Patents
Literature
93 results about "Ankle joint orthosis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Under the International Standard terminology, orthoses are classified by an acronym describing the anatomical joints which they contain. For example, an ankle foot orthosis ('AFO') is applied to the foot and ankle, a thoracolumbosacral orthosis ('TLSO') affects the thoracic, lumbar and sacral regions of the spine.
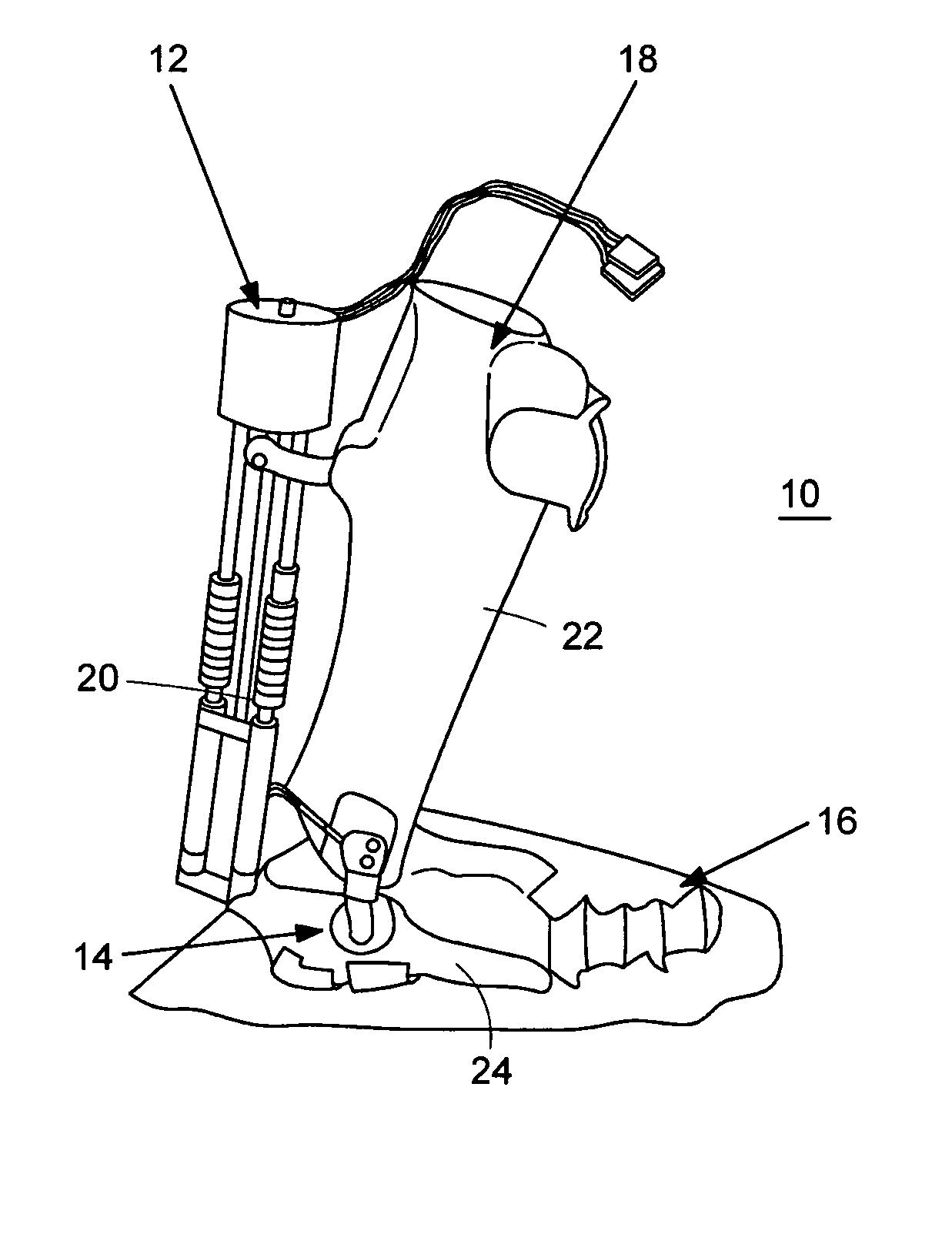
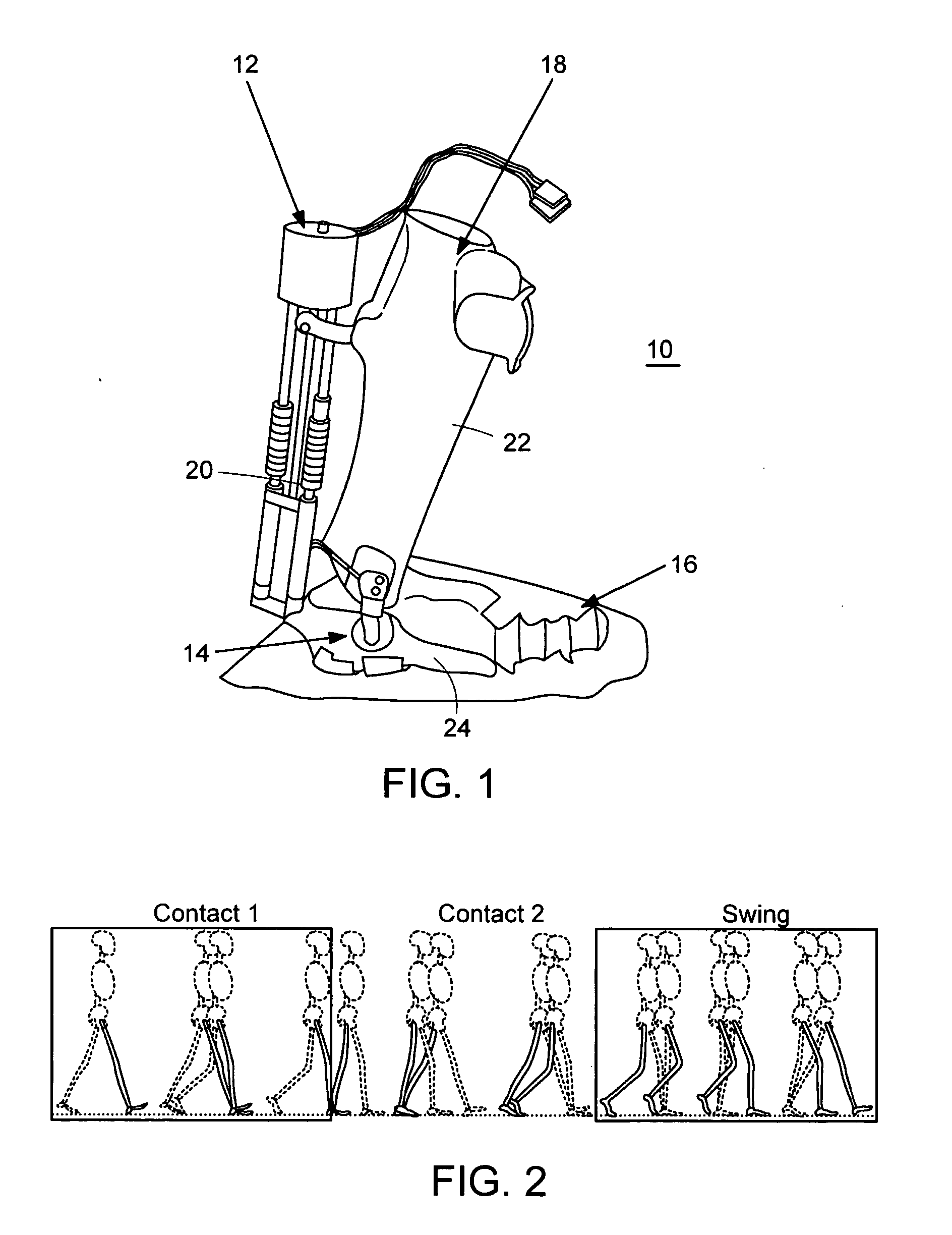
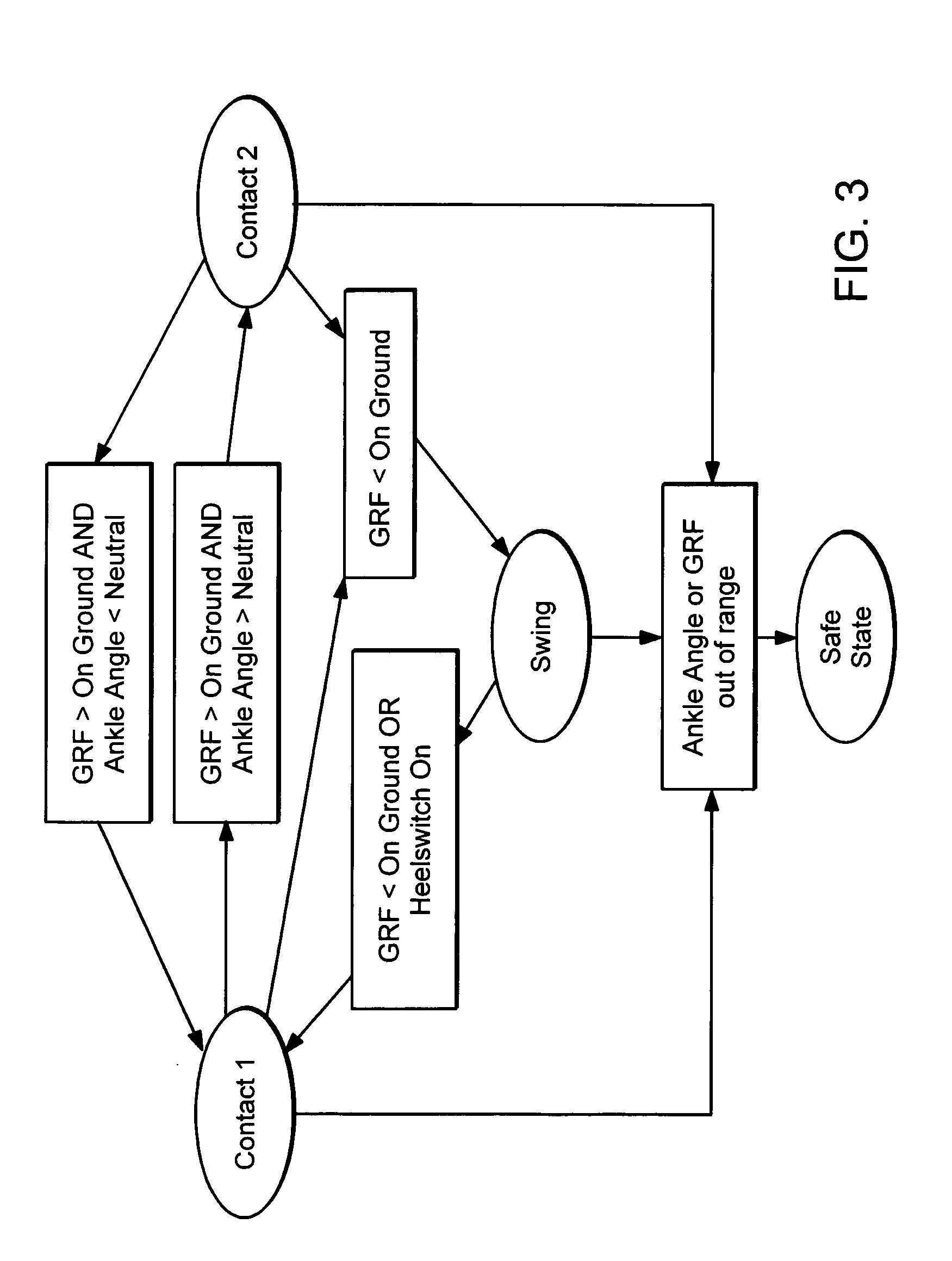
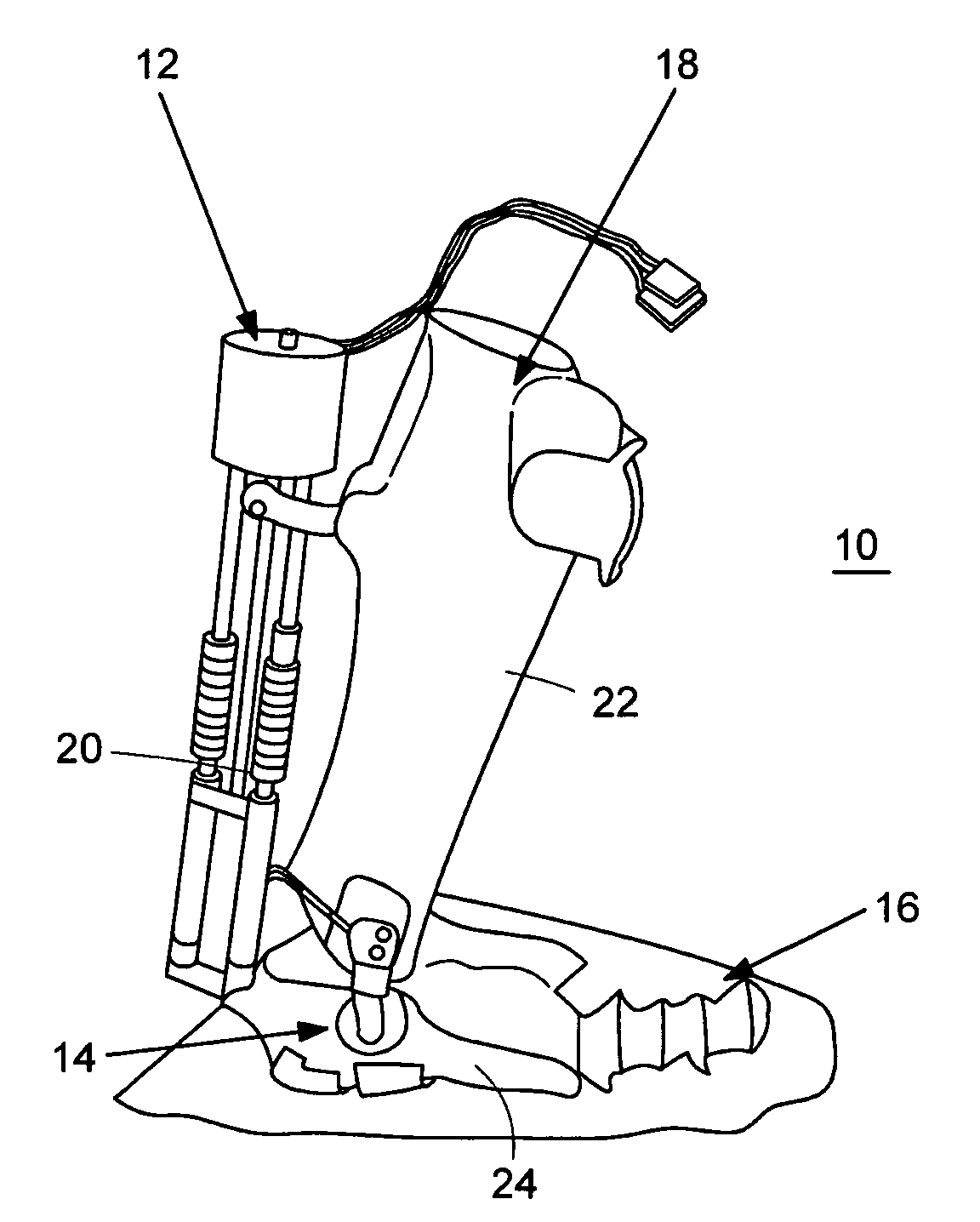
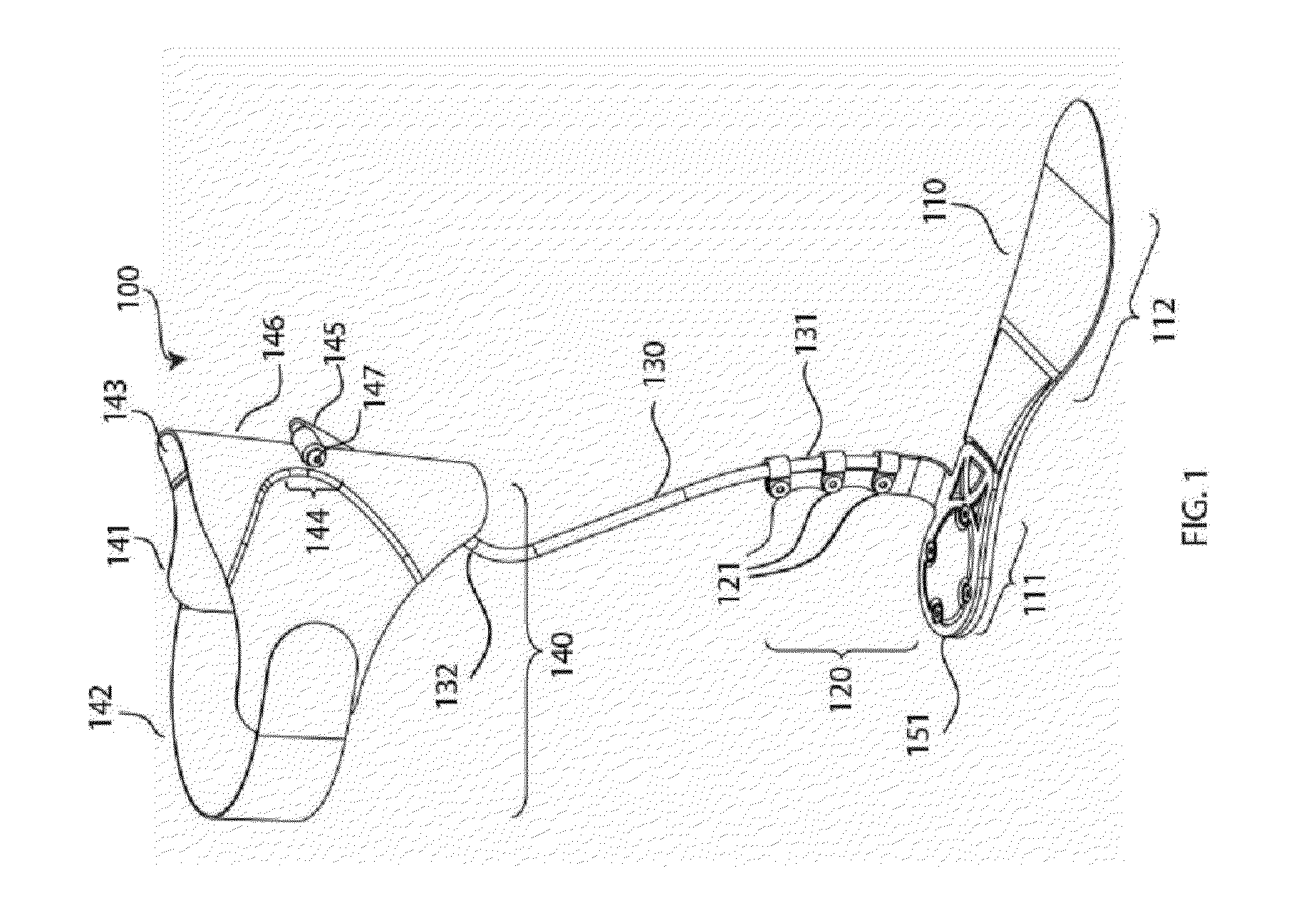
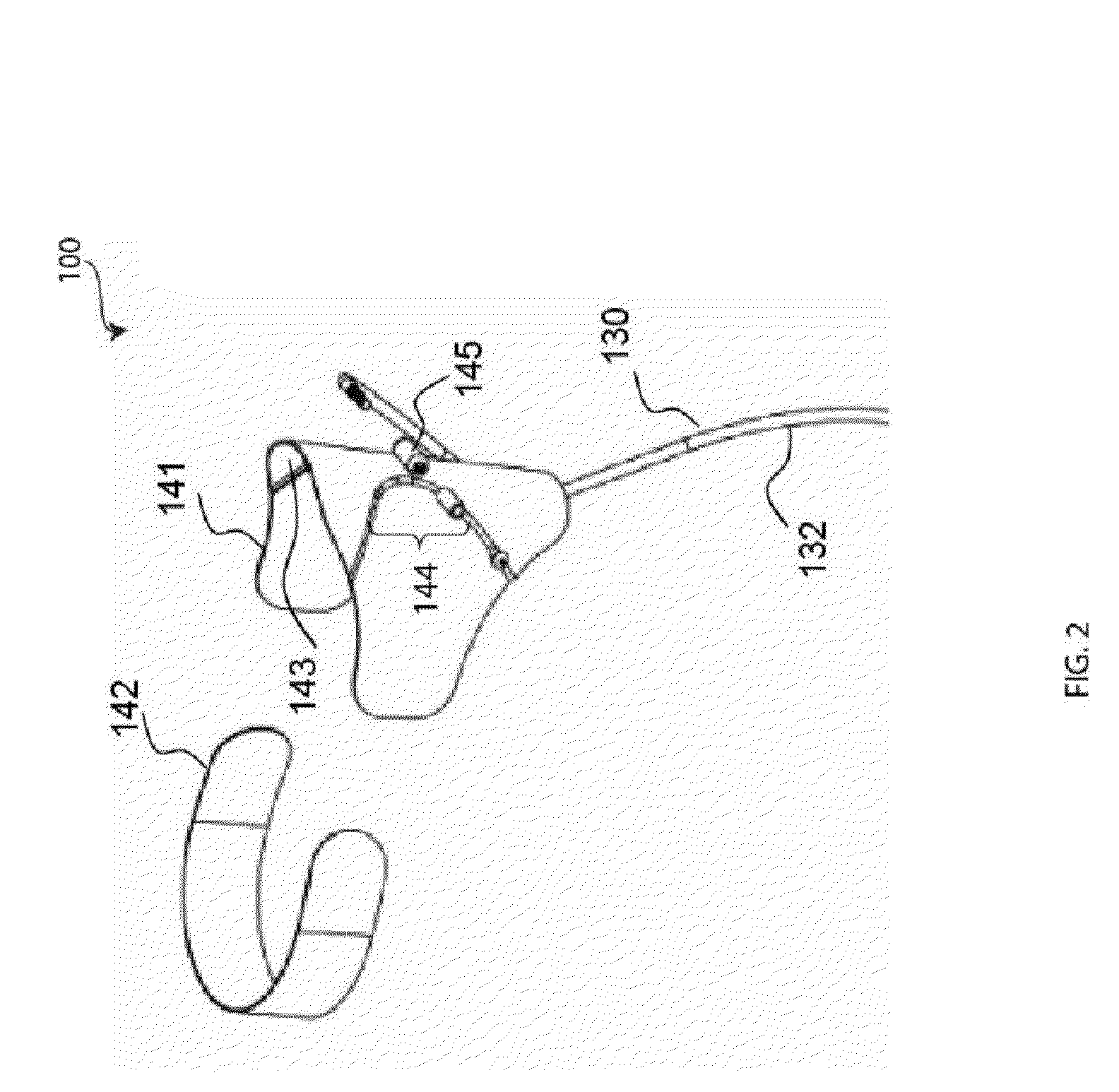
Active Ankle Foot Orthosis
ActiveUS20050070834A1Less kinematic differenceIncrease independenceWalking aidsNon-surgical orthopedic devicesWalking cyclePathology diagnosis
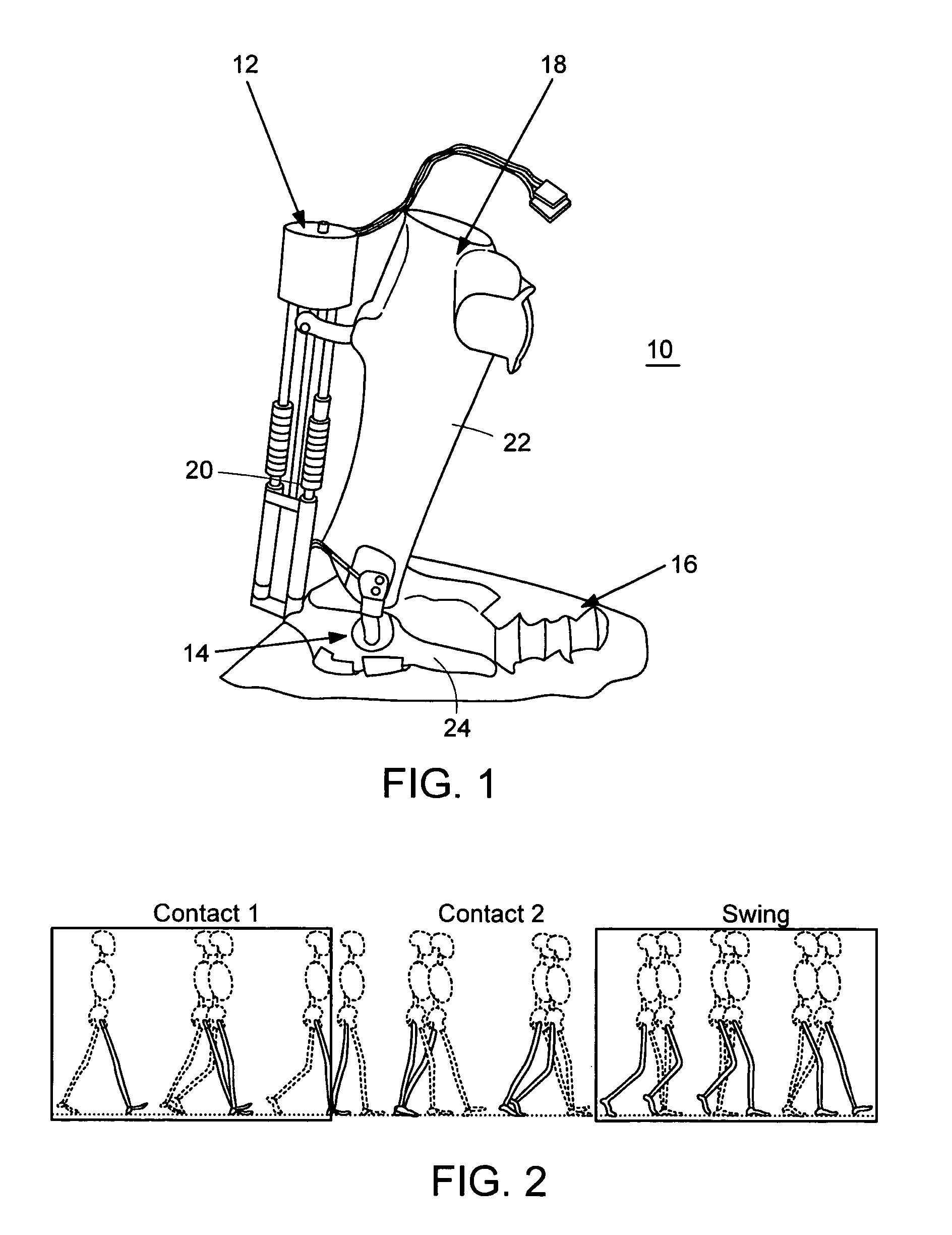
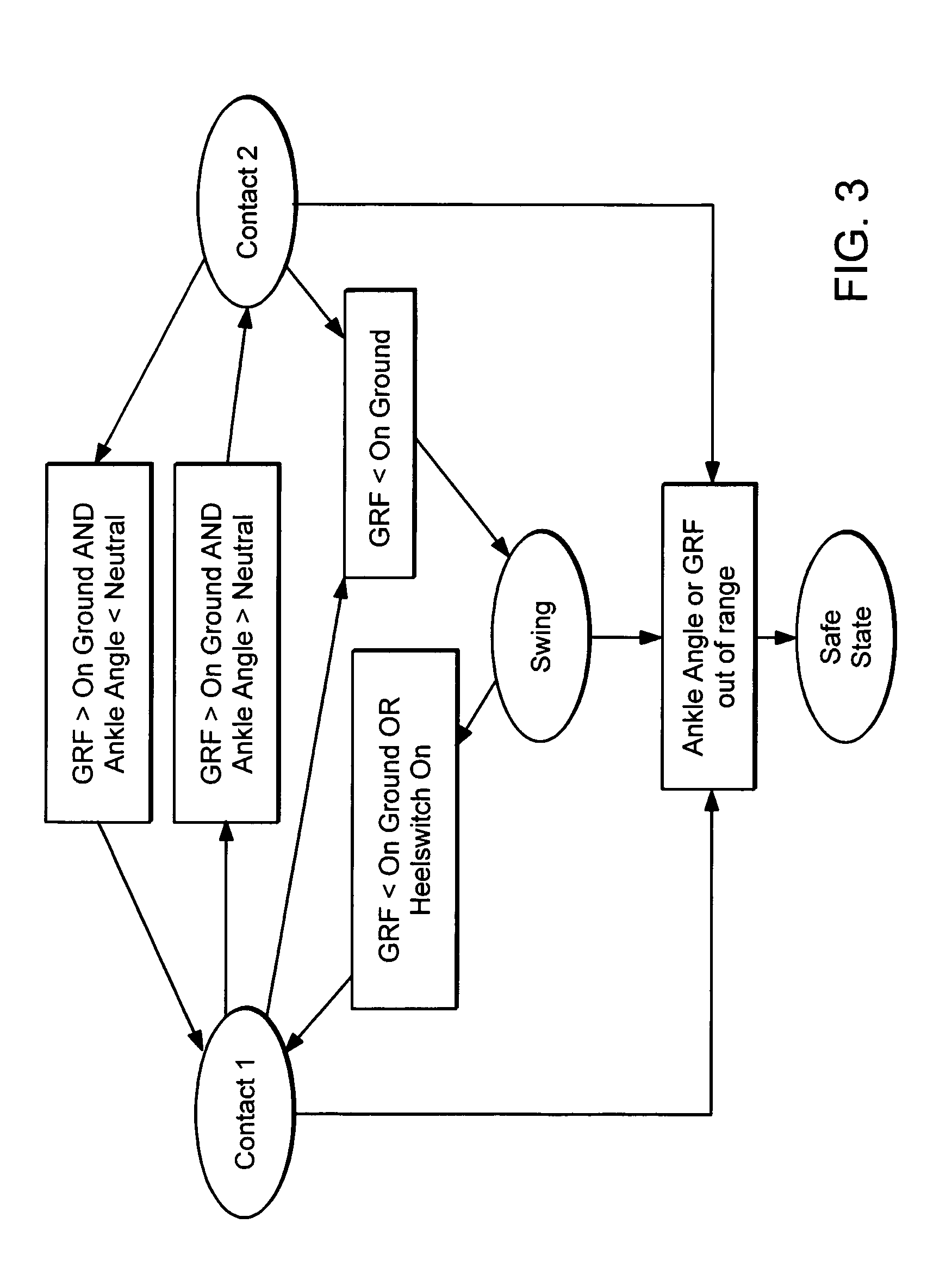
An Active Ankle Foot Orthosis (AAFO) is provided where the impedance of an orthotic joint is modulated throughout the walking cycle to treat ankle foot gait pathology, such as drop foot gait. During controlled plantar flexion, a biomimetic torsional spring control is applied where orthotic joint stiffness is actively adjusted to minimize forefoot collisions with the ground. Throughout late stance, joint impedance is minimized so as not to impede powered plantar flexion movements, and during the swing phase, a torsional spring-damper (PD) control lifts the foot to provide toe clearance. To assess the clinical effects of variable-impedance control, kinetic and kinematic gait data were collected on two drop foot participants wearing the AAFO. It has been found that actively adjusting joint impedance reduces the occurrence of slap foot, allows greater powered plantar flexion, and provides for less kinematic difference during swing when compared to normals.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Active ankle foot orthosis
ActiveUS8075633B2Increase independenceGreat easeWalking aidsNon-surgical orthopedic devicesWalking cyclePostural orientation
An Active Ankle Foot Orthosis (AAFO) is provided where the impedance of an orthotic joint is modulated throughout the walking cycle to treat ankle foot gait pathology, such as drop foot gait. During controlled plantar flexion, a biomimetic torsional spring control is applied where orthotic joint stiffness is actively adjusted to minimize forefoot collisions with the ground. Throughout late stance, joint impedance is minimized so as not to impede powered plantar flexion movements, and during the swing phase, a torsional spring-damper (PD) control lifts the foot to provide toe clearance. To assess the clinical effects of variable-impedance control, kinetic and kinematic gait data were collected on two drop foot participants wearing the AAFO. It has been found that actively adjusting joint impedance reduces the occurrence of slap foot, allows greater powered plantar flexion, and provides for less kinematic difference during swing when compared to normals.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Ankle-foot orthosis
ActiveUS6945947B2Variable propertySmooth transitionRestraining devicesFeet bandagesMedicineKnee orthosis
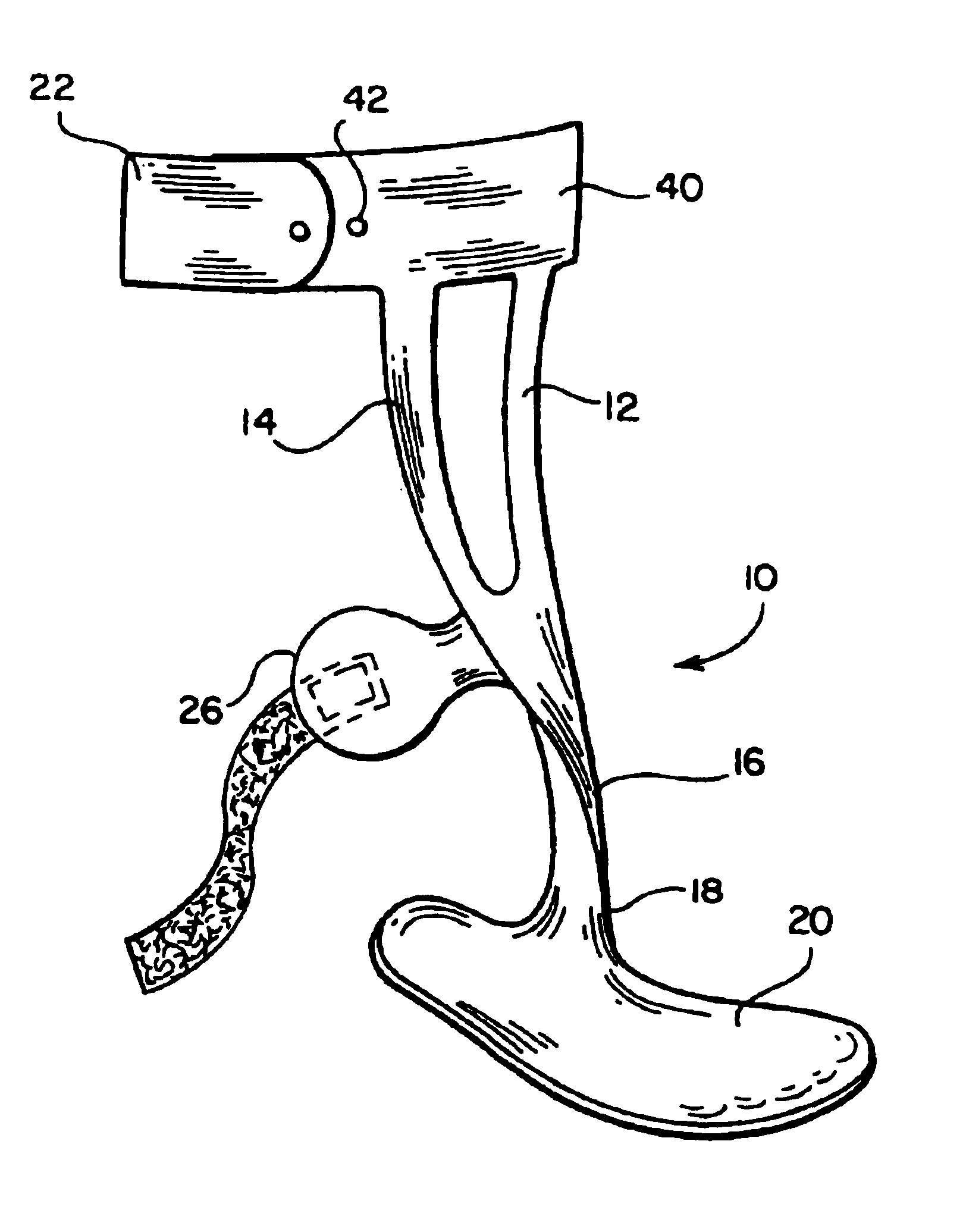
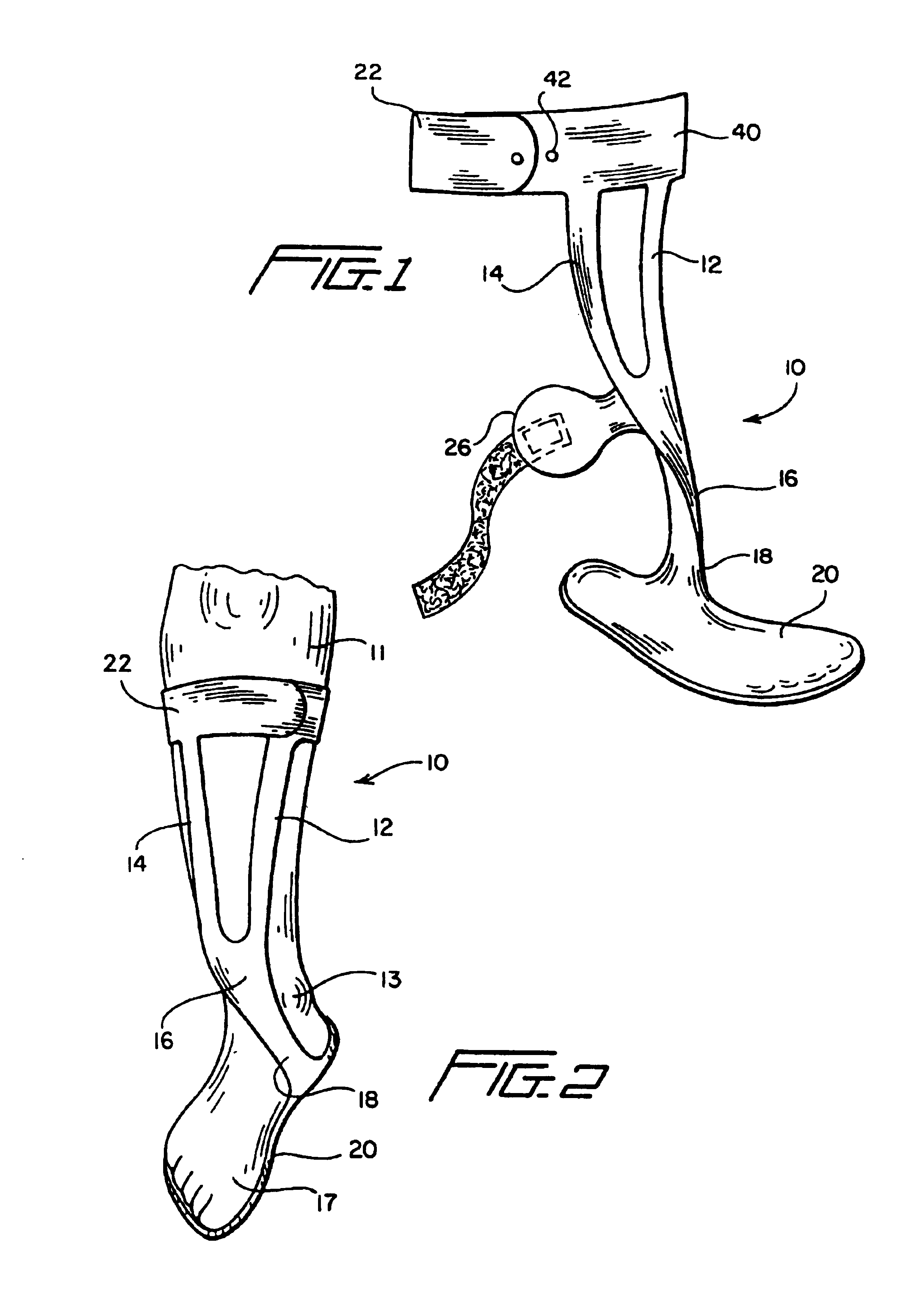
An ankle-foot orthosis having a structural frame formed from at least one layer of fabric impregnated with a hardened structural resin. The frame includes at least one anterior support member that extends downwardly from an upper leg engaging portion to define an anterior ankle portion which extends to a medial portion connected to a foot plate.
