Patents
Literature
297 results about "Torsional load" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The torsional load is imposed on the sample by the rotational oscillation of the lower test die half. There's also the exceptional braking power of Buell's 375 mm zero torsional load (ZTL) inside-out disc with a six piston brake calliper which reduces weight but maximises power and rider feedback.
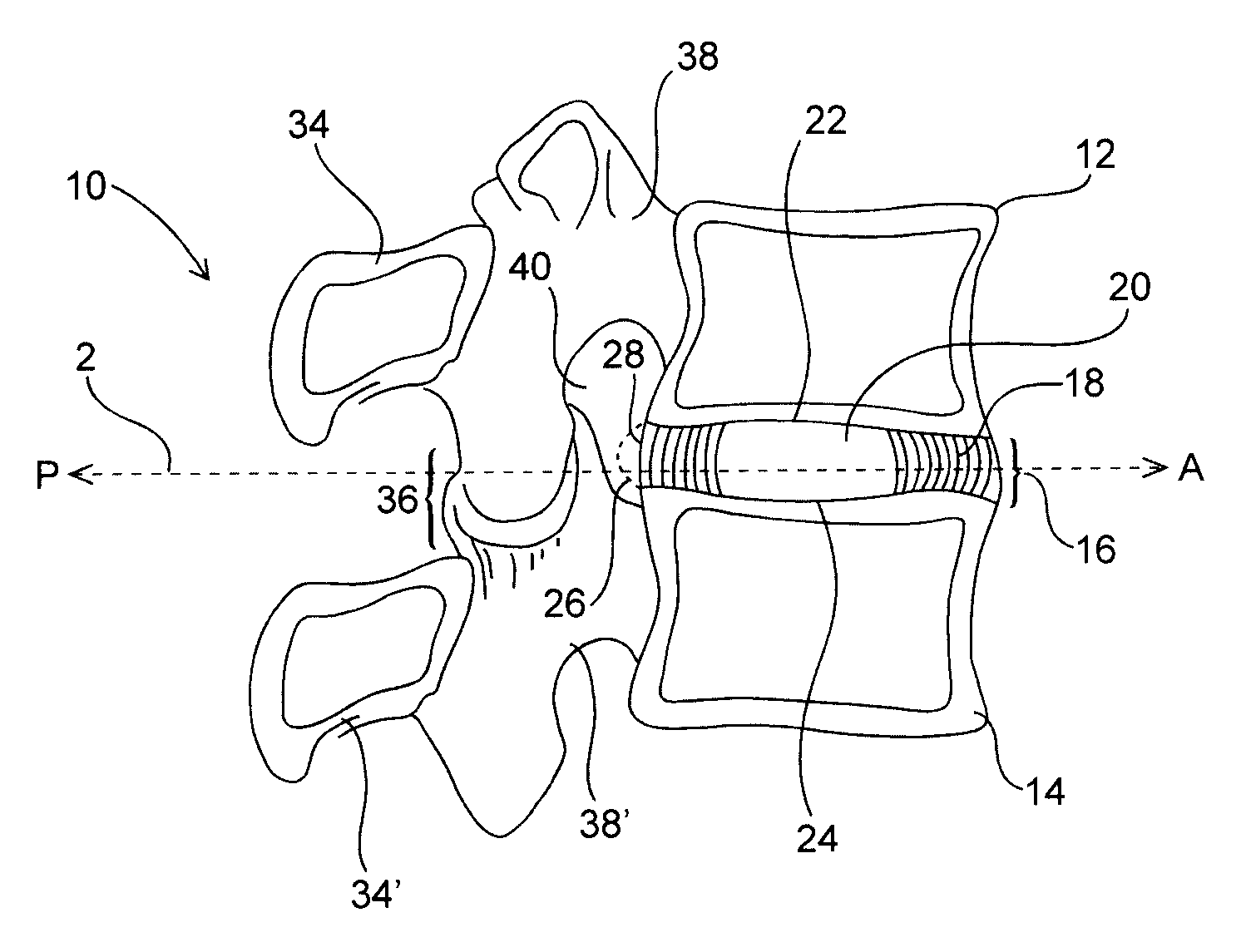
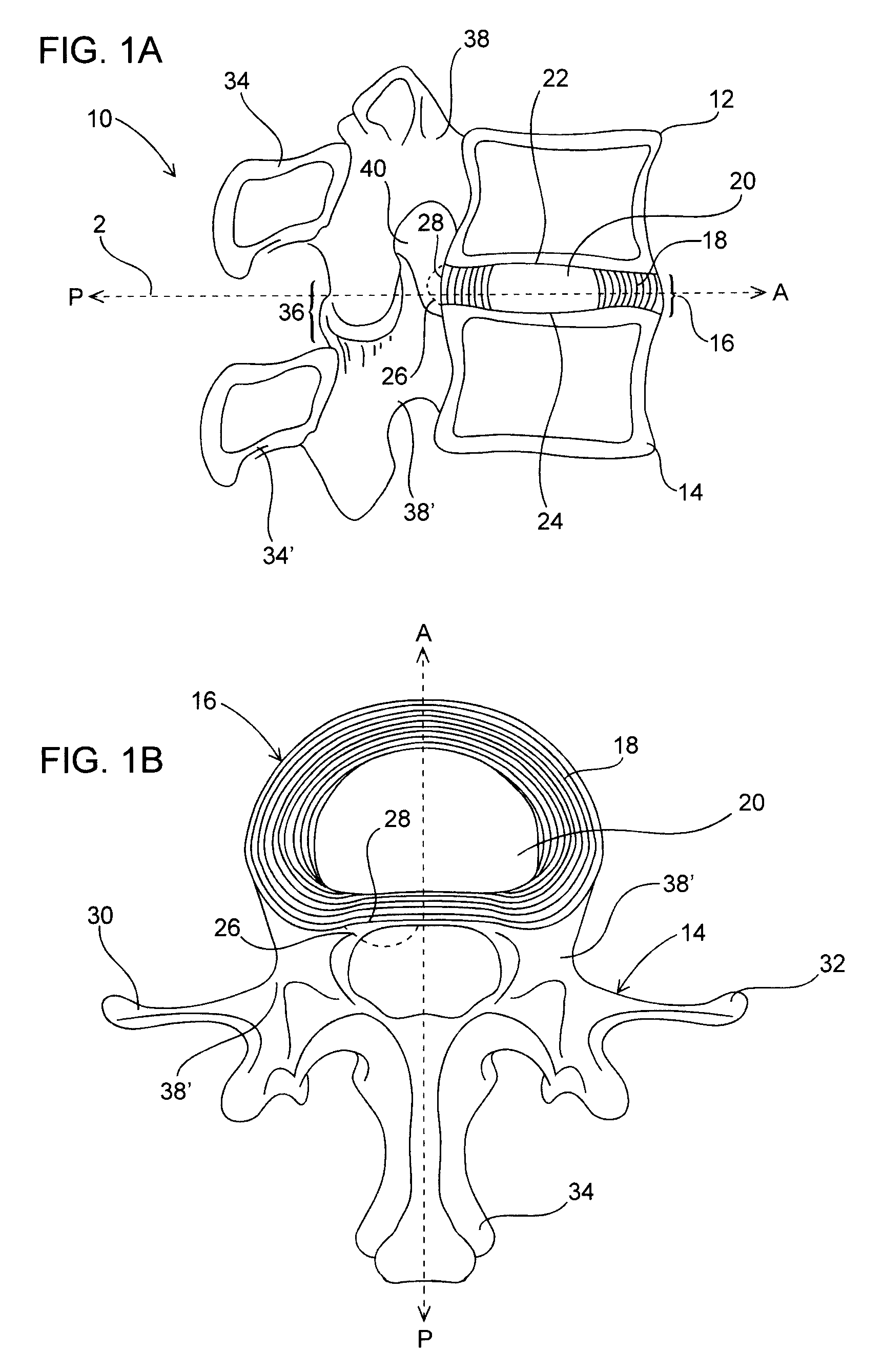
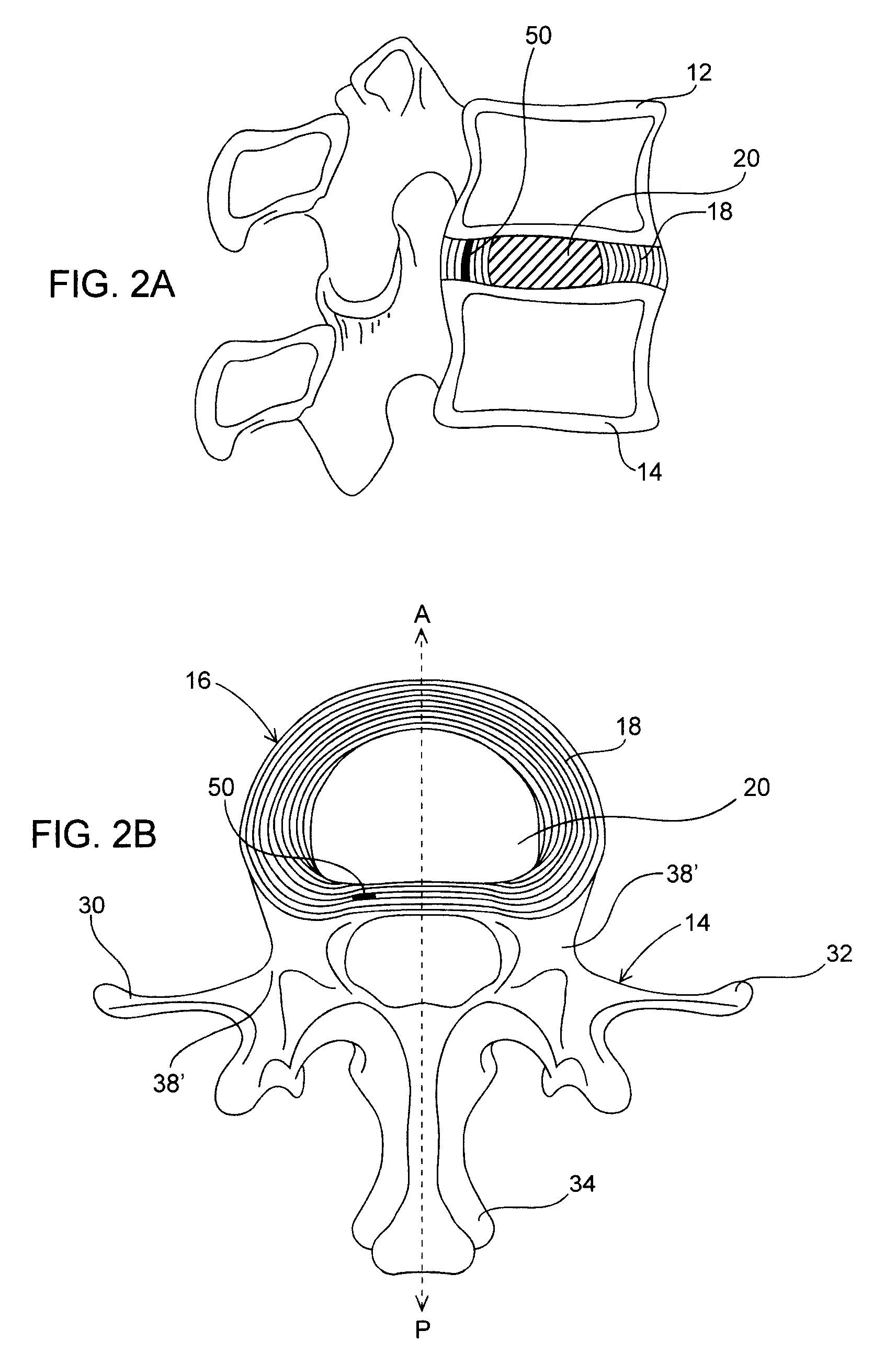
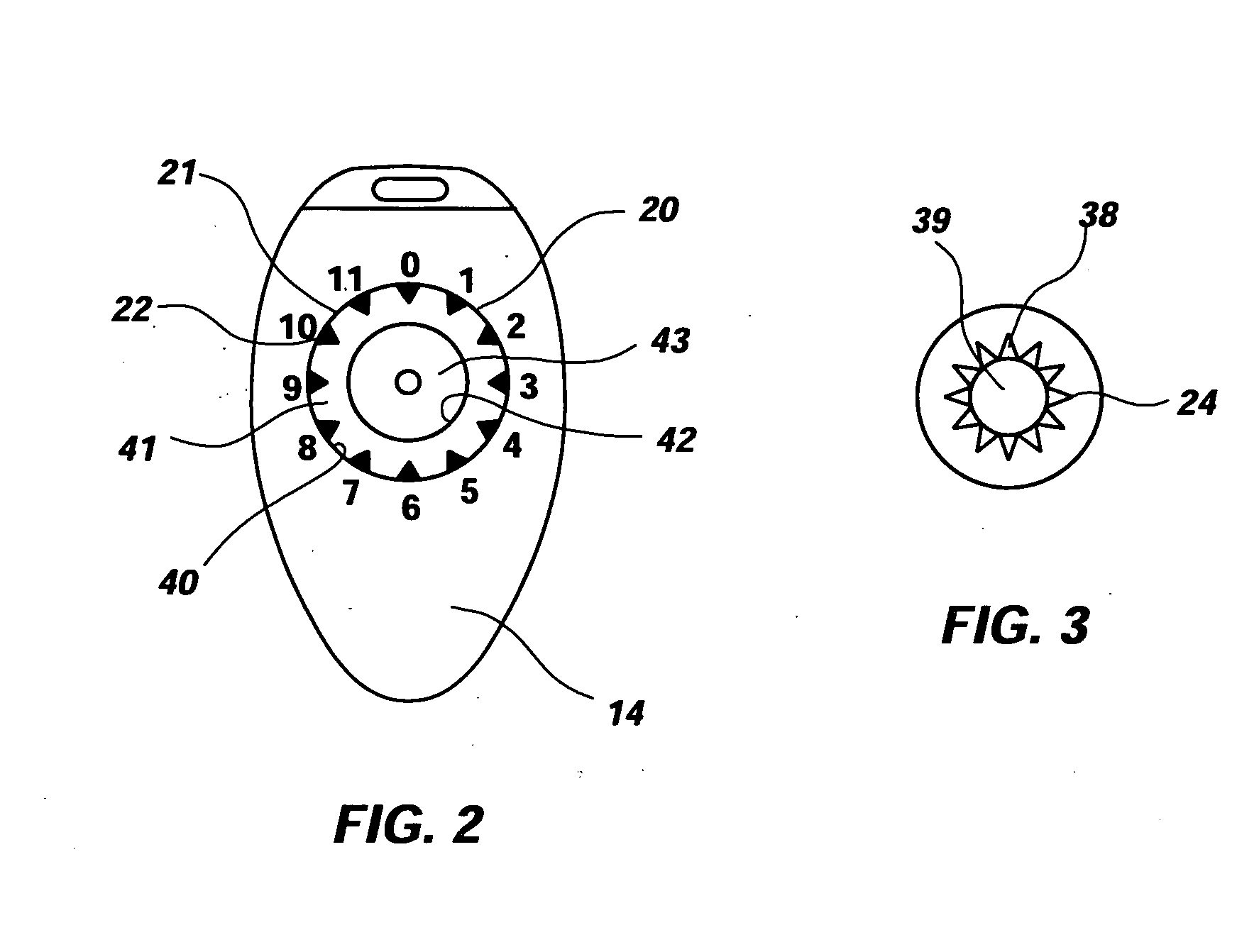
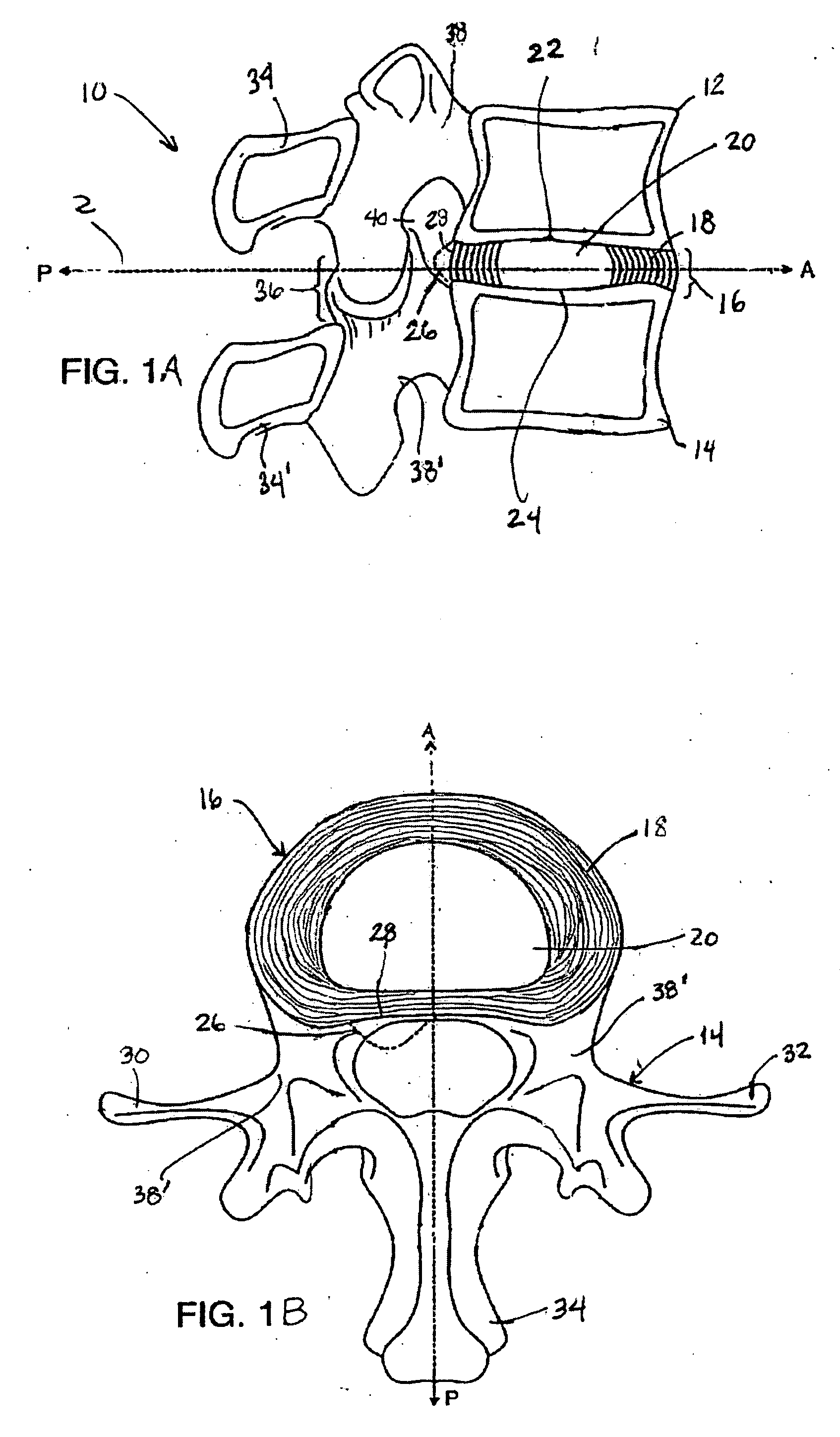
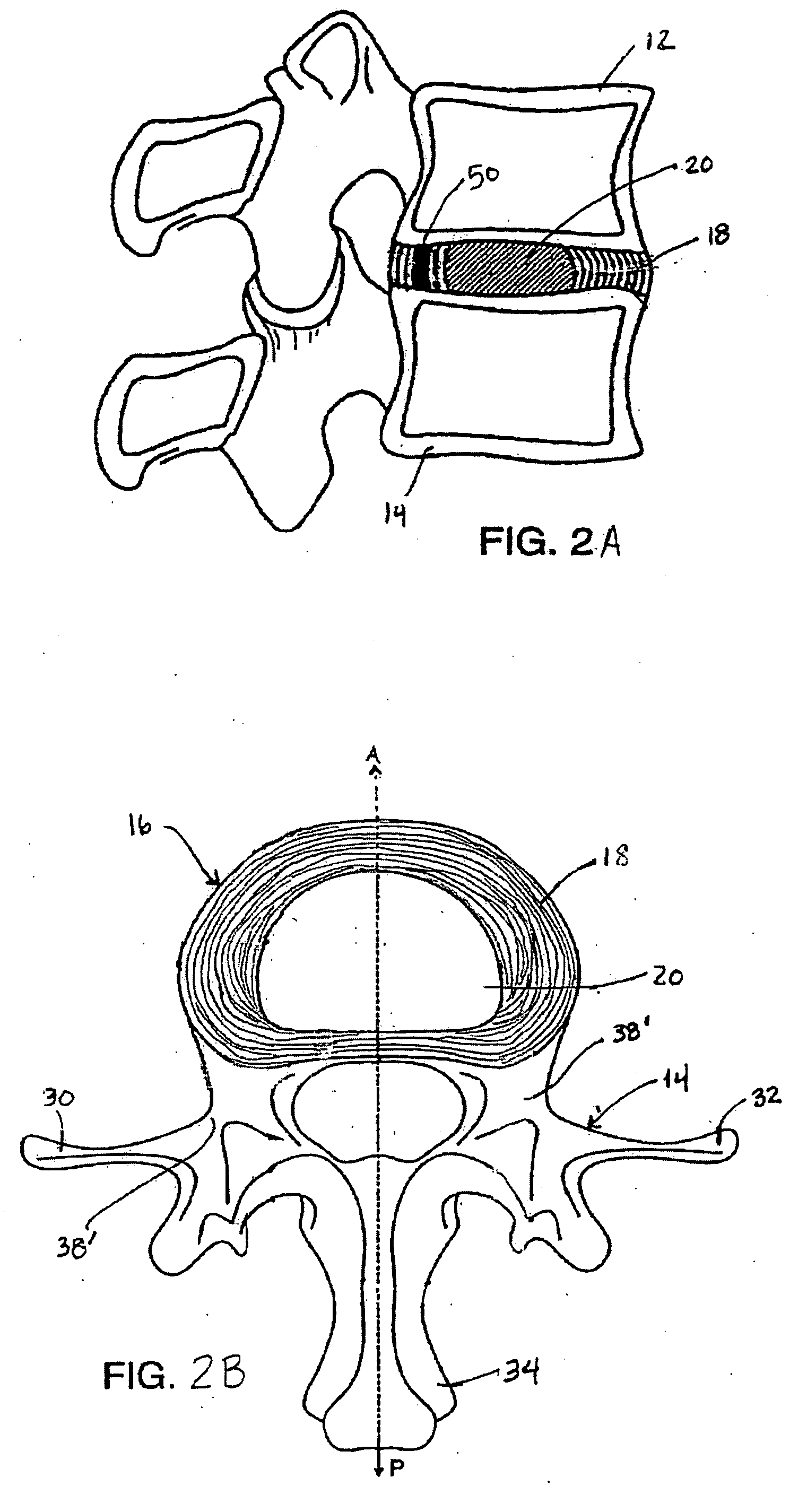
Spinal disc annulus augmentation
Intervertebral disc implants are provided for augmenting the annulus of the disc in a manner to bear at least part of the axial and / or torsional load on the annulus so that rents, fissures and subsequent herniation of the disc are prevented or substantially delayed. An aspect of the subject devices is that they have an operative height dimension that is equal to or less than the disc height of a normally functioning, healthy disc. Methods and tools are also provided for the minimally invasive implantation of the device within an intervertebral disc.
