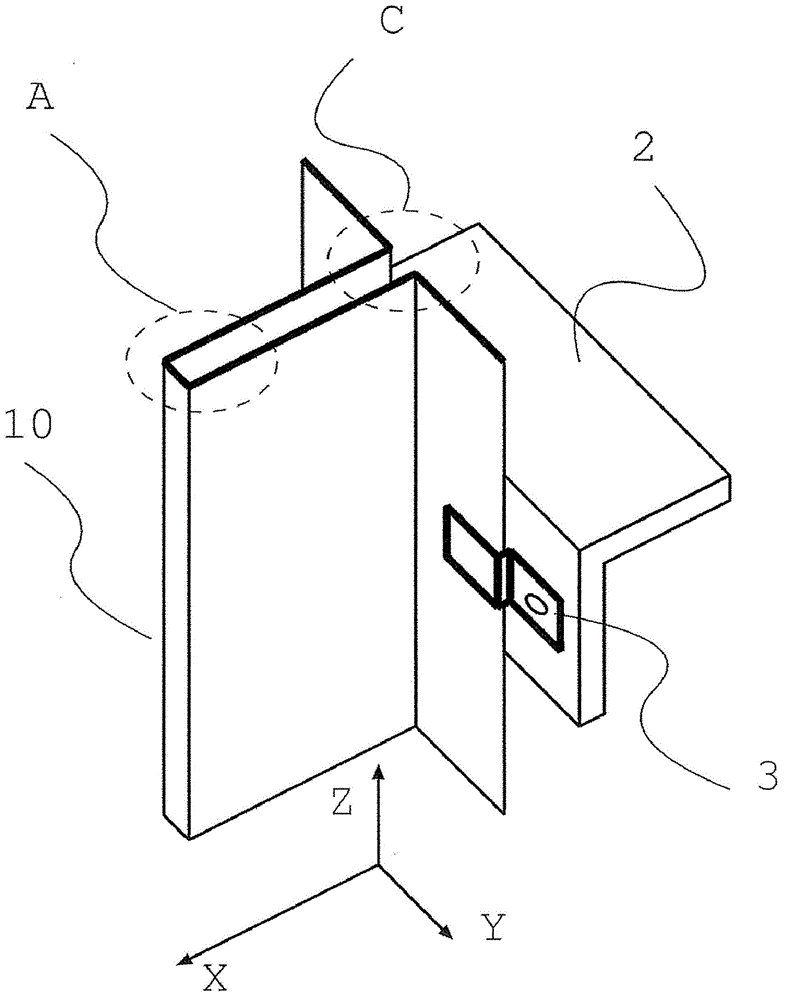
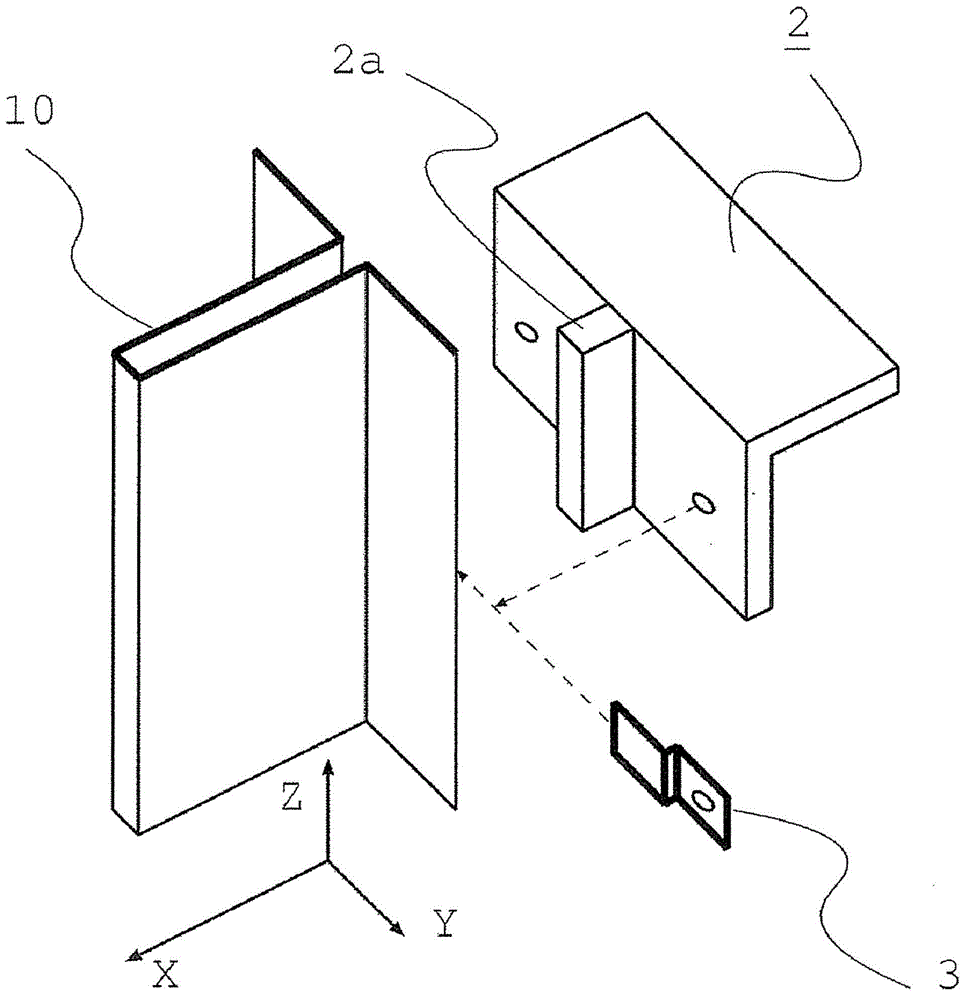
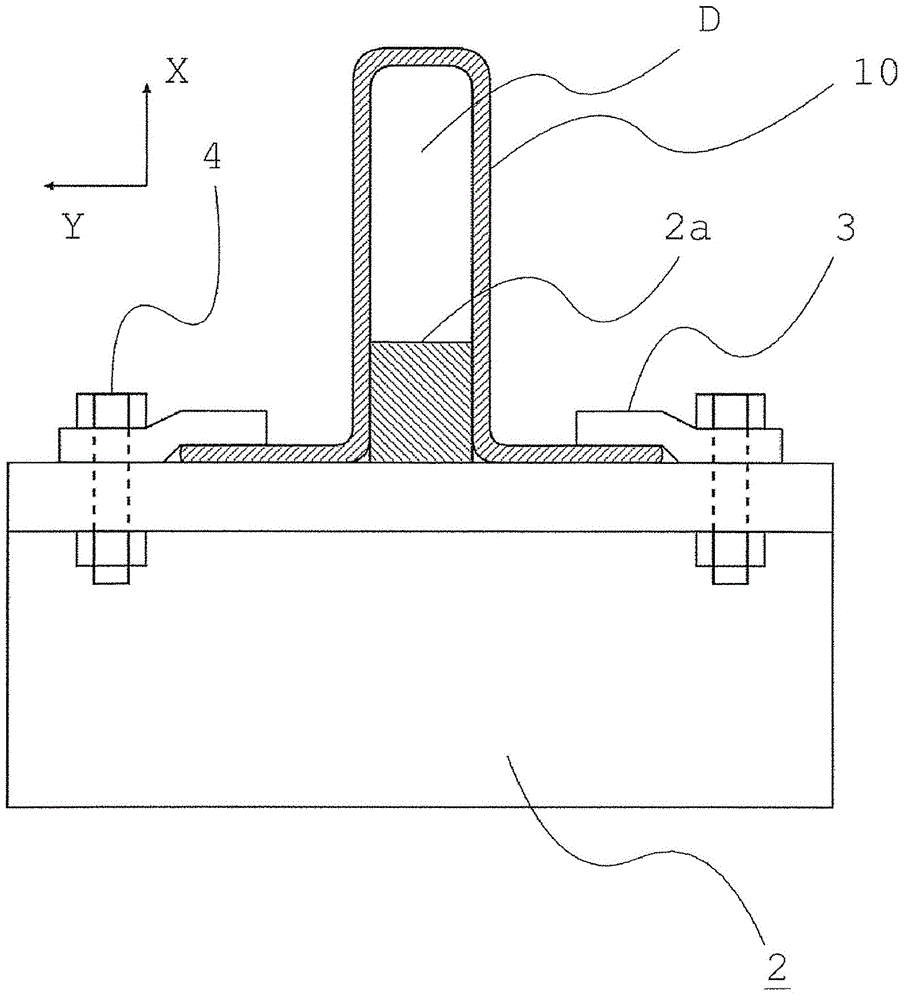
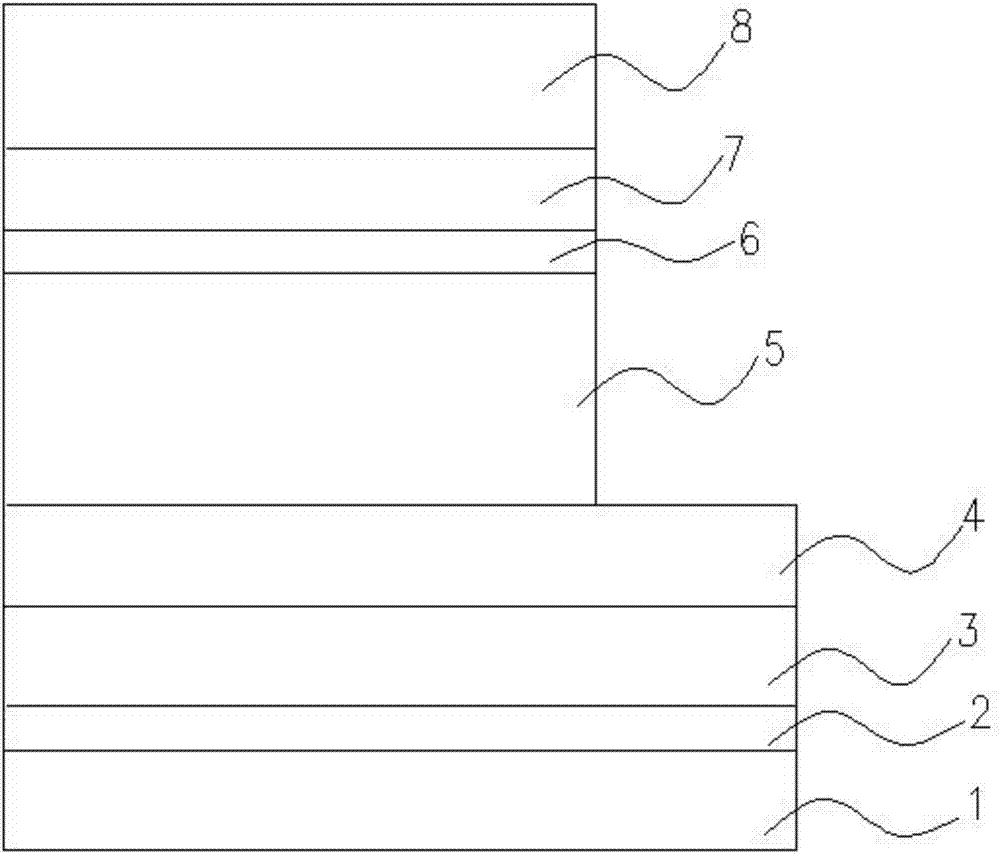
Patents
Literature
172results about How to "Curb tilt" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
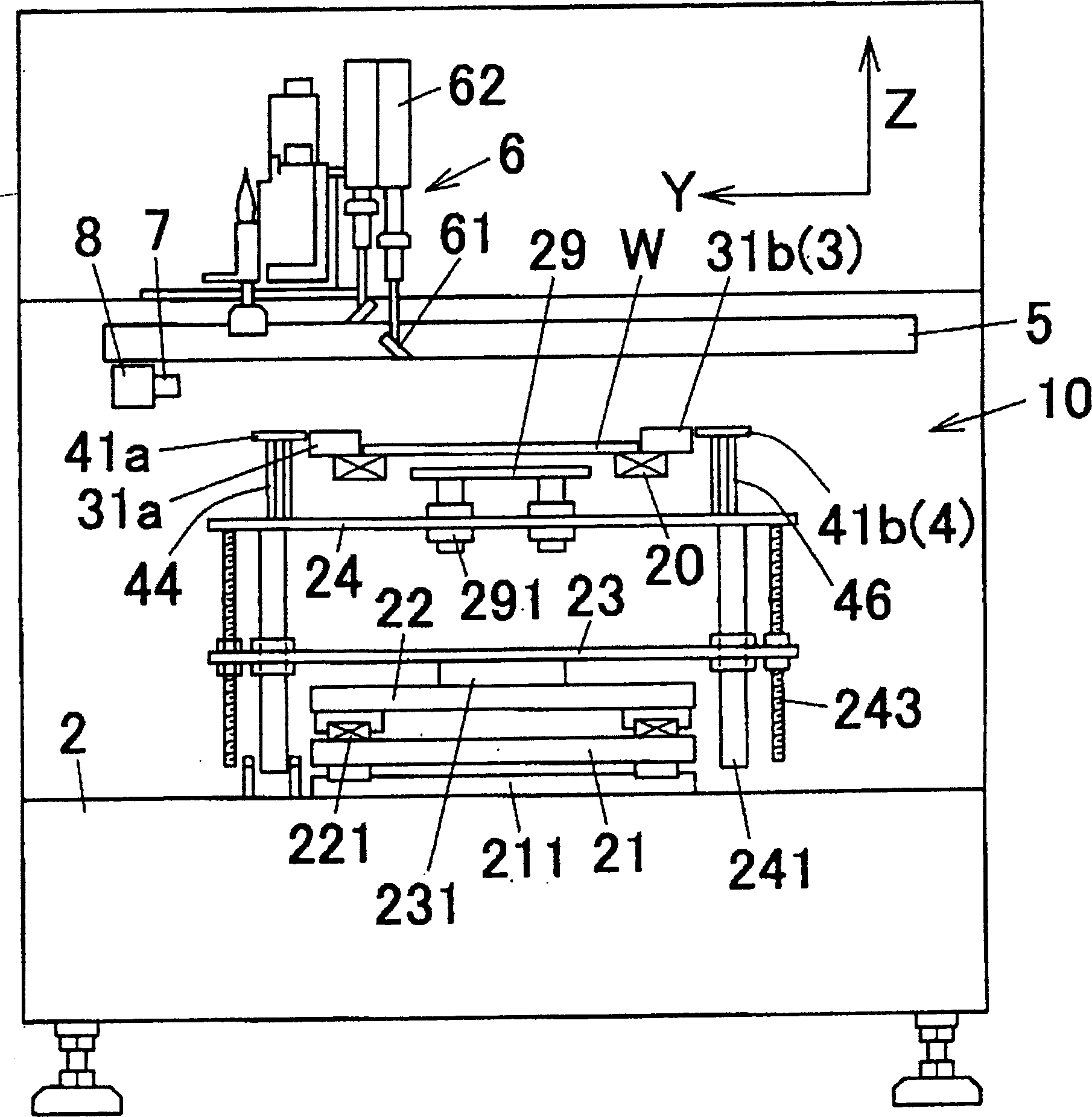
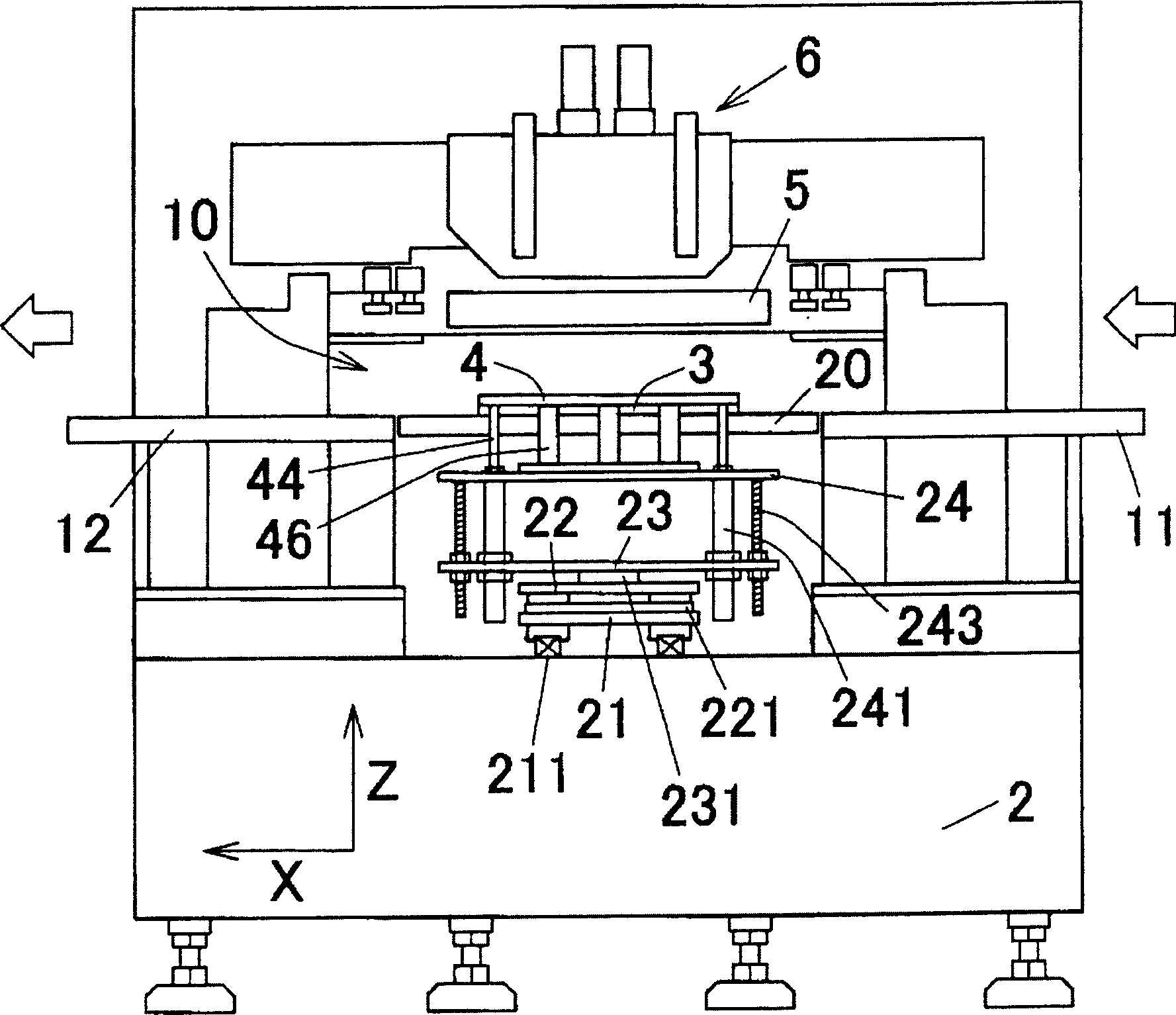
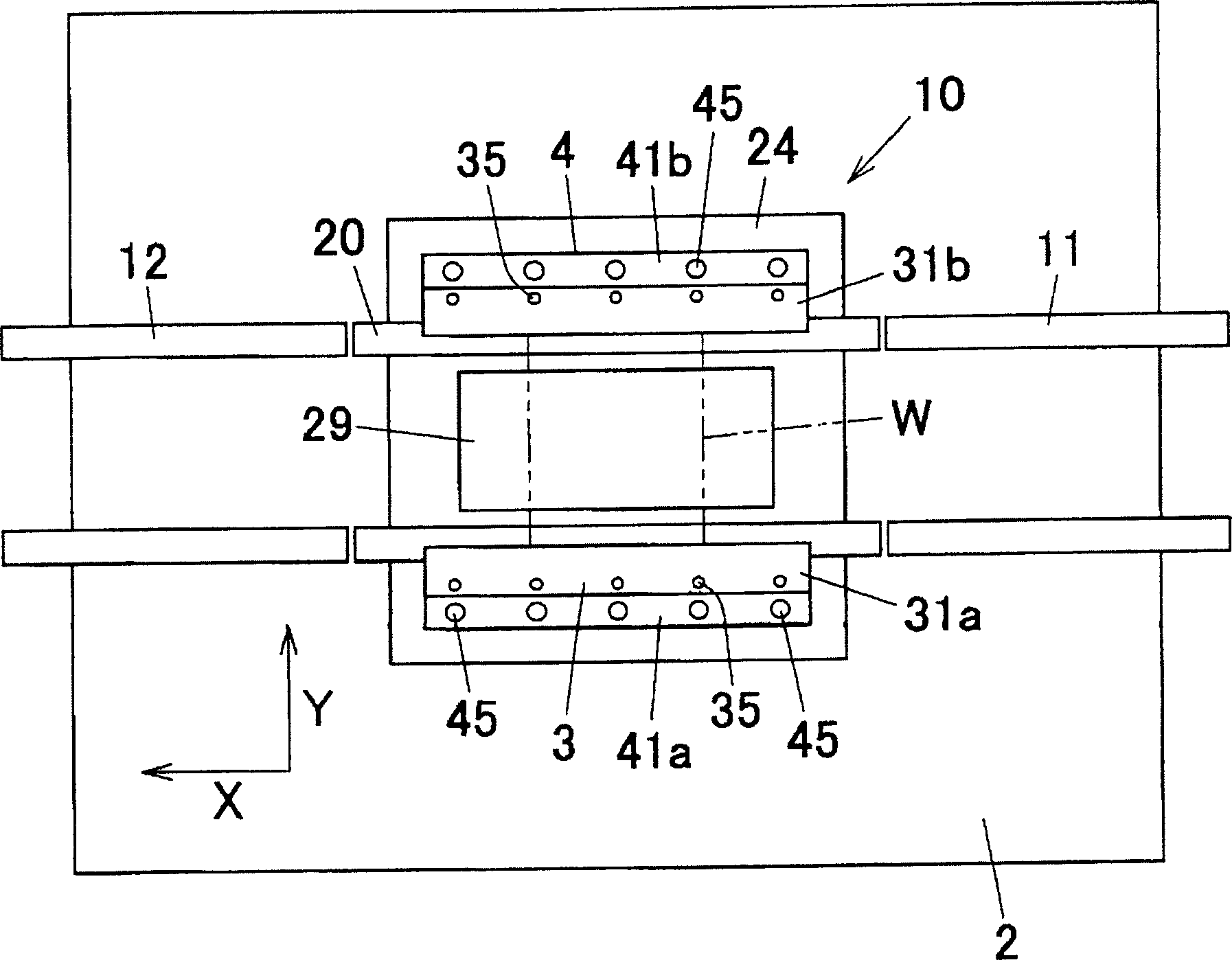
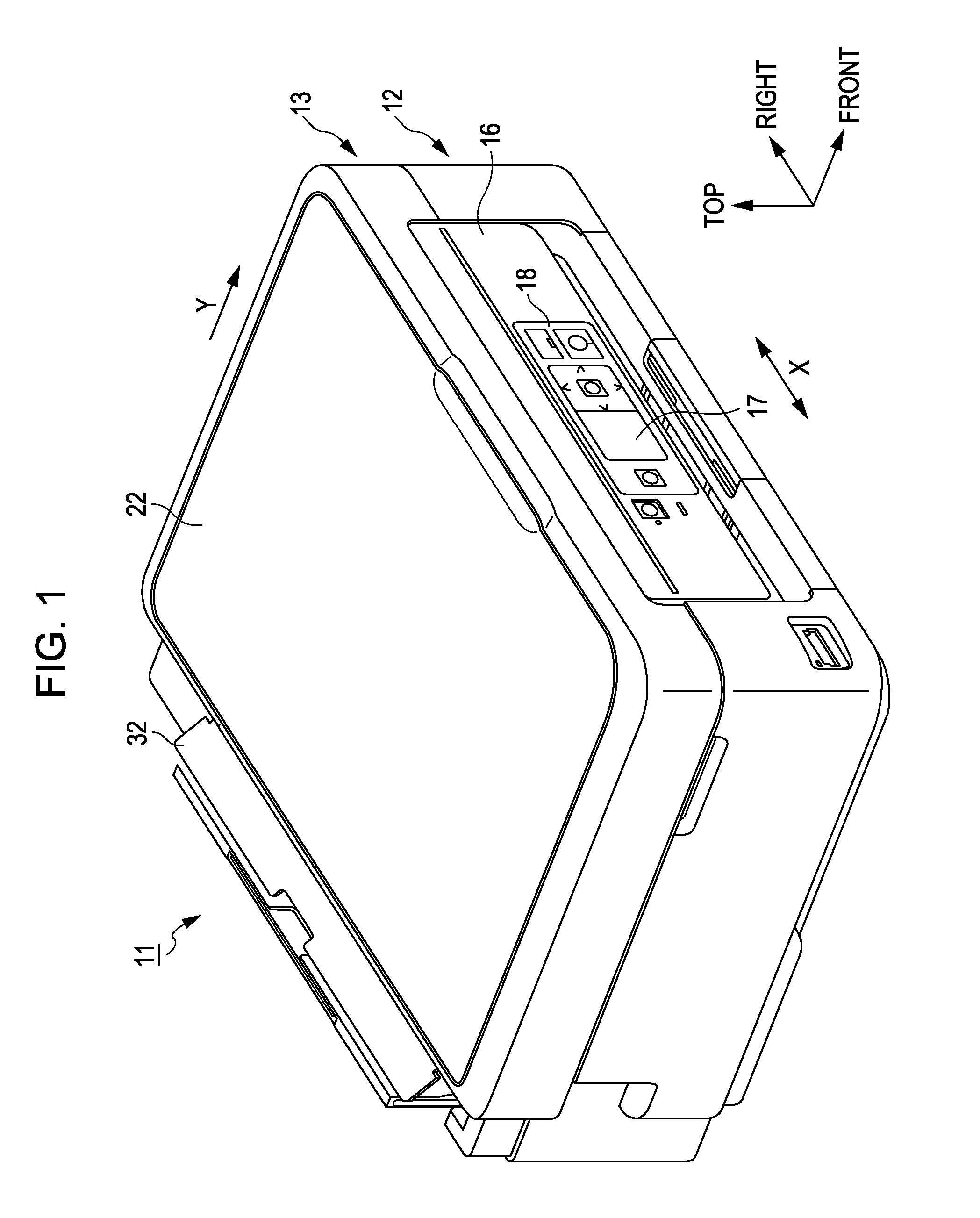
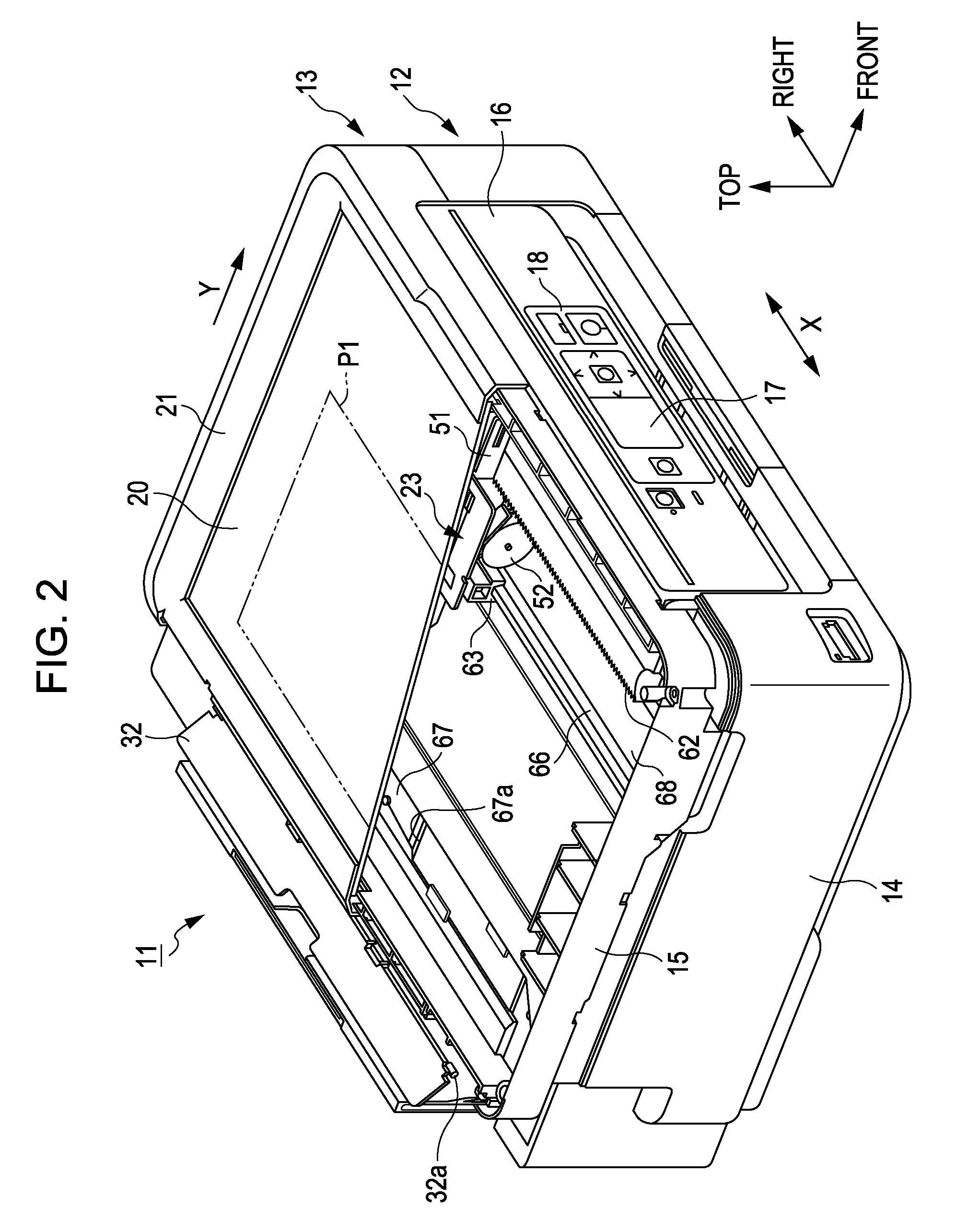
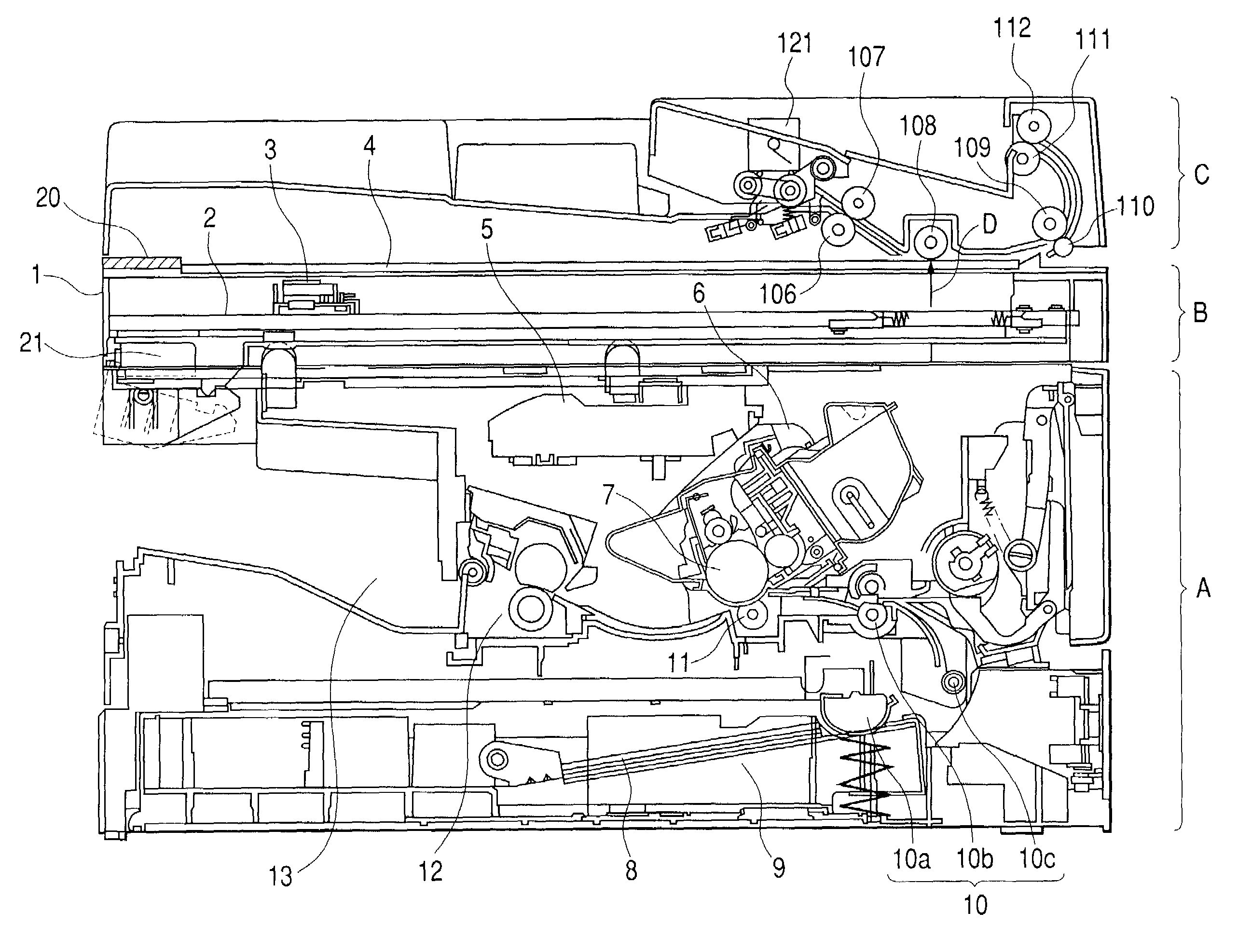
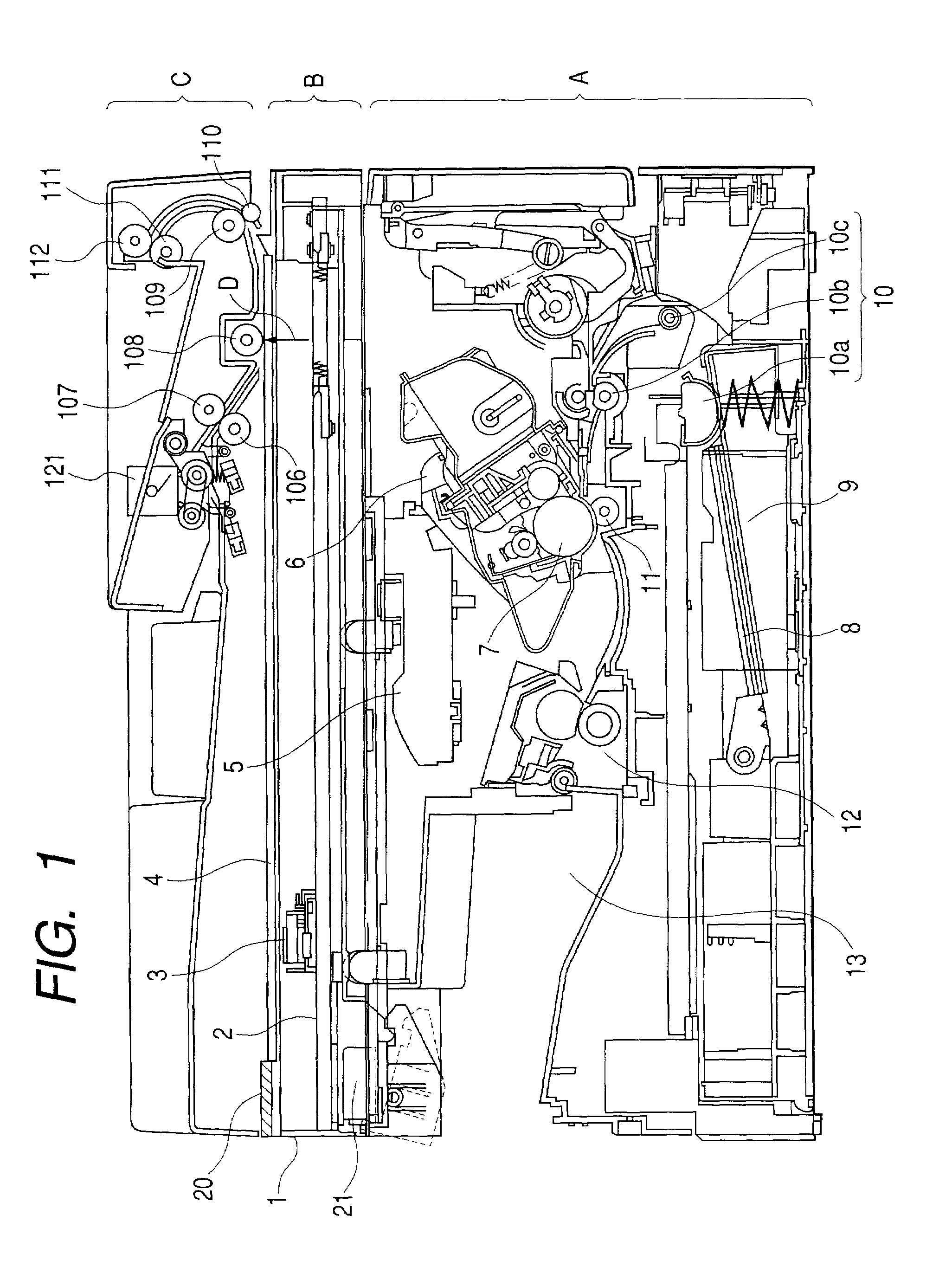
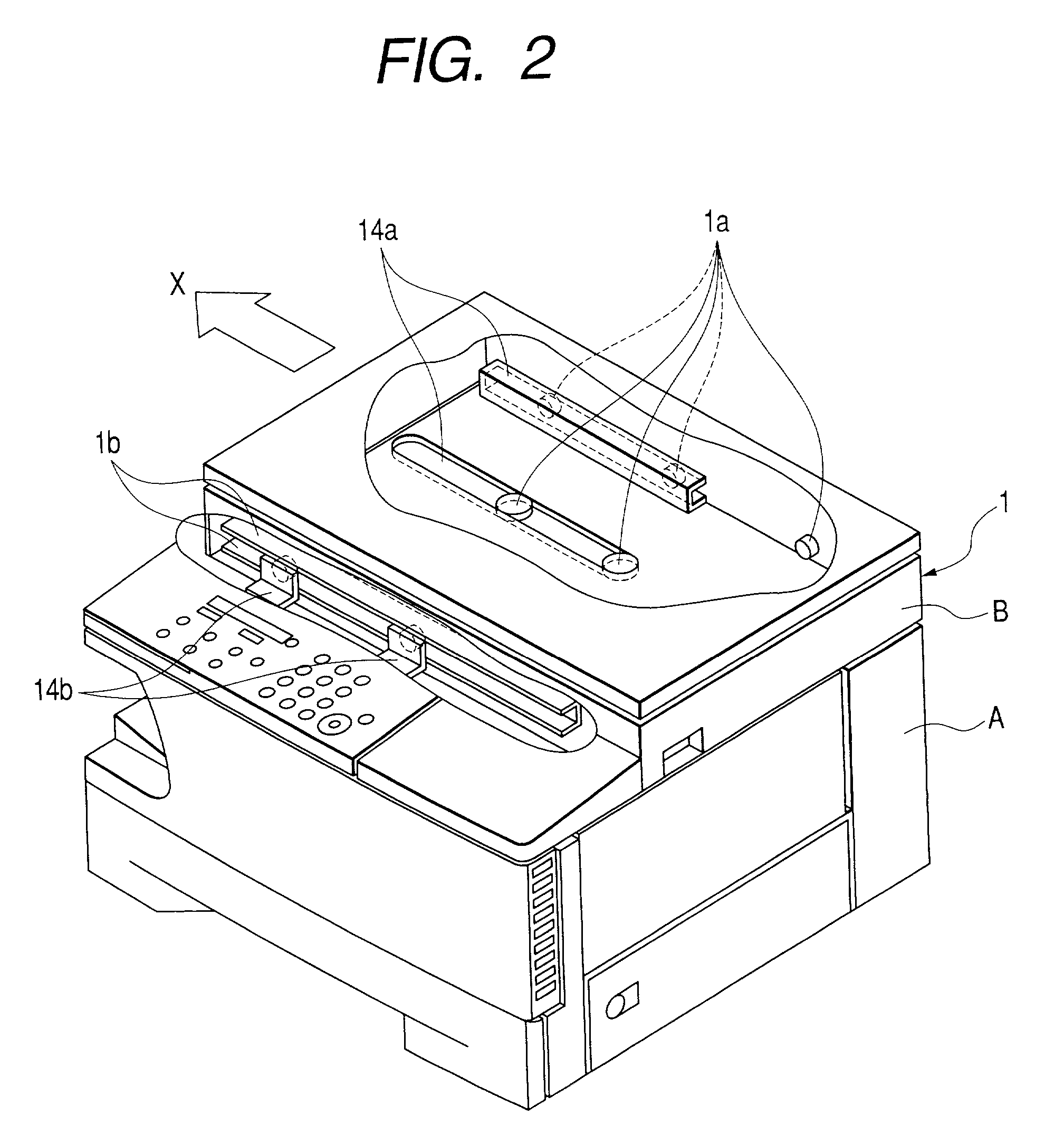
Printing apparatus
ActiveCN1846994AAdjustable clamping pressureAdjust clamping pressurePrinted circuit assemblingScreen printersStencil printingEngineering
Owner:YAMAHA MOTOR CO LTD
Au Alloy Bonding Wire
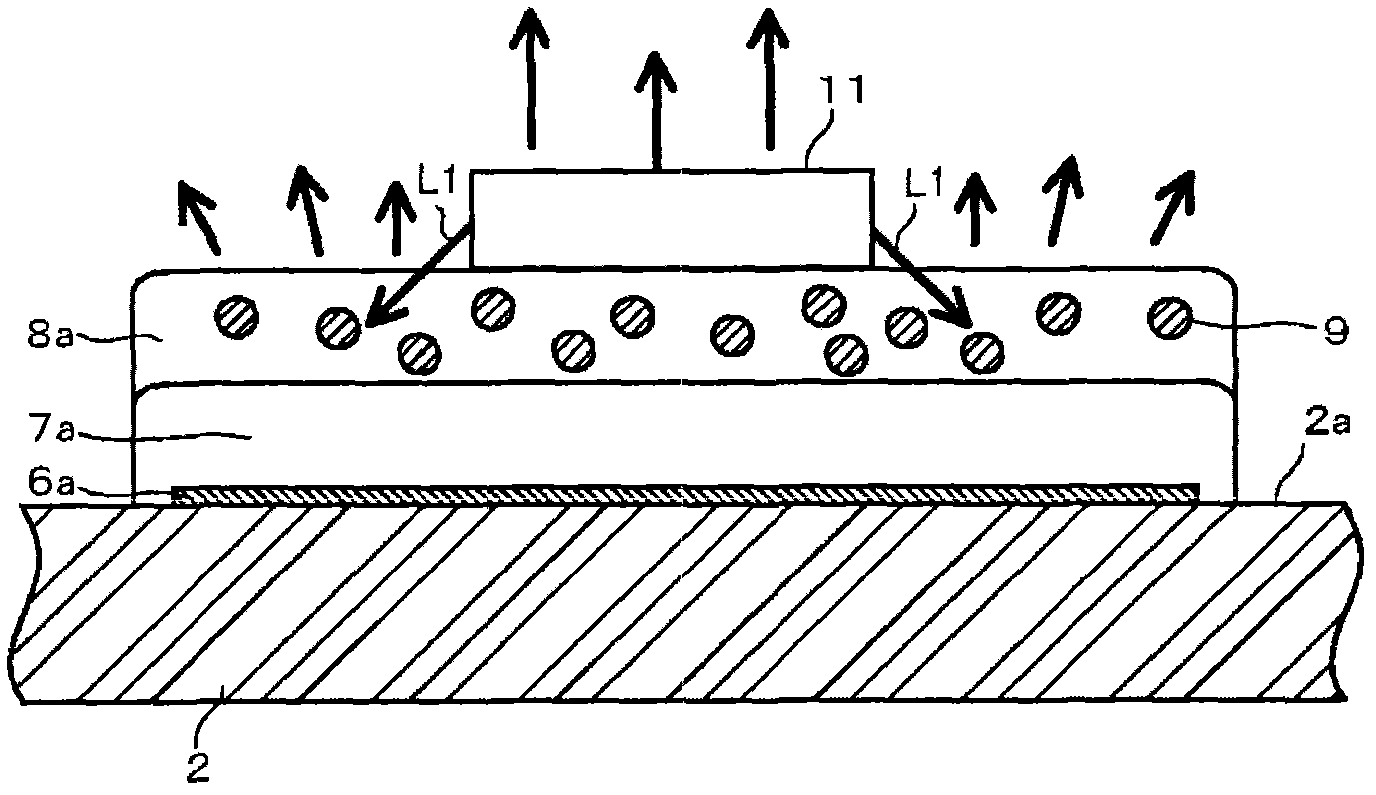
InactiveUS20080050267A1Improve adhesionCurb tiltSolid-state devicesWelding/cutting media/materialsTrace elementAlloy
Provided is a thin Au alloy bonding wire having desired strength, good bondability and stability over time, and improved circularity of a squashed ball and sphericity of a melted ball. The Au alloy bonding wire contains, in an Au alloy matrix containing 0.05 to 2 mass % in total of at least one selected from Pd and Pt of high purity in Au of high purity, as trace elements, 10 to 100 ppm by mass of Mg, 5 to 100 ppm by mass of Ce, and 5 to 100 ppm by mass of each of at least one selected from Be, Y, Gd, La, Eu and Si, the total content of