Patents
Literature
50 results about "In plane shear" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
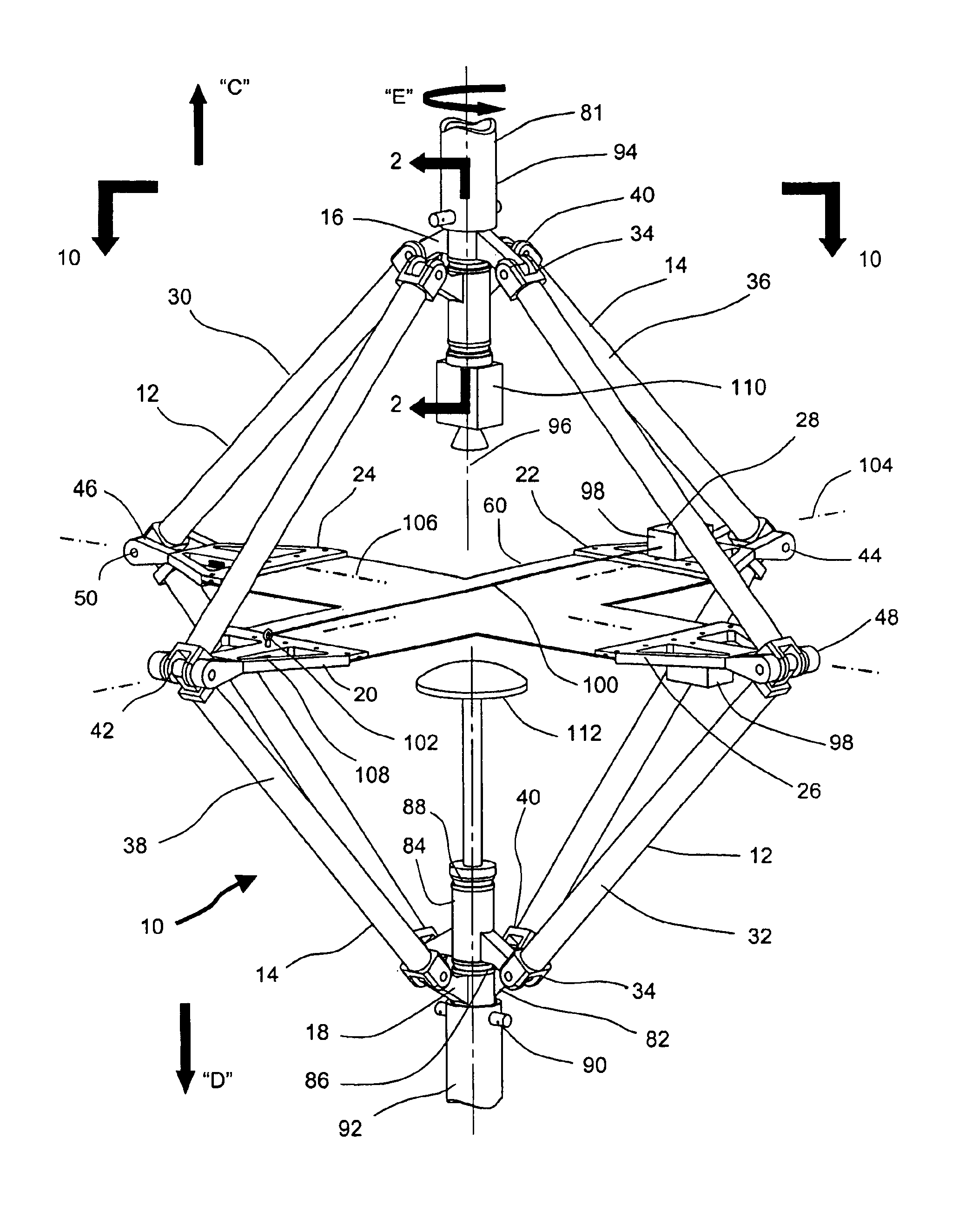
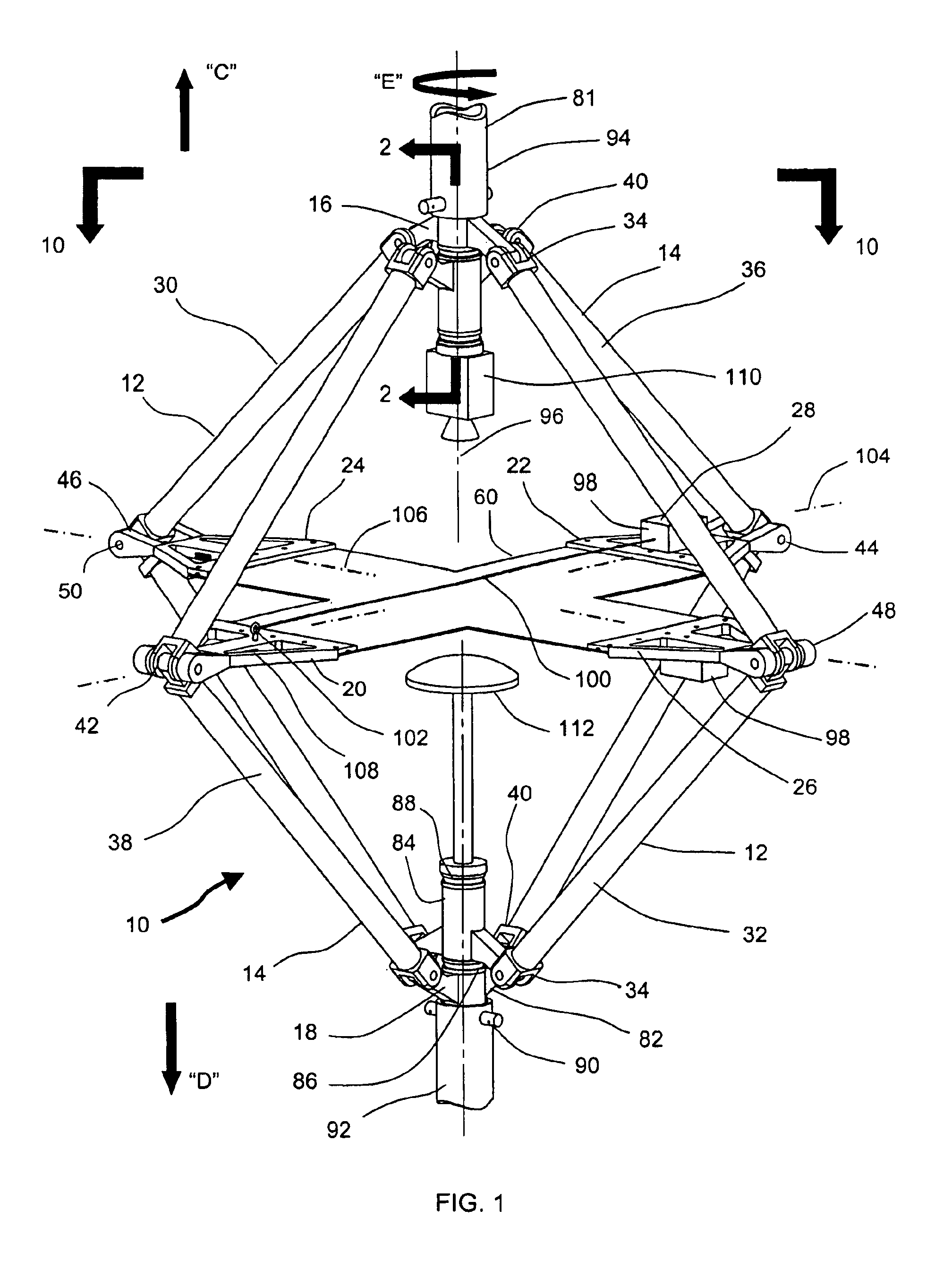
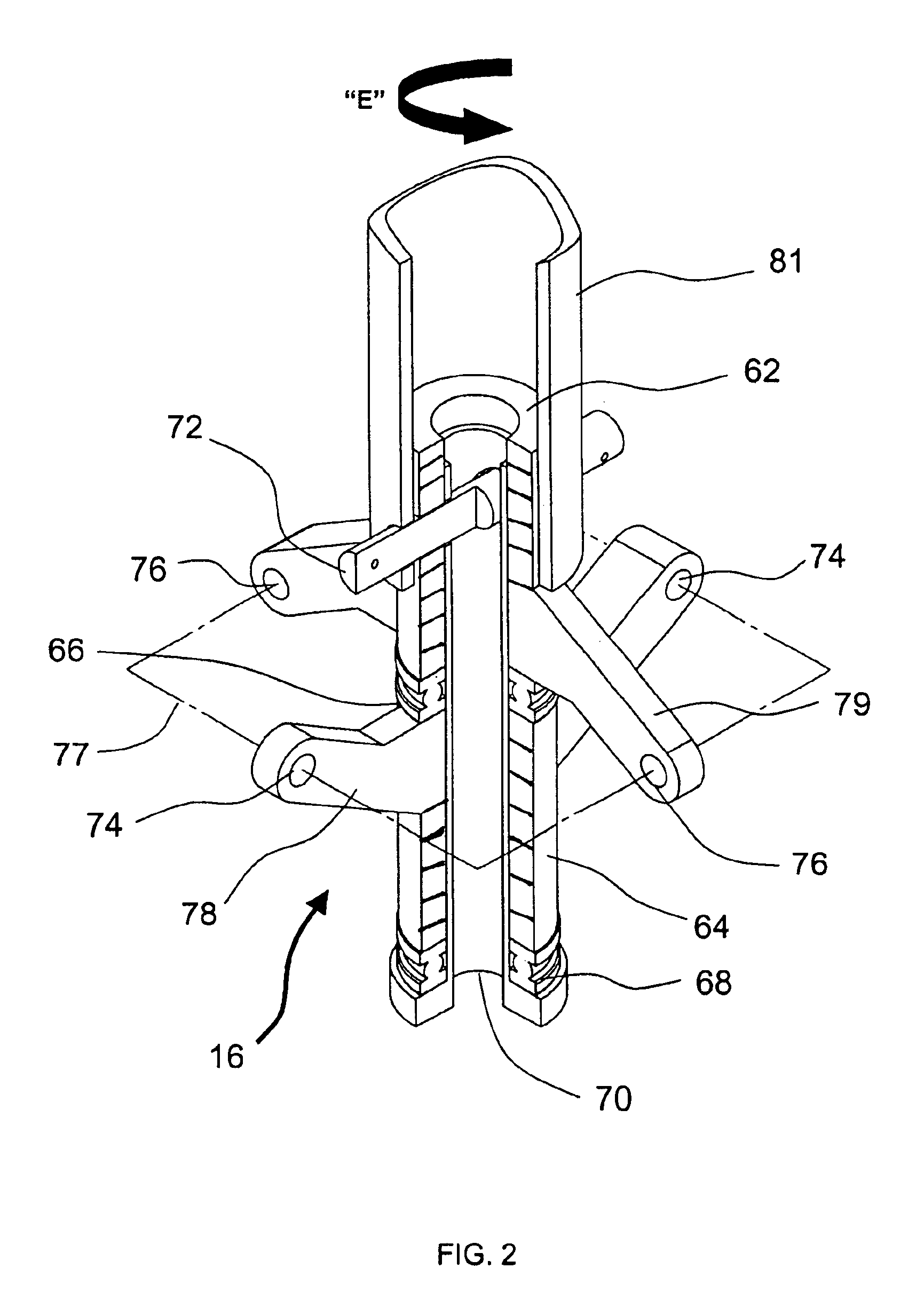
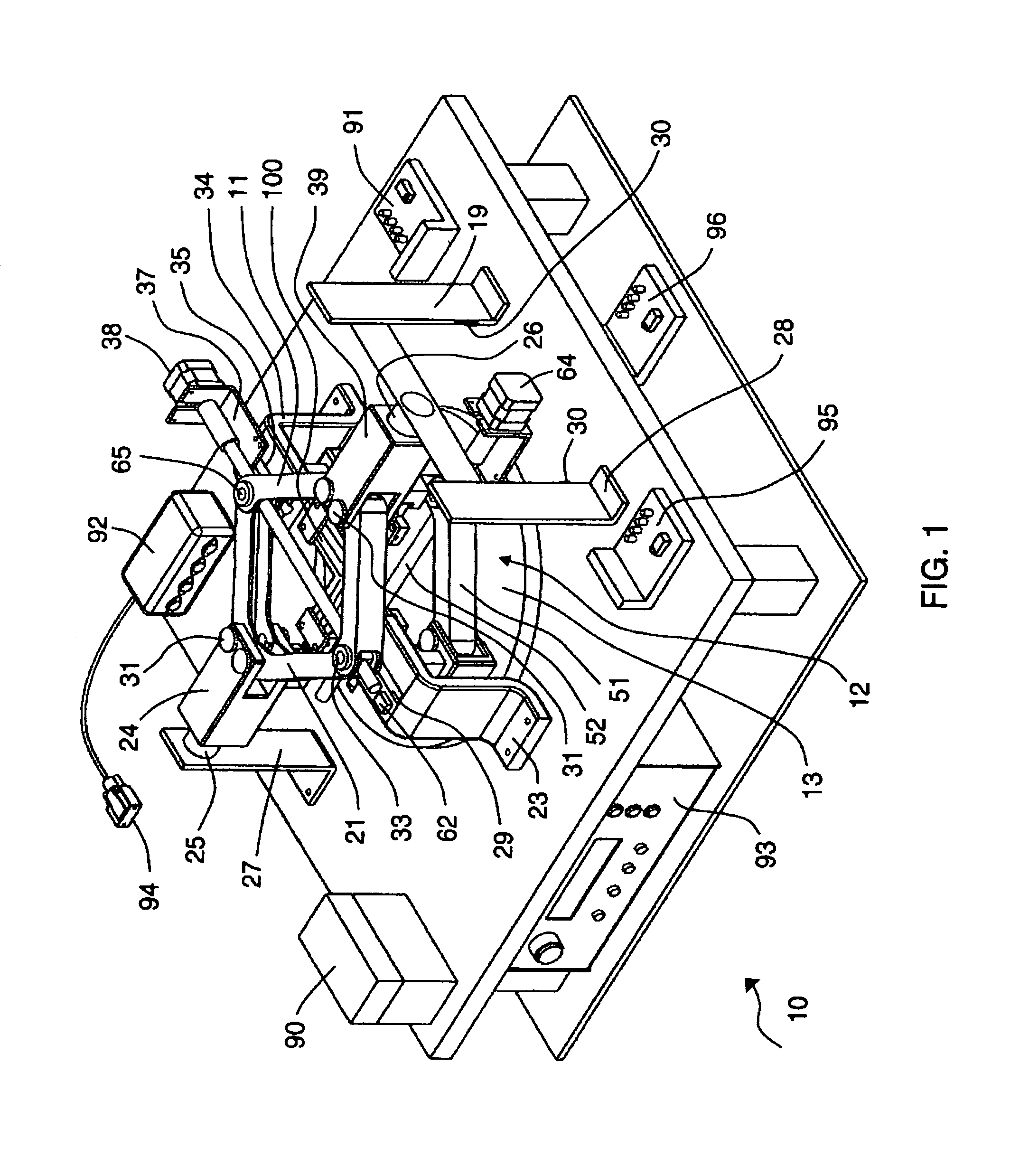
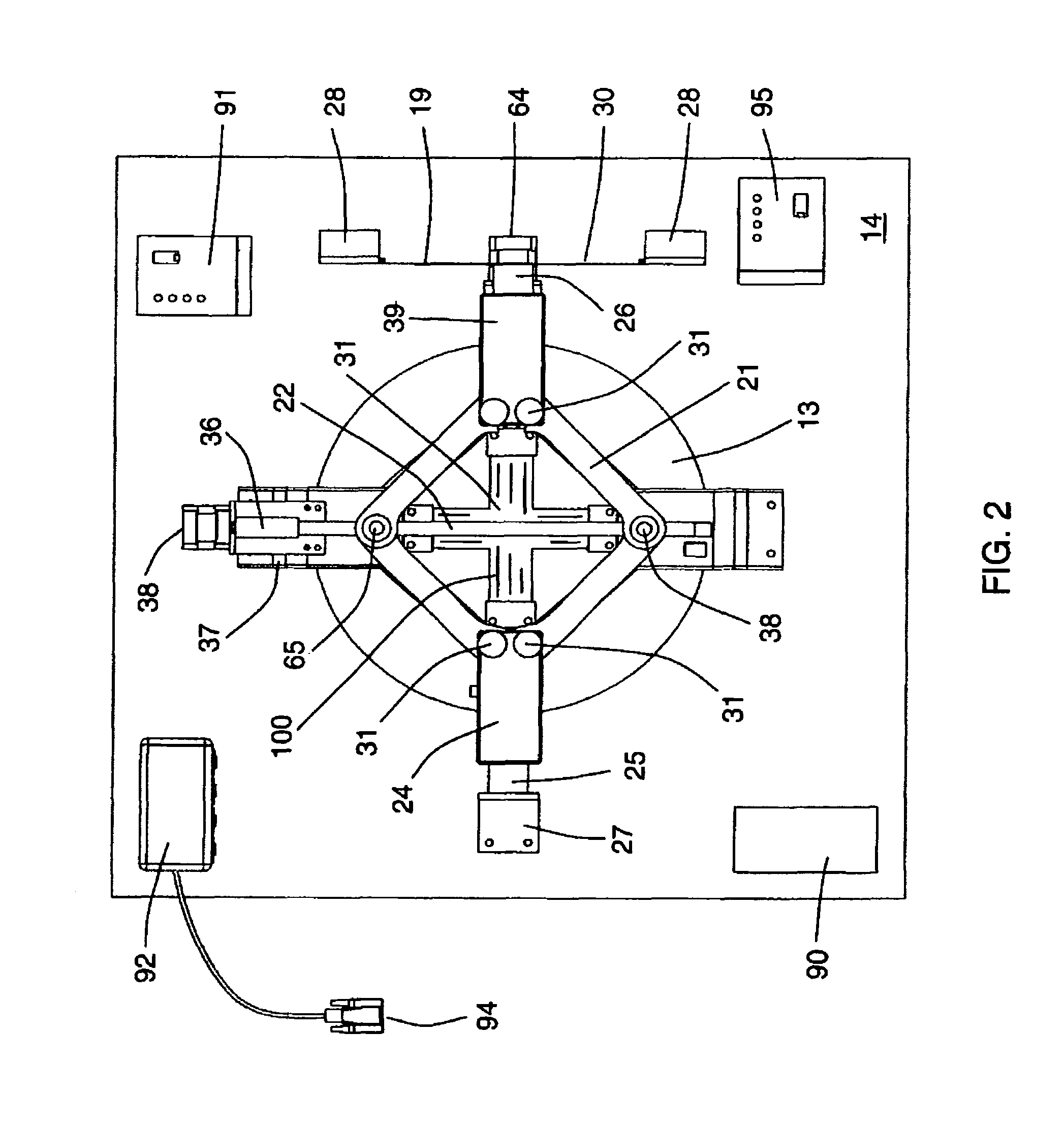
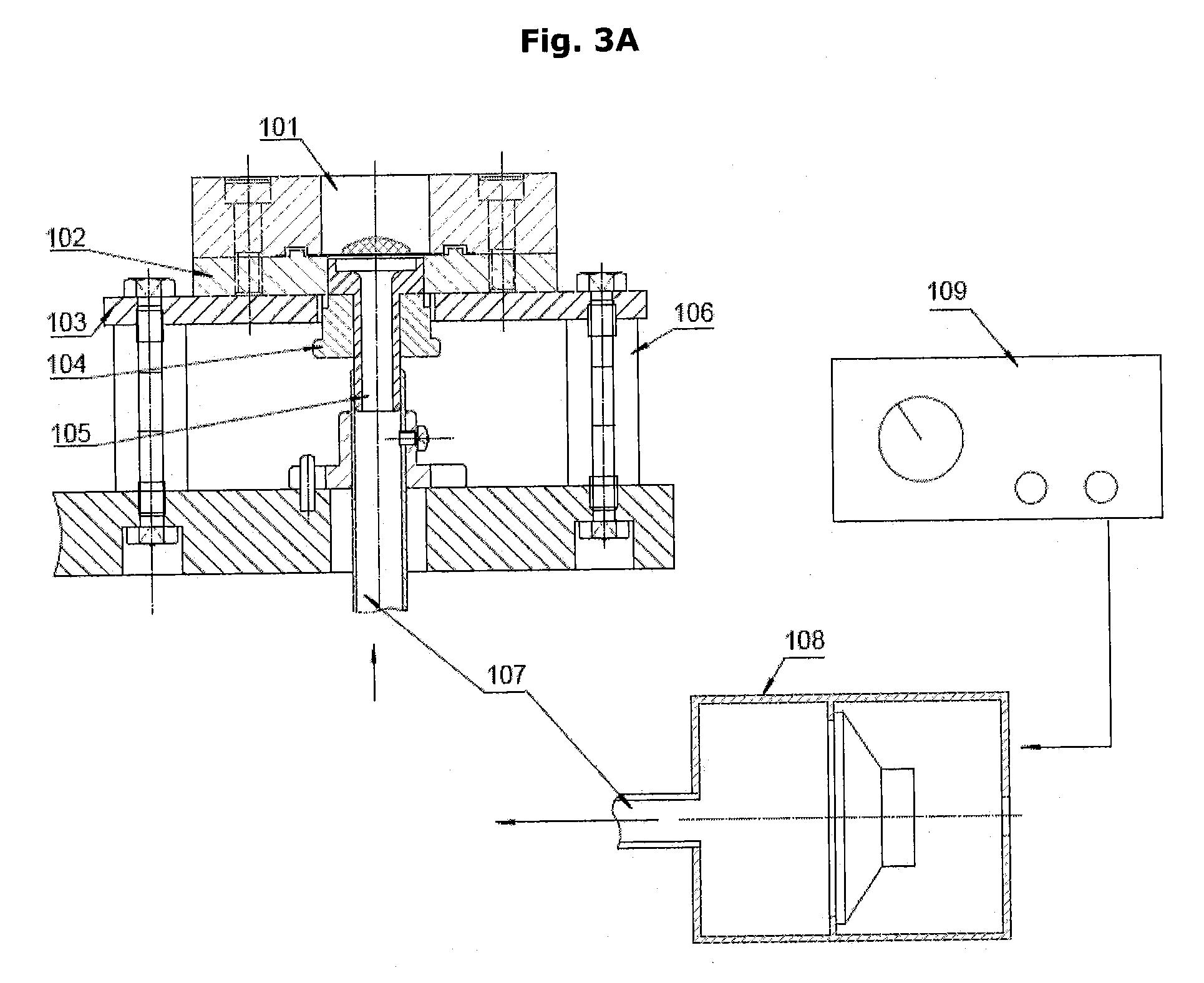
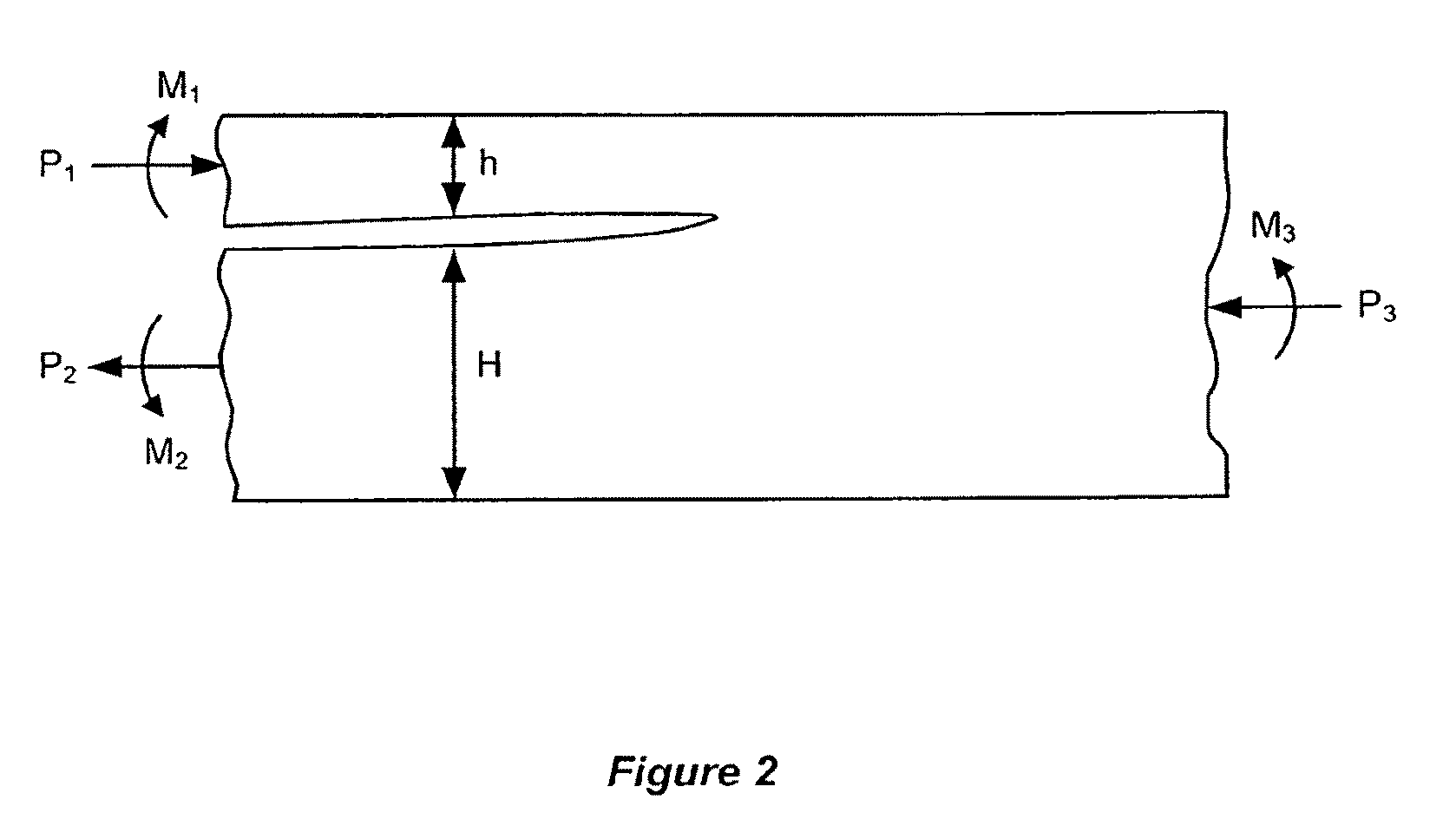
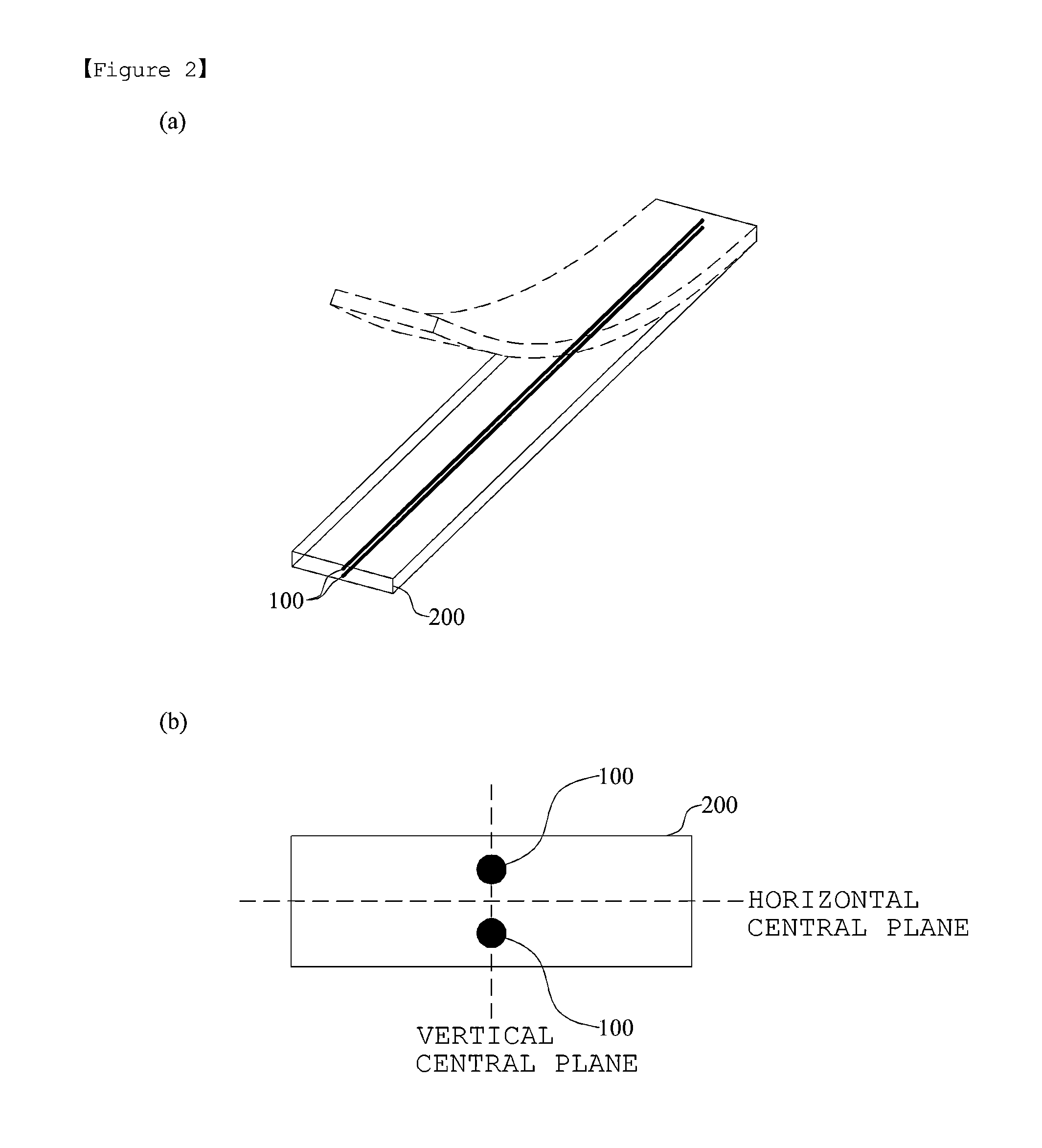
Combined in-plane shear and multi-axial tension or compression testing apparatus
ActiveUS6860156B1Provide flexibilityIncrease distanceMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesMaterial strength using repeated/pulsating forcesEngineeringTorsional load
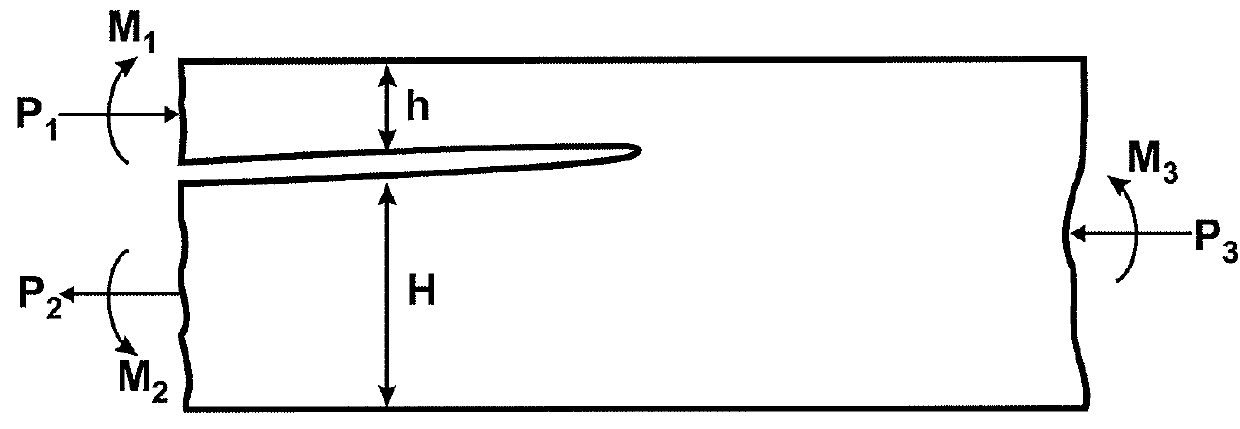
An in-plane shear and multi-axial tension or compression testing apparatus having four-bar linkages pivotable to two sleeves on an opposite vertices with the sleeves of each vertex rotationally attached to each other. Lateral links of each linkage are pivotally attached to load transfer plates in which the plates secure a test specimen. Each linkage is rotatable to the other linkages while the vertices are subjected to a compression or tensile load. The vertices are also capable of rotation by a testing machine for shear testing. During compression or tension of the vertices of the apparatus, the plates respectfully move toward or away from each other thereby applying compression or tension to the specimen. The bars of one linkage can be rotated with respect to the other, thereby applying torsional loading to the specimen.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
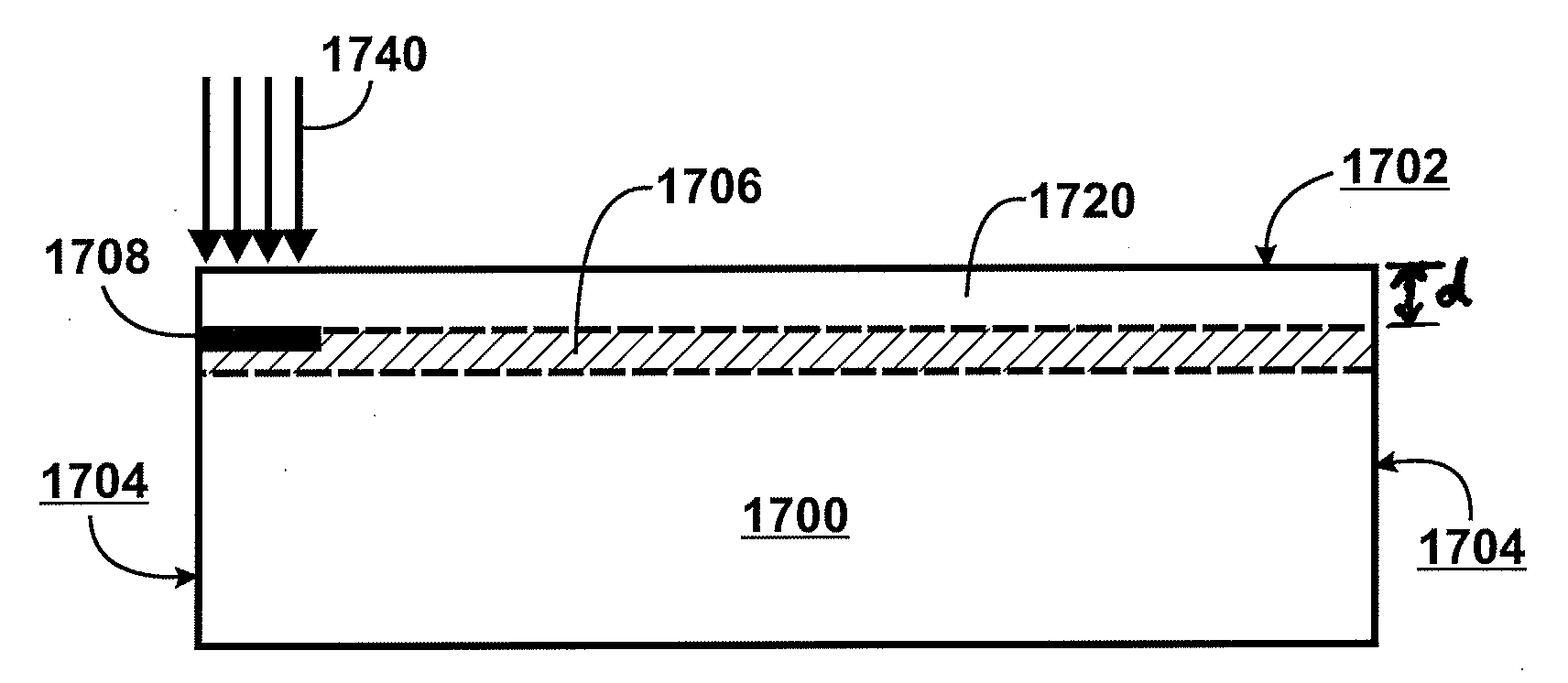
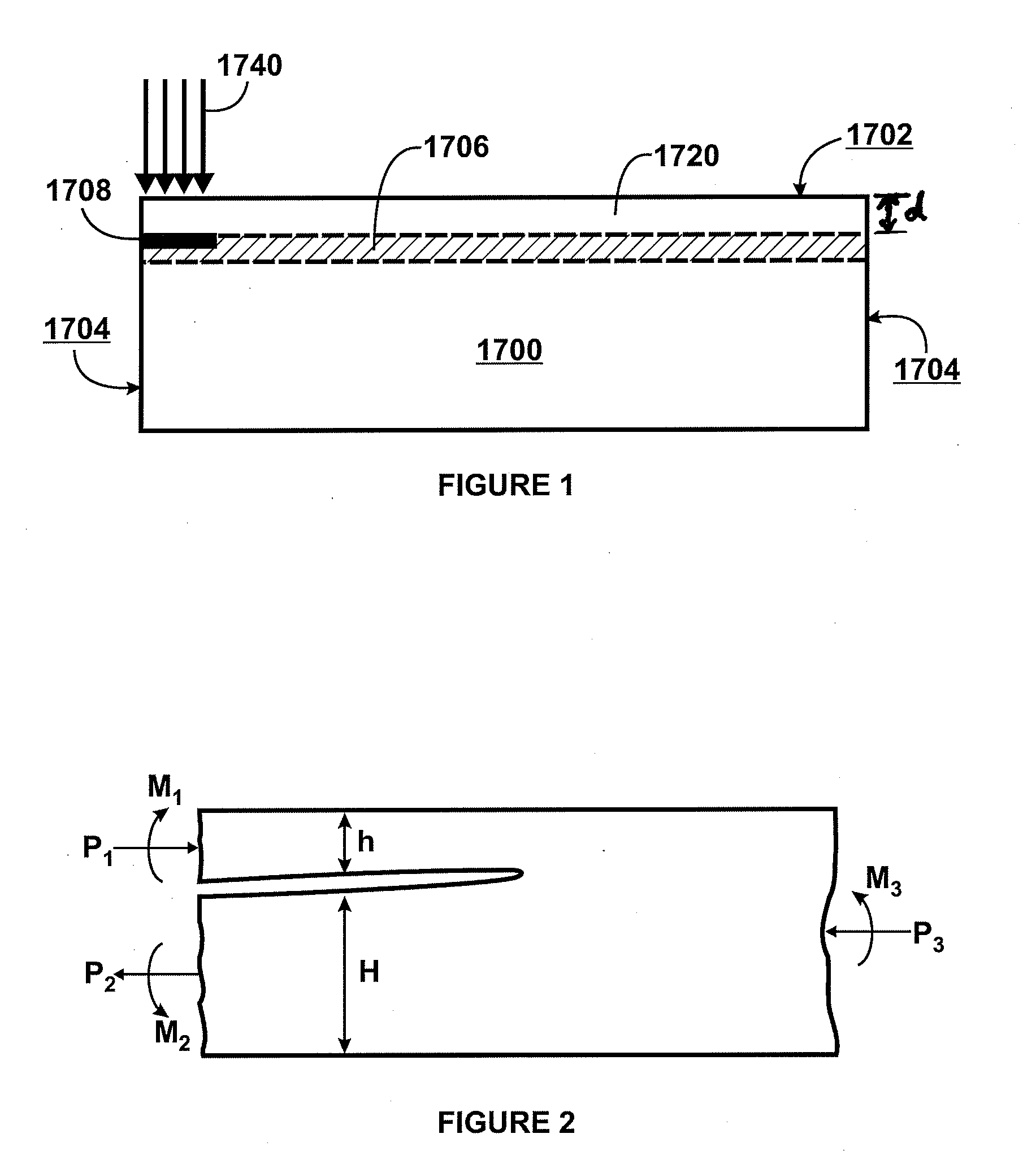
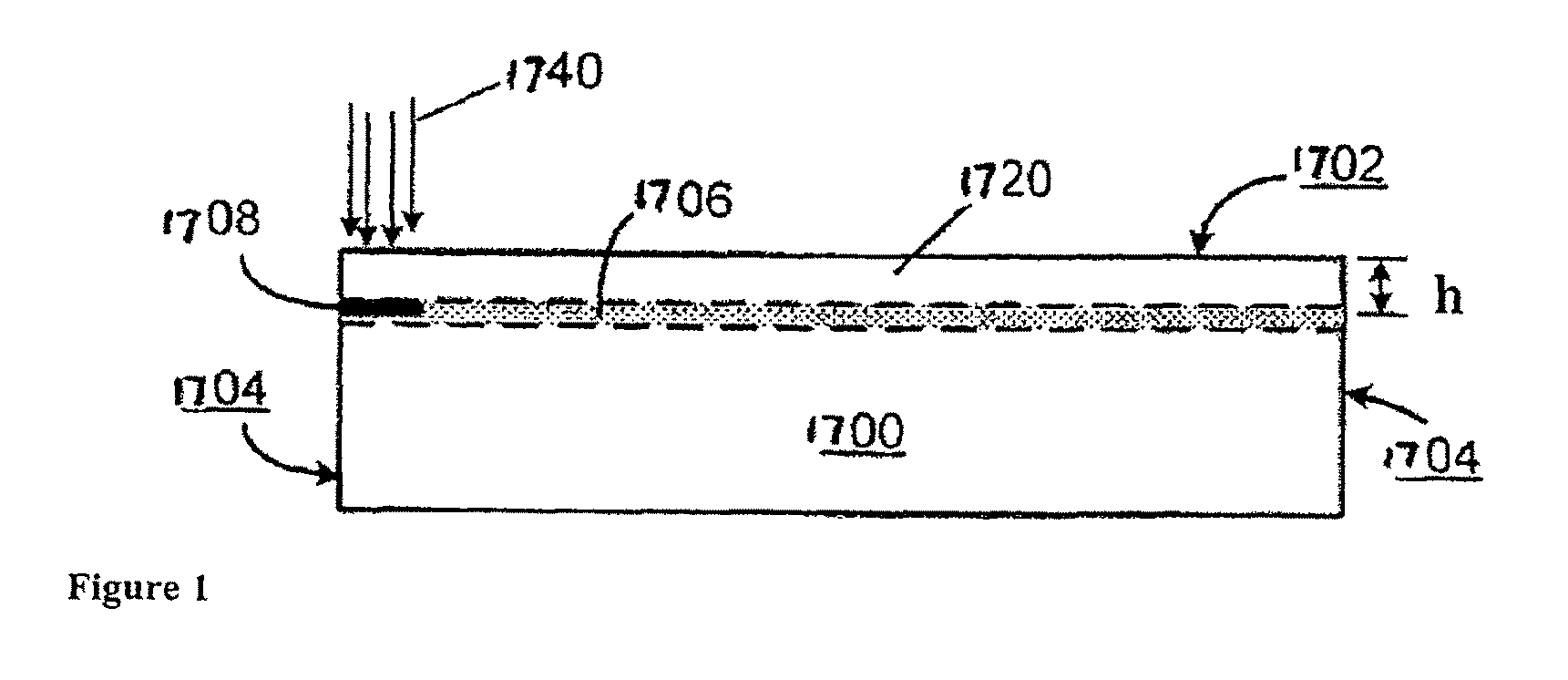
Layer transfer of films utilizing controlled shear region
ActiveUS20090277314A1Quality improvementImprove efficiencySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMetal working apparatusEngineeringThermal treatment
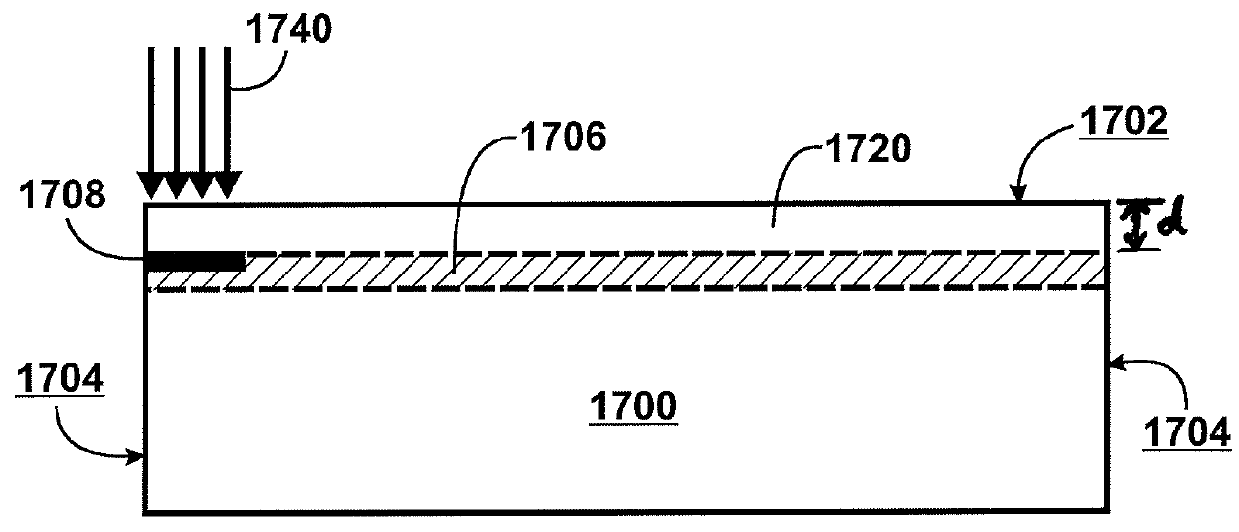
A film of material may be formed by providing a semiconductor substrate having a surface region and a cleave region located at a predetermined depth beneath the surface region. During a process of cleaving the film from the substrate, shear in the cleave region is carefully controlled. According to certain embodiments, an in-plane shear component (KII) is maintained near zero, sandwiched between a tensile region and a compressive region. In one embodiment, cleaving can be accomplished using a plate positioned over the substrate surface. The plate serves to constrain movement of the film during cleaving, and