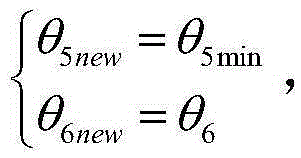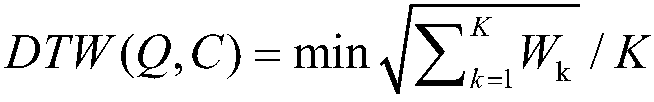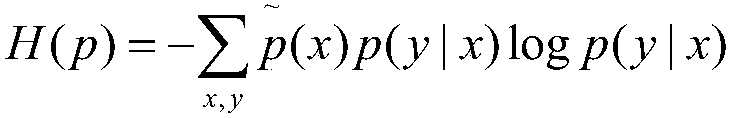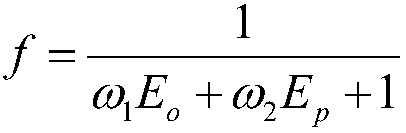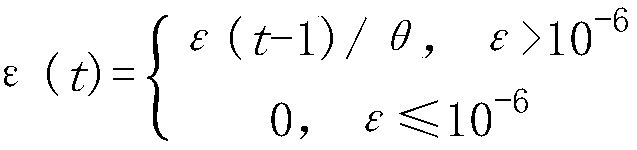Patents
Literature
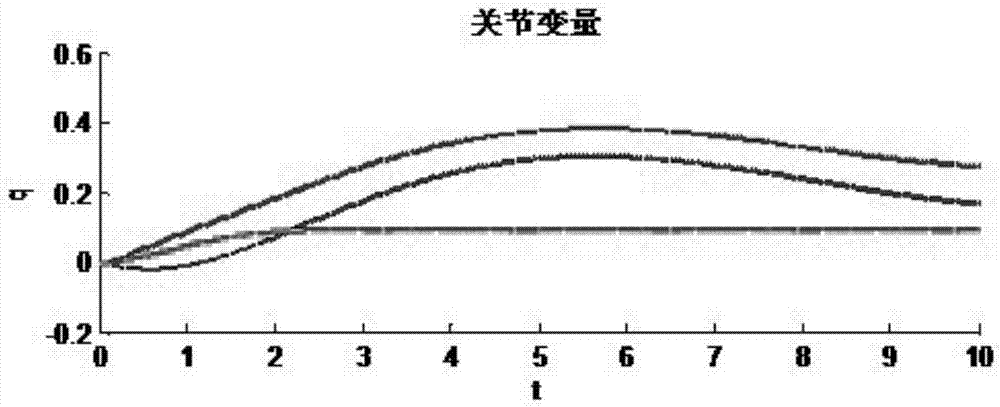
85 results about "Joint variable" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Joint Variation : Joint variation is a variable which is proportional to the product of two or more other variables.
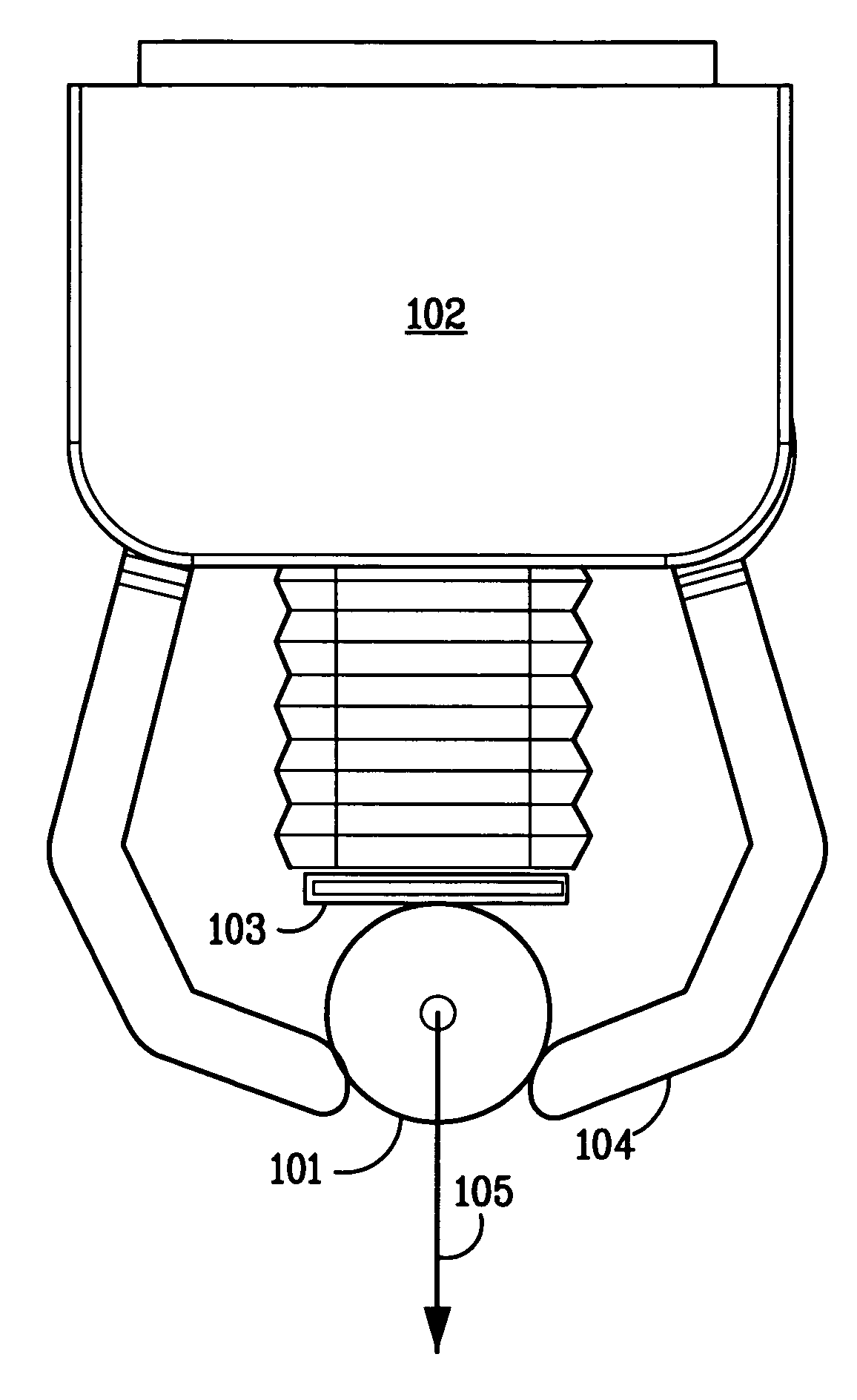
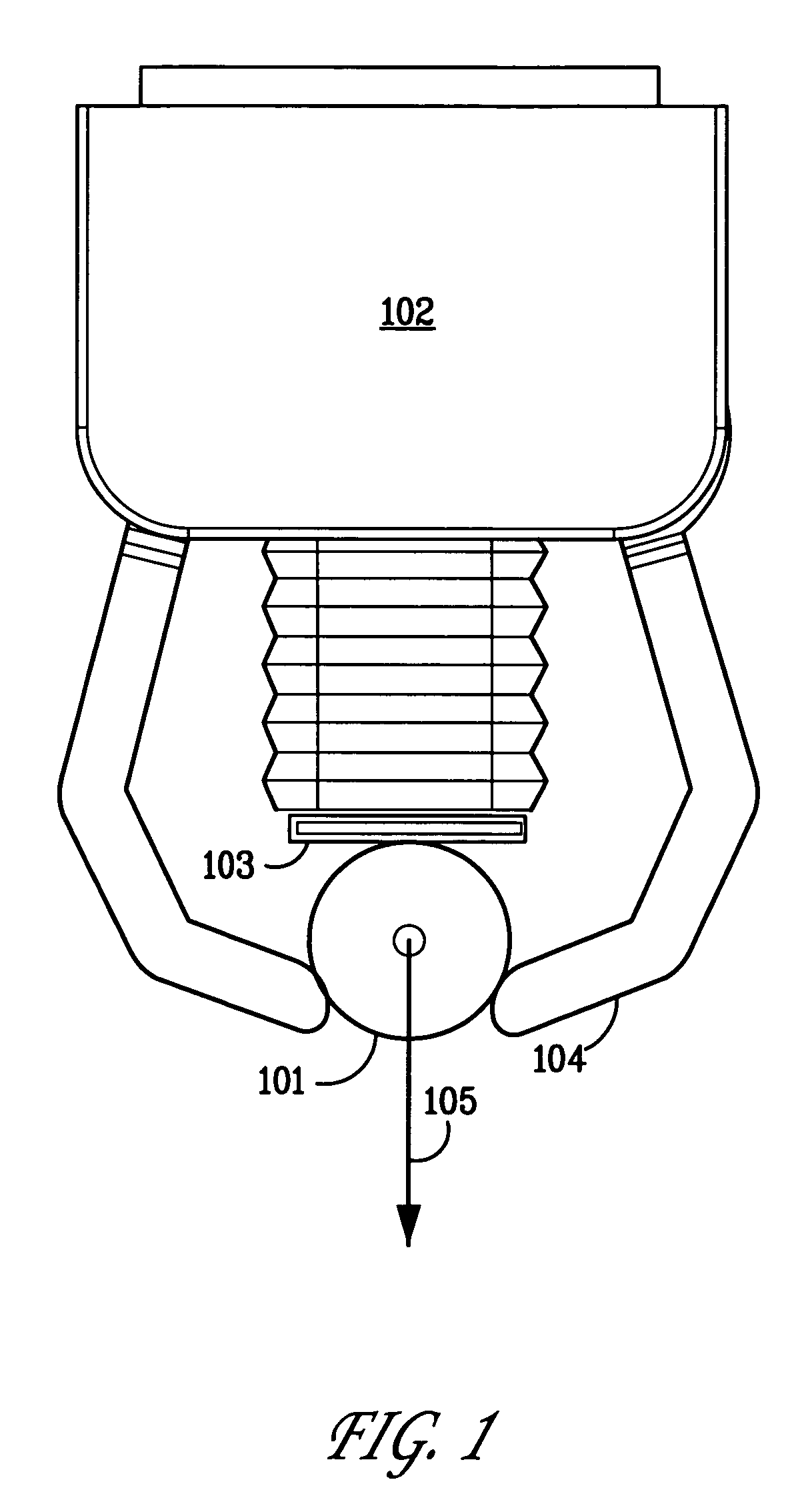
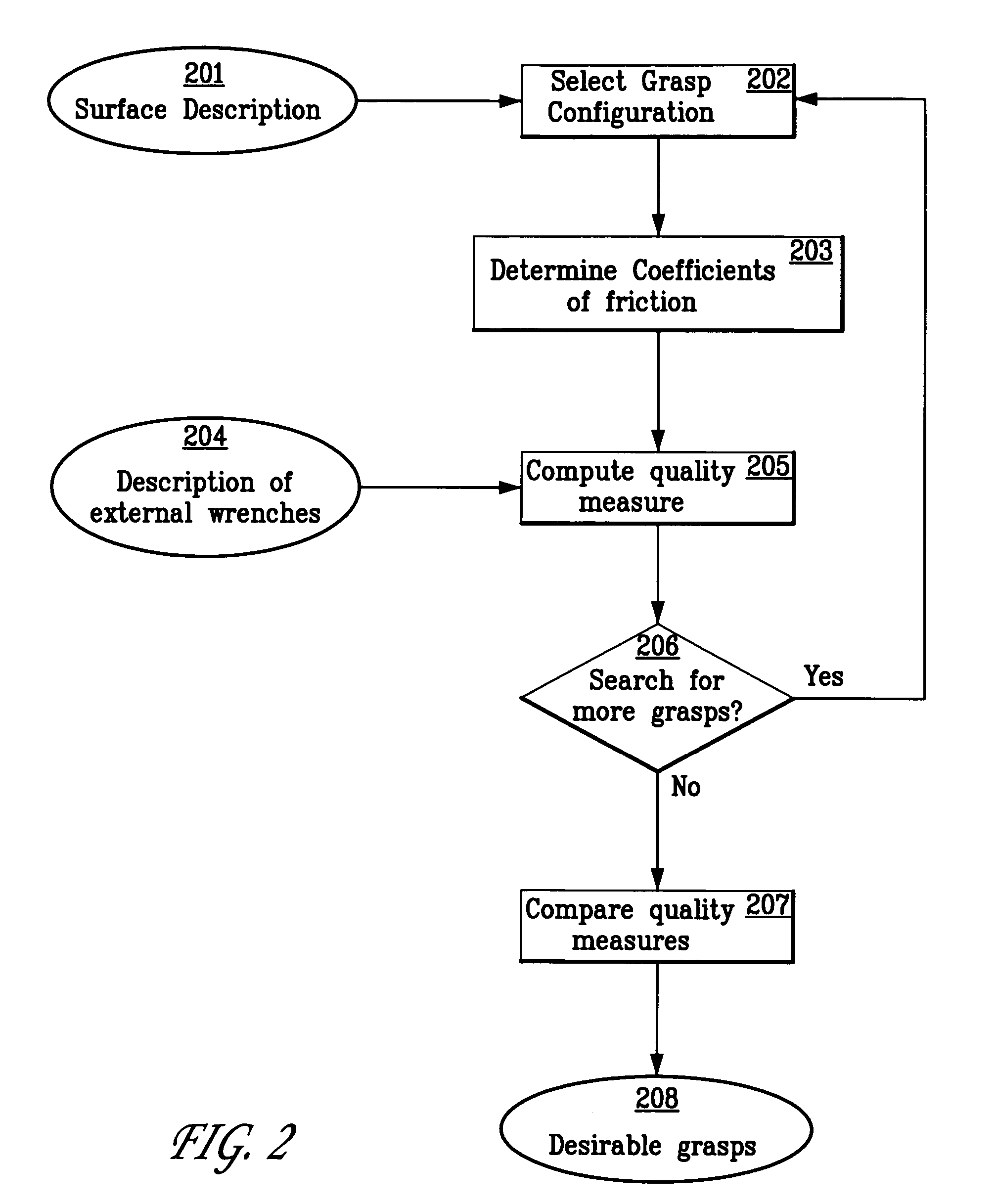
System and method for computing grasps for a robotic hand with a palm
A system and method for automatically computing desirable palm grasp configurations of an object by a robotic hand is disclosed. A description of the object's surface is obtained. A grasp configuration of a robotic hand comprising a palm and one or more fingers is selected, which specifies a hand configuration and joint variables of the hand, and a plurality of contact points on the object's surface for the palm and fingers. The coefficient of friction at each of the contact points is determined, and a description of one or more external wrenches to which may apply to the object is acquired. The ability of the robotic hand to hold the object against the external wrenches in the selected configuration is then computed. In some embodiments, a plurality of grasp configurations may be compared to determine which are the most desirable. In other embodiments, the space of hand configurations, or the smaller space of palm contact configurations, may be searched to find the most desirable grasp configurations.
Owner:STRIDER LABS
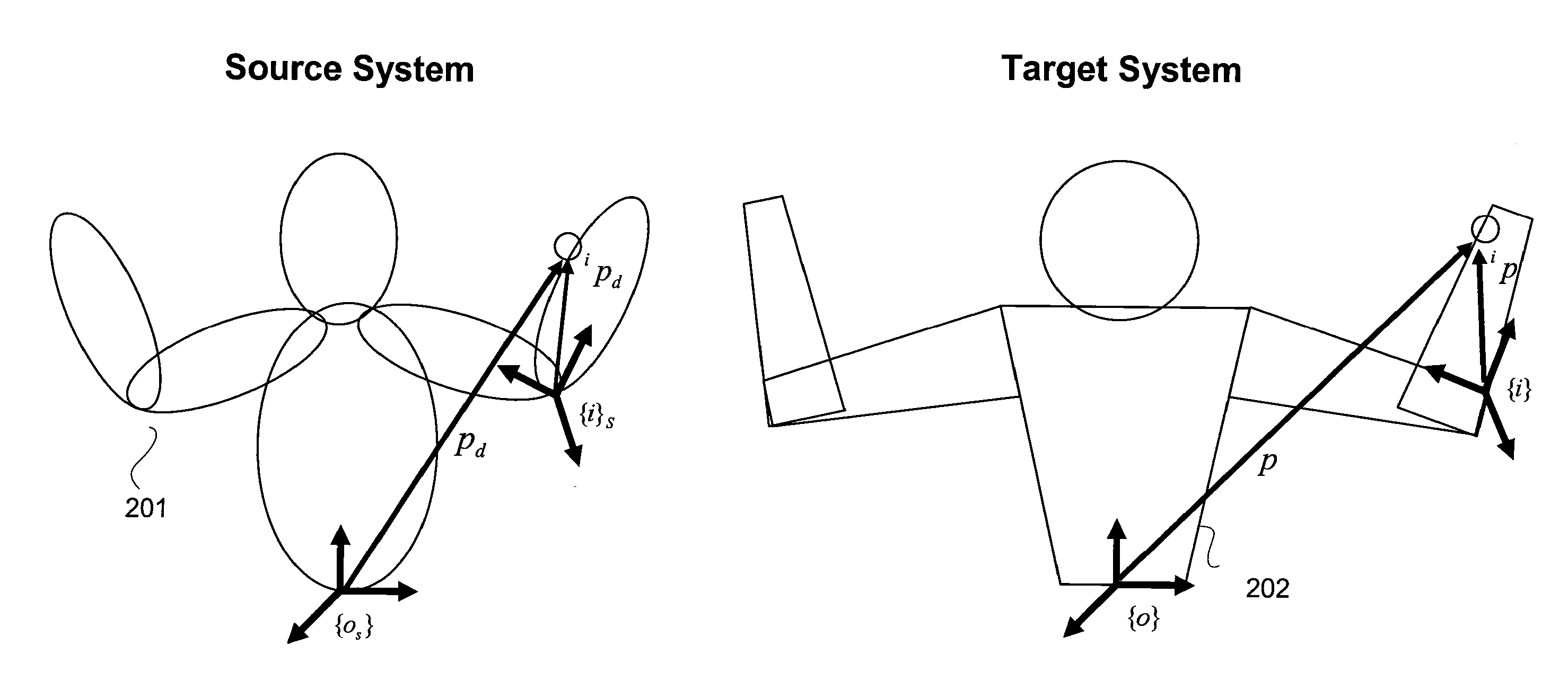
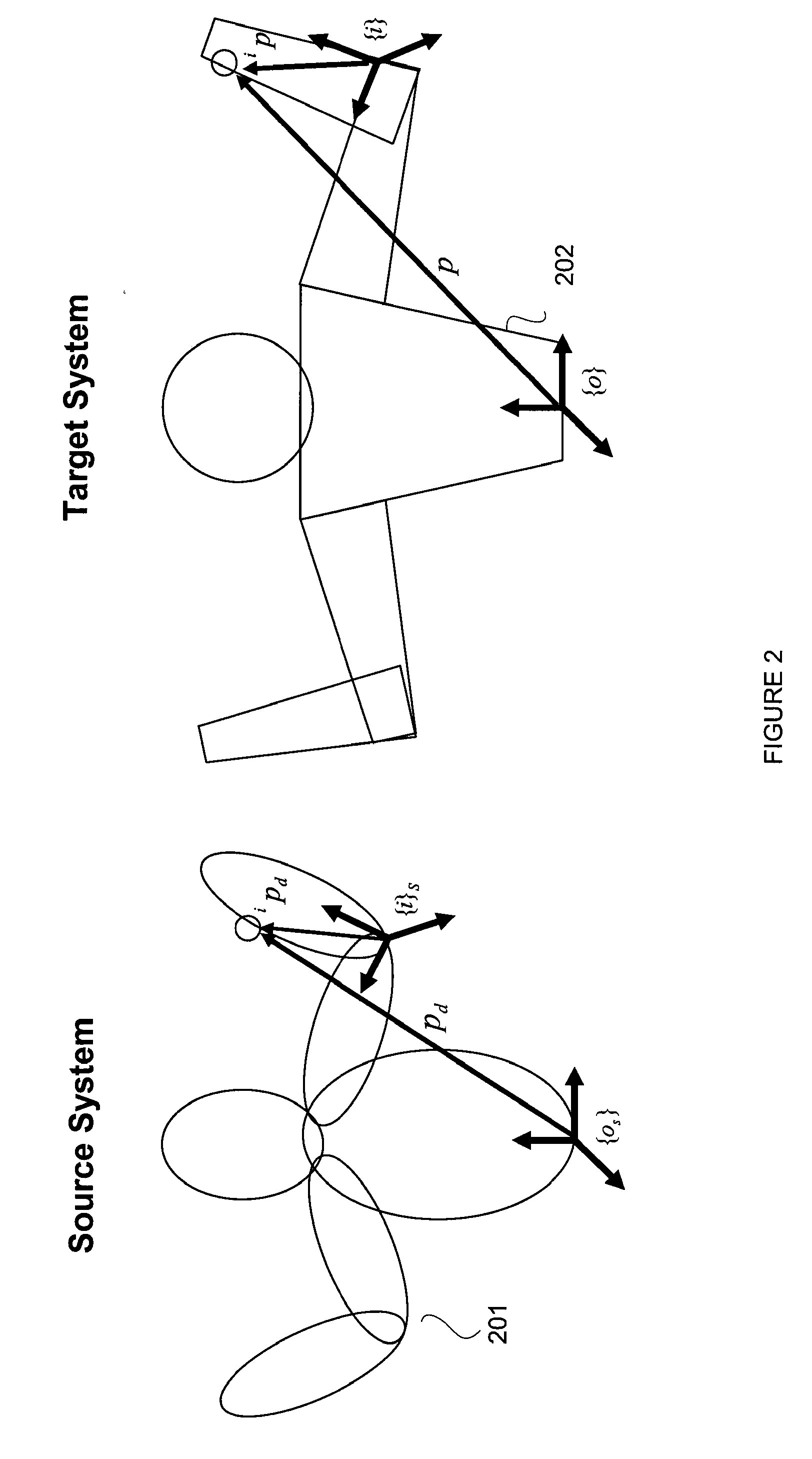
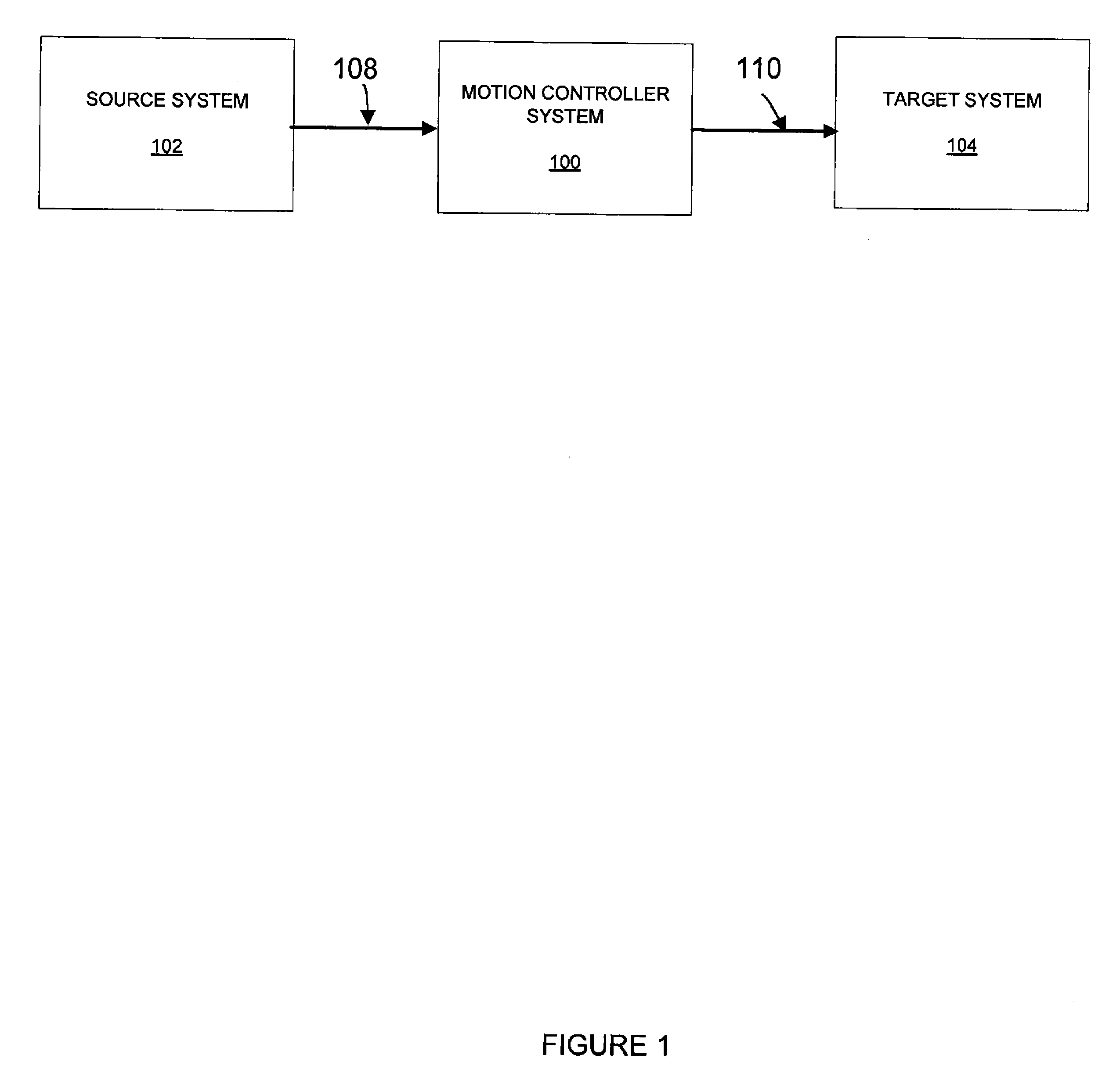
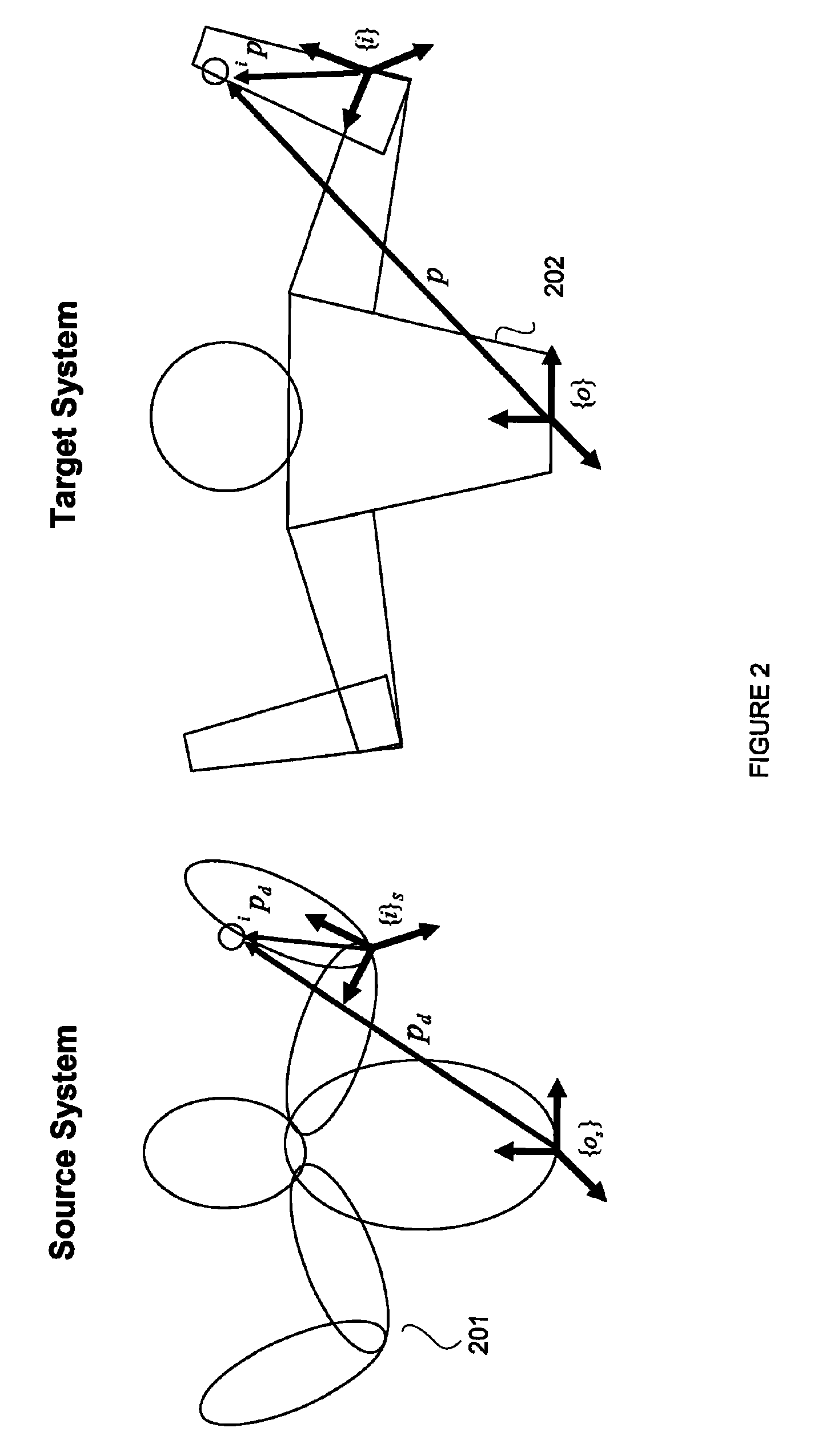
Reconstruction, Retargetting, Tracking, And Estimation Of Motion For Articulated Systems
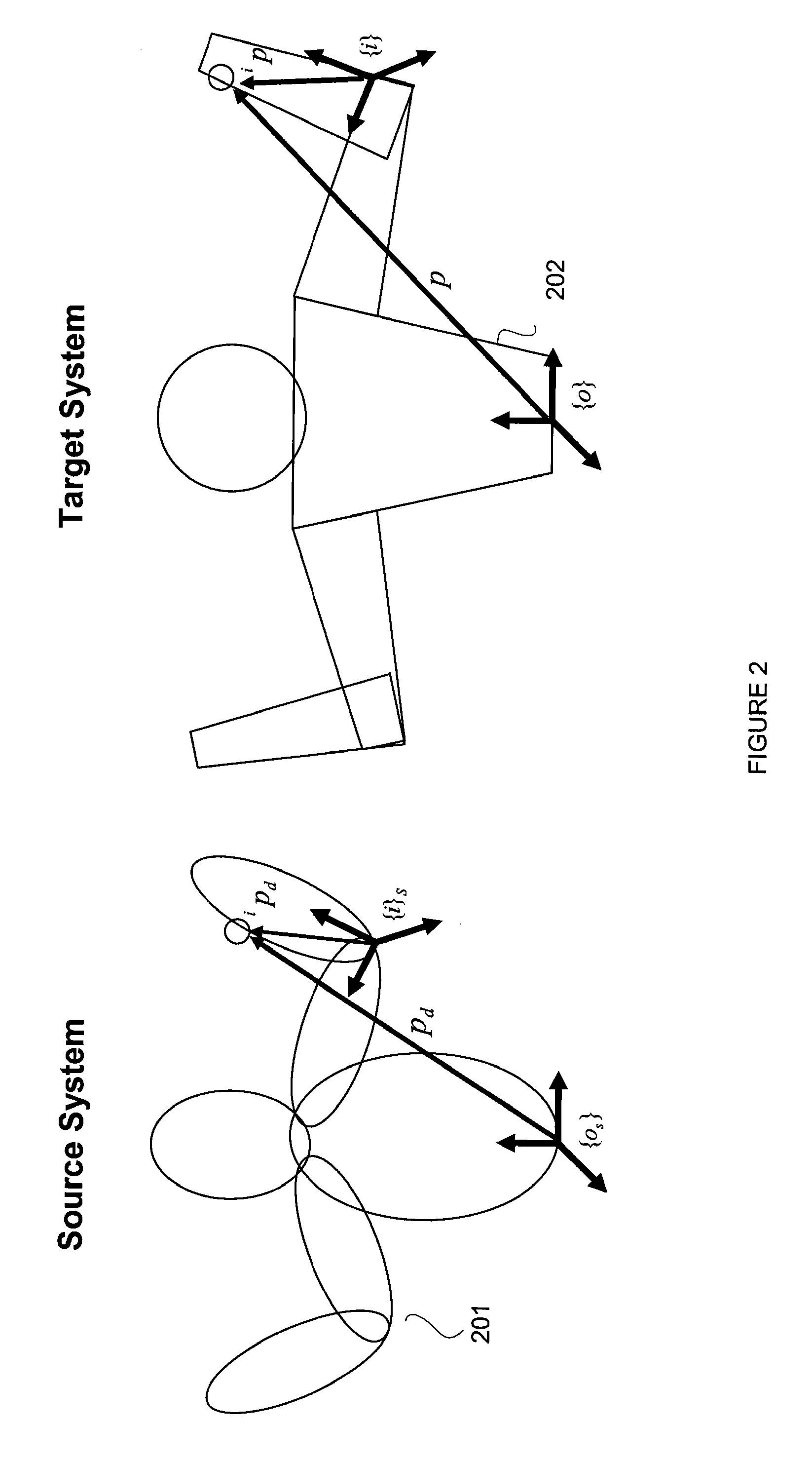
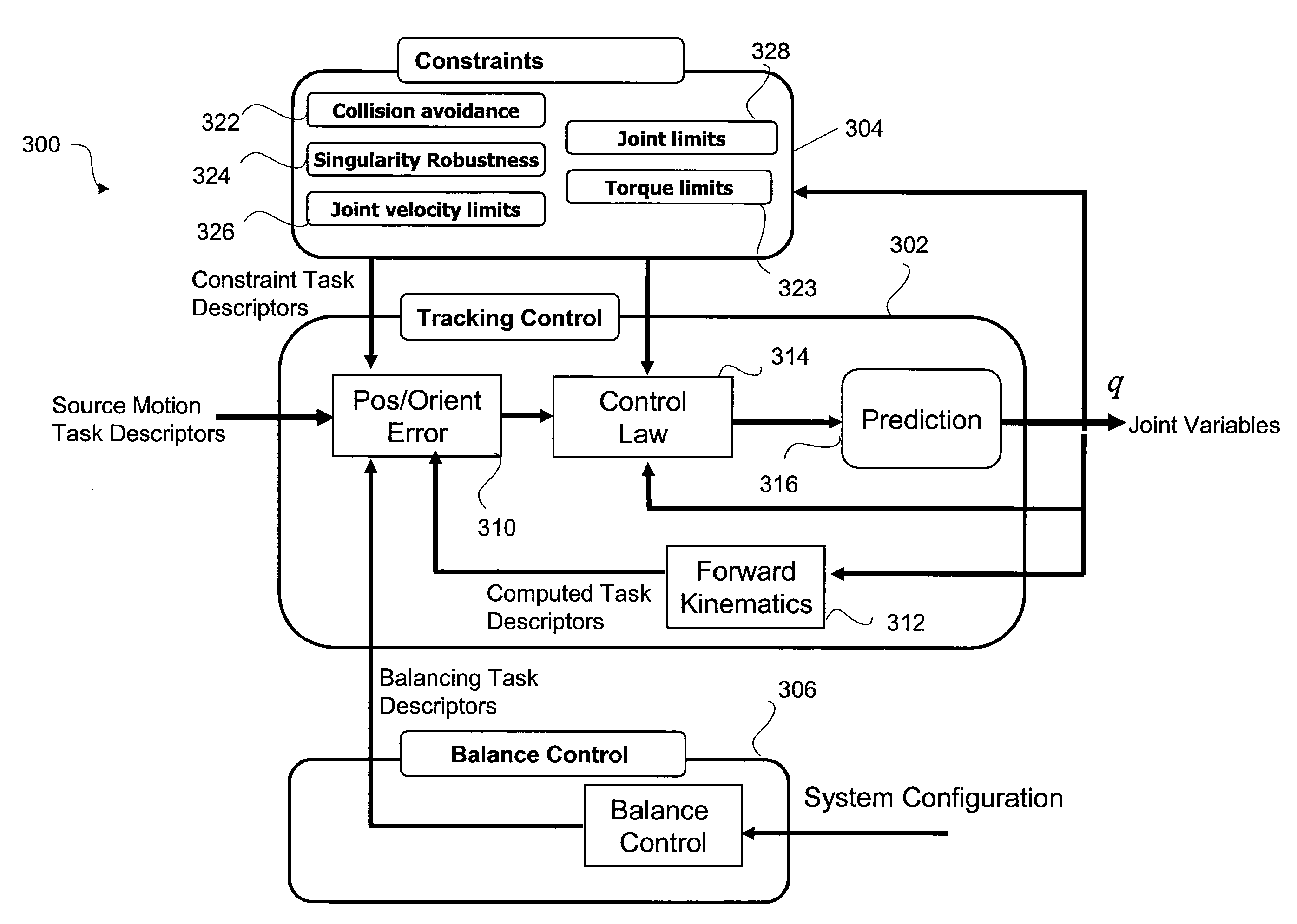
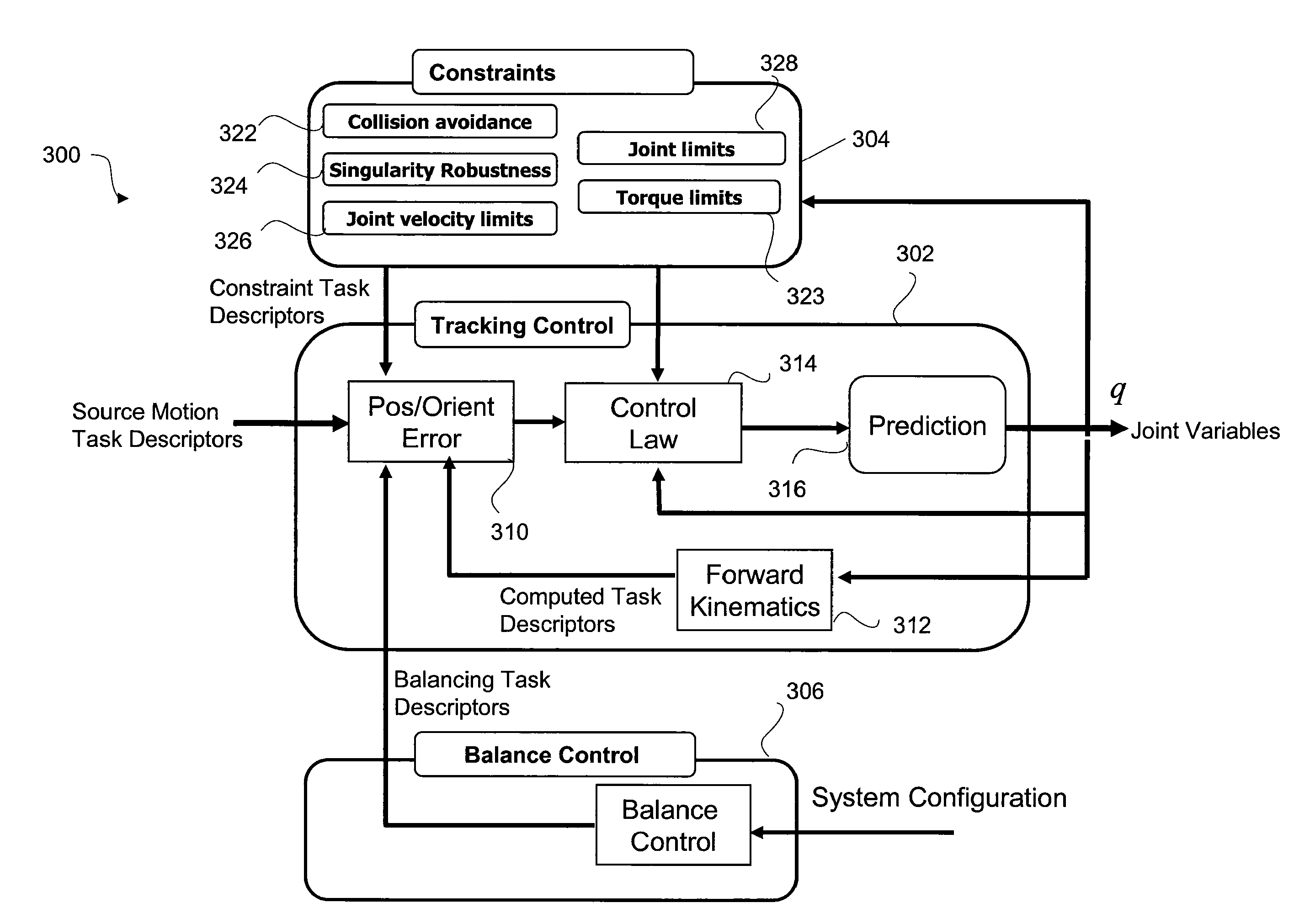
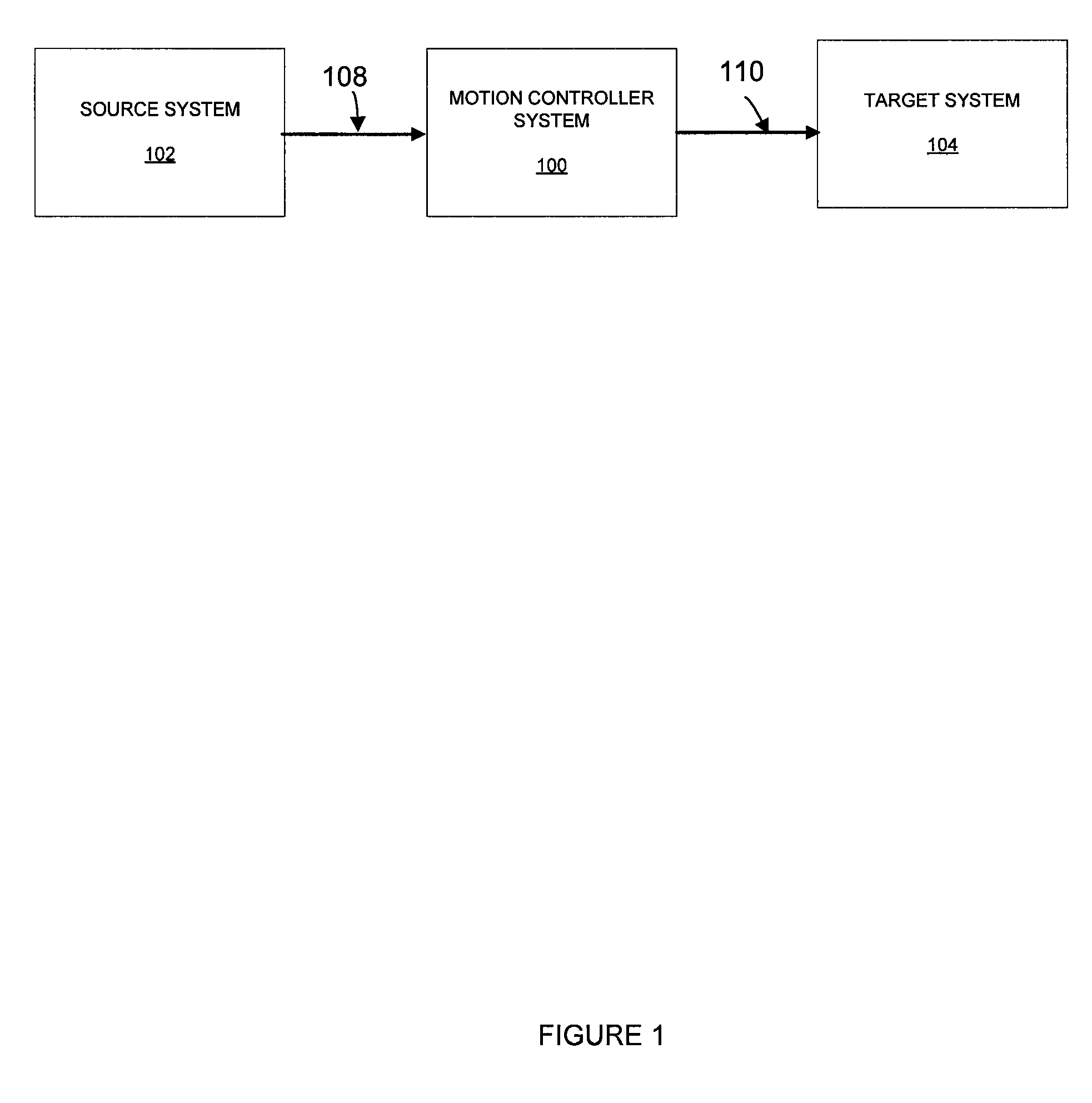
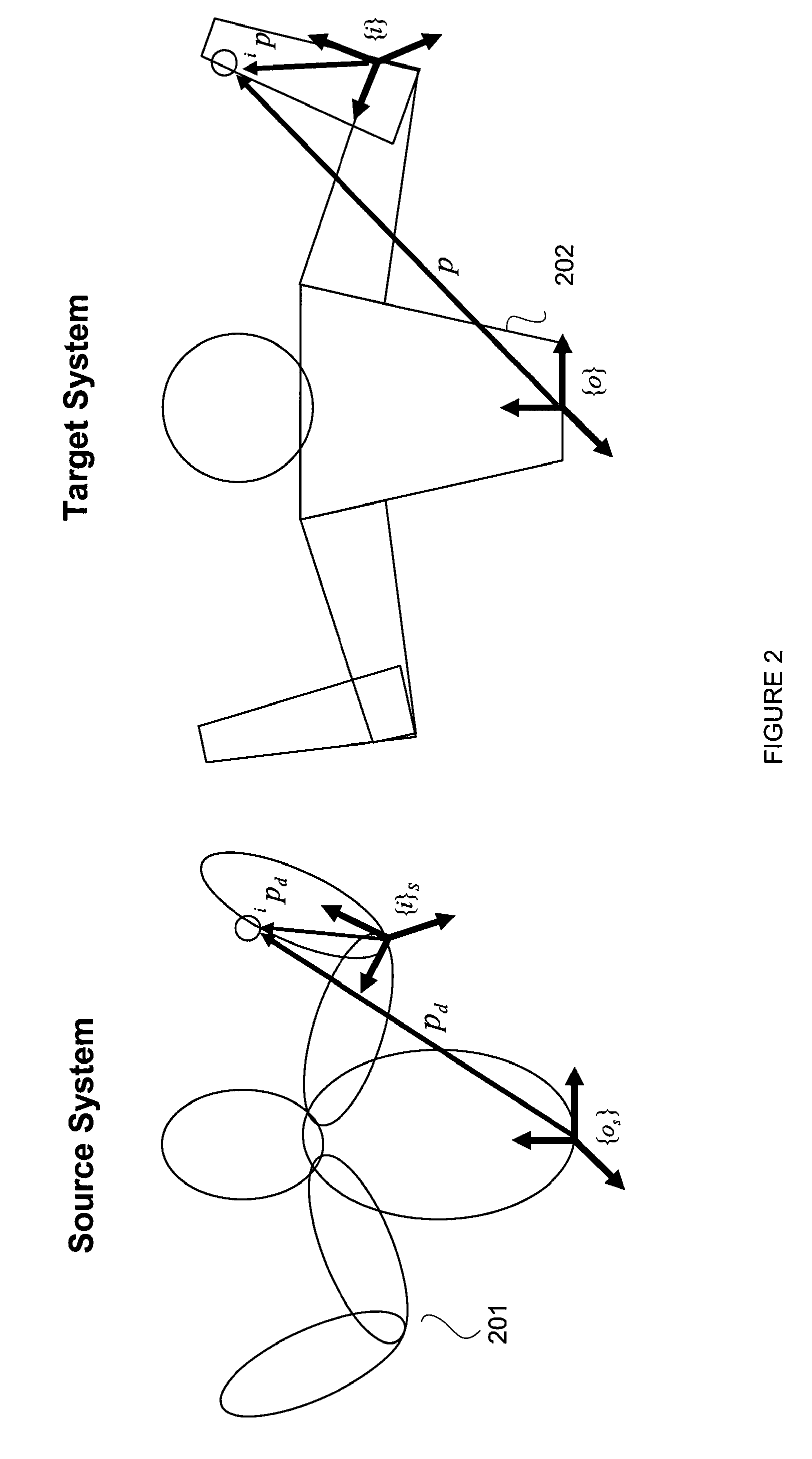
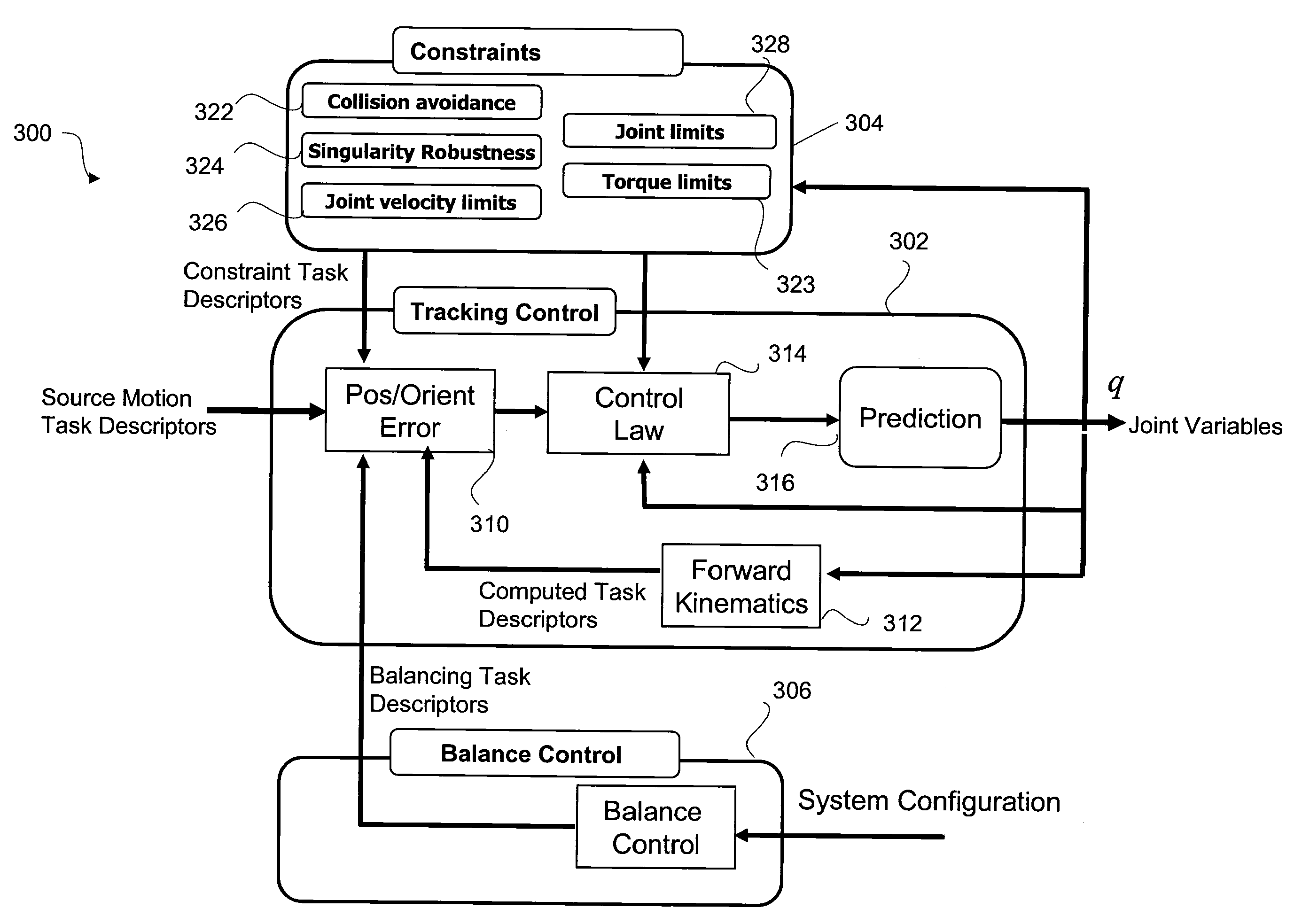
