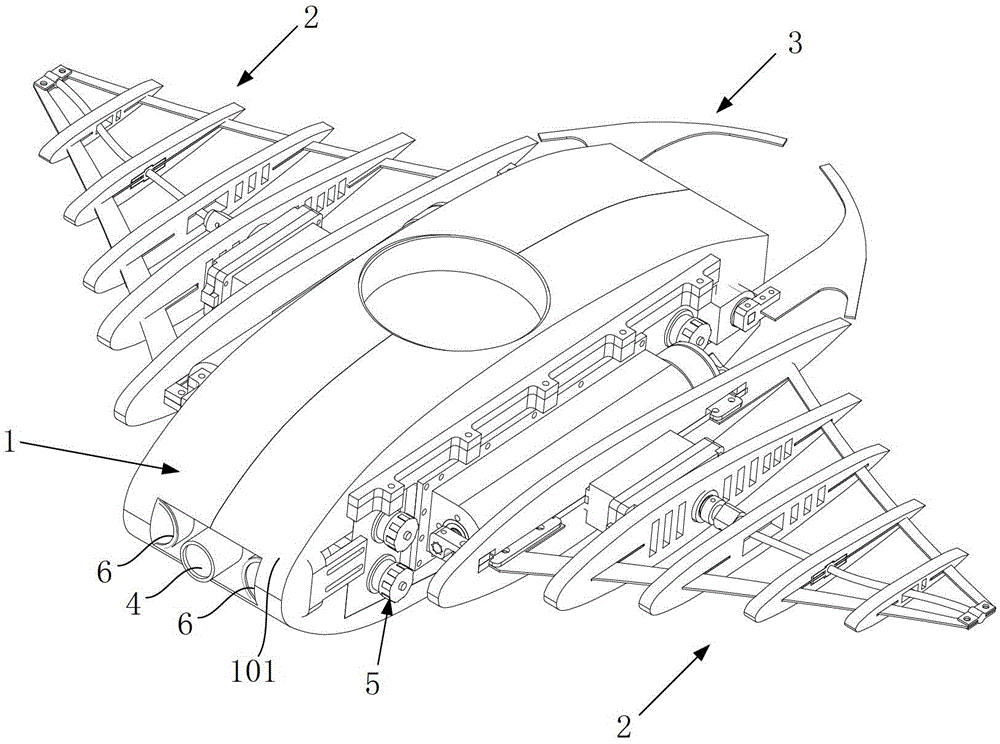
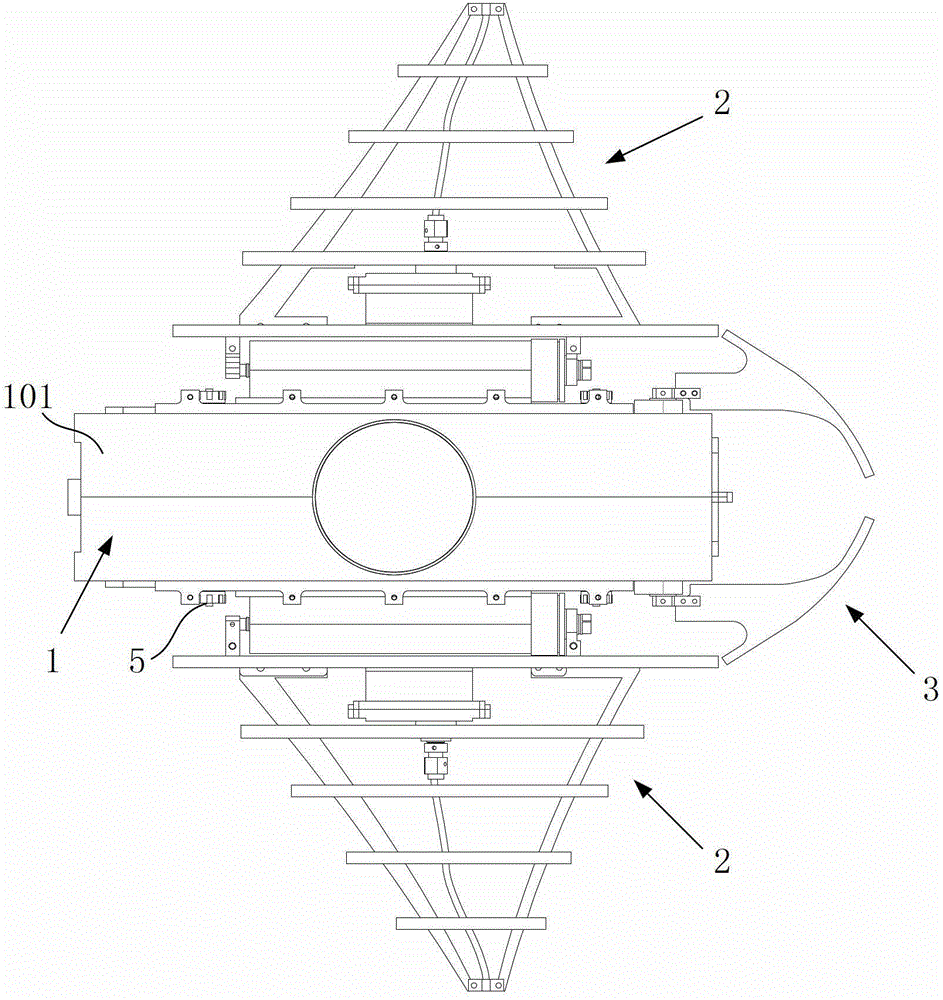
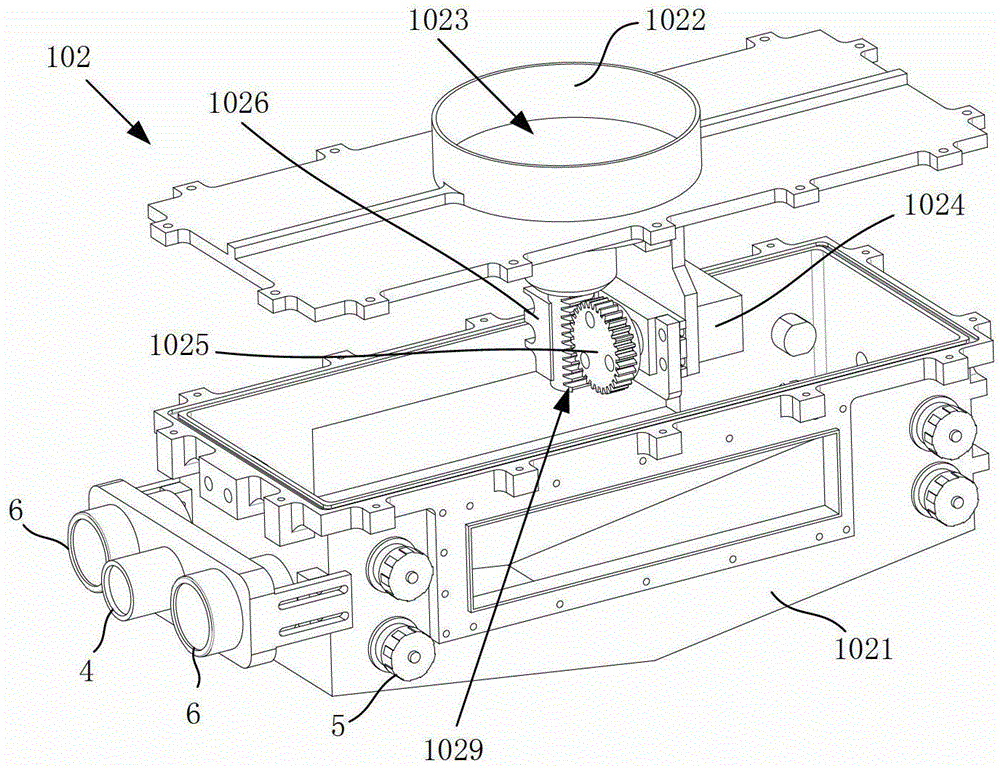
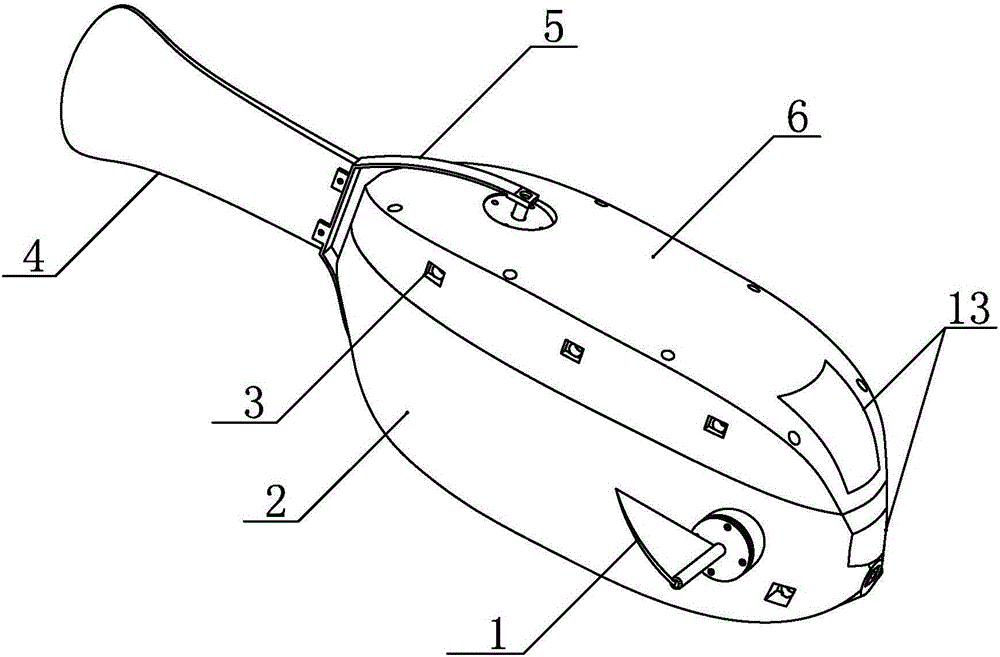
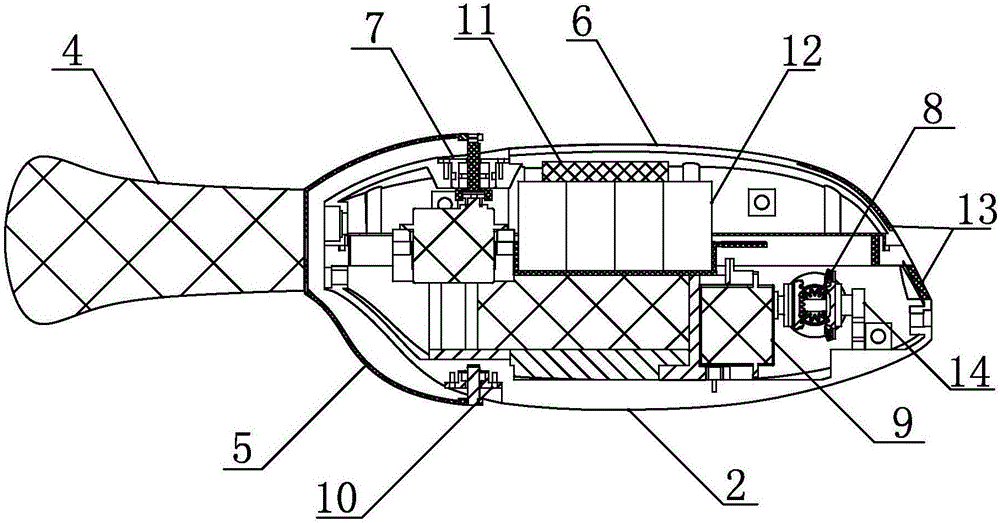
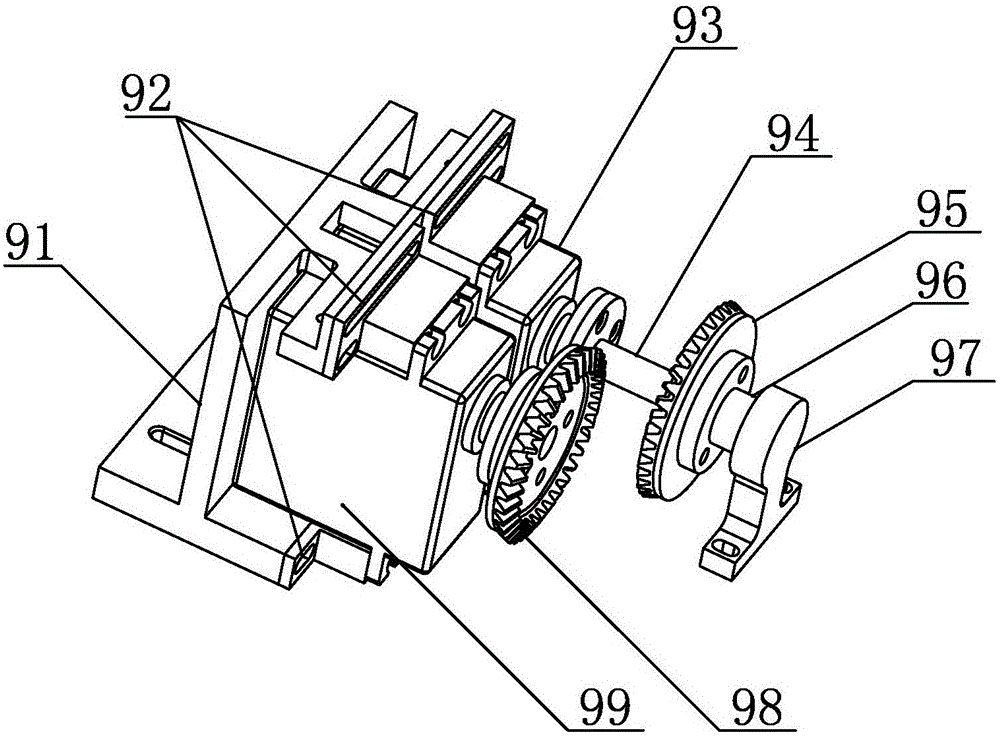
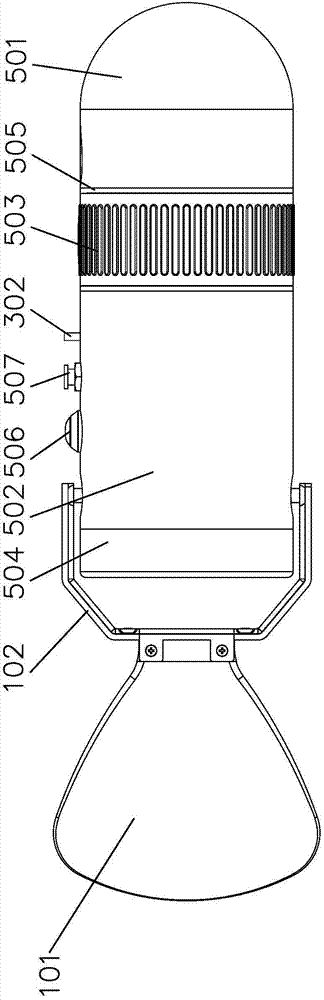
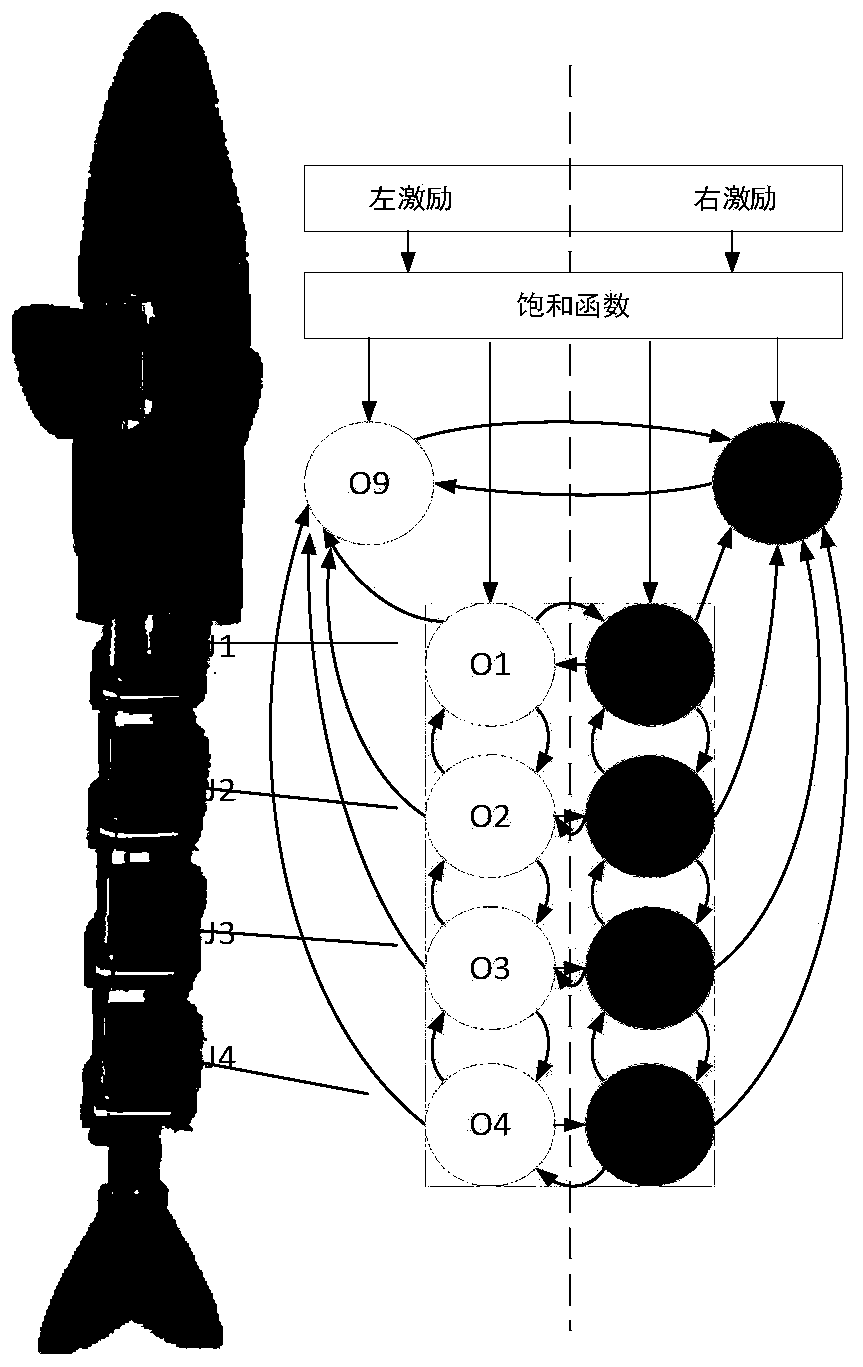
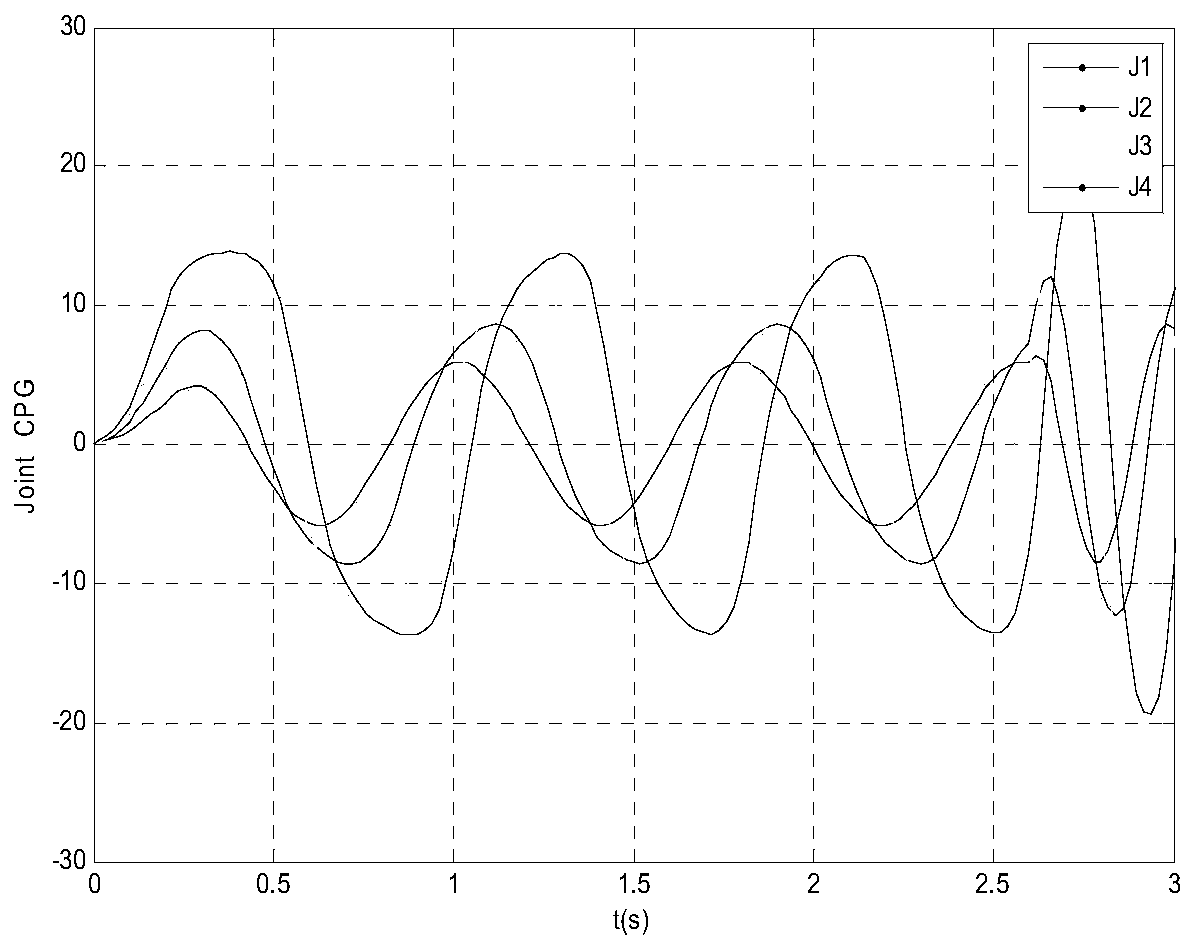
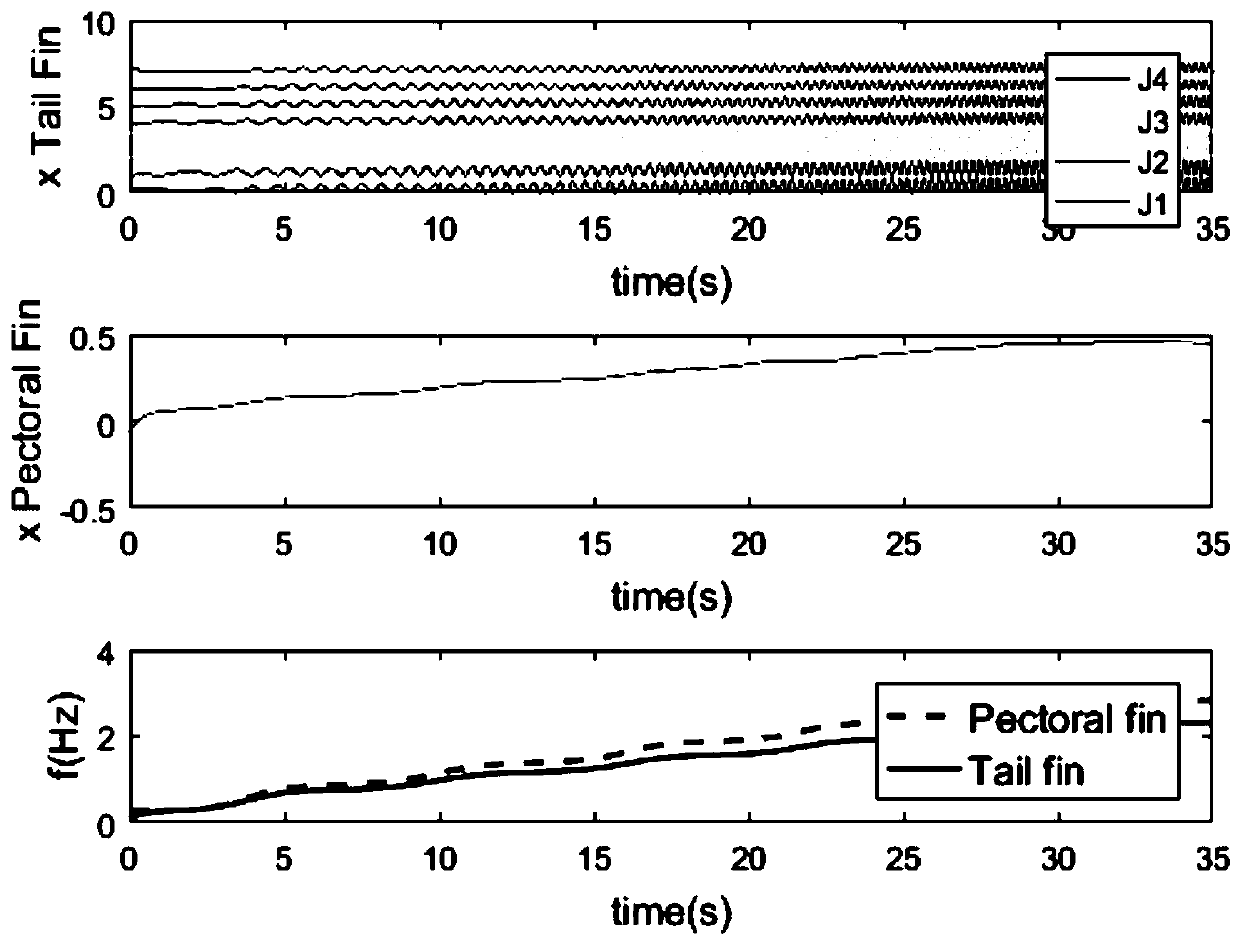
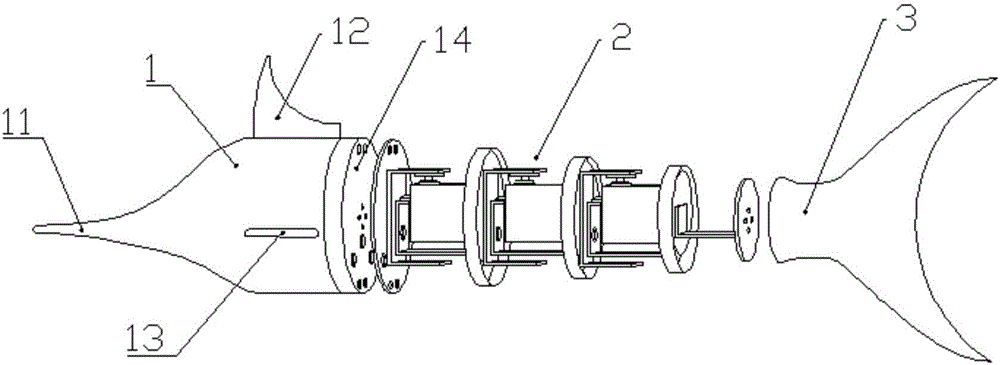
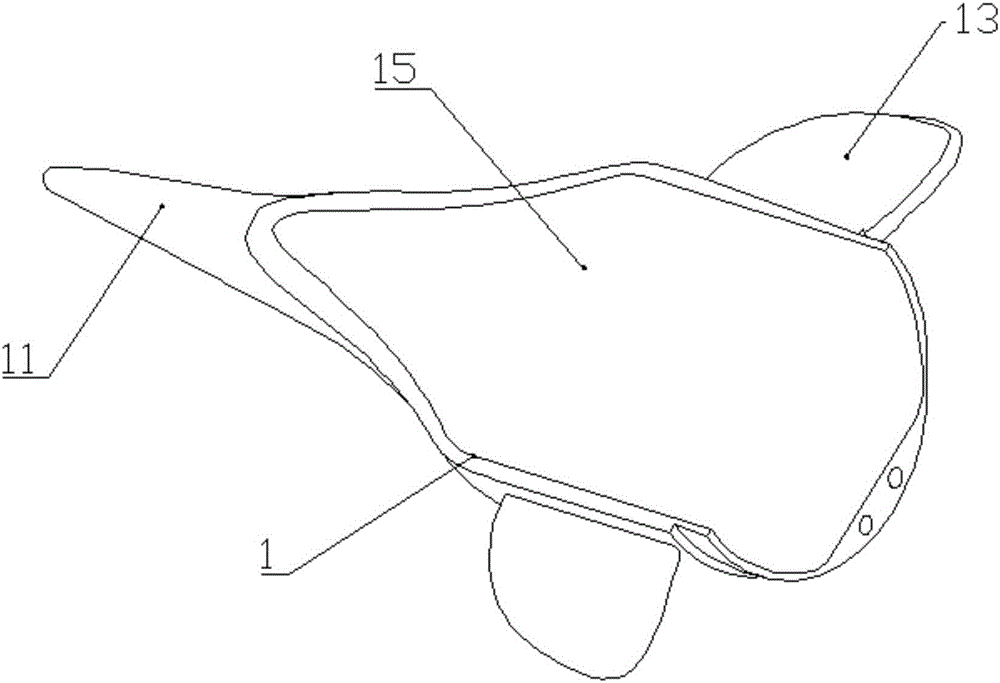
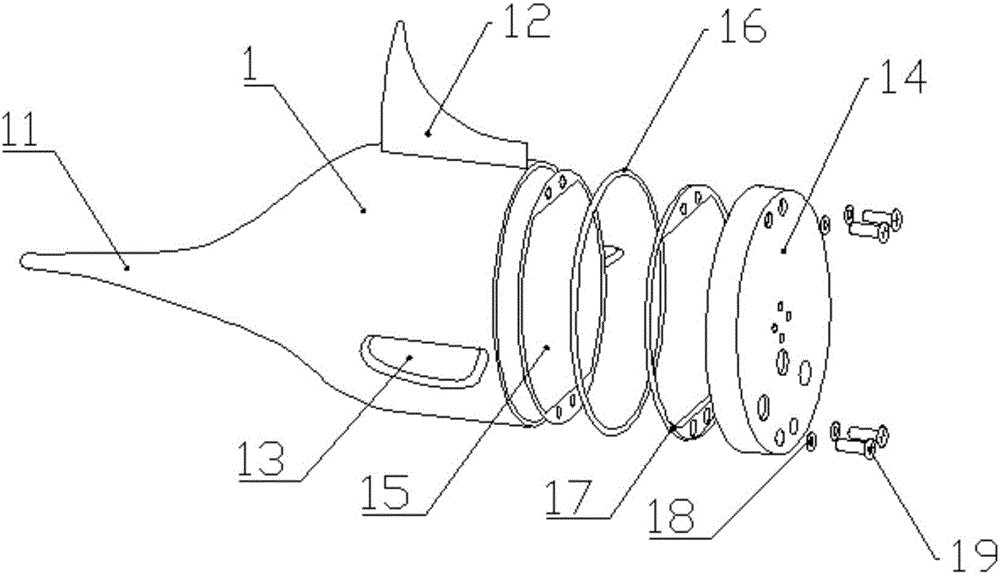
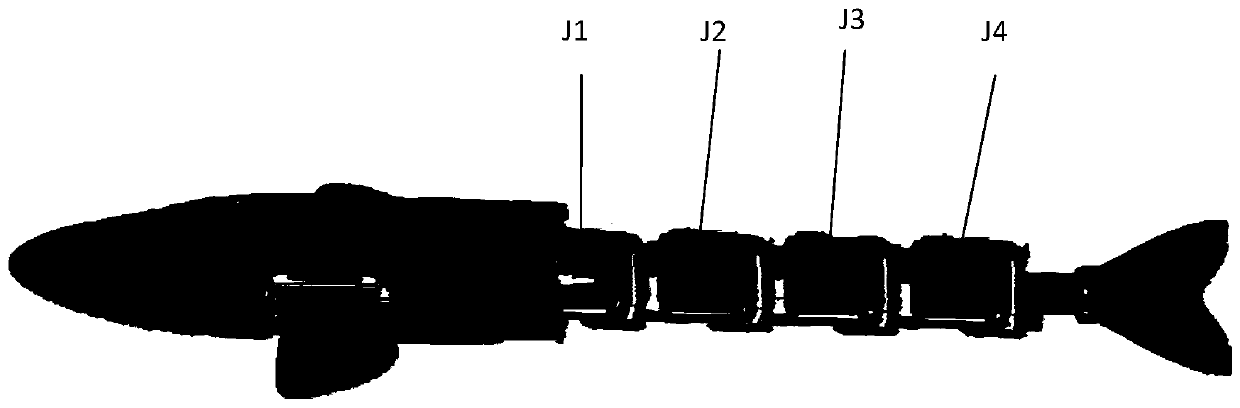
Patents
Literature
200 results about "Robot fish" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
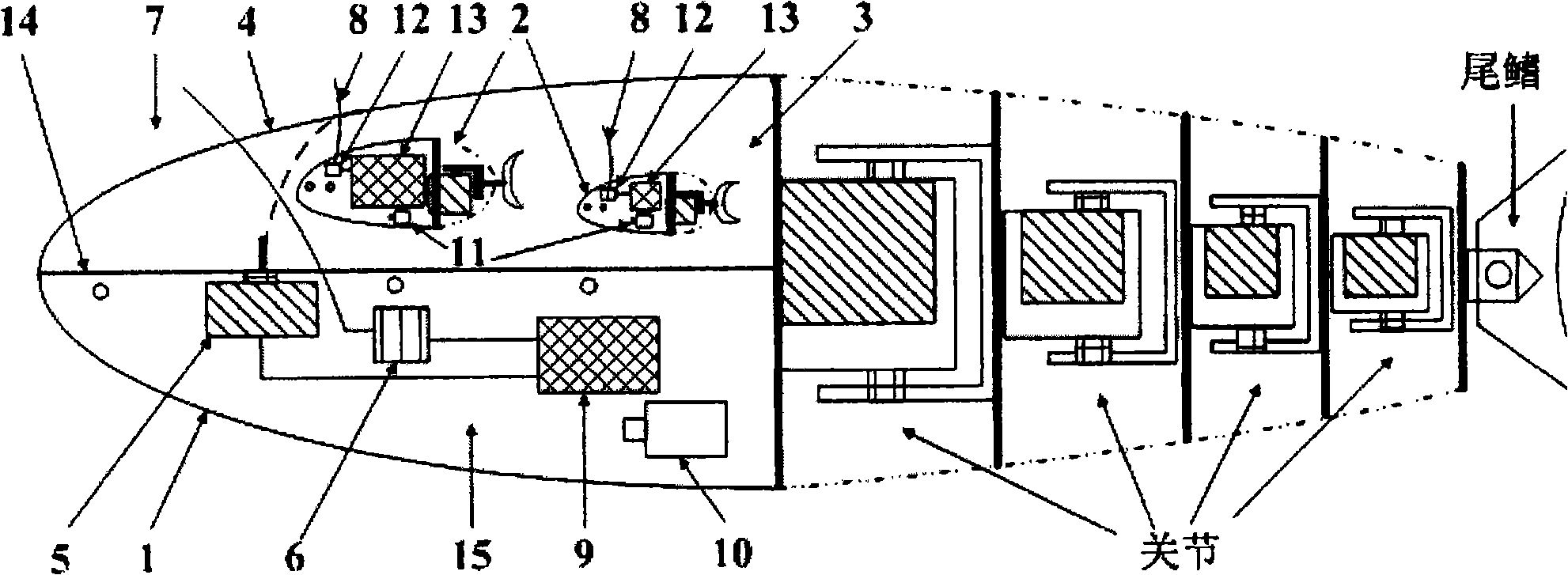
A robot fish is a type of bionic robot, which has the shape and locomotion of a living fish. Since the Massachusetts Institute of Technology first published research on them in 1989, there have been more than 400 articles published about robot fish. According to these reports, approximately 40 different types of robot fish have been built, with 30 designs having only the capability to flip and drift in water. Most robot fish are designed to emulate living fish which use Body-caudal fin (BCF) propulsion. BCF robot fish can be divided into three categories: Single Joint (SJ), Multi-Joint (MJ), and smart material-based design. The most important parts of researching and developing robot fish are advancing their control and navigation, enabling them to 'communicate' with their environment, making it possible for them to travel along a particular path, and to respond to commands to make their 'fins' flap.
