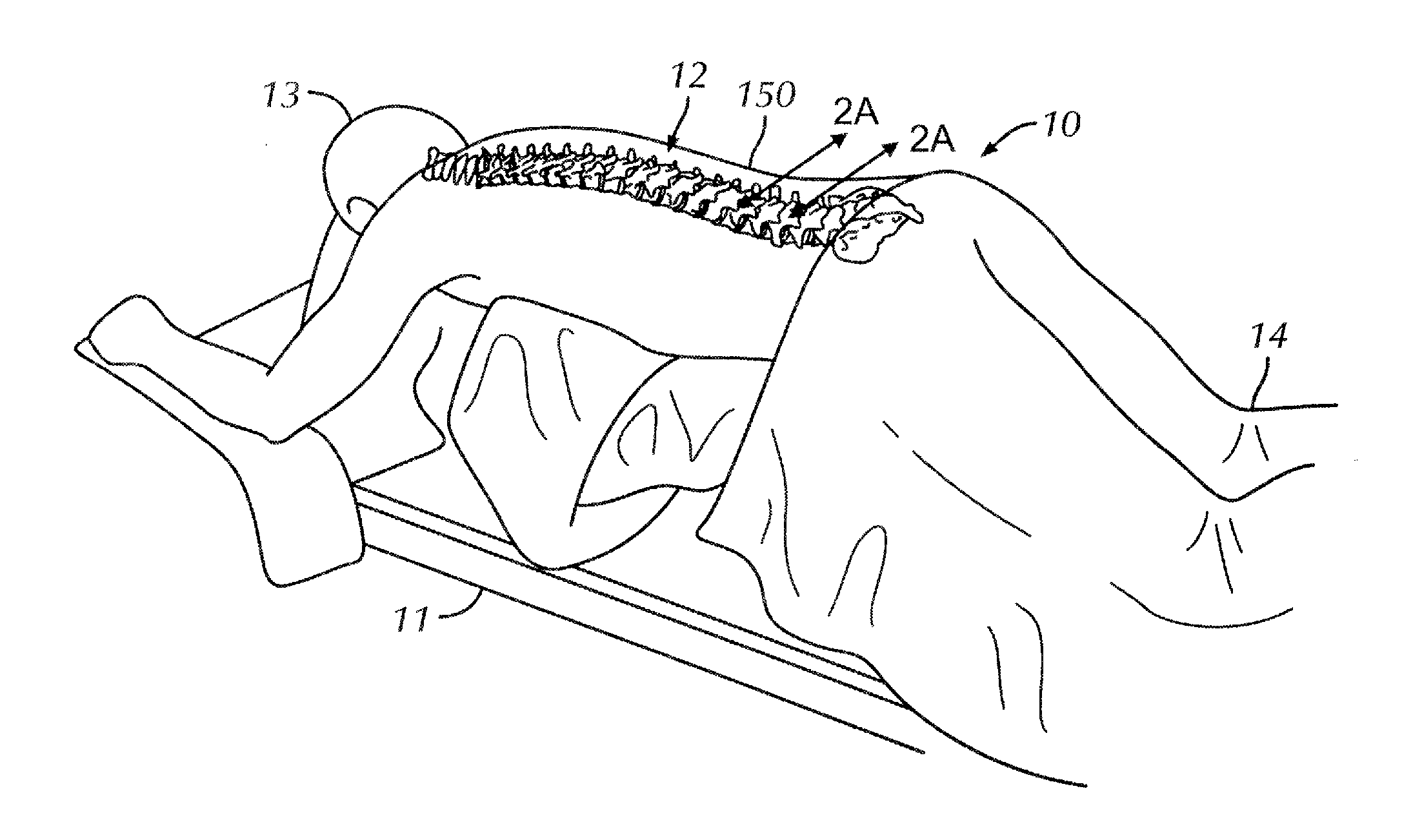
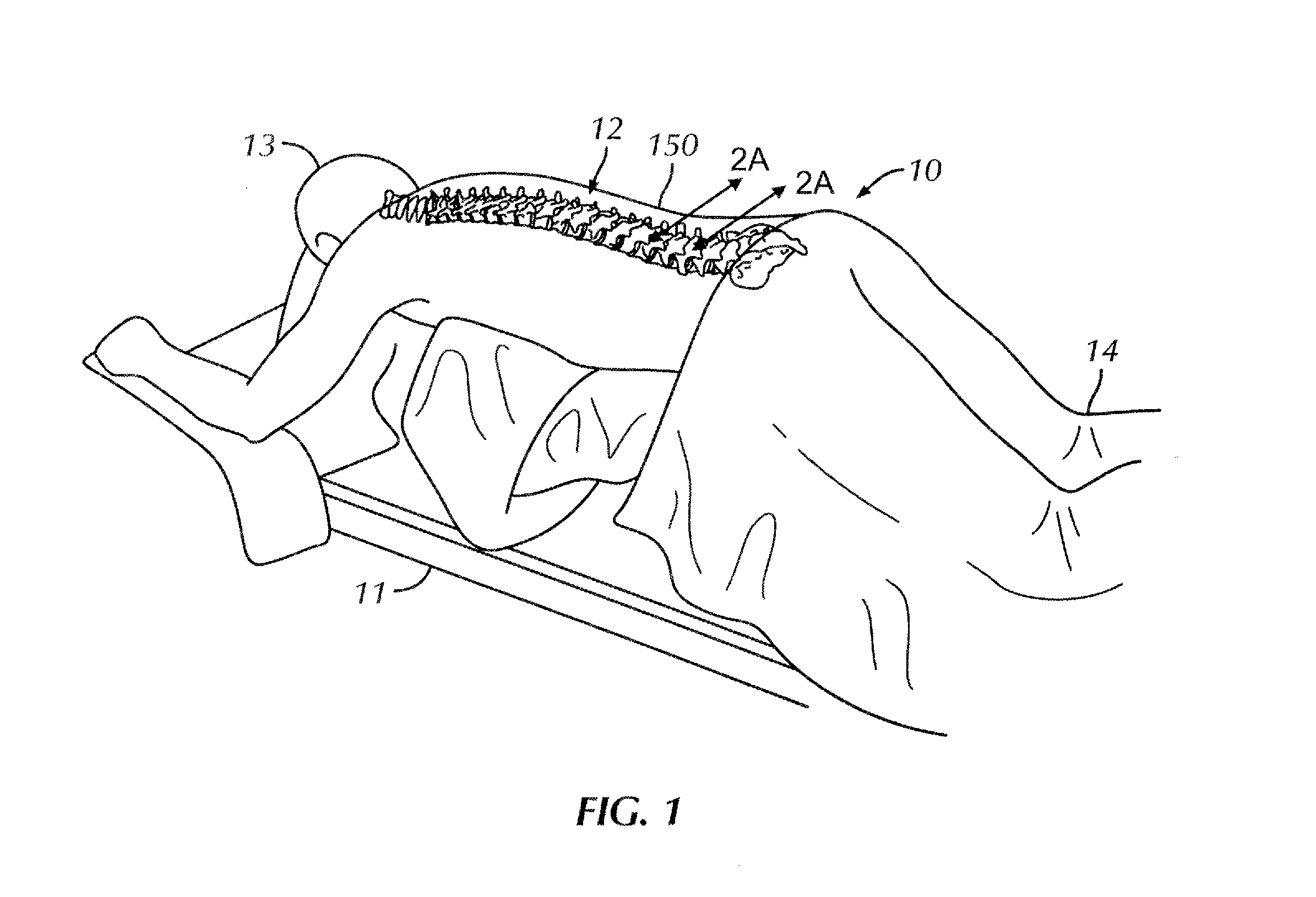
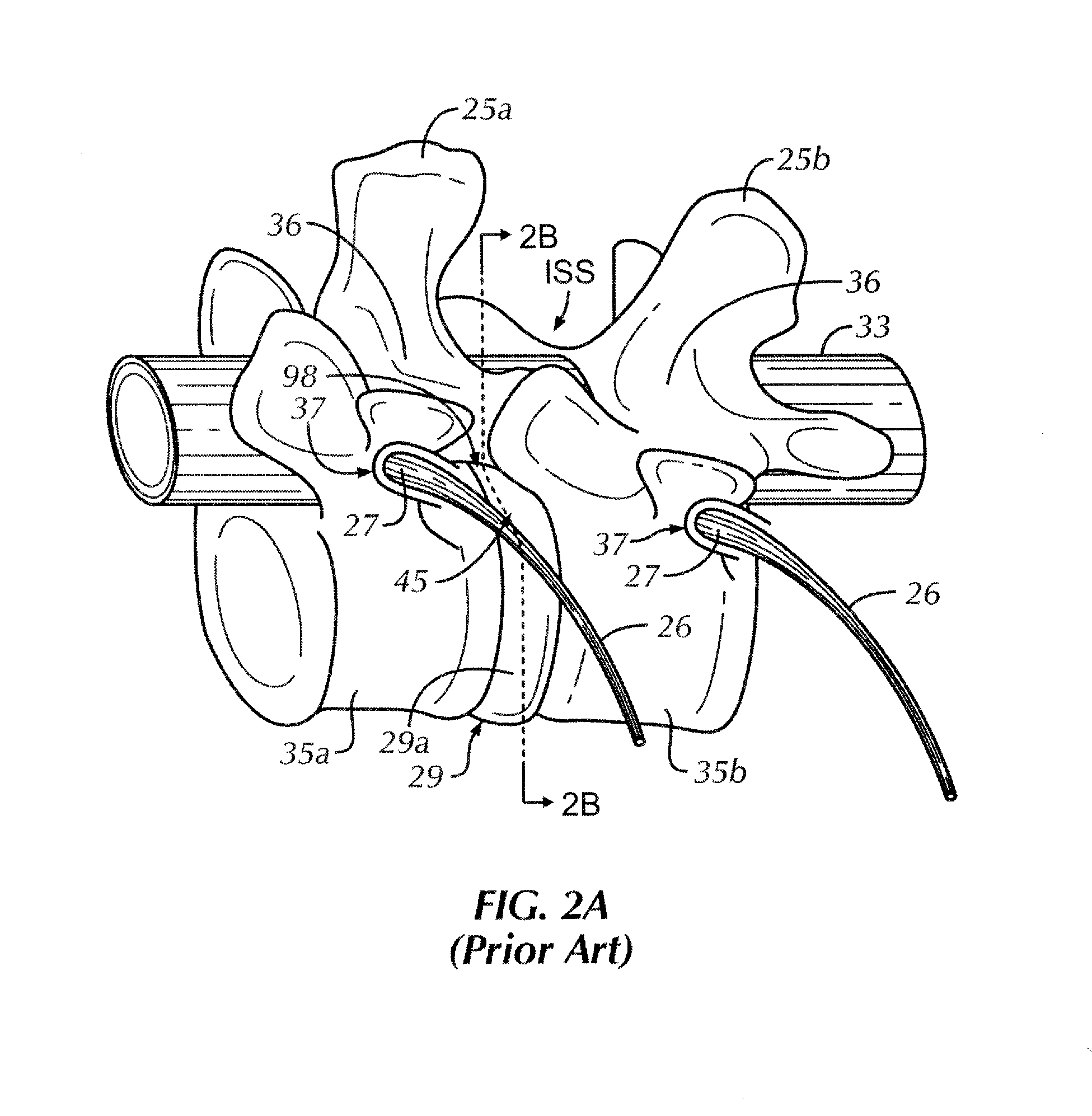
Patents
Literature
320 results about "Spinal operation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
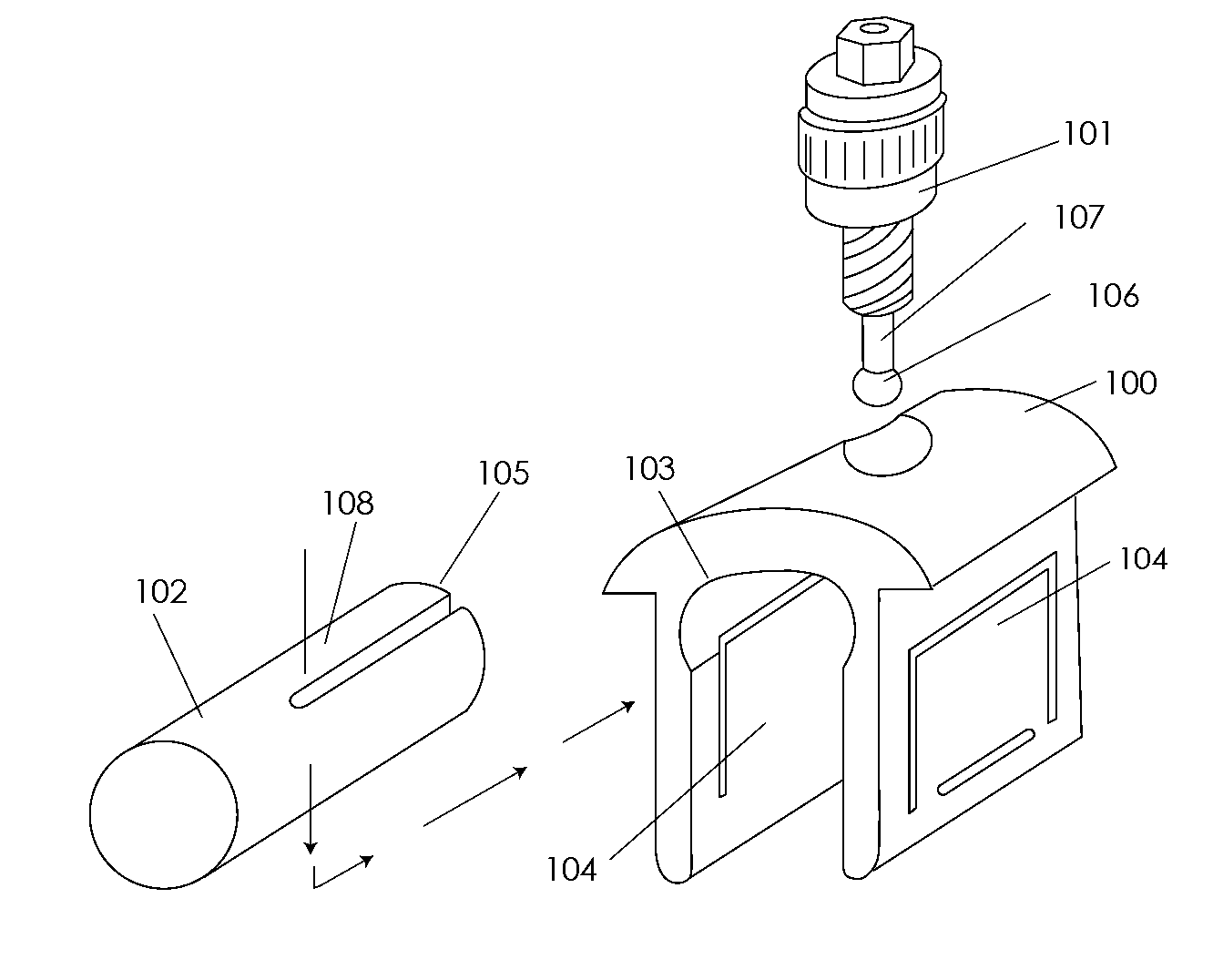
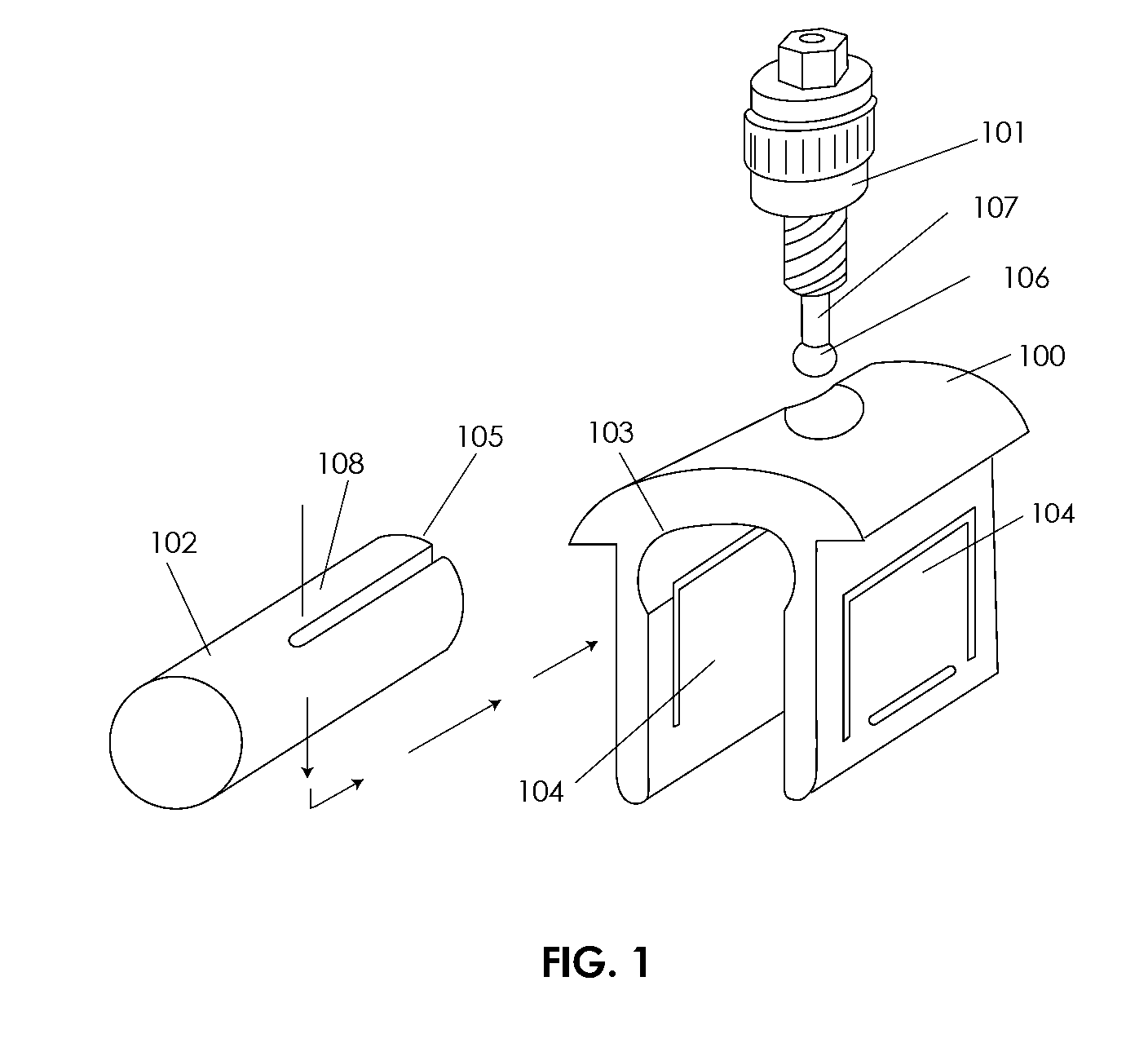
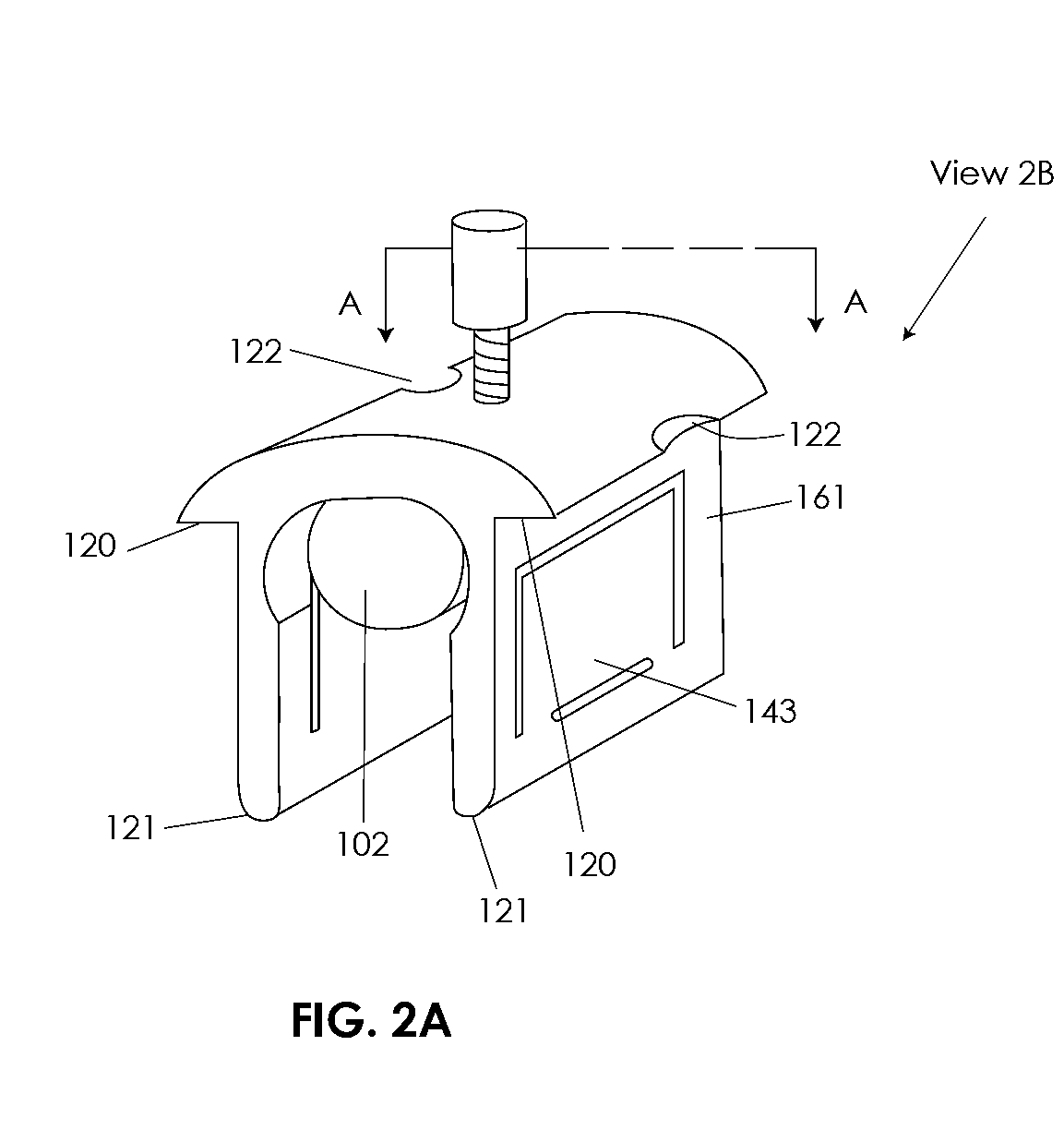
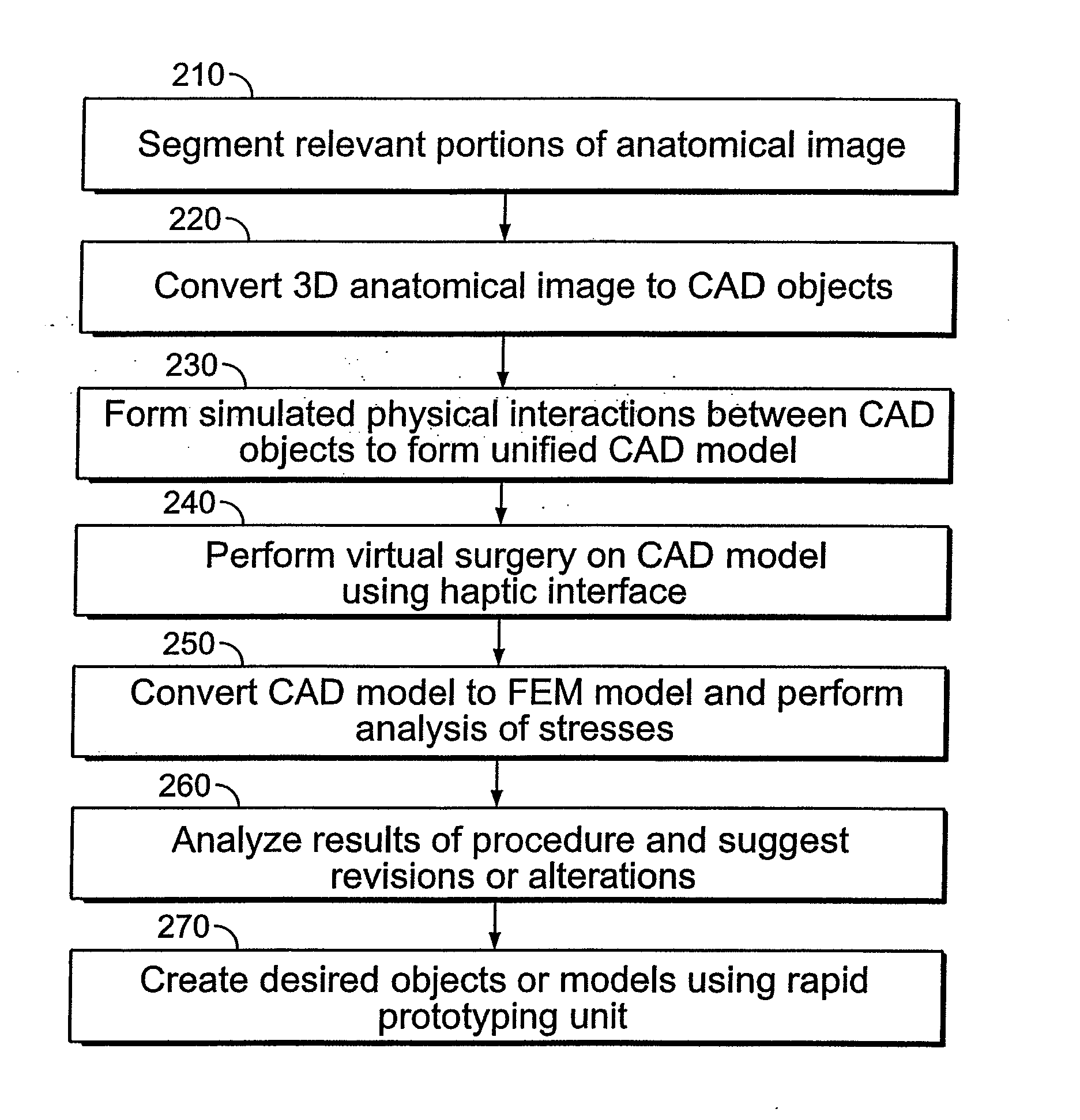
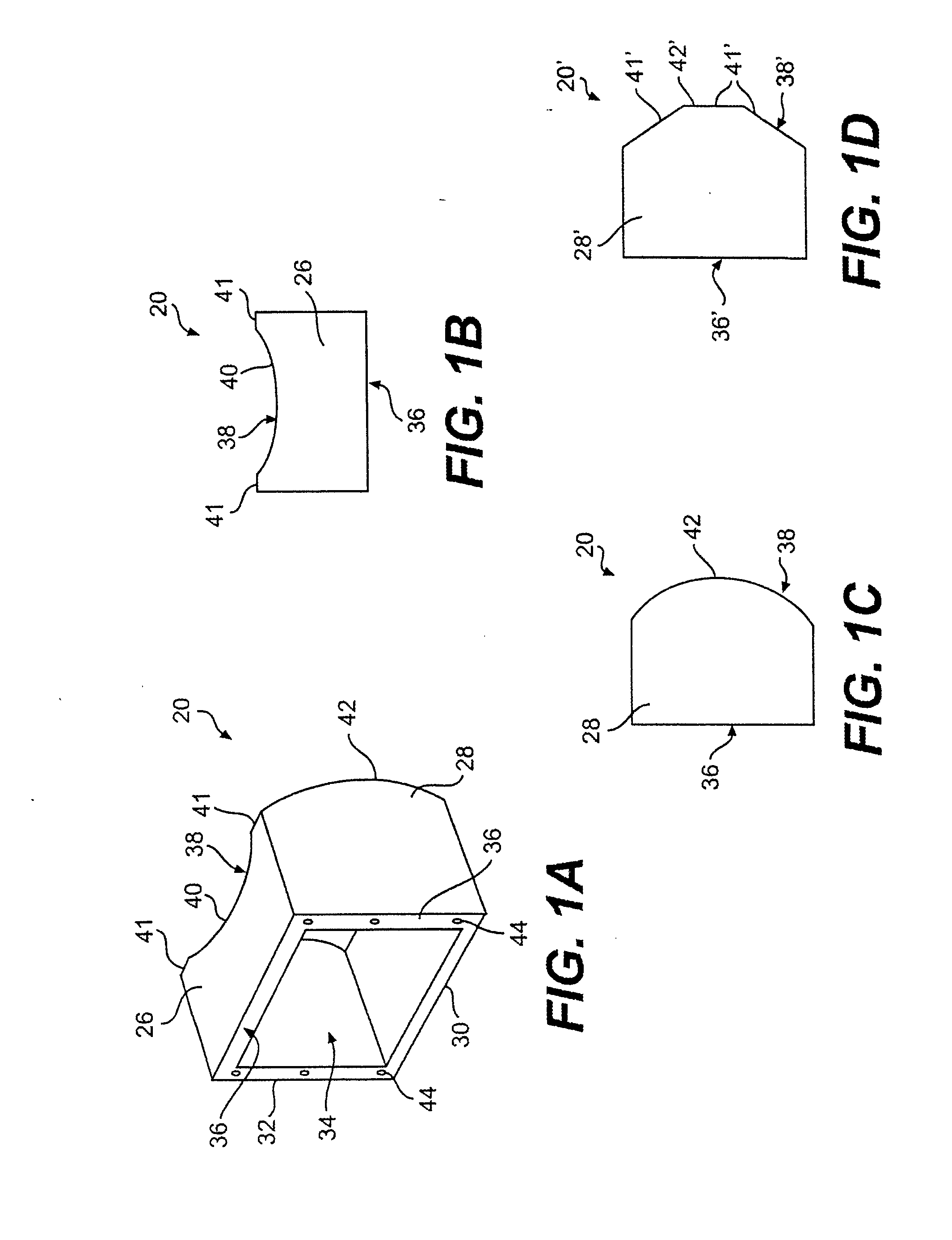
Computerized Planning Tool For Spine Surgery and Method and Device for Creating a Customized Guide for Implantations
InactiveUS20100217336A1Minimal effortMaximize accuracyMedical simulationAdditive manufacturing apparatusTouch PerceptionFinite element software
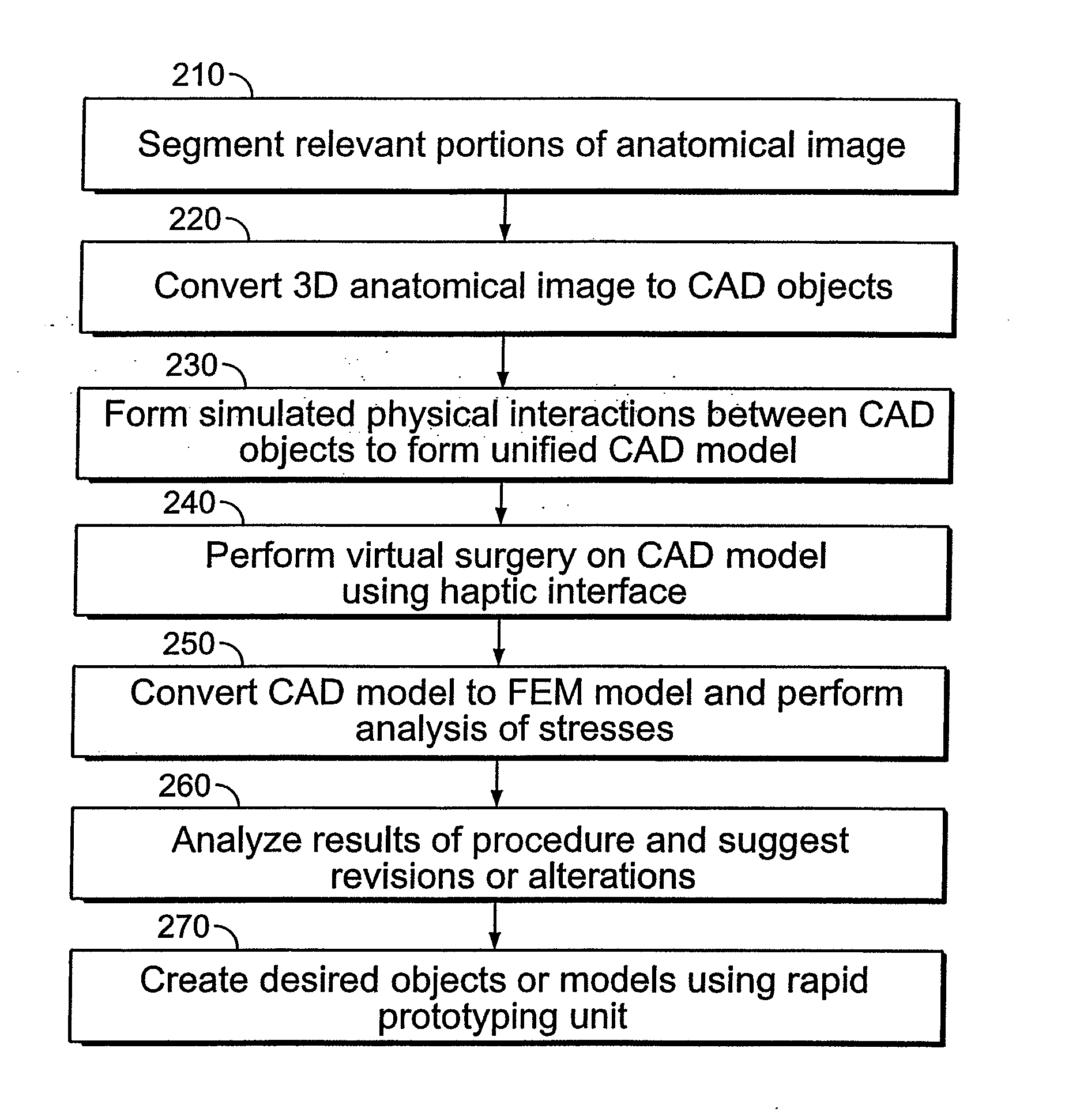
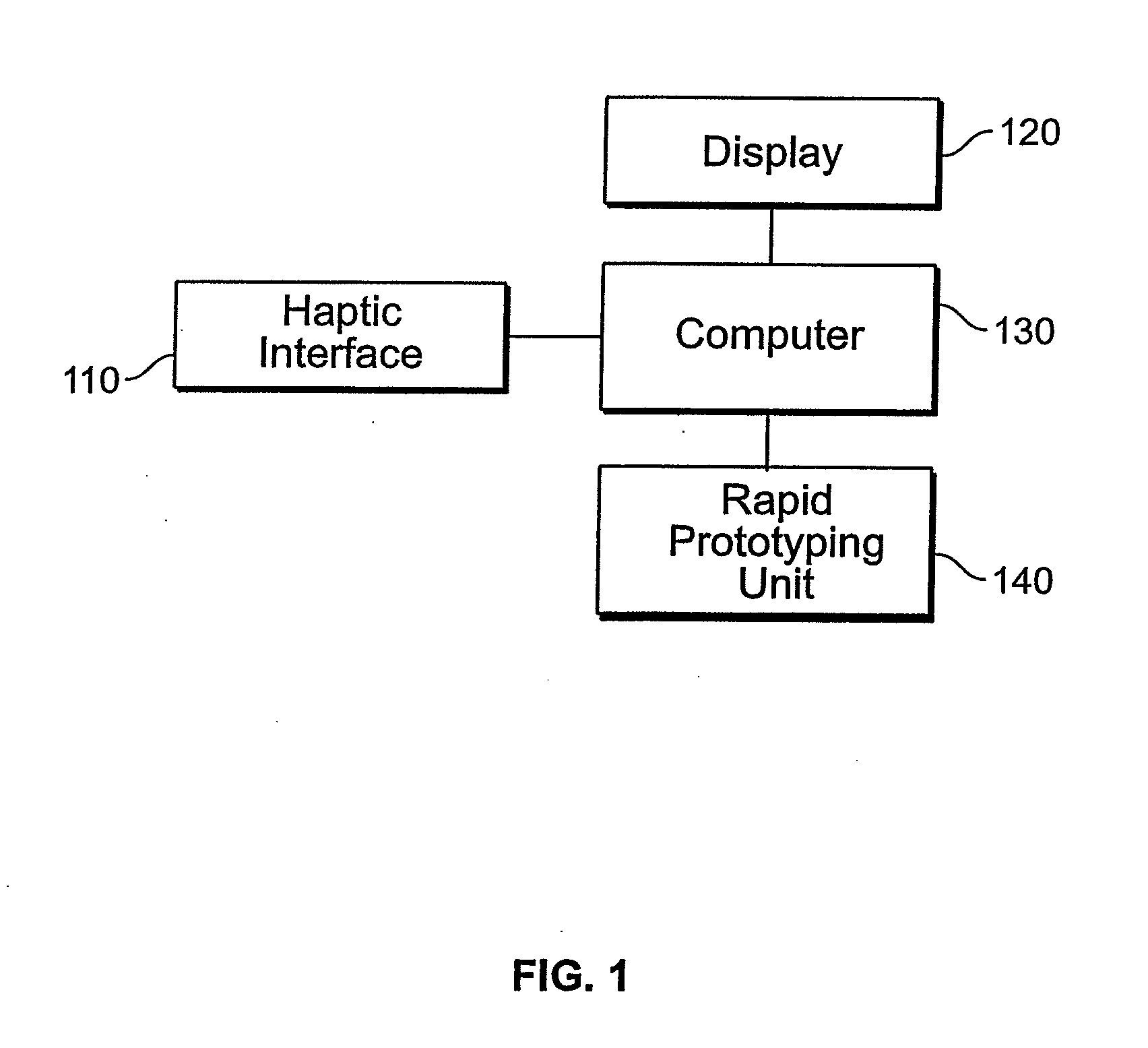
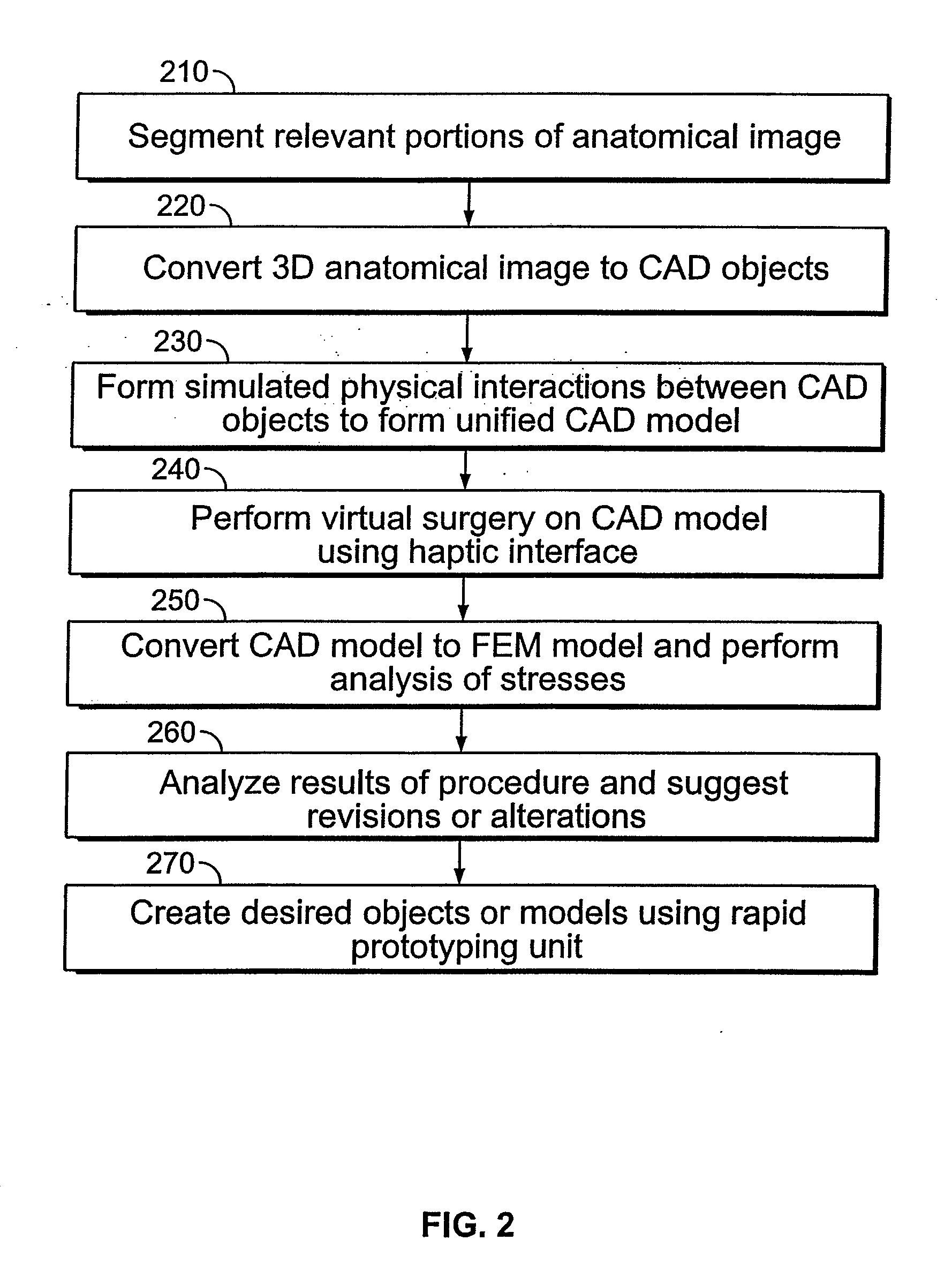
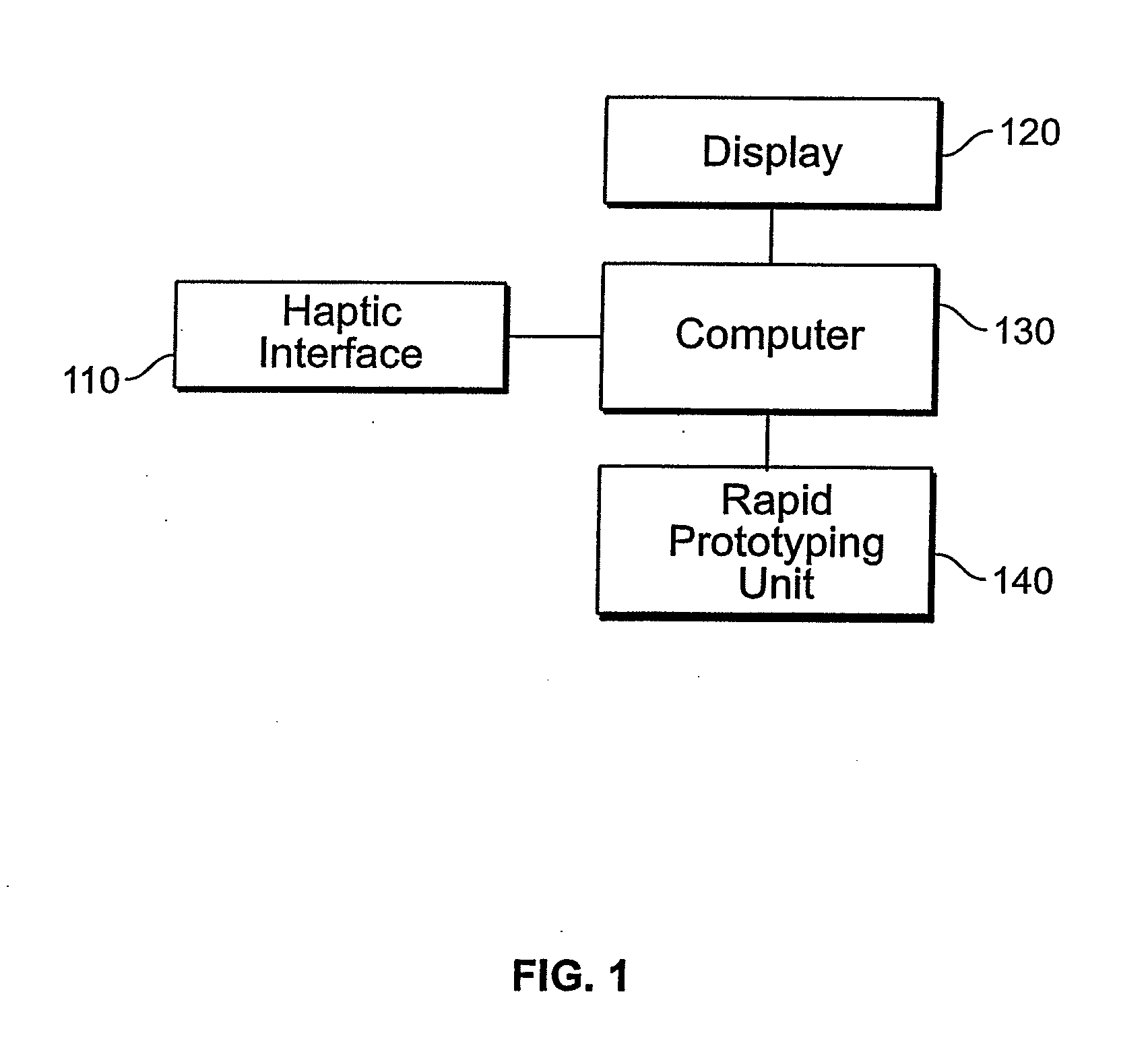
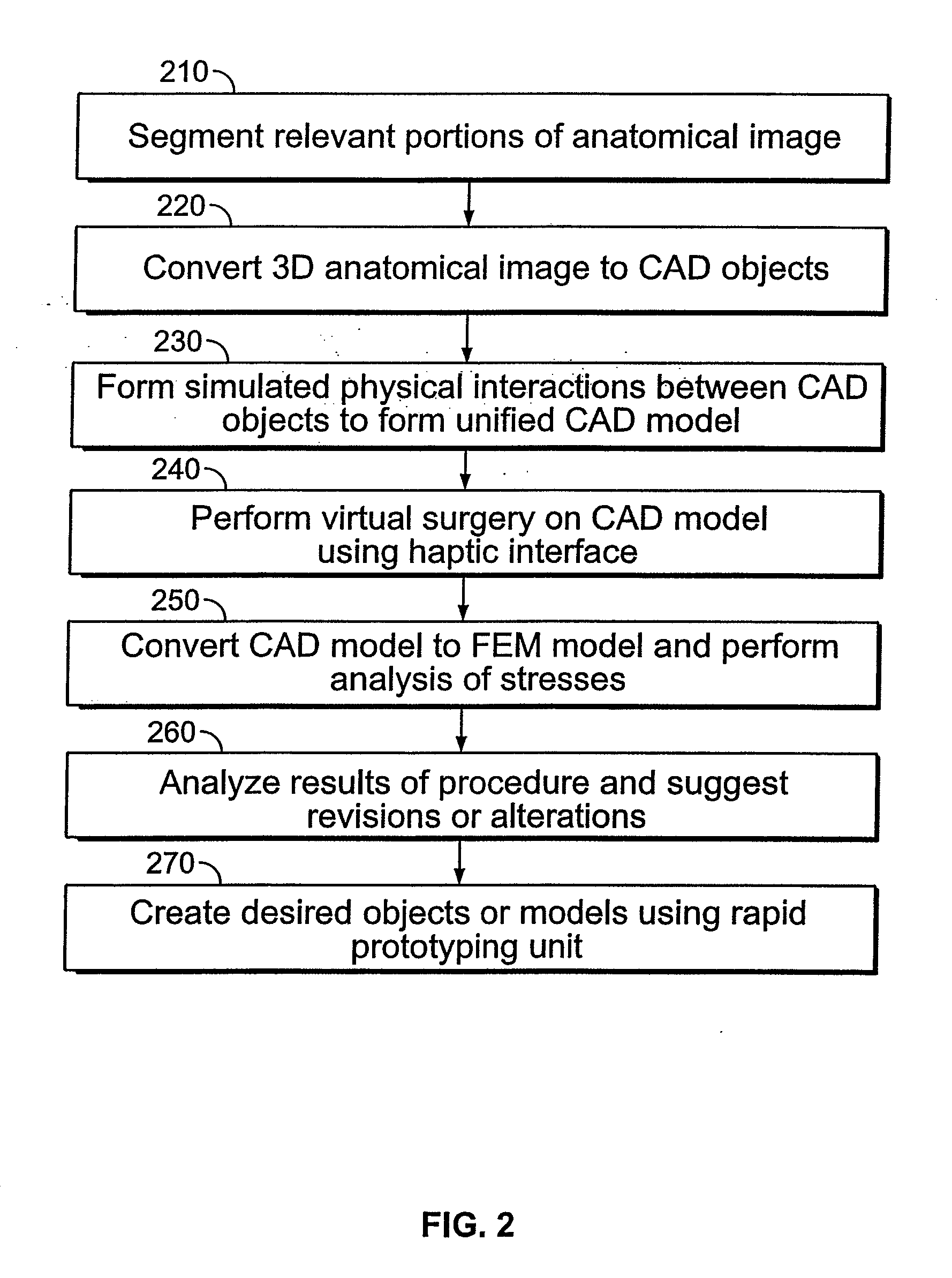
A system for planning a spine surgery, comprising a haptic interface capable of providing force feedback to the user and a computer adapted to simulate a surgical procedure by responding to inputs from the haptic interface and outputting haptic feedback to the haptic interface is provided.The system further comprising a rapid prototyping unit including a unit that is adapted to create models of the anatomical region where the surgical procedure will be performed in its current unoperated condition and in the predicted postoperative condition. Further the rapid prototyping unit is adapted to create a three dimensional guide to be used in the surgical procedure as well as suggest revisions to the surgical procedure. The system further comprises a computer that simulates loading of the spine and planned implanted hardware using finite element software.
