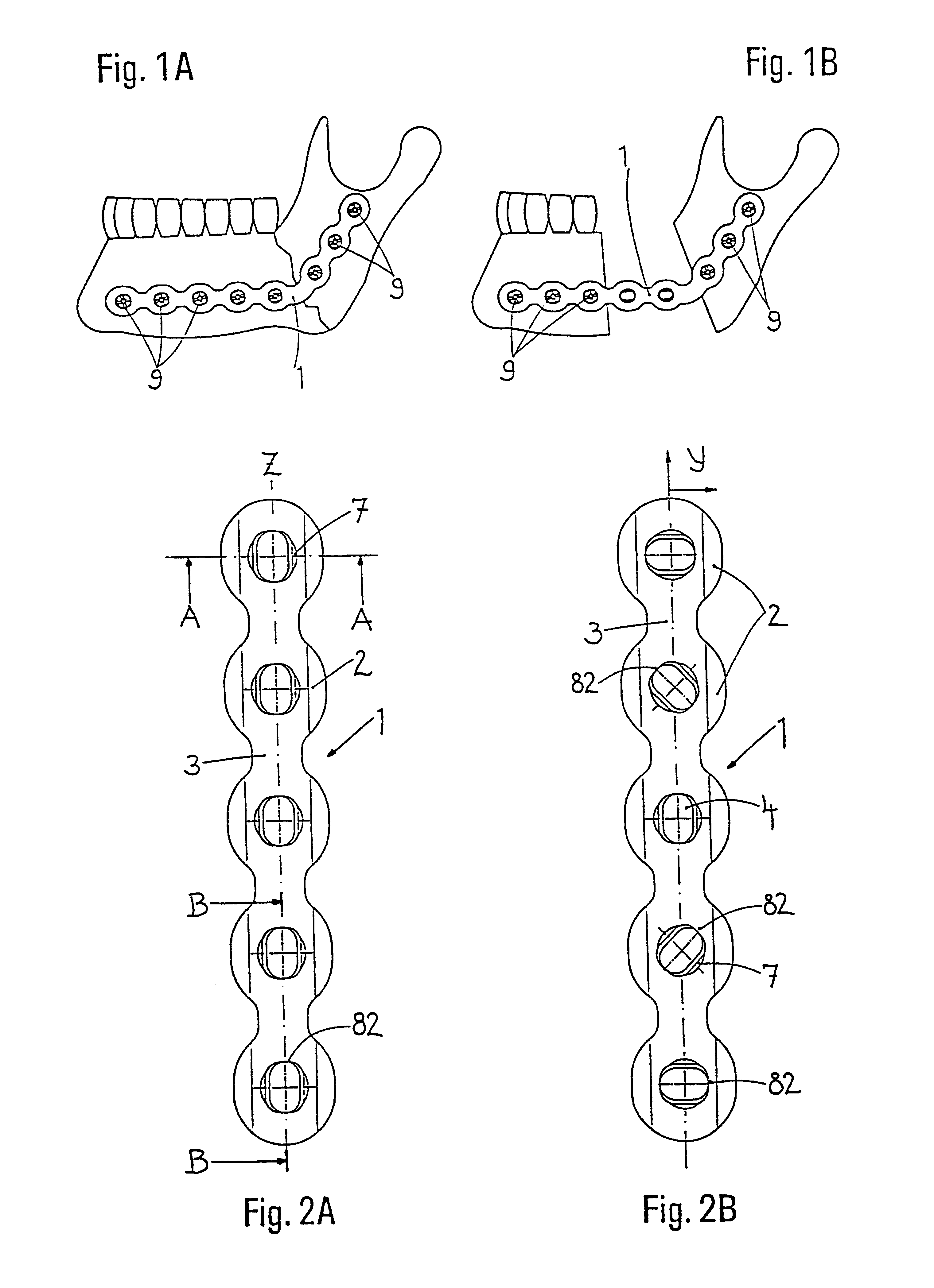Patents
Literature
2984 results about "Screw head" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
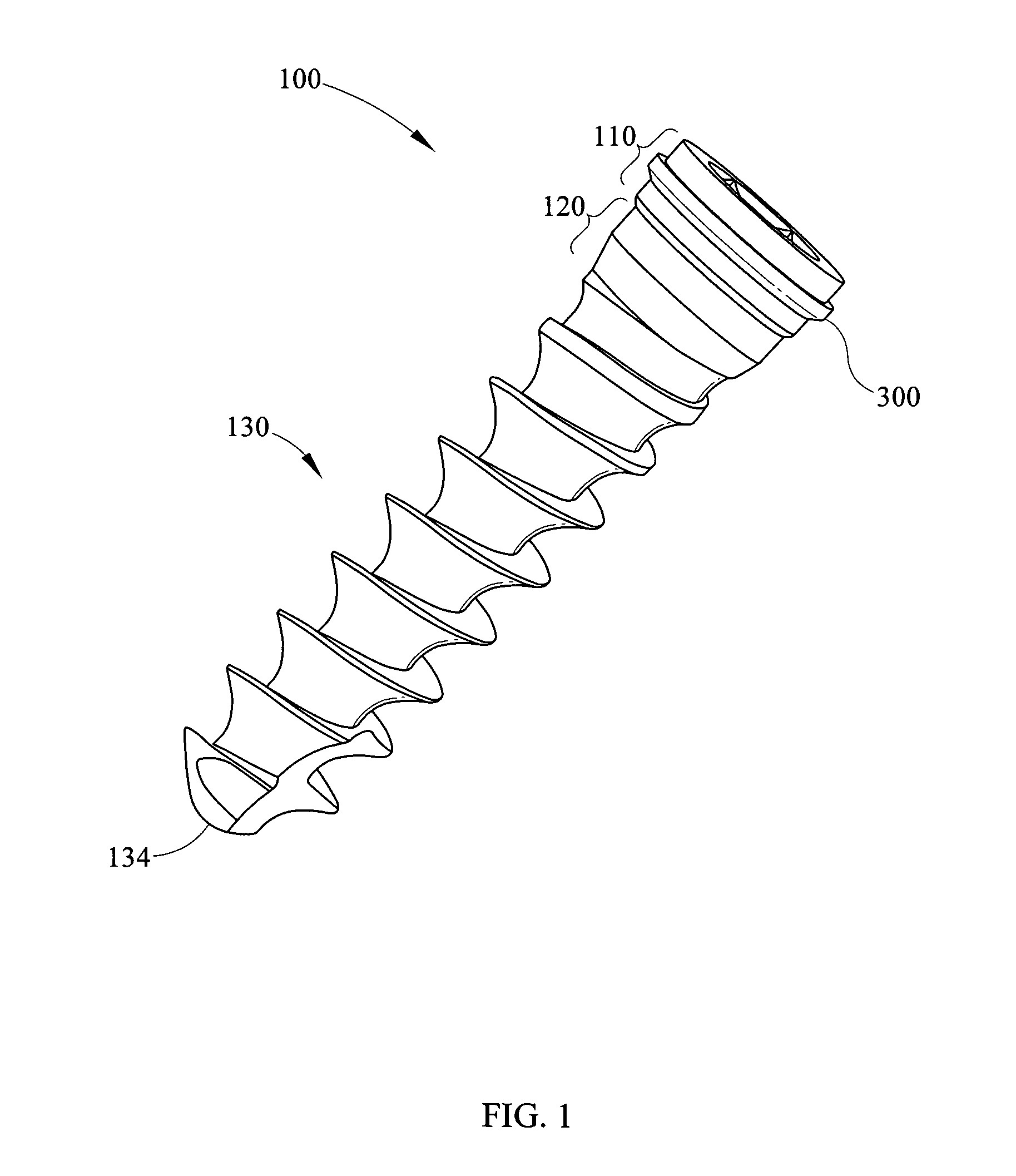
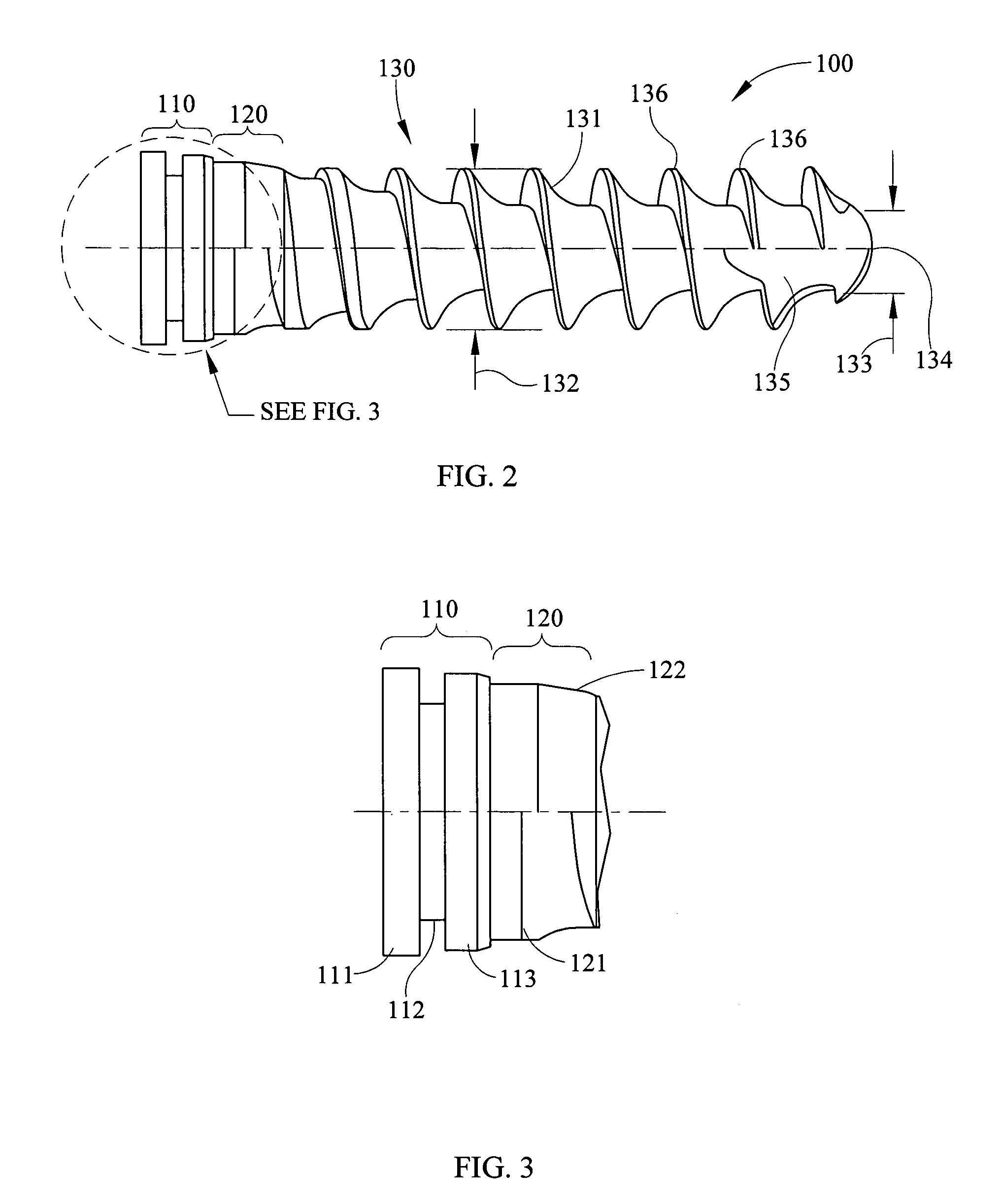
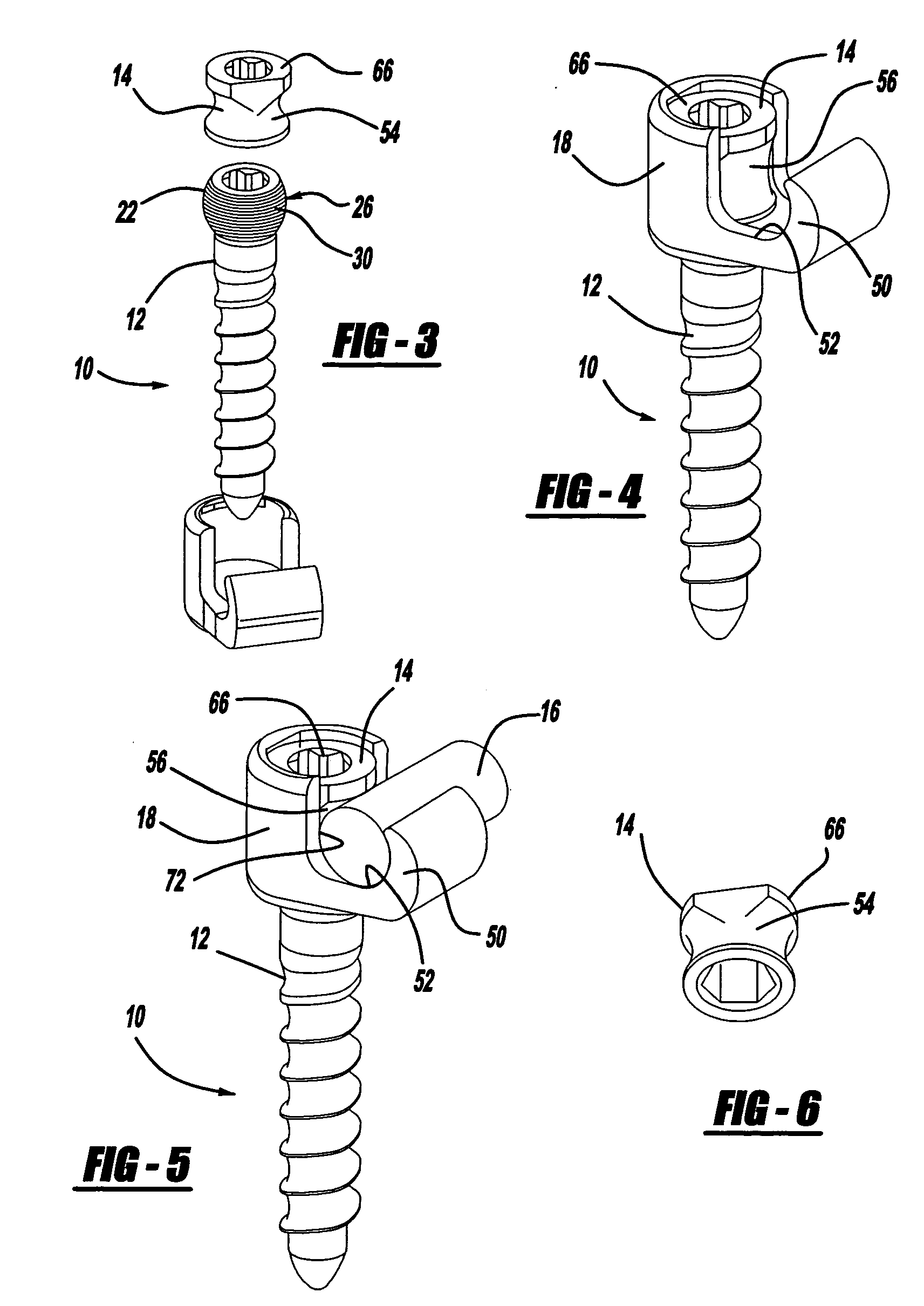
The head of a screw is where your screw will stop. Only the threaded part will be beneath the surface of your project, leaving the head outside, or flush with, the surface. Some head shapes help to create the look of the finished product, but they also usually have a purpose beyond aesthetics.
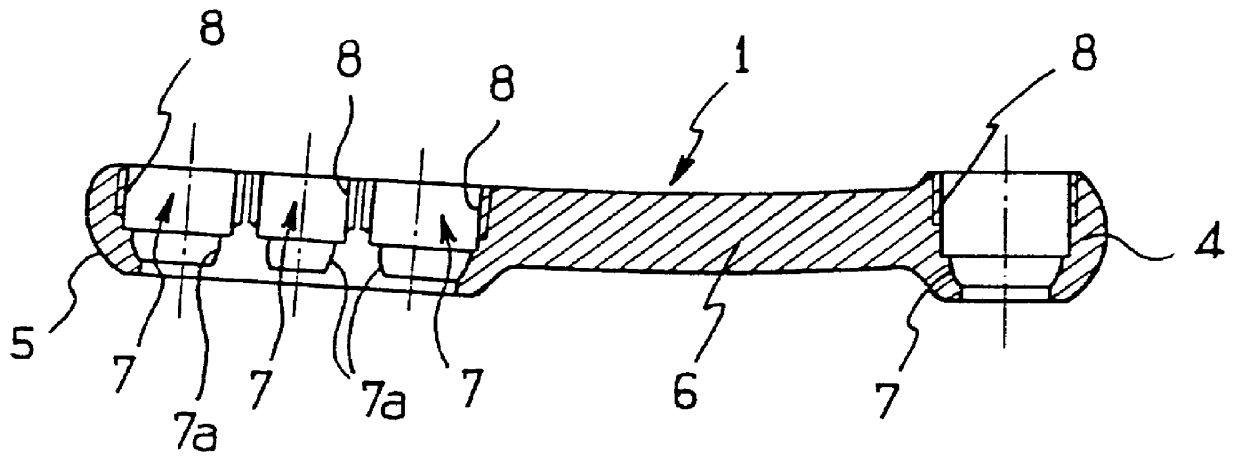
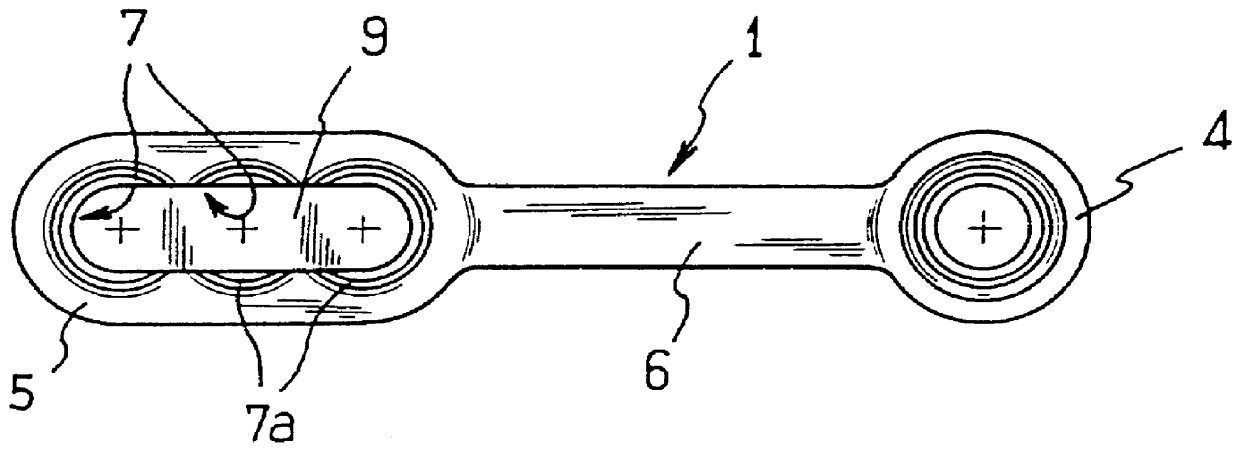
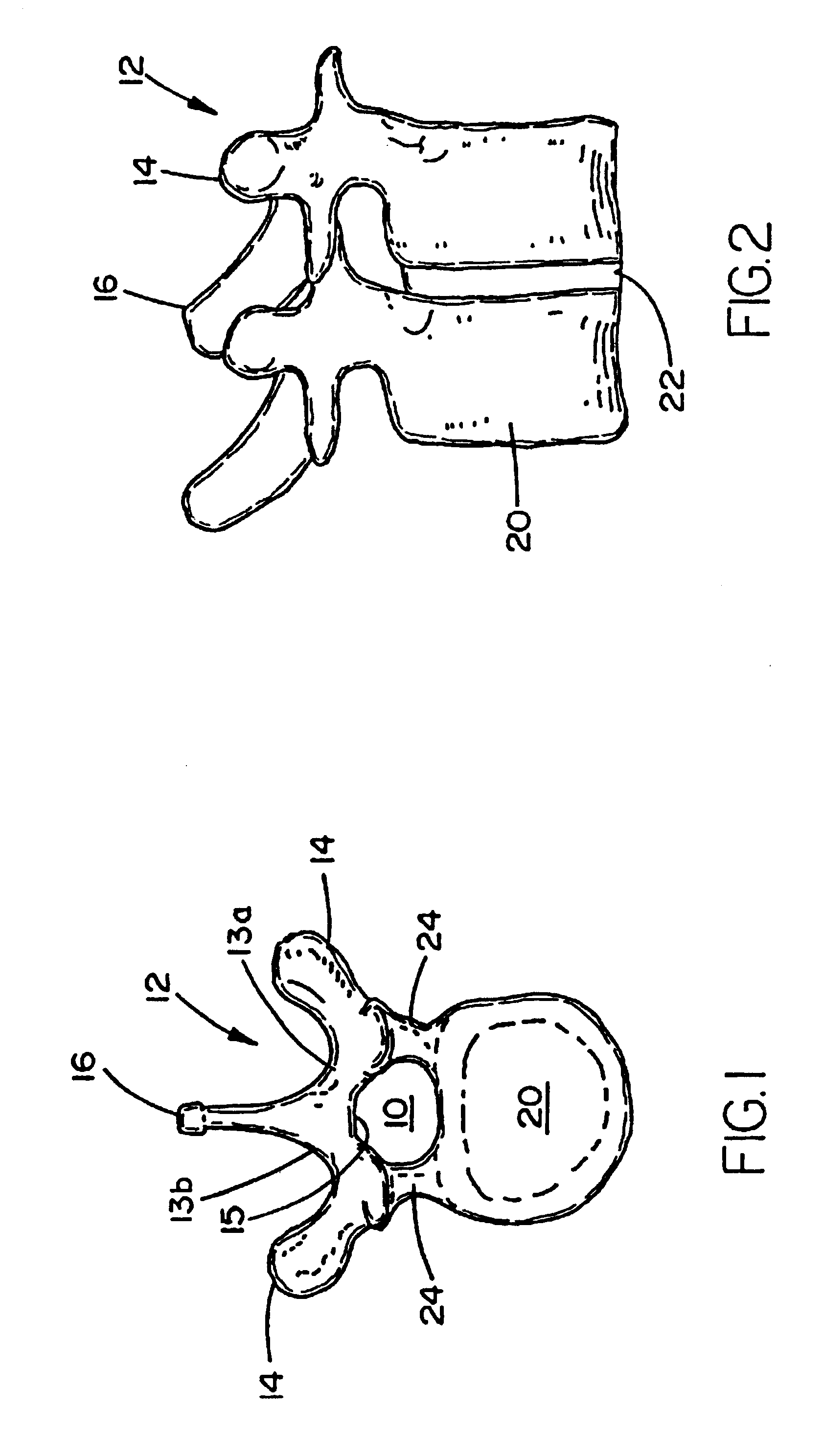
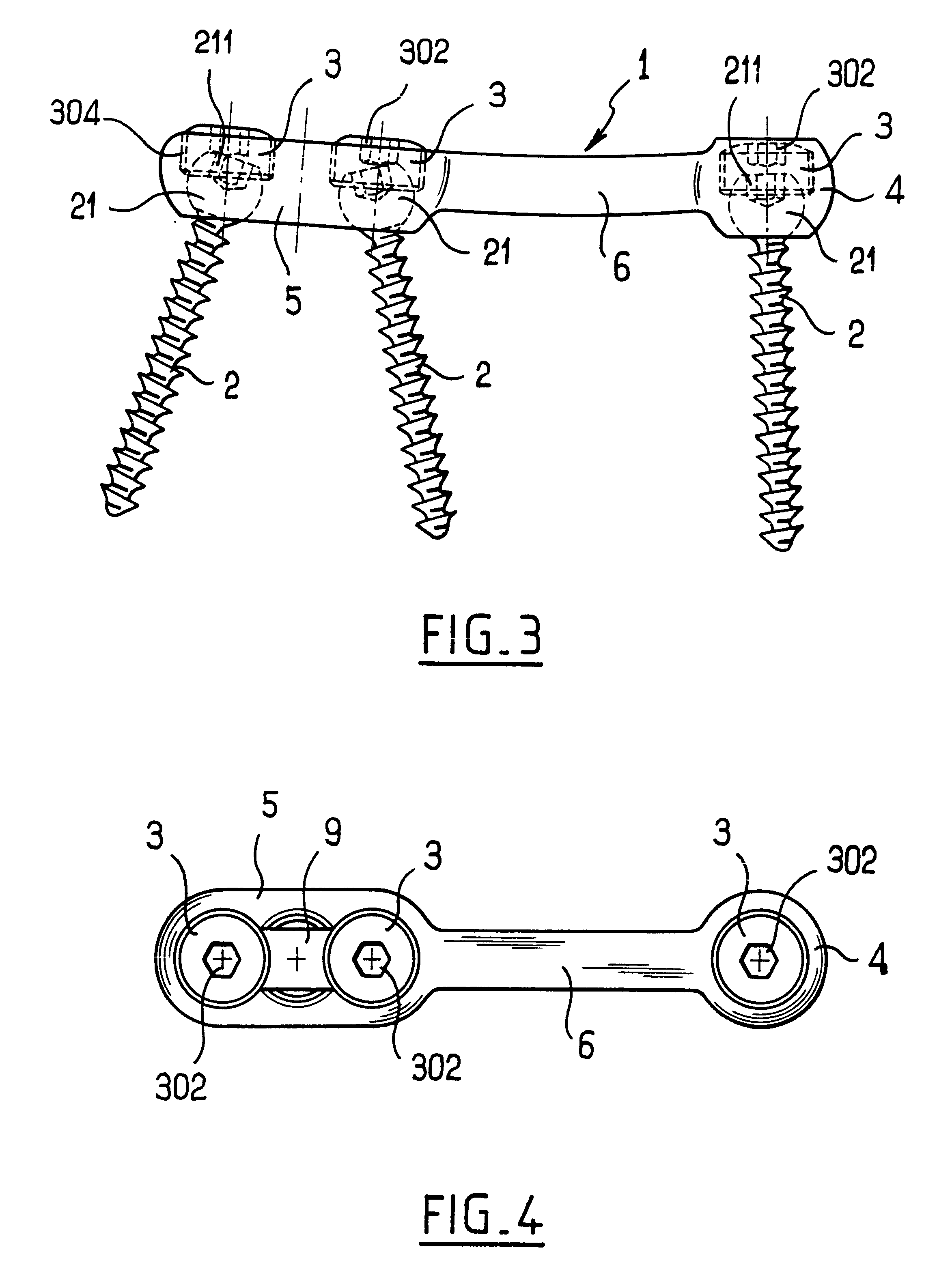
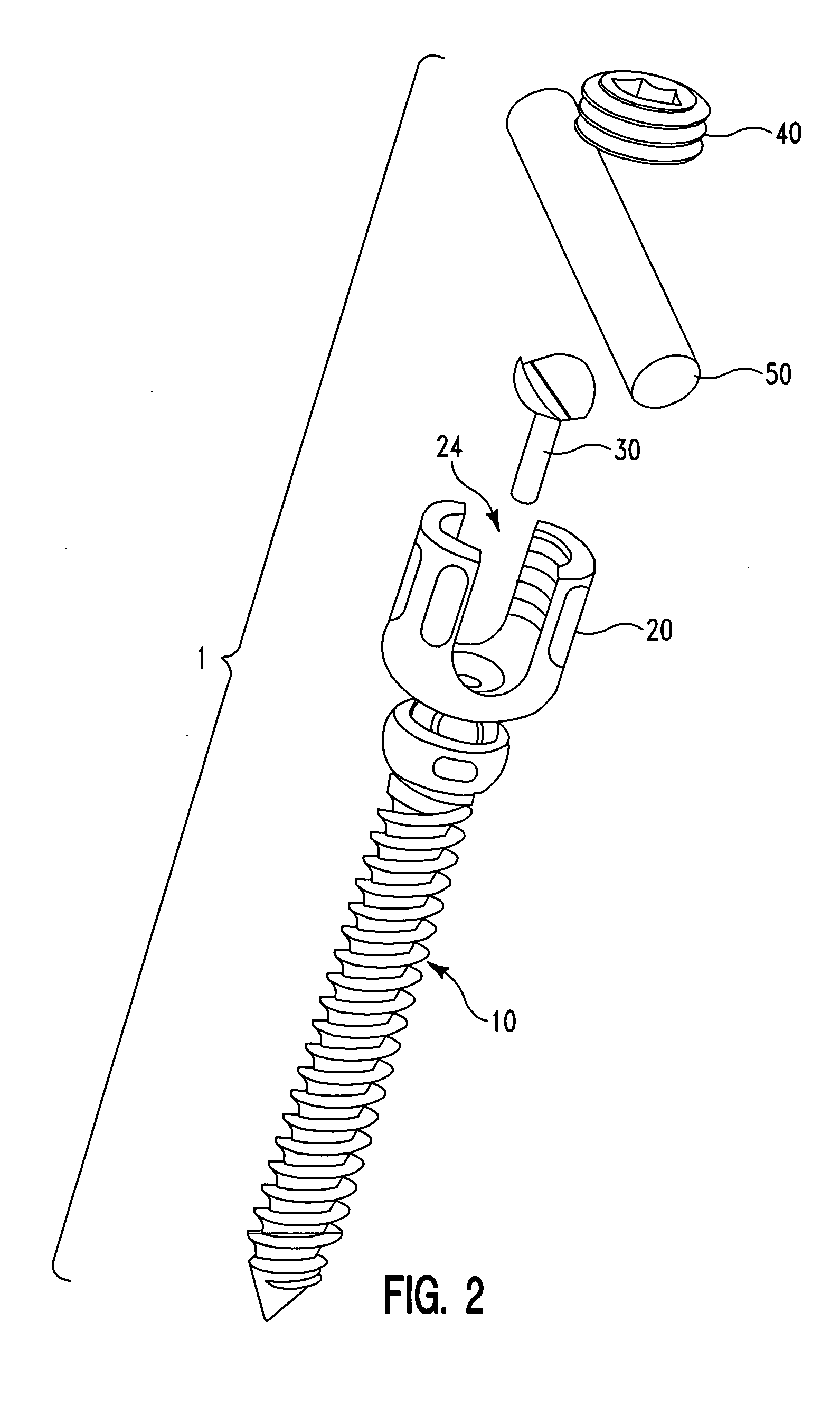
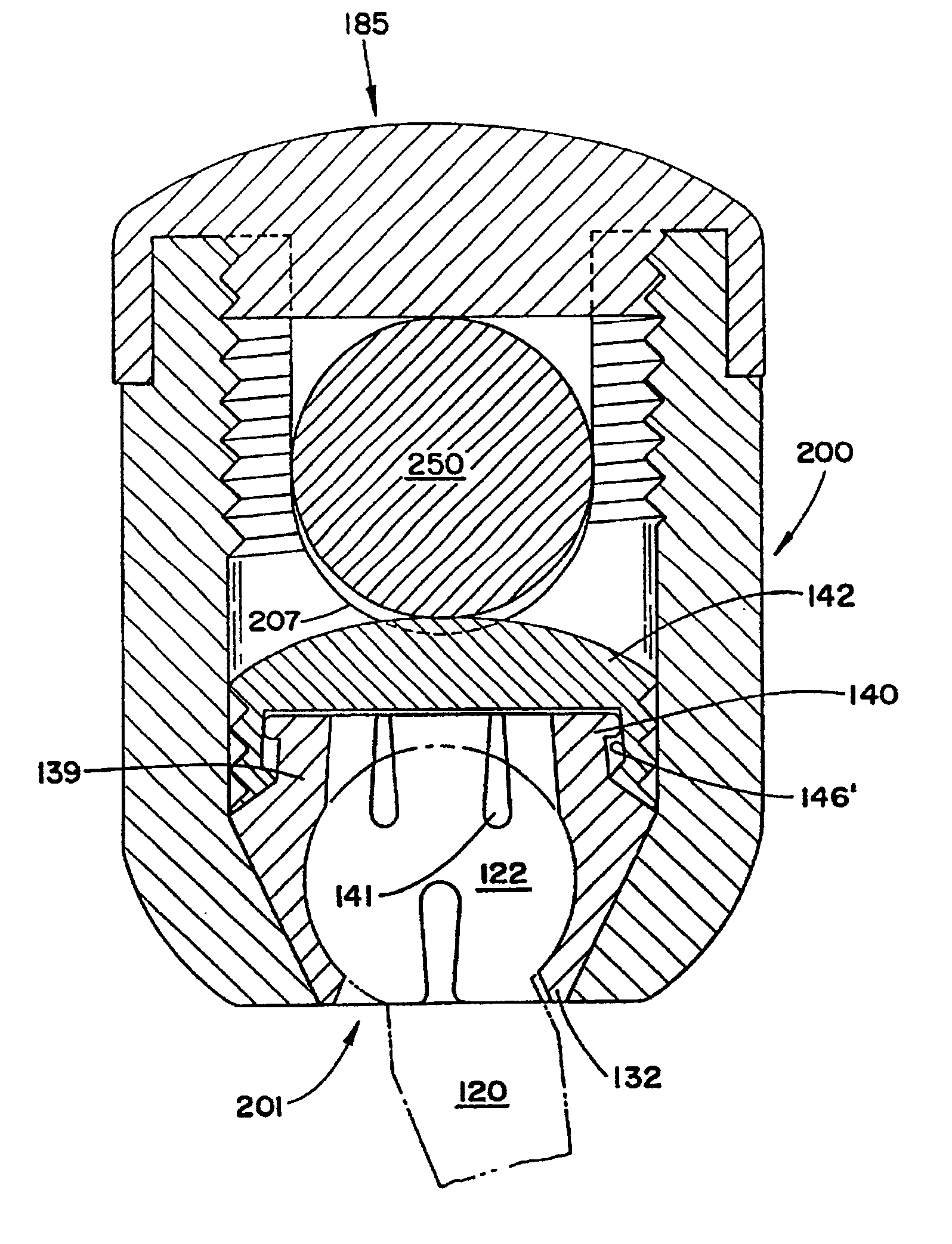
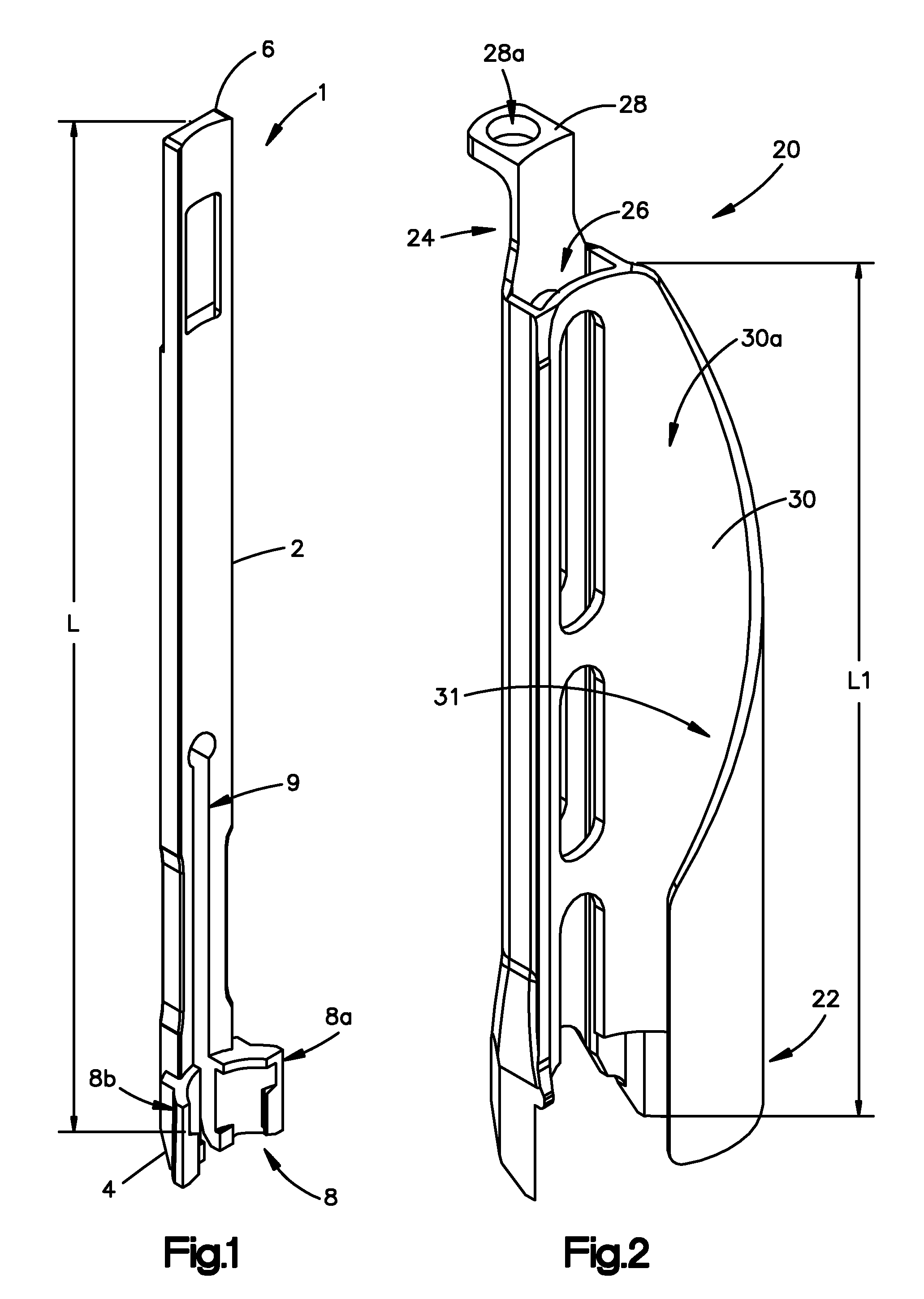
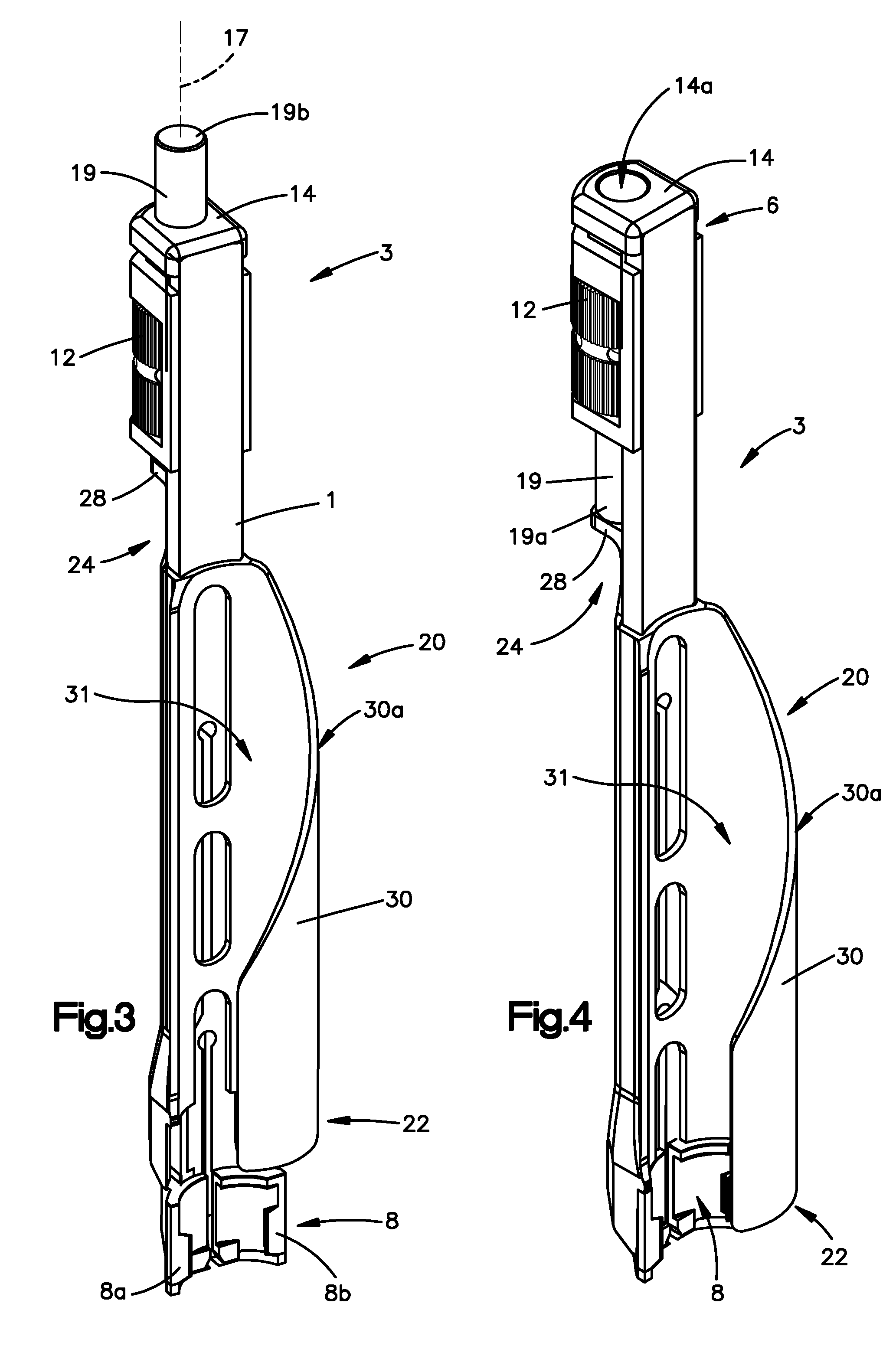
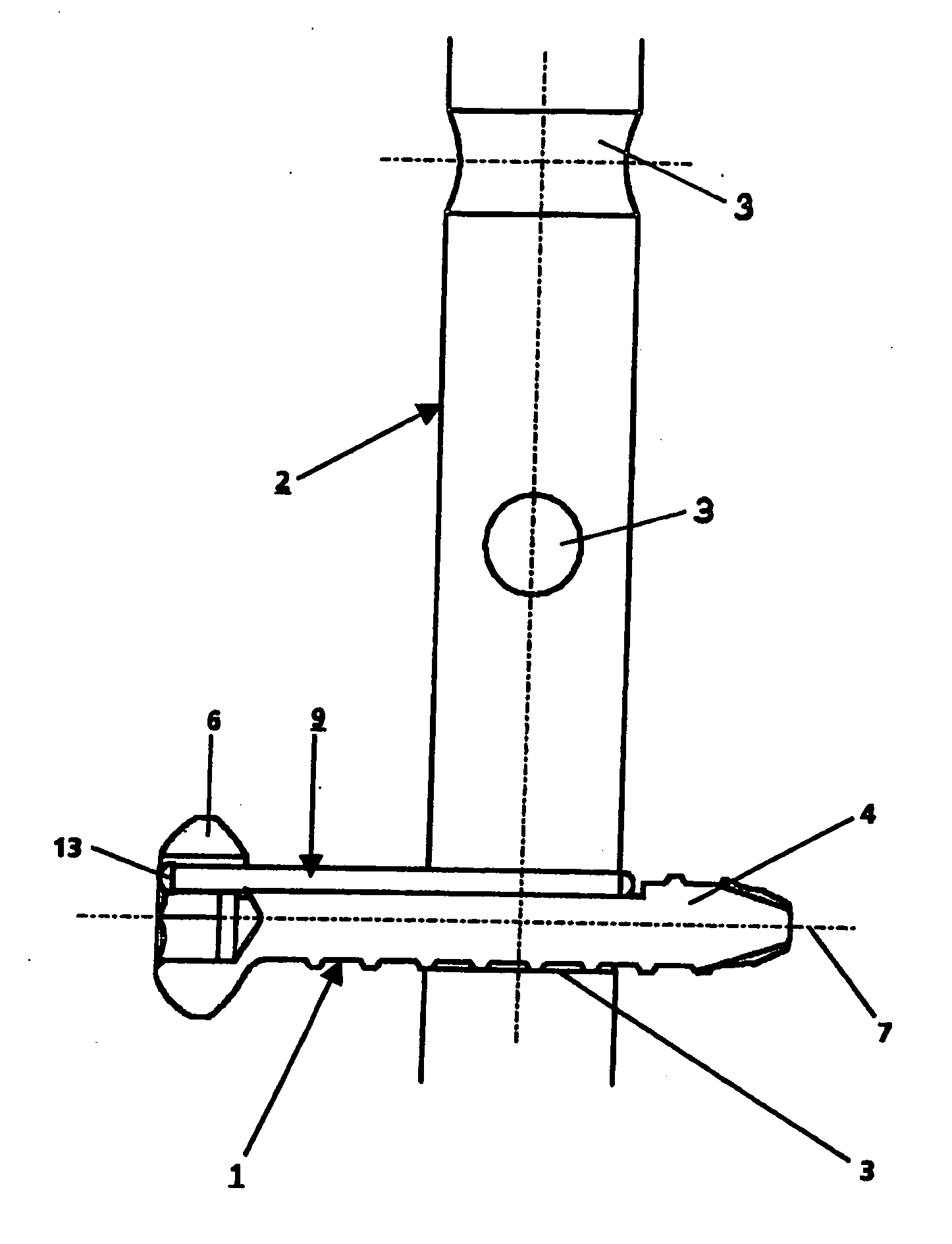
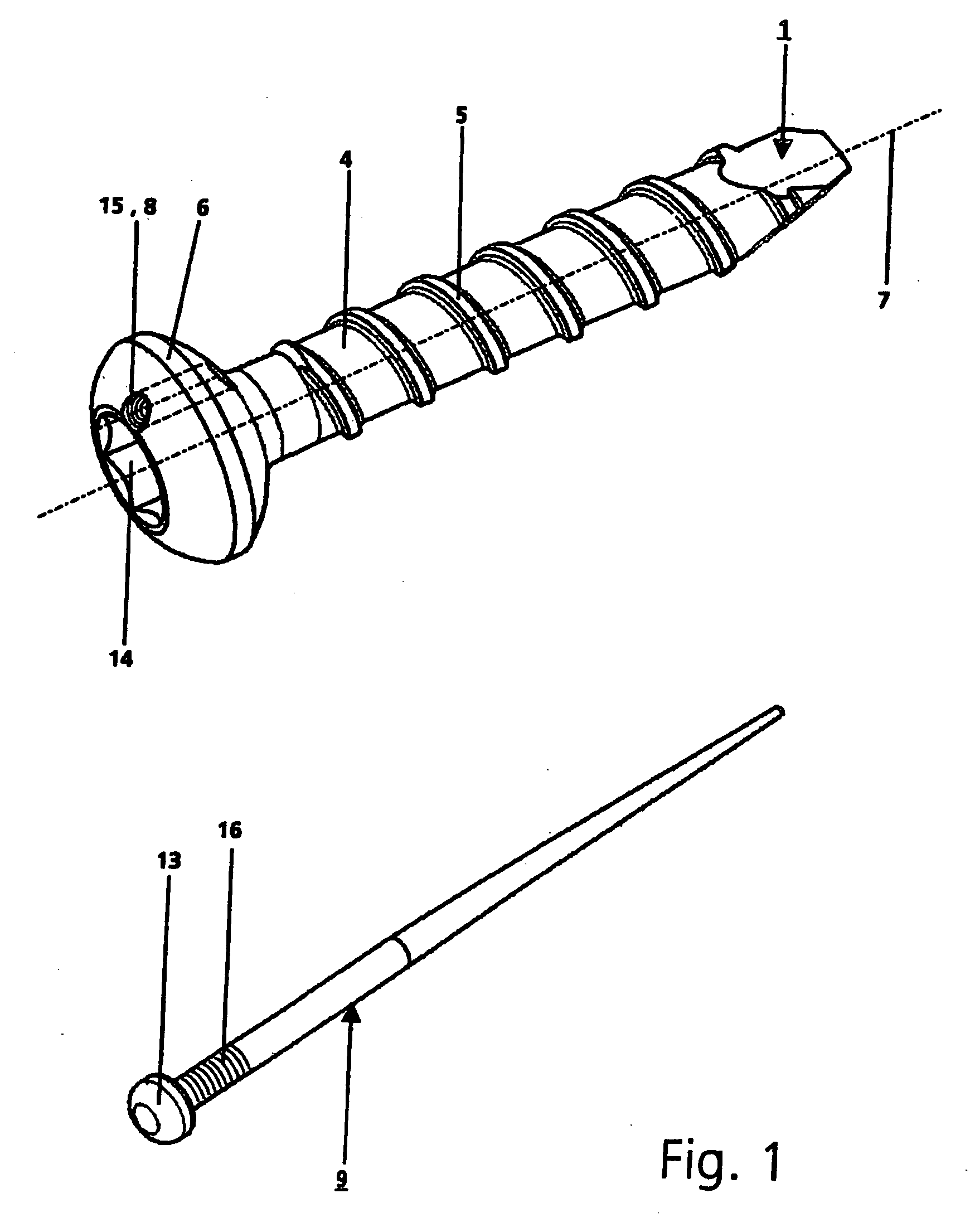
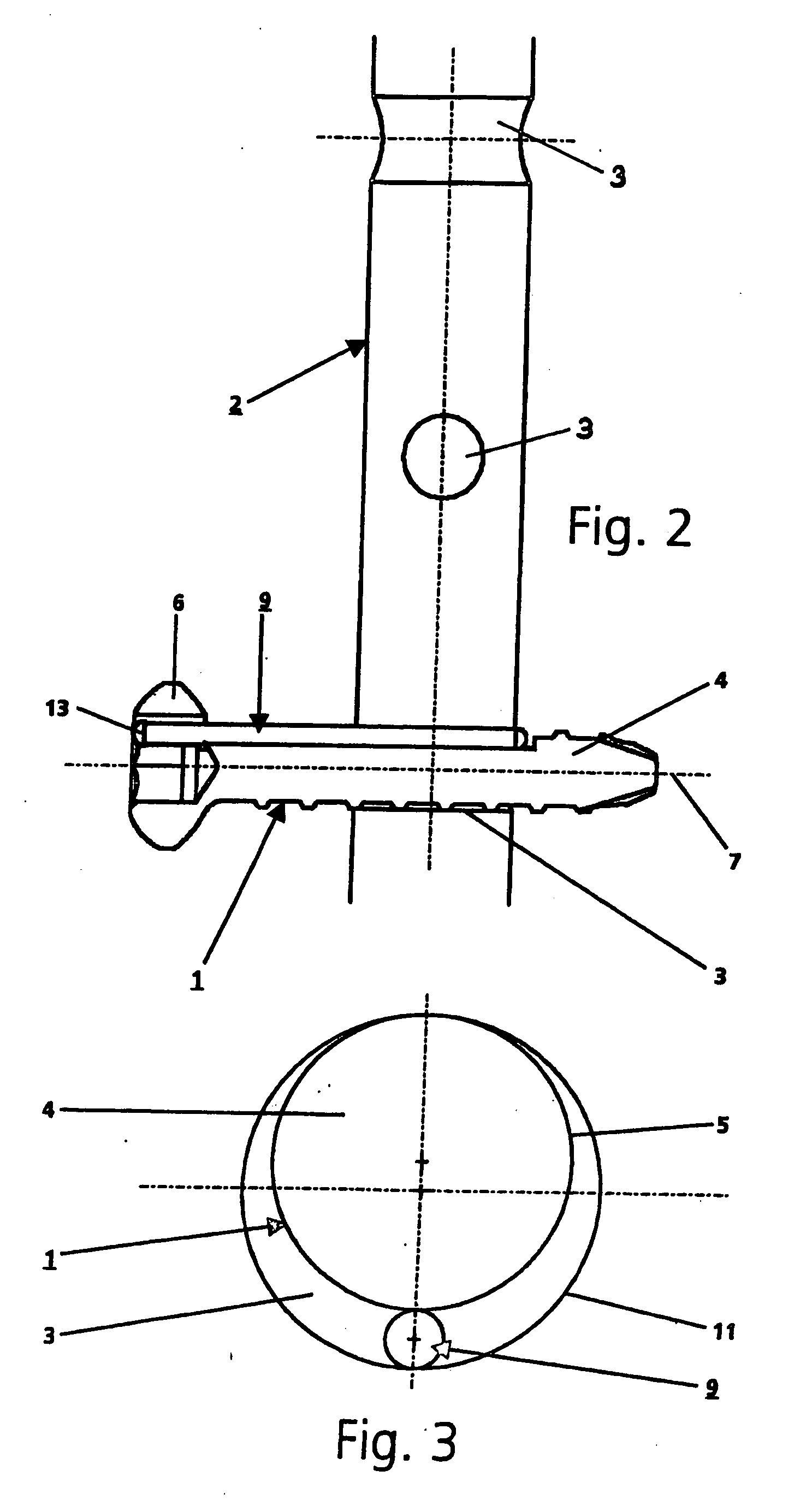
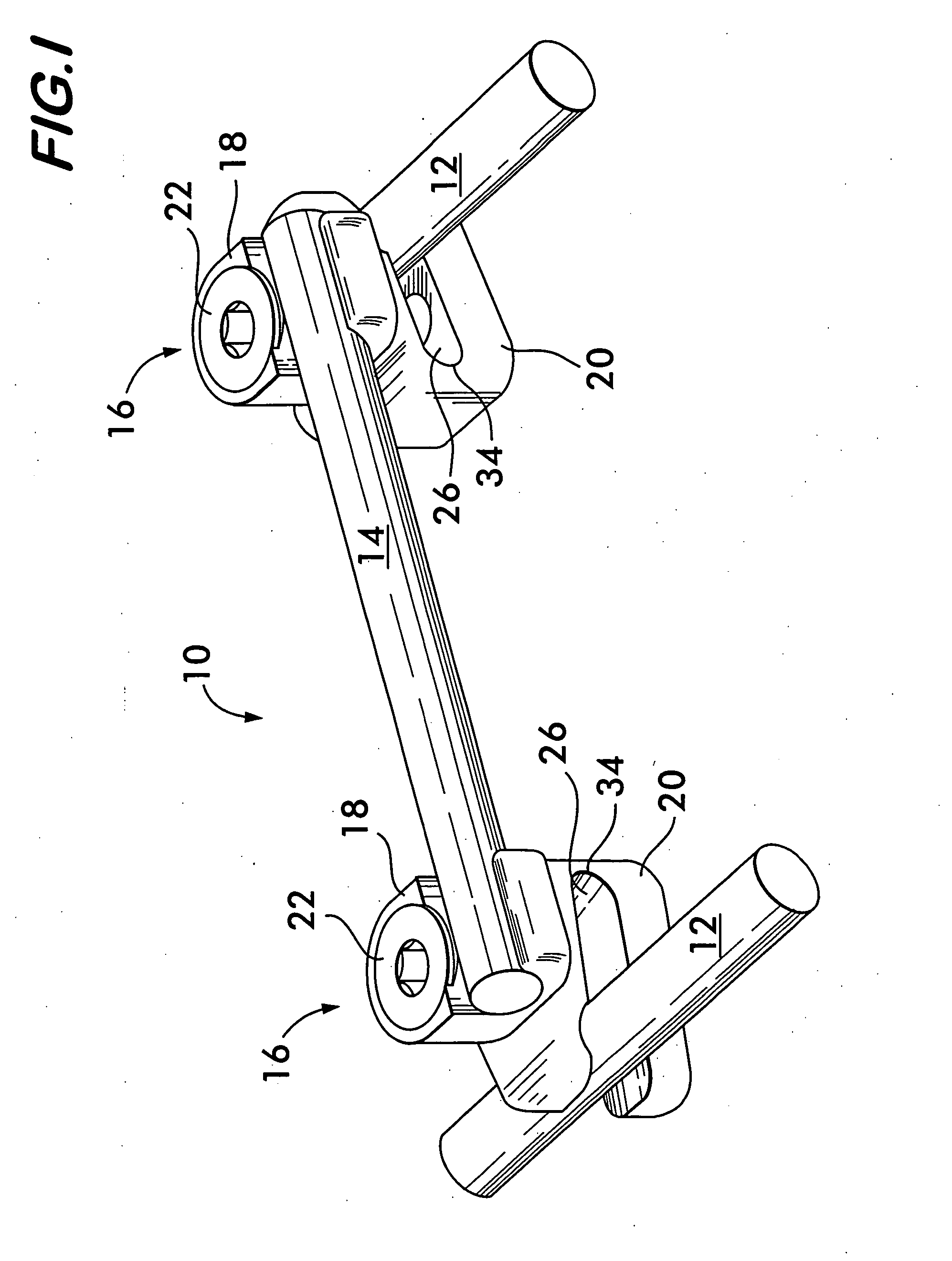
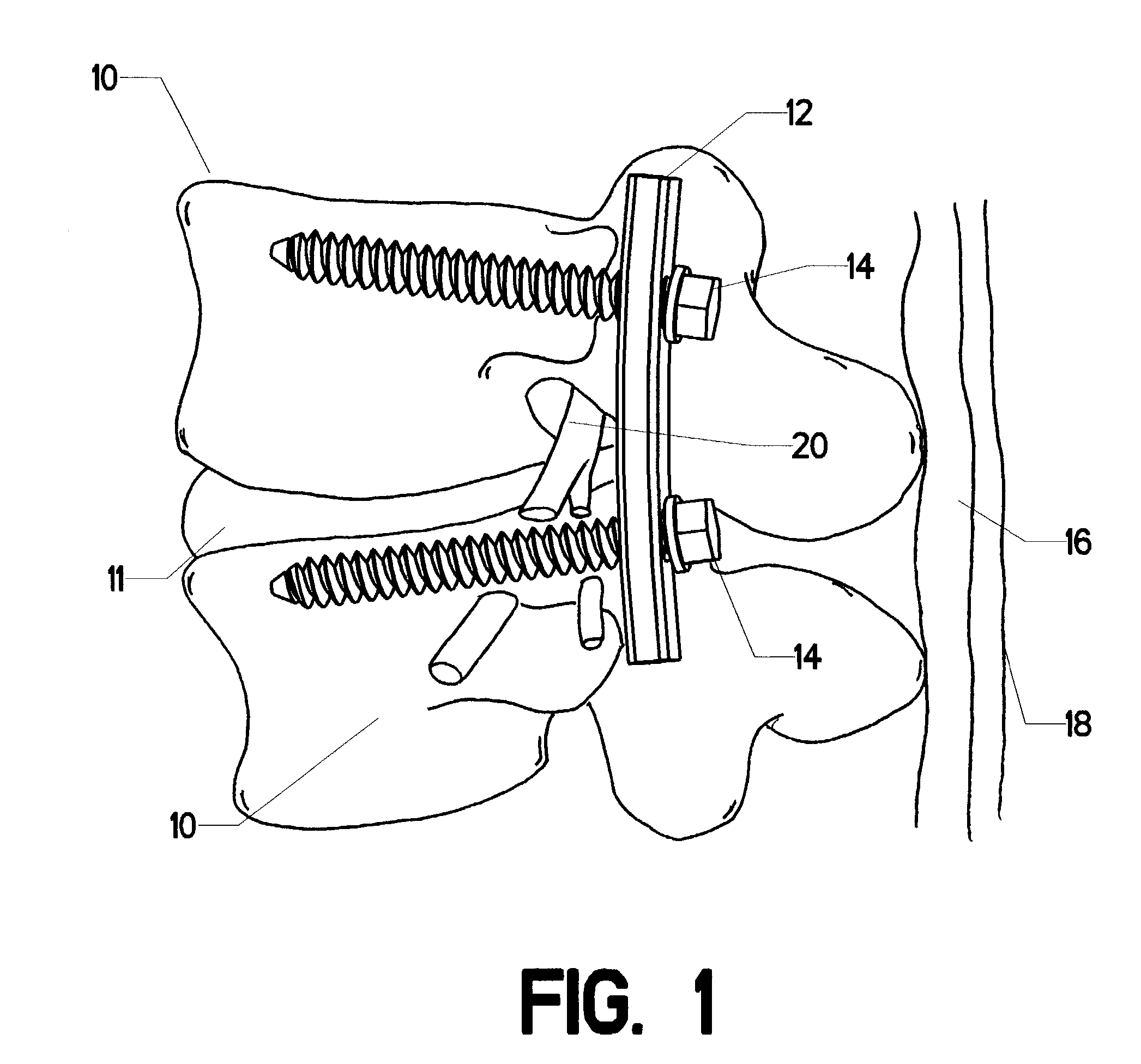
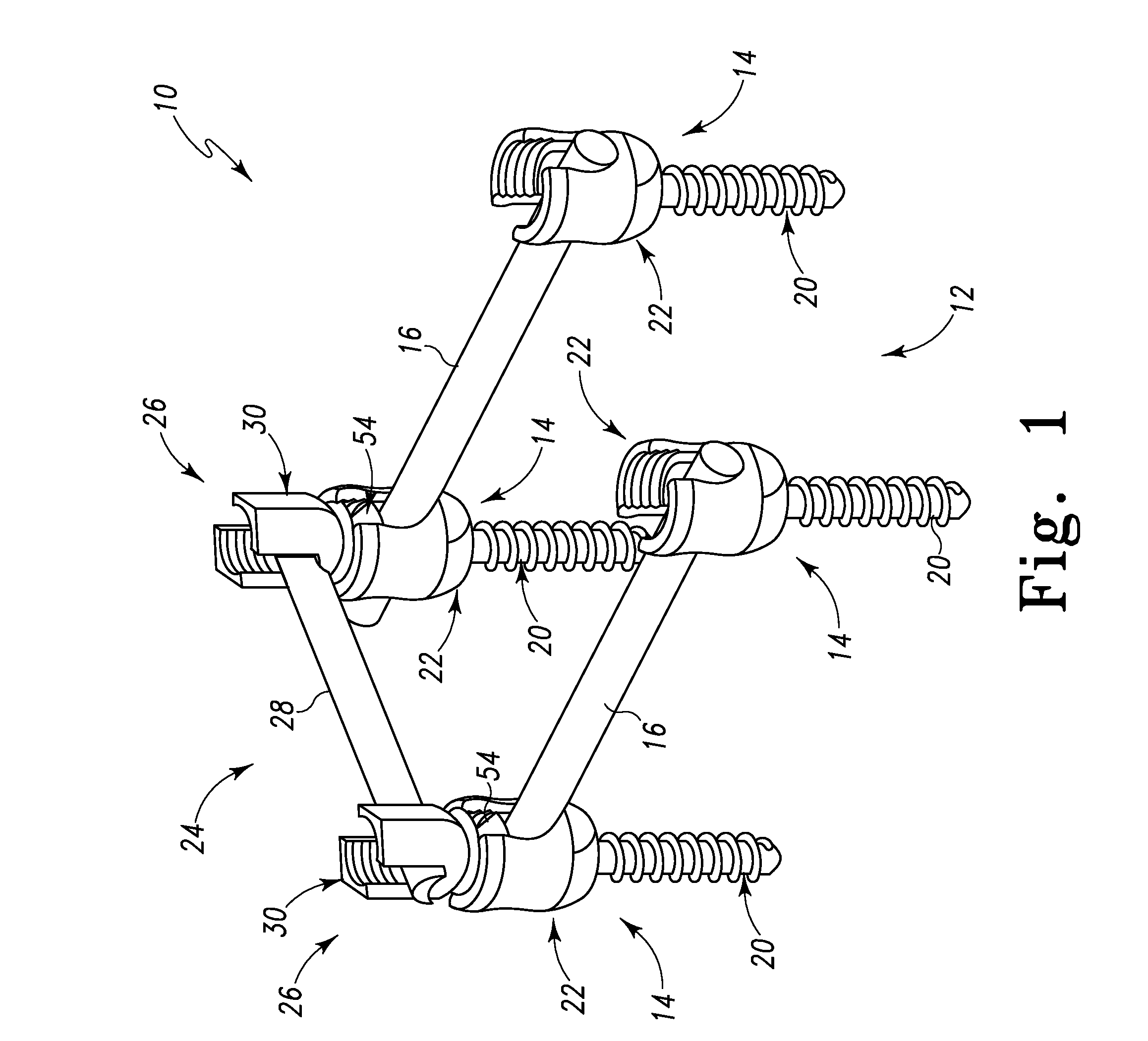
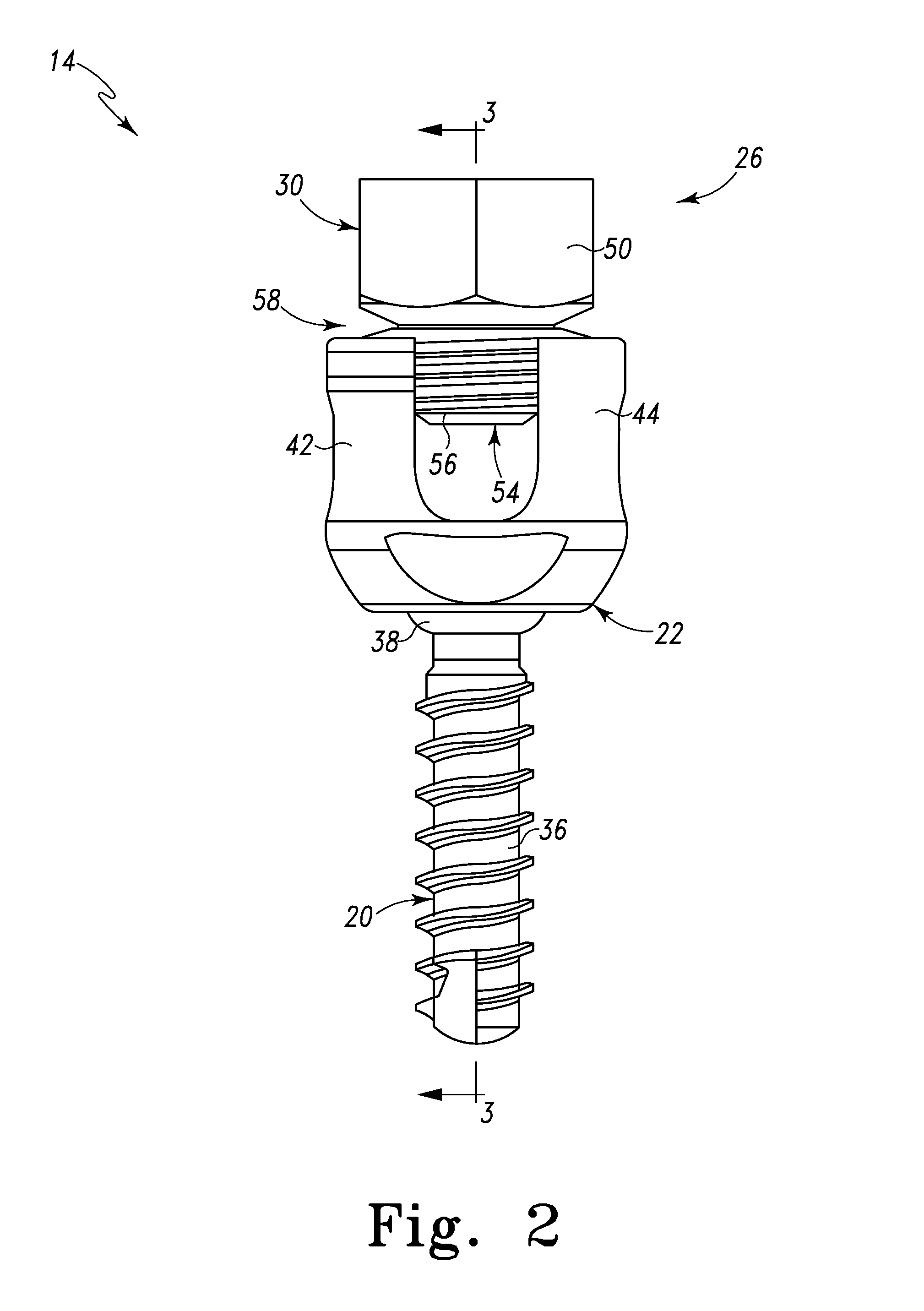
Bone fixing device, in particular for fixing to the sacrum during osteosynthesis of the backbone
InactiveUS6022350ADegree of stiffness attenuationReduce frictionInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsSacrumBone fixation devices
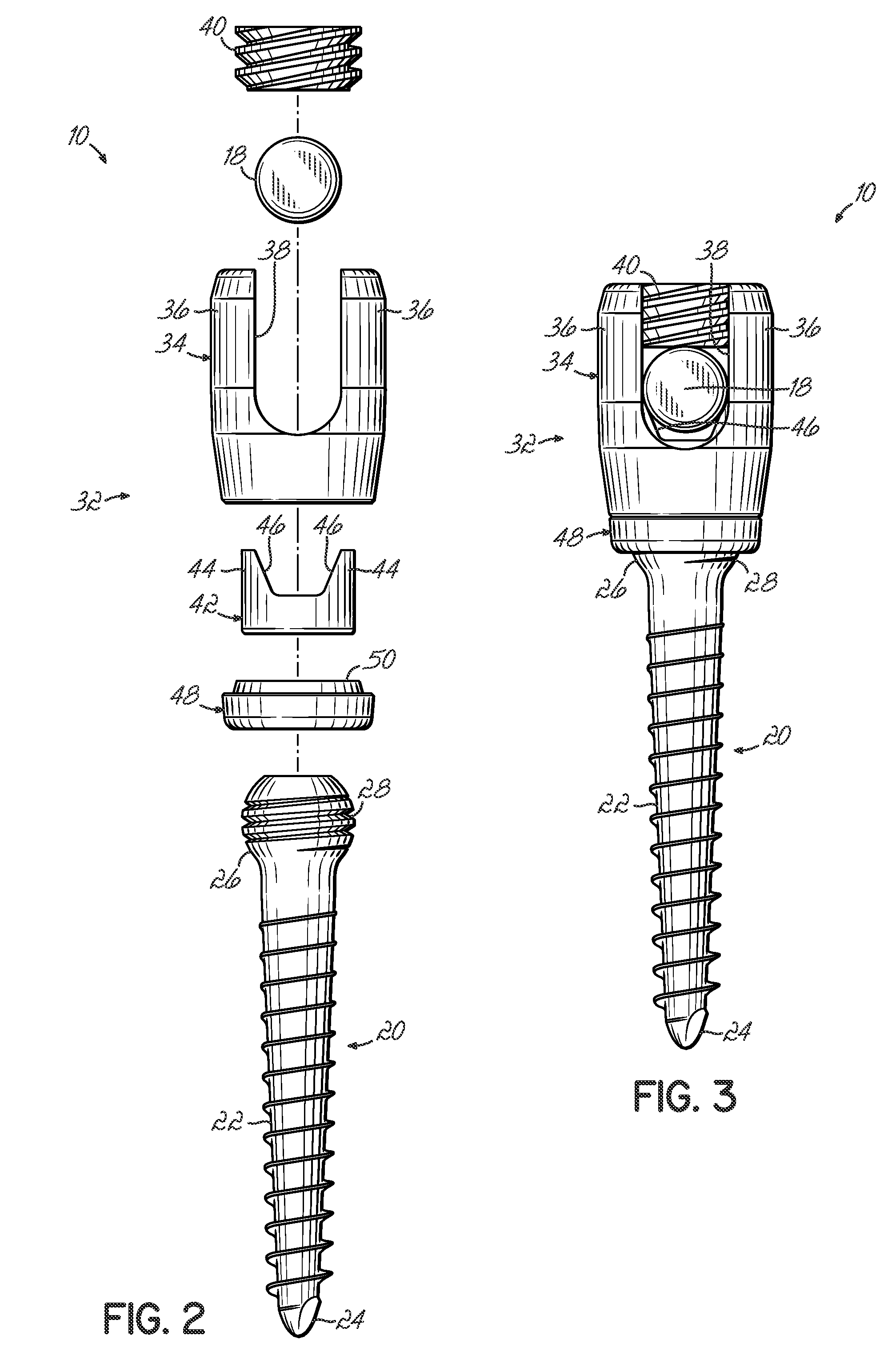
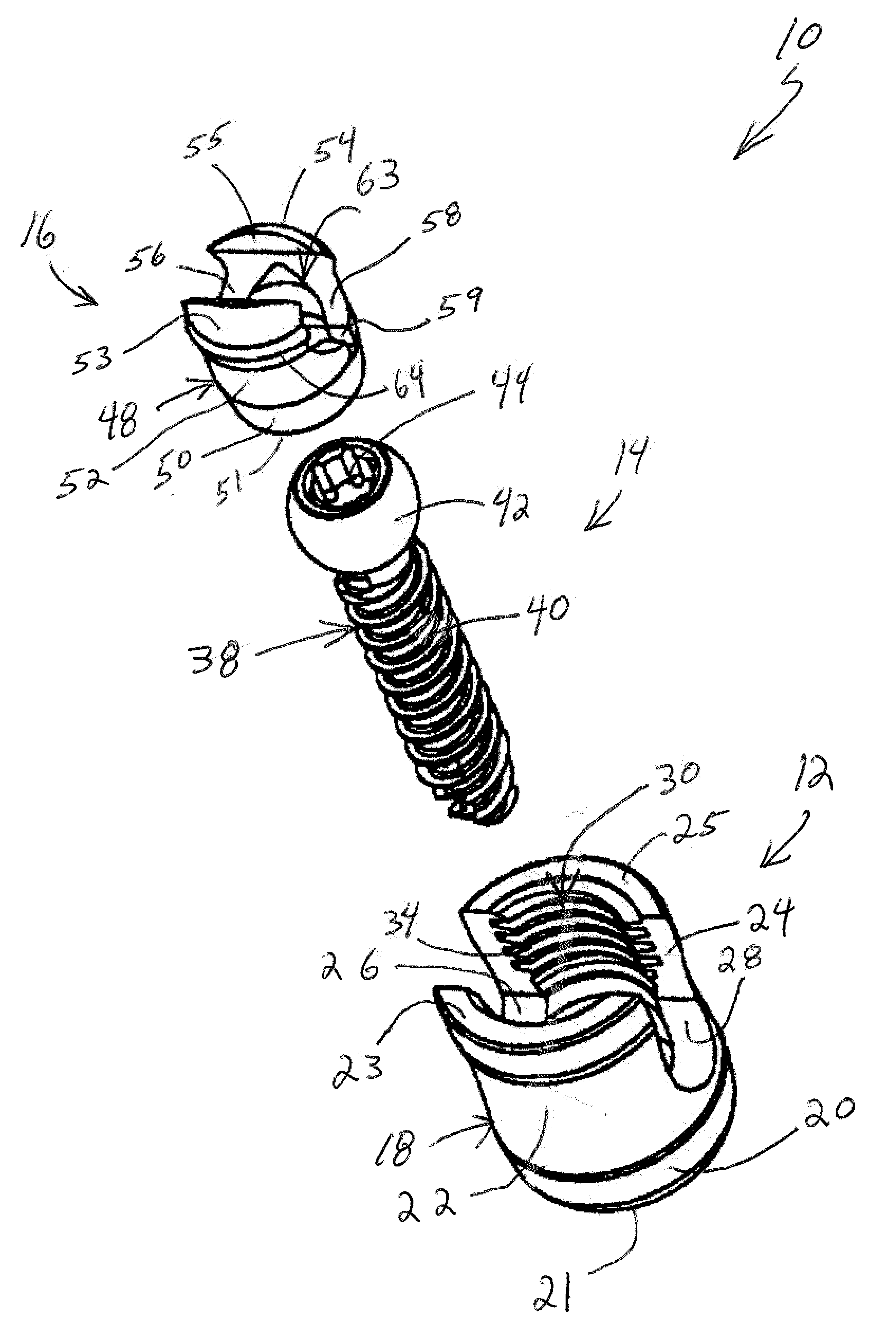
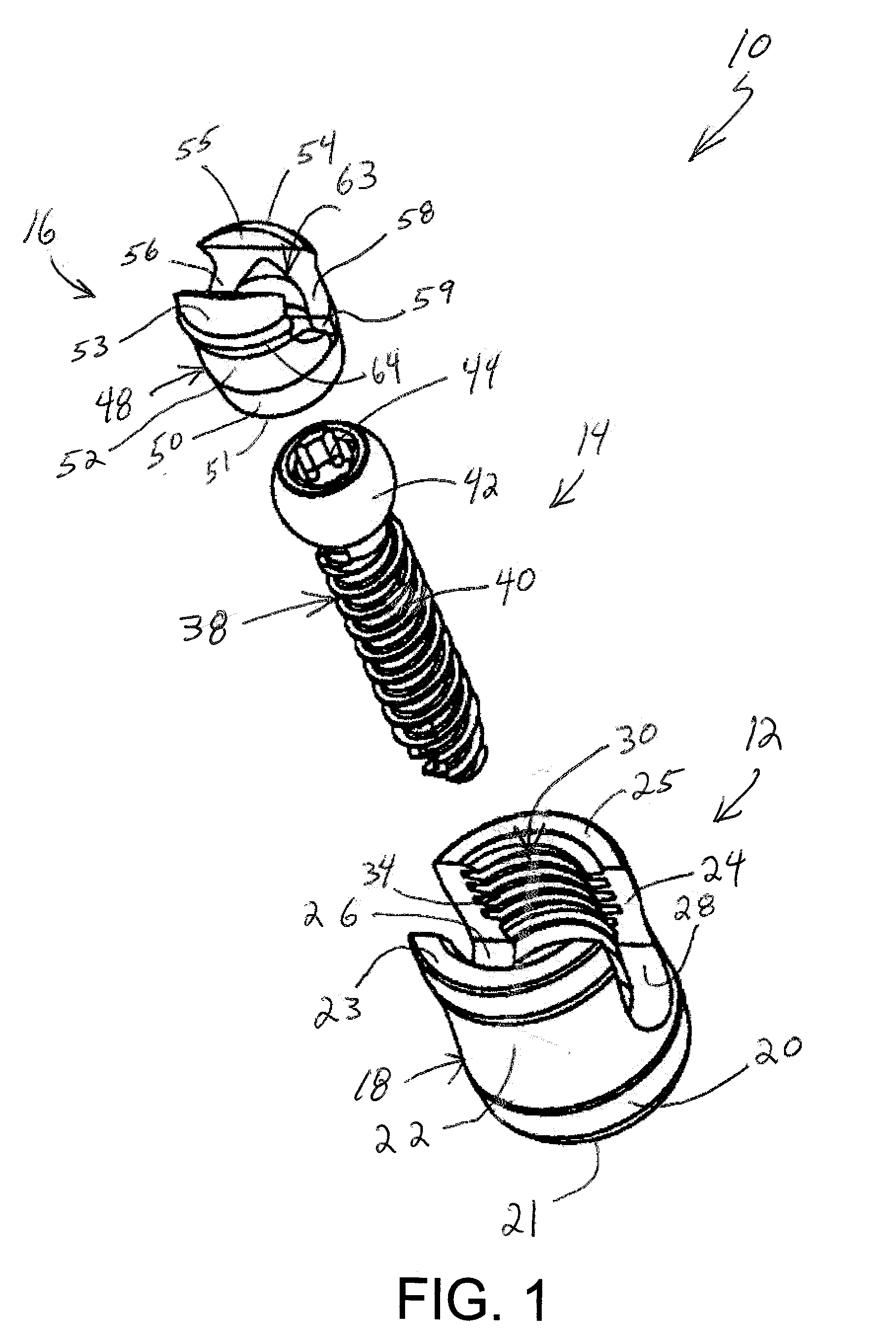
