Patents
Literature
1031results about "Fluid pressure measurement by optical means" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
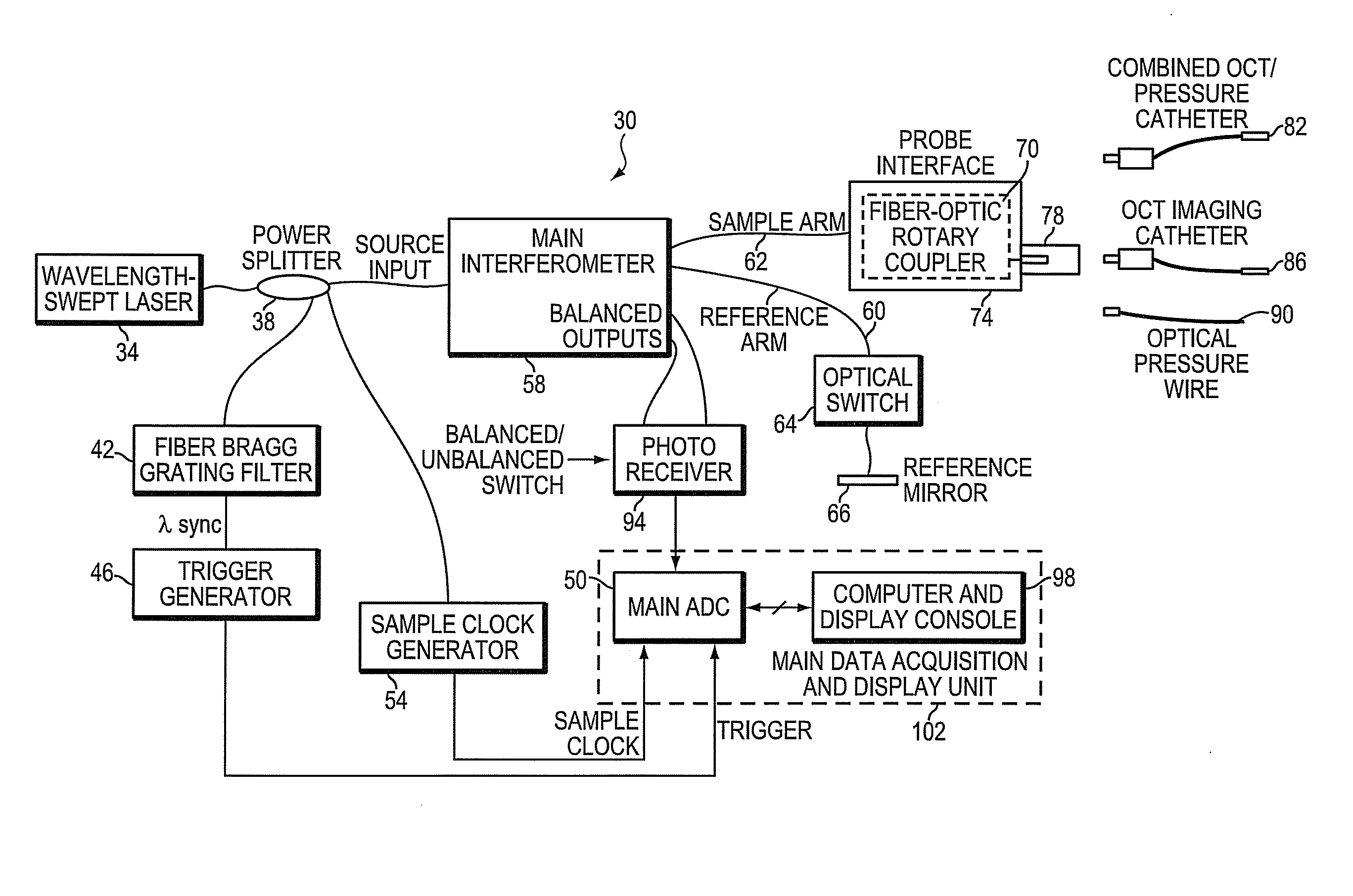
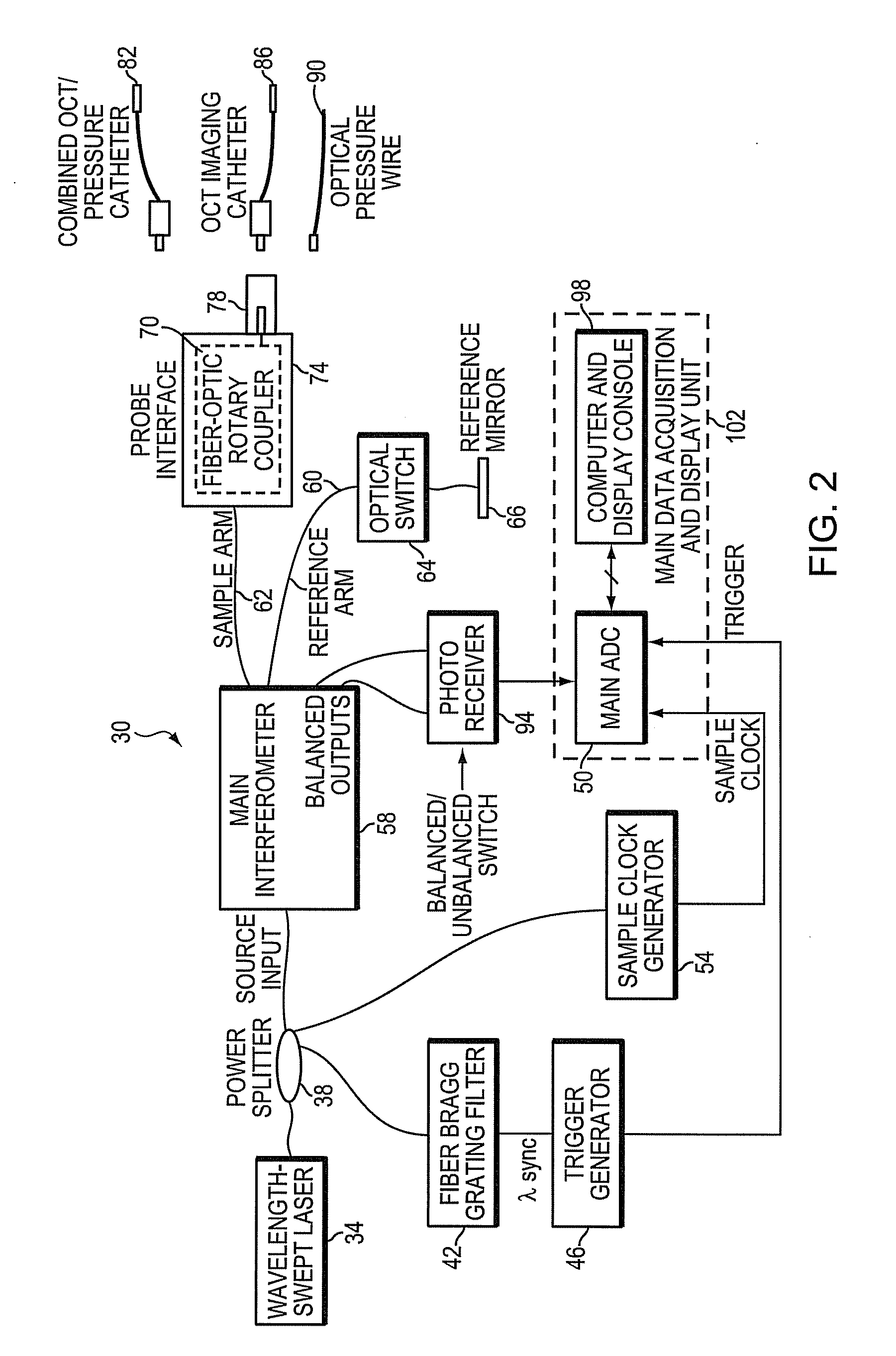
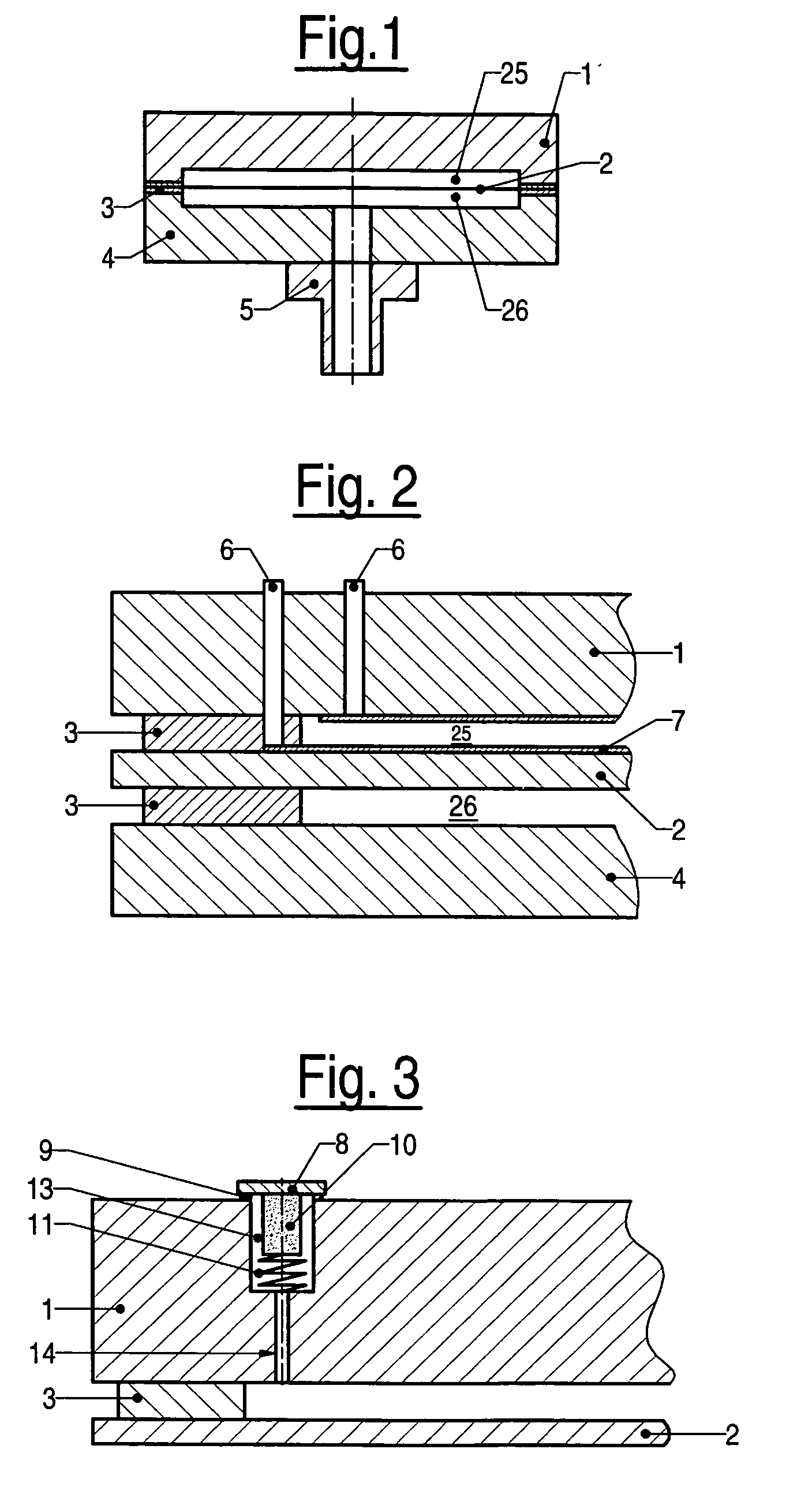
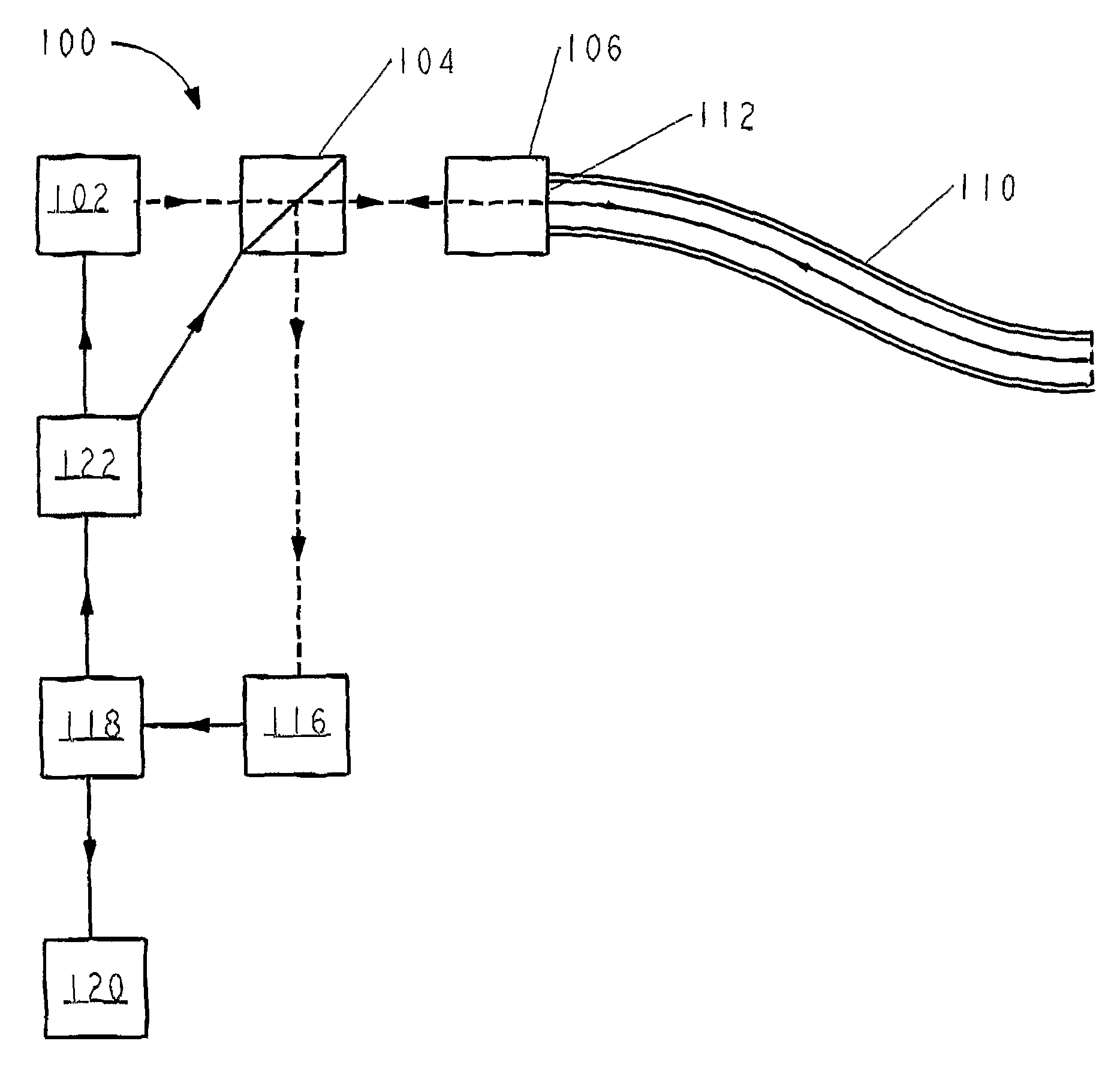
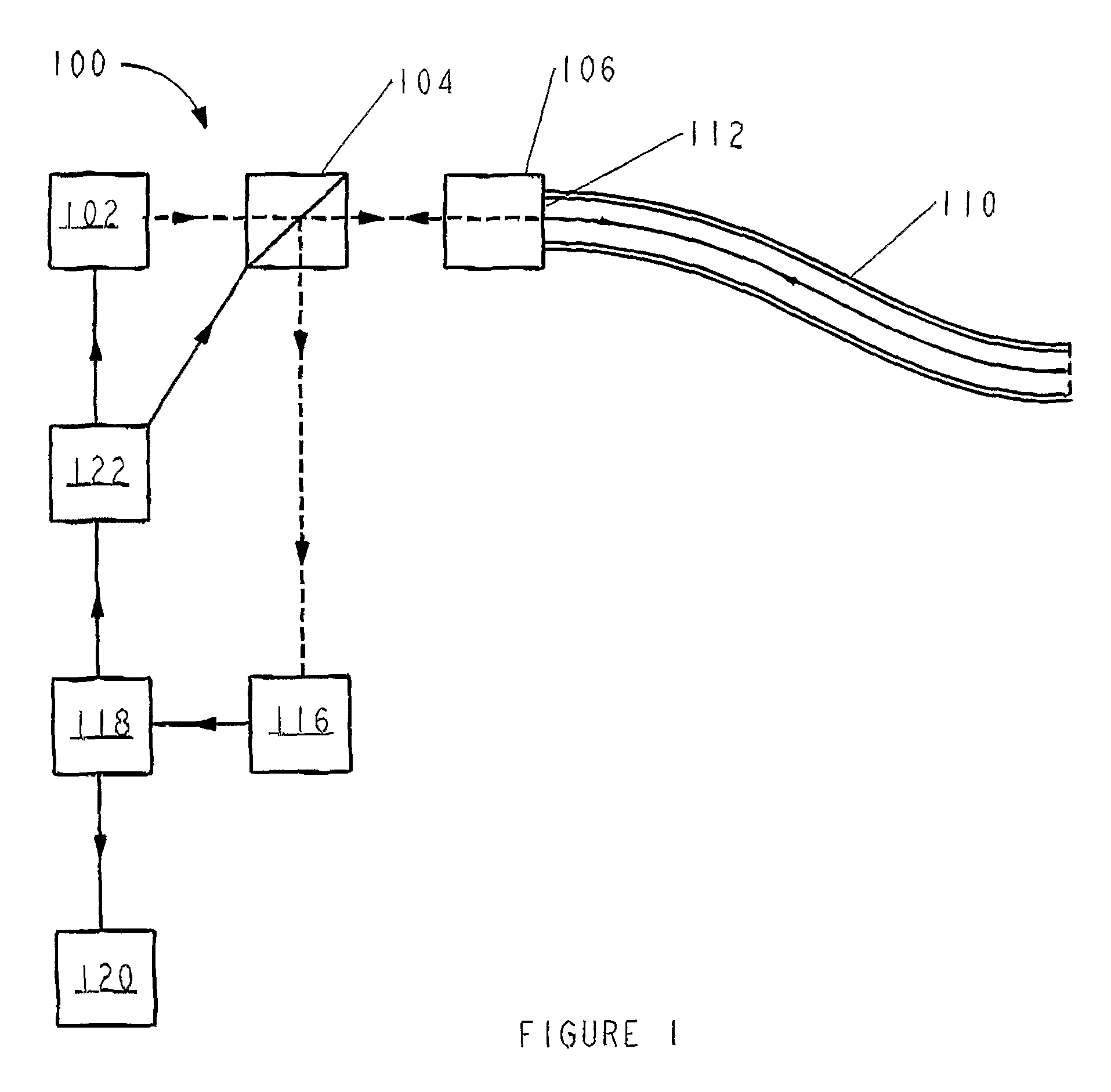
Intravascular optical coherence tomography system with pressure monitoring interface and accessories
ActiveUS20110178413A1PressureEasy to useRadiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometryPhotovoltaic detectorsPhotodetector
An optical coherence tomography system and method with integrated pressure measurement. In one embodiment the system includes an interferometer including: a wavelength swept laser; a source arm in communication with the wavelength swept laser; a reference arm in communication with a reference reflector; a first photodetector having a signal output; a detector arm in communication with the first photodetector, a probe interface; a sample arm in communication with a first optical connector of the probe interface; an acquisition and display system comprising: an A / D converter having a signal input in communication with the first photodetector signal output and a signal output; a processor system in communication with the A / D converter signal output; and a display in communication with the processor system; and a probe comprising a pressure sensor and configured for connection to the first optical connector of the probe interface, wherein the pressure transducer comprises an optical pressure transducer.
Owner:LIGHTLAB IMAGING
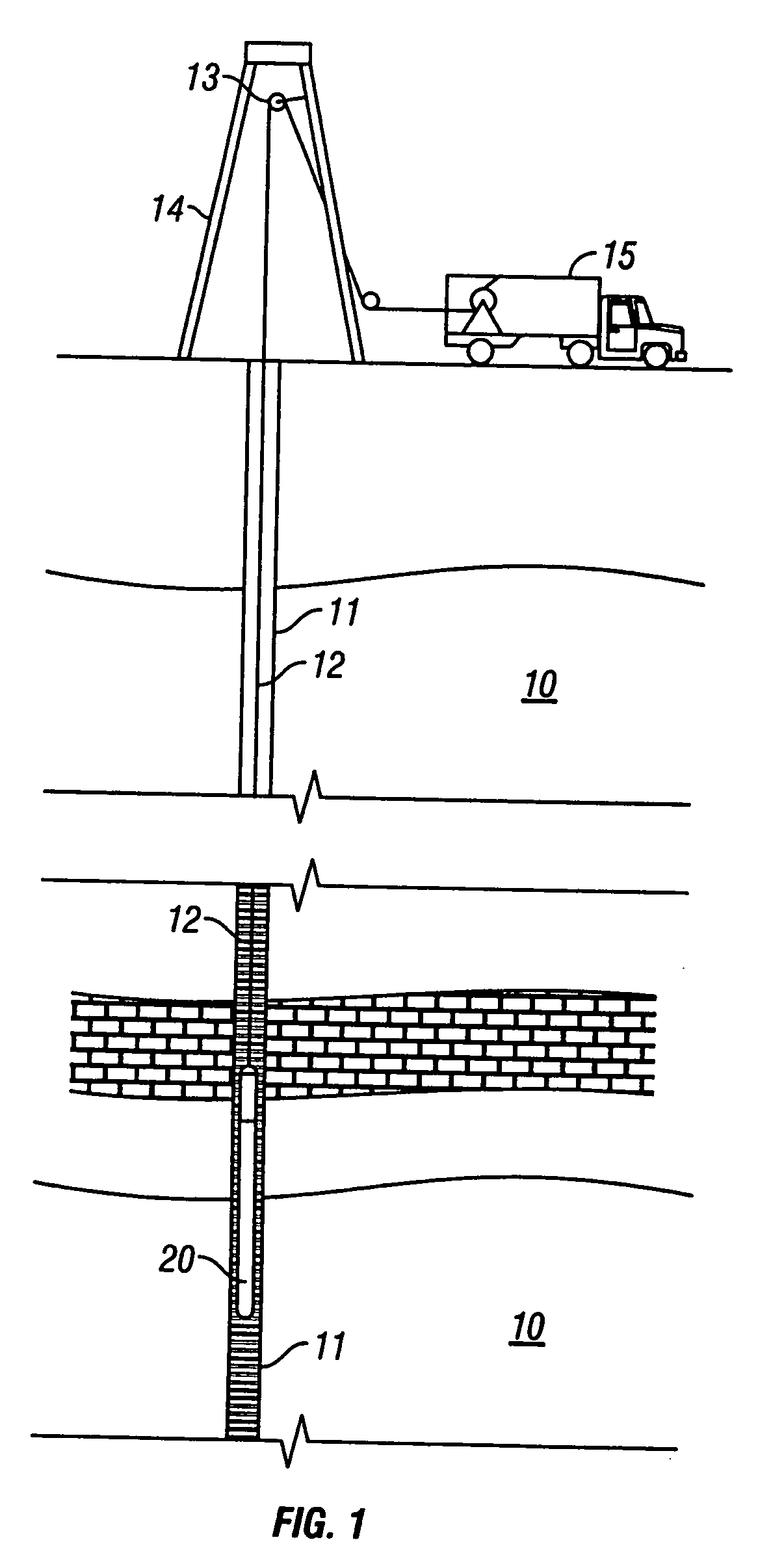
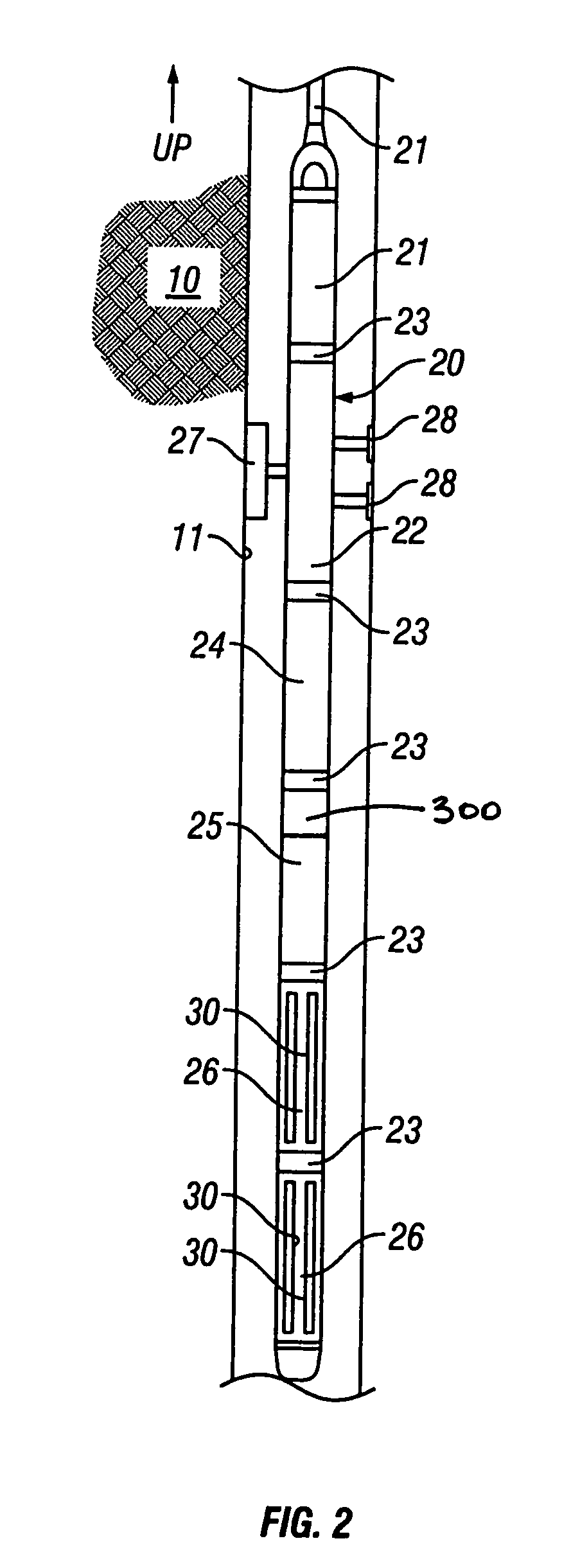
