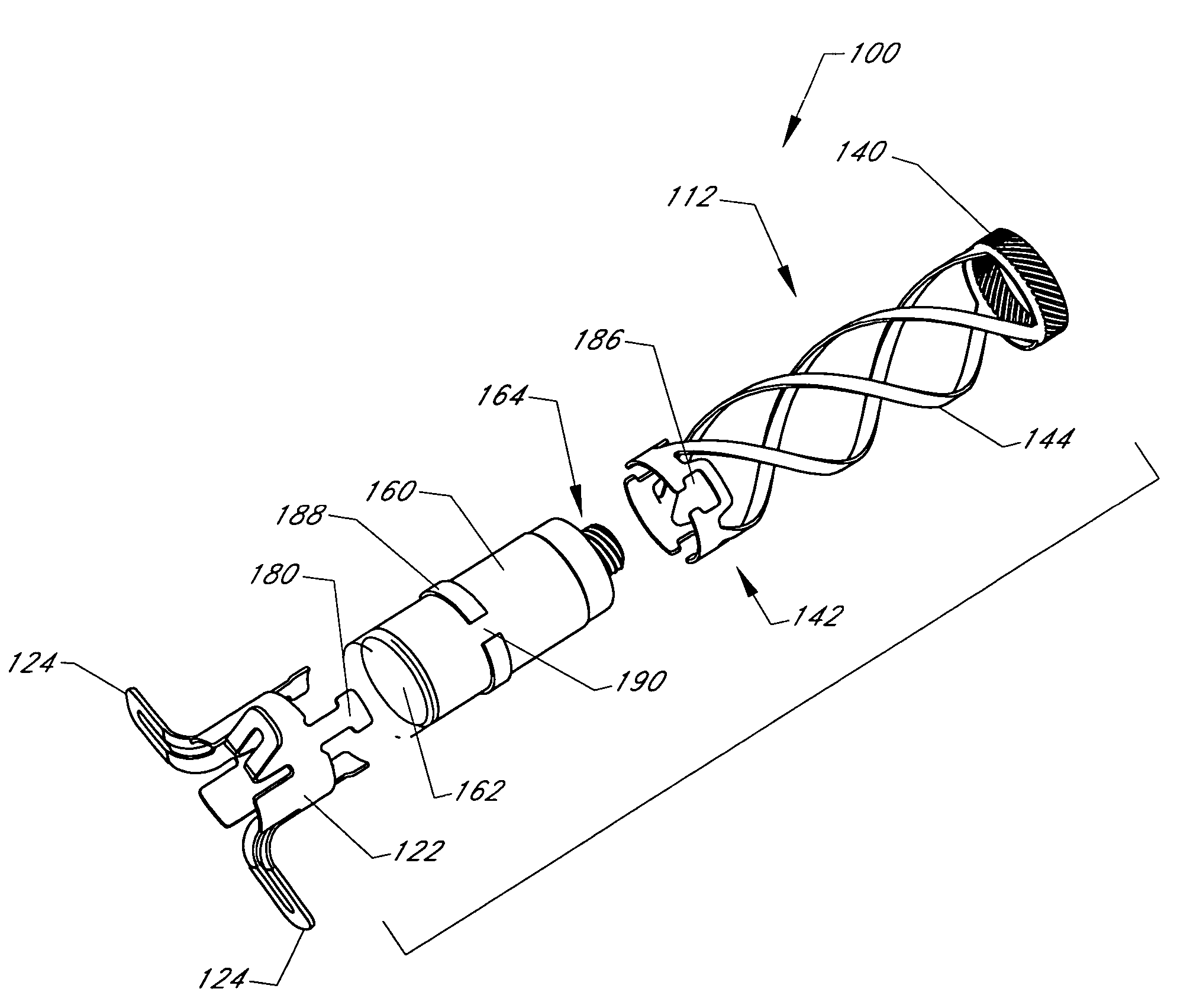
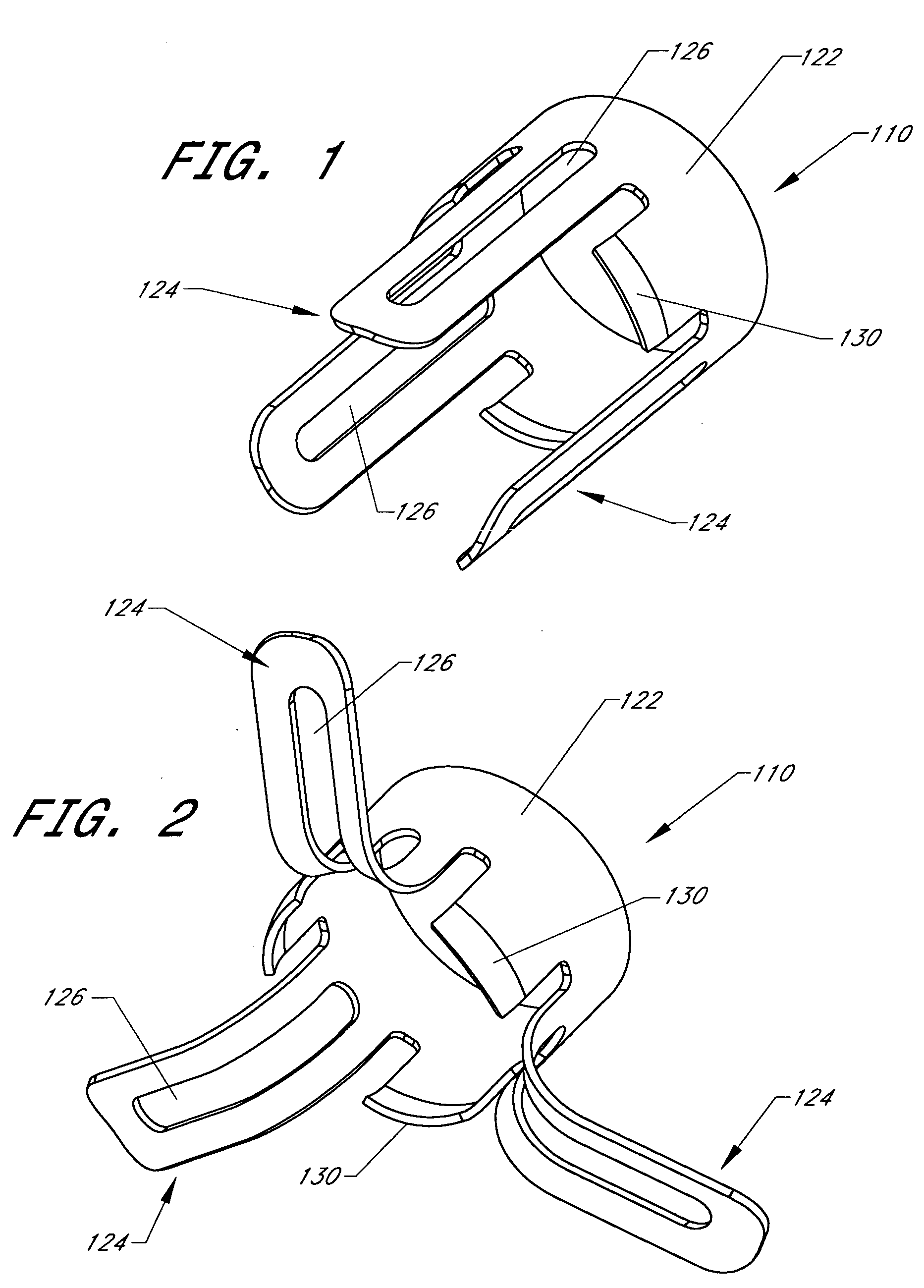
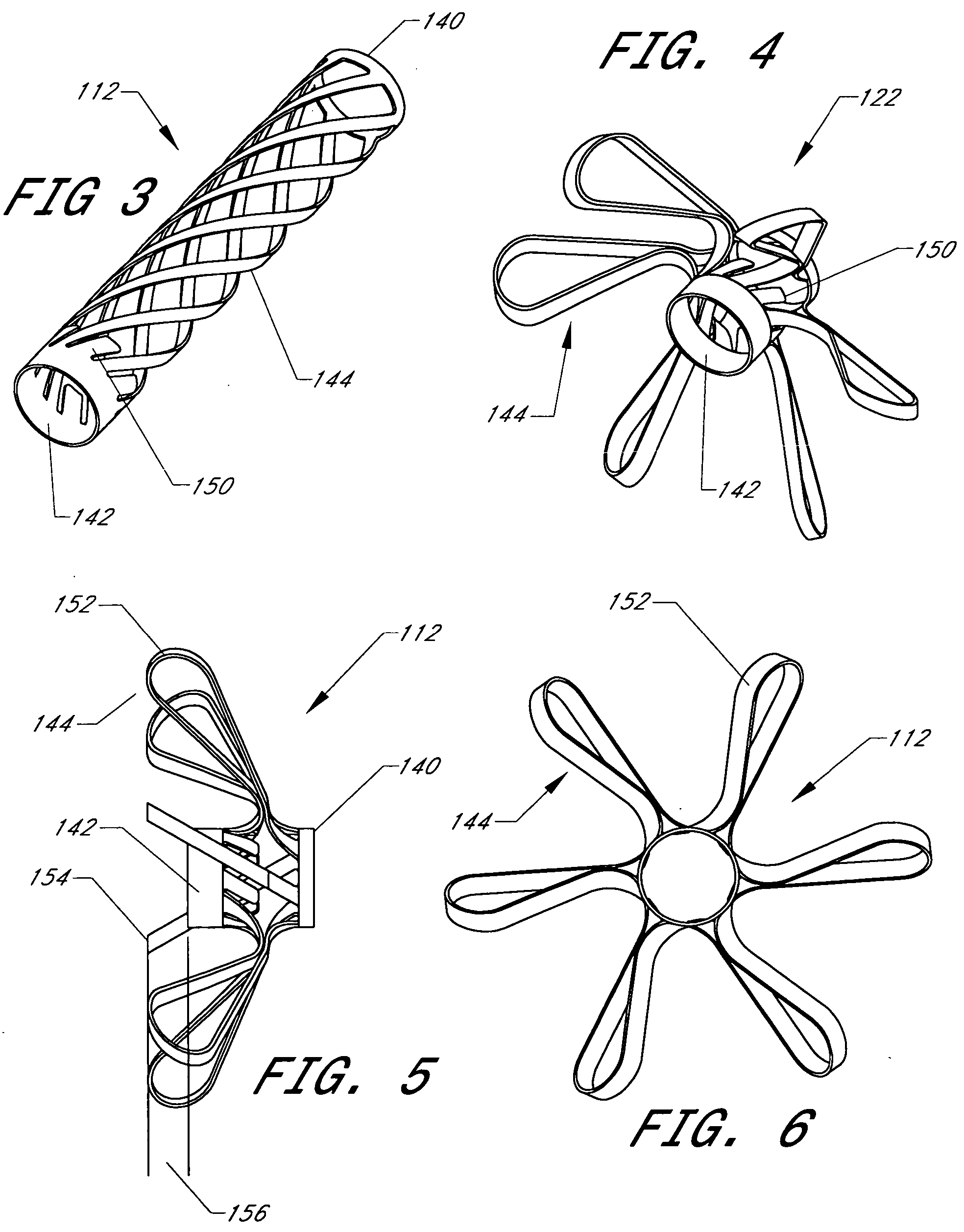
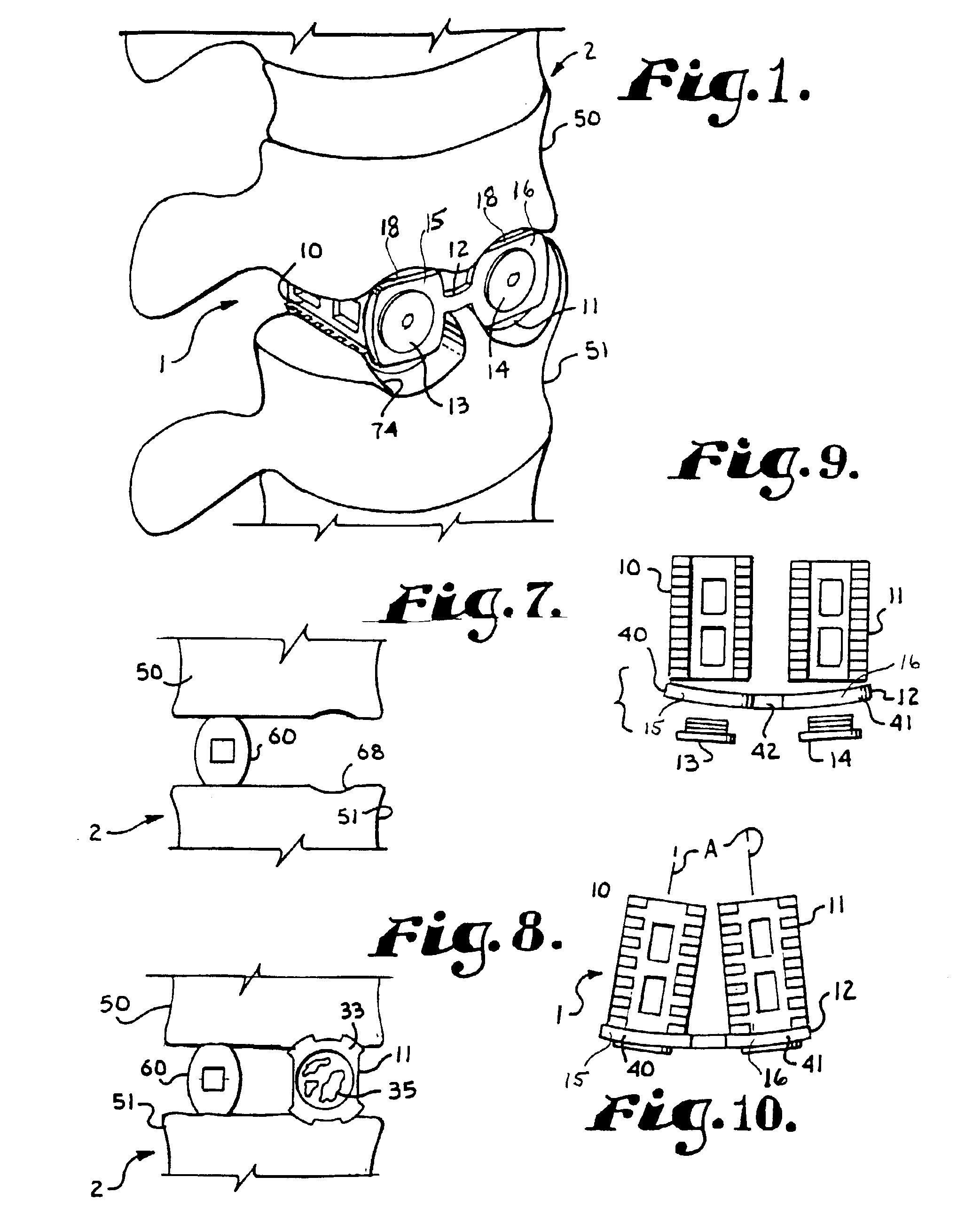
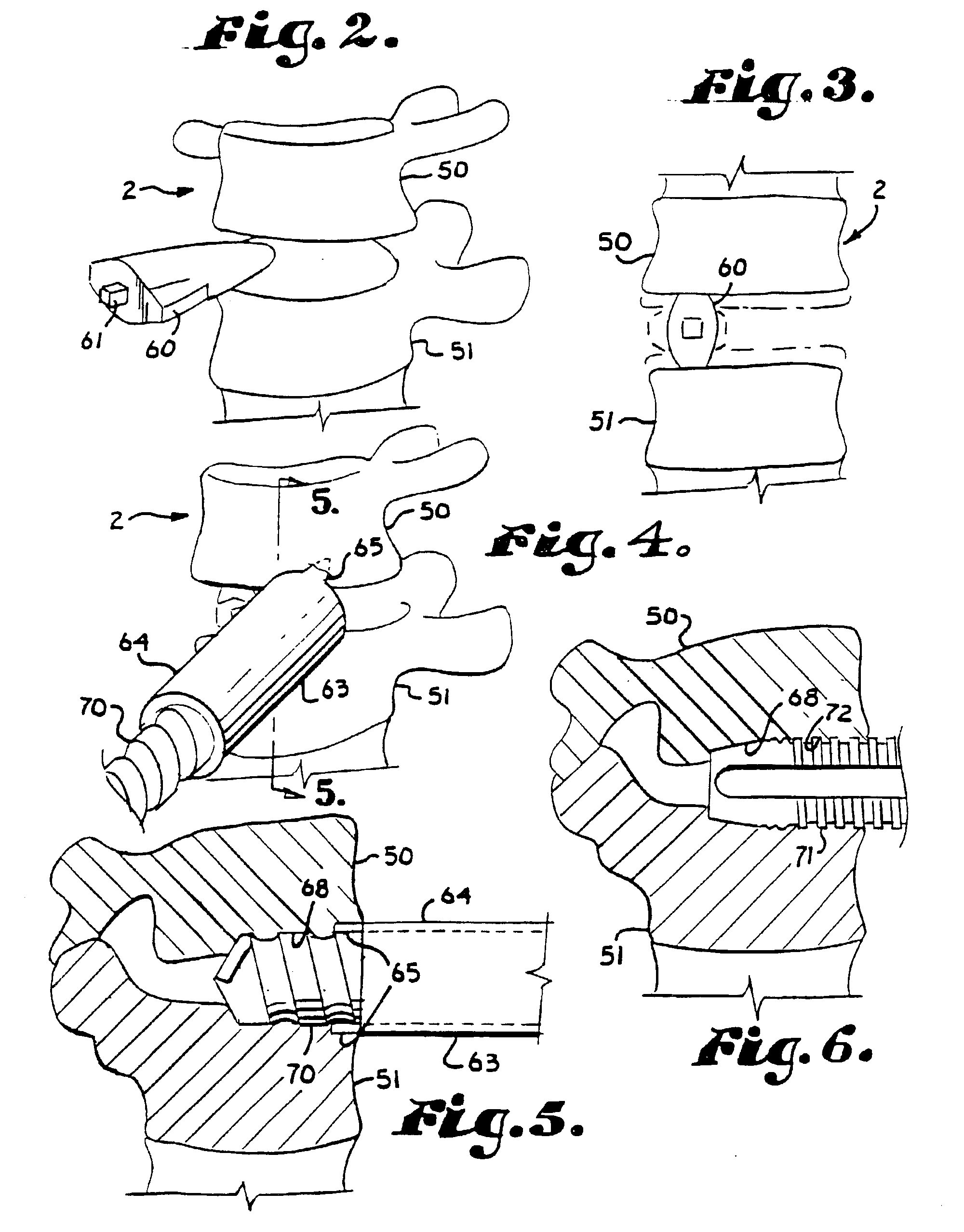
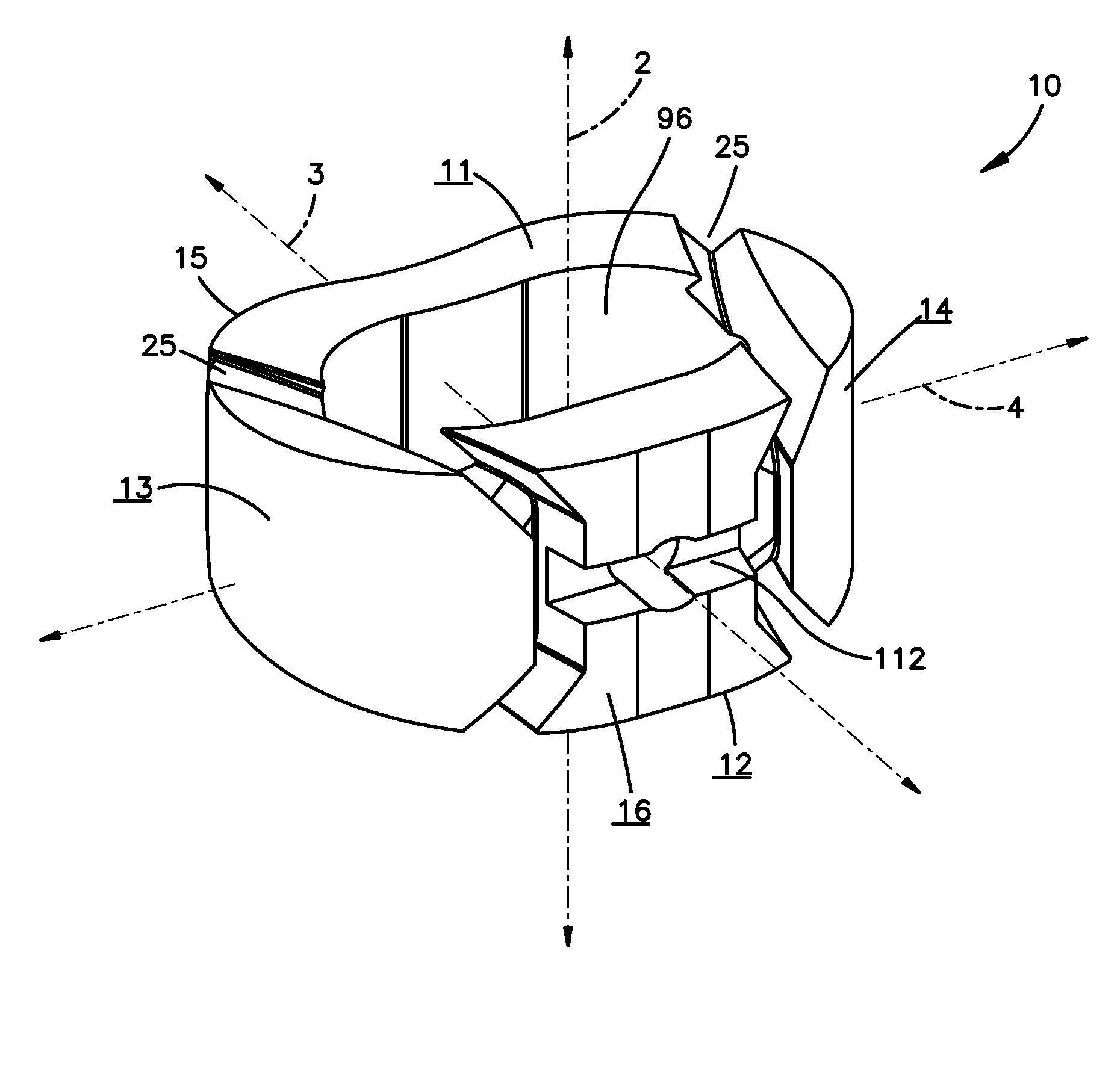
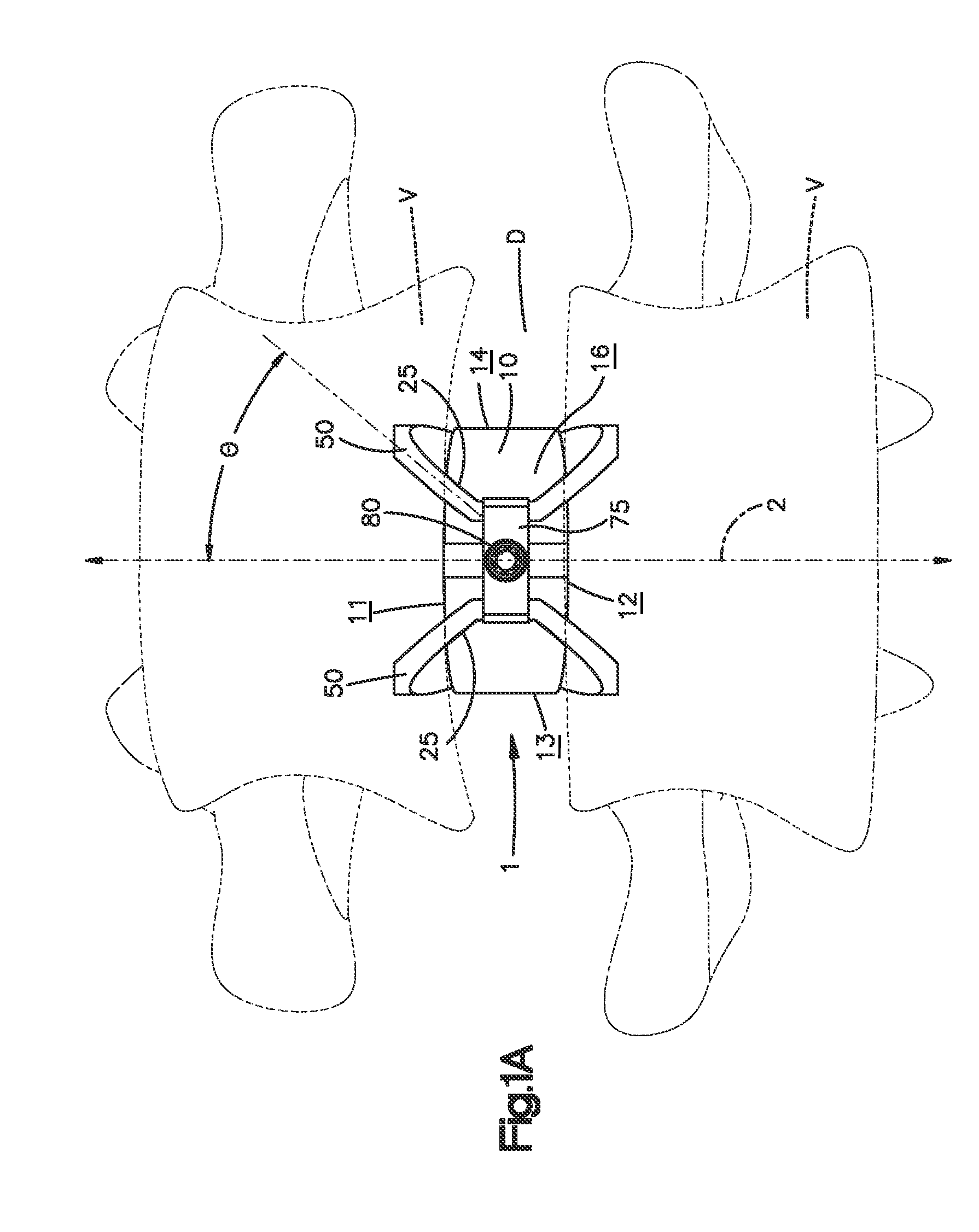
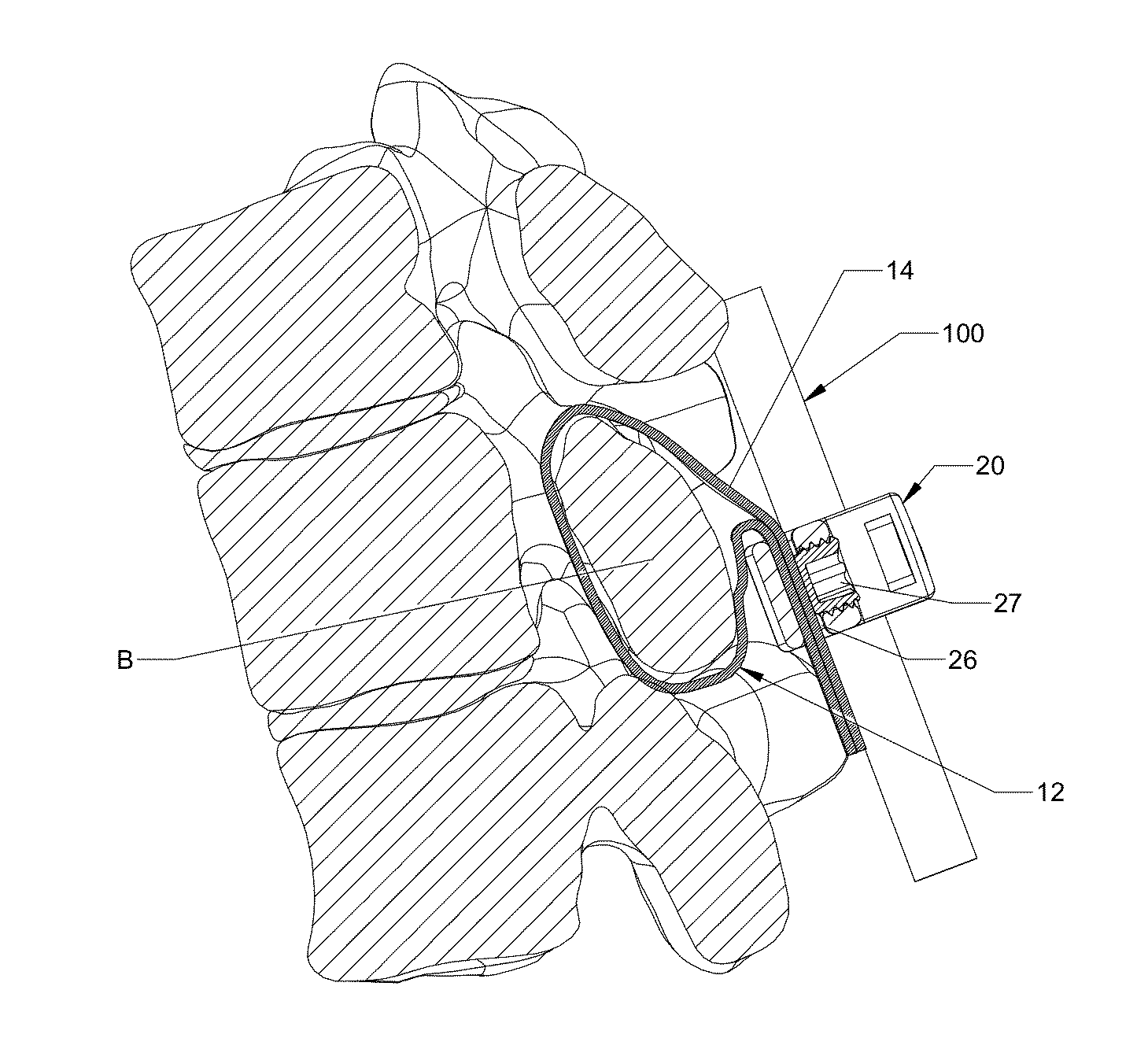
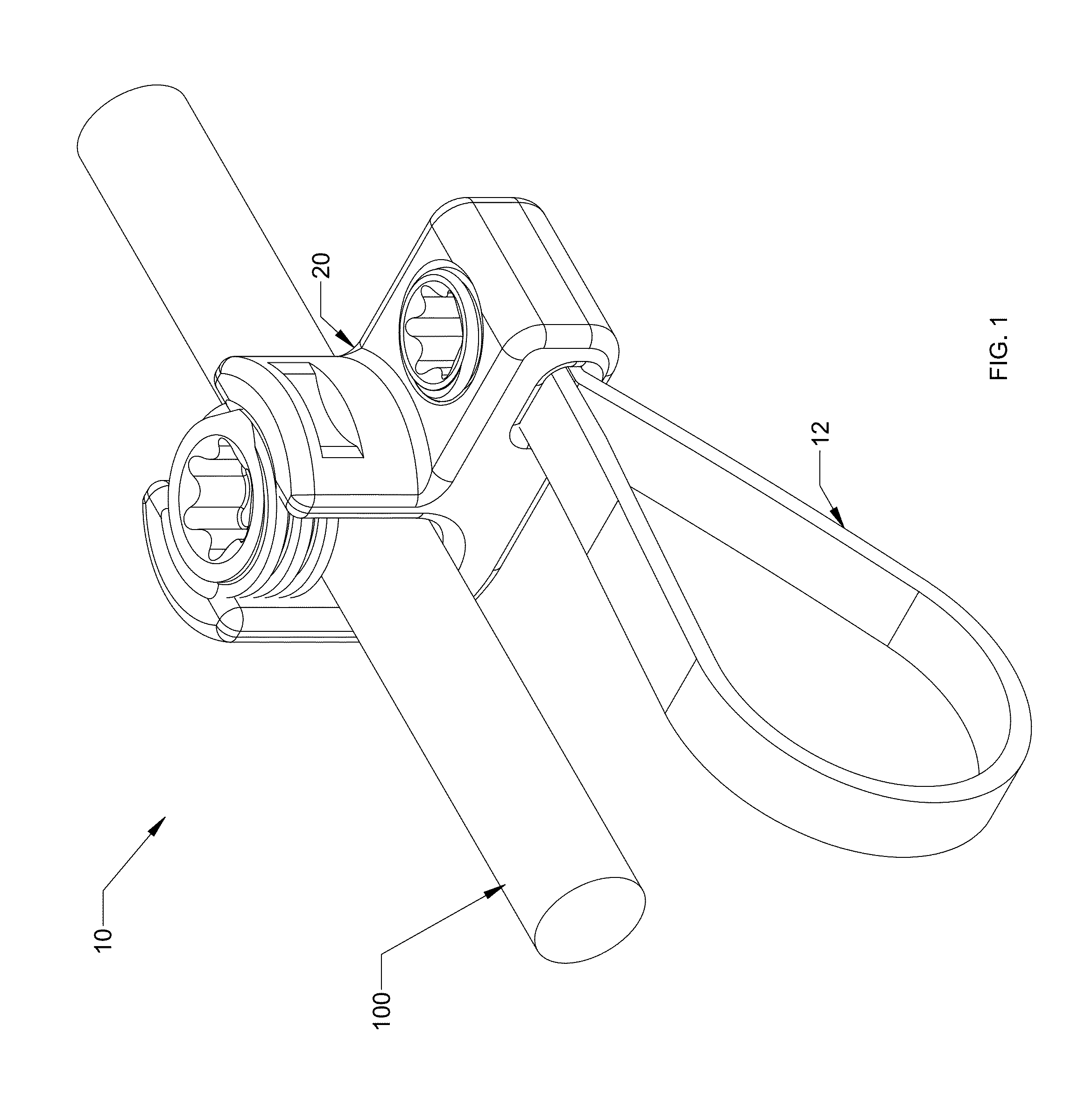
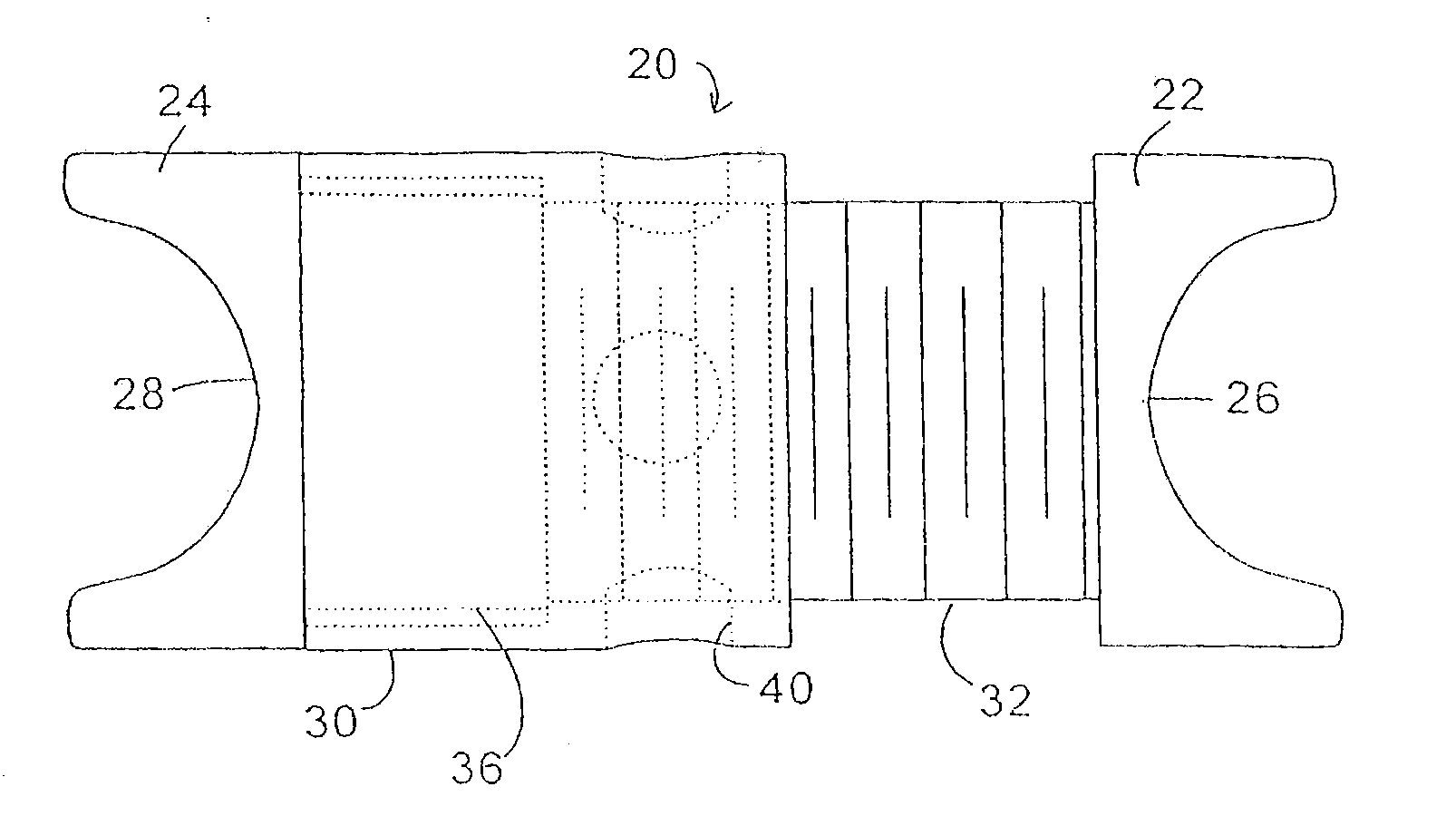
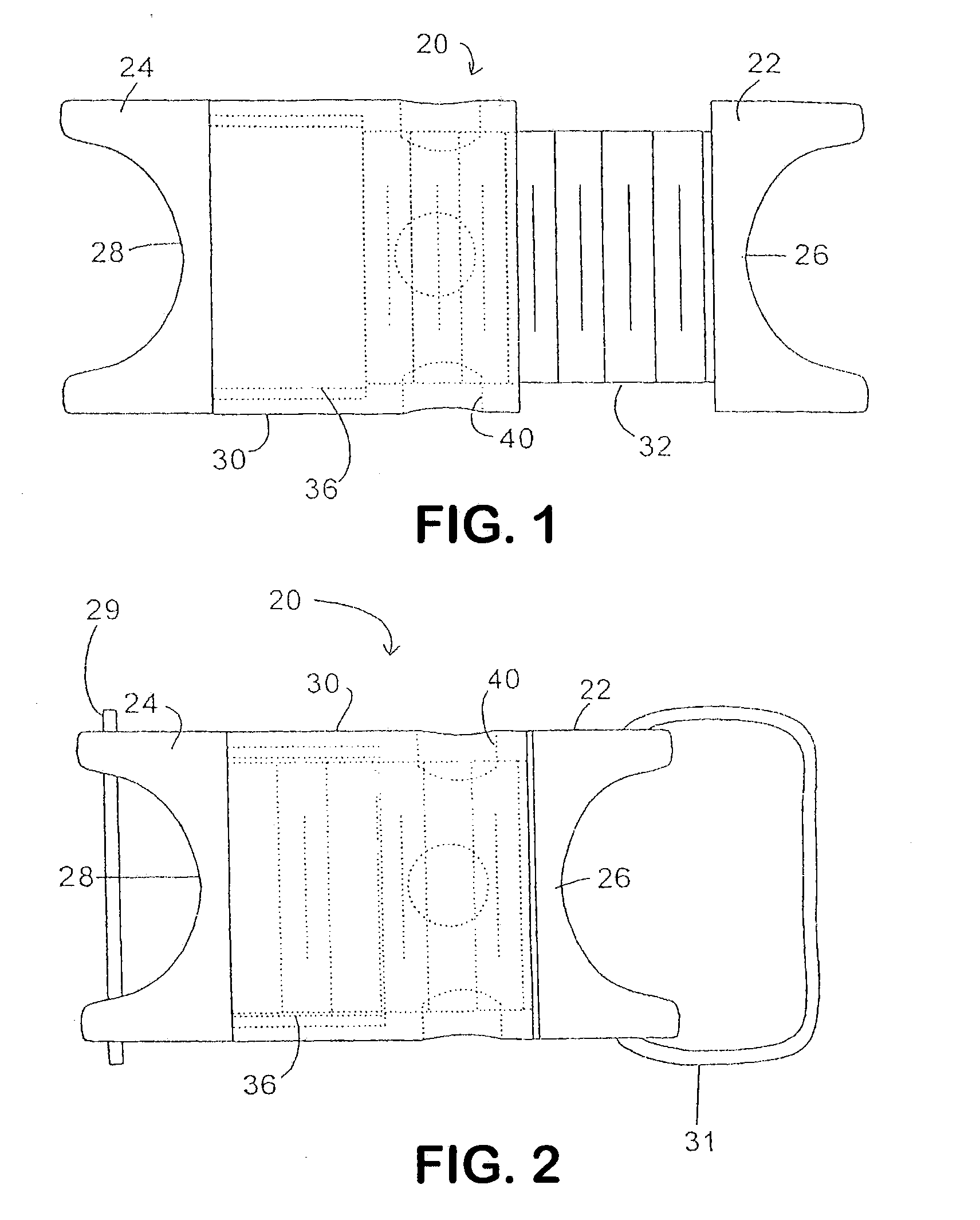
