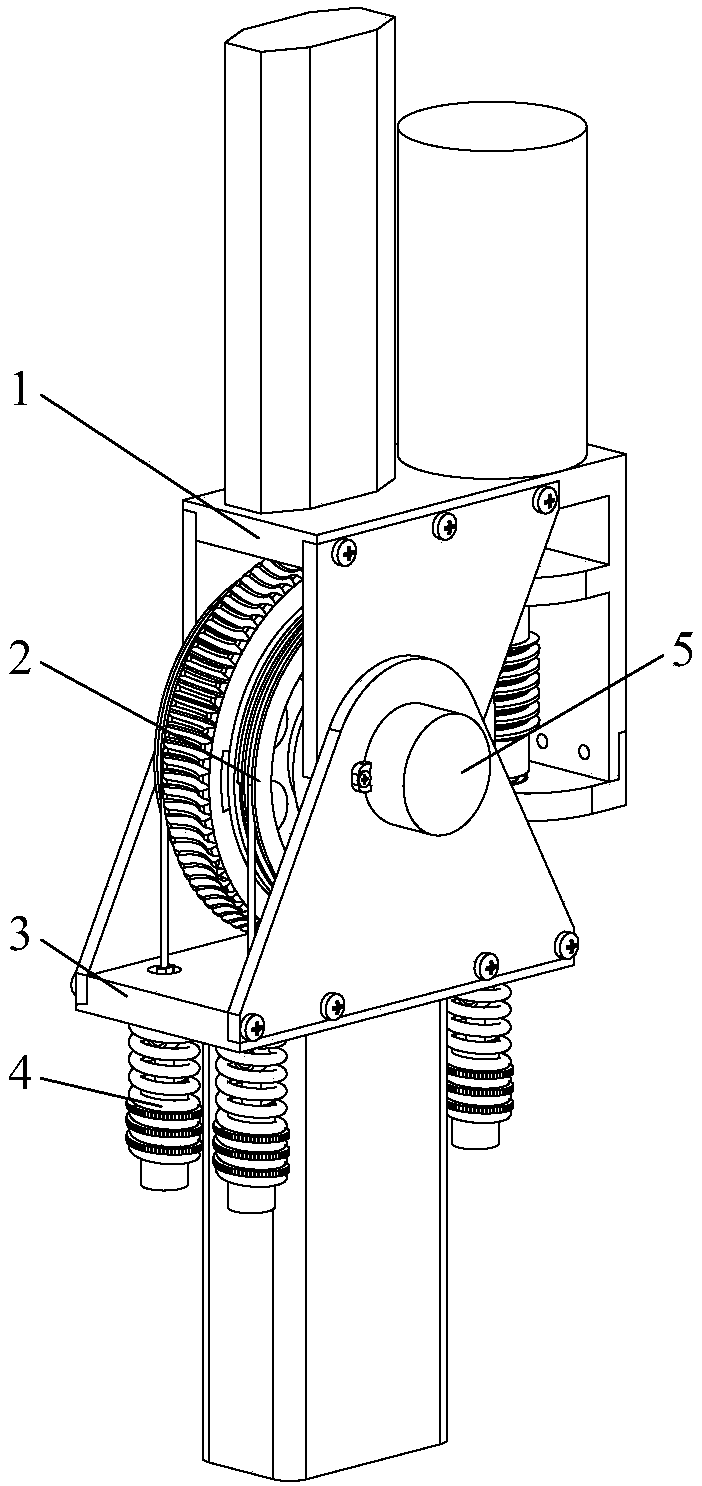
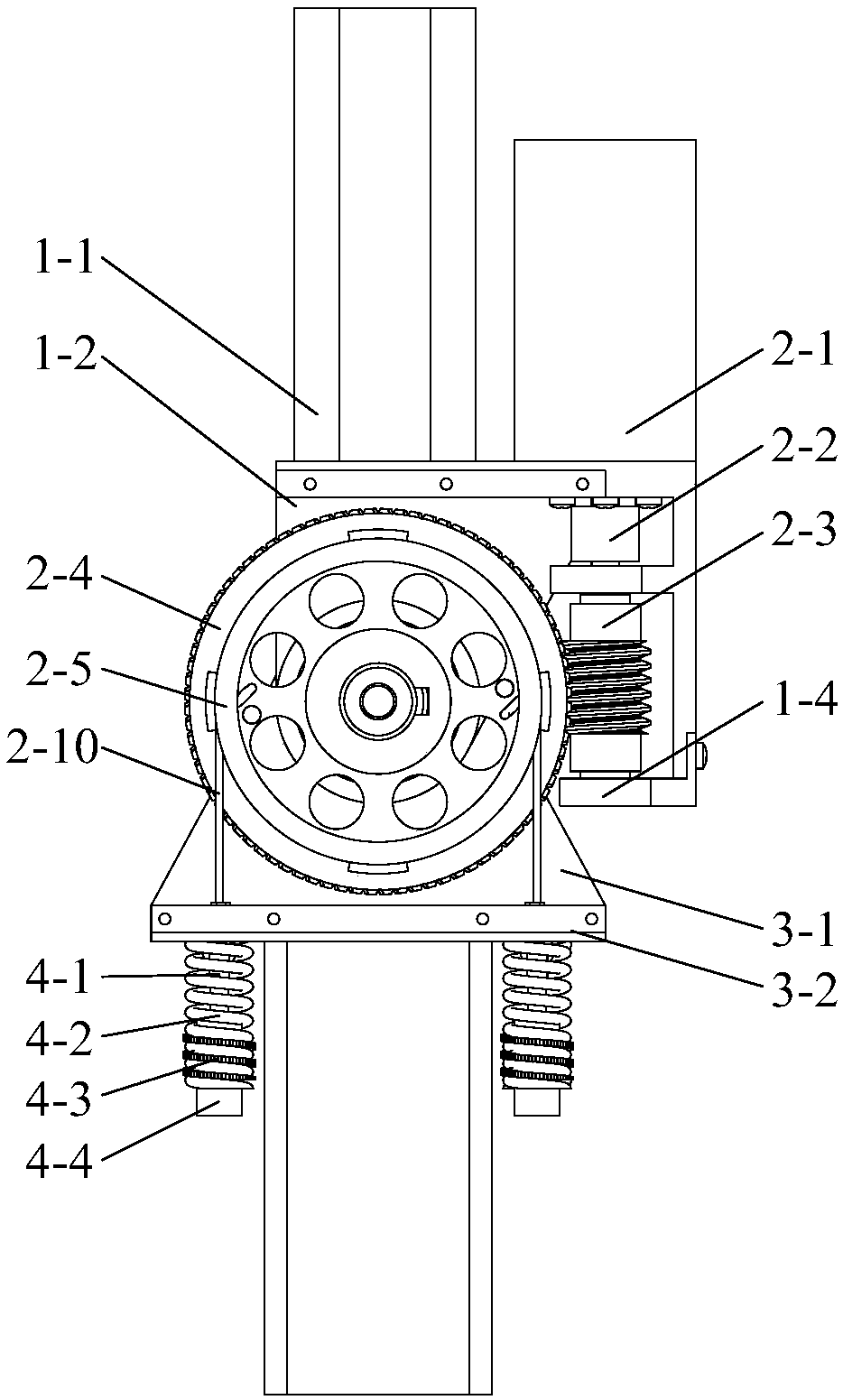
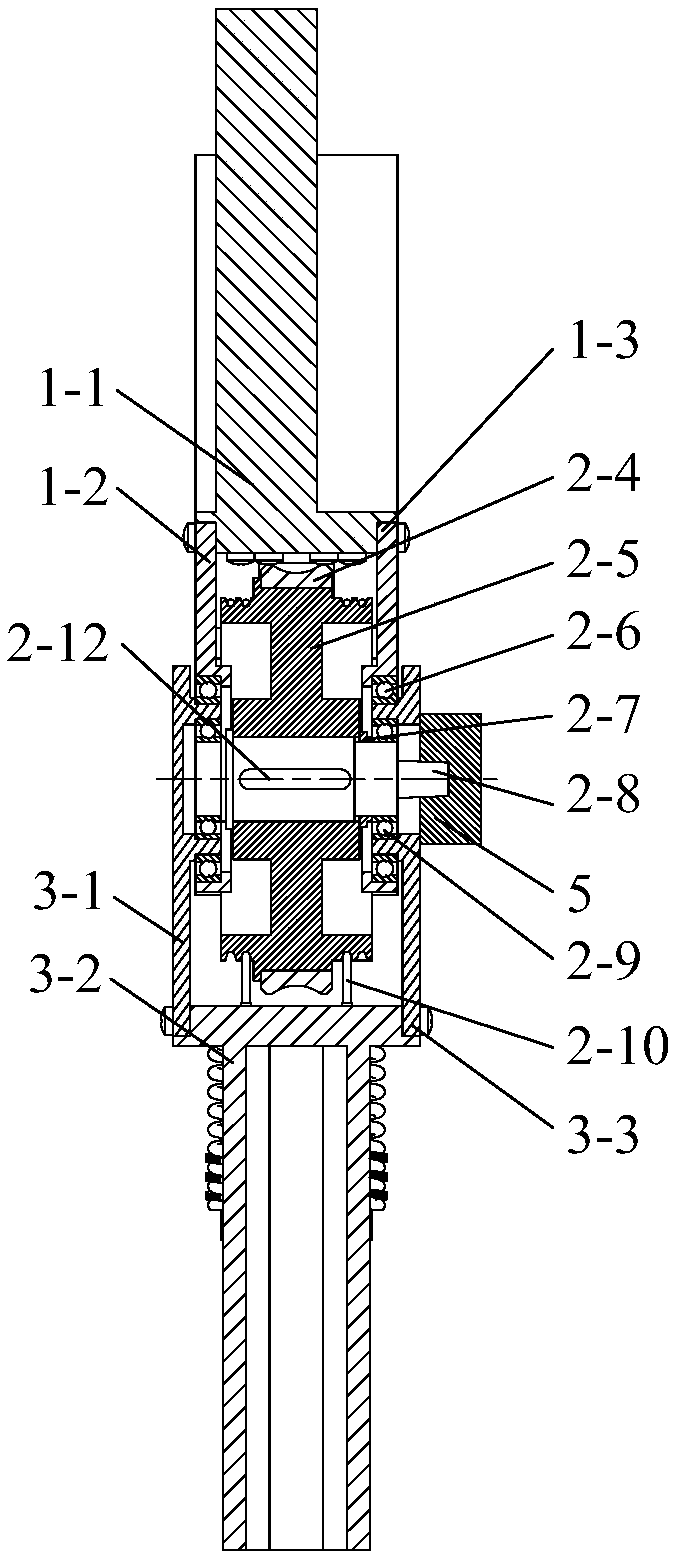
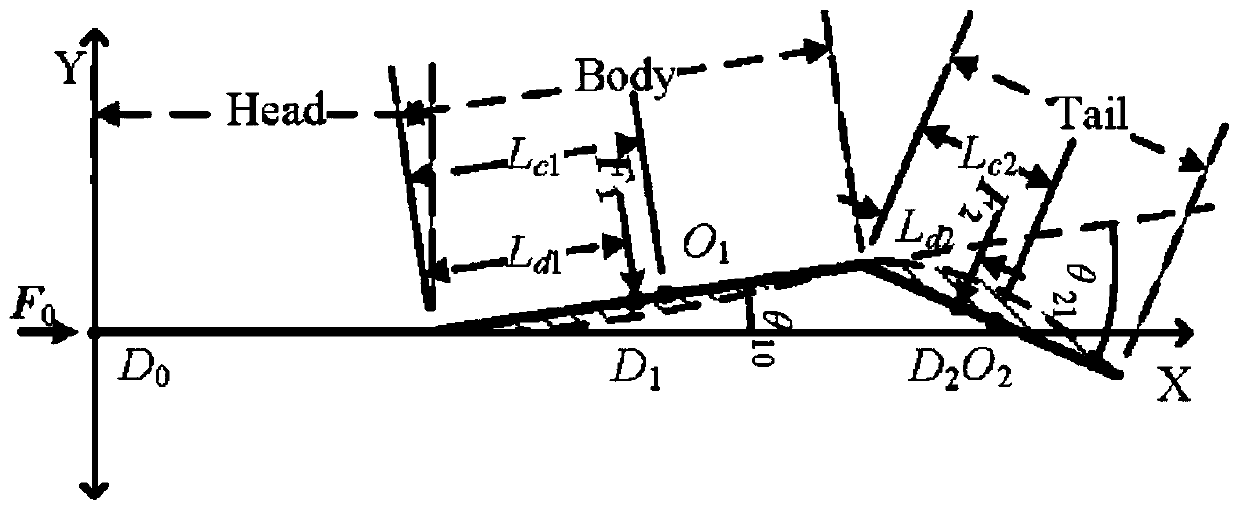
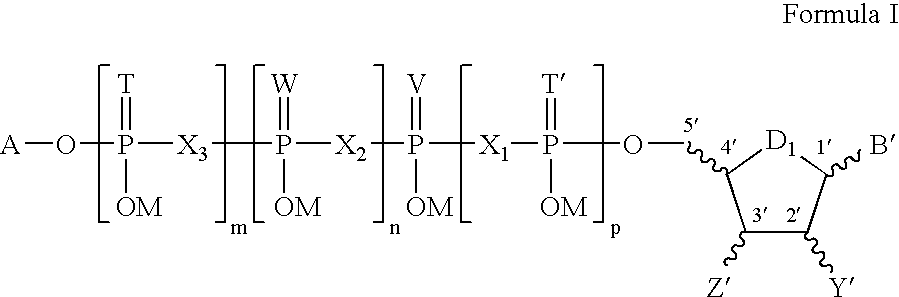Patents
Literature
100 results about "Joint stiffness" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Joint stiffness may be either the symptom of pain on moving a joint, the symptom of loss of range of motion or the physical sign of reduced range of motion.
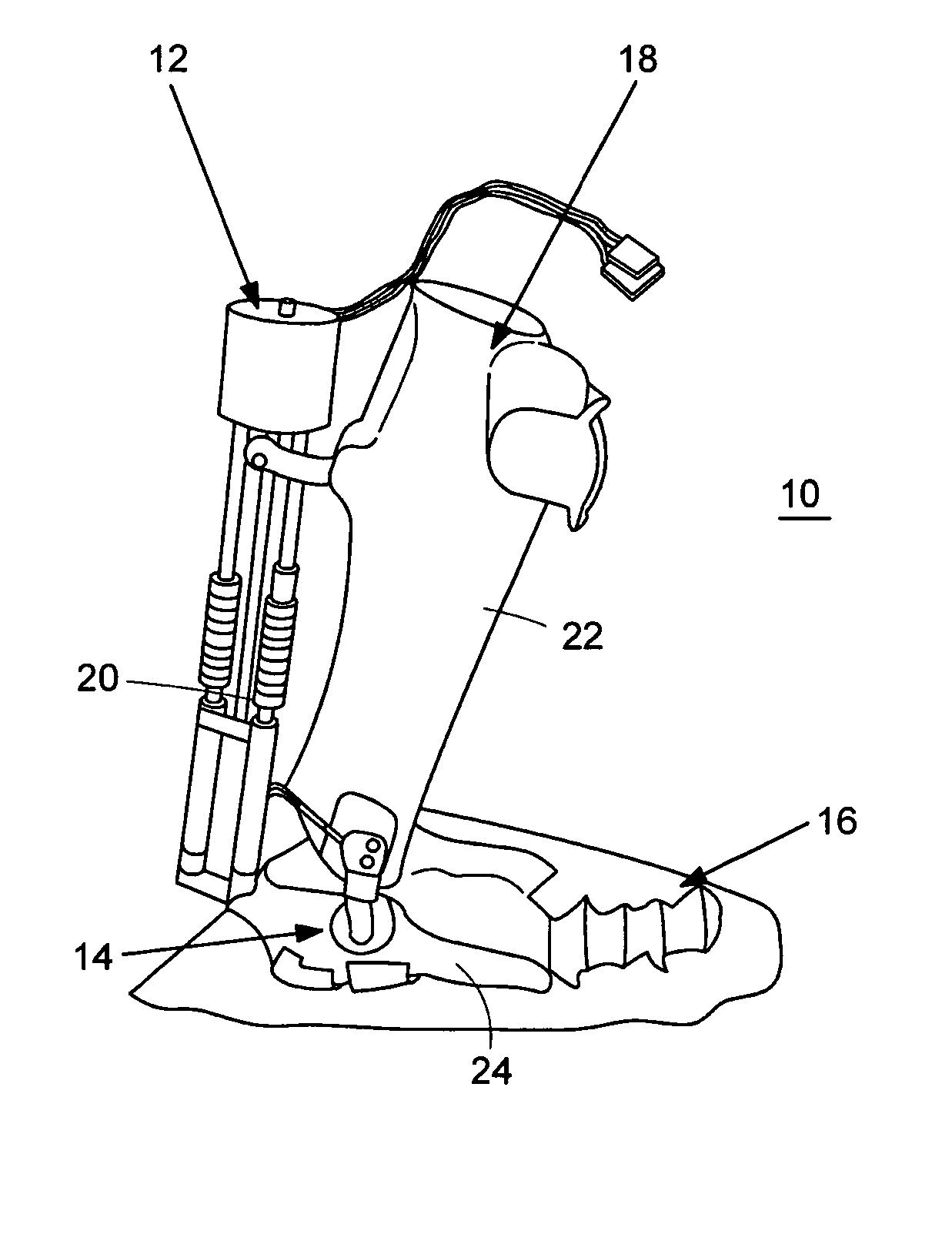
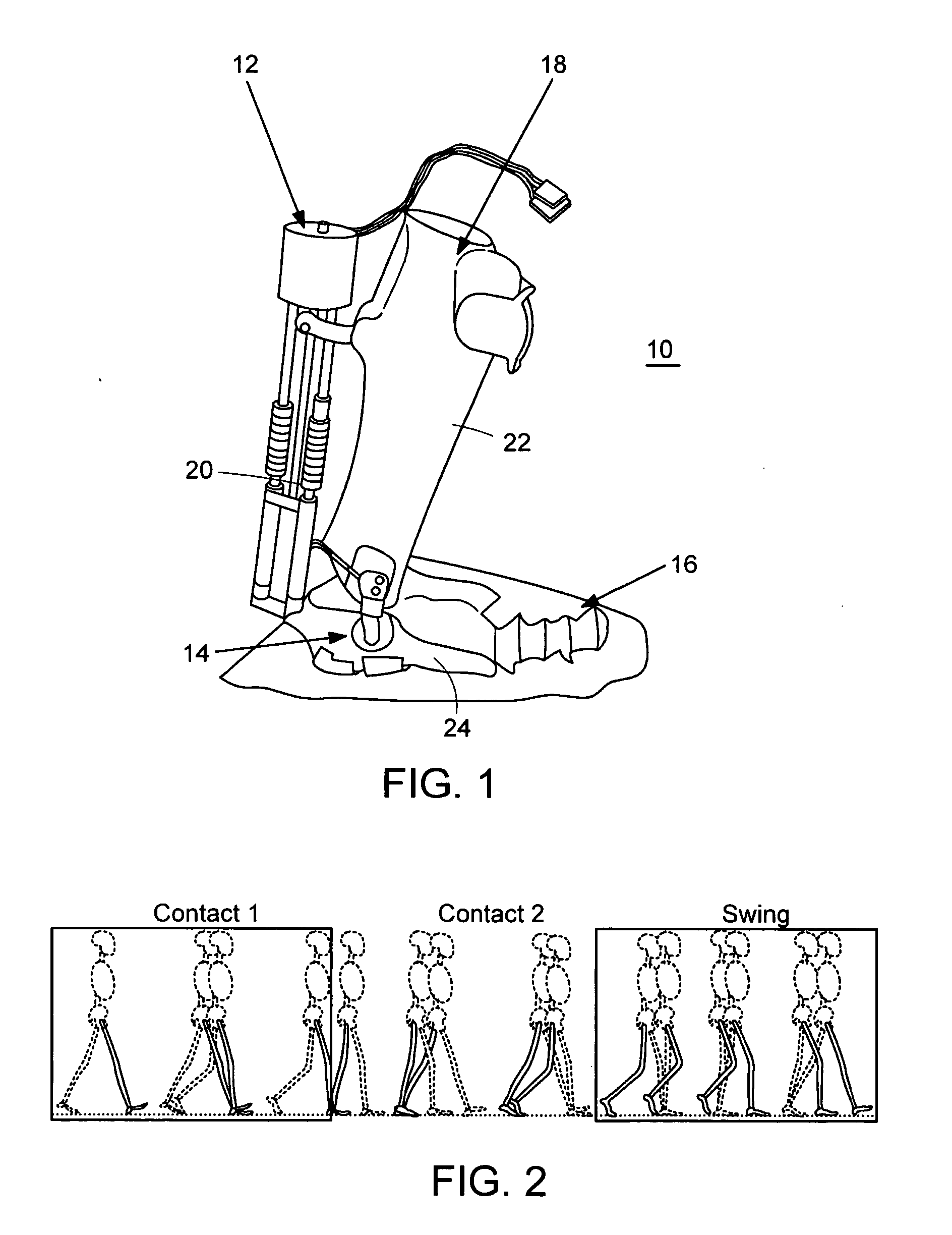
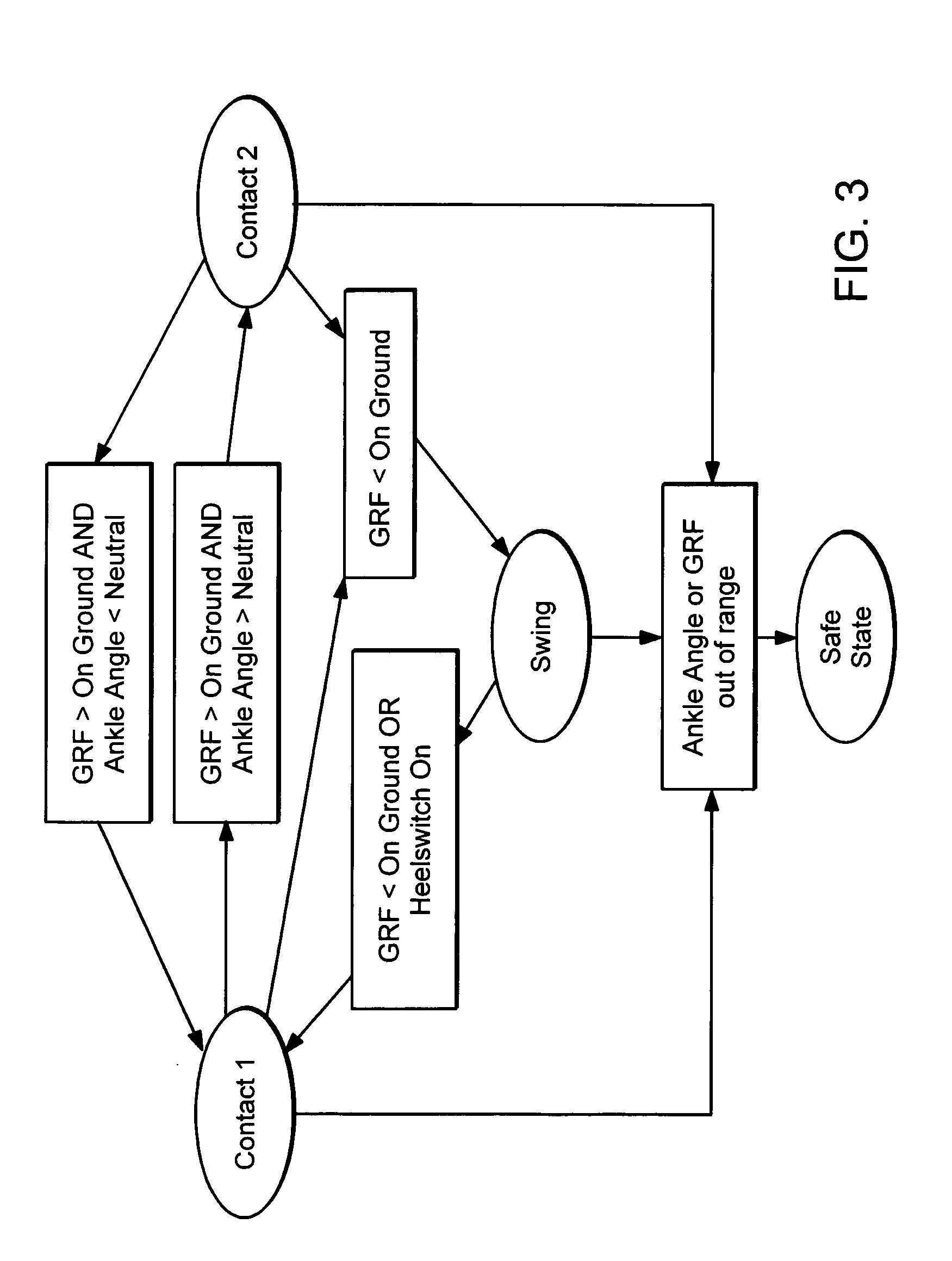
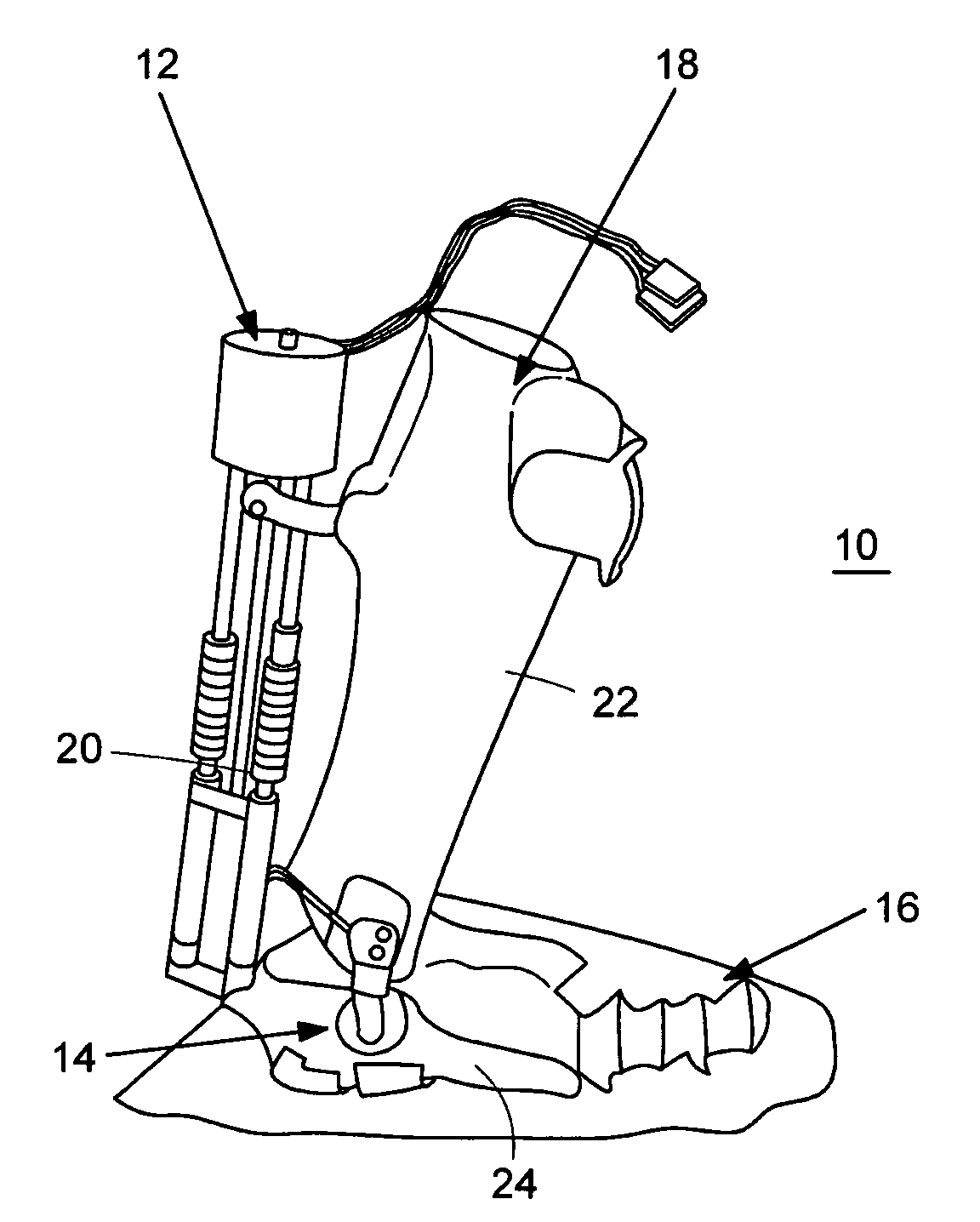
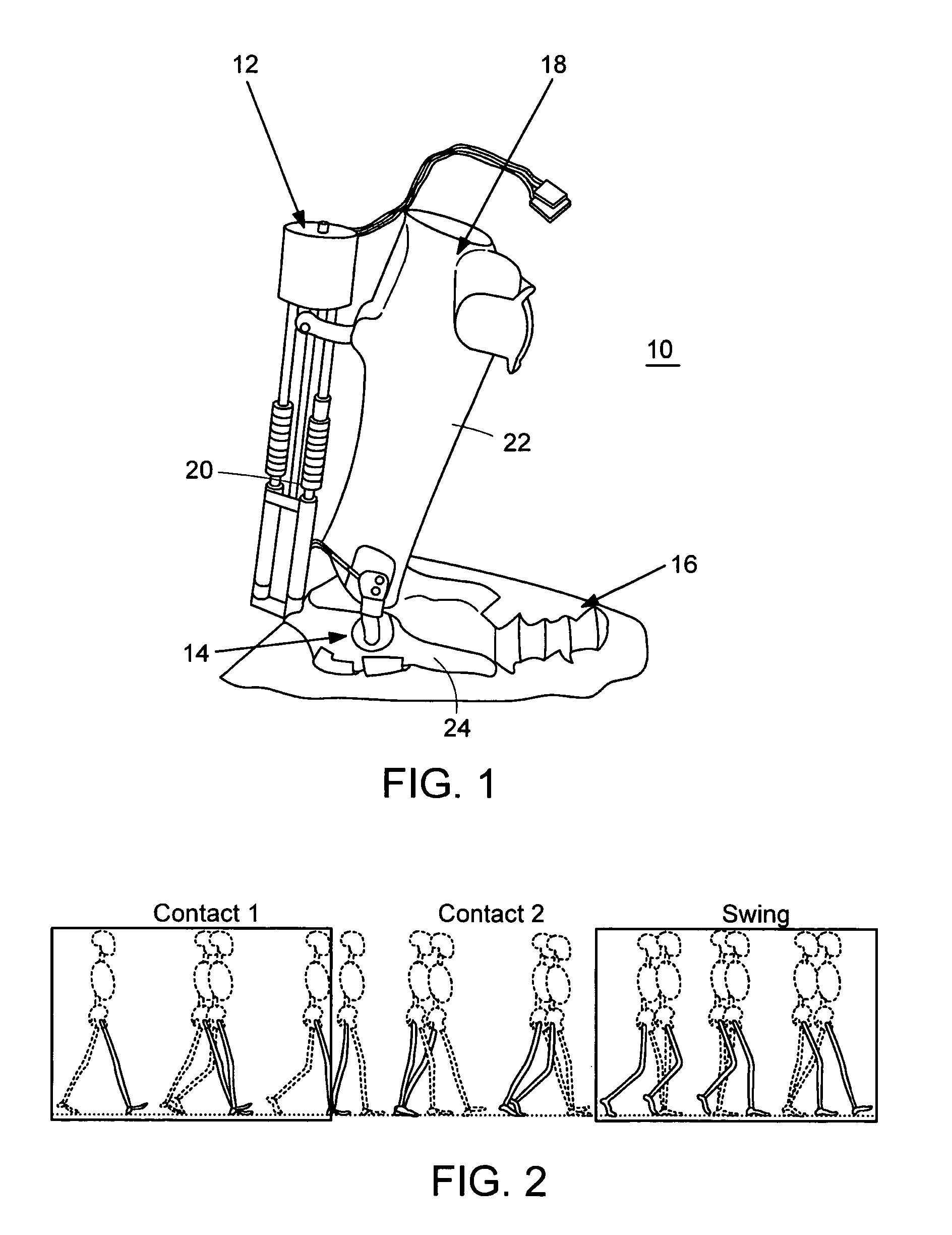
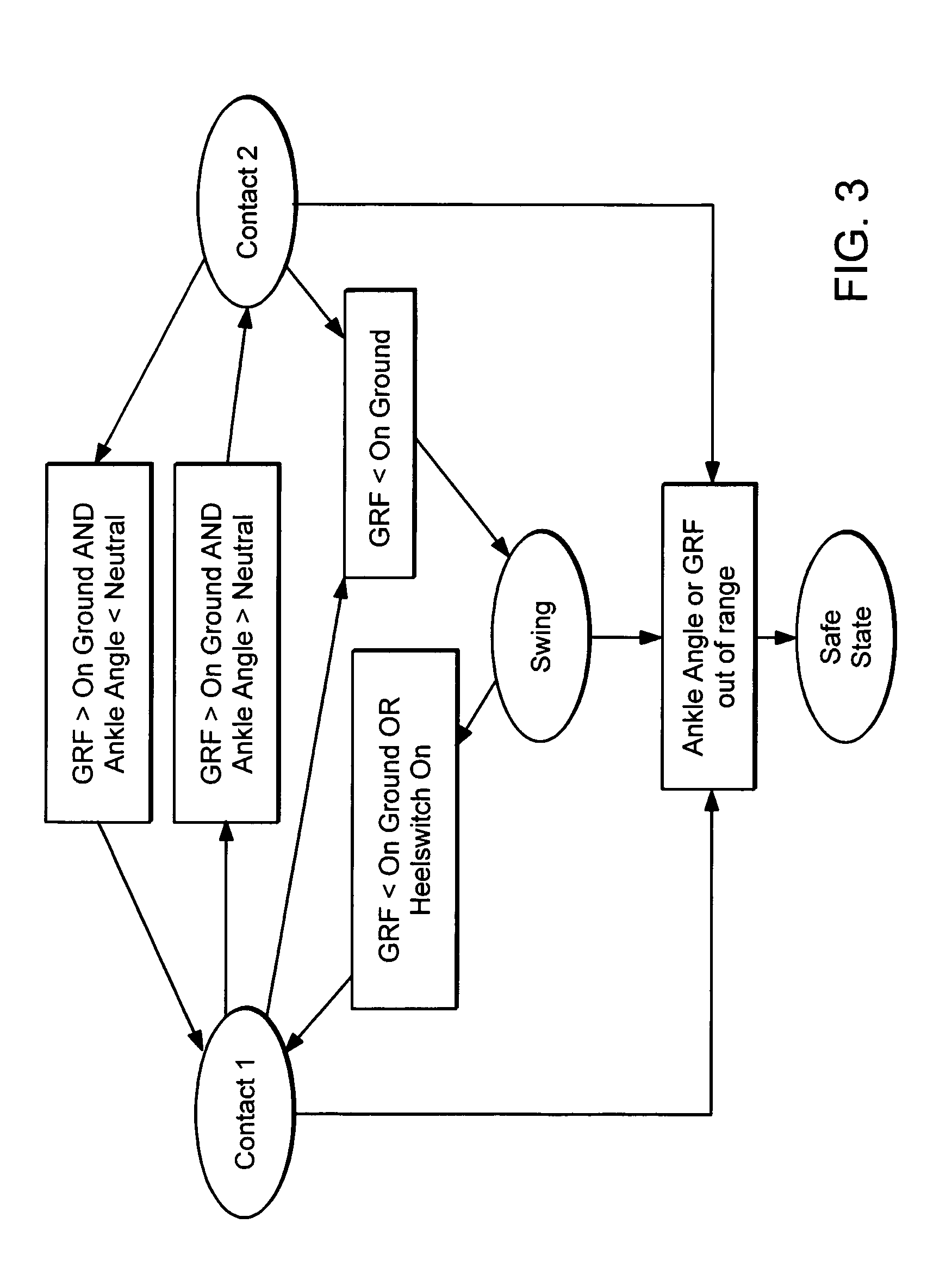
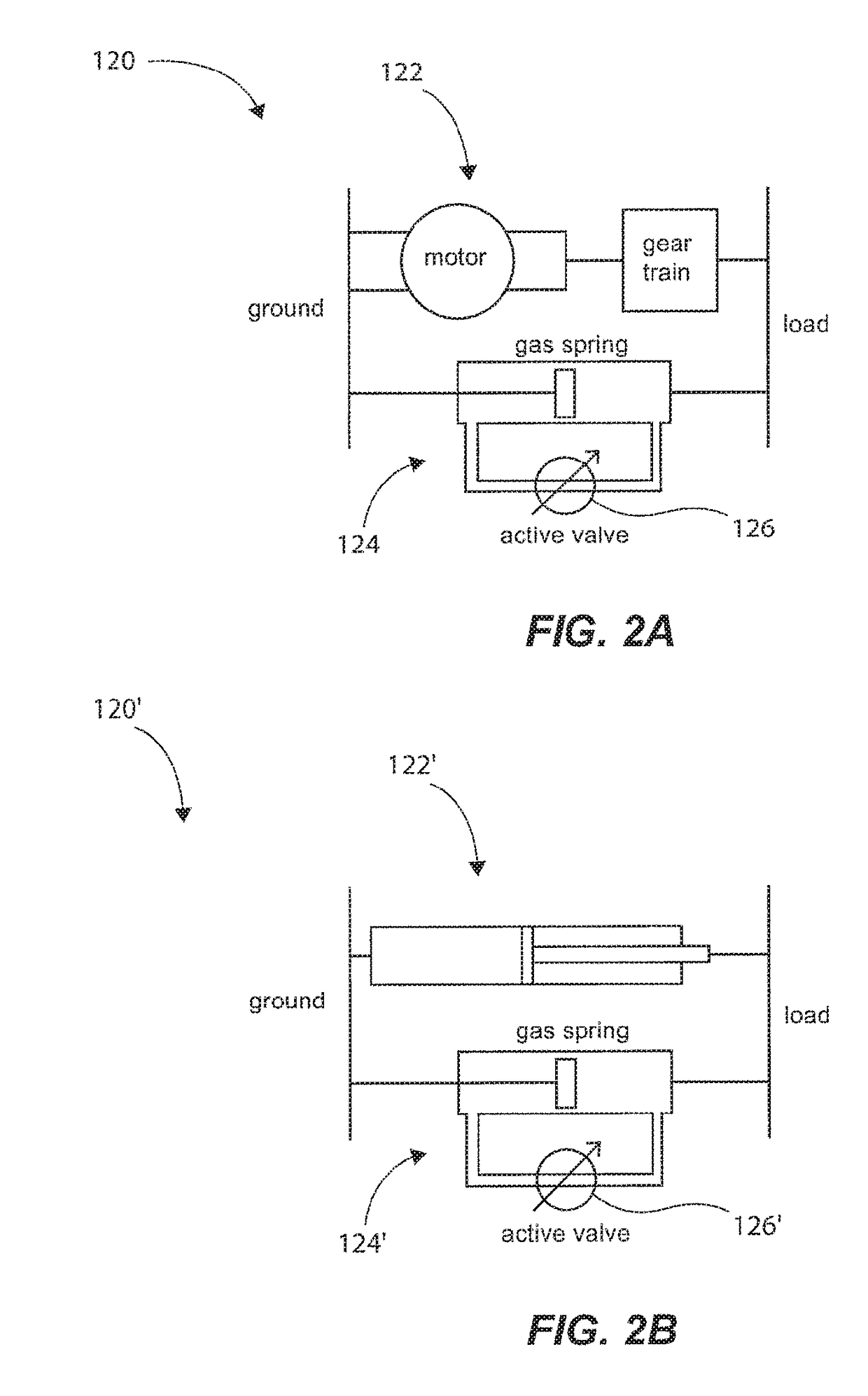
Active Ankle Foot Orthosis
ActiveUS20050070834A1Less kinematic differenceIncrease independenceWalking aidsNon-surgical orthopedic devicesWalking cyclePathology diagnosis
An Active Ankle Foot Orthosis (AAFO) is provided where the impedance of an orthotic joint is modulated throughout the walking cycle to treat ankle foot gait pathology, such as drop foot gait. During controlled plantar flexion, a biomimetic torsional spring control is applied where orthotic joint stiffness is actively adjusted to minimize forefoot collisions with the ground. Throughout late stance, joint impedance is minimized so as not to impede powered plantar flexion movements, and during the swing phase, a torsional spring-damper (PD) control lifts the foot to provide toe clearance. To assess the clinical effects of variable-impedance control, kinetic and kinematic gait data were collected on two drop foot participants wearing the AAFO. It has been found that actively adjusting joint impedance reduces the occurrence of slap foot, allows greater powered plantar flexion, and provides for less kinematic difference during swing when compared to normals.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Active ankle foot orthosis
ActiveUS8075633B2Increase independenceGreat easeWalking aidsNon-surgical orthopedic devicesWalking cyclePostural orientation
An Active Ankle Foot Orthosis (AAFO) is provided where the impedance of an orthotic joint is modulated throughout the walking cycle to treat ankle foot gait pathology, such as drop foot gait. During controlled plantar flexion, a biomimetic torsional spring control is applied where orthotic joint stiffness is actively adjusted to minimize forefoot collisions with the ground. Throughout late stance, joint impedance is minimized so as not to impede powered plantar flexion movements, and during the swing phase, a torsional spring-damper (PD) control lifts the foot to provide toe clearance. To assess the clinical effects of variable-impedance control, kinetic and kinematic gait data were collected on two drop foot participants wearing the AAFO. It has been found that actively adjusting joint impedance reduces the occurrence of slap foot, allows greater powered plantar flexion, and provides for less kinematic difference during swing when compared to normals.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
