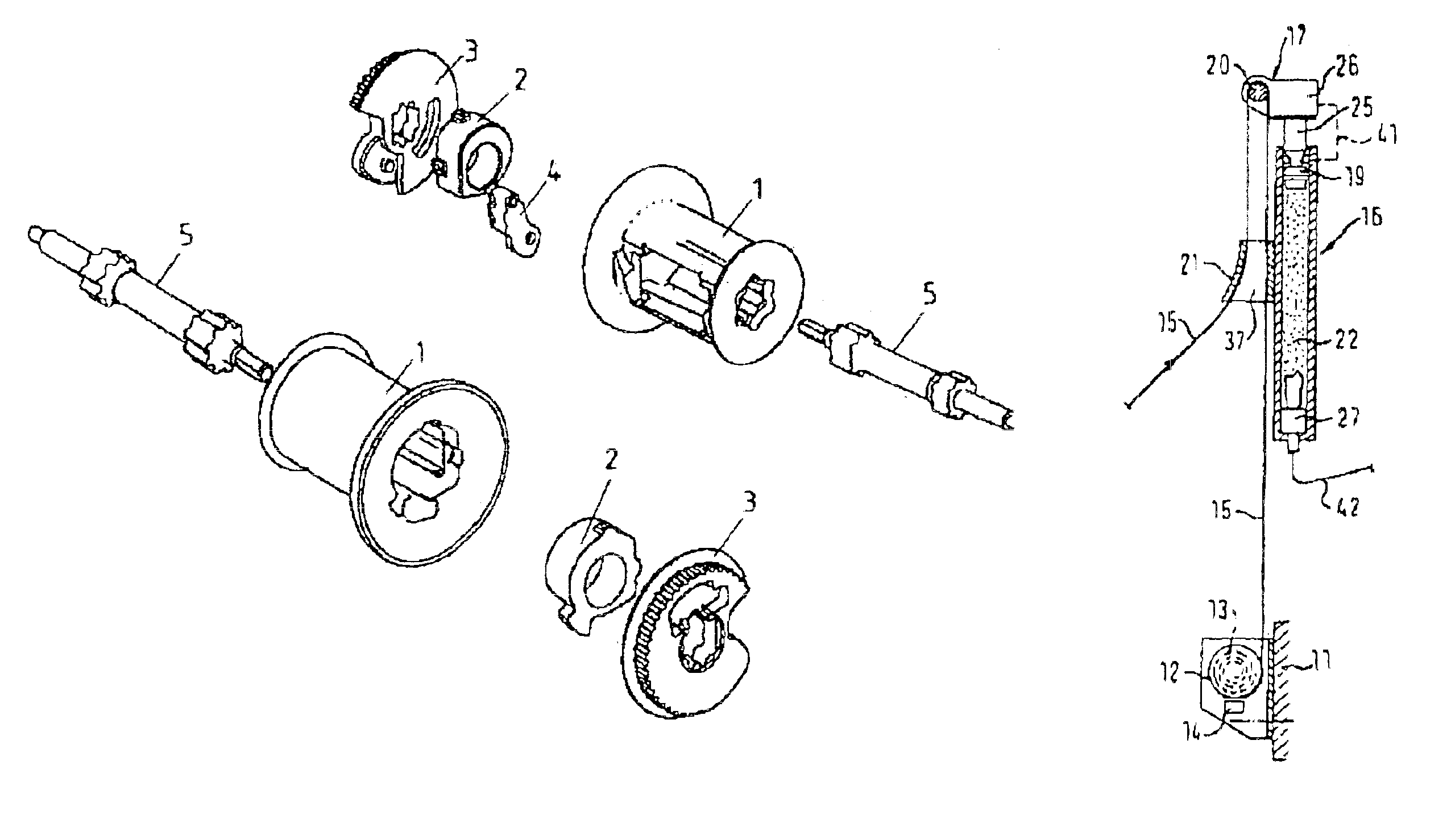
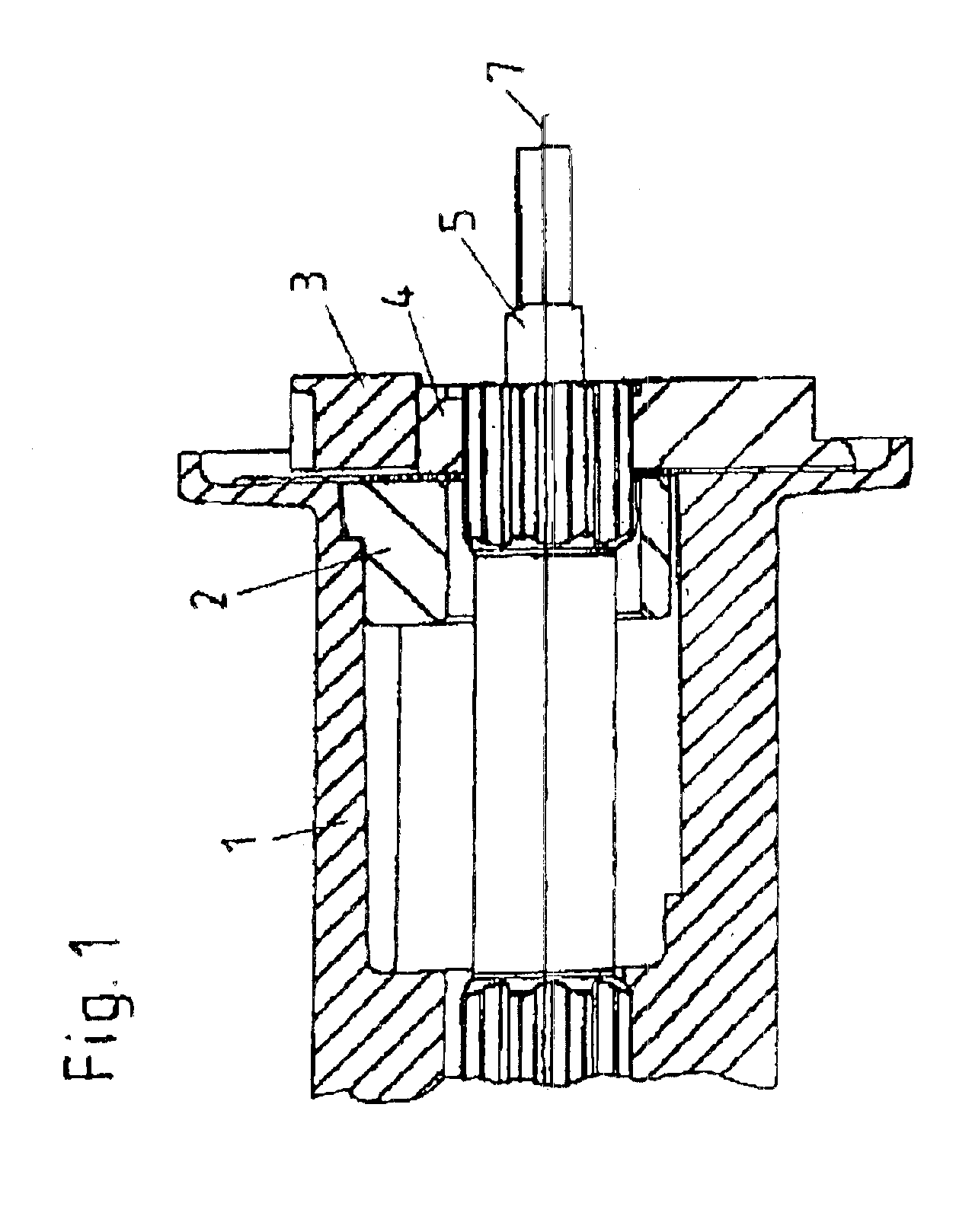
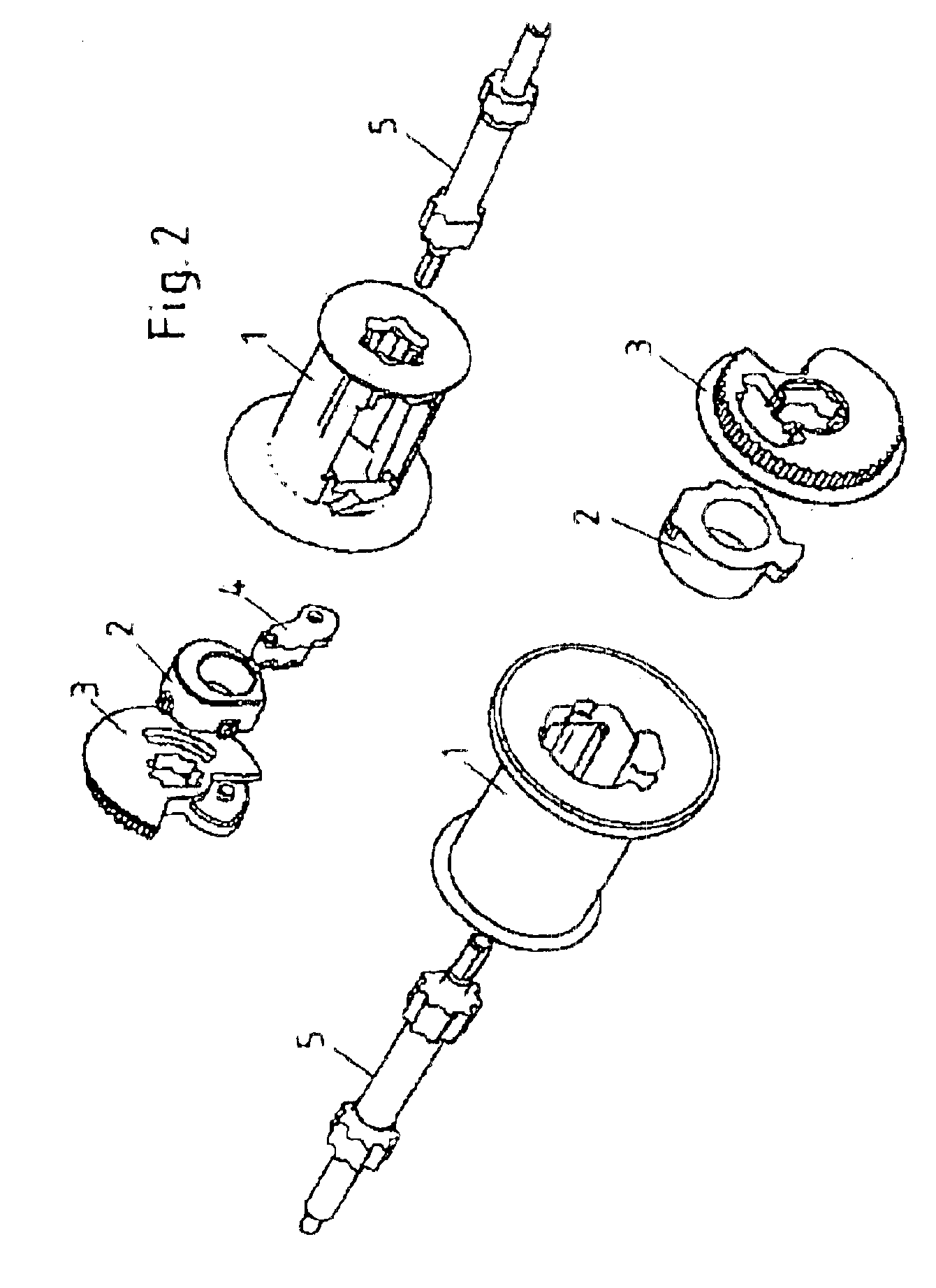
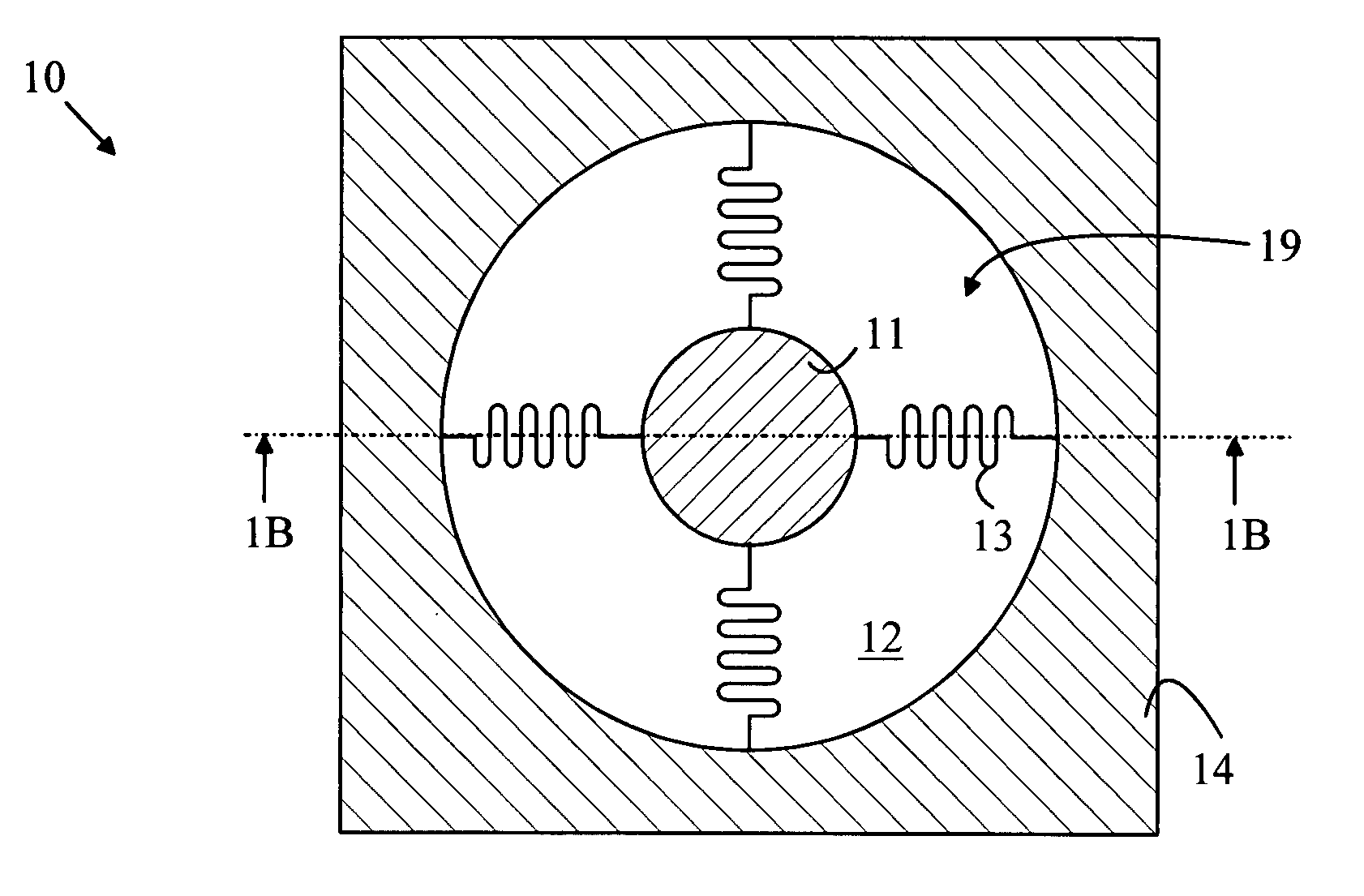
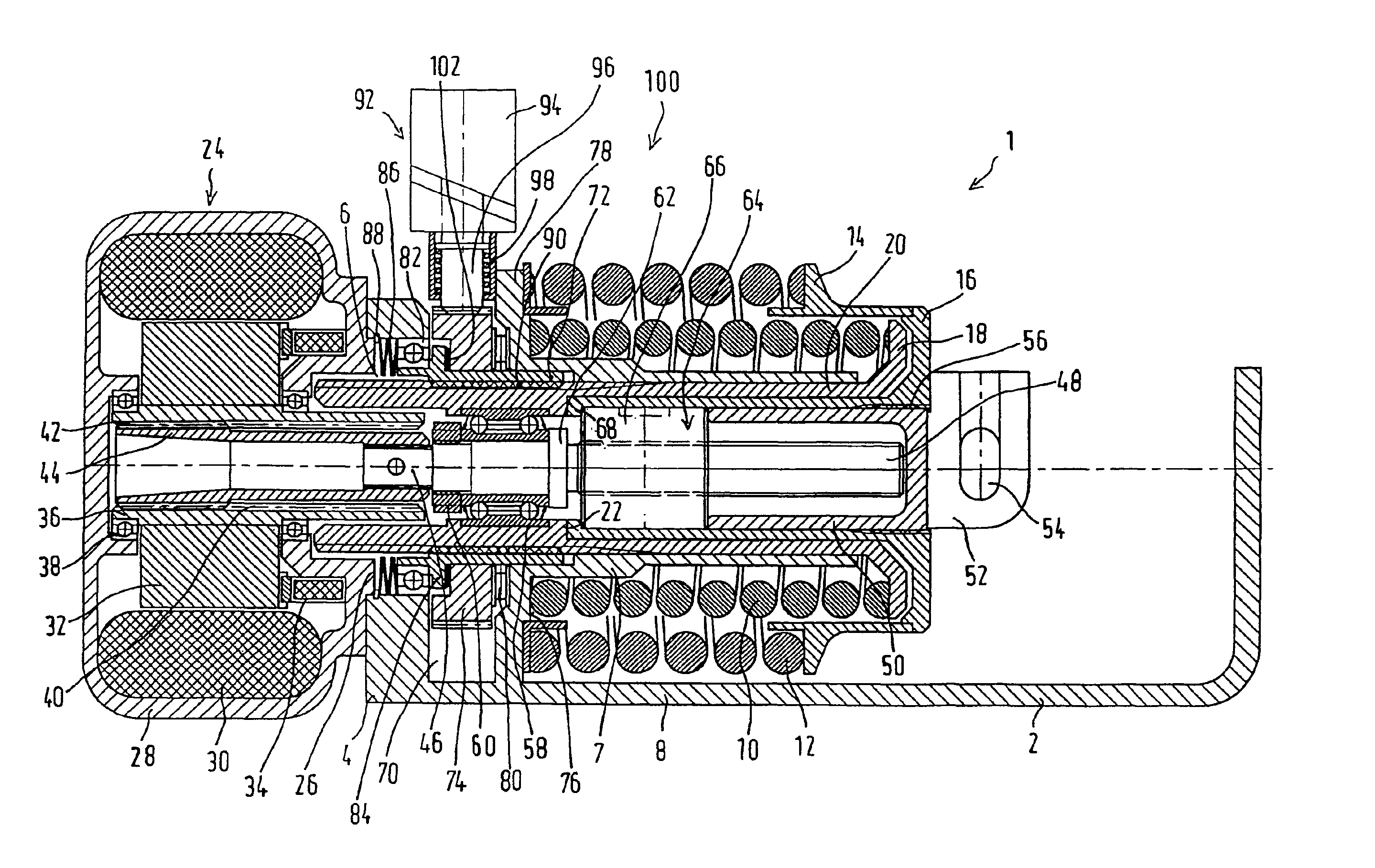
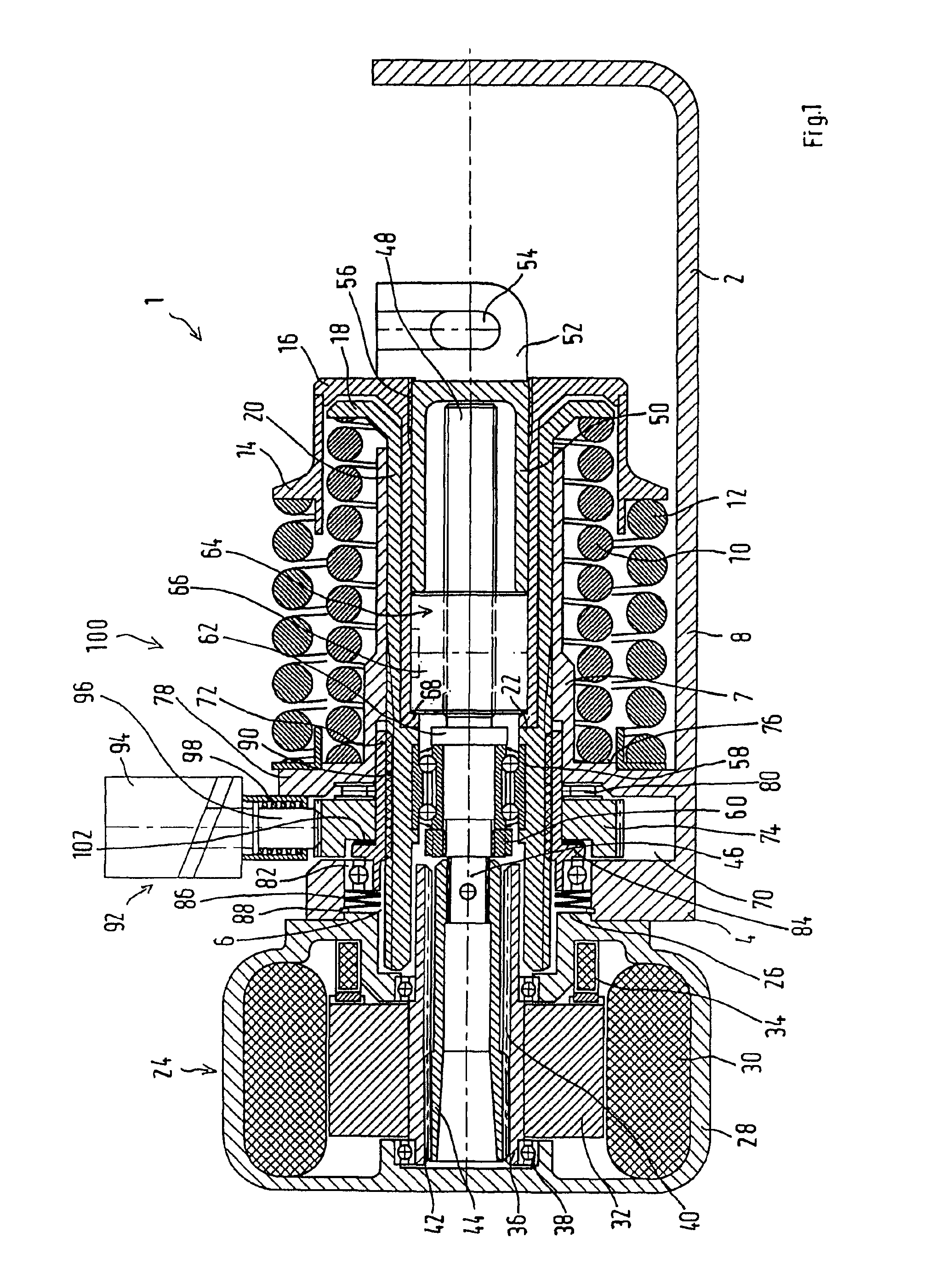
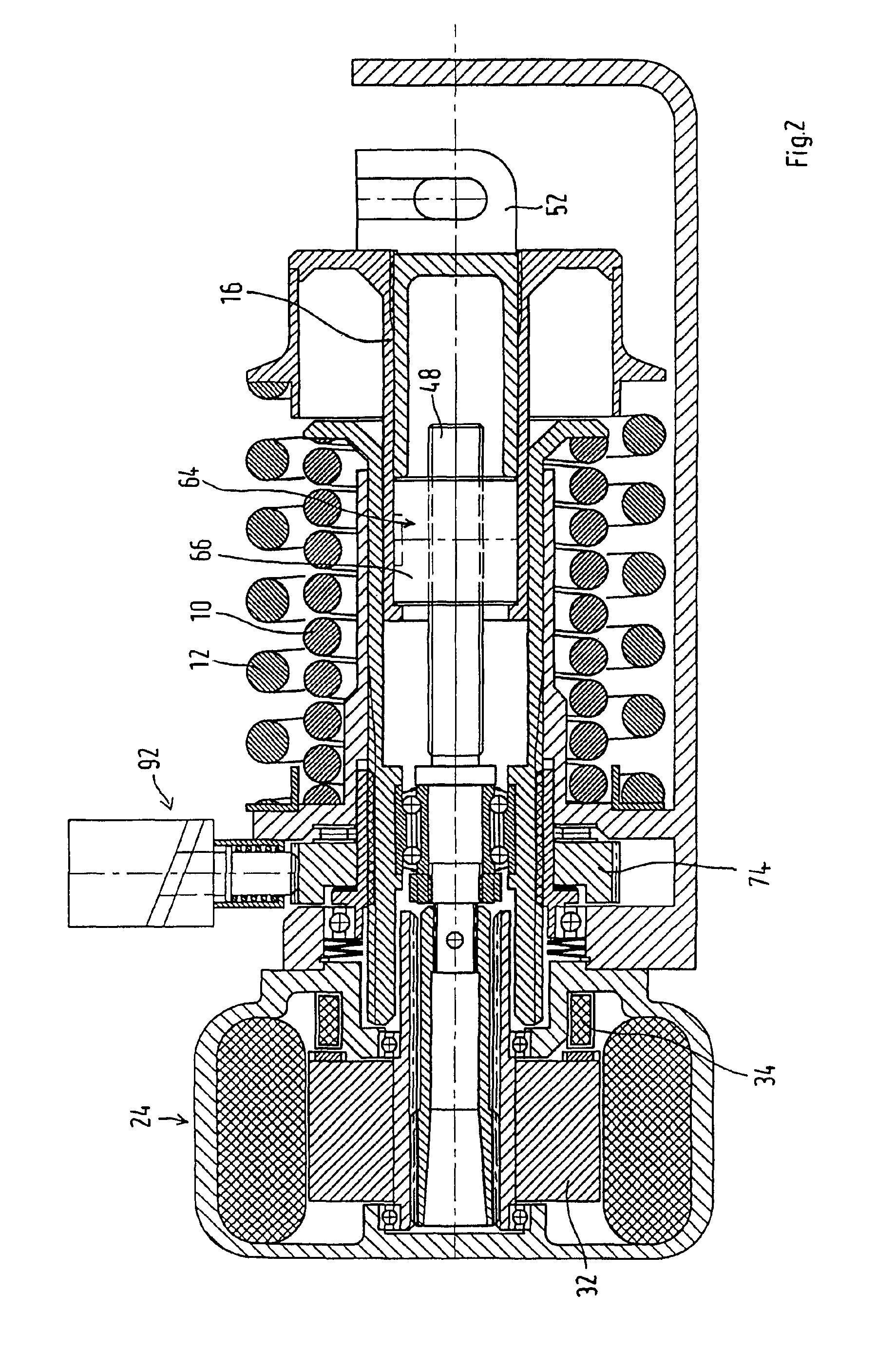
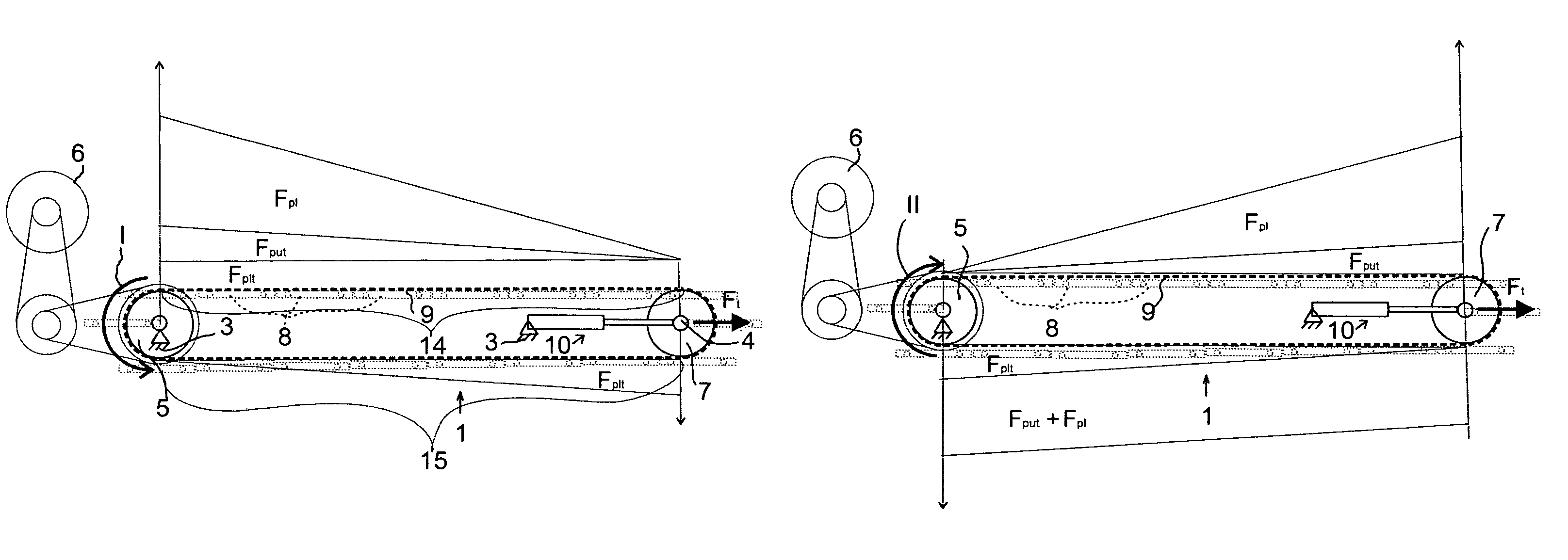
Patents
Literature
129 results about "Force level" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
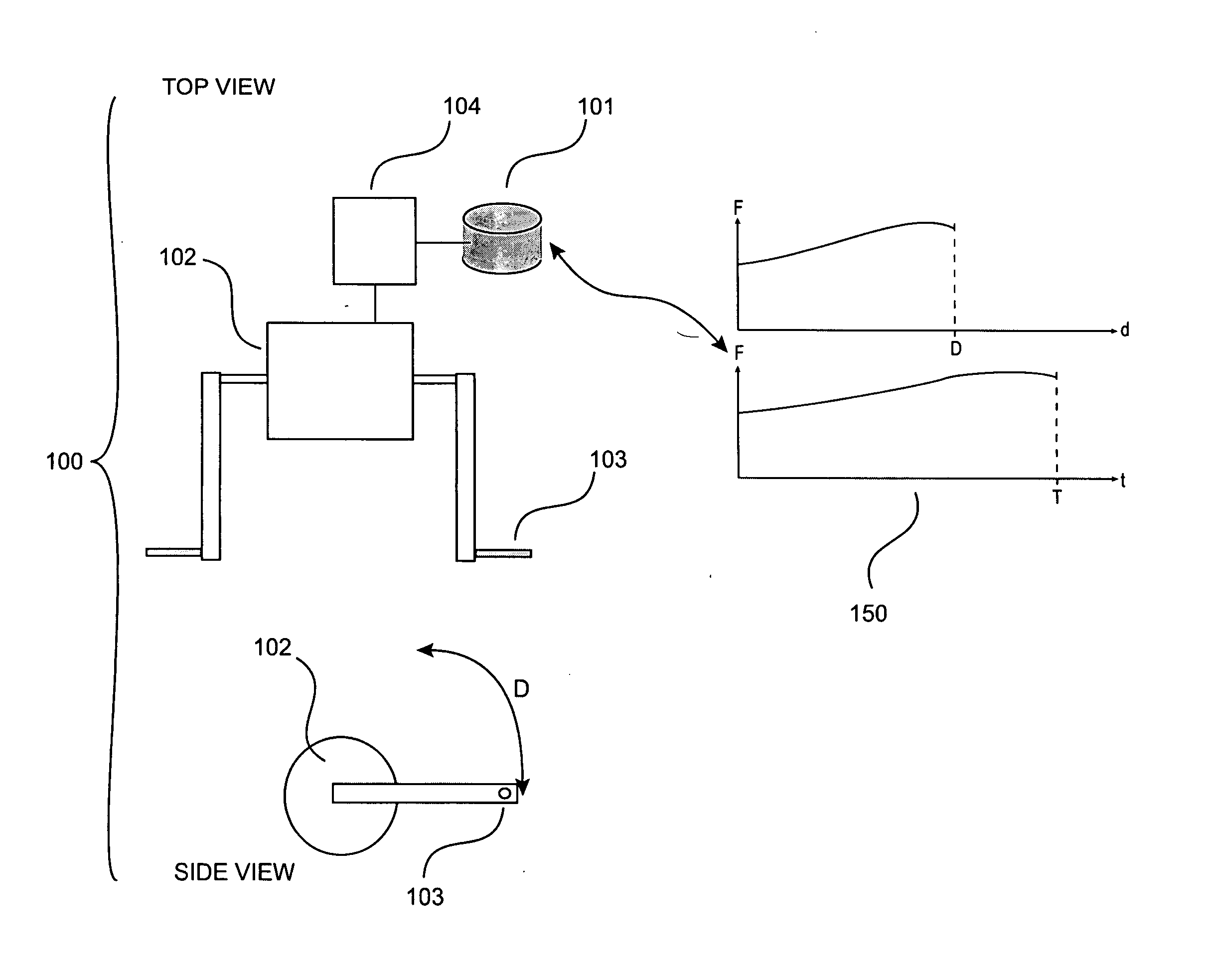
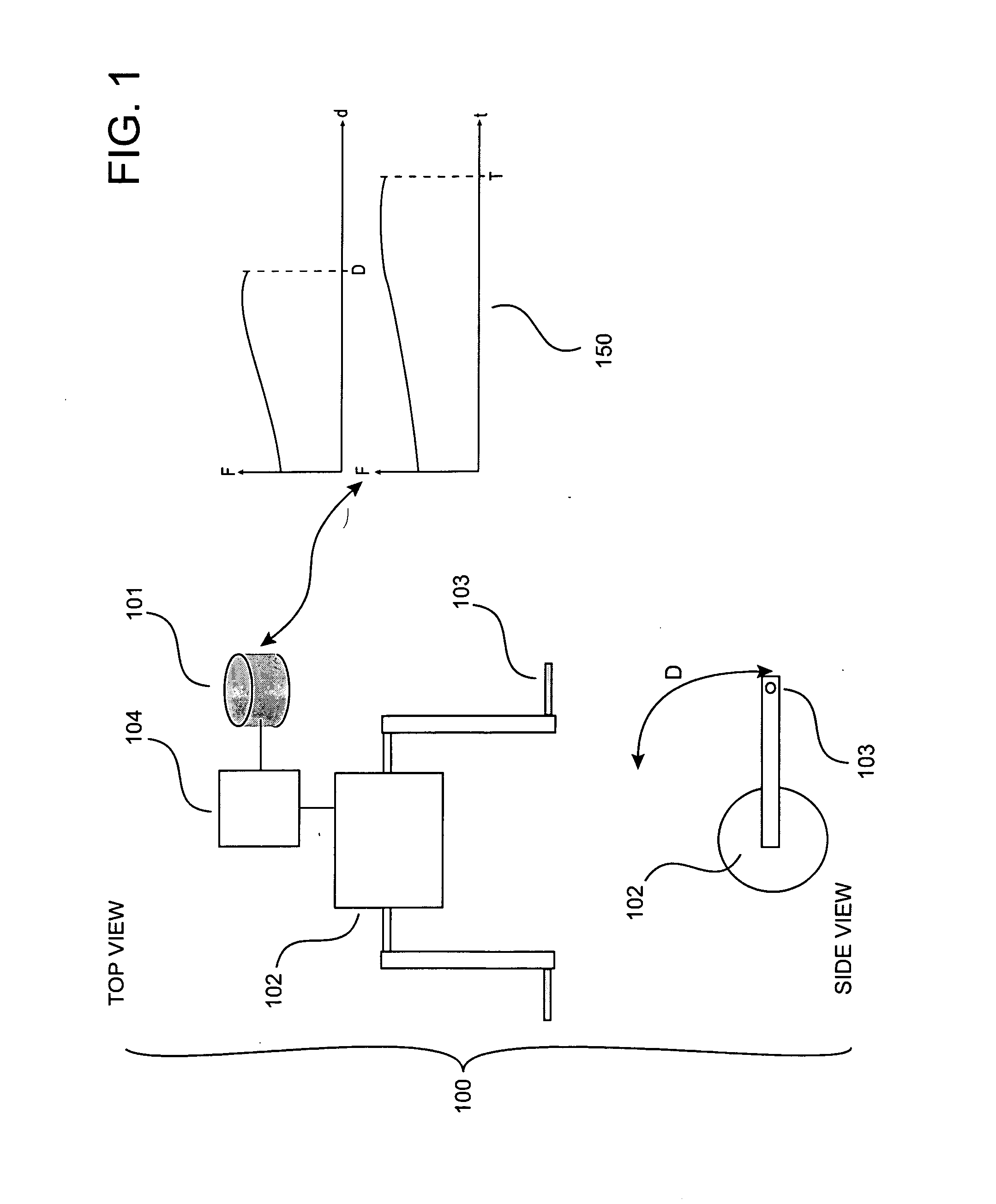
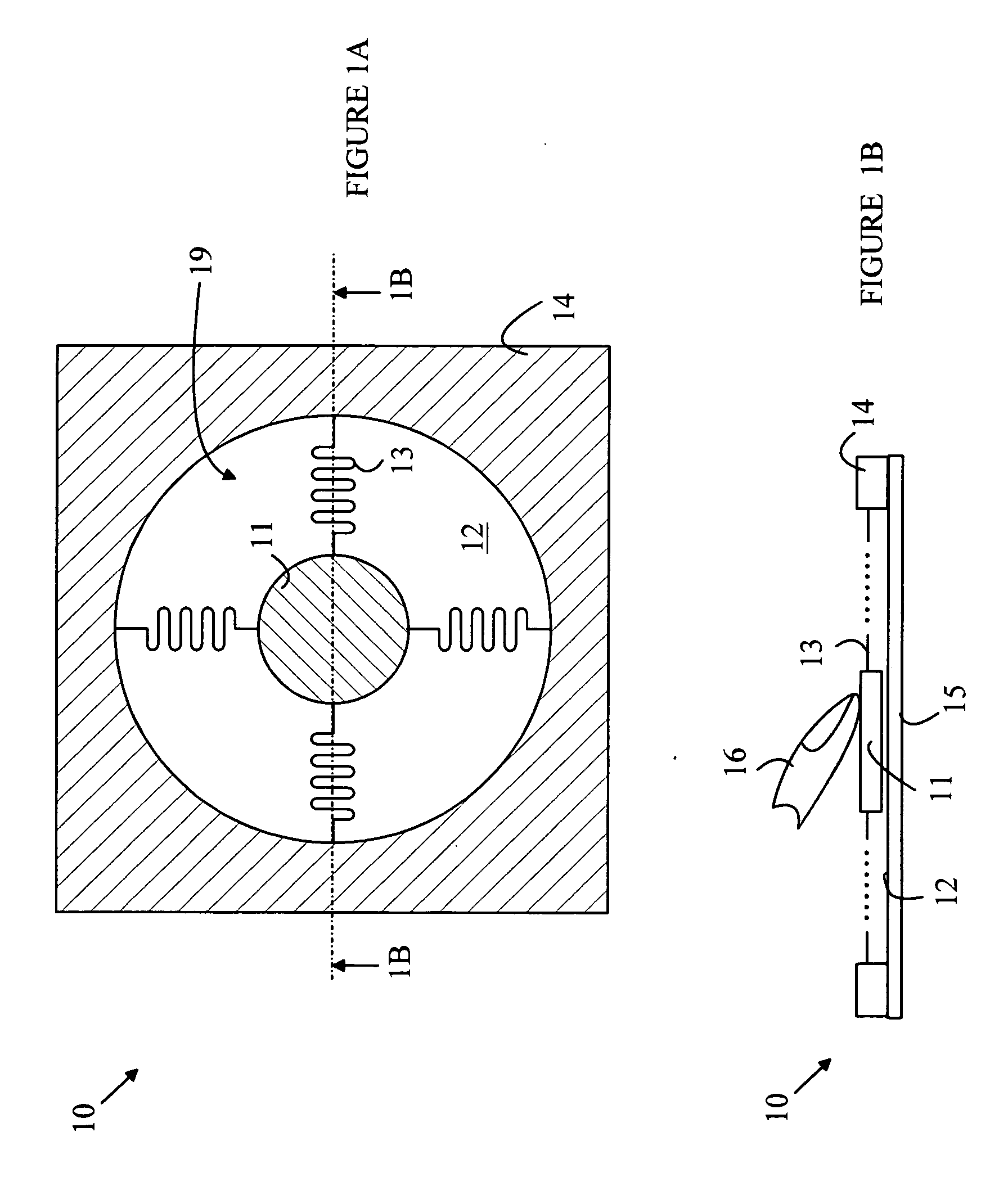
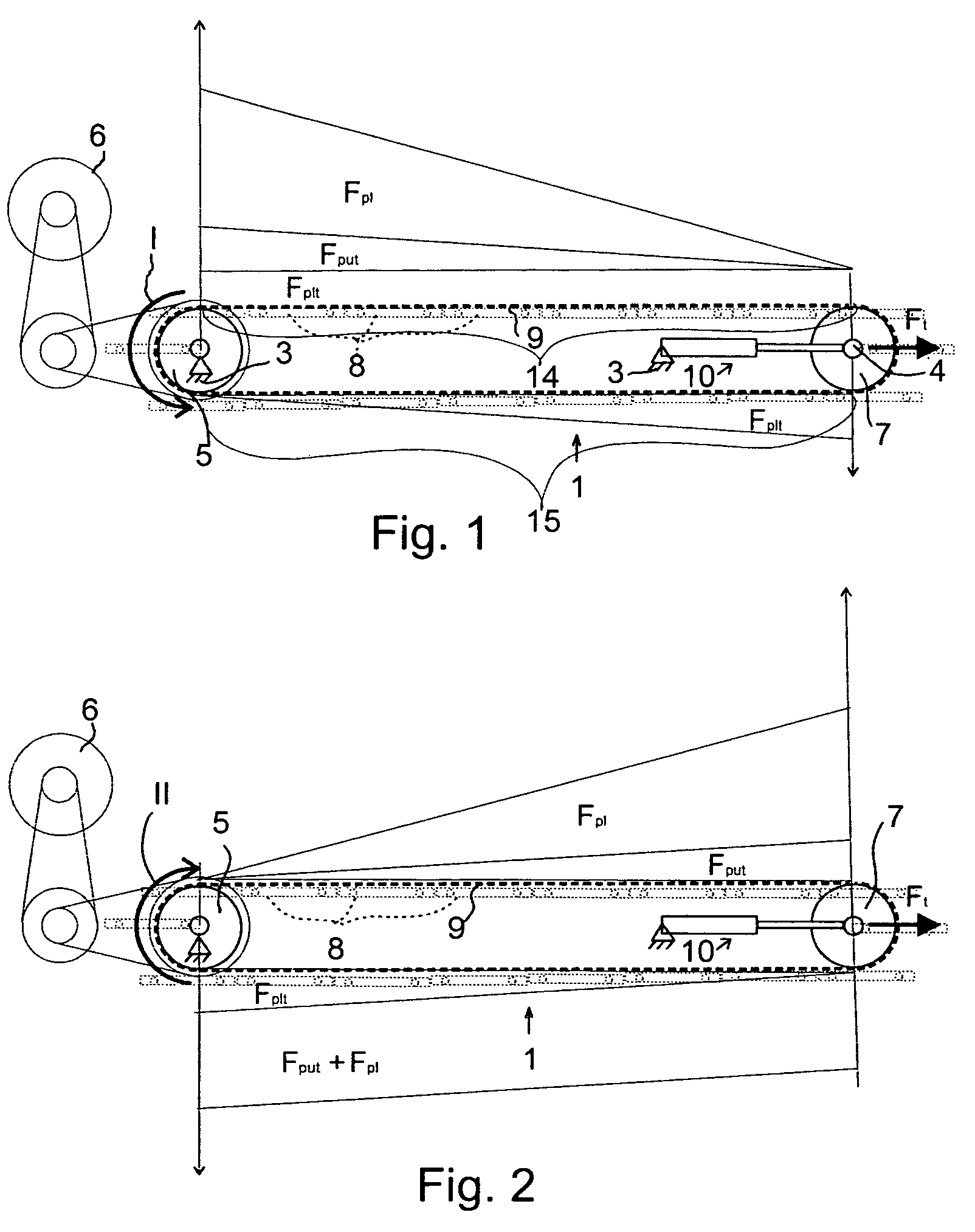
The force continuum is broken down into six broad levels. Each level is designed to be flexible as the need for force changes as the situation develops. It is common for the level of force to go from level two, to level three, and back again in a matter of seconds.
Programmable adaptable resistance exercise system and method
InactiveUS20070202992A1Quantity maximizationMinimizing effort expendedMuscle exercising devicesTime profileRange of motion
A programmable adaptive resistance exercise system and method. New type of resistance allows a user to maximize amount of muscle growth benefit while minimizing the effort to attain that level. Resistance level may be controlled by computer based on position or any derivate thereof with respect to time. Resistance is adaptive since force level