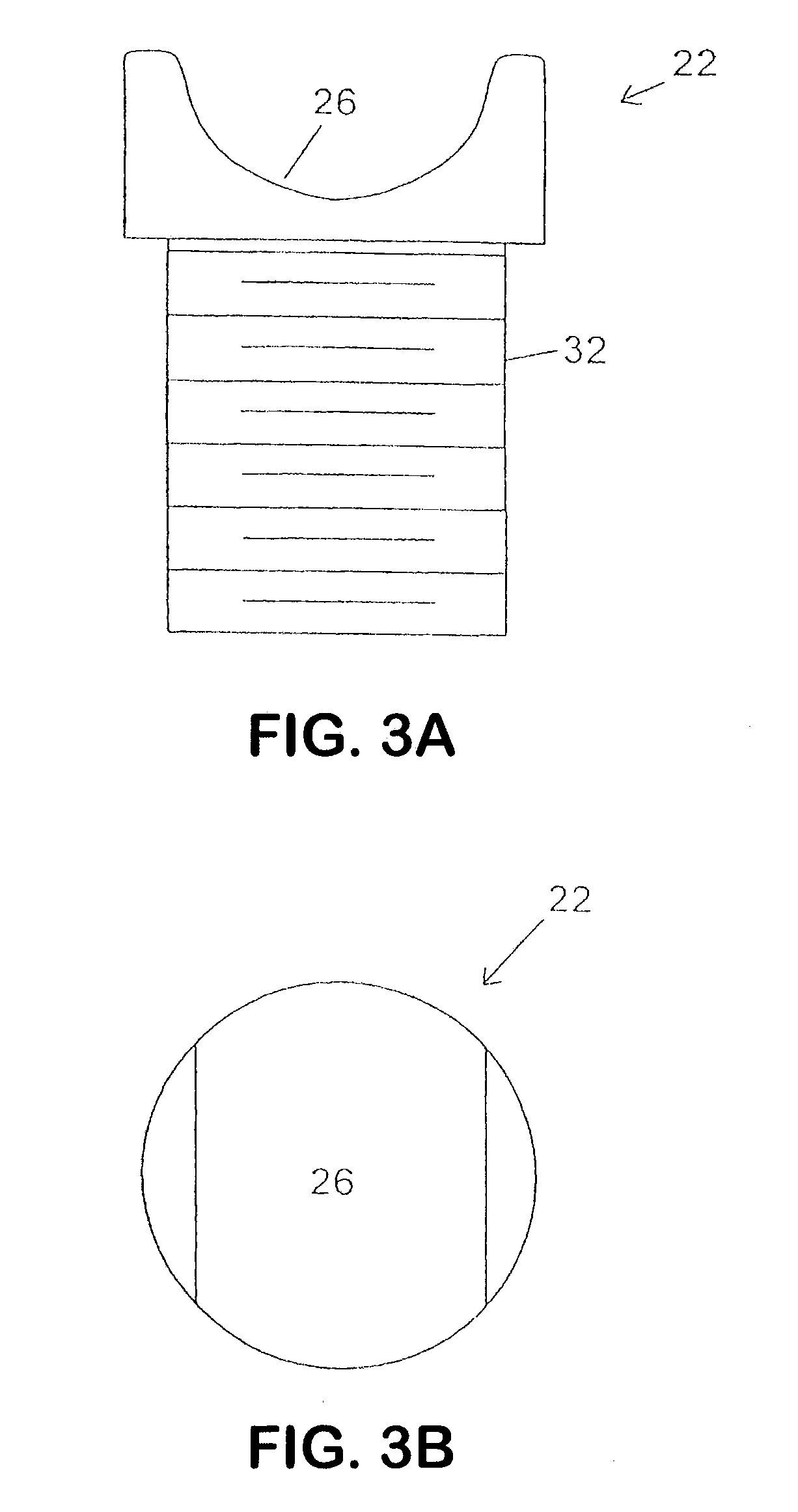
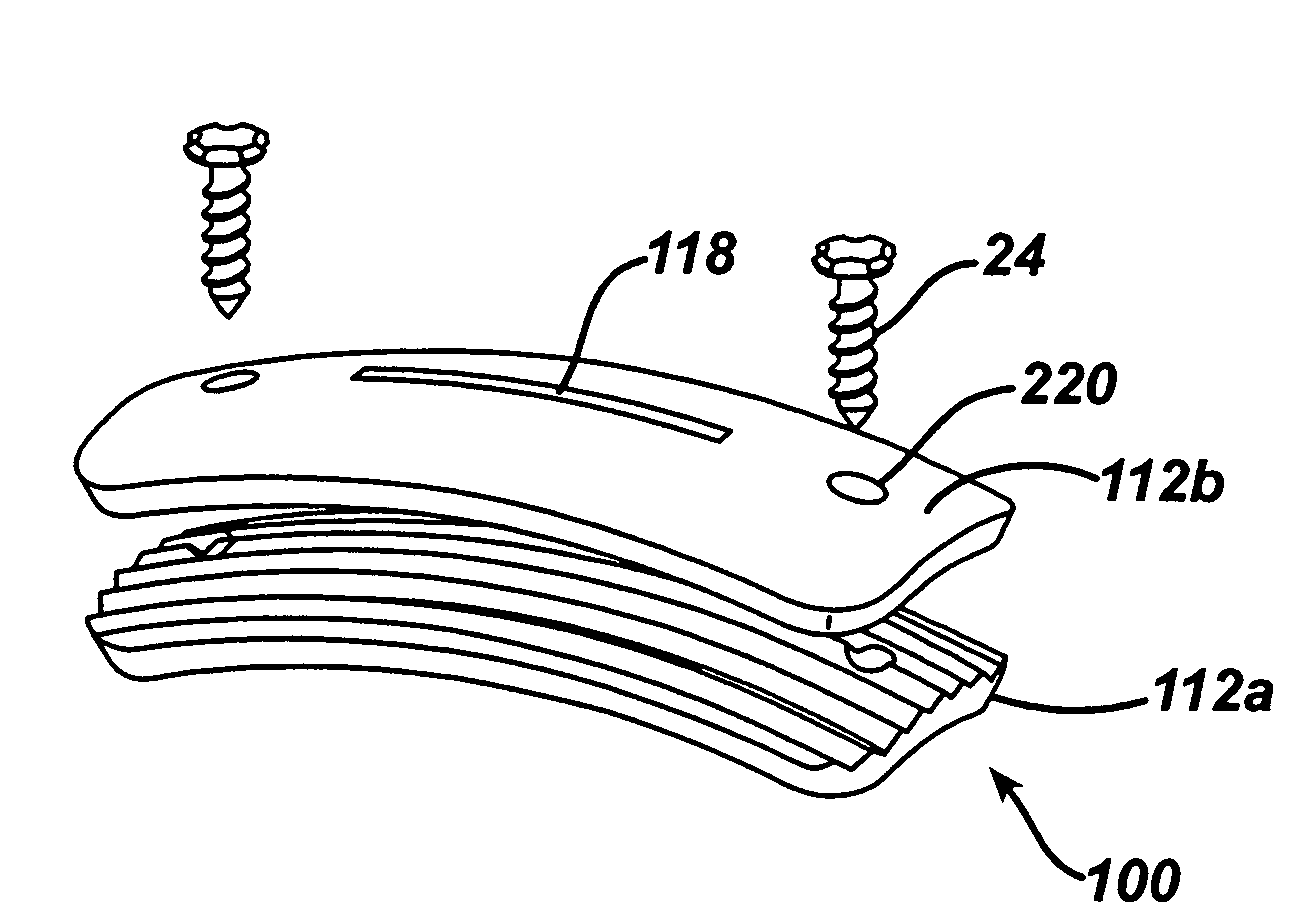
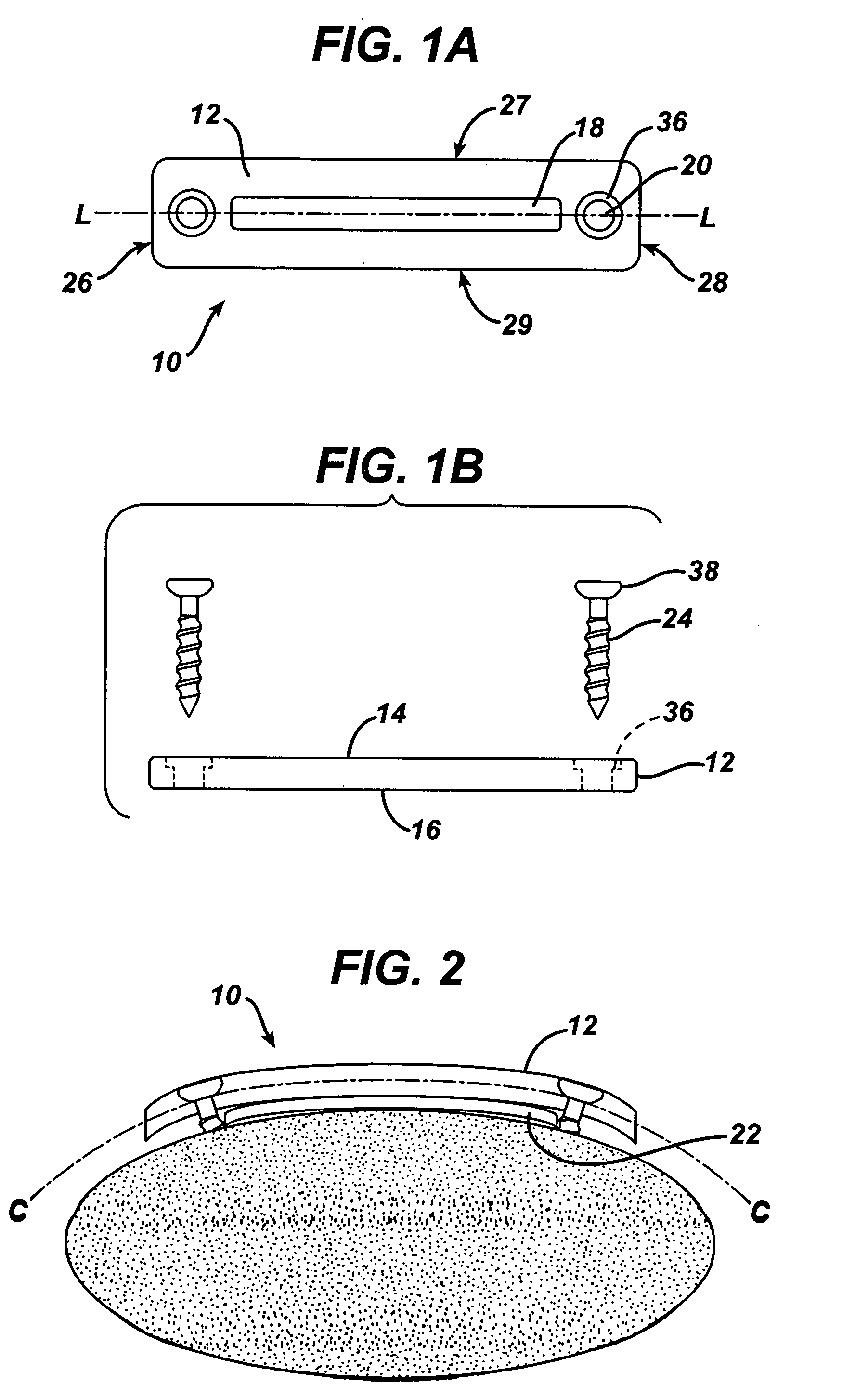
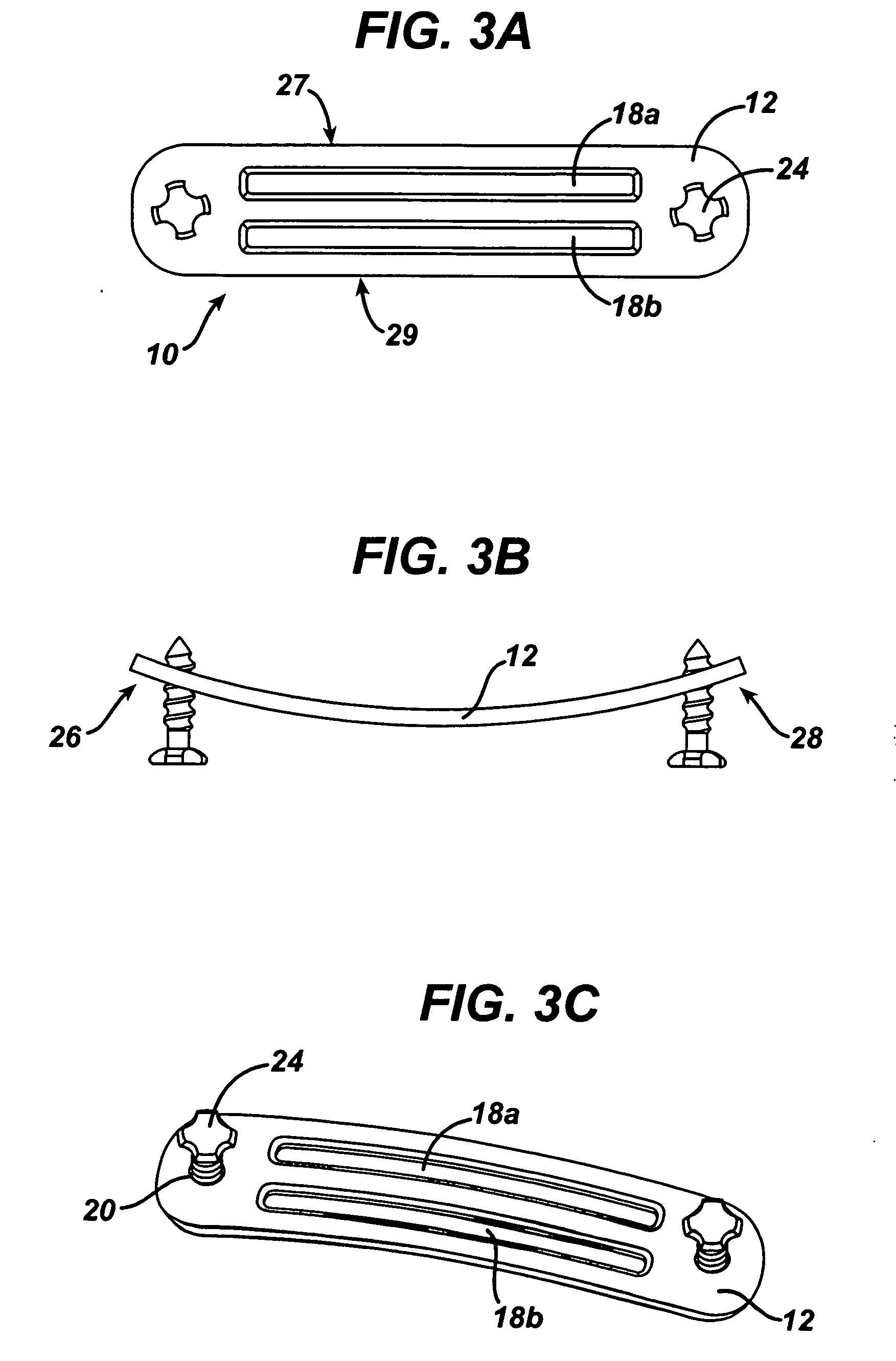
Implant fixation methods and apparatus
Various exemplary methods and devices are provided for fixing an implant to native tissue, such as, bone. The devices can include first and second plate bodies, each having an upper surface and a lower tissue contacting surface. The bodies can provides a large contact area for fixing the