Patents
Literature
33results about How to "Reduced stress shielding" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Bone replacement materials
ActiveUS20070203584A1Easy adhesionFacilitate cell growthAdditive manufacturing apparatusBone implantBone tissueBone tissue engineering
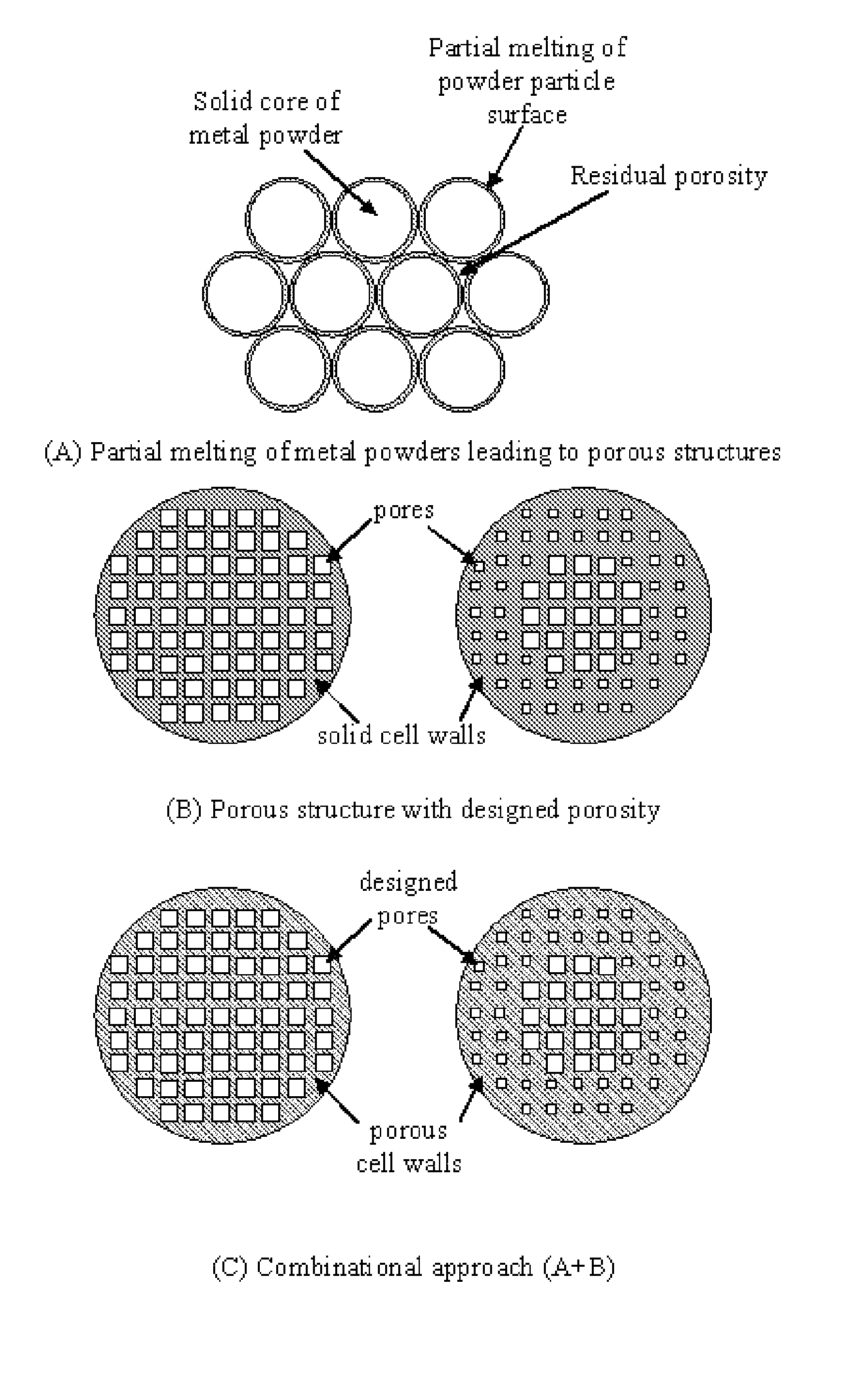
Particular aspects provide novel devices for bone tissue engineering, comprising a metal or metal-based composite member / material comprising an interior macroporous structure in which porosity may vary from 0-90% (v), the member comprising a surface region having a surface pore size, porosity, and composition designed to encourage cell growth and adhesion thereon, to provide a device suitable for bone tissue engineering in a recipient subject. In certain aspects, the device further comprises a gradient of pore size, porosity, and material composition extending from the surface region throughout the interior of the device, wherein the gradient transition is continuous, discontinuous or seamless and the growth of cells extending from the surface region inward is promoted. Additional aspects provide a device for bone tissue engineering, comprising a metal or metal-based composite member / material comprising an interior porous structure, wherein the pore size, porosity and material composition is selected to provide a device having an optimal density and / or elastic modulus and / or compression strength for a specific recipient. Novel methods for fabricating the devices are also provided.
Owner:WASHINGTON STATE UNIVERSITY
Prosthesis for restoring motion in an appendage or spinal joint and an intervertebral spacer
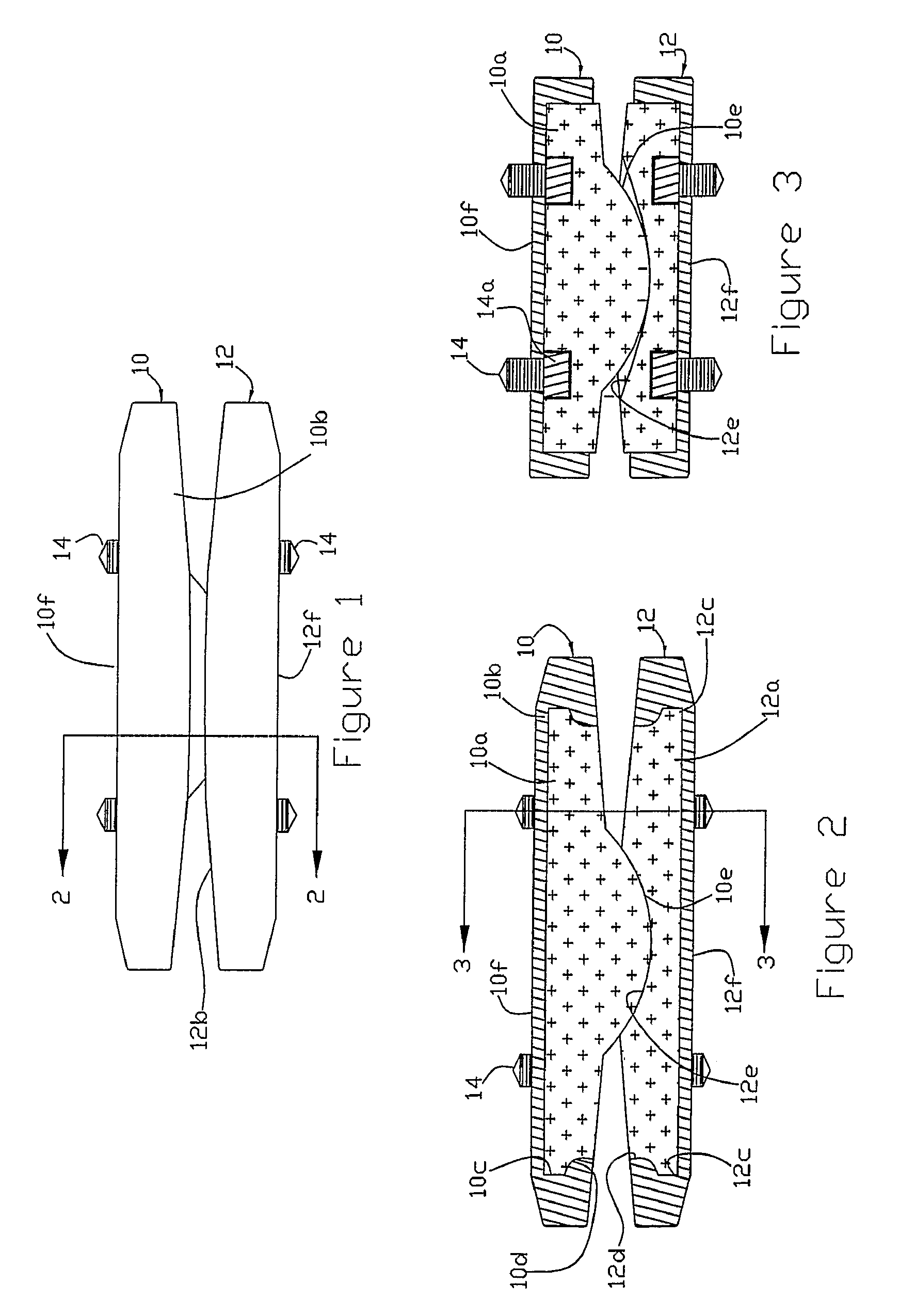
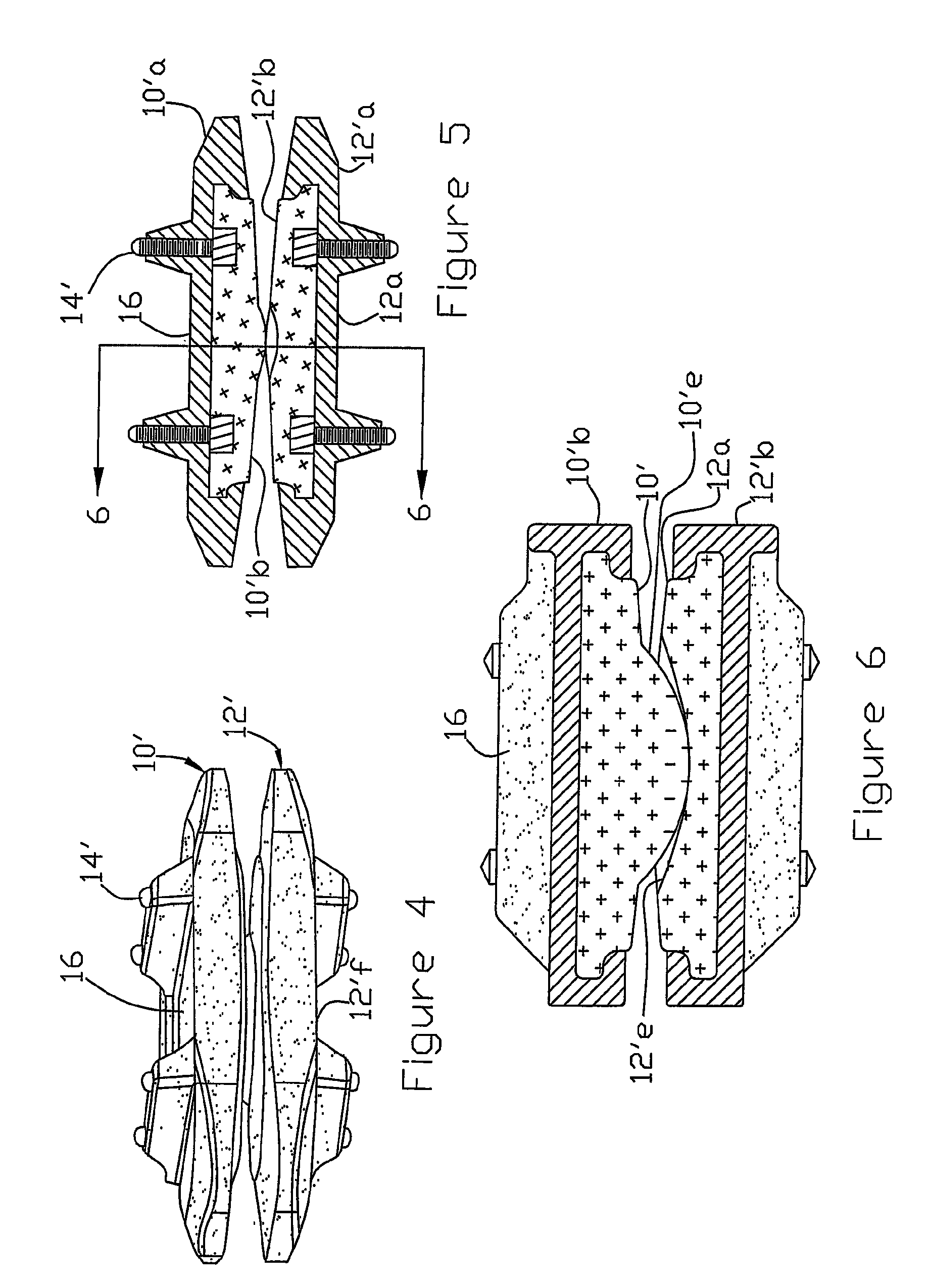
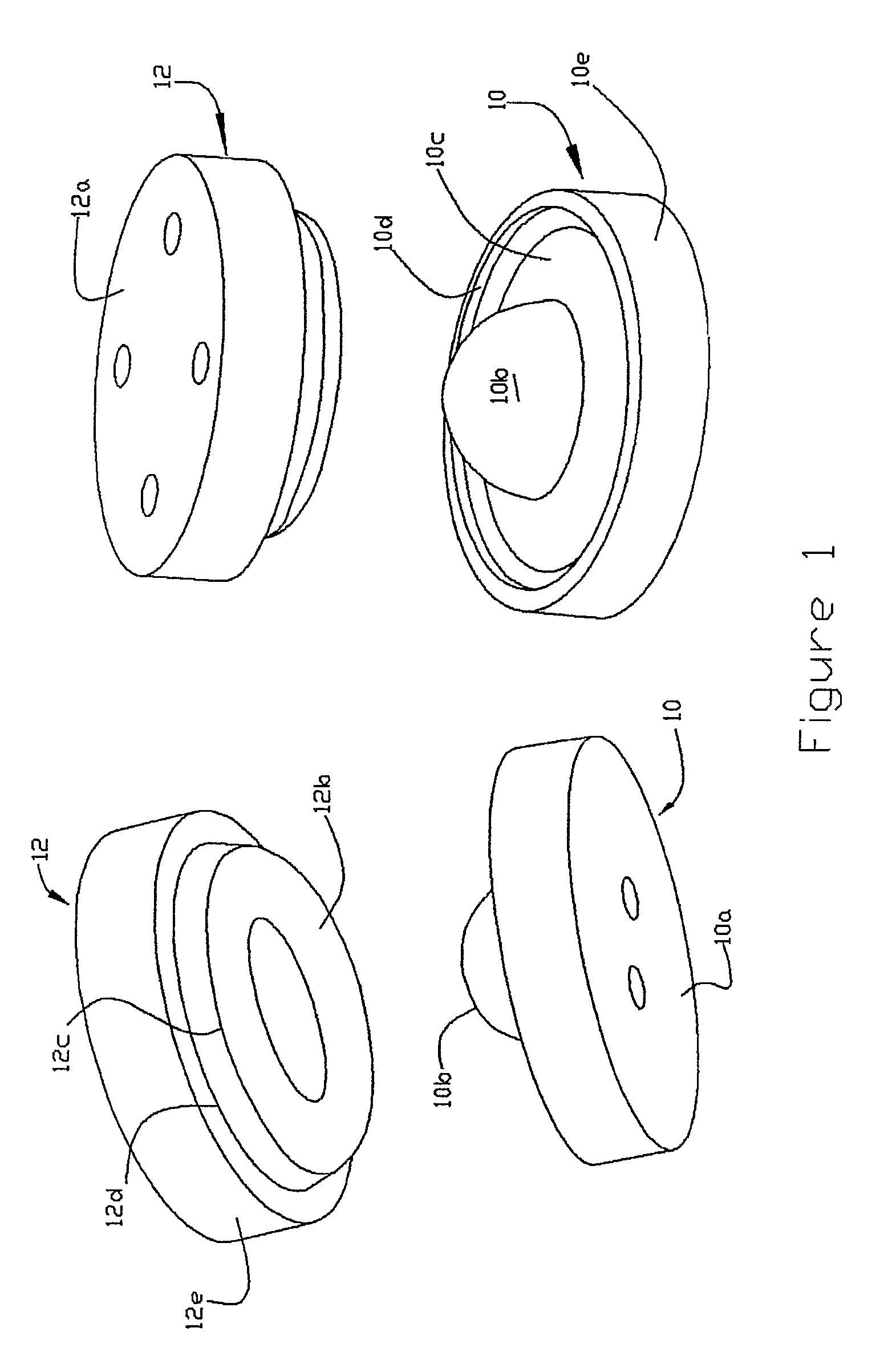
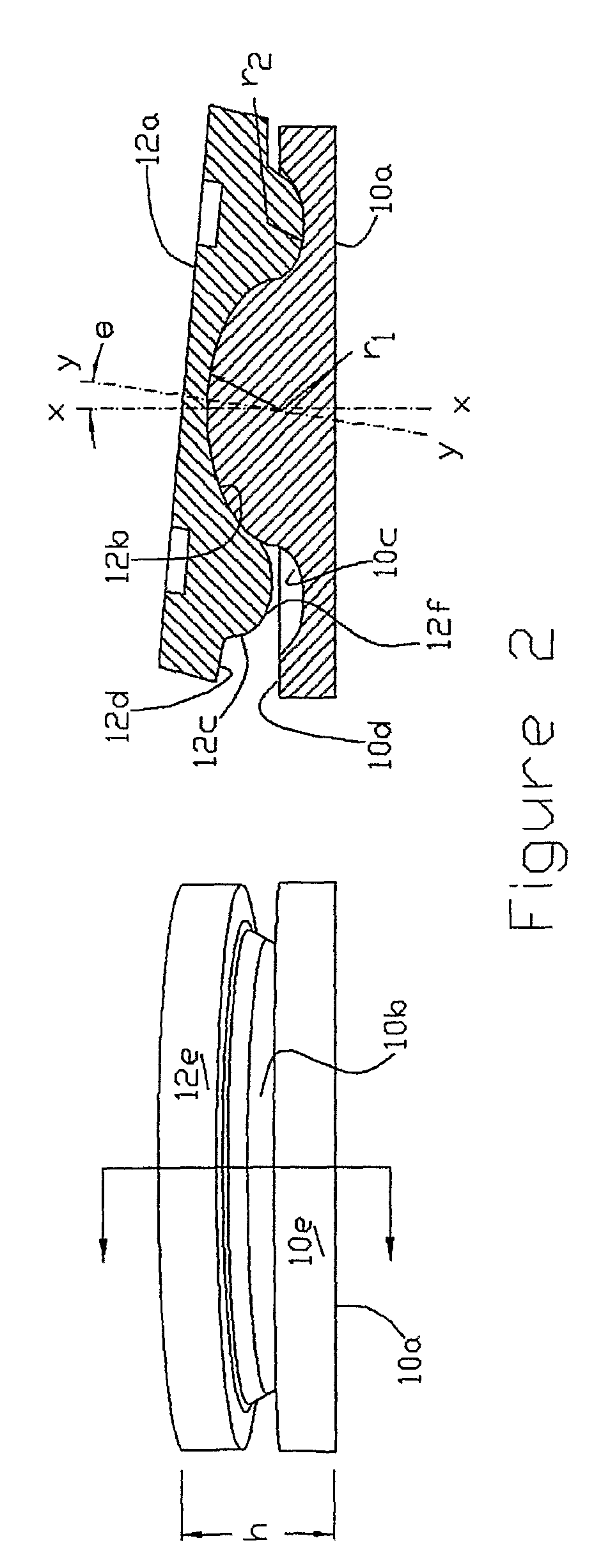
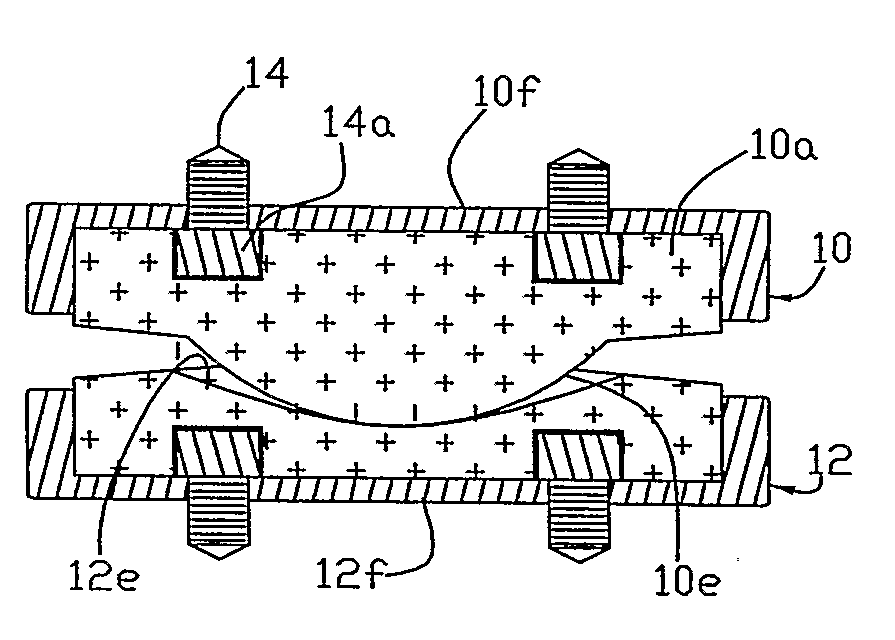
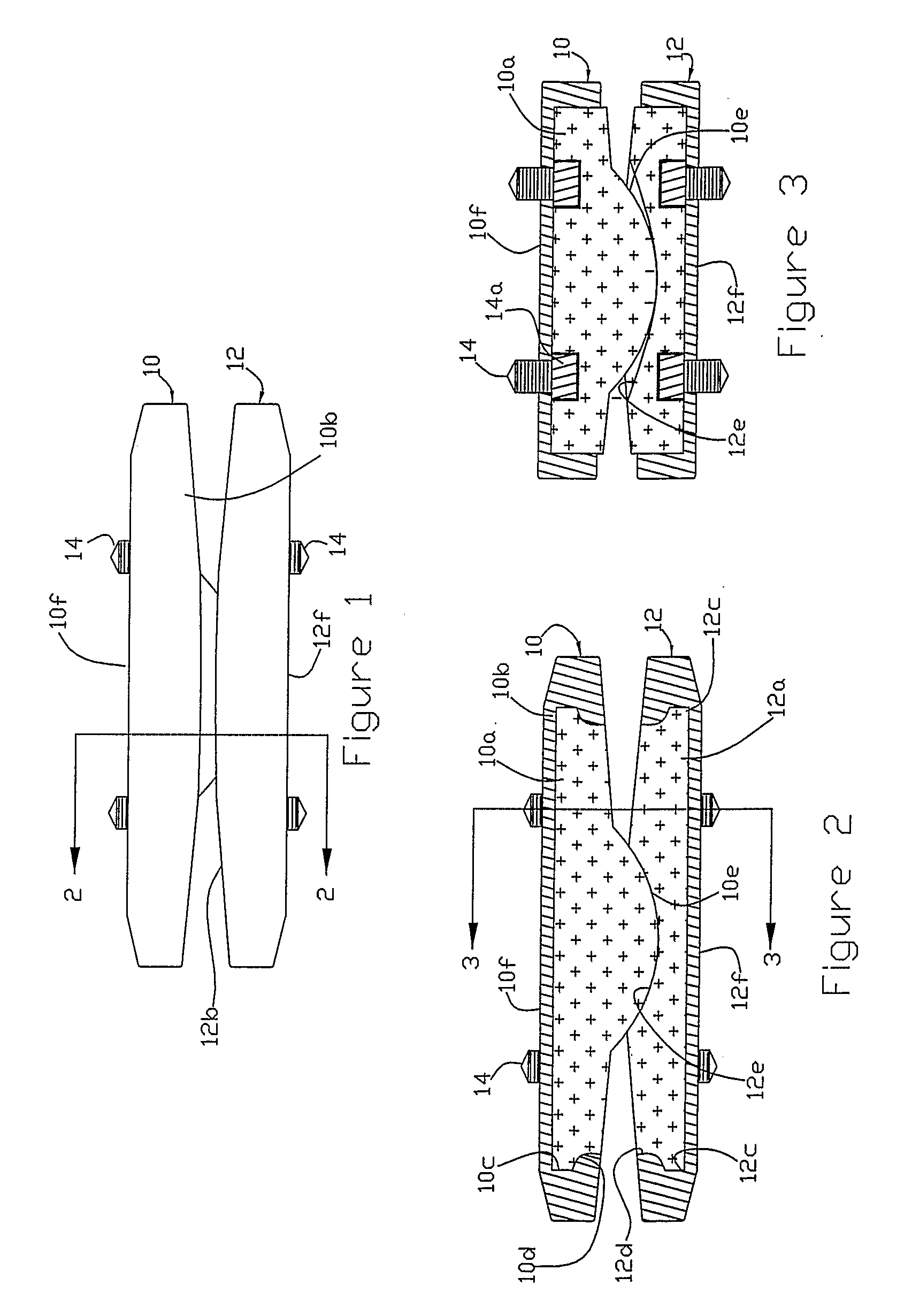
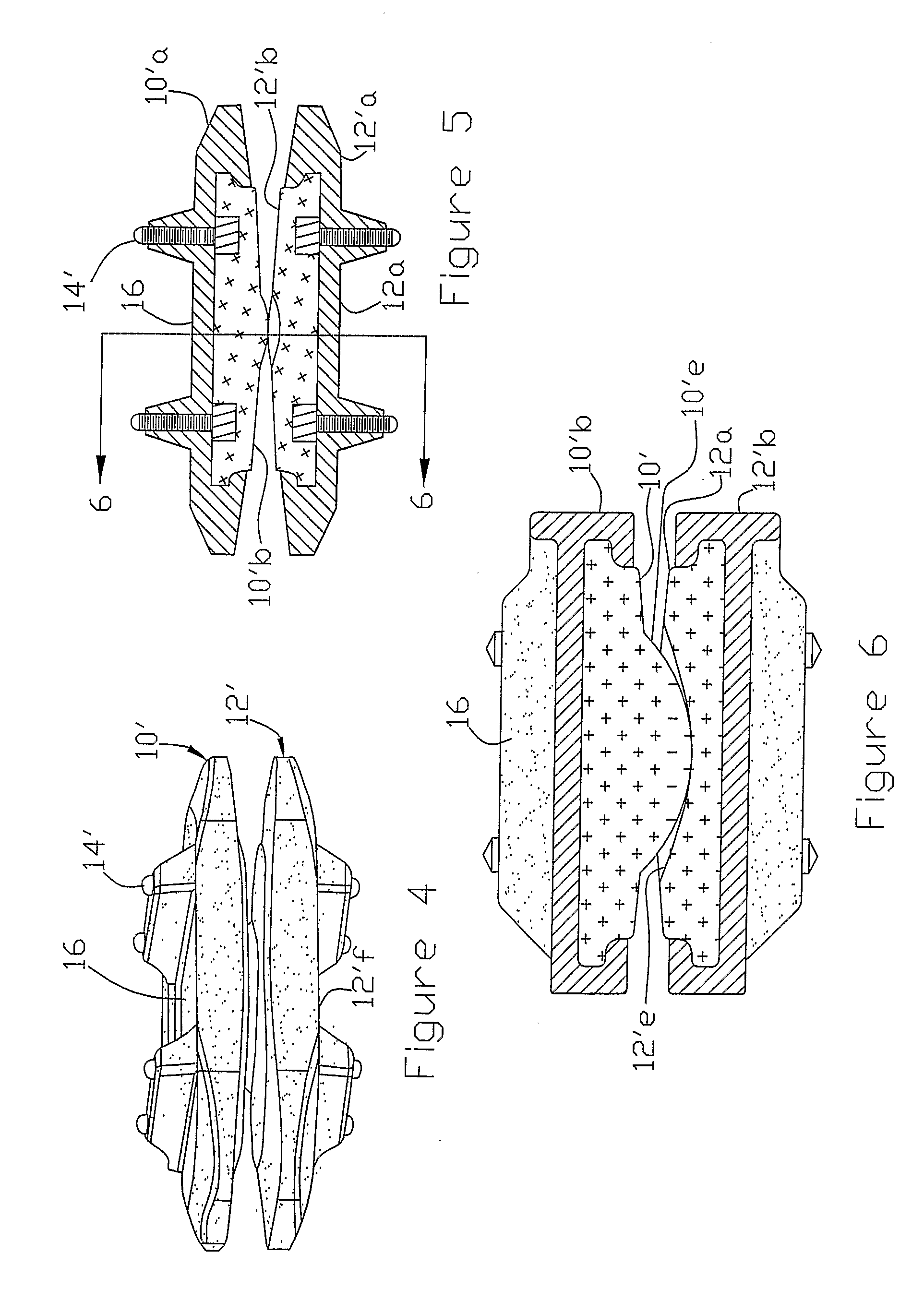
A motion restoring prosthesis to be interposed between the ends of two bones adjoining a mammalian appendage or spinal joint is formed of two components with the components having inner cooperating articulating surfaces and outer bone engaging surfaces. At least one of the components has an inner section made of relatively hard, stiff material defining one or the articulating surfaces and an outer section made of a softer material defining the bone engaging surface. The softer material having a hardness / stiffness characteristic compatible with the bone to reduce stress shielding and more evenly distribute the forces from the articulating surfaces to the associate bone interface.
Owner:SEASPINE
Motion restoring intervertebral device
Owner:SEASPINE
Prosthesis for restoring motion in an appendage or spinal joint and an intervertebral spacer
ActiveUS20090082868A1Reduced stress shieldingProlong lifeJoint implantsSpinal implantsProsthesisAppendage
A motion restoring prosthesis to be interposed between the ends of two bones adjoining a mammalian appendage or spinal joint is formed of two components with the components having inner cooperating articulating surfaces and outer bone engaging surfaces. At least one of the components has an inner section made of relatively hard, stiff material defining one or the articulating surfaces and an outer section made of a softer material defining the bone engaging surface. The softer material having a hardness / stiffness characteristic compatible with the bone to reduce stress shielding and more evenly distribute the forces from the articulating surfaces to the associate bone interface.