used throughout exercise range is based on current and past performance data. Level of effort and force versus time profile combinations are unlimited. Rest calculated based on the current and past performance data. May utilize hardware having a motor, an exercise interface (such as an bar or handle for example), a position sensor, digital input device to identify someone, computer configured to control the motor and exercise interface using current and past personal training data, calculate an exercise program based on preference and a time for subsequent workout, optionally alert a user when time to workout.
Owner:GRASSHOFF ERIC
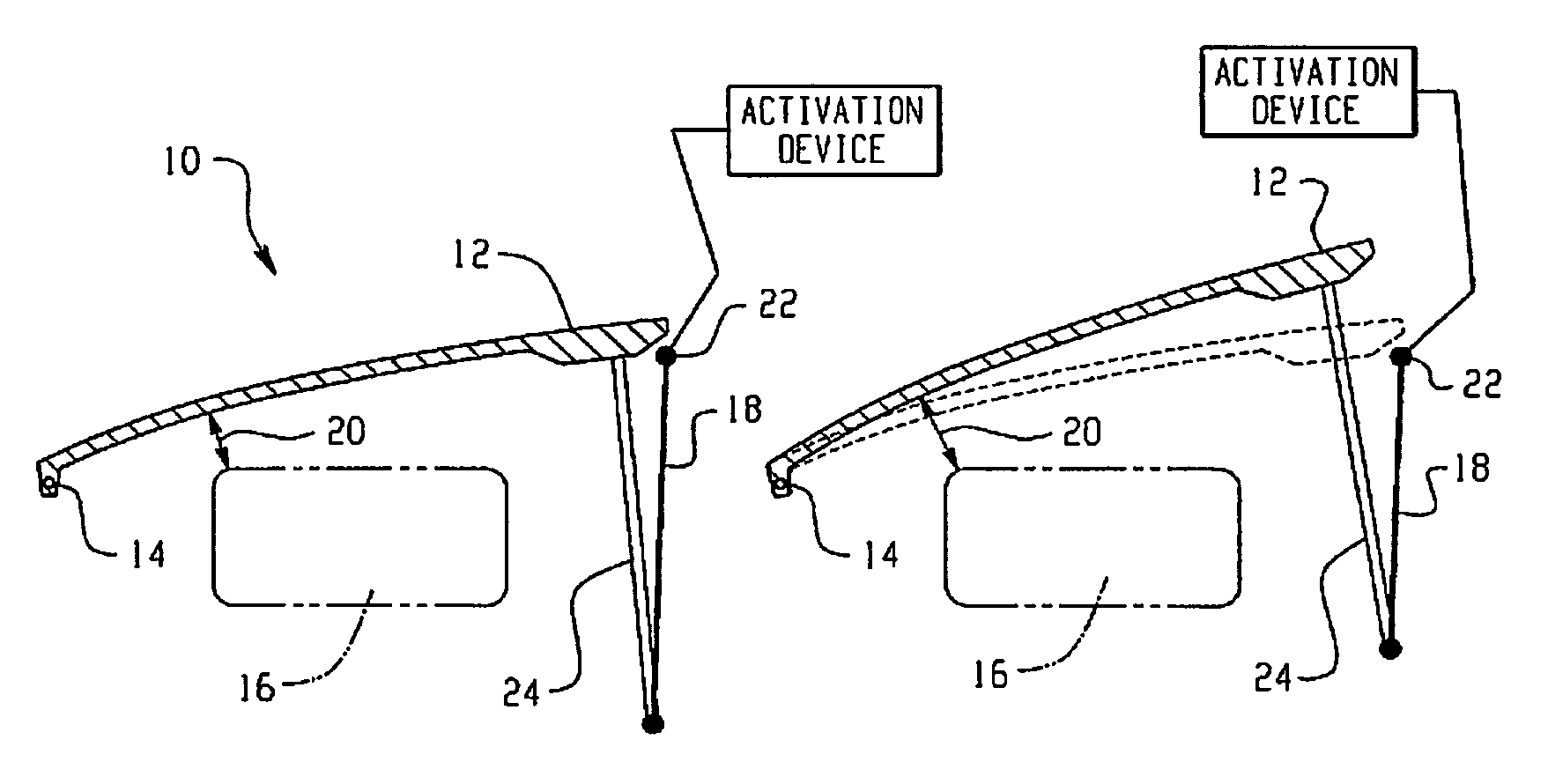
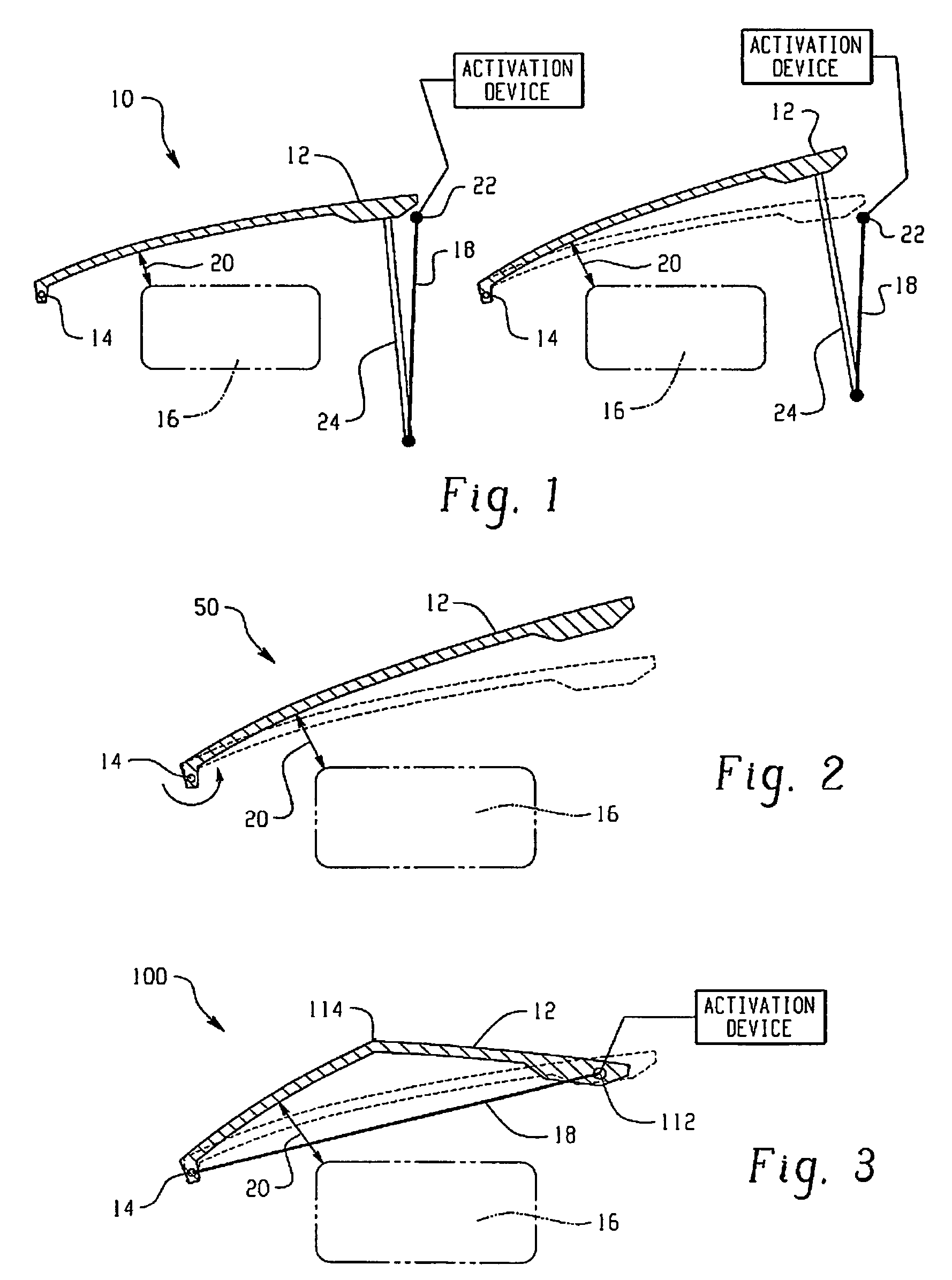
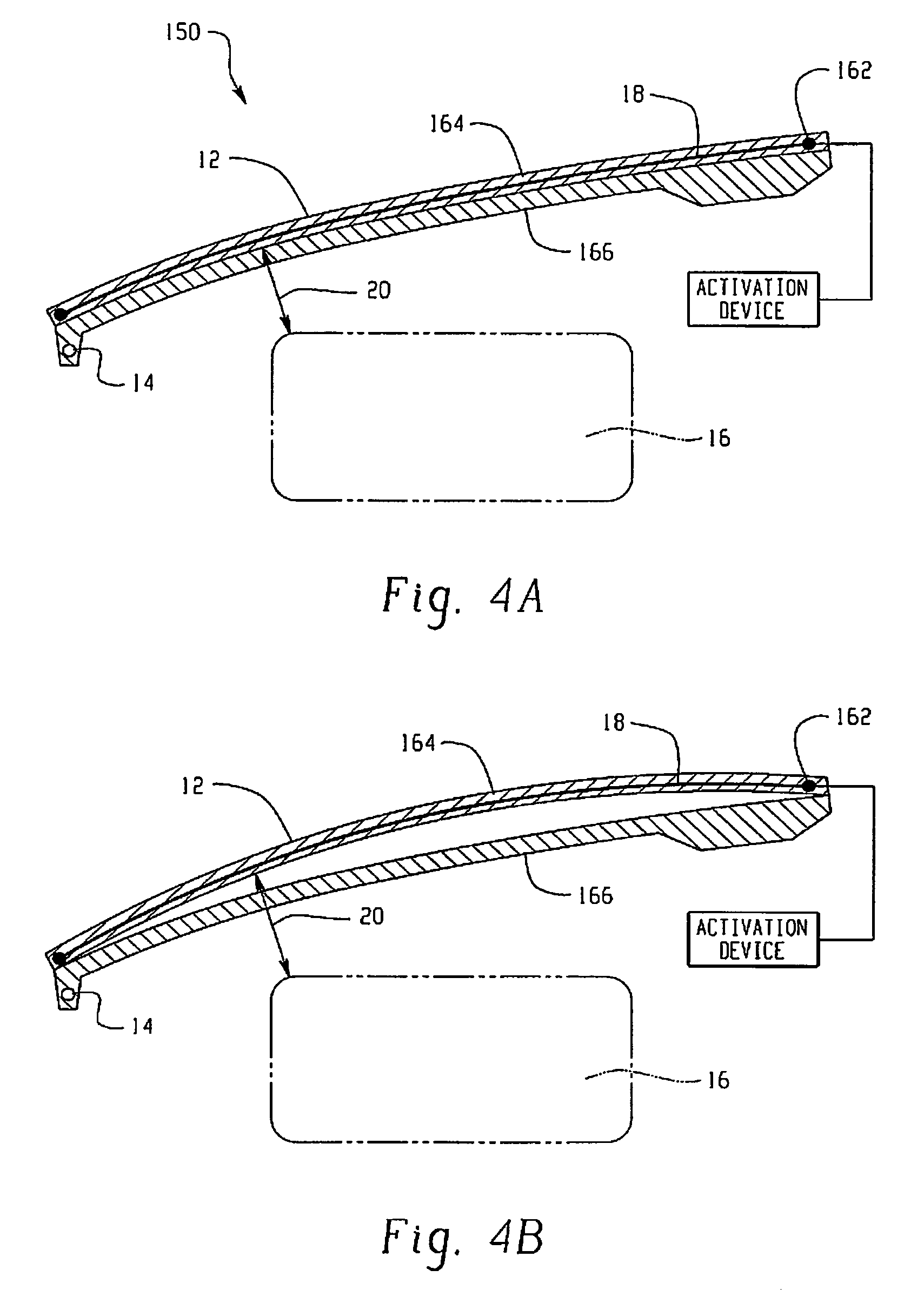
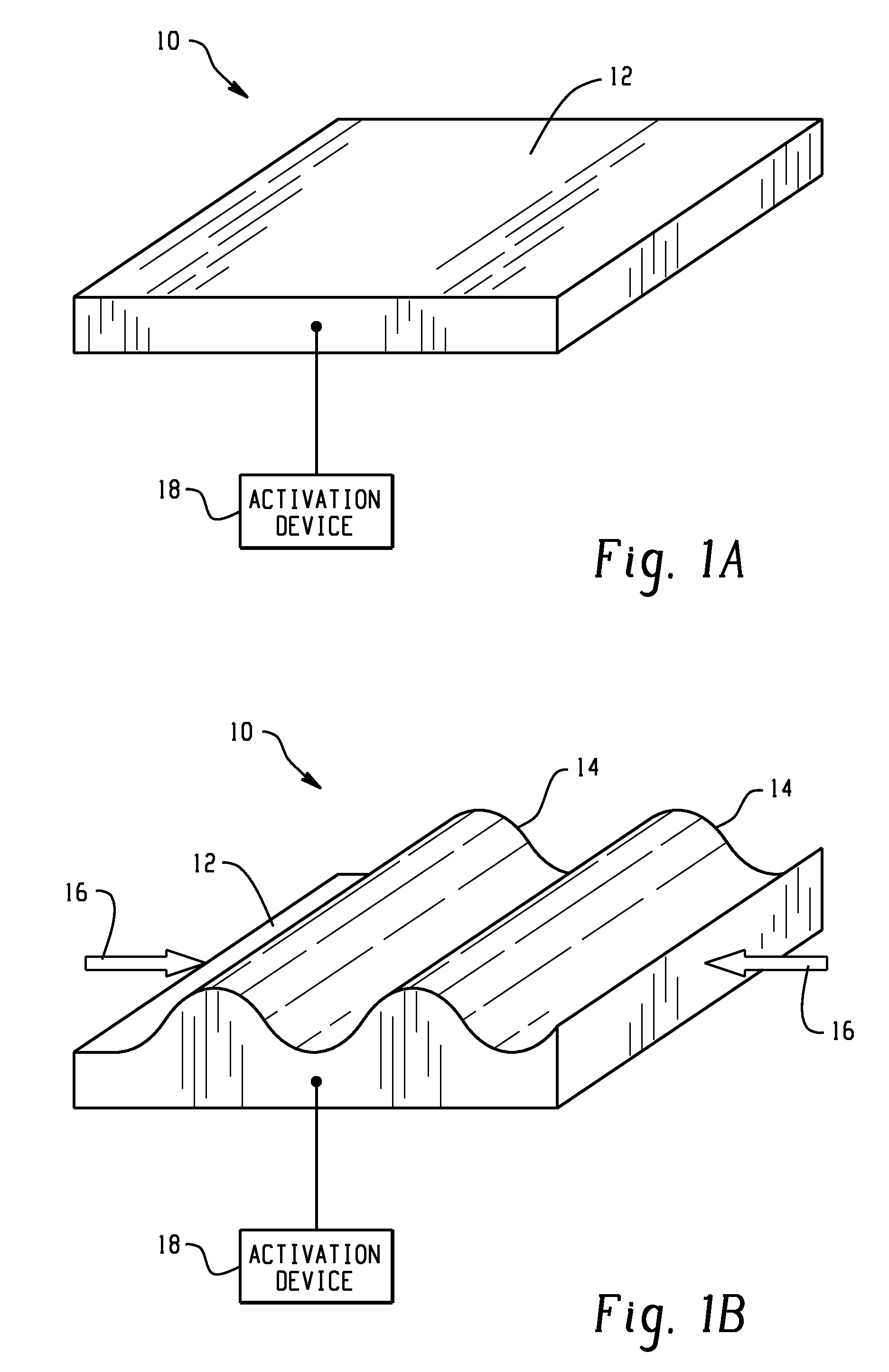
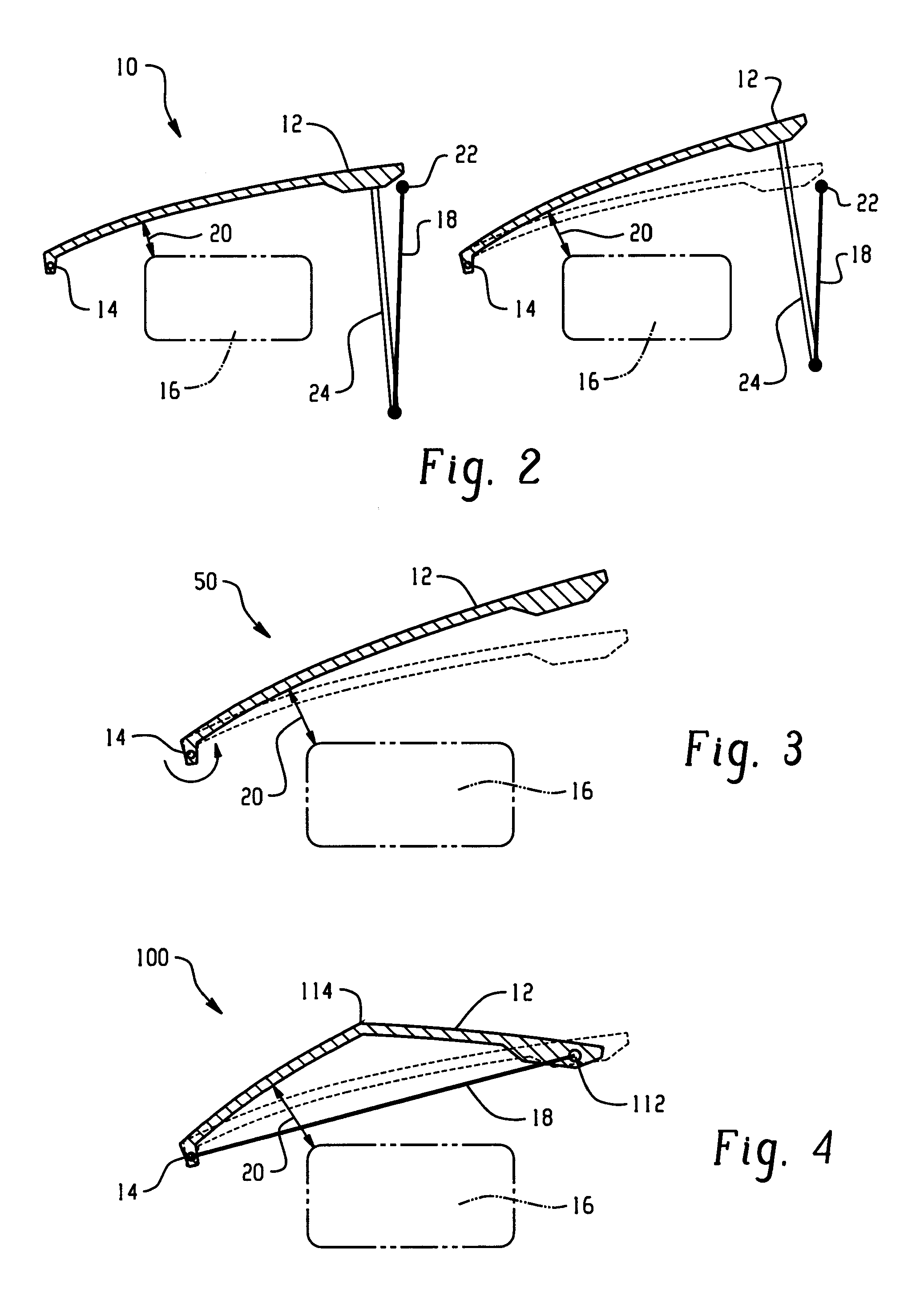
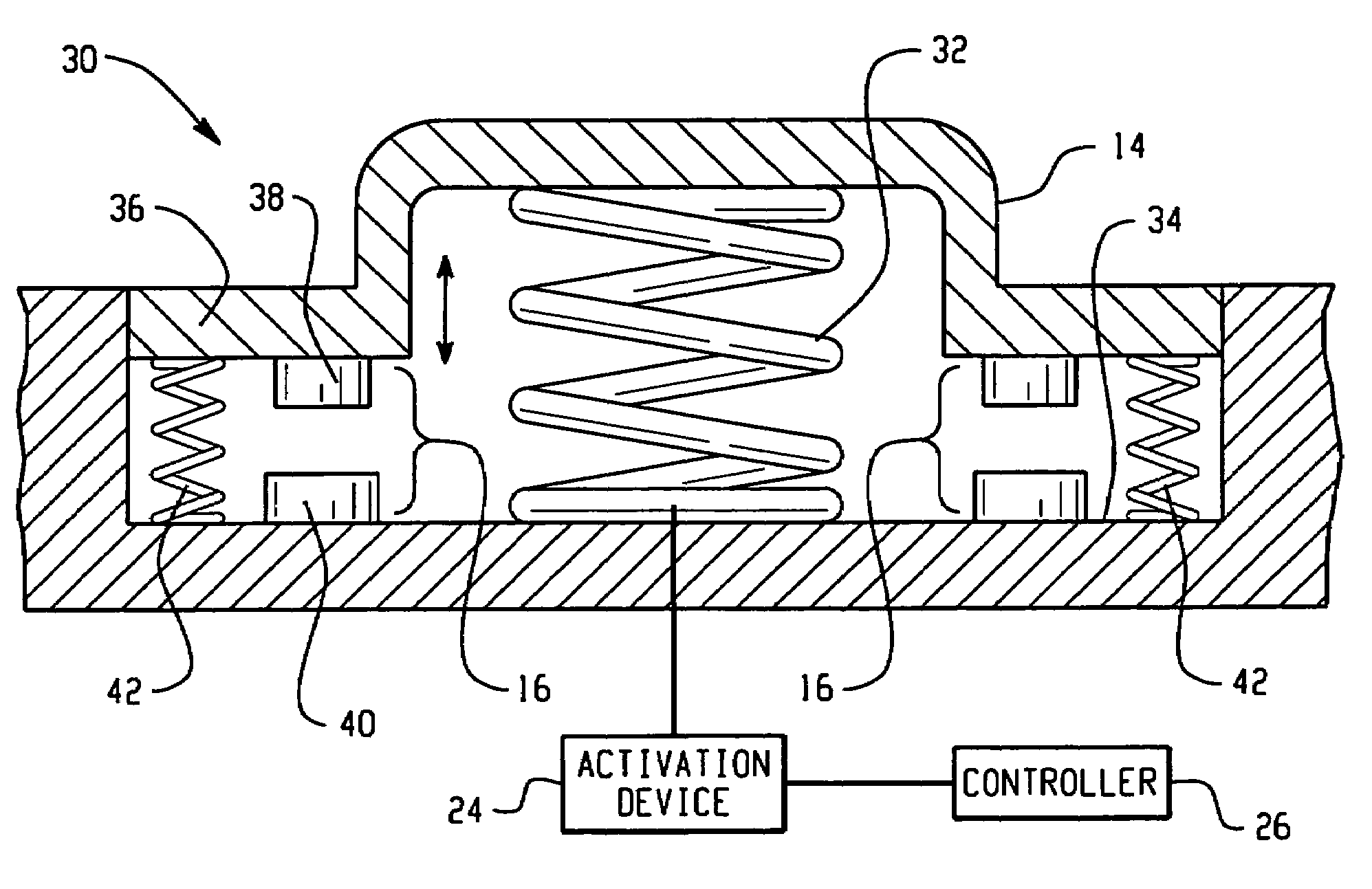
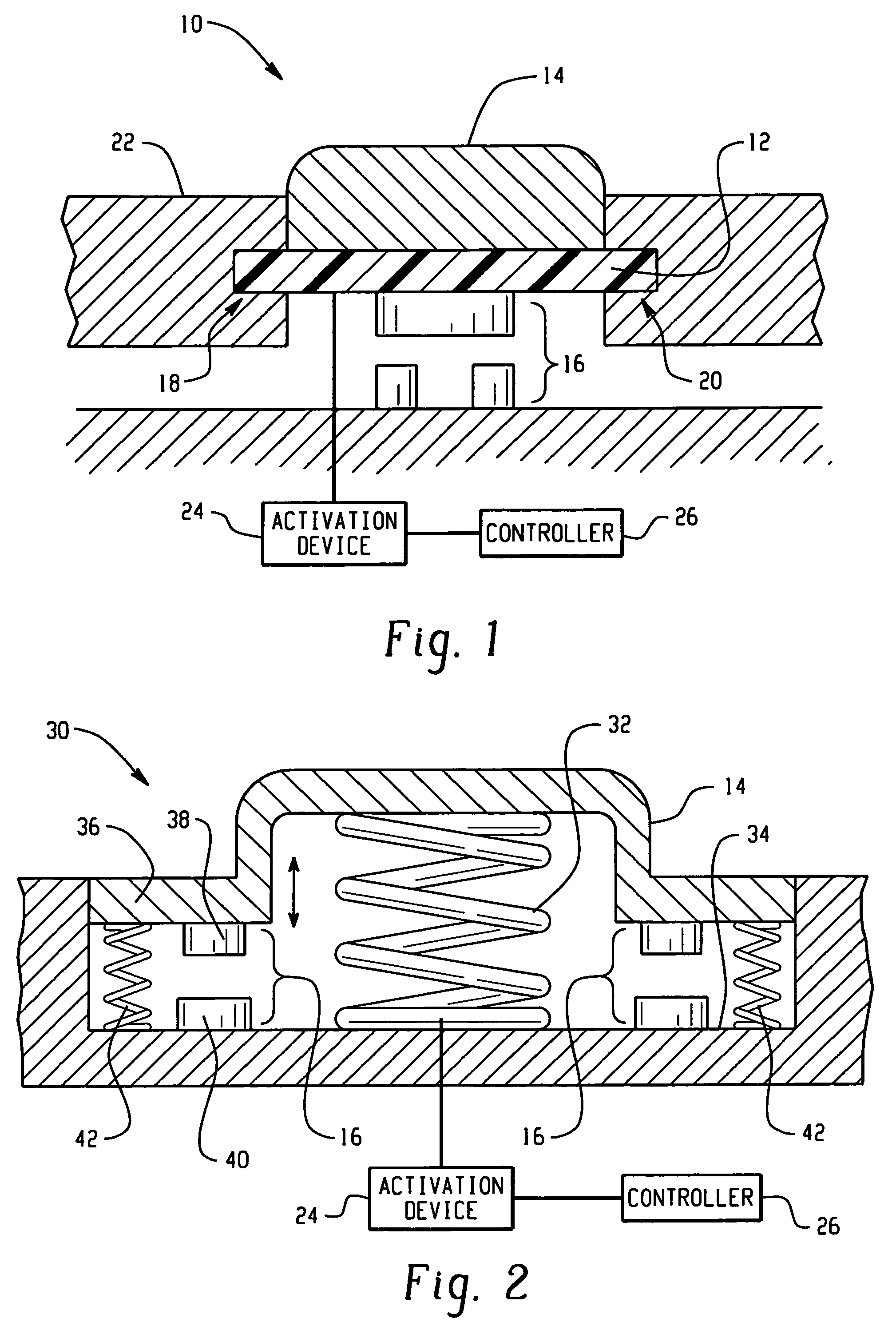
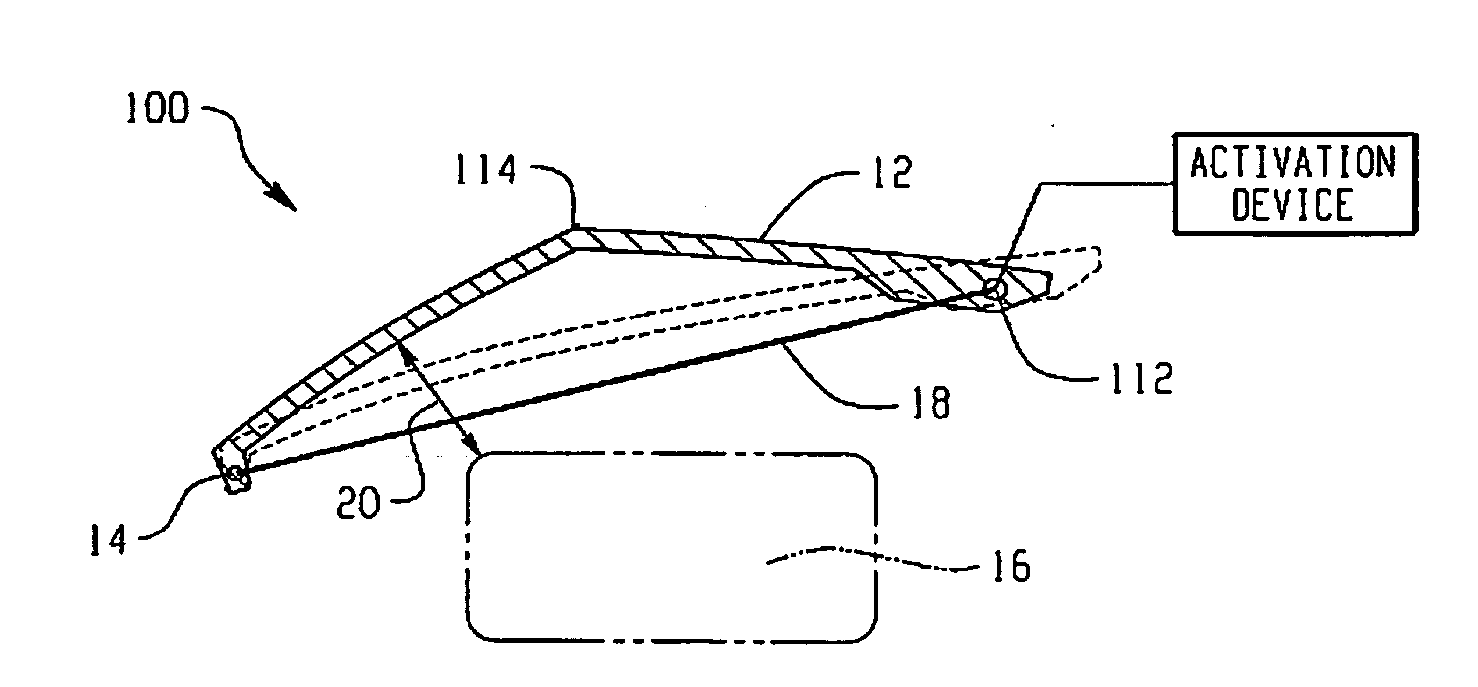
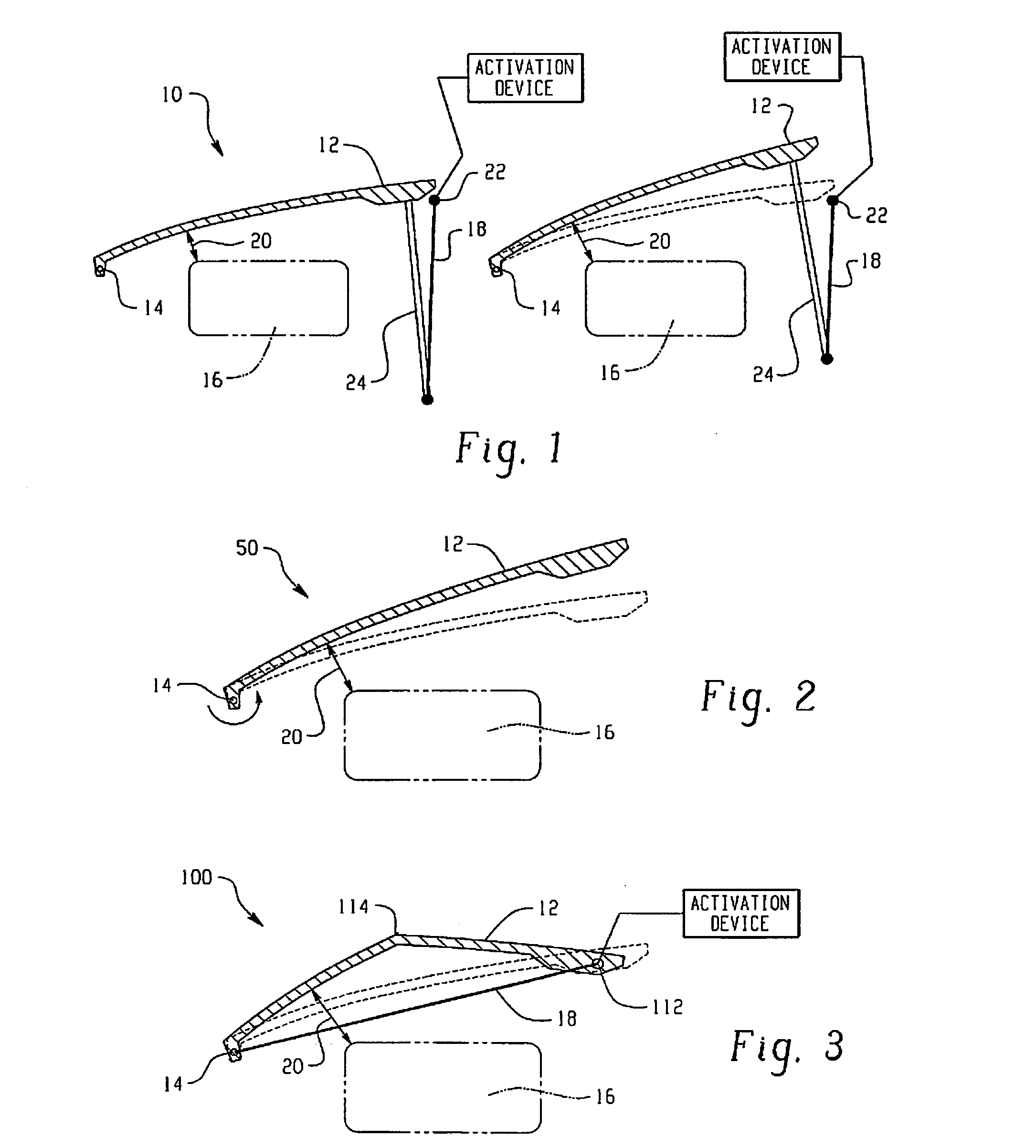
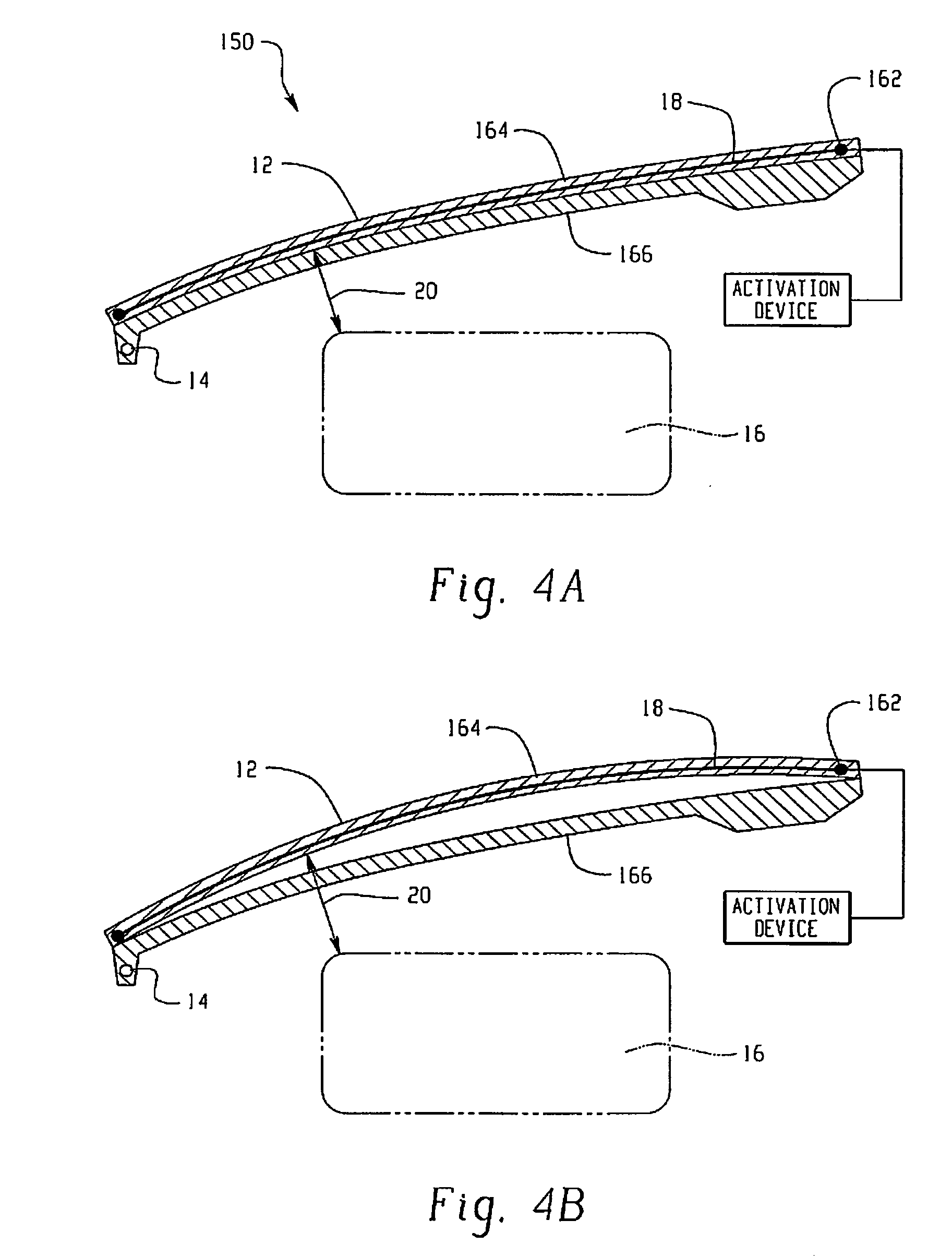
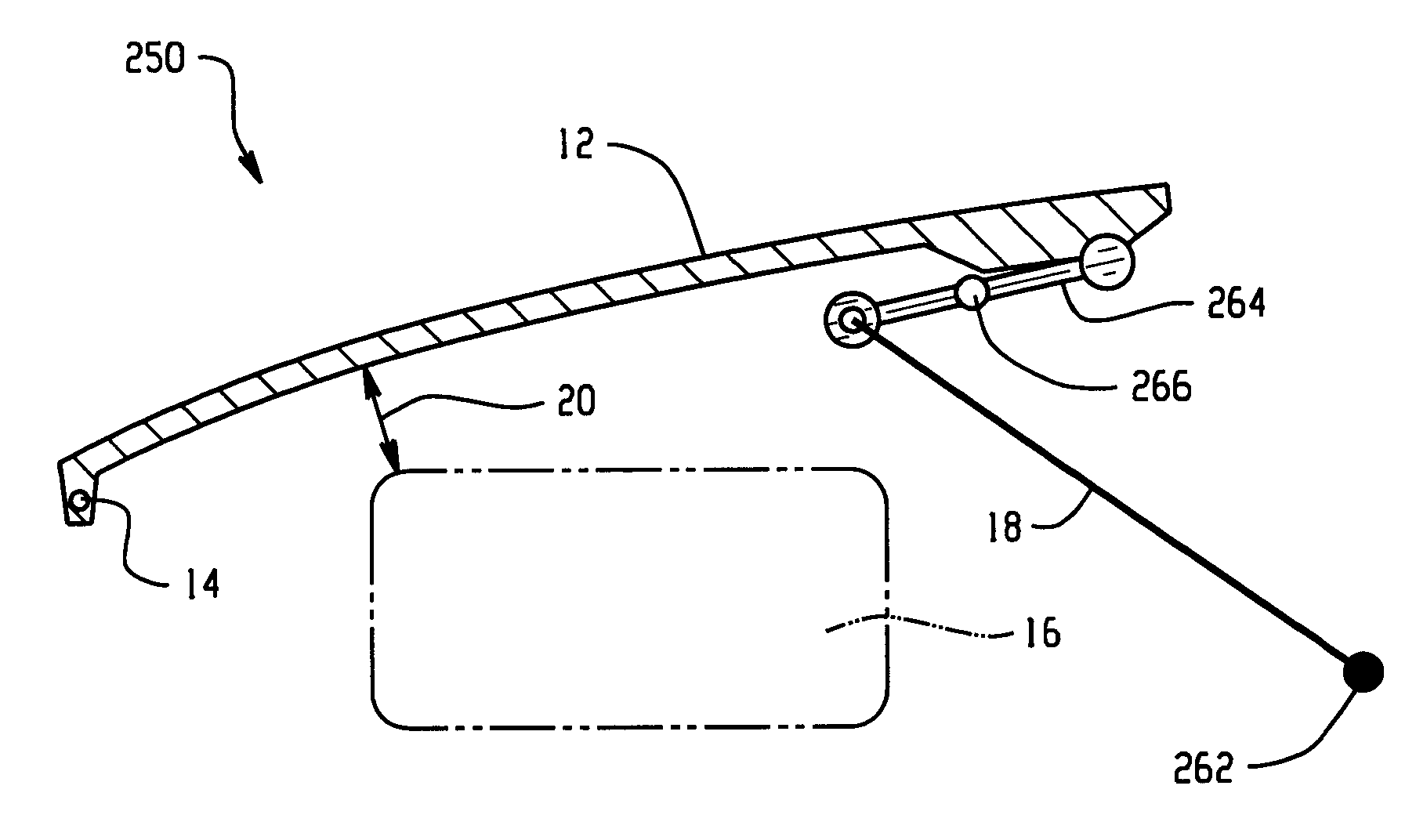
Hood lift mechanisms utilizing active materials and methods of use
InactiveUS7063377B2Clearance distanceIncrease distanceVehicle seatsSuperstructure subunitsIonic polymer–metal compositesEnergy absorption
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC +1
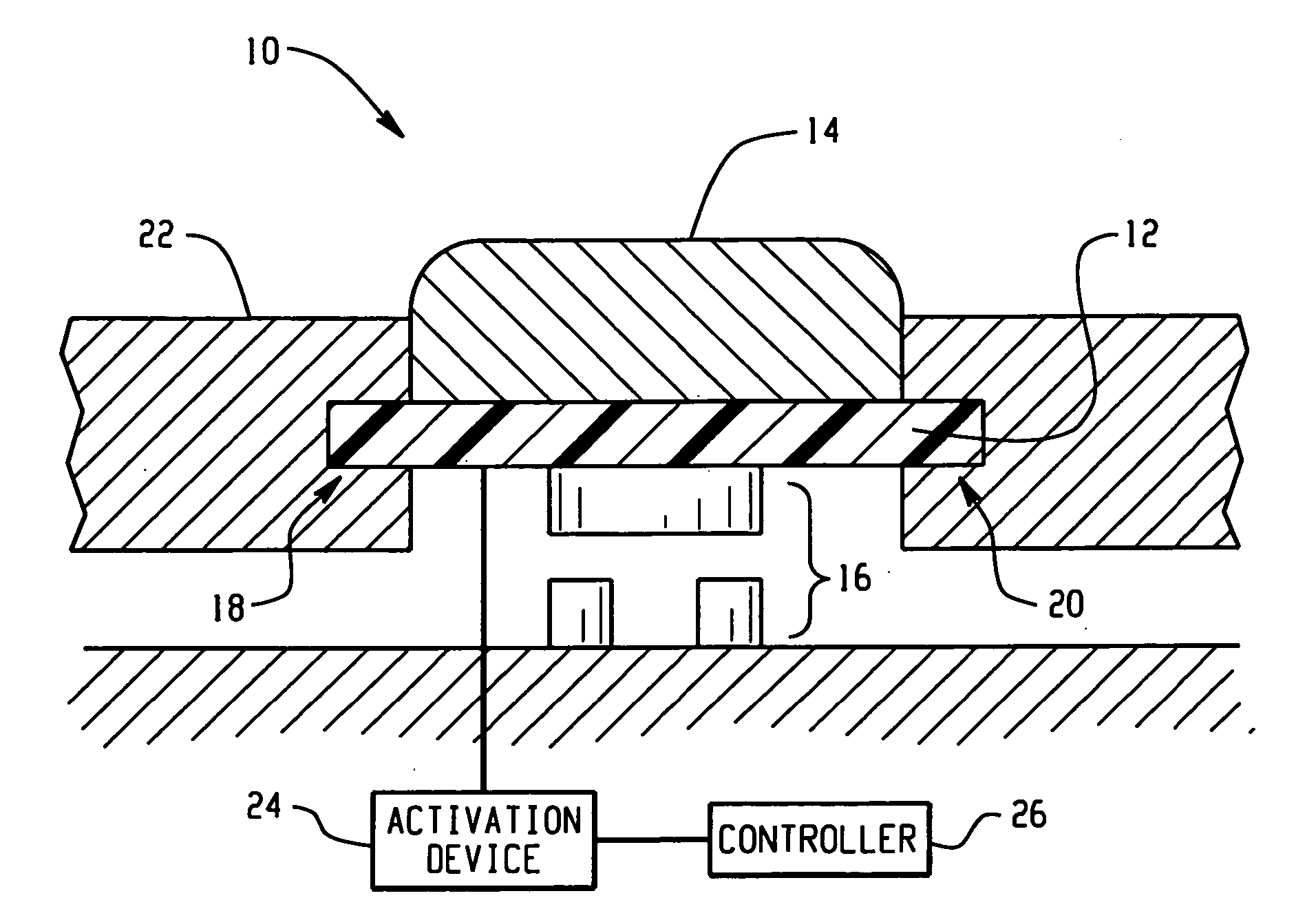