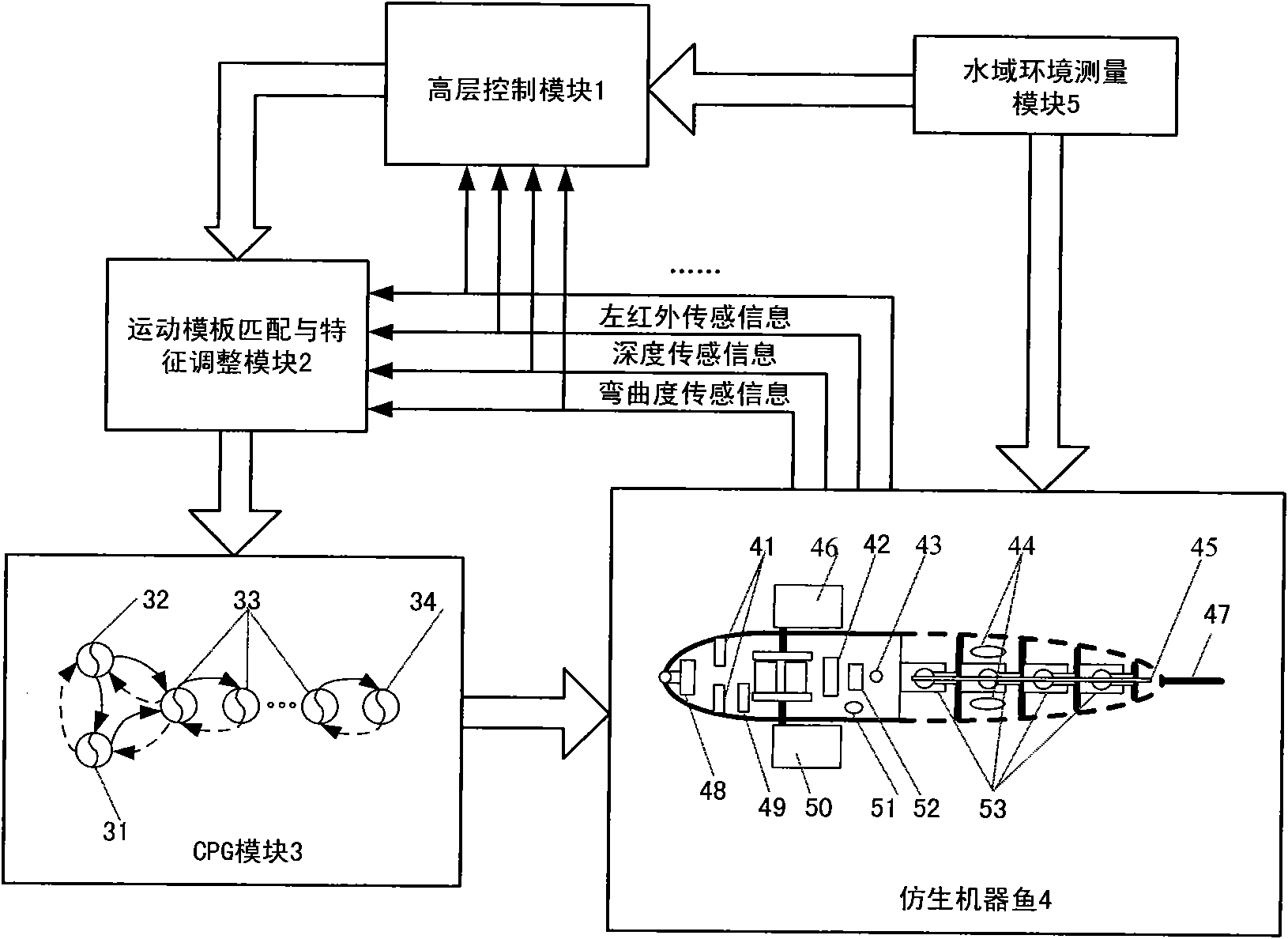
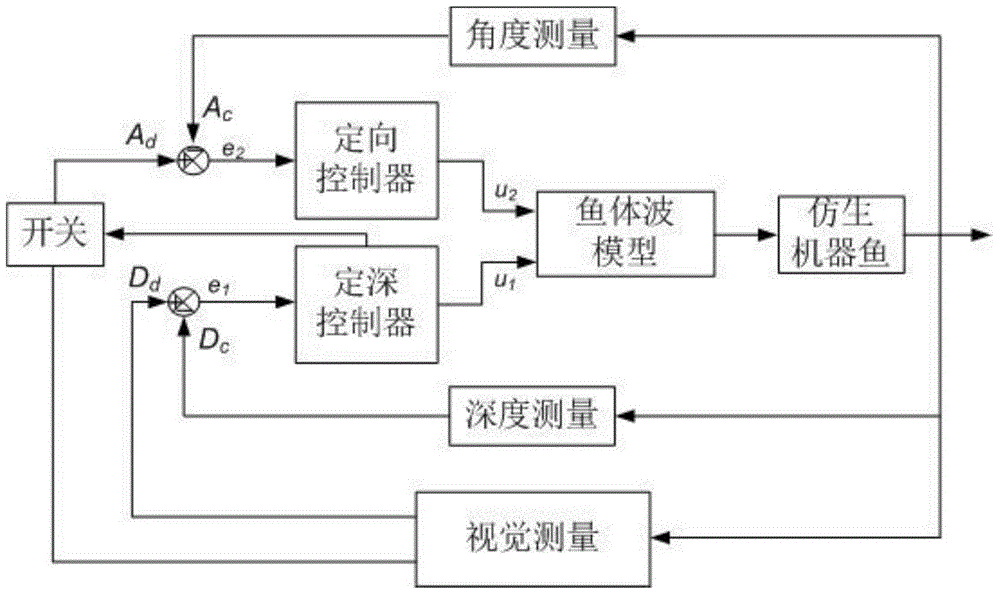
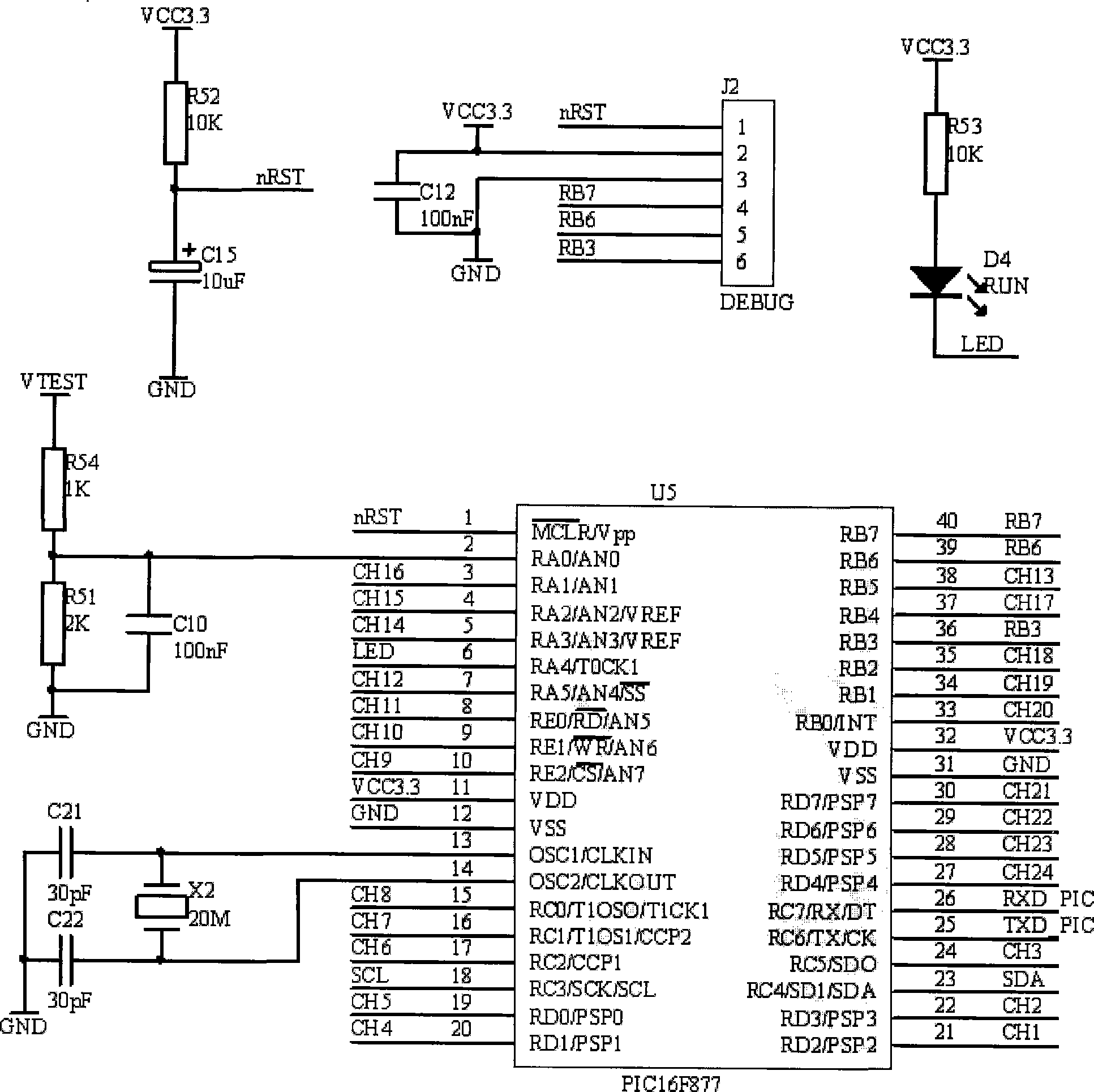
CPG feedback control method of biomimetic robot fish movement
ActiveCN101916071AFlexible Autonomous Swimming ControlImprove applicabilityAdaptive controlComputer moduleEngineering
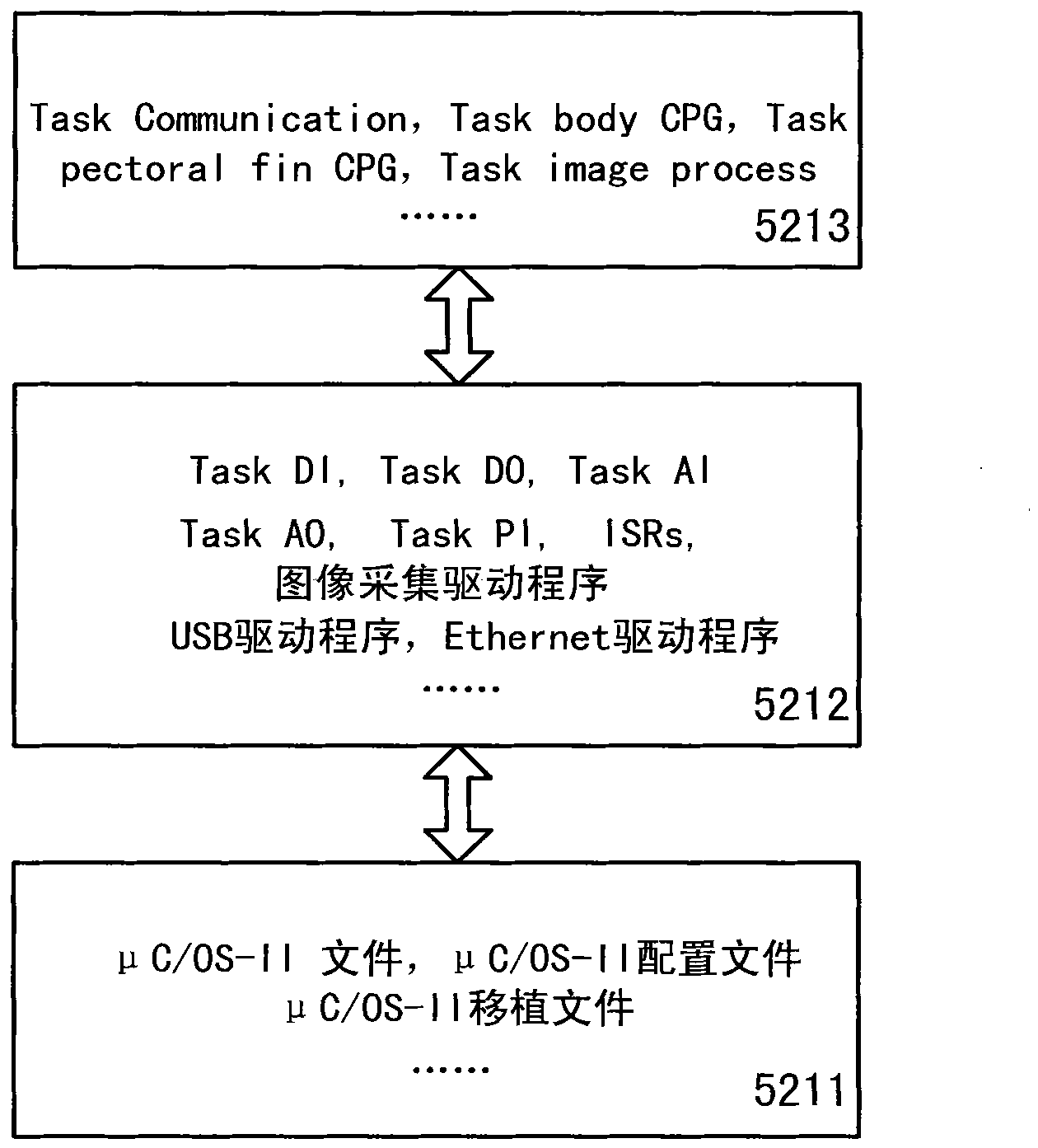
The invention relates to a CPG (Certified Program Generator) feedback control method of biomimetic robot fish movement, comprising the following steps of: providing a CPG feedback control model for receiving feedback signals by using different parts of a high-level control module, a CPG, a motor neuron, and the like; receiving biomimetic robot fish body state information and water environment information by the high-level control module; transmitting a corresponding command by treating the information and making a decision; and selecting a corresponding movement moulding plate to determine a suitable CPG configuration, wherein the suitable CPG configuration is used for controlling the parts of the biomimetic robot fish body to carry out rhythmic movement and non-rhythmic movement. The invention provides a reference for the feedback control theoretical design of the biomimetic robot fish movement and can realize mobile, flexible and independent autokinetic movement.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
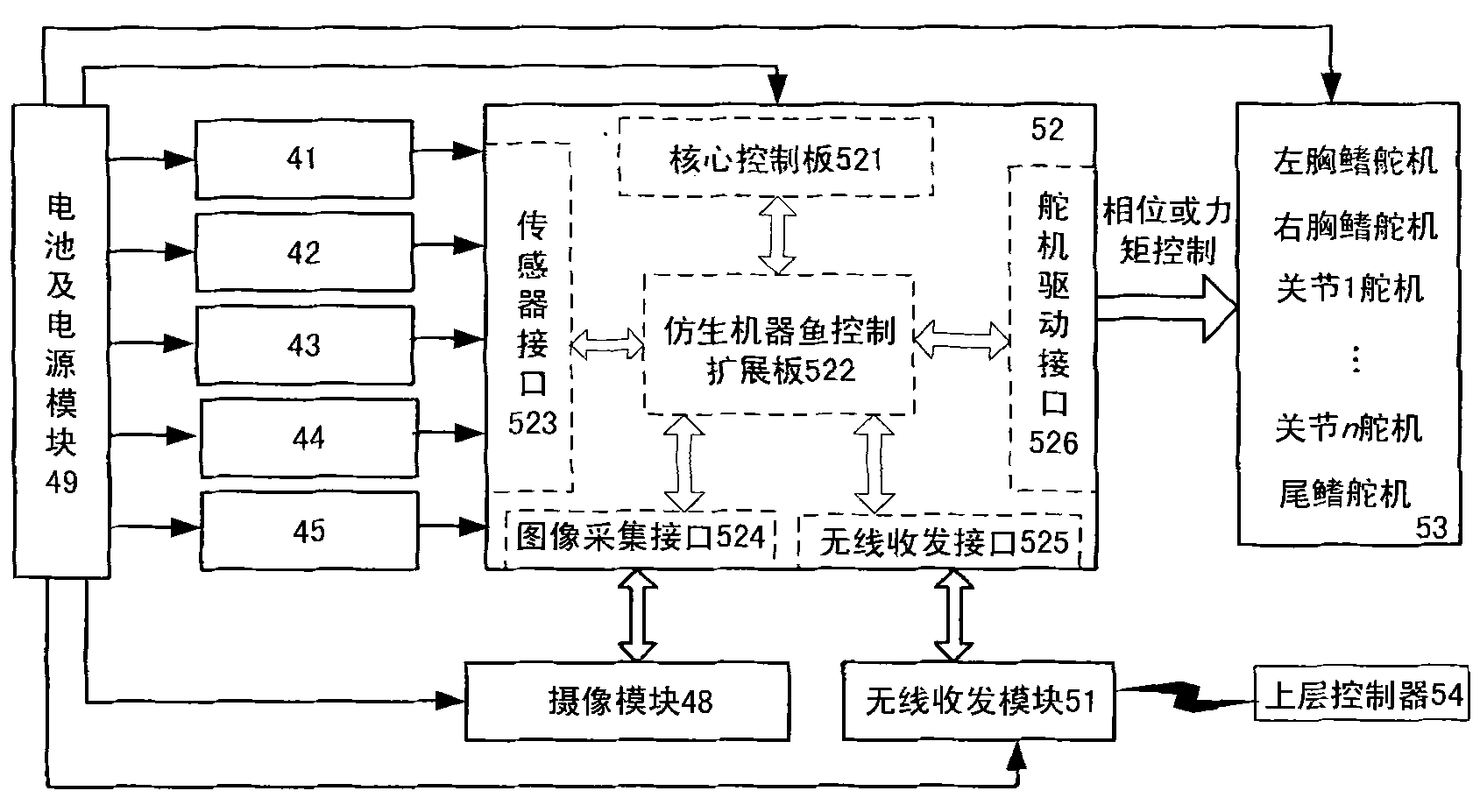
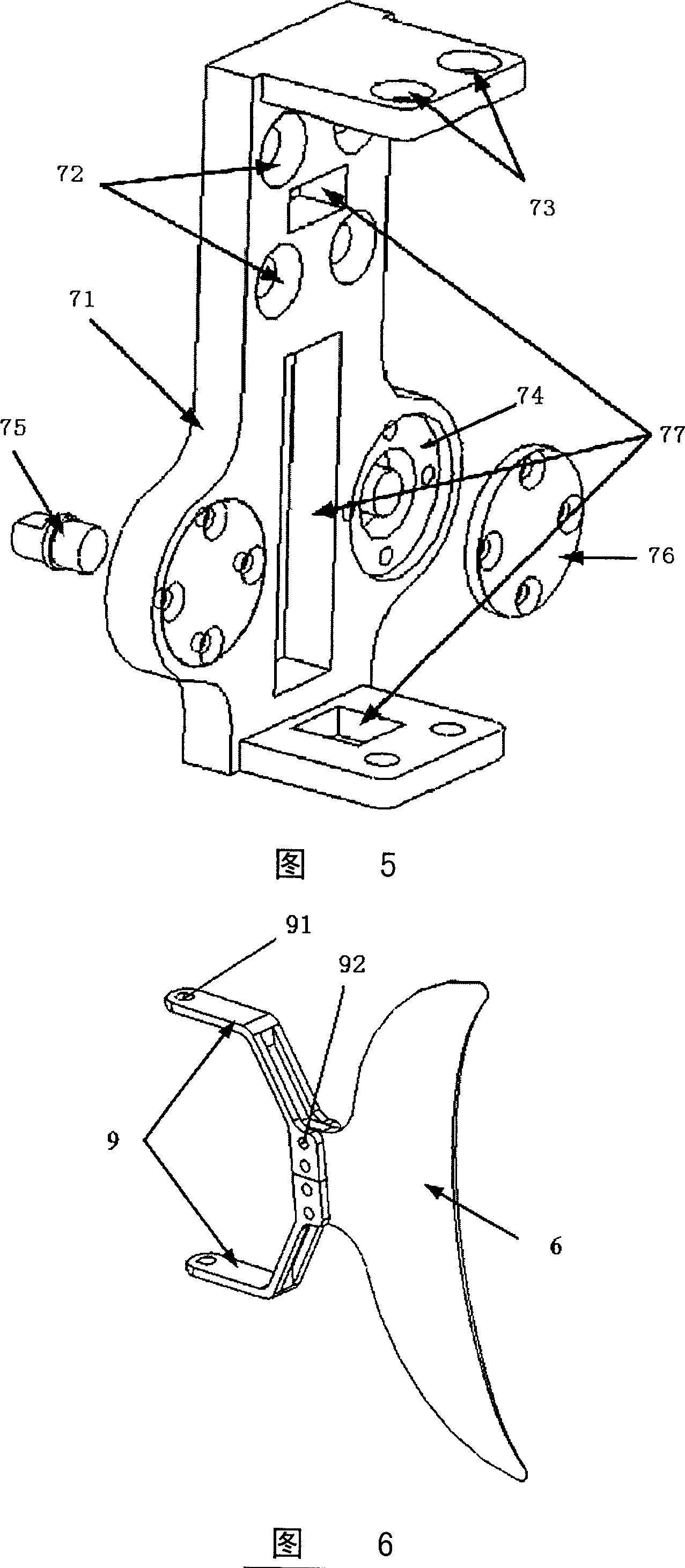
Bionic robot fish
ActiveCN1939805ACompact structureLifelike shapePropulsive elements of non-rotary typeMicrocontrollerBionics
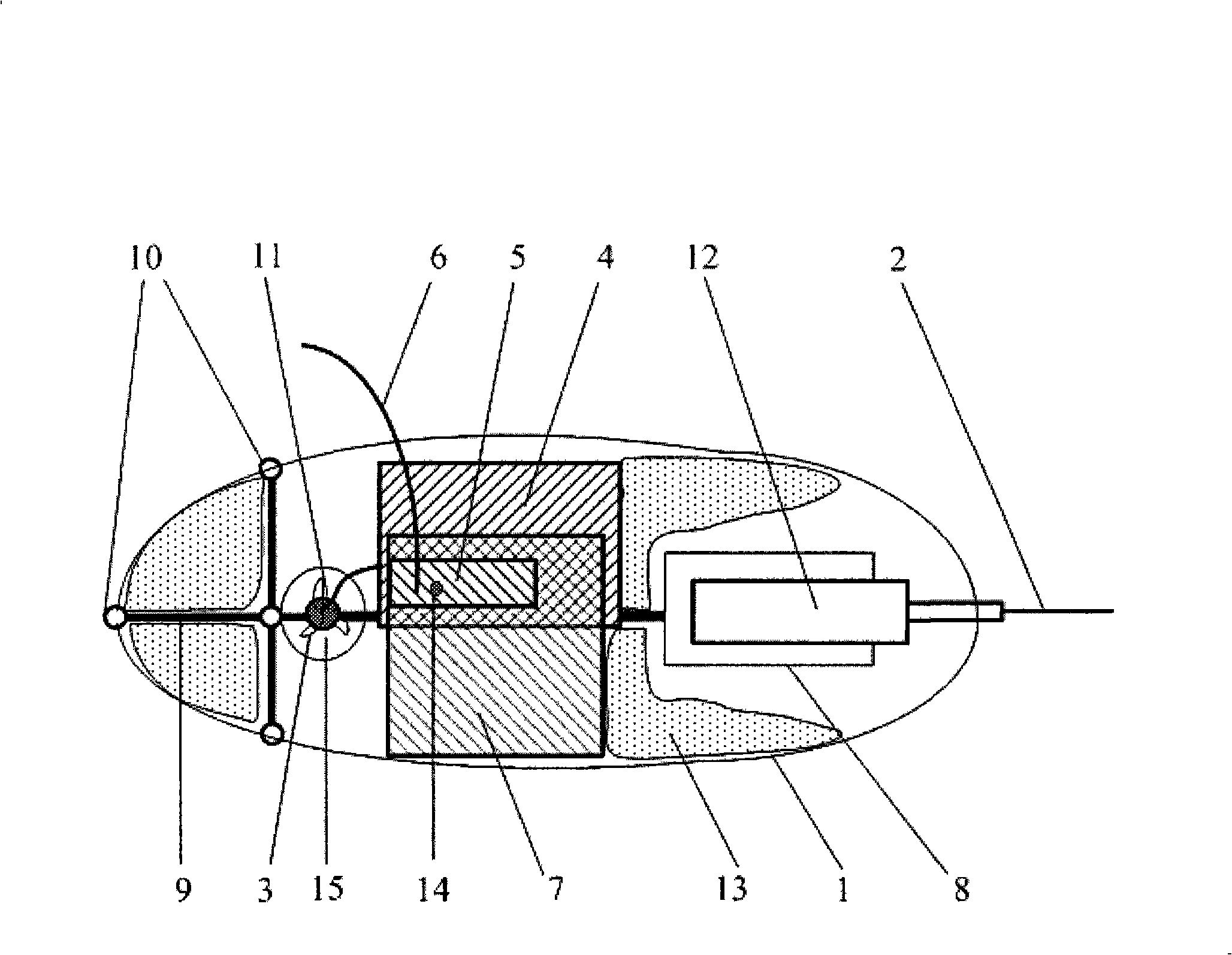
A bionic mechanical fish is composed of casing consisting of upper and lower halves, chest fins driven by step motor, tail unit consisting of tail fin, skin, frame, and fixing plate, and driven by linear motor, detecting unit consisting of miniature camera head, infrared sensor and pressure sensor, control unit comprising microcontroller, information acquisition module, motor driver and communication module, and float regulating unit consisting of linear motor and piston-cylinder reciprocating unit.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Modularized bionic robot fish
InactiveCN1962358AImprove reliabilityEasy maintenancePropulsive elements of non-rotary typeSpecial purpose vesselsBionicsModularity
The invention relates to a machine fish, wherein it is characterized in that: it comprises a fish head module sealed, left and right chest fin modules, at least two driving modules, and caudal fin; said fish head module has controller and main motor for floating the left and right chest fin modules whose main axles via movable sealing device are connected to the main motor; the left and right chest fin modules both have assist motors to drive the chest fins up and down; the axle of chest fin via the movable sealing device is connected to the assist motors; the driving module via the swing rod is connected; the first driving module via the head-tail connector is fixed on the back of fish head module; the caudal fin via the connector is connected to the back of driving module. The invention can be used in underwater detection, etc.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Bionic robot fish having up-down movement module and tail module
InactiveCN101301926ADive depth controlEasy to adjustPropulsion power plantsPropulsive elements of non-rotary typeCircular discBionics
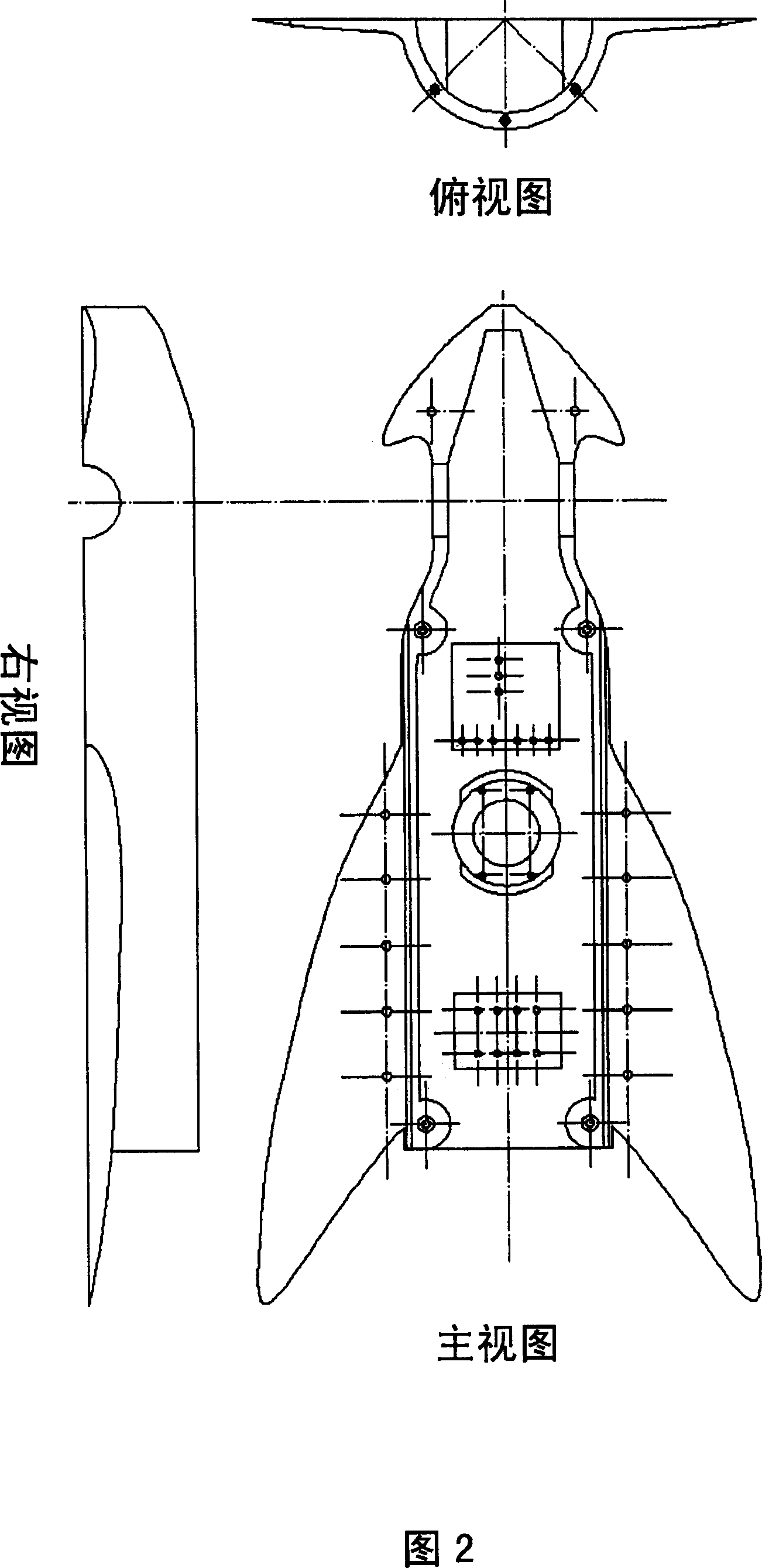
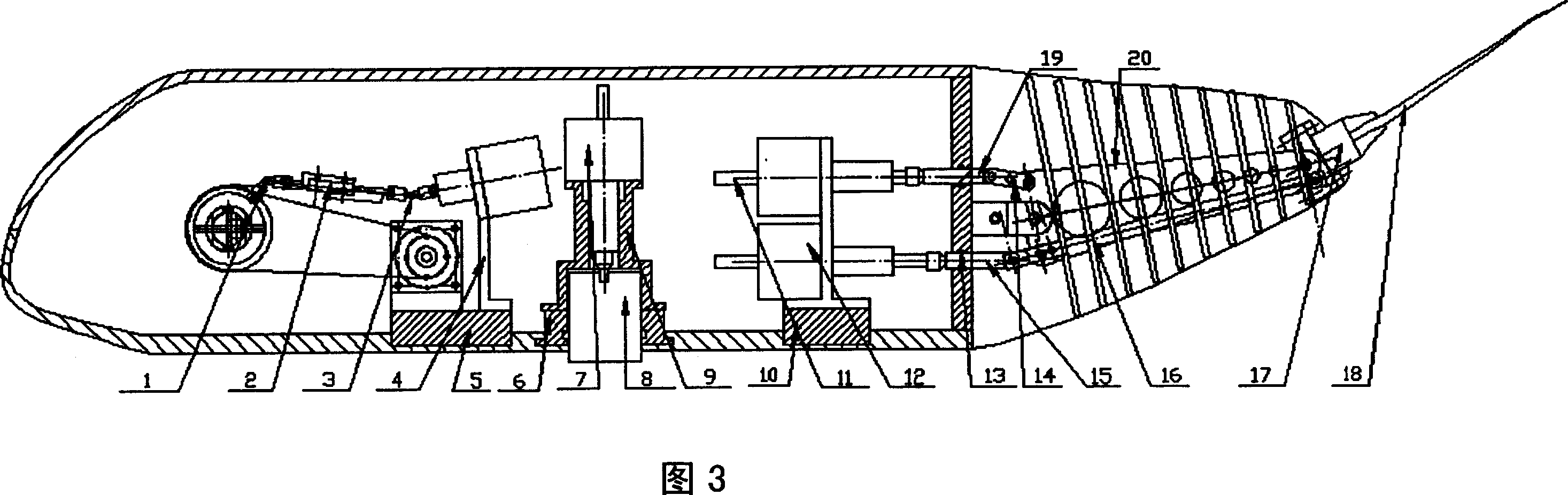
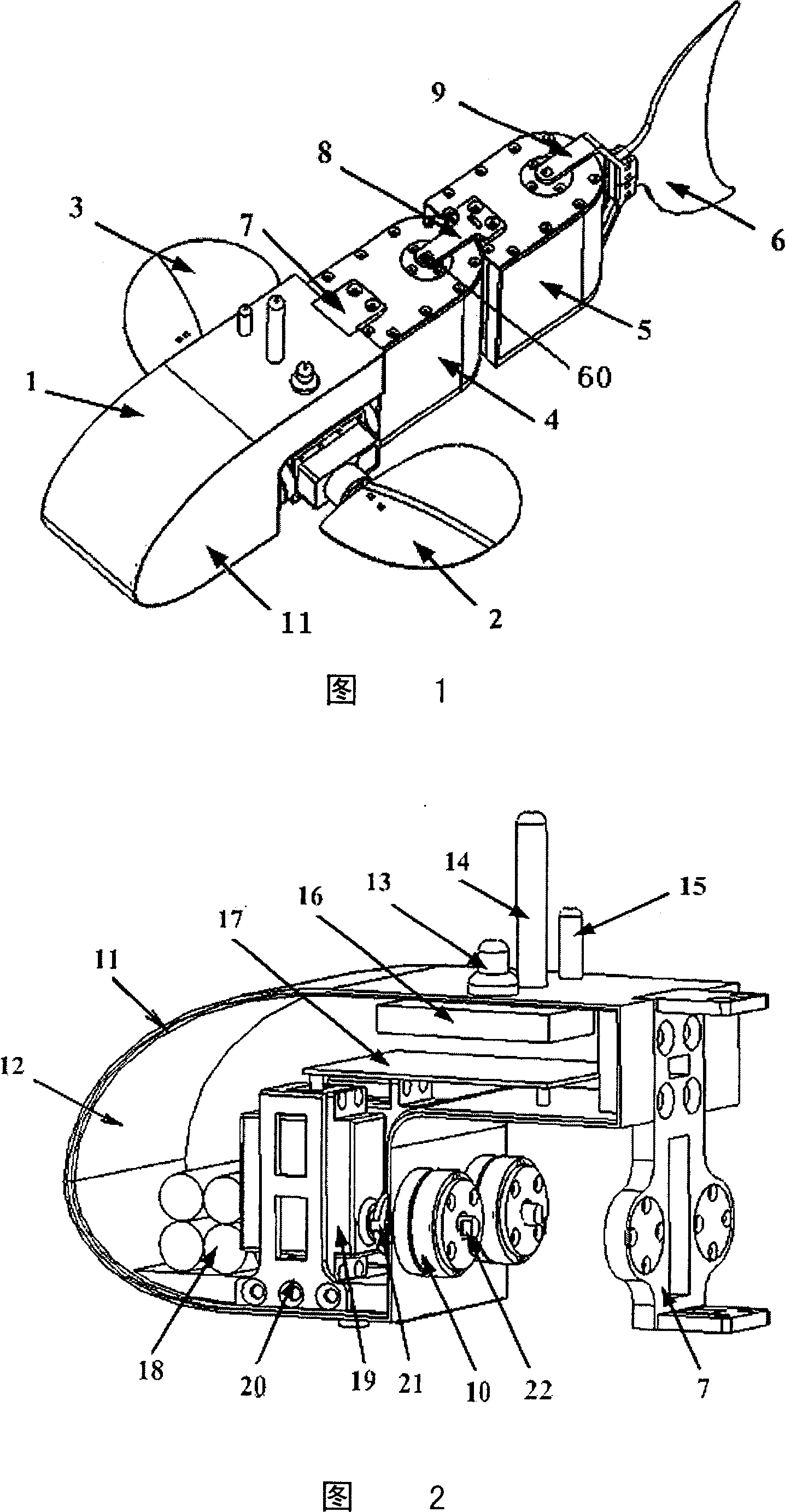
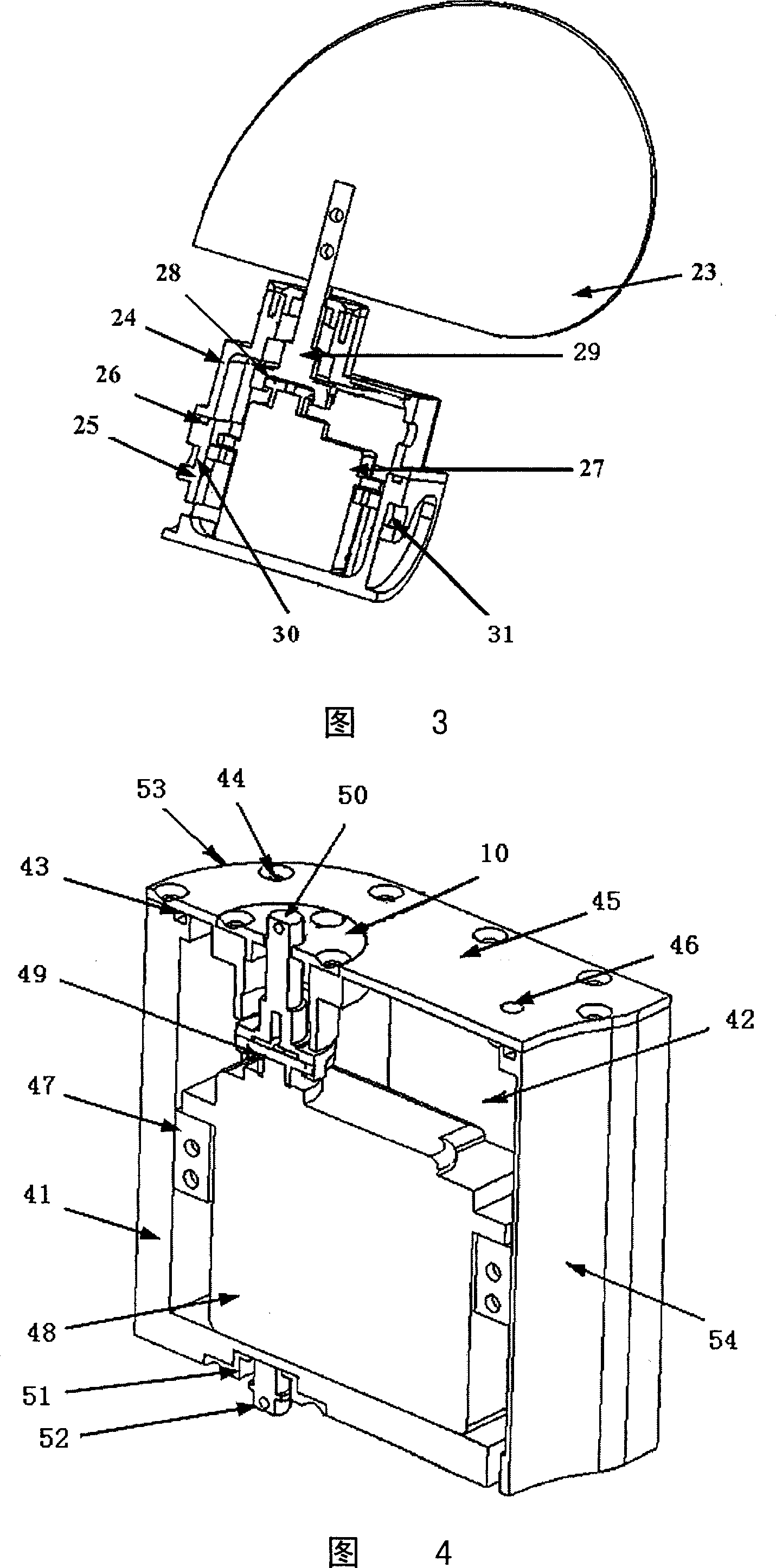
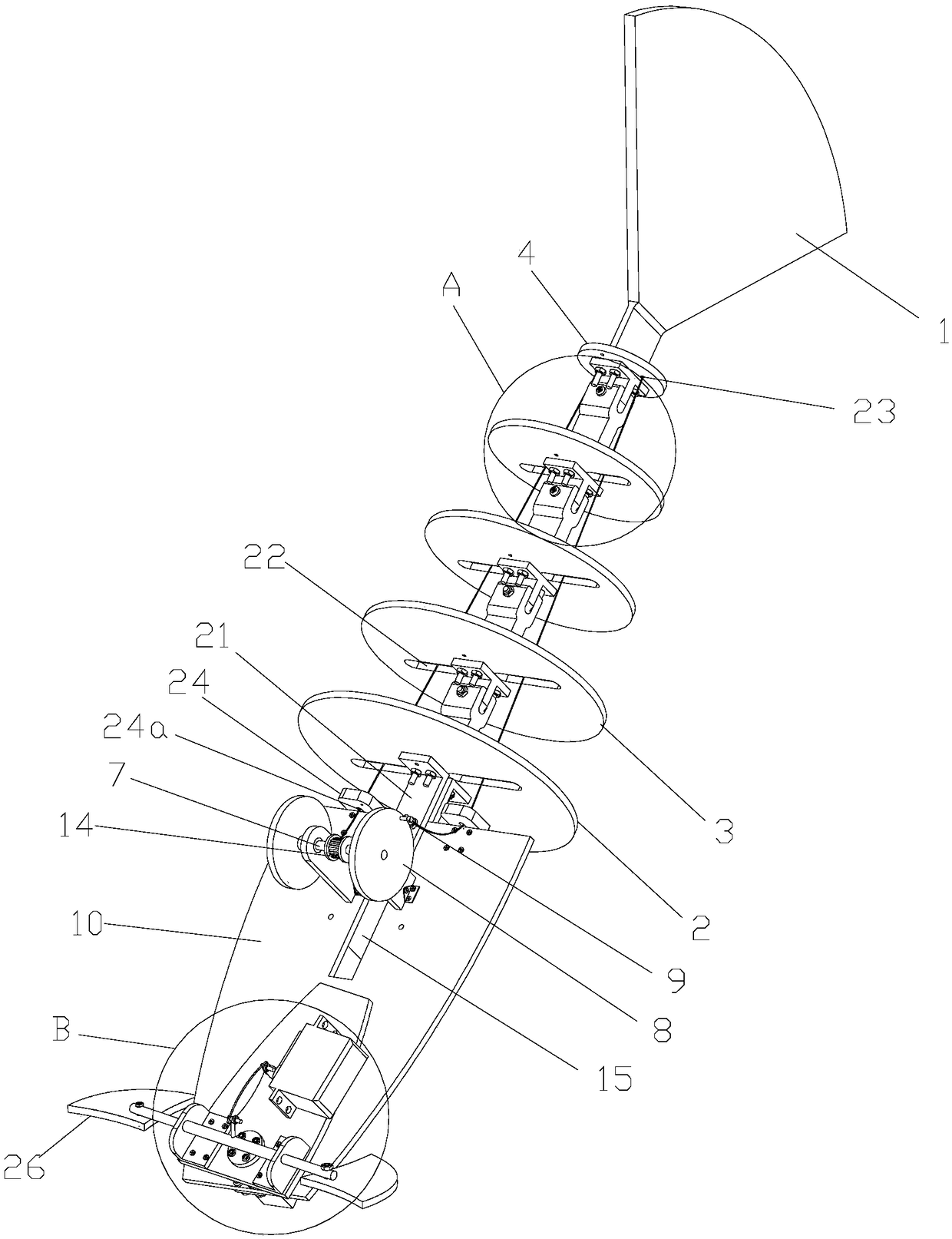
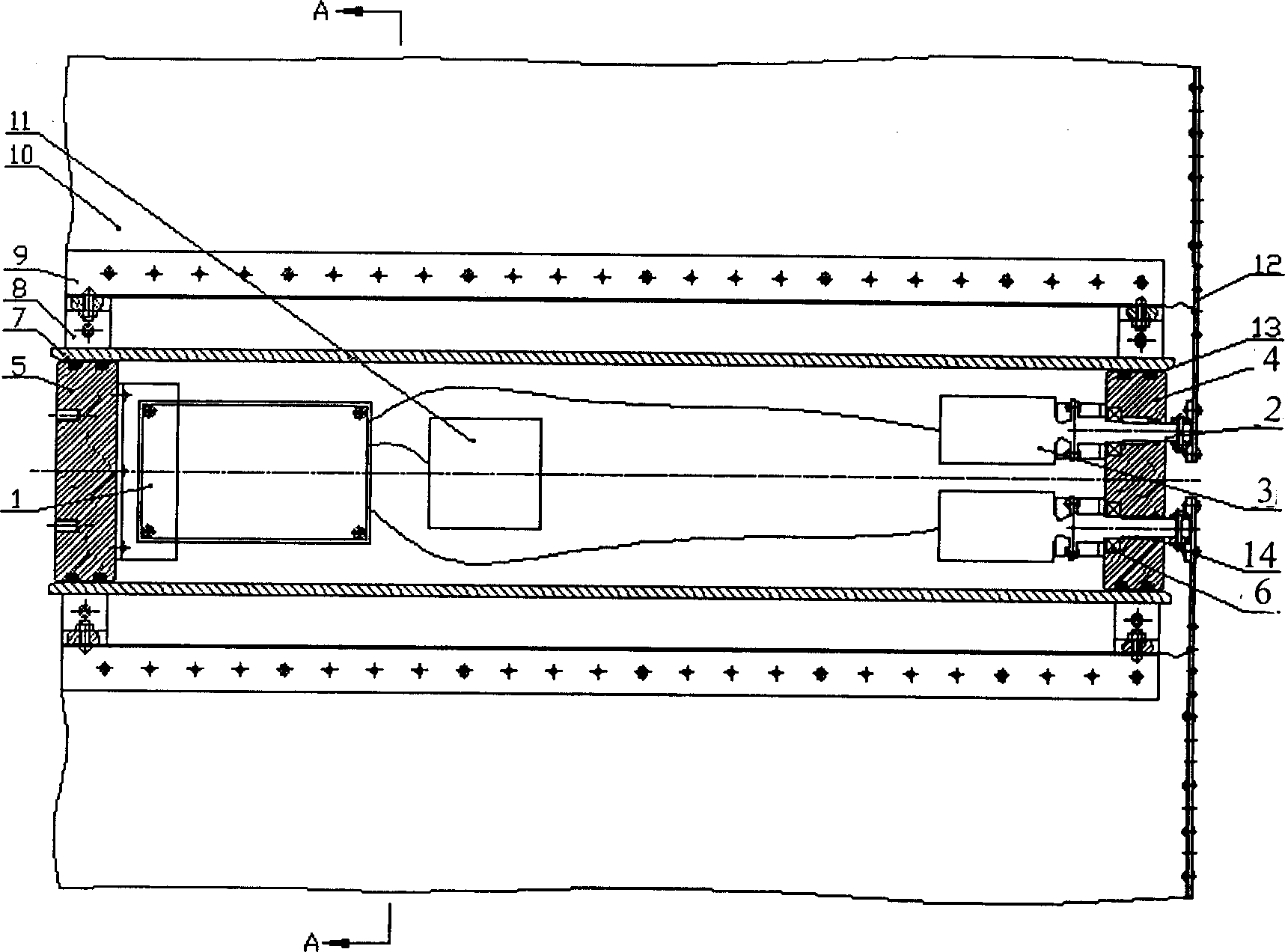
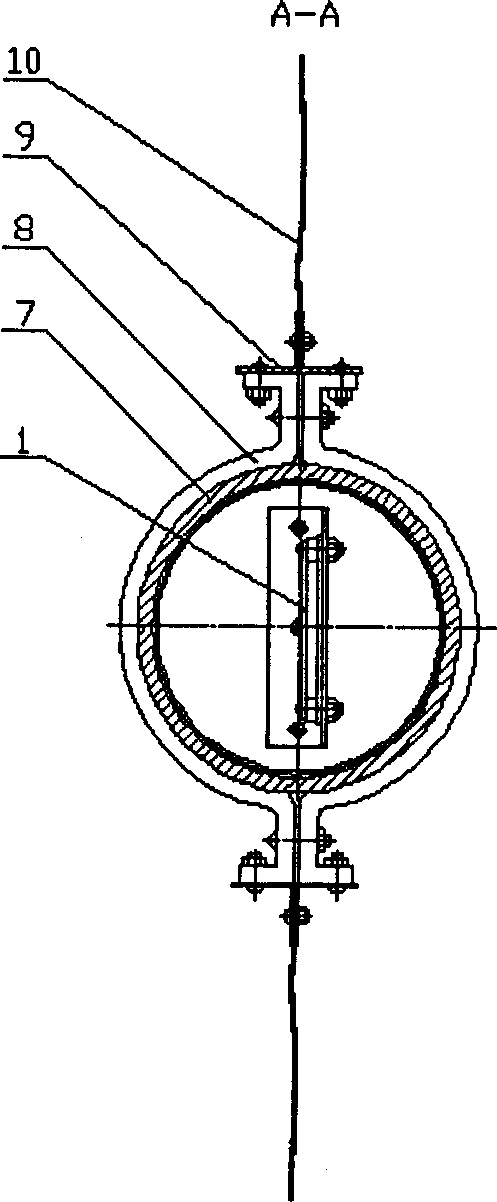
The invention provides a bionic robot fish provided with a rising module and a tail module, relating to the bionic robot fish used underwater and aiming at solving the defects of the existing bionic robot fishes that the rising speed is low; rising characteristics are indistinct and adjusting the tail fin movement-diameter is inconvenient, etc. The other end of a screw (11) is fixedly connected with a piston (4) through a screw end closure (3), the piston (4) is arranged in a cylinder (1), and one end of a cylinder end closure (6) is fixedly connected with the cylinder (1); a straight-spur cone gearwheel (38) is arranged on a central shaft (43) and two ends of a central shaft (43) are rotationally connected with two sides of a box body (39), and two sets of sliding mechanism assemblies (84) are respectively arranged on a first disk (22) and a second disk (44) through a first eccentric shaft (25) and a second eccentric shaft (41). The bionic robot fish provided by the invention has a better rising characteristic and better bionic effect and can easily realize the adjusting to the tail fin movement-diameter of the robot fish so as to lead the swaying of the fish body to be rare and the moving stability to be better.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Bionic robot fish propelled by oscillating and twisting compound motion of pectoral fins
InactiveCN103144756ARealize up and down swing motionAchieve swingPropulsive elements of non-rotary typeEngineeringSkeletal structures