Be, Y, Gd, La, Eu and Si being 5 to 100 ppm by mass, or as trace elements, Mg, Be, and at least one selected from Y, La, Eu and Si, or as trace elements, 10 to 100 ppm by mass of Mg, 5 to 30 ppm by mass of Si, 5 to 30 ppm by mass of Be, and 5 to 30 ppm by mass of at least one selected from Ca, Ce and Sn.
Owner:TANAKA DENSHI KOGYO KK
Intermittent coating method and apparatus
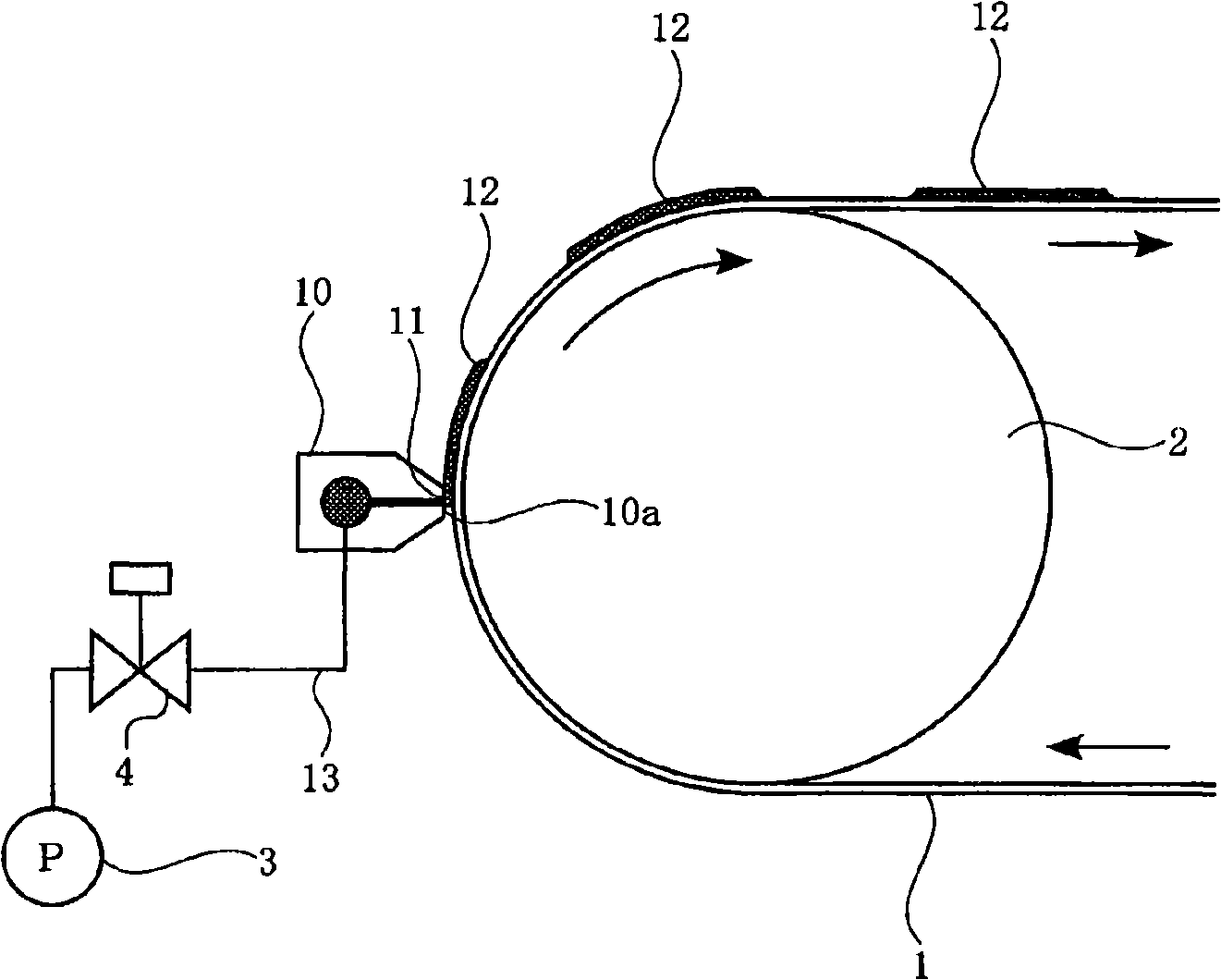
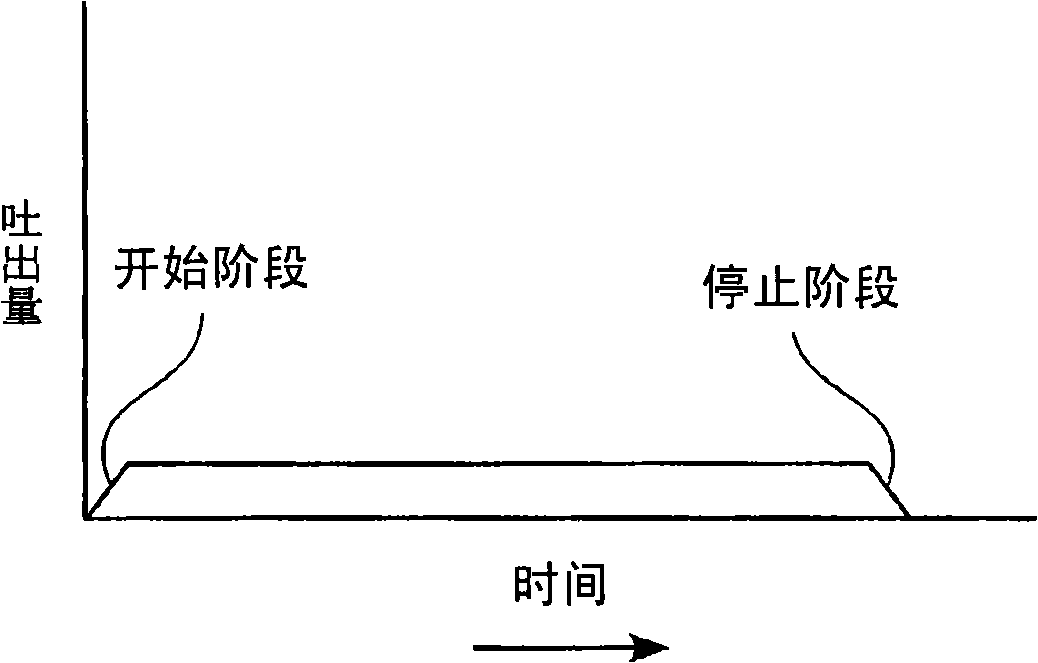
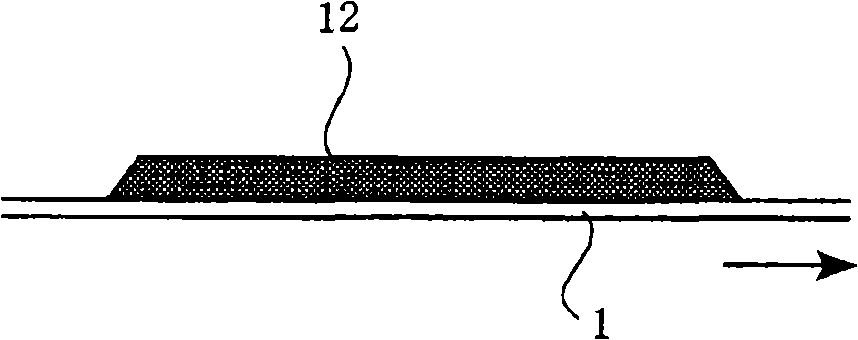
The technical problems of the present invention reside in that coating liquor can be coated on a substrate web with certain even thickness when the mobile substrate web is coated with coating liquor intermittently from head of a coating model. Coating liquor (12) is coated on the mobile sheet substrate web (1) intermittently from a discharge opening (11) located at front end surface (10a) of the coating model head (10), while coating liquor is coated intermittently on the substrate web, the process as shown below: the coating model head and the substrate web are moved in same direction when the coating model head provides coating liquid to the substrate web; the coating model stopping moving or moving along the direction opposite to the substrate web, coating liquor being coated from the coating model head to the moving substrate web; When coating liquor is stopped providing to the substrate web from the coating model head, the coating model head and the substrate web are moving alongsame direction.