Owner:LAURIMED
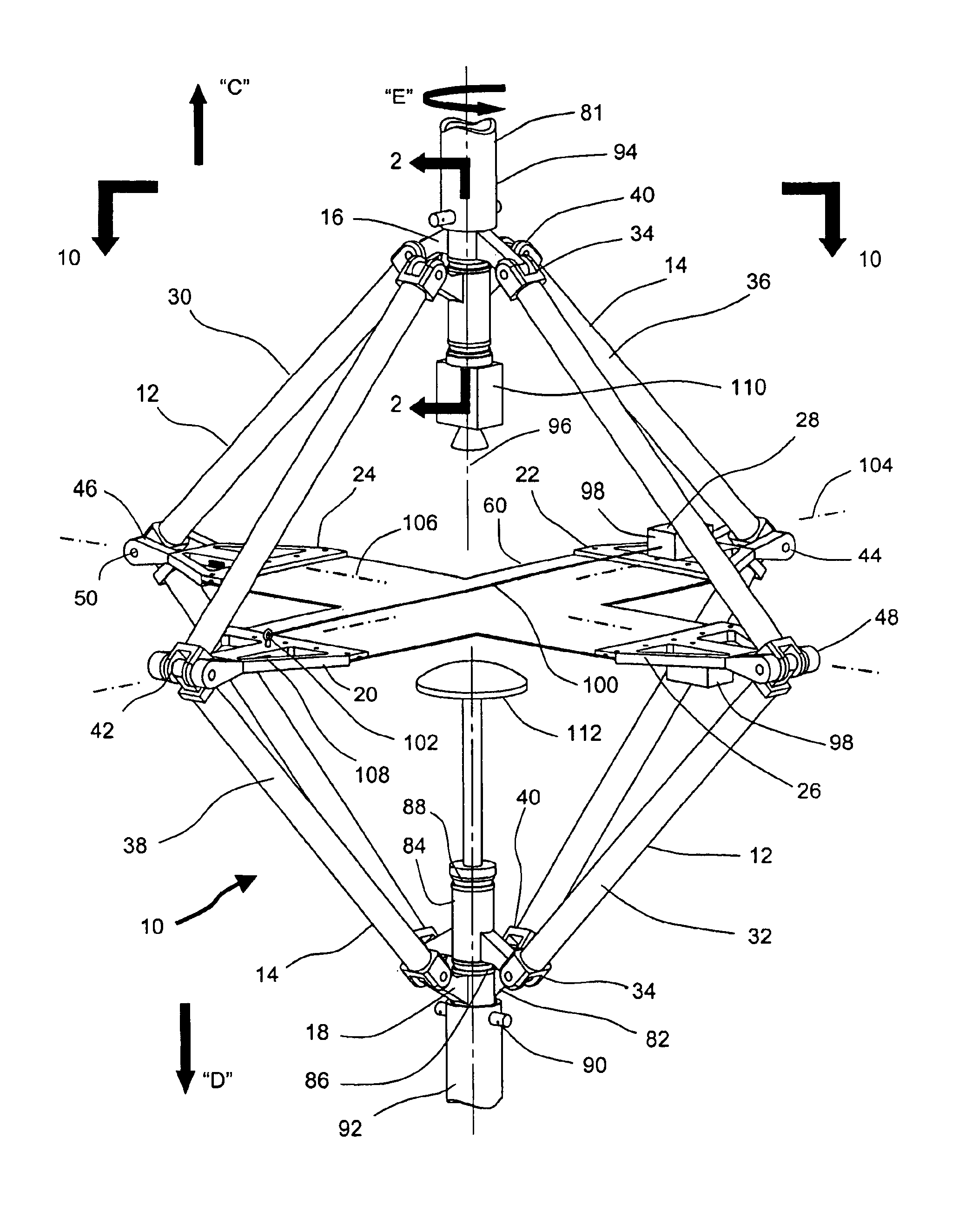
Combined in-plane shear and multi-axial tension or compression testing apparatus
ActiveUS6860156B1Provide flexibilityIncrease distanceMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesMaterial strength using repeated/pulsating forcesEngineeringTorsional load
An in-plane shear and multi-axial tension or compression testing apparatus having four-bar linkages pivotable to two sleeves on an opposite vertices with the sleeves of each vertex rotationally attached to each other. Lateral links of each linkage are pivotally attached to load transfer plates in which the plates secure a test specimen. Each linkage is rotatable to the other linkages while the vertices are subjected to a compression or tensile load. The vertices are also capable of rotation by a testing machine for shear testing. During compression or tension of the vertices of the apparatus, the plates respectfully move toward or away from each other thereby applying compression or tension to the specimen. The bars of one linkage can be rotated with respect to the other, thereby applying torsional loading to the specimen.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
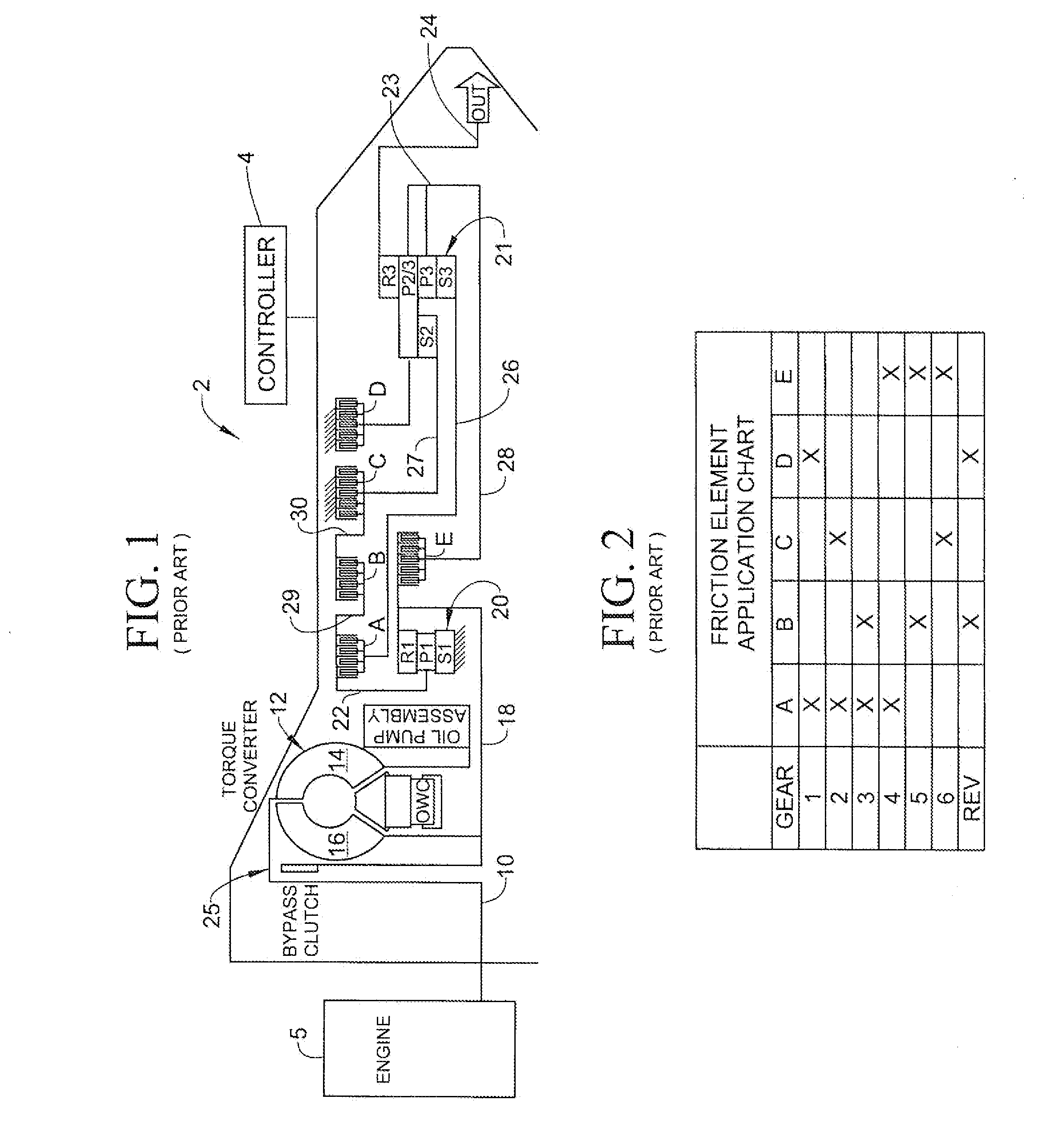
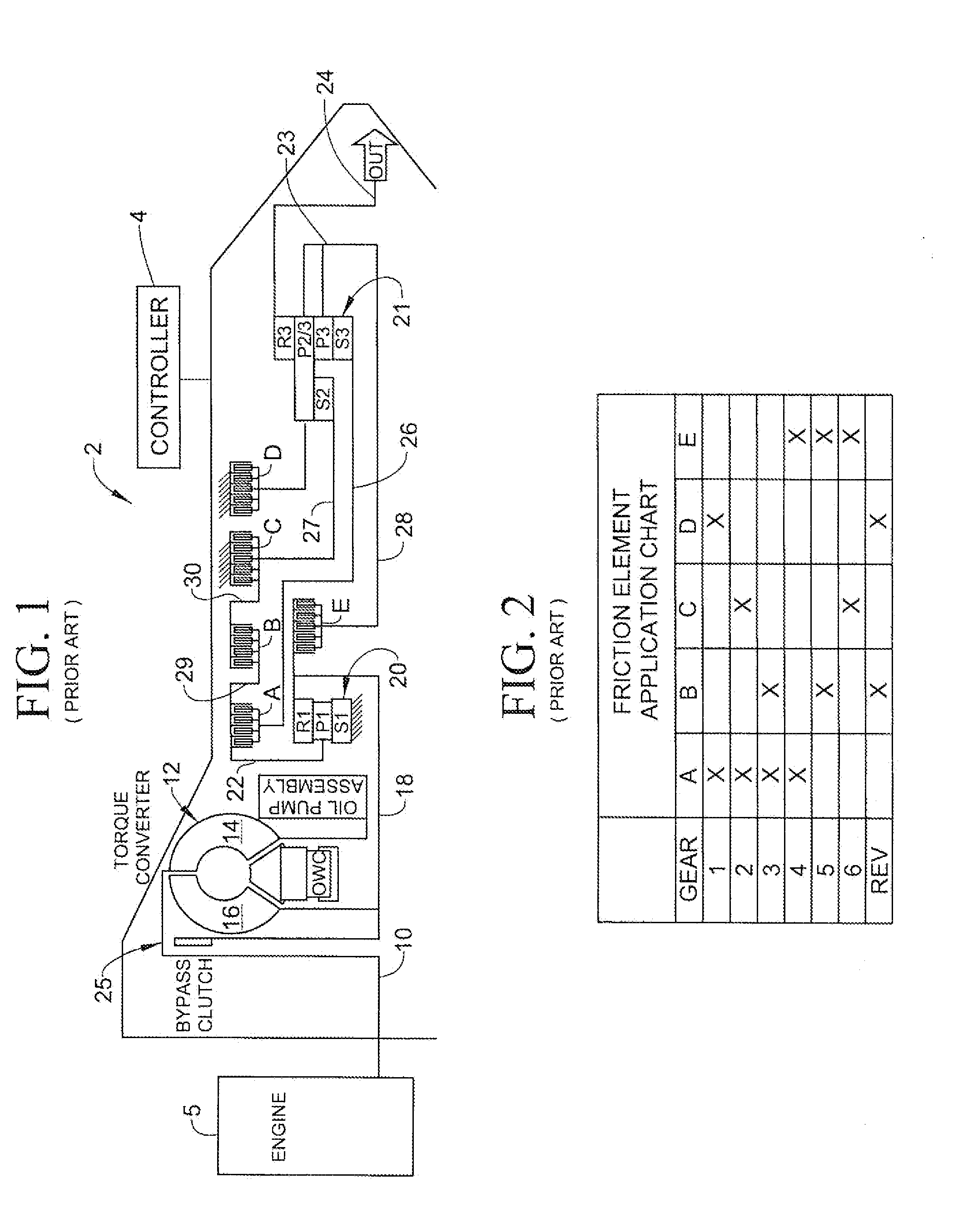
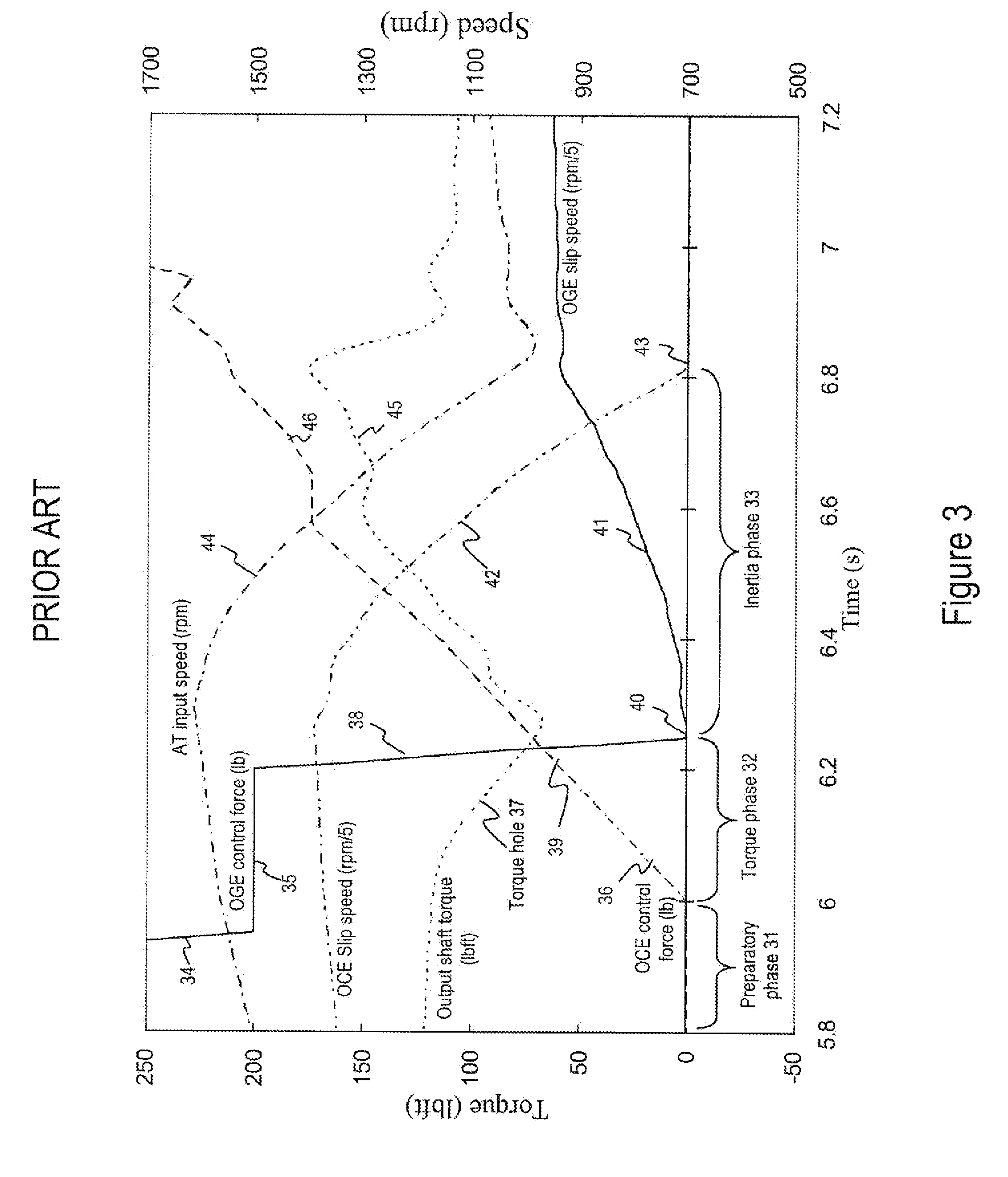
Closed-Loop Torque Phase Control for Shifting Automatic Transmission Gear Ratios Based on Friction Element Load Estimation
ActiveUS20100318269A1Increased torque capacityReducing torque capacityDigital data processing detailsGearing controlClosed loopTorque transmission
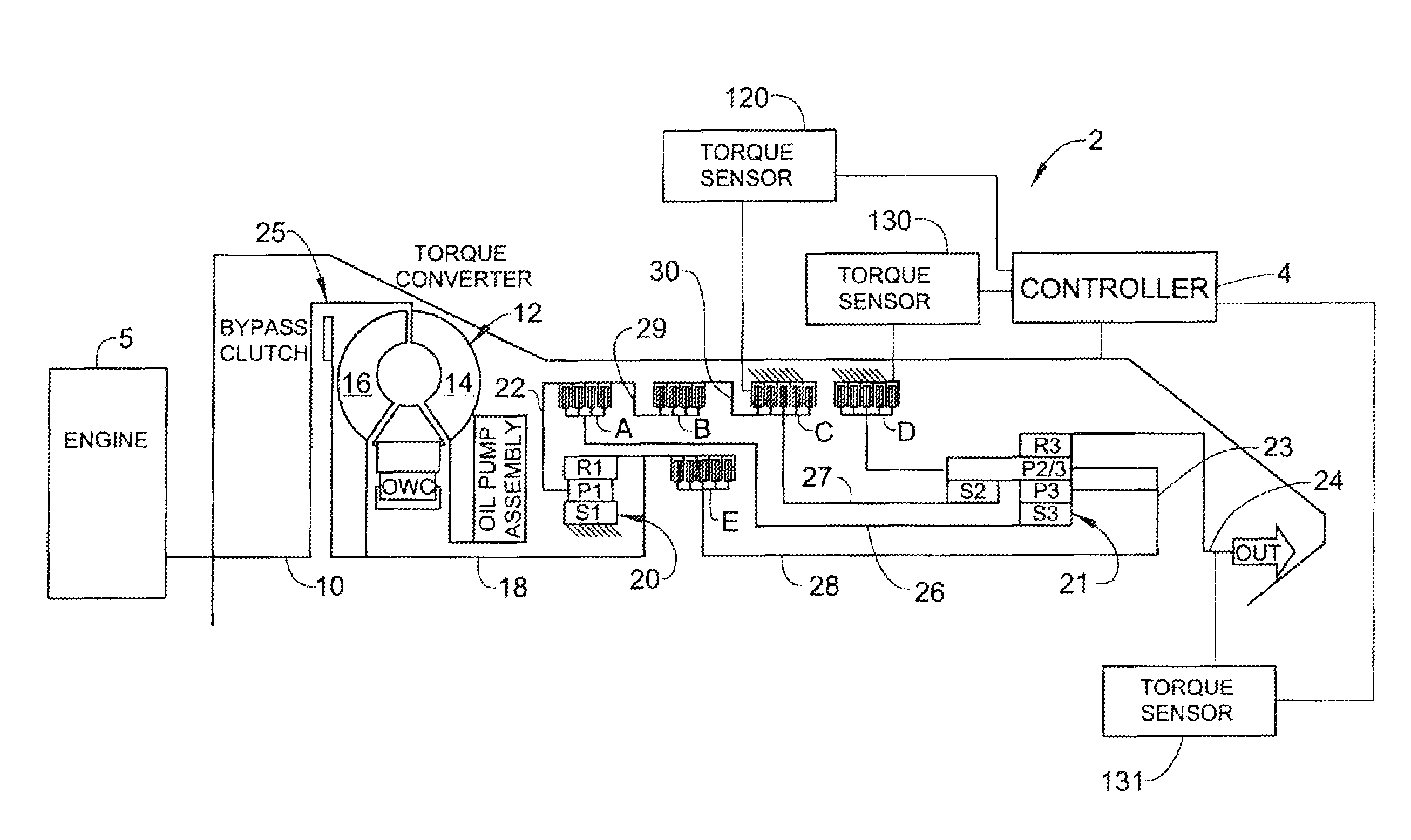
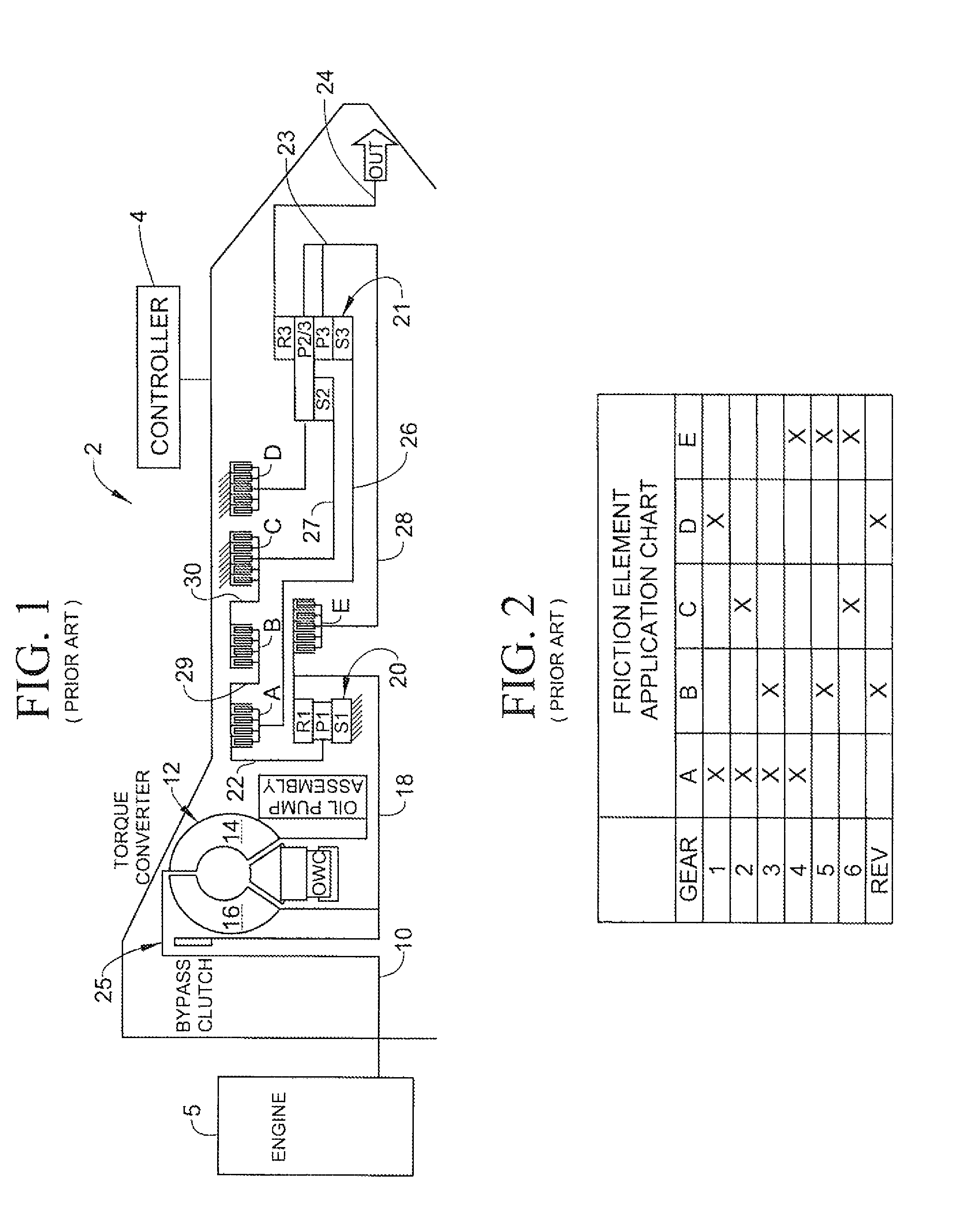
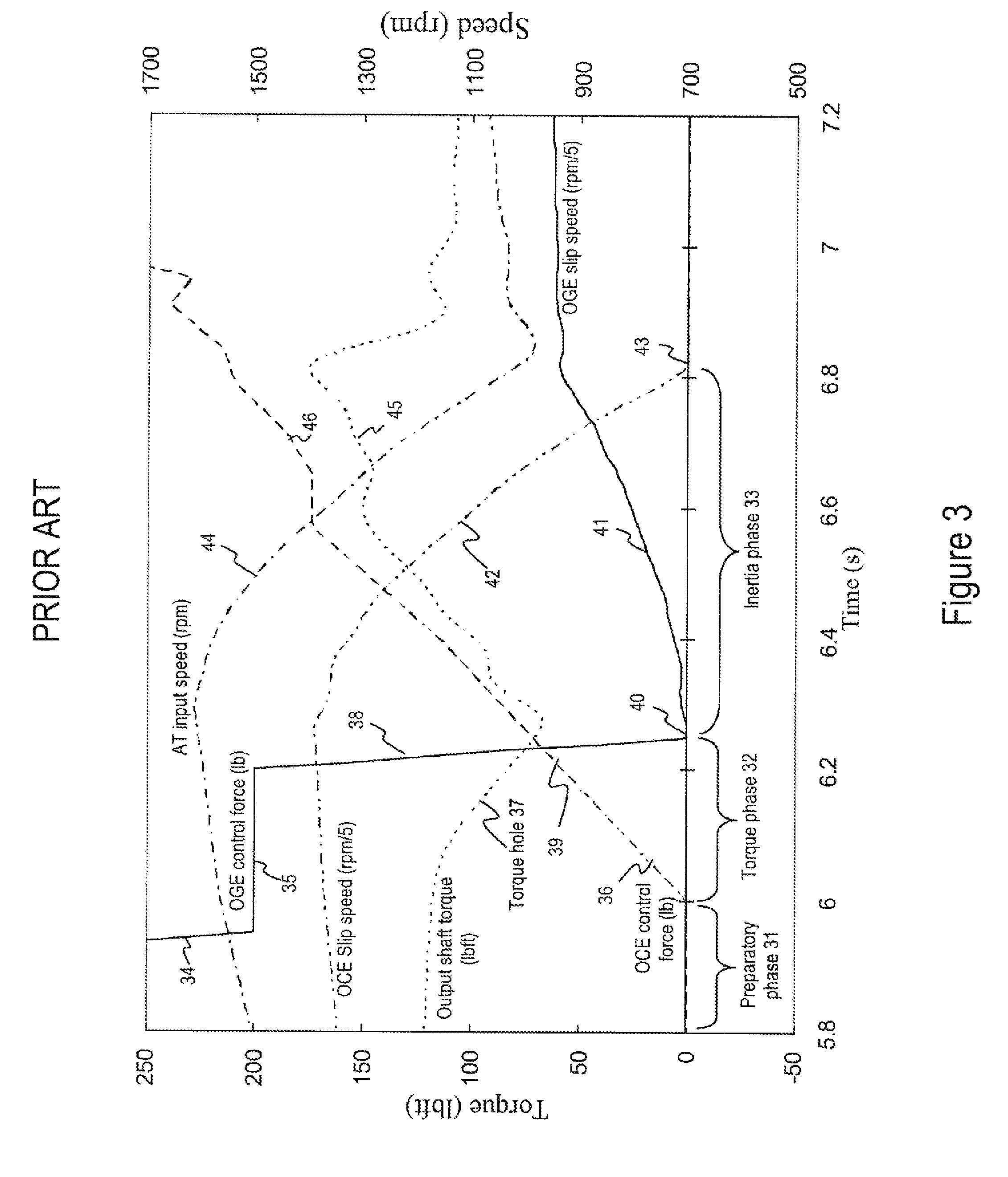
A closed loop shift control apparatus and method based on estimated torque in friction elements controls a torque transfer phase when shifting from a low gear configuration to a high gear configuration for an automatic transmission system. When pressure actuated friction elements are selectively engaged and released to establish torque flow paths in the transmission, estimates of torsional load exerted on the off-going friction element are used to predict the optimal off-going friction element release timing for achieving a consistent shift feel. The estimated torque is preferably calculated by using estimated torque signals generated as a function of speed measurements represented either the engine speed and turbine output speed or transmission output speed and wheel speed under dynamically changing conditions.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Rotor blade tip section
A main rotor blade includes a tip section having a splice cap, a structural tip spar, a core and an upper and lower tip skin. The tip section is mounted to a central blade section by mounting the tip spar to a main blade spar. The tip spar includes a first surface substantially parallel to a second surface. The first and second surfaces each extend from a shear web therebetween to define the generally C-shape in cross section. The shear web generally carries rotor blade torsional loads and eliminates the heretofore required structural core. A section of the tip spar overlaps a section of the main blade spar. The tip section thereby transfers the loads carried thereby through interaction between the overlapped spar sections. The tip section core and skins need not be structural members as the tip spar carries rotor blade tip section torsional loads.
