Patents
Literature
77 results about "Ionic polymer–metal composites" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
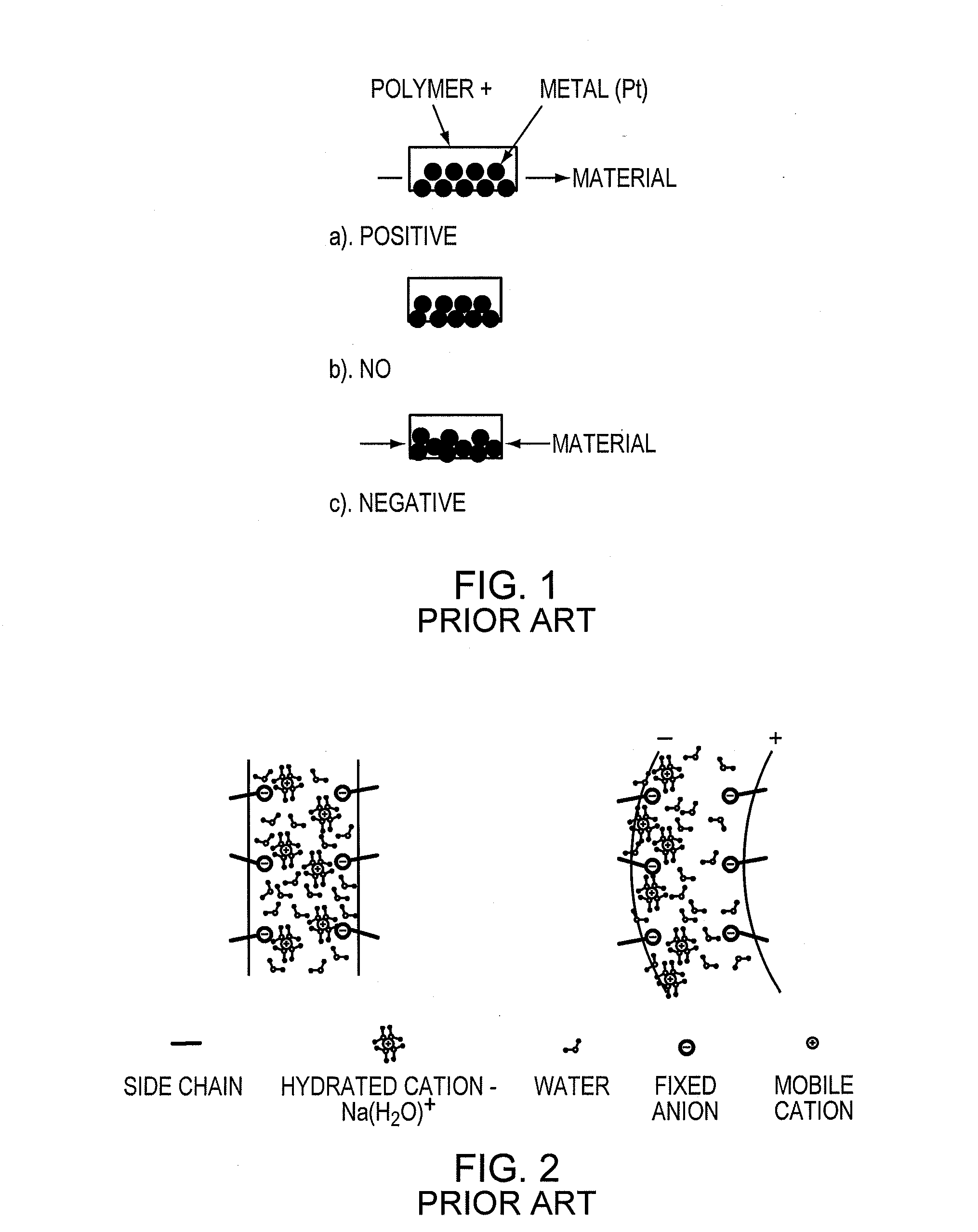
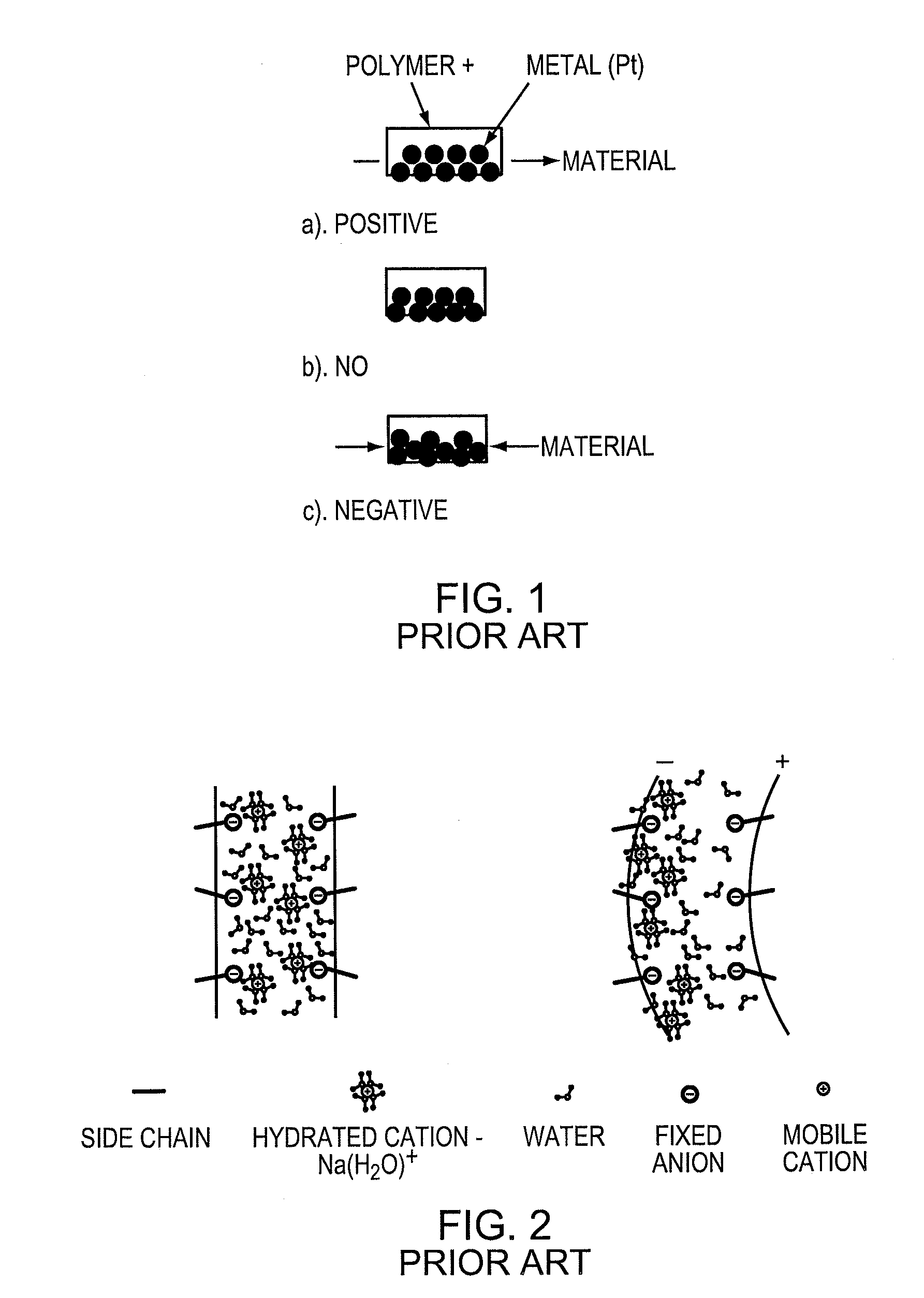
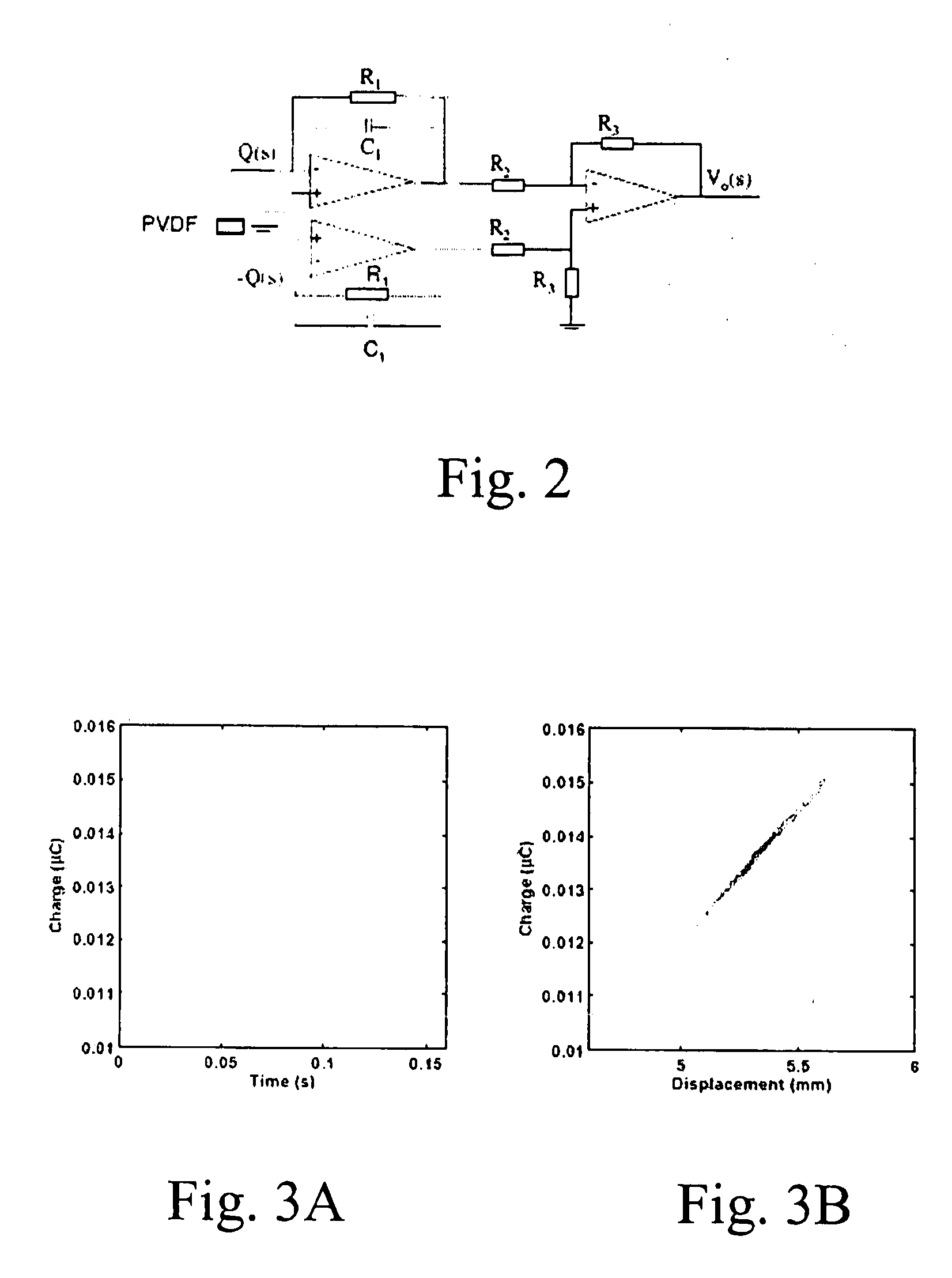
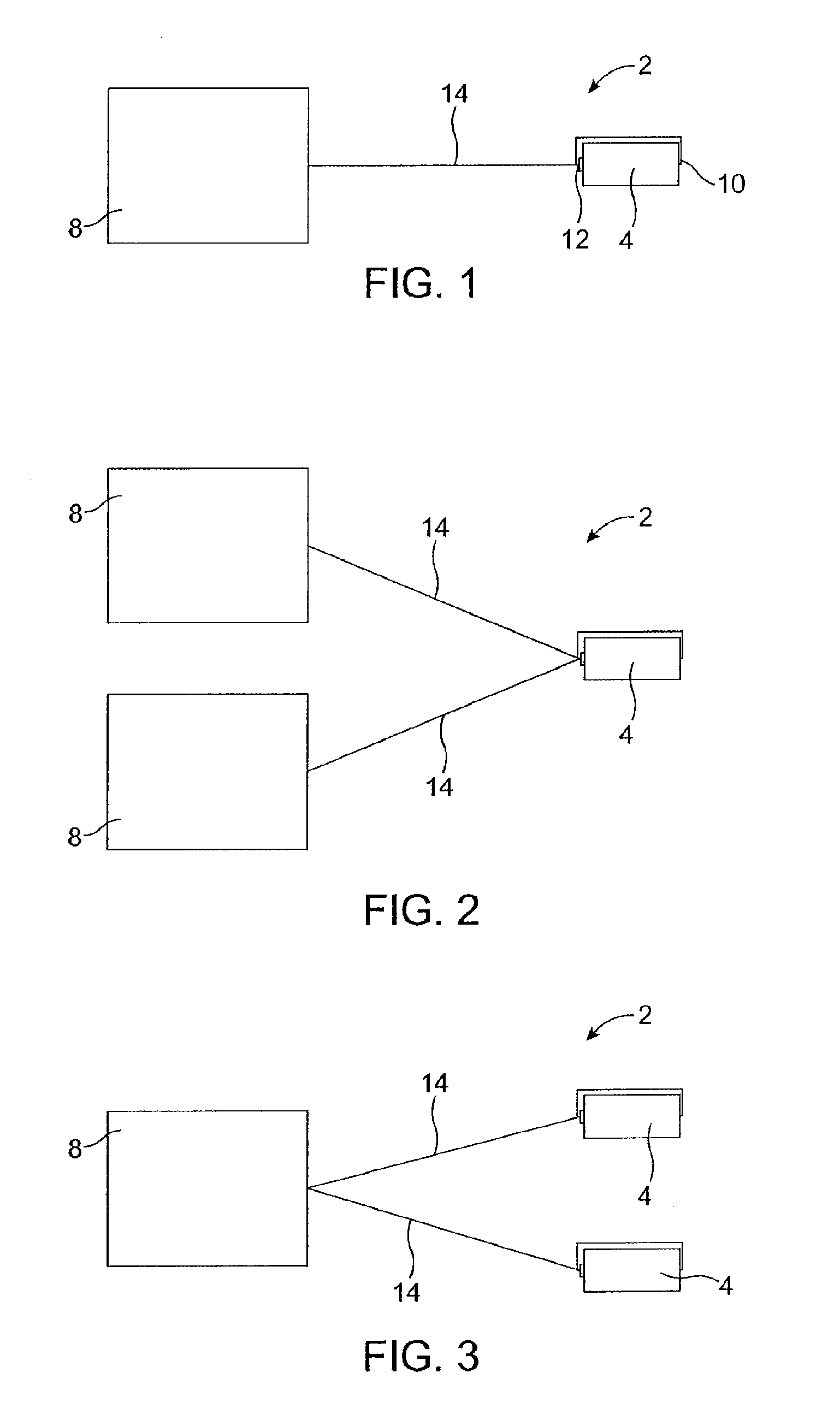
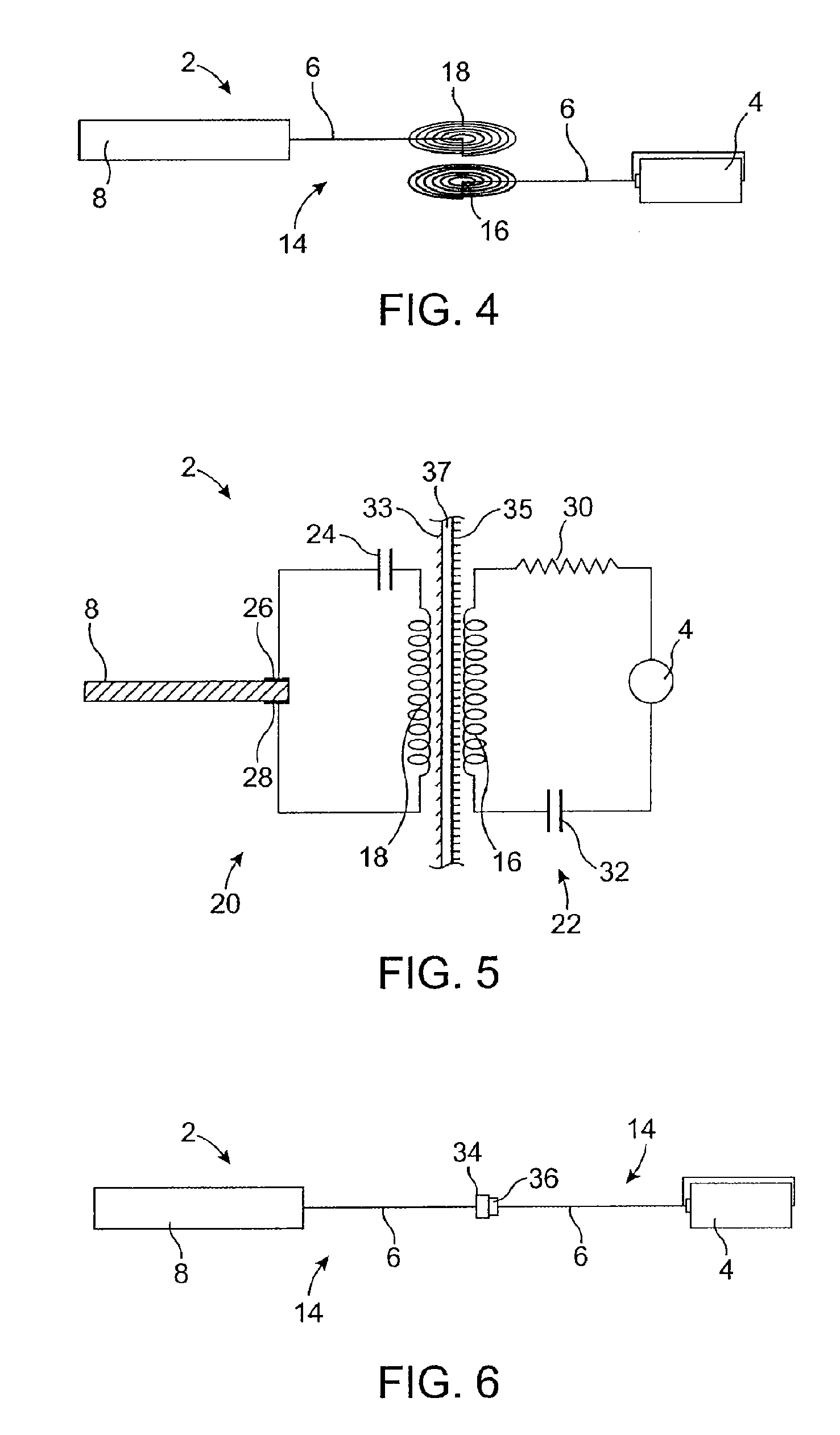
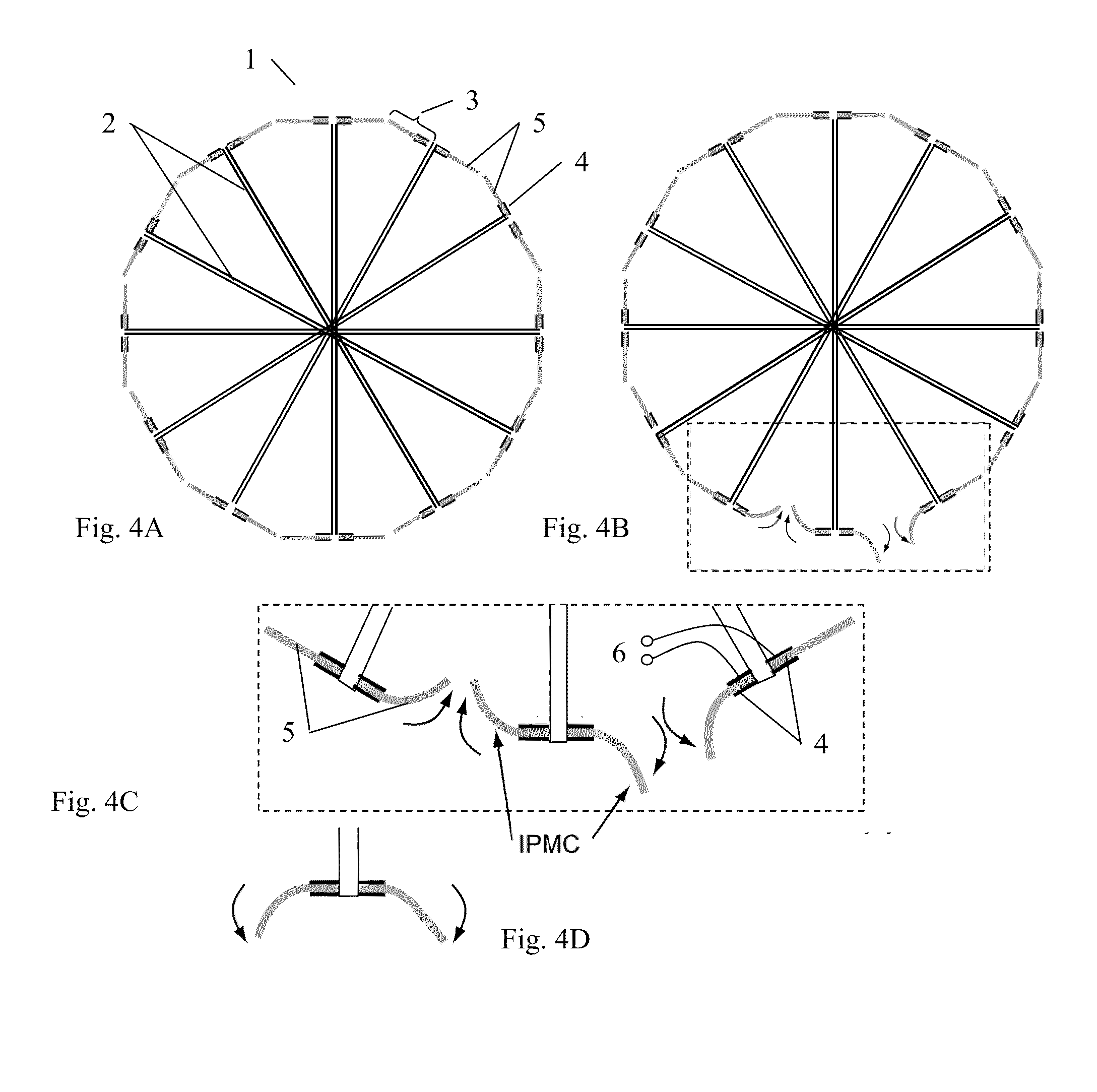
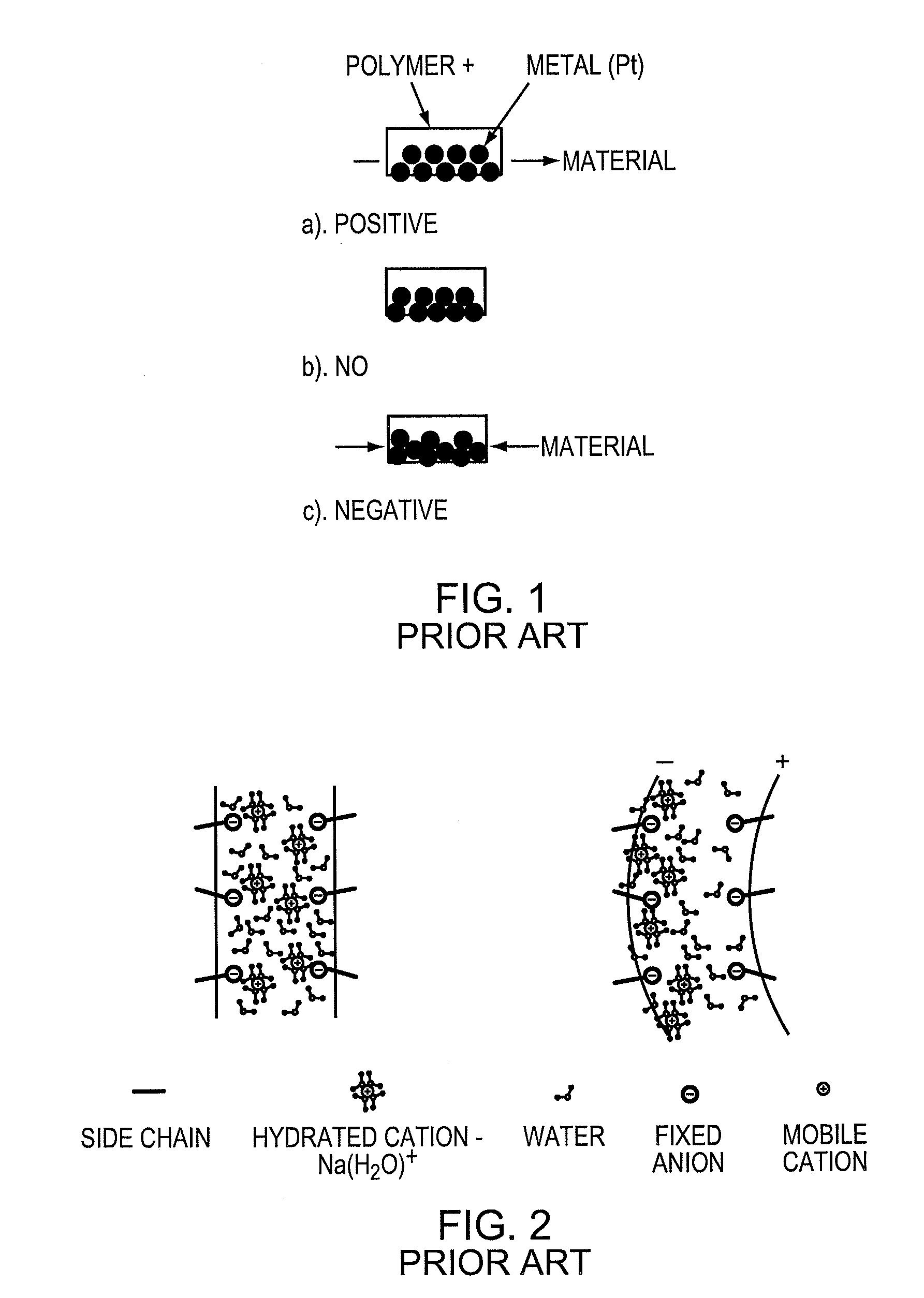
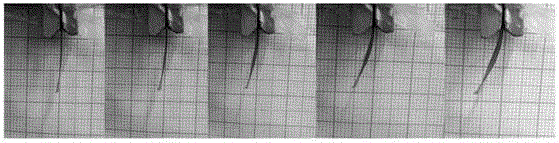
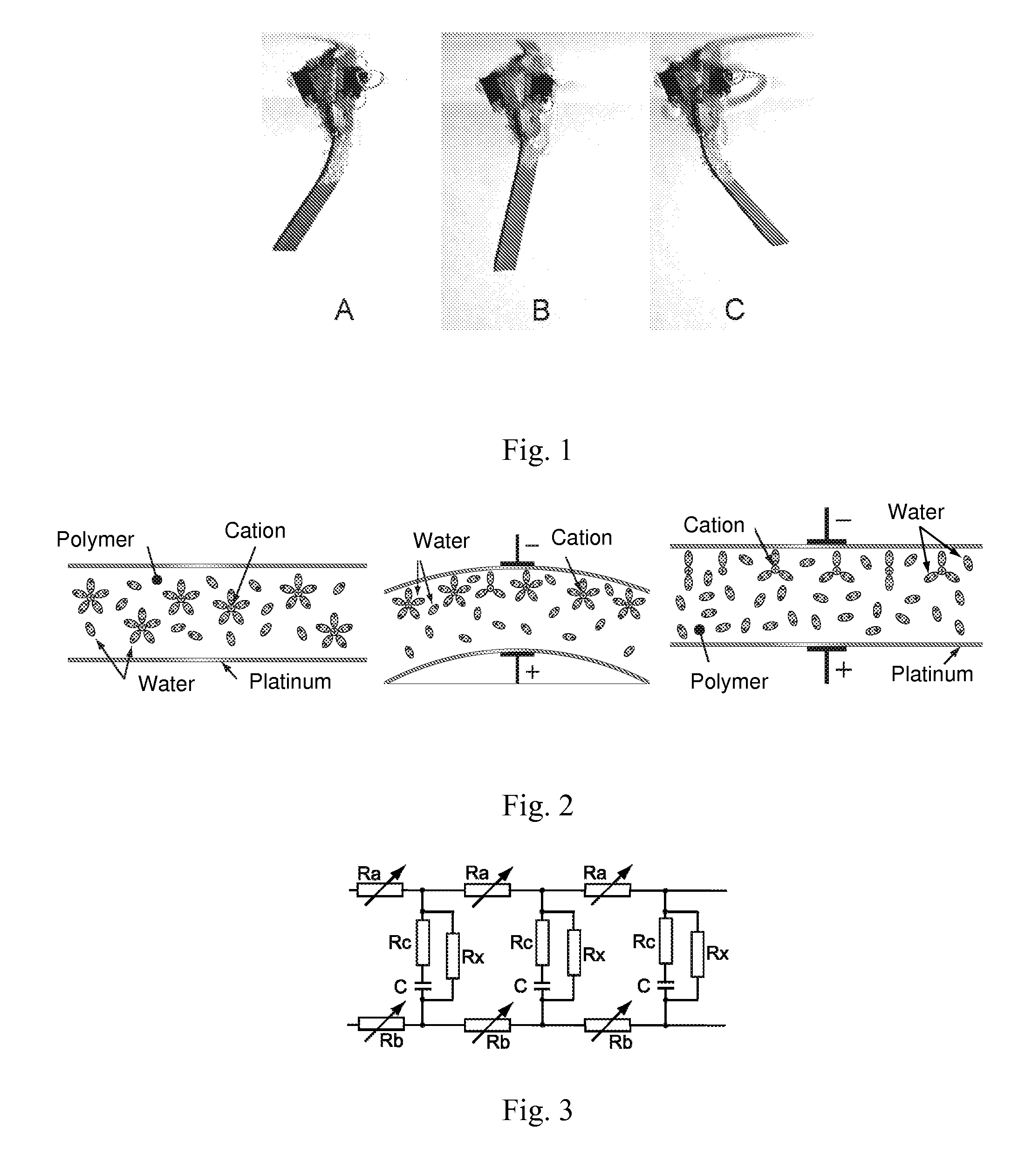
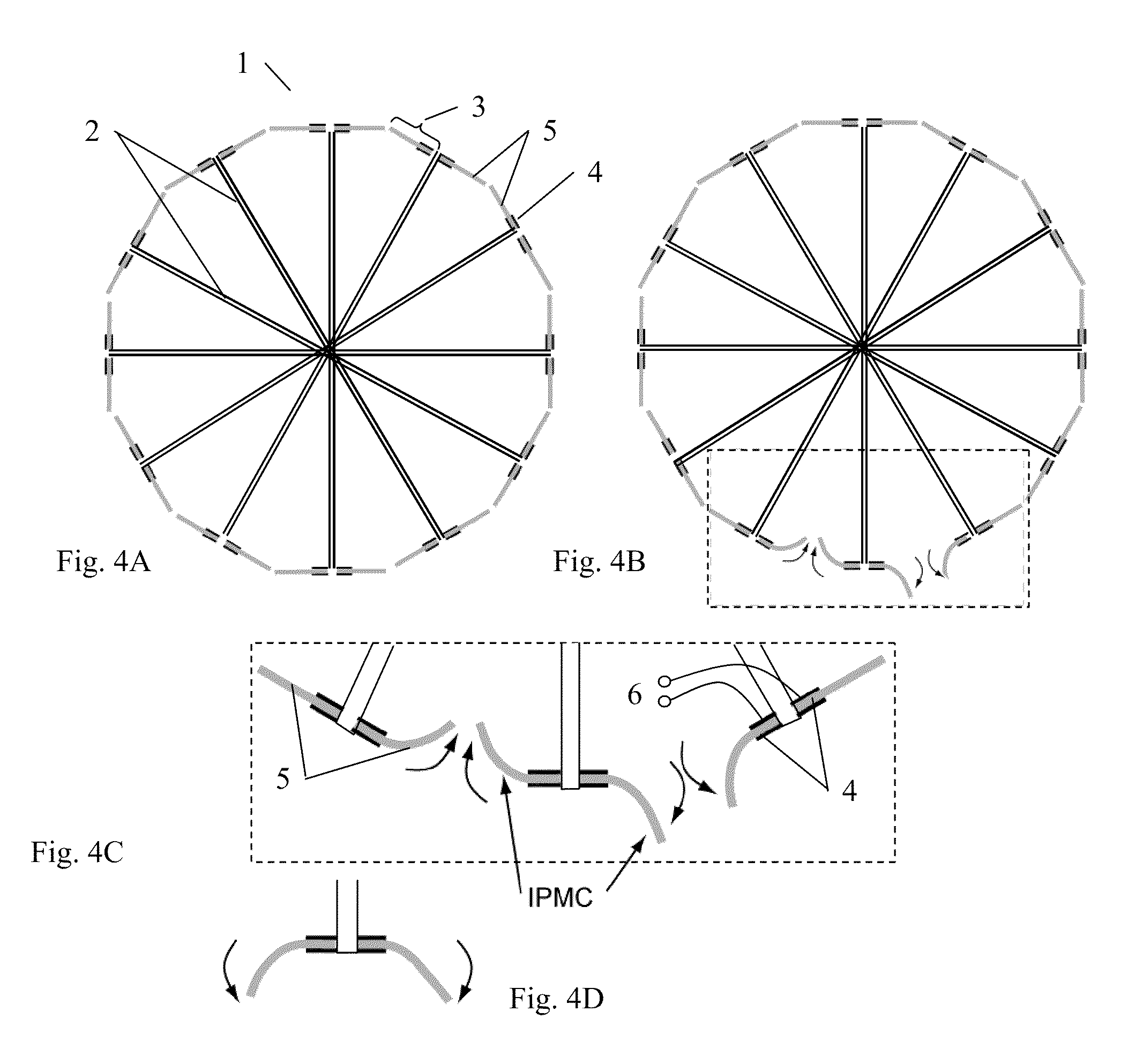
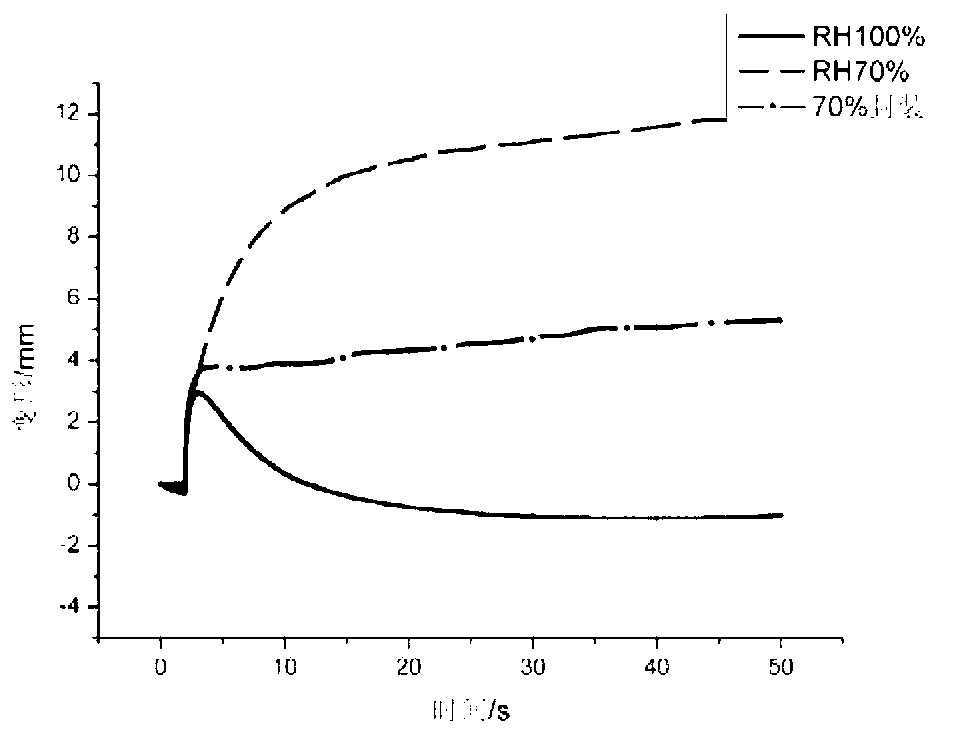
Ionic polymer–metal composites (IPMCs) are synthetic composite nanomaterials that display artificial muscle behavior under an applied voltage or electric field. IPMCs are composed of an ionic polymer like Nafion or Flemion whose surfaces are chemically plated or physically coated with conductors such as platinum or gold. Under an applied voltage (1–5 V for typical 10mmx40mmx0.2mm samples), ion migration and redistribution due to the imposed voltage across a strip of IPMCs result in a bending deformation. If the plated electrodes are arranged in a non-symmetric configuration, the imposed voltage can induce all kinds of deformations such as twisting, rolling, torsioning, turning,twirling, whirling and non-symmetric bending deformation. Alternatively, if such deformations are physically applied to an IPMC strips they generate an output voltage signal (few millivolts for typical small samples) as sensors and energy harvesters. IPMCs are a type of electroactive polymer. They work very well in a liquid environment as well as in air. They have a force density of about 40 in a cantilever configuration, meaning that they can generate a tip force of almost 40 times their own weight in a cantilever mode. IPMCs in actuation,sensing and energy harvesting have a very broad bandwidth to kilo HZ and higher. IPMCs were first introduced in 1998 by Shahinpoor, Bar-Cohen, Xue, Simpson and Smith (see references below) but the original idea of ionic polymer actuators and sensors goes back to 1992-93 by Adolf, Shahinpoor, Segalman, Witkowski, Osada, Okuzaki, Hori, Doi, Matsumoto, Hirose, Oguro, Takenaka, Asaka and Kawami as depicted below...