Owner:DIGNITY HEALTH
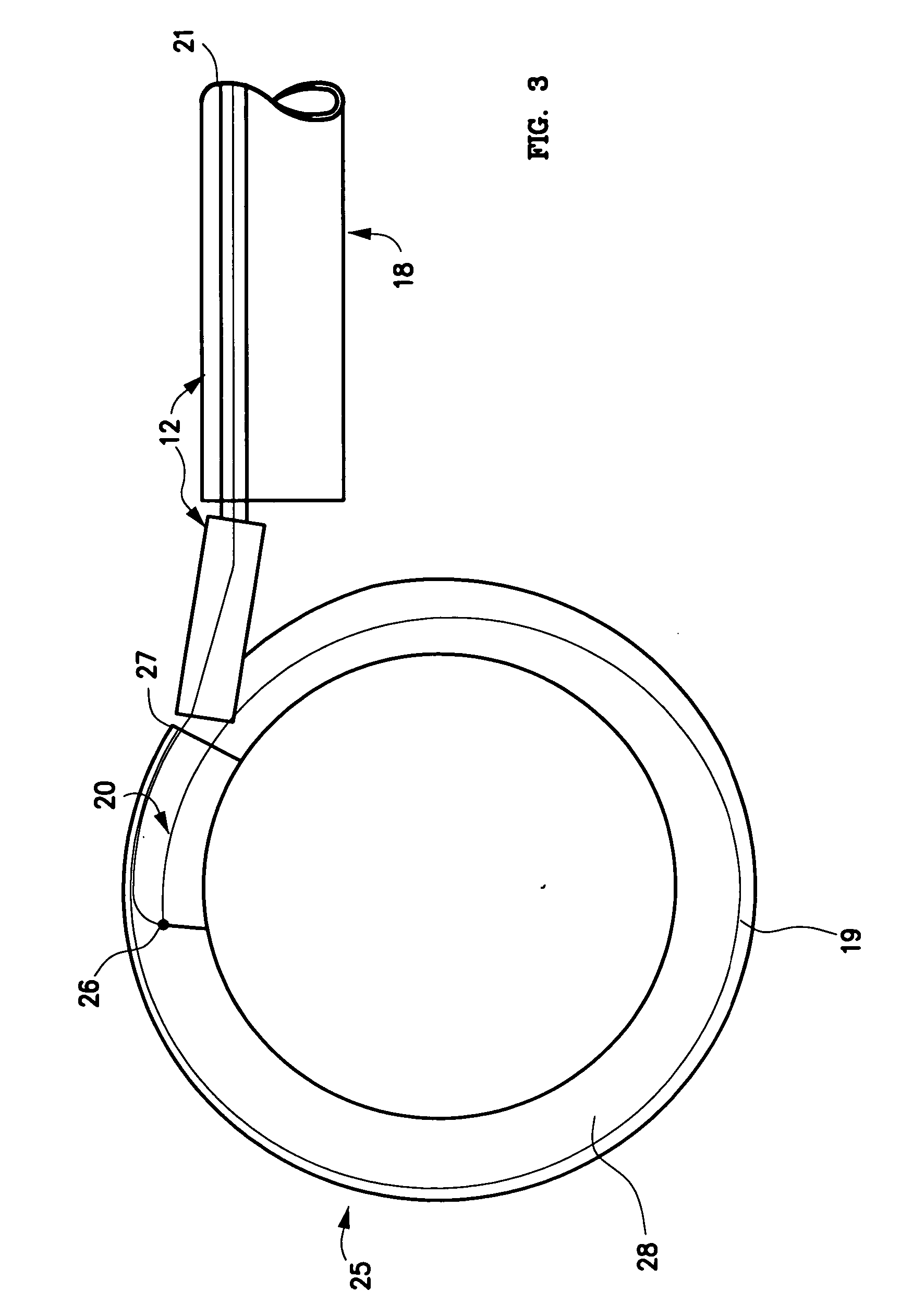
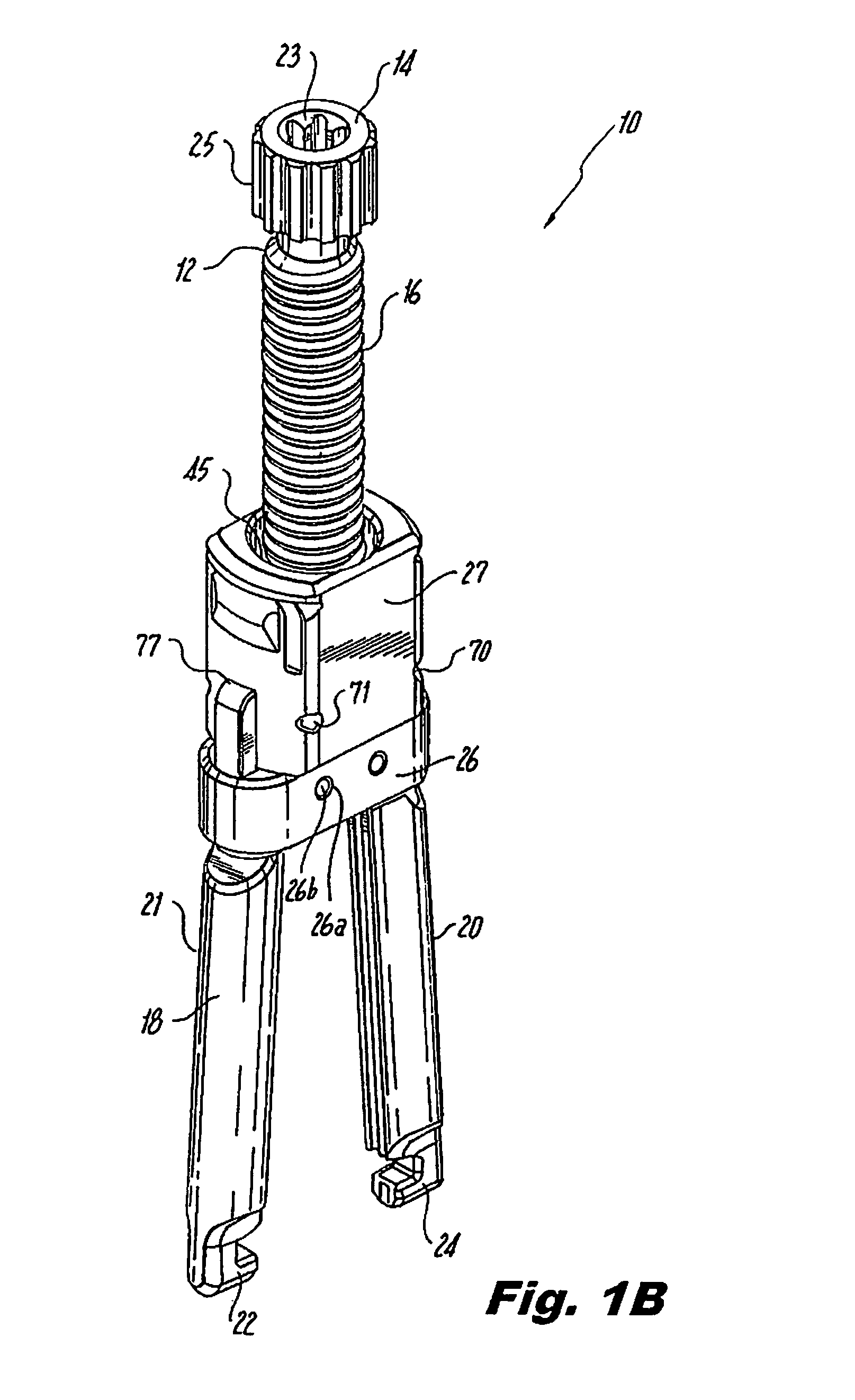
Exchange system for axial spinal procedures
InactiveUS20070066977A1Increase the cross-sectional areaInternal osteosythesisCannulasSpinal columnDrill
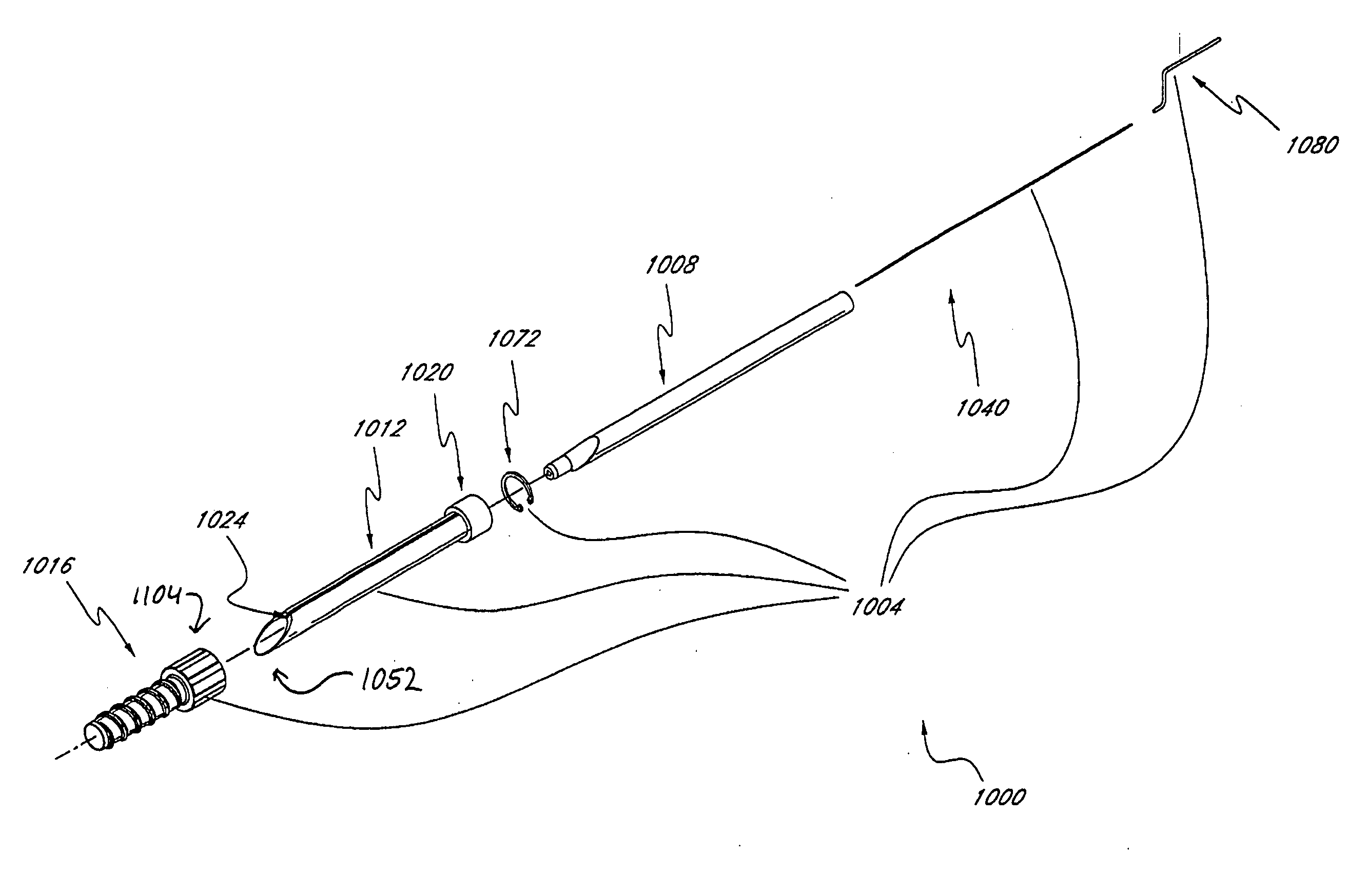
An exchange system is disclosed, for providing a protected path to a subcutaneous procedure site. An exchange cannula is provided with a central lumen, and a drill wire lumen that serves as a portal for a drill wire for coupling the assembly to bone. The wall thickness of the exchange cannula may be eccentric, to accommodate the drill wire lumen within the exchange cannula wall. A tensioning handle may be carried over the exchange cannula, for engaging adjacent tissue. The exchange cannula may have a proximal “T” handle. An exchange rod is movably positionable within the central lumen of the exchange cannula.
Owner:TRANS1
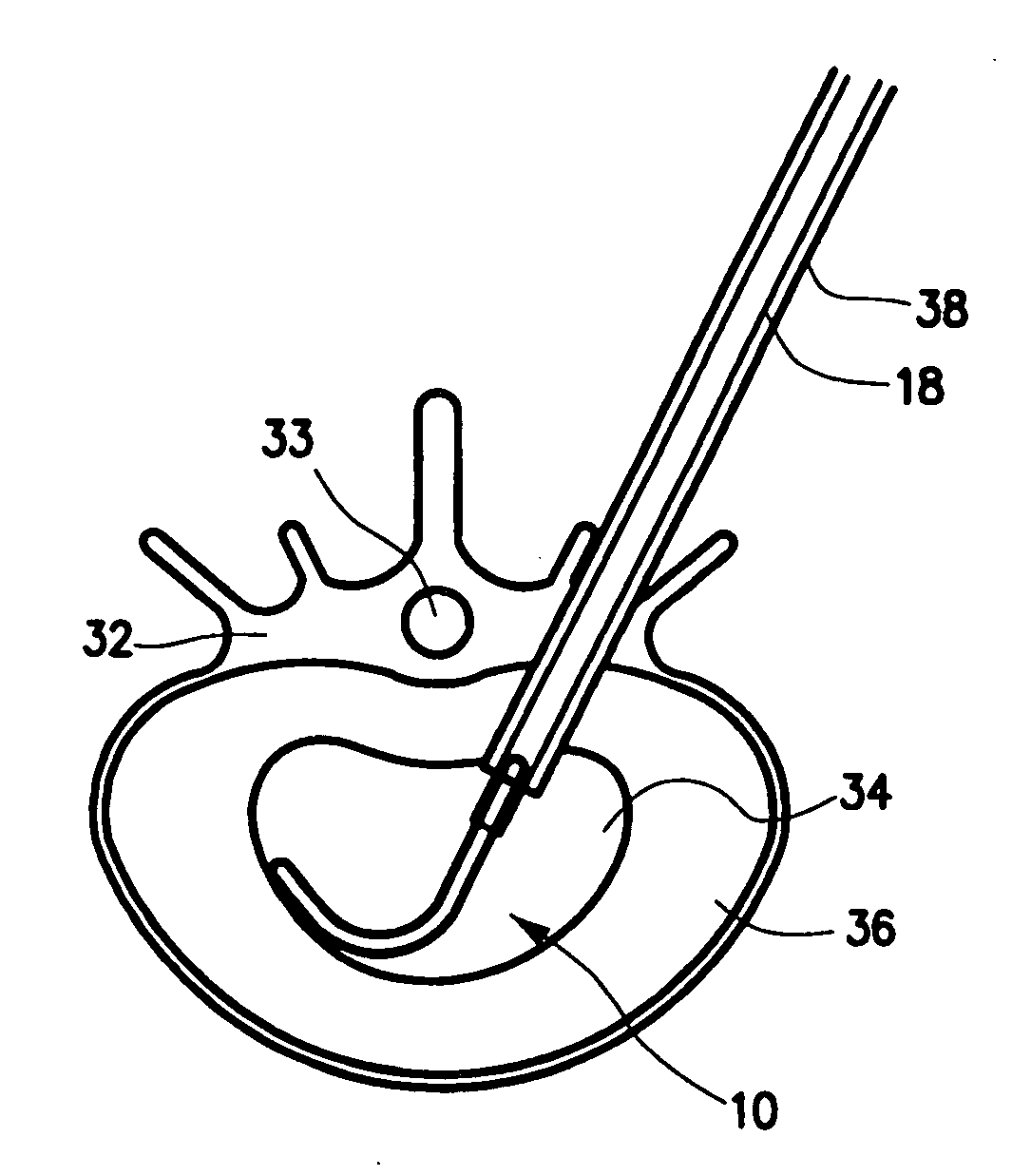
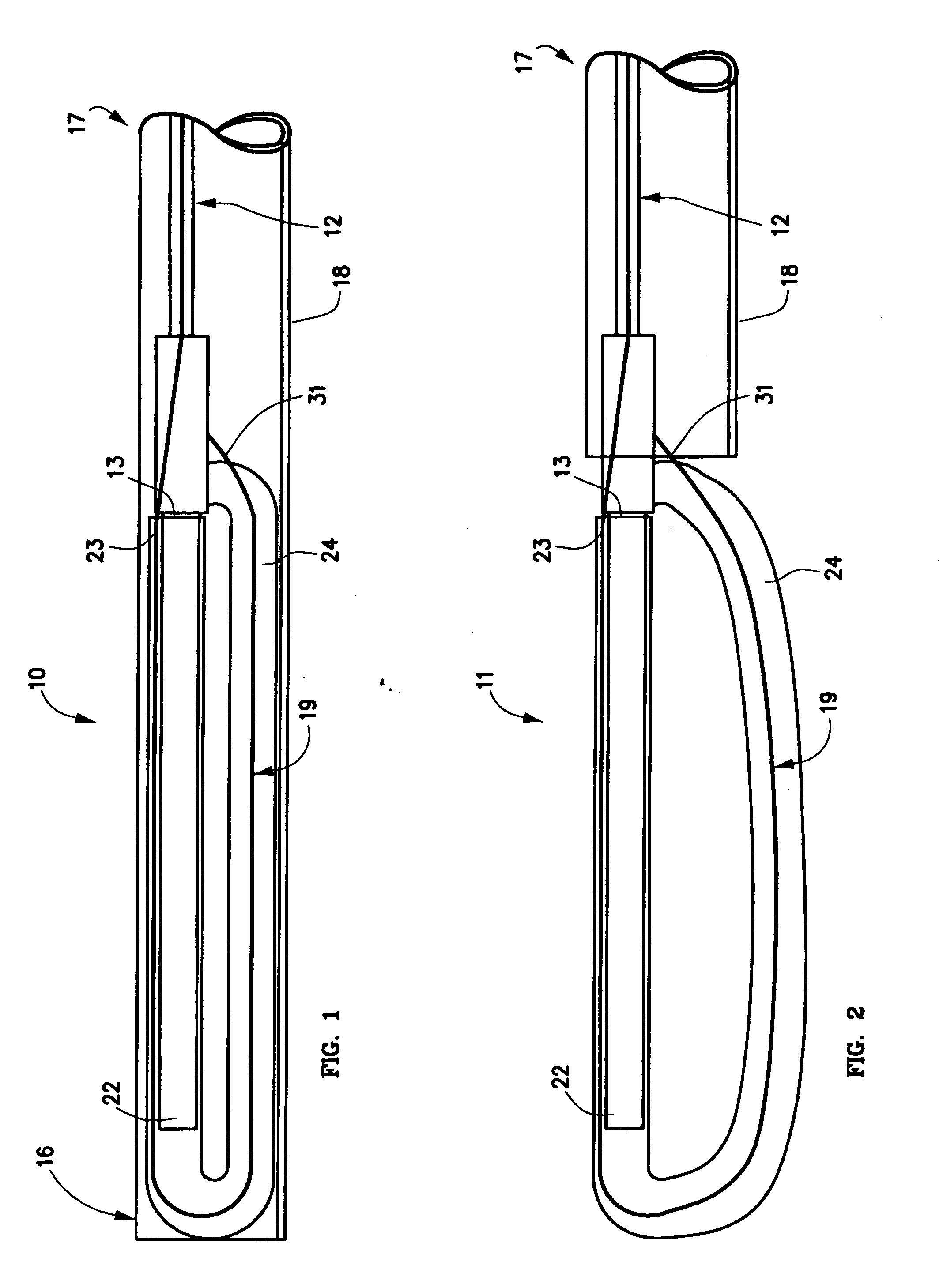
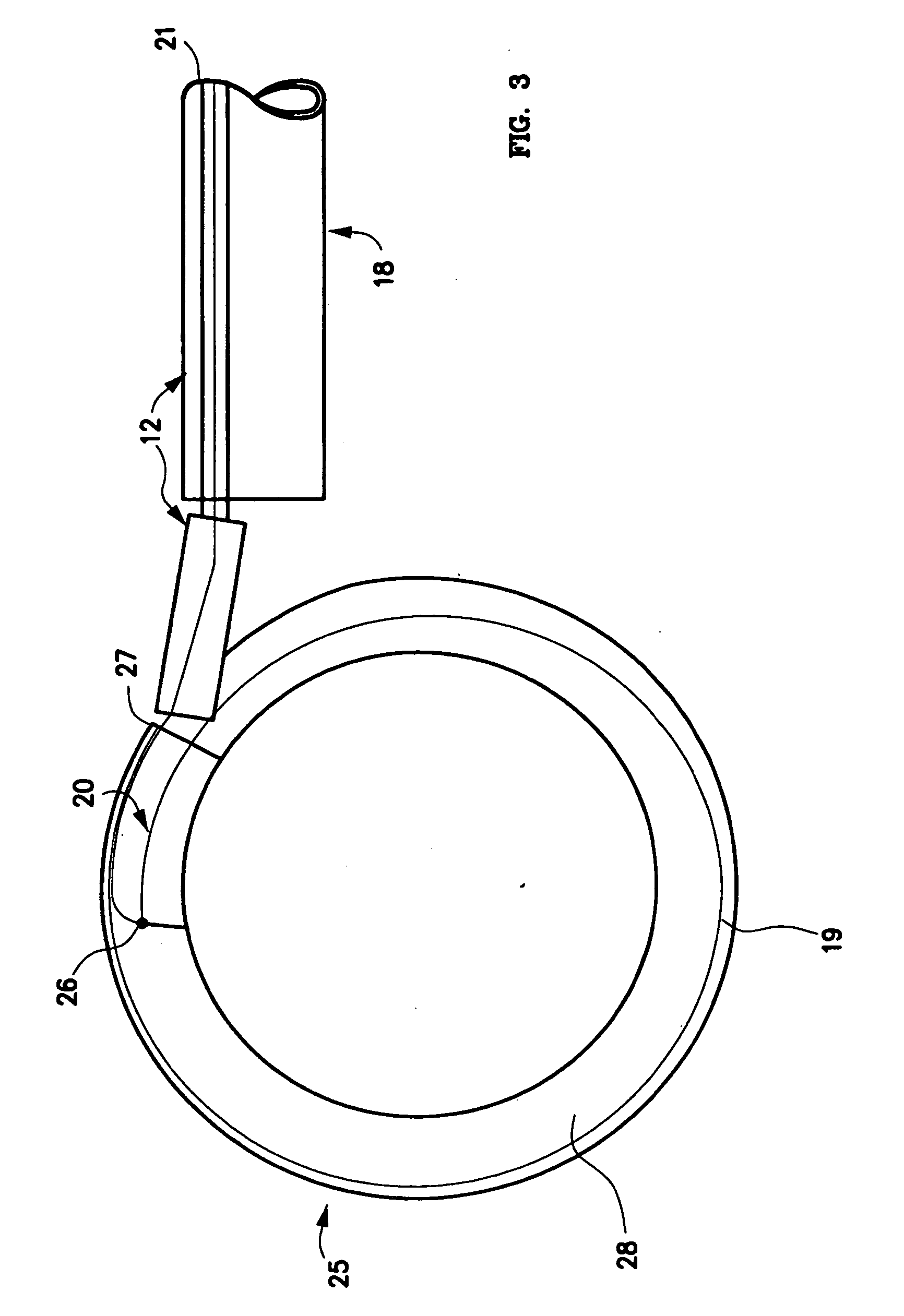
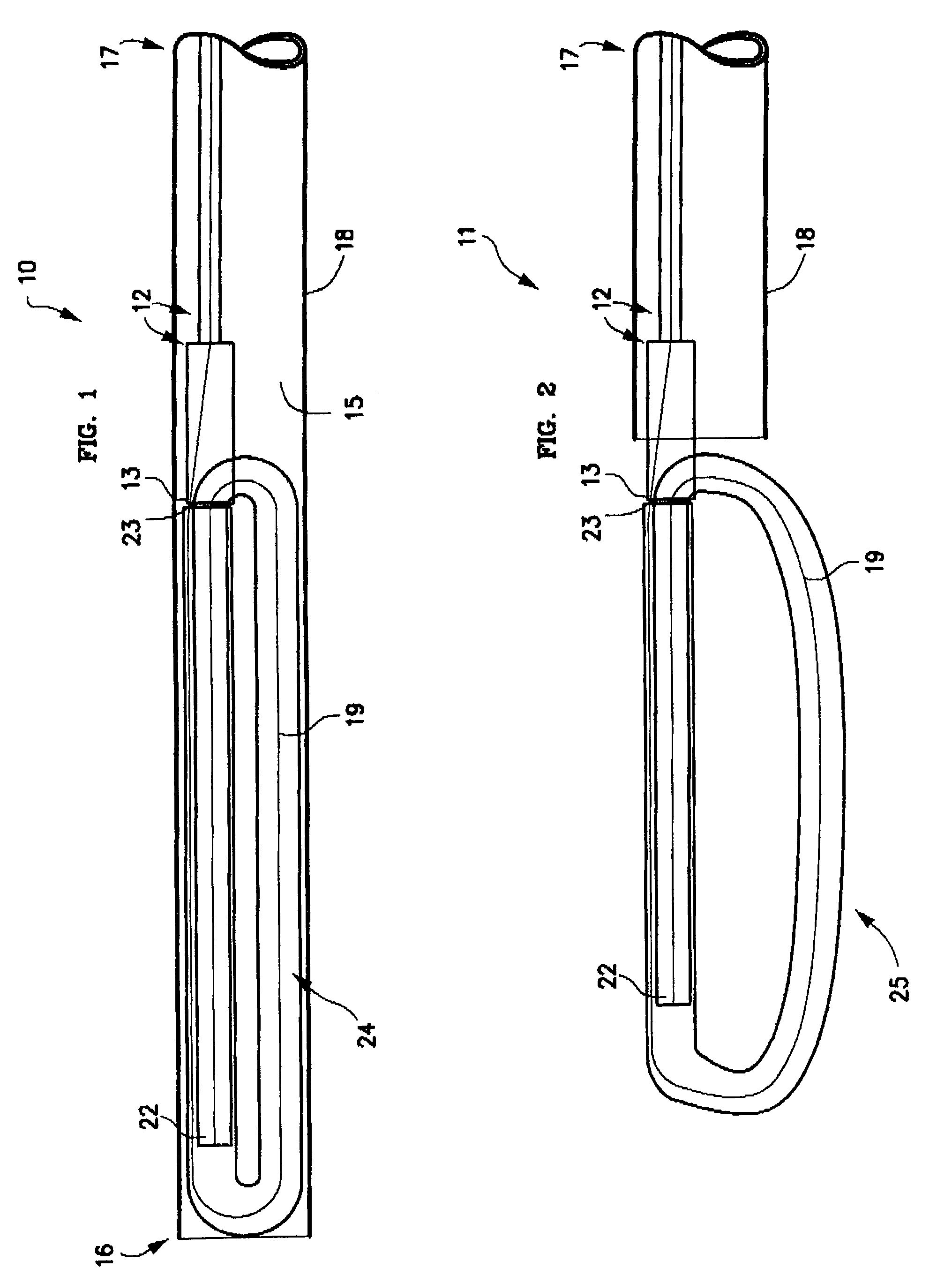
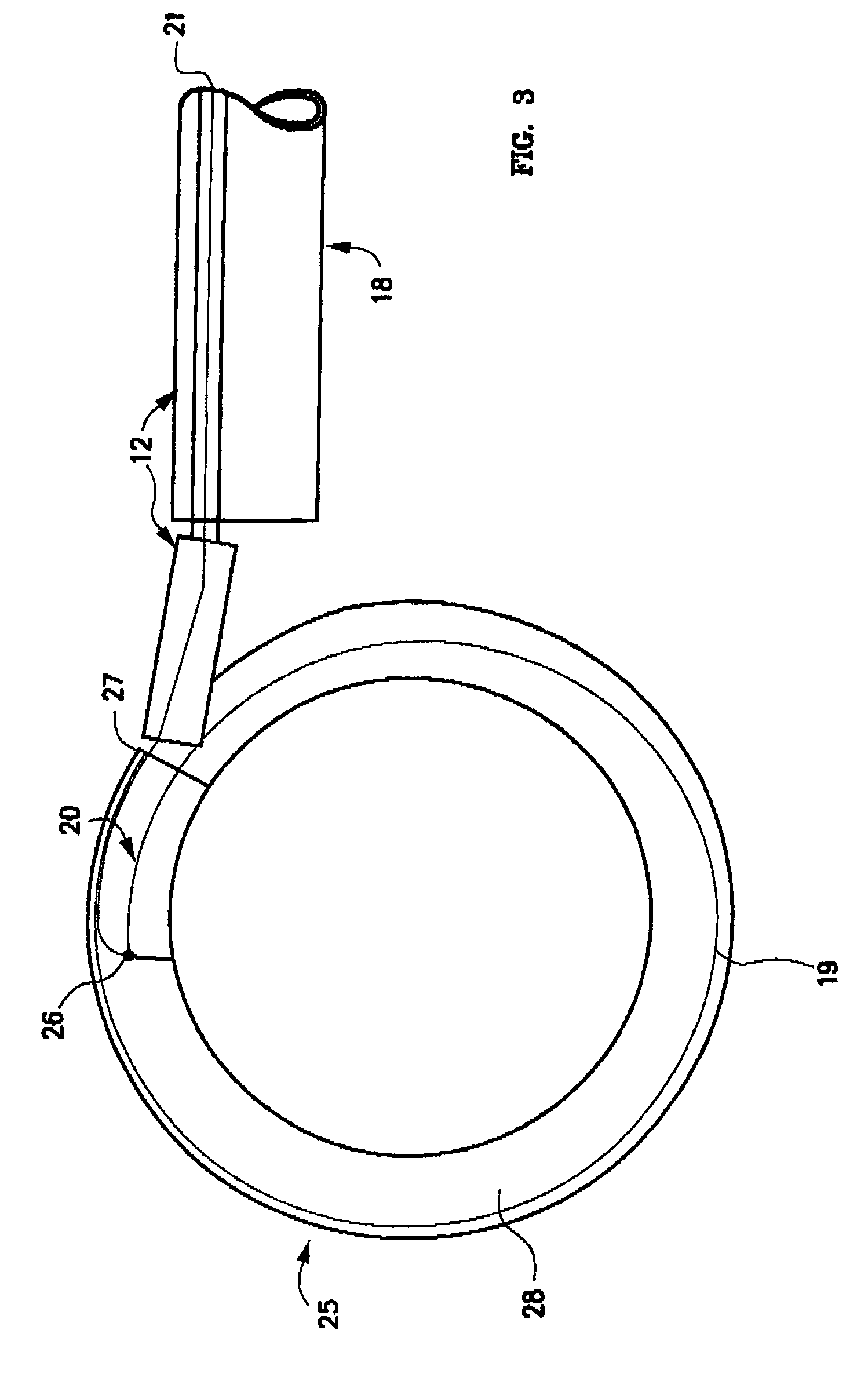
Mechanical apparatus and method for artificial disc replacement
InactiveUS20060287726A1Easy to integrateFree from painSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisPolyesterClosed loop
The present invention relates to a device and method which may be used to reinforce the native annulus during spinal surgery. The device is a catheter based device which is placed into the inter-vertebral space following discectomy performed by either traditional surgical or endoscopic approaches. The distal end of the catheter is comprised of an expansile loop which may be increased in diameter by advancement of a portion of the catheter via its proximal end, such proximal end remaining external to the body. The expansile loop may be formed of a woven or braided material and may be made of a polymer such as nylon, polyurethane, polyester, polyethylene, polypropylene or any of the well known and biocompatible polymers. Alternatively the expansile portion of the catheter may be formed from a metallic braid of stainless steel, elgiloy, Nitinol, or other biocompatible metals. The expansile loop may be formed such that when the loop is diametrically contracted the loop feeds into its other end, similar to a snake eating its own tail. Stabilization of the outer portion of the loop and pulling out the inner portion will thereby increase the overall diameter of the loop while maintaining it as a closed loop or torus. The present invention comprises four embodiments and can be used to 1) facilitate disk fusing, 2) perform an artificial replacement of the nucleus, 3) perform an artificial replacement of the annulus, or 4, perform an artificial replacement of both the nucleus and annulus.