Owner:KAUPTHING BANK
Active control of an ankle-foot orthosis
ActiveUS7650204B2Reduce the amount of noiseAdapt quicklyProgramme-controlled manipulatorPerson identificationGravitational forceOrthotic device
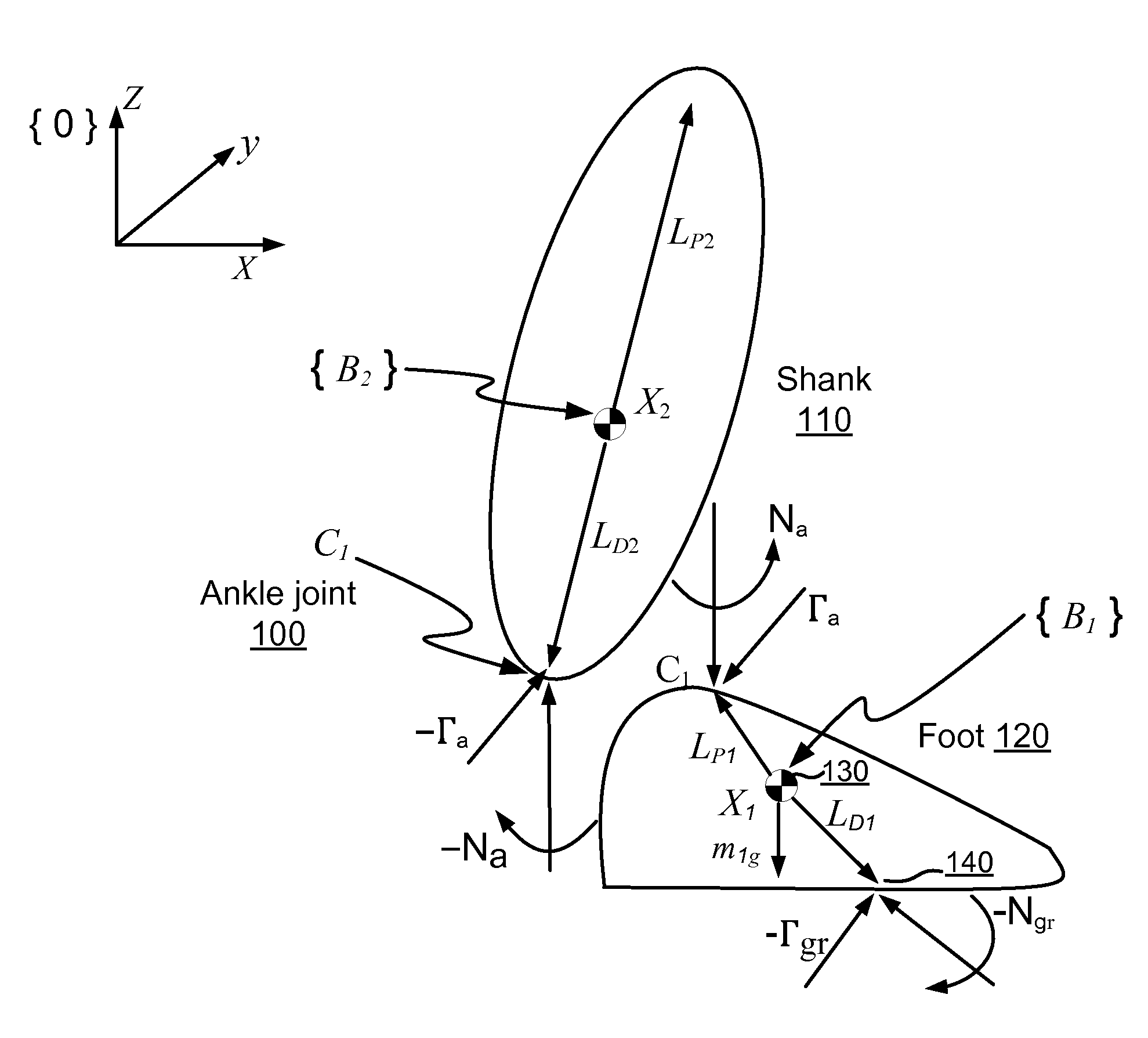
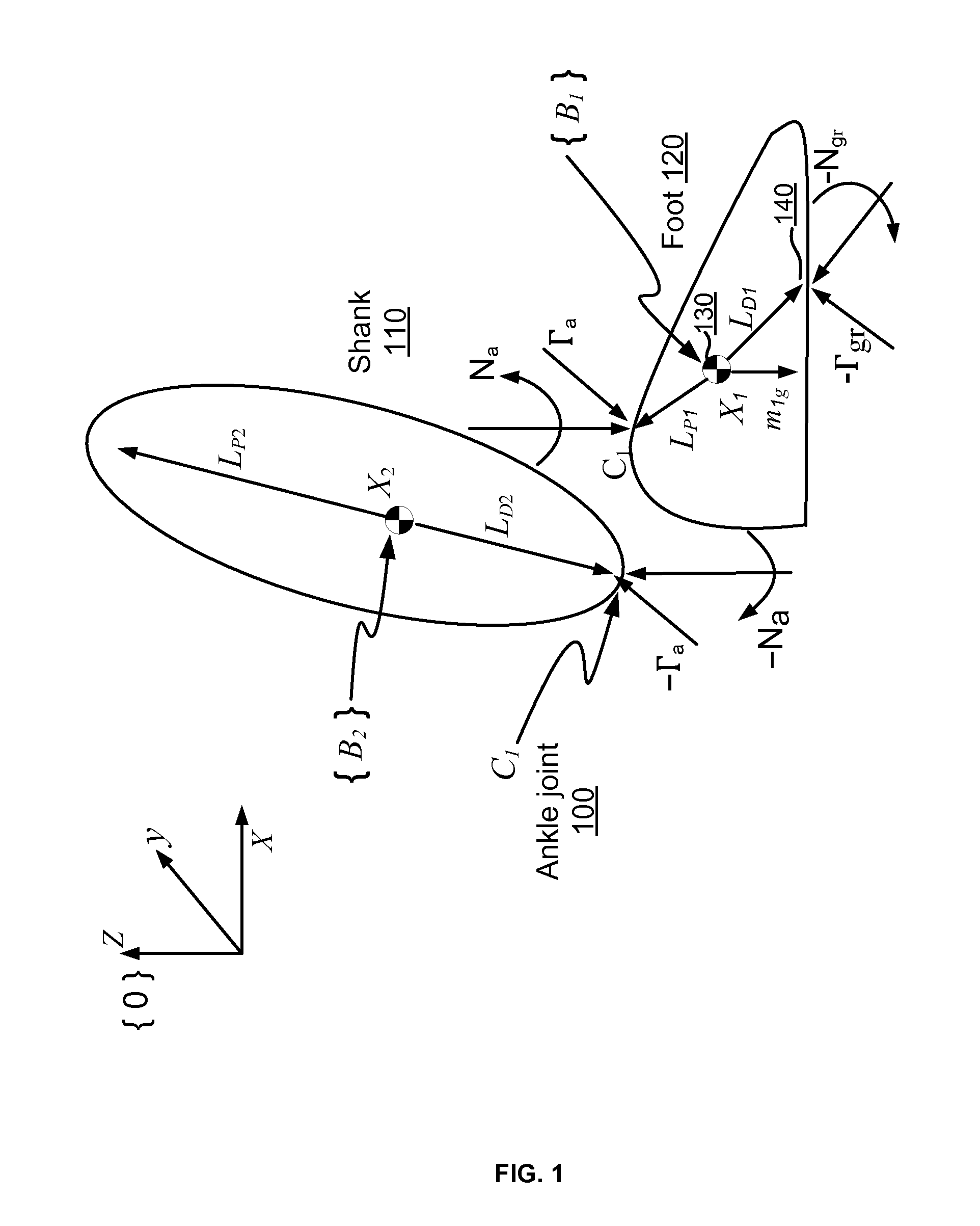
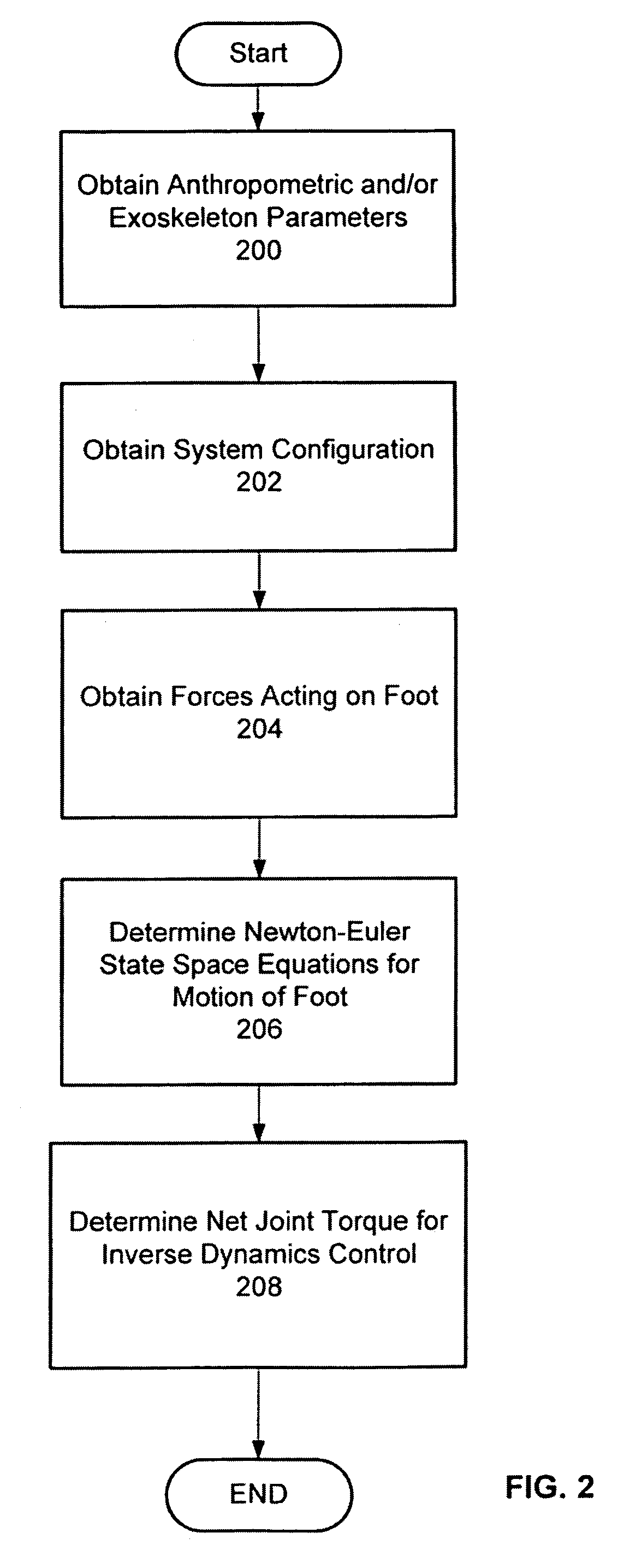
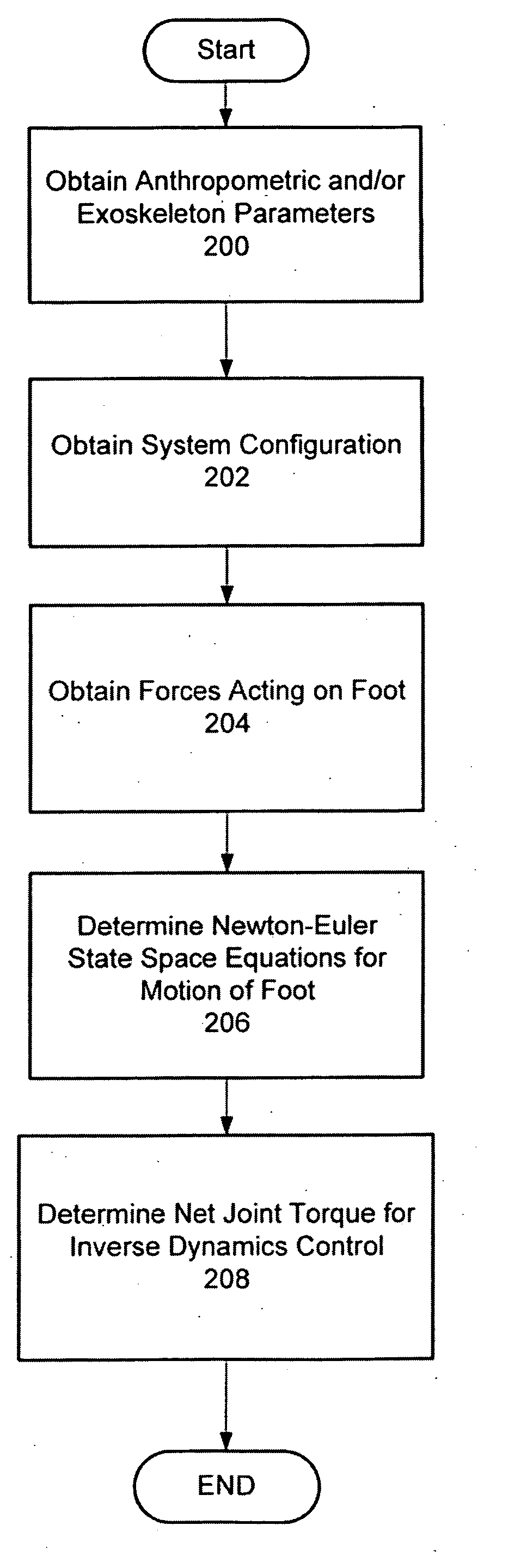
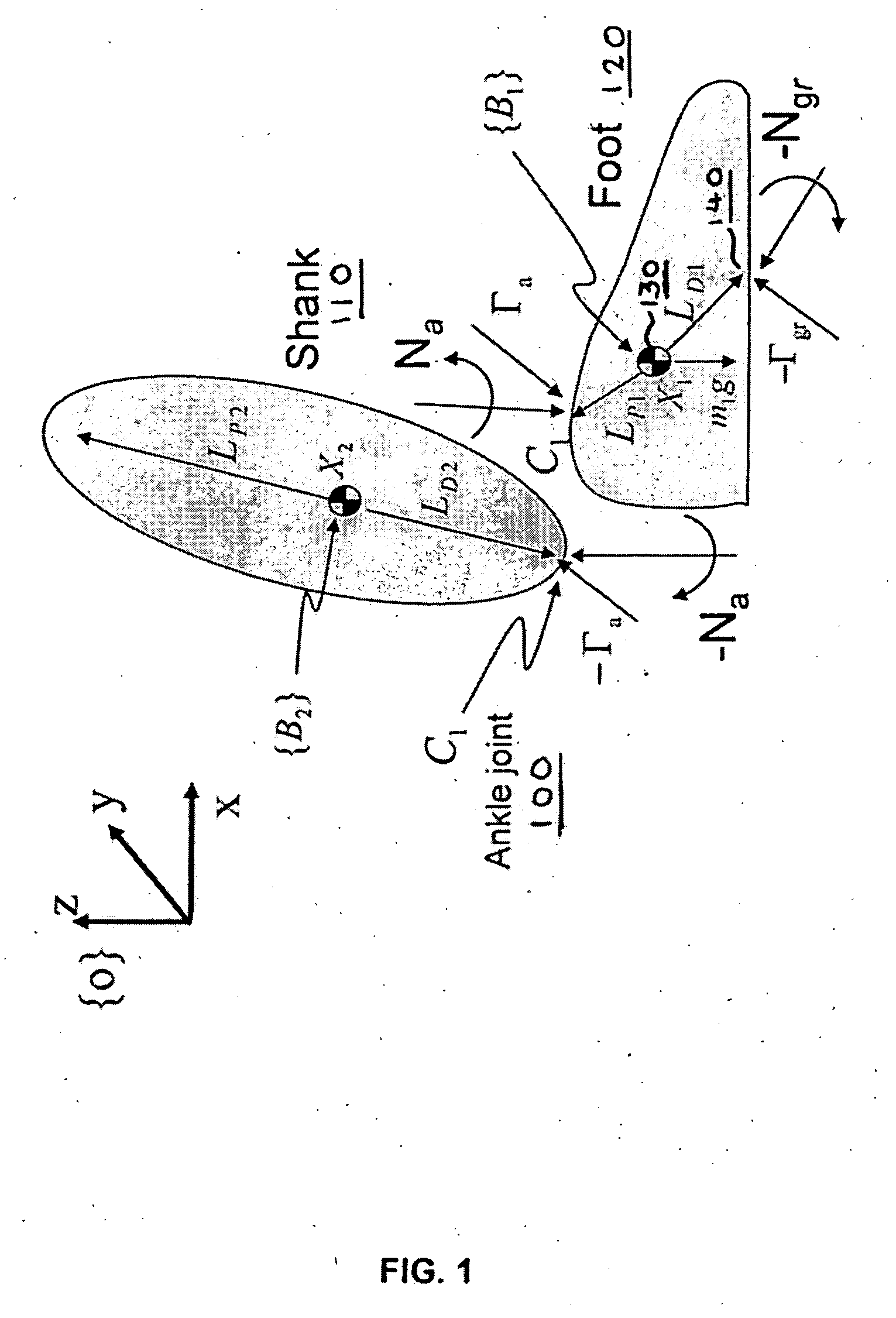
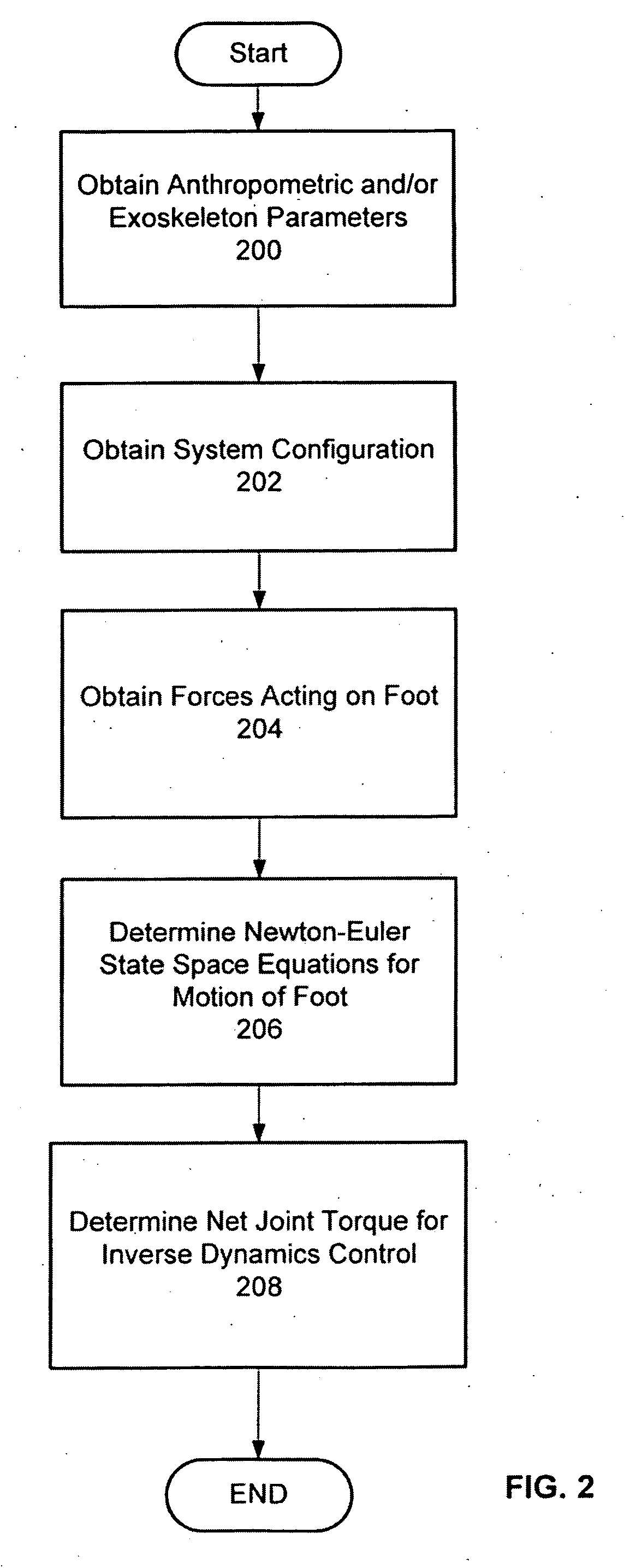
Techniques are provided for controlling a human-exoskeleton system including an ankle-foot orthosis by receiving system parameters for the human-exoskeleton system, receiving generalized coordinates such as an orientation of the foot, and determining a joint torque for controlling the ankle-foot orthosis to compensate for one or more components of forces acting on the foot. Forces selected for compensation include gravitational forces as well as external forces such as ground reaction forces. Techniques are provided for determining an ankle joint torque for partial or complete compensation of forces acting on the foot about an axis of rotation. The provided techniques mitigate the amount of interference between voluntary control and assist control, thereby allowing humans to quickly humans adapt to an exoskeleton system.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
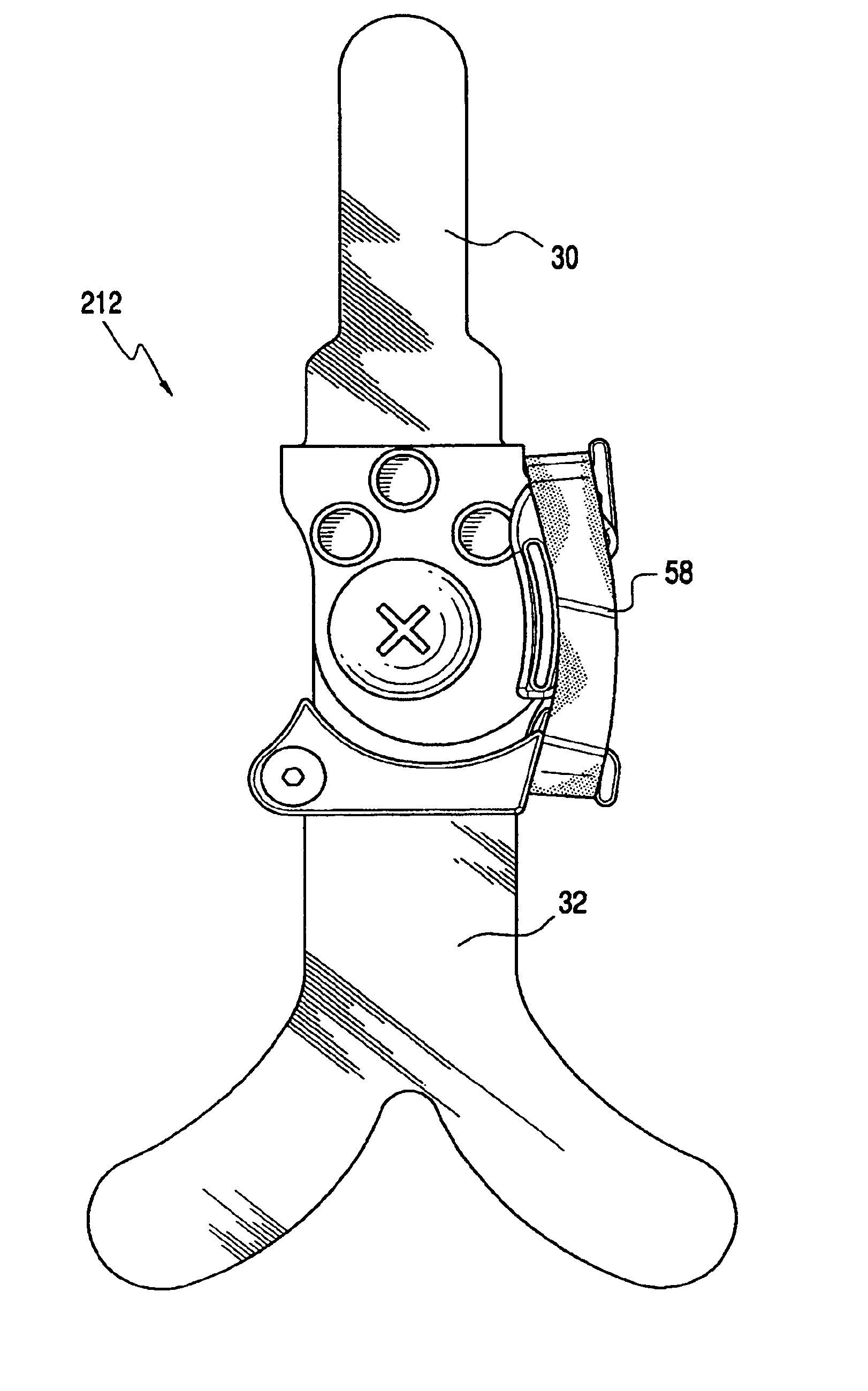
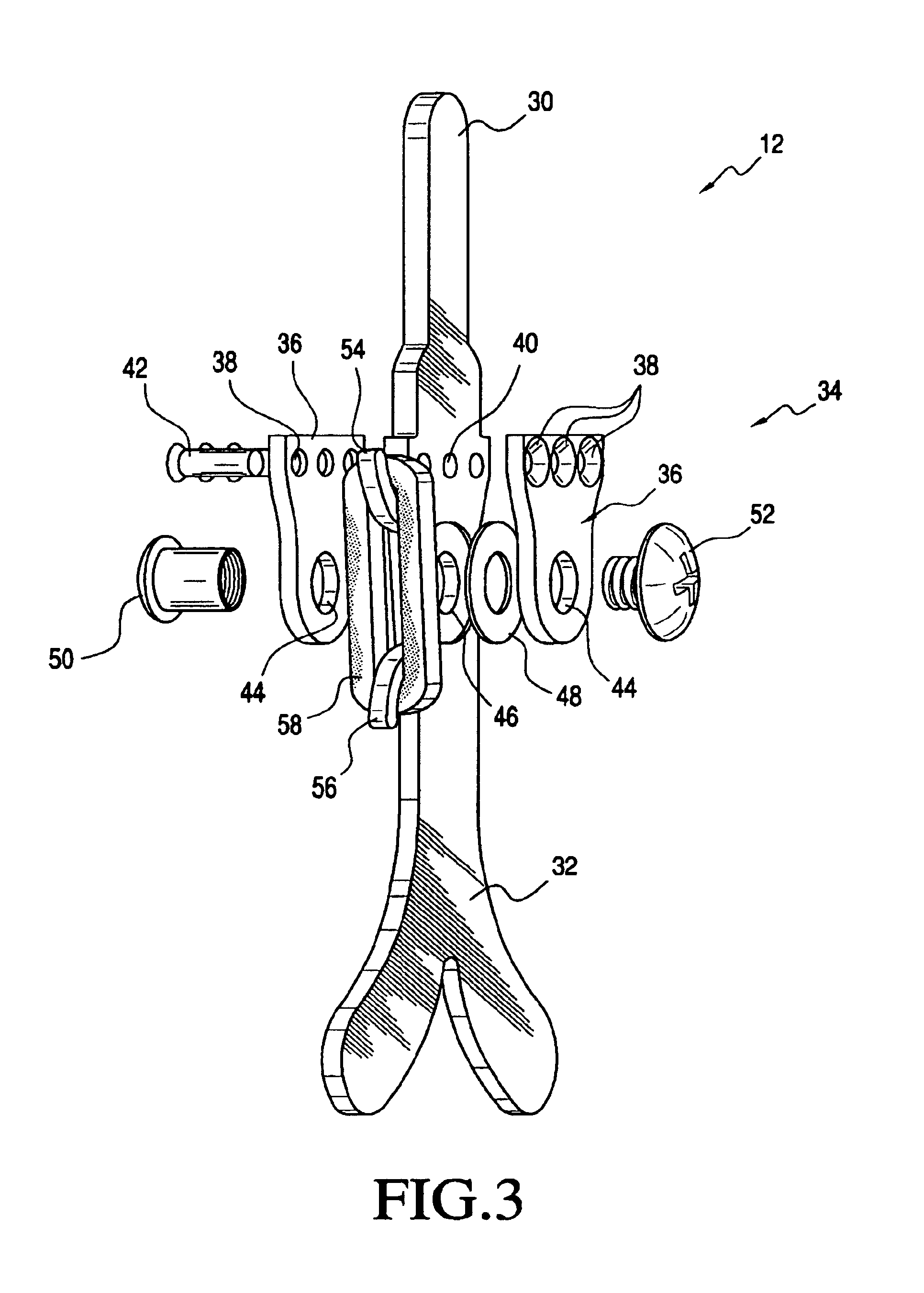
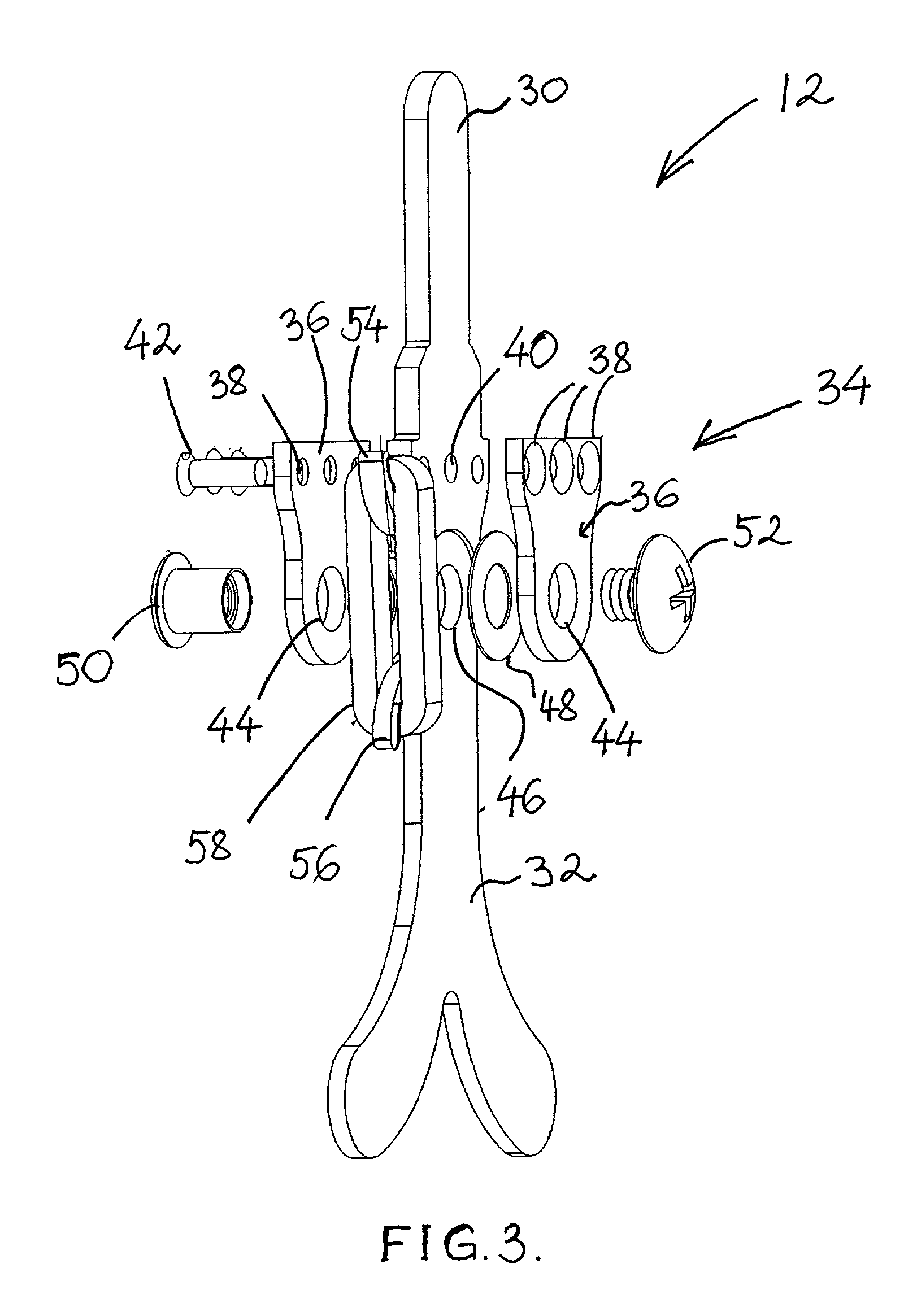
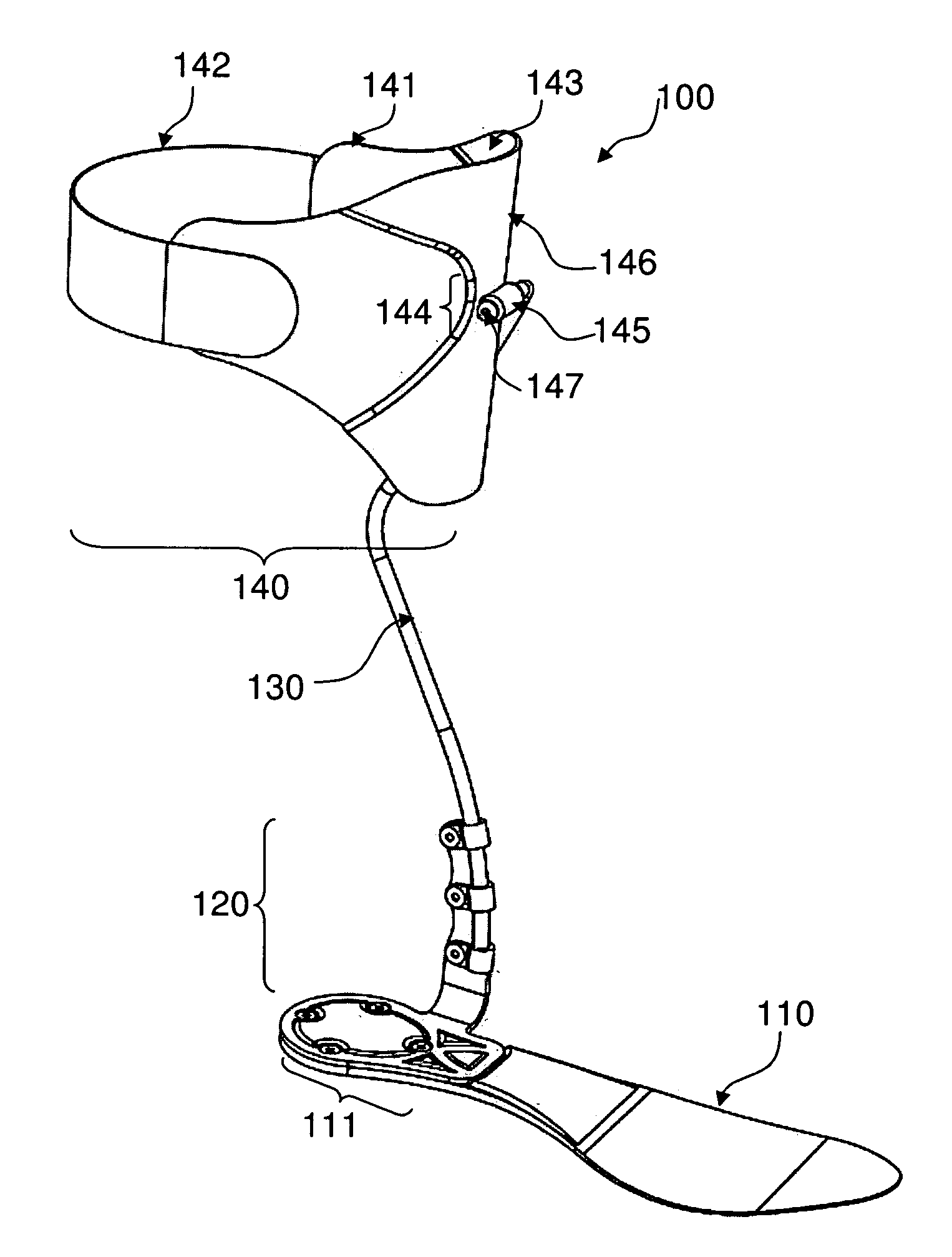
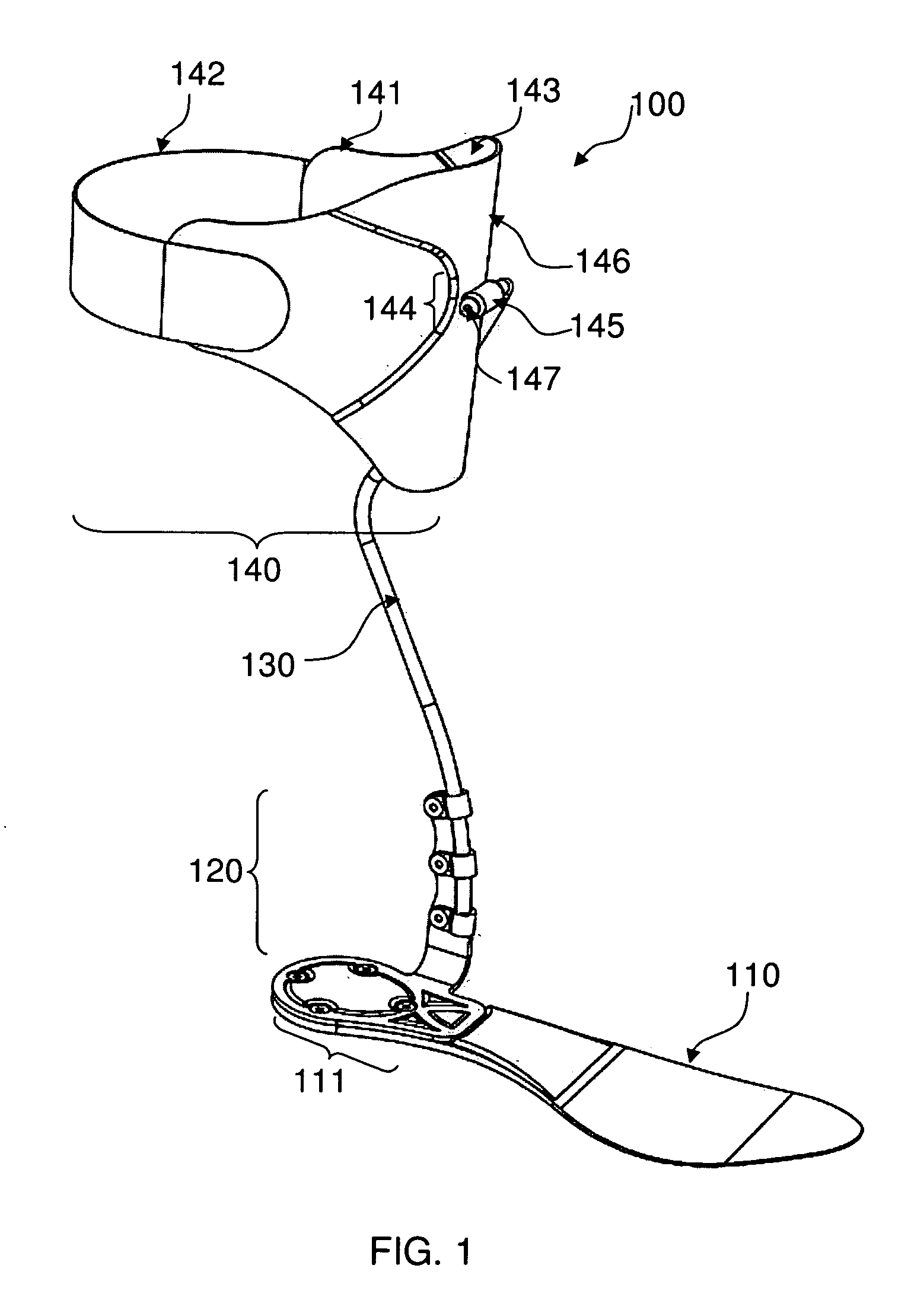
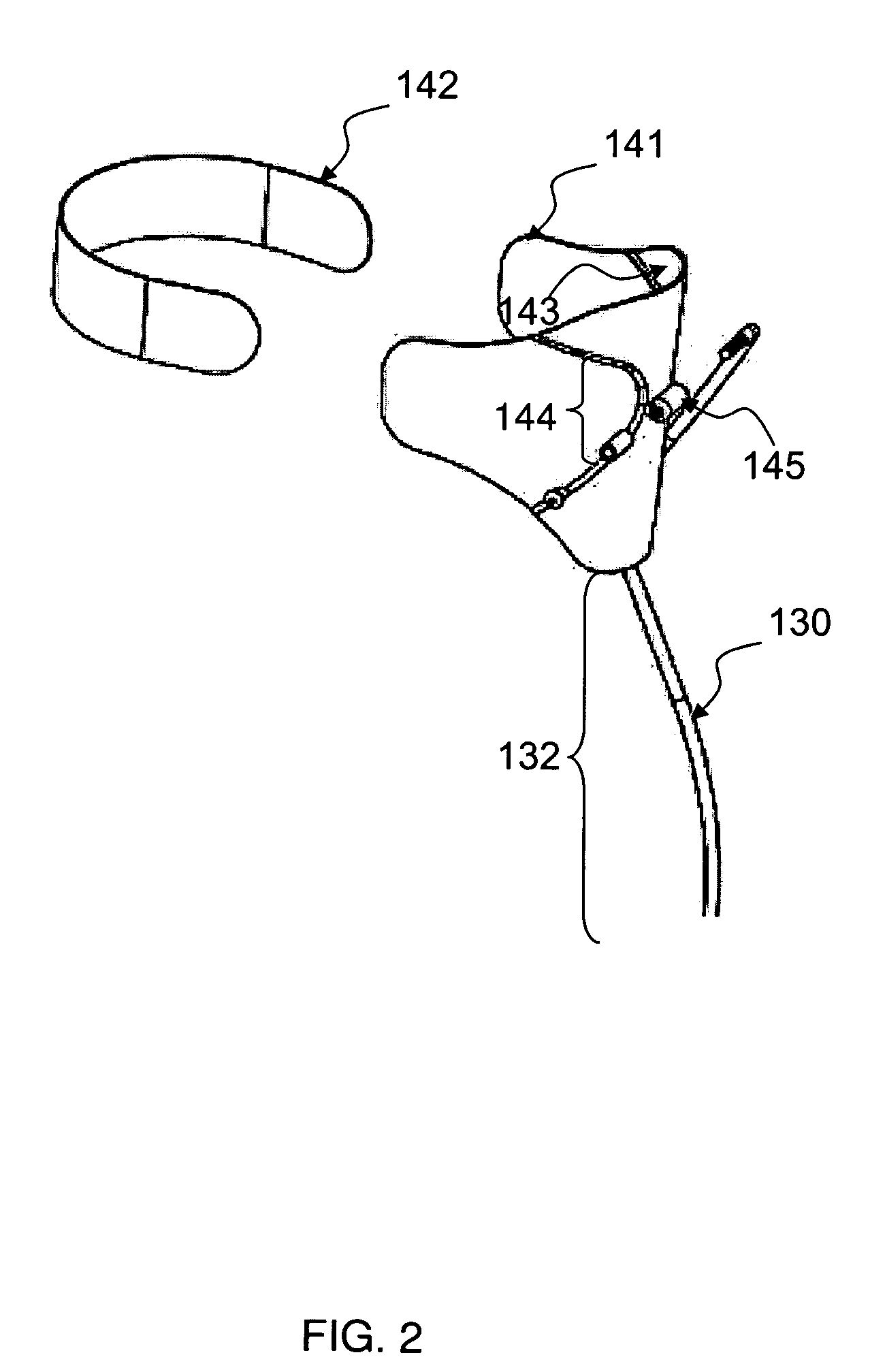
Tension assisted ankle joint and orthotic limb braces incorporating same
An improved limb brace joint includes a band that operates in tension to rotationally bias first and second longitudinal members of the joint. The band of the joint biases the rotation of the members to provide a dorsiflexion and / or plantarflexion assist when used in an ankle foot orthosis.