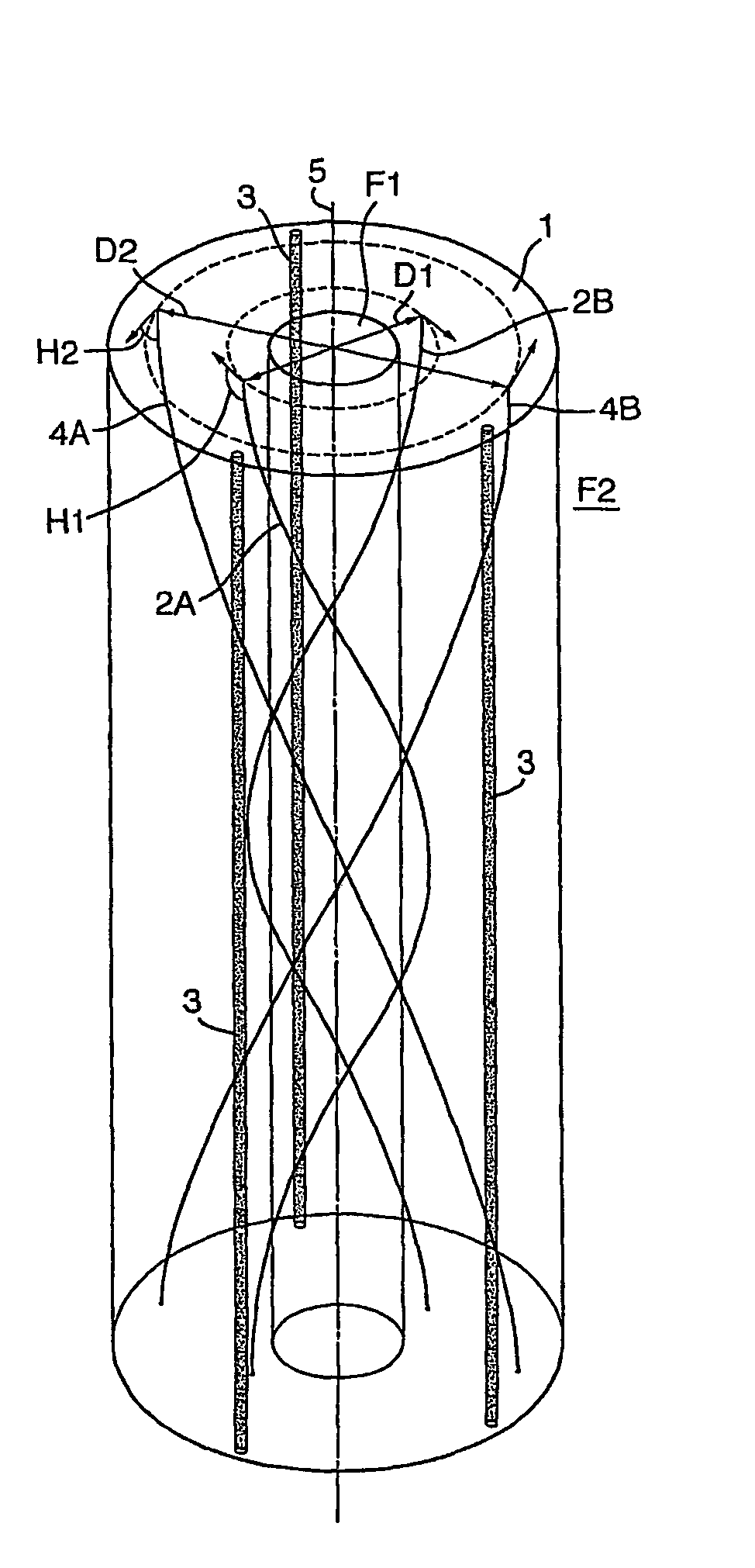
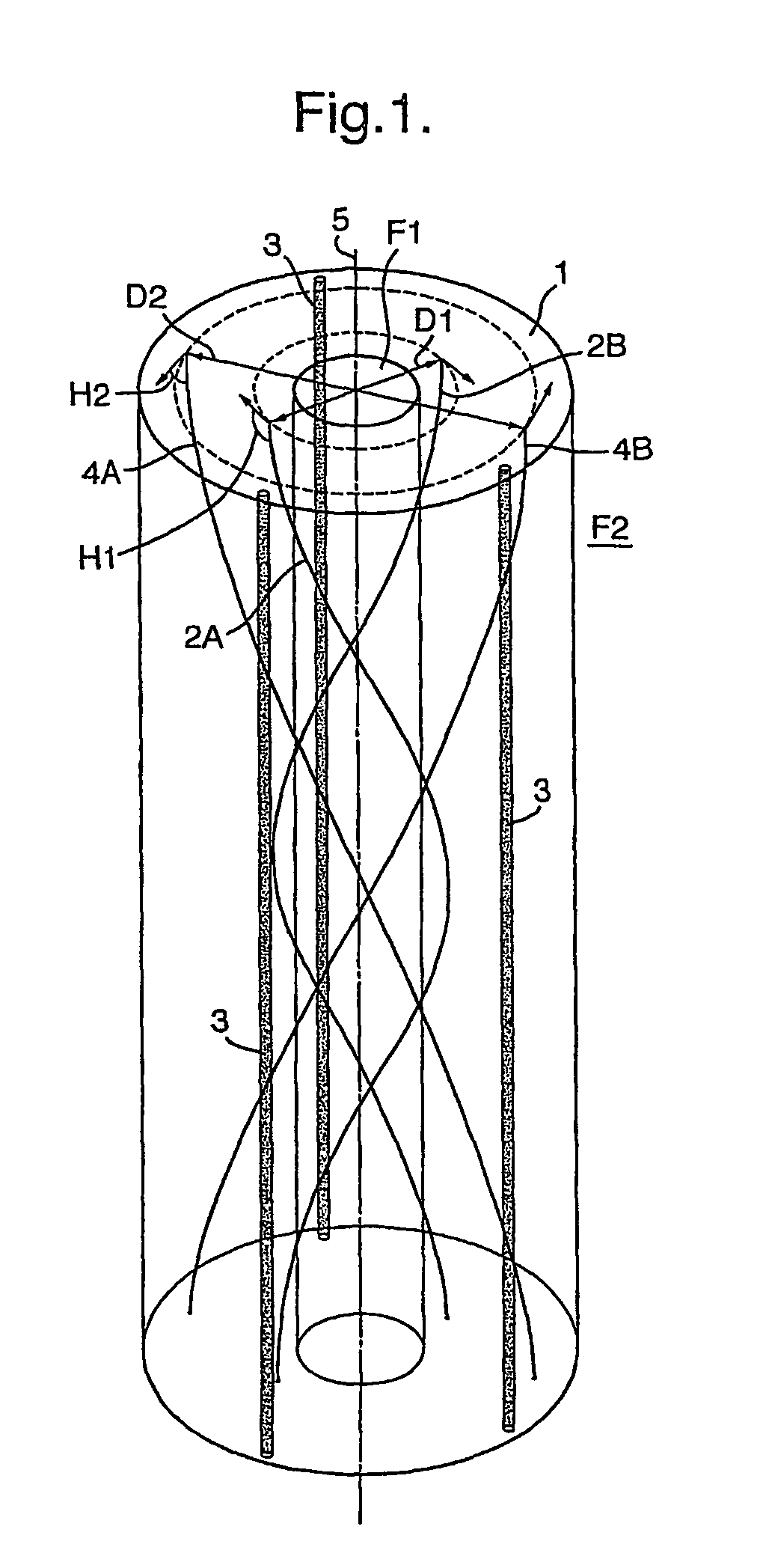
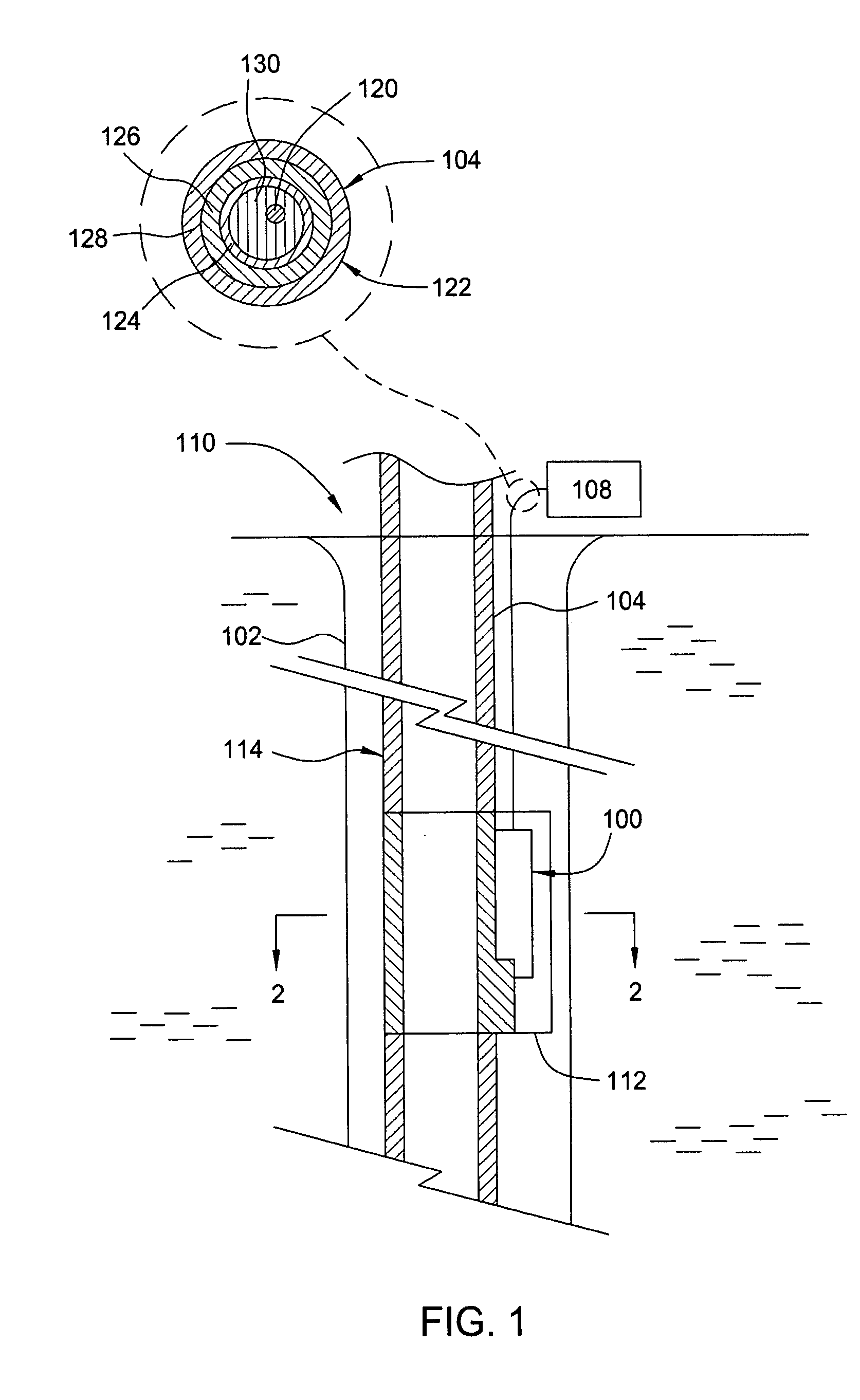
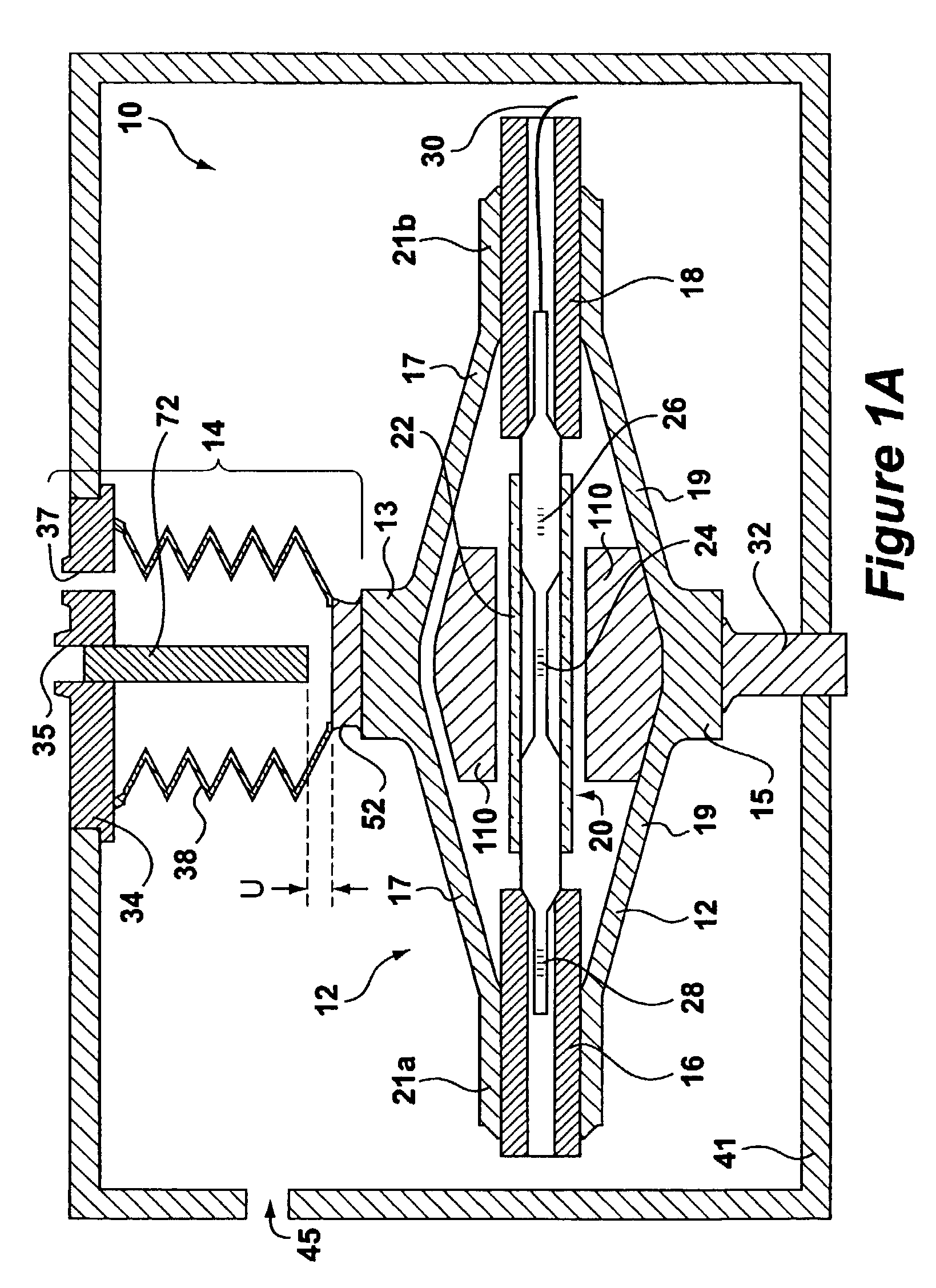
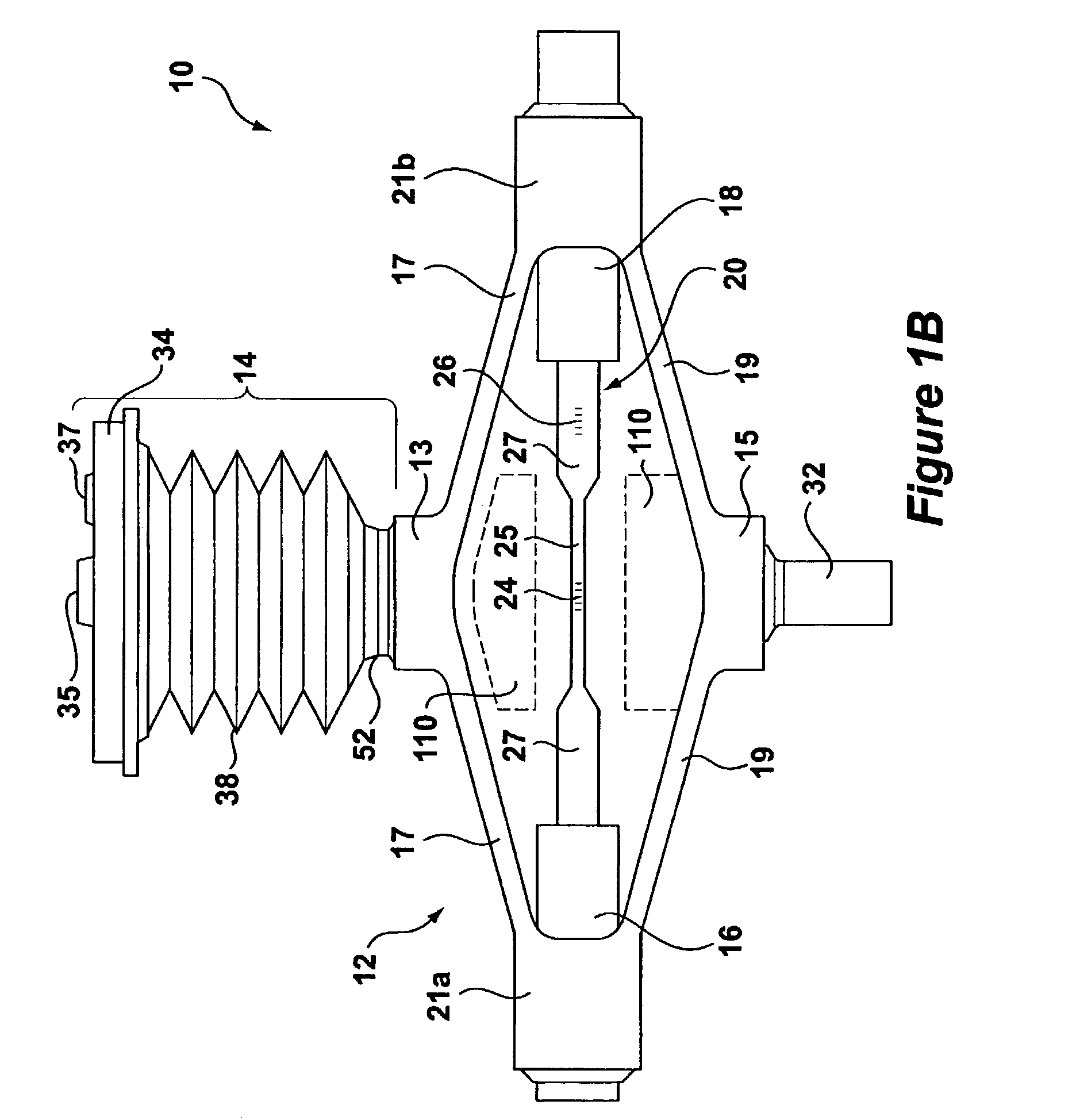
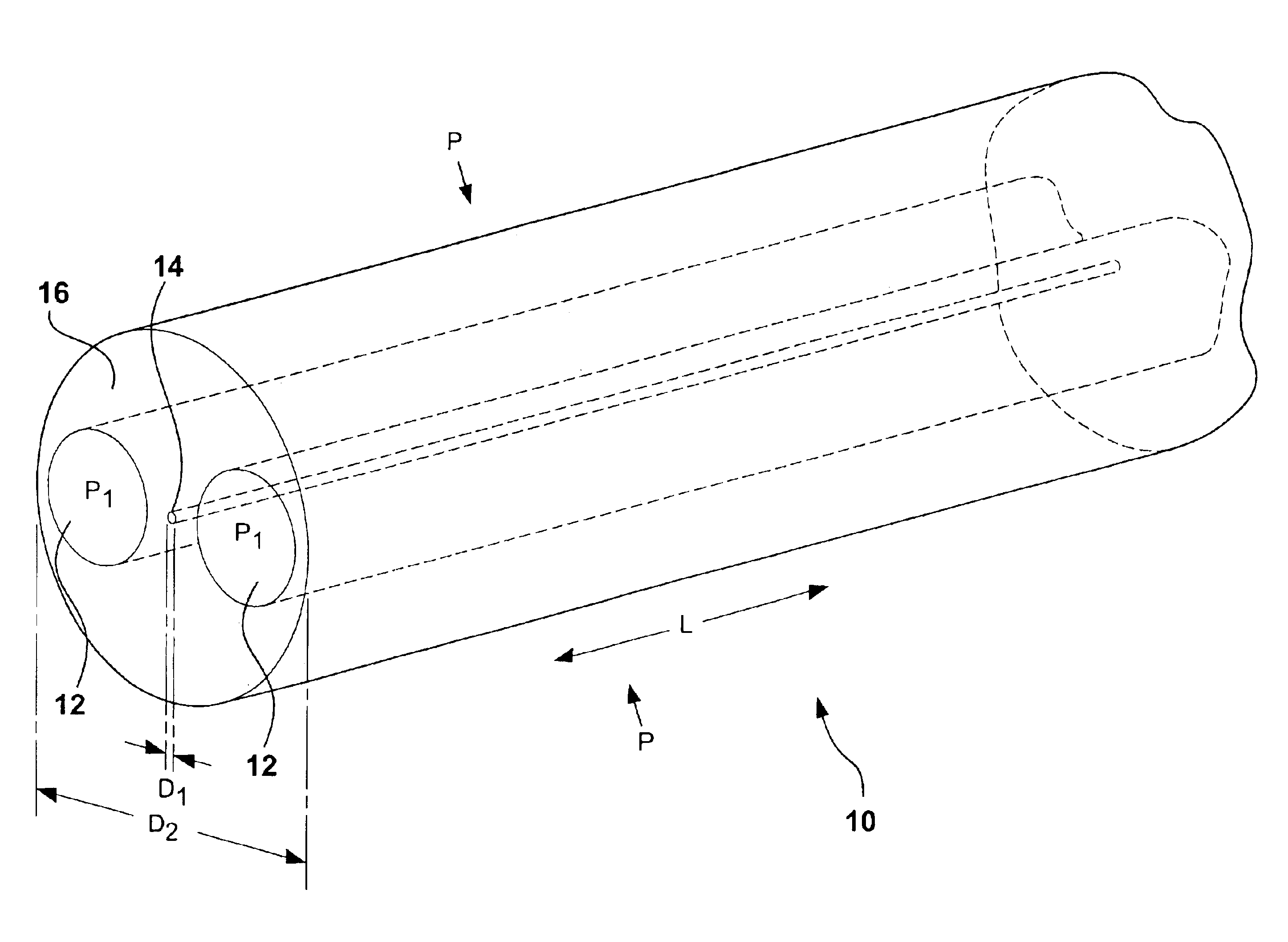
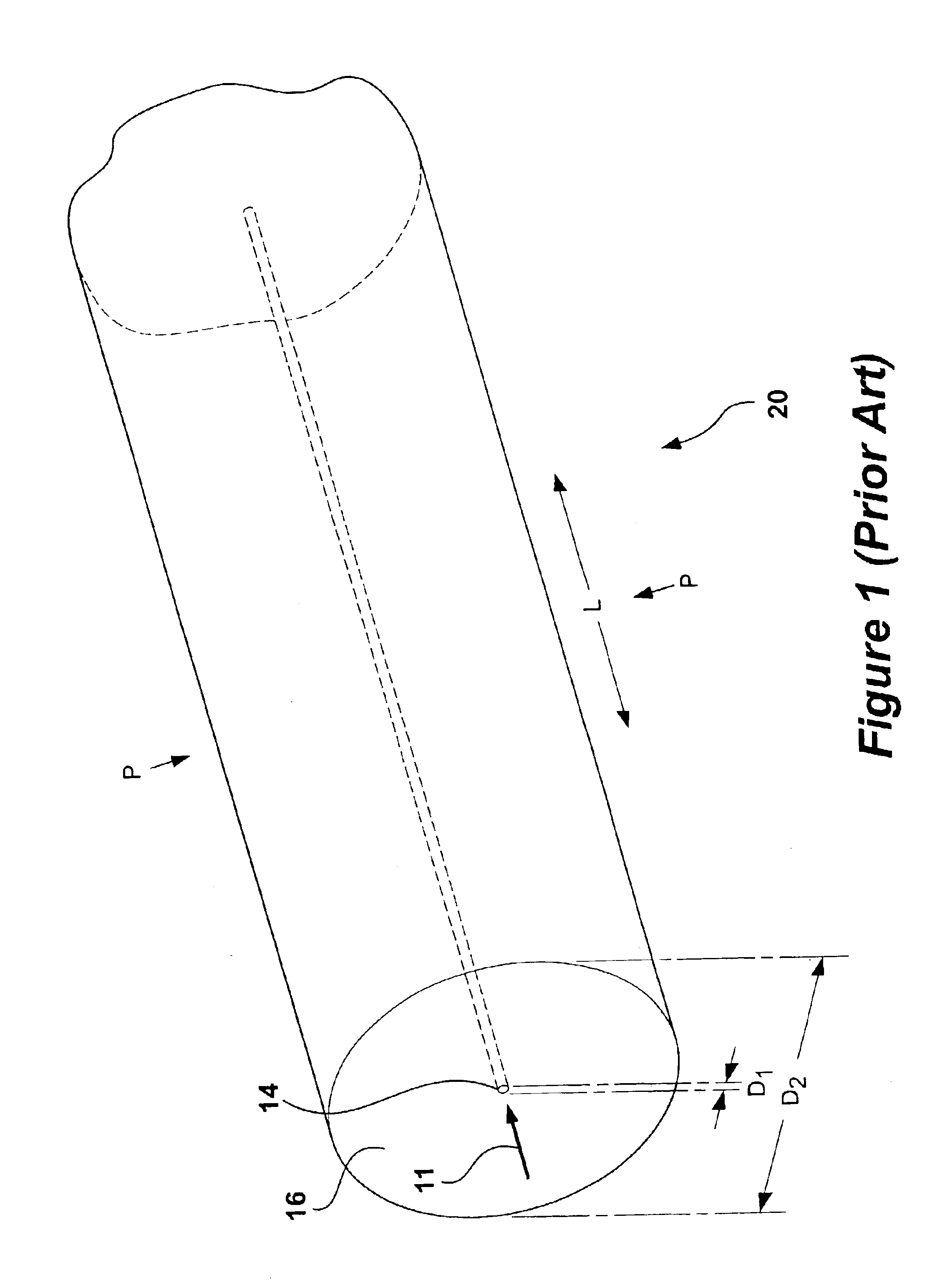
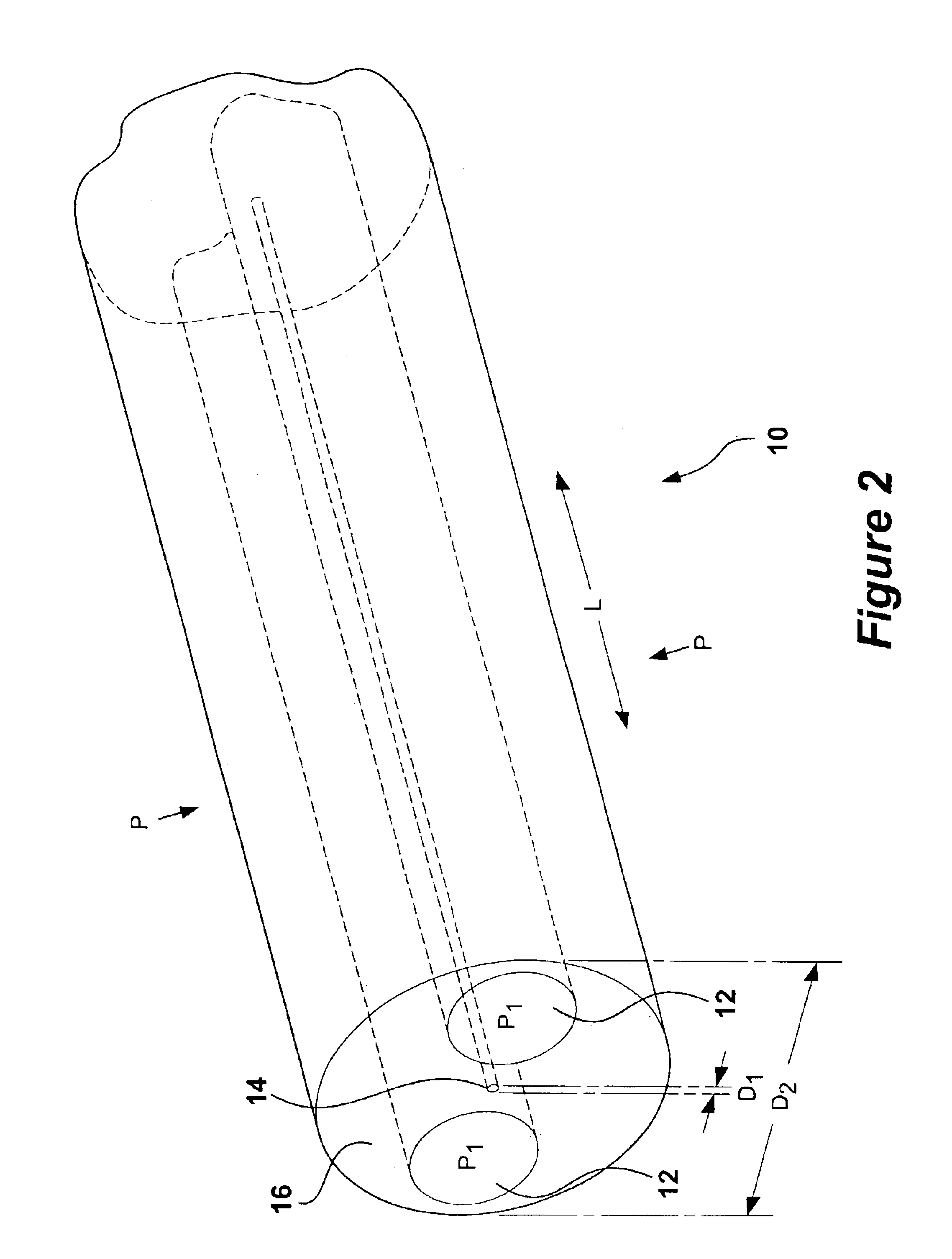
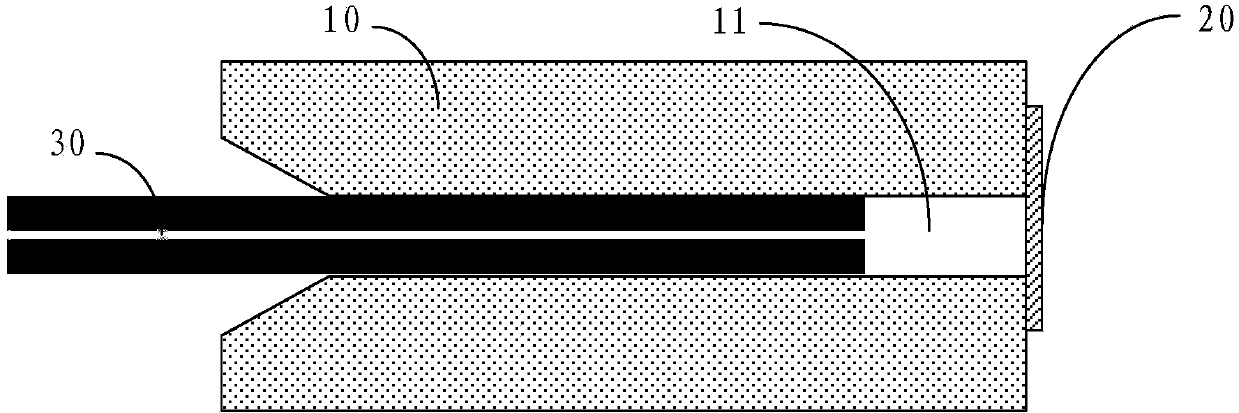
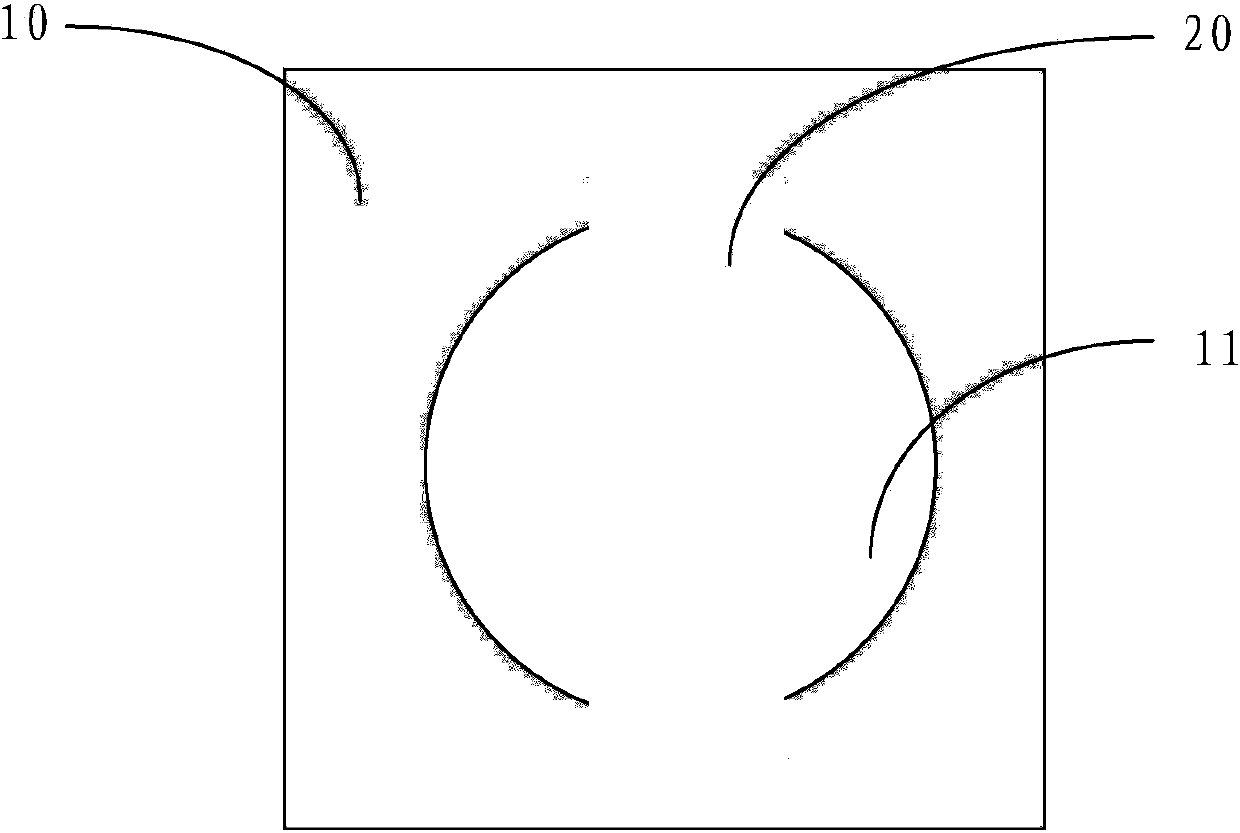
Instrumented Tabular Device for Transporting a Pressurized Fluid
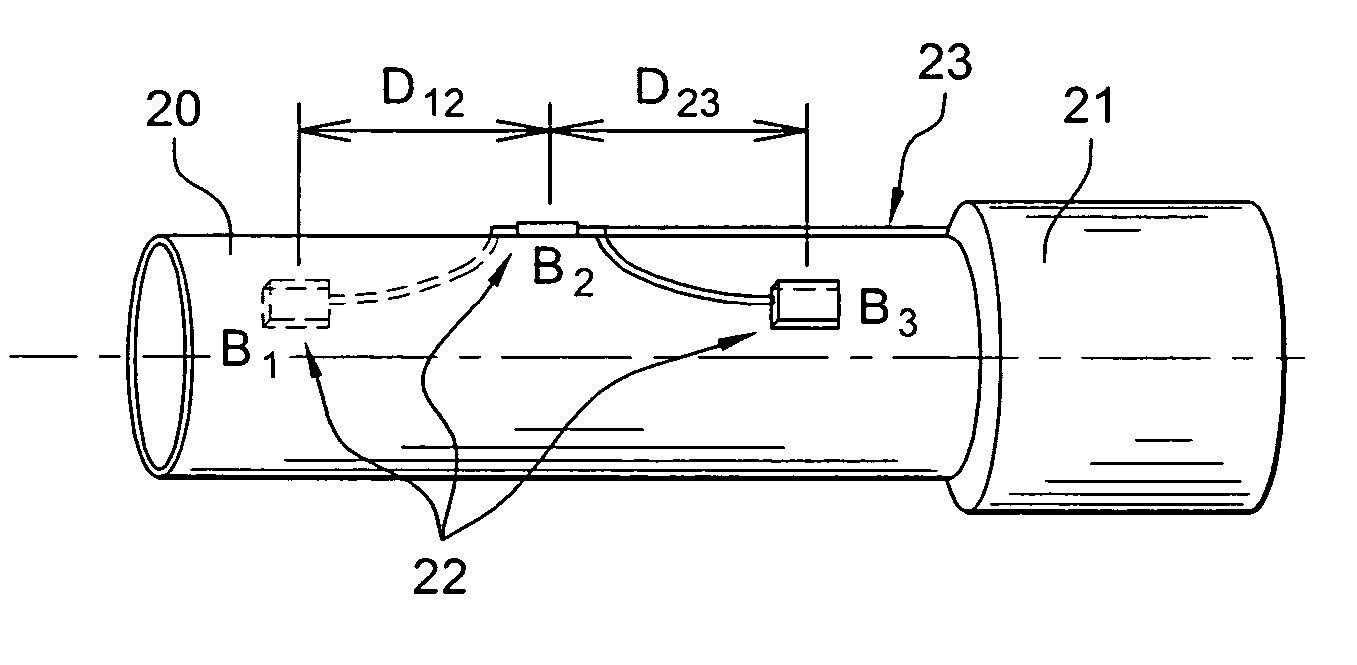
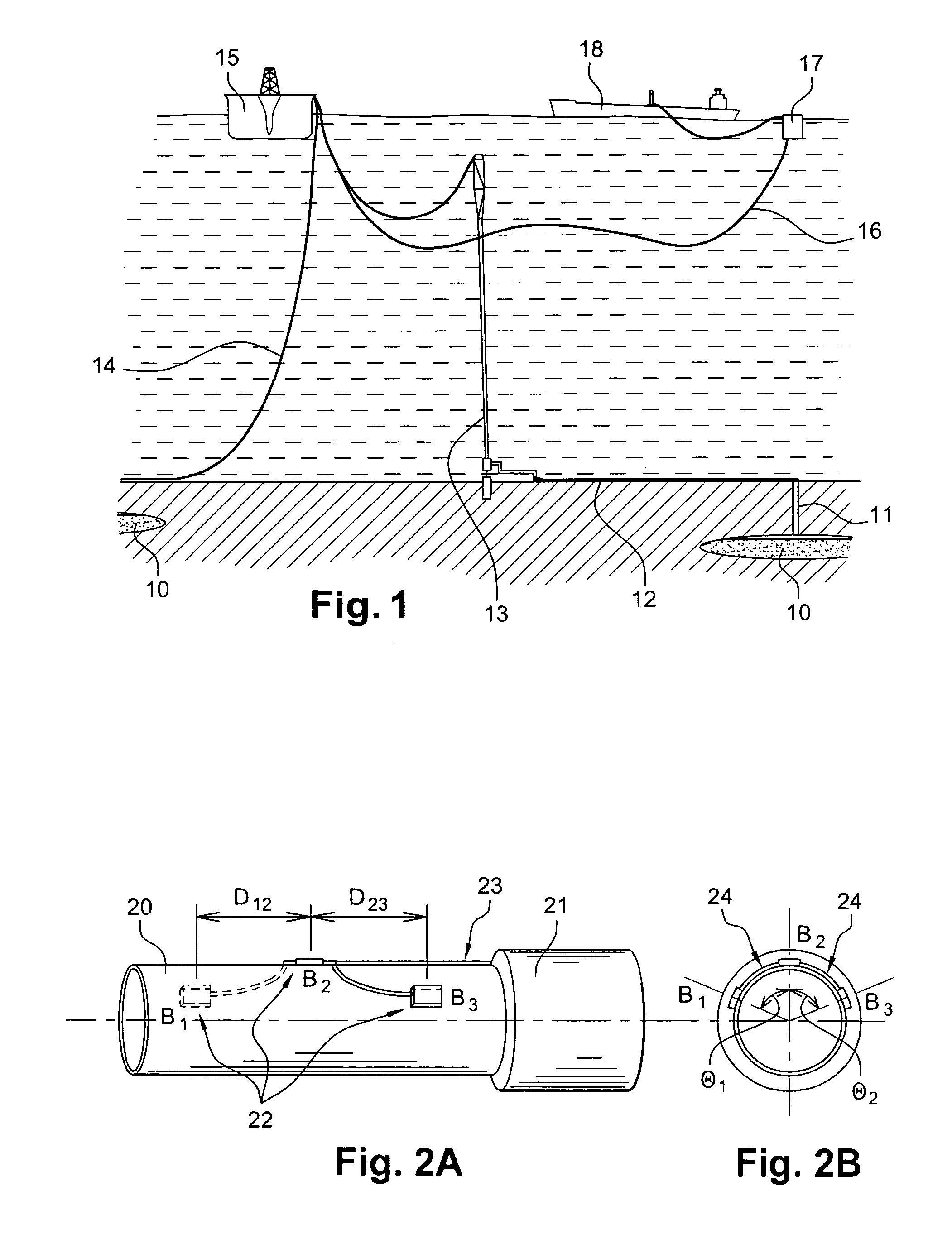
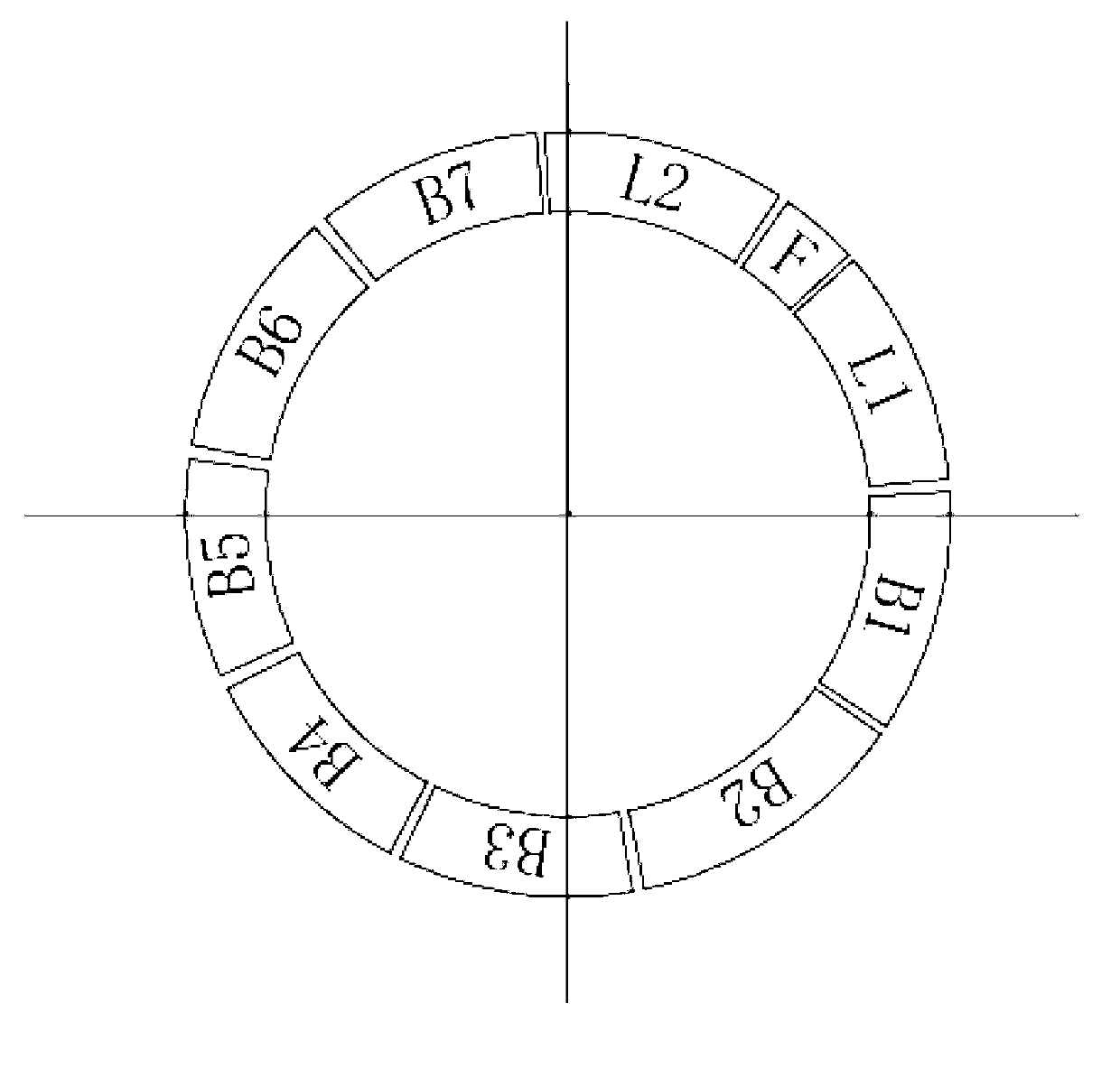
InactiveUS20070284112A1Low insertion lossDrilling rodsForce measurement by measuring optical property variationGratingEngineering
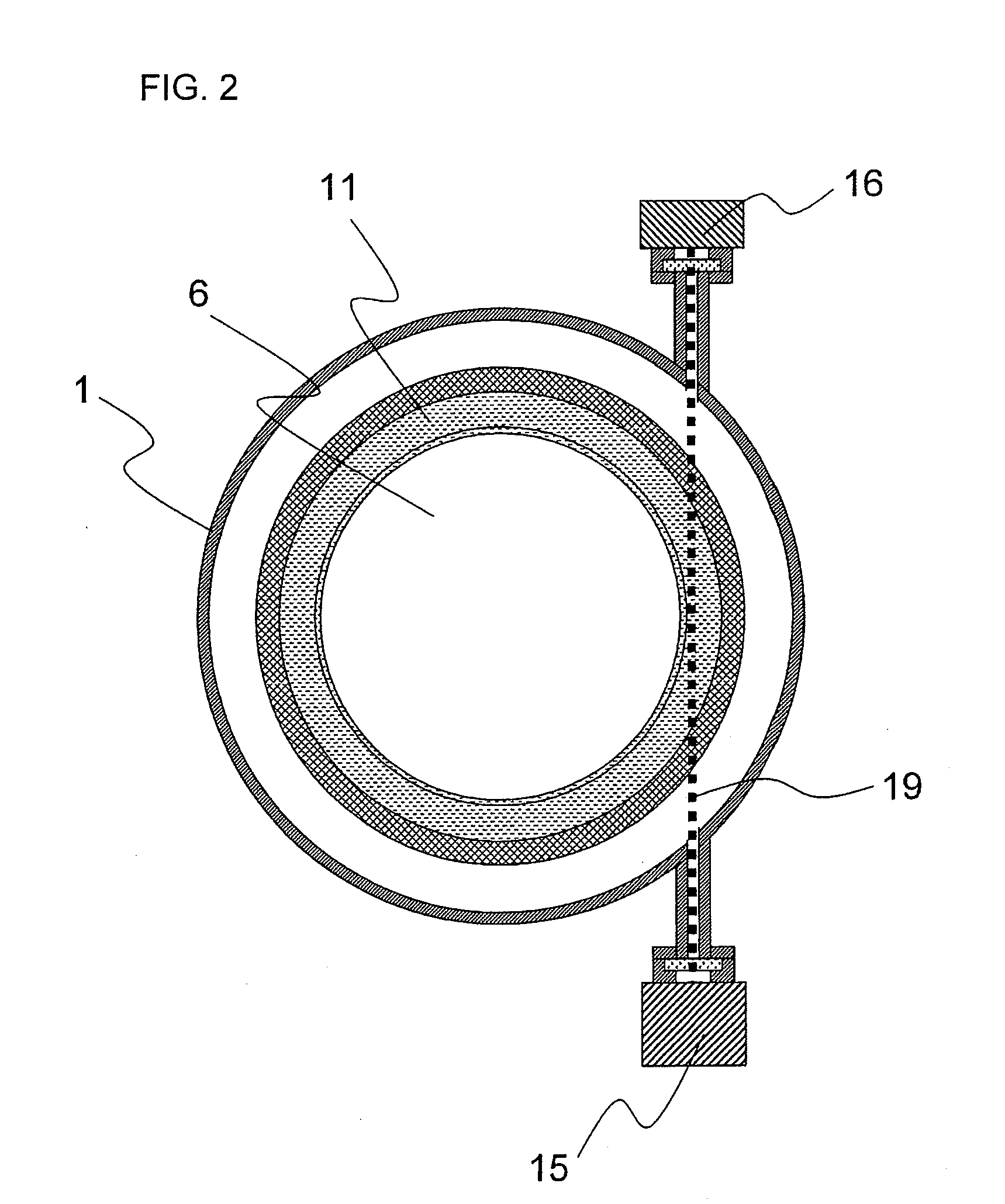
The invention relates to an instrumented tubular device for transporting a pressurized fluid notably in the field of oil exploration and in that of the transport of gas or hydrocarbons. This device comprises a tube (20) in which this fluid flows, with which are associated means for measuring the main deformations of this tube, and means for measuring the temperature of the fluid in the tube. This tube is equipped with measurement means integral with its surface and offset by at least one remote optical cable towards an electronic measurement system. These measurement means are means for assembling at least two non-parallel optical fibers which comprise at least three assemblies (B1, B2, B3) of at least two optical gages with Bragg gratings attached to at least three measurement locations (22) and connected to the remote optical cable (23) via optical fibers. At least one assembly further comprises a temperature gage.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