Owner:OUROBOROS MEDICAL INC
Method and apparatus for spinal procedures
InactiveUS7189240B1Assist in removeExcision instrumentsEndoscopic cutting instrumentsSpinal columnSpinal stenosis
A method of treating spinal stenosis, in which a rasp is brought through a part of a spinal channel and then axially moved so that the rasp removes a stenosis in the spinal channel. Optionally, a shield protects a spinal cord or other sensitive tissues in the spinal channel.
Owner:KYPHON
Electromagnetic apparatus and method for nerve localization during spinal surgery
An electromagnetic pedicle awl utilizes a tightly focused time-varying magnetic flux to create a localized electromotive force (EMF) near the tip of a pedicle awl. The localized EMF creates localized eddy currents in nearby nerves which in turn excite ionic nerve channels, the excitation being detected by an electromyographic recording device. In comparison to the electrically stimulated pedicle awl of the prior art, the electromagnetic pedicle awl only excites nerves directly in front of and directly to the side of the tip. The electromagnetic pedicle awl is comprised of a tapered awl or drill tip in combination with a solid core surrounded by a solenoid. A pulsed electric current source drives the solenoid to create a time-varying magnetic field in the vicinity of the tapered tip. The awl or drill tip may be stationary with respect to the solenoid or it may rotate. The electromagnetic pedicle awl in combination with an EMG detector connected to a patient is very sensitive to the pedicle hole position with respect to adjacent nerves and reduces false placement failure.
Owner:WOLF II ERICH
Mechanical apparatus and method for artificial disc replacement
InactiveUS20060287730A1Easy to integrateFree from painSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisLamina terminalisClosed loop
The present invention relates to a device and method which may be used to reinforce the native annulus during spinal surgery. The device is a catheter based device which is placed into the inter-vertebral space following discectomy performed by either traditional surgical or endoscopic approaches. The distal end of the catheter is comprised of an expansile loop which may be increased in diameter by advancement of a portion of the catheter via its proximal end, such proximal end remaining external to the body. The expansile loop may be formed such that when the loop is diametrically contracted the loop feeds into its other end, similar to a snake eating its own tail. Stabilization of the outer portion of the loop and pulling out the inner portion will thereby increase the overall diameter of the loop while maintaining it as a closed loop or torus. The expansile loop can use an attachment means to secure it to substantially healthy tissues of the annulus, nucleus, or endplates. The present invention comprises four embodiments and can be used to 1) facilitate disk fusing, 2) perform an artificial replacement of the nucleus, 3) perform an artificial replacement of the annulus, or 4, perform an artificial replacement of both the nucleus and annulus.
Owner:OUROBOROS MEDICAL INC
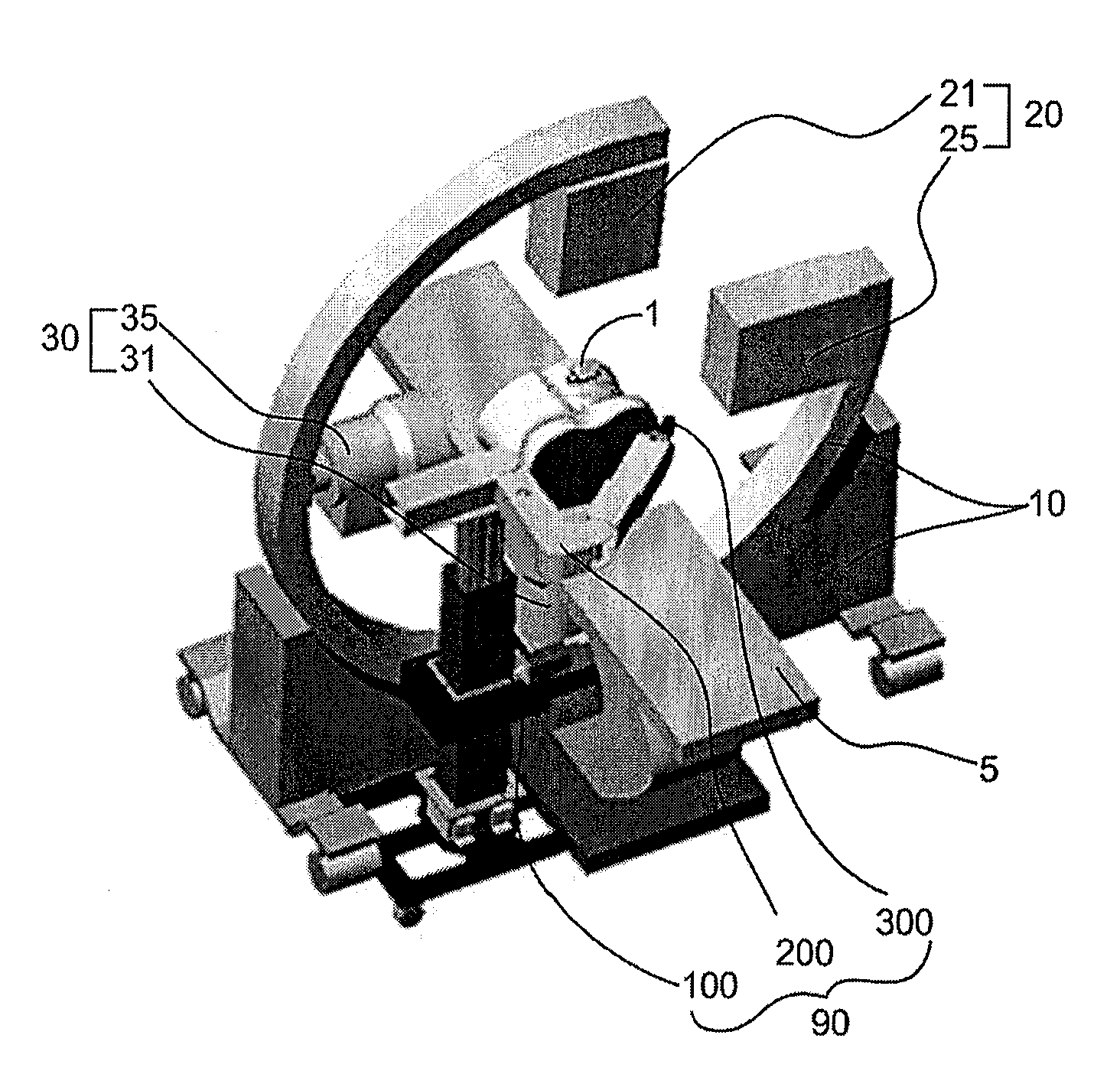
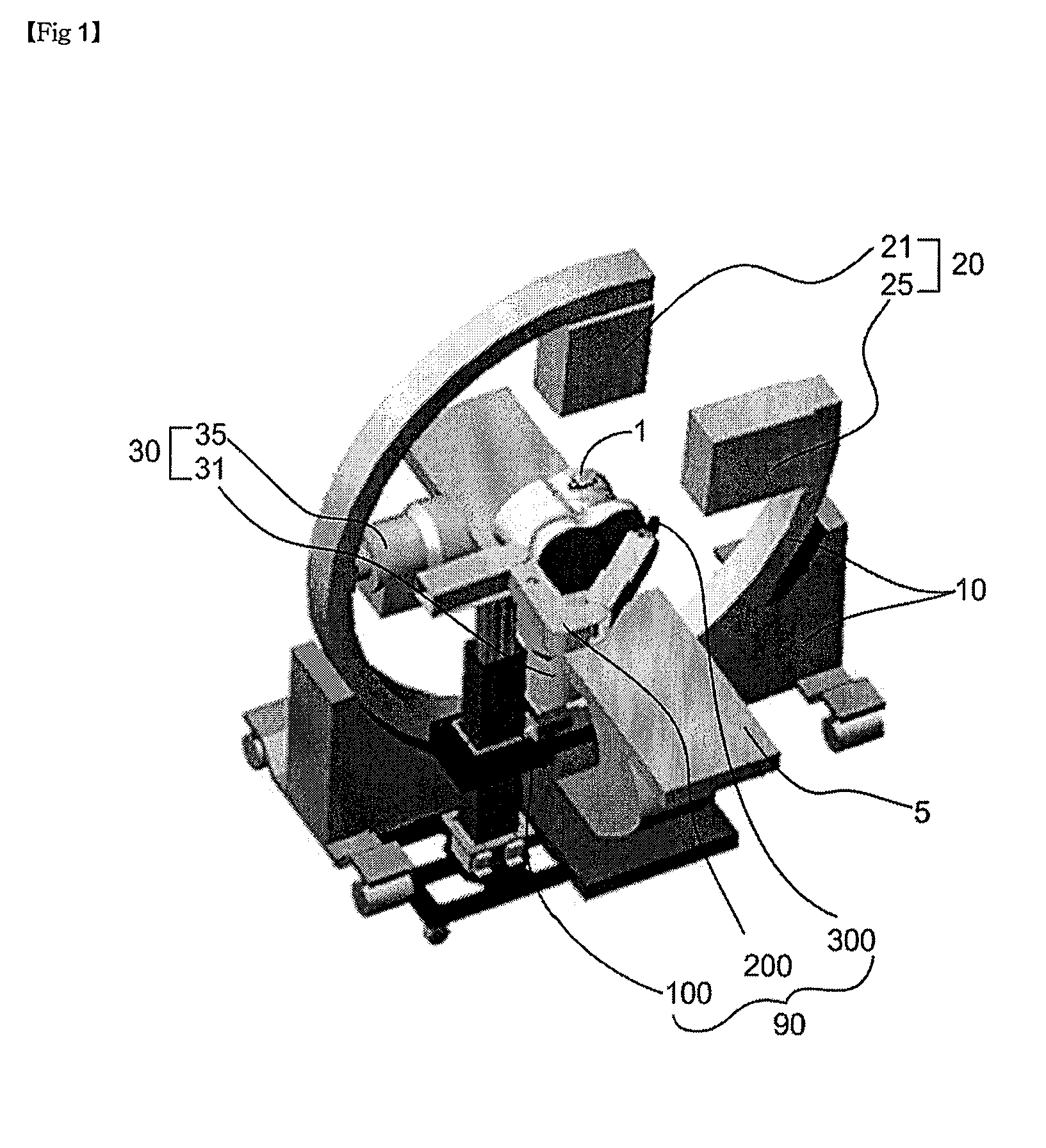
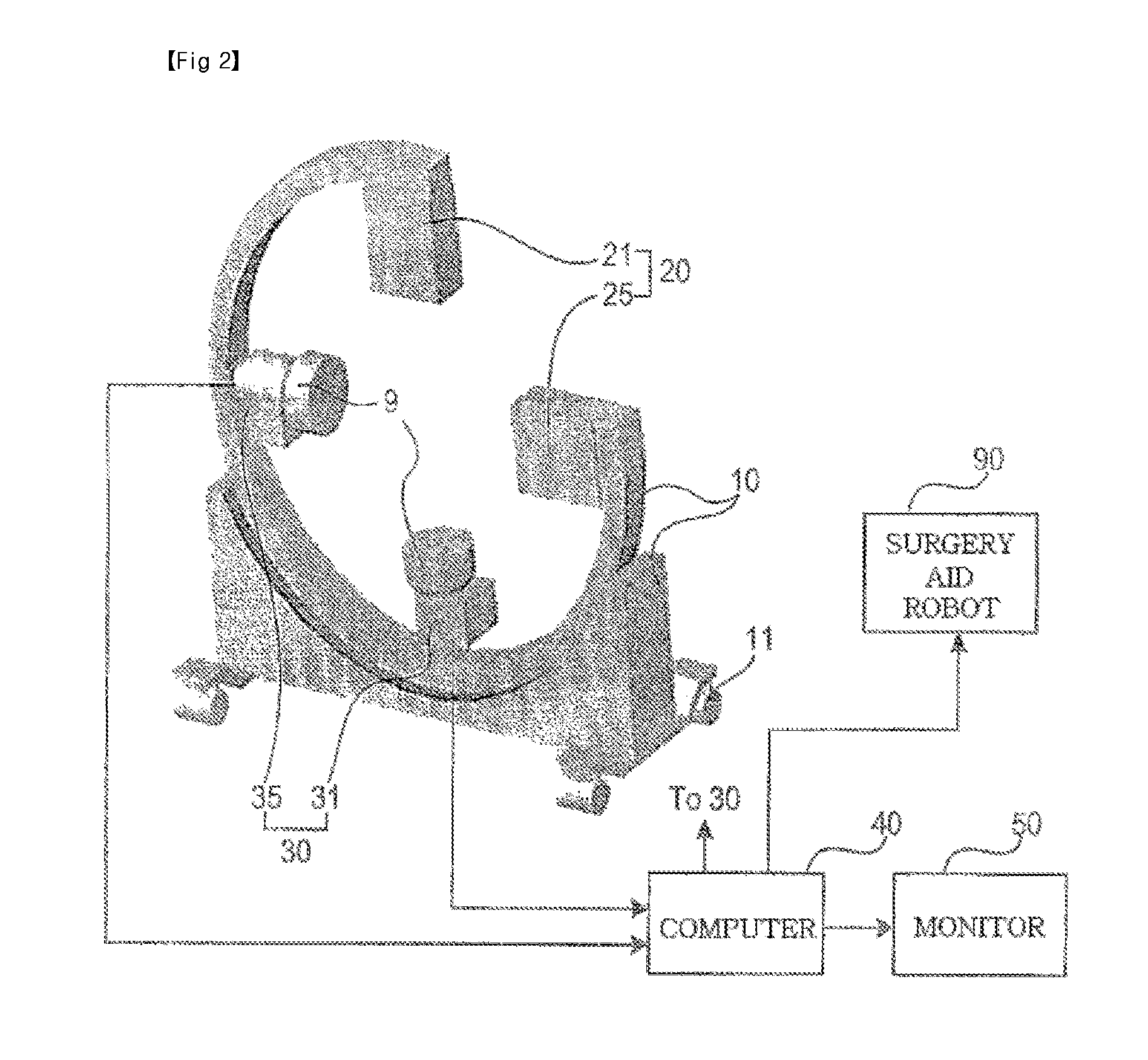
Bi-planar fluoroscopy guided robot system for minimally invasive surgery and the control method thereof
InactiveUS8046054B2Accurate three-dimensional surgery planAccurate surgery planMasksUmbrellasLess invasive surgeryProgram planning
Disclosed is a computer-integrated surgery aid system for minimally invasive surgery and a method for controlling the same. The system includes a surgery planning system for creating three-dimensional information from two-dimensional images obtained by means of biplanar fluoroscopy so that spinal surgery can be planned according to the image information and a scalar-type 6 degree-of-freedom surgery aid robot adapted to be either driven automatically or operated manually.
Owner:IUCF HYU (IND UNIV COOP FOUND HANYANG UNIV)
Minimally invasive surgical spinal exposure system
ActiveUS7150714B2Increase the areaImprove visualizationDiagnosticsSurgical field illuminationSpinal columnLess invasive surgery
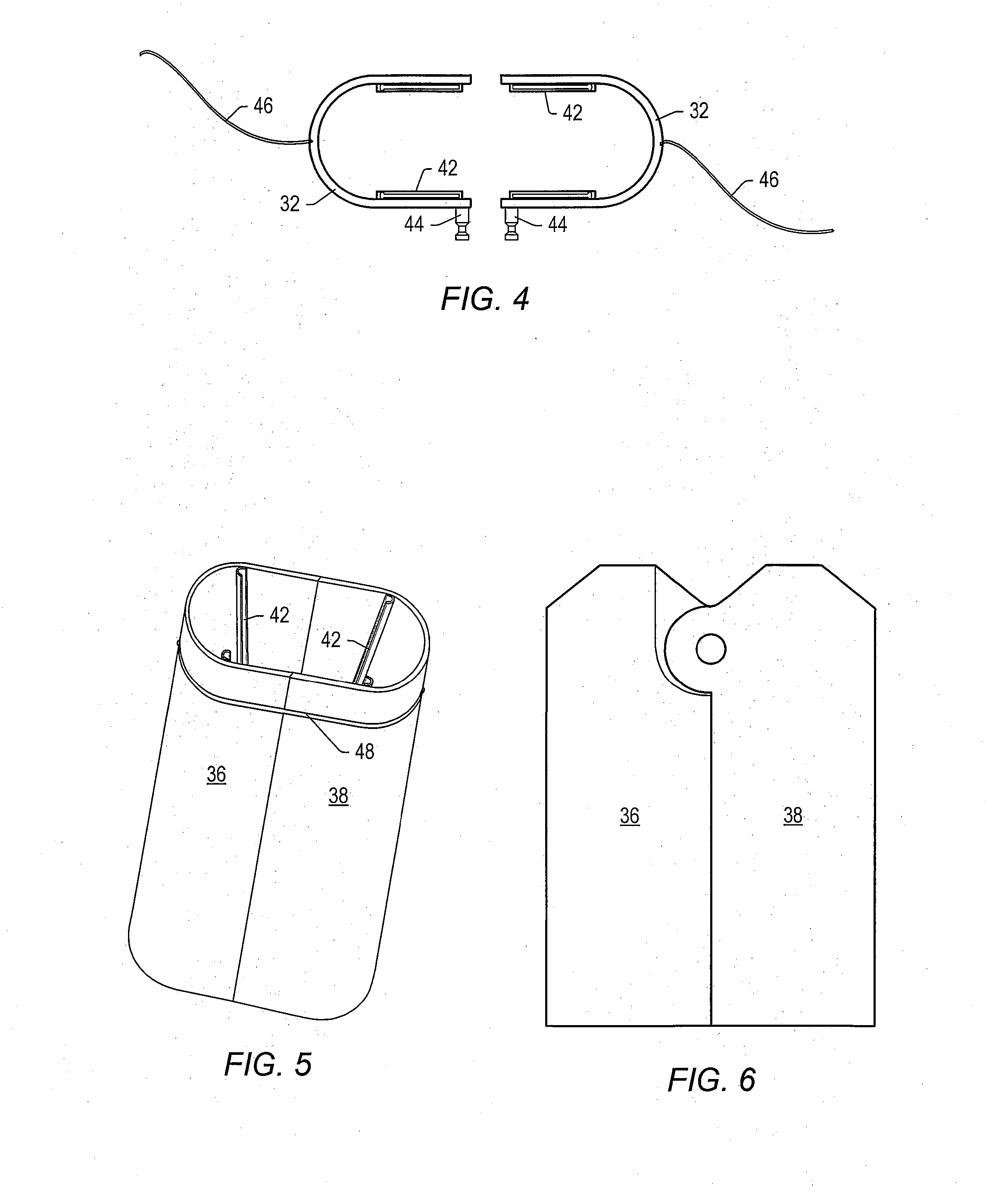
A minimally invasive retractor system is shown which has a support frame having two opposing pairs of horizontally oriented sides. The sides of the frame can be adjusted to vary an interior space of the frame. Four retractor blades are mounted on the frame for engaging tissue within a surgical site. Each retractor blade has an elongate body portion with a length which is oriented perpendicularly to the frame in use. One of the retractor blades can be equipped with a light source and a suction source which are integral to the blade. The blade also has an integral power source for powering the light source. The blade can also house a tissue retractor such as a dural retractor for retracting the dural sack of a patient during spinal surgery.