together with a localized thermal treatment reduces shear developed during the cleaving process. According to other embodiments, the KII component is purposefully maintained at a high level and serves to guide and drive fracture propagation through the cleave sequence. In one embodiment, the high KII component is achieved by adiabatic heating of silicon through exposure to E-beam radiation, which imparts a highly abrupt thermal gradient and resulting stress at a precisely defined depth in the silicon.
Owner:SILICON GENERAL CORPORATION
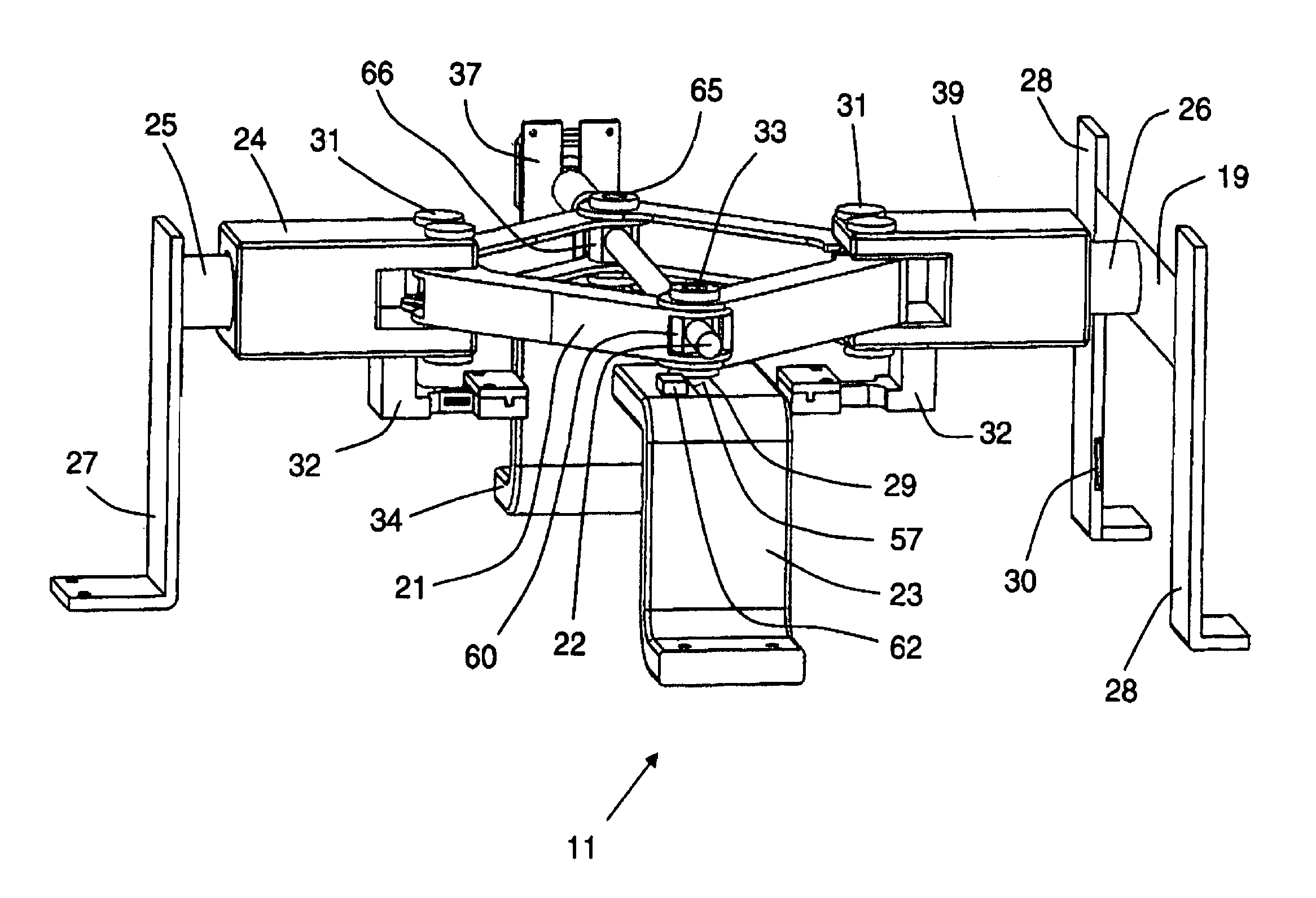
Compact and stand-alone combined multi-axial and shear test apparatus
ActiveUS8082802B1Low costFurther flexibilityForce measurementMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesJackscrewEngineering
A testing apparatus is disclosed that includes a turntable, an upper scissor jack assembly and a lower scissor jack assembly positioned in parallel planes, about a longitudinal axis and affixed to a base. The apparatus is powered by at least three motors with supporting controllers. The lower assembly is affixed to the base mechanically via the turntable which allows the lower assembly to rotate with respect to the upper assembly. There are two loading plates attached to the hinges of each scissor jack. The test specimen is secured by the loading plate. Each scissor jack operates by a screw-gear powered by one of the motors. Upon energizing a stepper motor; the screw-gear positions a scissor jack to apply a tension or compression on the specimen. While subjected to tension or compression, the lower jack assembly can be rotated with respect to the upper assembly for in-plane shear loading.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
Layer transfer of films utilizing controlled propagation
ActiveUS20100055874A1Quality improvementImprove efficiencySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesSemiconductorSilicon
A film of material may be formed by providing a semiconductor substrate having a surface region and a cleave region located at a predetermined depth beneath the surface region. During a process of cleaving the film from the substrate, shear in the cleave region is carefully controlled to achieve controlled propagation by either KII or energy propagation control. According to certain embodiments, an in-plane shear component (KII) is maintained near zero by adiabatic heating of silicon through exposure to E-beam radiation. According to other embodiments, a surface heating source in combination with an implanted layer serves to guide fracture propagation through the cleave sequence.