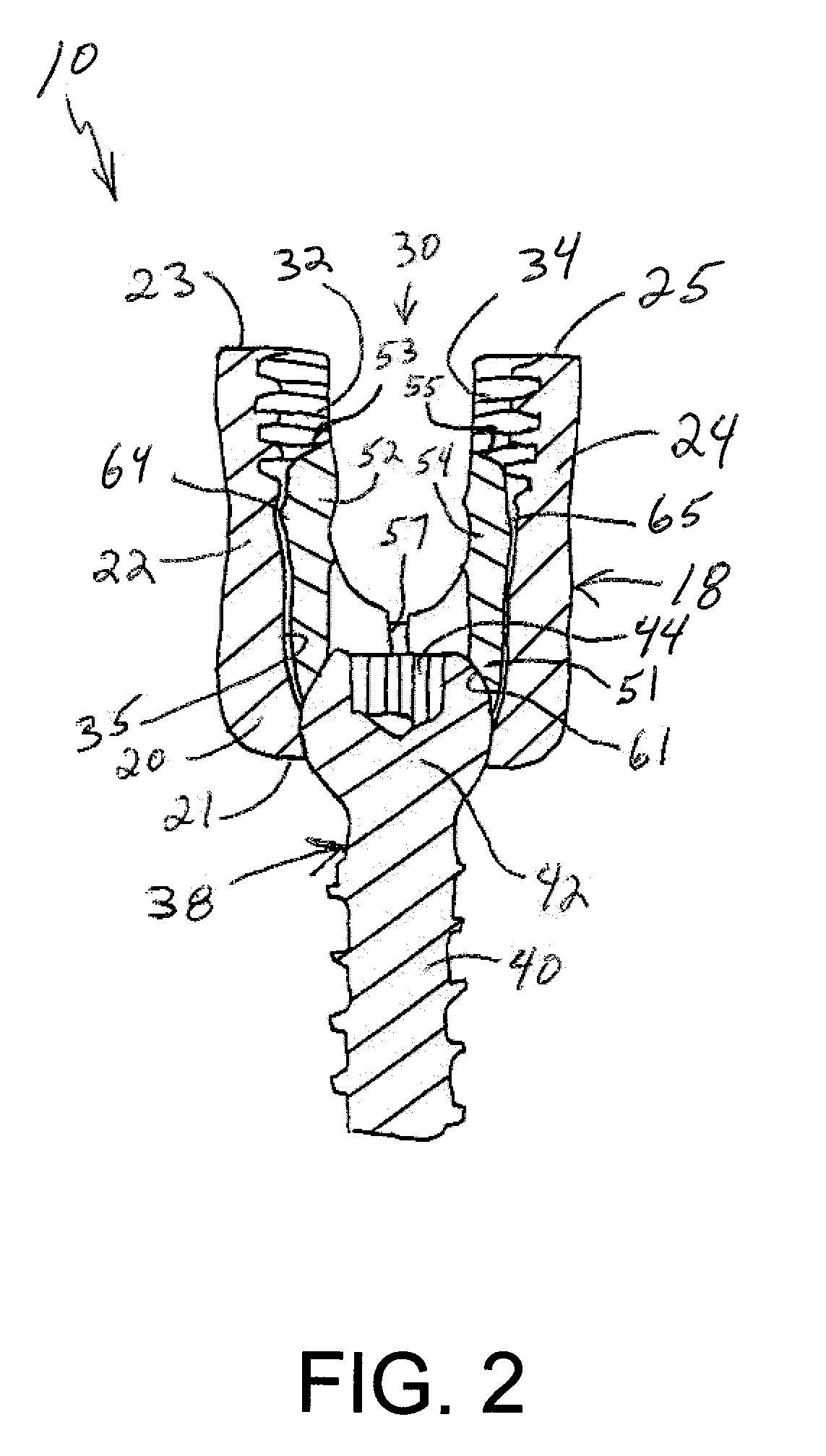
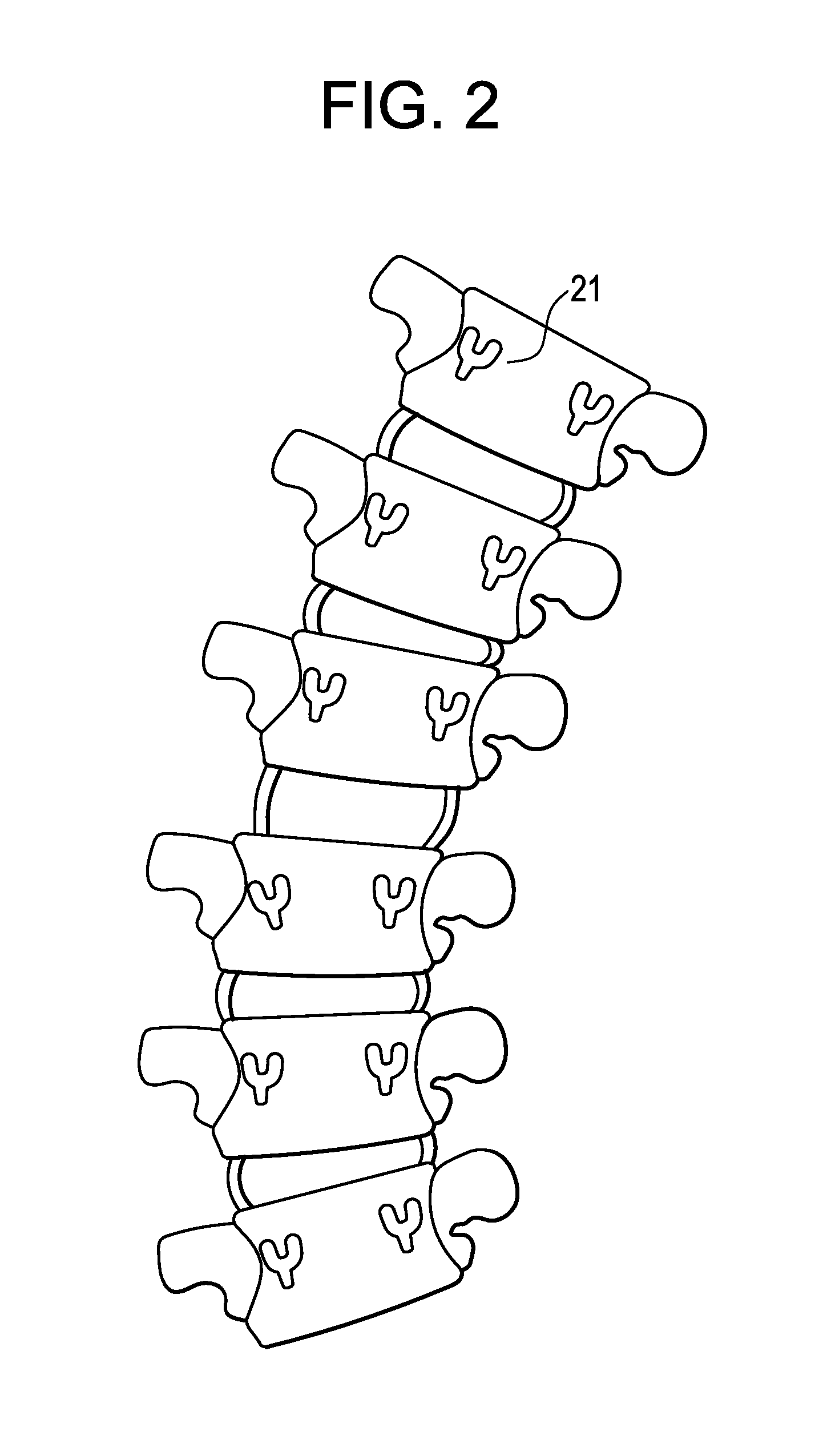
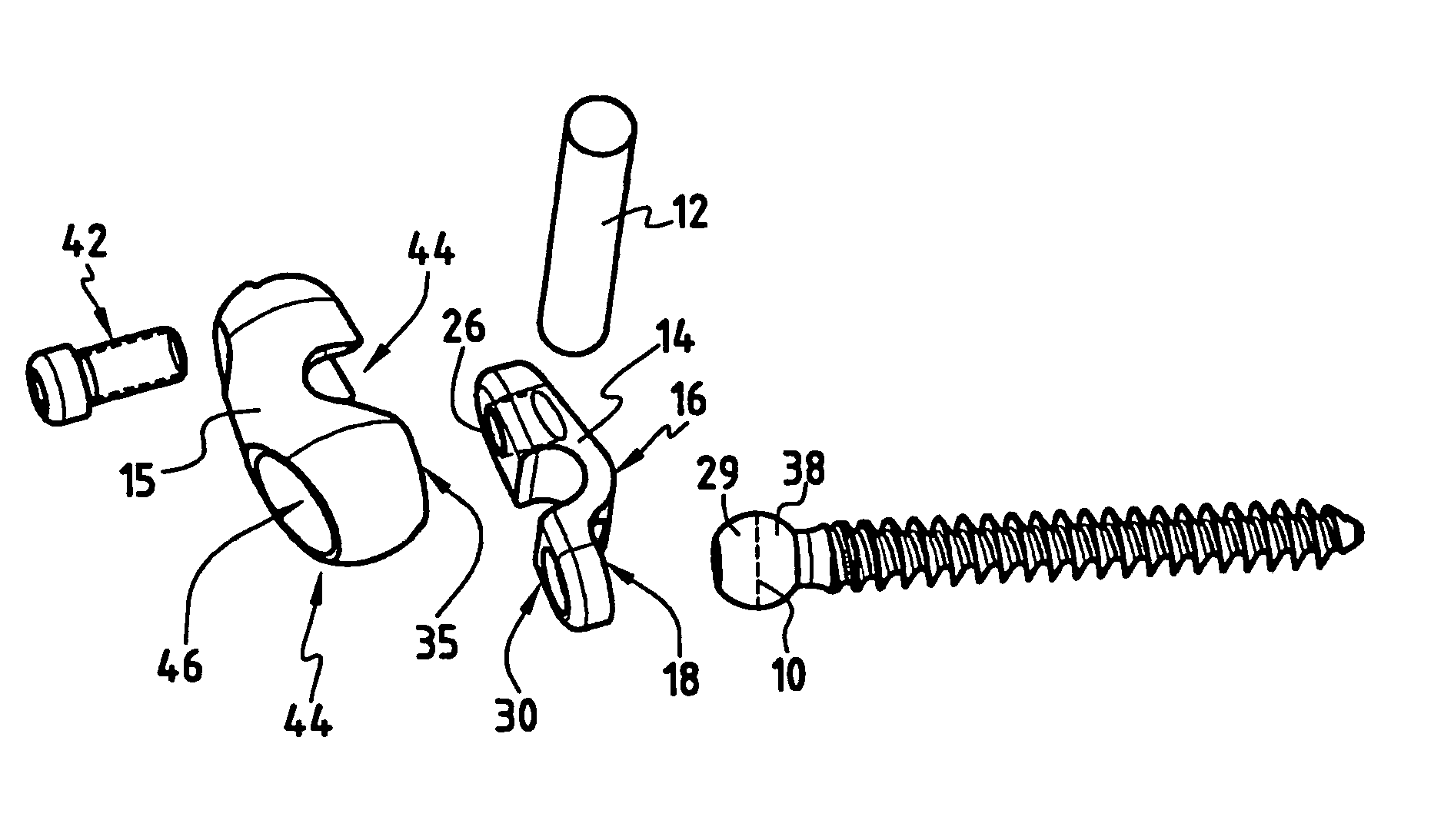
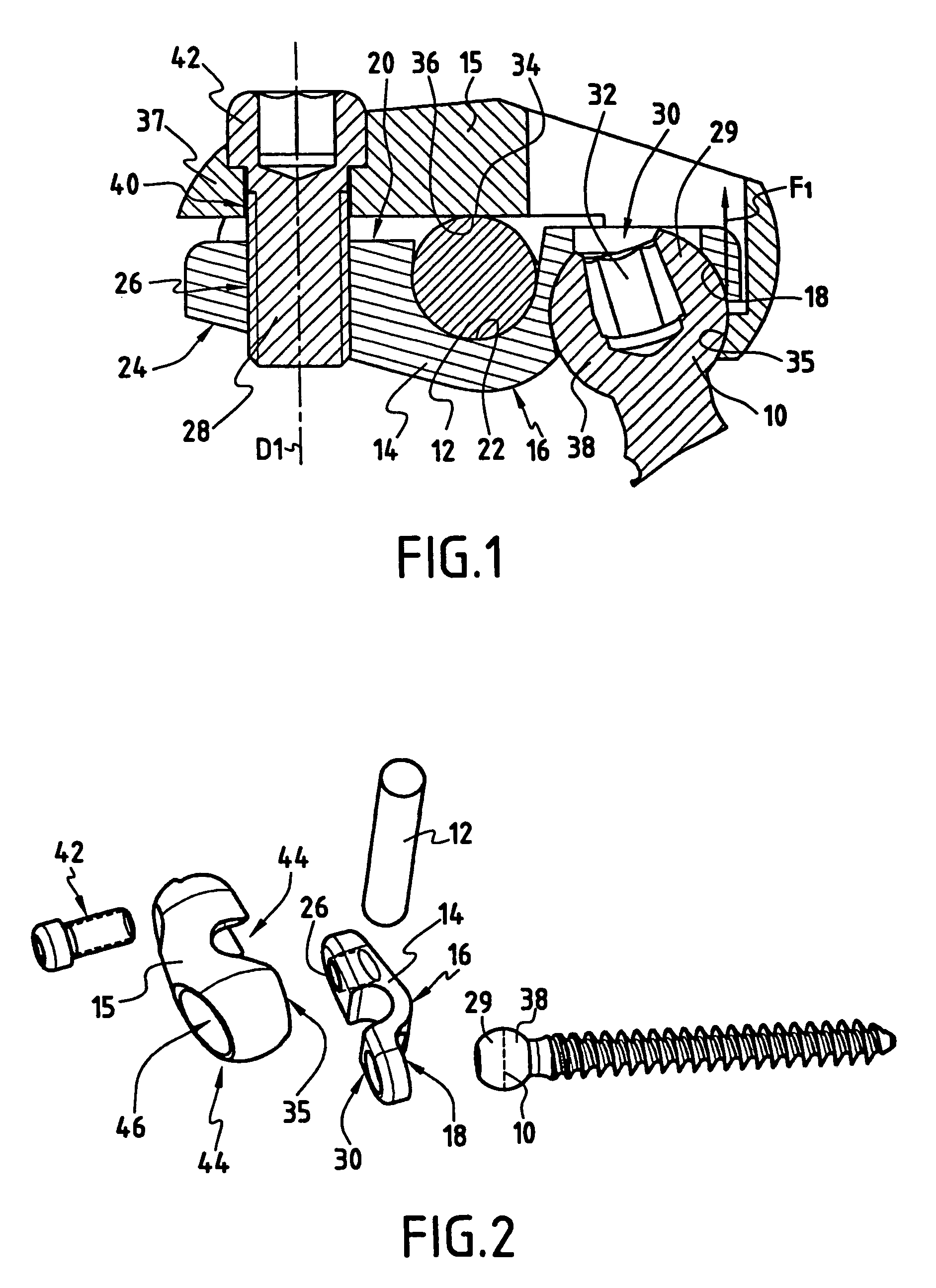
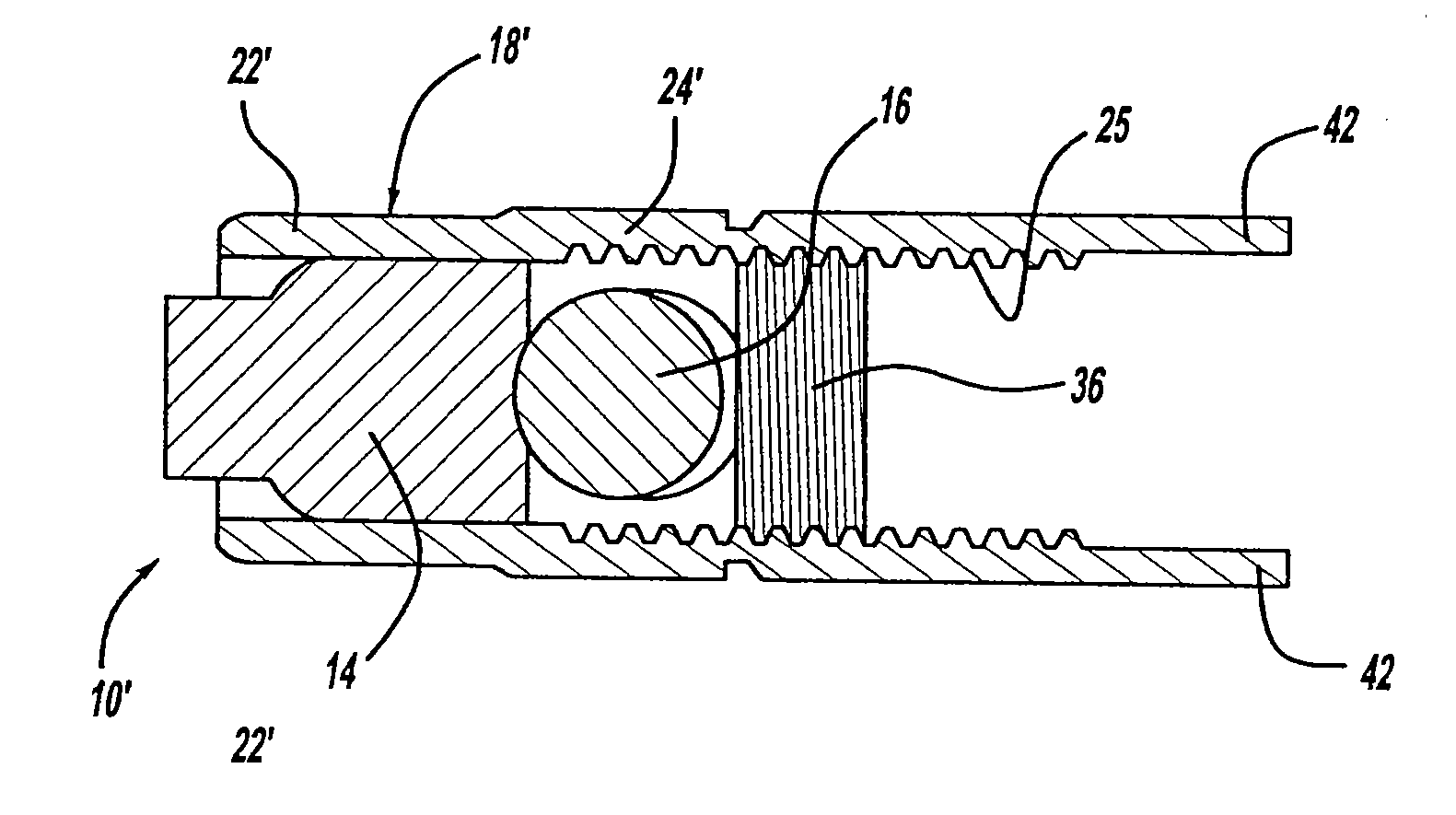
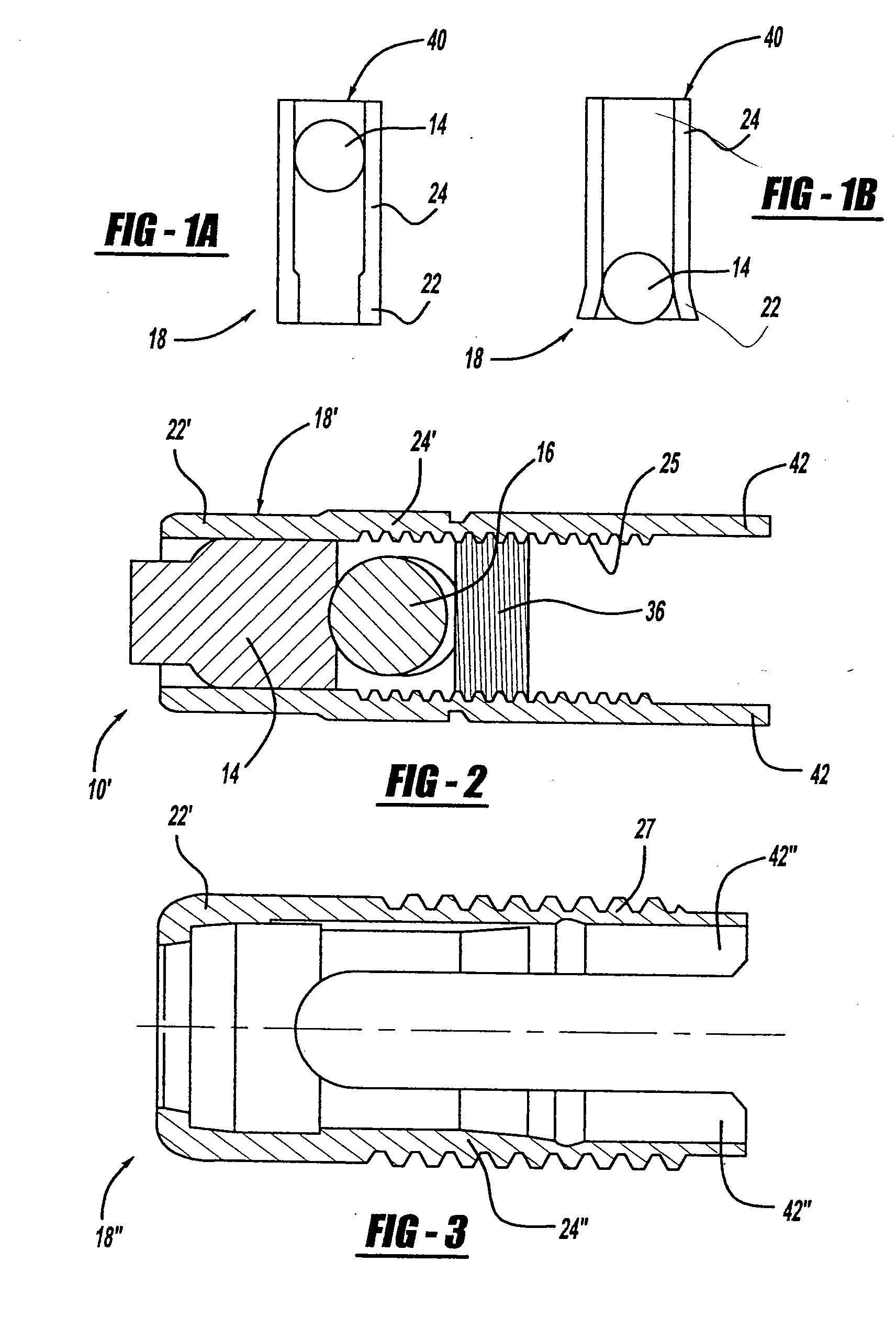
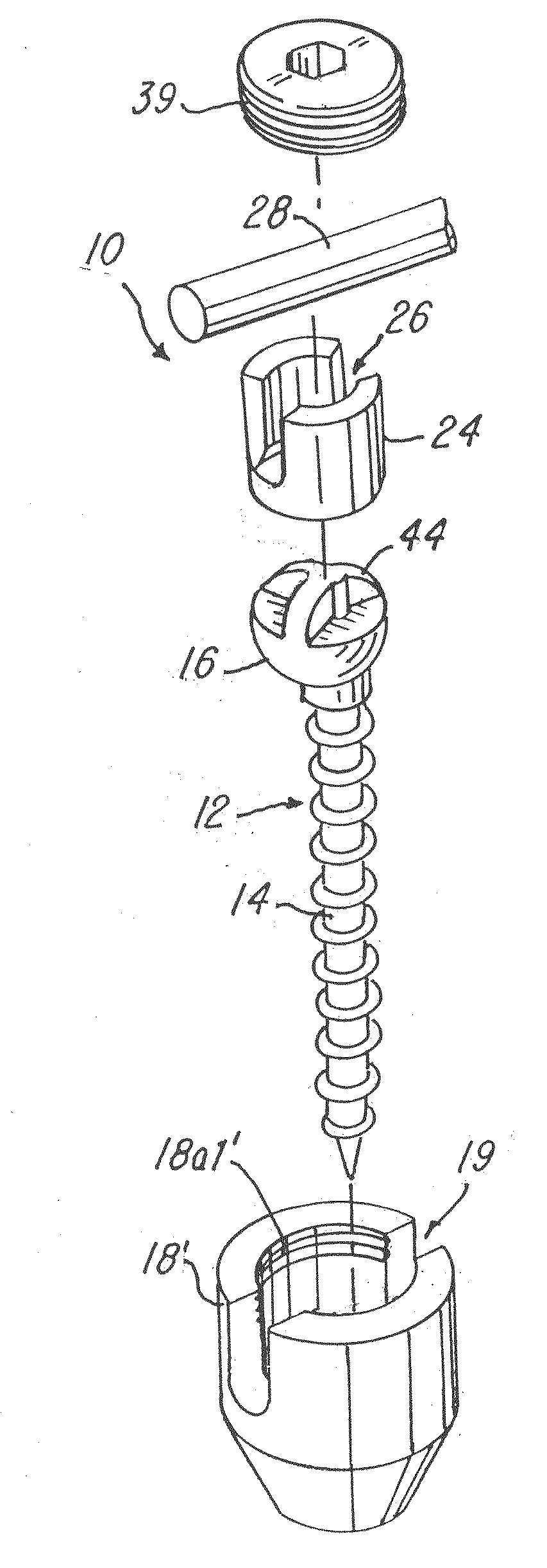
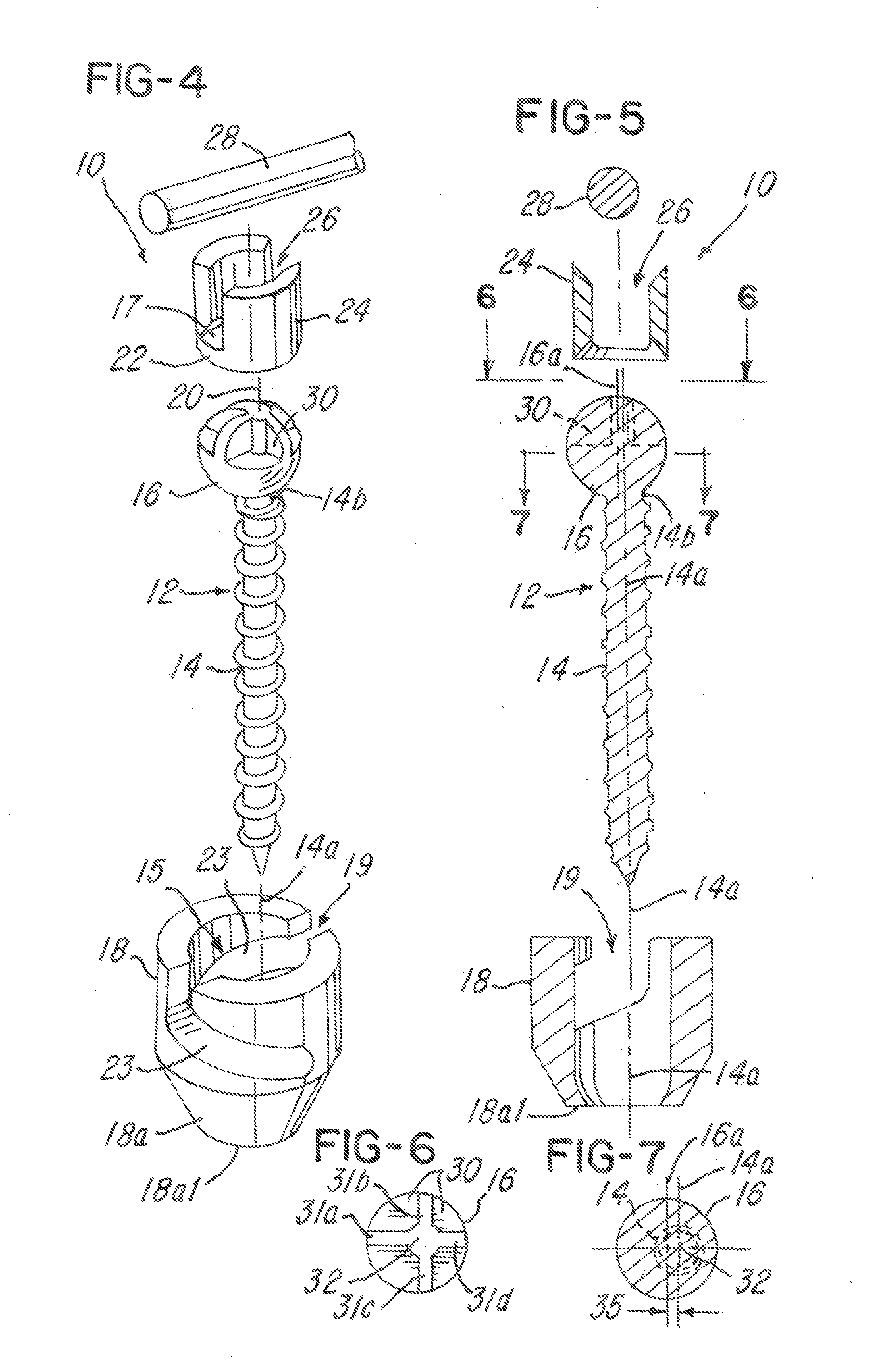
A bone fixing device, in particular for fixing to the sacrum for osteosynthesis of the backbone, comprises elongate link means receiving at least one bone-fastening screw, which passes through an orifice formed in the link means. In the bottom of the link means there is included a bearing surface of essentially circular cross-section. The head of the screw includes an essentially spherical surface for bearing against said bearing surface. The link means include a first thread in the vicinity of said orifice. The device further includes a plug having a second thread suitable for co-operating with the first thread, the plug being suitable for coming into clamping contact against said screw head to hold it in a desired angular position. According to the invention, the link means are constituted by a single-piece plate-shaped element having the orifice and the first thread formed therein, and said bearing surface is essentially spherical.
Owner:STRYKER EURO OPERATIONS HLDG LLC
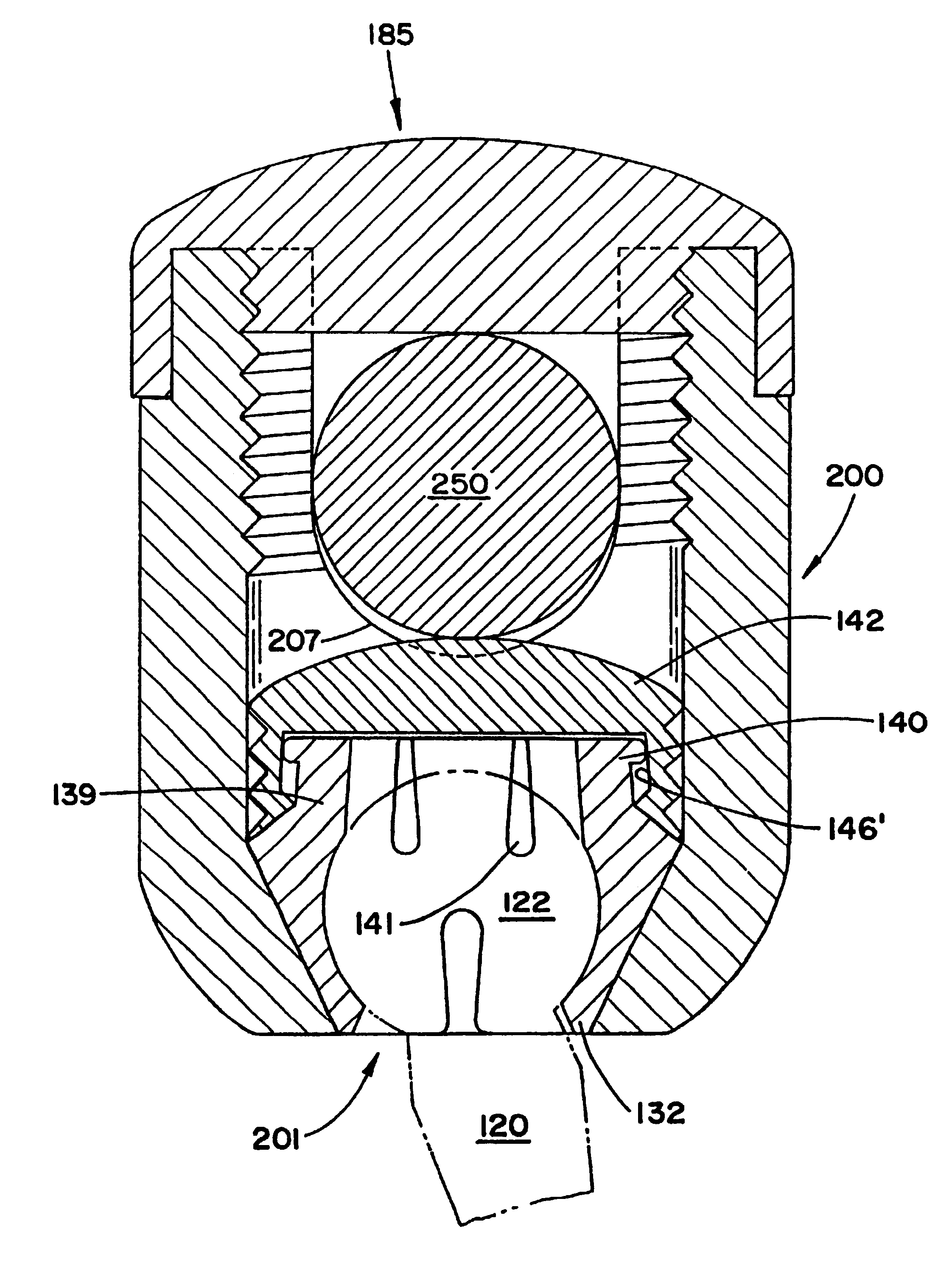
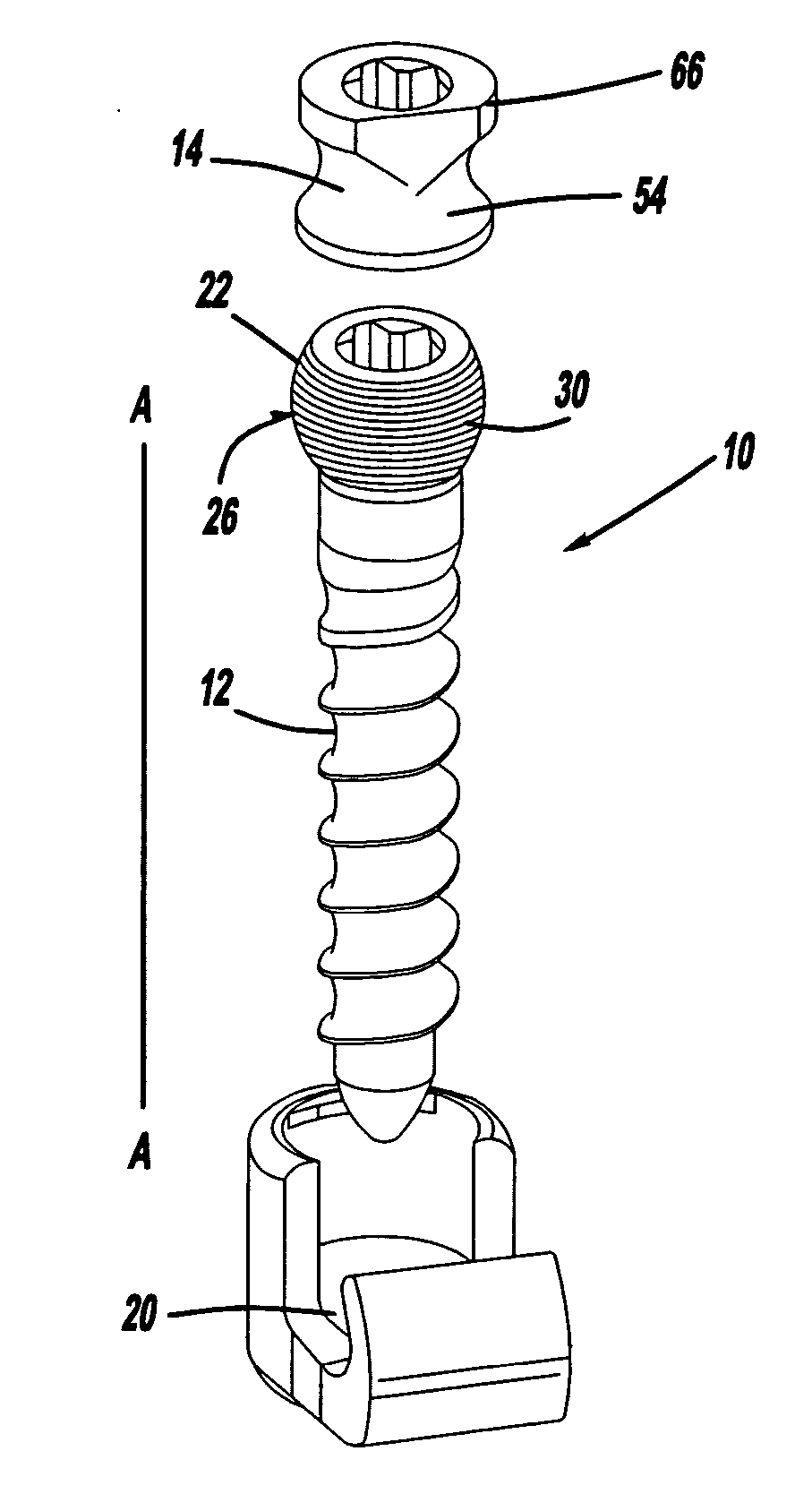
Polyaxial pedicle screw having a threaded and tapered compression locking mechanism