Owner:ZIMMER BIOMET SPINE INC
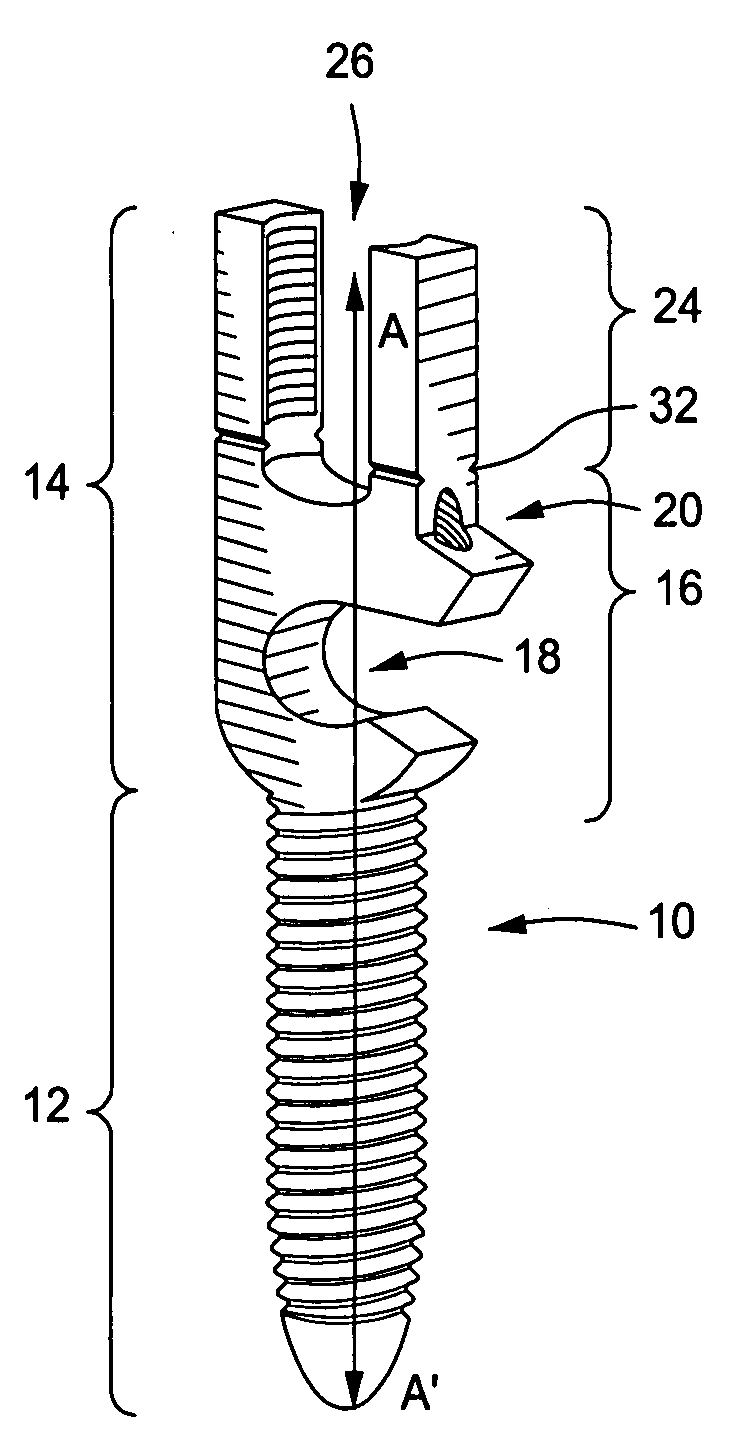
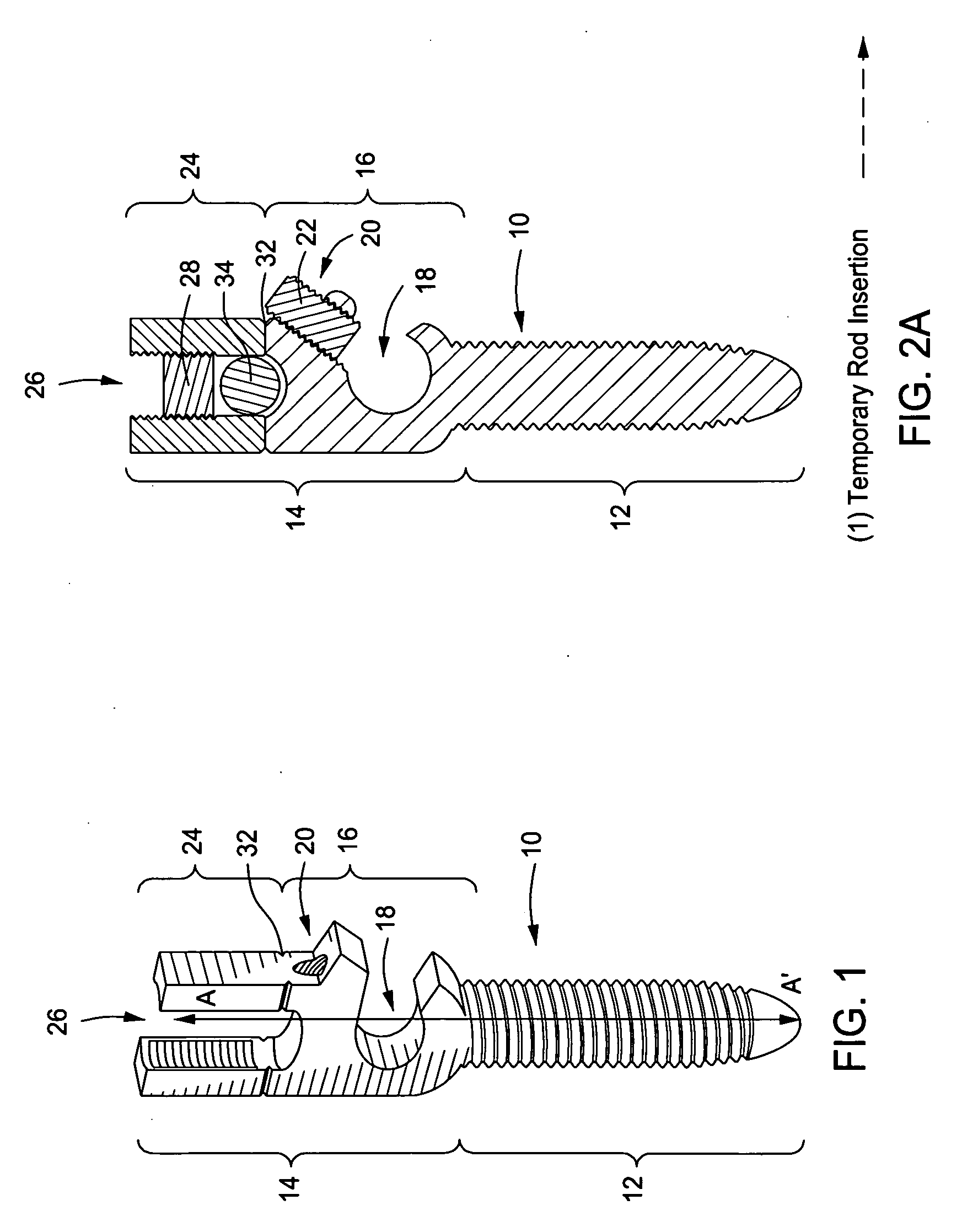
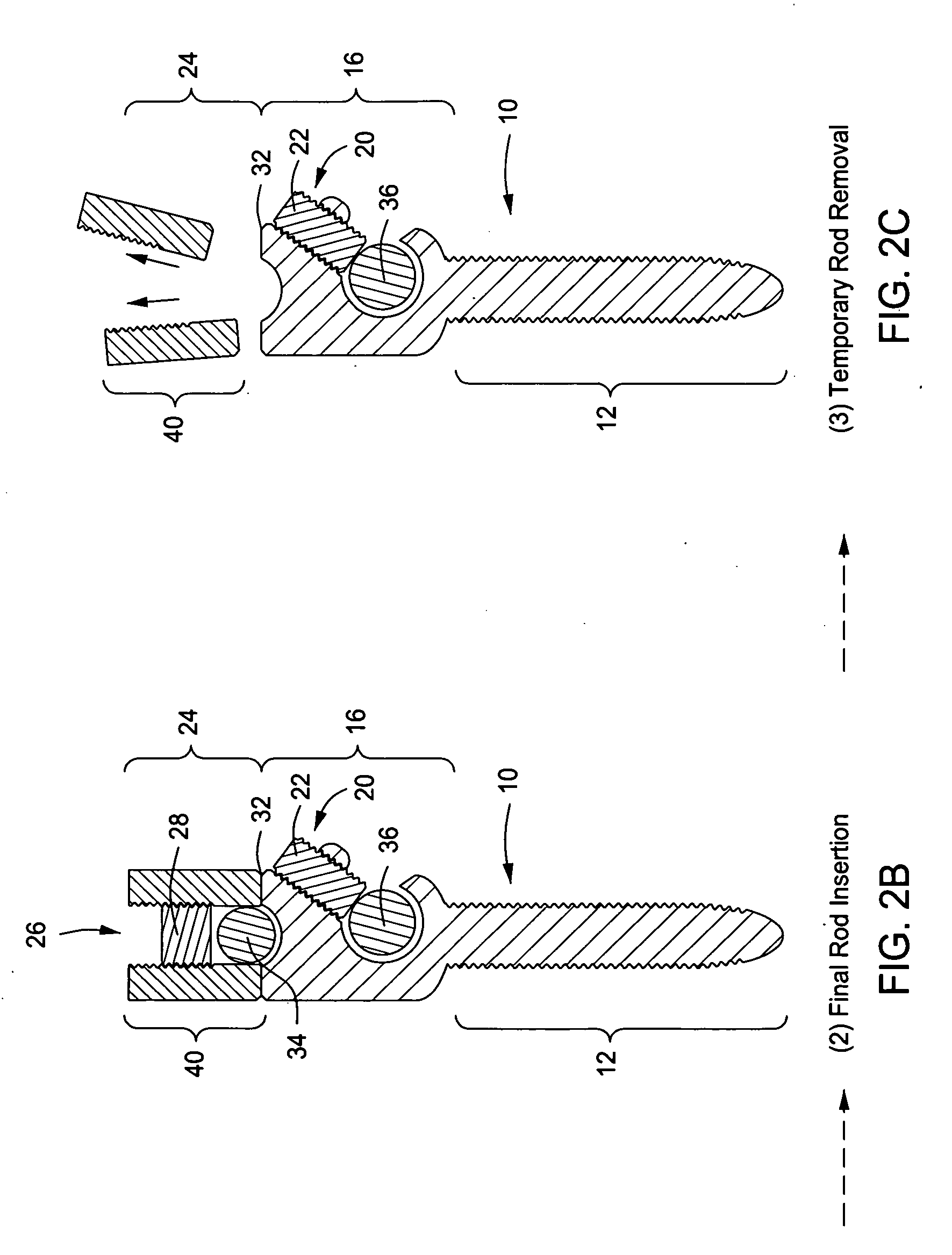
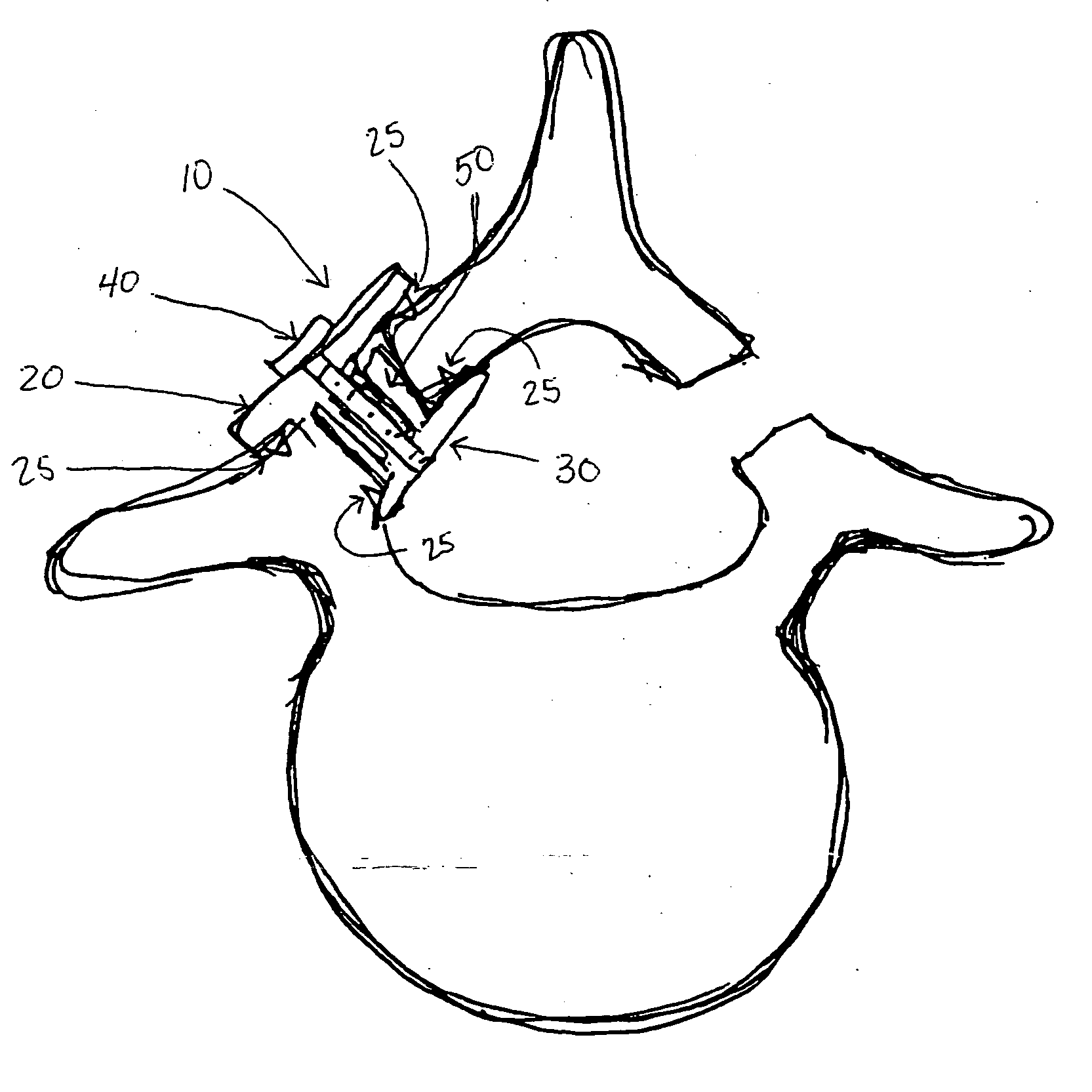
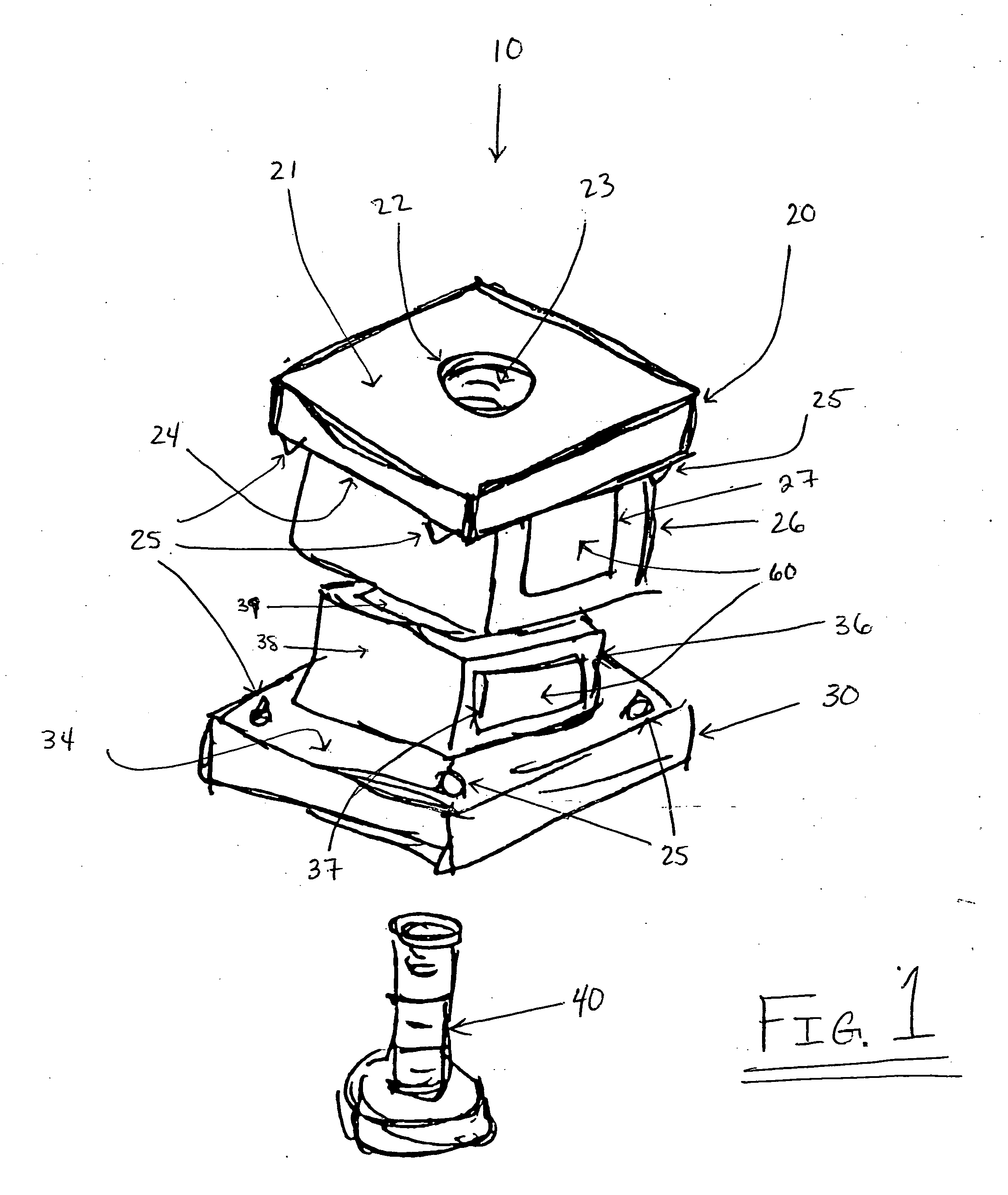
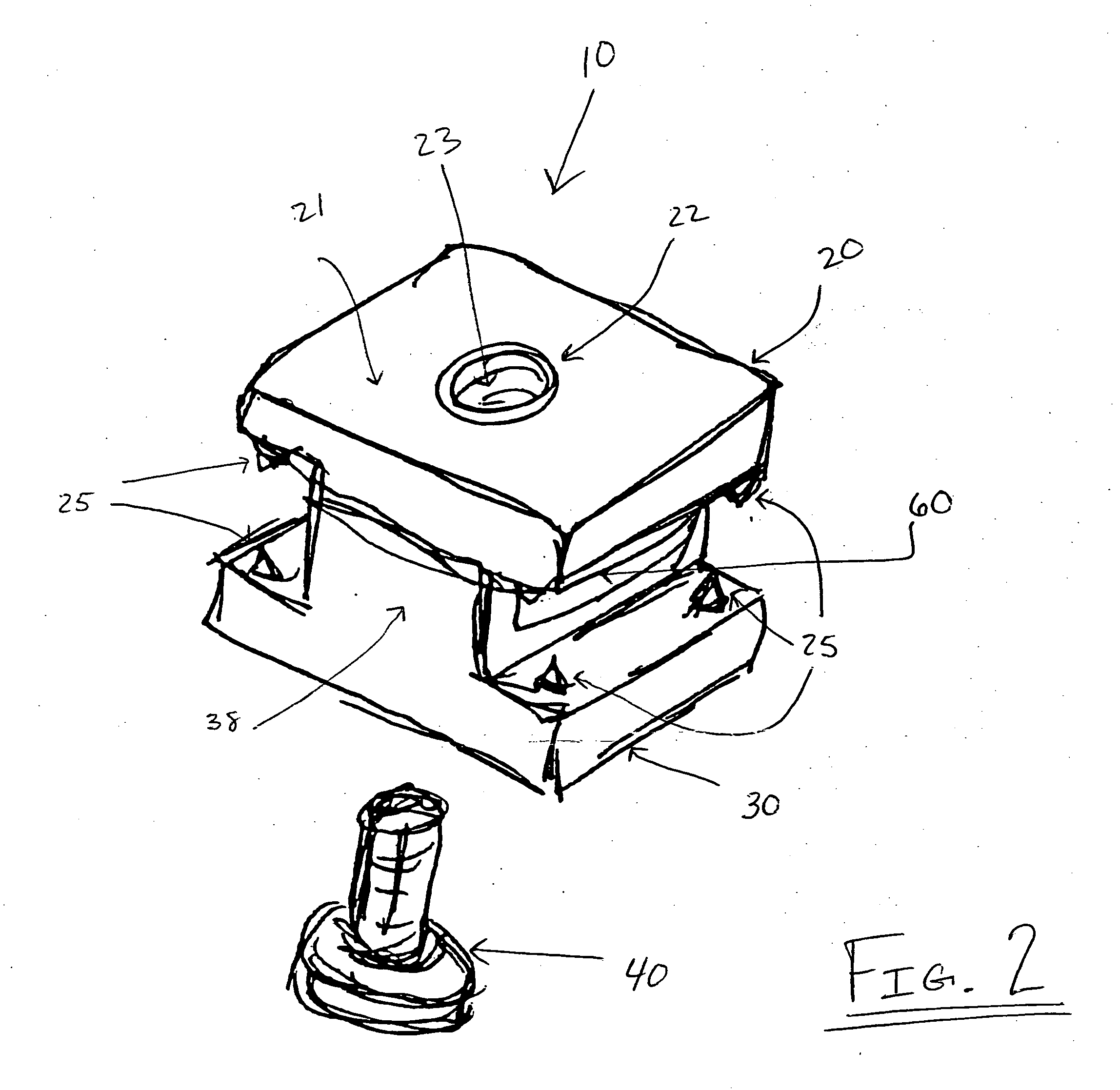
Bone anchoring assembly
InactiveUS20070233086A1Easy to fixHigh strengthInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsTrauma surgeryEngineering
A bone anchoring assembly for use in spinal surgery or trauma surgery includes an anchoring element having a shaft and a receiving part having a substantially U-shaped cross-section with a base connected to said shaft and two free legs forming a channel for receiving a rod having an at least partially structured surface. The bone anchoring assembly further includes a locking member cooperating with the receiving part for locking said rod in the channel. At least on the locking member or in the receiving part an engagement portion for engaging said structured surface of the rod is provided. The locking member, the rod and the receiving part cooperate in such a manner that as soon as the engagement portion comes into engagement with the structured surface the rod is held in the receiving part in a form-locking manner preventing movement of the rod.
Owner:BIEDERMANN TECH GMBH & CO KG
Mechanical apparatus and method for artificial disc replacement
InactiveUS20060287727A1Increase the diameterEasy to integrateSuture equipmentsBone implantPolyesterClosed loop
The present invention relates to a device and method which may be used to reinforce the native annulus during spinal surgery. The device is a catheter based device which is placed into the inter-vertebral space following discectomy performed by either traditional surgical or endoscopic approaches. The distal end of the catheter is comprised of an expansile loop which may be increased in diameter by advancement of a portion of the catheter via its proximal end, such proximal end remaining external to the body. The expansile loop may be formed of a woven or braided material and may be made of a polymer such as nylon, polyurethane, polyester, polyethylene, polypropylene or any of the well known and biocompatible polymers. Alternatively the expansile portion of the catheter may be formed from a metallic braid of stainless steel, elgiloy, Nitinol, or other biocompatible metals. The expansile loop may be formed such that when the loop is diametrically contracted the loop feeds into its other end, similar to a snake eating its own tail. Stabilization of the outer portion of the loop and pulling out the inner portion will thereby increase the overall diameter of the loop while maintaining it as a closed loop or torus. The present invention comprises four embodiments and can be used to 1) facilitate disk fusing, 2) perform an artificial replacement of the nucleus, 3) perform an artificial replacement of the annulus, or 4, perform an artificial replacement of both the nucleus and annulus.
Owner:OUROBOROS MEDICAL INC
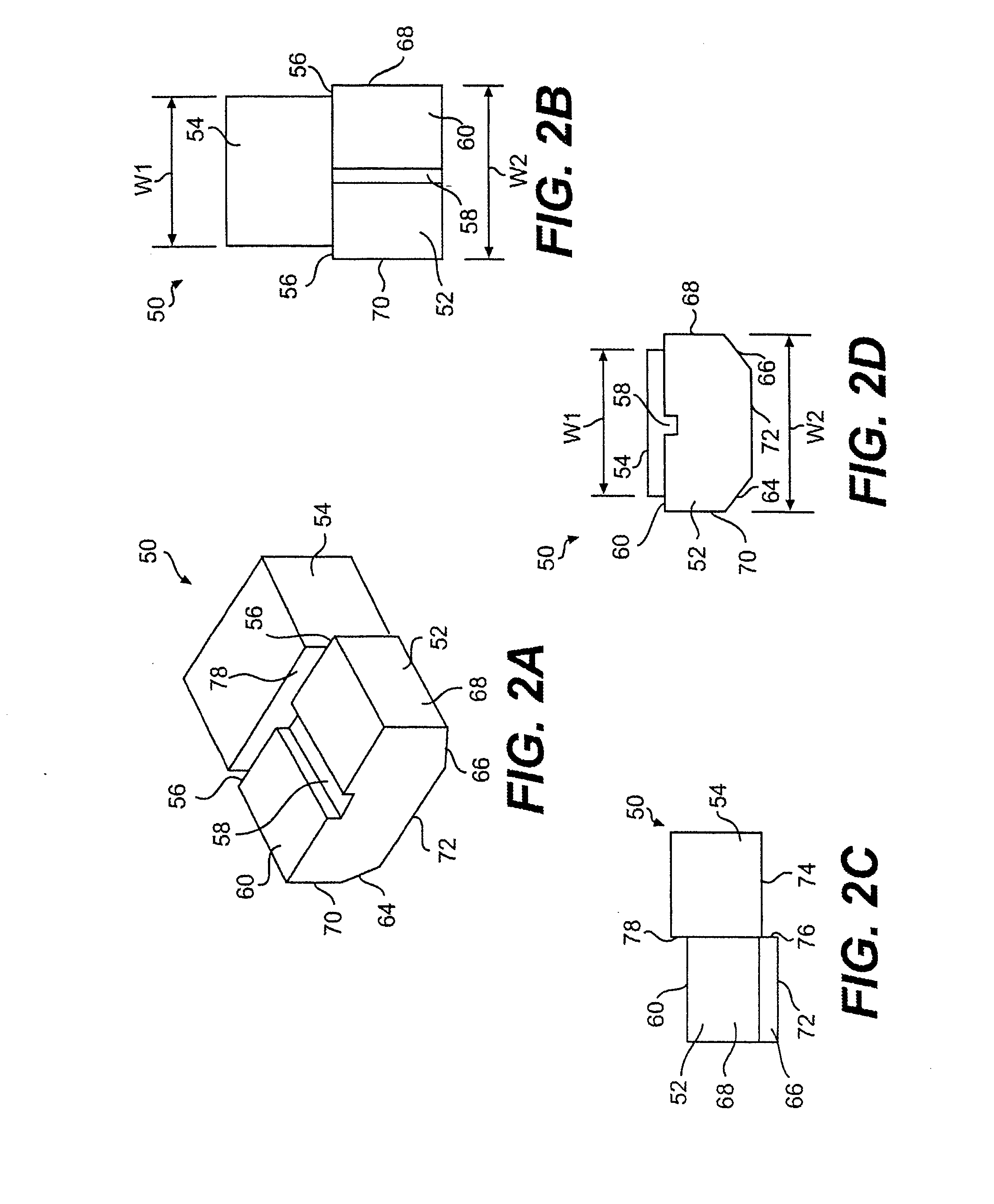
Spine surgery method and implant
ActiveUS20130310939A1Maximizing boney ingrowth surface areaMaximizing bone graft-host contactBone implantSpinal implantsBiomedical engineeringSpine surgery
An implant has a first contact surface to contact a first vertebral body endplate and a second contact surface to contact a second vertebral body endplate adjacent the first vertebral body. The implant is deployable, when positioned within an intradiscal space between the first and second vertebral bodies, from a first non-expanded condition where the first contact surface has a first effective footprint area A1 to a second expanded condition where the first contact surface has a second effective footprint area A2. The ratio A2 / A1 is at least 1.05.
Owner:FABIAN HENRY F +1
Device and method for variably adjusting intervertebral distraction and lordosis
InactiveUS20090099568A1Large depthImprove rigidityInternal osteosythesisSpinal implantsDistractionSpinal column
A removably insertable surgical apparatus is configured for insertion between adjacent vertebrae during spinal surgery and adjusted in-situ to produce varying degrees of distraction, neural-decompression, lordotic, kyphotic and / or scoliotic adjustment in the spine.