Owner:SILICON GENERAL CORPORATION
Reinforcing fiber base material for preforms, process for the production of laminates thereof, and so on
ActiveUS20090068428A1Excellent characteristicsGood drapabilityPaper/cardboard layered productsNon-woven fabricsVitrificationYarn
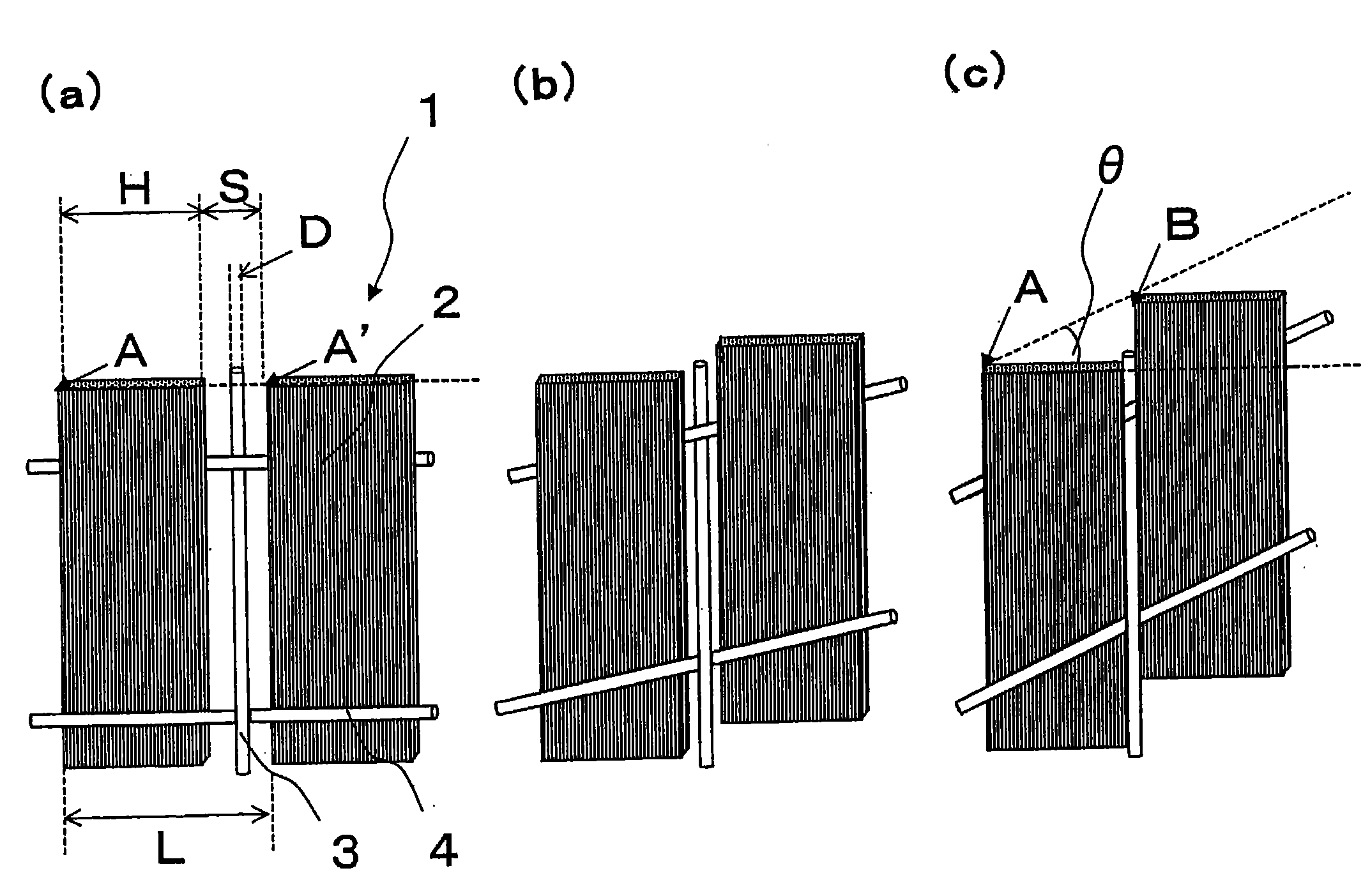
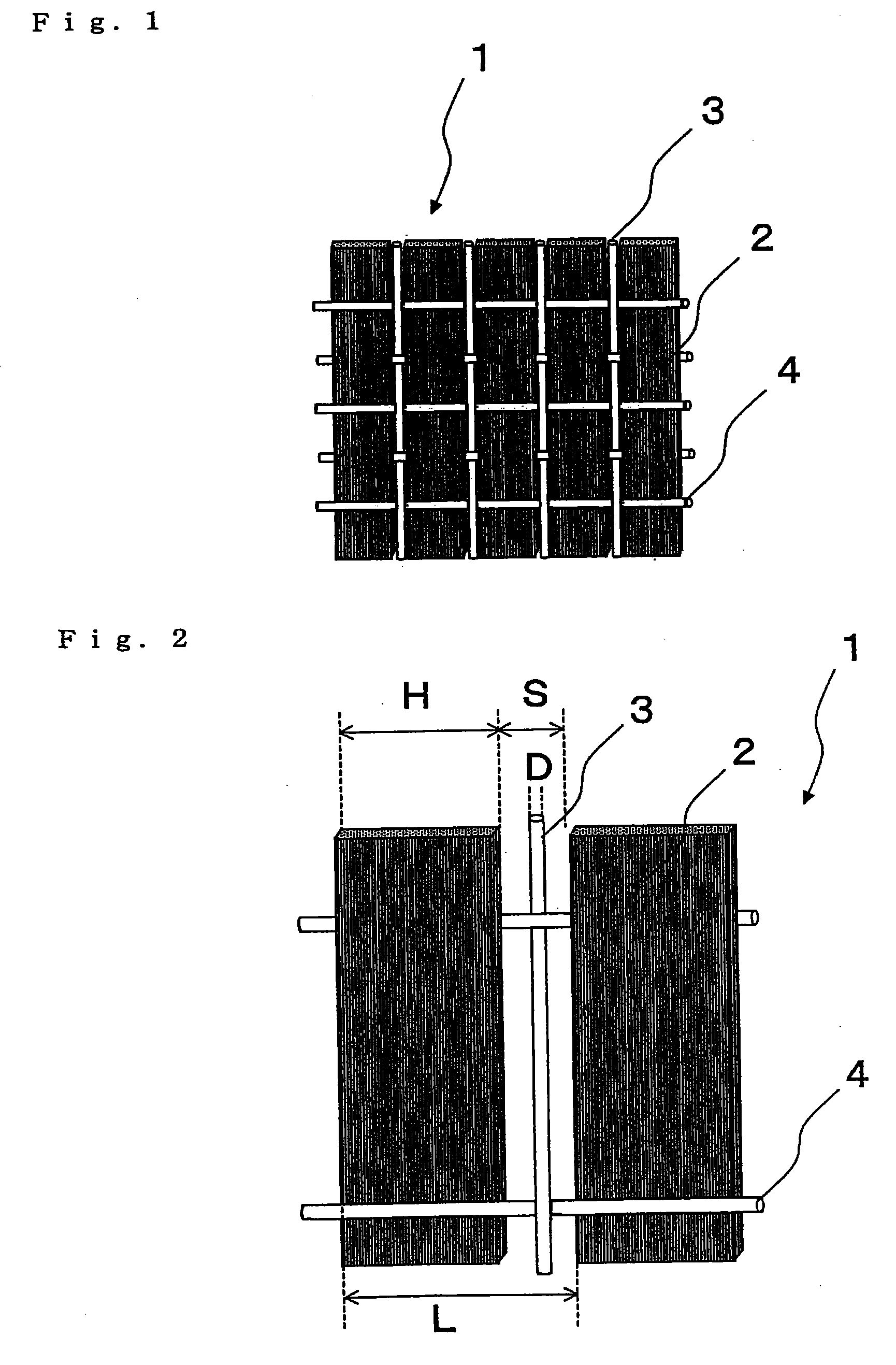
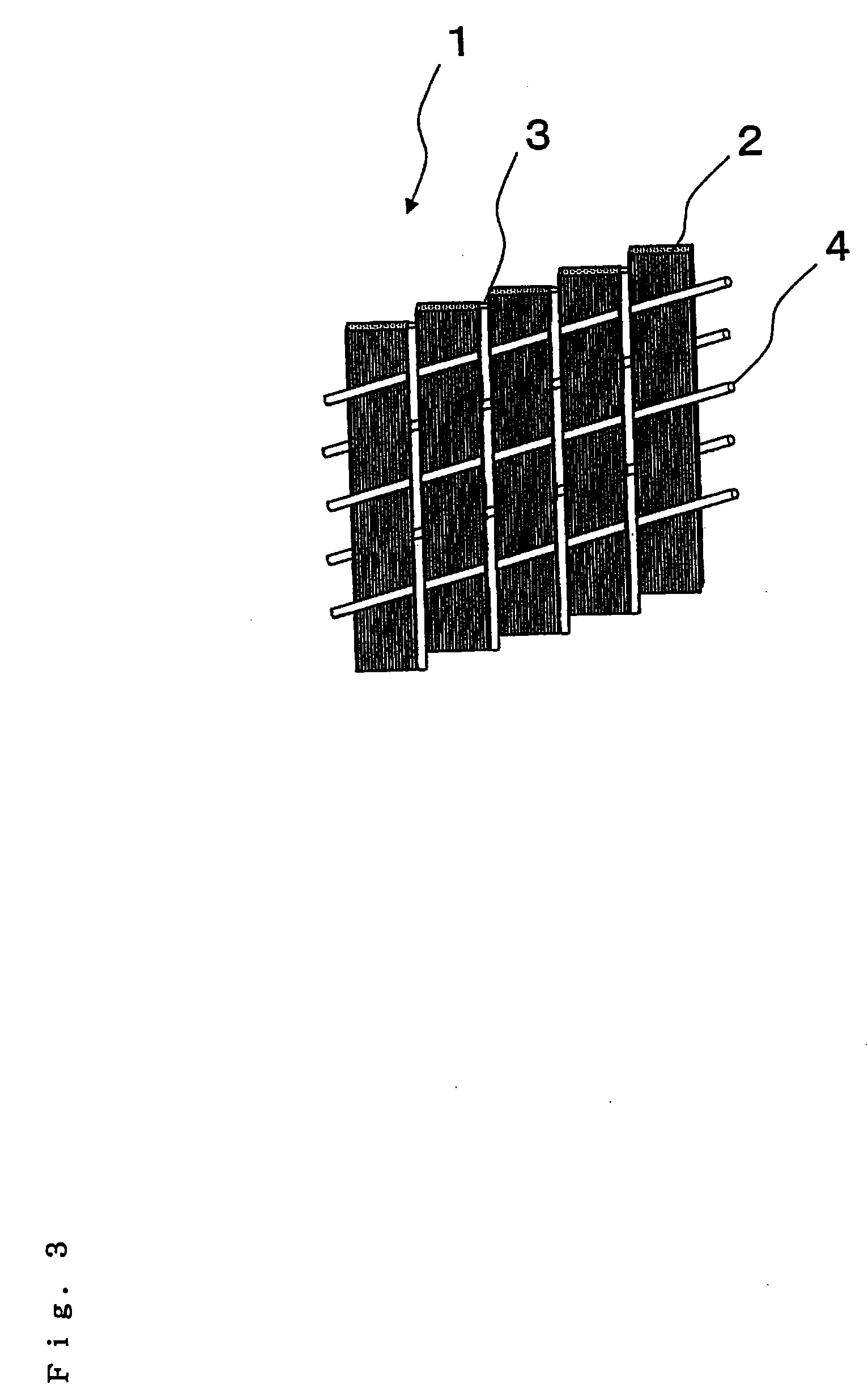
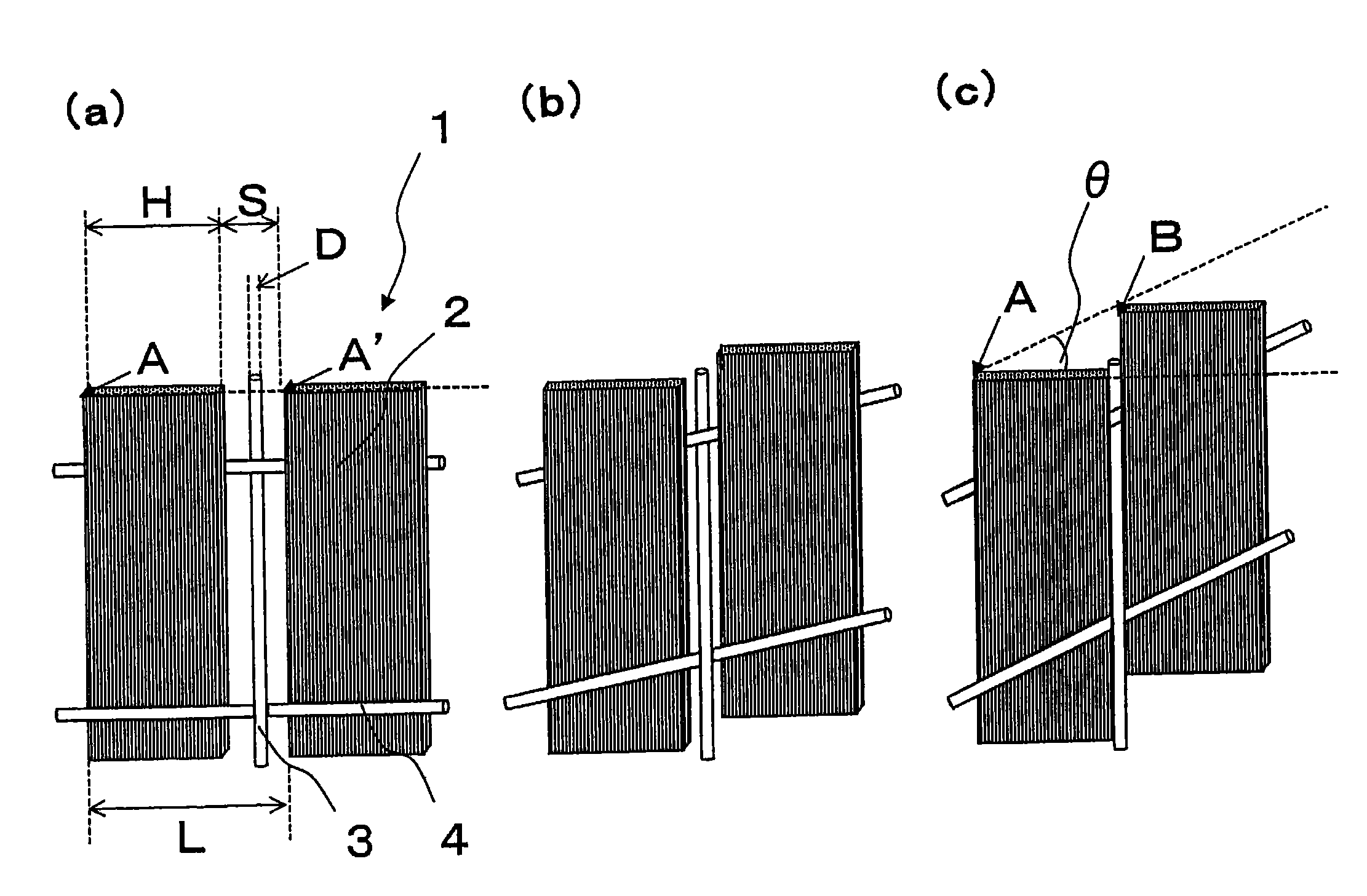
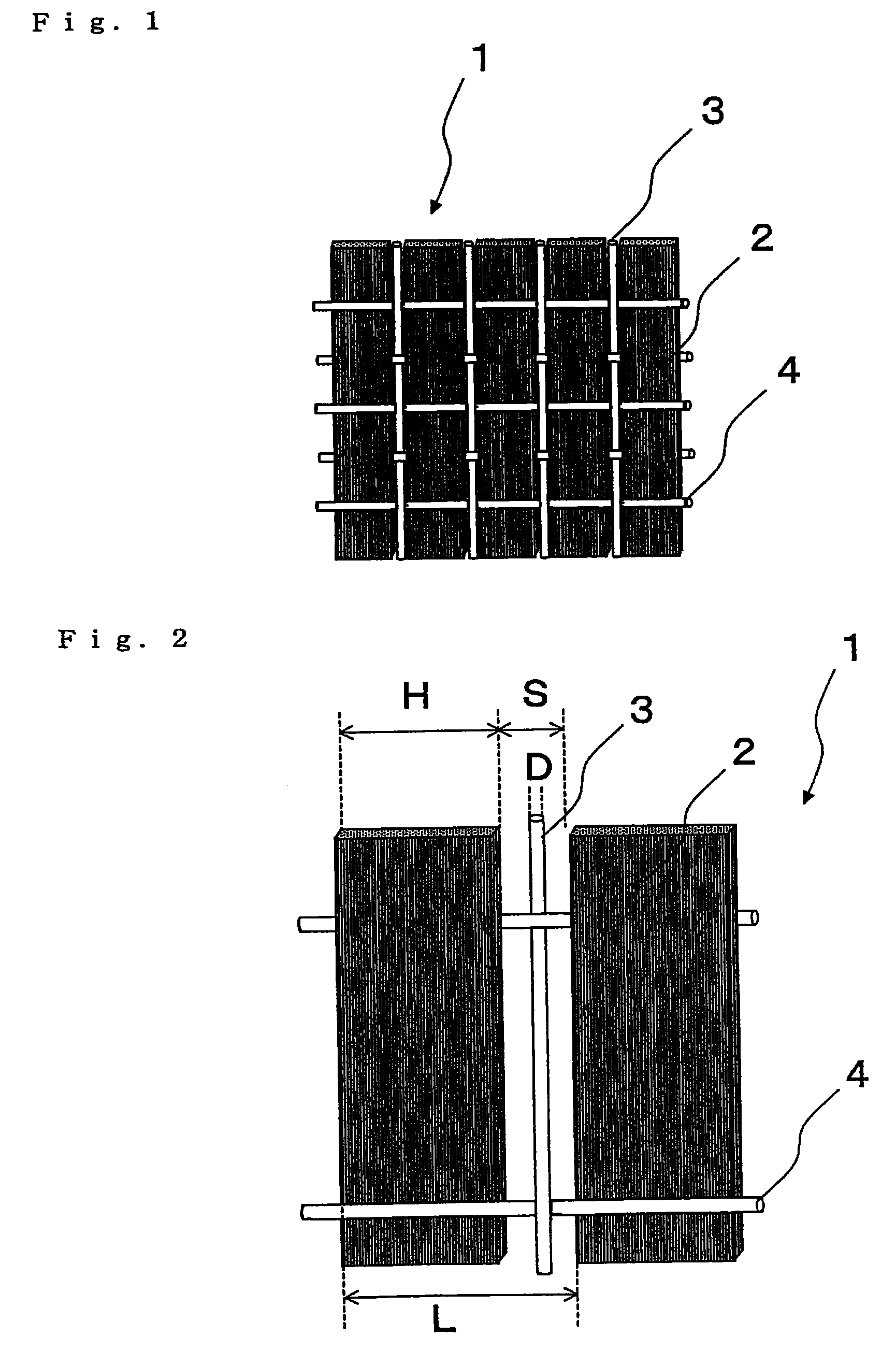
The invention provides (1) a reinforcing fiber base material having a weave constituted of both reinforcing fiber filaments arranged in one direction in parallel with each other and auxiliary yarns arranged in another direction, which satisfies the relationship: L=H / cos θ (wherein L is the length of auxiliary yarn covering one reinforcing fiber filament and H is the width of the filament as determined in such a state where the reinforcing fiber filaments are unified only with the auxiliary yarns; and 3°≦θ (in-plane shear strain)≦30°) and wherein 2 g / m2 to 40 g / m2 of an adhesive resin having a glass transition temperature between 0° C. and 95° C. is adhesed to at least one side thereof in spots, lines, or discontinuous lines; (2) a laminate obtained by laminating layers of the above reinforcing fiber base material, wherein the adhesive resin adhesed to each layer of base material partially bonds to a facing layer of base material over the whole surface thereof, with the maximum length of each bonding joint being not less than 1 mm and not more than the width H of a reinforcing fiber filament; and (3) a preform, obtained by shaping the laminate, having a reinforcing fiber volume fraction (Vpf) of 45% to 62%.
Owner:TORAY IND INC
Reinforcement method for continuous filament reinforced metallic matrix composite
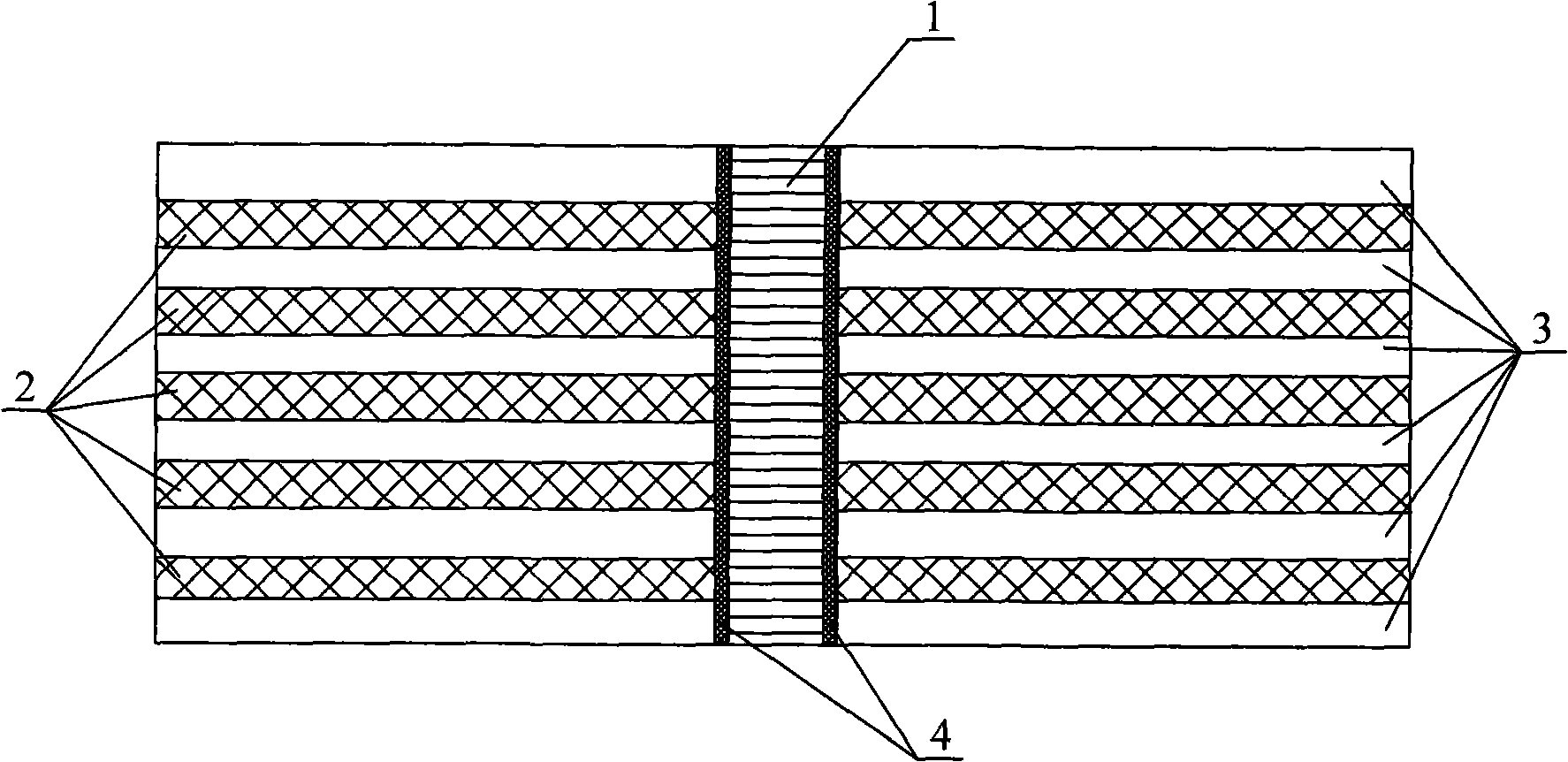
The invention discloses a reinforcement method of a continuous fiber-reinforced metal matrix composite, relates to the fiber-reinforced metal matrix composite, and aims at solving the problems that the rigidity and the strength character of a structural piece of the fiber-reinforced metal matrix composite are low along the thickness direction, the strength of in-plane shear and interlaminar shear is low, the impact ductility is low, and delamination is easy to occur. The reinforcement method is realized according to the steps as follows: after a fiber prefabricated part (2) is prepared, a wire (1) is added in the fiber prefabricated part (2), the fiber prefabricated part (2) and a composite material matrix (3) are processed through molten metal infiltration by heating, and the reinforcement to the continuous fiber-reinforced metal matrix composite is completed after cooling. Because the wire originally has high strength and high toughness and has stronger binding capacity with the matrix, the existence of the wire effectively strengthens the strength between fibrous composite layers or the strength along the weak direction such as thickness, etc., increases the interlaminar strength, the impact ductility and the damage tolerance of fibrous composite, and avoids the demixion.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
