Patents
Literature
105 results about "Dorsal fin" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
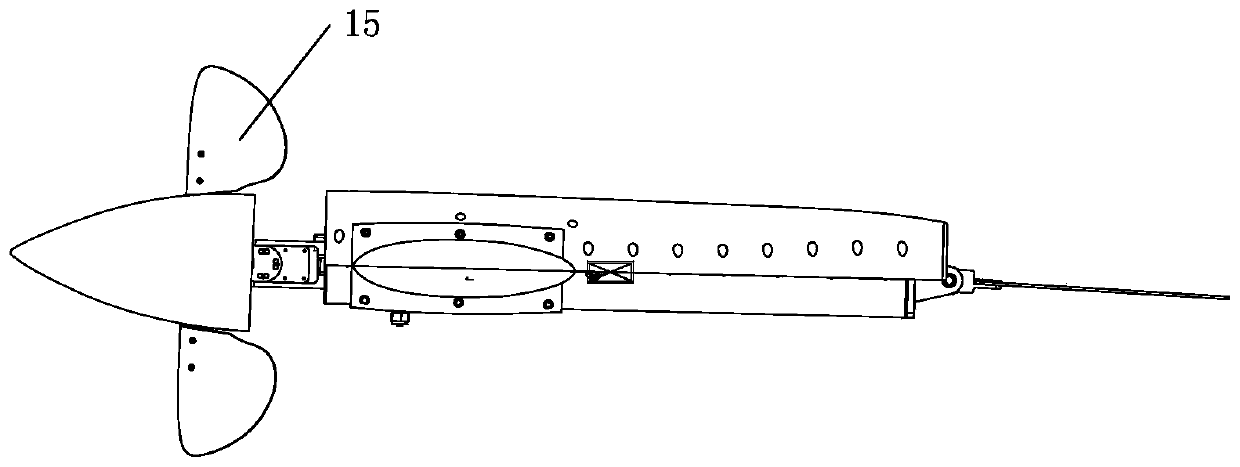
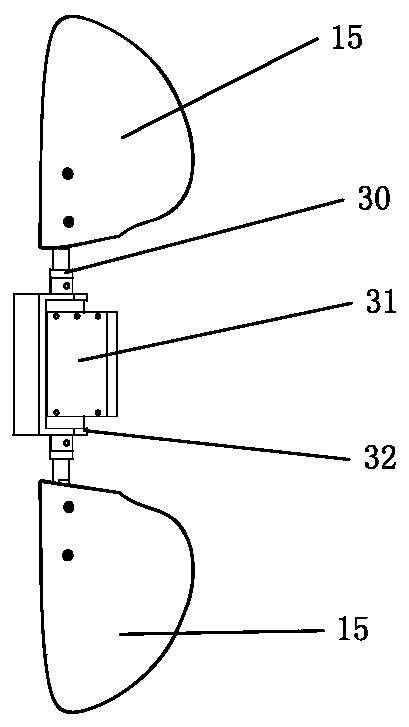
A dorsal fin is a fin located on the back of most marine and freshwater vertebrates such as fishes, cetaceans (whales, dolphins, and porpoises), and the (extinct) ichthyosaur. Most species have only one dorsal fin, but some have two or three.
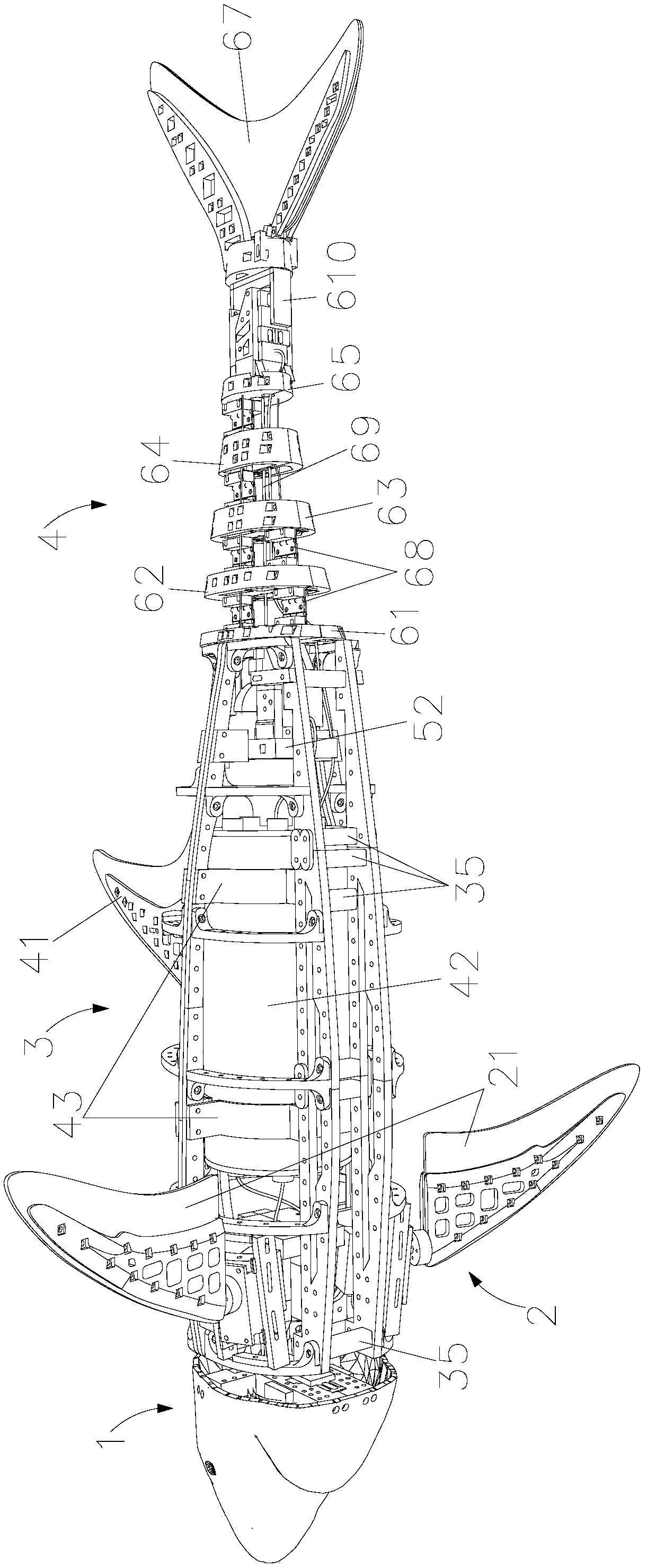
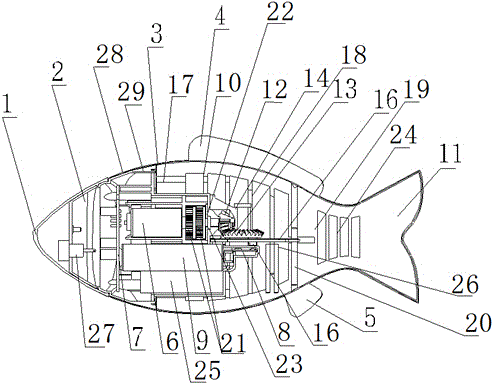
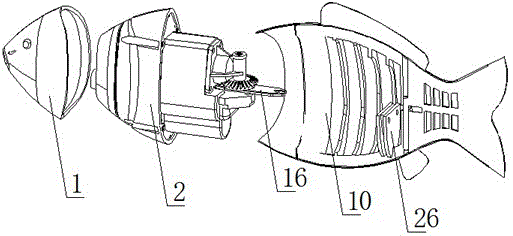
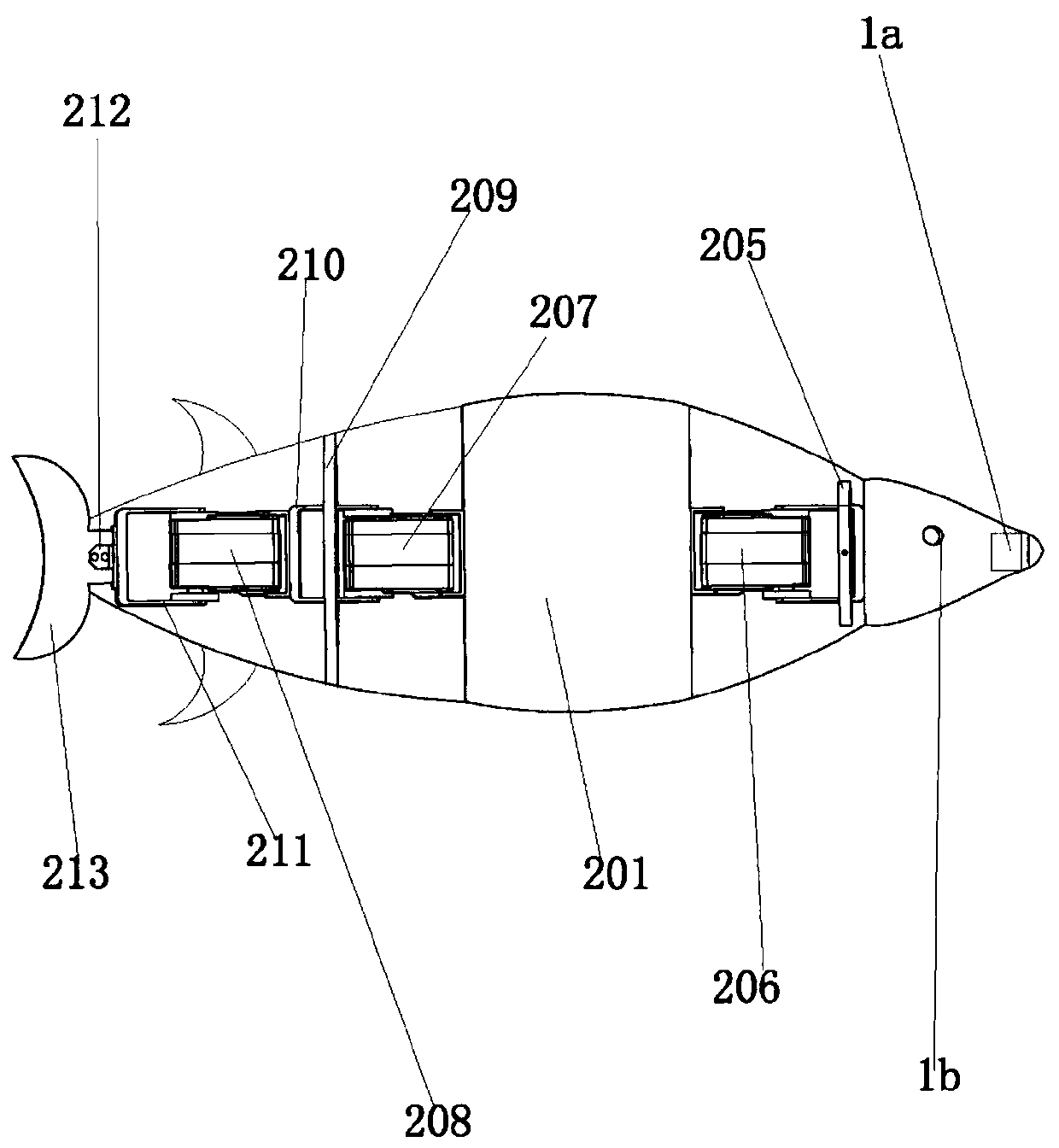
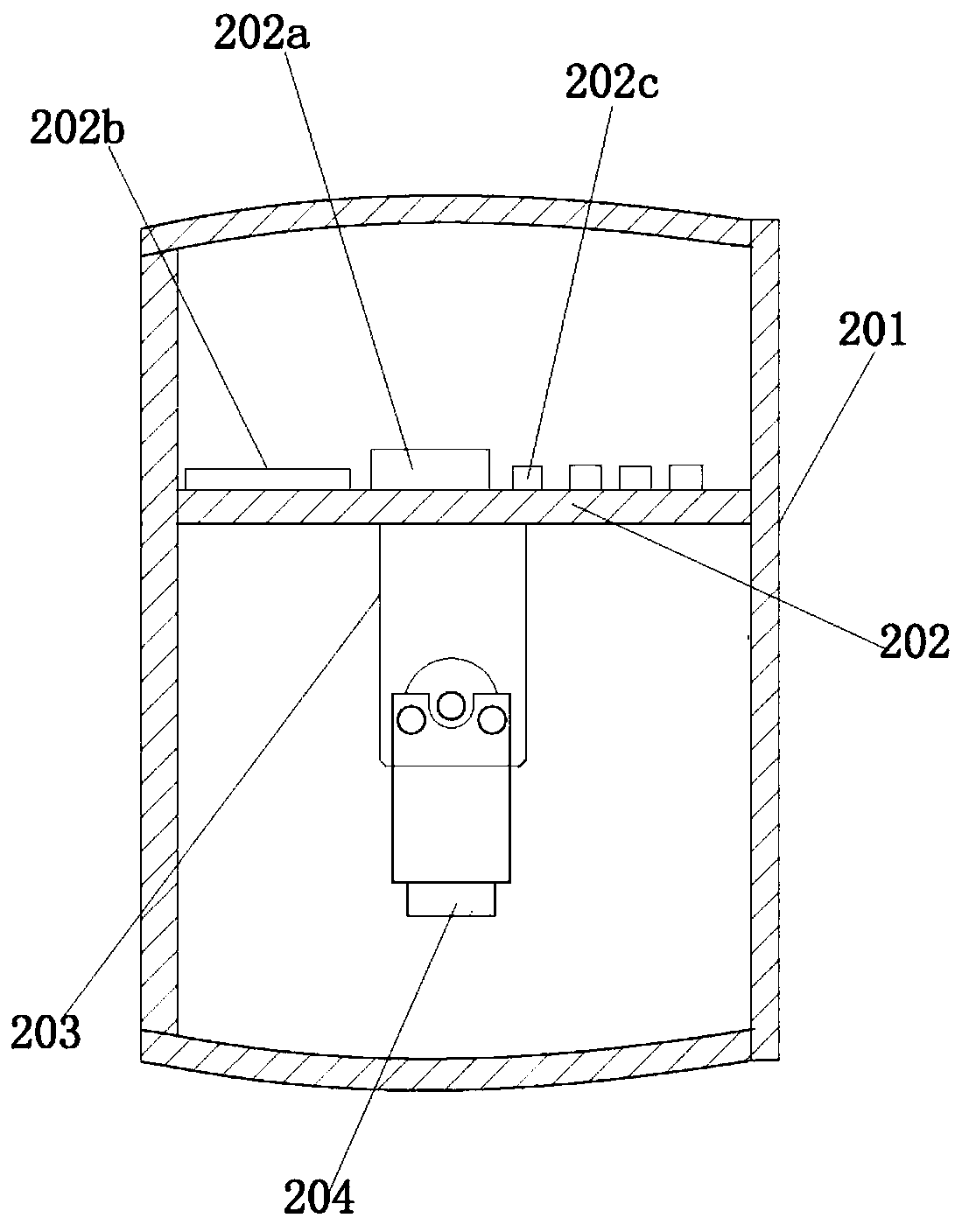
Biomimetic robotic dolphin
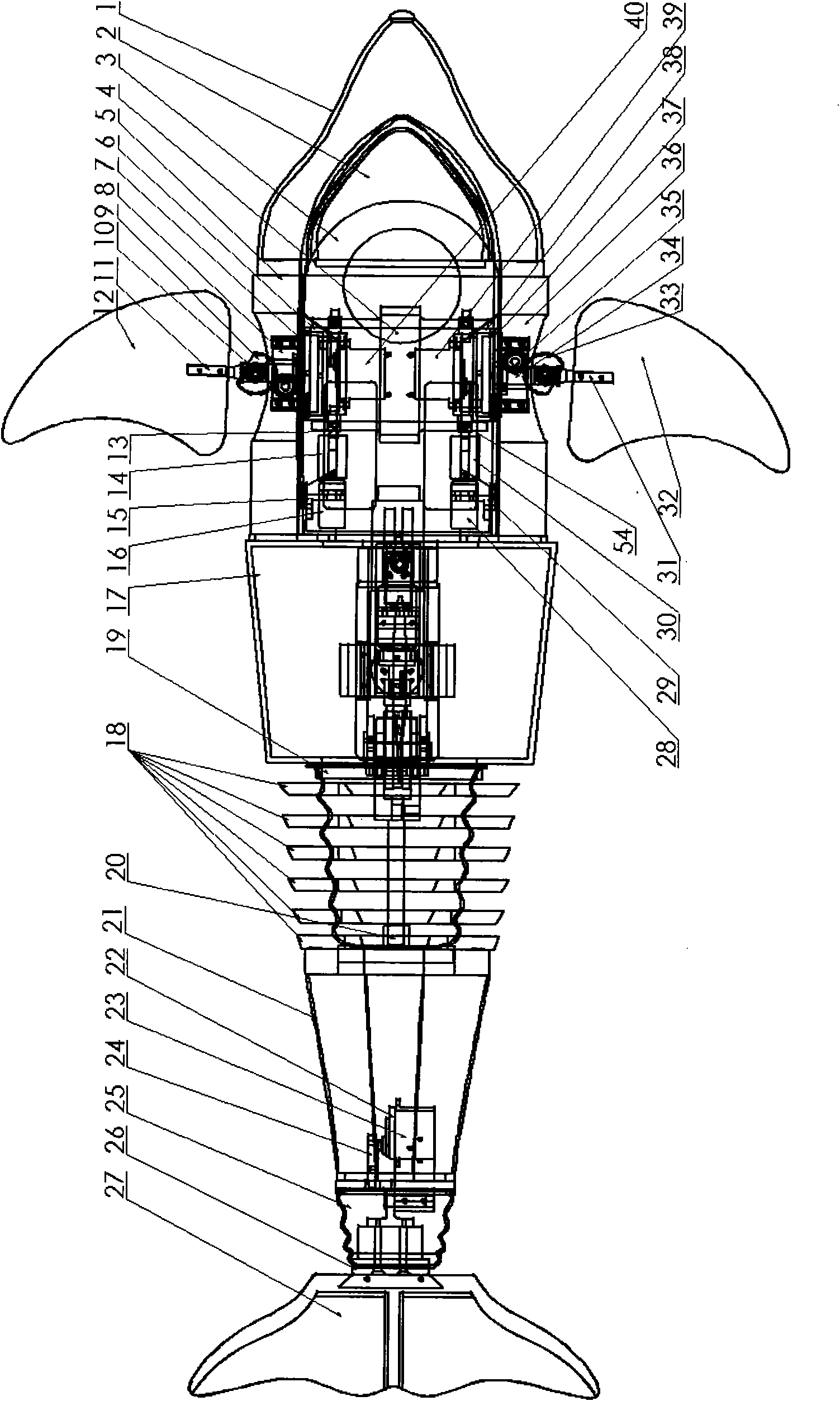
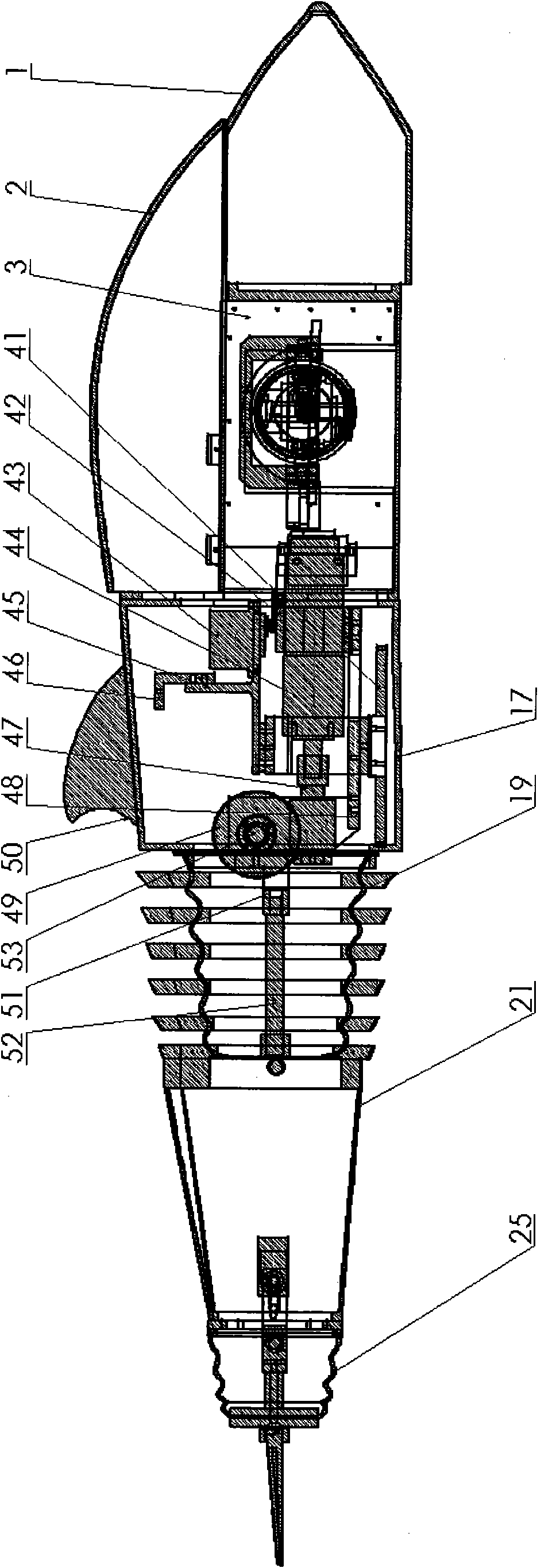
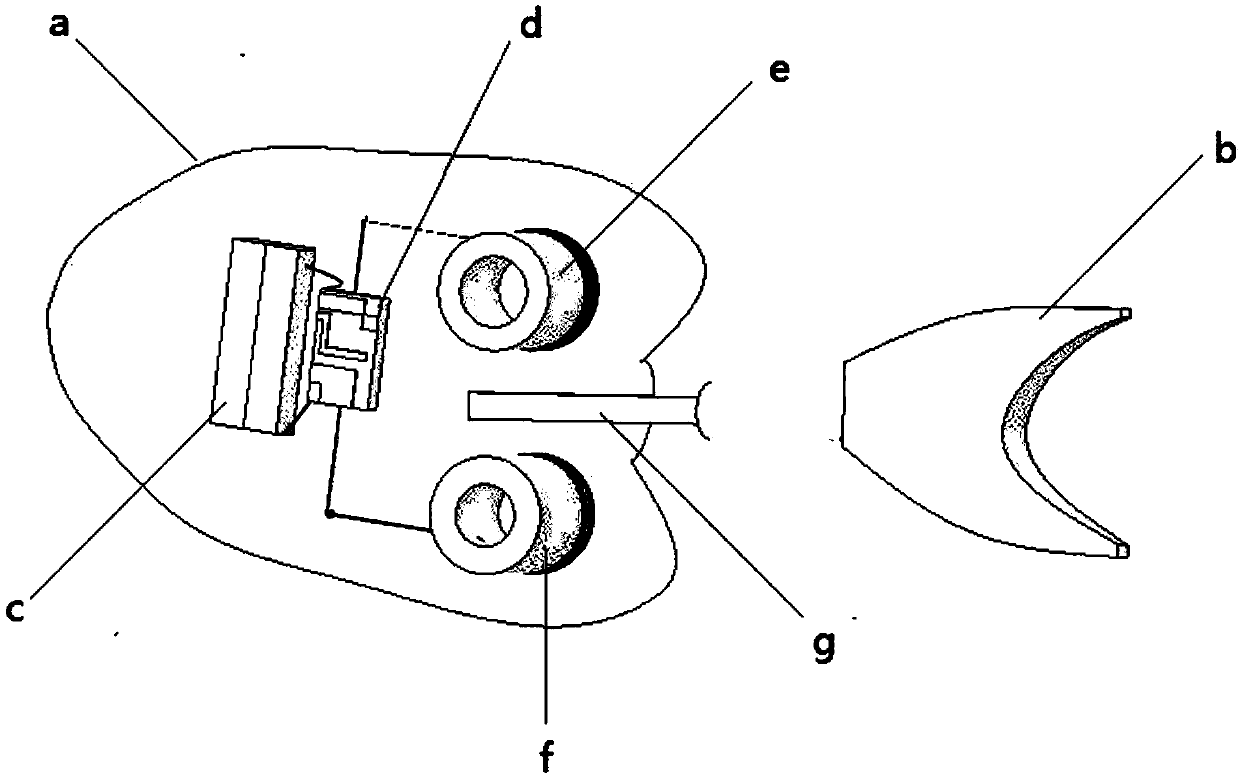
InactiveCN101913419ACompact structureLifelike shapePropulsion power plantsPropulsive elements of non-rotary typeBeak shapeEngineering
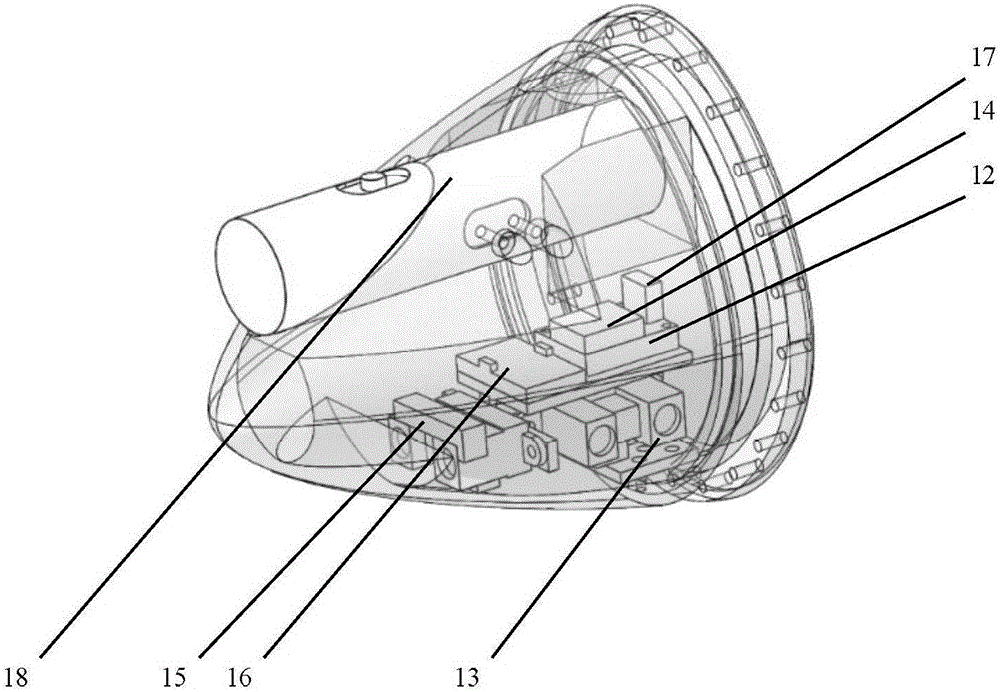
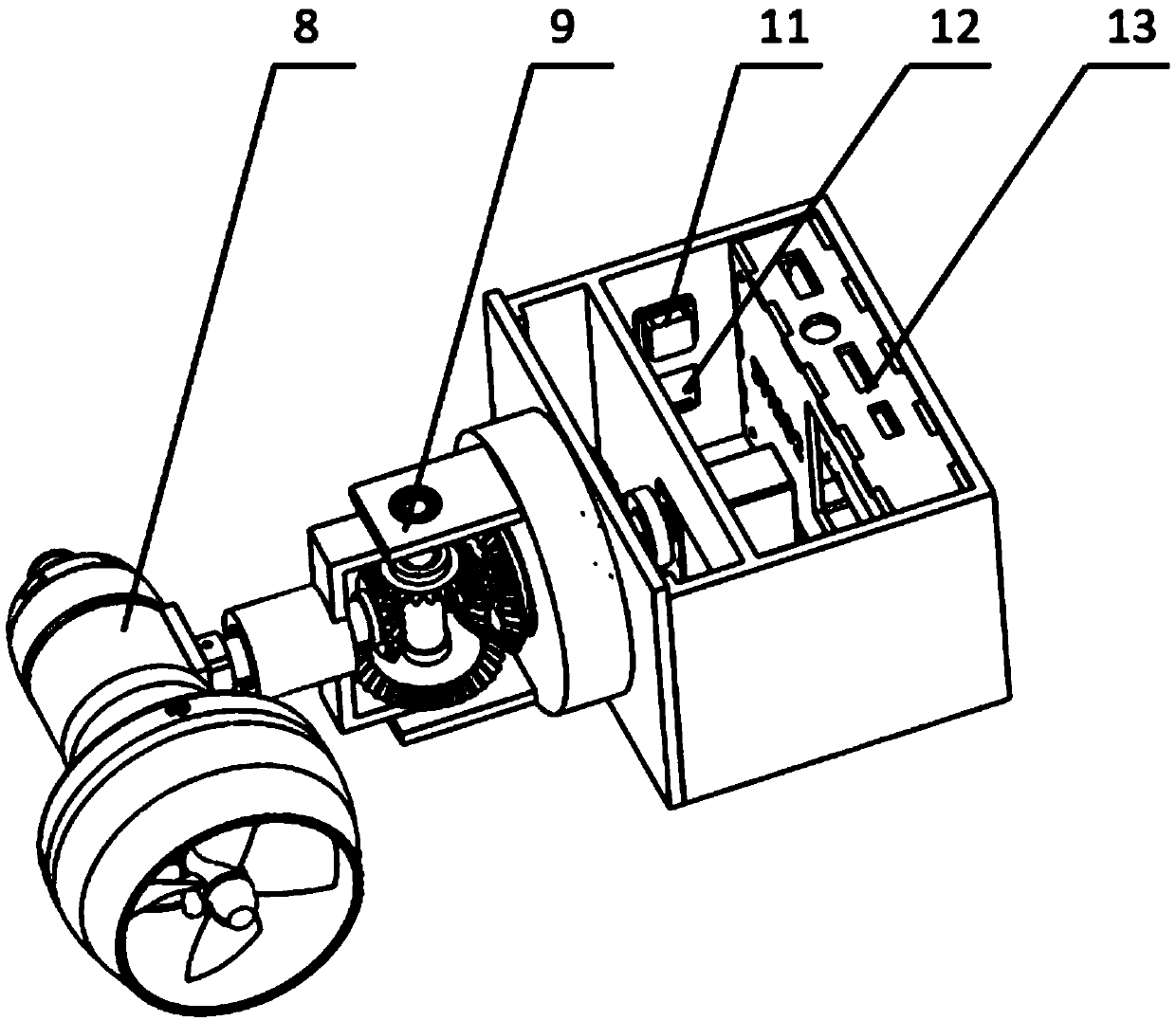
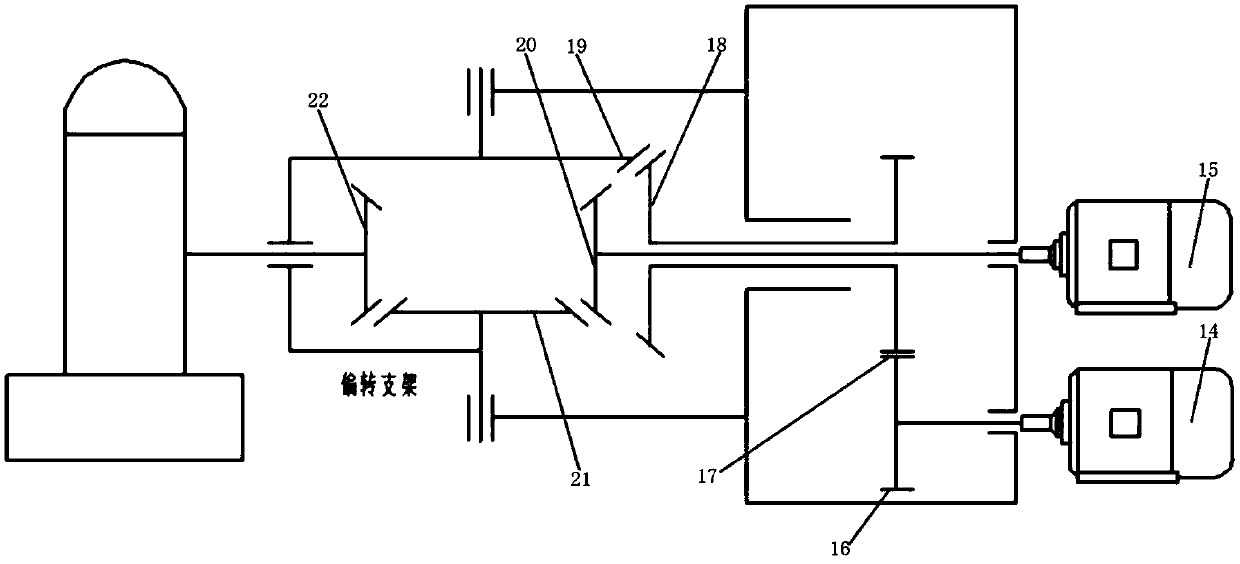
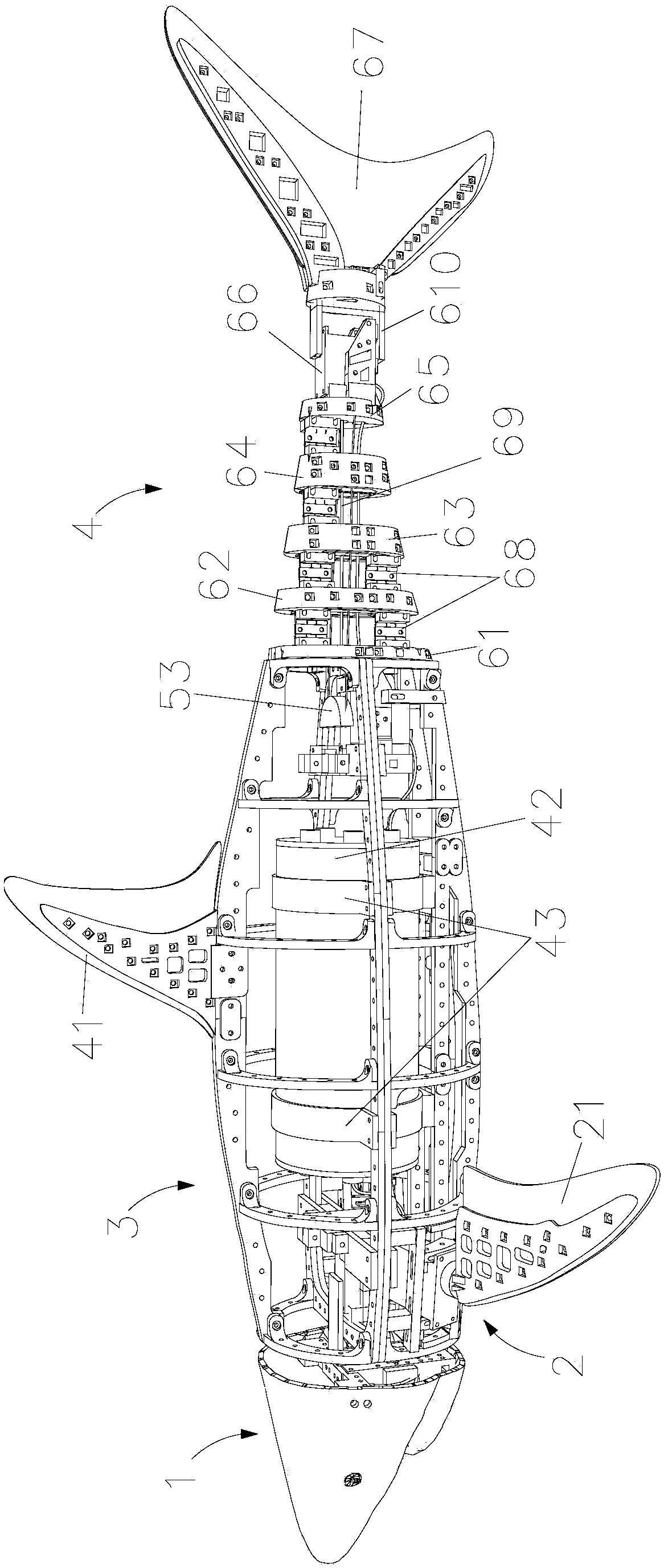
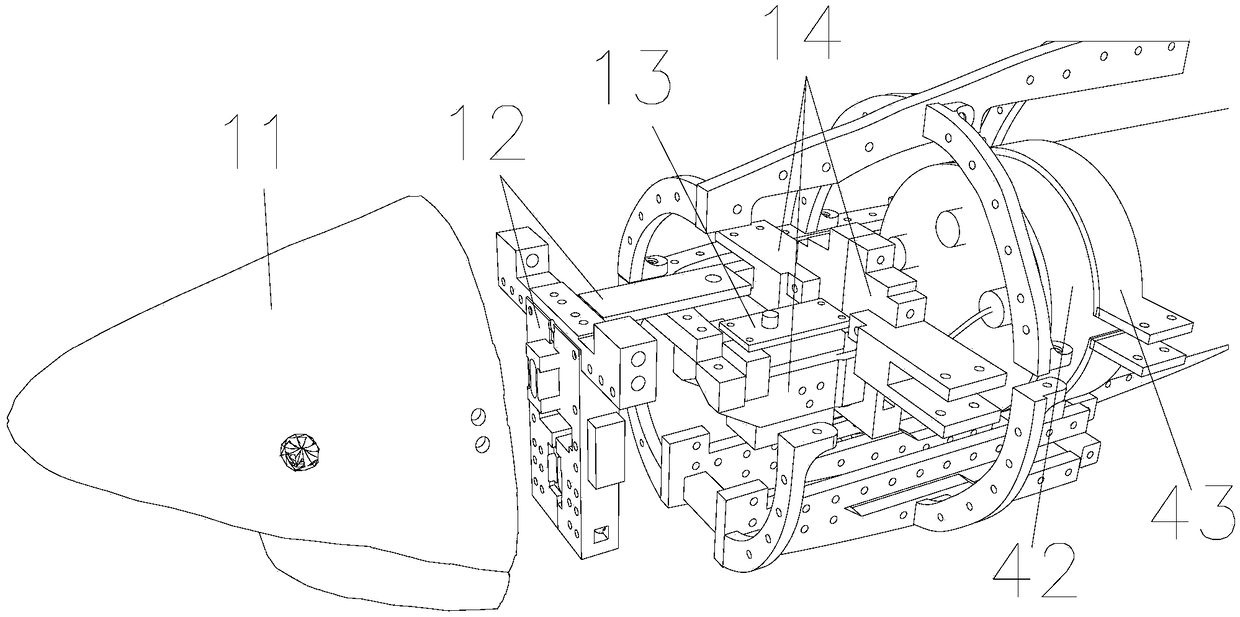
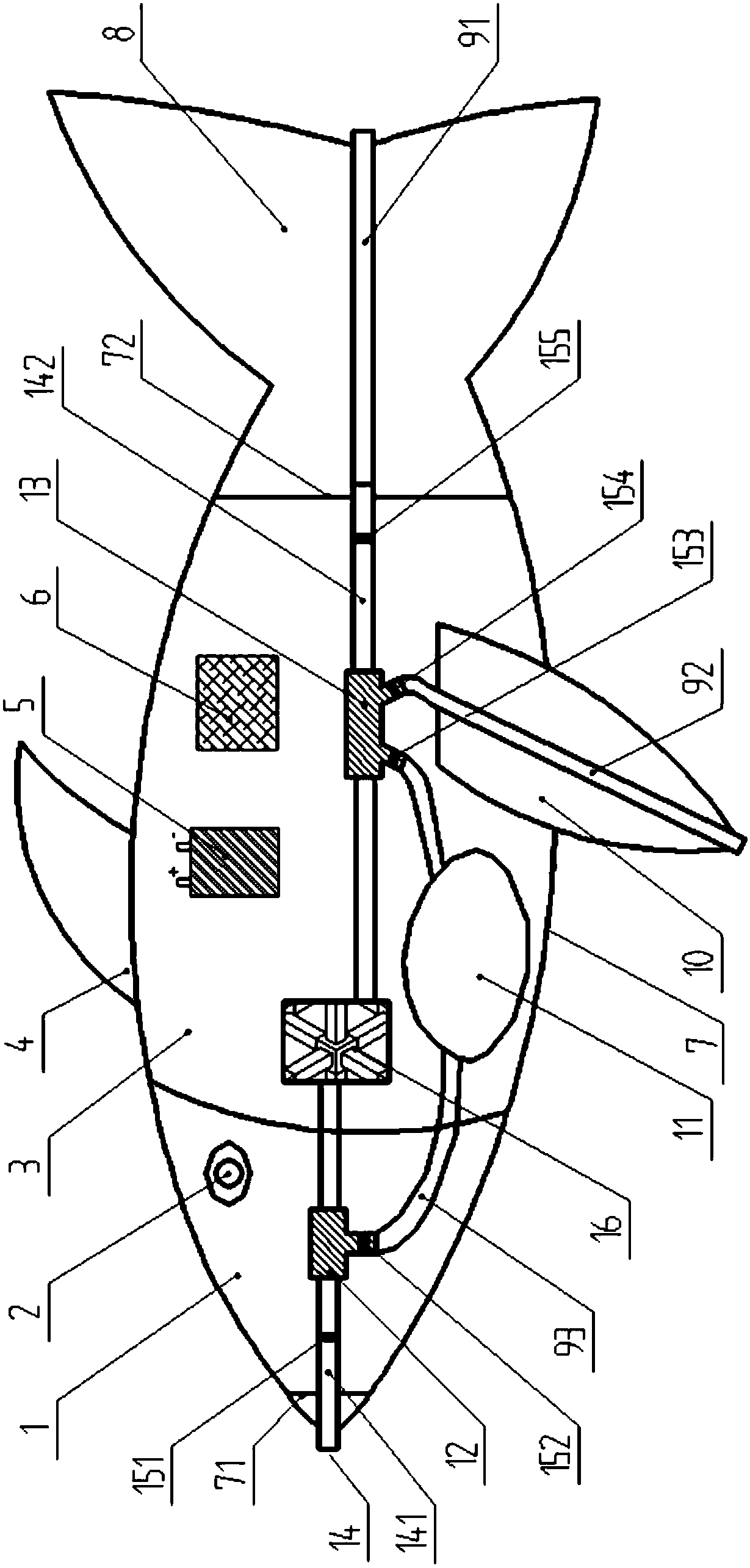
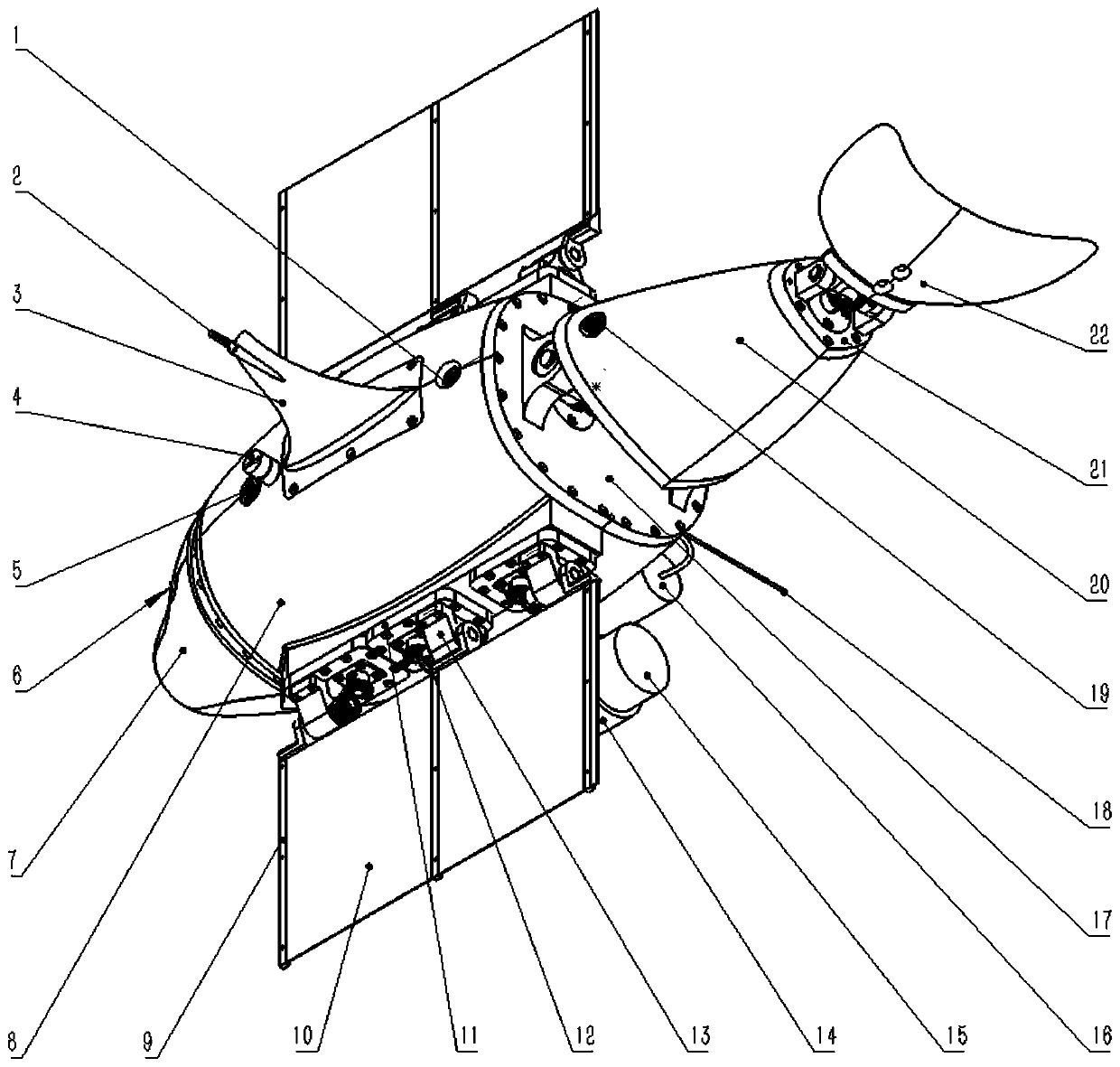
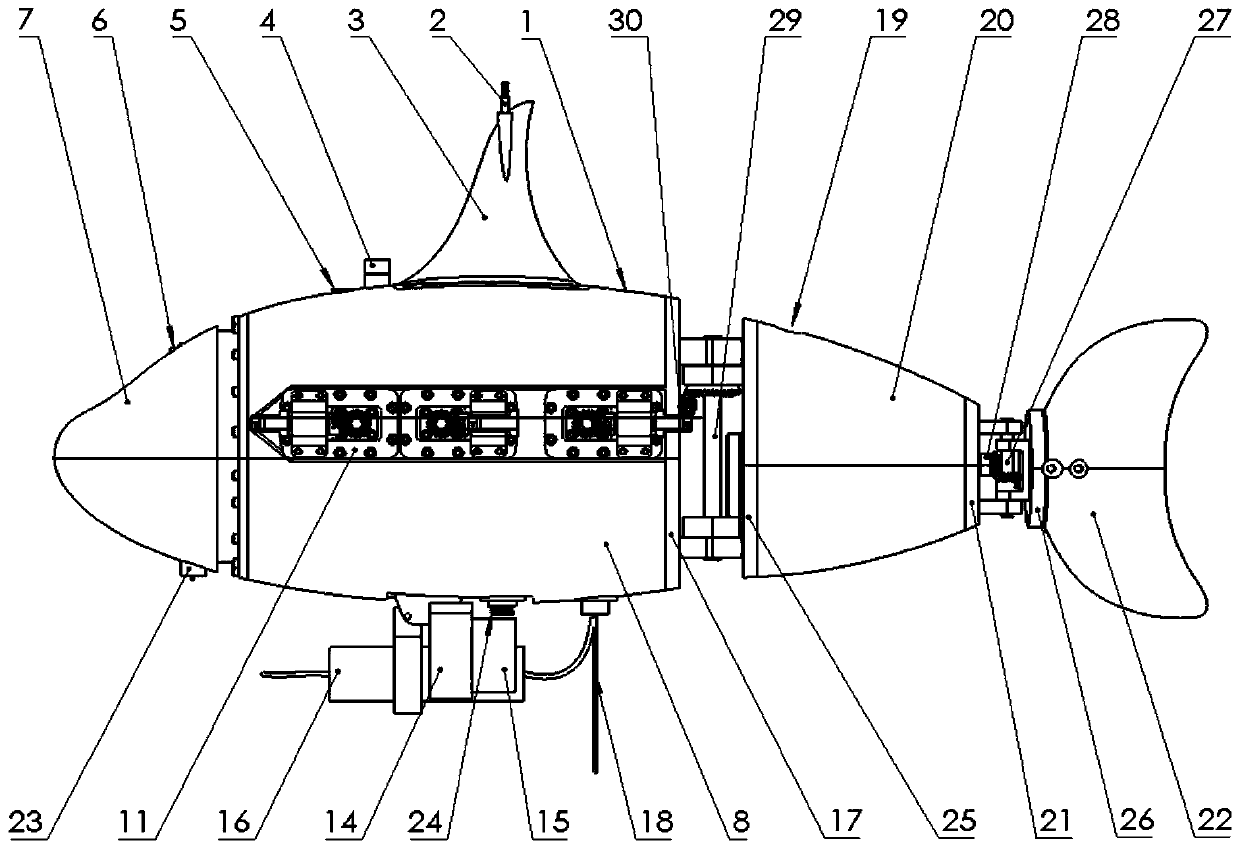
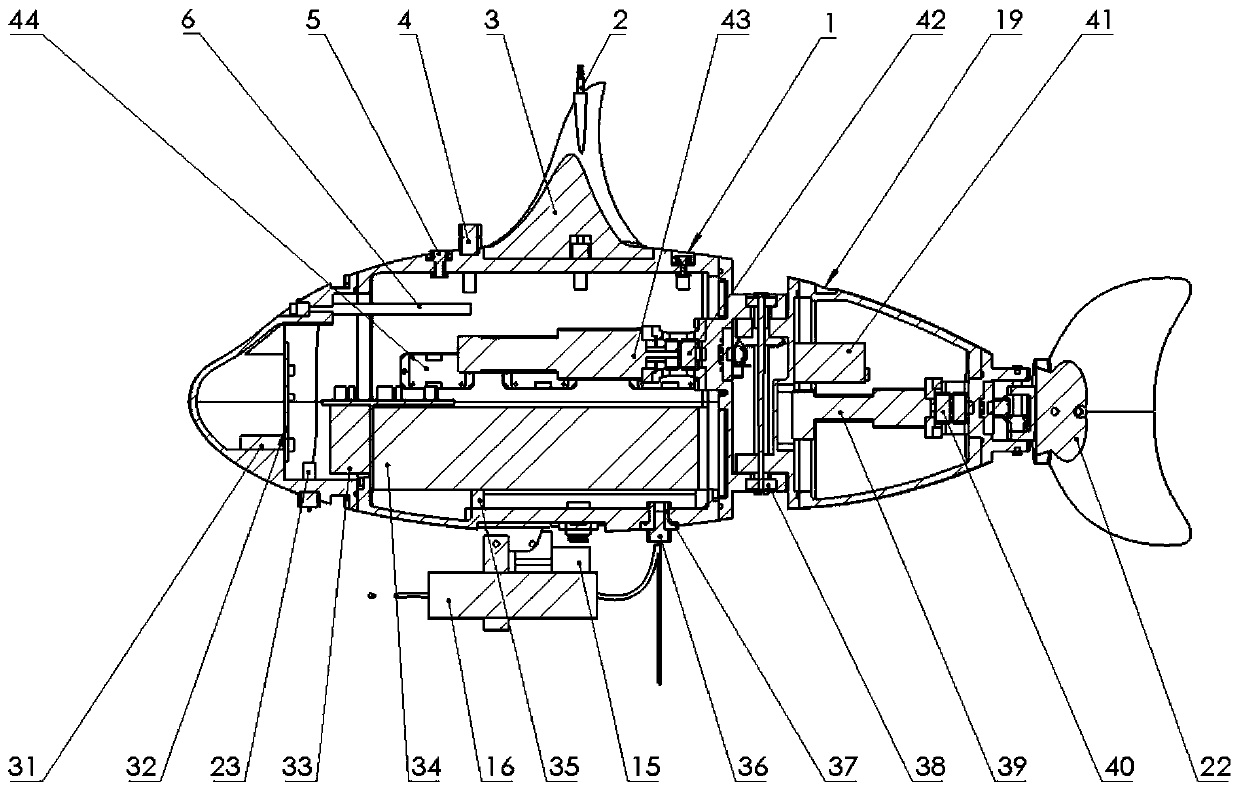
The invention discloses a biomimetic robotic dolphin. The biomimetic robotic dolphin comprises a beak part, a head shell, a pectoral fin mechanism, a main advancing mechanism, a tail part, a control part and a dolphin skin, wherein the beak part, the head shell and the pectoral fin mechanism form a streamlined head for the robotic dolphin; a left pectoral fin and a right pectoral fin are arranged on the two sides outside the head of the robotic dolphin and driven by six steering engines to swing, flap and turn respectively; the main advancing mechanism consists of a main flapping mechanism, a turning mechanism, a main advancing mechanism shell, a main advancing mechanism rubber pipe, a supporting frame and a dorsal fin which are driven by a direct current motor and the steering engines to realize flapping and turning of the body; the tail part comprises connecting nuts, a tail part skeleton and a tail fin flapping mechanism which are driven by the steering engines to realize the flapping of the tail fin; the control part consists of a control board, a communication module and a motor driver and is used for controlling the movement of the dolphin; and the dolphin skin is sleeved outside the mechanical structure of the robotic dolphin to realize integral sealing. The biomimetic robotic dolphin has the advantages of compact structure, realistic appearance and capability of providing an experiment platform for manufacturing tools for underwater operation.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Bionic robotic dolphin for water quality monitoring