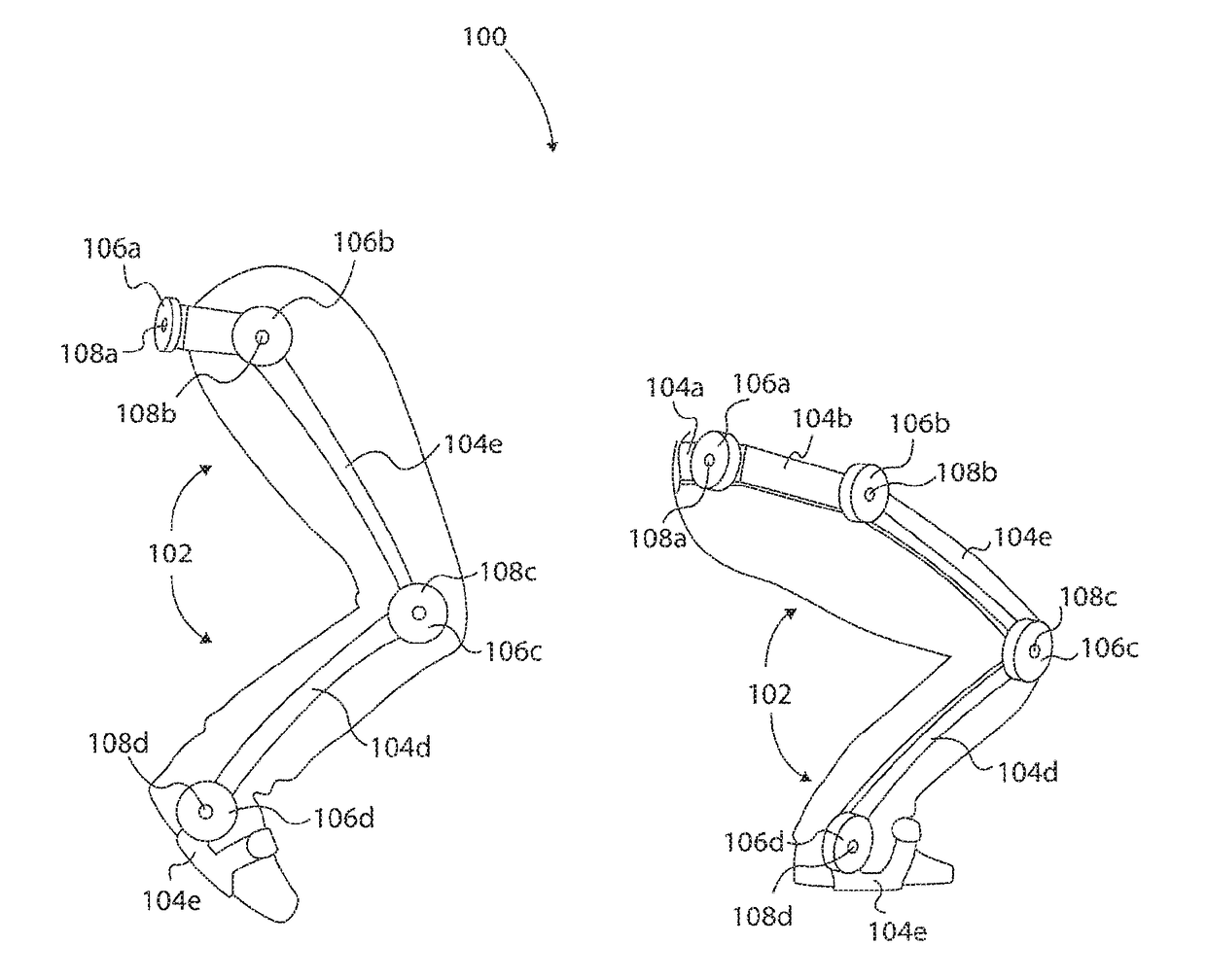
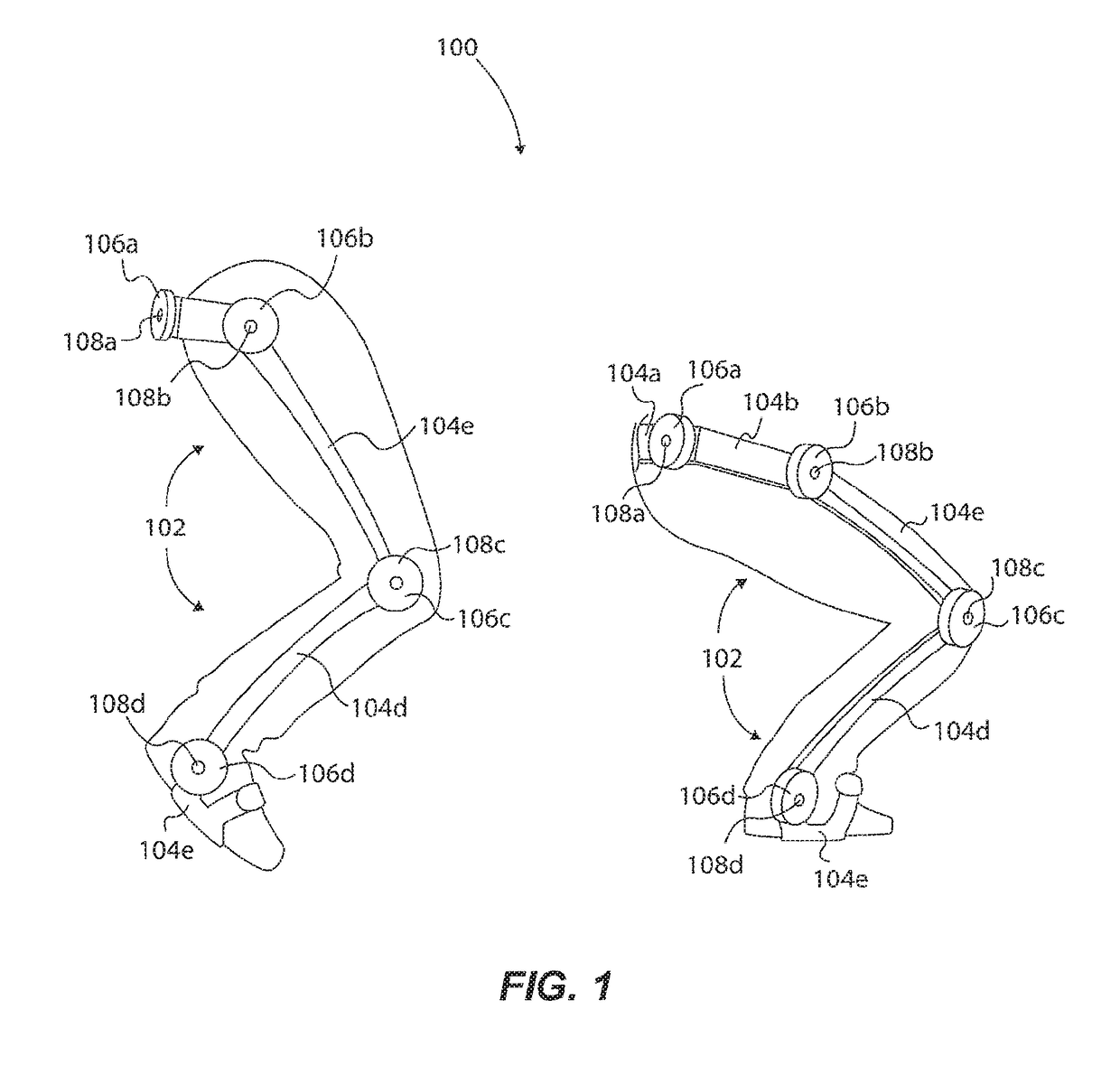
Tunable Actuator Joint Modules Having Energy Recovering Quasi-Passive Elastic Actuators for Use within a Robotic System
ActiveUS20180193172A1Minimize power consumptionReduce the required powerProgramme-controlled manipulatorJointsRobotic systemsStored energy
A tunable actuator joint module of a robotic assembly comprises an output member and an input member, where the output member is rotatable about an axis of rotation. A primary actuator (e.g., a motor) is operable to apply a torque to rotate the output member about the axis of rotation. A quasi-passive elastic actuator (e.g., rotary or linear pneumatic actuator) comprising an elastic component is tunable to a joint stiffness value and is operable to selectively release stored energy to apply an augmented torque to assist rotation of the output member and to minimize power consumption of the primary actuator. The tunable actuator joint module comprises a control system having a valve assembly controllably operable to switch the quasi-passive elastic actuator between an elastic state and an inelastic state during respective portions of movement of the robotic assembly (e.g., a hip or knee joint of an exoskeleton). Associated systems and methods are provided.
Owner:SARCOS CORP
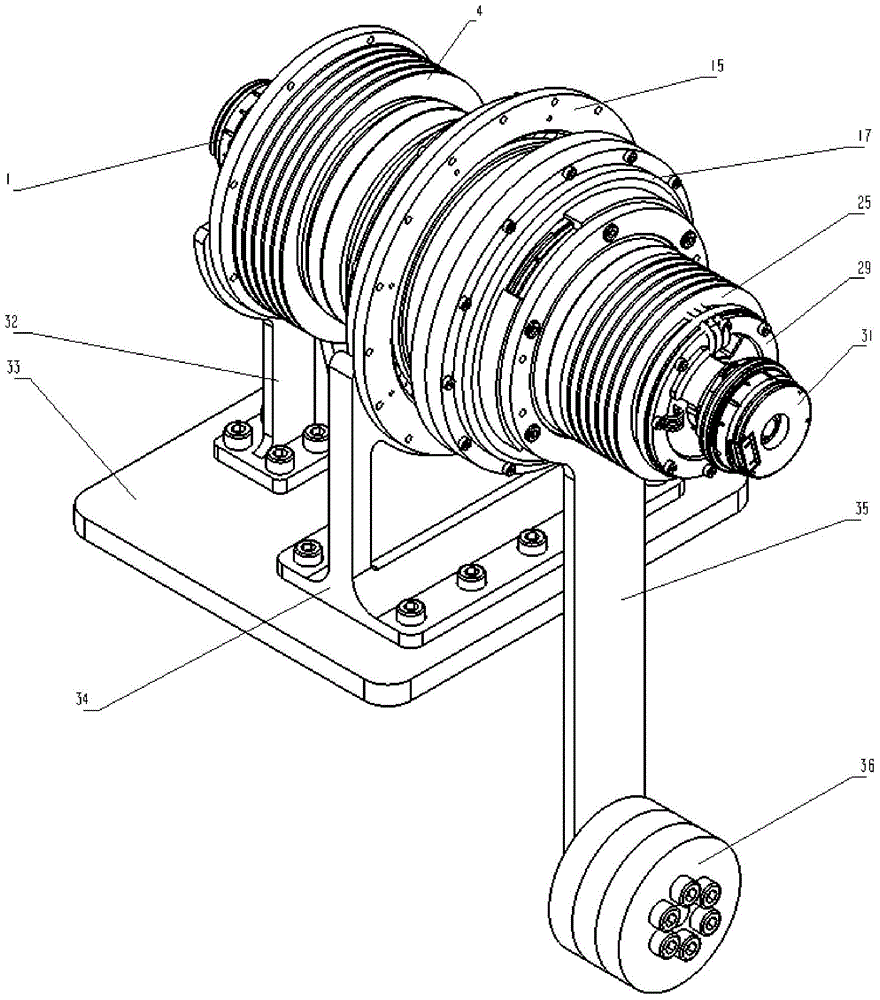
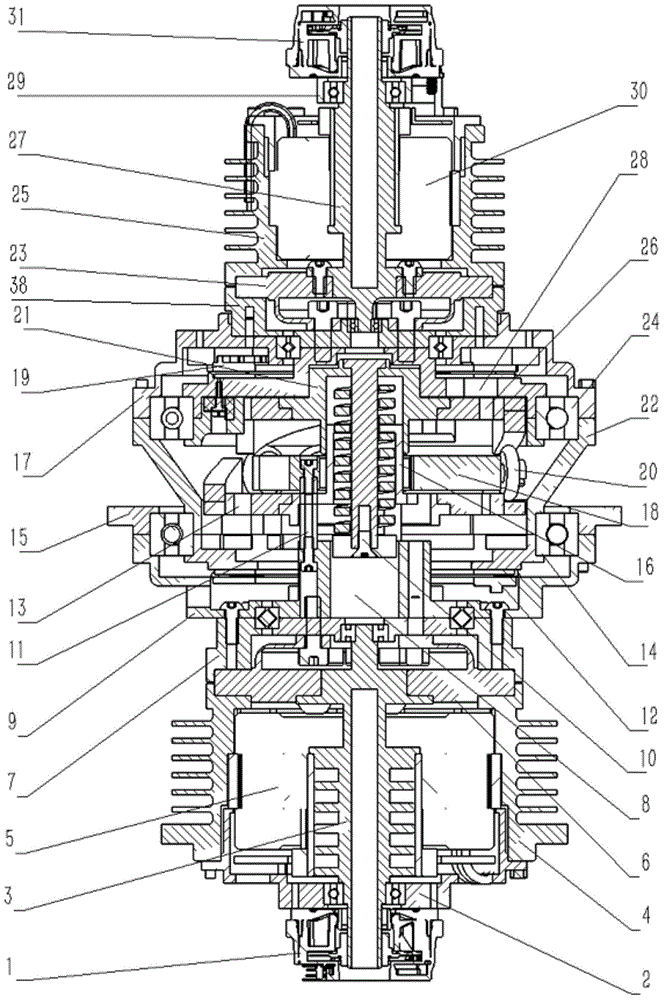
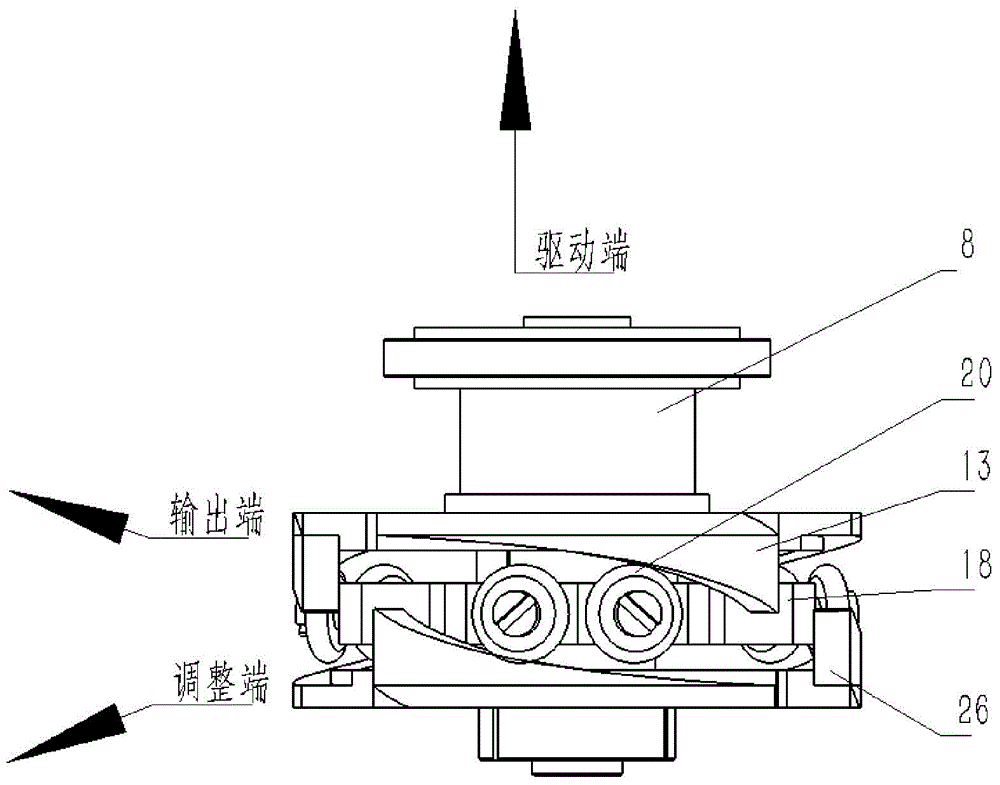
Stiffness-adjustable flexible joint actuator mechanism
ActiveCN104985608AReduce frictional resistanceAccurate transmissionJointsVariable stiffnessDrive motor
The invention discloses a stiffness-adjustable flexible joint actuator mechanism. The actuator mechanism is divided into an actuation end, an adjustment end and a flexible joint. The actuation end provides power for movement of the flexible joint, the adjustment end is responsible for changing stiffness of the flexible joint, and the flexible joint has the functions of relieving impact and adjusting stiffness. The actuator mechanism is additionally provided with a drive motor, and the joint can be actively driven to move. By the adoption of a variable-stiffness system in a curved bevel and rotary wheel matching structure, friction resistance is little and transmission is precise. Four absolute type encoders are installed, effective detection is achieved in the work process, sensitivity is high, and the fault rate is low. A shell is fully closed, the structure is compact, and the actuator mechanism can work in the severe environment. Changes of joint stiffness are linearly controllable from great flexibility to complete stiffness.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Synchronous displacement adjustment type variable-stiffness joint driver and adjustment method for robot joint stiffness