Owner:SIKORSKY AIRCRAFT CORP
Dual-rotor, single input/output starter-generator
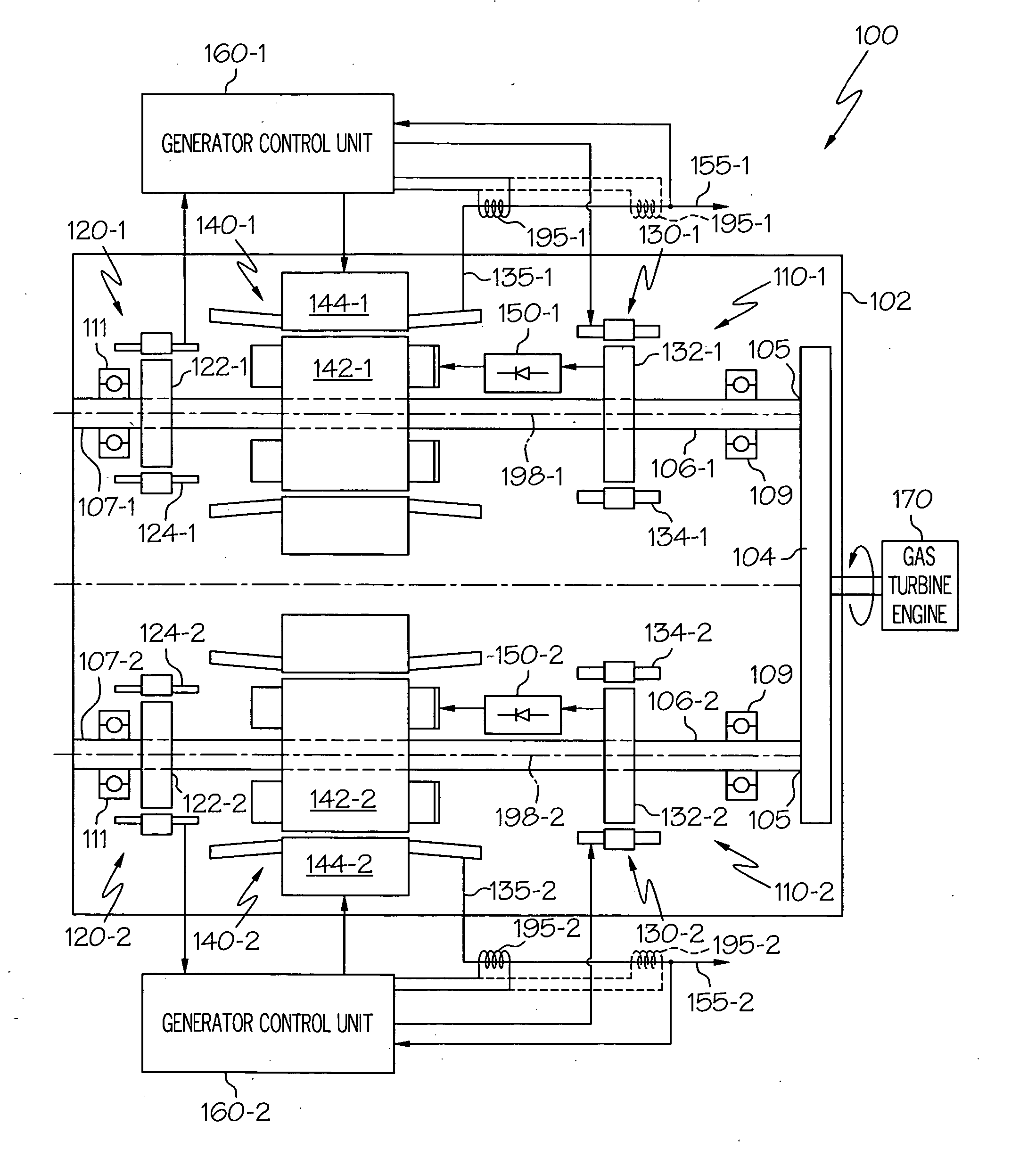
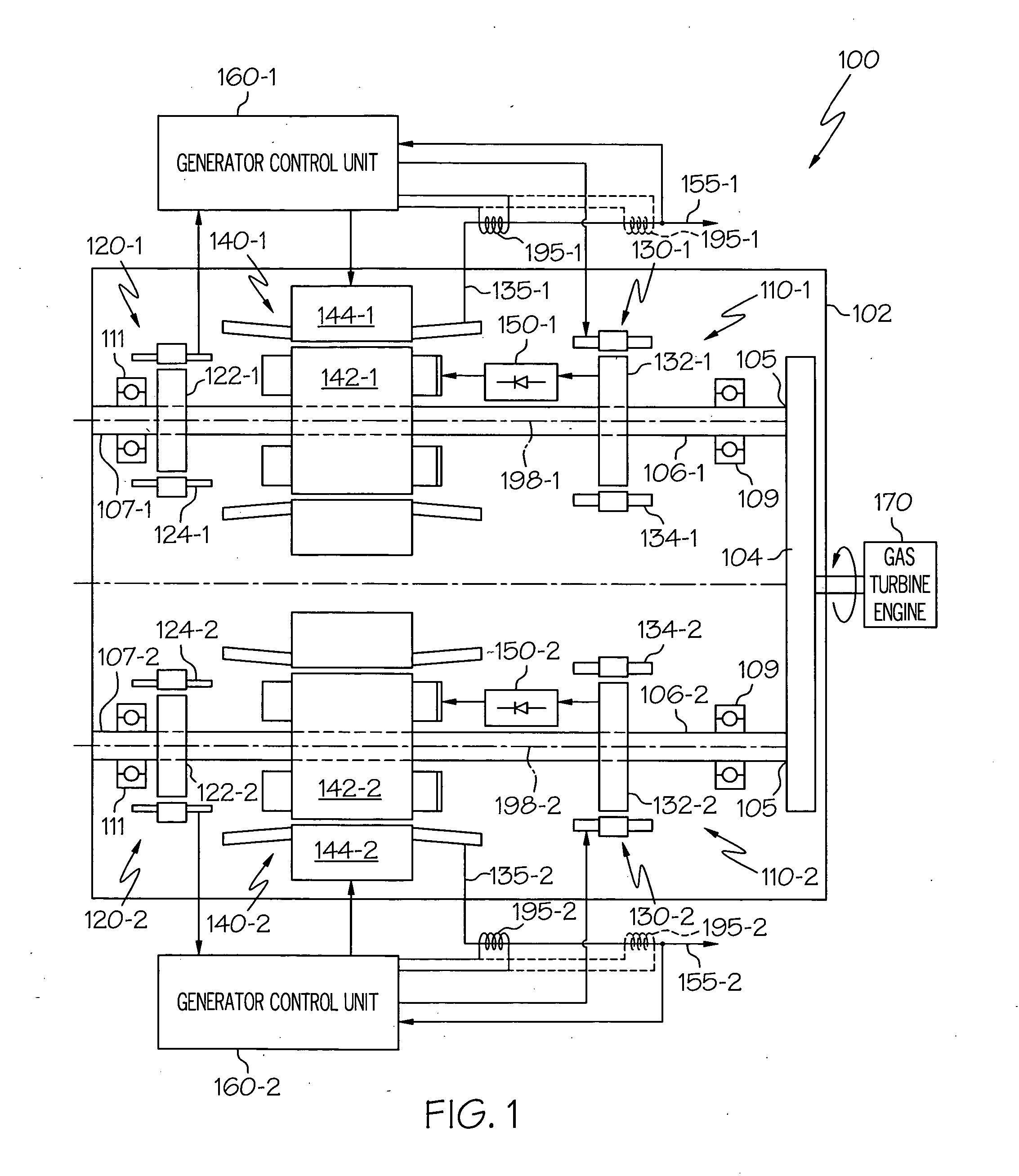
InactiveUS20060087123A1Shorten the lengthOverhung momentSteam useEfficient propulsion technologiesStarter generatorTorsional load
A starter-generator includes redundant motor / generator sets disposed within a common housing. Each motor / generator set is electrically and mechanically independent of one another, with the exception of a common input / output gear. The starter-generator is configured such that if one of the motor / generator sets experiences a predetermined torsional load, it will decouple from the input / output gear, allowing the other motor / generator set to continue operation uninterrupted.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Multiplexed torque brake system for a solar concentrator assembly
InactiveUS20090095283A1Reduce design loadDesign economySolar heating energySolar heat devicesDesign loadSolar concentrator
A multiplexed torque brake (MTB) system for preventing the accumulation of torsional forces at a center drive and thereby significantly reducing the design load requirements for trough frames of a corresponding solar concentrator assembly (SCA). In one embodiment, an MTB system for an SCA having a plurality of solar reflector frames spaced along a length of the SCA includes a plurality of brake mechanisms arranged at locations spaced apart from each other along the length of the SCA, each of the brake mechanisms coupled to a corresponding one of a plurality of supporting pylons and configured to constrain the solar reflector frames from rotating when subjected to torsional loads, the brake mechanisms adapted to transfer the torsional loads to the corresponding supporting pylons.
Owner:GOSSAMER SPACE FRAMES
E-fixture
InactiveUS20060101921A1Material strength using tensile/compressive forcesMaterial strength using steady torsional forcesInternal pressureDegrees of freedom
A device and a method are disclosed for testing a curved panel assembly, which simulates a segment of an aircraft fuselage barrel section, subjected to combined loading. The device includes an axial load head assembly attached to the test panel assembly via one axial load fitting and configured to apply an axial load to the test panel assembly, and an axial-torsion reaction box connected to the axial load head assembly via linear journal bearing assemblies, where the axial-torsion reaction box is configured to be rotated by a pair of torsional loading systems to apply a torsional load to the test panel assembly. The device also includes a gore section attached to hoop load fittings of the test panel assembly, configured to provide degrees of freedom that constrain the test panel assembly to load and deflect as it would naturally in an actual fuselage barrel, form a plenum box to apply an internal pressure load, and provide hoop loading systems that complete the full hoop load application to the test panel assembly. A fixed reaction box attached to the test panel assembly via another axial load fitting rigidly attaches the test panel to the self-reacting frame, completing the internal load path of the overall system.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
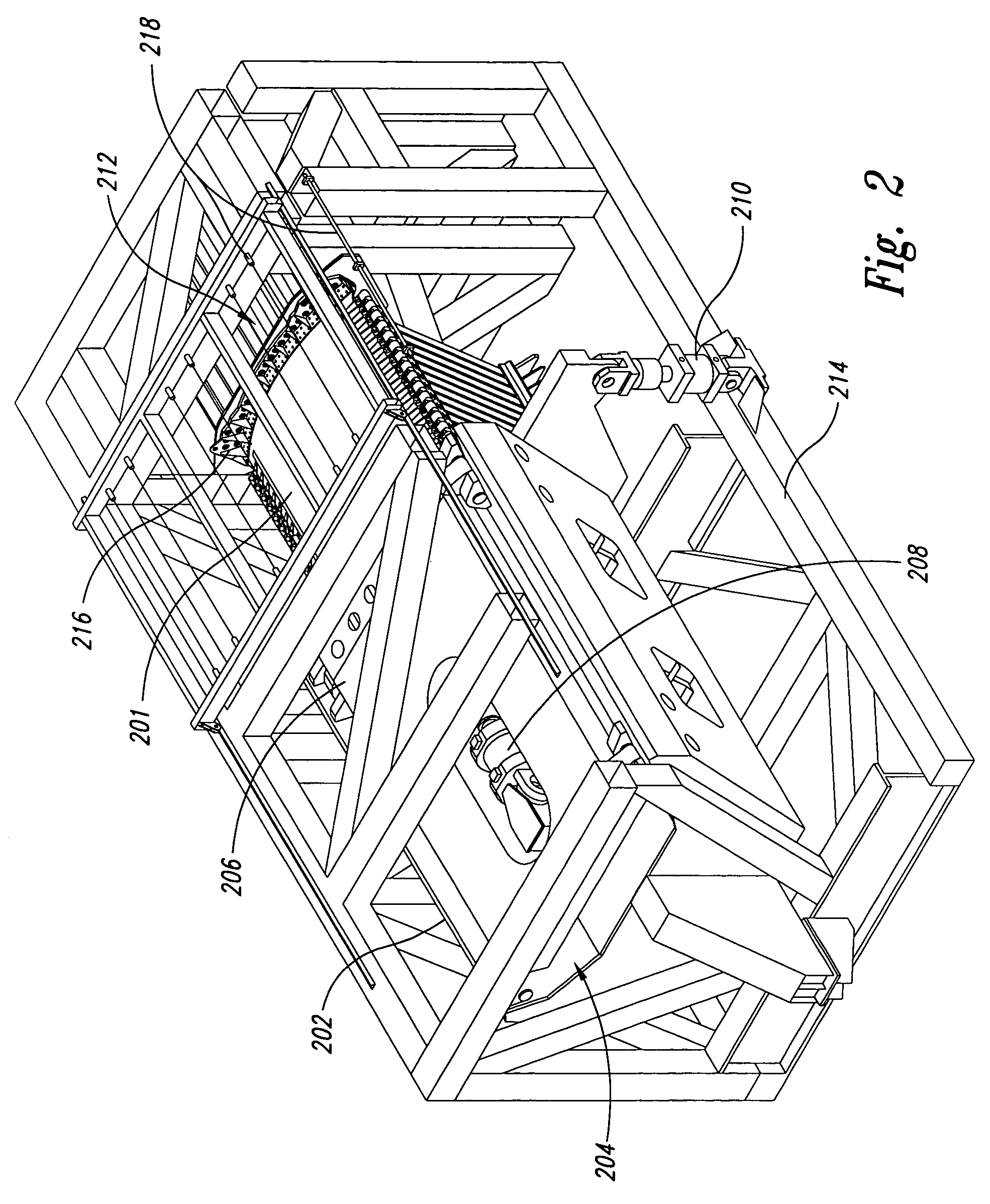
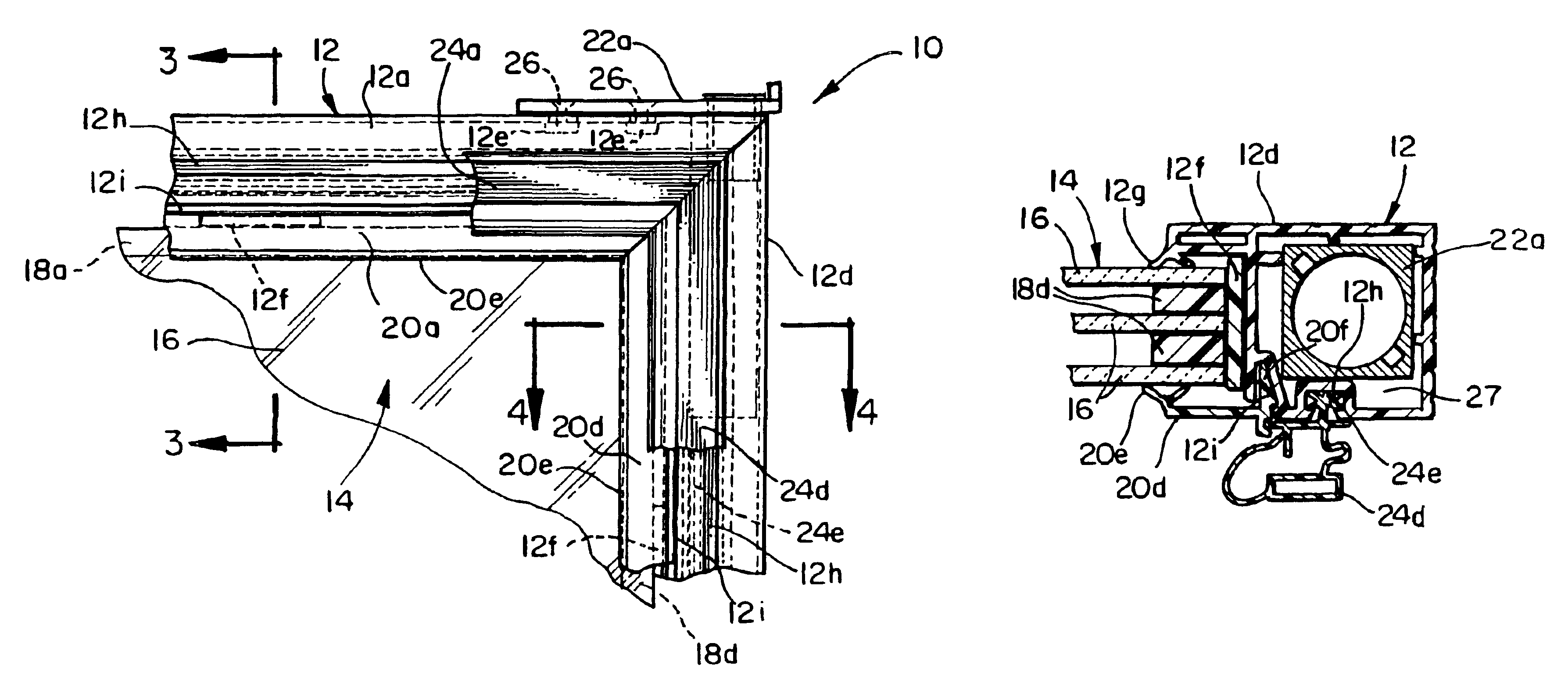
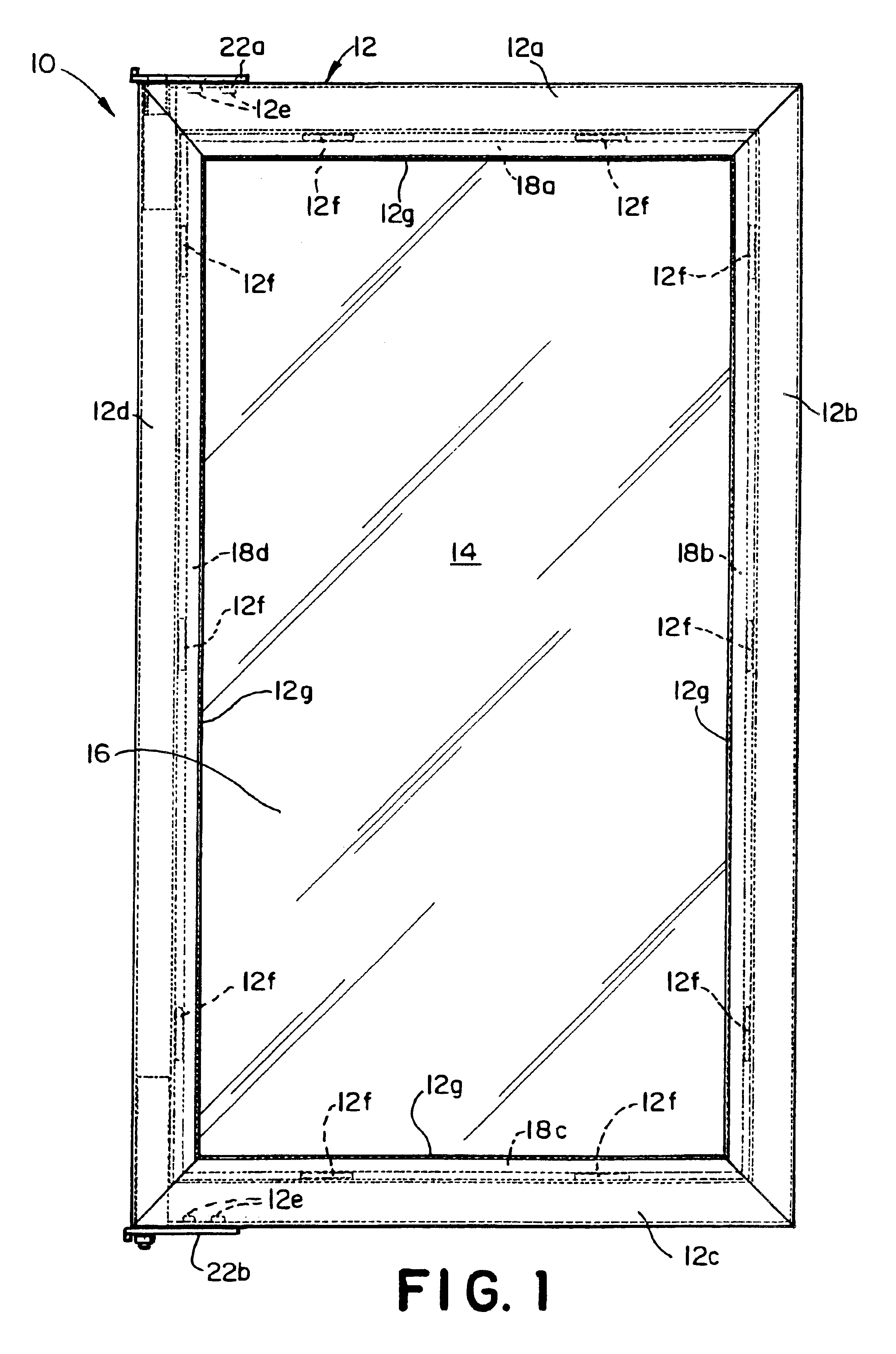
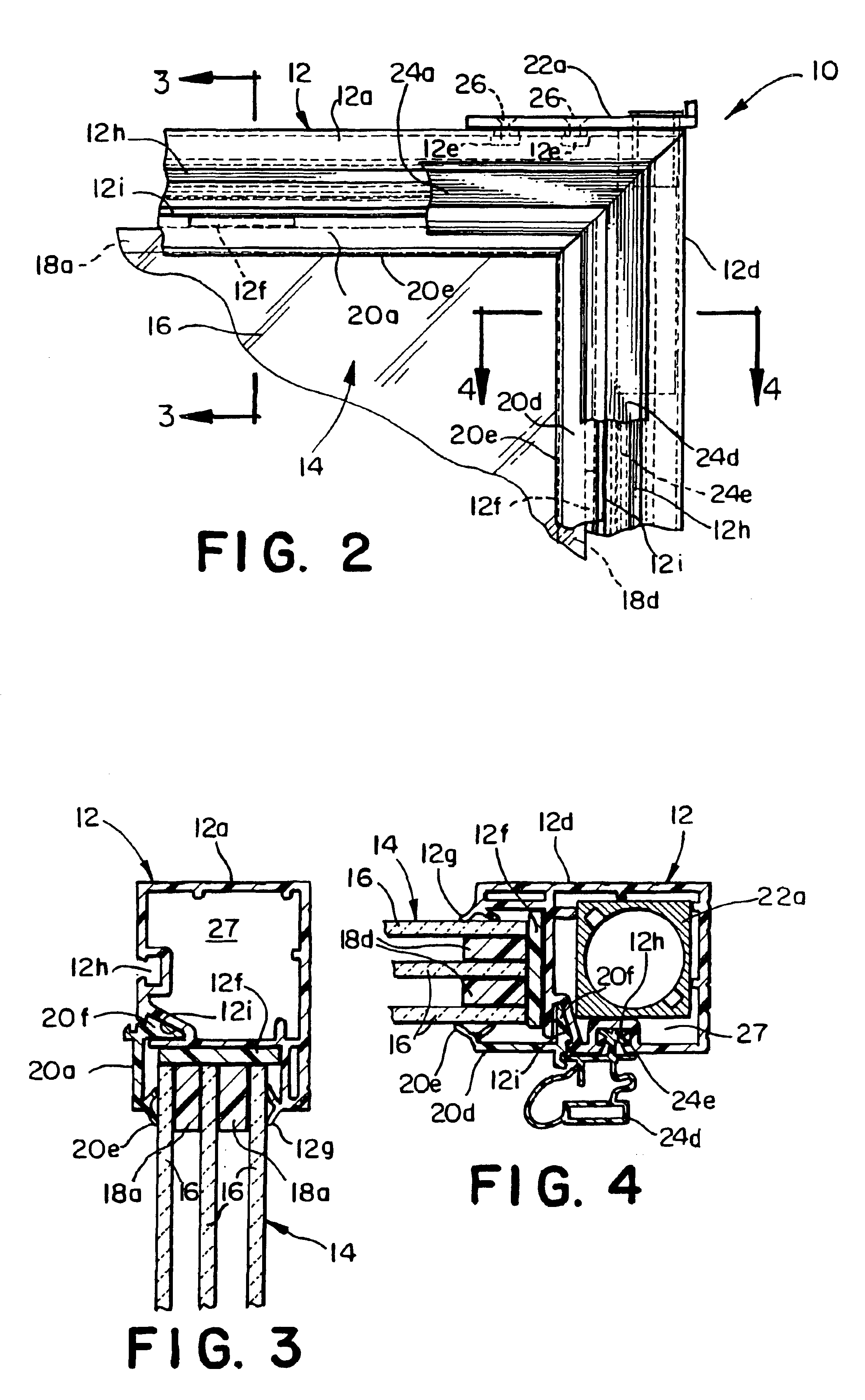
Refrigerator door assembly
InactiveUS7043886B1Improve structural rigidityEasy constructionShow cabinetsDomestic cooling apparatusRefrigerator carEngineering
A refrigerator door assembly for mounting within an opening of a refrigerator cabinet for movement relative to the refrigerator consisting in combination the following components within a hollow rigid plastic welded structural door frame: a multi-paned insulated glass pack drop-in unit, a bushing means and a hinge means, each secured in the door frame and cooperating to support the dynamic and torsional loads of the glass pack unit.