Owner:TOWNSEND IND INC
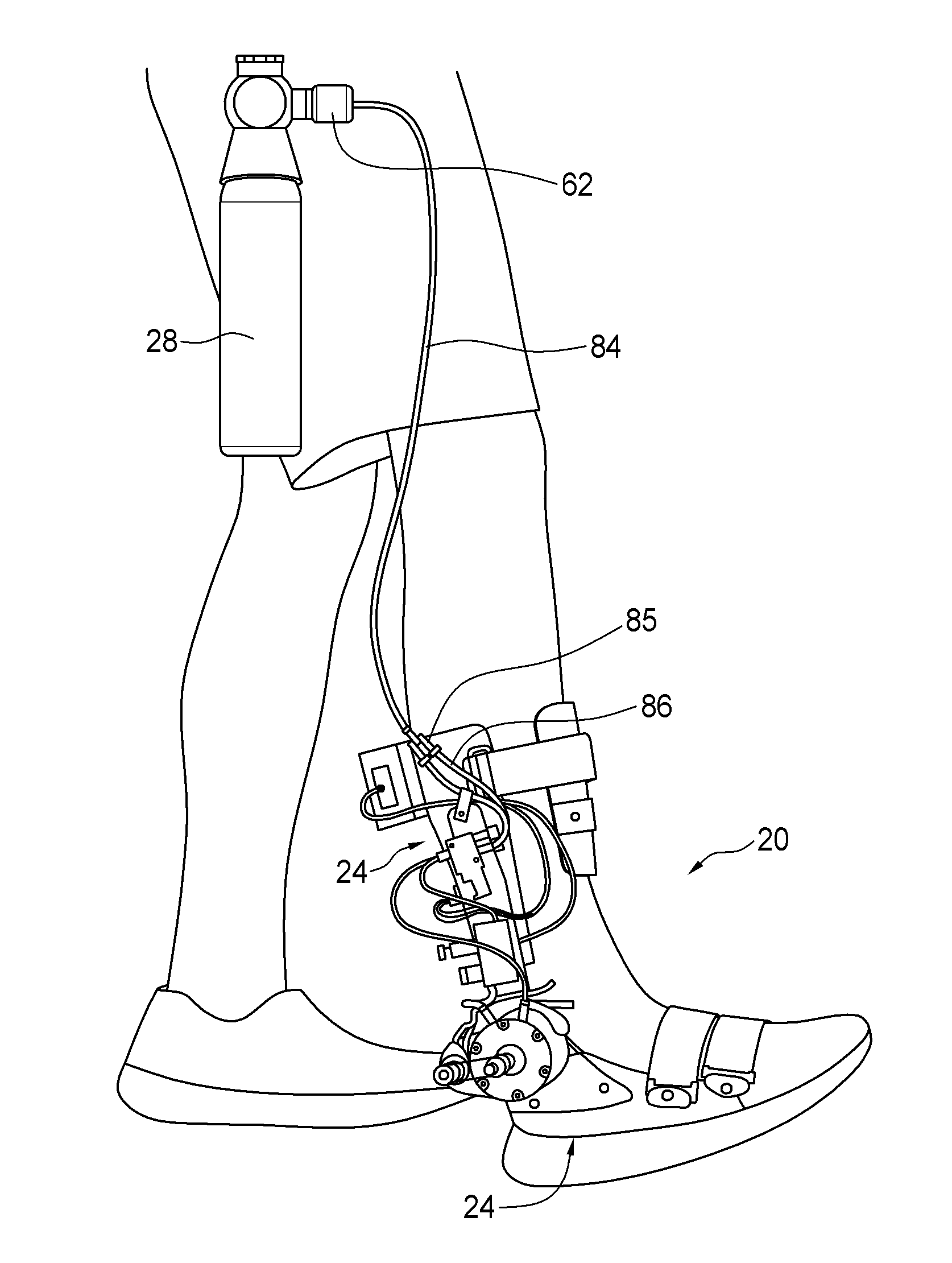
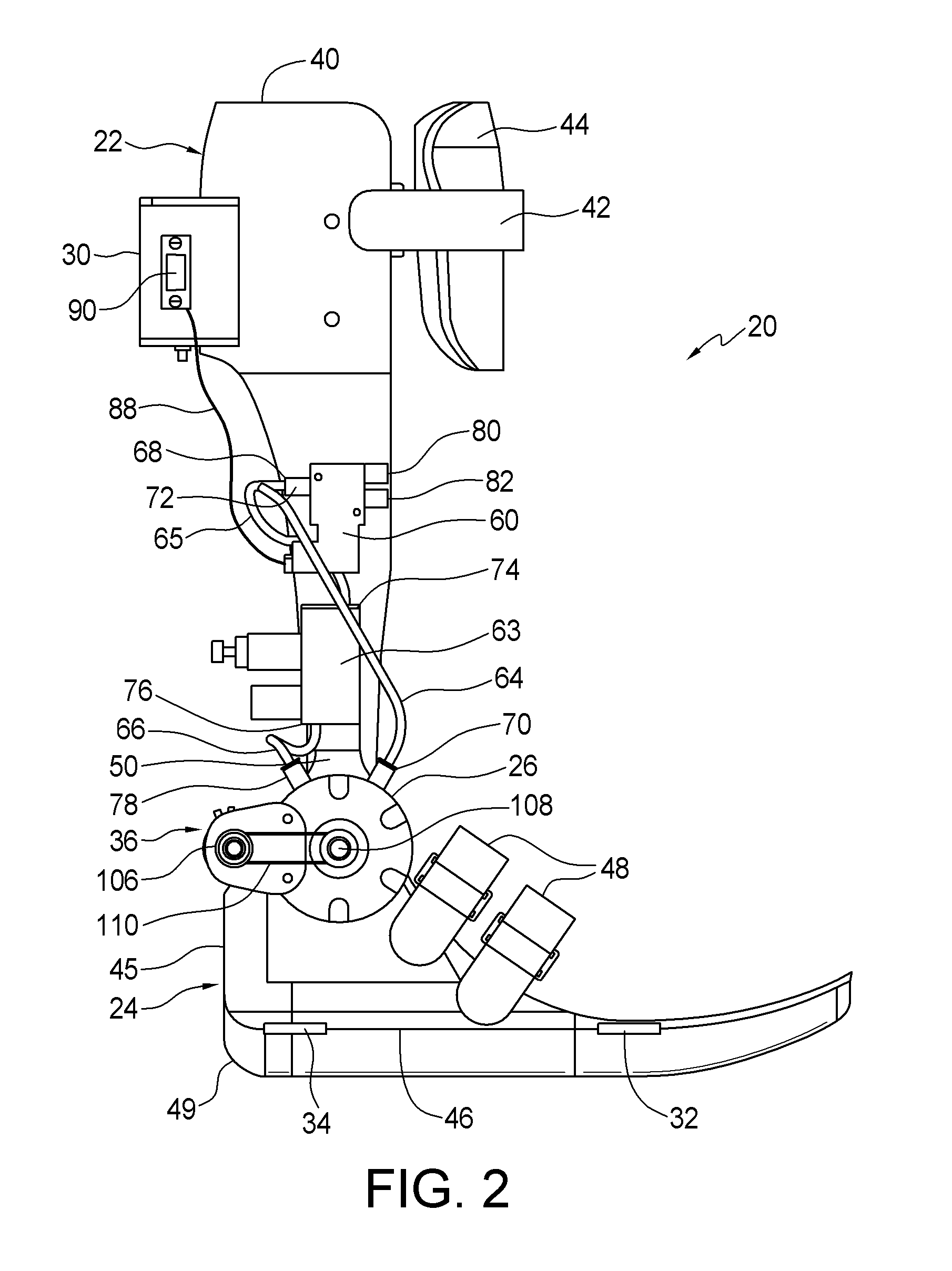
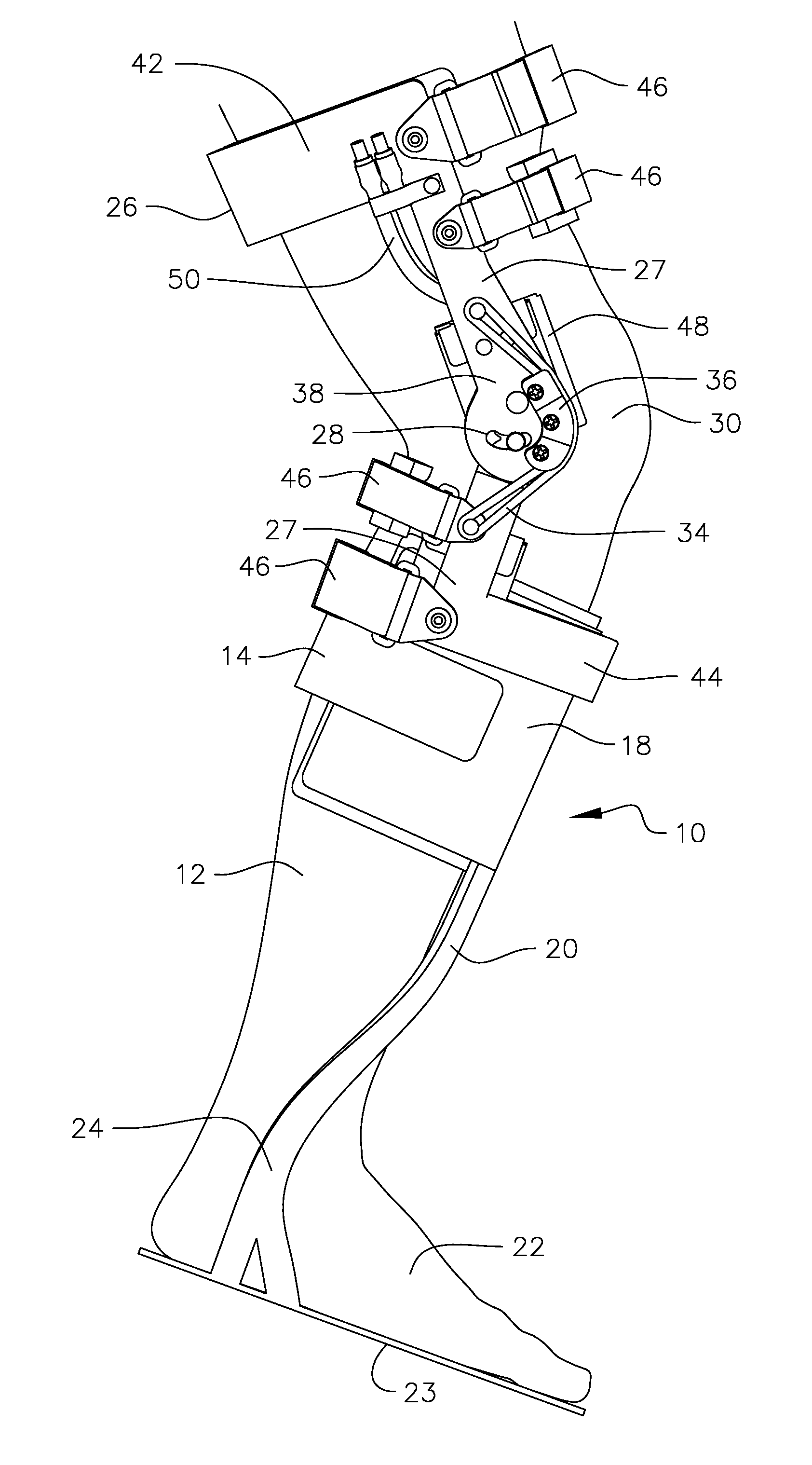
Portable active pneumatically powered ankle-foot orthosis
A portable active fluid-powered ankle foot orthosis. A lower leg mount and a foot bed are pivotally coupled at or proximate to an ankle position. A fluid powered rotary actuator is configured to receive power from a wearable fluid power source and provide controlled force and resistance to aid or inhibit relative rotation of the foot bed and the lower leg mount. An integral controller is provided for receiving data from sensors and controlling the fluid powered rotary actuator to actively assist gait of a user.
Owner:HSIAO WECKSLER ELIZABETH T +6
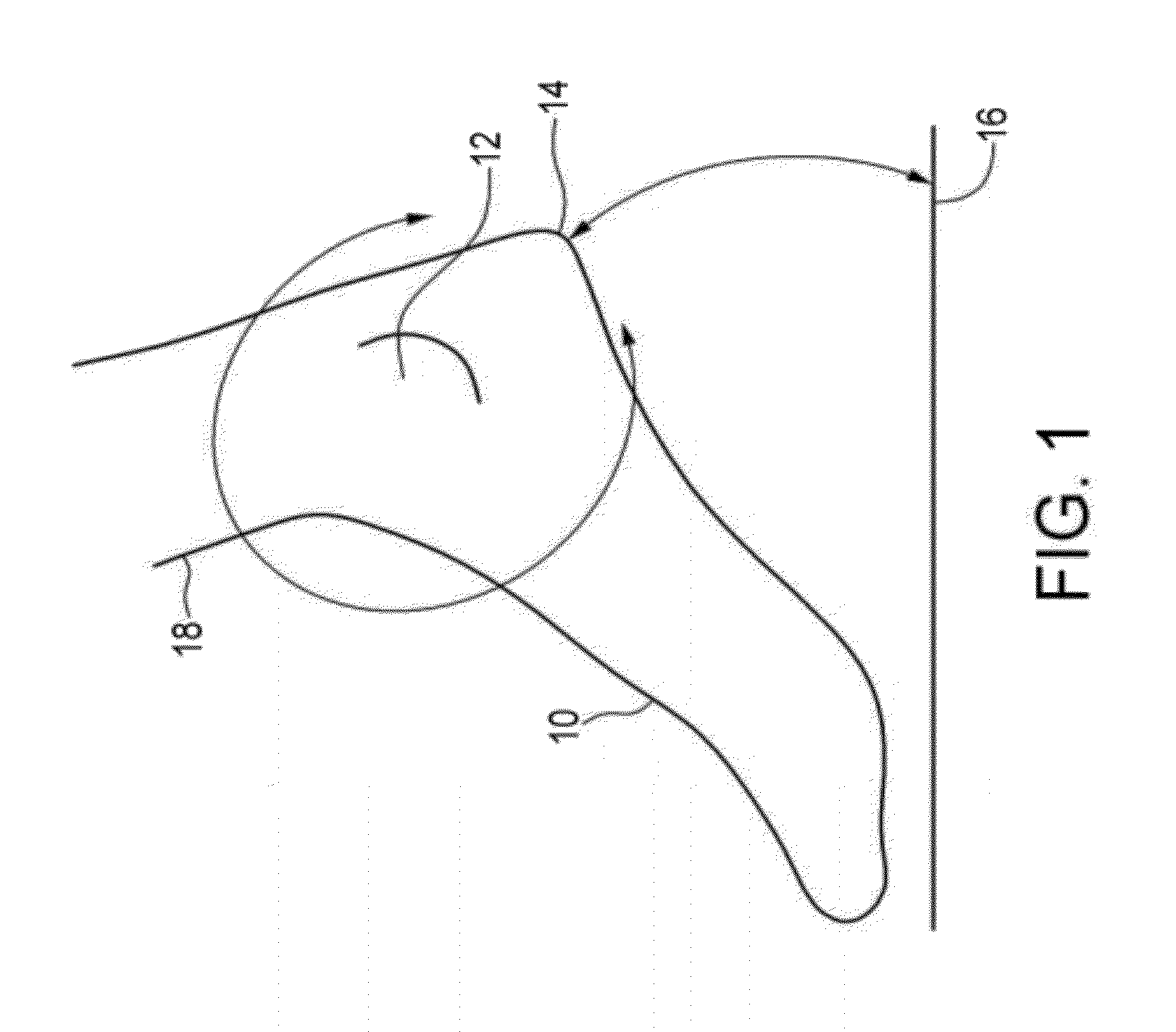
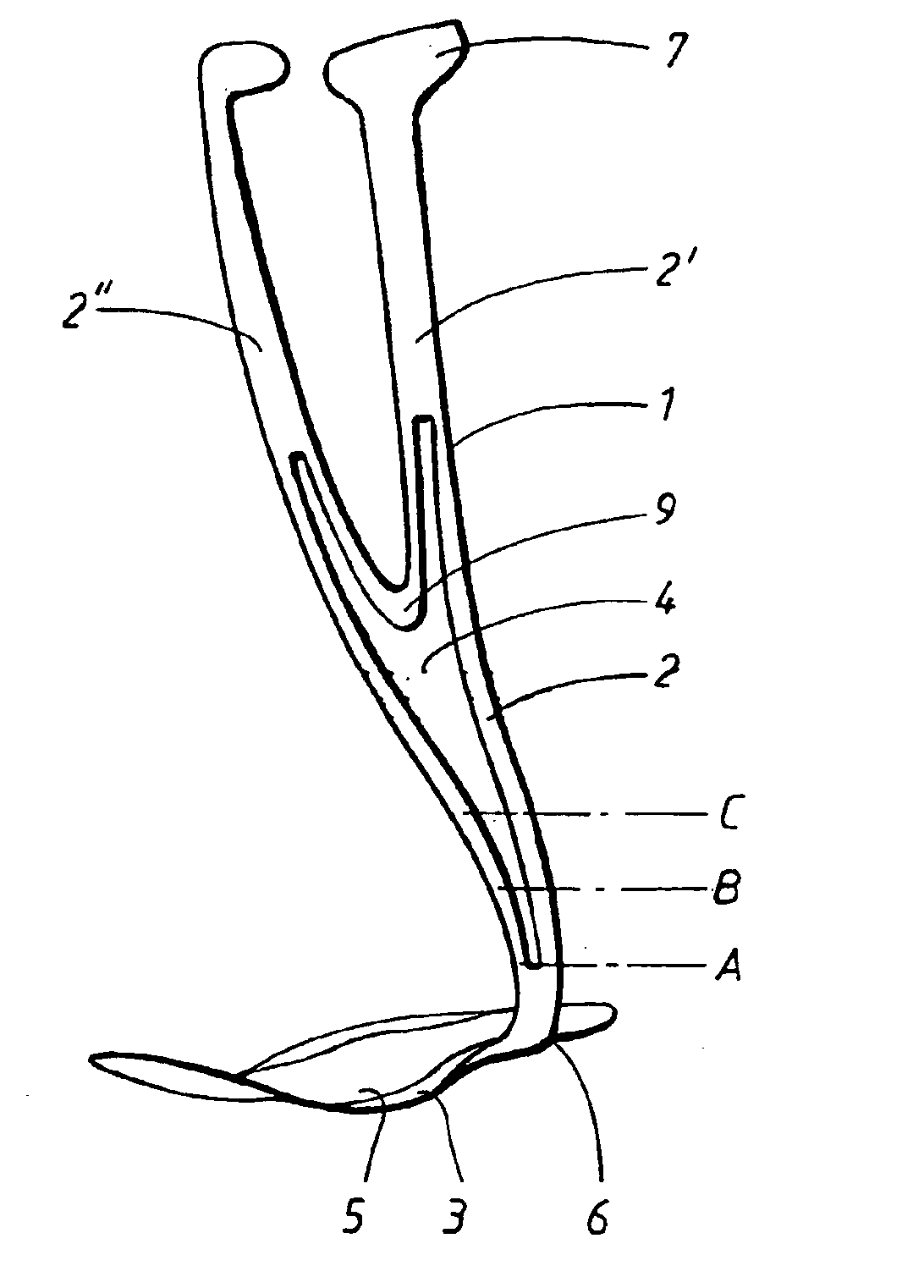
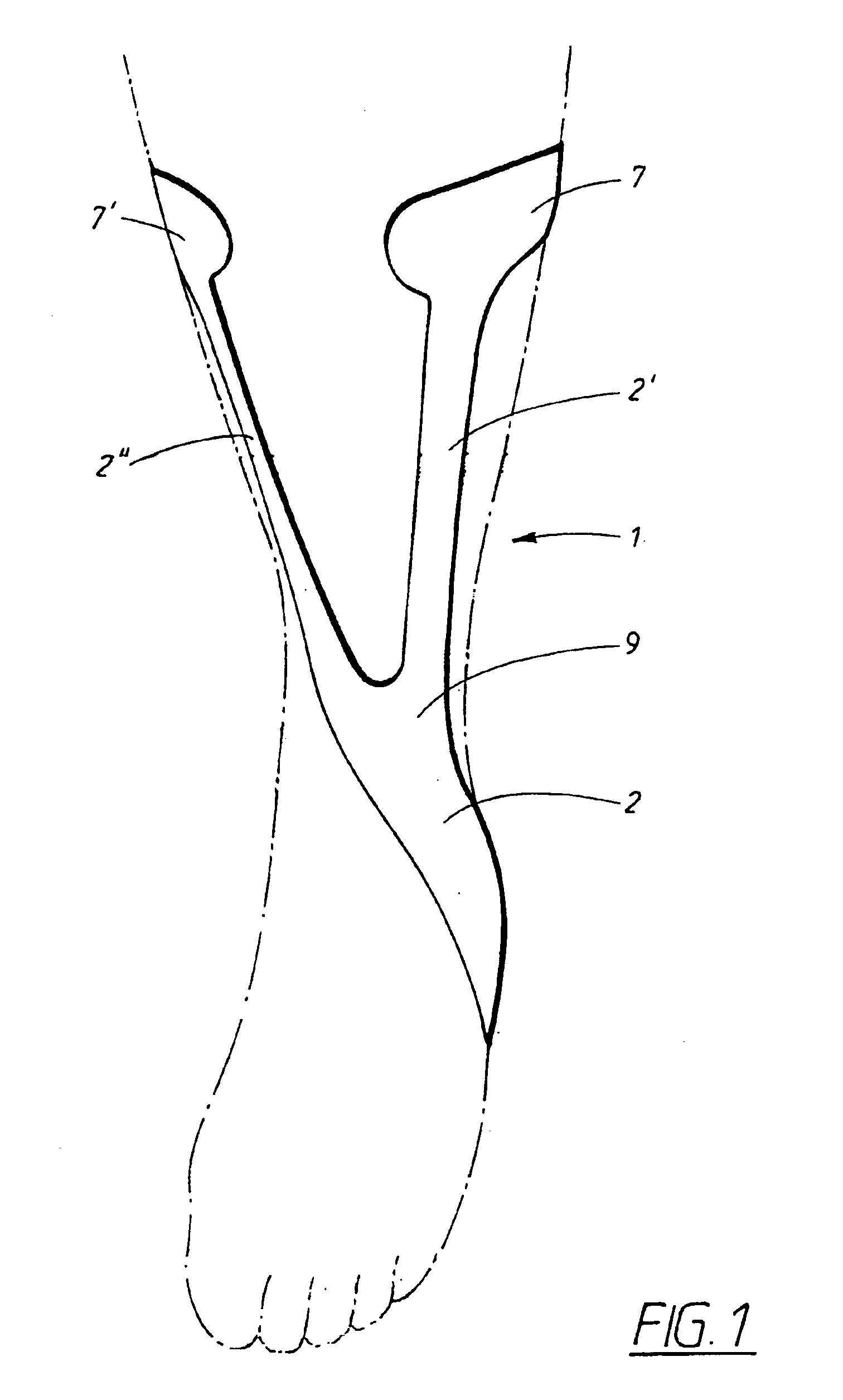
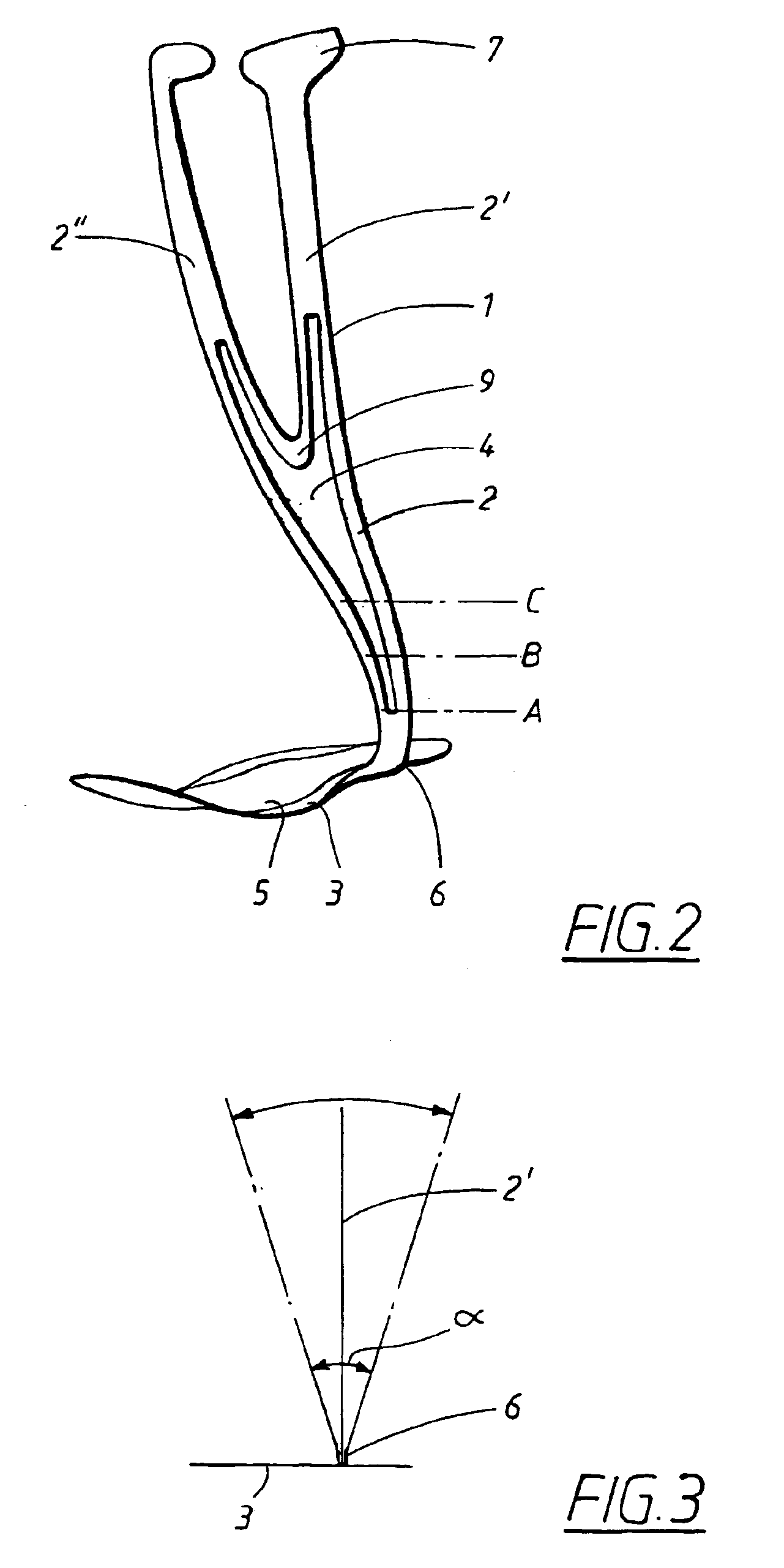
Ankle-foot orthosis
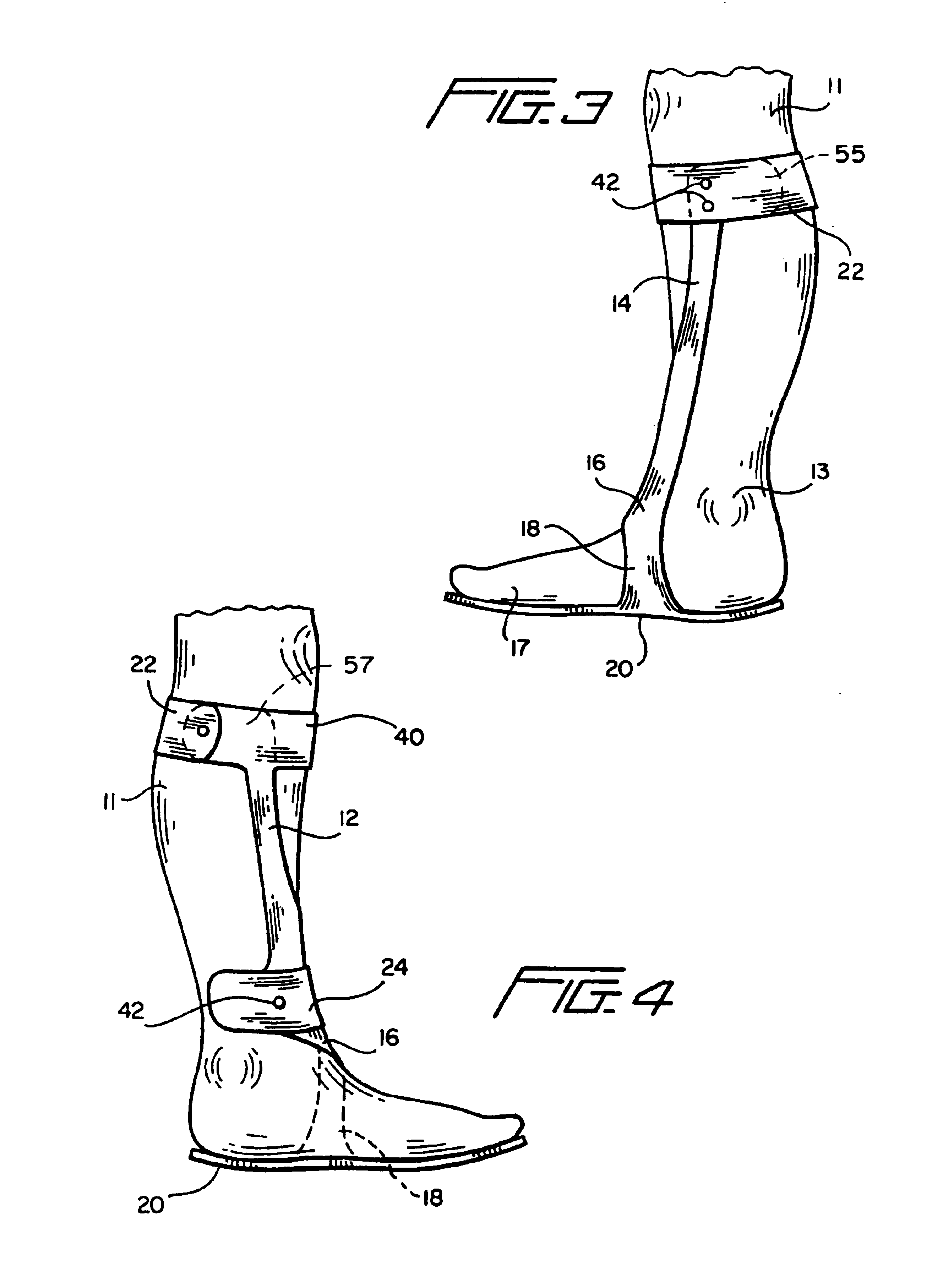
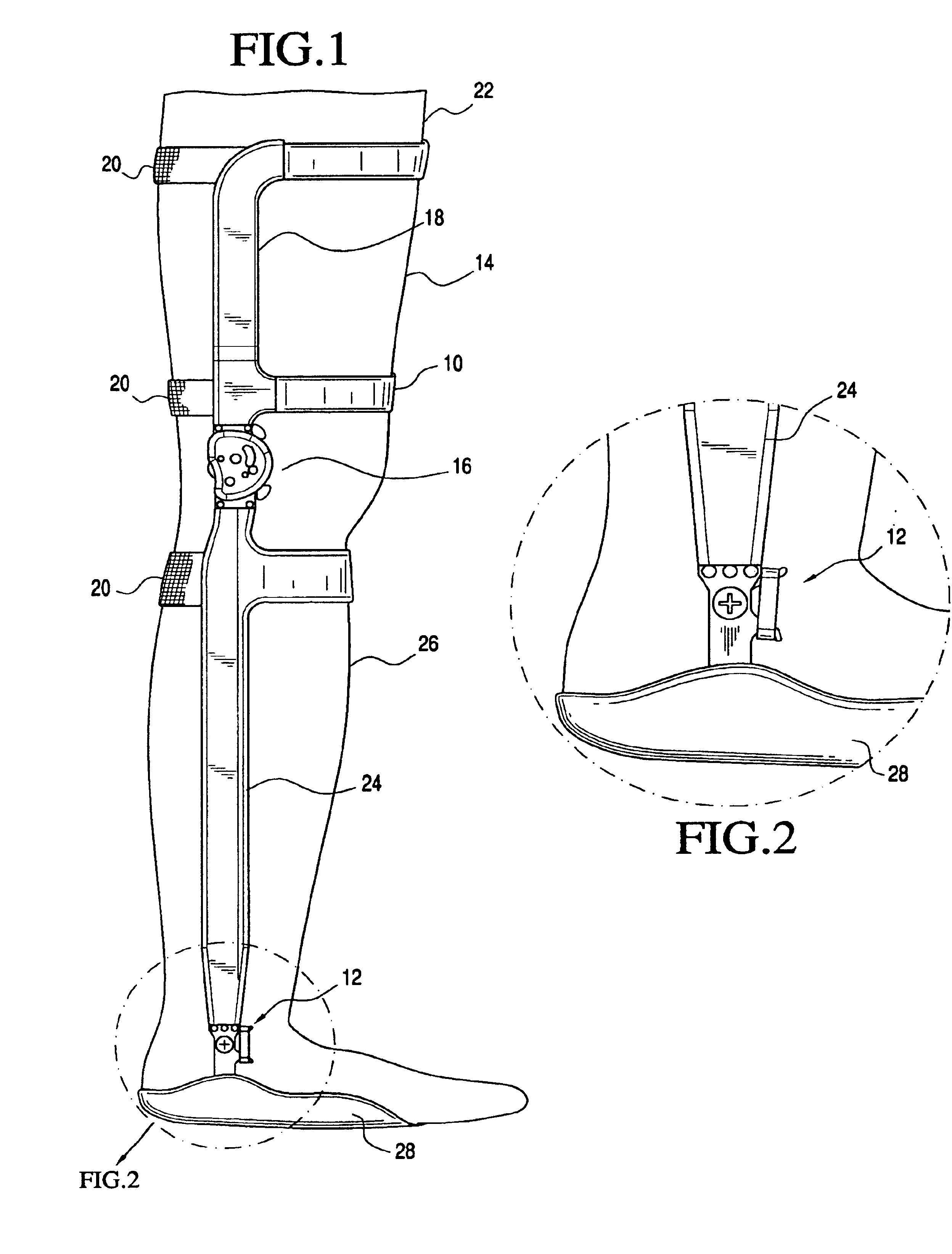
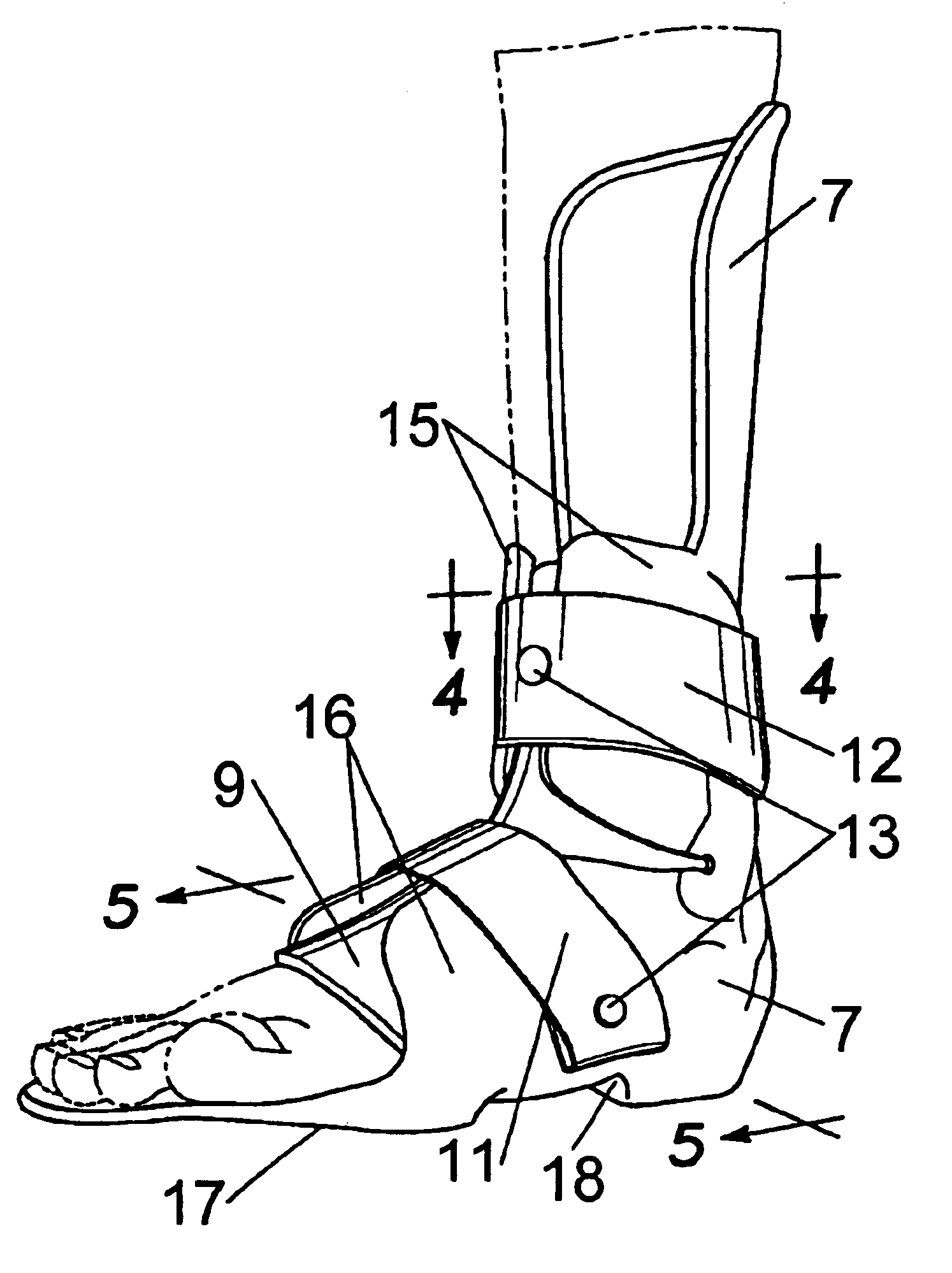
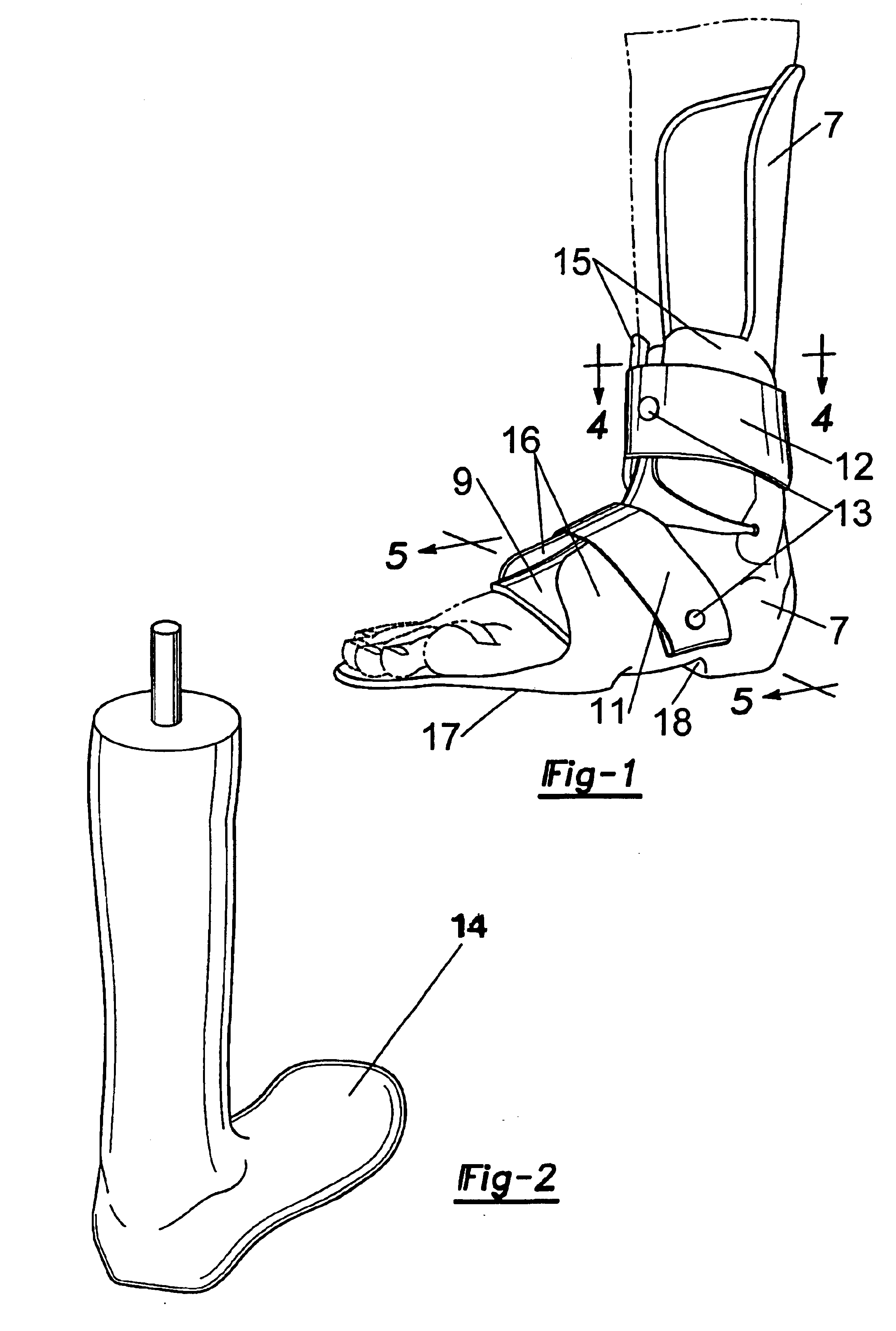
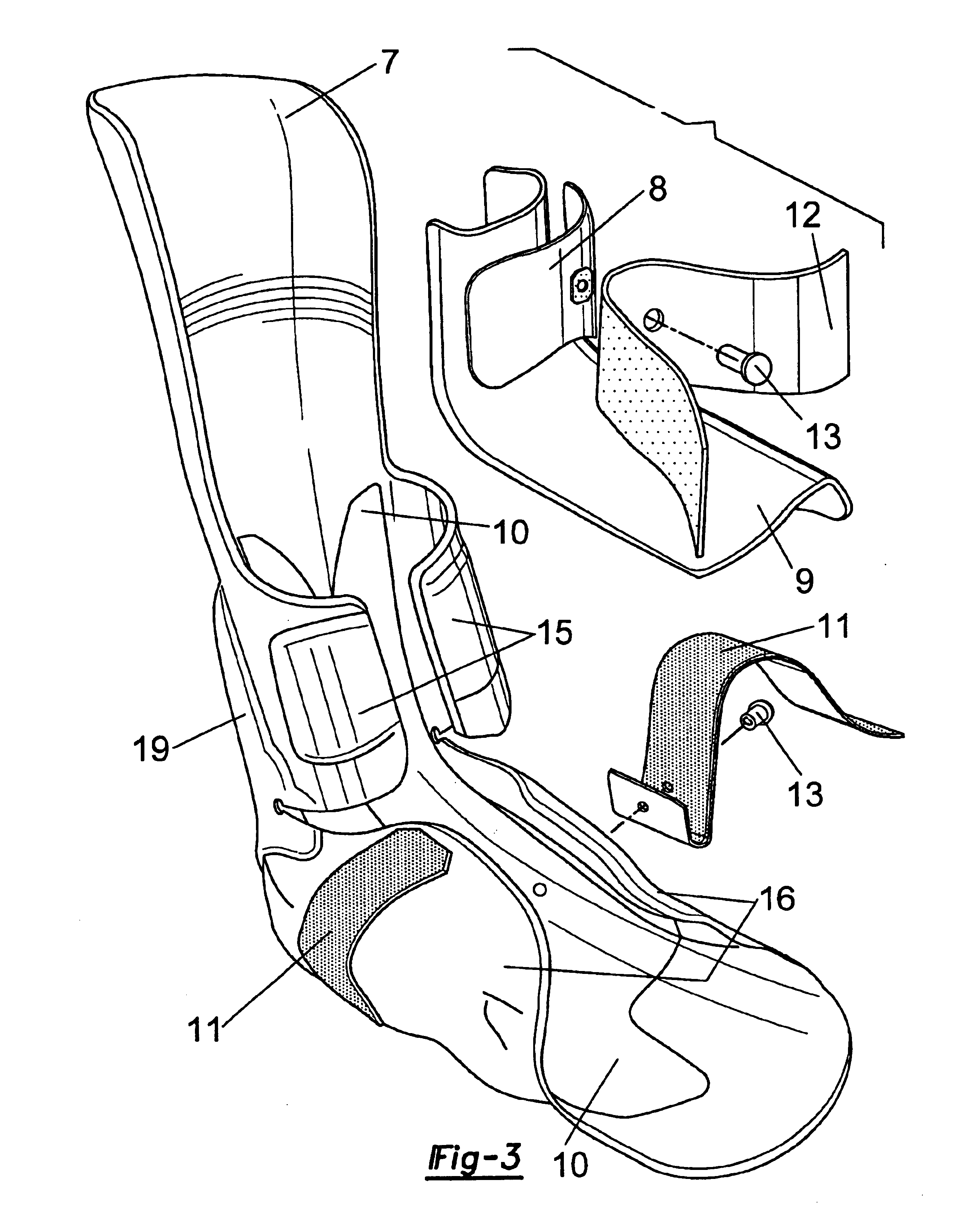
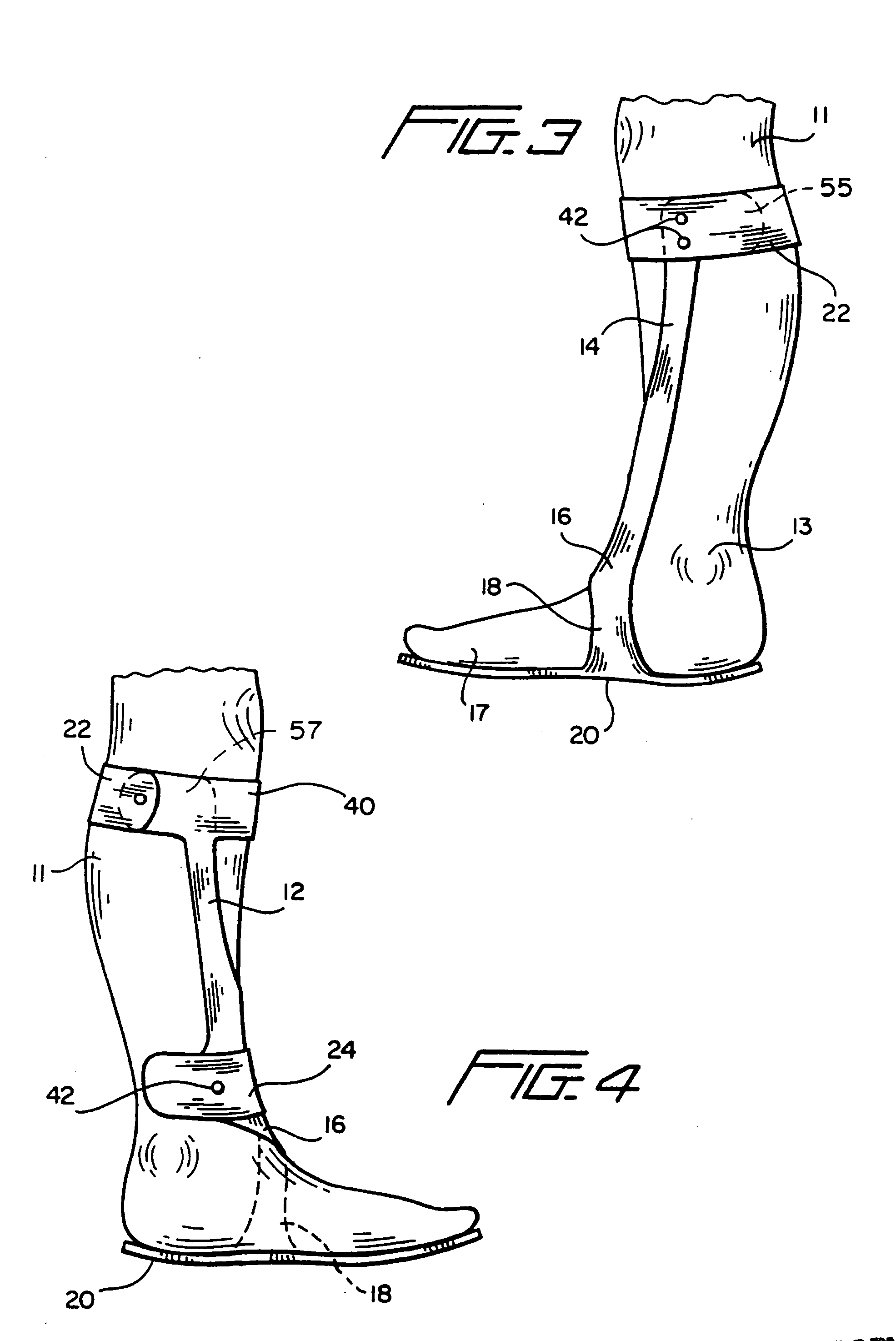
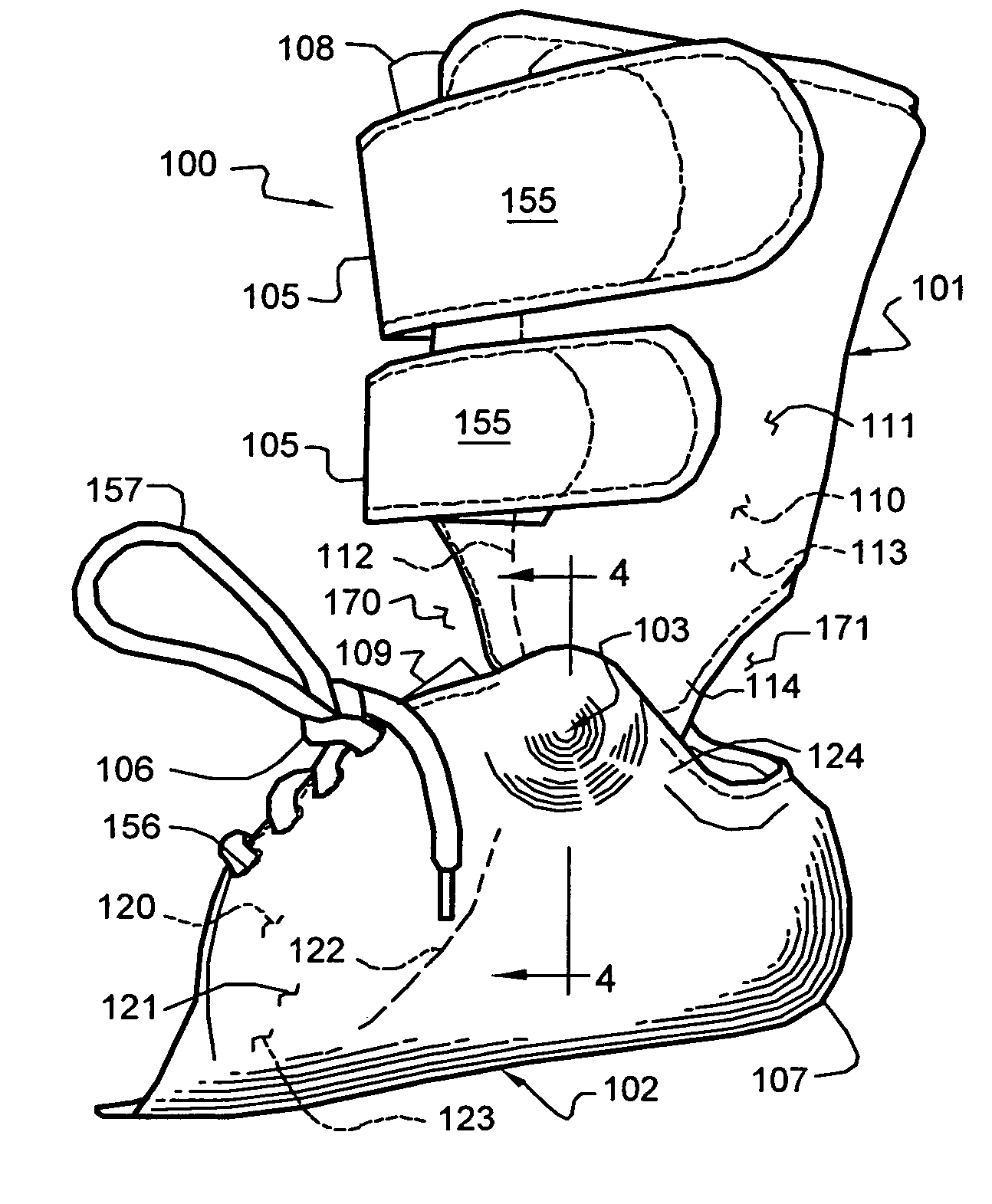
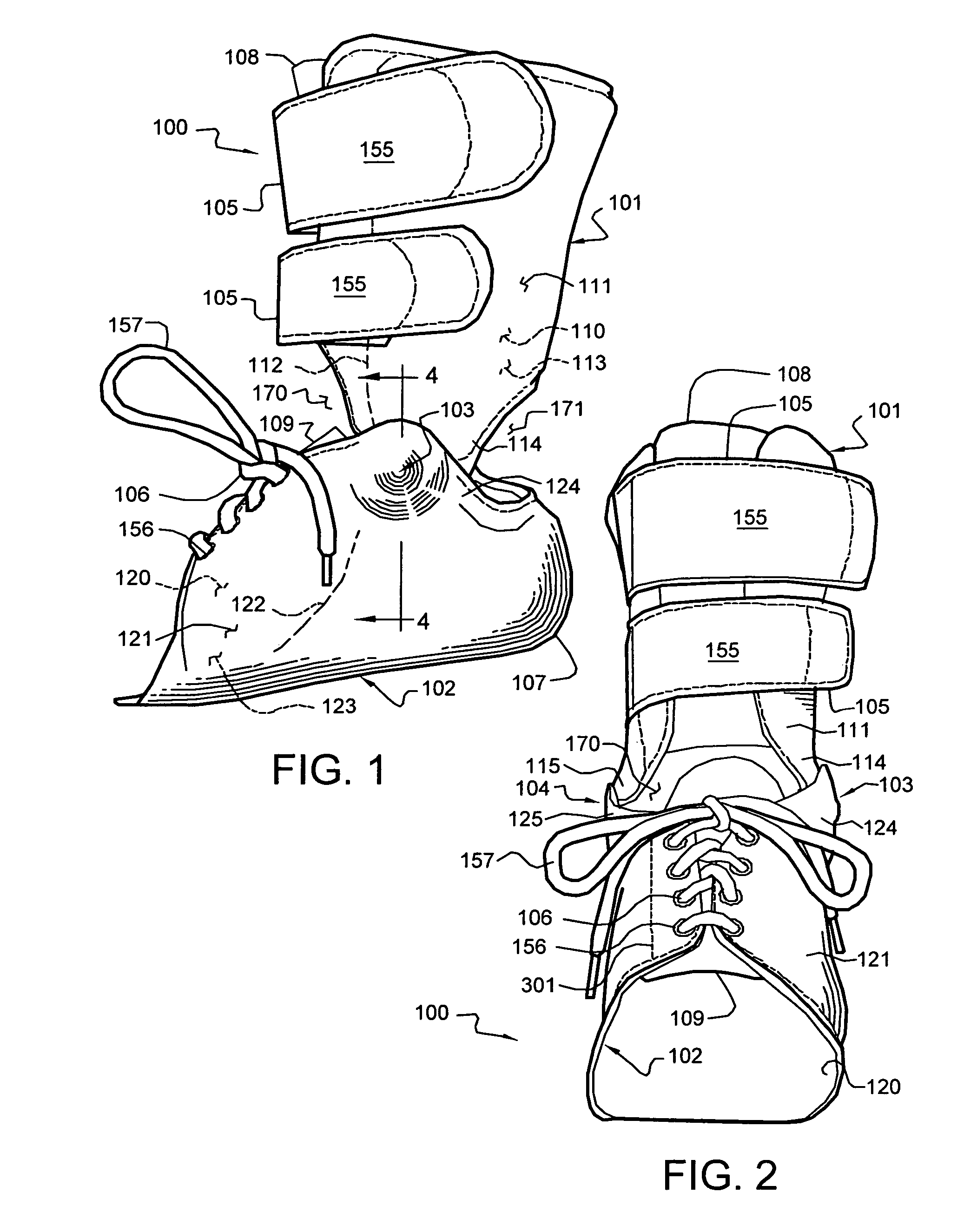
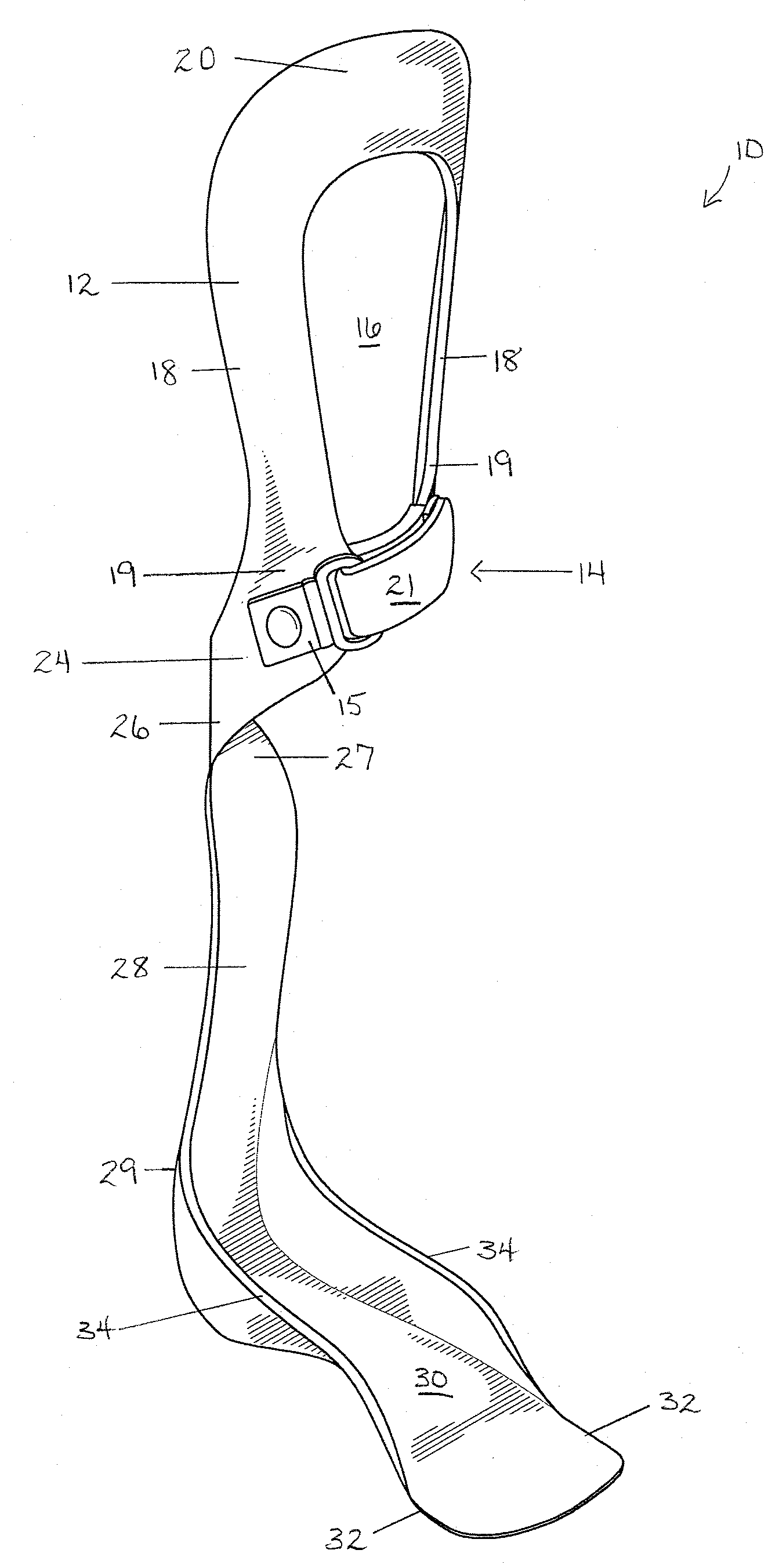
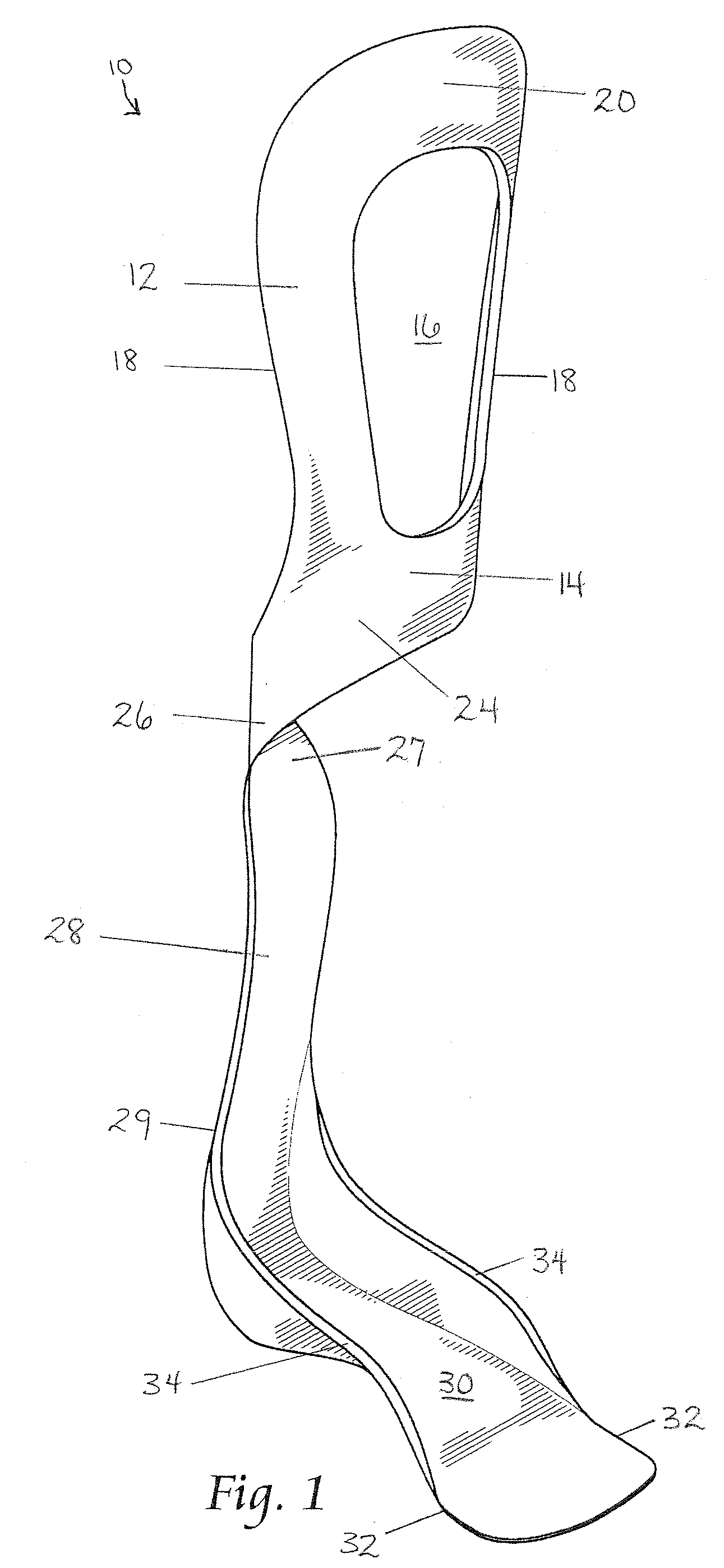
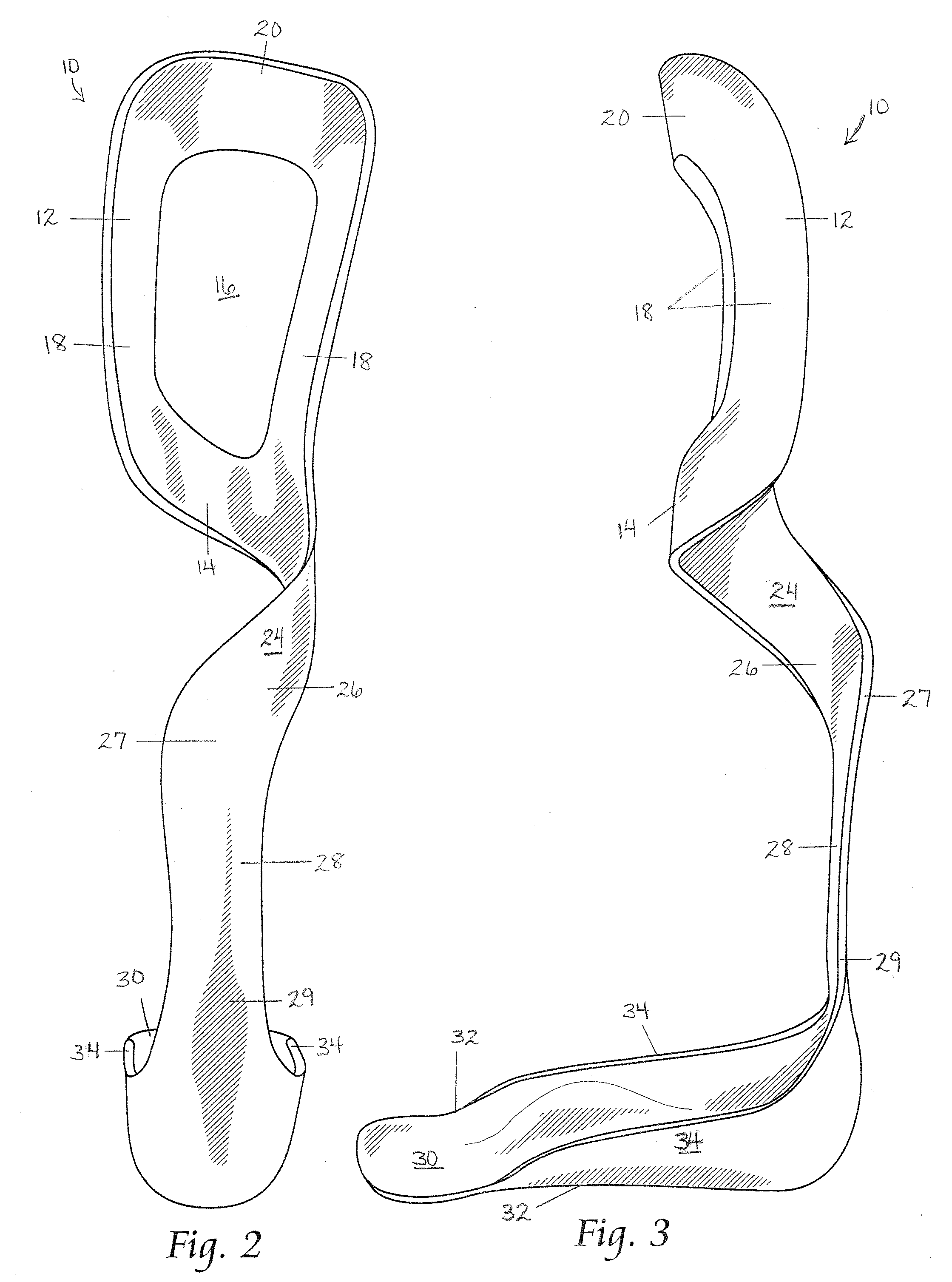
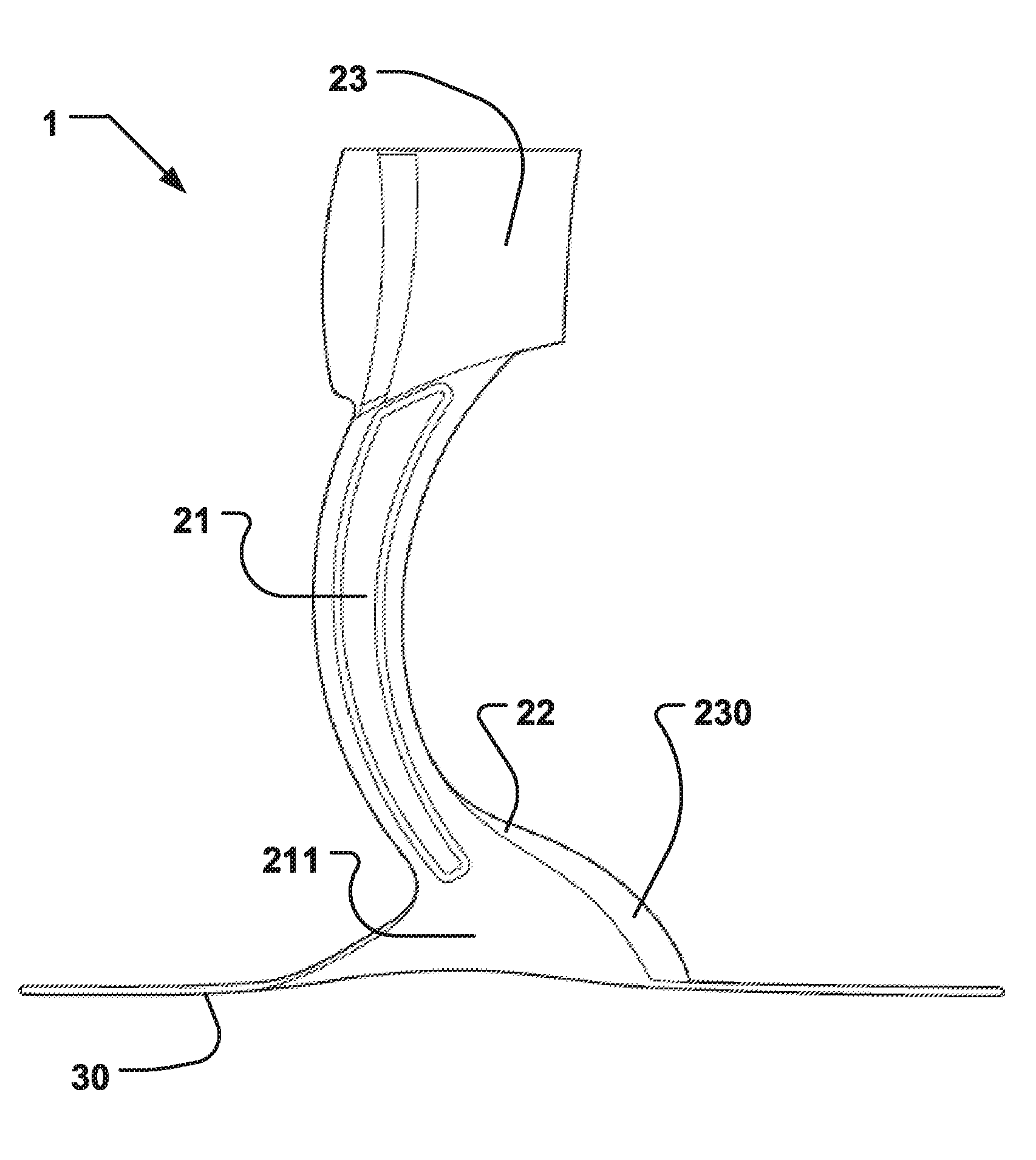
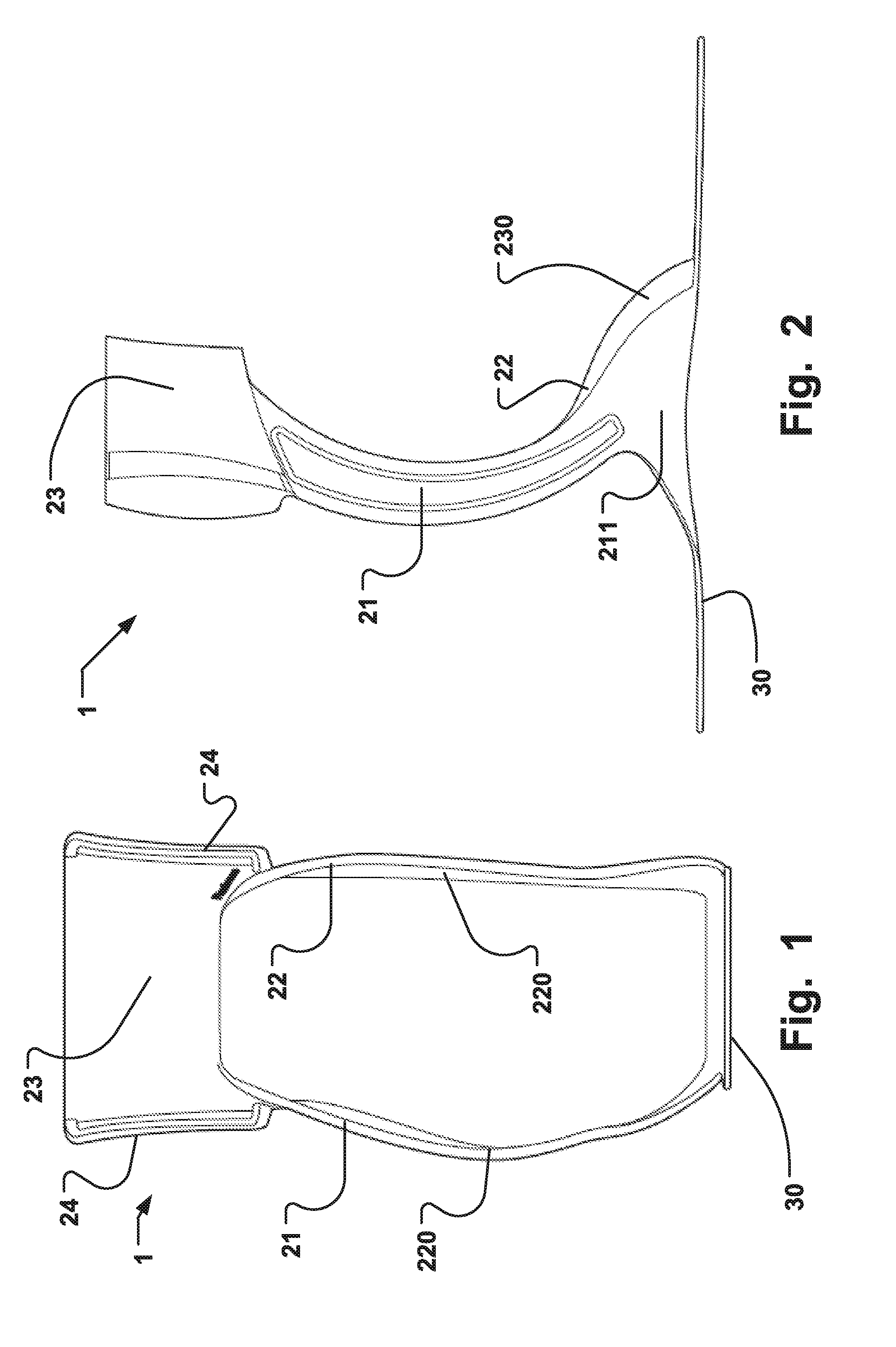
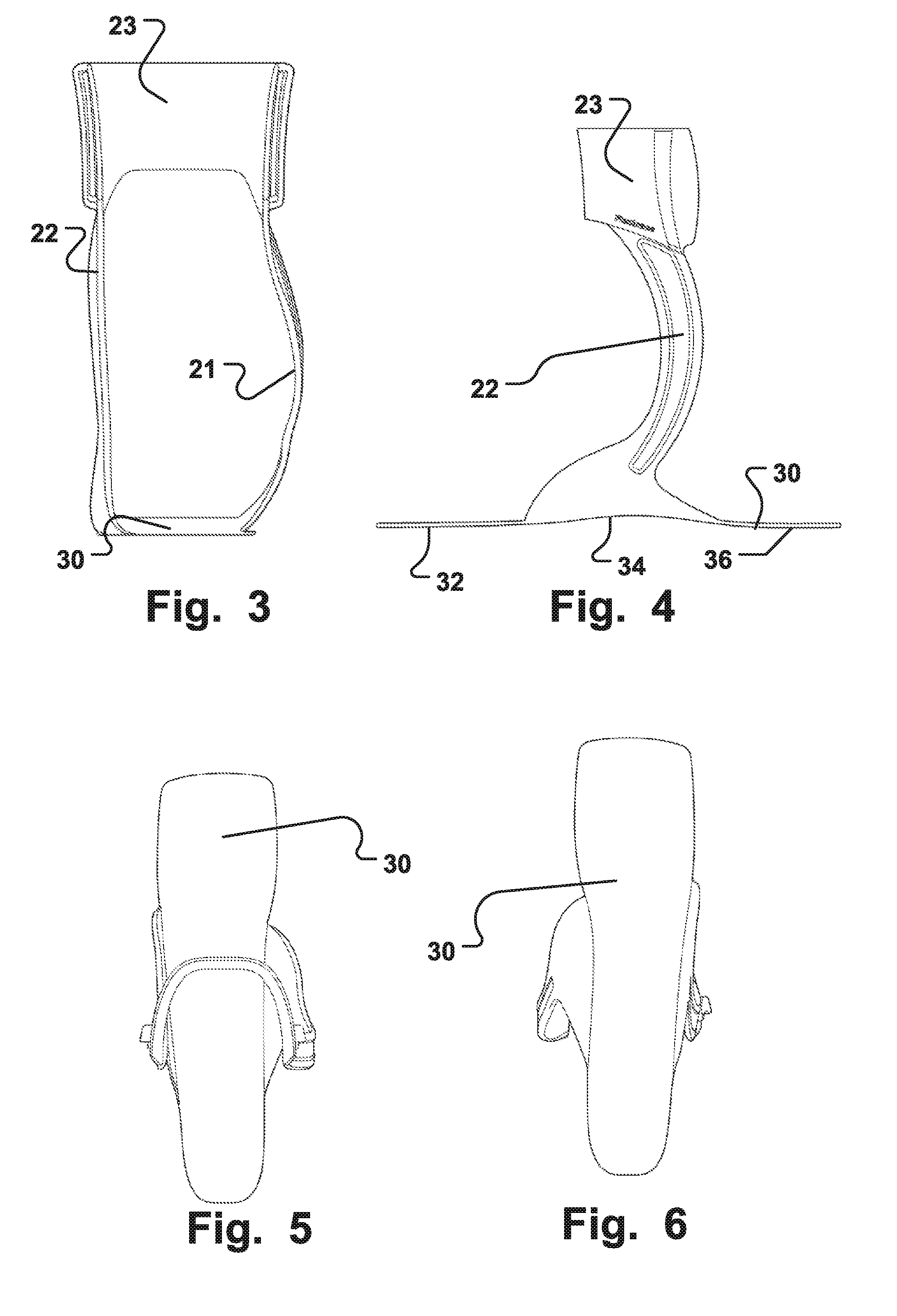
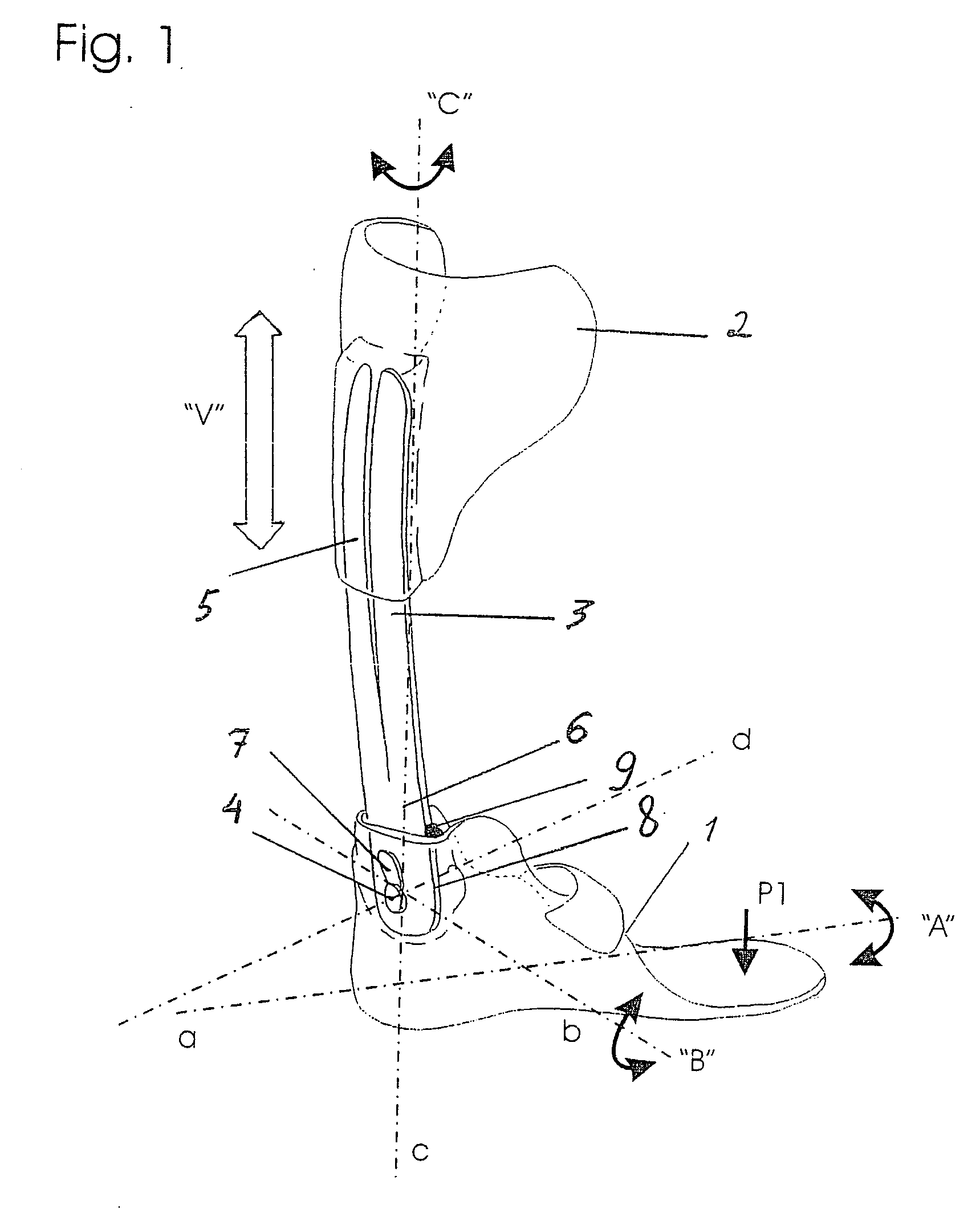
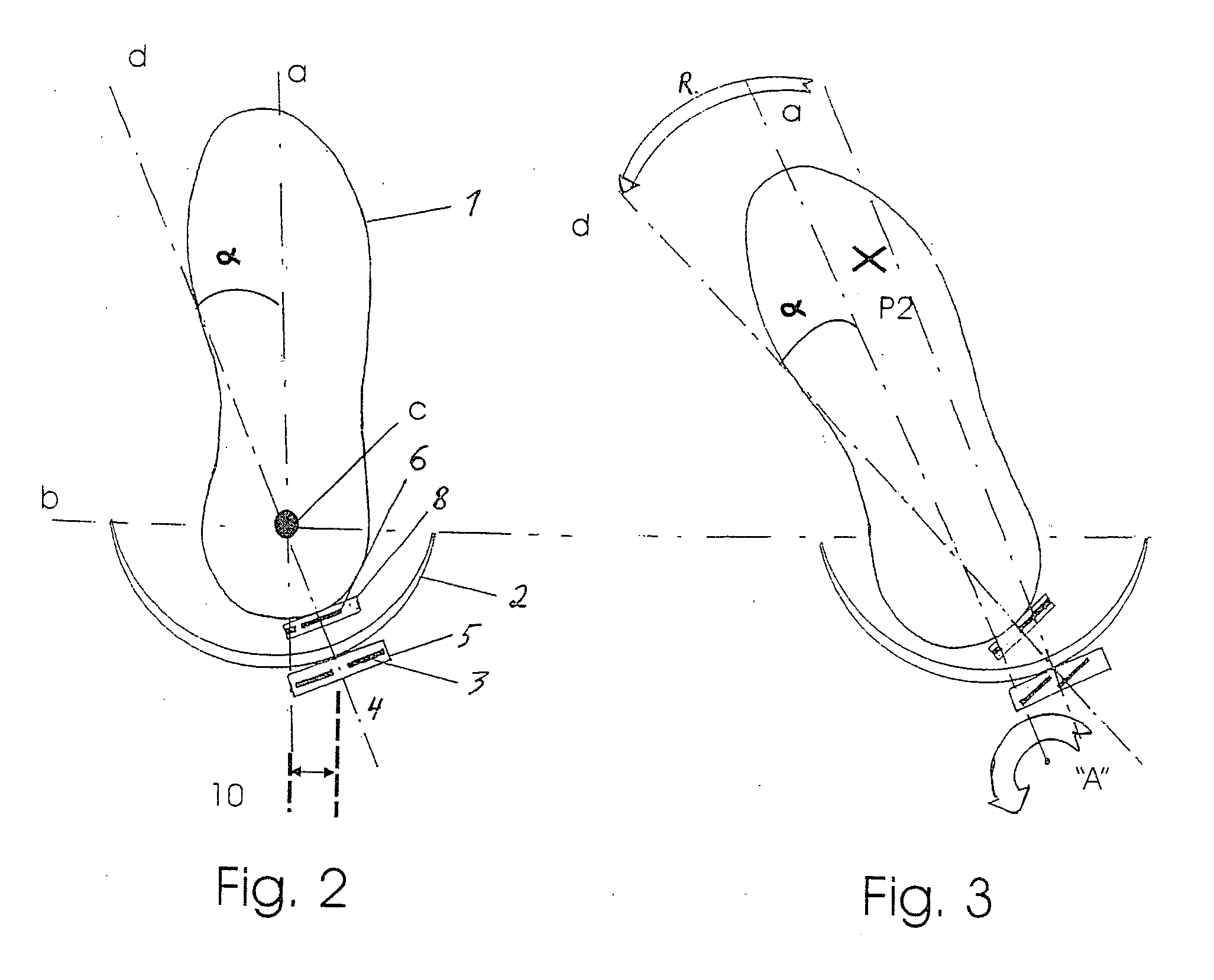
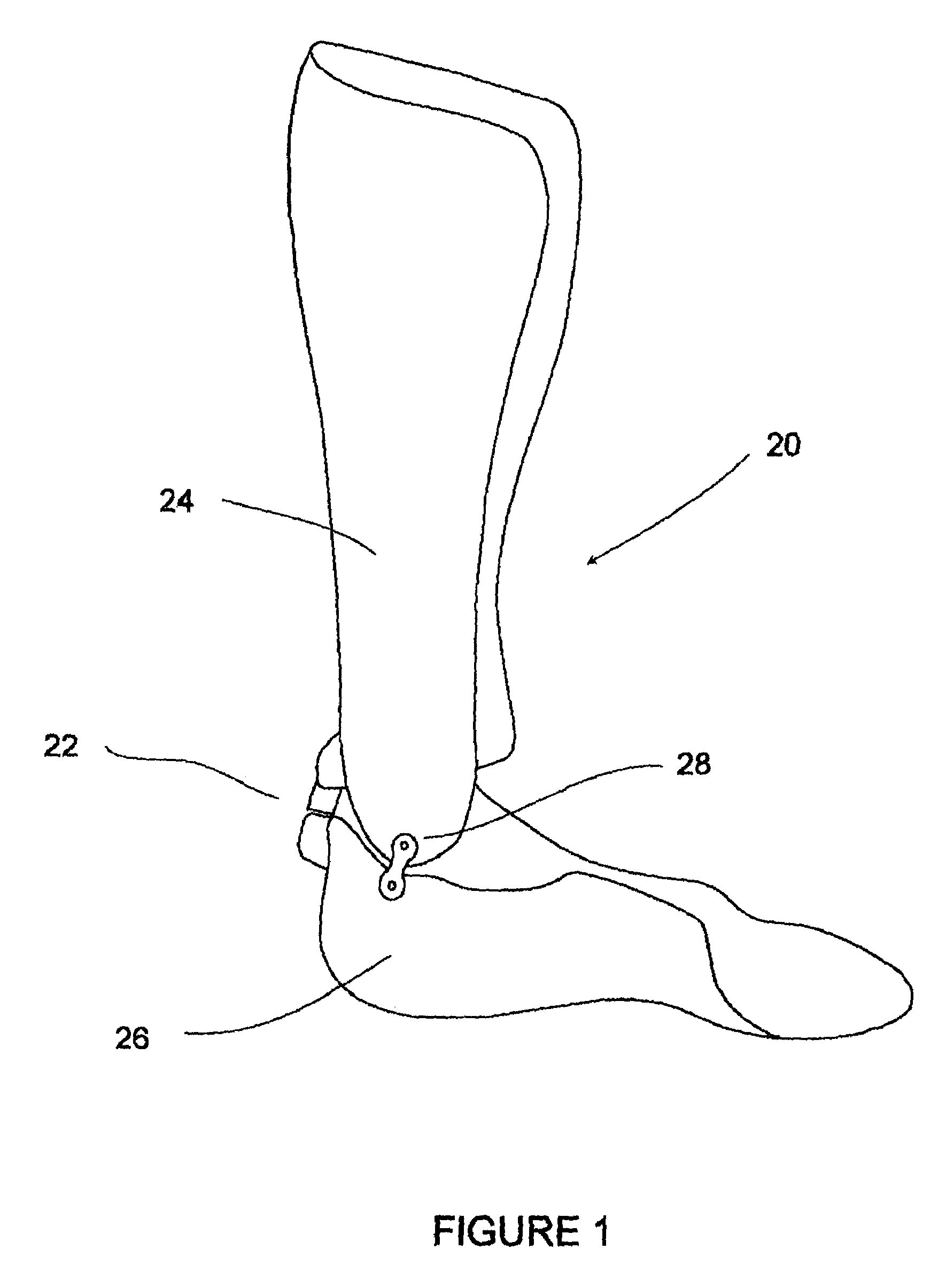
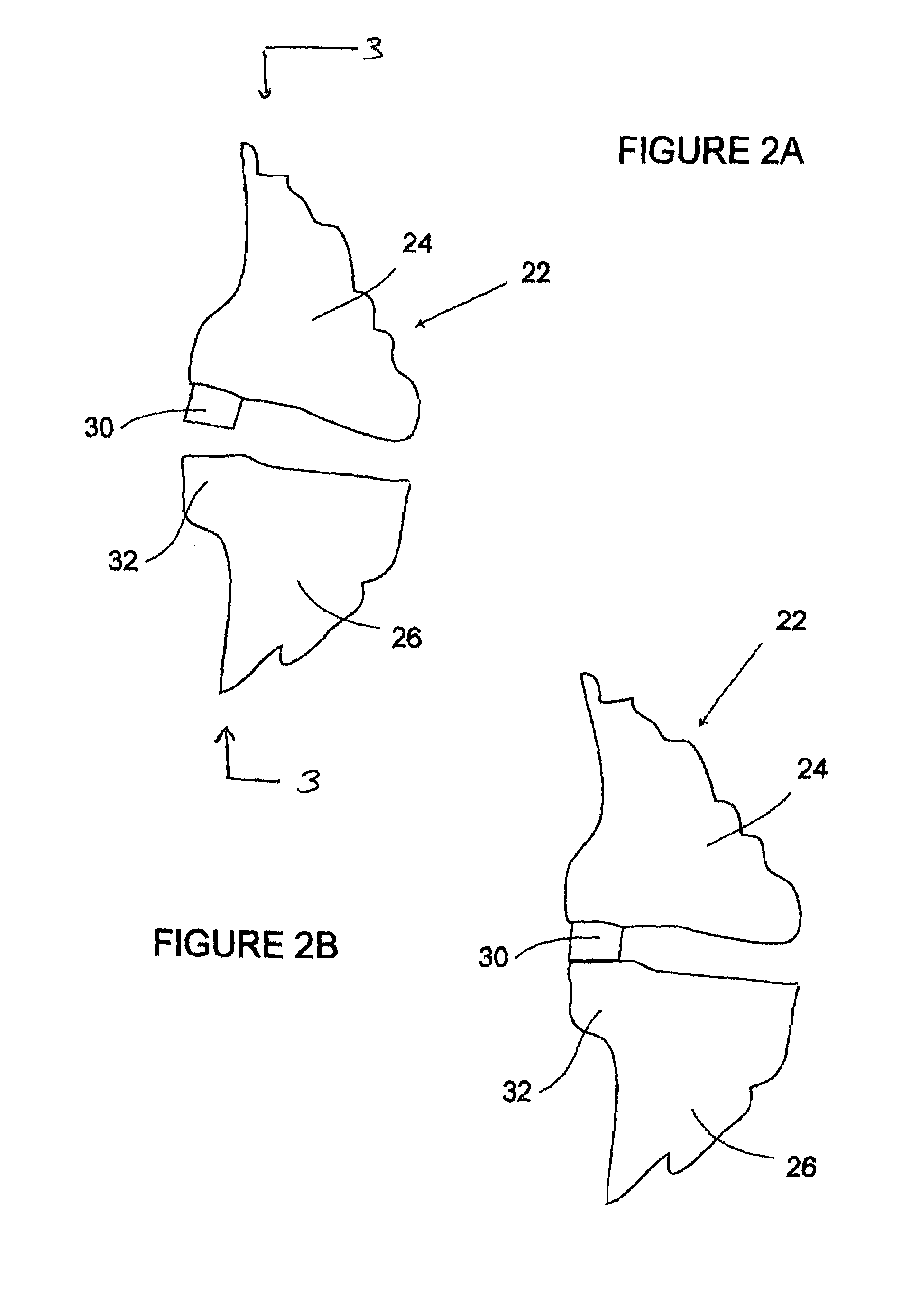
The present invention provides an ankle-foot orthosis (1) that comprises a strut (2) extending over the front of the lower leg and anterior of the lateral ankle, a foot plate (3) extending beneath the sole of the foot and a fastening means for the fastening the orthosis (1) to the leg. The strut comprises a bifurcation zone (9) and two strut branches (2′, 2″) arranged to extend on the outside of the lower leg on each side of the tibia. Thus the present invention provides an orthosis (1) with high resistance against wear and tear, high wear comfort for the patient and an orthosis (1) enabling an almost normal gait.
Owner:CAMP SCANDINAVIA
Portable active fluid powered ankle-foot orthosis
A portable active pneumatically-powered ankle foot orthosis. A lower leg mount and a foot bed are pivotally coupled at or proximate to an ankle position. A pneumatically powered rotary actuator is configured to receive power from a wearable fluid power source and provide controlled force and resistance to aid or inhibit relative rotation of the foot bed and the lower leg mount. Embedded sensors provide feedback from the device.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Articulated custom ankle-foot orthosis systems
ActiveUS20050096576A1Guaranteed wearRestraining devicesNon-surgical orthopedic devicesPronationsEngineering