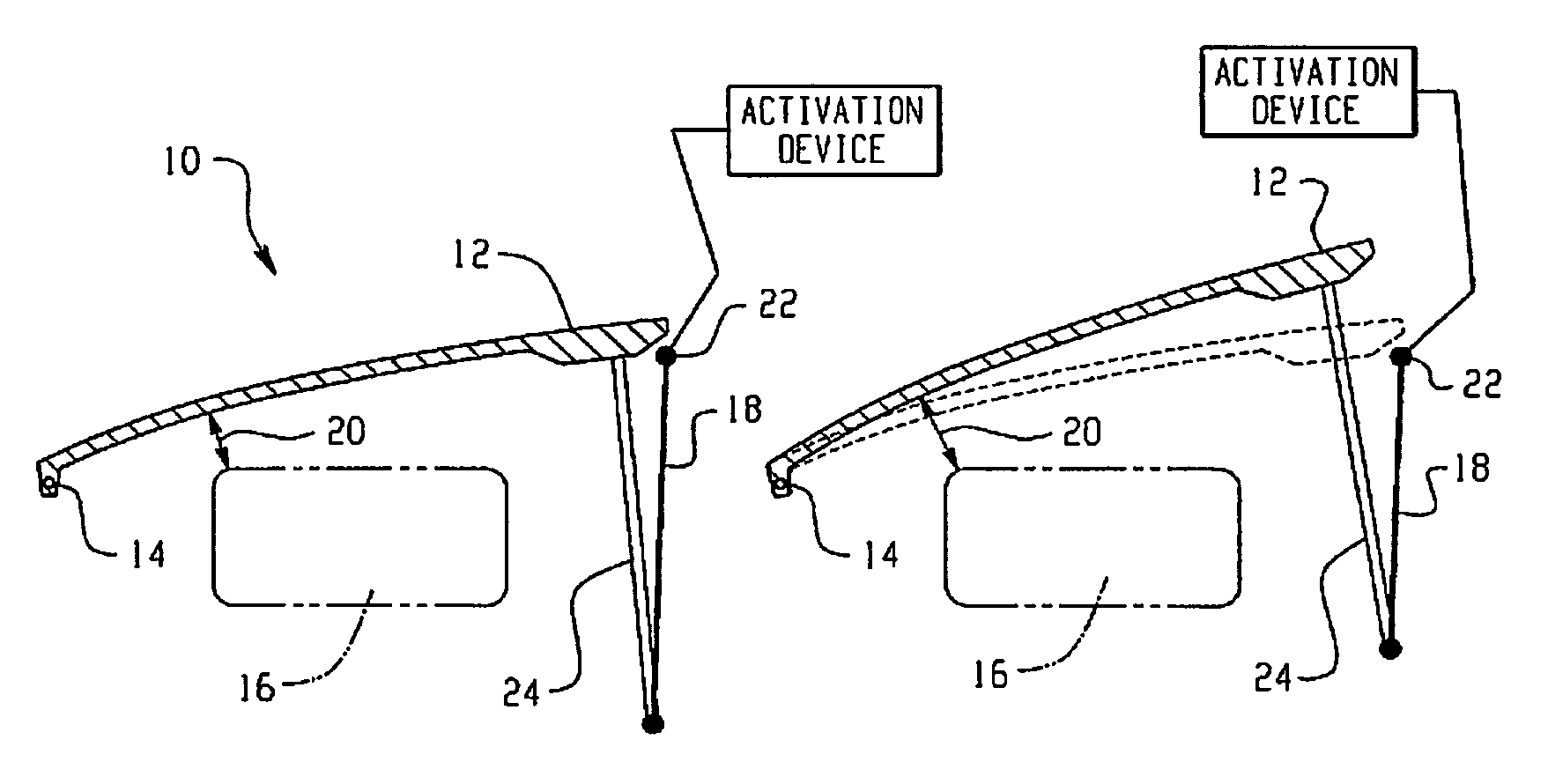
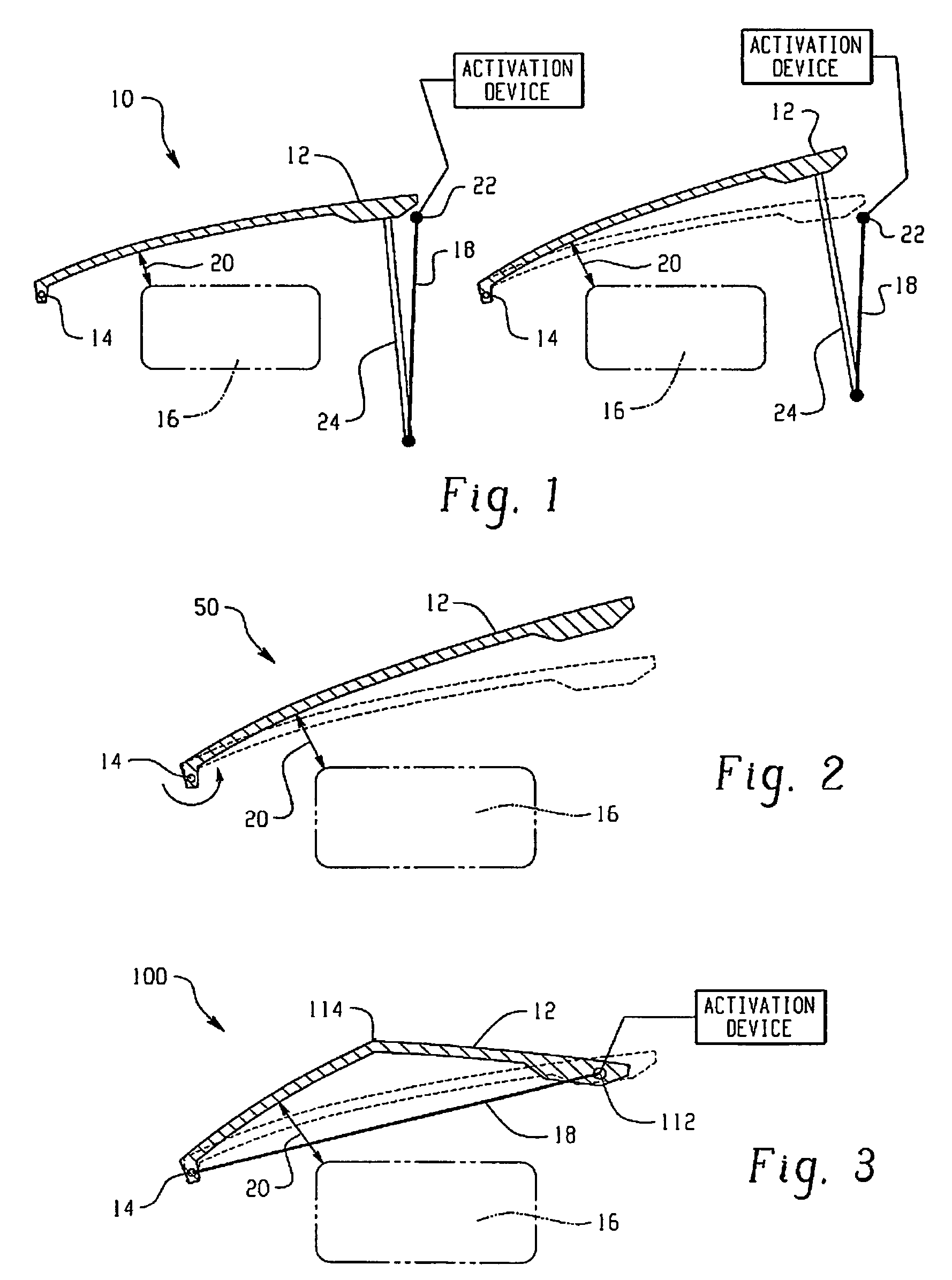
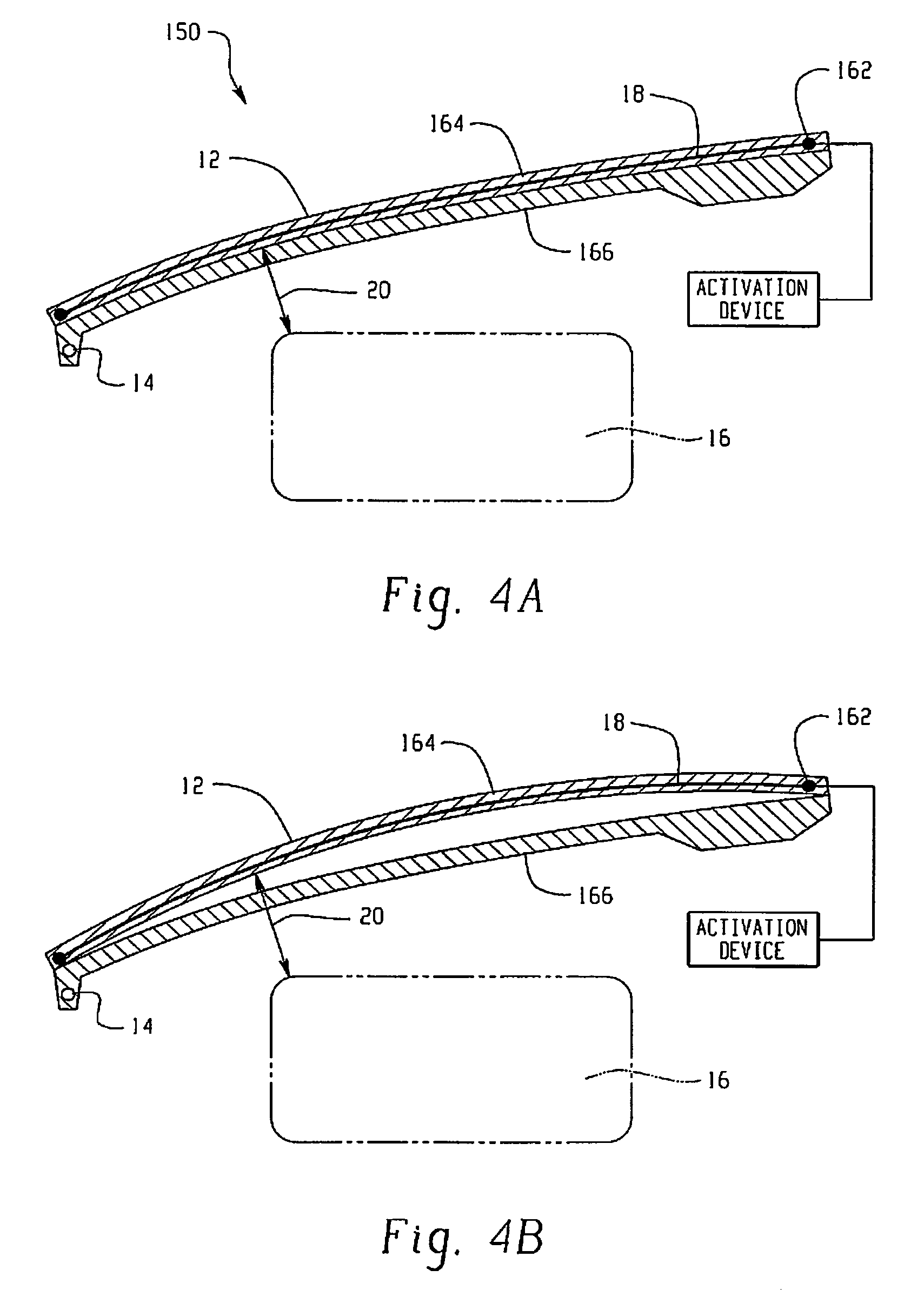
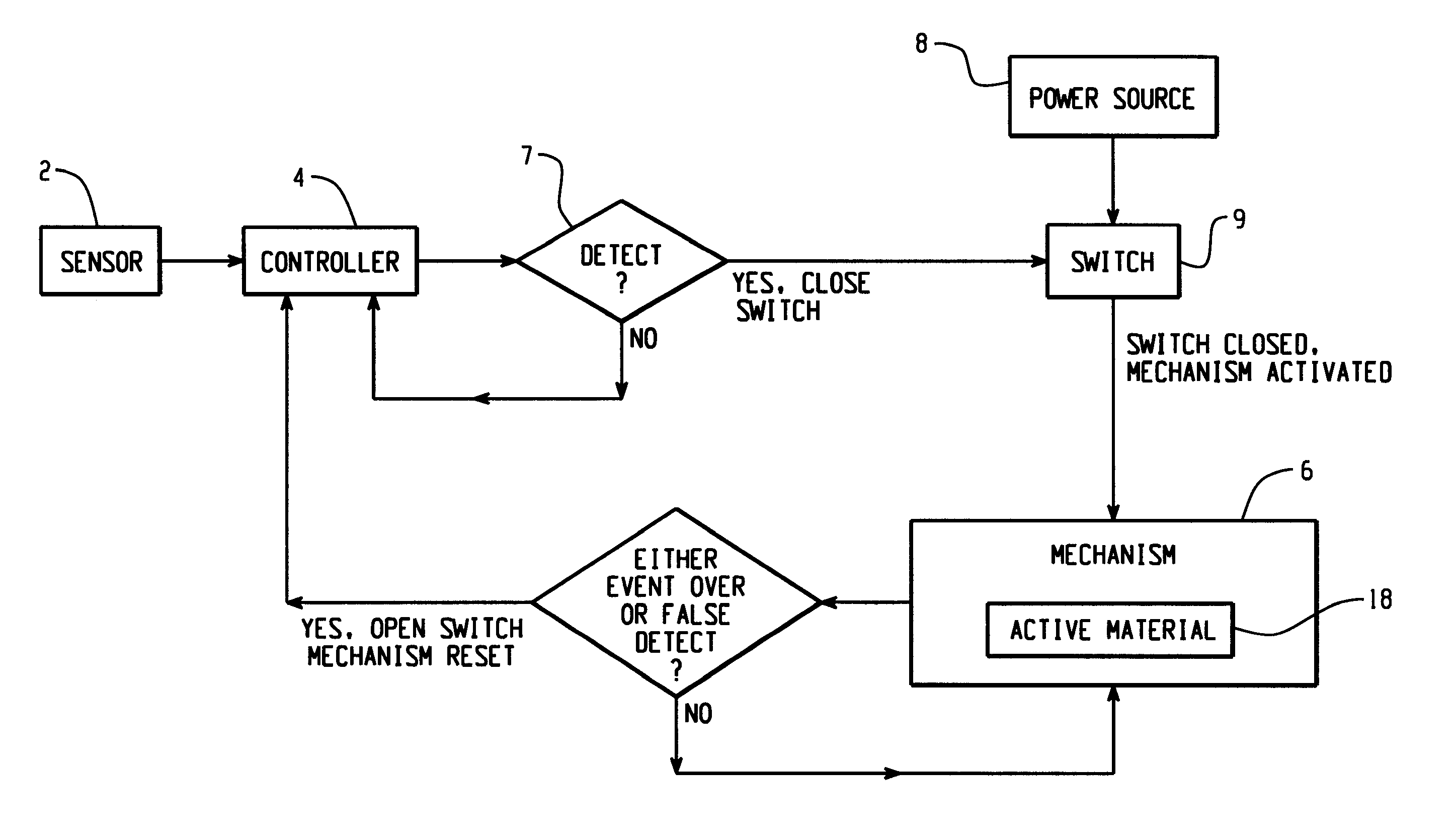
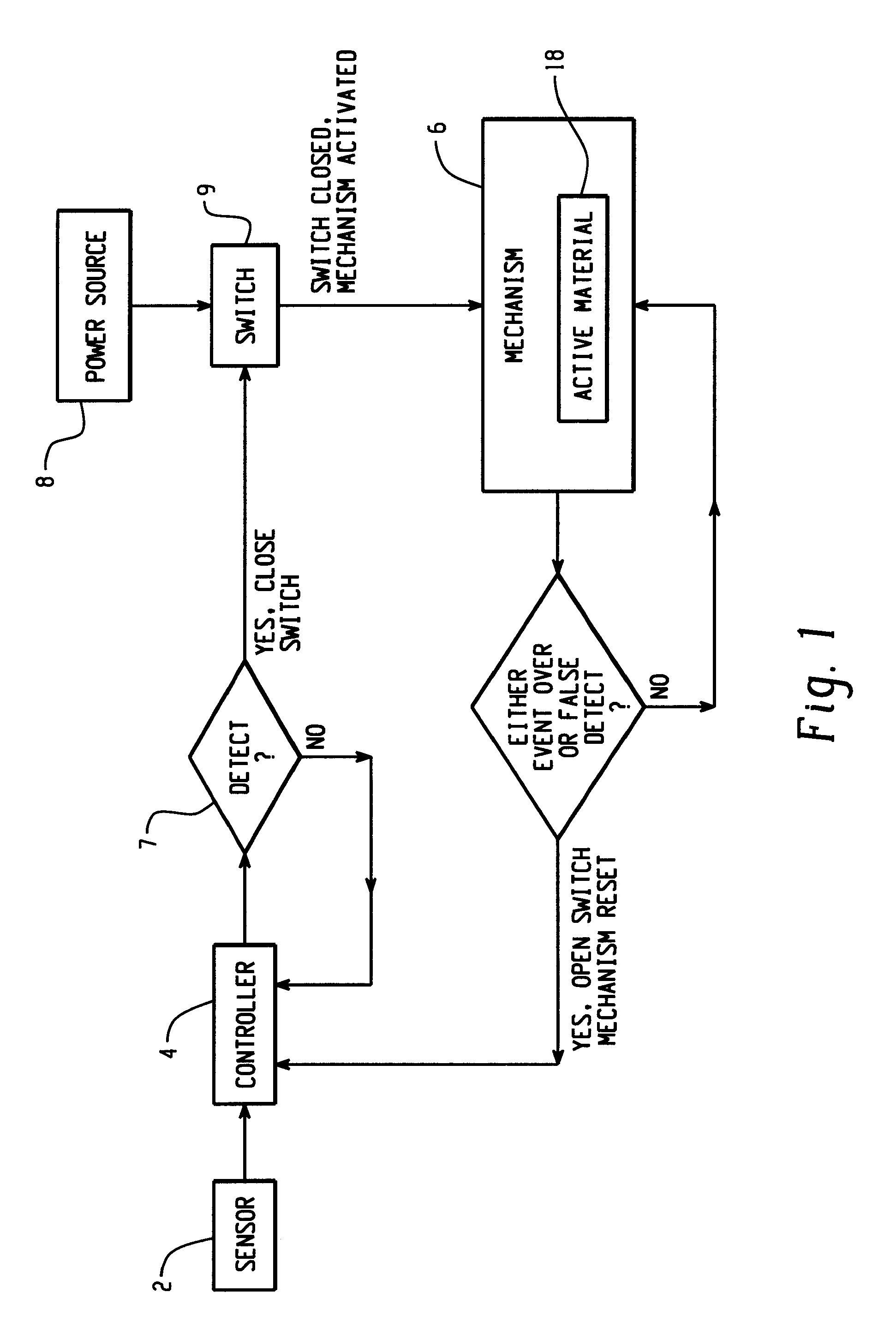
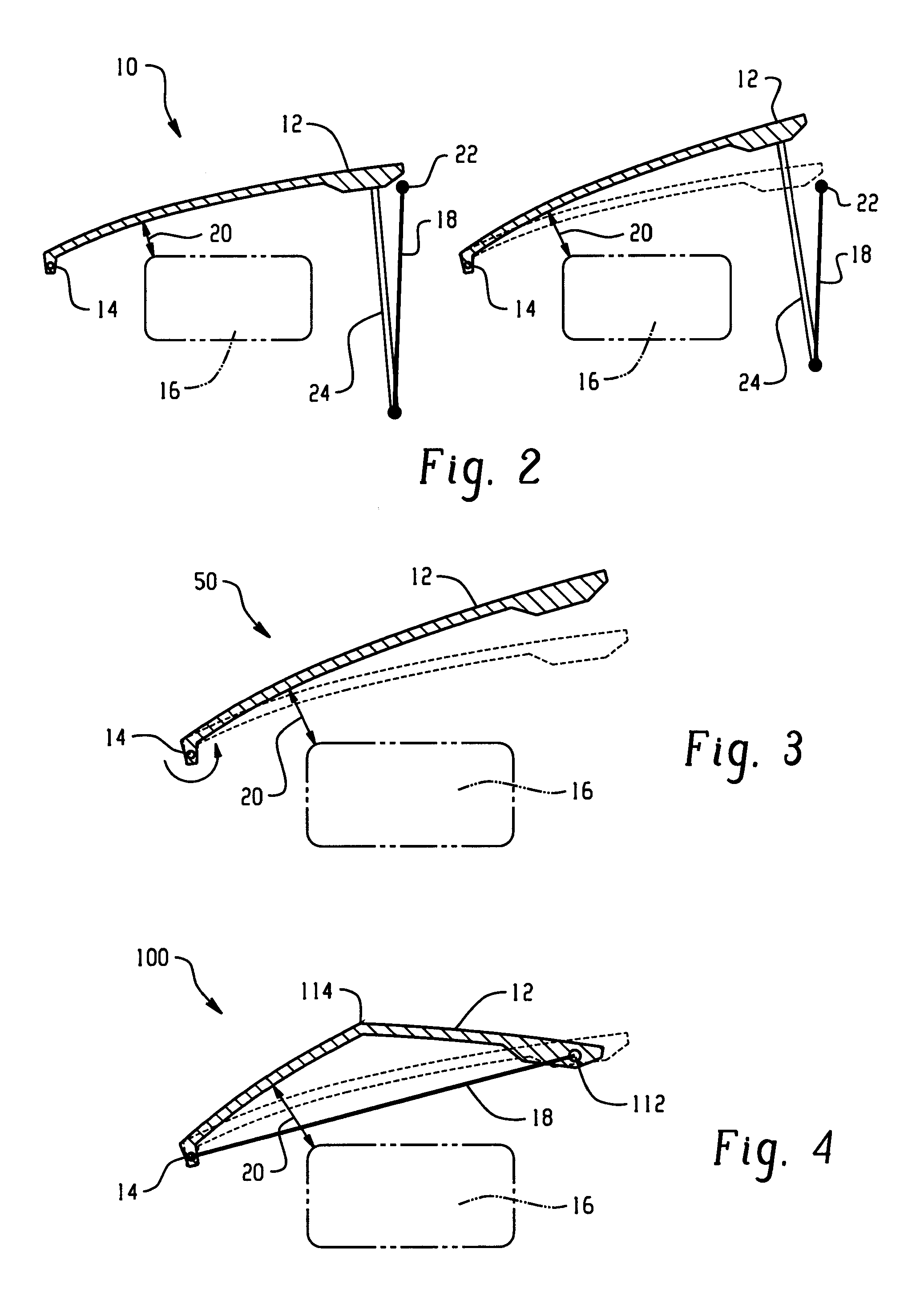
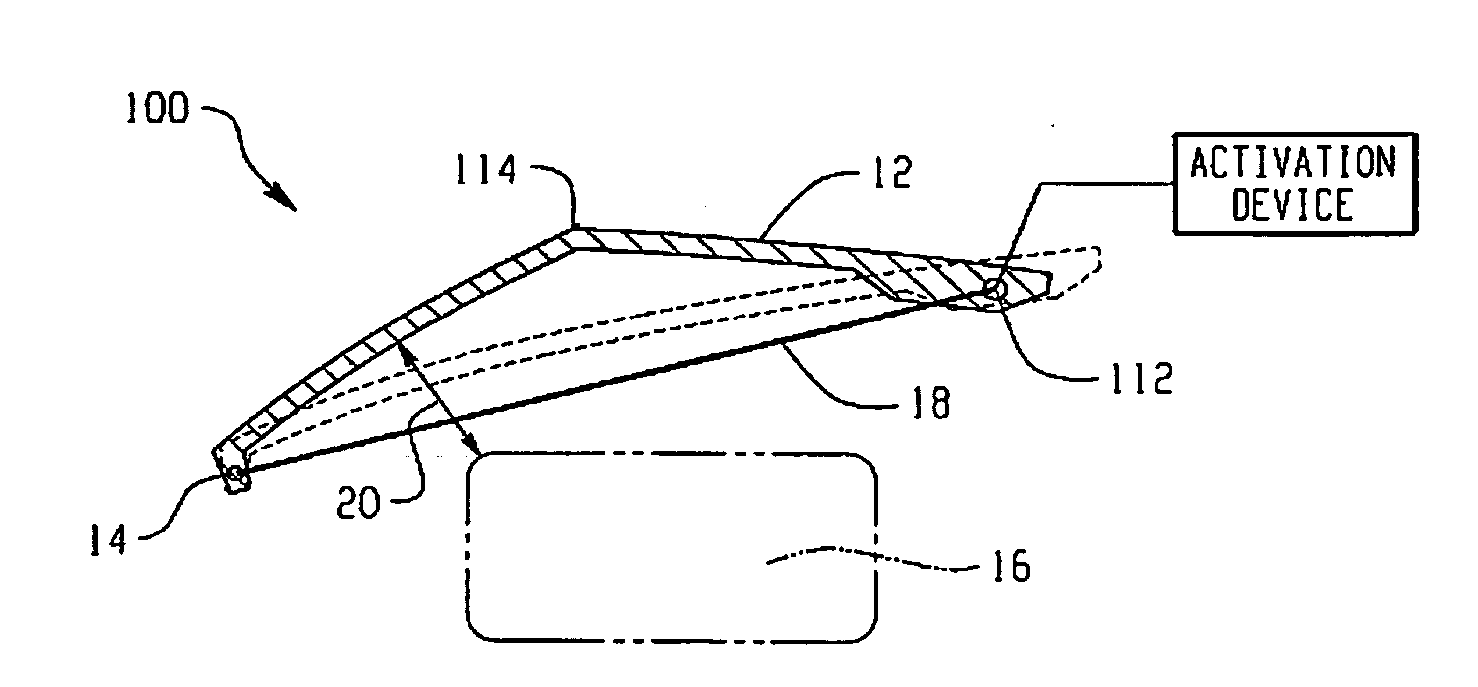
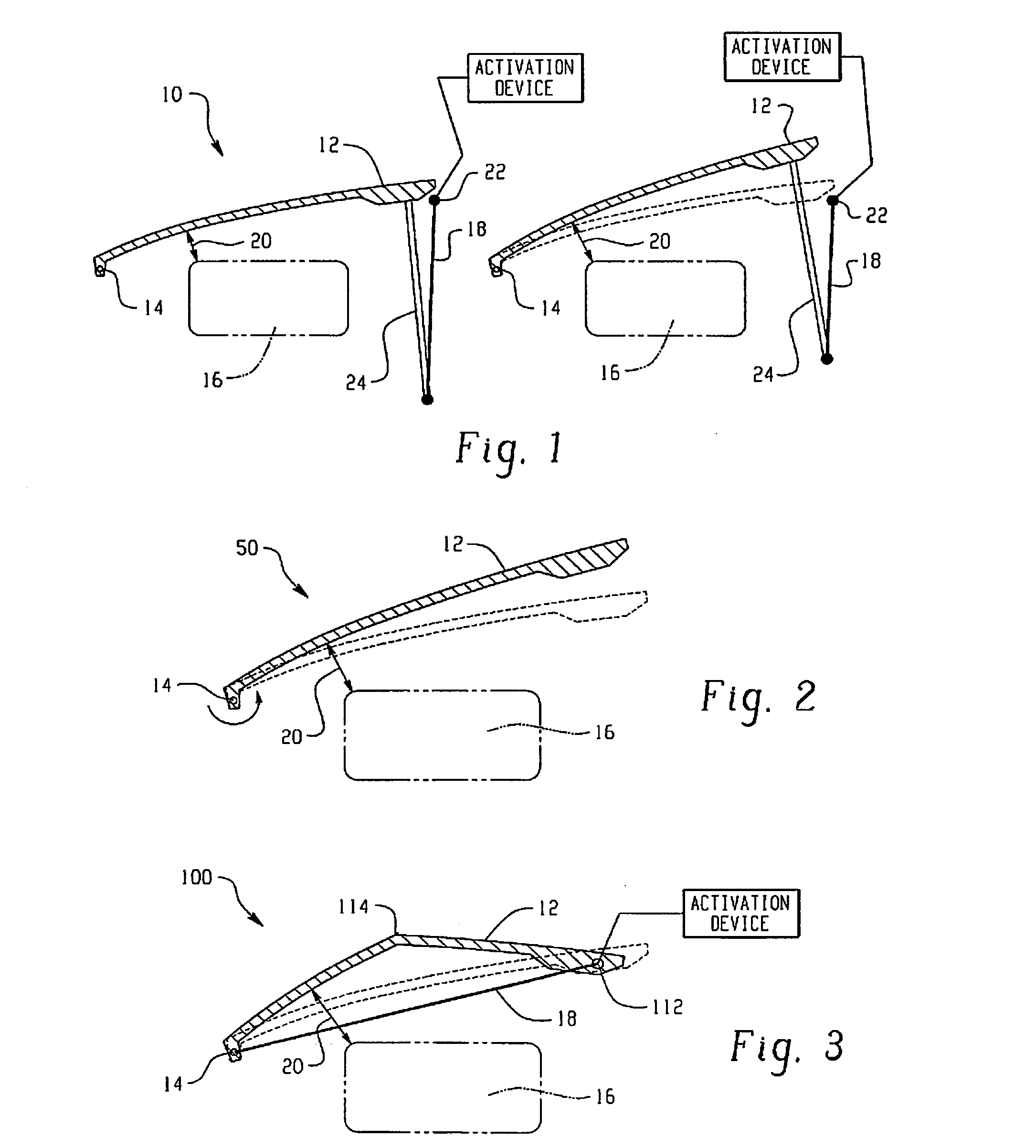
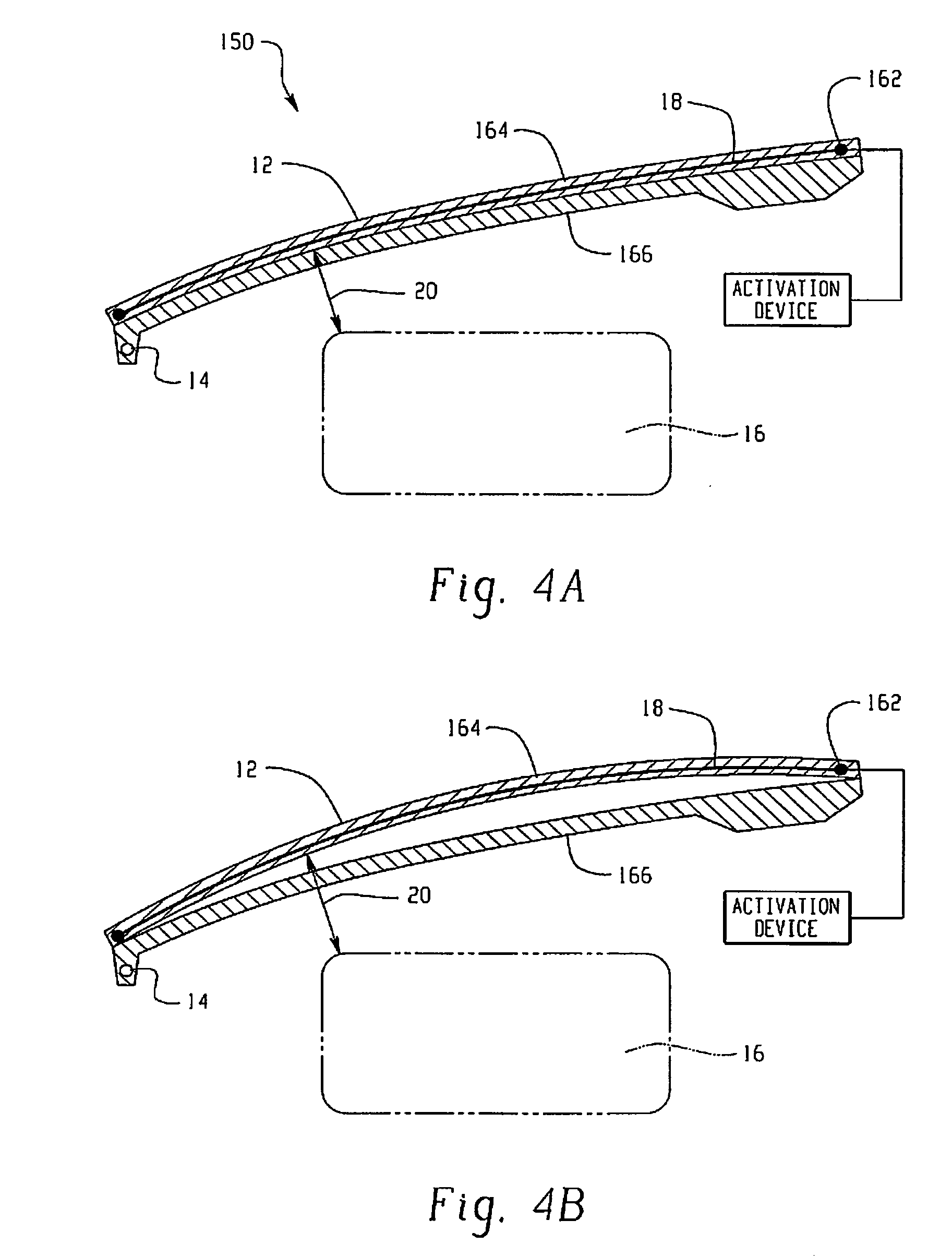
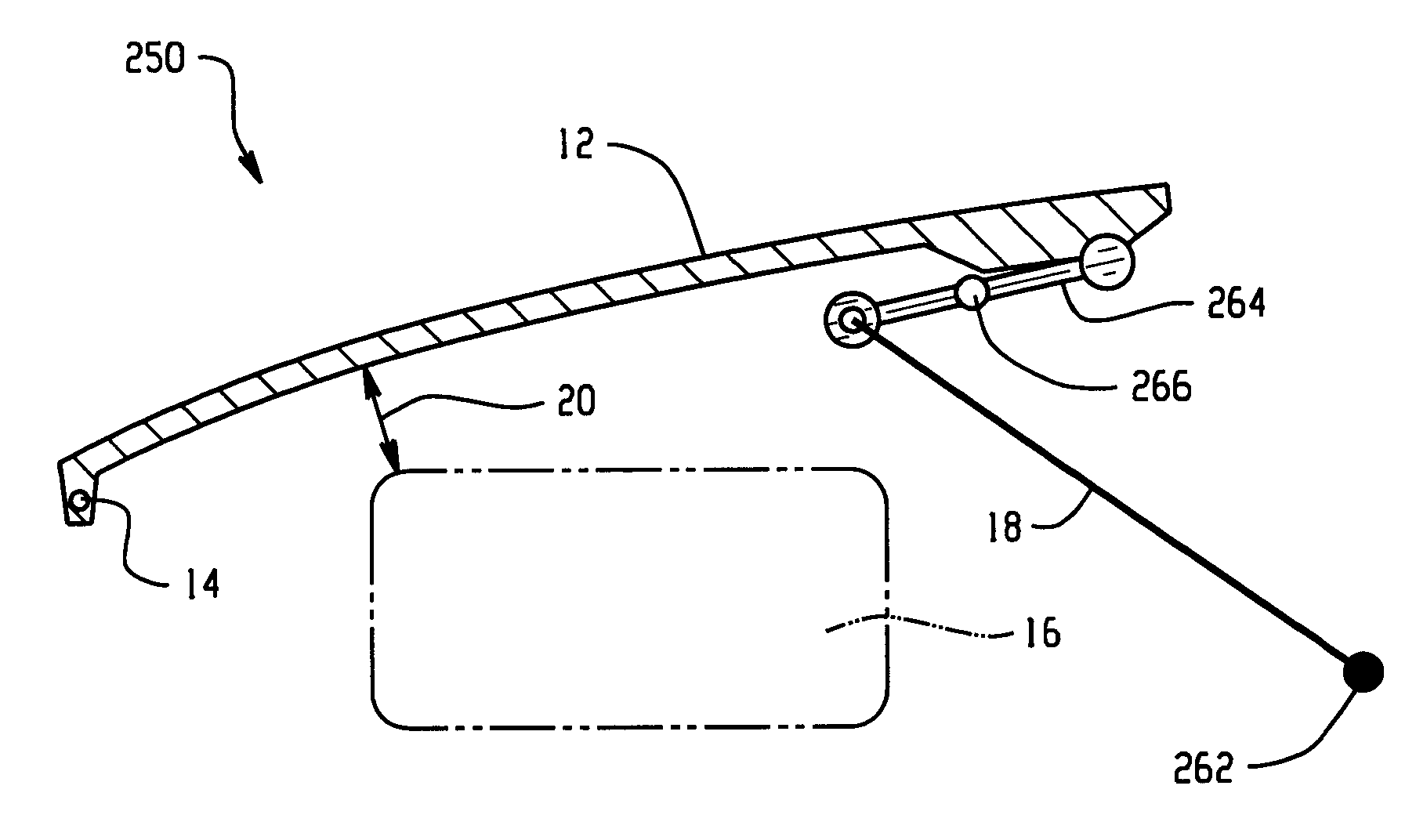
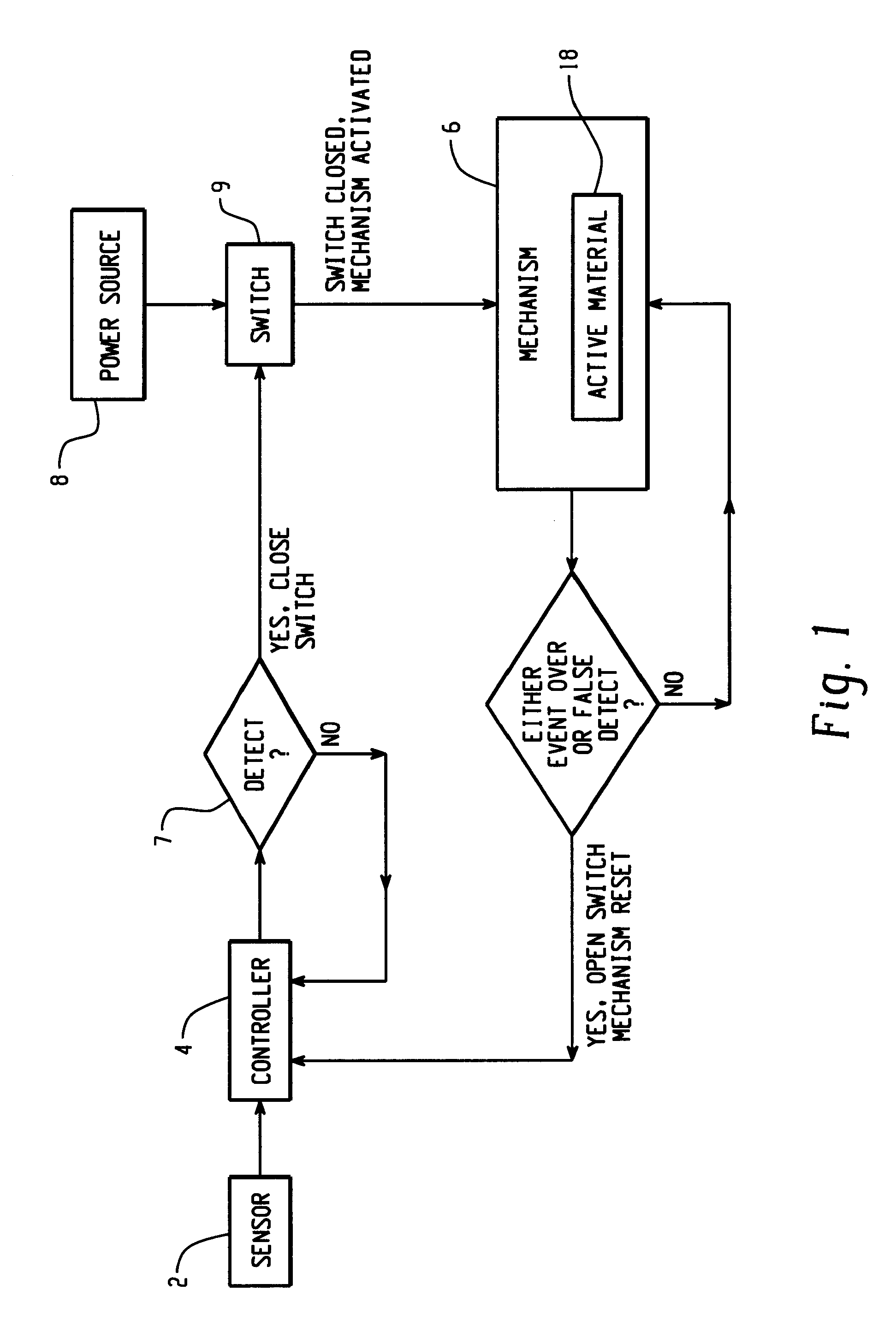
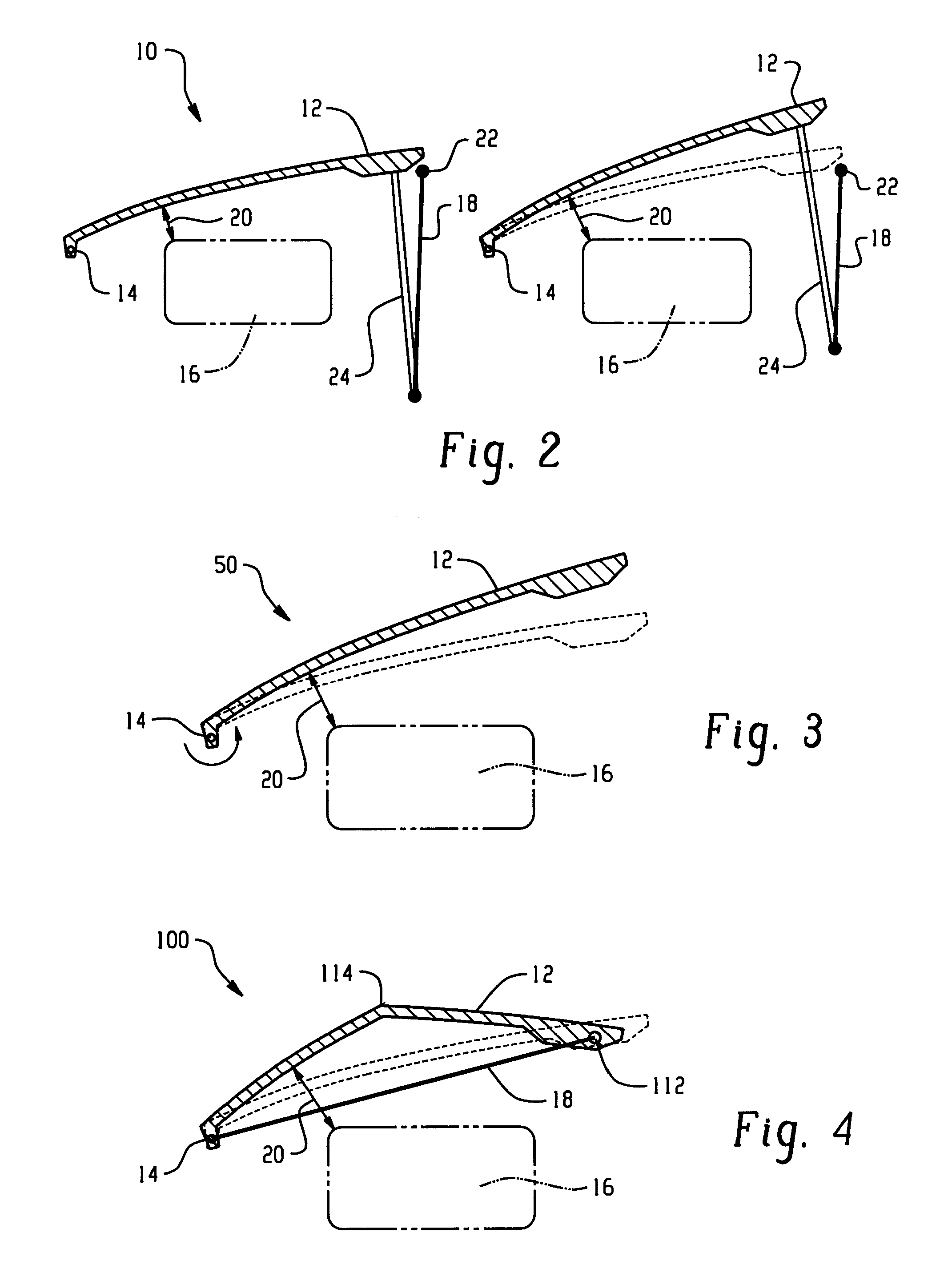
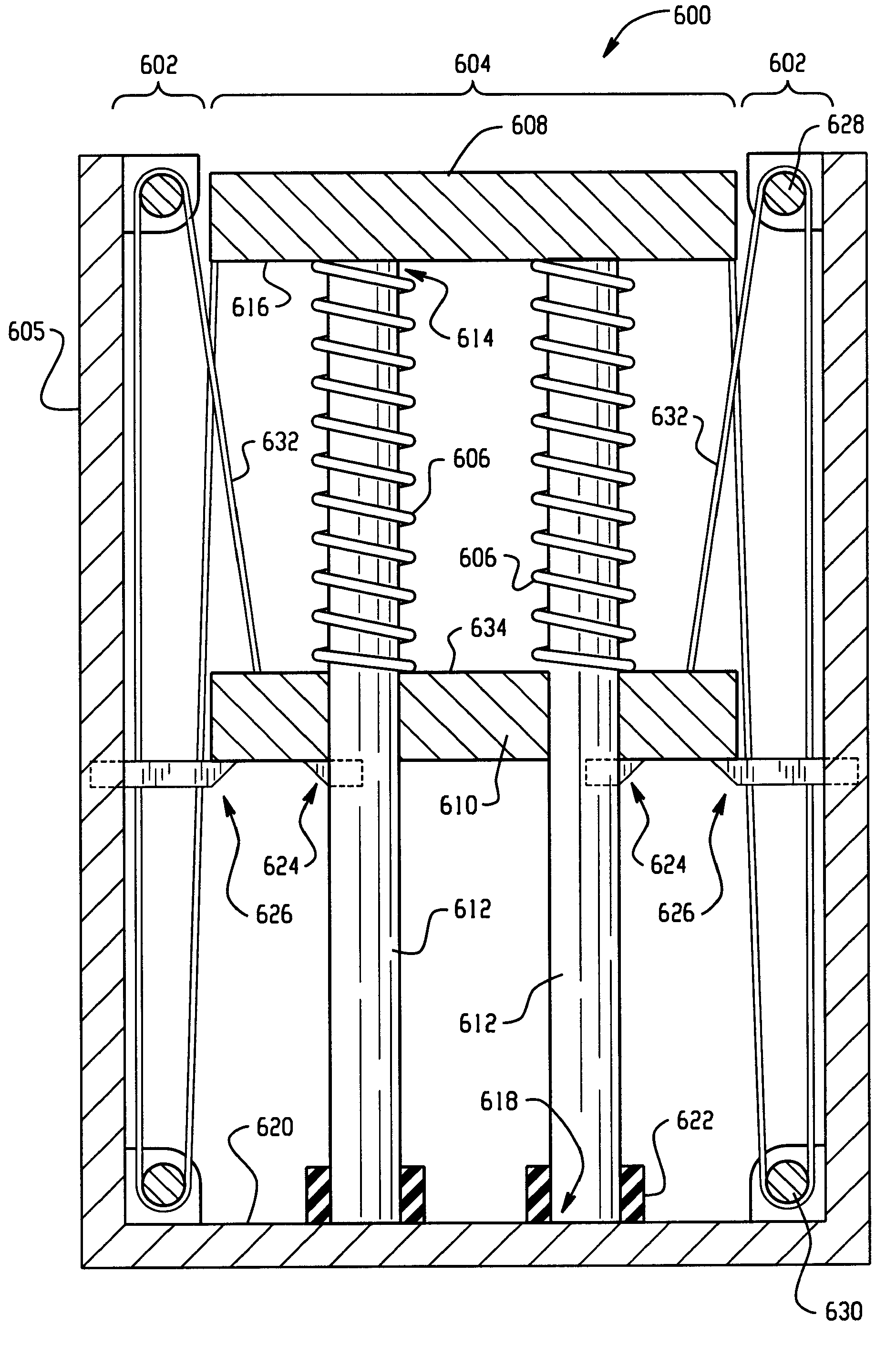
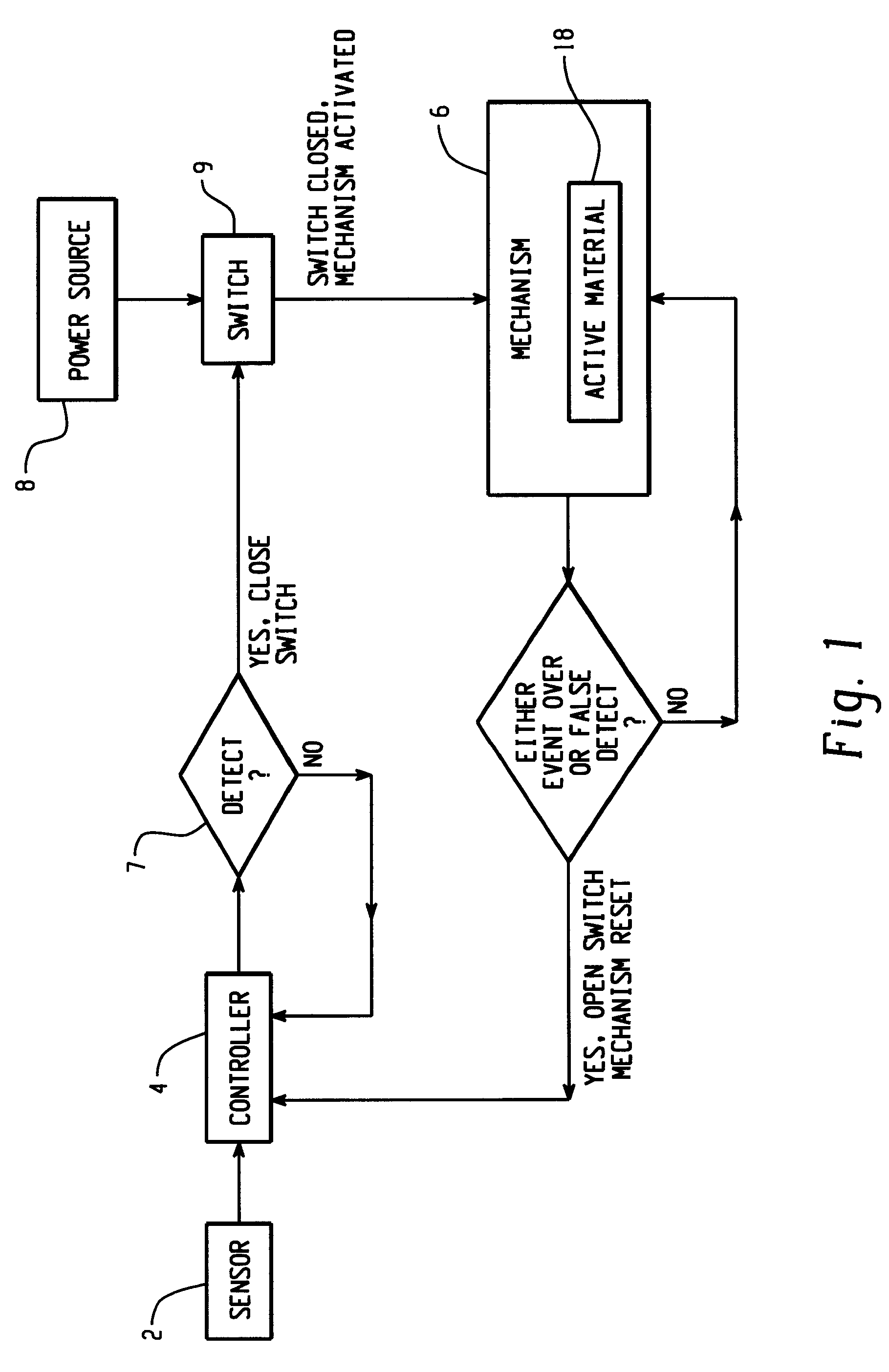
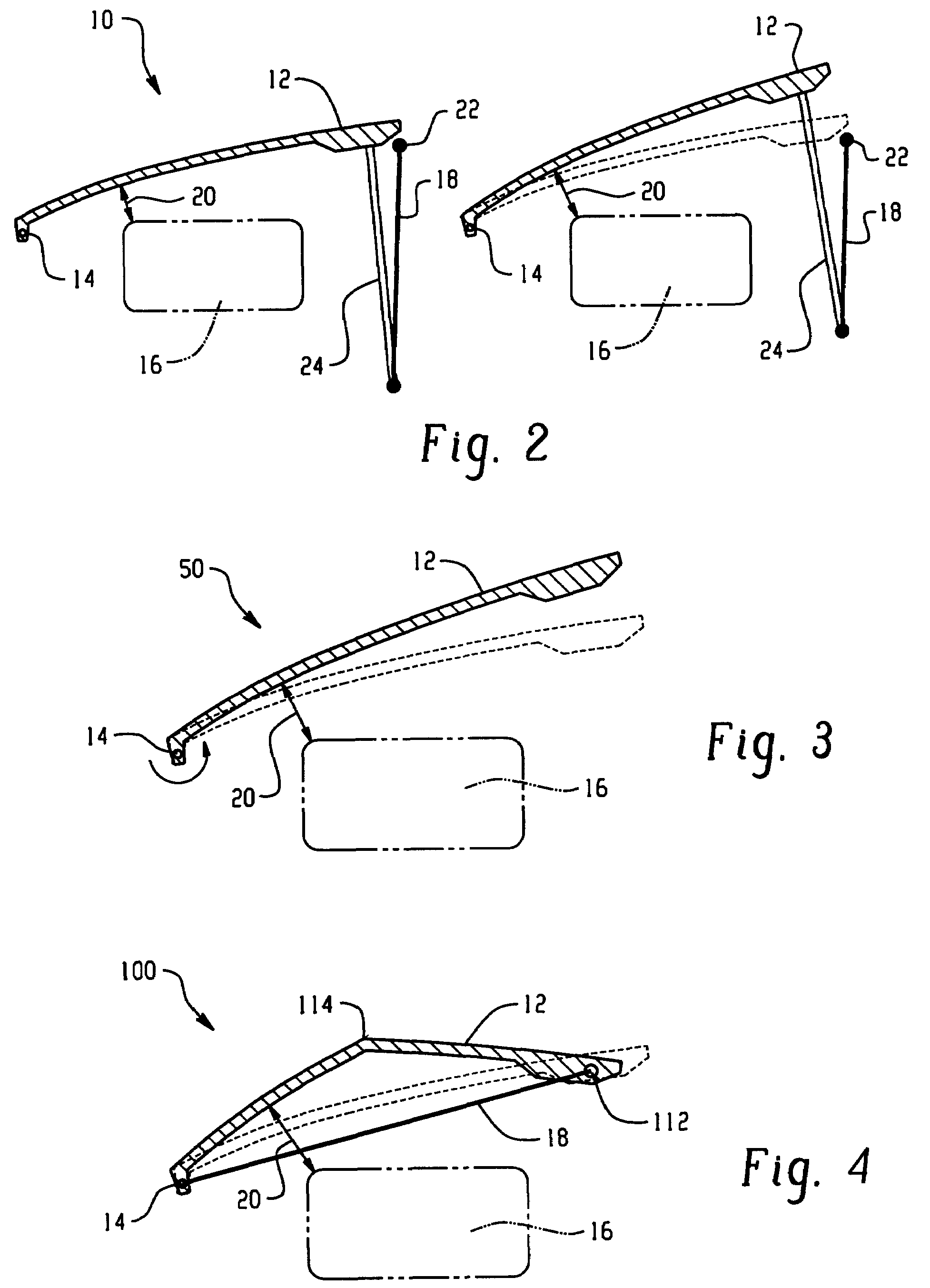
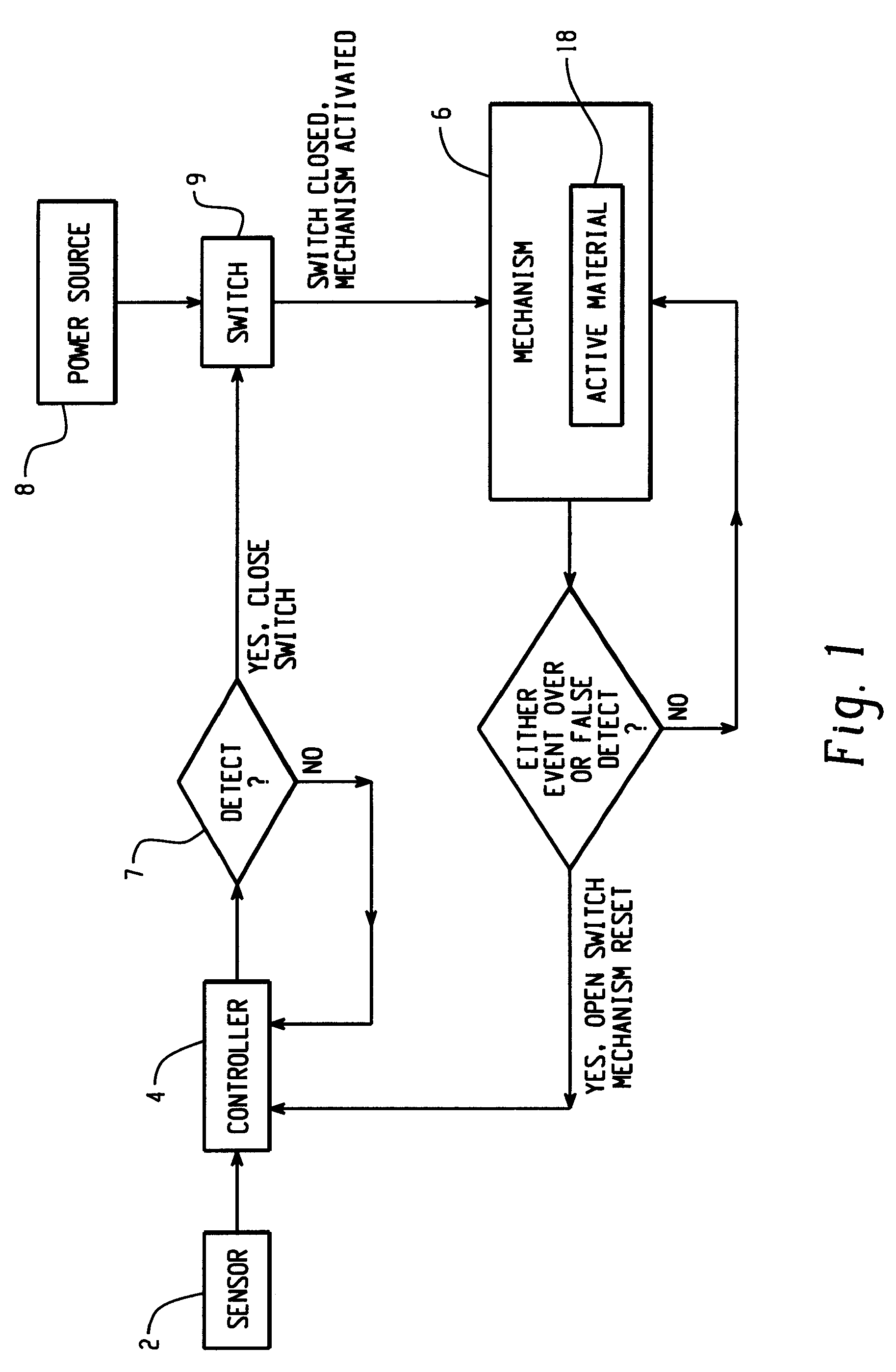
Hood lift mechanisms utilizing active materials and methods of use
InactiveUS7063377B2Clearance distanceIncrease distanceVehicle seatsSuperstructure subunitsIonic polymer–metal compositesEnergy absorption
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC +1
Hood lift mechanisms utilizing active materials and methods of use
A hood lift mechanism for reversibly increasing the energy absorption capability at appropriate force levels of a vehicle hood includes a vehicle hood; an active material in operative communication with the vehicle hood, wherein the active material comprises a shape memory alloy, a ferromagnetic shape memory alloy, a shape memory polymer, a magnetorheological fluid, an electroactive polymer, a magnetorheological elastomer, an electrorheological fluid, a piezoelectric material, an ionic polymer metal composite, or combinations comprising at least one of the foregoing active materials; and an activation device in operative communication with the active material, wherein the activation device is operable to selectively apply an activation signal to the active material and effect a reversible change in a property of the active material, wherein the reversible change results in an increased clearance distance between the vehicle hood and an underlying component.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN +1