Owner:SEASPINE
Bio-medicinal porous titanium material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101912635AReduce Insufficient StrengthReduced stress shieldingProsthesisNatural boneBiocompatibility
The invention discloses a bio-medicinal porous titanium material. The porous titanium material comprises at least two layers, the porosity of the material is enlarged layer by layer from inside to outside, the porosity of the innermost layer is 0 to 50 percent, the porosity of the outermost layer is 30 to 90 percent, and the size of aperture is 50 to 500 microns. The porous titanium material has excellent corrosion resistance and biocompatibility, has the mechanical property matched with natural bones, meanwhile can provide a good transmission passage for growth of bone cells, and can solve the stress shielding phenomenon and the problems of loosening, breakage and the like.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Biomedical titanium-niobium-based shape memory alloy as well as preparation method, processing method and application method thereof
The invention relates to a biomedical titanium-niobium-based shape memory alloy as well as a preparation method, a processing method and an application method thereof. The alloy comprises the following chemical compositions by weight percent: 28-39% of niobium, 0.35-5.5% of tin, 0.3-5.5% of aluminum, 0.5-5.5% of silicon, 0.2-5.5% of zirconium and the allowance of titanium. The alloy has the advantages of low elasticity modulus, good biocompatibility and mechanics compatibility, no toxic nickel element, good mechanical property and corrosion resisting property, excellent cold working property and low cold-working hardening ratio; the alloy can be used for cold working with large deformation such as cold rolling, cold wire drawing and the like, and the working cost is low. The titanium-niobium-based shape memory alloy is of the ideal and novel biological shape memory alloy material that replaces the TiNi shape memory alloy and can be widely used for an ultra-flexible bracket, an orthodontics dental arch wire and an orthopedics implantation instrument and the like in the fields of the medical treatment, the sports goods and the like.
Owner:GRINM MEDICAL INSTR BEIJING CO LTD
Biodegradable implant and method for manufacturing same
InactiveUS20120035740A1Reduce biodegradationBetter presentBone implantSpecial surfacesManganeseBiodegradable implants
This invention relates to a biodegradable implant including magnesium, wherein the magnesium contains, as impurities, (i) manganese (Mn); and (ii) one selected from the group consisting of iron (Fe), nickel (Ni) and mixtures of iron (Fe) and nickel (Ni), wherein the impurities satisfy the following condition: 0< / (i)≦5, and an amount of the impurities is 1 part by weight or less but exceeding 0 parts by weight based on 100 parts by weight of the magnesium, and to a method of manufacturing the same.