InactiveUSRE37665E1Improve locking effectEasy to compressInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsCouplingLocking mechanism
A polyaxial orthopedic device for use with rod implant apparatus includes a screw having a curvate head, a two-piece interlocking coupling element which mounts about the curvate head, and a rod receiving cylindrical body member having a tapered socket into which both the screw and the interlocking coupling element are securely nested. The interlocking coupling element includes a socket portion which is slotted and tapered so that when it is radially compressed by being driven downwardly into the tapered socket in the cylindrical body it crush locks to the screw. The securing of the rod in the body member provides the necessary downward force onto the socket portion through a contact force on the top of the cap portion. Prior to the rod being inserted, therefore, the screw head remains polyaxially free with respect to the coupling element and the body. In a preferred embodiment, the cap portion and the socket portion are formed and coupled in such a way that when the cap portion is compressed toward the socket portion, there is an additional inward radial force applied by the cap portion to the socket portion, thereby enhancing the total locking force onto the head of the screw.
Owner:FASTENETIX L L C
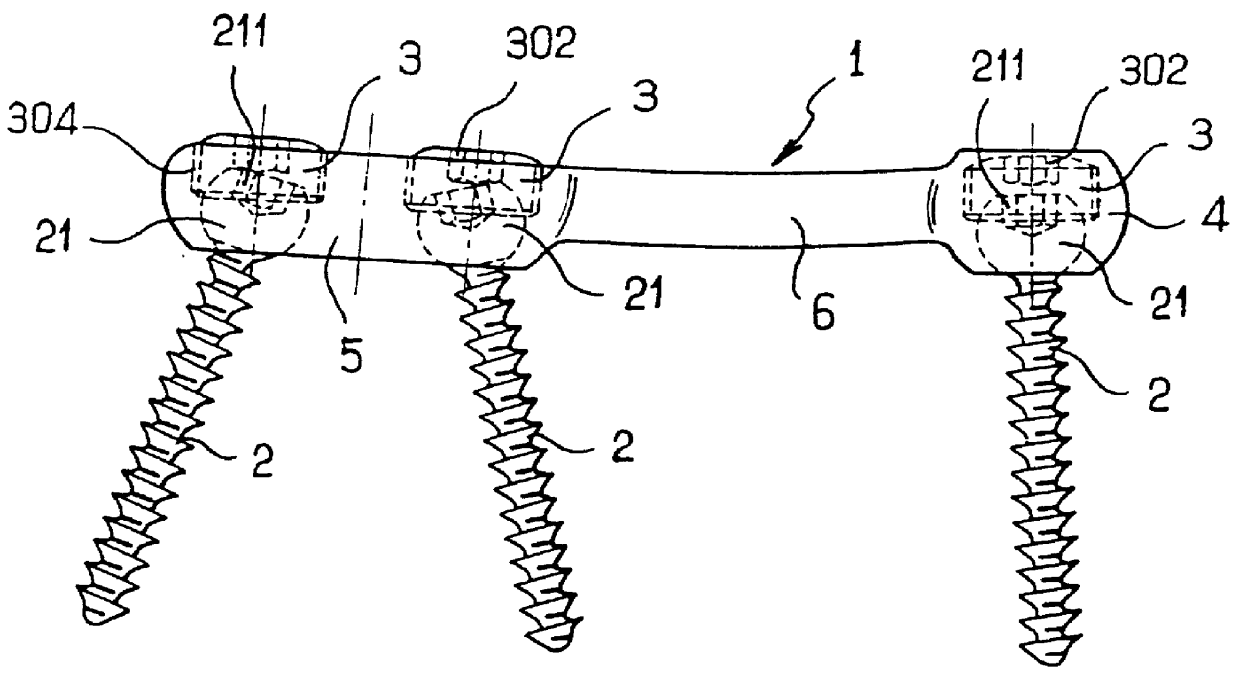
Device for fixing the sacral bone to adjacent vertebrae during osteosynthesis of the backbone