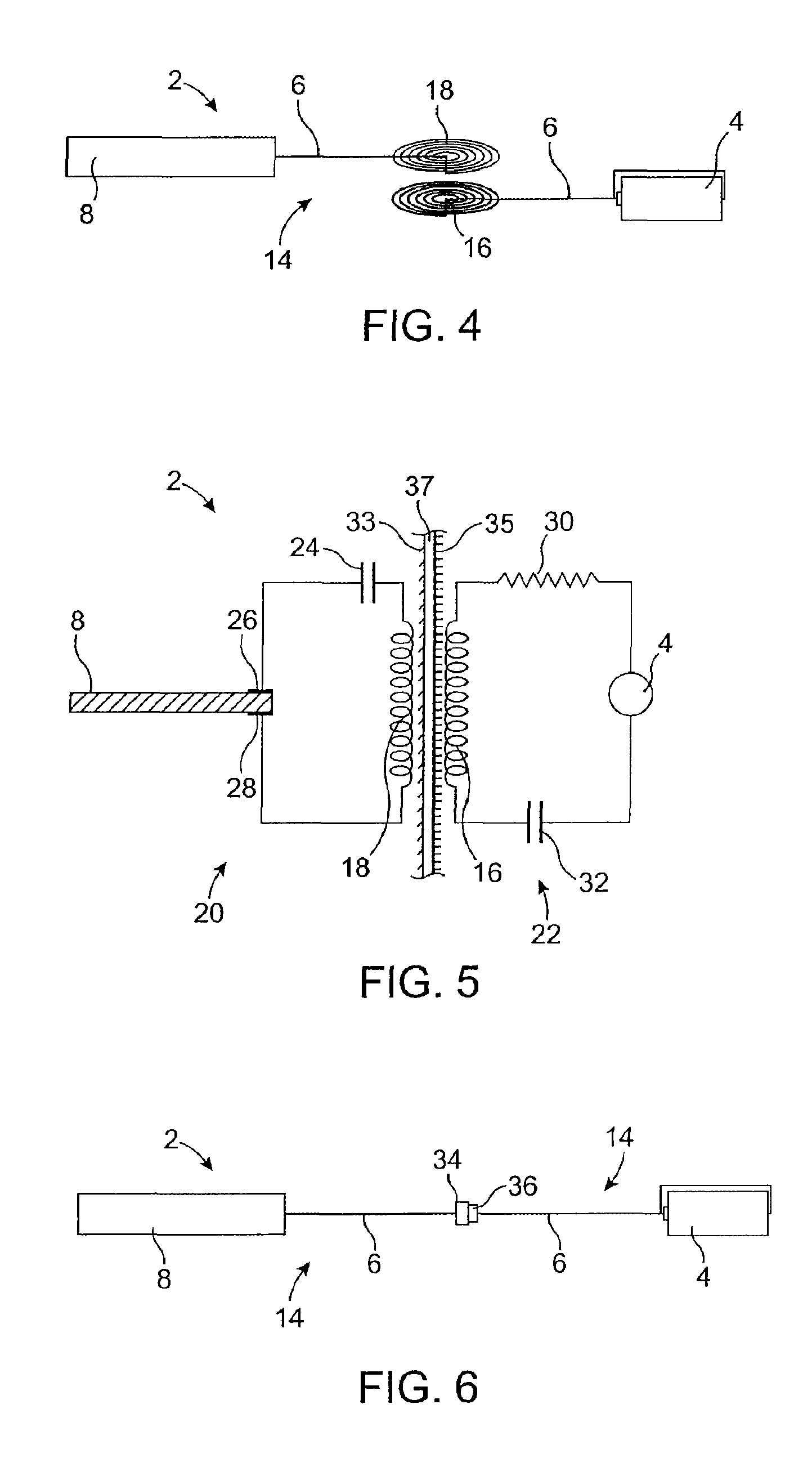
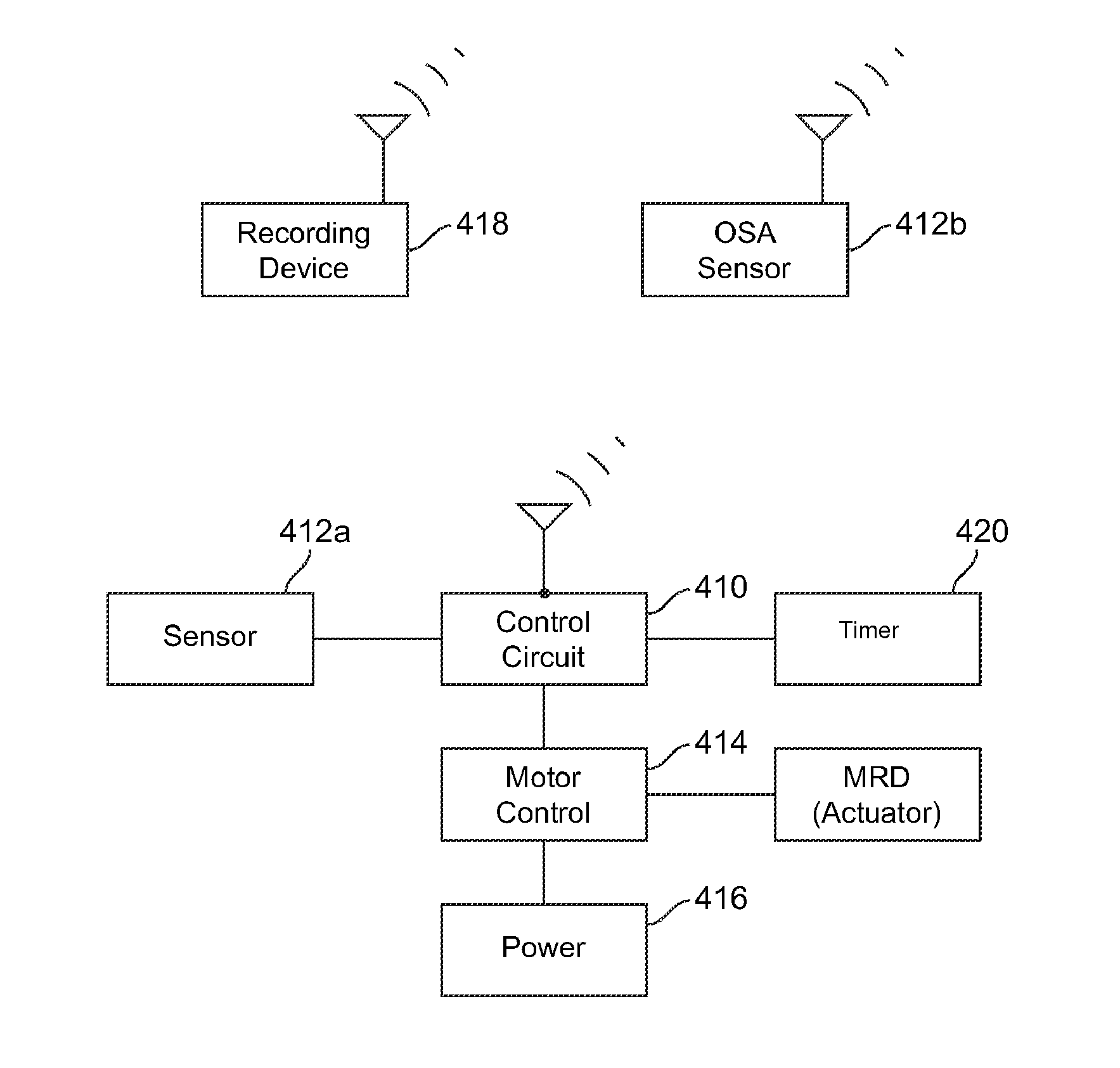
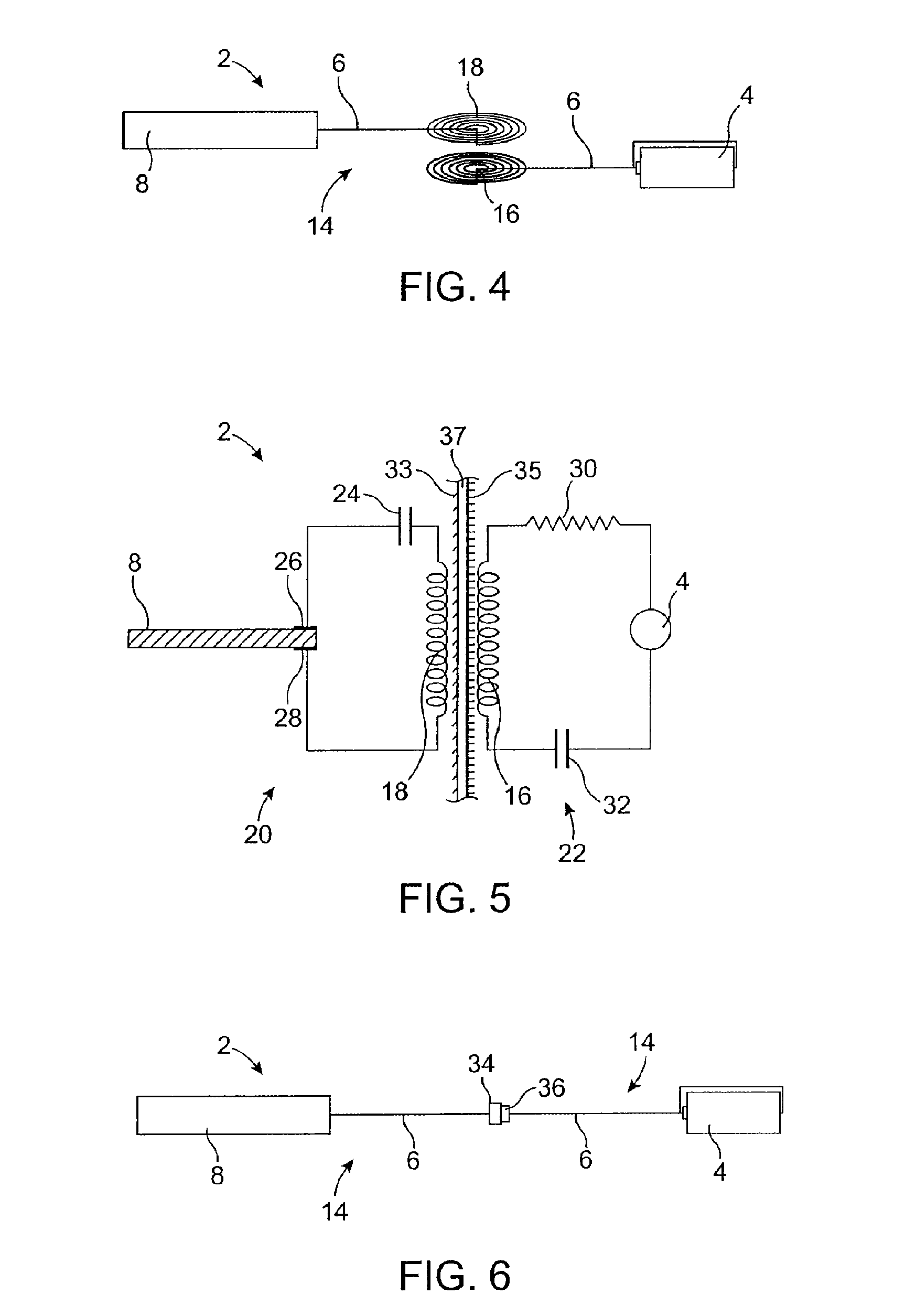
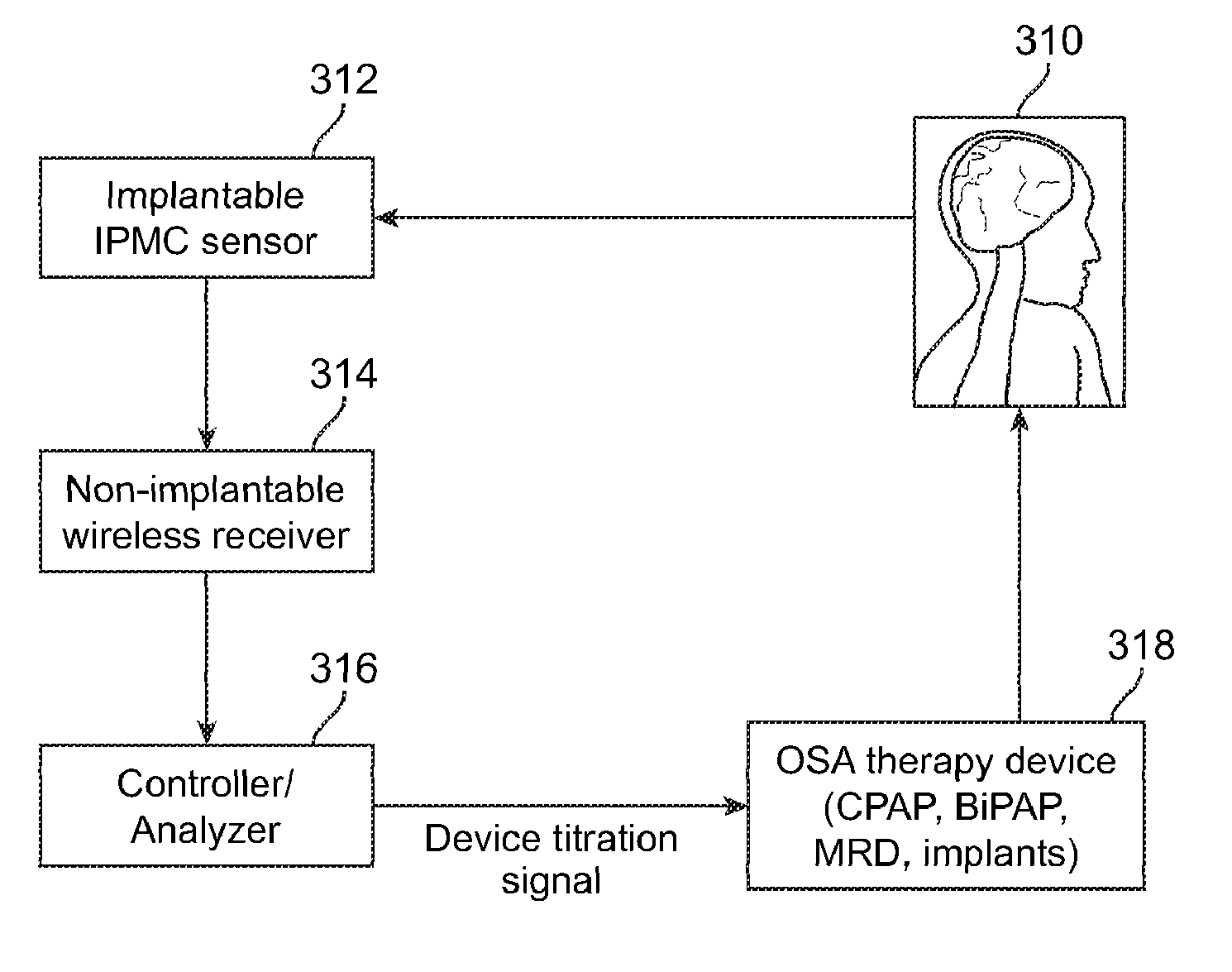
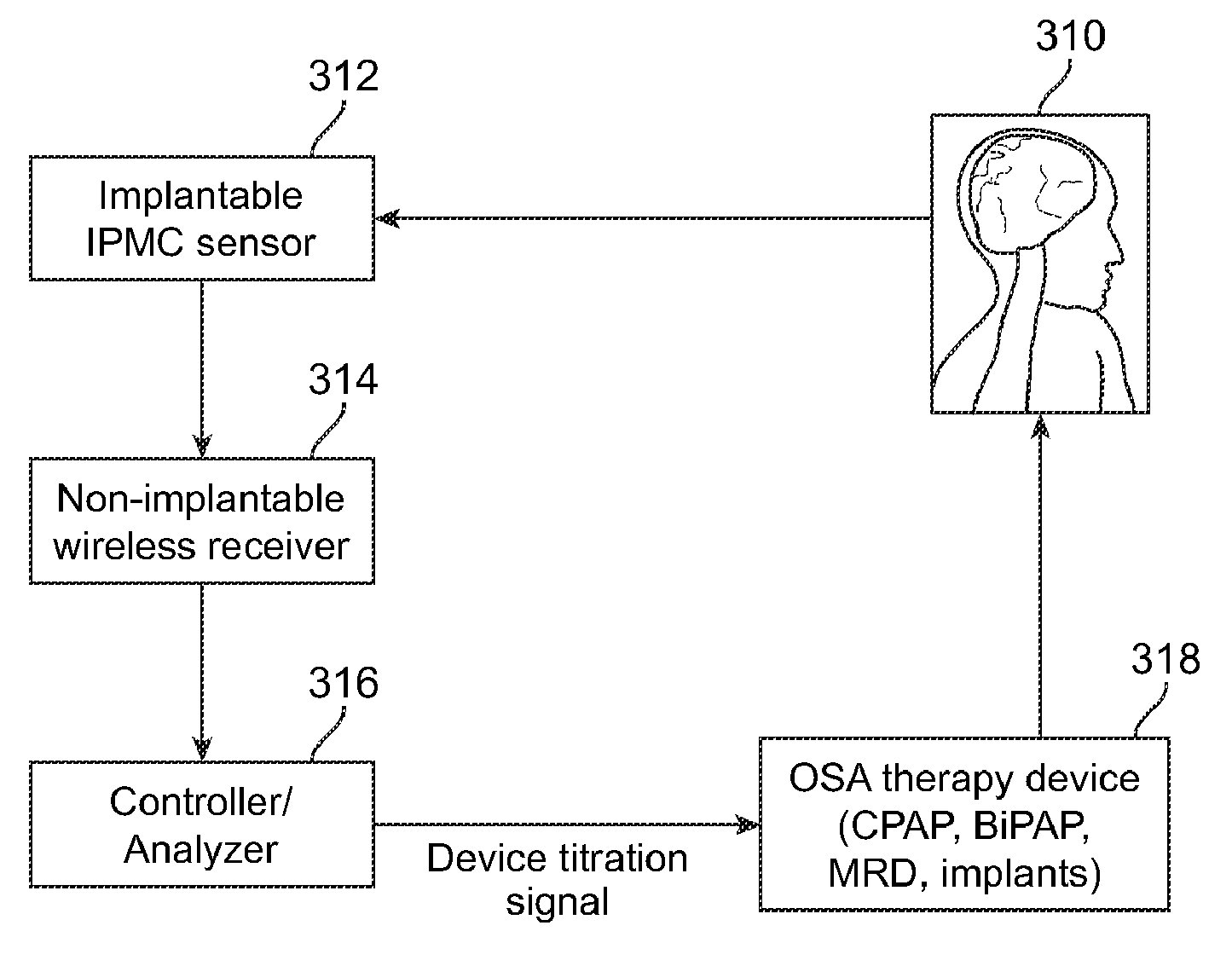
Implantable obstructive sleep apnea sensor
ActiveUS8813753B2Surgical adhesivesInternal osteosythesisIonic polymer–metal compositesSensor system
Owner:MEDTRONIC XOMED INC
Smart mandibular repositioning system
InactiveUS8578937B2Restraining devicesEndoradiosondesIonic polymer–metal compositesPositioning system
Systems and methods for detecting an obstructive sleep apnea event are disclosed herein. The systems and methods may use an electrical output generating ionic polymer metal composite sensor attached to a region in an airway passage in an oral cavity. The electrical output may be wirelessly transmitted as a signal for indication of an obstructive sleep apnea event. The signal may be further processed by a smart mandibular repositioning system for treatment of the obstructive sleep apnea event.
Owner:MEDTRONIC XOMED INC
Control of aerodynamic forces by variable wetted surface morphology
InactiveUS20090001222A1Vehicle body stabilisationServomotor componentsIonic polymer–metal compositesActuator
Systems and methods for providing dynamic control to a vehicle in a dynamic fluid. The systems and methods of the invention relate to one or more morphable surfaces that can be controlled by a controller and an actuator in an active manner to provide asperities that interact with a fluid moving across the morphable surfaces. By controlling the size, shape and location of the asperities, one can exert control authority over the motion of the vehicle relative to the fluid, including a speed, a direction and an attitude of the vehicle. Examples of materials that provide suitable morphable surfaces include ionic polymer metal composites and shape memory polymers, both of which types of material are commercially available. Useful morphable surface systems have been examined and are described.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