Owner:THERMOSEAL INDS
Cantilever rear suspension for a bicycle
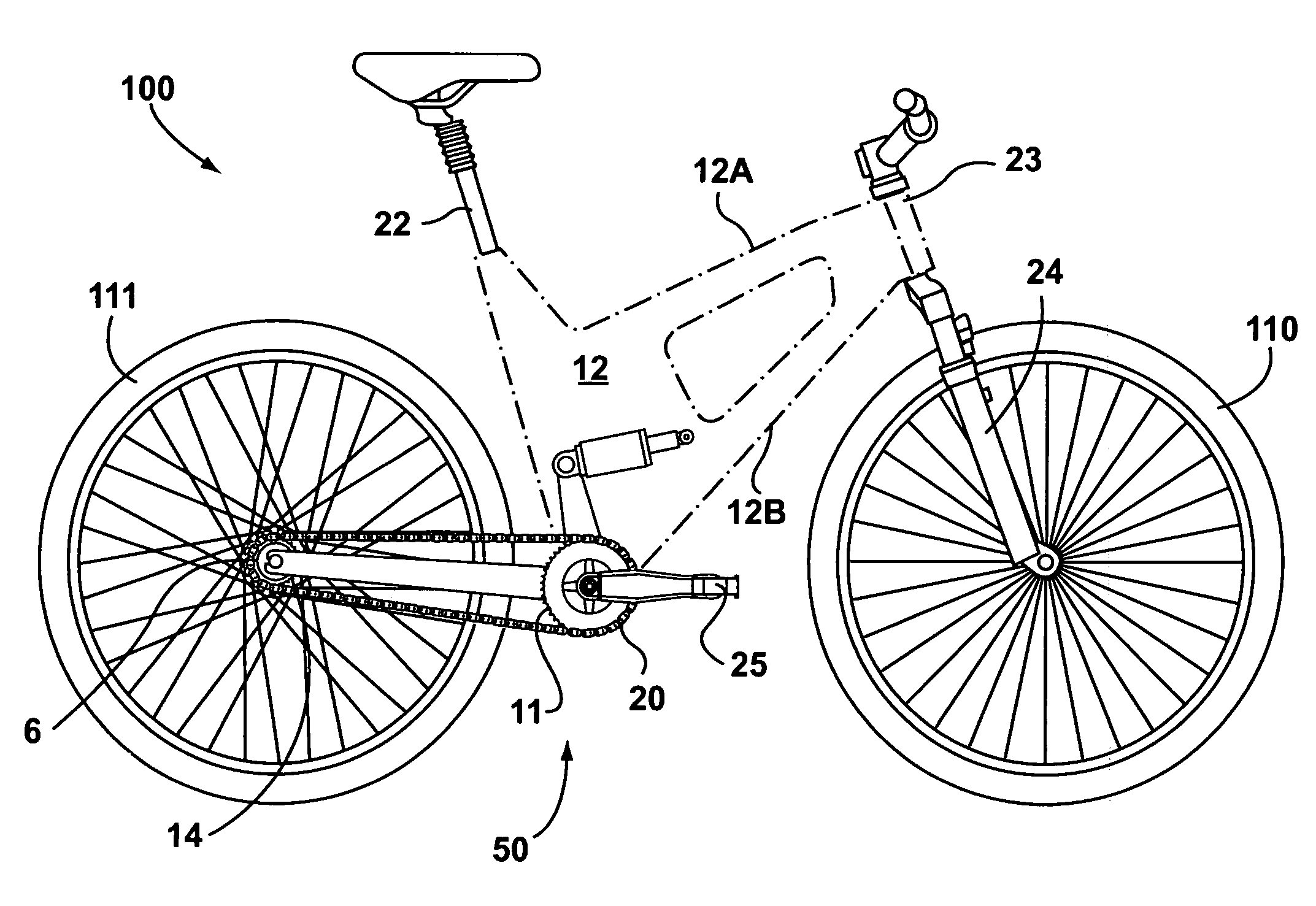
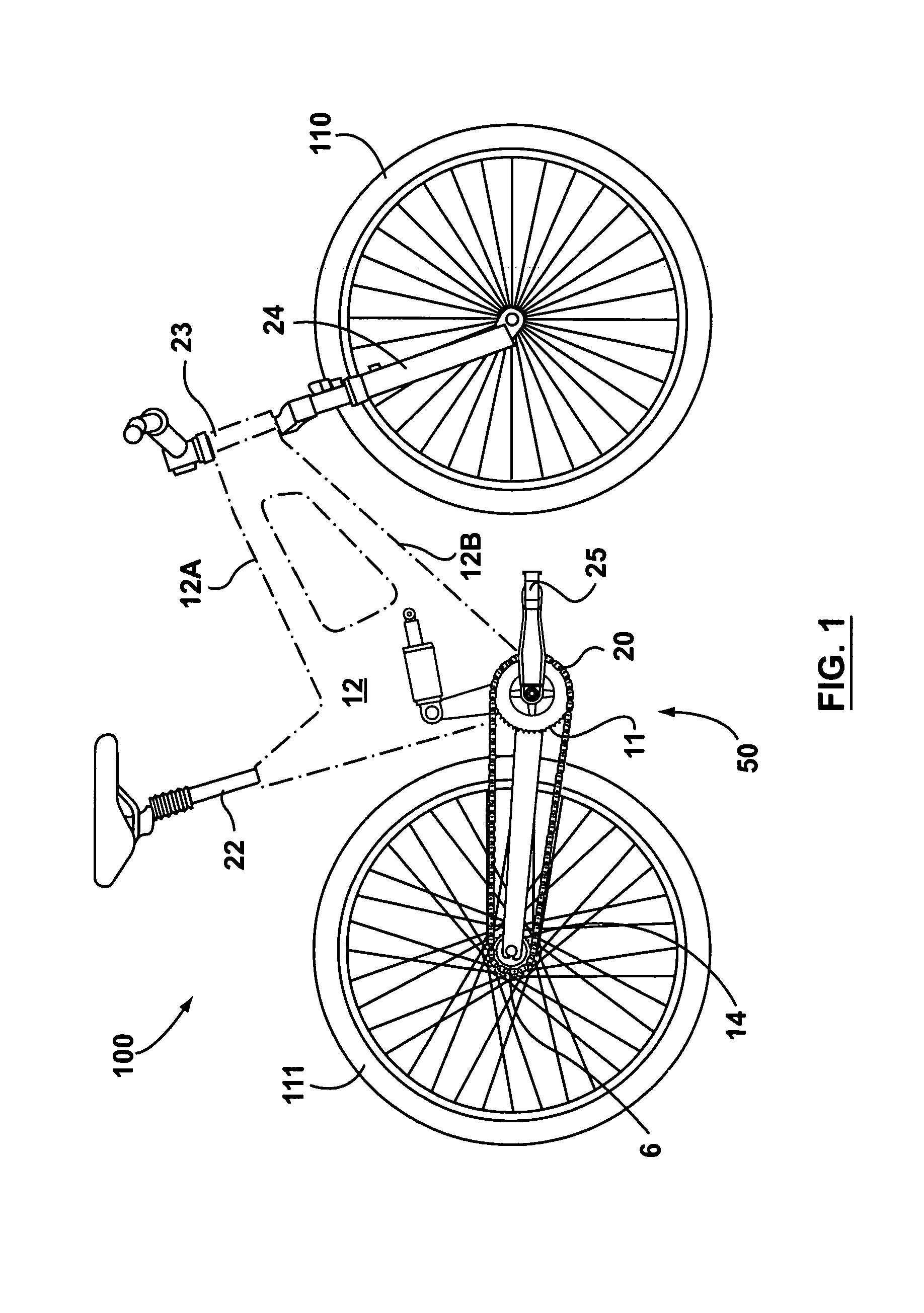
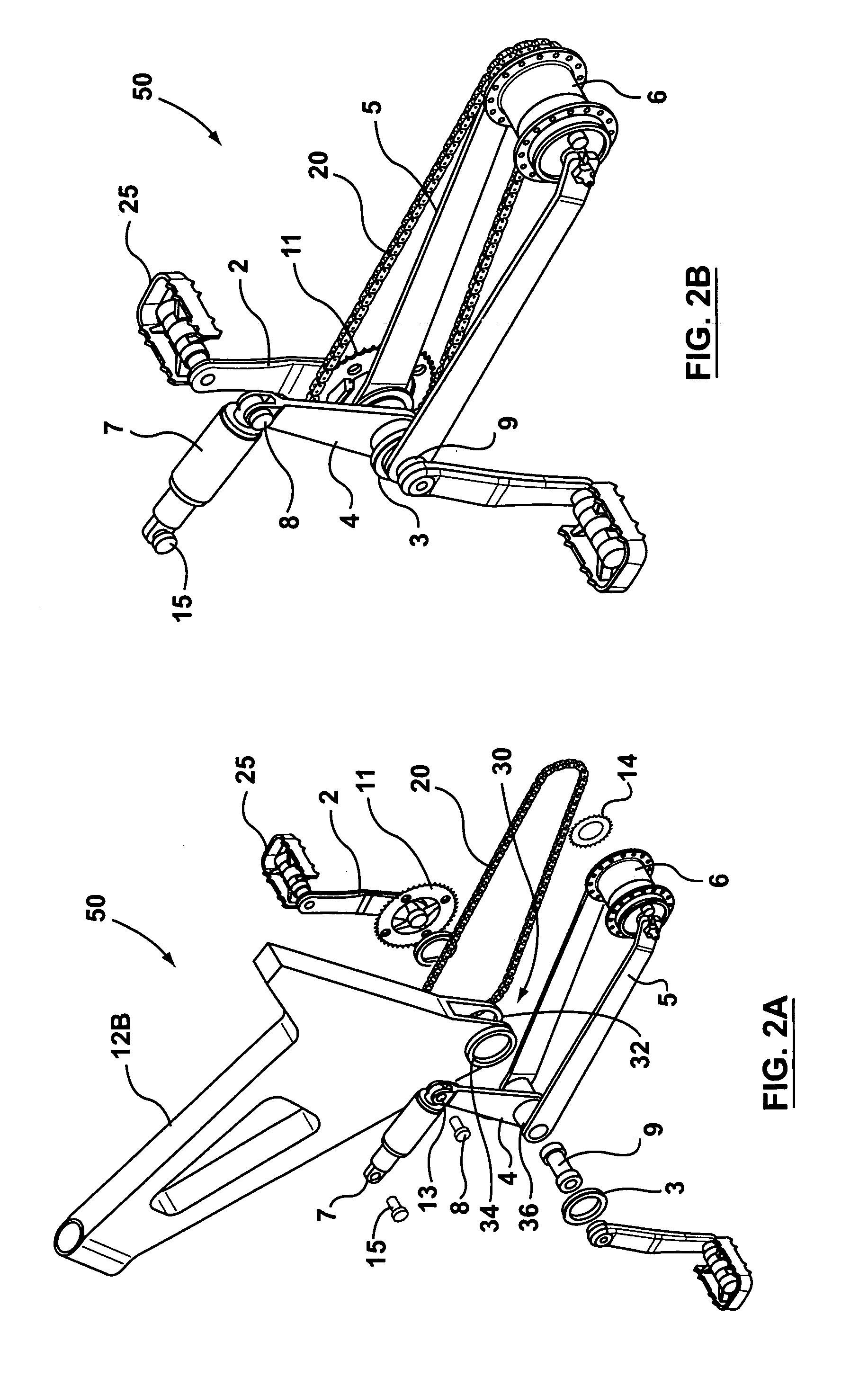
ActiveUS7104562B2Reduce unwanted playIncrease surface areaPassenger cyclesChildren cyclesRotational axisEngineering
A bicycle is equipped with a rear wheel suspension having a swing arm with one or more generally cantilevered side arms, which are capable of withstanding bending and torsional loads and isolating said loads from the rider. A bottom portion of the bicycle frame includes a pedal sleeve. A pedal or crank assembly rotates within the pedal sleeve about a rotational axis with a fixed location relative to the frame. The swing arm is pivotally secured to the frame for movement about the rotational axis. A shock-absorbing element is connected between the swing arm and the frame.
Owner:GINGL MANFRED
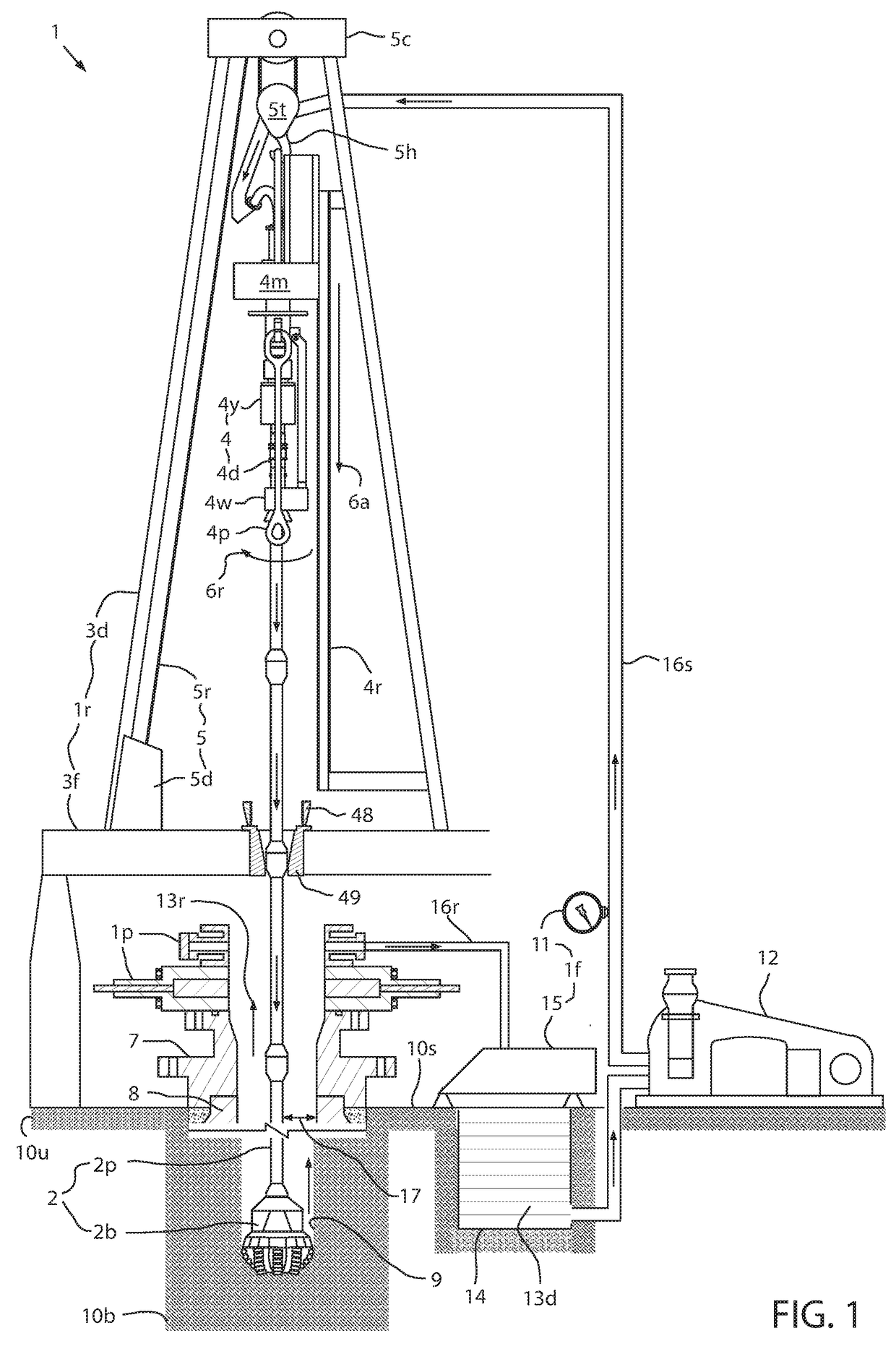
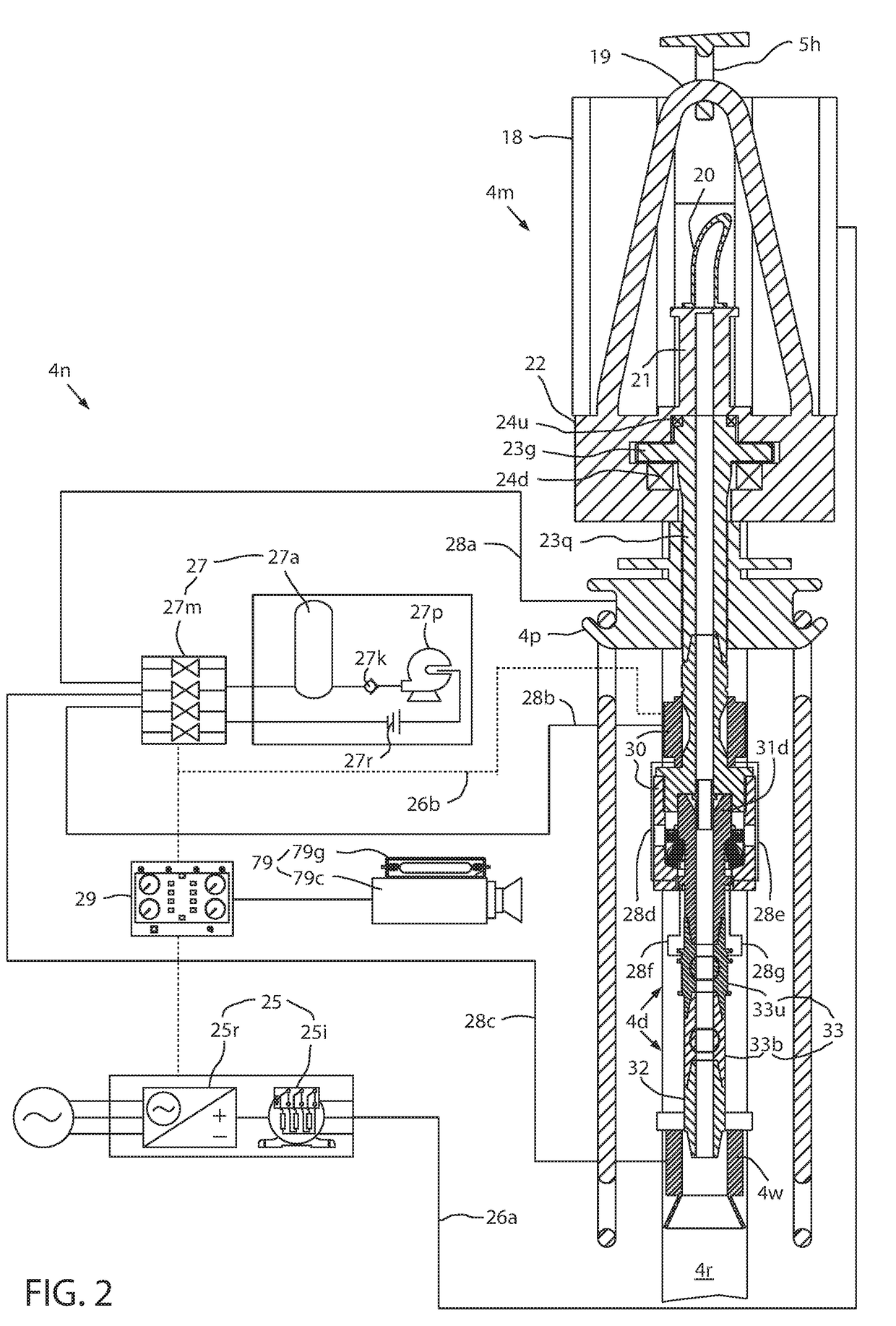
Modular connection system for top drive
The present disclosure generally relates to a modular connection system for a top drive. The modular connection system may include two tubular components, each having a bore, a seal profile, and two or more load transfer features. The first tubular component may be inserted to the second tubular component to make a connection to transfer fluid, axial loads, and torsional loads. Each of the two tubular components may also include a coupler configured to transfer pressured fluid, data, or other signals.