A control system and method generate joint variables for motion or posing of a target system in response to observations of a source system. Constraints and balance control may be provided for more accurate representation of the motion or posing as replicated by the target system.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Reconstruction, Retargetting, Tracking, And Estimation Of Pose Of Articulated Systems
A control system and method generate joint variables for motion or posing of a target system in response to observations of a source system. Constraints and balance control may be provided for more accurate representation of the motion or posing as replicated by the target system.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
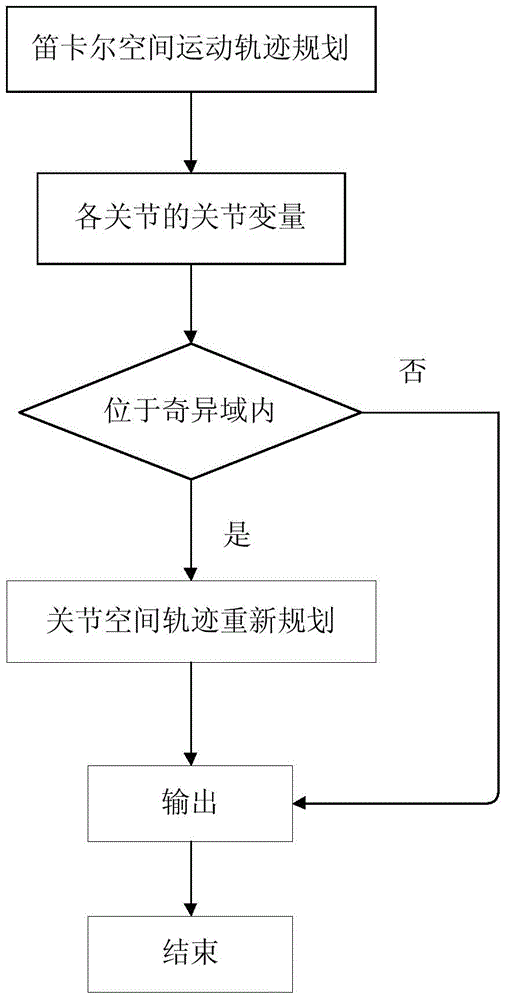
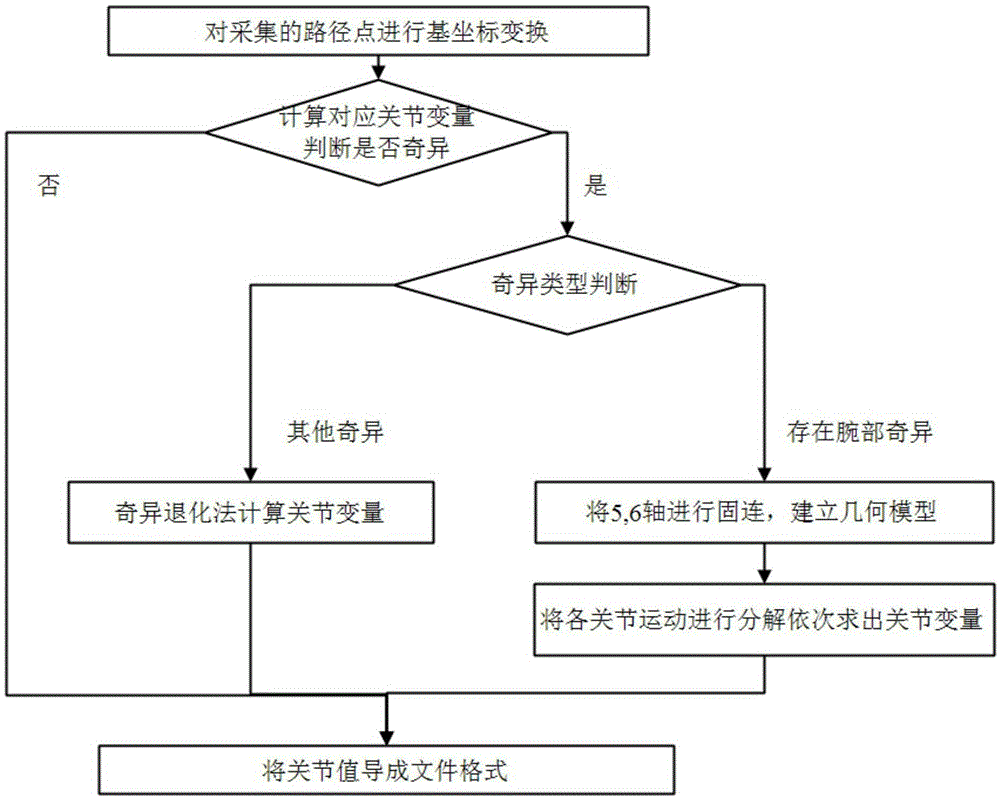
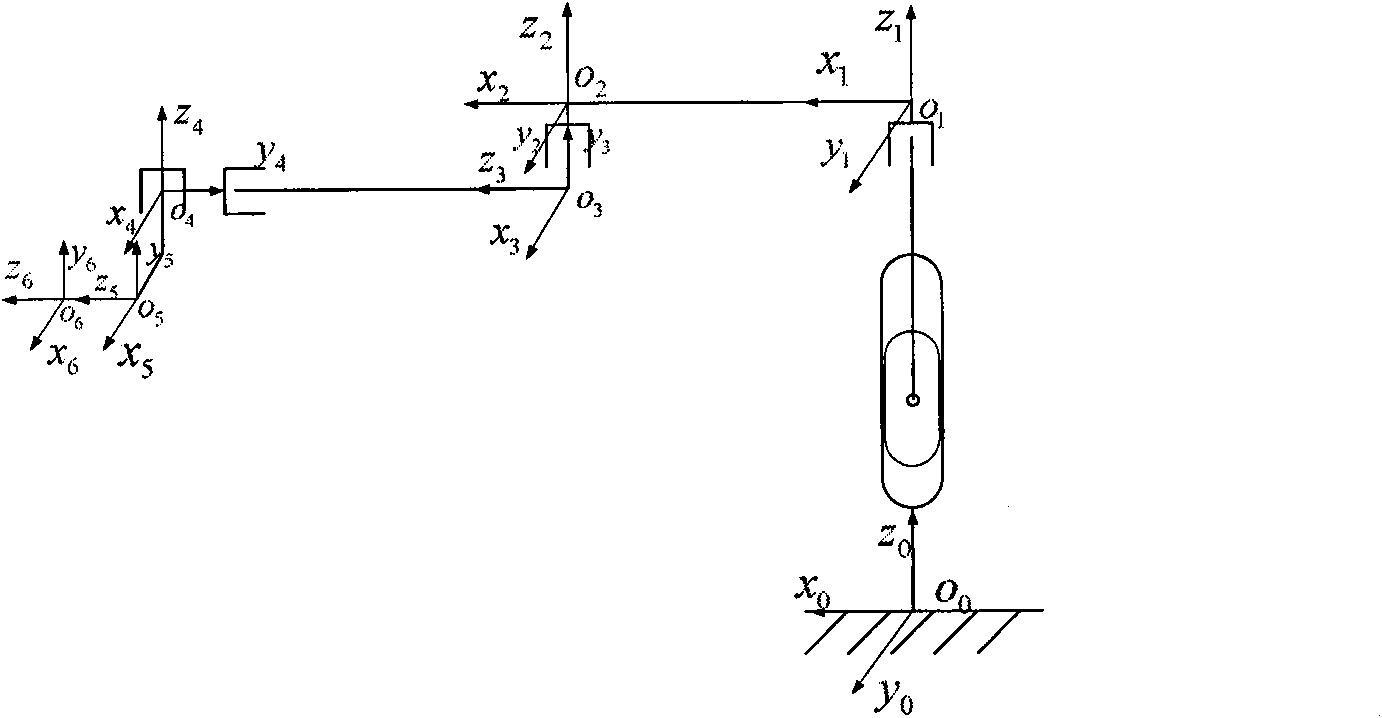
Method of six-DOF industrial robot passing singular region
InactiveCN103909522APass smoothlySolve the unstable operationProgramme-controlled manipulatorEngineeringSacroiliac joint
The invention discloses a method of a six-DOF industrial robot passing a singular region. The method includes the steps of 1, planning a motion curve of the six-DOF industrial robot in the Cartesian space; 2, subjecting coordinates and attitudes of interpolation points in the motion curve to inverse kinematic solution so as to obtain angular displacements, angular velocities and angular acceleration joint variables of joints of the six-DOF industrial robot at the interpolation points; 3, setting the singular region for the six-DOF industrial robot, calculating the joint variables of the interpolation points, judging whether the interpolation points are in the singular region or not, and if yes, further judging the type of singular configuration; 4, allowing the six-DOF industrial robot to pass the singular region. The method has the advantages that the method is simple and feasible and the problem that at present, the six-DOF industrial robot moves unstably due to abrupt change in the joint angular velocity when the six-DOF industrial robot encounters the singular region is well solved.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Reconstruction, retargetting, tracking, and estimation of pose of articulated systems
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Reconstruction, retargetting, tracking, and estimation of motion for articulated systems