tissue implant to bone, such that the implant can be securely held in position without requiring penetration of the implant. In one embodiment, the plate bodies can include at least one aperture for receiving a fixation device and a tissue implant receiving opening through which a tissue implant can be threaded prior to fixing the plate bodies to bone.
Owner:DEPUY SPINE INC (US)
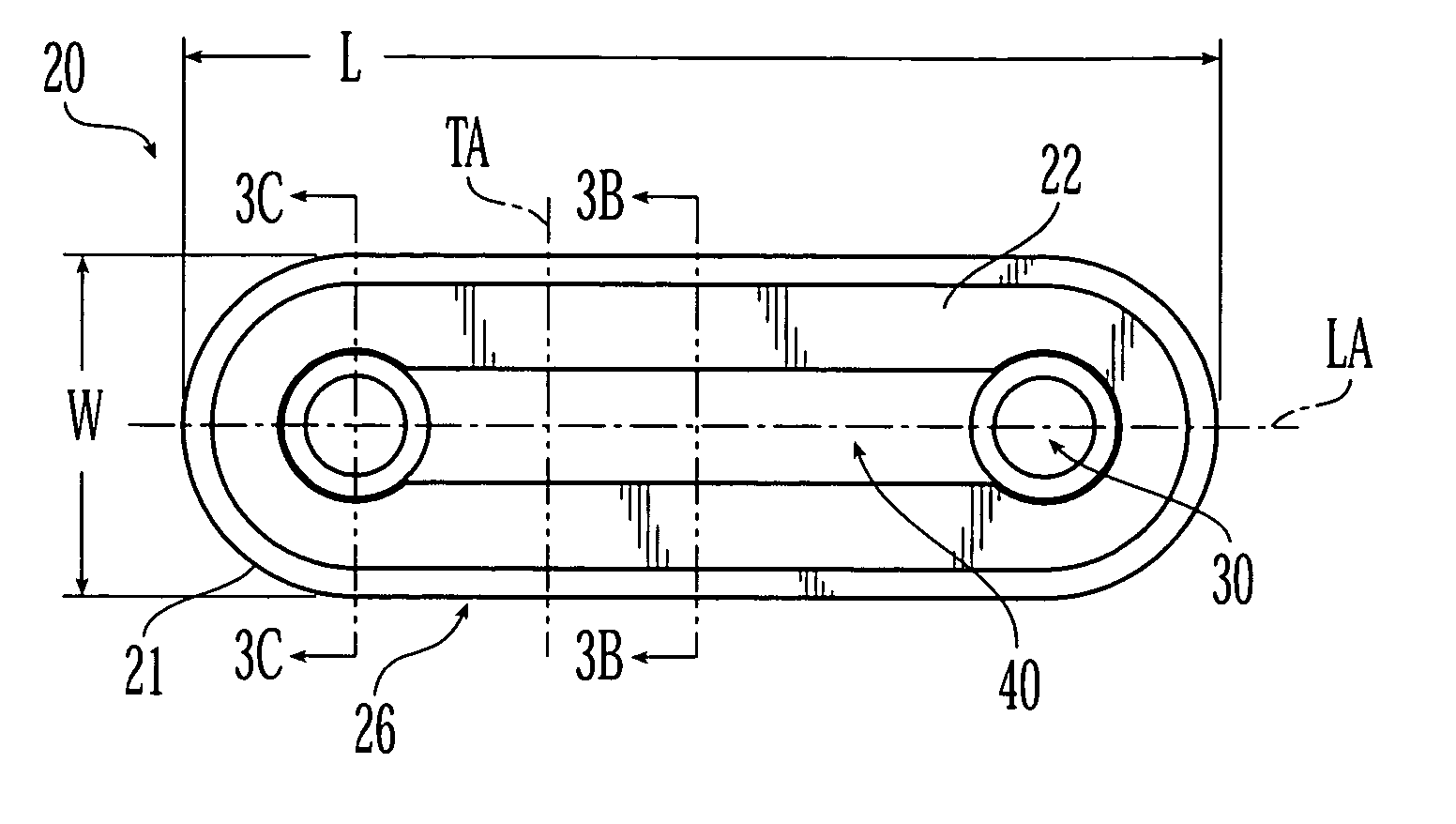
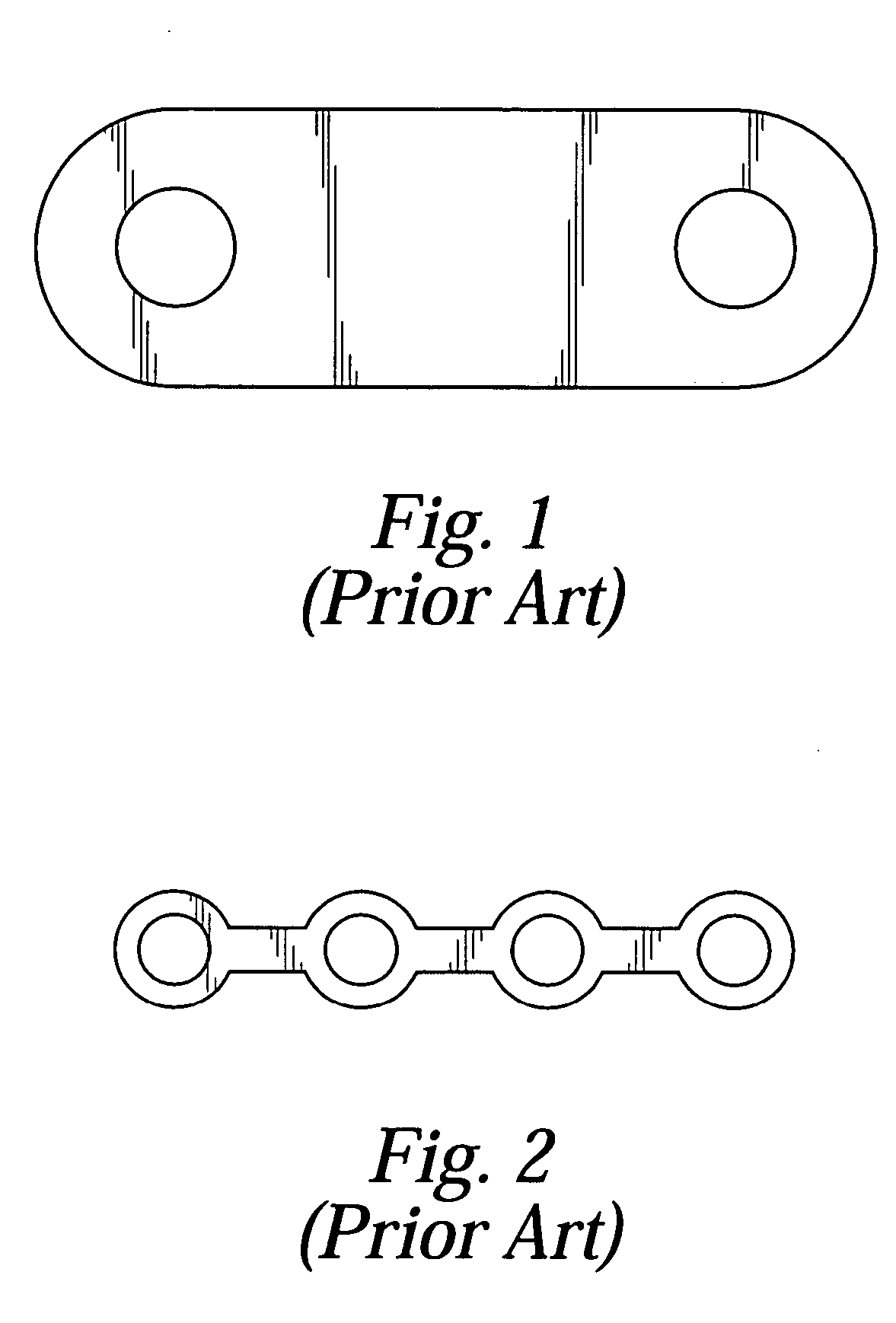