ActiveCN105775082AFlexible snorkelingAchieving locomotion controlTransmission systemsTesting waterComputer monitoringEngineering plastic
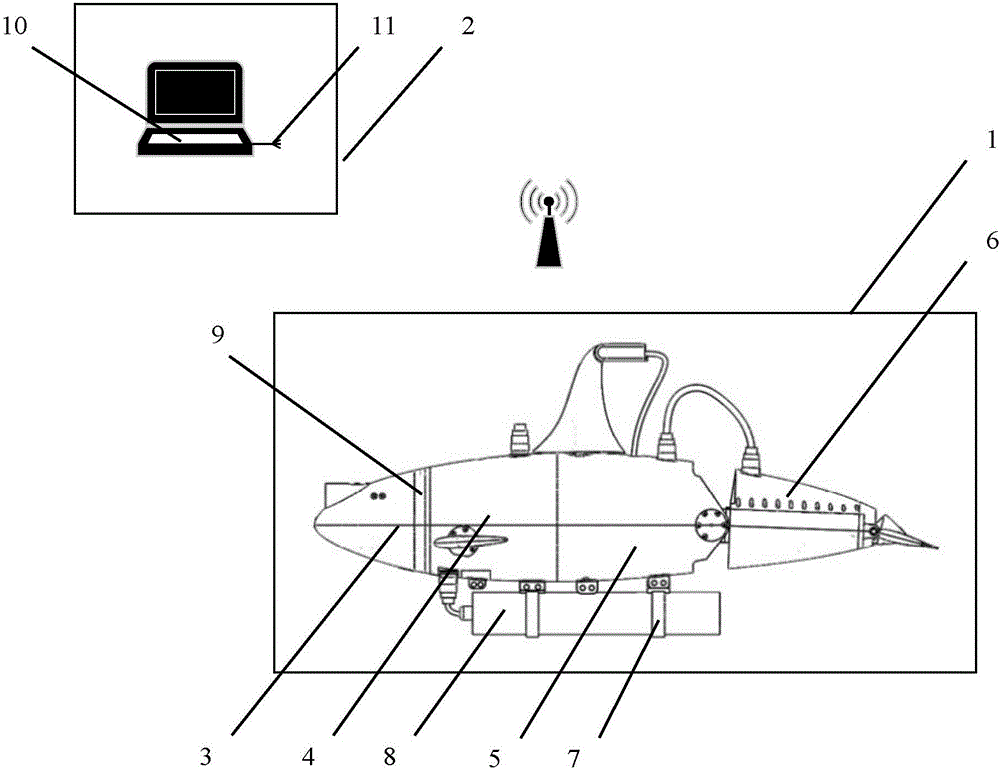
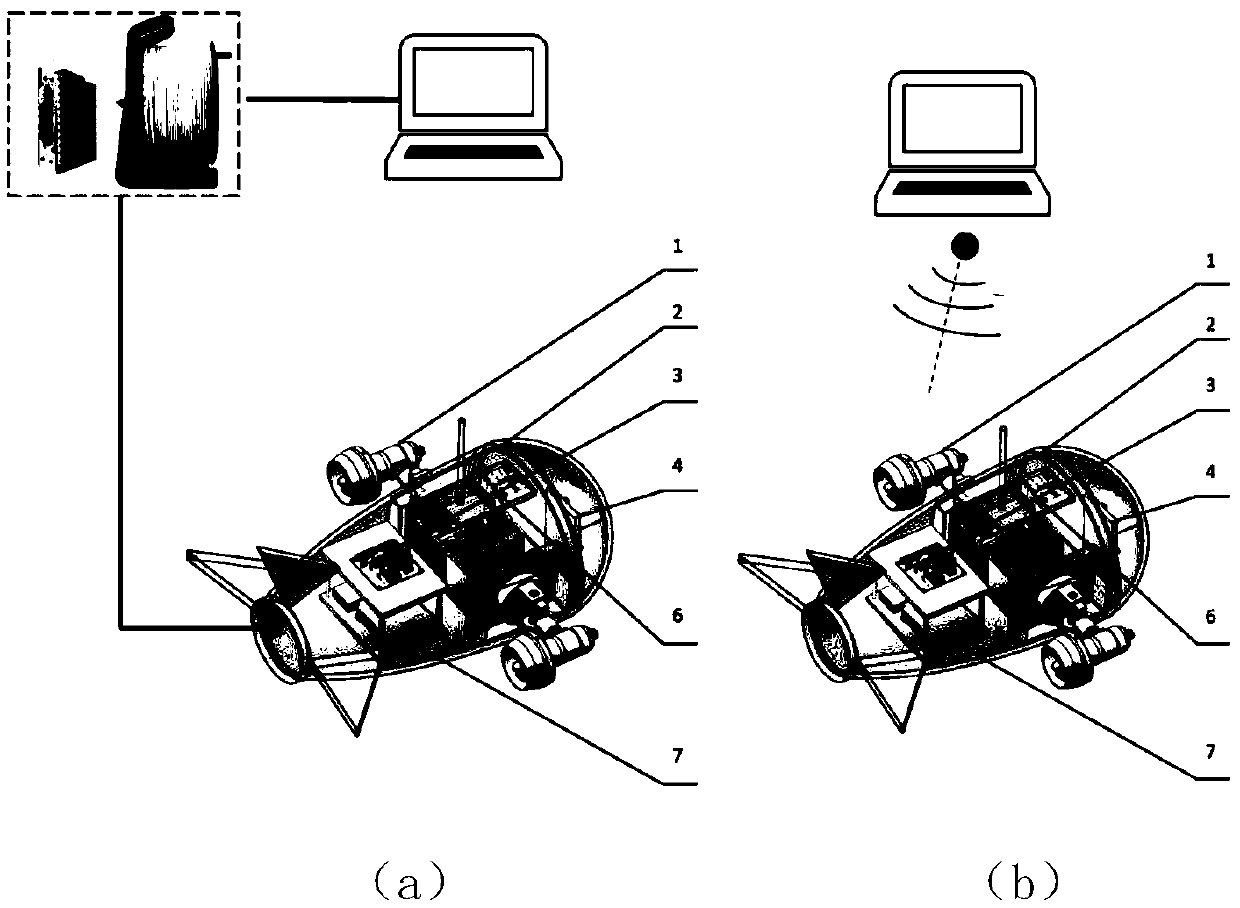
The invention discloses a bionic robotic dolphin for water quality monitoring. The bionic robotic dolphin comprises a bionic robotic dolphin body and an upper computer monitoring system. Information interaction between the bionic robotic dolphin body and the upper computer monitoring system is achieved in a radio frequency mode. According to the bionic robotic dolphin body, killer whale spindle low-resistance streamline appearance is adopted, a pressure-resistance shell is manufactured with polyformaldehyde engineering plastic, and the bionic robotic dolphin body comprises a water quality sensor module, a transparent head cabin, a pectoral fin cabin, a master control cabin and a tail joint cabin. The water quality sensor module is provided with different types of water quality sensors according to water quality monitoring requirements. A pectoral fin driving module is mounted in the pectoral fin cabin. The master control cabin is provided with a dorsal fin driving module and a tail joint driving module. The tail joint cabin is provided with a tail fin driving module. Maneuvering motions of advancing, steering, diving, floating and the like of the bionic robotic dolphin body can be achieved. By utilizing high maneuvering, low disturbance, non-pollution and the like of the bionic robotic dolphin body, water quality monitoring tasks are completed in narrow, complex and dynamic underwater environments by carrying the water quality sensors.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Modular underwater robot based on integrated vector propellers
InactiveCN109515651AImprove robustnessFunctionalUnderwater vesselsUnderwater equipmentAttitude controlControl signal