A control system and method generate joint variables for motion or posing of a target system in response to observations of a source system. Constraints and balance control may be provided for more accurate representation of the motion or posing as replicated by the target system.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
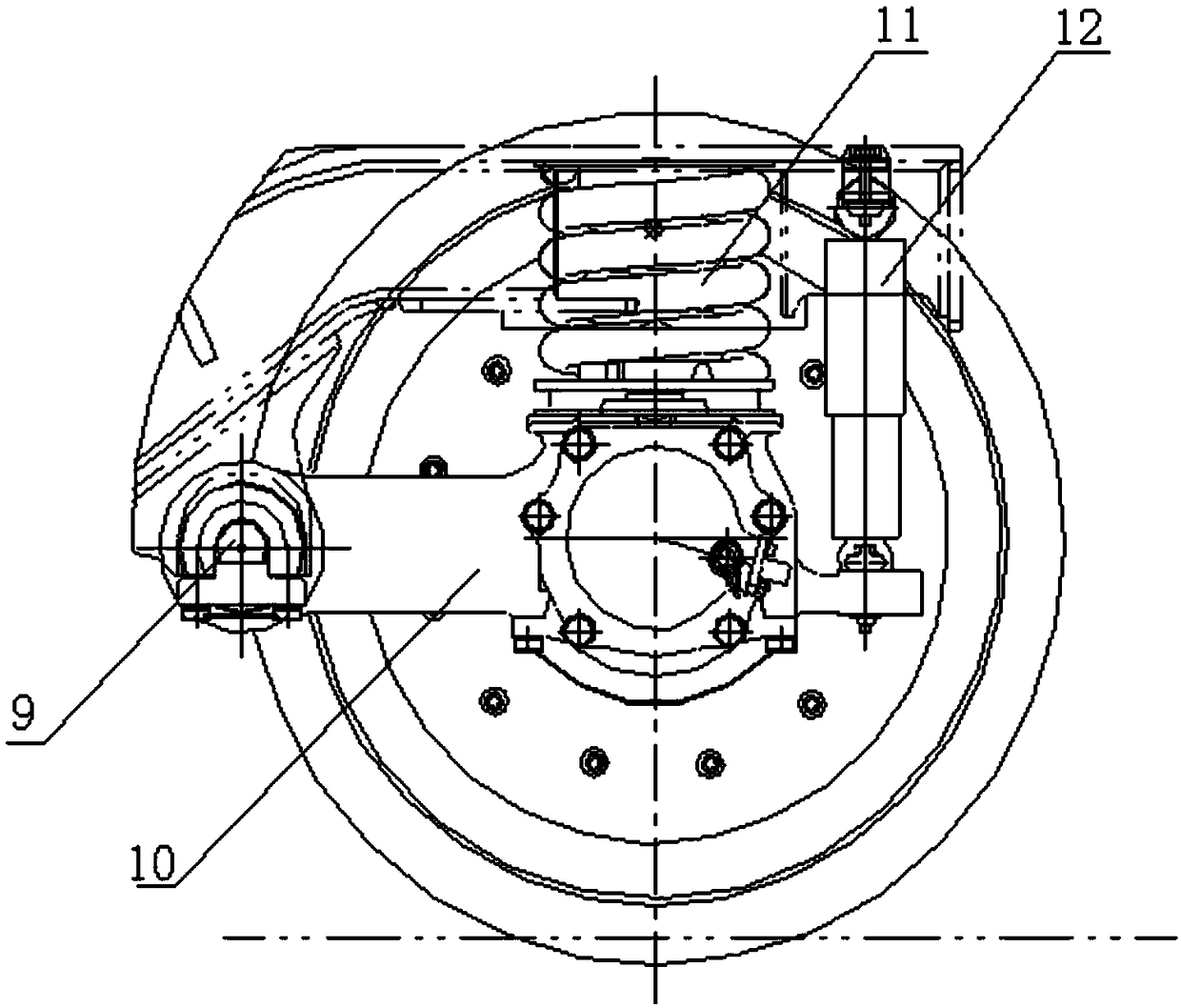
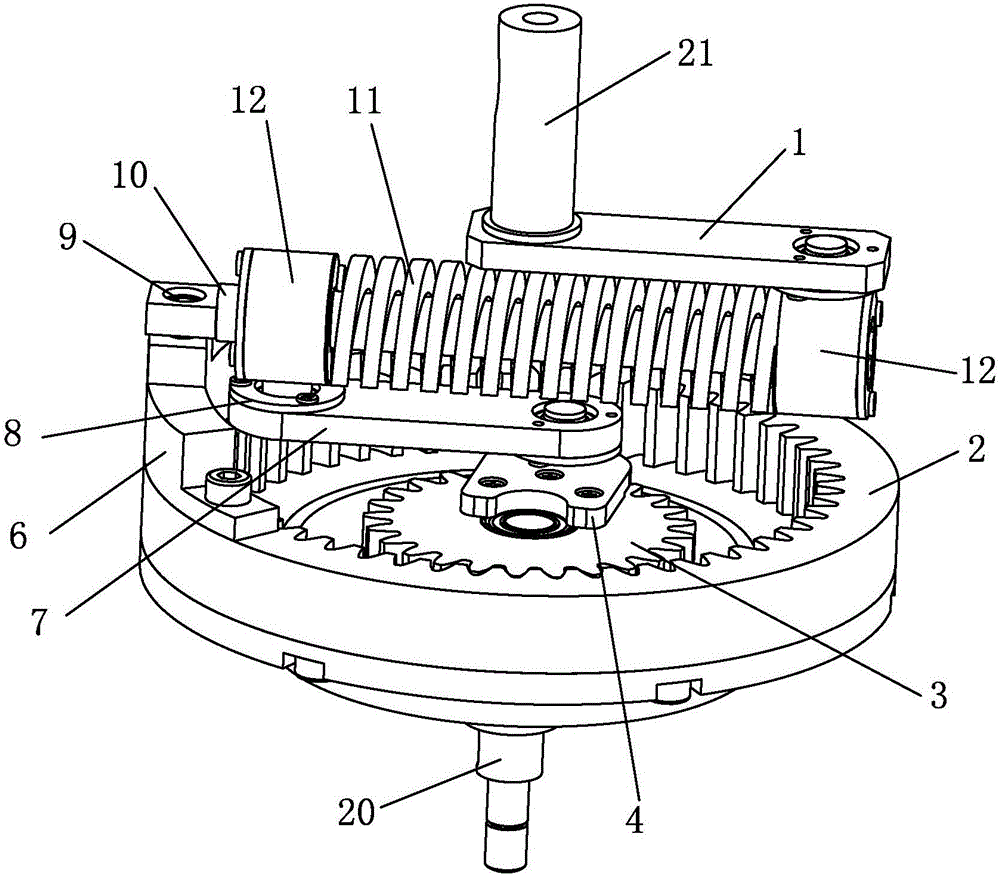
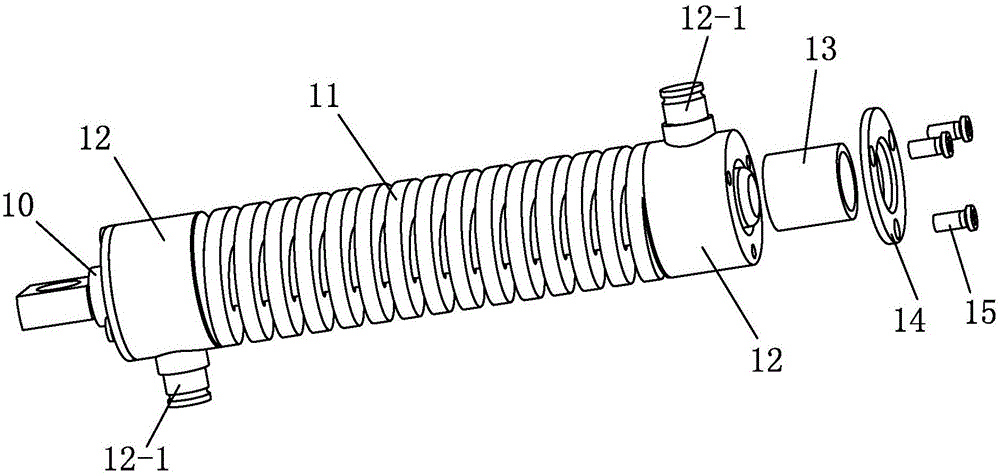
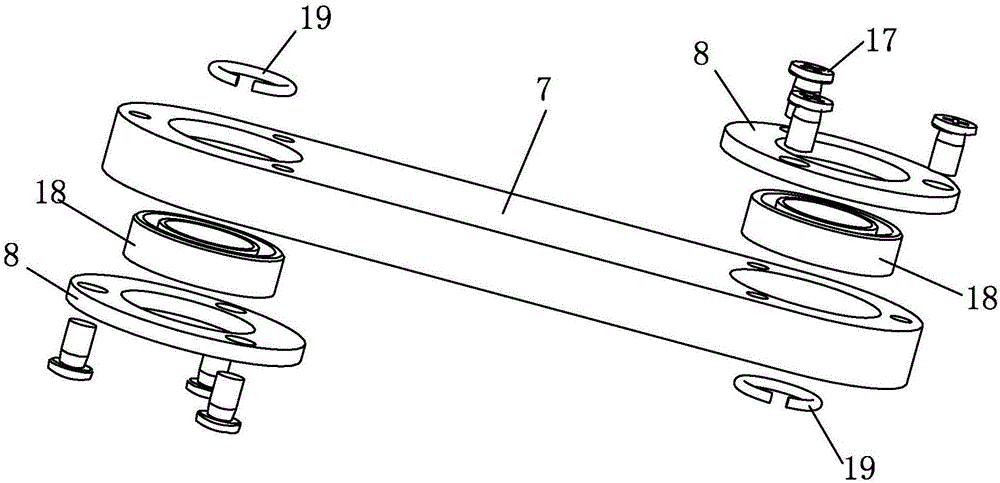
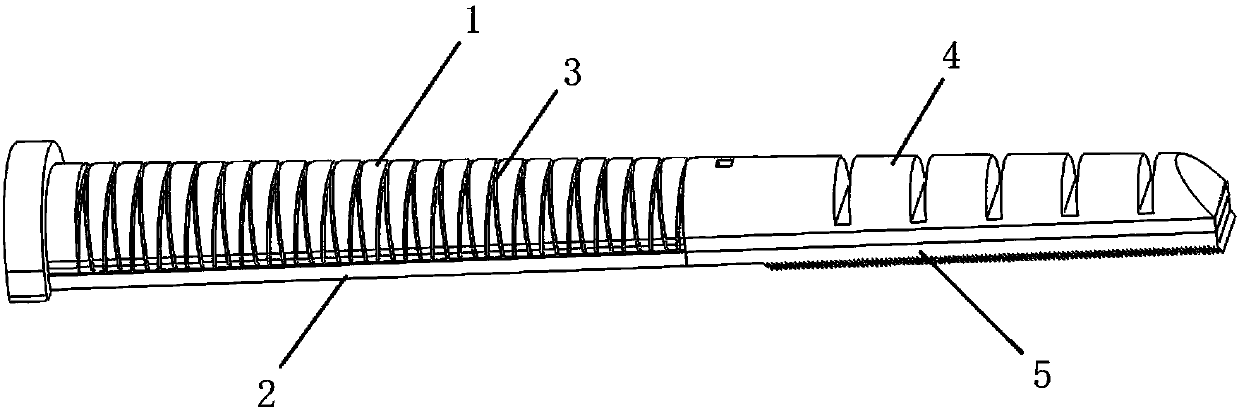
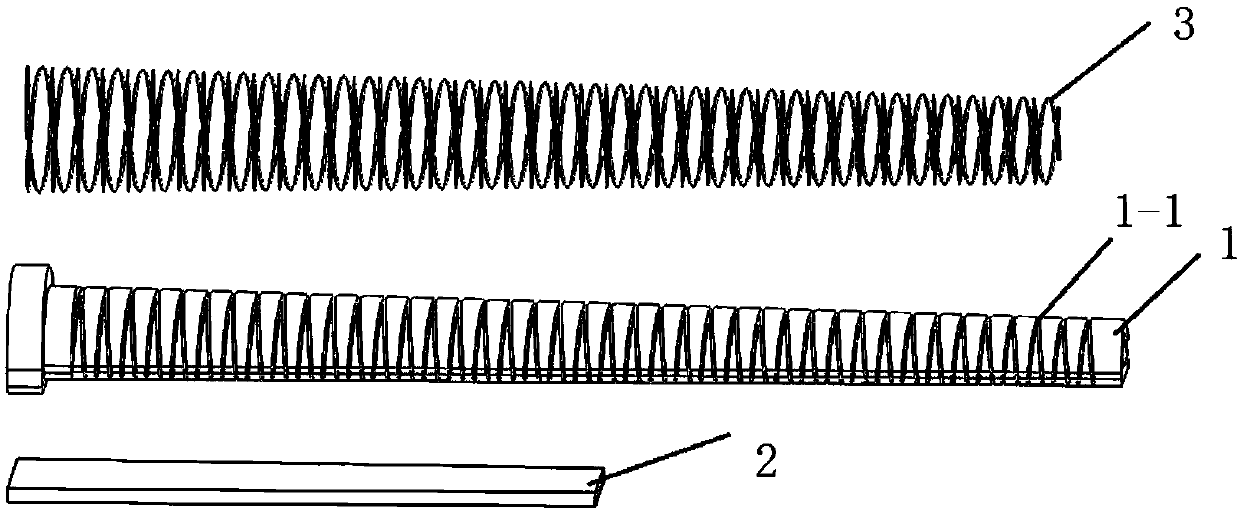
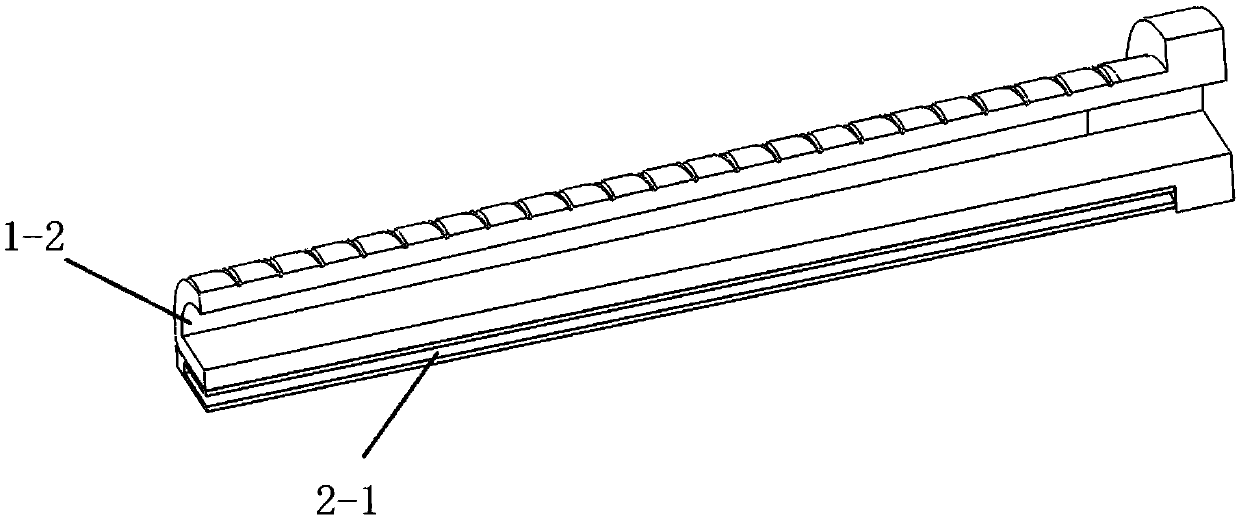
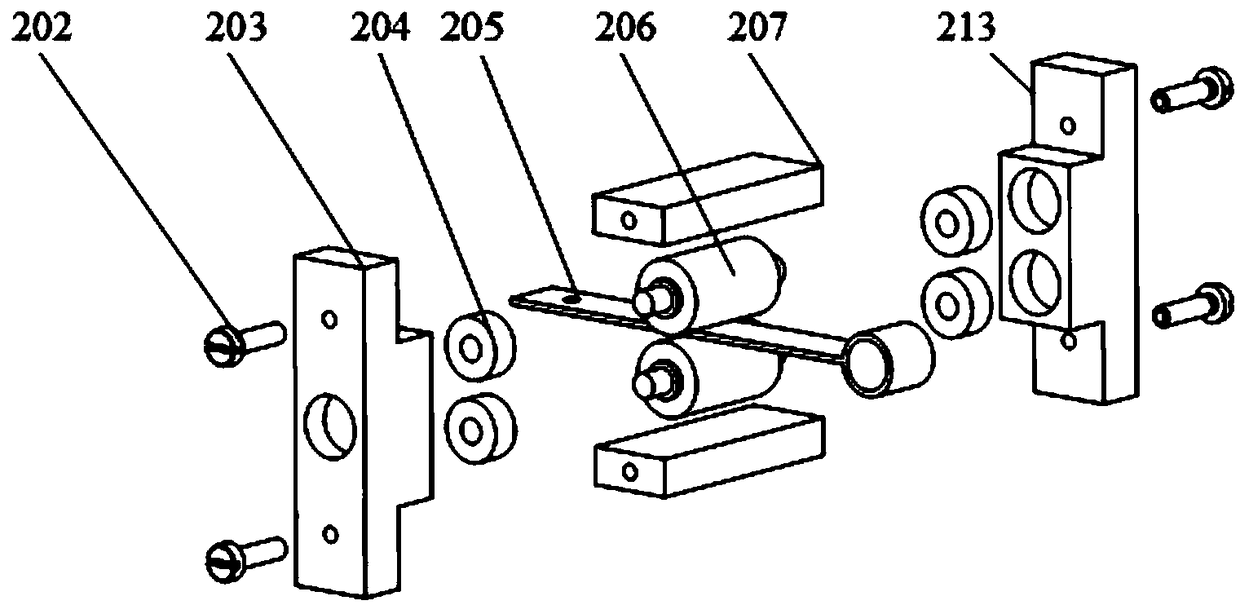
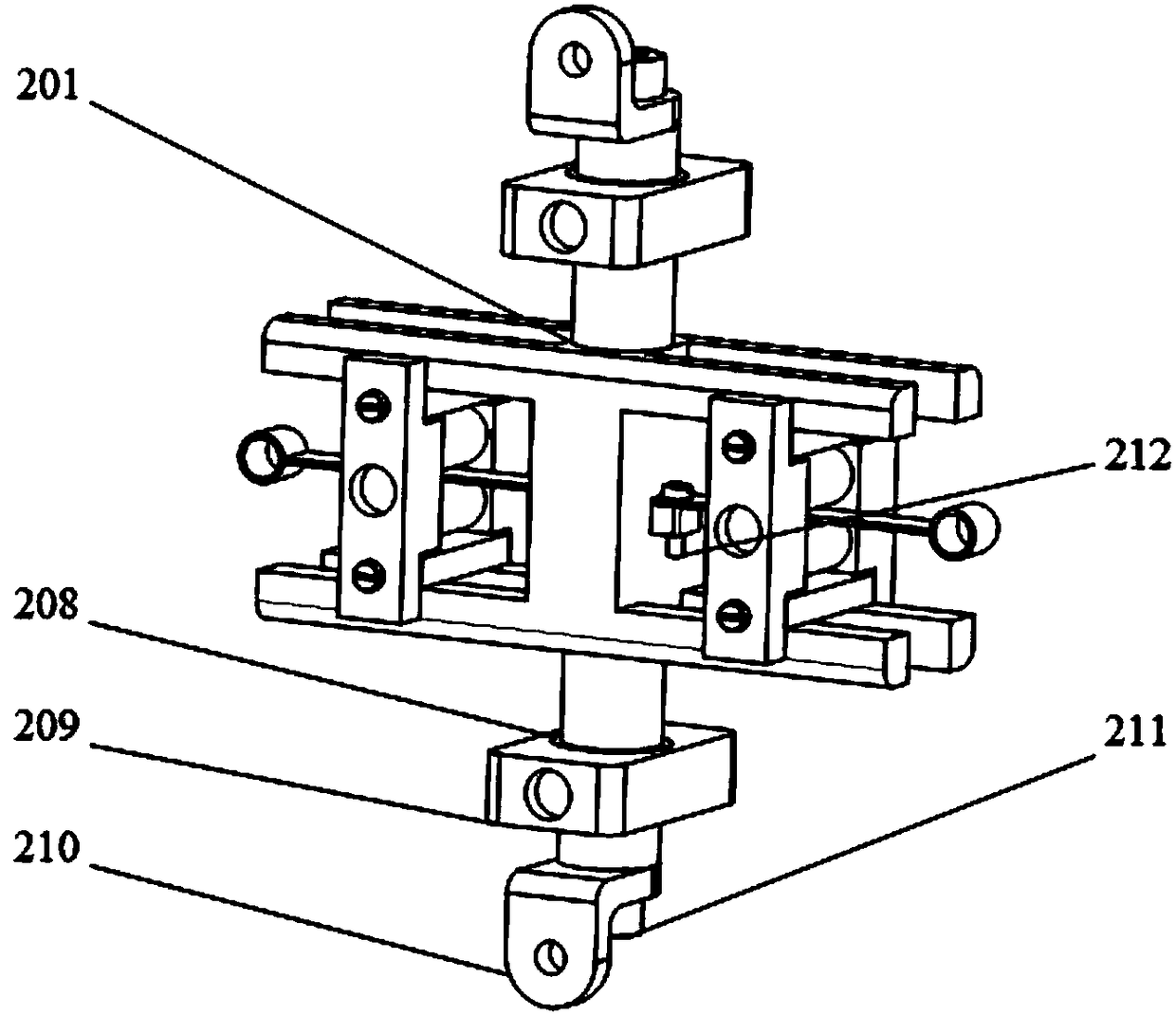
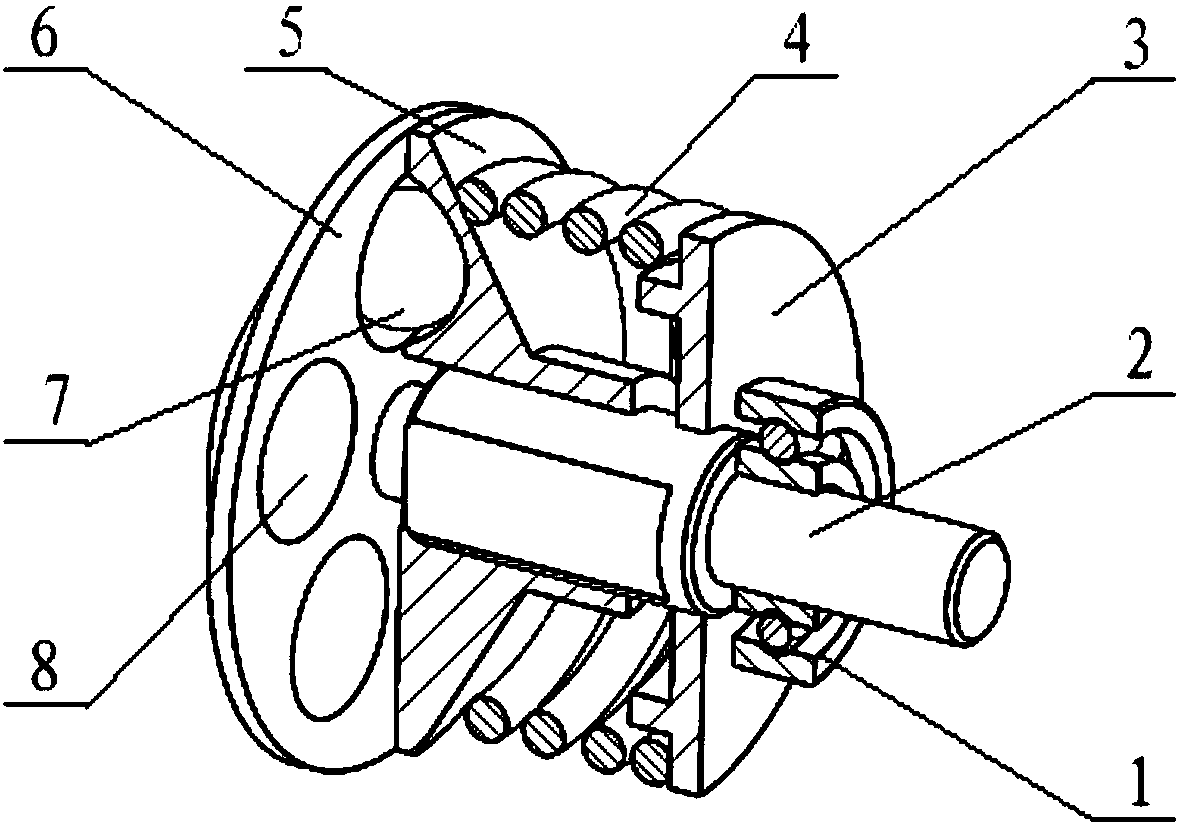
Rotating arm joint variable in stiffness and series of positioning device having same
PendingCN109455191AImprove dynamic performanceAdapt to different requirementsBogiesAxle-boxes mountingJoint variablePetroleum engineering
The invention relates to a rotating arm joint variable in stiffness. The rotating arm joint comprises an outer sleeve, a main spring, auxiliary springs and a mandrel, an oil pipeline is wound around the surface of the mandrel, the main spring is formed by vulcanizing rubber and a metal piece into a whole part, the metal piece part of the main spring is in press fit with the mandrel, the auxiliarysprings are in press fit with the two ends of the main spring, and each auxiliary spring is also formed by vulcanizing the rubber and the metal piece into a whole part corresponding to the main spring; the outer sleeve is in press fit with the peripheries of the main spring and auxiliary springs, the outer sleeve and the main spring define an oil chamber, and upper and lower openings of the oil chamber are communicated with two ports of the oil pipeline respectively. The oil pipeline is arranged between the mandrel and the main spring, and the oil chamber is formed between the main spring andthe outer sleeve. During running of a car, the oil chamber is compressed when the springs are deformed by a force, oil flows in the pipeline to generate a damping force, and the purpose of changing stiffness is achieved. A series of positioning devices having the rotating arm joint can meet different requirements of a linear line and a curved line, and the dynamic performance of the car is improved.