The invention discloses a bionic robot fish propelled by oscillating and twisting compound motion of pectoral fins, and the configuration refers to the bionic model of Myliobatidae fishes. The bionic robot fish comprises a body part, oscillating pectoral fins and a tail part, wherein the body part is provided with a floating-sinking mechanism to achieve floating and diving of the bionic robot fish, and the floating and the diving are controlled by the tail part mounted at the rear end of the body part; the oscillating pectoral fins are mounted on two sides of the body part and adopt flexible pectoral fin skeletal structures combined by both fin rays and skeleton straight plates; and the oscillating pectoral fins can be respectively driven to conduct oscillating and twisting compound motion to obtain an effective attack angle through an oscillating driving mechanism and a twisting driving mechanism so as to obtain the pectoral fin oscillating propelled bionic robot fish which is bionically propelled. The bionic robot fish has the advantages that bionic distribution of spanwise flexibility and chordwise flexibility of fin faces is realized, oscillating movement of the pectoral fins is achieved, the controllable oscillation degree is high and the controllable oscillation frequency range is wide; and the bionic robot fish has the flexible and twisting performances.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Bionic robot fish three-dimensional tracking method based on embedded visual guidance
InactiveCN104881045AReduce couplingAccurately control tasksTarget-seeking controlPattern recognitionVisual perception
The invention discloses a bionic robot fish three-dimensional tracking method based on embedded visual guidance. The method comprises: step 1, setting an artificial landmark, an embedded visual system automatically identifying the artificial landmark, combing with dimension information of the artificial landmark, obtaining information of three-dimensional position where a target is in; step 2, obtaining depth of information of the three-dimensional position where a target is in, using a control method based on a fuzzy sliding mode, guiding a bionic robot fish to swim to target depth and the bionic robot fish keeping swimming on the target depth; step 3, and when the bionic robot fish keeping swimming at the target depth, through multistage orientation control, ensuring the bionic robot fish tracks the target. On the basis of flexible motion of the robotic fish, the method realizes accurate control tasks.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
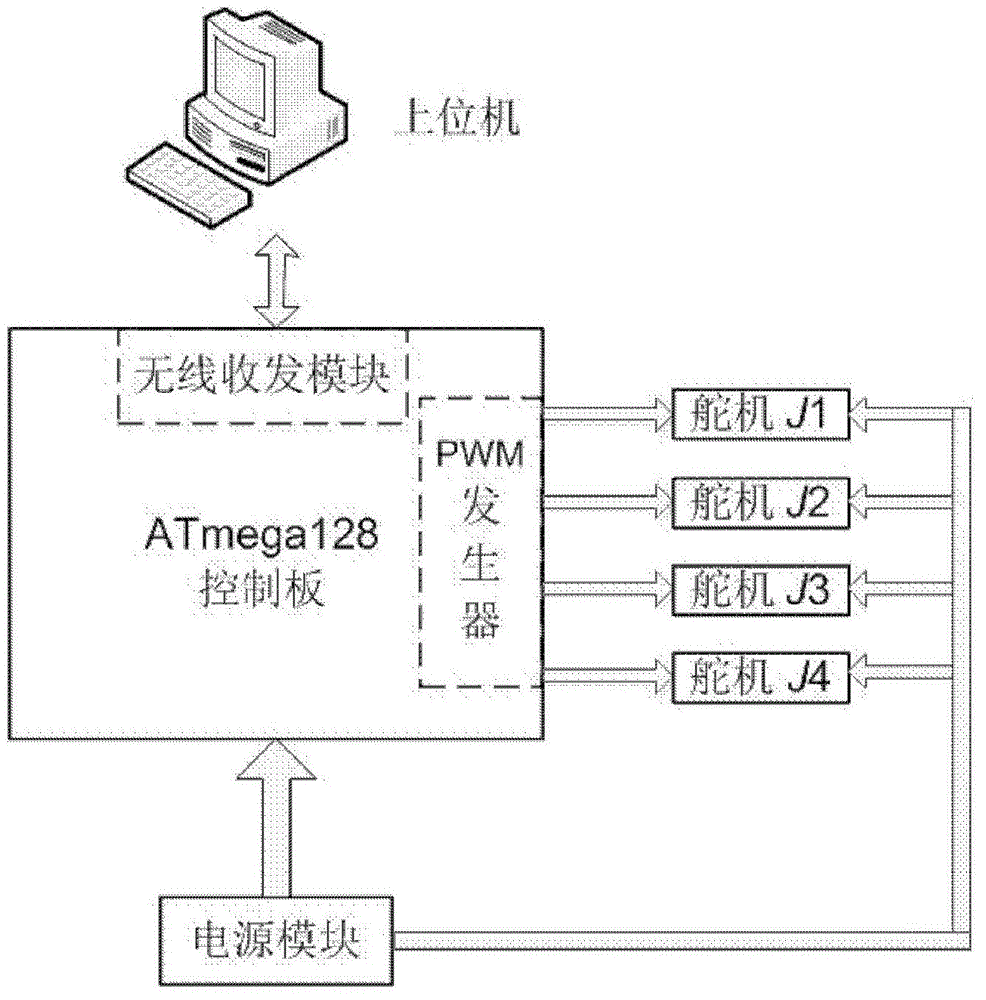
Information treating platform of small-sized both feet robot
InactiveCN101398687AIncrease typeTotal factory controlProgramme total factory controlInformation processingLimited resources
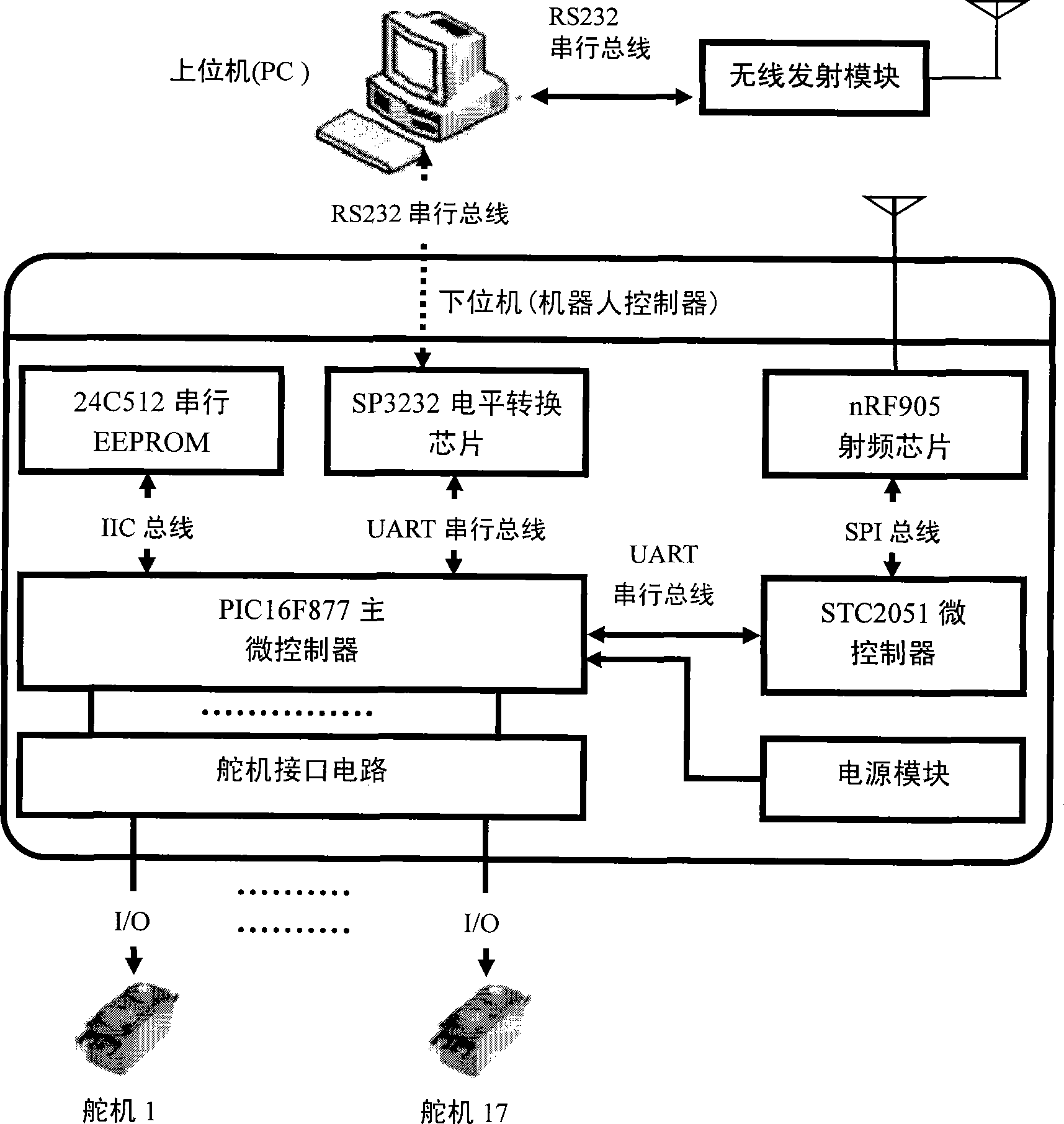
The invention provides an information processing platform of a double-foot robot and relates to a manual intelligent technology, and more information processing technologies fit for a robot are integrated in the limited space and limited resource of the robot. The platform comprises robot controller hardware, a communications protocol and control system software. A robot controller considers a steering engine control module as a core. A wireless communications module, a wired communications module, a data storage module and a power supply module are respectively connected with the steering engine control module. The power supply module provides stable voltage to every module. A PC machine transmits data to the information processing platform by the wired communications module or the wireless communications with the communications protocol to be processed by the controller, and the data is stored at the data storage module for reading and transferring later. The information processing platform can be used as a universal platform for controlling a steering engine, and the information processing platform can not only be used on a humanoid robot, but also used for controlling mechanisms using a three-wire steering engine as a joint, such as a joint, a mechanical hand, a robot fish, etc. of other robot.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Bionic robot fish
ActiveCN106005336ASolve the problem of underwater enduranceBatteries circuit arrangementsPropulsive elements of non-rotary typeNanogeneratorNew energy
The invention discloses a bionic robot fish which comprises a fish head part, a fish body part and a fish tail part, wherein a friction electric nano power generator covers the bionic robot fish; and the bionic robot fish further comprises a fish tail driving mechanism arranged on the fish tail part, a gravity center adjusting mechanism arranged on the fish body part, a pectoral fin swinging mechanism arranged on the fish head part and a power accumulation device connected with the friction electric nano power generator. The problem of submerged endurance of the robot fish is solved by sufficiently utilizing a new energy source, namely ocean energy.
Owner:DALIAN MARITIME UNIVERSITY
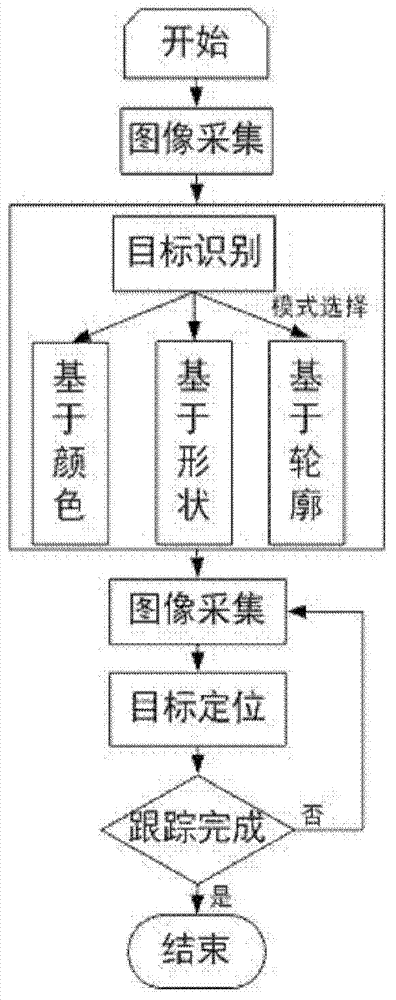
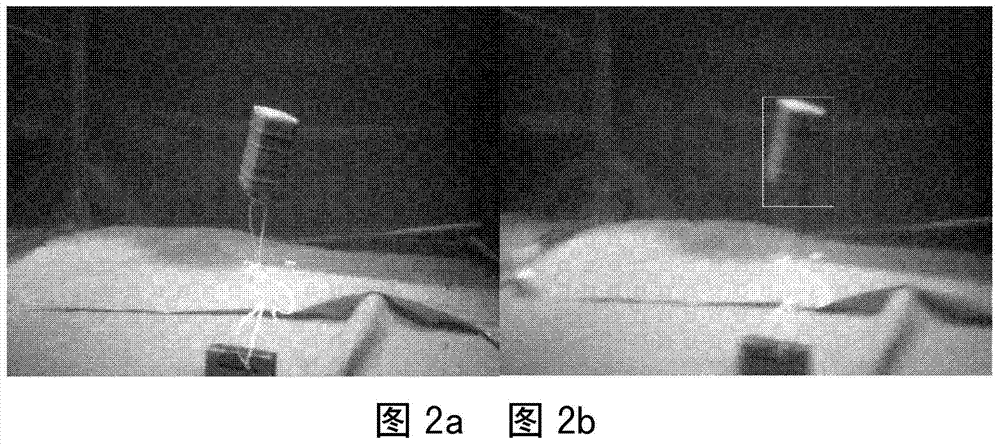
Underwater active vision tracking method applied to bionic robot fish
ActiveCN104298996APrecise positioningSmall amount of calculationCharacter and pattern recognitionEngineeringFeature description
The invention relates to an underwater active vision tracking method applied to a bionic robot fish, which comprises embedded visual system based active target identification and target positioning. The method comprises the steps of S1, acquiring a digital underwater image by a digital camera; S2, carrying out target identification based on one of color features, shape features and contour features, and acquiring an underwater target region of one of the color features, the shape features and the contour features; and S3, carrying out feature description on the target on the underwater target region of one of the color features, the shape features and the contour features by adopting a weighted color histogram, and realizing positioning for the underwater target according to the target feature description. The underwater active vision tracking method provided by the invention does not need to carry out preprocessing on the image, is small in calculation amount, good in real-time performance, accurate in positioning and applicable to scenes in which system resources are limited and the environment is relatively simple; and the underwater active vision tracking method is also applicable to active vision tracking under different environments and particularly to embedded visual applications on the bionic robot fish.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