ActiveCN104669261AEasy to adjustAdjust energy savingProgramme-controlled manipulatorJointsVariable stiffnessEngineering
The invention discloses a synchronous displacement adjustment type variable-stiffness joint driver. The synchronous displacement adjustment type variable-stiffness joint driver comprises a base, a swing arm position control assembly, a variable-stiffness adjustment assembly and an angular deviation measurement assembly, and is characterized in that the swing arm position control assembly is used for moving a swing arm to a specified equilibrium position point; the variable-stiffness adjustment assembly is used for changing the stiffness value of the driver according to the requirement of an actual task; the angular deviation measurement assembly is used for measuring and acquiring angular deviations for subsequent data processing and real-time stiffness control. The synchronous displacement adjustment type variable-stiffness joint driver is used for the variable-stiffness control of a robot joint, and can realize the flexibility of a driving system in terms of control without adding sensors, and thereby human safety is improved in the process of human-machine interaction. In addition, because of the special structural design, the energy consumption of a robot can be reduced, the joint structure is more compact, and good shock resistance and flexible dynamic characteristic lay a solid foundation for the movement of the robot in complex environments.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
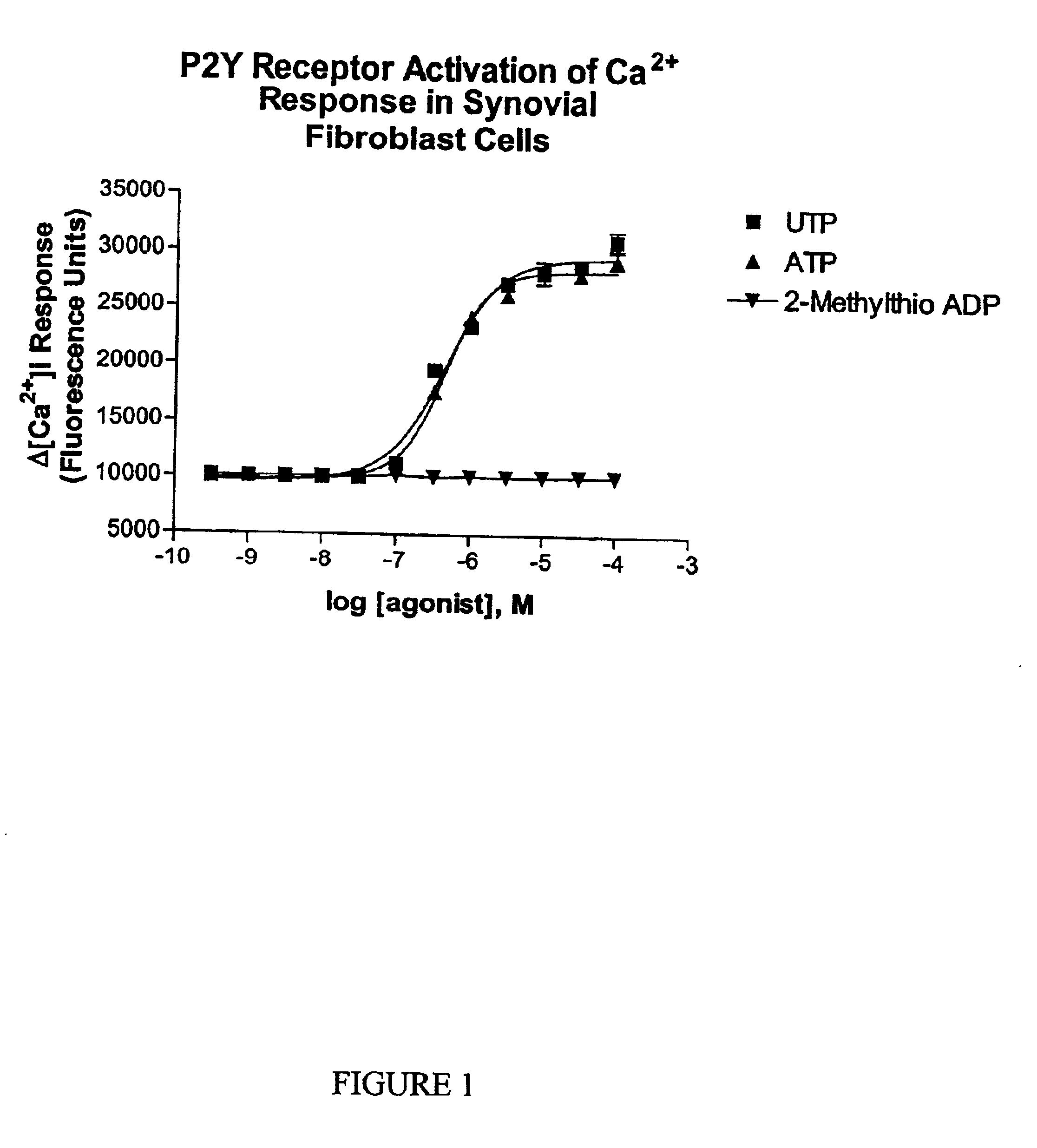
Joint lubrication with P2Y purinergic receptor agonists
InactiveUS7109181B2Enhance joint lubricationTreat osteoarthritisBiocideAerosol deliveryPhospholipidUridine Nucleotides
The present invention is directed to a method of altering the amount or composition of synovial fluids secreted from joints in a subject in need of such treatment. The method comprises administering to a subject a pharmaceutical composition comprising a P2Y purinergic receptor agonist in an amount effective to alter the amount or composition of synovial fluids. The P2Y purinergic receptor agonist is administered in an amount effective to stimulate secretion of synovial fluid, lubricin, hyaluronic acid, or surface-active phospholipids; to enhance joint lubrication; or to treat osteoarthritis. The pharmaceutical compositions useful in the present invention comprise a P2Y purinergic receptor agonist of Formula I and include, but are not limited to: uridine-, adenosine-, cytidine-5′-di- or triphosphates, dinucleoside polyphosphates, and analogs thereof. The invention is useful for treating conditions associated with reduced joint lubrication and joint stiffness, such as osteoarthritis.