Owner:CRRC CHANGCHUN RAILWAY VEHICLES CO LTD
NSGA-II algorithm-based multi-objective optimization method for mechanical arm in redundant space
ActiveCN105676636AIncrease load carrying capacityGuaranteed positioning accuracyAdaptive controlRedundant codeAngular velocity
The embodiment of the present invention provides an NSGA-II algorithm-based multi-objective optimization method for a mechanical arm in a redundant space. The method comprises the steps of converting the point-to-point transfer task of the mechanical arm in the operating space from a Cartesian space into a joint space, conducting the parameterized treatment on joint variables based on the sine seven-times polynomial interpolation method, adopting an obtained parameter sequence code as an individual in an NSGA-II algorithm-based population, figuring out an optimized solution for the motion trajectory of the mechanical arm based on the NSGA-II algorithm to enable the sum of the average values of all joint torques to be minimum, the torque of a largest joint to be minimum and the maximum angular velocity of joints to be minimum, and selecting a most optimal solution out of an obtained pareto non-dominated solution set. Based on the above method, the sum of the average values of all joint torques, the torque of the largest joint and the maximum angular velocity of joints are optimized according to the described motion trajectory. According to the technical scheme of the invention, when the point-to-point transfer task is executed in the operating space with the constraint conditions of the task to be met, multiple objects of the mechanical arm can be optimized at the same time according to the above described planning path.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
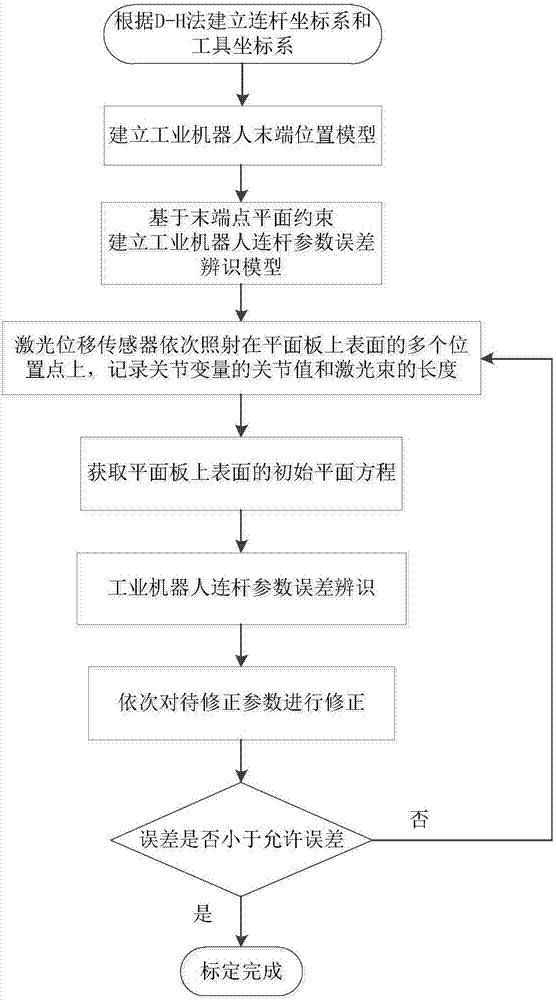
Calibration method of connecting rod parameters of industrial robot based on end-point plane constraint
The invention belongs to the field of calibration of connecting rod parameters of an industrial robot, in particular to a calibration method of the connecting rod parameters of the industrial robot based on end-point plane constraint. The calibration method comprises the following steps: (1) establishing a connecting rod coordinate system and a tool coordinate system of the industrial robot, and thus obtaining the end position coordinate of the industrial robot; (2) conducting plane constraint for an end point, and establishing an error identification model of the connecting rod parameters ofthe industrial robot; (3) transforming the postures of the industrial robot, recording the joint values of joint variables and the length of a laser beam, and calculating the initial parameter of a plane equation according to the position coordinates of the first three poses; (4) conducting error identification for the connecting rod parameters of the industrial robot; and (5) correcting parameters to be corrected in order, and verifying the precision of the corrected industrial robot. The calibration method can conduct calibration in the larger working space of the industrial robot, can realize fully automatic calibration, and has high calibration precision and low cost.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
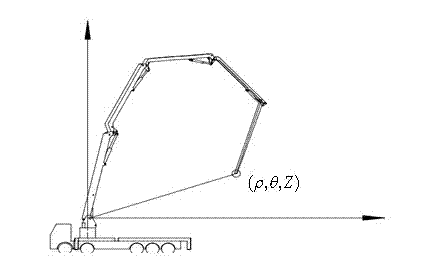
Method for compensating for deflection of concrete pump truck arm support
ActiveCN102345390AEffective control errorRealize intelligent controlBuilding material handlingControl systemEngineering
The invention discloses a method for compensating for the deflection of a concrete pump truck arm support, belonging to the technical field of concrete pump truck arm supports. In the method, a terminal is used for compensating in real time; an arm support deformation data sheet which corresponds to a series of pouring locus coordinates is established by testing; and when operating personnel controls a pouring gate to move to the start pouring point of a specified pouring locus, a control system is used for calling a corresponding locus planning program, arm support deformation data and a joint variable inverse solution program by computing an angle value fed back by each joint arm inclination angle sensor and resolving the joint variable of each compensated pouring point to control the application of pouring gate movement. The method for compensating for the deflection of the arm support has the beneficial effects of easiness for controlling, high accuracy, easiness for implementing and capability of effectively compensating for the deflation of the arm support in the intelligent control process.
Owner:JIANGSU XCMG CONSTR MASCH RES INST LTD
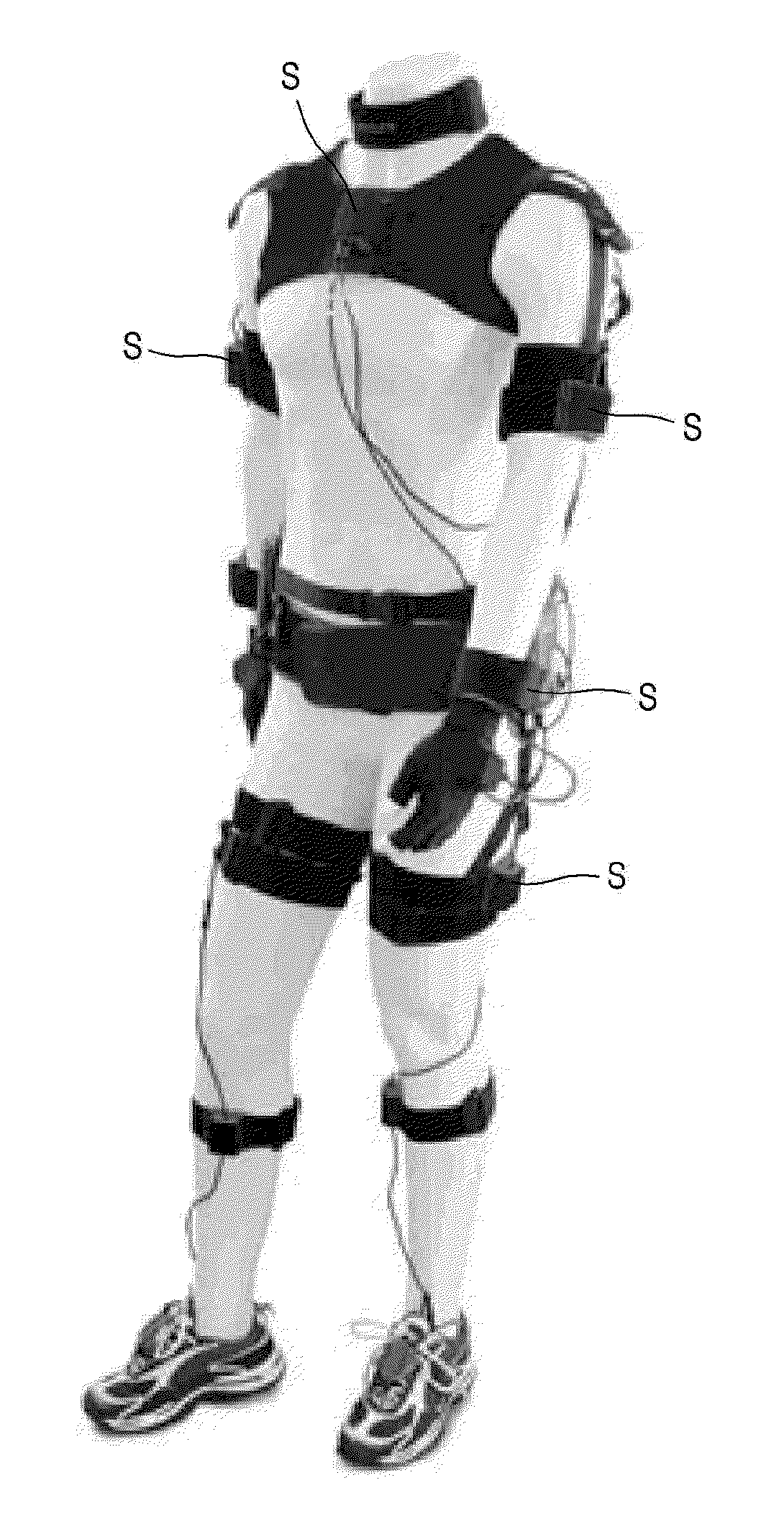
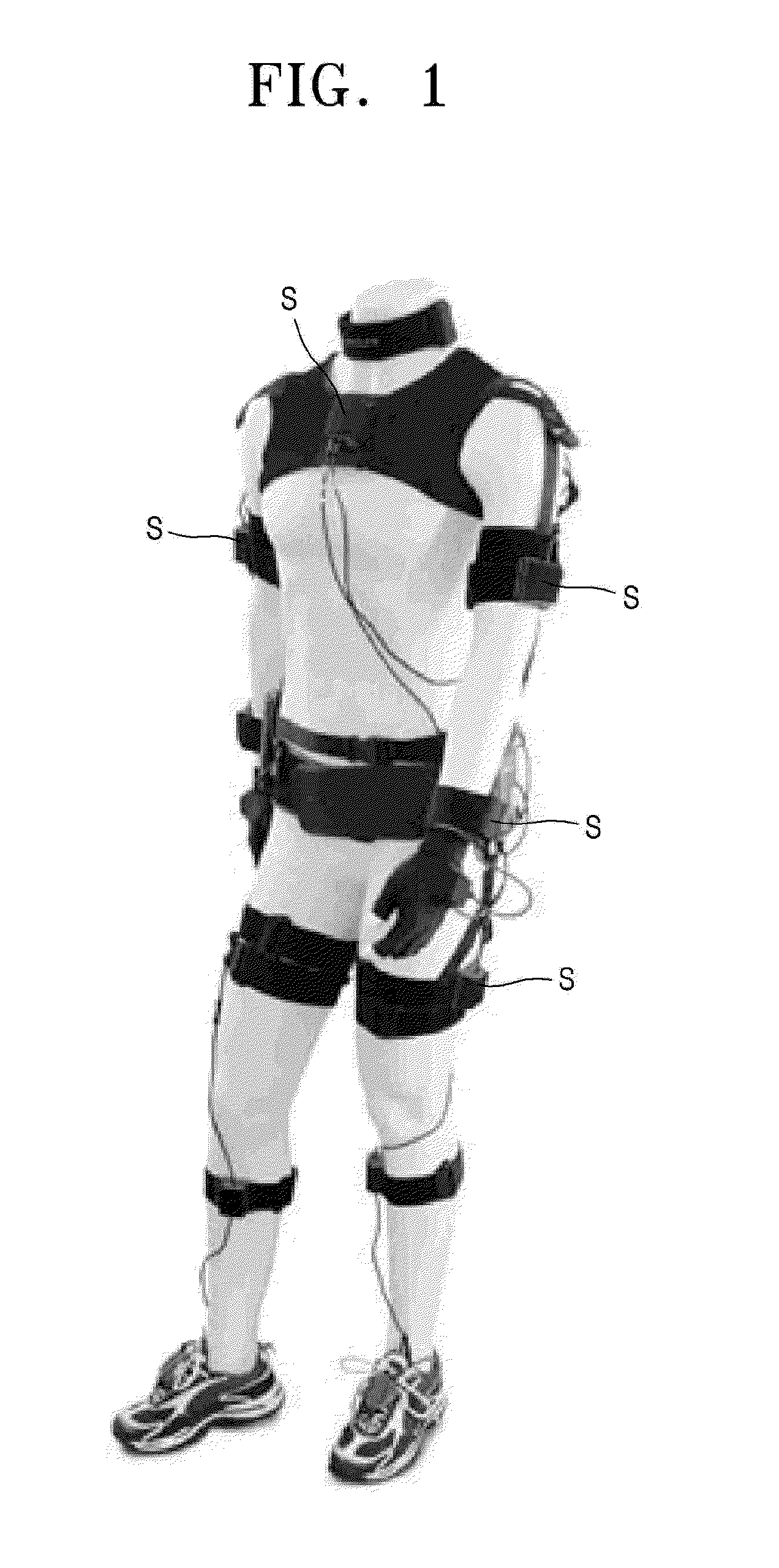
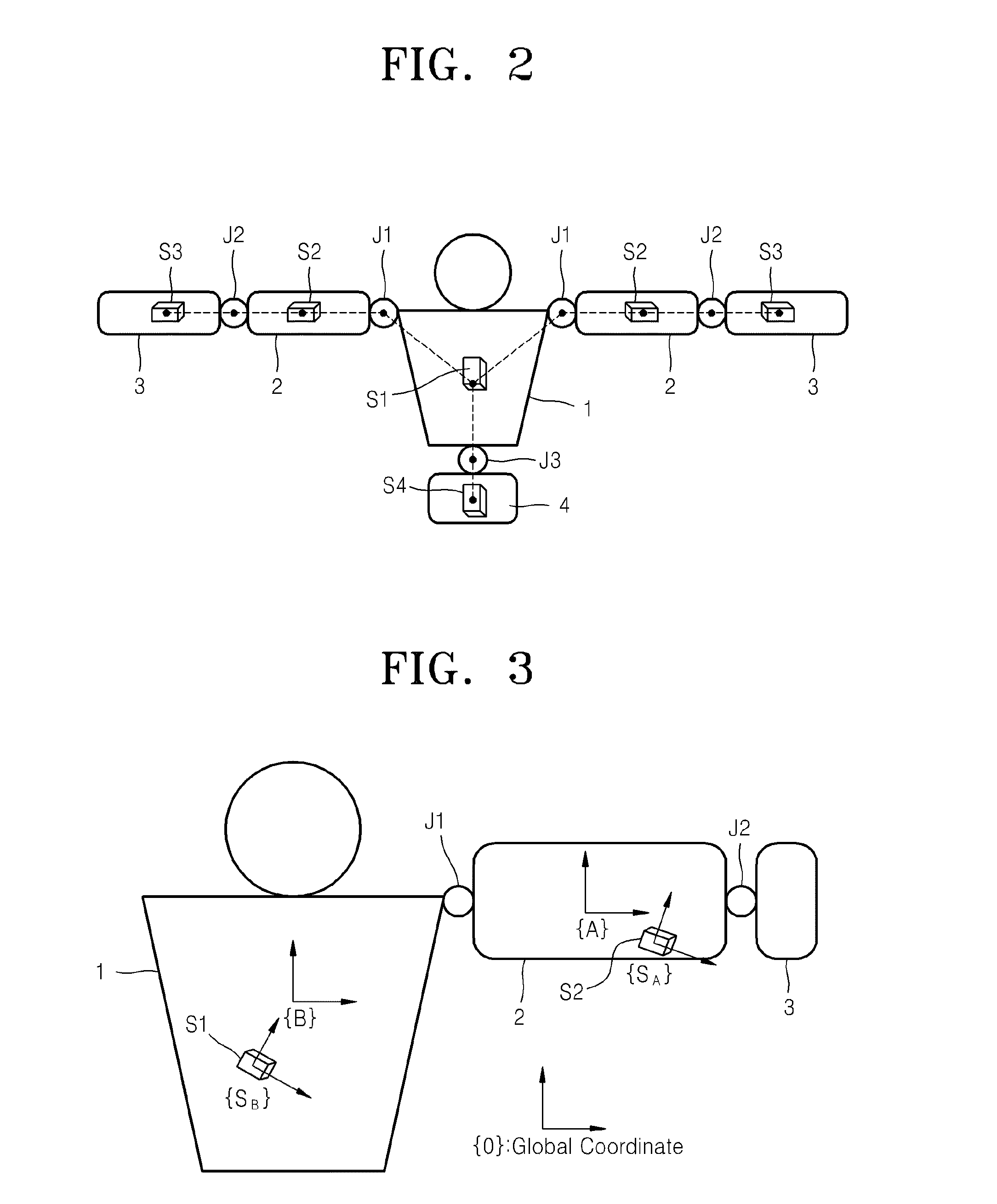
Method of motion tracking
ActiveUS20140156218A1Input/output for user-computer interactionImage analysisInertial coordinate systemBody region
A motion of a model including a joint, at least one body part that rotates with respect to the joint, and a plurality of inertial sensors attached to each body part and measuring a rotational motion of the body part is tracked by obtaining a rotational matrix of a sensor coordinate system fixed to each of the inertial sensors with respect to an inertial coordinate system fixed to ground, by using a signal measured by the inertial sensor attached to each body part; obtaining a rotational matrix of the sensor coordinate systems with respect to a body part coordinate system fixed to each body part, by using an obtained rotational matrix value of the sensor coordinate system; obtaining a rotational matrix of each body part coordinate system with respect to the inertial coordinate system, by using a calculated rotational matrix of the sensor coordinate systems; and calculating a joint variable with respect to each body part, by using a calculated rotational matrix of the body part coordinate system.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
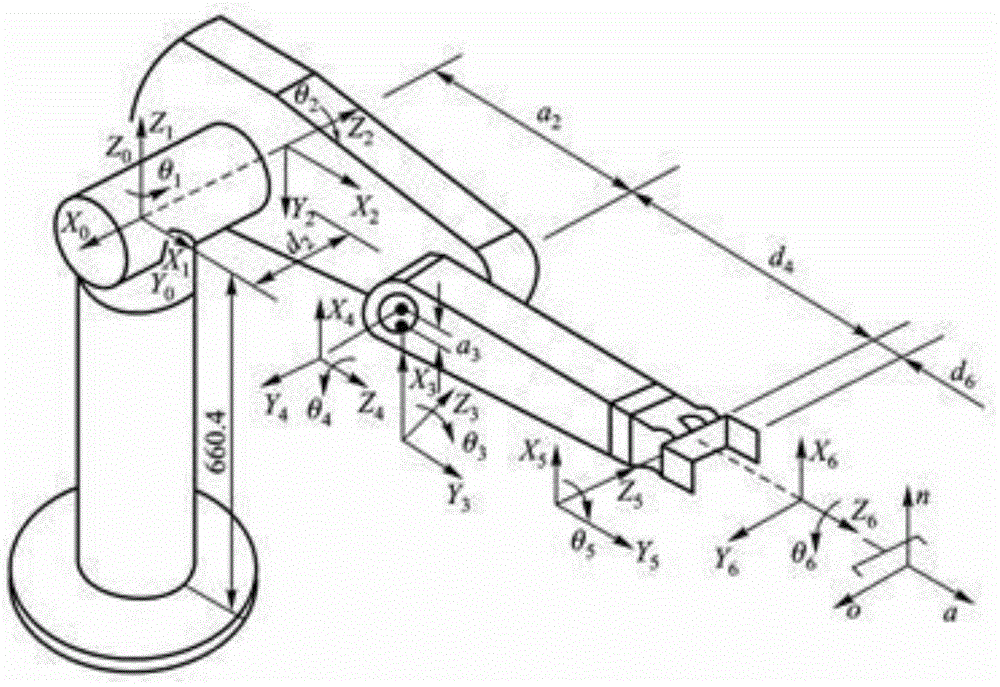
Robot path planning method for passing through wrist singular point
ActiveCN105382835AAchieve accurate reproductionConvenient teachingProgramme-controlled manipulatorSimulationIntegrated operations
The invention discloses a robot path planning method for passing through a wrist singular point. The robot path planning method comprises the following steps that the terminal of a teaching robot is operated and dragged to complete an integrated operation, and the coordinate transformation and kinematics inverse solution of an industrial robot are conducted by collecting path points; when a joint variable value corresponding to a current pose of the industrial robot is in the boundary of a wrist singular zone and a joint variable value corresponding to an original target pose is within the wrist joint singular zone, a fifth shaft and a sixth shaft of a robot are fixedly connected; according to a connecting rod transformational matrix of a third connecting rod coordinate system relative to a basal coordinate system, a product of the connecting rod transformational matrix of a tool coordinate system relative to a connecting rod coordinate system, and a product of the connecting rod transformational matrix of the tool coordinate system relative to the basal coordinate system, a position vector of the third connecting rod coordinate system relative to the basal coordinate system is calculated, and in this way, equations are established and solved to acquire all joint variable values of a processed target pose, and accordingly a path for passing through an accurate position of the wrist singular point can be acquired.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
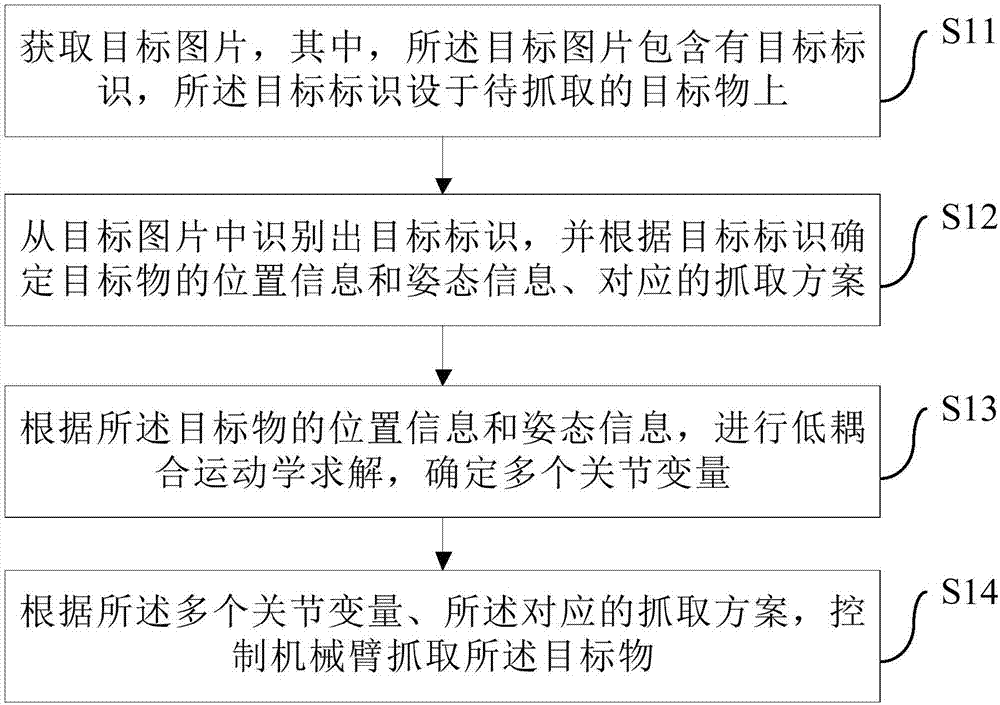
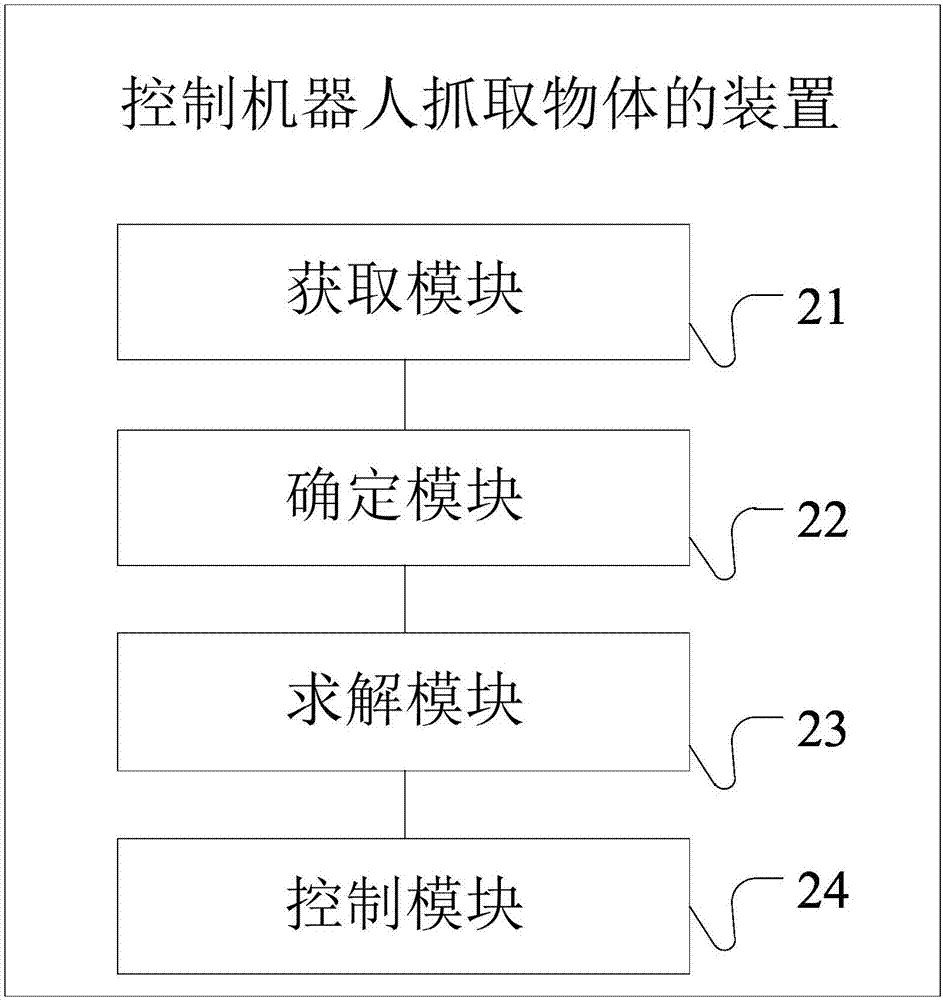
Method and device for controlling robot to grab object
ActiveCN107571260ASimple calculationFlexible computingProgramme-controlled manipulatorAlgorithmComputer vision
The invention provides a method and device for controlling a robot to grab an object. The method comprises the steps that a target picture is obtained, and the target picture contains a target mark which is arranged on the to-be-grabbed object; the target mark is identified from the target picture, position information and posture information of the target object and a corresponding grabbing scheme are determined according to the target mark; low-coupling kinematics solution is conducted, and thus, a plurality of joint variables are determined; and a mechanical arm is controlled to grab the target object according to the multiple joint variables and the corresponding grabbing scheme. According to the scheme, by identifying the target mark of the target object, the position information andthe posture information of the target object and the corresponding grabbing scheme are determined; the multiple joint variables are obtained through calculation based on low-coupling kinematics solution; and accordingly, the target object is grabbed according to the multiple joint variables and the corresponding grabbing scheme, and the technical problems that by means of an existing method, the target object identifying process is complex, the cost is high, and the joint variable calculating efficiency is low are solved.