Owner:U & I INC
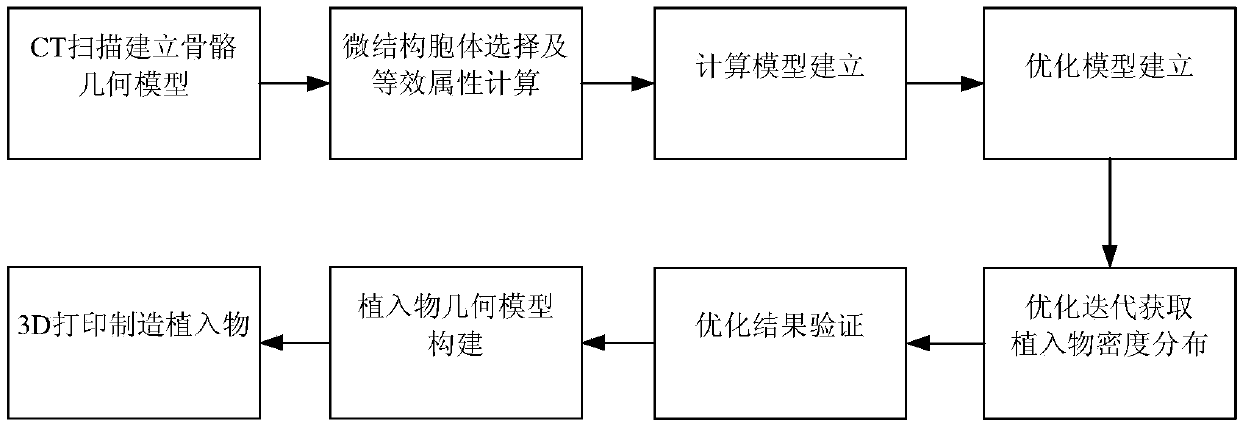
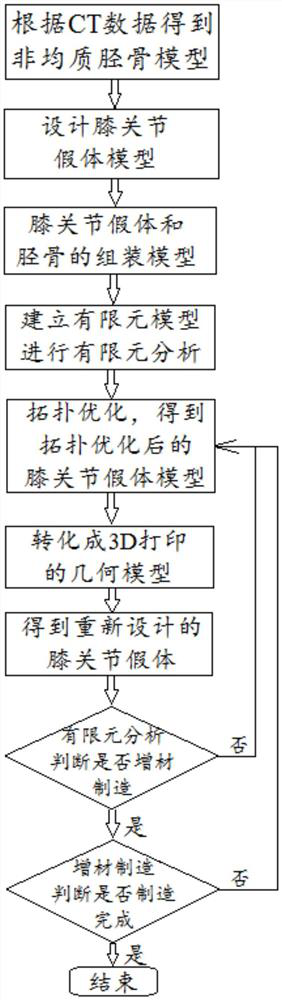
Variable-density porous metal orthopedic implant preparation method based on topology optimization technology
InactiveCN107563056AEfficient designExtended service lifeSpecial data processing applications3D modellingComputed tomographyDensity distribution
The invention discloses a variable-density porous metal orthopedic implant preparation method based on a topology optimization technology. The method comprises the steps that a bone geometric model isestablished through CT scanning, a microstructure is selected, and the porosity, the pore size of the microstructure and wall thickness conditions of the microstructure serve as constraint conditionsof topology optimization; attributes of an equivalent entity unit are calculated through a homogenization method, and a finite element is used for calculating the chemical performance of an implantedthrough the equivalent entity unit; the density distribution in the implant area is obtained through the density method topology optimization technology, and the porosity, the pore size of the microstructure and the wall thickness conditions of the microstructure serve as constraint conditions of topology optimization; a geometric model of the variable-density gradient porous orthopedic implant is constructed on the basis of the position information of a finite element node unit; the variable-density porous metal orthopedic implant is manufactured through 3D printing processing. The bone absorption is low, the mechanical property is good, the service life is long, and the probability of correction operations after the implant is implanted for a period of time can be reduced.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Prosthesis with resorbable collar
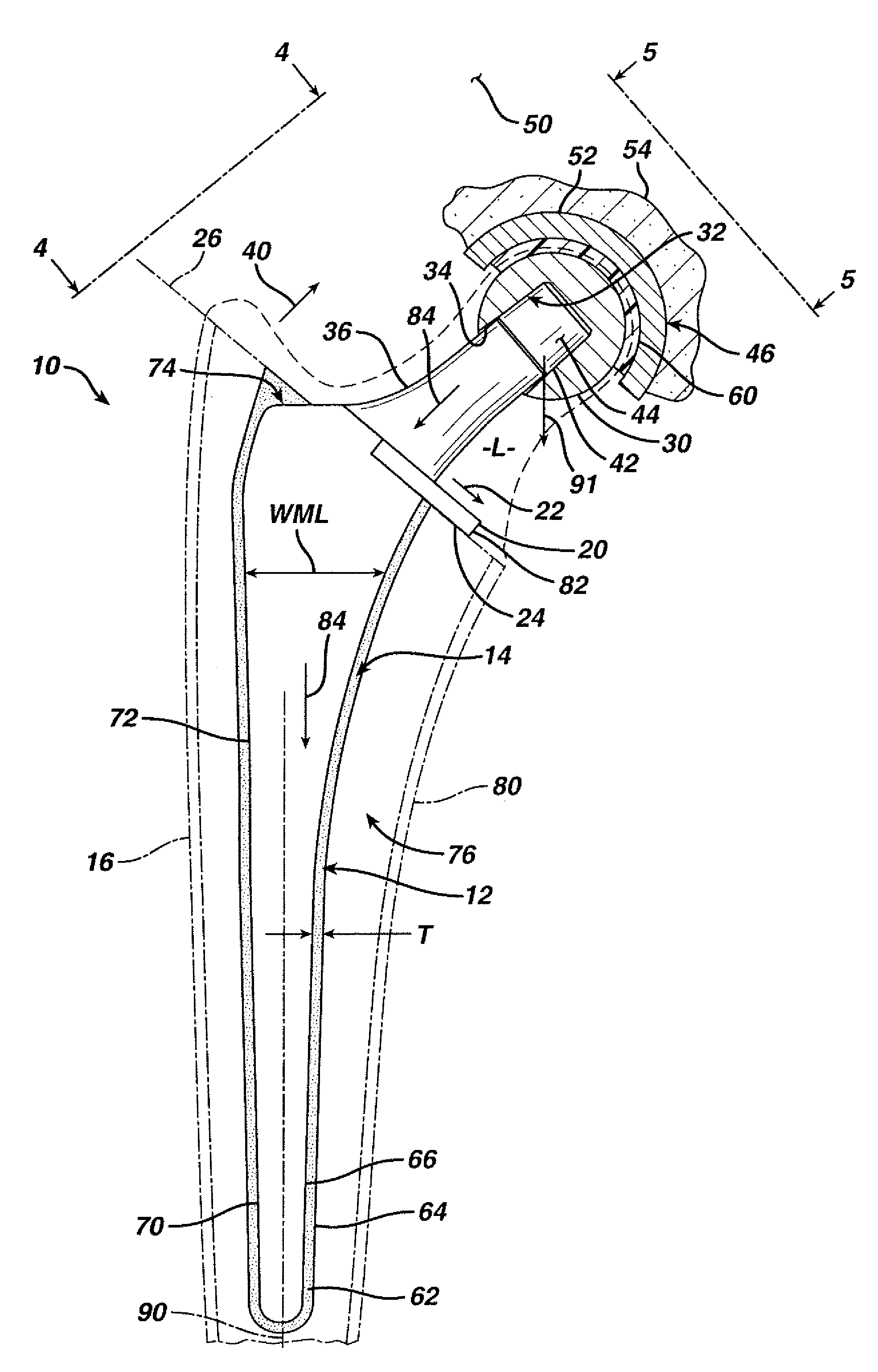
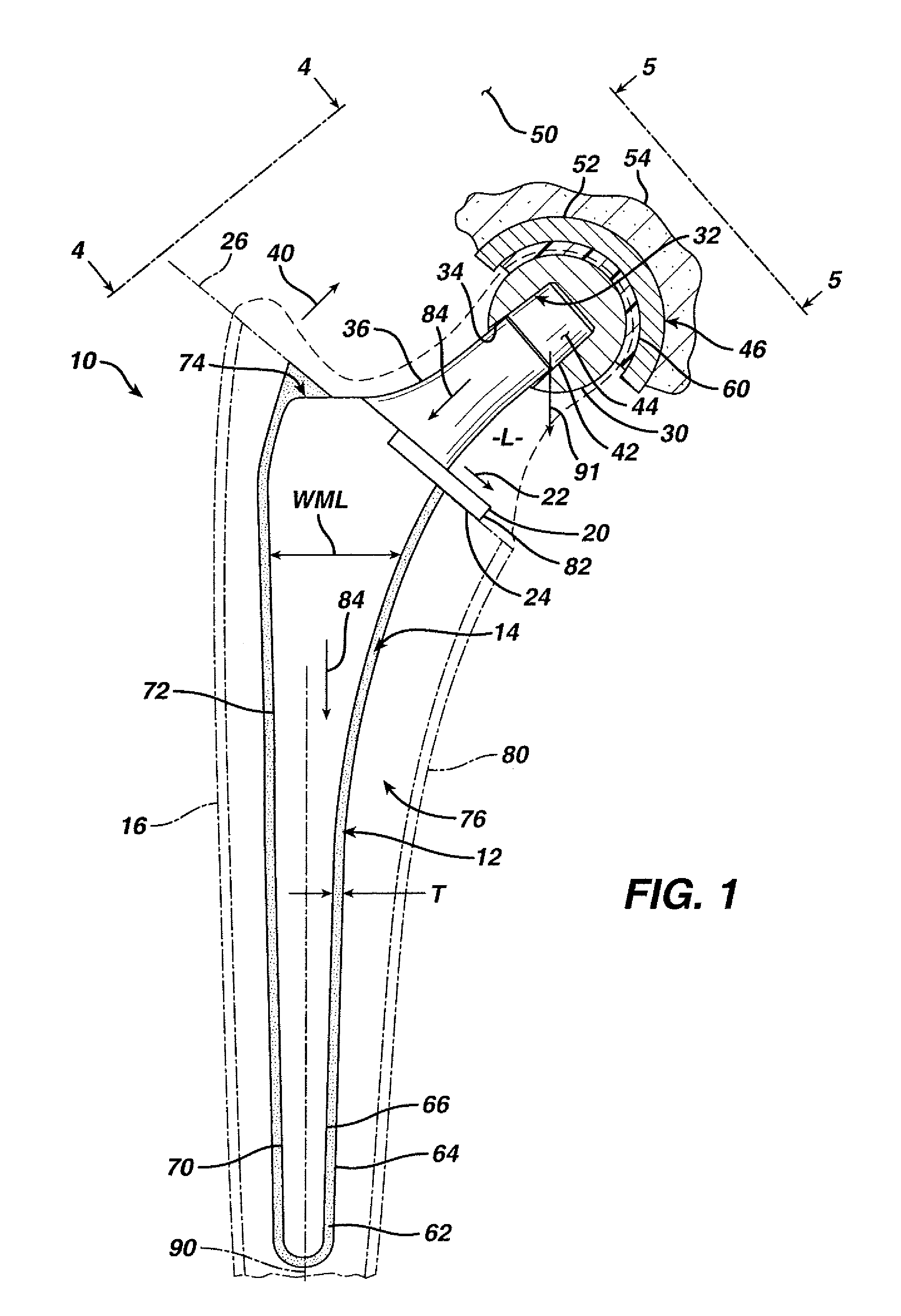
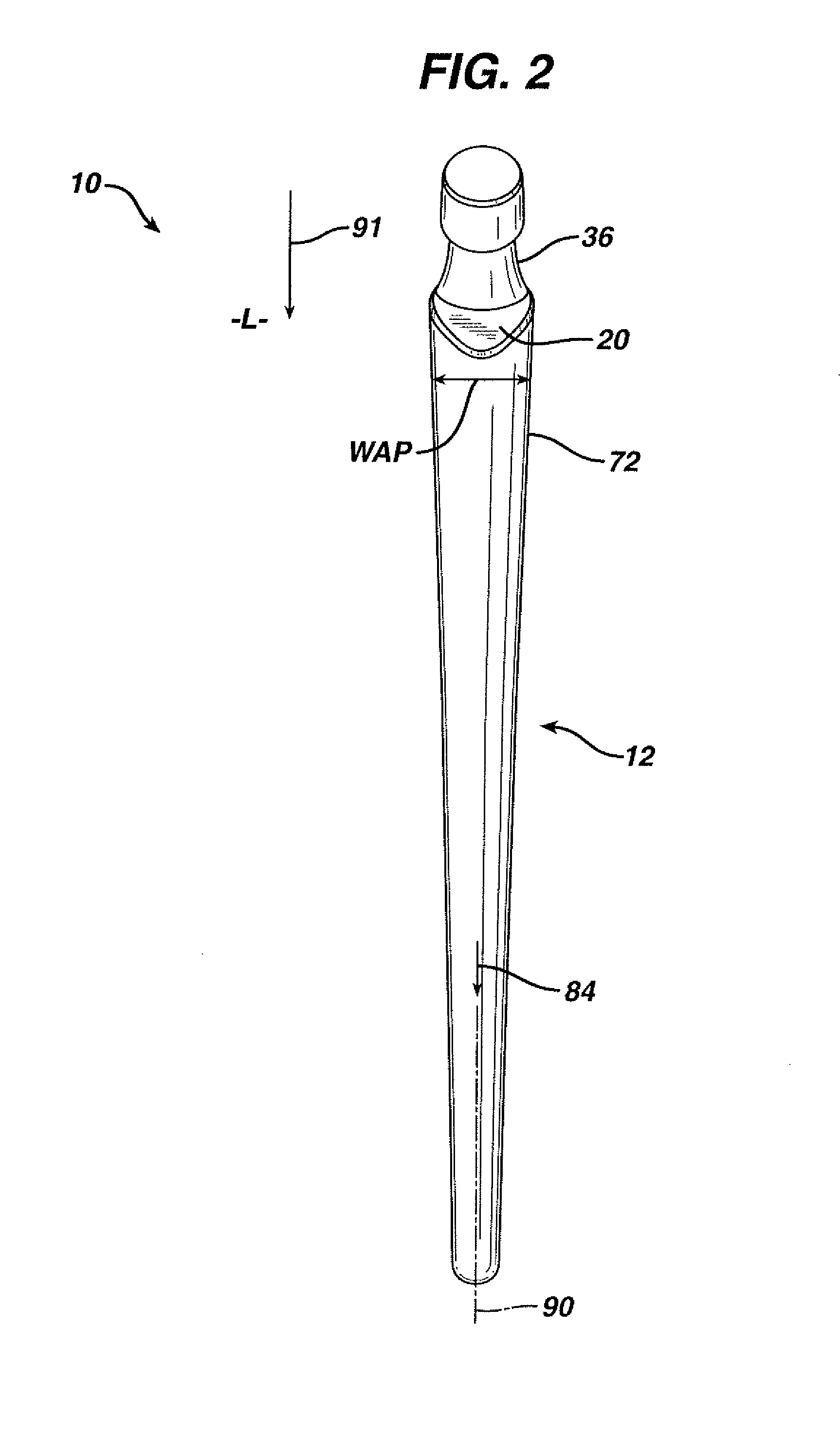
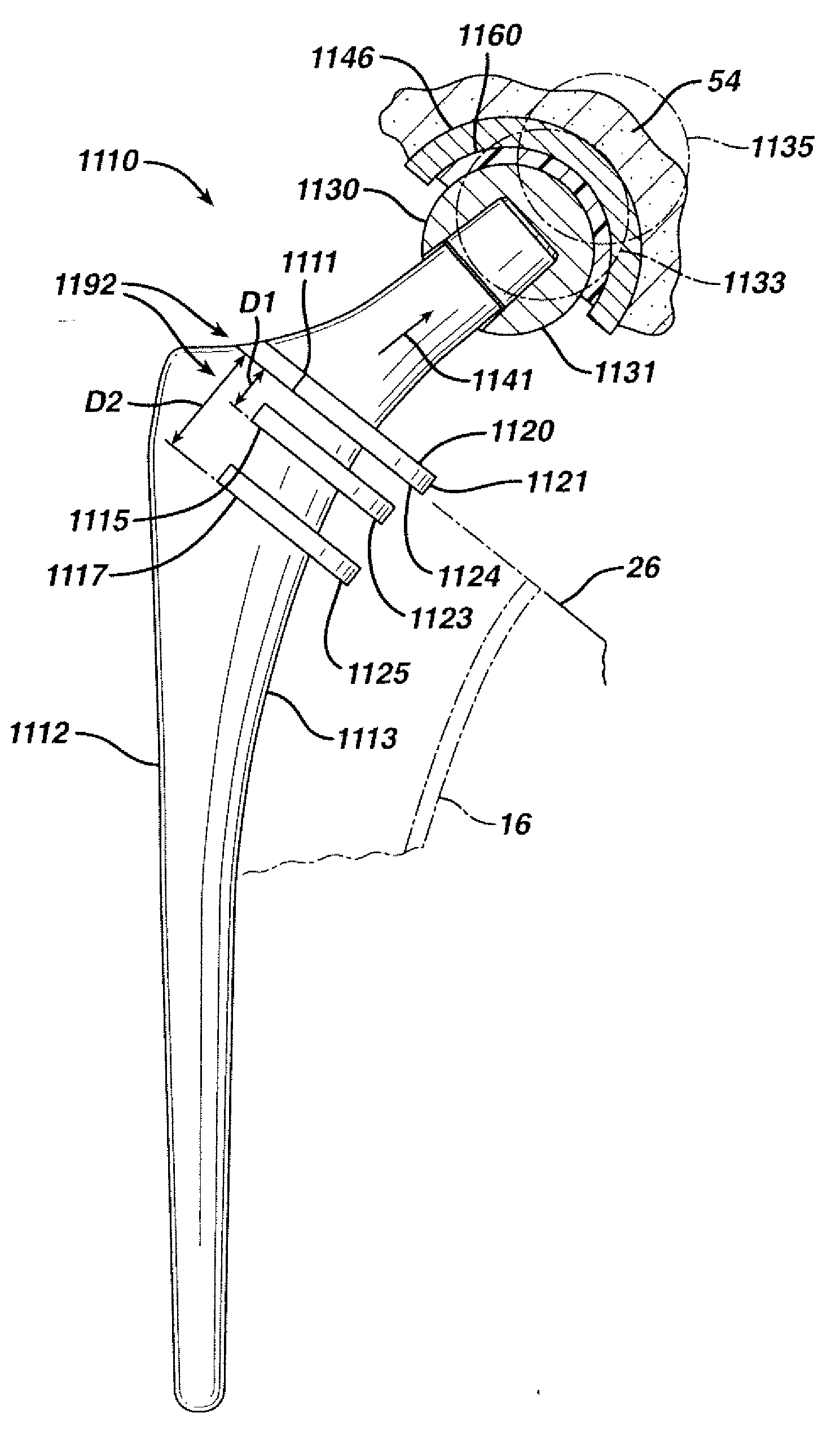
InactiveUS7261741B2Precise positioningReduced stress shieldingDiagnosticsJoint implantsProsthesisTarsal Joint
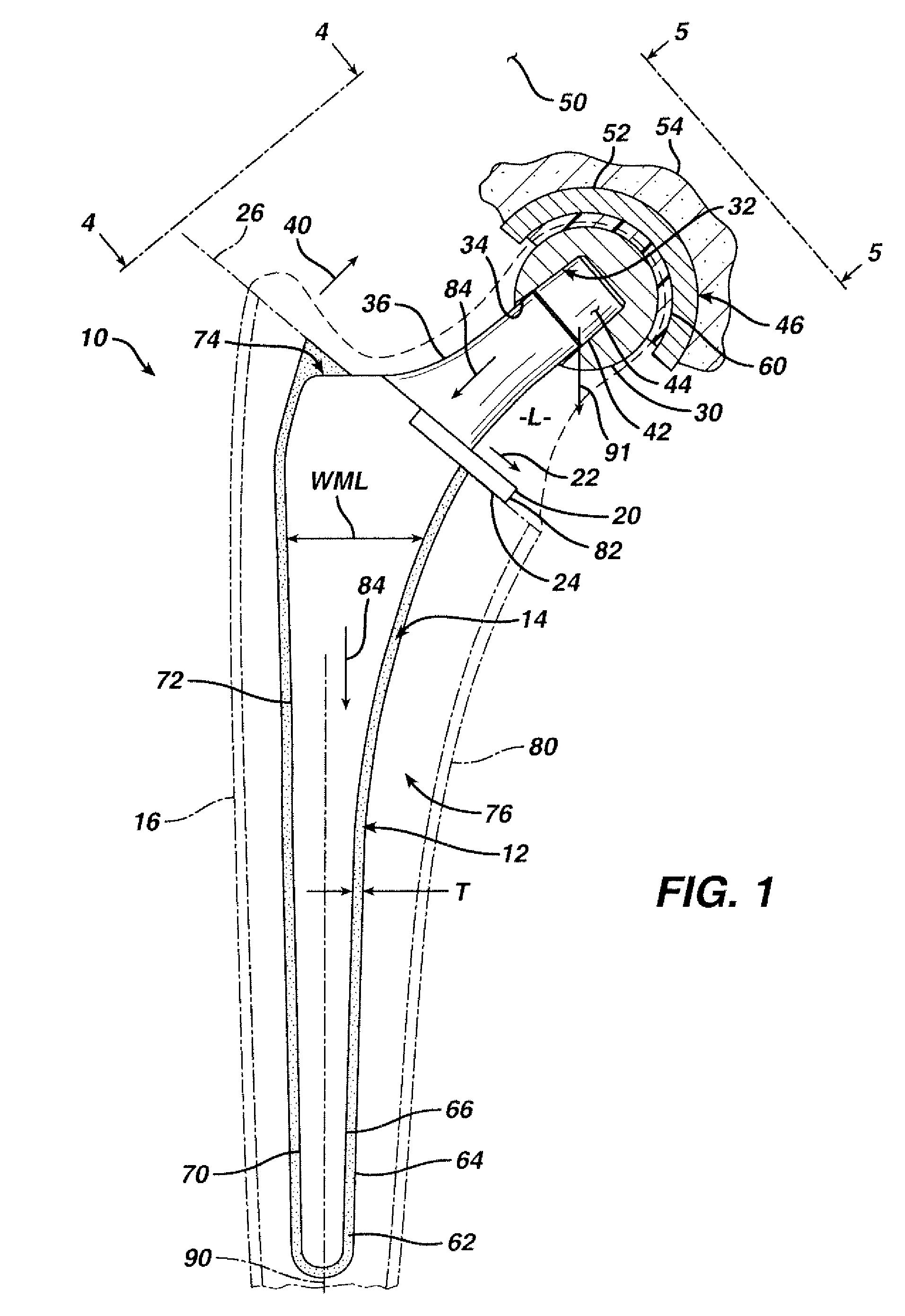
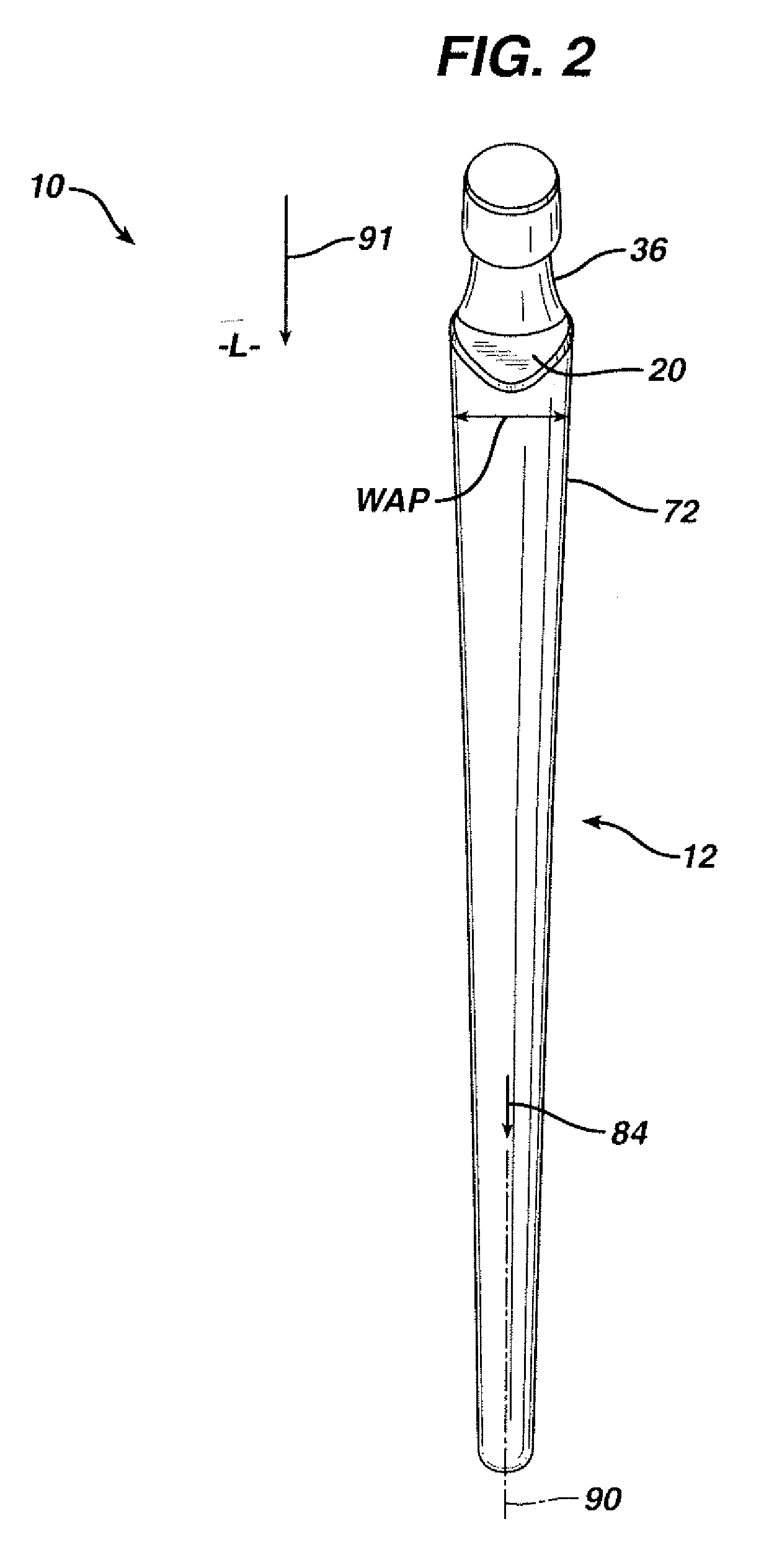
A articulating hemiarthroplasty prosthesis (10) for use in arthroplasty is provided. The prosthesis includes a stem (12) for implantation at least partially within the medullary canal (14) of a long bone (16) and a collar (20). The collar (20) is operably associated with the stem (12) and extends outwardly therefrom. At least a portion of the collar (20) includes a resorbable material. The prosthesis includes a head (30) and a cup (46) for engagement with the head (30).
Owner:DEPUY PROD INC
Bone replacement materials
ActiveUS9327056B2Low densityReduce stiffnessAdditive manufacturing apparatusBone implantPorosityChemical composition