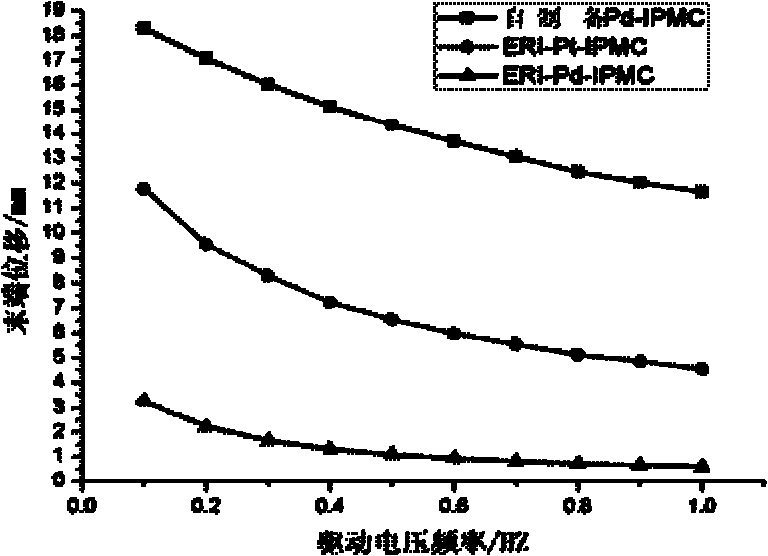
Preparation process of palladium electrode ion polymer and metal composite
InactiveCN102168260AIncrease profitImprove electrical actuation performanceLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingIonic polymer–metal compositesChemical plating
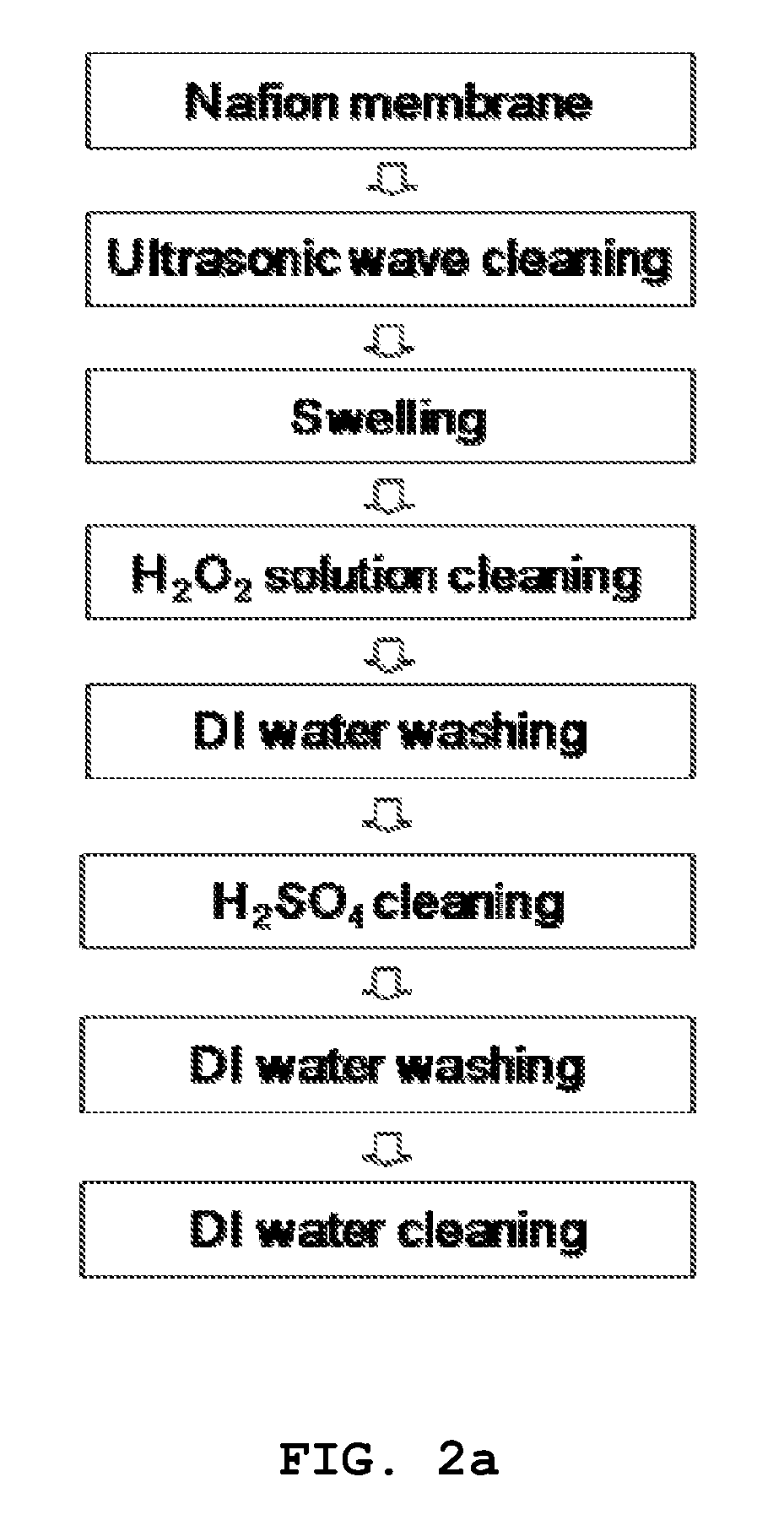
The invention discloses a preparation process of a palladium electrode ion polymer and metal composite, which is used for preparing a palladium metal electrode IPMC (Ion Polymer Metal Composite) by using immersion reduction plating and chemical plating methods in which an ion exchange membrane is used as a matrix material and [Pd (NH3)4] C12 is used as a main salt. The preparation process comprises the following four main steps of: (1) pretreatment of the matrix membrane: carrying out roughening, surface cleaning, foreign ion removal and full swelling on the matrix membrane; (2) immersion reduction plating including two processes, i.e., ion exchange and ion reduction: subjecting a pretreated Nafion membrane to repeated palladium ion immersion and exchange, and reducing the pretreated Nafion membrane with NaBH4 by adopting ultrasonic waves to form palladium metals on the surface and the internal surface of the ion exchange membrane; (3) chemical plating: wherein the thickening electrodes on the outer surface of a core material to compact internal surface electrodes by using an improved chemical plating method; and (4) postprocessing of the composite. The preparation process has a higher popularization value due to relatively improved efficiency, relatively lower cost and excellent actuation response.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Auto-titration of positive airway pressure machine with feedback from implantable sensor
ActiveUS8336553B2RespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesPositive airway pressureElectricity