The invention discloses a modular underwater robot based on integrated vector propellers. The integrated vector propellers are distributed on the left and right sides of an underwater robot cabin, sothat multidimensional thrust can be generated to realize navigation attitude and depth measurement and own attitude control; tail fins and dorsal fins are respectively fixed on two sides of the tail and the back of the underwater robot cabin; a power module, a load module and a communication module are arranged in the underwater robot cabin; the power module is used for supplying power to the underwater robot; and the communication module is respectively connected with the load module and the integrated vector propellers and is used for transmitting acquired data of the load module and a ground upper computer and transmitting control signals of the integrated vector propellers and the ground upper computer. The modular underwater robot disclosed by the invention has excellent maneuverability, functionality and intelligence while ensuring the stability of the underwater robot, improves the exploration ability under complex sea conditions, and has wide application prospects.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Artificial propagation method for advanced fry of yellow catfish
ActiveCN101263793AImprove developmentEnhance physical fitnessClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaBroodstockRed mullet
The invention relates to an artificial propagation method of yellow catfish fry, which is characterized in that: sexually mature yellow catfish over three years are chosen as the parent fishes; the female and male ratio is 3:1; a plurality of barrels are arranged in a spawning pond as fish nests; parent fish density in the spawning pond is 1 to 2 groups / m2; each group of parent fishes uses a barrel; the sand with a thickness ranging form 1cm to 5cm is arranged at the bottom of the barrel for the debonding of fish eggs; in spawning season, exogenous hormone is injected to the basal behind the dorsal fins of the parent fishes to induce ovulation and spermiation; an inversed conical container with smooth inner wall is used as the hatching barrel; fertilized eggs are arranged in the hatching barrel for hatching in flowing water; the dissolved oxygen in the water of the hatching barrel is larger than 5.5 mg / L; when hatching is over, fry is arranged in a cement pool for temporary rearing for 40 to 70 hours, then the fry is packaged in plastic bags with water and oxygen. The artificial propagation method of yellow catfish fry has the advantages that, well developed yellow catfish fry can be acquired; the operation is simple; the utilization rate of parent fishes is high; scale production of yellow catfish fry can be realized, and the invention has significant meaning for the intensive culture of yellow catfish.
Owner:沈阳华泰渔业有限公司
Biomimetic machine shark
