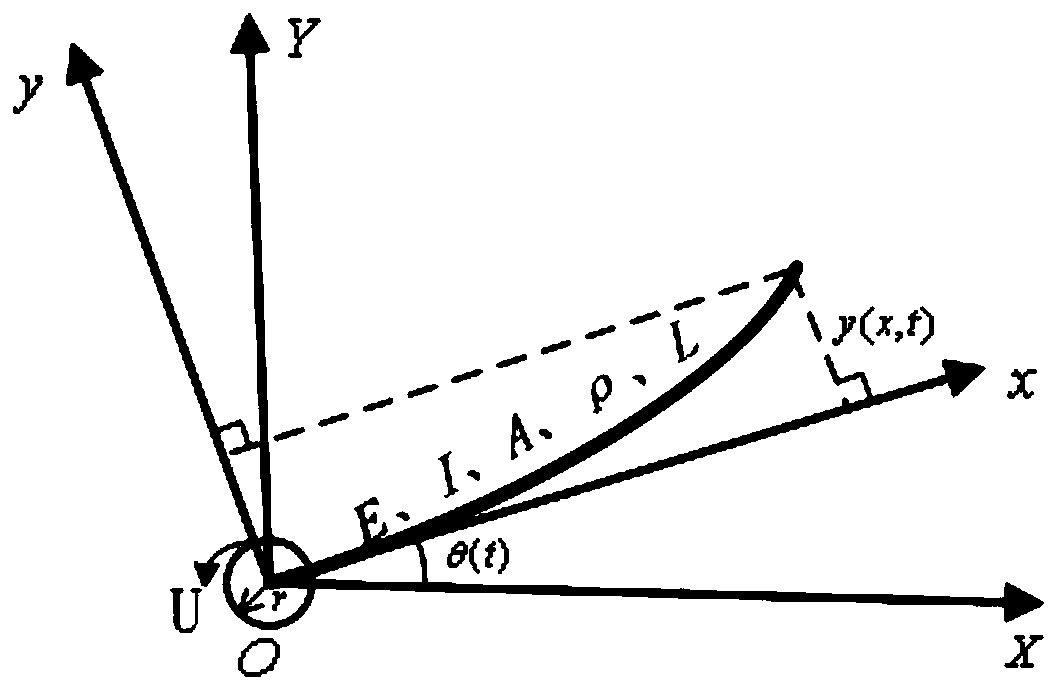
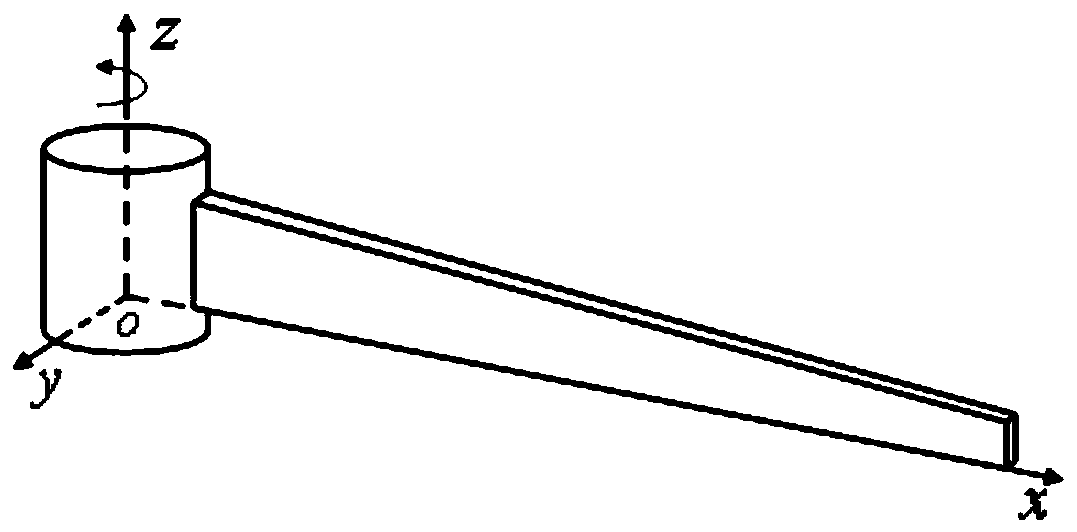
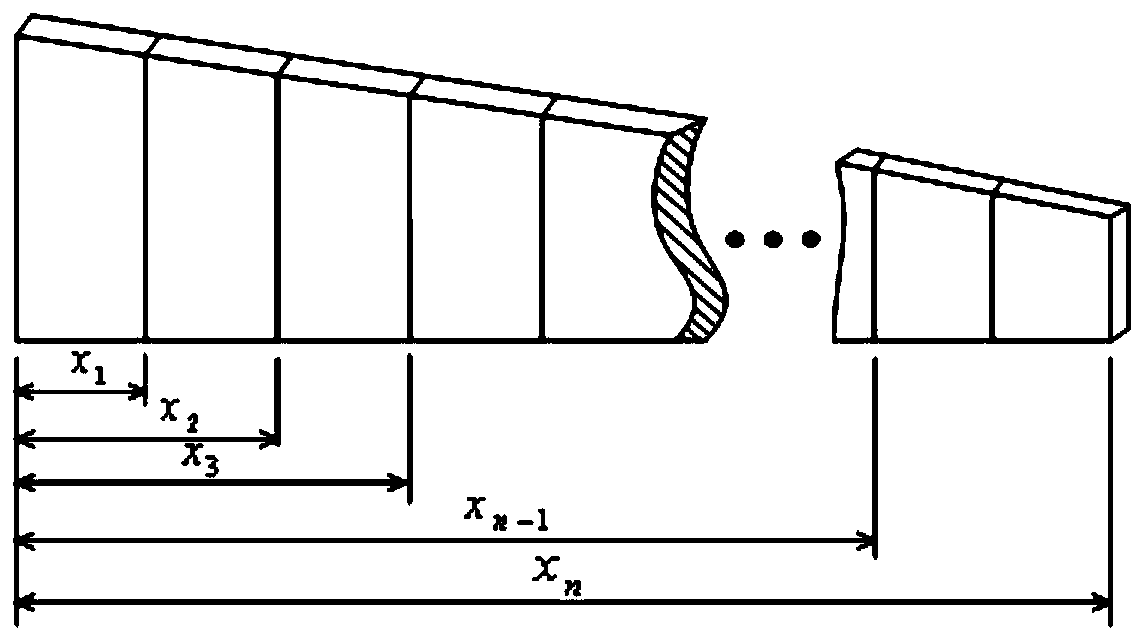
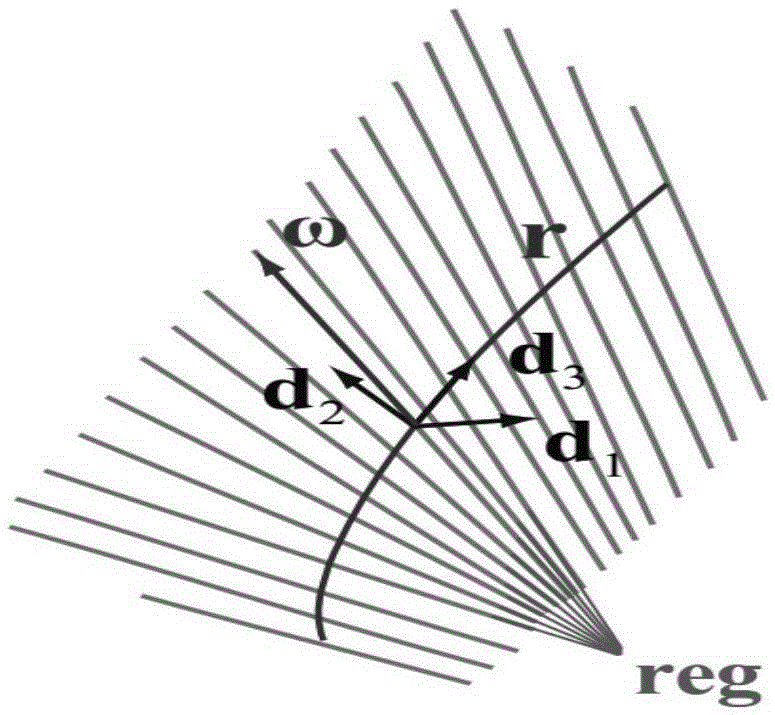
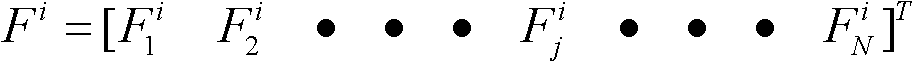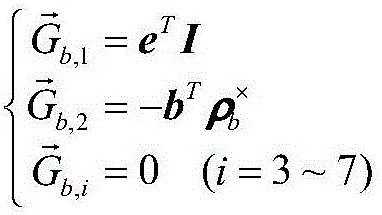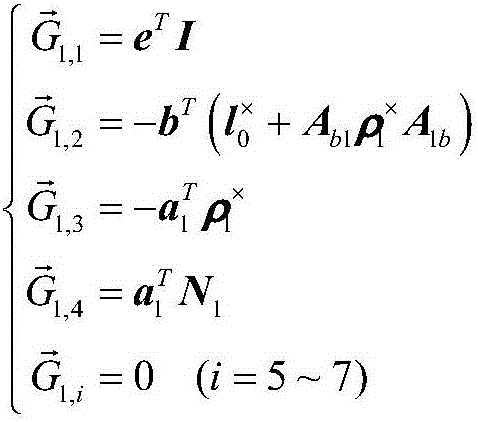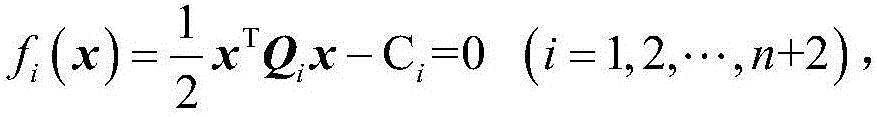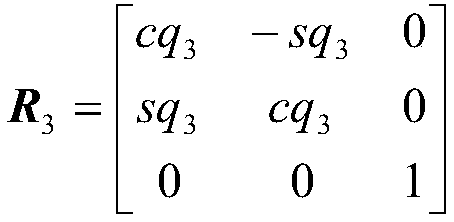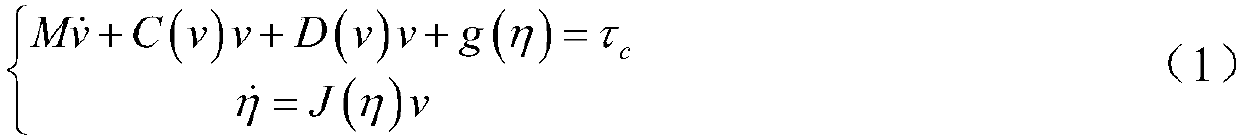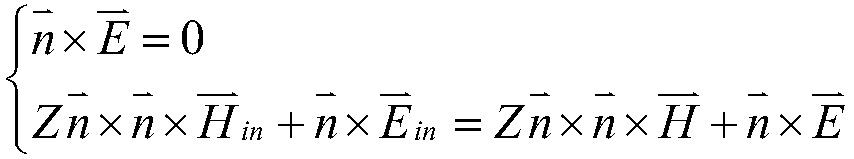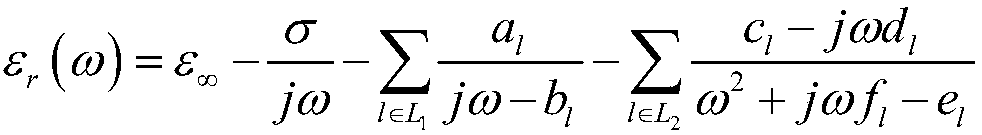Patents
Literature
73 results about "Generalized coordinates" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In analytical mechanics, specifically the study of the rigid body dynamics of multibody systems, the term generalized coordinates refers to the parameters that describe the configuration of the system relative to some reference configuration. These parameters must uniquely define the configuration of the system relative to the reference configuration. This is done assuming that this can be done with a single chart. The generalized velocities are the time derivatives of the generalized coordinates of the system.
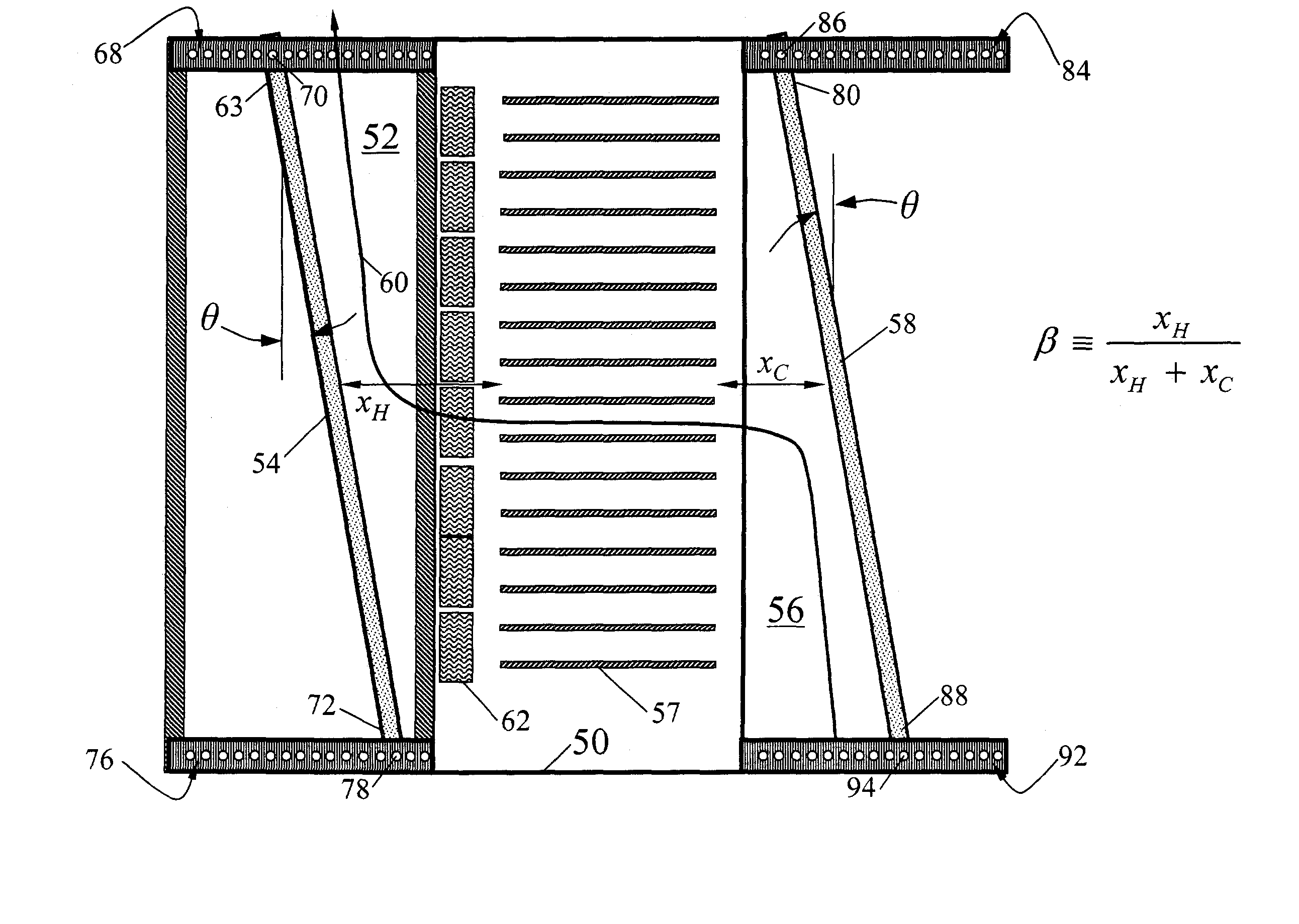
Cooling using complimentary tapered plenums
InactiveUS7085133B2Efficiently and effectively coolsEfficiently and effectivelyHeat exchange apparatusCooling/ventilation/heating modificationsCooling mediumGeneralized coordinates
Where a fluid cooling medium cools a plurality of heat-producing devices arranged in a row along a generalized coordinate direction, with a space between each adjacent pair of devices, each space may have a partition that defines a boundary between a first plenum and a second plenum. The first plenum carries cooling medium across an entrance and thence into a first heat-producing device located on a first side of the partition facing the first plenum. The second plenum carries cooling medium away from a second heat-producing device located on a second side of the partition facing the second plenum and thence across an exit. The partition is disposed so that the first plenum becomes smaller in cross-sectional area as distance increases from the entrance, and the second plenum becomes larger in cross sectional area as distance decreases toward the exit.
