Patents
Literature
341 results about "Torsional strength" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Torsional Strength. Measure of the ability of a material to withstand a twisting load. It is the ultimate strength of a material subjected to torsional loading, and is the maximum torsional stress that a material sustains before rupture.
Magnetic pulse connecting method and joint structure for thin-wall metal pipelines
InactiveCN101905375AIncreased processing flexibilityHigh strengthNon-electric welding apparatusHeat-affected zoneEngineering
The invention discloses a magnetic pulse connecting method and a joint structure for thin-wall metal pipelines and provides a safe and high-efficiency magnetic pulse connecting method and a magnetic pulse connecting joint structure for similar and dissimilar thin-wall metal pipelines. A coil-magnetic concentrator composite inductor or a coil inductor is connected with electromagnetic pulse forming equipment so that the pipelines of various metal materials or various structure shapes can be connected in a magnetic pulse way. The transition area of the joint connecting interface is small, the brittle phase or intermetallic compound almost cannot be generated, and the joint almost has no heat affected area and torsion deformation and has high strength and corrosion-resistance property; the tension strength and torsion strength of the joint are respectively higher than those of weak base metal; the subsequent cleaning procedure and post-weld heat treatment are not needed; and the connected pipeline satisfies certain rigidity requirement, cannot be subjected to the plastic deformation in the magnetic pulse connecting process and has high process flexibility.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Transport system
ActiveUS20110172875A1Easy to optimizeImprove rigidityVehicle testingRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesTransport systemTransit system
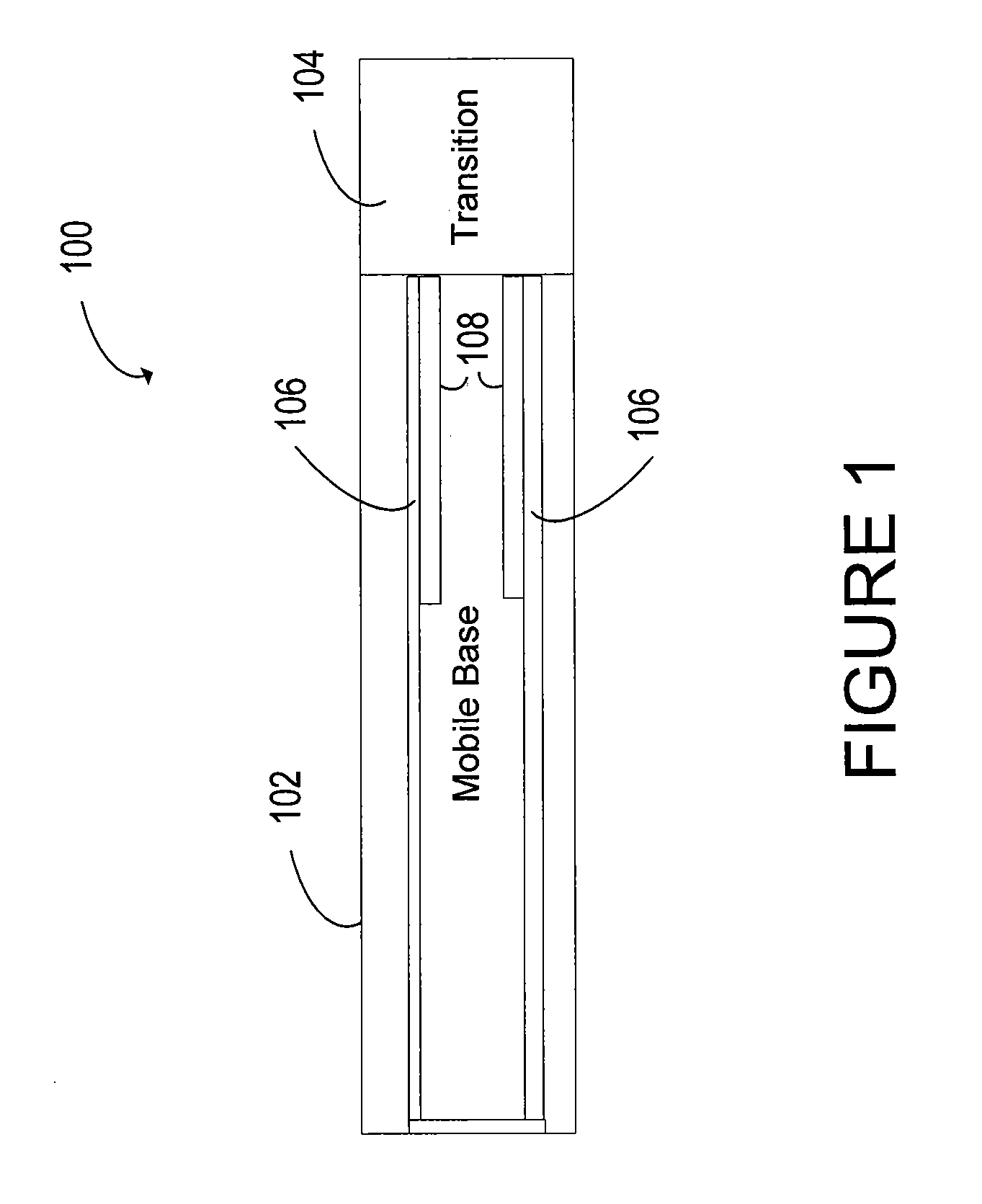
A mobile moving system that faculties freight movement includes movable approach ramps and a mobile base. The mobile base includes material handling devices configured to move freight longitudinally between a loading position, a transport position, and an unloading position. Parallel pocket members having a hollow-box-like shape are positioned along a portion of the plurality of the material handling devices to increase the torsional strength and rigidity of the material handling devices. The parallel pocket members are spaced apart and dimensioned so that each of the plurality of parallel pocket members may receive one or more prongs of an industrial vehicle.
Owner:INNOVATIVE TRANSPORT SOLUTIONS
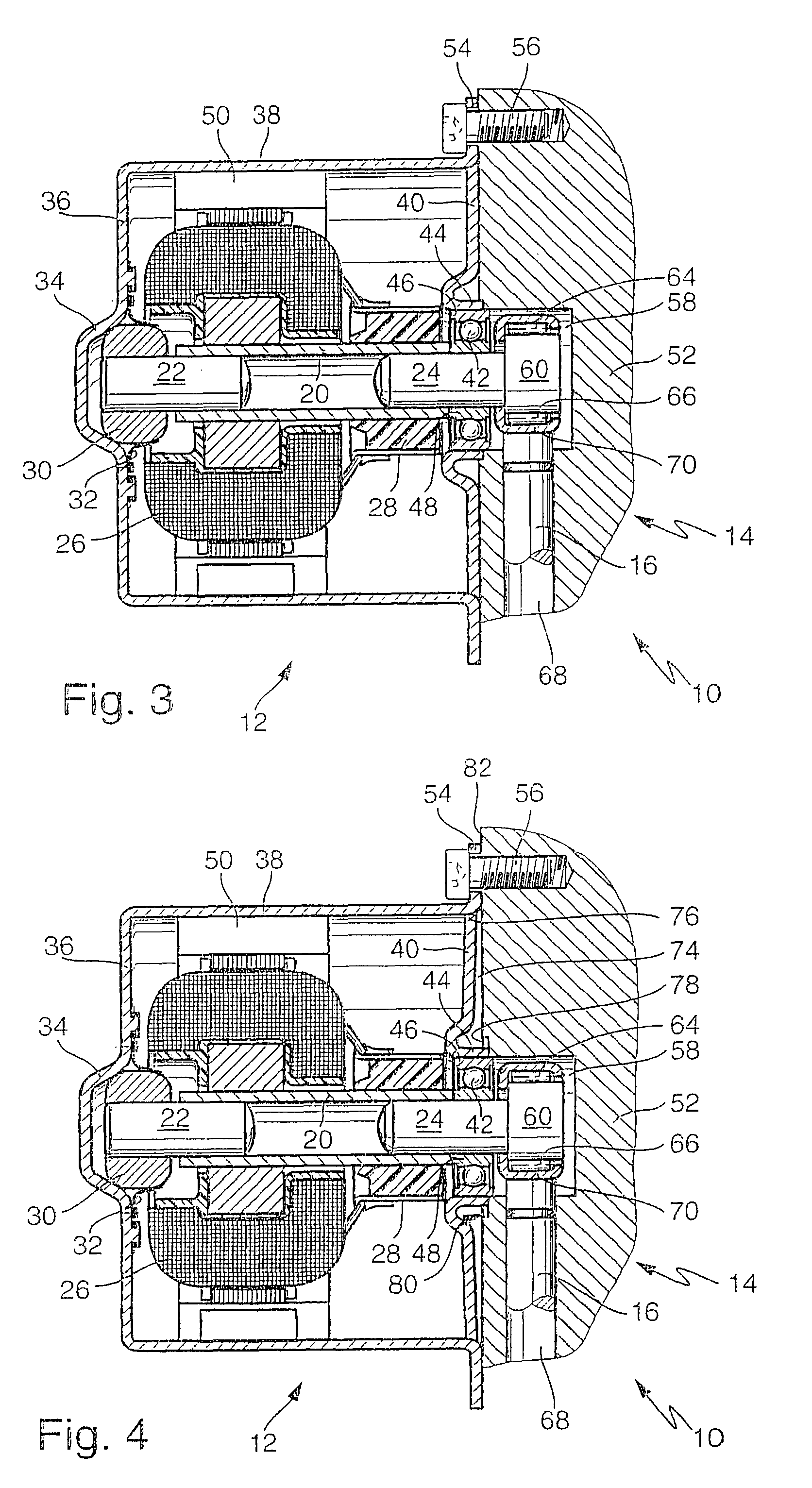
Pump aggregate for a hydraulic vehicle braking system
InactiveUS7168929B2Easy to bendImprove rigidityPositive displacement pump componentsBraking componentsRadial piston pumpTorsional strength
A pump unit for a hydraulic vehicle brake system with traction control has an electric motor driving a radial piston pump. A rotor shaft of the pump unit has a hollow shaft with two standardized, hardened cylindrical pins that are press-fitted into the ends of the hollow shaft. The rotor shaft can be produced simply, economically, and without metal-cutting machining. The hollow shaft has high bending and torsional strength. The rotor shaft has a small diameter at the bearing points, which makes a small bearing diameter and thus a small installation space for the pump unit possible.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Axle with non-round tapered ends affixed into fork leg dropouts with openings that match the axle ends for a bicycle fork
ActiveUS7494145B2Increased torsional strengthFacilitate easeWheel based transmissionFrictional rollers based transmissionEngineeringTorsional strength
Owner:HAYES BICYCLE GROUP
Resorbable Scaffolds For Bone Repair And Long Bone Tissue Engineering
ActiveUS20110307073A1Sufficient bendingAvoid insufficient compressionBone implantMechanical propertyPolycaprolactone
Bioresorbable scaffolds for bone engineering, such as repair of bone defects, particularly long bone defects, or augmentation of bone length are described. Scaffolds are porous and comprise multiple side channels. In one embodiment, scaffolds are made from layers of micro-filament meshes comprising polycaprolactone (PCL) or a PCL-composite sequentially laid in incremental 60 degrees of rotation to produce a 0 / 60 / 120 degree layering pattern, providing for the formation of interconnected pores. The scaffold can comprise a central channel filled, packed or infused with suitable agents such as bioactive agents. Furthermore, the scaffolds are stiff but yet fracture resistant and with sufficient bending, compressive and torsional strength suitable for bone engineering. The slow degradation of the scaffold is sufficient for the 3D matrix to maintain structure integrity and mechanical properties during the remodelling process.