Systems and methods for detecting and treating an obstructive sleep apnea event are disclosed herein. The systems and methods may use an electrical output generating ionic polymer metal composite sensor attached to a region in an airway passage in an oral cavity. The electrical output may be wirelessly transmitted as a signal for indication of an obstructive sleep apnea event. The signal may be further analyzed by a positive airway pressure system for treatment of the obstructive sleep apnea event.
Owner:MEDTRONIC XOMED INC
Control device and method of cooling fan of ATCA (Advanced Telecom Computing Architecture) system
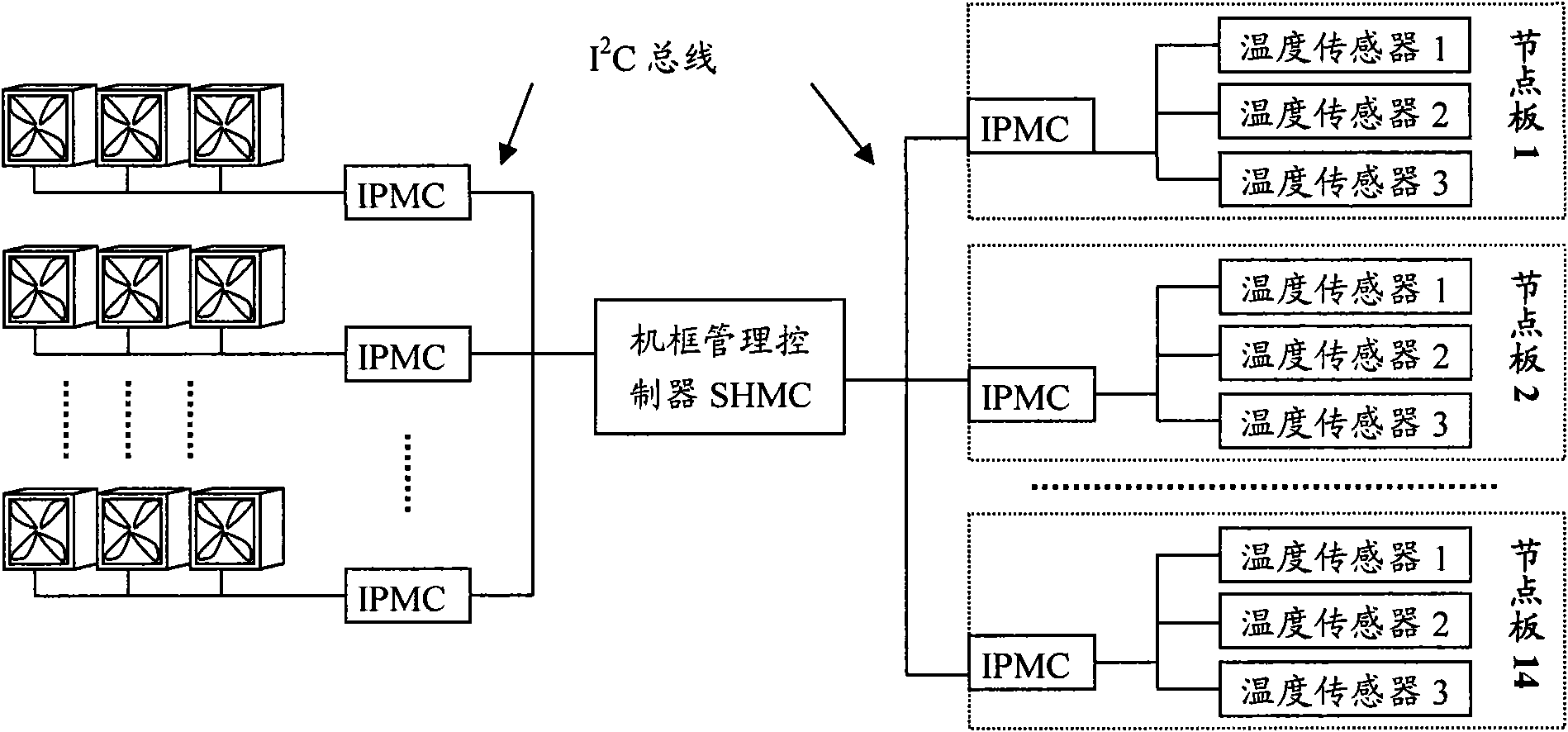
ActiveCN101871465AReduce noise pollutionGuaranteed Cooling RequirementsPump controlCooling/ventilation/heating modificationsIonic polymer–metal compositesGusset plate
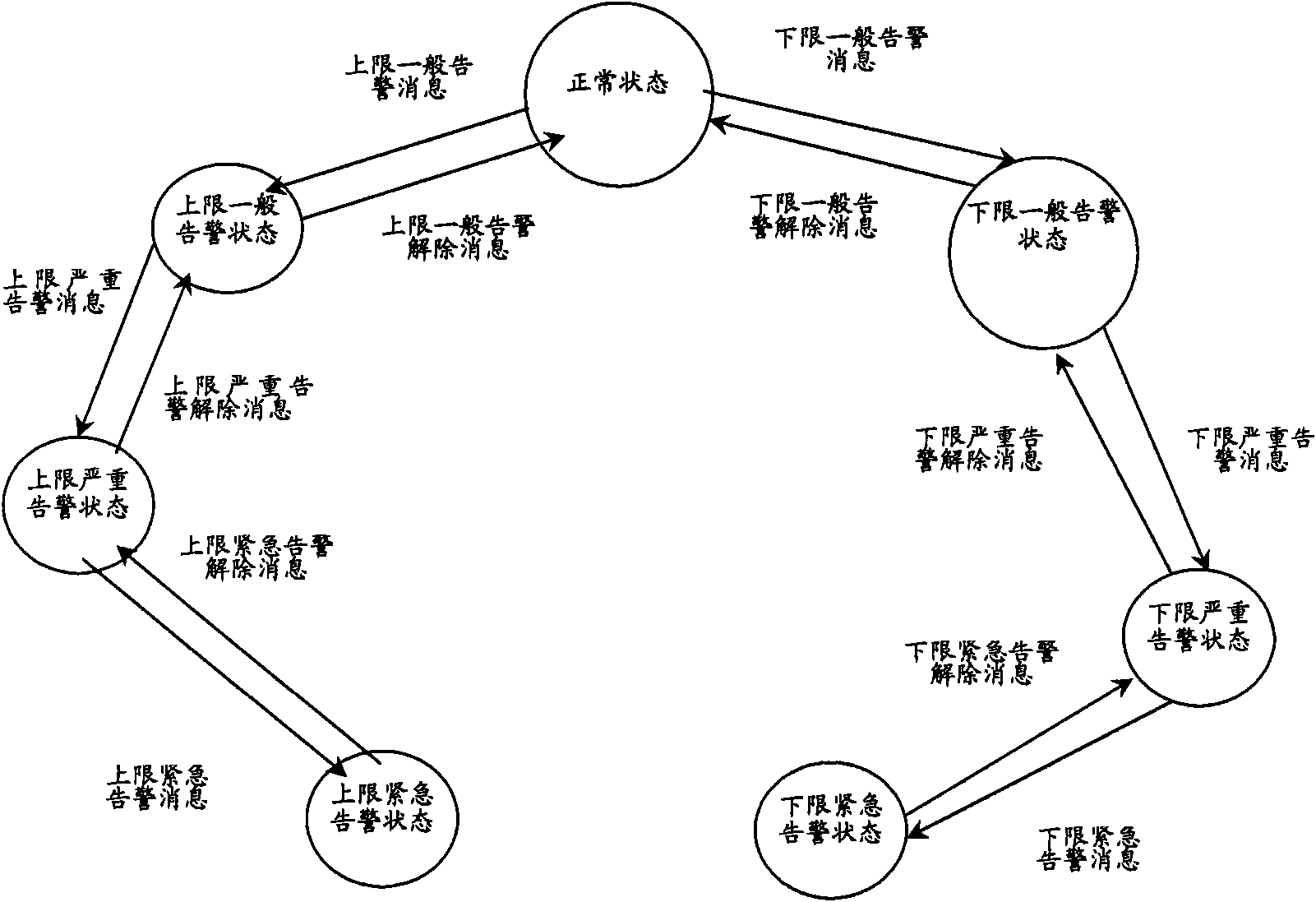
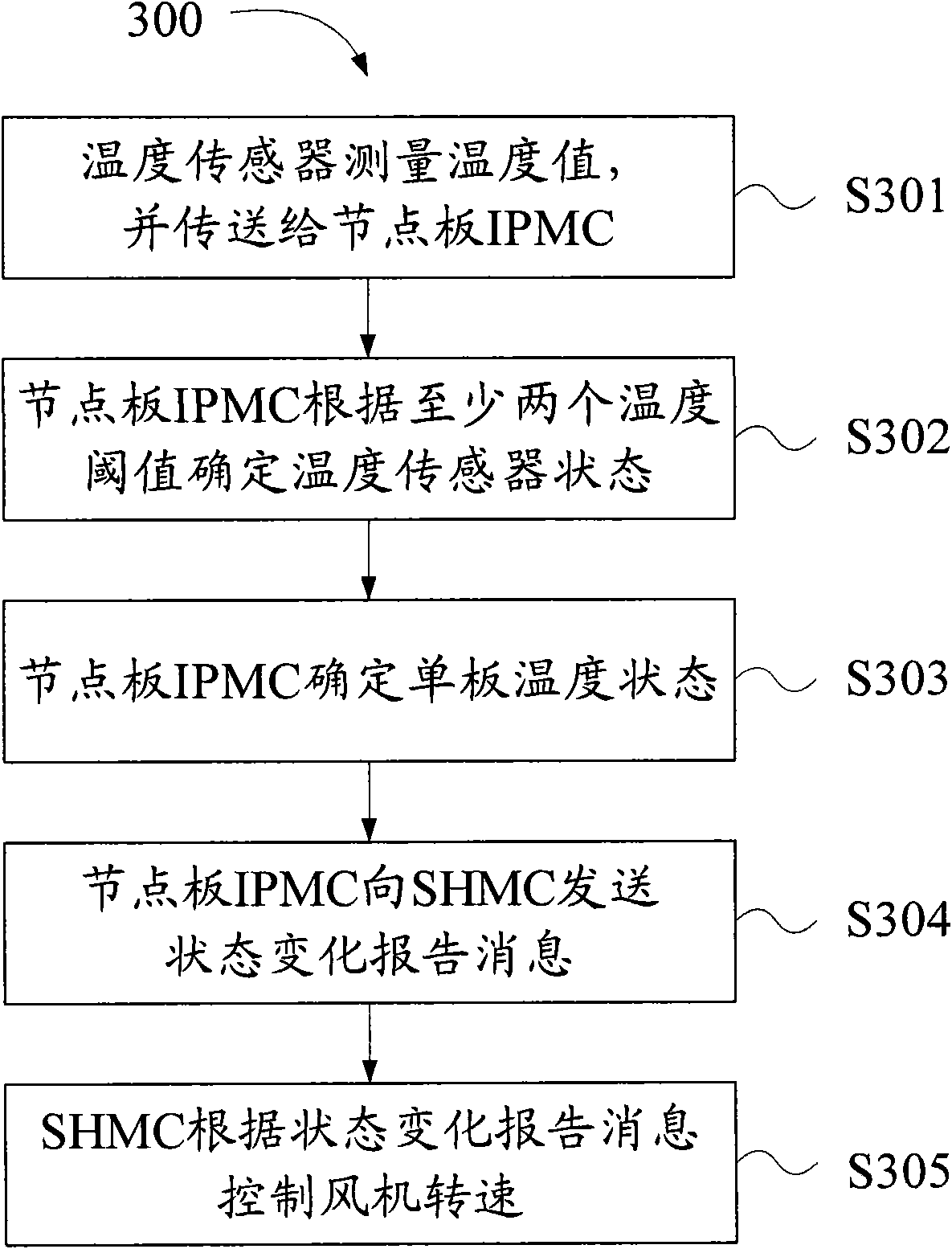
The invention provides control device and method of a cooling fan of an ATCA (Advanced Telecom Computing Architecture) system. The device comprises temperature sensors, a gusset plate IPMC (Ionic Polymer-Metal Composite) connected with the temperature sensors, and an SHMC (Shelf Management Controller) connected with the gusset plate IPMC, wherein the temperature sensors are used for measuring the temperature values of the areas where the temperature sensors are arranged and transmitting the temperature values to the gusset plate IPMC; the gusset plate IPMC is used for determining the states of the temperature sensors according to the temperature values of the temperature sensors on the gusset plate IPMC and temperature threshold values, determining single-plate temperature states and sending a state change report message to the SHMC according to the changes of the single-plate temperature states, and each temperature sensor at least comprises two temperature threshold values; and the SHMC is used for controlling the speed of the cooling fan according to the state change report message. By adopting the device and the method, the optimal control on the cooling fan can be realized, and energy saving control and noise reduction are realized while the cooling requirement of the system is guaranteed.