Owner:IBM CORP
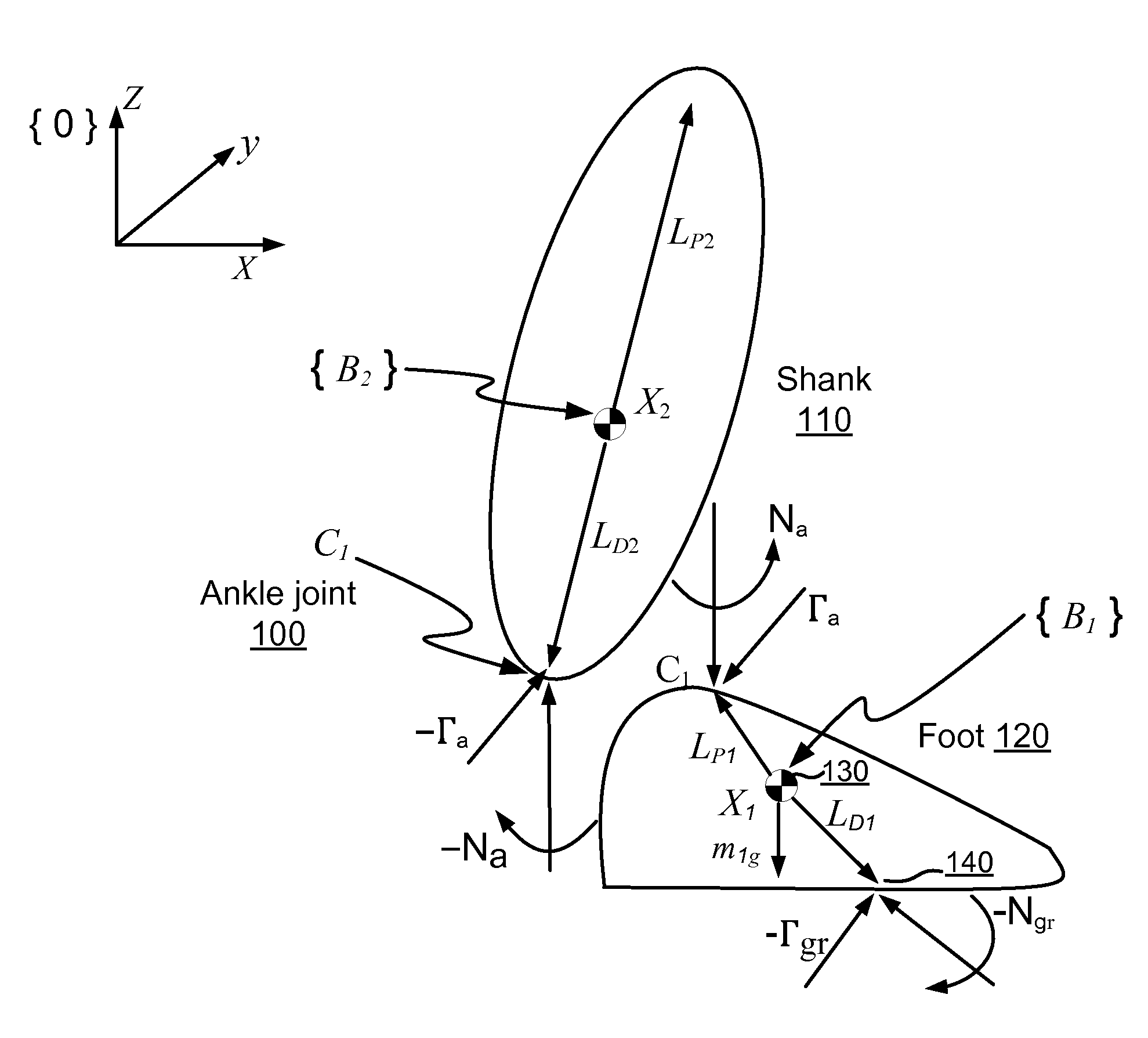
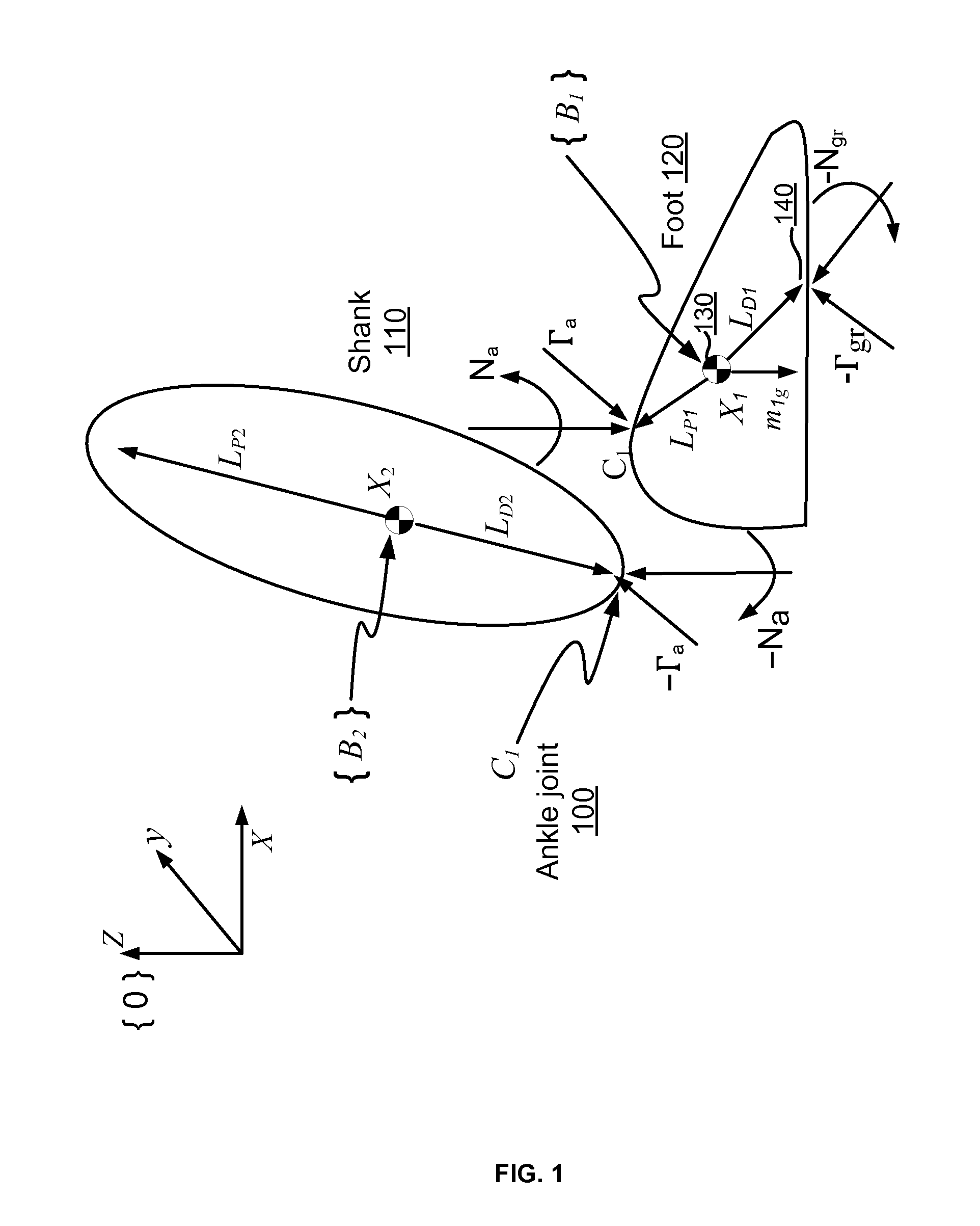
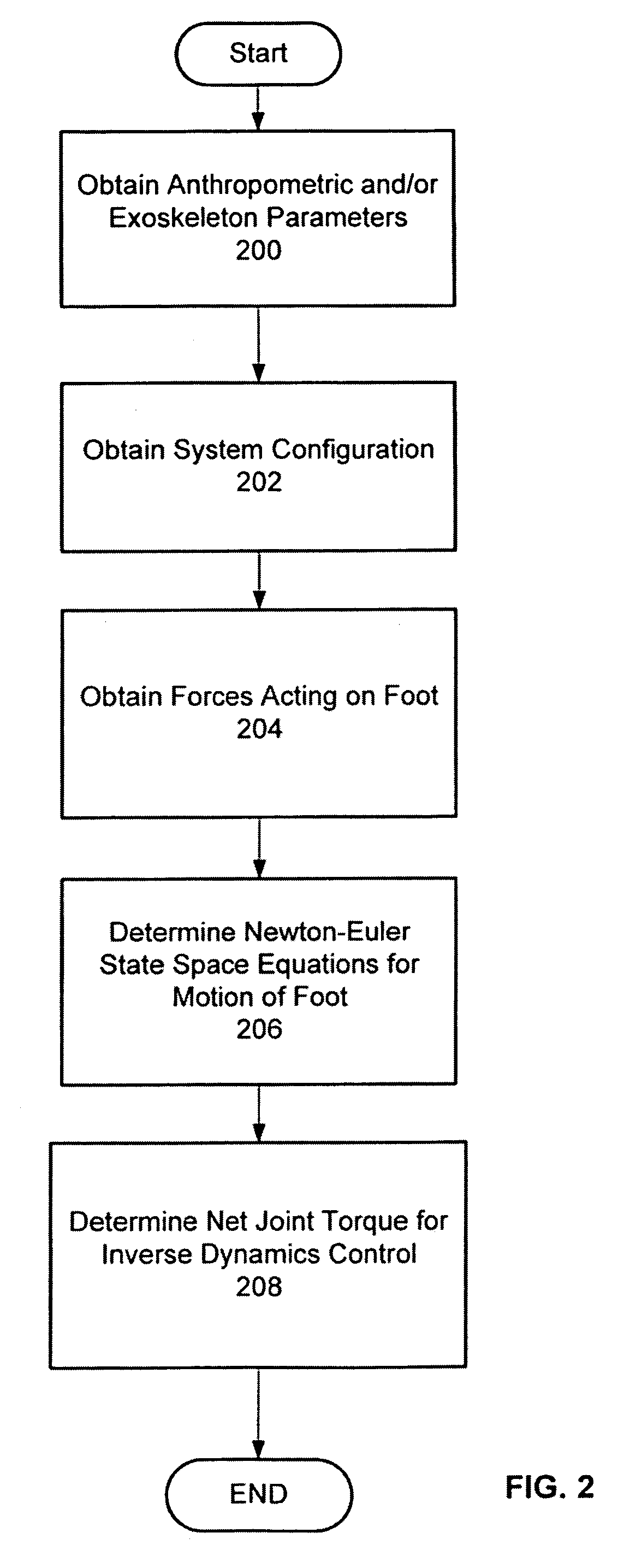
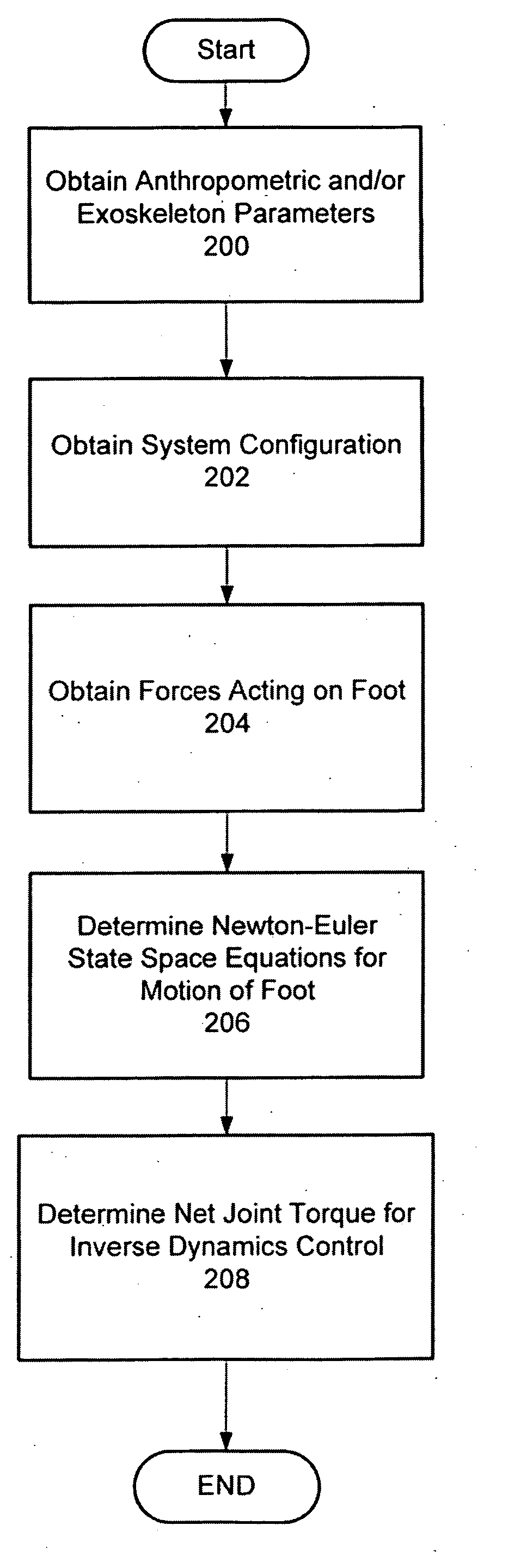
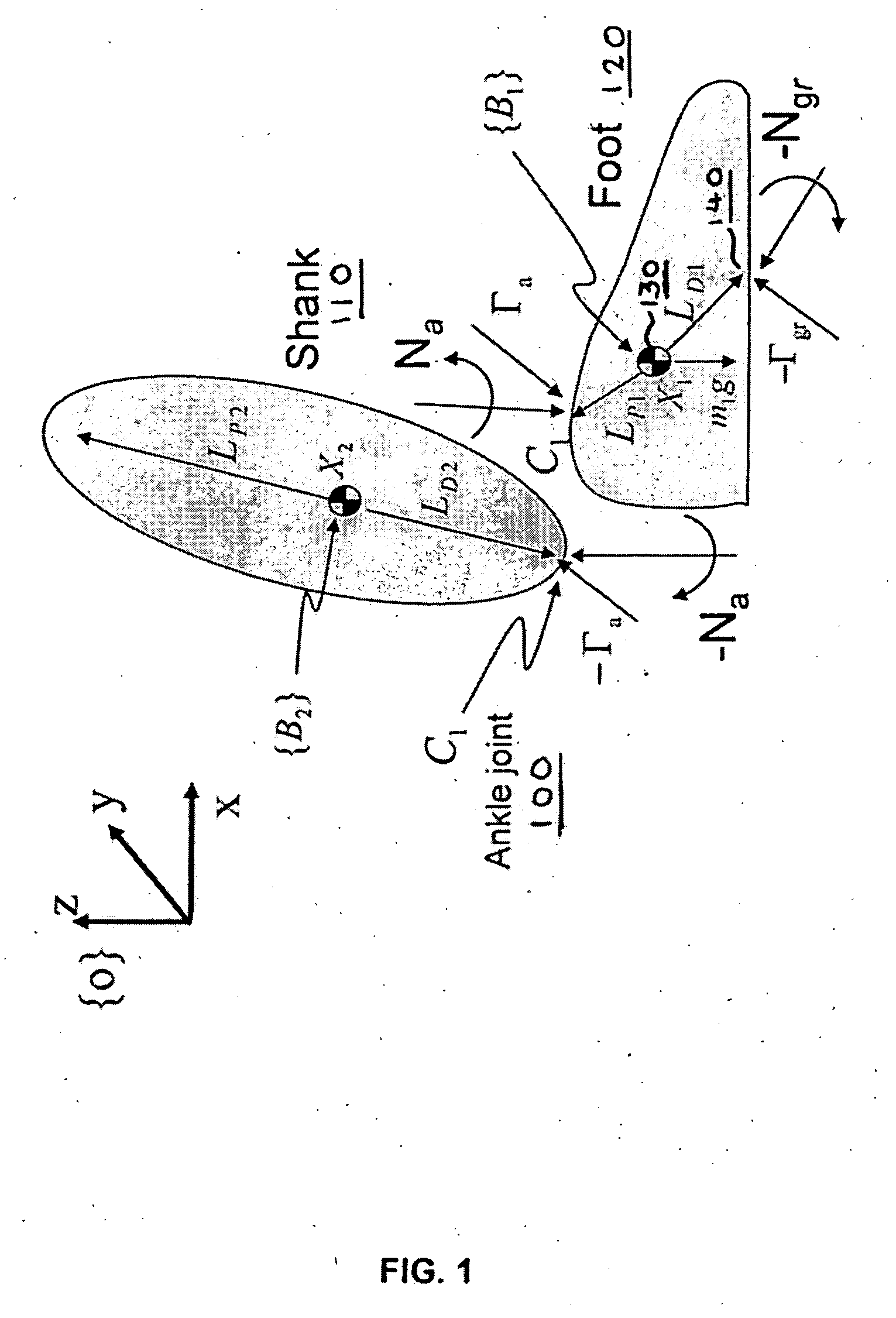
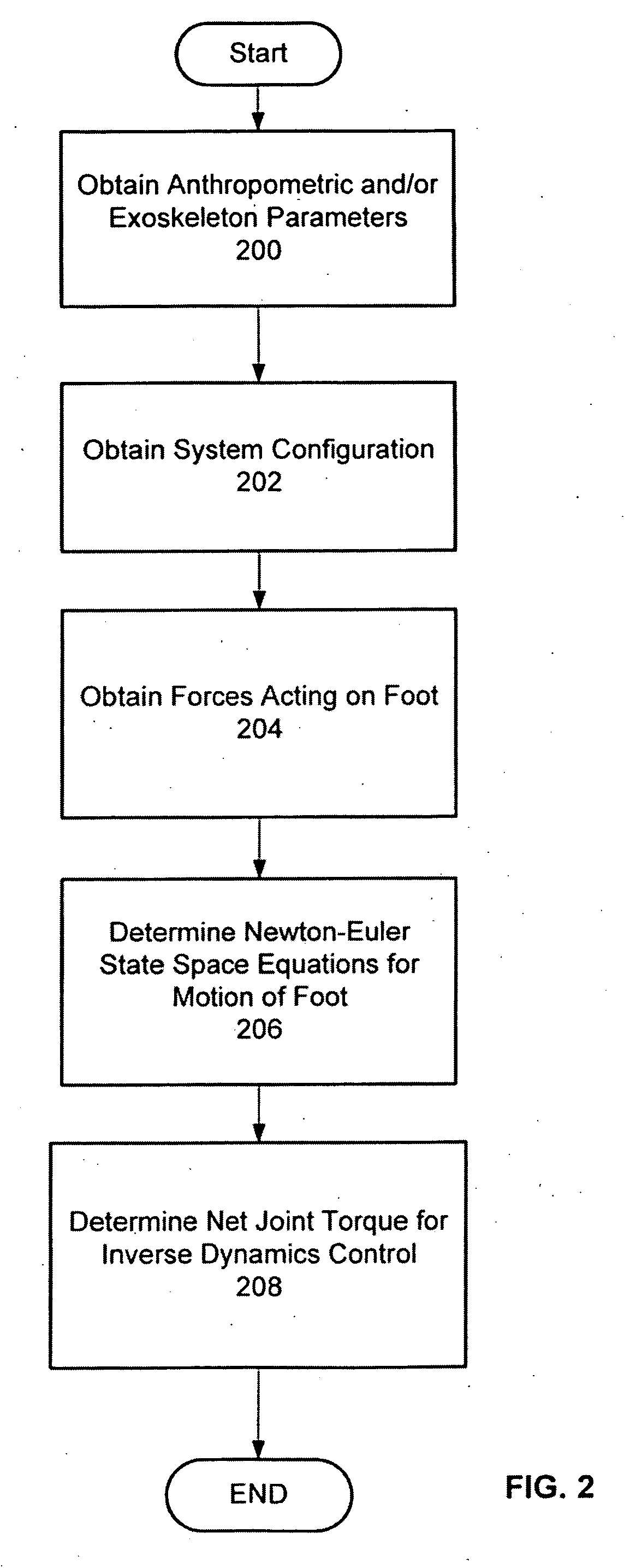
Active control of an ankle-foot orthosis
ActiveUS7650204B2Reduce the amount of noiseAdapt quicklyProgramme-controlled manipulatorPerson identificationGravitational forceOrthotic device
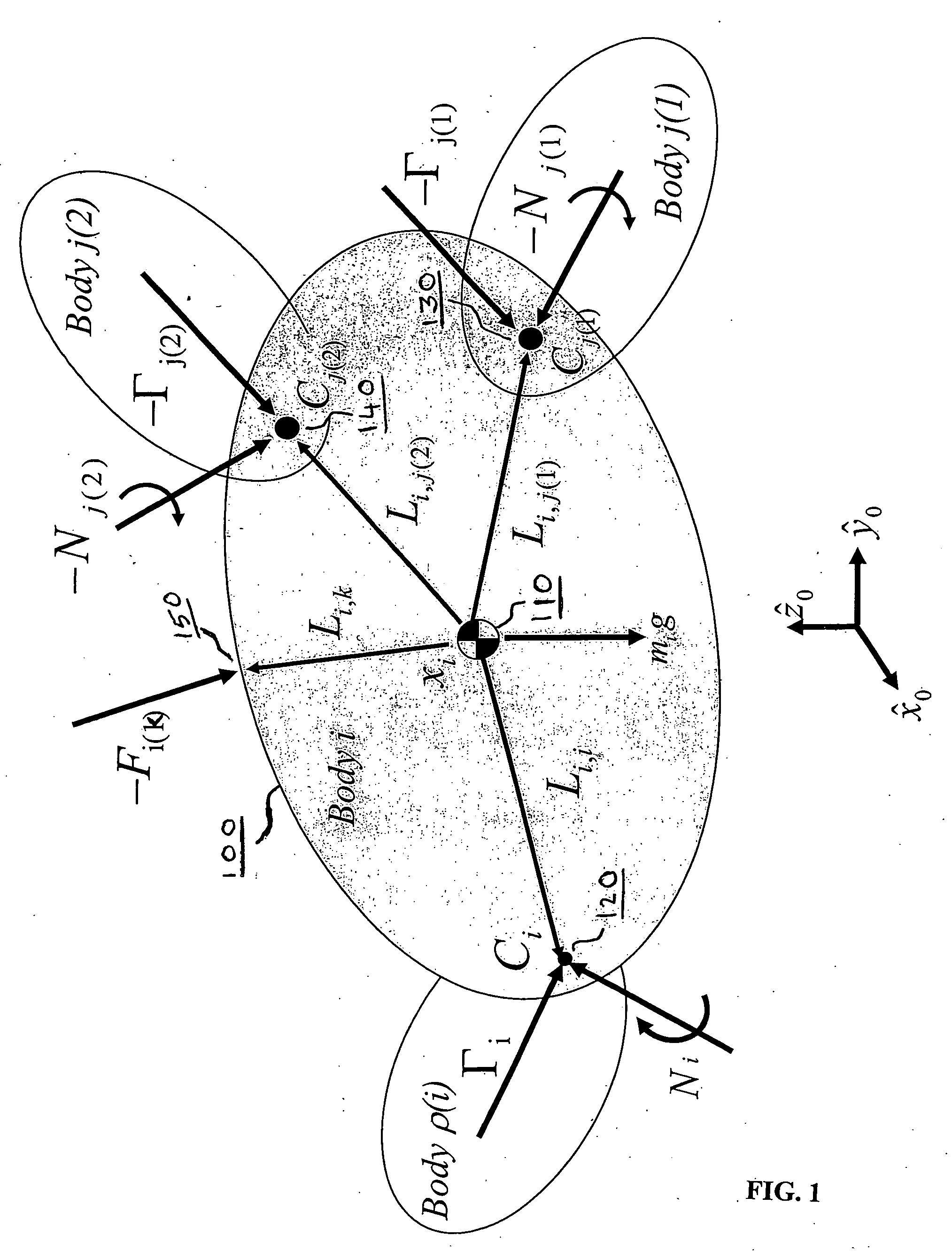
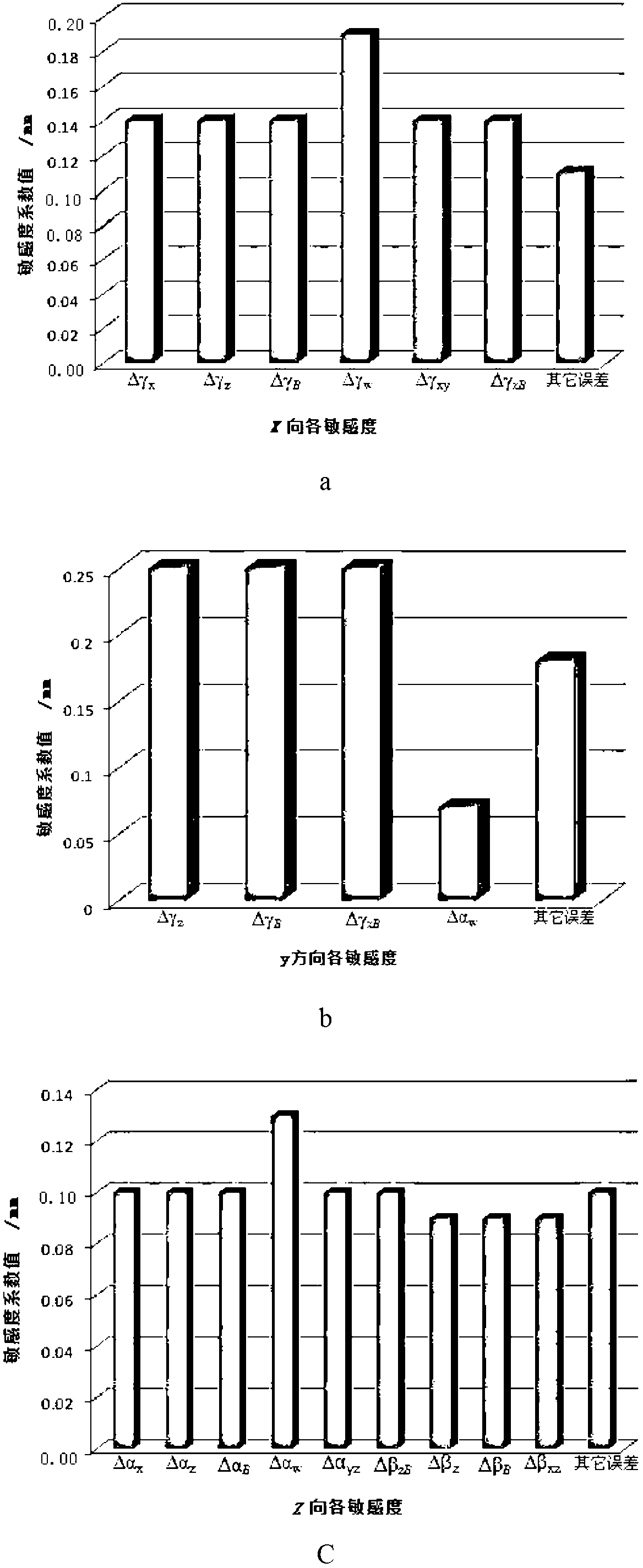
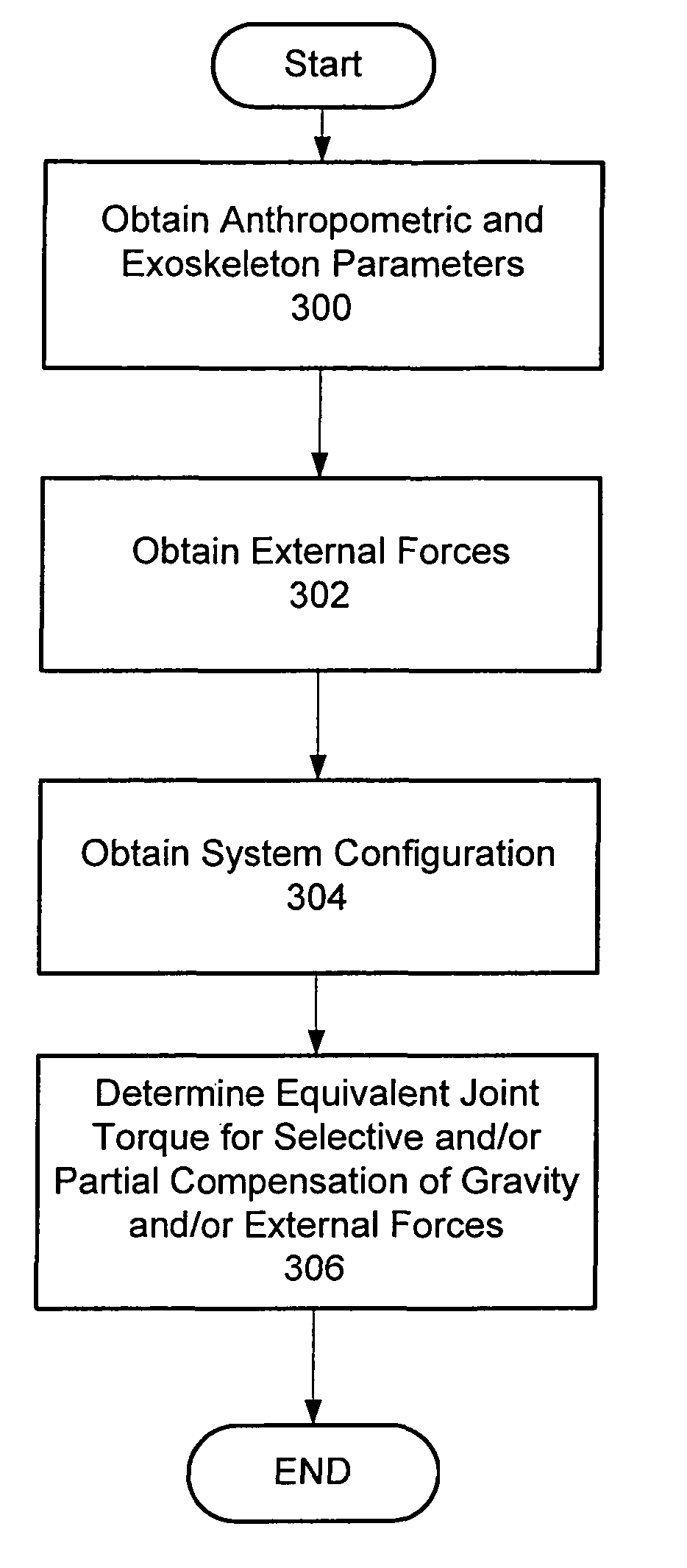
Techniques are provided for controlling a human-exoskeleton system including an ankle-foot orthosis by receiving system parameters for the human-exoskeleton system, receiving generalized coordinates such as an orientation of the foot, and determining a joint torque for controlling the ankle-foot orthosis to compensate for one or more components of forces acting on the foot. Forces selected for compensation include gravitational forces as well as external forces such as ground reaction forces. Techniques are provided for determining an ankle joint torque for partial or complete compensation of forces acting on the foot about an axis of rotation. The provided techniques mitigate the amount of interference between voluntary control and assist control, thereby allowing humans to quickly humans adapt to an exoskeleton system.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Progressive health monitoring method for cable system based on hybrid monitoring during generalized displacement of support
InactiveCN102221478AMonitor and evaluate health statusObvious non-linear featuresStructural/machines measurementMulti objective optimization algorithmLinear relationship
The invention provides a progressive health monitoring method for a cable system based on hybrid monitoring during generalized displacement of a support. Whether a mechanics calculation benchmark model of the structure requires to be updated against is decided by monitoring of a generalized coordinates of the structural support; considering the similar linear relationship among the current data vector of the monitored quantity and the initial value vector of the monitored quantity, the unit damage monitored quantity change matrix and the current nominal damage vector, in order to overcome the defects, a method using the linear relationship to approach the nonlinear relationship by section is adopted so that a large section is divided into a plurality of continuous small sections; the linear relationship in each small section is sufficiently accurate; and suitable algorithms such as a multi-objective optimization algorithm and the like can be utilized in each small section so as to calculate the non-inferior solution of the damage vector of the current cable, thus exactly determining the position and the damage degree of a damaged cable.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
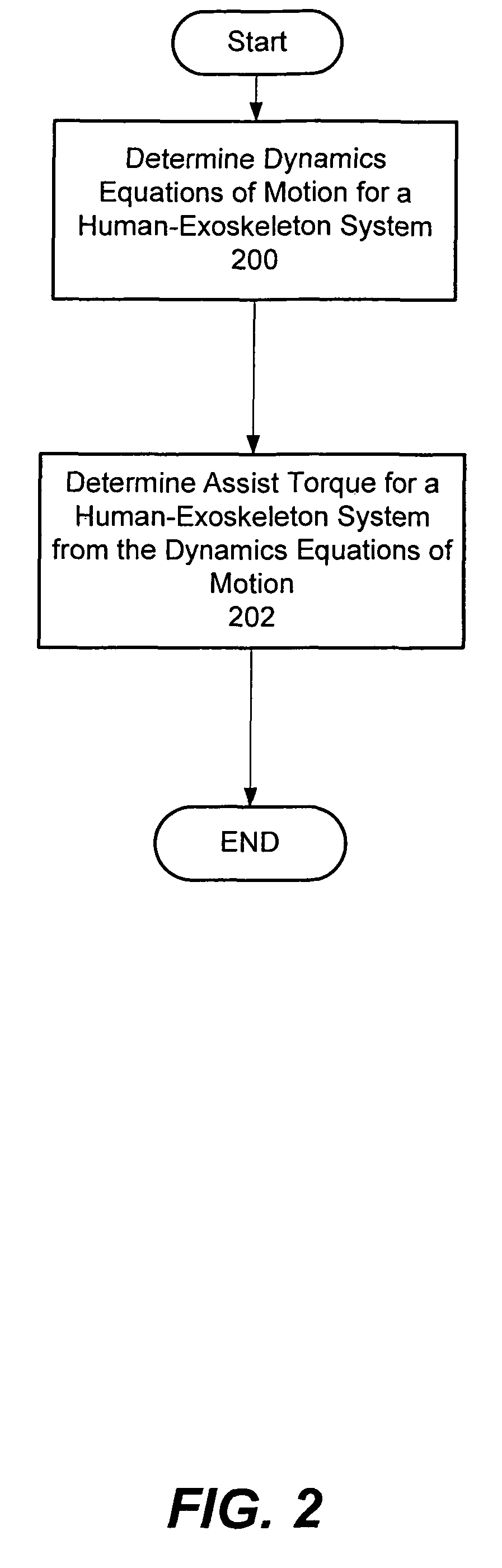
Exoskeleton controller for a human-exoskeleton system
ActiveUS20060247904A1Reduce the amount of noiseAdapt quicklyProgramme-controlled manipulatorPerson identificationActuatorExoskeleton
Techniques are provided for controlling an exoskeleton actuator at a joint of a human-exoskeleton system by receiving system parameters for the human-exoskeleton system, receiving generalized coordinates for the human-exoskeleton system, and determining an equivalent joint torque for the exoskeleton actuator to compensate for a selected force. While providing partial or complete compensation of selected gravitational and external forces, one embodiment of the present invention mitigates the amount of interference between voluntary control and assist control, thereby allowing humans to quickly humans adapt to an exoskeleton system.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Spatial complex flexible structure multi-body system dynamics modeling and calculating method
InactiveCN107220421AImproving computational efficiency in dynamics simulationsGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationComputing MethodologiesSimulation
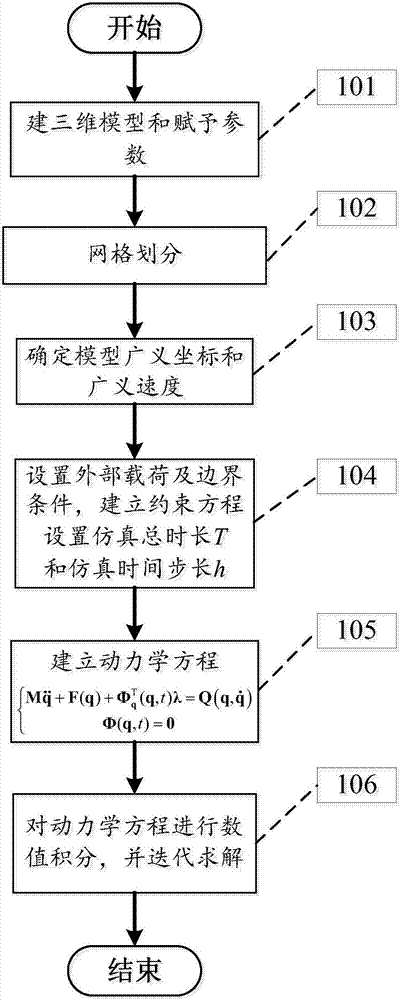