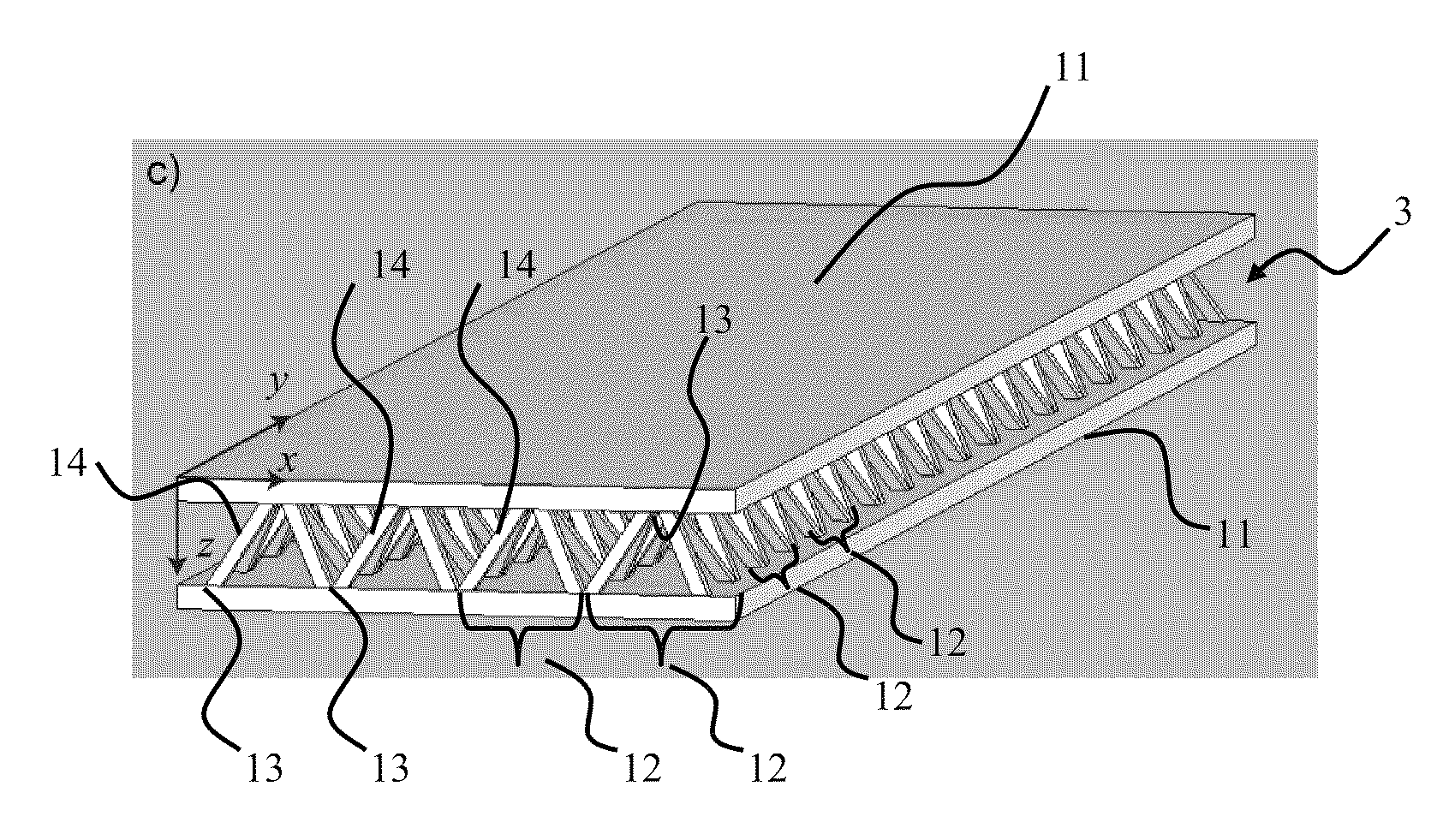
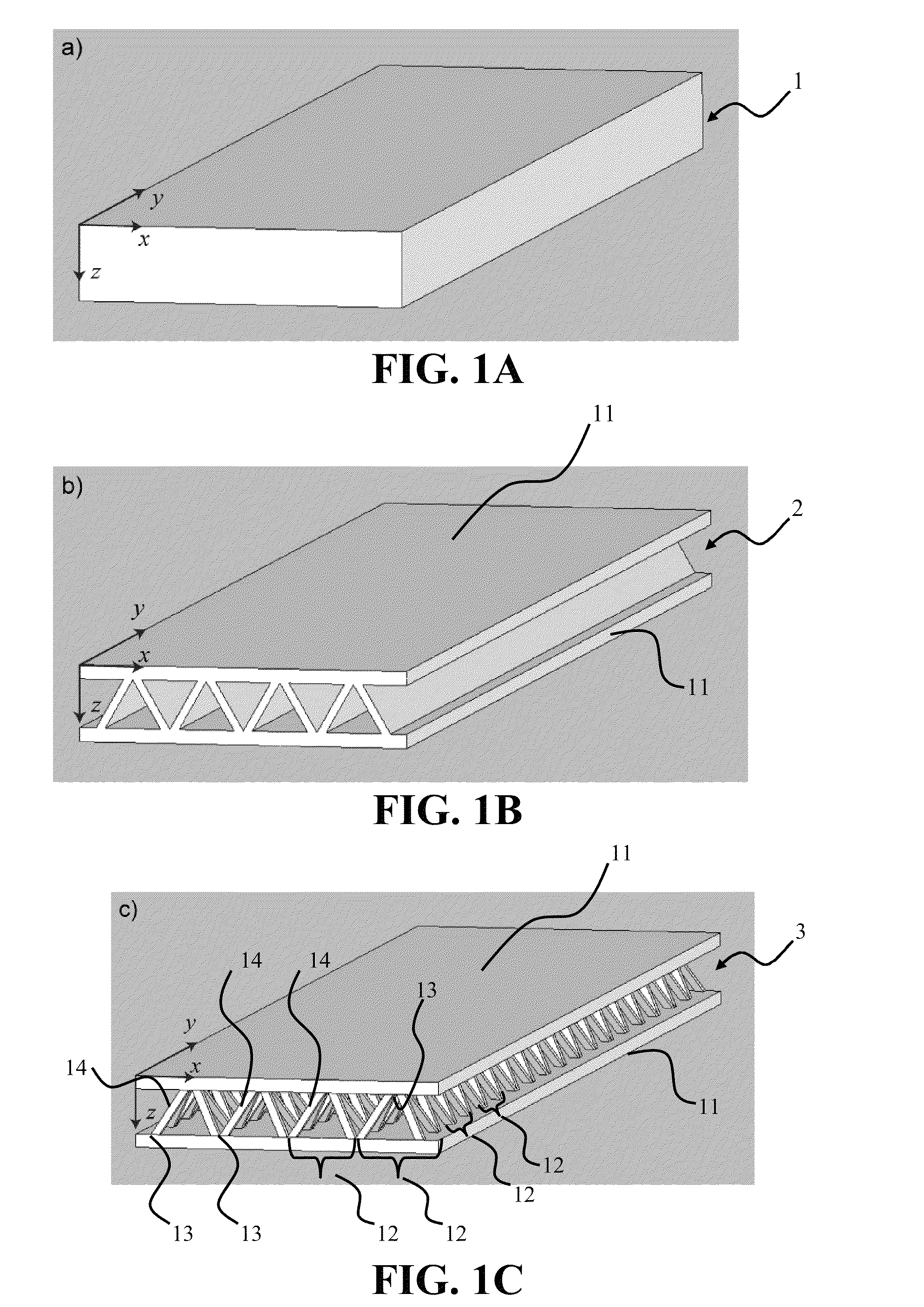
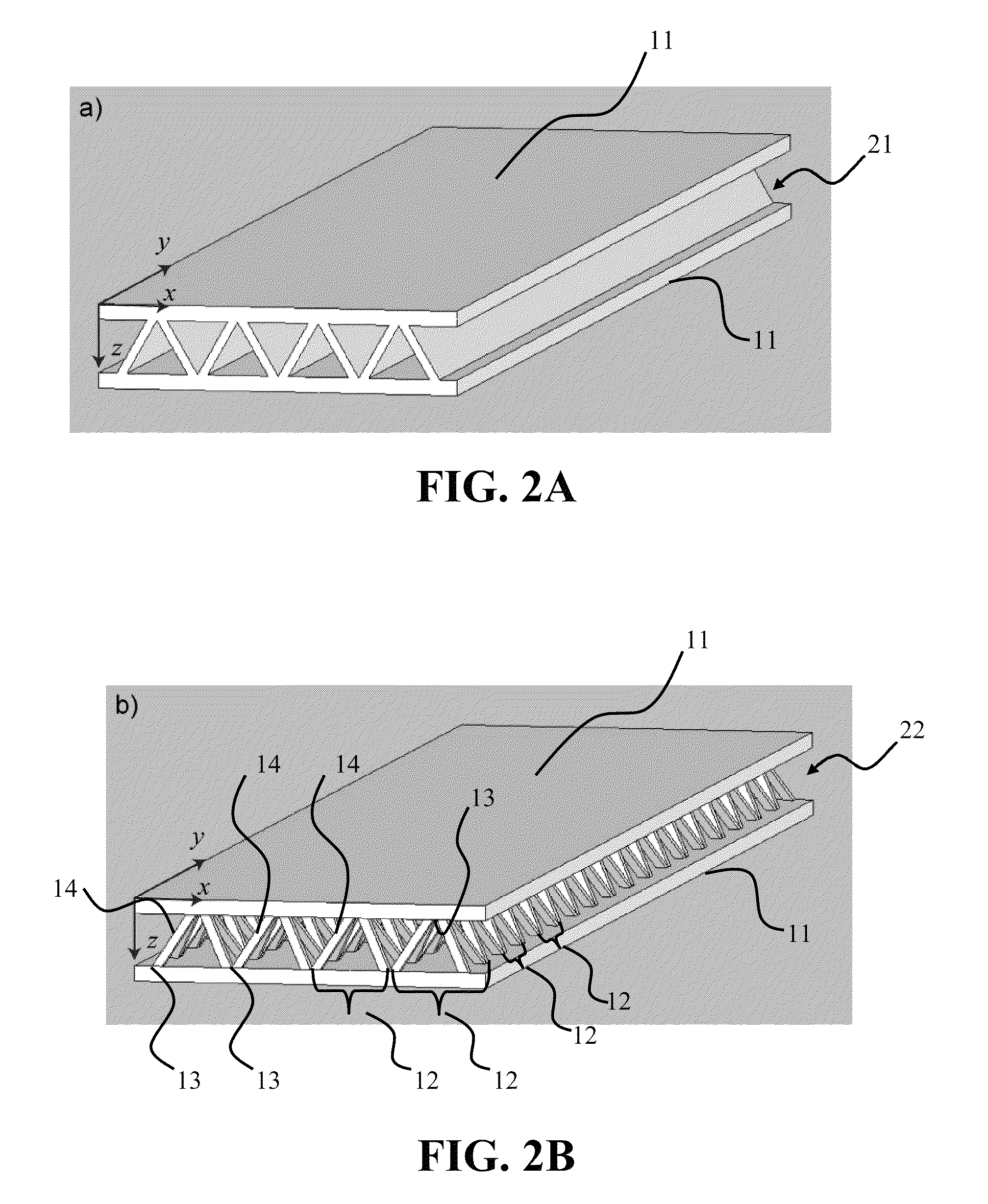
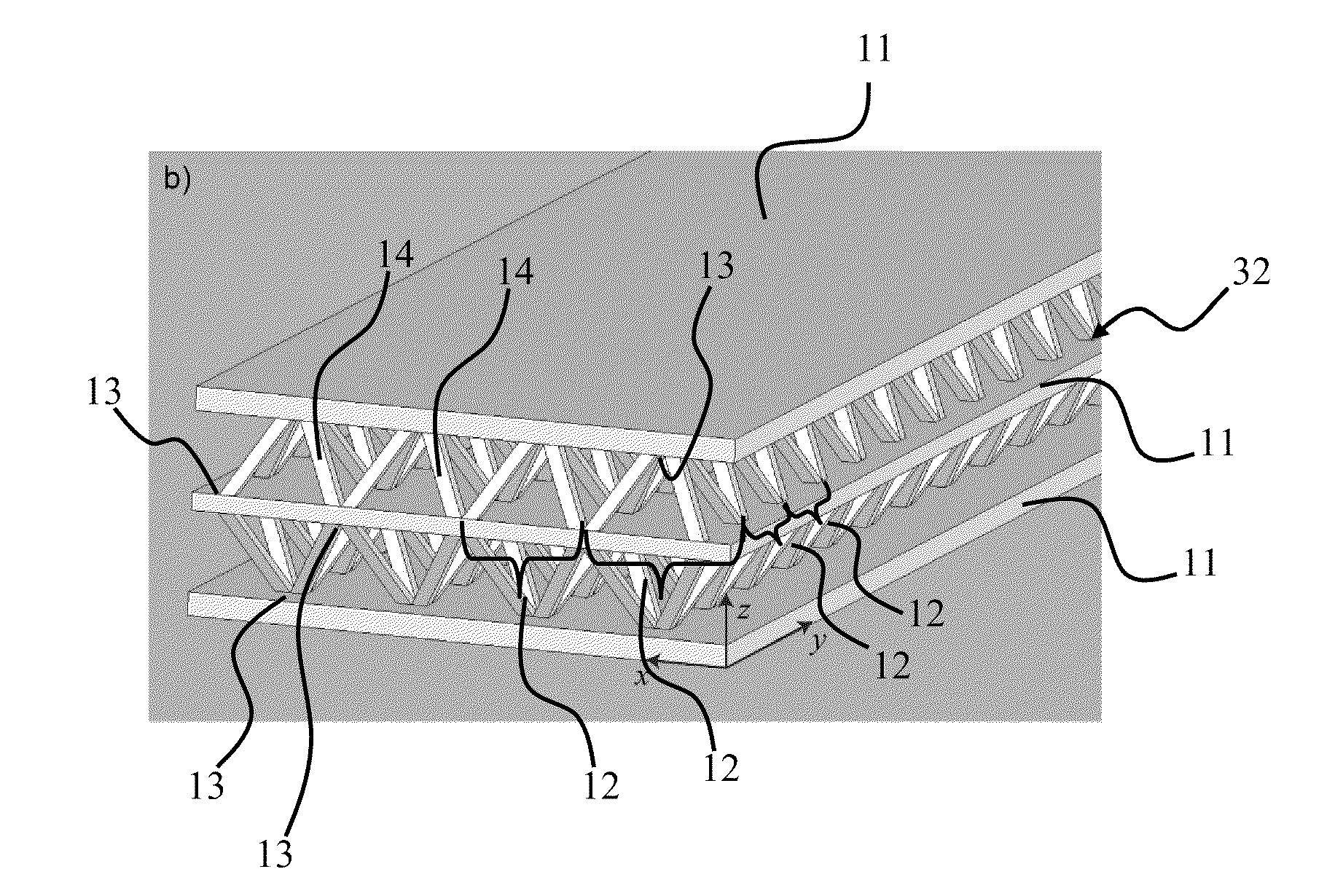
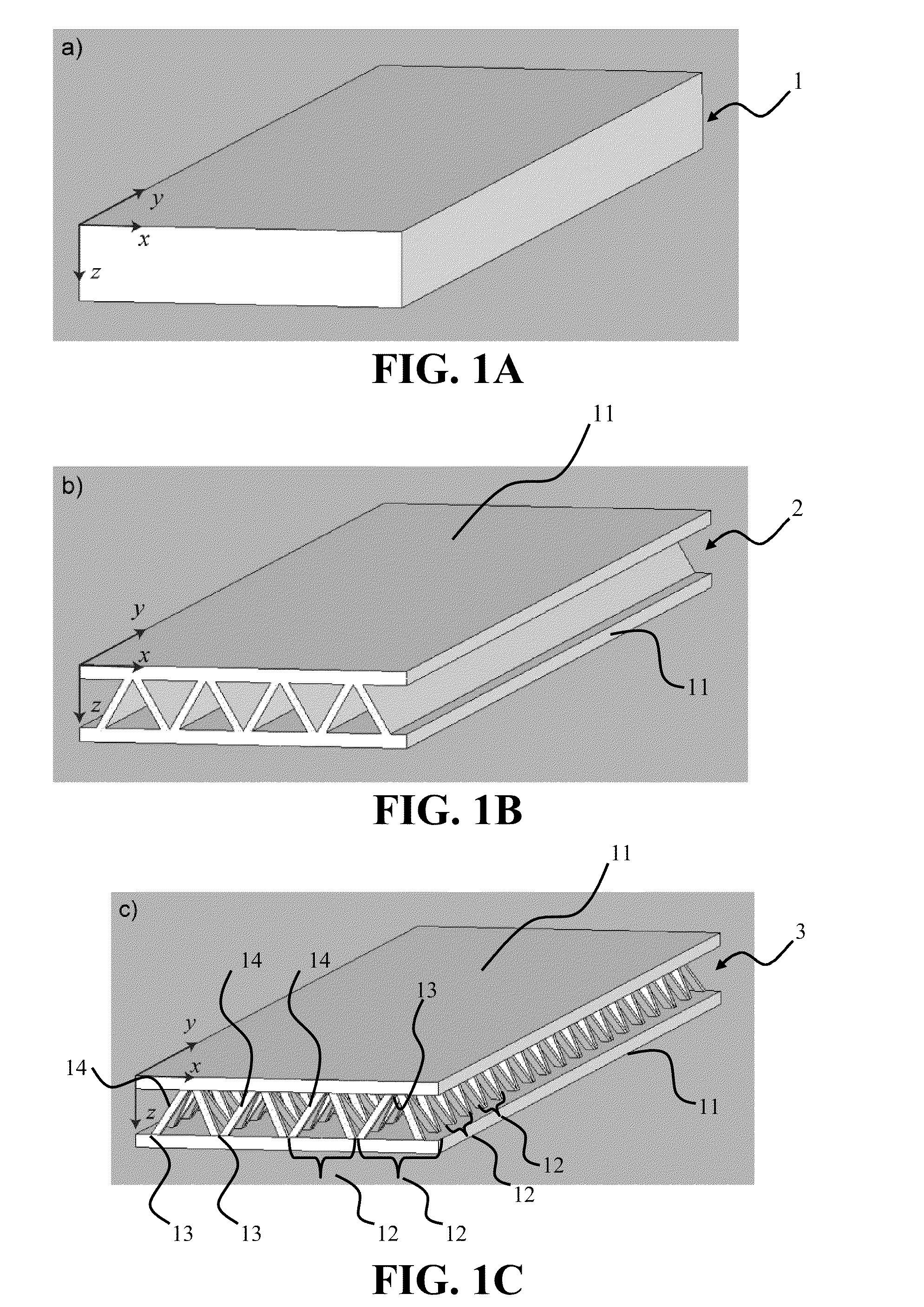
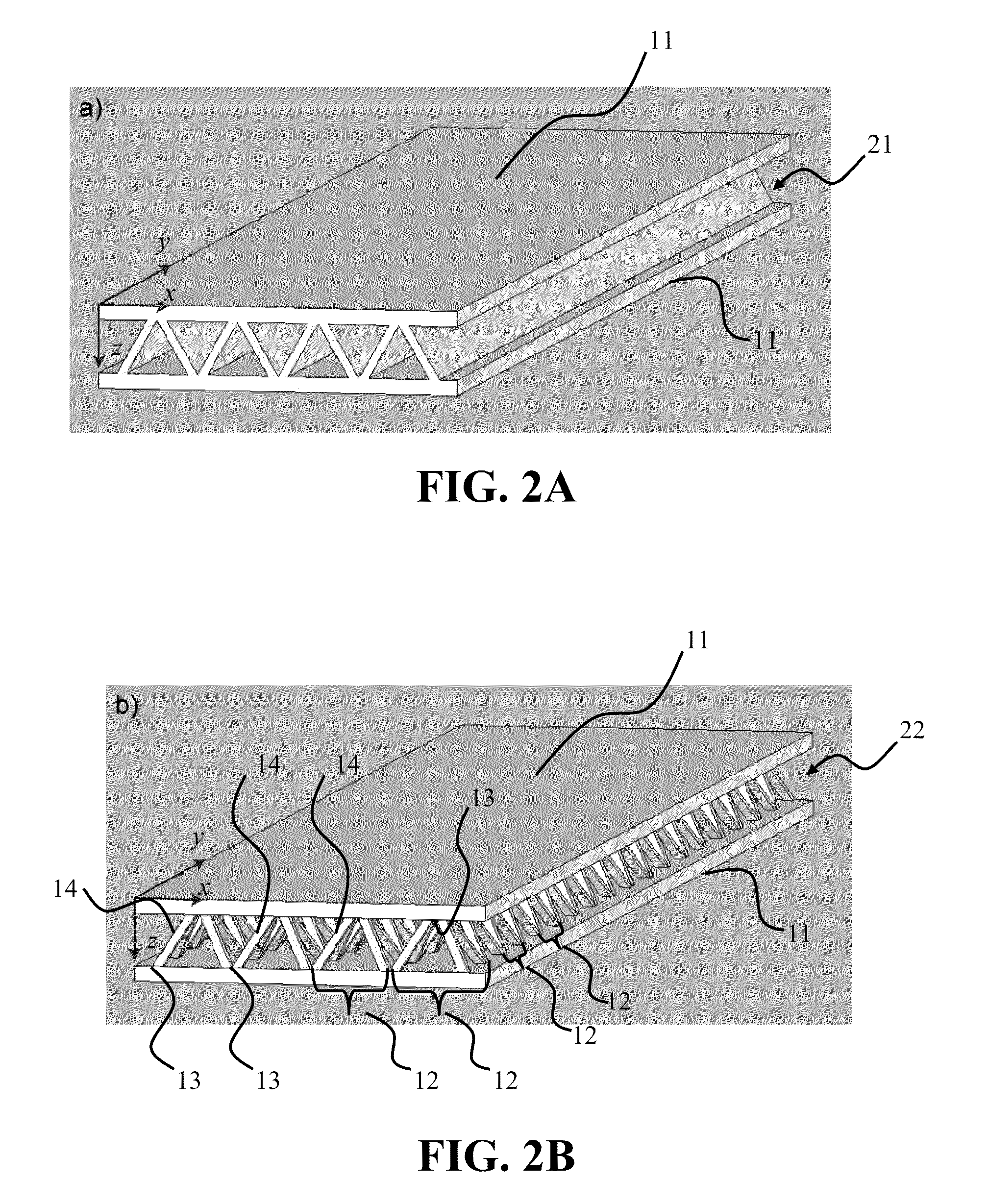
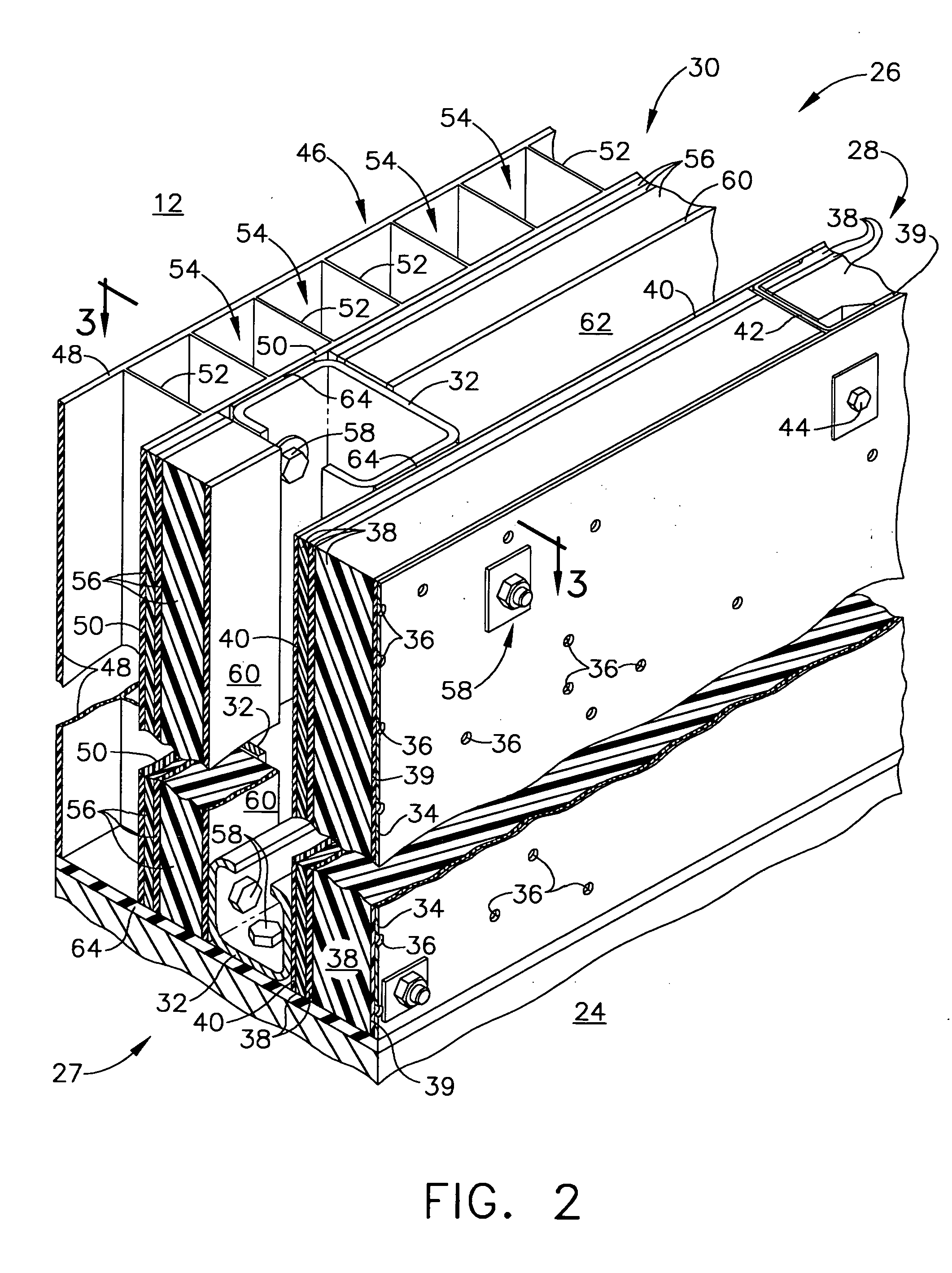
Manufacture of lattice truss structures from monolithic materials
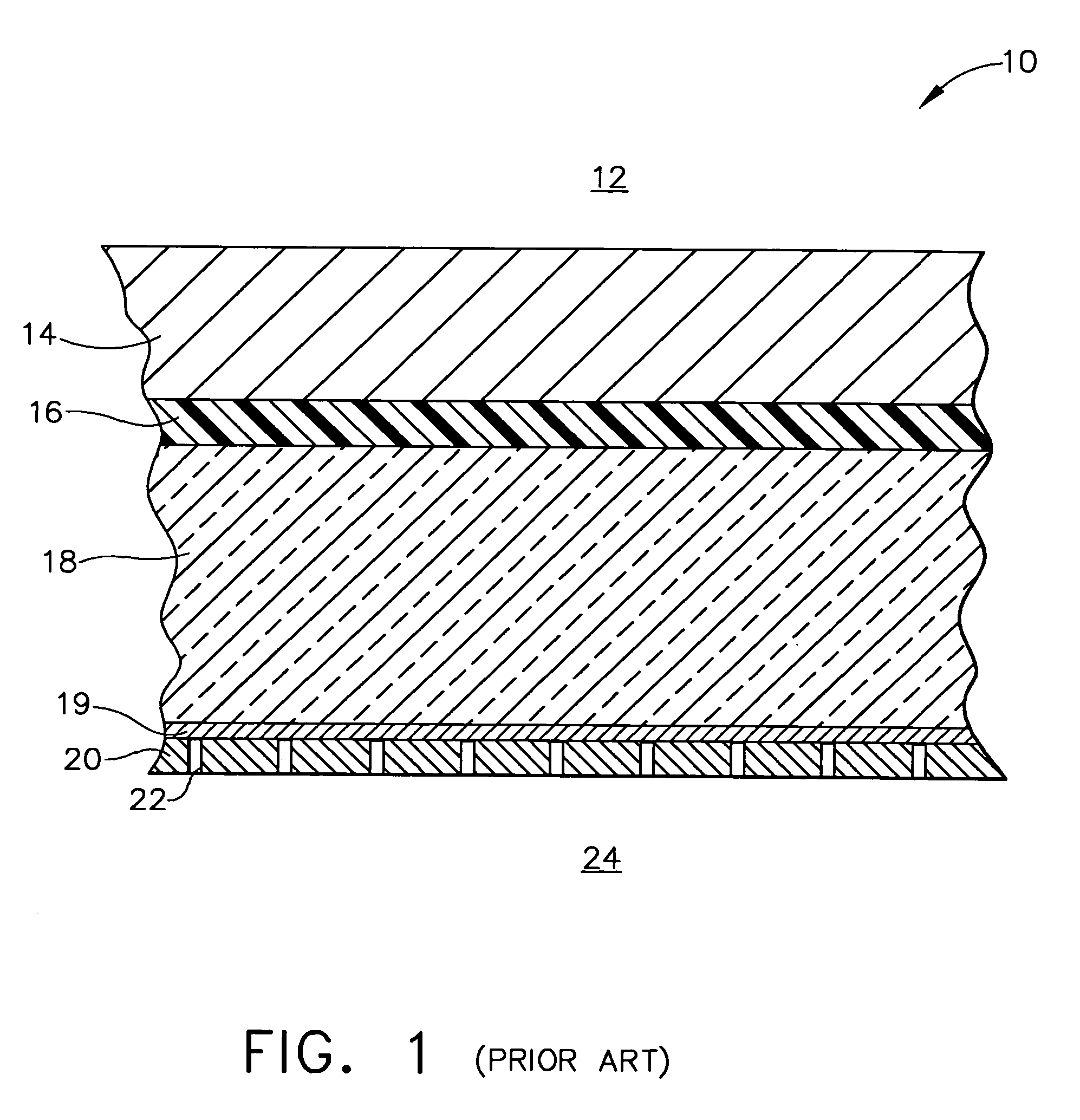
ActiveUS8176635B2Low densityImprove stress resistanceDecorative surface effectsFloorsBond interfaceBonding process
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND
Thermal-acoustic enclosure
An enclosure for apparatus that, during operation, generates heat and / or sound energy comprises at least one wall defining at least a portion of the enclosure hollow interior. The wall comprises in sequence outwardly from the enclosure hollow interior an inner panel, an outer panel, a support frame between the inner and outer panels to hold the inner and outer panels spaced apart, and a vibrator isolator between the support frame and the panels. Panels or panel segments of the wall primarily are made of non-metallic composites to provide a structurally strong, lightweight enclosure that includes enhanced acoustic characteristics and reduced heat transfer through enclosure walls, along with fire protection and in-plane shear loading capabilities.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Dynamic vibrational method and device for vocal fold tissue growth
InactiveUS20100291045A1Induced differentiationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiocideCultured cellBiology
Dynamic vibrational methods and devices for inducing differentiation of stem cells into vocal fold fibroblast-like cells or for generating vocal fold-like tissue from cultured cells. Also provided are matrices providing sustained release of growth factors, and bioreactors generating and delivering a high frequency vibration with in-plane shear stress to cultured cells.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF DELAWARE
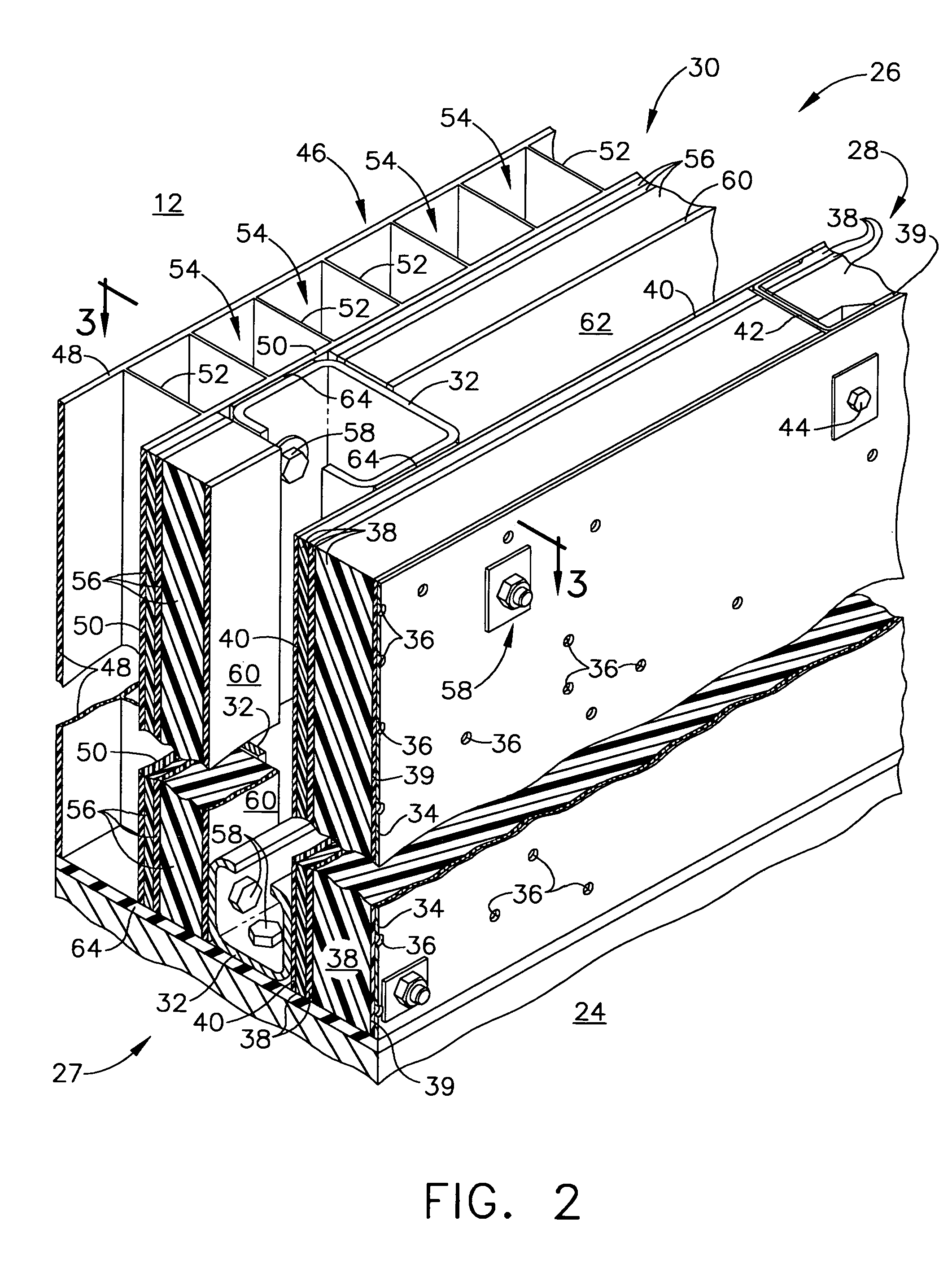
Manufacture of Lattice Truss Structures from Monolithic Materials
ActiveUS20090282773A1Low densityImprove stress resistanceDecorative surface effectsFloorsBond interfaceBonding process
Methods and systems to manufacture lattice-based sandwich structures from monolithic material. Such methods and systems eliminate the bonding process which is conventionally used to join lattice based truss cores to facesheets to form sandwich structures. This bonded interface is a key mode of failure for sandwich structures which are subjected to shear or bending loads because the nodes transfer forces from the face sheets to the core members while the topology for a given core relative density dictates the load carrying capacity (assuming adequate node-bond strength exists). An aspect comprises a core and related structures that provide very low density, good crush resistance and high in-plane shear resistance. An aspect of the truss structures may include sandwich panel cores and lattice truss topology that may be designed to efficiently support panel bending loads while maintaining an open topology that facilitates multifunctional applications.