Provided are devices for bone tissue engineering, comprising a metal or metal-based composite member comprising an interior macroporous structure with porosity varying from 0-90% (v), the member comprising a surface region having a surface pore size, porosity, and composition designed to encourage cell growth and adhesion thereon, to provide a device engineered for a particular recipient subject. Engineered devices may further comprises a gradient of pore size, porosity, and material composition extending from the surface region throughout the interior of the device, wherein the gradient transition is continuous, discontinuous or seamless to promote cell in-growth. Additional aspects provide methods for bone tissue engineering, comprising use of a metal or metal-based composite member comprising an interior porous structure, wherein the pore size, porosity and material composition is selected to provide a device having an optimal density and / or elastic modulus and / or compression strength for a specific recipient. Fabrication methods are provided.
Owner:WASHINGTON STATE UNIVERSITY
Preparation method for medical antibacterial titanium alloy
The invention discloses a preparation method for a medical antibacterial titanium alloy and belongs to the technical field of biomedical material preparation. The method comprises the following stepsthat Ti power, Nb power, Zr power and Ag powder are weighed according to the mass percentages of 52-62% of Ti, 15-38% of Nb, 5-13% of Zr and 2-10% of Ag; all the powder is put into a ball milling tankfor ball milling; the powder is taken out after ball milling and dried at low temperature, and the mixed powder is obtained; the mixed powder is put into a graphite mold and then put into a dischargeplasma sintering furnace, axial pressure of 60-70 MPa is applied, sintering is carried out at the vacuum degree of 2-10 Pa, the temperature is increased to the sintering temperature of 900-1,000 DEGC, the temperature is kept for 2-5 minutes, then the vacuum is kept continuously, the temperature is lowered to the room temperature, and the Ti-Nb-Zr-Ag alloy is obtained. The prepared Ti-Nb-Zr-Ag alloy has low elastic modulus (38-49 GPa) and high strength (880-1,200 MPa) and is antibacterial.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Device for variable fixation of bone fragments
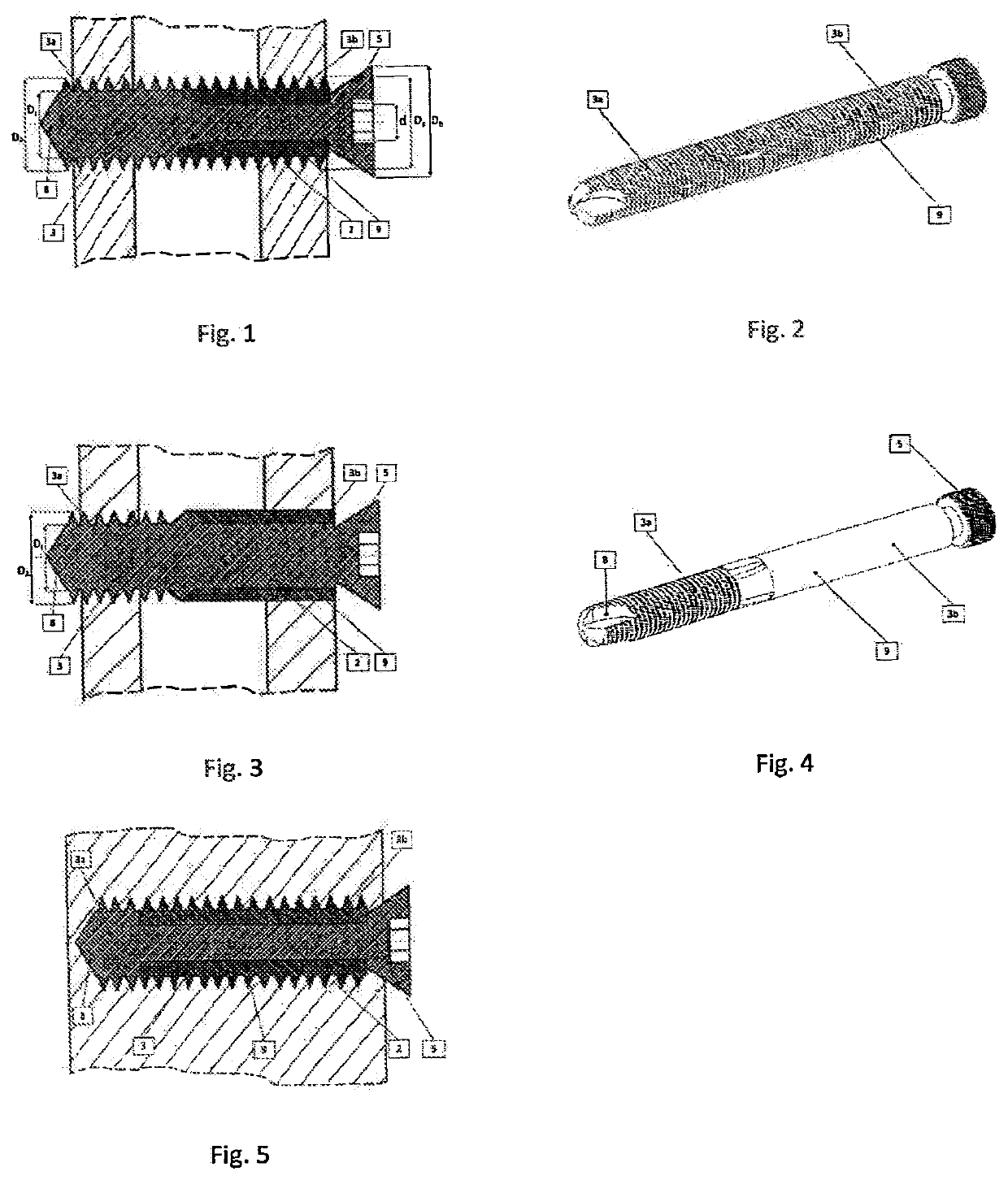
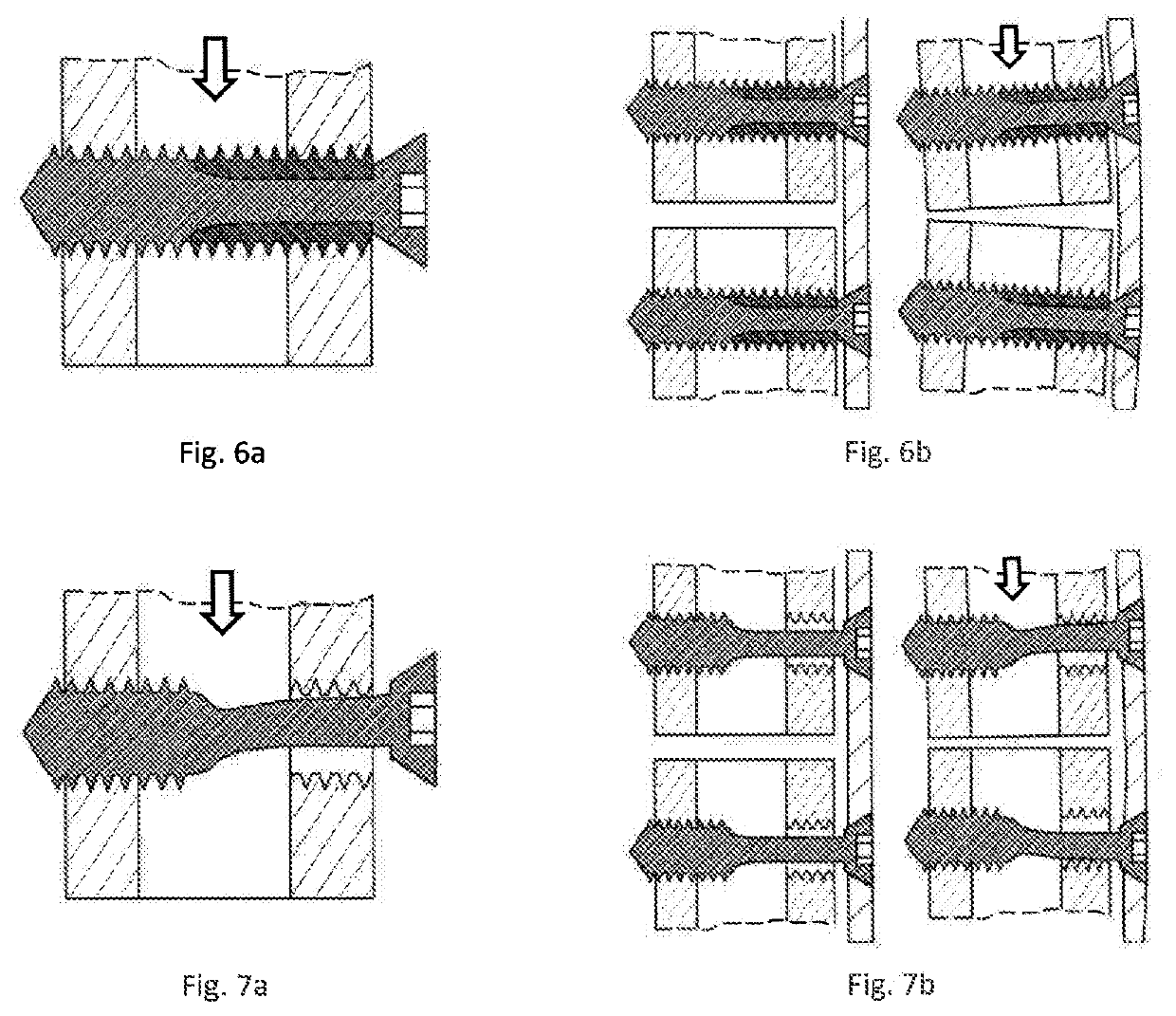
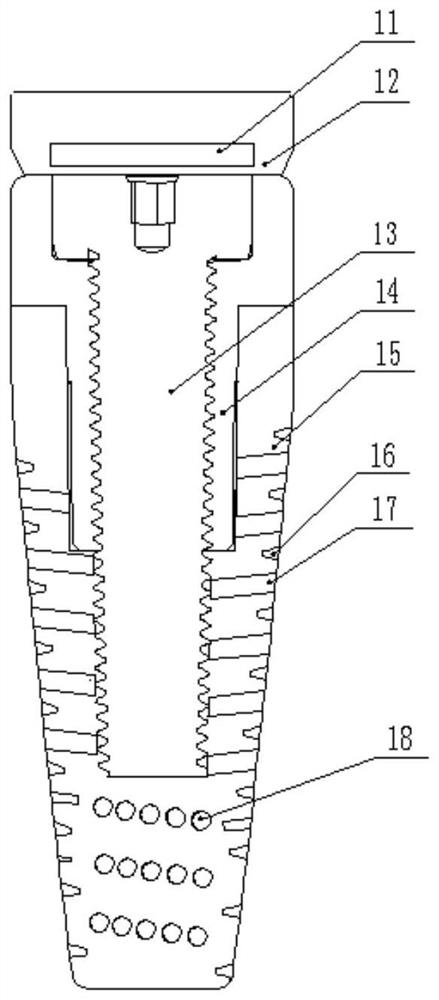
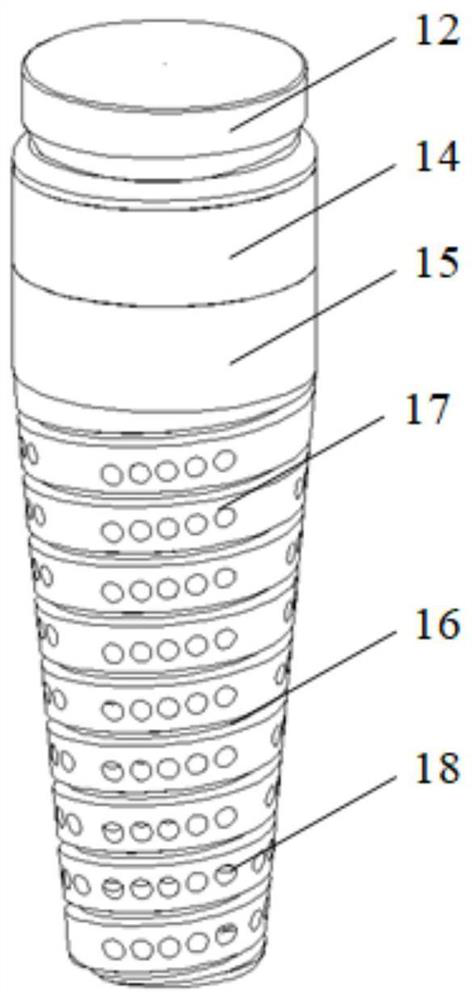
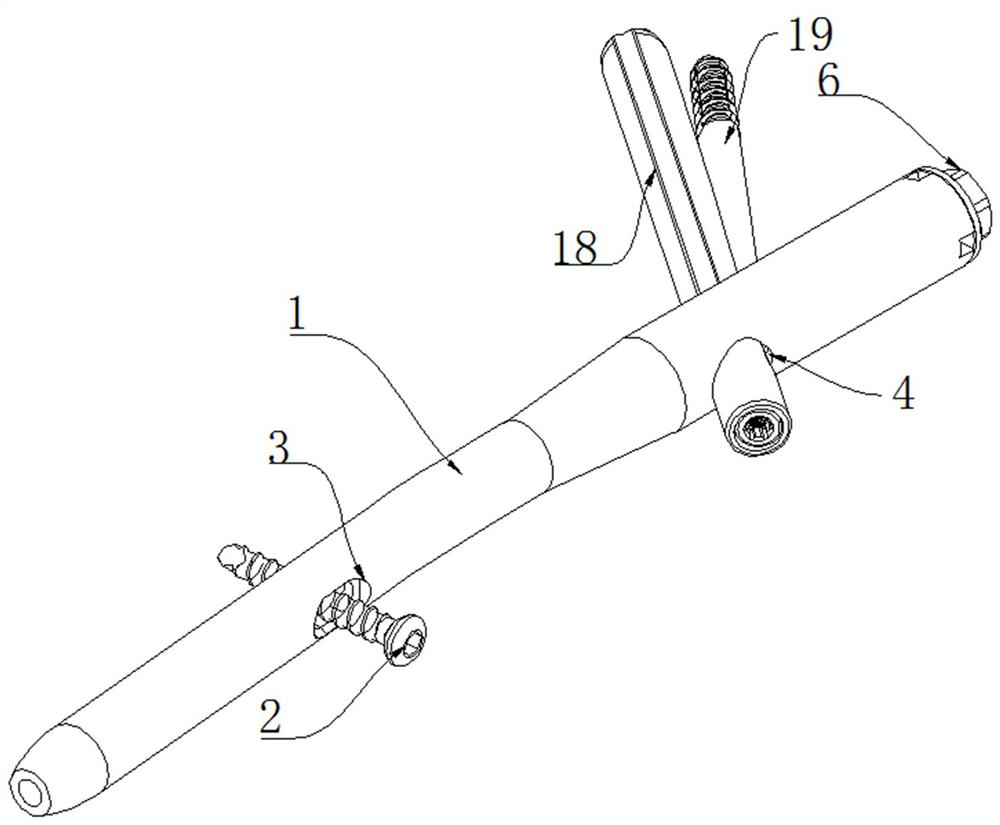
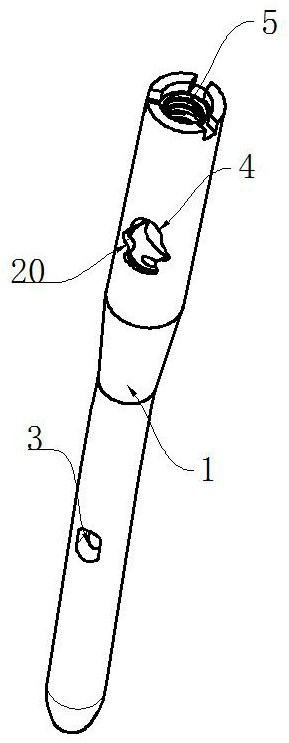
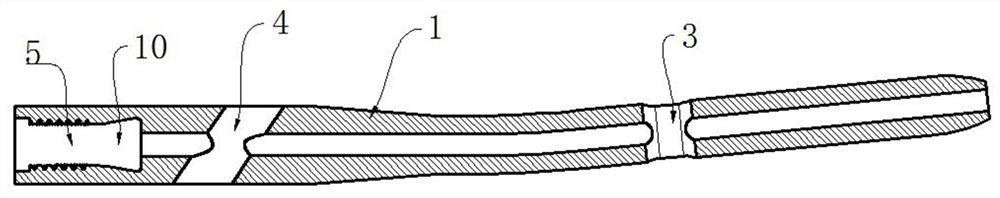
ActiveUS10610275B2Reduced mechanical propertiesLock firmlyFastenersBone platesBone splintersDistal portion
Device for bone fixation with a head portion (5), a tapering front portion (8) and a shaft (3) between said head portion (5) and said tapering front portion (8), said shaft (3) having a distal portion (3a) adjacent to said tapering front portion (8) and a proximal portion (3b) adjacent to said head portion (5); whereby said distal portion (3a) being provided with a thread and having a constant outer diameter DA and an inner core diameter DI; at least the proximal portion (3b) of said shaft (3) has a core (2) consisting of a biologically non-degradable material with degradation rate BND and having a diameter d≤DI; a sleeve (9) surrounding said core and consisting of a biologically degradable material with degradation rate BD, whereby BD>BND and said sleeve (9) being fixed to said core in a non-rotatable manner.
Owner:BIOMECH INNOVATIONS SA
Prosthesis with resorbable collar
InactiveUS20070067042A1Precise positioningReduced stress shieldingBone implantJoint implantsMedicineProsthesis