Owner:NANJING AVATARMIND ROBOT TECH CO LTD
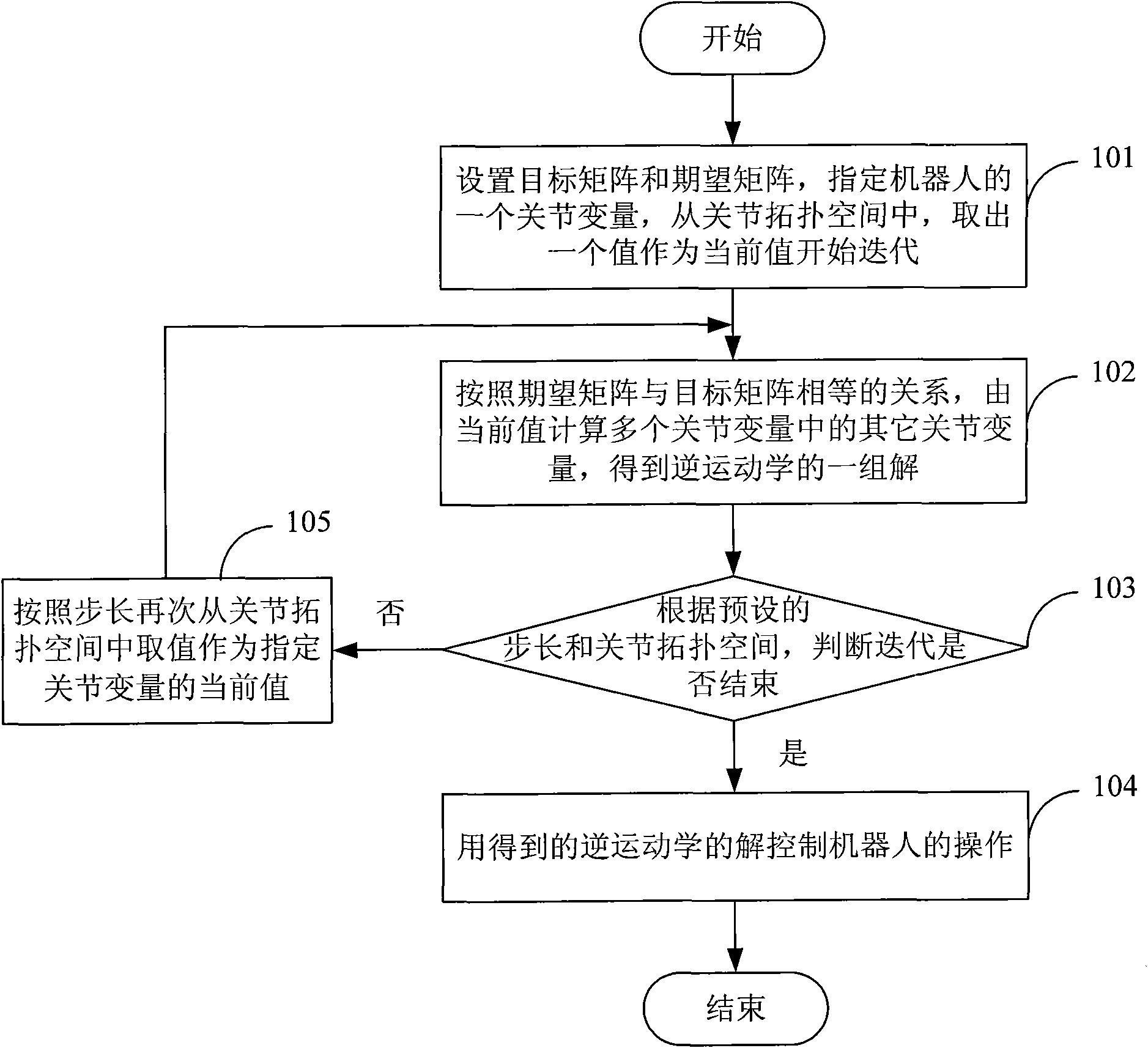
Method and device for controlling robot operations
InactiveCN101648376AHigh speedOvercoming the drawbacks of inverse kinematic solutionsProgramme-controlled manipulatorKinematics equationsControl theory
The invention discloses a method and a device for controlling robot operations, belonging to field of robots. The method comprises the following steps: 1. taking a kinematical equation as a target matrix, setting an expected matrix according to mission requirements, appointing a joint variable in a plurality of joint variables of a robot, and selecting a value from a joint topological space as a current value for starting iteration; 2. calculating other joint variables according to the equivalent relation of two matrixes and taking all calculated joint variables as a set of solutions of inverse kinematics; and 3. judging whether the iteration is finished or not, if so, utilizing the obtained solutions to control the robot operations, and otherwise, selecting a value from the joint topological space as a current value as an appointed joint variable according to the step length and executing the step 2. The device comprises an initiating module and an iteration module. The invention improves the solving speed of inverse kinematics and the controlling speed the robot operations, reduces the consumed time, improves the efficiency and has better universality.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
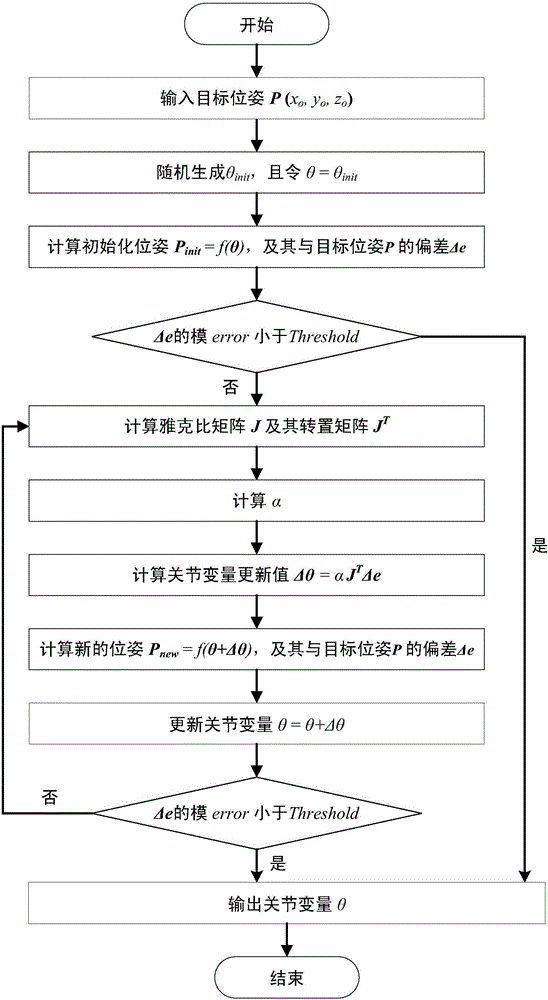
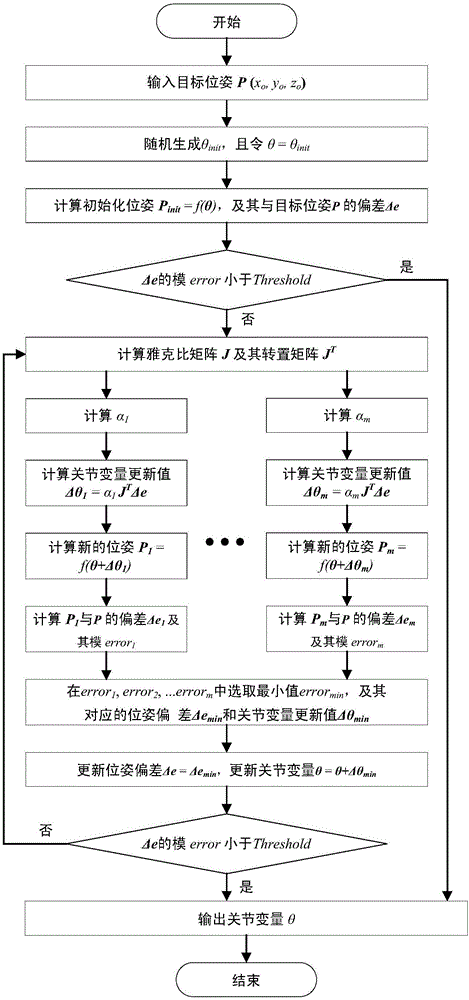
Rapid solution method and rapid solution system for high-degree-of-freedom robot inverse kinematics
ActiveCN106844985AImprove real-time performanceAccelerated Inverse Kinematics SolvingProgramme-controlled manipulatorDesign optimisation/simulationKinematics equationsDegrees of freedom
The invention provides a rapid solution method and a rapid solution system for high-degree-of-freedom robot inverse kinematics. The method includes the steps of 1, substituting a joint variable theta into a robot kinematics equation to obtain a Jacobian matrix J, and transposing the Jacobian matrix J to obtain a transposed Jacobian matrix JT; 2, generating a group of speculative values, calculating corresponding joint variable update values for the speculative values, substituting each joint variable update value into a robot forward kinematics equation to obtain corresponding poses Pk, calculating pose deviation delta ek between each pose Pk and a target pose P and calculating a modulus errork of the pose deviation delta ek; 3, selecting a minimum value errormin, corresponding pose deviation delta emin and joint variable update values delta theta min from a set of the modulus errork, updating the pose deviation delta e=delta emin and updating a joint variable theta=theta+delta theta min; 4, judging whether the errormin meets errormin<threshold or not, outputting the joint variable theta and finishing if the errormin meets errormin<threshold, otherwise, returning to the step 1 and continuing execution.
Owner:INST OF COMPUTING TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
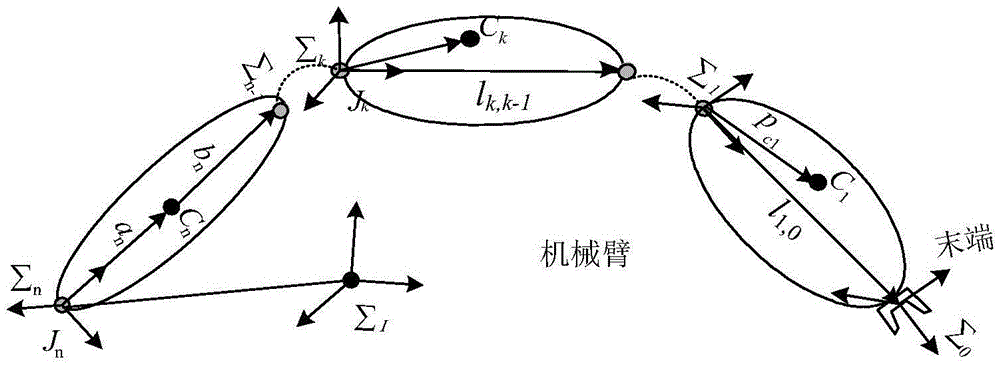
Tail end Cartesian space rigidity modeling method for rope-driven linkage mechanical arm
ActiveCN109249428AAchieve stiffnessEasy to controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorVirtual workEngineering
The invention discloses a tail end Cartesian space rigidity modeling method for rope-driven linkage mechanical arm. The method includes: calculating integral joint equivalent rigidity of a mechanicalarm linkage rope, calculating according to a velocity-stage kinematic relation between a driving rope and a mechanical arm joint to obtain a Jacobian matrix Gq from a joint space to a driving space, acquiring integral joint equivalent rigidity of the driving rope of the mechanical arm according to a virtual work principle and a variational principle, and calculating mechanical arm joint equivalentrigidity Kq; calculating according to a velocity-stage kinematic relation between a mechanical arm joint variable and a tail end pose to obtain a Jacobian matrix Jq from the joint space to the tail end Cartesian space, and acquiring an equivalent rigidity Ke, in the tail end Cartesian space, of the mechanical arm joint equivalent rigidity Kq according to the virtual work principle and the variational principle. Rigidity analysis and control of the rope-driven linkage mechanical arm can be realized, and the method can be applied to rigidity analysis, statics analysis, force control and the like of the rope-driven linkage mechanical arm.
Owner:SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL TSINGHUA UNIV
Method for capturing non-cooperative target by virtue of space robot
ActiveCN107529498ARealize synchronous captureImprove efficiencyProgramme-controlled manipulatorToolsGeometric modelingClosed loop
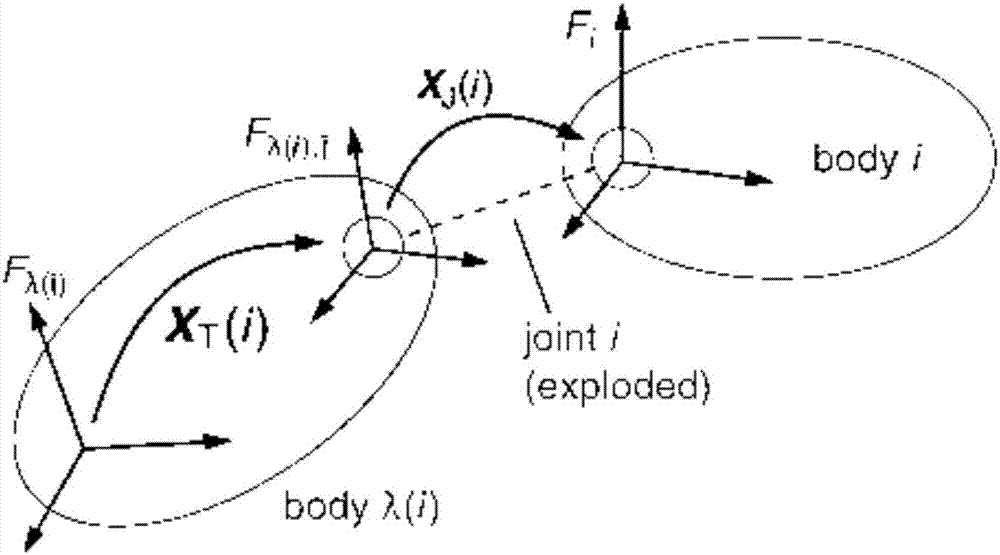
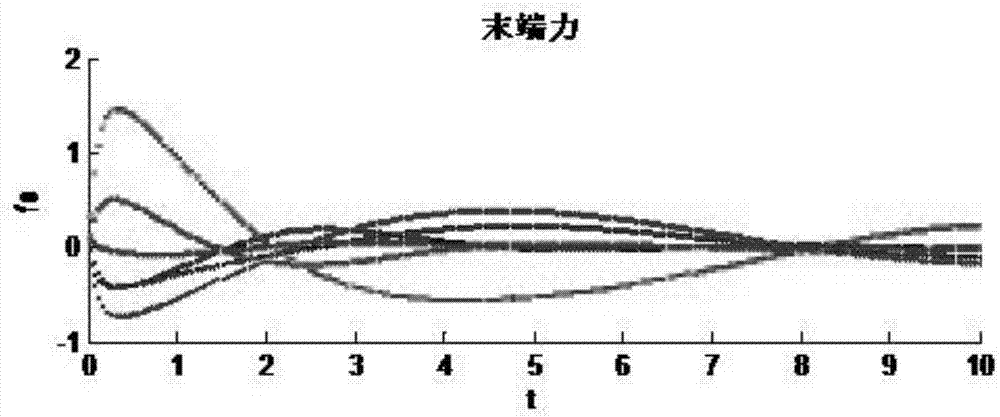
The invention discloses a method for capturing a non-cooperative target by virtue of a space robot. The method comprises the following steps: topologically representing the space robot, and establishing a geometric model and a joint model of the space robot; establishing an inverse dynamical model of the space robot based on a recursion Newton-Euler algorithm, establishing a positive dynamical model of the space robot based on a combination object algorithm, and establishing a dynamical model of the space robot based on a Lagrange mechanics algorithm; and forming a closed loop system by virtueof the space robot and a non-cooperative target combination object, establishing a closed loop dynamical model, and finishing the capturing of the non-cooperative target by virtue of the space robot.The combined solving of a joint variable and a mechanical arm terminal force of the space robot is realized based on a space vector and many-body dynamics and matrix theories, and the method is applicable to multiple types of opened or closed loop robot systems.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Robot control method based on natural language understanding
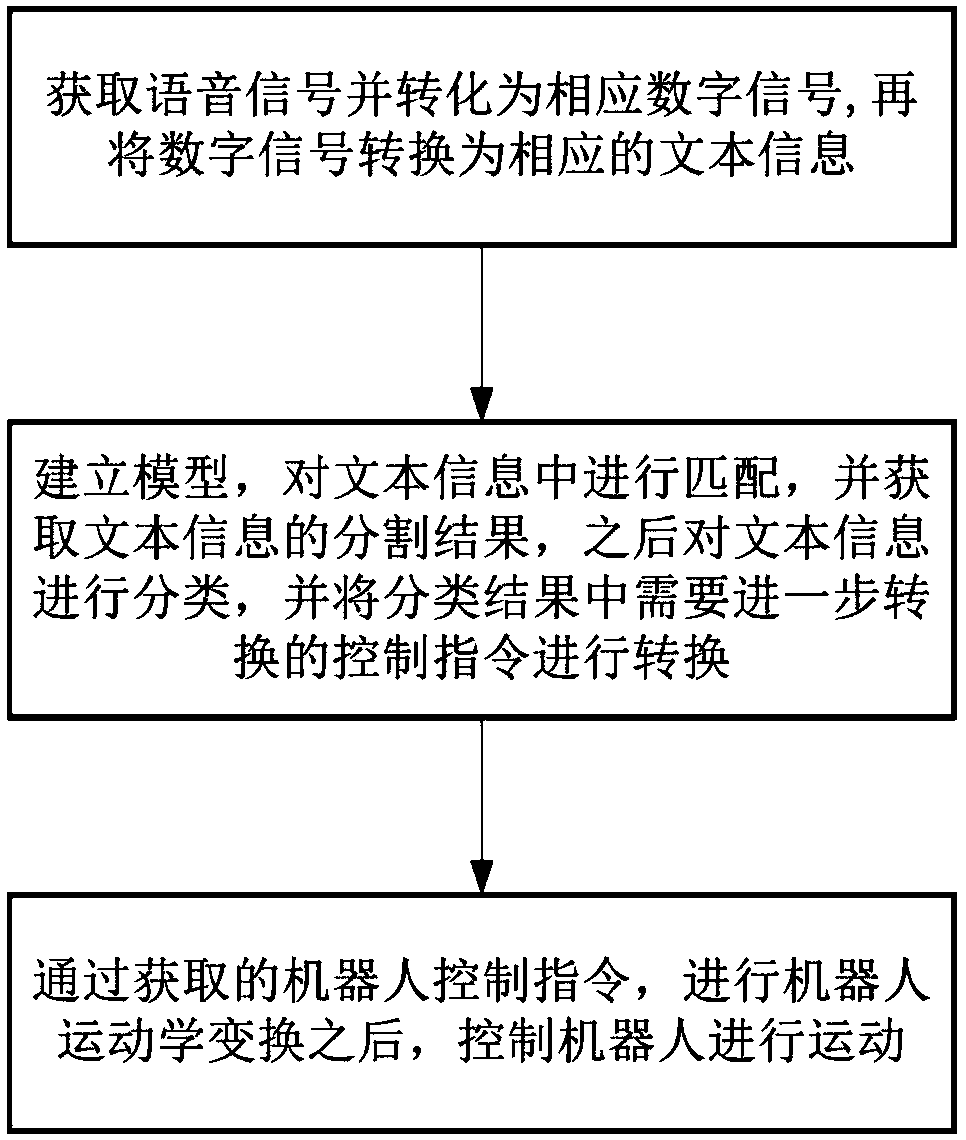
InactiveCN108447477AEasy to controlSpeech recognitionSpecial data processing applicationsNatural language understandingActuator
The invention provides a robot control method based on natural language understanding, and the method comprises the steps: (1) acquiring a speech signal and converting the speech signal into a corresponding digital signal, and then converting the digital signal into corresponding text information through a dynamic time warping algorithm; (2) establishing a model, and carrying out the matching of the key information and redundant information contained in the text information, obtaining a segmentation result of the text information, and then classifying the text information through a classifierestablished through a maximum entropy model, and then converting a control instruction to be converted further in the classification result; (3) carrying out the reverse solving of the obtained spatial coordinates of a tail executor of a mechanical arm into a joint variable of a rotating joint through a robot control command, and controlling the robot to move.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Variable-rigidity mechanism based on geometrical features
The invention relates to a joint variable-rigidity mechanism, in particular to a variable-rigidity mechanism based on geometrical features. The variable-rigidity mechanism aims to solve the problems that an existing variable-rigidity mechanism is complex in structure and poor in linearity, gaps and friction exist between the mechanism and a rod when the mechanism moves through a fulcrum, and consequently the position precision is low. The variable-rigidity mechanism comprises an output rod, a rigidity adjusting inner gear ring, a fulcrum gear, a fulcrum frame, a fulcrum bar, a middle rod, a spring, a shaft sleeve and two sliding blocks, wherein the sliding blocks are arranged at the two ends of the middle rod correspondingly, the spring is arranged on the middle rod located between the two sliding blocks in a sleeving mode, the shaft sleeve is arranged between the sliding blocks and the middle rod in a sleeving mode, and the shaft sleeve is axially positioned through bearing end covers arranged on the sliding blocks; and the fulcrum gear is engaged with the rigidity adjusting inner gear ring, and the fulcrum gear is arranged below the fulcrum frame and detachably connected with the fulcrum frame. The variable-rigidity mechanism is applied to a robot elbow joint.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
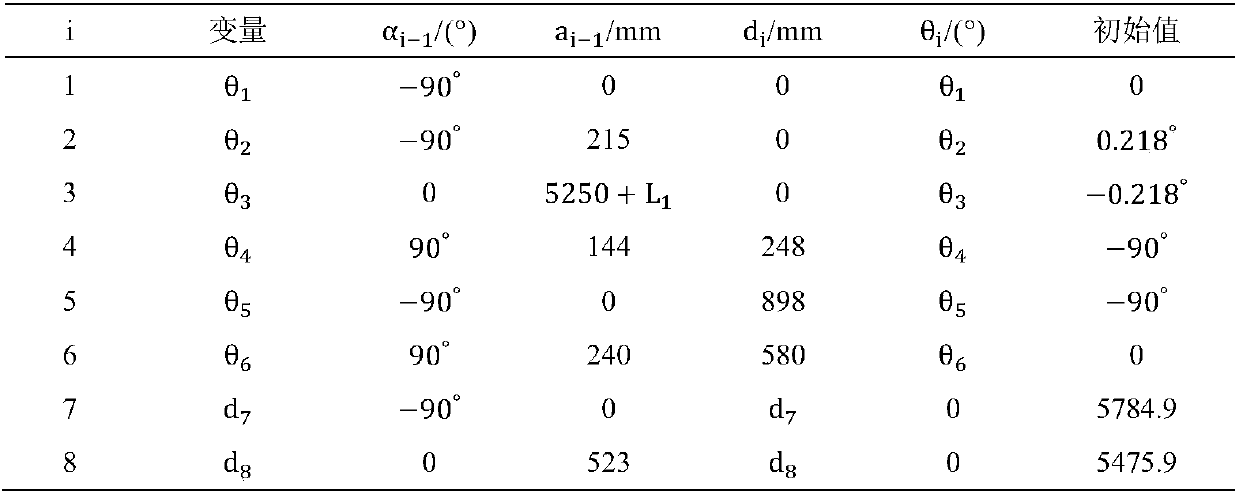
Method for achieving automatic positioning of cross section parallel hole for rock drilling machine rapidly and accurately
InactiveCN104265274AEasy to control intelligentlySimple calculationSurveyAutomatic control for drillingHydraulic cylinderClosed loop
The invention discloses a method for achieving automatic positioning of a cross section parallel hole for a rock drilling machine rapidly and accurately. The method for achieving automatic positioning of the cross section parallel hole for the rock drilling machine rapidly and accurately comprises the steps that the structural components of a drilling arm positioning mechanism of the hydraulic rock drilling machine and the movement of all mechanisms are analyzed, the joint coordinate system of the drilling arm positioning mechanism of the hydraulic rock drilling machine is established according to a structure model of a drilling arm system of the hydraulic rock drilling machine by means of the D-H method, the coordinate system of a drilling arm positioning system and connecting rod parameters are analyzed, and the functional relationships between the coordinates of a positioning tail end in a base coordinate system and all joint variables are calculated; cross section parallel hole regional planning for the hydraulic rock drilling machine is conducted; all the joint variables are solved; the pre-positioned position of the positioning tail end during drilling of the rock drilling machine is determined, the pre-positioned coordinates of the positioning tail end in the base coordinate system and all target joint variables are calculated, and a control module is driven in real time through a closed loop to adjust all hydraulic cylinders, so that whether the positioning tail end reaches a preset position is judged. By the adoption of the method for achieving automatic positioning of the cross section parallel hole for the rock drilling machine rapidly and accurately, the difficulty of solving the joint variables of the drilling arm system of the hydraulic rock drilling machine is greatly lowered.
