Tail end Cartesian space rigidity modeling method for rope-driven linkage mechanical arm
A technique of Cartesian space and modeling method, which is applied in the field of stiffness modeling of Cartesian space at the end of a rope-driven linkage manipulator, and can solve problems such as stiffness modeling of a rope-driven linkage manipulator
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0021] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments.
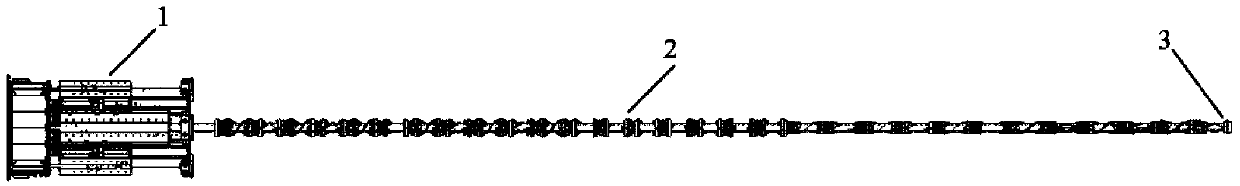
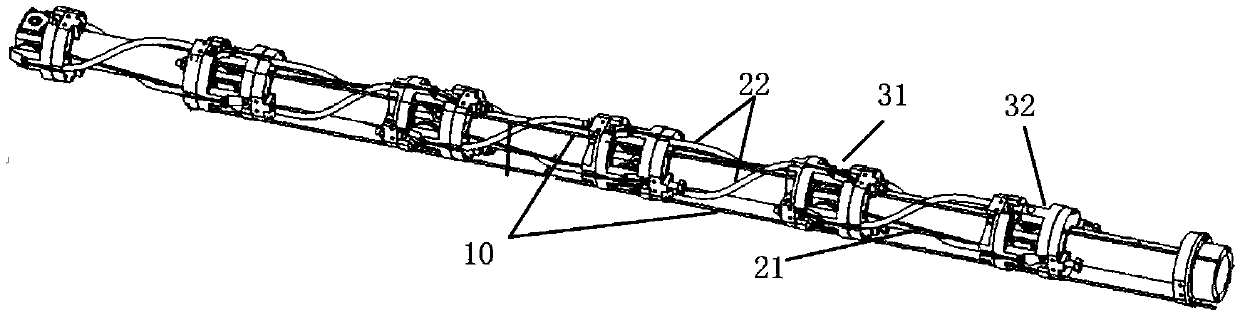
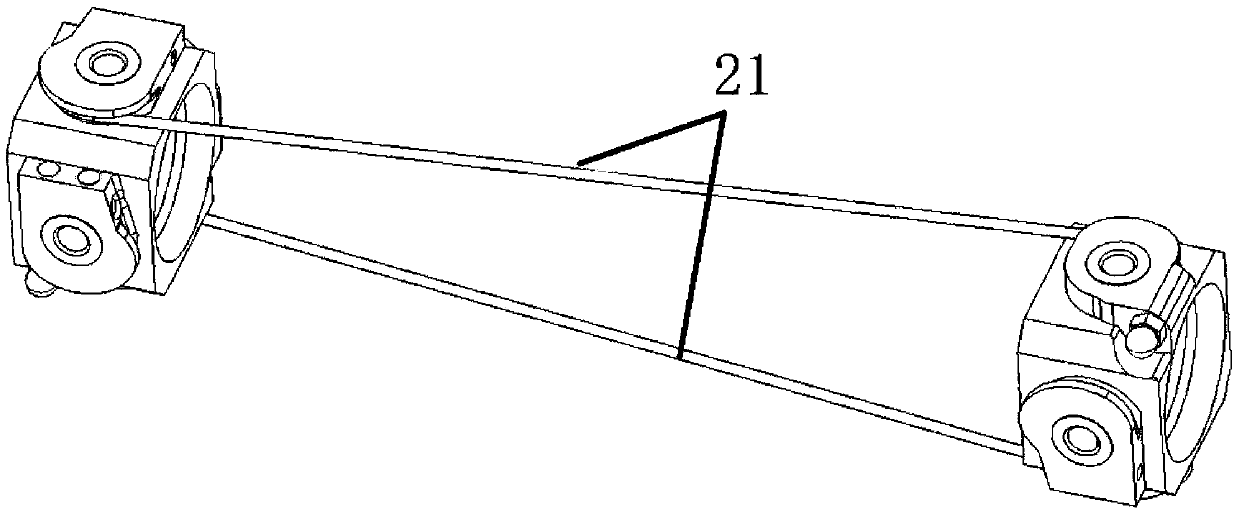
[0022] The specific embodiment of the present invention proposes a method for modeling the end Cartesian space stiffness of the rope-driven linkage manipulator, aiming at solving the mathematical model of the equivalent stiffness of the rope-driven linkage manipulator joints and the equivalent stiffness of the end Cartesian space Express and solve problems to realize the stiffness analysis, static analysis, force control, etc. of this type of manipulator. figure 1 The rope-driven linked manipulator model is given, which includes three parts: the drive box 1, the main body of the manipulator 2 and the end effector 3. The drive box 1 drives the rope to pull the main body of the manipulator to move through the motor. The ropes of this type of manipulator include driving ropes and linkage ropes. The equivalent stiffness of the joints is jointly gen...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com