Owner:TRANS CORP
Expandable osteoimplant
InactiveUS20080091270A1Improve conformityIncrease contactBone implantSpinal implantsLamina terminalisIncrease size
An osteoimplant comprising an expandable, biocompatible material. The expandable material may be demineralized bone particles such as demineralized cancelous chips or demineralized cortical fibers or may be another material such as a polymer. The osteoimplant has a first state and a second expanded state. The osteoimplant may be used with another device or on its own. The osteoimplant may be inserted into a device such as an intervertebral body fusion device in the compressed state. The osteoimplant may be rehydrated to expand to an increased size, for example as far as permitted by the confines of the intervertebral body fusion device and spinal endplates, thereby aiding in greater vertebral endplate contact and conformity in spinal surgery.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
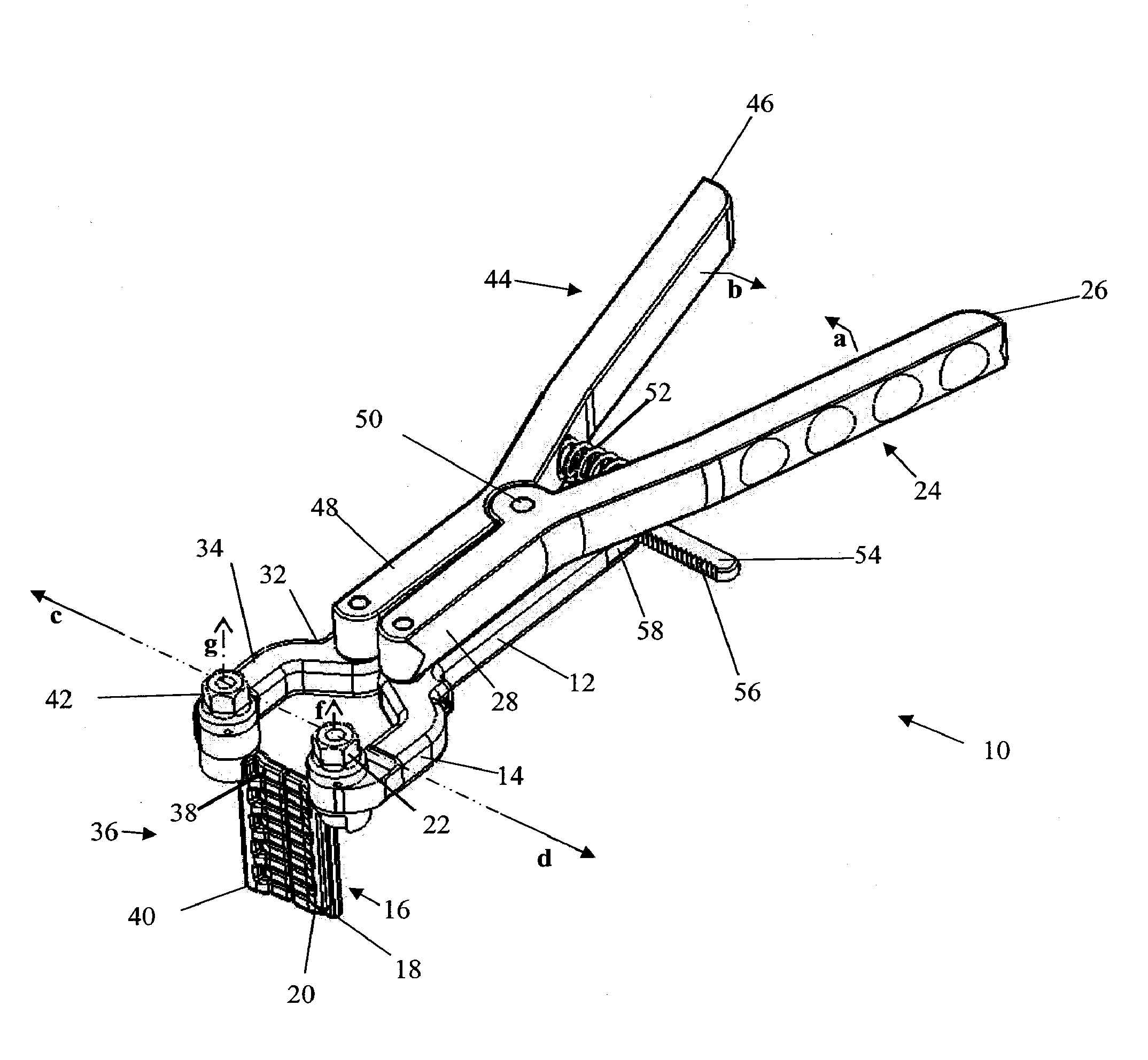
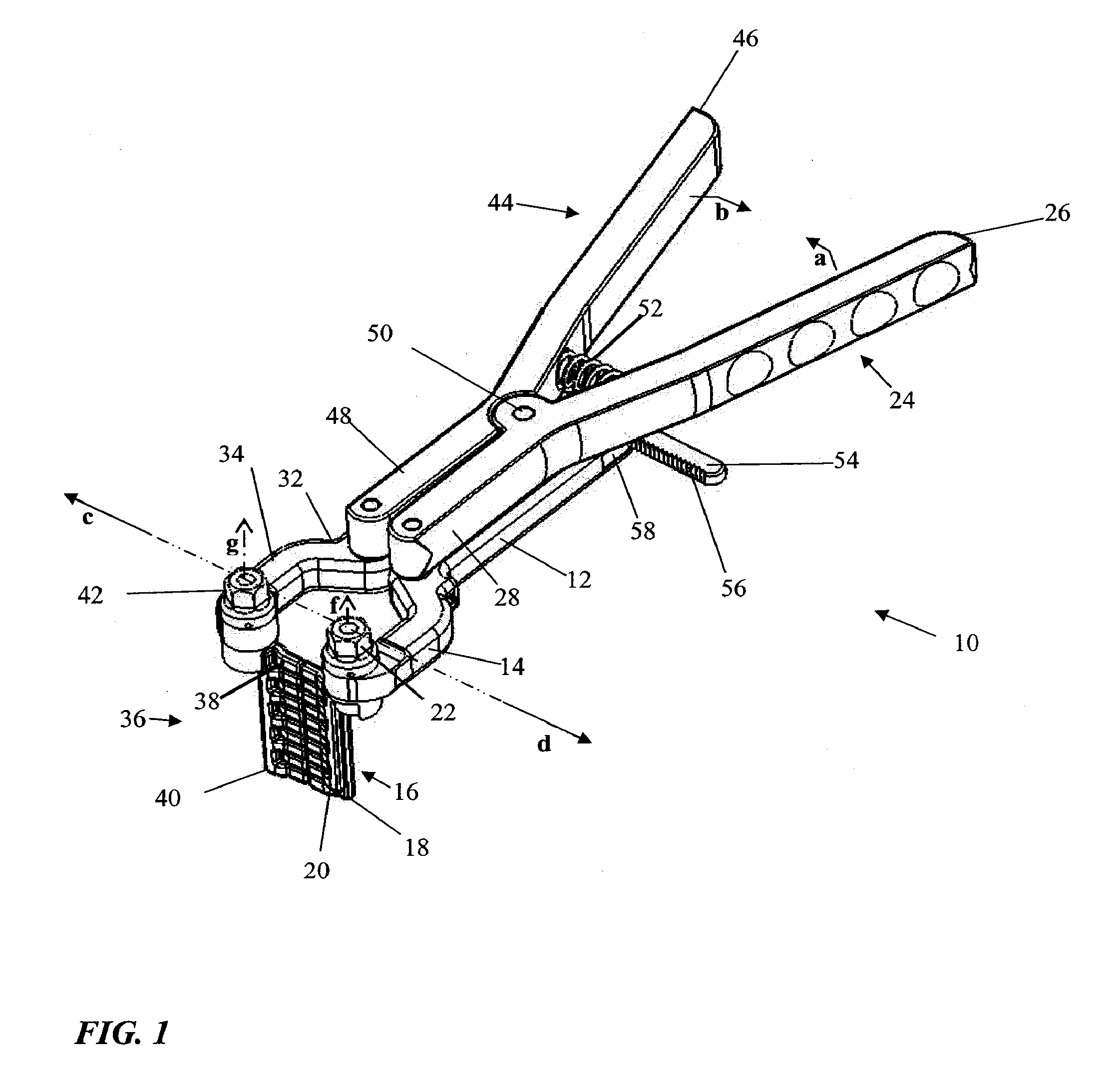
System and method for performing spinal surgery
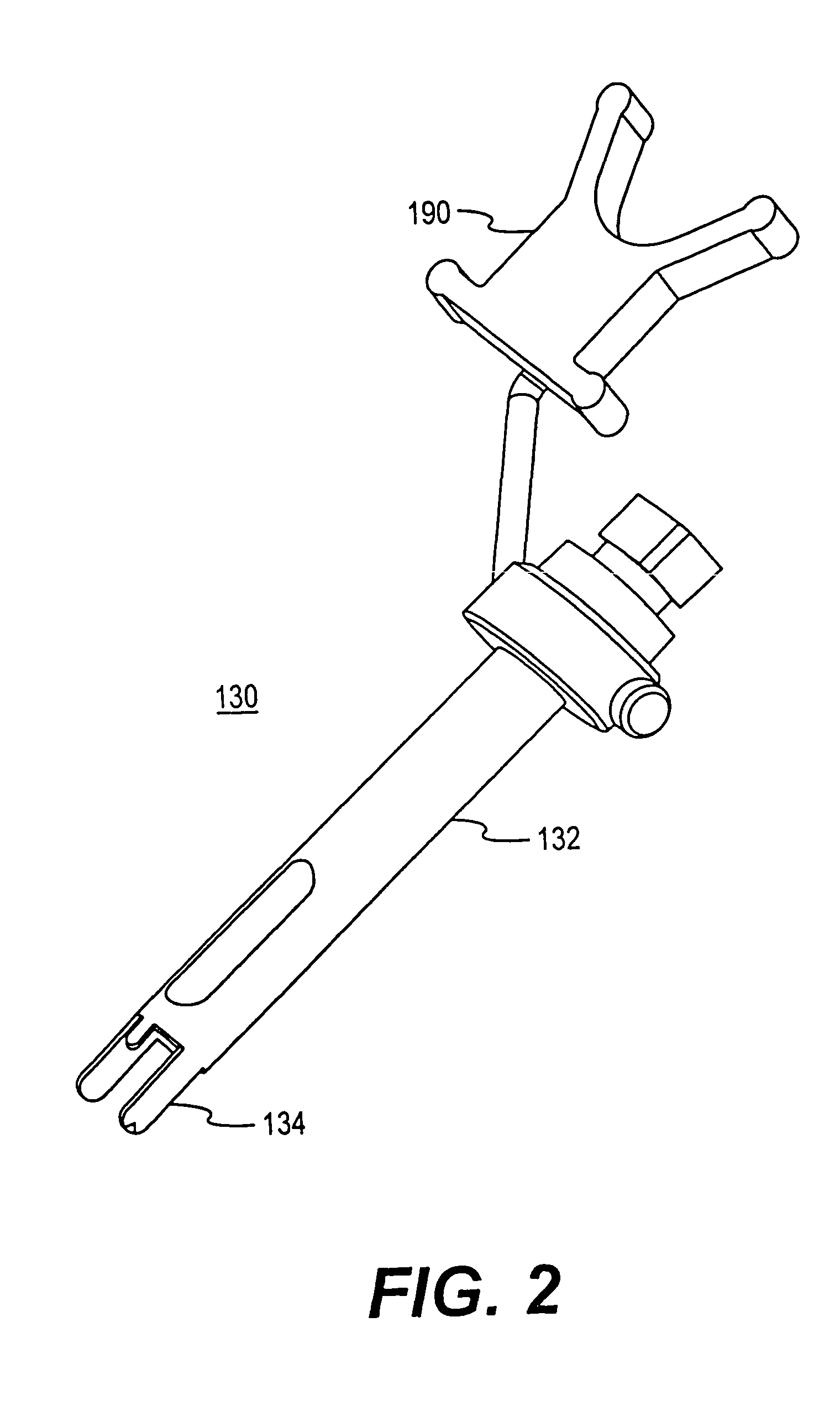
ActiveUS20110172714A1Improve stabilitySmooth rotationInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsVertebraSpinal operation
Systems and methods for surgical spinal correction are disclosed. A system including a plurality of bone screws, spinal rods, manipulators, and / or transverse couplers is disclosed for the manipulation of the spinal column is disclosed. A method of achieving, in a single action, manipulation and / or rotation of the spinal column using the disclosed system is disclosed. Also disclosed is a method of conducting spinal surgery to correct spinal deformities wherein spinal rods are pre-bent in a physiological sagittal plane prior to attachment of the vertebrae using bone screws.
Owner:K2M
Mechanical apparatus and method for artificial disc replacement
InactiveUS20070162135A1Increase the diameterEasy to integrateSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisLamina terminalisClosed loop
The present invention relates to a device and method which may be used to reinforce the native annulus during spinal surgery. The device is a catheter based device which is placed into the inter-vertebral space following discectomy performed by either traditional surgical or endoscopic approaches. The distal end of the catheter is comprised of an expansile loop which may be increased in diameter by advancement of a portion of the catheter via its proximal end, such proximal end remaining external to the body. The expansile loop may be formed such that when the loop is diametrically contracted the loop feeds into its other end, similar to a snake eating its own tail. Stabilization of the outer portion of the loop and pulling out the inner portion will thereby increase the overall diameter of the loop while maintaining it as a closed loop or torus. The expansile loop can use an attachment means to secure it to substantially healthy tissues of the annulus, nucleus, or endplates. The present invention comprises four embodiments and can be used to 1) facilitate disk fusing, 2) perform an artificial replacement of the nucleus, 3) perform an artificial replacement of the annulus, or 4, perform an artificial replacement of both the nucleus and annulus.
Owner:OUROBOROS MEDICAL INC
Spinal Rod Link Reducer
ActiveUS20090198279A1Process stabilityEffectively derotateSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisReducerManipulator
The present invention includes a rod link reducer of a spinal fixation system that includes a first and a second spinal rod manipulator; a first spinal rod manipulator joint connected to the first spinal rod manipulator and a second spinal rod manipulator joint connected to the second spinal rod manipulator; a first and a second translatable transverse shaft connected to the first and second joints, respectively; and a universal reducer connected to both the first and second translatable transverse shafts, wherein the universal reducer, the shafts and the linkers provide movement and temporary fixation of a spine that has been manipulated into a final position during spinal surgery.
Owner:GLOBUS MEDICAL INC
Computerized Planning Tool For Spine Surgery and Method and Device for Creating a Customized Guide for Implantations
InactiveUS20120150243A9Minimal effortMaximize accuracyMedical simulationAdditive manufacturing apparatusTouch PerceptionFinite element software
A system for planning a spine surgery, comprising a haptic interface capable of providing force feedback to the user and a computer adapted to simulate a surgical procedure by responding to inputs from the haptic interface and outputting haptic feedback to the haptic interface is provided.The system further comprising a rapid prototyping unit including a unit that is adapted to create models of the anatomical region where the surgical procedure will be performed in its current unoperated condition and in the predicted postoperative condition. Further the rapid prototyping unit is adapted to create a three dimensional guide to be used in the surgical procedure as well as suggest revisions to the surgical procedure. The system further comprises a computer that simulates loading of the spine and planned implanted hardware using finite element software.
Owner:DIGNITY HEALTH
Image guided spinal surgery guide, system and method for use thereof
InactiveUS7763035B2Improve proper placementPermit trackingBone implantSurgical navigation systemsThree-dimensional spaceNavigation system
Owner:SOFAMOR DANEK GRP INC +1
System and methods for restoring the structural integrity of bone
InactiveUS20050107877A1Encourages reformationPrevent slippingInternal osteosythesisBone implantCouplingBones fusion
A laminoplasty device including a superior attachment panel, inferior base panel, and a coupling screw for use in repair of lamina after spinal surgery. The interior of the fully assembled laminoplasty device contains a fusion corridor in which bone fusion material can be placed to facilitate regeneration of the lamina.
Owner:NUVASIVE
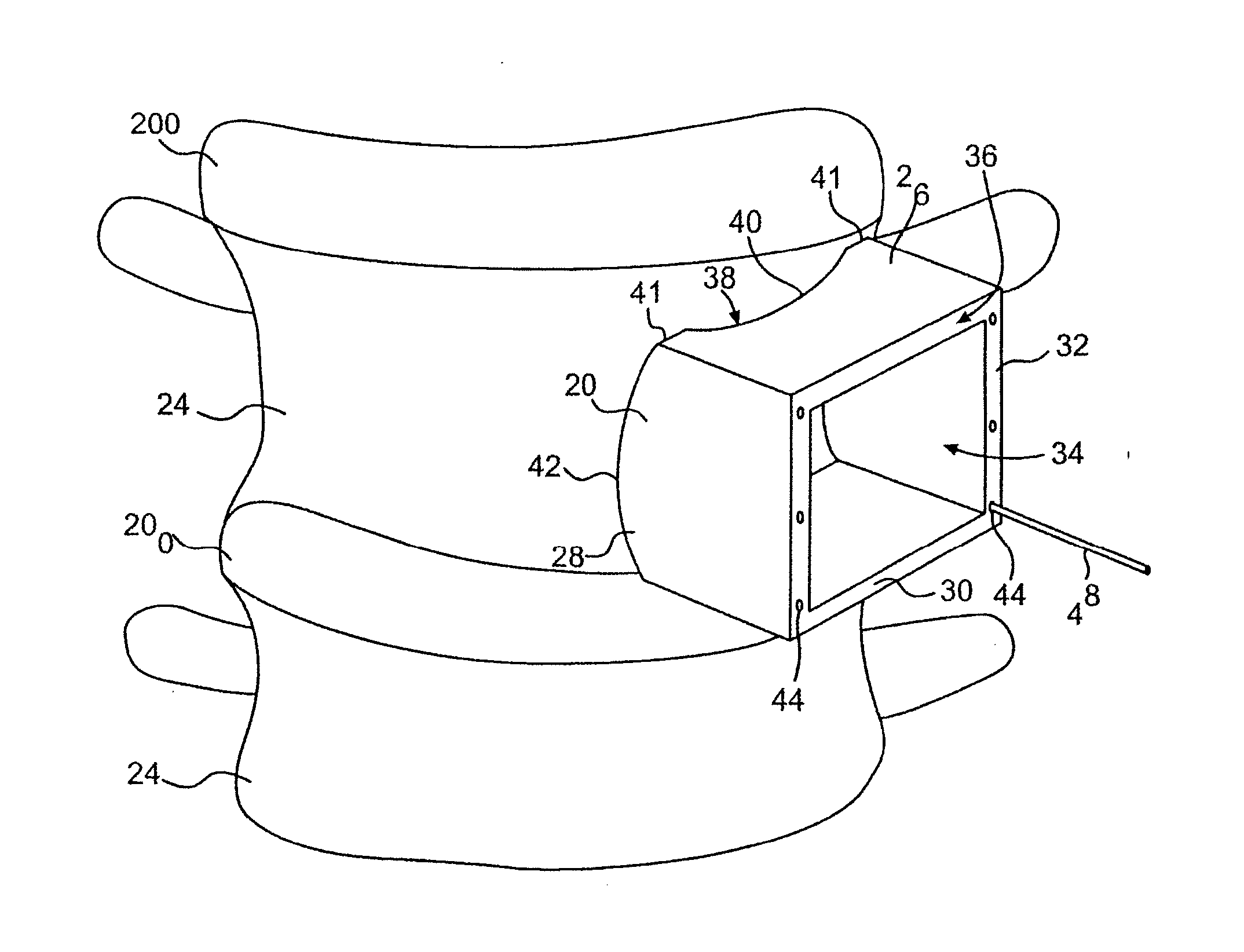
Device and method for tissue retraction in spinal surgery
InactiveUS20090076516A1Maintaining soft tissue retractionLess manipulationProsthesisBone platesSpinal columnIntervertebral space
The invention relates to a system and methods for retracting soft tissue during spinal repair or reconstruction procedures, particularly procedures within intervertebral sites of degenerated discs and associated neural compression. A retractor system includes an implantable bone plate, two or more retractor blades, the bone plate and retractor blades being mutually engageable; and a mechanism to adjust the retractor blade relative to the bone plate. In some embodiments, the retractor system may be applied to span more than one intervertebral space. An implanted retractor system provides an aperture for a clear operating field, and protects collateral tissue. A method for retracting soft tissue to facilitate spinal surgery includes securing a bone plate to adjacent vertebral bodies, engaging one or more retractor blades to the bone plate; and adjusting the angular position of the retractor blade relative to the bone plate so as to retract tissue lying external to the bone plate.
Owner:TRANS CORP
Mechanical apparatus and method for artificial disc replacement
InactiveUS7601172B2Easy to integrateFree from painSuture equipmentsBone implantLamina terminalisClosed loop
The present invention relates to a device and method which may be used to reinforce the native annulus during spinal surgery. The device is a catheter based device which is placed into the inter-vertebral space following discectomy performed by either traditional surgical or endoscopic approaches. The distal end of the catheter is comprised of an expansile loop which may be increased in diameter by advancement of a portion of the catheter via its proximal end, such proximal end remaining external to the body. The expansile loop may be formed such that when the loop is diametrically contracted the loop feeds into its other end, similar to a snake eating its own tail. Stabilization of the outer portion of the loop and pulling out the inner portion will thereby increase the overall diameter of the loop while maintaining it as a closed loop or torus. The expansile loop then uses an attachment means to secure it to substantially healthy tissues of the annulus, nucleus, or endplates. The present invention comprises four embodiments and can be used to 1) facilitate disk fusing, 2) perform an artificial replacement of the nucleus, 3) perform an artificial replacement of the annulus, or 4, perform an artificial replacement of both the nucleus and annulus.
Owner:OUROBOROS MEDICAL INC
Surgical retractor and method of use
A surgical retractor may be provided for a surgical procedure such as spinal surgery. The surgical retractor may include a pair of tissue retainers and a pair of separators. The separators may be positioned in channels of the tissue retainers to move distal ends of the tissue retainers apart, retract tissue, and enlarge an opening in a patient. In some embodiments, a nerve root retractor may be removably coupled to a surgical retractor to retain dura on one side of the spinal column and provide working room for the surgical procedure.
Owner:THEKEN SPINE
Minimally-invasive retroperitoneal lateral approach for spinal surgery
InactiveUS20120035730A1Realize distributionMinimize traumaSurgerySpinal implantsSpinal columnIntervertebral spaces
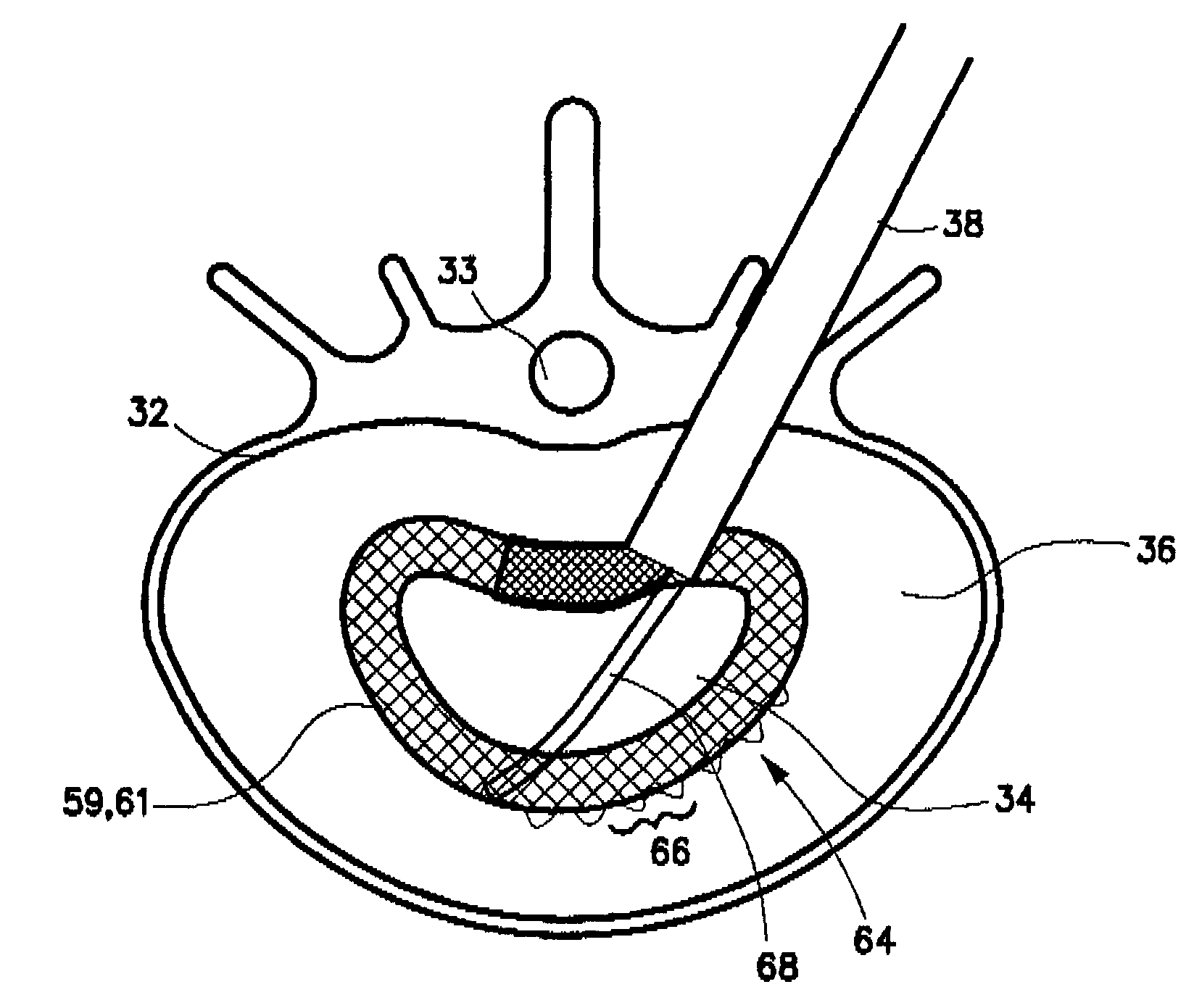
A method is disclosed for introducing a spinal disc implant into an intervertebral space of a subject. The subject is placed in a lateral position, and the anterior face of the spinal disc intervertebral space is accessed, between the L5 and S1 vertebrae, from an anterior and lateral retroperitoneal approach. An operative corridor to the anterior face of the spinal disc space is established by introducing a retractor instrument anterolaterally to the spinal disc space between the anterior superior iliac spine and the anterior inferior iliac spine. The damaged spinal disc contents are removed from the intervertebral space through the operative corridor, and the implant is advanced into the intervertebral space at an oblique angle and pivoted to position the implant substantially laterally within the intervertebral space. Elongated retractor and insertion instruments, as well as a modified disc implant, are also disclosed for carrying out the method.