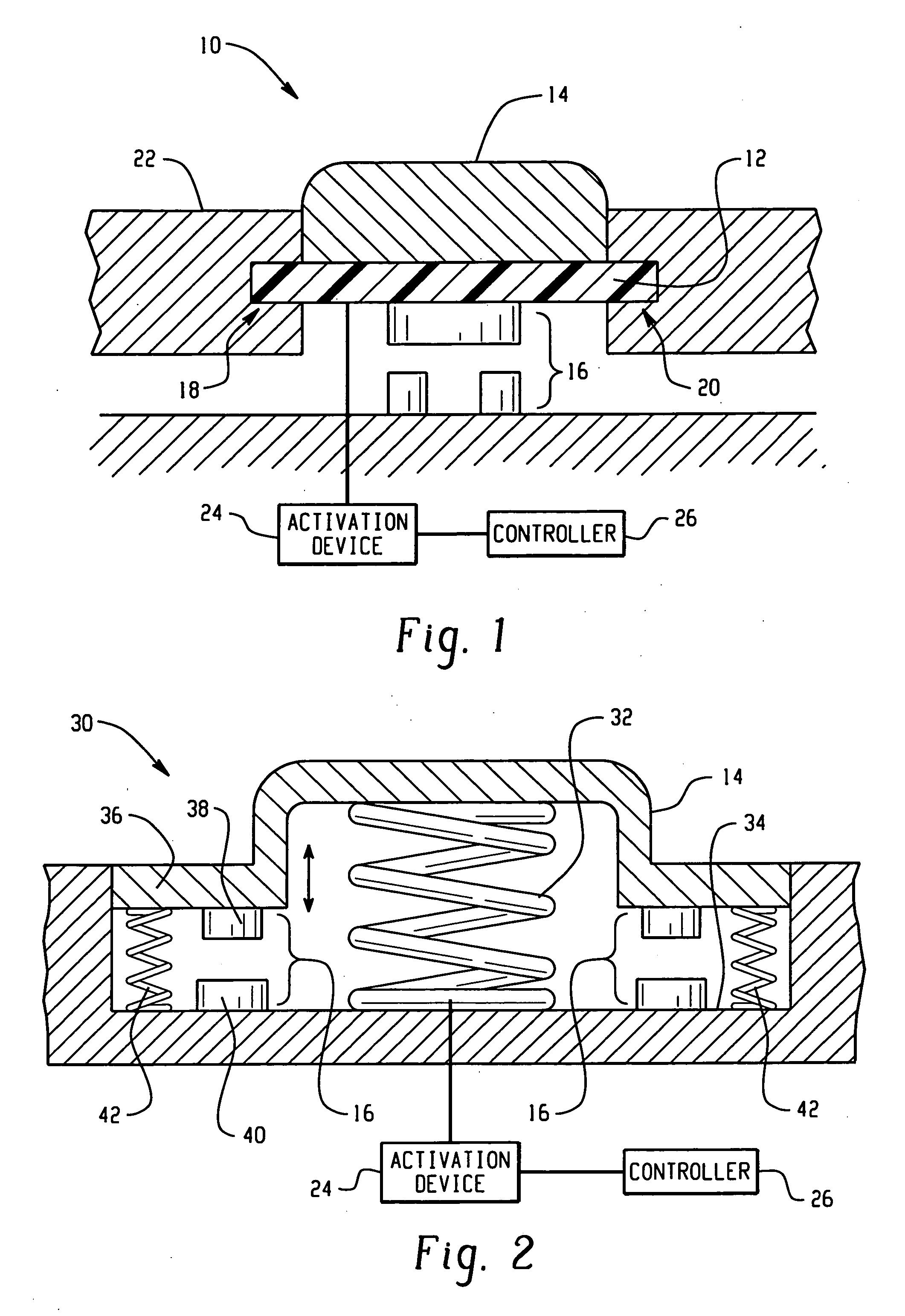
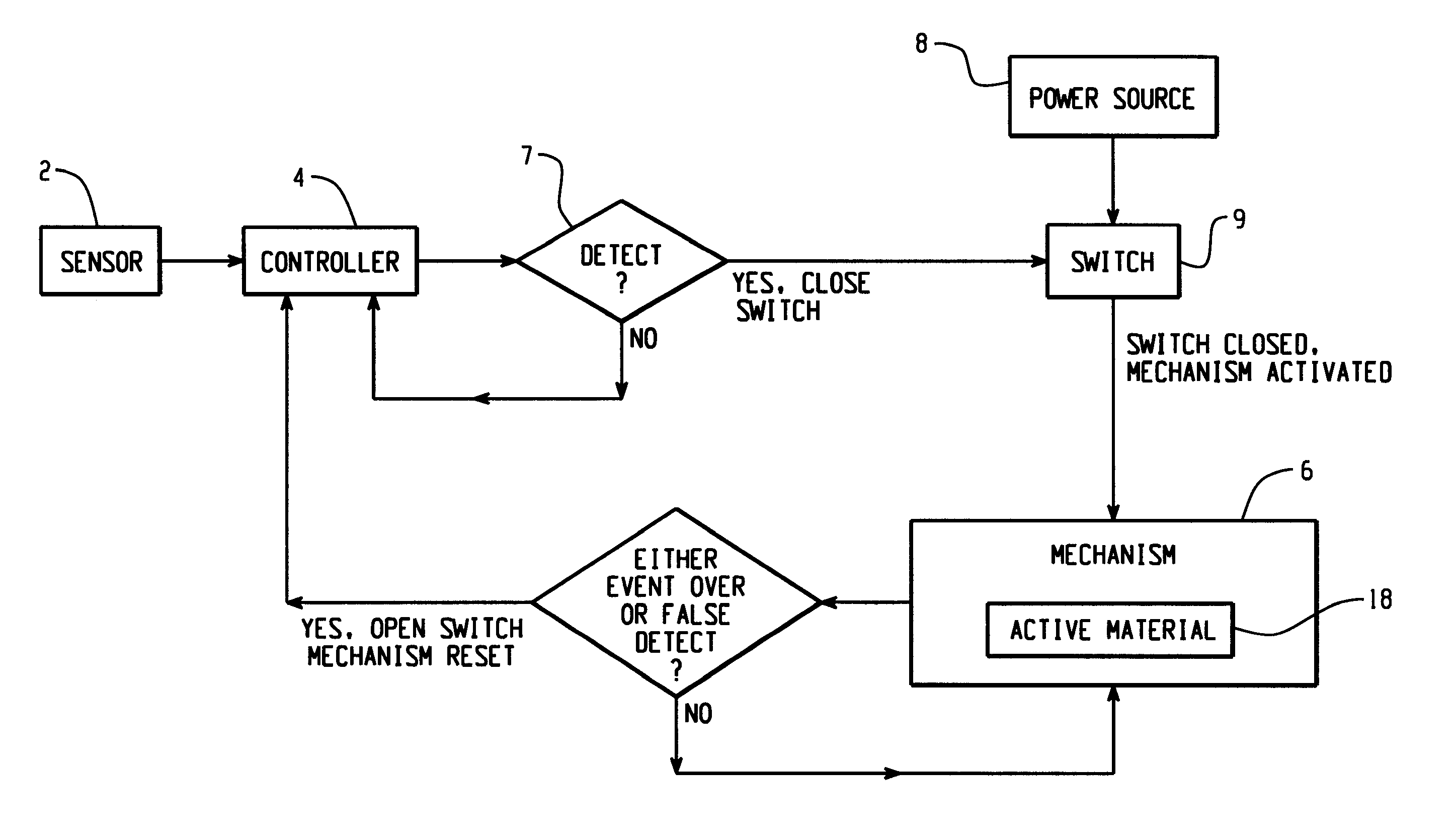
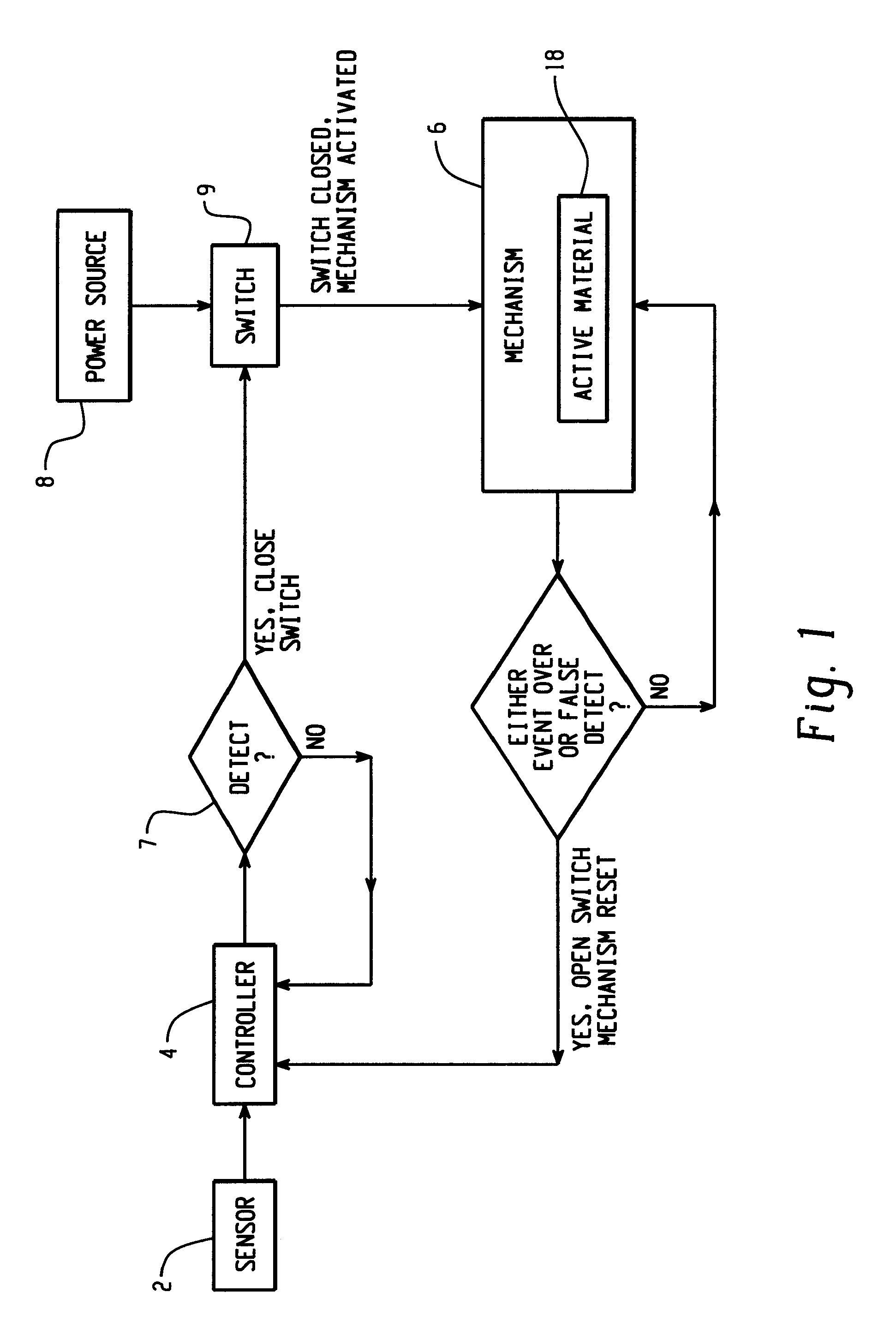
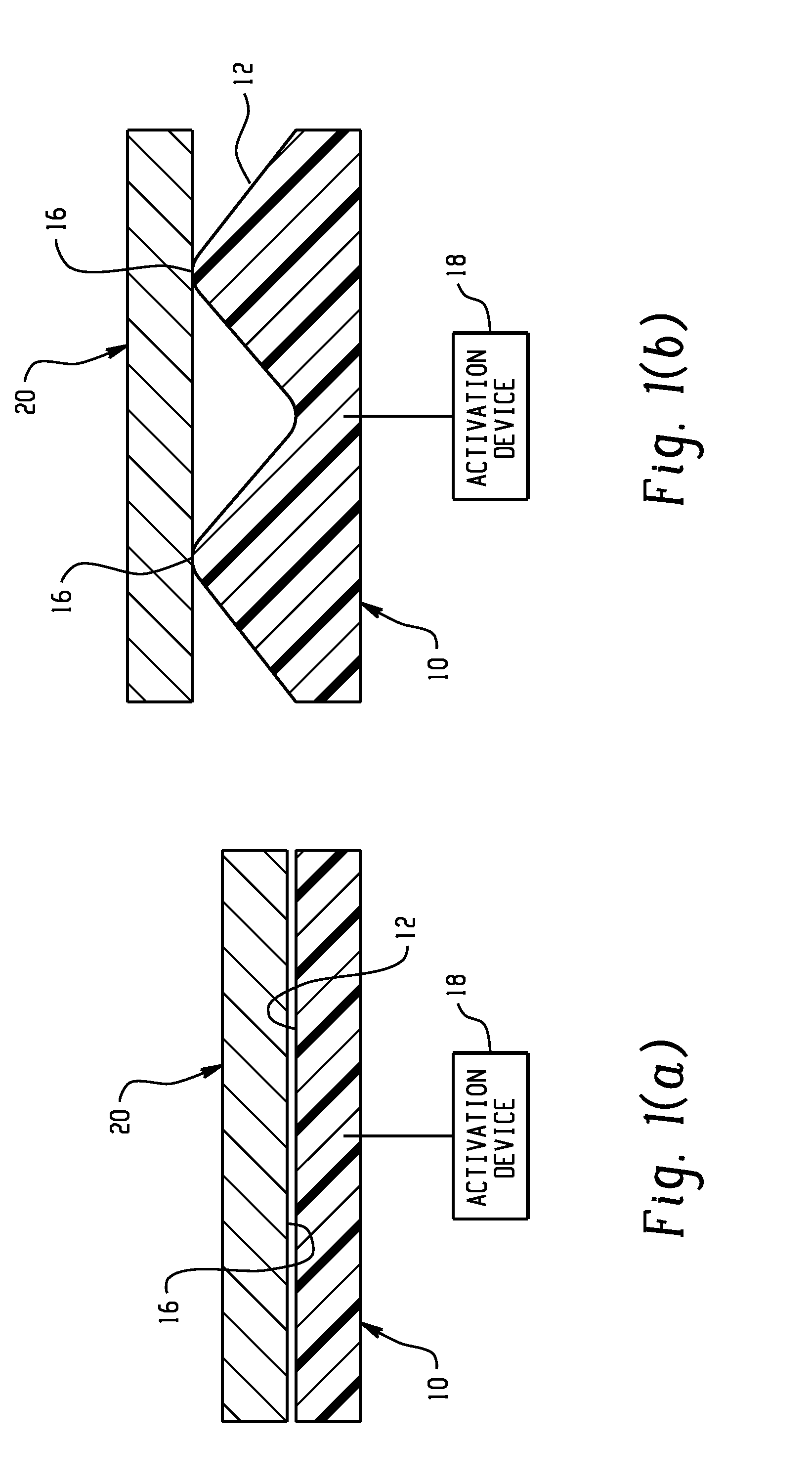
Active material based lockout mechanisms
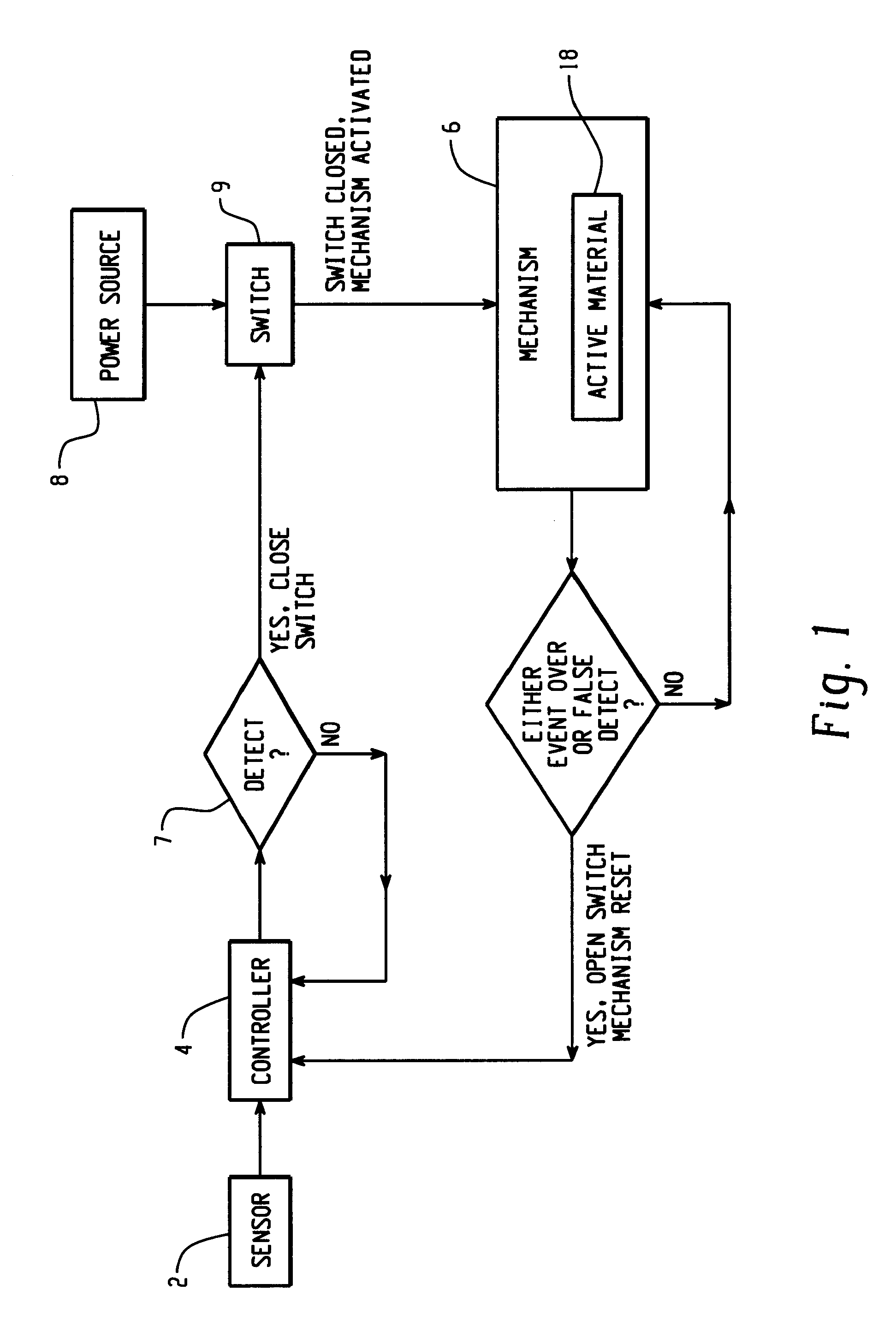
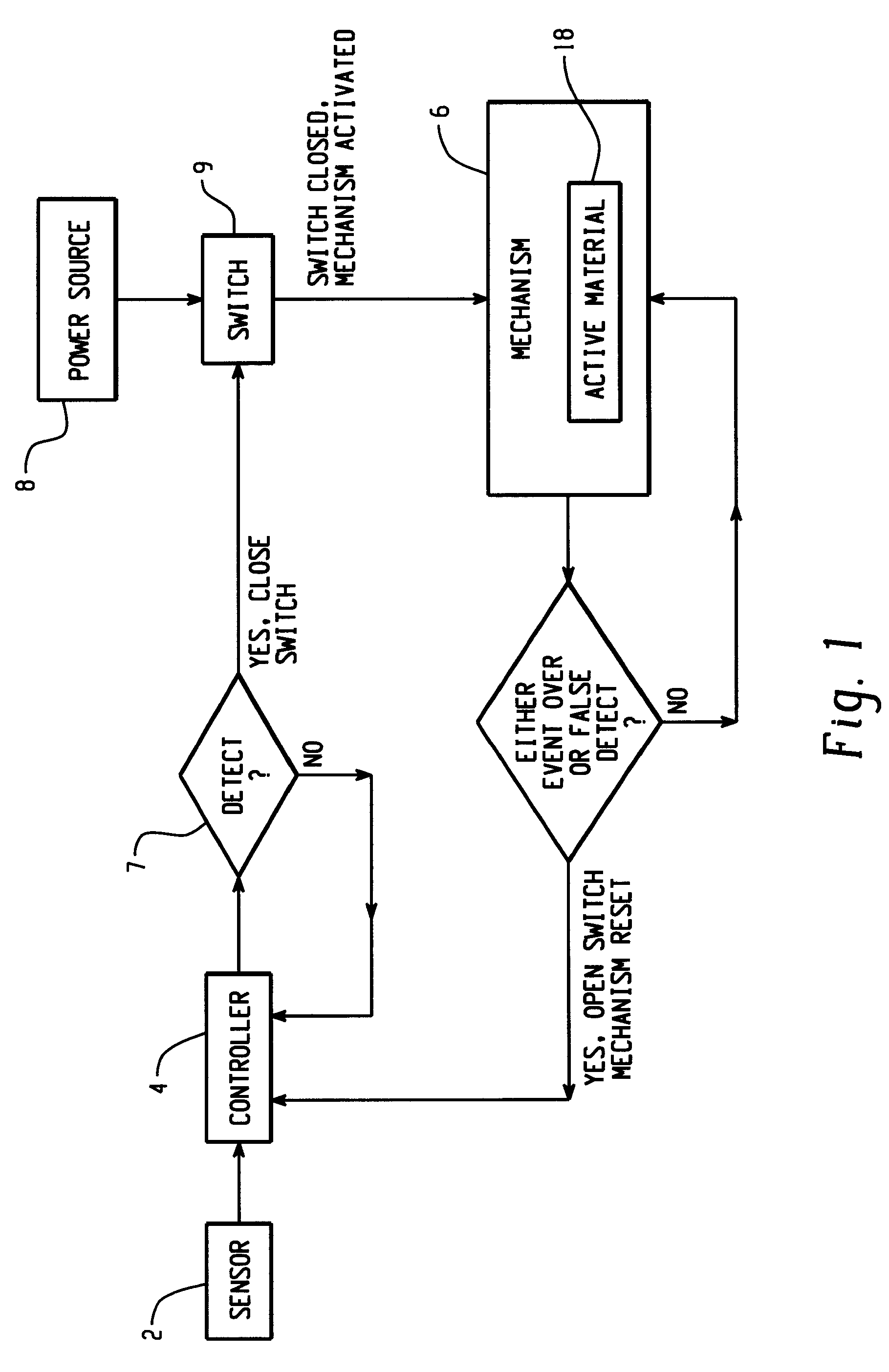
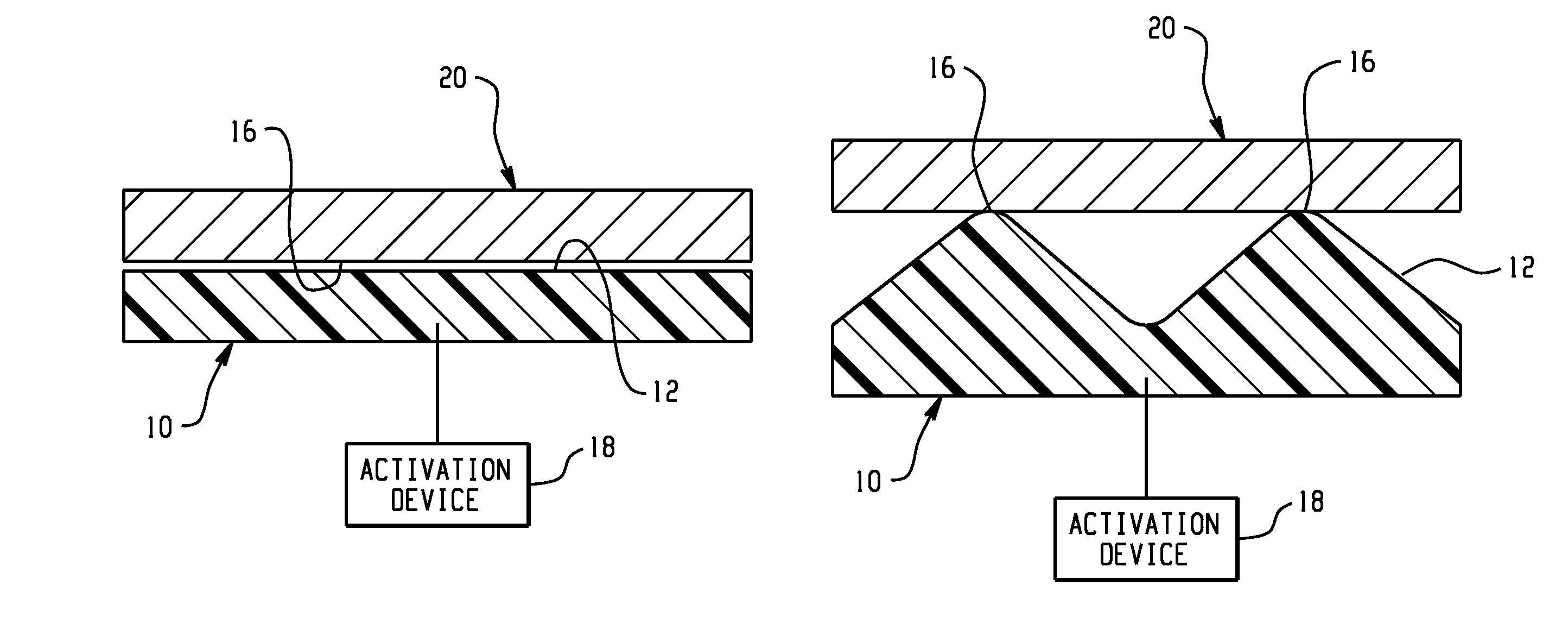
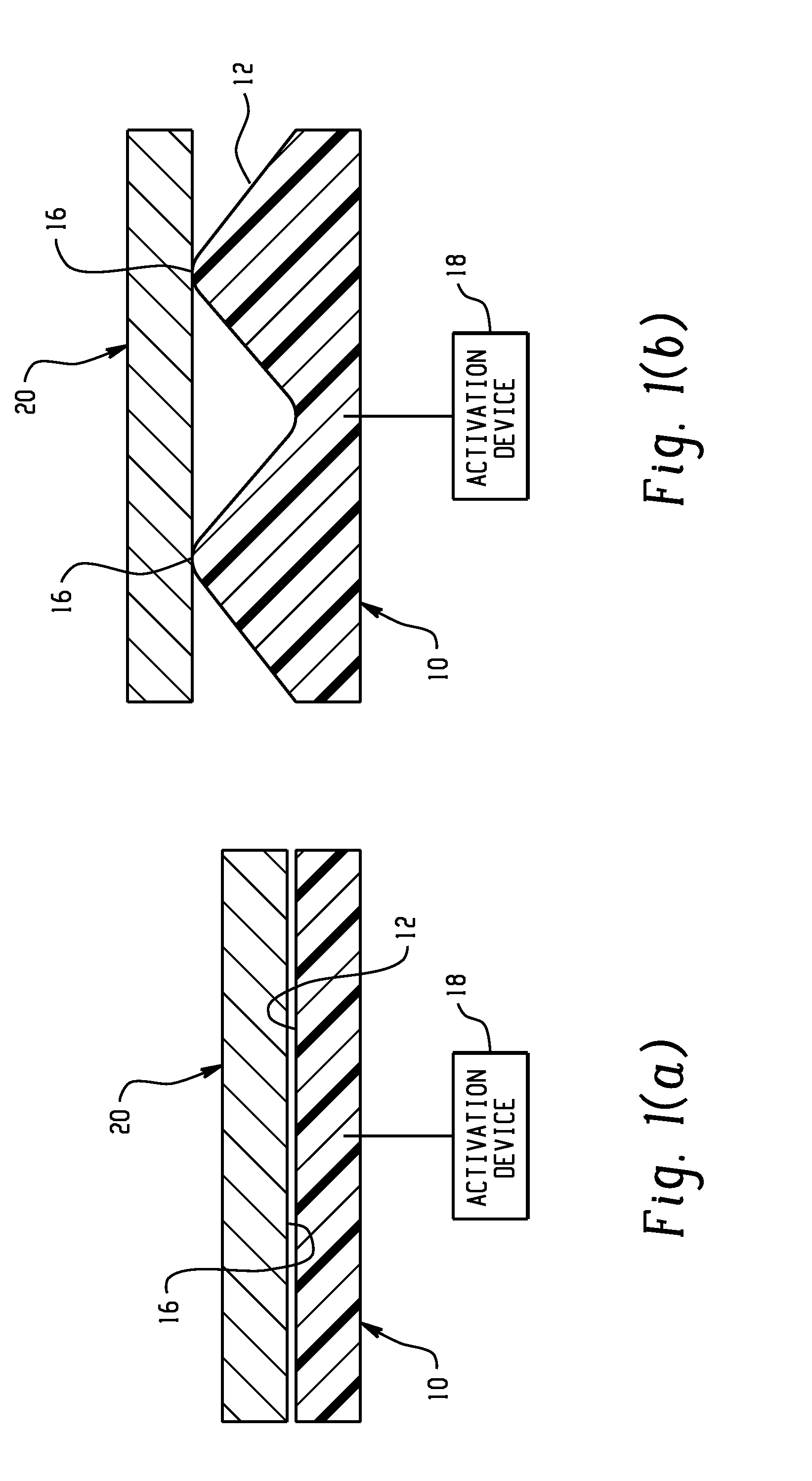
Control mechanisms and methods of use include the use of active materials as a blocking element. The control mechanisms generally include a tactile control in operative communication with an electrical circuit, wherein actuation of the tactile control closes the electrical circuit to activate a function. The blocking element includes an active material that is intermediate to the electrical circuit and the tactile control. The active material is adapted to change at least one attribute such as a modulus property in response to an activation signal. The change in the at least one attribute selectively changes a force level for actuating the tactile control.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
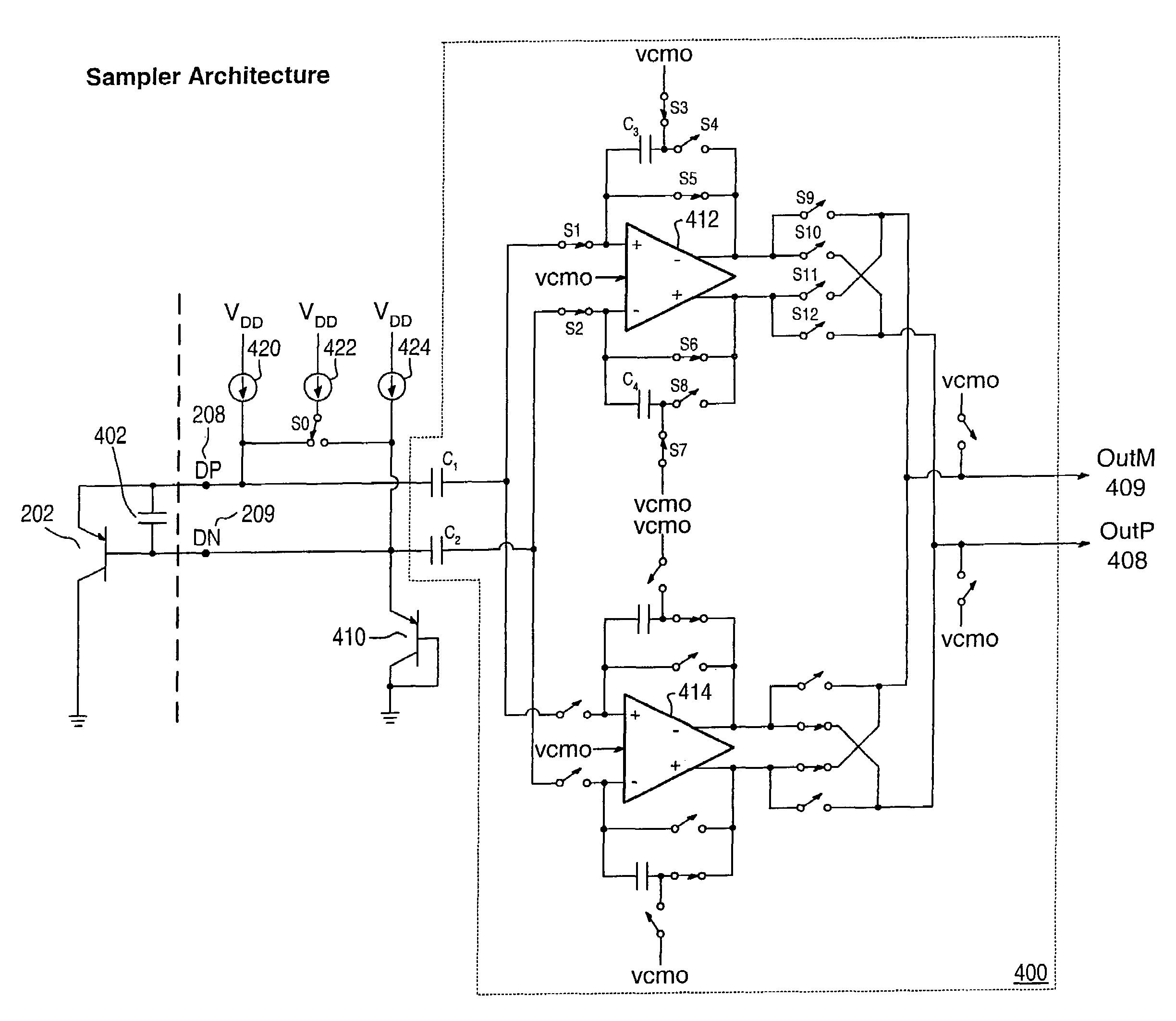
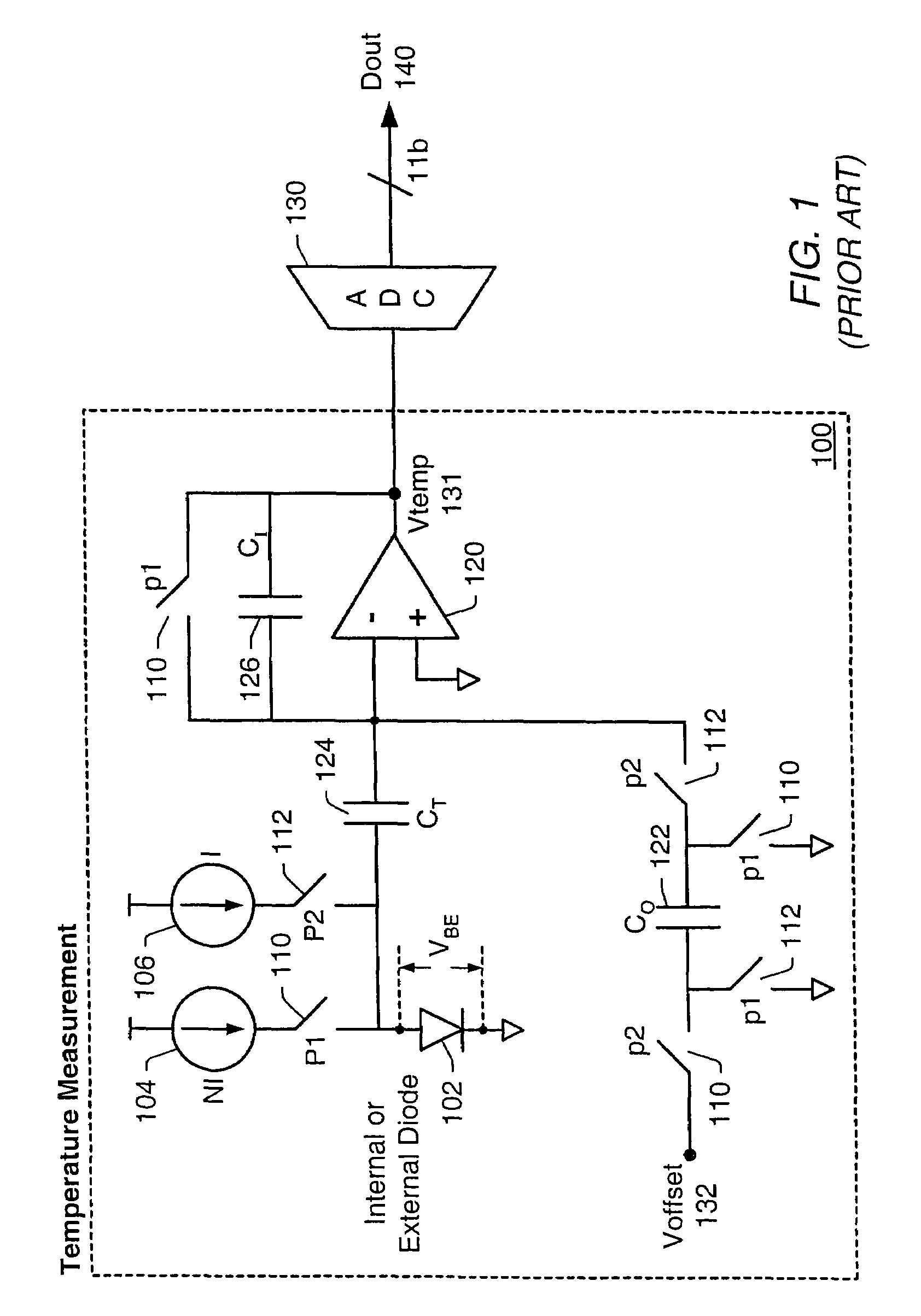
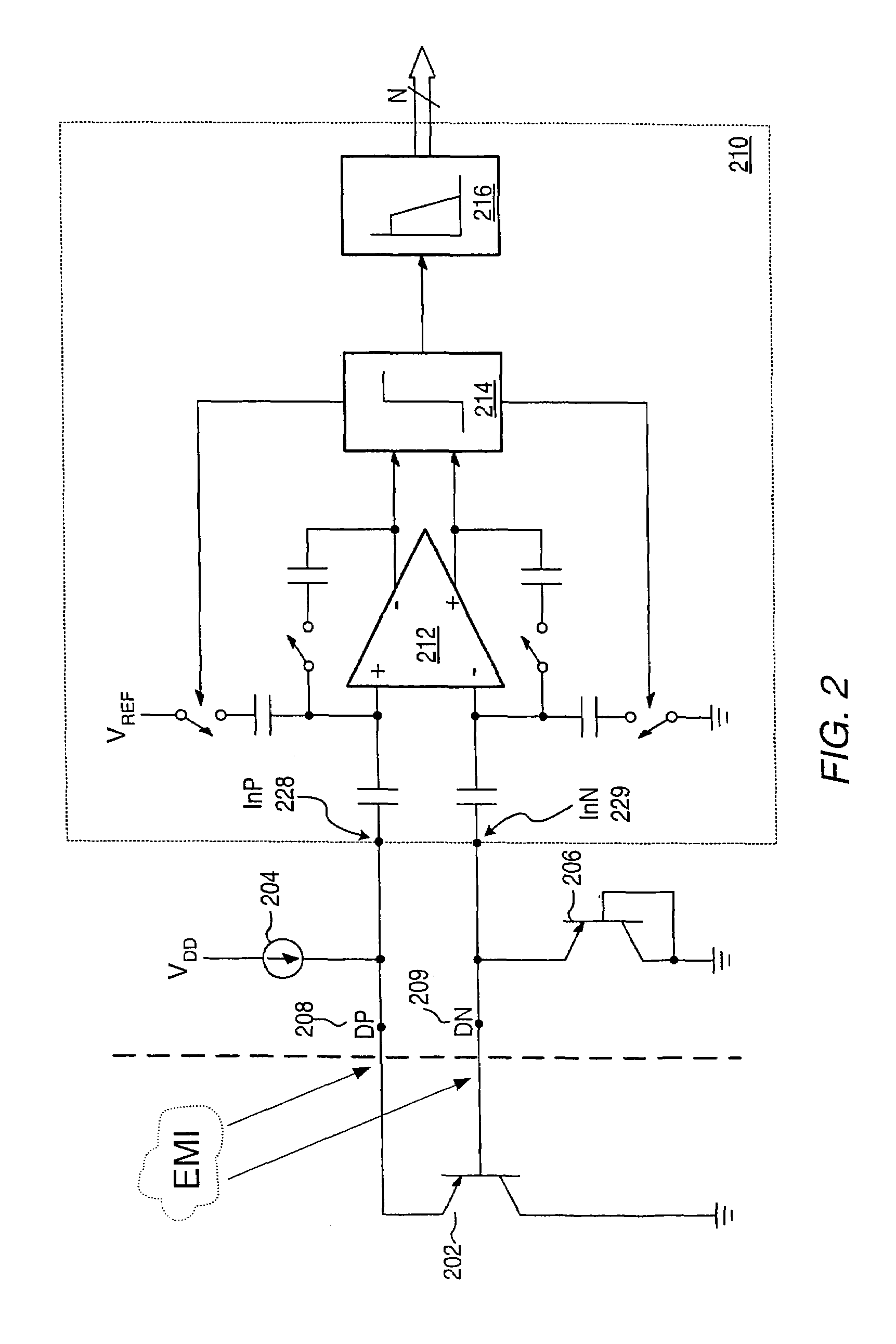
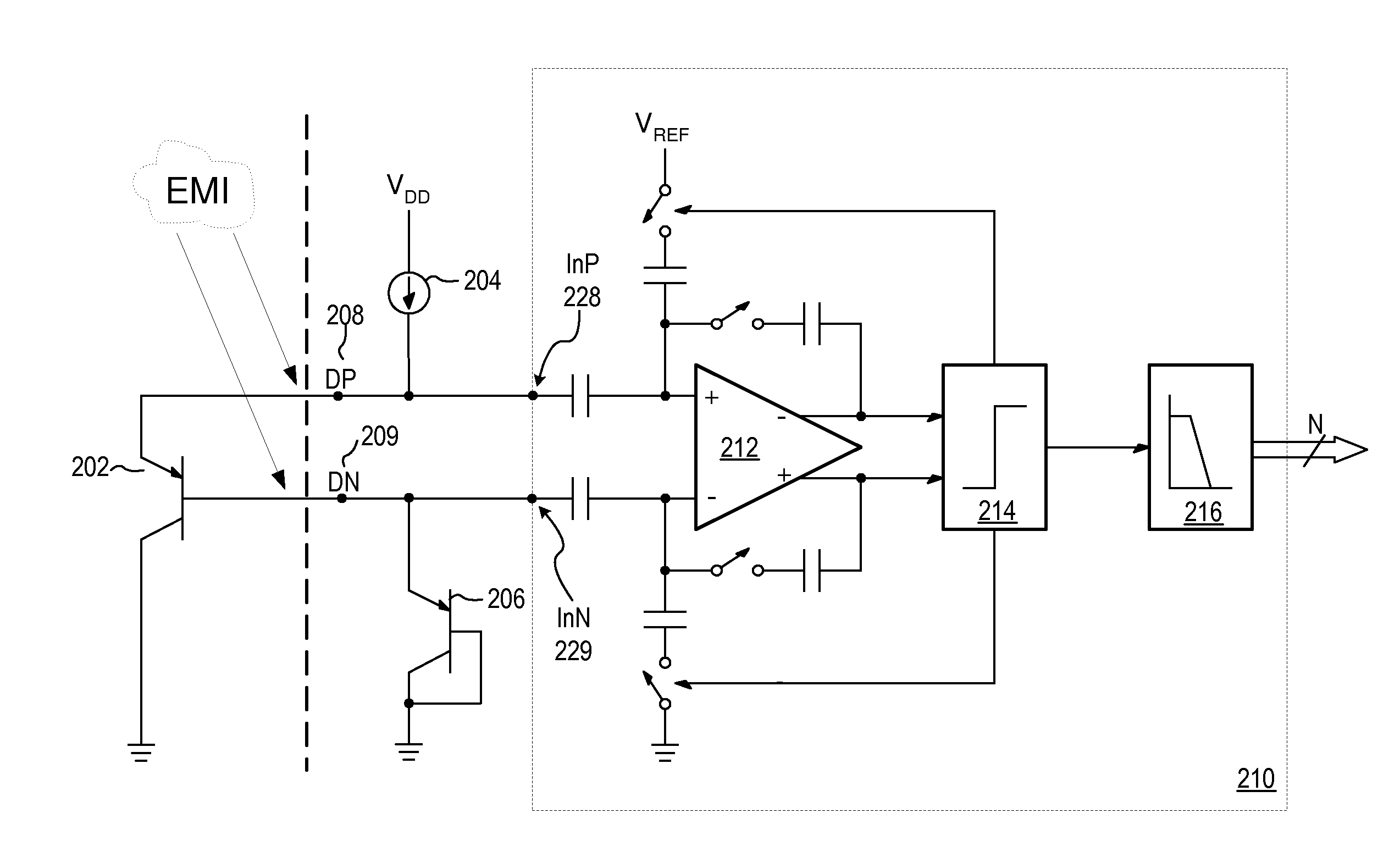
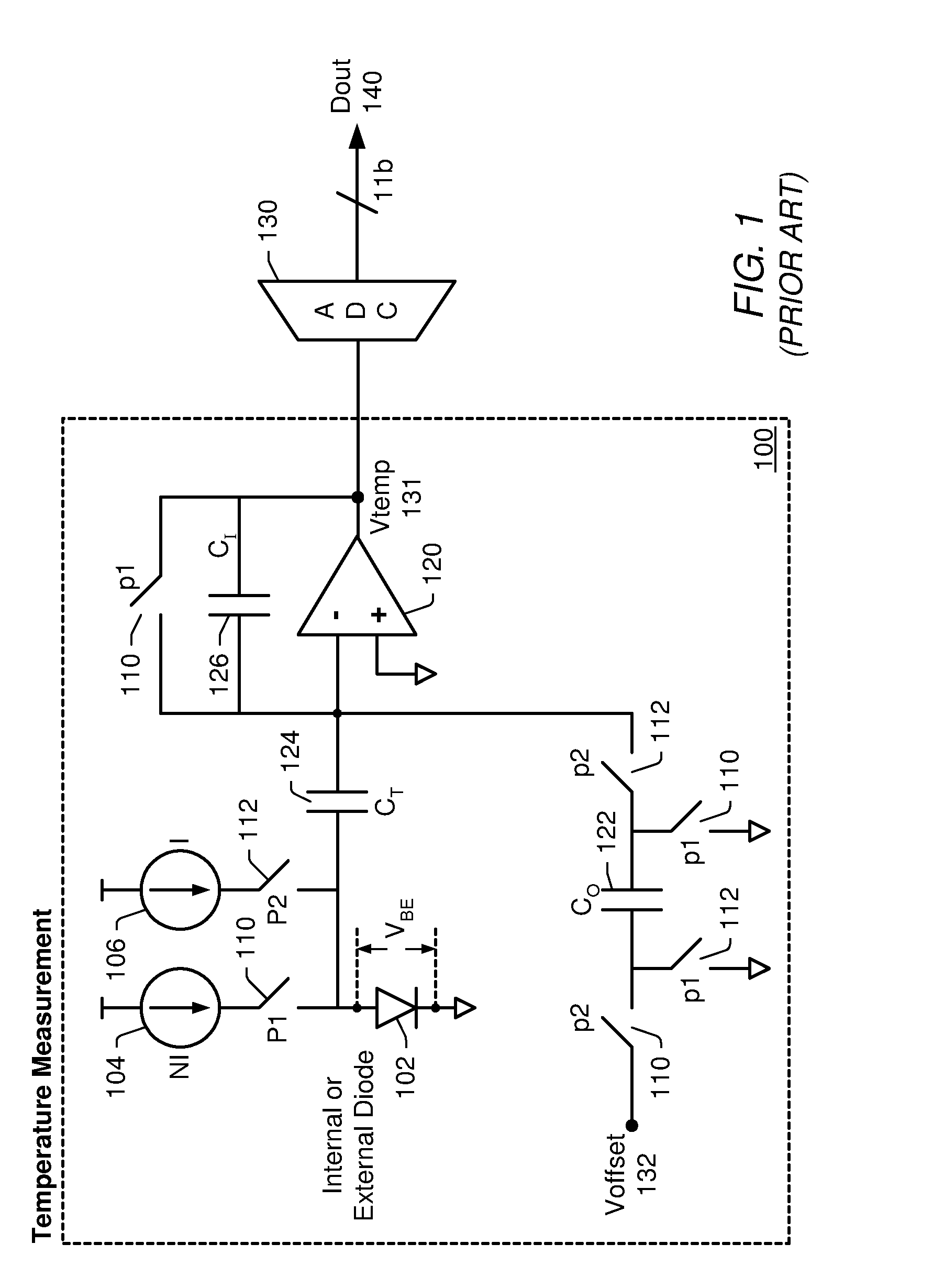
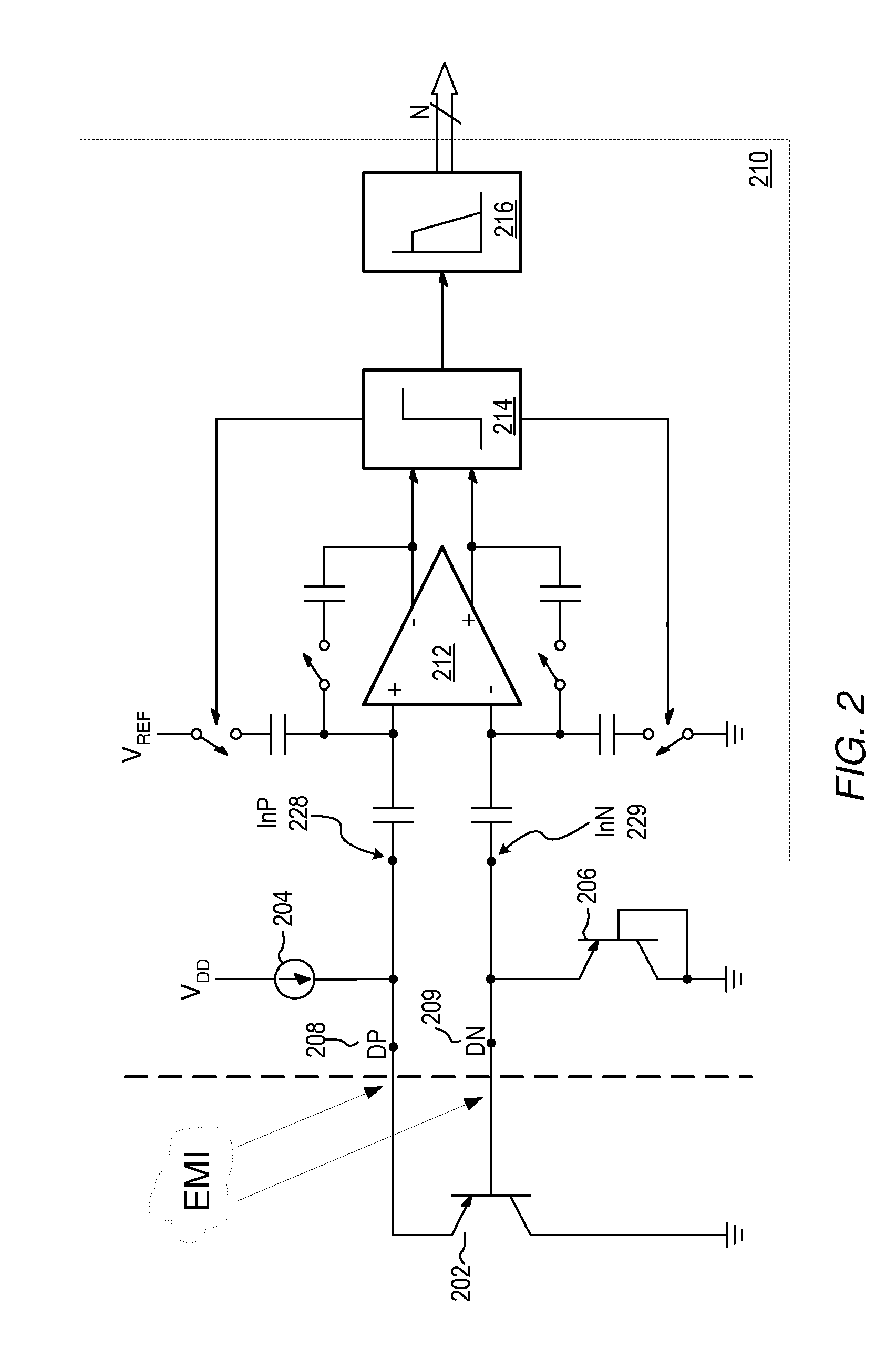
Proportional settling time adjustment for diode voltage and temperature measurements dependent on forced level current
ActiveUS7429129B2Increase conversion rateMinimizing temperature measurementThermometer detailsThermometers using material expansion/contactionAc componentsShunt capacitors
A temperature sensor circuit and system providing accurate digital temperature readings using a local or remote temperature diode. In one set of embodiments a change in diode junction voltage (ΔVBE) proportional to the temperature of the diode is captured and provided to an analog to digital converter (ADC), which may perform required signal conditioning functions on ΔVBE, and provide a digital output corresponding to the temperature of the diode. DC components of errors in the measured temperature that may result from EMI noise modulating the junction voltage (VBE) may be minimized through the use of a front-end sample-and-hold circuit coupled between the diode and the ADC, in combination with a shunt capacitor coupled across the diode junction. The sample-and-hold-circuit may sample VBE at a frequency that provides sufficient settling time for each VBE sample, and provide corresponding stable ΔVBE samples to the ADC at the ADC operating frequency. The ADC may therefore be operated at its preferred sampling frequency rate without incurring reading errors while still averaging out AC components of additional errors induced by sources other than EMI.