A custom articulated ankle-foot orthosis (AFO) system is disclosed that is formed on a cast of the wearer's foot. It has an adjustably tightenable calf section hingedly connected to an adjustably tightenable foot section. It is made of thermally formable plastic sheet, is lined inside and outside, and is padded inside. The brace permits dorsal / plantar flexion while supporting the ankle against supination and pronation. The apparatus and methods of manufacture are disclosed.
Owner:ARIZONA AFO INC
Ankle Foot Orthosis
Disclosed is an ankle foot orthotic device for assisting a user during gait. The device comprises: a foot support having a shape and size configured to the plantar aspect of a user foot, the foot support having a forward portion and a rearward portion and a heel plate coupled to an upper surface of the rearward portion. The device further comprises: an upper rod having a longitudinal axis and a lower end connected to an offset and a lower rod having: a longitudinal axis; a lower end connected to the heel plate; and an upward end connected to the offset.
Owner:YAAD ADVANCED ORTHOPEDICS
Tension assisted ankle joint and orthotic limb braces incorporating same
An improved limb brace joint includes a band that operates in tension to rotationally bias first and second longitudinal members of the joint. The band of the joint biases the rotation of the members to provide a dorsiflexion and / or plantarflexion assist when used in an ankle foot orthosis.
Owner:TOWNSEND INDUSTRIES INC
Method and orthotic system for rehabilitating neurologically impaired gait
InactiveUS20110105969A1Accurate forceMinimal frictional effectNon-surgical orthopedic devicesImpaired proprioceptionOrthotic device
Owner:MEDICAL ALLIANCE
Ankle Foot Orthosis Device
The present invention discloses an ankle foot orthosis device that is adjustable to a patient's drop foot. The device may include, inter alia, a foot-support that is sized to fit into a corresponding patient's footwear; an elongate member that is mechanically coupled to the foot-support; and a lower leg holder that is coupled to the elongate member. The lower portion of the elongate member may extend from the foot-support's heel portion upwards and rearwards towards a corresponding lower leg's calf and may further extend forwardly towards the corresponding lower leg's shin. Forward tilting of the lower leg in the gait cycle causes the elongate member to bend forward, which in turn causes the development of potential energy in the device that may be released during the gait cycle's toe-off and swing phase, thereby compensating for the energy lost in the drop foot.
Owner:YAAD ADVANCED ORTHOPEDICS
D-DAFO (Deroos-dynamic ankle foot orthosis)
InactiveUS6860864B2Correct misalignmentUnwanted motionRestraining devicesNon-surgical orthopedic devicesSupporting systemTibia
The D-DAFO (DeRoos-Dynamic Ankle Foot Orthosis) invention is a dynamic support system designed to maintain the correct alignment of the bones in the foot and ankle. The D-DAFO's dynamic stability allows the patient's tibia to rotate forward anteriorly and yet supported, while continuously providing the support to hold the patient in sub-talar neutral, and / or improved alignment for function, while simultaneously maintaining tone and extension synergy.