Owner:OSTEOPORE KOREA +2
Propeller shaft and method of producing the same
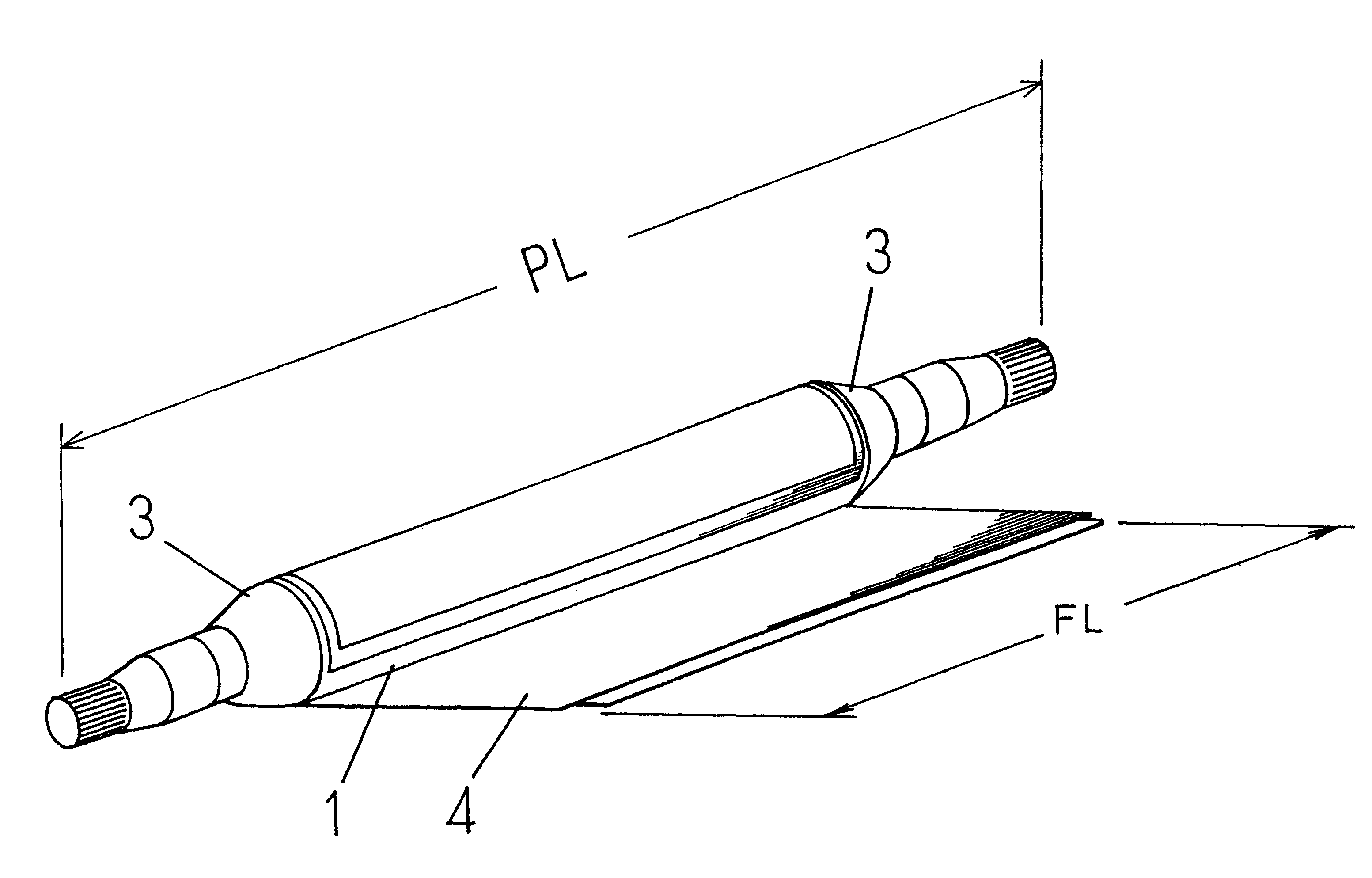
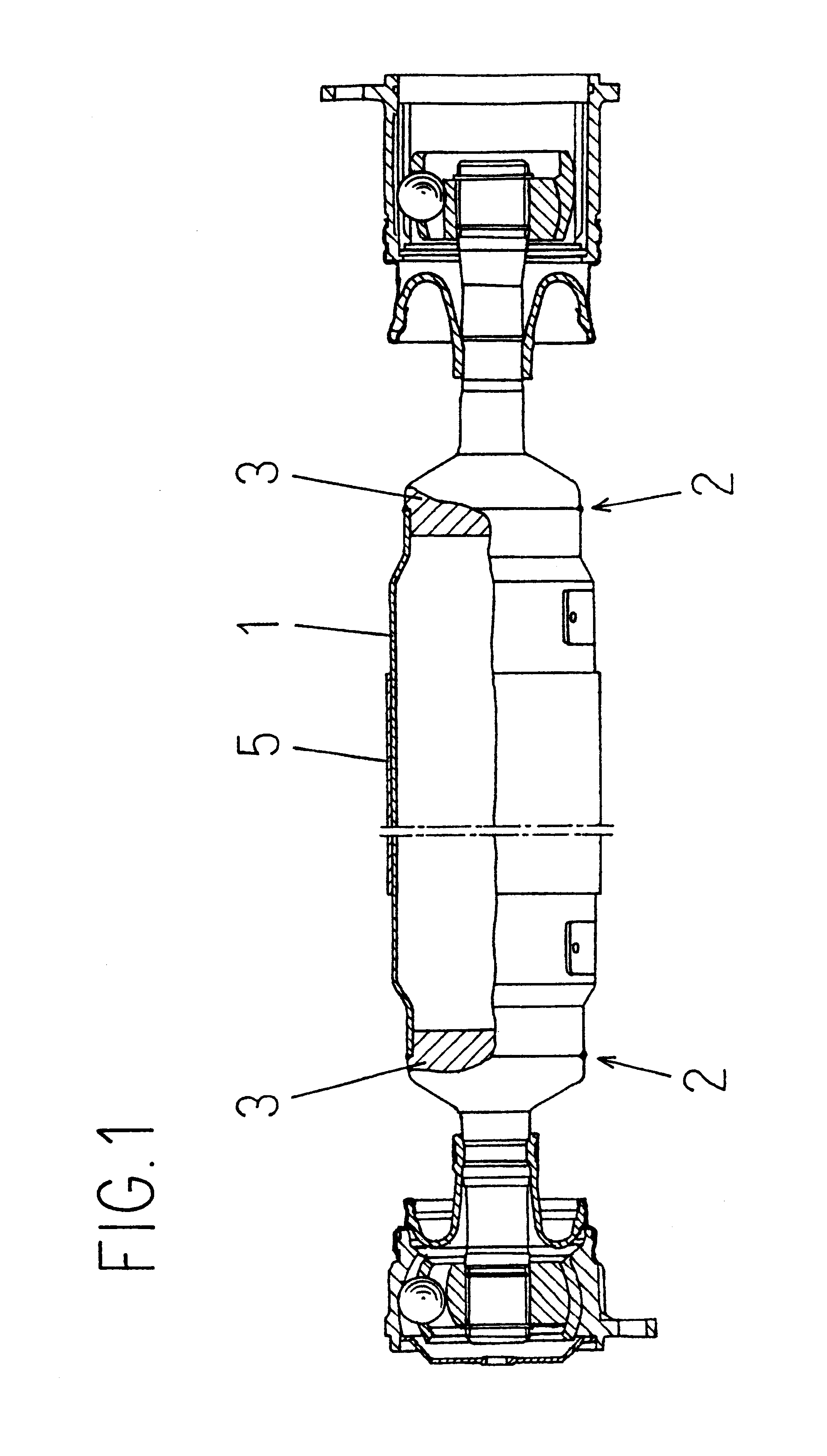
InactiveUS6287209B1Improve staminaLong-term reliabilityShaftsRotary machine partsDrive shaftPropeller
A propeller shaft has a metal pipe (1) with a joint element (3) joined at an end thereof. A fiber reinforced plastic layer (5) having a thickness that achieves a flexural rigidity satisfying a required natural bending frequency is formed on an outer circumference of the metal pipe (1) satisfying a static torsional strength required as a propeller shaft. The fiber reinforced plastic layer (5) has an interface strength between the reinforcing fiber and the matrix within a range of 20 to 200 MPa as measured by the microdroplet method.
Owner:MITSUBISHI CHEM CORP +1
Display device and liquid crystal display device
InactiveUS20050117086A1Increased torsional strengthSuppressing increaseDigital data processing detailsElectrical apparatus contructional detailsLiquid-crystal displayDisplay device
In a display device in which a display panel is supported from the back by a back frame, the back frame is composed of a pair of long side portions and a pair of short side portions each having an angular structure in section. Whereby, torsional strength is increased while suppressing increase in weight. This leads to increase in torsional strength while suppressing increase in weight even in a large-sized display screen.
Owner:SHARP KK
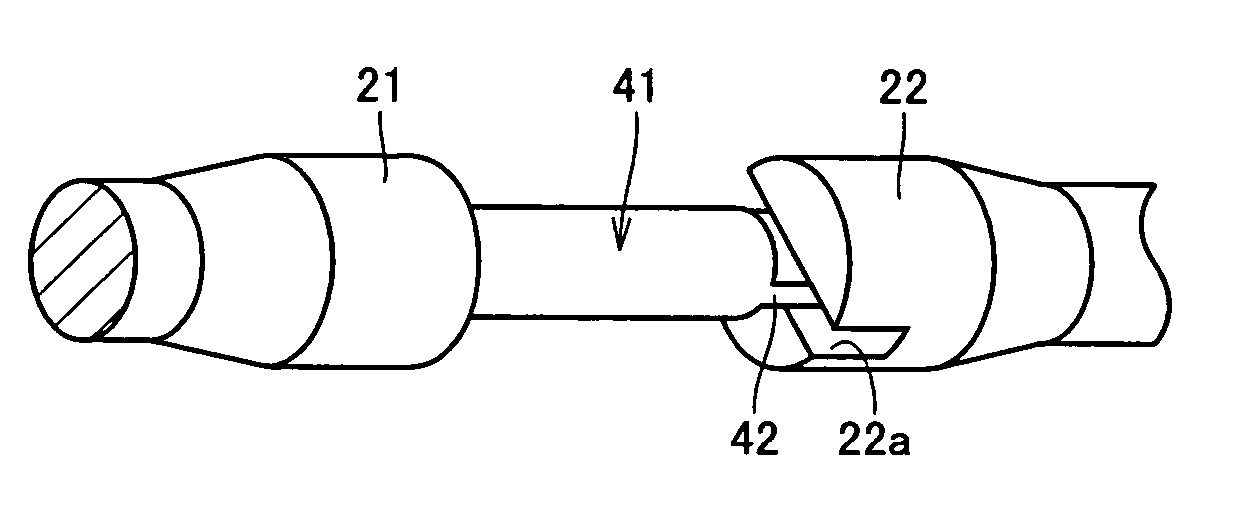
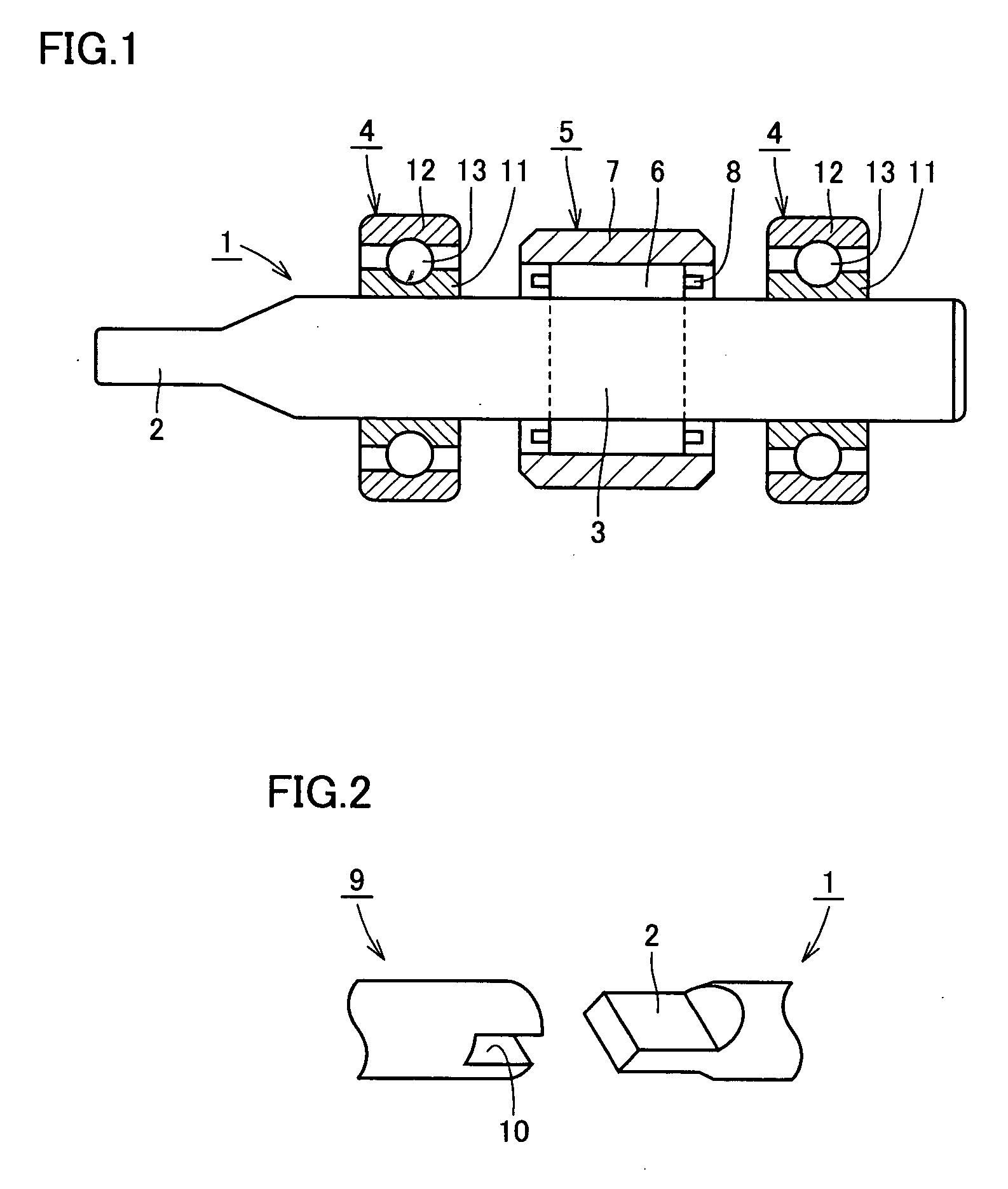
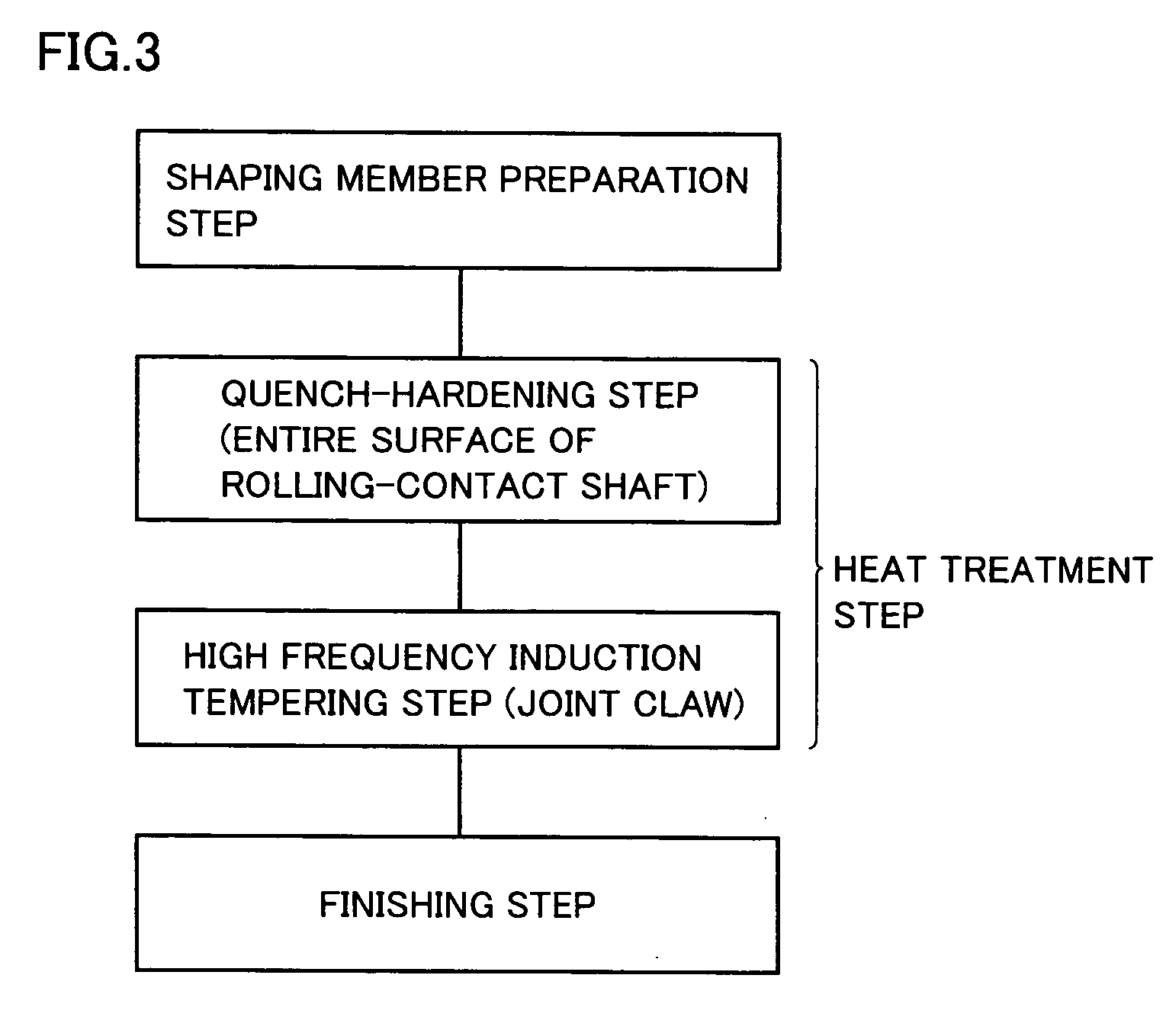
Rolling-contact shaft with joint claw
ActiveUS20070034301A1Improve contact fatigue lifeShaftsBearing componentsEngineeringMechanical engineering
A steel-made rolling-contact shaft with a joint claw improved in both the rolling contact fatigue life at the raceway and the static fracture strength (torsional strength) at the claw includes a joint claw at one end, and has a portion of the outer cylindrical surface functioning as a raceway of a needle roller qualified as a rolling element of a needle bearing. The joint claw is subjected to tempering by induction heating. A nitrogen-enriched layer is formed at the surface layer of the rolling-contact shaft with a joint claw. The grain size number of austenite grains in the nitrogen-enriched layer exceeds number 10. The hydrogen content of the rolling-contact shaft with ajoint claw is not more than 0.5 ppm.