InactiveCN109319075ASimple structureRealistic Bionic EffectPropulsive elements of non-rotary typeUnderwater vesselsMicrocontrollerMicrocomputer
The invention provides a biomimetic machine shark, and relates to the field of biomimetic underwater vehicles. The biomimetic machine shark comprises a shark head, a pectoral fin system, a dorsal fin,a shark body framework, a device cabin and a shark tail driving system; the shark head is connected with the shark body framework through a head steering engine, and the head steering engine is fixedto the front part of the shark body framework and can control the shark head to swing left and right; the pectoral fin system realizes floating upward and diving downward of the machine shark duringmoving by changing the angles of pectoral fins; a dorsal fin is fixed to the shark body framework, the device cabin is placed in the shark body framework, and the shark body framework is provided withthreaded holes to connect steering engines and other extending devices; a singlechip microcomputer, batteries and the like are placed in the device cabin; and the shark tail driving system realizes the condition that a main steering engine drives a whole tail part to swing flexibly through traction of a linkage piece, and a caudal fin steering engine is arranged at a last caudal joint to controla caudal fin to swing individually. According to the biomimetic machine shark, the structure is simple, the biomimetic effect is vivid, the expansibility is high, and three-dimensional motion under water can be realized.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Impeller of centrifugal fan
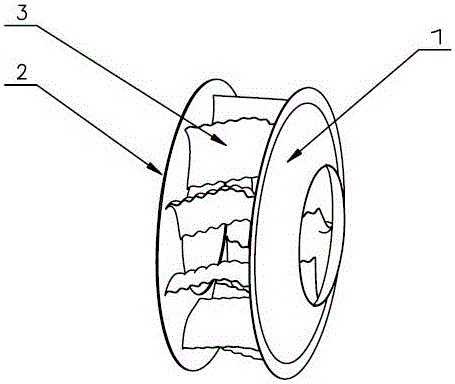
The invention discloses an impeller of a centrifugal fan. The impeller of the centrifugal fan comprises a front coil (1) and a back coil (2). A plurality of blades (3) are welded and fixed between the front coil and the back coil, vertical fracture surfaces of the blades are undulate, and horizontal fracture surface are circular-arc-shaped. The vertical fracture surfaces of the blades simulate the shell shape of a humpback and the horizontal fracture surfaces of the blades simulate the dorsal fin shape of the humpback. The eddy separation position at outlets of the blades is changed, the distance between eddy centers is enlarged, and the disturbance of eddy separation to flow is restrained, so that aerodynamic noise is reduced. The impeller of the centrifugal fan has the advantages of bionic noise reduction, good aerodynamics, high efficiency and the like.