Owner:PANTHEON SPINAL
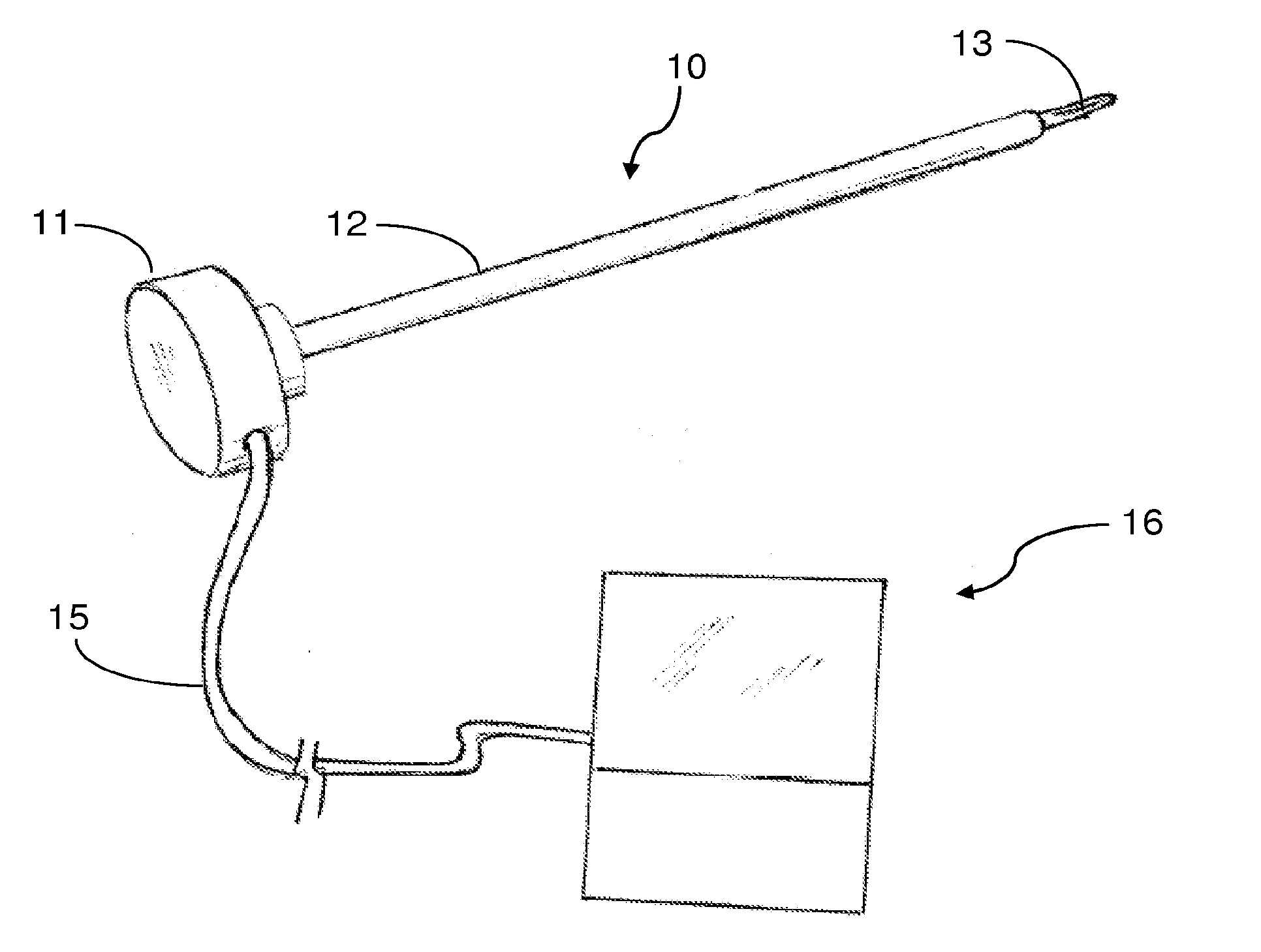
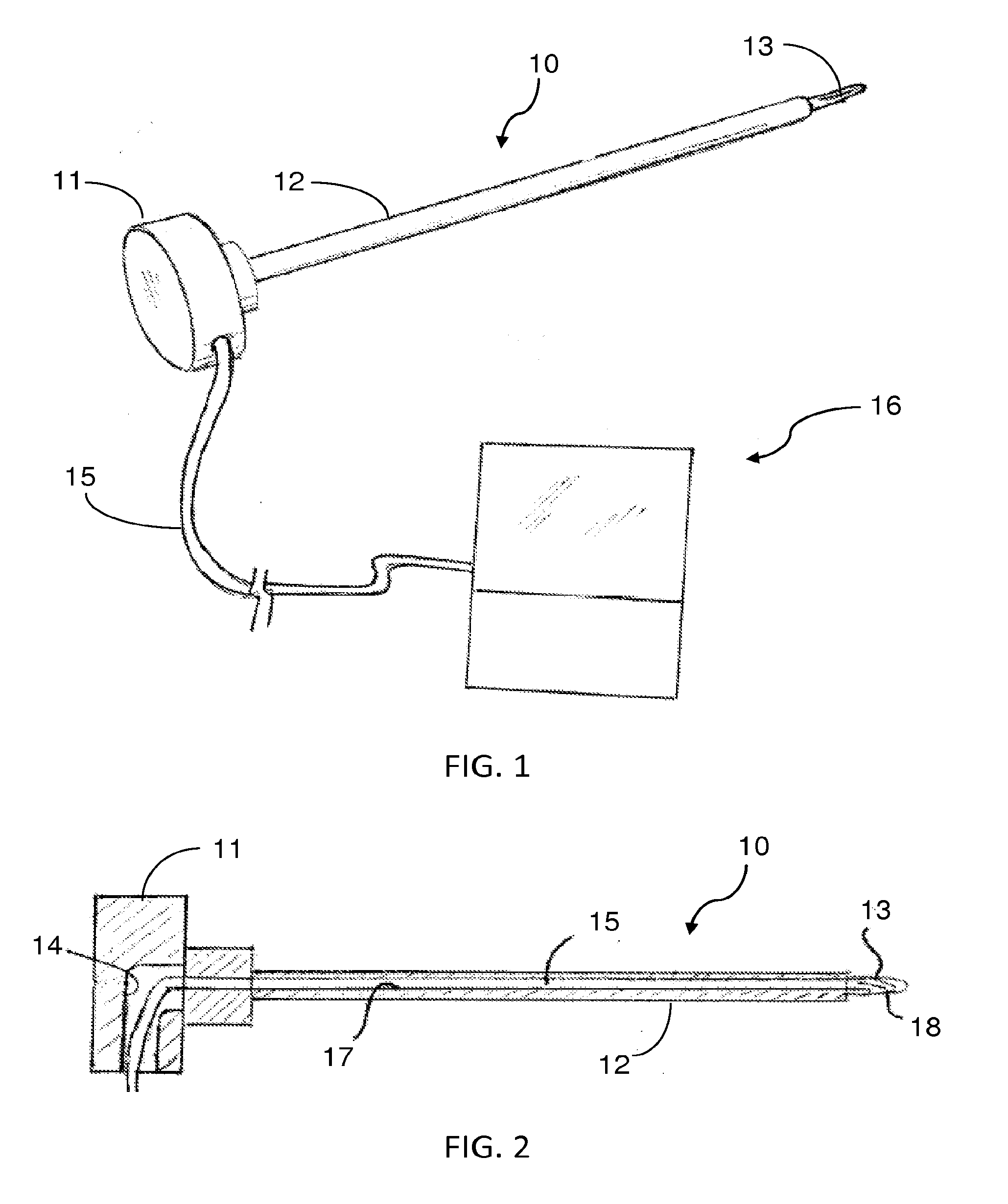
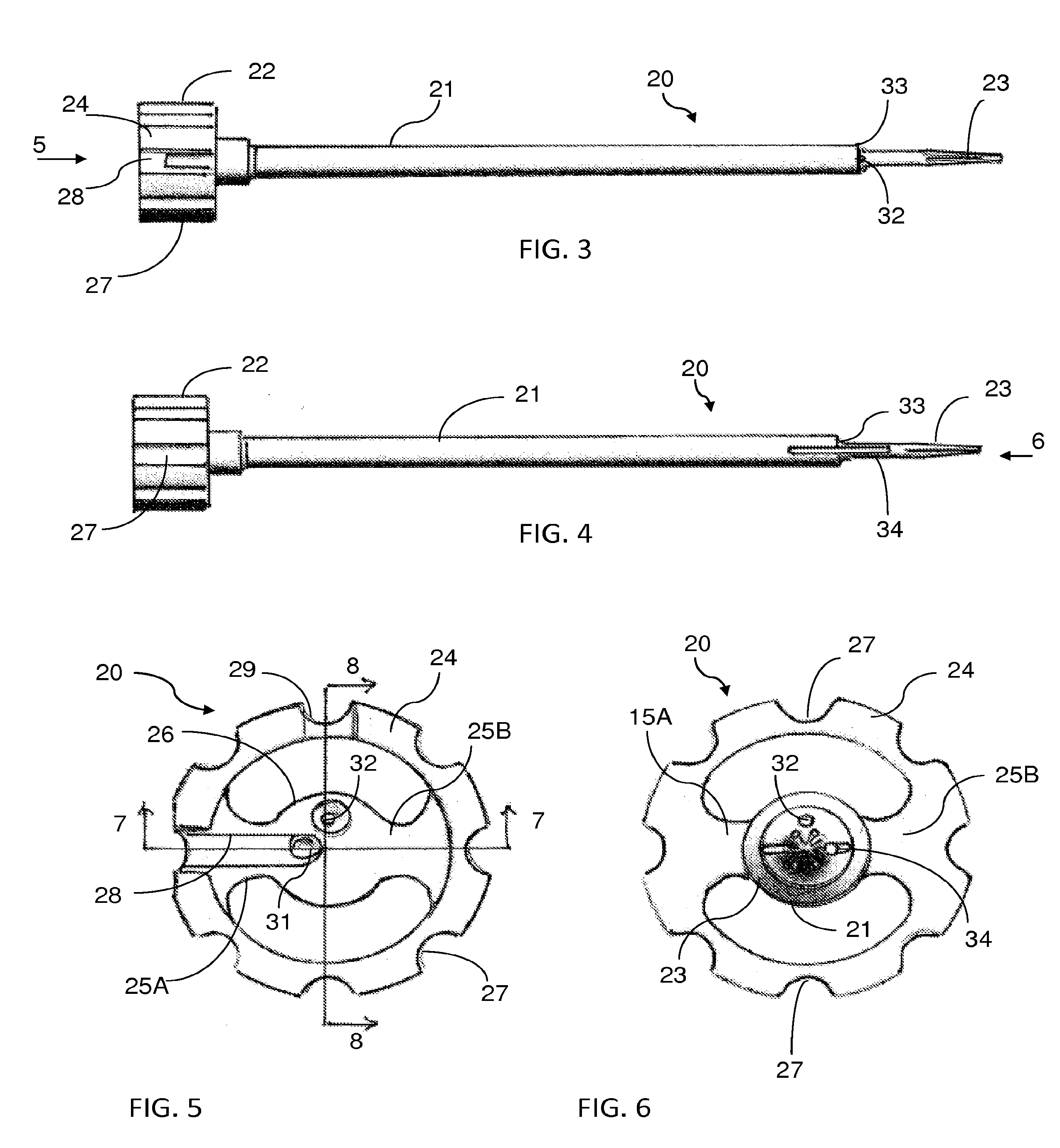
Illuminated endoscopic pedicle probe with dynamic real time monitoring for proximity to nerves
InactiveUS20150342621A1Prevent breachDirectly and accurately determinedSpinal electrodesElectromyographyVisual observationMonitoring system
An endoscopic pedicle probe for use during spinal surgery to form a hole in a pedicle for reception of a pedicle screw has an enlarged proximal end for cooperation with the hand of the surgeon and an elongate shaft terminating in a distal tip that may be pushed through the pedicle to form the hole. An integrated endoscope and light extend through the shaft to enable the surgeon to visually observe the target area, and a conduit extends through the shaft to convey a fluid to irrigate the target area. In a preferred form the probe is connected with an electromyographic or mechanomyographic monitoring system to alert the surgeon when a breach is about to occur. In a further embodiment, two endoscopes are associated with the probe. The complete probe may be disposable, or just the tip may be detachable for disposal or replacement.
Owner:OPTICAL SPINE LLC
Apparatus and method for performing spinal surgery
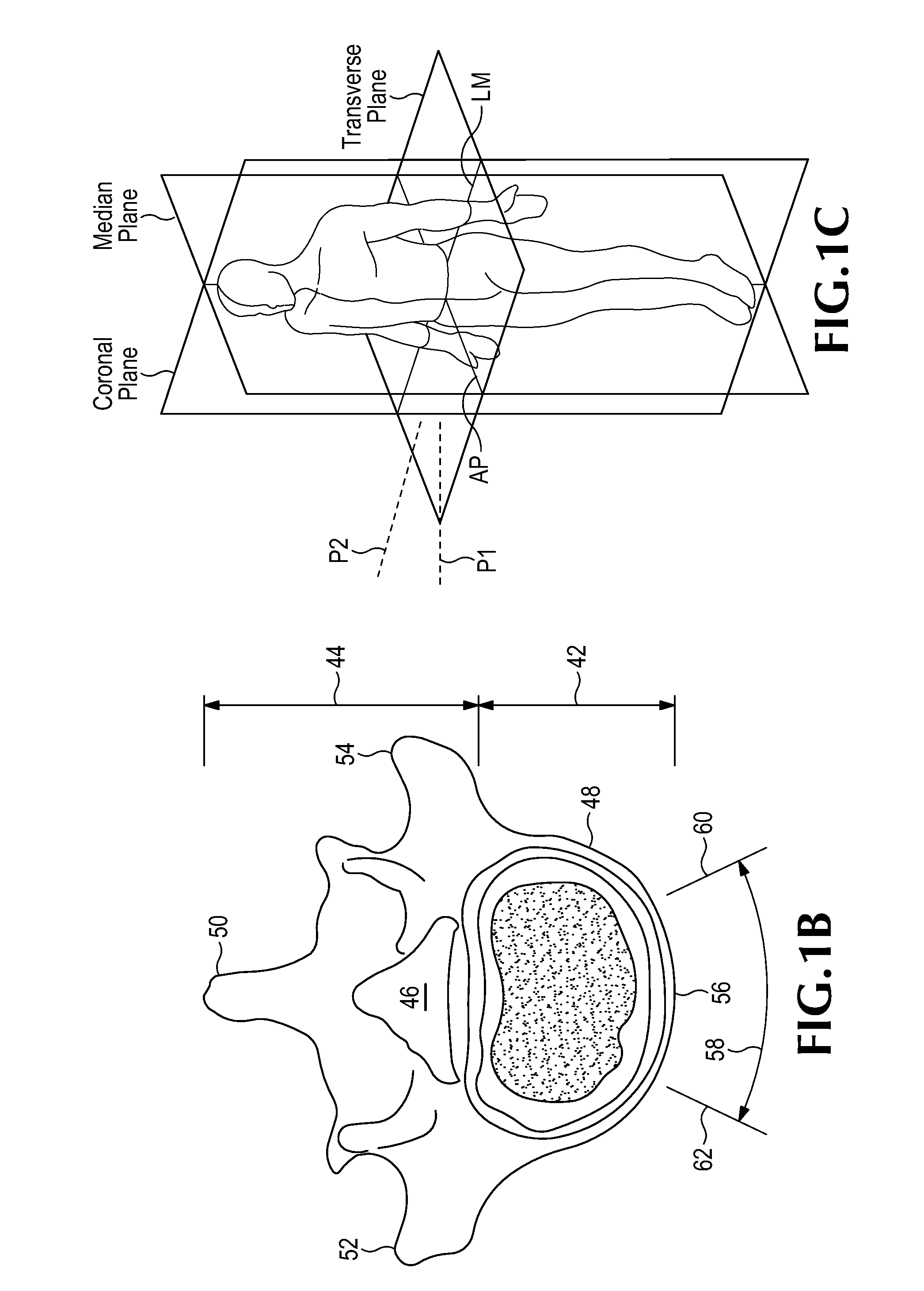
InactiveUS20080045966A1DiagnosticsNon-surgical orthopedic devicesLamina terminalisIntervertebral disc
A cutting guide for use in spinal surgery includes a sidewall defining an internal cavity. A chisel guide, for use with the cutting guide, includes a first block member to be inserted into the internal cavity of the cutting guide to position the first block member adjacent the vertebral body. The chisel guide also includes a second block member connected to the first block member. An apparatus for creating a cavity in a-vertebral body endplate and in an intervertebral disc may be a compressor or a distractor having at least one cutting implement thereon. A tensioner determines a proper elongation distance in a prosthesis implanted in a vertebral body.
Owner:DYNAMIC SPINE
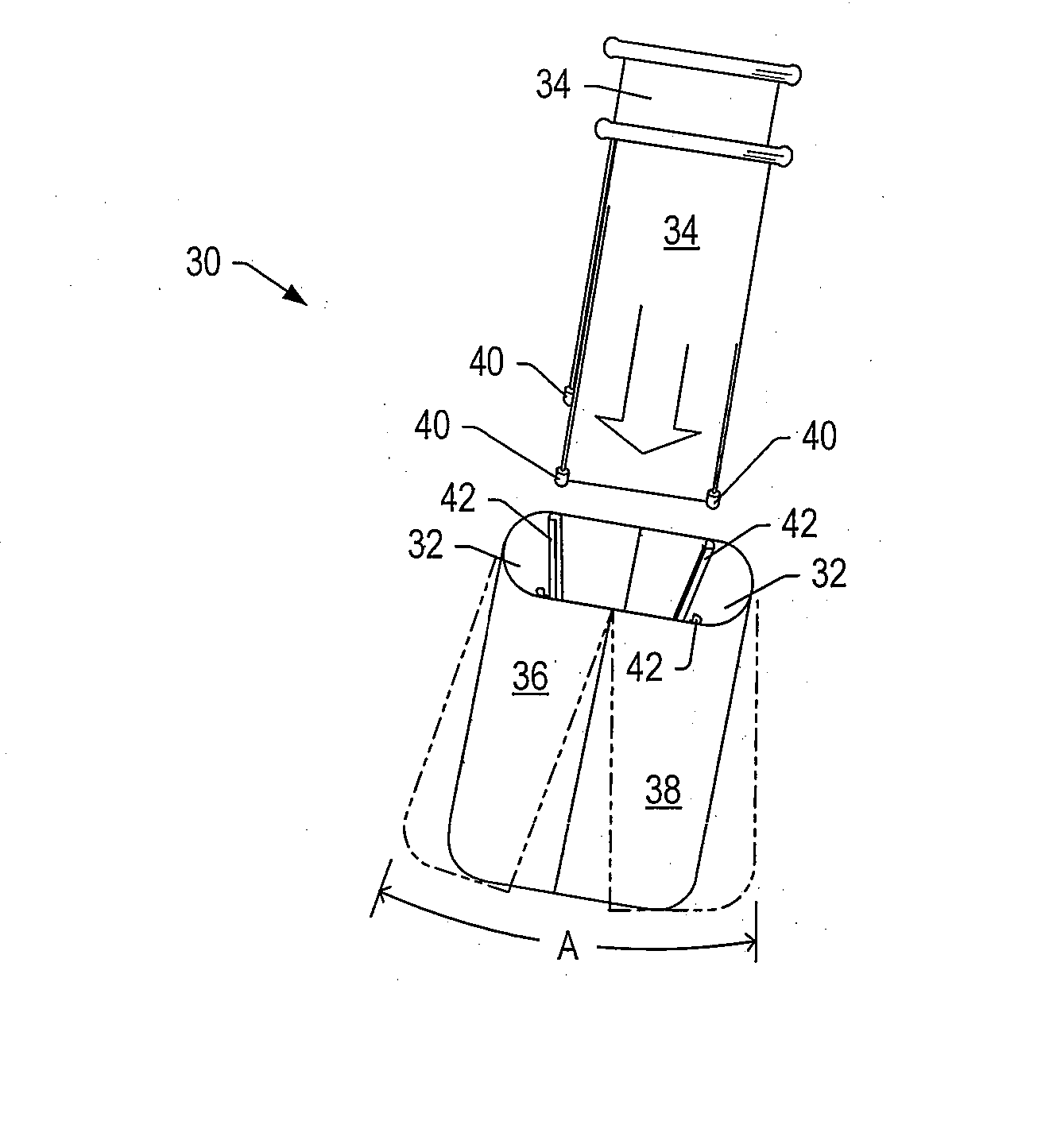
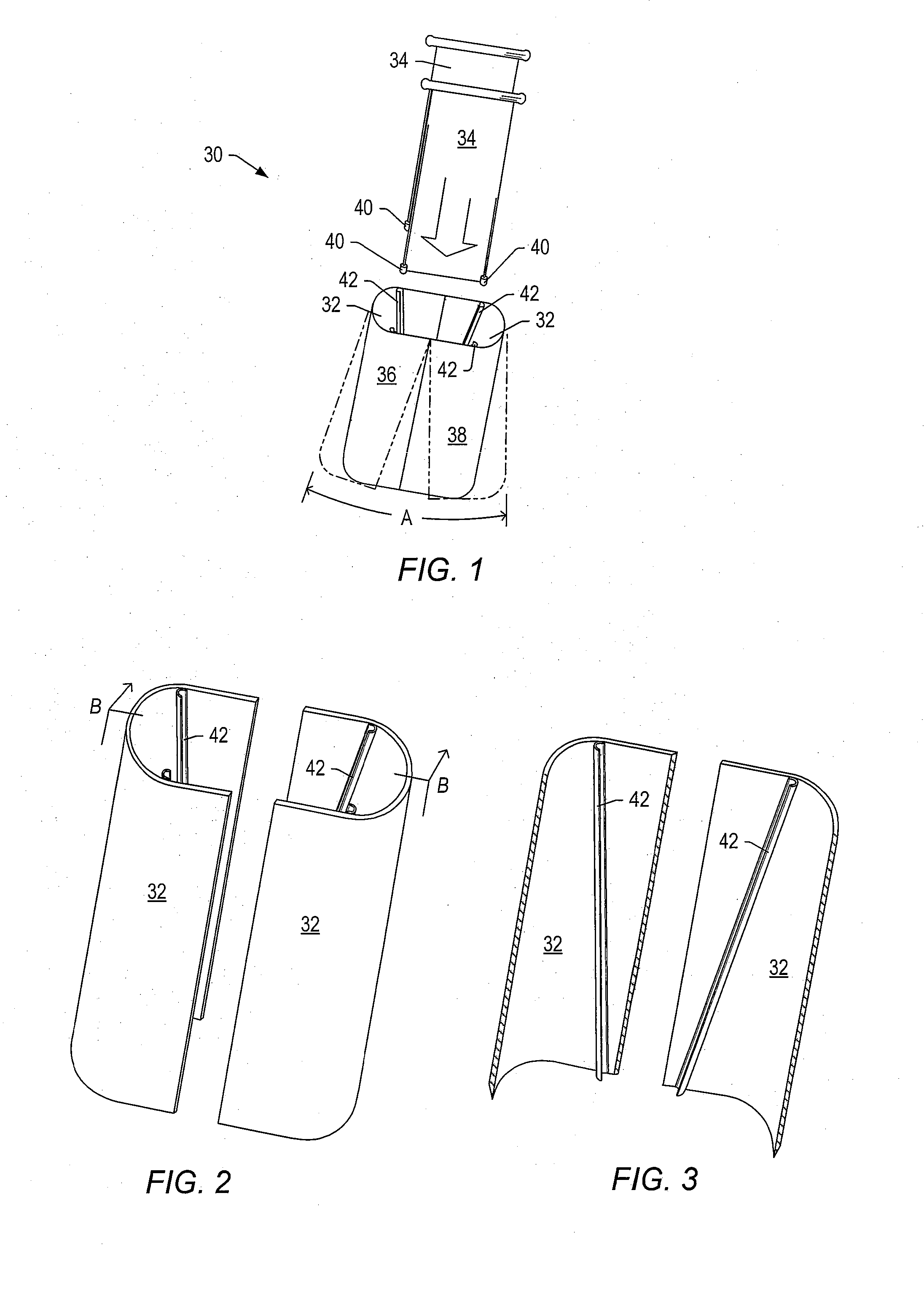
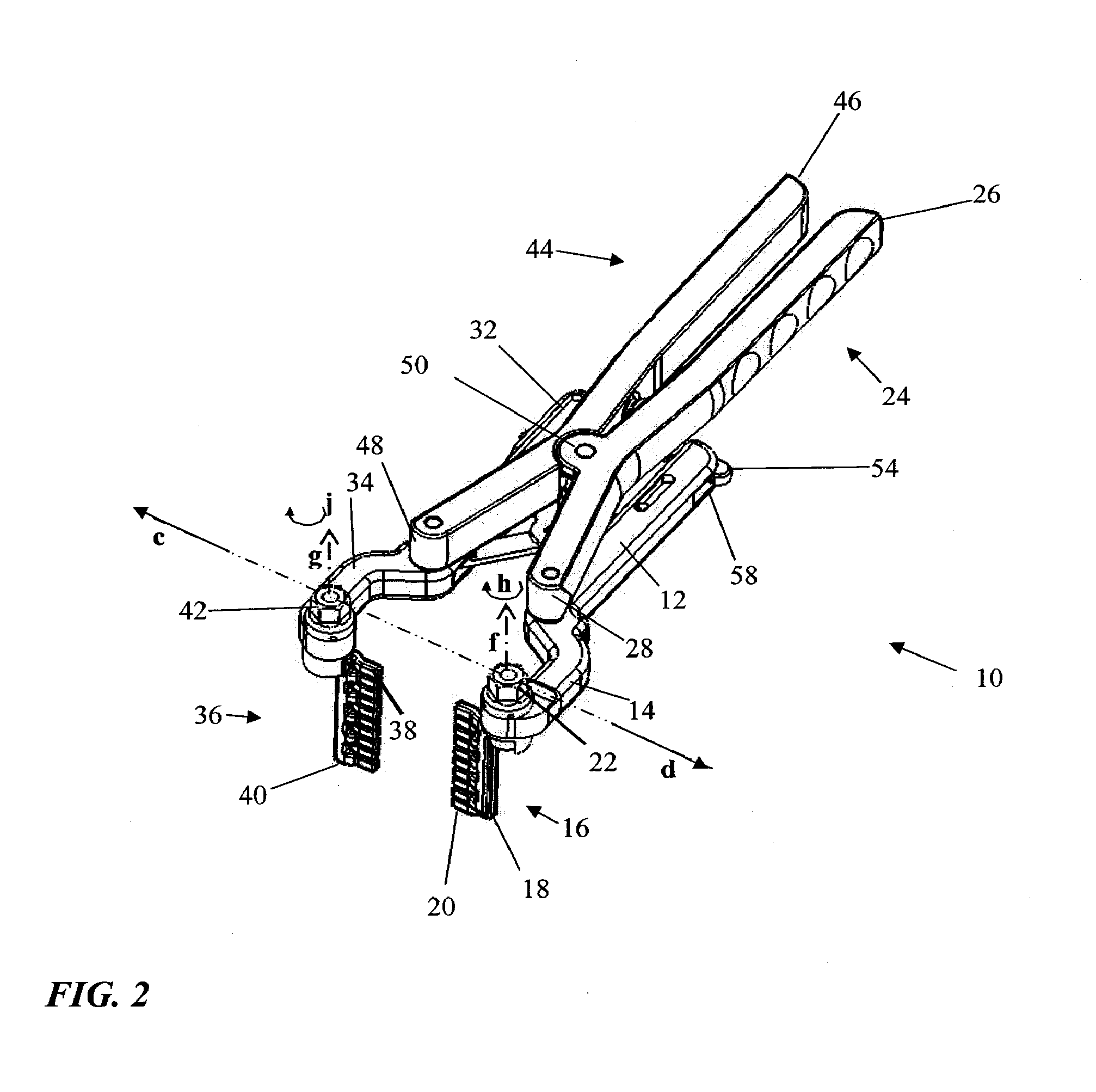
Retractor
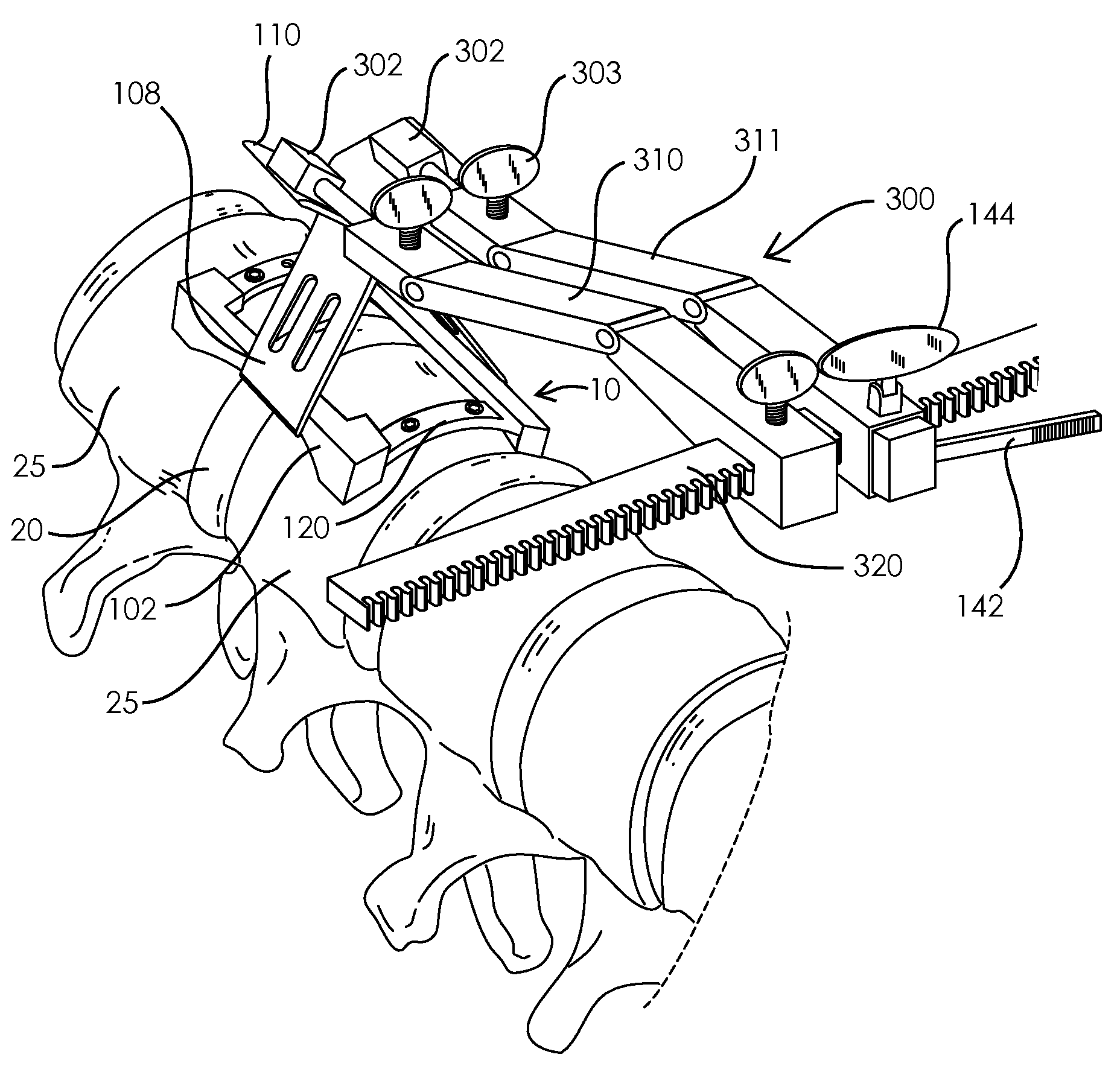
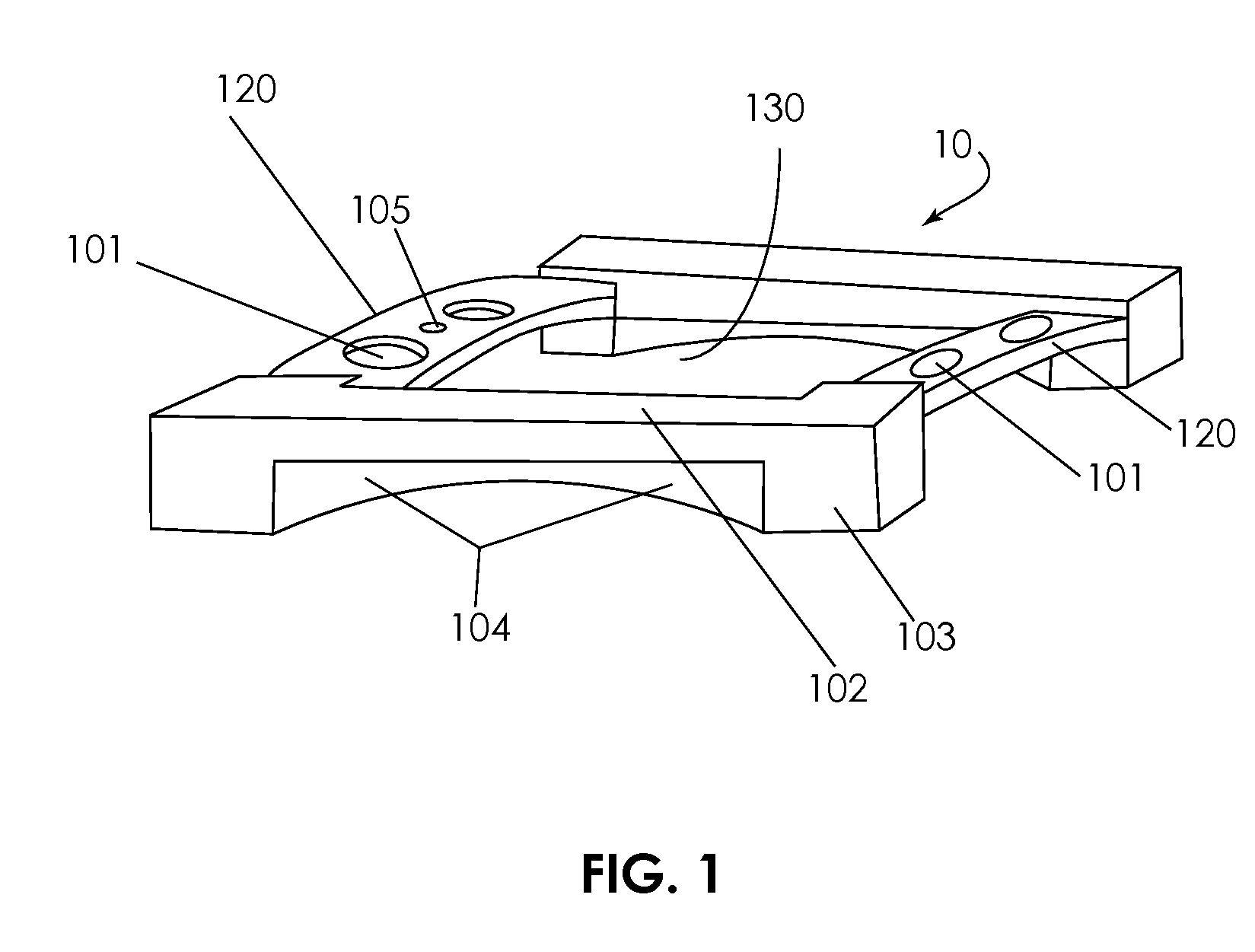
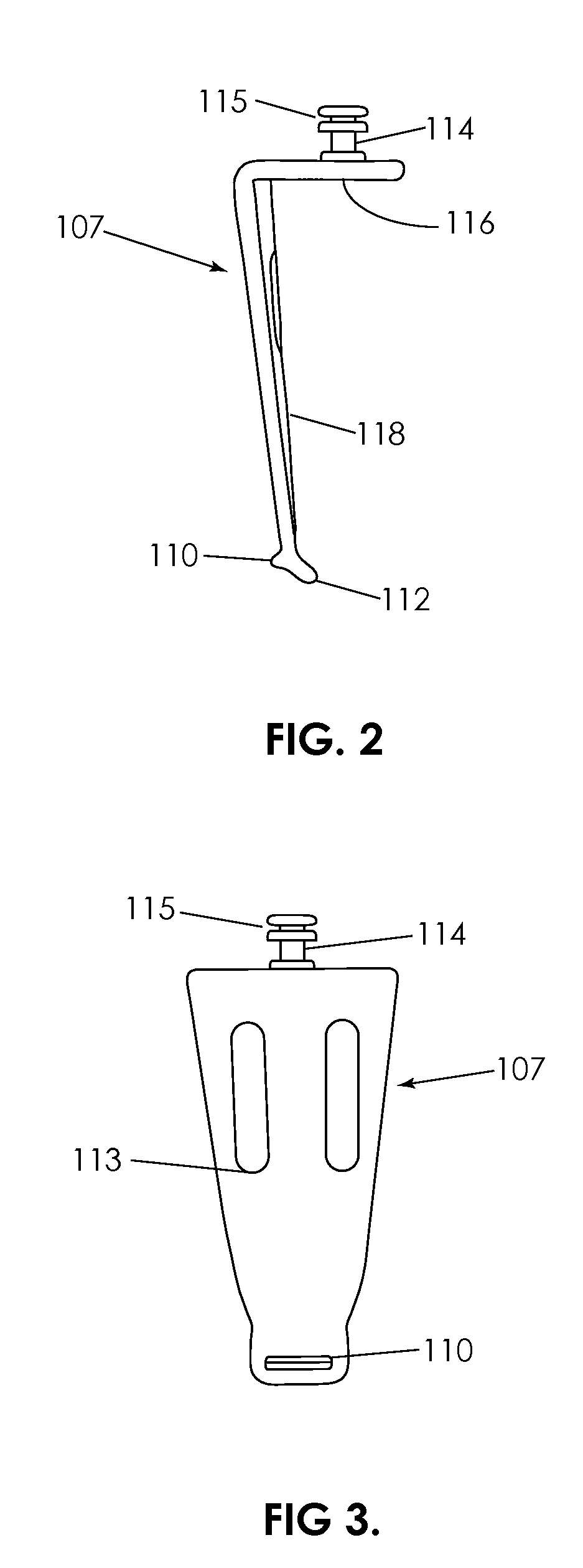
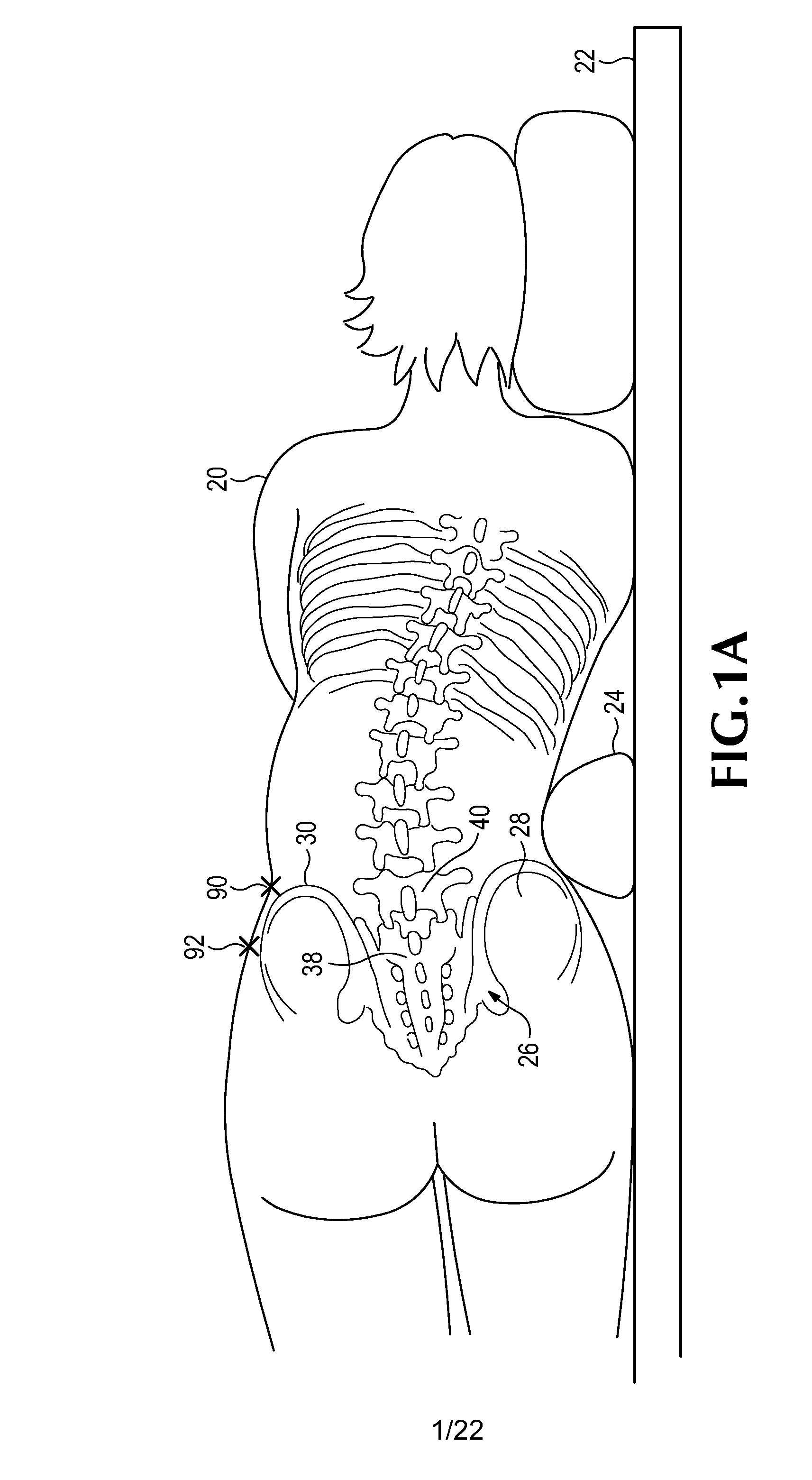
A retractor for use in surgical operations comprises a pair of blade assemblies which are adapted to open about a set of axes that are not parallel to a third spatial axis. The retractor further comprises a pair of arms, which are adapted to move the pair of blade assemblies apart from one another in the third spatial axis. In operation, the blade assemblies are closed to assume a low profile, inserted into a relatively small incision, and stretched apart from each other, thereby stretching the skin about the incision to form an aperture longer than the incision. The blade assemblies are then opened by rotating the blades about the set of axes, thereby stretching the skin around the incision in a second direction that is substantially perpendicular to the first direction (i.e. the direction of the incision.) The retractor thus forms an aperture for passage of surgical instruments and viewing of the surgical field by surgical personnel. In some embodiments, the retractor features a pair of removable handles that may be removed from the arms during surgery in order to afford the surgeon improved space management about the incision. In specific embodiments, the invention provides a method of performing an operation, e.g. a spinal operation, on a patient using the disclosed retractor.