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND
Sandwich panel
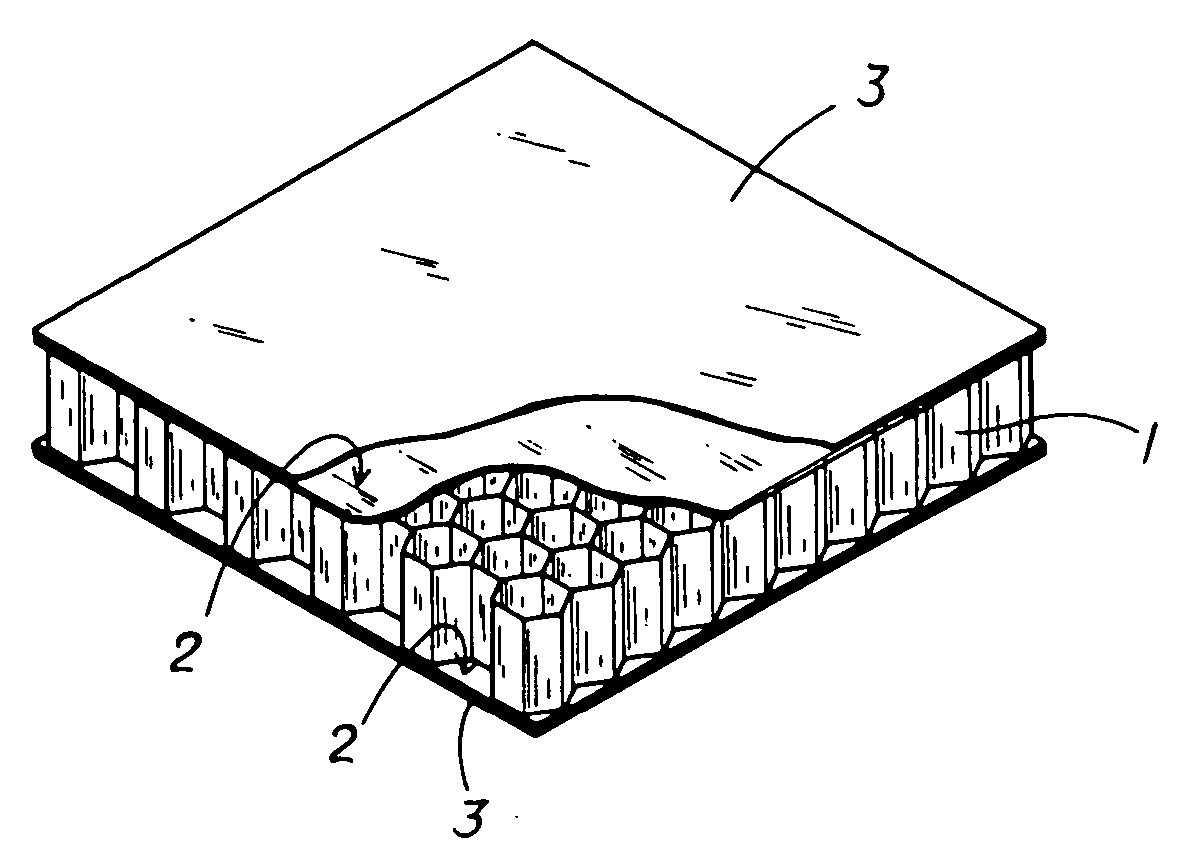
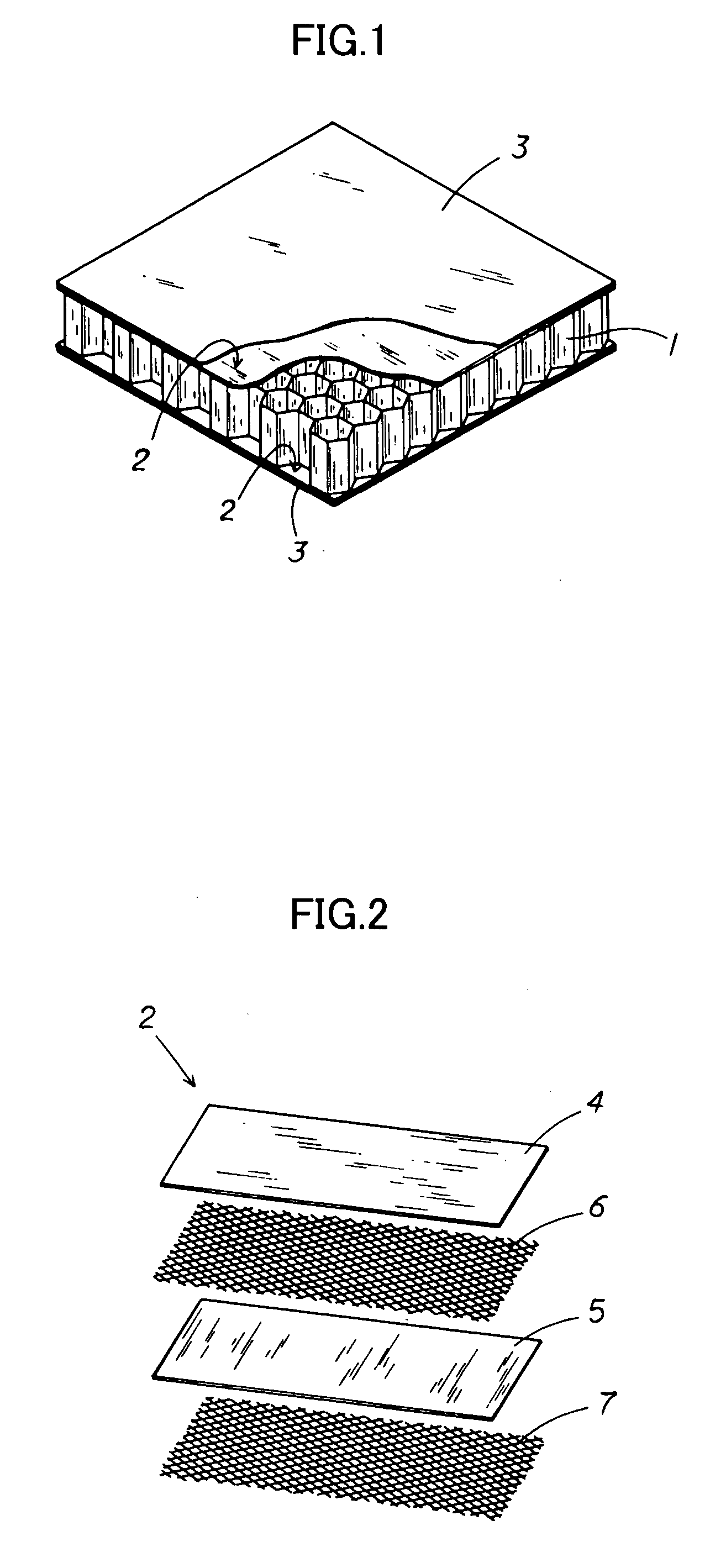
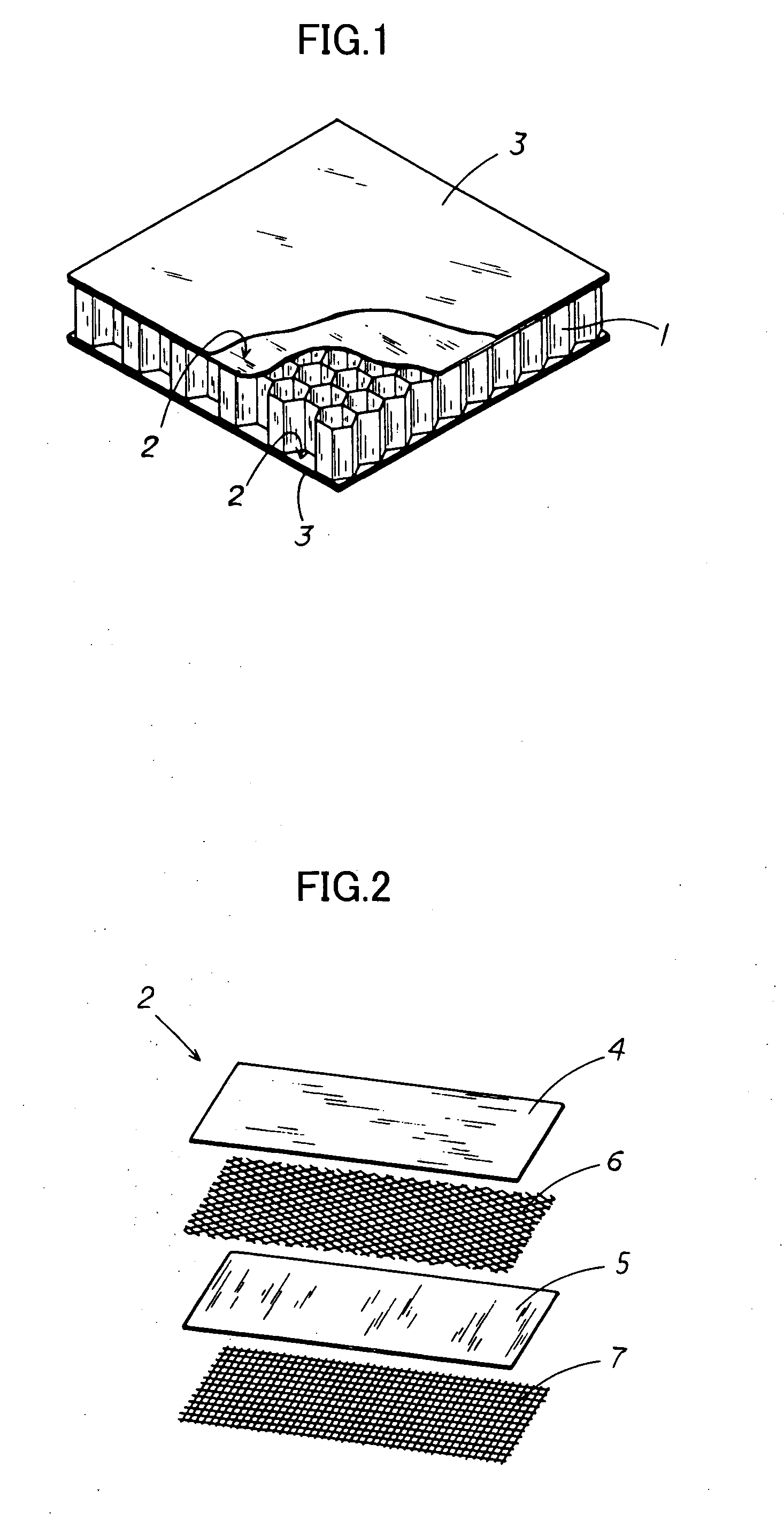
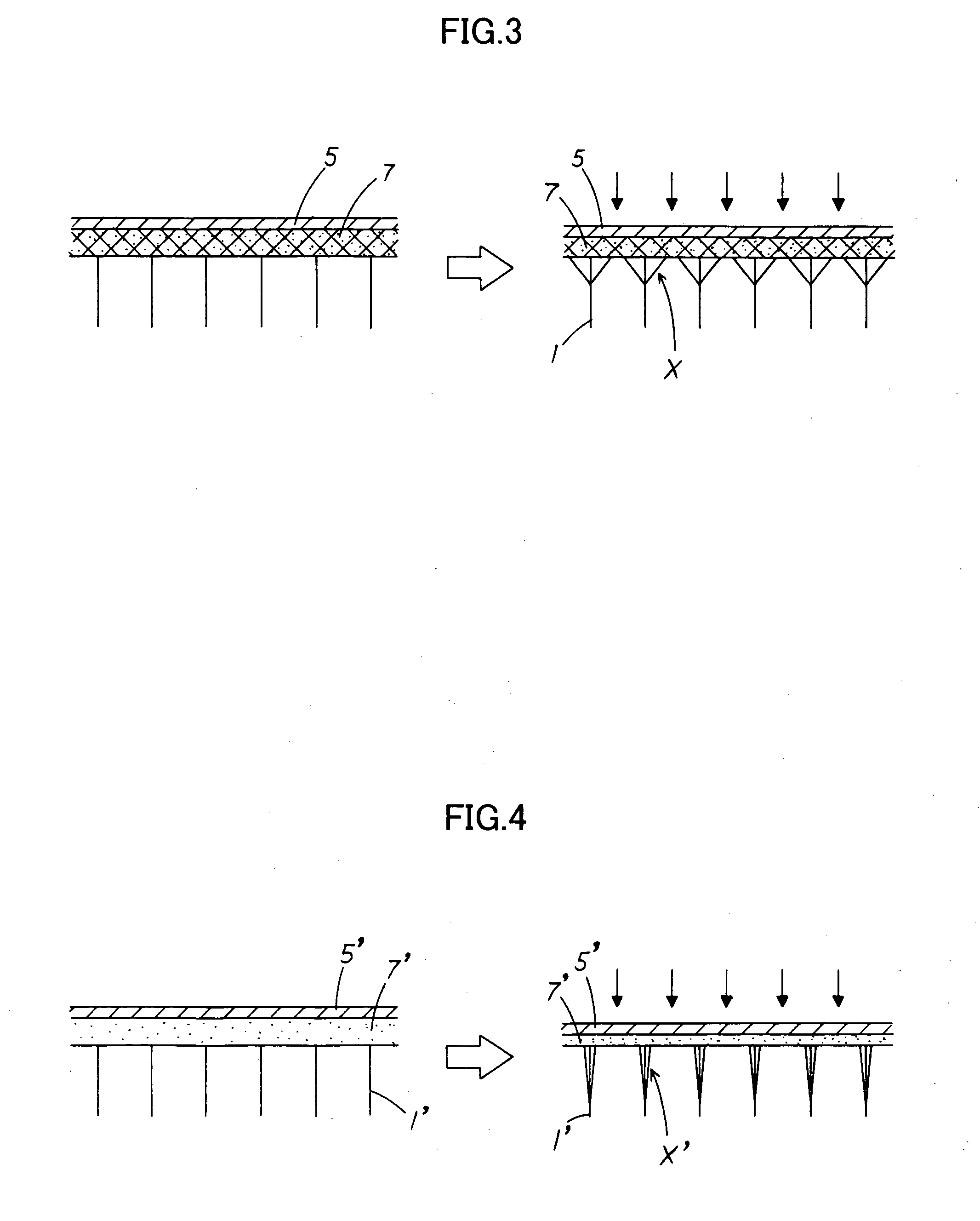
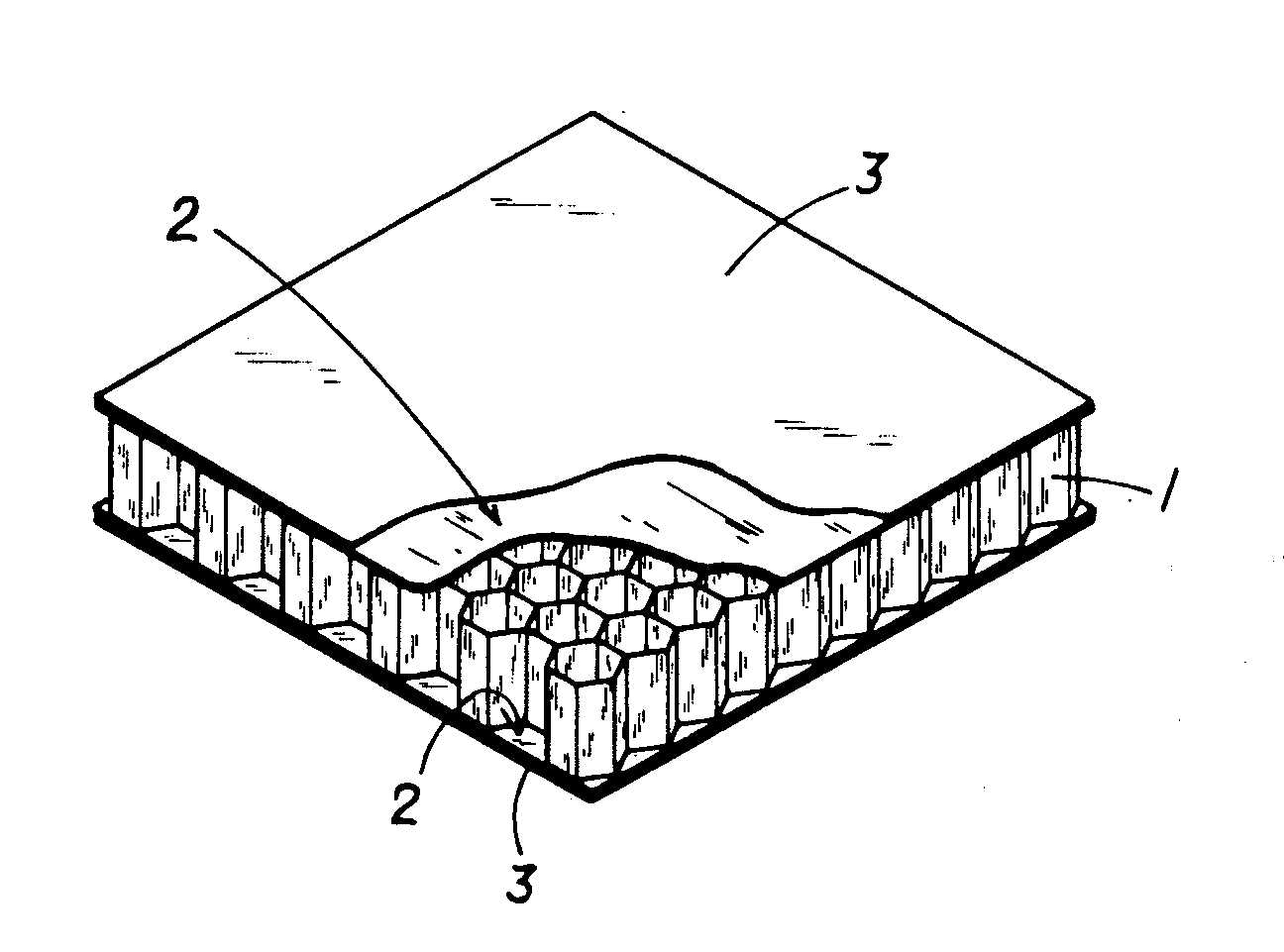
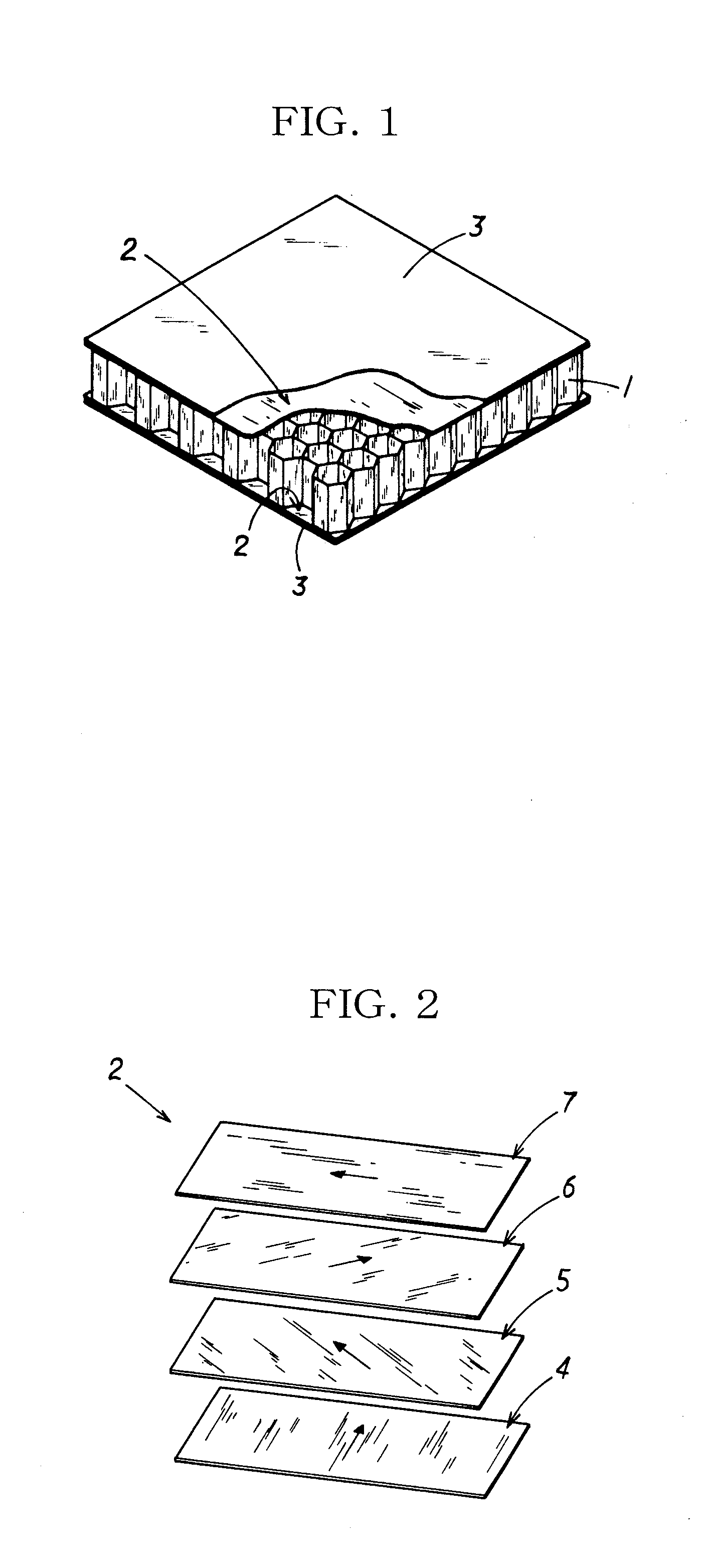
ActiveUS20080131645A1Improve practicalityReduce weightSynthetic resin layered productsBuilding componentsFiberSandwich board
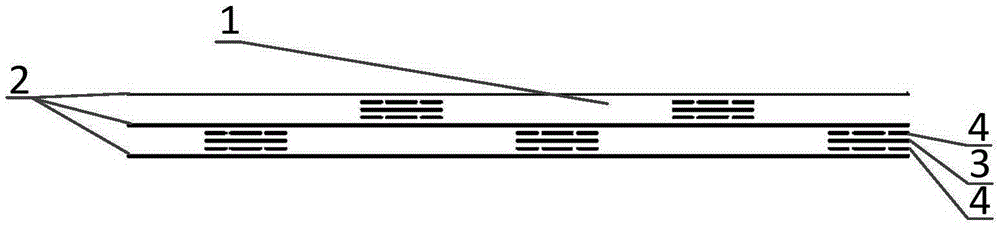
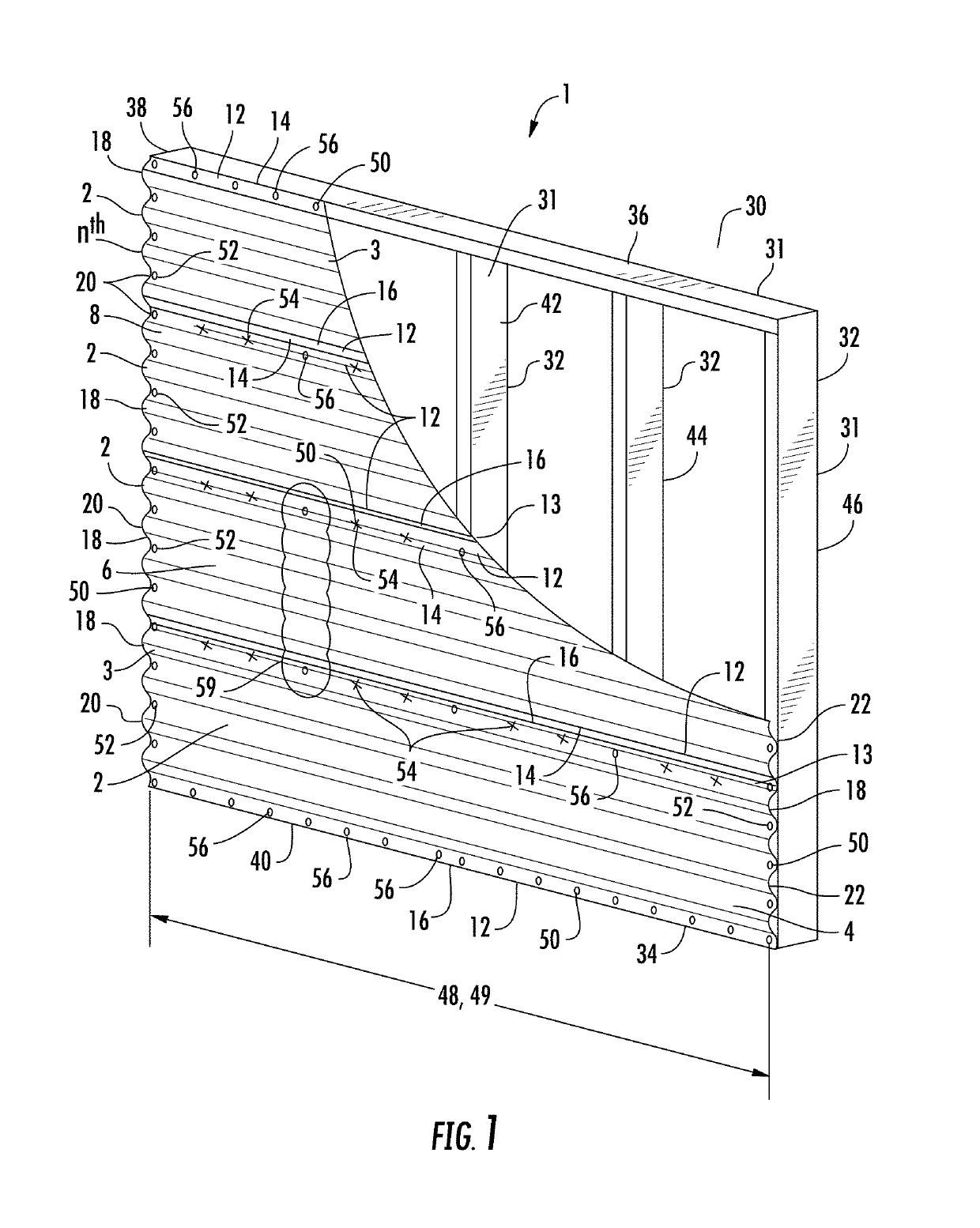
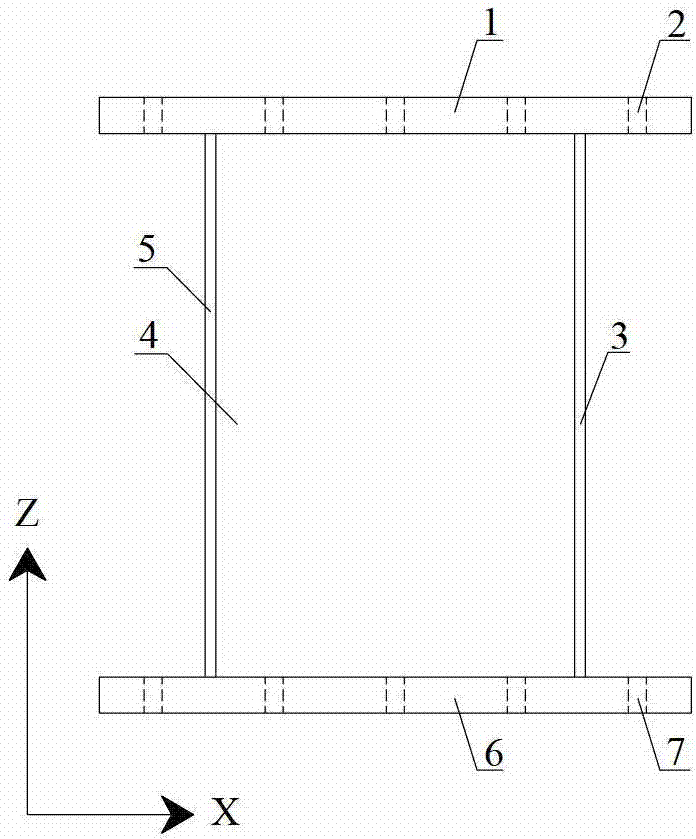
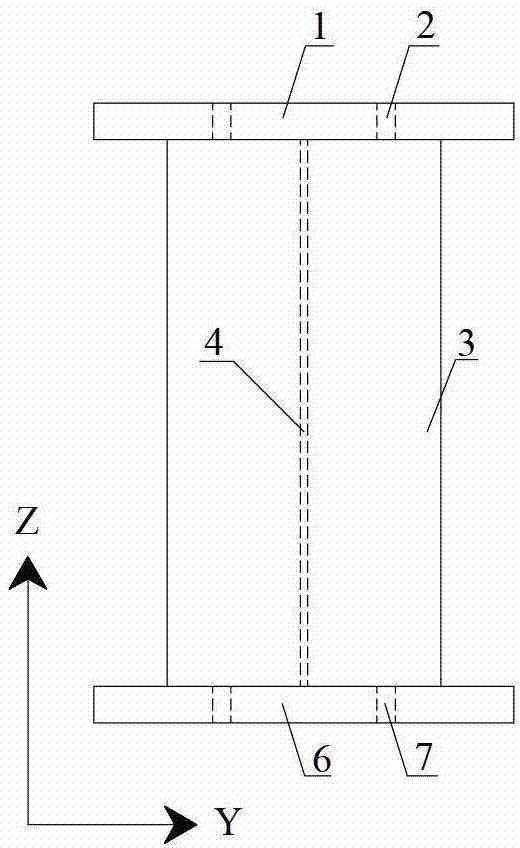
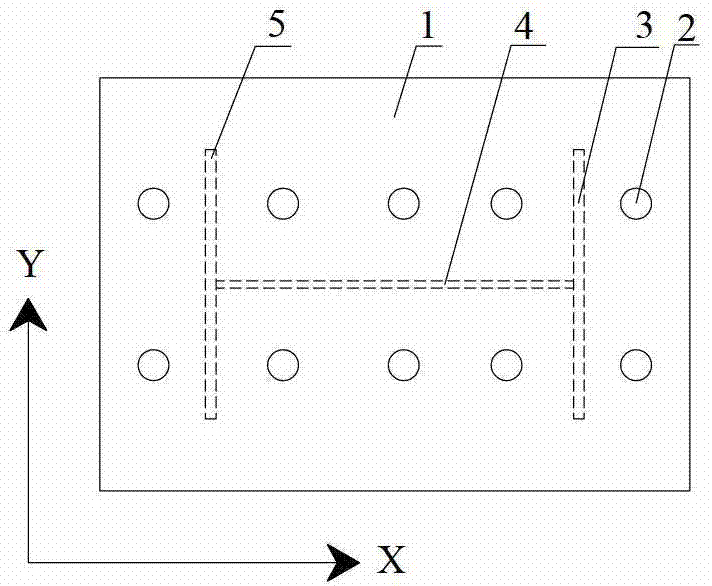
A sandwich panel that has excellent practicality as an inner wall material used in aircraft, for example, whereby the abovementioned requirements of flexural strength, peel strength, and in-plane shear strength can be satisfied while having reduced weight. A sandwich panel in which a middle material 2 and a surface material 3 that are each formed by laminating a plurality of fiber bodies are laminated from inside to outside on the upper and lower surfaces of a hollow columnar core 1, wherein the middle material 2 is composed of a set of unidireactional fiber bodies 4, 5 whose fibers are aligned in one direction, fibers in a first unidireactional fiber body 4 are in a direction that is substantially parallel to an edge of the sandwich panel, fibers in a second unidireactional fiber body 5 are in a direction that is substantially orthogonal to an edge of the sandwich panel, and bonding layers 6, 7 having a resin content ratio of 50% or higher are provided between the unidireactional fiber bodies 4, 5 and between the hollow columnar core 1 and an inside unidireactional fiber body 5.
Owner:JAMCO +1
Layer transfer of films utilizing controlled propagation
ActiveUS8293619B2Simplify the transfer processReduce energy costsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesSemiconductorSilicon
A film of material may be formed by providing a semiconductor substrate having a surface region and a cleave region located at a predetermined depth beneath the surface region. During a process of cleaving the film from the substrate, shear in the cleave region is carefully controlled to achieve controlled propagation by either KII or energy propagation control. According to certain embodiments, an in-plane shear component (KII) is maintained near zero by adiabatic heating of silicon through exposure to E-beam radiation. According to other embodiments, a surface heating source in combination with an implanted layer serves to guide fracture propagation through the cleave sequence.
Owner:SILICON GENERAL CORPORATION
Thermal - acoustic enclosure
An enclosure for apparatus that, during operation, generates heat and / or sound energy comprises at least one wall defining at least a portion of the enclosure hollow interior. The wall comprises in sequence outwardly from the enclosure hollow interior an inner panel, an outer panel, a support frame between the inner and outer panels to hold the inner and outer panels spaced apart, and a vibrator isolator between the support frame and the panels. Panels or panel segments of the wall primarily are made of non-metallic composites to provide a structurally strong, lightweight enclosure that includes enhanced acoustic characteristics and reduced heat transfer through enclosure walls, along with fire protection and in-plane shear loading capabilities.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method for observing rock and soil sample shear band inclination angle evolution rules under two types of formation conditions
InactiveCN104848838AFully automatedQuick measurementIncline measurementClassical mechanicsComputational physics
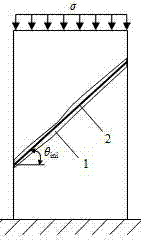
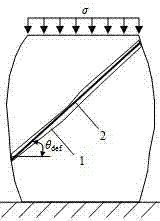
The invention provides a method for observing rock and soil sample shear band inclination angle evolution rules under original and real-time formation conditions. The method includes acquiring a digital image, comprising speckle surfaces, of a sample by shooting devices under a loading condition; by a digital image correlation method, acquiring maximum shear strain fields of the sample under the original and real-time formation conditions; by an interpolation method, acquiring maximum shear strain fields good in smoothness in an area comprising measured shear bands; deleting redundant data according to roughly-estimated widths and inclination angles of the measured shear bands to acquire positions of all points on center lines of the measured shear bands, and acquiring inclination angles of planer shear bands and spatial shear bands by a fitting method. The method has the advantages that the rules that the shear band inclination angles evolve according to stress, strain and time under the original and real-time formation conditions can be acquired; automated, rapid and accurate measurement of the shear band inclination angles can be achieved; the method is suitable for measuring the inclination angles of plane inclination strain concentration bands and spatial shear planes of various materials.