Owner:WEATHERFORD TECH HLDG LLC
Multi-axial pedicle fixation assembly and method for use
ActiveUS20120209335A1Avoid assemblySuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisPlastic surgeryTorsional load
An implantable orthopedic assembly comprises a bone fixator and head assembly for securing a stabilizing rod to the spine. The head assembly allows multi-axial repositioning of the bone fixator relative to the head assembly. A primary drive interface located on the bone fixator may be used to adjust the depth of bone penetration when the bone fixator and head assembly are substantially coaxial. A secondary drive interface located on the head assembly may be used to adjust the depth of bone penetration while independently adjusting the stabilizing rod position when the bone fixator and the head assembly are not coaxial, transferring torsional loads to the bone fixator.
Owner:ORTHOFIX US LLC
Frame structure for vehicle
InactiveUS20120119546A1Increased torsional stiffnessInhibit weight gainVehicle seatsSuperstructure subunitsRotational axisEngineering
In a frame structure for a vehicle having a reinforcement body provided inside a frame body, the frame body comprises a first face portion and a second face portion extending in a direction substantially perpendicular to a rotational-axis direction of a bending moment occurring when a torsional load acts on a vehicle body, and third face portions positioned between the first and second face portions, and the reinforcement body comprises third-face connection portions connected to the third face portions, a first-face connection portion connected to the first face portion at a corner portion, a first-face non-contact portion provided away from the first face portion, a second-face connection portion connected to the second face portion at a corner portion, and a second-face non-contact portion provided away from the second face portion.
Owner:MAZDA MOTOR CORP
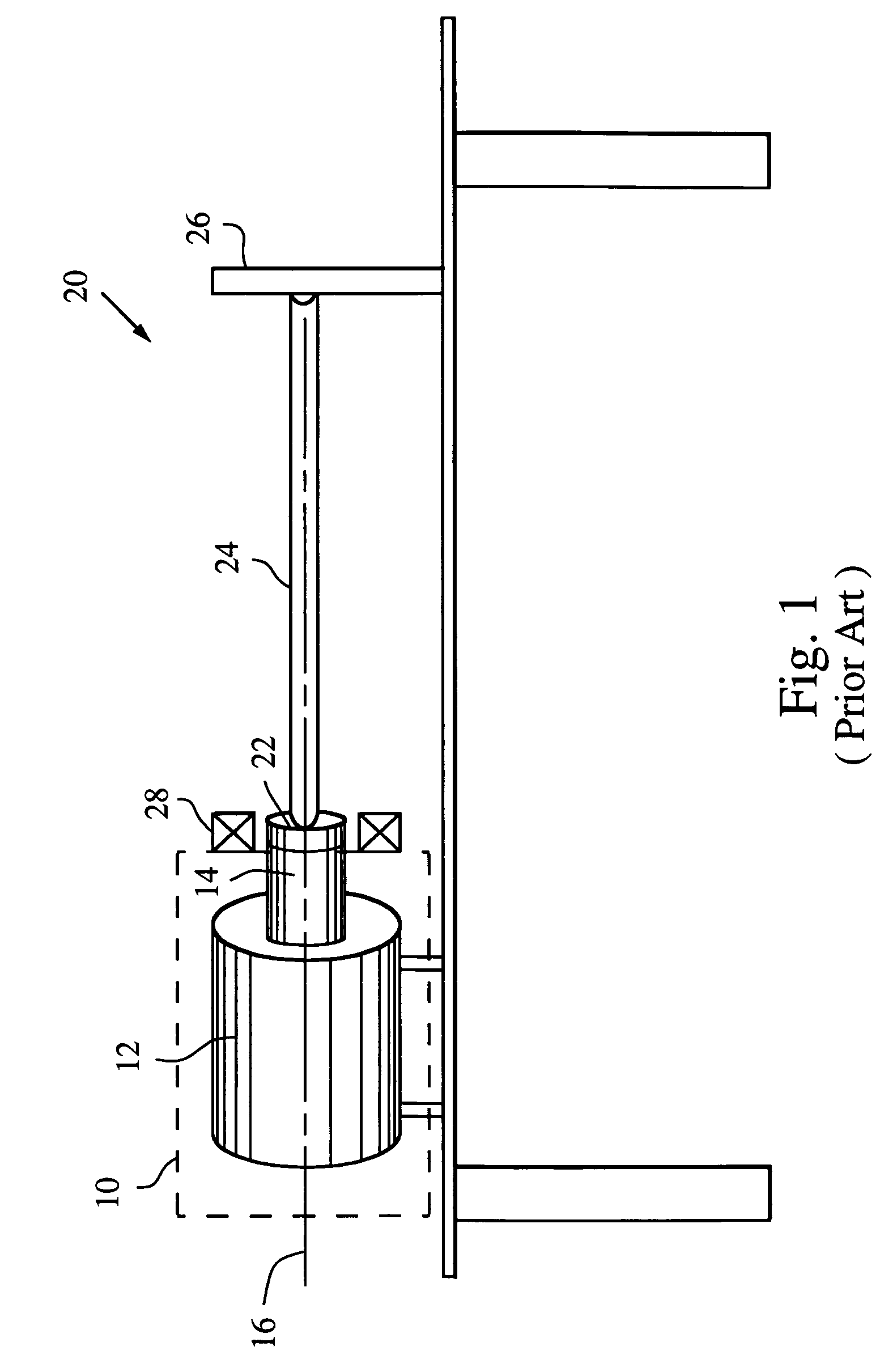
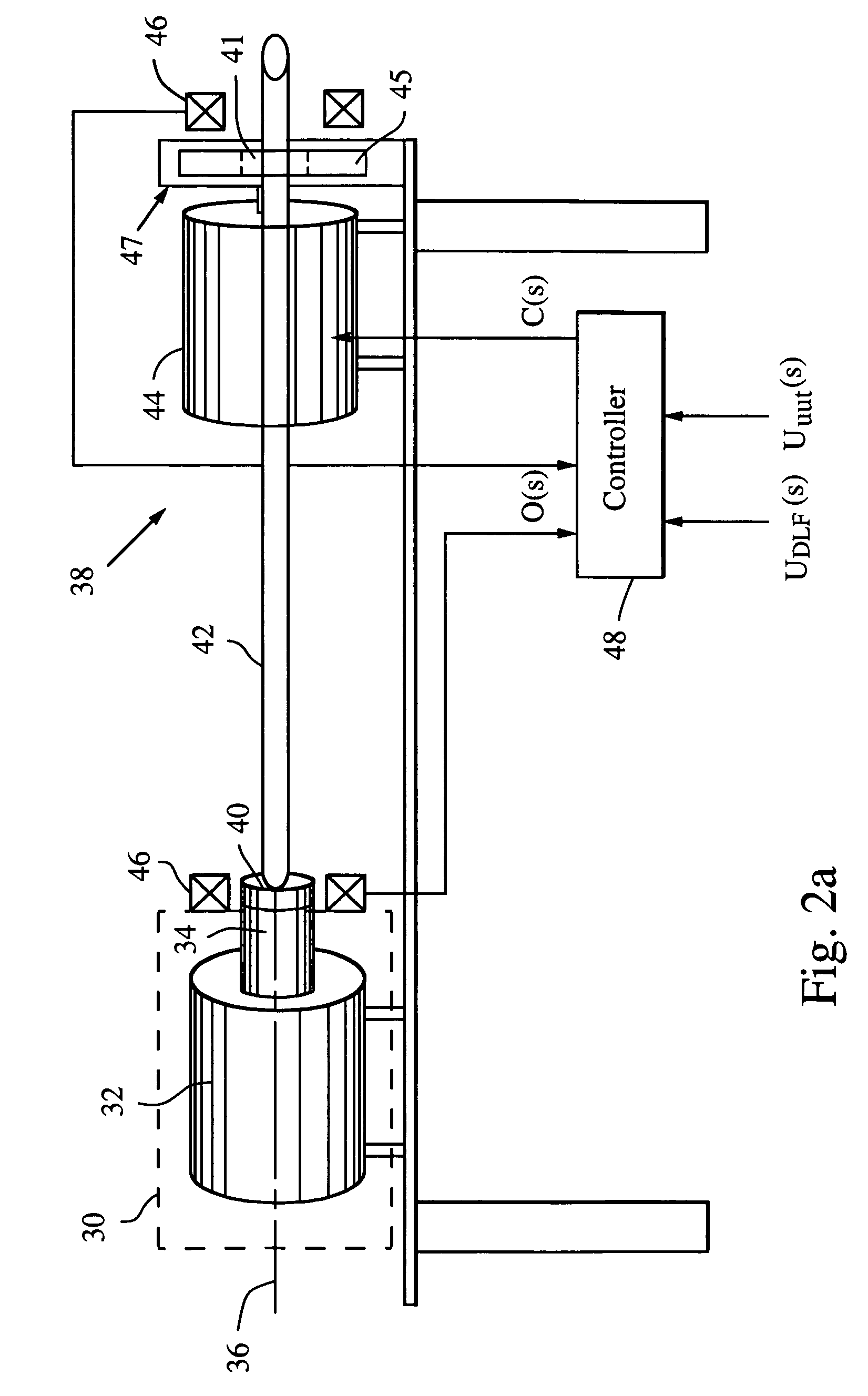
Dynamic load fixture for rotary mechanical systems
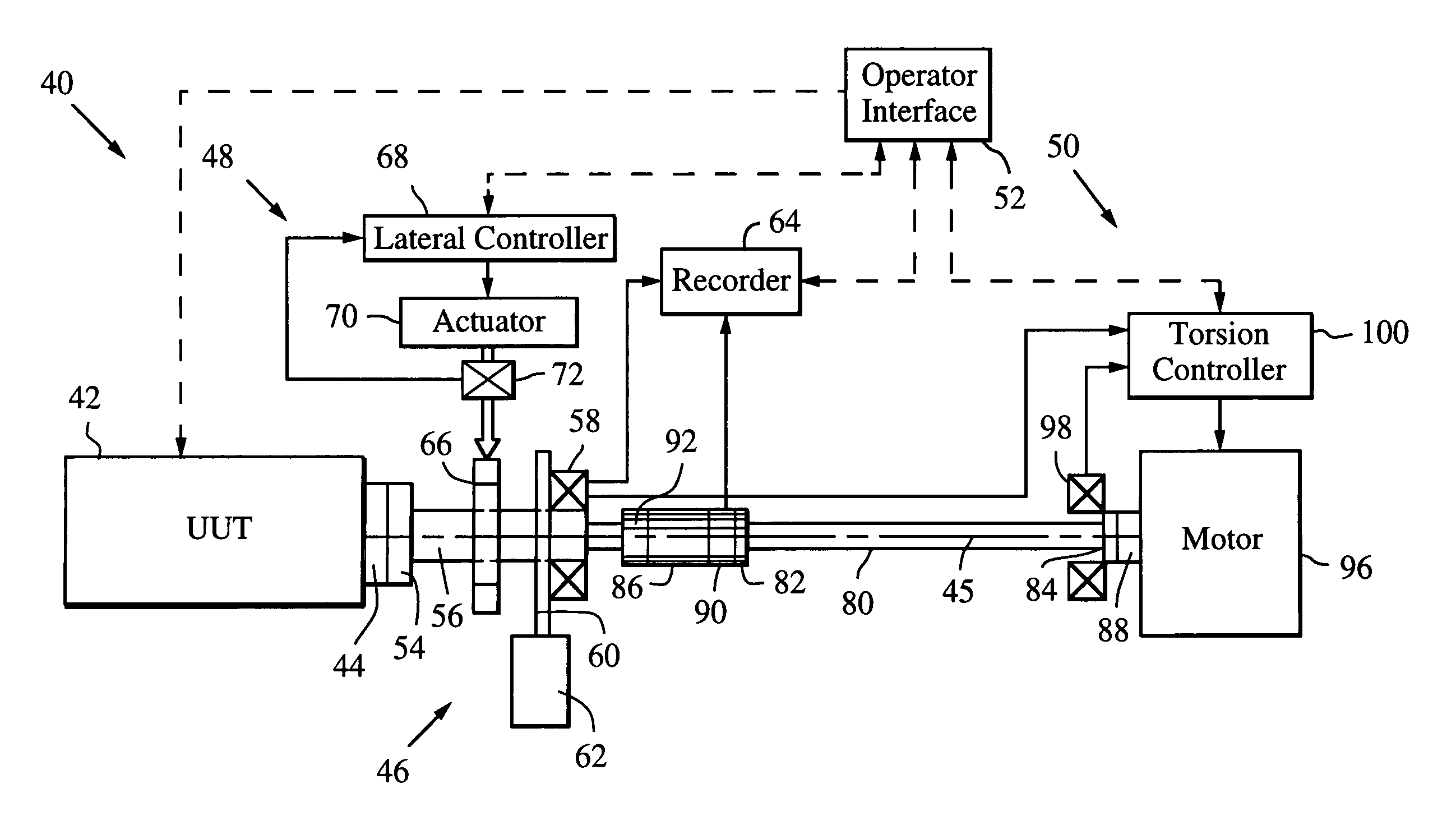
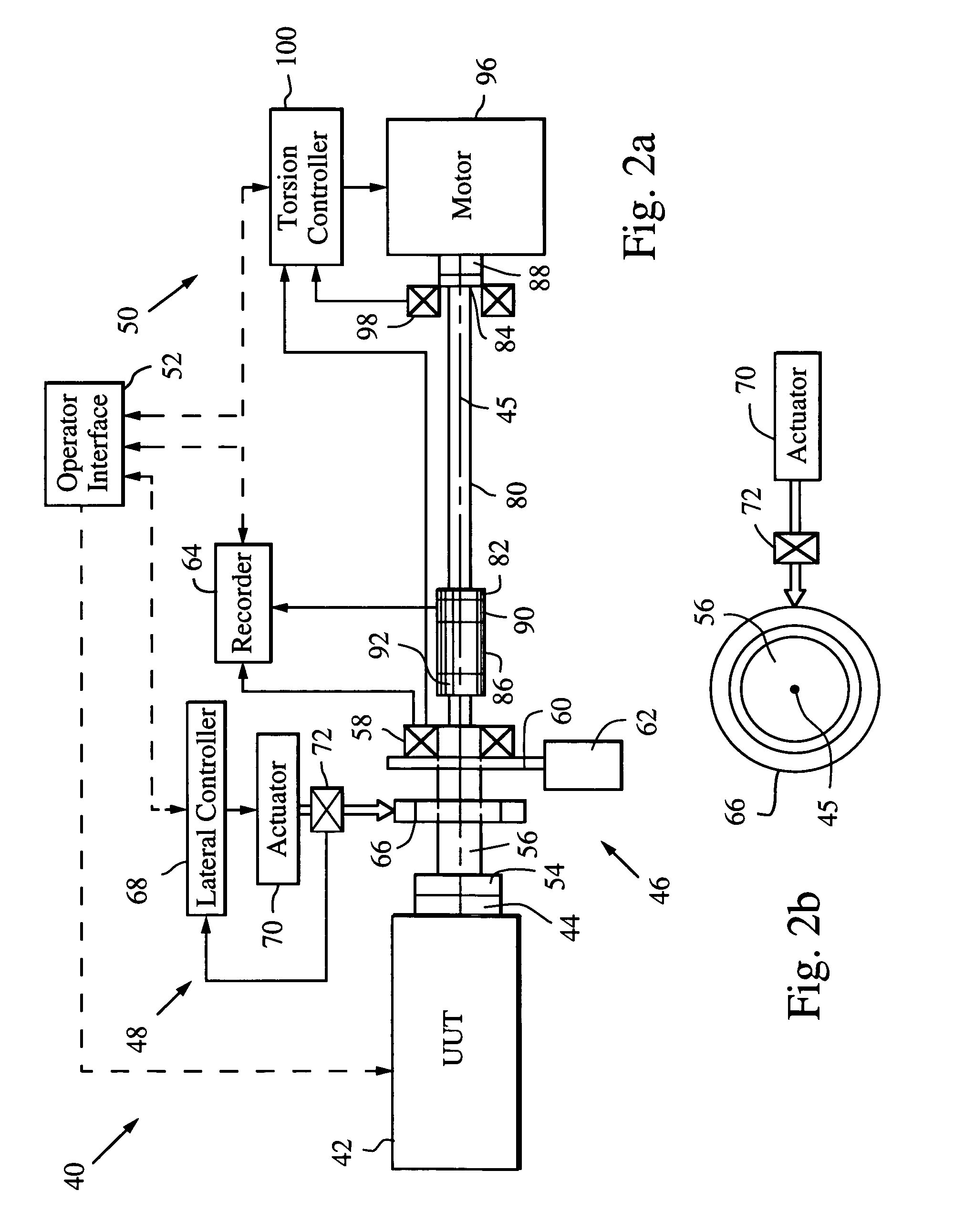
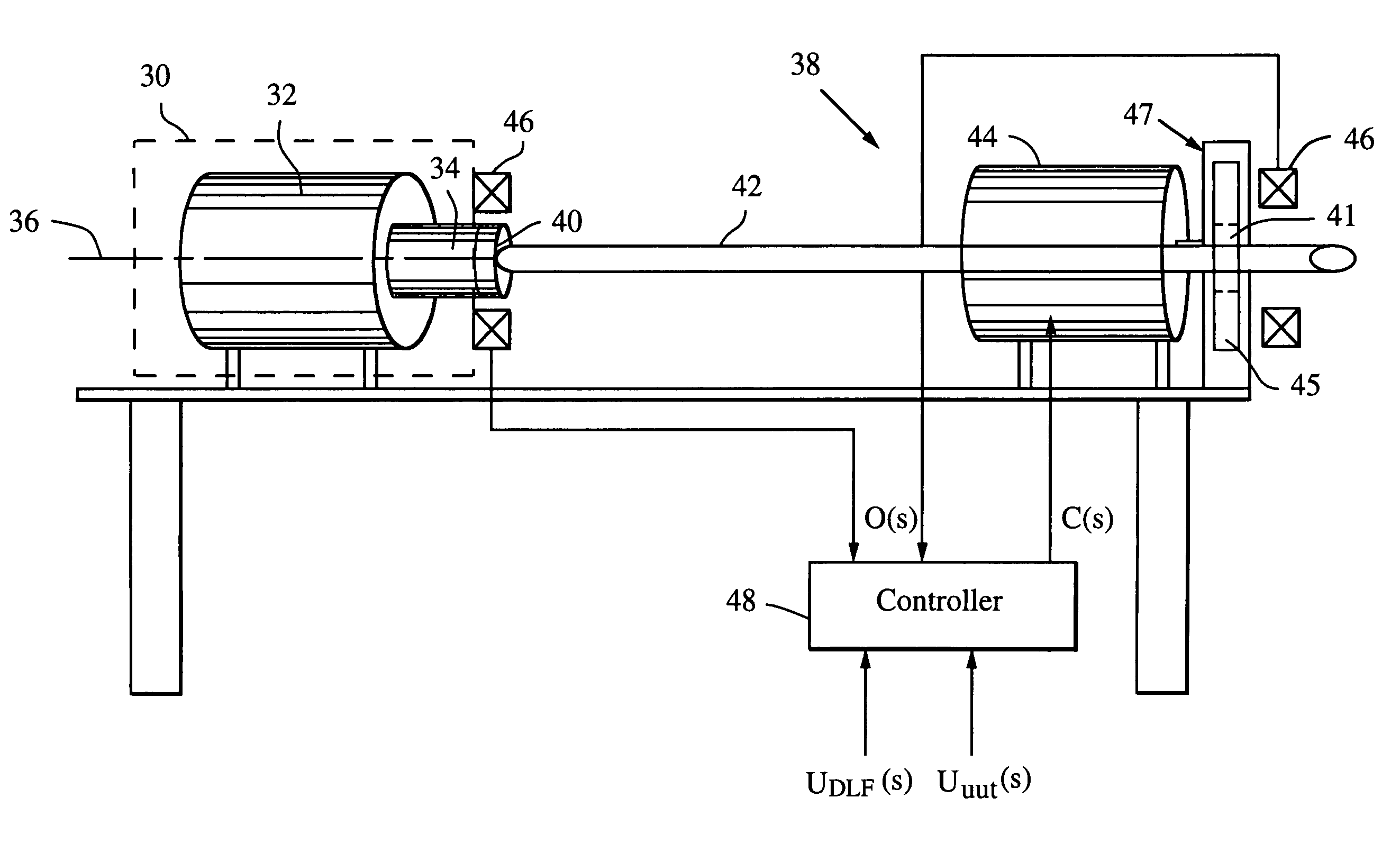
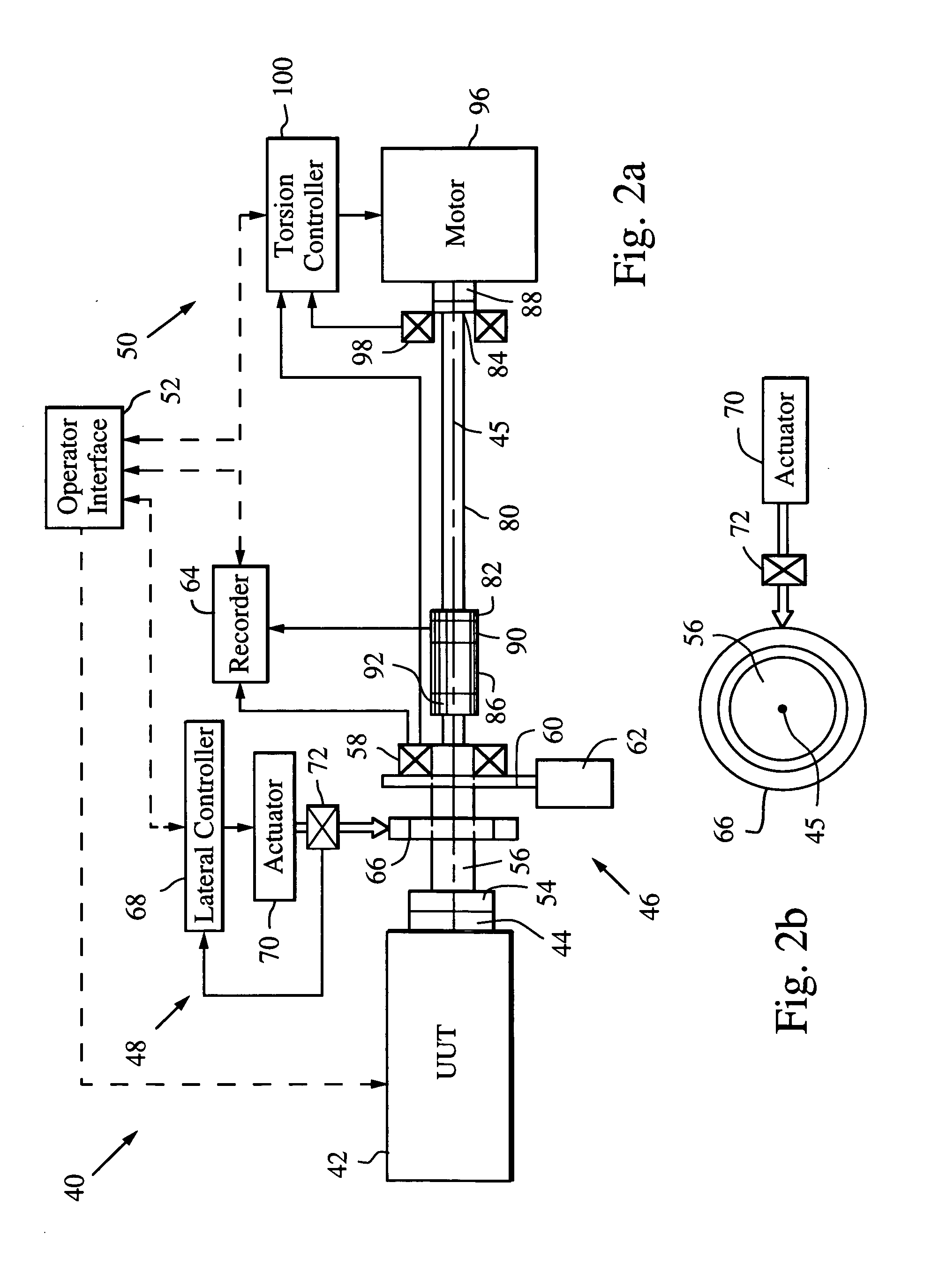
ActiveUS7080565B2Affect accuracyMaintain accuracyMachine part testingWork measurementDrive shaftAngular rotation
A dynamic load fixture (DLF) for testing a unit under test (UUT) includes a lateral load system that applies a time-varying lateral load profile to the UUT drive shaft and an encoder that measures its angular rotation. An isolation stage suitably constrains the encoder from rotating about the axis while allowing it to move in other directions in which the application of the lateral force induces motion. The lateral load system includes a load bearing around the drive shaft, an actuator that applies a lateral force to the load bearing, a force sensor for measuring the applied lateral force, and a lateral controller for adjusting a command signal to the actuator to implement a lateral load profile. The DLF may also include a torsion load system that applies a time-varying torsion load profile to the drive shaft.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