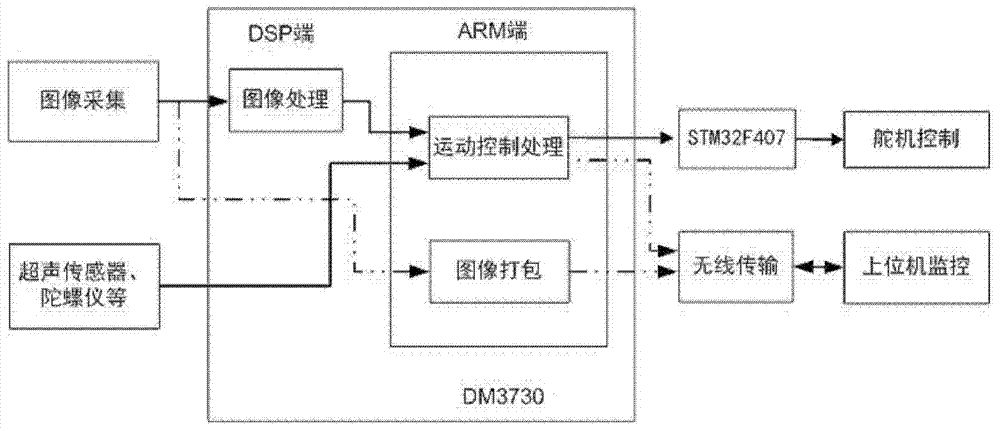
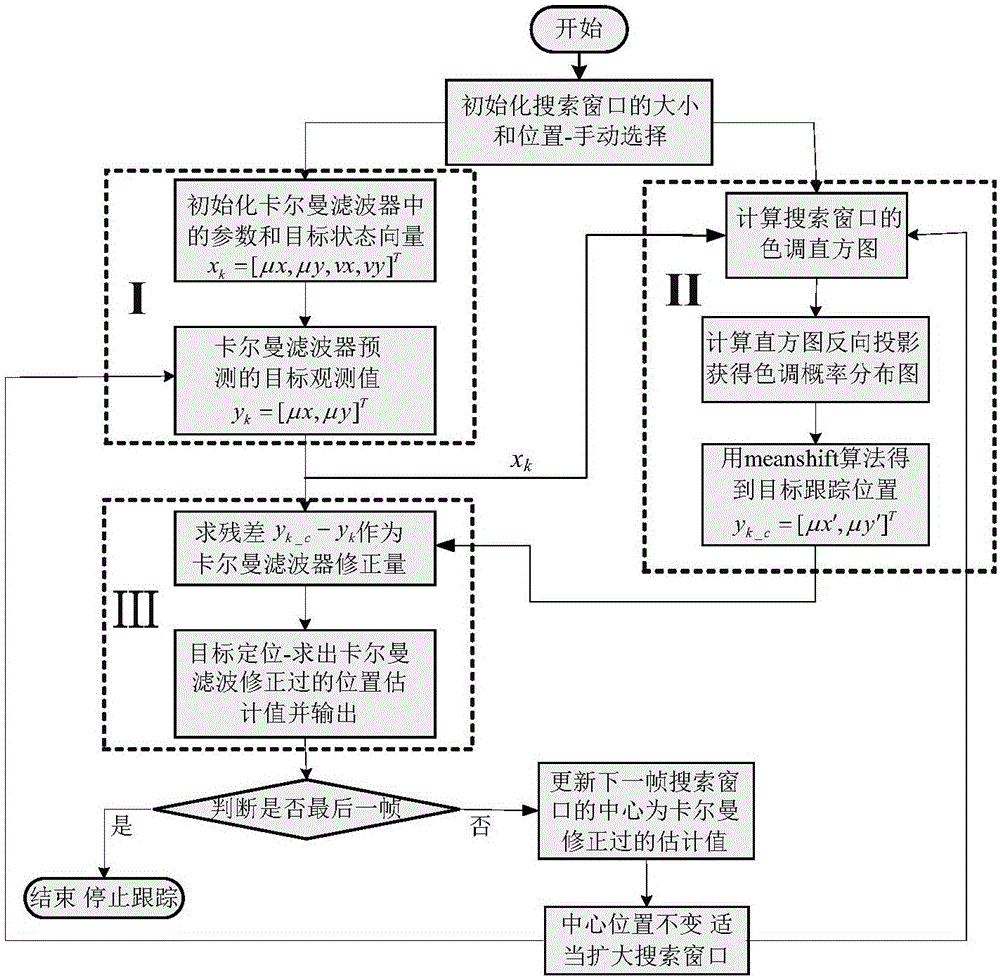
Camshift (continuously adaptive mean-shift) robot fish tracking method based on embedded Kalman filter
The invention discloses a Camshift (continuously adaptive mean-shift) robot fish tracking method based on an embedded Kalman filter. The Camshift robot fish tracking method is suitable for complicated underwater environments of robot fishes, the accuracy of the robot fish tracking quick motion is improved, and the real-time performance is good. The Camshift robot fish tracking method comprises the following steps of firstly, utilizing the Kalman filter to predict the possible position of a motion object in the next frame of image; then, using Camshift to search in the relative reduction range, so as to effectively enhance the accuracy of tracking a quick motion object; then, utilizing the observing value obtained by the Camshift to correct the observing value obtained by the Kalman filter, so as to further improve the accuracy of target tracking. Compared with the prior art, the Camshift robot fish tracking method has the advantages that the real-time performance and accuracy of the target tracking algorithm can be comprehensively considered, and the purpose of the robot fish accurately tracking the target in real time is realized.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY +2
Backward swimming control method of biomimetic carangiform robot fish
ActiveCN102745320ARich sports modeImprove mobilityPropulsive elements of non-rotary typeControl signalChain type
The invention discloses a backward swimming control method of a biomimetic carangiform robot fish, based on a CPG (Central Pattern Generator) to control the robot fish to swim. The backward swimming control method comprises the following steps: firstly, building a CPG chain type network topology according to the characteristics of fish swimming to reduce a CPG parameter number and reduce the complexity of a model; secondly, by reasonably regulating parameters of the CPG model, enabling an output signal of the CPG model to satisfy the following condition, in a direction from the head to the tail of the robot fish, phases of the control signal of a steering engine of the robot fish sequentially lag, and amplitudes are sequentially reduced, so that backward propelling force is produced, and backward swimming of the robot fish is realized. The backward swimming control method has the promotion action in deeply understanding a backward swimming motion mechanism of fishes and also provides guidance for enriching motion modals of underwater robots and improving the maneuvering ability of the underwater robots.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Underwater miniature bionic machinery fish
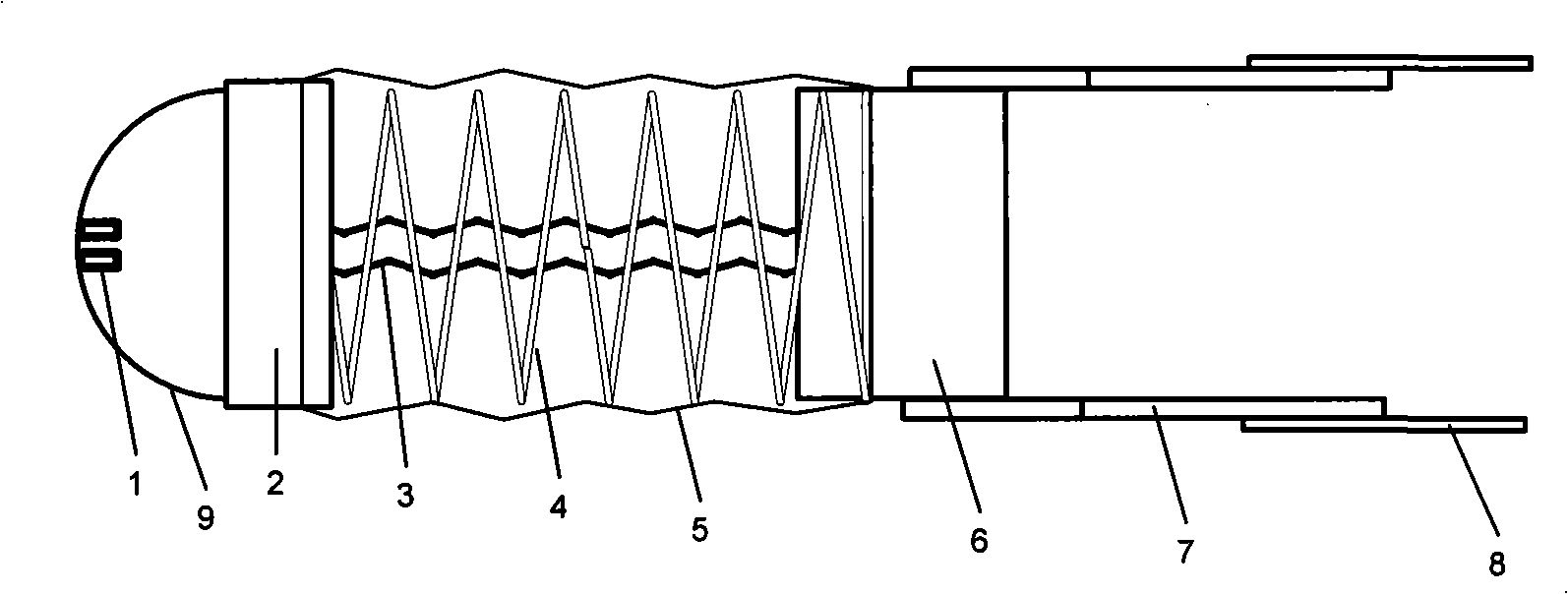
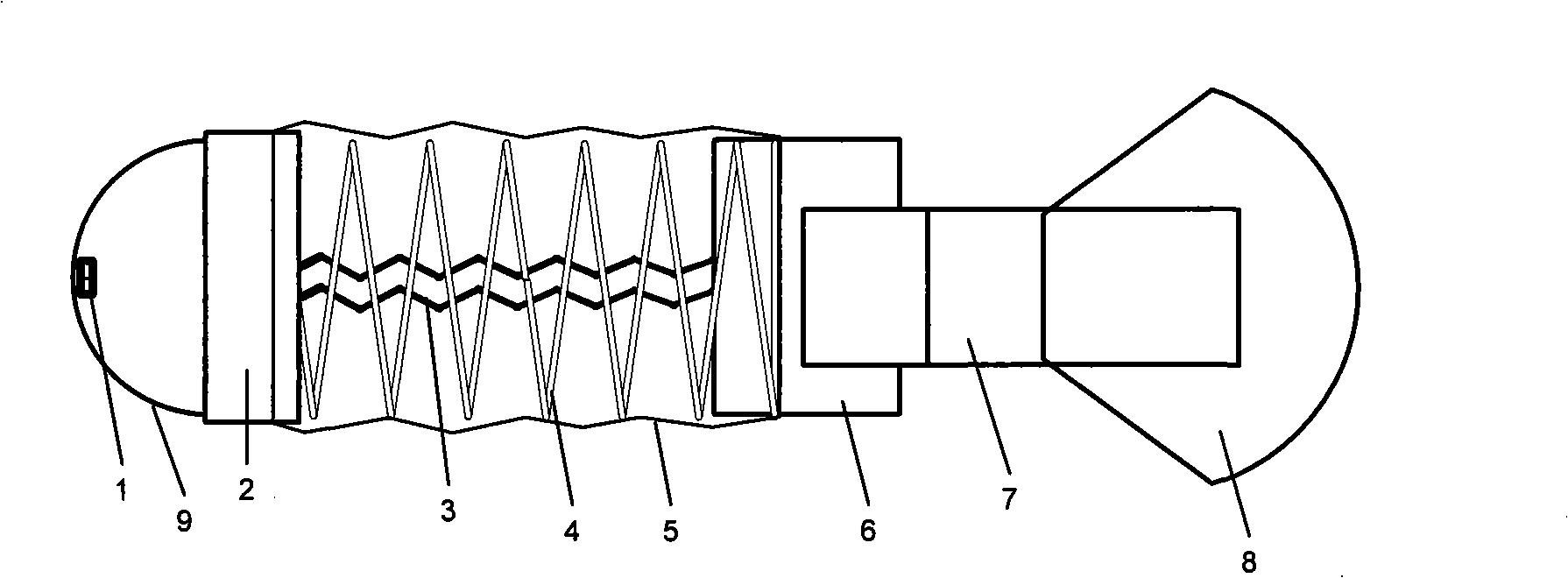
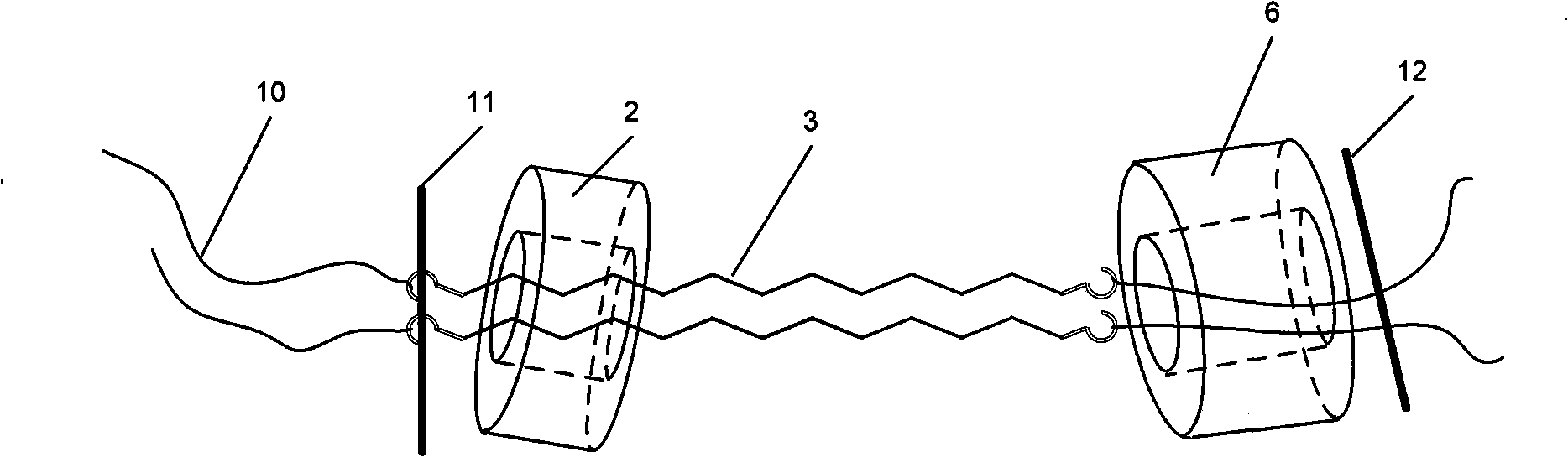
InactiveCN101293565ASimple barrierReduce volumePropulsive elements of non-rotary typeLow noiseLow voltage
The invention provides an underwater minitype biomimetic robot fish, comprising a hemispherical head, a body and a pushing tail. The front end of the hemispherical head is provided with two minitype infrared photoelectric sensors; the body is connected between the hemispherical head and the pushing tail, which is a telescopic body that consists of a memory alloy spring and a light compression spring that is sheathed outside the memory alloy spring; the pushing tail is provided with two ICPF fish tails which are arranged in parallel at the two sides of the telescopic shell. The memory alloy spring and the ICPF are respectively connected with an external circuit by light leads. The invention provides the underwater minitype biomimetic robot fish with power supplied by low voltage, driven by novel intelligent material and ultra-low noise. The underwater minitype biomimetic robot fish is designed by combining the characteristics of floating and submergence of jellyfish and tail swing advancing of fishes after researching multiple motion types of normal fishes.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
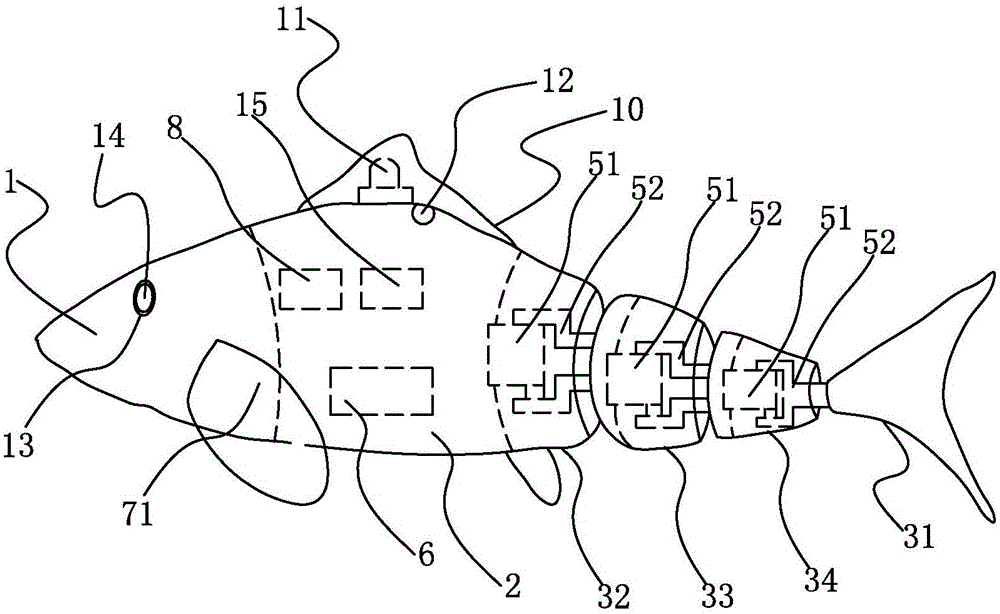
Novel automatic bionic robot fish
InactiveCN105711778AImprove mobilityStrong autonomyPropulsive elements of non-rotary typeUnderwater equipmentMicrocontrollerCommunication unit
The invention relates to a robot fish for underwater detection tasks, and aims at providing a novel automatic bionic robot fish which is good in self-stability and maneuverability, high in automatic performance and capable of adapting the complex underwater operation environment. The novel automatic bionic robot fish comprises a main cabin. The main cabin is composed of an upper shell and a lower shell which are sealed; a fin simulating assembly is arranged outside the main cabin, and the fin simulating assembly comprises a pair of pectoral fins and a tail fin. The main cabin is internally provided with a pectoral fin assembly, a tail fin assembly, a sensing module and a control module. The pectoral fin assembly comprises a pectoral-fin steering engine fixing mechanism and two pectoral-fin power transmission mechanisms; the tail fin assembly comprises a tail-fin power transmission mechanism and a passive rotating mechanism; the sensing module comprises a visual sensor, an infrared distance sensor, an IMU attitude sensor and a plurality of pressure sensors; the control module comprises a microcontroller, a sensor-information collecting pressing board, a steering engine control unit and a communication unit.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Single-joint robot fish and underwater propulsion platform