The invention provides a spatial complex flexible structure multi-body system dynamics modeling and calculating method. The method comprises the steps of 101, building a three-dimensional model and giving parameters; 102, performing mesh generation on the model; 103, calculating a mesh unit generalized coordinate vector q and a generalized velocity vector; 104, building a mesh model constraint equation; 105, according to the mesh unit type, the generalized coordinate vector, the generalized velocity vector and the constraint equation, building a multi-body system dynamics equation on the basis of a first-class lagrange equation; 106, calculating the built multi-body system dynamics equation, and completing modeling calculating of the spatial complex flexible structure multi-body system dynamics problem. The simple and effective dynamics modeling method is provided for the flexible structure multi-body system, and the calculating efficiency is improved.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Recognition method of critical geometrical error source of machine tool
The invention discloses a recognition method of a critical geometrical error source of a machine tool and belongs to the technical field of machine precision designing. The recognition method of the critical geometrical error source of the machine tool is characterized by comprising the steps that the machine tool is abstracted into a multi-body system according to the structure and motion characteristics of the machine tool, relevance of parts of the machine tool is described by a topological structure and a low-order body array, a generalized coordinate system is built in the multi-body system, coupling relationship of error amounts of parts of the machine tool is described by a homogeneous transformation matrix, a characteristic matrix and a motion equation of the relative movement between two adjacent bodies of the machine tool are elicited, a precision model of a machining center is built, an ordinary mathematical model used for error sensitivity analysis of a four-shaft machine tool is built with a matrix differential method according to the precision model of the precision horizontal machining center, influence degrees on the whole space error of all error elements are compared by calculating the geometrical error sensitivities of all parts, and finally the critical error source influencing the machining precision of the machine tool is recognized.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH +1
Exoskeleton controller for a human-exoskeleton system
ActiveUS7774177B2Reduce the amount of noiseAdapt quicklyProgramme-controlled manipulatorDigital data processing detailsActuatorSacroiliac joint
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
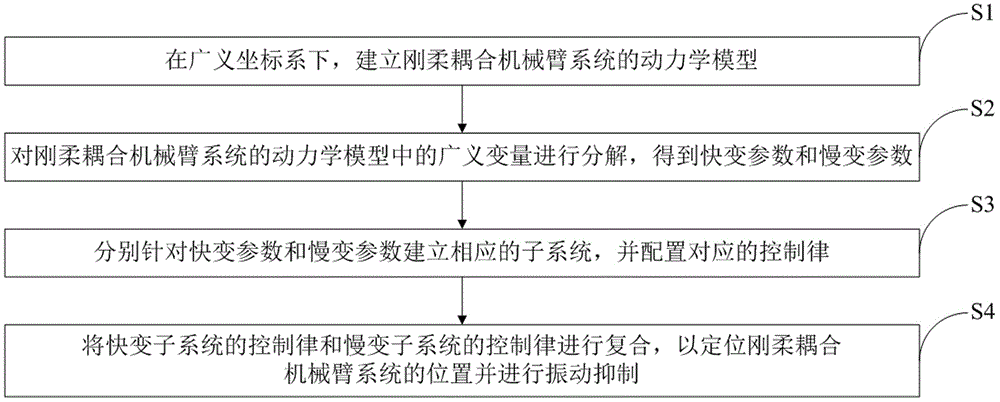
Vibration suppression algorithm of spatial flexible mechanical arm
ActiveCN106094528AReduce vibrationSuppression of flexural vibrationAdaptive controlVibration controlDynamic models
The invention discloses a vibration suppression algorithm of a spatial flexible mechanical arm. The algorithm is implemented as follows: S1, a dynamic model of a rigid-flexible coupling mechanical arm system is established under a generalized coordinate system; S2, a generalized variable in the dynamic model of the rigid-flexible coupling mechanical arm system is decomposed to obtain a quick-changing parameter and a slow-changing parameter; S3, corresponding sub systems are established for the quick-changing parameter and the slow-changing parameter and corresponding control laws are configured; and S4, the control laws of the quick-changing parameter and the control law of the slow-changing parameter are combined, thereby localizing the rigid-flexible coupling mechanical arm system and carrying out vibration suppression. According to the invention, the dynamic model of the rigid-flexible coupling mechanical arm system is established and is decomposed into the quick-changing and the slow-changing sub systems with different dimensions; and the rigid attitude motion state and the flexible vibration state of the platform are separated and controllers are designed respectively to carry out combined controlling. Therefore, a flexibility vibration control problem of in-orbit flexible mechanical arm operation is solved.
