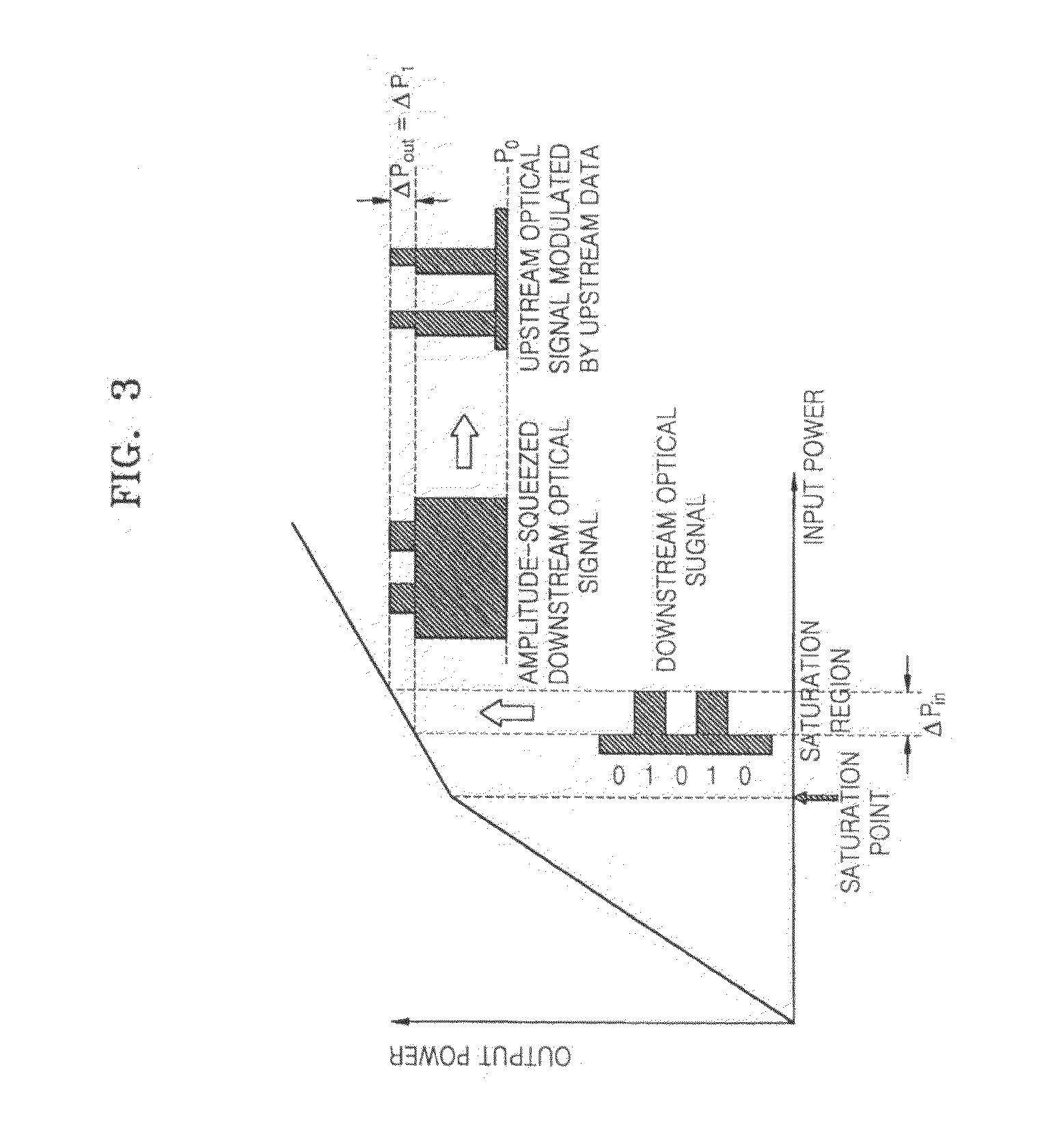
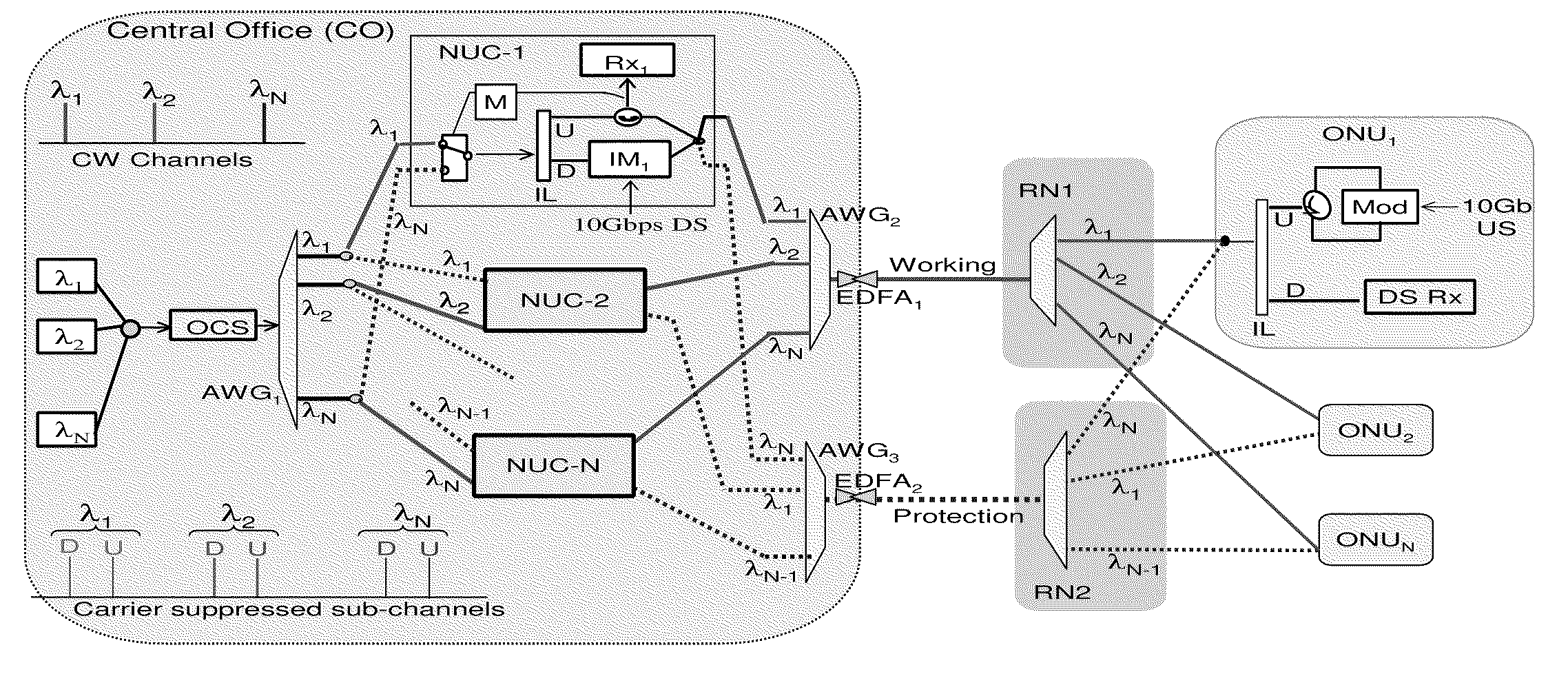
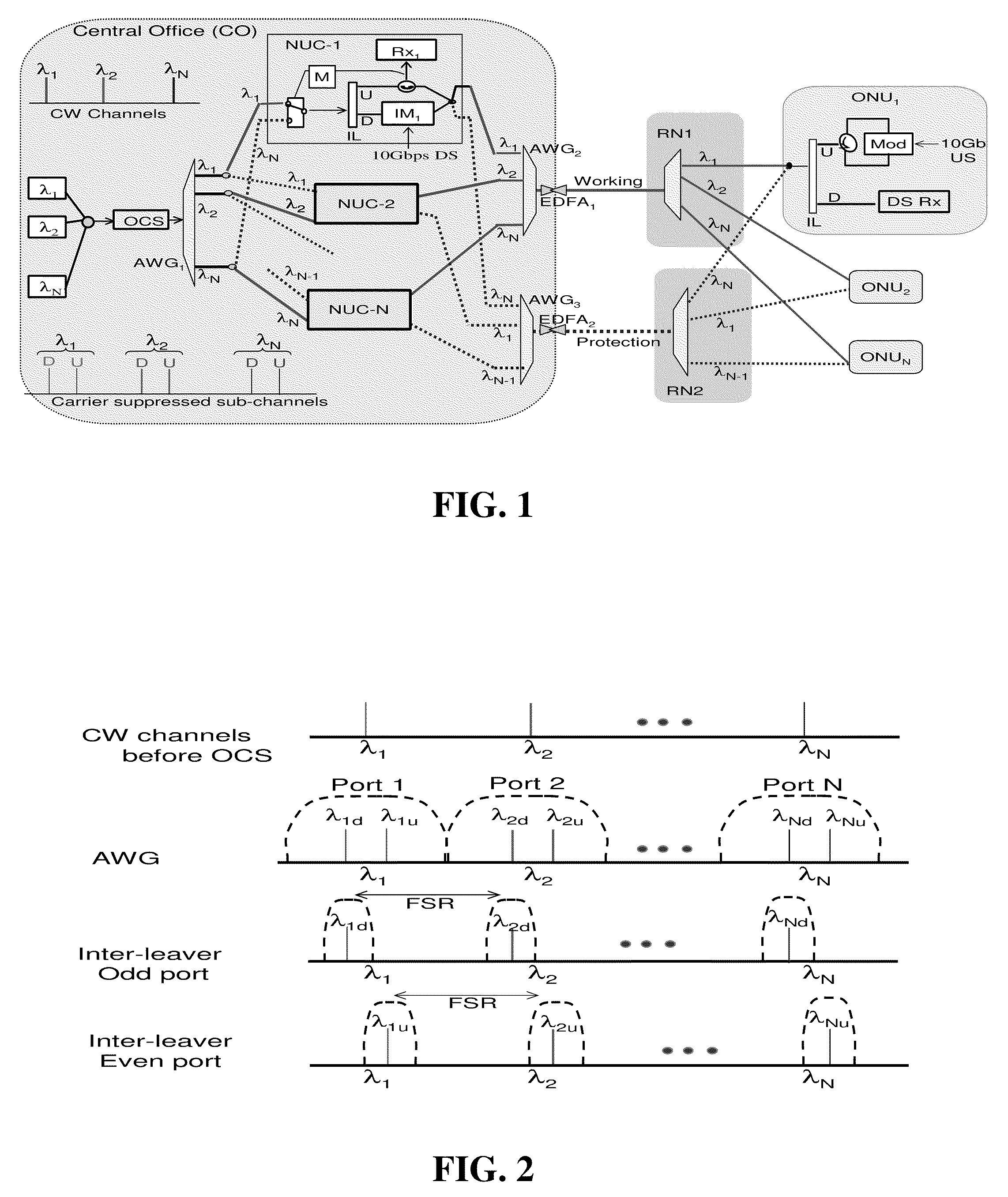
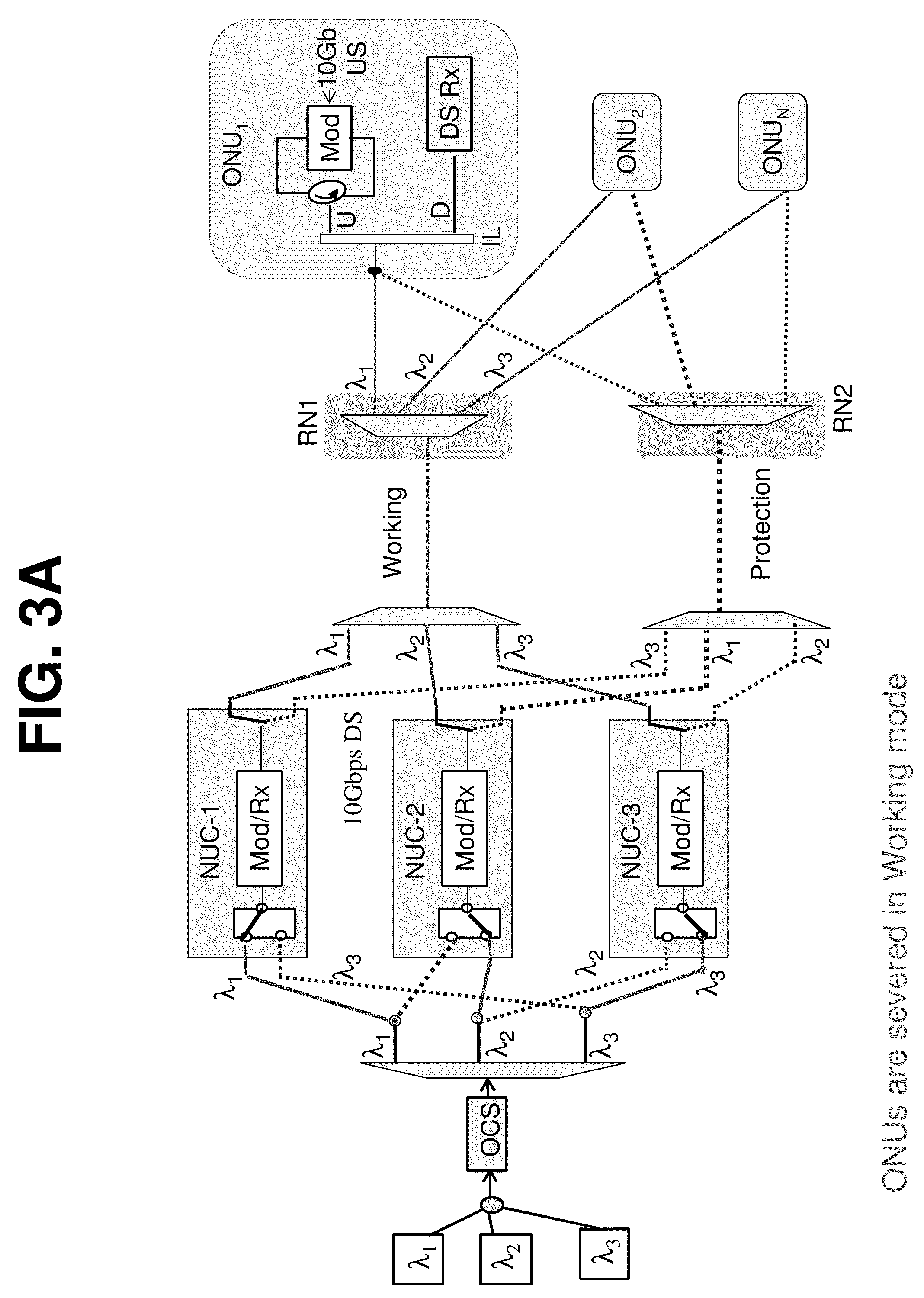
Patents
Literature
314 results about "Wavelength division multiplexing passive optical networks" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
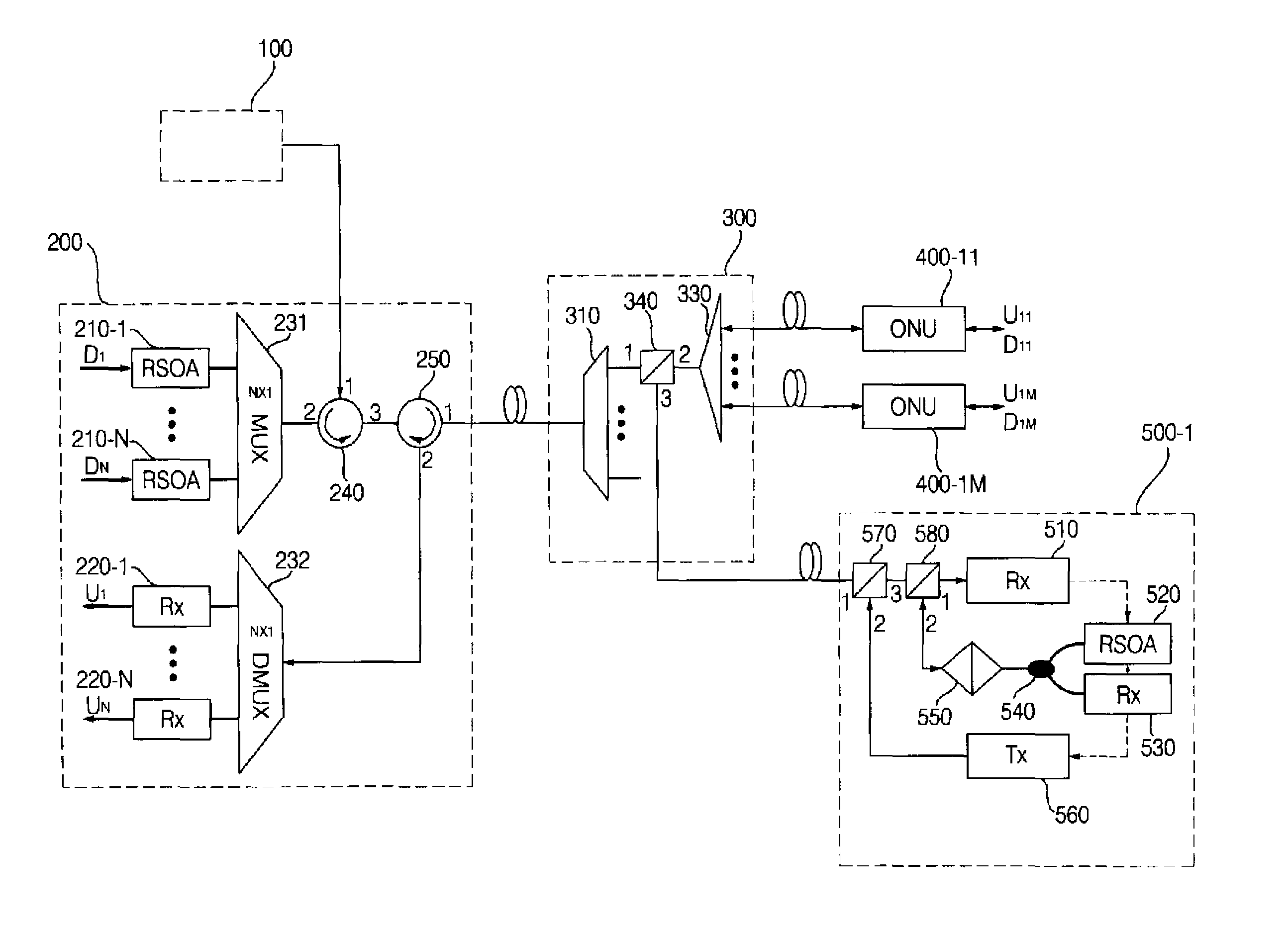
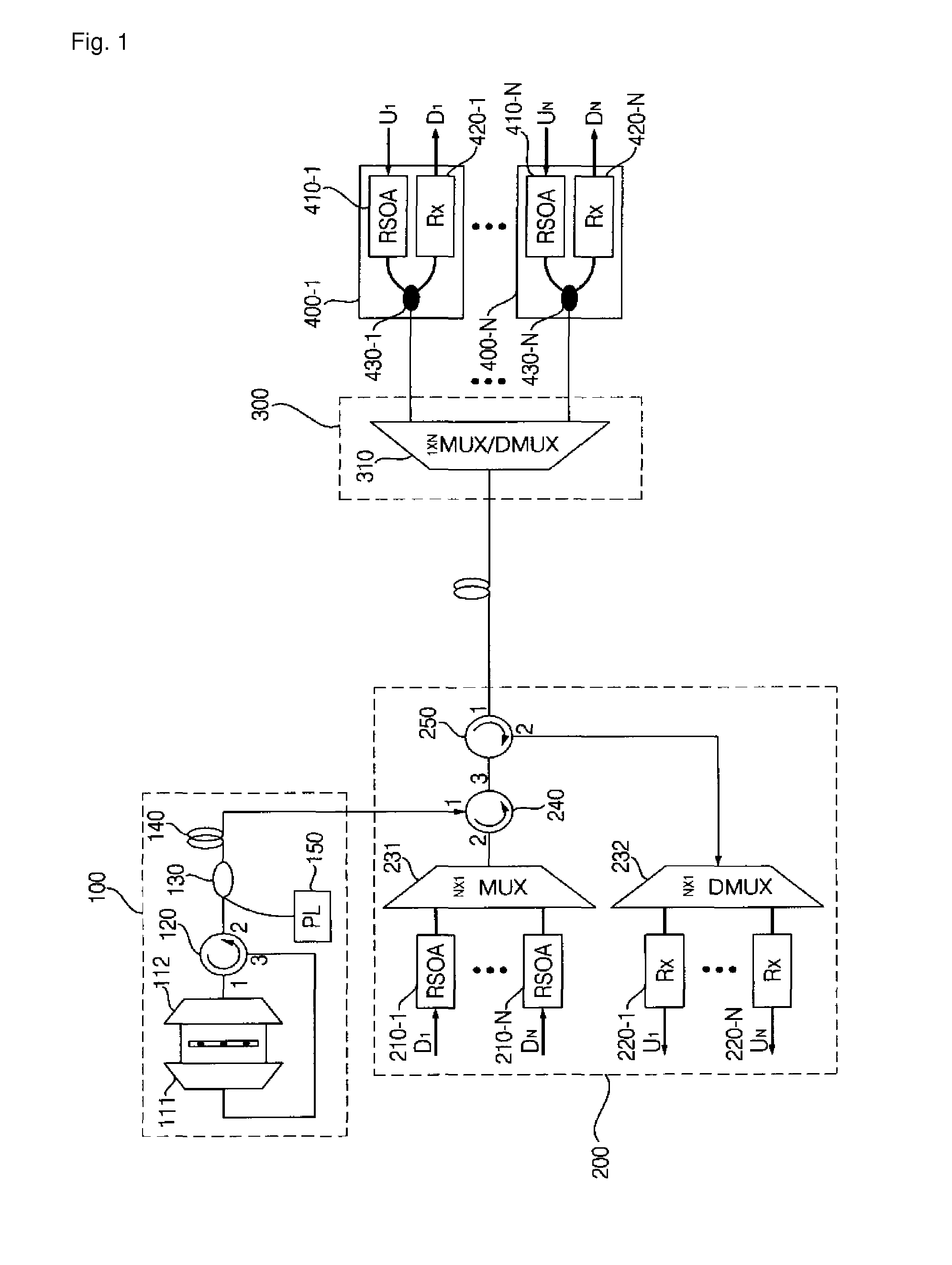
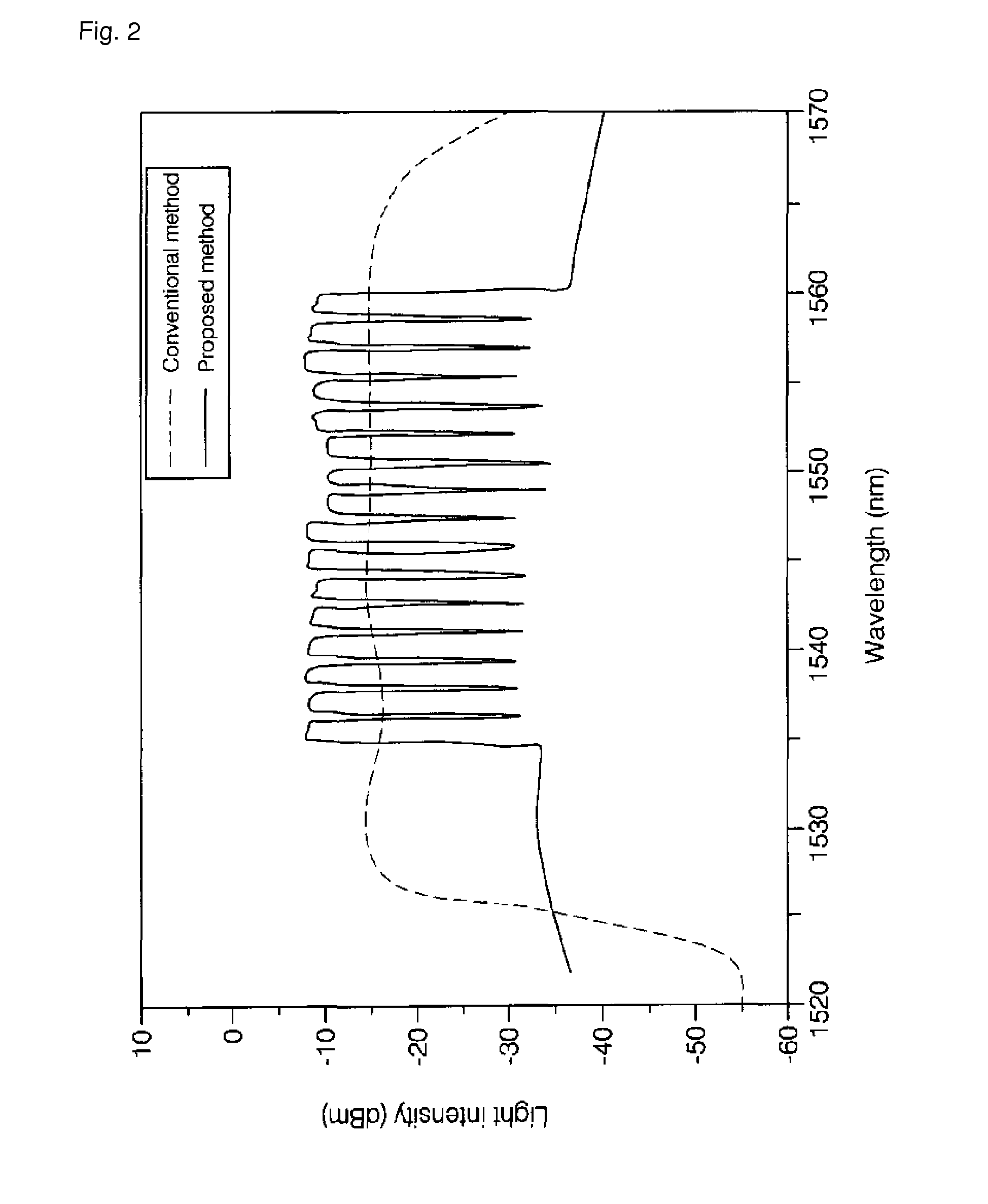
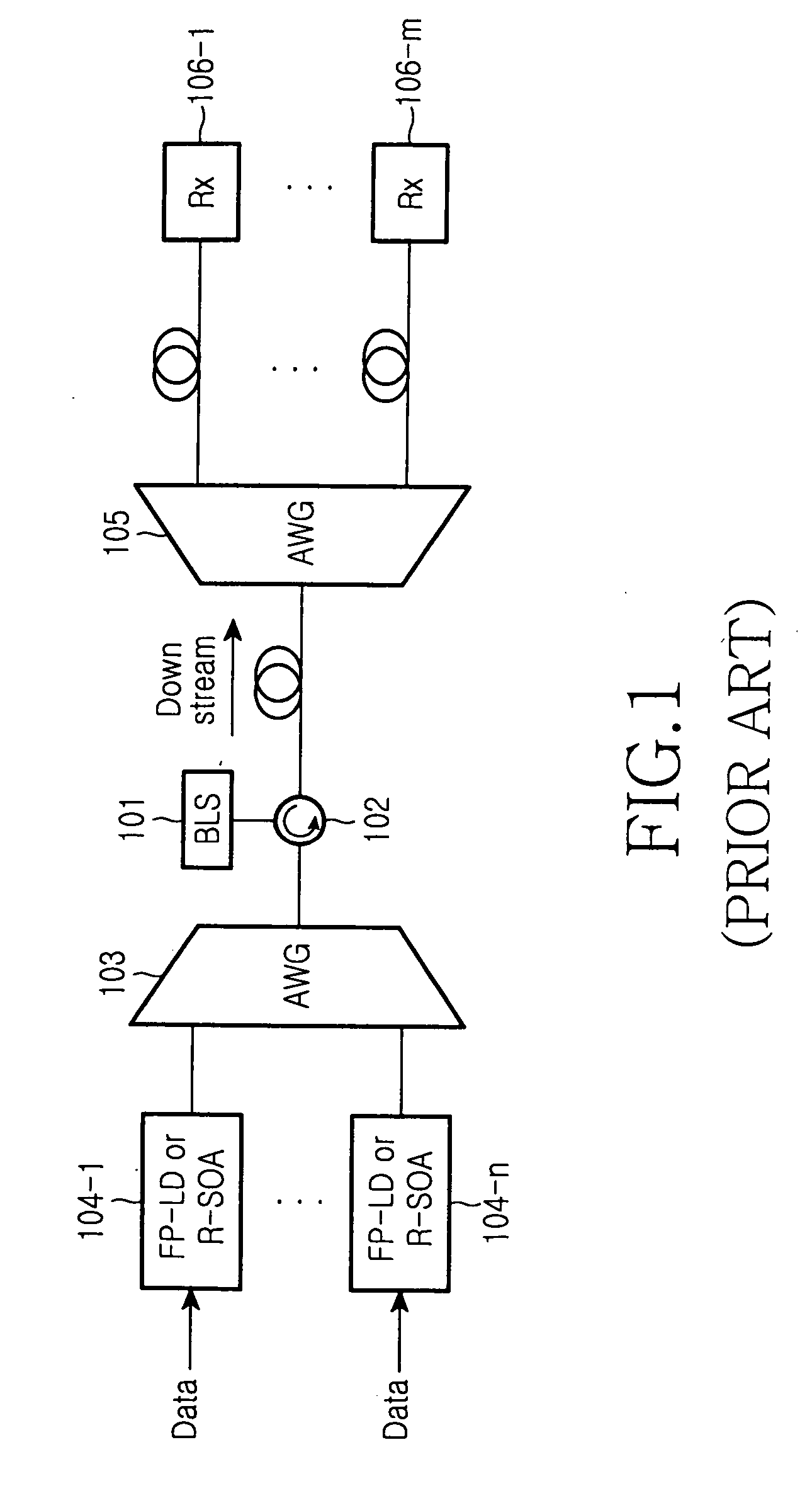