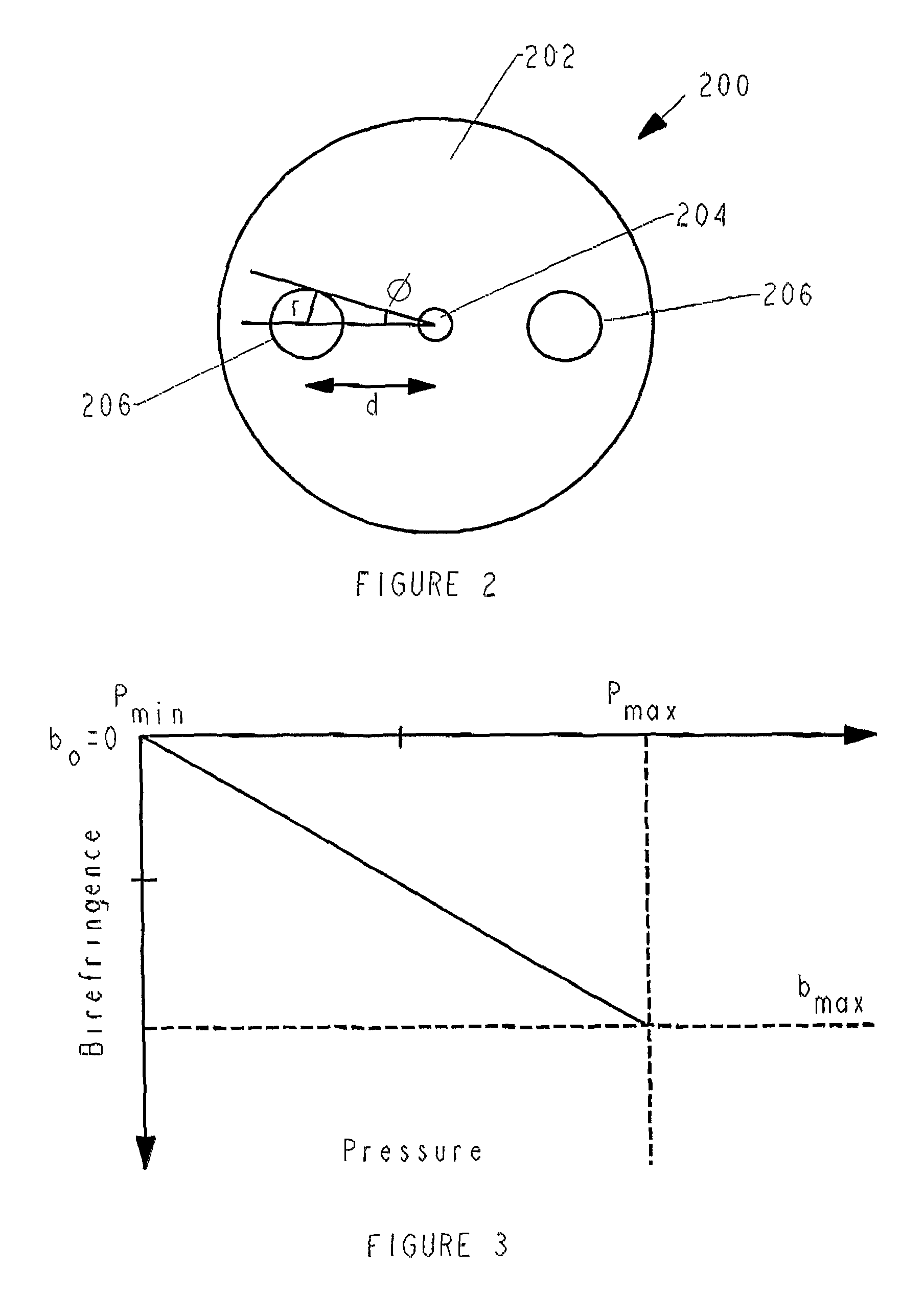
Anisotropic distributed feedback fiber laser sensor
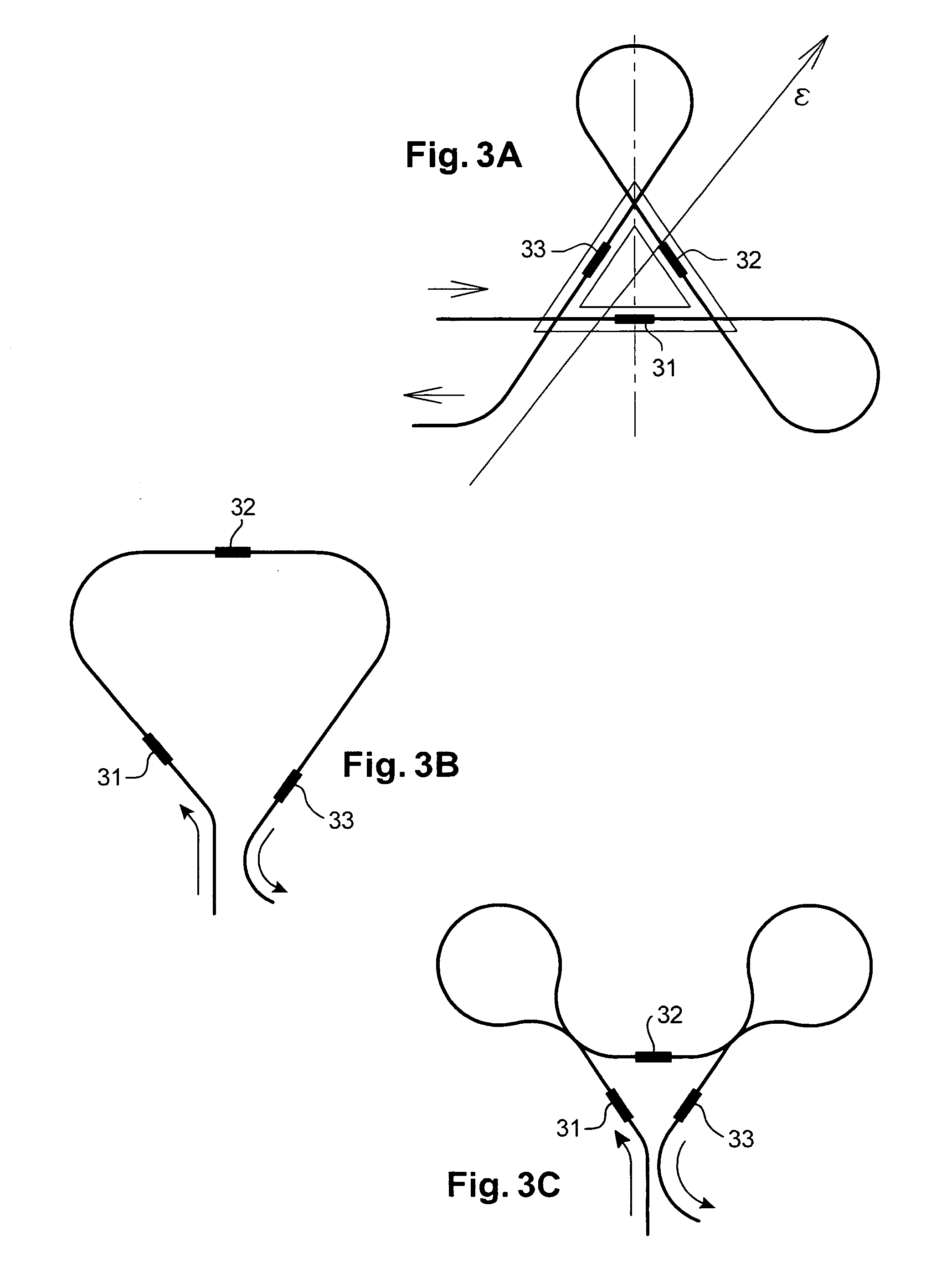
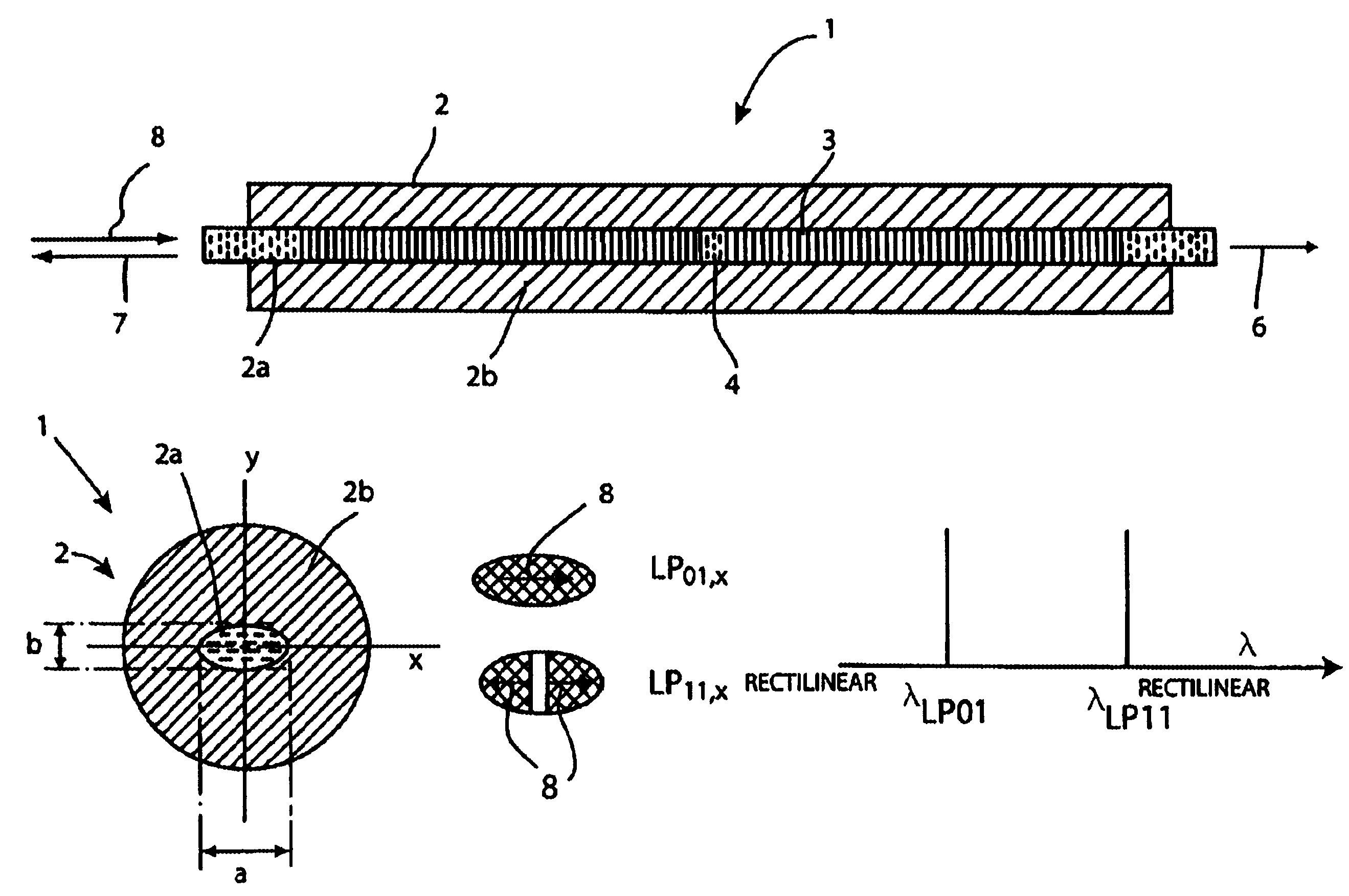
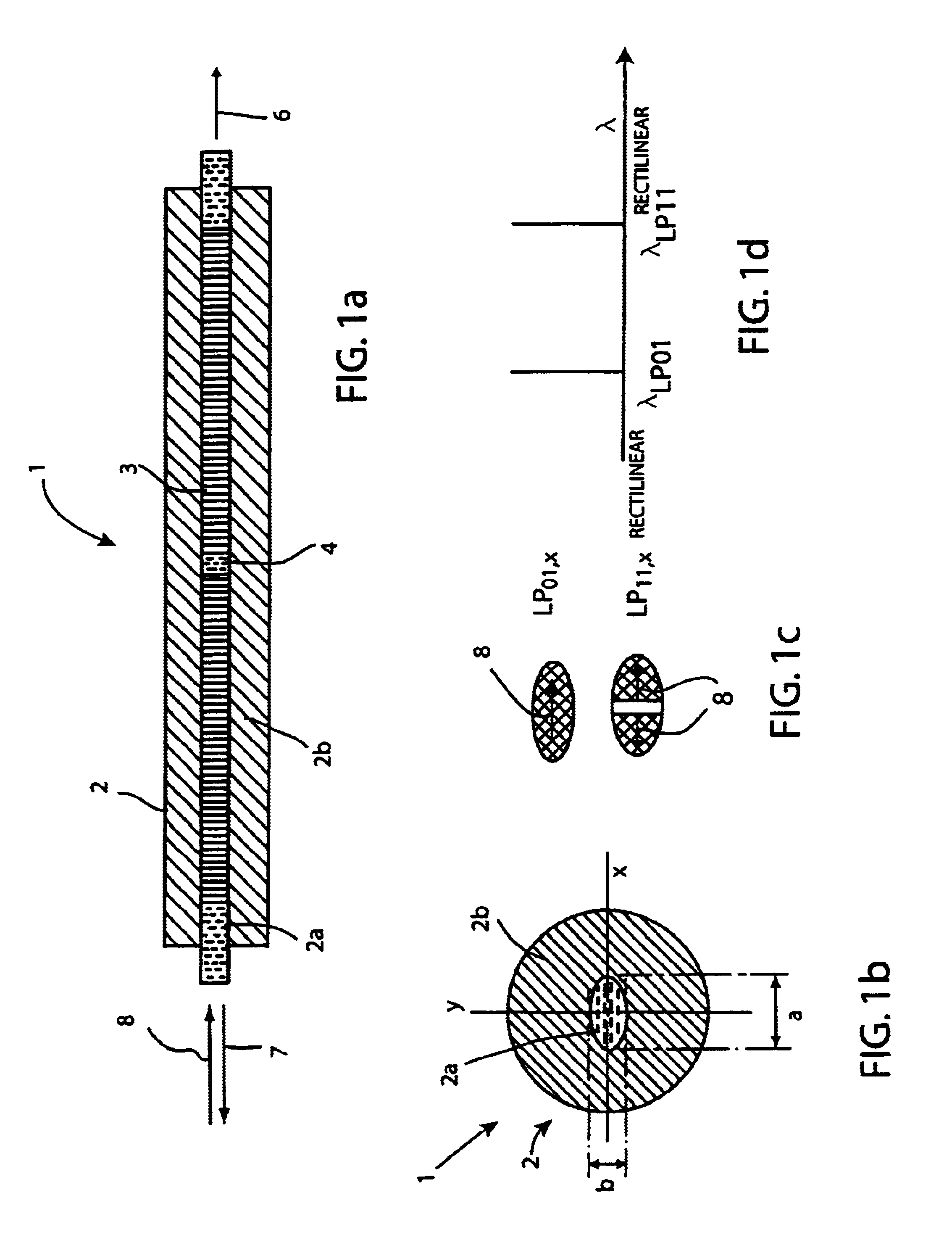
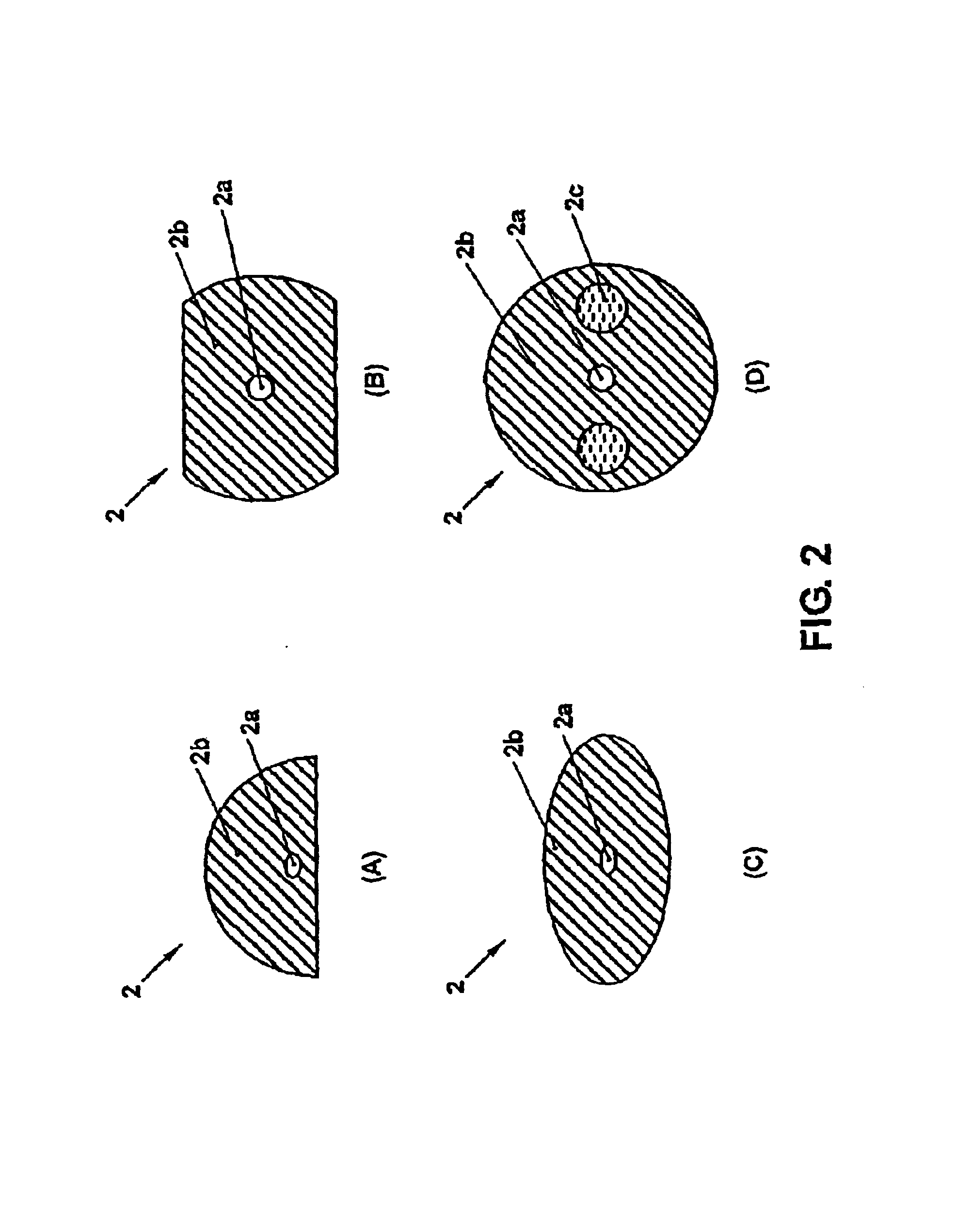
The invention relates to a DFB fiber laser sensor (1). A measurement quantity makes it possible to induce a linear birefringence between mode pairs of the laser-amplifying fiber (2) and to measure an associated beat frequency (Δν1, Δν2, Δν3). According to the invention, the laser-amplifying fiber (2) has a nonrotationally symmetrical structure, so that it is possible to detect isotropic pressures p, acoustic waves or chemical substances that can be added radially to the laser-amplifying fiber (2). In a second aspect of the invention, an emission wavelength range and parameters (a, b, ΔN) of the laser-amplifying fiber (2) and also a grating period L of the fiber Bragg grating resonator (3) are coordinated with one another such that at least two different spatial modes (LP01, LP11even, LP11odd, LP21even) are propagatable and it is possible to measure beat frequencies (Δν1, Δν2, Δν3) between oscillatory longitudinal laser modes assigned to them. Exemplary embodiments relate to: rotationally asymmetrical fiber types, a choice of special spatial modes (LP11odd, LP21even) and / or multiple fiber Bragg gratings (3) for reducing the beat frequencies (Δν1, Δν2, Δν3) below 100 GHz; and elimination of temperature influences e.g. by the detection of a plurality of beat frequencies (Δνa, Δνb, Δνc, Δνd) between different pairs of spatial modes (LP01, LP11even, LP11odd, LP21even) and / or polarization modes (X, Y).