Owner:SHANGHAI AEROSPACE CONTROL TECH INST
Mechanical arm motion control method
InactiveCN103331756AImplement trackingSimple calculationManipulatorMathematical modelAngular velocity
A mechanical arm motion control method comprises the following steps of: (1) establishing complete corresponding transformation transfer matrices of n connecting rods, working out linear velocities and angular velocities of the connecting rods, (2) calculating centers of mass of the connecting rods to obtain inertia tensors, working out total kinetic energy and total potential energy of a mechanical arm, obtaining a partial derivative of the difference between the total kinetic energy and the total potential energy to a generalized coordinate q of the mechanical arm, obtaining a relationship between a driving force vector tau and q, q', establishing a mathematical model, and (3) performing iterative calculation on set time with a variable gain iterative control algorithm for each time point, acquiring an error between each time point and expected pose qd, subtracting the errors from the current pose q(0) to obtain an initial error e'1(0), taking the driving force vector tau as system input, performing the iterative calculation on the set time with the variable gain iterative control algorithm, obtaining the driving force vector tau required to control the mechanical arm to reach the expected pose at each time point. The method is higher in control precision and good in flexibility, and is applicable to non-linear and time-varying occasions.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Active control of an ankle-foot orthosis
ActiveUS20060270950A1Reduce the amount of noiseAdapt quicklyProgramme-controlled manipulatorPerson identificationGravitational forceOrthotic device
Techniques are provided for controlling a human-exoskeleton system comprising an ankle-foot orthosis by receiving system parameters for the human-exoskeleton system, receiving generalized coordinates such as an orientation of the foot, and determining a joint torque for controlling the ankle-foot orthosis to compensate for one or more components of forces acting on the foot. Forces selected for compensation can include gravitational forces as well as external forces such as ground reaction forces. Techniques are provided for determining an ankle joint torque for partial or complete compensation of forces acting on the foot about an axis of rotation. One embodiment of the present invention mitigates the amount of interference between voluntary control and assist control, thereby allowing humans to quickly humans adapt to an exoskeleton system.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Simulation method for elastic waverider hypersonic flight vehicle
ActiveCN103970957AThin bodyReflect aerodynamic/propulsion/elastic coupling propertiesSustainable transportationSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationElastic vibrationDamping ratio
The invention provides a simulation method for an elastic waverider hypersonic flight vehicle. The method includes the following steps that considering influences of aerodynamic heating and variable section inertia moment, an elastic model of a hypersonic flight vehicle free beam structure is established; a model superposition method is used for solving an elastic vibration equation, the intrinsic frequency, damping ratio and intrinsic vibration mode of each mode are solved, and on this basis, an elastic vibration generalized coordinate equation of the waverider flight vehicle is obtained; a computational fluid dynamics method is used for obtaining aerodynamic force and engine propulsion of the flight vehicle; on the basis of analyzing thrust, aerodynamic force and aeroelasticity, a rigid body-elastic coupling model of the hypersonic flight vehicle is established. The simulation method is suitable for performing modeling and simulation on the waverider flight vehicle. On this basis, the established model of the waverider hypersonic flight vehicle is more accurate, and the aerodynamic / propelling / elastic coupling characteristics of the flight vehicle can be reflected better in the process of model simulation.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Stable tether dragging control method for space debris
ActiveCN107643689AClearing task successfullyStable removalAdaptive controlEngineeringRelative motion
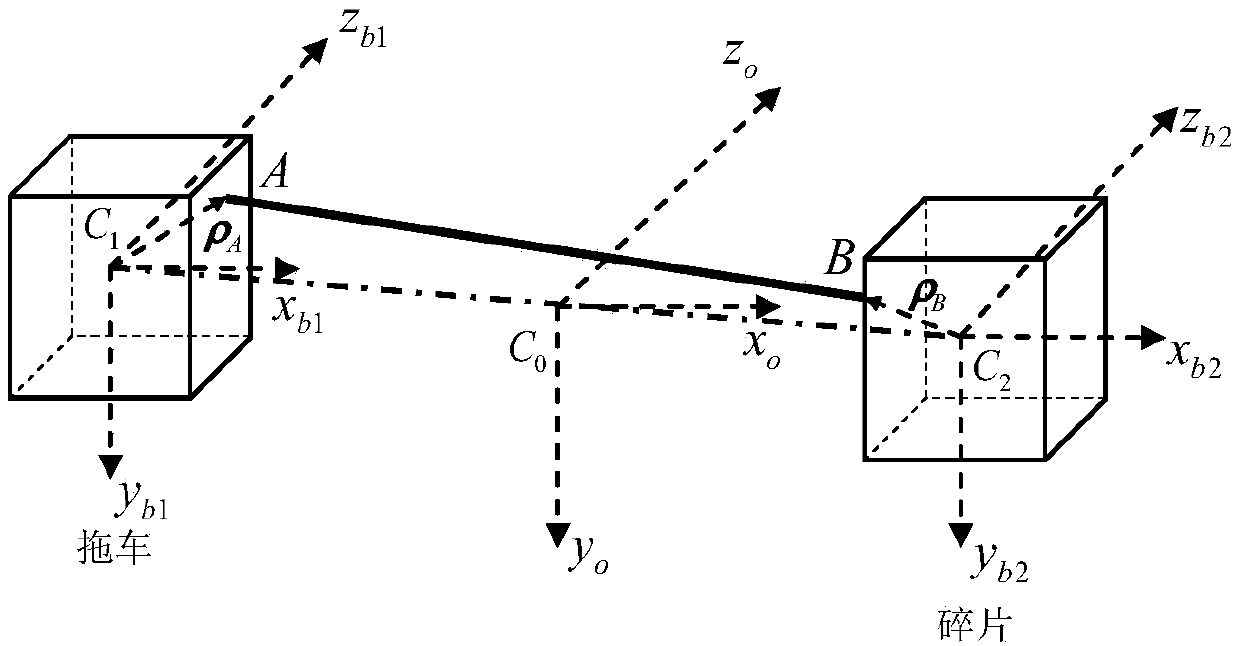
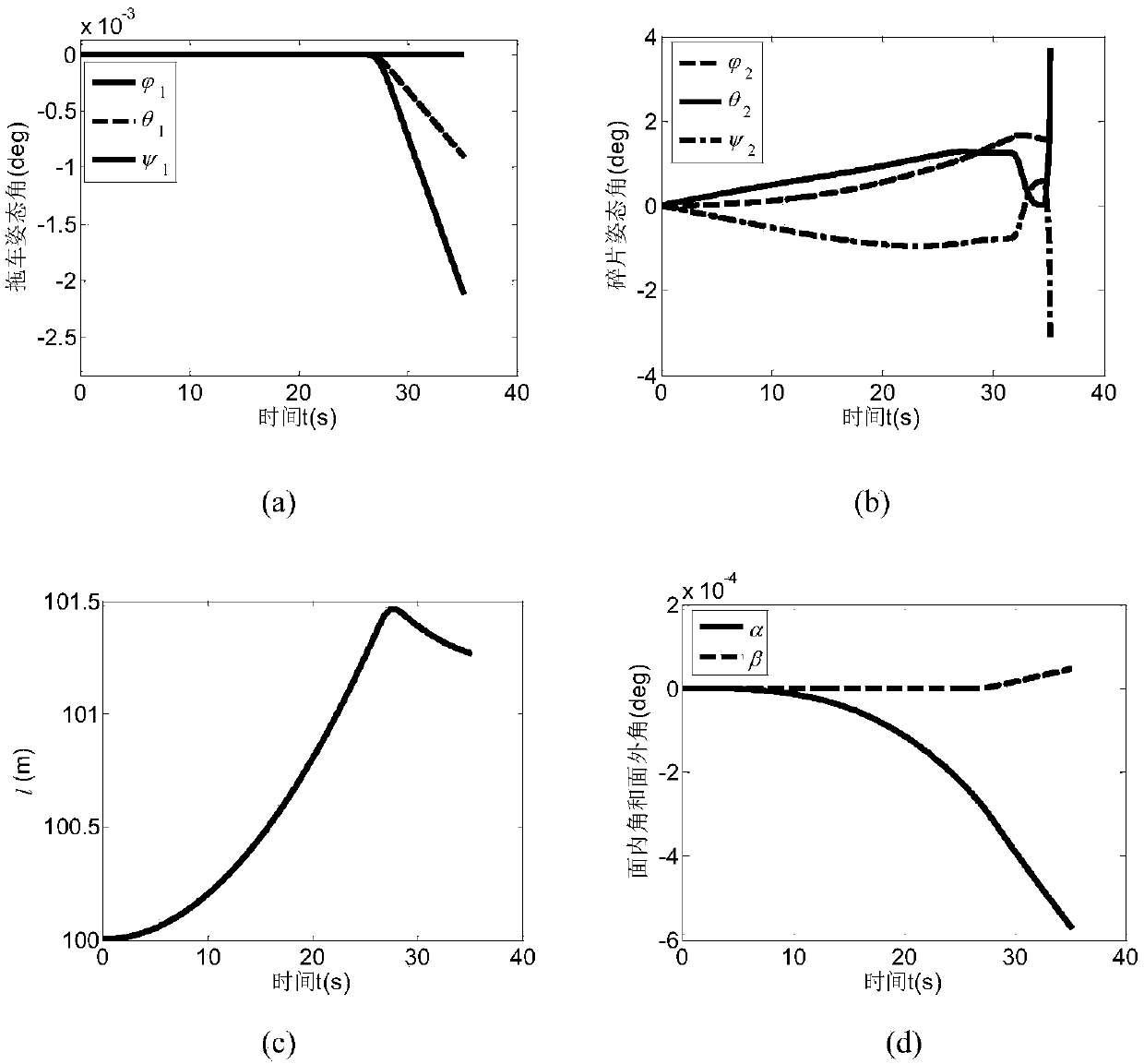
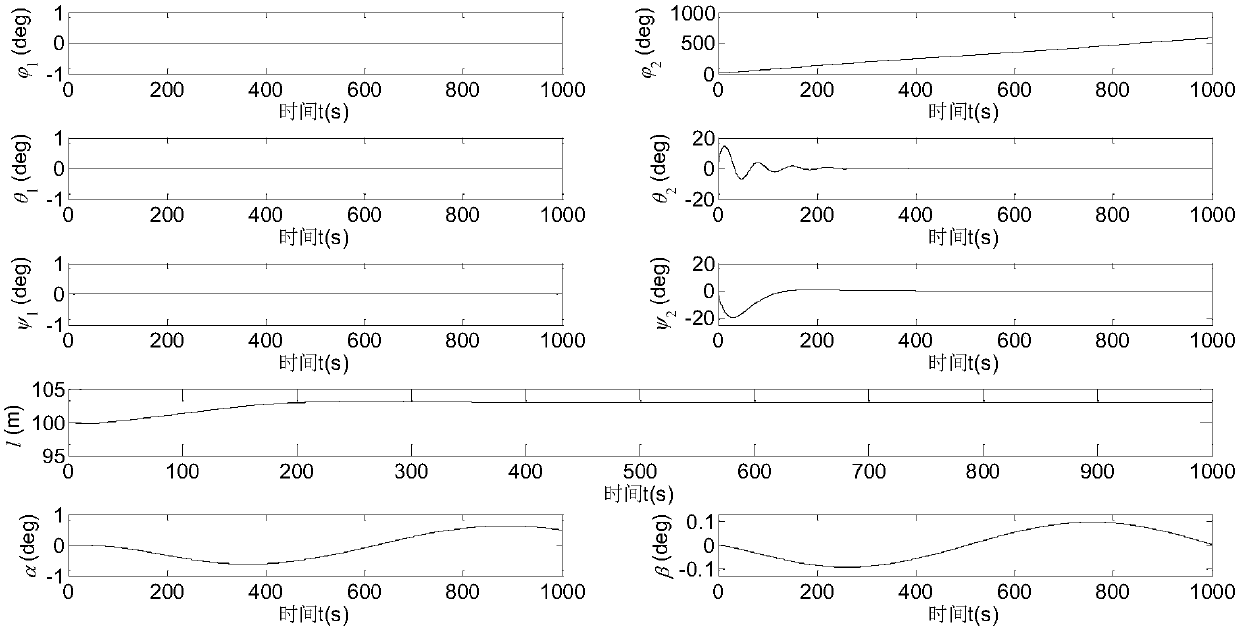
The invention, which belongs to the attitude dynamics and control field of the spacecraft, relates to a stable tether dragging control method for space debris, especially to the relative motion and flexible tether control method of the spacecraft. According to the invention, appropriate generalized coordinates are selected and an accurate three-dimensional orbital attitude coupling dynamics modelof a tether trailer system is established by using a lagrange method, wherein the debris and the trailer are viewed as rigid bodies and the tether is considered as a mass-free spring damping. A methodfor estimating the de-tumbling capability for specific debris by the tether before de-tumbling on the debris by the tether is put forward. For the initially rotating space debris, an offset control strategy using an original tether length and a connection point offset value as control inputs is designed to realize debris de-tumbling and stabilizing the jittering of the system, so that the reliable guarantee is provided for tether dragging elimination of the space debris.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Self-adaptive finite time convergence sliding-mode control method of robot
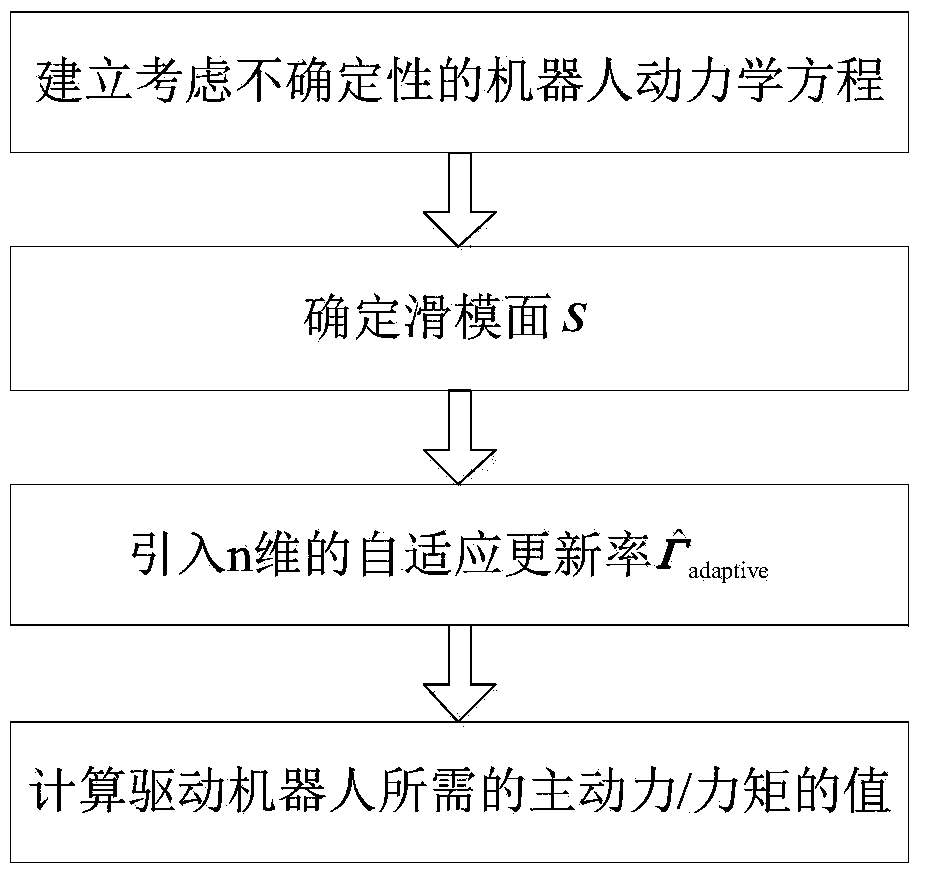
ActiveCN105171758AReduce chatteringSolve the influence of different dynamic characteristicsProgramme-controlled manipulatorSpecial data processing applicationsRobotic systemsCoordinate vector
The invention relates to a self-adaptive finite time convergence sliding-mode control method of a robot and belongs to the technical field of control. The method comprises steps as follows: establishing a robot kinetic equation considering uncertainty, determining a sliding mode surface, then introducing n-dimensional self-adaptive updating rate, calculating value of active power / moment required for driving the robot finally, and driving a robot system based on the value so as to enable generalized coordinate vectors of the robot to converge to a steady-state or trace command signals in finite time. The method has the characteristics and benefits as follows: firstly, the problem of chattering of the sliding-mode control is solved greatly while high-precision control is realized; secondly, possible influence of different dynamic characteristics in all directions of freedom degrees of the robot system can be eliminated; thirdly, the problem of moment saturation and chattering of the robot system at the starting stage can be solved; fourthly, kinetic compensation guaranteeing real-time performance of the control can be realized. The method is applicable to the robot systems with structure types of parallel connection, series connection, series-parallel connection and the like.