Owner:YANSHAN UNIV
Inverse kinematics solving method and device for service robot in intelligent space
InactiveCN108255058AImprove controlPrevent inversionAdaptive controlGenetic algorithmsDiscretizationContinuum function
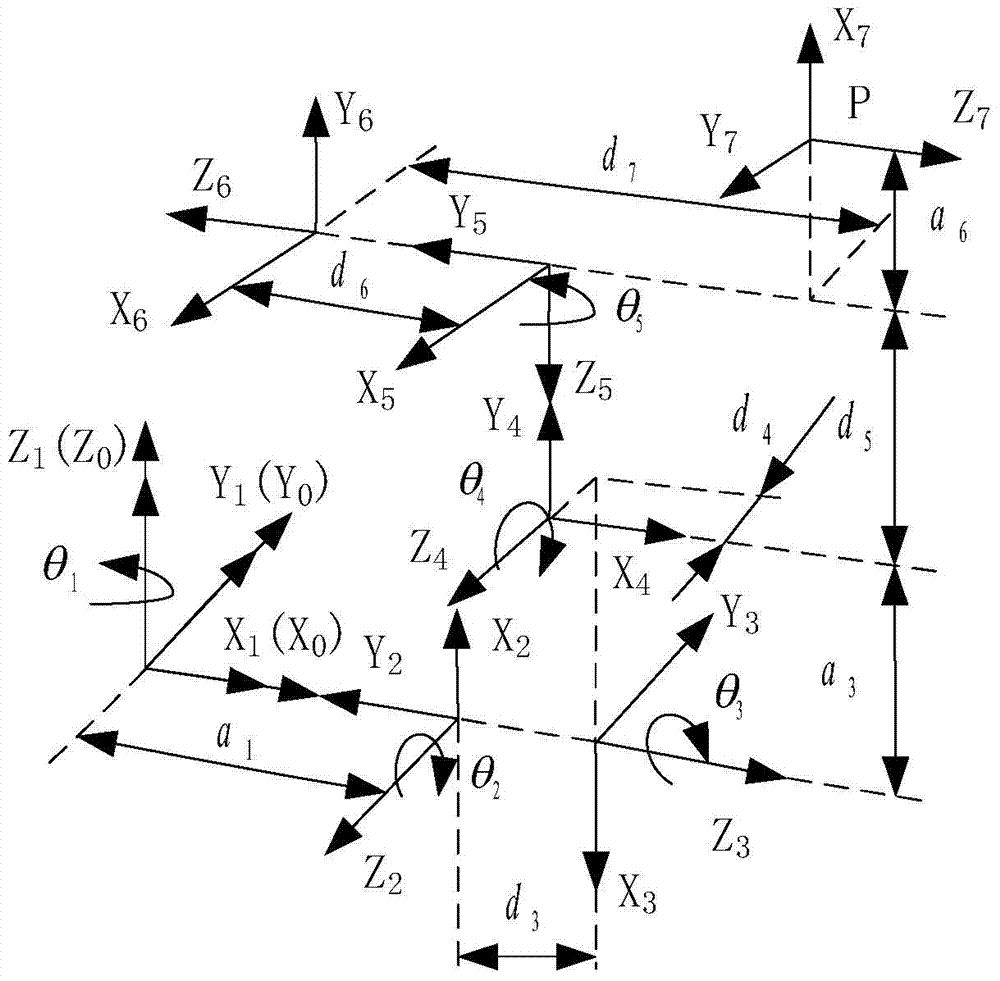
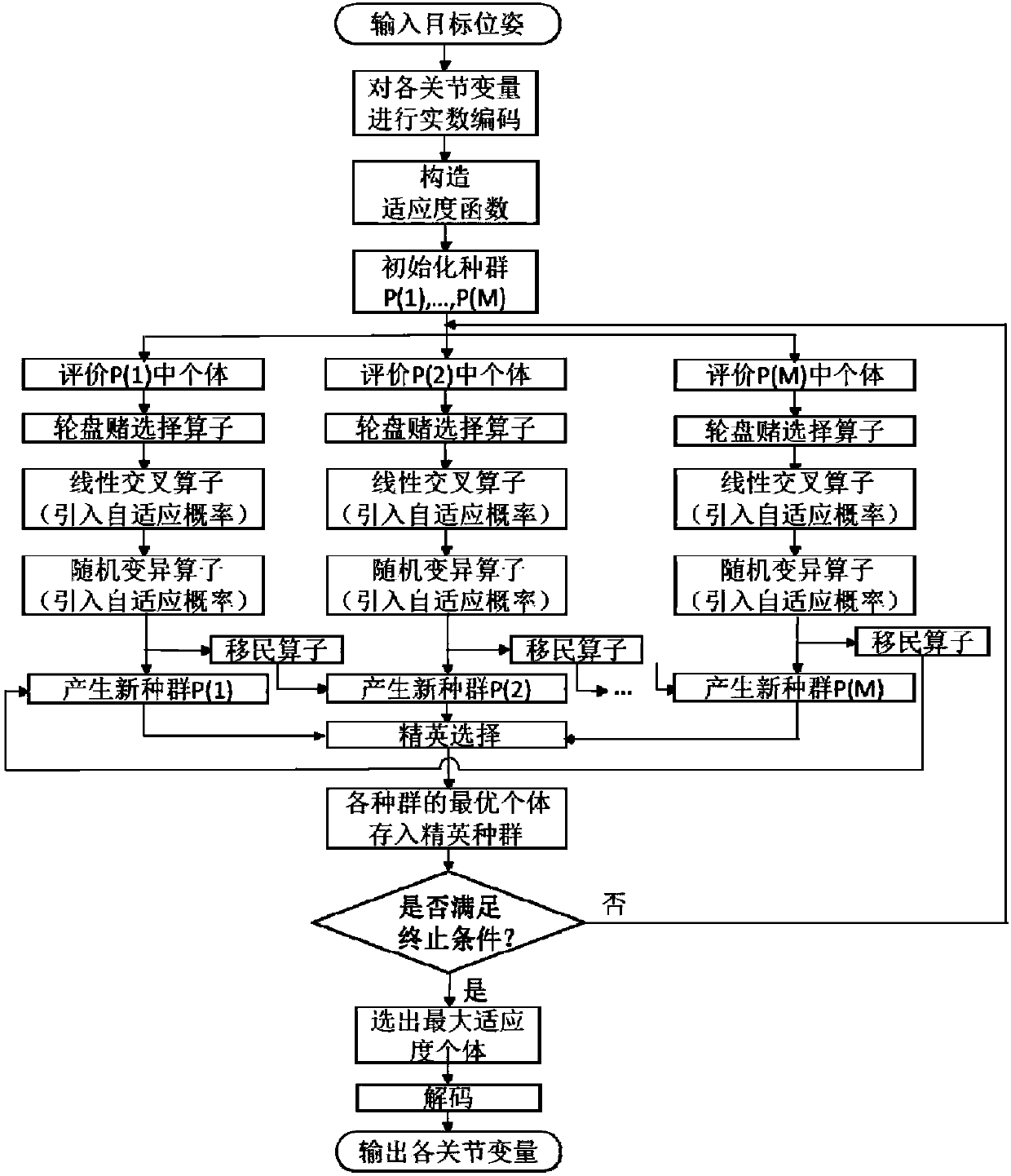
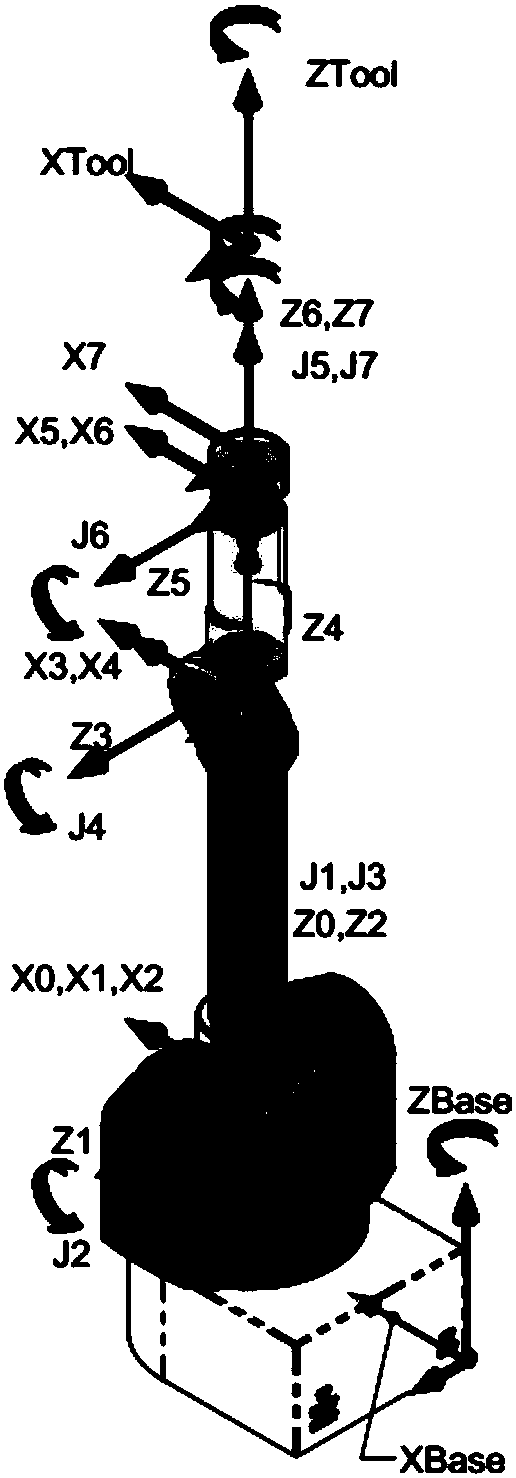
The invention discloses an inverse kinematics solving method and device for a service robot in a smart space. The method includes the following steps that: the forward kinematics model of the robot isestablished by using a D-H parameter method; real number coding is performed on the joint variables of the robot; an adaptive function is constructed with difference between a current pose and a target pose adopted as an optimization objective; and a genetic algorithm is used to perform optimization solution on the joint variables, so that the optimal solution of the inverse kinematics problem isobtained. The method of the invention does not need to be limited to robot configurations, and a plurality of populations are introduced, so that parallel optimization search can be realized, and therefore, the method can cope with the increase of the degree of freedom of the robot; the real number coding is adopted for the individuals, and mapping errors occurring during continuous function discretization when binary coding is adopted can be avoided; and on the basis of the real number coding, crossover operation adopts a linear crossover mode, mutation operation adopts a random mutation mode, and adaptive crossover and mutation probabilities are introduced, and therefore, a better solution can be effectively protected in the later stage of evolution, and convergence speed and precisioncan be guaranteed.
Owner:山东大学深圳研究院
Dynamic scaling planning method for floating base and mechanical arm in neutral buoyancy test
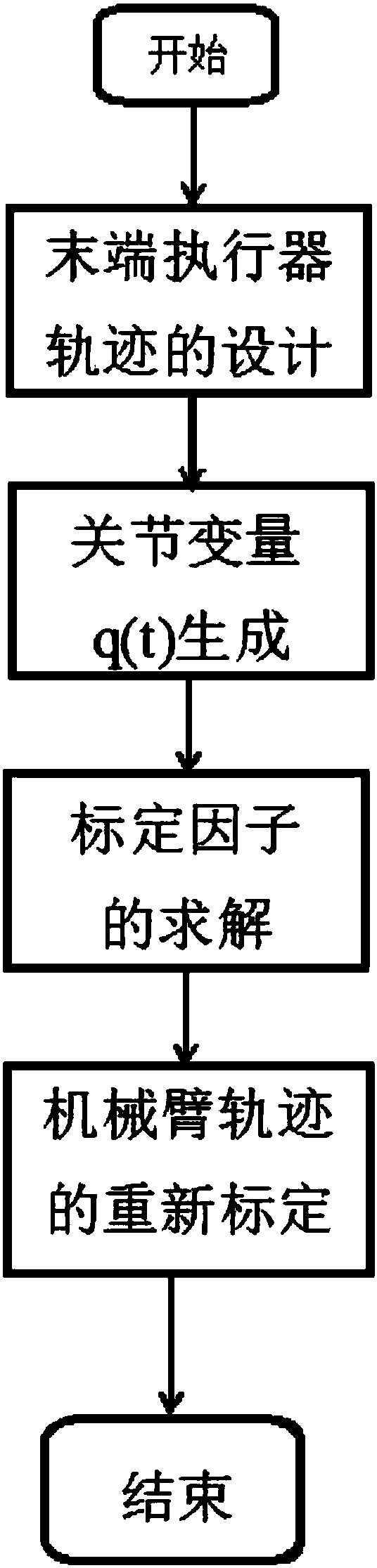
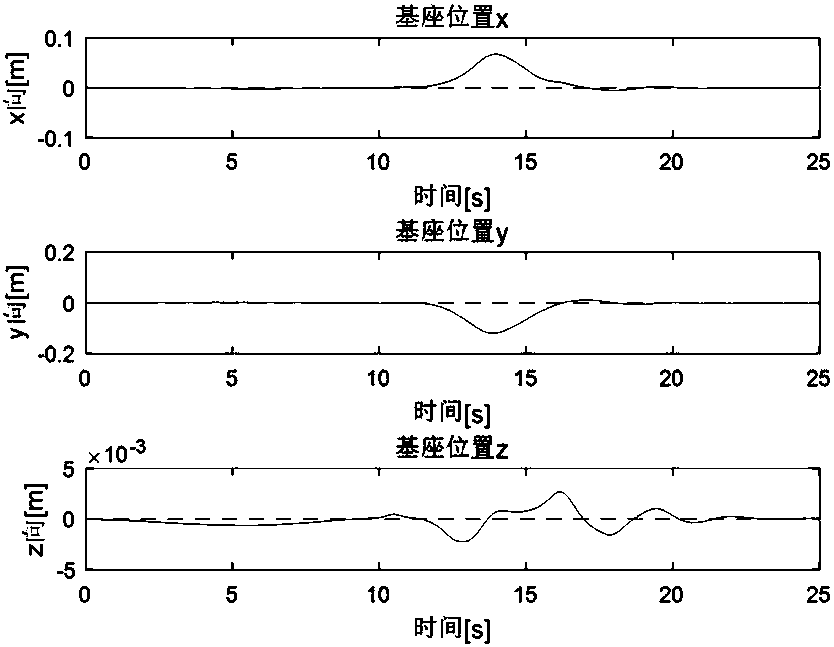
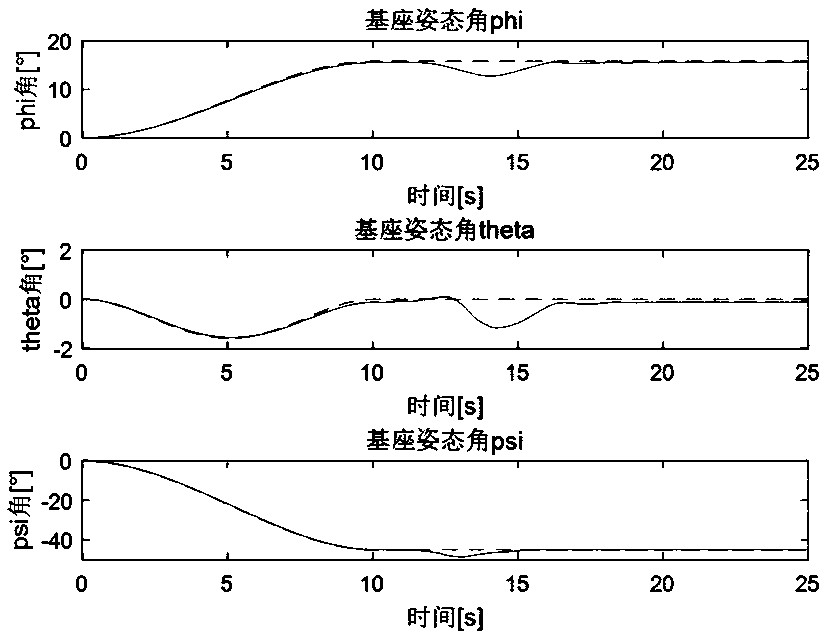
ActiveCN107145640APose stabilityPose stability depends on the static stability of the base itselfGeometric CADProgramme-controlled manipulatorPoint sequenceEngineering
A dynamic scaling planning method for a floating base and a mechanical arm in a neutral buoyancy test comprises the following steps of I, setting a trajectory of an executor at the tail end of the mechanical arm in a pond coordinate system, inserting a path point sequence in the trajectory, and dividing the trajectory into n sections for execution; II, establishing n third-order polynomial equations, and calculating path points into a corresponding joint variable q(t); III, solving a calibration factor; and IV, solving the recalibrated mechanical arm, and respectively solving dynamic scaling of the trajectory in each section of joint space trajectory through the same rule to form a plurality of new trajectories. According to the dynamic scaling planning method for the floating base and the mechanical arm in the neutral buoyancy test, through dynamic time calibration for the motion trajectory, new joint angular speed and angular acceleration of the mechanical arm are formed, thus, inertia forces and environmental forces of the mechanical arm are changed so that the stability of positions and postures of the base is realized by the planning method which cannot keep the stability of positions and postures of the base originally.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Double-joint variable-cross-section soft-body hand with wedged transverse-pattern structure
InactiveCN110497439AIncrease stiffnessIncrease frictionGripping headsEngineeringAtmospheric pressure
The invention discloses a double-joint variable-cross-section soft-body hand with a wedged transverse-pattern structure. The double-joint variable-cross-section soft-body hand structurally comprises abracket and three soft-body fingers fixed on the bracket. The soft-body hand has the characteristics of being low in mass, easy to control, low in price, easy to manufacture and the like, can clamp complex fragile objects, and has high flexibility, safety and adaptability; and compared with other existing soft-body fingers, the soft-body fingers of the soft-body hand have the advantages of beinggreater in bending and higher in responding speed under a same atmospheric pressure due to variable-cross-section cavities, and similar to the human finger profile.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
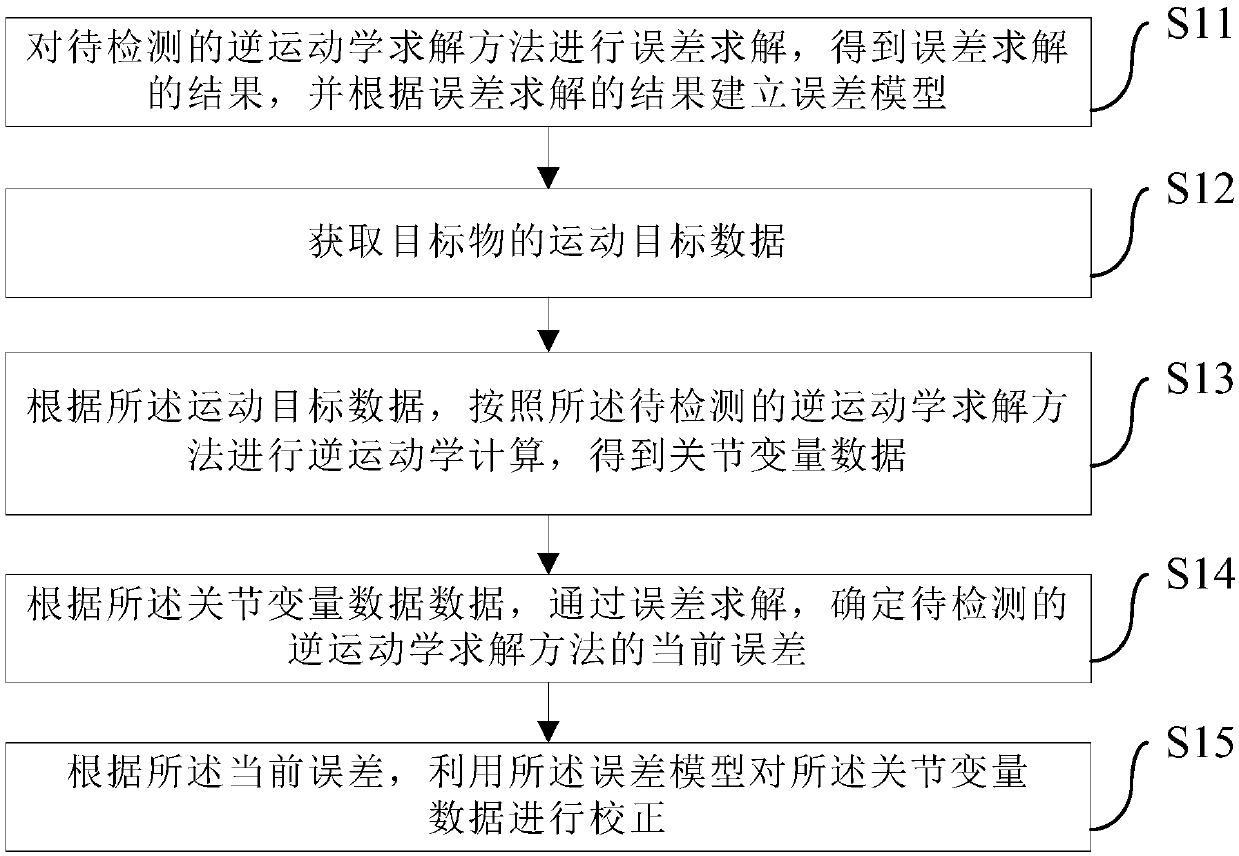
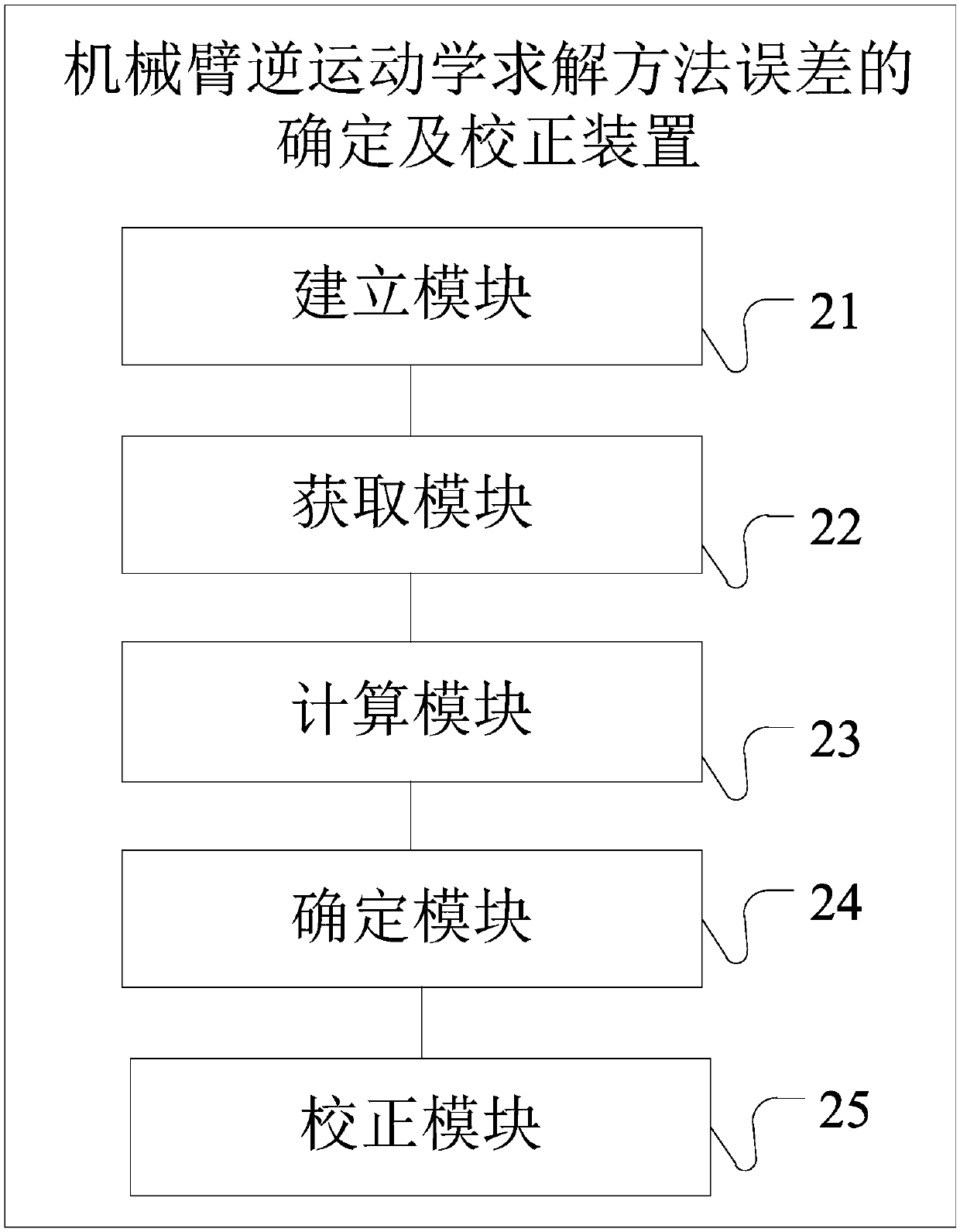
Method and device for determining and correcting inverse kinematics solving method error of mechanical arm
ActiveCN107553496AReal-time correctionOK real timeProgramme-controlled manipulatorAlgorithmData error
The invention provides a method and device for determining and correcting an inverse kinematics solving method error of a mechanical arm. The method comprises the steps of (1) conducting error solvingon an inverse kinematics solving method to be detected to obtain an error solving result and establishing an error model according to the error solving result; (2) acquiring motion target data of a target object; (3) conducting inverse kinematics computation through the inverse kinematics solving method to be detected according to the motion target data to obtain joint variable data; (4) determining the current error of the inverse kinematics solving method to be detected through error solving according to the joint variable data; and (5) correcting the joint variable data through the error model according to the current error. Through the scheme, the error model is established before operation; the current error is determined through error solving during operation; corresponding data correction is conducted through the error model. Thus, the technical problems that the inverse kinematics solving method error cannot be determined on line in real time and data errors cannot be corrected in time by means of an existing method are solved.