Owner:DATANG MOBILE COMM EQUIP CO LTD
Dynamic roughness for aerodynamic applications
InactiveUS20090065650A1Aircraft stabilisationBoundary layer controlsIonic polymer–metal compositesEngineering
Systems and methods for providing dynamic control to a surface immersed in a dynamic fluid. The systems and methods of the invention relate to one or more morphable surfaces that can be control in an active manner to provide asperities that interact with a fluid moving across the morphable surfaces. By controlling the size, shape and location of the asperities, one can exert control authority over the motion of the surface relative to the fluid. Examples of materials that provide suitable morphable surfaces include ionic polymer metal composites and shape memory polymers, both of which types of material are commercially available. Useful morphable surface systems have been examined and are described.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Integrated actuator sensor structure
ActiveUS20100109595A1Piezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesElement comparisonElectricityIonic polymer–metal composites
An integrated sensory actuator (10) which uses an electroactive polymer is provided. The sensory actuator is comprised of an actuating member (12) made of an ionic polymer-metal composite; a sensing member (14) made of a piezoelectric material; and an insulating member (16) interposed between the actuating member and the sensing member. The sensory actuator may further include a compensation circuit adapted to receive a sensed signal from the sensing member and an actuation signal from the actuating member and compensate the sensed signal for feedthrough coupling between the actuating member and the sensing member.
Owner:BOARD OF TRUSTEES OPERATING MICHIGAN STATE UNIV
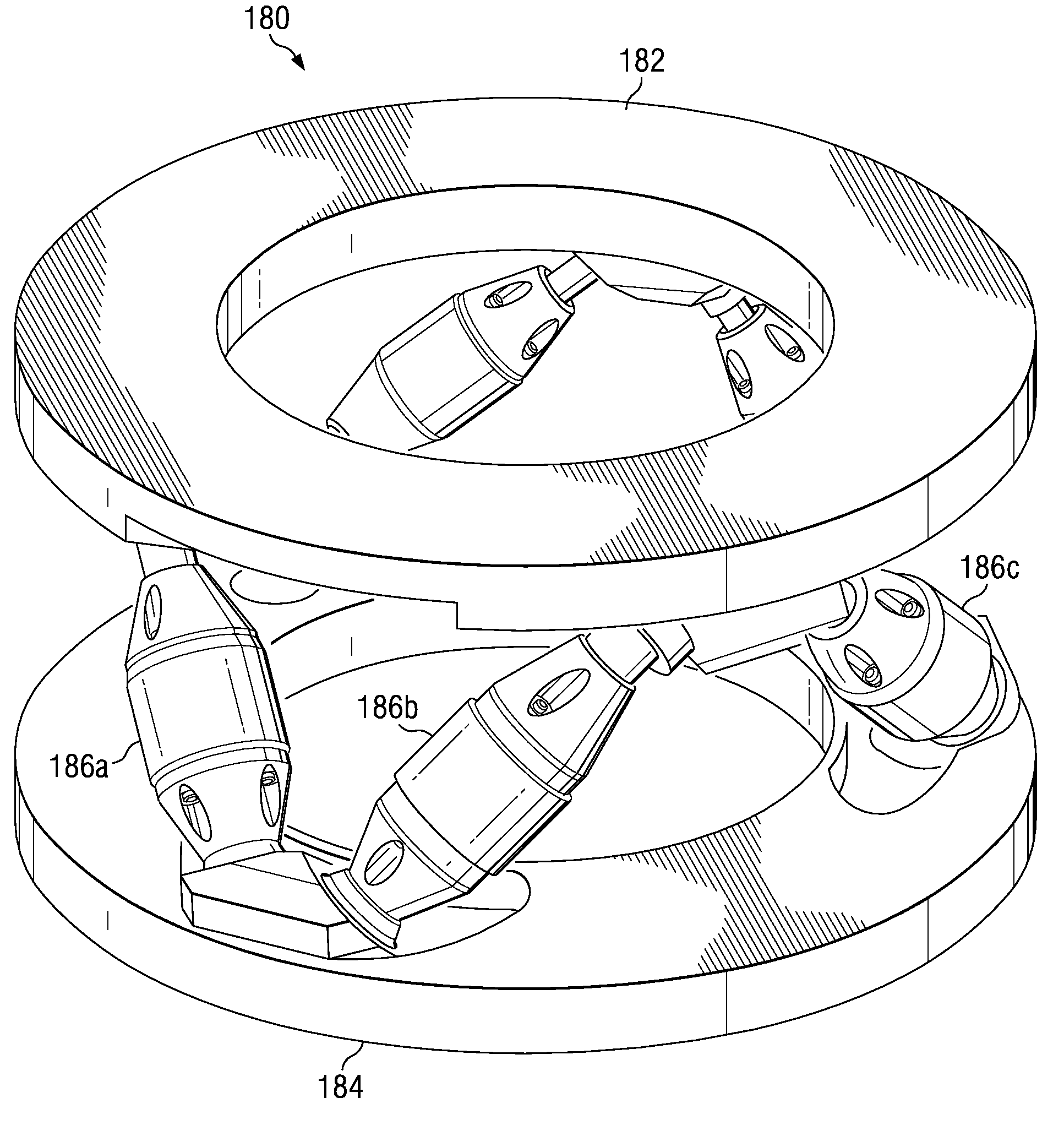
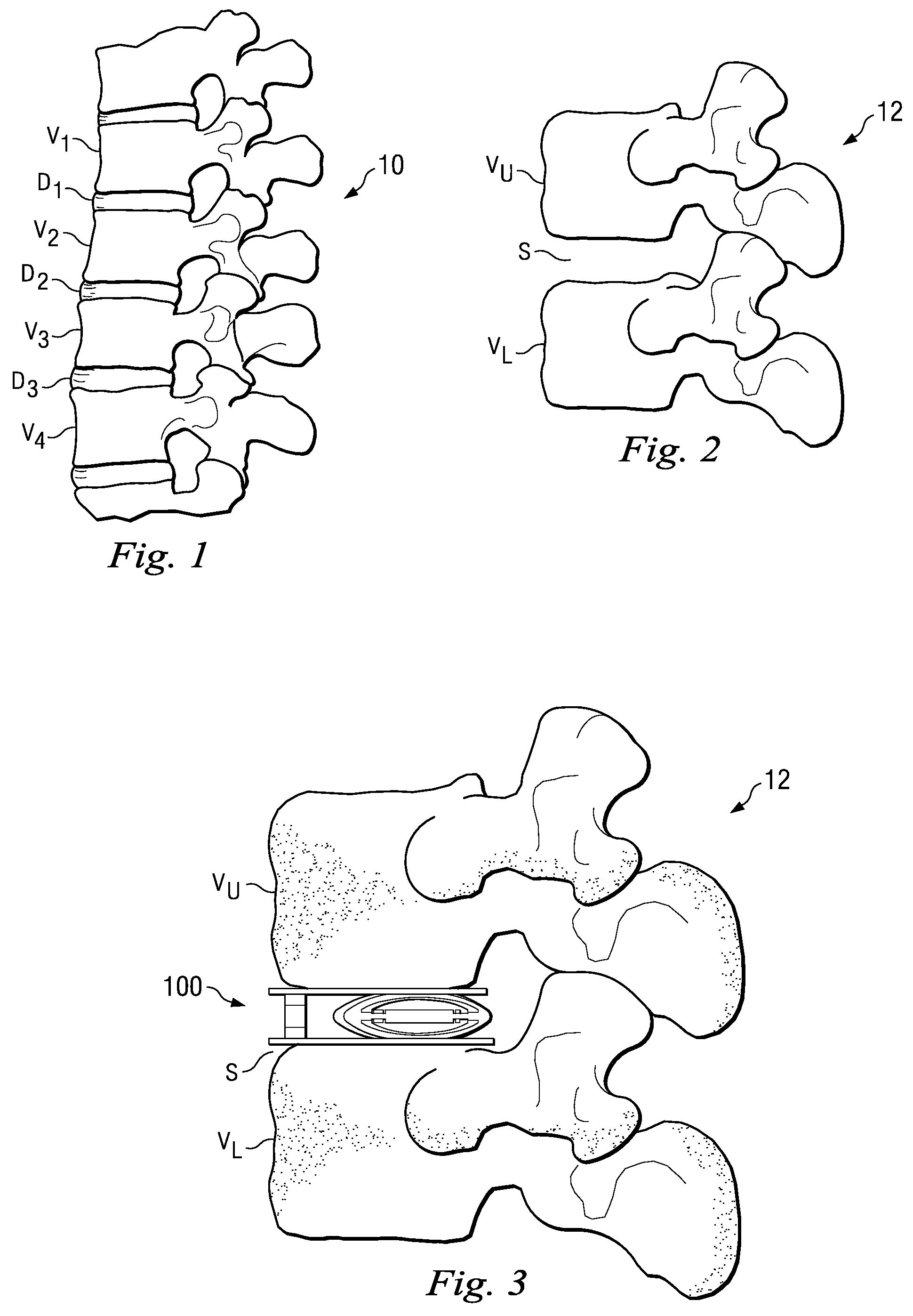
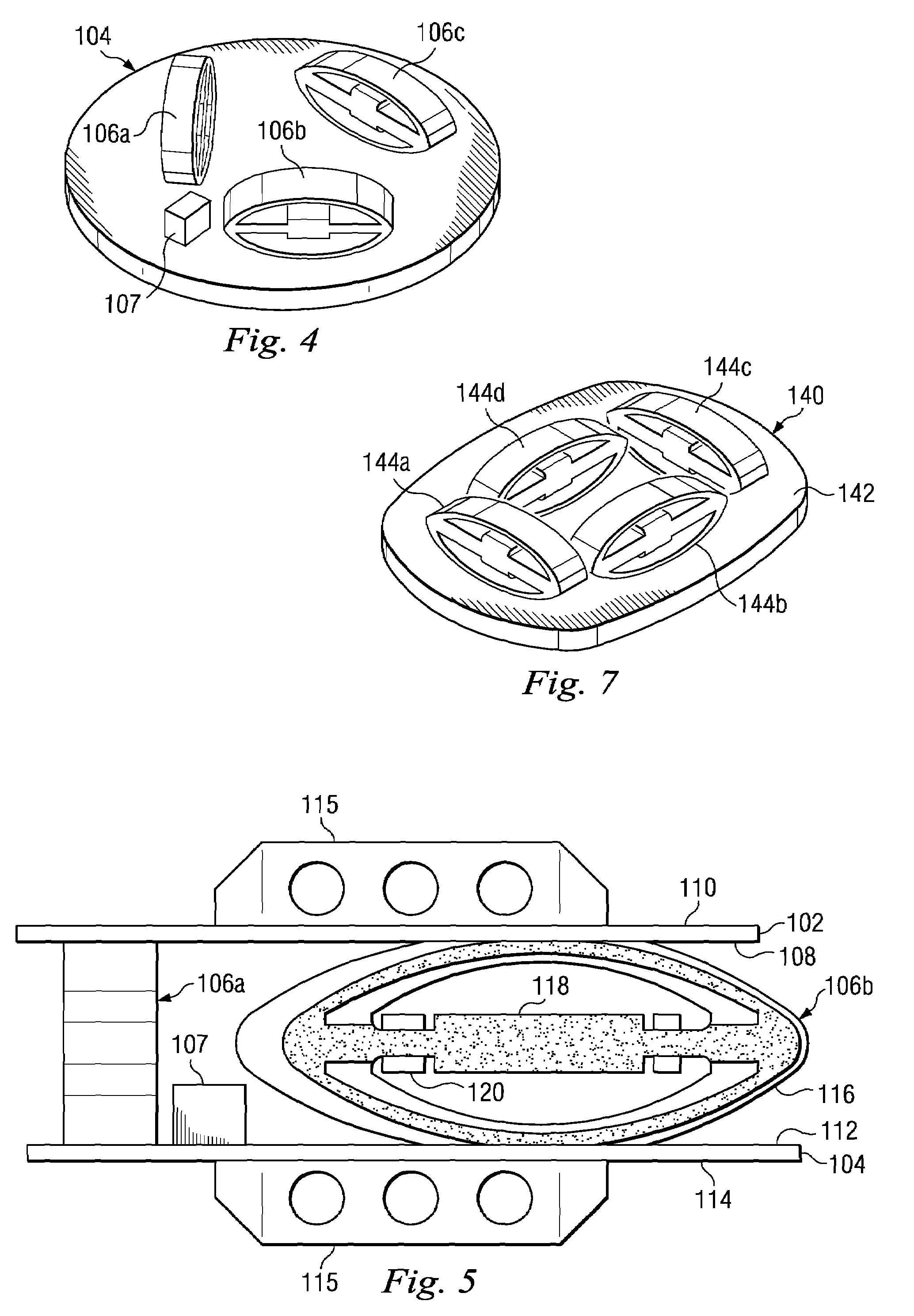
Active Vertebral Prosthetic Device
InactiveUS20080167718A1Spinal implantsCoatingsIonic polymer–metal compositesPhysical medicine and rehabilitation
An active vertebral prosthetic device system may include an actuatable displacement element having an upper side and a lower side. The actuatable displacement element may be configured for placement between an upper vertebral body and a lower vertebral body and may be configured to alter the overall distance between the upper and the lower vertebral bodies in situ. A controller may be operable to post-surgically actuate the actuatable displacement element. In some aspects, the displacement element maybe a piezoelectric motor, an electroactive polymer, an ionic polymer metal composite, and an actuator.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Auto-Titration of Positive Airway Pressure Machine With Feedback From Implantable Sensor
ActiveUS20090078257A1Low stiffnessRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesIonic polymer–metal compositesPositive airway pressure
Systems and methods for detecting and treating an obstructive sleep apnea event are disclosed herein. The systems and methods may use an electrical output generating ionic polymer metal composite sensor attached to a region in an airway passage in an oral cavity. The electrical output may be wirelessly transmitted as a signal for indication of an obstructive sleep apnea event. The signal may be further analyzed by a positive airway pressure system for treatment of the obstructive sleep apnea event.
Owner:MEDTRONIC XOMED INC
Novel uses of electroactive polymer materials
InactiveUS20090293664A1Precise positioningFlexibilityProgramme-controlled manipulatorMechanical apparatusIonic polymer–metal compositesManipulator
Novel applications of electroactive polymer materials, particularly of ionic polymer metal composite (IPMC). Such applications include manipulators with combined electromechanical and electroactive actuators. Applications are particularly suitable in low gravity environment.
Owner:UNIV OF TARTU
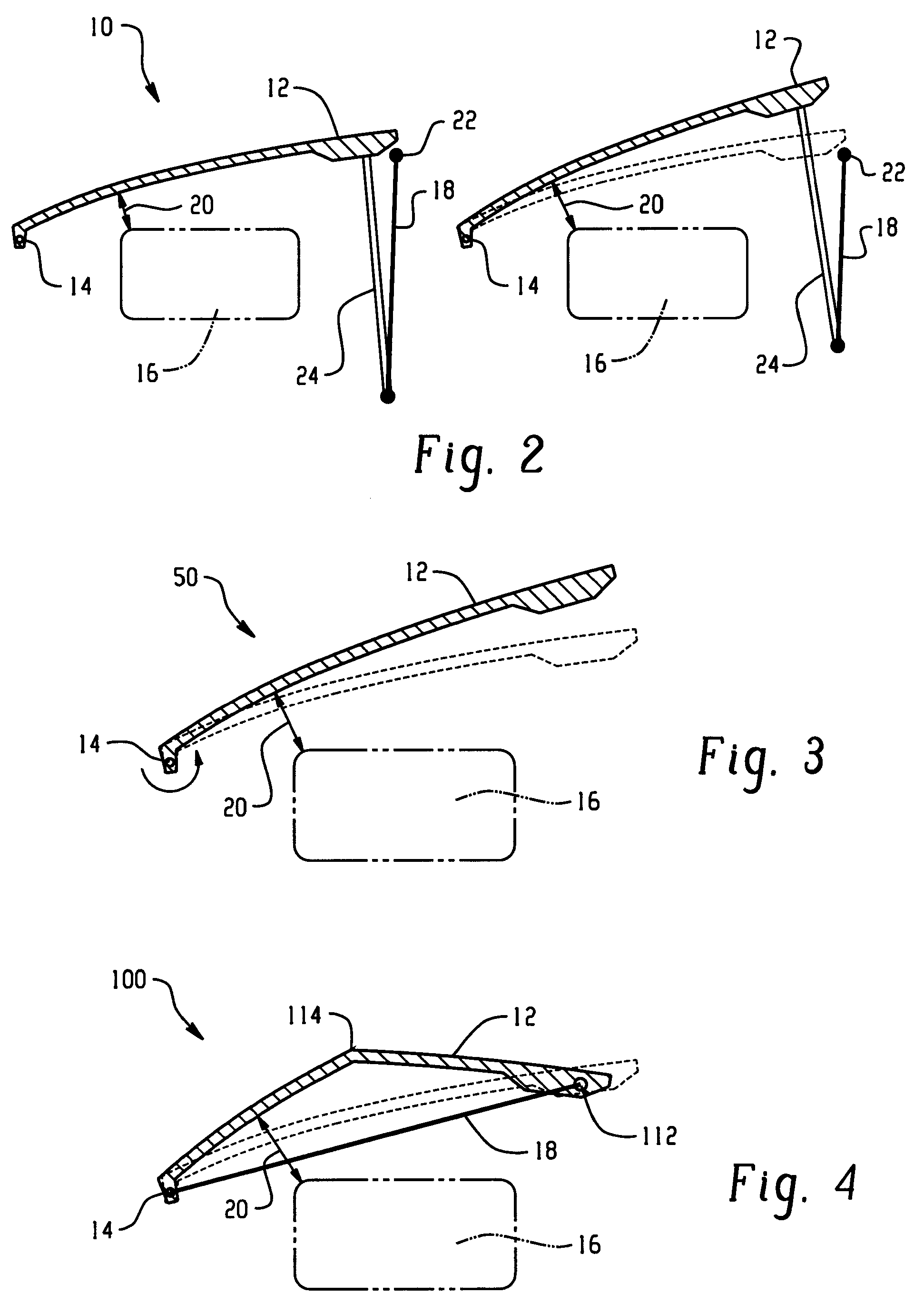
Hood lift mechanisms utilizing active materials and methods of use
InactiveUS20060028051A1Increased clearance distanceClearance distanceVehicle seatsAnti-theft devicesIonic polymer–metal compositesElastomer
A hood lift mechanism for reversibly increasing the energy absorption capability at appropriate force levels of a vehicle hood includes a vehicle hood; an active material in operative communication with the vehicle hood, wherein the active material comprises a shape memory alloy, a ferromagnetic shape memory alloy, a shape memory polymer, a magnetorheological fluid, an electroactive polymer, a magnetorheological elastomer, an electrorheological fluid, a piezoelectric material, an ionic polymer metal composite, or combinations comprising at least one of the foregoing active materials; and an activation device in operative communication with the active material, wherein the activation device is operable to selectively apply an activation signal to the active material and effect a reversible change in a property of the active material, wherein the reversible change results in an increased clearance distance between the vehicle hood and an underlying component.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC +1
Hood lift mechanisms utilizing active materials and methods of use
A hood lift mechanism for reversibly increasing the energy absorption capability at appropriate force levels of a vehicle hood includes a vehicle hood; an active material in operative communication with the vehicle hood, wherein the active material comprises a shape memory alloy, a ferromagnetic shape memory alloy, a shape memory polymer, a magnetorheological fluid, an electroactive polymer, a magnetorheological elastomer, an electrorheological fluid, a piezoelectric material, an ionic polymer metal composite, or combinations comprising at least one of the foregoing active materials; and an activation device in operative communication with the active material, wherein the activation device is operable to selectively apply an activation signal to the active material and effect a reversible change in a property of the active material, wherein the reversible change results in an increased clearance distance between the vehicle hood and an underlying component.