InactiveUS6290703B1Degree of stiffness attenuationReduce frictionInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsSacral BoneBone fixation devices
Owner:STRYKER EURO OPERATIONS HLDG LLC
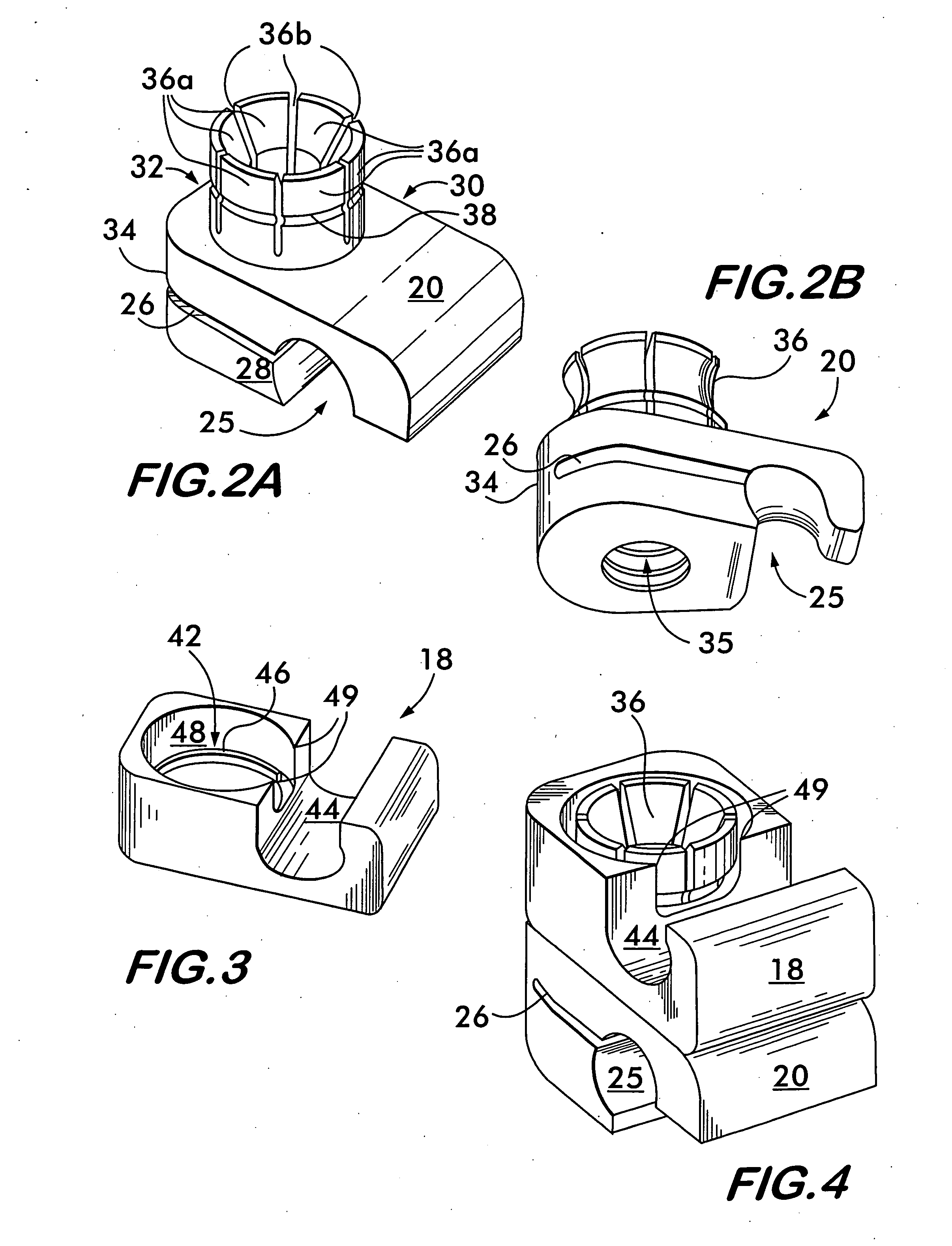
Blockable bone plate
InactiveUS6730091B1Cost effective productionLow costSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisEngineeringIliac screw
The blockable bone plate consists of a plurality of plate members which are connected to each other via webs. A screw hole is provided in at least some plate members, preferably in each plate member. The screw hole is surrounded by a spherical countersink on the upper surface of the plate. Provided internally in the screw hole there is an engagement contour which consists of contour valleys and contour peaks partially running in a horizontal and radial peripheral direction on the wall of the screw hole. The engagement contour is preferably produced by milling and has for example a pointed, round, trapezoidal or serrated configuration. A blocking thread is provided under the screw head of the screw intended for blocking. As the screw is screwed in, the blocking thread engages in the engagement contour. The particular advantages lie in increased security against the screw coming loose and in the possibility of also inserting the screw through the plate at an inclination. Furthermore, a bone plate is proposed which has the shape of an arc of a circle in the longitudinal axis of the plate and which requires less bending, particularly on the human lower jaw, and adapts to the bone in a more ideal manner.