Owner:NANJING AVATARMIND ROBOT TECH CO LTD
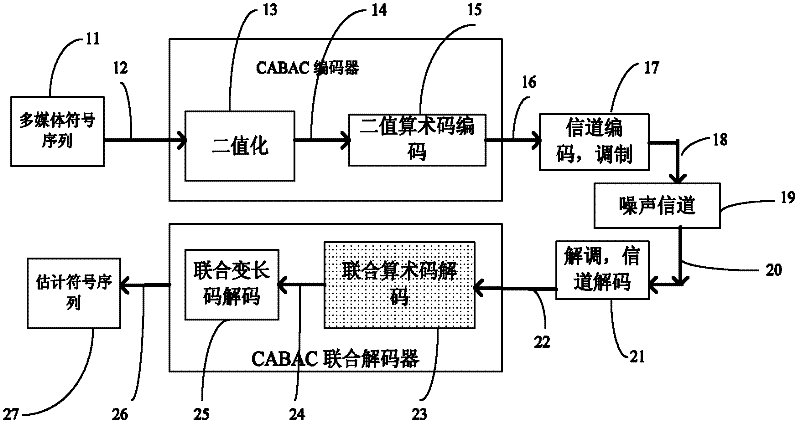
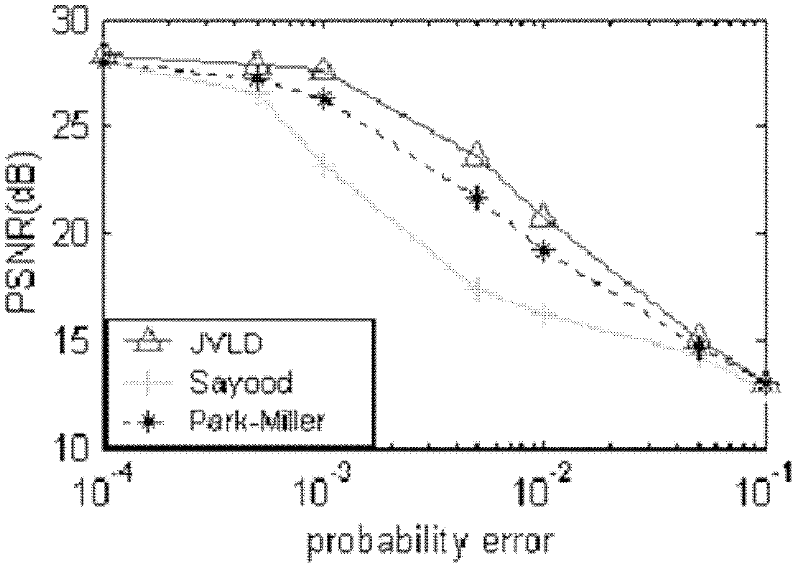
Joint source-channel decoding method for video/image transmission
InactiveCN102655588AGood bit error resistance performancePrevent and reduce bit error propagationPulse modulation television signal transmissionDigital video signal modificationVariable-length codeVideo transmission
The invention discloses a joint source-channel decoding method for video / image transmission, which is applicable to video transmission of a video coding standard H.264 and HEVC (high efficiency video coding), and image transmission of JPEG2000 (joint photographic experts group). Two modules (namely, a joint source-channel arithmetic-code decoder and a joint source-channel variable-length-code decoder) are mainly used in the method disclosed by the invention; decoding information outputted by the joint source-channel arithmetic-code decoder can be used as input information of the joint source-channel variable-length-code decoder, and then an optimal decoding symbol sequence is obtained through carrying out further searches on cellular pictures of joint variable length codes; and meanwhile, at the joint source-channel arithmetic-code decoder part, invalid search paths can be deleted by using the codon structure information of the variable length codes, thereby improving the decoding performance. The method is low in computing complexity and small in time delay, and therefore the method is applicable to actual video and image transmission systems.
Owner:ZHEJIANG GONGSHANG UNIVERSITY
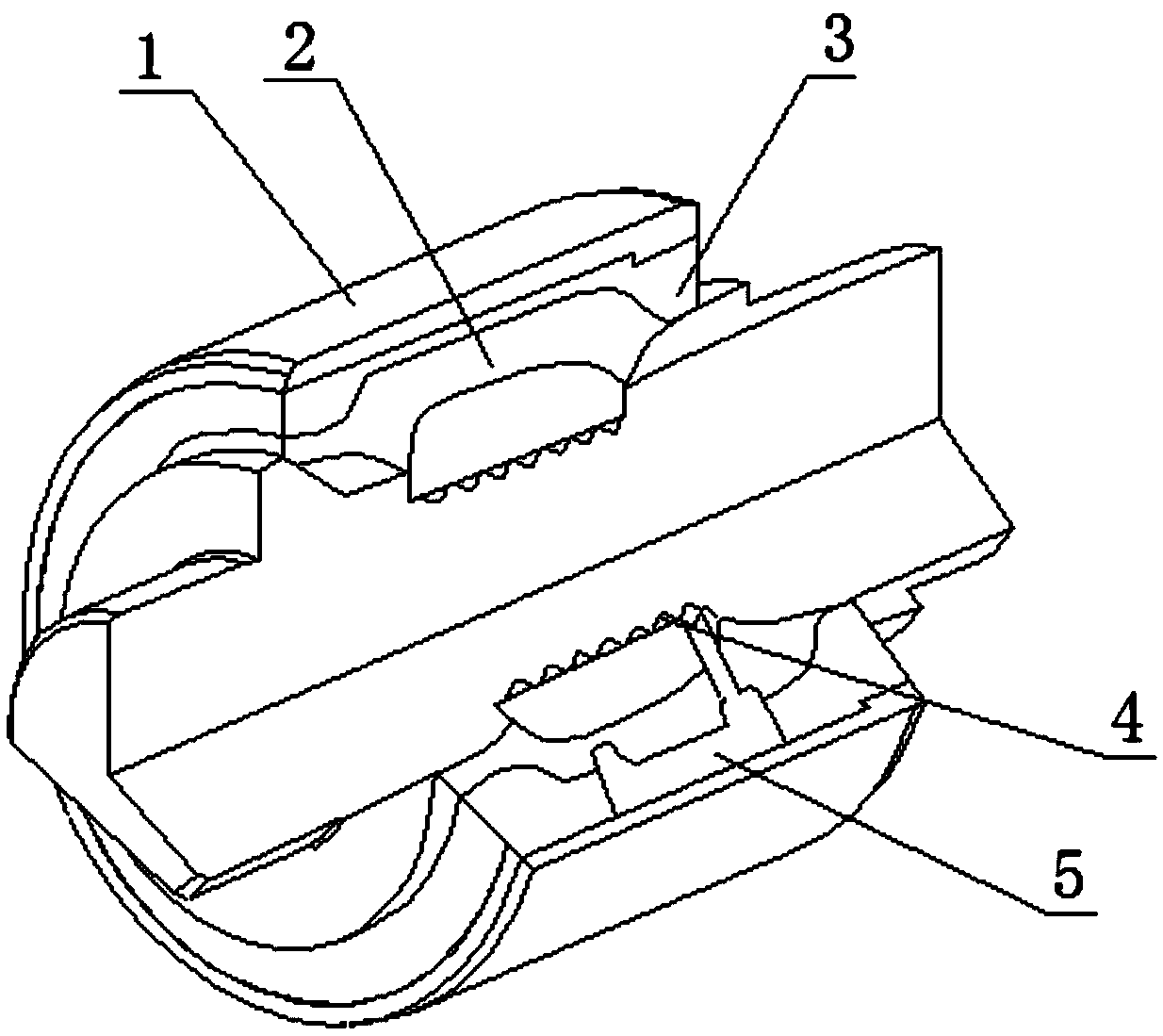
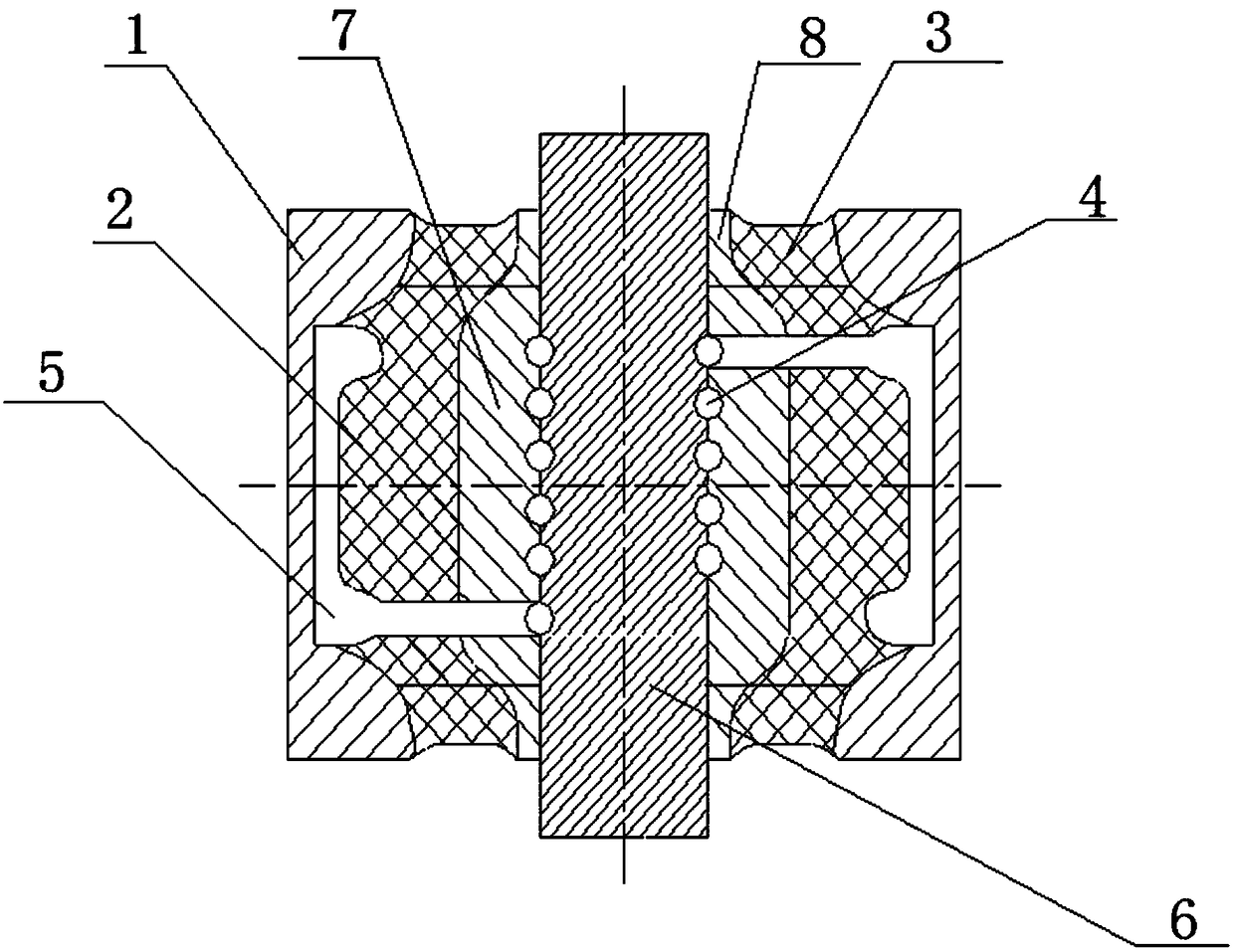
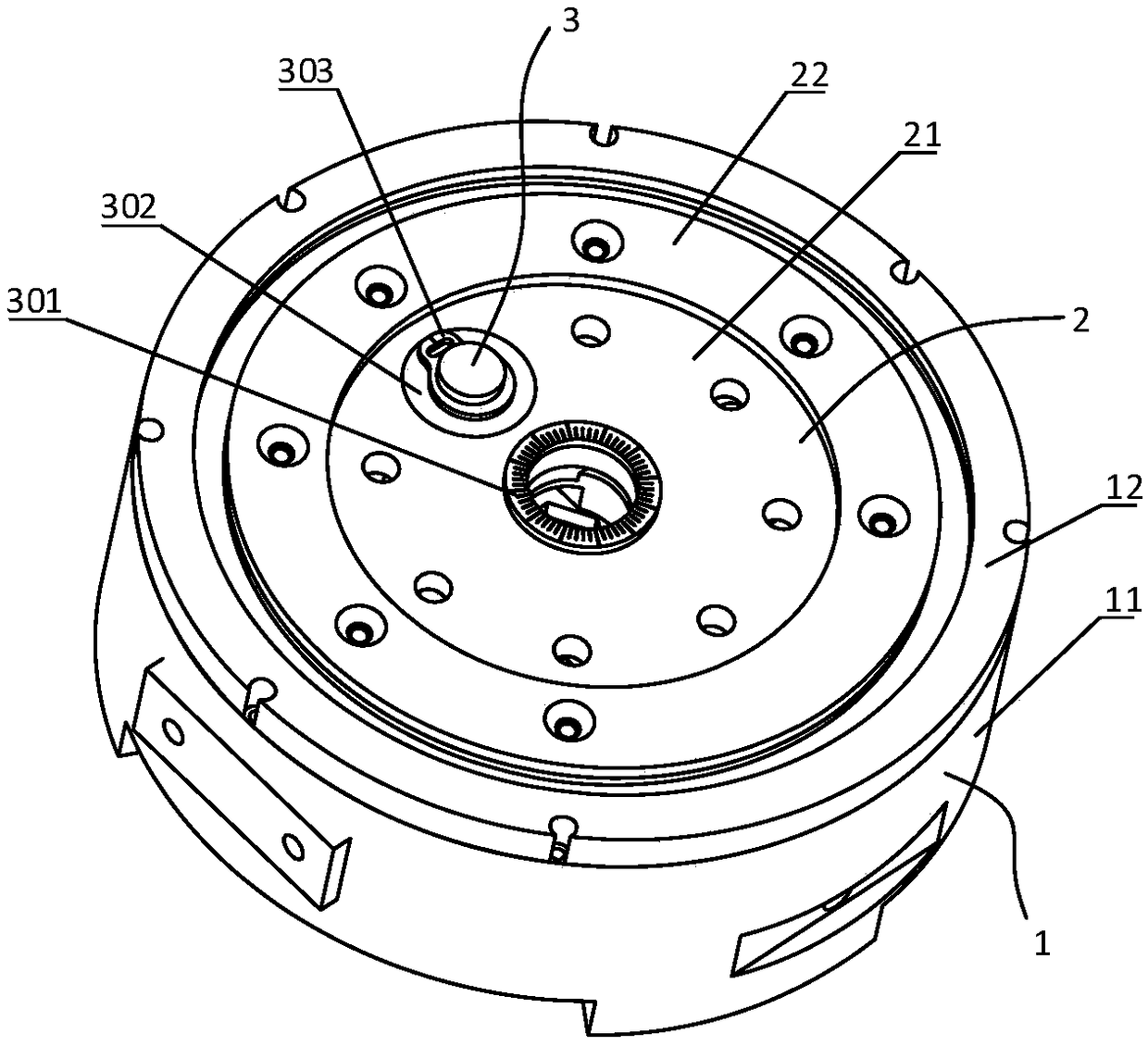
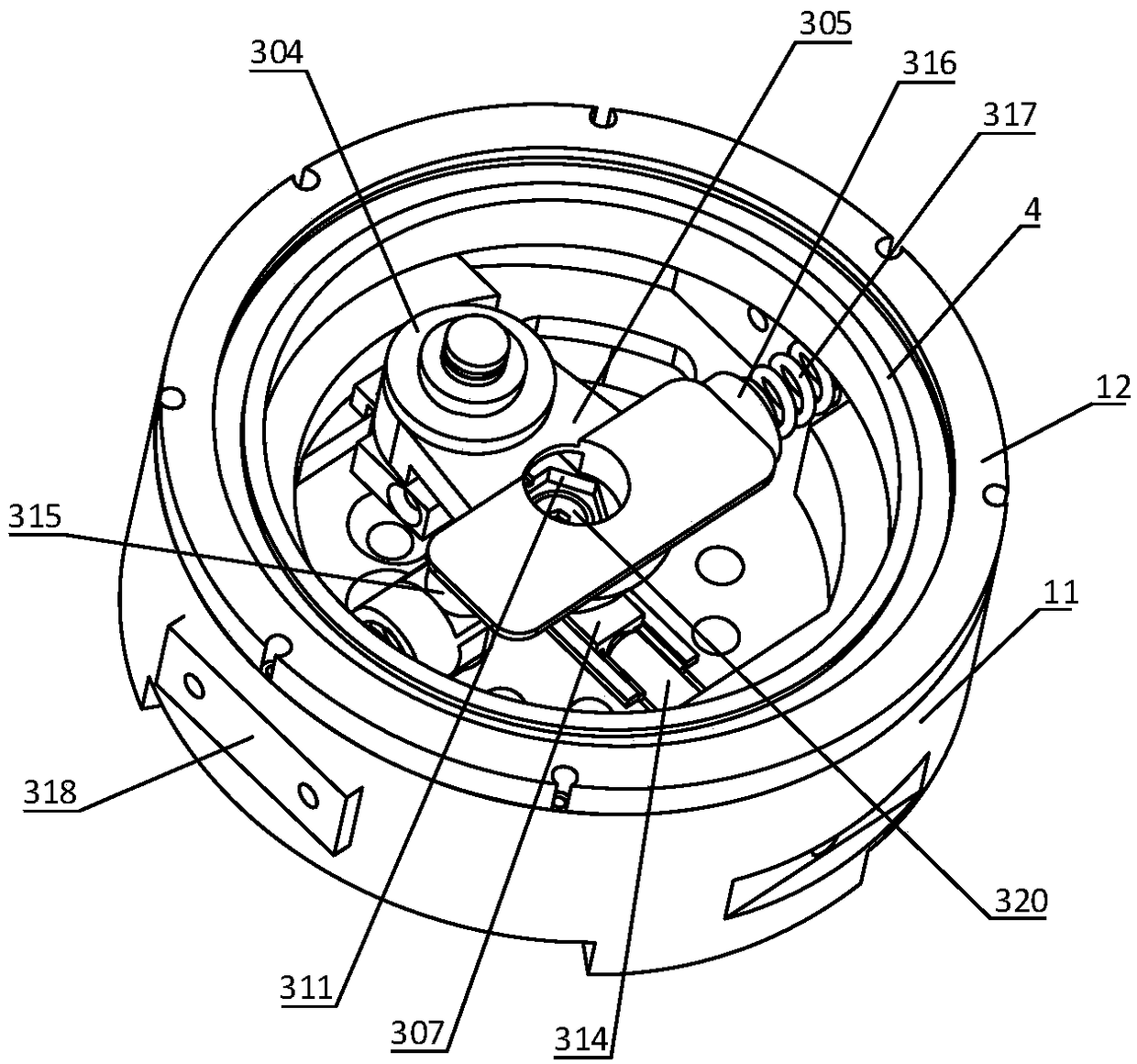
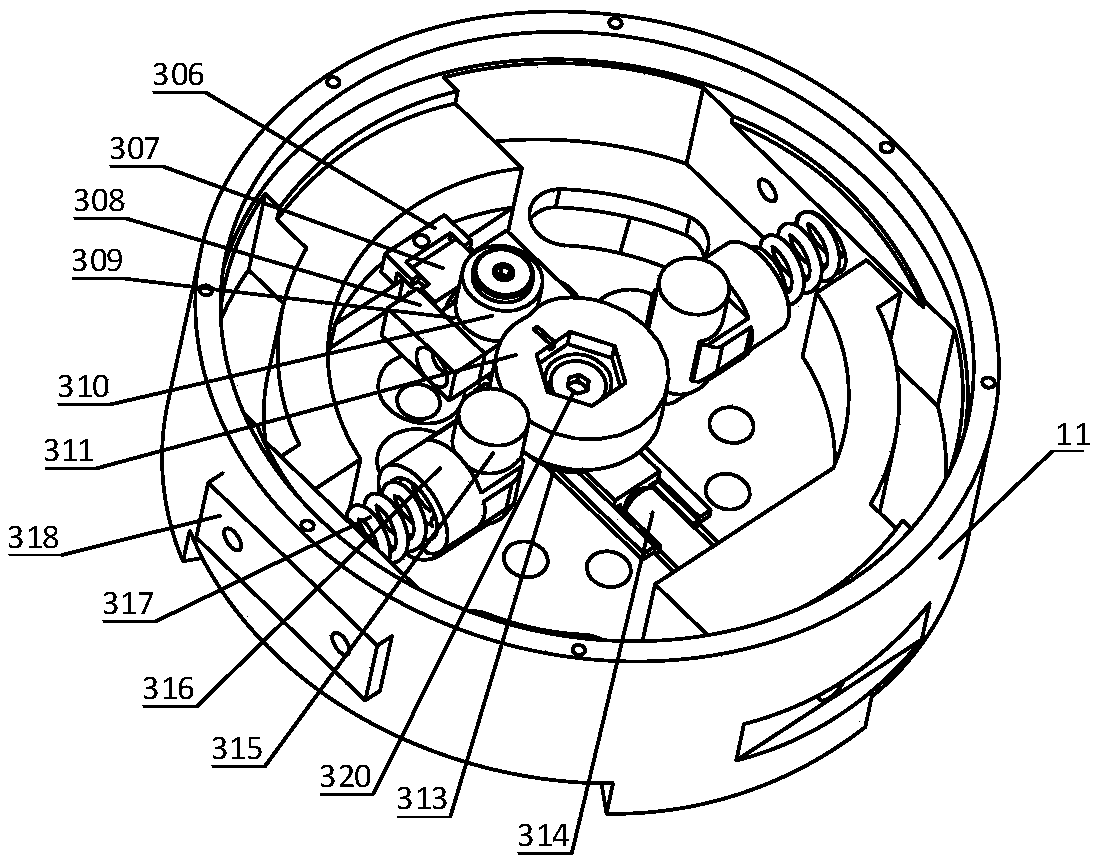
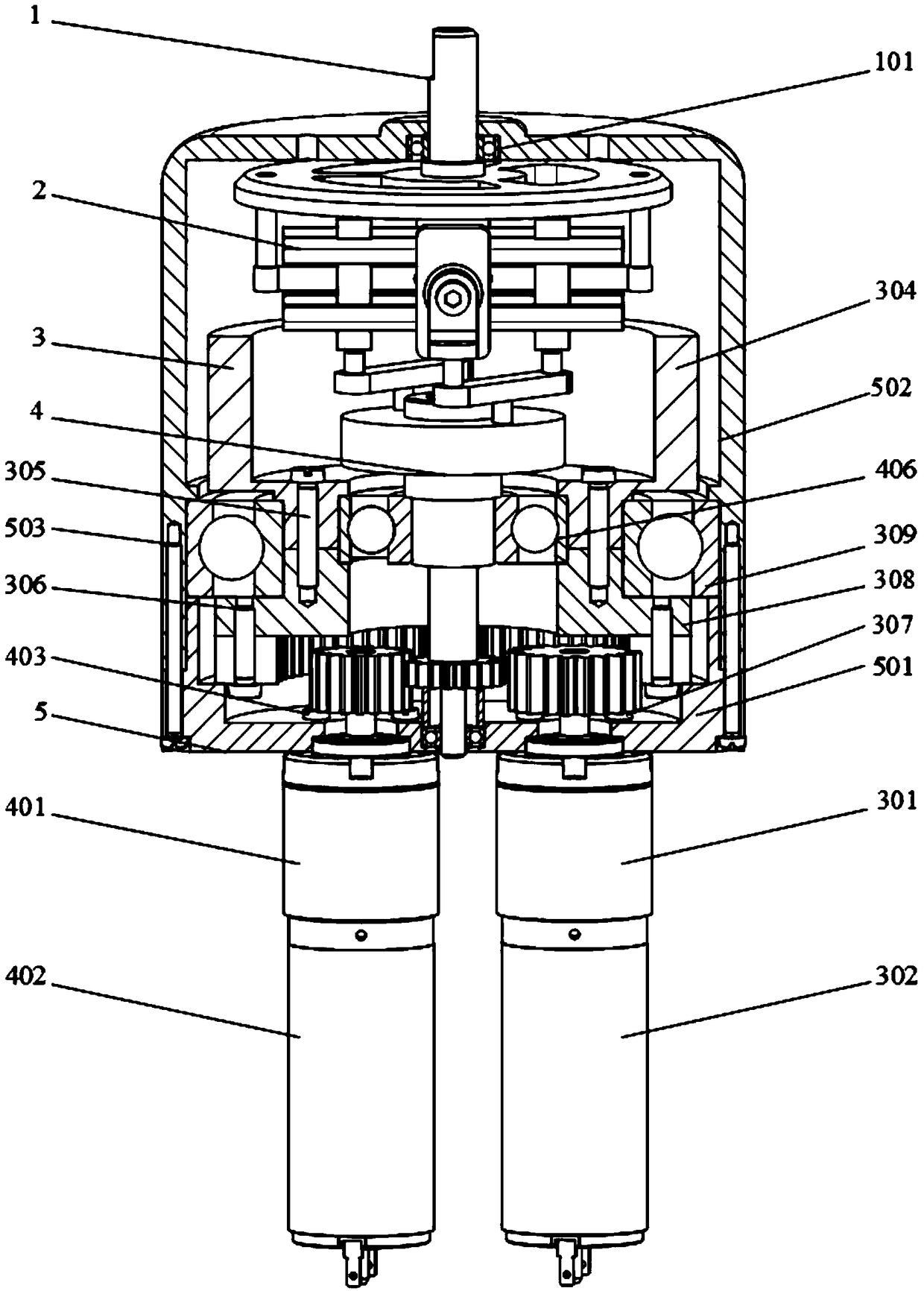
Robot joint variable stiffness module capable of locally linearly adjusting stiffness value
The invention discloses a robot joint variable stiffness module capable of locally linearly adjusting a stiffness value, comprising an input part, an output part and a stiffness adjustment part. The invention can adjust the stiffness of the module only by adjusting the position of a lever fulcrum. As the position of the lever fulcrum changes, the force arm ratio of the lever also changes between zero and infinity, and the stiffness value of the module changes between zero and infinity. A bearing is provided between the input part and the output part to withstand non-torque loads and enables the input part and the output part to rotate relative to each other. When the output part of the variable stiffness module is subjected to an external transient load, the load is transferred by a cam lever and absorbed by a compression spring, thereby reducing external impact, achieving flexible drive output, and improving the robustness and operational stability of the robot. The invention has theadvantages of compact structure, low cost and linear adjustment within a specified range, so that the invention can be conveniently applied to various interactive devices, especially flexible robot joints.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
Stable seismic quality factor Q estimation method based on variational mode decomposition
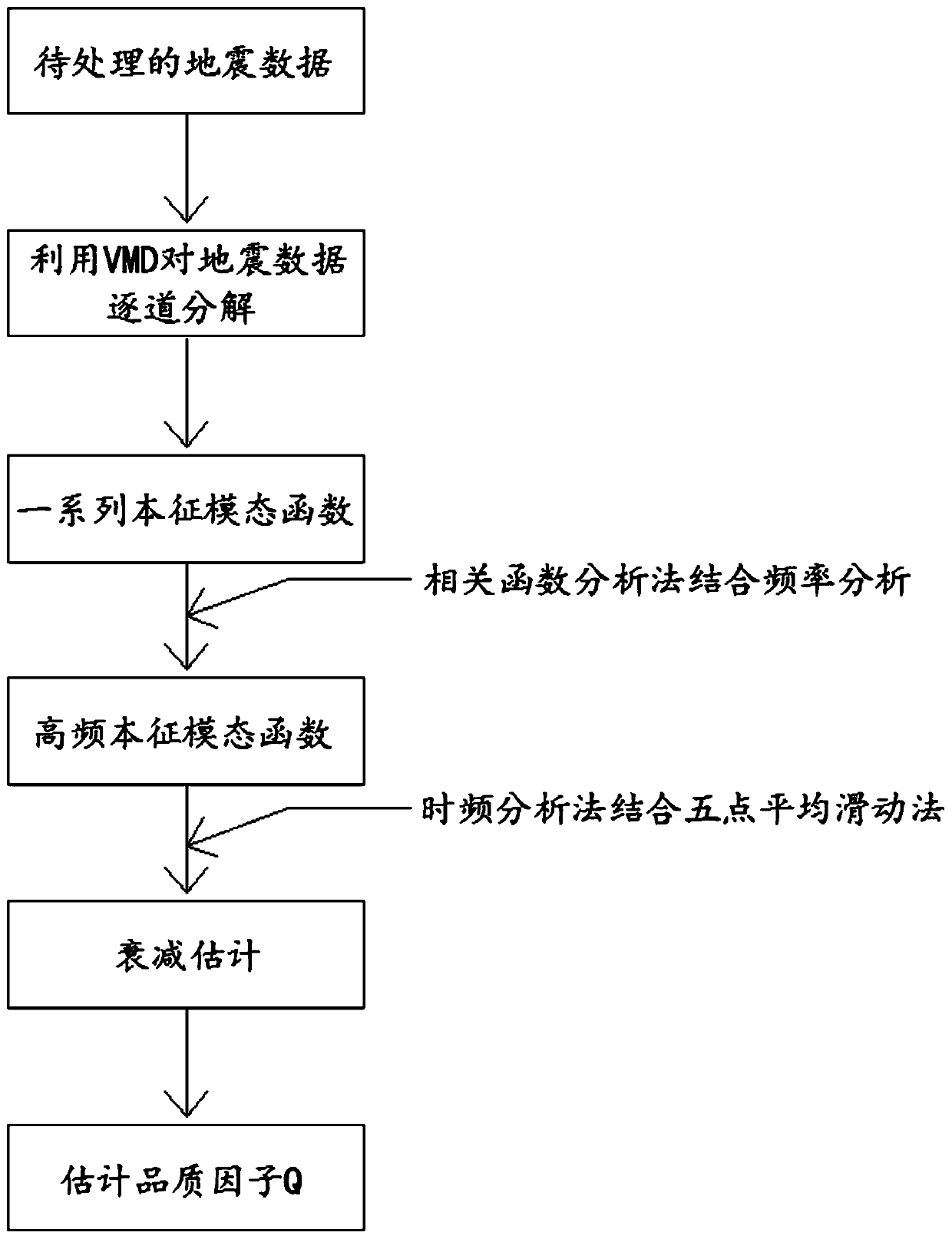
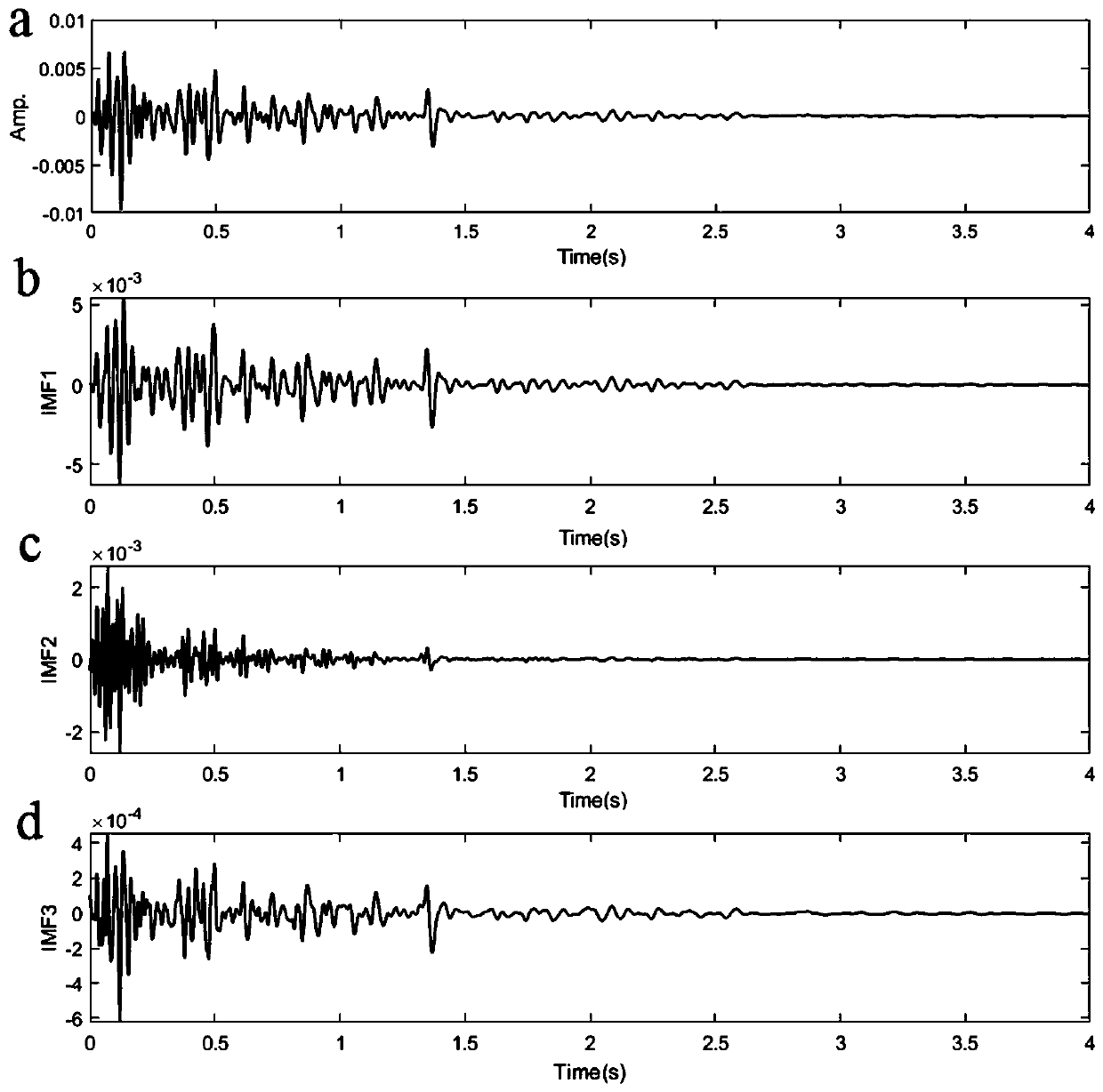
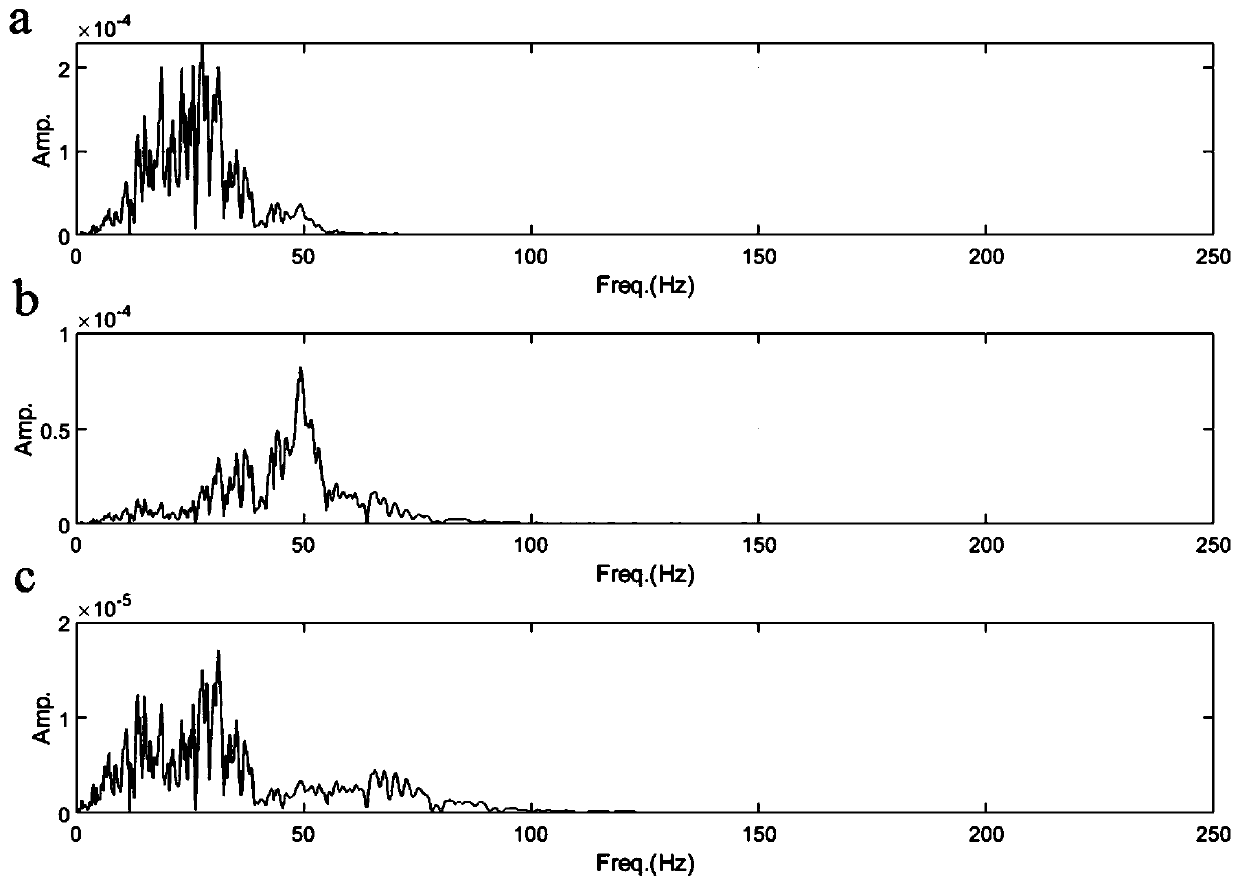
ActiveCN110187388AImprove estimation accuracyImprove stabilitySeismic signal processingSpectral bandsTime–frequency analysis
The invention provides a stable seismic quality factor Q estimation method based on variational mode decomposition, belonging to the field of oil and gas exploration geophysical processing methods. The method comprises the following steps of: decomposing seismic data into a series of intrinsic mode functions by adopting variational mode decomposition, then preferably selecting a main contributionintrinsic mode function component of a seismic signal by using a correlation function method, preferably selecting a high-frequency intrinsic mode function by combining frequency analysis, preferablyselecting a logarithmic amplitude spectral band for estimating attenuation of data points of adjacent layers of the seismic data by using a time-frequency analysis method based on variational mode decomposition combined with a five-point average sliding method for the high-frequency intrinsic mode function, and providing a stable stratum quality factor Q estimation value of a seismic channel by combining the least square method. The stable seismic quality factor Q estimation method based on variational mode decomposition overcomes the defect of long transmission time for the time-frequency joint variable estimation quality factor, avoids the mutual influence of different frequency bands, avoids the influence of noise and improves the estimation precision and stability of the quality factorQ.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIV OF INFORMATION TECH