Owner:CHUGAI RO CO LTD
Optical unit
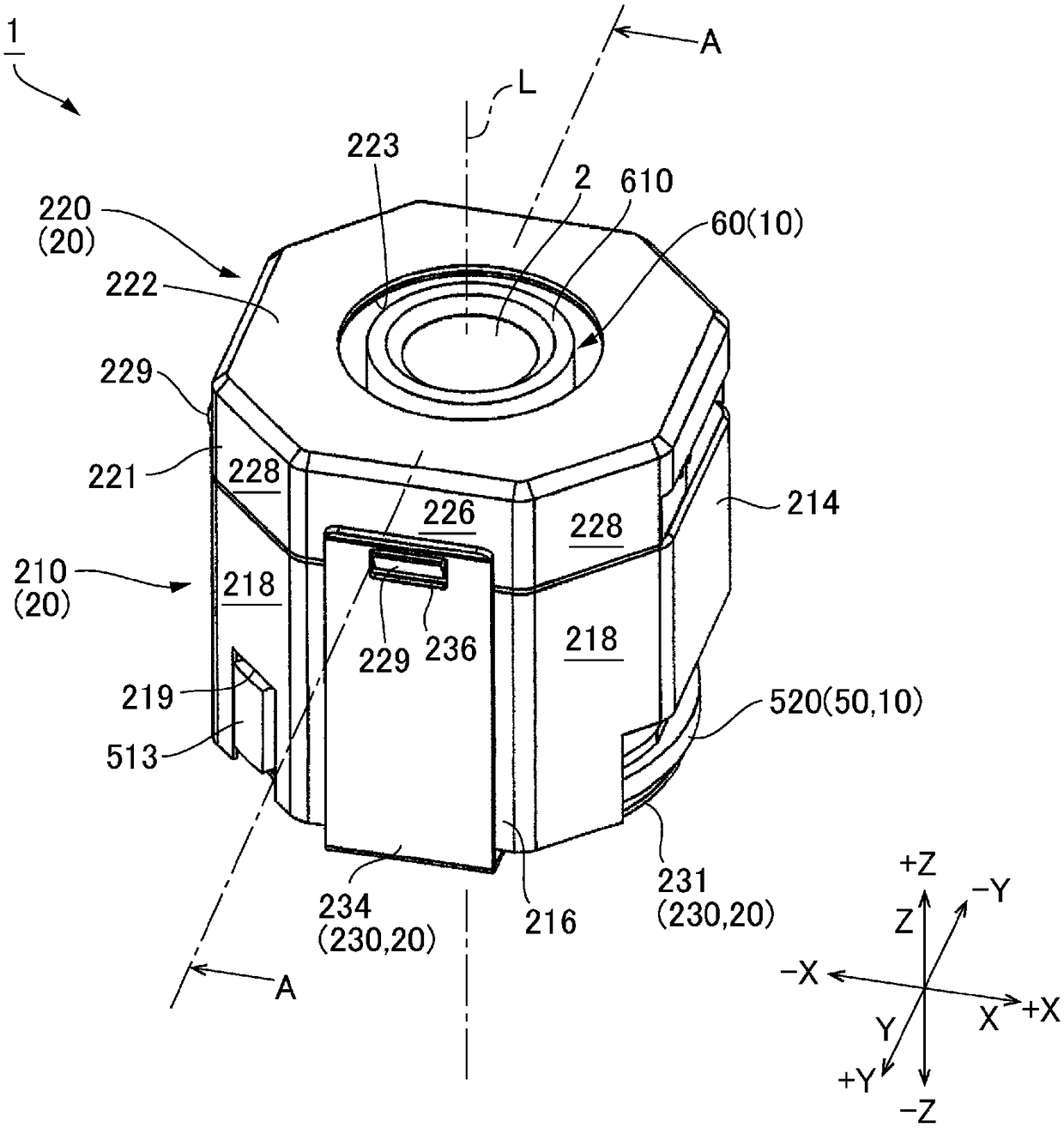
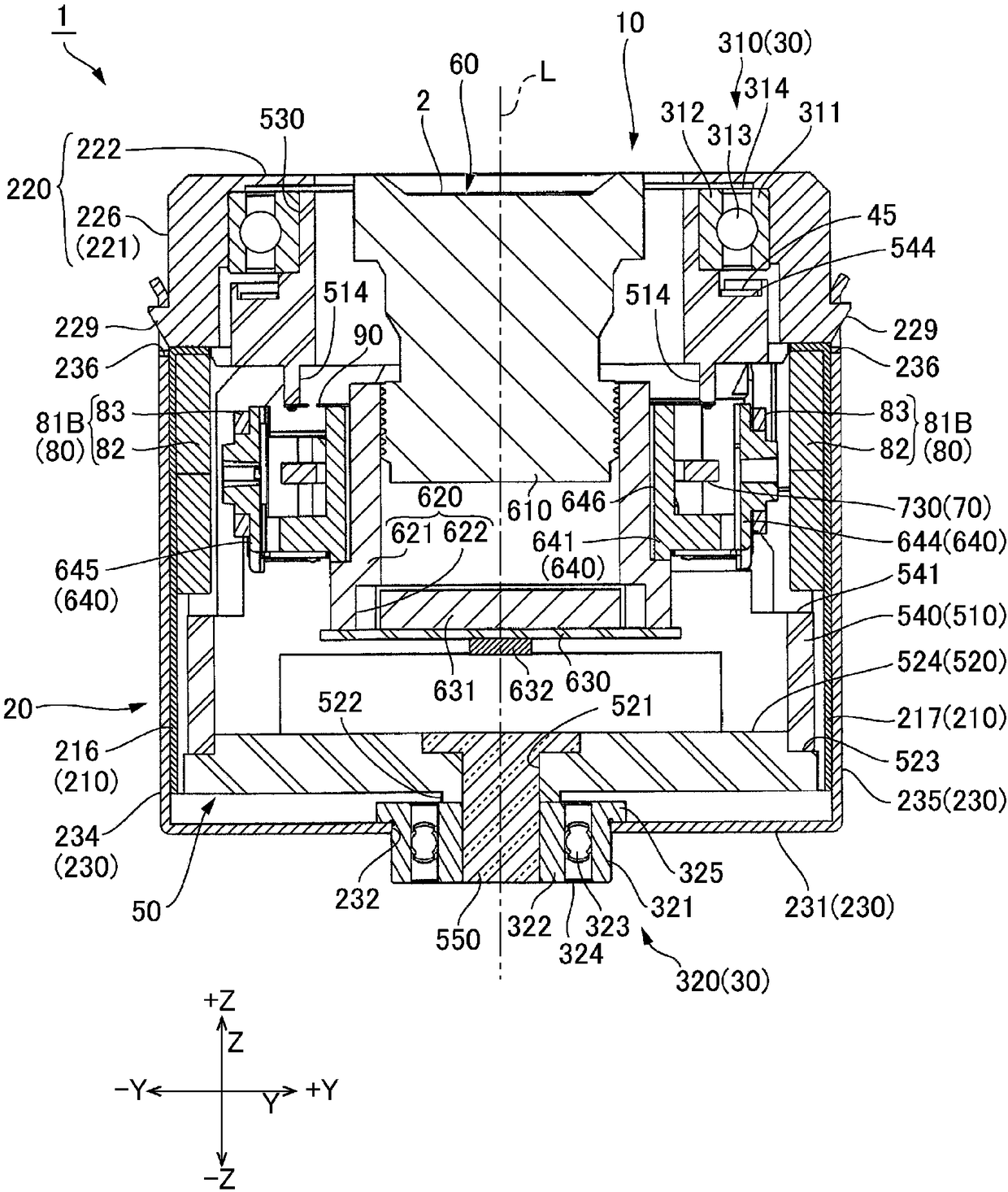
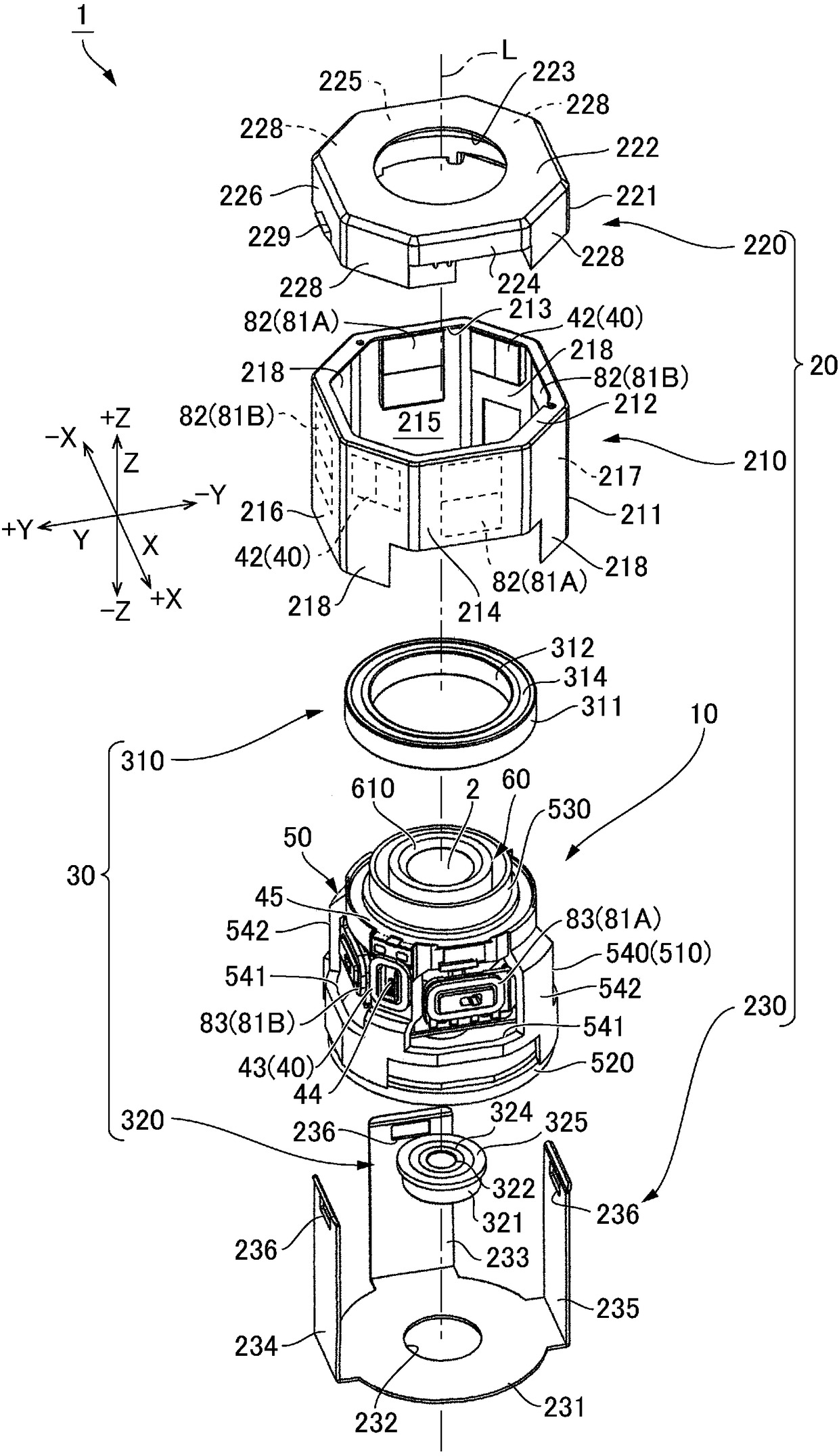
An optical unit capable of reducing wobbling of an optical module that rotates about an optical axis while rotating, and reducing the risk that the rotary bearing portion is damaged by impact is disclosed. The optical unit (1) includes a subject-side rotary bearing part (310) located on a subject side of an optical module (60) and an image-side rotary bearing part (320) located on an image side ofthe optical module. The two rotary bearing parts disposed on both the subject side and the image side of the optical module (60) make it possible to restrain the tilt of the optical module (60) and restrain backlash during a rotation of the optical module (60) around an optical axis. This prevents the optical module (60) from becoming a cantilever state and a twisting load from being applied dueto an impact. Thus, it is possible to reduce the possibility of breakage of the rotary bearing parts due to an impact. A movable body (10) includes a rotary bearing holder (50) which swingably supports the optical module. A rolling magnetic-drive mechanism (40) is disposed between the rotary bearing holder (50) and a fixed body.
Owner:SANKYO SEIKI MFG CO LTD
Balance measuring apparatus for tyre
The invention discloses a balance measuring apparatus for tyre so disposed that a upper rim shaft is inserted an insertion hole of a driving shaft which is rotarily driven by a lower rim shaft, and a hollow operation sleeve slides to a cooperation position, a plurality of balls (12) in the upper and lower parts of the circumferential wall which is maintained on the driving shaft and on which the insertion hole is formed being configured to match an annular groove (14a) which is formed on the peripheral surface of the upper rim shaft (14), so that the upper rim shaft (14) is firmly locked circumferentially at the upper and lower positions. In rotation, the invention can inhibit inclination or vibration and swinging of the upper rim shaft (14) in order to increase measuring accuracy.
Owner:YAMATO SCALE CO LTD
Differential Gearing for Vehicle
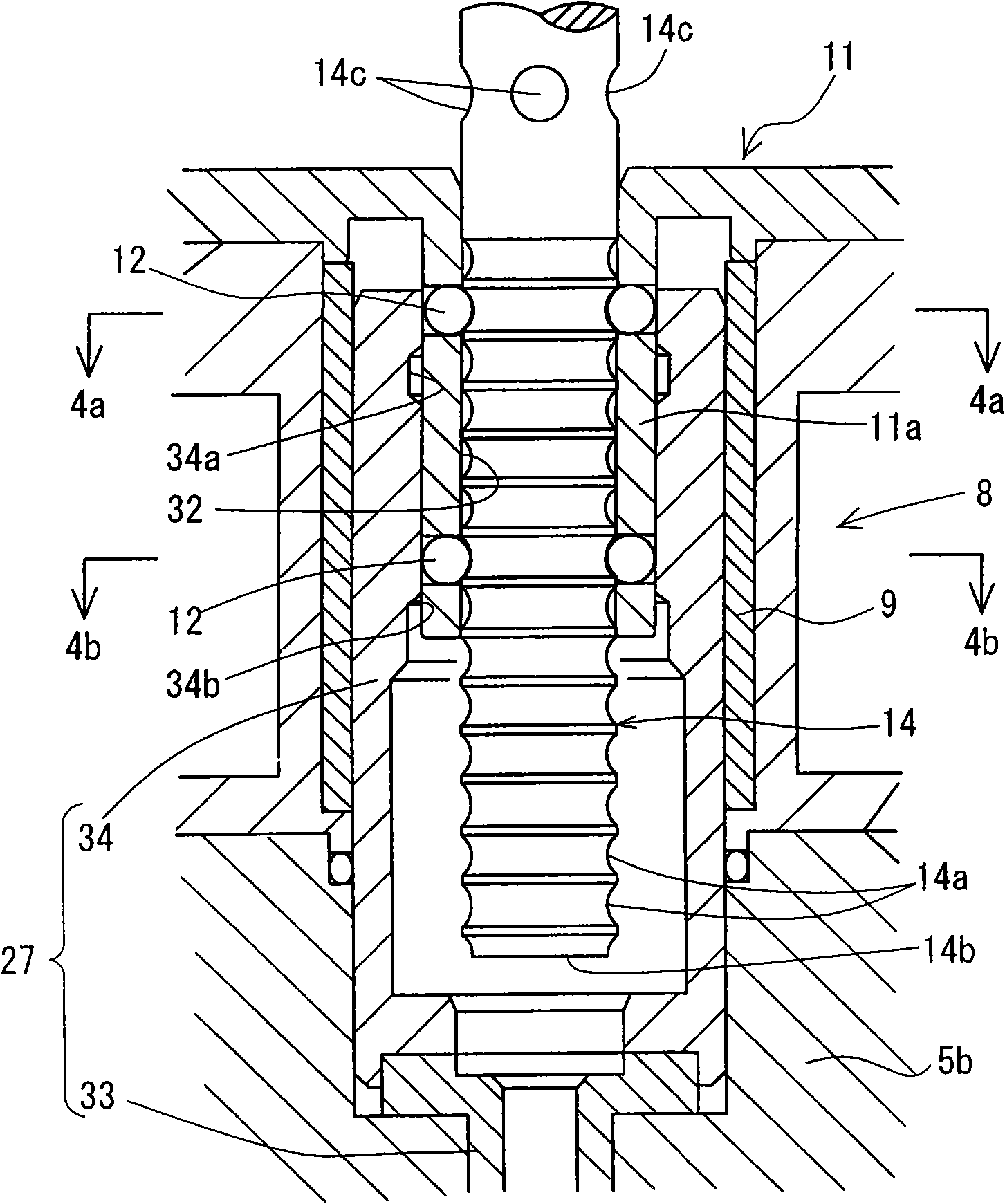
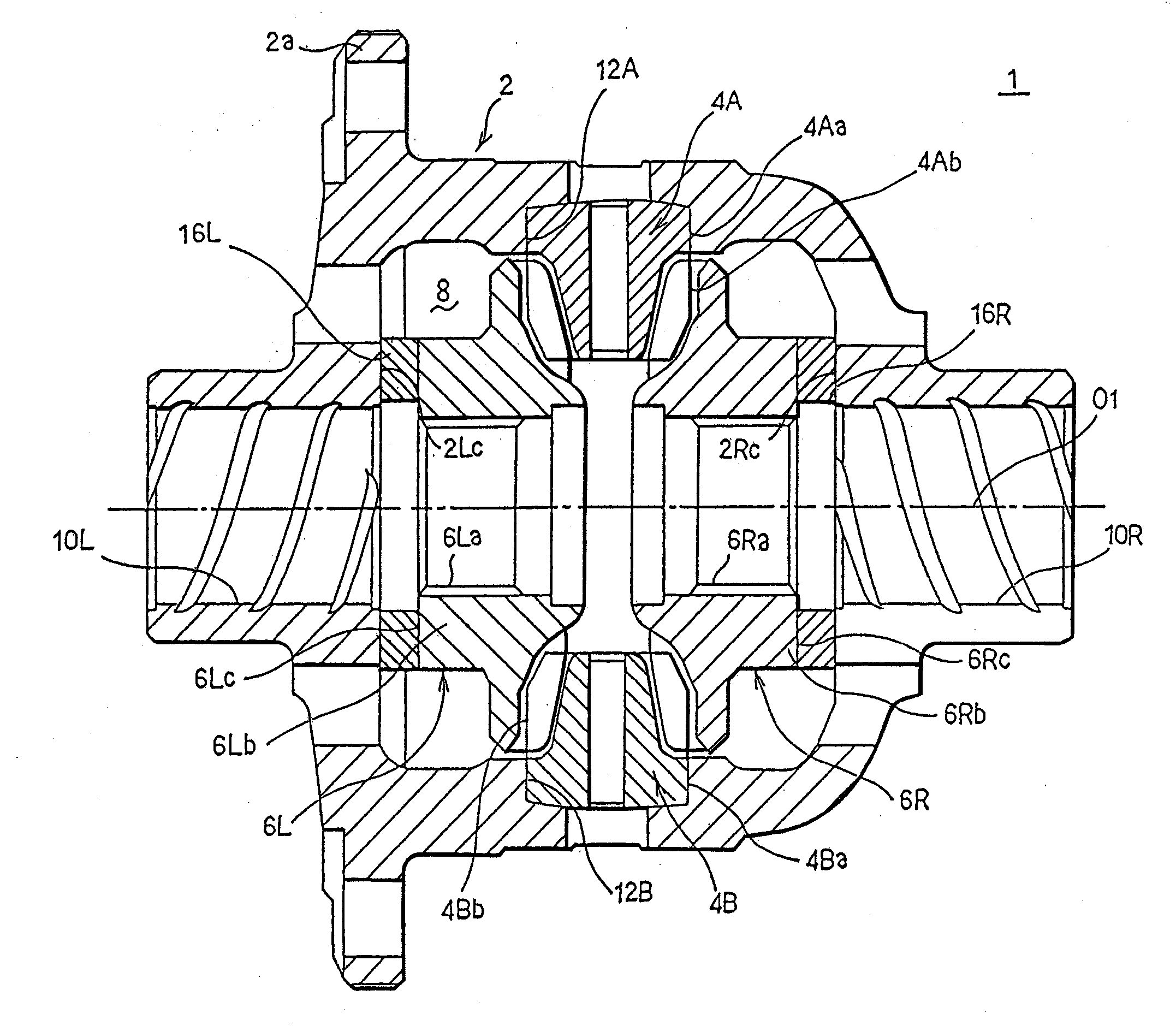
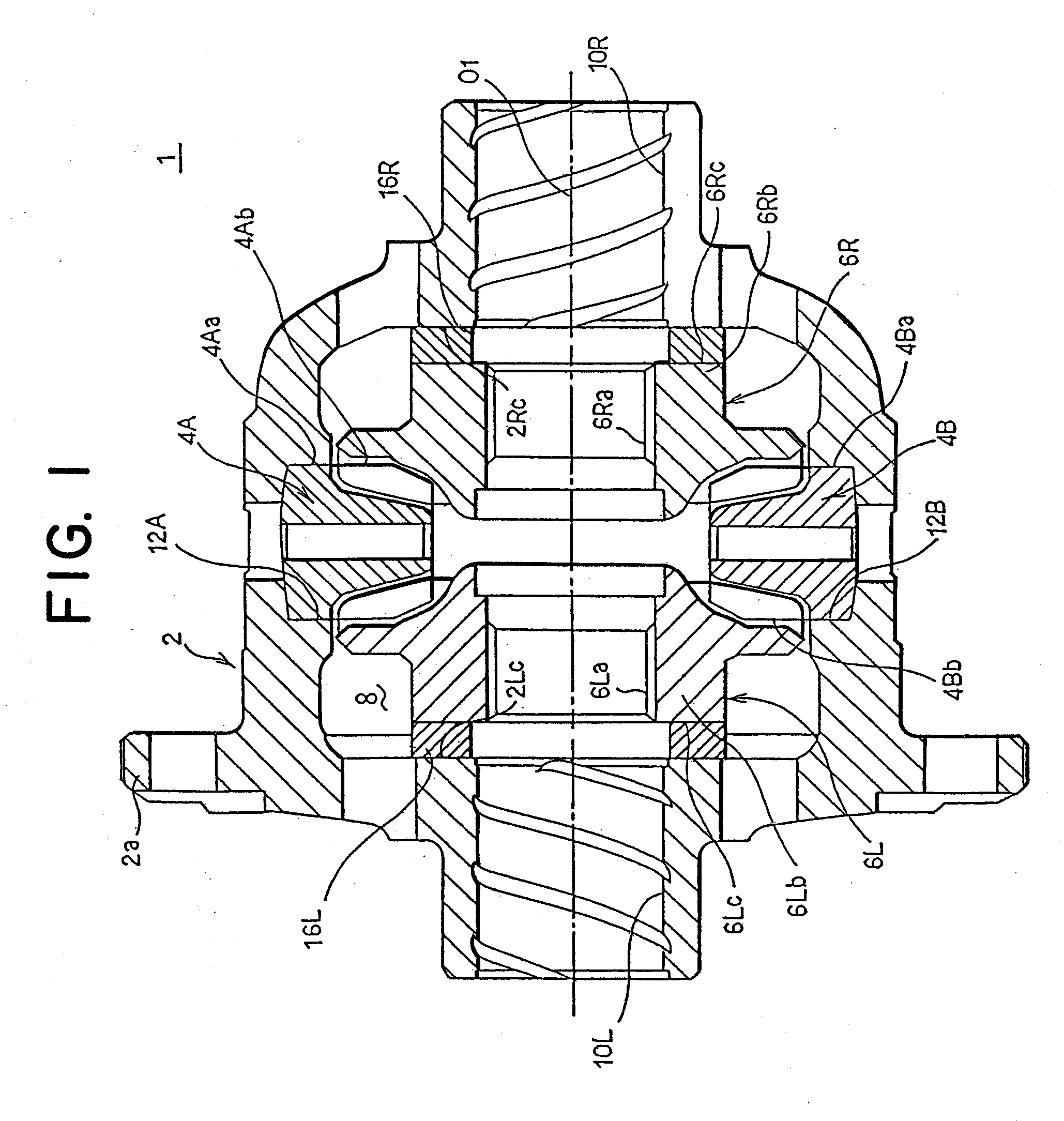
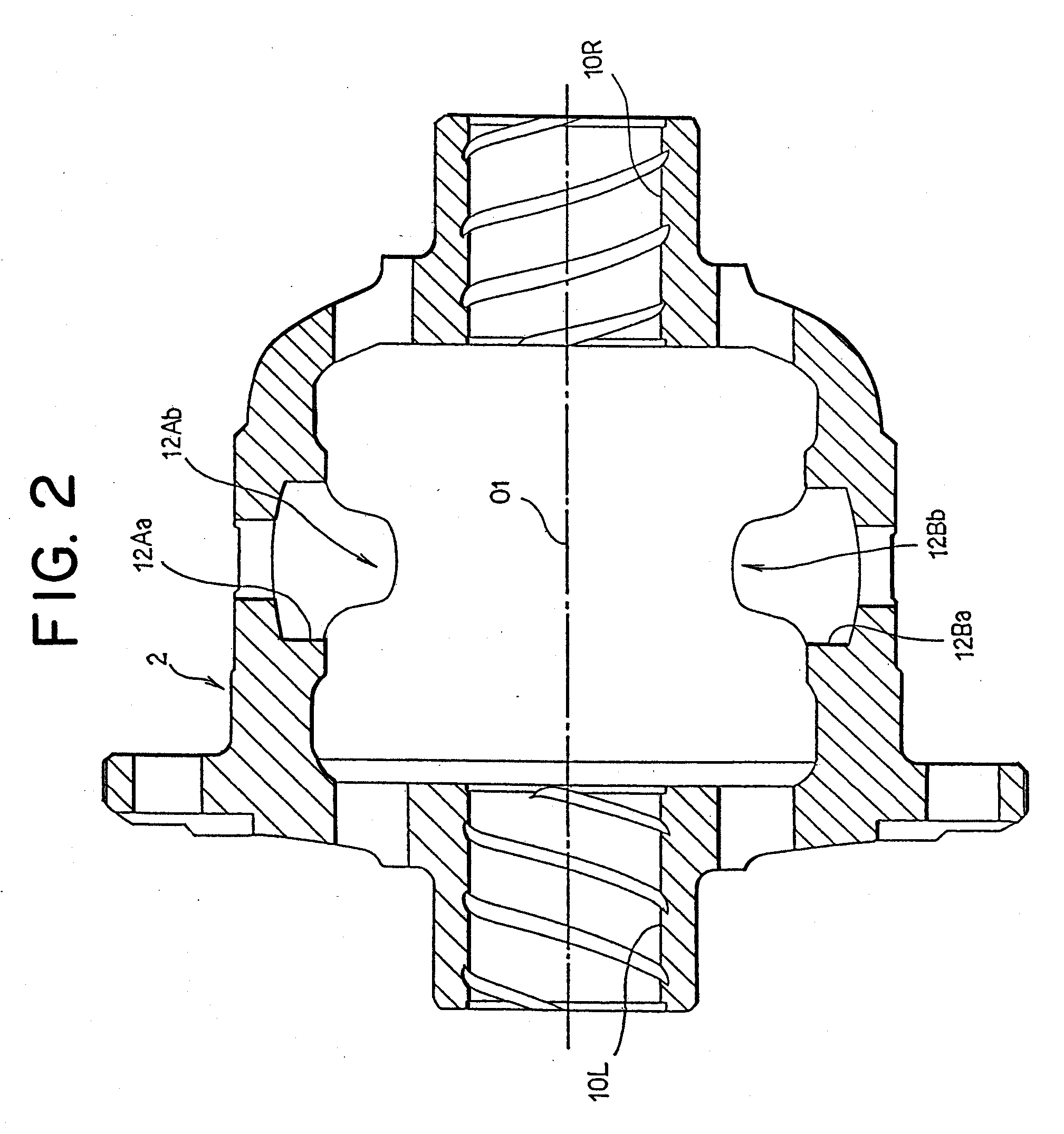
A plurality of pinion gears 4A, 4B which are rotatably held within a differential case 2, a pair of left and right side gears 6L, 6R disposed in meshing engagement with the pinion gears and connected to left and right axles, respectively, and thrust washers 16L, 16R interposed between the rear surfaces of the side gears and the internal surface of the differential case are provided. The differential case is of a one-piece type, and is formed with an opening 2b in its sidewall, which is used in assembling the pinion gears and the like. The internal surface of the differential case is formed with pinion gear holders 12A, 12B. The pinion gears are inserted, followed by the insertion of the side gears. The side gears are spaced from the pinion gears by an amount corresponding to the thickness of the thrust washers, and this allows the side gears to be inserted in following relationship with the pinion gears.