Owner:NTN CORP
Resorbable scaffolds for bone repair and long bone tissue engineering
ActiveUS8702808B2Increased torsional strengthProvide strengthBone implantMechanical propertyPolycaprolactone
Bioresorbable scaffolds for bone engineering, such as repair of bone defects, particularly long bone defects, or augmentation of bone length are described. Scaffolds are porous and comprise multiple side channels. In one embodiment, scaffolds are made from layers of micro-filament meshes comprising polycaprolactone (PCL) or a PCL-composite sequentially laid in incremental 60 degrees of rotation to produce a 0 / 60 / 120 degree layering pattern, providing for the formation of interconnected pores. The scaffold can comprise a central channel filled, packed or infused with suitable agents such as bioactive agents. Furthermore, the scaffolds are stiff but yet fracture resistant and with sufficient bending, compressive and torsional strength suitable for bone engineering. The slow degradation of the scaffold is sufficient for the 3D matrix to maintain structure integrity and mechanical properties during the remodelling process.
Owner:OSTEOPORE KOREA +2
Plastic pipe adhesive joint
InactiveUS20030155768A1High strengthFluid pressure sealed jointsJoints with sealing surfacesThreaded pipeEngineering
A method of joining two pipe ends, by forming male threads on an end of a first pipe with a steep taper angle, forming matching female threads on an end of a second pipe, and applying adhesive material to the threads before twisting the pipes to fully engage the male and female threads, thereby spreading the adhesive material across adjacent load-bearing surfaces of the threads. The threads have multiple start locations for thread engagement so that the pipe ends may be twisted to achieve full engagement in less than one full relative rotation. The male and female threads are formed with a squeeze angle between matching surfaces of the threads between 0.5 and 5.0 degrees. The finished joint provides immediate leak-tightness, and immediate tensile, compressive and torsional strength and does not protrude outside of the pipe profile. The technique may also be used to join pipes constructed of dissimilar materials, particularly by using a coupler that has the appropriate threading, and securing the coupler to a non-threaded pipe end using any convenient means, such as a mechanical fit, or fusion bonding.
Owner:HOLLINGSWORTH ELMONT E +1
Impact resistant aircraft fuselage
ActiveUS20090140096A1Sufficient residual torsional strengthIncreasing resistance to damageGas turbine type power plantsPiston type power plantsPropellerTorsional strength
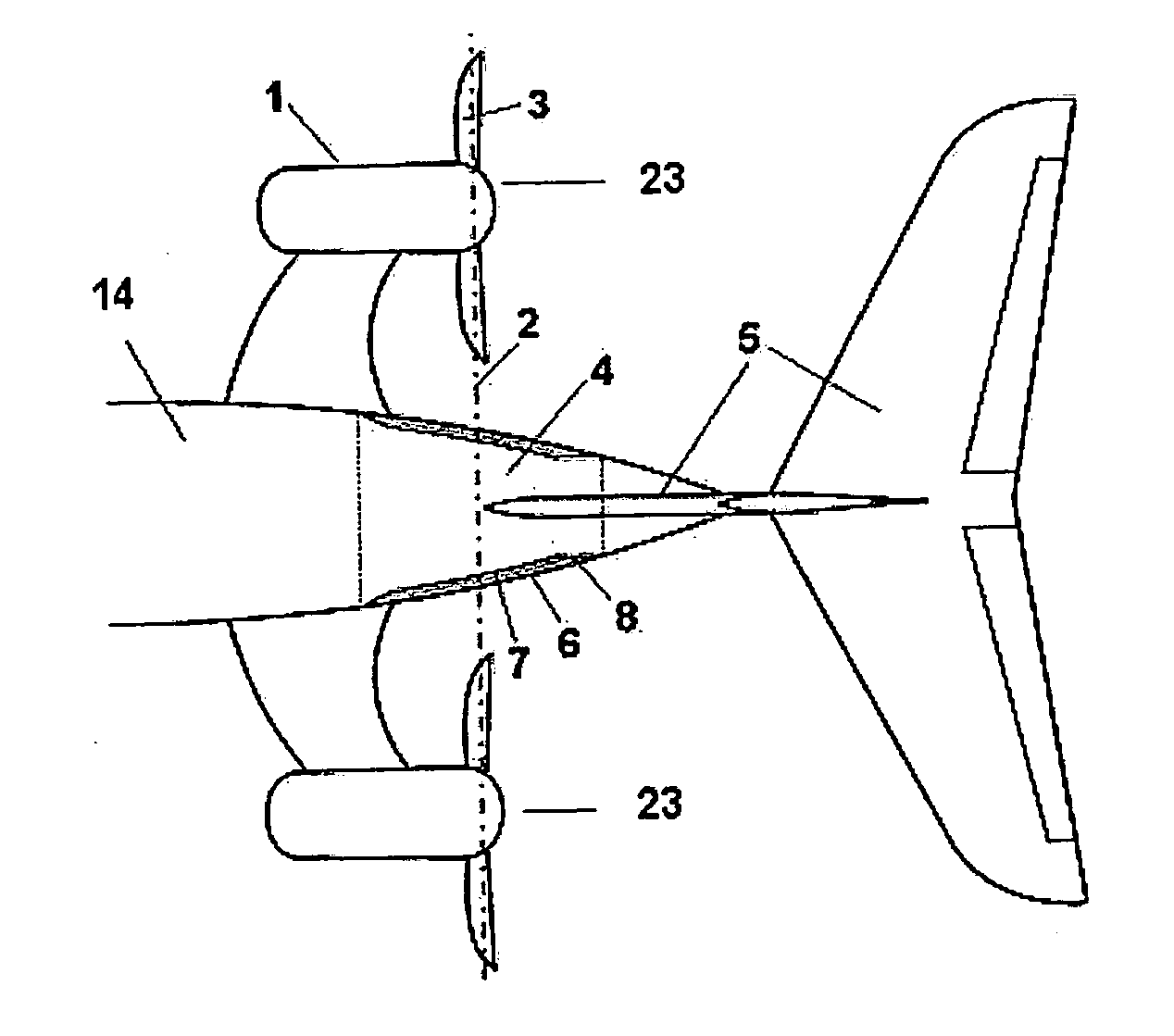
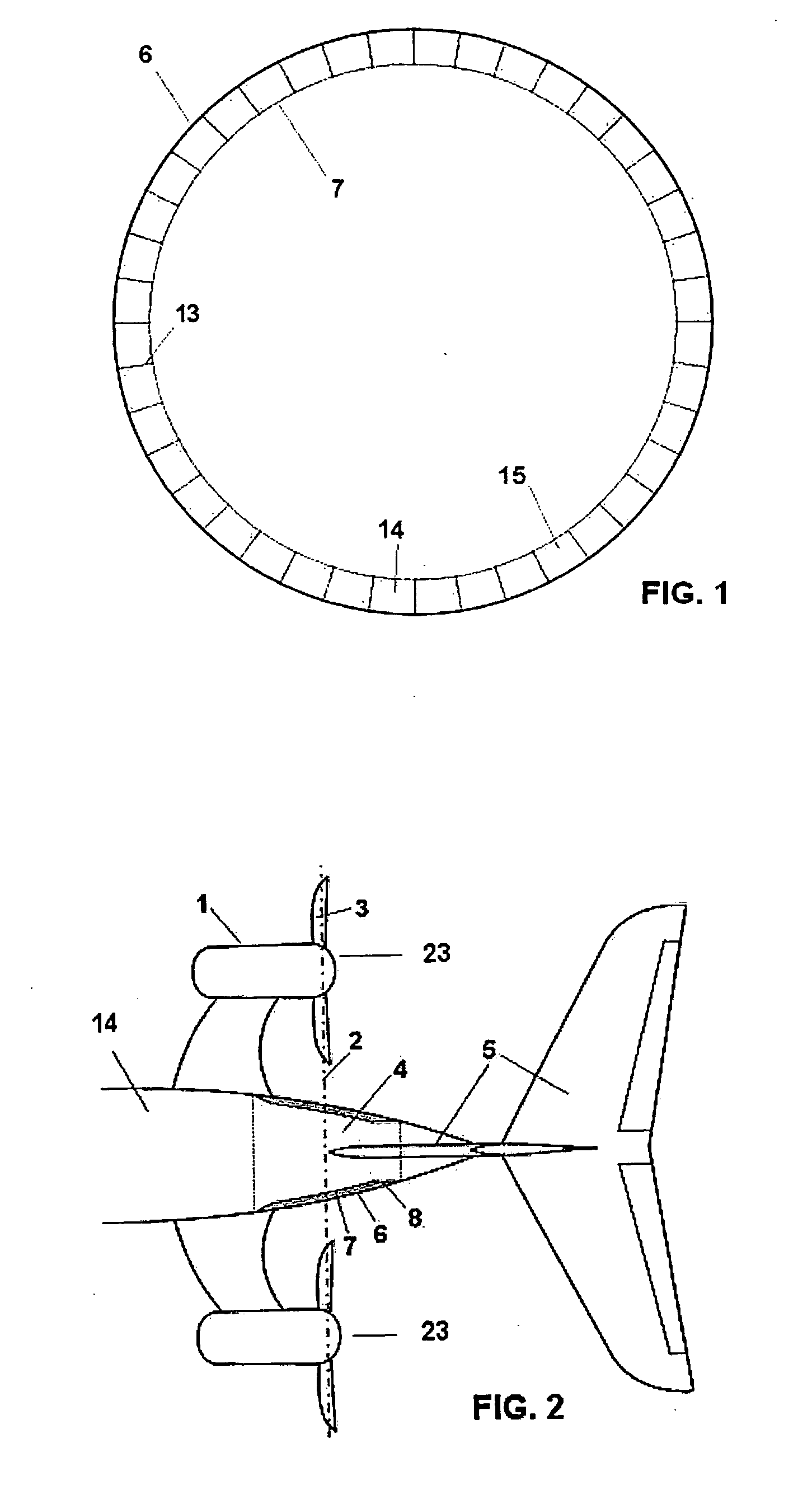
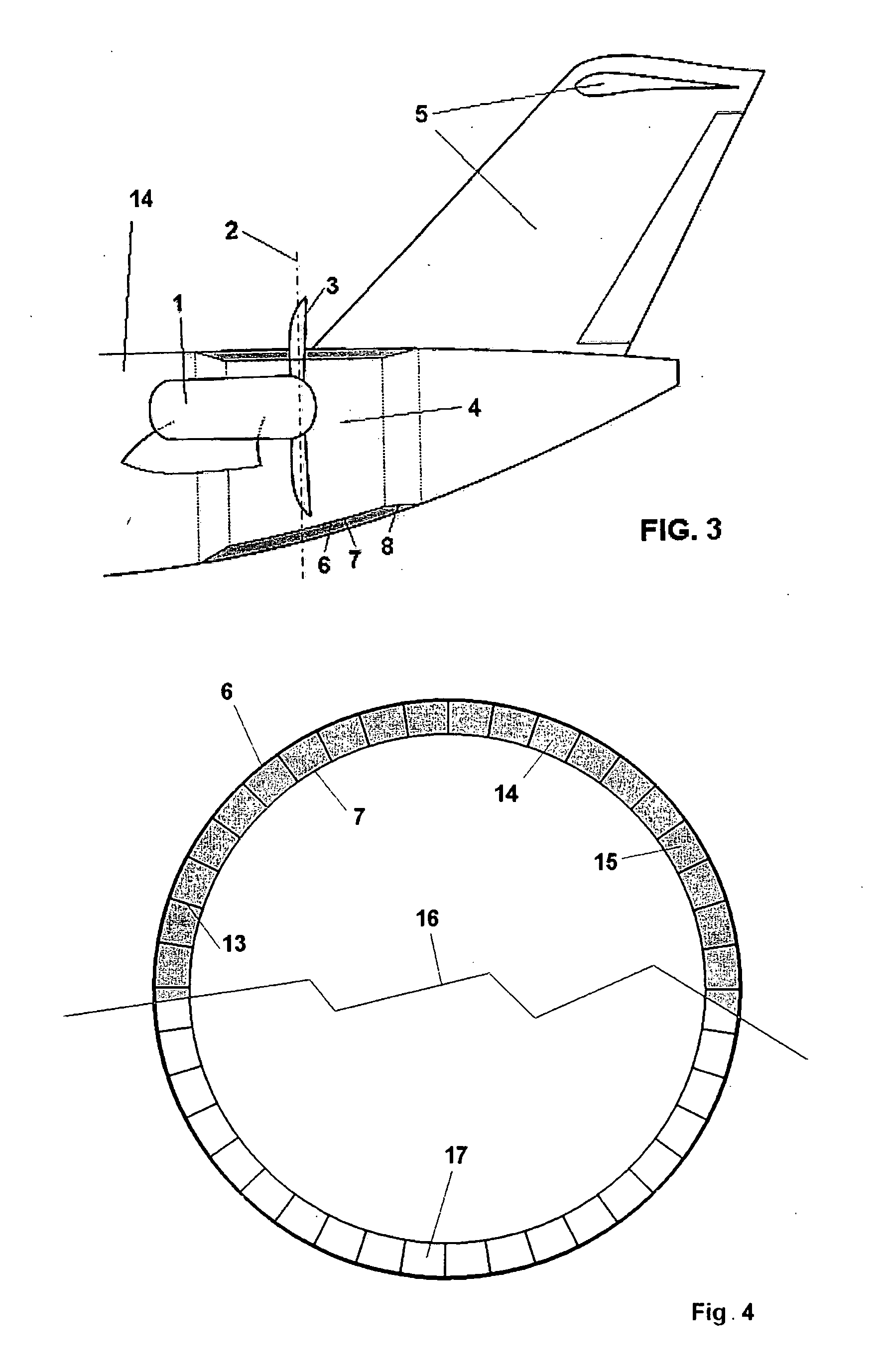
The invention relates to a structural configuration of the rear fuselage (4) of an aircraft with propeller engines (1) comprising propellers (23) formed in turn by blades (3), the mentioned propeller engines (1) being located at the rear part of the aircraft and the empennage (5) of the aircraft in turn being located behind the plane of the propellers (23), characterized in that the structural configuration of the rear fuselage (4) comprises an outer skin (6) and an inner skin (7), both skins (6, 7) being joined by means of radial elements (13) configuring cells (14), such that the obtained structural configuration maximizes the torsional strength of the rear fuselage (4) of the aircraft in the event of damage of the mentioned rear fuselage (4) due to the detachment of one of the blades (3) of the propeller engines (1).