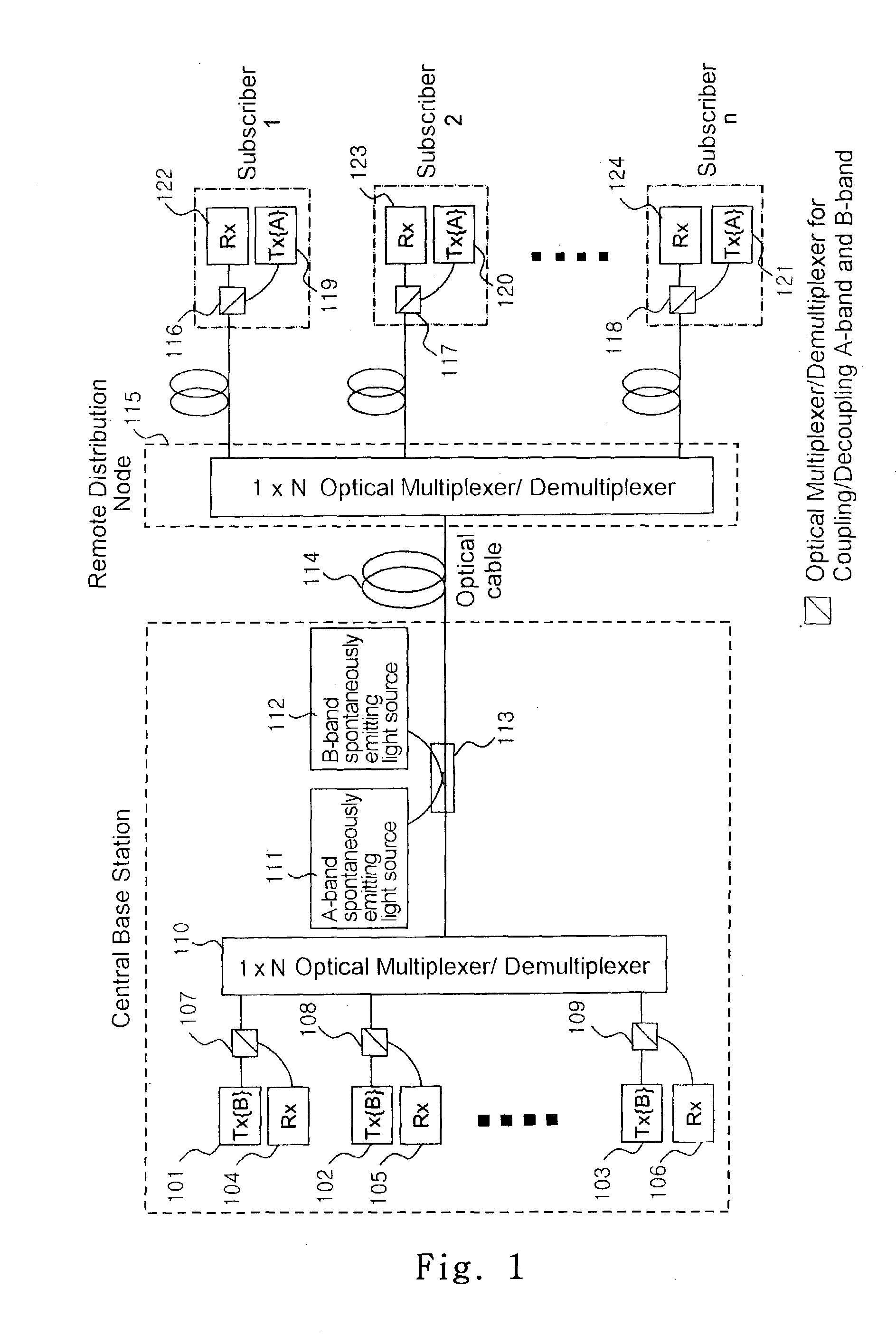
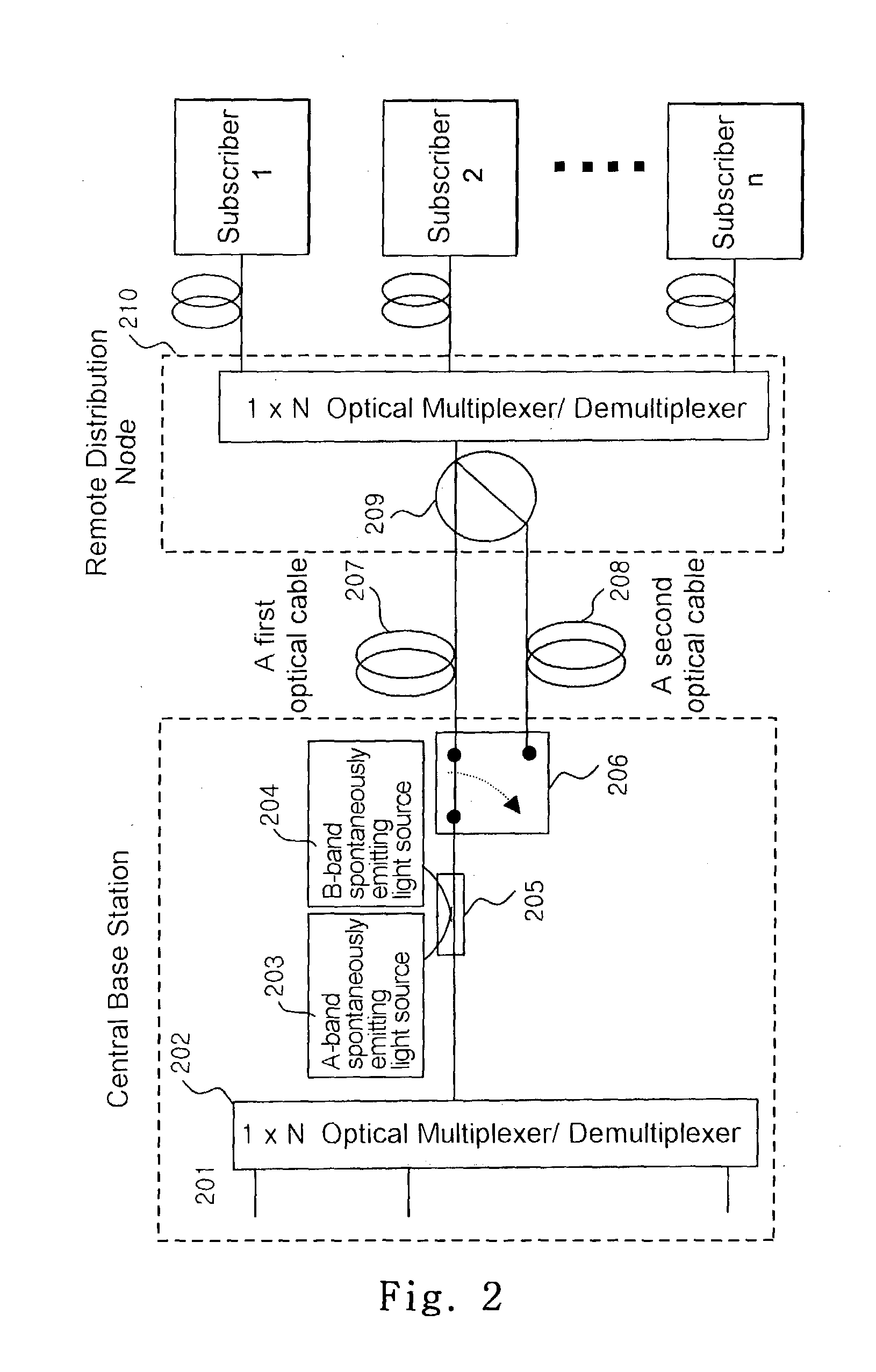
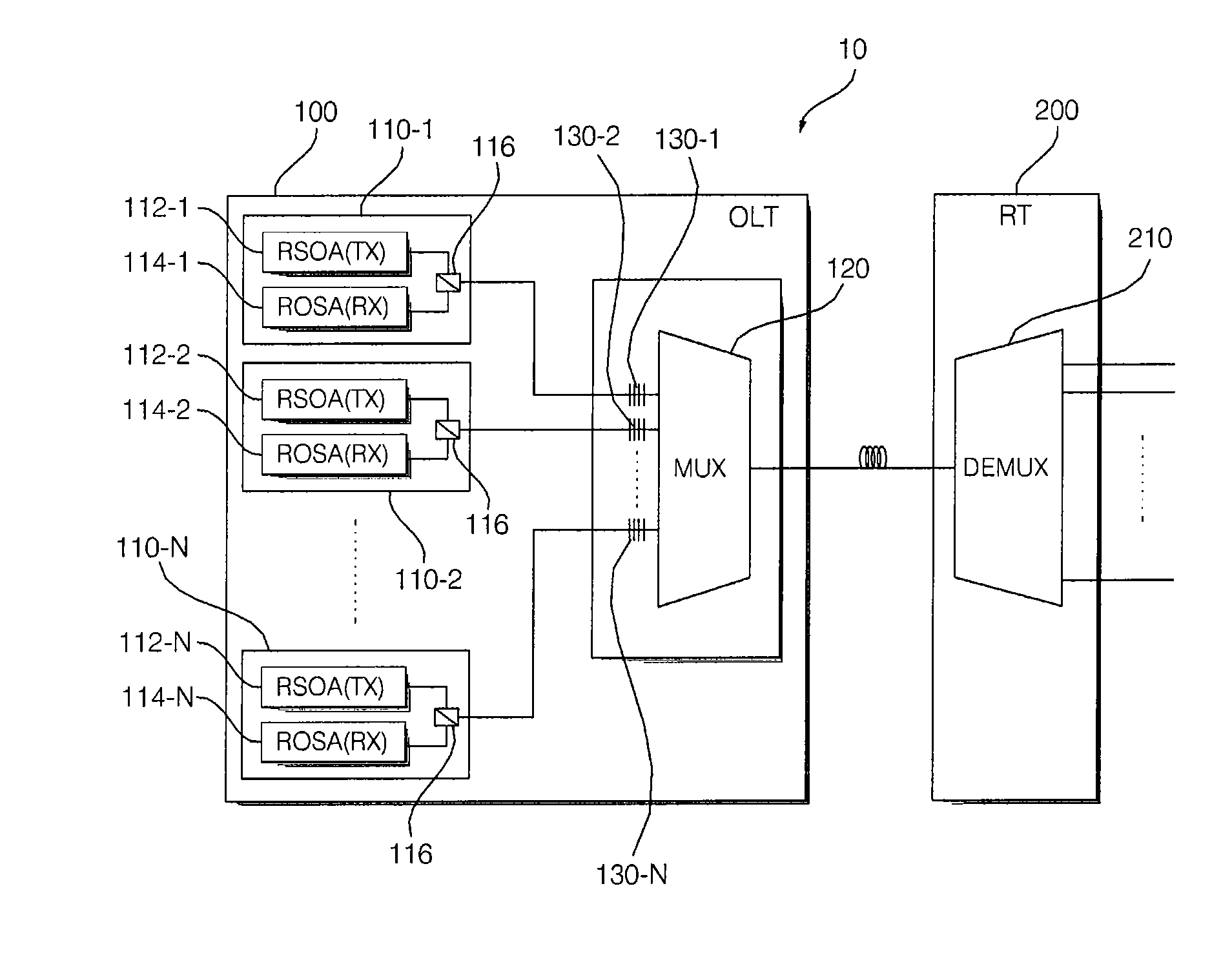
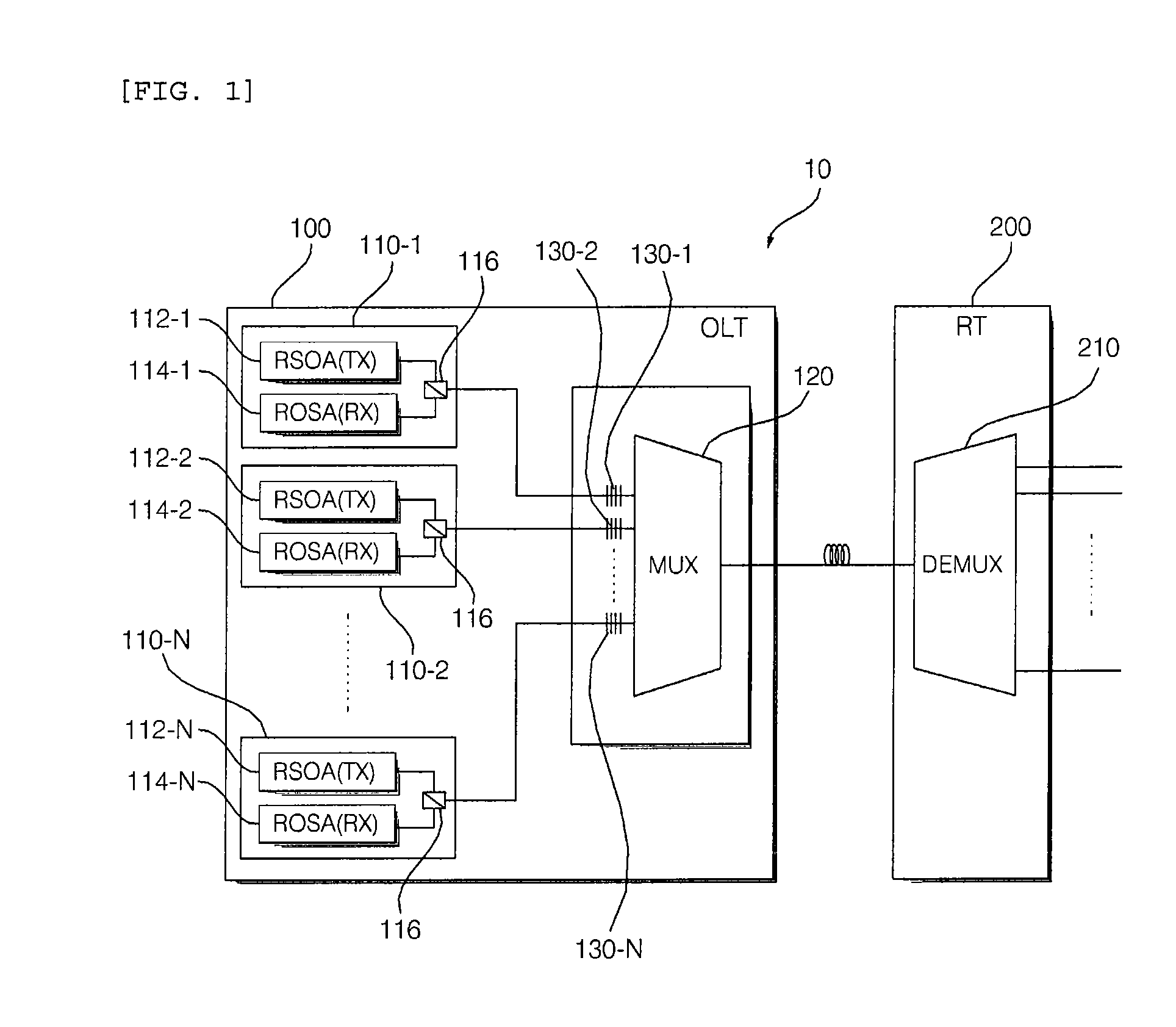
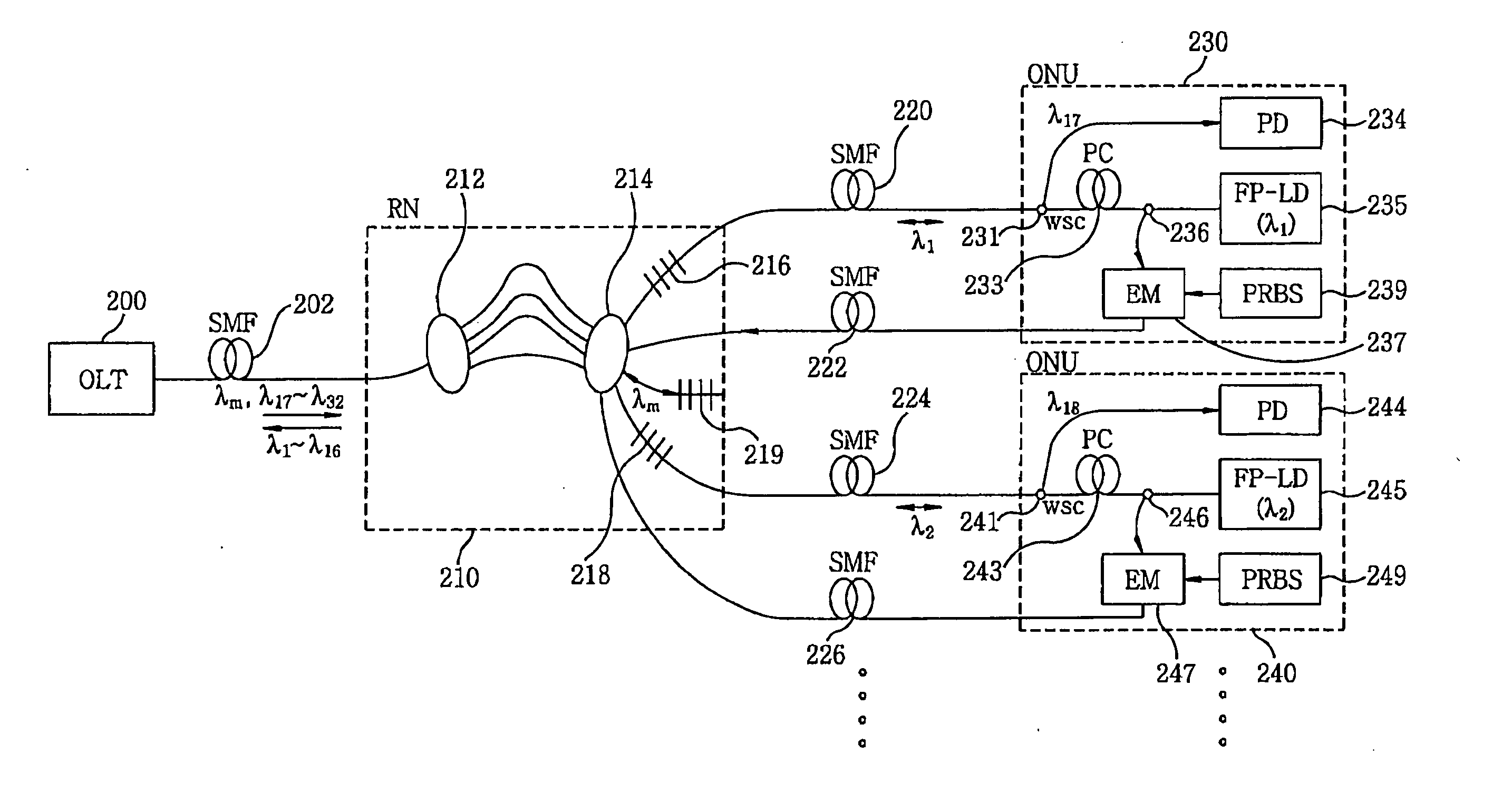
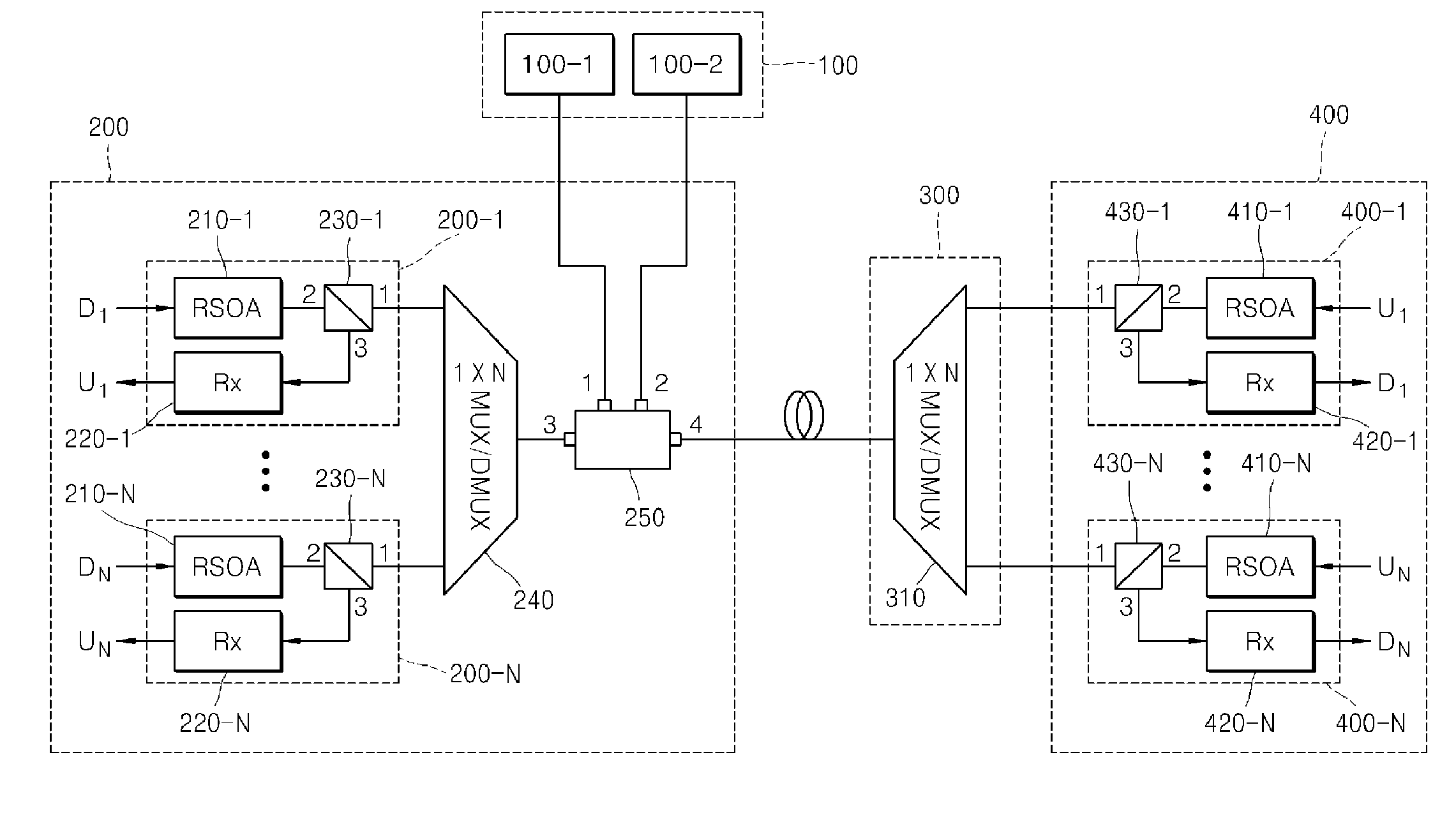
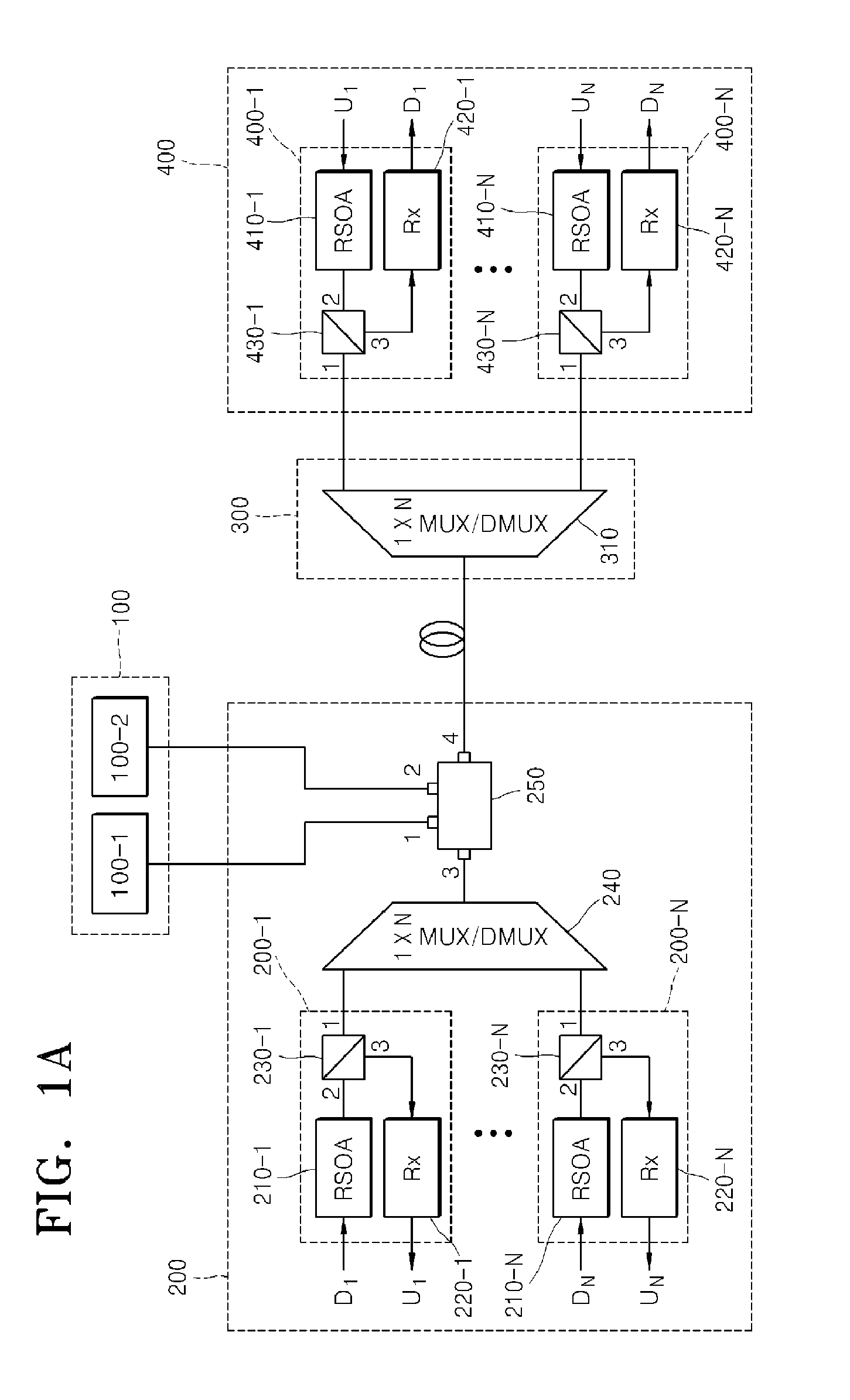
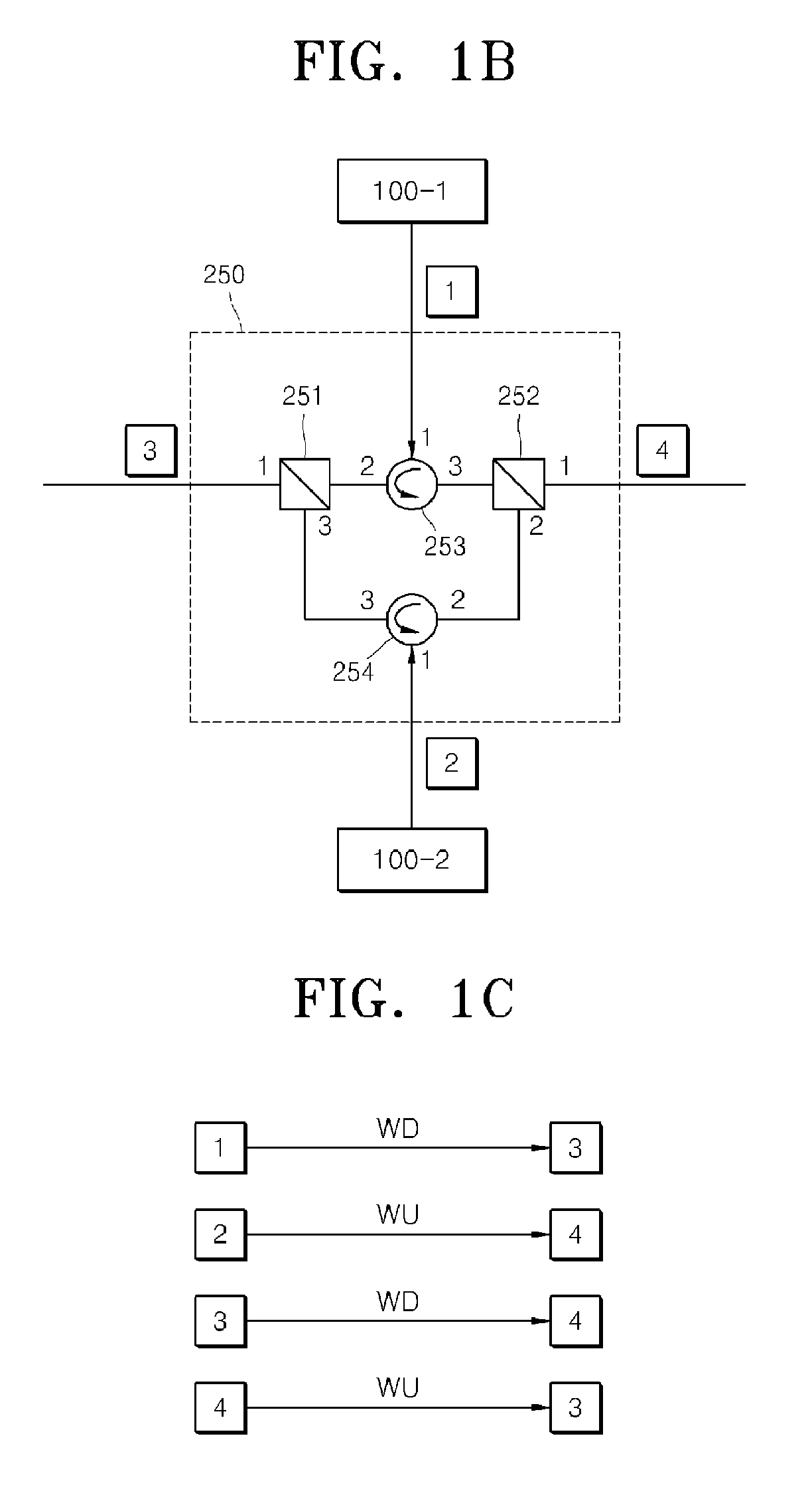
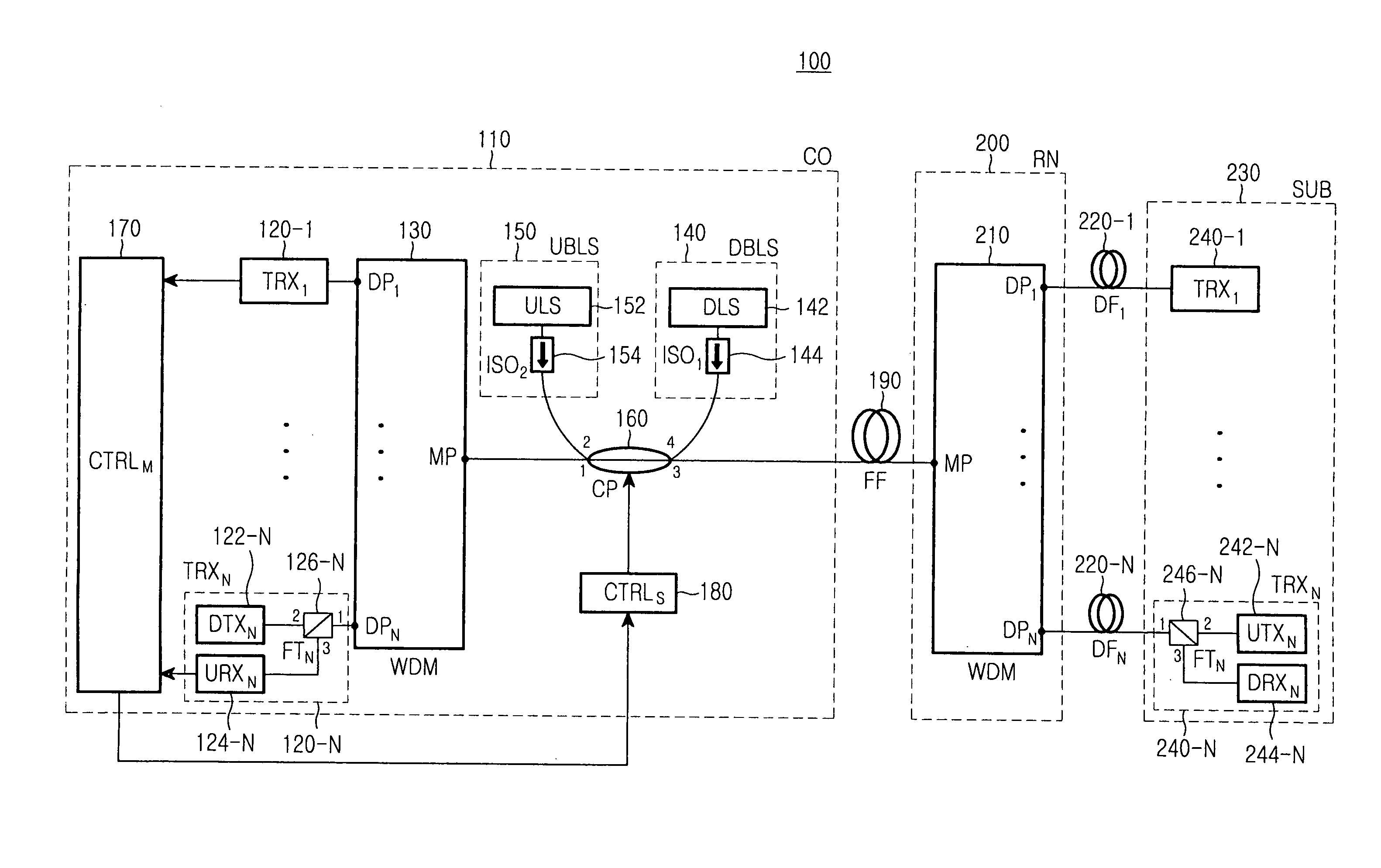
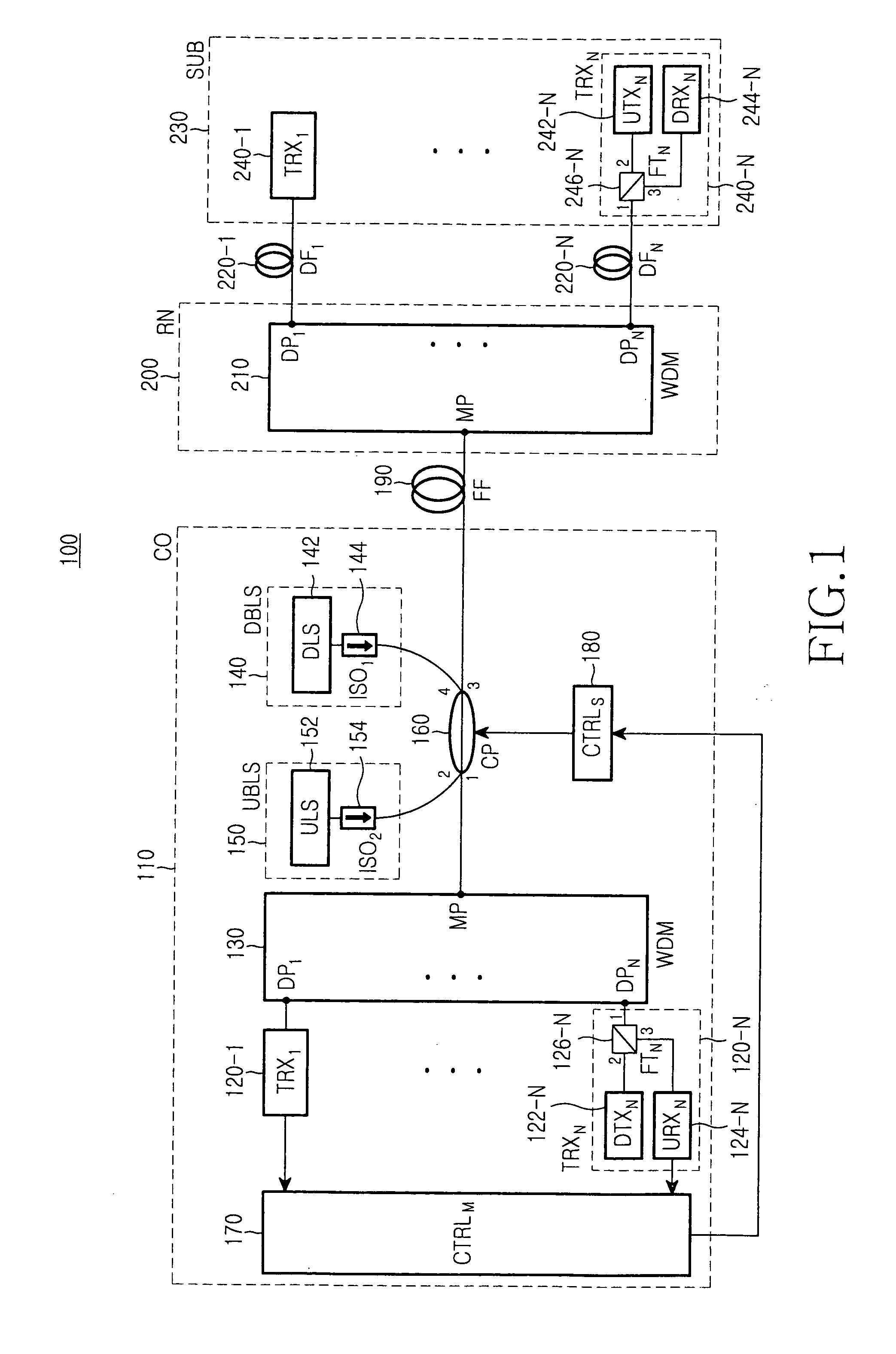
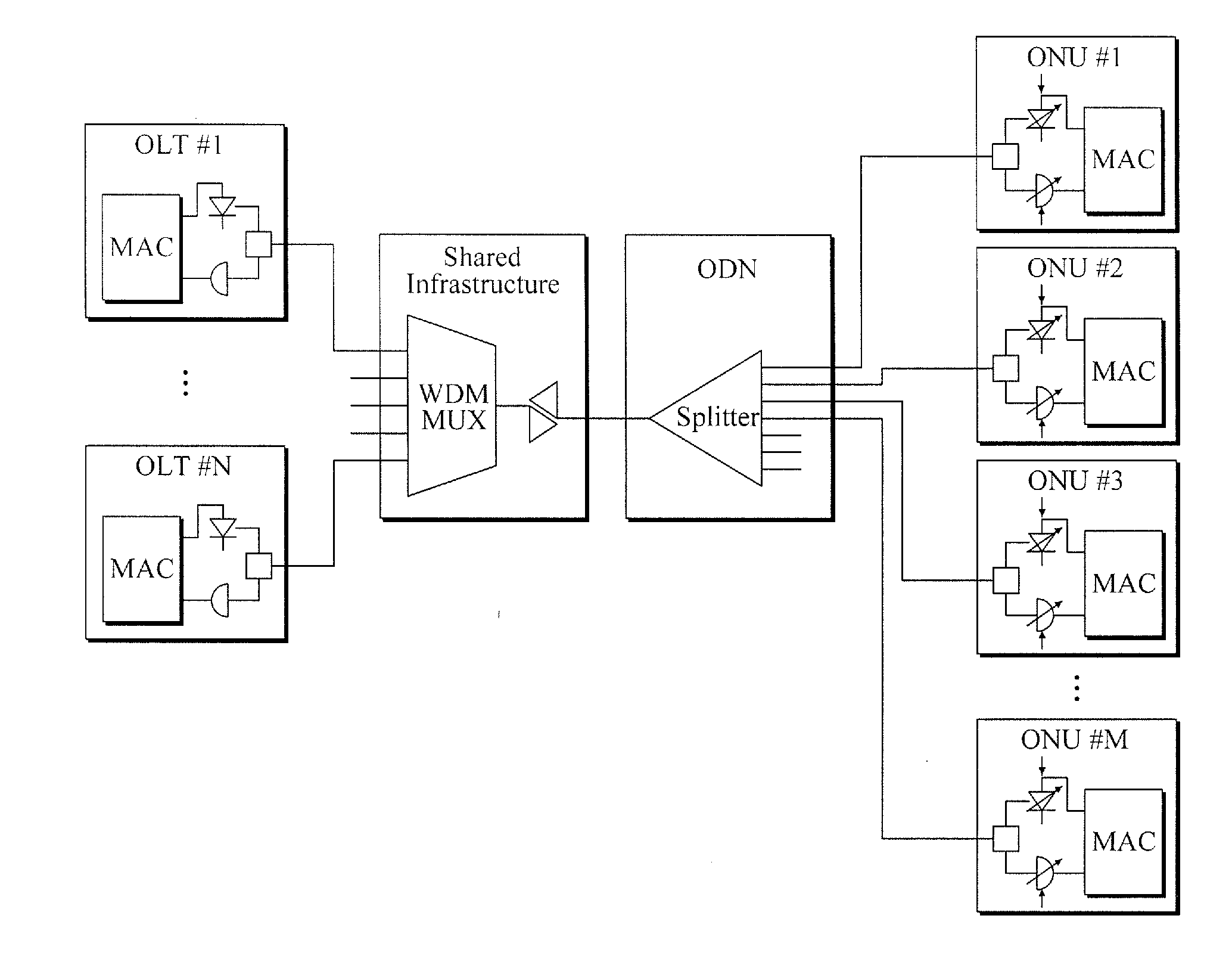
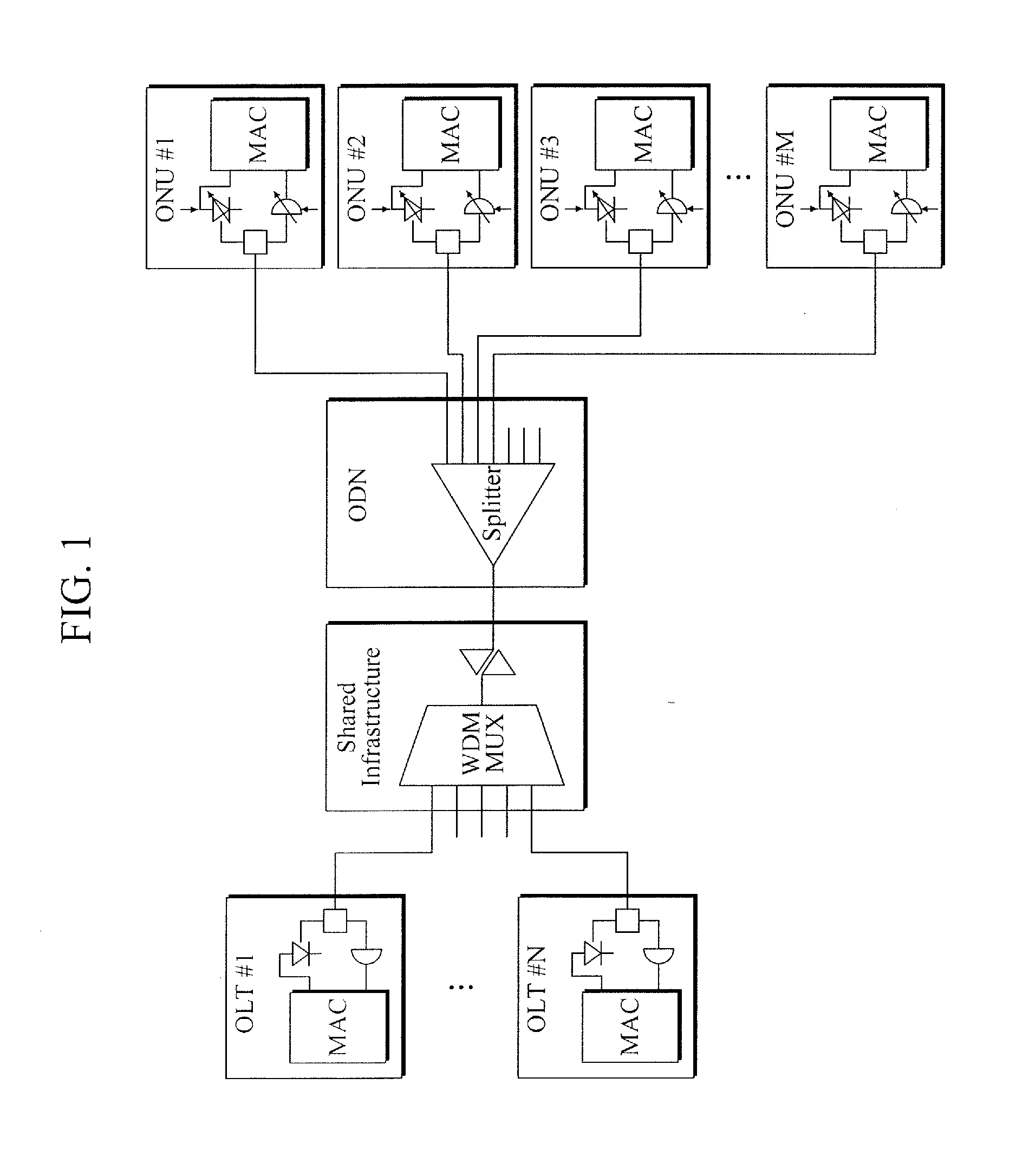