Owner:ZHUZHOU ELECTRIC LOCOMOTIVE CO
Underwater bio-robot fish system energy supply device based on piezoelectric material
ActiveCN102957339AReduce weightLong duration of energy supplyElectrical storage systemPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesElectricityUnderwater
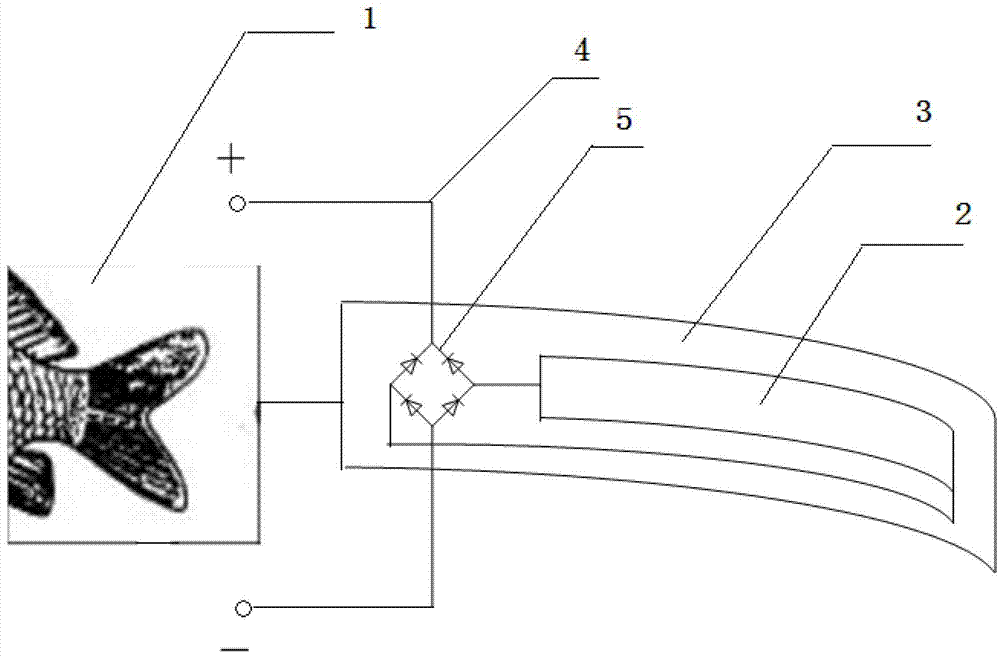
The invention provides an underwater bio-robot fish system energy supply device based on a piezoelectric material. The underwater bio-robot fish system energy supply device based on the piezoelectric material comprises a flexible material substrate, a piezoelectric thin film, a rectifying circuit, a transmitting circuit and an energy storing device, wherein the flexible material substrate comprises a free end and a fixed end, and the fixed end is fixedly arranged on a tail fin or a dorsal fin; the piezoelectric thin film is fixedly arranged on the flexible material substrate; and the transmitting circuit and the energy storing device are implanted or fixedly arranged in the body or head of a fish. According to the underwater bio-robot fish system energy supply device based on the piezoelectric material, disclosed by the invention, the piezoelectric material is deformed by collecting vibration generated by the motion of an organism, and a stimulation device continuously generates electric signals after current is rectified by the rectifying circuit and is transmitted and stored so as to control the nerves of the organism to move. The underwater bio-robot fish system energy supply device disclosed by the invention has the characteristics of light weight, long energy supply continuing time and the like, and can reduce the load in the fish generated due to the weight of an energy supply system so as to realize long-term and long-distance control in a bio-robot fish system.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Method for removing blood released during filleting from the backbone of fish, and device for removing such blood
ActiveUS8956205B2Reducing entry of bloodReduce entryPoultry processingFish filletingRemove bloodFish fillet
In a method for removing blood released during filleting from the backbone and the indentations therein in the region of the vertebrae of fish that are conveyed in a row with the head forwards and the belly downwards, the removal of blood is carried out at the same time and in the same place as the cutting of the backbone. The backbone, which is freed of ray bones and rib bones, is guided through a cutting gap and is cut clear on the belly side of the fish over the entire length of the fish as far as the root of the dorsal fin to leave a backbone stump. The fish fillet flesh is covered by covering surfaces which converge at the cutting gap and of which at least two covering surfaces form the cutting gap. Pressurized cleaning fluid is sprayed onto the backbone that is guided between the covering surfaces through the cutting gap during cutting. A device for removing said released blood comprises a backbone cutting device having two backbone cutting circular blades, which are arranged obliquely in an inverted V shape and form the covering surfaces, and having fish guiding means forming covering surfaces that cover the fish fillet flesh. A cleaning device comprises at least one cleaning nozzle aligned with the cutting gap. An actuating device actuates the cleaning device and the backbone cutting device simultaneously. The covering surfaces protect the fish fillet flesh from being sprayed with the cleaning fluid.
Owner:NORDISCHER MASCHINENBAU RUD BAADER GMBH CO KG
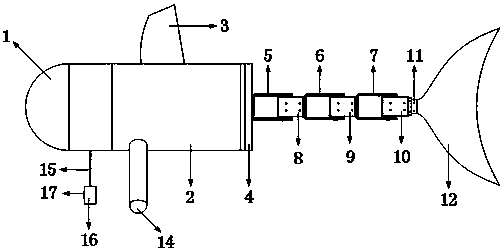
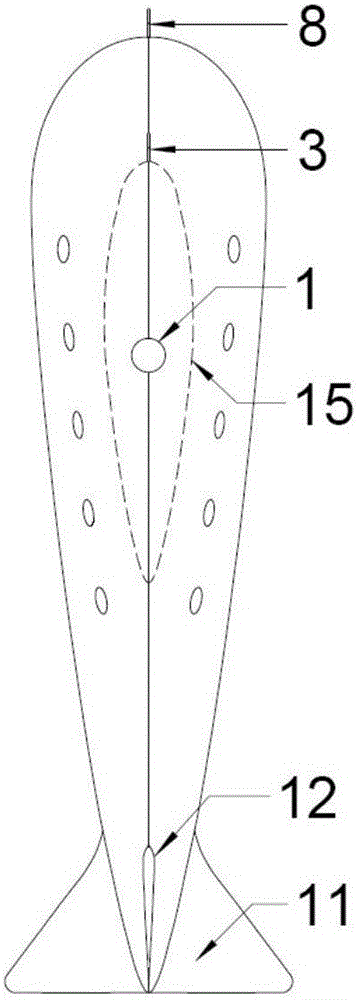
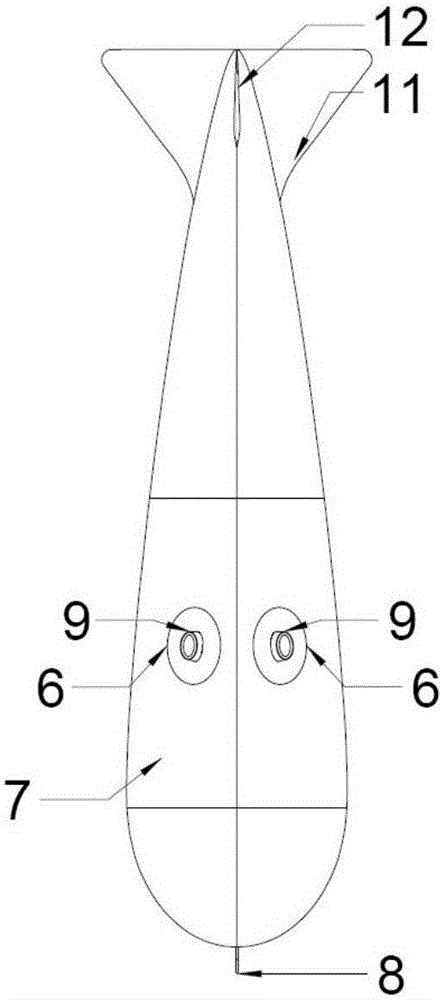
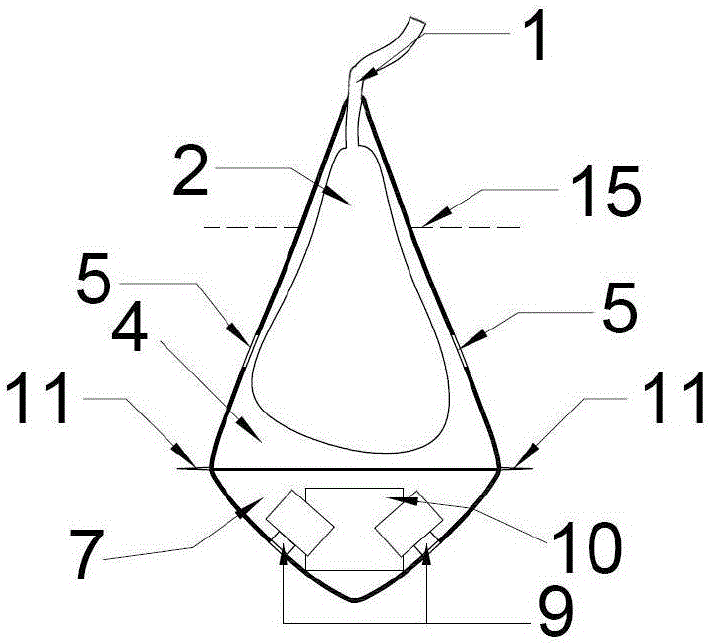
Dorsal fin aerial carrier and task system antenna integrated configuration
InactiveCN109305323AInfluence of aerodynamic characteristicsImprove Field MaintenanceAircraft stabilisationAntenna supports/mountingsCopperFuselage
The invention belongs to the field of aircraft overall aerodynamic integrated layout design, and particularly relates to a dorsal fin aerial carrier and task system antenna integrated configuration. An existing aerial carrier antenna is an exposed copper cable antenna which is long in length, the copper cable antenna is exposed outside a fuselage and is likely to be affected by wind, rain, salt fog and the like when special tasks are executed in a special area, environmental corrosion of equipment is accelerated, consequently, a copper cable is broken, an antenna support pulley and a steel cable are abraded and even broken, and reliability is low. According to the dorsal fin aerial carrier and task system antenna integrated configuration, by designing an environment-friendly antenna mounting cabin, an aerial carrier antenna and a task system antenna are mounted and arranged in a fuselage structure, and the original aerodynamic characteristic of an aircraft is not affected negatively tothe maximum limit.
Owner:SHAANXI AIRCRAFT CORPORATION
Method for artificially releasing, listing and marking fishes without spines or with spines and without spinal teeth
InactiveCN102301965ADoes not affect balanceDoes not affect activityClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaBody balanceMedicine
The invention discloses a method for artificially releasing, listing and marking fishes without spines or with spines and without spinal teeth. The method comprises the following steps of: narcotizing a fish; passing a hanging line through a hanging ring on a signboard; after threading the hanging line through a needle, passing the needle through the gap between a first axonost and a second axonost in dorsal fin subcutaneous muscle of the fish; after leading out the hanging line by the needle, crossing the hanging line at two sides of the dorsal fin in front of the dorsal fin to form a coil; connecting the crossed two ends of the hanging line; shearing the redundant hanging line; and then completing by putting the signboard right ahead of the dorsal fin. Before being listed, the fishes are necessary to temporarily cultivate. After being listed, the marked fishes are necessary to temporarily cultivate. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the listing and marking problem of the fishes without the spines on fins or with the spines and without the spinal teeth, in particular small-scale fishes, can be solved; furthermore, after the fishes are listed, the body balance and the movement of the fishes cannot be influenced; the damage on the fishes is low; the survival rate is high; the mark shedding rate can be obviously reduced; and the accuracy of the releasing effect evaluation by using the listing, marking and releasing return-catching method is increased.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
Individual marking method of takifagu obscurus
InactiveCN103222433AHigh retention rateNot easy to fall offClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaAbdominal cavityGrowth data
The invention discloses an individual marking method of takifagu obscurus, which comprises the steps of disinfecting a PIT mark and a syringe, narcotizing the takifagu obscurus, placing the disinfected mark in a syringe needle, allowing the syringe needle to pierce skin at the rear edge of the back of a dorsal fin of the takifagu obscurus, inserting the needle to an abdominal cavity by clinging the inner side of the cling, pushing the mark to between the skin and a muscle of the takifagu obscurus, and drawing out the needle. With the adoption of the method, the retention rate of the mark can be increased, the mark does not fall off easily, the degree of injury of a takifagu obscurus body is low during marking, and the normal activity of the takifagu obscurus is not influenced. The mark is 8-10g, and the early marking of the takifagu obscurus provides a precondition for obtaining precise growth data required by selective breeding.
Owner:FRESHWATER FISHERIES RES CENT OF CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERY SCI
Bionic robot fish oriented to environment monitoring
PendingCN110356536APH value real-time detectionSolubility real-time detectionMeasurement devicesPosition/course control in two dimensionsSolubilityWater quality
A bionic robot fish oriented to environment monitoring comprises a fish body, a fish head, a caudal fin, a dorsal fin and a ventral fin, wherein the fish body is provided with a counterweight module and a battery; the fish head is mounted on one end of the fish body; the fish head is provided with a pitching module for controlling the upward floating and downward diving of the robot fish and a left and right turning module for changing the swimming direction of the robot fish; the caudal fin is mounted on the other end of the fish body through a swimming module; the dorsal fin is mounted at the dorsum of the fish body; and the ventral fin is mounted at the ventral side of the fish body. The bionic robot fish oriented to environment monitoring can detect multiple parameters such as pH values, solubility, temperature, ammonia nitrogen content, electrical conductivity, water hardness, turbidity and the like in different waters in real time. The bionic robot fish can cruise according to apredetermined path and detect water quality data of positions in the predetermined path. In addition, the bionic robot fish adopts a modular design in mechanical design, thereby reducing repeated design and repeated processing, decreasing relevant development cost, and shortening the research and development period.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Underwater high-simulation robotic fish mechanism and system
ActiveCN105059511ABeautiful swimmingSimple structurePropulsive elements of non-rotary typeTransmission with mechanical gearingElectric machineryEngineering
The invention discloses an underwater high-simulation robotic fish mechanism and system. The robotic fish mechanism and system comprise a front shell, a control cabinet, fish skin, a dorsal fin, an anal fin, a power mechanism and a tail swinging mechanism, wherein the power mechanism is positioned in the control cabinet, and comprises a driving motor, a master control circuit, a slave control circuit and a power source; the tail swinging mechanism comprises a crank mechanism, fish bones and a tail fin; the crank mechanism comprises a first bevel gear, a second bevel gear, a bearing pedestal, a magnet and a swing rod; the output end of the power source is electrically connected with the input end of the master control circuit; the output end of the master control circuit is electrically connected with the input end of the driving motor; the slave control circuit is positioned under the crank mechanism and is in communication connection with the master control circuit; the driving motor is fixedly mounted in the control cabinet; a shaft hole is formed in the tail end of the control cabinet. The underwater high-simulation robotic fish mechanism and system disclosed by the invention drive a robotic fish to swim by adopting a single joint, so that the design is artful, and the structure is reasonable.
Owner:中科步思德(洛阳)智控科技有限公司
Pasteurized swimming crab back fin
InactiveUS20100272873A1Package sterilisationMeat/fish preservation by freezing/coolingReady to eatHand held
The present invention is directed to a method and system for preparing a pasteurized swimming crab back (PSCB) fin leg (“crab leg”) for individual consumption. In particular, the method and system of the present invention results in a pasteurized, hand-held, all natural food product for consumption by a consumer. The PSCB product is a ready to eat crab leg that has been trimmed, cleaned, thermo processed and packed in a hermetically sealed can or cup.
