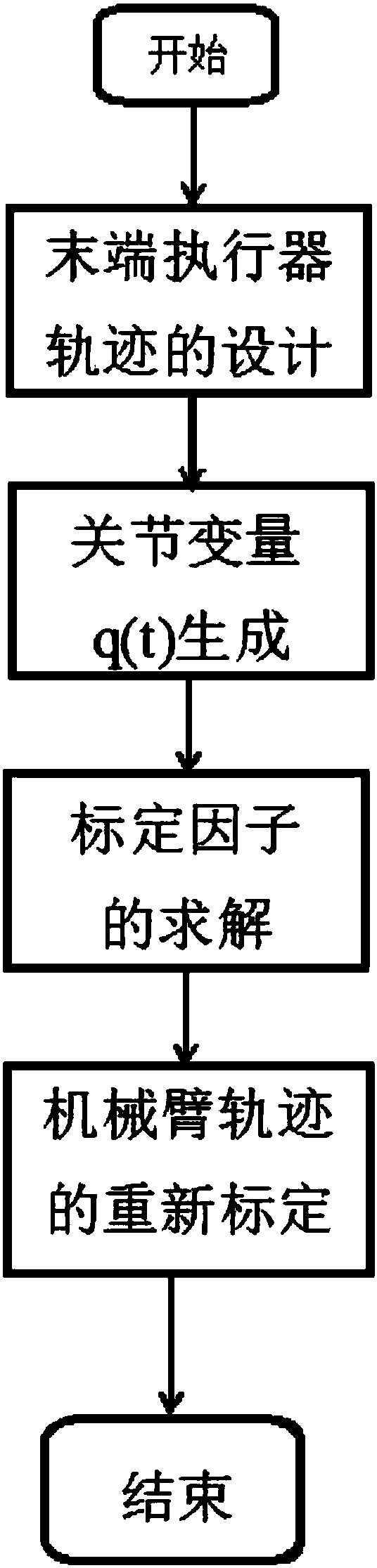
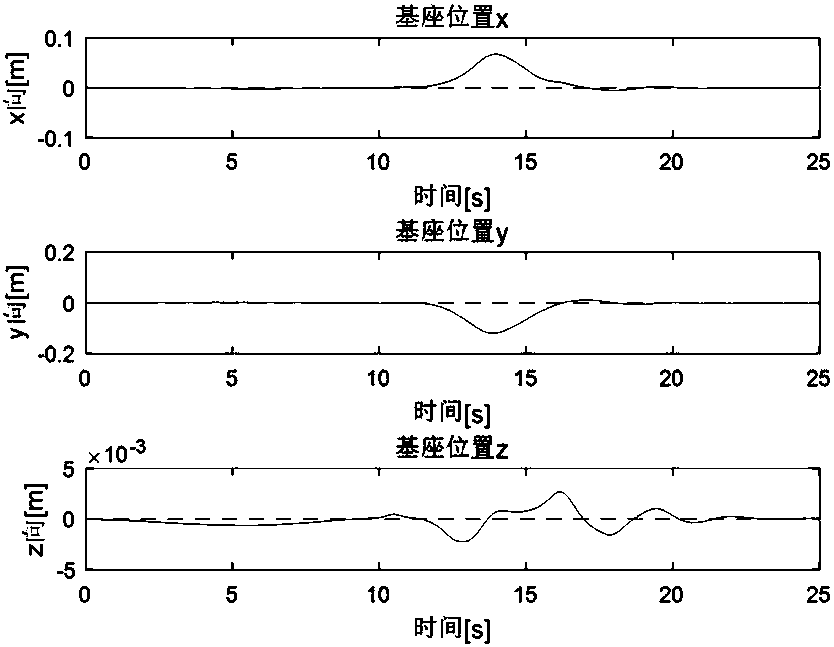
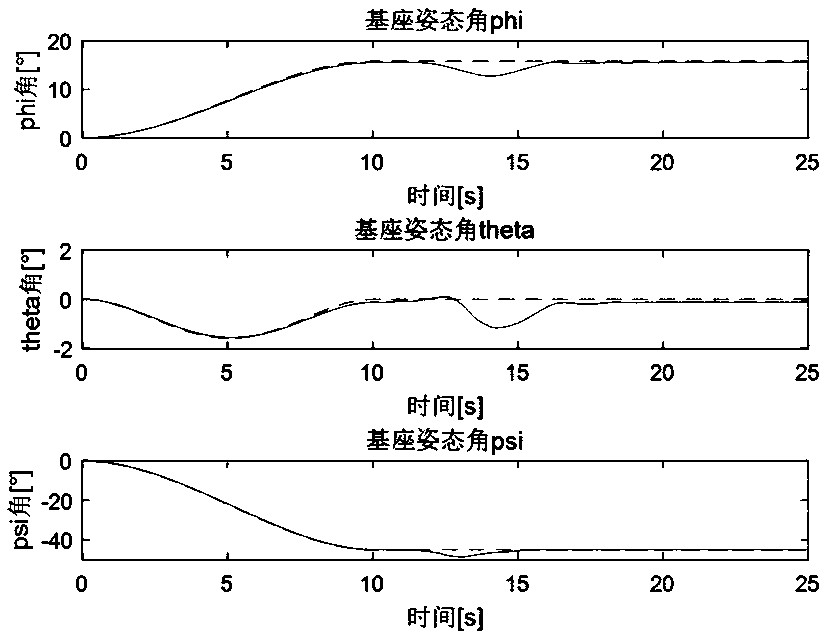
Dynamic scaling planning method for floating base and mechanical arm in neutral buoyancy test
A technology of a robotic arm and a base is applied in the field of dynamic scaling planning of a floating base and a robotic arm in a neutral buoyancy experiment. strong effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0101] In this group of simulation experiments, the initial position coordinates of the base are set to [0 0 0], the initial posture of the base is [0°0° 0°], and the initial joint angle of the end effector of the manipulator is [-30° 30 °]. The goal of the task is to make the end effector of the manipulator reach the coordinates [0.5 0.5 0.2] while the base position remains at [0 0 0]. The position in the simulation is uniformly represented by the coordinates in the pool coordinate system, and the unit is meter. The attitude is uniformly represented by Euler angles, and the unit is degree. In the simulation test, the base uses a position tracking slide film controller based on the approach rate, the parameter c is set to diag(2.1,2.1,2.1,8,8,8), and the parameter b is set to diag(5.8,5.8,5.8, 20,20,20). The robotic arm uses a PID controller to output control signals to the joint angle, and the controller gain coefficient K p Set to diag(300,200), differential gain coeffic...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com