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS SL
Shaft for light-weight golf clubs
InactiveUS6767422B1Improve rigidityHigh strengthPaper/cardboard wound articlesPedestrian/occupant safety arrangementFiberFlexural strength
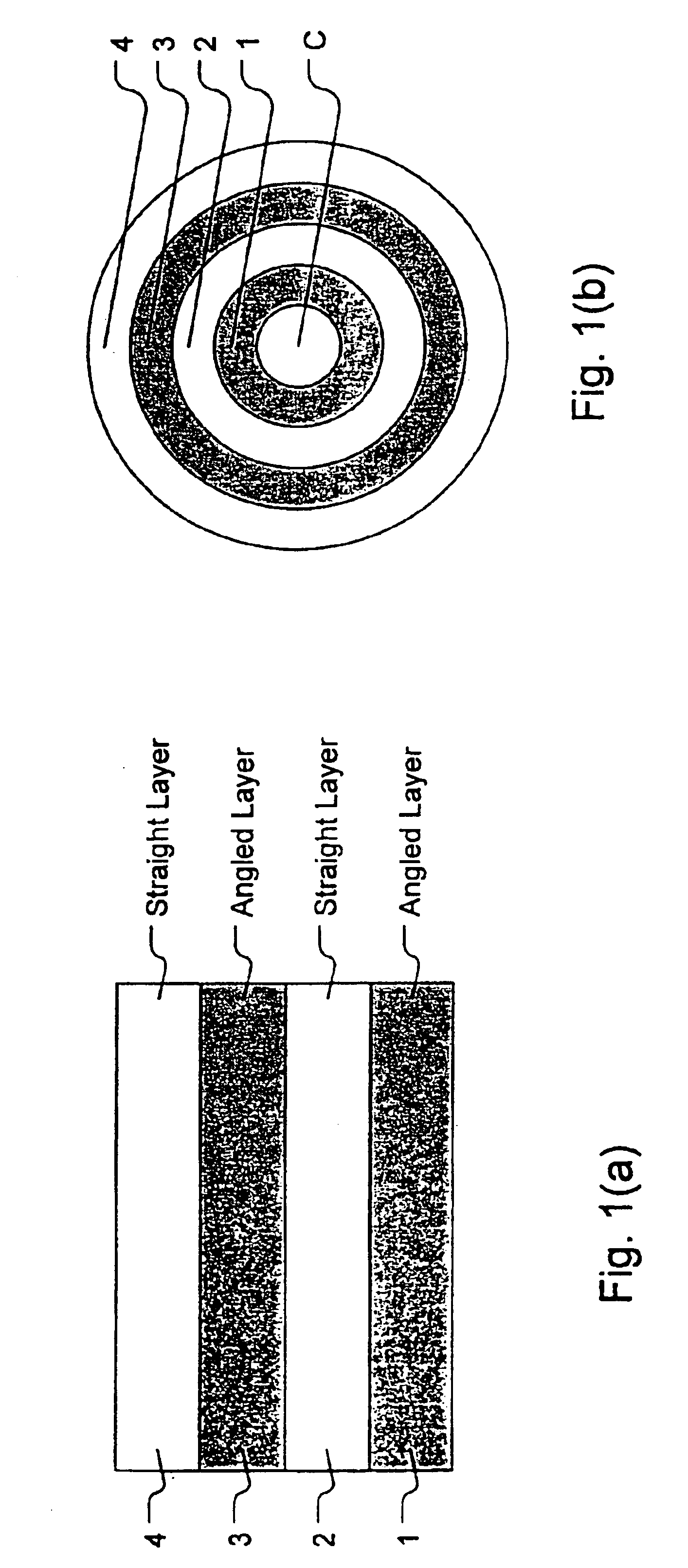
A golf club shaft is 35-50 percent lighter than a conventional shaft while maintaining the outer diameter and structural characteristics of conventional shafts. The shaft has at least four layers of fiber reinforced material. The fiber reinforced layers are from innermost to outermost: a first angled layer; a first straight layer; a second angled layer; and a second straight layer. The angled layers are formed by bonding together two materials, each with fibers aligned in different directions. The second angled layer maintains the proper strength and rigidity of the shaft while keeping the shaft as light weight as possible. Aligning the second layer's fibers at an angle of 35-75 degrees with respect to the longitudinal direction of the shaft ensures proper weight and strength characteristics of the shaft. The resulting shaft is light-weight and exhibits the flexural rigidity, flexural strength, torsional rigidity, torsional strength, and crushing strength of conventional shafts.
Owner:MITSUBISHI RAYON CO LTD
Ultra high torque double shoulder tool joint
InactiveCN1261948AIncrease the cross-sectional areaWide front section with large cross-sectional areaDrilling rodsDrilling casingsNoseTorsional strength
An ultra high torque double shoulder tool joint for maximizing the torsional strength of a threaded connection by correlating a transverse cross-sectional counter-bore area of the box (12) and pin (10). The pin (10) includes a base section (74) and a nose section (24). The nose section (24) defines a cross-sectional nose area (28). The pin external threads (22) include a taper no greater than 1 / 12. The box (12) include a cross-sectional counterbore area (46) and a cross-sectional box area (52). The overall strength of the tool joint is dependent upon the torsional strength of the threaded connection, the cross-sectional nose area (28) and the cross-sectional counter-bore area (46).
Owner:GRANT PRIDECO LP
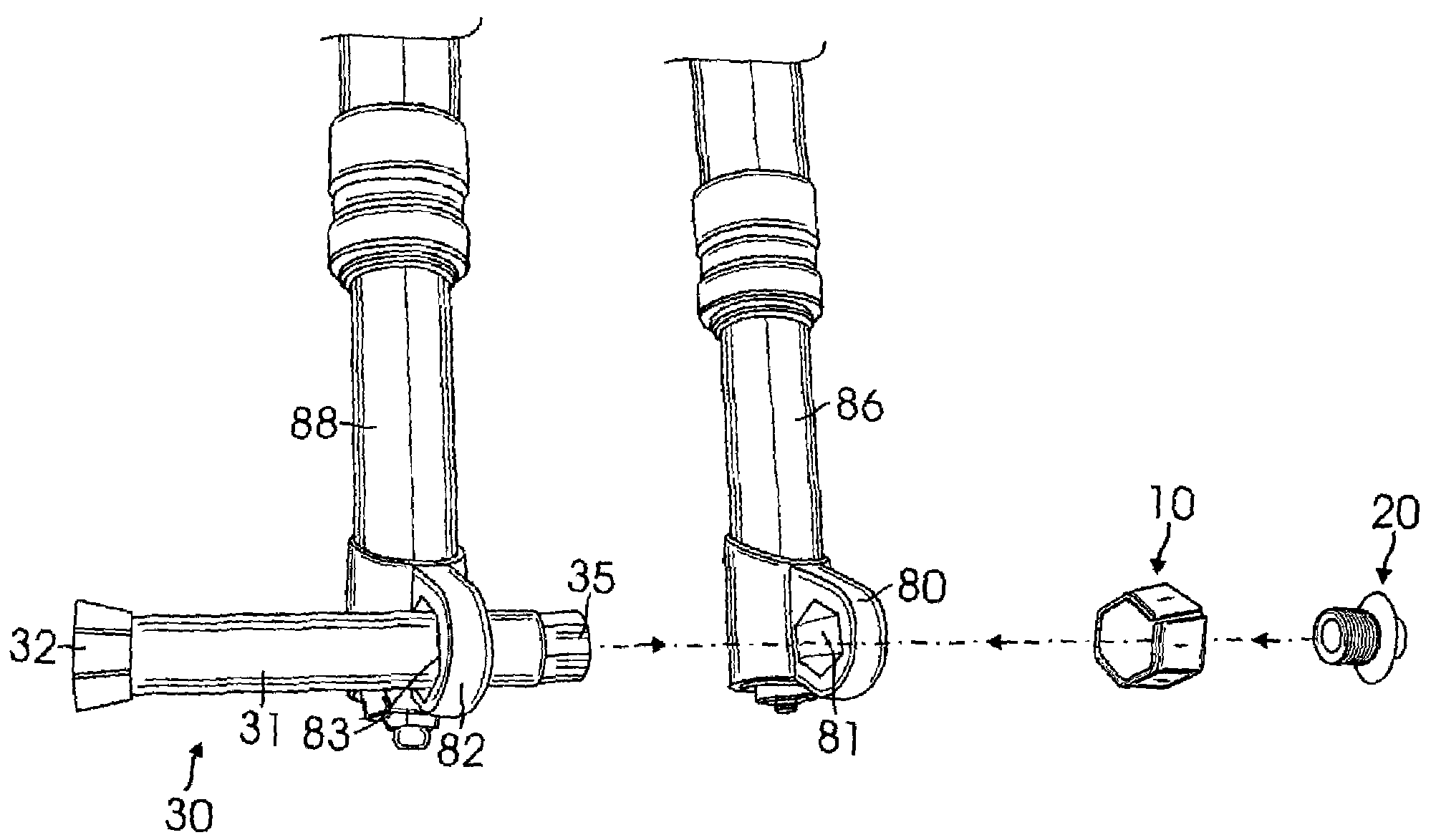
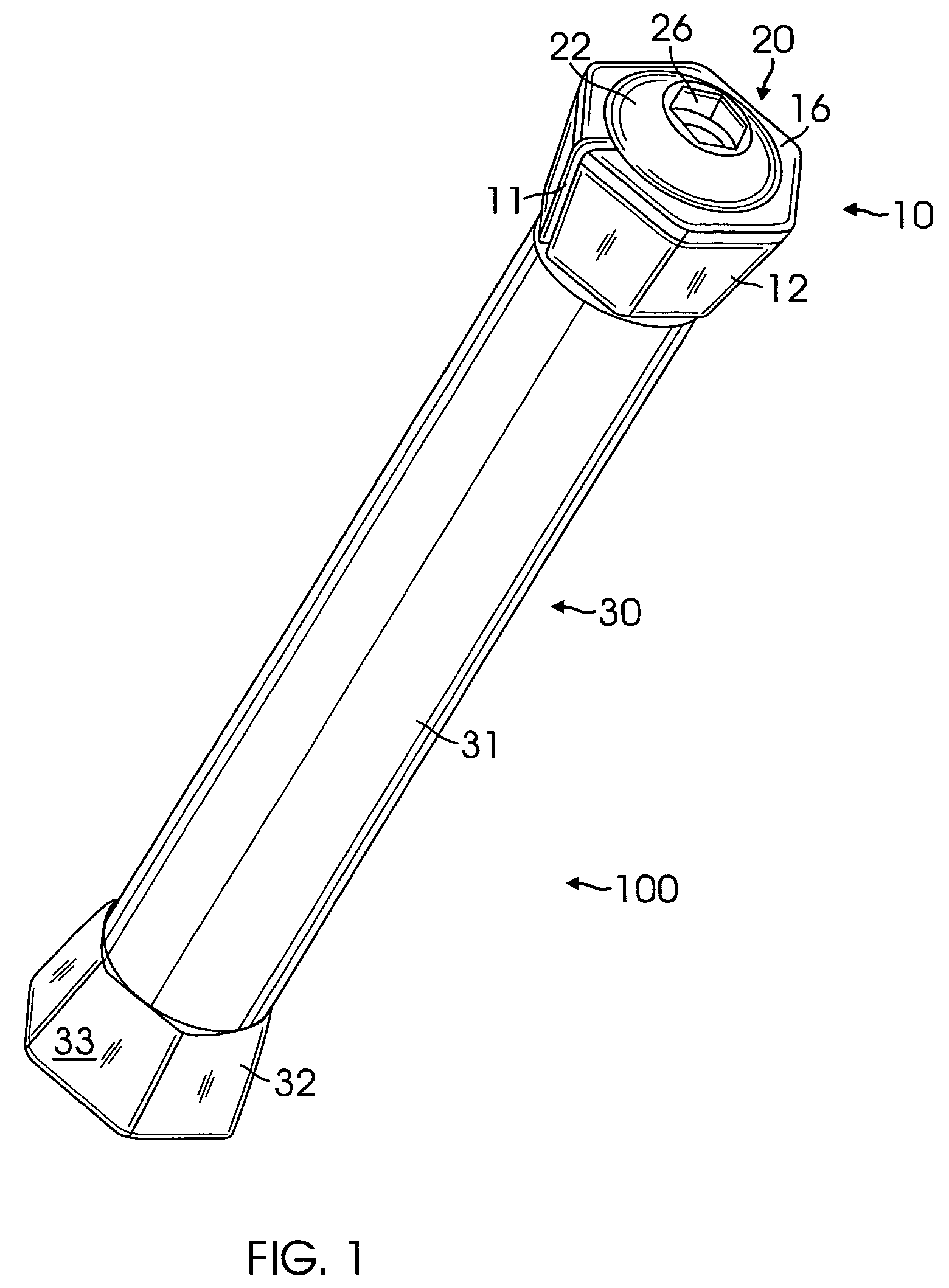
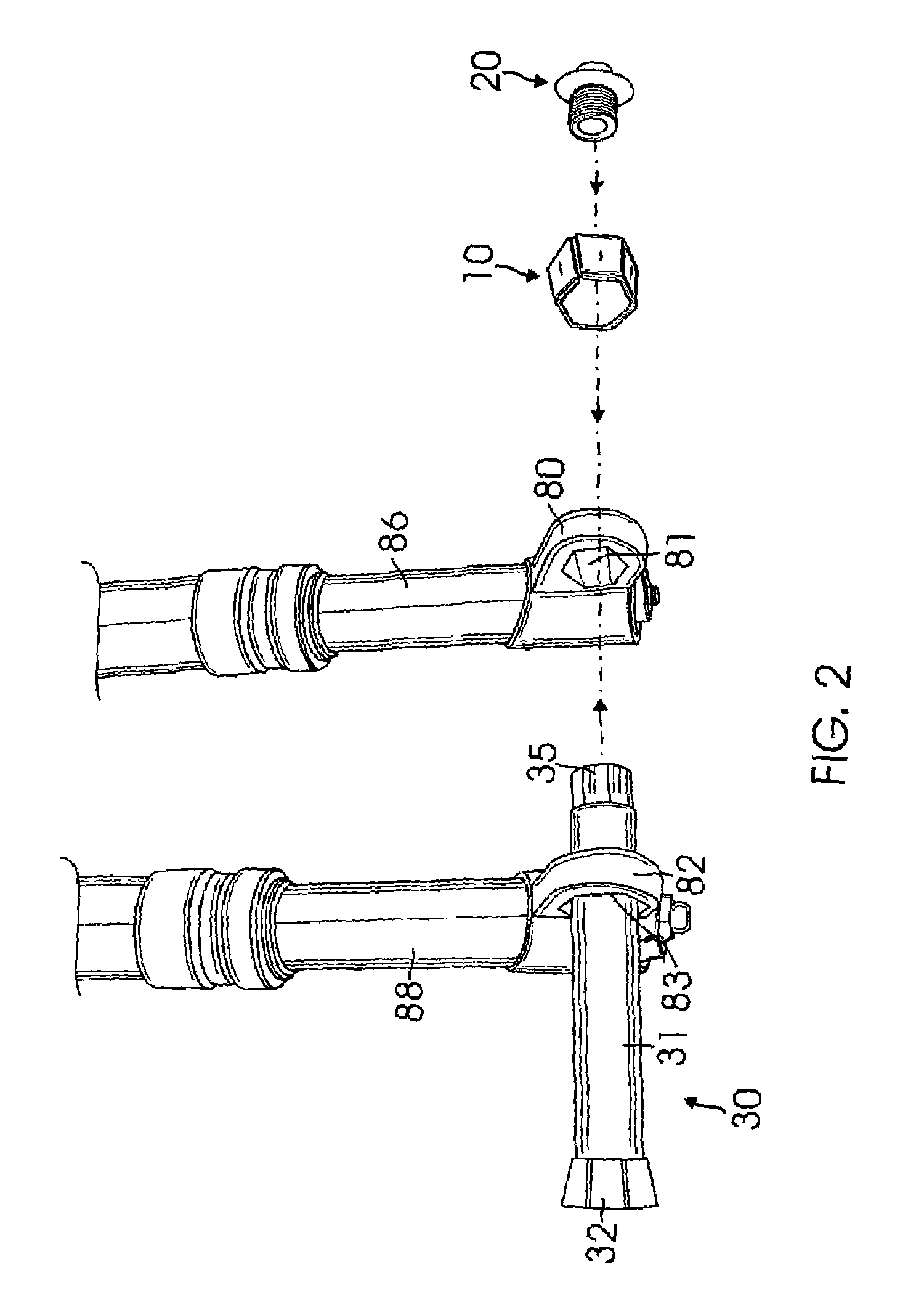