An articulating hemiarthroplasty prosthesis (10) for use in arthroplasty is provided. The prosthesis includes a stem (12) for implantation at least partially within the medullary canal (14) of a long bone (16) and a collar (20). The collar (20) is operably associated with the stem (12) and extends outwardly therefrom. At least a portion of the collar (20) includes a resorbable material. The prosthesis includes a head (30) and a cup (46) for engagement with the head (30).
Owner:DEPUY PROD INC
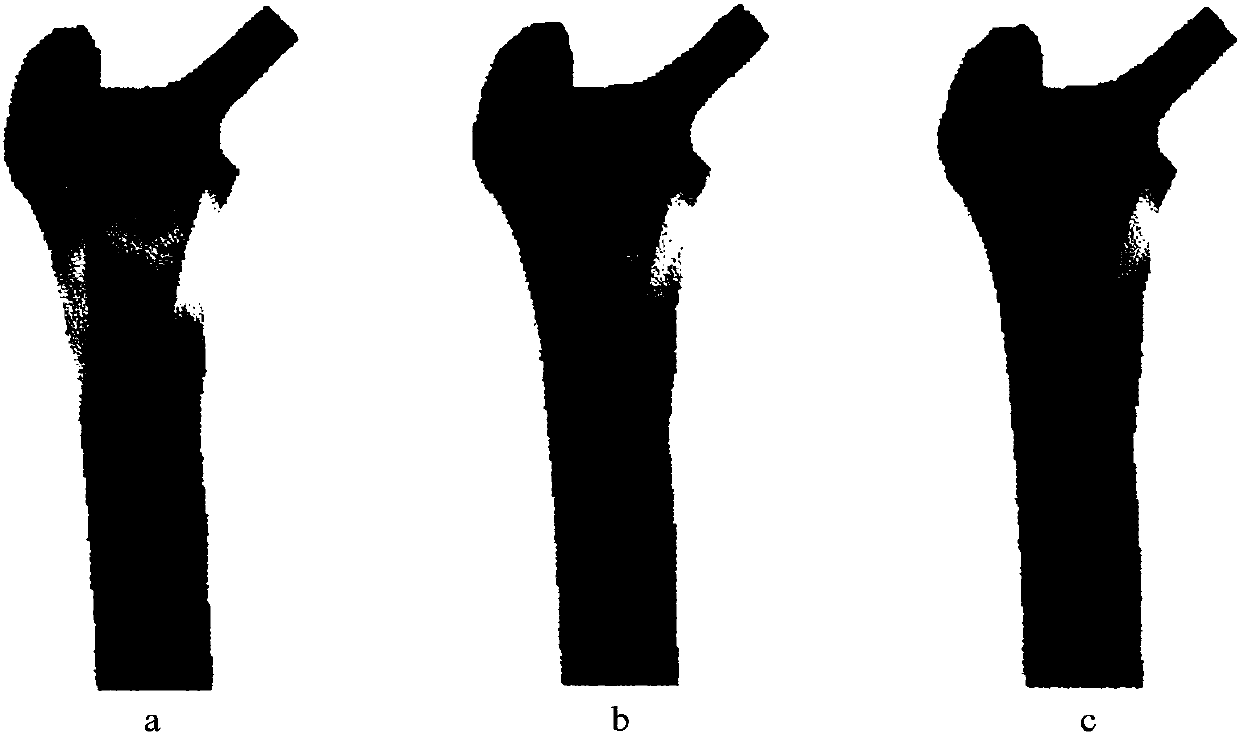
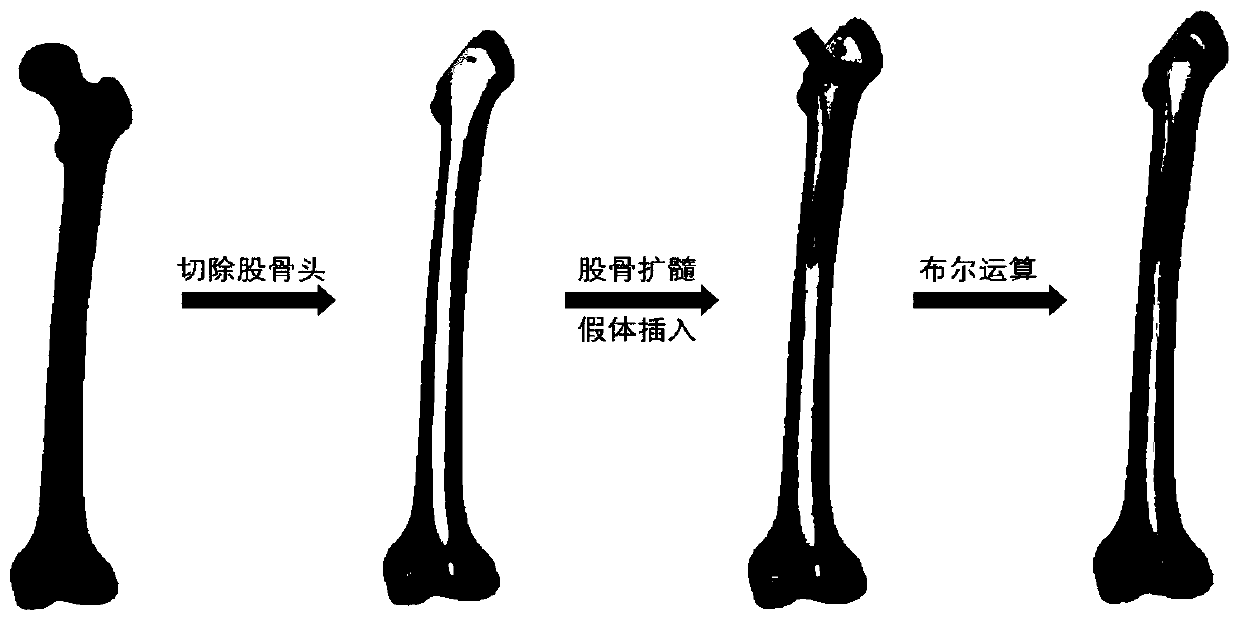
Method for designing femoral stem prosthesis
InactiveCN110840626AReduced strain energyExtend your lifeJoint implantsTomographyHuman bodyComputer printing
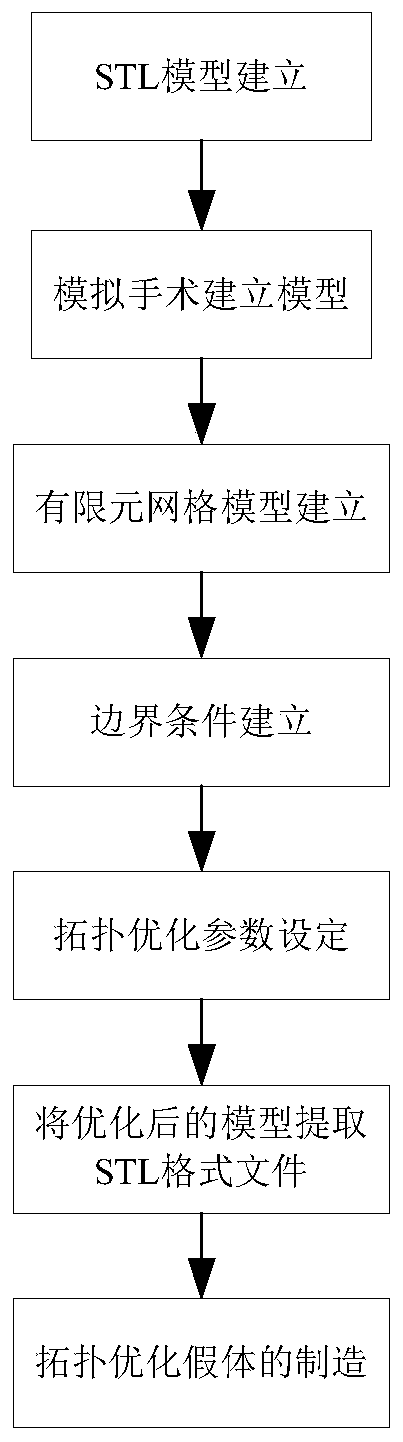
The invention relates to the technical field of medical instruments, in particular to a method for designing a femoral stem prosthesis, and solves the problem that the existing femoral stem prosthesisis made of a material with high elastic modulus, so that the difference between the high elasticity and that of human femur is large, resulting in different degrees of stress shielding, the problem that the manufacturing process can hardly satisfy the manufacture requirement on customization and complex interior structure, so that high matching prostheses meeting the individual needs cannot be implemented, and other problems. The method comprises establishing an STL model, carrying out simulation operation to establish a model, establishing a finite element mesh model, establishing model material properties, establishing boundary conditions, setting topological optimization parameters and extracting an STL format file from the optimized model; and carrying out post-processing of fairing and the like to remove chessboard patterns in the software Inspire to obtain an optimized femoral stem model; manufacturing an optimized prosthesis with ti6al4v, and finishing the manufacture by meansof an electron beam melting technique through an Arcam Q10 plus metal printer. The method for designing the prosthetic stem structure adopts integral forming and has no need for cutting, splicing andother processing, and the structure is good in biocompatibility.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Expanding Interbody Spacers
ActiveUS20190274838A1Reducing rasping requirementImprove matchJoint implantsSpinal implantsPorosityHigh stiffness
An expandable interbody spacer includes a first endplate surface located on a first side of the spacer and adapted to contact a vertebral endplate surface of a first vertebral body, a second endplate surface located on a second, opposed, side of the spacer and adapted to contact a vertebral endplate surface of a second, opposed, vertebral body and an expansion mechanism adapted to selectively apply a distracting force between the first endplate surface and the second endplate surface, whereby actuation of the expansion mechanism causes the spacer to transition between a compressed insertion configuration to an expanded fusion configuration. The spacer also includes one or more of a deformable surface, a porosity to promote bone on-growth or through-growth, a stiffness substantially equivalent to cortical bone, and structure distributing loads through the spacer substantially without transferring the loads through higher-stiffness structures.