Owner:广东若贝特设备制造有限公司
Modeling method of space three-body flexible tethered satellite formation system under non-inertial reference coordinate system
ActiveCN109002050ASimplify the modeling processImprove accuracyCosmonautic vehiclesCosmonautic partsDynamic equationInstability
The invention belongs to the technical field of spacecraft flight, and particularly relates to a modeling method of a space three-body flexible tethered satellite formation system under a non-inertialreference coordinate system. The modeling method comprises the following steps that firstly, a satellite formation system model and a non-inertial reference system fixed to the system centroid are established; secondly, a flexible tether connecting a satellite is discrete into a plurality of tether units, and the satellite and tether unit particles are numbered; and finally, dynamic equations ofdiscrete element particles under the non-inertial reference system are established, and then the dynamic equations of the satellite formation system are derived. According to the modeling method of the space three-body flexible tethered satellite formation system under the non-inertial reference coordinate system, modeling is carried out under the non-inertial reference system, redundant steps such as selecting generalized coordinates and coordinate transformation are not required, and simultaneously flexibility of the space tether is considered, so that the method is faster and more accuratein describing various space dynamic behaviors of a formation system and revealing spin stability and instability states of the system. In addition, the modeling method of the space three-body flexibletethered satellite formation system under the non-inertial reference coordinate system can further be extended to modeling of a four-body or multi-body space tethered formation system and has great practical value.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
System and method for simulating motion of a multibody system
InactiveUS20090228244A1Great evolutionAvoid excessive errorComputation using non-denominational number representationDesign optimisation/simulationMomentumForward dynamic
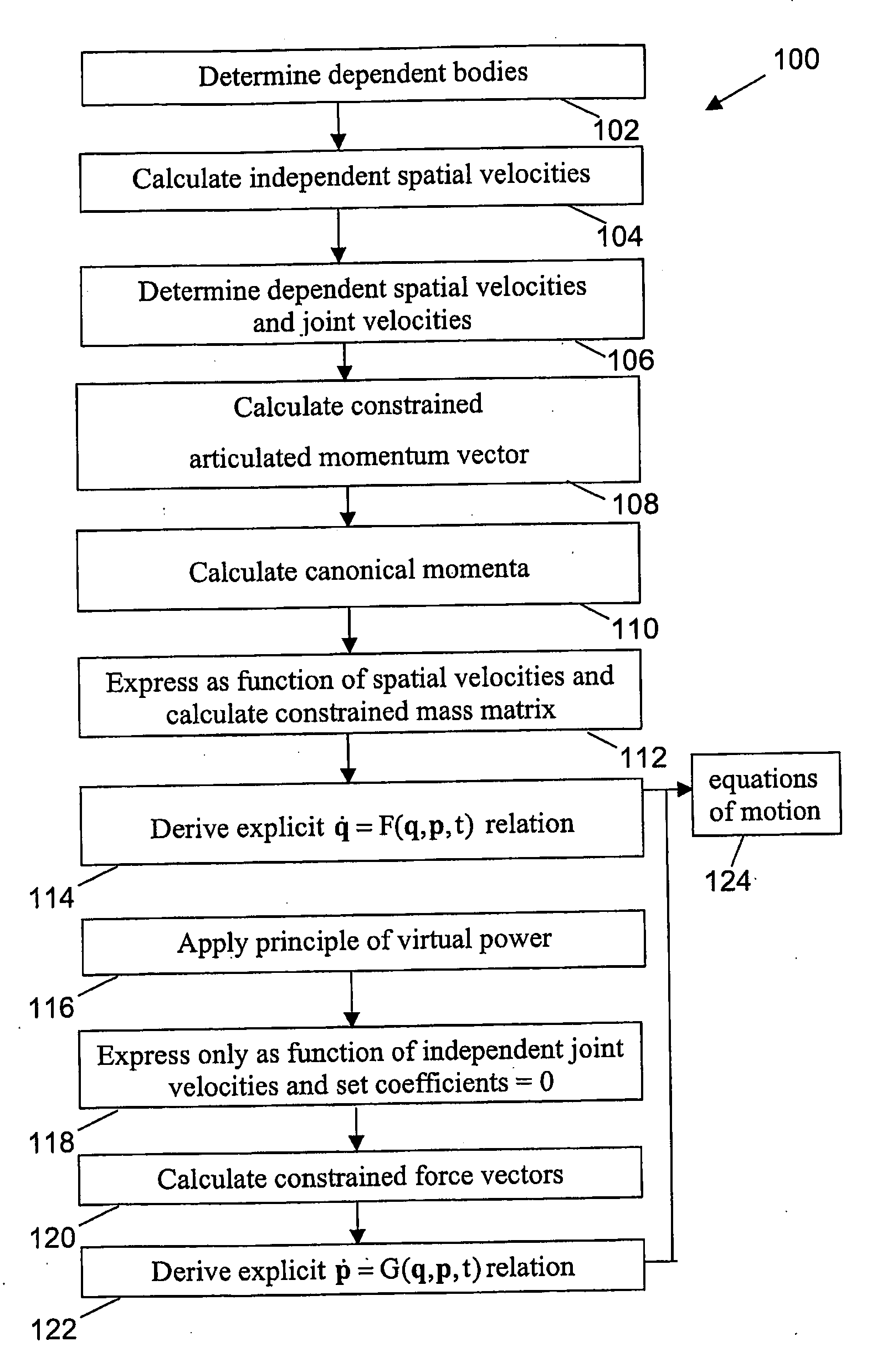
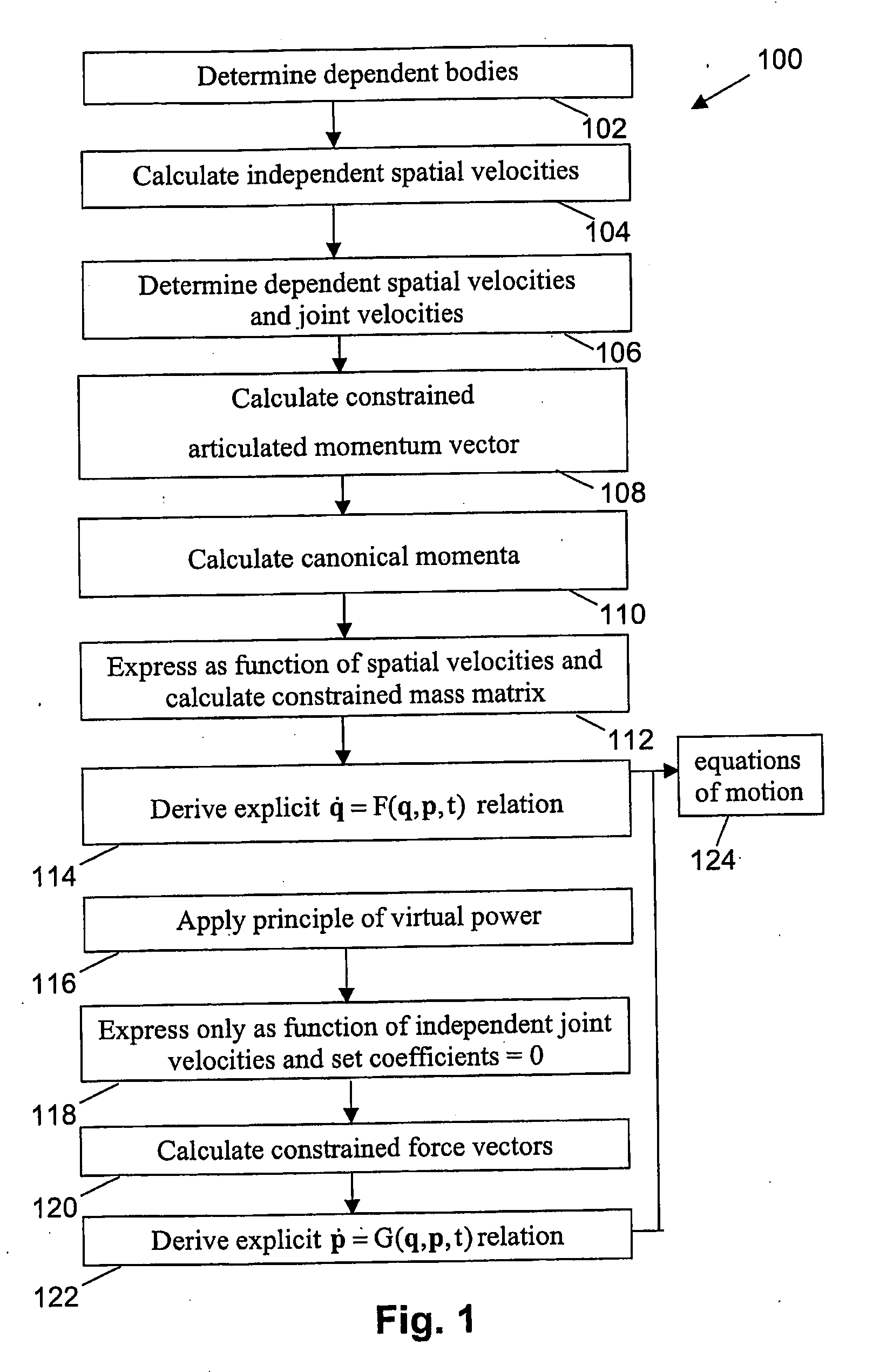
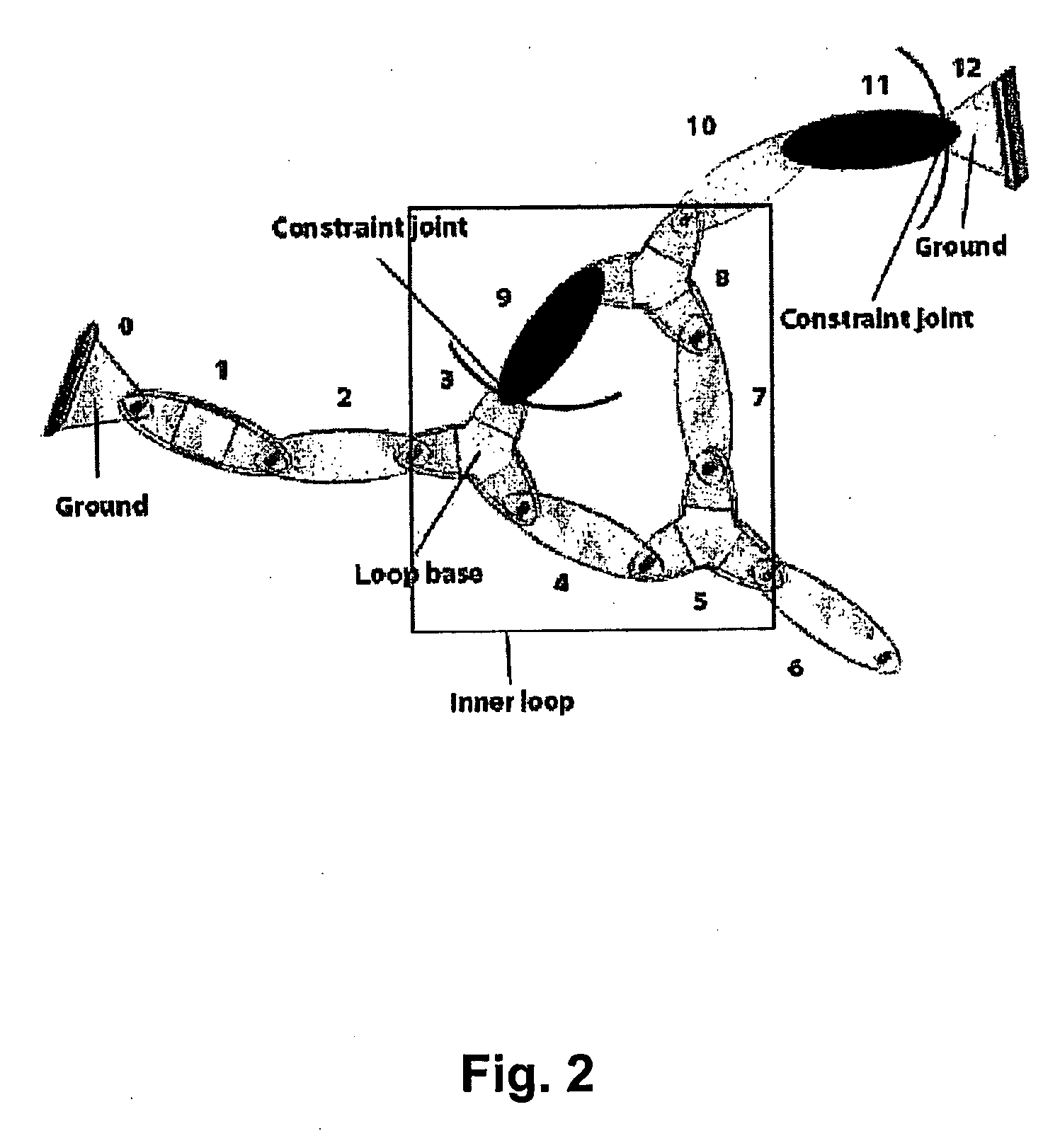
The present invention relates to a method and system for describing the motion of a closed-loop multibody mechanism. In this case, equations of motion need to be obtained for constrained multibody systems. The invention is based on a forward dynamics formulation resulting in a recursive Hamiltonian formulation for closed-loop systems using generalised co-ordinates and conjugated canonical momenta. The method allows to limit the number of arithmetical operations necessary to obtain the equations of motion with a good evolution of the constraints violation errors. Calculations can be performed based on constrained articulated momentum vectors.
Owner:VRIJE UNIV BRUSSEL
Inhaul cable time varying cable force course recognizing method based on extended kalman filter
InactiveCN104713673AApply for online assessmentImprove recognition accuracyTension measurementVibration controlEngineering
An inhaul cable time varying cable force course recognizing method based on an extended kalman filter comprises the following steps of utilizing an established inhaul cable motion equation taking inhaul cable end displacement and flexural rigidity into consideration to choose a plurality of steps of inhaul cable vibration control modes, dispersing horizontal inhaul cable vibration into a vibration mode function and generalized coordinate mode, using extended state variables containing inhaul cable force to convert an inhaul cable vibration differential equation into a state space equation, an observation equation based on inhaul cable acceleration and a monitored acceleration time travel curve of a real bridge inhaul cable, and using a predicting process and an updating process of the extended kalman filter to recognize inhaul cable time varying cable force courses. The inhaul cable time varying cable force course recognizing method can recognize the time varying cable force courses in the situation of known or unknown external simulation (wind load and other environment load) monitoring data. The inhaul cable time varying cable force course recognizing method can accurately recognize the time varying cable force courses in real time and is especially suitable for online evaluation of inhaul cables.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Dual quaternion solution of six degrees of freedom parallel robot forward kinetics
ActiveCN105807712AQuick position calculationFast pose calculationNumerical controlRobotic systemsAlgebraic equation
The invention discloses a dual quaternion solution of six degrees of freedom parallel robot forward kinetics. According to the method, dual quaternions are taken as generalized coordinates of a parallel robot system, a forward kinetic equation set is a quadratic algebraic equation about the dual quaternions, a high-efficiency value algorithm is brought forward for the equation set, and least square solutions of the position and attitude of such a six degrees of freedom parallel robot motion platform can be rapidly calculated. For a parallel robot not including redundancy driving, a least square solution is also an exact solution.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS +2