Owner:LIAONING TECHNICAL UNIVERSITY
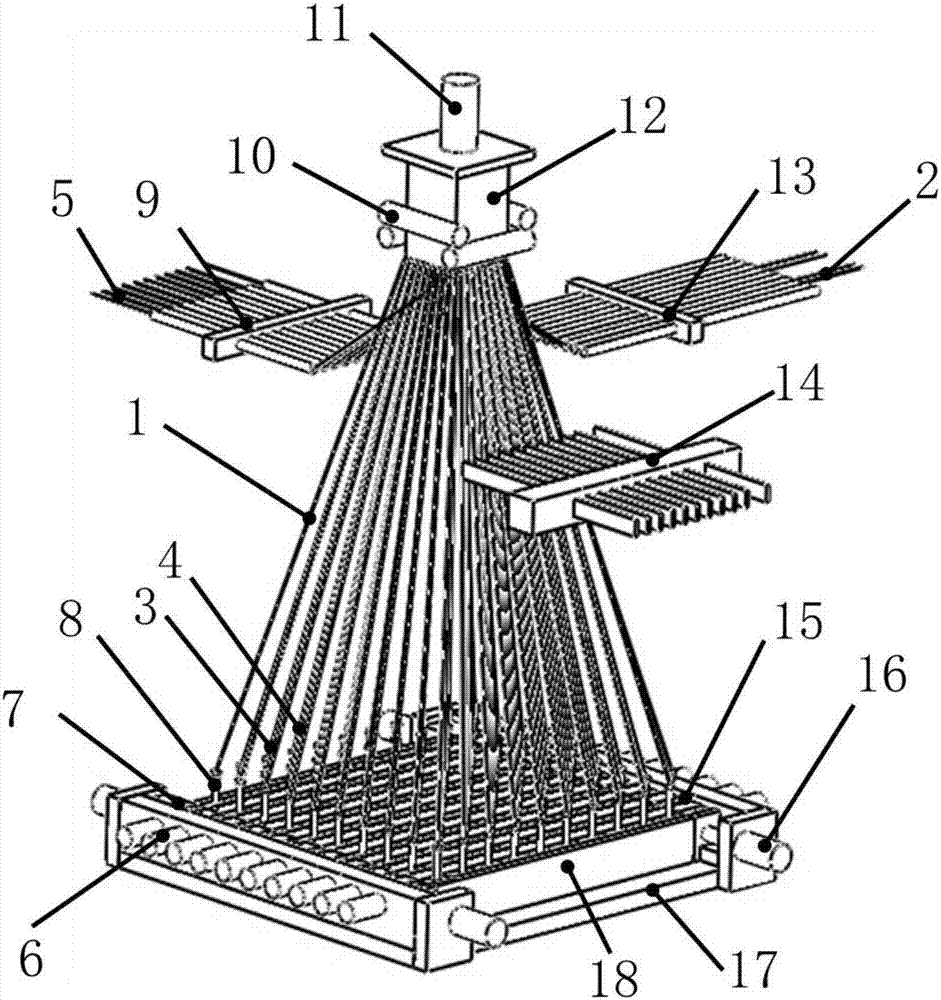
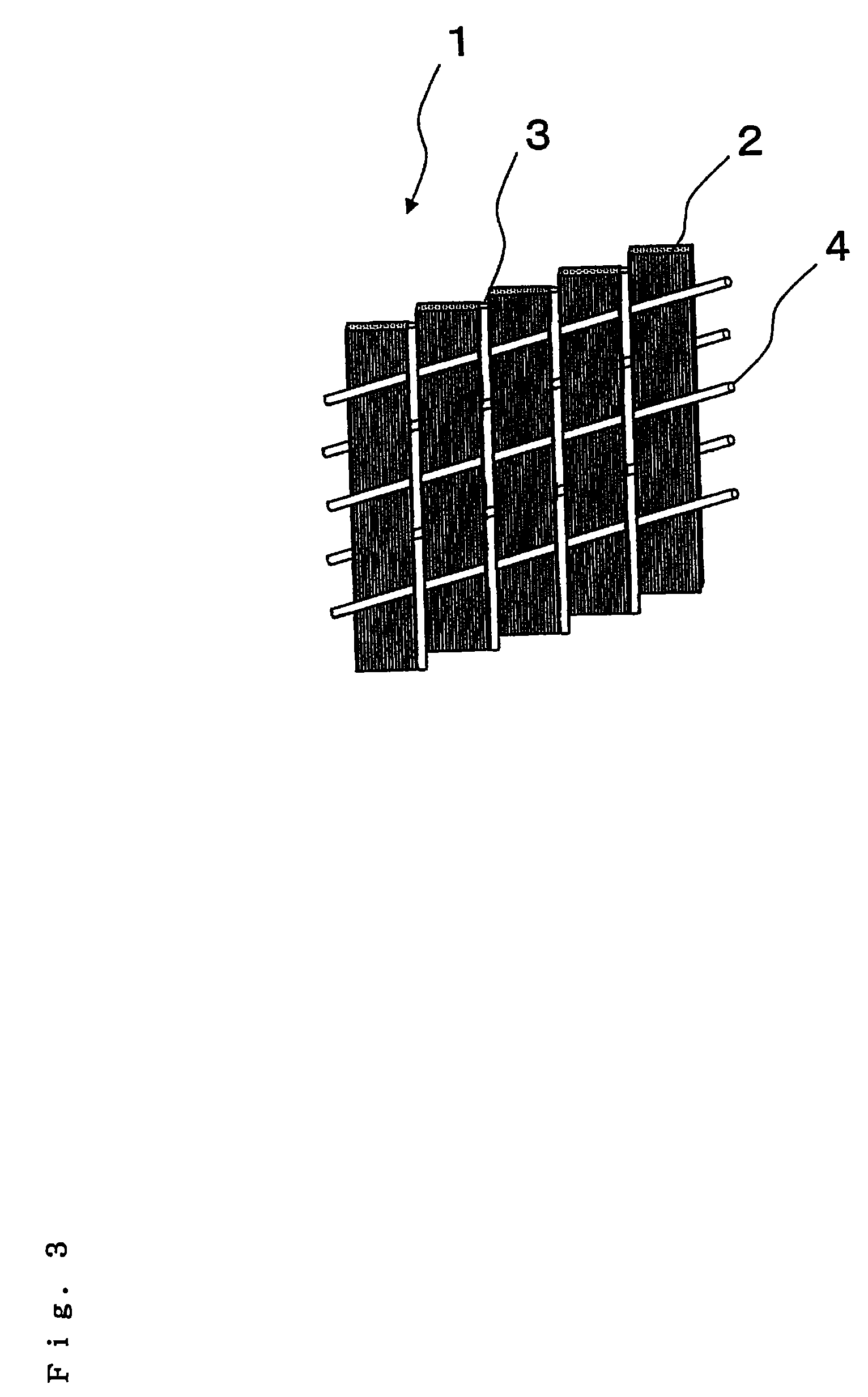
Weaving method for multi-layer and multi-direction fabric
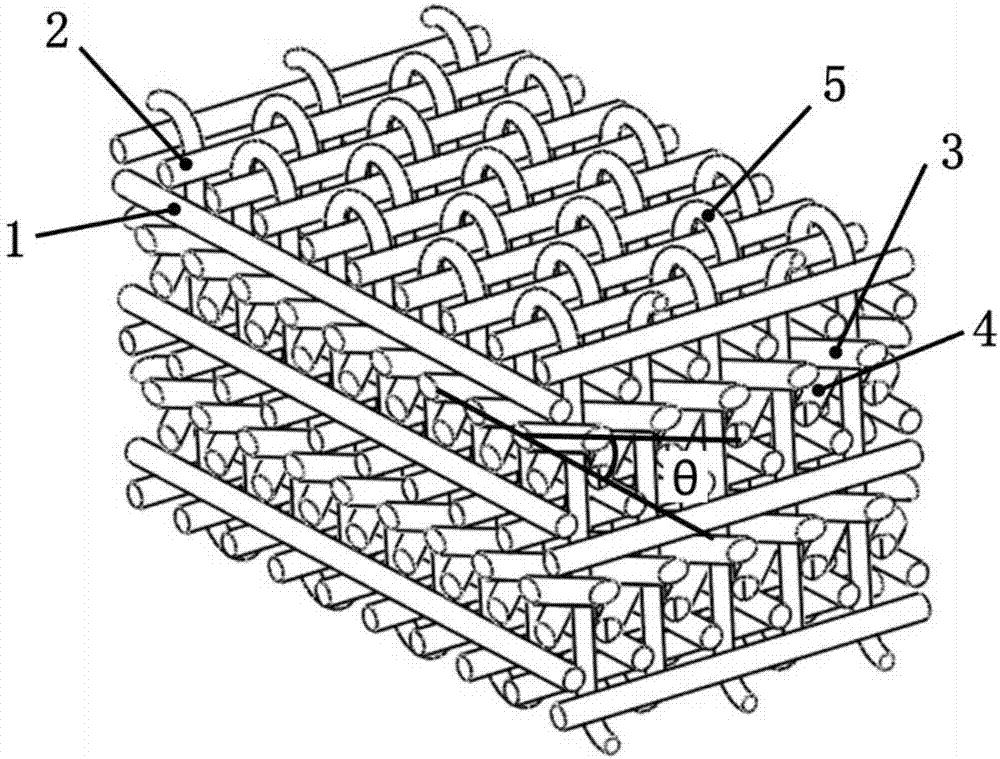
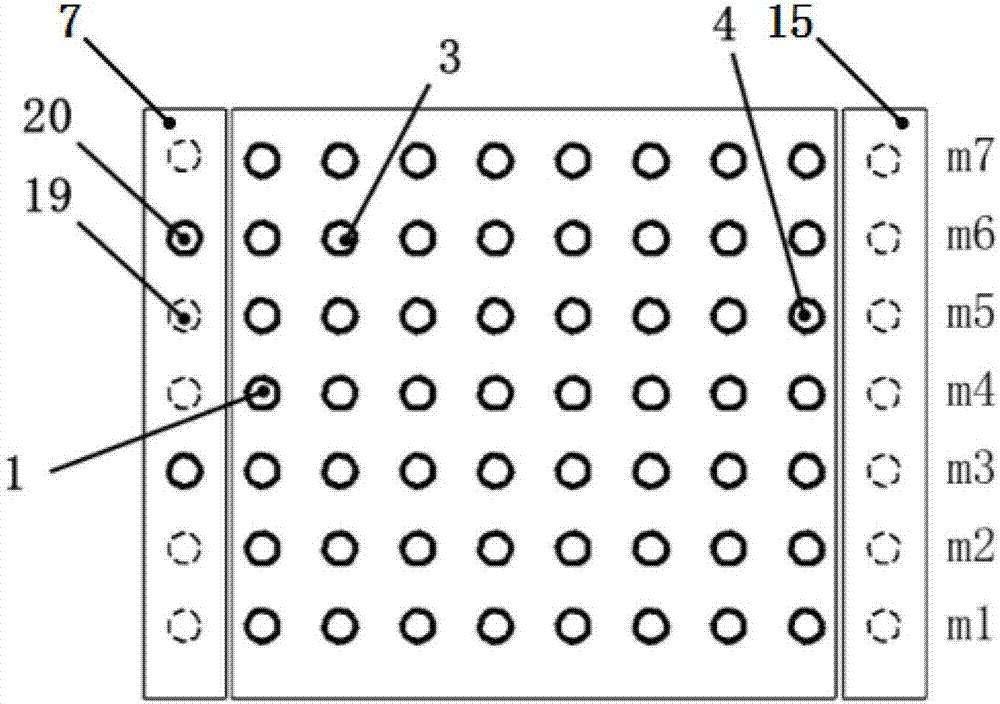
ActiveCN106939462ASolve the problem of controllable adjustment of tilt angleImproved in-plane shear performanceMulti-ply fabricsEngineeringOblique angle
The invention discloses a weaving method for a multi-layer and multi-direction fabric, characterized in that the weaving method comprises following steps: (1) arranging main yarn; (2) arranging oblique yarn and side yarn; (3) moving the oblique yarn; (4) introducing normal yarn; (5) introducing weft yarn; (6) compressing yarn; and (7) repeating the steps (3) to (6) until a target length of the fabric i.e., the multi-layer and multi-direction fabric is obtained. The weaving method for the multi-layer and multi-direction fabric can flexibly design the arrangement of an oblique yarn layer in the fabric, which solves the problem that control and adjustment on an oblique angle of the oblique yarn is difficult, and is conductive to the improvement of in-plane shear properties of composites. Moreover, the method has advantages of easy operation, high production efficiency, and stable process, and can meet demands of low cost production of high-performance composites.
Owner:TIANJIN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
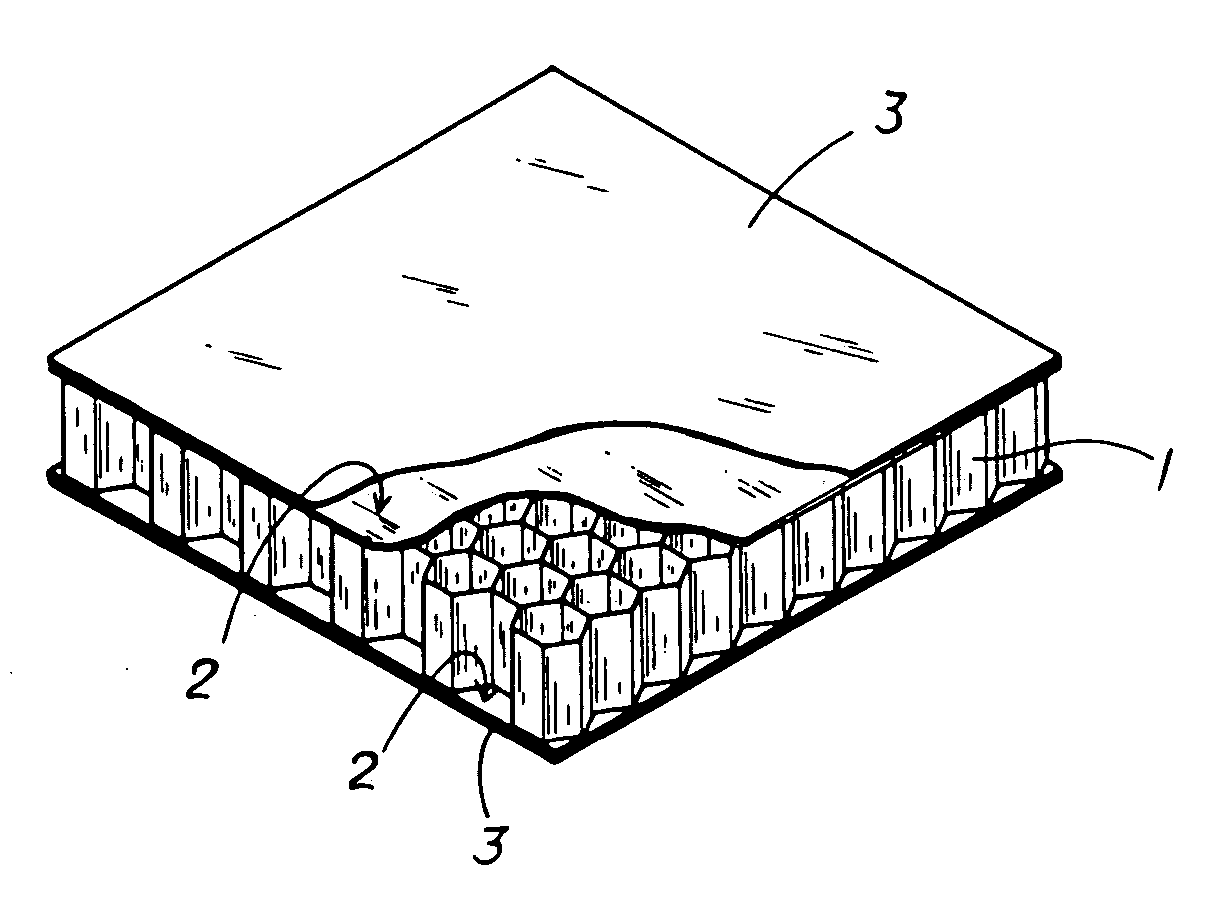
Thin slab layer for formation of honeycomb structure, honeycomb structure and preparation method thereof
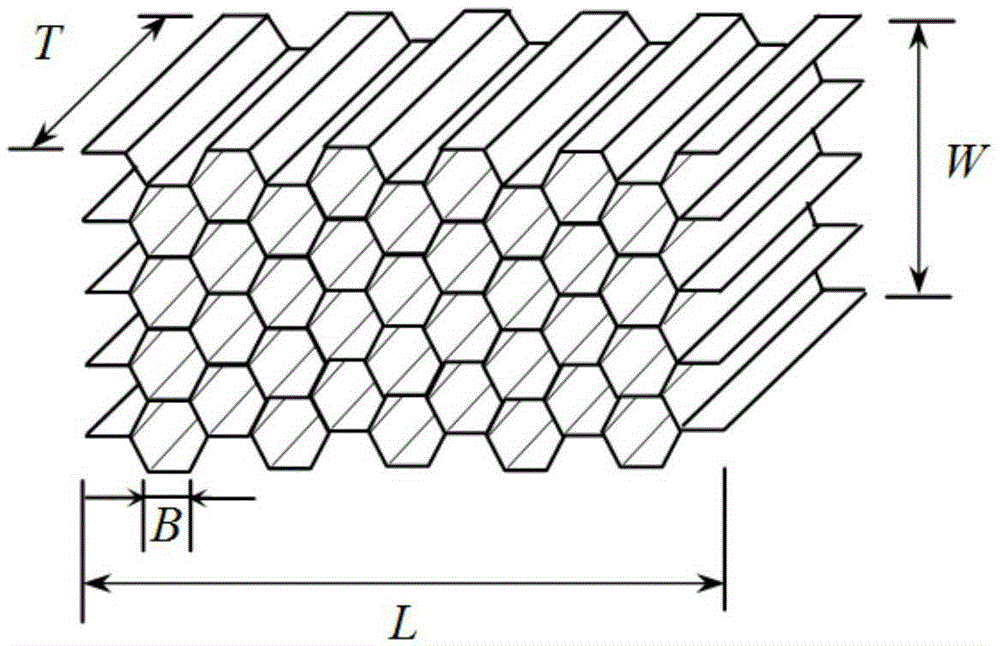
The invention provides a thin slab layer which enhances through a strengthening layer such as carbon fiber or a functional material and is used for formation of a honeycomb structure, a honeycomb structure and its preparation method. According to the honeycomb structure, a strengthening layer of cell wall width is glued at the place where the honeycomb cell walls are glued with each other, so as to achieve the following effects: under the circumstance of not increasing the honeycomb structural cell density, plane compression strength / modulus and in-plane shear strength / modulus of the honeycomb structure are greatly raised, honeycomb structure compression amount during the honeycomb structure forming process is greatly reduced, and process window for honeycomb structure formation is expanded so as to ensure that the appearance of a honeycomb structural product is more accurate; and under the circumstance of not increasing the honeycomb structural cell density, functions of the honeycomb structure are increased: if the strengthening layer is carbon fiber cloth, heat-conducting property of the honeycomb structure is enhanced; and if the strengthening layer is a wave-absorbing material, absorbing property of the honeycomb structure is improved.
Owner:北京金轮沃德科技有限公司
Positioning system and method of spacecraft subjected to space junk collision
ActiveCN106645406AQuick responseSmall amount of calculationAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesSensor arrayEngineering
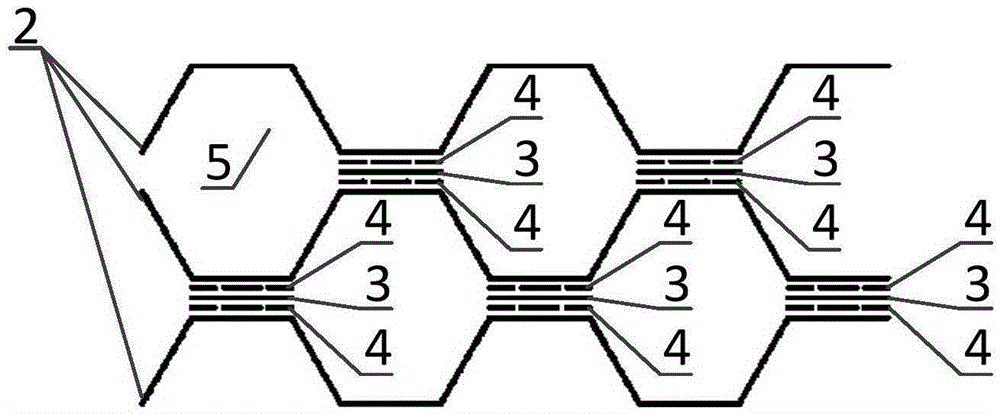
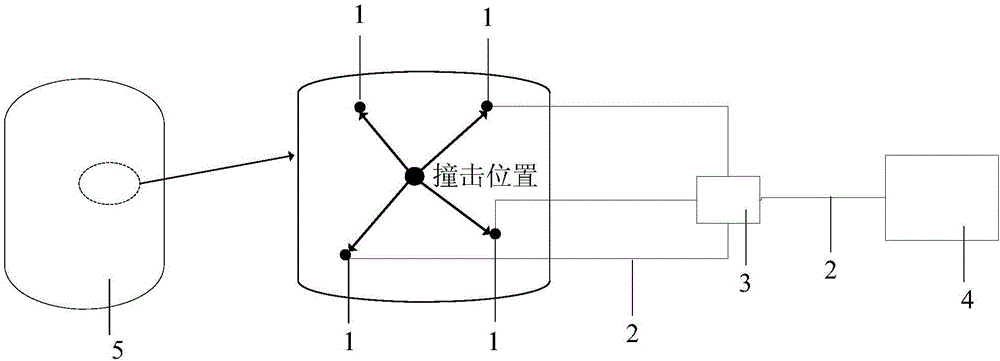
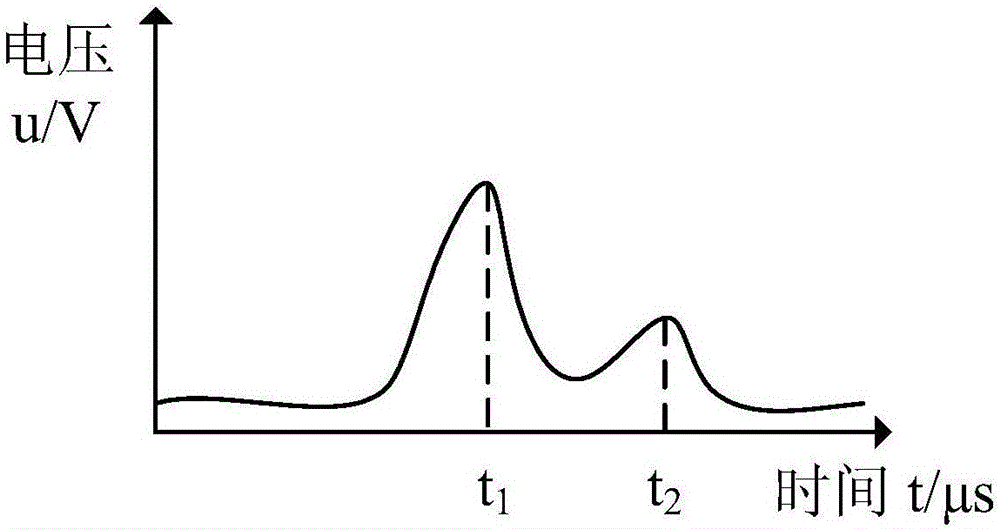
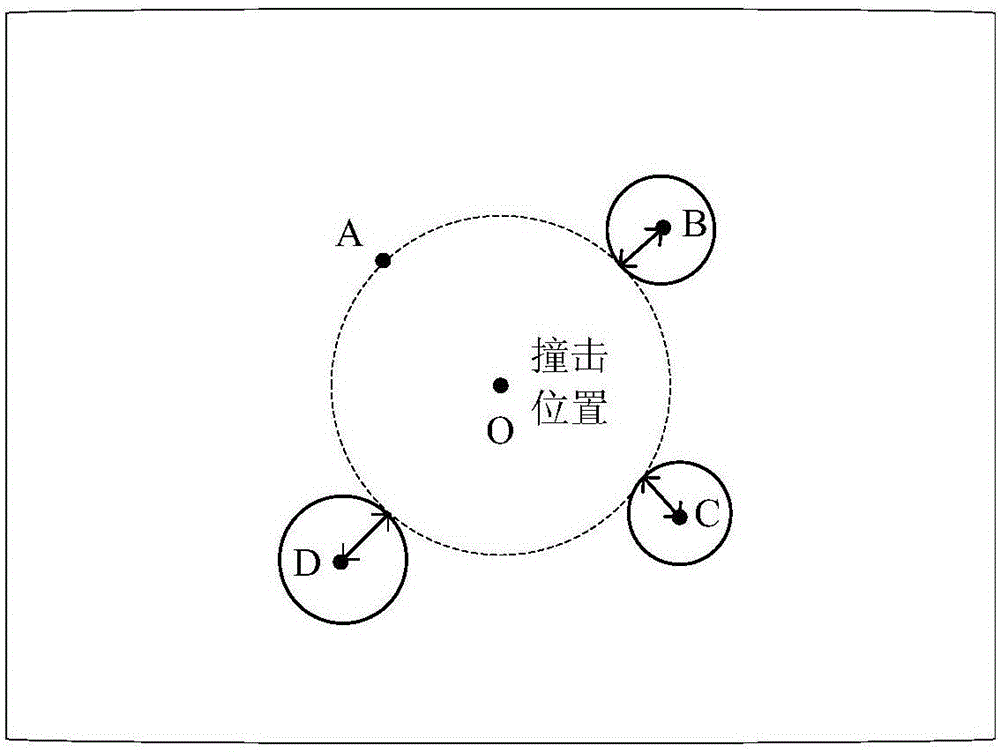
The invention provides a positioning system and method of a spacecraft subjected to space junk collision. The positioning system comprises in-plane shearing wave piezoelectric sensors (1), a data transmission line (2), a charge amplifier (3) and a data processing unit (4), wherein the in-plane shearing wave piezoelectric sensors (1) are glued and fixed on an inner surface of a spacecraft structure (5); a sensor array is composed of the plurality of in-plane shearing wave piezoelectric sensors (1) and the in-plane shearing wave piezoelectric sensors (1) are connected with the charge amplifier (3) through the data transmission line (2); and the charge amplifier (3) is connected with the data processing unit (4) through the data transmission line (2). After collision occurs, the data processing unit (4) is used for acquiring data of the in-plane shearing wave piezoelectric sensors (1) in real time, and the positioning system is used for carrying out collision positioning of space junks through in-plane shearing wave SHO (Super High Output) wave and a four-point geometric positioning method, so that high-precision positioning of a collision position can be realized.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF SPACECRAFT SYST ENG
Layer transfer of films utilizing controlled shear region
ActiveUS9362439B2Limit regionReduce developmentSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMetal working apparatusEngineeringThermal treatment
Owner:SILICON GENERAL CORPORATION
Structural systems with improved sidelap and buckling spans
ActiveUS10370851B2Improve ductilityHigh strengthRoof covering using slabs/sheetsConstruction materialEngineeringUltimate tensile strength
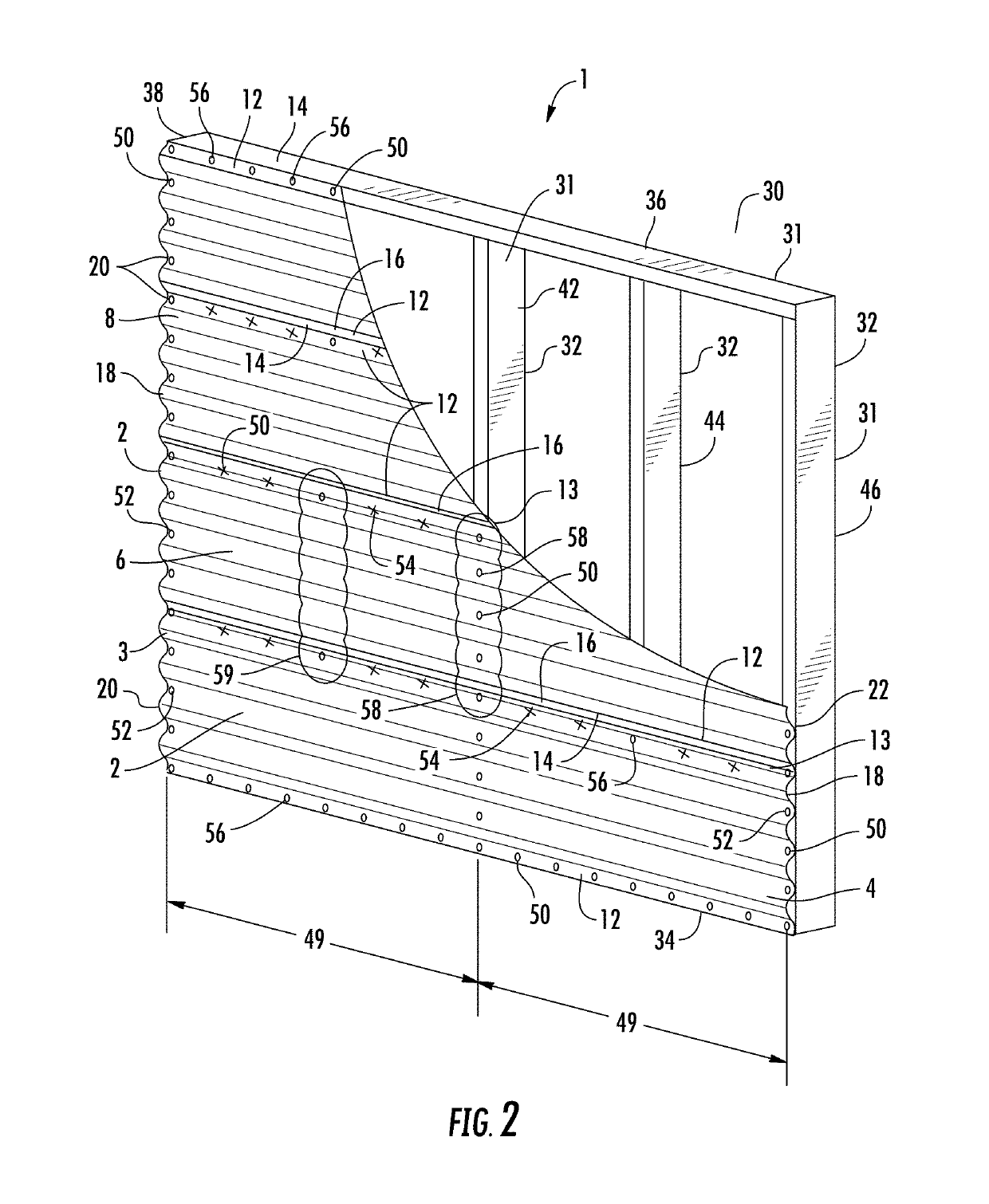
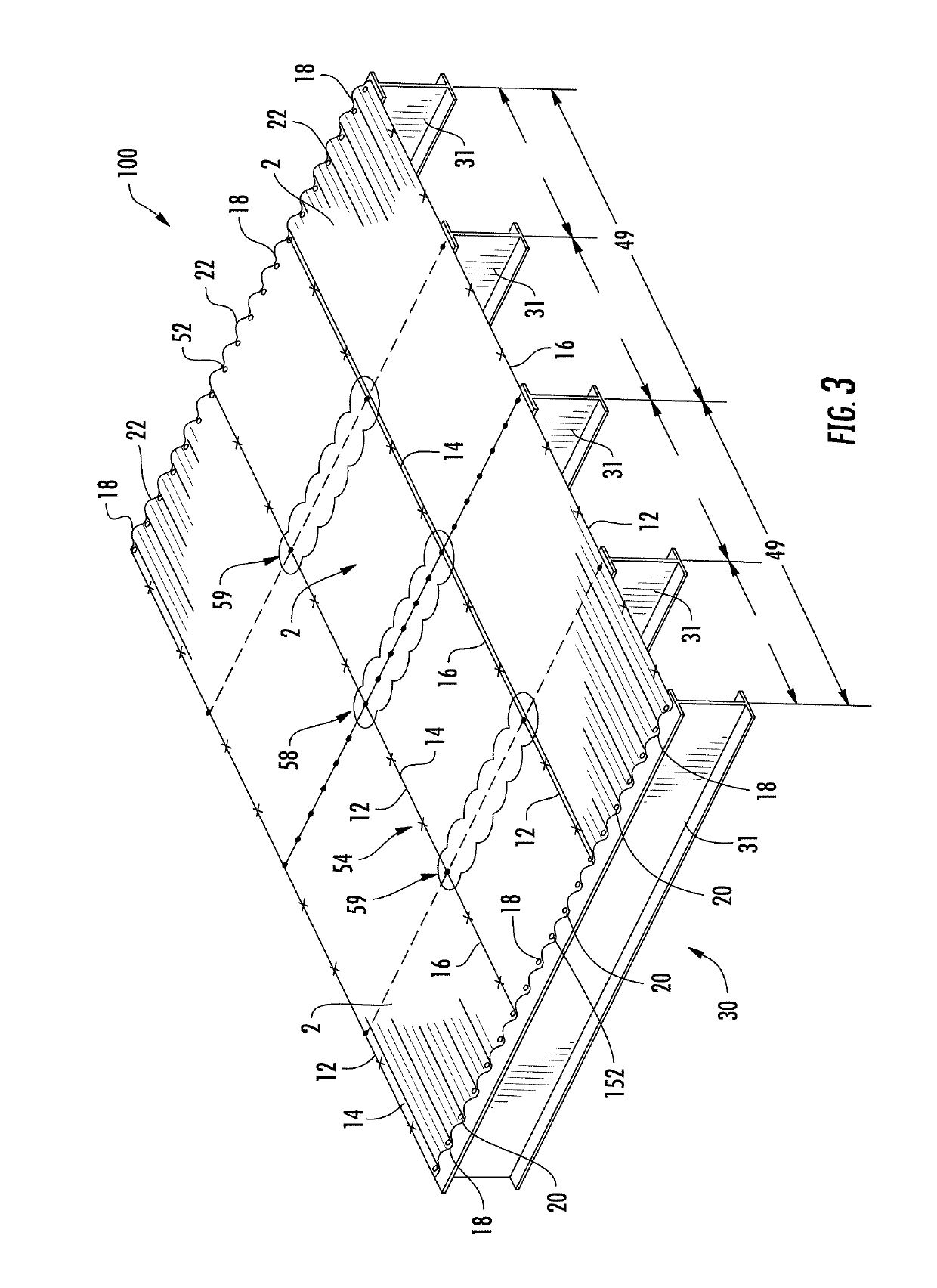
The invention relates to structural panel systems which utilize different configurations to increase the flexibility of the panel systems. The increased flexibility of the panel systems may be achieved through the use of improved connection patterns and / or improved sidelap strength. The improved sidelap strength may be achieved through the use of a reinforcing member between edges of the panels or other sidelap configurations that improve the strength of the system along the sidelaps. The increased flexibility may also be achieved through the use of orienting flutes of the panels in the same direction as the supports members of the panel systems. The different aspects of the invention that improve the flexibility of the systems may be utilized alone or in combination with each other to improve the wall panel systems or roof panel systems, or combinations thereof, to improve the displacement capacity of the panel systems for in-plane shear loading.