Owner:MICROCHIP TECH INC
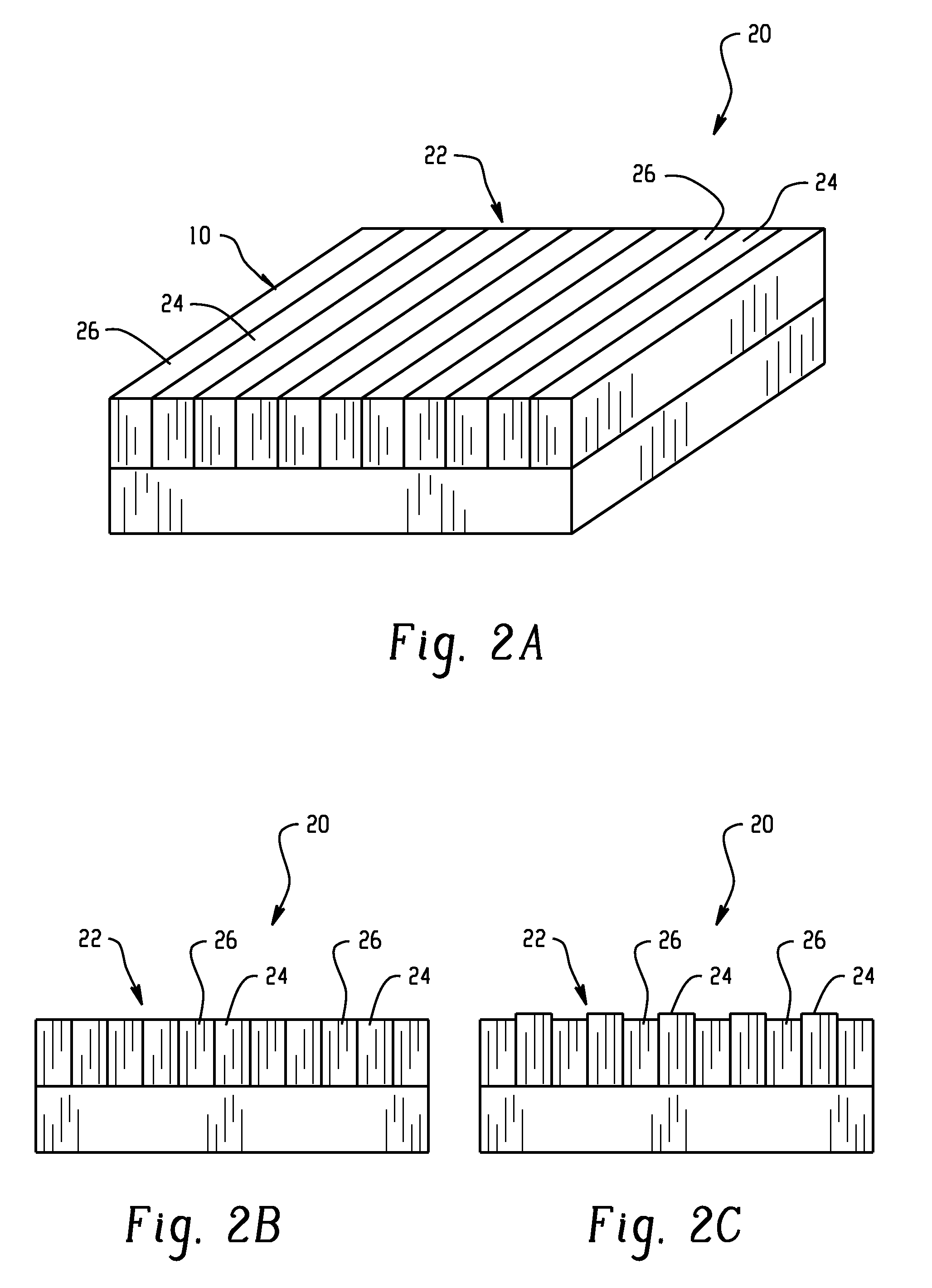
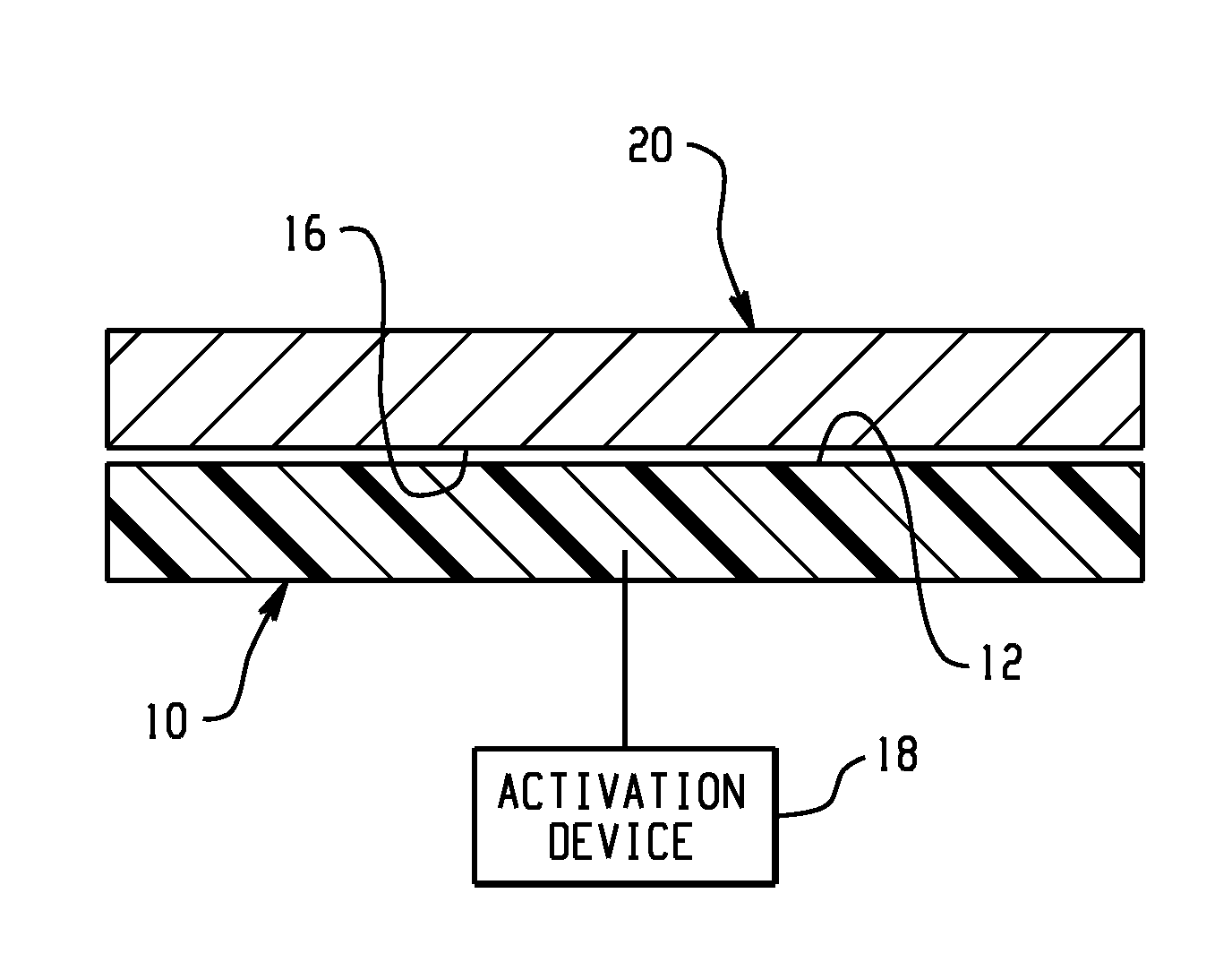
Active material based bodies for varying surface texture and frictional force levels
InactiveUS20090047197A1Efficient changeBacterial antigen ingredientsLavatory sanitoryEngineeringBiological activation
A device for selectively controlling and varying surface texture includes a body having at least one surface, and an active material in operative communication with the at least one surface, wherein the active material is configured to undergo a change in a property upon receipt of an activation signal, wherein the change in a property is effective to change a texture of the at least one surface.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Hood lift mechanisms utilizing active materials and methods of use
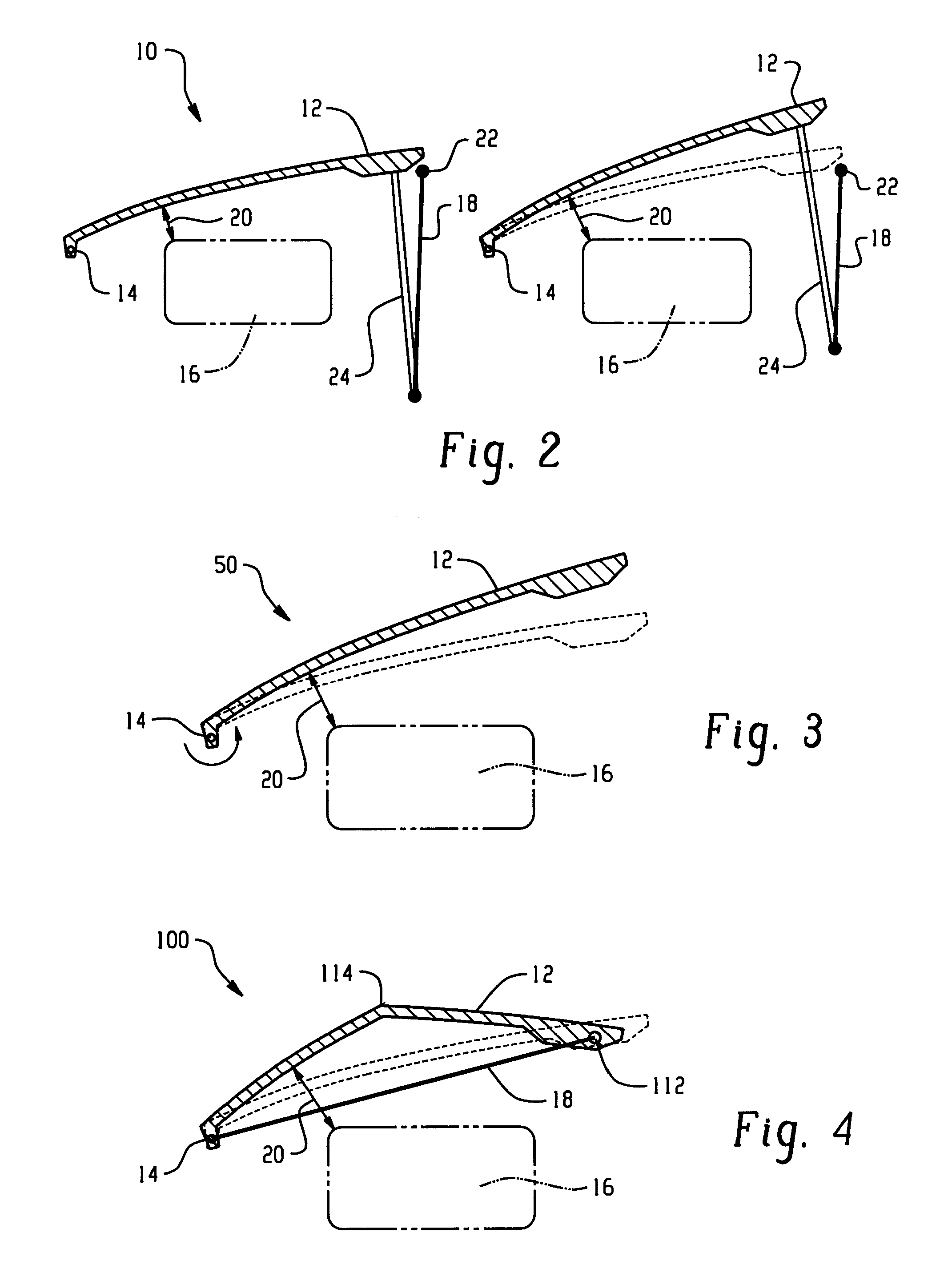
A hood lift mechanism for reversibly increasing the energy absorption capability at appropriate force levels of a vehicle hood includes a vehicle hood; an active material in operative communication with the vehicle hood, wherein the active material comprises a shape memory alloy, a ferromagnetic shape memory alloy, a shape memory polymer, a magnetorheological fluid, an electroactive polymer, a magnetorheological elastomer, an electrorheological fluid, a piezoelectric material, an ionic polymer metal composite, or combinations comprising at least one of the foregoing active materials; and an activation device in operative communication with the active material, wherein the activation device is operable to selectively apply an activation signal to the active material and effect a reversible change in a property of the active material, wherein the reversible change results in an increased clearance distance between the vehicle hood and an underlying component.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN +1
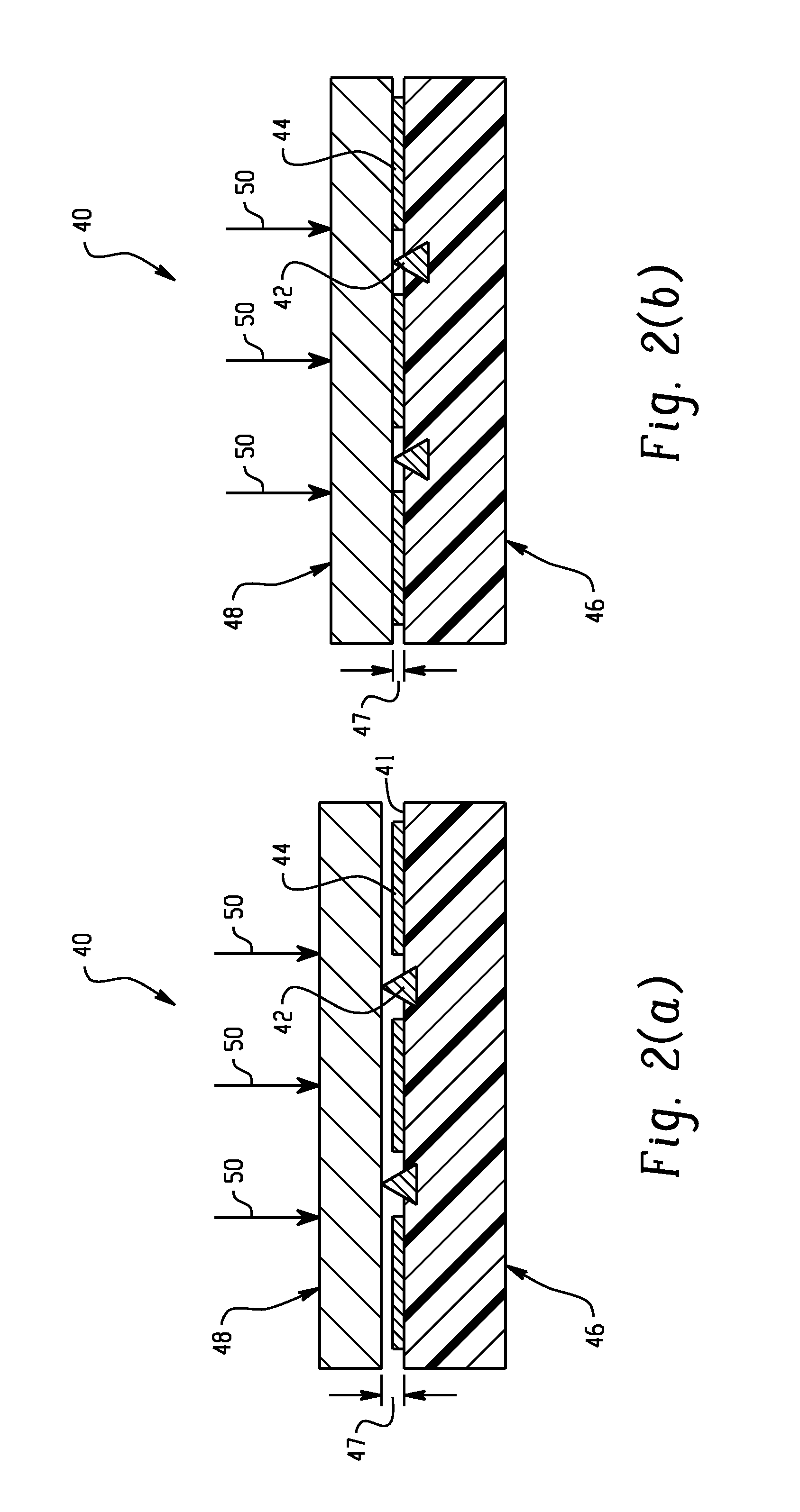
Active material based bodies for varying frictional force levels at the interface between two surfaces
A device for selectively controlling and varying a frictional force level at an interface between two bodies, includes a first contact body having at least one surface, a second contact body having at least one surface in physical communication with the first contact body, and an active material in operative communication with a selected one or both of the first contact body and the second contact body, wherein the active material is configured to undergo a change in a property upon receipt of an activation signal wherein the change in a property is effective to change the frictional force level at the interface between the at least one surface of the first contact body and the at least one surface of the second contact body.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Active material based lockout mechanisms
ActiveUS7332688B2Contact surface shape/structureDashboard fitting arrangementsEngineeringBiological activation