Owner:INSPIRE PHARMA
Cryogenic Enhancement of Joint Function, Alleviation of Joint Stiffness and/or Alleviation of Pain Associated With Osteoarthritis
ActiveUS20140343543A1Prevents nerve signalingMinimally invasiveCatheterSurgical instruments for coolingSacroiliac jointPain reduction
A method in which a location is determined on the skin that is proximate to a sensory nerve that is associated with a painful condition. At least one needle of a cryogenic device is inserted into the location on the skin such that the needle is proximate to the sensory nerve. The device is activated such that the at least one needle creates a cooling zone about the sensory nerve, thereby eliminating or reducing severity of the painful condition.
Owner:PACIRA CRYOTECH INC
Controllable variable-stiffness flexible elbow joint rehabilitation robot
InactiveCN102764188AEnsure training safetyImprove flexibilityChiropractic devicesVariable stiffnessDrive wheel
The invention discloses a controllable variable-stiffness flexible elbow joint rehabilitation robot. The rehabilitation robot mainly comprises a wearable exoskeleton mechanism and non-linear driving mechanisms, wherein the wearable exoskeleton mechanism has one degree of freedom, is used for simulating the motion of an elbow joint, and mainly comprises a large arm, a small arm, a driving wheel and supporting frames; each non-linear driving mechanism comprises a motor lead screw and a connecting rod-spring non-linear mechanism; and the connecting rod-spring non-linear mechanism consists of a Robert linear mechanism and a linear spring, and the output force of the connecting rod-spring non-linear mechanism and the length change of a steel wire rope are in secondary non-linear relation. The rehabilitation robot is driven by two non-linear driving systems, and the structures of the two non-linear driving systems are similar to those of human joints. Due to the compliance of the driving systems, the safety of a patient is relatively high in the rehabilitation training process. The output force of the connecting rod-spring non-linear mechanism and the length change of the steel wire rope are in a relation of a quadratic polynomial, and the joint stiffness and the joint angle can be independently controlled, so the control accuracy of joint positions cannot be affected while the whole system keeps the flexibility.
Owner:上海博又博科贸有限公司
Compact variable-stiffness rotary flexible joint
ActiveCN106914917AAchieve stiffnessRealize functionProgramme-controlled manipulatorJointsVariable stiffnessEngineering
The invention discloses a compact variable-stiffness rotary flexible joint. The compact variable-stiffness rotary flexible joint comprises a joint driving disk, a joint output disk, a joint driven inner disk, a first cam, a first driven variable-stiffness adjusting seat, a first group of compression springs, a plain shaft, a first variable-stiffness adjusting seat, a turbine lead screw structure, a second variable-stiffness adjusting seat, a second group of compression springs, a second driven variable-stiffness adjusting seat, a second cam, a cylindrical gear, a worm, an absolute encoder, a motor and a circular-arc rack. By adopting the flexible joint, flexible driving output can be realized, external impact is reduced, and the service life of a robot is prolonged; meanwhile, joint stiffness can increase and decrease sequentially along with the increase of the flexible deformation angle of the joint, the robustness and running stability of the robot are enhanced, the joint stiffness can be adjusted actively under the own driving action, and the adaptability to different working tasks is enhanced; moreover, the flexible joint has an online flexible deformation detection function, so that feedback results of flexible deformation and output torque can be obtained, and online stiffness adjustment is realized.
Owner:HEBEI UNIV OF TECH
Industrial robot variable parameter stiffness identification and modeling method
ActiveCN110161850AGet to work quicklyReduce workloadProgramme controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorSimulationActuator
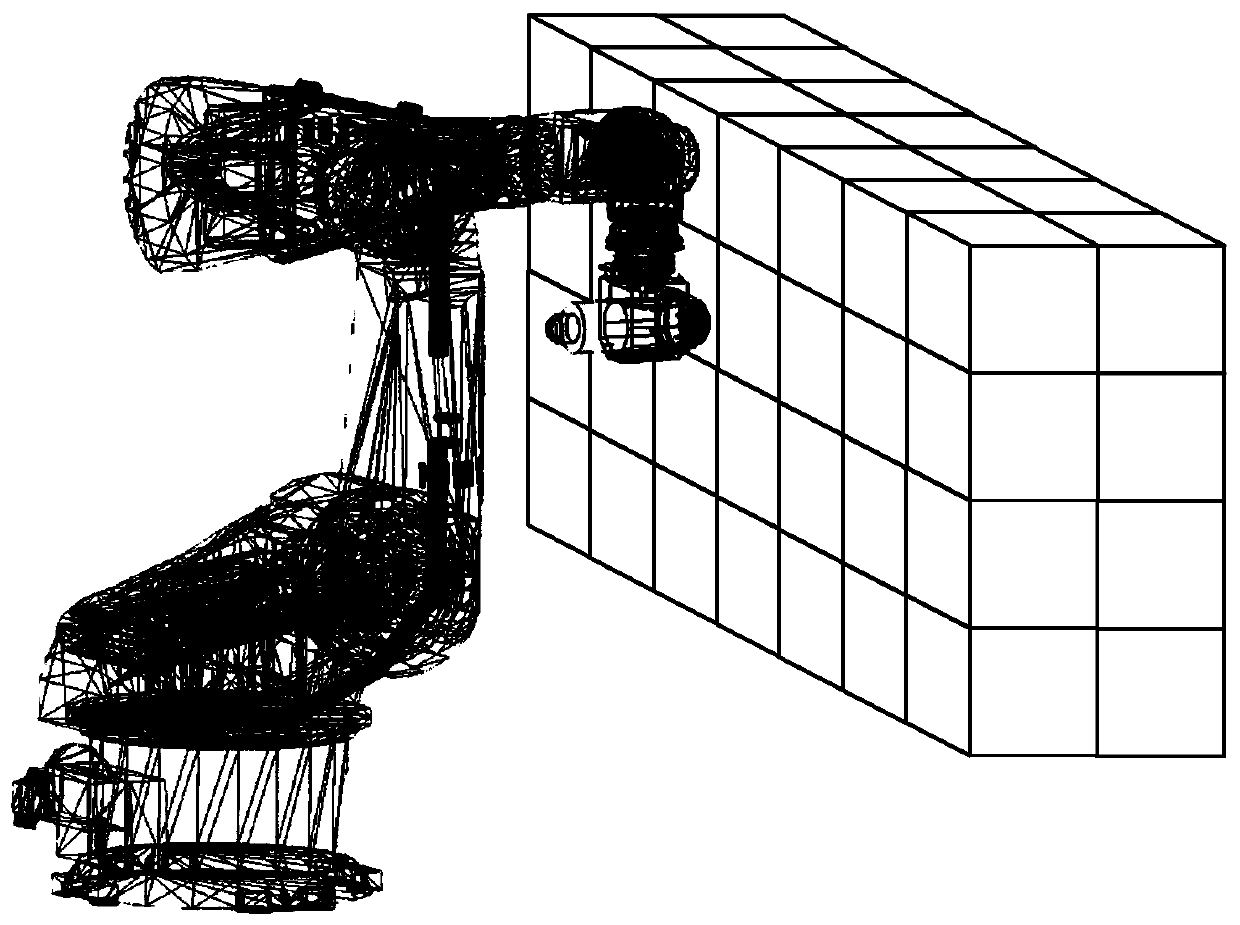
The invention discloses an industrial robot variable parameter stiffness identification and modeling method, which belongs to the technical field of industrial robot stiffness identification. In the method, the effective working space of the robot is divided to multiple cubic regions; in view of a working task for a certain processing region, through applying different loads to an end effector under multiple positions and multiple postures in the region, based on the relationship between a load and end deformation, the robot joint stiffness in the interval can be identified and acquired, and accurate stiffness control on the robot at different working intervals during the processing process is realized. The method can realize accurate evaluation on the stiffness performance of the robot during the working process, the end deformation during the loaded processing process is thus accurately predicted, the effects of improving the processing precision and the quality are further achieved,and the application requirements of the robot in the field of high precision machining such as milling and hole making can be met.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
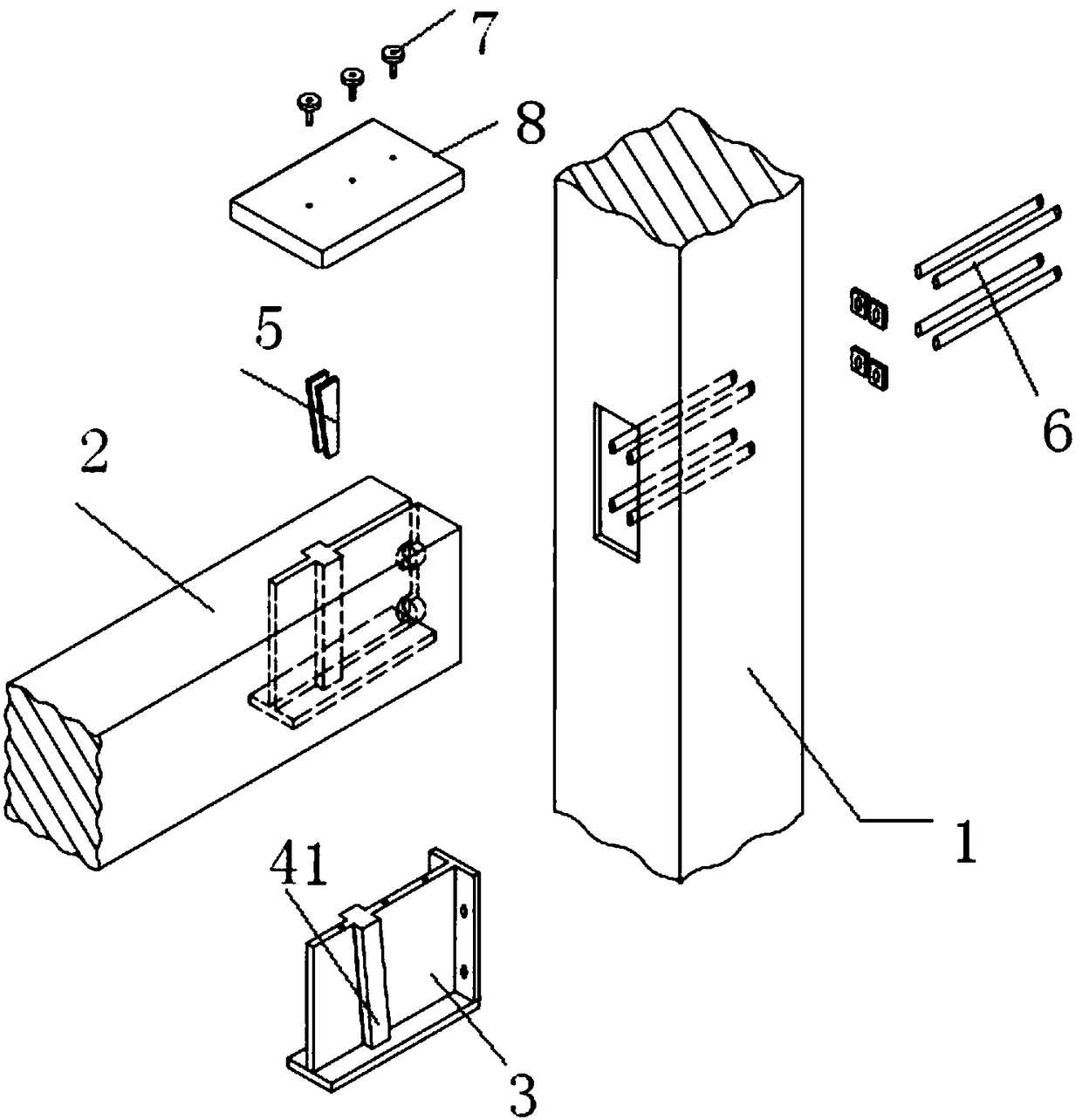
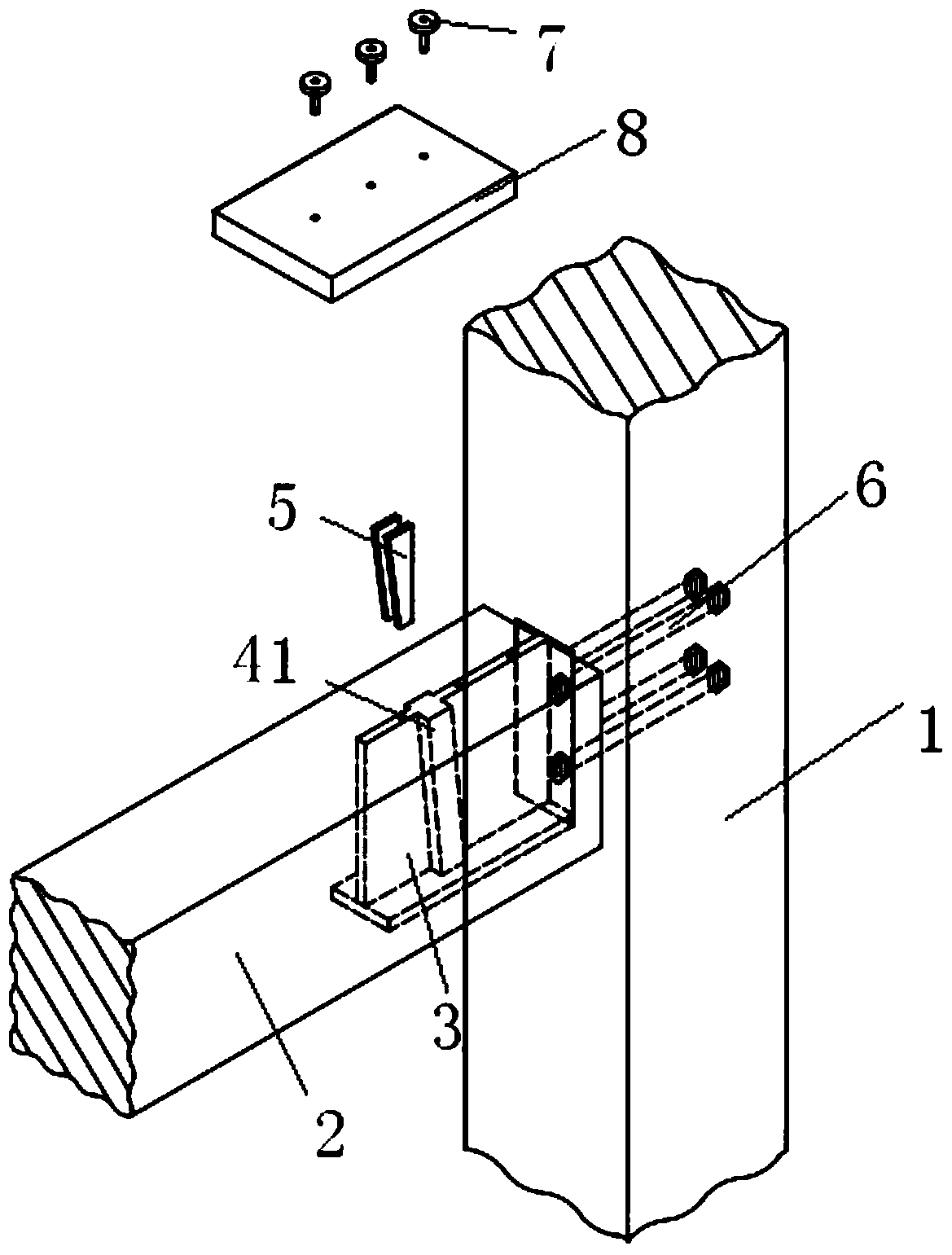
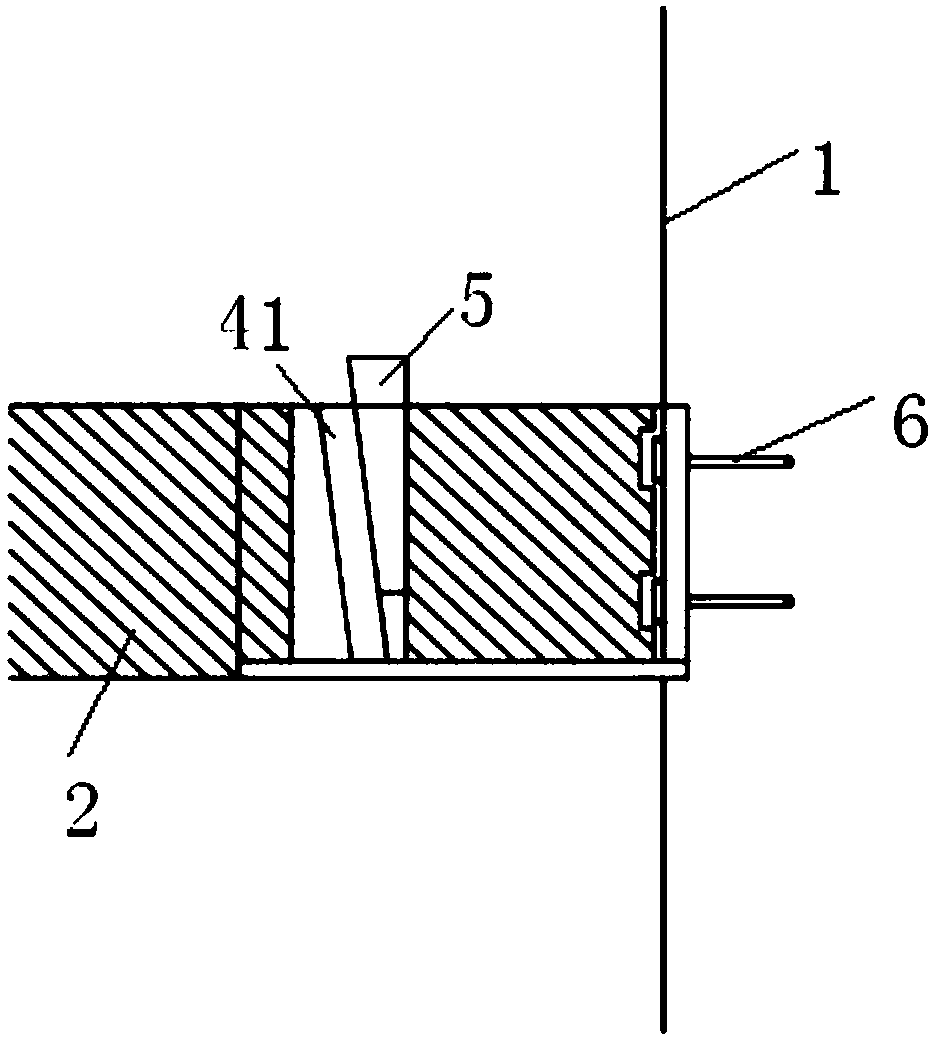
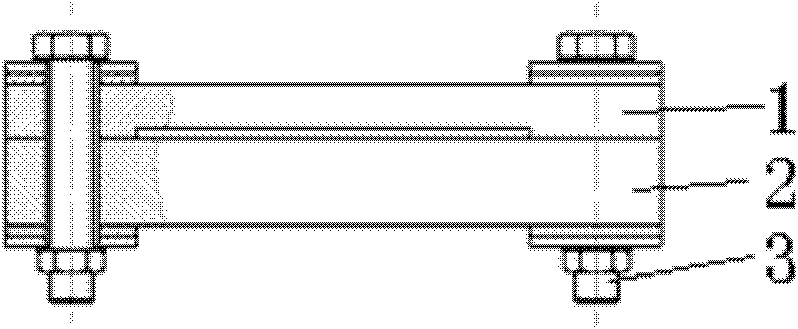
Assembly wood structure beam column embedded steel bar joint
InactiveCN103603431AImprove carrying capacityGood node stiffnessBuilding constructionsAdhesiveHigh energy