Owner:JTEKT CORP
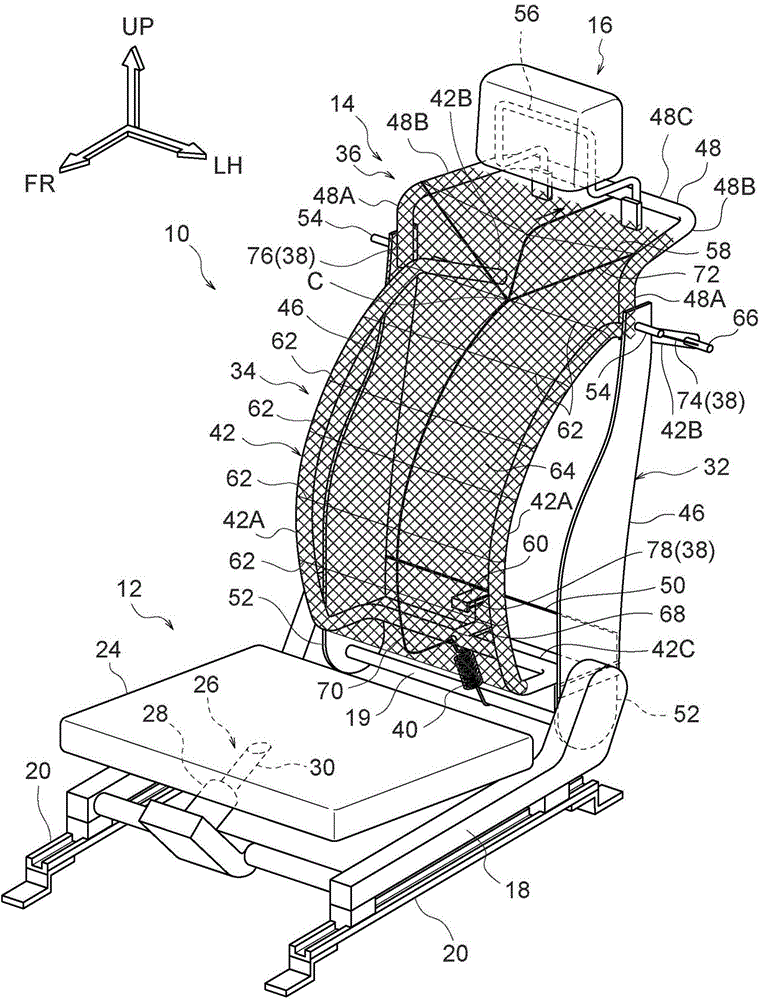
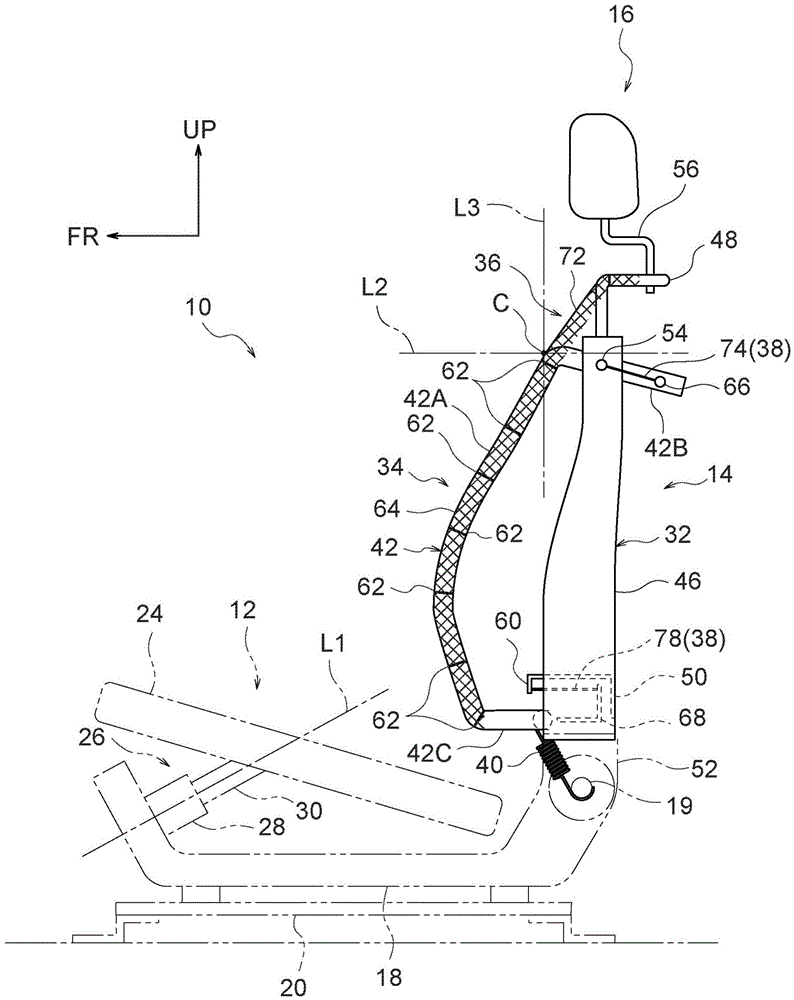
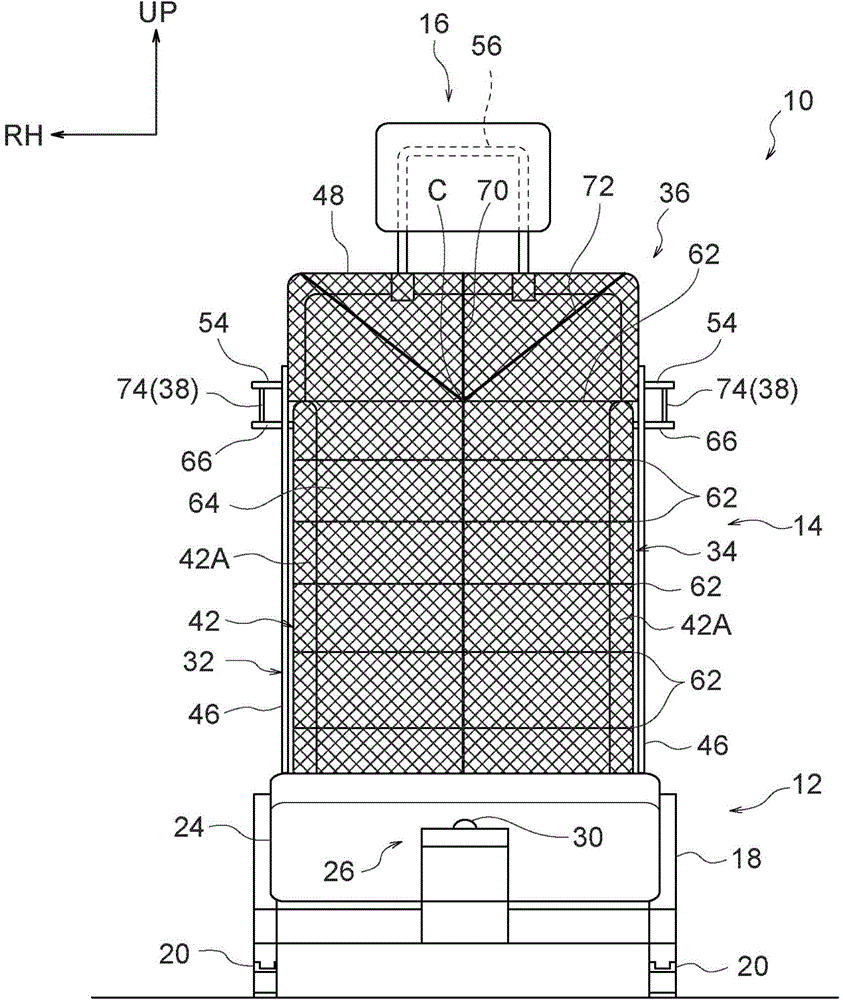
Vehicle seat
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Elevator apparatus
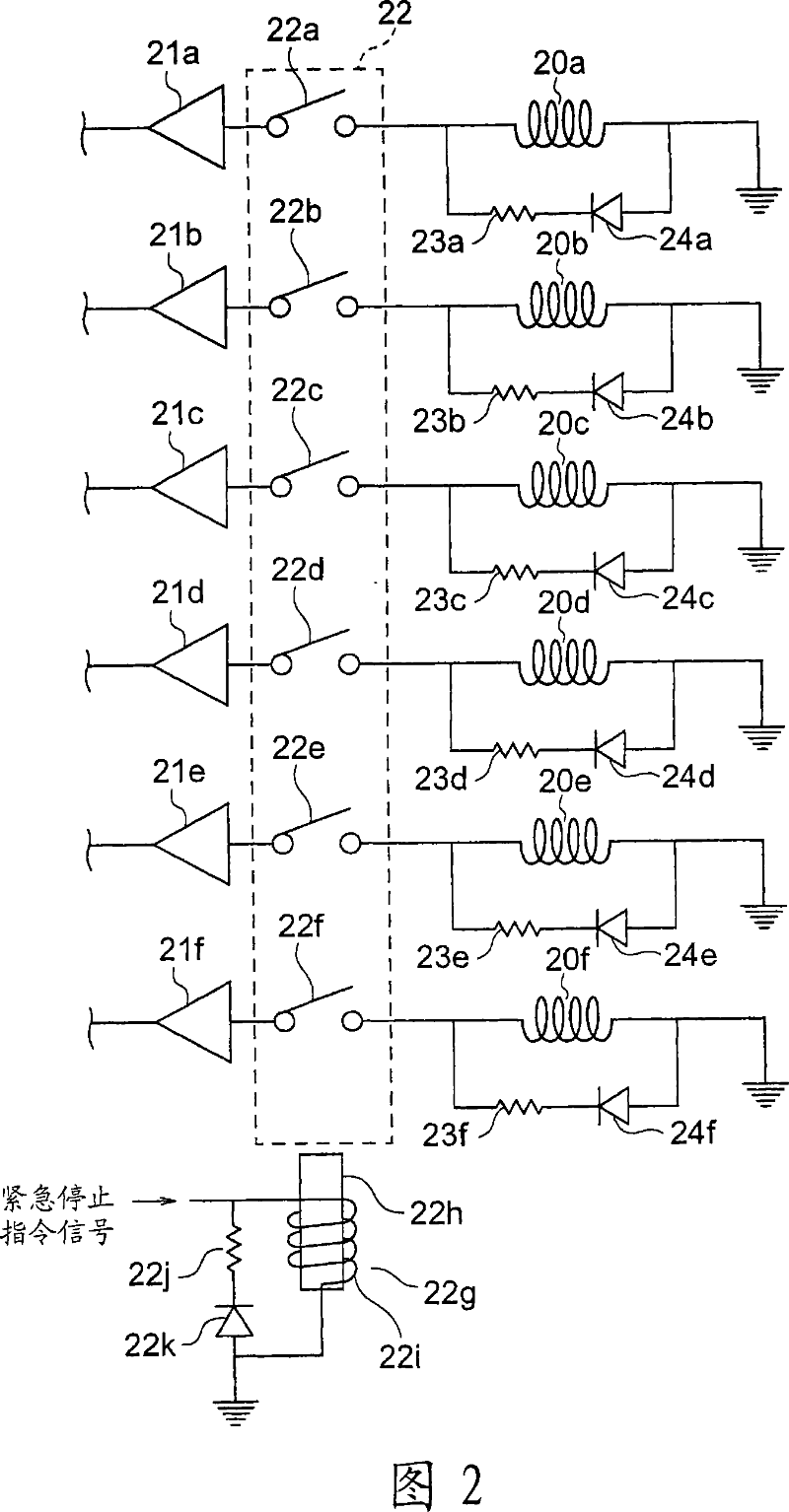
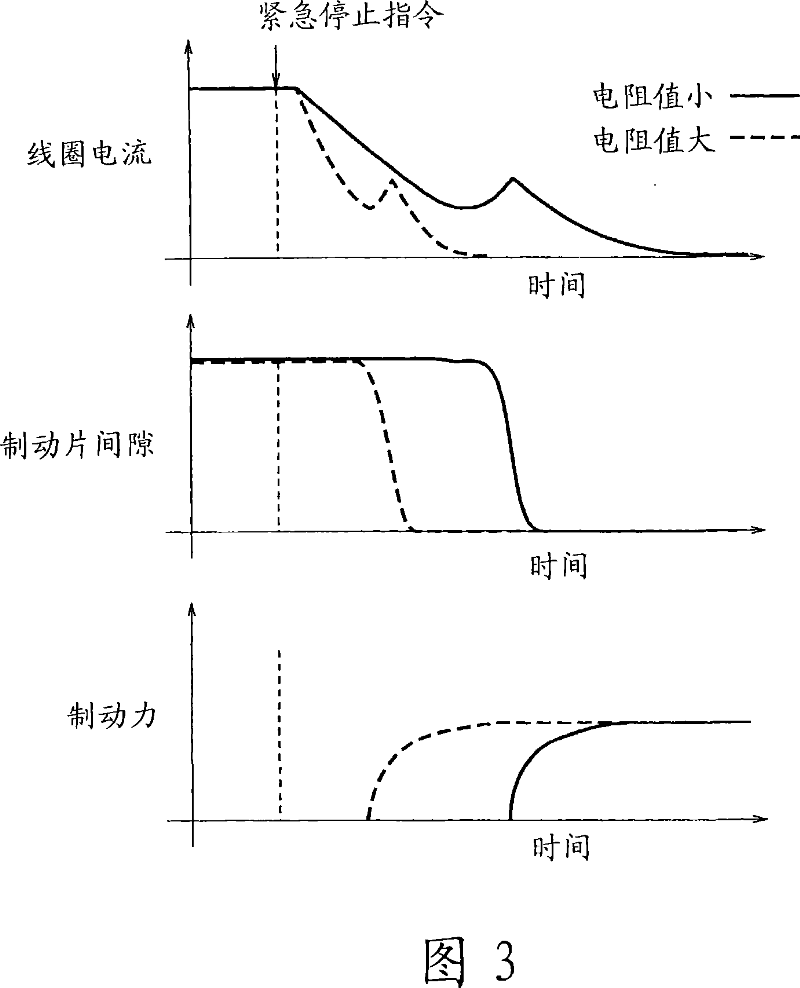
An elevator device in which an elevator car is lifted and lowered by drive force of drive devices. Each of the drive devices has a drive sheave, a motor for rotating the drive sheave, and a brake device for braking rotation of the drive sheave. The brake device has brake bodies belonging to different groups. In emergency braking, the brake device causes the brake bodies to generate force for each group at a different timing.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Lens driving device and camera module
InactiveCN102445744AReduce the numberLow costProjector focusing arrangementCamera focusing arrangementComputer moduleMiniaturization
A lens driving device prevents its holder from tilting while driving the lens, and has a small number of components, low cost, and small size. The lens driving device includes a base, a holder, magnets, and magnetic plates. The base includes a projection having a hook-shaped cross section. The holder includes a rotation inhibitor which comes into contact with the projection of the base. The holder is supported to the base by one shaft. One magnetic plate is located further from the shaft than the center of the magnet is. The other magnetic plate is located closer to the shaft than the center of the magnet is. The magnetic forces generated between the magnetic plates and the magnets make the holder subjected to a torque on the shaft. The torque allows the rotation inhibitor to be slightly pressed against the projection.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
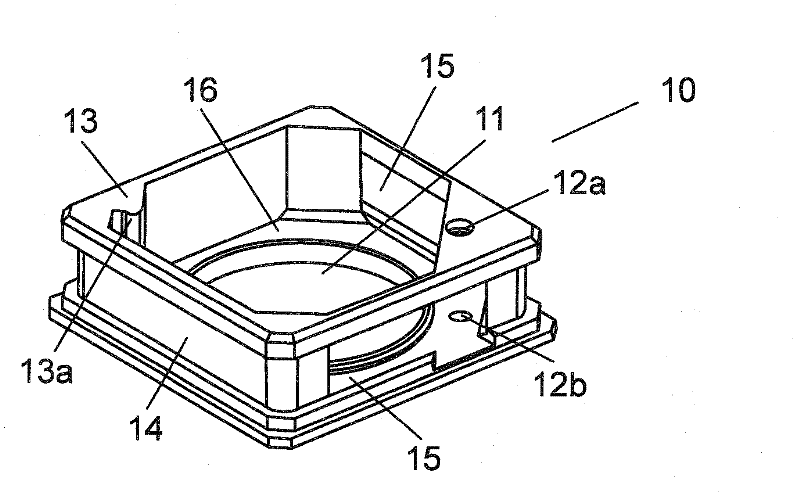
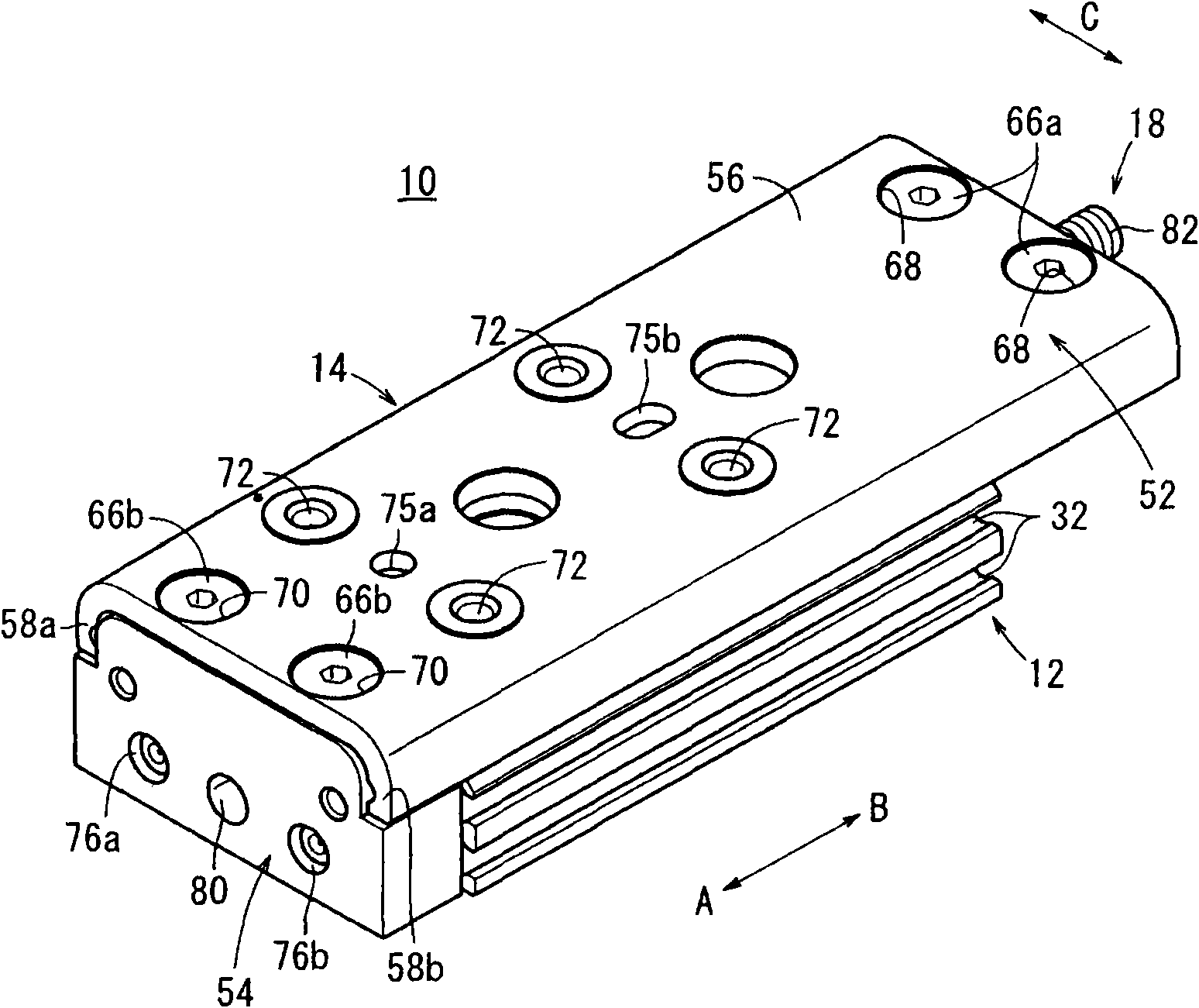
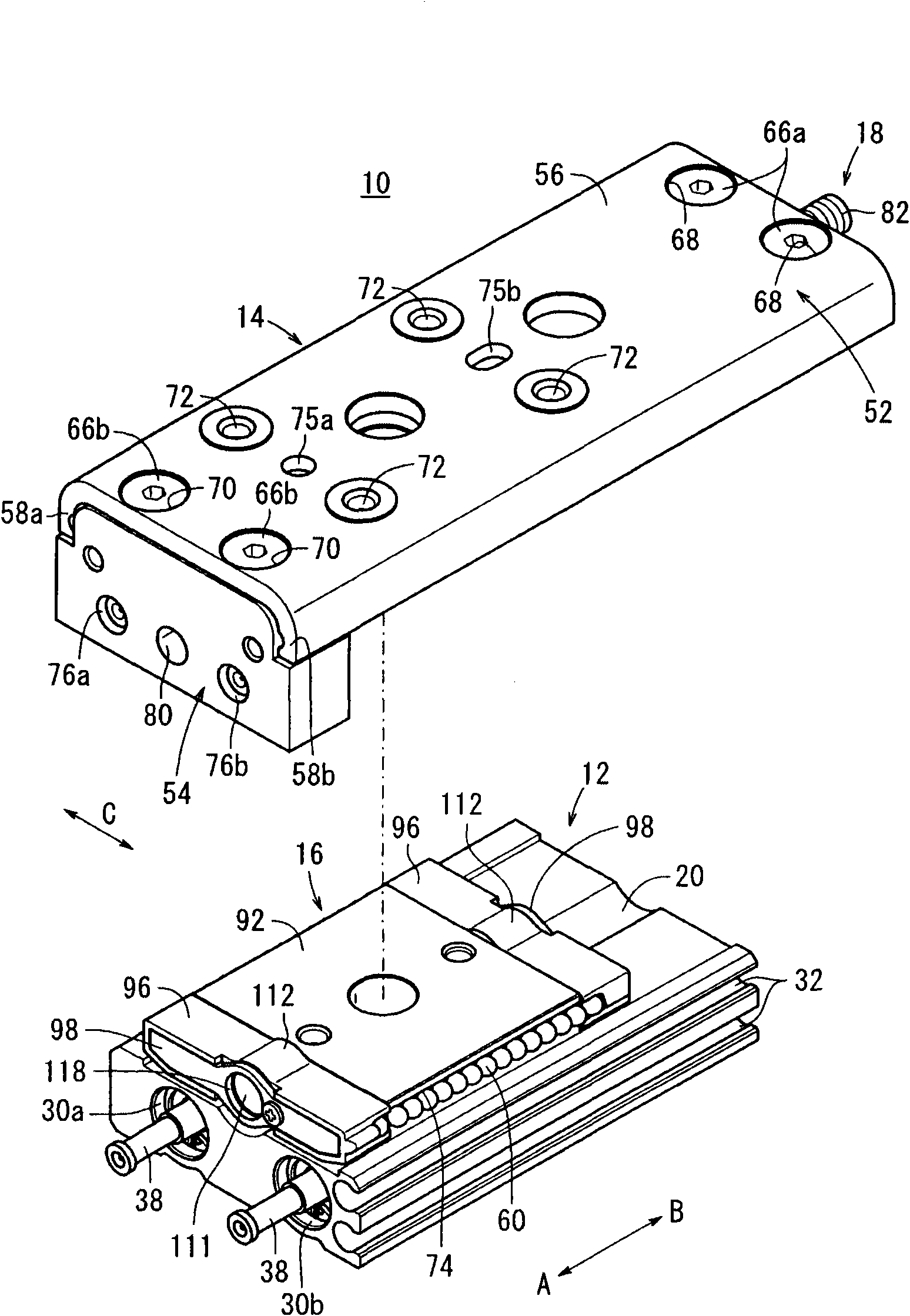
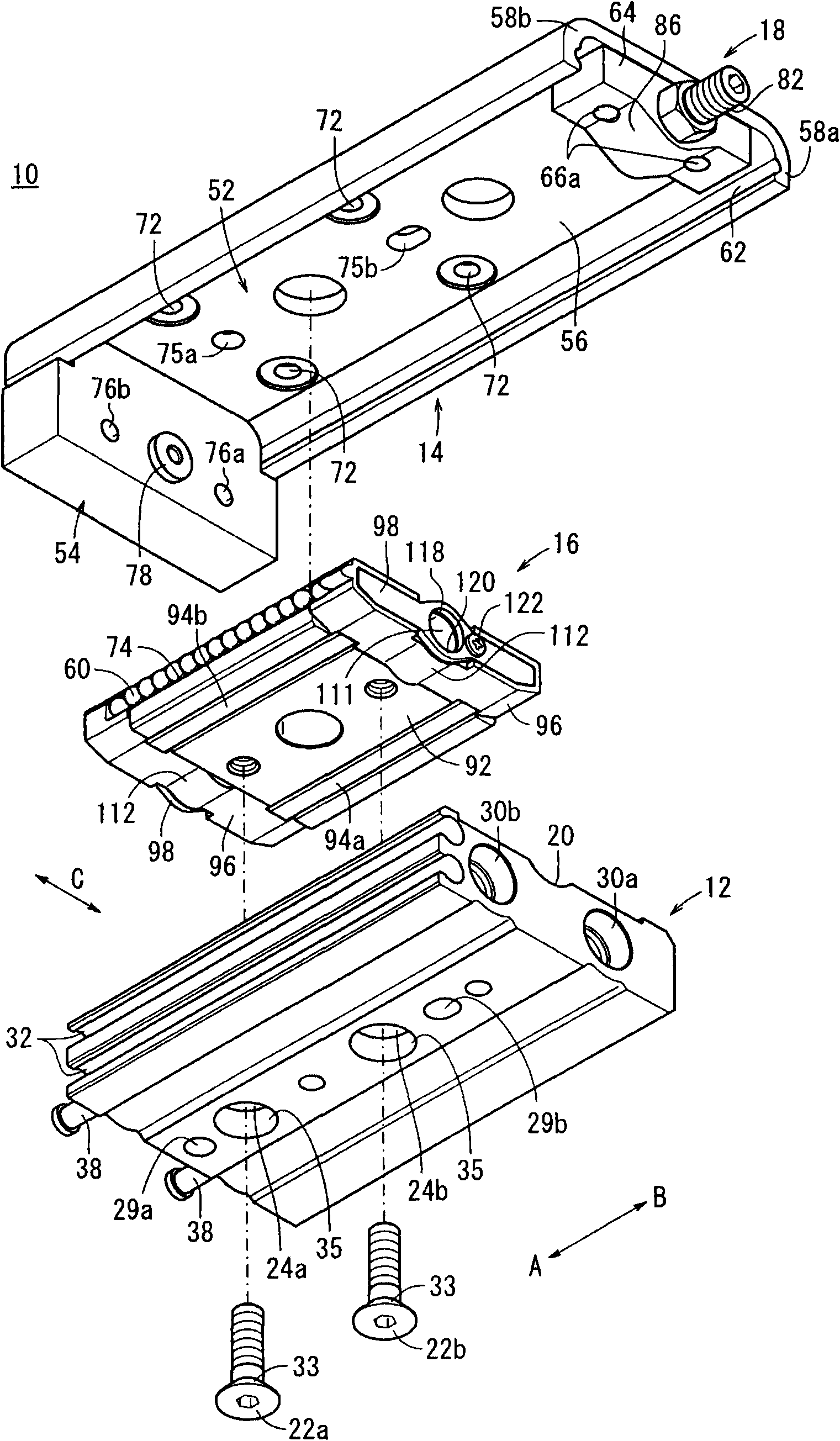
Linear actuator
A linear actuator (10) includes a cylinder main body (12). With respect to the cylinder main body (12), a slide table (14) is disposed for reciprocal displacement through a guide mechanism (16), which is disposed on the cylinder main body. A stopper mechanism (18) having a stopper bolt (82) is disposed on one end of the slide table (14) centrally in a widthwise direction perpendicular to the longitudinal direction of the slide table (14). In addition, when the slide table (14) is displaced along the cylinder main body (12), one end of the stopper bolt (82) comes into abutment with an end of a cover (96) of the guide mechanism (16), whereupon the slide table (14) becomes engaged therewith and movement of the slide table (14) is stopped.