Owner:NEXUS SPINE L L C
Manufacturing method of atlas and axis titanium alloy prosthesis
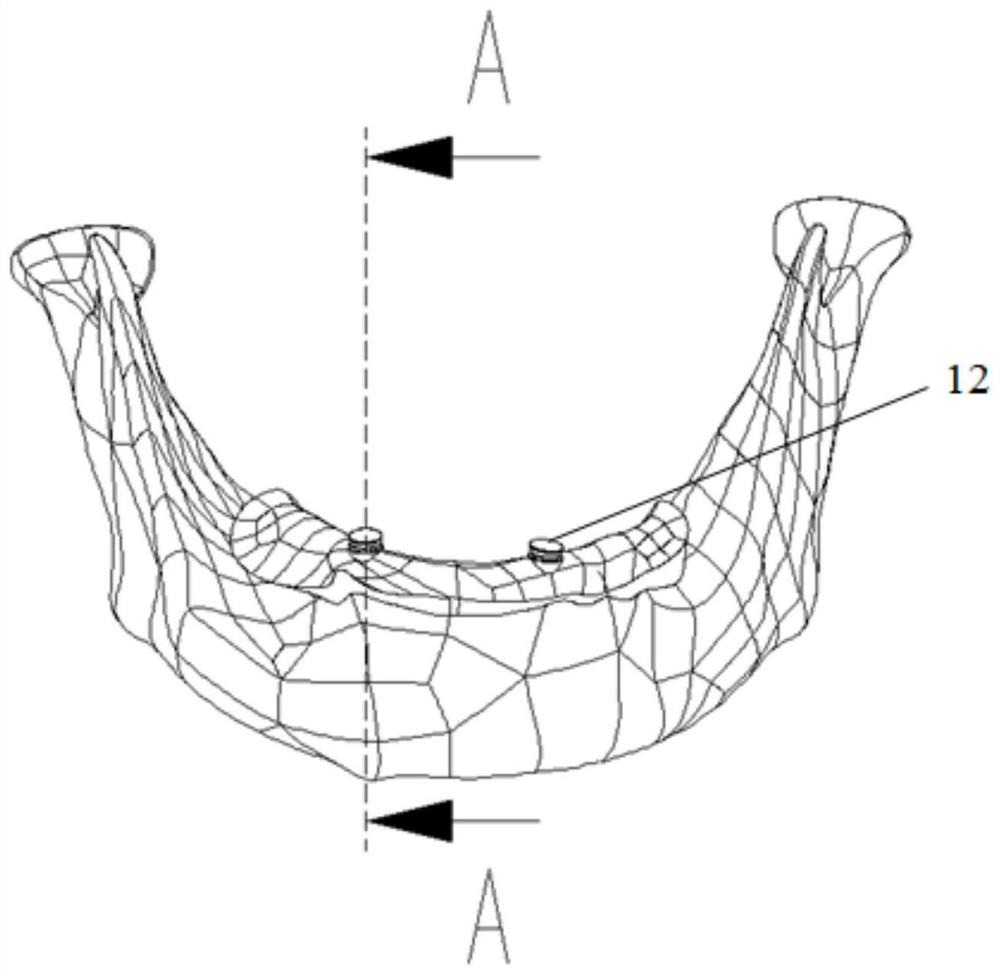
InactiveCN106618810ALow elastic modulusReduced stress shieldingSpinal implantsTomographyData fileNoise reduction
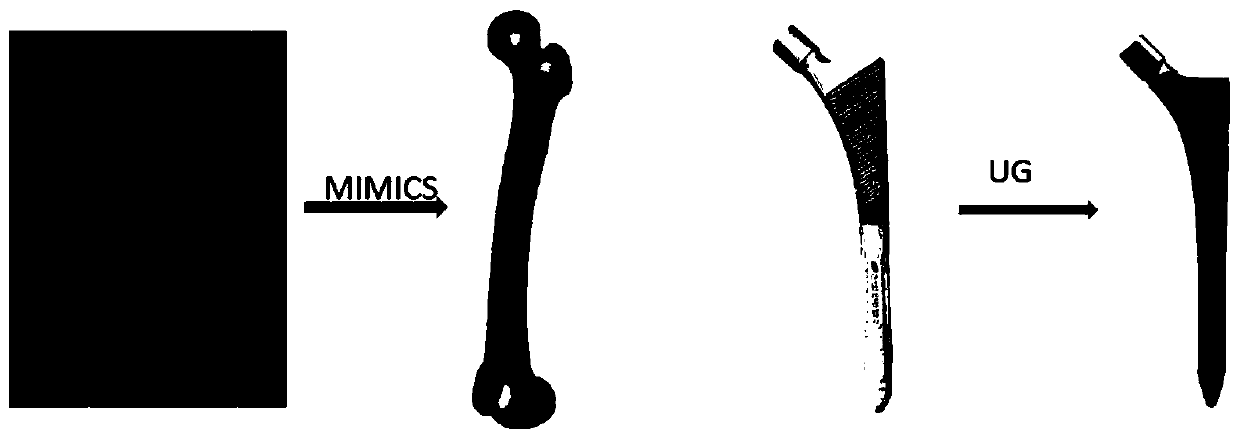
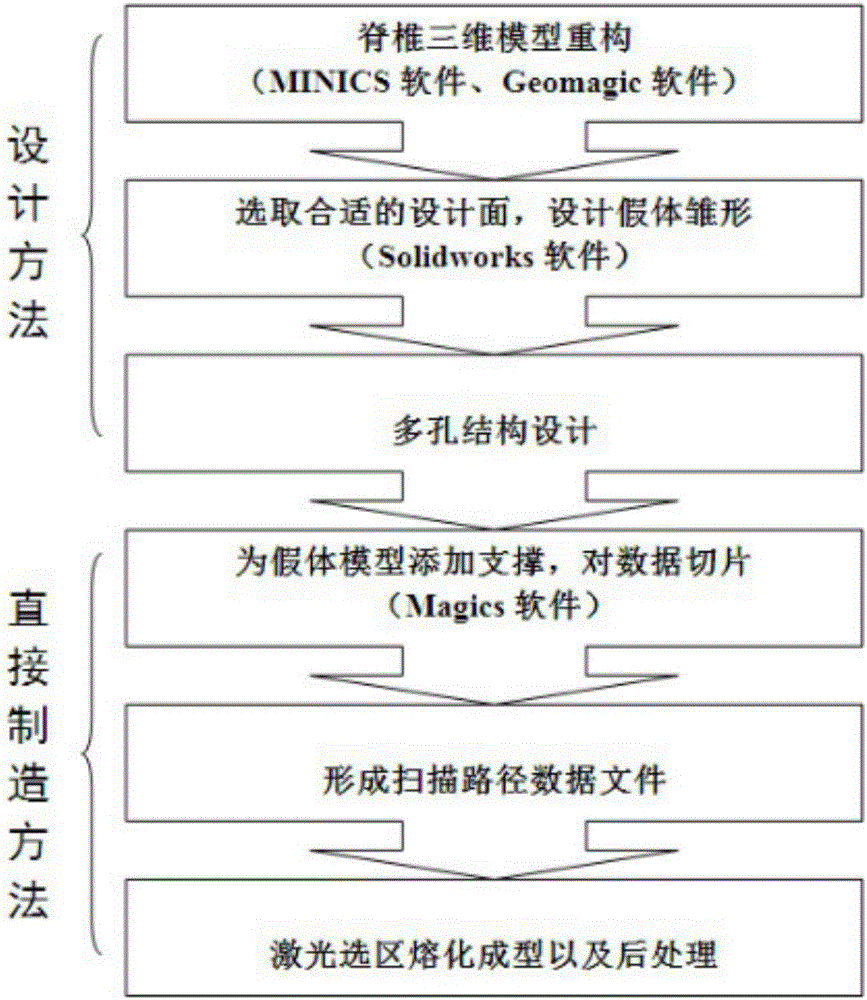
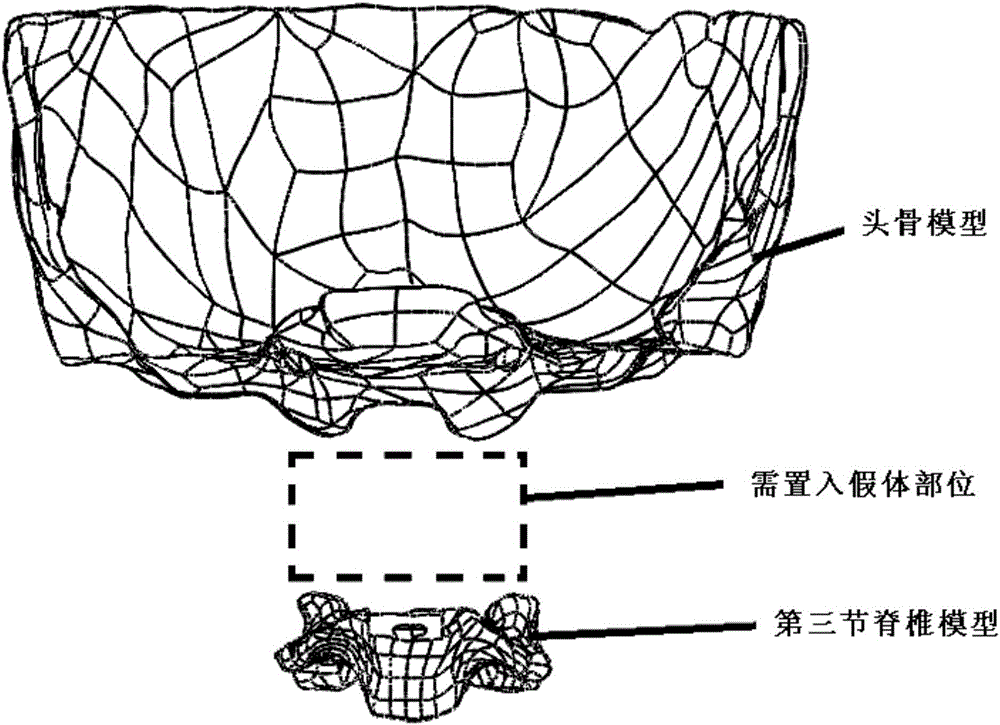
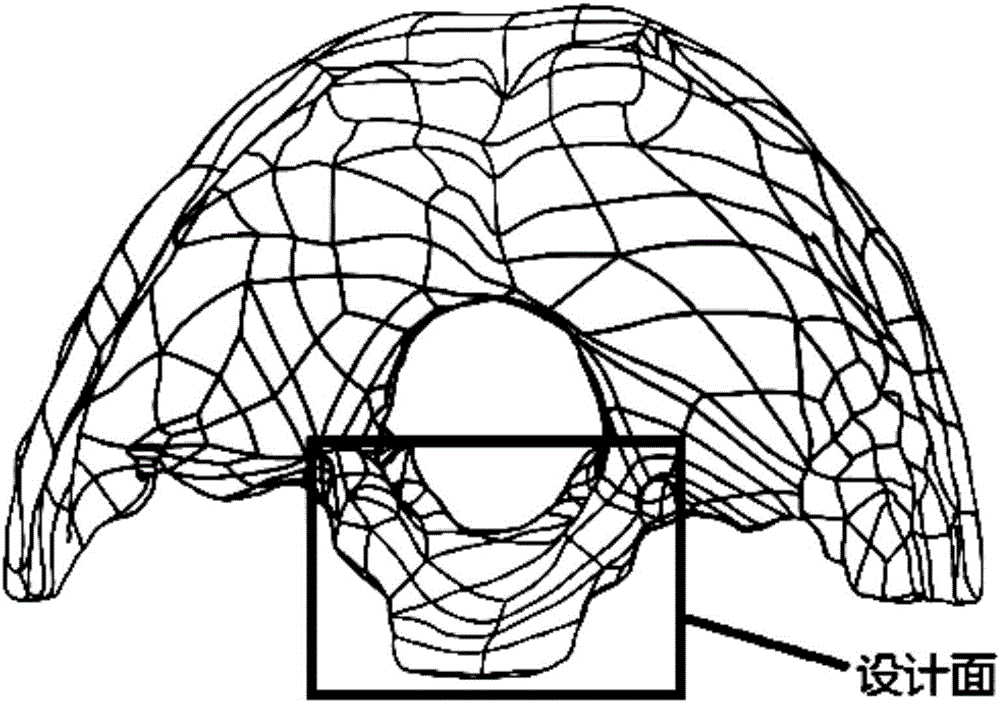
The invention discloses a manufacturing method of an atlas and axis titanium alloy prosthesis. The method comprises the steps of uploading CT tomography data of DICOM format of the spine medical image into the MINICS software, establishing three dimensional model data of spine to be reconstructed, implementing noise reduction by using the Geomagic software, exporting a 3D data file of step format, importing the file into the SolidWorks software, selecting the right design surfaces in the third section of the spine and the skull, establishing a prosthesis prototype between the two design surfaces, making sure the prosthesis and two design surfaces are completely fit. In order to reduce the modulus of elasticity of the prosthesis, and achieve the light weight design, the inside of the prosthesis is filled with porous grids by using SolidWorks. The porous structure on the prosthesis surface is also designed.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Internal fixation system and use method thereof
ActiveCN109330674AAvoid troubleReliable and strong internal fixation effectFastenersBone platesForcepsInternal fixation
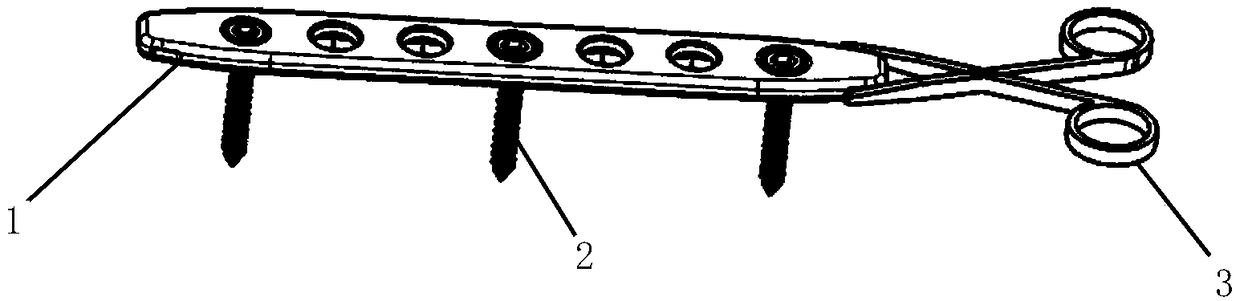
The invention relates to an internal fixation system and a use method thereof. The internal fixation system comprises a bone fracture plate of an inert biological material and a bone fracture screw ofone or more capable of degrading a magnesium alloy, and may further comprise an internal fixation extraction forceps in actual use. The invention also discloses a use method of the aforementioned internal fixation system. The internal fixation system and the use method have the advantages of a traditional internal fixation system, and utilize the feature that the position that the bone fracture plate is in contact with the bone fracture screw easily generates galvanic corrosion so that corrosion residual screws can be simply and quickly cut off when taking out the bone fracture plate, and screw rod parts of the remaining bone fracture screws can remain in a human body, thereby reducing the hospitalization rate and hospitalization time of patients, and improving the surgical satisfaction of the patients.
