Proximal tibia bone cement pressurizing device
A compression device and bone cement technology, applied in the field of medical devices, can solve the problems of easy early loosening, less bone cement, and bone cement intrusion, etc., and achieve the effect of increasing life expectancy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
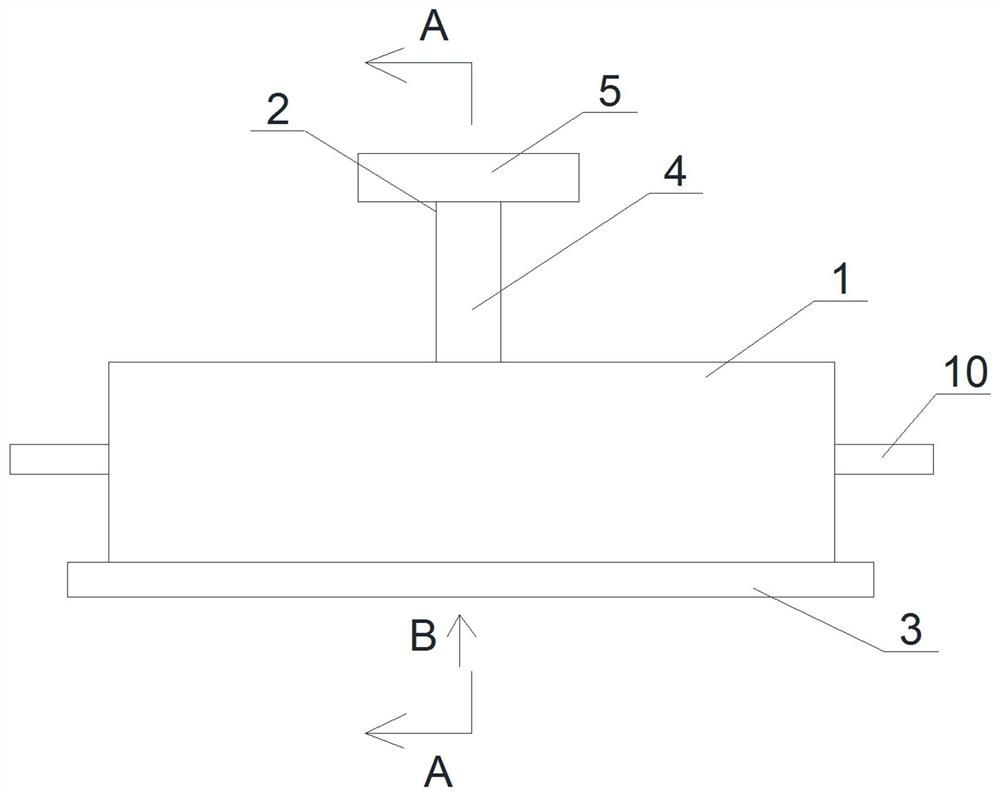
[0030] Such as Figure 1 to Figure 4 As shown, a proximal tibial bone cement pressurization device includes a cylinder body 1, a pressure plate 6 located in the cylinder body 1 and sealingly connected with the cylinder body 1 to move along the length direction of the cylinder body 1, and a pressure plate 6 The top of the cylinder is fixedly connected and the driving mechanism 2 that drives the pressure plate 6 to move in the vertical direction, the baffle 3 located under the cylinder 1 and used to block the bottom of the cylinder 1, the size of the baffle 3 is larger than that of the cylinder 1 Cross-sectional size, the bone cement is located in the cylinder 1 and on the lower surface of the compression plate 6, and the bone cement is pressed into the cancellous bone at the proximal end of the tibia by applying pressure to the compression plate 6. The cylinder 1 is vertically The height in the direction is 20 mm, the wall thickness is 2 mm, the thickness of the compression pla...