Owner:MEYER GRANT C
Ankle-foot orthosis
InactiveUS20050234378A1Natural and dynamic gaitMaintain positionRestraining devicesNon-surgical orthopedic devicesKnee orthosisOrthotic device
An ankle-foot orthosis having a structural frame formed from at least one layer of fabric impregnated with a hardened structural resin. The frame includes at least one anterior support member that extends downwardly from an upper leg engaging portion to define an anterior ankle portion which extends to a medial portion connected to a foot plate.
Owner:KAUPTHING BANK
Active driving ankle foot orthosis with plantar pressure detection function
The invention discloses an active driving ankle foot orthosis with a plantar pressure detection function. The active driving ankle foot orthosis comprises a shank fixing component, a foot sensing component and an active driving component. The active driving component drives a driving bevel gear through a direct current motor; the driving bevel gear is meshed with a driven bevel gear; the driven bevel gear is mounted on a transmission shaft; a synchronous pulley, a synchronous belt and a tensioning screw are respectively formed at two ends of the transmission shaft. Seven film pressure sensors and an accelerometer are arranged in the foot sensing component. The active driving ankle foot orthosis has the advantages that on one hand, an intelligent pressure sensing foot is designed according to body bionics, a sensing heel and a sole are mutually connected through a spring steel sheet, the segmented structure of a human foot is simulated, and toes and the sole can be freely bent during walking, and on the other hand, active driving free degree is designed on the sagittal plane of an ankle joint, foot drop of a patient is prevented, meanwhile, power for the patient to go ahead is effectively provided through the driving of the direct current motor, and the walking load of the patient is reduced.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Molded ankle-foot orthoses and methods of construction
InactiveUS8512269B1Function increaseReduce deformityFeet bandagesNon-surgical orthopedic devicesTibiaEngineering
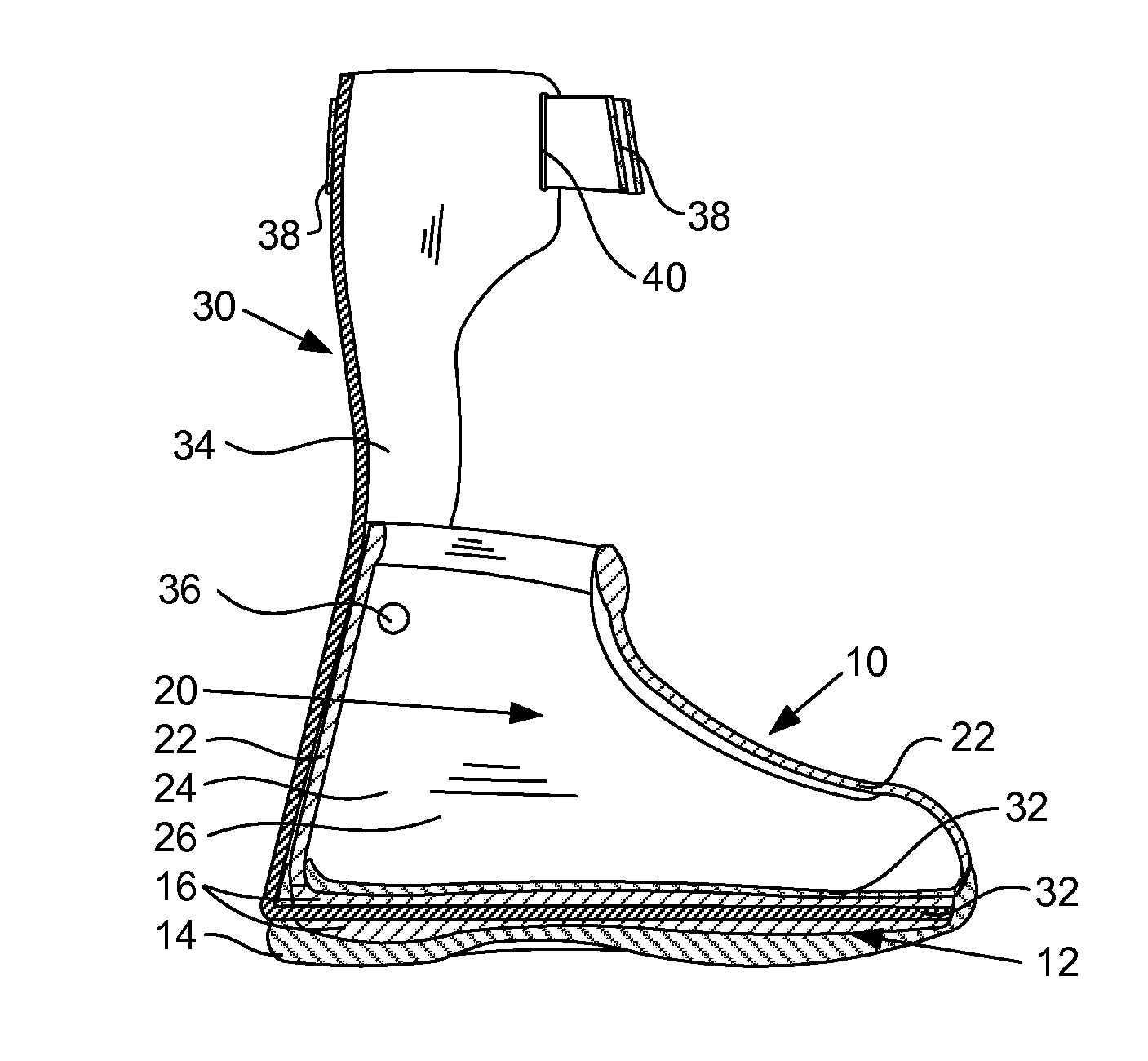
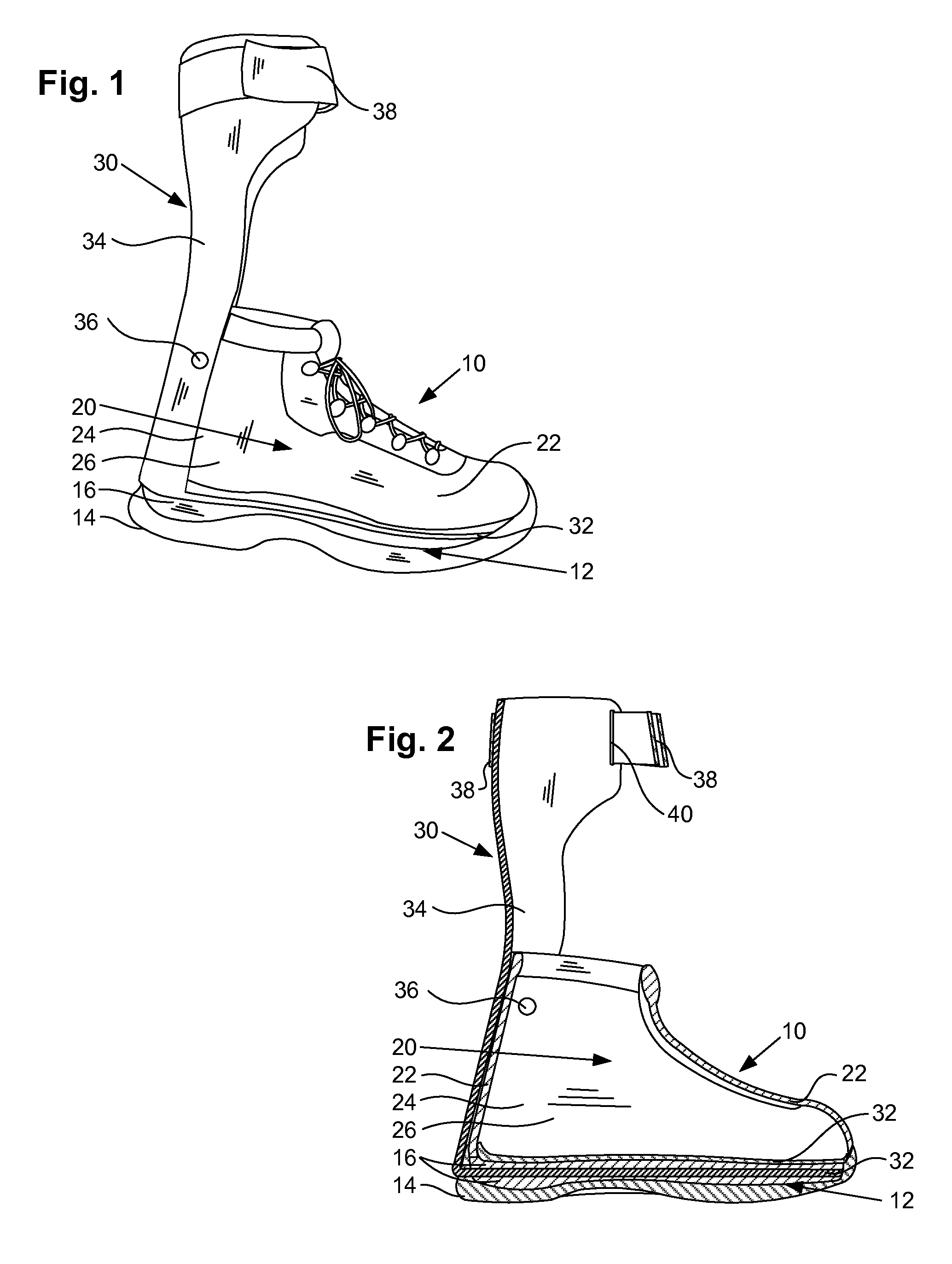
Disclosed is an ankle-foot orthosis that includes a boot and a pre-tibial shell. The boot includes an inner shell and outer shell between which are included padding and / or structural supports according to the needs of the patient to be treated. The pre-tibial shell likewise includes an interior layer and an exterior layer. Both the boot and the pre-tibial shell are custom molded to a casting made from an injured foot while taped in a non-weight-bearing position and corrected to a position of neutral pathology. Also disclosed is a method for constructing the disclosed ankle-foot orthosis.