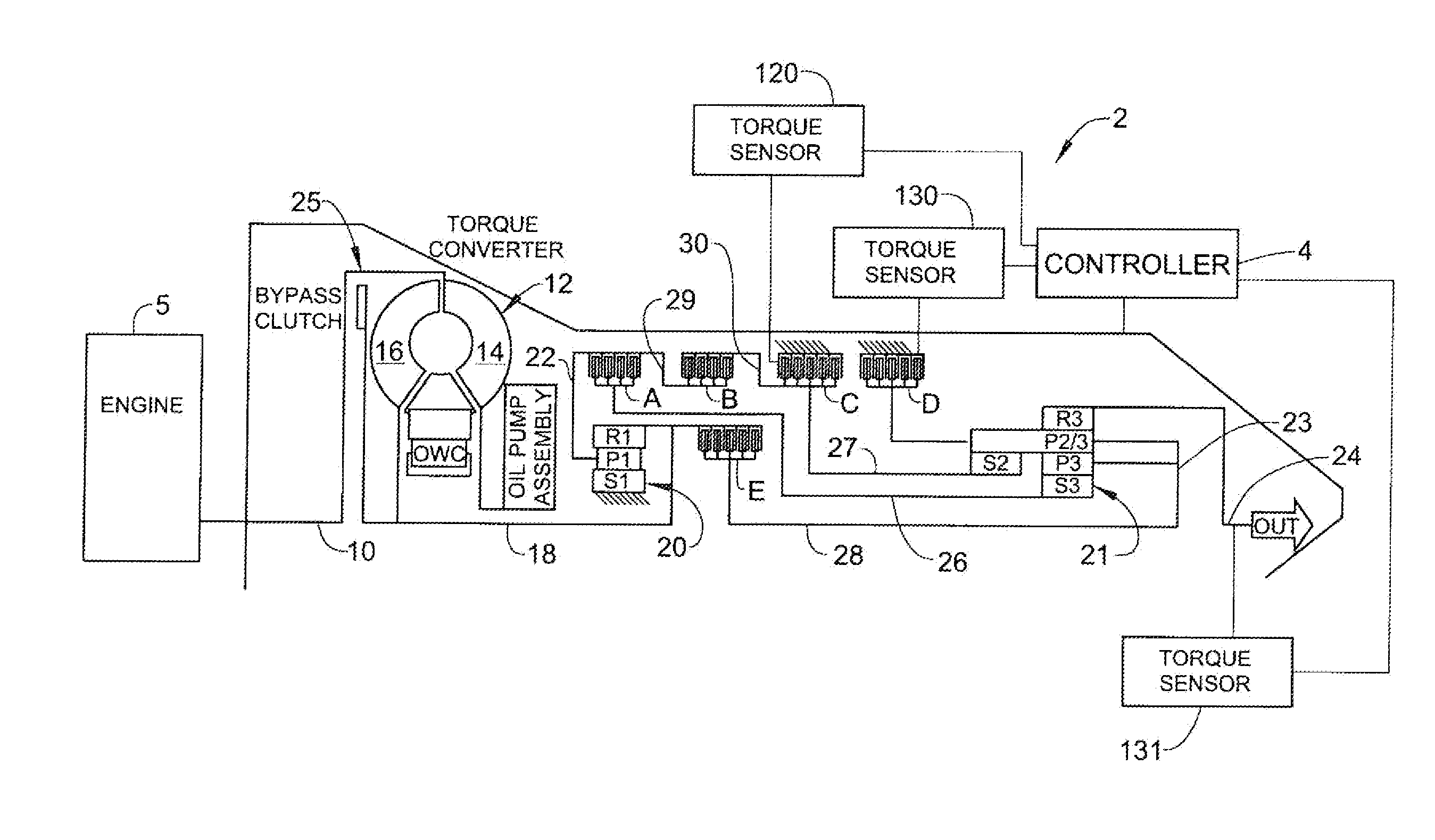
Closed-Loop Torque Phase Control for Shifting Automatic Transmission Gear Ratios Based on Friction Element Load Sensing
ActiveUS20100262344A1Improve shift feelIncreased torque capacityDigital data processing detailsGearing controlLoad sensingClosed loop
A closed loop shift control apparatus and method based on friction element load controls a torque transfer phase when shifting from a low gear configuration to a high gear configuration for an automatic transmission system. When pressure actuated friction elements are selectively engaged and released to establish torque flow paths in the transmission, measurements or estimates of torsional load exerted on the off-going friction element are used to predict the optimal off-going friction element release timing for achieving a consistent shift feel. The ideal timing to release the off-going friction element is uniquely defined when torque load exerted onto the off-going friction element becomes substantially zero. An on-coming clutch engagement process is controlled by a closed loop control based on measurements or estimates of on-coming clutch torque capacity for a constant shift feel under dynamically changing conditions.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
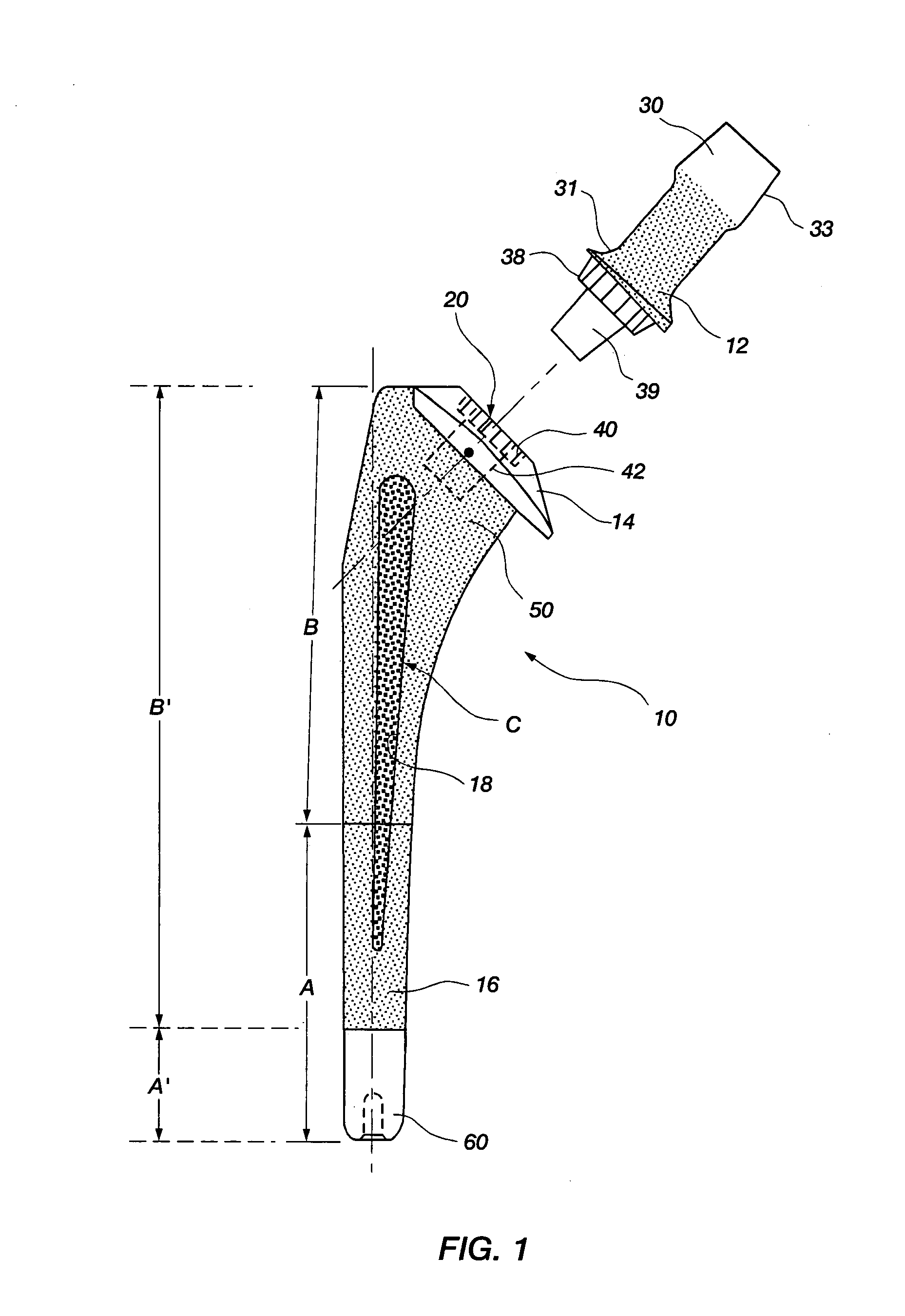
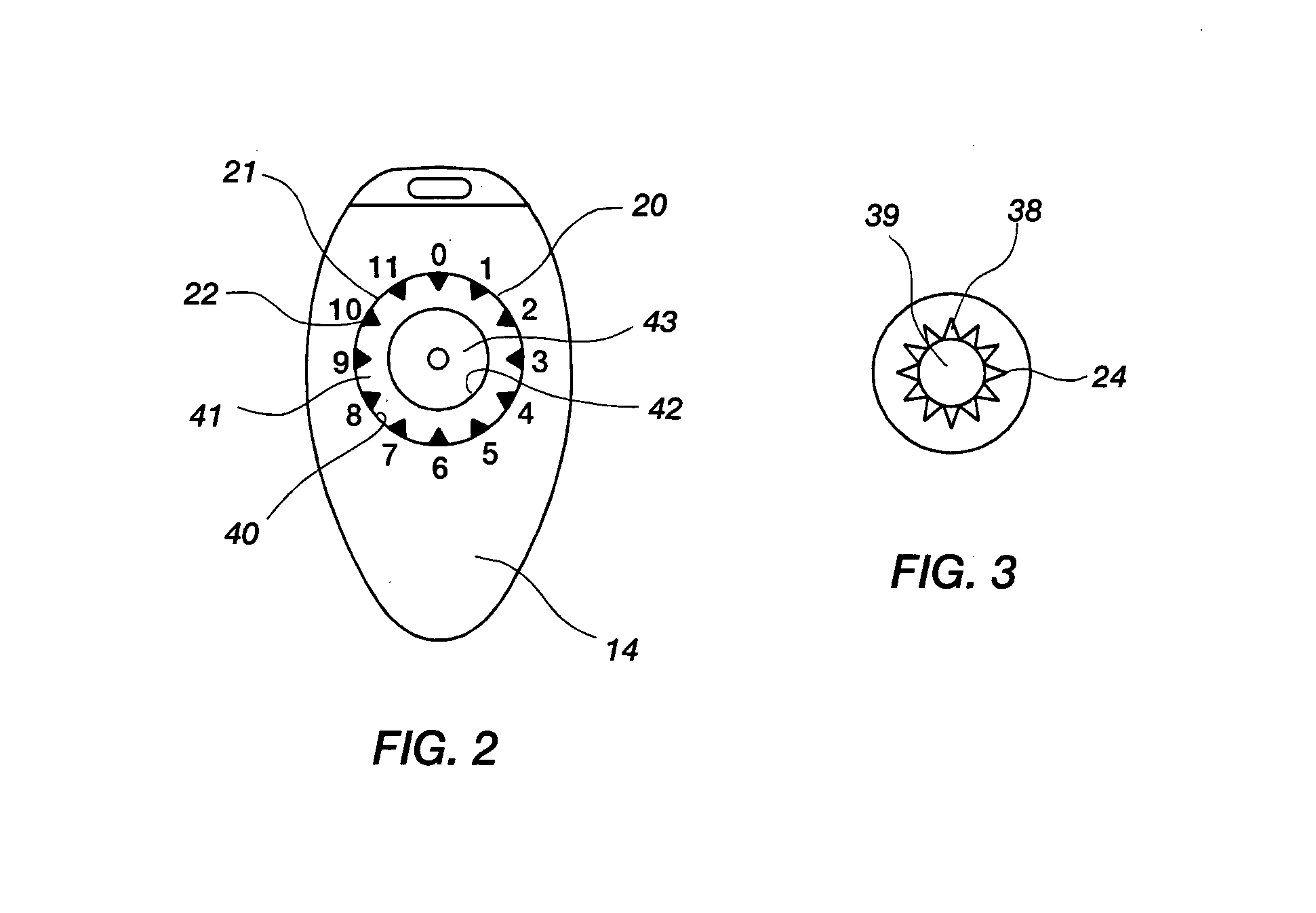
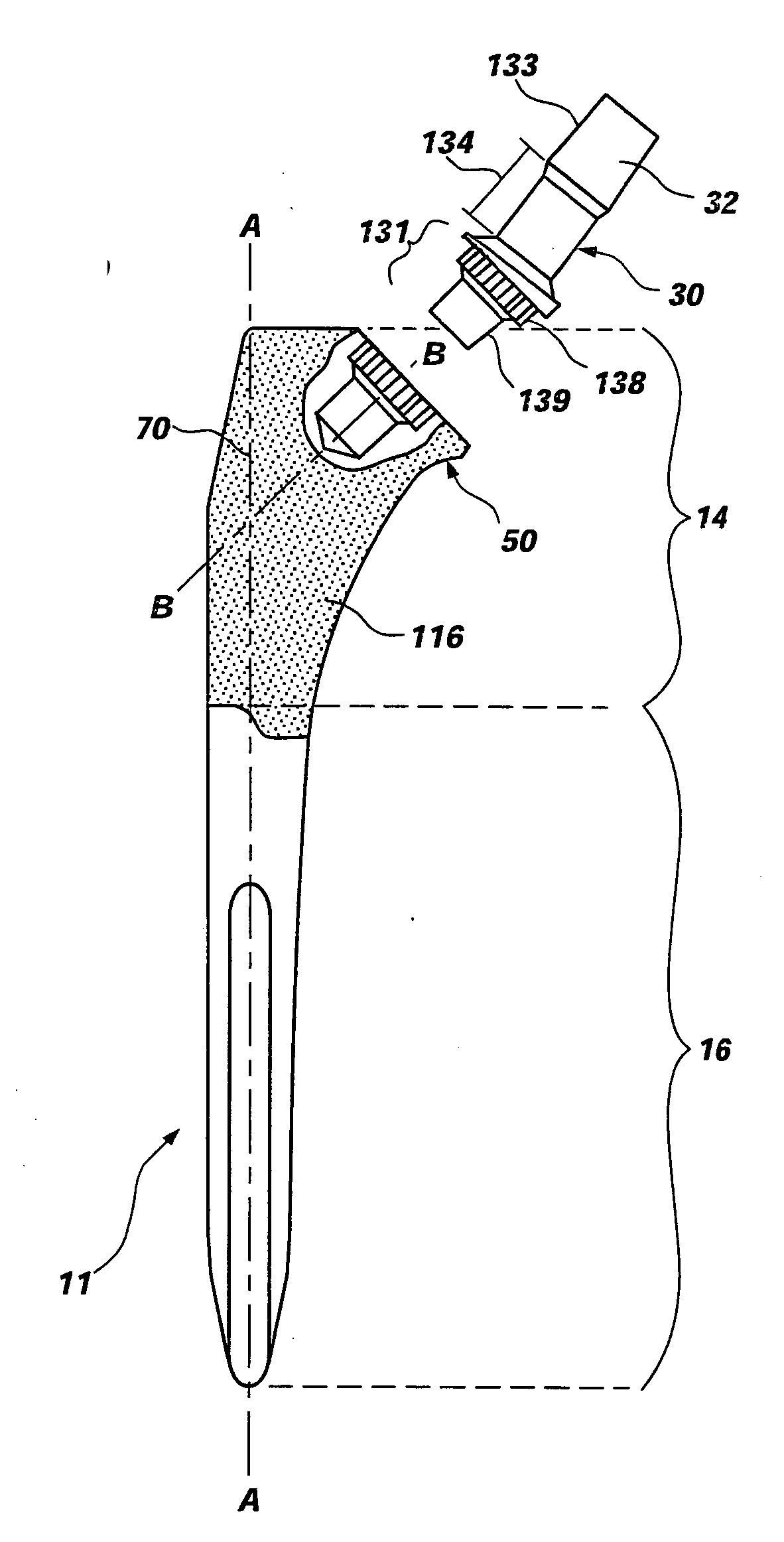
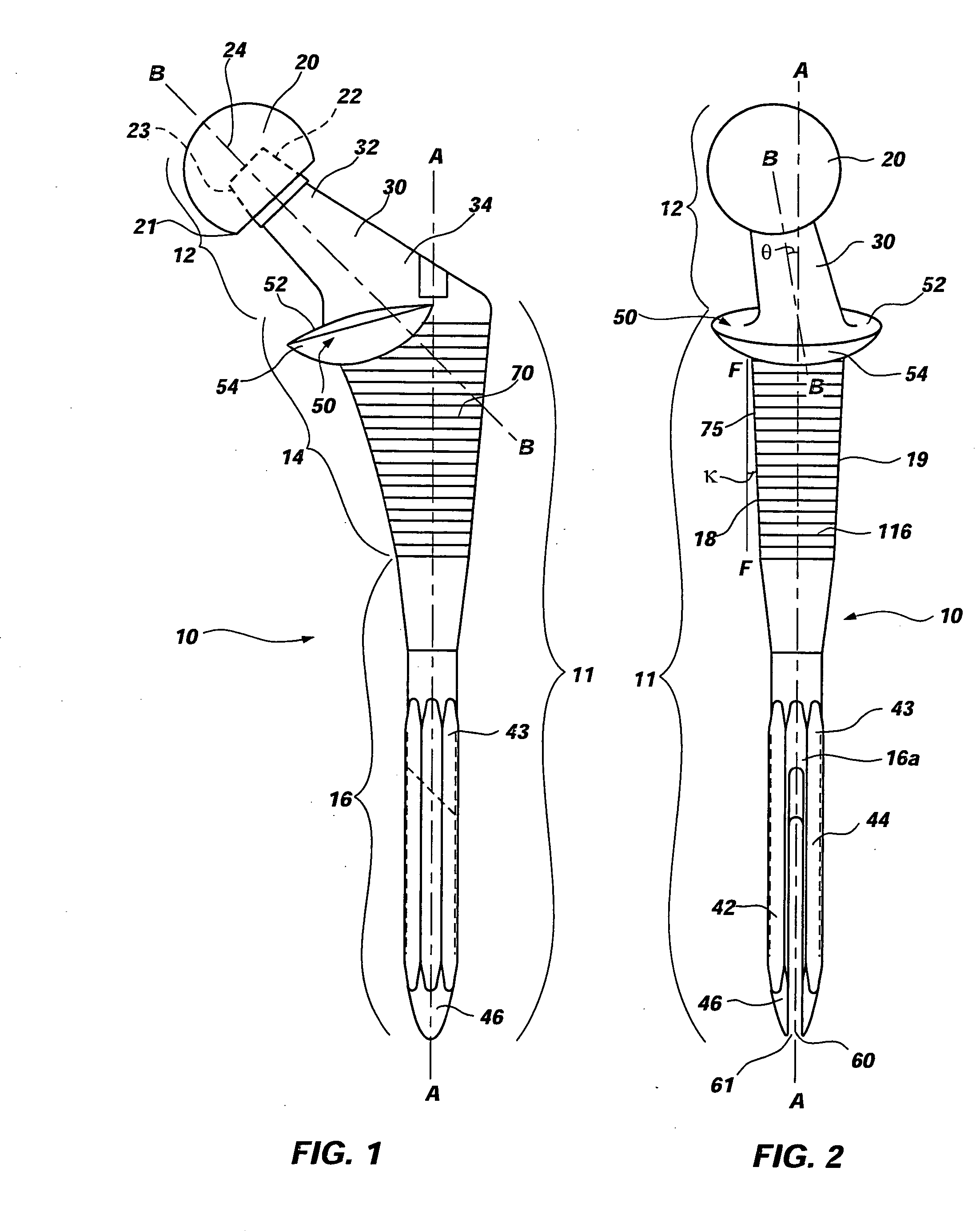
Differential porosity prosthetic hip system
A prosthetic femoral implant for use in a hip joint, as a ball and socket type joint, is disclosed. The implant includes a modular neck having a variety of adjustable positions to adjust the lateral offset and version angle of the femoral implant in relation to the femur. The implant further includes a broad, full collar for providing a compression force increasing the interdigitation between the interface of the bone, implant and cement. The implant also includes a stem having a depression having a roughened porous surface for resisting the increased torsional loads placed on the implant due to the increased lateral offset and version angle. The stem further comprises three distinct zones, each zone having its own roughened surface creating a tripartite differential porosity.
Owner:ENCORE MEDICAL ASSET CORP
Spinal disc annulus augmentation
InactiveUS20060271196A1Augmenting intervertebral disc annulusSpinal implantsSpinal columnSpinal Disk Implant
Intervertebral disc implants are provided for augmenting the annulus of the disc in a manner to bear at least part of the axial and / or torsional load on the annulus so that rents, fissures and subsequent herniation of the disc are prevented or substantially delayed. An aspect of the subject devices is that they have an operative height dimension that is equal to or less than the disc height of a normally functioning, healthy disc. Methods and tools are also provided for the minimally invasive implantation of the device within an intervertebral disc.