Owner:SPINAL ELEMENTS INC
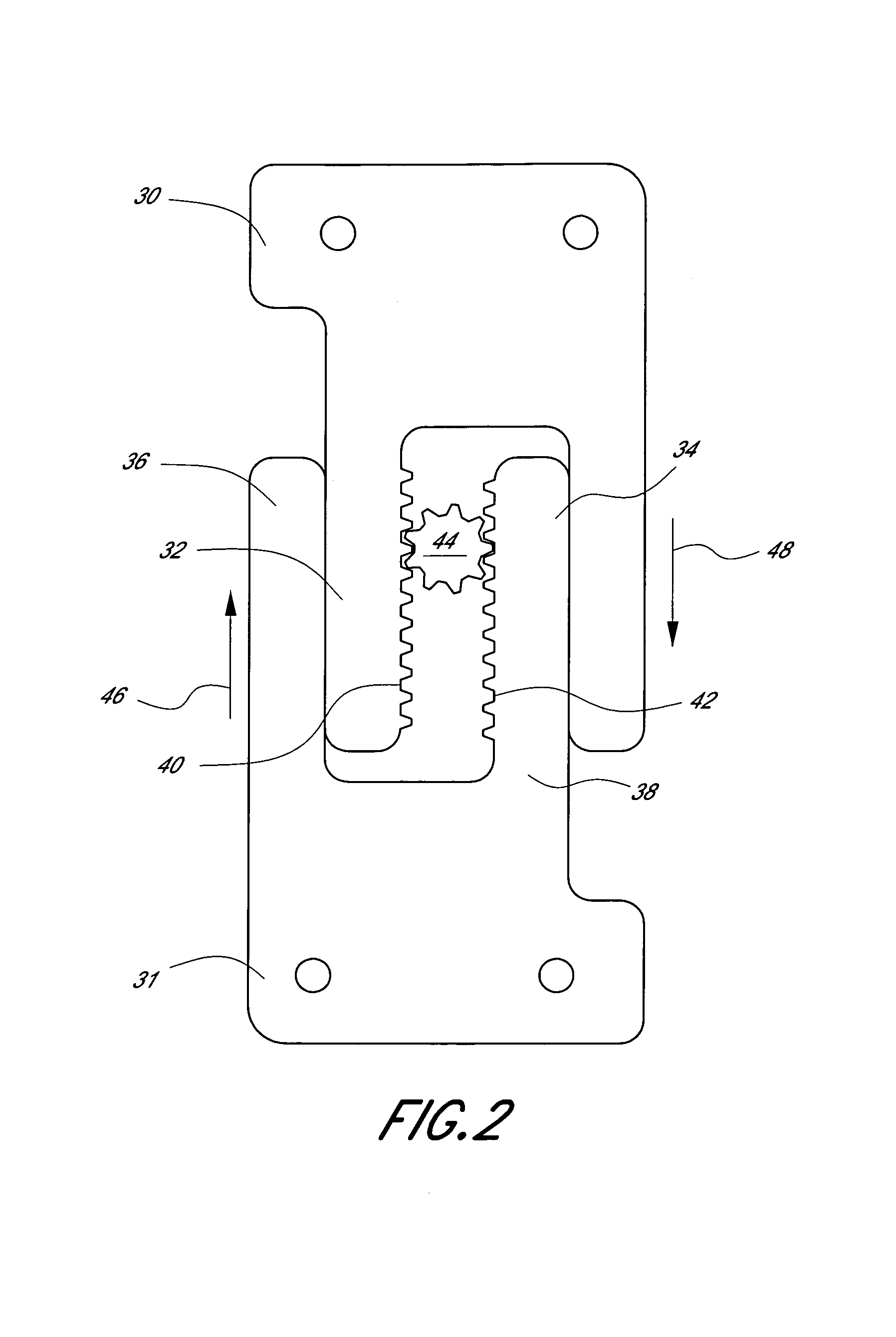
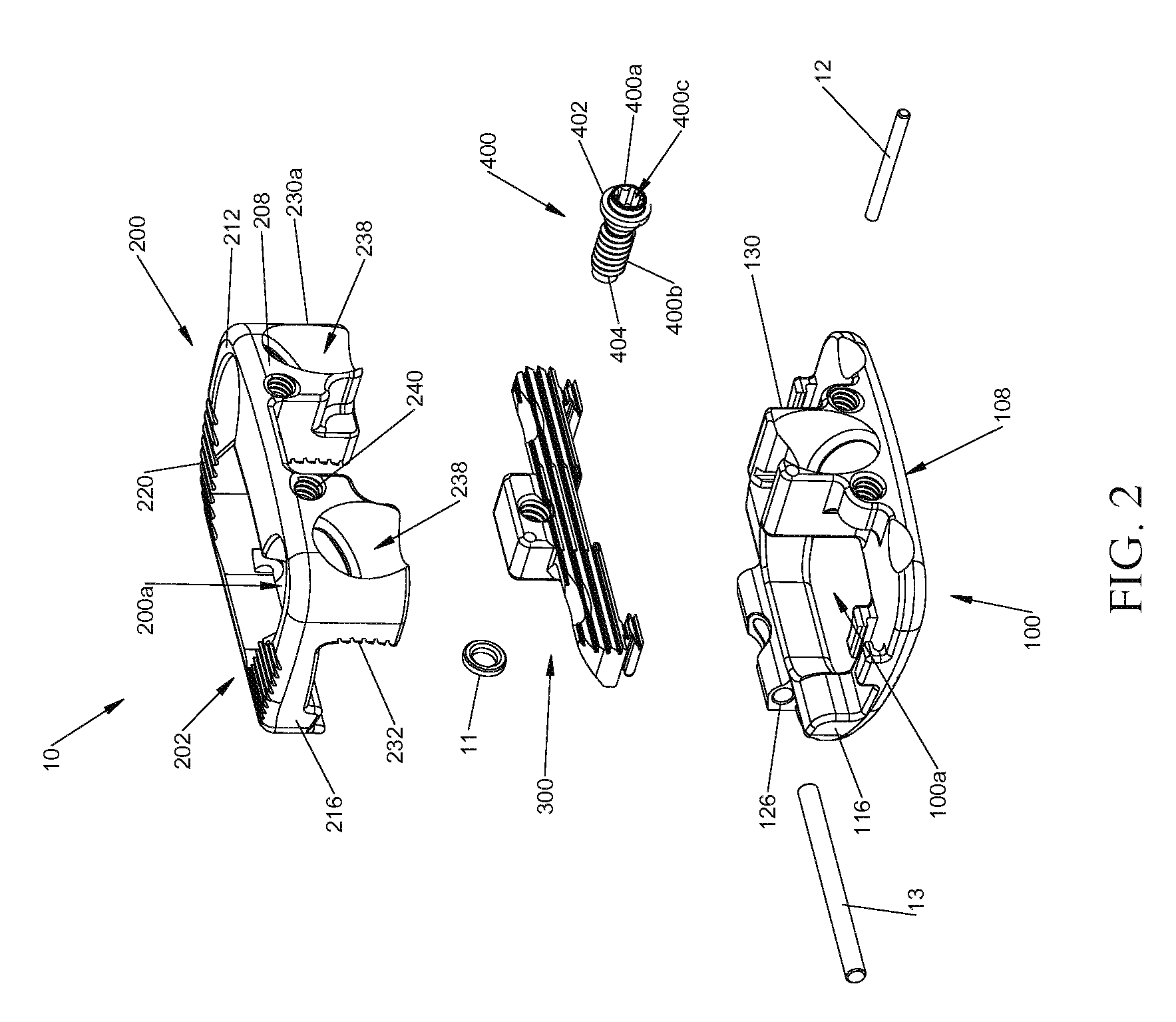
Compressible fixation apparatus for spinal surgery
A spinal fixation apparatus is configured with a pair of endpieces and an intermediate compressible portion. The compressible portion may comprise a pair of mating sliders comprising toothed arms attached to the endpieces. A gear engages the toothed arms. When the gear is rotated, the sliders bring the endpieces together, compressing the apparatus.
Owner:SMART DISC
Surgical instrument system and method for providing retraction and vertebral distraction
An instrument for spinal surgery for retracting soft tissue and mounting between a superior spinous process and an inferior spinous process includes a relatively rigid frame, a first retractor blade mounted to the frame and a distractor element movably mounted to the frame. The distractor element has a body, a proximal end and a distal end. The distractor element has a thickness and a length. The distractor element is configured for mounting between the superior and inferior spinous processes in a working configuration. The distractor element is generally tapered at the distal end in an insertion configuration. The instrument also includes an insertion shaft attached to the proximal end and a first shaft joint mounted between the frame and the insertion shaft.
Owner:DIETZE JR DONALD DAVID +1
Method for directed cell in-growth and controlled tissue regeneration in spinal surgery
ActiveUS20100028309A1Prevention and minimization of uncontrolled adhesionPrevention and minimization of and scar formationBiocideSurgerySpinal columnMammal
The present invention relates to a method for directed cell in-growth and controlled tissue regeneration to prevent post-surgical or post-traumatic adhesion and fibrosis formation on the injured surface of a tissue selected from the group consisting of spinal column tissue, dura mater, and spinal nerves in a mammal, comprising the step of providing, covering and separating the tissue with a bioactive biofunctional, non-porous, microscopically multilayered collagen foil biomatrix, and to a method for treating a defect in a mammal comprising the step of providing, covering and separating said tissue with a bioactive biofunctional, non-porous, microscopically multilayered collagen foil biomatrix.
Owner:BAXTER INT INC +1
Expandable spinal interbody spacer and method of use
An expandable spinal implant configured for positioning within a space between adjacent vertebral bodies includes an upper body, a lower body, a ratchet mechanism, and a plurality of bone screws. The upper body and lower body are pivotably affixed at a first end and are capable of movement relative to each other. The ratchet mechanism is slidably disposed on one of the upper and lower body and is capable of engaging the opposite one of the upper and lower body thereby permitting movement of the upper and lower body relative to each other in a first direction, but not in a second direction. An insertion instrument capable of being attached to the expandable spinal instrument and a method of performing spinal surgery is also disclosed.
Owner:K2M
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com