Owner:苏州卓恰医疗科技有限公司
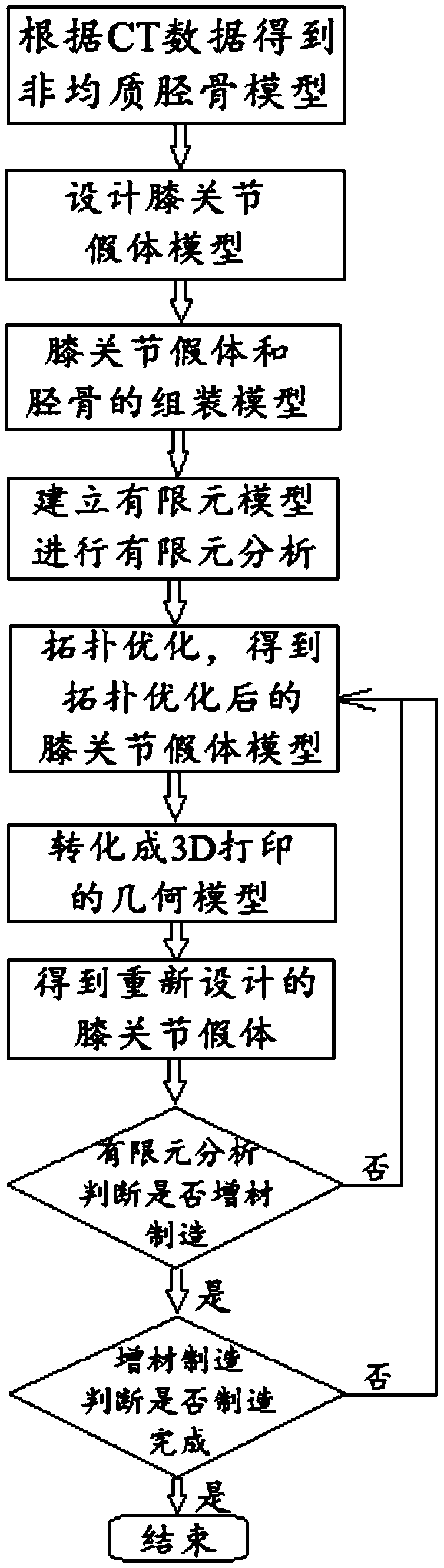
Manufacturing method of individualized customized knee joint bionic prosthesis based on 3D printing
ActiveCN110833472AUniform stress distributionGood biomechanical propertiesJoint implantsTomographyElement analysisKnee Joint
The invention discloses a manufacturing method of an individualized customized knee joint topological optimization bionic prosthesis based on 3D printing, which relates to the technical field of medical artificial joints. The problem that the manufacturing method is urgently needed to reduce prosthesis looseness or fracture around the prosthesis is solved, and the method comprises the steps: establishing and assembling a tibia model and a knee joint prosthesis model, and performing finite element analysis and topological optimization; carrying out fairing; designing a specific structure of themodel, optimally reserving an internal region by adopting a solid structure, optimally reserving an outer layer region and optimally removing the region by adopting a grid structure, and forming a gradient between the regions; introducing back an assembly state of a tibia model, performing finite element analysis, comparing with a first finite element analysis result, judging whether 3D manufacturing and application are performed or not, and performing topological optimization again if the 3D manufacturing and application cannot be performed. The prosthesis prepared by the invention reduces the problem of prosthesis looseness or prosthesis peripheral fracture, provides space for ligament stop point implantation and internal bone grafting, is light in weight, and is beneficial to bone tissue ingrowth.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Dental implant and dental implant manufacturing method
PendingCN112043433AHigh modulus of elasticityImprove bindingDental implantsAdditive manufacturing apparatusOsseointegrationBone tissue
The invention discloses a dental implant and a dental implant manufacturing method. The dental implant comprises an implant body, a fixing screw, a fixing abutment and a treatment cap. The implant body comprises an end part and a conical part. The implant body is provided with the end part and the conical part which are connected in an up-down mode, an external thread is arranged on the conical part, and the external thread is divided into a first pore area with a first pore and a second pore area with a second pore in an up-down mode, so that when the implant body is combined with the bone tissue, the first pore area set as a through hole is conveniently combined with the bone tissue of the dense bone, and the second pore area set as a blind hole is conveniently combined with the bone tissue of the cancellous bone; and therefore, the elasticity modulus of the implant body is optimized, the osseointegration performance of the dental implant is improved, the strength is proper, the stress shielding is smaller, the biomechanical property is good, and the problems that an existing dental implant is poor in osseointegration performance and relatively large in stress shielding are solved.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECH
Multi-material porous distal femur implant and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN112690930AImprove adaptabilityReduced stress shieldingAdditive manufacturing apparatusJoint implantsTissue engineeredBiomedical engineering
The invention discloses a multi-material porous distal femur implant and a manufacturing method thereof. The implant comprises a hard gradient porous distal femur implantation trunk and soft hydrogel cartilage; the hard gradient porous distal femur implantation trunk is of a porous structure, and the outer contour includes a conical femur body and two quasi-sphere-like imitated femur ankles; the soft hydrogel cartilage includes two semi-circular-ring-shaped coverings, and the two semi-circular-ring-shaped coverings are covered with the two imitated femur ankles respectively. According to the multi-material porous distal femur implant, the bionic design that a hard material and a soft material are combined is adopted, the structural composition of the normal distal femur of a human body can be imitated to the maximum extent; by adopting a way of combining the soft material and corresponding stem cells, after being implanted, the soft material can be stimulated through tissue engineering to generate blood capillaries, so that the adaptability of the implant in the human body is improved; and moreover, by adopting a way of combining hydroxyapatite and titanium alloy, the brittleness problem of a single-material hydroxyapatite implant can be avoided.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH +1
Biomedical titanium-niobium-based shape memory alloy as well as preparation method, processing method and application method thereof
The invention relates to a biomedical titanium-niobium-based shape memory alloy as well as a preparation method, a processing method and an application method thereof. The alloy comprises the following chemical compositions by weight percent: 28-39% of niobium, 0.35-5.5% of tin, 0.3-5.5% of aluminum, 0.5-5.5% of silicon, 0.2-5.5% of zirconium and the allowance of titanium. The alloy has the advantages of low elasticity modulus, good biocompatibility and mechanics compatibility, no toxic nickel element, good mechanical property and corrosion resisting property, excellent cold working property and low cold-working hardening ratio; the alloy can be used for cold working with large deformation such as cold rolling, cold wire drawing and the like, and the working cost is low. The titanium-niobium-based shape memory alloy is of the ideal and novel biological shape memory alloy material that replaces the TiNi shape memory alloy and can be widely used for an ultra-flexible bracket, an orthodontics dental arch wire and an orthopedics implantation instrument and the like in the fields of the medical treatment, the sports goods and the like.
Owner:GRINM MEDICAL INSTR BEIJING CO LTD
An orthopedic implant device
ActiveCN114027960BAvoid misjudgmentNo artifactsInternal osteosythesisOrthopedic departmentFibrous composites
The invention discloses an orthopedic implant device. The main body of the intramedullary nail adopts a core-shell structure. The main body core is laminated with continuous fiber composite materials to improve the bending strength. Fiber composite material to improve torsional strength. By forming an expansion cavity in the cap hole of the intramedullary nail body, and taking out the unit at the same time to form an expansion structure, the surface of the expansion structure fits or partially fits with the side wall of the expansion cavity, which increases the The shear force area, that is, correspondingly reduces the requirements for the shear strength of the material, and at the same time forms a clamping force between the two, and the combined application of the clamping force avoids the application of the take-out unit in the prior art when using continuous fiber composite materials. When on the main body of the intramedullary nail, the force is placed on the thread with low shear strength, causing the thread to collapse and / or spread.
Owner:江苏百易得医疗科技有限公司
An Adaptive Late Stabilized Femoral Stem Prosthesis
Owner:深圳协同创新高科技发展有限公司