Owner:GE OIL & GAS UK LTD
Optical sensor with co-located pressure and temperature sensors
ActiveUS20070006663A1Fluid pressure measurement by electric/magnetic elementsForce measurement by measuring optical property variationFiberRefractive index
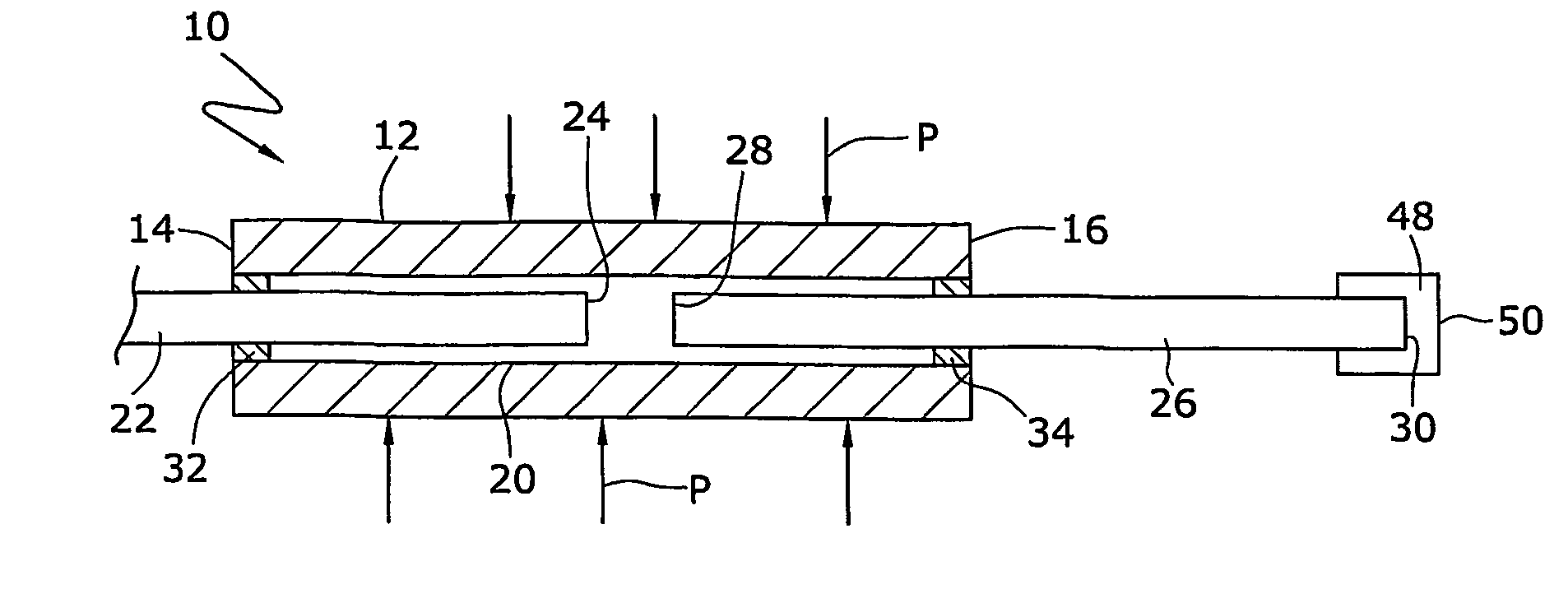
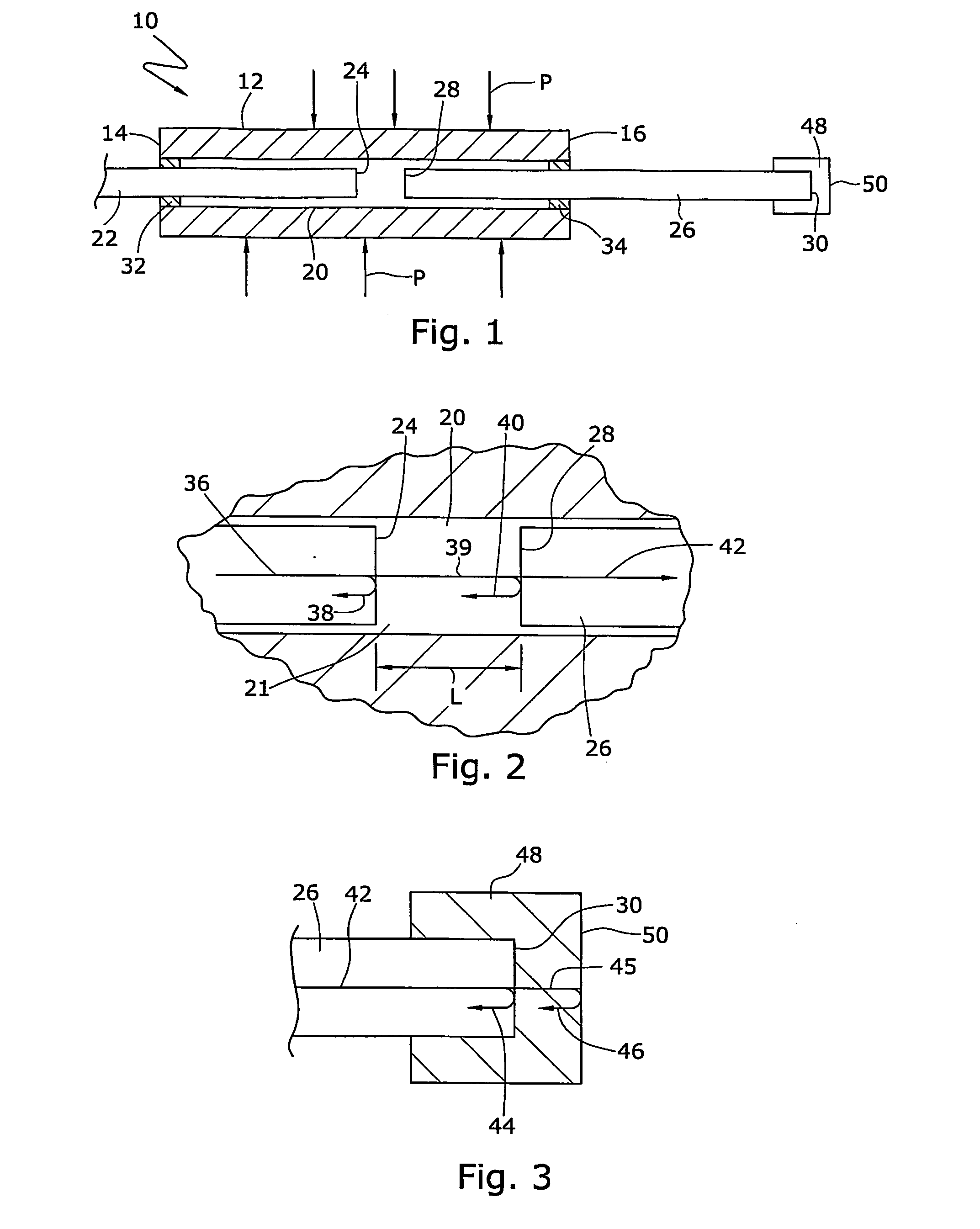
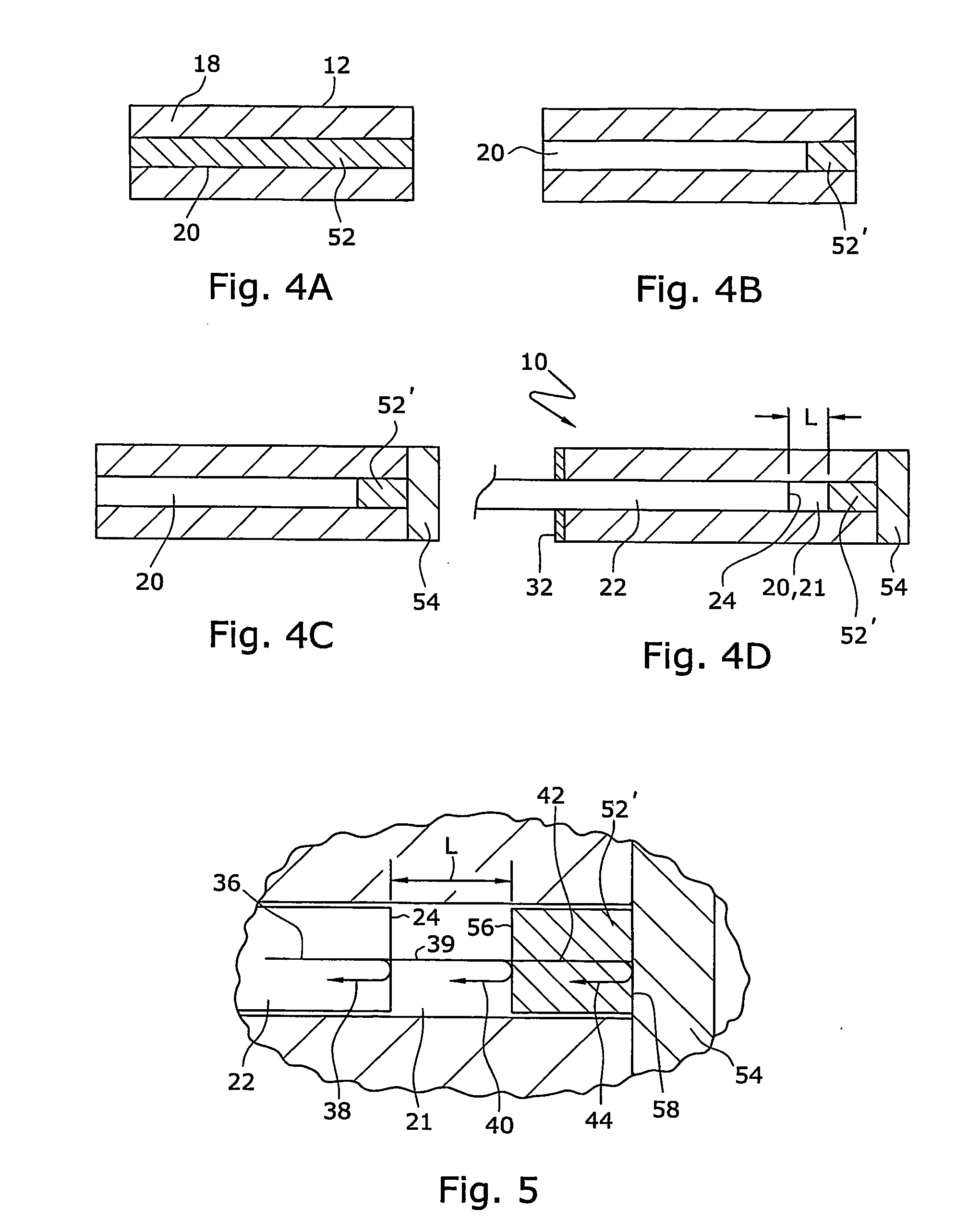
An optical sensor (10) that provides for concurrent pressure and temperature measurements at substantially the same location includes at least one launch fiber (22) and at least one temperature sensitive material (52) having a refractive index that changes with a change in temperature. The launch fiber and temperature sensitive material are spaced from each other across a gap (21) having length (L). A reflecting fiber (26) can be provided adjacent the temperature sensitive material. The optical sensor (10) also includes a sealed cavity (20). The launch fiber (22) and reflecting fiber (26) can be attached to the tube and at least partially disposed within the cavity. Changes in pressure change the length (L) of the gap (21).
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
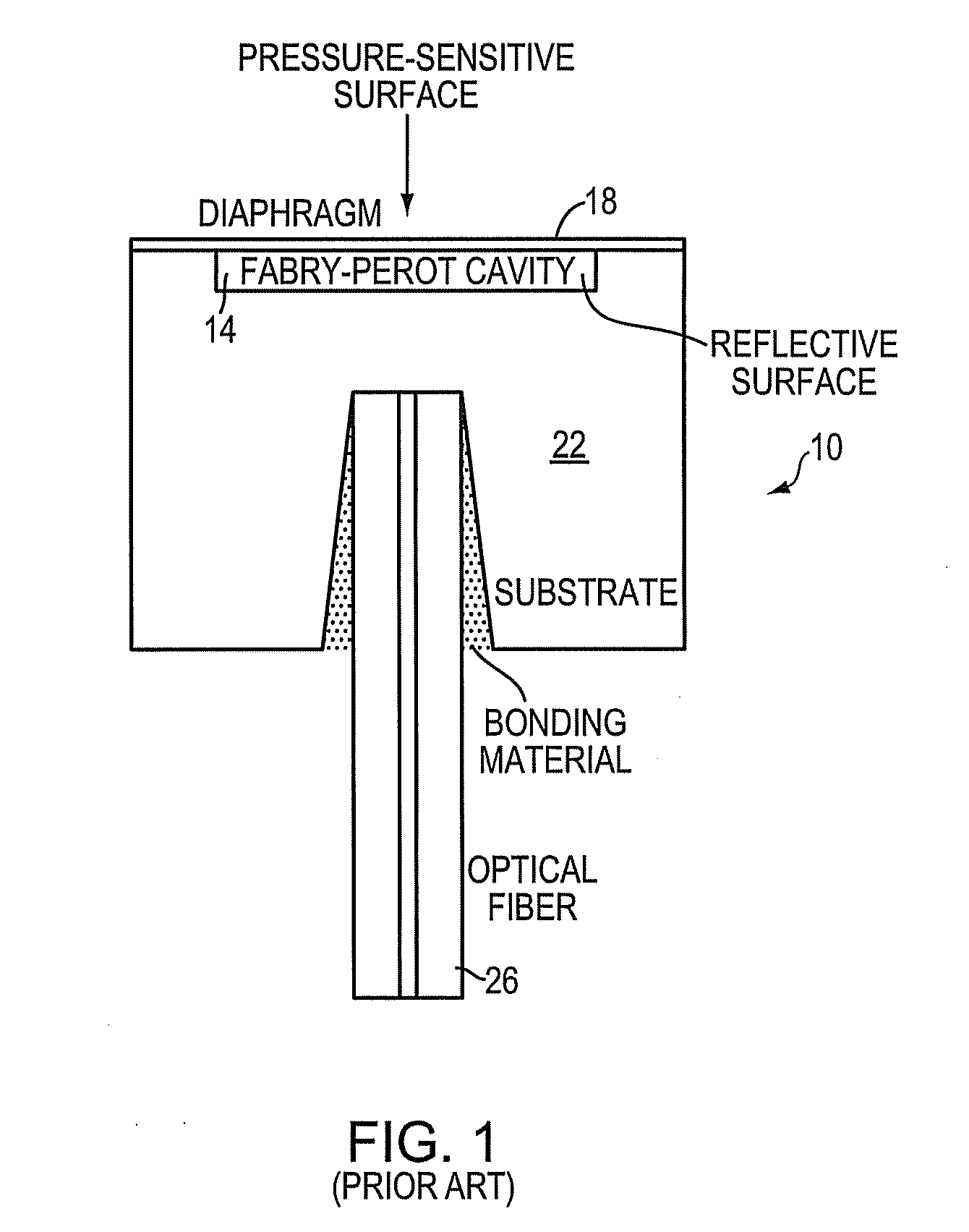
High-stability optical fiber Fabry-Perot pressure sensor packaged without glue and manufacturing method
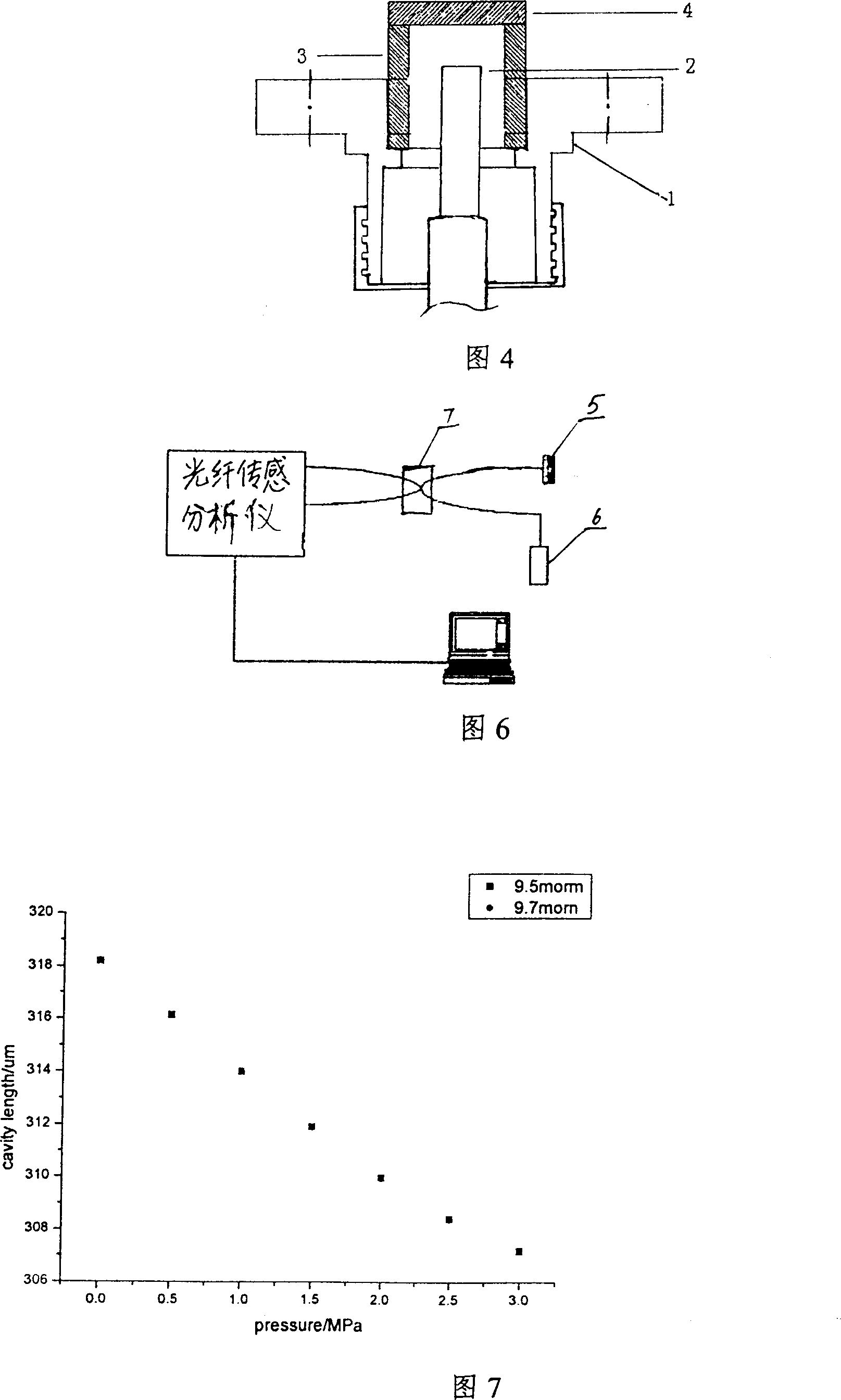
ActiveCN102384809AEliminate the effects ofEasy to achieve airtightFluid pressure measurement by electric/magnetic elementsOptical light guidesEngineeringCo2 laser
The invention provides a high-stability optical fiber Fabry-Perot pressure sensor packaged without glue and a manufacturing method. The sensor comprises a sensor head, a sensor body with a through-hole in middle, and an optical fiber, wherein a four-layer structure (comprising a first monocrystalline silicon piece, a first Pyrex sheet glass, a second monocrystalline silicon piece and a second Pyrex sheet glass) is adopted by the sensor head; a first reflecting surface of a Fabry-Perot cavity is formed by the back surface of the first monocrystalline silicon piece; the second monocrystalline silicon piece is used for providing a second reflecting surface of the Fabry-Perot cavity; the second Pyrex sheet glass is in butt fusion with the sensor body; and the optical fiber is fixedly arrangedin the sensor body by adopting a CO2 laser, and thereby non-glue packaging is realized. When the first layer of monocrystalline silicon piece is deformed by external pressure changes, the length of the optical fiber Fabry-Perot cavity is changed; and after a broadband light source is accessed to the sensor, the change of the cavity length can be extracted through collecting a reflection spectrum of the sensor or extracting low-coherence interference fringes of the sensor, and thereby pressure information is obtained. By adopting the structure, the influences of environmental changes such as the temperature, the humidity, and the like can be effectively eliminated, and the measurement accuracy can be greatly improved.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
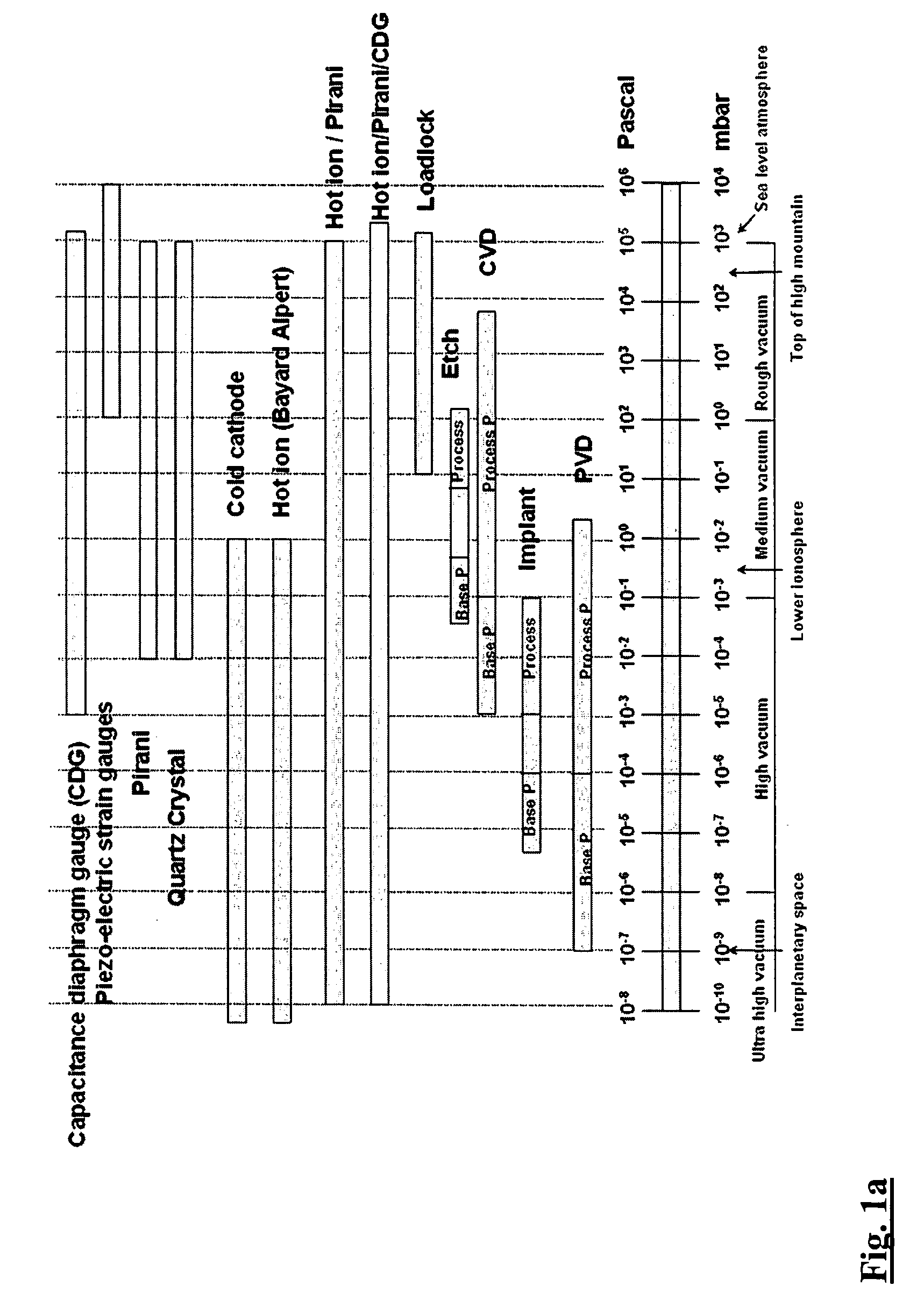
Plasma processing apparatus and plasma processing method
InactiveUS20100025369A1Curb tiltReduce in quantityElectric discharge tubesVacuum gauge using ionisation effectsEngineeringRadio frequency
To monitor the thickness of a focus ring consumed during wafer processing. A plasma processing apparatus includes a vacuum chamber 1, workpiece mounting means 5, high frequency electric power introducing means 4 and radio-frequency bias electric power introducing means 7 and processes a surface of a workpiece 6 using a plasma that is converted from a gas introduced into the vacuum chamber 1 by the action of a high frequency electric power introduced by the high frequency electric power introducing means 4. The plasma processing apparatus further includes an annular member 11 surrounding the workpiece 6 mounted on the workpiece mounting means 5, and a pair of tubes having an aspect ratio of 3 or higher and disposed on a side wall of the vacuum chamber 1 to face each other. Each tube is vacuum-sealed at a tip end thereof with a glass material. One of the tubes has a light source 15 disposed facing to the interior of the vacuum chamber on the atmosphere side of the glass material, and the other tube has light receiving means 16 disposed facing to the interior of the vacuum chamber on the atmosphere side of the glass material. The light receiving means 16 receives light passing across the surface of the annular member 11.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
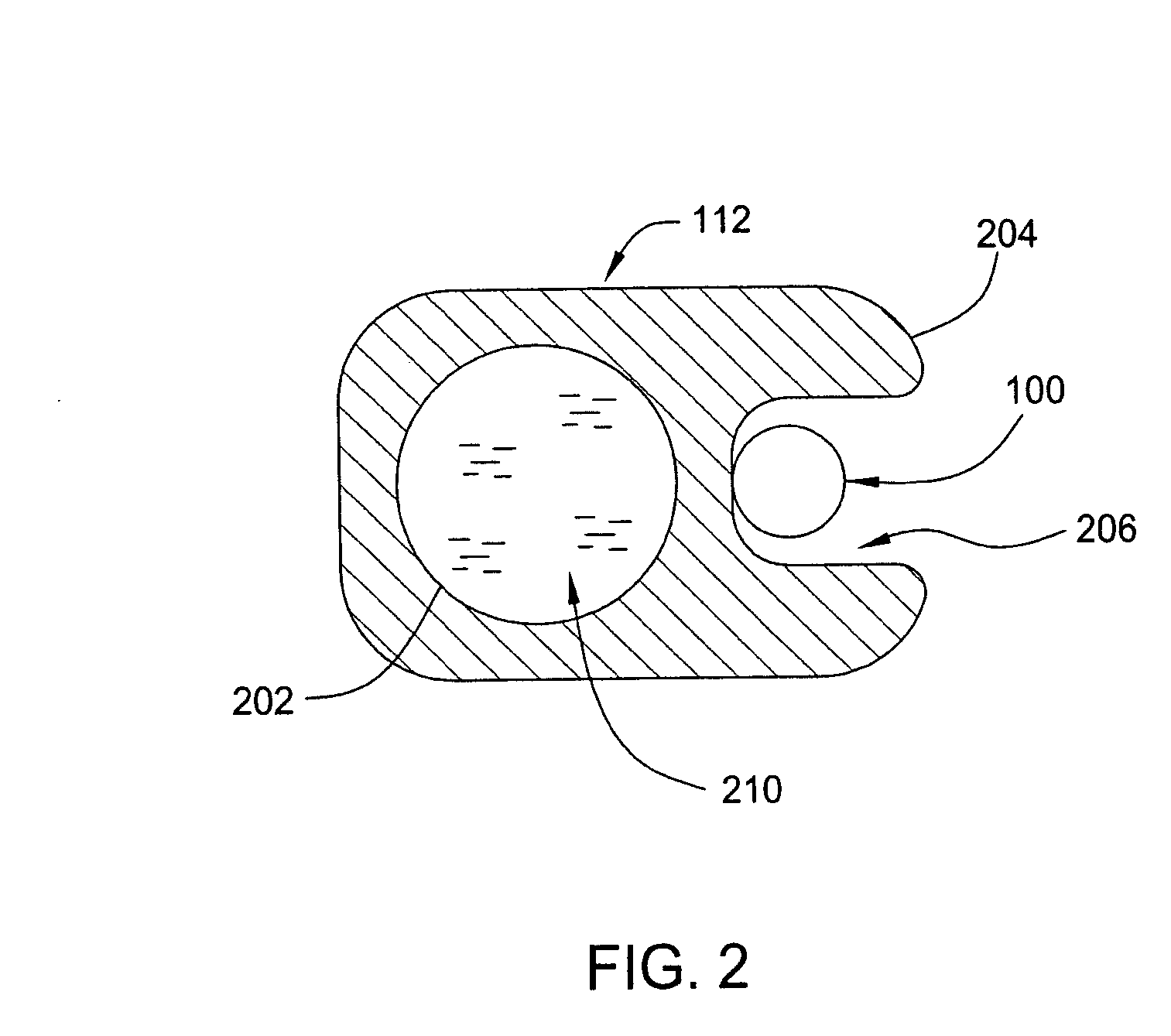
Pressure sensor assembly and method of using the assembly
A pressure sensor assembly comprises a sensor housing having a flexible wall that is configured to deform in response to a pressure difference between the interior and exterior of the sensor housing; —a first fiber optical cable section that is bonded to the flexible wall of the sensor housing such that the length of the first fiber optical cable section changes in response to deformation of the wall in response to the said pressure difference; a second fiber optical cable section which is bonded to a thermal reference body, which body is connected to the sensor housing by a strain decoupled connection mechanism, such as a tack weld or flexible glue, and is configured to deform substantially solely in response to thermal deformation, such that the length of the second fiber optical cable section solely changes in response to thermal deformation of the thermal reference body.