Axle with non-round tapered ends affixed into fork leg dropouts with openings that match the axle ends for a bicycle fork
ActiveUS20080116658A1Increased torsional strengthFacilitate easeWheel based transmissionFrictional rollers based transmissionEngineeringTorsional strength
The present invention relates to a bicycle fork comprising an improved axle with non-round tapered ends affixed into dropouts with openings to match the axle ends through a taper-lock affixation for improving the torsional strength of the fork and facilitate ease of the axle installation. The improved axle consists of a first non-round end with interior female threads connecting an intermediate cylindrical portion which connects to a second non-round tapered end. An improved tapered split non-round nut having a cylindrical bolt possessing male threads lock the nut to the first end of the axle, wherein said bolt has an another preferred embodiment which connects a rotatable handle for ease of the axle installation.
Owner:HAYES BICYCLE GROUP
Flexible drill bit and angled drill guide for use with the same
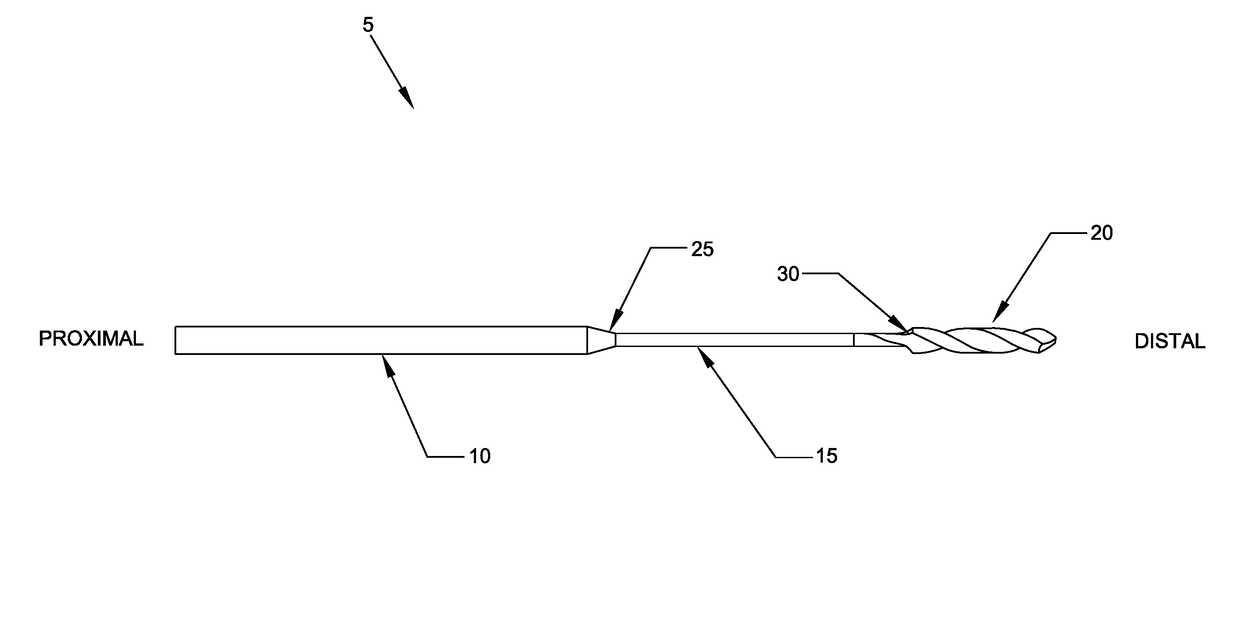
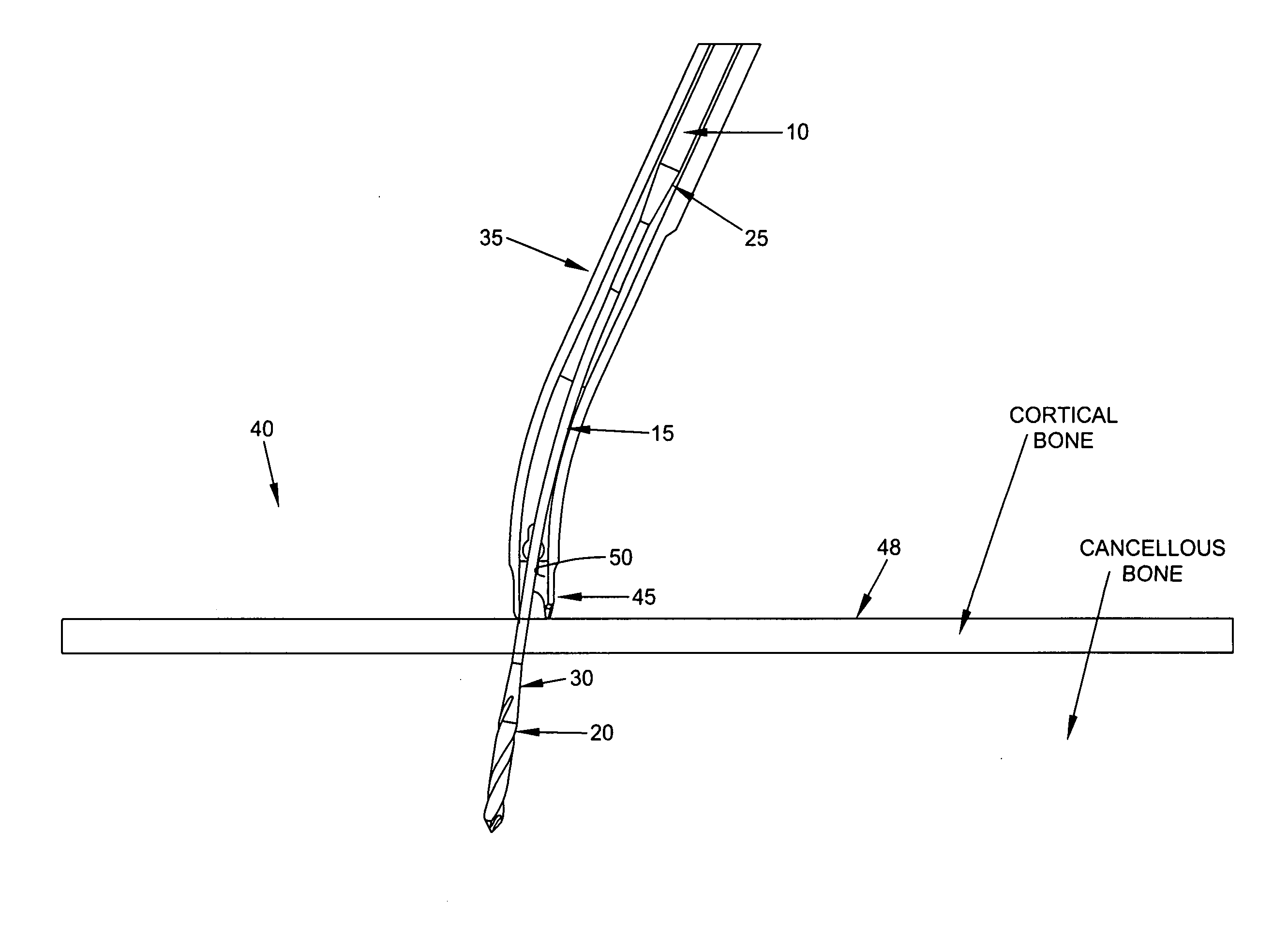
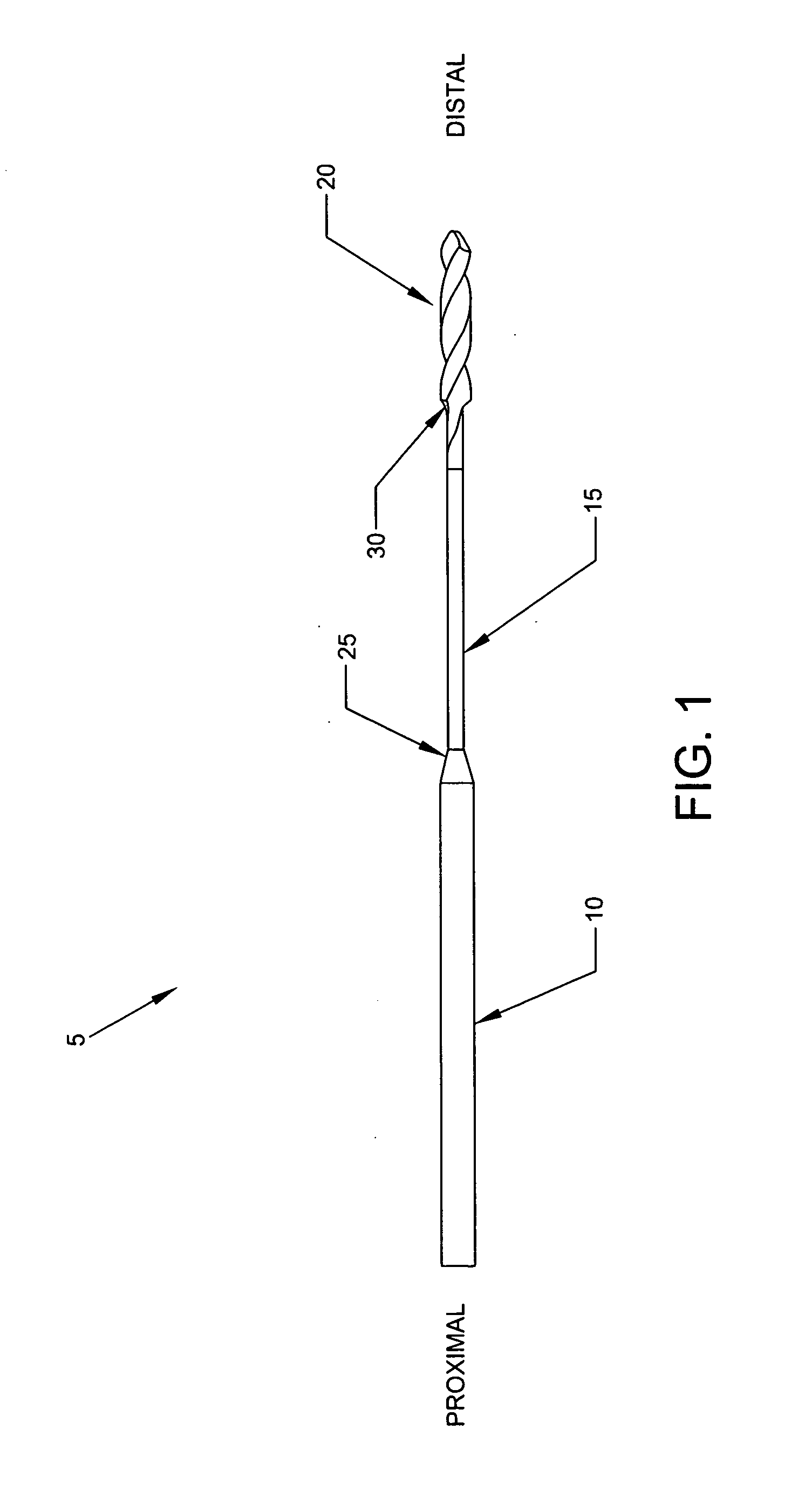
ActiveUS10022131B1Solve the lack of flexibilityIncreased torsional strengthBone drill guidesEngineeringStructural engineering
A flexible drill bit comprising: a proximal shaft portion for connecting to a source of turning; a distal cutting tip portion for boring into a material; and an intermediate shaft portion extending between the proximal shaft portion and the distal cutting tip portion, the intermediate shaft portion being characterized by (i) sufficient longitudinal flexibility so as to permit the flexible drill bit to be passed along a curve, and (ii) sufficient torsional strength to permit the flexible drill bit to bore into the material. Apparatus for drilling a hole in material, the apparatus comprising: an angled drill guide comprising a curved distal section, a less-curved proximal section, and a lumen extending therebetween, wherein the less-curved proximal section comprises a flat extending therealong for reducing the effective diameter of the less-curved proximal section so as to minimize interference between the angled drill guide and the side wall of an access cannula.