Owner:SMC CORP
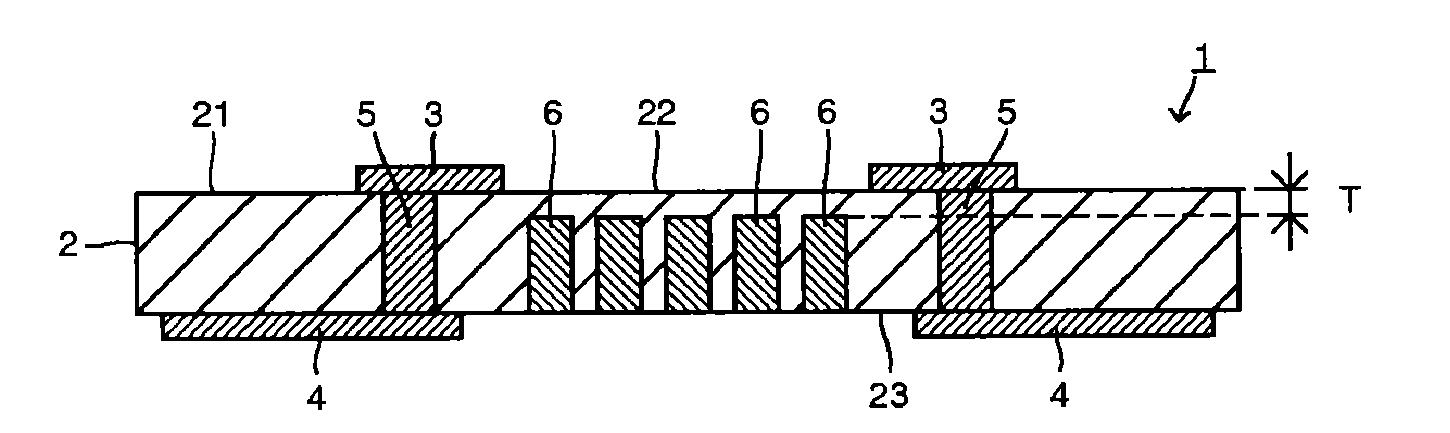
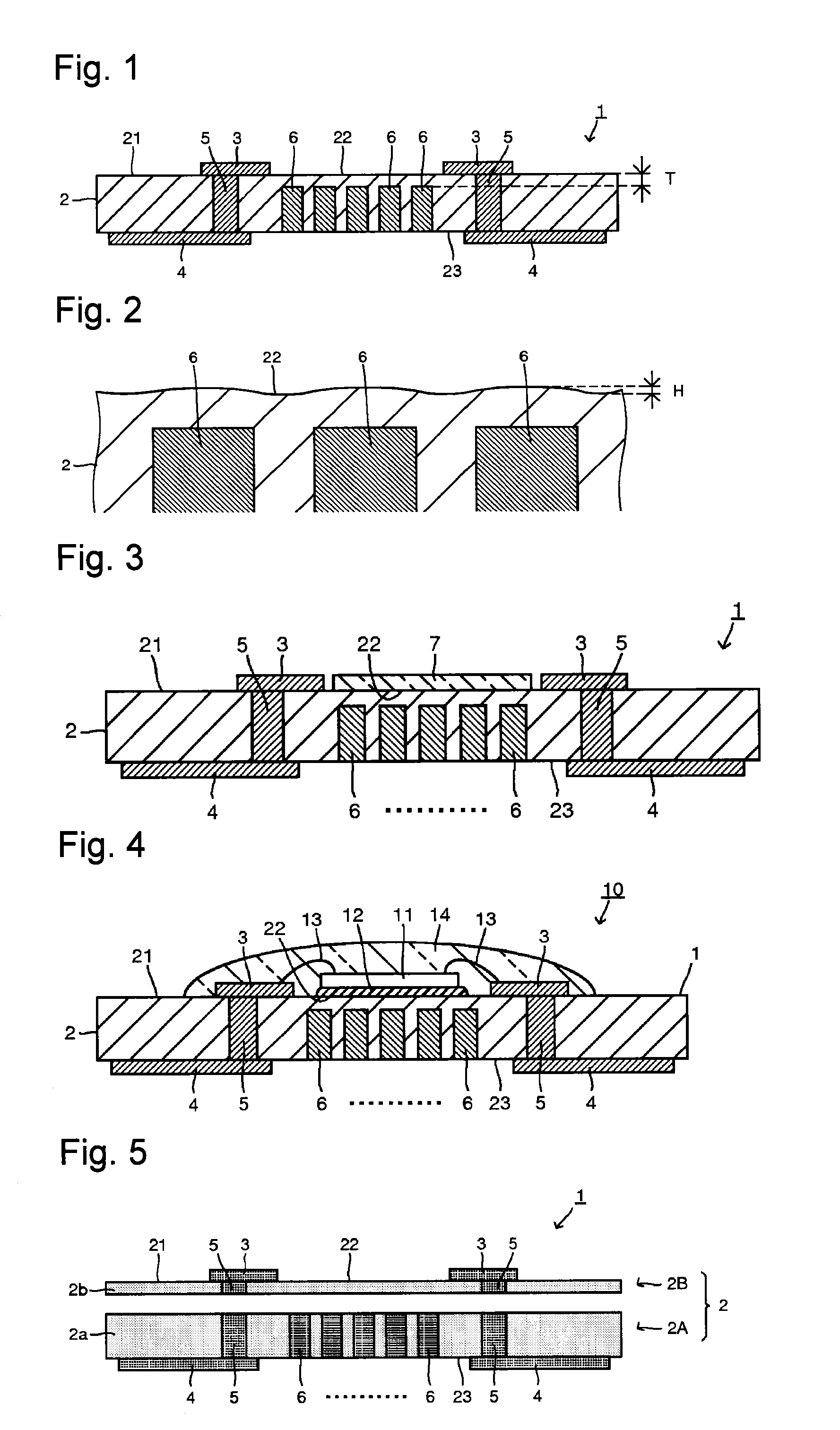
Stacked type solid electrolytic capacitor and method for manufacturing same
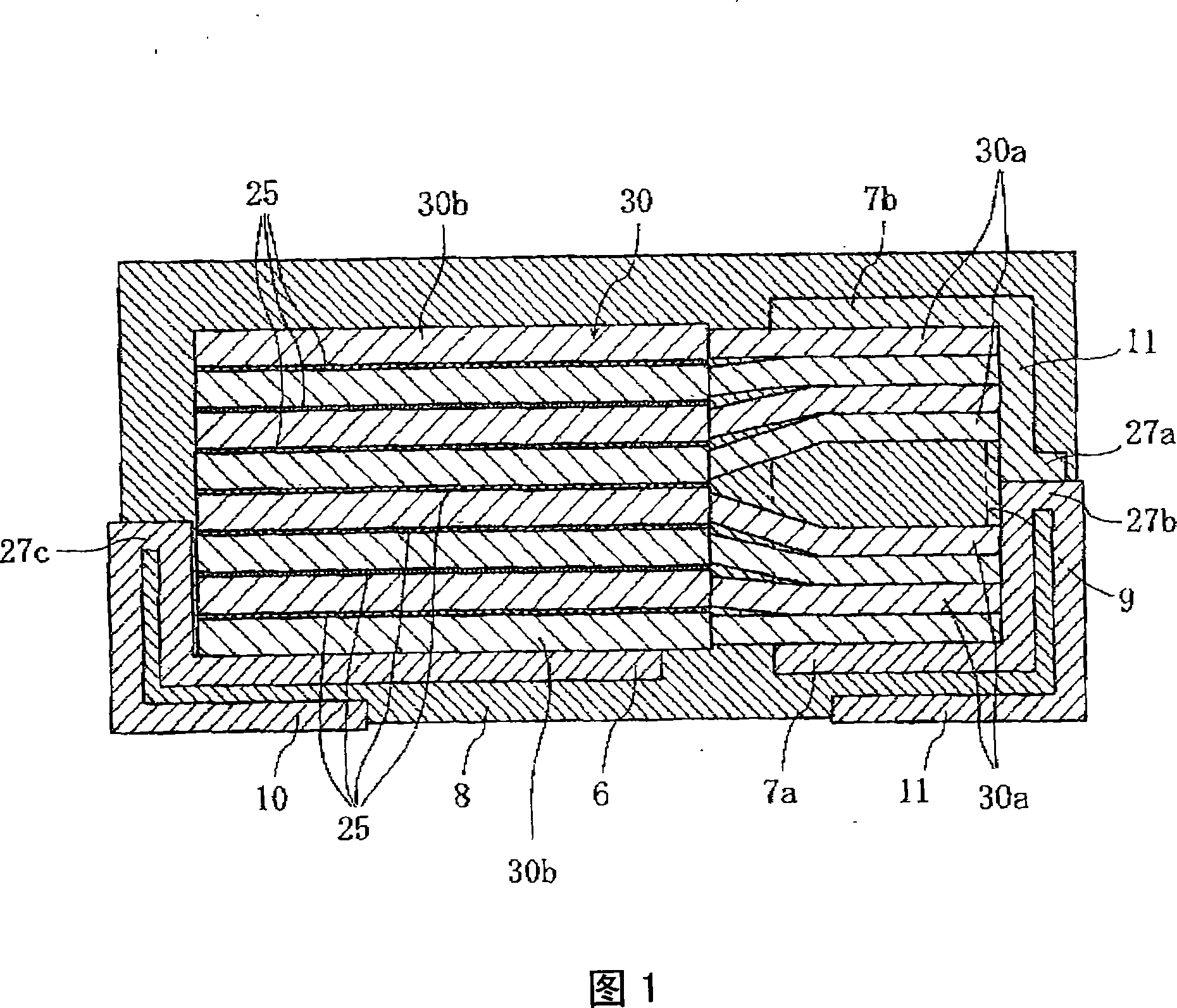
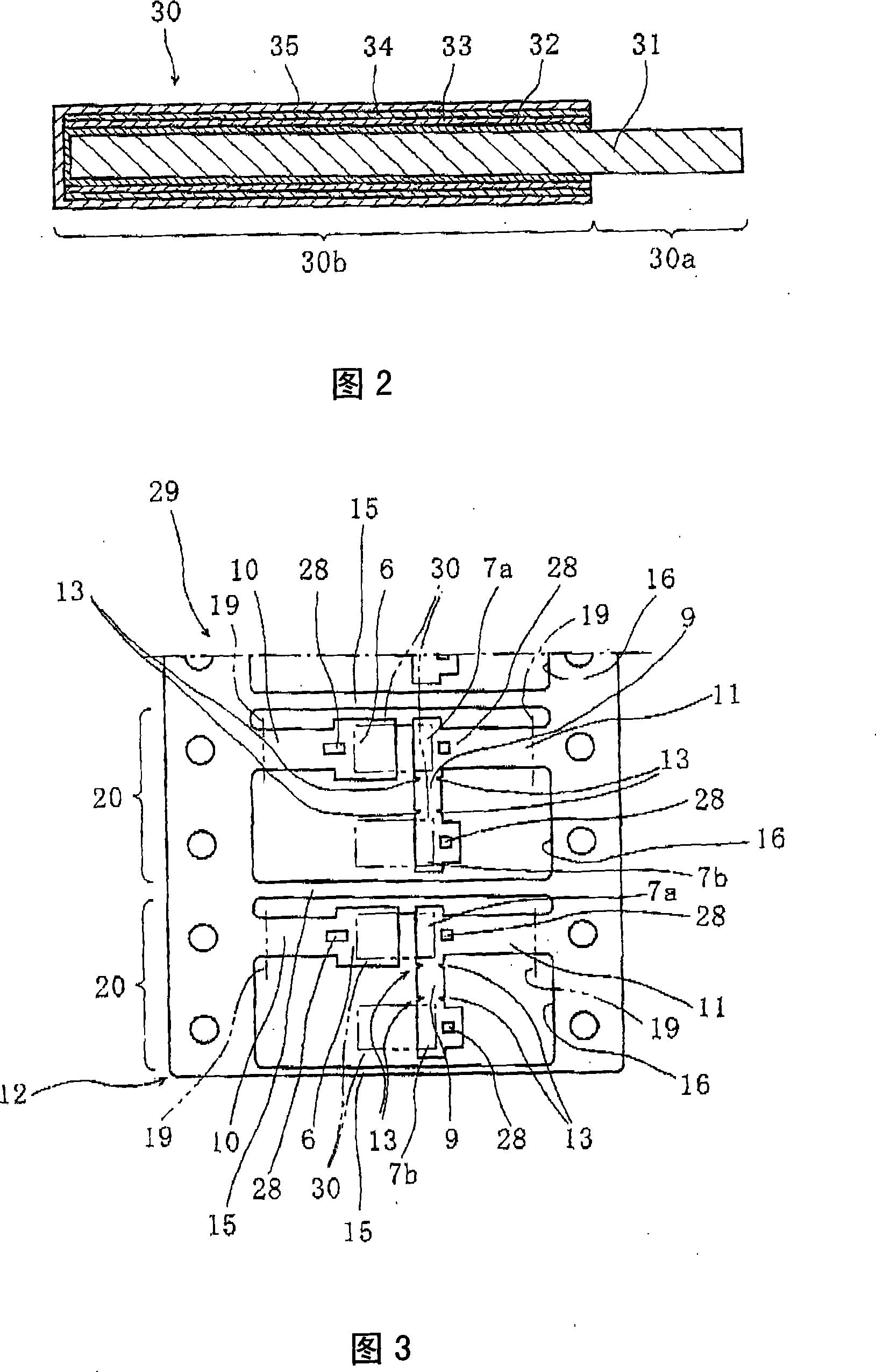
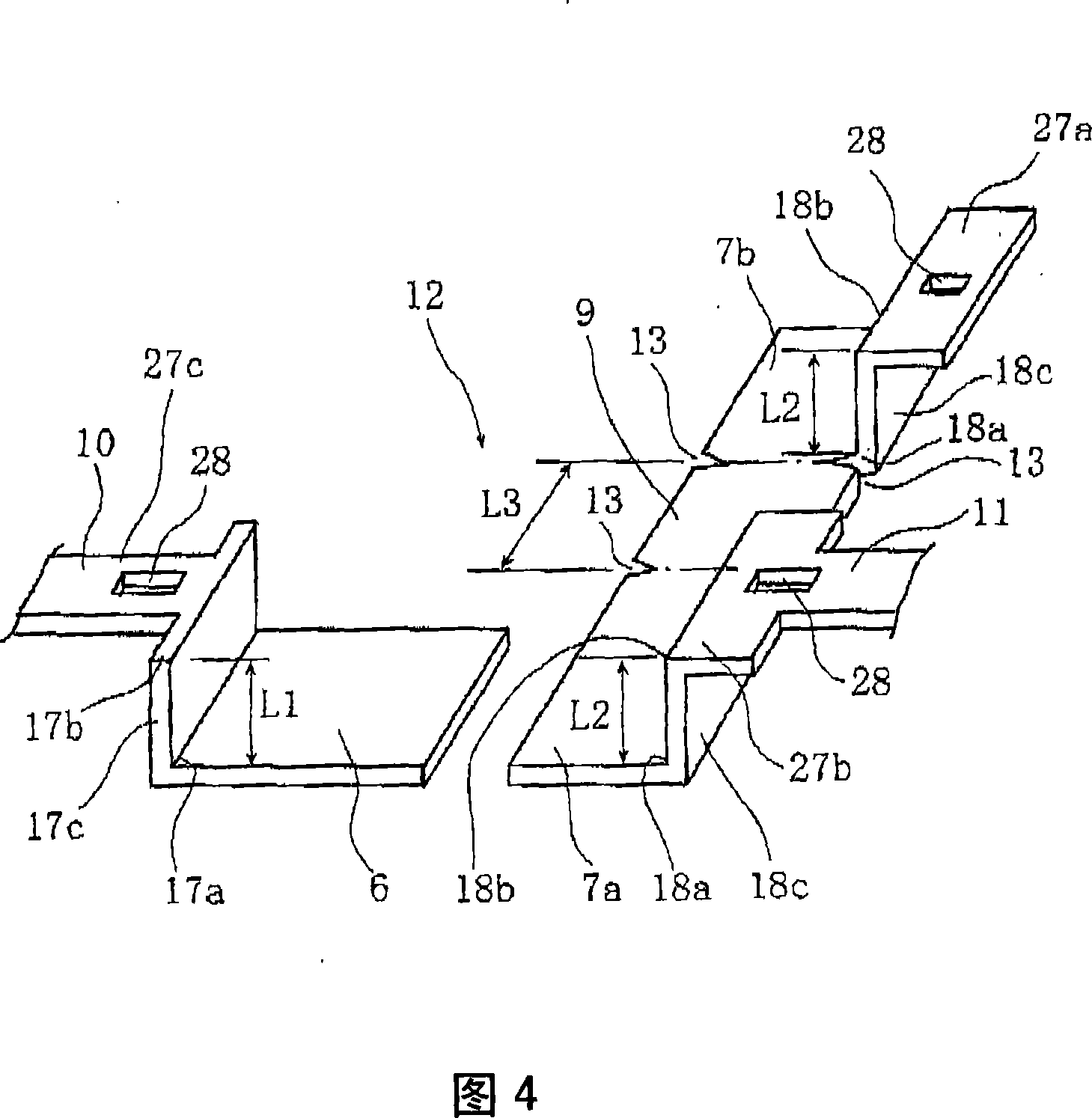
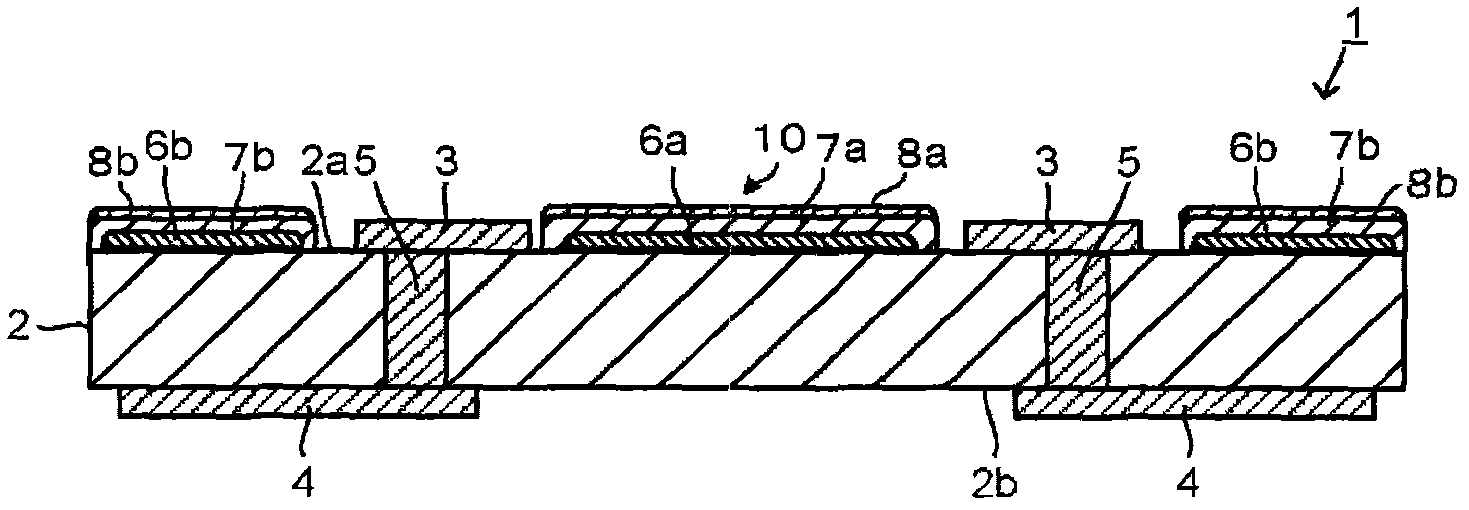
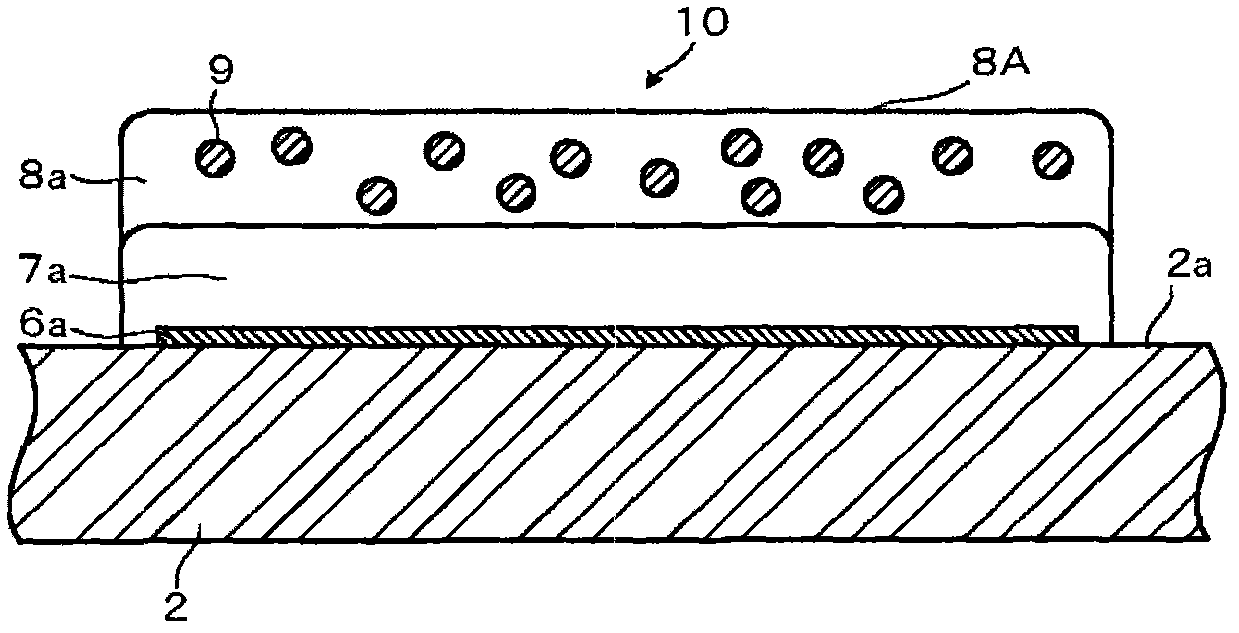
ActiveCN101176172ALower on-resistanceEasy to power onSolid electrolytic capacitorsCapacitor electrodesCapacitanceElectrolytic capacitor
A solid electrolytic capacitor has a structure wherein a capacitor element (30) is arranged by being stacked, and an anode section (30a) is fixed by being welded on anode mounting planes of anode mounting sections (7a, 7b) provided on an anode terminal. The solid electrolytic capacitor is characterized in that the two anode mounting sections (7a, 7b) are provided, the anode mounting sections (7a, 7b) are arranged in parallel, and the adjacent anode mounting sections (7a, 7b) are mutually connected by a connecting section (9).
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD +1
Sealed cell
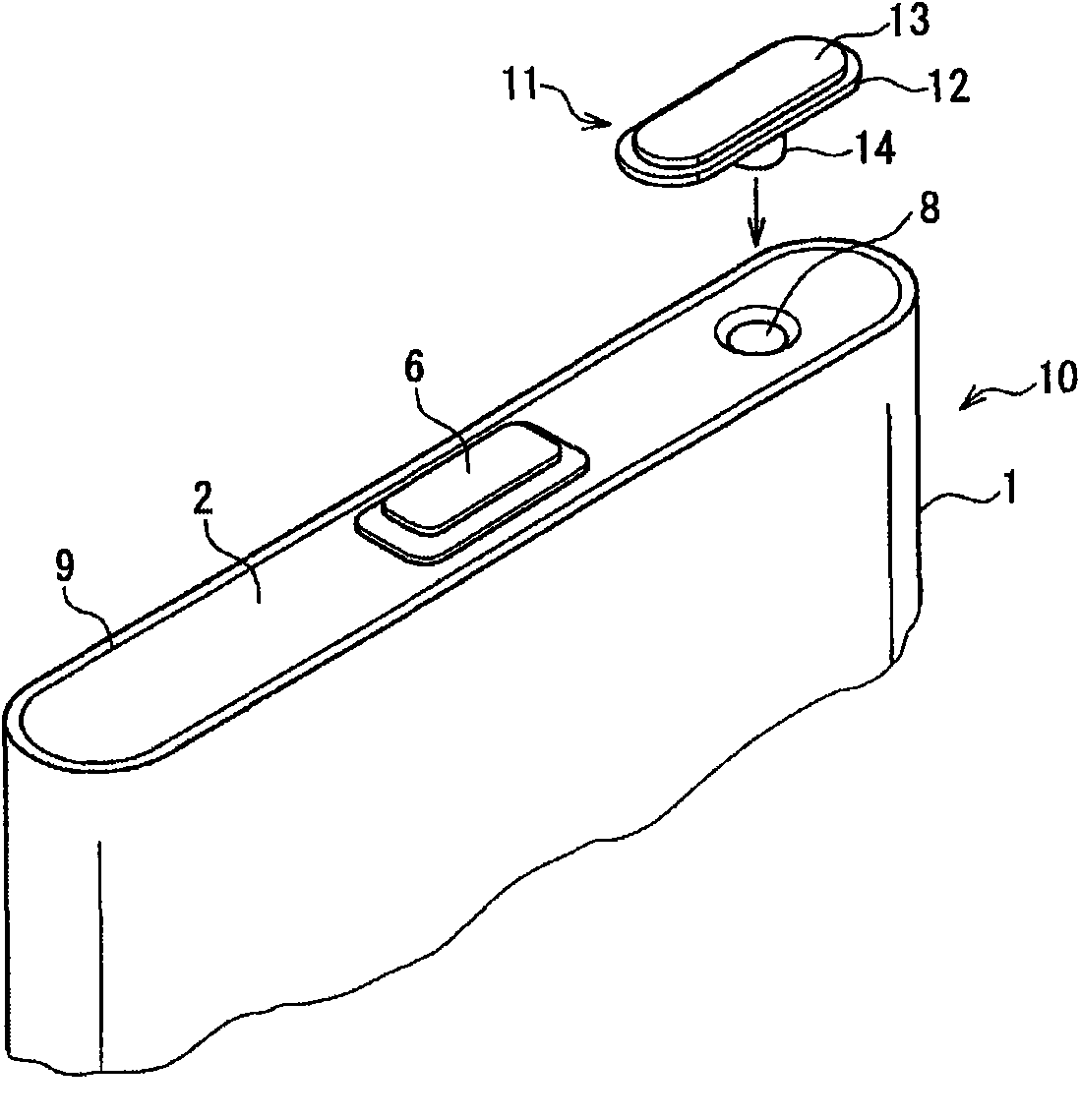
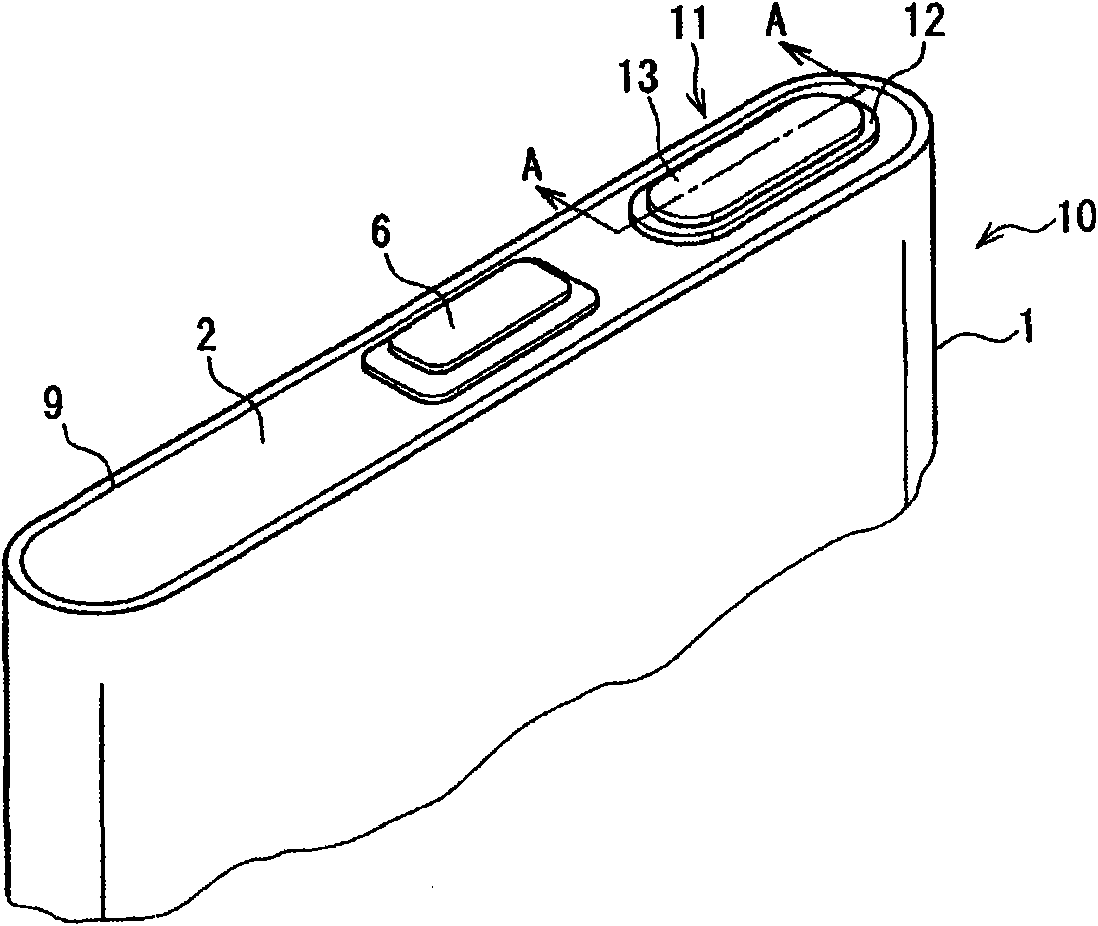
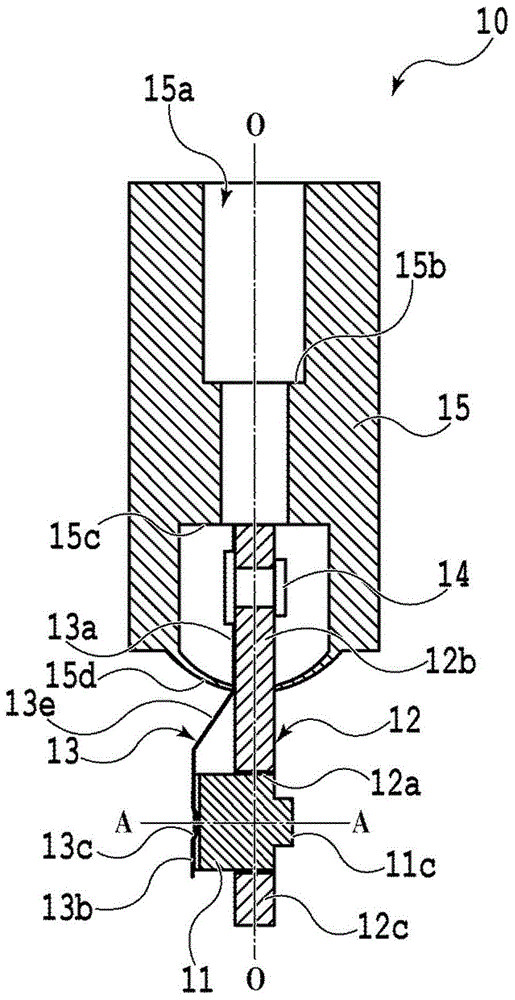
InactiveCN101626088ASuppress floatingCurb tiltSecondary cellsCell component detailsEngineeringWelding
The present invention provides a sealed cell which can restrain floating and inclining of a sealing body, and avoid bad welding. The sealed cell adopts an opening of a sealing body (2) for sealing, wherein, the opening is used for canning externally, a sealing body (11) is inserted into a hole (8) formed on the sealing body (2), the hole (8) forming makes the diameter increased following a surface of a taper face (15) towards to the package body (2), an interval (16) forms between the taper face (15) and the sealing body (11), and the sealing body (11) is welded on the package body (2). The taper face (15) is benefit for eccentricity and inclining of the sealing body (11) in installing. A biting sheet generated in inserting the sealing body is stored in the interval (16). The floating and inclining of the sealing body (11) caused by sandwiching of the biting sheet can be restrained and bad welding is avoided.