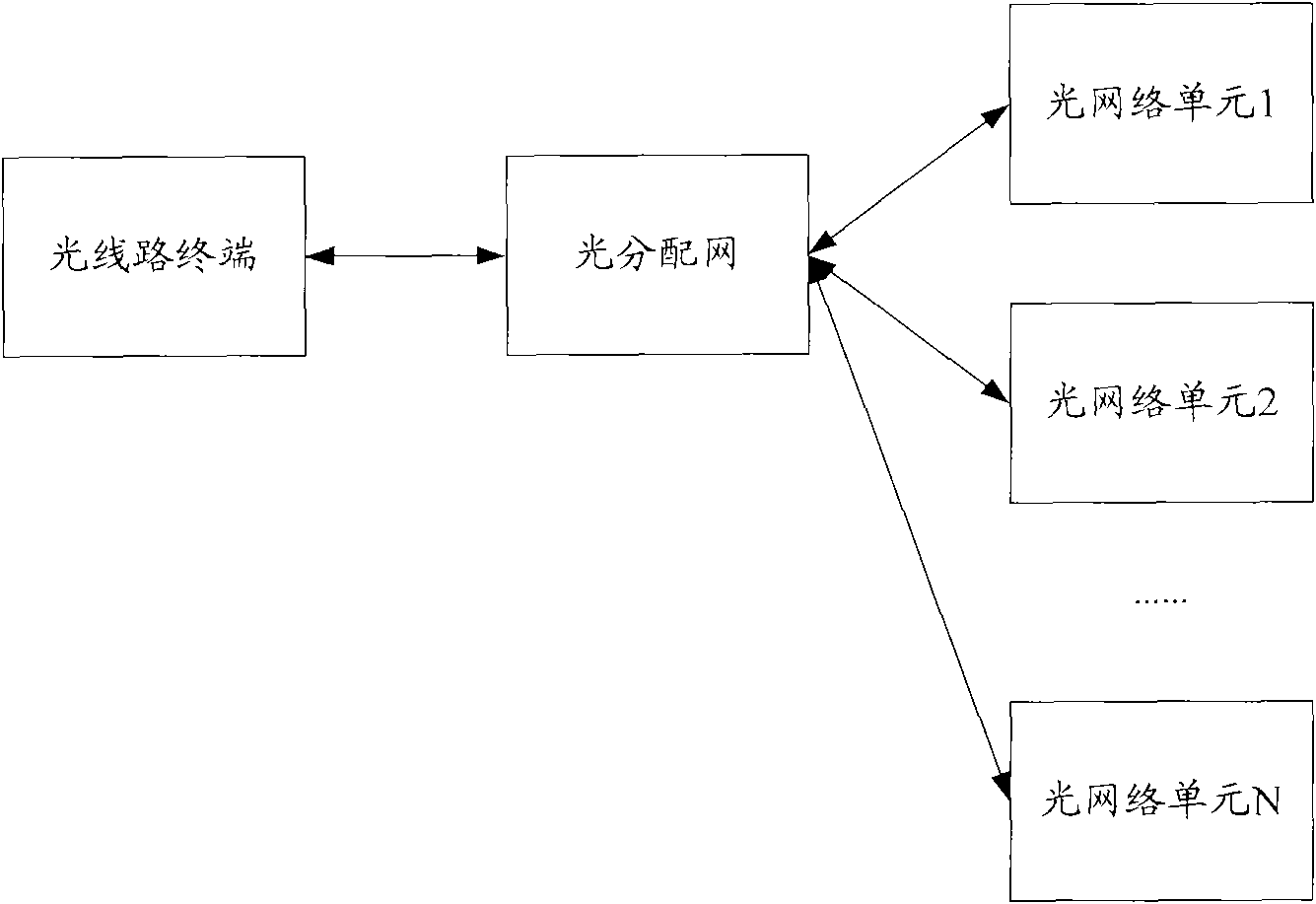
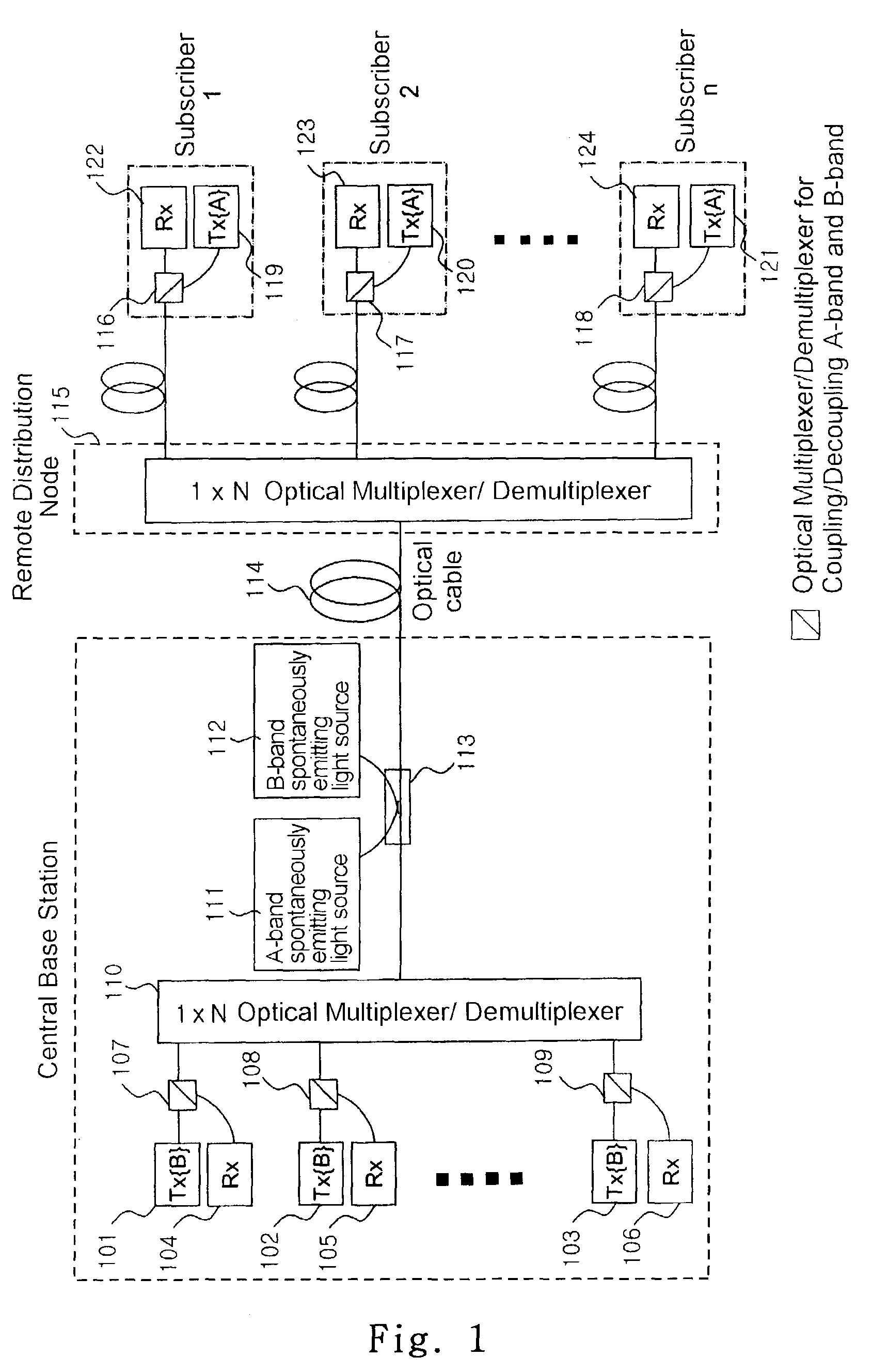
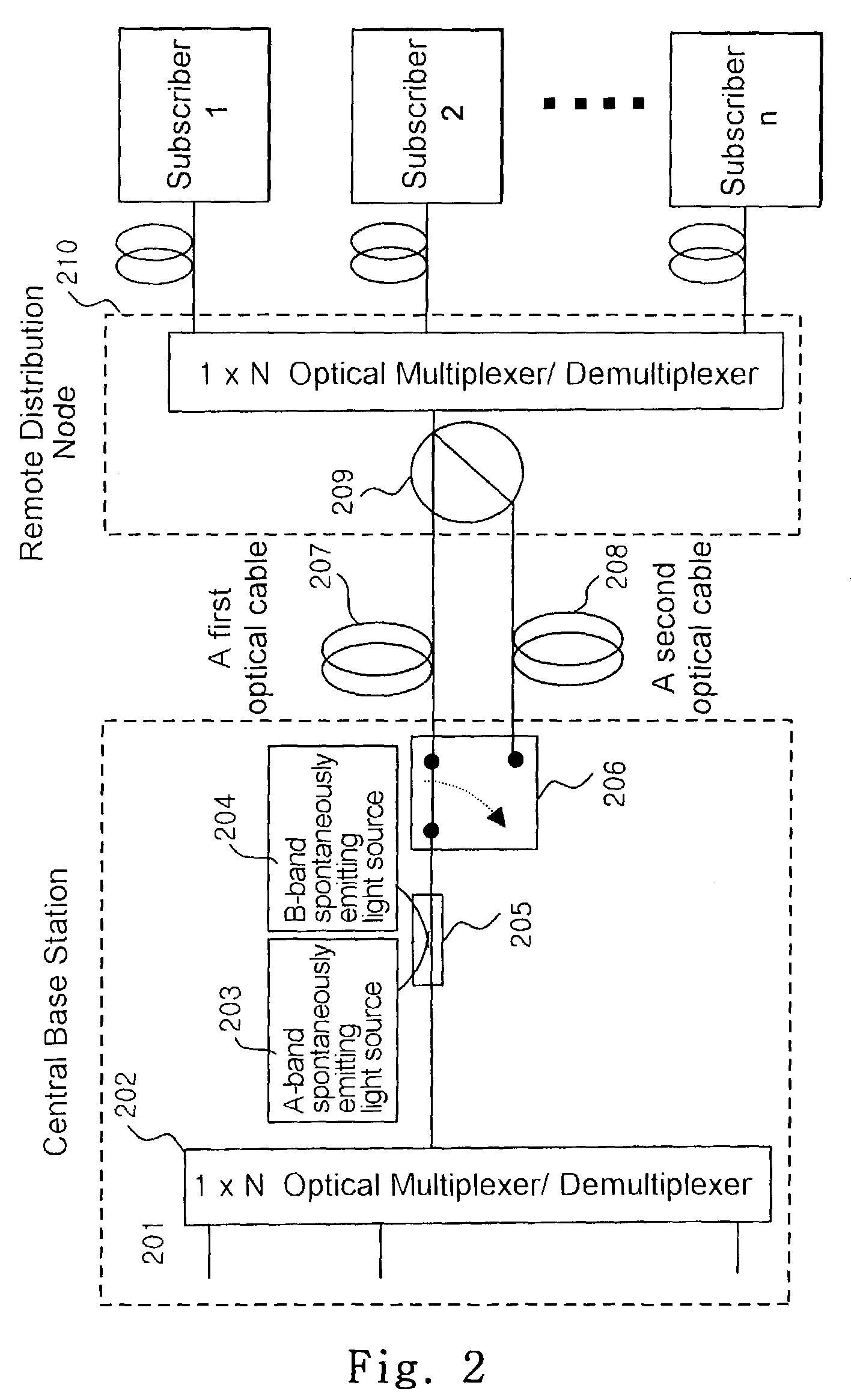
Wavelength division multiplexing-passive optical network system
ActiveUS9008513B2Preventing most of the lossIncrease distanceWavelength-division multiplex systemsMultimode transmissionOptical line terminationOptical transmitter
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
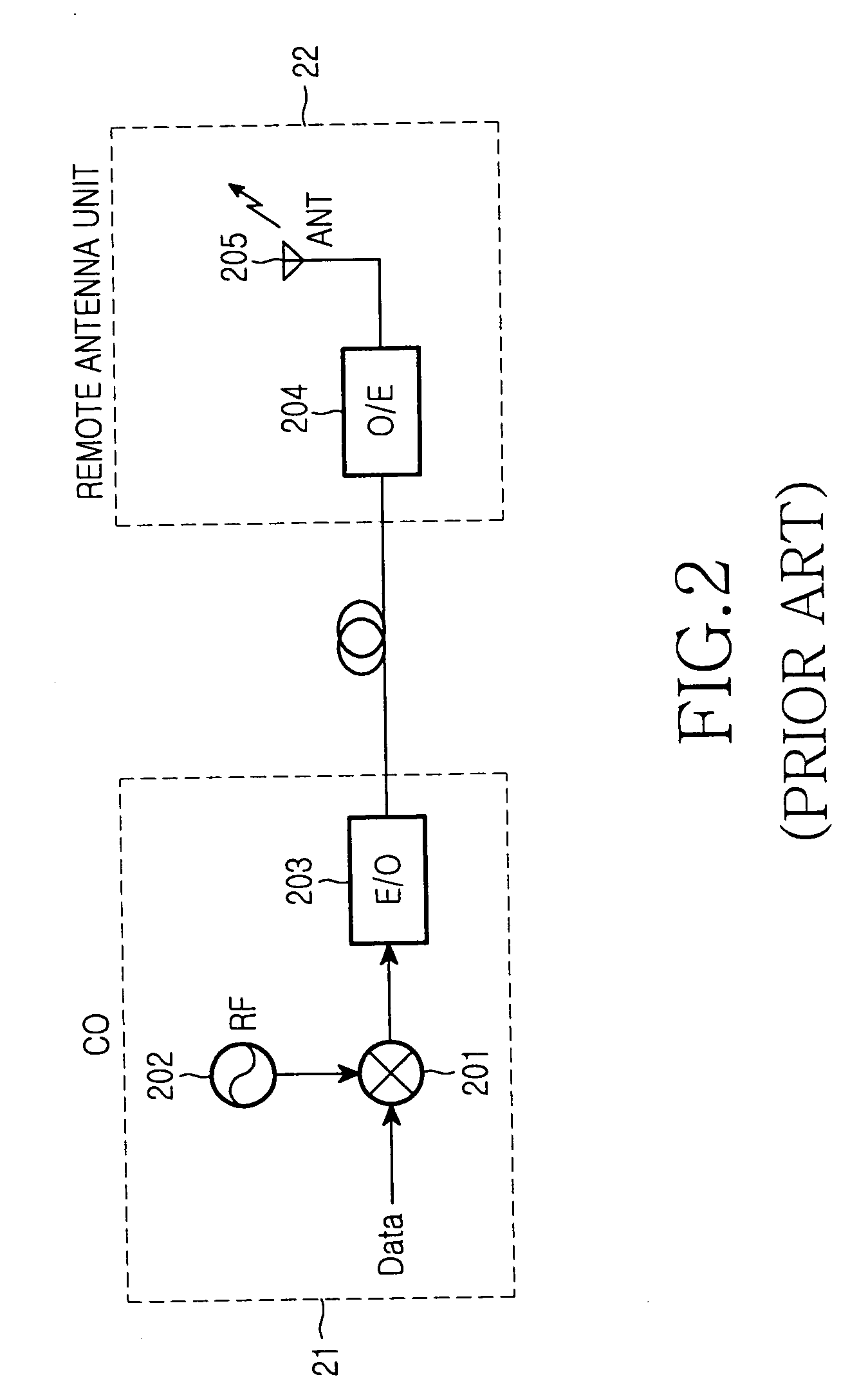