Owner:STANO WILLIAM SCOTT +1
Active control of an ankle-foot orthosis
ActiveUS20060270950A1Reduce the amount of noiseAdapt quicklyProgramme-controlled manipulatorPerson identificationGravitational forceOrthotic device
Techniques are provided for controlling a human-exoskeleton system comprising an ankle-foot orthosis by receiving system parameters for the human-exoskeleton system, receiving generalized coordinates such as an orientation of the foot, and determining a joint torque for controlling the ankle-foot orthosis to compensate for one or more components of forces acting on the foot. Forces selected for compensation can include gravitational forces as well as external forces such as ground reaction forces. Techniques are provided for determining an ankle joint torque for partial or complete compensation of forces acting on the foot about an axis of rotation. One embodiment of the present invention mitigates the amount of interference between voluntary control and assist control, thereby allowing humans to quickly humans adapt to an exoskeleton system.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Articulated custom ankle-foot orthosis systems
ActiveUS7691076B2Guaranteed wearRestraining devicesNon-surgical orthopedic devicesPronationsEngineering
Owner:ARIZONA AFO INC
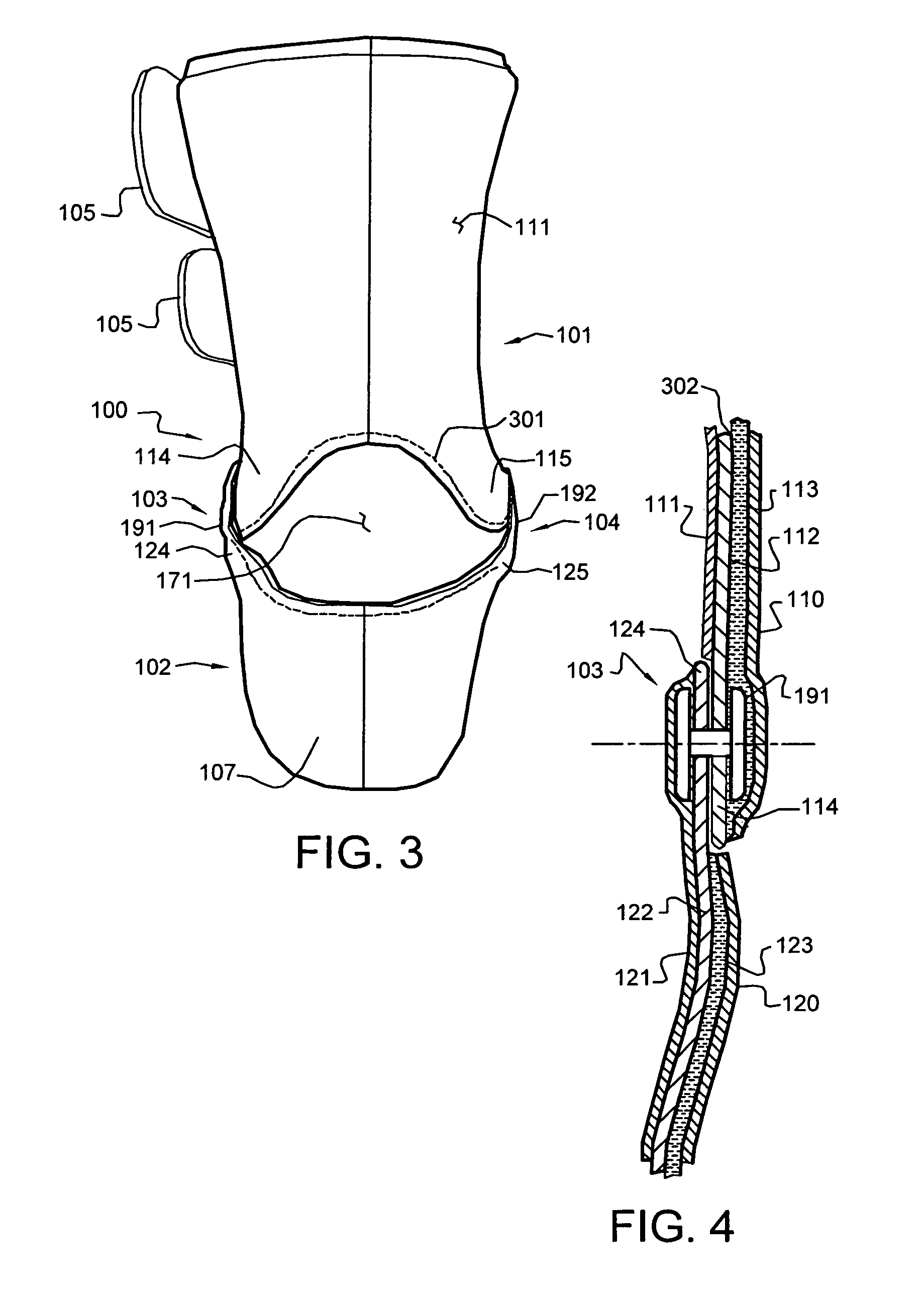
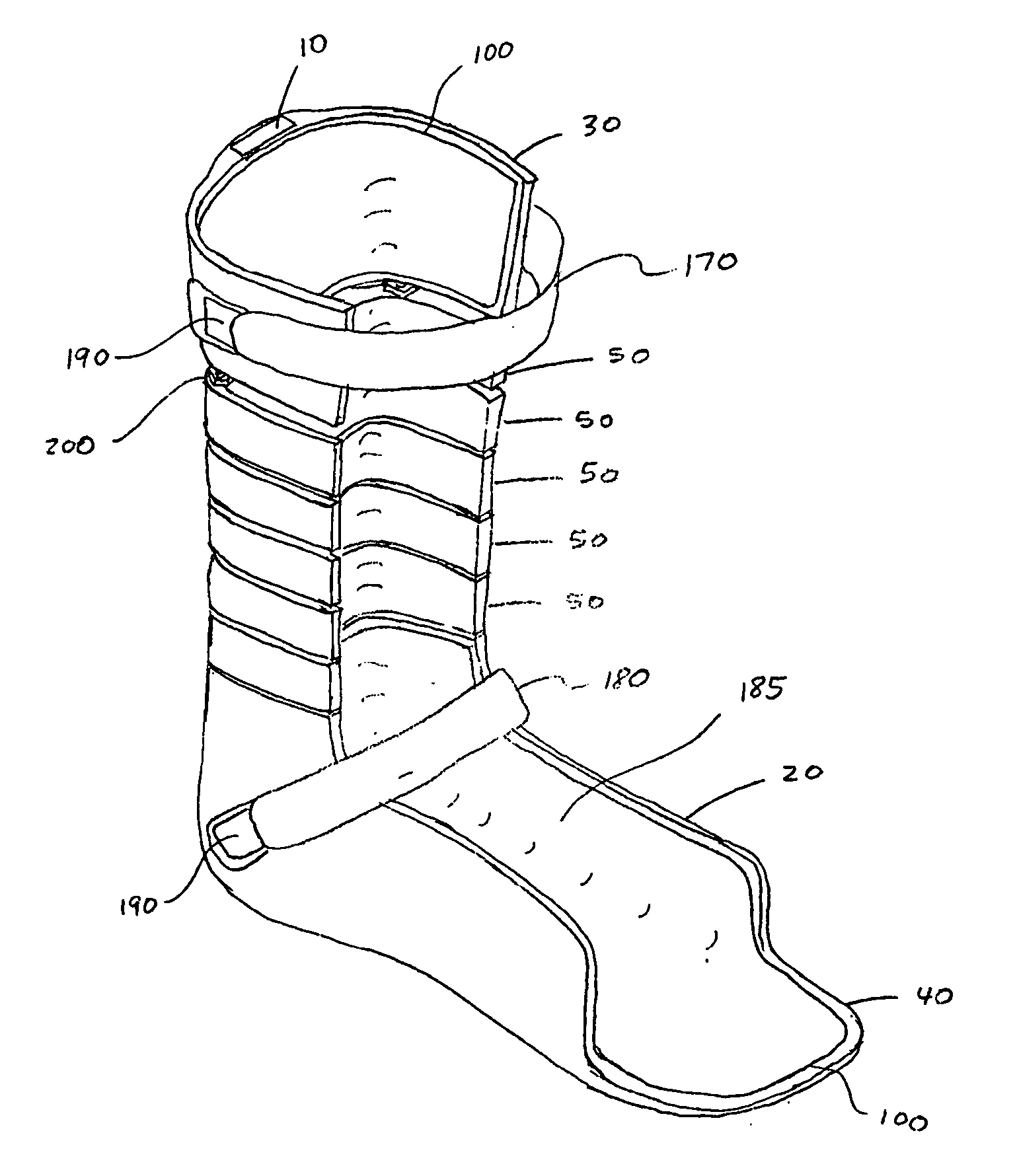
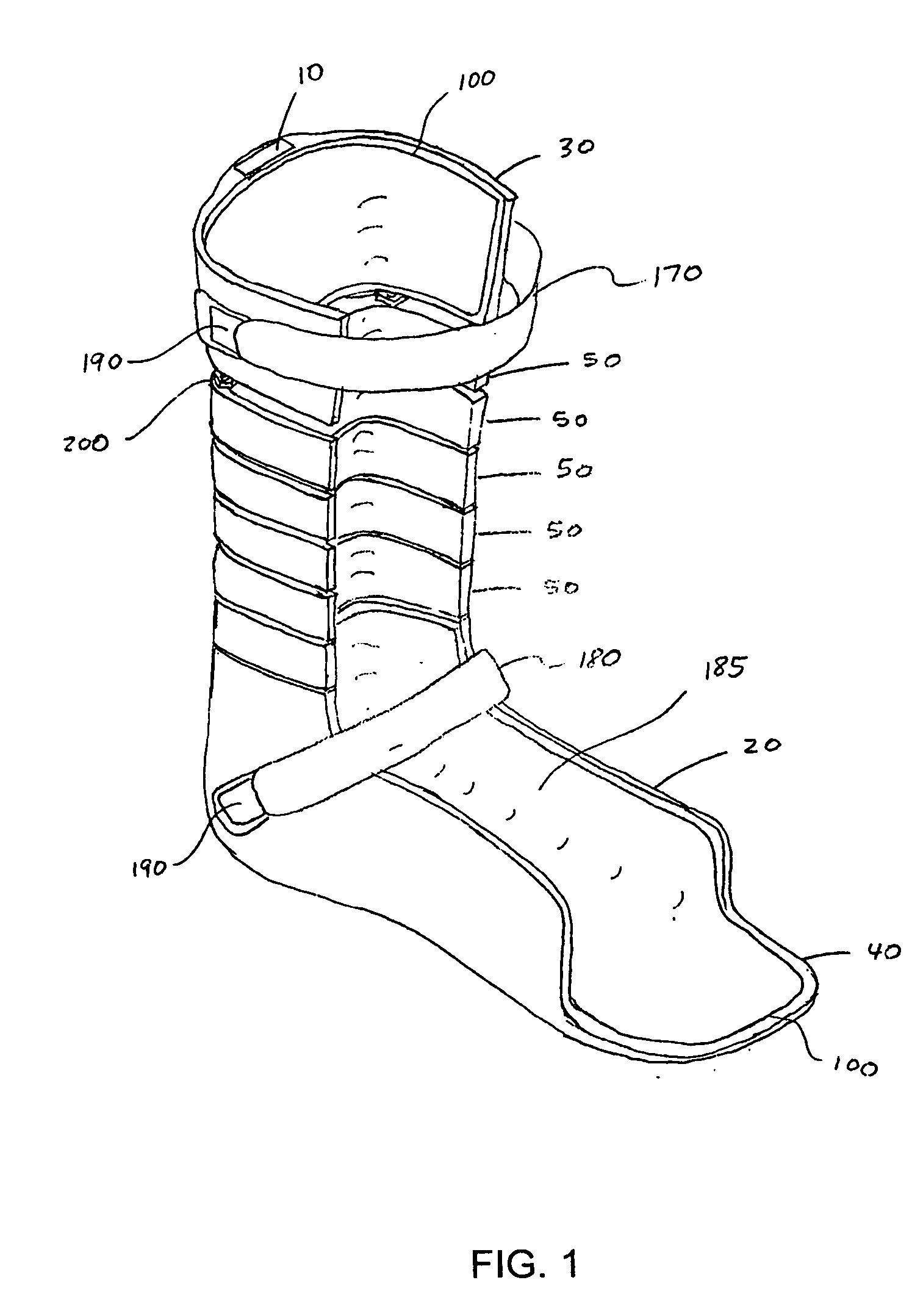
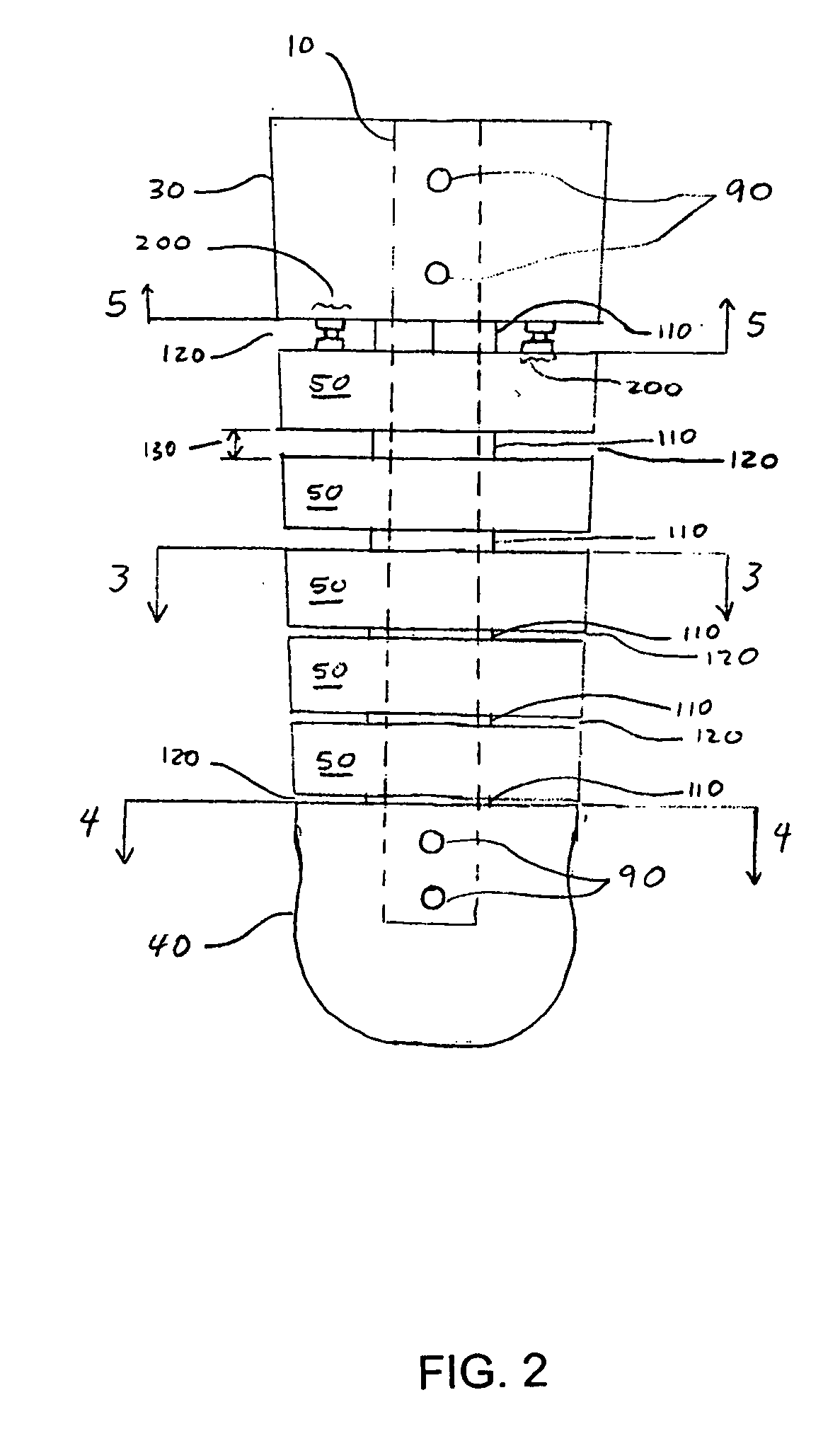
Ankle-foot orthosis
ActiveUS20050273028A1Expanding and narrowing width of gapIncrease stiffnessNon-surgical orthopedic devicesFoot dorsiflexionCattle calf
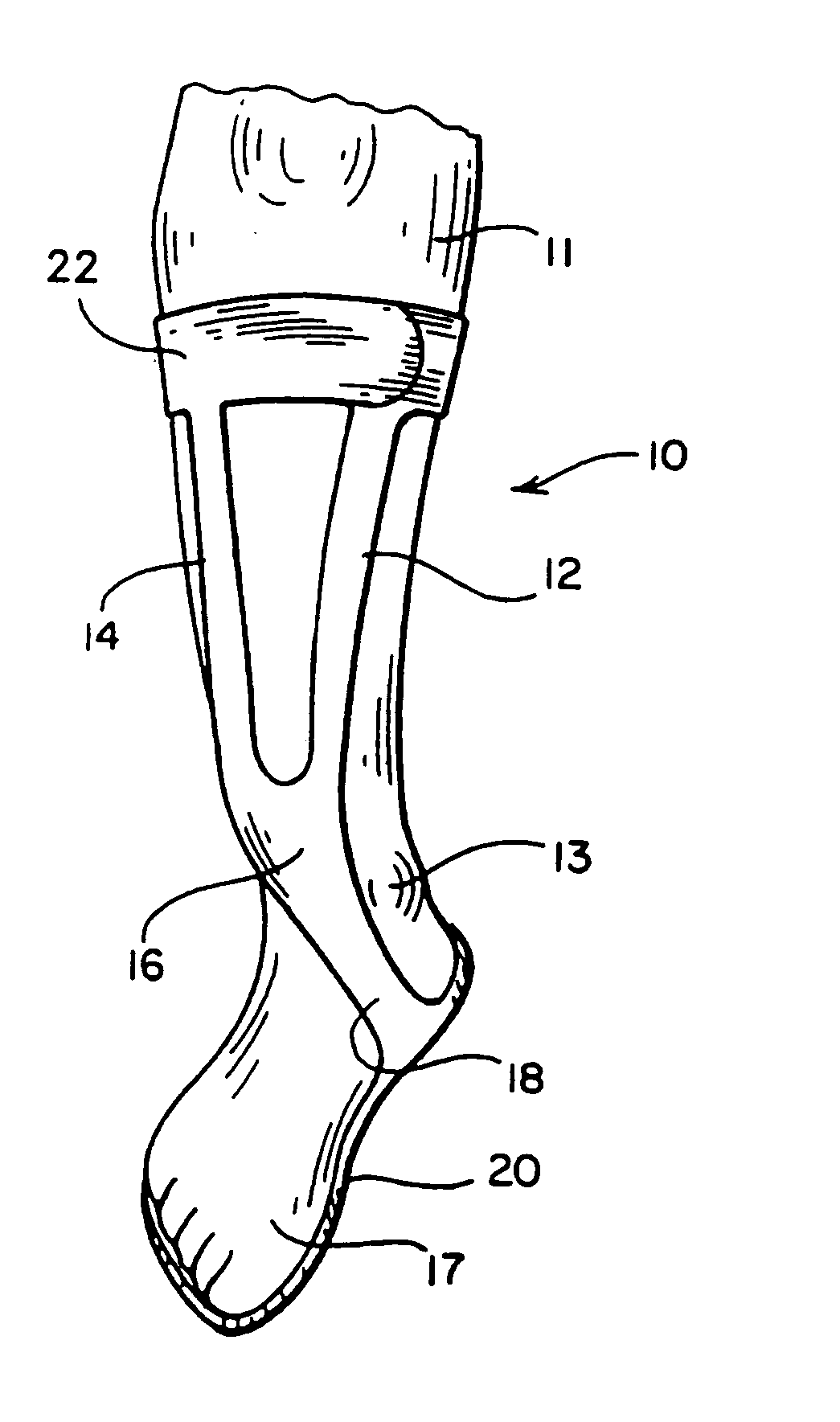
An ankle-foot orthosis for aiding or enhancing a user's foot and ankle movement, wherein the orthosis comprises at least one strut member, a calf shell, a foot shell, and a plurality of segments. Gaps formed between adjacent segments, an uppermost segment and the calf shell, and a lowermost segment and the foot shell have gap widths, wherein gaps at a higher location have larger gap widths than those at a lower location. Therefore, in dorsiflexion, the gaps close in series from bottom to top, gradually increasing the orthosis stiffness, creating a progressive dorsiflexion stop, and decreasing the magnitude of loads transferred into the user. In plantar flexion, the gaps similarly decrease in series from bottom to top, gradually increasing the orthosis stiffness, creating a progressive plantar flexion stop, and decreasing the magnitude of loads transferred into the user.
Owner:RONAN REYNOLDS +2
Ankle foot orthosis and method therefor
An ankle foot orthosis that provides a patient with forward flexing, energy loading, and balance control. The orthosis may also be adjustable for size and fit. The orthosis couples opposing stabilization forces that help to provide optimal balance control.
Owner:WARNER MITCHELL S
Orthotic clubfoot device
The present invention relates to an orthotic device wherein the patient's feet are maintained at a desired angle while allowing the patient to move in an otherwise normal manner and preventing blister formation. The orthotic device generally comprises an orthotic splint assembly, two ankle foot orthosis and two custom molded inserts secured to the ankle foot orthosis.
Owner:WASHINGTON UNIV IN SAINT LOUIS
Ankle foot orthosis
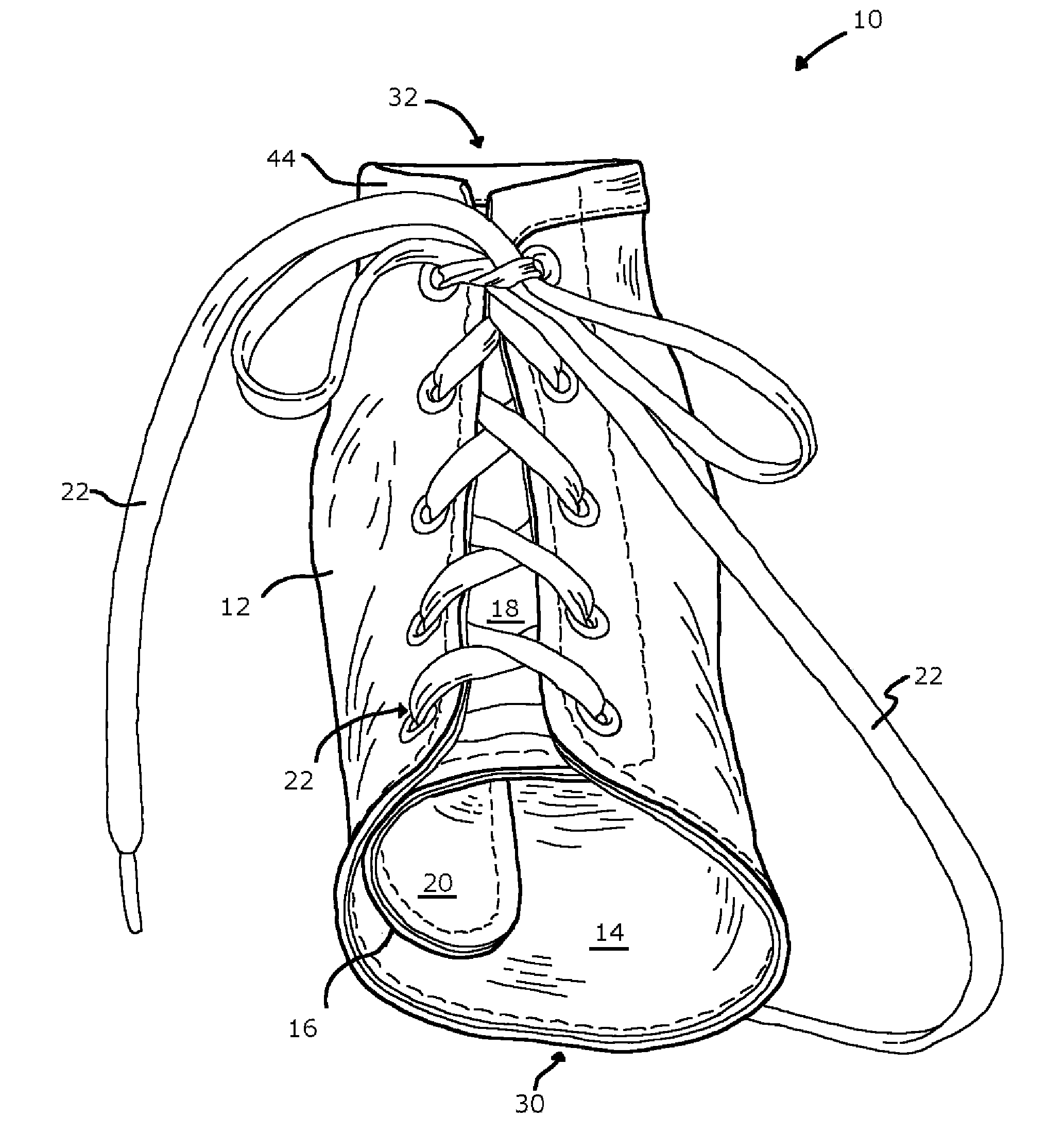
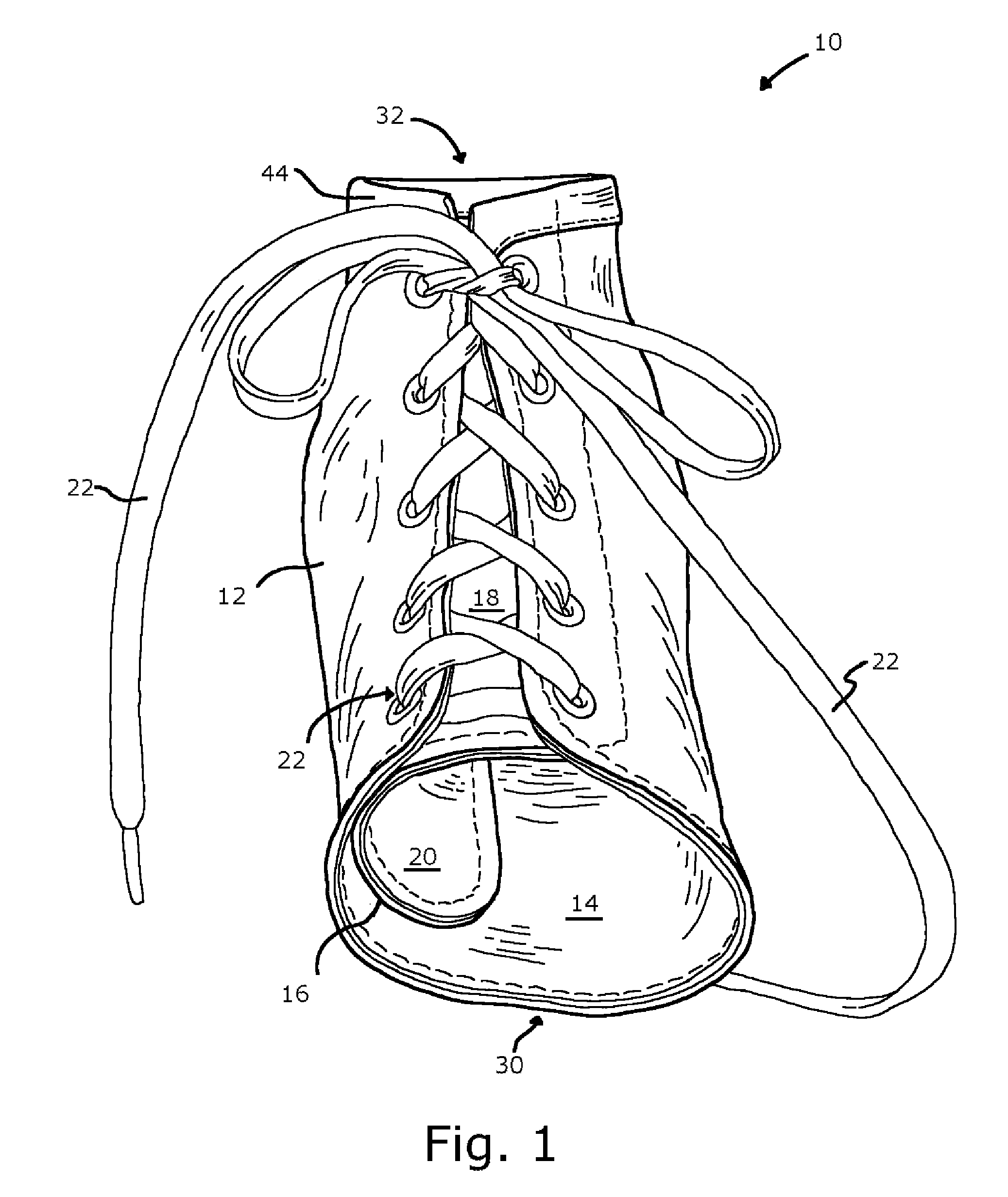
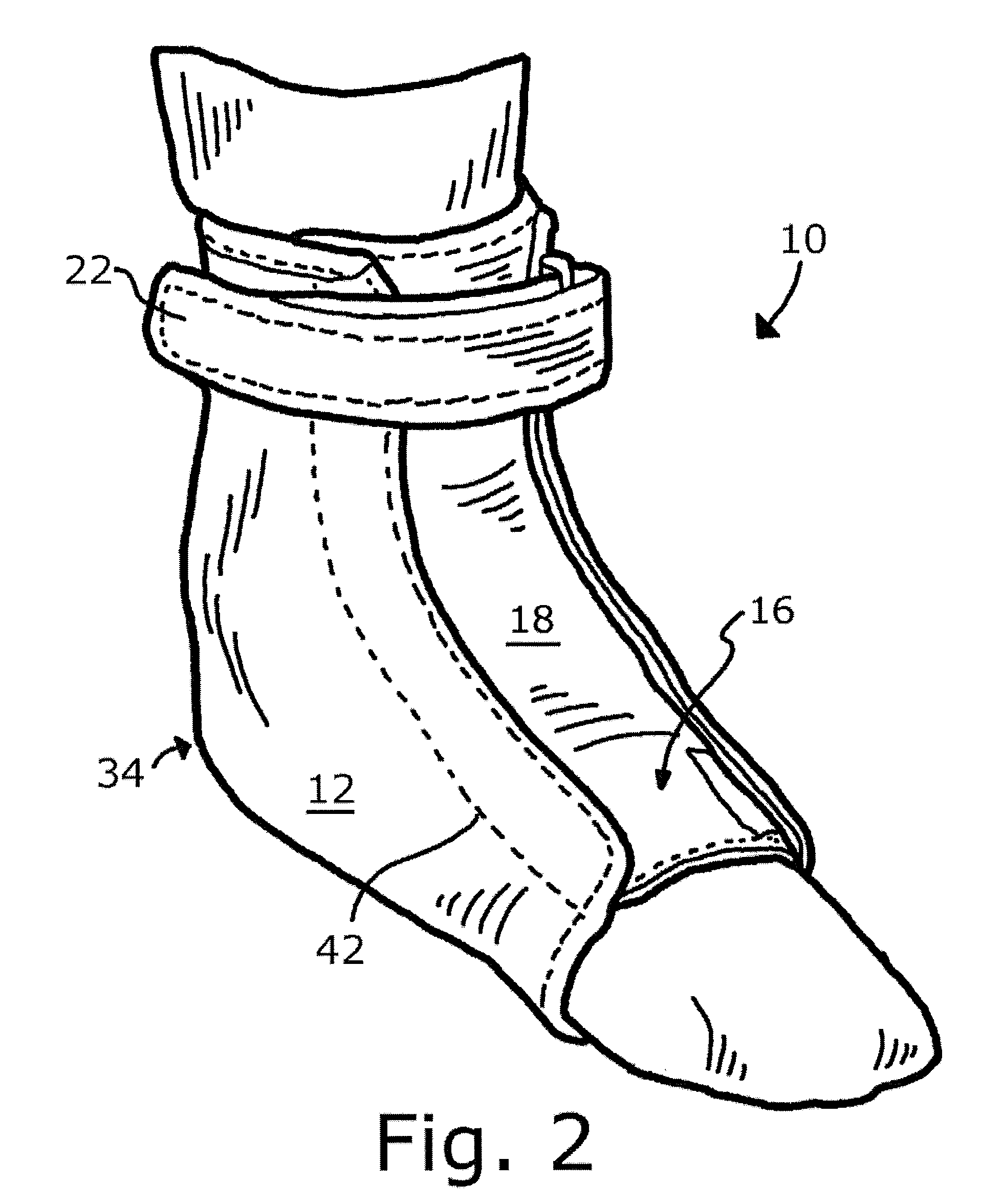
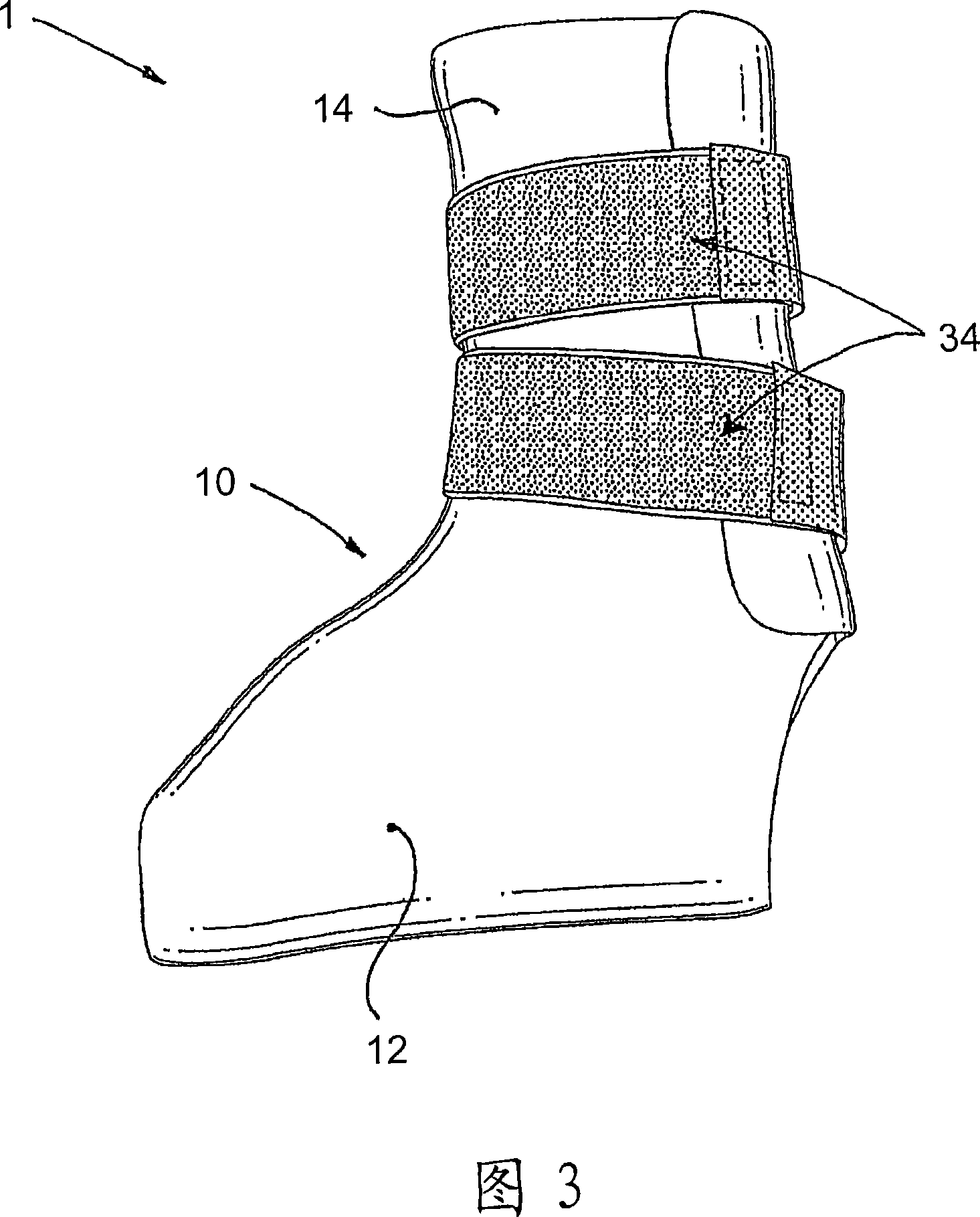
InactiveCN101115452AEasy to manufactureCheap manufacturingMedical scienceOrthotic deviceAnkle joint orthosis
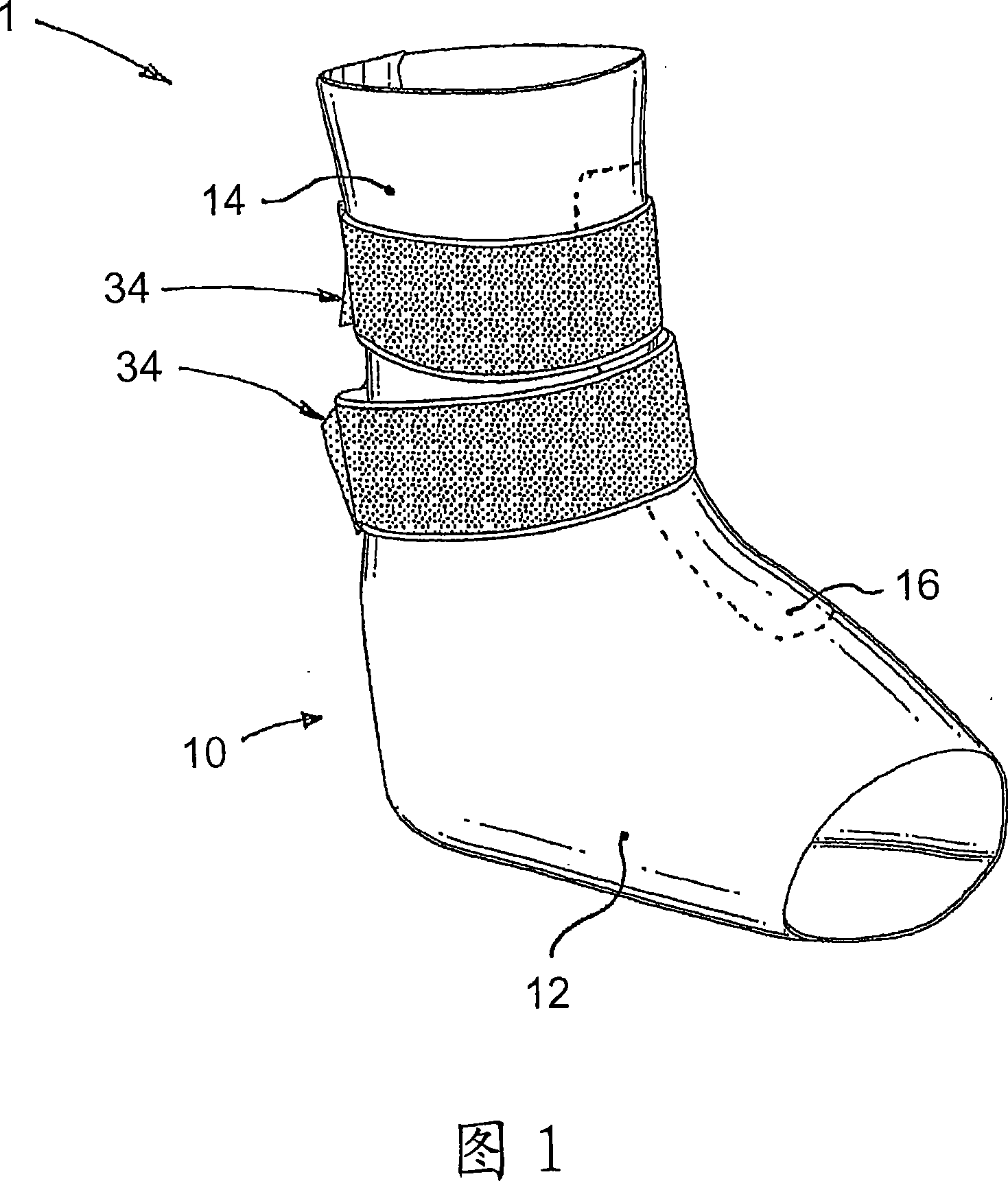
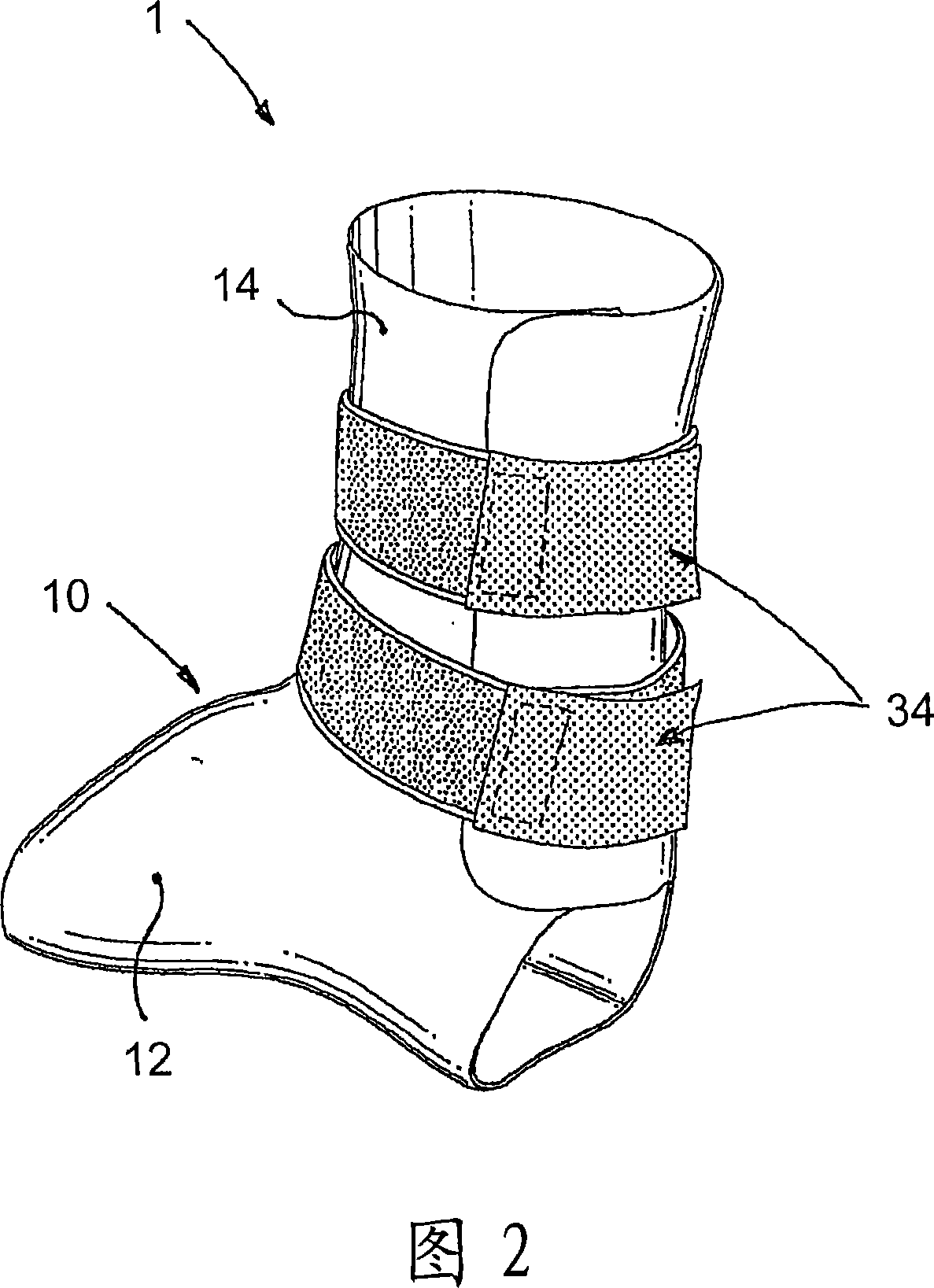
A preferred embodiment of the invention provides an ankle-foot orthosis (1) for resisting plantarflexion of a patient's foot, comprising a resiliently flexible sock-like orthotic structure (1) formed of first (12) and second (14) tubular sections set at an angle to one another, wherein the second tubular section is capable of being opened for insertion of the patient's foot and lower leg into respective ones of said first and second tubular sections, the orthosis further comprising at least one closure member (34) that can be passed round at least part of the periphery of the second tubular section and secured in place to urge the second tubular section towards a closed position in which the second tubular section is closely fitted to the lower leg of the patient.
Owner:罗伯特·约翰·瓦特
Ankle-foot orthosis
ActiveUS7335177B2Effective lengthIncrease stiffnessNon-surgical orthopedic devicesKnee orthosisOrthotic device
An ankle-foot orthosis for aiding or enhancing a user's foot and ankle movement, wherein the orthosis comprises at least one strut member, a calf shell, a foot shell, and a plurality of segments. Gaps formed between adjacent segments, an uppermost segment and the calf shell, and a lowermost segment and the foot shell have gap widths, wherein gaps at a higher location have larger gap widths than those at a lower location. Therefore, in dorsiflexion, the gaps close in series from bottom to top, gradually increasing the orthosis stiffness, creating a progressive dorsiflexion stop, and decreasing the magnitude of loads transferred into the user. In plantar flexion, the gaps similarly decrease in series from bottom to top, gradually increasing the orthosis stiffness, creating a progressive plantar flexion stop, and decreasing the magnitude of loads transferred into the user.
Owner:RONAN REYNOLDS +2
Ankle-Foot Orthosis Element and a Manufacturing Method Therefor
InactiveUS20140257162A1Stable supportEasy to placeInsertsNon-surgical orthopedic devicesEngineeringOrthotic device
The disclosure is related to an ankle-foot orthosis element and a method of manufacturing therefor and provides for stability in a lateral direction as well as in a front-rear direction of an ankle-foot orthosis element. Moving or sliding of the orthosis in relation to the shoe is prevented. In one embodiment an ankle-foot orthosis element is provided, which comprises a base plate element (30), at least one supporting element (21, 22) supported by the base plate element (30); a top section (23) supported by the at least one supporting element (21, 22) and wherein the base plate element (30) comprises a concave shape for fixation of the ankle-foot orthosis element in a foot wear, such as a shoe or a sport shoe.
Owner:FLEXBRACE INT
Dynamic Ankle Orthesis
InactiveUS20060276736A1Easy to optimizeImprove stabilityRestraining devicesNon-surgical orthopedic devicesEngineeringOrthotic device
A dynamic ankle orthesis as subject of the present invention comprises a shoe insert (1) having a heel, a cuff (2) and a springy means (3, 6) for coupling the shoe insert (1) and the cuff (2). The springy means is coupled at its lower part (6) to the shoe insert (1) by means of a pivot (4) located at the heel of the shoe insert (1). The orthesis according to the present invention allows control and assistance of the foot during rotation around each of the three axes of rotation of the foot and heel in a distinct way during each of the phases of a step.