Owner:HITACHI MAXELL ENERGY LTD
Hoisting and lowering driving engagement multi-row chain
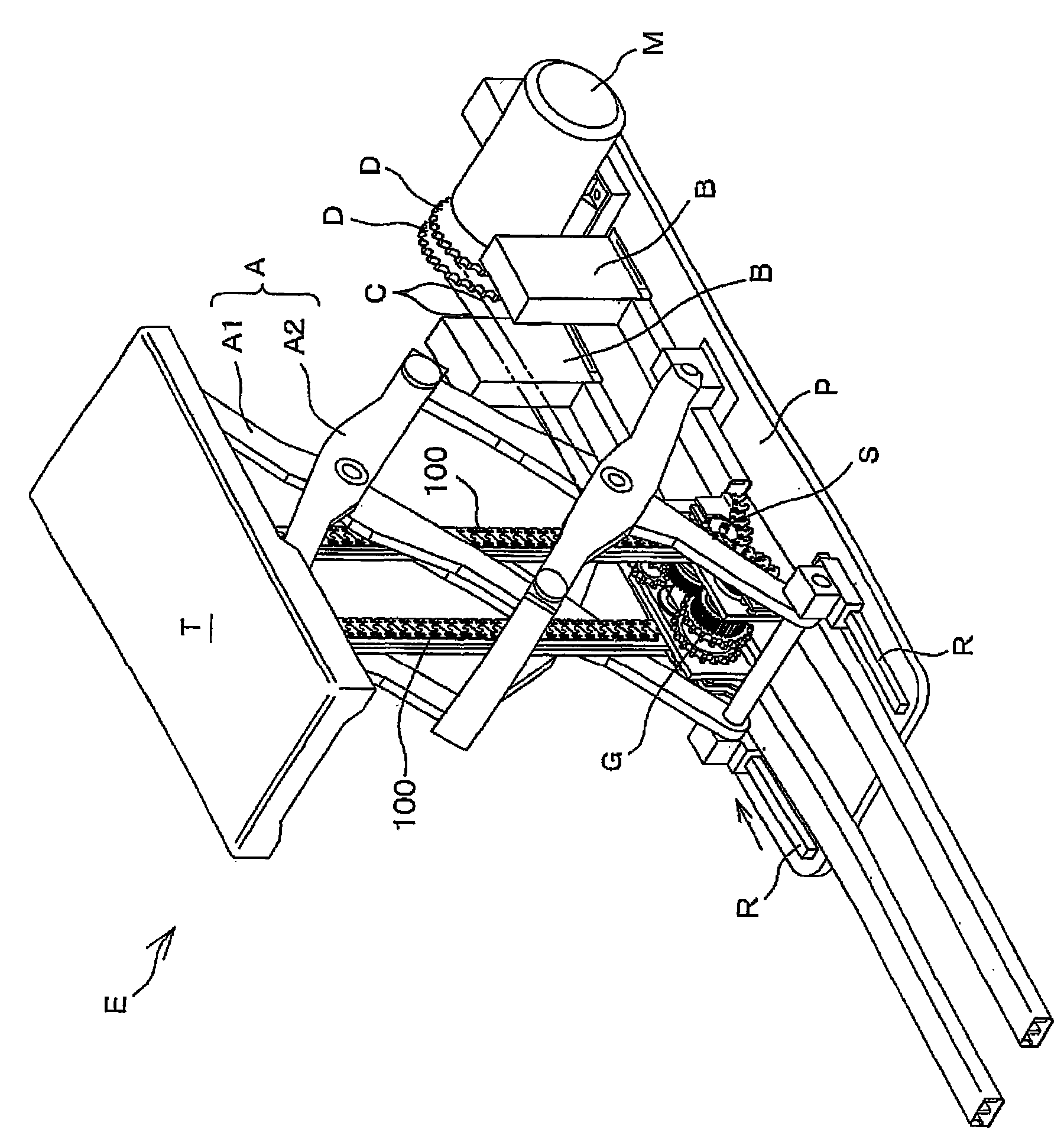
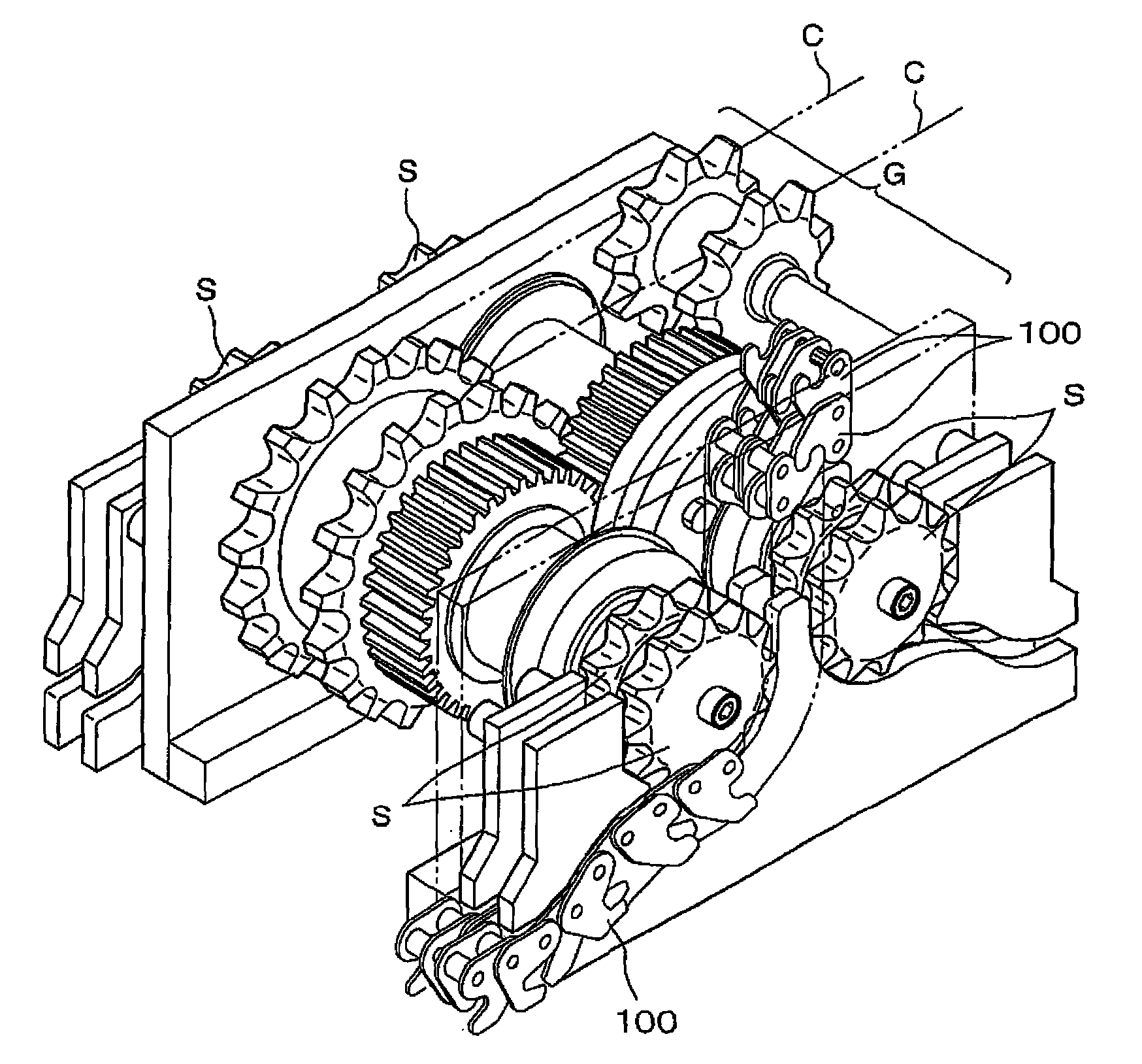
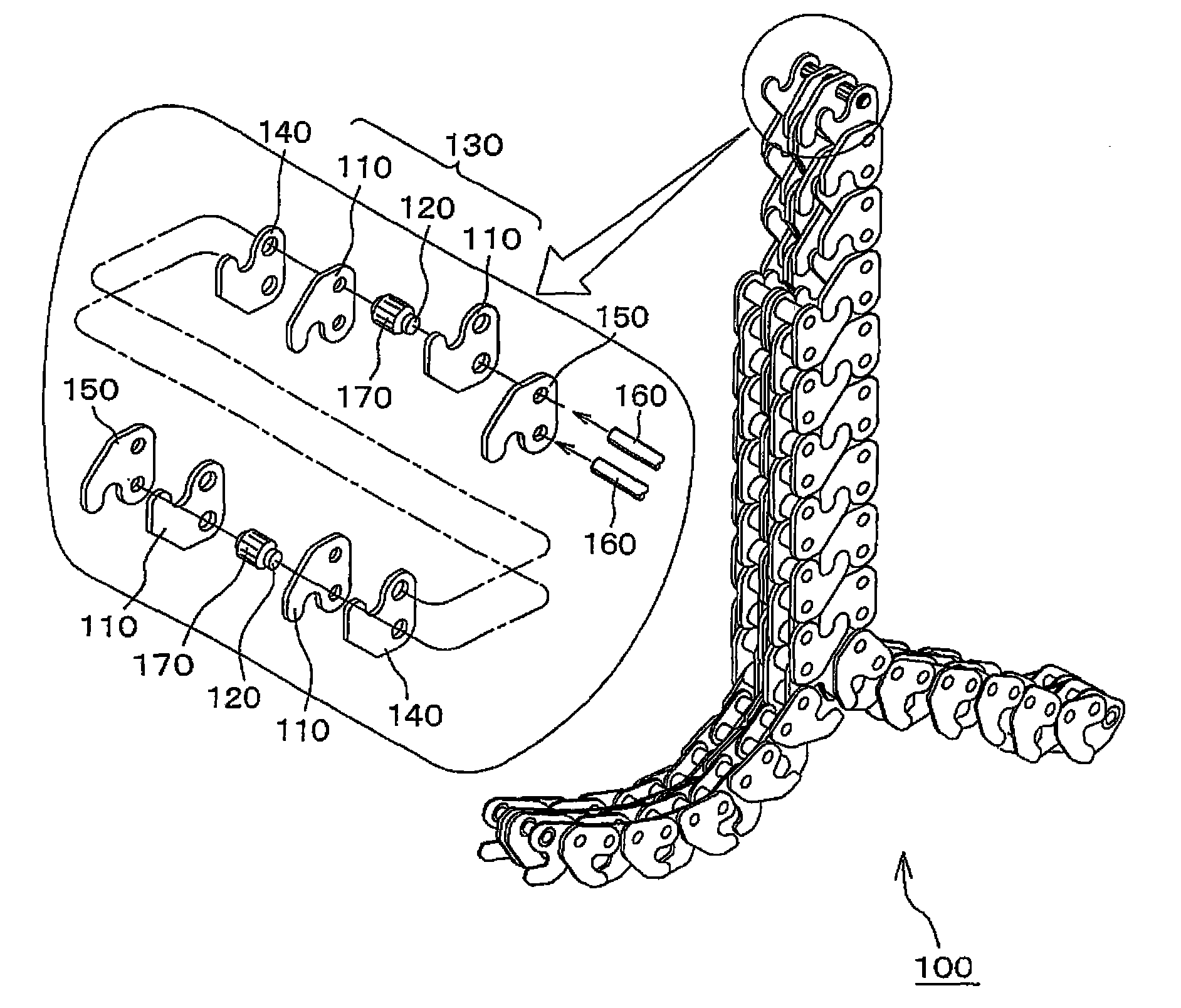
InactiveCN101654214ACurb bendingImprove mesh balanceLifting framesFriction gearingsMiniaturizationEngineering
Aspects of the invention provide a hoisting and lowering driving engagement multi-row chain in which the weight of the chain is balanced across the chain width direction so as to improve the load balance. This allows the weight of articles to be hoisted and lowered more stably hoisted and at higher positions, and results in an improvement of endurance of the chain, reduction of driving noise, miniaturization of the chain size, while the biasing or deflecting of intermediate tooth plates and inner tooth plates in the chain width direction is suppressed. The hoisting and lowering driving engagement mluti-row chain 100 includes, inner tooth plates 110, a bushing 120, intermediate tooth plates 140, outer tooth plates 150 and connecting pins 160, and the inner tooth plates 110, the intermediate tooth plates 140 and the outer tooth plates 150 are manufactured by blanking with molds in same shape from a same direction, and at least one of the inner tooth plates 110, the intermediate tooth plates 140 and the outer tooth plates 150 are connected with other plates in a state of back reversion.
Owner:TSUBAKIMOTO CHAIN CO
Anti-pulling system
An anti-pulling system comprises an upper connecting plate, a lower connecting plate, an upper layer of sliding mechanism, a lower layer of sliding mechanism and intermediate layers, the upper layer of sliding mechanism and the lower layer of sliding mechanism are respectively connected with the upper connecting plate and the lower connecting plate, the intermediate layer is connected between the upper layer of sliding mechanism and the lower layer of sliding mechanism, and the upper layer of sliding mechanism and the lower layer of sliding mechanism have the same structure, are mounted opposite from each other, and can slide in directions perpendicular to each other. The upper (lower) layer of sliding mechanism comprises n sets of upper (lower) guide rails and upper (lower) sliders, the upper (lower) guide rails are mounted in parallel, the upper (lower) sliders are slidably fitted on the upper (lower) guide rails, the top surfaces of the upper guide rails are connected with the upper connecting plate, the top surfaces of the lower guide rails are connected with the lower connecting plate, and the intermediate layers are respectively connected with the bottoms of the upper sliders and the lower sliders. Under the load action of an earthquake or wind, the anti-pulling system can resist the high upward pulling force of a building structure, meanwhile, the anti-pulling system can allow a seismic isolation structure to slide, resist upsetting moment and enhance the anti-leaning or anti-shaking capability of the building structure, and the anti-pulling system can be used along with intermediate seismic isolation rubber bearings and dampers to form a foundation seismic isolation system which can provide the capability of resisting and balancing the horizontal leaning moment of the structure.
Owner:柳州东方工程橡胶制品有限公司
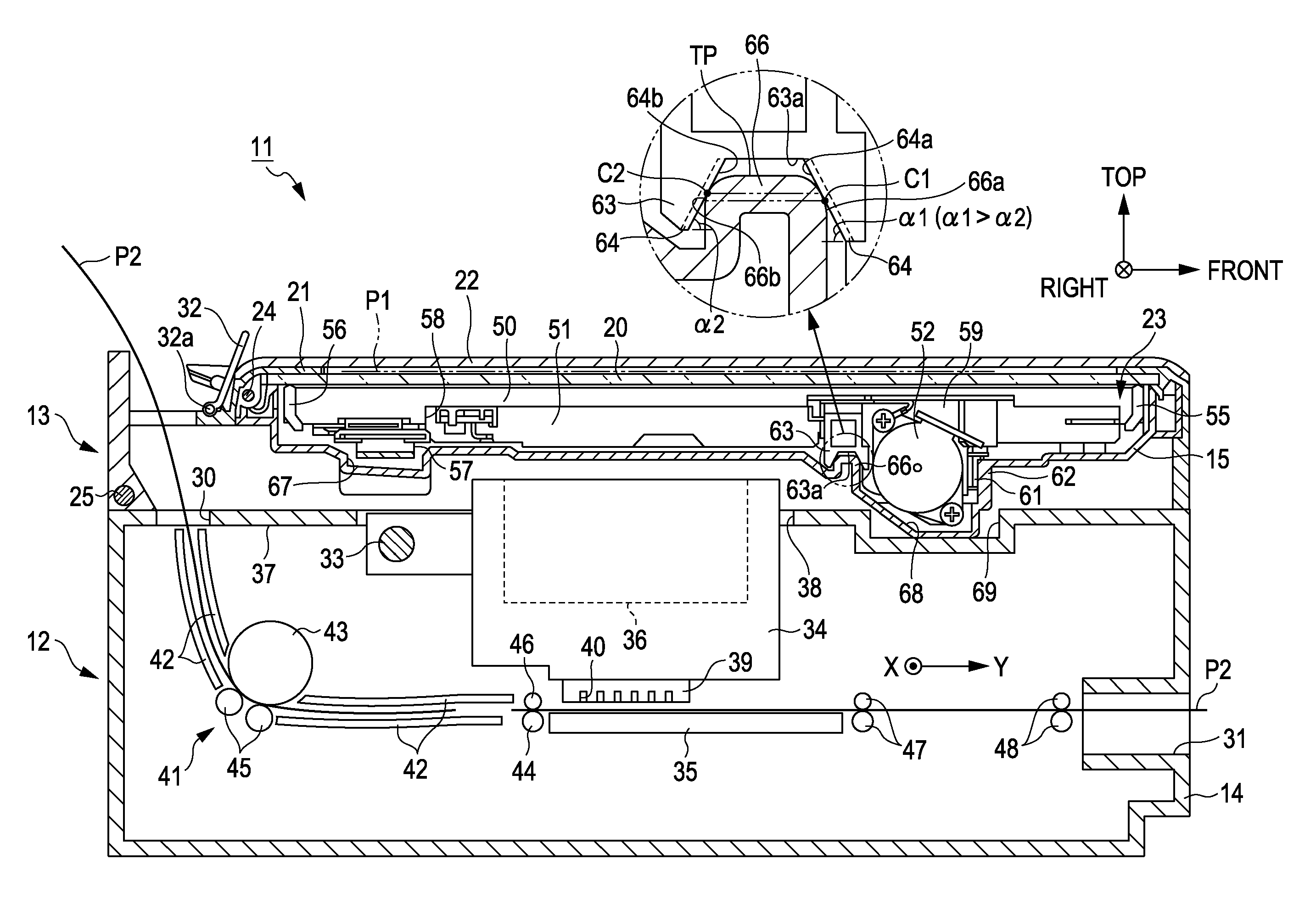
Cooling system of engine for small-sized vehicle
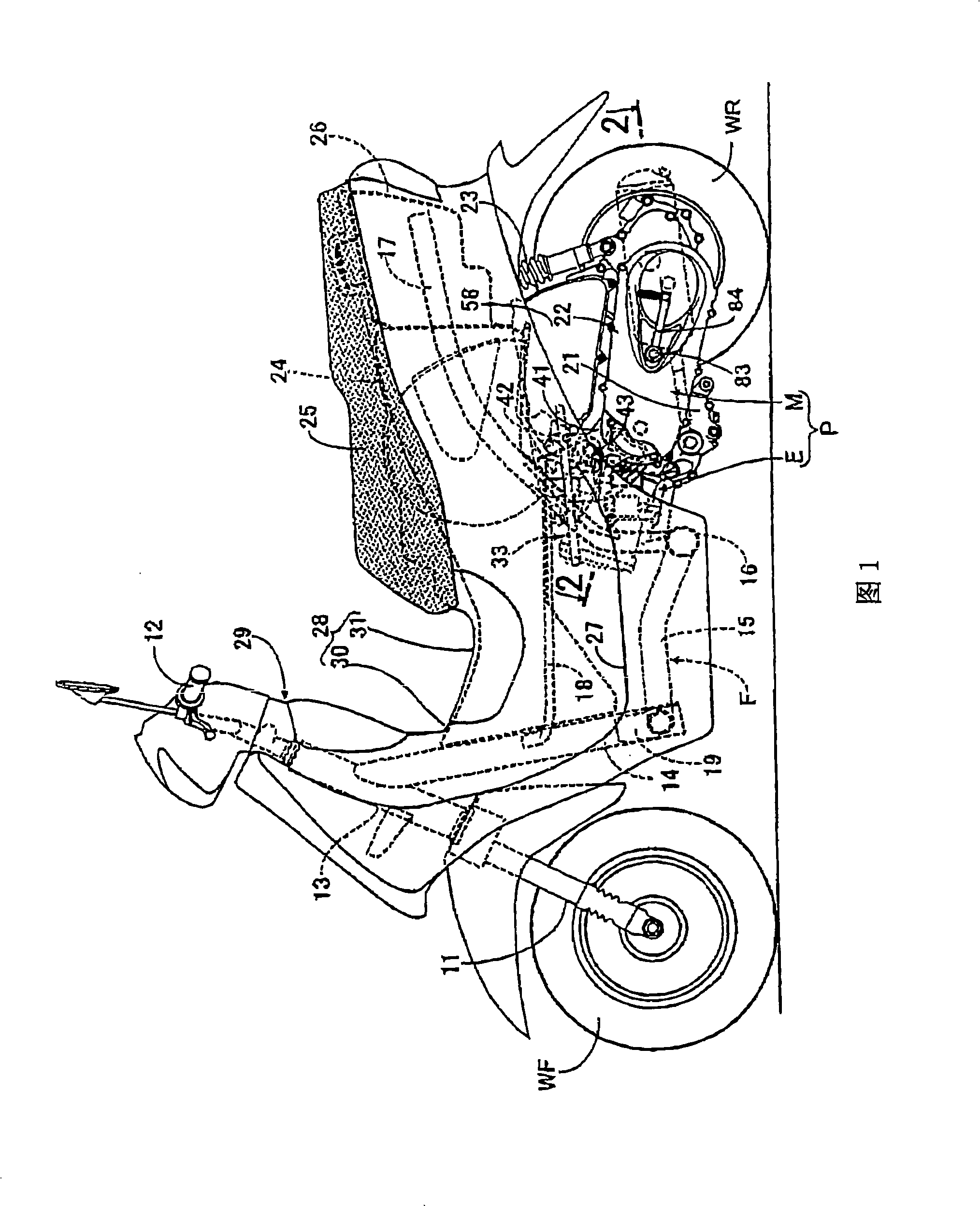
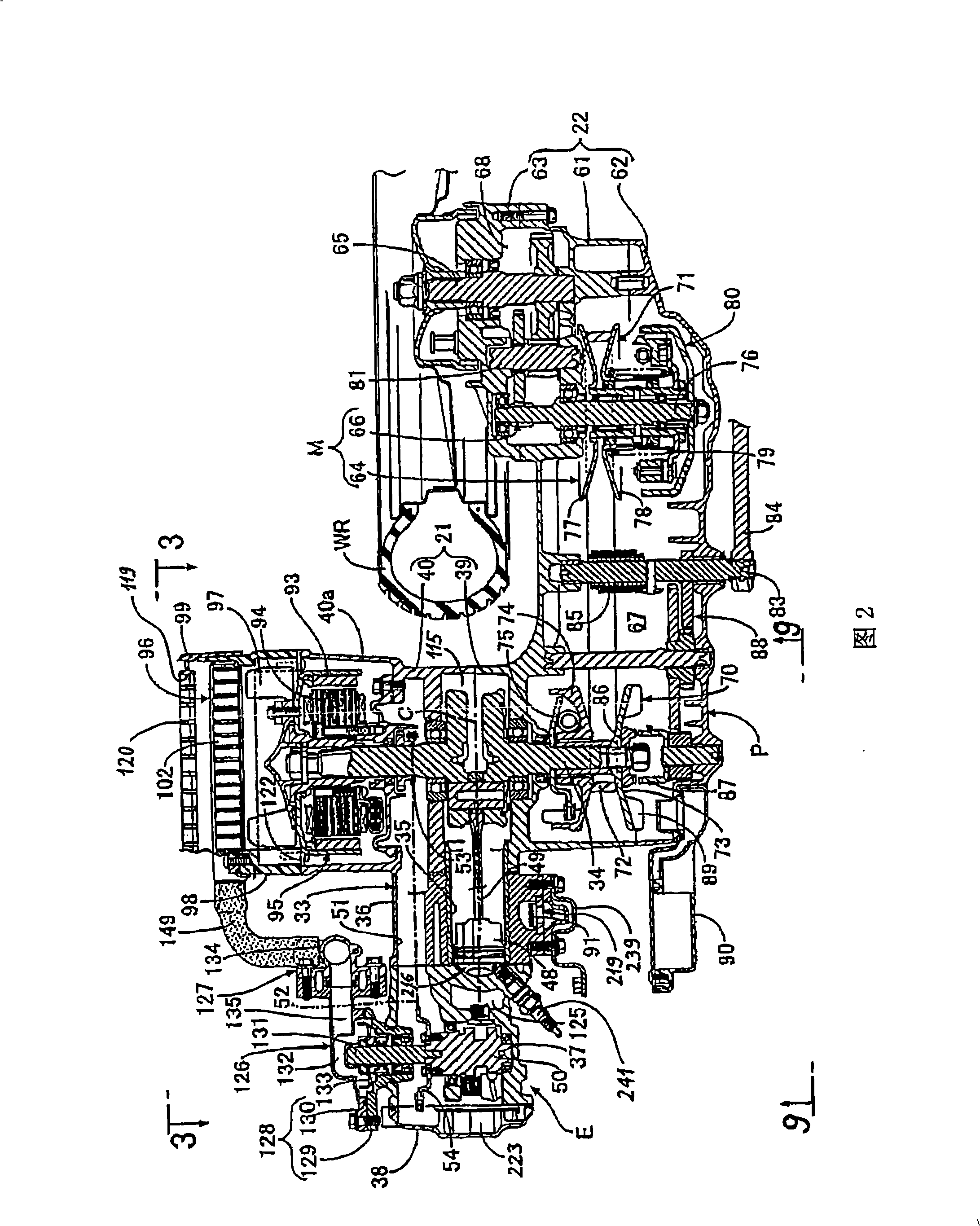
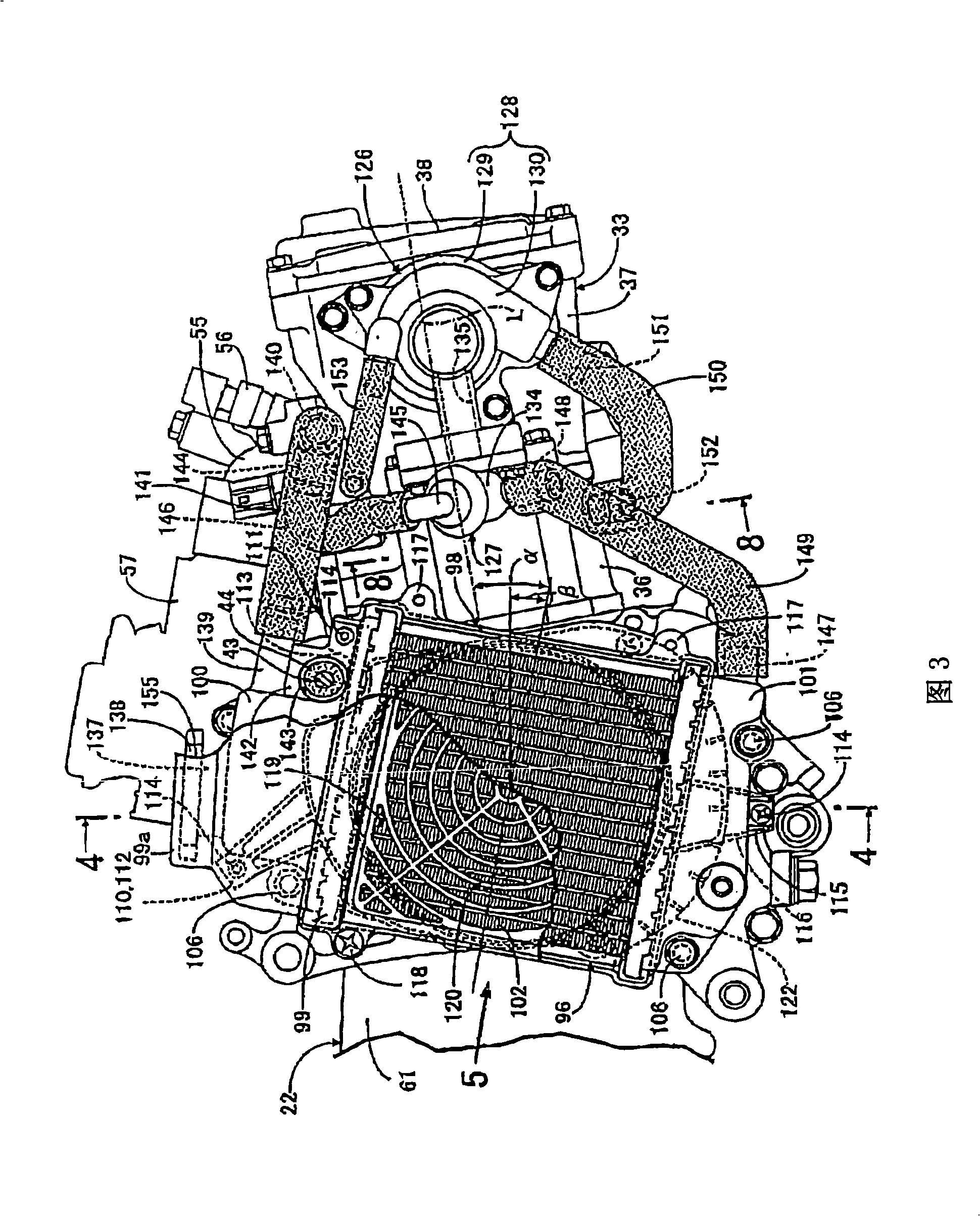
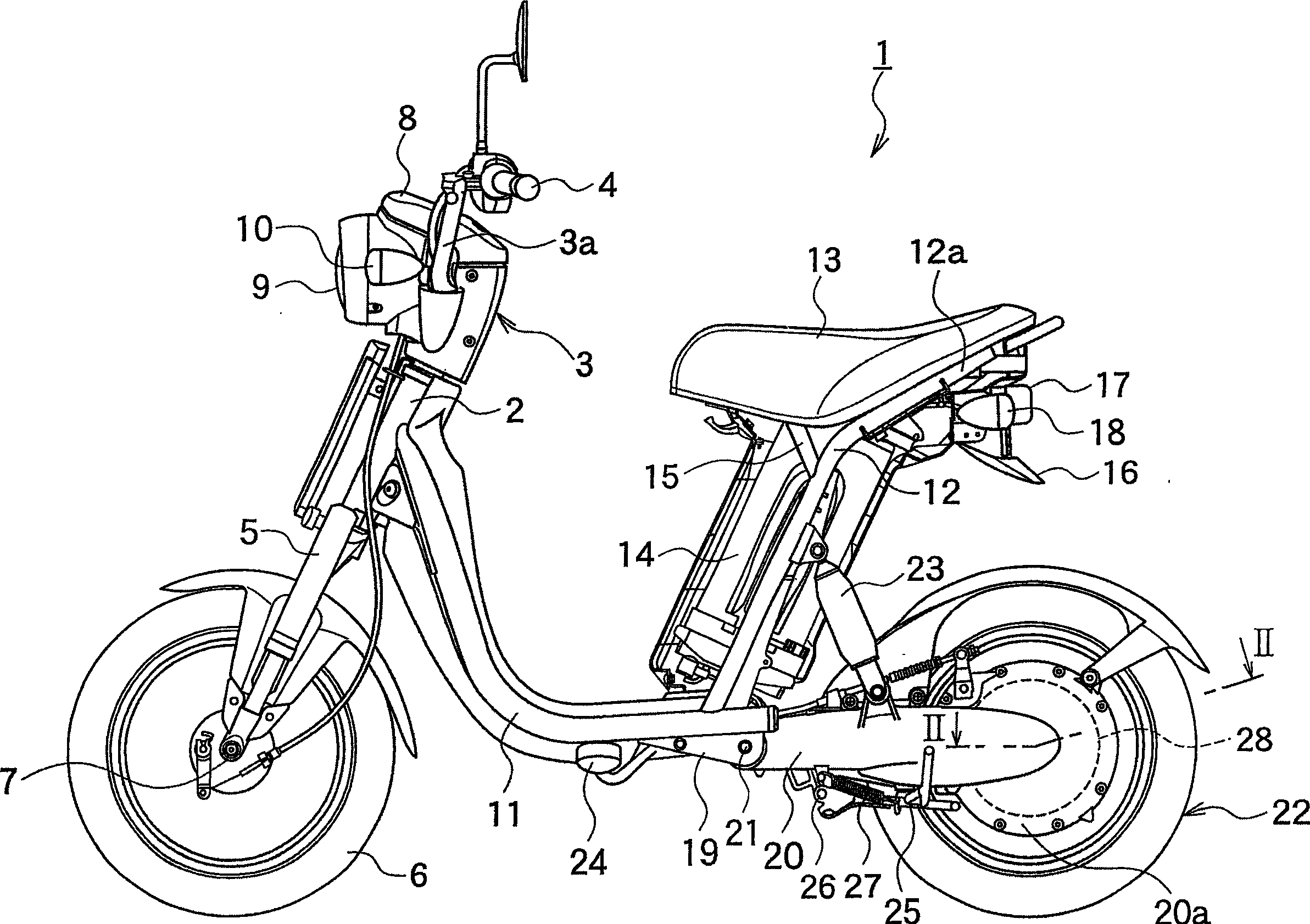
In order to reduce the number of parts, to enable air to bleed from a water jacket and to simplify a conduit layout around a radiator in a cooling system of an engine for a small-sized vehicle, an engine main unit is rockably supported by a body frame via a supporting shaft and the radiator at least a part of which is arranged on the downside of the supporting shaft in a side view is supported by a crankcase on the side of the crankcase. A radiator 96 is arranged on the side of a crankcase with a front end arranged in front of a supporting shaft; from a side view, a leading-out pipe 140 provided to an engine main unit 33 for leading cooling water from an uppermost part of a water jacket of the engine main unit 33 and an inlet pipe 139 provided to an upper tank 100 of the radiator 96 on the upside of the supporting shaft 43 are coupled via a conduit 141 passing the upside of the supporting shaft 43 in a side view to be higher from the leading-out pipe 140 to the side of the inlet pipe 139.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Focusing apparatus for optical device
InactiveUS20130222929A1Minimizing manufacturingMinimizing manufacturing and assemblyProjector focusing arrangementCamera focusing arrangementElectrical and Electronics engineering
Provided is a focusing apparatus for an optical device, the focusing apparatus including a lead screw rotatably installed in the optical device, a carriage screw-coupled to the lead screw to move in a longitudinal direction of the lead screw in response to rotation of the lead screw, a lens barrel receiving at least one lenses and moving along the longitudinal direction of the lead screw, and a bridge extending from an outer circumferential surface of the lens barrel to enclose the carriage, in which the bridge moves the lens barrel in response to movement of the carriage.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Slide valve
The invention provides a slide valve preventing inclination in back pressure in a simple construction. The slide valve at least has a valve main body drawing out a valve body having an inlet side port in an opening; a valve seat configured to be in the valve body and having at least one outlet side port, relative to a valve body opening, in a valve body surface; and a valve core assembly at least comprising a plunger driven by a solenoid and a connection rod, a valve core and a leaf spring assembled on the plunger in an integrated mode. The slide valve opens and closes the outlet side port. The valve core is maintained to be at the connection rod, opens and closes at least one outlet side port and slides on a valve seat surface of a valve seat. The valve core also has a sealing surface opening and closing the outlet side portion and a back surface opposite to the sealing surface. The leaf spring is abutted against the back surface of valve core and presses the valve core on the valve seat surface of the valve seat. A protrusion forms on the leaf spring. A step portion comprising a bottom surface abutted against the protrusion forming on the leaf spring forms on the back surface of the valve core.