Owner:HARBOR SEAFOOD
Carp electrode transforation implantation brain stereotaxic method
InactiveCN102028546APrecise positioningReduce mechanical damageSurgeryDiagnostic recording/measuringAquatic animalFront edge
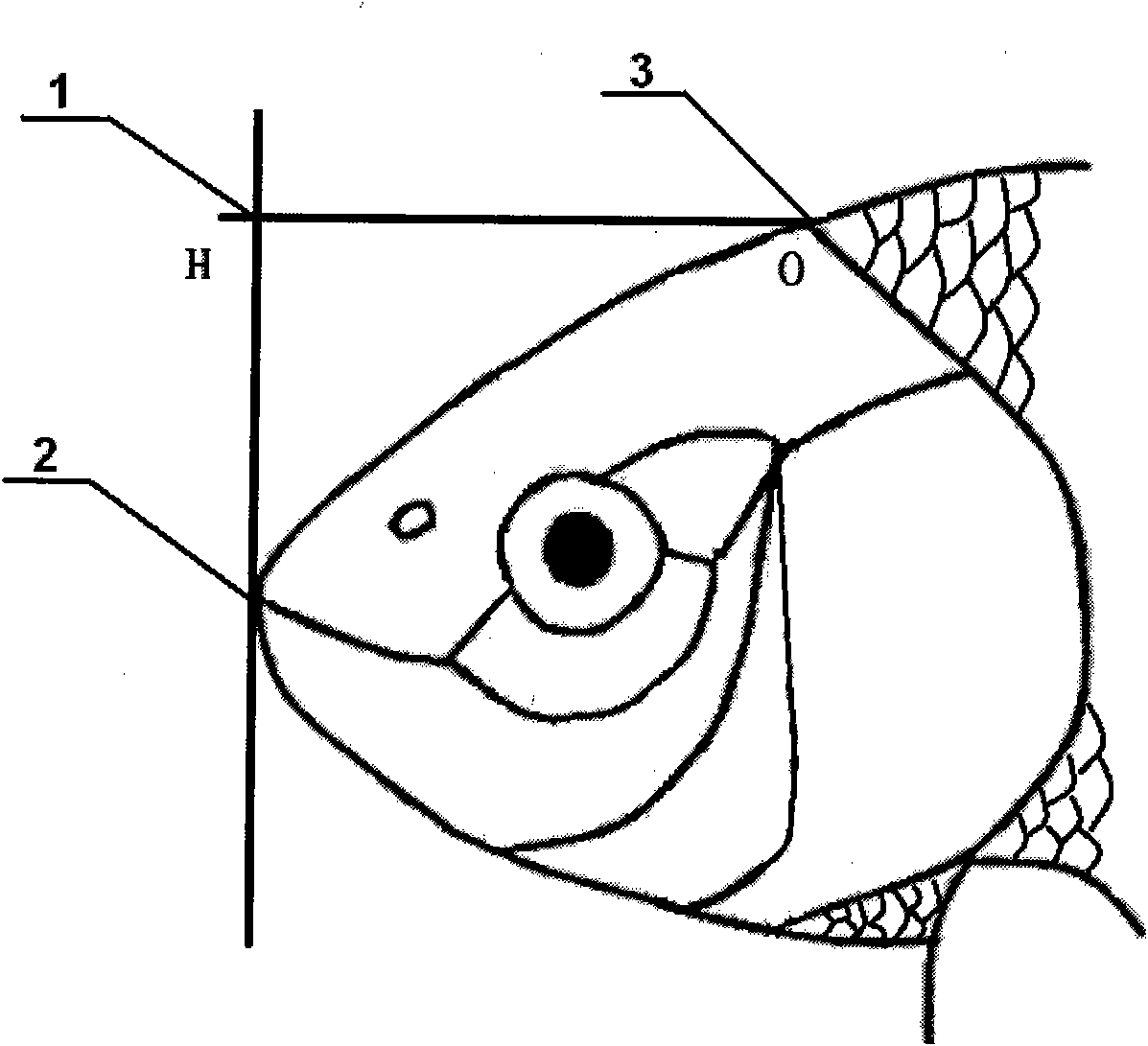
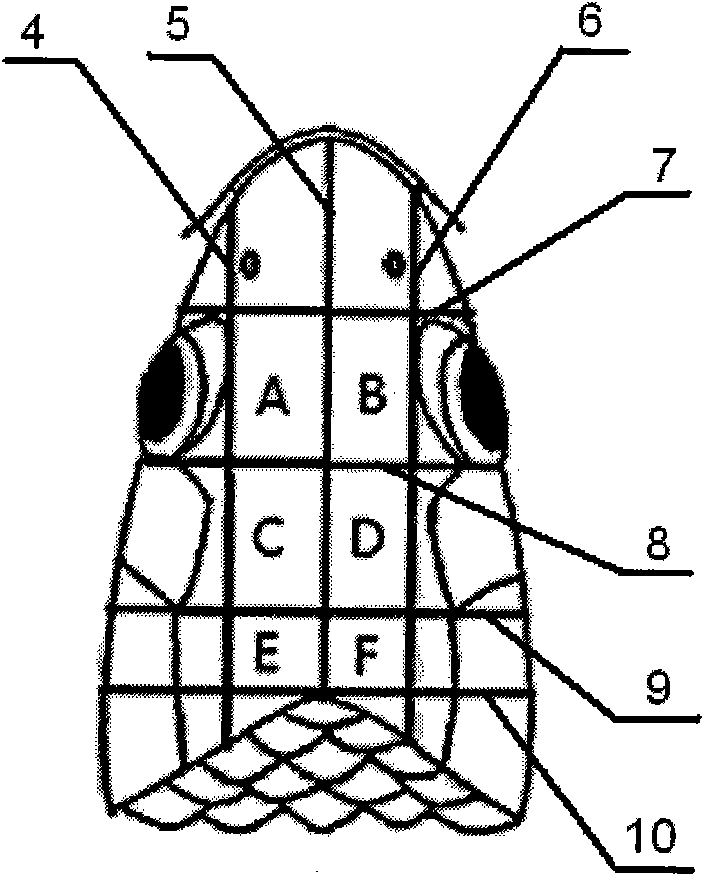
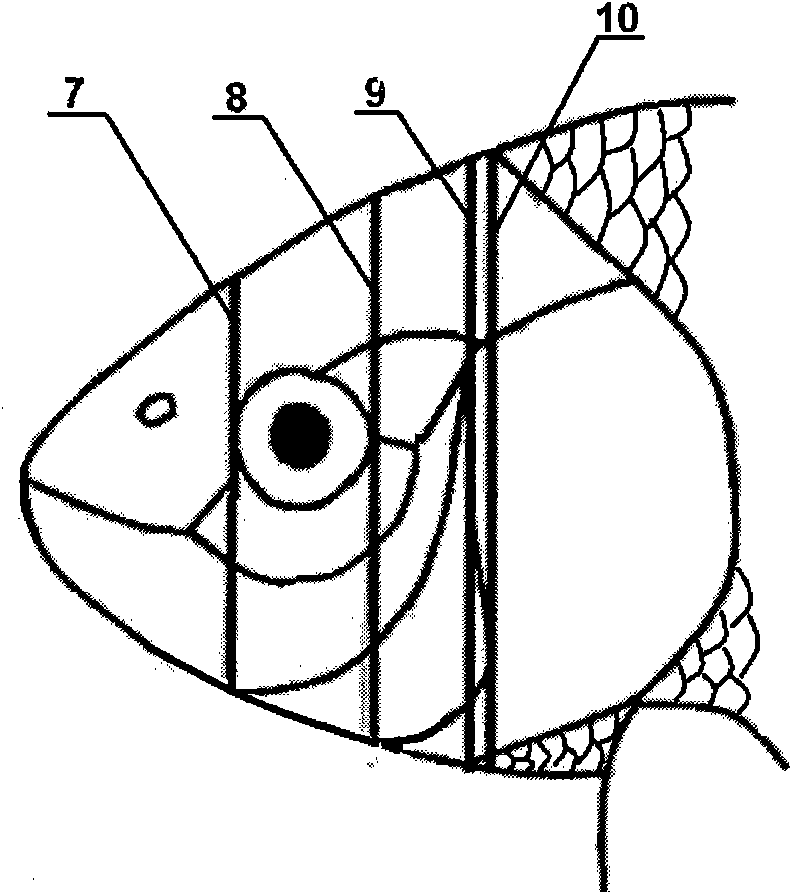
The invention discloses a carp electrode transforation implantation brain stereo positioning method, which belongs to the technical field of brain stereo positioning. The invention mainly solves the problem of accurate positioning in electrode implantation into brain without craniotomy. The method comprises the following steps: drawing a straight line centrally from the carp mouth to the intersection point between the head and the first scale of the trunk, and drawing a straight line parallel to the central line based on the upper edges of two orbits respectively; drawing a connection line along the front edges of the two orbits; drawing a connection line along the rear edges of the two orbits; drawing a connection line between the joint moving joint points of the operculum bones on the two sides and the orbit bones; and drawing a line through the joint between the head and the first scale of the trunk and vertical to the central line. The skull surface is divided into 6 areas by the 7 lines, each area representing a coordinate system. The mouth, dorsal fin and operculum on the two sides clamp 4 points for fixing; in the positioning of a brain stereotaxic instrument, an electrode is implanted into the brain along a skull hole, and magnetic resonance imaging equipment navigates and corrects deviation so as to realize three-dimensional accurate positioning without craniotomy. The invention is applicable to the collection of brain wave of aquatic animals or control on biological behavior by conduction of electrical signals.
Owner:YANSHAN UNIV
Underwater bionic robotic fish driven by fluid conveying pipe
PendingCN108408006AUnlimited waterRange of controlPropulsion based emission reductionPropulsive elementsWater storageElectricity
The invention discloses an underwater bionic robotic fish driven by a fluid conveying pipe. The underwater bionic robotic fish includes a fish head, a fish body, a dorsal fin, a tail fin, pectoral fins, a water sac, a water pump, a fluid conveying pipe system, a controller and a power supply. The interior of the fish body is a closed cavity, and the water pump, the controller and the fluid conveying pipe system are all installed in the cavity. Flutter occurs when the internal flow of a fluid conveying hose of the tail fin exceeds the critical flow velocity, so that the tail fin is driven to swing to provide power for the fish to move forwards. A fluid hose of the pectoral fins also flutters when the internal flow exceeds the critical flow velocity, so that the left and right pectoral finsswing up and down, and the steering of the fish can be controlled while the propulsion power is provided. The water storage capacity in the water sac is controlled by the water pump and the fluid conveying pipe system, and the weight of the fish body is increased or reduced so as to achieve the sinking and floating of the fish body. The required power for electrical equipment is provided by the power supply, and various motion forms of the bionic fish is controlled by the controller. According to the underwater bionic robotic fish driven by the fluid conveying pipe, the fish movement can be simulated, the disturbance to underwater creatures is reduced, and the risk of being trapped is reduced.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Quantified and optimal batch tagging method for sparidae fish based on tagging effect
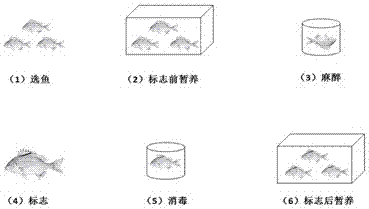
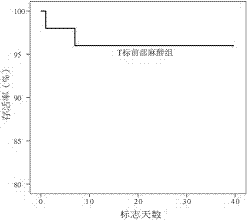
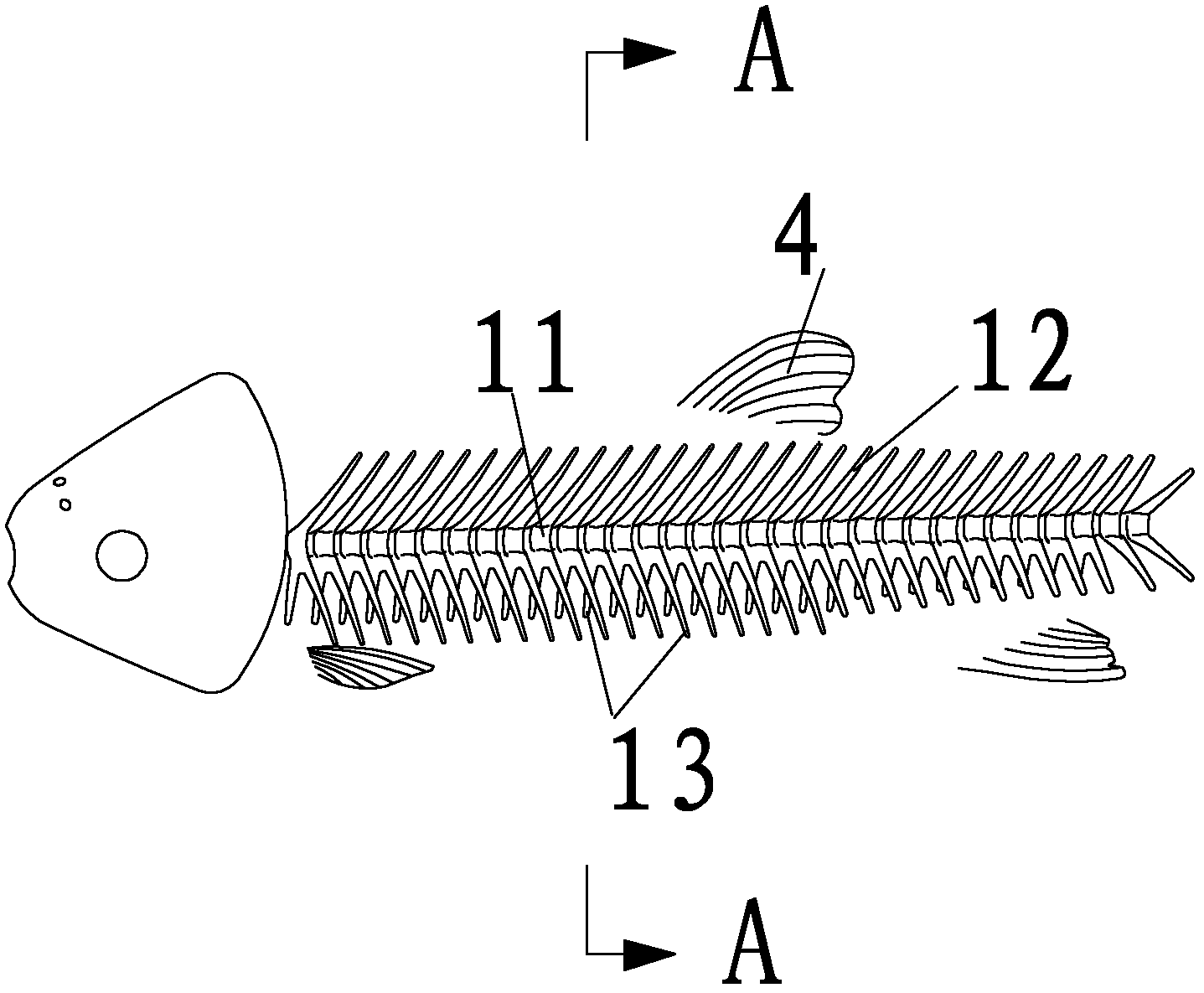
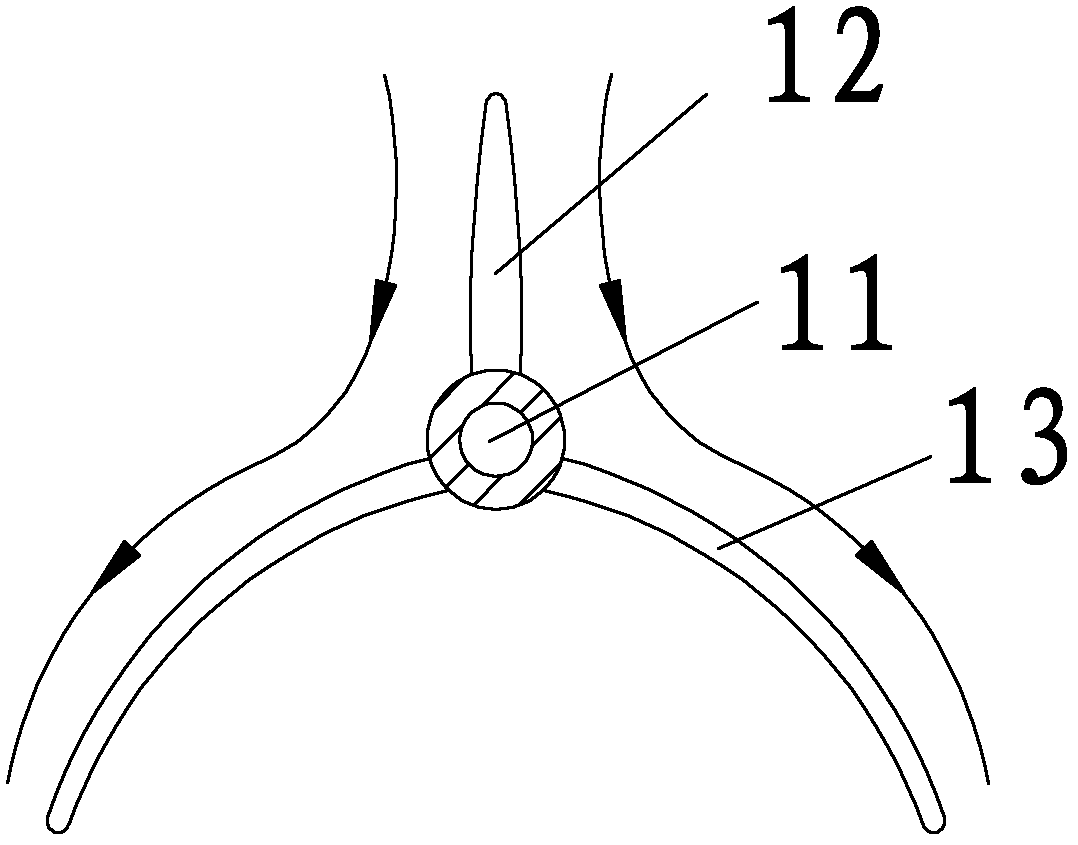
The invention discloses a tagging method for sparidae fish. The method comprises selecting fish, temporary rearing before tagging, anaesthetizing, disinfecting and temporary rearing after tagging. According to the invention, through operations such as selecting T-type labels, anaesthetizing before tagging and tagging muscles at front part under dorsal fin base, the survival rate of tagged sparidae fish is increased to the most and the tagging shedding rate is reduced. the tagging method is simple and practical; the flow is clear; the efficiency and effect of tagging and releasing are greatly increased; the tag and releasing can be operated based on evidence; the tagging has less influence on the growth of tagged sparidae fish and the method is suitable for the tagging and releasing of sparidae fish.
Owner:GUANGDONG OCEAN UNIVERSITY
Method for separating loin from backbone meat of crisp grass carp
The invention relates to a method for separating loin and backbone meat of a crisp grass carp. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: (1) cutting along the two sides of a dorsal fin, moving a cutting edge from a neural spine to rib bones to separate loin together with strip-shaped backbone meat which is surrounded by intramuscular bones from the spine, and then cutting to separate belly meat; and (2) stripping the intramuscular bones together with the backbone meat from the loin by cutting along the outer side of the intramuscular bones, cutting close to the outer side of the intramuscular bones at the ends to move apart the edge of the loin from the backbone meat, and pressing the loin by one hand or tools while pulling the departed edge of the loin, to completely separate the whole backbone meat and the intramuscular bones surrounding the backbone meat from the loin. The invention has the following advantages: the fish meat is maintained to the greatest extent; the utilization rate and added value of fish meat are increased; convenience is created for the processing, cooking and service of fish meat; and the backbone meat with intramuscular bones can be further processed.
Owner:广东省中山食品水产进出口集团有限公司
Method for removing blood released during filleting from the backbone of fish, and device for removing such blood
ActiveUS20140227953A1Reduce entryResistance to influencePoultry processingFish filletingRemove bloodFish fillet
In a method for removing blood released during filleting from the backbone and the indentations therein in the region of the vertebrae of fish that are conveyed in a row with the head forwards and the belly downwards, the removal of blood is carried out at the same time and in the same place as the cutting of the backbone. The backbone, which is freed of ray bones and rib bones, is guided through a cutting gap and is cut clear on the belly side of the fish over the entire length of the fish as far as the root of the dorsal fin to leave a backbone stump. The fish fillet flesh is covered by covering surfaces which converge at the cutting gap and of which at least two covering surfaces form the cutting gap. Pressurised cleaning fluid is sprayed onto the backbone that is guided between the covering surfaces through the cutting gap during cutting. A device for removing said released blood comprises a backbone cutting device having two backbone cutting circular blades, which are arranged obliquely in an inverted V shape and form the covering surfaces, and having fish guiding means forming covering surfaces that cover the fish fillet flesh. A cleaning device comprises at least one cleaning nozzle aligned with the cutting gap. An actuating device actuates the cleaning device and the backbone cutting device simultaneously. The covering surfaces protect the fish fillet flesh from being sprayed with the cleaning fluid.