Integrated wired and wireless WDM PON apparatus using mode-locked light source
InactiveUS20060182446A1Low costEfficient wireless integrationIndoor gamesWavelength-division multiplex systemsMode-lockingBroadband
Integrated wired and wireless wavelength division multiplexing passive optical network (WDM PON) apparatus using a light source mode-locked to fed incoherent light includes: a fed light generator for providing fed light for up / downstream signals via a broadband light source emitting an incoherent optical signal; a central office (CO) for receiving, mode-locking, and downstream-optical-transmitting the incoherent optical signal generated by the fed light generator and receiving and optical-detecting an upstream optical signal transmitted from a subscriber unit; and the subscriber unit for receiving, mode-locking, and upstream-optical-transmitting the incoherent optical signal generated by the fed light generator and receiving and optical-detecting a downstream optical signal transmitted from the CO, wherein a wired optical transmitter for transmitting a baseband wired signal and a wireless optical transmitter for transmitting a high frequency radio frequency (RF) signal are comprised for up / downstream optical transmission of the CO and the subscriber unit.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method for operating wavelength-division-multiplexed passive optical network
InactiveUS20060115271A1Avoid wastingEasy to useTime-division optical multiplex systemsWavelength-division multiplex systemsControl channelLength wave
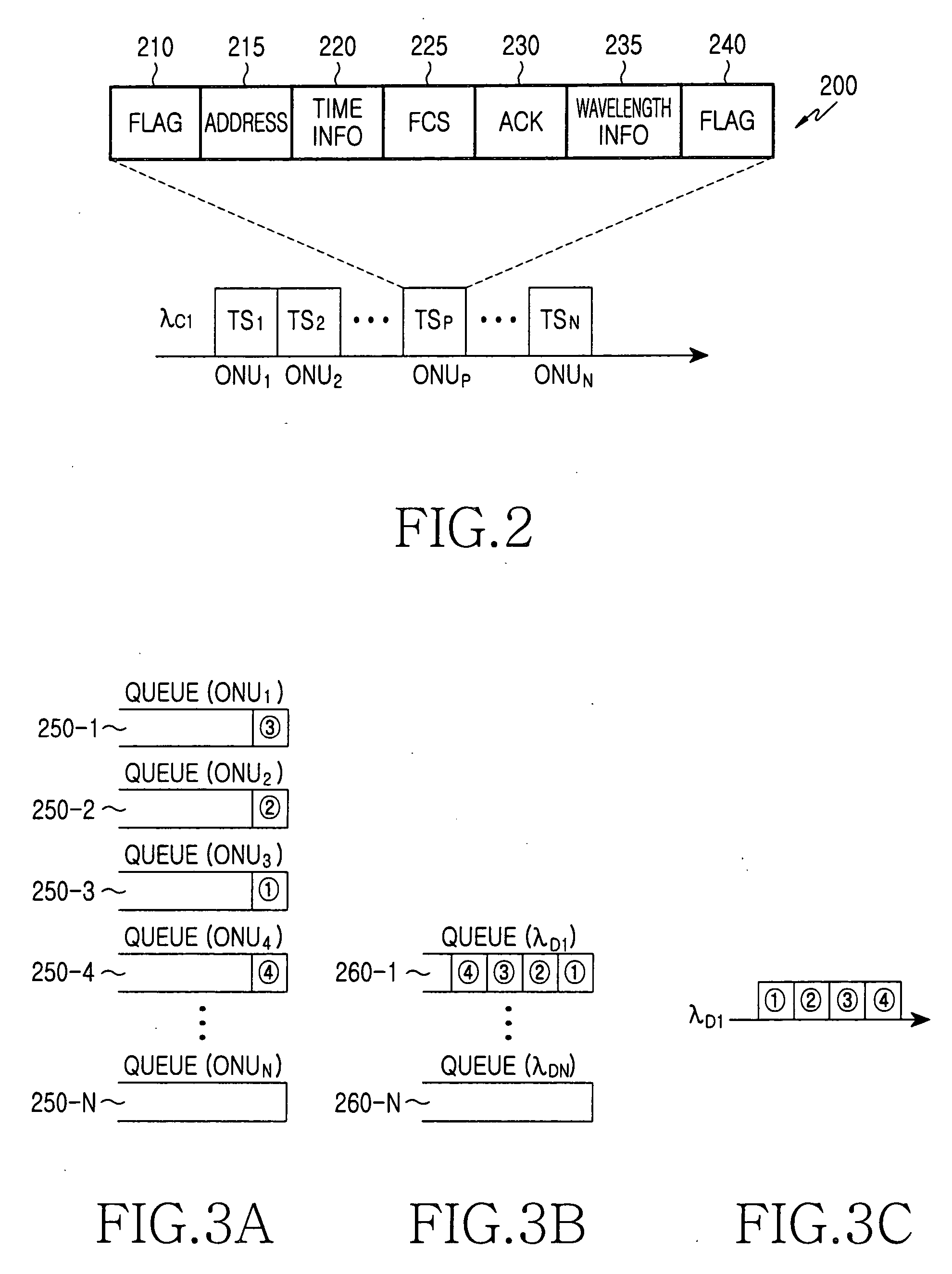
Disclosed is a method for operating a wavelength-division-multiplexed passive optical network (WDM-PON) including an optical line terminal (OLT) and a plurality of optical network units (ONUs), each of which is connected to the OLT and communicates with the OLT. The method comprises the steps of transmitting a first control