Owner:MEDARTIS AG
Device and method for percutaneous placement of lumbar pedicle screws and connecting rods
InactiveUS7306603B2High positioning accuracyLow costInternal osteosythesisCannulasPedicle screwBiomedical engineering
A minimally invasive method for stabilizing adjacent vertebrae to be fused is accomplished with a device configured to interlink the pedicles of the adjacent vertebrae and including multiple pedicle screws. Each of the pedicle screws has a screw head configured to receive a connecting rod in a position, in which the rod and the receiving pedicle screw are vertically aligned.
Owner:THEKEN SPINE
Fixed and variable locking fixation assembly
InactiveUS7001389B1Smoother transitionFacilitate smoothingSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisFastenerEngineering
A locking screw assembly is provided which allows installation into a plate-like member using relatively little force, but which requires relatively great force for removal. The fastener has an annular locking ring provided within a groove in the head of the screw to allow the screw to sit within or flush with the anterior surface of the plate. The through-hole in the plate which receives the locking screw comprises an entrance, a collar section, an undercut, and an exit. The locking ring resides within the undercut. The locking ring has a leading surface that is chamfered or radiused and a trailing surface that is flat. The chamfer allows the locking ring to easily be inserted into the through-hole by interacting with a lead chamfer in the entrance. After installation, the flat trailing surface abuts a lip adjoining the collar section and the undercut and prevents the screw from being easily removed from the through-hole.
Owner:THEKEN SPINE
Polyaxial pedicle screw assembly
InactiveUS20050192571A1More lateral range of motionSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisPedicle screwBiomedical engineering
A pedicle fixation assembly and method for assembly comprises a screw head comprising a male bulbous end; a bone fixator component comprising a female concave semi-spherical socket for receiving the screw head; a locking saddle pin for engaging the screw head and the bone fixator component; and a blocker for engaging the screw head and for securing the longitudinal member.
Owner:CUSTOM SPINE INC
Slidable bone plate system
The invention is directed to a bone plate system. The bone plate system comprises a base plate having two generally parallel elongated screw slots extending therethrough. Two bone screws are provided that are capable of securing the base plate to a bone by insertion through the screw slots into the bone. Each bone screw has a screw head and a threaded portion extending therefrom. An interference device is attached to the base plate and retains the bone screws while permitting the bone screws to toggle and to controllably slide in the screw slots of the base plate. This design is particularly useful for joining adjacent vertebral bodies, as it permits controlled settling of the vertebral bodies, thereby enhancing the healing process.
Owner:NUVASIVE
Polyaxial pedicle screw having a threaded and tapered compression locking mechanism
InactiveUSRE39089E1Improve locking effectSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisCouplingLocking mechanism
A polyaxial orthopedic device for use with rod implant apparatus includes a screw having a curvate head, a two-piece interlocking coupling element which mounts about the curvate head, and a rod receiving cylindrical body member having a tapered socket into which both the screw and the interlocking coupling element are securely nested. The interlocking coupling element includes a socket portion which is slotted and tapered so that when it is radially compressed by being driven downwardly into the tapered socket in the cylindrical body it crush locks to the screw. The securing of the rod in the body member provides the necessary downward force onto the socket portion through a contact force on the top of the cap portion. Prior to the rod being inserted, therefore, the screw head remains polyaxially free with respect to the coupling element and the body. In a preferred embodiment, the cap portion and the socket portion are formed and coupled in such a way that when the cap portion is compressed toward the socket portion, there is an additional inward radial force applied by the cap portion to the socket portion, thereby enhancing the total locking force onto the head of the screw.
Owner:FASTENETIX L L C
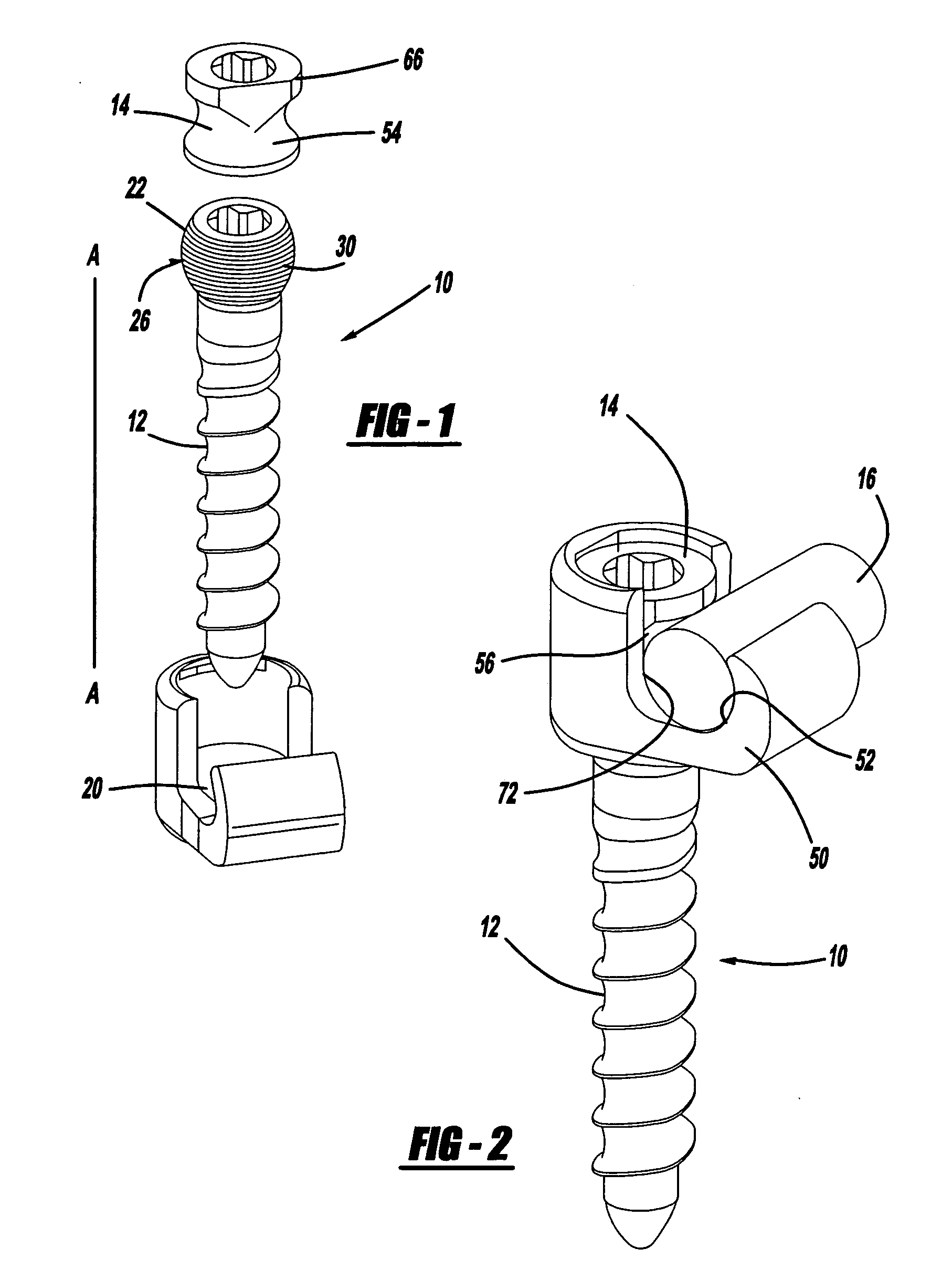
Biased angle polyaxial pedicle screw assembly
A pedicle screw assembly and method of assembly comprises a longitudinal member; a screw head comprising a bulbous end, wherein the screw head has a slot adapted to receive the longitudinal member; a bone fixator component comprising a concave socket having a biased angled top and a rounded bottom adapted to receive the screw head; a locking pin adapted to engage the screw head, the bone fixator component, and the longitudinal member; and a blocker adapted to engage the screw head and to secure the longitudinal member. Additionally, the bone fixator component may be configured as any of a bone screw and a hook.
Owner:CUSTOM SPINE INC
Removable polyaxial housing for a pedicle screw
InactiveUS20080009862A1Ease of insertionEase of alterationSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisScrew threadSurgery
A polyaxial body is selectively removable from a pedicle screw in a spinal fixation system without disruption of the screw's placement in the patient's spine. The polyaxial body according to various embodiments of this invention may be locked relative to the screw head and coupled to the spine rod without deformation of the screw or body components while still allowing for subsequent removal of the body from the screw head. The head of the pedicle screw is threadably engaged with a retainer ring on the polyaxial body thereby permitting selective removal of the body from the screw head without disrupting the placement of the screw in the spine. This allows for the pedicle screw to remain in the spine as the fixation system is adjusted as required by the surgeon for subsequent and reliable reanimation.
Owner:ZIMMER BIOMET SPINE INC
Cervical plate with backout protection
The present invention provides a cervical plate with backout protection. In particular, a bushing residing in each of a plurality of through holes has a bottom edge that aligns with a protrusion on a screw head. The bottom edge aligning with the protrusion inhibits reverse threading or backing out of the bone screw.
Owner:ZIMMER BIOMET SPINE INC
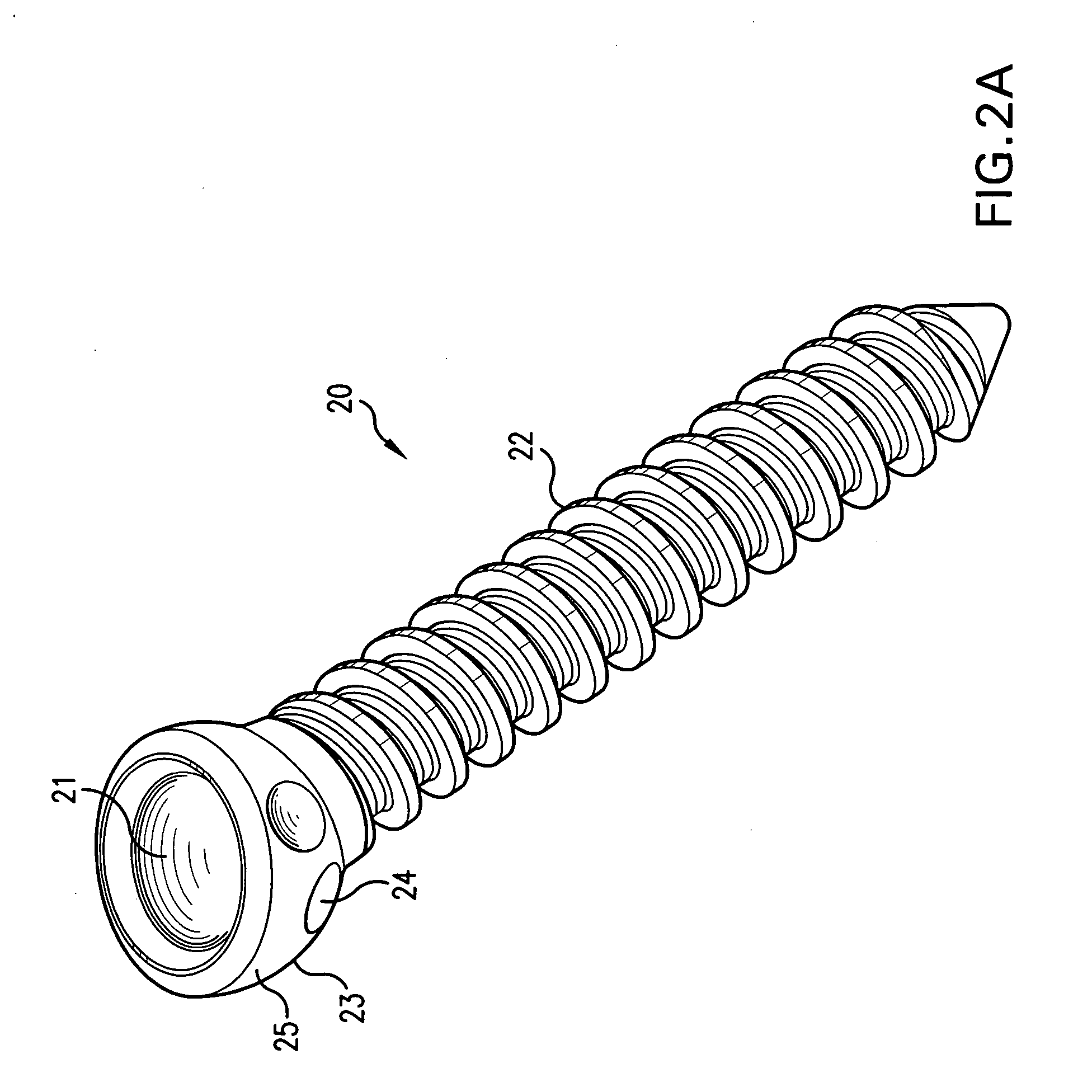
Bone screws and methods of use thereof
ActiveUS20110060373A1Prevent escapeFaster advanceSuture equipmentsDental implantsBone defectBiomedical engineering
The invention features bone screws having a threaded screw body and a screw head attached to one end of the screw body, the bone screw further including: a) an interior channel extending longitudinally through the screw head and through at least a portion of the screw body, wherein the interior channel has a width of less than 5.0 millimeters; and b) a plurality of radially-disposed delivery channels connecting the interior channel to the exterior of the screw body, each delivery channel having exterior openings. The invention further features devices that include a bone screw and a delivery manifold detachably attached to the screw head of the bone screw. In addition, the invention features methods of treating a patient having a bone defect by using a bone screw described herein.
Owner:INNOVISION CO LTD
Minimally invasive fixation sysyem
ActiveUS20070270842A1Reduce the amount of noiseInternal osteosythesisDiagnosticsSet screwSurgical site
A minimally invasive fixation system and method for providing access to a surgical site. The fixation system may include a holding assembly, the holding assembling preferably including a lateral implant holder which may be attached to a pedicle screw and a sleeve positioned in connection with the lateral implant holder to prevent the lateral implant holder from separating from the pedicle screw. The sleeve may further include a tissue protection portion to keep the tissue out of the surgical site. A holding sleeve may be operably connected to the holding assembly and pedicle screw and may be used to insert the pedicle screw into the body. Multiple constructs may be inserted into the body so that a portion of the holding assembly extends from the body and provides access to and visualization of the surgical site. A rod holder may also be used to insert a rod into the head of the screw. The rod may be held by the rod holder so that the rod may be angulated as the rod is inserted into the screw heads. Once the rod is positioned in the screw heads, locking caps and / or set screws may be positioned over the rod and engage the screw heads so that the position of the rod may be fixed with respect to the screws. In some embodiments, a movement mechanism may be used to move the screws relative to each other to compress and / or distract the vertebrae.
Owner:SYNTHES USA
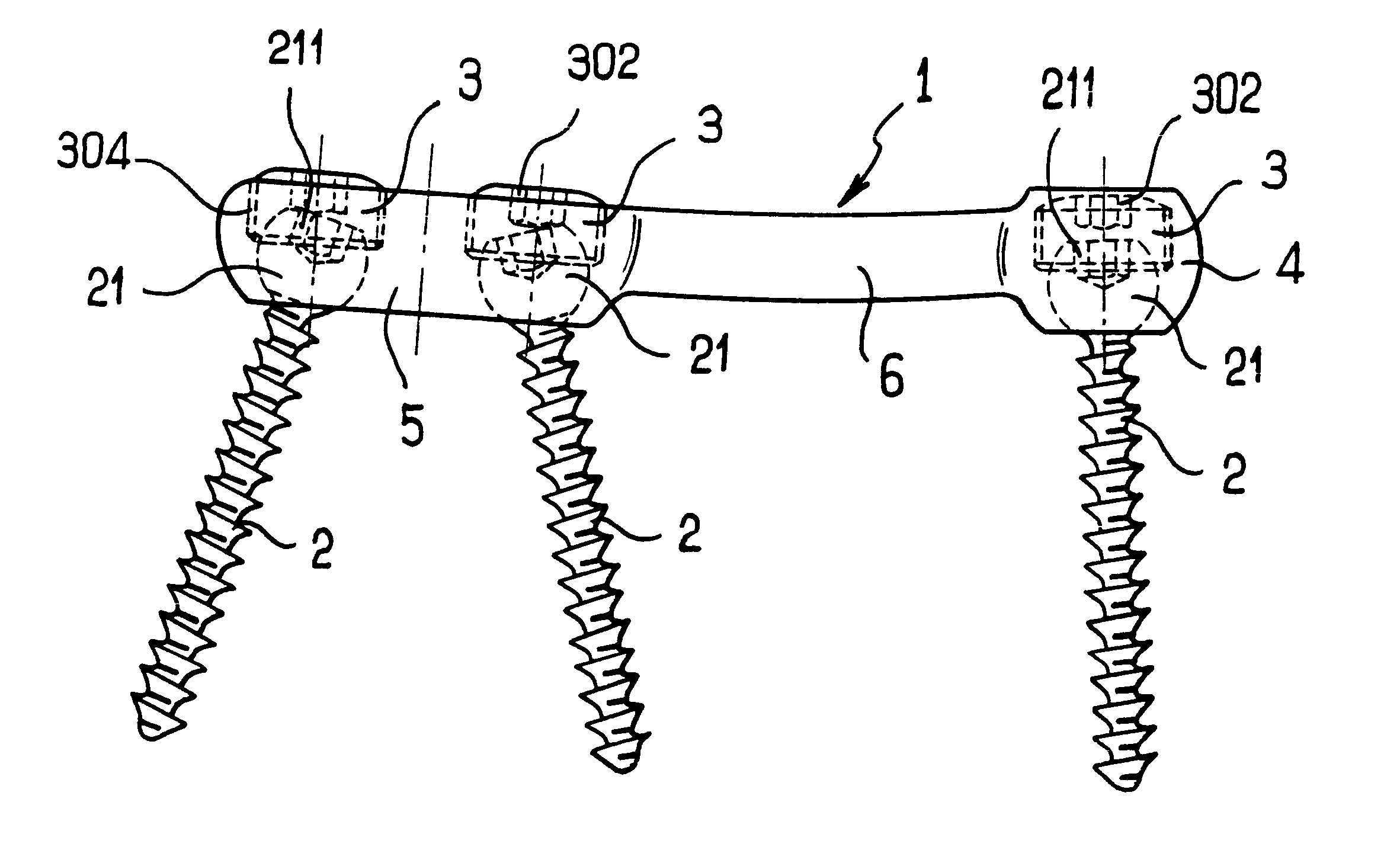
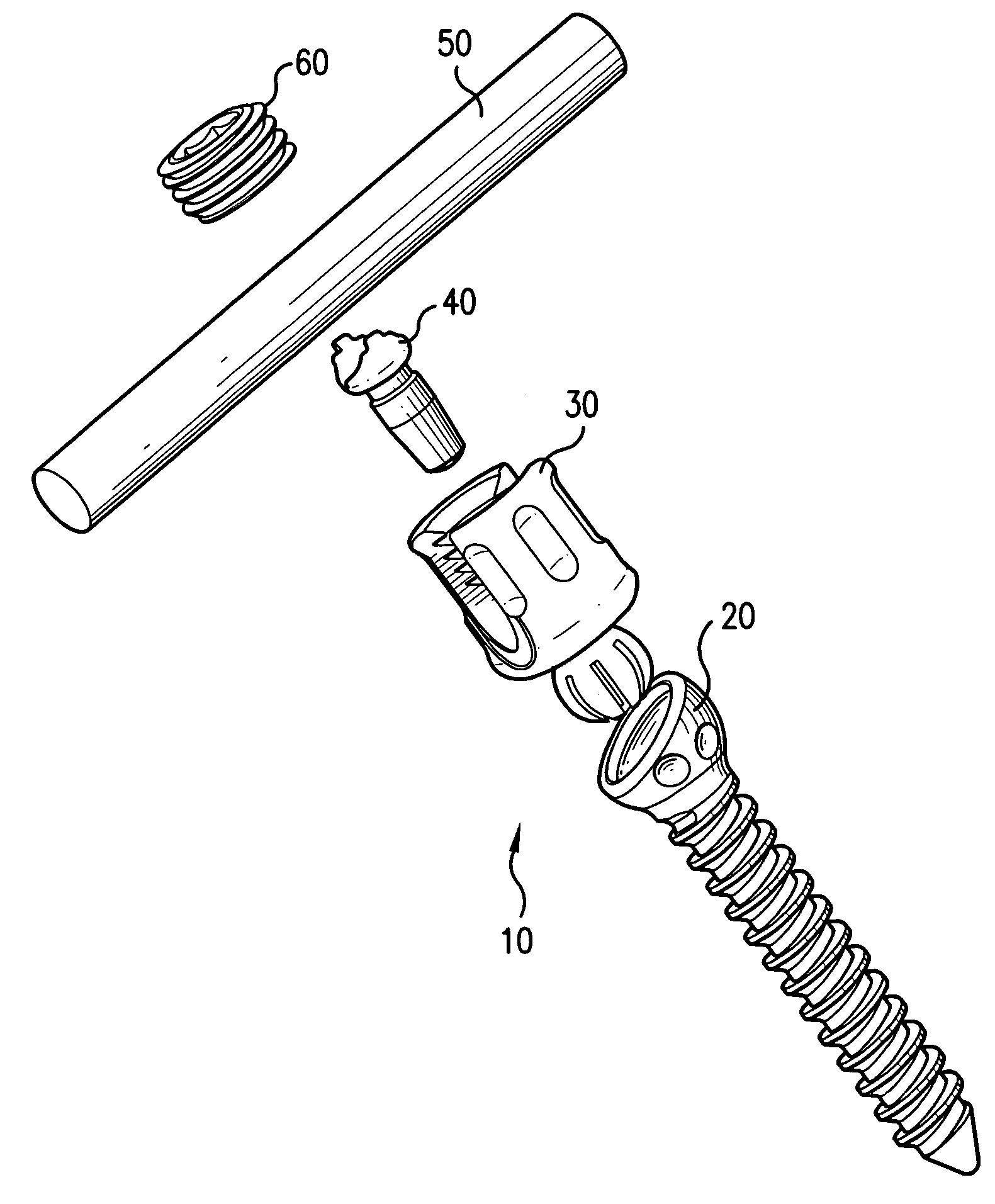
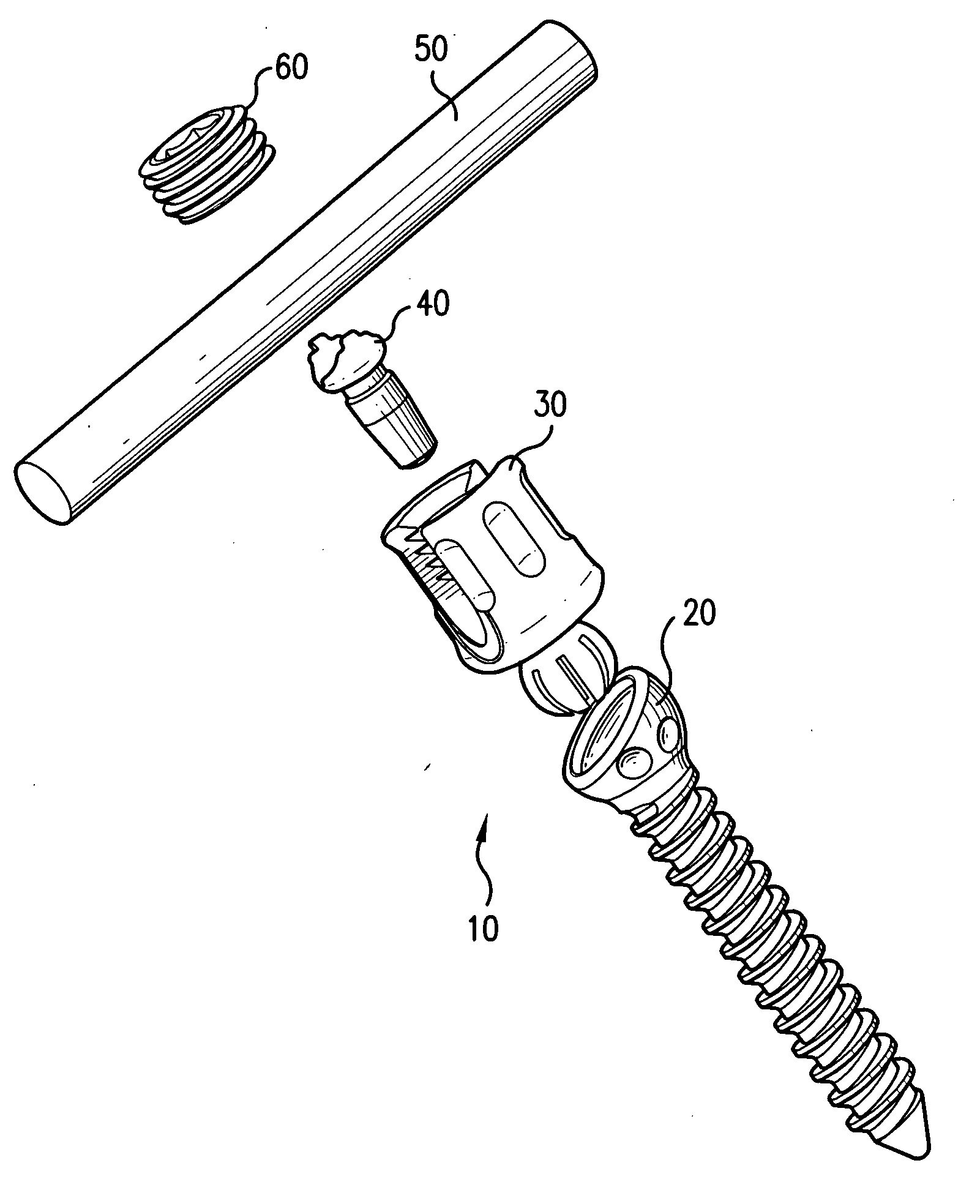
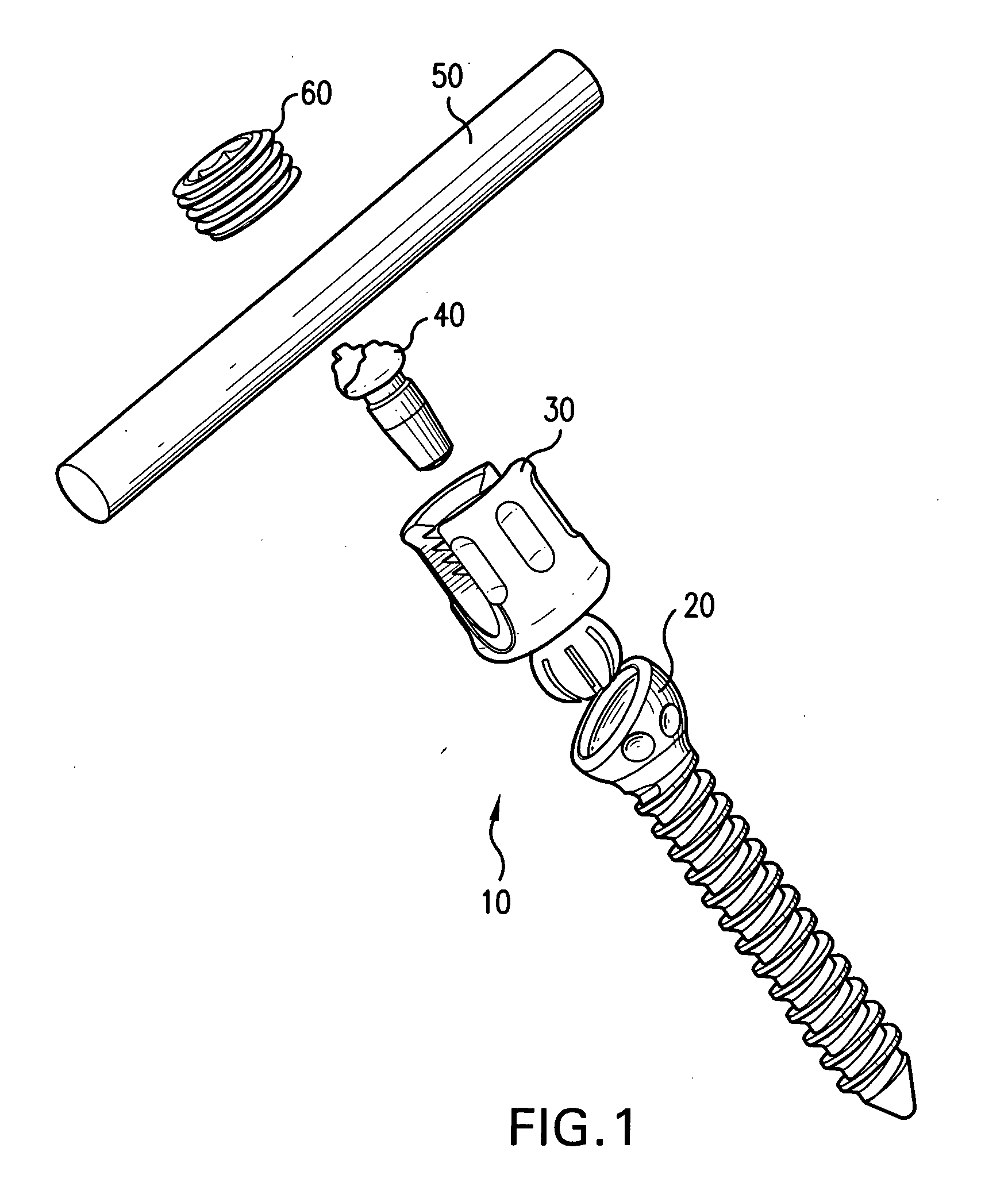
Screw and rod fixation assembly and device
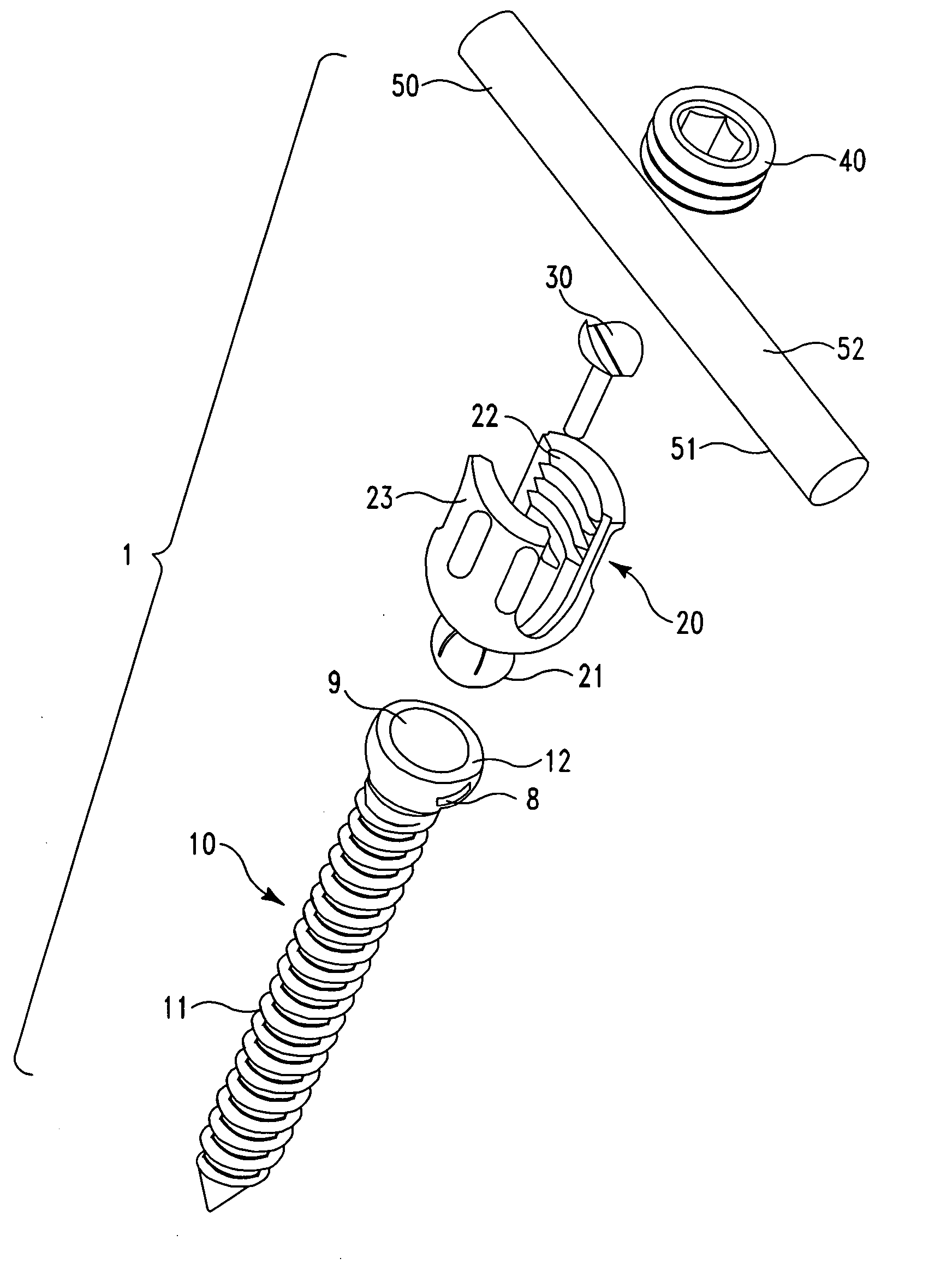
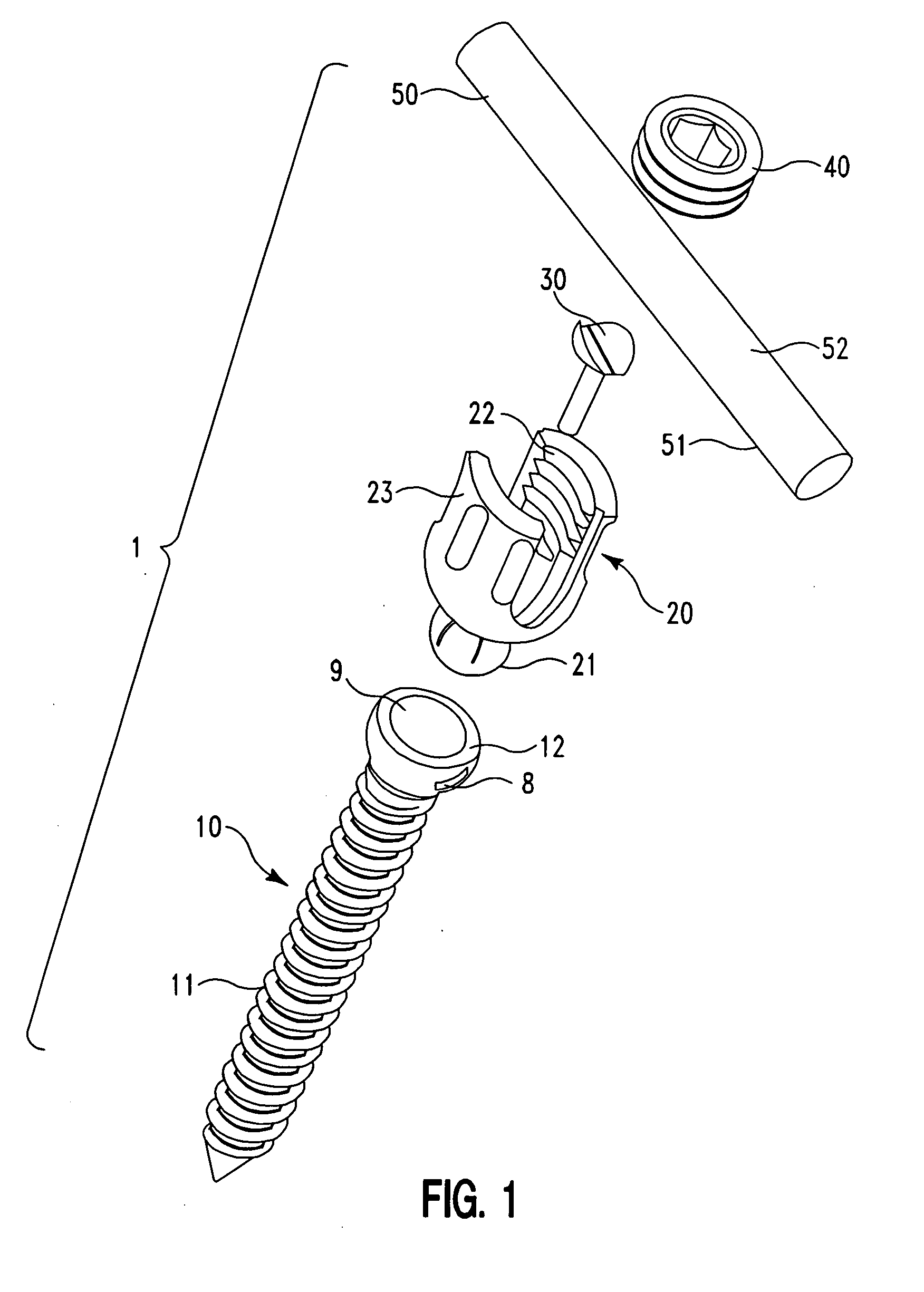
A screw and rod fixation assembly for fixing a screw and a rod, the assembly having a screw including a screw head, a body portion including a screw head receiving device for receiving the screw head and a rod receiving device for receiving a rod therein, the rod receiving device being offset from the screw head receiving device, and a locking device for locking a rod within the rod receiving device. A medical device for fixing a screw and a rod, the assembly having a screw including a screw head, a body portion having a receiver for receiving the screw head and an offset slot for receiving a rod therein, and a lock for locking the rod within the assembly. A receiving member for receiving and maintaining a rod therein, the receiving member having a body portion having a receiver for receiving a screw head and an offset slot for receiving a rod therein. A rod receiving device having a body portion having a receiver for receiving a screw therein and a rod seat offset within the body portion.