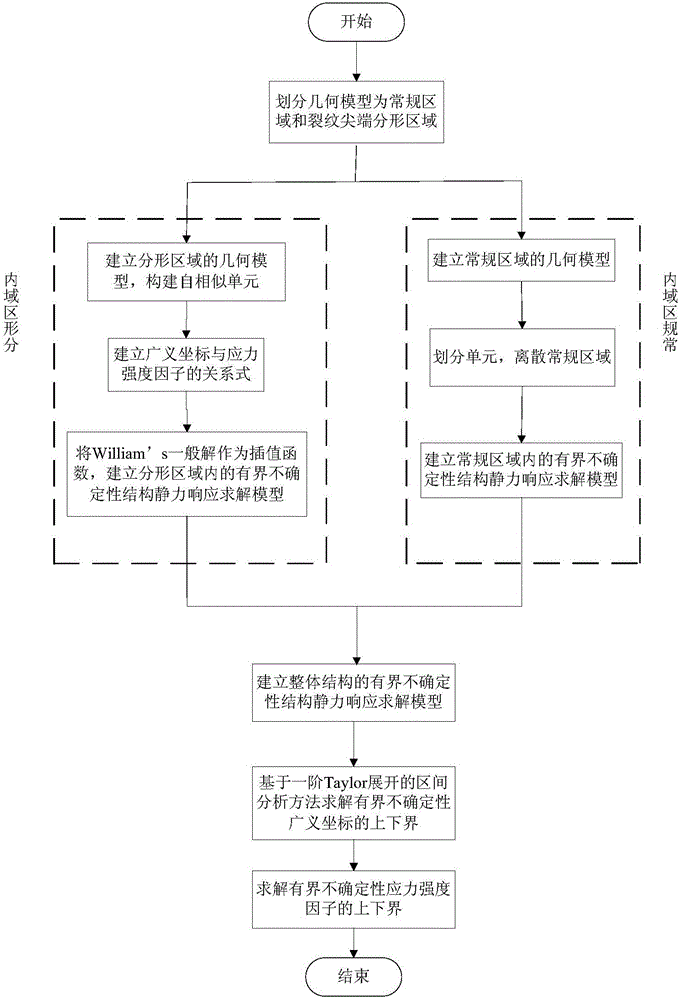
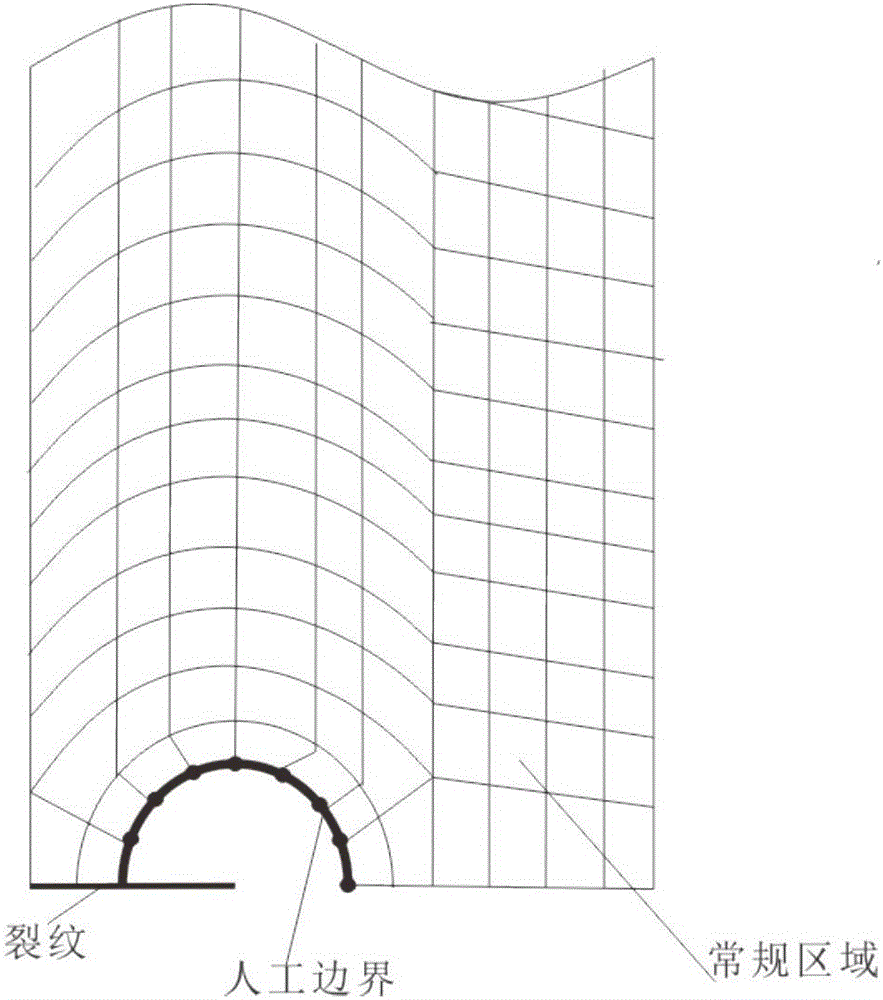
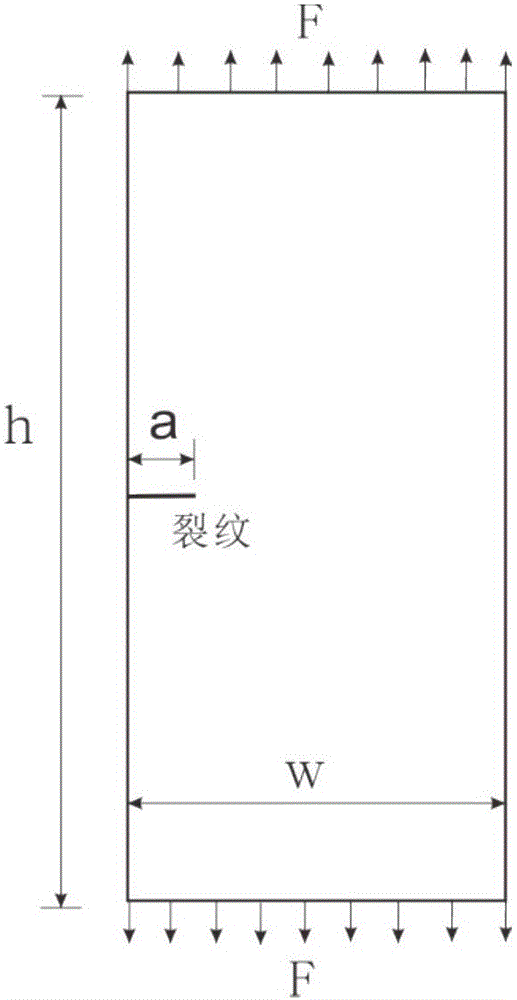
Method for predicting upper and lower bounds of bounded uncertain plane crack stress intensity factors based on fractal theory
ActiveCN105808884AHigh precisionImprove computing efficiencyDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsPredictive methodsGeometric modeling
The invention discloses a method for predicting upper and lower bounds of bounded uncertain plane crack stress intensity factors based on a fractal theory. According to a geometric model including a crack structure, the geometric model is divided into a conventional region and a fractal region of crack tips by using an artificial boundary to establish a bounded uncertain structural static force response solution model in the conventional region; a William's general solution is used as an interpolation function to establish a bounded uncertain structural static force response solution model in the fractal region; then, assembly is performed to obtain a whole bounded uncertain structural static force response solution model including a crack structure, the upper and lower bounds of bounded uncertain generalized coordinates are calculated by adopting a first-order Taylor expansion based interval analysis method, and further the upper and lower bounds of the bounded uncertain plane crack stress intensity factors are calculated. The upper and lower bounds of the bounded uncertain plane crack stress intensity factors are calculated are accurately and efficiently obtained by adopting the method, and objective and effective data is provided for reliability evaluation and design of structures.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Space coordinate monitoring based cable system health monitoring method applied in supporting seat generalized displacement
InactiveCN102323080AMonitor and evaluate health statusEffective Health MonitoringStructural/machines measurementReference modelControl engineering
The invention discloses a space coordinate monitoring based cable system health monitoring method applied in supporting seat generalized displacement. The need of updating a mechanical calculation reference model of a structure is decided by monitoring the supporting seat generalized coordinates of the structure, based on space coordinate monitoring, and the mechanical calculation reference model of the structure is updated only when the supporting seat generalized coordinates of the structure vary, so that a new mechanical calculation reference model of the structure included in the supporting seat generalized coordinates of the structure is obtained, and a unit damage monitored quantity variance matrix is obtained by calculating on the basis of the model. A noninferior solution of a current cable damage vector can be calculated quickly with appropriate algorithms such as a multi-target optimization algorithm and the like according to approximate linear relations between a current numeric vector of a monitored quantity and an initial vector of the monitored quantity, the unit damage monitored quantity variance matrix, a unit damage scalar quantity and a cable system current damage vector to be resolved, so that the position and damage degree of the damaged cable can be determined accurately relatively when supporting seat generalized displacement occurs.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
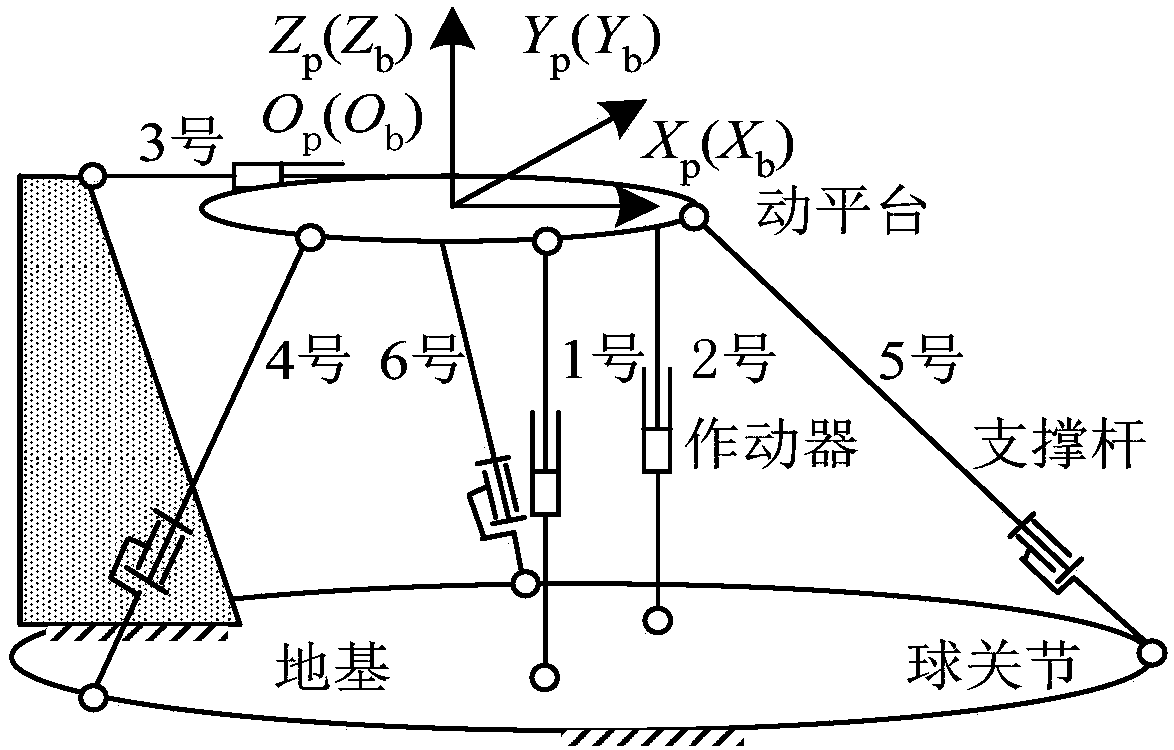
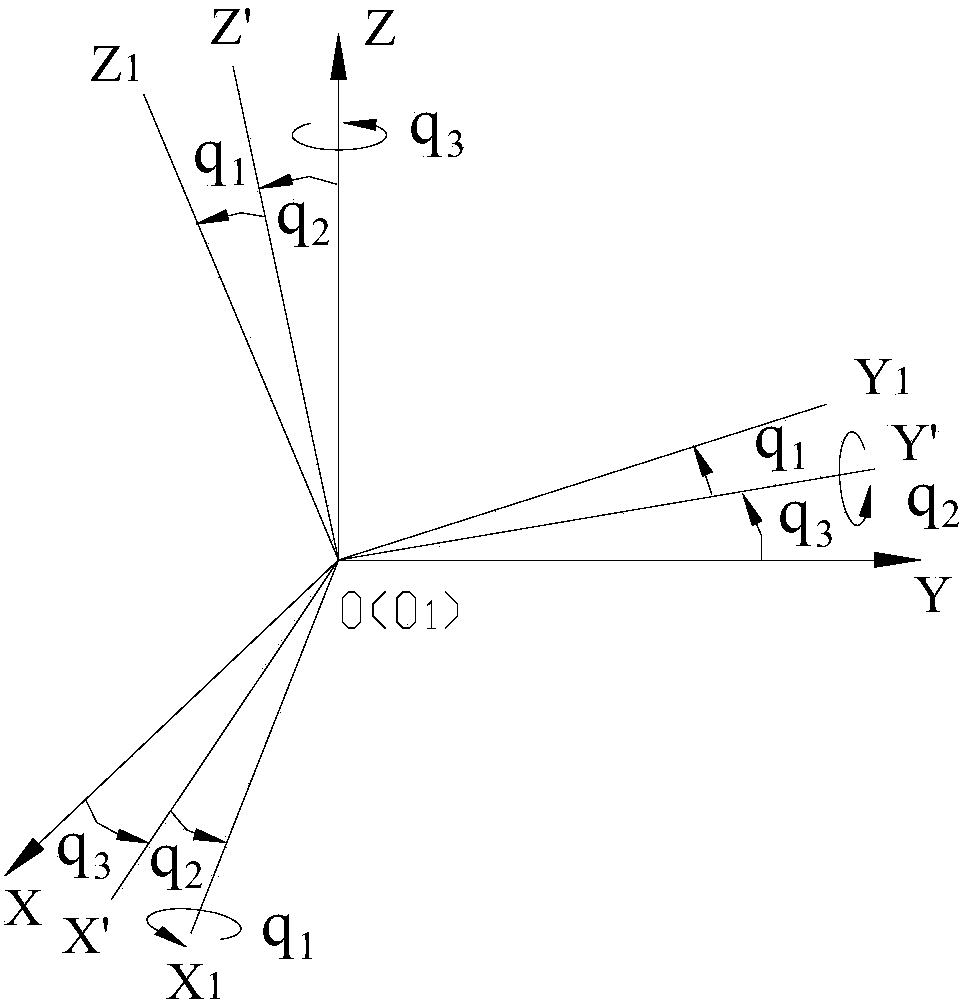
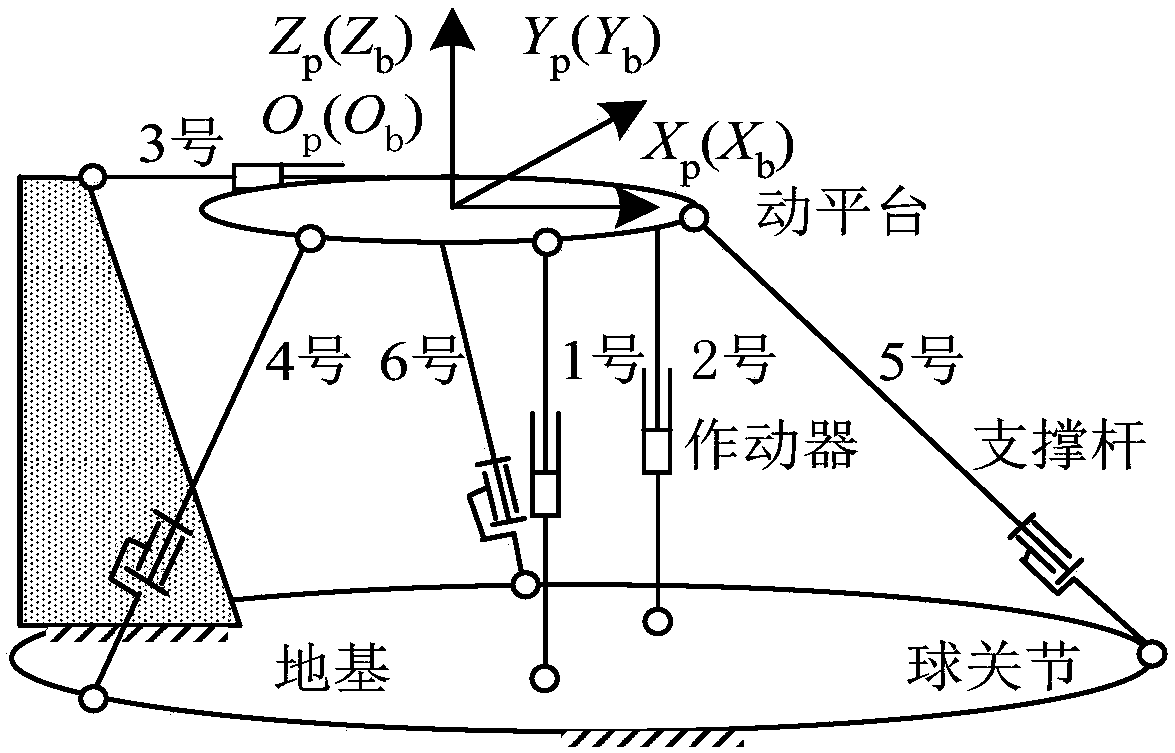
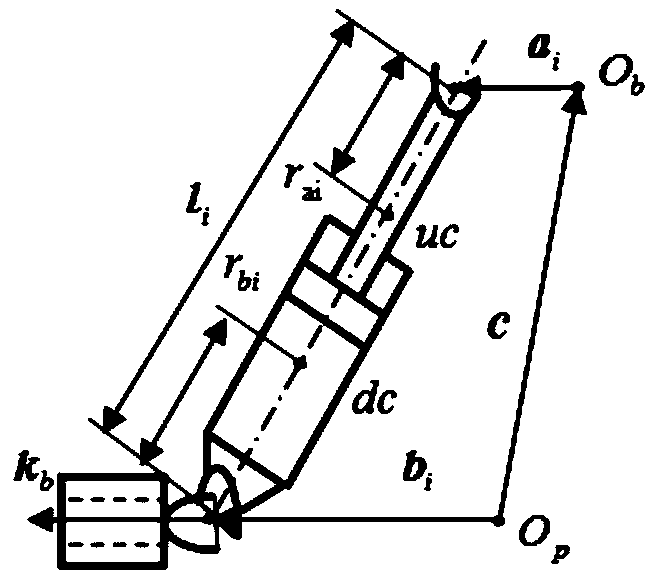
Method for controlling attitude angle of three-degree-of-freedom parallel mechanism based on kinematics normalization
InactiveCN108334114AHigh precisionImprove real-time performanceProgramme-controlled manipulatorControl without using feedbackKinematicsThree degrees of freedom
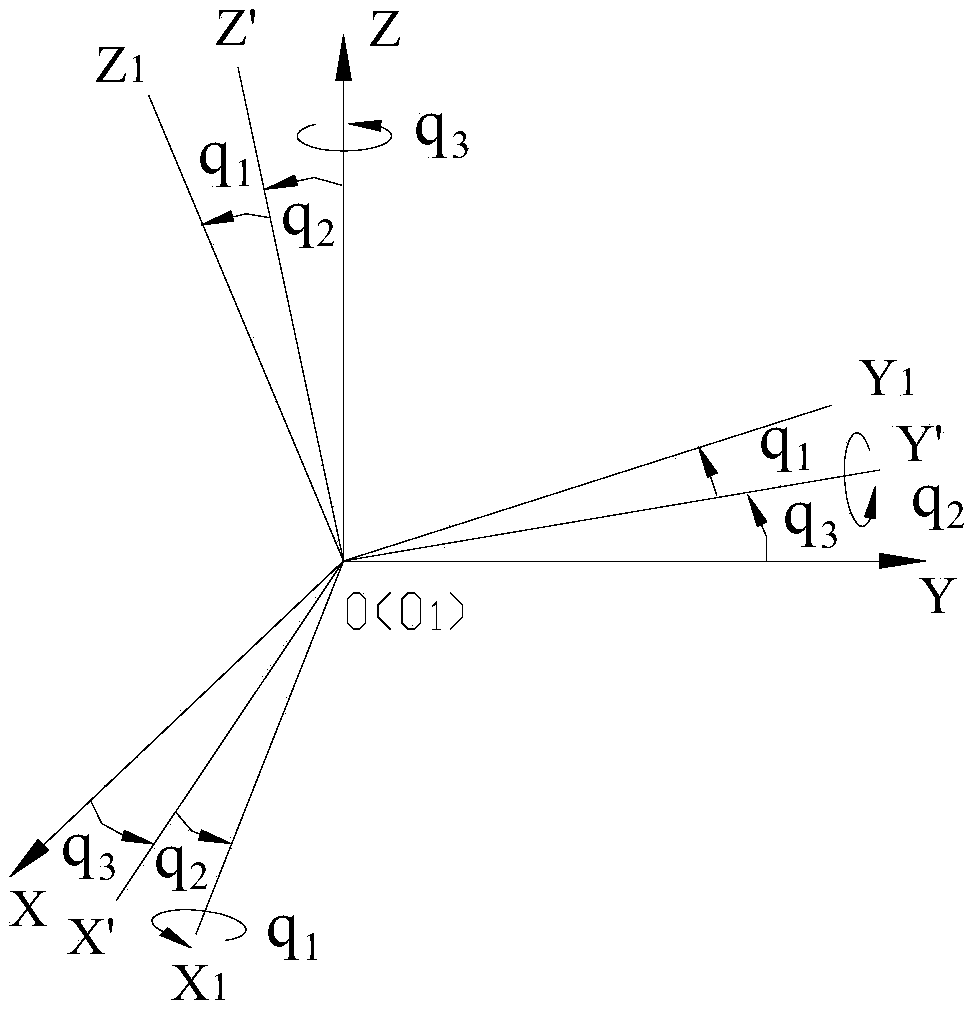
The embodiment of the invention provides a method for controlling the attitude angle of a three-degree-of-freedom parallel mechanism based on kinematics normalization. The parallel mechanism comprisesthree sets of actuators, three sets of support rods and a movable platform. The control method comprises the steps of establishing a body coordinate system OB-XbYbZb at the center of a circle where ahinge point on the movable platform is located, and establishing a fixed reference coordinate system Op-XpYpZp on the earth, wherein when the parallel mechanism is located at a working initial position, the body coordinate system coincides with the reference coordinate system; describing the attitude of the movable platform by applying the generalized coordinates of the body coordinate system relative to the reference coordinate system, wherein the generalized coordinates comprise three euler angles, and the three euler angles are composed of a transverse rocking angle, a longitudinal rockingangle and a yaw angle; acquiring a rotation matrix of the body coordinate system relative to the reference coordinate system; according to the length of the actuators or the length of the support rods, and applying the kinematics normalization algorithm to obtain the attitude angle of the movable platform based on the relation between the rotation matrix and the kinematics.
