Solid-state imaging device, method for driving solid-state imaging device, and electronic apparatus
A camera device, solid-state technology, applied in TV, electrical components, color TV, etc., can solve the problem of unable to read the global shutter, and achieve the effect of large dynamic range, noise reduction, and expansion of effective pixel area
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 approach
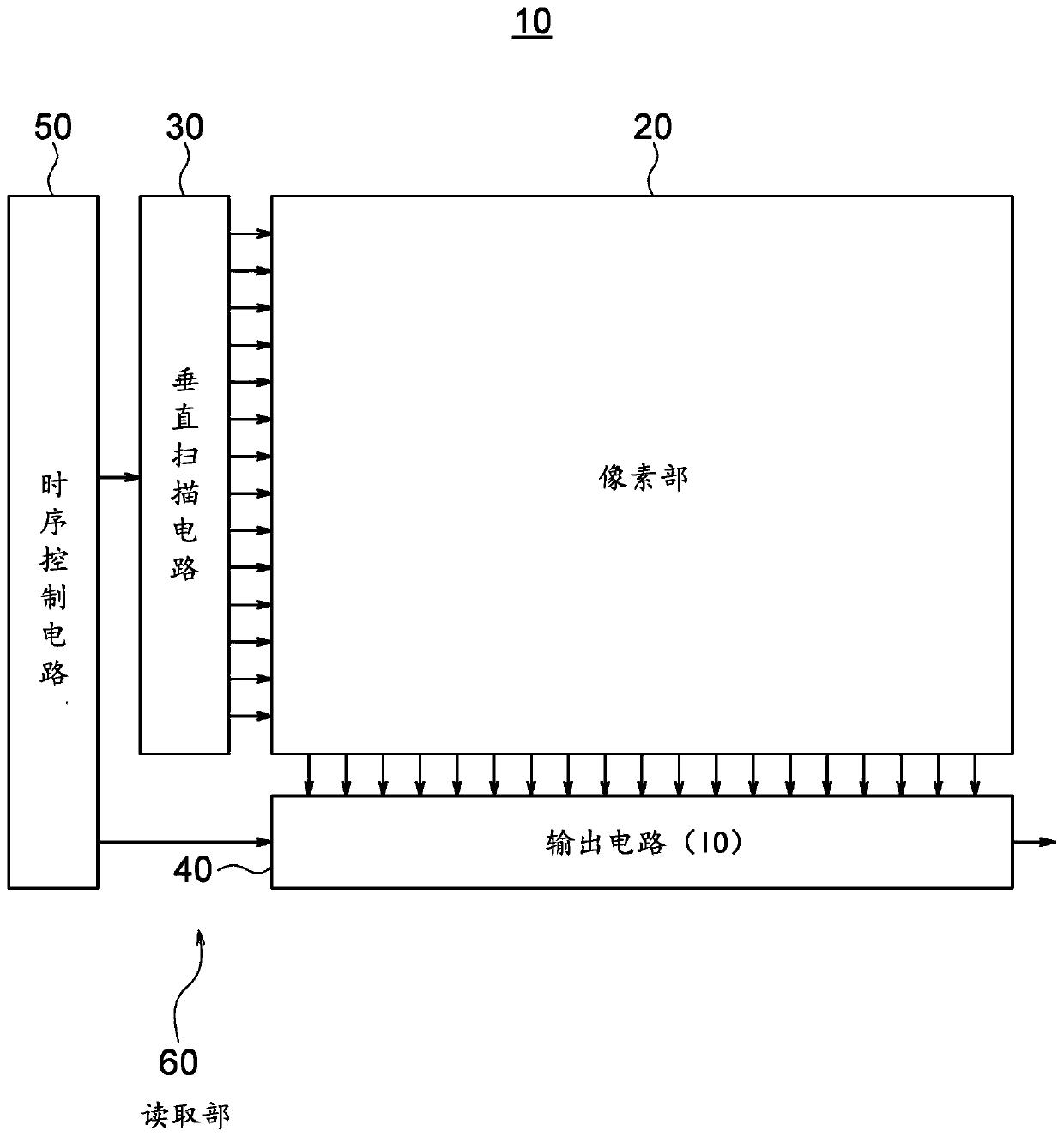
[0067] figure 1 It is a block diagram showing a configuration example of the solid-state imaging device according to the first embodiment of the present invention.
[0068] In the present embodiment, the solid-state imaging device 10 is constituted by, for example, a CMOS image sensor including digital pixels (Digital Pixels) as pixels.
[0069] Such as figure 1 As shown, this solid-state imaging device 10 includes a pixel unit 20 as an imaging unit, a vertical scanning circuit (row scanning circuit) 30, an output circuit 40, and a timing control circuit 50 as main constituent elements.
[0070] Among these components, for example, the vertical scanning circuit 30, the output circuit 40, and the timing control circuit 50 constitute a pixel signal reading unit 60.