Owner:RICHELSOPH MARC +1
Biased angle polyaxial pedicle screw assembly
ActiveUS20050192573A1Accurate distanceSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisEngineeringPedicle screw
A pedicle screw assembly and method of assembly comprises a longitudinal member; a screw head comprising a bulbous end, wherein the screw head has a slot adapted to receive the longitudinal member; a bone fixator component comprising a concave socket having a biased angled top and a rounded bottom adapted to receive the screw head; a locking pin adapted to engage the screw head, the bone fixator component, and the longitudinal member; and a blocker adapted to engage the screw head and to secure the longitudinal member. Additionally, the bone fixator component may be configured as any of a bone screw and a hook.
Owner:CUSTOM SPINE INC
Top Loading Polyaxial Spine Screw Assembly With One Step Lockup
A top loading polyaxial spinal rod screw assembly is configured for simultaneous or one step lockup of angular orientation of a rod holder portion of the screw assembly relative to a bone screw and of a spinal rod within the rod holder portion of the screw assembly. The spinal rod and the angular orientation of the rod holder holding the spinal rod are thus fixed upon receipt of a lockup component of the present assembly. Components of the present spinal rod screw assembly cooperate to allow reception of a spinal rod in a rod holder that is adapted for pivotal retention on a bone screw and to lock or fix the spinal rod within the rod holder while also locking or fixing the angular orientation of the rod holder relative to the bone screw upon receipt of a lockup cap component of the screw assembly in the rod holder. In one form, the present screw assembly is defined by a three-piece polyaxial screw head assembly for a bone screw. The three-piece polyaxial screw head assembly includes a spine rod holder or head configured for pivotal connection with the bone screw, a head insert configured for reception in the spine rod holder, and a lockup (end) cap configured for reception in the spine rod holder. The lockup cap is configured to interact with the head insert to fix an angular position or orientation of the spine rod holder relative to the bone screw at the same time as fixing a spinal rod that has been received in the spine rod holder relative to the spine rod holder.
Owner:LIFE SPINE INC
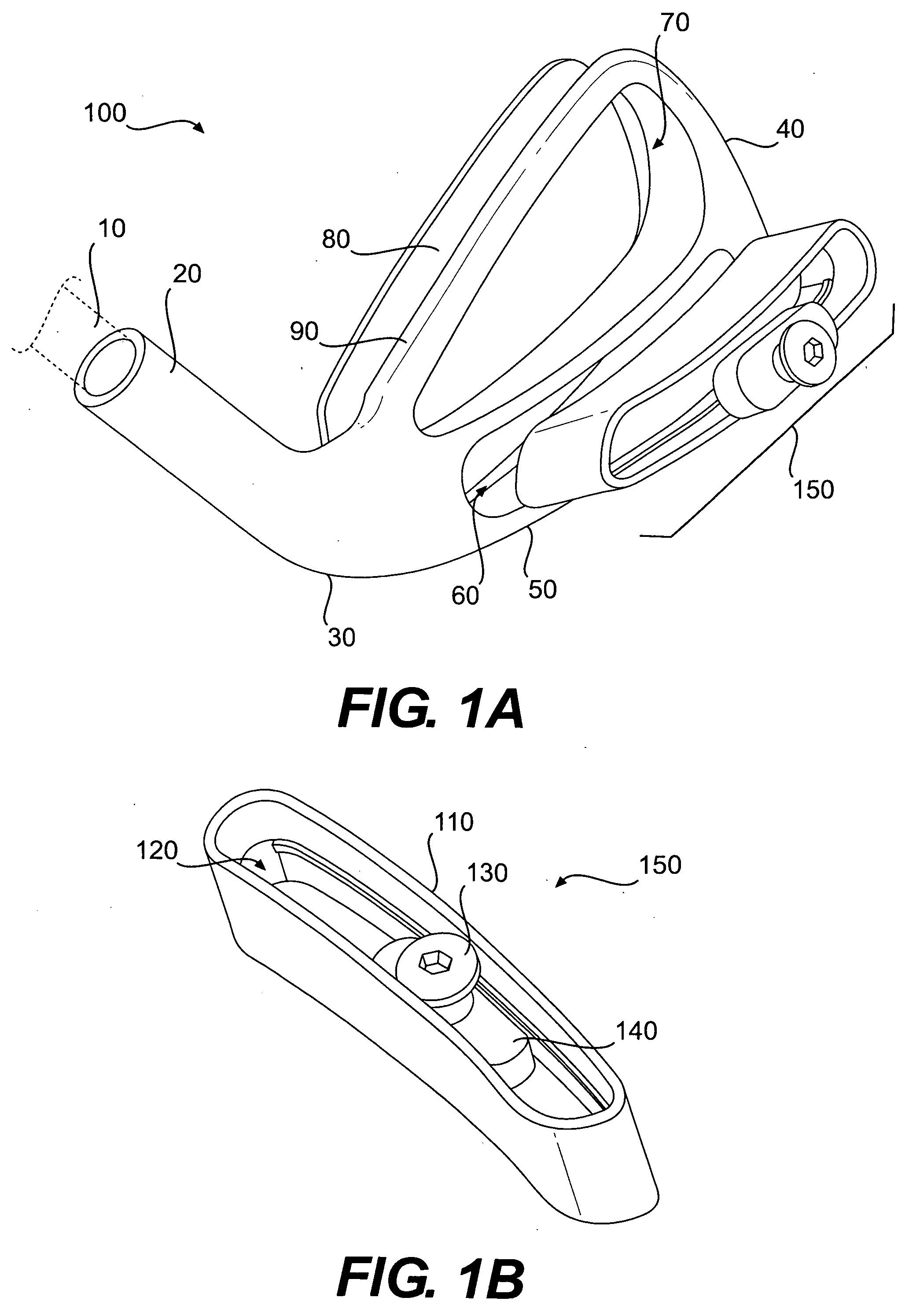
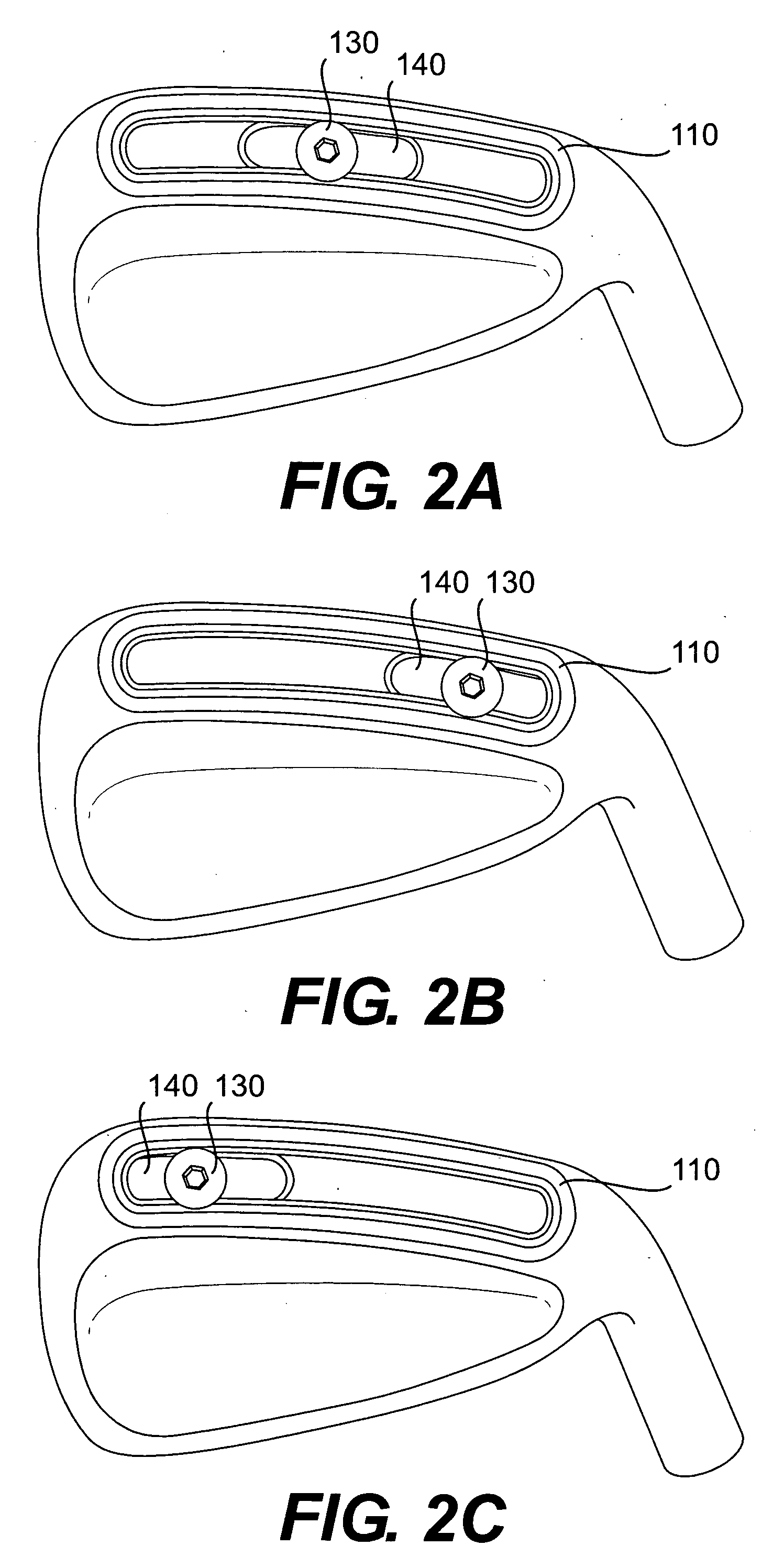
Adjustable weight golf clubs
InactiveUS20080020861A1Adjustable center of gravityGolf clubsStringed racketsEngineeringGravity center
The present invention relates to golf clubs having a movable weight which may be used to adjust the center of gravity of the golf club head. The golf club may include a slidable weight movable to various positions along a slot between the heel and the toe of the club. The head may include a cavity shaped to receive an insert. In one embodiment, a slidable weight consisting of a screw and a weight which may engage with each other may be configured to move along the length of the insert. During assembly, the weight may be inserted into an opening in the end of the insert and slid along a close fitting channel running the length of the insert. The weight's position along the channel may be secured by engaging the screw and tightening down the screw with a portion of the insert secured between the screw head and the weight. The assembled insert and slidable weight may then be press fit into the cavity in the head. By adjusting the position of the weight and screw within the insert, the center of gravity of the golf club may be adjusted.
Owner:HILCO TAG
Image Guided Intra-Operative Contouring Aid
A method of contouring spinal rods, and systems therefor. The surgeon uses image guided surgery instruments to identify the locations of the screw heads through which the rod will pass. These locations allow a computer to form a best fit line that corresponds to the shape of a rod that can pass through the screw heads. This best fit line is then displayed on a projection table from both its coronal and sagittal views. The surgeon then shapes the rod using these 2-D images as a template.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
Device for fixing a rod and a spherical symmetry screw head
Owner:ZIMMER SPINE AUSTIN
Locking screw for an intramedullary nail
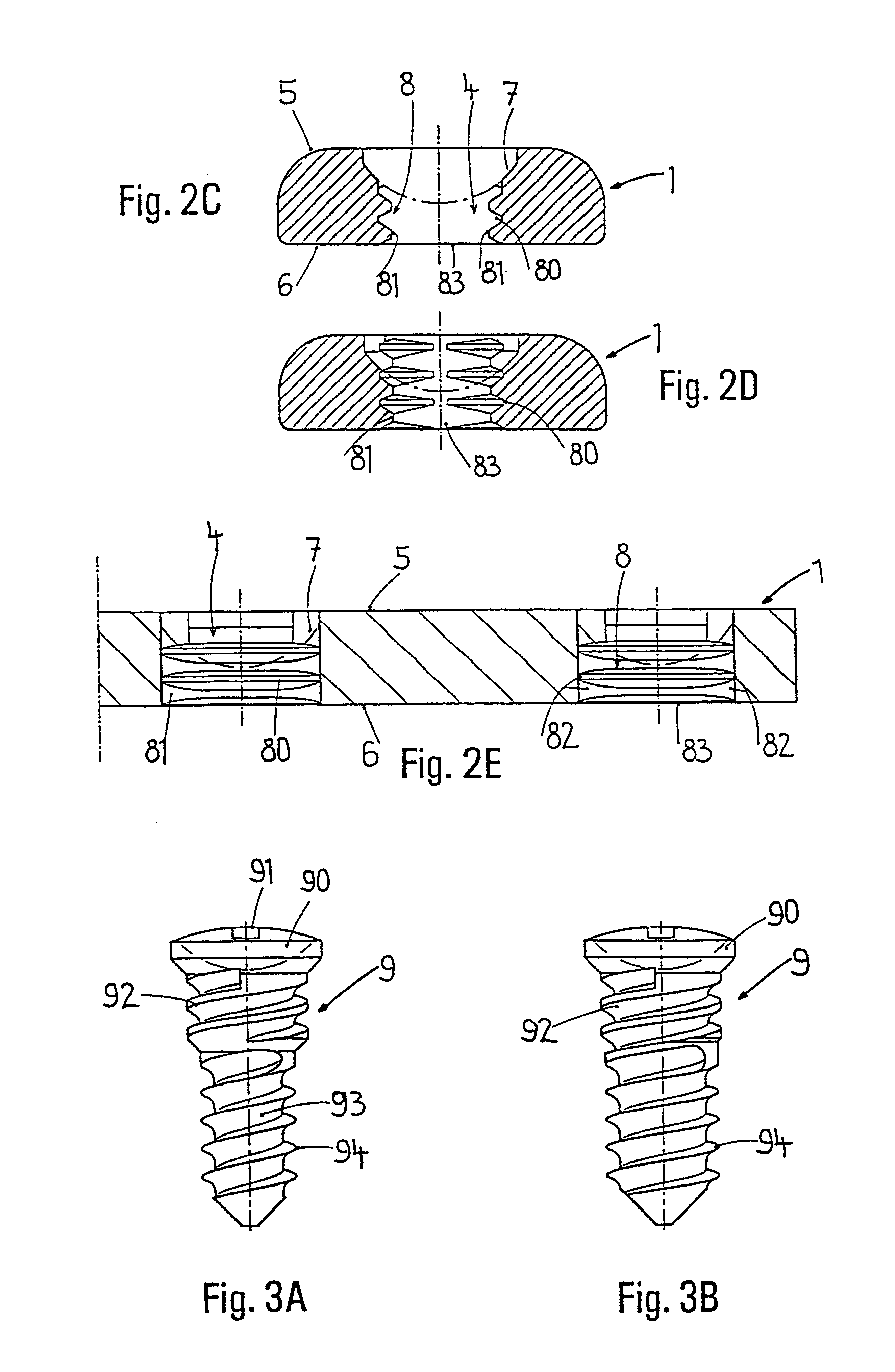
ActiveUS20060064095A1Avoid piercingImprove guidanceInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsEngineeringScrew thread
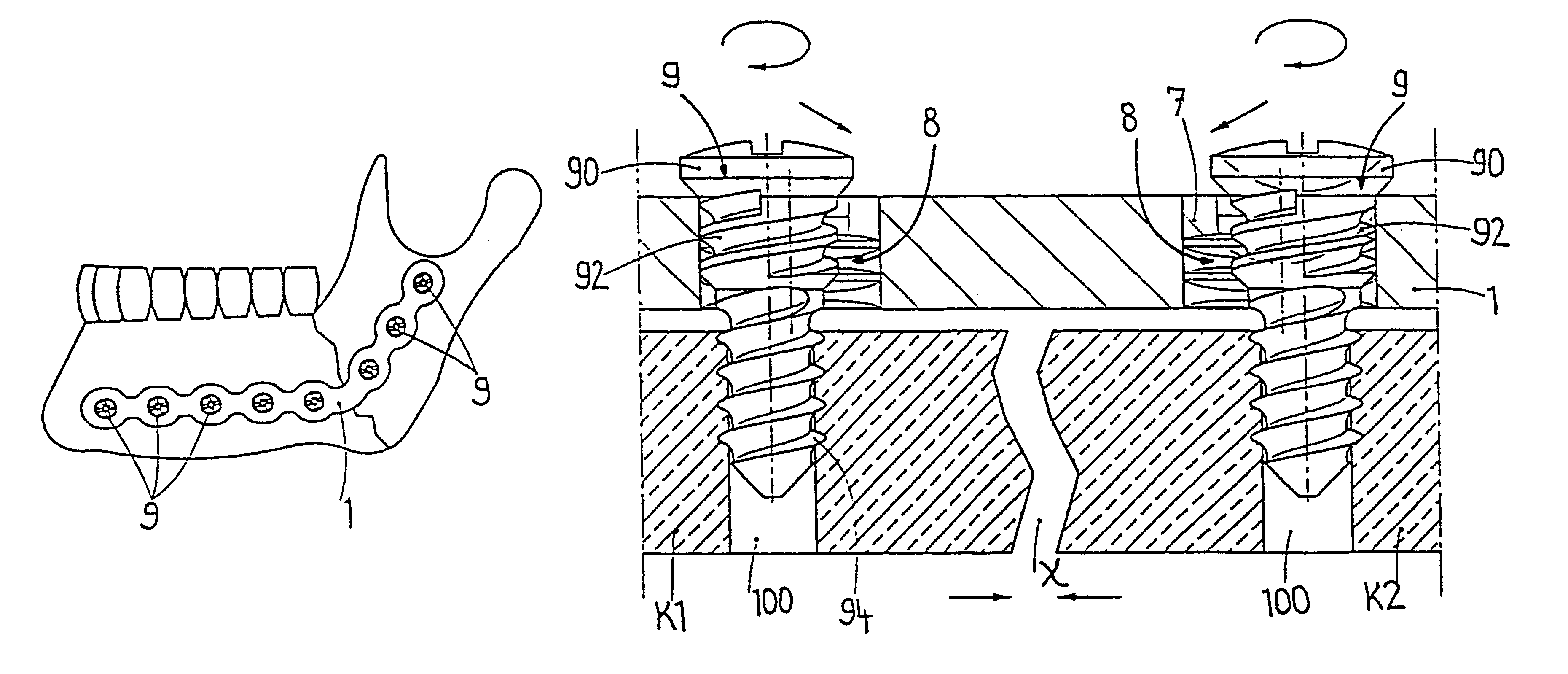
A locking screw for an intramedullary nail having at least one transverse hole. The locking screw has a central longitudinal axis and includes a screw shank, which is at least partially provided with an external thread, and a screw head. The diameter of the screw head is greater than the outer diameter of the external thread, and the screw head includes a passage extending generally parallel to the longitudinal axis of the screw and the external thread. The passage is configured to receive a longitudinal wedge element. As a result, any gap between the locking screw and the intramedullary nail is eliminated and the screw is wedged in position in the transverse hole of the intramedullary nail.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC +1
Rod to rod connector
InactiveUS20070049932A1Improve the immunityInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsBearing downEngineering
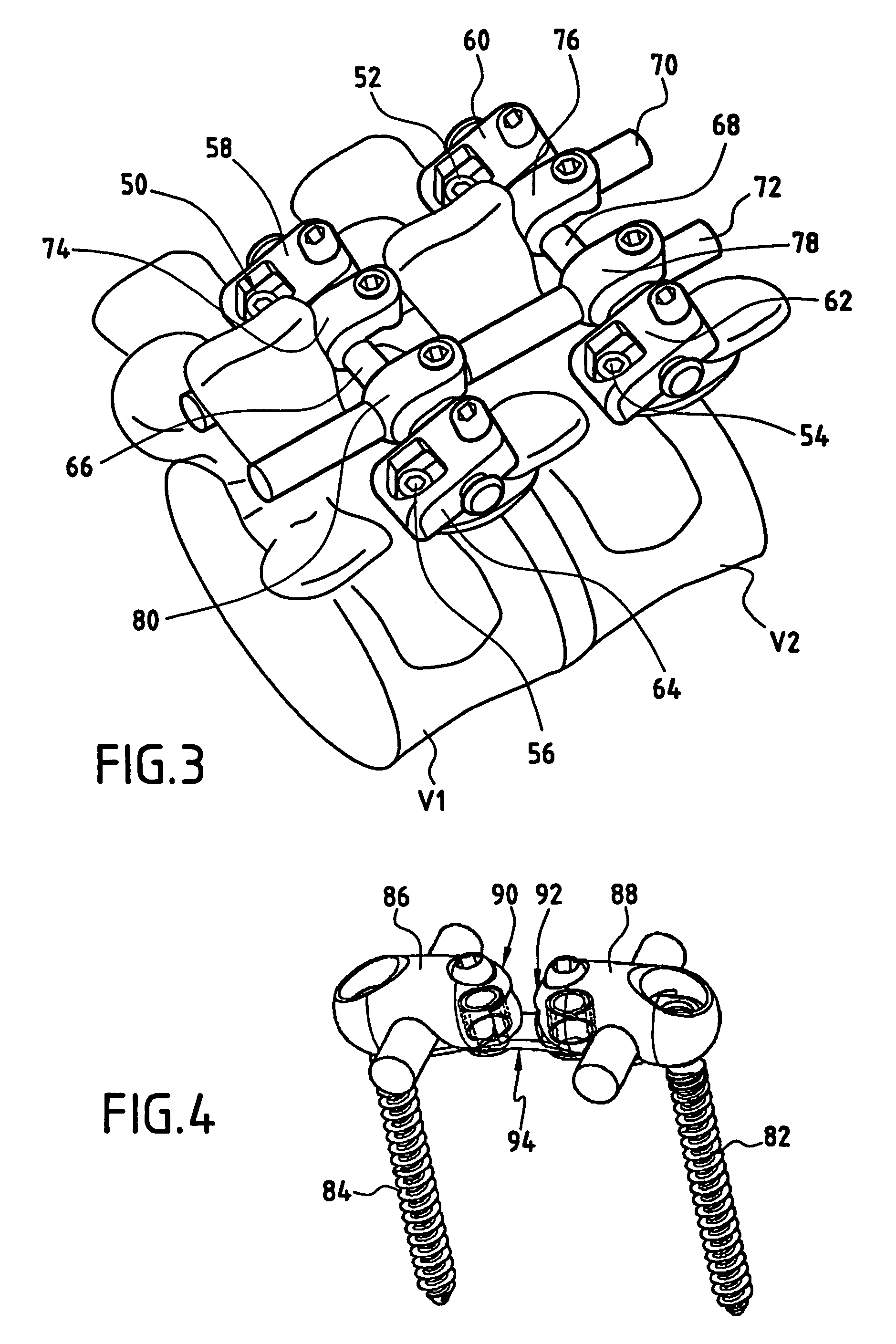
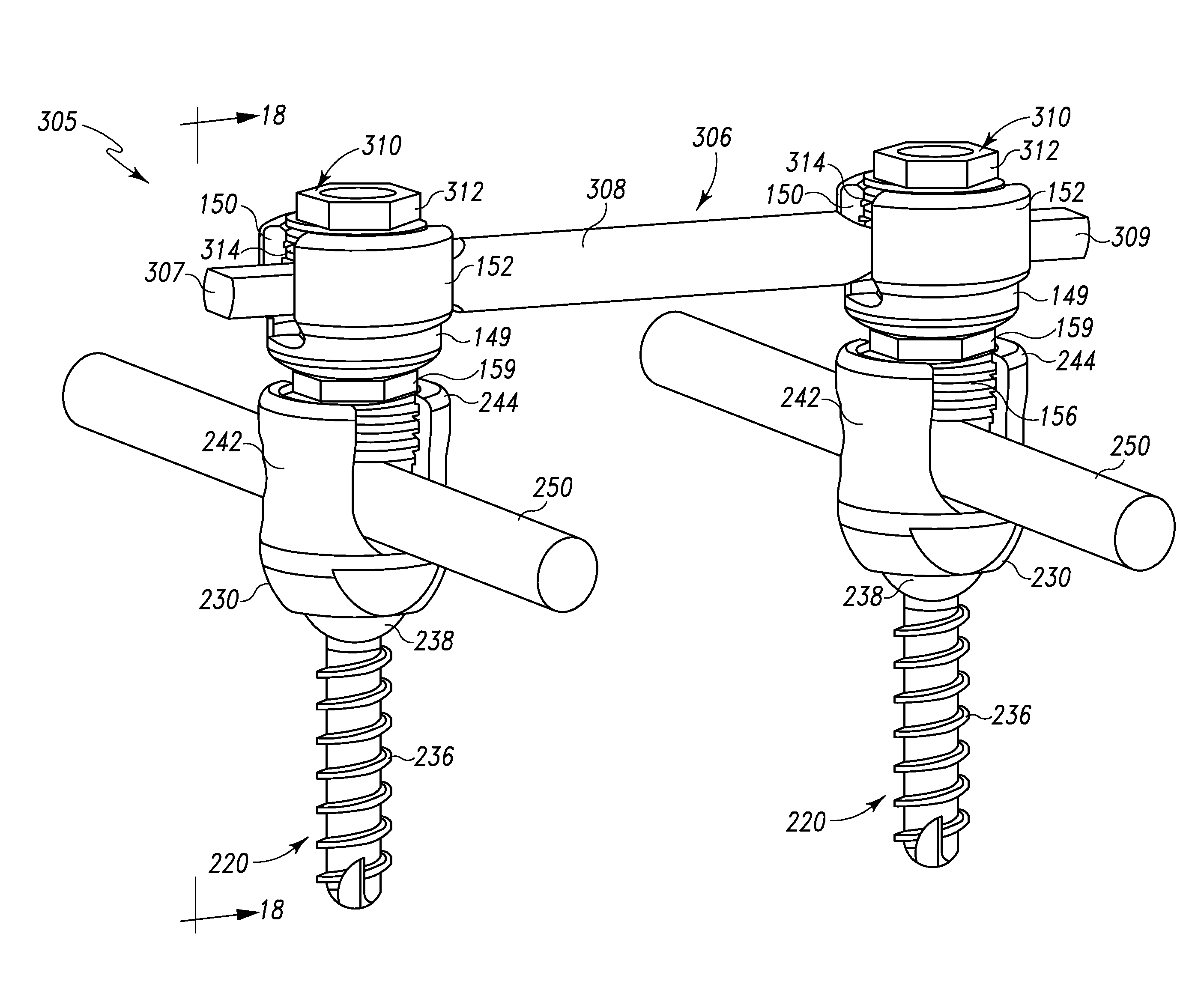
The invention is a rod to rod connector that can be used to interconnect two generally parallel spinal rods of a spinal rod and anchor system. The connector comprises a transverse rod and two pairs of clamping bodies, one for each spinal rod. Each pair connects one of the longitudinal spinal rods to the transverse rod in infinitely adjustable angular relationship. One of the two clamping bodies of each pair comprises a C-shaped channel for accepting the spinal rod. The channel is in communication with a slot that defines a hinge. A threaded screw hole passes transversely through the slot and permits a screw to squeeze the hinge, thereby causing the C-shaped channel to close around and clamp the rod. The second clamping body is similar to the first except that there is no slot or hinge and the screw hole preferably is not threaded, but includes a countersink for seating a chamfered screw head. Also, an angular portion of the screw hole intersects the C-shaped channel. The two clamping bodies are aligned with each other so that their screw holes are coaxial so that a single screw can pass through both holes thereby clamping both rods in the C-shaped channels and fixing the angle between the two clamping bodies and, hence, the two rods. The first clamp clamps the spinal rod by squeezing the hinge to cause the C-shaped channel to squeeze around the rod. The second clamp clamps the transverse rod by virtue of the bottom of the screw head bearing down on the transverse rod over the portion of the screw hole that intersects the C-shaped channel.