Owner:舒天艺
Underwater robot trajectory tracking backstepping control method
InactiveCN107807522AEasy to controlImprove stabilityTarget-seeking controlAdaptive controlKinematics equationsAngular degrees
The invention discloses an underwater robot trajectory tracking backstepping control method, and is used for solving the technical problem of poor practicality of the present underwater robot controlmethod. According to the technical scheme, firstly the tracking error of generalized coordinates is defined and then the generalized velocity error is defined based on the six-degree-of-freedom kinematic equation (which is expressed in the specification) of an underwater robot body coordinate system, the first Lyapunov function and the second Lyapunov function are selected and the control law is selected so that underwater robot control can be realized. The Lyapunov function is adopted so that the control stability is high, the position error and the angle error tend to be zero and thus the practicality is great.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV +1
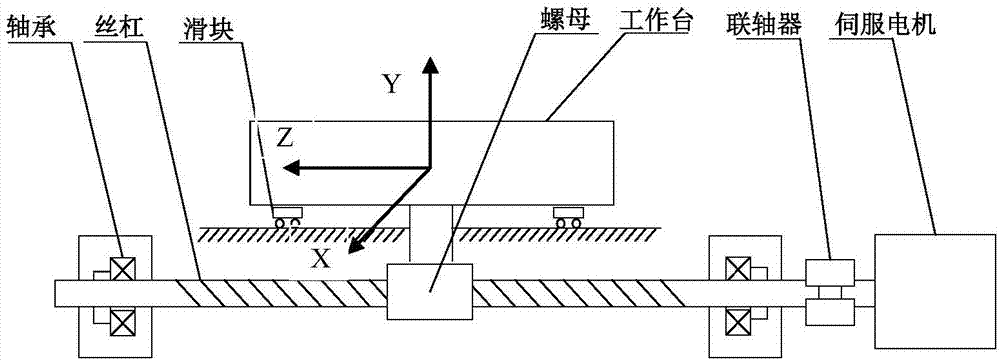
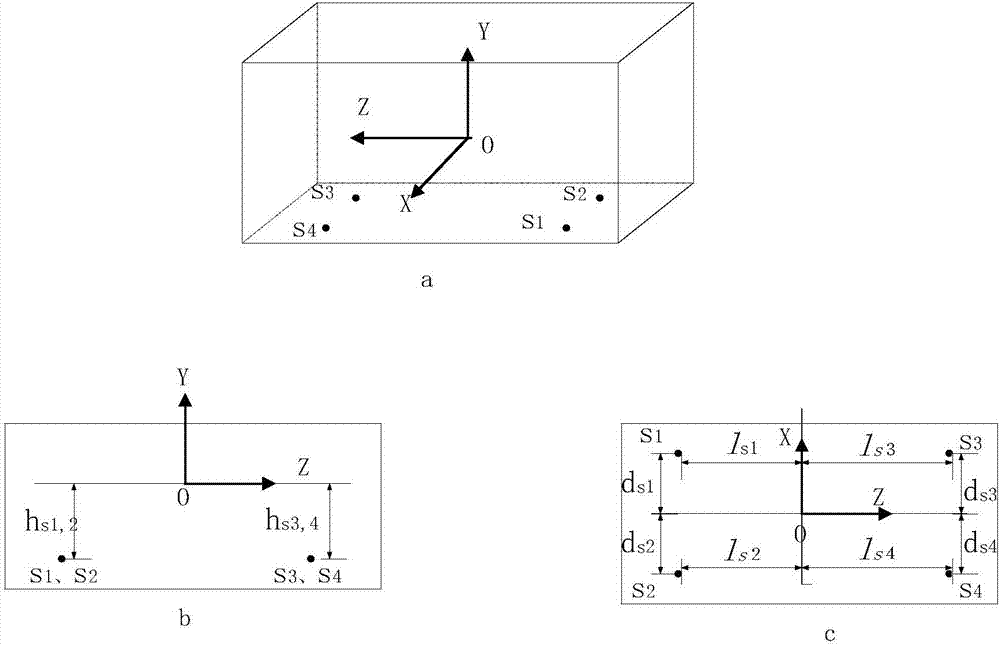
Modeling method for modal of double-drive feeding system of numerical control machine tool
InactiveCN107102620ASimple relationshipIntuitive modeling methodProgramme controlComputer controlNumerical controlModel method
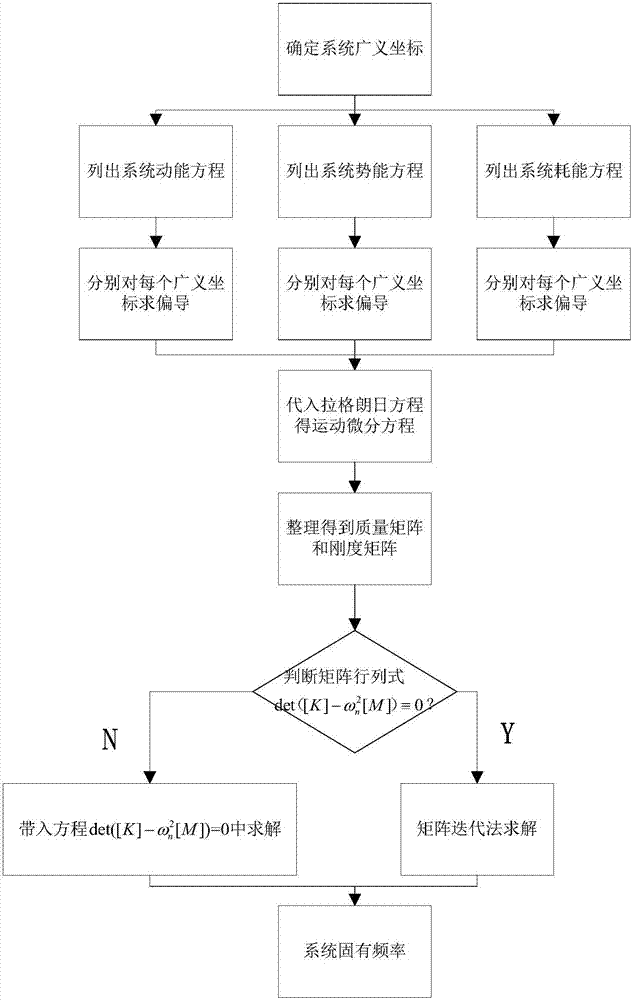
The invention proposes a modeling method for the modal of a double-drive feeding system of a numerical control machine tool, and the method comprises the steps: 1, determining the generalized coordinates of a system; 2, building a kinetic energy expression of a machine tool feeding system; 3, building a potential energy expression of the feeding system; 4, building an energy consumption expression of the feeding system; 5, building the position transformation relation between the coordinates of a sliding block and the coordinates of a workbench; 6, substituting an energy expression into a Lagrange equation, and obtaining a movement differential equation of the feeding system; 7, solving modal parameters, and solving the modal intrinsic frequency. The method is more visual, and the variable can be controlled. The change of the intrinsic frequency can be observed according to the change of a variable. The relation between the variable and the intrinsic frequency is more visual.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Attitude angle control method of three-degree-of-freedom parallel mechanism
InactiveCN108664040AHigh precisionImprove real-time performanceControl without using feedbackKinematicsThree degrees of freedom
The embodiment of the invention provides an attitude angle control method of a three-degree-of-freedom parallel mechanism. The method comprises the steps of establishing a body coordinate system Ob-XbYbZb at the center of a circle, where the hinge point on the movable platform is located, establishing a fixed reference coordinate system Op-XpYpZp on the ground, the body coordinate system overlapping with the reference coordinate system when parallel mechanism is located at the working initial position, describing the posture of the moving platform by applying a body coordinate system relativeto the generalized coordinates of the reference coordinate system, wherein the generalized coordinates comprise three euler angles including transverse rocking angles, longitudinal rocking angles andyaw angles; acquiring a rotation matrix of the body coordinate system relative to the reference coordinate system; and obtaining the relation between the angular velocity, the angular acceleration andthe eulerian angle derivative of the moving platform in the body coordinate system; obtaining translational displacement of the moving platform according to the expected attitude angle; and obtainingthe movement rule of each actuator in the parallel structure by means of a kinematics reversal method according to the attitude angle and the translation displacement of the moving platform.
Owner:舒天艺
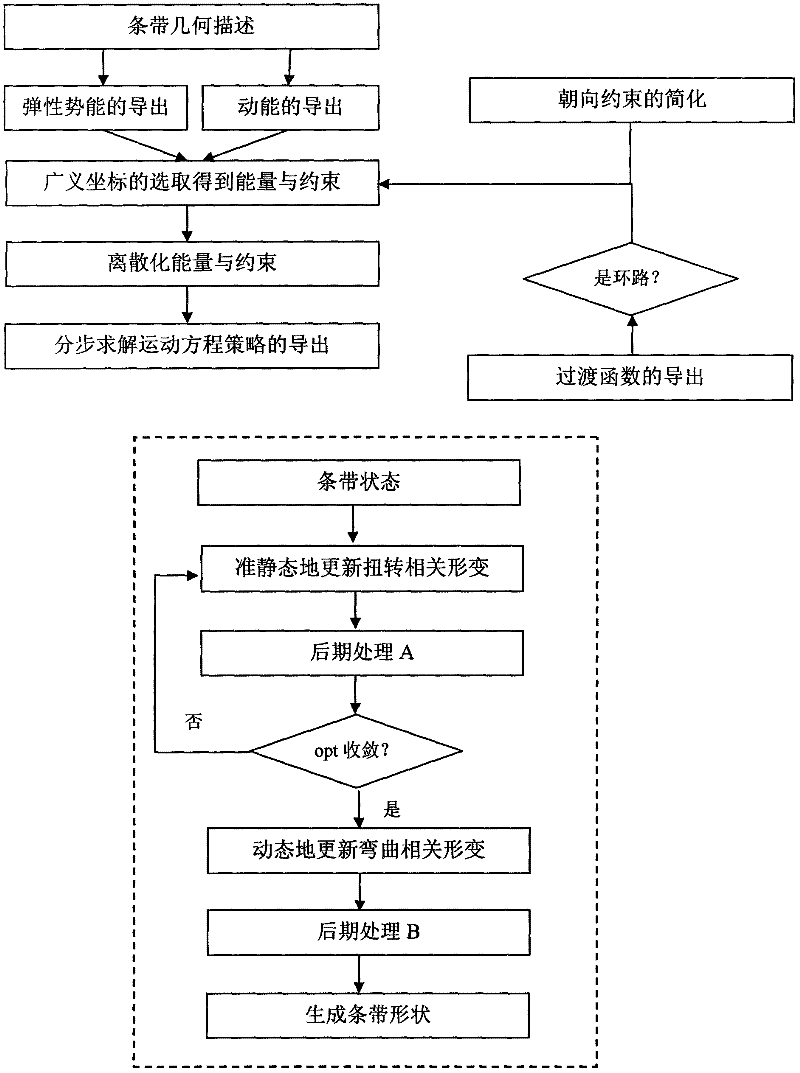
Geometric accurate inflexible stripe simulation method
InactiveCN102393968AAccurately represent the interesting stateEnhanced interactionAnimationThin shellsQuaternion
The invention discloses a geometric accurate inflexible stripe simulation method. A special ruled surface is used for describing a two-dimensional curved surface corresponding to an inflexible stripe, a thin shell model is combined to obtain an energy model described by a stripe center line; compared with the traditional method that the thin shell model is directly applied to the two-dimensional curved surface and triangle or quadrilateral dispersion is carried out, the simulation method has the advantages that algorithm complexity is greatly reduced and solving efficiency is improved. A 'quaternion-center line node coordinate-shielding failure rate curvature ratio' generalized coordinate is used for describing the stripe center line, the obtained motion equation can be stably and efficiently solved, and an external force and a moment are convenient to apply. Finally solving of the motion equation is simplified into two steps of quasi-statically updating deformation of a twisting part and dynamically updating the deformation of a curved part by utilizing the fact that frequency of deformation of the twisting part of a stripe is higher than the frequency of the curved part, thus calculation overhead is reduced while accuracy of dynamic track is hardly reduced.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
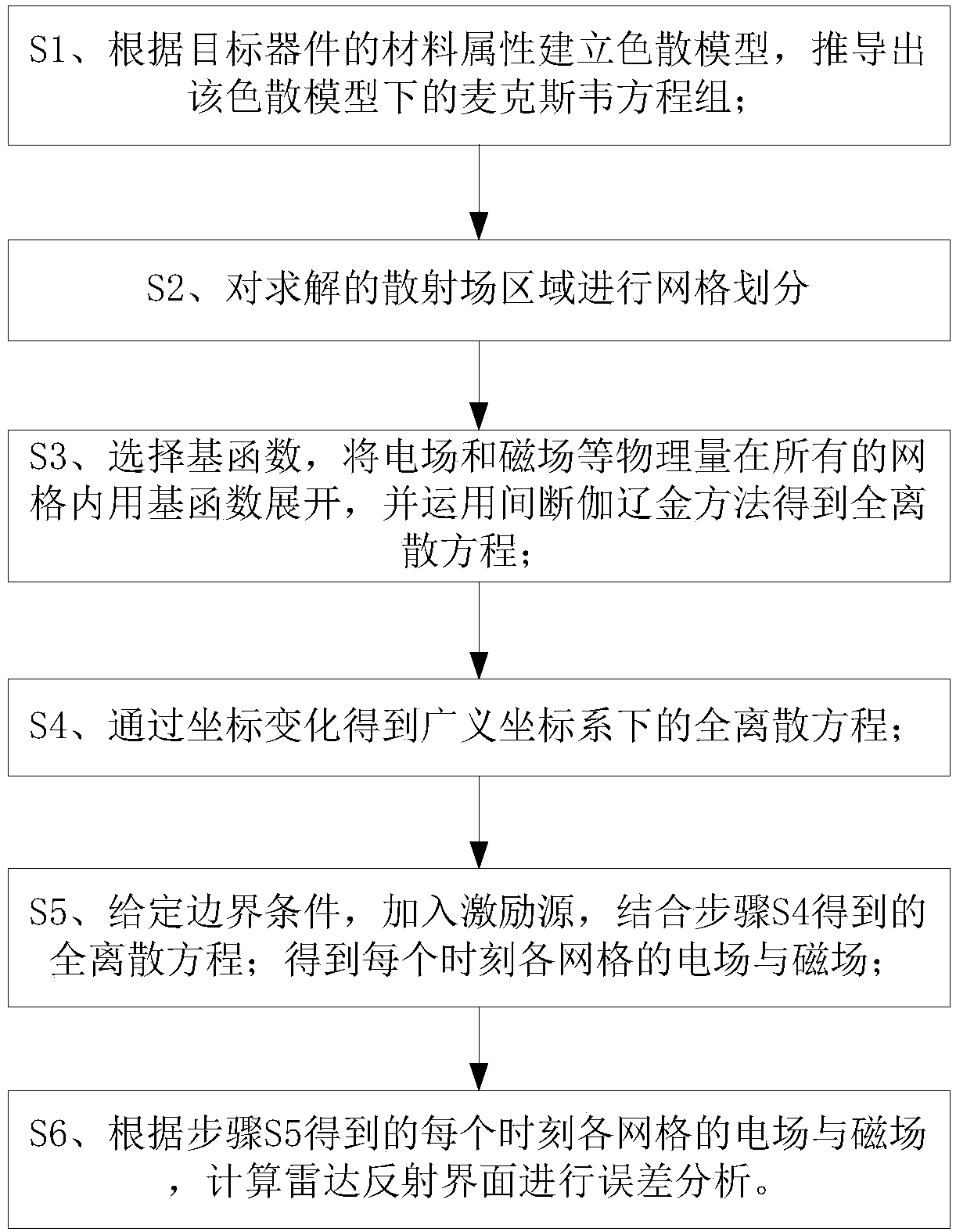
Method for obtaining electromagnetic property of any chromatic dispersion material based on generalized coordinate system
InactiveCN108021533ASolve dispersionHigh precisionComplex mathematical operationsMaxwell's equationsElectromagnetic field
The invention discloses a method for obtaining the electromagnetic property of any chromatic dispersion material based on a generalized coordinate system. The method is applied in the field of three-dimensional electromagnetic field numerical value obtaining. By establishing the link between a generalized chromatic dispersion model and a traditional chromatic dispersion model, a corresponding coefficient is selected according to the material property of a target device, a specific chromatic dispersion model is obtained, and therefore a Maxwell equation set satisfied by the chromatic dispersionmaterial is deduced; spatial discretization is conducted on a Maxwell equation weak form through an intermittent galerkin method to form a semi-discrete form, and time discretization is conducted through a leapfrog time format to obtain a full-discrete format; due to the high dependency of units in the method, the same target device can be divided through different grids, it is ensured that parallel computing can be applied, and the chromatic dispersion problem of a multi-dimensional device can be solved at high precision, high speed and low computing cost, and the universality of the methodis increased by deducing the full-discrete format under the generalized coordinate system.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Gust mitigation analysis method based on state space form vortex grid method
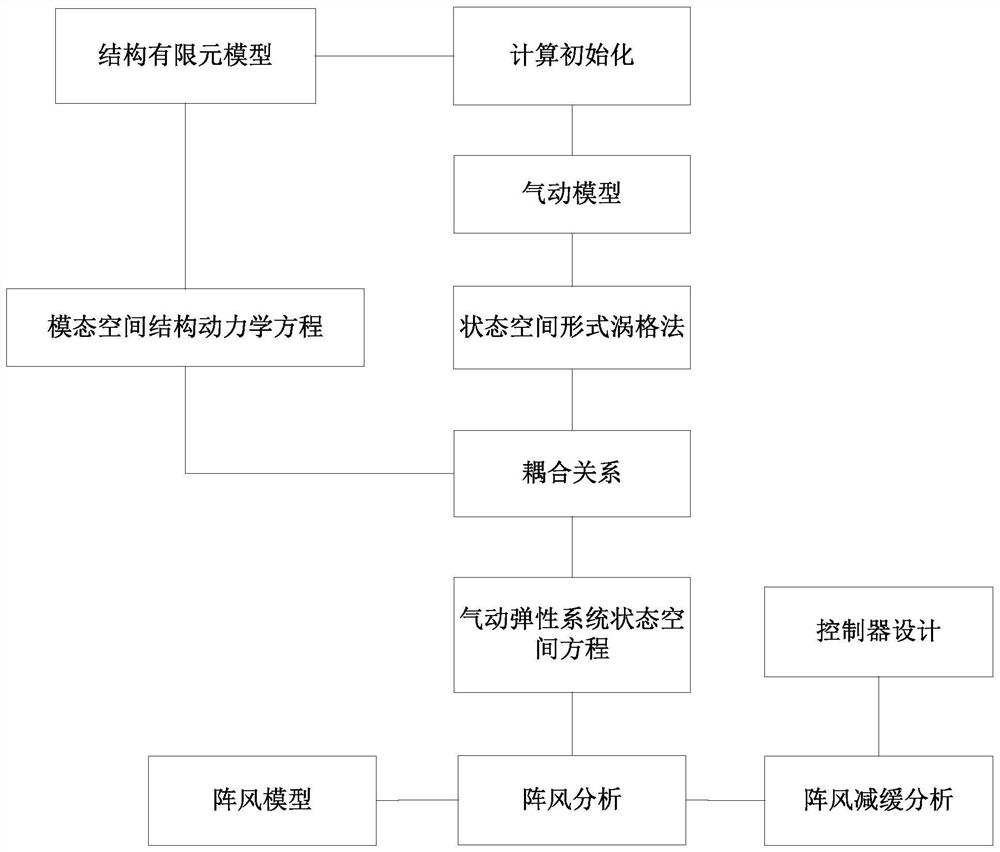
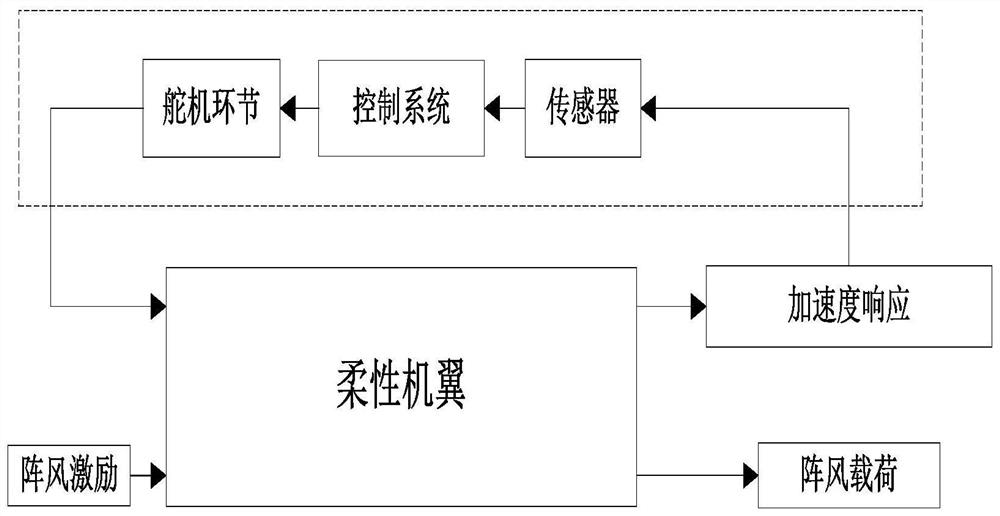
ActiveCN113128085AAccurate calculationSimple designSustainable transportationDesign optimisation/simulationTime domainLoop control
The invention discloses a gust alleviation analysis method based on a state space form vortex grid method, and the method comprises the following steps: establishing an aerodynamic grid according to a given model, and establishing a relationship among model attachment vortex intensity, trailing vortex intensity and wing surface induced velocity according to the state space form vortex grid method; forming an aeroelastic coupling equation after the relation between the generalized coordinates of the finite element mode and the control surface mode and the wing surface induced velocity is obtained through interpolation, wherein the aeroelastic coupling equation is also in the state space form, a given gust model serves as external excitation, and aeroelastic gust analysis can be conducted; on the basis of the aeroelastic coupling equation, taking the acceleration of a certain point of a wing as system output, forming control surface deflection input signals after the acceleration passes through a controller, building a closed-loop control system, and carrying out aeroelastic gust slowing-down simulation analysis. According to the method, gust analysis precision can be improved, frequency domain and time domain conversion is avoided, and analysis efficiency is improved.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Vibration reduction method of single-connecting-rod flexible mechanical arm
InactiveCN111015737AEasy to controlStable controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorElectric machineryEngineering
The invention discloses a vibration reduction method of a single-connecting-rod flexible mechanical arm. In a generalized coordinate system, a bending vibration equation is established based on an Euler-Bernoulli beam theory. Parameter discretization is carried out through finite segmentation, and a flexible mechanical arm kinetic model is established. The kinetic model is analyzed to obtain characteristic parameters such as natural vibration frequency of the mechanical arm. The motion of the mechanical arm is set to be accelerated, constant-speed and decelerated three-section motion, the current signal time of a control motor at different motion stages is designed according to the inherent frequency of the mechanical arm, motion trajectory planning and motion parameter configuration are conducted on the flexible mechanical arm, and vibration reduction of transverse motion is achieved. According to the method, on the basis that the instruction shaping vibration suppression method is analyzed, a feedforward method is generated through combining the track, instruction operation is simple and rapid, the structure of the mechanical arm does not need to be changed, the vibration reduction effect is obvious, and the method has good application value in the aspect of vibration reduction of industrial flexible mechanical arm rotating motion.