Owner:STRYKER PUERTO RICO LLC
Large-axle-load railway vehicle bogie
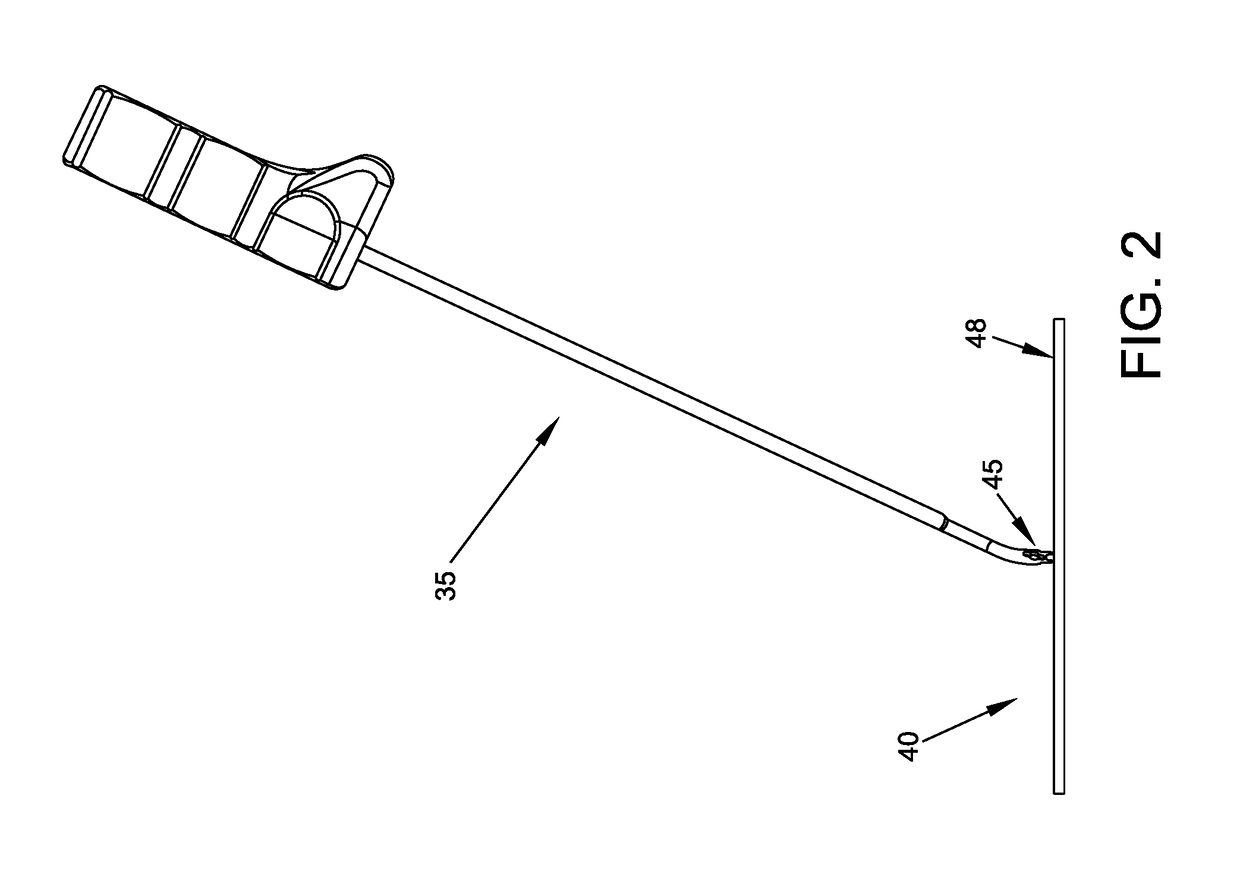
ActiveCN103625493AImprove flexural strengthIncreased torsional strengthBogiesBogie-underframe connectionsBogieAir spring
The invention relates to a large-axle-load railway vehicle bogie which comprises a framework. The framework is composed of side beams, a cross beam, an auxiliary beam, two wheel pairs, a primary suspension device, a secondary suspension, a traction device, a foundation brake device, a traction motor and a gearbox. The primary suspension device is composed of a steel spring and a rotating arm shaft box, and the rotating arm shaft box is connected with the framework through the steel spring. The wheel pairs comprise wheel shafts and wheels fixed at the two ends of each wheel shaft, and the wheel shafts are connected with the rotating arm shaft box. The secondary suspension device comprises an air spring, a side-rolling preventing torsion bar and a height control device which all are arranged on the framework. The height of side beam vertical plates and the outer radius and the thickness of the cross beam are increased, the overall bending strength and the torsional strength of the bogie are greatly improved, the load bearing ability of a motor lifting seat and a gearbox lifting seat is greatly improved, the vertical load bearing ability of the side beams is greatly improved, and 17 tons of axle load can be met.
Owner:CRRC QINGDAO SIFANG CO LTD
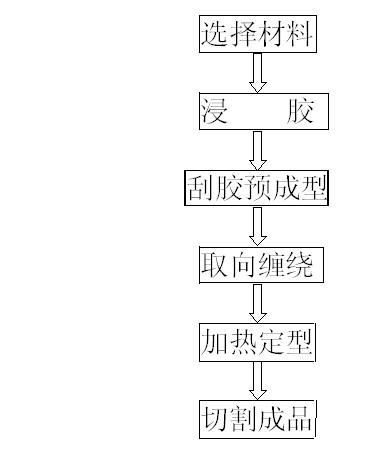
Production process of large-calibre epoxy glass fiber and braided strap winding extrusion draw pipe
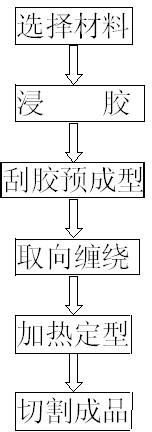
The invention discloses a production process of a large-calibre epoxy glass fiber and braided strap winding extrusion draw pipe, comprising the following steps of: (1) selecting materials: selecting glass fiber filaments, epoxy resins and glass fiber braided straps as materials, and carrying out orientation distribution on the glass fiber braided straps; (2) dipping glue; (3) scraping the glue for performing; (4) carrying out orientation winding; (5) carrying out heat forming; and (6) cutting into finished products. In the invention, the outer diameter of a produced epoxy glass fiber extrusion draw pipe produced by the production process disclosed by the invention is 10-1000 mm, and therefore, cracking phenomenon is prevented from being generated in the extruding and drawing process of anextrusion draw pipe with a diameter larger than 30 mm in the traditional process and the production of the epoxy glass fiber extrusion draw pipe with the diameter larger than 30 mm becomes real; the production process is simple to operate, greatly enhances the torsional strength and the split strength of the extrusion draw pipe and reduces the operational risks of enterprises; in addition, a product produced by the process meets the requirements on design and quality, effectively enlarges the application range of the epoxy glass fiber extrusion draw pipe and is one of significant innovations of the production process of the large-calibre epoxy glass fiber and braided strap winding extrusion draw pipes throughout history.
Owner:盐城市强力电工绝缘材料厂(有限合伙)
Plastic pipe adhesive joint
InactiveUS7237810B2High strengthFluid pressure sealed jointsJoints with sealing surfacesThreaded pipeFull Relative
A method of joining two pipe ends, by forming male threads on an end of a first pipe with a steep taper angle, forming matching female threads on an end of a second pipe, and applying adhesive material to the threads before twisting the pipes to fully engage the male and female threads, thereby spreading the adhesive material across adjacent load-bearing surfaces of the threads. The threads have multiple start locations for thread engagement so that the pipe ends may be twisted to achieve full engagement in less than one full relative rotation. The male and female threads are formed with a squeeze angle between matching surfaces of the threads between 0.5 and 5.0 degrees. The finished joint provides immediate leak-tightness, and immediate tensile, compressive and torsional strength and does not protrude outside of the pipe profile. The technique may also be used to join pipes constructed of dissimilar materials, particularly by using a coupler that has the appropriate threading, and securing the coupler to a non-threaded pipe end using any convenient means, such as a mechanical fit, or fusion bonding.
Owner:HOLLINGSWORTH ELMONT E +1
Cylinder lock having improved torsional strength
A cylinder lock includes a latch retractor housing having inner and outer cover plates, inner and outer drive spindles extending respectively through the inner and outer cover plates, a sleeve surrounding the outer drive spindle and having a flange contacting the outer cover plate, an outer shell surrounding the inner drive spindle and the latch retractor housing, and at least one rigid coupling member or tube disposed within the outer shell and engaging and coupling together the inner and outer cover plates and the flange, thereby reinforcing the outer drive spindle and the latch retractor housing and increasing torsional and compression strengths thereof. A reinforcing ring is further provided to couple the outer drive spindle to the outer handle for reinforcement.
Owner:TLHM CO LTD
Device for testing static torsional strength and vibration strength of transmission assembly
The invention discloses a device for testing the static torsional strength and vibration strength of a transmission assembly. The device comprises a test bed and a slide block, wherein a loading mechanism on the slide block comprises a loading motor, and a half shaft which is connected to the output end of the loading motor through a transmission mechanism; the test bed is provided with a supporting mechanism consisting of a suspension fixing device and a controllable upward and downward stretching device; a transmission and an engine are fixed through a suspension point, so that the static torsional strength of a transmission shell can be inspected; and moreover, an entire power assembly is lifted to a specified height and returned quickly by using the upward and downward stretching device, so that instantaneous impact caused by gravity is generated for simulating the bumpy road condition of an entire vehicle, the suspension position strength of the transmission is tested, and the test result is closer to the practical road condition of the entire vehicle. The device has a simple and compact structure, is easy to install, and is suitable to be taken as a testing device for performing static torsional vibration test on the transmission shell of an automobile engine; and the installation space is saved, and the testing accuracy of the transmission is increased.
Owner:BAODING WEIYI AUTOMOBILE CO LTD
Flexible drill bit
ActiveUS20130261628A1Increased torsional strengthSolve the lack of flexibilityBone drill guidesEngineeringTorsional strength
A flexible drill bit comprising:a proximal shaft portion for connecting to a source of turning;a distal cutting tip portion for boring into a material; andan intermediate shaft portion extending between the proximal shaft portion and the distal cutting tip portion, the intermediate shaft portion being characterized by (i) sufficient longitudinal flexibility so as to permit the flexible drill bit to be passed along a curve, and (ii) sufficient torsional strength to permit the flexible drill bit to bore into the material.
Owner:STRYKER PUERTO RICO LLC
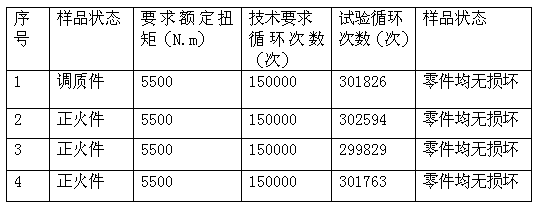
Freestyle scooter
Owner:STEINBACH ROBERT
Opto-electronic combined trailing cable used for hydrophone system
ActiveCN104851512ASmall sizeHigh densityPlastic/resin/waxes insulatorsCommunication cablesHydrophoneTorsional strength
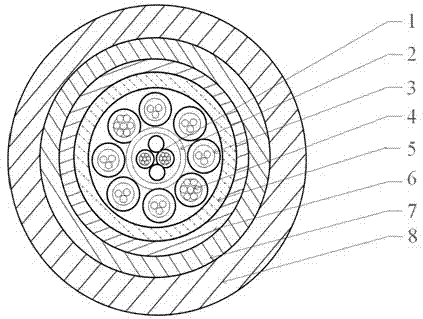
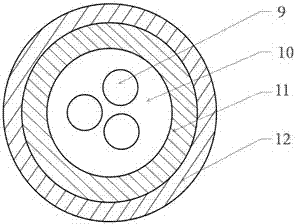
The invention relates to an opto-electronic combined trailing cable used for a hydrophone system. The cable comprises a shielding signal line, power lines, optical units, and an outer sheath. The cable is characterized in that the shielding signal line is on the center of the cable, the power lines and the optical units are stranded around the shielding signal line to form a cable core, a nonmetal reinforcing element wraps out of the cable core, and the outer sheath wraps the nonmetal reinforcing element. Low-density or medium-density polyethylene is used in the cable to ensure the density of the opto-electronic combined trailing cable slightly larger than density of seawater, and by using seawater buoyancy, energy source loss in the hydrophone system is reduced. Optical fibers are high-strength anti-bending single-mode fibers, and torque balance is realized in the cable structure and technology, and transmission loss of the optical fibers is controlled, so as to ensure reliability of optical signal transmission and obtain better detection effect. The opto-electronic combined trailing cable is high in tensile and torsional strength, and flexibility of the optical fiber is ensured, and the cable has good transmission stability and reliability.