Owner:ORTEC INC
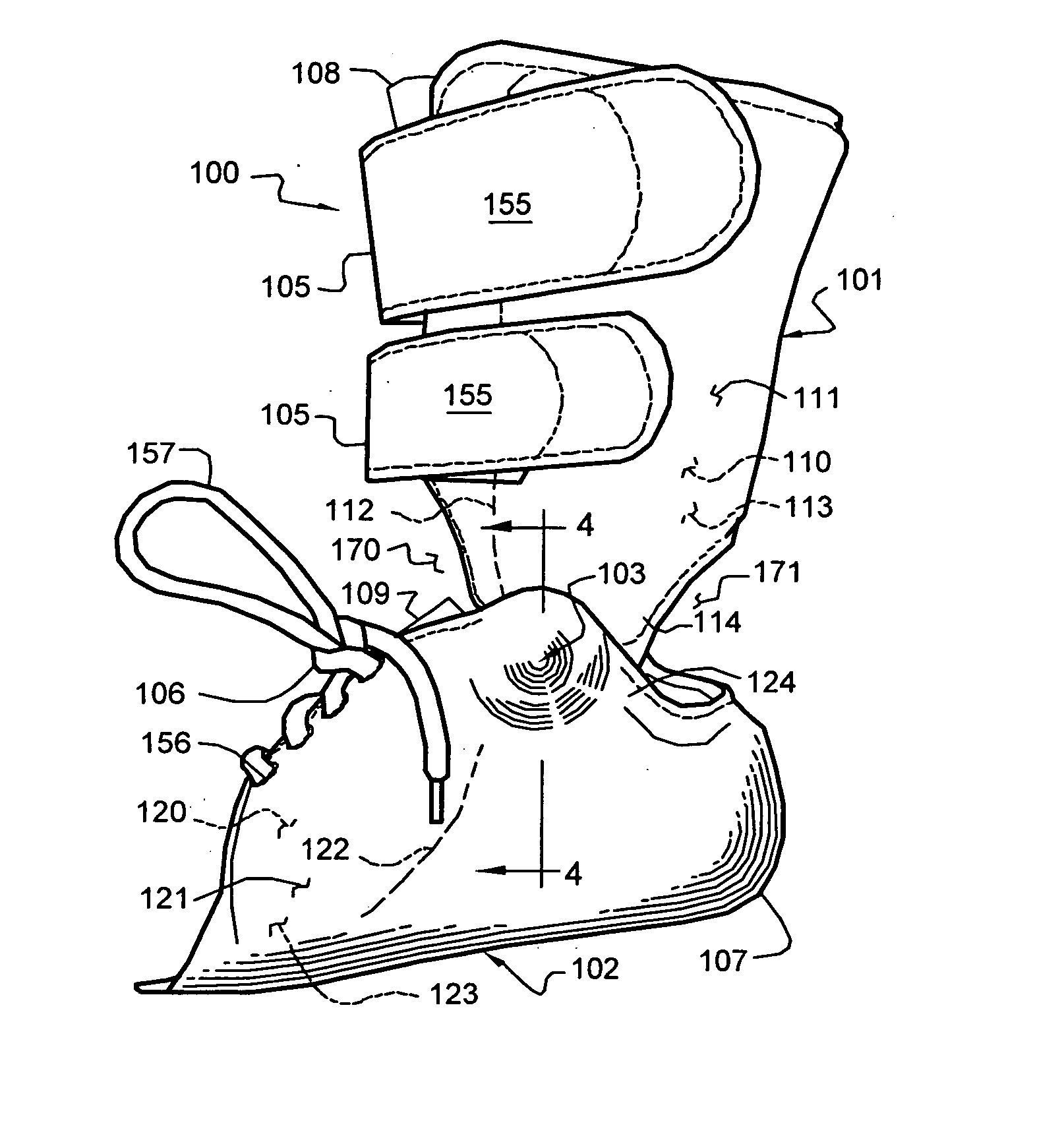
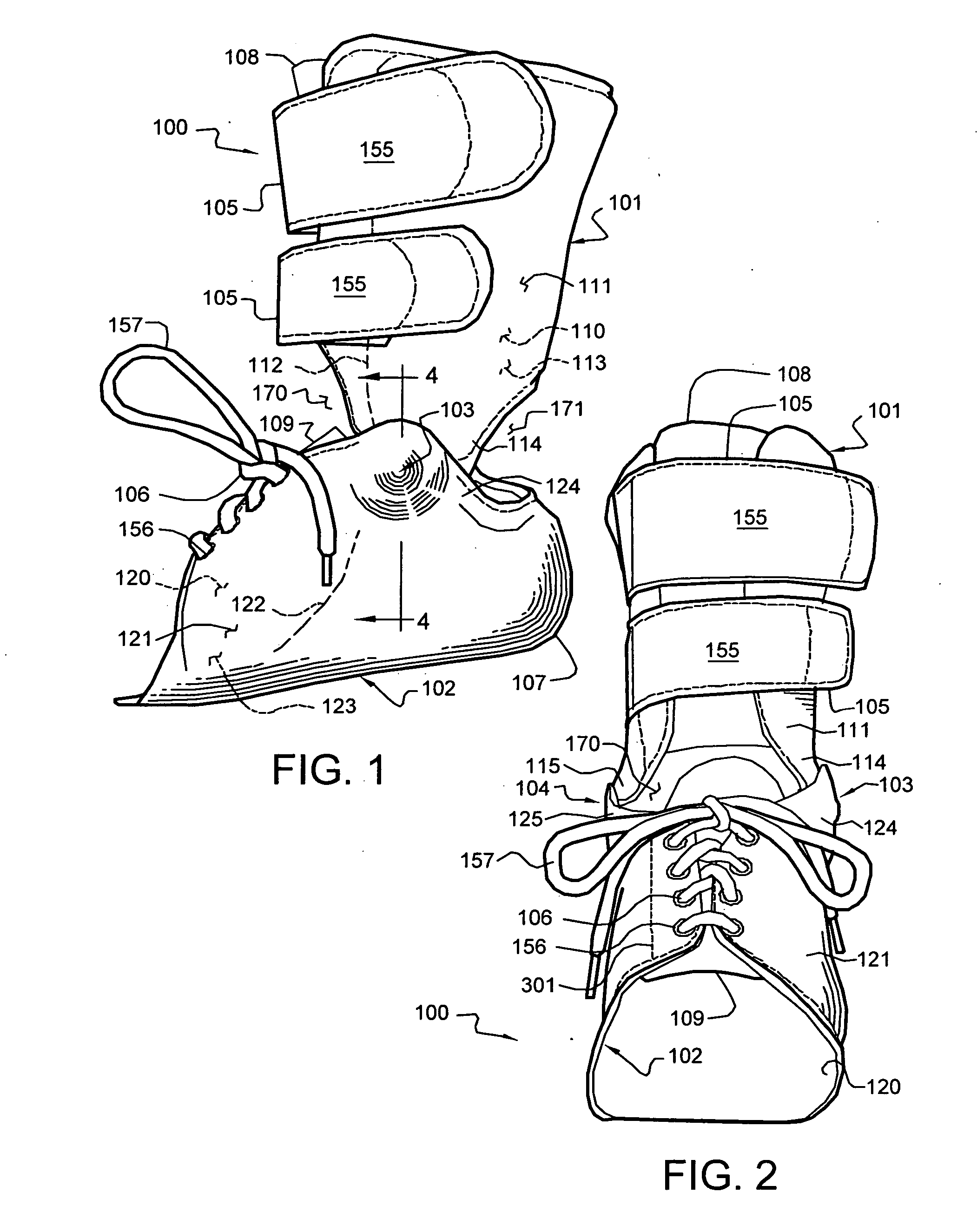
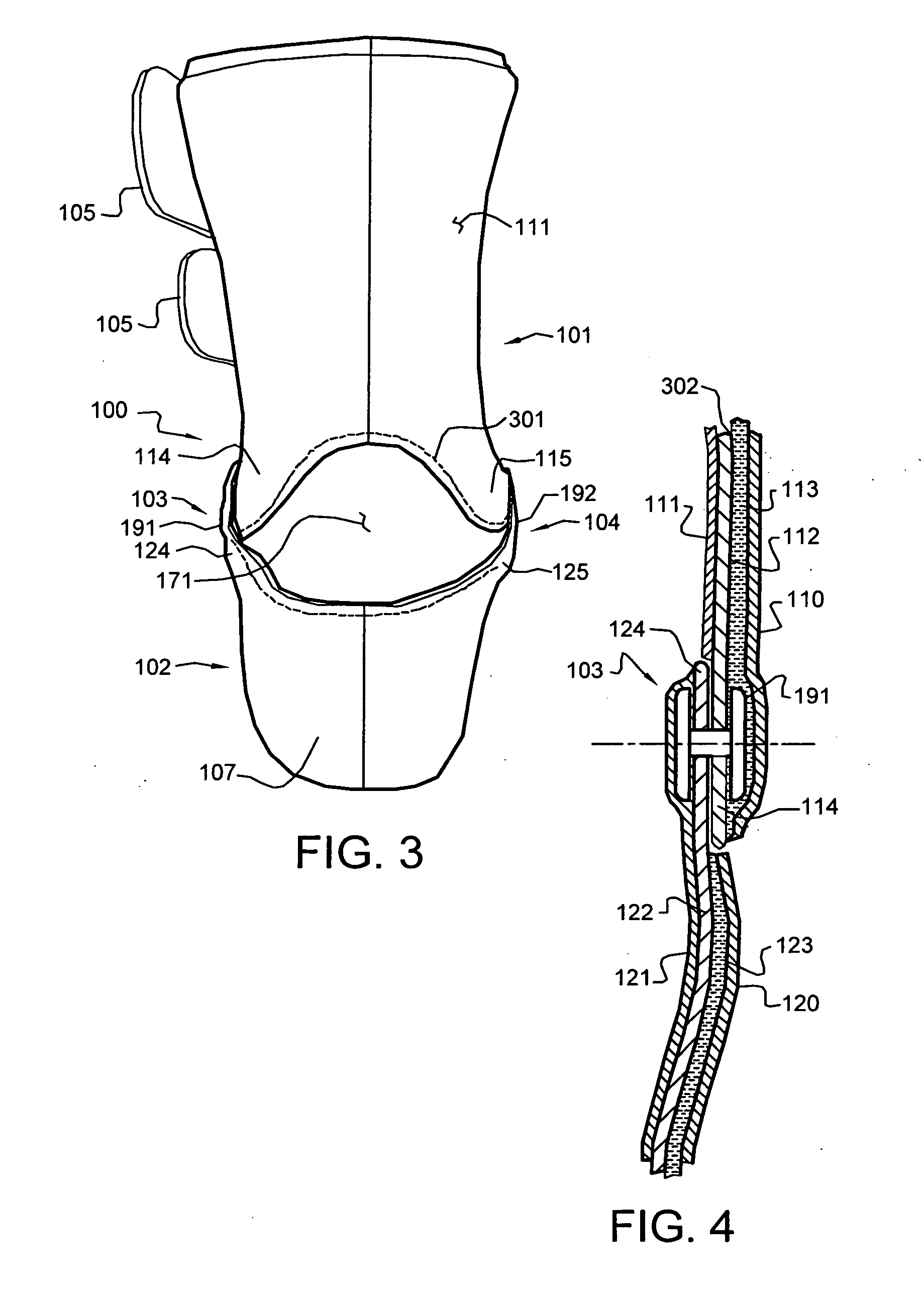
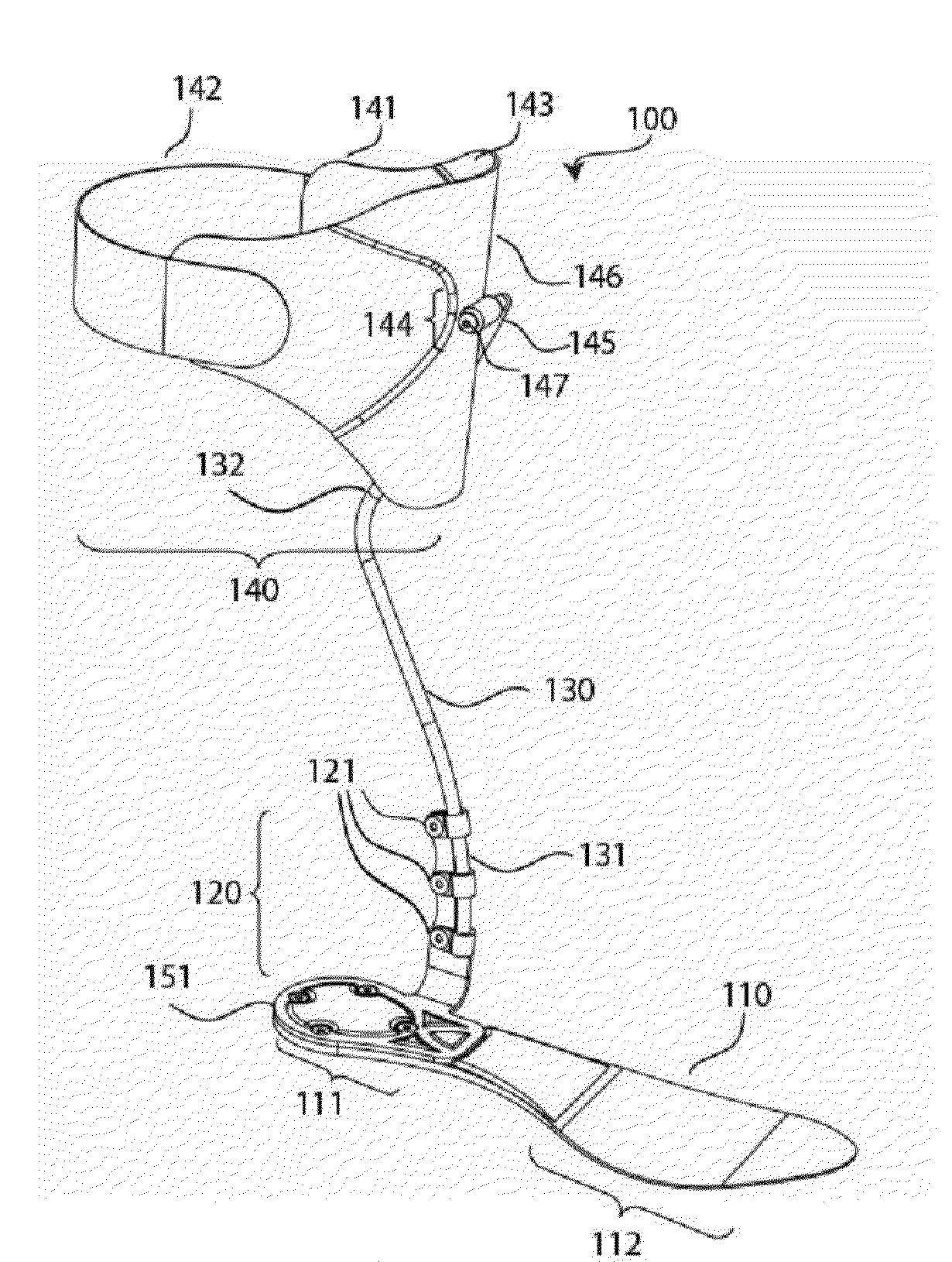
Ankle-Foot Orthosis
An Ankle-Foot Orthosis, or AFO, has a vertical portion and a horizontal portion joined together. The horizontal portion is fixed to a shoe, which is selected by a user, by separating at least part of the sole such that the horizontal portion can be adhered near or between a midsole of the sole of a shoe. The horizontal portion provides the necessary structure needed to connect a shoe to the vertical portion of the AFO such that a user suffering with a weakness or deformity can walk with a more normal gait. In an alternate embodiment, the AFO is removable from a shoe such that it can be replaced onto the same or a different shoe.
Owner:SCHWARTZ NATHAN
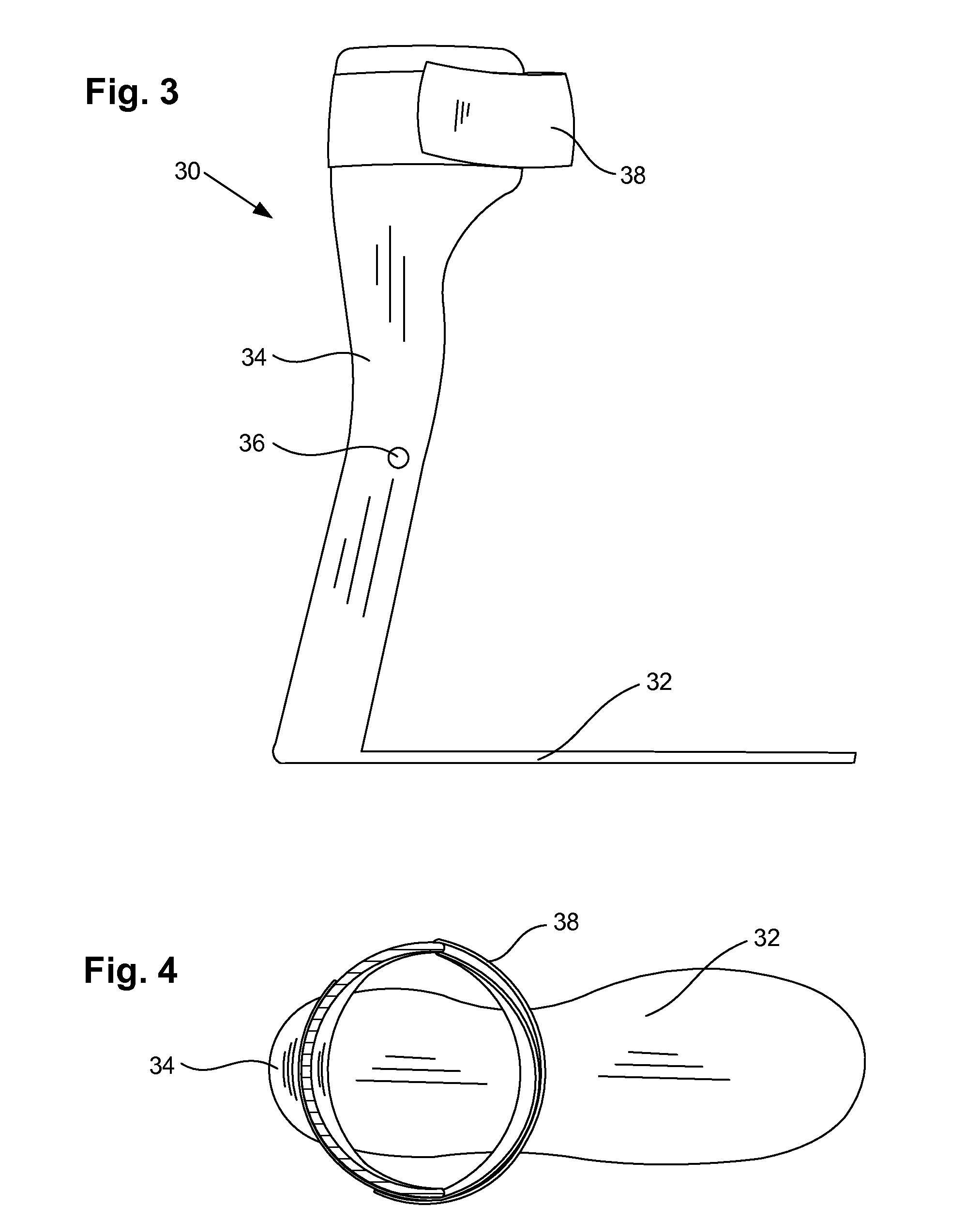
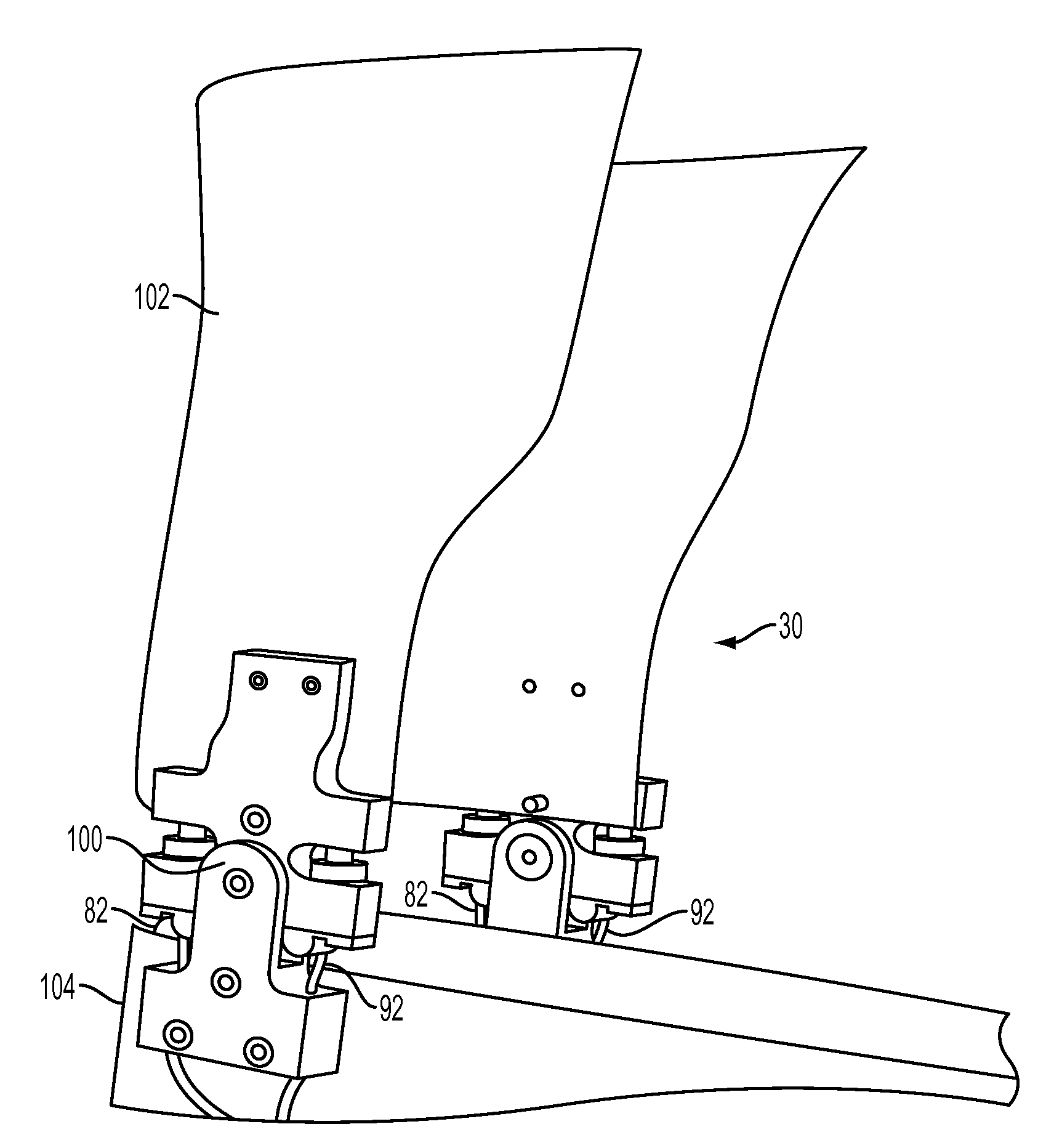
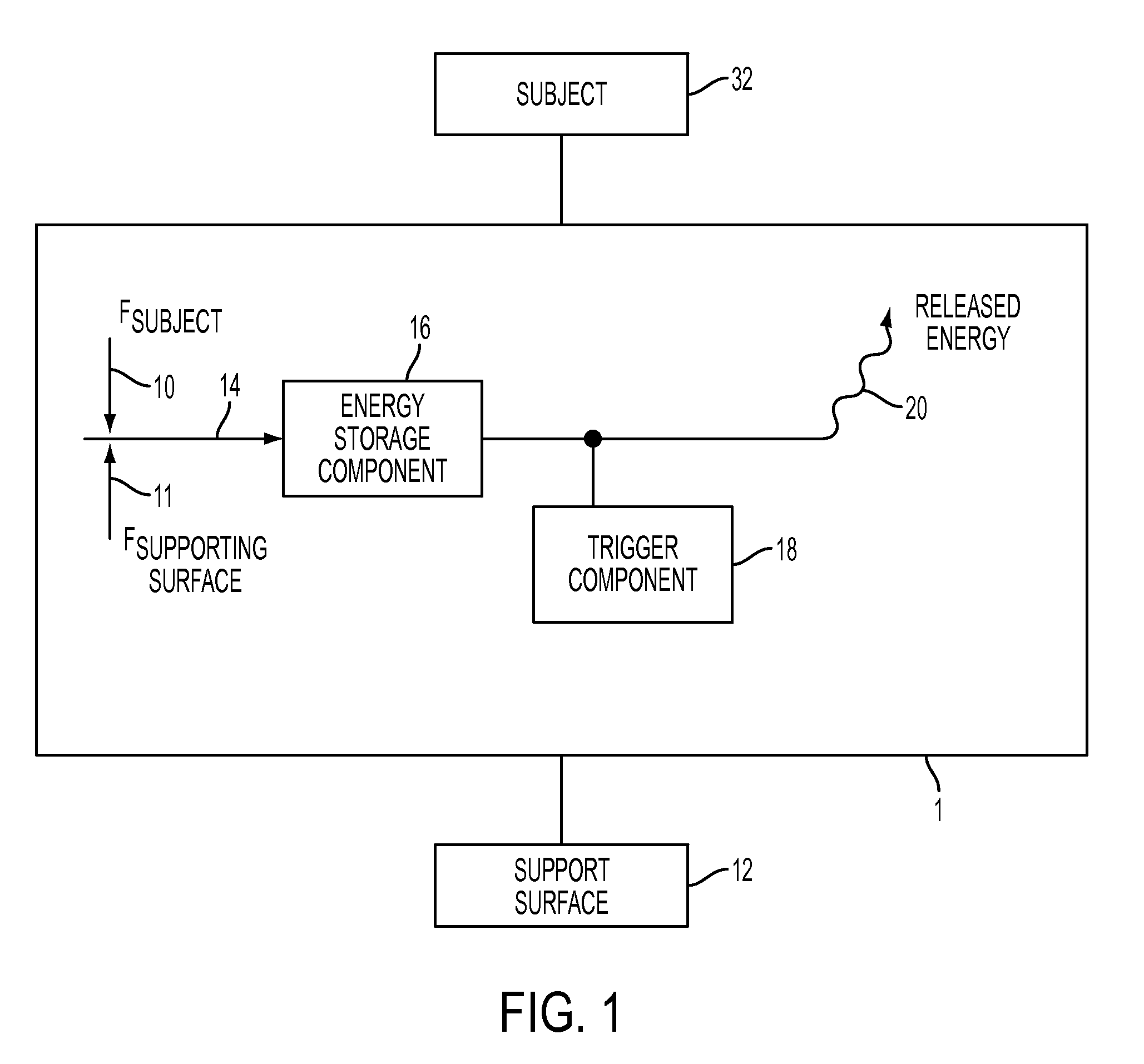
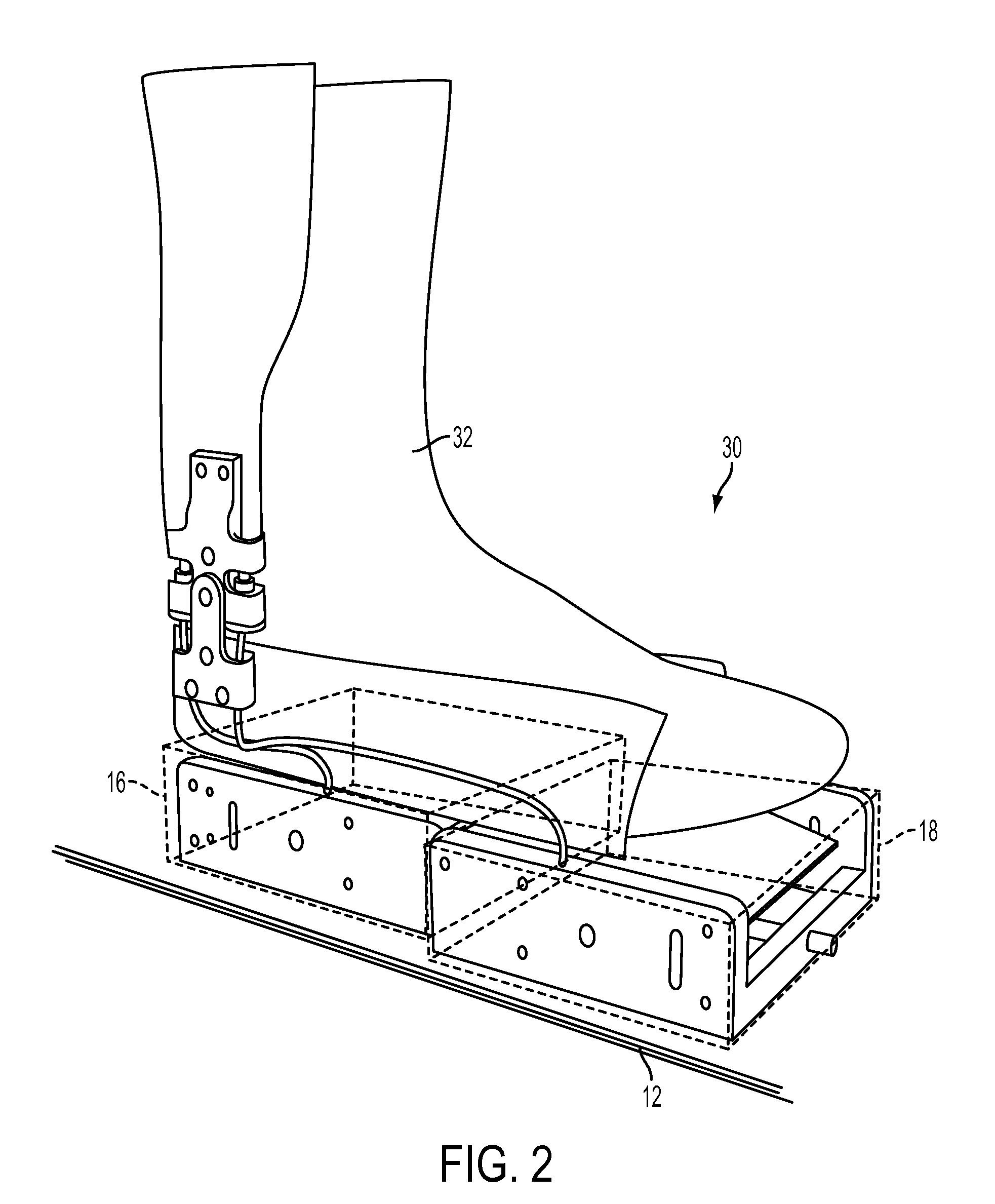
Method and System for Energy Returning Ankle Foot Orthosis (ERAFO)
InactiveUS20100076346A1Augment weak powerImprove walking performanceChiropractic devicesPerson identificationStored energyEngineering
An orthotic device / system and method including at least one energy storage component and at least one trigger component which prevents release of the stored energy until the desired point in the movement cycle of an extremity. Use of the device / system and method permits, among other things, the orthosis to capture energy from the force present between a patient and a supporting surface and return it at a specified point in the movement cycle of the subject's extremity.
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND
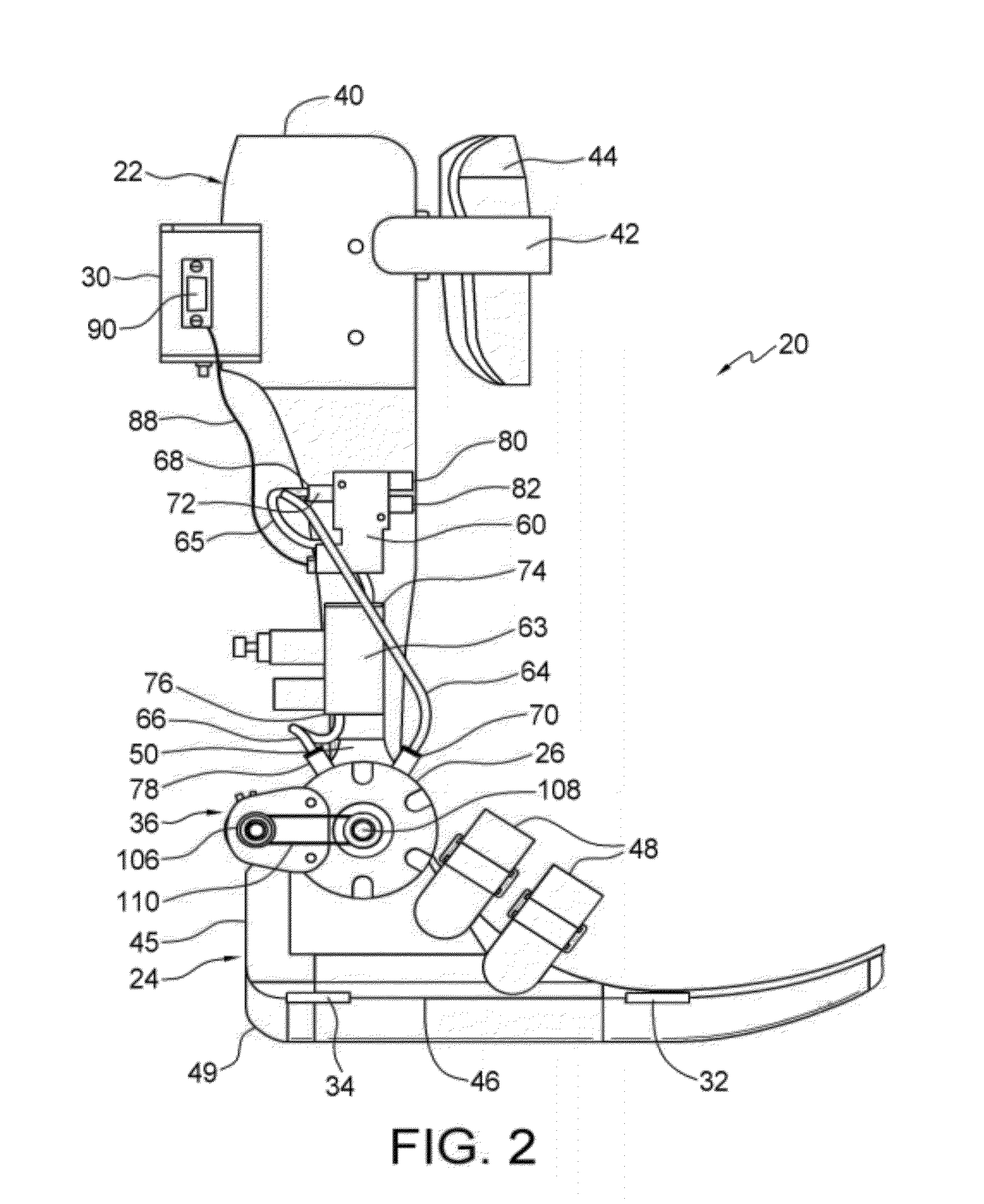
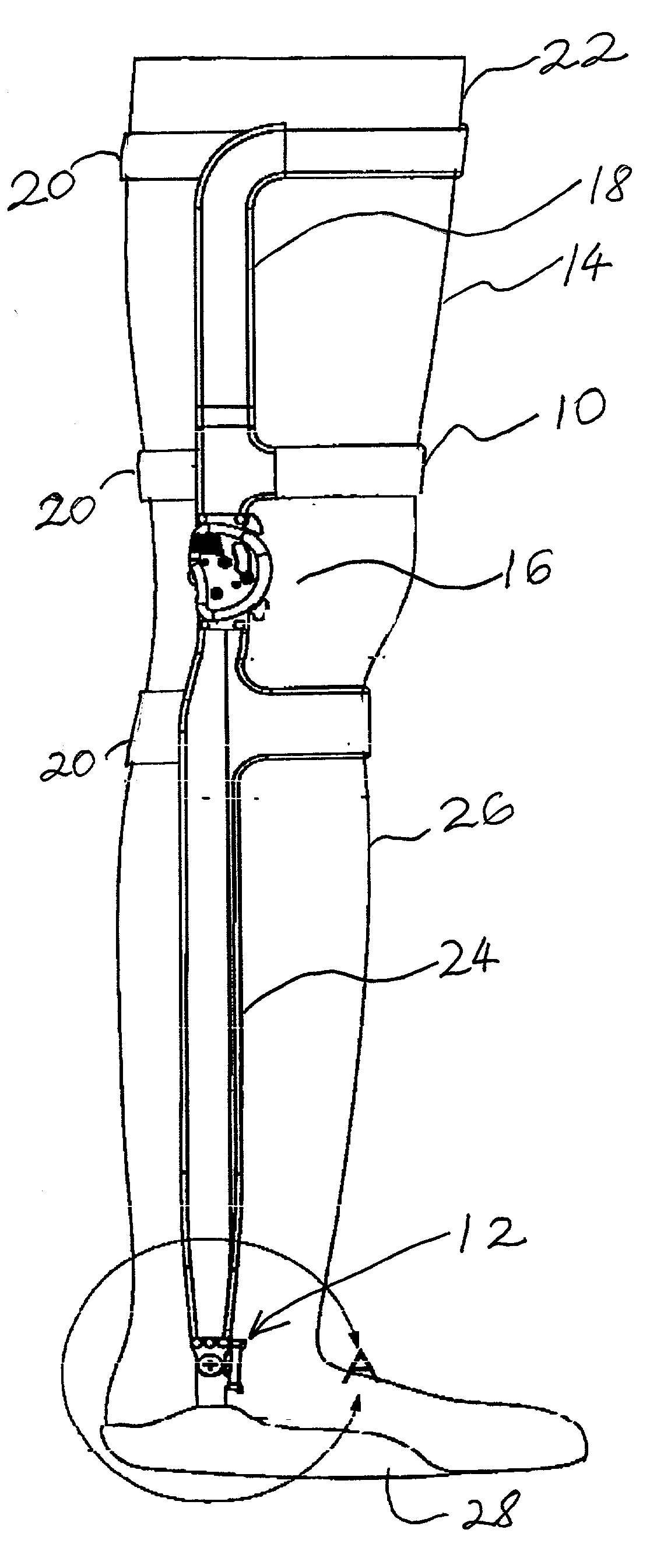
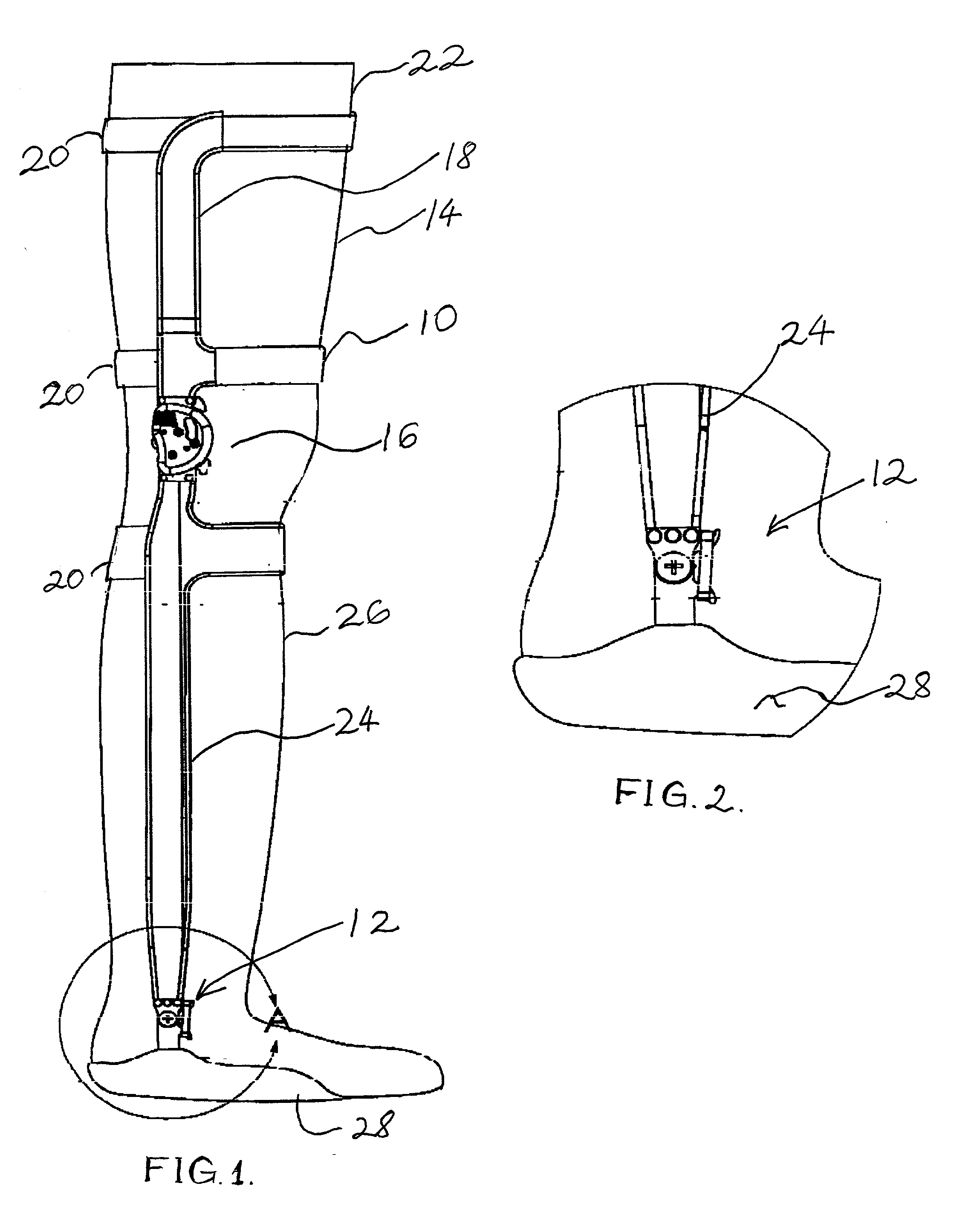
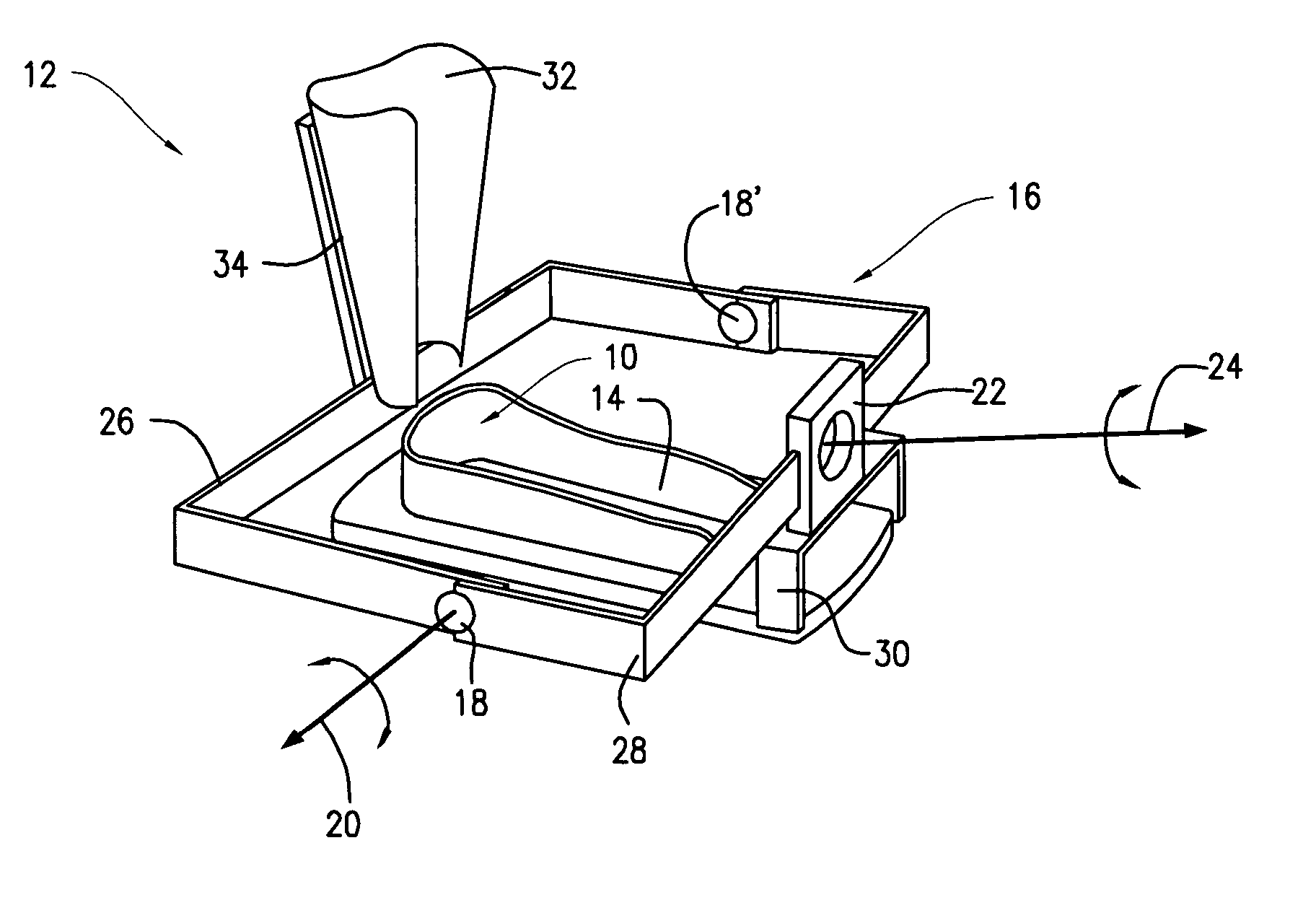
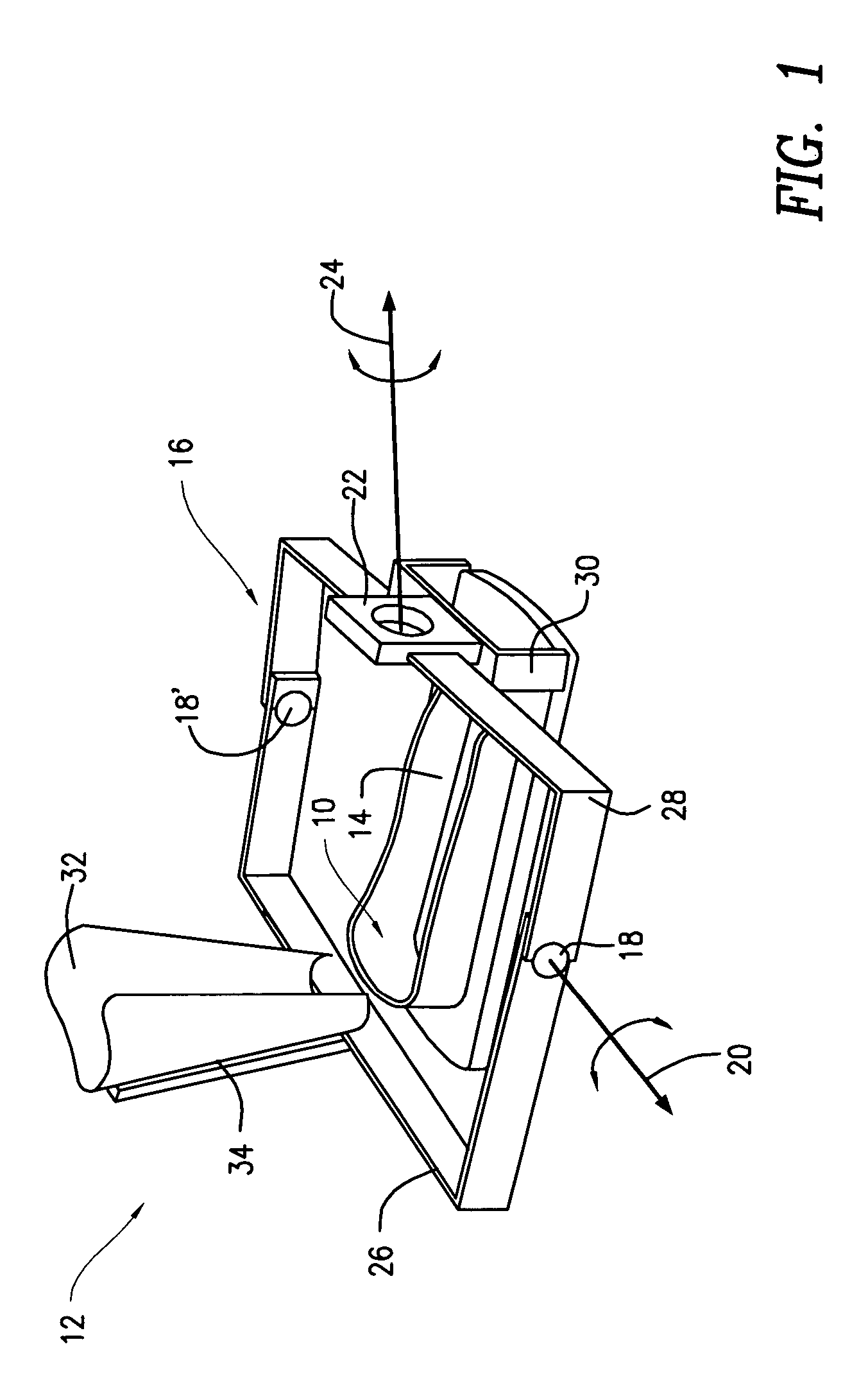
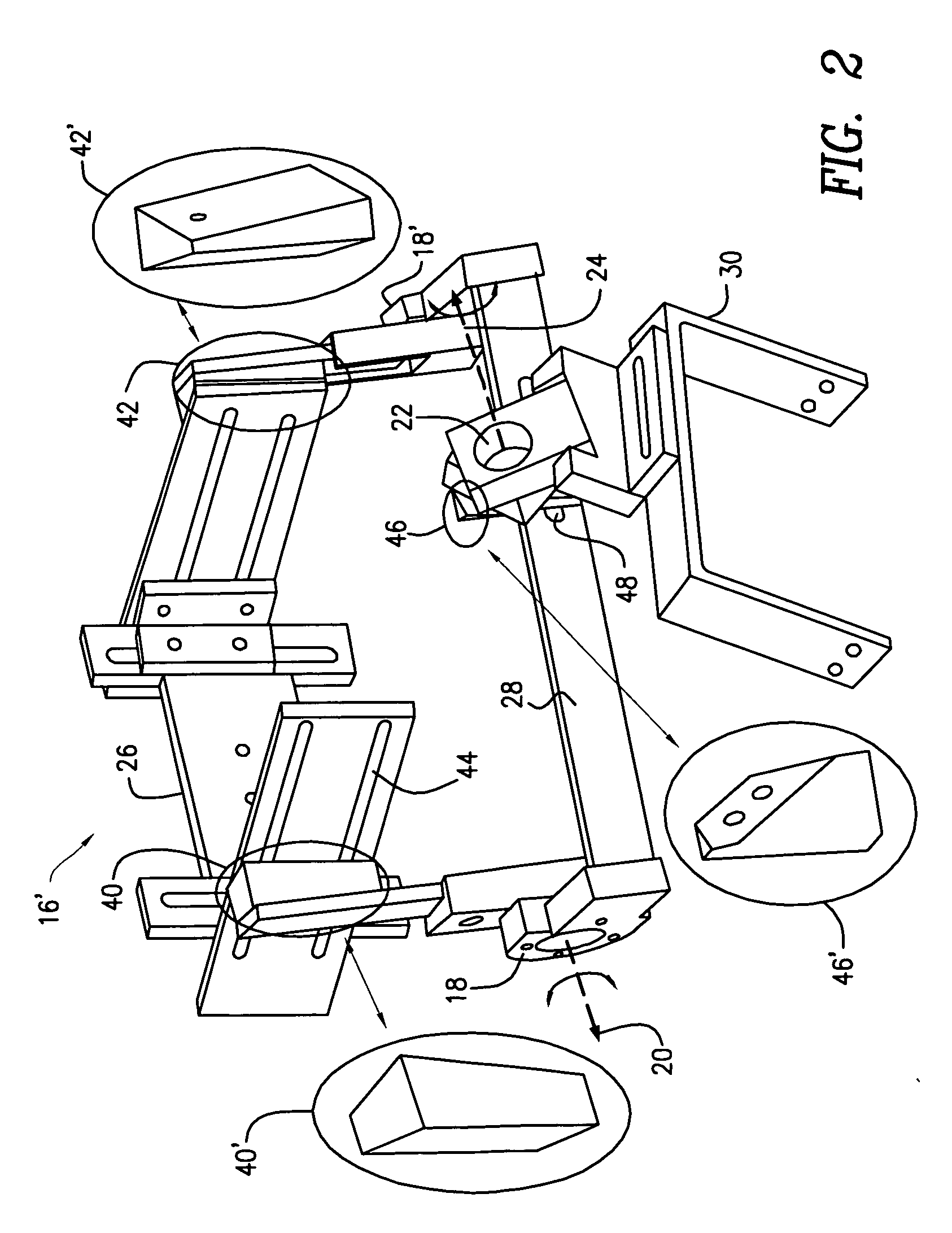
Ankle-foot orthosis device