Owner:SHELL USA INC
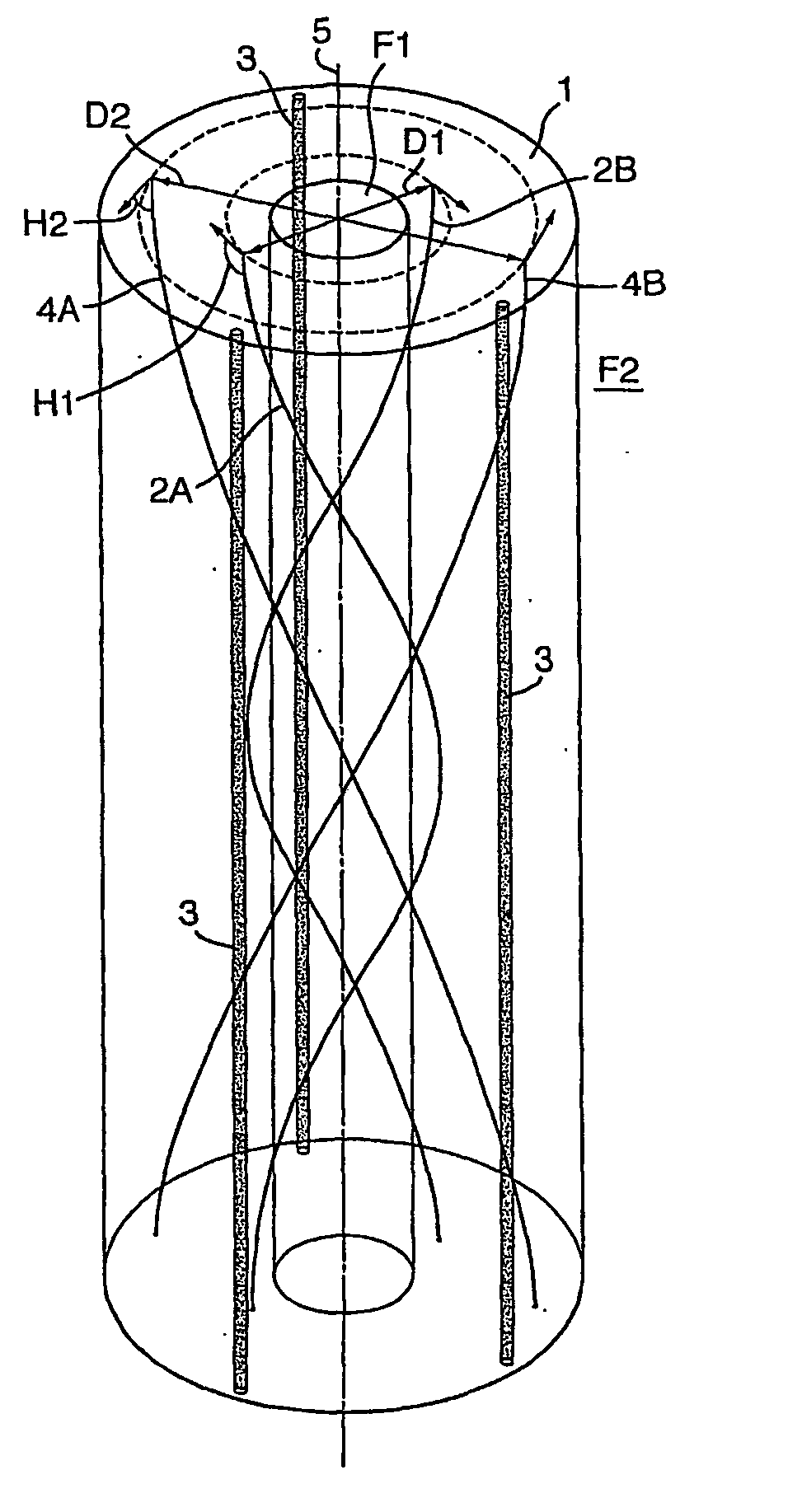
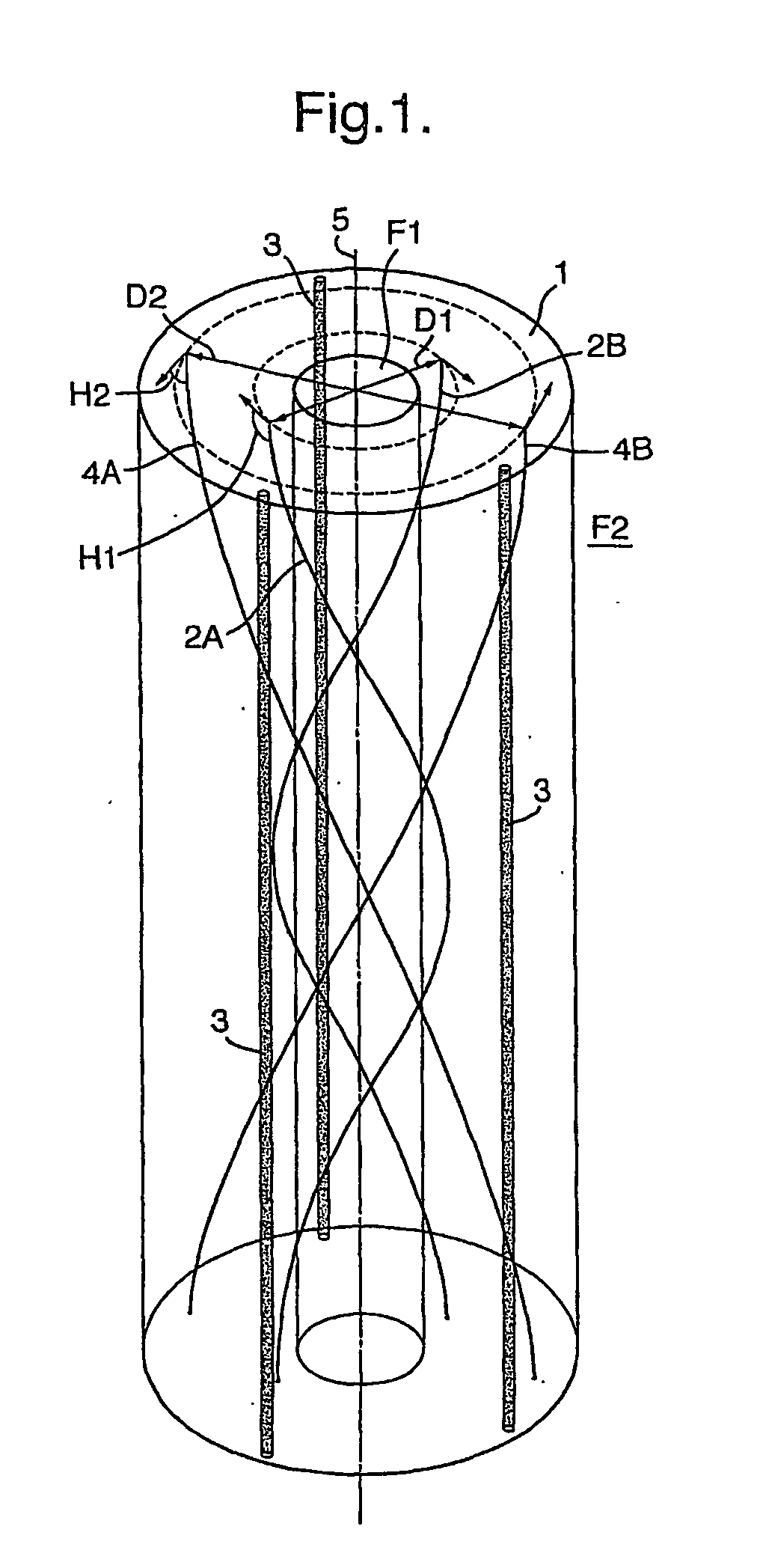
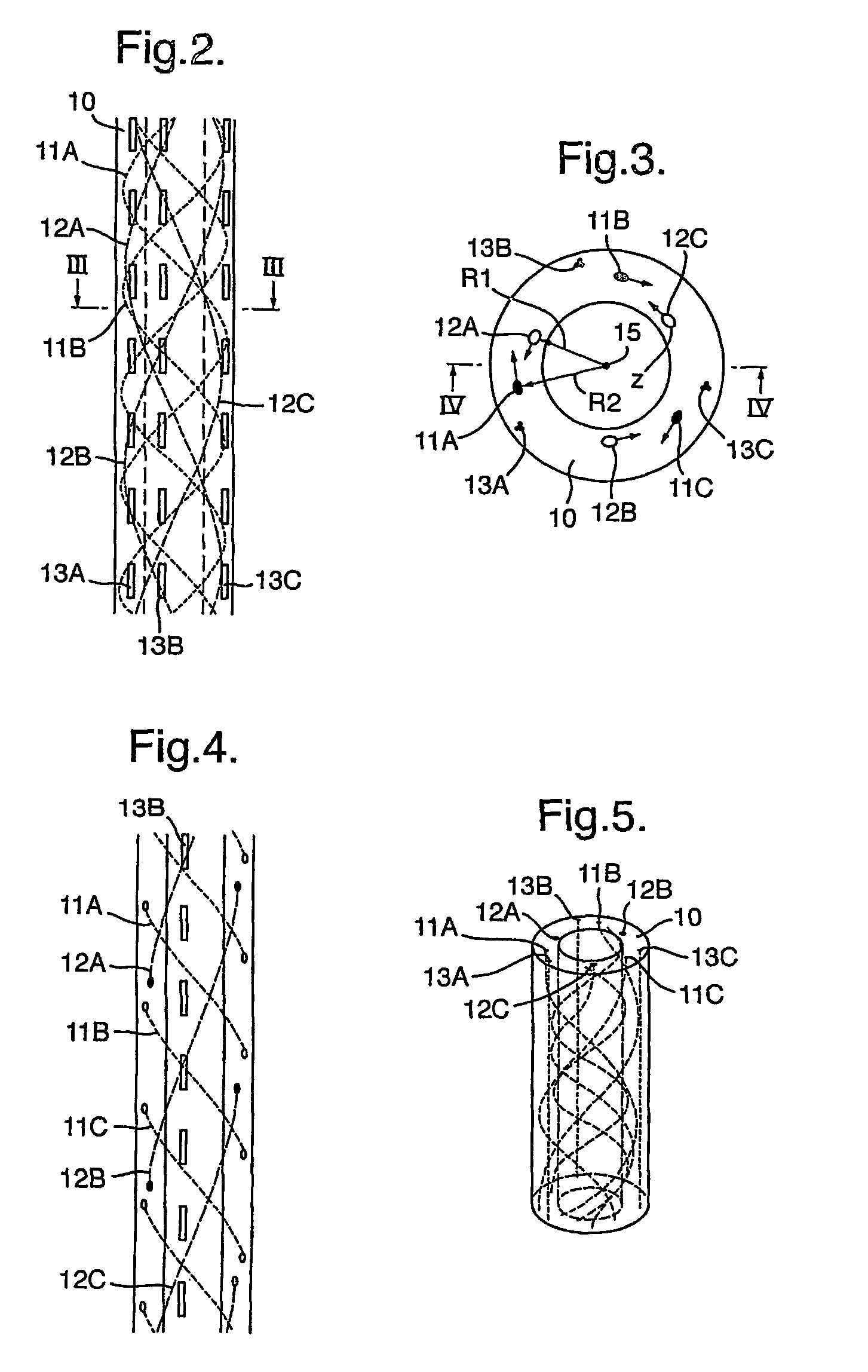
Coiled optical fiber assembly for measuring pressure and/or other physical data
A method and system are disclosed for measuring pressure and other physical data such as the temperature, elongation, torsion and bending at any point along the length of an elongate carrier tube by means of one or more coiled optical fibers that are embedded in the wall the tube such that deformation of the carrier tube induces strain in each optical fiber. In use a pulsed laser light source transmits a sequence of light pulses of a selected wavelength from an upstream end of each fiber into a coiled substantially uniform light guide channel provided by the optical fiber and a light sensor assembly detects any shift in wavelength of the light pulses backscattered from various locations along the length of the light guide channel. A signal processing assembly then calculates a strain pattern along the length of the fiber, and a pressure difference between the interior and exterior of the tube, at various locations along the length of the carrier tube. Preferably several fibers are wound at different pitch angles and in different directions and at different diameters in the wall of the carrier tube and the signal processing assembly calculates bending, torsion and both radial and axial deformation of the carrier tube on the basis of a comparison of the strain patterns induced on different optical fibers.
Owner:SHELL USA INC
Method and apparatus for determining an optimal pumping rate based on a downhole dew point pressure determination
ActiveUS20040231408A1Reduce capacityReduce pressureElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingFluid pressure measurement by electric/magnetic elementsLight energyDew
The present invention provides a down hole spectrometer for determination of dew point pressure to determine an associated optimal pumping rate during sampling to avoid precipitation of asphaltenes in a formation sample. A sample is captured at formation pressure in a controlled volume. The pressure in the controlled volume is reduced. Initially the formation fluid sample appears dark and allows less light energy to pass through a sample under test. The sample under test, however, becomes lighter and allows more light energy to pass through the sample as the pressure is reduced and the formation fluid sample becomes thinner or less dense under the reduced pressure. At the dew point pressure, however, the sample begins to darken and allows less light energy to pass through it as apshaltenes begin to precipitate out of the sample. Thus, the dew point is that pressure at which peak light energy passes through the sample. The dew point pressure is plugged into an equation to determine the optimum pumping rate for a known mobility, during sampling to avoid dropping the pressure down to the dew point pressure to avoid asphaltene precipitation or dew forming in the sample. The bubble point can be plugged into an equation to determine the optimum pumping rate for a known mobility, during sampling to avoid dropping the pressure down to the bubble point pressure to avoid bubbles forming in the sample.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Optical interferometric pressure sensor
InactiveUS20070089524A1Raise the gradeFluid pressure measurement by mechanical elementsFluid pressure measurement by optical meansOptical reflectionEngineering
A capacitive vacuum measuring cell has a first housing body and a membrane, both of Al2O3 ceramic or sapphire. The membrane is planar with a peripheral edge joined by a first seal to the first housing body to form a reference vacuum chamber. A second housing body of Al2O3 ceramic or sapphire opposite the membrane, is joined to the peripheral edge of the membrane by a second seal to form a measurement vacuum chamber. A port connects the vacuum measuring cell to a medium to be measured. At least in the central area of the first housing body, an optical transparent window is formed and at least the central region of the membrane has an optically reflective surface. Outside the reference vacuum chamber, in opposition to and at a distance from the window, an optical fibre is arranged for feeding in and out light onto the surface of the membrane.
Owner:INFICON GMBH
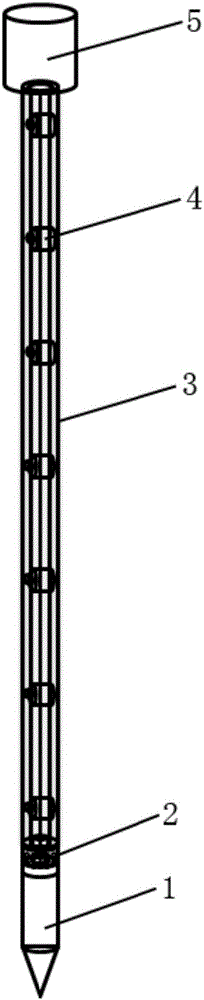
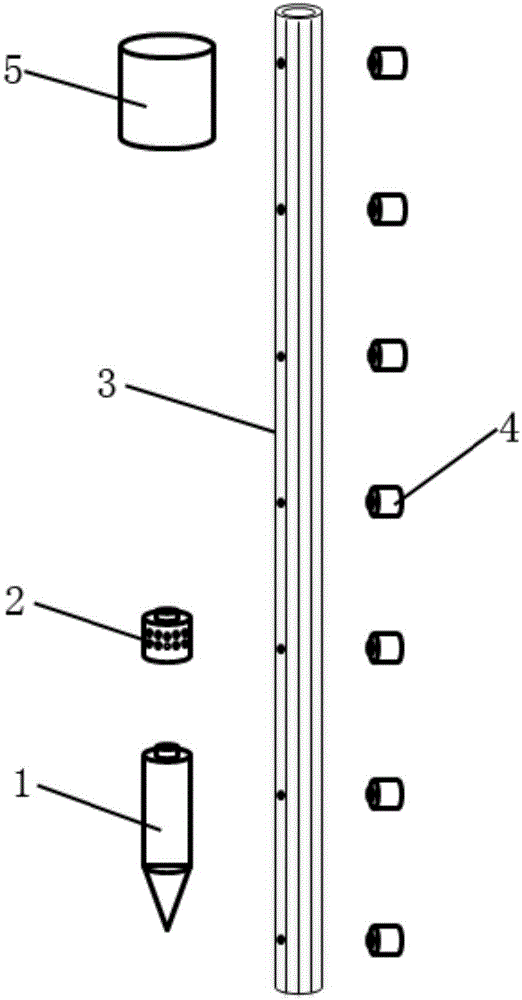
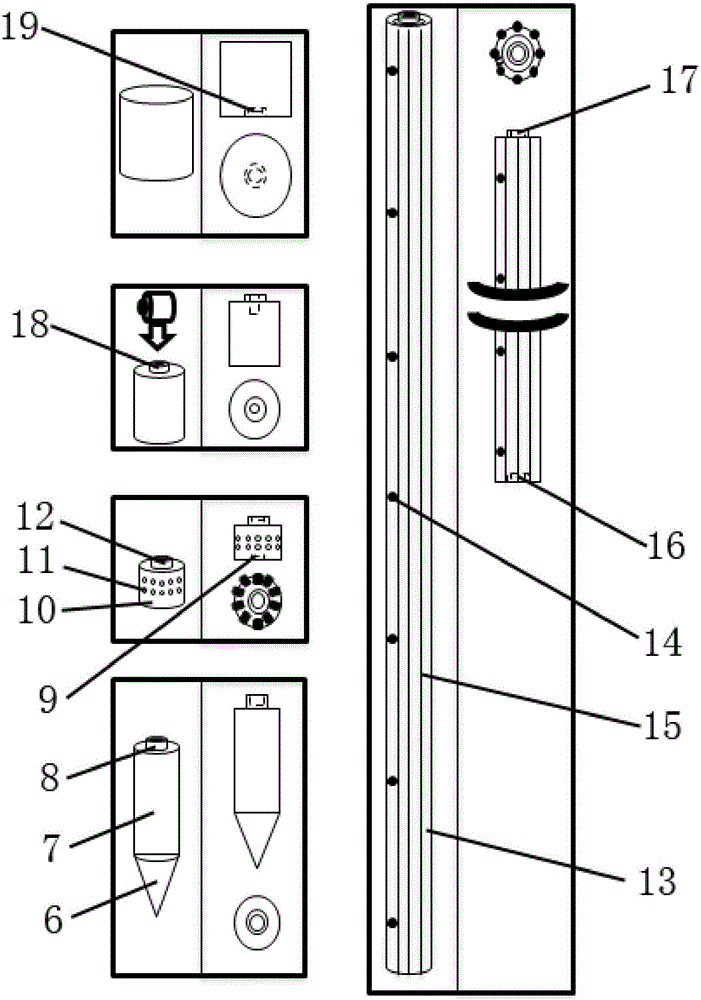
Penetration type multifunctional submarine sediment in-situ observation probe rod
ActiveCN106802132APore water pressure real-time monitoringPorosity real-time monitoringForce measurement by measuring optical property variationUsing optical meansProcess mechanismOcean bottom
The invention relates to a penetration type multifunctional submarine sediment in-situ observation probe rod, including a static sounding probe, a resistivity measuring module, a deformation measuring tube and a control cabin which are connected in sequence from bottom to top. The resistivity measuring module includes a resistivity measuring module main body, and point electrodes are distributed at equal intervals on the outer circumferential surface of the resistivity measuring module main body. The deformation measuring tube is of a tubular structure, includes a deformation rubber tube and embedded pore water pressure sensors inside the deformation rubber tube, eight stress and strain measuring optical fibers are distributed at equal intervals along an axial direction on the outer wall of the deformation rubber tube, a row of water drainage holes are distributed along the axial direction, and each water drainage hole is connected with an embedded pore water pressure sensor. The penetration type multifunctional submarine sediment in-situ observation probe rod provided by the invention can realize CPTU detection and can also perform long-term in-situ observation, and add dynamic change process observation of pore water pressure and sediment deformation of different depths; and deformation observation and pore pressure observation are effectively combined, and taking static sounding data for reference, and a dynamic change process mechanism of seabed sediments are interpreted from different angles.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF MARINE GEOLOGY
Coiled optical fiber assembly for measuring pressure and/or other physical data
A method and system are disclosed for measuring pressure and other physical data, such as the temperature, elongation, torsion and bending at any point along the length of an elongate carrier tube by means of one or more coiled optical fibers that are embedded in the wall the tube such that deformation of the carrier tube induces strain in each optical fiber. In use a pulsed laser light source transmits a sequence of light pulses of a selected wavelength from an upstream end of each fiber into a coiled substantially uniform light guide channel provided by the optical fiber and a light sensor assembly detects any shift in wavelength of the light pulses backscattered from various locations along the length of the light guide channel. A signal processing assembly then calculates a strain pattern along the length of the fiber, and a pressure difference between the interior and exterior of the tube, at various locations along the length of the carrier tube. Preferably several fibers are wound at different pitch angles and in different directions and at different diameters in the wall of the carrier tube and the signal processing assembly calculates bending, torsion and both radial and axial deformation of the carrier tube on the basis of a comparison of the strain patterns induced on different optical fibers.
Owner:SHELL USA INC
Pressure sensor assembly suitable for use in harsh environments
A sensor for sensing the pressure of a first fluid is provided. In one embodiment, sensor for sensing the pressure of a first fluid includes a fiber optic based sensing element disposed in a housing. A buffer fluid is disposed in the housing and is in fluid communication with the sensing element. A pressure transmitter is coupled to the housing for maintaining a predefined relationship between pressures of the first fluid and buffer fluid. A connector assembly is coupled to the housing and is coupled by an optical fiber is the sensing element. The sensor having a connector assembly is suitable for use in harsh conditions, such as within oil and gas well applications.