Control mechanisms and methods of use include the use of active materials as a blocking element. The control mechanisms generally include a tactile control in operative communication with an electrical circuit, wherein actuation of the tactile control closes the electrical circuit to activate a function. The blocking element includes an active material that is intermediate to the electrical circuit and the tactile control. The active material is adapted to change at least one attribute such as a modulus property in response to an activation signal. The change in the at least one attribute selectively changes a force level for actuating the tactile control.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
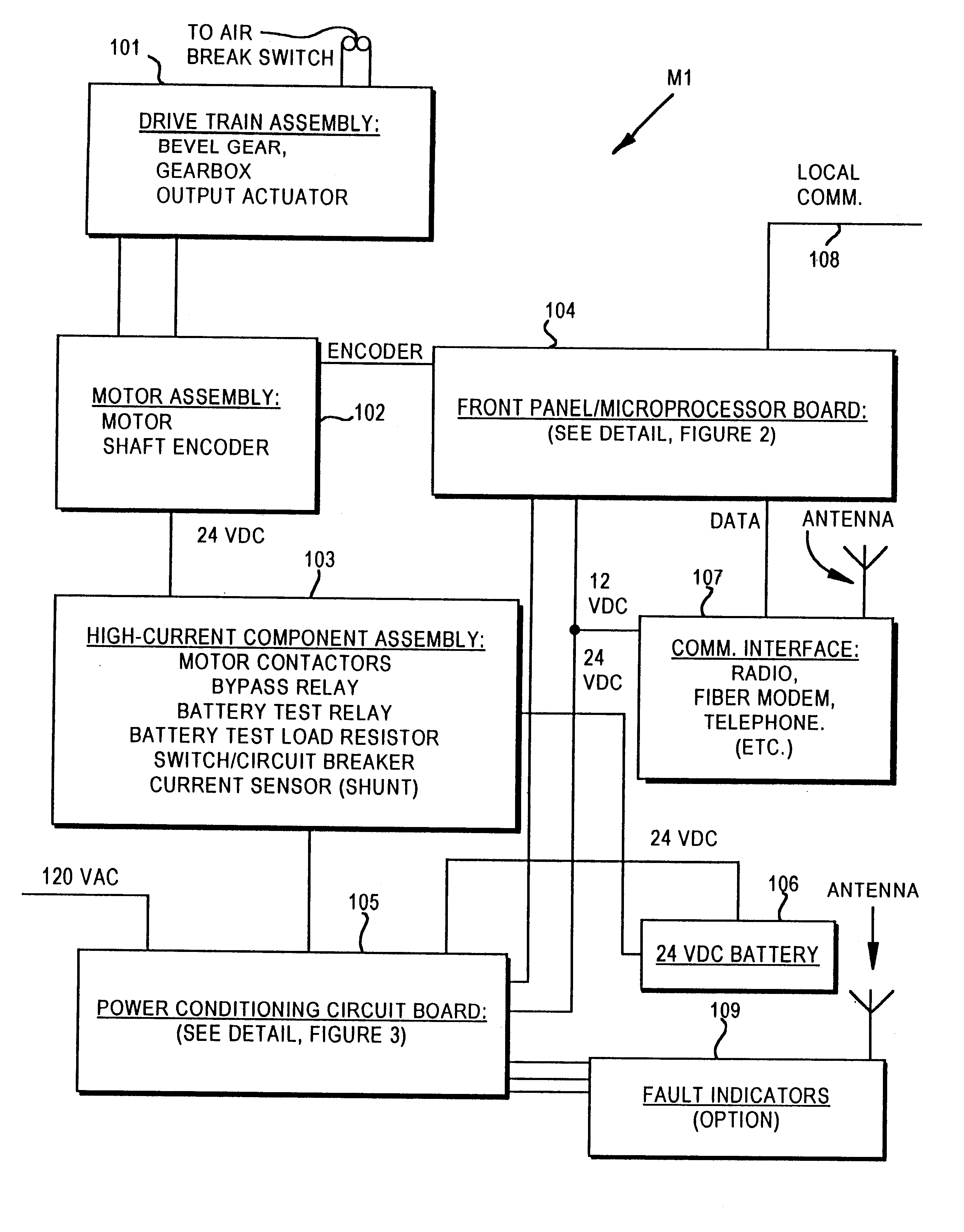
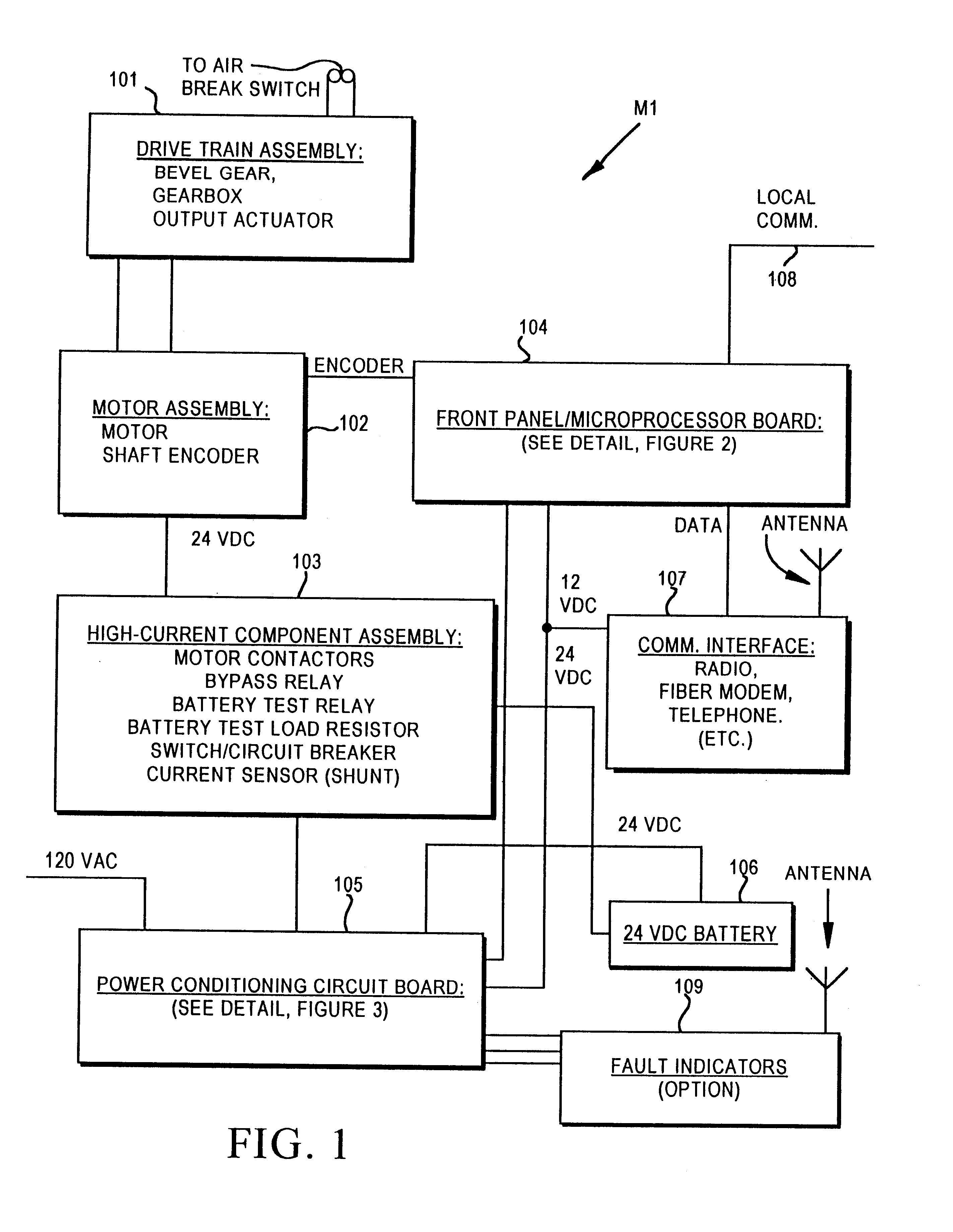
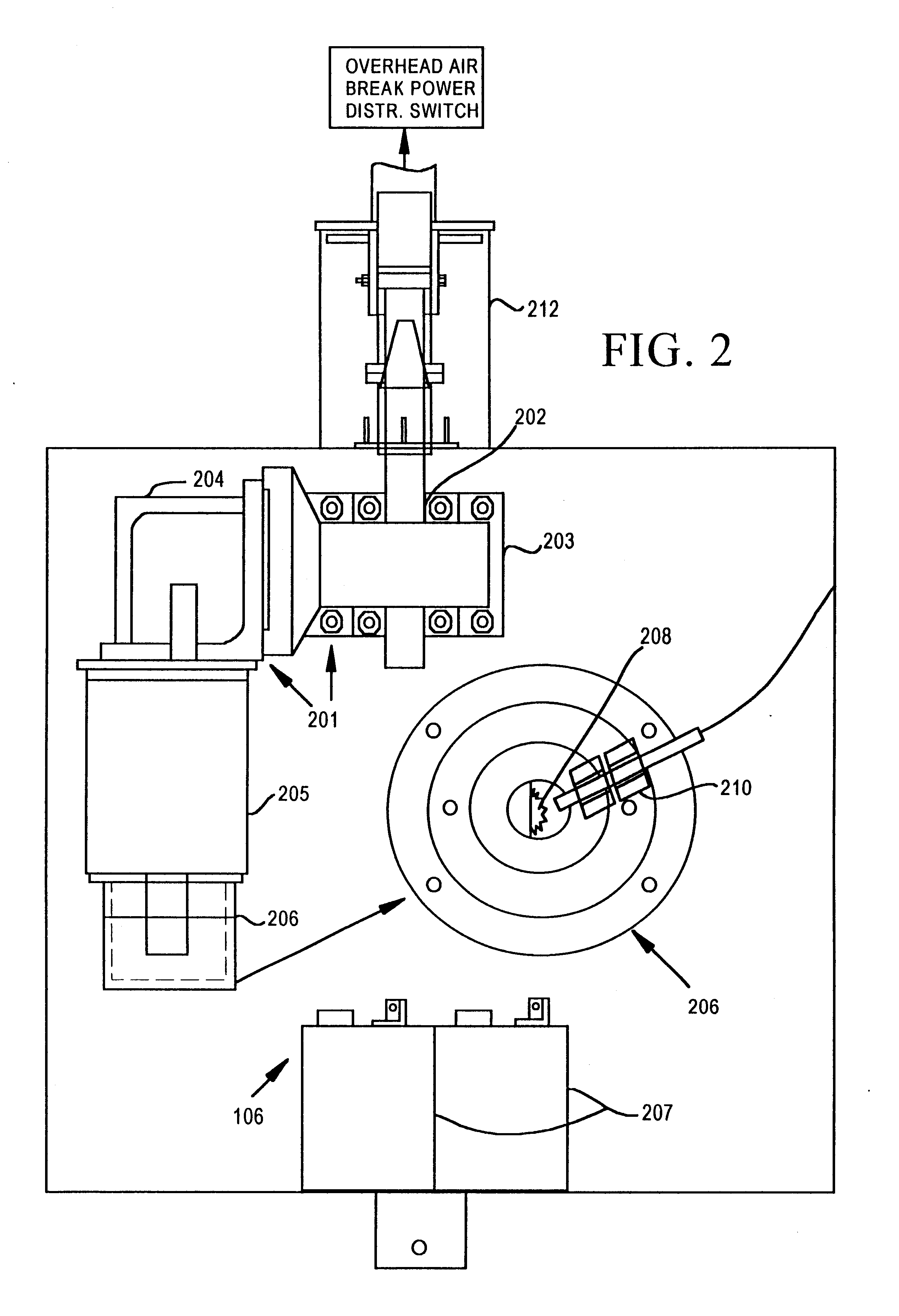
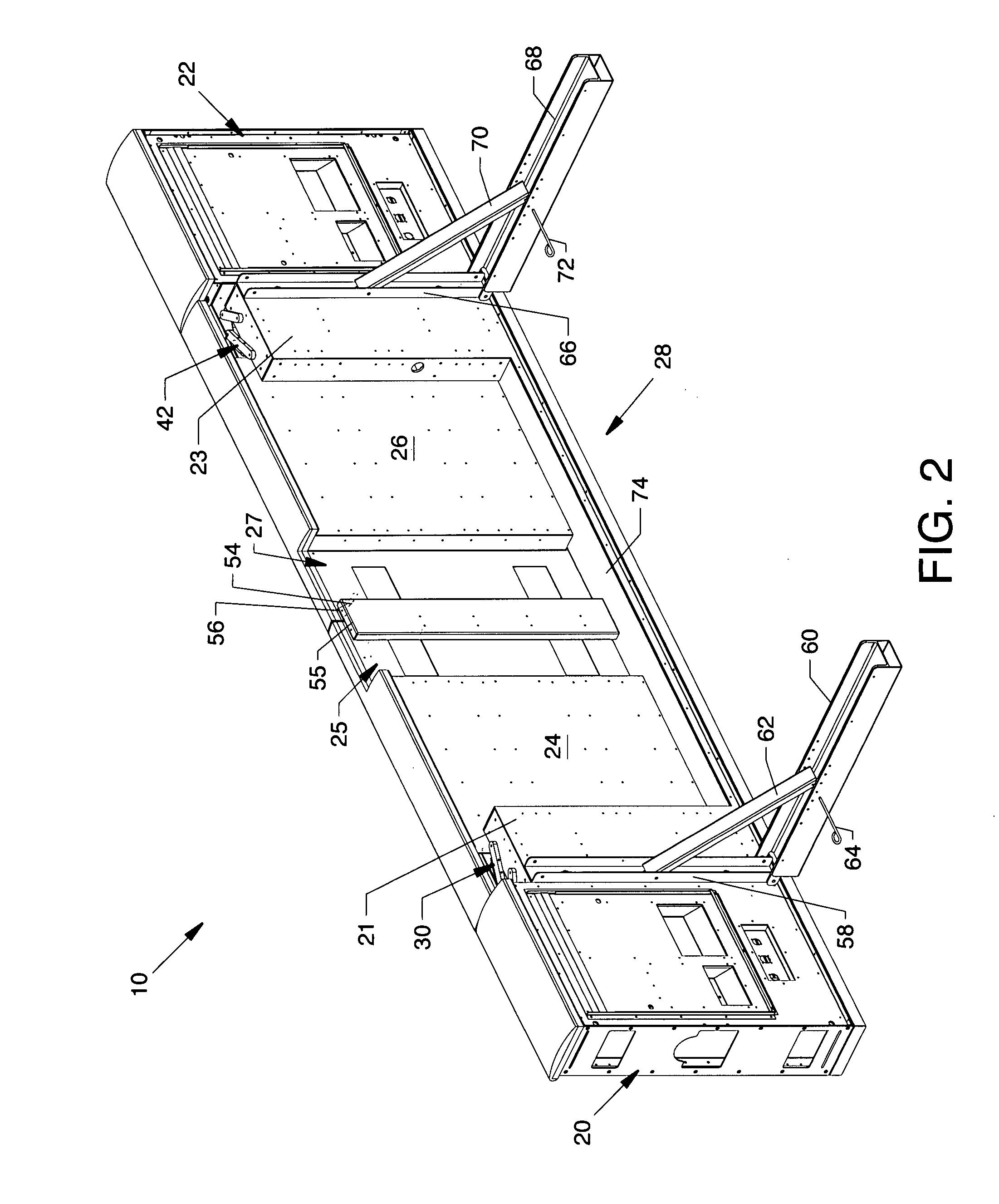
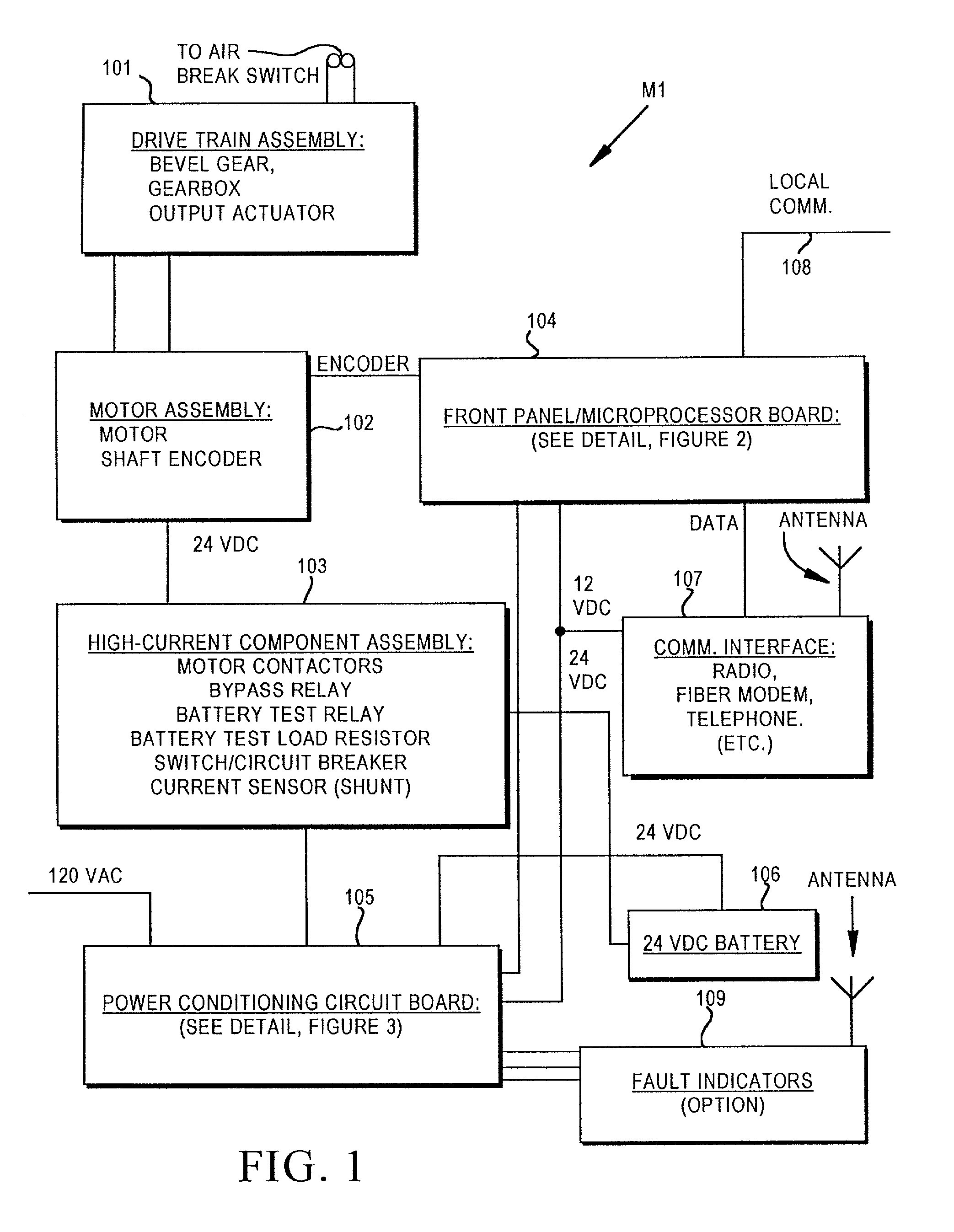
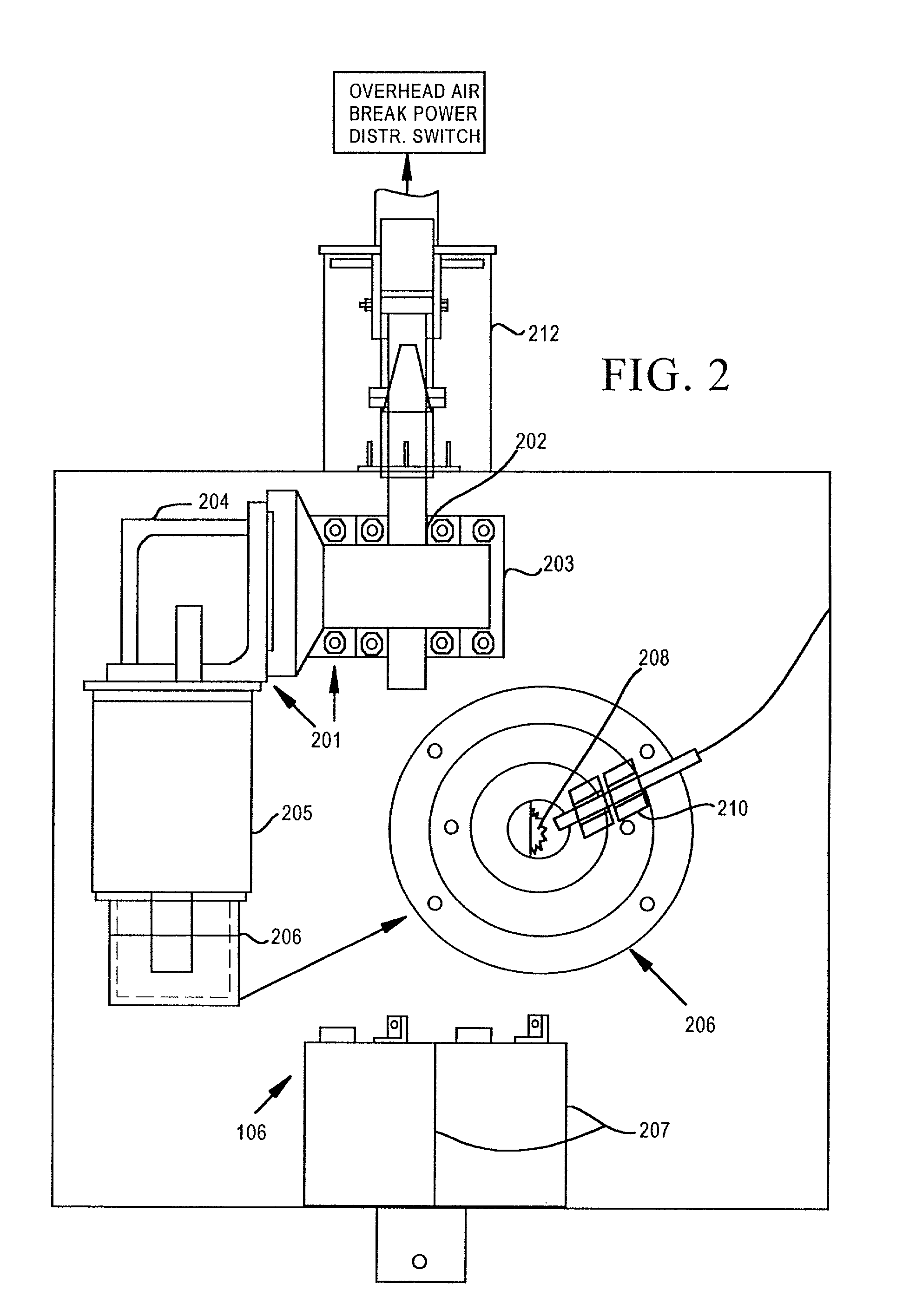
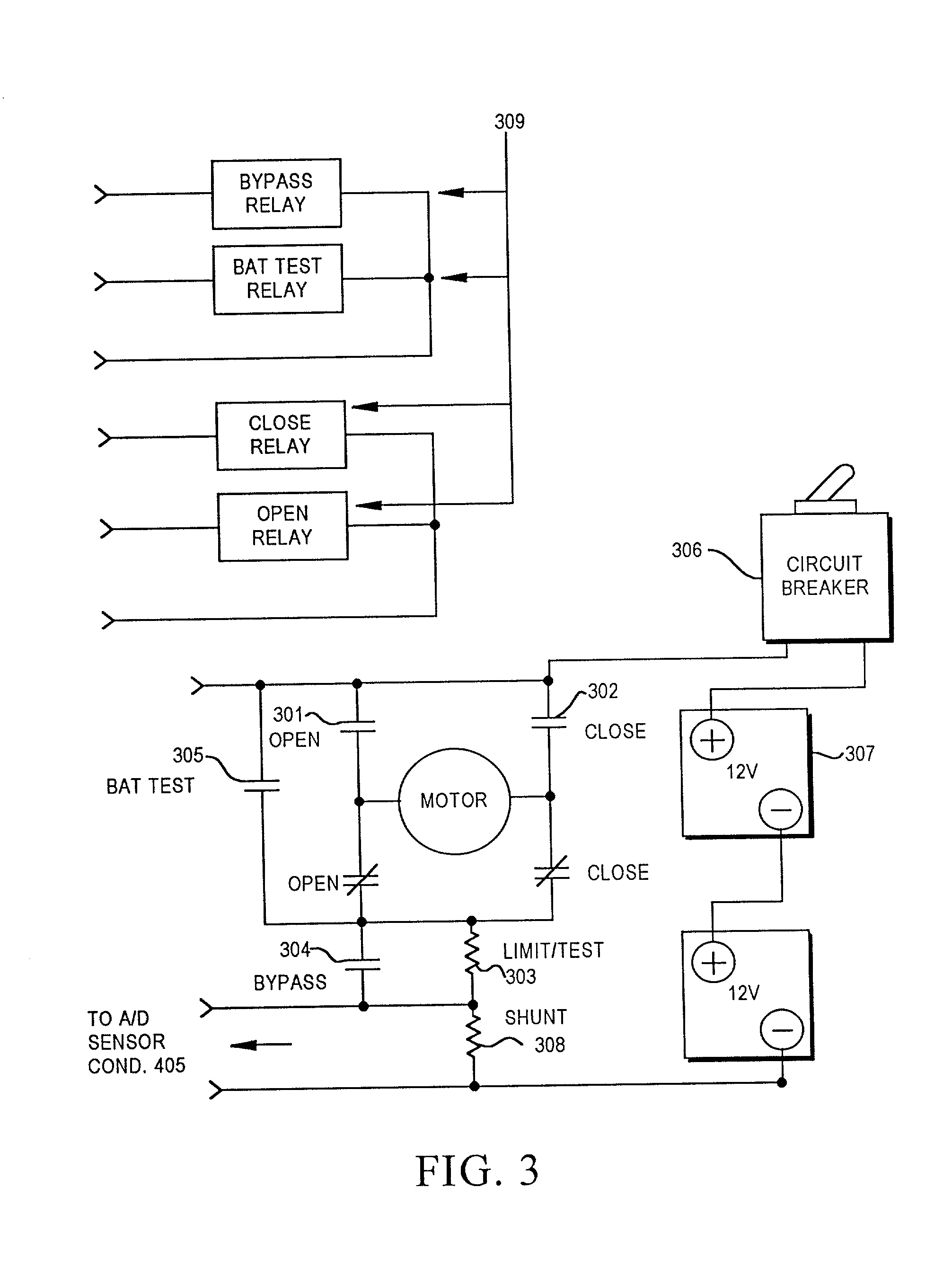
Motor operator for over-head air break electrical power distribution switches
InactiveUS6215263B1DC motor speed/torque controlElectrothermal relaysTime informationMicrocontroller
A motor operator for an overhead power switch is disclosed including a microcontroller, a unique and powerful array of well-integrated sensors, a motor and drive developing substantial torque and speed and coupled to a switch actuator and responsive to the microcontroller, and a sophisticated program algorithm stored in memory at the actuator site for dynamically controlling, i.e., governing the various control modes as called for by changing conditions. The sensors include an encoder associated with the motor and drive that develops position information signals fed to the dynamic microcontroller to compute real time information including position, speed, and stopping distance used in conjunction with remote operate commands to open, close and monitor status of the switch in the various ways disclosed. Under the supervision of the microcontroller, a motor drive power switching circuit selectively applies a source of power, such as from an on site battery, to an electric motor to drive the switch toward open or closed position at different speeds, output force levels such as at different torques, and in continuous or incremental movements depending on conditions determined by the microcontroller in response to sensor inputs.
Owner:S&C ELECTRIC
Modular base side bearing
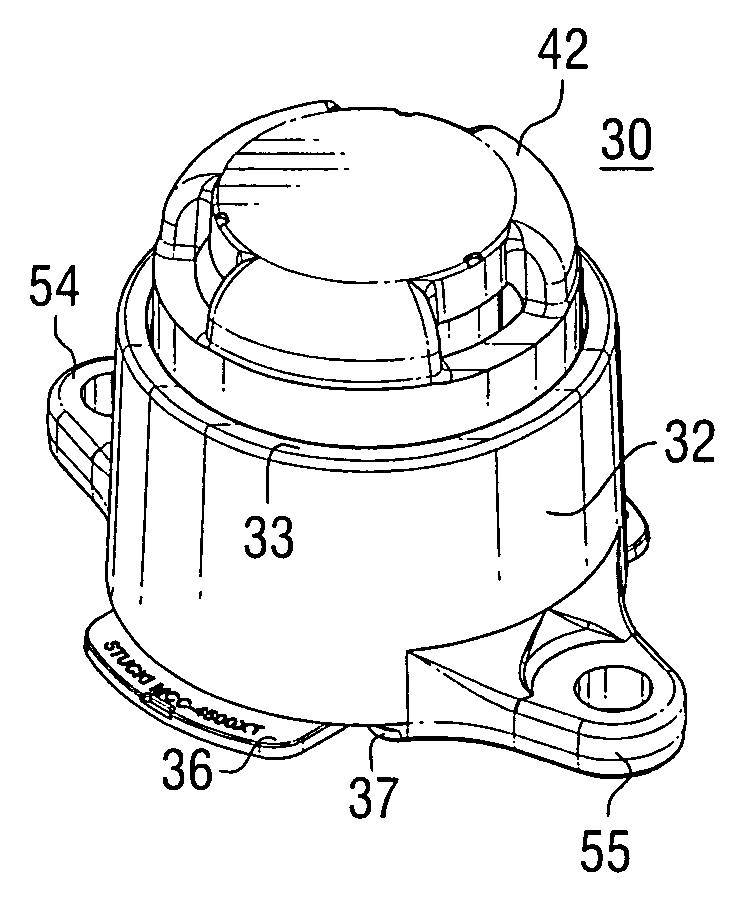
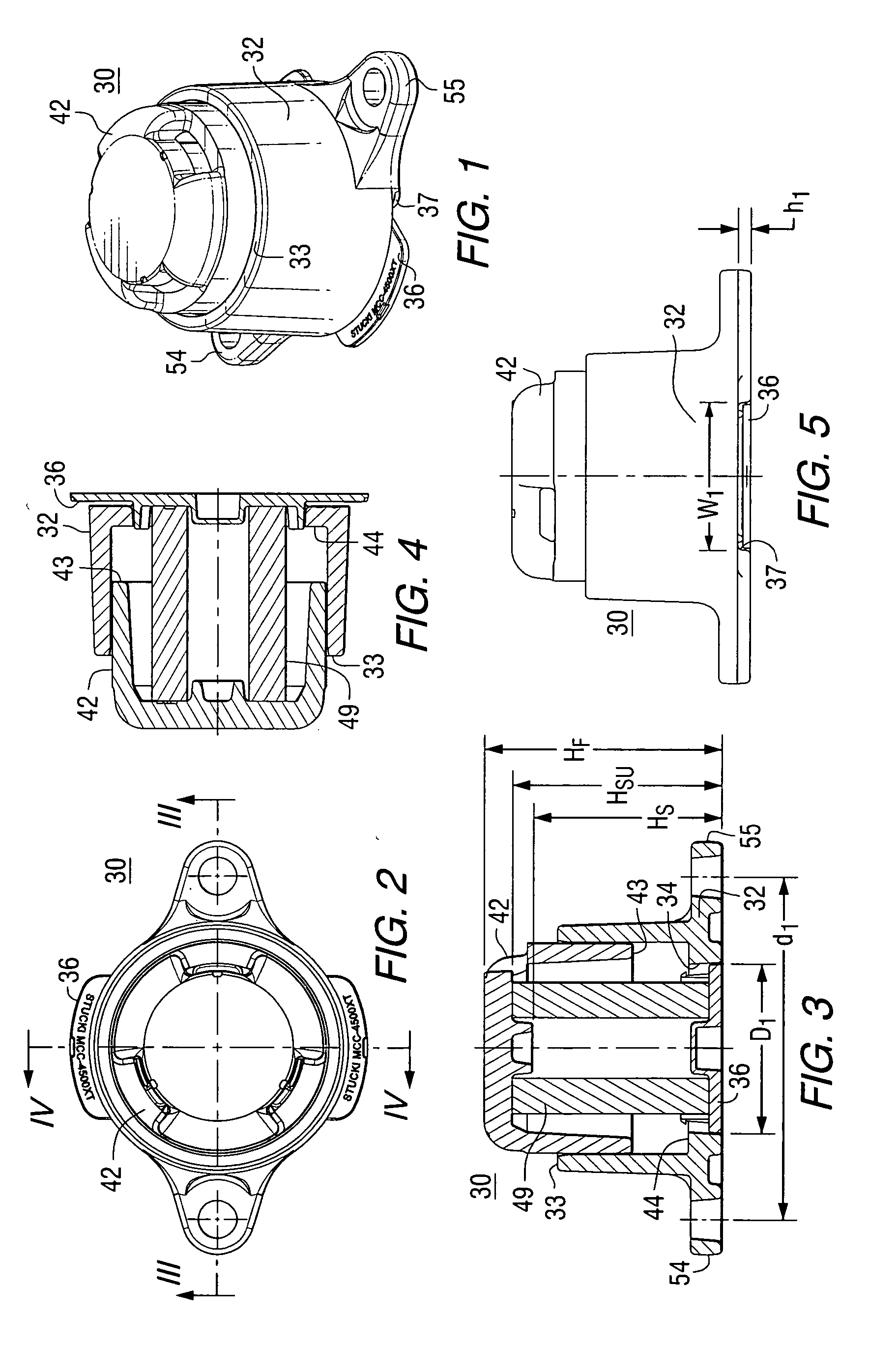
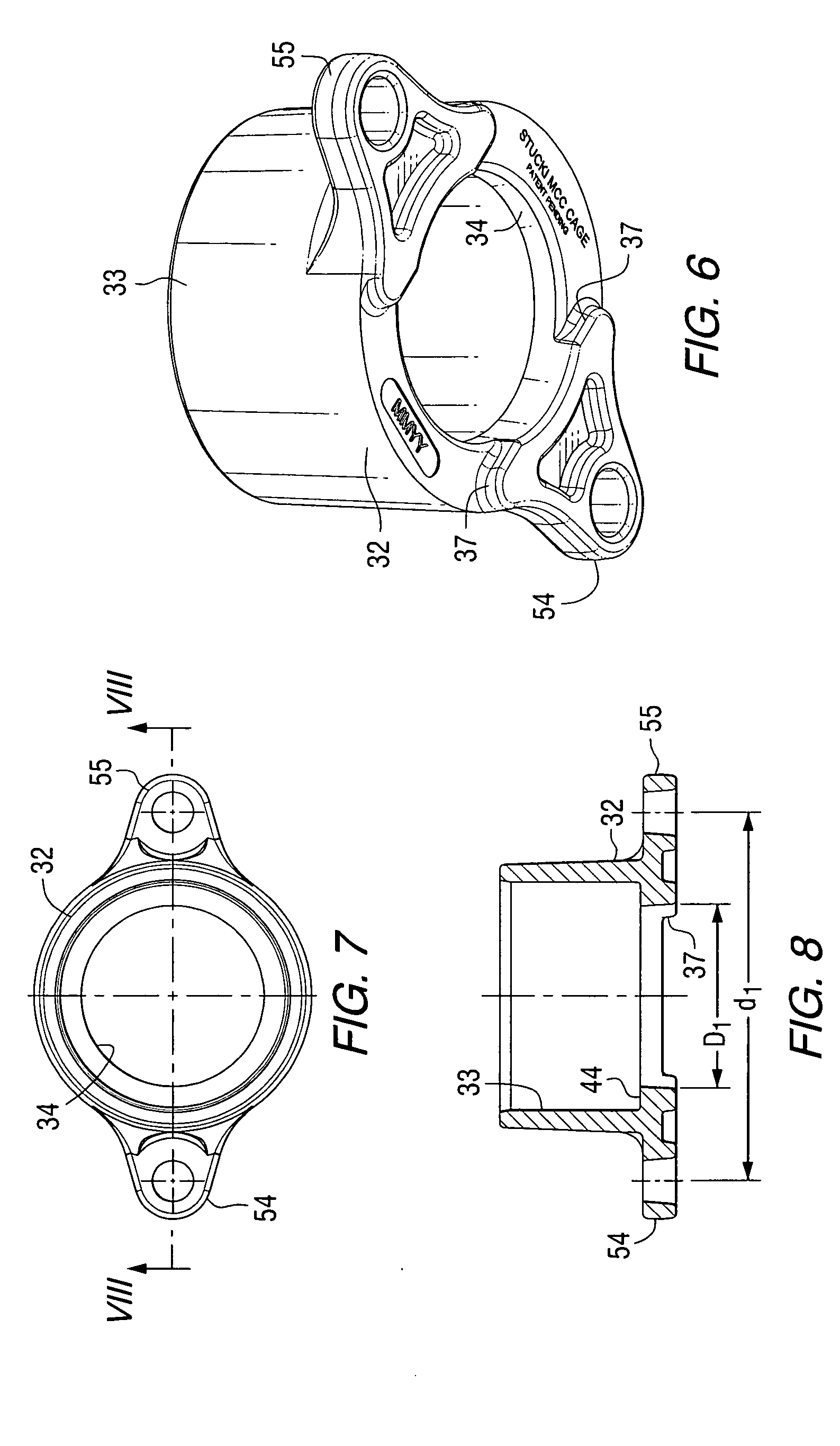
A modular base side bearing assembly has a cage with upstanding side walls defining a bearing cavity and a central bottom opening to receive a modular base on which a bearing element supported on a central base portion thereof. The modular base has externally visible tabs identifying a force level corresponding to the modular base, in which the thickness of the central base portion corresponds such force level. The modular bases are interchangeable with modular bases having central base portions of differing thickness, or zero-thickness, such that the same cage, bearing element, and wear cap can be used with different modular bases to provide different force levels. The modular base is movable vertically relative to the cage to accommodate uneven mounting surfaces.