InactiveCN104118549ASimple structureImprove sealingPropulsive elements of non-rotary typeUnderwater equipmentSacroiliac jointPropulsor
The invention relates to a single-joint robot fish and an underwater propulsion platform, and relates to an underwater propulsion device, aiming at providing a single-joint robot fish and an underwater propulsion platform which are simple in structure, low in cost and simple and convenient to operate. The single-joint robot fish comprises an outer shell, a bionic propulsion mechanism, a power energy module, a control communication module and a posture adjusting mechanism, wherein the bionic propulsion mechanism comprises a tail fin, a C-shaped skeleton, an upper main shaft and a lower main shaft; the tail fin is fixedly connected with the rear end of the C-shaped skeleton; the outer ends of the upper main shaft and the lower main shaft are fixedly connected with two ends of the C-shaped skeleton respectively; the power energy module comprises a battery and a propulsion driving device; the output end of the propulsion driving device is connected with the inner ends of the upper main shaft and the lower main shaft; the control communication module comprises an integrated main control board and an antenna; the posture adjusting mechanism comprises a circumferential rotation driving device and a circumferential rotation counter weight which are arranged in the outer shell; the circumferential rotation driving device is used for driving the circumferential rotation counter weight to rotate around the axis of the outer shell in front-rear direction.
Owner:BORUIZHI TIANJIN INFORMATION TECH
Light-weight and small-sized mangneto swinging bionic robot fish
InactiveCN103950526AReduce complexityEasy control forwardPropulsive elements of non-rotary typeTransmission with non-mechanical gearingPolyvinyl chlorideEngineering
The invention discloses light-weight and small-sized mangneto swinging bionic robot fish, which comprises a fish body, a magnetic motive force fish tail, a U-shaped block and a charging pile, wherein the fish body and the magnetic motive force fish tail are connected through the U-shaped block, the charging pile is arranged at the lower end of the surface, connected with the fish tail, of the fish body, the fish body comprises an infrared sensing probe, a second waterproof casing I, a second waterproof casing II, a control switch and a waterproof soft plug, the second waterproof casing II is arranged at the outer surface of the fish body, and the magnetic motive force fish tail comprises an magnetic induction coil, a rotating shaft, a PVC (polyvinyl chloride) tube pipe, a round permanent magnet and a flexible fish tail. The light-weight and small-sized mangneto swinging bionic robot fish has the advantages that the structure is simple, the weight is light, and the size is small; a magnetic motive force pushing mechanism does not need any waterproof protection, and the complexity of the mechanism is greatly reduced, the energy consumption is low, and the cruising capability is improved; the energy consumption power of a magnetic motive force mode is 1 / 4 of that of a motor, and in addition, the work voltage range is wider; the control is simple and convenient, and the advancing, the acceleration, the turning, the sinking and floating and the like of the robot fish can be easily controlled through controlling the current direction and the current intensity of the coil.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV OF SCI & TECH
BP neural network-based multimodal motion method and system of robot fish
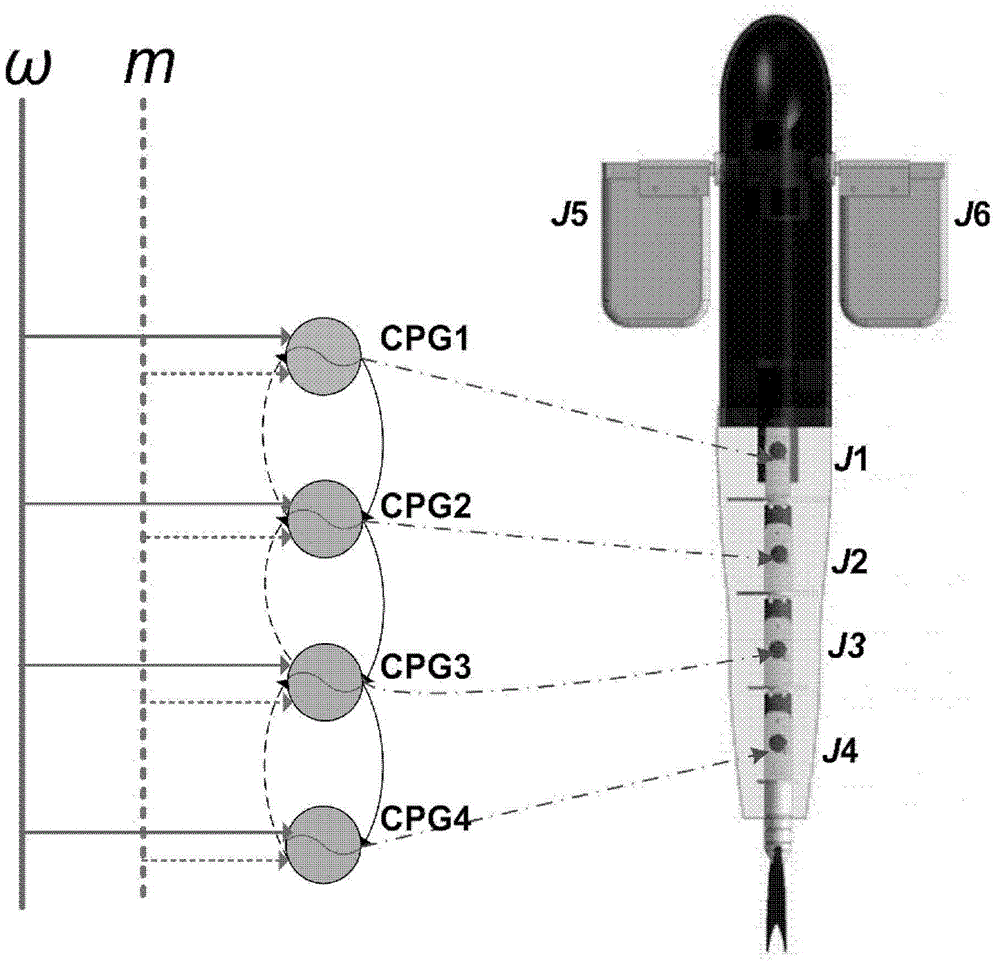
ActiveCN110286592AImprove the ability to perceive the environmentEnable multimodal movementAdaptive controlNetwork packetDynamic models
The invention provides a BP neural network-based multimodal motion method and system of robot fish. The method comprises the steps of building a CPG model; carrying out dynamic modeling on robot fish with pectoral fins at four joints, inhibiting pectoral fin CPGs by tail fin CPGs in a one-way manner, determining left and right input stimuluses, downlink and uplink phase coupling coefficients, uplink and downlink coupling coefficient weights and CPG frequencies corresponding to various joints by using nonlinear oscillator models as CPG neurons; building a BP neural network model; obtaining variations of joint angles on the basis of the CPG model, storing variation values of the joint angles as data packets for carrying out BP neural network training, and transmitting the trained data to a controller of the biomimetic robot fish; and driving swinging of various joints by using CPG signals and carrying out swimming and turning motions of the robot fish. According to the BP neural network-based multimodal motion method and system of the robot fish, multimodal motions of the robot fish are learned by using the BP neural network, so that the target of learning the multimodal motion processes of the robot fish through the BP neural network is finally achieved and the autonomy and the adaptability of a robot fish system are improved.