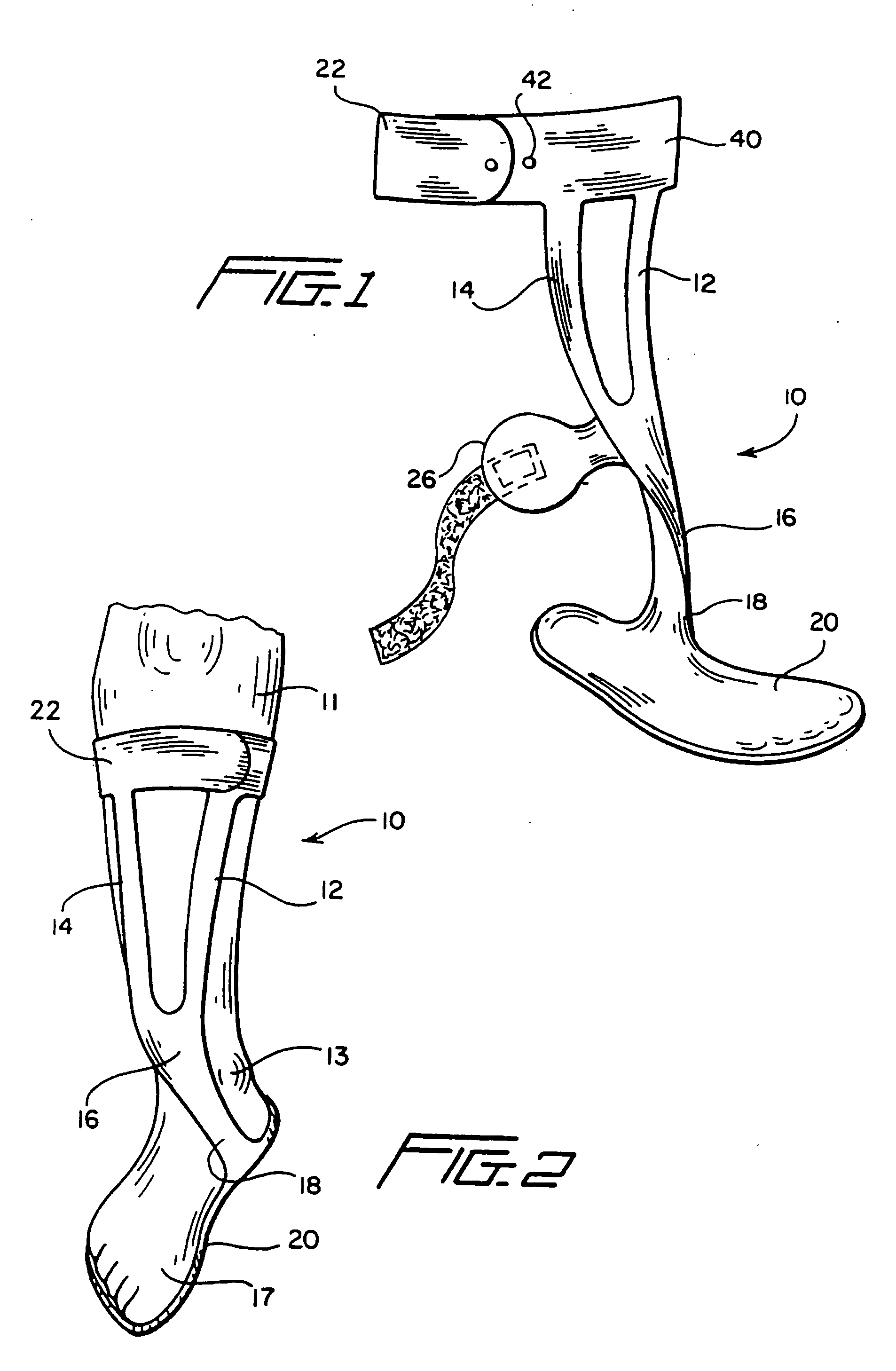
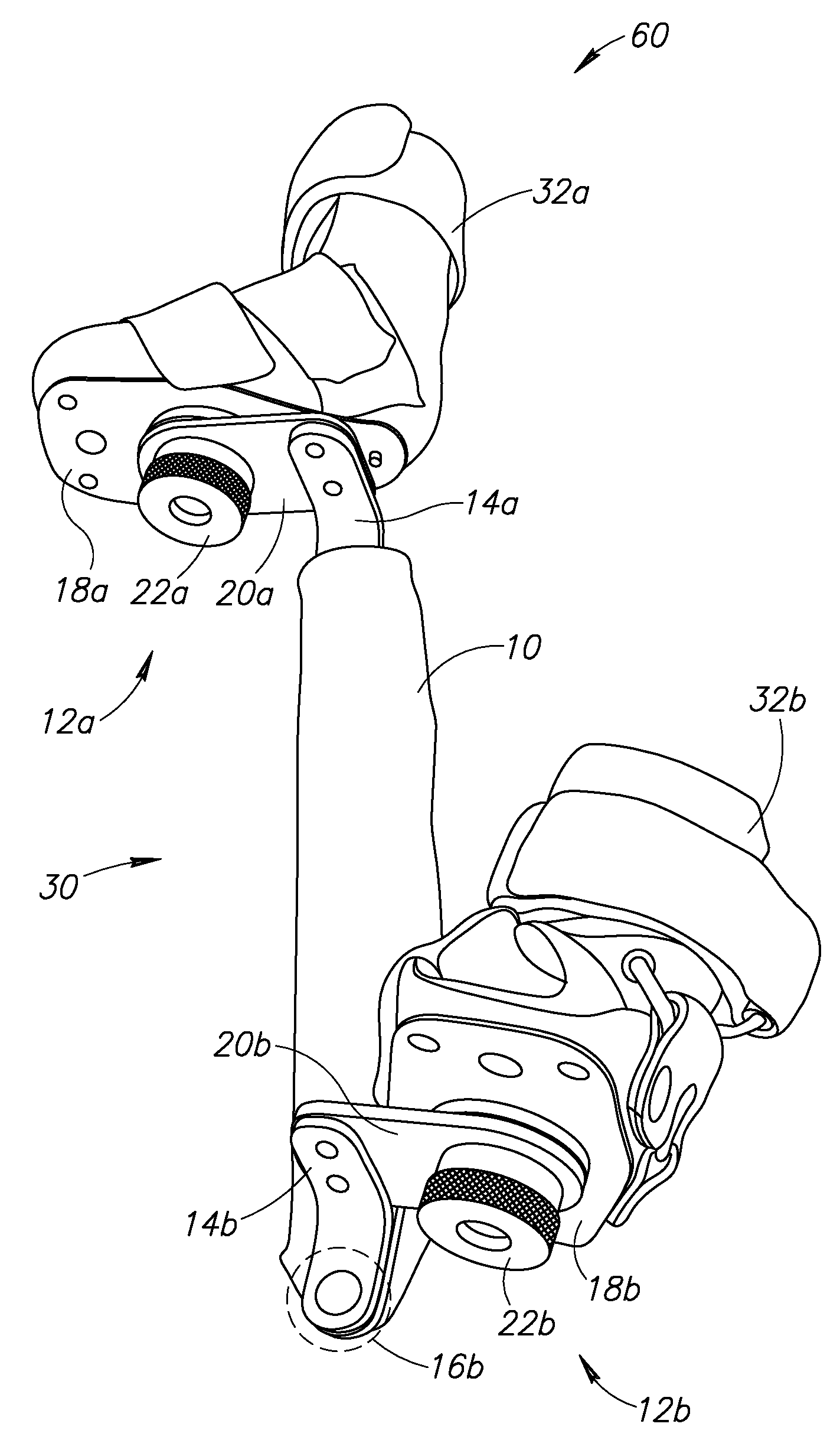
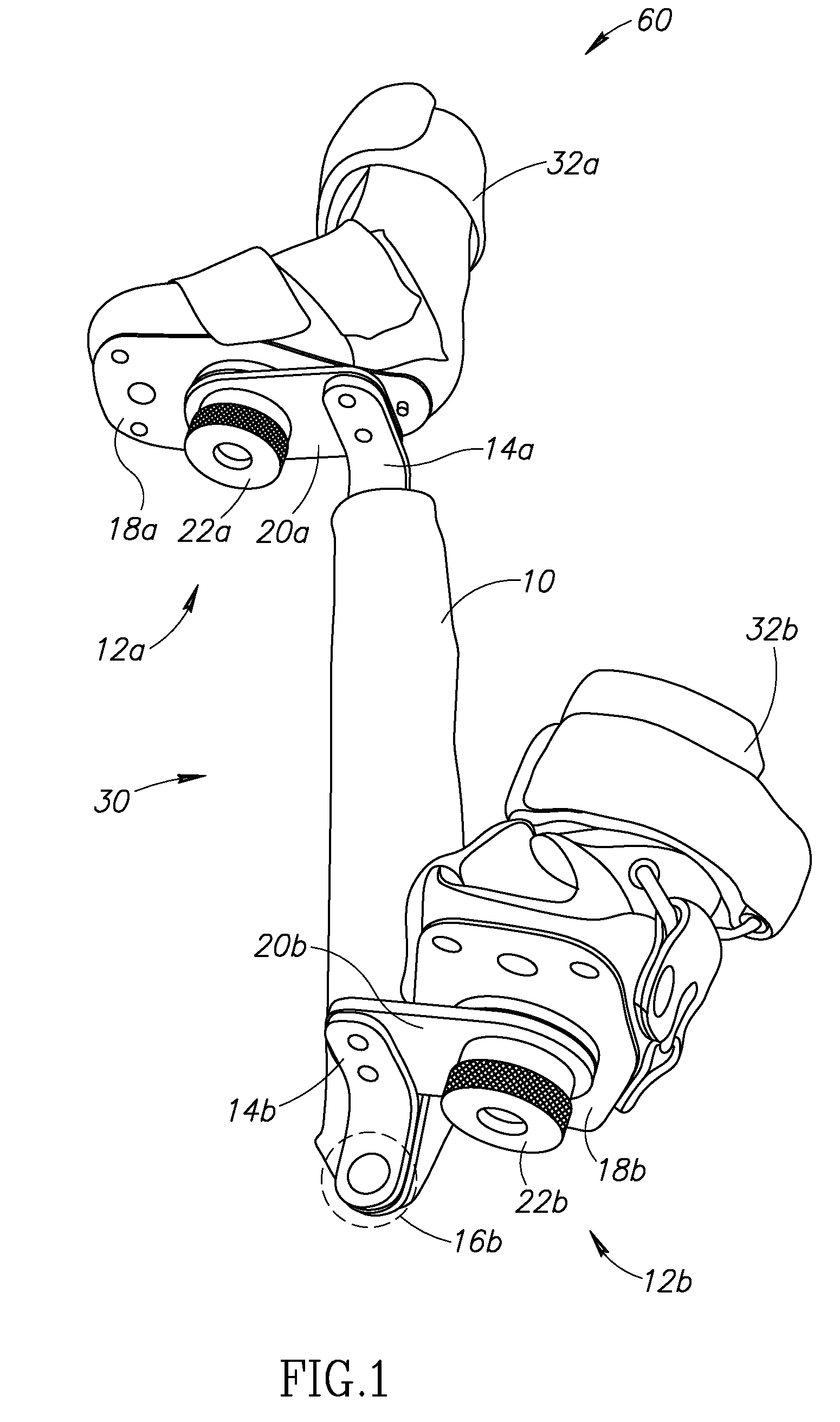
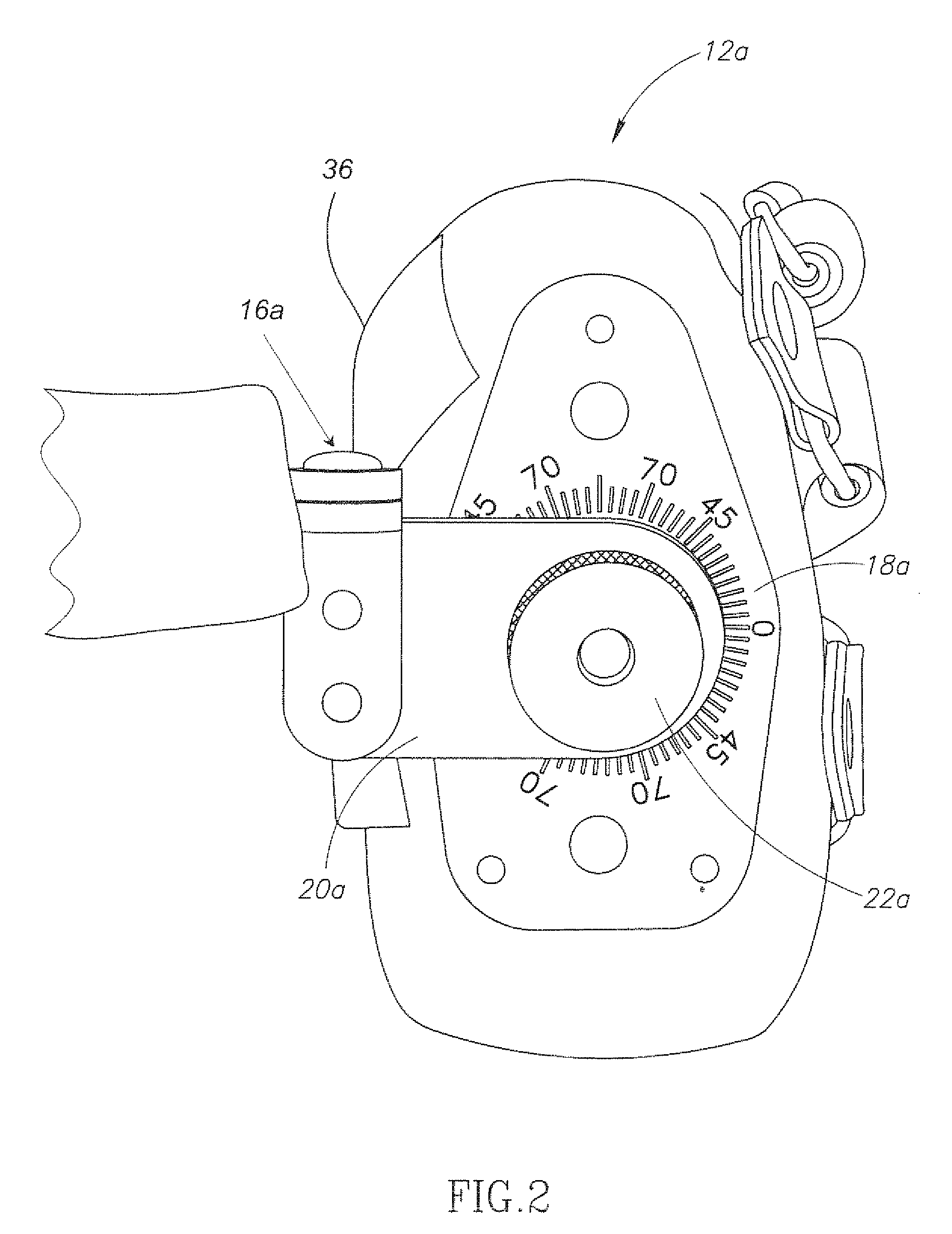
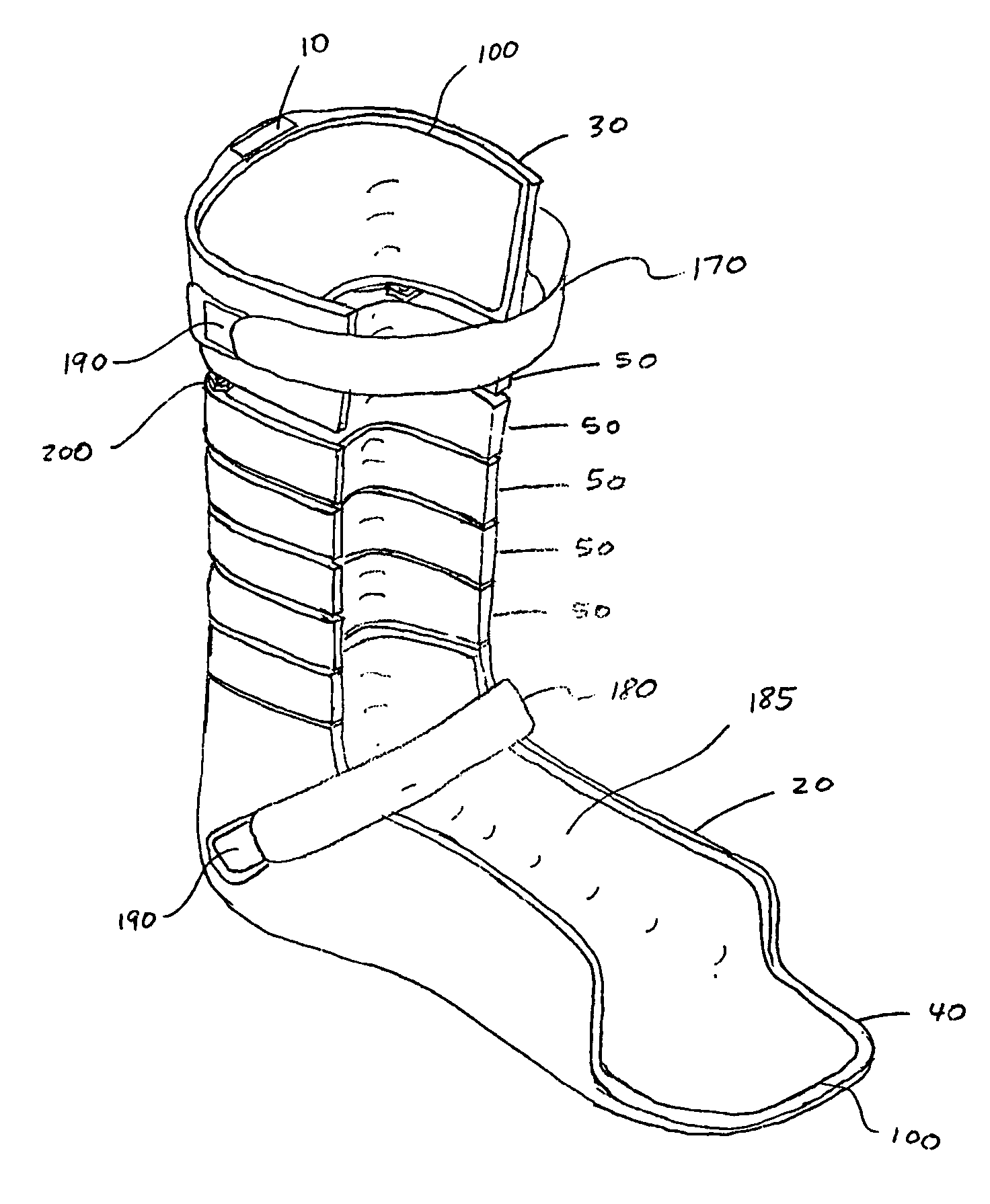
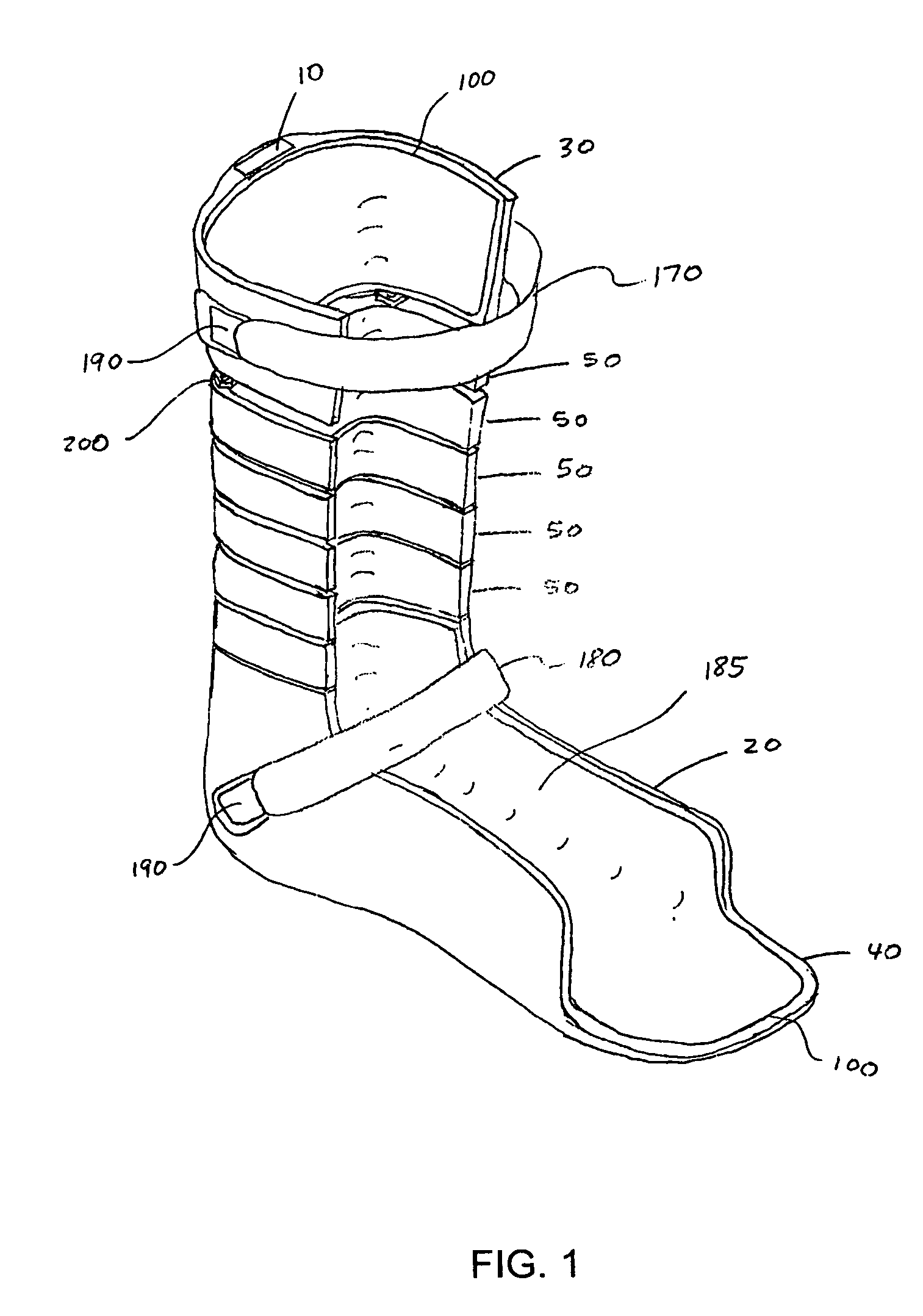
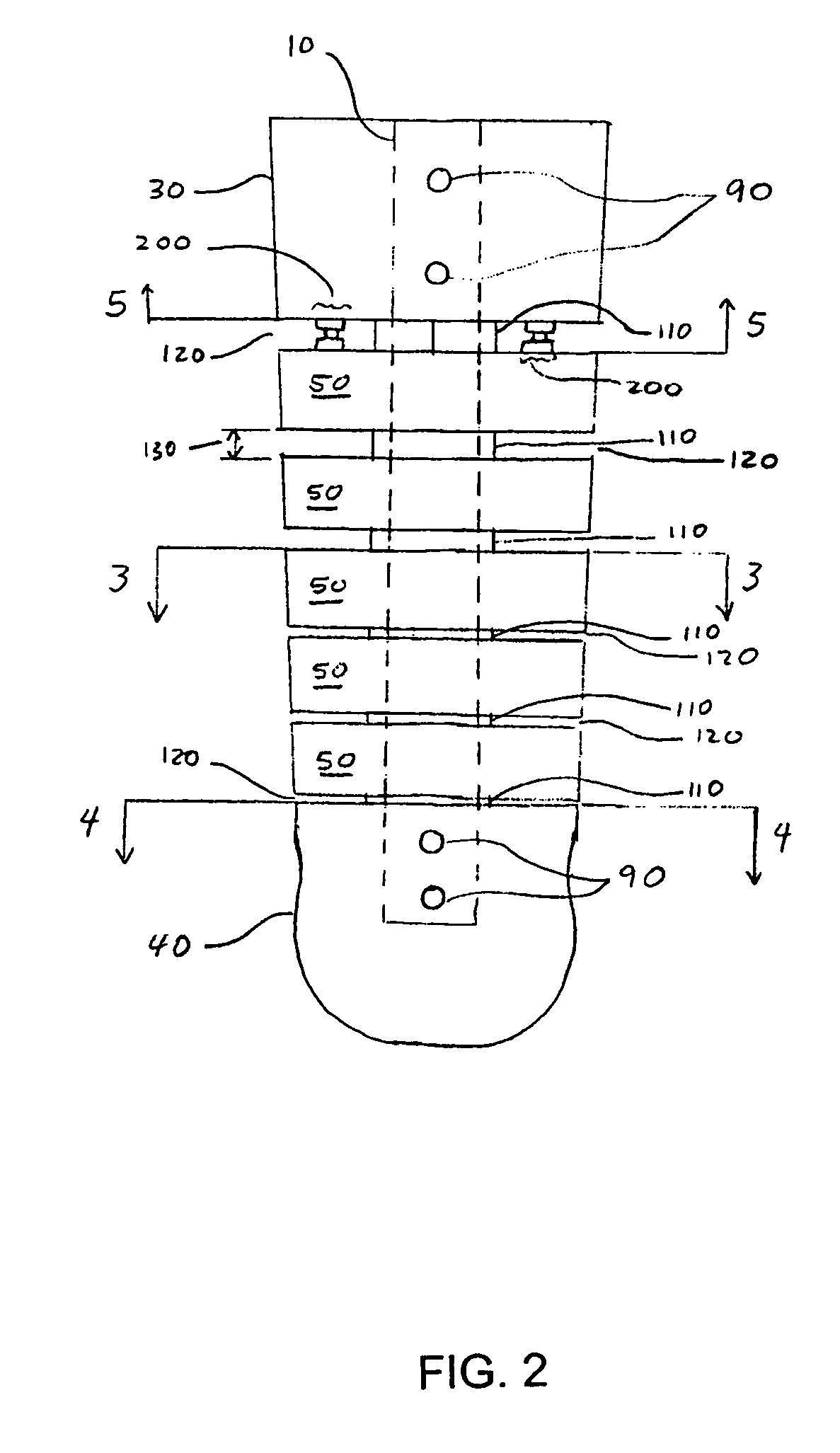
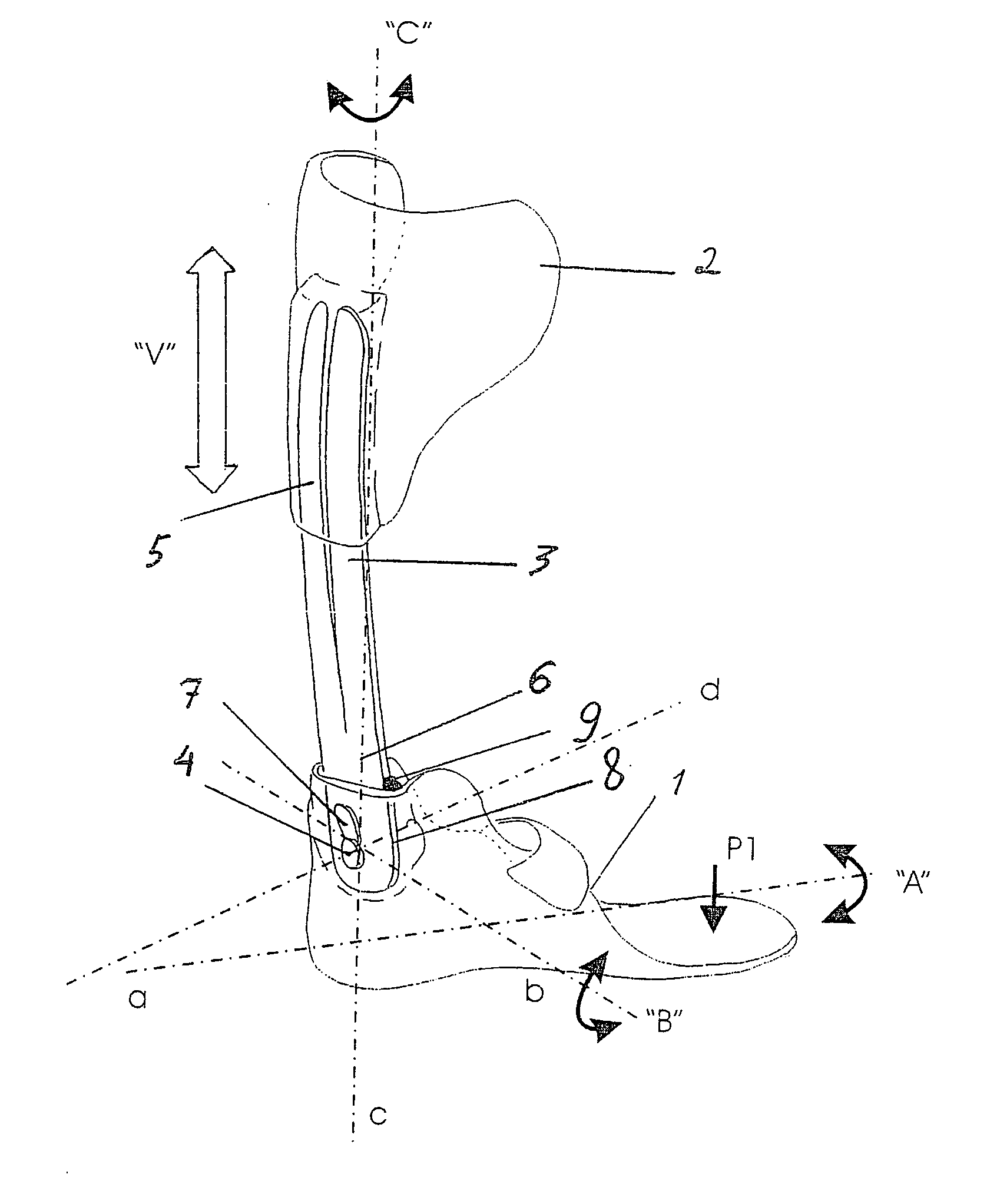
An ankle-foot orthosis comprising a leg member 12; a foot member 14; a frame 16 connecting the leg member to the foot member, wherein the frame comprises a first revolute joint 18 that rotates about a first axis 20 and a second revolute joint 22 that rotates about a second axis 24, wherein the first and second axes are non-parallel. The frame can further comprise a foot member segment 30 secured to the foot member 14 and extending to the second revolute joint 22. The orthosis can comprise a first force-torque sensor 36 located on the leg member, a second force-torque sensor 38 located on the foot member, and an encoder positioned on one of the revolute joints. The invention includes a method of measuring ankle-foot-related forces comprising positioning a subject's leg and foot in an ankle-foot orthosis; collecting data from the first and second force-torque sensors; and analyzing the collected data to determine the motion of the subject's ankle.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF DELAWARE
Methods of making and using an ankle-foot orthosis
InactiveUS7018350B2Function increaseImprove performanceNon-surgical orthopedic devicesKnee orthosisOrthotic device
The present invention is directed, to an improved orthosis and posterior plantar flexion stop for the orthosis, as well as to methods of making and using the orthosis and posterior stop, plus components used to make the orthosis and stop. The ankle-foot orthosis and plantar flexion stop of the present invention improve on the function and performance of the orthosis, while also making the orthosis attractive and easier to use than prior devices.
Owner:HINSHON PATRICK SCOTT
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com