The invention discloses an assembly wood structure beam column embedded steel bar joint which comprises a wood beam, a wood column, an embedded steel bar, adhesives, an assembly connector, a joint fastener and a steel base plate. The wood beam is connected with the wood column through the assembly connector, the embedded steel bar and the joint fastener, the embedded steel bar is embedded into a pre-bored or reserved duct or formed channel at a beam end, the assembly connector is fixed to a column body through the joint fastener, the joint fastener is fixed on one side of the wood column back to the wood beam through the steel base plate, and cross grains of the embedded steel bar position at the beam end are strengthened by the aid of self-tapping screws. The joint has high bending resistance, joint stiffness, energy-dissipating capacity and ductility, can ensure a reliable structure under a small earthquake and can also control structural damage when the structure greatly deforms under a large earthquake, and ideal effects of high bearing capacity, high energy dissipation and high ductility are achieved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
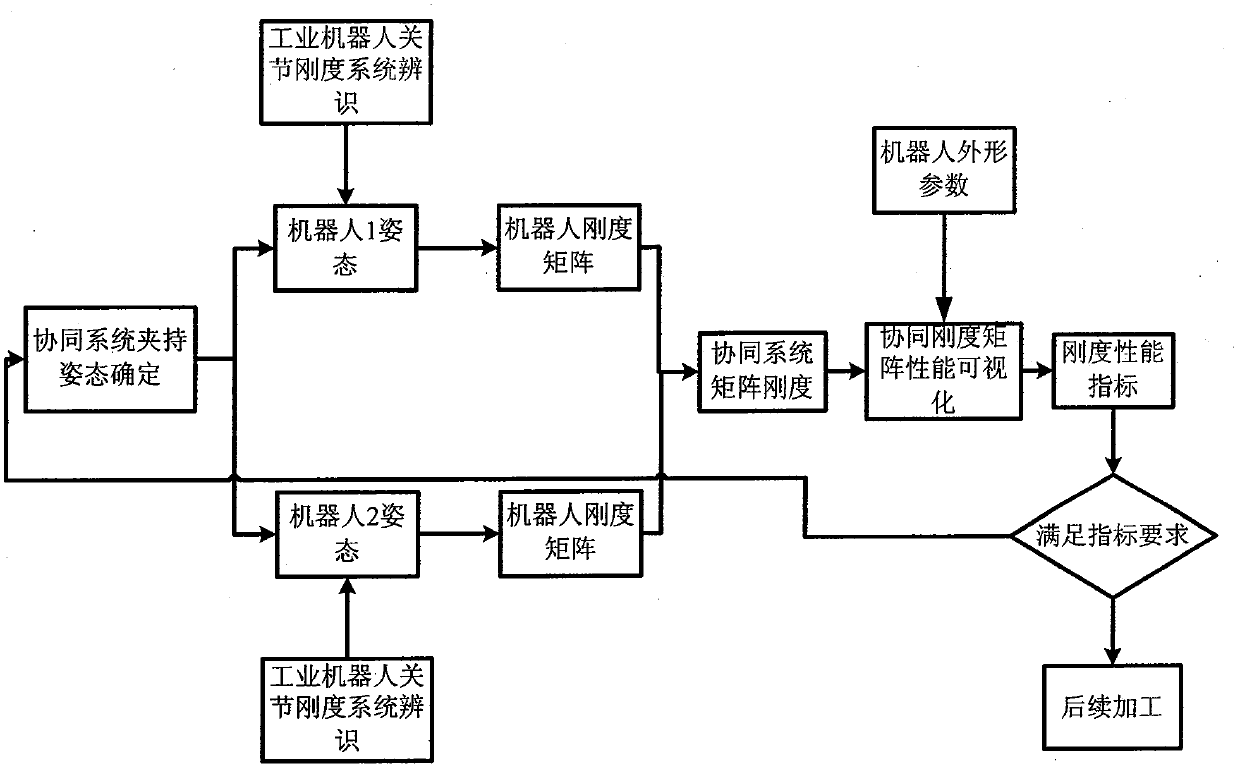
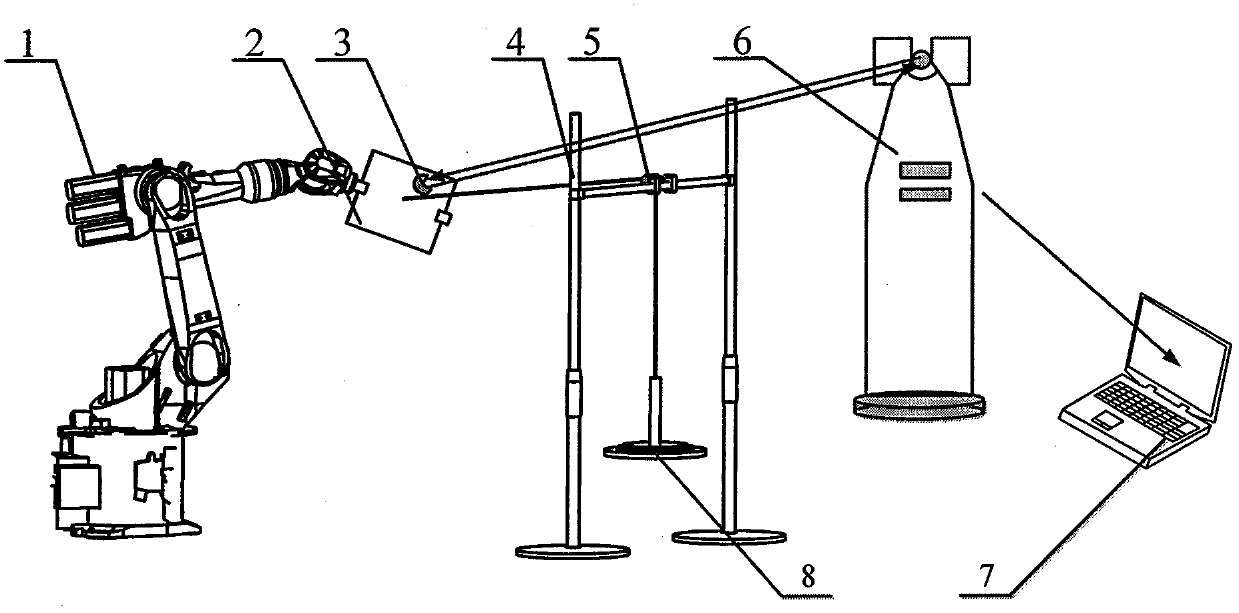
Multi-robot synergistic system static stiffness real-time performance evaluation method
InactiveCN107414834AImprove machining accuracyThe method steps are simpleProgramme controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorSimulationJoint stiffness
The invention provides a multi-robot synergistic system static stiffness real-time performance evaluation method without additional devices. The method comprises the steps that based on a robot kinematics transfer matrix and a robot end operation stiffness matrix, a robot joint stiffness identification scheme is established and implemented, and accurate robot practical joint stiffness is acquired; by employing robot system software to feed back real-time joint angles, a robot jacobian matrix is established, and a multi-robot synergistic system overall stiffness matrix is formed through the robot jacobian matrix and joint stiffness parameters identified by a robot; robot real-time stiffness is subjected to visual characterization through robot stiffness matrix ellipsoids, and the maximum value of system stiffness matrix characteristic values is selected as an evaluation index for carrying out robot stiffness evaluation; finally, through a GUI design interface, a stiffness performance evaluation visual interface is designed based on a double-KUKA KR-16 robot synergistic system.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
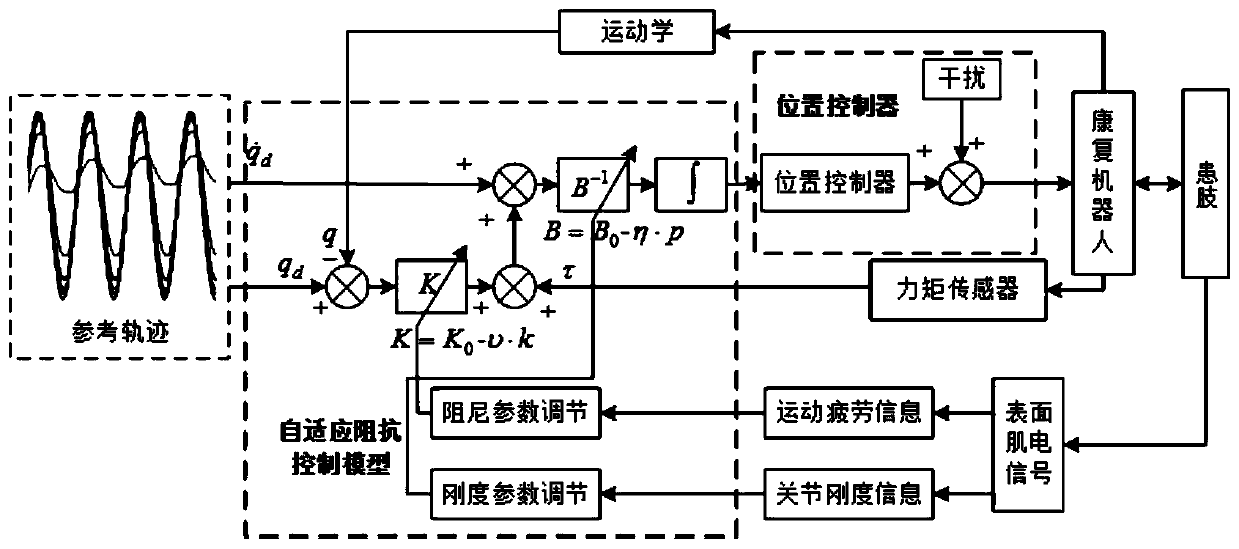
Rehabilitation robot control method based on joint stiffness and muscle fatigue
ActiveCN110355761APrevent harmfulImprove securityProgramme-controlled manipulatorRelative variationIntermediate frequency
The invention discloses a rehabilitation robot control method based on joint stiffness and muscle fatigue. According to the rehabilitation robot control method, the joint angle signals and the surfaceelectromyogram signals of a subject are collected, individual physiological parameters of the muscles are identified through a genetic algorithm in combination with a positive and negative dynamics principle, a personalized joint skeletal muscle model is established, and joint stiffness information in the moving process is calculated; the median frequency of the surface electromyogram signal in the moving process is calculated, and the fatigue information of the subject is acquired by utilizing the relative variation value; and self-adaptive adjustment is carried out on the parameters of an impedance model by adopting the joint stiffness information and the motion fatigue information, meanwhile, the rigidity and the damping parameters are restrained through a saturation function, and theself-adaptive impedance control method of the rehabilitation robot is realized. According to the rehabilitation robot control method, the rigidity information related to joints and the fatigue information related to the muscles are considered at the same time, the rigidity information and the fatigue information are introduced into the rehabilitation robot for control, the safety of joints and muscles in the rehabilitation training process can be considered, and safe and effective rehabilitation training is realized.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
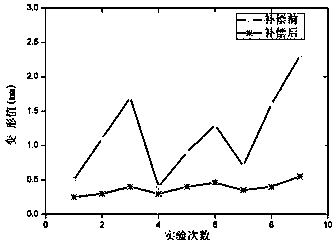
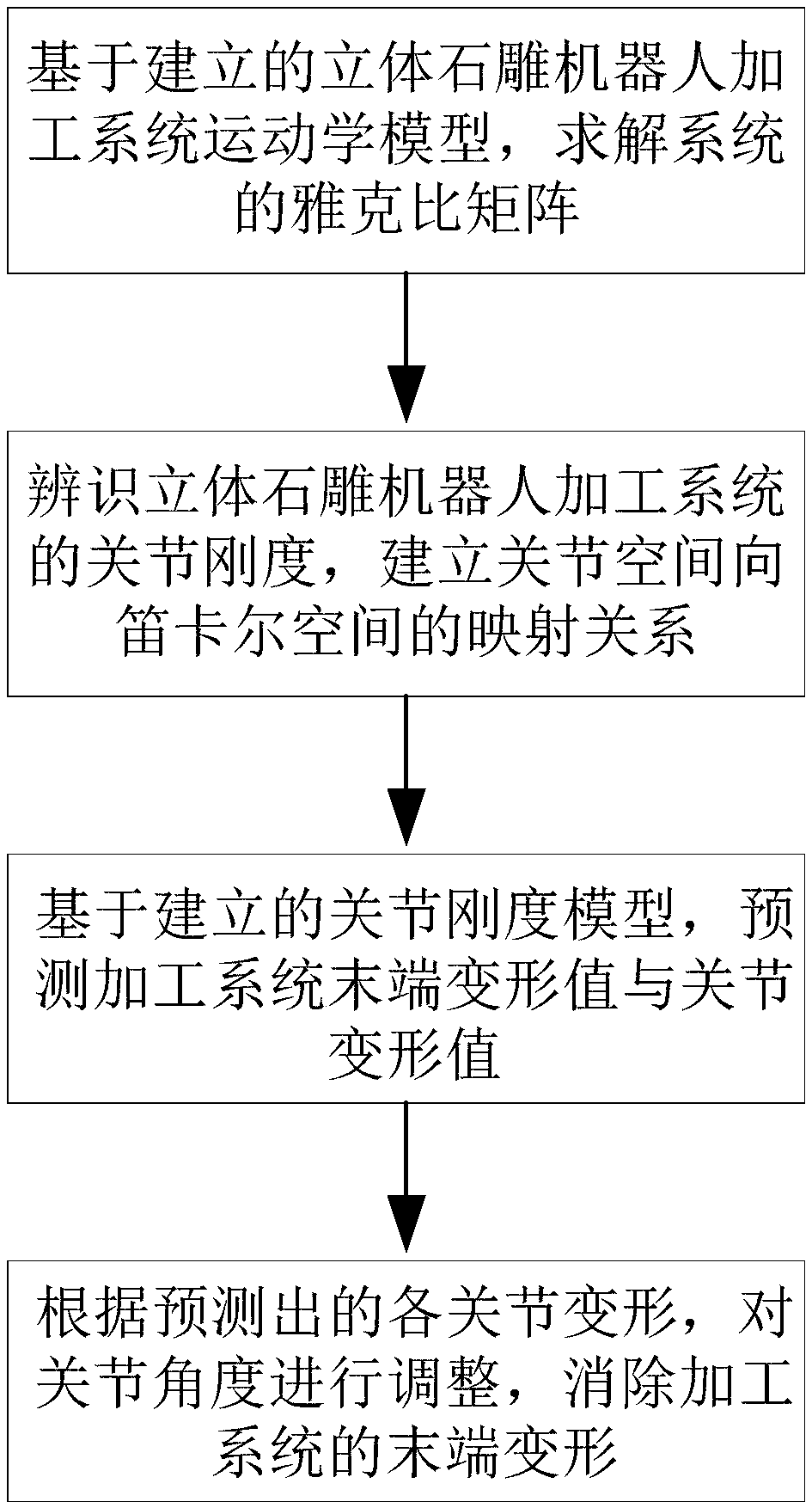
Deformation prediction and compensation method of three-dimensional stone carving robot processing system
ActiveCN109434829ADistortion Value EliminationImprove trajectory accuracyProgramme-controlled manipulatorModel makingStructural deformationStone carving
The invention relates to a deformation prediction and compensation method of a three-dimensional stone carving robot processing system. The deformation prediction and compensation method comprises thesteps that a kinematic model of the three-dimensional stone carving robot processing system is constructed, and a Jacobian matrix of the three-dimensional stone carving robot processing system is solved; a robot stiffness identification experiment is designed, the joint stiffness of the three-dimensional stone carving robot processing system is identified, and the mapping relationship of stiffness from a joint space to a Cartesian space at the end is established; according to the position and posture of the three-dimensional stone carving robot processing system and the external force received during processing, a joint stiffness model is used for predicting the tail end deformation value and each joint deformation value of the three-dimensional stone carving robot processing system; andaccording to the predicted deformation of each joint, the angle of each joint is adjusted to eliminate the deformation at the tail end of the robot processing system for processing three-dimensional stone carvings. The quantitative compensation of the structural deformation value of any three-dimensional stone carving robot processing system is realized, and the tool path precision of the three-dimensional stone carving robot processing system is improved when stone is processed.