Owner:SAGINOMIYA SEISAKUSHO INC
Substrate for light-emitting element and light-emitting device
InactiveUS20120201037A1Improve flatnessLow heat resistanceLighting support devicesLayered productsHeat resistanceLight emitting device
To provide a substrate for light-emitting element, which is excellent in the planarity of the mounting surface to be provided with a light-emitting element, has a low heat resistance and can suppress the tilt of the light-emitting element. A substrate for light-emitting element, which comprises a substrate main body 2 made of a sintered product of a glass ceramics composition comprising a glass powder and a ceramics filler and having a mounting surface 21, of which a part constitutes a mounting portion 22 on which a light-emitting element is to be mounted, and thermal vias 6 embedded in the substrate main body 2 and extending from a non-mounting surface 23 which is a surface opposite to the mounting surface 21 to the vicinity of the mounting surface 21 so as not to be in contact with the mounting surface 21.
Owner:ASAHI GLASS CO LTD
Image reading apparatus
ActiveUS8659807B2Curb tiltSuppress tilting of the reading sensorPictoral communicationEngineeringMechanical engineering
An image reading apparatus comprises: a guide portion that is linked to a driving portion and extends so as to guide the movement of a reading carriage; a guide rail that guides the reading carriage while supporting the reading carriage; and an interlocking portion that is provided in the reading carriage, has a first sliding surface that makes contact with the guide rail on the side of the guide rail facing the guide portion and a second sliding surface that makes contact with the guide rail on the side of the guide rail that is on the opposite side as the guide portion. The position at which the first sliding surface of the interlocking portion makes contact with the guide rail is lower on the guide rail than the position at which the second sliding surface of the interlocking portion makes contact with the guide rail.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Suspended aerial rail train
PendingCN107985328AAvoid damageGuaranteed service lifeElevated railway with suspended vehicleBogie-underframe connectionsBogieEngineering
The invention belongs to the field of transportation equipment, particularly provides a suspended aerial rail train, and aims at solving the problem that a bogie of a suspended aerial rail train in the prior art is easily damaged when a train body bears large lateral force. To achieve the aim, the suspended aerial rail train comprises a suspension arm used for connecting a bogie and a train body,and damping parts arranged on the two sides of the suspension arm, wherein one end of the suspension arm is fixedly connected with the bogie, the other end of the suspension arm is in pivot connectionwith the train body, and the two ends of the damping parts are in pivot connection with the bogie and the train body respectively. When bearing external lateral force, the train body can transmit thelateral force to the suspension arm instead of the bogie through the damping parts. Therefore, the suspended aerial rail train has the advantages that the bogie can be prevented from being damaged when the train body tilts under lateral force, and thus the service life of the bogie is prolonged.
Owner:ZHONGJIAN AIR TRAIN BEIJING TECH CO LTD
Moulding forming device,its head and method for making optical element
InactiveCN1834046AHigh shape accuracyCurb tiltGlass pressing apparatusGlass press-moulding apparatusEngineeringSupport surface
The invention discloses to a pressing molder, relative production of its pressure head and optical element. Wherein, when pressing the molding mould, first, using the first pressure head (11) to compress the main body mould (4) on the support surface (23) (reference surface) of flange (22) of lower mould (2), to process the positioning between the main body mould (4) and the lower mould (2); with said positioning state, using the second pressure head (12) to support the upper mould (3) to compress and mold the molding blank (w); when the molding blank (w) is pressed molded, non-incline fixing the main body mould (4) and lower mould (2) and fixing the first pressure head (11), therefore, the second pressure head (12) that guided by the first pressure head (11) can non-incline compress upper mould (3), and the relative incline between upper and lower moulds (3, 2) can be restrained; the invention can be used to produce the optical element with high shape accuracy.
Owner:HOYA CORP
Supporting structure of elevator guide rail
The invention provides a supporting structure of an elevator guide rail. In the prior art, if the up-down interval of a carrier becomes longer, the horizontal load of an elevator car and a counterweight, when an earthquake happens, may result in the bending of the guide rail, and then the bending strength cannot be ensured. Therefore, if a guide rail having a larger cross section is required, the problem of higher cost of the guide rail arises. The supporting structure of the elevator guide rail includes a steel plate forming guide rail provided with a U-shaped forming part, and a carrier supporting the steel plate forming guide rail, wherein one face of the steel plate forming guide rail and one face of the carrier are defined in that the surfaces of the faces are contacted with each other in the plane determined by the head direction of the steel plate forming guide rail and the axial direction of the steel plate forming guide rail.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Epitaxial structure for improving light output power of ultraviolet LED
PendingCN106935690AImprove blocking efficiencyReduce leakageSemiconductor devicesUltravioletElectron blocking layer
The invention discloses an epitaxial structure for improving light output power of an ultraviolet LED. The epitaxial structure comprises a substrate, a GaN buffer layer, a non-doped GaN layer, a doped N-type GaN layer, a AlGaN / GaN multi-quantum well structure, an insertion layer, an electron barrier layer EBL and a P-type GaN layer which are sequentially arranged from bottom to top, wherein the substrate employs a sapphire substrate, the thickness of the GaN buffer layer is 20-25 nanometers, the growth temperature of the GaN buffer layer is 530-550 DEG C, the GaN buffer layer is recrystallized under heat preservation for 6 minutes at 1,050 DEG C, the thickness of the non-doped GaN layer is 2.0-2.5 micrometers, the growth temperature of the non-doped GaN layer is 1,050 DEG C, the thickness of the doped N-type GaN layer is 2.5-3.0 micrometers, the Si doping concentration is 5*10<18>cm<-3>, the growth temperature is 1,050 DEG C, and the multi-quantum well AlGaN / GaN structure is formed by alternatively growing multi-quantum well AlGaN layers and multi-quantum well GaN layers according to six periods. By improving the crystal quality of an ultraviolet LED chip, the electron barrier effect of the electron barrier layer is optimized, the electron leakage is reduced, so that the efficiency reduction of an ultraviolet LED device is improved, and the light output power is improved.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
Original feeding apparatus, original reading apparatus, and image forming apparatus
InactiveUS7199910B2Smooth slidingEasy to installElectrographic process apparatusArticle feedersImage formationComputer science
Owner:CANON KK
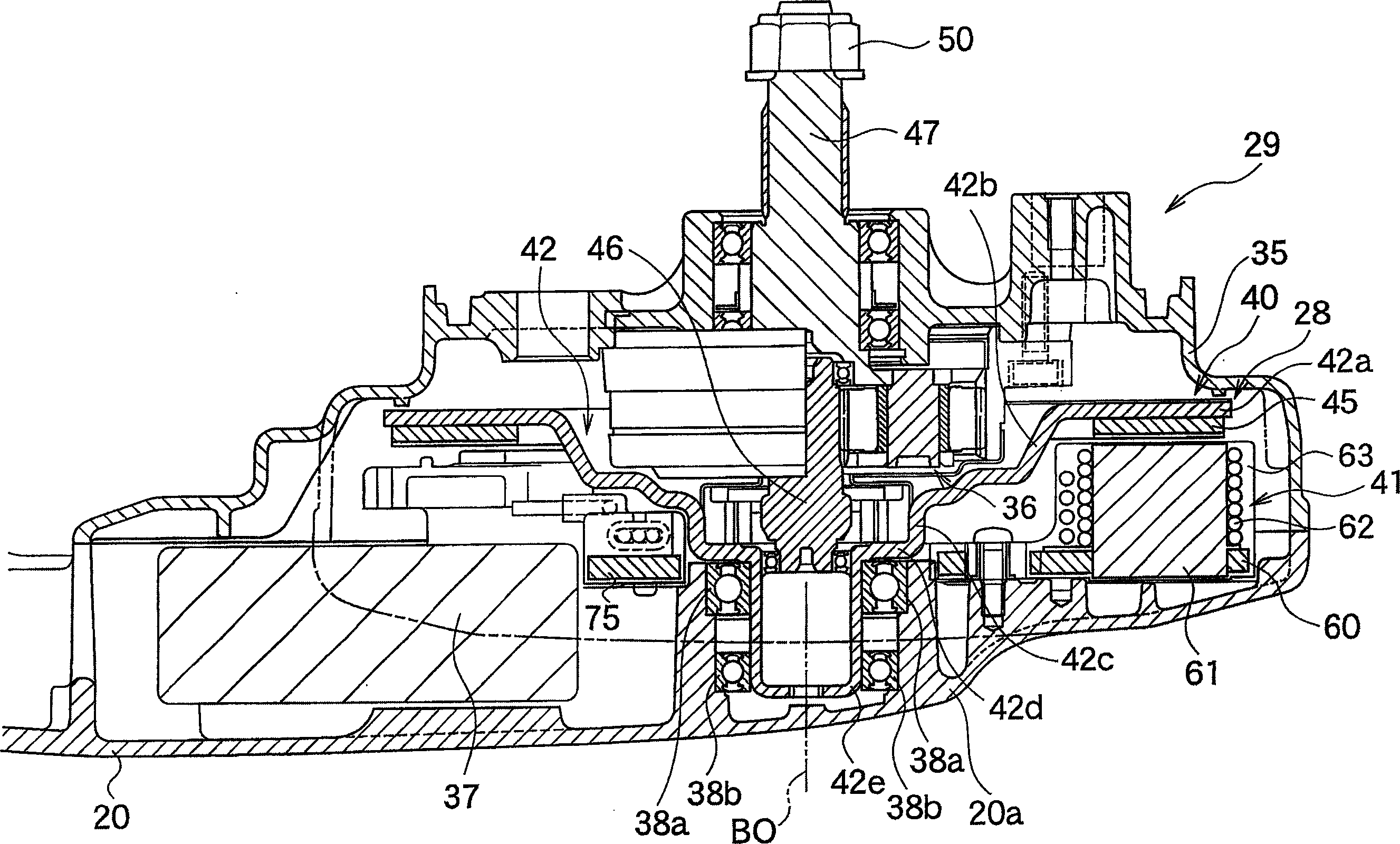
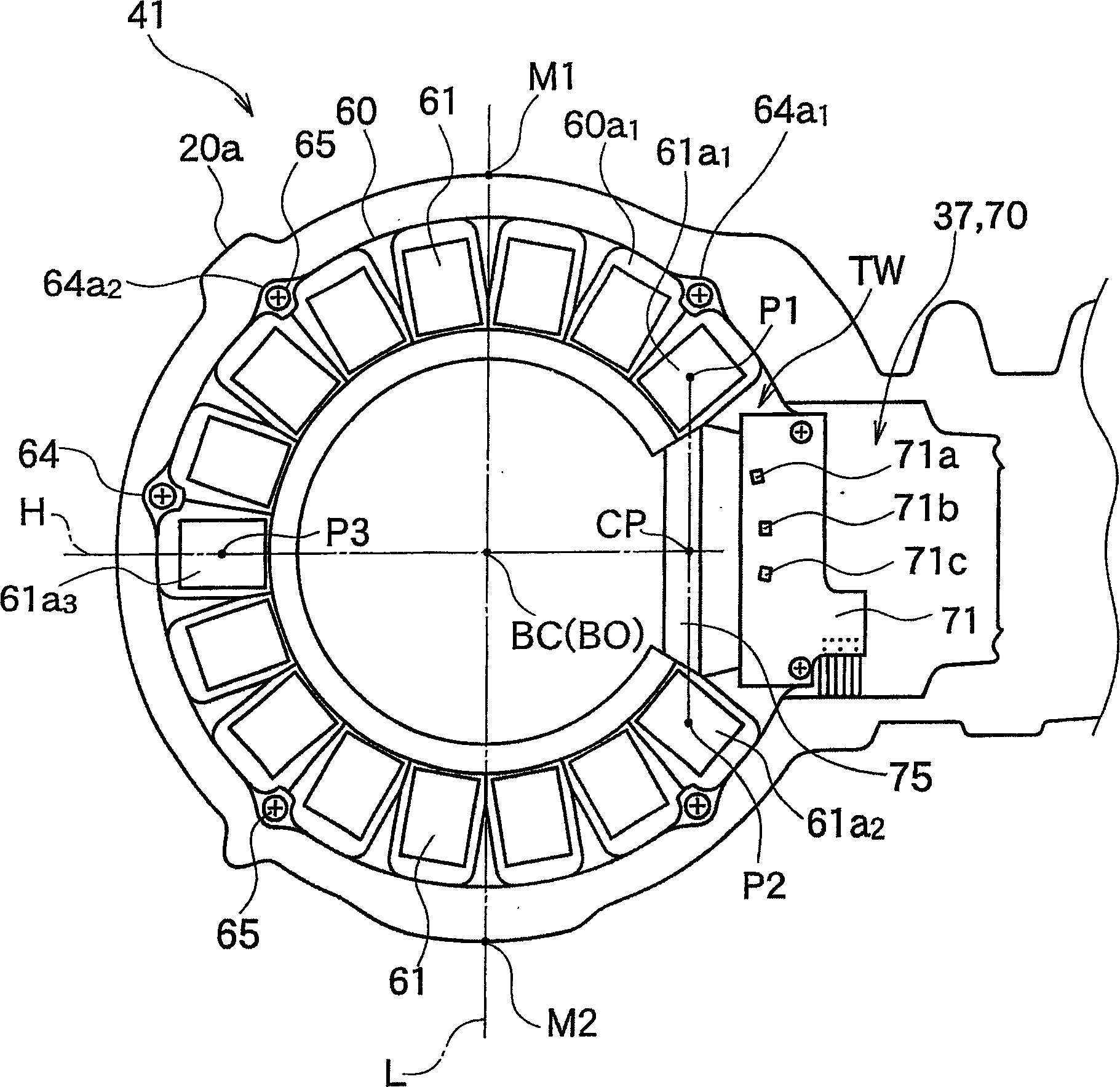
Axial gap type motor generator
The invention relates to an axial gap dynamo-electric machine comprising a rotor having a revolving shaft supported by a bearing and a magnet for generating a magnetic field, a stator yoke disposed so as to oppose the rotor, and a plurality of teeth being disposed on the magnet-opposed surface of the stator yoke substantially in the shape of a partly removed circle, wherein a removed portion is free of teeth, the partially removed circle having a midpoint at a predetermined point in relation to a center axis of the bearing and opposing the magnet at a predetermined gap. The invention aims to provide an improved axial gap dynamo-electric machine having a structure in which some of the teeth in the stator are missing, to limit inclination of a rotor caused by such missing of the teeth. Therefore, the invention provides that circumferential pitches among the plurality of teeth are set to differ from each other, in particular, so that an attractive force of the magnet is set to increase towards the removed portion.
Owner:YAMAHA MOTOR CO LTD
Substrate for mounting light-emitting element and light-emitting device
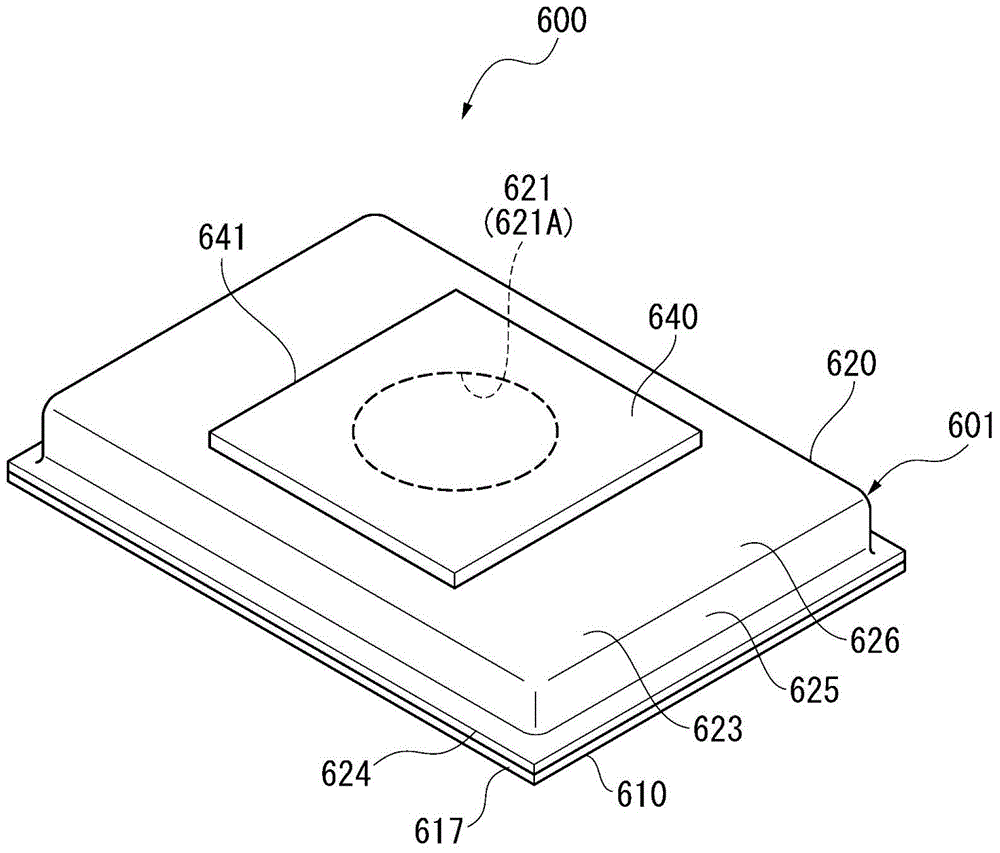
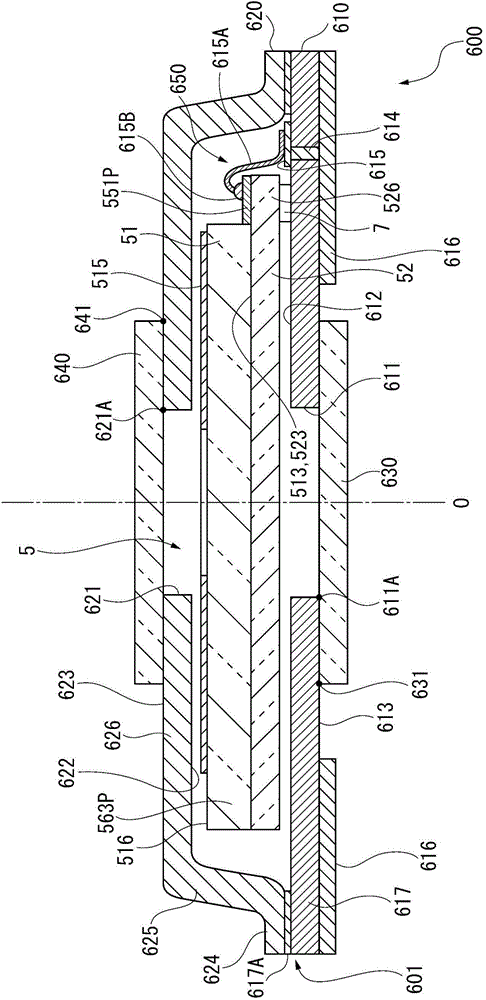
InactiveCN102280559ACurb tiltImprove flatnessSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesHeat resistanceAlloy
To provide a substrate for a light-emitting element, being less susceptible to the loss of light supplied from a light emitting element, having high utilization efficiency of light, being excellent in flatness of a mounting surface on which a light-emitting element is to be mounted, and having a low heat resistance, when used for a light-emitting device. A substrate 1 for mounting a light-emitting element, which comprises a substrate main body 2, a reflection layer 6 composed mainly of silver (Ag) or a silver alloy, formed on a part of the substrate main body 2, a first protective layer 7 composed mainly of a sintered product of a glass powder, formed so as to cover the entire surface of the reflection layer 6, and a second protective layer 8 a part which constitutes a mounting portion 10 on which a light-emitting element is to be mounted, formed on the first protective layer 7, wherein the first protective layer 7 contains substantially no alumina filler, and further the second protective layer 8 is made of a sintered product of a glass powder containing a ceramic filler 9.