Bone fixation implants
InactiveUS20050216008A1Reduce the possibilityIncrease pressureInternal osteosythesisBone implantMetallic materialsEngineering
The present invention is generally directed to an improved bone fixation implant that provides tactile indication of the top surface of the implant. In one embodiment, an implant comprises a top surface, a bottom bone-contacting surface, and recessed portion disposed in the top surface of the implant to provide a tactile indicator for readily identifying the top surface of the implant. In another embodiment, the top surface indicator may be in the form of an elongated top surface groove that is recessed below the top surface of the implant. The implant may further include at least two fastener holes for receiving fasteners therethrough to secure the implant to the bone. In preferred embodiments, the implant may be made of a resorbable or metallic materials. In another embodiment of the present invention, an implant may comprise transverse slots preferably disposed between at least some of the fastener holes.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
Retaining element for an implant and ampoule for preserving said implant
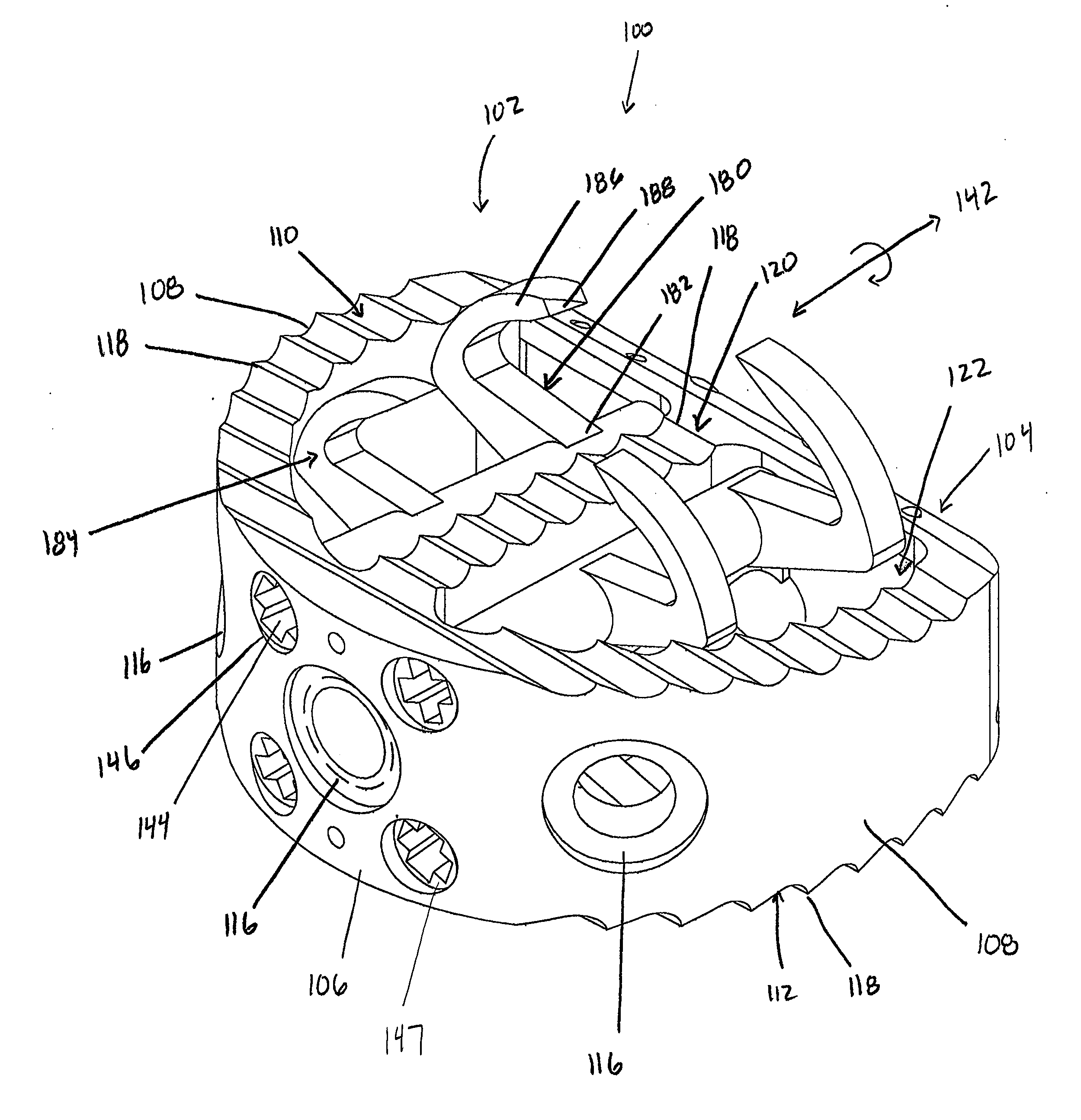
InactiveUS6261097B1Easy to operateGood adhesionDental implantsTransverse incisionMechanical engineering
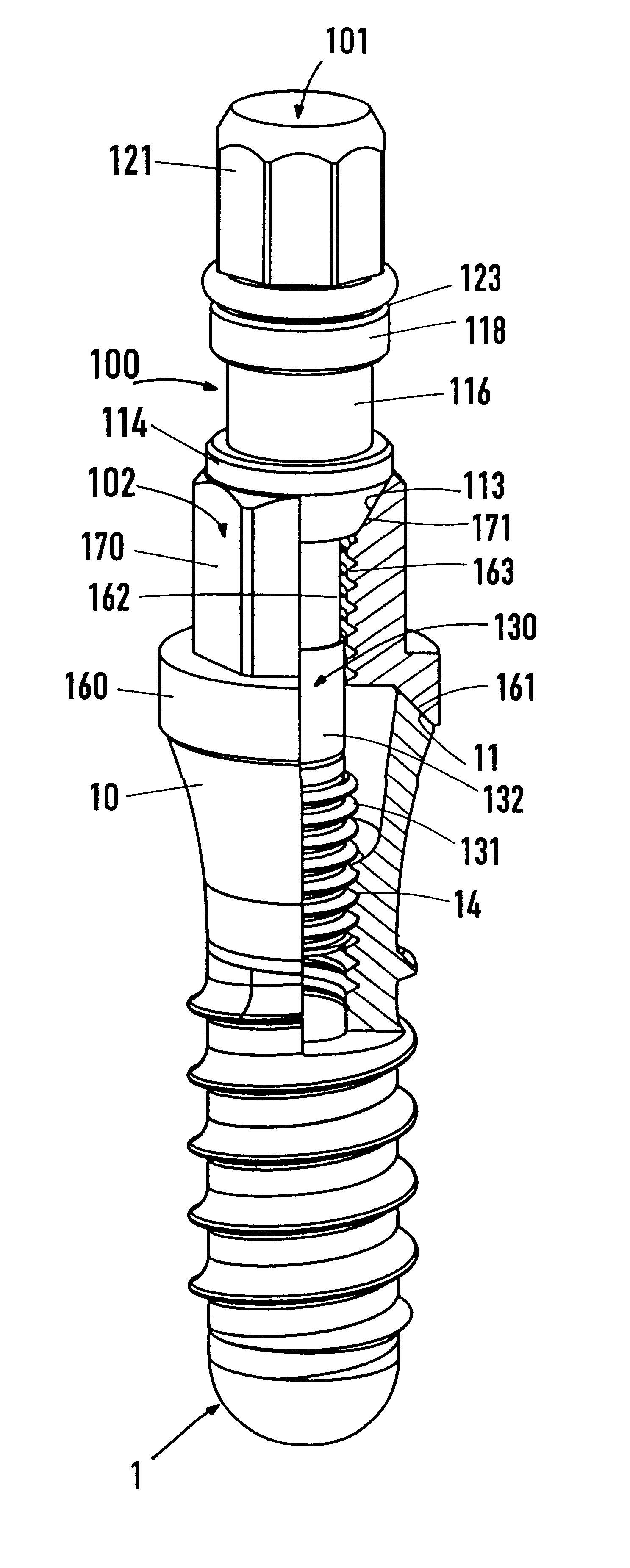
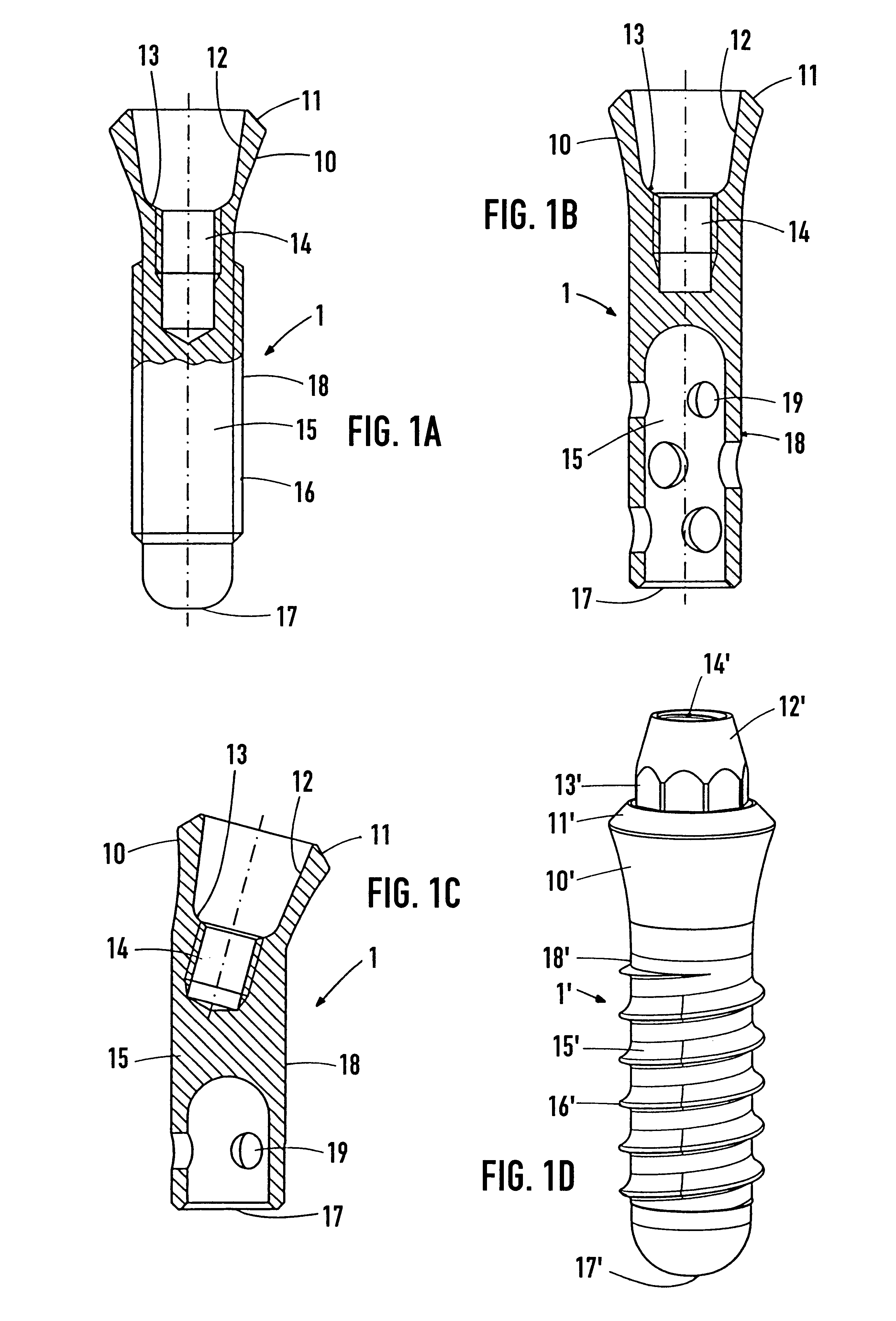