Owner:UNIV OF MICHIGAN THE +1
Hood lift mechanisms utilizing active materials and methods of use
ActiveUS7556117B2Pedestrian/occupant safety arrangementAutomatic initiationsIonic polymer–metal compositesEnergy absorption
Hood lift mechanisms for reversibly increasing the energy absorption capability at appropriate force levels of a vehicle closure includes a vehicle closure; an active material in operative communication with the vehicle closure, wherein the active material comprises a shape memory alloy, a ferromagnetic shape memory alloy, a shape memory polymer, a magnetorheological fluid, an electroactive polymer, a magnetorheological elastomer, an electrorheological fluid, a piezoelectric material, an ionic polymer metal composite, or combinations comprising at least one of the foregoing active materials; and an activation device in operative communication with the active material, wherein the activation device is operable to selectively apply an activation signal to the active material and effect a reversible change in a property of the active material, wherein the reversible change results in an increased clearance distance between the vehicle closure and an underlying component.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC +1
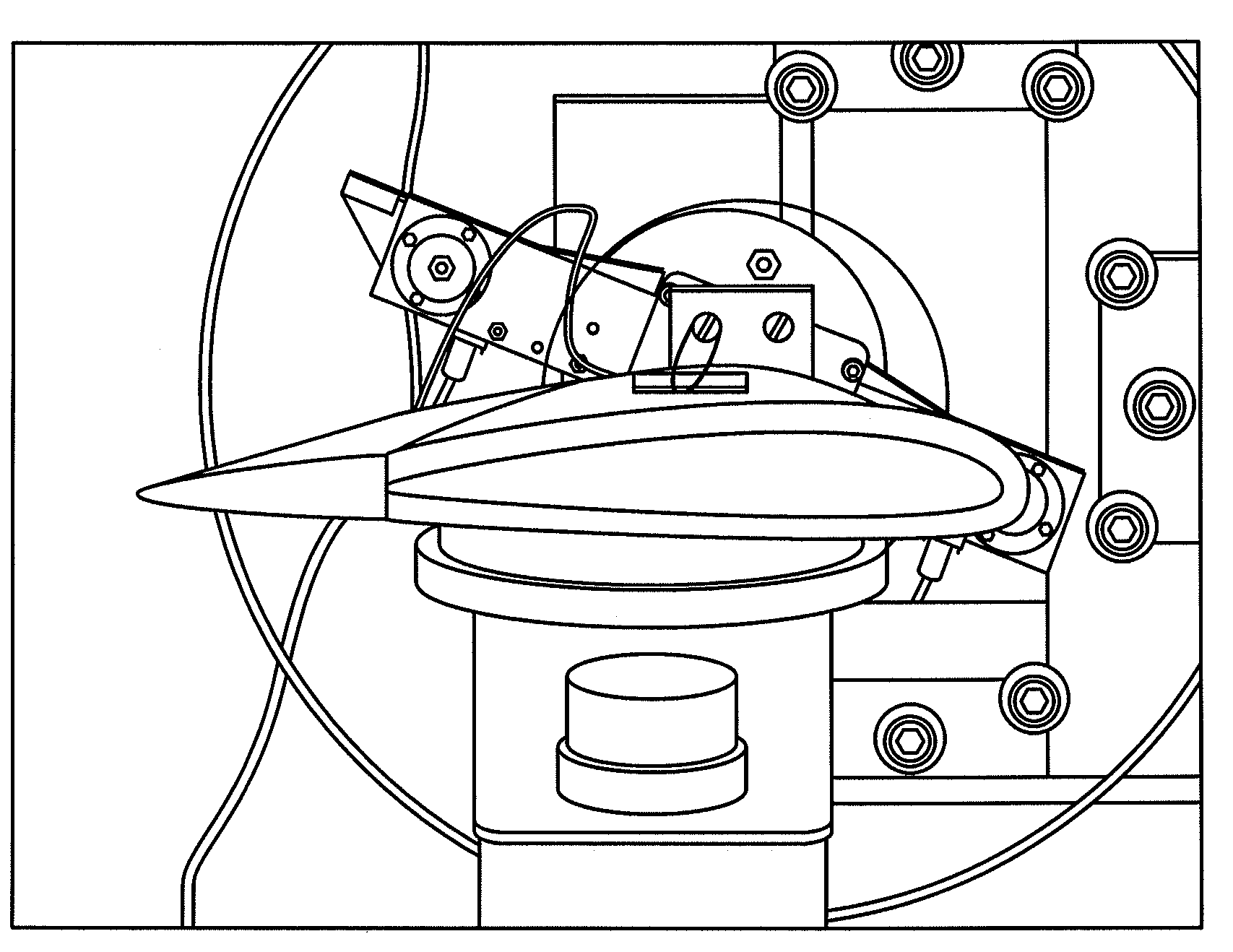
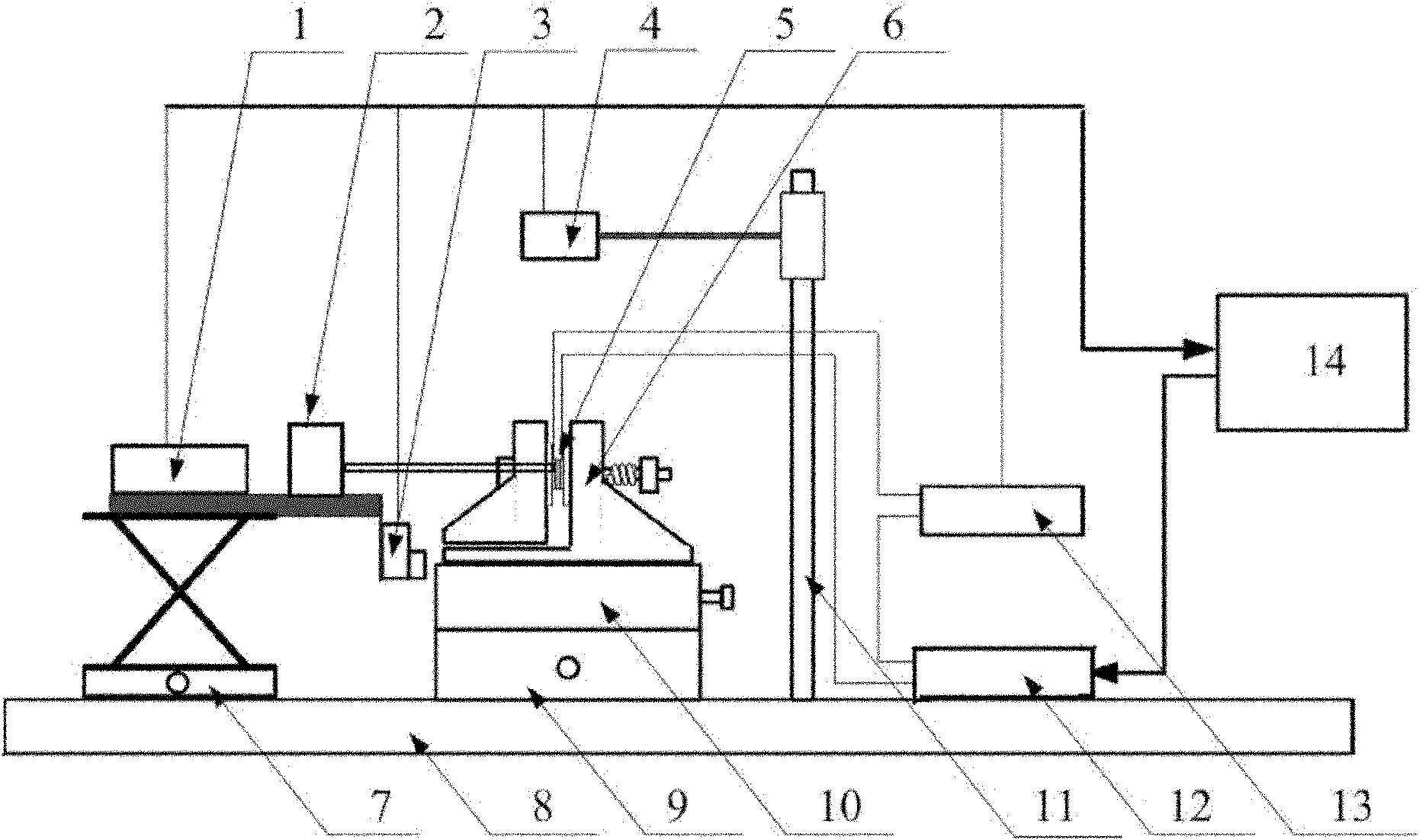
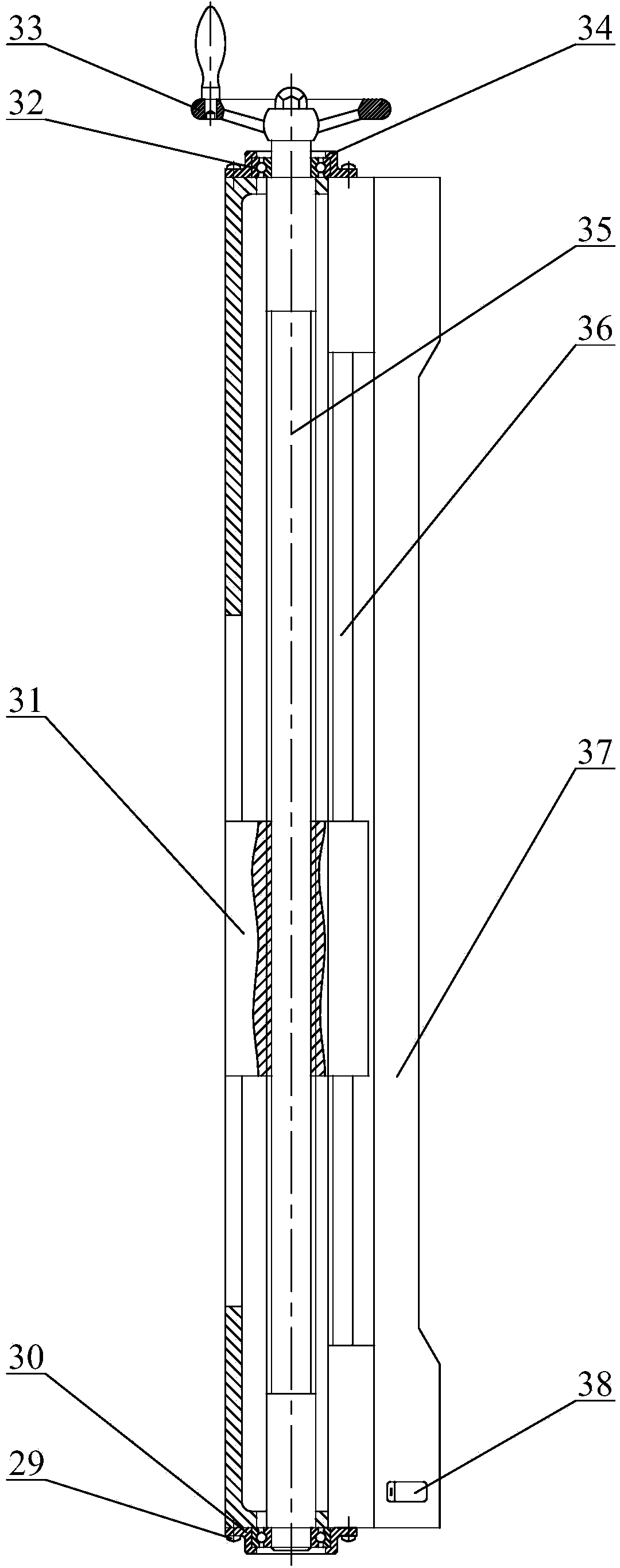
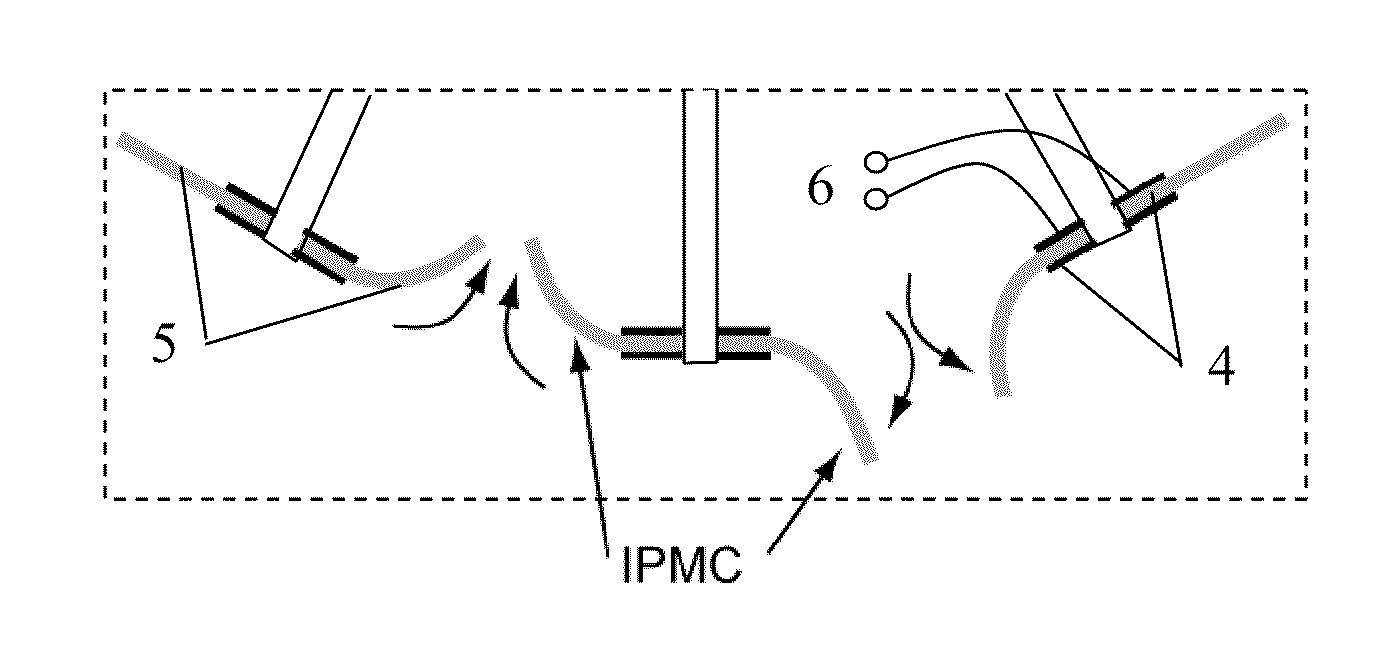
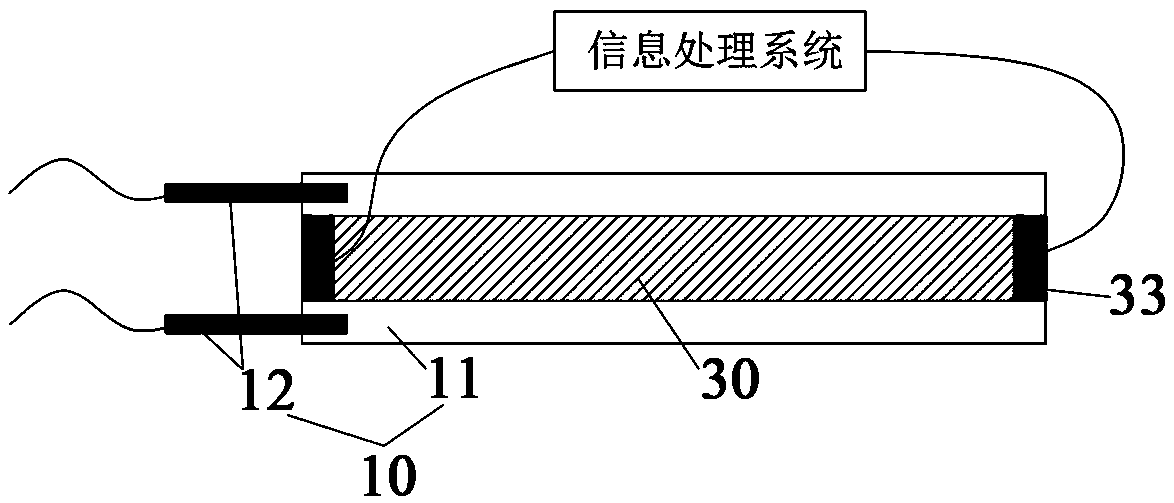
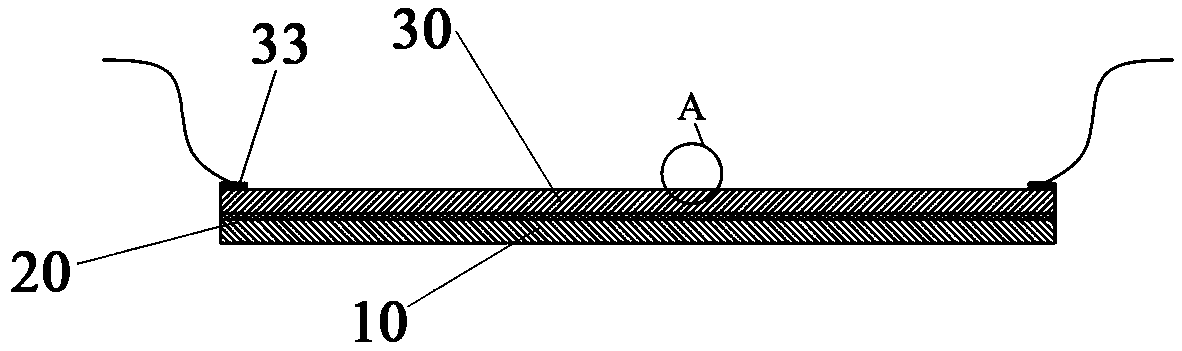
Device for testing comprehensive mechanical and electrical properties of ionic polymer-metal composite (IPMC)
InactiveCN102116689AGood choiceEasy to installCurrent/voltage measurementForce measurementIonic polymer–metal compositesEngineering
The invention discloses a device for testing comprehensive mechanical and electrical properties of an ionic polymer-metal composite (IPMC). The device comprises a base frame and is characterized in that a lifting platform, a Y-directional movable platform and an X-directional movable platform are arranged on the base frame, wherein a demountable sample fixture is arranged on the X-directional movable platform, a resonance displacement input device, a displacement sensor and a micro-force sensor are arranged on the lifting platform, and a CCD (charge-coupled device) camera is arranged above the sample fixture; and a power amplifier (PA), a current / voltage test board and a computer system are also arranged on the base frame, wherein the PA, the current / voltage test board and a sample are electrically connected together to form an electrical property test circuit, the computer system acquires the measured data output by the displacement sensor, the micro-force sensor, the CCD camera and the current / voltage test board so as to generate an excitation signal, and then the PA performs measurement control on the sample.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Dynamic roughness for aerodynamic applications
InactiveUS8302904B2Aircraft stabilisationBoundary layer controlsIonic polymer–metal compositesEngineering
Systems and methods for providing dynamic control to a surface immersed in a dynamic fluid. The systems and methods of the invention relate to one or more morphable surfaces that can be control in an active manner to provide asperities that interact with a fluid moving across the morphable surfaces. By controlling the size, shape and location of the asperities, one can exert control authority over the motion of the surface relative to the fluid. Examples of materials that provide suitable morphable surfaces include ionic polymer metal composites and shape memory polymers, both of which types of material are commercially available. Useful morphable surface systems have been examined and are described.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Ionic artificial muscle drive based small robot fish and moving method thereof
ActiveCN104002947AImprove mobilityPropulsive elements of non-rotary typeIonic polymer–metal compositesEngineering
The invention relates to an ionic artificial muscle drive based small robot fish and a moving method thereof and belongs to the technical field of intelligent material applications. A fish body of the robot fish is driven by a pectoral fin drive system and a tail fin drive system coordinately. The pectoral fin drive system comprises a U-shaped rack in the fish body and a left pectoral fin drive mechanism and a right pectoral fin drive mechanism. Each of the pectoral fin drive mechanisms comprises three ionic polymer metal composite (IPMC) material sheets, a rotation disc, a rotation shaft and a pectoral fin film, and vertical wing flapping and shaking can be achieved. The tail fin drive system comprises an electrode clamping units fixed at the tail, an IPMC material sheet and a tail fin, and one-way or two-way swinging of the fish body in the axial plane can be achieved. A control panel and a battery are disposed in the fish body, and moving modes such as linear cruising, speeding up / speeding down / sudden stopping, left and right / turning and floating / diving are achieved by setting appropriate drive signals.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
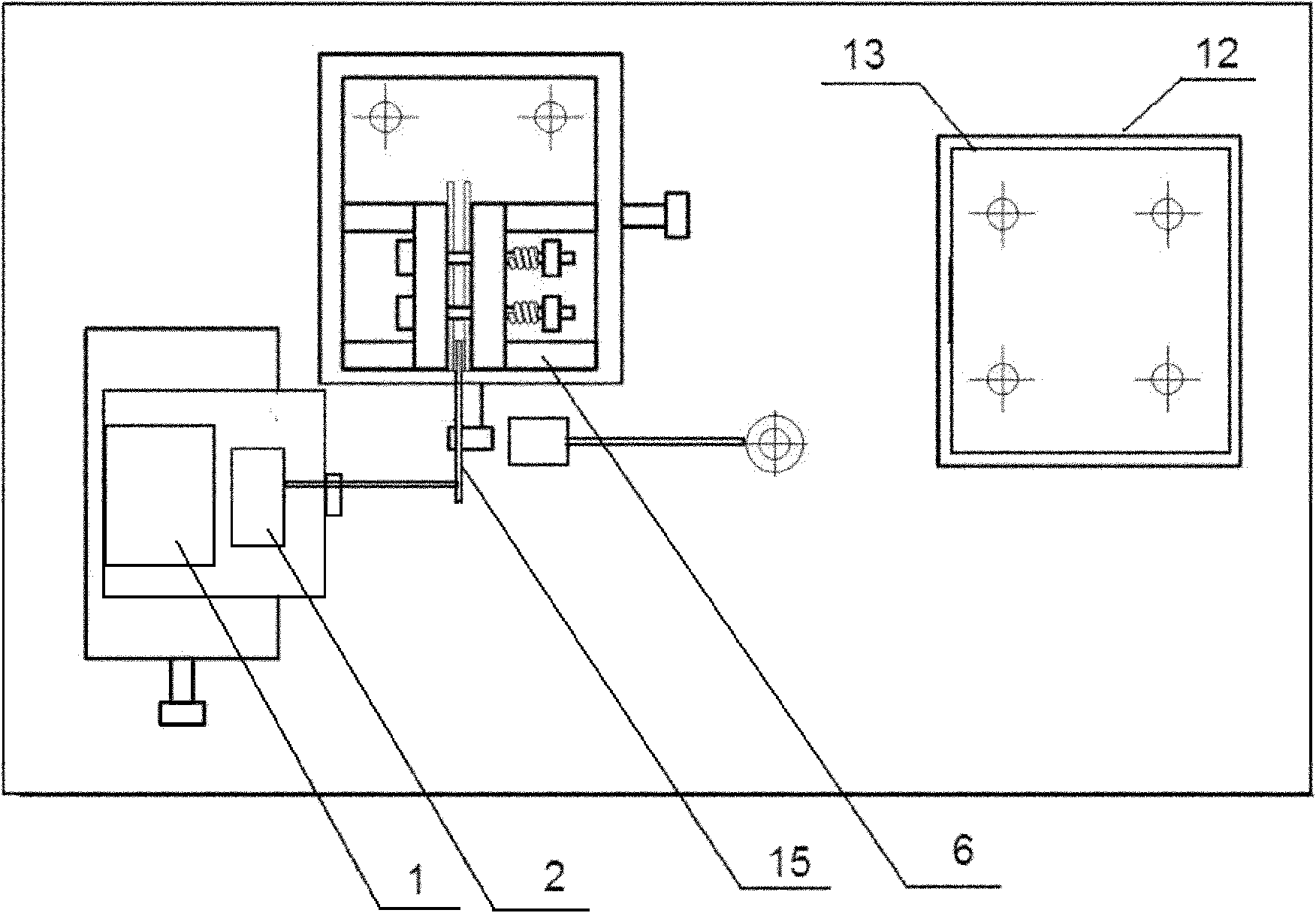
Experimental platform aiming at comprehensive performance testing of IPMC (Ionic Polymer Metal Composite) artificial muscle material
InactiveCN103439191APrecise feedingPrecise positioningMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesMaterial resistanceLow noiseIonic polymer–metal composites
The invention aims to provide an experimental platform aiming at comprehensive performance testing of an IPMC (Ionic Polymer Metal Composite) artificial muscle material. The experimental platform mainly comprises a sample clamping module, a sample tension testing module, a sample displacement testing module, a feeding module and the like, wherein the feeding module mainly consists of a horizontal feeding mechanism and a vertical feeding mechanism; the sample clamping module is fixed on a supporting seat of the vertical feeding mechanism; a vertical pedestal of the vertical feeding mechanism is fixed on a slide block of the horizontal feeding mechanism; the slide block is matched with a driving lead screw to realize horizontal movement; the sample tension testing module and the sample displacement testing module are fixed on a platform pedestal of the feeding module. A non-contact measurement method is adopted in an experimental process to avoid interference of personal factors during measurement; the experimental platform generally has various characteristics of simple structure, easiness in operation, low manufacturing cost, small size, convenience in daily maintenance, low noise, no limitation of experimental conditions, no pollution and the like.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
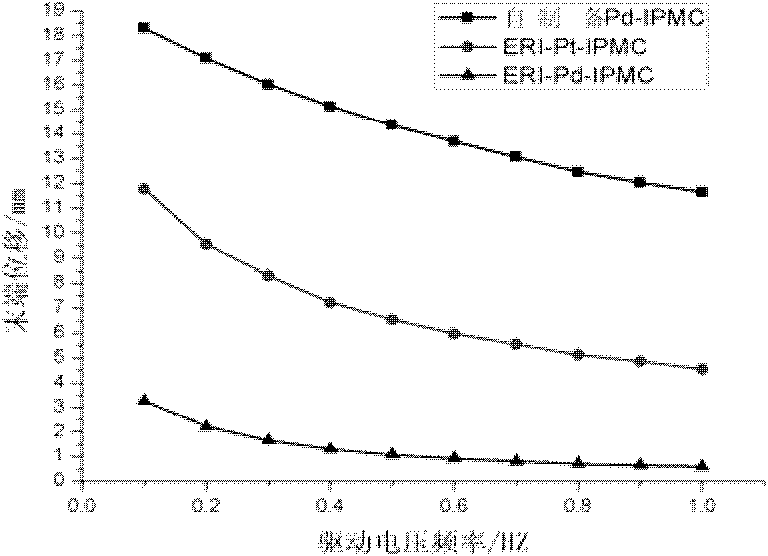
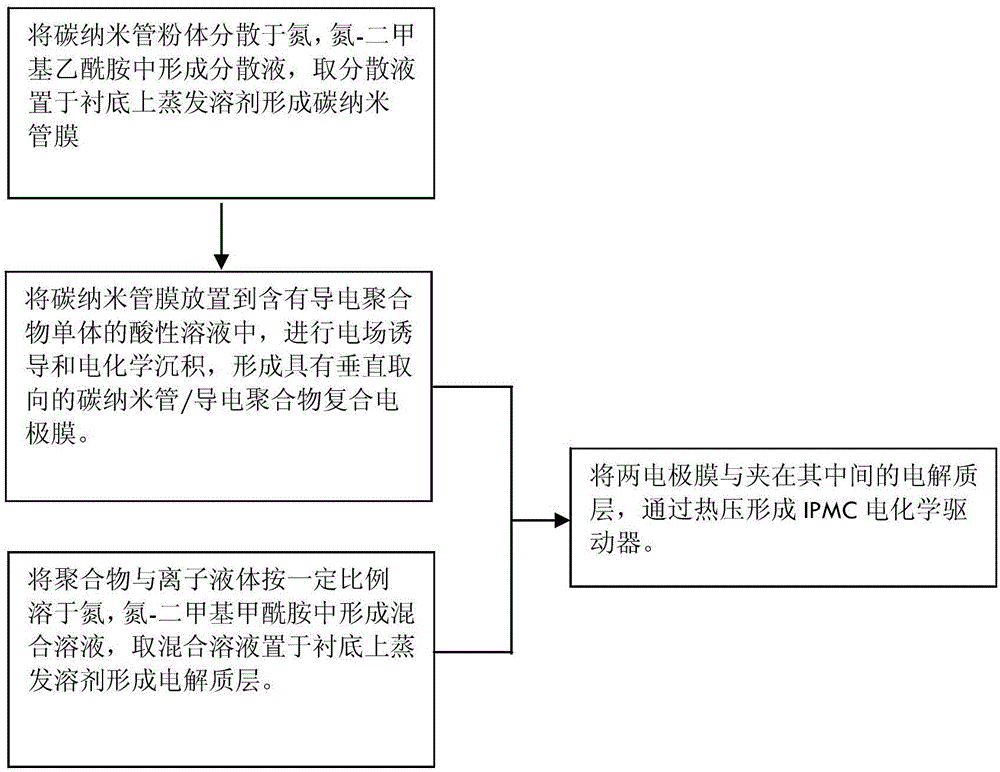
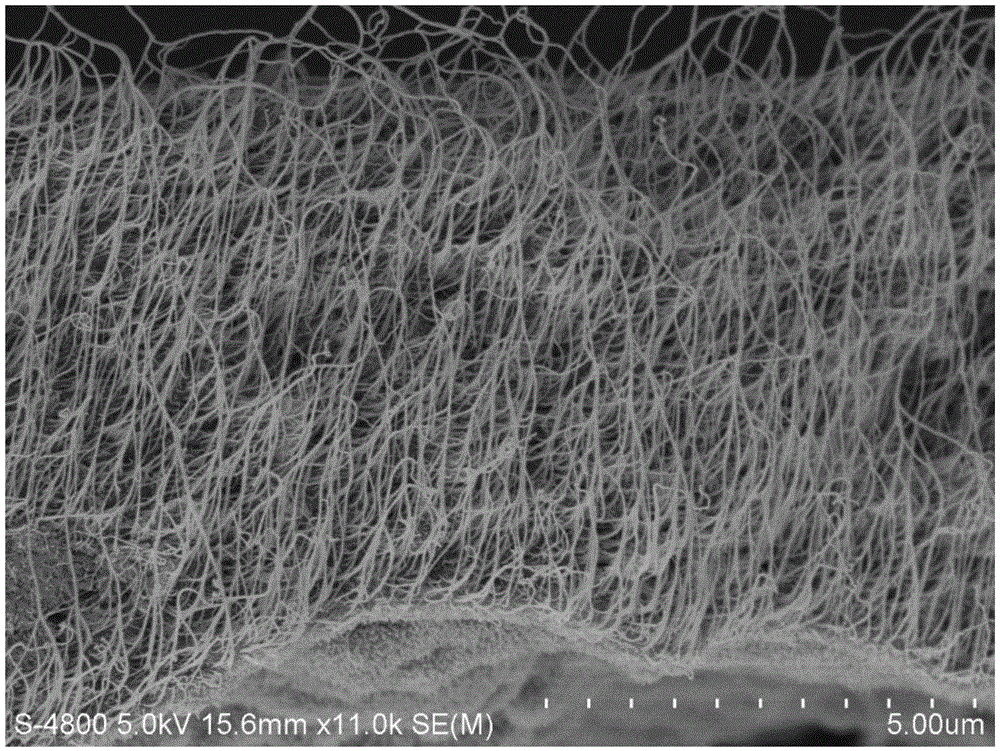
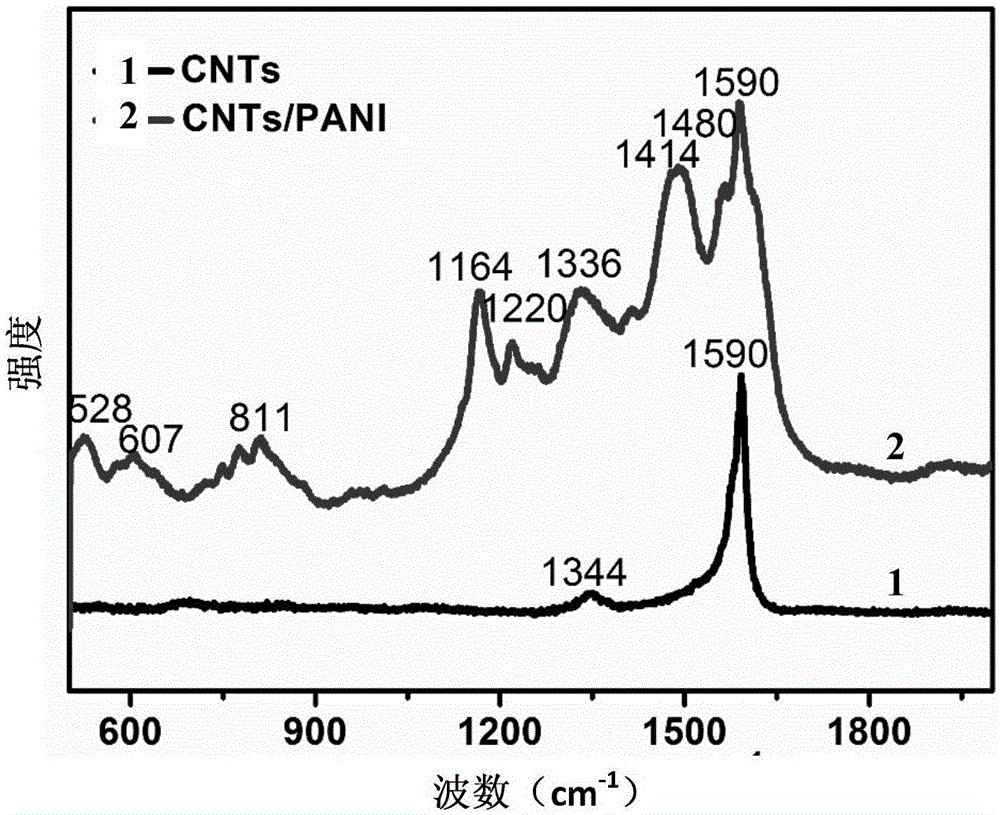
Ionic polymer metal composites (IPMC) electrochemistry driver, preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN106299105ALow costSimple processPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyPiezoelectric/electrostrictive devicesIonic polymer–metal compositesConductive polymer composite
The present invention discloses an IPMC electrochemistry driver, a preparation method and an application thereof. The preparation method can comprise the steps of providing a carbon nano tube film mainly formed by interlacing a plurality of unordered carbon nano tubes, establishing a three-electrode reaction system by the substances, such as the carbon nano tube film, an acid solution containing a conductive polymer monomer, an auxiliary electrode, etc., to carry out the electrodeposition reaction, and obtaining a carbon nano tube / conductive polymer composite electrode film having a vertical orientation by adjusting and controlling the conditions, such as the electrolyte concentration, the current, the voltage, the reaction time, etc.; providing a polymer electrolyte layer bearing an ionic liquid; and fixedly clamping the electrolyte layer between two composite electrode films, thereby obtaining the IPMC electrochemistry driver. The IPMC electrochemistry driver of the present invention has an excellent electro mechanical response performance, for example, an actuation displacement is large, the response speed is fast, the stability is high, and the service life is long, has wide application prospect in the biomimetic intelligent material field, is simple in preparation technology and low in cost, and is suitable for the large-scale production.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF NANO TECH & NANO BIONICS CHINESE ACEDEMY OF SCI
Selective plating process for IPMC (Ionic Polymer Metal Composite) drive
InactiveCN102953053ARealize the functions of complex driversMaking meetLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingPlatinumIonic polymer–metal composites
The invention discloses a selective plating process for an IPMC (Ionic Polymer Metal Composite) drive. The selective plating process is characterized by comprising the following steps: firstly, pretreating a substrate material; secondly, producing a non-plating region on the pretreated ion exchange membrane pretreated in the first step according to the use requirement of the drive to be isolated from a plating region; enabling an electrode not to be plated in the non-plating region in the subsequent work procedure by a mask method; when the line width is greater, directly covering by using a high-temperature-resistant electroplating adhesive tape to enable the blocked part not to be plated, and when the line width is smaller, producing a reverse covering layer by using the electroplating adhesive tape to expose a blocking line and isolating different electrode regions by generating silver chloride precipitation; and thirdly, depositing an electrode layer on the plating region by adopting soaking and reduction plating and producing a platinum, palladium, silver or copper metal electrode or a platinum-palladium composite electrode and a silver-copper composite electrode.