Embodiment 2
[0033] Such as Figure 1 to Figure 4As shown, a proximal tibial bone cement pressurization device includes a cylinder body 1, a pressure plate 6 located in the cylinder body 1 and sealingly connected with the cylinder body 1 to move along the length direction of the cylinder body 1, and a pressure plate 6 The top of the cylinder is fixedly connected and the driving mechanism 2 that drives the pressure plate 6 to move in the vertical direction, the baffle 3 located under the cylinder 1 and used to block the bottom of the cylinder 1, the size of the baffle 3 is larger than that of the cylinder 1 Cross-sectional size, the bone cement is located in the cylinder 1 and on the lower surface of the compression plate 6, and the bone cement is pressed into the tibial plateau by applying pressure to the compression plate 6, and the height of the cylinder 1 in the vertical direction is 30mm, the wall thickness is 3mm, the thickness of the compression plate 6 is 10mm, the barrel 1 is made ...
Embodiment 3
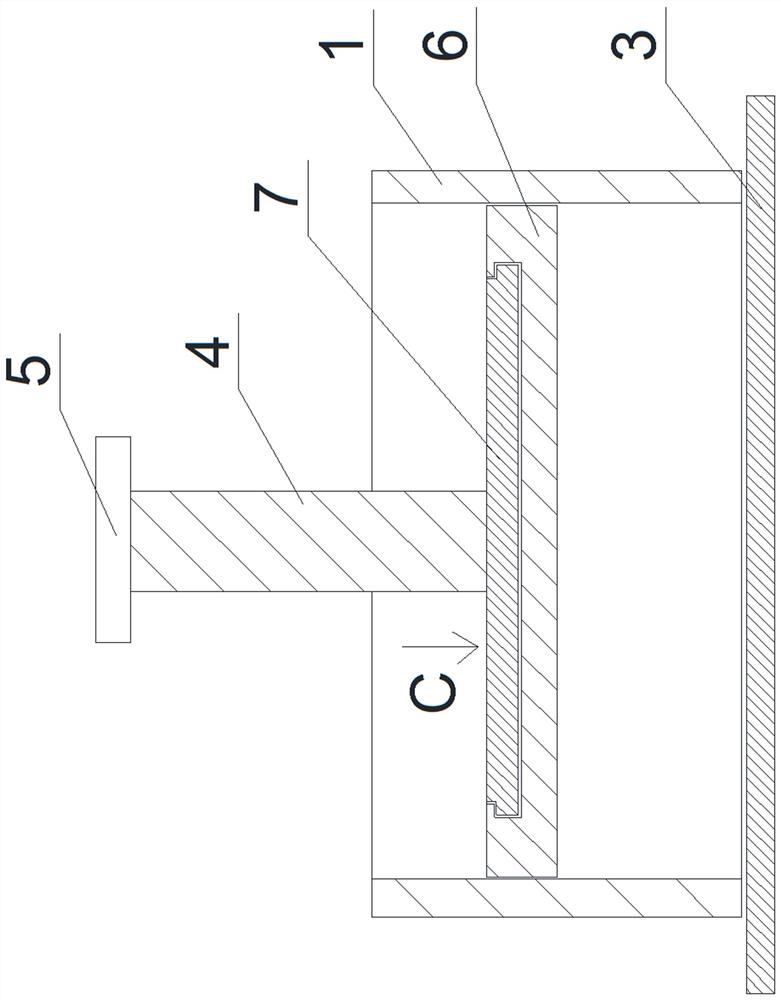
[0037] Such as Figure 9 As shown, the difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is only that: the operating rod 4 is covered with a limiting plate 16, the limiting plate 16 is threadedly connected with the outer surface of the operating rod 4, and the cross-sectional area of the limiting plate 16 is Greater than the cross-sectional area of the cylinder body 1, the limit plate 16 is located on the horizontal plane, and the outer surface of the operating rod 4 is provided with threads and scale values, which is convenient for controlling the amount of bone cement in the cylinder body 1, and the limit plate 16 is in contact with the cylinder body. The top of the body 1 touches to prevent the operation rod 4 from continuing to move downward, thereby controlling the amount of bone cement in the cylinder body 1 entering the spongy bone at the proximal end of the tibia. threaded hole, turn the limit plate 16, the limit plate 16 moves relative to the length direction of...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Height | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Wall thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com