Owner:NUCOR CORP
Smart soft composite actuator
ActiveUS20150001994A1Large deformationSimple structureMicromanipulatorPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesEngineeringActuator
Disclosed is a smart soft composite actuator which enables user-desiring deformation by changing the position of smart material functioning as an active component, wherein the smart soft composite actuator comprises a smart material whose shape is changeable based on an external signal; and a matrix for supporting the smart material and determining an external shape, wherein the smart material is positioned inside the matrix or in a surface of the matrix, and at least one of in-plane shear deformation and out-of-plane deformation is realized by controlling the position of smart material.
Owner:SEOUL NAT UNIV R&DB FOUND
Sandwich panel
ActiveUS20100035018A1Improve practicalityReduce weightSynthetic resin layered productsCeramic layered productsFiberYarn
A sandwich panel that has excellent practicality as an inner wall material used in aircraft, for example, whereby the abovementioned requirements of flexural strength, peel strength, and in-plane shear strength can be satisfied while having reduced weight. A sandwich panel in which a middle material 2 and a surface material 3 that are each formed by laminating a plurality of fiber bodies are laminated from inside to outside on the upper and lower surfaces of a hollow columnar core 1, wherein the middle material 2 is composed of a set of unidirectional fiber bodies 4, 5 whose fibers are aligned in one direction, bonding layers 6, 7 having a resin content ratio of 50% or higher are provided between the unidirectional fiber bodies 4, 5 and between the hollow columnar core 1 and an inside unidirectional fiber body 5, the bonding layer 7 is composed of a woven fiber body 7 in which fibers are used for a warp yarn and a woof yarn that is orthogonal to the warp yarn, and the yarns are woven, and the woven fiber body 7 is formed so that any one of the warp yarn and the woof yarn is substantially parallel to the edge of the sandwich panel, and the other of the warp yarn and the woof yarn is substantially orthogonal to the edge of the sandwich panel.
Owner:JAMCO +1
Sandwich panel
ActiveUS20080318000A1Improve flexural strengthAdequate strength in-plane shear strengthLayered productsVehicle componentsYarnSandwich board
There is provided a lightweight sandwich panel of exceptional utility, which satisfies the flexural strength and in-plane shear strength requirements for an inner wall material used in aircraft. The sandwich panel comprises a laminating material in which a plurality of fiber bodies_is laminated, and a surface material, the laminating material and the surface material being laminated in the stated order from the inside to the outside on the upper and lower surfaces of a hollow columnar core. The laminating material comprises at least four unidirectional fiber bodies each of which has fibers aligned in a uniform direction and is laminated so that each of the fiber directions thereof is at approximately 0 , +45°, −45°, and 90°, respectively, in relation to one edge of the sandwich panel. The unidirectional fiber bodies are stitched together using a stitching yarn.
Owner:JAMCO +1
Reinforcing fiber base material for preforms, process for the production of laminates thereof, and so on
ActiveUS8236410B2Excellent characteristicsGood drapabilitySynthetic resin layered productsFibre chemical featuresYarnVitrification
The invention provides (1) a reinforcing fiber base material having a weave constituted of both reinforcing fiber filaments arranged in one direction in parallel with each other and auxiliary yarns arranged in another direction, which satisfies the relationship: L=H / cos θ (wherein L is the length of auxiliary yarn covering one reinforcing fiber filament and H is the width of the filament as determined in such a state where the reinforcing fiber filaments are unified only with the auxiliary yarns; and 3°≦θ (in-plane shear strain)≦30°) and wherein 2 g / m2 to 40 g / m2 of an adhesive resin having a glass transition temperature between 0° C. and 95° C. is adhesed to at least one side thereof in spots, lines, or discontinuous lines; (2) a laminate obtained by laminating layers of the above reinforcing fiber base material, wherein the adhesive resin adhesed to each layer of base material partially bonds to a facing layer of base material over the whole surface thereof, with the maximum length of each bonding joint being not less than 1 mm and not more than the width H of a reinforcing fiber filament; and (3) a preform, obtained by shaping the laminate, having a reinforcing fiber volume fraction (Vpf) of 45% to 62%.
Owner:TORAY IND INC
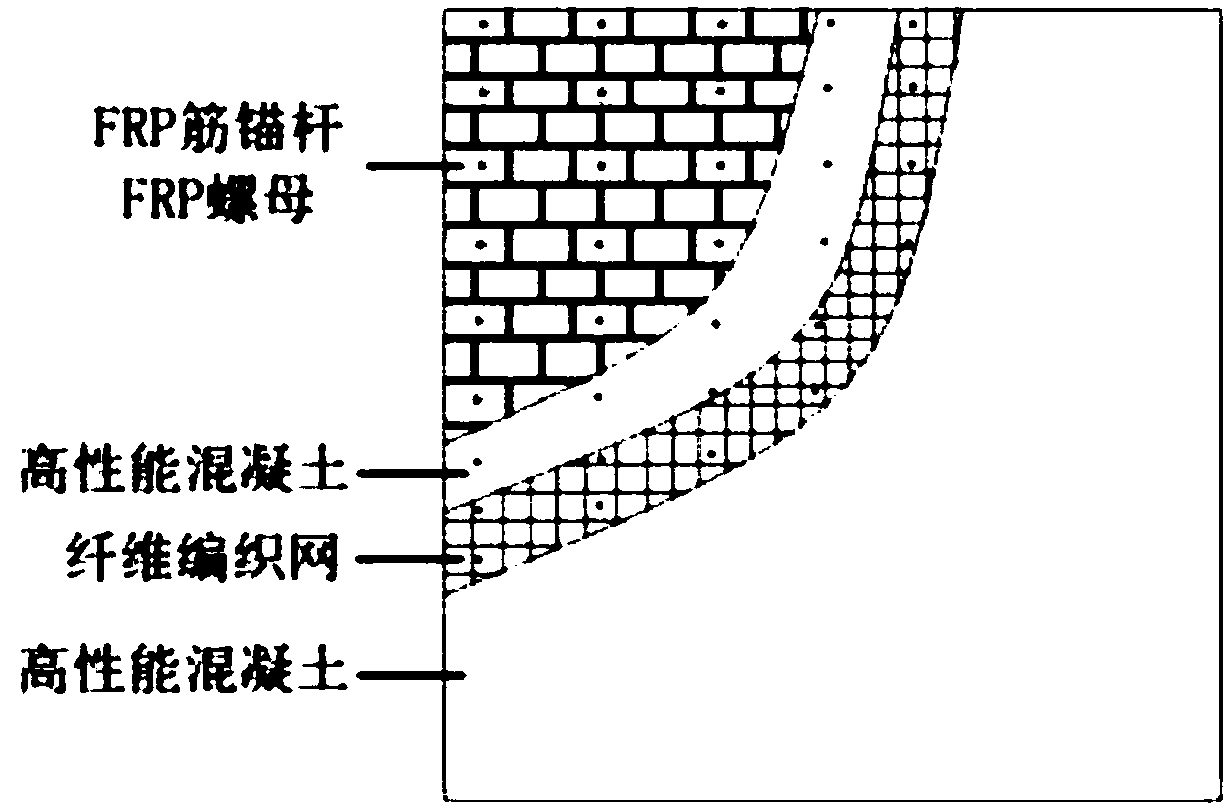
Reinforcement method of TRC for improving anti-seismic performance of multi-piece brick masonry wall
InactiveCN108532981AImprove seismic performanceImprove shear resistanceClimate change adaptationBuilding repairsFiberBrick masonry
The invention discloses a reinforcement method of TRC for improving an anti-seismic performance of multi-piece brick masonry wall, and belongs to the technical field of repair, reinforcement and construction of masonry walls. The reinforcement method comprises the steps that a plurality of penetrating circular holes are drilled in the wall to be reinforced, and fiber reinforced plastic (FRP) rib anchor rods are used for penetrating through the circular holes; the surface of the wall to be reinforced is coated with high-performance concrete, a fiber woven net is impregnated with epoxy resin, and the surface of the fiber woven net is coated with the high-performance concrete again; If one layer of fiber woven net can not meet the requirement of wall anti-seismic performance improvement, twoor more layers of fiber woven nets can be laid; and wet water curing is carried out until the high-performance concrete age is reached. According to the reinforcement method of TRC for improving the anti-seismic performance of the multi-piece brick masonry wall, in-plane shear resistance and out-of-plane bending resistance of the multi-piece brick masonry wall are improved, the risk of serious damage or even collapse of a masonry structure in earthquake is reduced, the inadaptability of a masonry material caused by the use of the epoxy resin in FRP reinforcement is avoided, deficiency of low reinforcement efficiency of engineered cementitious composite (ECC) reinforcement is effectively improved, and the integrity of multi-piece brick masonry wall is improved.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH
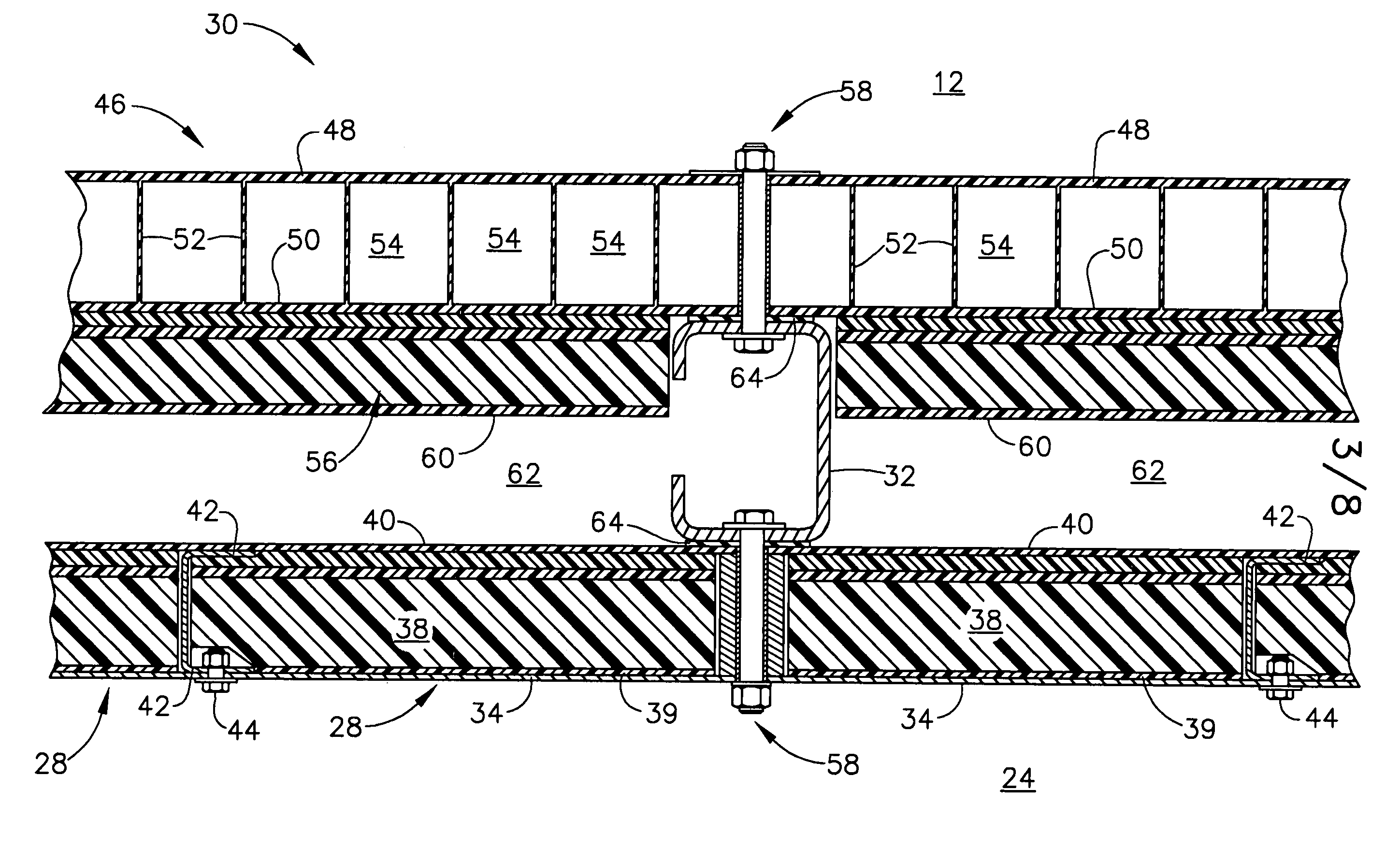
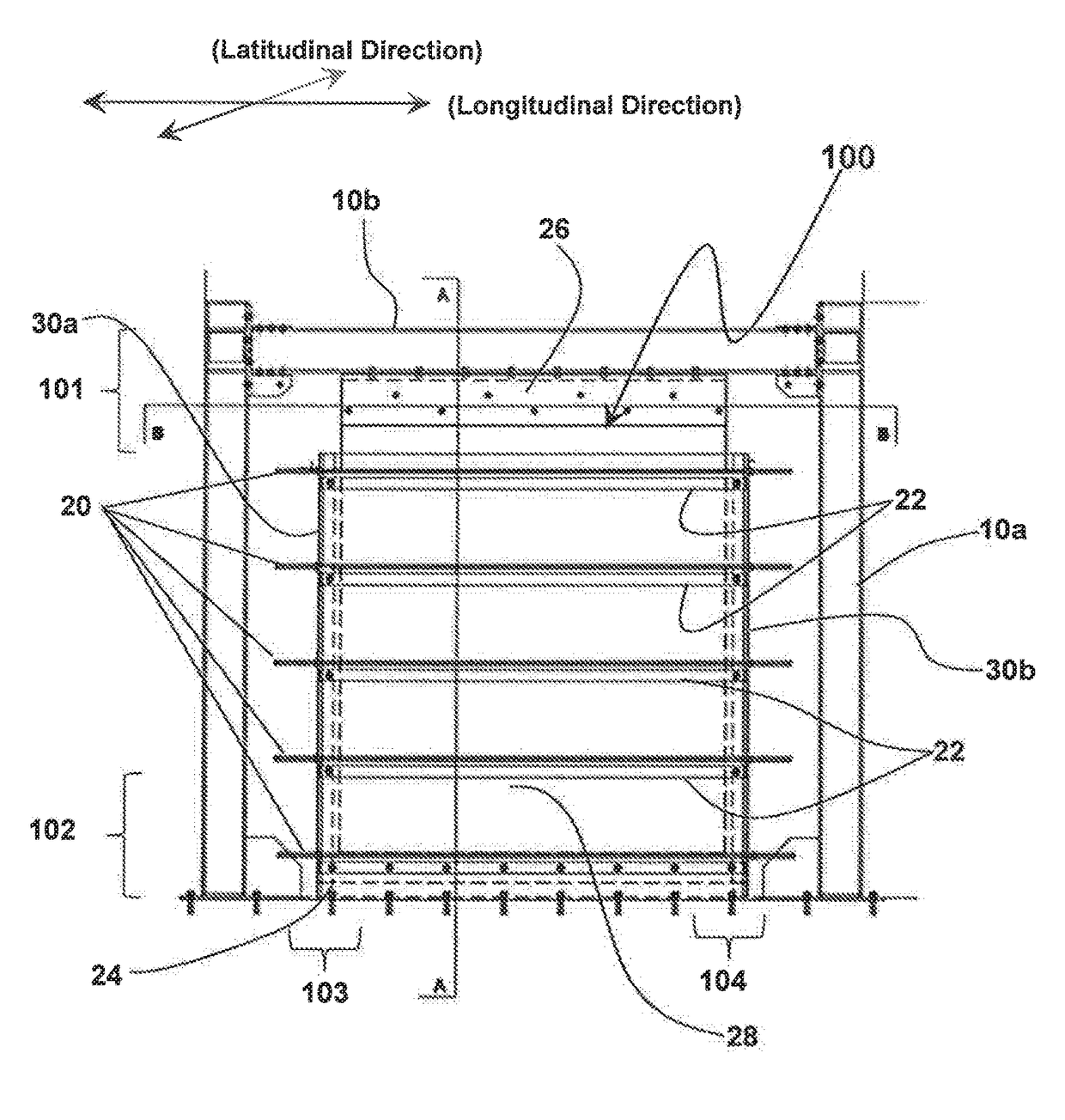
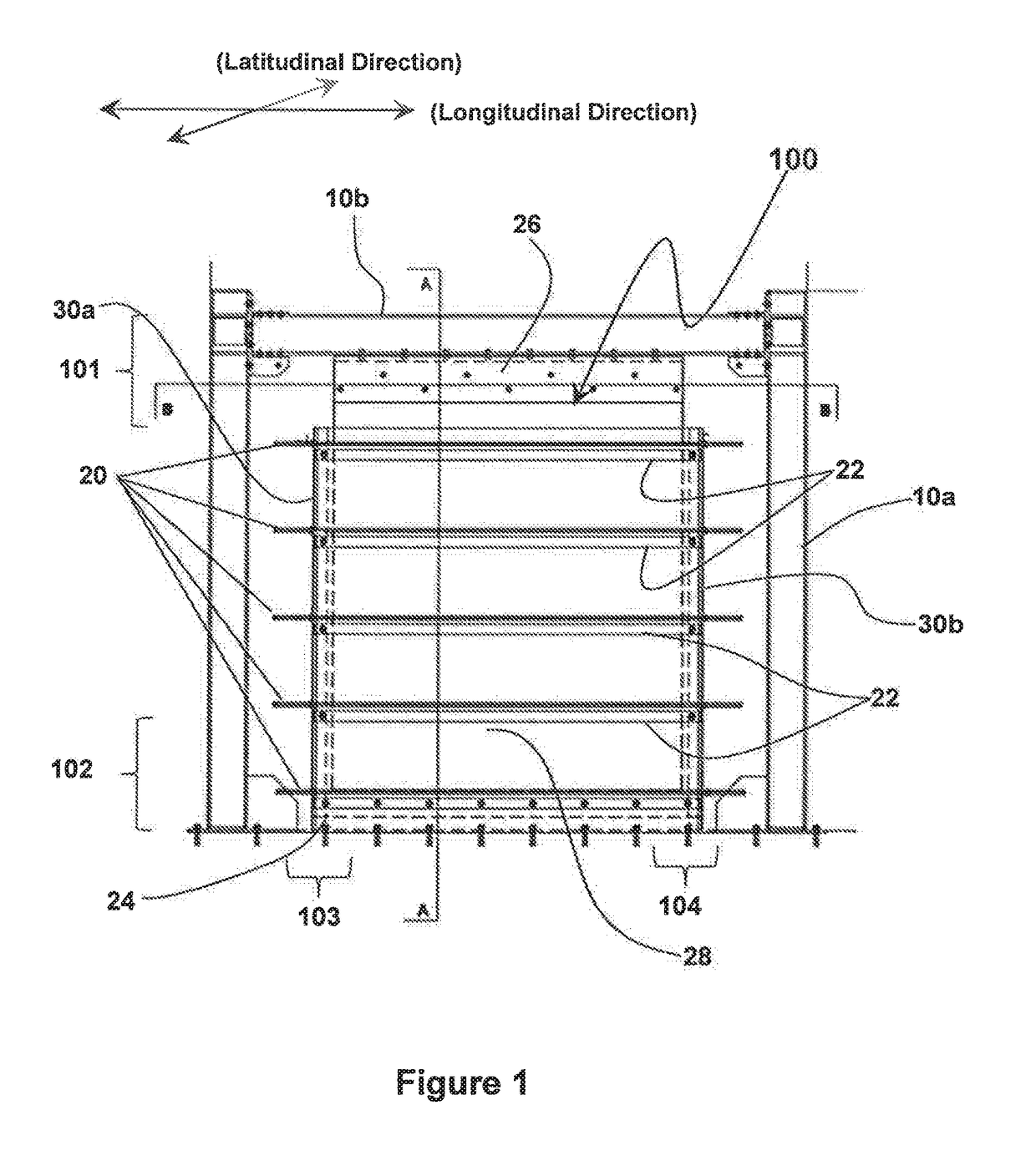
Wall panel damping device
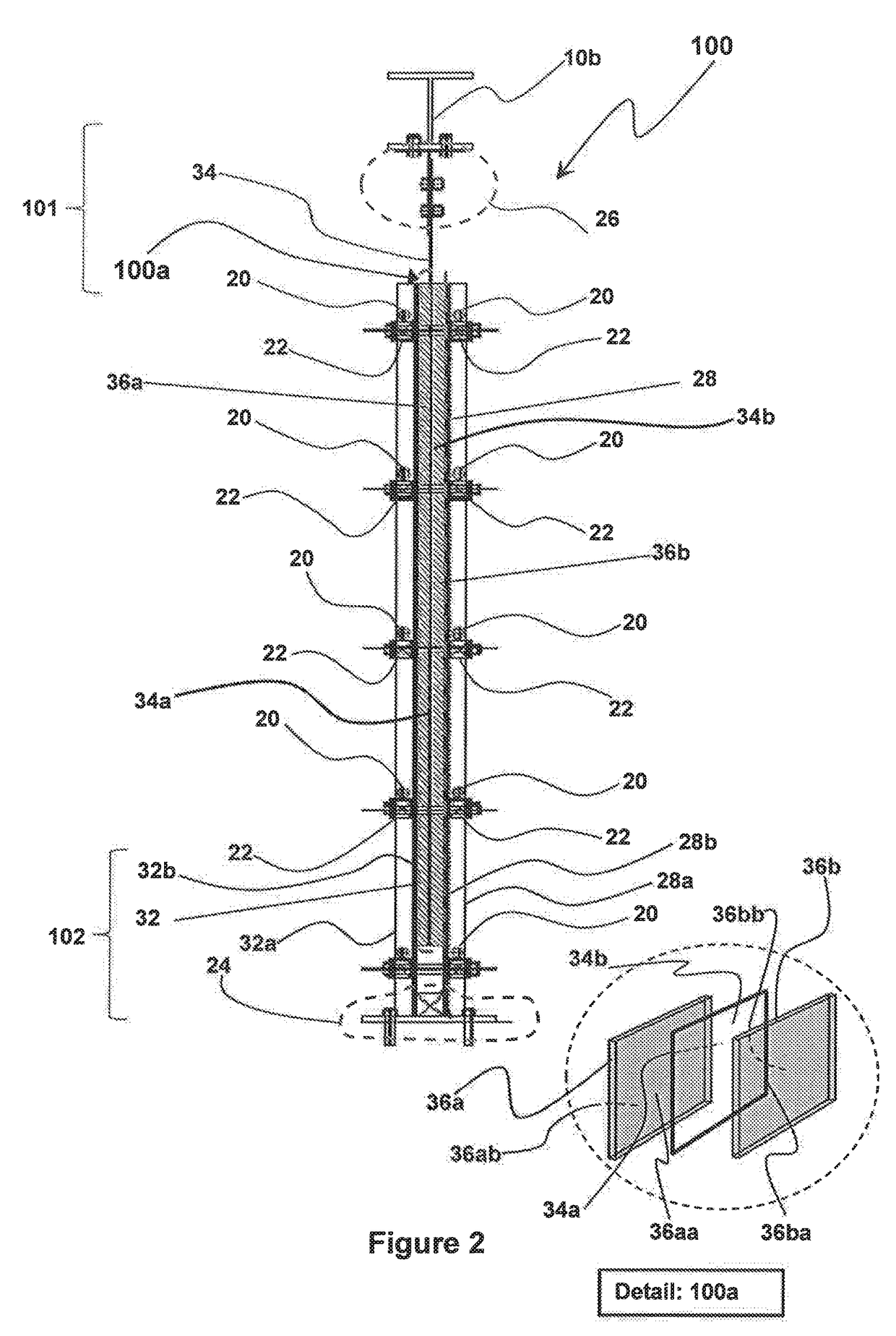
The present invention provides a viscoelastic wall panel damping device (100) that provides damping against multidirectional reacting dynamic loads that include in-plane shear force resistance and out of plane force resistance. The viscoelastic wall panel damping device (100) of the present invention, including an assembly (100a) having a pair of symmetrically opposing surfaces formed by a pair of damping element planar members (36a, 38b) that sandwiches a rigid planar member (34), The assembly (100a) being over-laid by a pair of face plates (28, 32), a proximal face plate (28) and a distal face plate (32). Aforementioned pair of face plates (28, 32) and the rigid planar member (34) of the assembly (100a) having a plurality of vertically oriented stiffener members (33) comprising of vertically oriented welded strips (33a) of steel disposed with stiffener elements (33b) at spatial intervals along the length of said welded strips of steel (33a). Aforementioned pair of face plates (28, 32) further being disposed at respective outer surfaces (28a, 32a) with a plurality of horizontal stiffener members (22).