Owner:ASAHI GLASS CO LTD
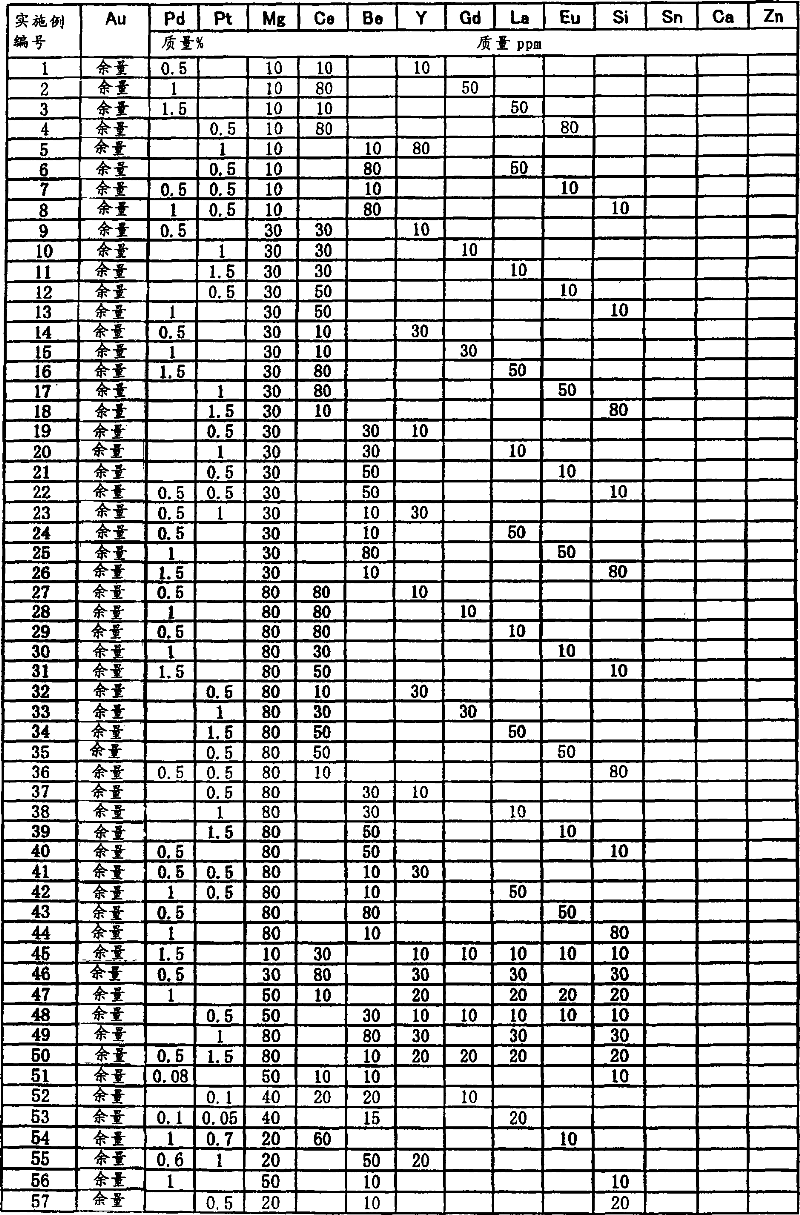
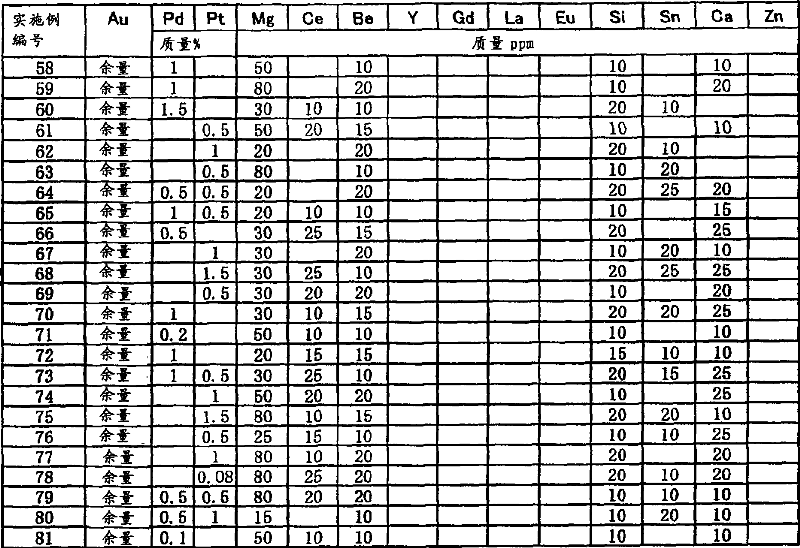
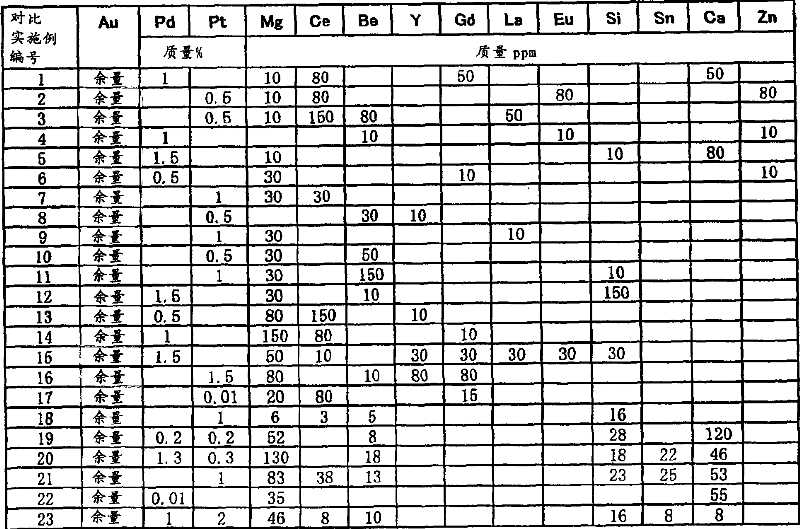
Au alloy bonding wire
ActiveCN101040372ADelays the effect of interdiffusionEasy to shapeSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingTrace elementAlloy
An Au alloy bonding wire which comprises an Au alloy matrix containing high purity Au and at least one of high purity Pd and Pt in a total amount of 0.05 to 2 mass %, and, incorporated in the matrix as a trace element, Mg in an amount of 10 to 100 mass ppm, Ce in an amount of 5 to 100 mass %, and at least one of Be, Y, Gd, La, Eu and Si in an amount of each element of 5 to 100 mass % and in a total amount of Be to Si of 5 to 100 mass ppm; an Au alloy bonding wire which comprises the above Au alloy matrix and, incorporated in the matrix as a trace element, Mg and Be and at least one of Y, La, Eu and Si; an Au alloy bonding wire which comprises the above Au alloy matrix and, incorporated in the matrix as a trace element, Mg in an amount of 10 to 100 mass ppm, Si in an amount of 5 to 30 mass ppm, Be in an amount of 5 to 30 mass ppm, and at least one of Ca, Ce and Sn in an amount of 5 to 30 mass ppm. The above bonding wire is a fine diameter Au alloy bonding wire which has a desired strength, exhibits good binding characteristics and good stability for a long period of time, and is improved in the circularity of a pressed ball and the sphericity of a molten ball.
Owner:TANAKA DENSHI KOGYO KK
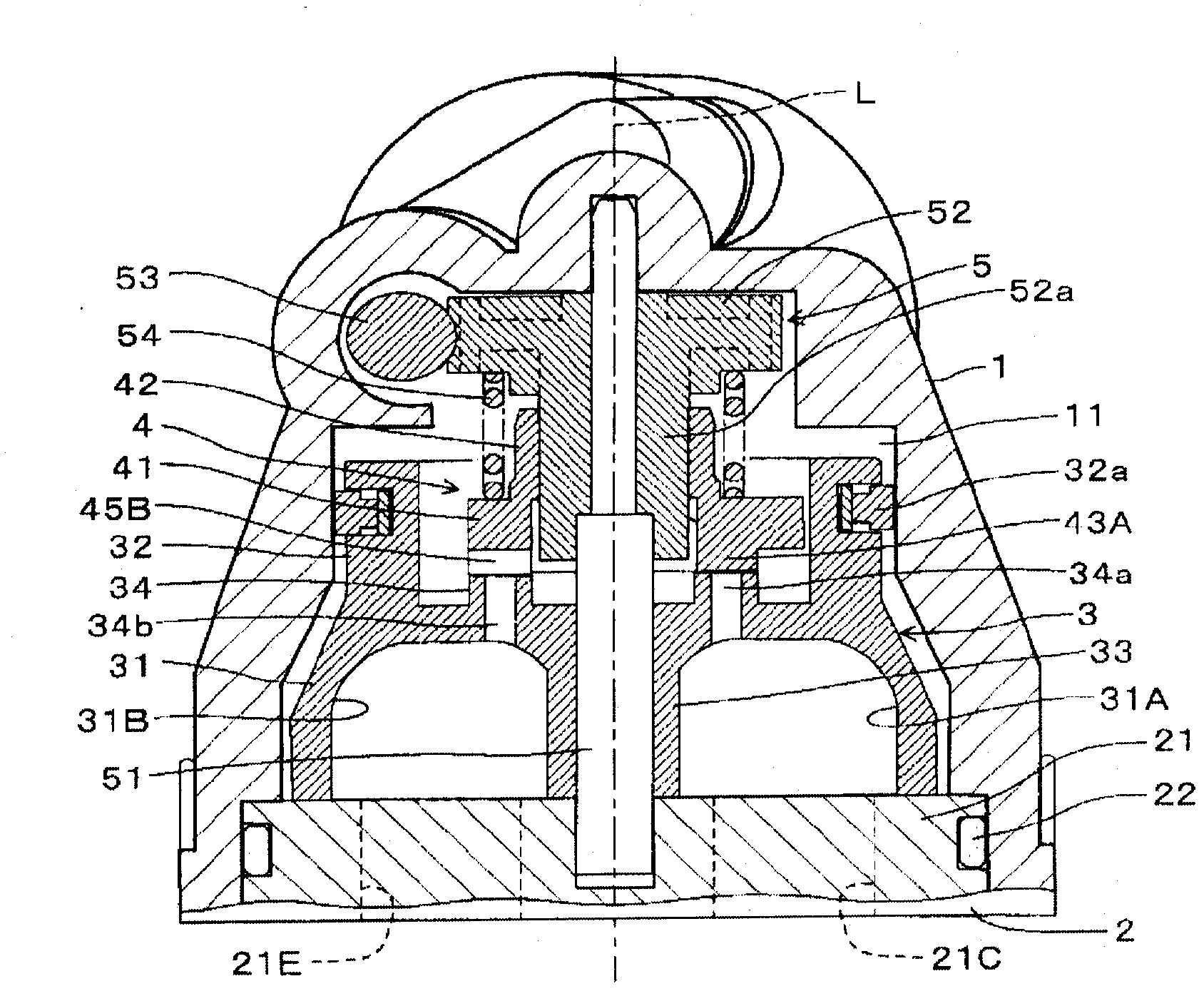
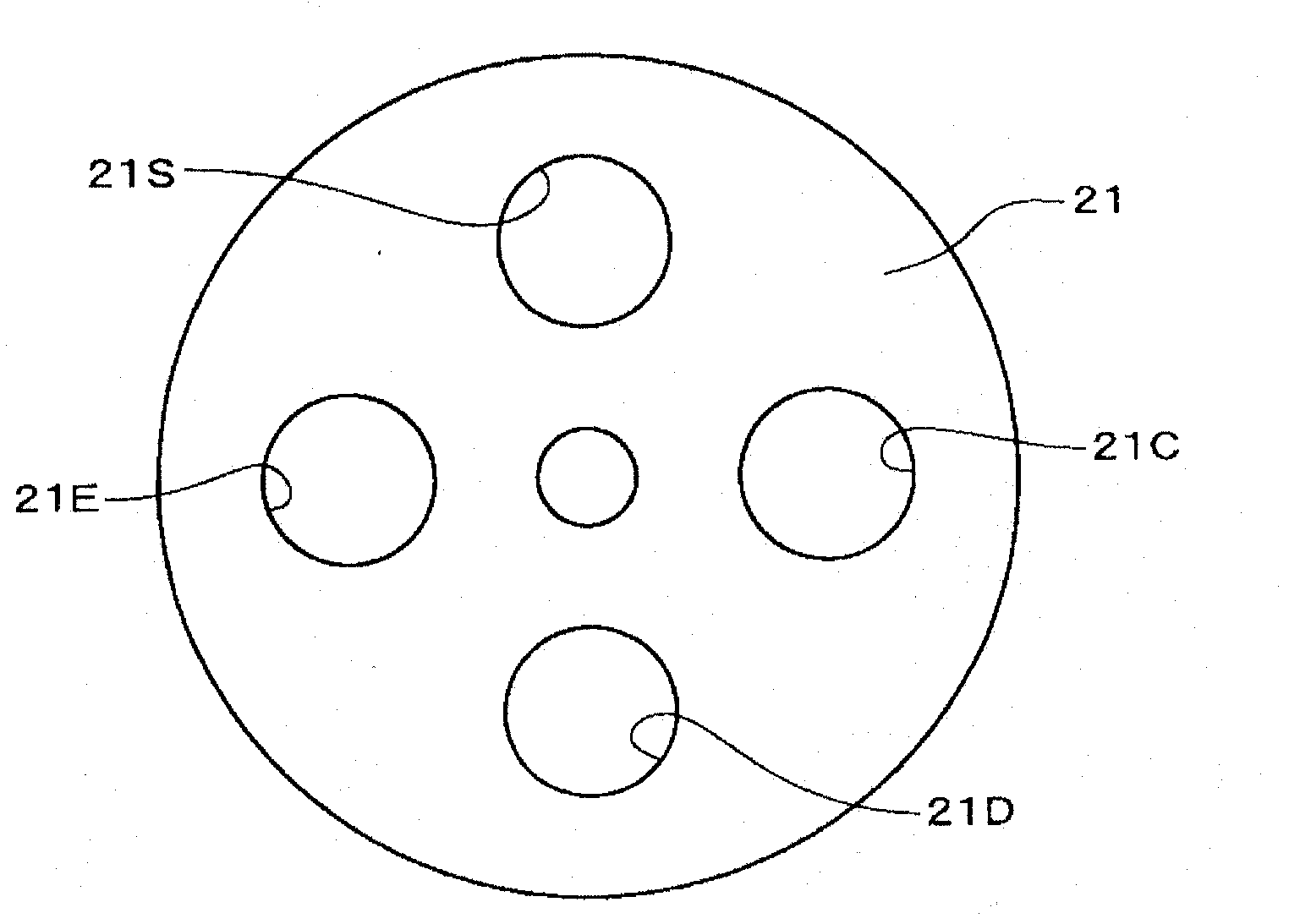
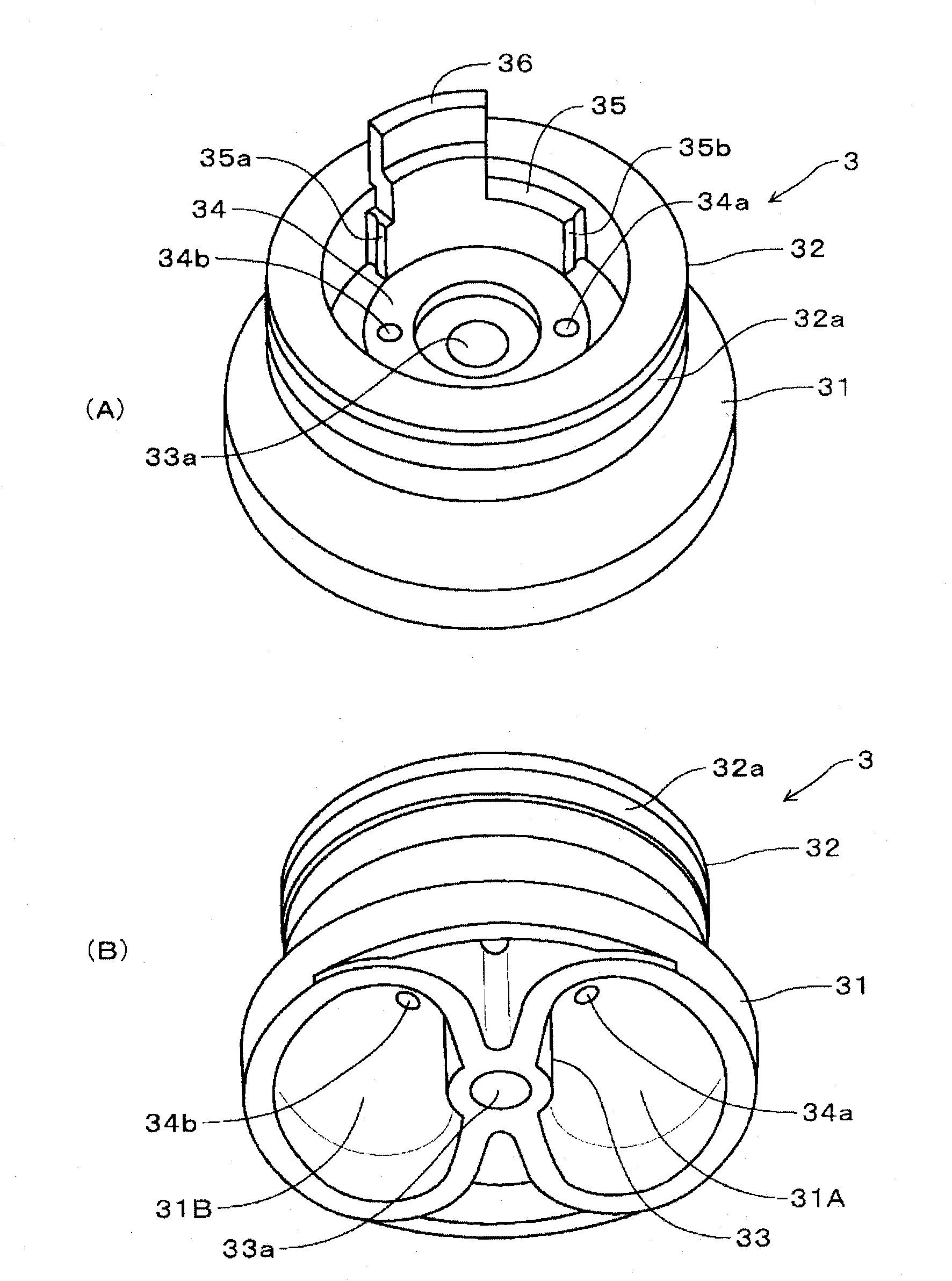
Flow path selector valve
InactiveCN102047014AReliable conversionPromote conversionOperating means/releasing devices for valvesMultiple way valvesEngineeringSwitching time
A flow path selector valve for switching between a cooling state and a heating state by rotation of a main valve (3) together with a auxiliary valve (4), wherein rotational operation of the main valve (3) and the auxiliary valve (4) are simplified to make operation of the main valve (3) reliable and to reduce a switching time. An outdoor heat exchanger-side communication passage (31A) and an indoor heat exchanger-side communication passage (31B) are formed in the main valve (3). An outdoor heat exchanger-side equalizing hole (34a) for connecting the outdoor heat exchanger-side communication passage (31A) to a valve chamber (11) is formed in the main valve. An indoor heat exchanger-side equalizing hole (34b) for connecting the indoor heat exchanger-side communication passage (31B) to the valve chamber (11) is formed in the main valve (3). A closing section (43A) for closing the outdoor heat exchanger-side equalizing hole (34a) and an equalizing hole opening section (45B) for opening the indoor heat exchanger-side communication passage (34b) are also formed in the auxiliary valve (4). A closing section for closing the indoor heat exchanger-side equalizing hole (34b) and an equalizing hole opening section for opening the outdoor heat exchanger-side communication passage (34a) are also formed in the auxiliary valve. A support section sliding on an auxiliary valve seat (34) is formed on the auxiliary valve (4). The main valve (3) is rotated 90 DEG by merely operating the auxiliary valve (4) in either forward or reverse directions, and this switches between the cooling state and the heating state.
Owner:SAGINOMIYA SEISAKUSHO INC
Electronic device and method for manufacturing this device
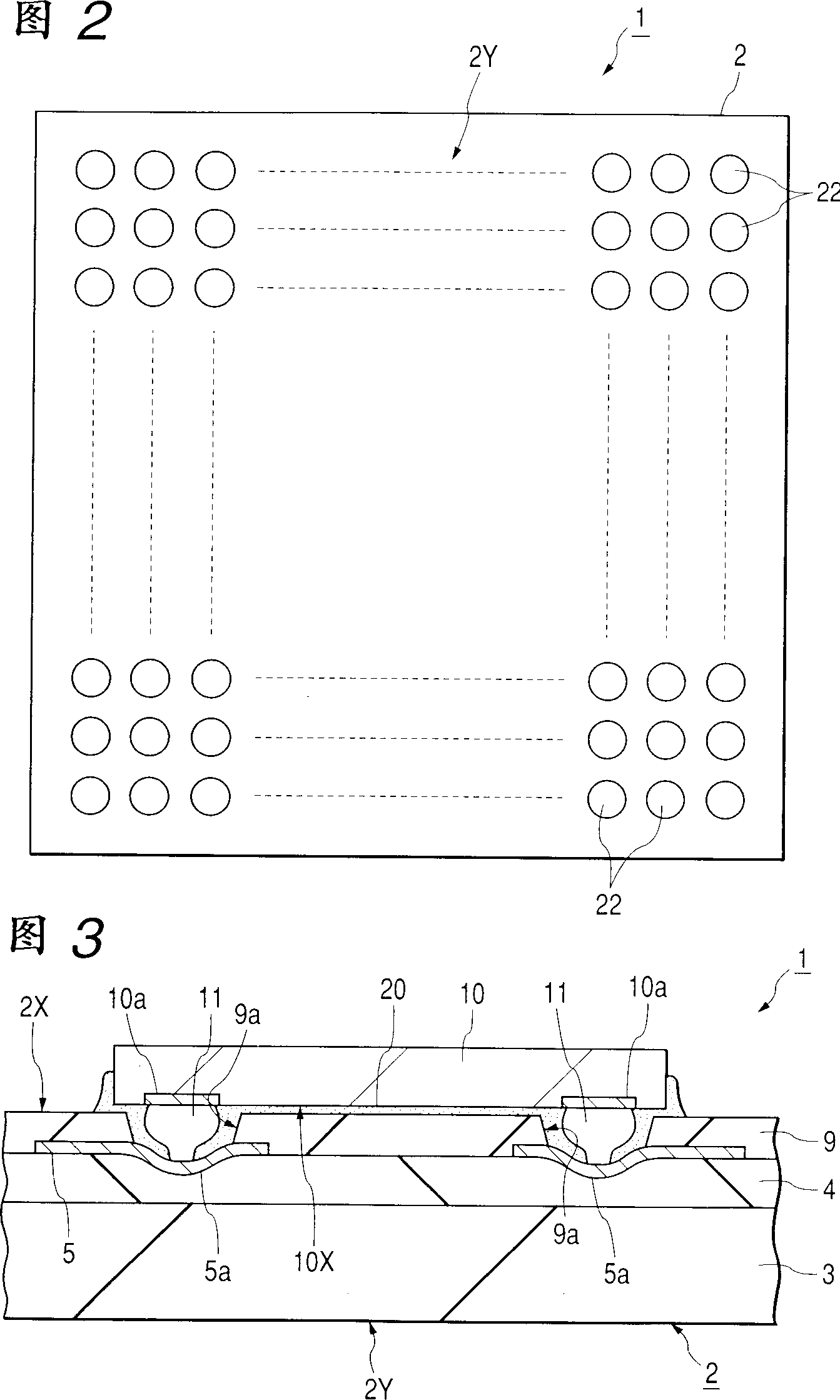
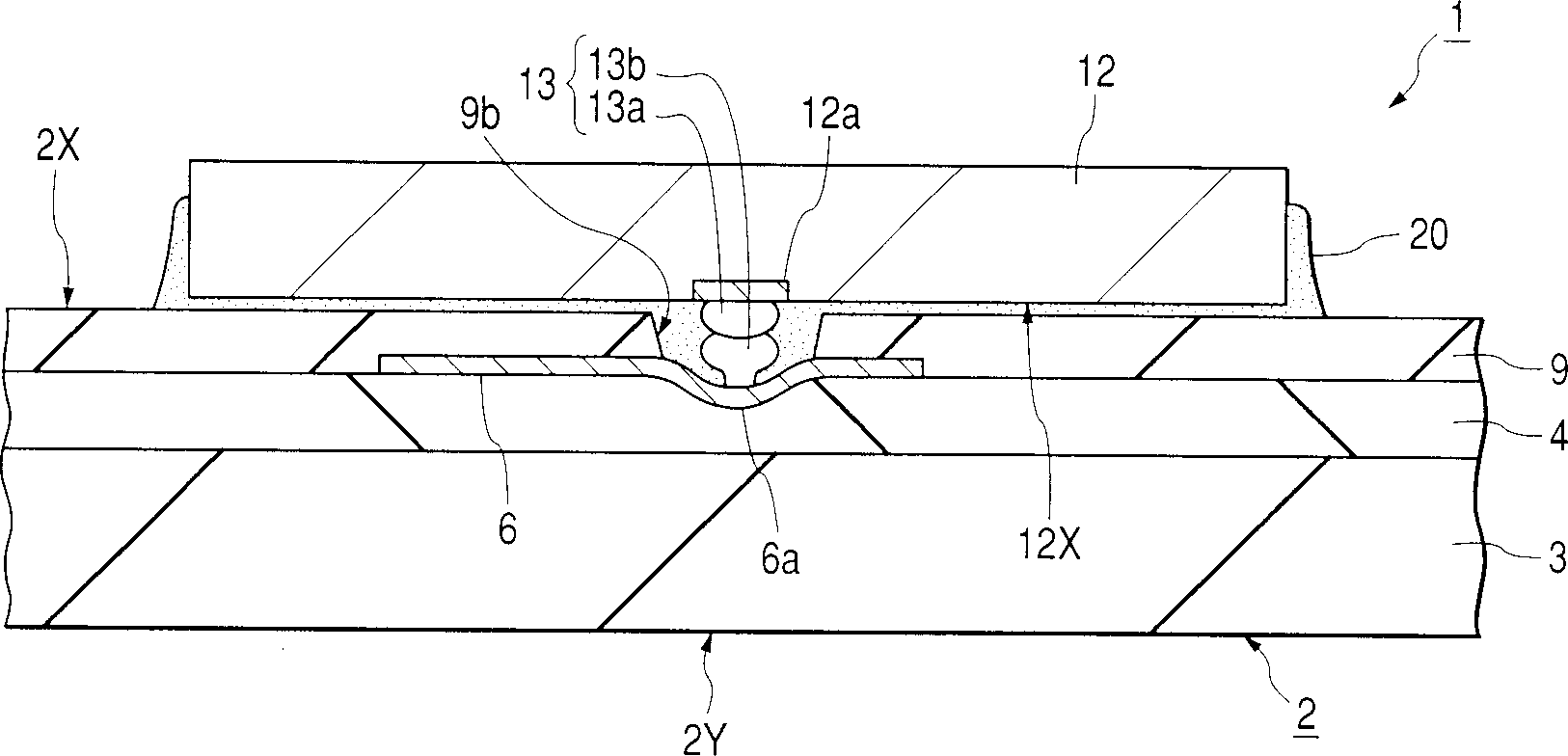
InactiveCN1340857ACurb tiltSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesElectrical connectionSemiconductor chip
An electronic device comprising: a semiconductor chip having plural electrode pads on one main surface thereof; a wiring board having plural connection parts; and plural salient electrodes disposed respectively between the electrode pads of the semiconductor chip and the connection parts of the wiring board to provide electrical connections between the two, the salient electrodes being arranged in an array not providing balance of the semiconductor chip with respect to one main surface of the wiring board, the plural connection parts of the wiring board being arranged at a deeper position than one main surface of the wiring board in a depth direction from the one main surface.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Optical filter device, optical module and electronic apparatus
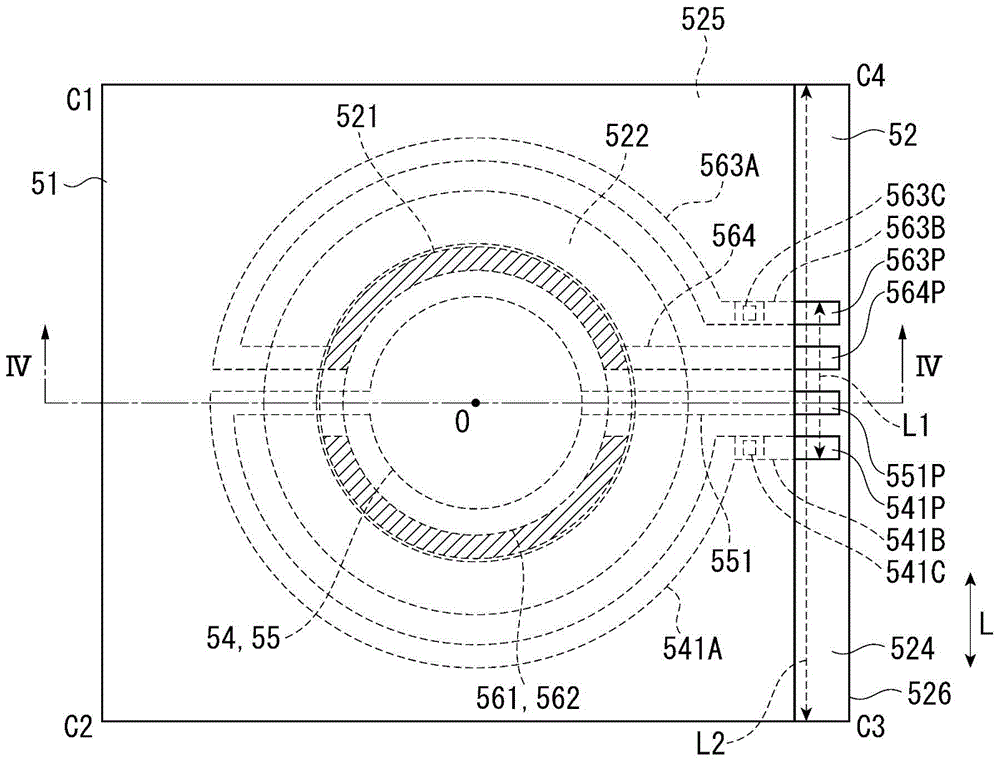
InactiveCN104076504ACurb tiltRaman scatteringSpectrum generation using multiple reflectionOptical ModuleComputer module
An optical filter device includes a wavelength variable interference filter provided with a movable substrate on which respective electrode pads are provided; a base substrate on which the wavelength variable interference filter is mounted, facing the movable substrate; and a fixing member that is disposed between the movable substrate and the base substrate and fixes the movable substrate and the base substrate. The fixing member is disposed at a position that overlaps the respective electrode pads, in a filter plan view.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com