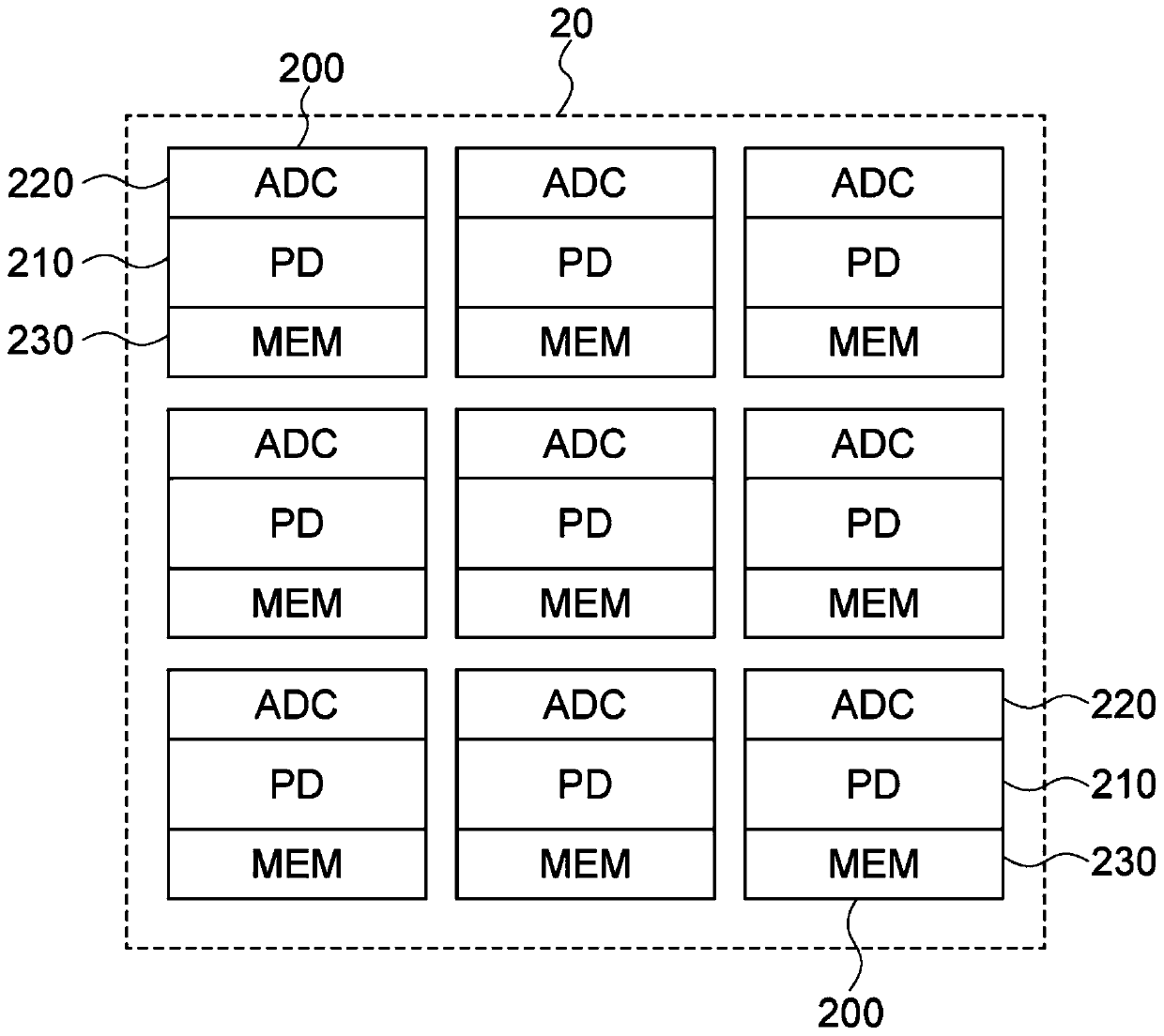
[0071] In the first embodiment, the solid-state imaging device 10 includes, as digital pixels, a photoelectric conversion reading unit, an AD (analog-to-digital) conversion unit, and a memory unit in the pixel uni...