Owner:HUAQIAO UNIVERSITY
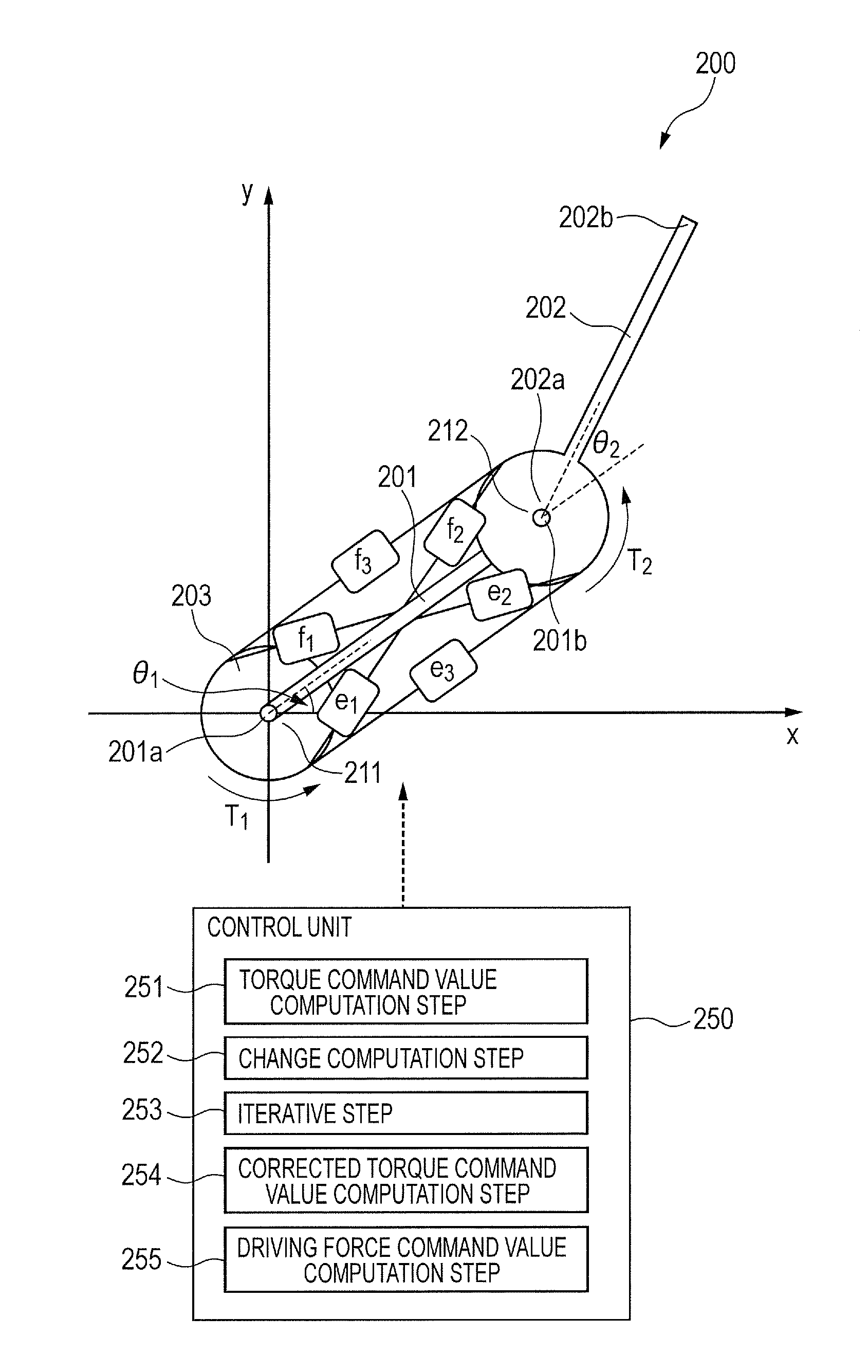
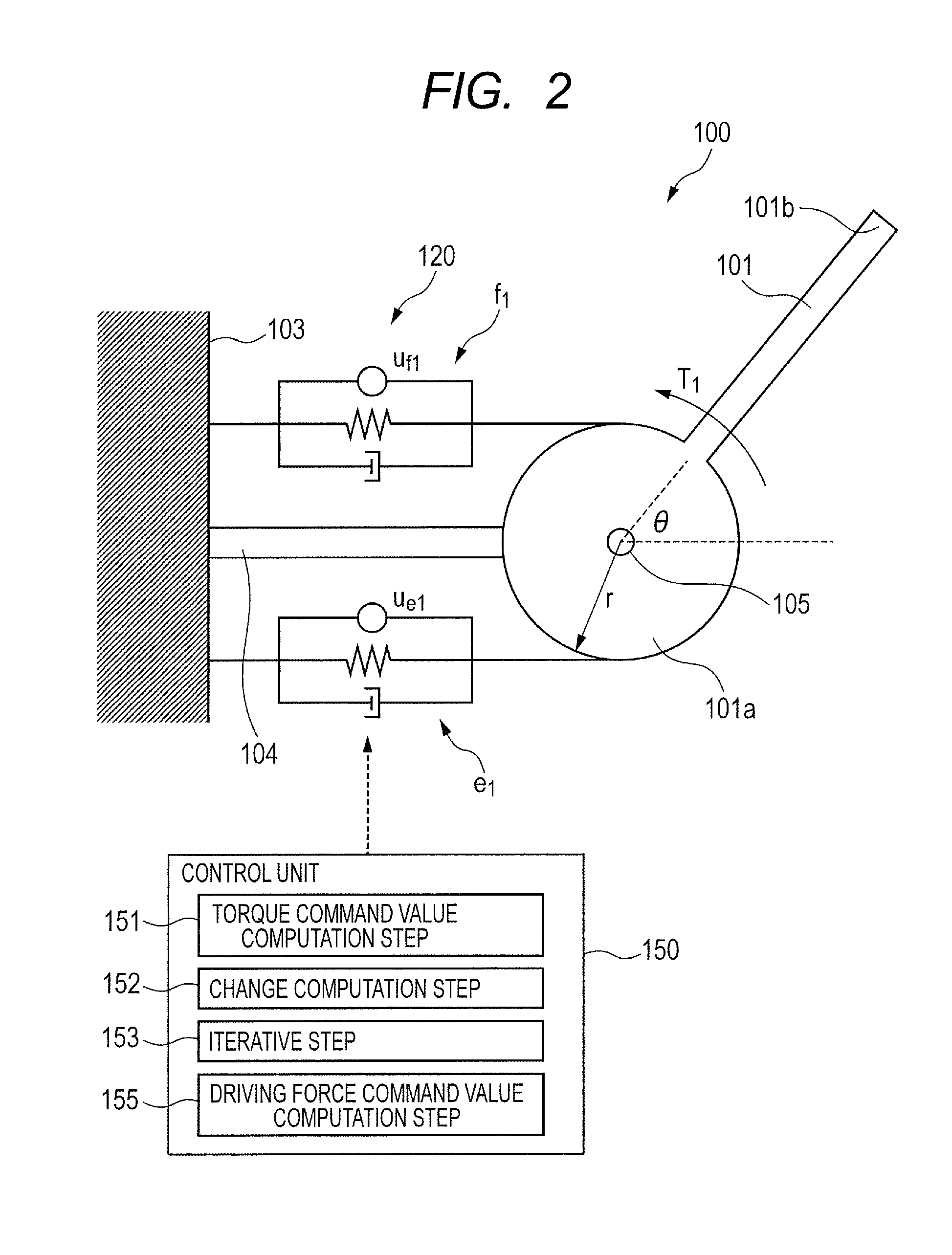
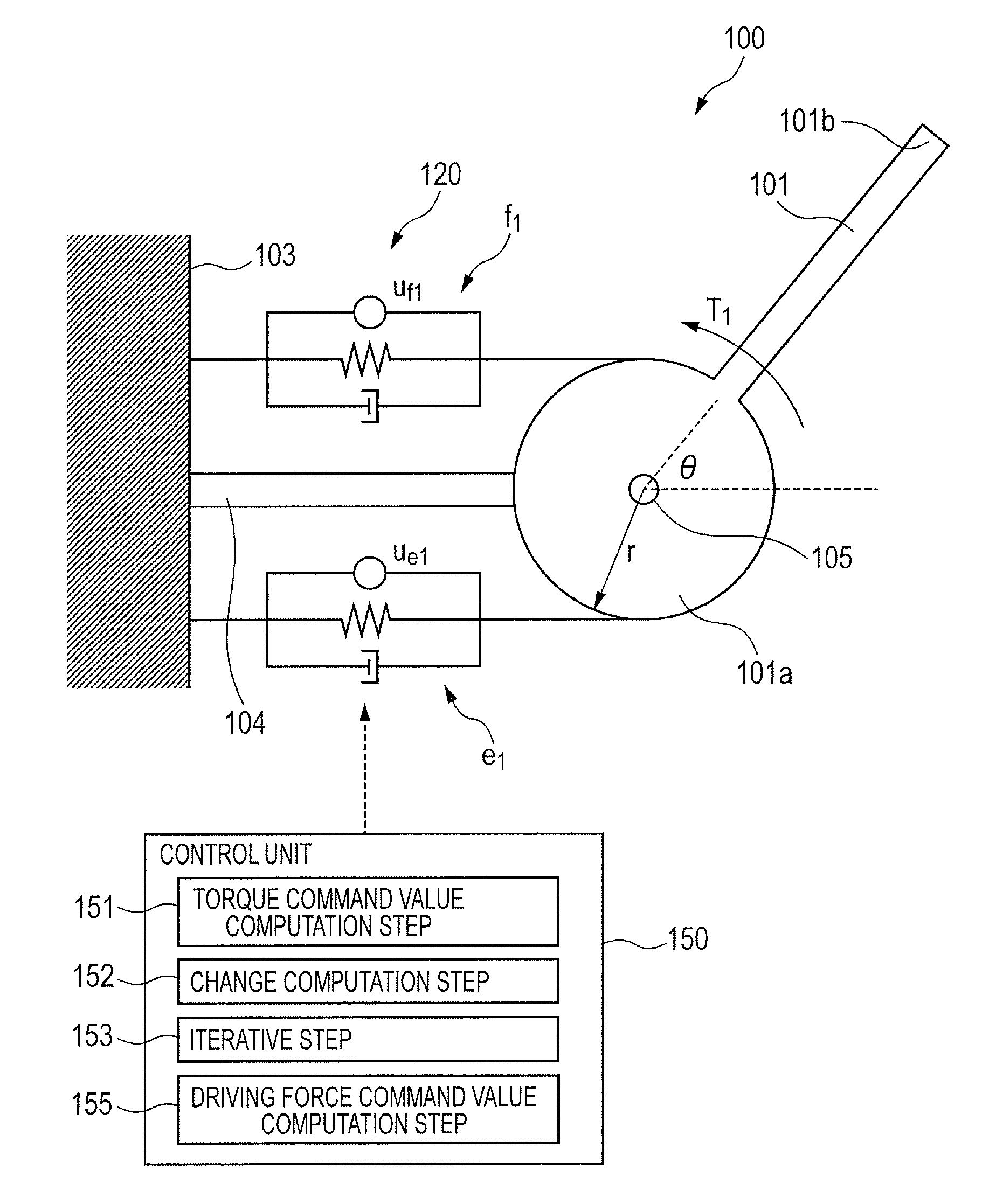
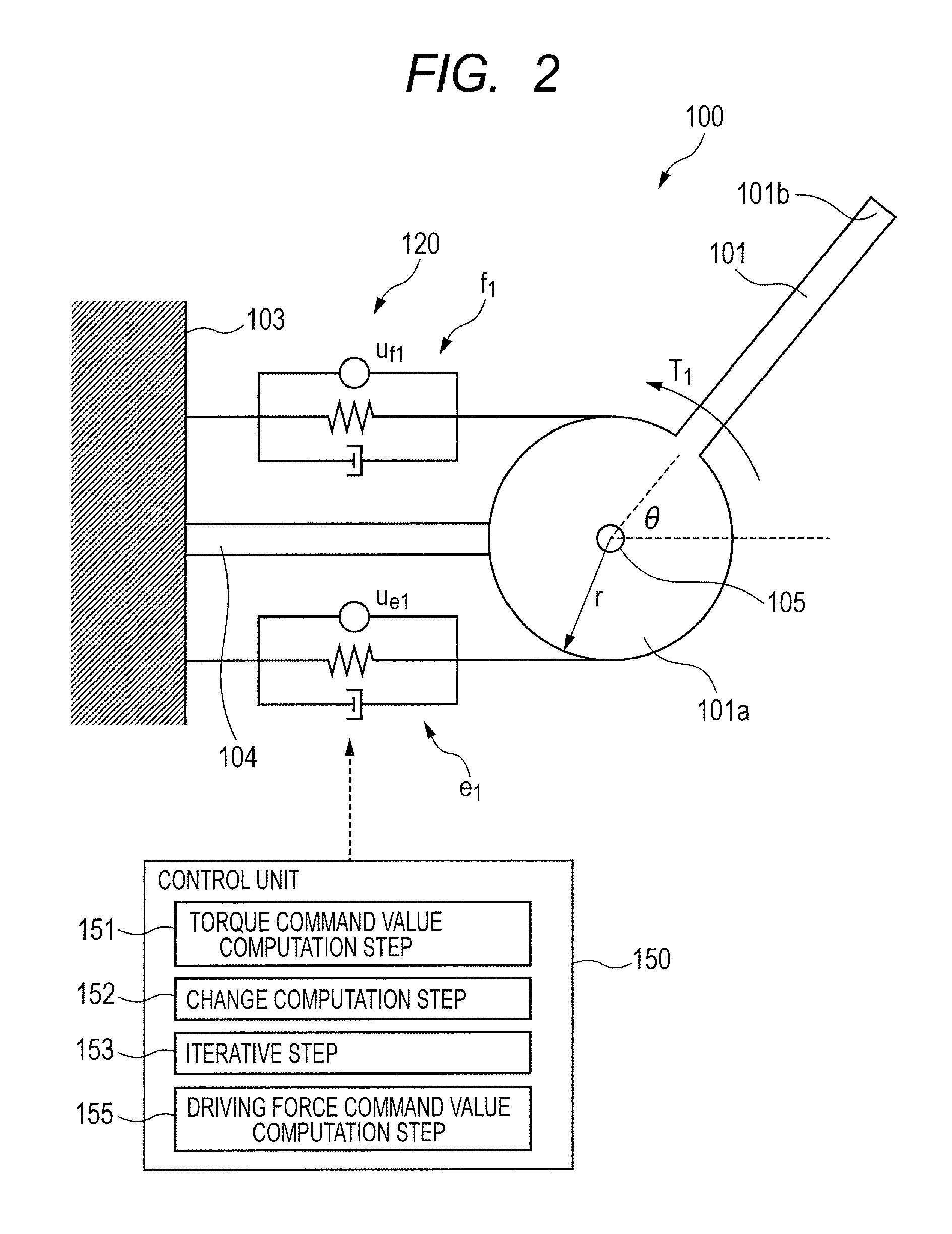
Control method of robot apparatus and robot apparatus
InactiveUS20130211596A1Optimizing stiffness of jointExtended operating timeProgramme controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorEngineeringActuator
A control method of a robot apparatus, the robot apparatus including a link and a pair of actuators, obtaining each driving force command value of each of the actuators, and controlling each of the actuators, the control method including: a torque command value computation step; a change computation step of computing a difference between the joint stiffness command value and a value and performing a computation of subtracting a value from the joint stiffness command value; an iterative step of iterating the computations of the torque command value computation step and the change computation step until the difference converges to a value equal to or smaller than a predetermined value; and a driving force command value computation step to compute each of the driving force command values when the difference is converged to a value equal to or smaller than the predetermined value.
Owner:CANON KK
Cryogenic enhancement of joint function, alleviation of joint stiffness and/or alleviation of pain associated with osteoarthritis
ActiveUS9610112B2Safe with no serious device-related adverse eventsAvoid signalingCatheterSurgical instruments for heatingSacroiliac jointPain reduction
Owner:PACIRA CRYOTECH INC
Fabricated steel-wood structure connecting joint
InactiveCN108547379AImprove carrying capacityGood node stiffnessBuilding constructionsEngineeringInverted-T shape
A fabricated steel-wood structure connecting joint comprises columns and beams. Short inverted-T-shaped steel connecting pieces are inserted into the ends of the beams, long bolts penetrate into the columns, one end of each long bolt is connected with the corresponding short inverted-T-shaped steel connecting piece, webs of the short inverted-T-shaped steel connecting pieces are connected with cover plates through short bolts, and the cover plates are arranged on the upper portions of the beams. The fabricated steel-wood structure connecting joint adopts the short inverted-T-shaped steel connecting pieces and has the advantages of great bearing capacity, joint stiffness, energy dissipation capacity and ductility performance.
Owner:XIJING UNIV
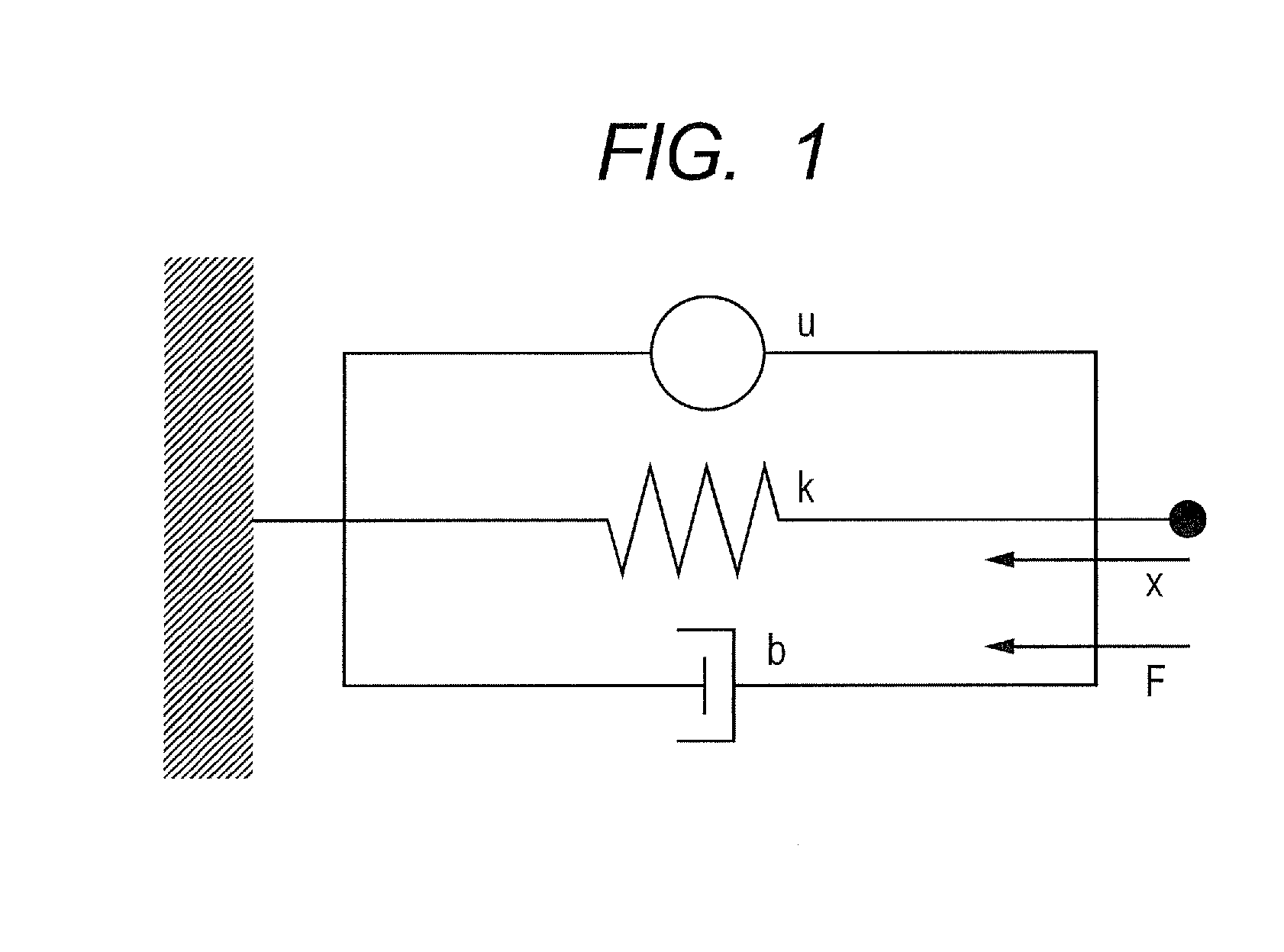
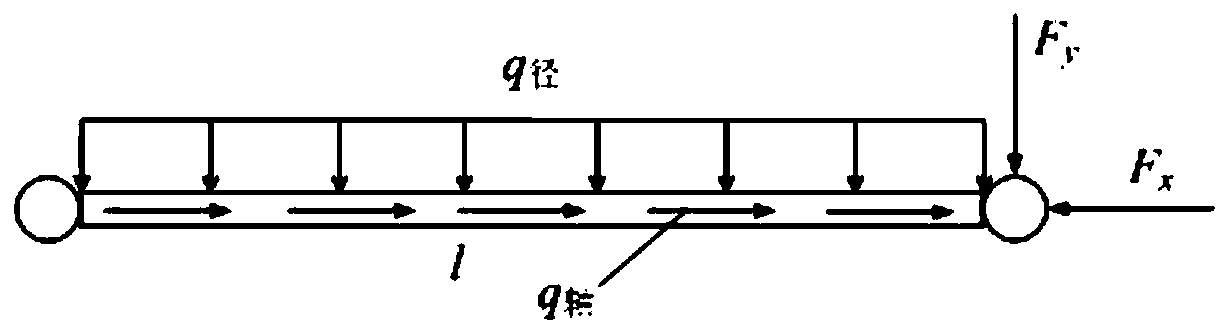
Method for obtaining mechanical joint stiffness
The invention discloses a method for obtaining mechanical joint stiffness. The method is implemented according to the following steps: firstly, a pulse excitation method is adopted so as to obtain resonance frequency of an actual structure; secondly, an upper contact layer and a lower contact layer of a joint are regarded as a virtual material so as to build a finite element analytical model of an overall structure comprising the joint; and thirdly, a group of initial values of normal stiffness Kn and tangent stiffness Kt is firstly preset, and the preset values of the normal stiffness Kn and the tangent stiffness Kt are revised after the natural frequency which is obtained through computing and the resonance frequency which is obtained through experiment are compared with each other so as to ensure that the natural frequency which is obtained through computing continuously approaches the resonance frequency which is obtained through experiment until the natural frequency which is obtained through computing is approximate enough with the resonance frequency which is obtained through experiment, then last preset group of values of the normal stiffness Kn and the tangent stiffness Kt is the joint stiffness final fixed value which is obtained through adopting the method. In the method adopted by the invention, the iterative method is adopted so as to continuously adjust the design variable, and the finally obtained design variable is the joint stiffness data.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF TECH
Robot system controlling method, robot system, and control apparatus for quadrupedal robot
InactiveUS8958915B2Eliminate needEasy to adjustProgramme controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorRobotic systemsFeedback control
An object of the present invention is to provide a robot system controlling method and robot system which perform link angle control and joint stiffness control through feedback control.