Owner:WEATHERFORD TECH HLDG LLC
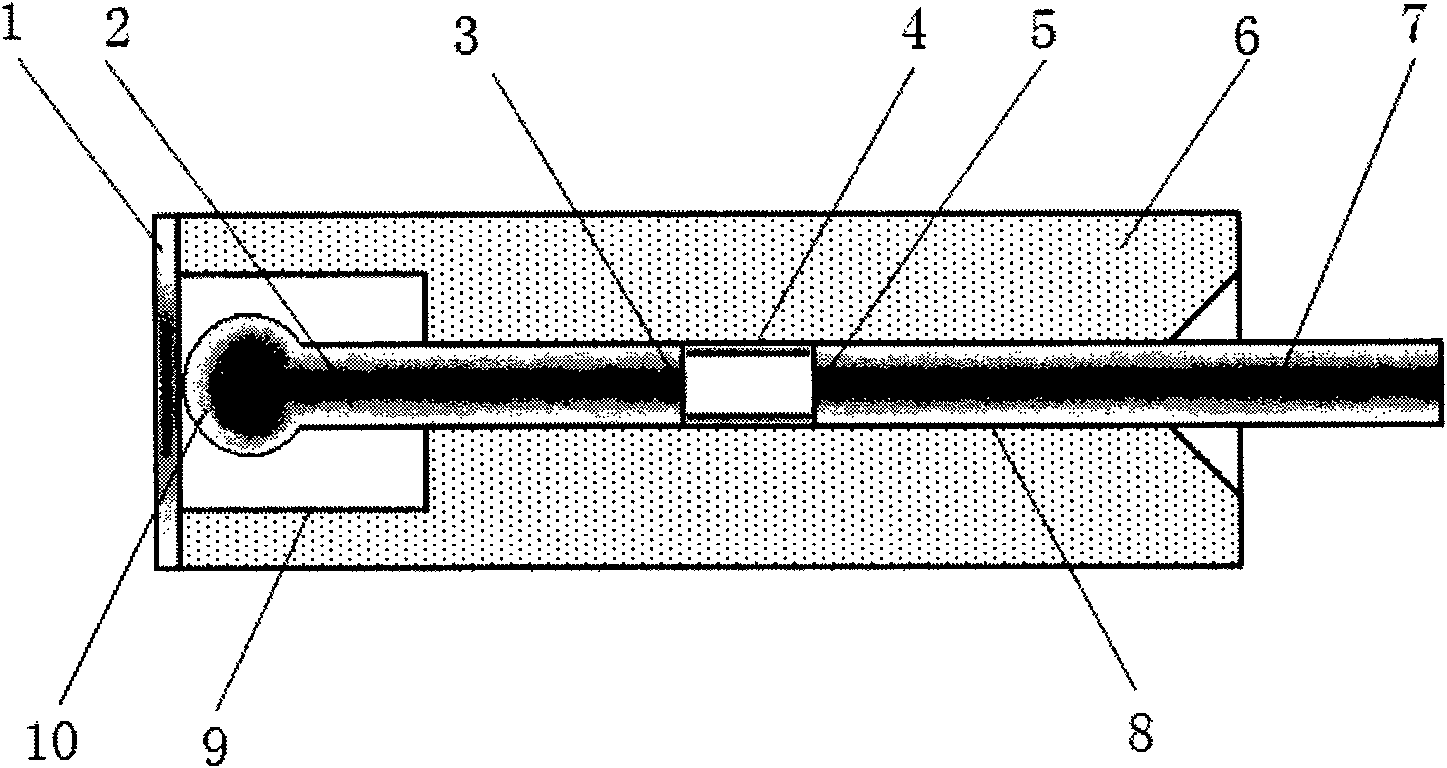
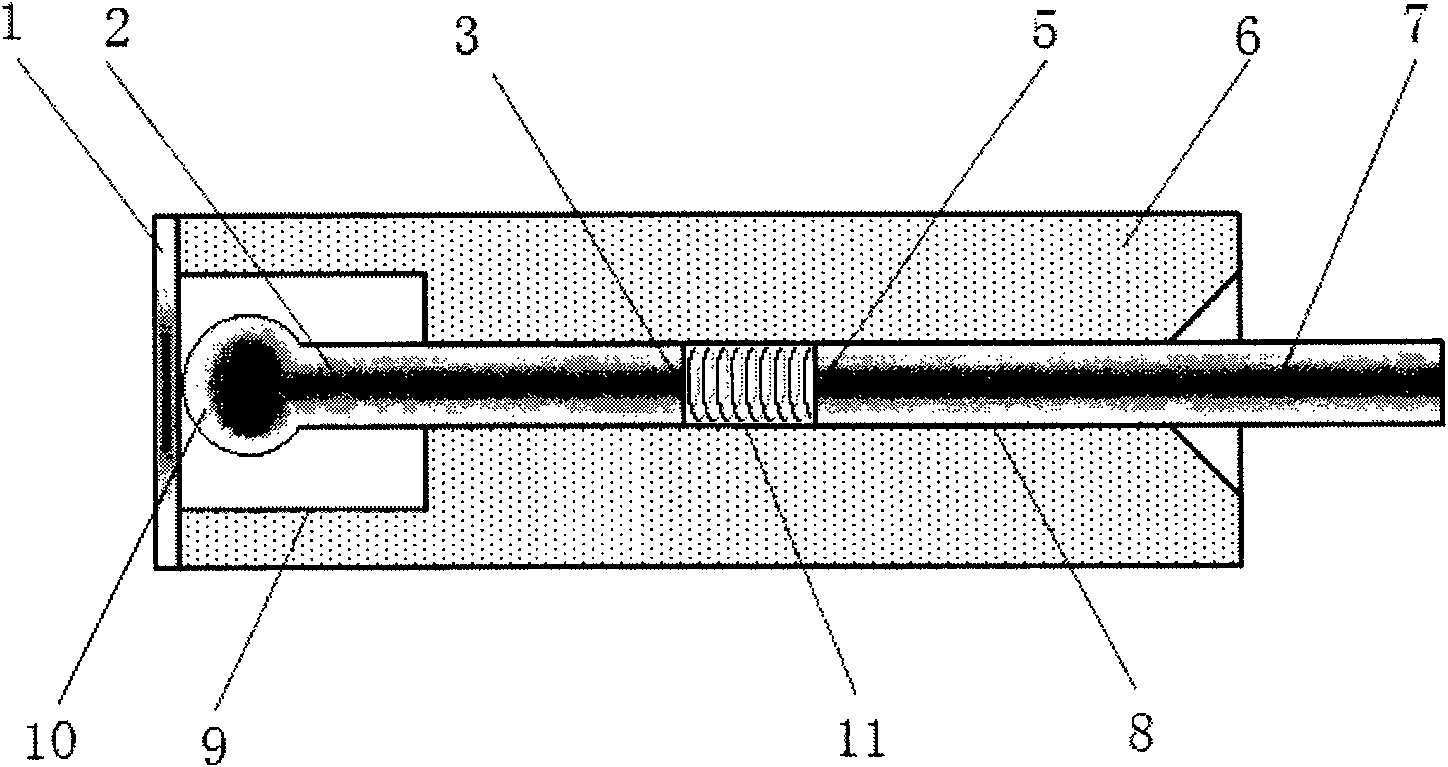
Optical fiber Fabry-Perot pressure sensor and fabrication method thereof
InactiveCN101858809AReduce measurement errorEnsure close contactCoupling light guidesFluid pressure measurement by optical meansEngineeringAlternative methods
The invention relates to a novel optical fiber Fabry-Perot pressure sensor and a fabrication method thereof. The optical fiber Fabry-Perot pressure sensor is used for detecting the relative pressure and absolute pressure of liquid and gas as well as sound wave signals, ultrasonic wave signals and the like. The structure of the optical fiber Fabry-Perot pressure sensor mainly comprises an optical fiber, an elastic diaphragm, a sensor body and a miniature spring. Two methods and an alternative method can be adopted to form a Fabry-Perot cavity and fabricate the sensor. The elastic diaphragm and the sensing optical fiber are tightly contacted in a plane-sphere point contact manner; when the outside pressure is changed to cause the deformation of the elastic diaphragm, the diaphragm can drive the optical fiber to axially move in the sensor body, so that the length of the Fabry-Perot cavity of the optical fiber is changed; after a broadband light source is connected, by scanning the spectrum of the light passing through the optical fiber Fabry-Perot pressure sensor or extracting low-coherence interference fringes, the change of the cavity length can be extracted, and thereby pressure information can be obtained. The structure can avoid the defect that the diaphragm of the conventional optical fiber Fabry-Perot pressure sensor cannot be over-deformed, and can obtain higher measurement precision.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Optical fiber distributed temperature and stress sensing device
InactiveCN101158592AAddress cross-sensitivity issuesSolving Measurement Range IssuesForce measurement by measuring optical property variationThermometers using physical/chemical changesObservational errorDiscriminator
The invention discloses a sensing device of optical fiber distribution type temperature and stress and mainly comprises a light source module (1), a frequency discriminator module (2), and a thermo tank module (3), which are all connected with one another by polarization-preserving fiber. The invention is a direct detection method which is based on optical fiber Raman scattering used as a carrier wave of temperature information, brillouin scattering used as a carrier wave of stress, rayleigh scattering used for measuring relative frequency of a outgoing laser beam to a frequency discriminator and Fabry-Perot etalon used for discriminating frequency and distributing sensing temperature and stress. The invention has the advantages of simple structure, fine stability, avoidance of outgoing power of the light source during coherent detection, outgoing frequency of the light source. Instability of acoustic modulation or electro-optic modulation frequency is directly referred to measure errors and the direct detection technology of the frequency discrimination is not sensitive to frequency drift of the light source and fluctuation of signal intensity.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
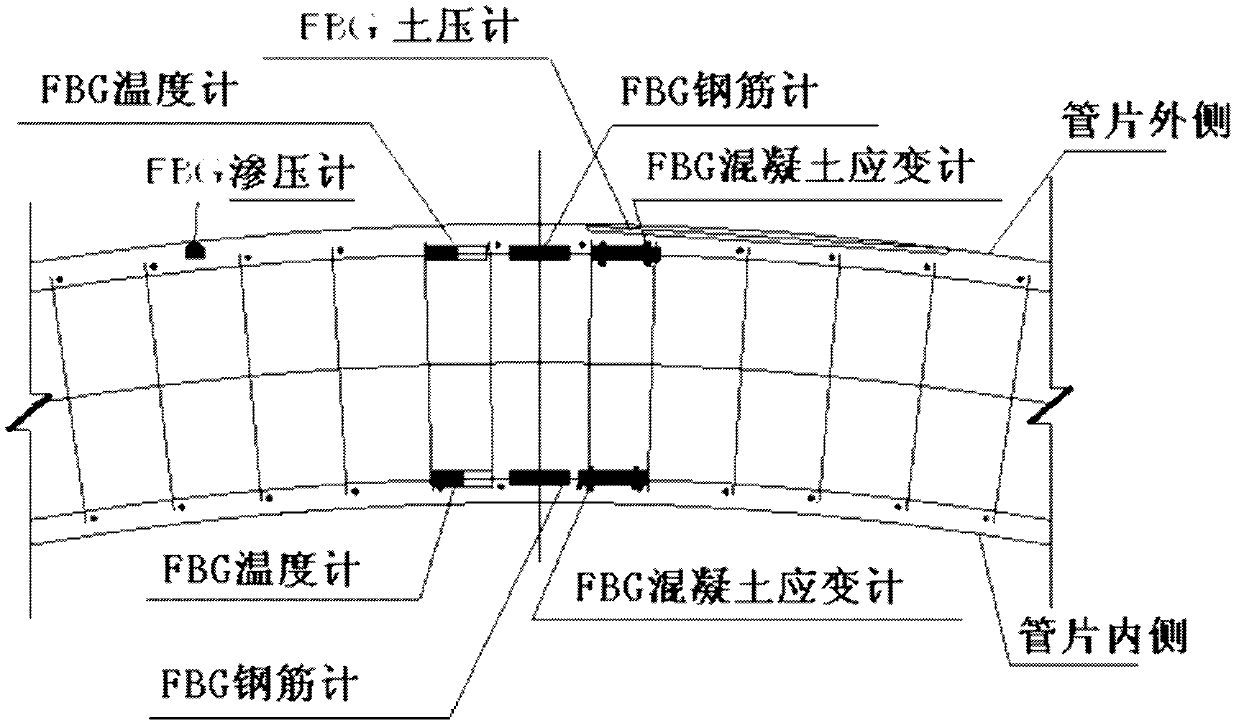
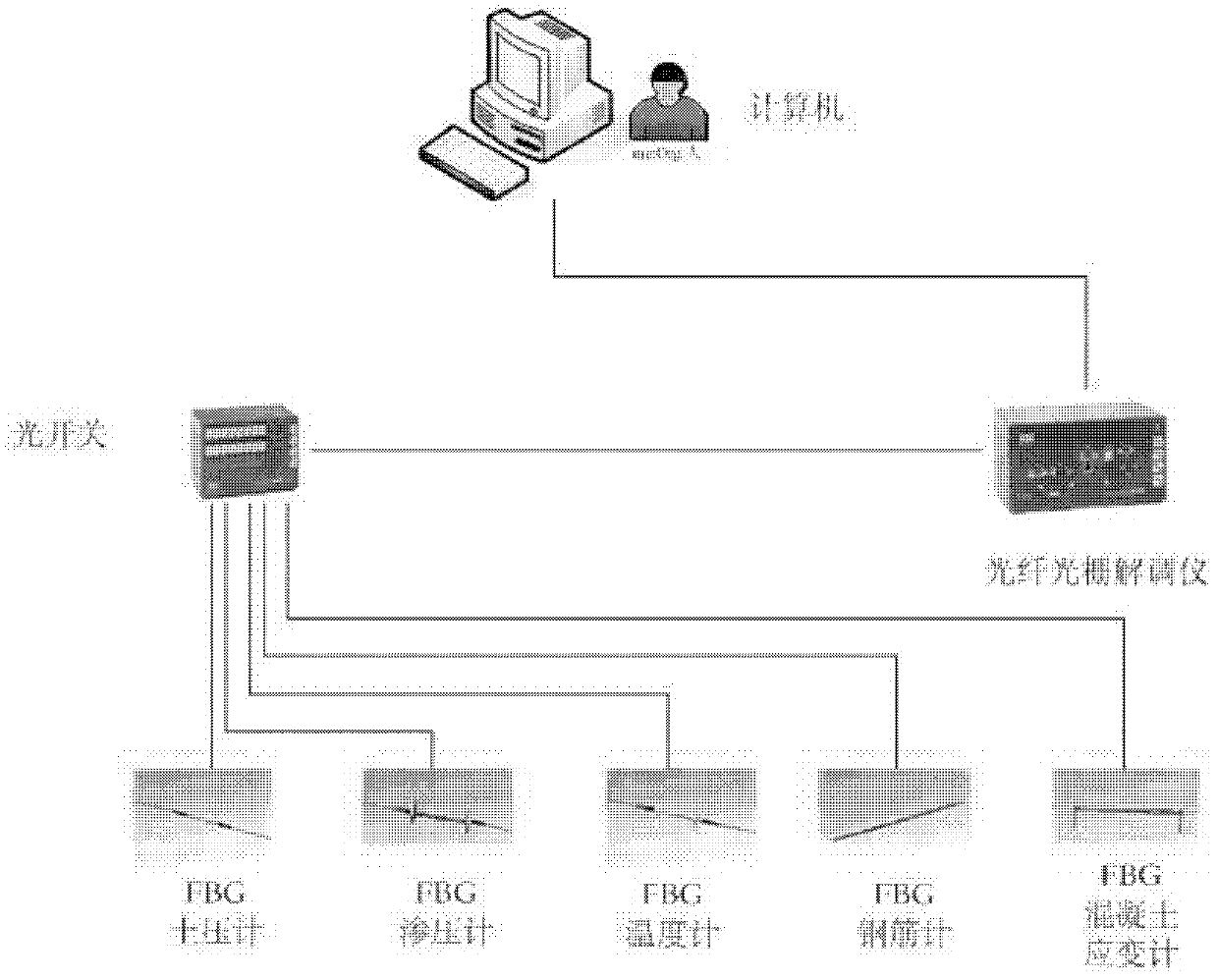
Multi-parameter real-time monitoring method and system for synchronous grouting behind segment wall of shield tunnel
ActiveCN103123252AFlexible and convenient layoutThe test effect is goodForce measurement by measuring optical property variationThermometers using physical/chemical changesGratingPore water pressure
The invention discloses a method and system for monitoring a plurality of control parameters of a synchronous grouting process behind a segment wall during shield tunnel piercing construction in a fiber grating sensing and optical fiber communication mode. The method and system is mainly characterized in the remote and real-time multi-parameter monitoring, namely various fiber grating sensors which are pre-buried in segment control positions are used to perform remote and real-time monitoring on control parameters of pore water pressure, soil pressure, segment temperature, concrete stress, rebar stress and other control parameters in synchronous grouting process behind a segment wall, and the grouting pressure can be adjusted according to the monitoring data so as to ensure the grouting to be finished smoothly and ensure the grouting quality. The method and system is strong in practical applicability and feasibility, can monitor any link in the synchronous grouting construction behind the tunnel segment wall and can improve the controllability of the synchronous grouting process and the grouting quality.
Owner:NANJING UNIV +1
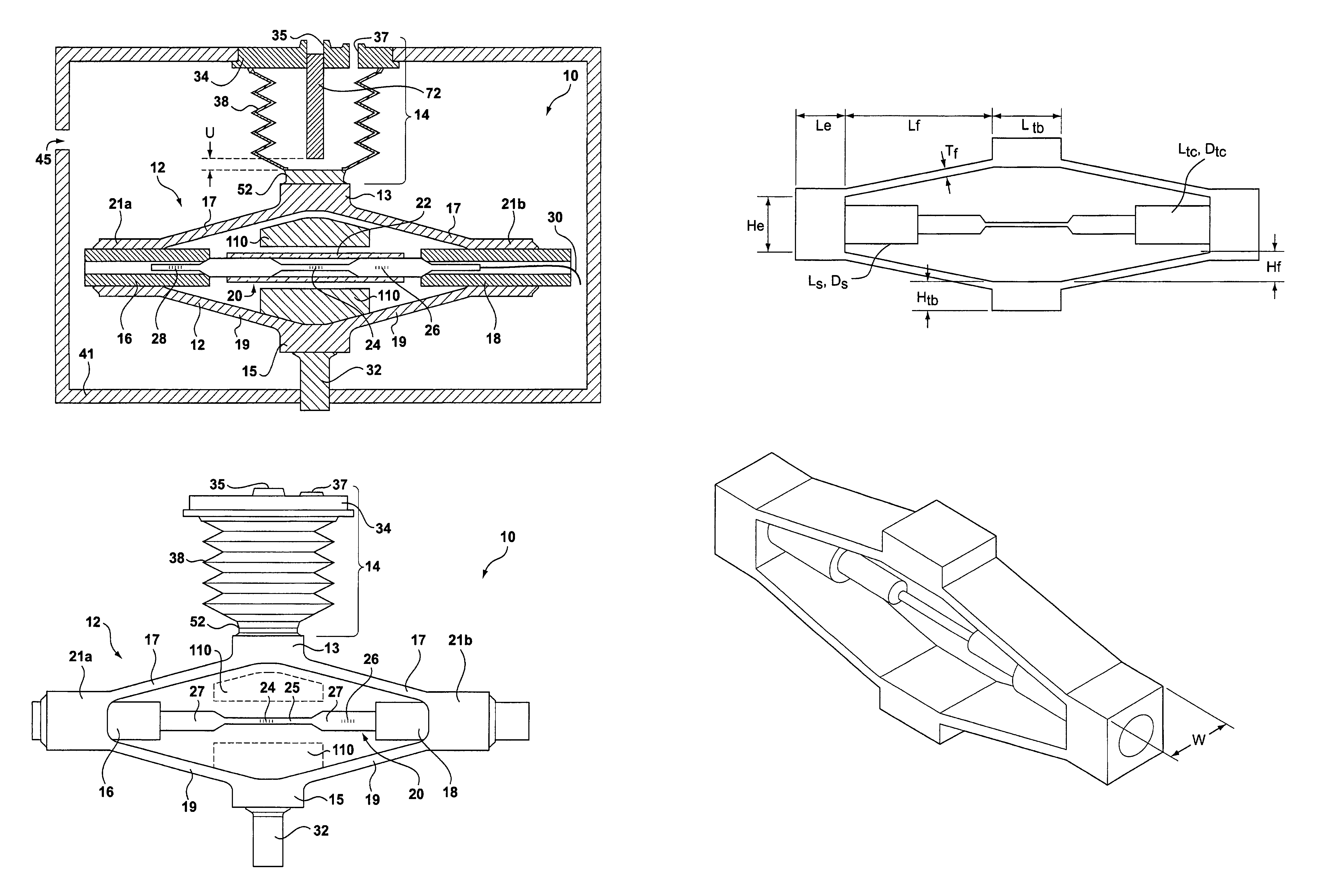
Optical differential pressure transducer utilizing a bellows and flexure system
InactiveUS7047816B2Fluid pressure measurement using elastically-deformable gaugesFluid pressure measurement by electric/magnetic elementsFiberGrating
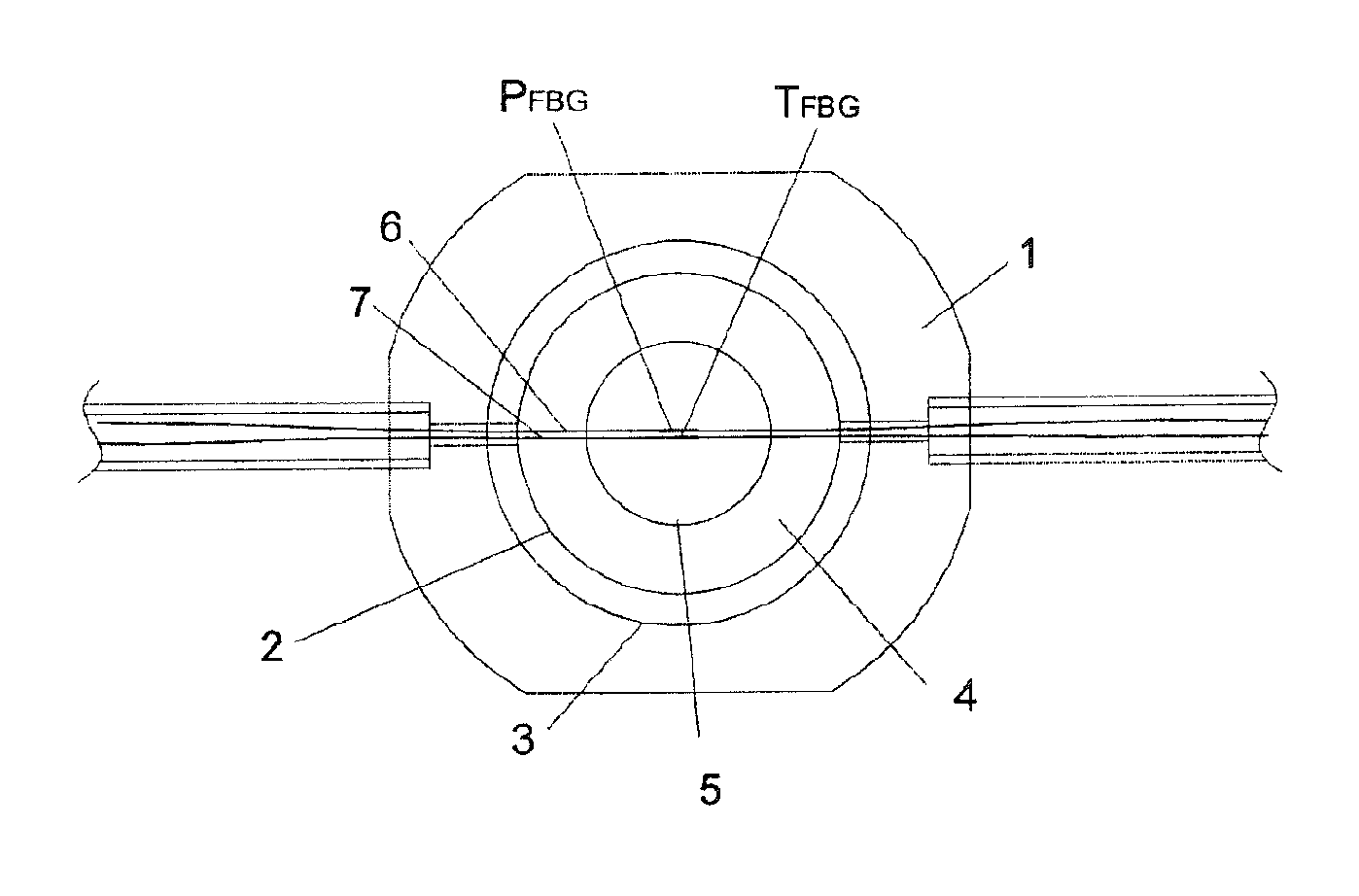
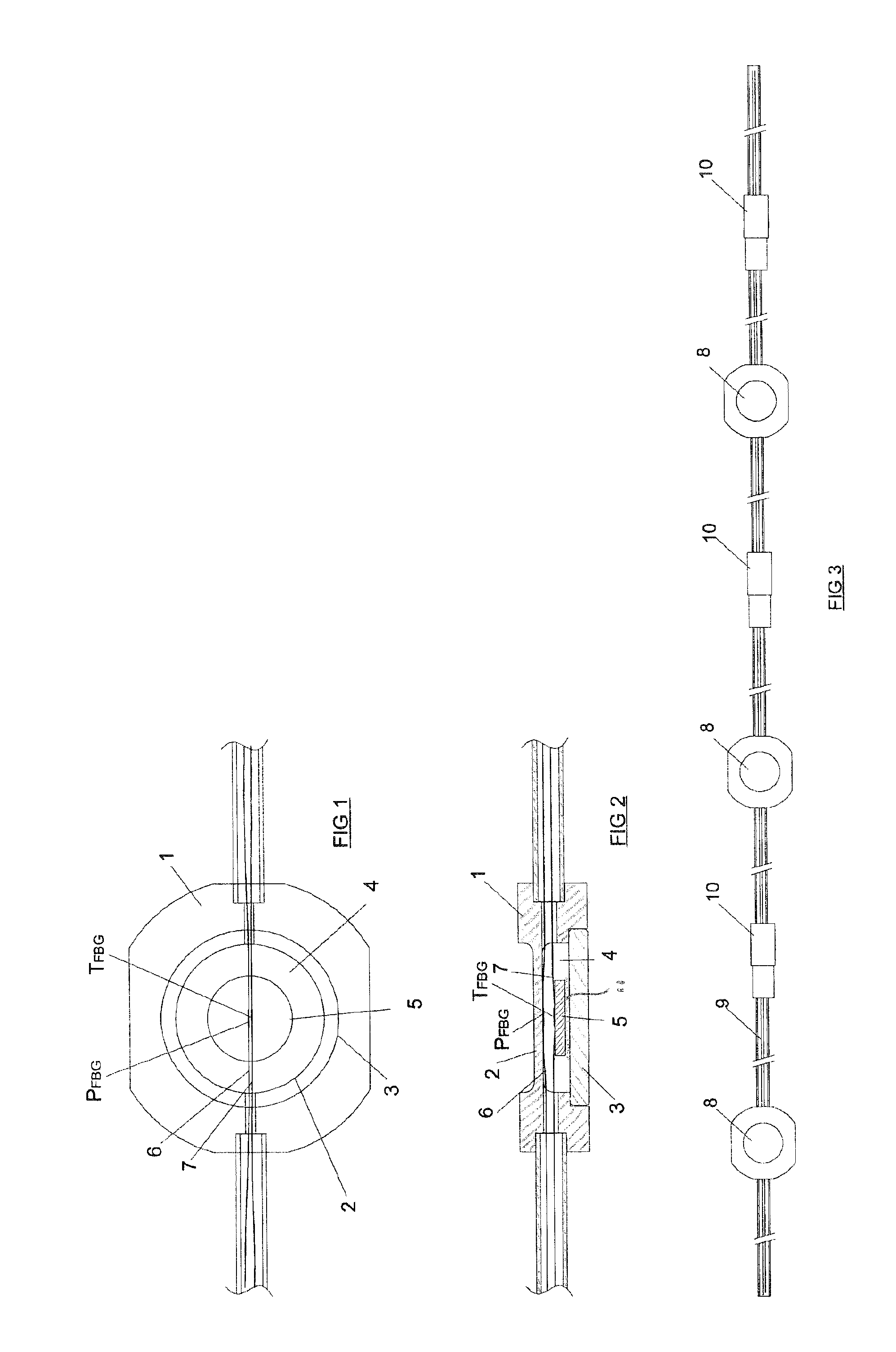
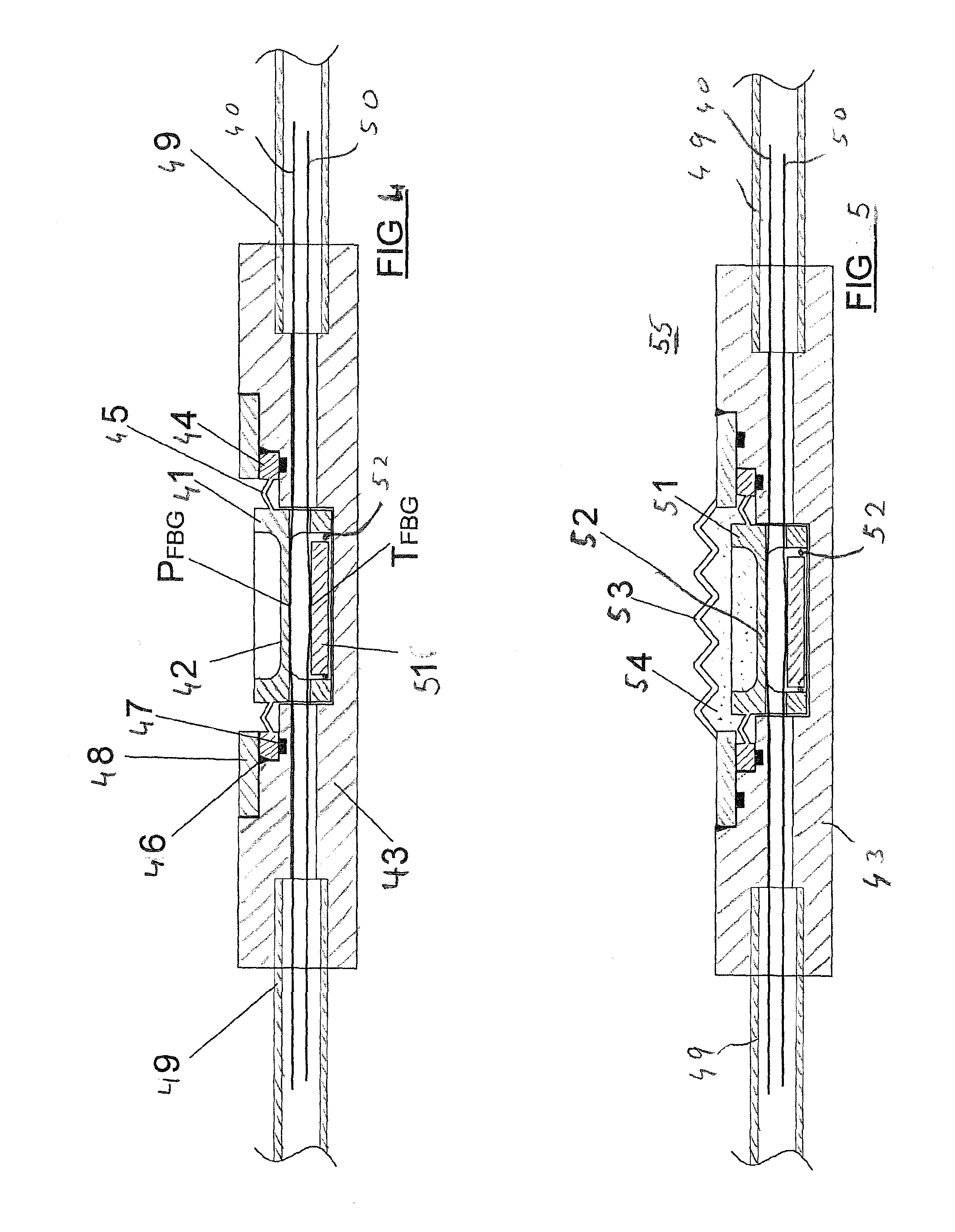
A pressure transducer that uses a rhomboidal flexure to provide displacement amplification to an optical sensing element is disclosed. The transducer includes an optical sensor disposed between sides of the flexure. The top portion of the flexure connects to a displacement device, such as a bellows. A first pressure port provides a first pressure to the bellows. A second pressure, preferably greater than the first pressure, is ported into a housing containing the flexure, which tends to compress the bellows and pull apart or expand the flexure. Such expansion pinches or compresses the optical sensing element between the sides of the flexure, and in particular stresses an optical sensing element containing a fiber Bragg grating. Assessing the Bragg reflection wavelength of the grating allows the differential pressure to be determined, although the transducer can also be used to sense an absolute pressure. A temperature compensation scheme, including the use of additional fiber Bragg gratings and thermal compensators axially positioned to counteract thermal effects of the optical sensing element, is also disclosed.
Owner:WEATHERFORD TECH HLDG LLC
Detecting method suitable for optical fiber distributed temperature and stress sensing device
InactiveCN101158591AAddress cross-sensitivity issuesSolve the problem of measuring range of large temperature 0~400℃Force measurement by measuring optical property variationThermometers using physical/chemical changesDiscriminatorRayleigh scattering
The invention discloses a detection method suitable for a sensing device of optical fiber distribution type temperature and stress. The sensing device of the optical fiber distribution type temperature and stress mainly comprises a light source module (1), a frequency discriminator module (2), and a thermo tank module (3), which are all connected with one another by polarization-preserving fiber. The detection method of the invention is a direct detection method which is based on optical fiber Raman scattering used as a carrier wave of temperature information, brillouin scattering used as a carrier wave of stress, rayleigh scattering used for measuring the relative frequency of a outgoing laser beam to the frequency discriminator and Fabry-Perot etalon used for discriminating frequency and distributing sensing temperature and stress. The invention has the advantages of simple structure, fine stability, avoidance of outgoing power of the light source during coherent detection, and outgoing frequency of the light source. Instability of acoustic modulation or electro-optic modulation frequency is directly referred to measure errors and the direct detection technology of frequency discrimination is not sensitive to the frequency drift of the light source and the fluctuation of signal intensity.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Optical fiber temperature-depth diving mark continuous measuring system
ActiveCN103759717AScientific and reasonable designHigh spatio-temporal resolutionMeasuring open water depthThermometers using physical/chemical changesSea temperatureBuoy
The invention relates to marine hydrology parameter monitoring, and particularly discloses an optical fiber temperature-depth diving mark continuous measuring system. The system comprises a communication buoy, a main floating ball, an instrument bin, a demodulating system, a temperature-depth chain, a mooring rope, an acoustical releaser and an anchoring weight, wherein the communication buoy comprises a solar cell, a big dipper communication plate card and a satellite combined antenna; the demodulating system comprises a demodulation module and a lithium battery and is arranged in the instrument bin, and the temperature-depth chain integrates a temperature sensor and a pressure sensor for measuring temperature and pressure, and the communication buoy, the main floating ball, the instrument bin, the temperature-depth chain, the releaser and the anchoring weight are successively connected through the mooring rope. The optical depth diving mark continuous measuring system provided by the invention has the advantages that the high density, real time, continuation and long-term observation of a temperature-depth vertical section from a sea surface to 500m underwater are realized, the data is exact and reliable, and the economic benefit is high; the optical fiber temperature-depth diving mark continuous measuring system is widely applied in different marine observation operations and provides a novel observation means for measuring sea temperature-depth.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Side-hole cane waveguide sensor
A side-hole optical cane for measuring pressure and / or temperature is disclosed. The side-hole cane has a light guiding core containing a sensor and a cladding containing symmetrical side-holes extending substantially parallel to the core. The side-holes cause an asymmetric stress across the core of the sensor creating a birefringent sensor. The sensor, preferably a Bragg grating, reflects a first and second wavelength each associated with orthogonal polarization vectors, wherein the degree of separation between the two is proportional to the pressure exerted on the core. The side-hole cane structure self-compensates and is insensitive to temperature variations when used as a pressure sensor, because temperature induces an equal shift in both the first and second wavelengths. Furthermore, the magnitude of these shifts can be monitored to deduce temperature, hence providing the side-hole cane additional temperature sensing capability that is unaffected by pressure. Additionally, the side-hole cane can be used to measure a differential pressure between a first pressure ported to the side-holes and a second external pressure.