Owner:NORDISCHER MASCHINENBAU RUD BAADER GMBH CO KG
Chinese white dolphin dorsal fin identification method based on convolutional neural network
PendingCN110837818AImprove efficiencyImprove positioning accuracyBiometric pattern recognitionImaging qualityTest sample
The invention discloses a Chinese white dolphin dorsal fin identification method based on a convolutional neural network, and the method comprises the steps: constructing a Chinese white dolphin dorsal fin image library with a position box and an identification tag, and dividing the Chinese white dolphin dorsal fin image library into a training sample and a test sample; training a convolutional neural network for positioning a dorsal fin region; respectively training three convolutional neural networks for identifying the left and right sides of the dorsal fin, the image quality of the dorsalfin and an individual to which the dorsal fin belongs; positioning a dorsal fin region of the image in the test sample through a convolutional neural network for positioning; and identifying the dorsal fin area through the three convolutional neural networks for identification, and outputting identification results of the left and right sides of the dorsal fin, the dorsal fin image quality and theindividual to which the dorsal fin belongs. According to the method, the feature learning capability of the convolutional neural network is fully utilized, automatic identification of the dorsal finof the Chinese white dolphin can be efficiently and accurately realized, and marine biologists are helped to analyze the individual habits and population characteristics of the Chinese white dolphin.
Owner:SHANTOU UNIV
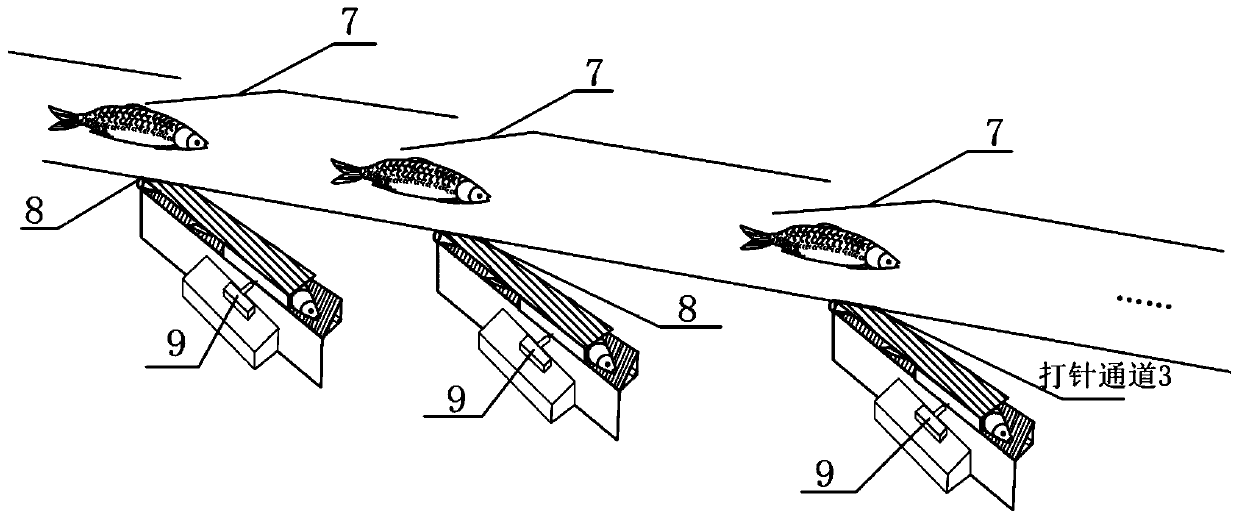
Grass carp vaccine identification and continuous automatic injection method and device thereof
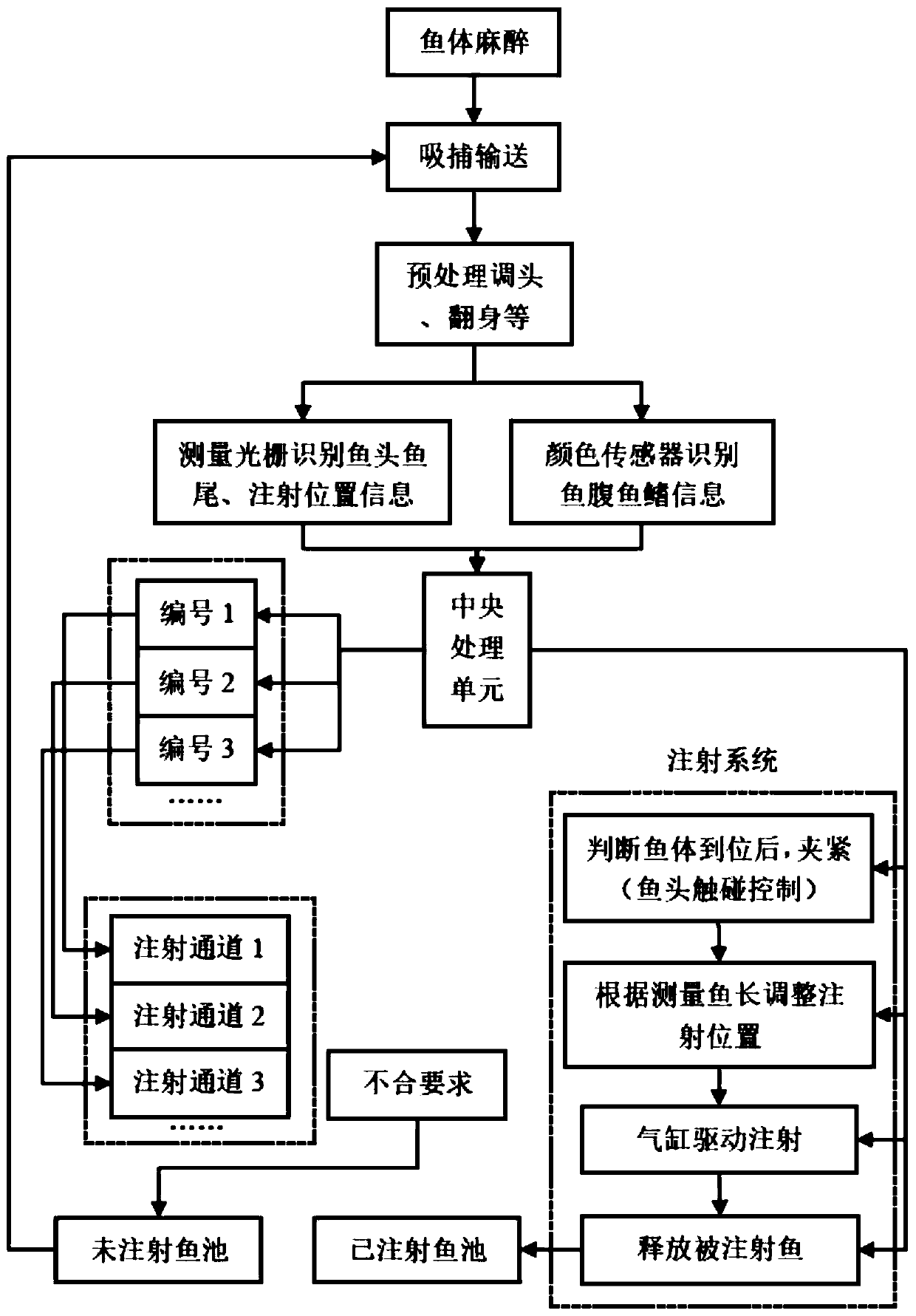
ActiveCN110664505ARealize machine recognitionReduce labor burdenClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaZoologyGrass Carp (fish)
The invention relates to a grass carp vaccine identification and continuous automatic injection method which comprises the following steps: S1, acquiring fish length, fish width and chromaticity information of grass carps in an ordered conveying process by using at least three groups of measuring gratings and at least one group of color sensors, wherein the chromaticity information is used for judging the positions of fish bellies and dorsal fins; S2, comparing a preset value with the obtained information by a control center, determining whether the positions of the fish length, the fish width, the fish belly and the dorsal fin meet requirements or not, and obtaining the injection position information; S3, returning the grass carps which do not meet the requirements to a fishpond along a conveying device, and placing the grass carps which meet the requirements into an injection channel from a conveying belt through a poking rod; and S4, adjusting the injection position according to theinjection position information by the injection channel, performing the injection, and after injection is completed, performing releasing to an aquaculture water area.
Owner:FISHERY MACHINERY & INSTR RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF FISHERY SCI
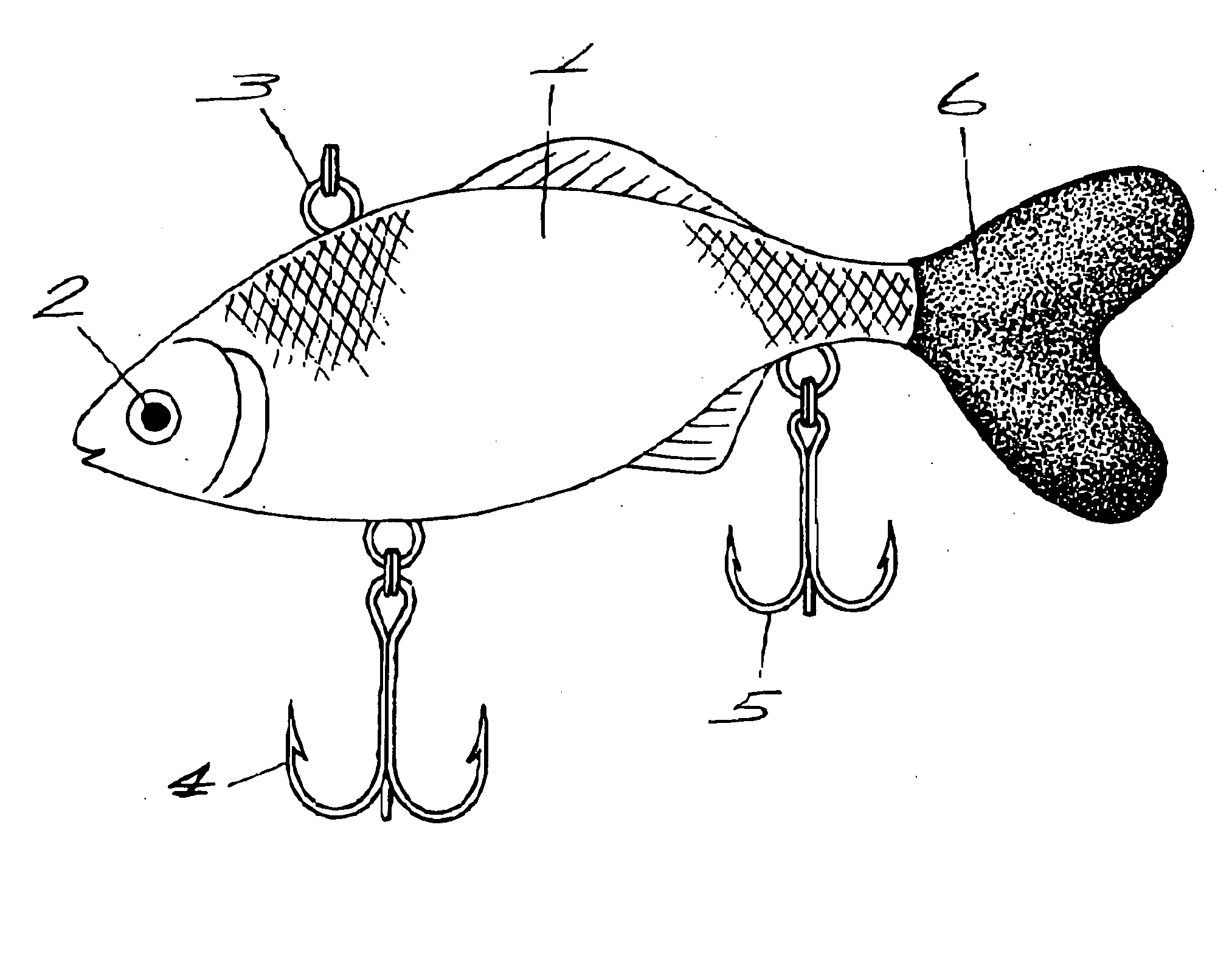
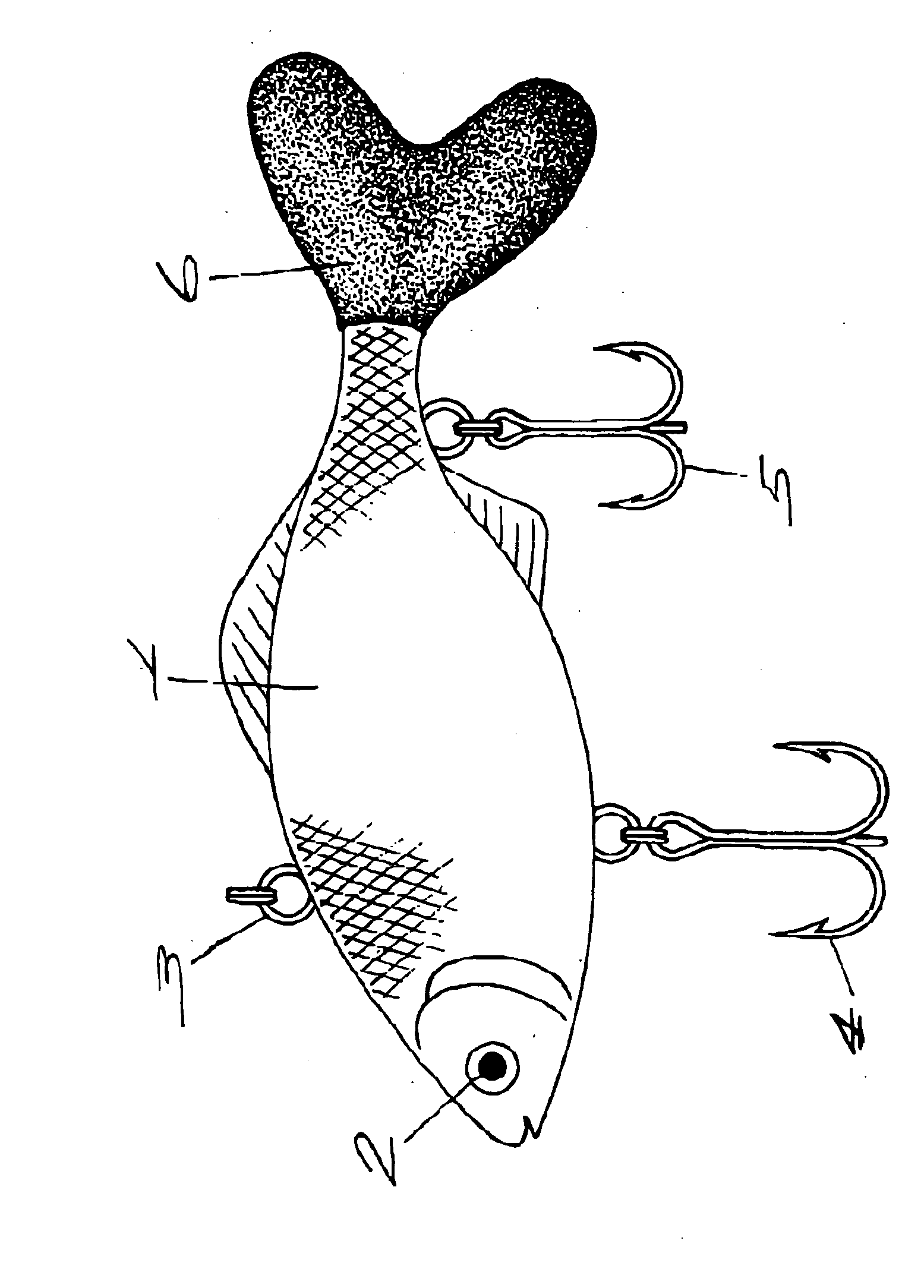
Lure
A lure having a shape that represents a small fish, a bug, or the like, including a tail fin part, a dorsal fin part or a pectoral fin part made of soft material like synthetic resin, rubber or the like, and the remaining portion made of hard material.