Owner:CANON KK
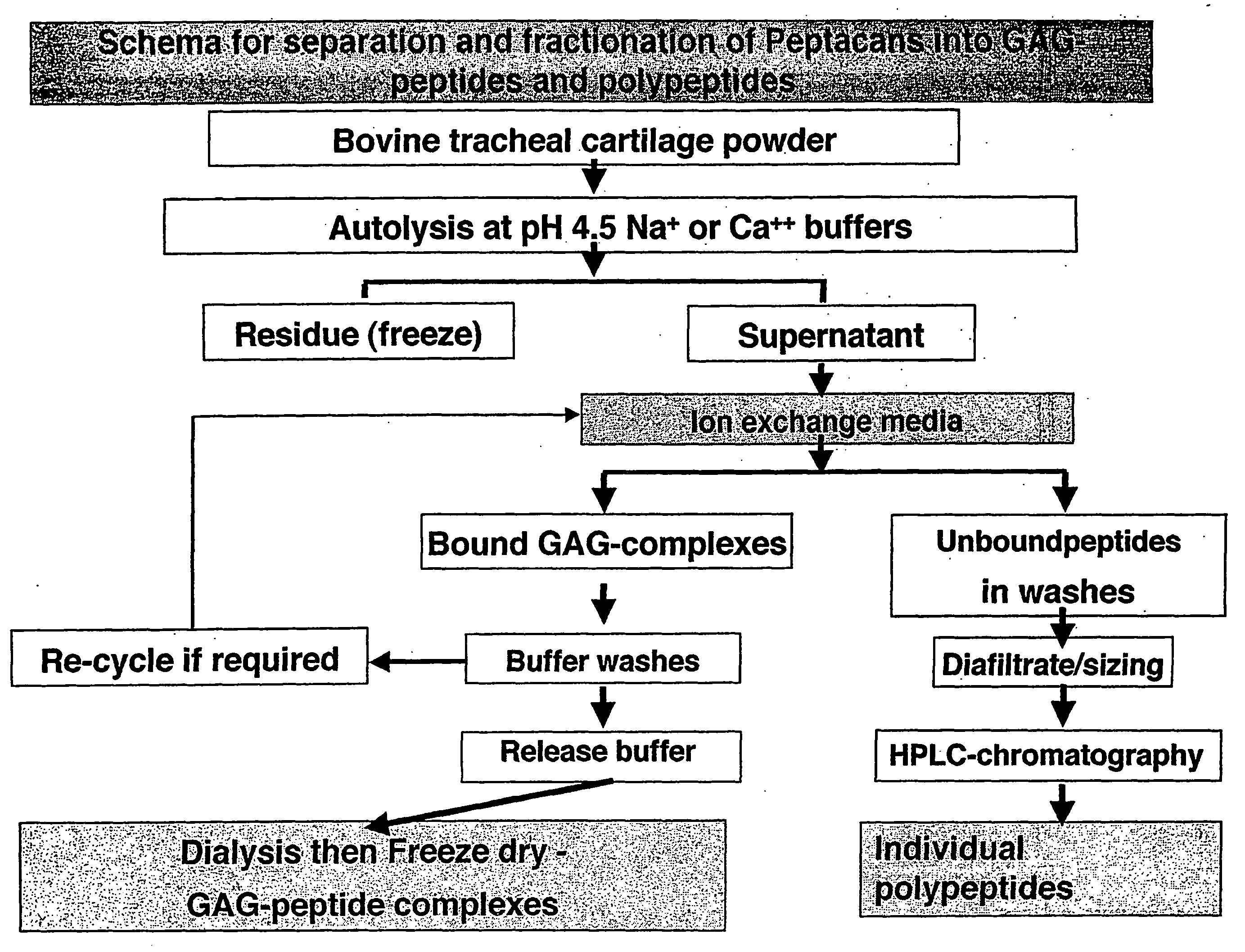
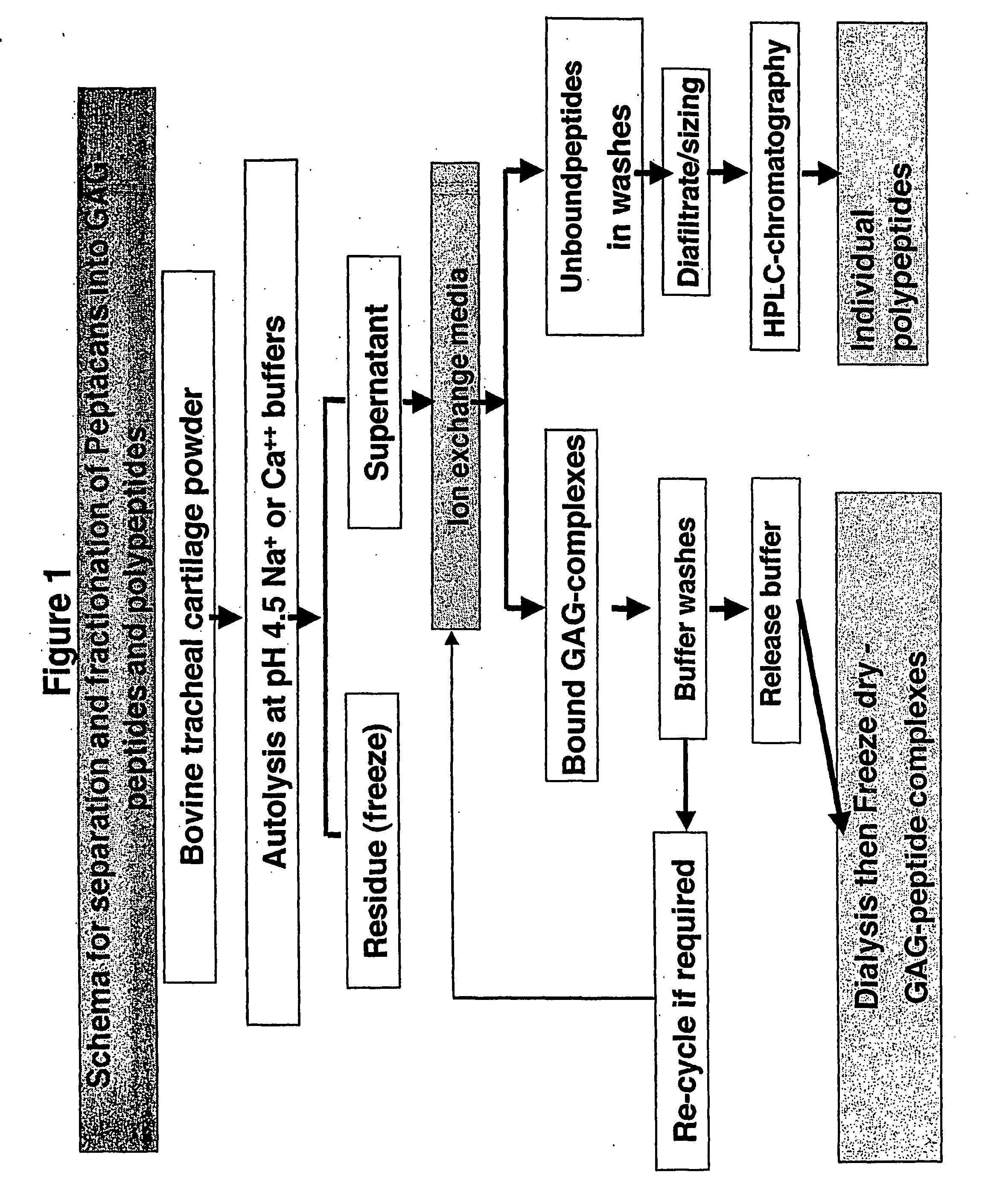
Glycosaminoglycan Peptides Derived From Connective Tissues And Use Thereof In The Prevention Of Arthritis And Other Degenerative Medical Conditions
InactiveUS20080200372A1Avoid seizuresLow mobilityOrganic active ingredientsSkeletal disorderProphylactic treatmentJoint stiffness
The inventors sought to provide compositions and methods of prophylaxis to prevent these harmful immune responses in patients and to prevent the related undesirable symptoms biological tissue such as for example inflammation, cell injury, tissue injury, tissue degradation, tenderness, redness, joint stiffness, joint swelling, restricted mobility and reduced strength. The inventors found that prophylactic therapy of an animal comprising administering a pharmaceutical composition comprising a GAG-peptide complex, optionally together with a connective tissue derived polypeptide, prevented the onset of at least one undesirable symptom.
Owner:INST OF NUTRACEUTICAL RES
Permanent magnet variable-stiffness flexible joint for robot
The invention belongs to the technical field of flexible robots, and provides a permanent magnet variable-stiffness flexible joint for a robot, wherein the permanent magnet variable-stiffness flexiblejoint is capable of simulating nolinear variable-stiffness muscle features of a bionic joint. A permanent magnet variable-stiffness mechanism is adopted as a stiffness adjusting component, a rope isused as force and motion transmission component, the stiffness changes along with change of air gaps between permanent magnets, by means of actions of a motor, a rope winch and a guide pulley, force and position decoupling of ropes at the two sides of a manipulator, so that only joint rotating angle instead of joint stiffness is changed, and namely the joint position is adjusted under the equal-stiffness condition; the effect of just changing joint stiffness instead of the joint position can be achieved, and work under corresponding stiffness condition is achieved according to different working conditions. The permanent magnet variable-stiffness flexible joint for the robot is concise in motion form, convenient to manufacture and easy to operate.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Robot joint variable stiffness actuator
The invention belongs to the technical field of robot joints, and particularly relates to a robot joint variable stiffness actuator. The robot joint variable stiffness actuator comprises a power output device and two power input devices. The power output device comprises a power output rack, a screw rod and friction circular truncated cones. The screw rod is installed on the power output rack andis in thread connection with the two friction circular truncated cones. The small diameter ends of the two friction circular truncated cones correspond to each other. The two power input devices are rotationally installed on the two sides of the power output rack respectively and are both connected with the two friction circular truncated cones. The joint turning angles and the joint stiffness arecontrolled by changing the relative turning directions of the two power input devices. According to the robot joint variable stiffness actuator, the two power input devices are symmetrically arrangedon the two sides of the power output device, the joint turning angles and the joint stiffness are controlled by changing the relative turning directions of two power input shafts. Furthermore, it canbe realized that a motor or joint components are protected by adopting the friction manner.
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF AUTOMATION - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Electrical heat and vibrating device
InactiveUS20060041207A1Highly effectiveEasy self-managementChiropractic devicesVibration massageJoint painHuman body
The Electrical Heat and Vibrating Device is a lightweight, portable, completely self-contained low voltage, and self-administered therapeutic apparatus. More particularly, this invention gives the wearer or user comforting sensations to facilitate a temporary reduction in joint stiffness, joint pain, and joint discomfort, within the human body.
Owner:GROSS JULIA
Dynamic stabile hip joint brace system
InactiveCN102846417AAchieve passive swingPromote reconstructionMedical scienceTissue repairCoxal joint
The invention discloses a dynamic stabile hip joint brace system for treating hip joint diseases, which is characterized by comprising a fixed seat bound to the waist of the human body, a movably seat bound to the knee of the human body, and an action actuator providing movement power, wherein fixed seat side lugs are arranged at the sides of the fixed seat, and movable seat side lugs are arranged at the sides of the movable seat above the knee; and the action actuator is hinged between the fixed seat side lugs and the movable side lugs through an action actuator seat and an action actuator rod, and the telescopic action actuator drives the hip joint through the movable seat to swing. Through the implementation of the invention, the hip joint is driven to swing in a safety range, the tissue reconstruction is effectively prompted, and the tissue repair is accelerated, and therefore, the therapeutic effect of the hip joint disease is effectively improved, and the therapeutic time is shortened; and the arthrodesis syndromes of traditional treatment methods of joint stiffness, muscle atrophy, osteoporosis and the like brought by long-term non-movement are avoided.
Owner:胡大勇 +1
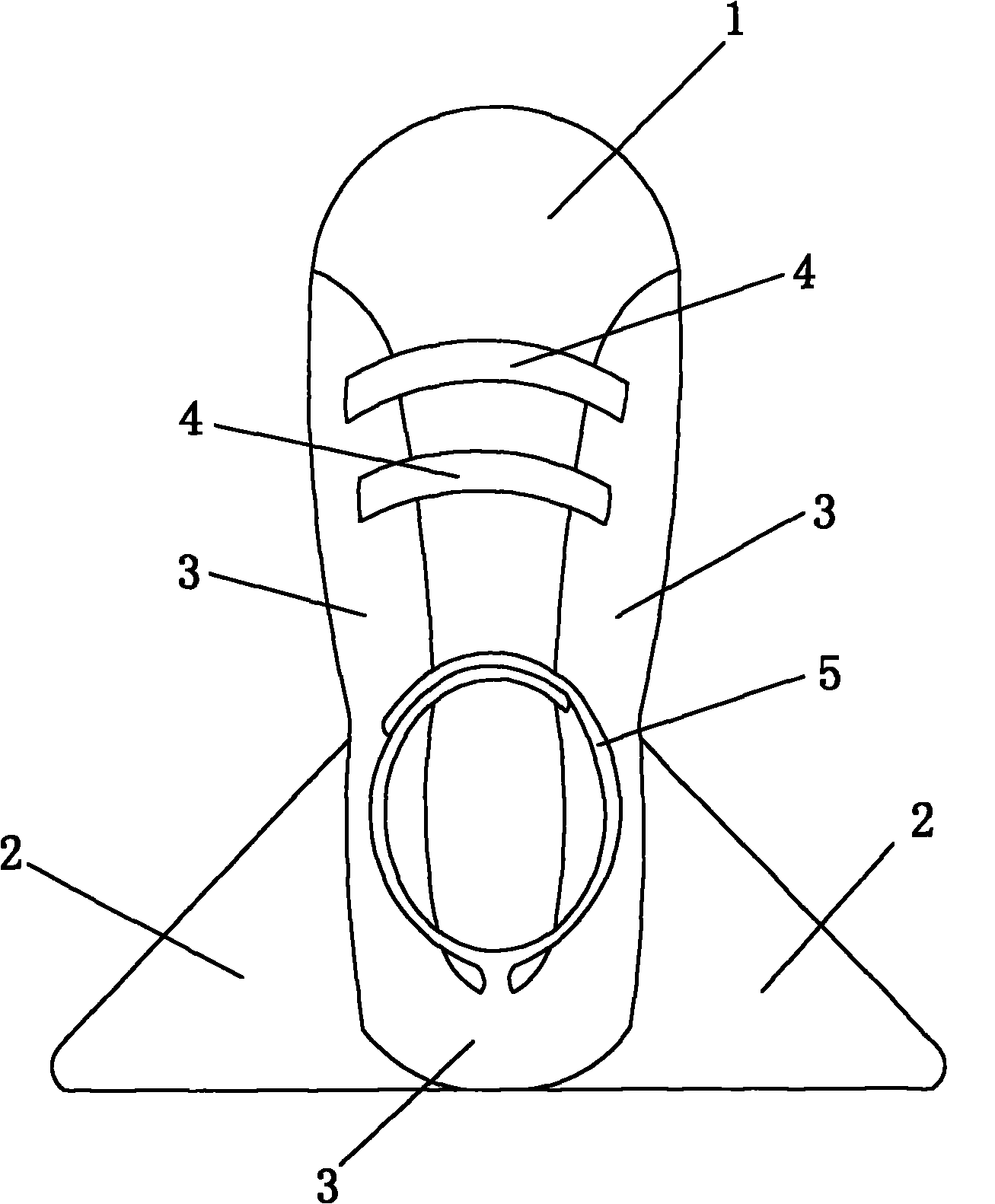
Improvement of ant-rotating shoes
InactiveCN101797193AAvoid pressure soresImprove comfortMedical scienceFootwearMuscle forceEngineering
The invention discloses an improvement of ant-rotating shoes. Two side wing plates of each anti-rotating shoe and the sole are combined into together, therefore, the stability is increased, and the unsoundness of the traditional heel nailed by wood plates is avoided. The soft upper and the hollow shoe insole can avoid the part in contact with feet generating sore, increase the comfort, and have the heat insulation function. The toes can not be covered by the upper and can expose out of the upper, thereby being convenient to observe the blood circulation of the toes. The overlapping length of the left upper and the right upper can be freely adjusted according to the size and fatness of the feet, therefore, the upper and the foot surface can be meshed. The invention has wide application, can be applied to patients with fracture accompanied by neurologic damage, patients in ankle joint fracture recovery period, paraplegics, patients in long-term sickbed, patients before and after artificial hip joint operation, and comas, can prevent foot drop, foot internal rotation and foot external rotation, has no influence on the sufficient motion of quadriceps femoris or ankle joint, prevent joint stiffness and muscular dystrophy, and performs active function on increasing the muscle force.