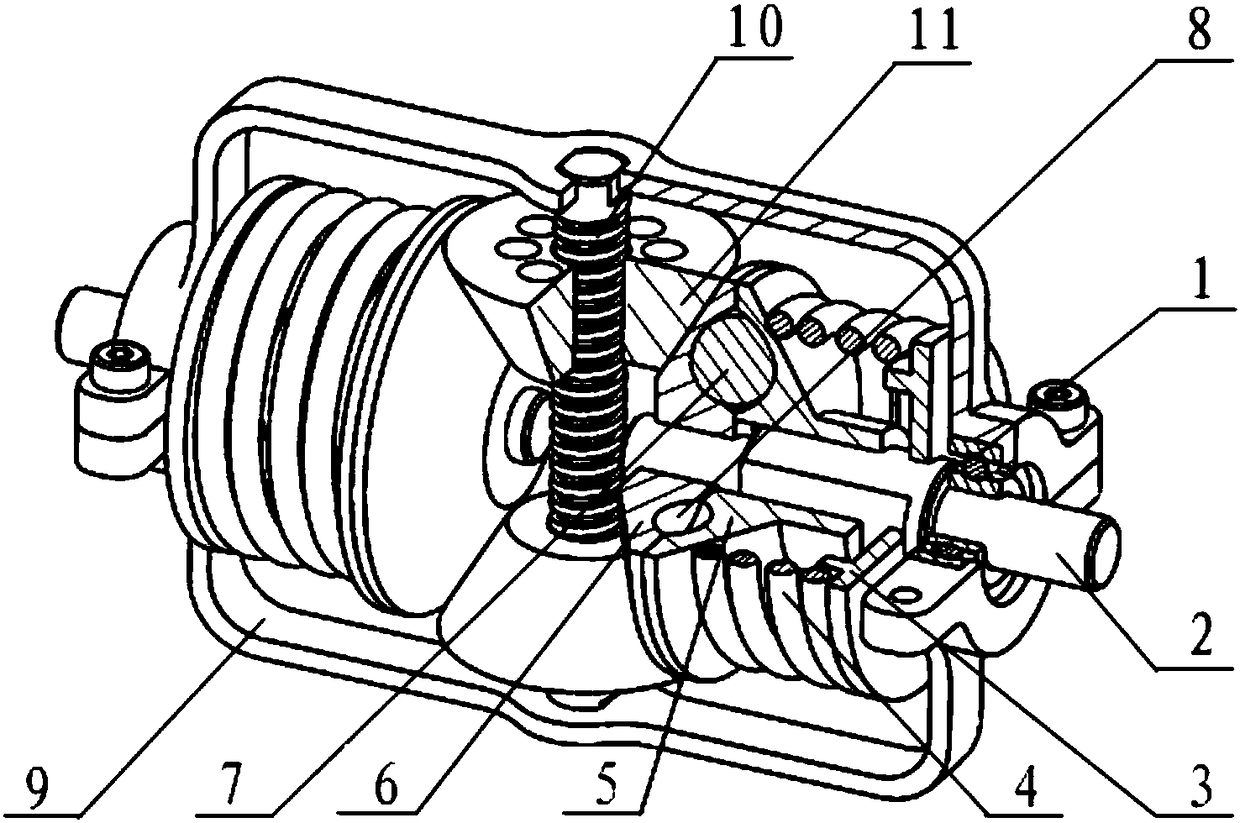
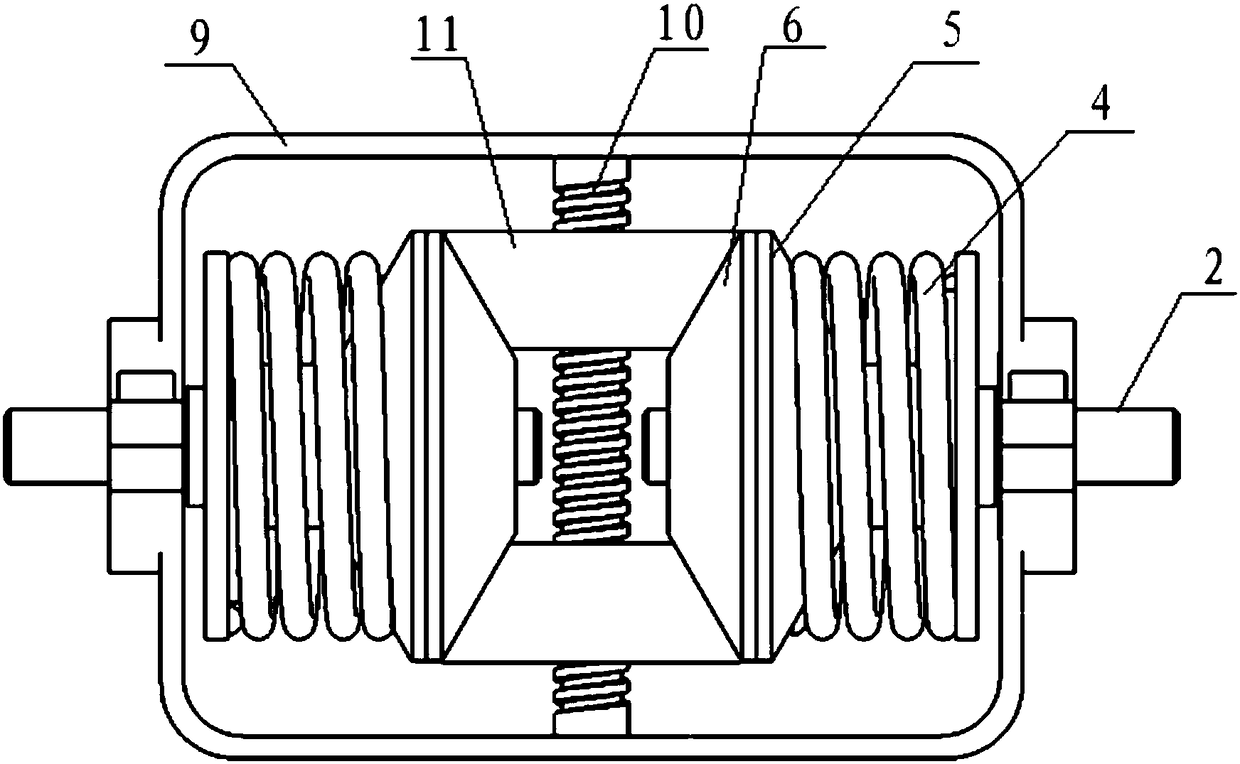
Rotation joint variable rigidity actuator
ActiveCN108942908AChanging the effective length of actionAchieve output stiffnessProgramme-controlled manipulatorJointsEffective actionActuator
The invention discloses a rotation joint variable rigidity actuator. The rotation joint variable rigidity actuator comprises a supporting machine base. The supporting machine base comprises a base, ashell and two base connecting screws. The base is located at the lower end of the shell. The lower end of the shell abuts against the upper end of the base. One ends of the two base connecting screwsboth penetrate through the base and extend into the shell. A torque output mechanism is arranged on the shell and provided with two parallel output disc connecting pins located in the shell. The two output disc connecting pins are provided with a rigidity adjusting mechanism. A main transmission mechanism is arranged on one side of the lower end of the base. According to the rotation joint variable rigidity actuator, the effective acting length of a leaf spring can be changed, output rigidity changes are achieved, fixed-rigidity output is achieved through synchronous rotation of the main transmission mechanism and a rigidity adjusting disc, variable rigidity output is achieved through asynchronous rotation, and output rigidity decoupling is facilitated; and accordingly, the algorithm is convenient to control, friction is reduced, energy consumption can be better reduced, an output disc can continuously rotate, the structure is compact, and the size is small.
Owner:YANSHAN UNIV
Robot joint variable stiffness actuator
The invention belongs to the technical field of robot joints, and particularly relates to a robot joint variable stiffness actuator. The robot joint variable stiffness actuator comprises a power output device and two power input devices. The power output device comprises a power output rack, a screw rod and friction circular truncated cones. The screw rod is installed on the power output rack andis in thread connection with the two friction circular truncated cones. The small diameter ends of the two friction circular truncated cones correspond to each other. The two power input devices are rotationally installed on the two sides of the power output rack respectively and are both connected with the two friction circular truncated cones. The joint turning angles and the joint stiffness arecontrolled by changing the relative turning directions of the two power input devices. According to the robot joint variable stiffness actuator, the two power input devices are symmetrically arrangedon the two sides of the power output device, the joint turning angles and the joint stiffness are controlled by changing the relative turning directions of two power input shafts. Furthermore, it canbe realized that a motor or joint components are protected by adopting the friction manner.
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF AUTOMATION - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
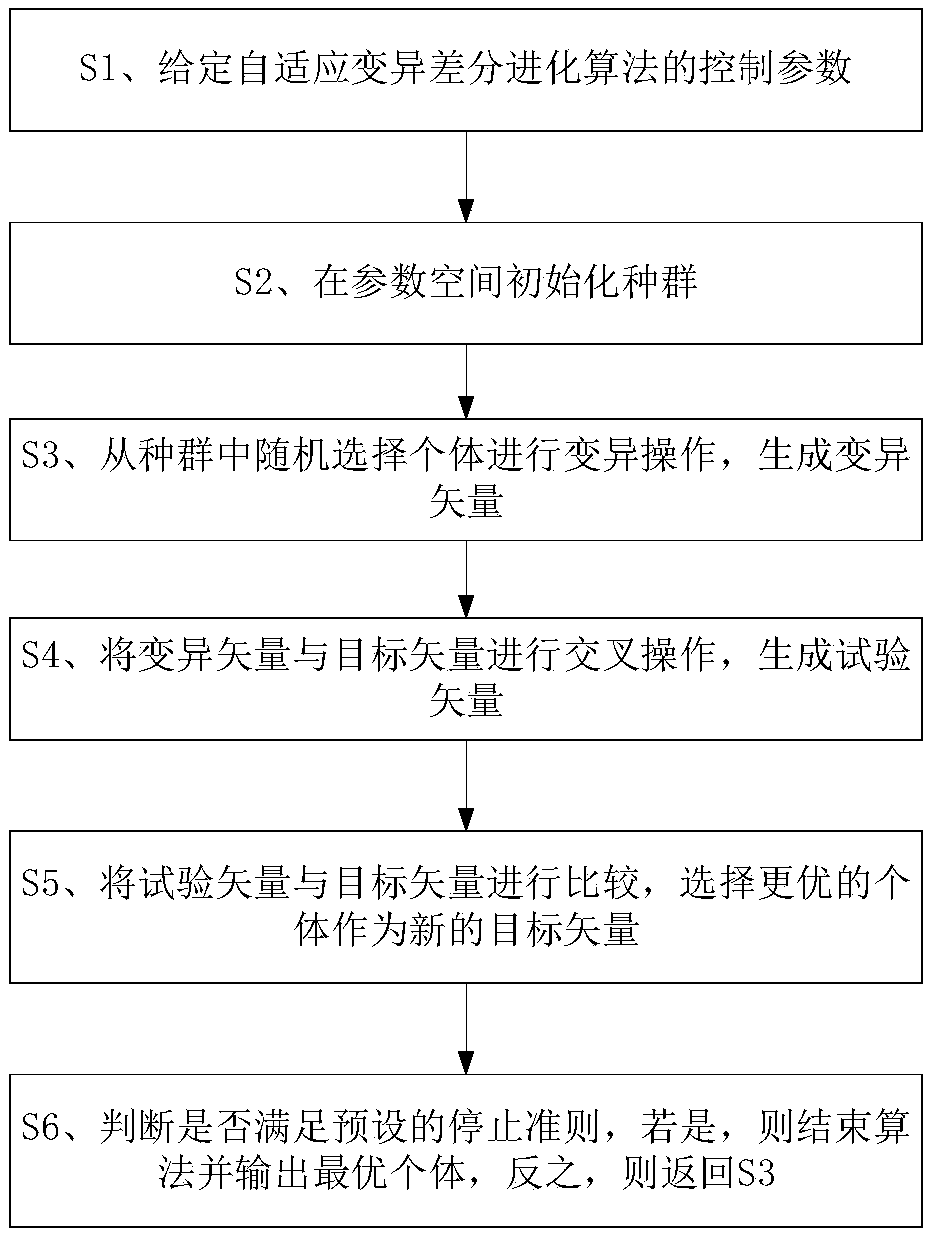
Mechanical arm control method
PendingCN109623814AImprove flexibilityGuaranteed pose accuracyProgramme-controlled manipulatorTotal factory controlComputer scienceForward kinematics
The invention discloses a mechanical arm control method. The mechanical arm control method comprises the following steps that (1) a forward kinematics model of the mechanical arm is established as system input, and a controls parameter of an adaptive mutation differential evolution algorithm is given; (2) population initializing is randomly carried out in parameter space; (3) individuals are randomly selected from population to perform mutation operation to generate a mutation vector; (4) the mutation vector and a target vector are subjected to cross operation to generate a test vector; (5) the test vector is compared with the target vector, and a better individual is selected as a new target vector; and (6) whether a preset stopping criterion is met or not is judged, if so, the optimal individual is ended and output to be as a joint variable quantity matrix of the mechanical arm, and otherwise, the step 3 is repeated. According to the mechanical arm control method, the shortest strokesolution is obtained while the accuracy of the posture of the mechanical arm is ensured, the flexibility of joints is improved, and the working efficiency is improved.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com