Owner:SAAL JEFFREY ALAN +1
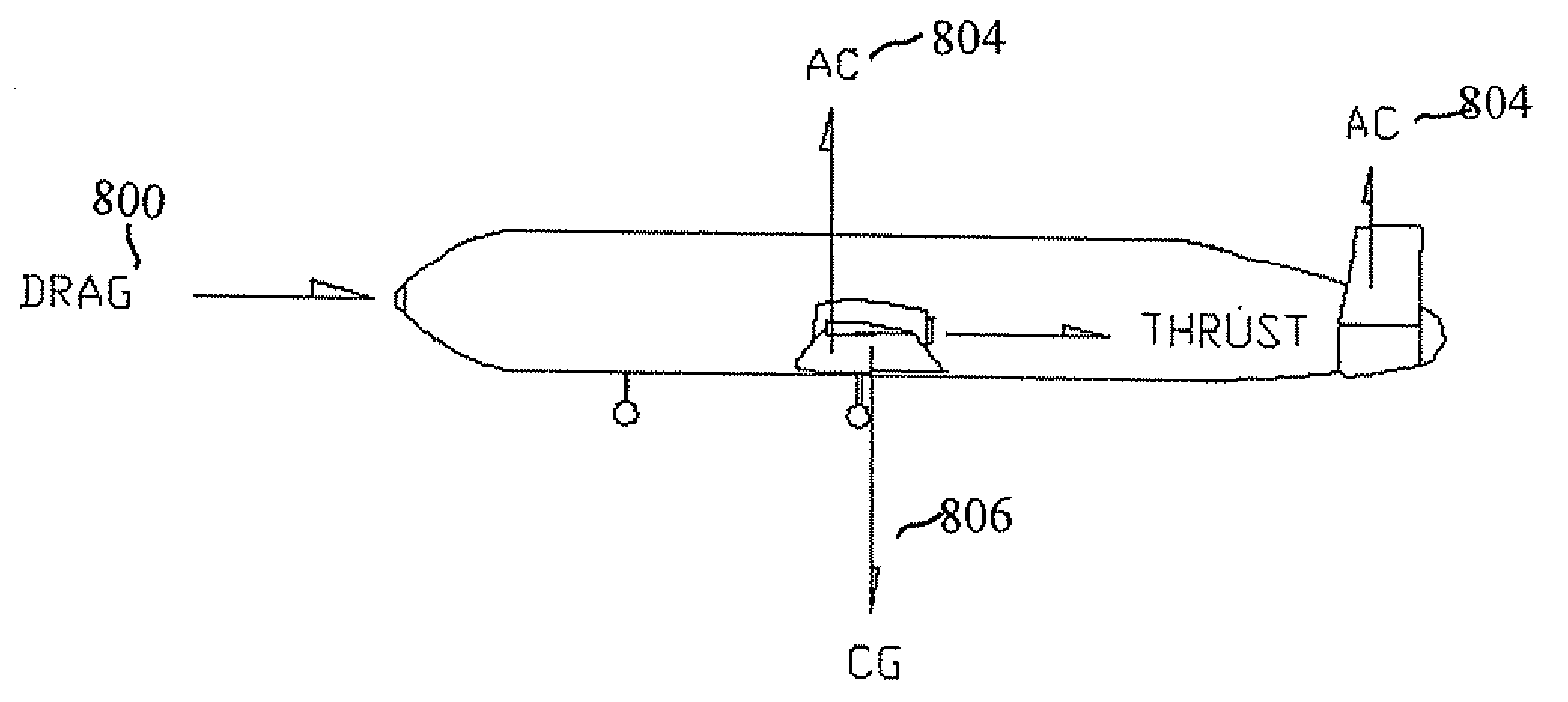
Methods for fuel-efficient transportation of cargo by aircraft
InactiveUS20090114773A1Much low speedHighly efficient flight profileUnmanned aerial vehiclesAir-treatment apparatus arrangementsTorsional loadUltimate tensile strength
Owner:HELOU JR ELIE
Differential porosity prosthetic hip system
A prosthetic femoral implant for use in a hip joint, as a ball and socket type joint, is disclosed. The implant includes a modular neck having a variety of adjustable positions to adjust the lateral offset and version angle of the femoral implant in relation to the femur. The implant further includes a broad, full collar for providing a compression force increasing the interdigitation between the interface of the bone, implant and cement. The implant also includes a stem having a depression having a roughened porous surface for resisting the increased torsional loads placed on the implant due to the increased lateral offset and version angle. The stem further comprises three distinct zones, each zone having its own roughened surface creating a tripartite differential porosity.
Owner:ENCORE MEDICAL ASSET CORP
Intrinsic stability in a total hip stem
A prosthetic device and method of using the device is disclosed. The device may include a bushing insert, a femoral head component, a neck component that may be either integral or modular, and a stem component having a proximal body portion and a distal portion. The proximal body portion may include such features as a recess for receiving a portion of the modular neck, a proximal conical flare having a bottom surface with a rounded contour, an anterior metaphyseal tapering flare, as well as other features. The distal portion may include a coronal slot, a sagittal slot, a helical slot, or a combination thereof. The above features may be provided for increasing the intrinsic stability of the device and for resisting torsional loads placed on the device.
Owner:ENCORE MEDICAL ASSET CORP
Auxiliary loading device for bogie frame strength test
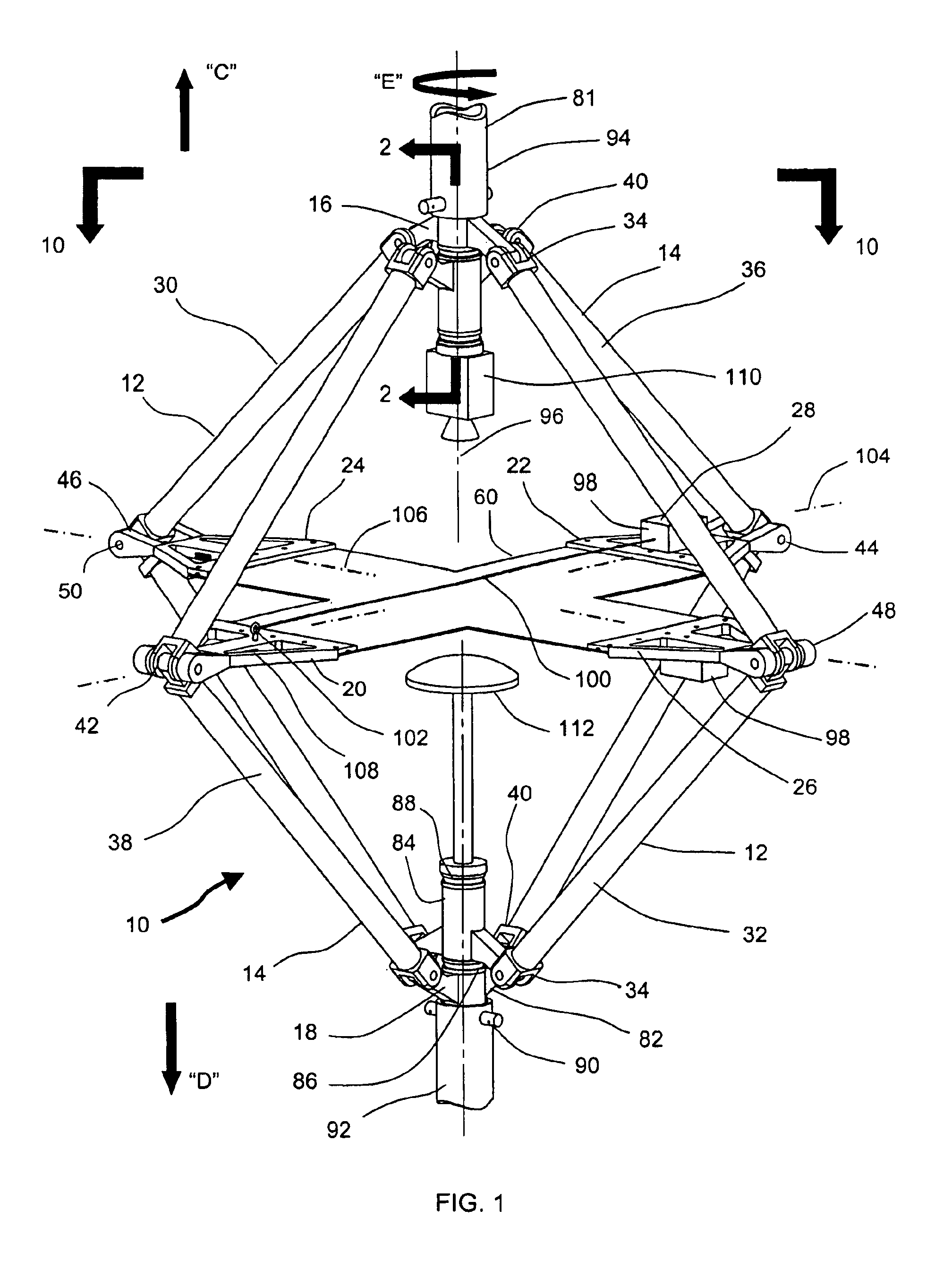
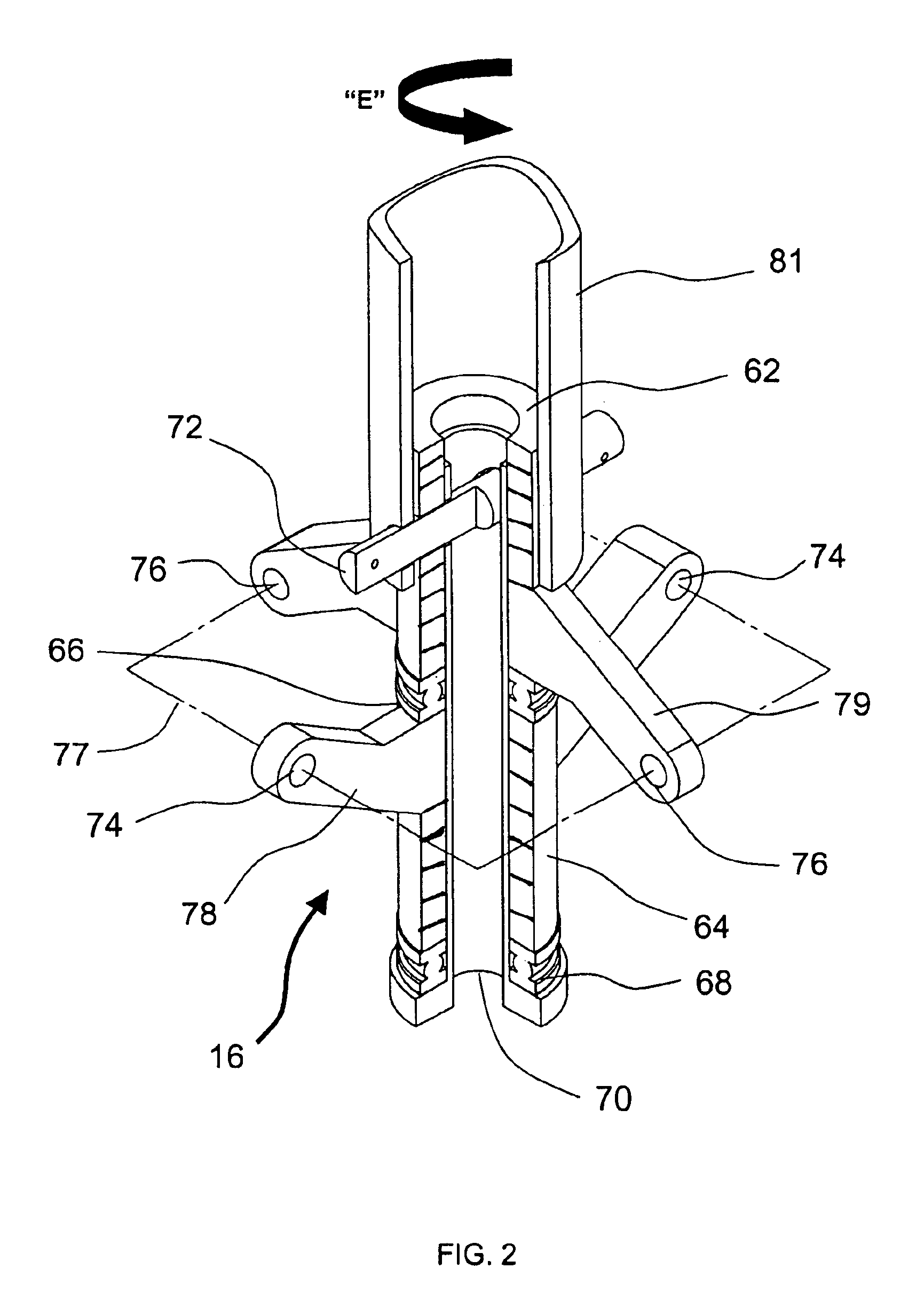
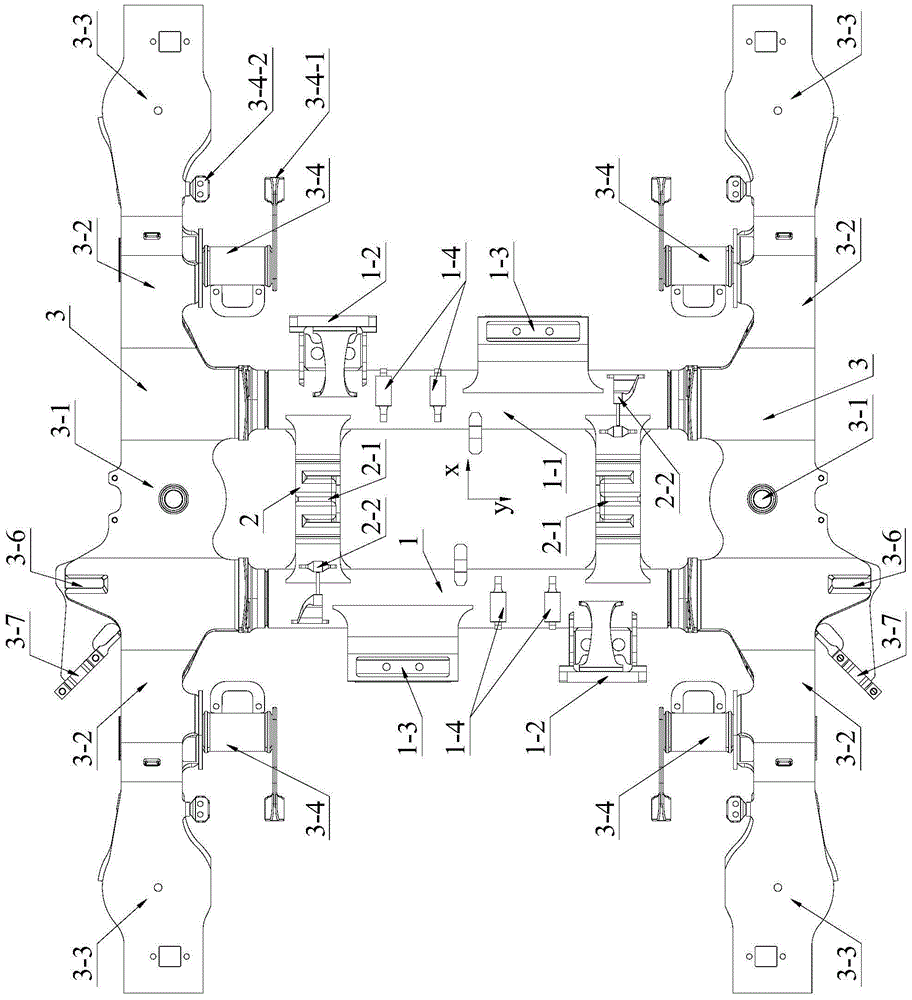
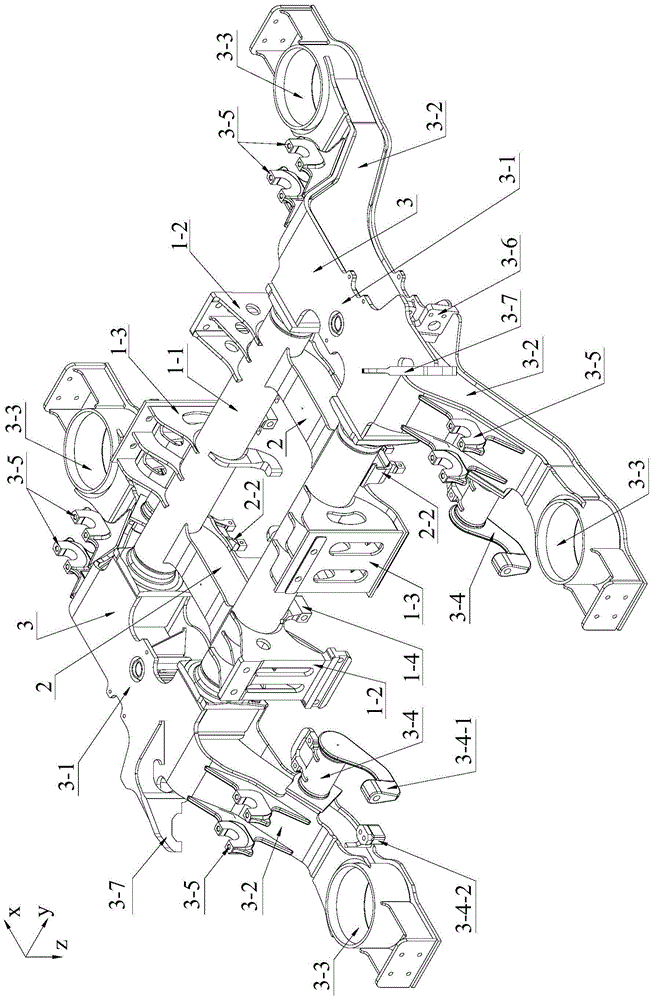
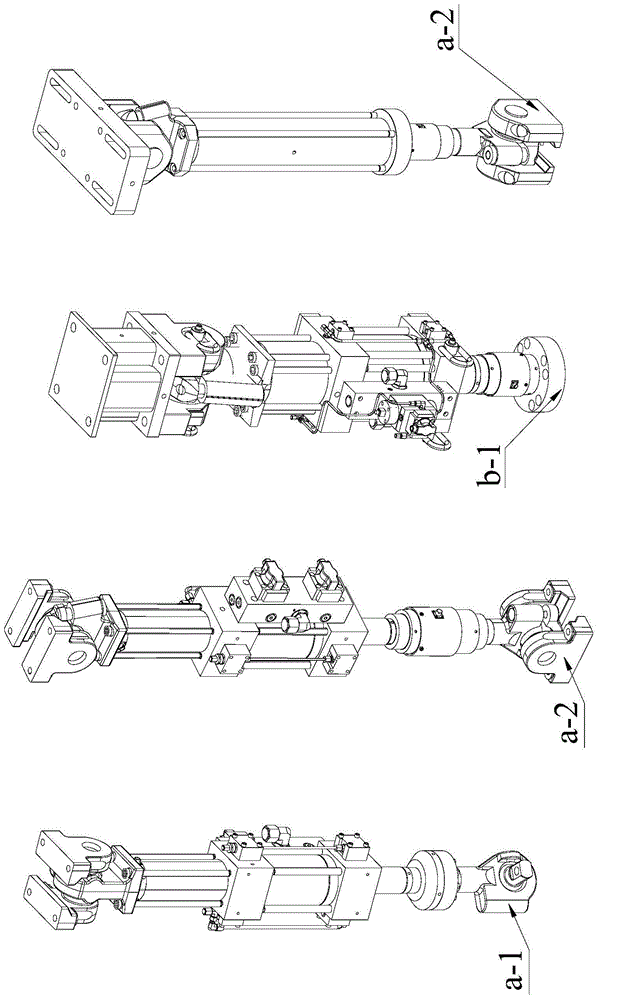
An auxiliary loading device for a bogie frame strength test belongs to the field of auxiliary loading devices for railway vehicle bogie frame strength tests and comprises four vertical torsion load loading seats, two vertical load loading seats, two groups of nut gaskets, transverse load loading units, four braking load loading sets, two snake-shaped swing resistant load loading seats, two gear box load loading seats, two longitudinal load and transverse restrain loading beams, two motor load loading seats, vertical restraint traction bases and two testing traction pull rods. The auxiliary loading device for the bogie frame strength test has the advantages that an original arrangement space is expanded through a plurality of force bearing load loading components with expanding structures, a bogie frame strength test needs not simplify the numbers of a stress loading points, the arrangement space among every application force driving component or force bearing component is sufficient, interference and conflicts cannot occur among the every application force driving component or force bearing component, and the testing results of a simulation bogie in a dynamic comprehensive force bearing state is more accurate and reliable.