Owner:CHANGAN UNIV
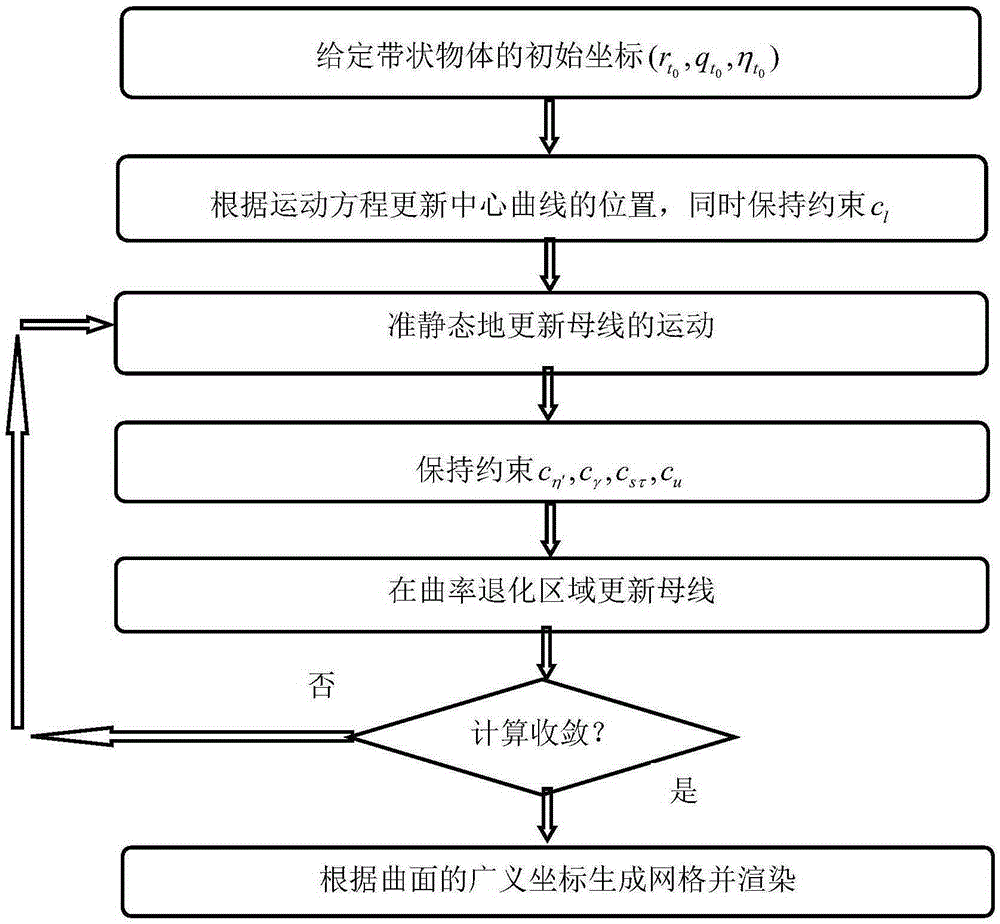
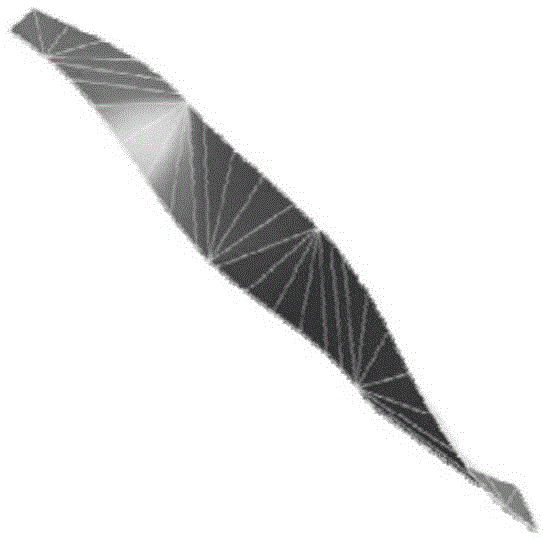
Geometric property descriptive model of banded object which cannot extend, and dynamics simulation method
ActiveCN105335552AGuaranteed inextensibilityLess freedomSpecial data processing applicationsExtensibilityDescription model
The invention discloses a geometric property descriptive model of a banded object which cannot extend, and a dynamics simulation method. For a banded object which cannot extend, a regular center curve is used as a descriptive model of geometric properties. The model comprises a center curve length-preserving constraint and a generatrix non-intersecting constraint, and a boundary condition. The method comprises establishing generalized coordinates to represent a banded curved surface, establishing an elastic potential energy model for a rectangular banded developable surface, the potential energy model being used for calculating internal stress in the rectangular banded developable surface; and calculating motion of the rectangular banded developable surface through a numerical simulation calculation method. The model can precisely describe geometric properties of a banded object, and can accurately ensure non-extensibility of the banded curve surface. In simulation, required freedom degree is relatively few, and large amount of length-preserving constraint is not needed, and a degradation condition which may occur in simulation can be processed. Thus, efficiency and stability of a computer is greatly improved than those of a conventional method.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Angle monitoring based loose cable recognizing method applied in supporting seat generalized displacement
InactiveCN102323091AMonitor and evaluate health statusStructural/machines measurementApparatus for force/torque/work measurementReference modelLinear relationship
The invention discloses an angle monitoring based loose cable recognizing method applied in supporting seat generalized displacement. The need of updating a mechanical calculation reference model of a structure is decided by monitoring supporting seat generalized coordinates of the structure, based on angle monitoring, and the mechanical calculation reference model of the structure is updated only when the supporting seat generalized coordinates of the structure vary, so that a new mechanical calculation reference model of the structure included in the supporting seat generalized coordinates of the structure is obtained, and a unit damage monitored quantity variance matrix is obtained by calculating on the basis of the model. A virtual damaged cable can be calculated and recognized according to approximate linear relations between a current strain vector and an initial strain vector, a virtual unit damage strain variance matrix and a current virtual damage vector. After a true damaged cable is identified with a nondestructive examination method, the remaining virtual damaged cables are loose support cables, i.e., cables of which the cable force need to be adjusted, and the cable length needing to be adjusted can be determined according to a relation between the loose degree and the virtual damage degree.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
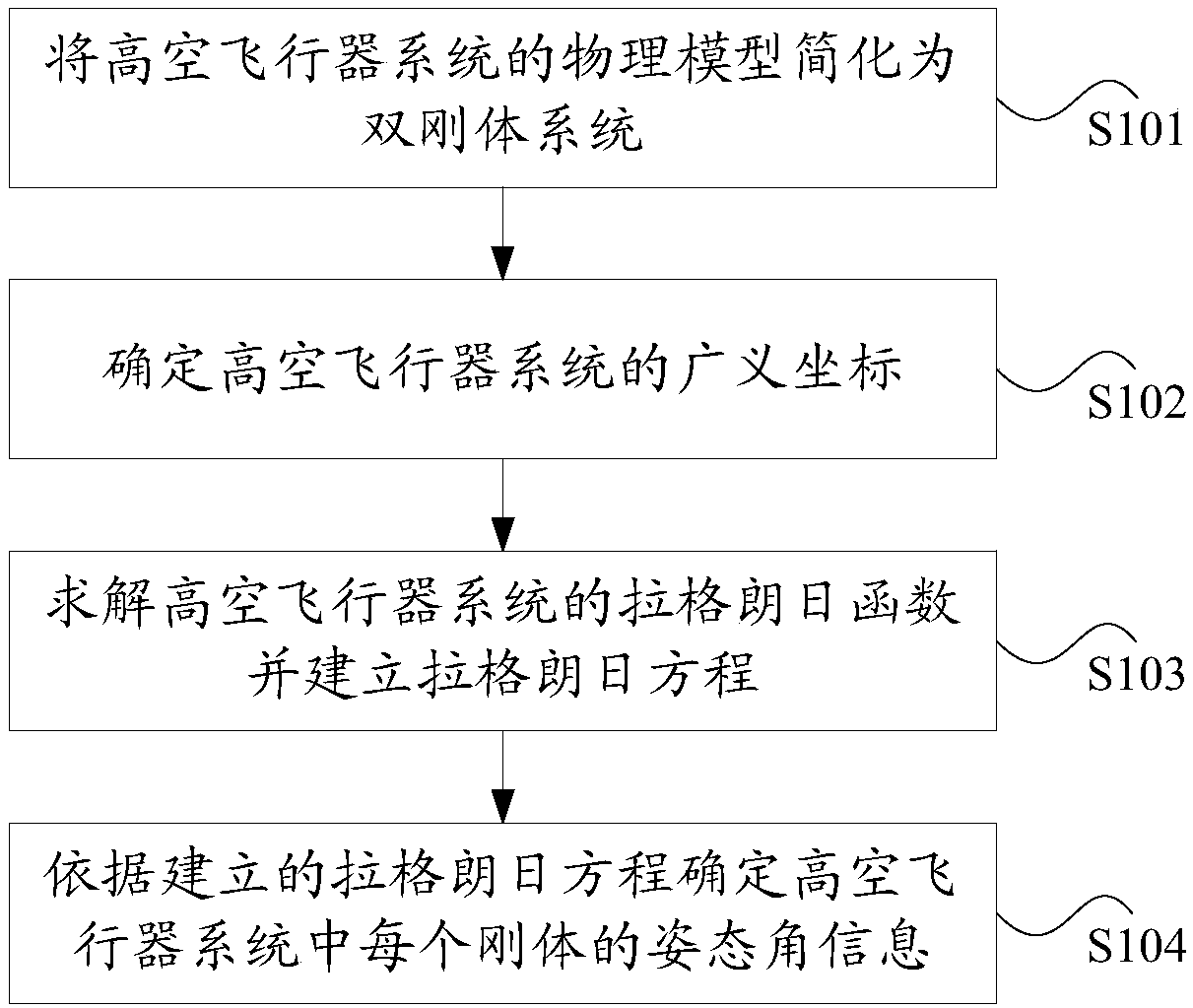
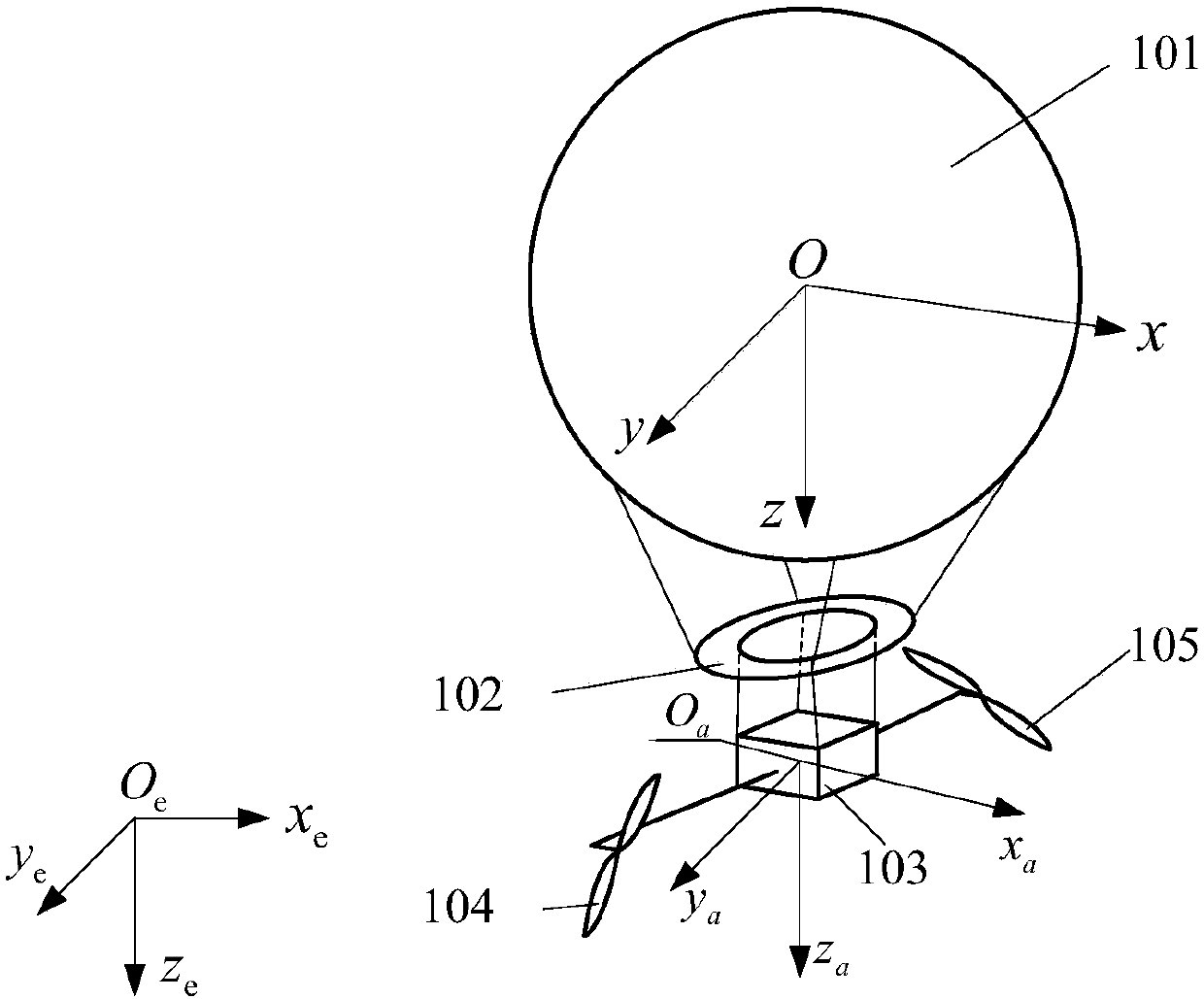
Modeling method and modeling device applied to high-altitude vehicle system
PendingCN108733858ASolve technical problems with large errorsReduce mistakesGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationModel methodPhysical model
The invention discloses a modeling method and a modeling device applied to a high-altitude vehicle system. The method comprises the following steps: simplifying a physical model of the high-altitude vehicle system to be a double-rigid-body system, wherein an aerostat and a pod are simplified to be one rigid body; determining generalized coordinates of the high-altitude vehicle system, wherein thegeneralized coordinates at least comprise attitude angle information of each rigid body in the high-altitude vehicle system; solving a lagrange function of the high-altitude vehicle system and building a lagrange equation; and determining the attitude angle information of each rigid body in the high-altitude vehicle system according to the built lagrange equation. The method and the device provided by the invention solve a technical problem that a result of modeling and simulation for the high-altitude vehicle system has larger error relative to actual conditions in the related technologies.
Owner:海口未来技术研究院
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com