no. 2 approach
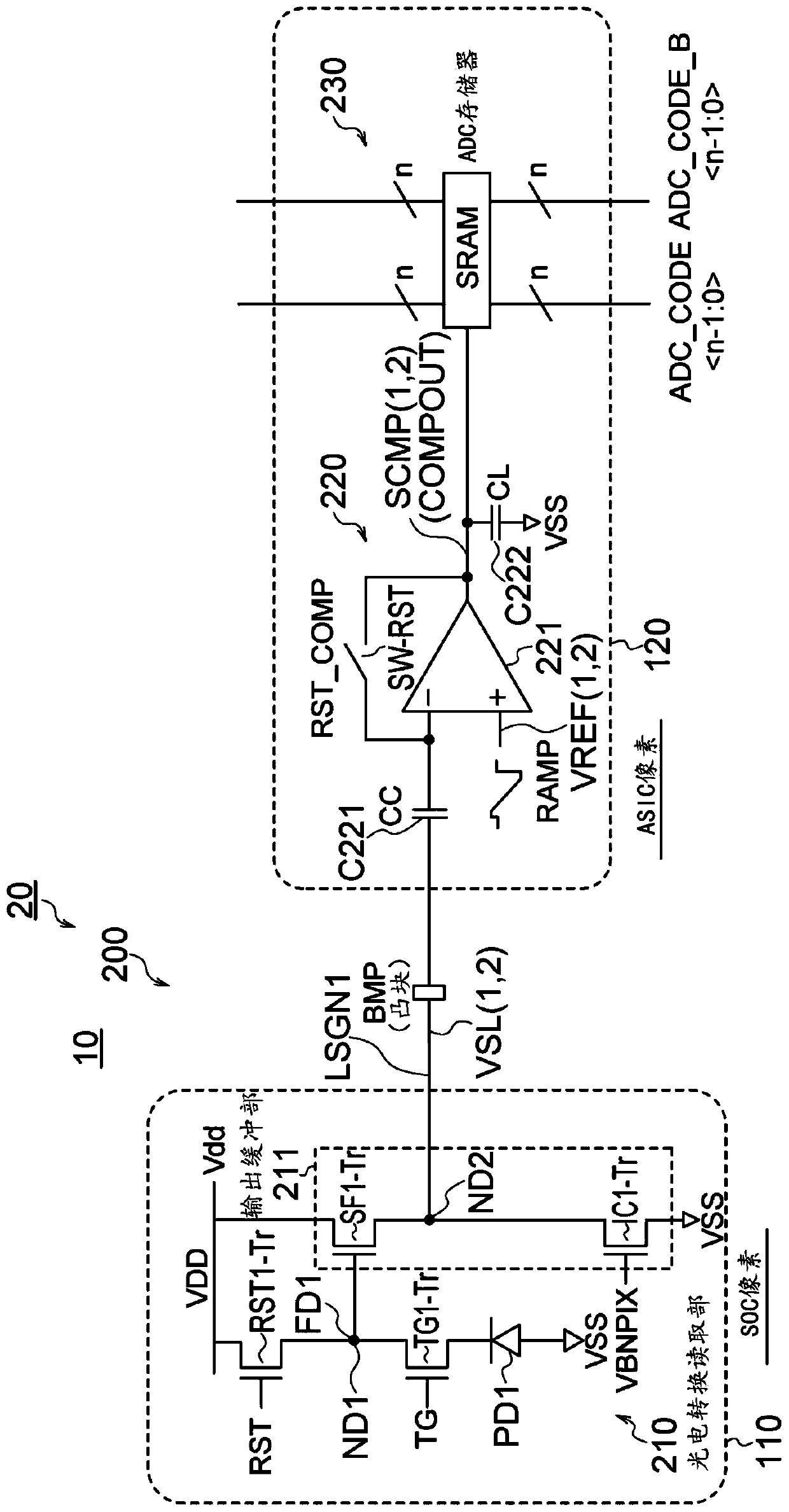
[0330] Figure 17 It is a circuit diagram showing a configuration example of a comparator according to the second embodiment.
[0331] The difference between the solid-state imaging device 10A of the second embodiment and the solid-state imaging device 10 of the first embodiment is as follows.
[0332] In the solid-state imaging device 10A of the second embodiment, the second noise band limiting capacitor C752 is connected to the input line of the voltage signal VSL to the auto-zero capacitor C711 of the first amplifier 710 from the pixel output buffer unit 211.
[0333] The source follower output of a pixel includes a typical parasitic capacitance of 1 to 2 pF that functions as a noise bandwidth limiting capacitor, but the source follower output of a DPS pixel is different from a typical rolling shutter CMOS image sensor that does not have these parasitic capacitances. different. Therefore, the higher frequency noise spectrum is transferred to the comparator, which overall ...
no. 3 approach
[0337] Figure 18 It is a circuit diagram showing a configuration example of a comparator according to the third embodiment.
[0338] The difference between the solid-state imaging device 10B of the third embodiment and the solid-state imaging device 10A of the second embodiment is as follows.
[0339] In the solid-state imaging device 10B of the third embodiment, the gate of the other NMOS transistor NT713 of the differential transistor pair DTP is connected to the third noise band limiting capacitor C753.
[0340] In the comparator 700B of the third embodiment, in order to suppress the AZ switching transistor noise during the AZ period, the parasitic capacitance of the third noise bandwidth limiting capacitor C753 connected to the node ND713 is small, so high voltage noise appears.
[0341] Therefore, adding the third noise bandwidth limiting capacitor C753 (CL3) will effectively reduce the AZ noise.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com