Owner:A STUCKI CO
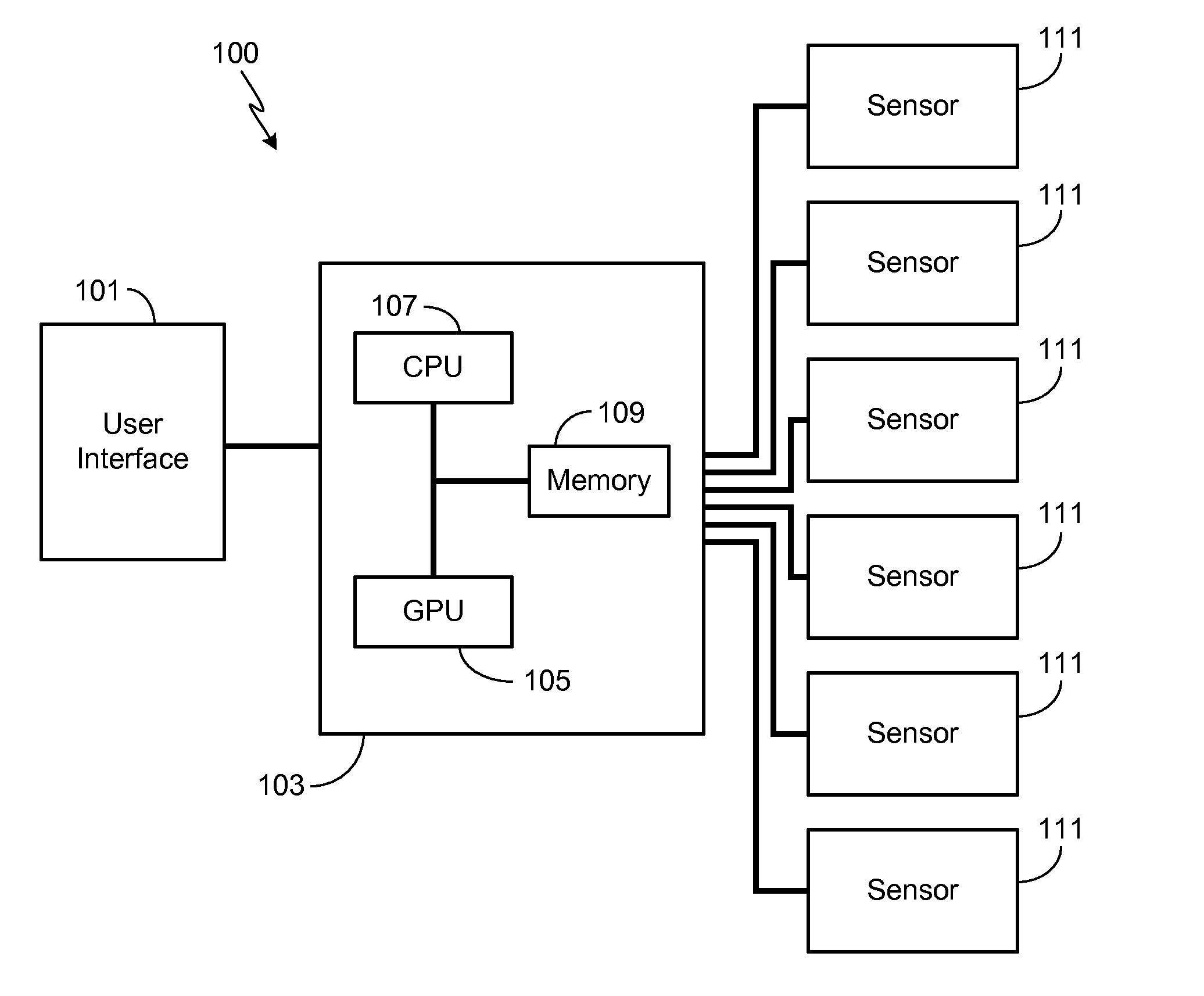
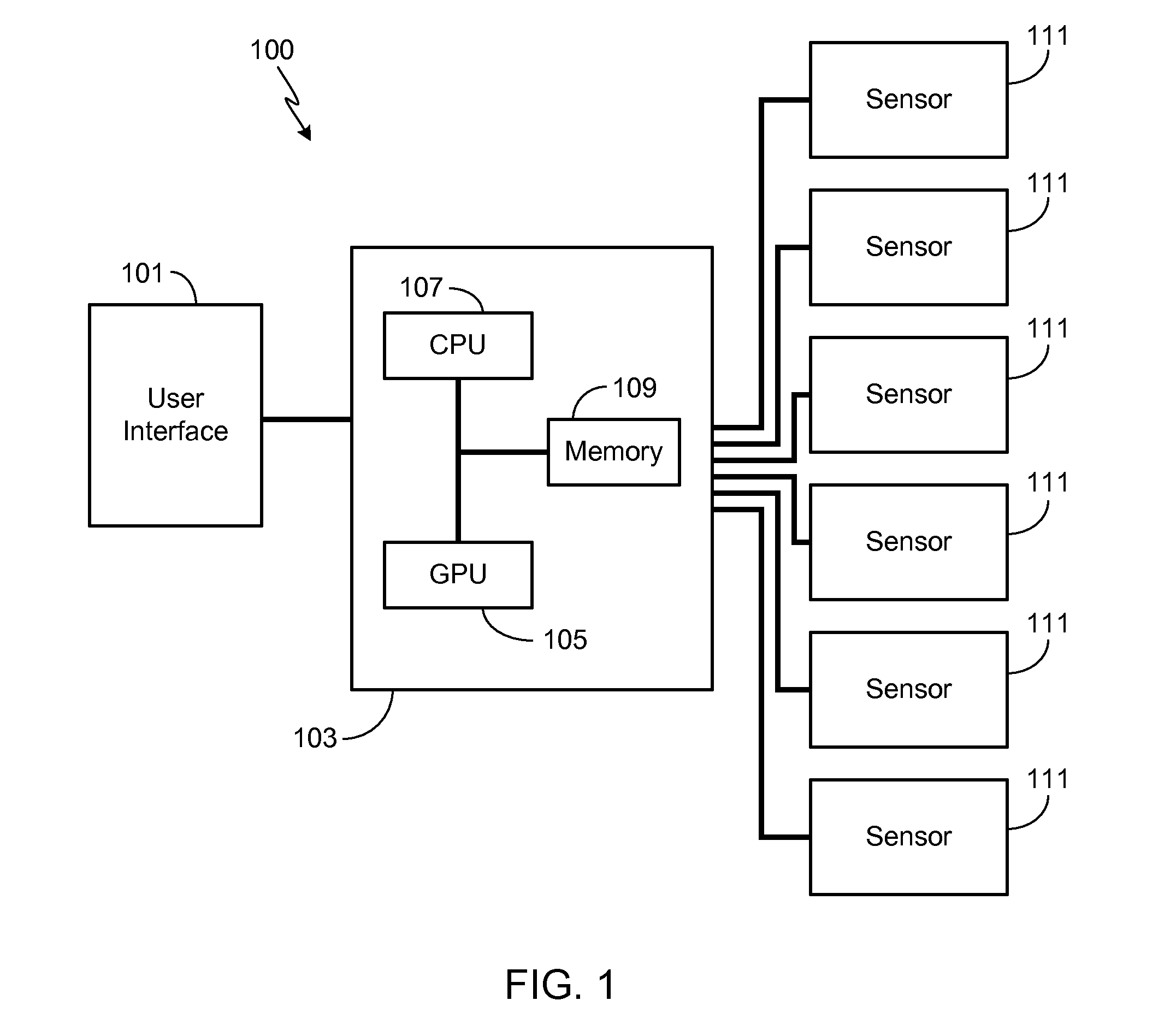
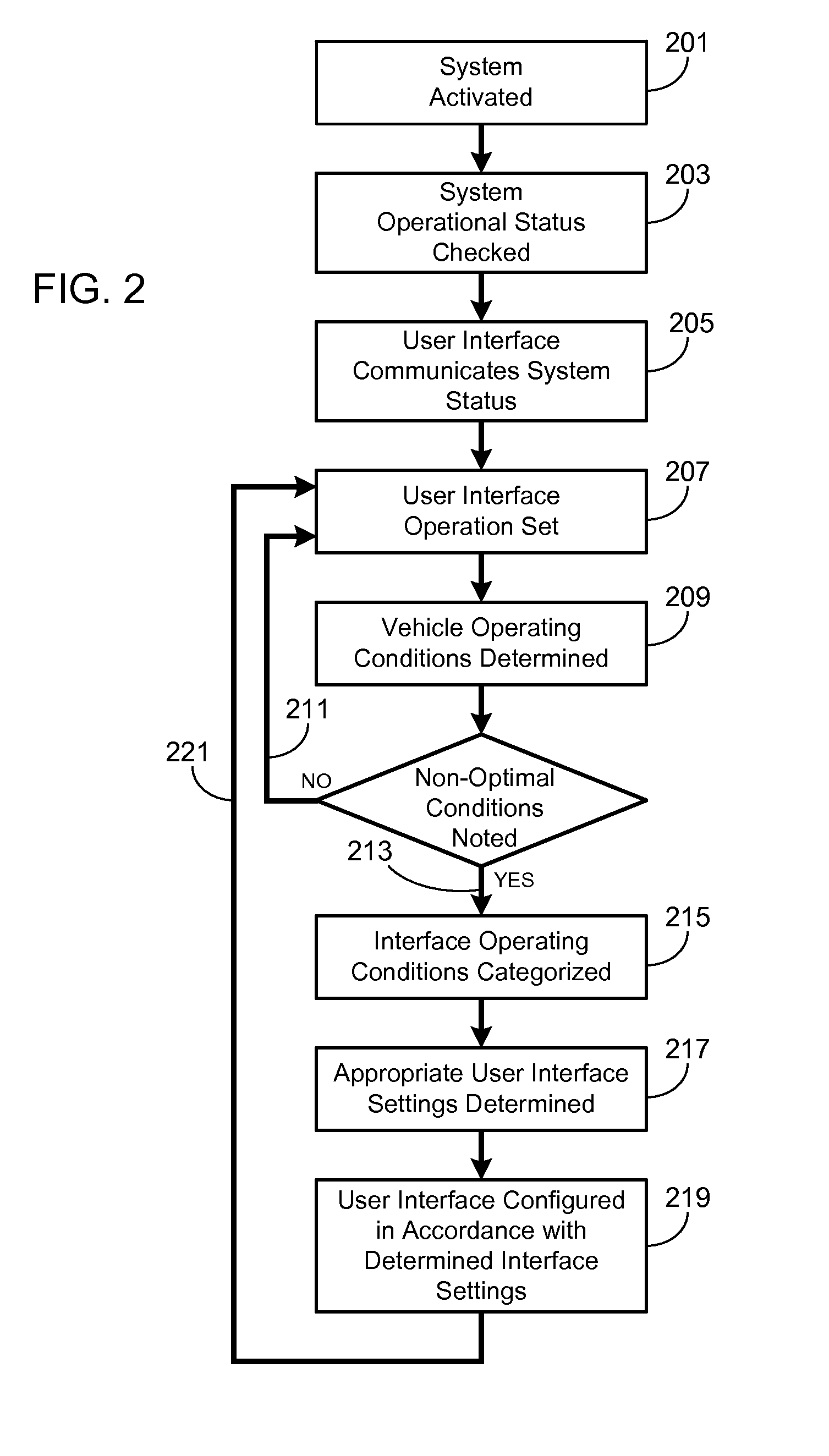
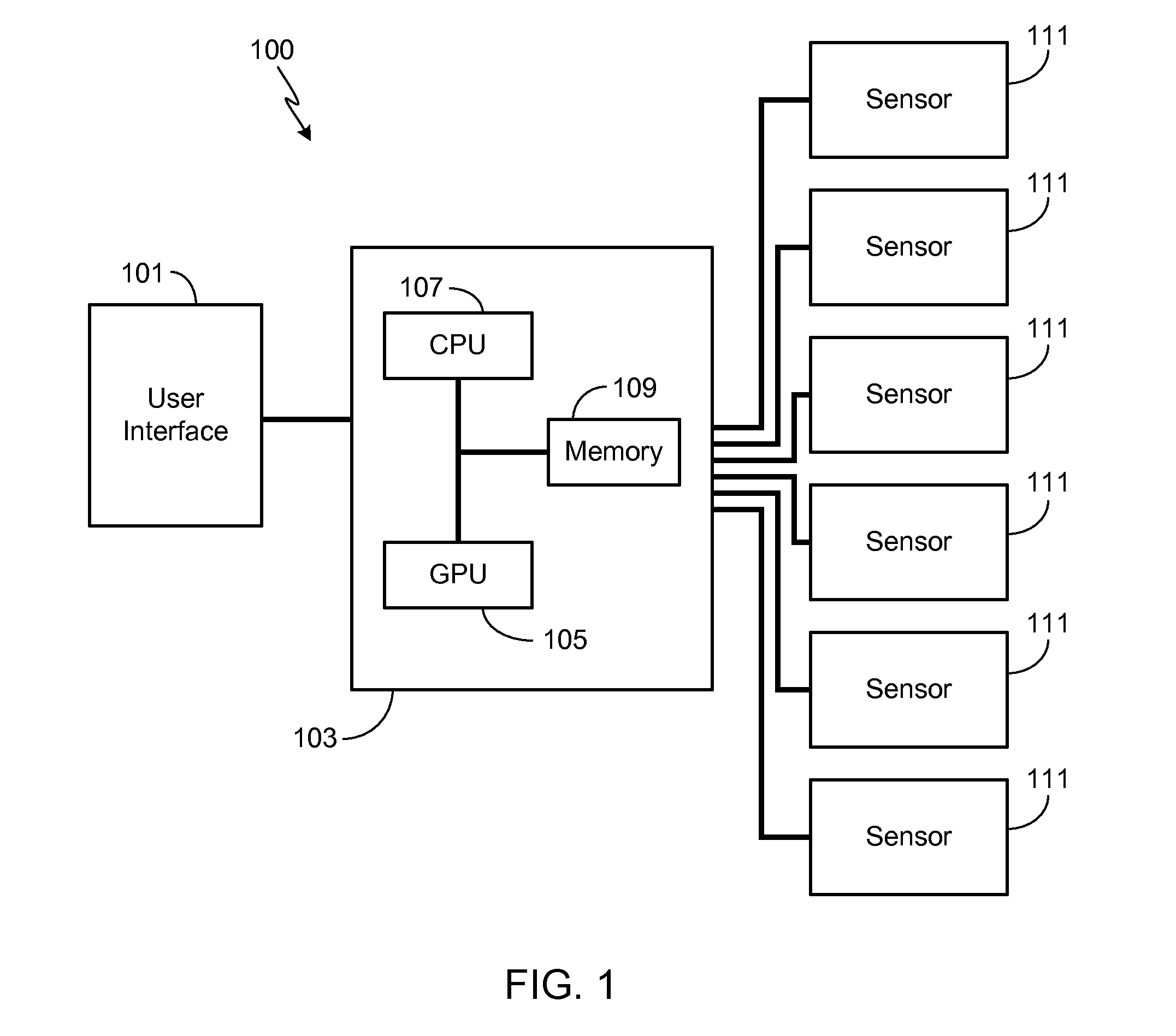
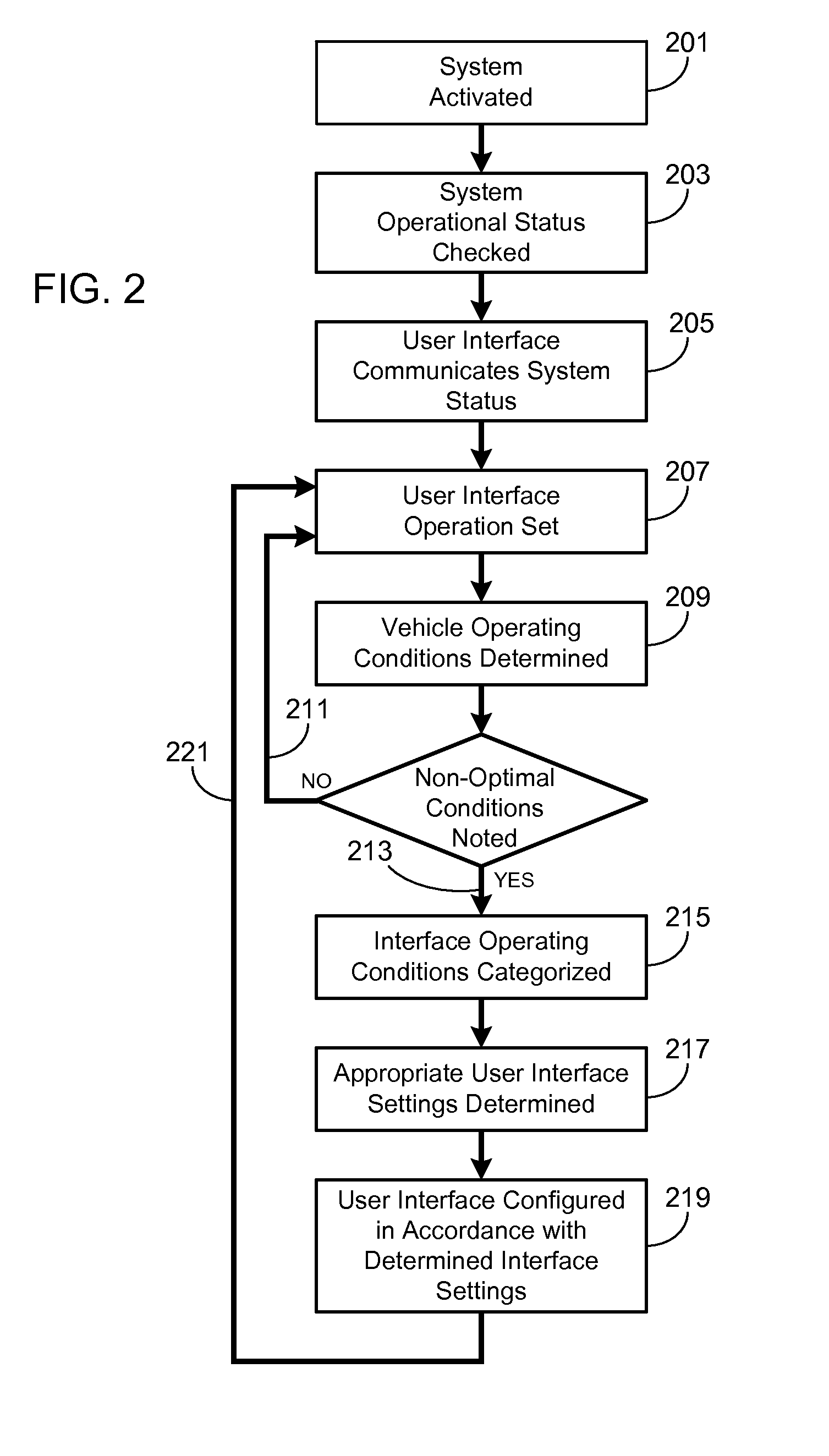
Adaptive Soft Buttons for a Vehicle User Interface
ActiveUS20110082619A1Improve user performanceExpands touch-sensitiveVehicle testingDashboard fitting arrangementsGraphical user interfaceEngineering
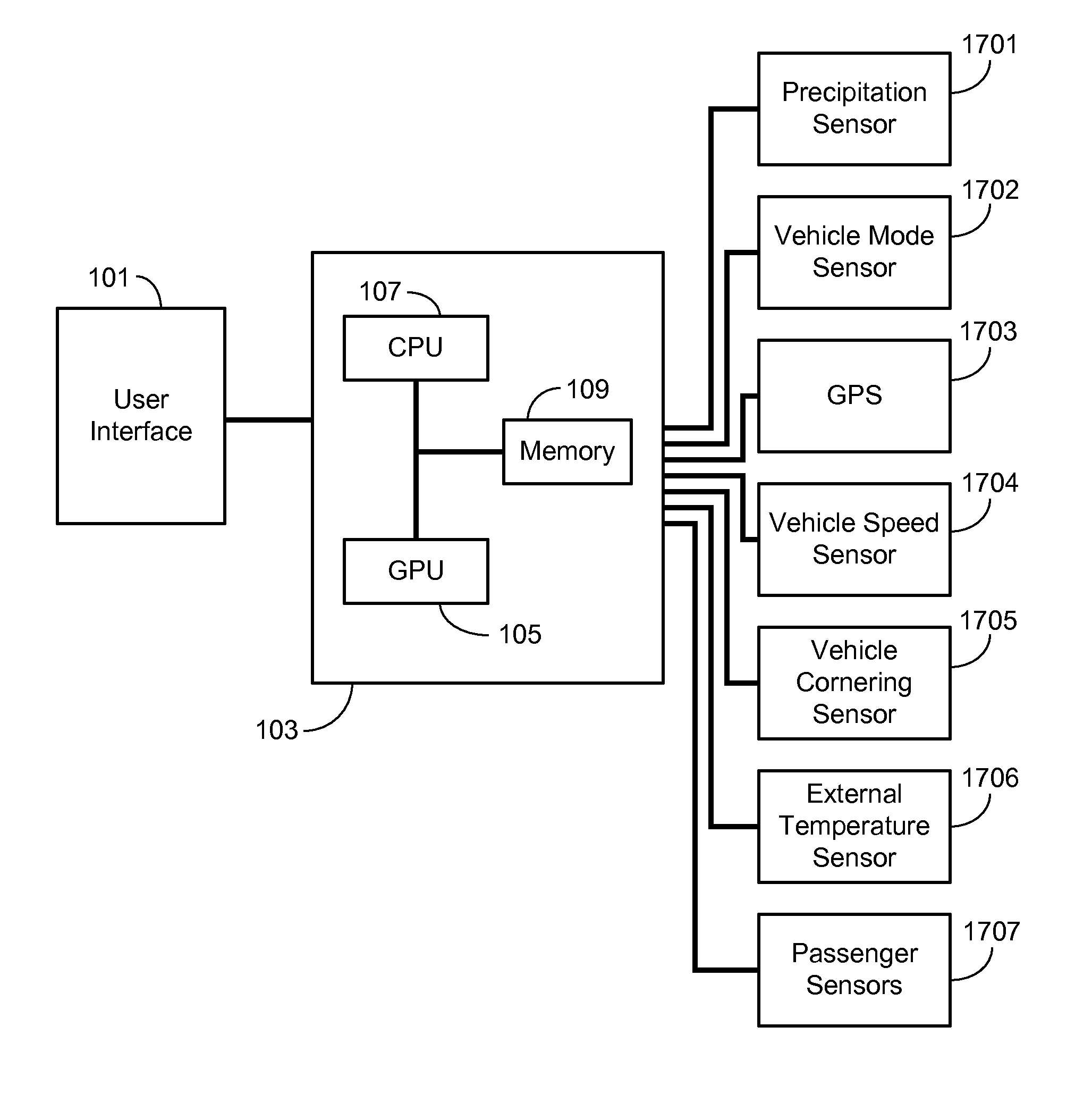
A system and a method are provided for configuring the touch-sensitive area and / or the tap duration associated with a plurality of touch-sensitive soft buttons of a vehicle user interface in response to varying vehicle conditions. In particular, as a monitored vehicle condition deteriorates, the system controller coupled to the vehicle user interface expands the touch-sensitive region and / or increases the tap duration of the touch-sensitive soft buttons, thereby improving the user's ability to successfully interact with the interface. Vehicle conditions that may be monitored and used to configure the touch-sensitive area and / or tap duration include passenger cabin vibration levels, vehicle speed, turn radius, lateral force levels, precipitation levels and external ambient temperature.
Owner:TESLA INC
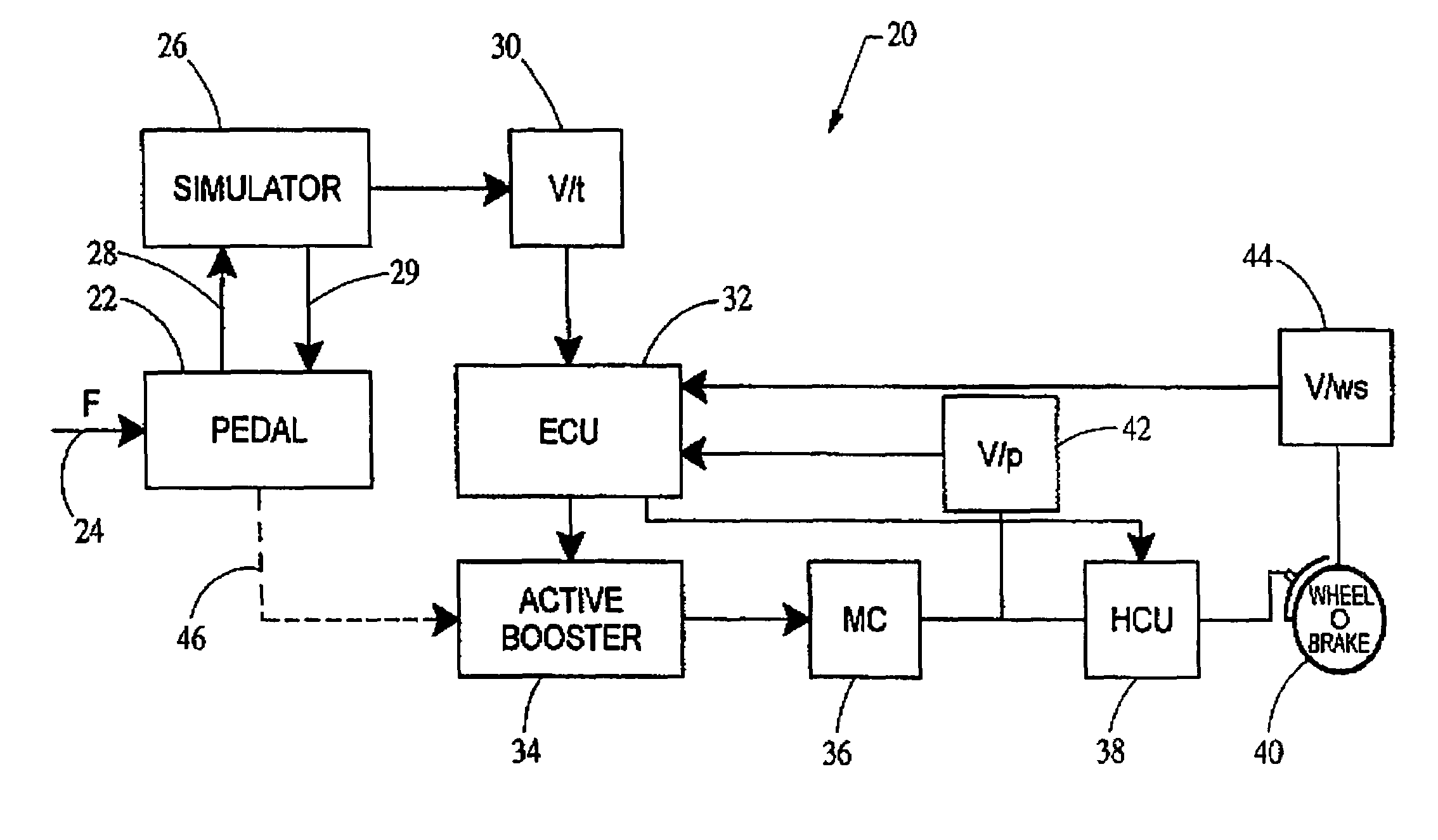
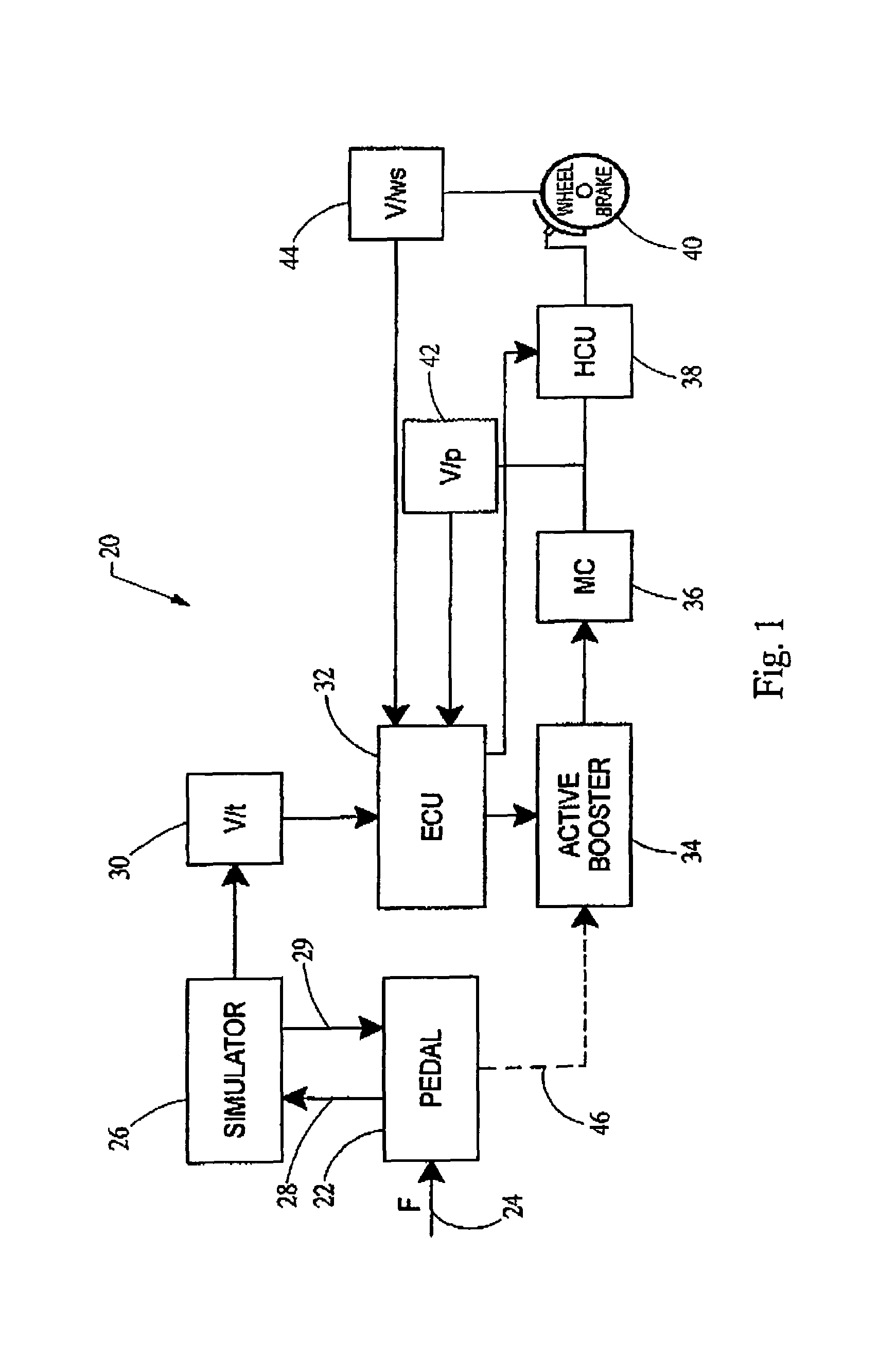
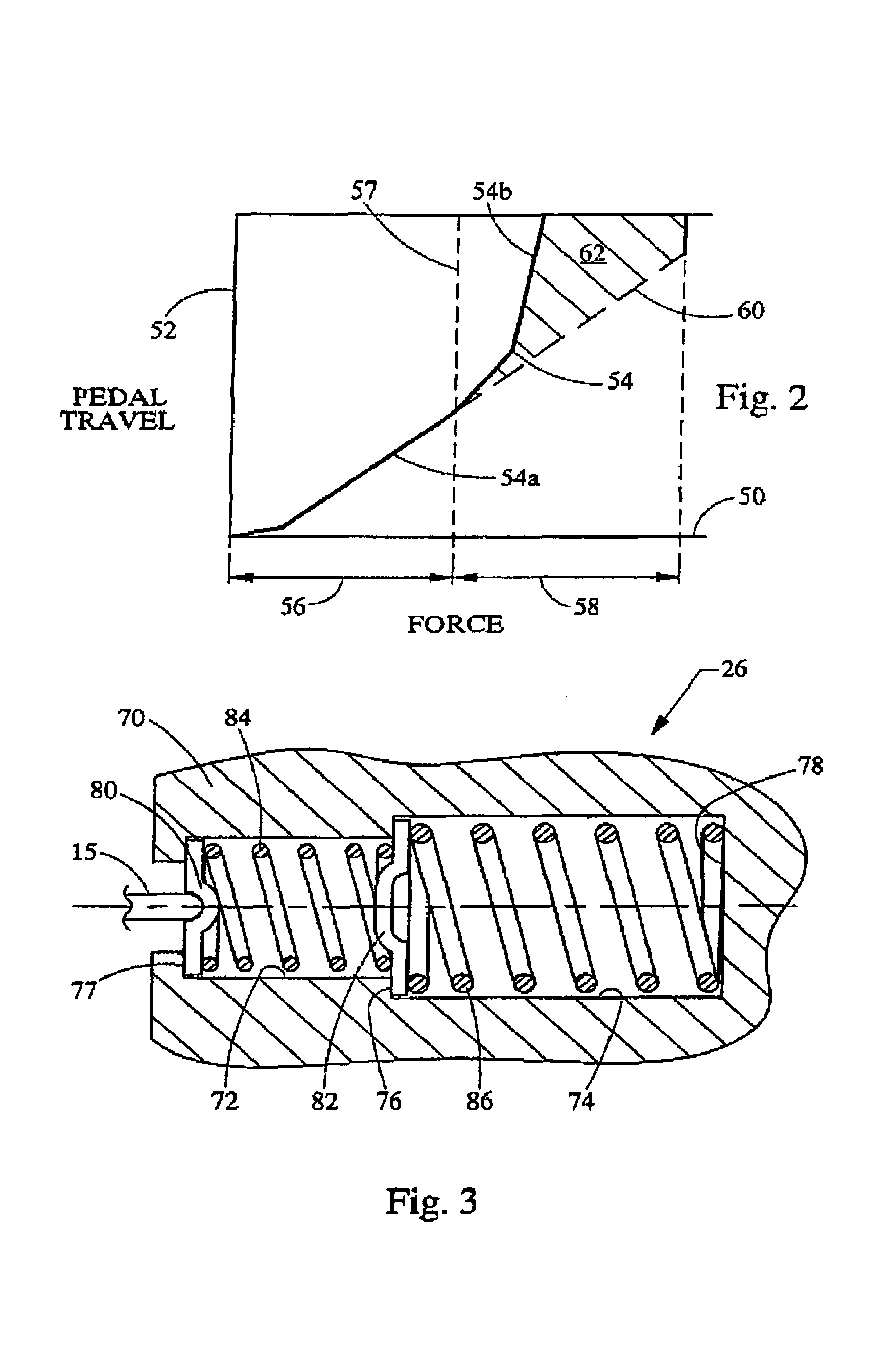
Brake pedal feel simulator
ActiveUS7357465B2Reduces simulation forceImprove abilitiesBraking action transmissionApplication and release valvesForce levelAutomotive engineering
A brake pedal feel simulator is provided which reduces the simulation force provided to the brake pedal during emergency or failed conditions. The simulator generally comprises a first spring having a first spring rate and a second spring having a second spring rate. The second spring rate is selected to be lower than the first spring rate. When a predetermined force level is achieved at the brake pedal and simulator, the spring rate provided by the simulator shifts to the second spring rate. In this manner, the rate resistance to translation of the brake pedal is reduced, thereby improving the operator's ability to brake the vehicle.