Owner:UNIVERSITI PUTRA MALAYSIA
Bidirectional energy dissipating soft steel energy dissipater
The invention discloses a bidirectional energy dissipating soft steel energy dissipater. The bidirectional energy dissipating soft steel energy dissipater comprises a core energy dissipating component which comprises three rectangular energy dissipating steel plates forming an I-shaped structure, the three rectangular energy dissipating steel plates are respectively a left side rectangular energy dissipating steel plate, a middle rectangular energy dissipating steel plate and a right side rectangular energy dissipating steel plate, and the middle rectangular energy dissipating steel plate is fixed between the left side rectangular energy dissipating steel plate and the right side rectangular energy dissipating steel plate. The dimension parameters of the three rectangular energy dissipating steel plates are specifically defined according to engineering needs and damping requirements. The bidirectional energy dissipating soft steel energy dissipater is combined design of two principles of bend yielding and shear yielding, simultaneously achieves in-plane shear yielding energy dissipating and out-plane bend yielding energy dissipating. A hard core adopts steel with a low yield point, the three rectangular energy dissipating steel plates are reasonably arranged to guarantee the yielding energy dissipating under set inter-story displacement deformation when an earthquake acts, structural damage is avoided, and a protection function is played.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Reinforcement method for continuous filament reinforced metallic matrix composite
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
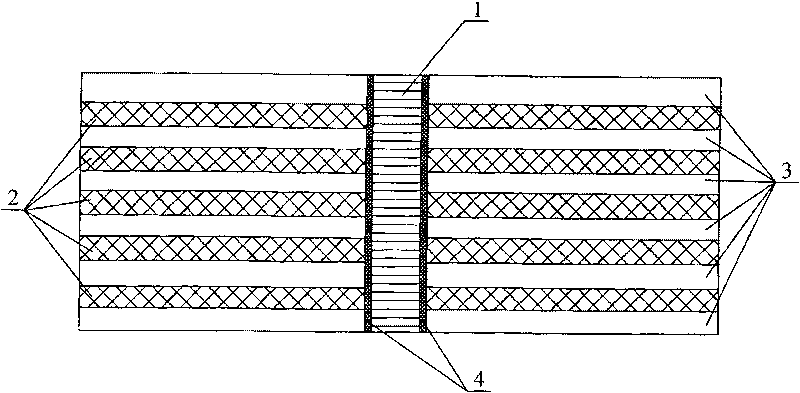
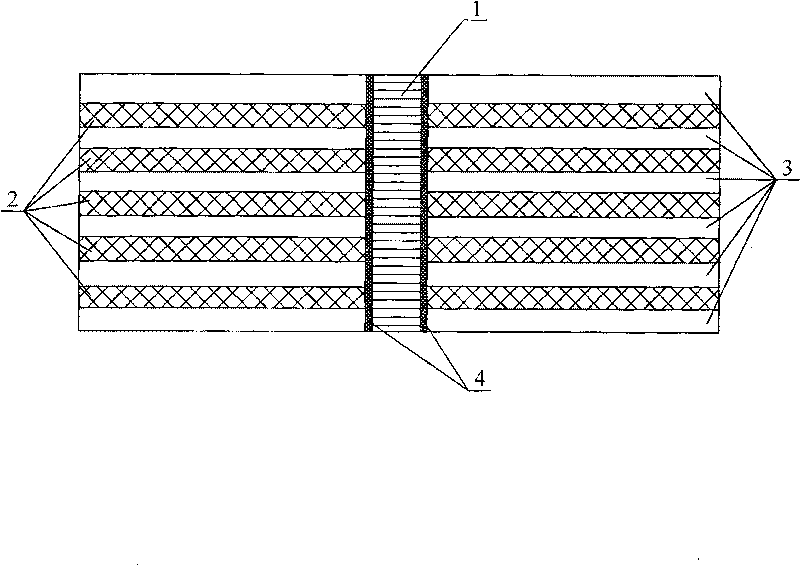
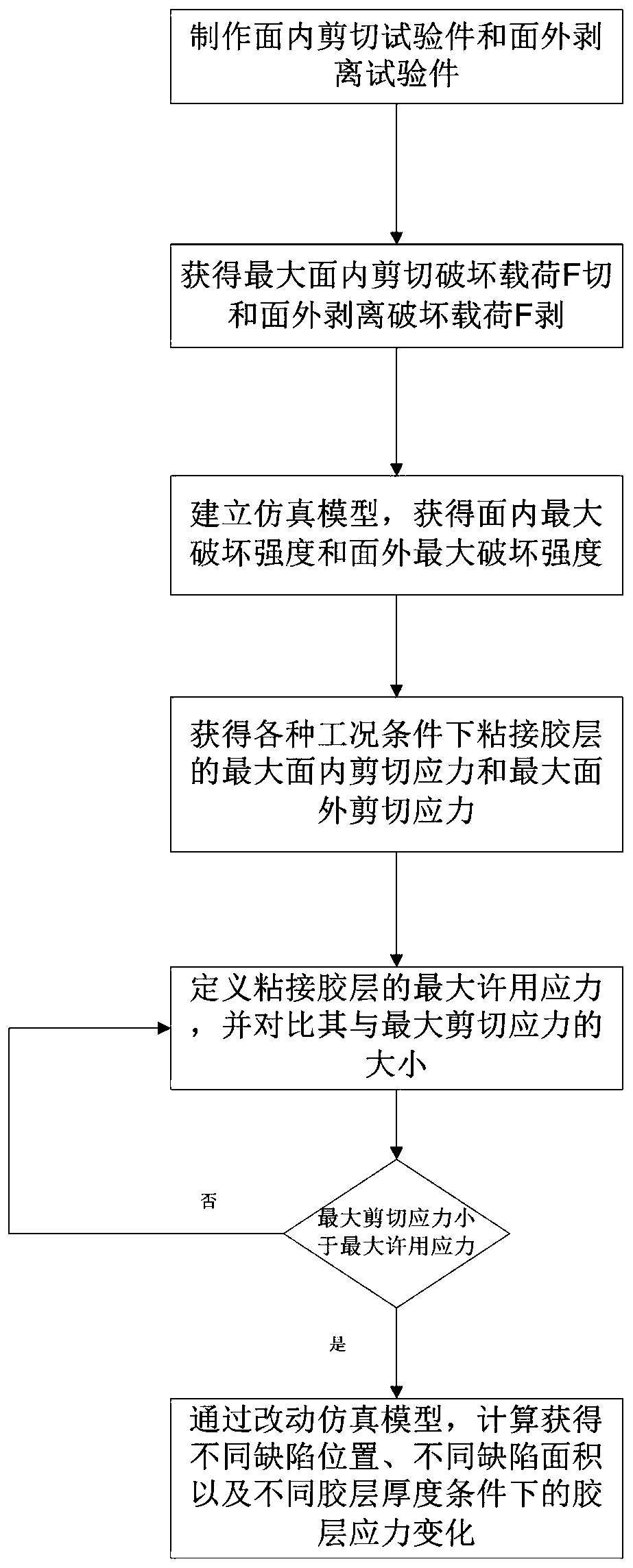
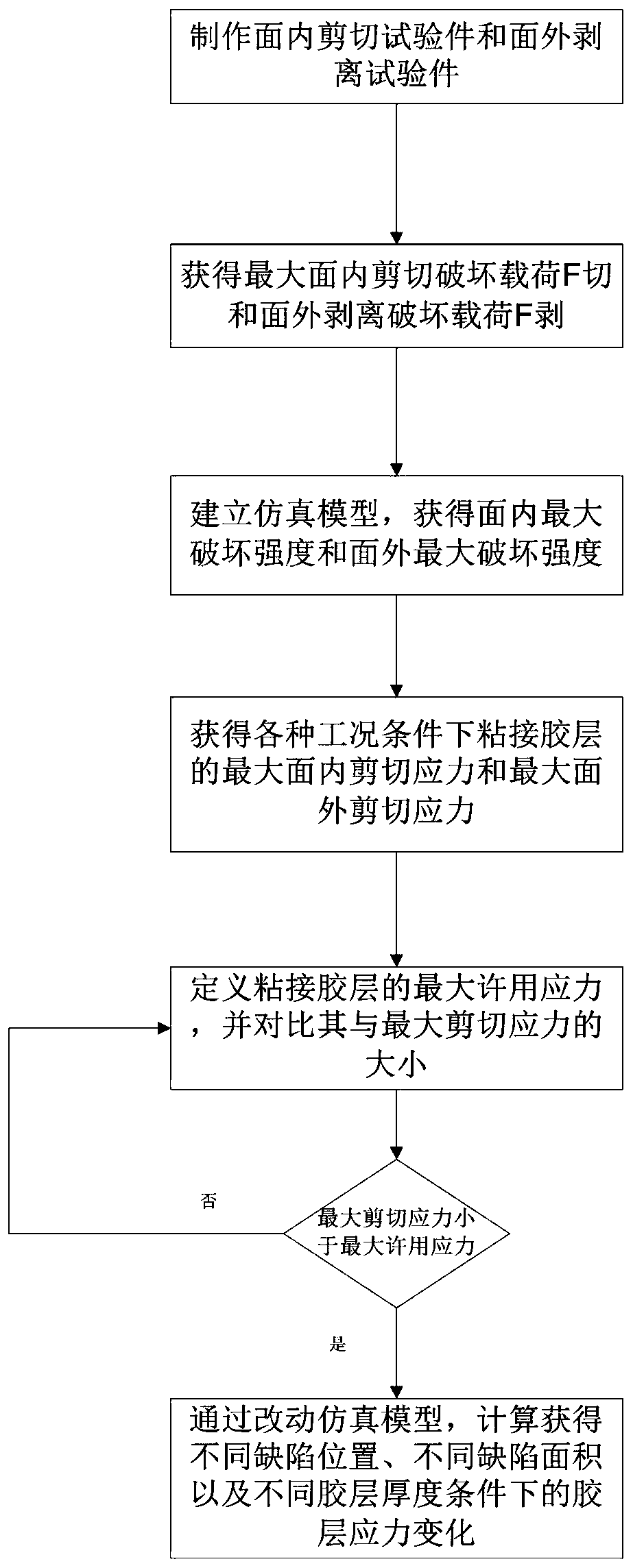
Bonding assembly performance evaluation method
ActiveCN109975205AAvoid errorsThe calculation result is accurateUsing mechanical meansMaterial analysisIn planeBreaking strength
The invention provides a bonding assembly performance evaluation method. According to the method, an in-plane shear test piece and an out-of-plane peel test piece are prepared so as to be adopted to perform an in-plane shear test piece and an out-of-plane peel test piece; a maximum in-plane shear breaking load F and an out-of-plane peeling breaking load F are obtained and are adopted as the inputof a simulation model, and simulation calculation is carried out, so that a maximum in-plane breaking strength sigmasin and a maximum out-of-plane breaking strength sigmasout can be obtained; the maximum allowable stress of an adhesive layer is defined; and the maximum in-plane shear stress gammajin and maximum out-of-plane shear stress gammajout of the adhesive layer under various working conditions are compared with each other, bonding schemes are evaluated, and the feasible region of the defect tolerance range of the adhesive layer is provided. Safety margin is determined on the basis of material strength calculated through the simulation model, and therefore, errors caused by material strength which is obtained by an original simulation model through an experiment can be decreased, andtherefore, the evaluation of bonding assembly performance design schemes is realized.
Owner:BEIJING AEROSPACE TECH INST
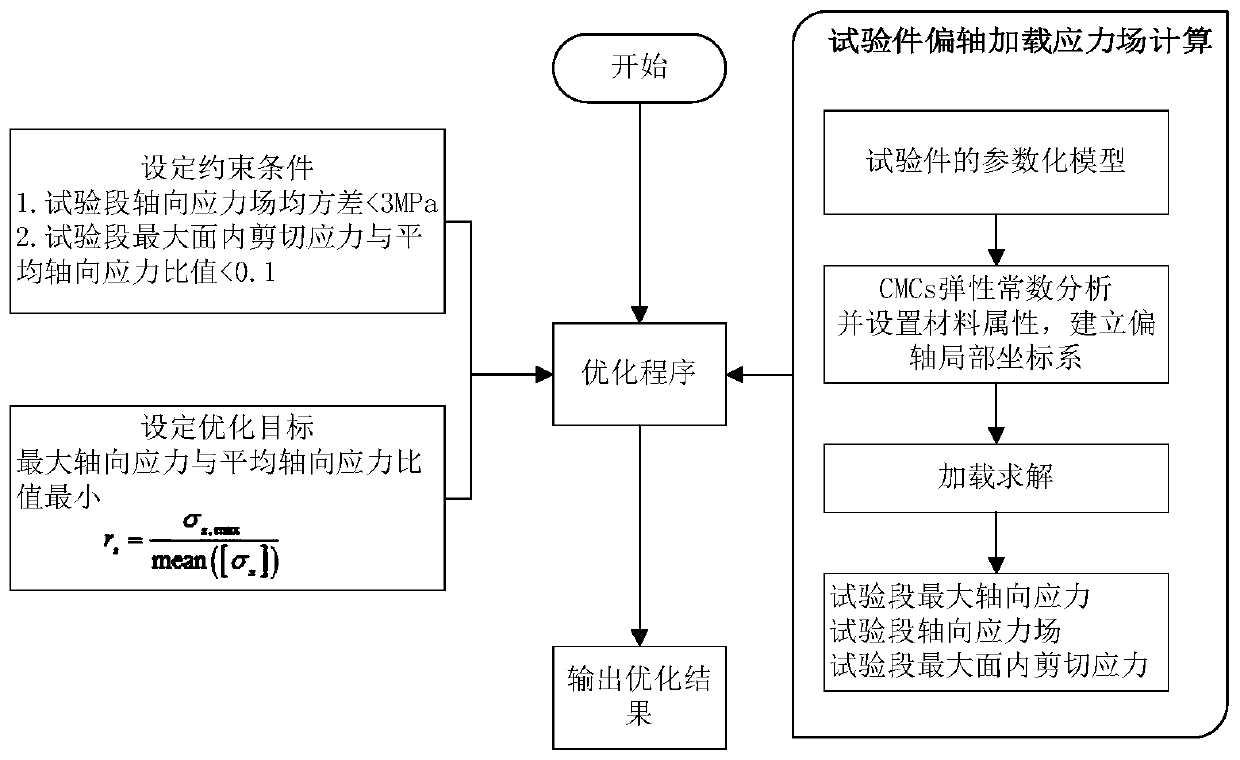
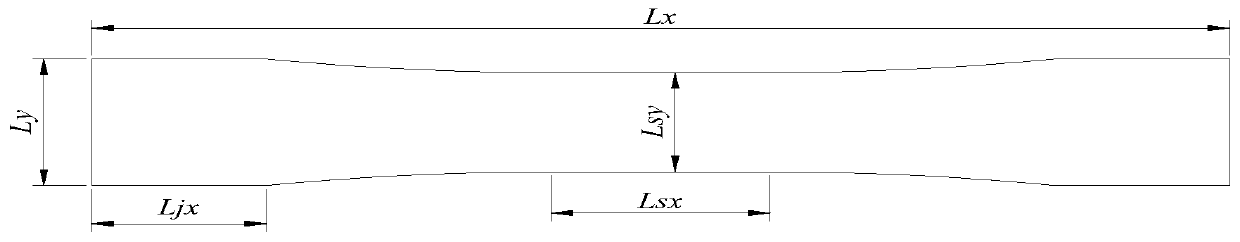
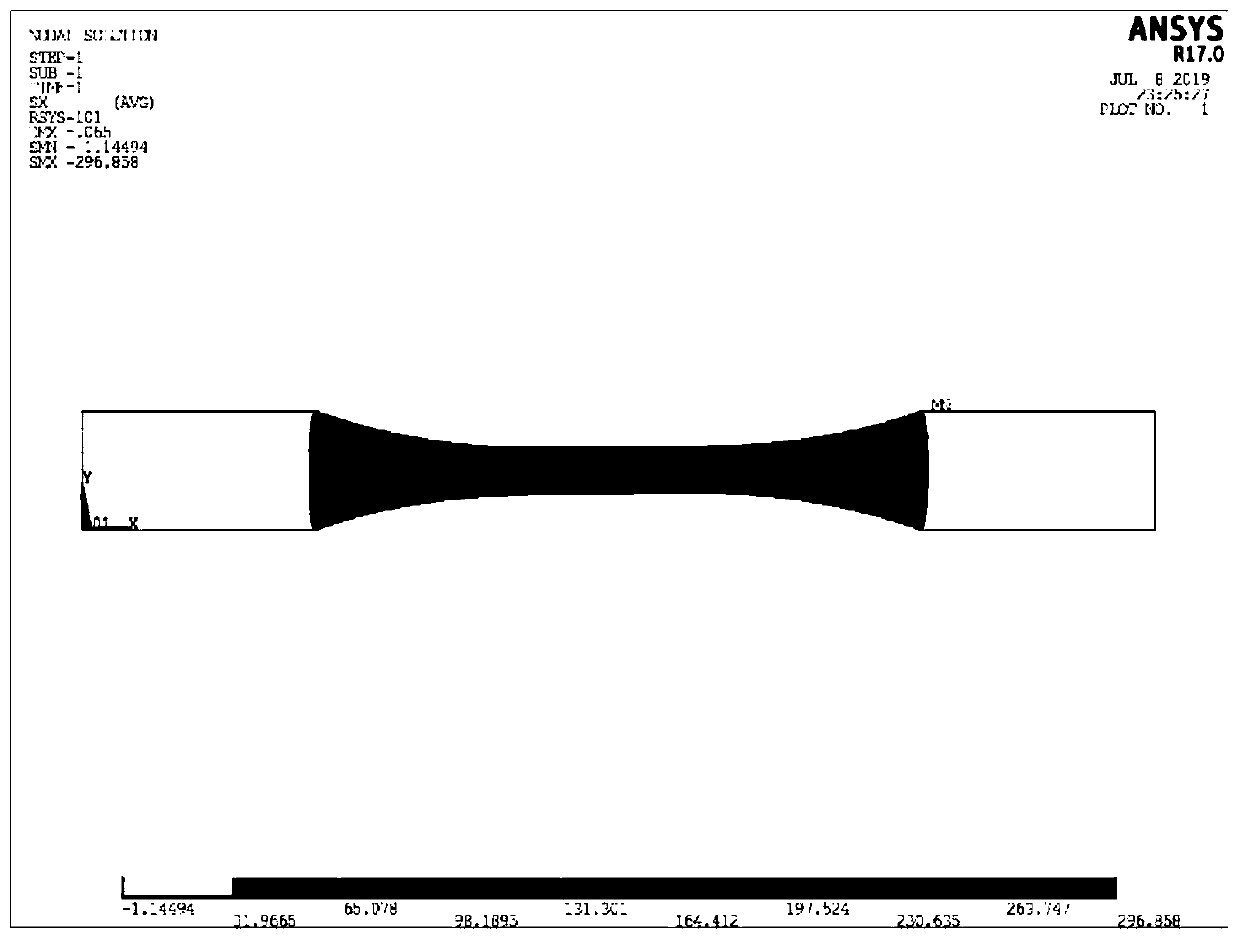
Optimal design method for off-axis tensile test piece of one-way ceramic matrix composite
ActiveCN110502793AAvoid failureFull load fiberSpecial data processing applicationsShear stressTensile testing
The invention discloses an optimal design method for off-axis tensile test piece of one-way ceramic matrix composite which comprises the following steps: based on a finite element method, establishinga parameterized model of a traditional ceramic matrix composite off-axis tensile test piece; calculating the elastic property of the composite material by utilizing a rigidity / flexibility average method; establishing an off-axis local coordinate system; loading and solving the model, and extracting the maximum axial stress and the maximum internal shear stress of the test section and the axial stress field of each node; constructing stress obtained through stress comparison parameter processing; setting an optimization constraint condition and an optimization target, substituting the optimization constraint condition and the optimization target into an optimization program for calculation, and outputting an optimization result; and carrying out optimized result verification and analysis.According to the invention, the test piece deformation caused by additional bending moment in the off-axis stretching process is effectively reduced; and the test piece is ensured not to fail due to in-plane shear stress. Therefore, the success rate of the test is improved, effective test data can be obtained, and a test basis is provided for researching the mechanical property of the test.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
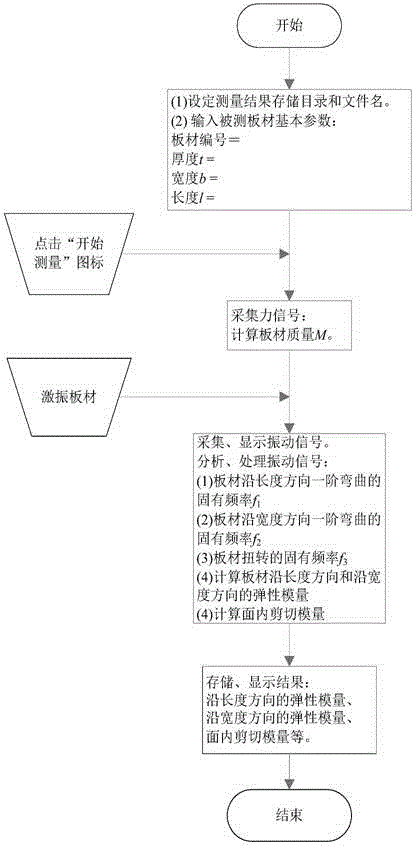
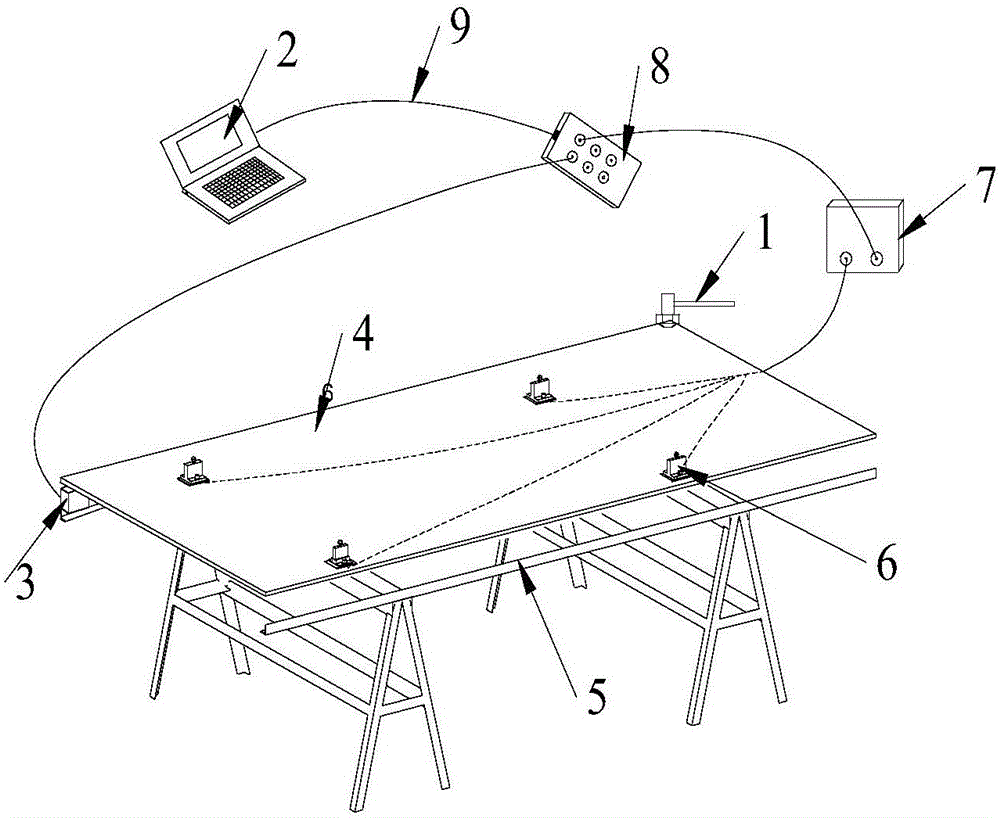
Nondestructive detection method for elastic modulus and in plane shear modulus of large-size wood based panel
InactiveCN106093197ARapid determinationEasy to measureAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesShear modulusNon destructive
The invention relates to a nondestructive detection method for the elastic modulus and the in plane shear modulus of a large-size wood based panel. The nondestructive detection method comprises: 1, placing a plate; 2, setting a measurement result storage directory and a file name, and inputting the basic parameters of the plate; 3, measuring the quality of the plate; 4, measuring the elastic modulus of the plate in a length direction, the elastic modulus of the plate in a width direction, and the in plane shear modulus; and 5, storing, and displaying the measurement result. According to the present invention, with the method, the main mechanical property indices such as the elastic modulus in the length direction, the elastic modulus in the width direction, the in plane shear modulus and the like can be nondestructively, quickly, conveniently and concurrently determined; and compared with the traditional detection method (small specimen bending measurement, tensile measurement, and the like), the method of the present invention has characteristics of non-destructive detection, time saving, cost saving, and convenient operation.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
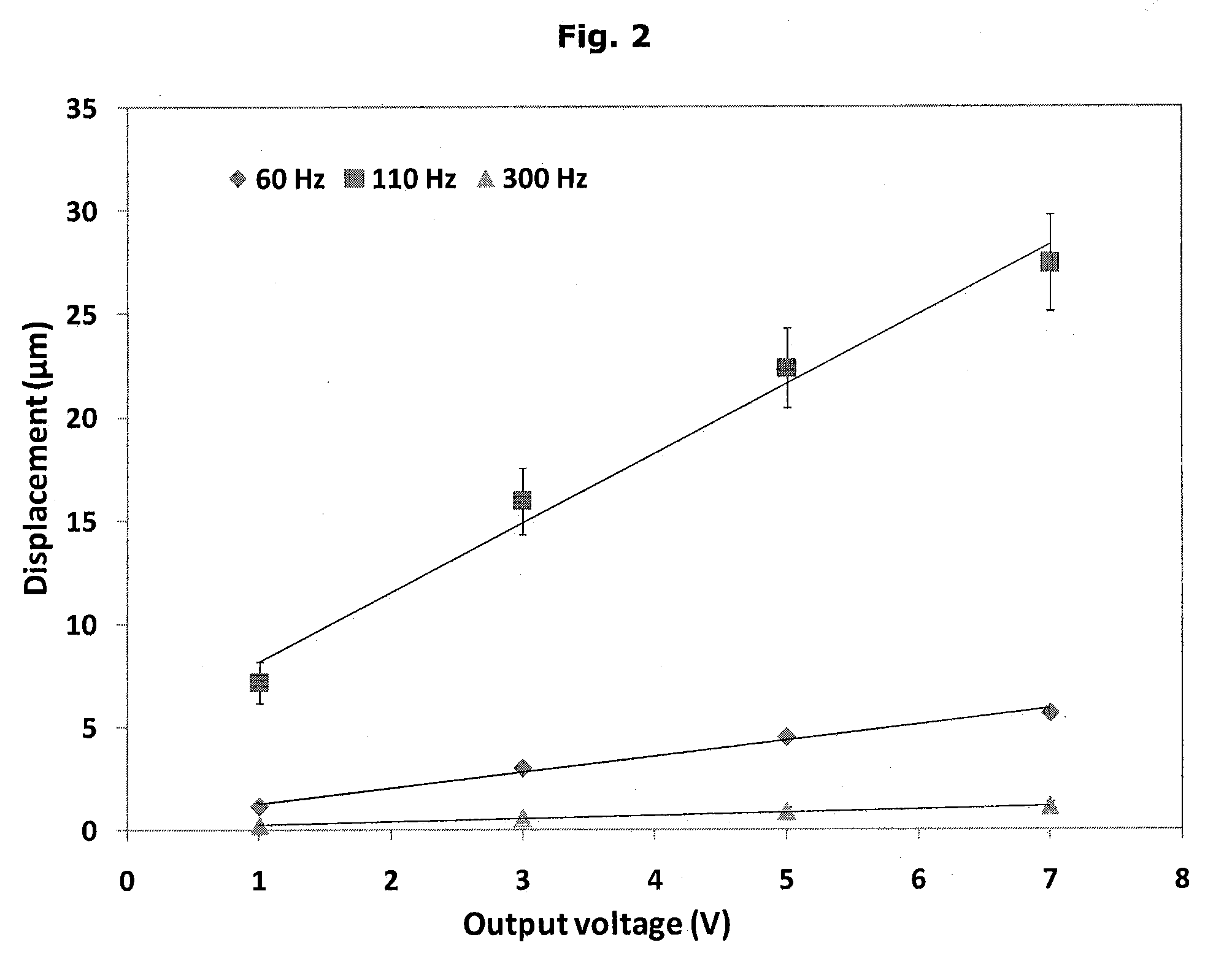
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com