Owner:AESCULAP AG
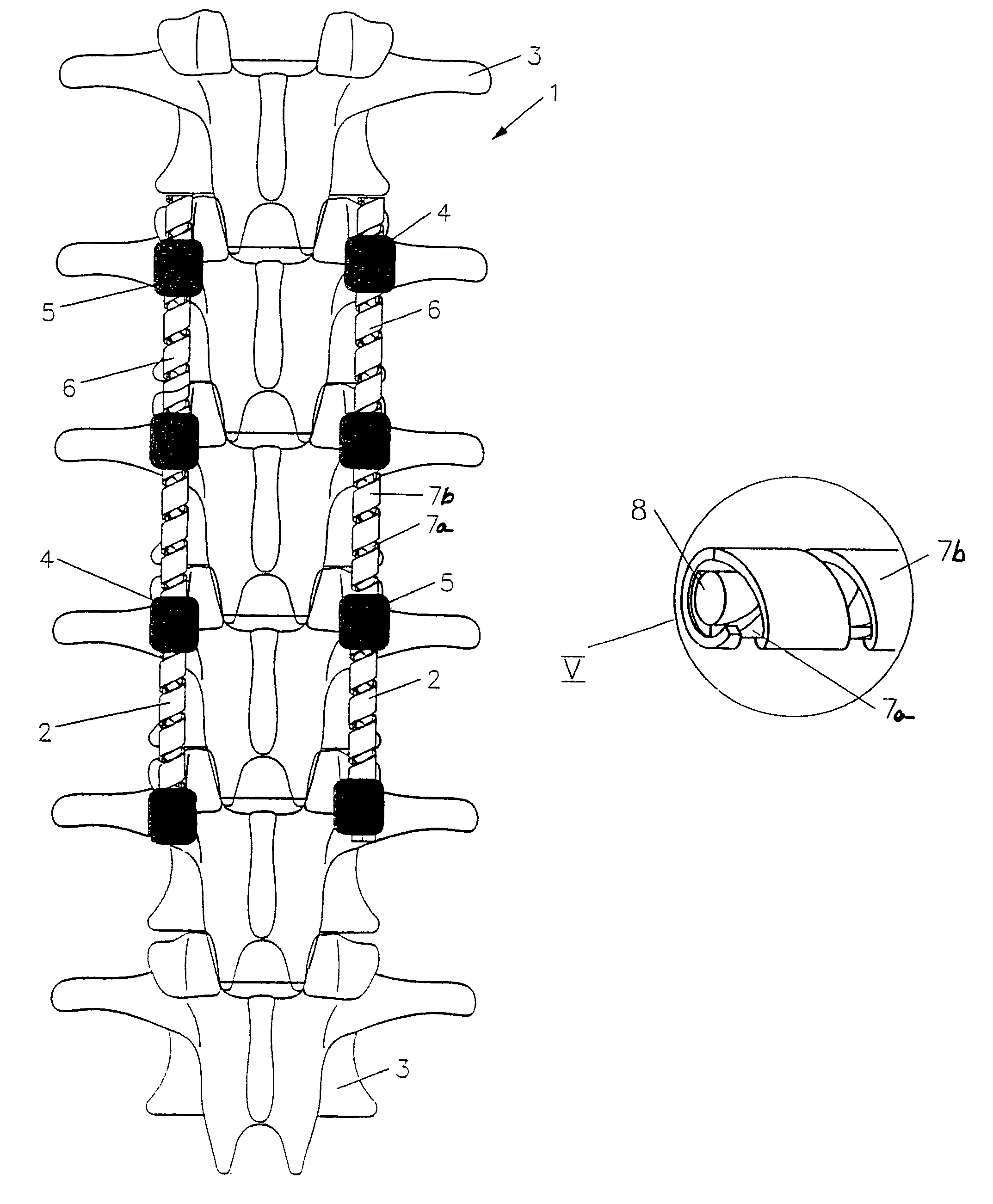
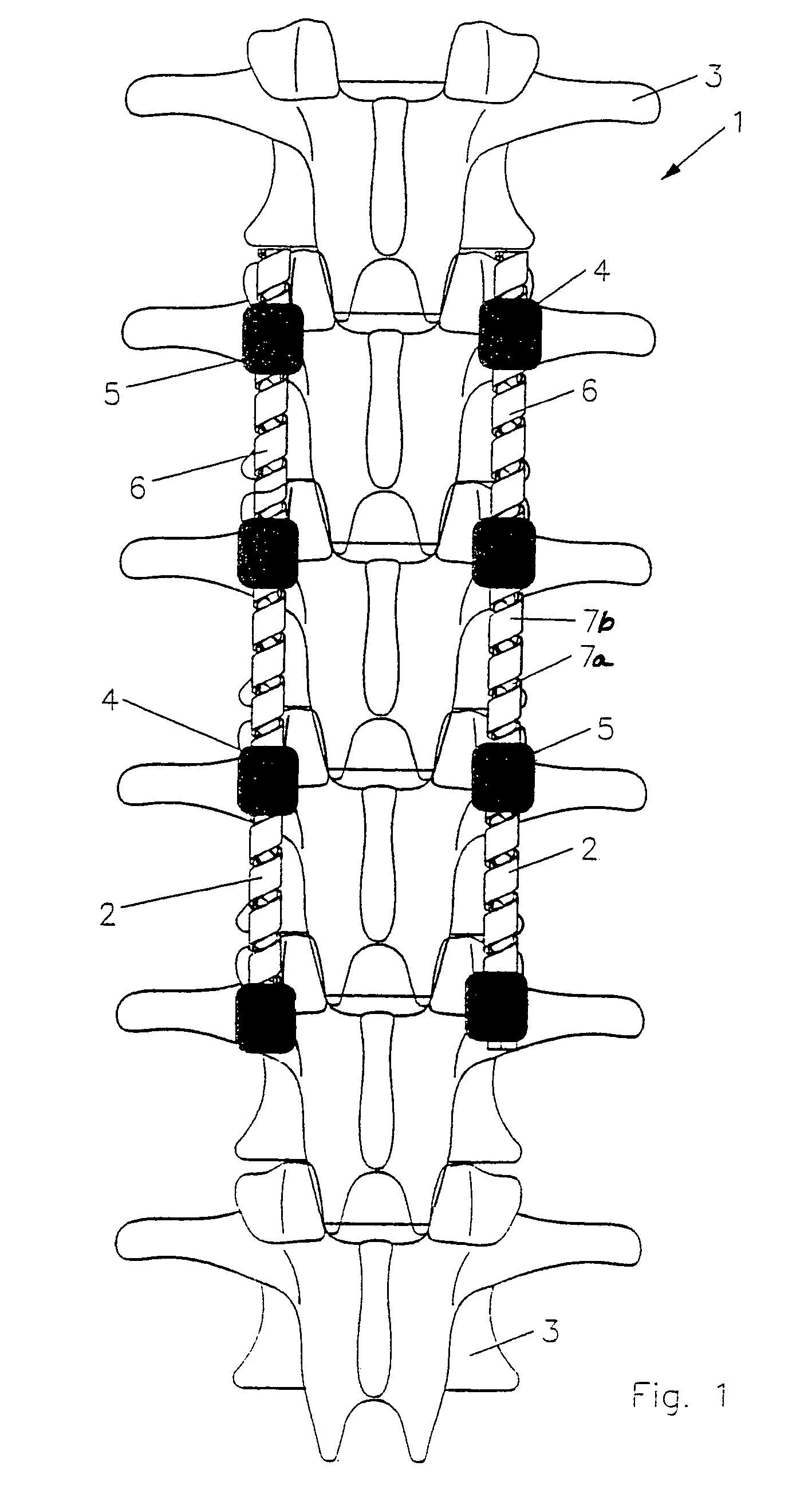
Implant for correction and stabilization of the spinal column
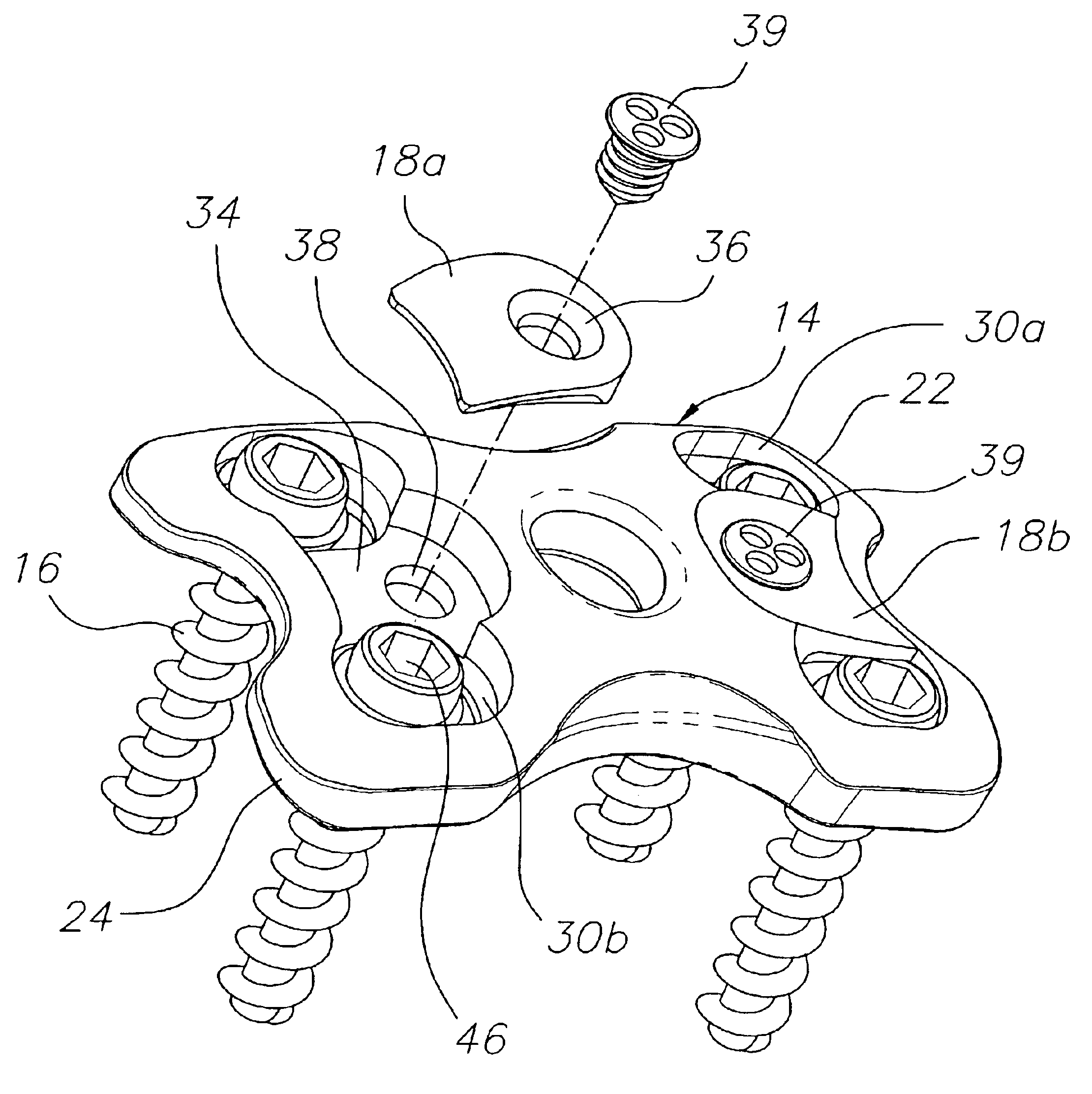
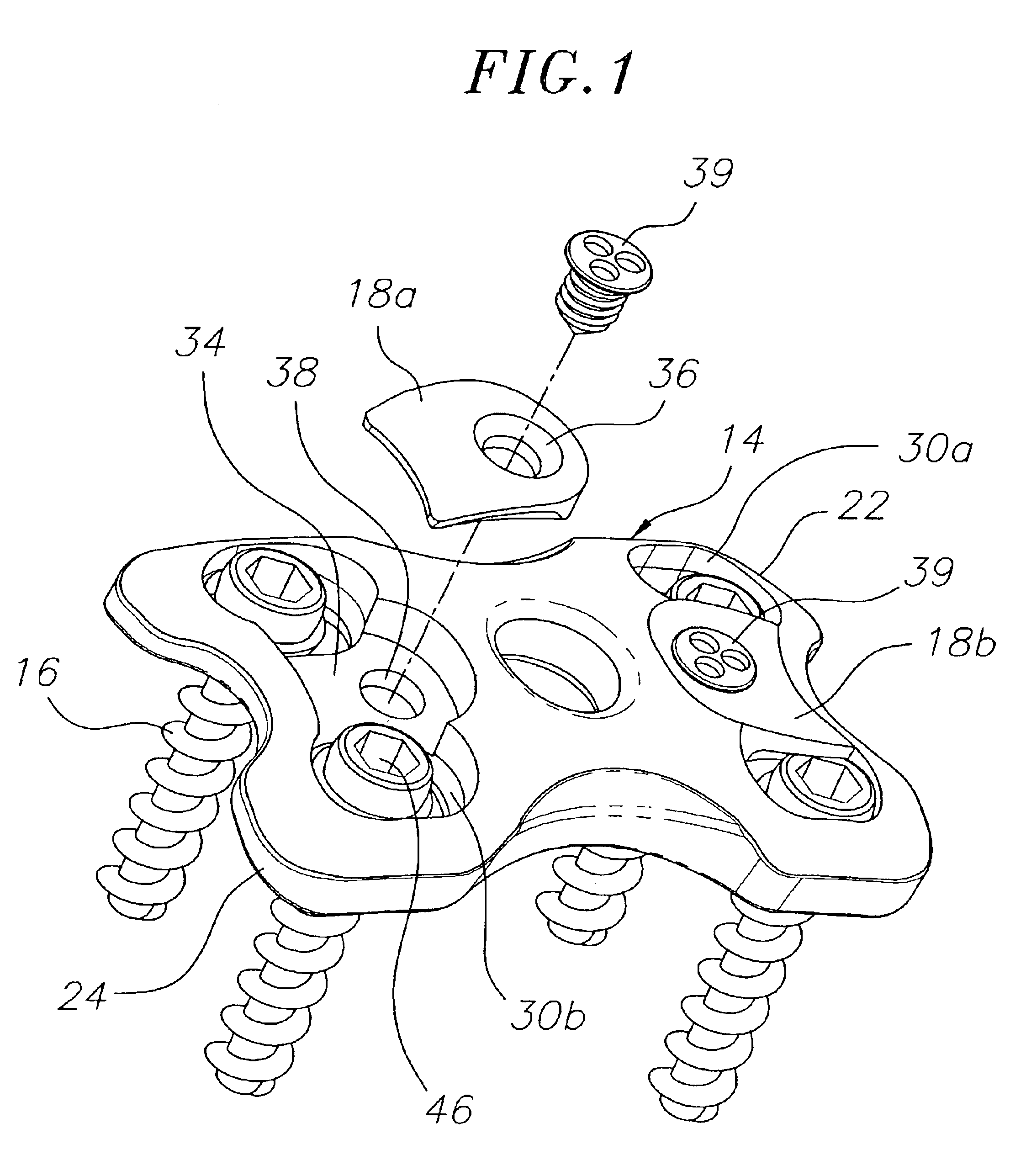
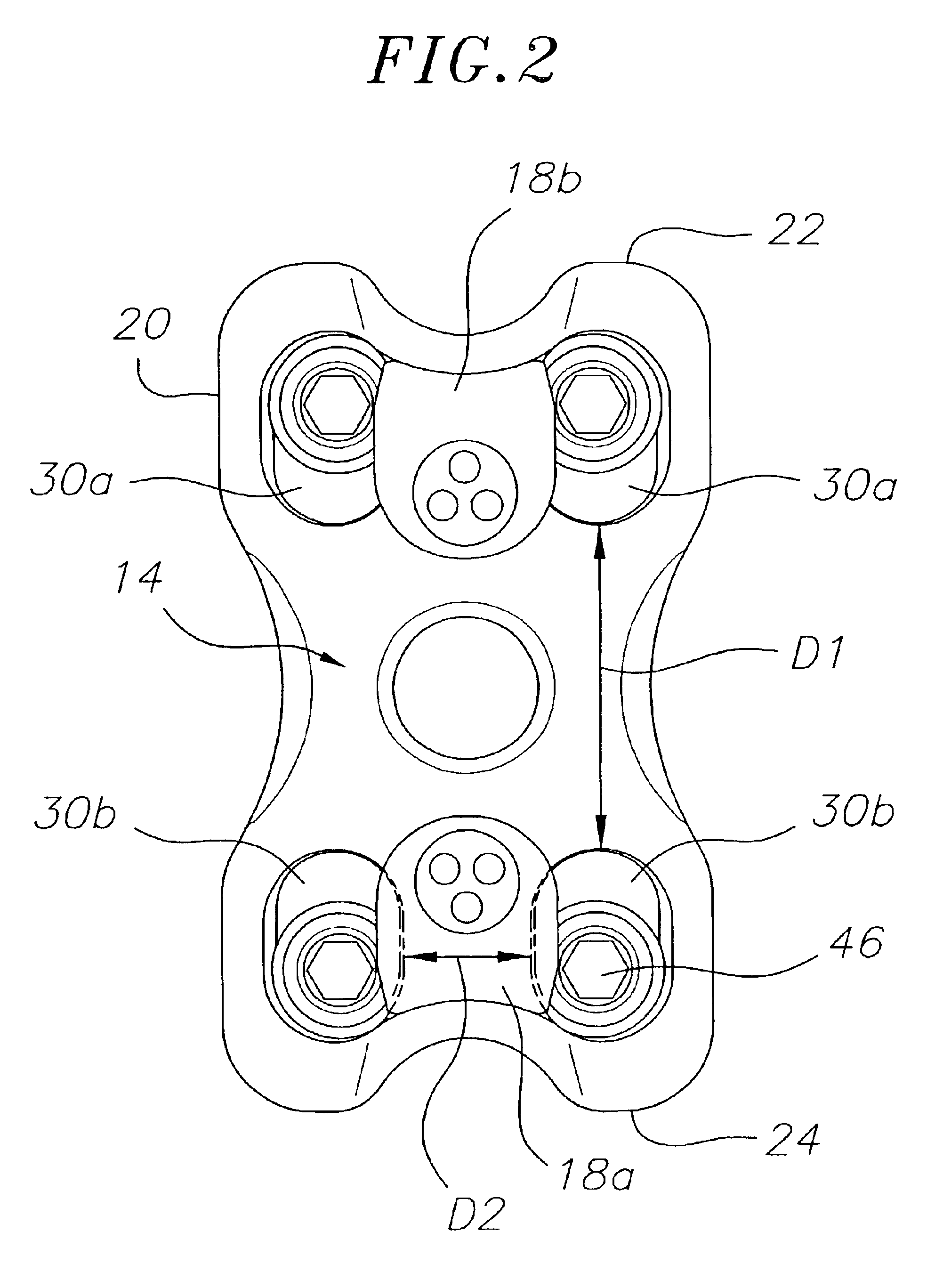
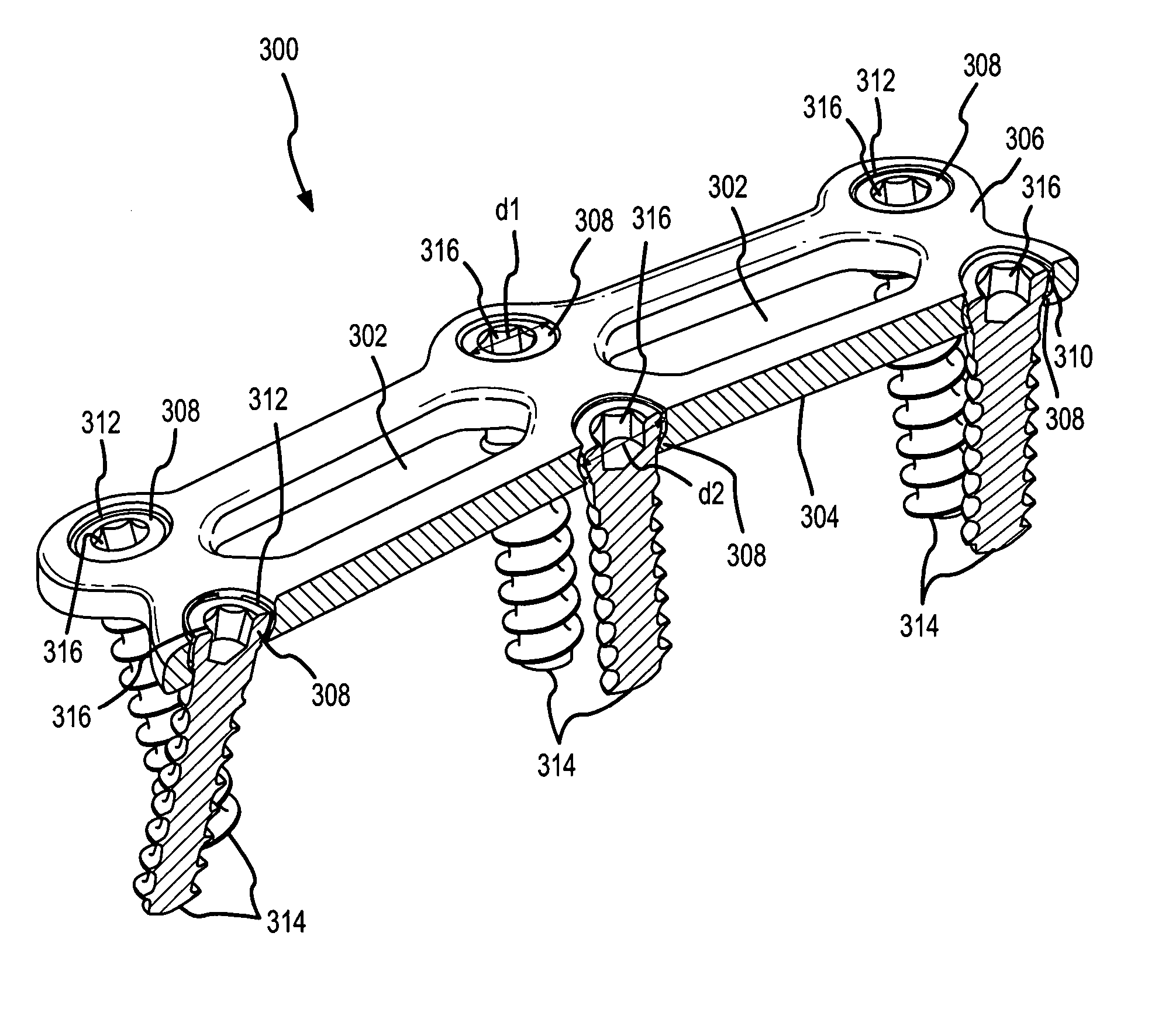
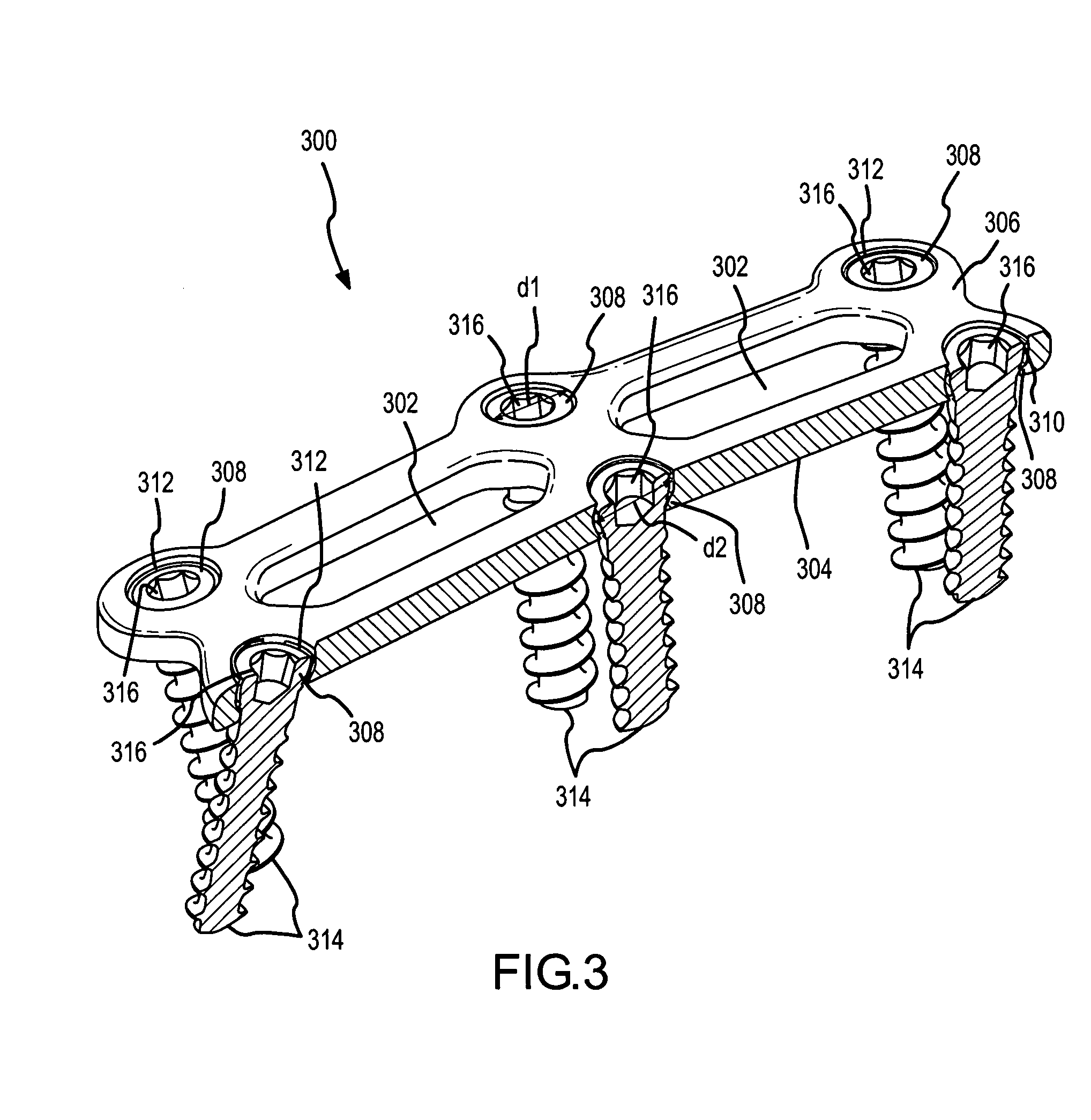
InactiveUS7651515B2Improve approximationLow mobilityInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsSpinal columnIliac screw
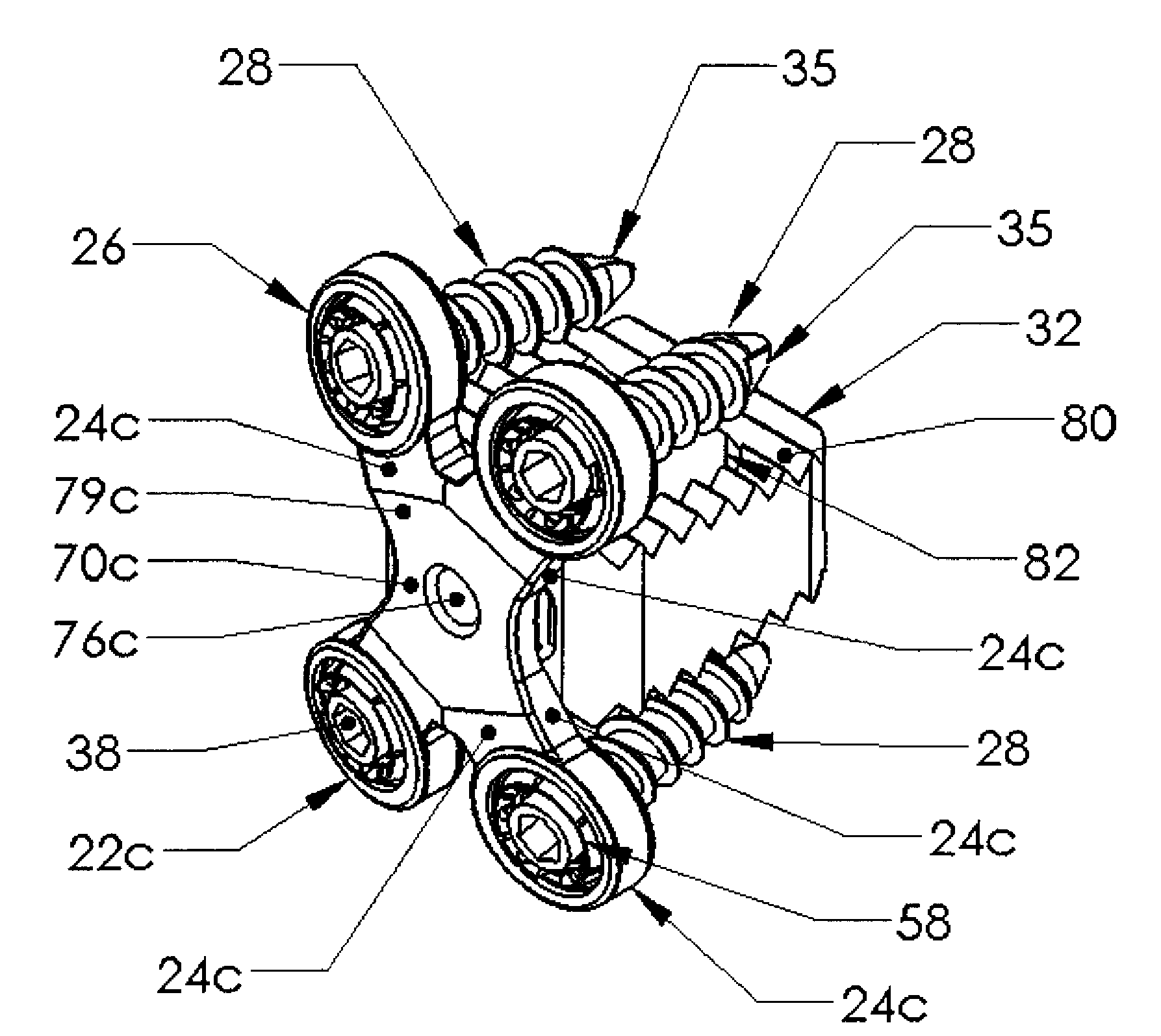
An implant for the correction and stabilization of the spinal column, comprising pedicle screws that can be screwed into the vertebrae of a spine, and of at least one connection element that connects the pedicle screws at the screw heads. This connection element is formed by a spiral whose spiral windings are arranged offset in the axial direction, following a screw line.