Owner:SHANDONG JIANZHU UNIV
Flexible dual-drive biomimetic fish with variable drive position
InactiveCN102114907ASimple structureImprove stabilityPropulsive elements of non-rotary typeShape-memory alloyEngineering
The invention discloses a flexible dual-drive biomimetic fish with a variable drive position, relating to a biomimetic robot fish which is used for solving the defects of poor stability and bad maneuverability of the traditional biomimetic fish. A movable tail fin driver and a fixed tail fin driver of the biomimetic fish respectively comprises an elastic basic sheet, a fish tail, a silicon gel layer, a shape memory alloy wire fixed seat and two shape memory alloy wires coated with insulating layers, wherein the movable tail fin driver and the fixed tail fin driver are parallel with a longitudinal centre line of a biomimetic fish body and symmetrically arranged relative to the longitudinal centre line of the biomimetic fish body; the two shape memory alloy wire fixed seats are respectivelyarranged in corresponding driver installing grooves, the shape memory alloy wire fixed seat on the fixed tail fin driver is fixedly connected with the biomimetic fish body through a shim, the shape memory alloy wire fixed seat on the movable tail fin driver is fixedly connected with one end of a rotating cross beam through a connecting sheet, and the other end of the rotating cross beam is fixedly connected with a steering engine shaft on the biomimetic fish body. The invention is used for underwater detection.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Microminiature floatable toy machine fish
The invention discloses a floatable and sinkable micro robot fish which relates to the technology of bionic robots; the robot fish is used for amusement and comprises a fish body, a fish tail and a floating and sinking propeller. A fixed skeleton is arranged in the fish body; a control module, a communication module, a rechargeable battery, an infrared sensor, a tail motor, a filler and other components are fixed on the skeleton; the skeleton is wrapped with a whole-fish-shape fish skin; the tail motor is connected with a swinging joint and used for the forward boosting and the direction control of the robot fish; the infrared sensor provides information about the obstruction in front of and below the robot fish; the filler is beneficial to keep the outer appearance of the robot fish; the fish tail is essentially composed of tail fins; the floating and sinking propeller is used for controlling the floating and sinking of the robot fish. The floatable and sinkable micro robot fish can be set in a plurality of sports modes including remote control, obstacle avoidance, preset programming and has the advantages of simple production, lifelike outer appearance and strong appreciation quality.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Carangid bionic robot fish
InactiveCN106005333AReasonable structureSimplify the design processPropulsive elements of non-rotary typeUnderwater vesselsData acquisitionComputer module
The invention provides a bionic robot fish of the family Trevally, belonging to the technical field of underwater robots, including a fish tail, a tail transmission mechanism, a tail steering gear, a battery, a controller, a pectoral fin steering gear, a switch and a fish body, and a pressure sensor , a sealing cylinder, an electronic compass, a buoyancy adjustment cylinder, a linear potentiometer, a buoyancy motor, a camera and a pectoral fin, the fish tail is connected with the tail steering gear through a tail transmission mechanism, a sealing cylinder and a buoyancy adjustment cylinder are arranged in the fish body, and the sealing cylinder A battery, a controller and a pectoral fin steering gear are arranged inside, a buoyancy motor is arranged at the rear end of the buoyancy adjustment cylinder, a switch and a camera are arranged on the head of the fish body. The beneficial effects of the present invention are: reasonable structure, novel and ingenious, capable of carrying a variety of information collection modules for data collection, at the same time adapting to the operation requirements in various environments, having good maneuverability and propulsion efficiency, and the modular design is easy to manufacture, Installation and commissioning simplifies the design and processing of complex parts and reduces costs.
Owner:HEBEI UNIV OF TECH
Ionic artificial muscle drive based small robot fish and moving method thereof
ActiveCN104002947AImprove mobilityPropulsive elements of non-rotary typeIonic polymer–metal compositesEngineering
The invention relates to an ionic artificial muscle drive based small robot fish and a moving method thereof and belongs to the technical field of intelligent material applications. A fish body of the robot fish is driven by a pectoral fin drive system and a tail fin drive system coordinately. The pectoral fin drive system comprises a U-shaped rack in the fish body and a left pectoral fin drive mechanism and a right pectoral fin drive mechanism. Each of the pectoral fin drive mechanisms comprises three ionic polymer metal composite (IPMC) material sheets, a rotation disc, a rotation shaft and a pectoral fin film, and vertical wing flapping and shaking can be achieved. The tail fin drive system comprises an electrode clamping units fixed at the tail, an IPMC material sheet and a tail fin, and one-way or two-way swinging of the fish body in the axial plane can be achieved. A control panel and a battery are disposed in the fish body, and moving modes such as linear cruising, speeding up / speeding down / sudden stopping, left and right / turning and floating / diving are achieved by setting appropriate drive signals.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Line-driven robotic fish
PendingCN109050851AReduce weightSimple joint structurePropulsive elements of non-rotary typeJoint componentEngineering
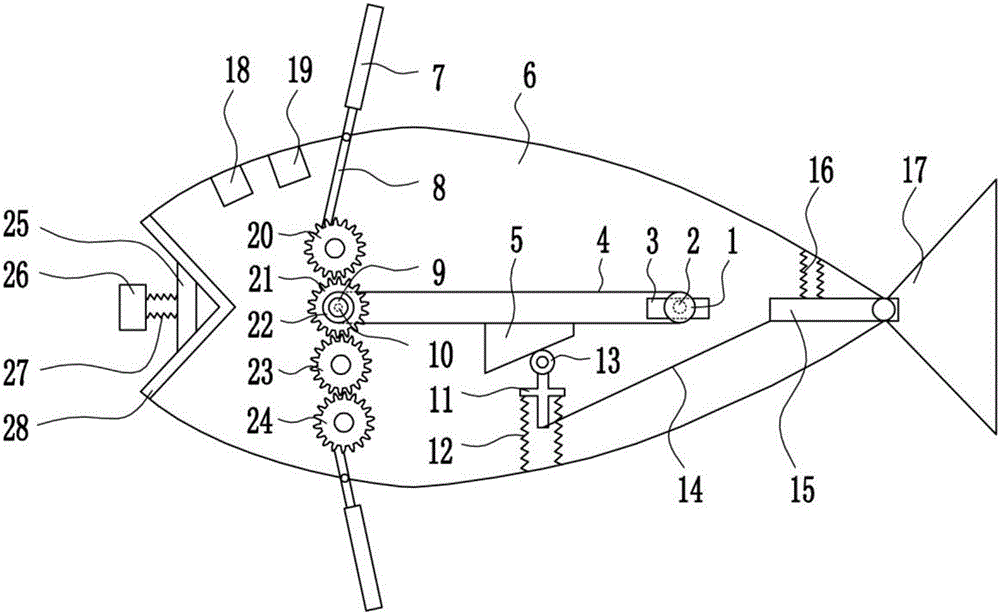
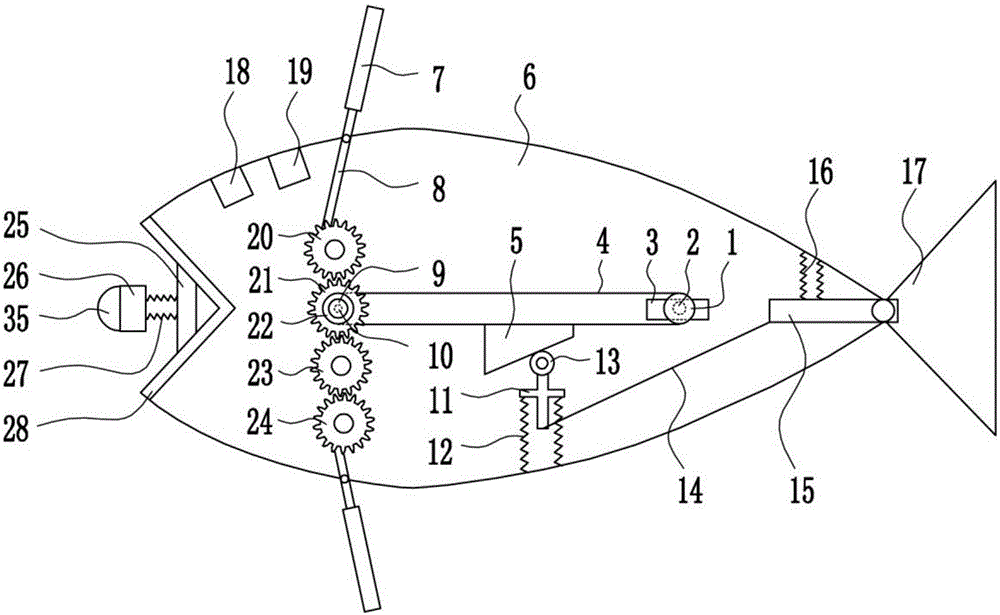
A line-driven robotic fish including fish head, fish body and tail, Fish tail comprise a tail fin and a support plate assembly, The support plate assembly is composed of a support plate connected in turn from the rear to the rear, at least one support plate II and one support plate III, wherein the front side of the support plate I is fixedly connected with the fish body, the rear side of the support plate III is fixedly connected with the caudal fin, the support plate I and the support plate II are connected with each other, and the adjacent support plates II and the support plate II and thesupport plate III are connected with each other through joint components; And two transmission wires arranged in parallel. The front end of the transmission wire is connected with the fish tail driving mechanism, and the rear end passes through the support plate I and the support plate II in turn and is fixedly connected with the support plate III after passing through the support plate I and thesupport plate II; The two driving wires are made of flexible material and are driven by the fish tail driving mechanism, so as to drive the supporting plates II and III to swing left and right; The thread-driven type robot fish of the invention has simple joint structure and reduces the whole weight of the robot fish while providing its own driving force.
Owner:CHONGQING THREE GORGES UNIV
Bionic machine fish
InactiveCN101318544AThe fish swim in the same postureRealistic effectPropulsive elements of non-rotary typeUnderwater equipmentLeft halfControl system
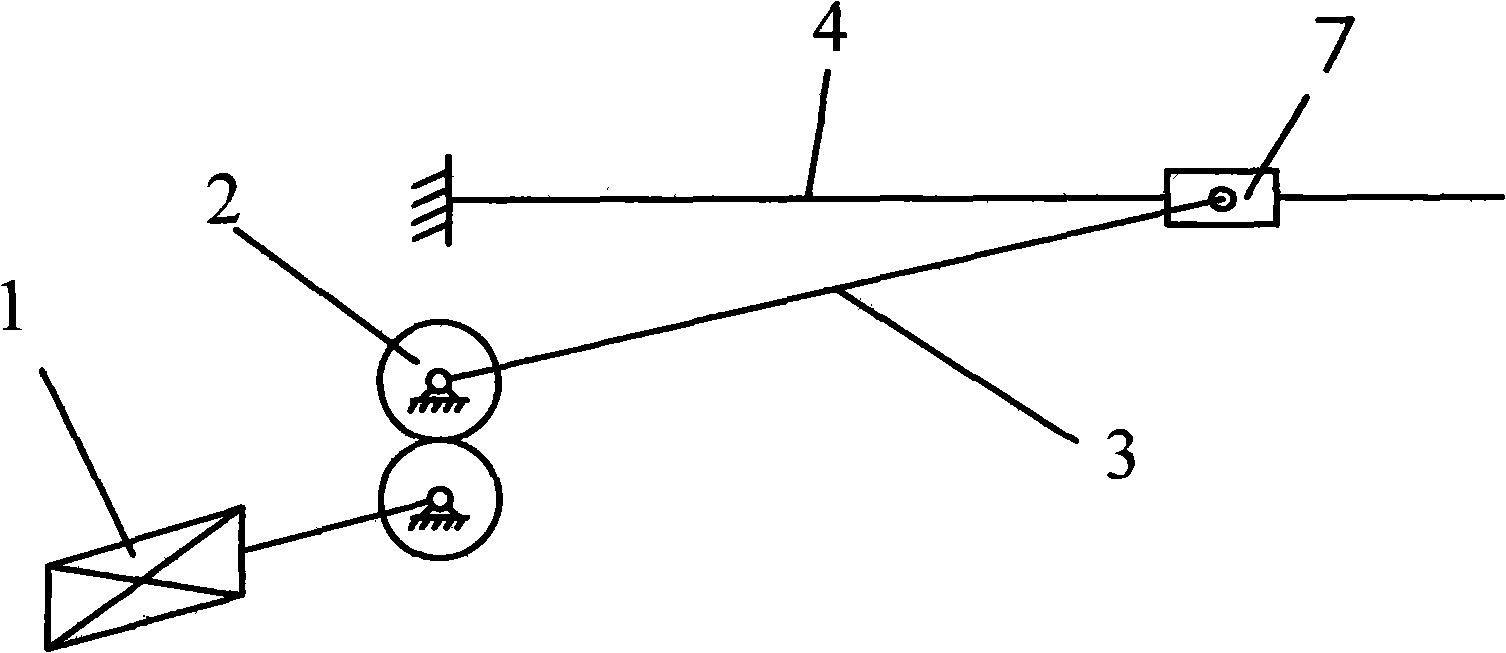
The invention discloses a biomimetic robot fish which can realize the advance with different speeds and turning left and right with different turning radii. A single freedom degree control mode is adopted and a servo electromotor is adopted to be reversed by a reversing gear set to drive a swing stem to swing; a pin roll at the tail end of the swing stem pushes an elastic thin plate one end of which is fixed on the skeleton of the robot fish and the other end is free to swing to-and-fro. The swimming modes of the robot fish are controlled to be different by controlling the differences of the swing mode of the elastic thin plate by a control system. The swing stem symmetrically swings left and right to lead the robot fish to advance; the advancing speed of the robot fish can be controlled by changing the swing amplitude and the frequency of the swing stem; the swing stem eccentrically swings at the left half; for example, eccentrically swinging at the left half can lead the fish to turn left; when the robot fish turns, the turning radius of the robot fish can be controlled by changing the swing amplitude and the frequency of the swing stem.
Owner:NANTONG GUANGYI ELECTROMECHANICAL CO LTD +1
Parent-subsidiary bionic machinery fish system
ActiveCN101314404AImprove efficiencyPropulsive elements of non-rotary typeUnderwater vesselsControl theoryFuture of robotics
The invention provides a composite bionic robot fish system, relating to a bionic robot technique. The system consists of a master robot fish (a master machine for short) and an auxiliary robot fish (an auxiliary machine for short). The master machine is large in volume and strong in exercise and journey continuation capacity, is provided with a carrying cabin, and can load one or a plurality of auxiliary machines; the auxiliary machines are small in volume, maneuverable and flexible, and the auxiliary machines with different functions can have different volumes; after the auxiliary machines are carried to a destination by the master machine, the auxiliary machines are separated from the master machine and then carry out missions under the leadership of the master machine or independently. The master machine can communicate with the auxiliary machines, so as to complete the coordination actions that the auxiliary machines go out of or into the cabin, etc. The system can provide a multi-underwater-robot working platform adapted to different environmental requirements according to the different environments or missions, and can give full play to each individual, which is favorable for improving efficiency and widening the application range of the system.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Robot-fish communication system
ActiveCN106313042ASimple structureImprove the decorative effectProgramme-controlled manipulatorCommunications systemEngineering
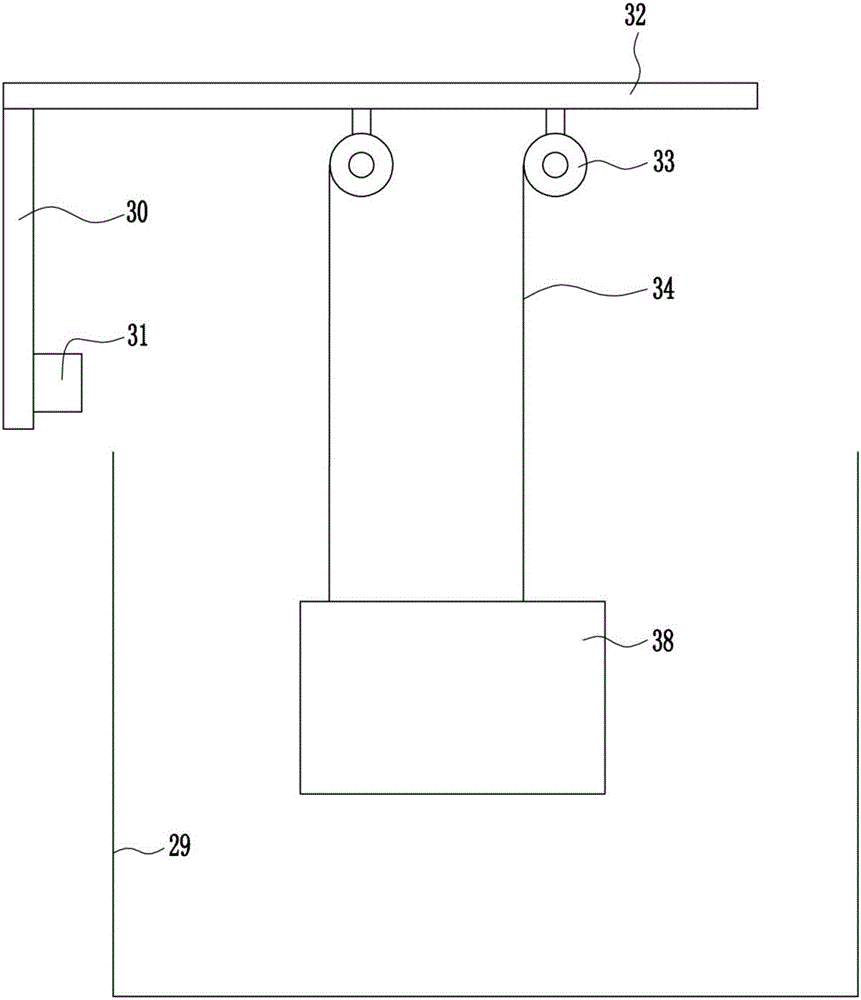
The invention relates to a communication system, in particular to a robot-fish communication system. In order to achieve the technical purposes that the structure is simple, the decoration effect is better, and the working process can be conveniently adjusted, the robot-fish communication system provided by the invention comprises a fish tank, a mounting plate, a switch, a top plate, electric wheels, second pulling ropes and a robot fish, wherein the robot fish is arranged in the fish tank, the mounting plate is arranged on the left side of the bottom of the top plate, the switch is arranged on the right side of the mounting plate, the electric wheels are arranged on the bottom of the top plate and wound with the second pulling ropes, and the lower ends of the second pulling ropes are connected with the top of the robot fish. The robot-fish communication system achieves the effects that the structure is simple, the decoration effect is better, and the working process can be conveniently adjusted.