Owner:SHANDONG HENGDA BRAND PACKAGE CO LTD
Hood lift mechanisms utilizing active materials and methods of use
ActiveUS7686120B2Vehicle seatsSuperstructure subunitsIonic polymer–metal compositesEnergy absorption
A hood lift mechanism for reversibly increasing the energy absorption capability at appropriate force levels of a vehicle hood includes a vehicle hood; an active material in operative communication with the vehicle hood, wherein the active material comprises a shape memory alloy, a ferromagnetic shape memory alloy, a shape memory polymer, a magnetorheological fluid, an electroactive polymer, a magnetorheological elastomer, an electrorheological fluid, a piezoelectric material, an ionic polymer metal composite, or combinations comprising at least one of the foregoing active materials; and an activation device in operative communication with the active material, wherein the activation device is operable to selectively apply an activation signal to the active material and effect a reversible change in a property of the active material, wherein the reversible change results in an increased clearance distance between the vehicle hood and an underlying component.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN +1
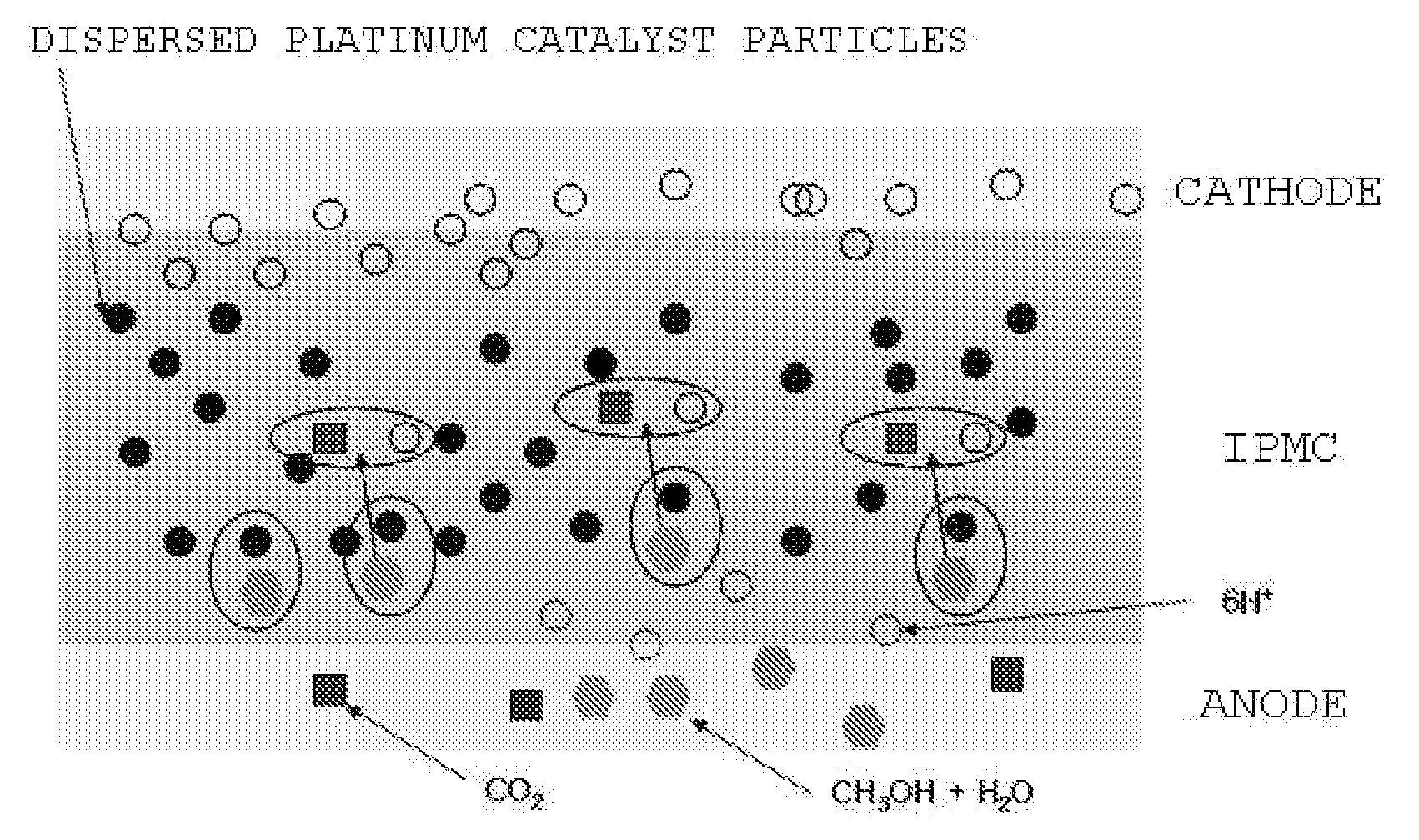
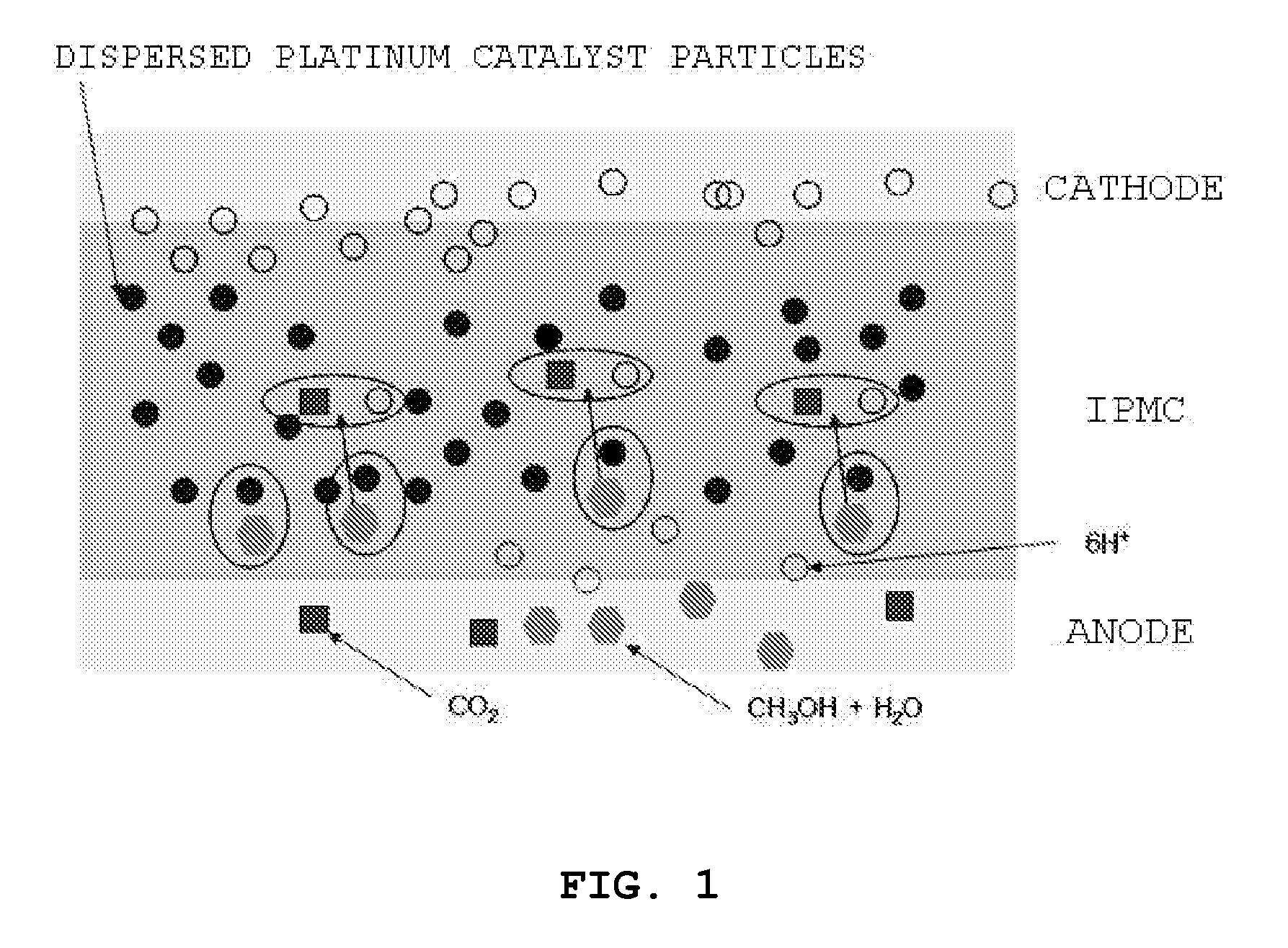
Ionic polymer metal composite electrolyte for fuel cell
InactiveUS20080003479A1Reduce crossoverSolid electrolytesFinal product manufactureIonic polymer–metal compositesPlatinum nanoparticle
Disclosed are an ionic polymer metal composite electrolyte for a fuel cell and a method of preparing the same. In detail, the invention provides an ionic polymer metal composite electrolyte for a fuel cell, in which an ionic polymer metal composite, in which platinum nanoparticles are dispersed in a Nafion membrane, is used as an electrolyte, in place of the Nafion membrane alone, upon the fabrication of a fuel cell having a polymer electrolyte, and also provides a method of preparing the same. The ionic polymer metal composite electrolyte of the invention can solve problems related to the cross-over of a conventional Nafion membrane, and thereby can be used as the polymer membrane of a methanol direct fuel cell, having improved open-circuit voltage.
Owner:KONKUK UNIV IND COOP CORP
3D preparing method of ionic polymer metal composite base membrane
InactiveCN110066485AReduce consumptionShorten the production cycleAdditive manufacturing apparatusCrystallographyIonic polymer–metal composites
The invention provides a 3D preparing method of an ionic polymer metal composite base membrane. The method comprises the steps of weighing a Nafion solution and BaTiO3 nanoscale powder according to aset mass ratio of Nafion to BaTiO3 at first, then concentrating the Nafion solution to the mass fraction of 15%, dropwise adding dimethyl sulfoxide with the volume fraction of 15% into the concentrated Nafion solution, then adding the BaTiO3 nanoscale powder into the mixed Nafion solution, stirring the mixed solution so that the solution can be sufficiently and uniformly mixed, and removing bubbles in the solution; concentrating and evaporating the obtained solution, and then conducting grinding to obtain nanoscale particles; extruding the obtained nanoscale particles to make Nafion precursorfilaments, and adopting a 3D printer for printing a design entity through the Nafion precursor filaments to obtain the base membrane. According to the 3D printing method, a 3D printing technology is adopted for base membrane printing, manufacturing of section-variable structures, hollow structures and other complicated structures is achieved, thick base membranes can be printed, and thicker and larger IMPCs can be prepared; through a reasonable solution preparing technology, the problem that bubbles are easily generated in a formed membrane is solved.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Capsule endoscope based on IPMC (ionic polymer metal composite) driving and driving method thereof
InactiveCN104873166ATo achieve the purpose of losslessEasy to swallowGastroscopesOesophagoscopesIonic polymer–metal compositesAttitude control
The invention relates to a capsule endoscope based on IPMC (ionic polymer metal composite) driving and a driving method thereof. The capsule endoscope based on the IPMC driving comprises a capsule front cover, a capsule main body structure and a capsule tail structure, wherein a plurality of slice IPMCs are arranged on the outer side of the capsule main body structure and on the capsule tail structure along the axial direction of a capsule. Under normal moving status of the capsule endoscope based on the IPMC driving, the slice IPMCs on the outer side of the capsule main body structure can be folded along the capsule, and are unfolded outwards after control signals are applied onto the slice IPMCs on the outer side of the capsule main body structure, and thereby can be used to achieve a deceleration or clamping function. When the slice IPMCs on the outer side of the capsule main body structure are respectively controlled, a posture adjustment for the capsule can be achieved. One or two IPMCs can be installed at the tail end of the capsule, and are used to achieve an active driving function. The capsule endoscope based on the IPMC driving and the driving method thereof use IPMC artificial muscle smart materials good in biocompatibility to achieve movement and posture control of the capsule endoscope based on the IPMC driving in a human body.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
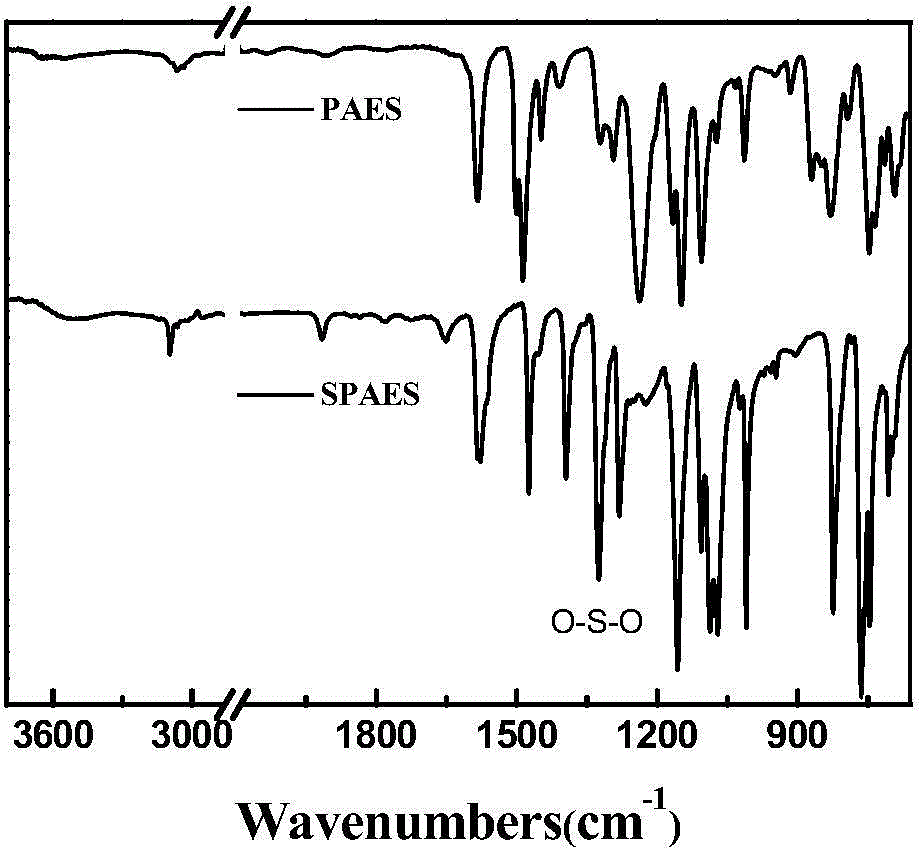
Sulfonated poly ether sulfone, and preparation method and application thereof in electrical actuator preparation
InactiveCN104804182AHigh ion exchange equivalentHigh ion exchange capacityPiezoelectric/electrostrictive/magnetostrictive devicesIonic polymer–metal compositesPolymer science
Sulfonated poly ether sulphone or a sulfonated poly ether sulphone derivative is a phenyl sulfone and 2,2-bis(4-hydroxyphenyl)propane or fluorene-9-bisphenol (BHPF) or polyethylene glycol modified fluorene-9-bisphenol sulfonated block polymer; sulfonated poly ether sulphone, the sulfonated poly ether sulphone derivative or the polyethylene glycol modified sulfonated poly ether sulphone derivative has the structural formula shown in the specification, wherein R1 refers to H or SO3H, and R2 refers to H or SO3H. Sulfonated poly ether sulfone can be used for preparing an ionic polymer-metal composite electrical actuator. Sulfonated poly ether sulfone has a higher ion-exchange equivalent, and a wider mechanical performance adjusting range, and is relatively low in cost.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIVERSITY OF LIGHT INDUSTRY
Uses of electroactive polymer materials
InactiveUS8395300B2Precise positioningSufficient forceProgramme-controlled manipulatorMechanical apparatusIonic polymer–metal compositesPolymer science
Novel applications of electroactive polymer materials, particularly of ionic polymer metal composite (IPMC). Such applications include manipulators with combined electromechanical and electroactive actuators. Applications are particularly suitable in low gravity environment.
Owner:UNIV OF TARTU
Packaging process capable of improving stability of ionic polymer metal composite (IPMC) driver
InactiveCN103280522AMoisture stableQuick bondingPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyIonic polymer–metal compositesAdhesive
The invention discloses a packaging process capable of improving the stability of an ionic polymer metal composite (IPMC) driver. The packaging process is characterized in that the packaging process is implemented by two methods, wherein one method comprises the steps of performing pre-packaging by using an ultraviolet gluing material, and depositing a Parylene coating or a gas barrier layer such as a dense oxide gas barrier layer at normal temperature; and the other method comprises the step of adhering an IPMC surface to a high-barrier thin film material by using light curing glue as an adhesive, so that the stability of water in the material is ensured. According to the packaging process, the curing time of a packaging layer is greatly reduced; in addition, heating is not required in the whole process, so that the water in the material can be accurately controlled; and the packaging process has high practical value.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Bionic sensing and executing integrated flexible actuator and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN109866480AChange the output resistor valueRealize the actuation effectSynthetic resin layered productsConverting sensor output electrically/magneticallyEngineeringIonic polymer–metal composites
The invention discloses a bionic sensing and executing integrated flexible actuator and a preparation method thereof. The flexible actuator comprises an ionic polymer metal composite (IPMC) actuatinglayer, an adhesive layer arranged on the IPMC actuating layer, and a bionic strain sensing element arranged on the adhesive layer; the bionic strain sensing element comprises a flexible substrate layer arranged on the IPMC actuating layer, a conductive layer arranged on the flexible substrate layer and a first electrode arranged on the conductive layer, wherein the flexible substrate layer is provided with bionic V-shaped groove arrays. When external vibration waves are transmitted to the bionic strain sensing element, and output resistance of the bionic strain sensing element reaches a presetvalue, the IPMC actuating layer is automatically started, actuating bending occurs, and the bionic strain sensing element layer is further driven to deform. The actuating degree of the actuator can be indirectly acquired according to an output resistance value, so that the purposes that sensing and executing are integrated and actuation is intelligent and controllable are achieved.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com