Owner:CONTINENTAL AUTOMOTIVE SYST INC
Linear motor force ripple identification and compensation with iterative learning control
InactiveUS20060170382A1Increase heightIncrease speedProgramme controlMotor control for low load efficiencyEngineeringPeak value
Embodiments of the present invention are directed to compensating for force ripple of an apparatus driven by a force produced by a linear motor. In one embodiment, a method of compensating for force ripple comprises generating force commands for a trajectory starting at a plurality of starting positions of the apparatus driven by the linear motor to produce different trajectory motions based on the same trajectory at the plurality of starting positions, the force commands each including peaks of large acceleration / deceleration and valleys of low force levels; calculating an average of the force commands during large acceleration / deceleration generated based on trajectory motions for the plurality of starting positions; calculating a variation ratio of the force command for each trajectory motion to the calculated average of the force commands; and compensating for force ripple in the apparatus based on the calculated variation ratio to control the force applied by the linear motor to the apparatus.
Owner:NIKON CORP
Exercise apparatus based on a variable mode hydraulic cylinder and method for same
ActiveUS7762934B1Security challengeDistance minimizationMuscle exercising devicesWater sourceEngineering
The invention is a hydraulic cylinder for use in exercise machines to deliver a controllable fast acting force. The invention uses a hydraulic cylinder with features that allow high acceleration rates, rapid changes of force level and direction, and positive force limitation. In the preferred embodiment, the hydraulic cylinder is composed of a rodless, hydraulic cylinder coupled to a cable and pulley system. A water source delivers water to generate a force against an inner bi-directionally moving piston to generate a regulated movement and force.The ends of the rodless hydraulic cylinder are sealed by both a water control spool valve and a controllable poppet style pressure relief valve. The water control spool valves adjustably permits water to enter and exit the hydraulic cylinder to regulate the direction and speed of movement of the piston. The pressure relief valve controls the desired maximum pressure and corresponding forces exerted on cylinder. Thus, both the internal speed and force of movement of the piston can be controlled. The invention can deliver high acceleration / speed, high force resistance; high acceleration / speed, low force resistance; low acceleration / speed, high force resistance; or low acceleration / speed, low force resistance exercise forces and movements depending on the water flow, internal pressure, and resulting generated forces.
Owner:FOI GRP
Hood lift mechanisms utilizing active materials and methods of use
InactiveUS20060028051A1Increased clearance distanceClearance distanceVehicle seatsAnti-theft devicesIonic polymer–metal compositesElastomer
A hood lift mechanism for reversibly increasing the energy absorption capability at appropriate force levels of a vehicle hood includes a vehicle hood; an active material in operative communication with the vehicle hood, wherein the active material comprises a shape memory alloy, a ferromagnetic shape memory alloy, a shape memory polymer, a magnetorheological fluid, an electroactive polymer, a magnetorheological elastomer, an electrorheological fluid, a piezoelectric material, an ionic polymer metal composite, or combinations comprising at least one of the foregoing active materials; and an activation device in operative communication with the active material, wherein the activation device is operable to selectively apply an activation signal to the active material and effect a reversible change in a property of the active material, wherein the reversible change results in an increased clearance distance between the vehicle hood and an underlying component.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC +1
Hood lift mechanisms utilizing active materials and methods of use
A hood lift mechanism for reversibly increasing the energy absorption capability at appropriate force levels of a vehicle hood includes a vehicle hood; an active material in operative communication with the vehicle hood, wherein the active material comprises a shape memory alloy, a ferromagnetic shape memory alloy, a shape memory polymer, a magnetorheological fluid, an electroactive polymer, a magnetorheological elastomer, an electrorheological fluid, a piezoelectric material, an ionic polymer metal composite, or combinations comprising at least one of the foregoing active materials; and an activation device in operative communication with the active material, wherein the activation device is operable to selectively apply an activation signal to the active material and effect a reversible change in a property of the active material, wherein the reversible change results in an increased clearance distance between the vehicle hood and an underlying component.
Owner:UNIV OF MICHIGAN THE +1
Hood lift mechanisms utilizing active materials and methods of use
ActiveUS7556117B2Pedestrian/occupant safety arrangementAutomatic initiationsIonic polymer–metal compositesEnergy absorption
Hood lift mechanisms for reversibly increasing the energy absorption capability at appropriate force levels of a vehicle closure includes a vehicle closure; an active material in operative communication with the vehicle closure, wherein the active material comprises a shape memory alloy, a ferromagnetic shape memory alloy, a shape memory polymer, a magnetorheological fluid, an electroactive polymer, a magnetorheological elastomer, an electrorheological fluid, a piezoelectric material, an ionic polymer metal composite, or combinations comprising at least one of the foregoing active materials; and an activation device in operative communication with the active material, wherein the activation device is operable to selectively apply an activation signal to the active material and effect a reversible change in a property of the active material, wherein the reversible change results in an increased clearance distance between the vehicle closure and an underlying component.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC +1
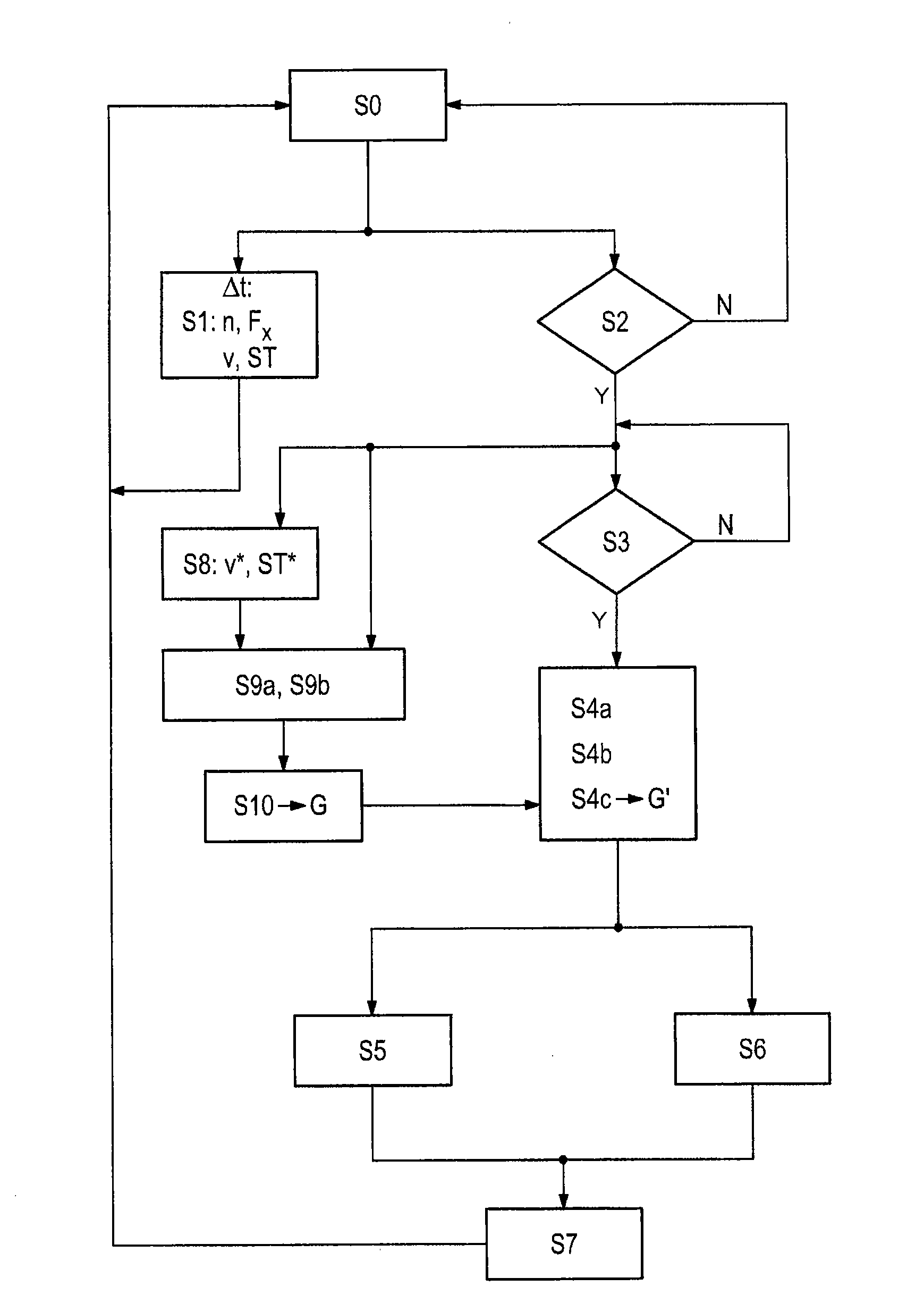
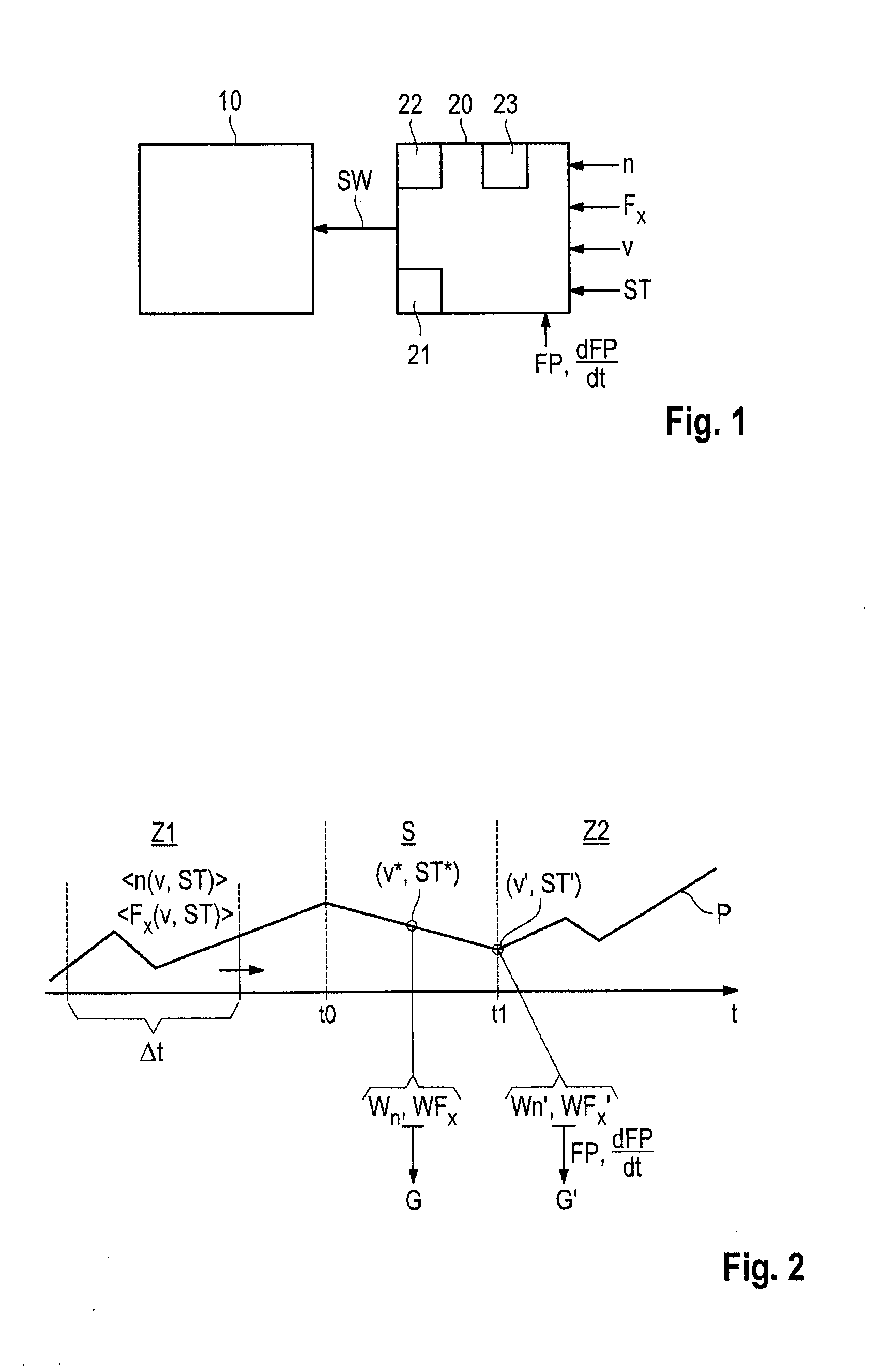
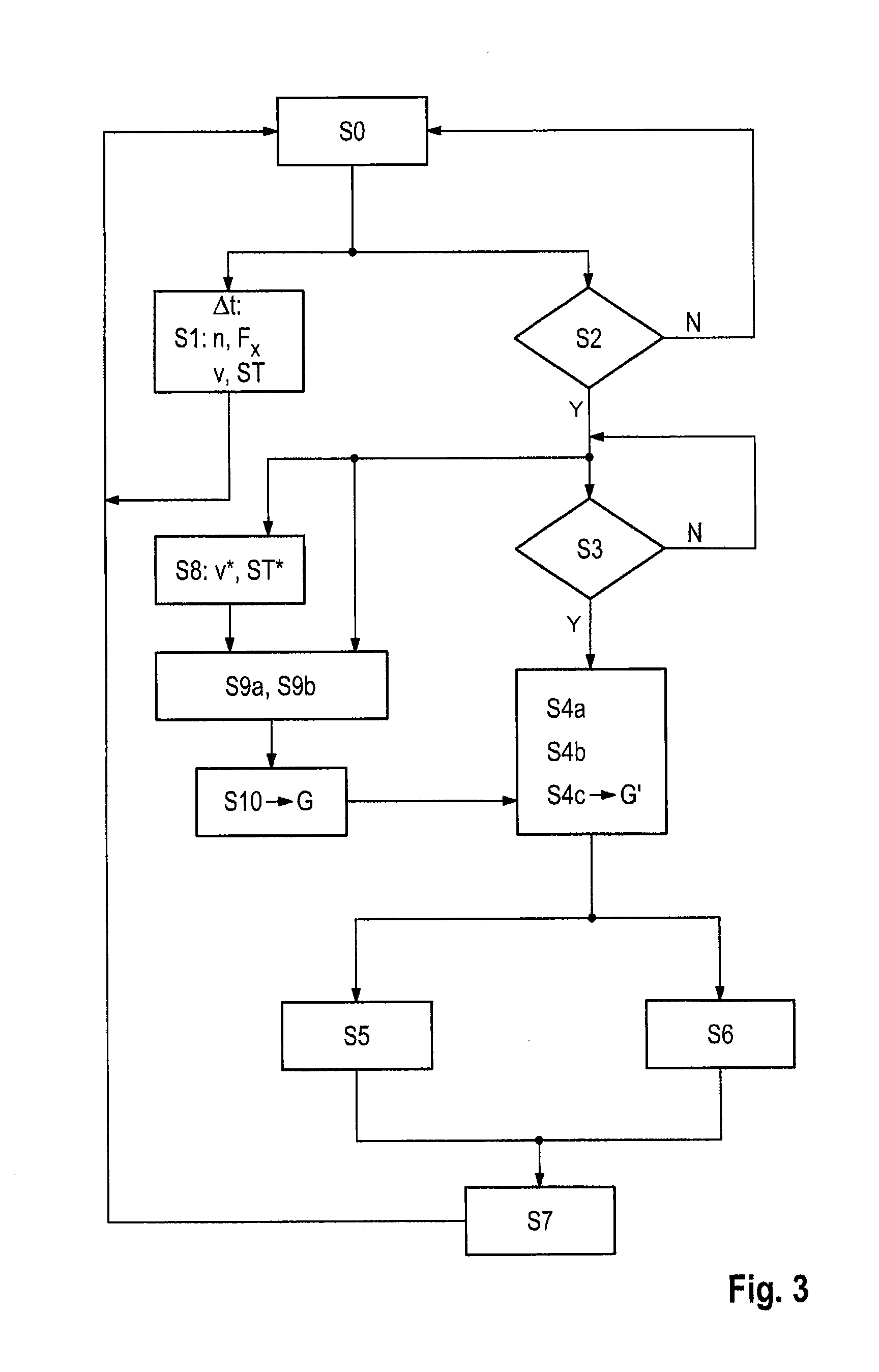
Gear selection method for an automatic transmission for a traction phase after a coasting phase of a motor vehicle
ActiveUS20110313631A1Digital data processing detailsRoad transportMobile vehicleAutomatic transmission
Disclosed herein is a gear selection method and device for an automatic transmission for a traction phase (Z2) after a coasting phase (S) of a motor vehicle. According to the method, in a traction phase (Z1) before the coasting phase (S), a sliding average value of the rotational speed level (n) and / or of the traction force level (Fx) is formed depending on the particular velocity (v) and particular gradient (ST) and is taken into consideration for defining at least one gear choice of the automatic transmission for the traction phase (Z2) after the particular coasting phase (S).
Owner:DR ING H C F PORSCHE AG
High output device for confirming thread presence in nuts and other threaded parts
ActiveUS7059055B2Quick testAvoid shutdownPlug gaugesMechanical counters/curvatures measurementsMotor driveEngineering
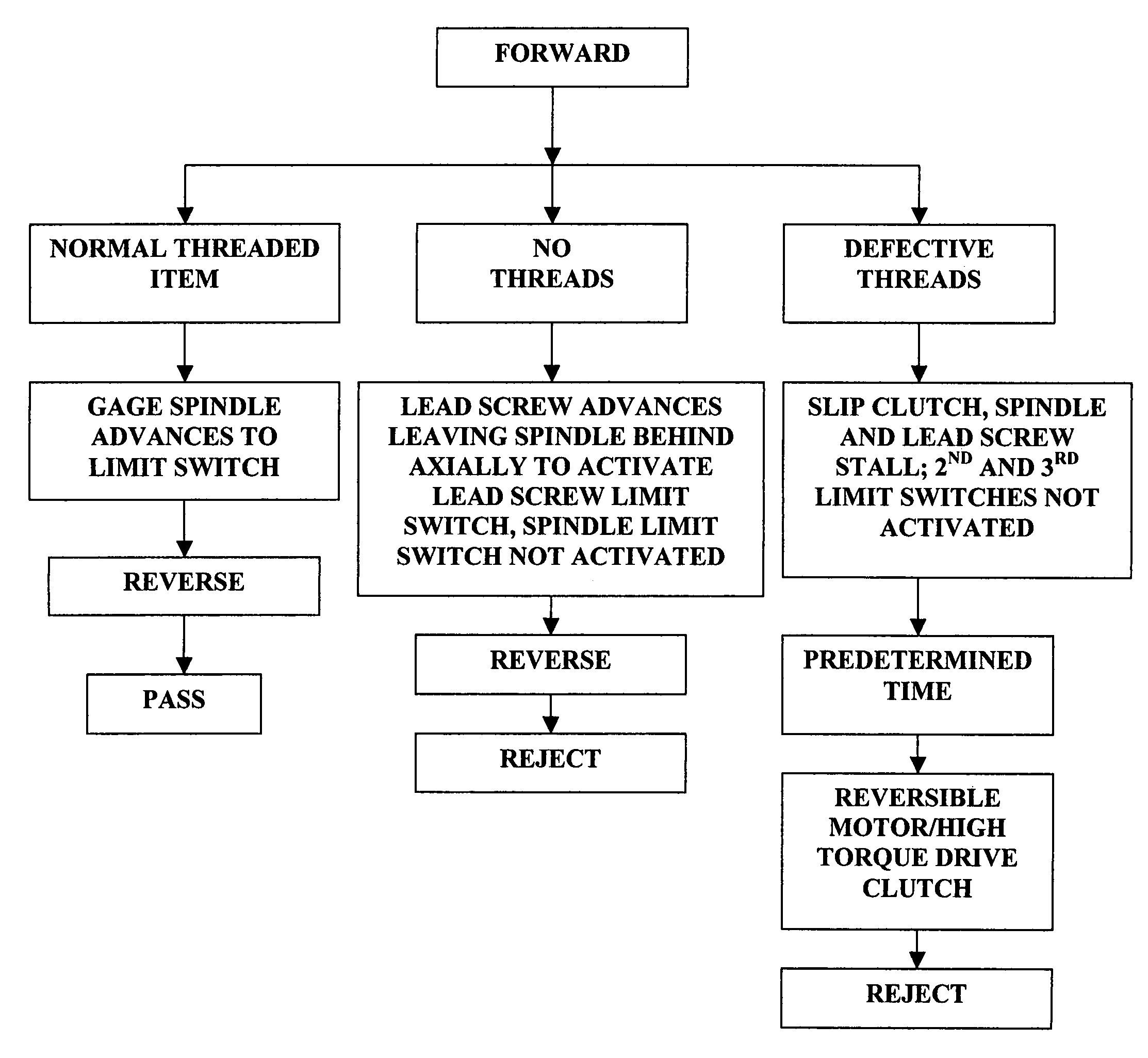
A device for confirming the presence of thread in nuts and other threaded parts has a threaded gage mounted on a holder which is connected through a clutch to a motor. The motor drives the holder to rotate the threaded gage to engage the threaded part. Switches are provided to stop and reverse the motor. The device identifies parts without threads and also damaged and incomplete threads. The device does not impart undue force levels to unthreaded, undersized parts or defective parts. The device confirms threads in threaded blind bores.
Owner:NEW VISTA CORP
Adaptive soft buttons for a vehicle user interface
ActiveUS8818624B2Improve user performanceExpands touch-sensitiveInput/output for user-computer interactionInstruments for road network navigationGraphical user interfaceEngineering
A system and a method are provided for configuring the touch-sensitive area and / or the tap duration associated with a plurality of touch-sensitive soft buttons of a vehicle user interface in response to varying vehicle conditions. In particular, as a monitored vehicle condition deteriorates, the system controller coupled to the vehicle user interface expands the touch-sensitive region and / or increases the tap duration of the touch-sensitive soft buttons, thereby improving the user's ability to successfully interact with the interface. Vehicle conditions that may be monitored and used to configure the touch-sensitive area and / or tap duration include passenger cabin vibration levels, vehicle speed, turn radius, lateral force levels, precipitation levels and external ambient temperature.
Owner:TESLA INC
Safety gate system having an electronic display
InactiveUS20080236045A1Provide securityPrevent tripping hazardGates/doorsFixed grillesComputer moduleDisplay device
A safety gate system having an electronic display for seamless integration into a barrier with electronic display capabilities. The safety gate system includes a post and a gate hinged to the post. The gate face and post carry electronic display modules which appear when the gate is closed, as continuous with and seamlessly integrated into the display of the barrier. Preferably, the hinges are four-bar hinges, most preferably two sets of paired four-bar hinges. The safety gate also includes a lower chase or sill which allows both signal wiring and power to pass under the gate. Braced rear legs compensate for the cantilever forces of the gates when open. A latch, preferably an electromagnetic latch, auto-releases in response to a pre-set sufficient force level, such as arising crowd surge forces, being applied to the gate, as well as being remotely releasable.
Owner:DAKTRONICS
Motor operator for over-head air break electrical power distribution switches
A motor operator for an overhead power switch is disclosed including a microcontroller, a unique and powerful array of well-integrated sensors, a motor and drive developing substantial torque and speed and coupled to a switch actuator and responsive to the microcontroller, and a sophisticated program algorithm stored in memory at the actuator site for dynamically controlling, i.e., governing the various control modes as called for by changing conditions. The sensors include an encoder associated with the motor and drive that develops position information signals fed to the dynamic microcontroller to compute real time information including position, speed, and stopping distance used in conjunction with remote operate commands to open, close and monitor status of the switch in the various ways disclosed. Under the supervision of the microcontroller, a motor drive power switching circuit selectively applies a source of power, such as from an on site battery, to an electric motor to drive the switch toward open or closed position at different speeds, output force levels such as at different torques, and in continuous or incremental movements depending on conditions determined by the microcontroller in response to sensor inputs.
Owner:S&C ELECTRIC
Safety belt apparatus
InactiveUS6871877B2Reduce disadvantagesImprove protectionBelt retractorsEnergy-absorbing device incorporationEngineeringBelt safety
A safety belt apparatus for a vehicle, having a belt reel, a belt buckle, a belt redirection apparatus mounted on the B-post of the vehicle. The apparatus also includes, a belt-force limiter with a torsion bar and a belt tensioner. In the event of an accident, the belt tensioner is triggered, and pretorsioning of the torsion bar is simultaneously effected. The pretorsion is preferably brought about by the forces that arise during belt tensioning. The pretorsion allows for the force limitation to start at an optimum force level with regard to the retention force and the protection of the occupant.
Owner:TAKATA PETRI ULM
Slide pad notebook pointing device with sealed spring system
InactiveUS20060290665A1Cathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingCircular discPointing device
A pointing device having top and bottom pucks that move on a stage is disclosed. The top puck moves over the top surface of the stage in response to a lateral force applied thereto. The top and bottom pucks are magnetically coupled such that the two pucks maintain a predetermined relative position with respect to one another. A position sensor generates a signal indicative of the location of the bottom puck. The pointing device can also include a pressure signal generator that generates a user present signal if the top puck is subjected to a force greater than a first force level. The determined pressure can also be used to simulate a button being pushed. Exemplary pressure signal generators utilize strain gauges, variable capacitors in the top puck, and circuits for detecting the vertical distance between the top and bottom pucks when the top puck includes a deformable member.
Owner:AVAGO TECH ECBU IP (SINGAPORE) PTE LTD
Active material based bodies for varying frictional force levels at the interface between two surfaces
A device for selectively controlling and varying a frictional force level at an interface between two bodies, includes a first contact body having at least one surface, a second contact body having at least one surface in physical communication with the first contact body, and an active material in operative communication with a selected one or both of the first contact body and the second contact body, wherein the active material is configured to undergo a change in a property upon receipt of an activation signal wherein the change in a property is effective to change the frictional force level at the interface between the at least one surface of the first contact body and the at least one surface of the second contact body.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Embedded button for an electronic device
An embedded button without having gap is disclosed according to the present invention. The button area just bends to operate instead of moving back and forth to operate within a through hole so that no water, vapor, or dust shall enter into the device. One of the embodiment comprises an inner bump configured on an inner side of an outer frame; a pressure switch is configured under the inner bump and touches the bottom surface of the bump; and an activating electrical signal is triggered when the button area is pressed by user with a force exceeding a threshold force level from outside surface of the outer frame of the electronic device.
Owner:UNEO INC
Brake actuator
InactiveUS6840354B2Small dimensionImprove securityAxially engaging brakesBraking action transmissionActuatorParking brake
Owner:KNORR BREMSE SYST FUR SCHIENENFAHRZEUGE GMBH
Travelator and method for controlling the operation of a travelator
InactiveUS7861843B2Easy to useAvoid damageConveyorsControl devices for conveyorsDrive wheelFree rotation
Travelator, the conveyor of which comprises a frame, which comprises a stationary first frame part and a second frame part that moves in relation to it. The drive wheel is mounted on a bearing allowing rotation onto the first frame part. The power unit rotates the drive wheel. The diverting wheel is mounted on a bearing allowing free rotation onto the second frame part. The transport surfaces are connected to a traction element which is formed as an endless loop, and which is led to pass over the drive wheel and the diverting wheel. The tightening device is arranged to act between the first frame part and the second frame part to move the diverting wheel linearly away from the drive wheel in order to exert tightening force on the traction element. The travelator comprises identification means for identifying the drive status of the conveyor, and adjustment means for adjusting the tightening force of the tightening device to different force levels based on the drive status identified. In the method the drive status of the conveyor is identified, and the tightening force of the endless traction element of the conveyor of the travelator is adjusted on the basis of the drive status identified.
Owner:KONE CORP
Sheet-to-tube resistance spot welding using servo gun
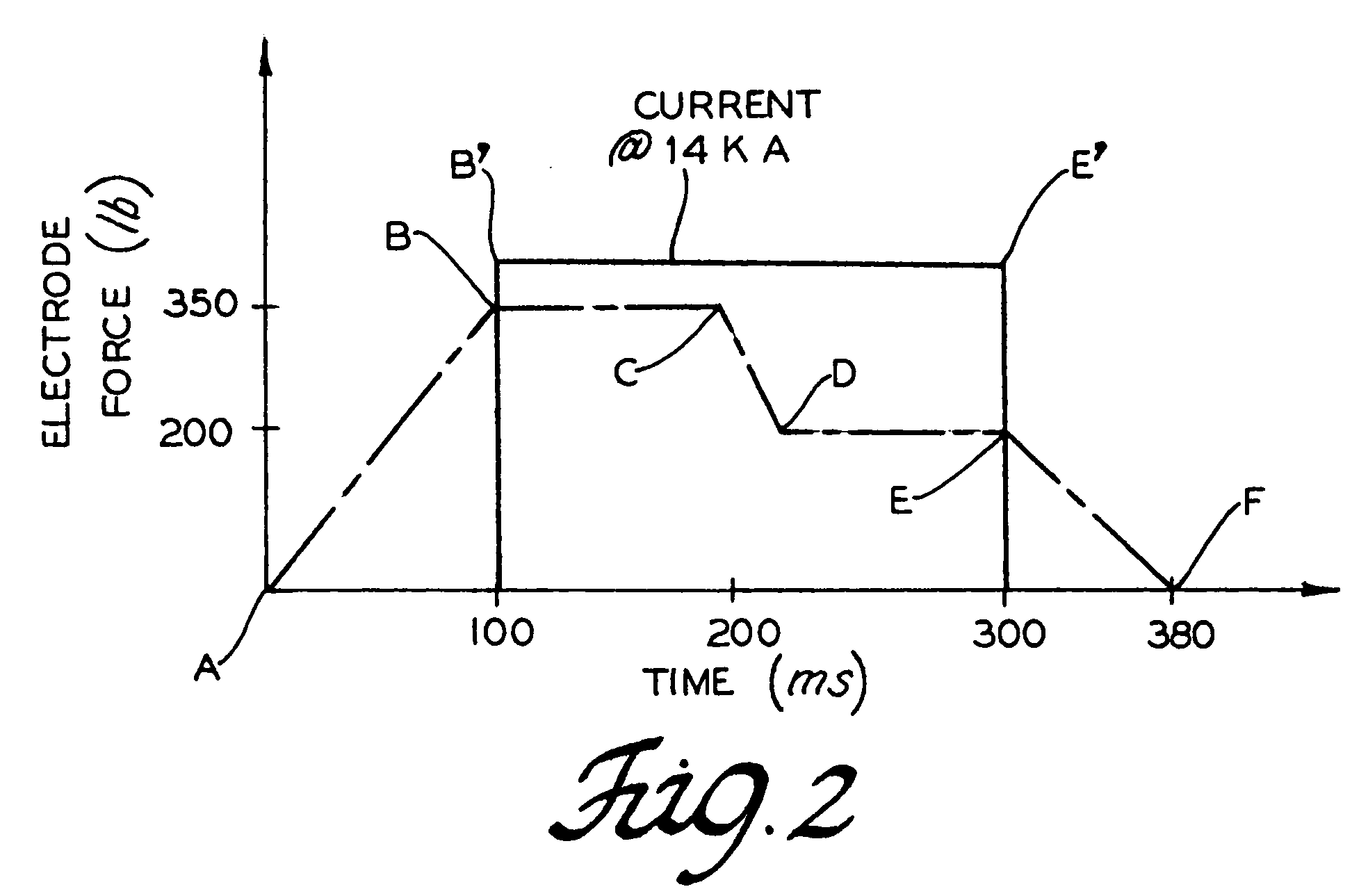
InactiveUS20050184031A1Reducing and eliminating crackEasy to controlWelding/cutting auxillary devicesArc welding apparatusElectrical resistance and conductanceEngineering
A method of spot welding a sheet overlapped to a tube with a servomotor-driven electrode applying a clamping force to the sheet. Over a first clamping time interval, the clamping force is increased to a first force level, at which point a welding current is applied to weld the sheet and tube together for a welding time interval. The first force level is maintained for a second clamping time interval, after which the clamping force is reduced to a second force level over a third clamping time interval and is maintained for a fourth clamping time interval. The welding current is removed upon expiration of the welding time interval and the clamping force is simultaneously reduced over a fifth clamping time interval, after which the electrode is disengaged from the sheet. The reduction in clamping force during the welding cycle reduces cracking of the spot weld.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Proportional Settling Time Adjustment For Diode Voltage And Temperature Measurements Dependent On Forced Level Current
ActiveUS20090009234A1Increase conversion rateMinimizing temperature measurementThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsElectronic switchingAc componentsShunt capacitors
A temperature sensor circuit and system providing accurate digital temperature readings using a local or remote temperature diode. In one set of embodiments a change in diode junction voltage (ΔVBE) proportional to the temperature of the diode is captured and provided to an analog to digital converter (ADC), which may perform required signal conditioning functions on ΔVBE, and provide a digital output corresponding to the temperature of the diode. DC components of errors in the measured temperature that may result from EMI noise modulating the junction voltage (VBE) may be minimized through the use of a front-end sample-and-hold circuit coupled between the diode and the ADC, in combination with a shunt capacitor coupled across the diode junction. The sample-and-hold-circuit may sample VBE at a frequency that provides sufficient settling time for each VBE sample, and provide corresponding stable ΔVBE samples to the ADC at the ADC operating frequency. The ADC may therefore be operated at its preferred sampling frequency rate without incurring reading errors while still averaging out AC components of additional errors induced by sources other than EMI.
Owner:MICROCHIP TECH INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com