Owner:WEATHERFORD TECH HLDG LLC
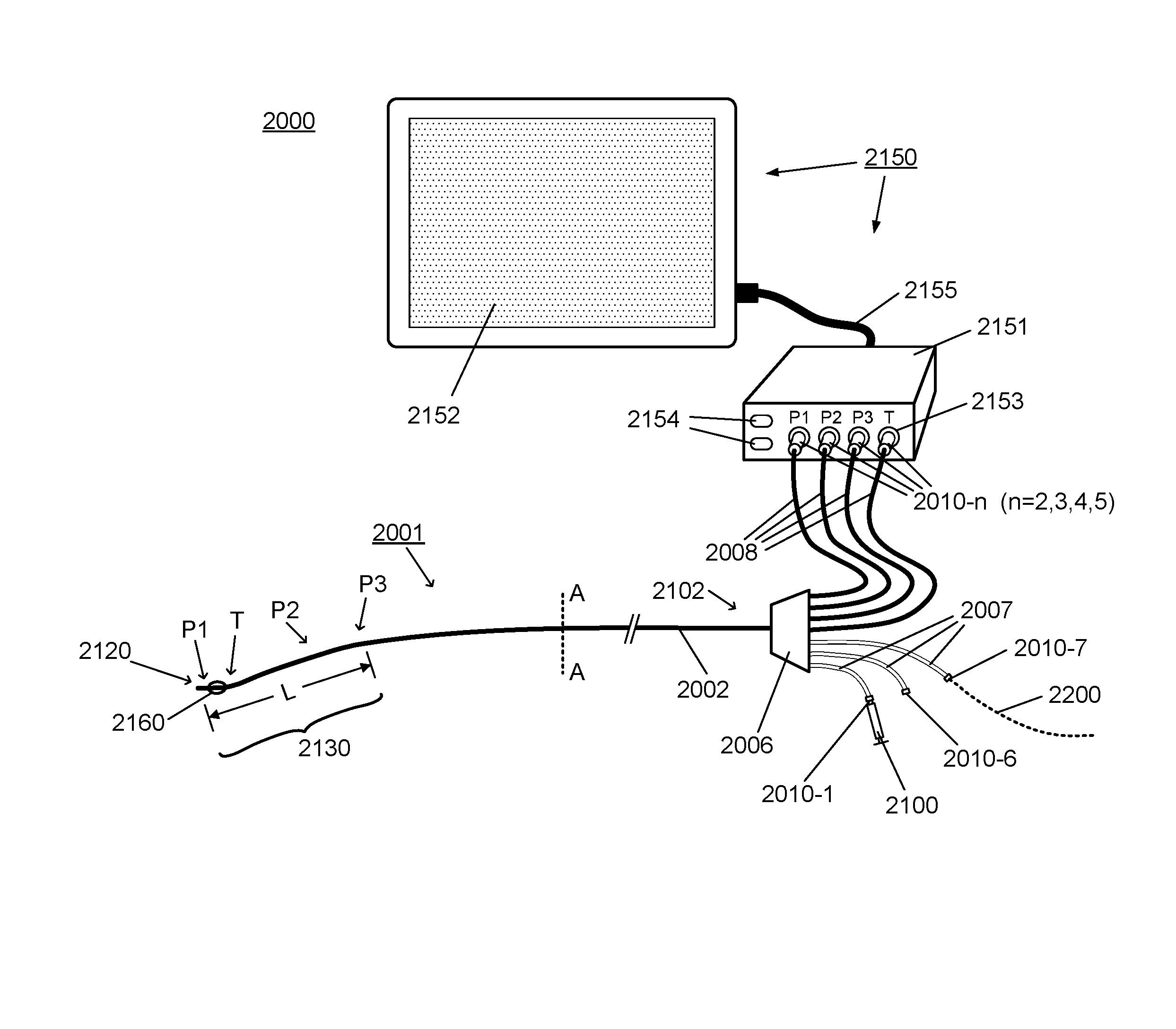
System and apparatus comprising a multi-sensor catheter for right heart and pulmonary artery catheterization
ActiveUS20170027458A1Reduce oneReduce disadvantagesMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesHeart valvesAtrial cavityRight atrium
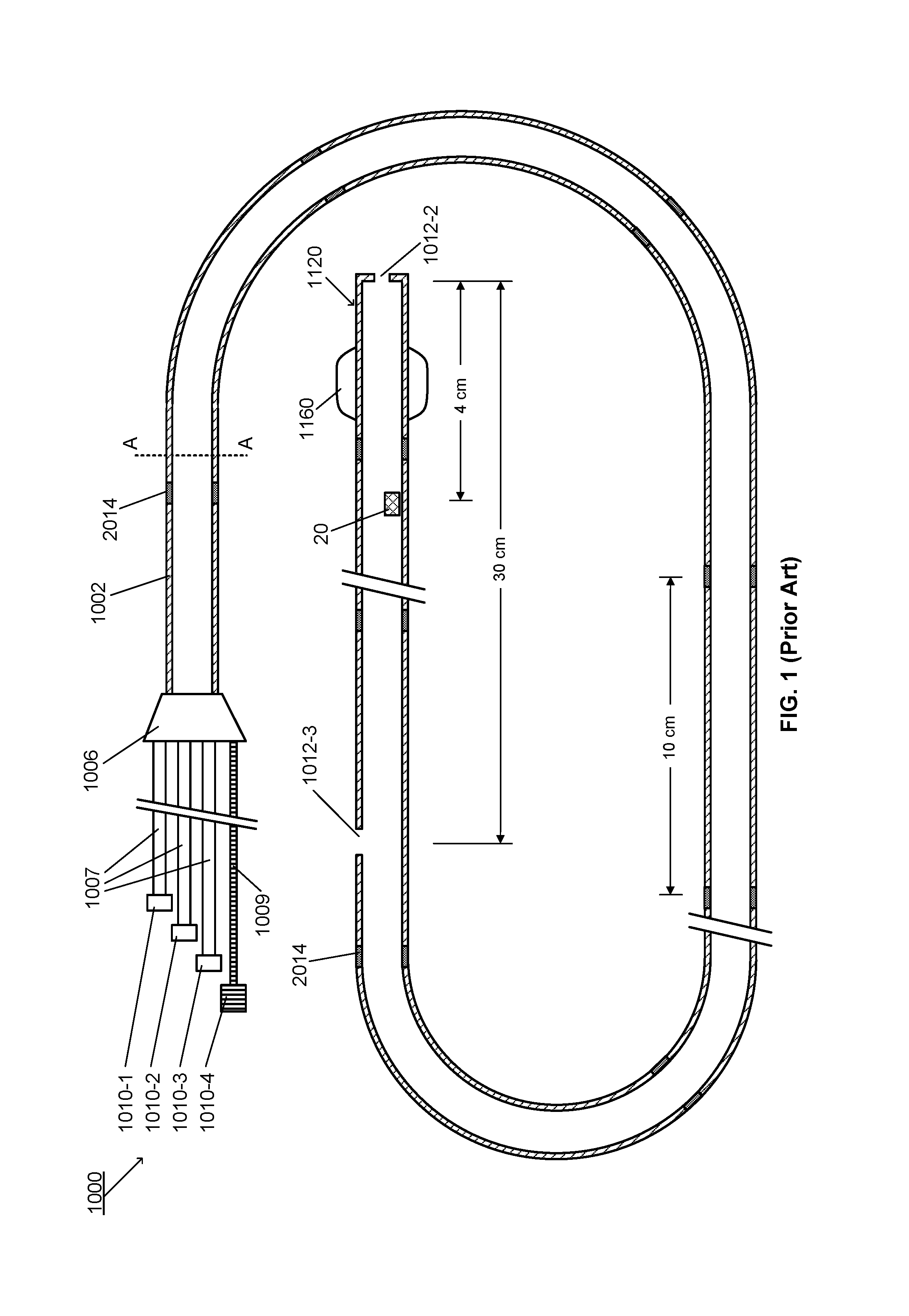
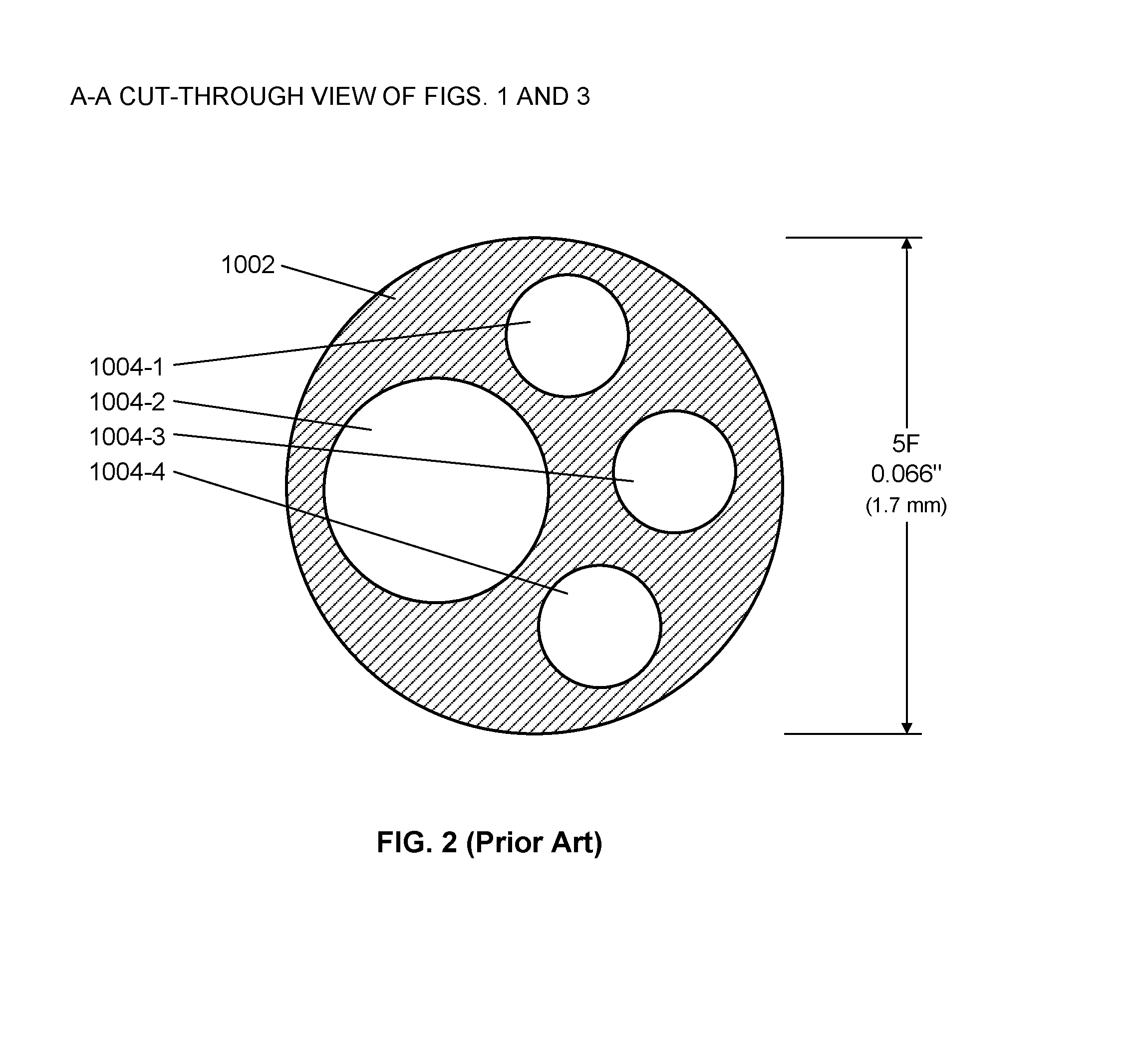
A system and apparatus comprising a multi-sensor catheter for right heart and pulmonary artery catheterization is disclosed. The multi-sensor catheter comprises multi-lumen catheter tubing into which at least three optical pressure sensors, and their respective optical fibers, are inserted. The three optical pressure sensors are arranged within a distal end portion of the catheter, spaced apart lengthwise within the distal end portion for measuring pressure concurrently at each sensor location. The sensor locations are configured for placement of at least one sensor in each of the right atrium, the right ventricle and the pulmonary artery, for concurrent measurement of pressure at each sensor location. The sensor arrangement may further comprise an optical thermo-dilution sensor, and another lumen is provided for fluid injection for thermo-dilution measurements. The catheter may comprise an inflatable balloon tip and a guidewire lumen, and preferably has an outside diameter of 6 French or less.
Owner:HEMOCATH LTD
Fabry-Perotw fiber-optic pressure sensor and manufacture method therefor
InactiveCN101017116AAvoid influenceEasy to manufactureForce measurement by measuring optical property variationCoupling light guidesFiberCutting glass
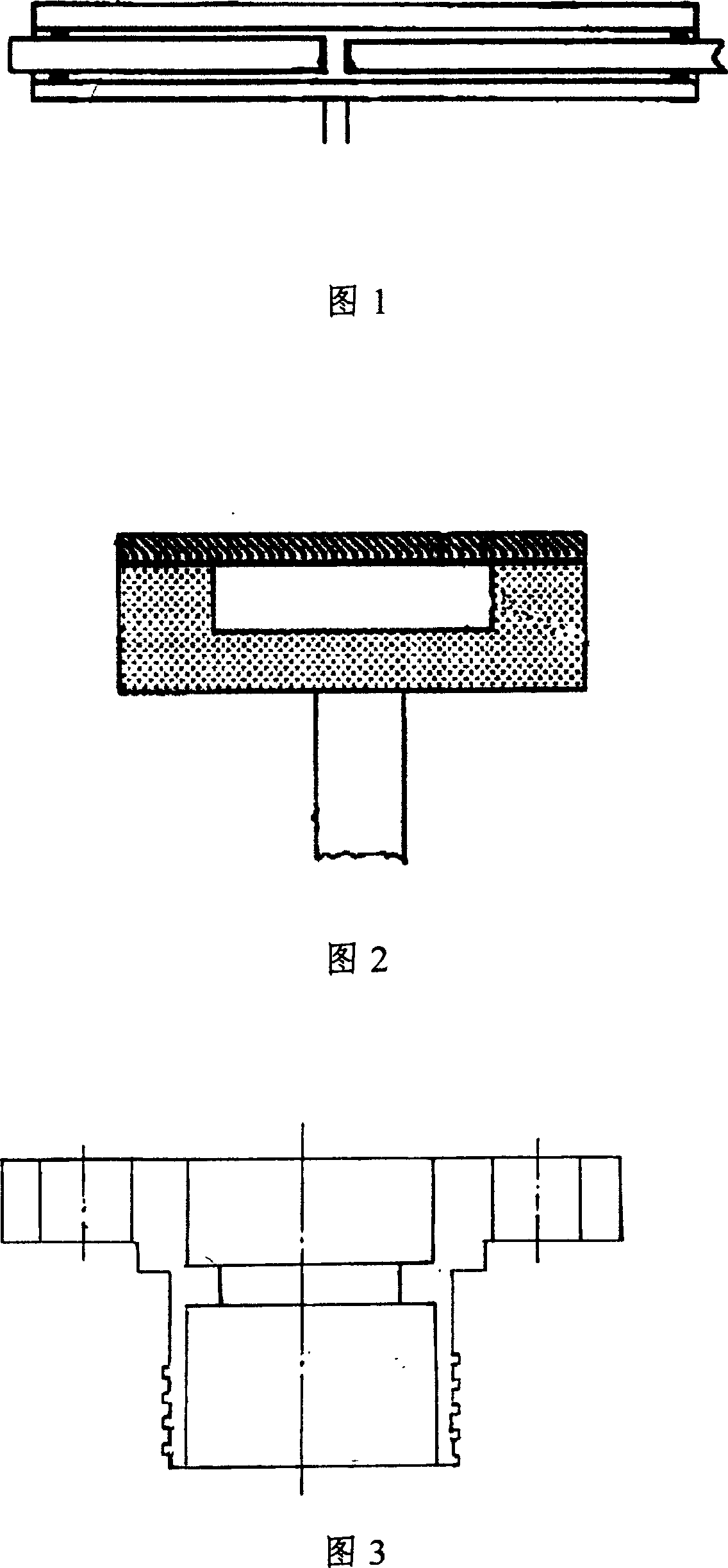
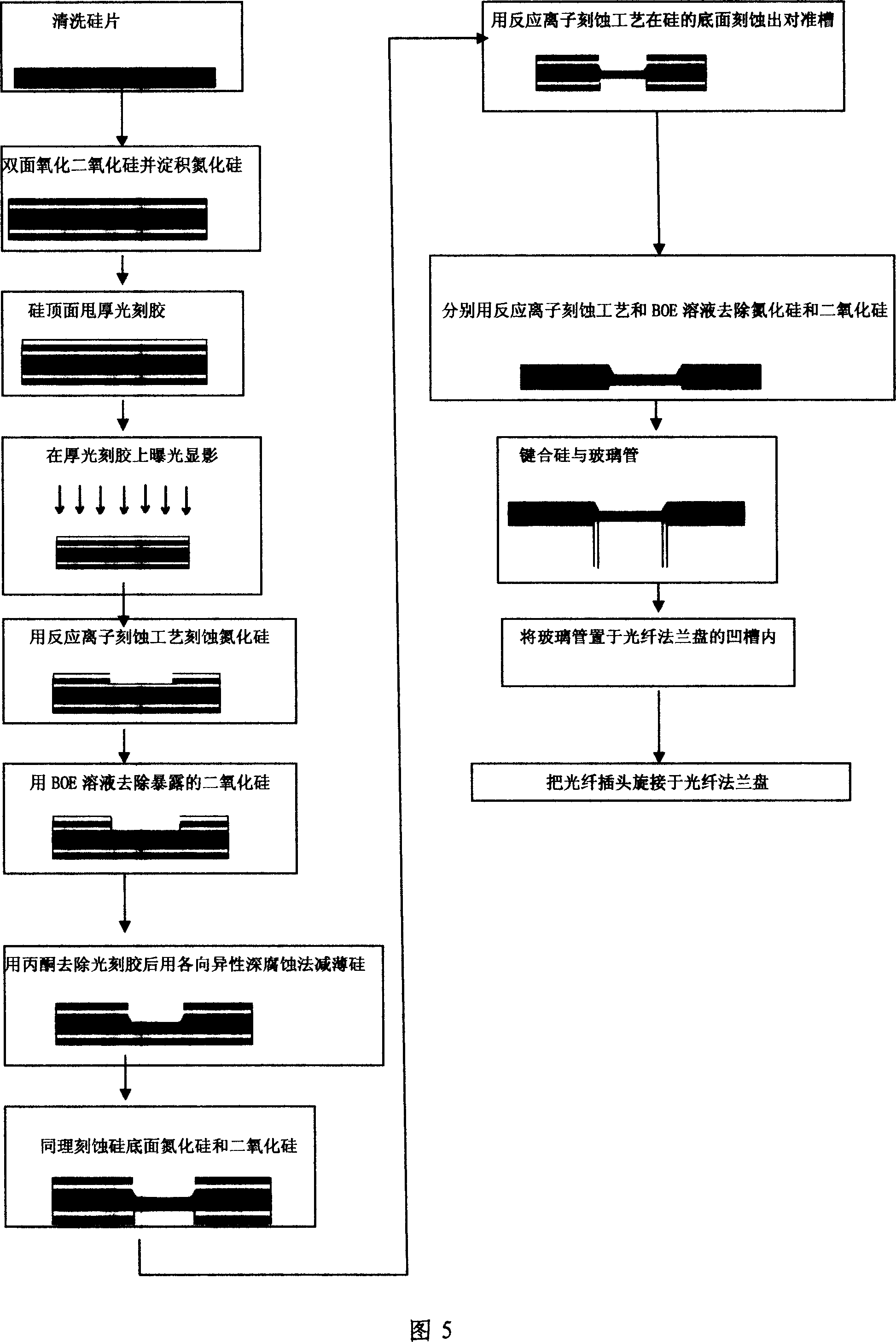
This invention discloses one Fabry-Perot fiber pressure sensor, which comprises single silicon slice, glass round tube, fiber flange disc and fiber plug and is characterized by the following: the single silicon slice and glass round tube one end are connected through anode keys; other end of round tube is added to fiber flange disc tank; the fiber plug is connected to flange disc with ceramics needle and silicon slice form the chamber. This invention also discloses one method for it, which comprises the following steps: putting the cut glass tube and silicon slice onto key furnace; the glass tube outer wall is coasted with epoxy resin to flange concave tank; connecting the fiber plug into fiber flange disc to form the chamber.
Owner:NANJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
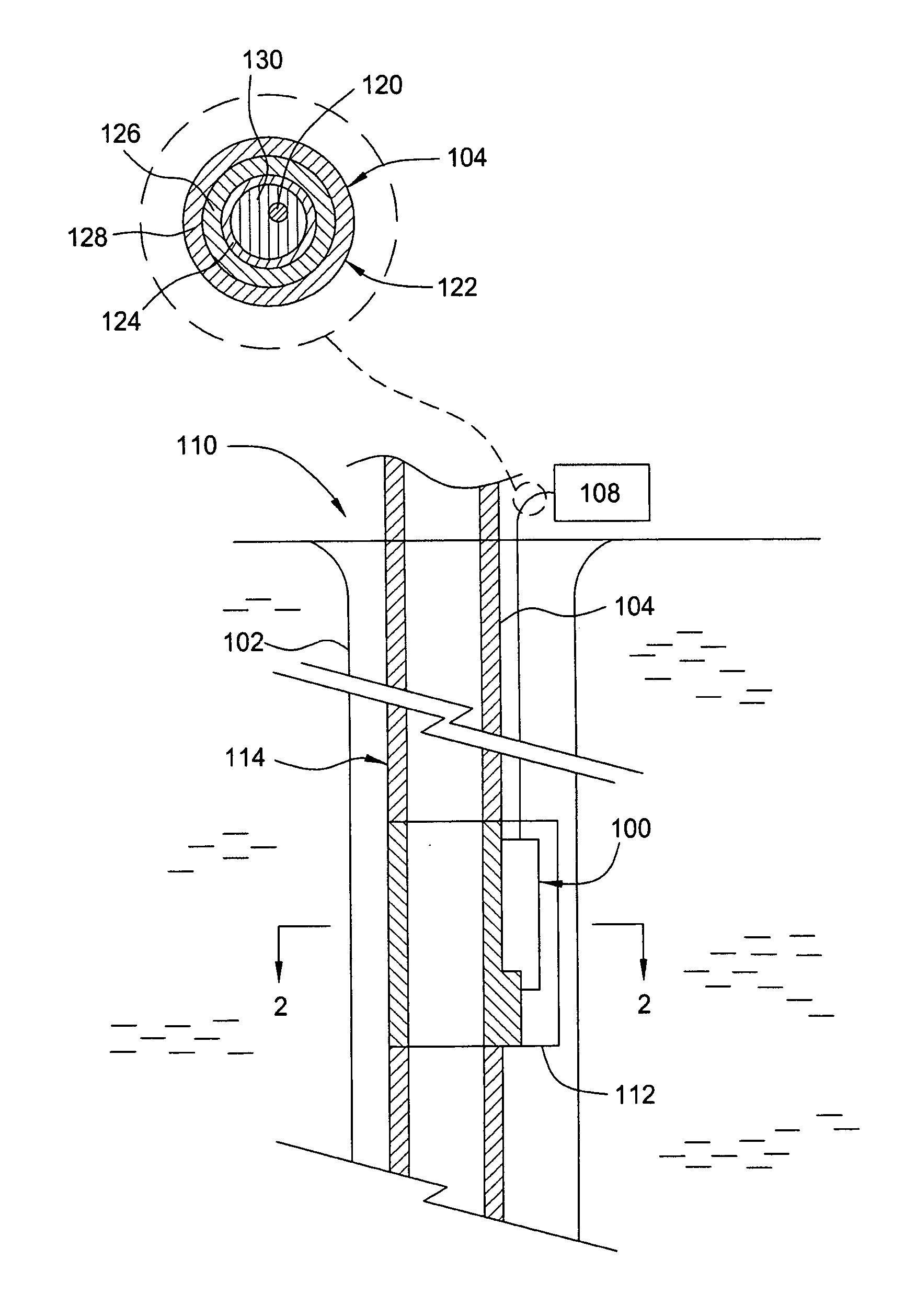
Fiber optic based method and system for determining and controlling position of a sliding sleeve valve
InactiveUS6995352B2Improve accuracy and reliabilityPhotometry using reference valueSurveyFiberSleeve valve
An apparatus and method for determining the position of a hydraulically actuated sliding sleeve valve in real time is disclosed. The apparatus comprises, in a preferred embodiment, a reference sensor and a position sensor, both of which constitute fiber optic windings wound around the hydraulic fluid cavity used to activate the sleeve. The sensors measure the pressure exerted by the hydraulic fluid in the cavity, with the reference sensor circumferentially lengthening to create an optical time delay indicative of the base line pressure of the hydraulic fluid. As the sleeve moves, the position sensor becomes increasingly exposed to the hydraulic fluid pressure and also begins to experience a time delay, which can be compared to the reference sensor's time delay to determine sleeve position.
Owner:WEATHERFORD TECH HLDG LLC
Method and apparatus for detecting pressure distribution in fluids
ActiveUS7940389B2Useful in detectionNot easy to detectFluid speed measurement using pressure differenceForce measurementPressure senseSingle mode fiber transmission
Owner:VIAVI SOLUTIONS INC
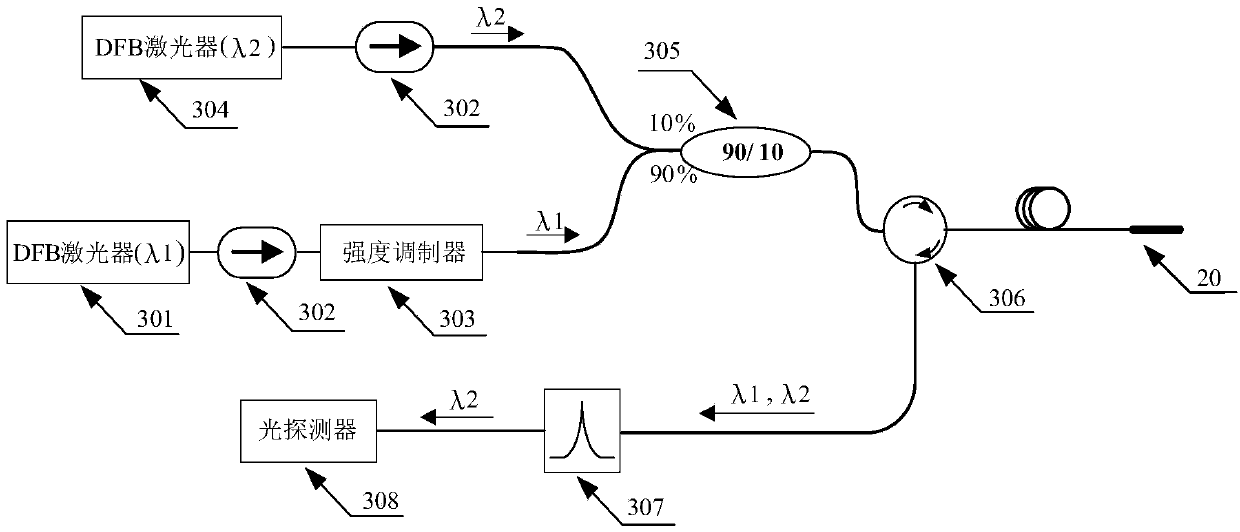
Method for the automated measurement of gas pressure and concentration inside sealed containers
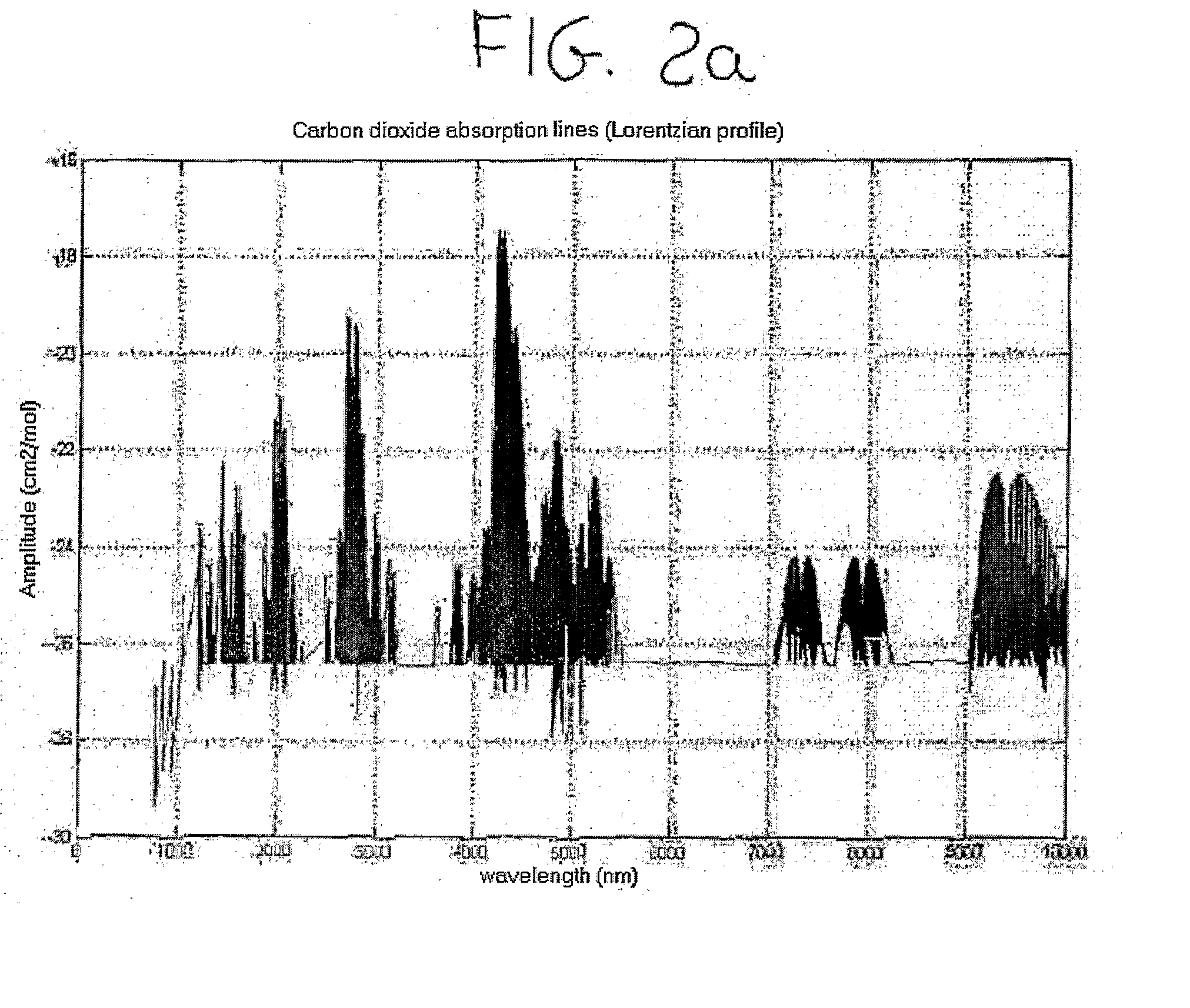
ActiveUS20100067012A1Color/spectral properties measurementsFluid pressure measurement by optical meansLight beamProduct gas
The device comprises a laser source which emits a beam of a predetermined wavelength towards an optically transparent closed container and detectors arranged to detect the laser beam which is attenuated by the gas absorption. The detectors provide the first data of absorption representative of a first absorption spectrum of the gas including distorted absorption lines and noise. The invention implements a method of calculation aimed at receiving and elaborating said first data. The output of the operation are parameters that represent a second absorption spectrum free of noise and distortion in the absorption lines. From these parameters we are able to determine the gas pressure and concentration in the container.