Owner:YANGTZE OPTICAL FIBRE & CABLE CO LTD
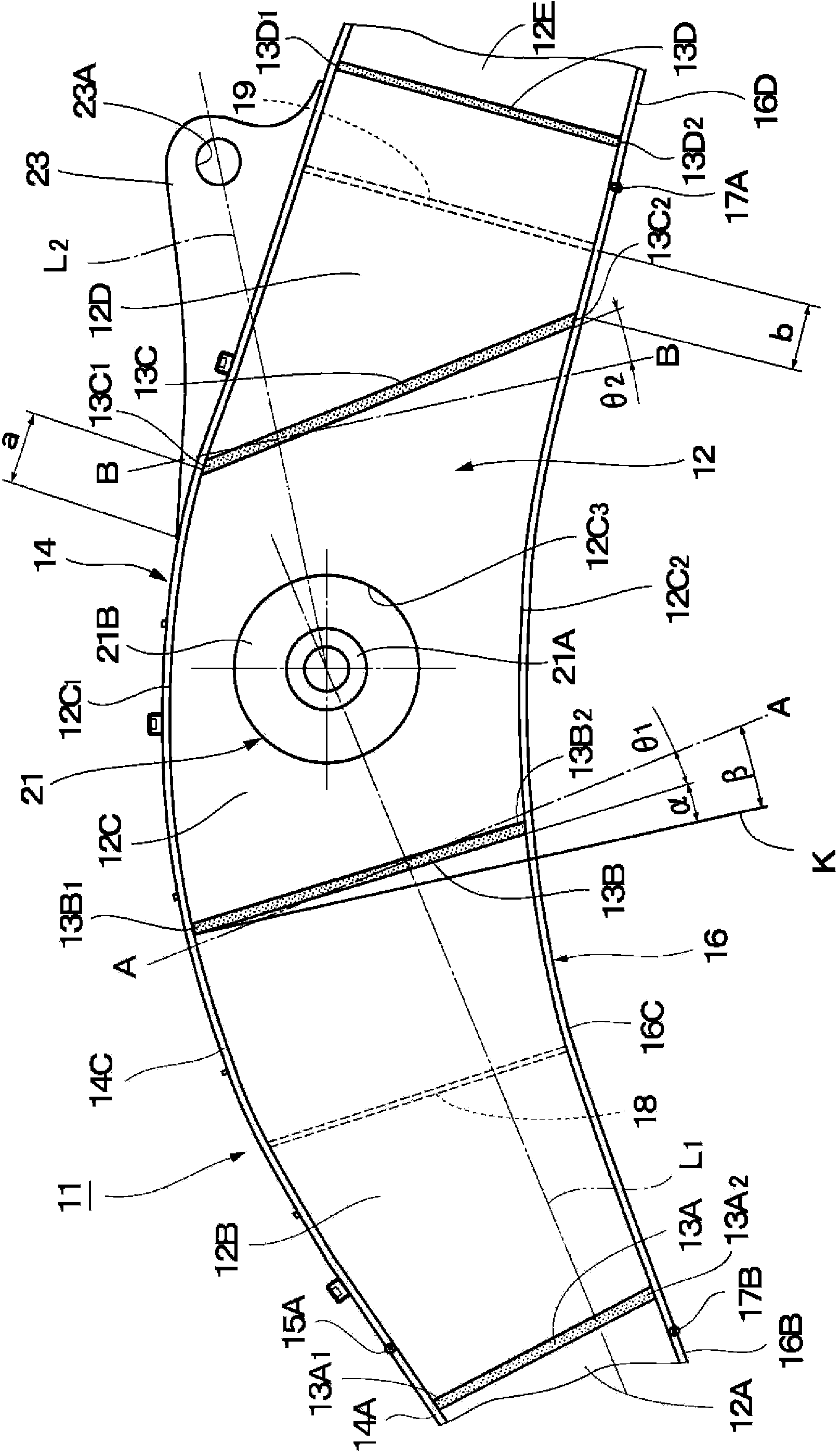
Boom for construction machine
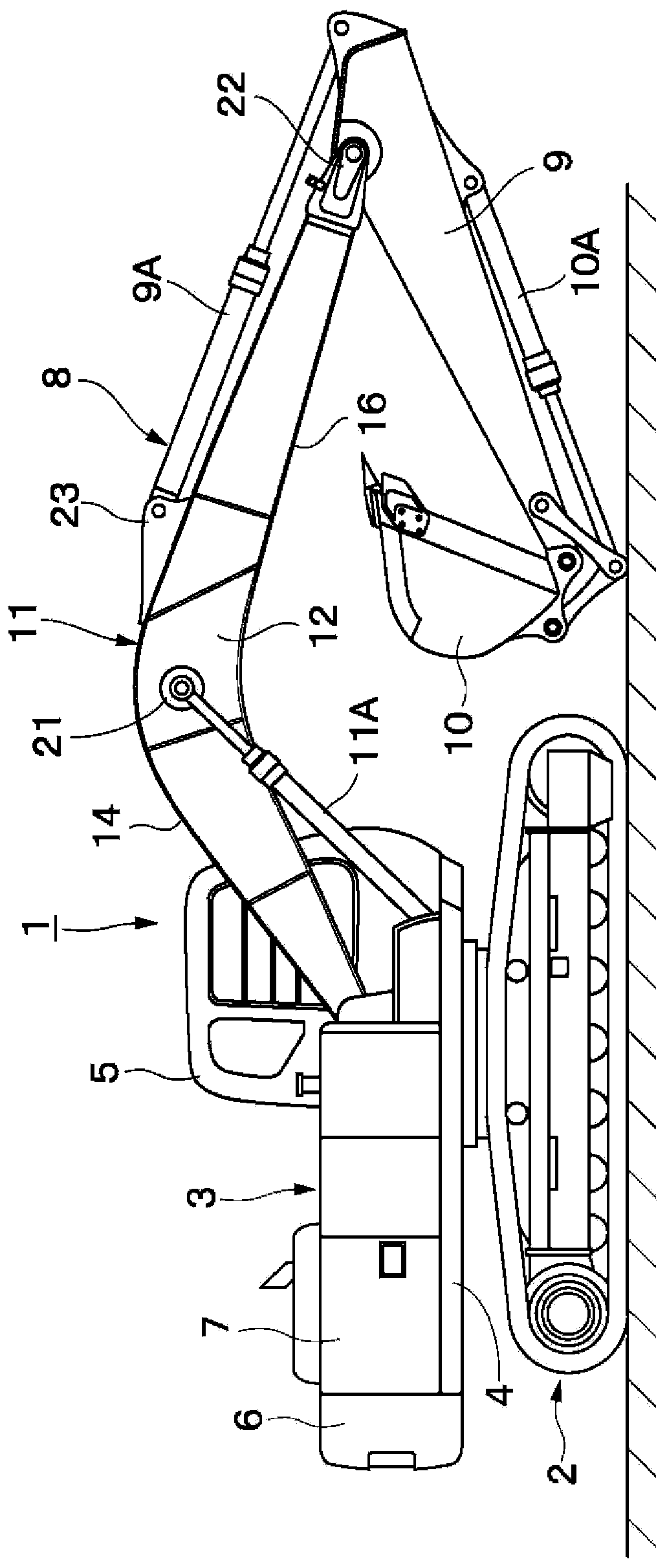
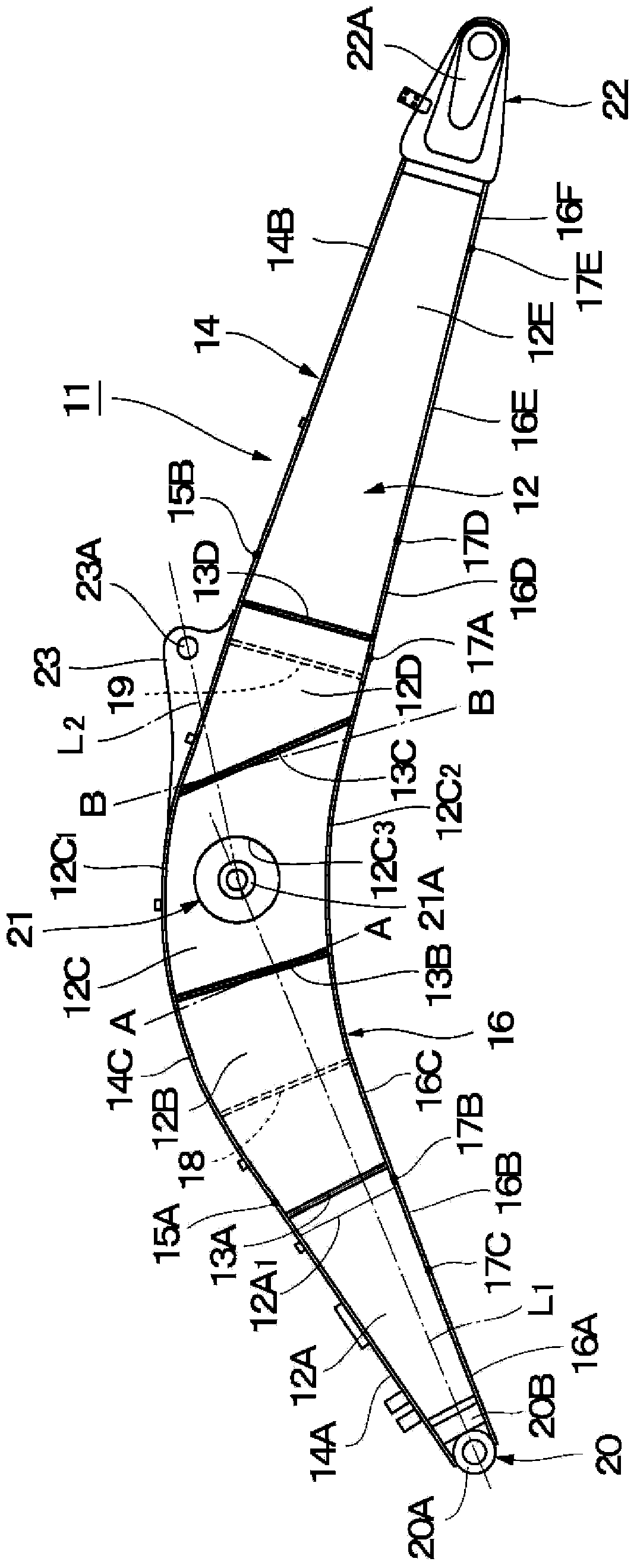
InactiveCN103403263AImprove welding strengthMechanical machines/dredgersFlexural strengthTorsional strength
Left and right web plates (12) of a boom (11) are each formed by joining first to fifth web materials (12A-12E) at the ends thereof in the front-back direction along weld lines (13A-13D). An upper flange plate (14) is formed by joining a back upper flange material (14A), a front upper flange material (14B), and an intermediate upper flange material (14C) at the ends thereof in the front-back direction along weld lines (15A, 15B). A lower flange plate (16) is formed by joining first to sixth lower flange materials (16A-16F) at the ends thereof in the front-back direction along weld lines (17A-17E). The weld lines (13A-13D) of the left and right web plates (12), and the weld lines (15A, 15B) of the upper flange plate (14) and the weld lines (17A-17E) of the lower flange plate (16) are disposed at different positions from each other in the front-back direction. Consequently, weight reduction can be achieved by reducing the overall weight while the bending strength, torsional strength, and the like of the boom (11) are ensured.
Owner:NIHON KENKI CO LTD
Novel earthquake damage control system for thin-wall hollow pier
InactiveCN104674649AReduce residual displacementReduce widthBridge structural detailsBridge erection/assemblyPre stressTorsional strength
The invention discloses a novel earthquake damage control system for a thin-wall hollow pier. The novel earthquake damage control system comprises a pier base, a thin-wall hollow pier, high-tenacity fiber-enhanced cement-based composite material expanded sections, an unbonded prestressed tendon and steel energy consumption elements, wherein the thin-wall hollow pier is arranged on the upper end surface of the pier base, so that the torsional strength and the energy-dissipating capacity of the thin-wall pier are improved. The high-tenacity fiber-enhanced cement-based composite material expanded sections are arranged on the inner side and the outer side of the lower part of thin-wall hollow pier; a series of steel energy consumption elements are arranged in the thin-wall hollow pier along the pier height; the lower part of the unbonded prestressed tendon is anchored on the pier base; and the upper part of the unbonded prestressed tendon is anchored at the center of the first steel energy consumption element from bottom to top. By virtue of the unbonded prestressed tendon, the self-resetting capacity of the pier after the earthquake is provided; and the crack width of the pier after the earthquake is reduced. By virtue of the high-tenacity fiber-enhanced cement-based composite material expanded sections, the axis-compression ratio of the bottom section of the thin-wall hollow pier is reduced; the shear-bearing capacity and the anti-bending capacity of the thin-wall hollow pier are increased; and the steel energy consumption elements can be arranged as rapid exchange components, so that the repairability after the earthquake is increased.
Owner:DALIAN MARITIME UNIVERSITY
Locking screw driver with increased torsional strength
InactiveUS20110245839A1Increased torsional strengthMetal working apparatusProsthesisEngineeringTorsional strength
An orthopedic tool for implanting a bone screw and a method of manufacturing the same. The orthopedic tool includes a head that is shaped to lock onto the bone screw and that has improved torsional strength.
Owner:ZIMMER INC
One-section type composite material vehicle transmission shaft preparation method
ActiveCN104985829ARaise the natural frequencyMeet the lengthCoatingsAgricultural engineeringShaft length
The present invention discloses a one-section type composite material vehicle transmission shaft preparation method, wherein the vehicle transmission shaft comprises a cross type universal joint and a cage type universal joint, the cross type universal joint and the cage type universal joint are respectively connected with both ends of a composite material pipe having inner threads, the cross type universal joint is connected with a vehicle power system, the cage type universal joint is connected with a rear bridge system by using a flange form, the composite material pipe is prepared through an outer thread mold provided with a spiral groove, and the cross type universal joint and the cage type universal joint are connected on both ends of the composite material pipe to prepare the vehicle transmission shaft. According to the present invention, the advantage that the natural frequency of the composite material-made transmission shaft is higher than the natural frequency of the steel-made transmission shaft is completely provided, and the composite material transmission shaft has characteristics of extremely high fatigue resistance, extremely high static torsional strength and the like, can meet the requirements of the vehicles on the transmission shaft length and angle changing during the movement process, and can be applied in passenger vehicles, trucks, commercial vehicles, sport utility vehicles, and other fore-laying rear-drive vehicles.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUAYU NEW MATERIAL TECH CO LTD
Thermal treatment method of spline shaft head of transmission shaft
ActiveCN103215428ADeepen the depthHigh surface hardnessFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesHeating timeDrive shaft
The invention discloses a thermal treatment method of a spline shaft head of a transmission shaft. The method is characterized by sequentially comprising a normalizing process and a medium-frequency induction quenching process, wherein the normalizing process sequentially comprises two steps of: (I) heating the spline shaft head by a push disc-type heating furnace, wherein the heating temperature is 850+ / -10 DEG C, and the heating time is 120 minutes; and (II) performing air cooling for 2-3 hours; the medium-frequency induction quenching process comprises two steps of: (I) quenching, wherein the surface quenching area of the spline shaft head comprises a spline part and a full-oil seal table part, and the depth of the hardening layer is 4-6mm; and (II) low-temperature tempering. Compared with the same kind of hardening and tempering and medium-frequency induction quenching technology (needing tempering at a high temperature of 680+ / -10 DEG C for 150 minutes), the method disclosed by the invention greatly saves resources on the premise of guaranteeing the static torsional strength and fatigue life of the spline shaft head, reduces the production cost, has positive social significance of low carbon and environmental protection, and remarkably improves the product competitiveness.