Owner:YG ISHII KOGEI
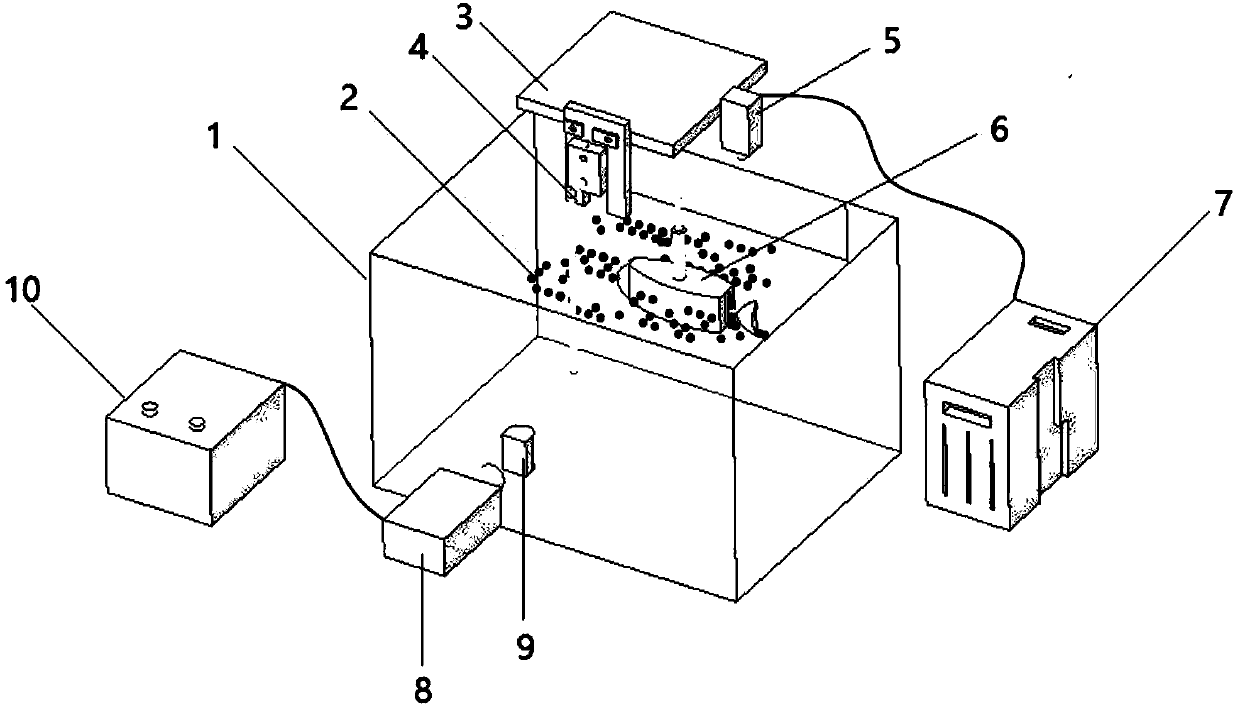
Device and method for measuring pressure field generated by fishtailing of bionic fish
PendingCN107588885AEfficient acquisitionEasy accessFluid pressure measurement by optical meansFishtailingCcd camera
Owner:CHINA THREE GORGES UNIV
Artificial breeding method of Barbatula nuda
InactiveCN106212333AHigh yieldImprove fertilization rateClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaBarbatula nudaInternational unit
The invention discloses an artificial breeding method of Barbatula nuda. The artificial breeding method comprises the following steps: firstly, collecting parent fishes: harvesting from a natural water area to select healthy wild fishes, and starting to collect parent Barbatula nuda in early March; secondly, stocking and breeding the parent fishes: putting the selected parent fishes into a temporary cement pond; after the parent fishes enter the pond, enabling the parent fished to stay in the pond for 1 to 2 days and then starting to feed bait; thirdly, preparing a parturifacient: mixing and proportioning 1000 international units of gonadotropin, 2mu g of luteinizing hormone releasing hormone No.2 and 1mg of domperidone for each kilo of female fish chorionic vill; fourthly, hastening spawning: injecting the parturifacient prepared in the third step into base muscle of dorsal fins of the parent fishes; fifthly, artificially inseminating: performing dry inseminating to obtain fertilized ova; sixthly, incubating, thus obtaining Barbatula nuda fries after 7 days. The developmental maturities of sexual glands of the parent fishes are basically consistent. A parent fish population centrally spawns, so that the induced spawning rate and the fertilization rate are improved. The whole technical process is performed within a controllable range, is little influenced by an external environment, and is convenient and reliable to operate.
Owner:辽宁省淡水水产科学研究院
Multi-degree-of-freedom bionic robot fish for real-time mobile monitoring of water quality and control method thereof
PendingCN110844026ASimplify the sampling processSimplify detectionTelevision system detailsTransmission systemsHydrometryFish development
The invention provides a multi-degree-of-freedom bionic robot fish for real-time mobile monitoring of water quality and a control method thereof. The bionic robot fish comprises a hard head shell, a hard fish body shell, a hard dorsal fin shell, a tail connecting piece, a fishtail component, an underwater lifting device, an underwater monitoring module, a battery, a main control circuit board, a data acquisition module, a 4G wireless communication module, a 4G antenna, a GPS antenna, a GPS positioning receiver module, a voltage stabilizing module, a radio receiving module, a water quality pH value detection sensor and a water quality turbidity value detection sensor. A short-range control method and a remote control method are provided, the bionic robot fish is wide in available range, convenient to carry, easy to operate and visual in display, the real-time acquisition of different water quality parameters and underwater environment images of different water areas can be realized, theremote operation can be achieved through 4G communication, and the cost is effectively saved; and the bionic robot fish is widely applied to underwater resource exploration, hydrological monitoring and the like, and a technical reserve is provided for future water quality monitoring robotic fish development.
Owner:NANJING GAOYUAN ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION ENG +1
Shallow water heritage photographic measurement device and measurement method thereof
InactiveCN105823418ARealize 3D mappingCamera attitude stabilizationUsing optical meansMeasurement deviceLow speed
The invention discloses a shallow water heritage photographic measurement device and a measurement method thereof. The shallow water heritage photographic measurement device comprises a high dorsal fin fish-shaped body, the upper half part is a water inlet cabin, the top of the water inlet tank is internally provided with an elastic air bag, the lower half part of the fish-shaped body is a device cabin, two slopes of a bottom plate of the device cabin are respectively provided with a camera, the photographing directions of the two cameras are orthogonal with the two slopes at the bottom part of the device cabin and are inclined towards the left side and the right side, and the purposes of achieving inclined photographing and acquiring side data of a three-dimensional object through a sealed and transparent photographing window are achieved. The tail part of the fish-shaped body is provided with a horizontal tail fin and a vertical tail fin for keeping directional stability of the fish-shaped body during an advancing photographing process. A high towing hook and a low towing hook are arranged in front of the fish-shaped body for being tied to a traction rope and tied to a general cable at the same interval. The whole set of system is towed forwardly at a low speed through two ends of the general cable, a measured area is passed linearly, and underwater target photographing is realized; and the same measured area is passed again in a right angle direction, each side surface of the target is photographed, and panoramic photographing is realized.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Dactylopteridae-imitated underwater robot
InactiveCN110203359AReduce the impactImprove movement stabilityUnderwater equipmentOcean bottomWorking environment
The invention belongs to the technical field of bio-robots, particularly relates to a dactylopteridae-imitated underwater robot and aims at solving the problems that a propeller propelling mode of anunderwater robot in the prior art is poor in work environment adaptability, the movement state is not stable, the actual work requirement is difficult to meet, and work efficiency is low in the low-speed movement process. The dactylopteridae-imitated underwater robot comprises a fish body, a dorsal fin, a pair of pectoral fins, a stern room and a tail fin. A control unit is arranged in the fish body. Under control of the control unit, the dactylopteridae-imitated underwater robot can adopt two propelling modes in water and has good maneuverability and movement stability, environment adaptability is high, stable movement can be achieved in the complex seabed environment, and meanwhile, the dactylopteridae-imitated underwater robot is provided with an information acquisition module and a detection module and can be used for underwater environment monitoring and underwater exploration.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for treating wheeleri or gloveri of globefish
A head part of a balloonfish is cut off at a neck part from a body with leaving a skin at a body side, the skin at the body side left in cutting off the head part and a skin at a back side are simultaneously peeled to a position of a dorsal fin. In peeling the skins, internal organs separated from the body in a form of attached to the skin at the body side are removed. The skins peeled to the position of the dorsal fin are returned to the original positions and the balloonfish body is covered with the skins to restore the balloonfish to its original external form.
Owner:荣水贸易株式会社
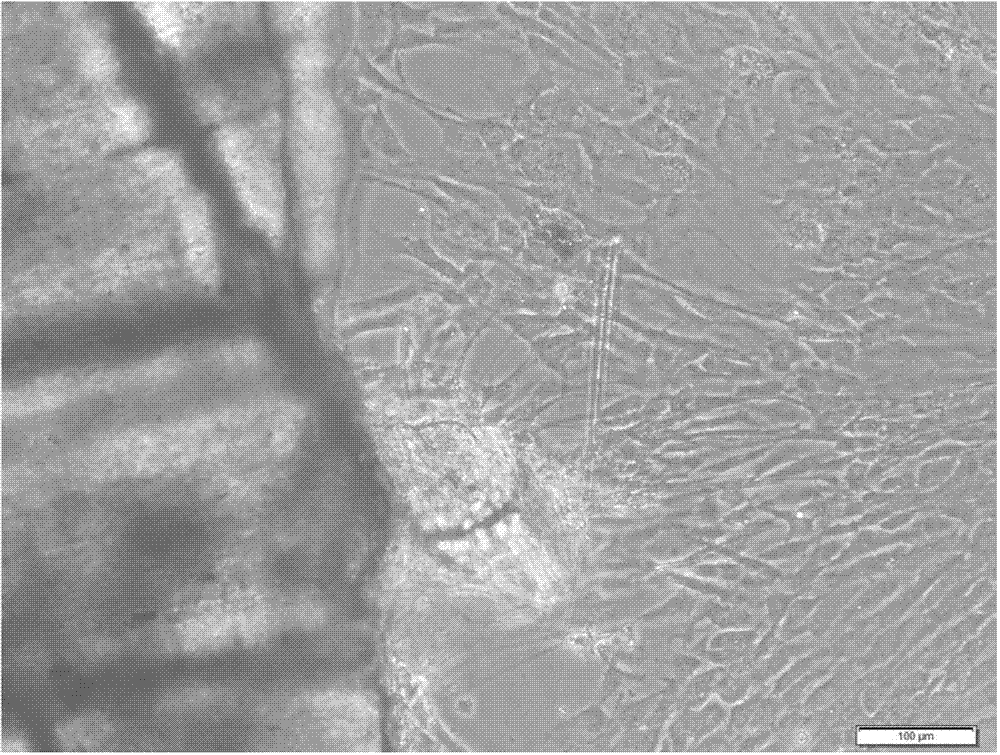
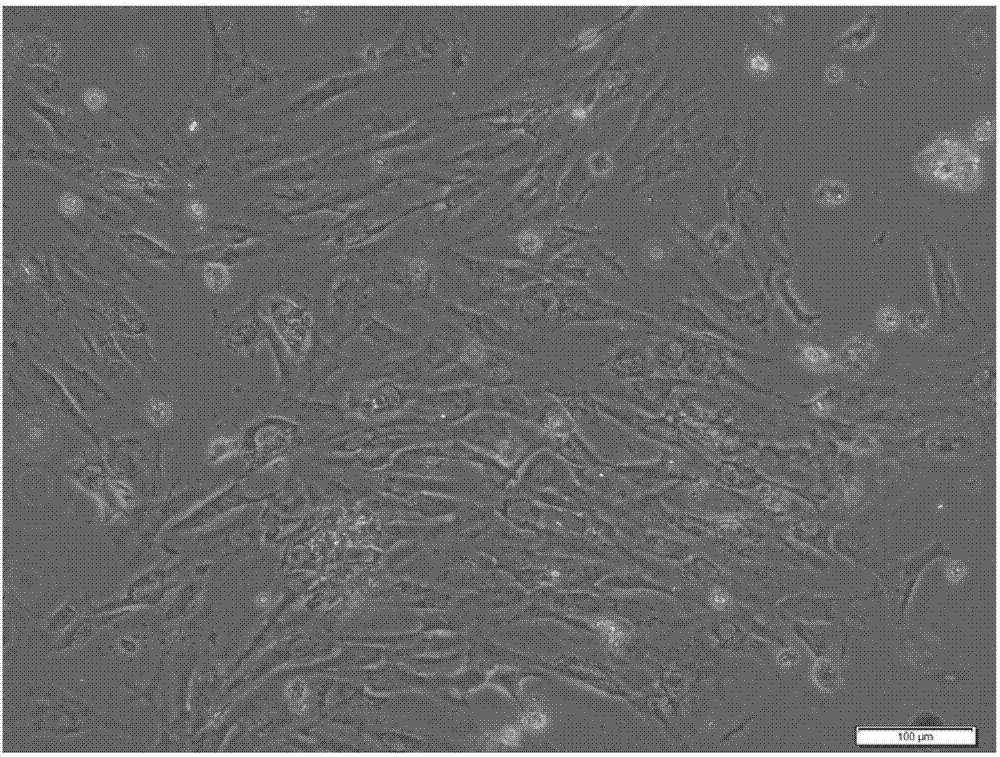
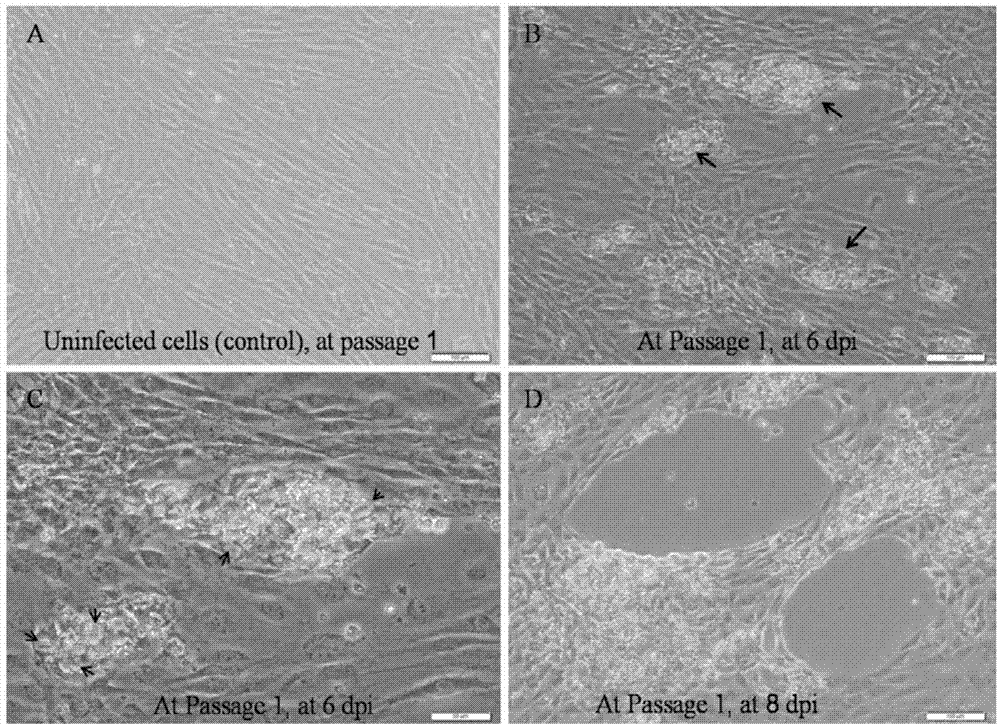
Silver crucian carp back fin cell line
InactiveCN104774802ASave human effortSave moneyMicroorganism based processesVertebrate cellsMaterial resourcesVirus
The invention relates to a silver crucian carp back fin cell line. The silver crucian carp back fin cell line is obtained through primary culture and subculture conducted on the back fin of a silver crucian carp, and a used cell culture fluid is prepared by using an M199 culture medium. The invention further provides an establishing method and application of the silver crucian carp back fin cell line. The silver crucian carp back fin cell line has the advantages that the established silver crucian carp back fin cell line can be subjected to continuous passage, and a large amount of silver crucian carp back fin cell lines can be provided. The silver crucian carp back fin cell line can be directly applied to research on silver crucian carp immunity related function genes and can be applied to a silver crucian carp virus infection experiment, a large amount of manpower and material resources are saved, and effect is better. The silver crucian carp back fin cell line can be subjected to multigelation and can be applied to important research in cell biology, virology, molecular biology, genetics, immunology and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI OCEAN UNIV
Multifunctional bionic tuna and control method thereof
InactiveCN110775229AEasy for free snorkelingFlexible sailing capabilityTesting waterPropulsive elements of non-rotary typeMarine engineeringBiology
The invention relates to a multifunctional bionic tuna and a control method thereof, and relates to the technical field of underwater bionic machines. The multifunctional bionic tuna comprises a fishhead, a fish body part, a rear fin, an anal fin, a tail fin, a flexible skin and a fish bone frame, wherein the flexible skin wraps the fish body part and is connected with the fish bone frame, a control cabin is arranged at the widest part of the fish body part, a control panel is installed in the control cabin, a floating submersible steering engine is arranged in the control cabin and is used for controlling a weight block at the centre of the fish body part, the floating submersible steering engine is mounted on the control panel and controlled by the control panel, the weight block is mounted on the rotary power output end of the floating submersible steering engine and can swing and rotate back and forth to enable the bionic tuna to freely float, and the bionic tuna can provide forward pushing force by means of tail swing so as to be convenient to advance; and moreover, the multifunctional bionic tuna has various functions of attracting fish groups, invisibility, water body detection and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI OCEAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com