Owner:CONSIGLIO NAT DELLE RICERCHE
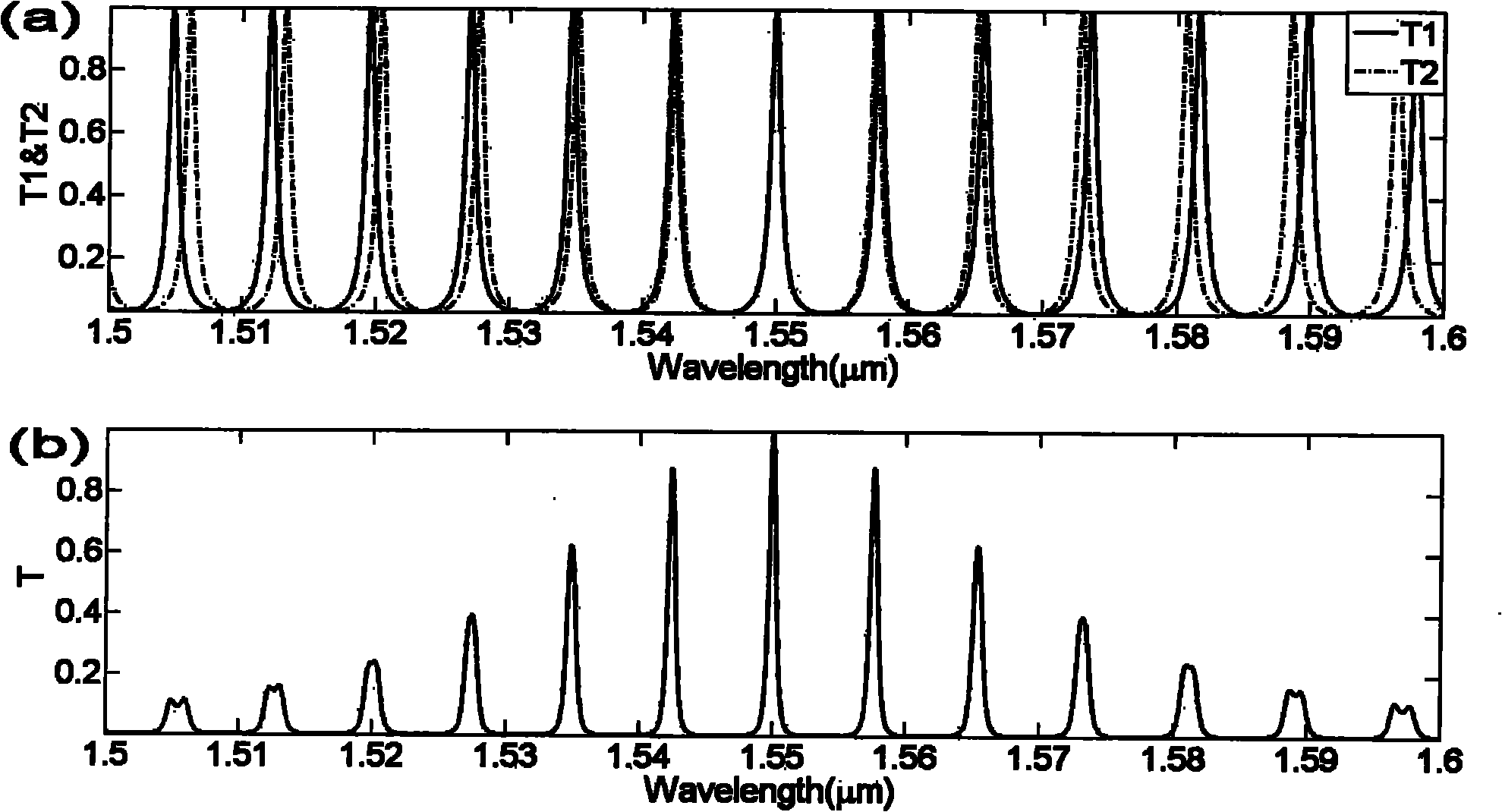
Photo sensor based on vernier effect of broadband light source and cascading optical waveguide filter
ActiveCN101871790ALow costHigh sensitivityPhase-affecting property measurementsThermometers using physical/chemical changesResonant cavityOptical power meter
The invention discloses a photo sensor based on the vernier effect of a broadband light source and a cascading optical waveguide filter, which comprises a broadband light source, an input waveguide, a connecting waveguide, an output waveguide, a reference ring-shaped resonant cavity coupled with the input waveguide and the connecting waveguide, a sensing ring-shaped resonant cavity coupled with the connecting waveguide and the output waveguide and two optical power meters. The sensing ring-shaped resonant cavity and the reference ring-shaped resonant cavity are different in optical length; adjacent resonance peaks are not coincident completely when one resonance frequency of the sensing ring-shaped resonant cavity is coincident with one resonance frequency of the reference ring-shaped resonant cavity. At least a part of waveguides in the sensing ring-shaped resonant cavity are influenced by a measured variable or at least a part of waveguides are in contact with a measured substance; the movement of a resonance line can be caused by measured variable influence or measured substance change; and the vernier effect of double resonant cavities can amplify the movement to be movement of total transmission spectrum envelop and can convert the movement into the change of transmission total output power, thereby detecting the measurement substance simply.
Owner:浙江光尖电机技术有限公司
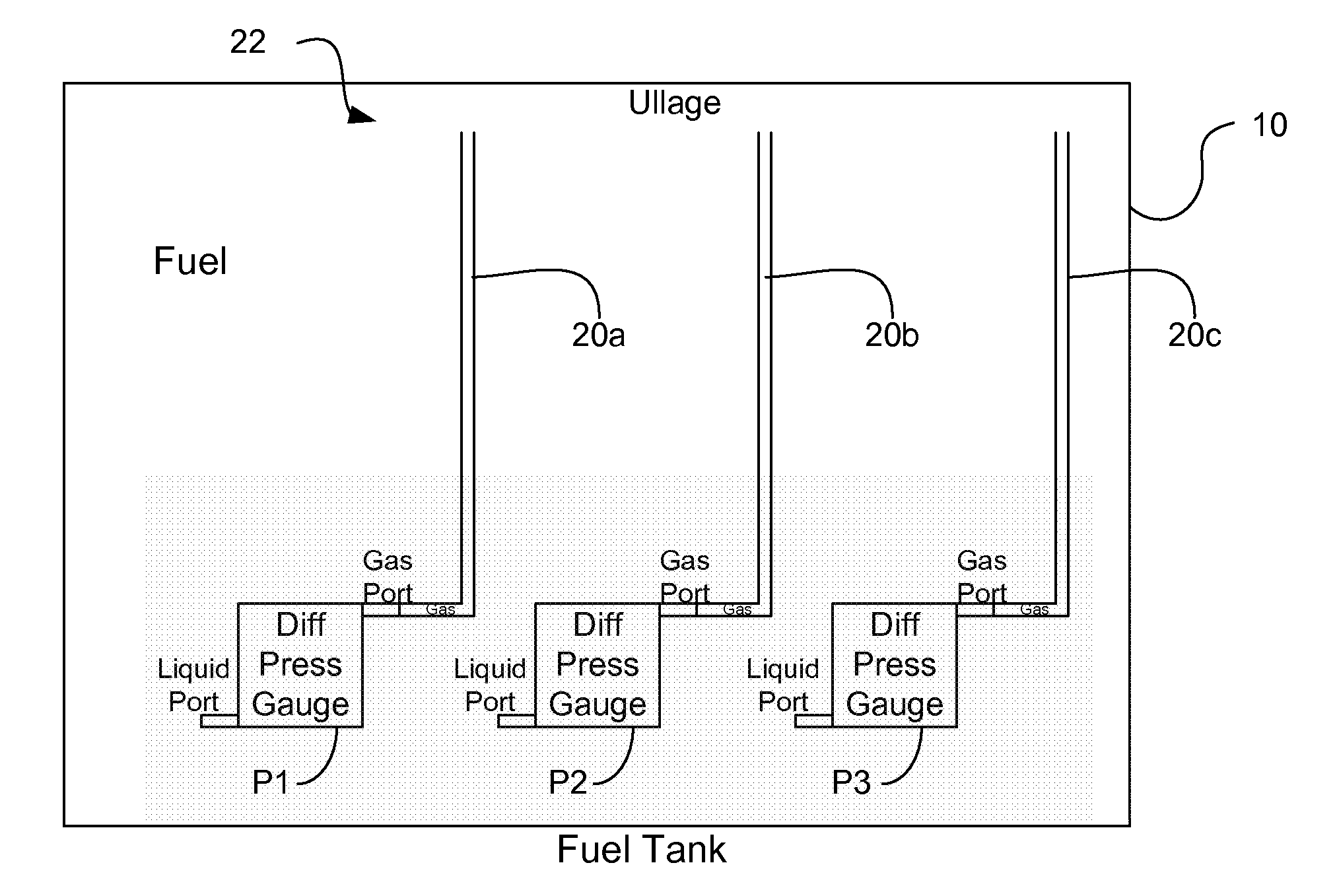
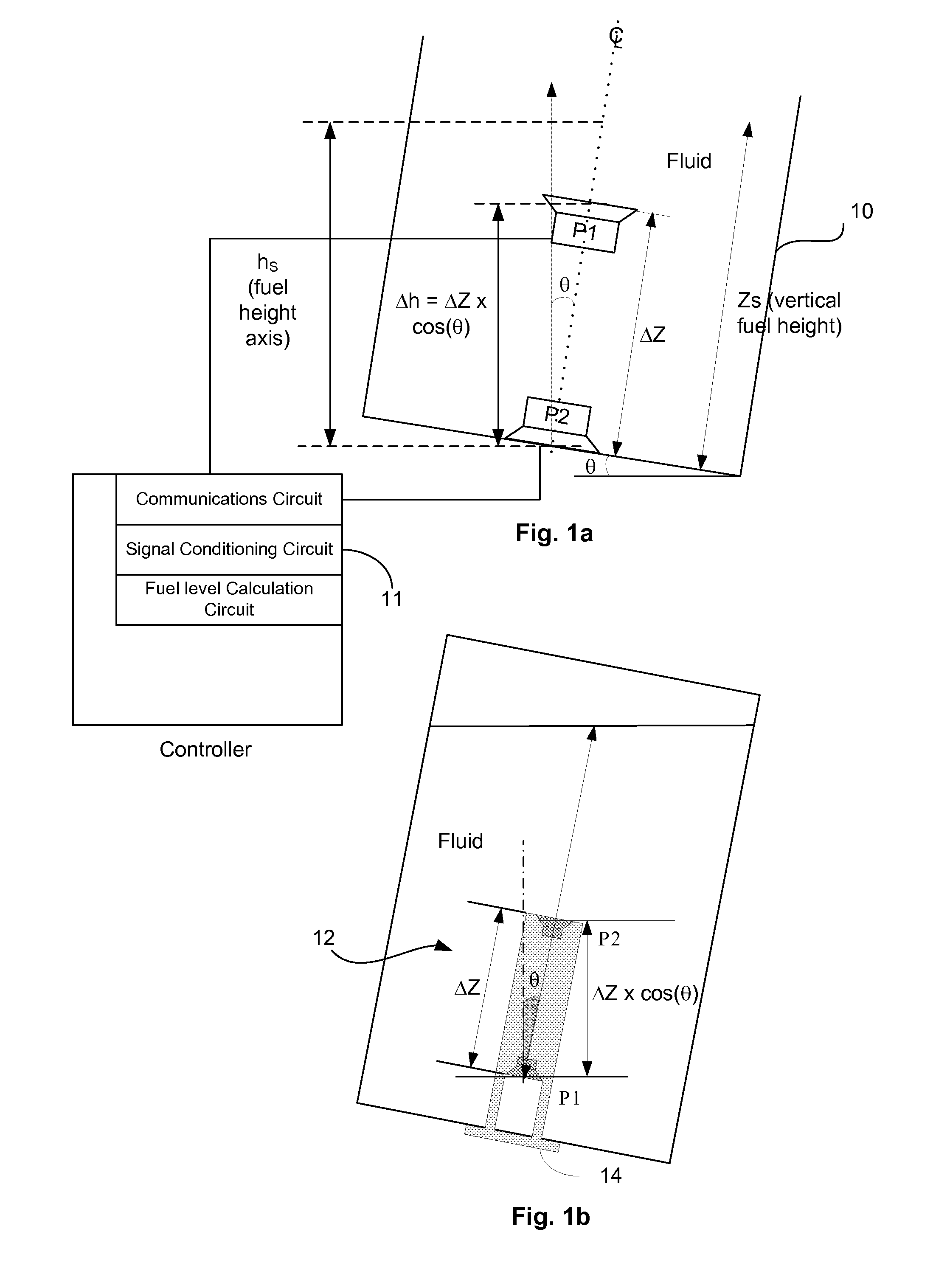
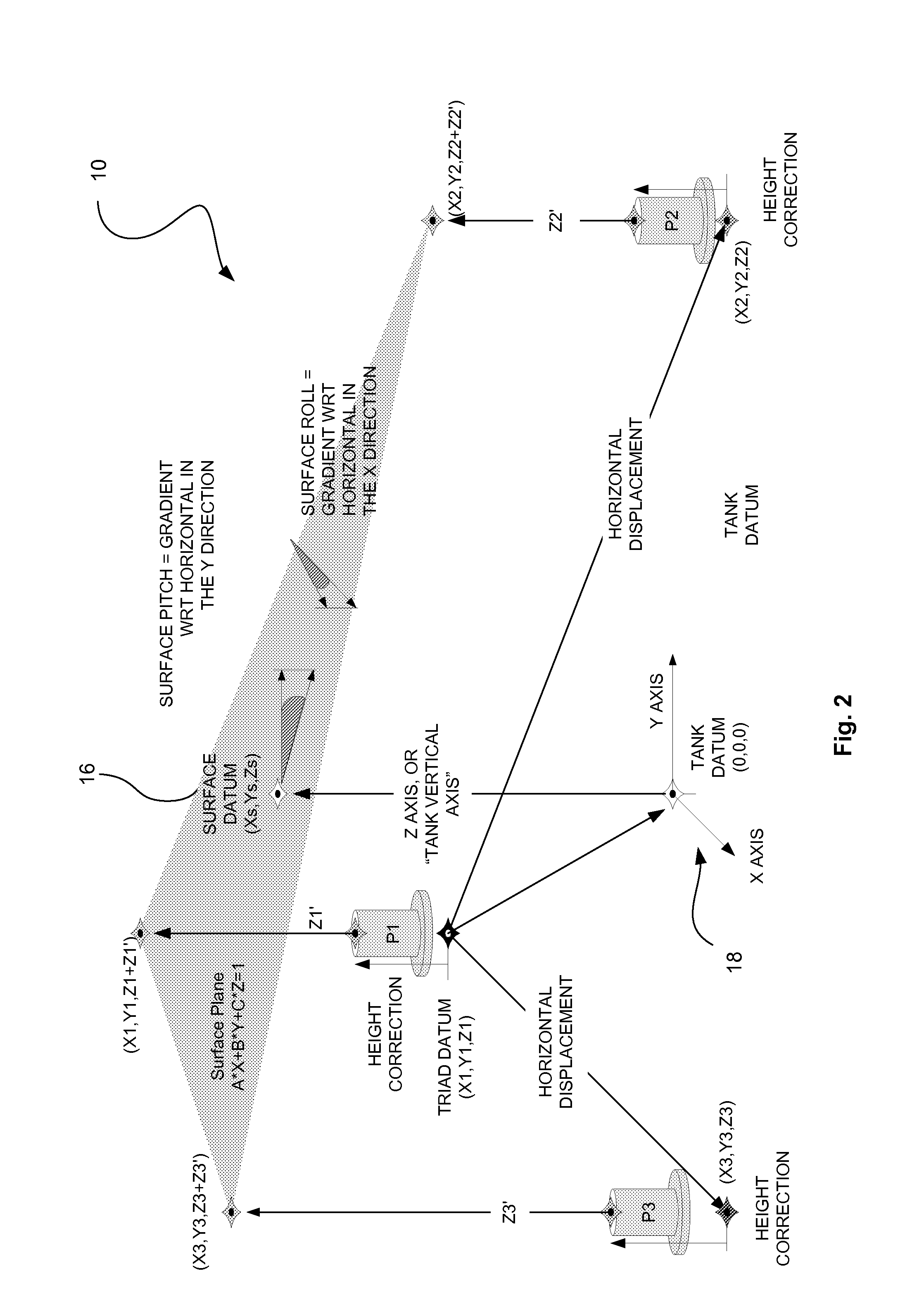
Aircraft fluid gauging techniques using pressure measurements and optical sensors
InactiveUS20150100253A1Flow propertiesFluid pressure measurement by mechanical elementsLevel measurementEngineering
A fluid level measurement system includes a first pressure sensor disposed inside a fluid tank at a first elevation relative to a height axis of the fluid tank, and a second pressure sensor disposed inside the fluid tank at a second elevation relative to the height axis of the fluid tank, the second elevation different from the first elevation. The first pressure sensor and the second pressure sensor are configured to provide a signal indicative of a sensed pressure, and fluid height is calculated from the difference in sensed pressure between the first and second pressure sensors relative to the sensed pressure of either the first or the second pressure sensor.
Owner:PARKER HANNIFIN CORP
Resonant type Fabry-Perot optical fiber sensor, manufacturing method and air pressure detecting method
ActiveCN103994851AImprove applicabilitySmall creepFluid pressure measurement by optical meansResonanceEngineering
The invention provides a resonant type Fabry-Perot optical fiber sensor which comprises a sensor body and a through hole penetrating through the sensor body. One end of the through hole is provided with a graphene thin film for sensing the to-be-detected air pressure in an attached mode, and the other end of the through hole is provided with transmission optical fibers which penetrate through the through hole and are matched with the through hole. According to the resonant type Fabry-Perot optical fiber sensor, the air pressure of gas is calculated in the mode that graphene thin film resonant frequency changes are caused by damp of the gas to the graphene thin film, so that a closed Fabry-Perot cavity is not needed, and the manufacturing difficulty is reduced; the the original measurement thin film deformation quantity is replaced by resonance to further conduct air pressure measurement, and thin film material creeping caused by repeated film deformation is effectively reduced; digital frequency signals after probe laser detection are output after the sensor conducts detection, and result analysis can be conveniently carried out compared with light wave signals of an interferometric sensor. Stimulation and detection are carried out through the single transmission optical fibers, and long-distance air pressure measurement can be achieved, and the applicability of the sensor is greatly improved.
Owner:THE HONG KONG POLYTECHNIC UNIV SHENZHEN RES INST
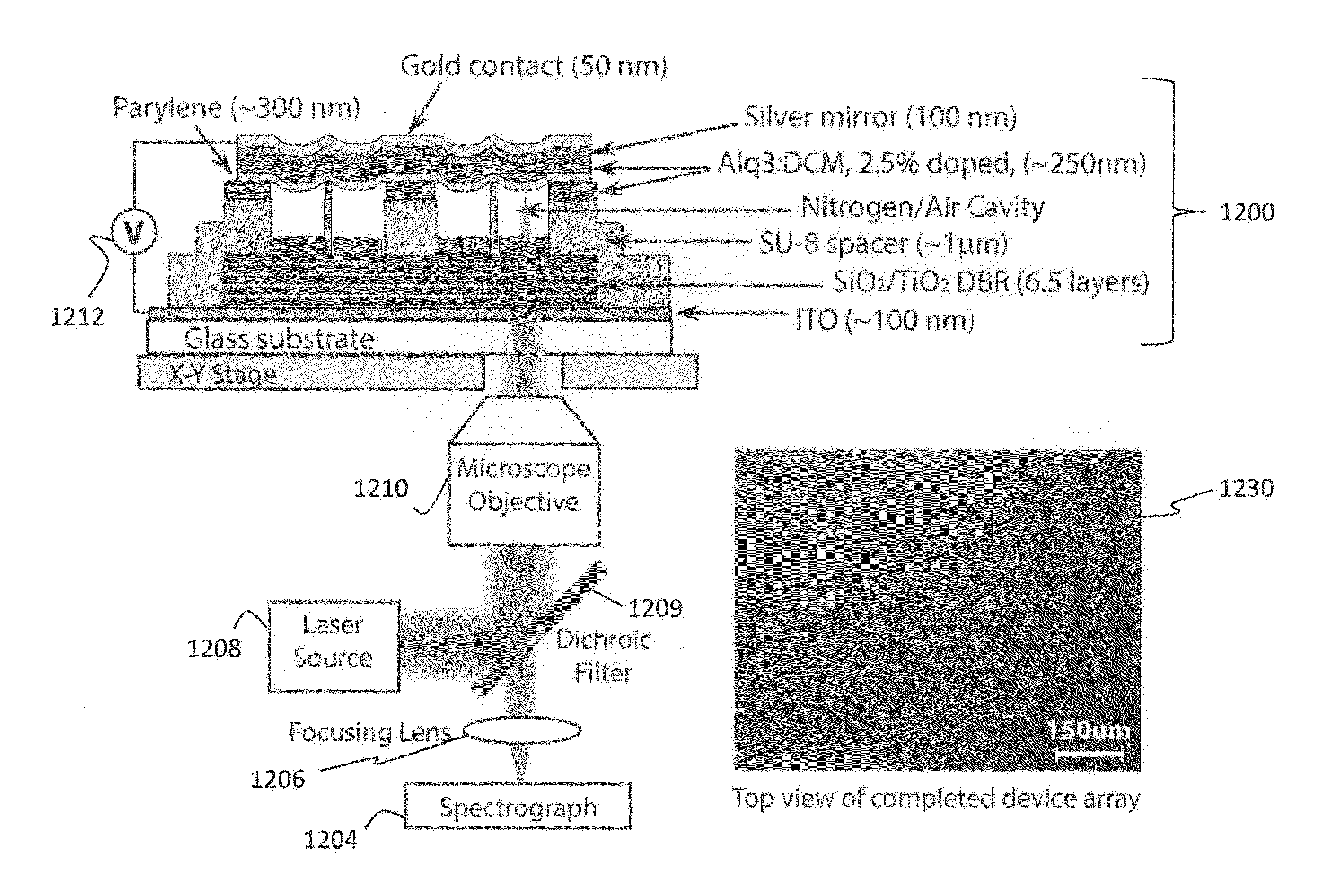
Method and applications of thin-film membrane transfer
ActiveUS20150311664A1Fluid pressure measurement by electric/magnetic elementsForce measurement by measuring optical property variationMicrocontact printingExternal bias
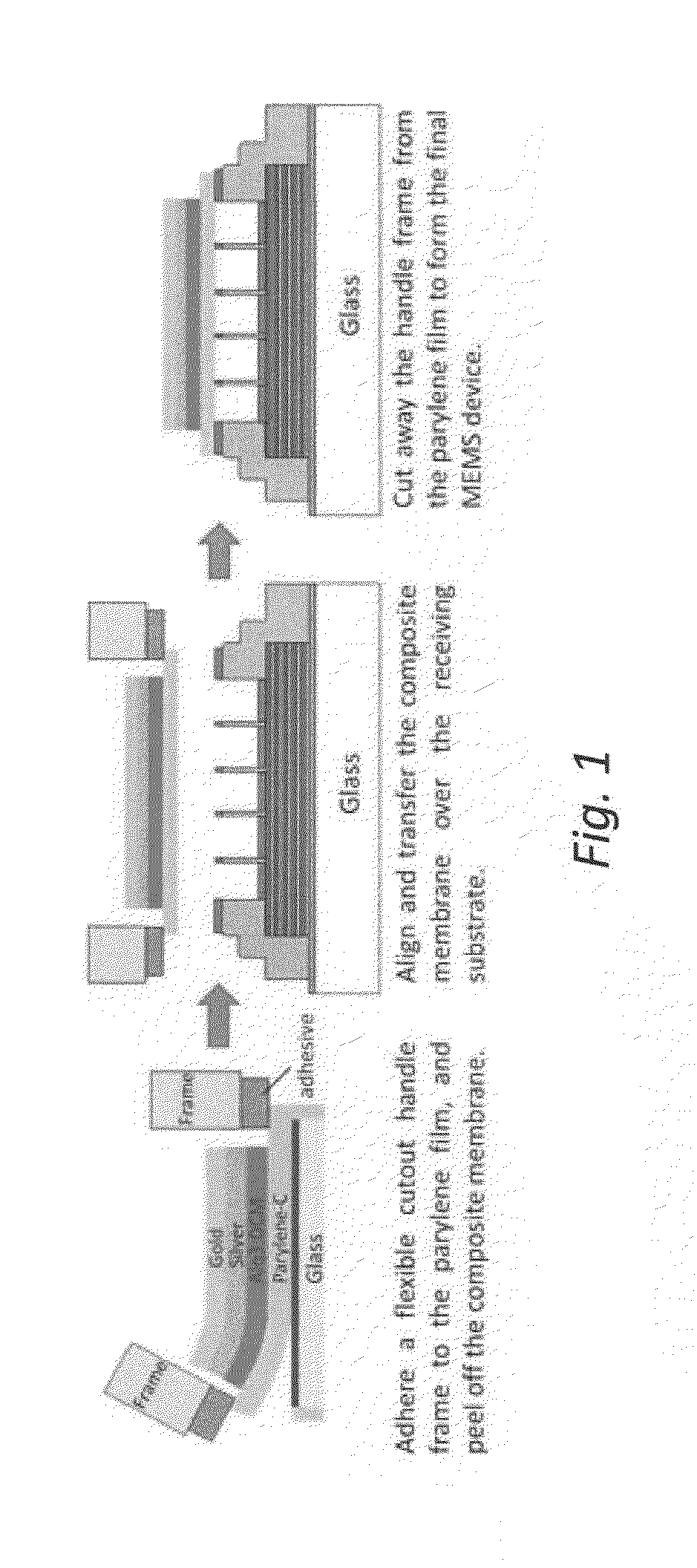
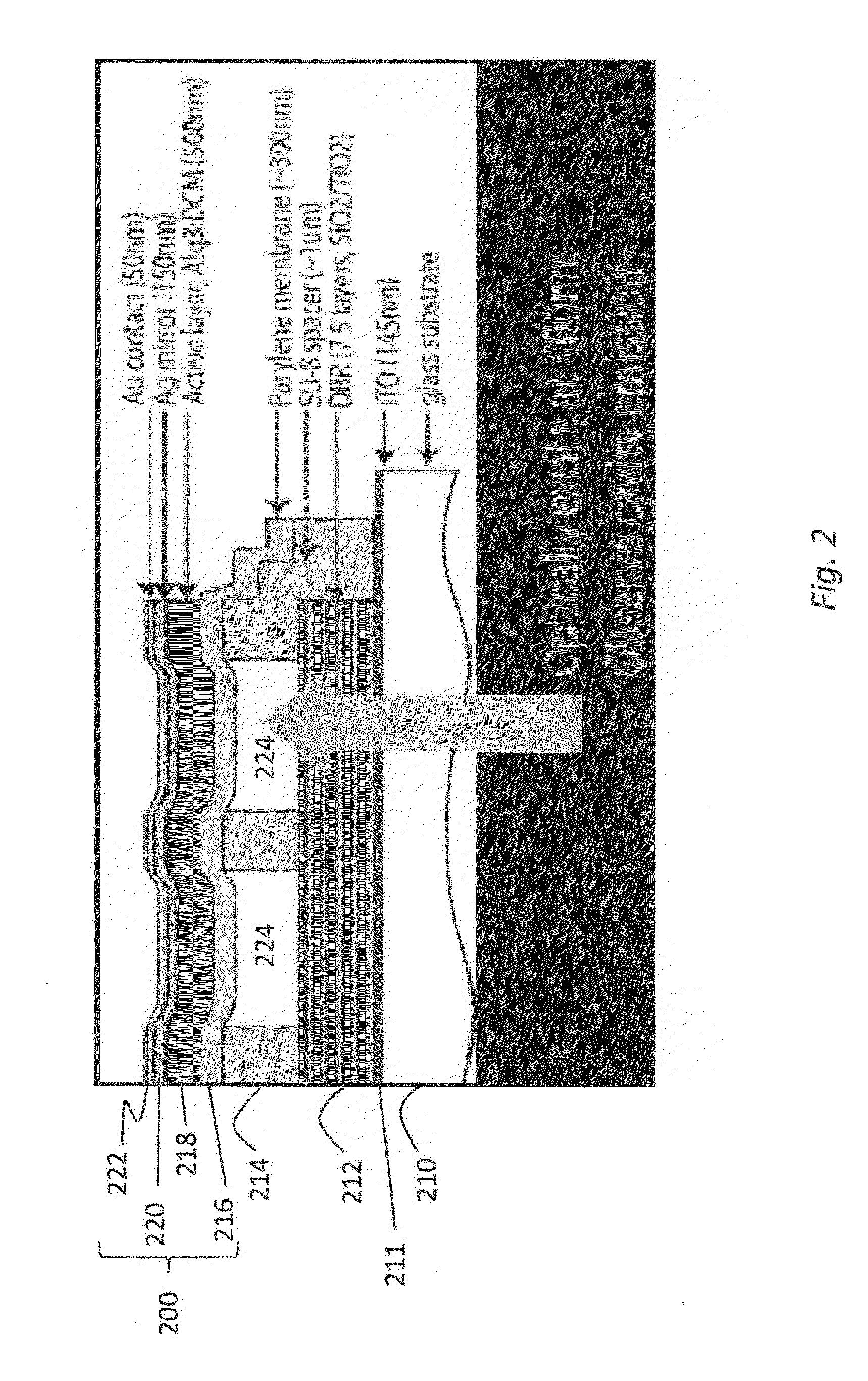
The disclosure relates to method and apparatus for micro-contact printing of micro-electromechanical systems (“MEMS”) in a solvent-free environment. The disclosed embodiments enable forming a composite membrane over a parylene layer and transferring the composite structure to a receiving structure to form one or more microcavities covered by the composite membrane. The parylene film may have a thickness in the range of about 100 nm-2 microns; 100 nm-1 micron, 200-300 nm, 300-500 nm, 500 nm to 1 micron and 1-30 microns. Next, one or more secondary layers are formed over the parylene to create a composite membrane. The composite membrane may have a thickness of about 100 nm to 700 nm to several microns. The composite membrane's deflection in response to external forces can be measured to provide a contact-less detector. Conversely, the composite membrane may be actuated using an external bias to cause deflection commensurate with the applied bias. Applications of the disclosed embodiments include tunable lasers, microphones, microspeakers, remotely-activated contact-less pressure sensors and the like.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com