Owner:ULRIKH GMBKH & KO KG
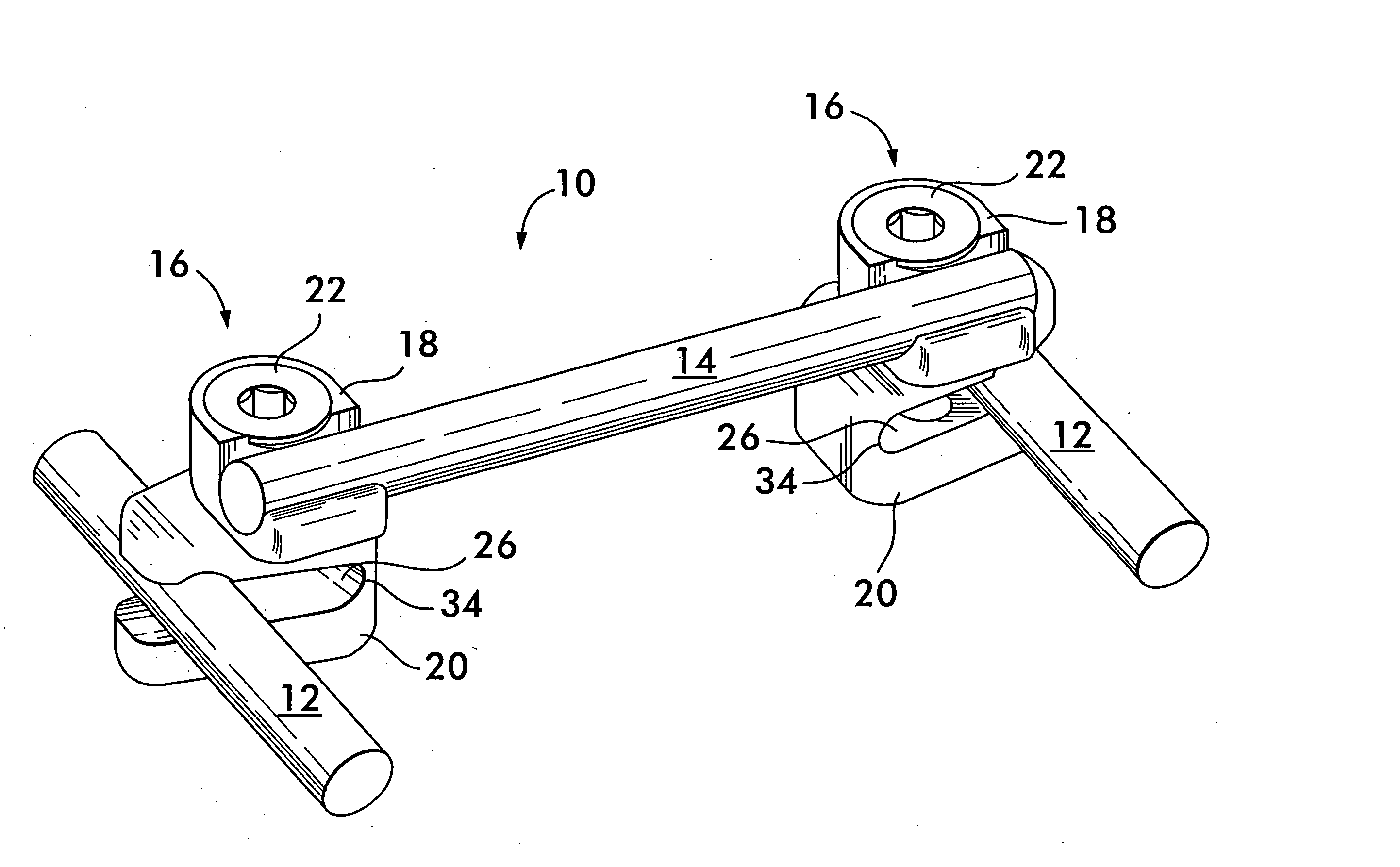
Connecting device for profiled bars with grooves
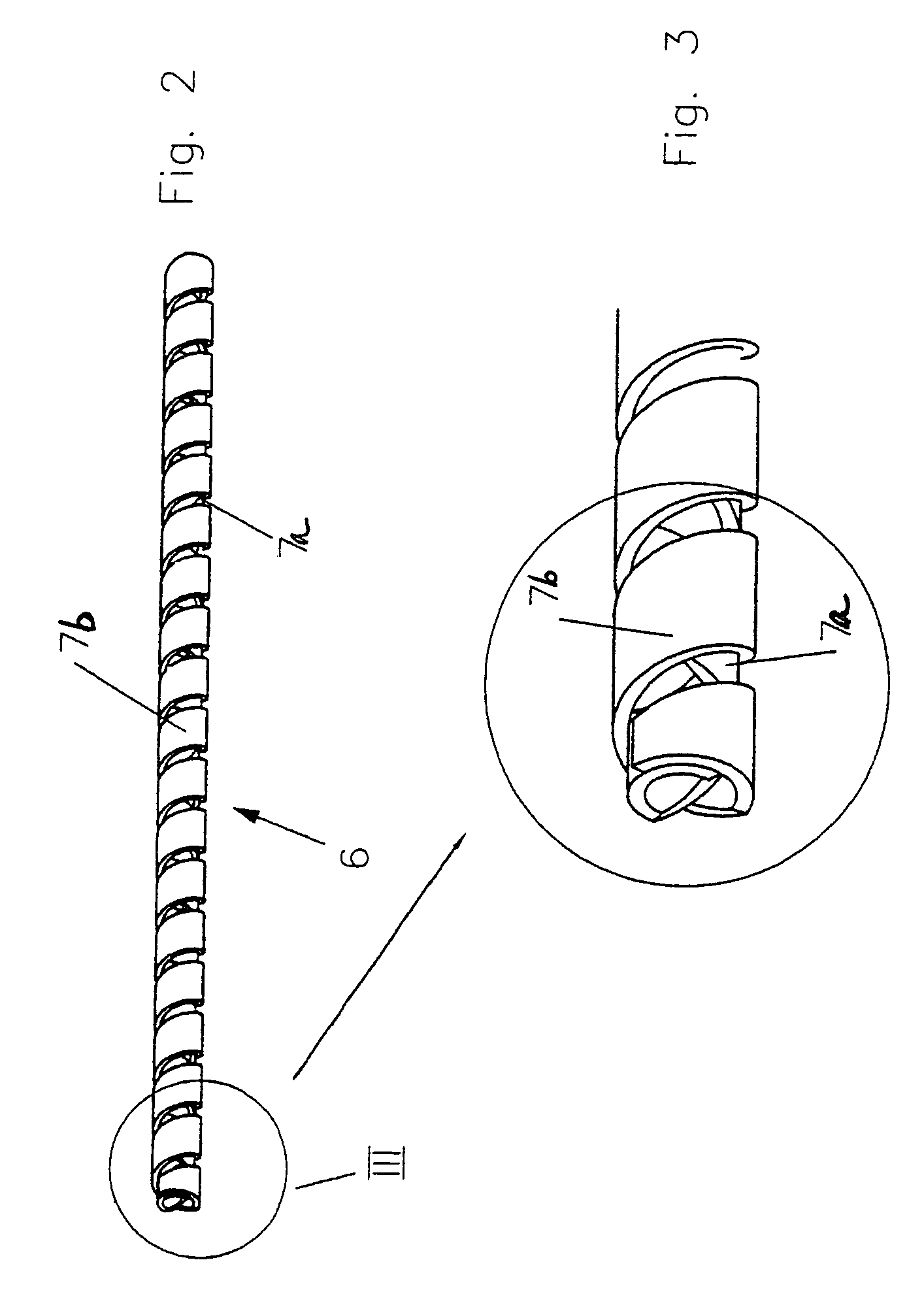
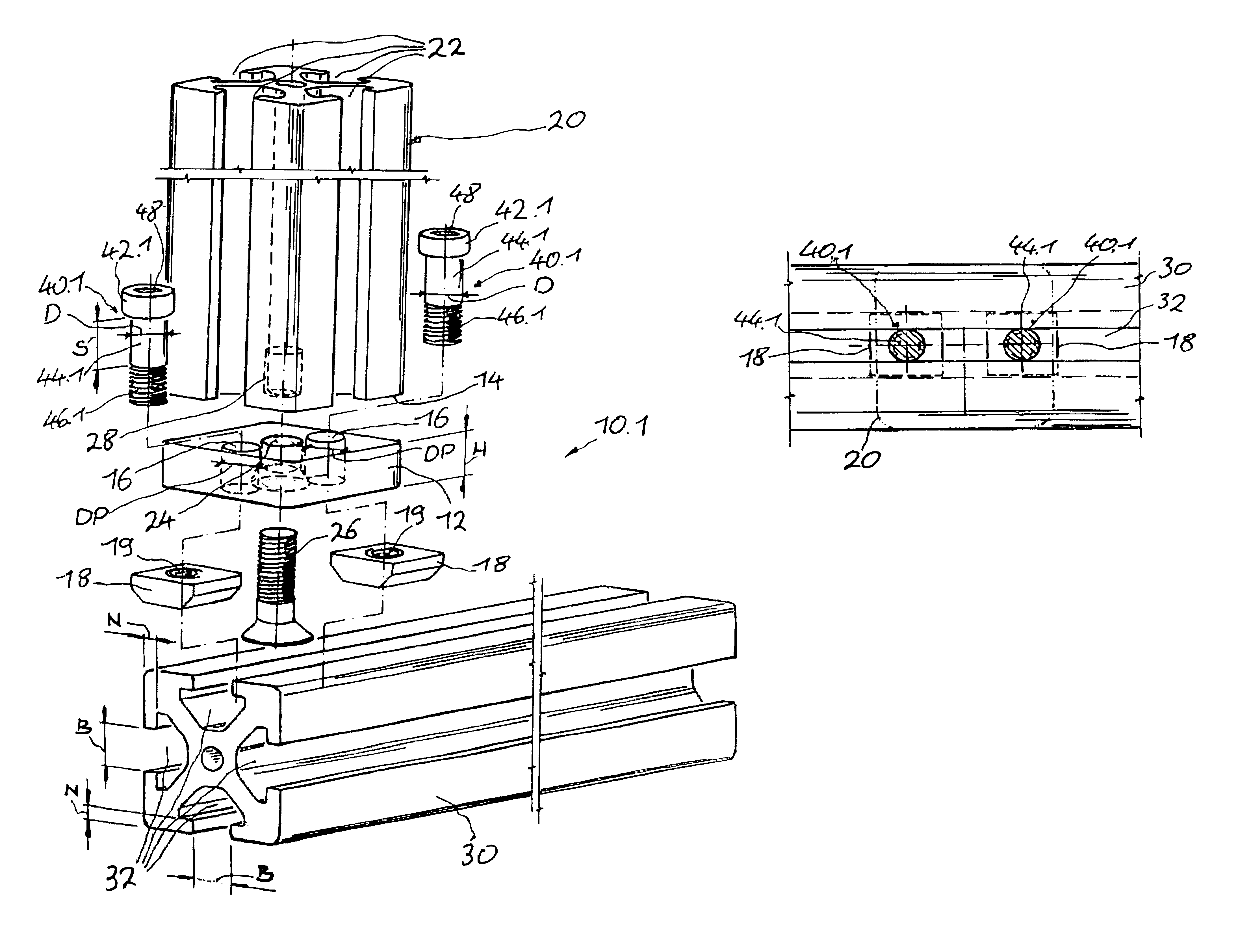
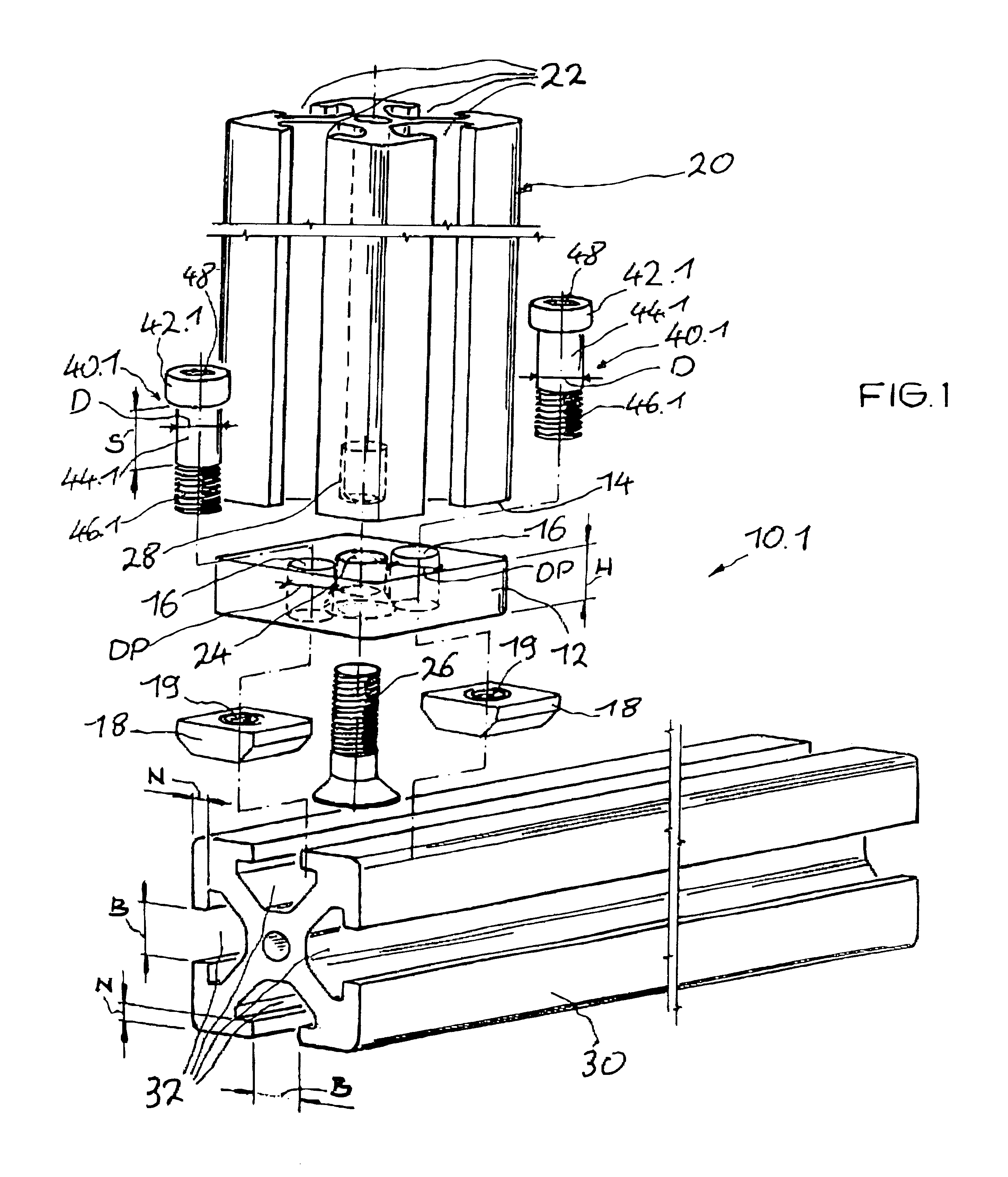
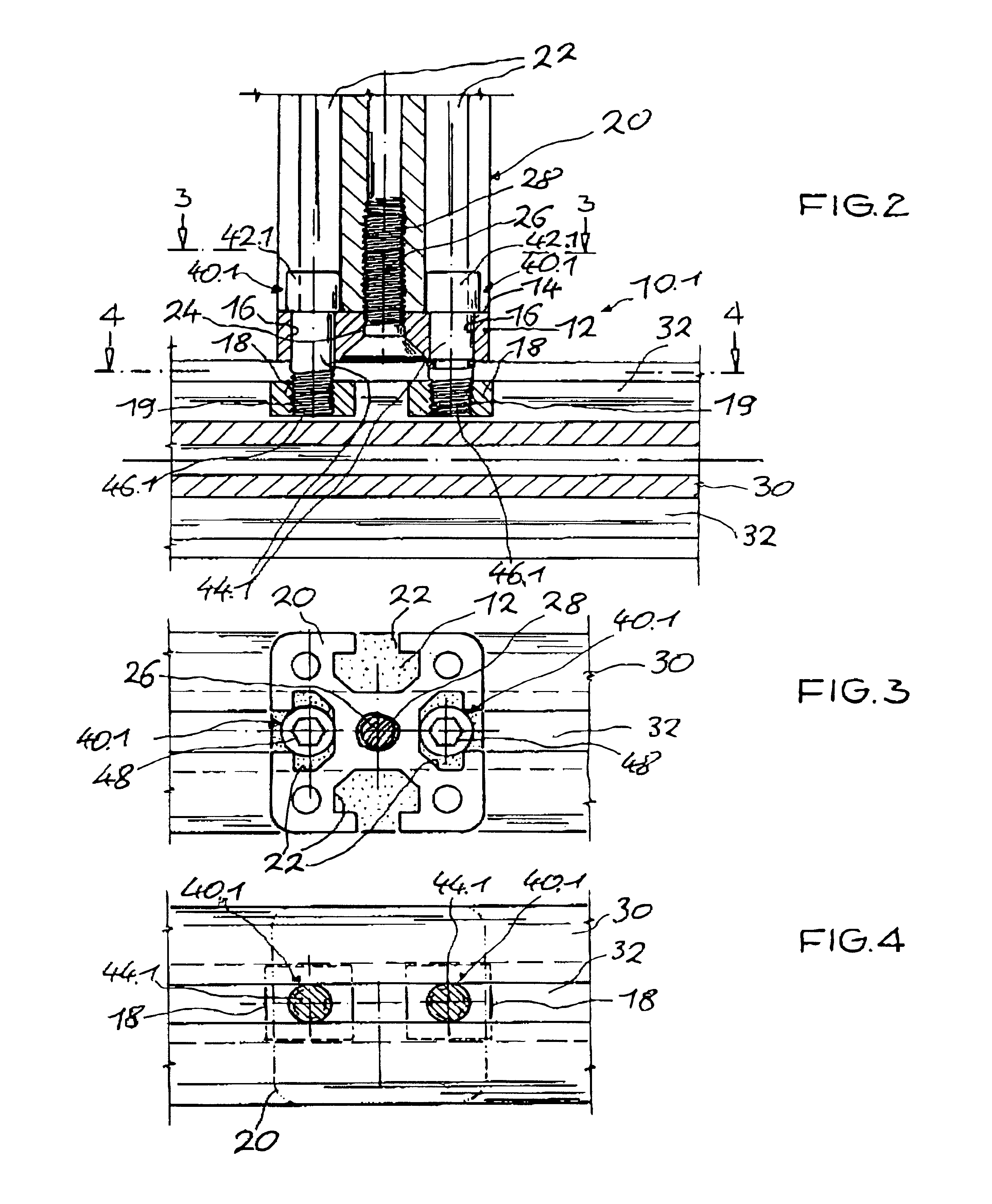
A connecting device for connecting at least two profiled bars that are essentially perpendicular to one another and have grooves, in conjunction with sliding blocks, one plate connector unit is fastened to the end of a first profiled bar and anchored in a groove in the second profiled bar by way of screw units they extend in recesses in the plate connector unit. The geometry of the screw head of the screw unit is configured such that it centers the screw unit within the groove in the first profiled bar and the engages with a centering effect in the groove in the second profiled bar.
Owner:FMS FORDER UND MONTAGE SYST SCHMALZHOFER
Screw and rod fixation assembly and device
The present invention provides for a screw and rod fixation assembly for fixing a screw and, optionally, a rod. The screw and rod fixation assembly includes a screw, fixing mechanism, a substantially annular ring, rod seating mechanism, and locking mechanism. The present invention also provides for a fixing mechanism for fixing a screw, wherein the fixing mechanism further includes an inner surface wall having a gripping portion and a non-gripping portion. Further, the present invention provides for a substantially annular ring for guiding and providing mechanical and frictional force to a screw head. Additionally, the present invention provides for a rod seating mechanism operatively engaged to the screw head and including at least one flexible portion capable of being compressed against a portion of a rod therein. Finally, the present invention provides for a locking mechanism for engaging the rod and the rod seating mechanism. The locking mechanism includes a deflecting mechanism for deflecting the at least one flexible portion of the rod seating mechanism against and around the rod as the locking mechanism further engages the at least one flexible portion of the rod seating mechanism.
Owner:AESCULAP IMPLANT SYST
Spinal fixation device
ActiveUS20090326580A1Reduce stimulationAdjustable flexibilitySuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisIliac screwBiomedical engineering
A spinal fixation assembly has a bone screw with head having a continuously curved spherical outer surface. The curved surface nests in a split annular bushing having a plurality of segments curving around the screw head. The bushing has an outward extending flange that fits into a recess in a socket in a fixation plate. The plate has at least three legs which extend from ends of a cross-member to form one of an H shaped, X shaped or A shaped configuration. Each socket is curved to rotatably receive rotation of the bushing. The socket recess is larger than the bushing flange to allow the bushing to tilt a predetermined amount depending on a thickness of the outward extending flange.
Owner:WESTMARK MEDICAL
Minimally invasive fixation system
A minimally invasive fixation system and method for providing access to a surgical site. The fixation system may include a holding assembly, the holding assembling preferably including a lateral implant holder which may be attached to a pedicle screw and a sleeve positioned in connection with the lateral implant holder to prevent the lateral implant holder from separating from the pedicle screw. The sleeve may further include a tissue protection portion to keep the tissue out of the surgical site. A holding sleeve may be operably connected to the holding assembly and pedicle screw and may be used to insert the pedicle screw into the body. Multiple constructs may be inserted into the body so that a portion of the holding assembly extends from the body and provides access to and visualization of the surgical site. A rod holder may also be used to insert a rod into the head of the screw. The rod may be held by the rod holder so that the rod may be angulated as the rod is inserted into the screw heads. Once the rod is positioned in the screw heads, locking caps and / or set screws may be positioned over the rod and engage the screw heads so that the position of the rod may be fixed with respect to the screws. In some embodiments, a movement mechanism may be used to move the screws relative to each other to compress and / or distract the vertebrae.
Owner:SYNTHES USA
Clamping screw extractor
InactiveUS20040068269A1Prevent rotationSleeve/socket jointsDispensing apparatusScrew extractorScrew thread
A tool for gripping and removing mechanical fasteners such as pedicle screws. With reference to FIG. 7, the device generally resembles a screwdriver, having a handle on one end, a long shaft in the middle, and fastener engaging means on the other end. The fastener engaging means comprises a set of two or more jaws having inward facing gripping surfaces positioned to grasp the external surfaces of a screw head. The jaws are formed as part of a collet slidably mounted within an outer thread sleeve. The thread sleeve is attached to the shaft. A tapered journal on the collet interacts with a tapered bore in the thread sleeve so that when the collet is pulled into the thread sleeve, the set of two or more jaws are squeezed together. The threaded engagements between the collet and the thread sleeve should be the reverse of the thread on the screw to be removed; i.e., if a right-hand screw is to be removed then the threaded engagement between the collet and the thread sleeve should be made with a left-hand thread. In operation, the jaws are placed over the screw head and the device is rotated in a counterclockwise direction (for removal of a screw with a right-hand thread). The inward facing surfaces on the jaws bear against the bolt head, thereby impeding the rotation of the collet relative to the thread sleeve. The left-hand threaded engagement between the collet and the thread sleeve therefore pulls the collet further into the thread sleeve, whereupon the tapered bore squeezes the jaws more tightly together. Thus, the reader will appreciate, applying torque to the device when it is in position on a screw head simultaneously torques the screw head and squeezes the jaws more tightly together. The inward facing surfaces are also provided with an undercut in order to accommodate axial misalignment between the jaws and the screw head.
Owner:MEDITRON DEVICES
Offset multiaxial or polyaxial screw, system and assembly
A capless multiaxial screw fixation assembly, including: a screw having a threaded portion and a screw head portion positioned at one end thereof; and, a retainer having a first end, a second end opposite the first end, and a bore for receiving the screw threaded portion so that the screw head portion is seated therein. At least one of the screw and the retainer is configured such that the retainer is able to pivot about the screw head portion in a non-symmetrical manner.
Owner:X SPINE SYST
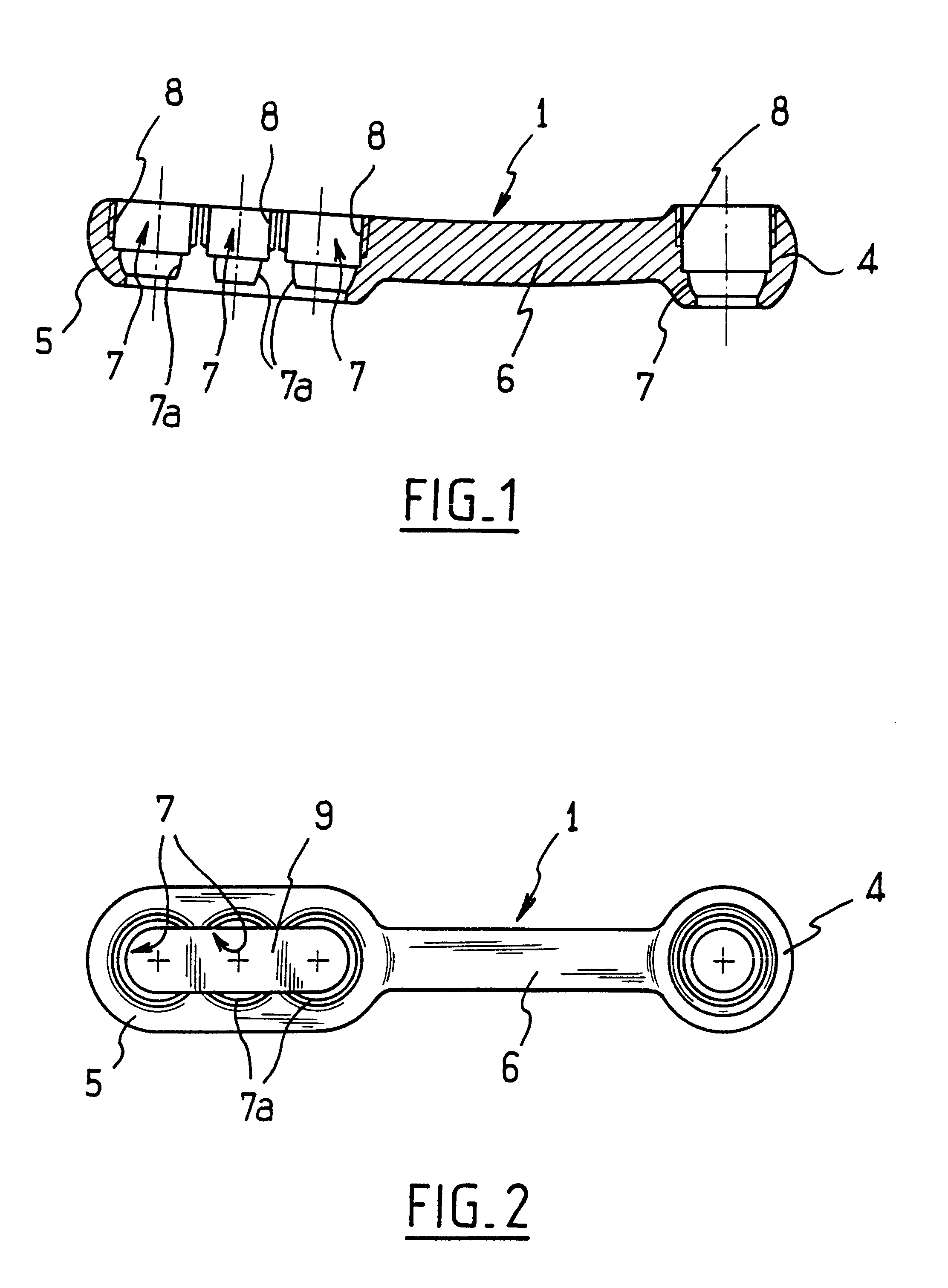
Posterior Cervical Cross Connector Assemblies
ActiveUS20100160981A1Increase construction heightSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisSet screwCross connection
A spinal cross connector head assembly and a cross connector assembly utilizing the spinal cross connector head assembly are configured for fixation to an existing spinal rod bone screw head. The spinal cross connector head assembly has one or more components which incorporate one or more breakaway portions that aid in the installation of the cross connector head assembly onto a polyaxial spinal rod bone screw assembly. The spinal cross connector assembly includes first and second spinal cross connector head assemblies each of which is configured for fixation to existing, adjacent spinal rod screw heads and connection with a cross connector rod. Each spinal cross connector rod head assembly has a dual breakaway system including a cross connector head component having a breakaway collar that, once detached, provides a polyaxial cross connector head, and a set screw component having a breakaway set screw that, once detached, provides fixation of the orientation of the polyaxial cross connector head relative to the polyaxial spinal rod bone screw head.
Owner:LIFE SPINE INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com