Owner:刘景瑞
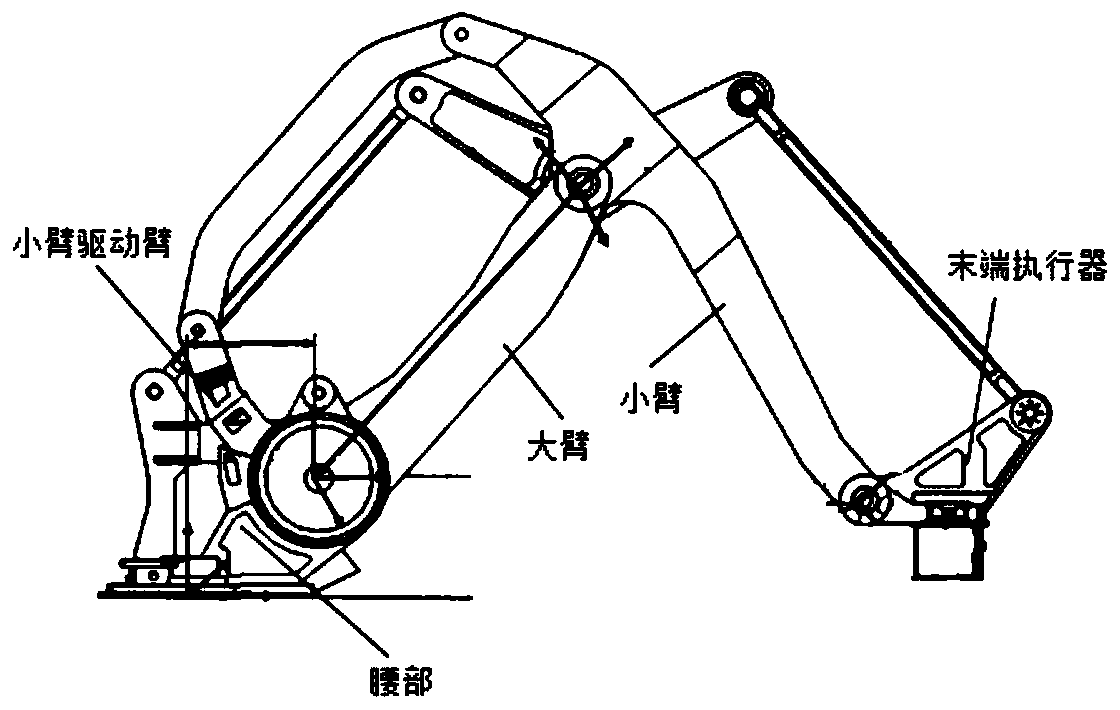
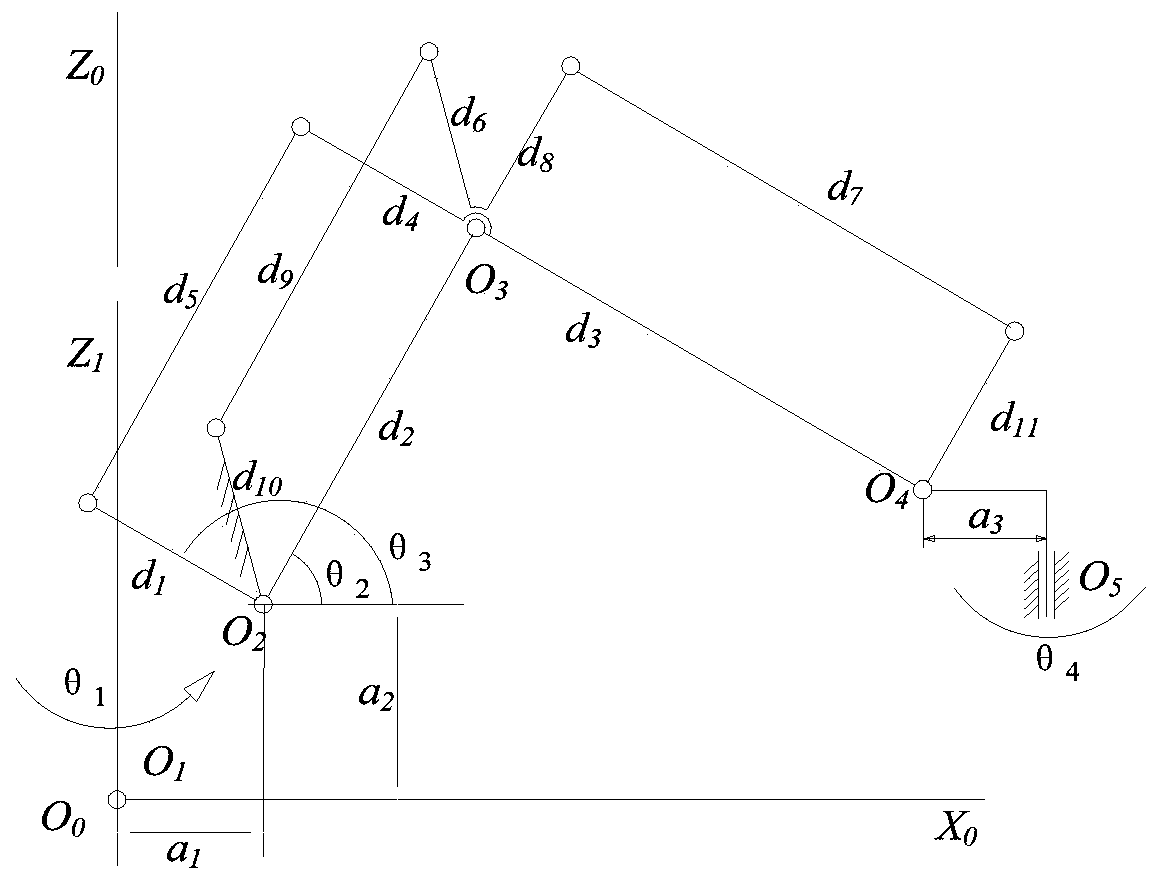
Heavy load stacking robot frequency response characteristic analyzing method and system
InactiveCN110549340AExact Rigid Body Dynamic EquationsHigh accelerationProgramme-controlled manipulatorStacking articlesKinematicsControl system
The invention provides a heavy load stacking robot frequency response characteristic analyzing method and system. For a high-speed heavy load stacking robot, kinematics analysis is performed, a forward kinematics solution and work space is obtained, a Jacobian matrix is obtained, and the relationship between a joint space and a Cartesian space is built; static stiffness analysis is performed on the stacking robot; a rigid-flexible coupling dynamical model is built through a Lagrange second-type equation, the joint flexibility of the high-speed heavy load stacking robot is described, and a vibration mode of the robot is analyzed; and the influence law of different joint stiffnesses on the system frequency response is obtained, and according to the influence law, movement of the high-speed heavy load stacking robot is controlled. The heavy load stacking robot frequency response characteristic analyzing method and system lay a foundation for building of the kinematics and dynamical model,subsequent trajectory planning and design of a control system.
Owner:LIAOCHENG UNIV
Compact variable-stiffness tandem elastic actuated joint
ActiveCN108481359AReduce usageCompact structureProgramme-controlled manipulatorJointsVariable stiffnessReduction drive
The invention discloses a compact variable-stiffness tandem elastic actuated joint which comprises an upper arm part, a driving part, a forearm part, a stiffness regulation part and an angle sensor. Aworm gear and a reel are fixed to a bolt together through mounting keys, worm gear transmission is introduced, and the use of a gear reducer is reduced, so that the joint has small size and a compactstructure and achieves the purpose of miniaturization design. The compact variable-stiffness tandem elastic actuated joint can realize bidirectional flexibility, and the joint stiffness K is equal to4kR2, wherein K is the joint stiffness, k is individual spring stiffness, and R is the radius of a wire lot of the reel. The joint stiffness can be calculated accurately. Two groups of springs are used, the requirement on the spring stiffness is lower than that of one group of springs, and the spring size can be reduced and the joint size is further reduced. The springs are arranged on the two sides of the reel, which is good for balance of internal and external side force.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
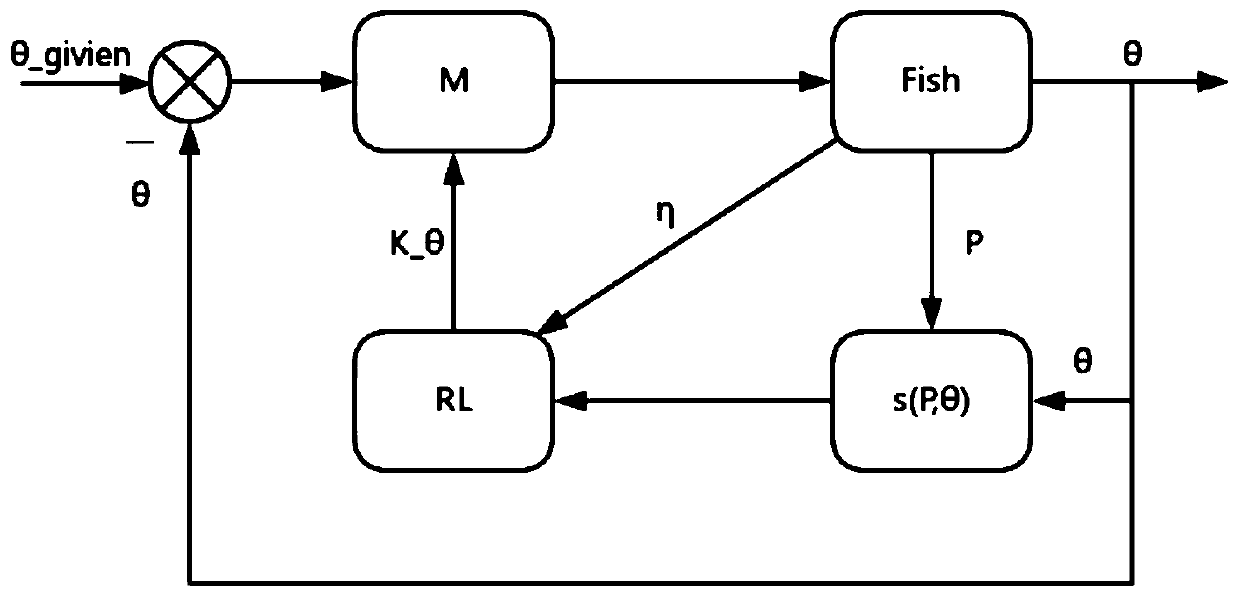
Control method and device for robot fish, equipment and storage medium
InactiveCN110262218AImprove propulsion efficiencyControllers with particular characteristicsReinforcement learning algorithmPropulsive efficiency
The application discloses a control method and device for a robot fish, equipment and a storage medium. A difference between a current first angle of a robot fish joint and a preset second angle is obtained; according to a negative work power currently outputted by a joint motor and a current first angle of the robot fish joint, a current optimal joint stiffness value of the robot fish joint is obtained from a pre-established Q table and is used as a proportion coefficient of a PID controller; PID controlling is performed on the difference to obtain a current optimal torque; the robot fish joint is driven by controlling the joint motor, so that the torque of the robot fish joint becomes the current optimal torque; and then the step of acquiring a difference is performed again. The Q table is established based on a reinforcing learning algorithm. Therefore, the propulsive efficiency of the robot fish is improved.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Control method of robot apparatus and robot apparatus
InactiveUS9044860B2Optimizing stiffness of jointExtended operating timeProgramme controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorActuatorControl theory
A control method of a robot apparatus, the robot apparatus including a link and a pair of actuators, obtaining each driving force command value of each of the actuators, and controlling each of the actuators, the control method including: a torque command value computation step; a change computation step of computing a difference between the joint stiffness command value and a value and performing a computation of subtracting a value from the joint stiffness command value; an iterative step of iterating the computations of the torque command value computation step and the change computation step until the difference converges to a value equal to or smaller than a predetermined value; and a driving force command value computation step to compute each of the driving force command values when the difference is converged to a value equal to or smaller than the predetermined value.
Owner:CANON KK
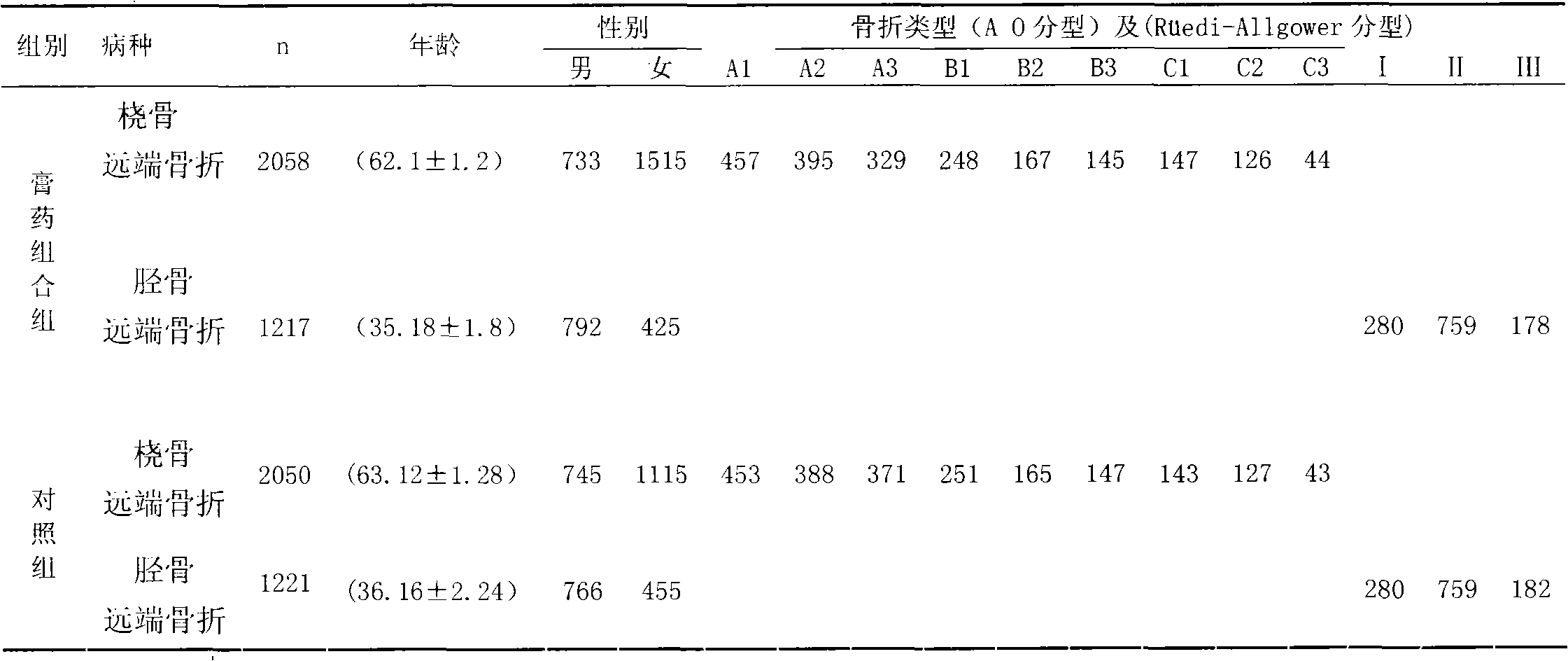
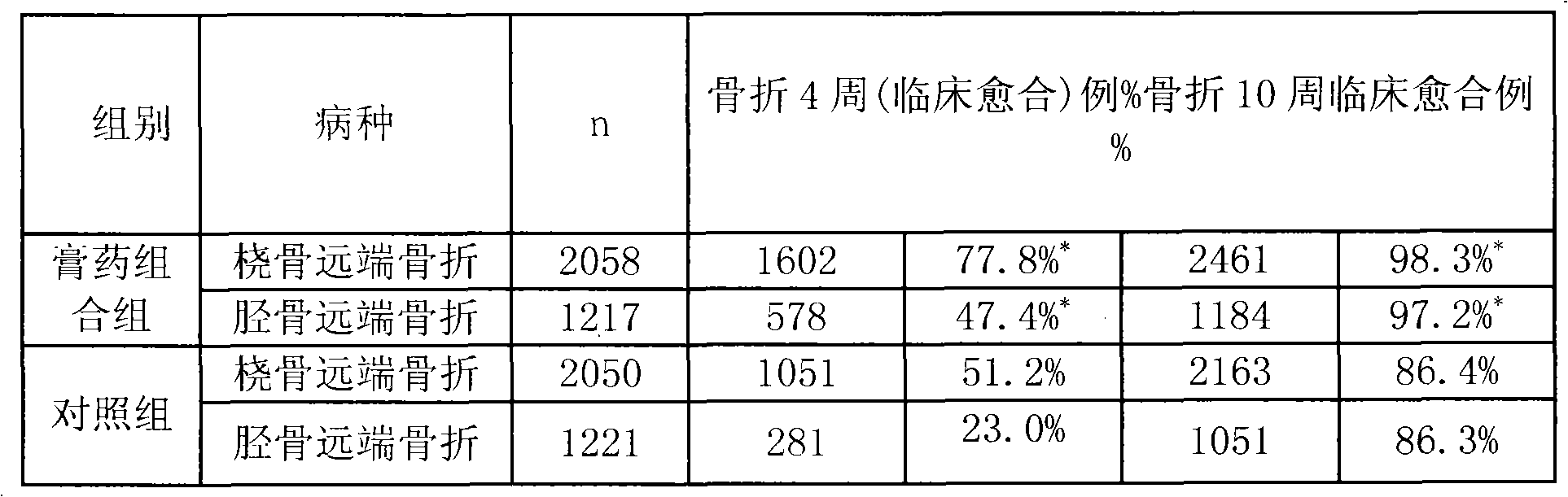
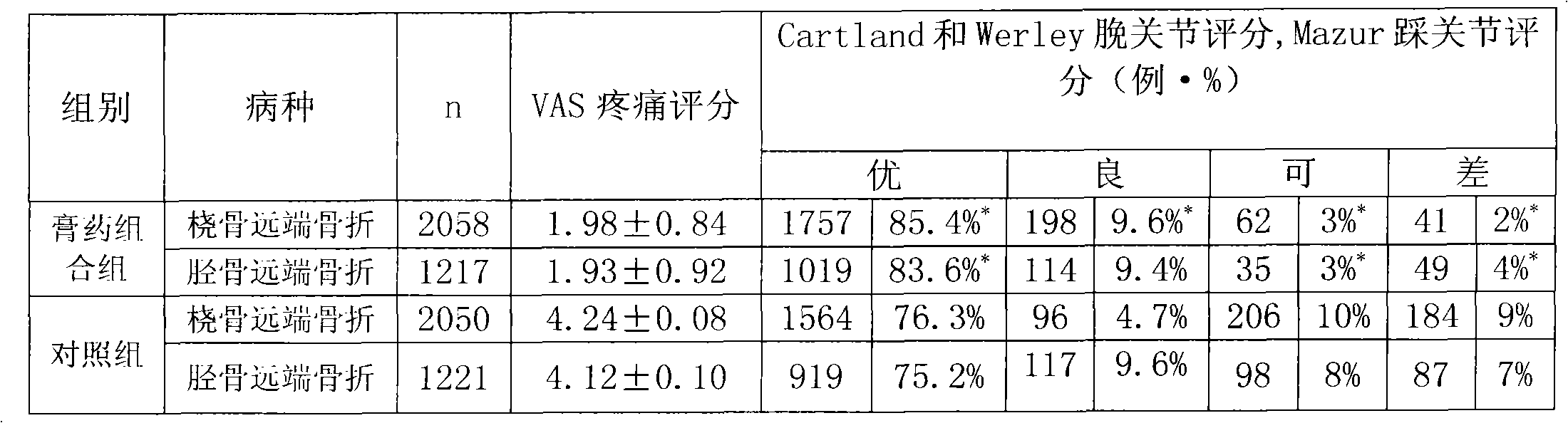
An external application plaster combination for treatment of fracture injuries and a preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103156992APromote healingEffective functional exerciseHeavy metal active ingredientsAnthropod material medical ingredientsMedicinal herbsSide effect
The invention belongs to the technical field of application of traditional Chinese medicine, and in particular relates to an external application plaster combination for treatment of fracture injuries and a preparation method thereof. The external application plaster combination is characterized by comprising two parts of, namely traumatology extinction paste, and traumatology bone-setting paste. During the treatment of a fracture injury, different pastes are used at different stages, wherein the traumatology extinction paste is externally applied at the injury position in the early fracture reduction, and before and after a surgery; while the traumatology bone-setting paste is applied in the middle and late period to reduce local swelling and pain of the injury, and effectively promote the healing of the fracture, allowing a patient to perform effective functional training relatively early for prevention and treatment of joint stiffness. Clinical applications have proves that the external application plaster combination which is prepared from pure Chinese medicinal herbs, has advantages of being fast in relieving swelling and pain, short in the recovery period, definite in curative effects, and non-side effects.
Owner:李天顺 +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com