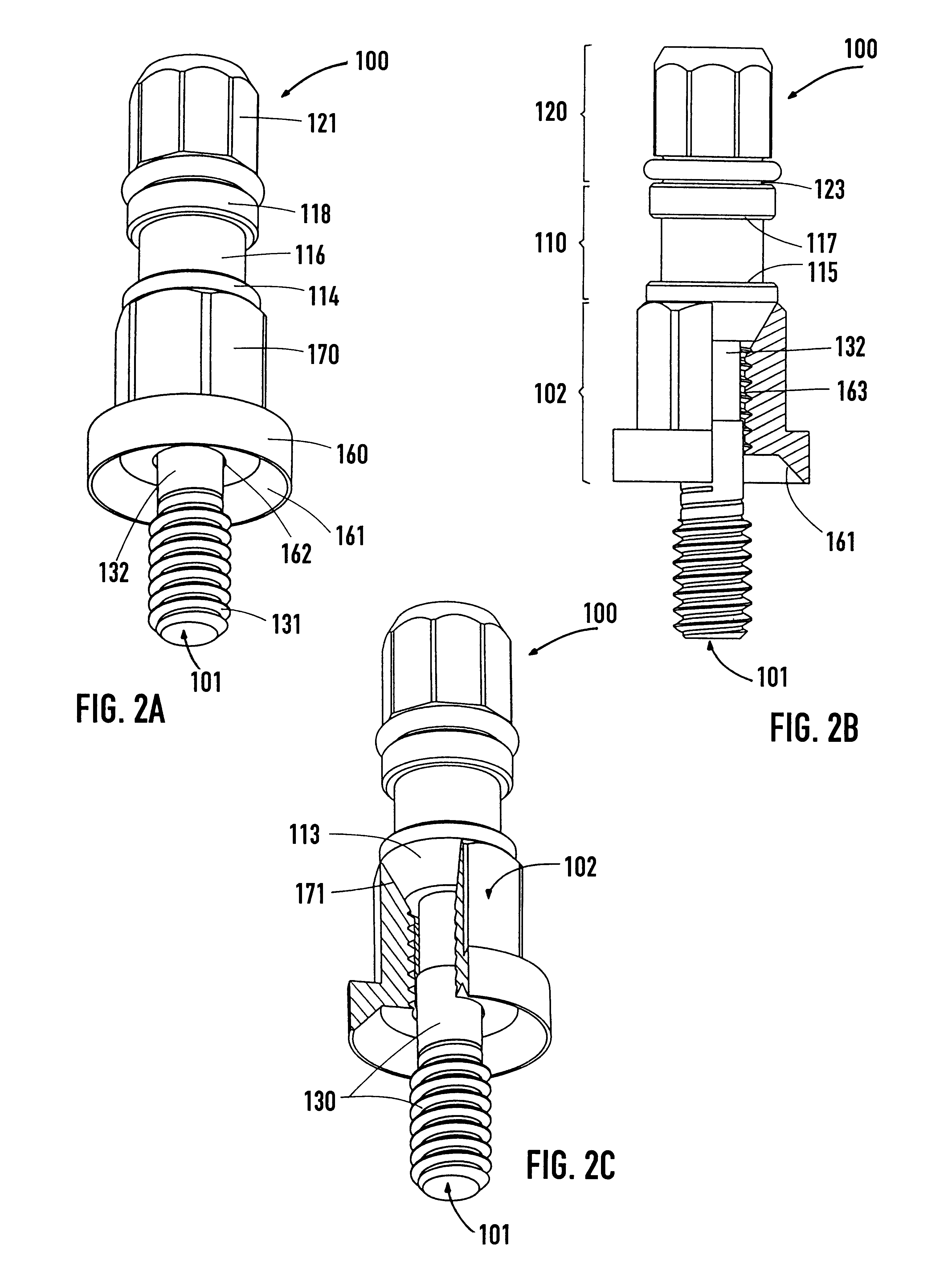
The proposal is for a holding element (100) which can be screwed into the internally threaded bore (14) of the implant (1) even during production of the latter and can thus be used to grip or hold the implant for the following production phases. Furthermore, the holding element (100) serves to fix an implant (1), which is screwed thereto, inside an ampoule (200) and for the application of a screwing-in tool for implantation. The particular feature of the ampoule (200) lies in the fact that it has a large-area, lateral cutout (231) in the casing and also a fixing part (210) for accommodating the holding element (100) in a clamped manner. The implant (1) can thus be pulled laterally out of the ampoule (200). The devices facilitate handling of the implant (1) during production and insertion into the bone.
Owner:STRAUMANN HLDG AG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com