Owner:HEFEI LINGXIANG INFORMATION TECH
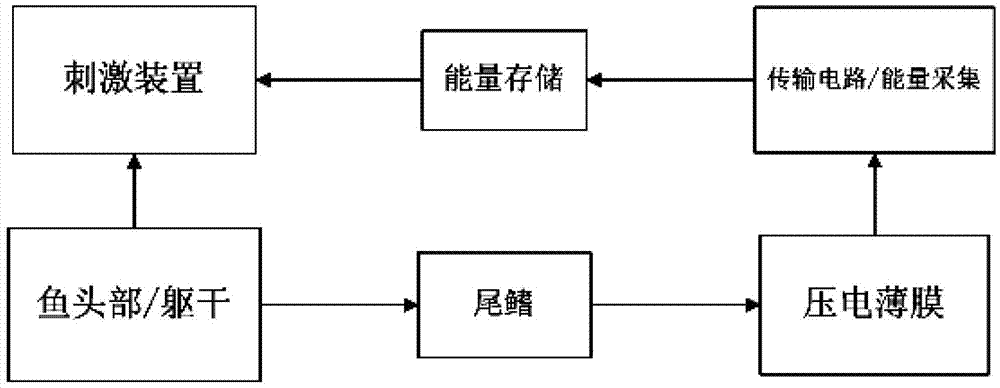
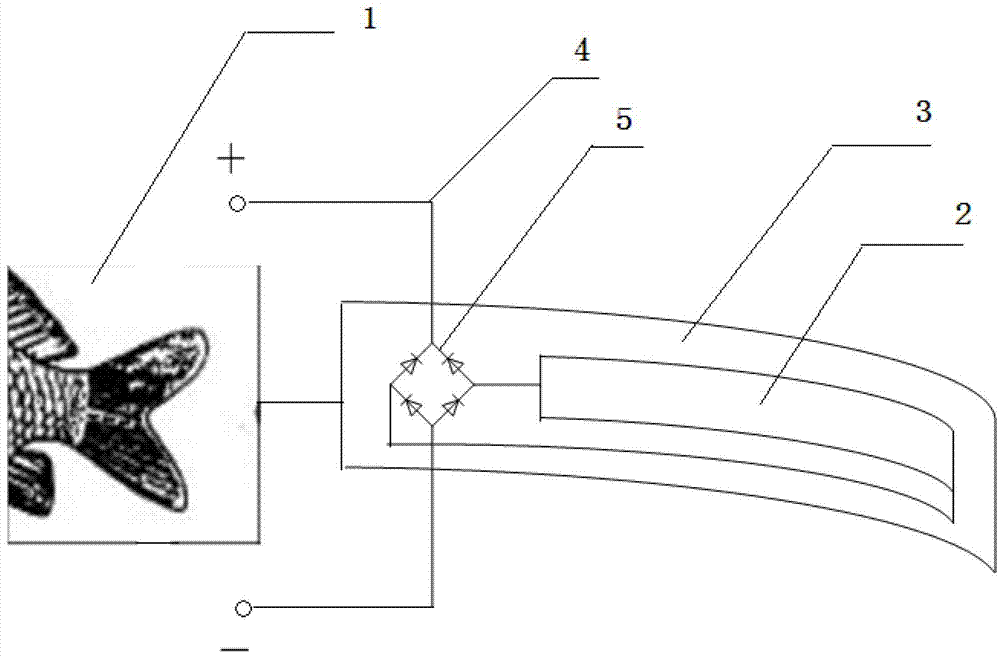
Underwater bio-robot fish system energy supply device based on piezoelectric material
ActiveCN102957339AReduce weightLong duration of energy supplyElectrical storage systemPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesElectricityUnderwater
The invention provides an underwater bio-robot fish system energy supply device based on a piezoelectric material. The underwater bio-robot fish system energy supply device based on the piezoelectric material comprises a flexible material substrate, a piezoelectric thin film, a rectifying circuit, a transmitting circuit and an energy storing device, wherein the flexible material substrate comprises a free end and a fixed end, and the fixed end is fixedly arranged on a tail fin or a dorsal fin; the piezoelectric thin film is fixedly arranged on the flexible material substrate; and the transmitting circuit and the energy storing device are implanted or fixedly arranged in the body or head of a fish. According to the underwater bio-robot fish system energy supply device based on the piezoelectric material, disclosed by the invention, the piezoelectric material is deformed by collecting vibration generated by the motion of an organism, and a stimulation device continuously generates electric signals after current is rectified by the rectifying circuit and is transmitted and stored so as to control the nerves of the organism to move. The underwater bio-robot fish system energy supply device disclosed by the invention has the characteristics of light weight, long energy supply continuing time and the like, and can reduce the load in the fish generated due to the weight of an energy supply system so as to realize long-term and long-distance control in a bio-robot fish system.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Waving bionic robot fish
InactiveCN1876488ASimple structureLight in massPropulsive elements of non-rotary typeLow noiseEngineering
The invention discloses a fluctuated bionic robot fish, which comprises a main body formed by a cylinder frame, two sealing covers, and a robot fin fixing element, wherein the frame of main body contains two helms, control circuit board and battery used to power the machine; two sides of main body via fin fixing element, are connected to two fluctuated fins made from flexible material; the front sealing cover has two rods connected to the driving helm, via the vibration of helm, to make two rods as the vibration source of fluctuated fin; the vibration source, via flexible fluctuated fin, is transmitted backwards to form the traveling wave to push the robot fish. The invention has simple structure and lower noise.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Bionic robot fish
ActiveCN106741774ABig propulsionIncrease flexibilityPropulsive elements of non-rotary typeUnderwater equipmentBionicsLong axis
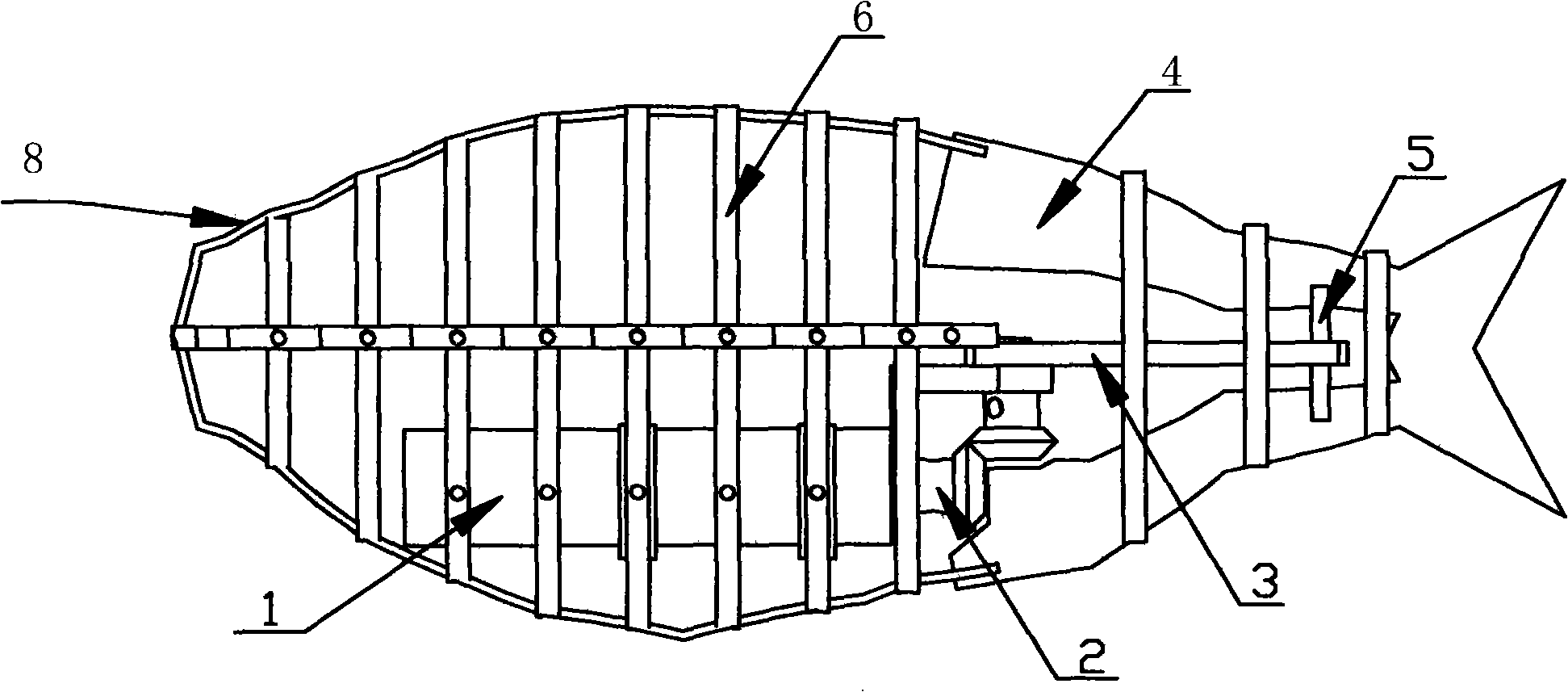
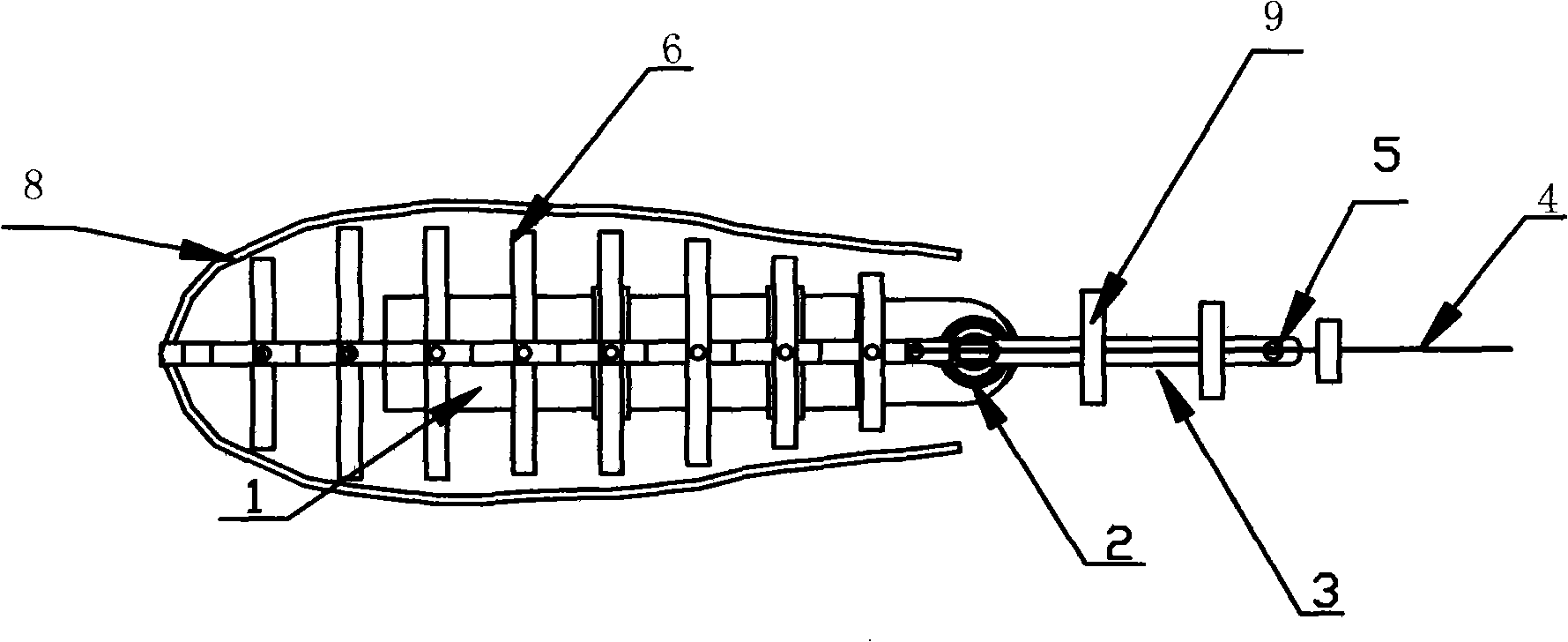
The invention discloses a bionic robot fish and relates to the technical field of underwater robots. The bionic robot fish structurally comprises a head portion, a body portion and a tail portion which are sequentially connected; the front end of the head portion is provided with a thin and long sharp-end structure; the outer surface of the head portion is of a streamline structure; the body portion comprises a fish skin and a propelling system; the overall shape of the fish skin is of a streamline structure; a plurality of grooves are distributed in the upper edge of the fish skin side by side in the direction of the long axis of the fish skin; the propelling system drives the body portion to swing to achieve underwater movement of the bionic robot fish; and the tail portion comprises a tail fin support and a tail fin. The bionic robot fish reduces fluid resistance during swimming, is reliable in work and is high in bionic degree.
Owner:CETC OCEAN INFORMATION CO LTD
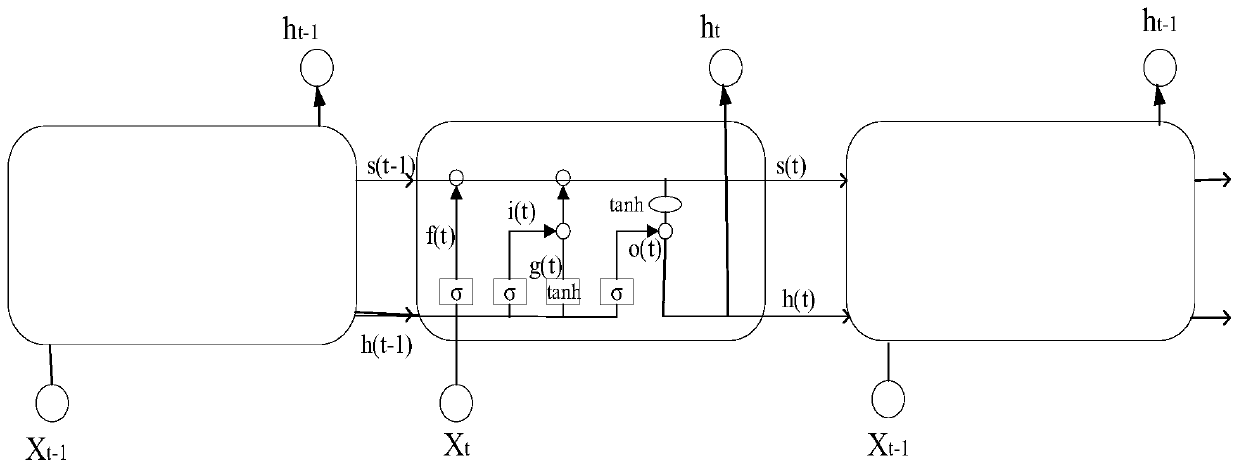
Bionic robot fish motion control method, controller and bionic robot fish
The invention provides a bionic robot fish motion control method, a controller and a bionic robot fish. The bionic robot fish motion control method comprises the follow steps: acquiring the angle of the fish tail fin joint and the corresponding bionic robot fish motion state tag to be stored in a data set, wherein the motion state tag of the bionic robot fish includes a straight-swimming motion state tag and a turning motion state tag; dividing the data set into a training set and a test set and normalizing; constructing an LSTM neural network model and training the LSTM neural network model by using the data from the normalized training set and testing the LSTM neural network model by using the test set so as to obtain the trained LSTM neural network model and obtain a bionic robot fish tail fin swing model; and outputting the motion state of the bionic robot fish corresponding to the present angle of the fish tail fin joint by using the bionic robot fish tail fin swing model. The motion state of the bionic robot fish can be accurately controlled and the control of the bionic robot fish can be better realized.
Owner:SHANDONG JIANZHU UNIV
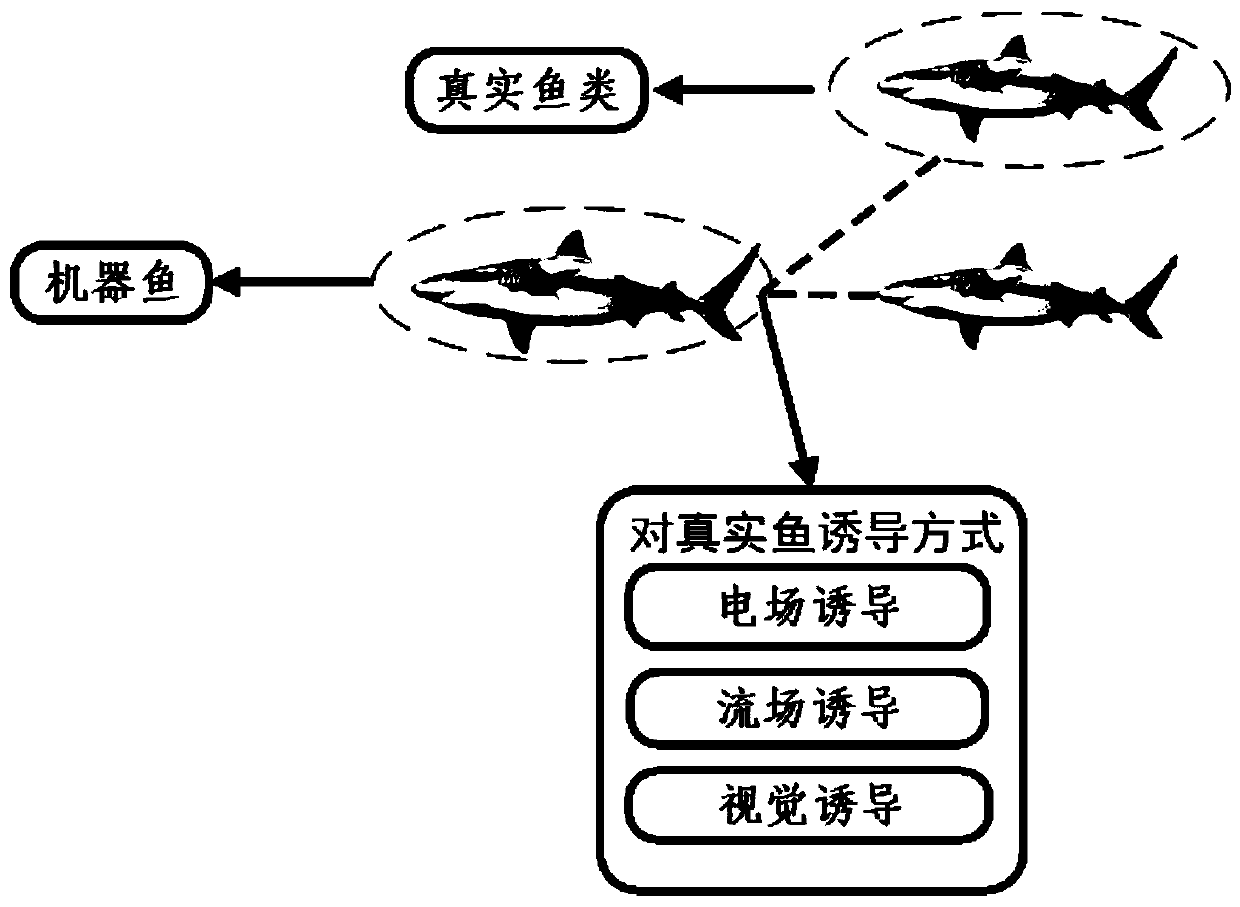
An underwater bionic guiding robotic fish and a method for guiding fish motions
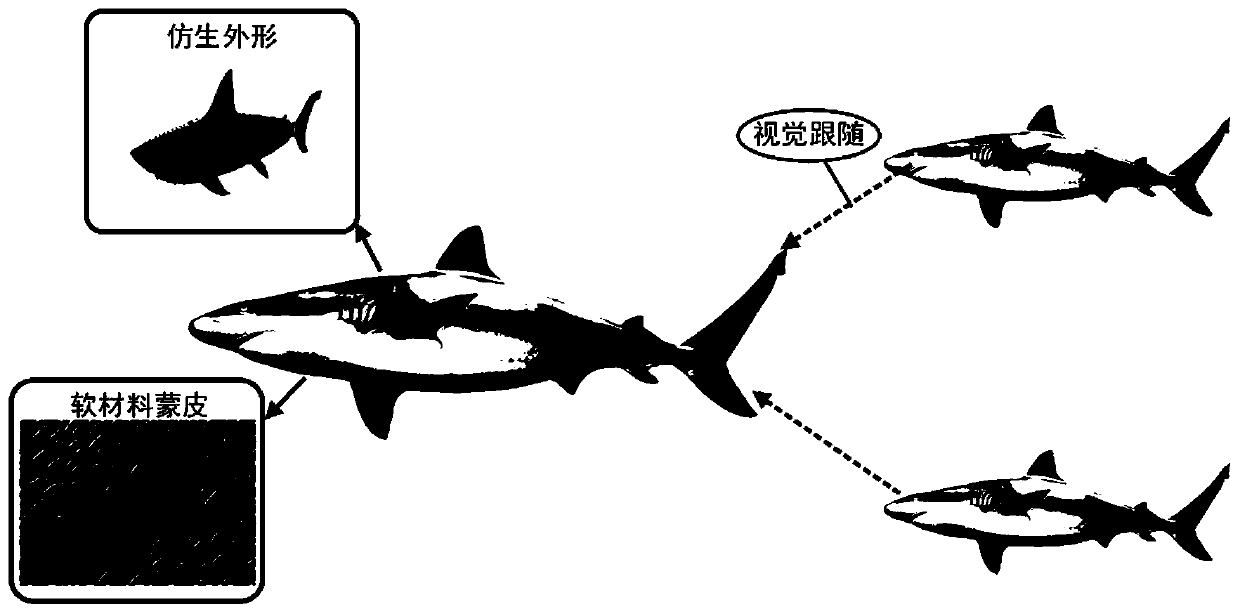
ActiveCN110228575AImprove task concealmentIncrease flexibilityClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaBionicsSoft materials
The invention provides an underwater bionic guiding robotic fish and a method for guiding fish motions. A variety of ways are combined and complemented to realize real fish guidance including visual guidance, wake field guidance and electric field guidance. A bionic robotic fish shape architecture simulating the real fish shape architecture and covered with a soft material skin is designed to simulate real fish in shape for visual guidance. Through swinging of bionic robotic fish tail fin in the water, a flow field similar to fish swimming is generated to induce real fish to follow in the lateral rear side to achieve flow field guidance. An electric signal emitting end of an underwater electric potential generating device is used to generate a high electric potential in the water, so thatthe tail portion of the bionic robot fish becomes an electric field positive pole, and electric field guiding is realized according to the positive pole seeking effect of the fish. Through combinationof a plurality of modes, the underwater bionic guiding robotic fish can realize a function of guiding real fish motions so as to provide a new method and approach to establishment of an underwater machinery-biology mixed cluster.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Bionic intelligent robot fish
ActiveCN105799876AAvoid the hassle of salvage rechargingTo achieve the purpose of full underwater operationPropulsive elements of non-rotary typeSpecial purpose vesselsEngineeringIntelligent control
The invention discloses a bionic intelligent robot fish. The bionic intelligent robot fish is provided with a streamline shell. The bionic intelligent robot fish is divided into a fish head, a fish body and a fish tail according to the shape structure of a biological fish. The fish body comprises a first part, a second part, a third part and a fourth part. The first part and the second part are fixedly connected, the second part and the third part are rotationally connected through a first drive mechanism, the third part and the fourth part are rotationally connected through a second drive mechanism, and the fourth part and the fish tail are rotationally connected through a third drive mechanism. A control module, a wireless charging module, a sinking and floating mechanism, an infrared sensor, a pressure sensor and a nine-axis attitude sensor are arranged in the body of the bionic robot fish. It is guaranteed that the purpose of fish intelligent control is achieved through a bionic robot.
Owner:NANJING LEPENG ELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com