Owner:XUCHANG YUANDONG DRIVE SHAFT +1
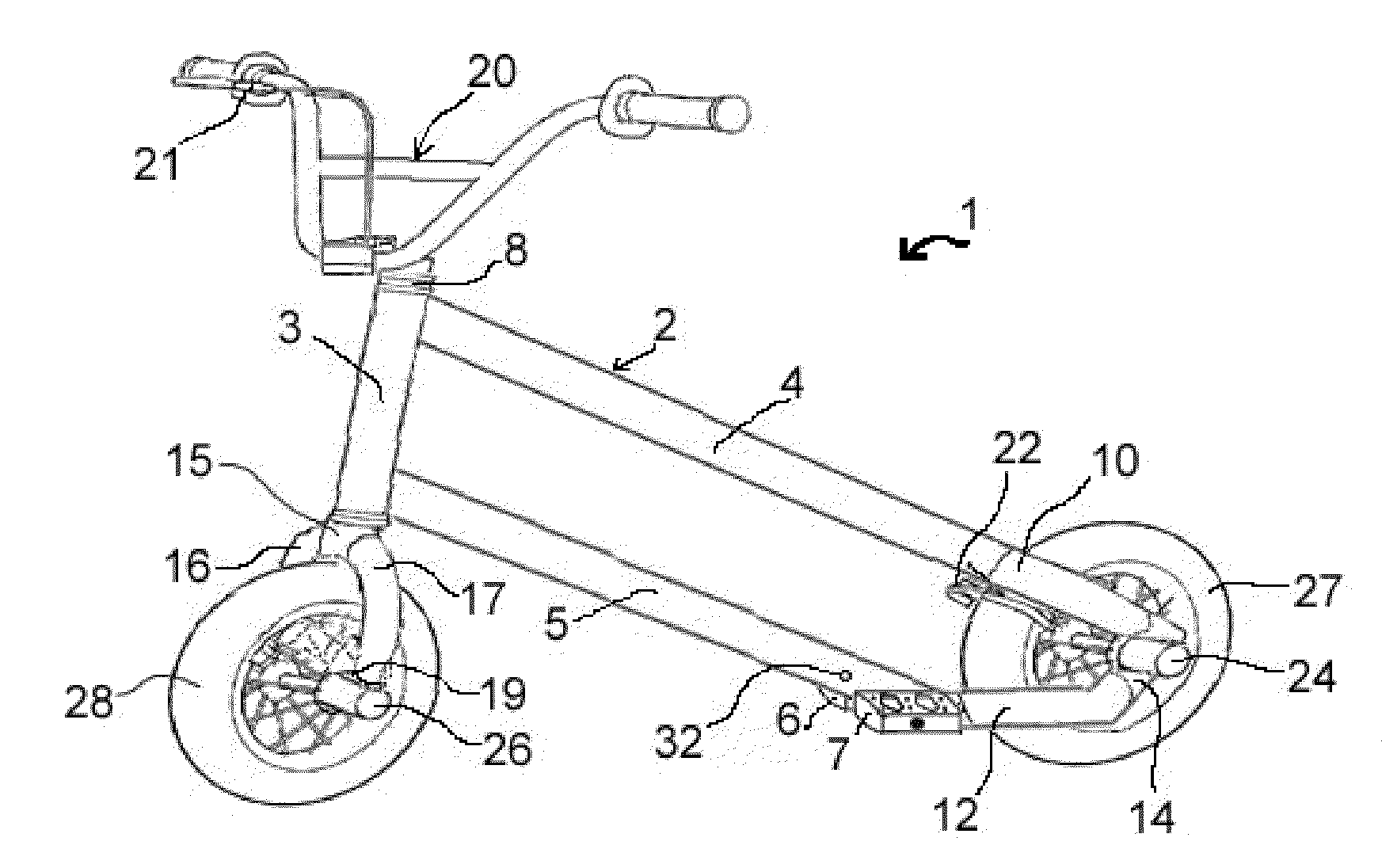
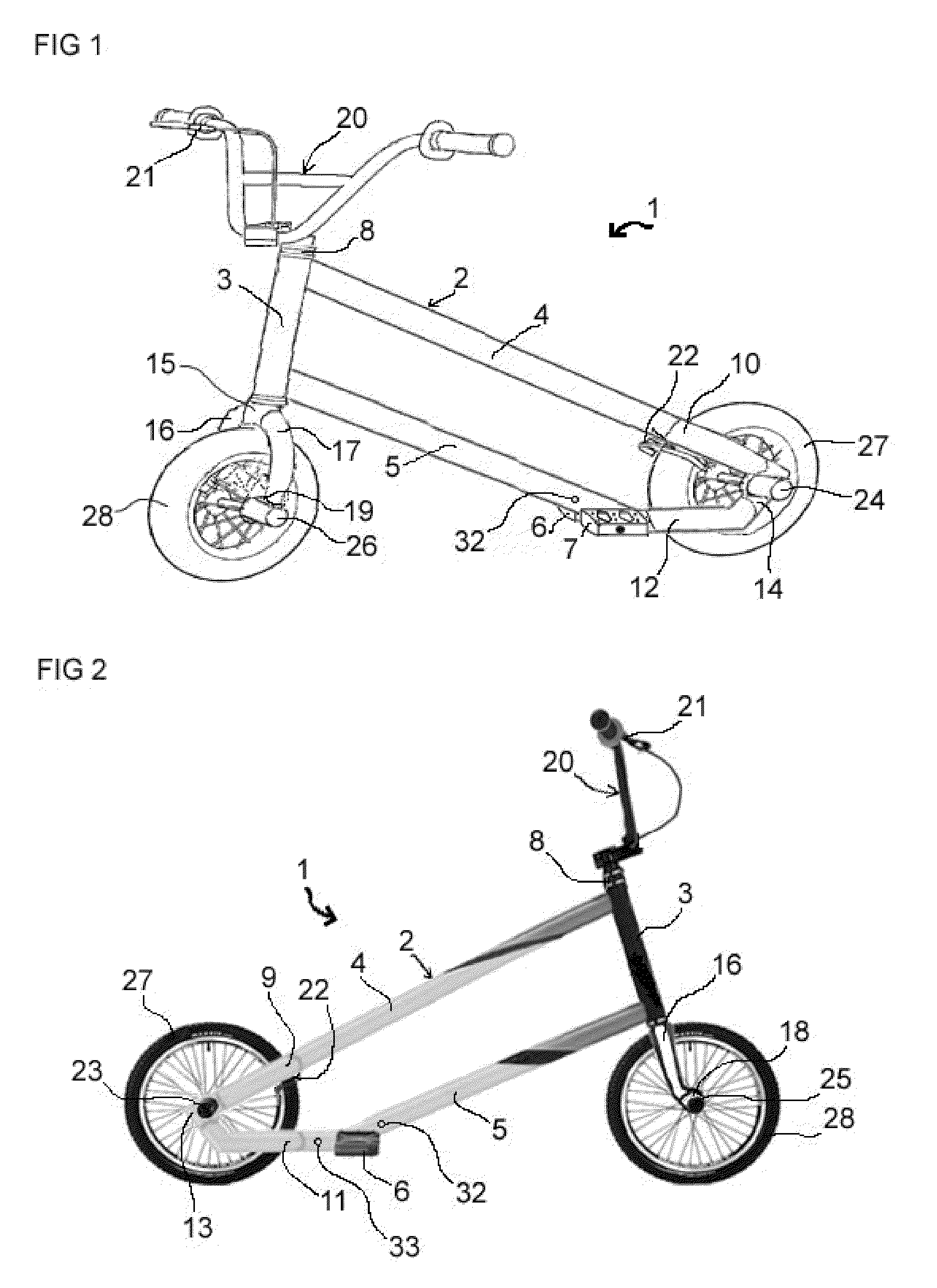
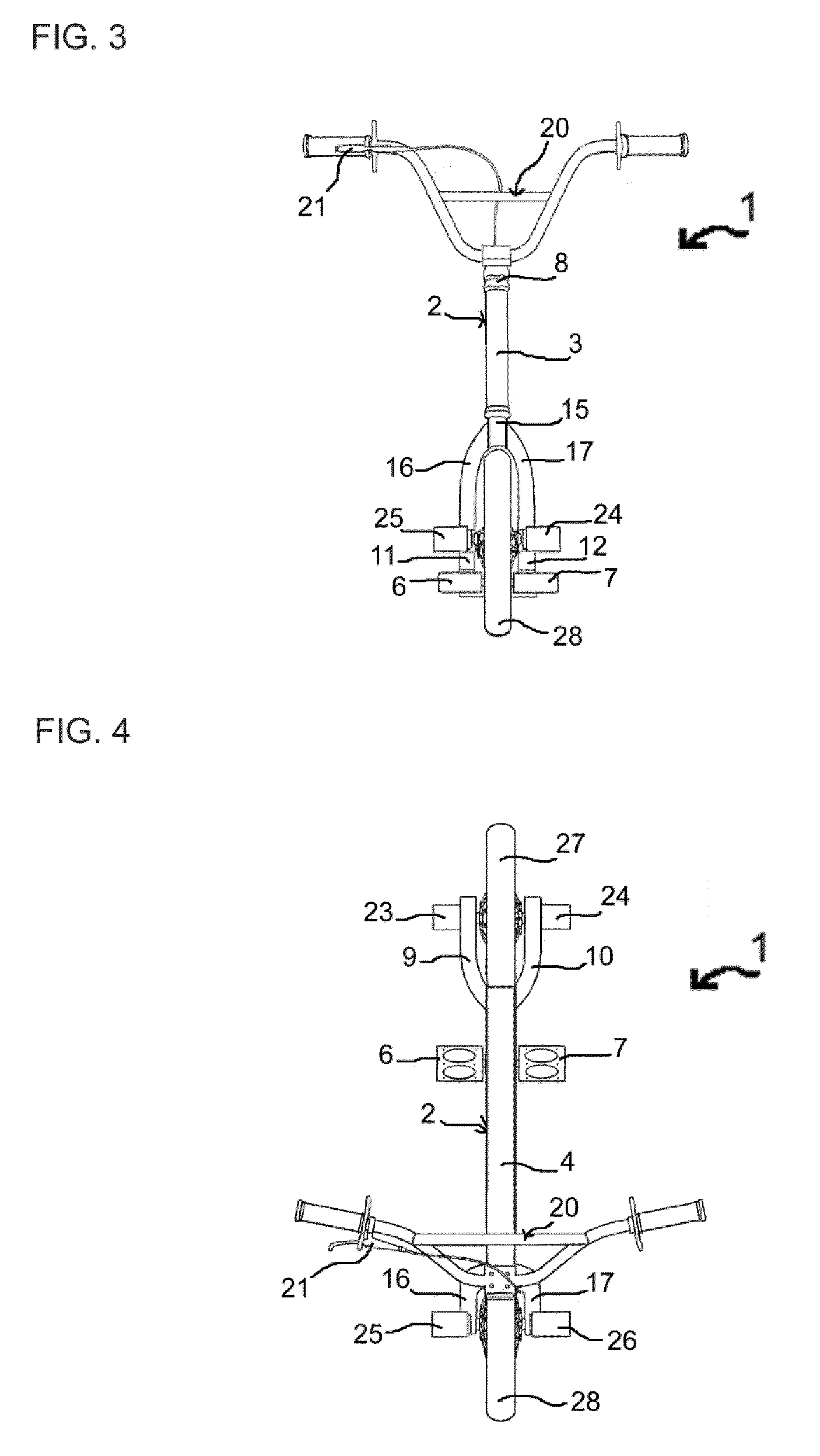
Freestyle Scooter
A scooter is presented which allows the rider to maintain a secure forward facing stance with both feet parallel to the direction of travel and a combined center of gravity of both rider and scooter centrally between the front and rear wheel irrespective of the vertical tilt of the scooter. The scooter comprises a frame with high torsional strength, suitable for attaching an adjustable footrest thereto. The footrest may comprise two pedals, one on each side of the frame, or a footboard sufficiently wide to allow the rider to place both feet parallel to the direction of travel thereon. The longitudinal position of the pedals or footboard may be adjustable by selectively attaching the pedals or footboard to one of two or more attachment features at the frame.
Owner:STEINBACH ROBERT
Shaft lever part for engineering machinery and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN101886158AStrong wear abilityReduce distortionShaftsIncreasing energy efficiencyTorsional strengthHardness
The invention relates to a shaft lever part for engineering machinery, comprising a core, a quench hardening layer and an intermediate layer between the quench hardening layer and the core. The surface hardness of the shaft lever part is not less than 50 HRC; the ratio DS / r of the depth DS of the quench hardening layer to the radius r of a shaft lever is 0.28-0.32; and the proportional relation of the depth DS of the quench hardening layer and the width b of the intermediate layer can be expressed as follows: b=(0.382-0.618)DS. The manufacturing method of the shaft lever part for engineering machinery comprises the procedures of tempering and heat treating, rough turning, surface induction quenching and stress-eliminated tempering. The shaft lever part for engineering machinery has stronggrain wearing resistance. The ratio of the depth DS of the hardening layer to the radius r of the shaft lever is 0.28-0.32. The shaft lever part for engineering machinery has highest value-added ratio of torsional strength, highest cost performance, smallest residual stress and longer service life.
Owner:YANTAI SHOUGANG DONGXING GRP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com