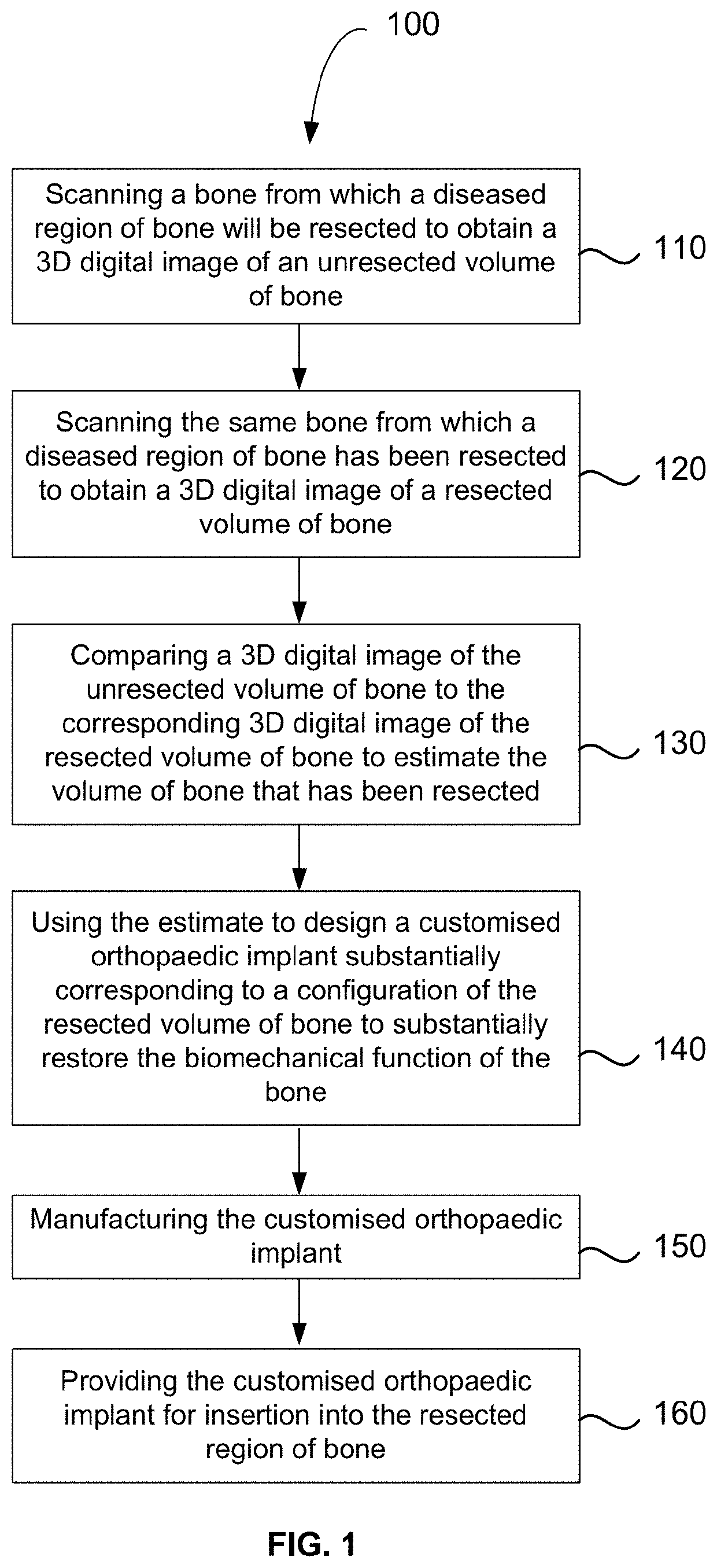
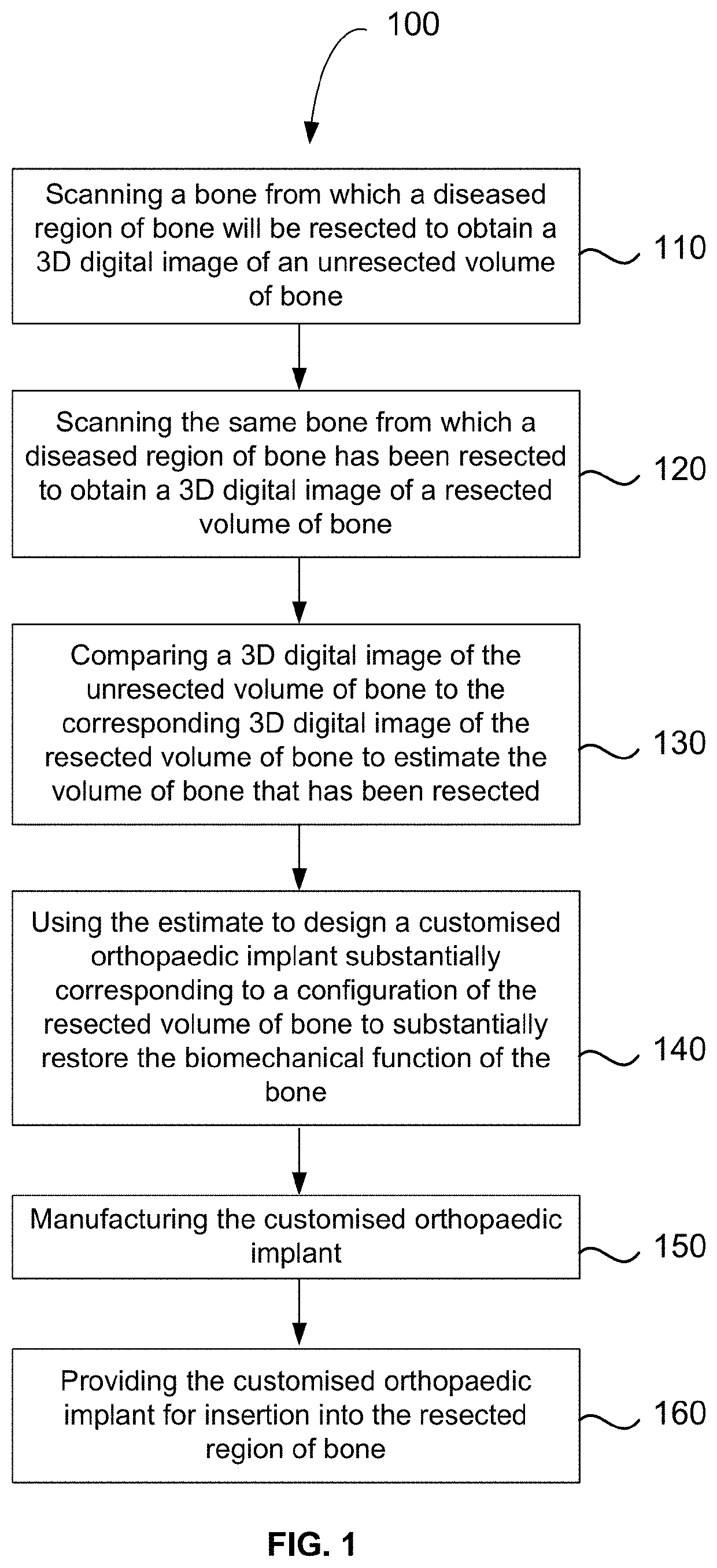
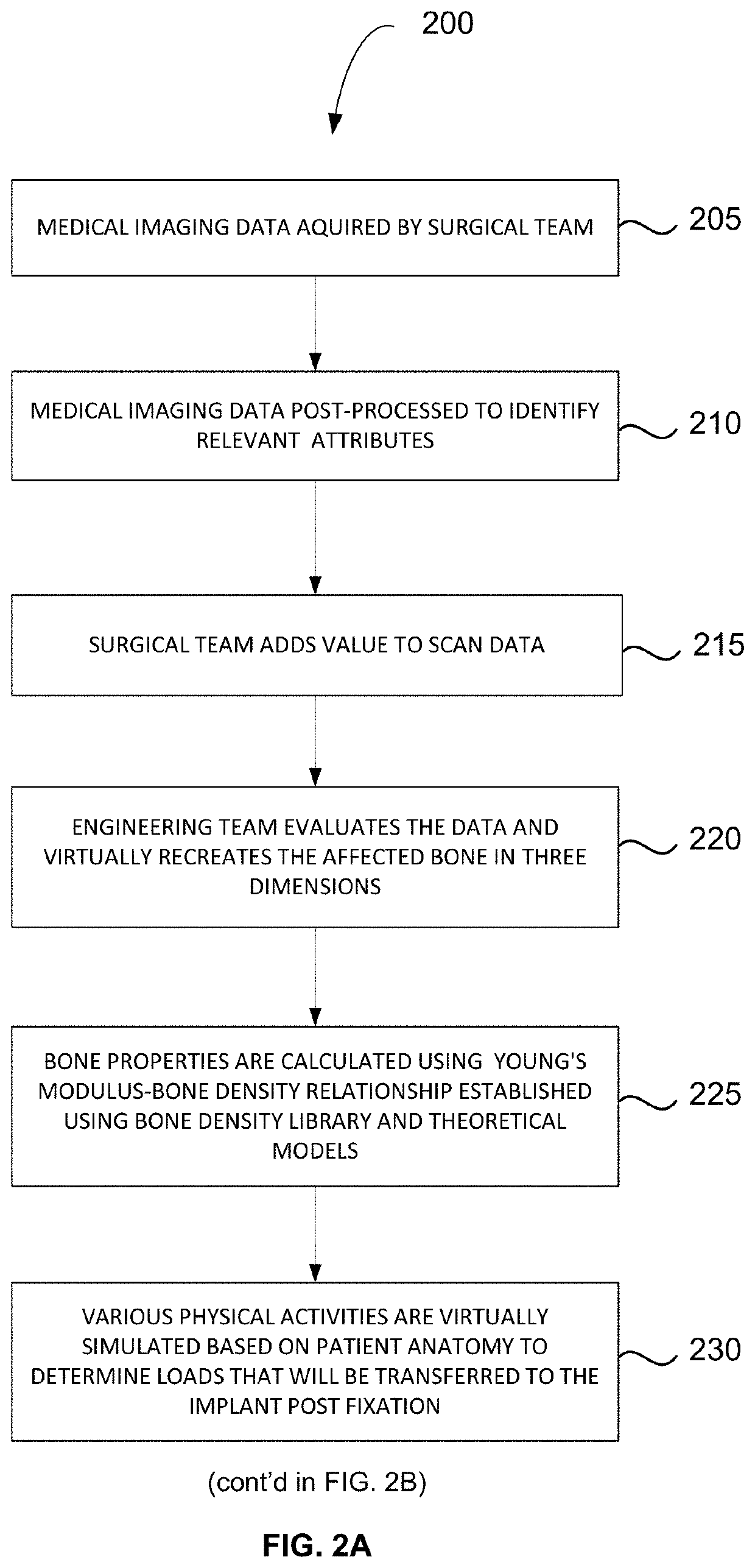
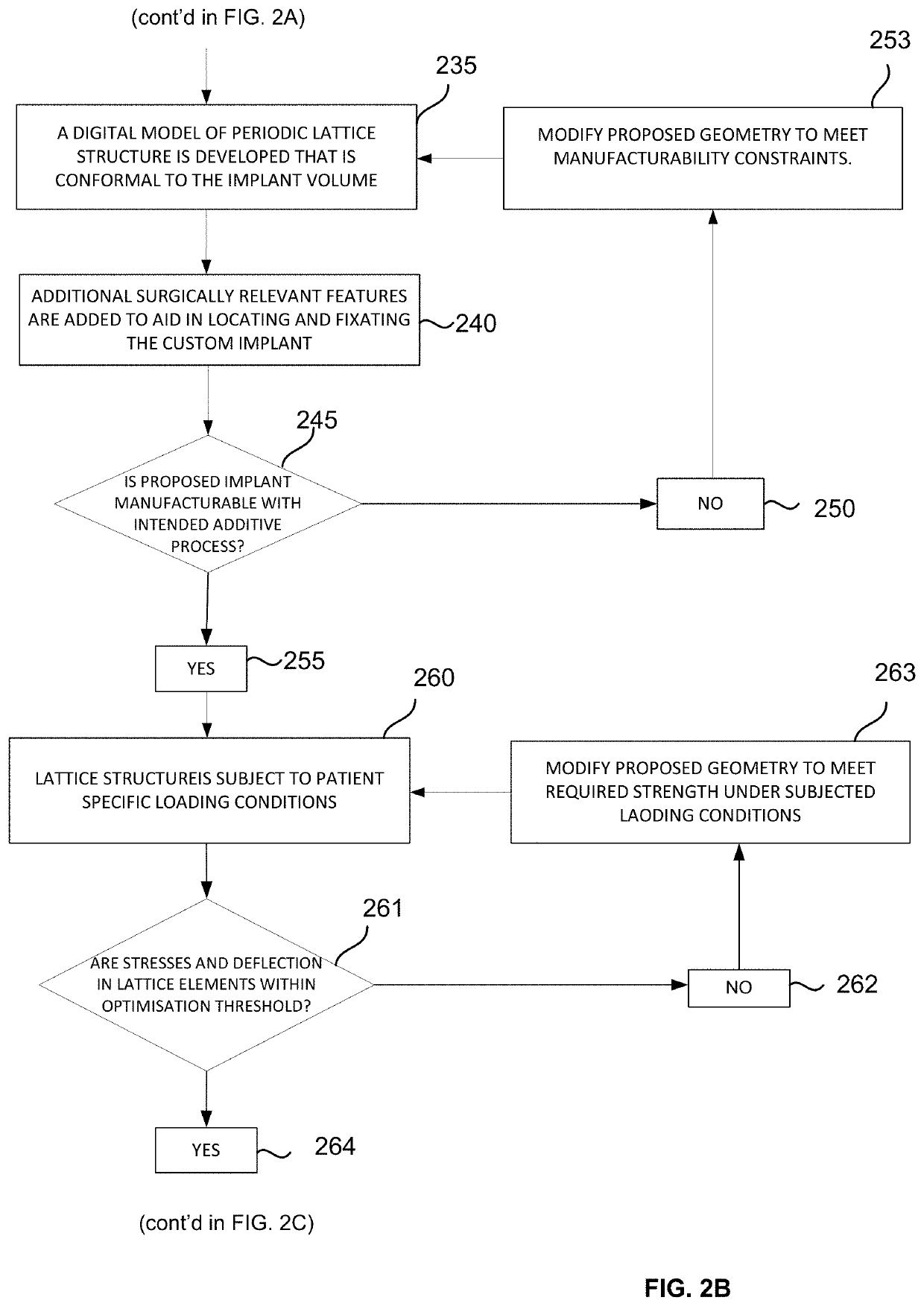
Method for producing a customised orthopaedic implant
ActiveUS10688726B2Easy to controlEnhance bone ingrowthAdditive manufacturing apparatusBone implantBiomechanicsDigital image
Owner:ROYAL MELBOURNE INST OF TECH
A method for manufacturing a multi-material porous distal femur implant
ActiveCN112690930BImprove adaptabilityReduce loosenessAdditive manufacturing apparatusJoint implantsHuman bodyBody of femur
The invention discloses a multi-material porous femoral distal implant and a manufacturing method thereof. The implant includes a hard gradient porous femoral distal implanted trunk and soft hydrogel cartilage; the hard gradient porous femoral distal The end-implanted torso is a porous structure, and the outer contour is divided into a conical femoral body and two spherical imitation femoral ankles; the soft hydrogel cartilage is two semi-circular coverings, respectively covering the two A simulated femoral ankle. The present invention adopts a bionic design combining hard materials and soft materials, which can imitate the structure of the normal distal femur of the human body to the greatest extent. By using the combination of soft materials and corresponding stem cells, tissue engineering can be used in After implantation, it stimulates the generation of capillaries and improves the adaptability of the implant in the human body. Moreover, the combination of hydroxyapatite and titanium alloy can avoid the brittleness problem of single-material hydroxyapatite implants.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH +1
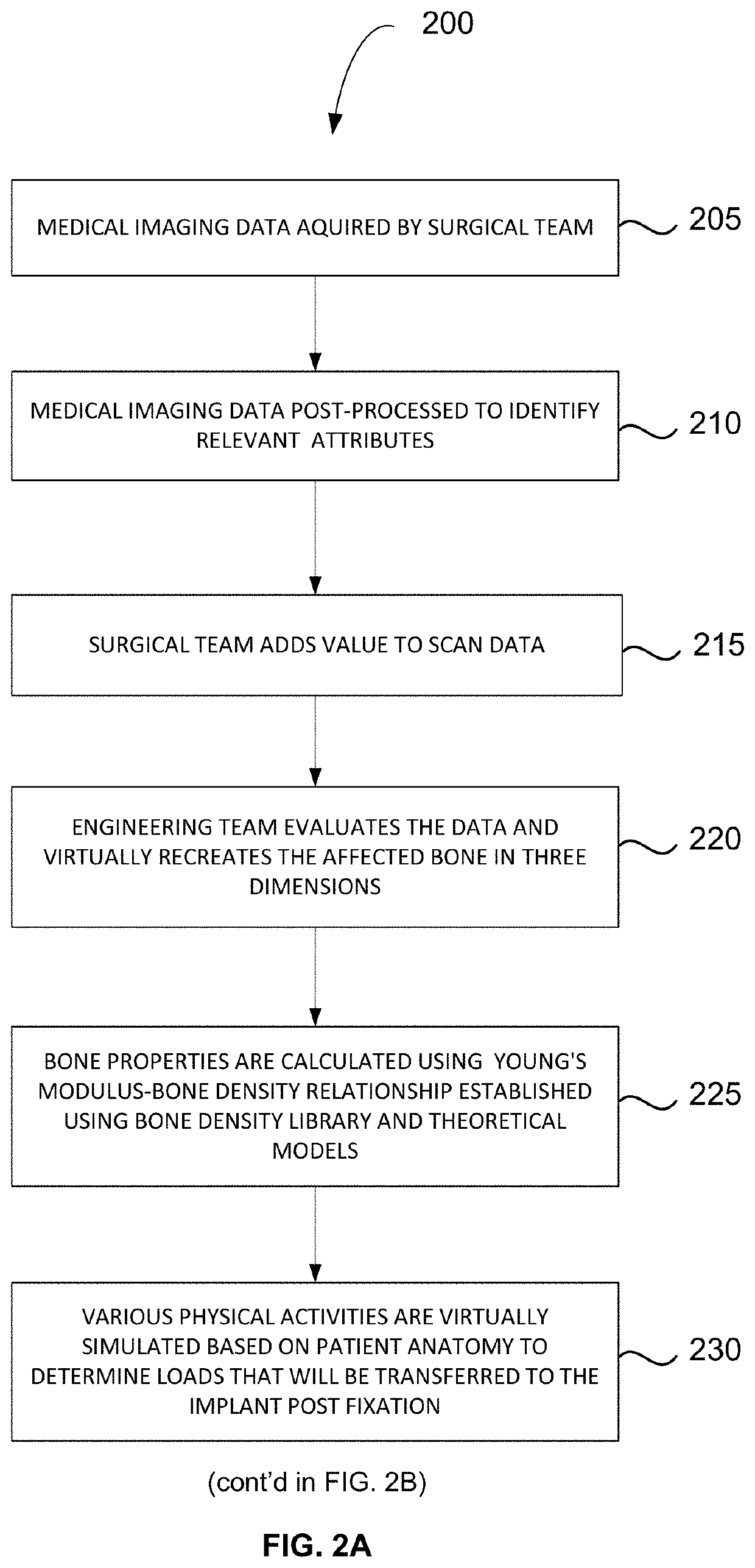
Method for producing a customised orthopaedic implant
PendingUS20200269516A1Enhance bone ingrowthEasy to controlAdditive manufacturing apparatusBone implantBiomechanicsBiomedical engineering
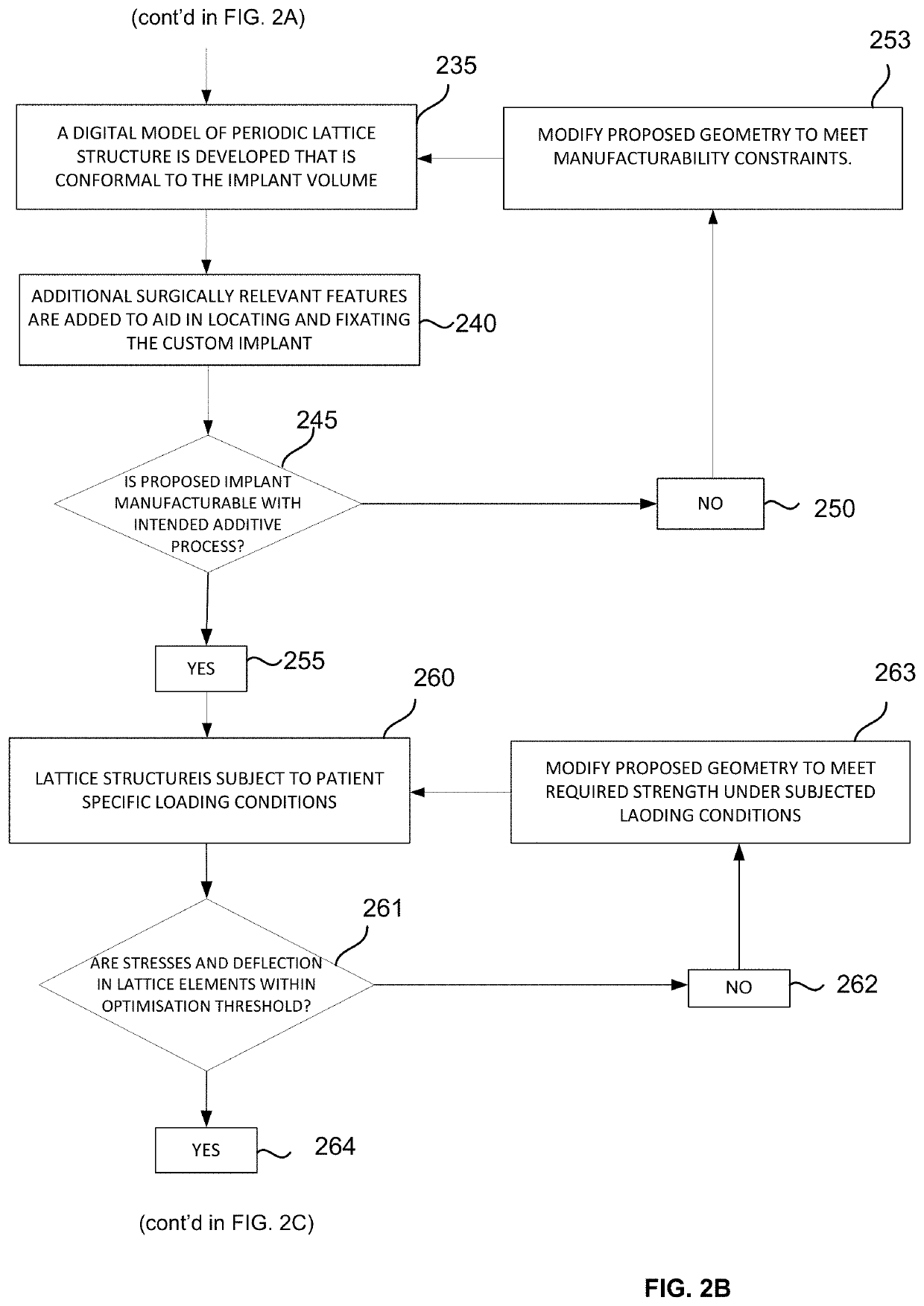
A customised orthopaedic implant is provided, the implant being formed of metal, the implant being substantially comprised of a lattice-type geometry that has a periodic arrangement and is conformal to a configuration of a region of bone that was resected to remove bone that is diseased and is optimised to substantially restore a biomechanical function of a bone from which the region of bone was resected on implantation of the customised orthopaedic implant in consideration of the anatomical function and of the properties of a bone type corresponding to the region of bone that was resected, together with patient-specific parameters and anticipated loads to which the implant will be subjected during various typical activities and movements.
Owner:ROYAL MELBOURNE INST OF TECH
Powder for preparing porous material by laser synthesis reaction
InactiveCN1803947AHigh mechanical strengthSolving Mechanical Compatibility IssuesLiquid surface applicatorsPowdery paintsAlloyMaterials science
Owner:SHENYANG POLYTECHNIC UNIV
A kind of internal fixation system and using method thereof
ActiveCN109330674BAvoid troubleReliable and strong internal fixation effectFastenersBone platesHuman bodyMg alloys
The invention relates to an internal fixation system and a use method thereof. The internal fixation system comprises a bone fracture plate of an inert biological material and a bone fracture screw ofone or more capable of degrading a magnesium alloy, and may further comprise an internal fixation extraction forceps in actual use. The invention also discloses a use method of the aforementioned internal fixation system. The internal fixation system and the use method have the advantages of a traditional internal fixation system, and utilize the feature that the position that the bone fracture plate is in contact with the bone fracture screw easily generates galvanic corrosion so that corrosion residual screws can be simply and quickly cut off when taking out the bone fracture plate, and screw rod parts of the remaining bone fracture screws can remain in a human body, thereby reducing the hospitalization rate and hospitalization time of patients, and improving the surgical satisfaction of the patients.
Owner:苏州卓恰医疗科技有限公司
Manufacturing method of personalized knee bionic prosthesis based on 3D printing
ActiveCN110833472BUniform stress distributionGood biomechanical propertiesJoint implantsTomographyElement analysisKnee Joint
The invention discloses a manufacturing method of an individualized customized knee joint topological optimization bionic prosthesis based on 3D printing, which relates to the technical field of medical artificial joints. The problem that the manufacturing method is urgently needed to reduce prosthesis looseness or fracture around the prosthesis is solved, and the method comprises the steps: establishing and assembling a tibia model and a knee joint prosthesis model, and performing finite element analysis and topological optimization; carrying out fairing; designing a specific structure of themodel, optimally reserving an internal region by adopting a solid structure, optimally reserving an outer layer region and optimally removing the region by adopting a grid structure, and forming a gradient between the regions; introducing back an assembly state of a tibia model, performing finite element analysis, comparing with a first finite element analysis result, judging whether 3D manufacturing and application are performed or not, and performing topological optimization again if the 3D manufacturing and application cannot be performed. The prosthesis prepared by the invention reduces the problem of prosthesis looseness or prosthesis peripheral fracture, provides space for ligament stop point implantation and internal bone grafting, is light in weight, and is beneficial to bone tissue ingrowth.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Orthopedic implant device
ActiveCN114027960AAvoid misjudgmentNo artifactsInternal osteosythesisShear stressOrthopedic department
The invention discloses an orthopedic implant device which comprises an intramedullary nail main body which is of a core-shell structure, the bending strength of a main body core is improved by laminating a continuous fiber composite material, and the torsional strength of a main body shell is improved by a continuous fiber composite material which is obliquely arranged with the main body core. An expansion containing cavity is formed in a sealing cap hole of the intramedullary nail main body, meanwhile, a taking-out unit forms an expansion structure, the surface of the expansion structure is attached to or partially attached to the side wall of the expansion containing cavity, the shearing stress area is increased through the arrangement, and the requirement for the shearing strength of materials is correspondingly lowered; meanwhile, a clamping force is formed between the expansion structureand the expansion containing cavity, and the resultant force application of the clamping force avoids the phenomenon that when a taking-out unit in the prior art is applied to an intramedullary nail main body prepared from a continuous fiber composite material, a stressed part is located at a thread with low shear strength, and consequently the thread is broken and / or expanded.
Owner:江苏百易得医疗科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com