Owner:CRRC CHANGCHUN RAILWAY VEHICLES CO LTD
Moldable fabric
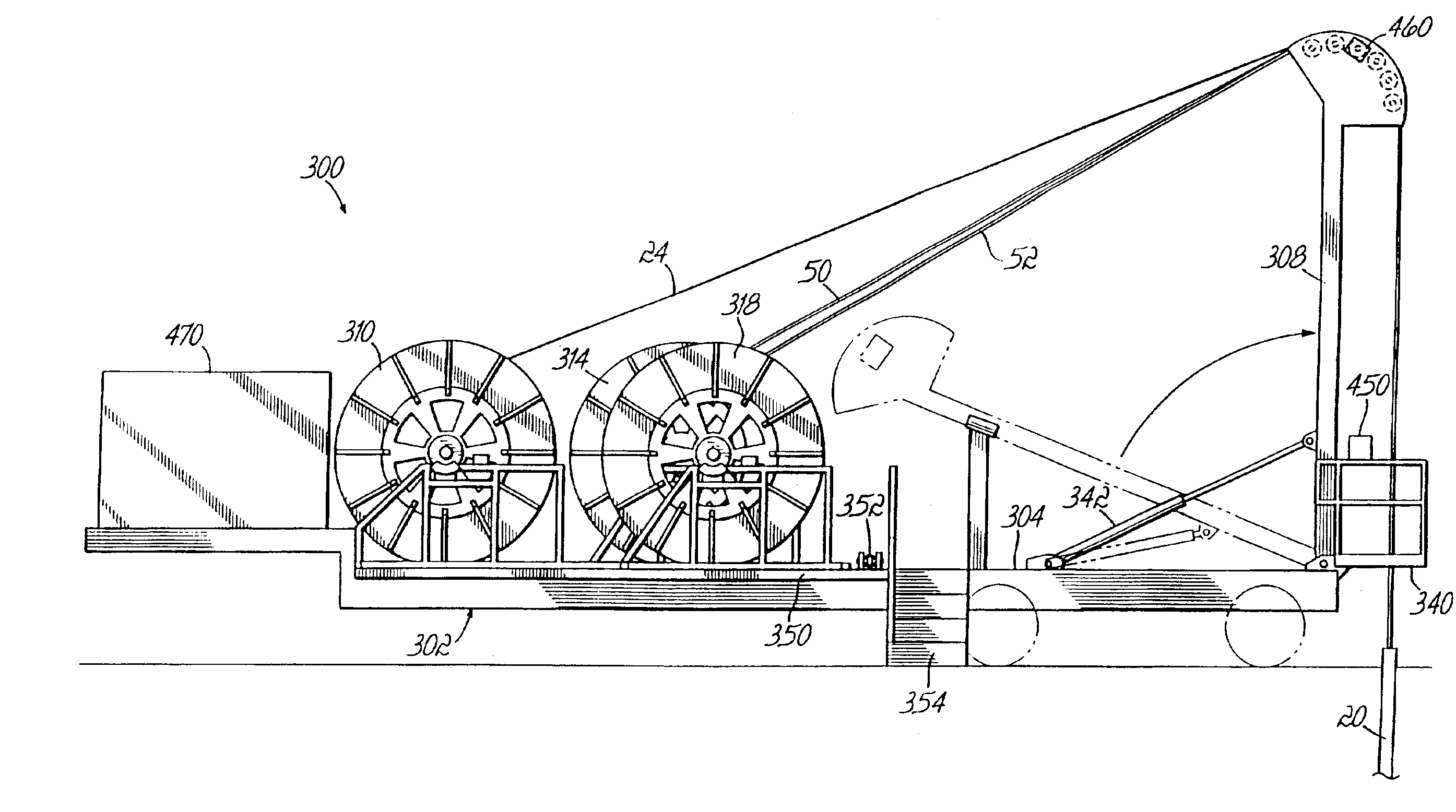
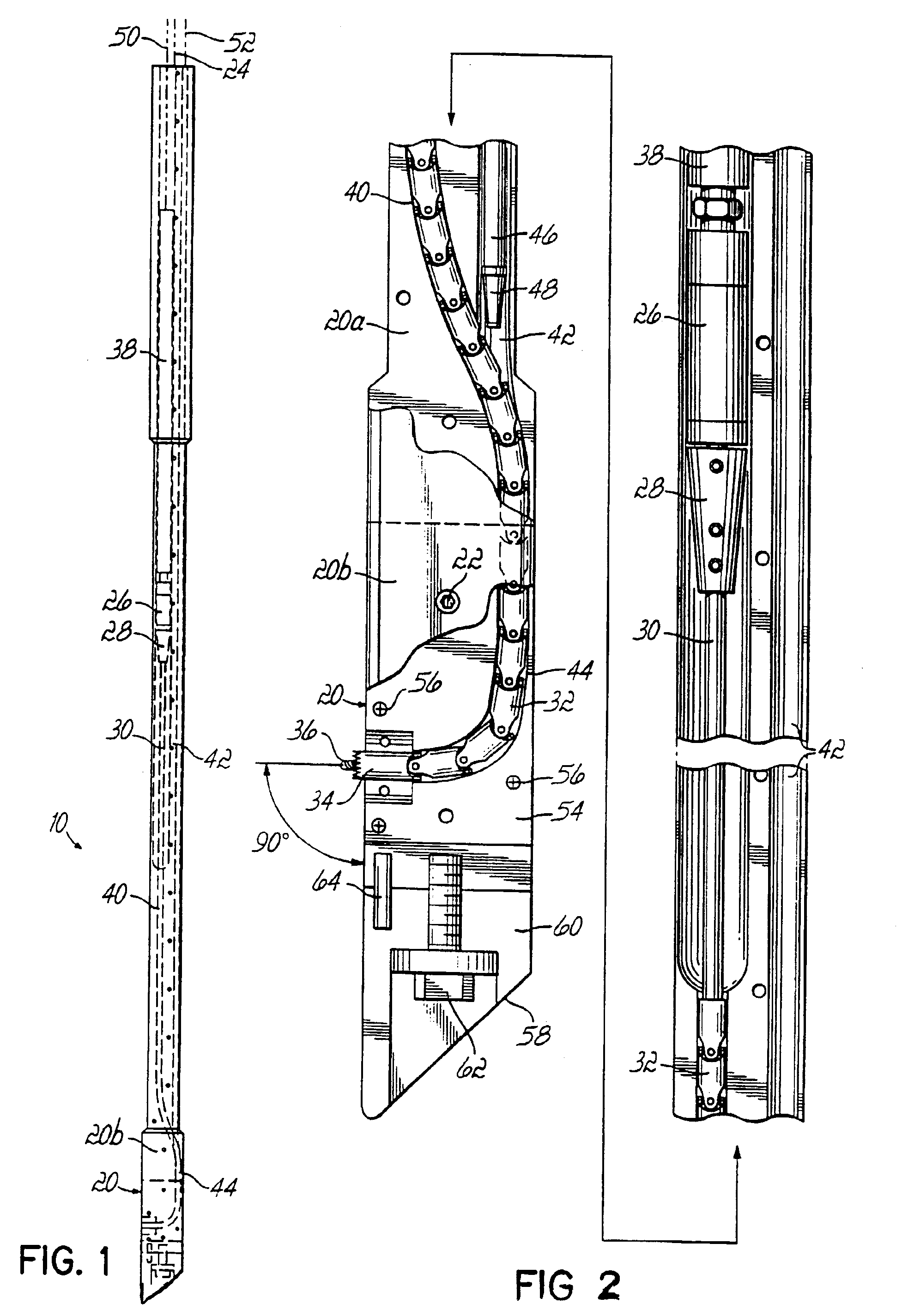
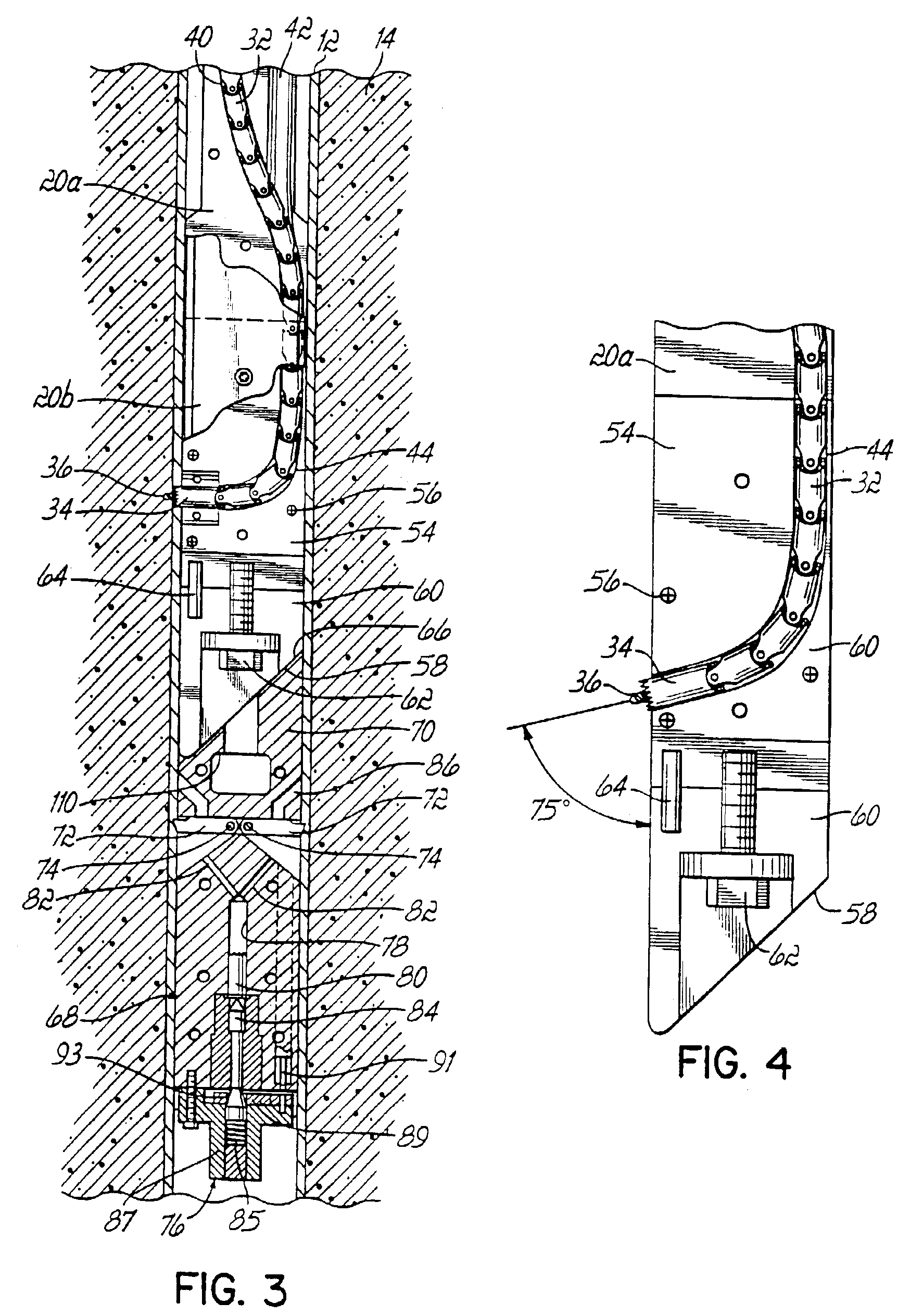
Apparatus for boring a hole from an inside of a casing outwardly at an angle relative to a longitudinal axis of the casing comprises a drill shoe having a longitudinal axis and being positionable in the casing, the shoe having first and second passageways which converge into a third passageway exiting the shoe, a torsional load transmitting element and a cutting element connecting to one end of the torsional load transmitting element, the torsional load transmitting element and cutting element being positioned in the first passageway during non-use and in the third passageway during use, and a fluid conduit and a nozzle connected to one end of the fluid conduit, the fluid conduit and nozzle being positioned in the second passageway during non-use and in the third passageway during use.
Owner:BATESVILLE SERVICES
Dynamic load fixture for application of torsion loads for rotary mechanical systems
ActiveUS7165465B2Efficient reproductionImprove response bandwidthMachine part testingWork measurementNegative feedbackAerodynamic load
A dynamic load fixture (DLF) applies a torsion load to a unit under test (UUT) to achieve the demanding aerodynamic load exposures encountered by a control actuation system (CAS) in flight. Instead of fixing the end of the torsion bar, the DLF controls the application of torque to the torsion bar, hence the UUT via a DLF motor. The dynamic load can be independent of the angular rotation of the UUT, which allows the DLF to more effectively reproduce desired acceptance tests such as torque-at-rate and nonlinear loads. Furthermore, application of the loads through a torsion bar allows the system the compliance needed to generate precise loads while allowing for the flexibility of changing torsion bars to test a wide variety of UUT on one test platform. To achieve the demanding aerodynamic load exposures encountered by a CAS in flight, the controller must be able to respond both very fast and very precisely. Control is enhanced by the thorough characterization of the DLF and application of either “classic” negative feedback control or “modern” state-space control methods of linear observers and quadratic optimum control.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Damper pulley assembly having a safety device
Owner:DAYCO EURO
E-fixture
A device and a method are disclosed for testing a curved panel assembly, which simulates a segment of an aircraft fuselage barrel section, subjected to combined loading. The device includes an axial load head assembly attached to the test panel assembly via one axial load fitting and configured to apply an axial load to the test panel assembly, and an axial-torsion reaction box connected to the axial load head assembly via linear journal bearing assemblies, where the axial-torsion reaction box is configured to be rotated by a pair of torsional loading systems to apply a torsional load to the test panel assembly. The device also includes a gore section attached to hoop load fittings of the test panel assembly, configured to provide degrees of freedom that constrain the test panel assembly to load and deflect as it would naturally in an actual fuselage barrel, form a plenum box to apply an internal pressure load, and provide hoop loading systems that complete the full hoop load application to the test panel assembly. A fixed reaction box attached to the test panel assembly via another axial load fitting rigidly attaches the test panel to the self-reacting frame, completing the internal load path of the overall system.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
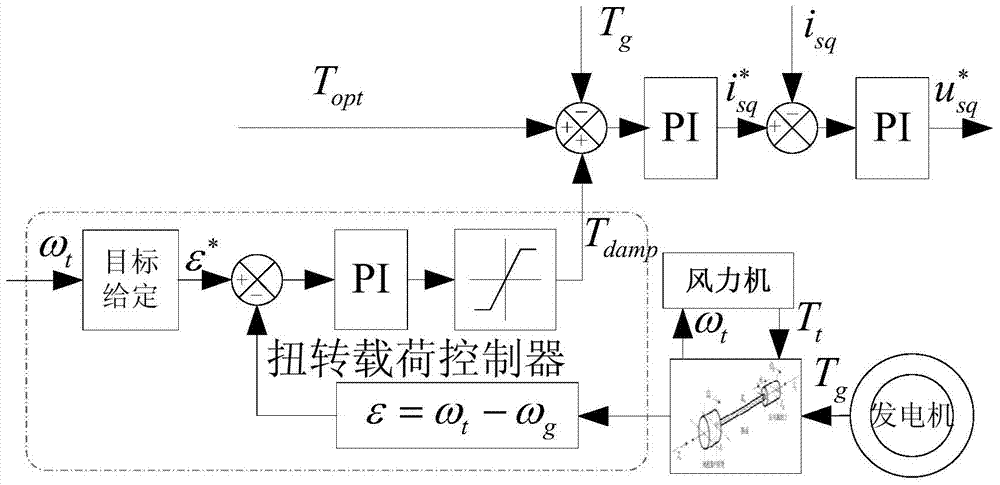
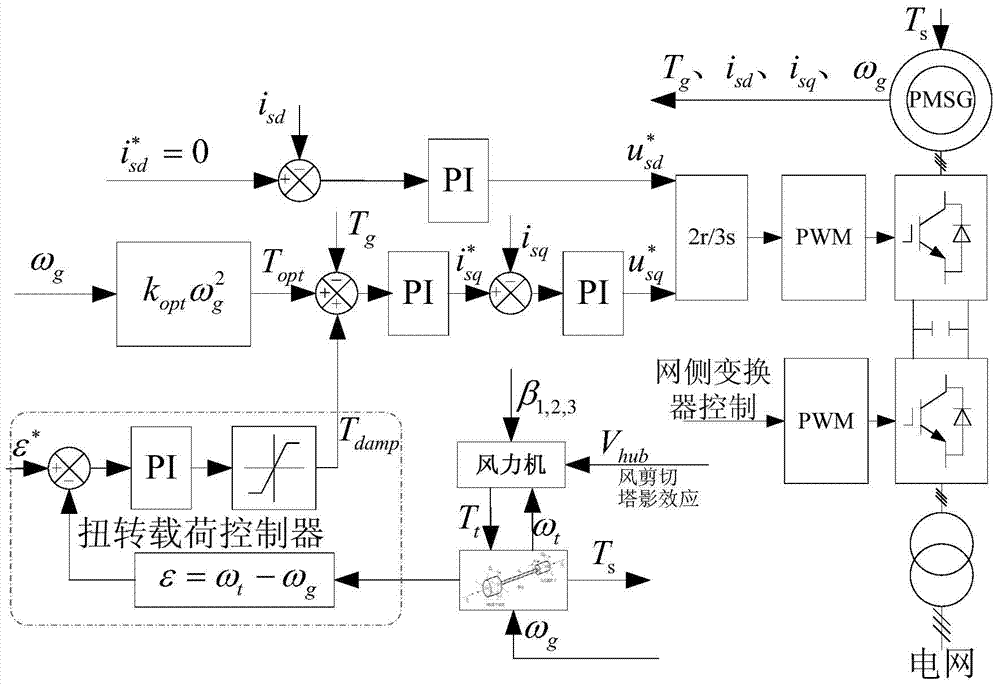
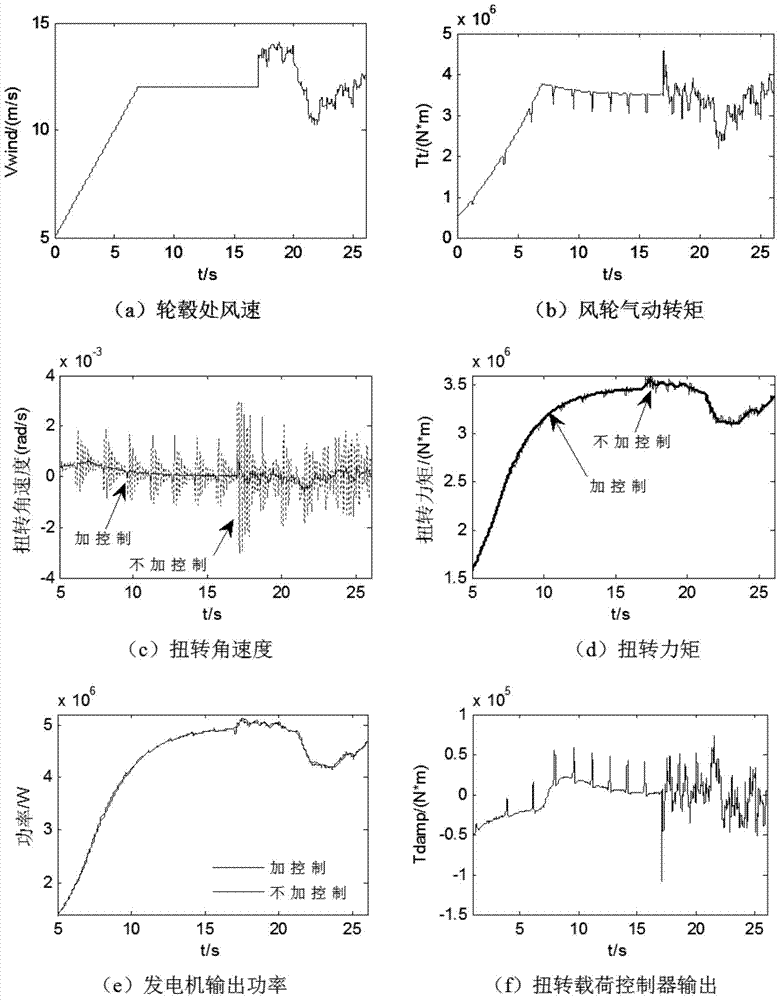
Torsion load controller for restraining torsional vibration of wind turbine generator and control method
ActiveCN104329220AIncrease dampingAvoid couplingWind motor controlMachines/enginesElectricityTorsional vibration
The invention provides a torsion load controller for restraining the torsional vibration of a wind turbine generator and a control method. The controller takes torsion angular speed as feedback quantity; the torsion angular speed is a quantity related to the rotation speed and the accelerated speed of a wind wheel; the deviation between the rotate speed and the accelerated speed is subjected to a PI regulator and amplitude limiting, and then serves as controller output; the controller output is overlapped to the torque of a generator; parameters of the PI regulator in the torsion load controller are set; the target of the torsion angular speed during torsional vibration restraining is subjected to optimization design. The controller has high feasibility and applicability, and can quicken the maximum power tracking to a certain extent.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
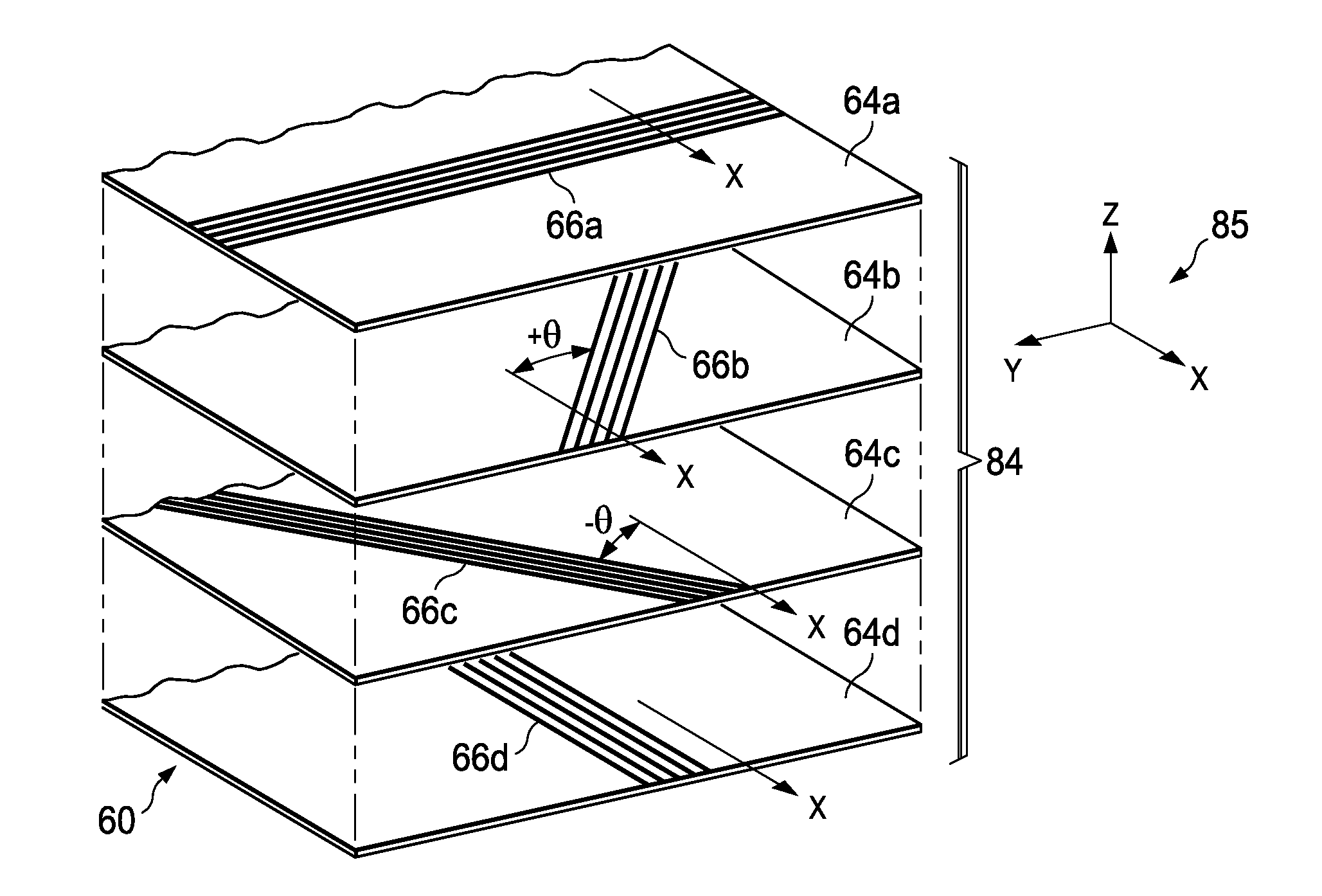
Optimized Cross-Ply Orientation in Composite Laminates
ActiveUS20130330503A1Reduce weightImprove suppression propertiesSynthetic resin layered productsLaminationComposite laminatesEngineering
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Dynamic load fixture for rotary mechanical systems
ActiveUS20060070461A1Efficient reproductionImprove response bandwidthMachine part testingWork measurementDrive shaftAngular rotation
A dynamic load fixture (DLF) for testing a unit under test (UUT) includes a lateral load system that applies a time-varying lateral load profile to the UUT drive shaft and an encoder that measures its angular rotation. An isolation stage suitably constrains the encoder from rotating about the axis while allowing it to move in other directions in which the application of the lateral force induces motion. The lateral load system includes a load bearing around the drive shaft, an actuator that applies a lateral force to the load bearing, a force sensor for measuring the applied lateral force, and a lateral controller for adjusting a command signal to the actuator to implement a lateral load profile. The DLF may also include a torsion load system that applies a time-varying torsion load profile to the drive shaft.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Closed-loop torque phase control for shifting automatic transmission gear ratios based on friction element load sensing
ActiveUS8255130B2Improve shift feelIncreased torque capacityDigital data processing detailsGearing controlLoad sensingClosed loop
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Damped Axle Shaft
InactiveUS20090197690A1Damp energyRotating vibration suppressionHydroxy compound active ingredientsRelative displacementTorsional load
An axle shaft which is inherently damped very near the source of the oscillation, via inner and outer axle components with a damping ring that couples between them, wherein the inner component which serves as the axle shaft, has a torsional stiffness different from (i.e., less than) that of the outer component which serves as a concentrically disposed axle sleeve. Under torsional load, both the inner and outer components transmit the torsional load, wherein the inner component twists more than the outer component, resulting in relative displacement therebetween. The damping ring experiences the relative displacement and consequently damps energy of the twist, whereby powerhop and associated driveline disturbances, such as for example axle shutter, are reduced.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Frame structure for vehicle
InactiveUS8641131B2Increased torsional stiffnessInhibit weight gainVehicle seatsSuperstructure subunitsRotational axisEngineering
In a frame structure for a vehicle having a reinforcement body provided inside a frame body, the frame body comprises a first face portion and a second face portion extending in a direction substantially perpendicular to a rotational-axis direction of a bending moment occurring when a torsional load acts on a vehicle body, and third face portions positioned between the first and second face portions, and the reinforcement body comprises third-face connection portions connected to the third face portions, a first-face connection portion connected to the first face portion at a corner portion, a first-face non-contact portion provided away from the first face portion, a second-face connection portion connected to the second face portion at a corner portion, and a second-face non-contact portion provided away from the second face portion.
Owner:MAZDA MOTOR CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com