channel including allocation information of downstream data channels and allocation information of time slots for the downstream data channels to each of the plurality of ONUs; and transmitting downstream data to the plurality of ONUs using their associated downstream data channels, each having at least one time slot, based on the information included in the first control channel.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
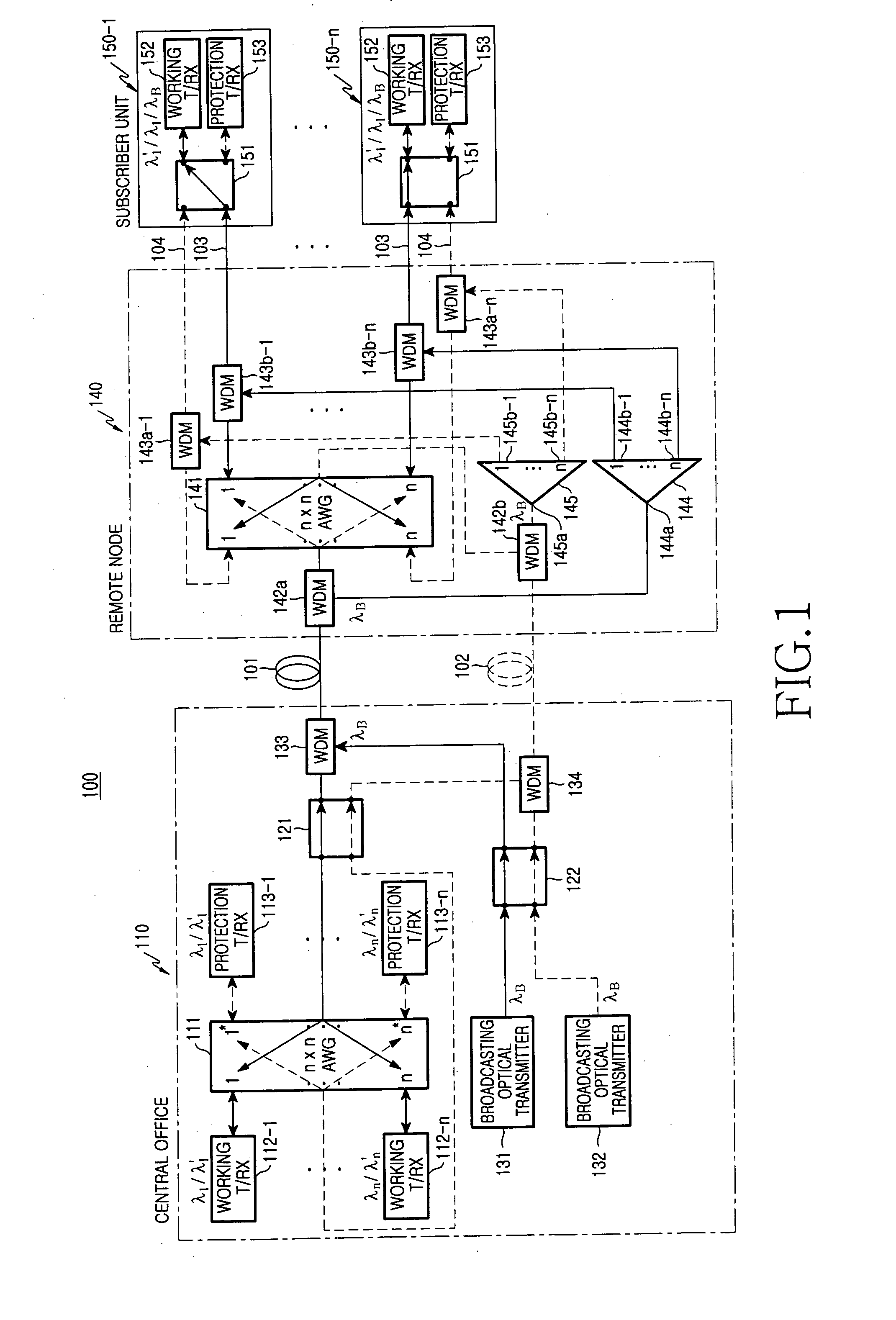
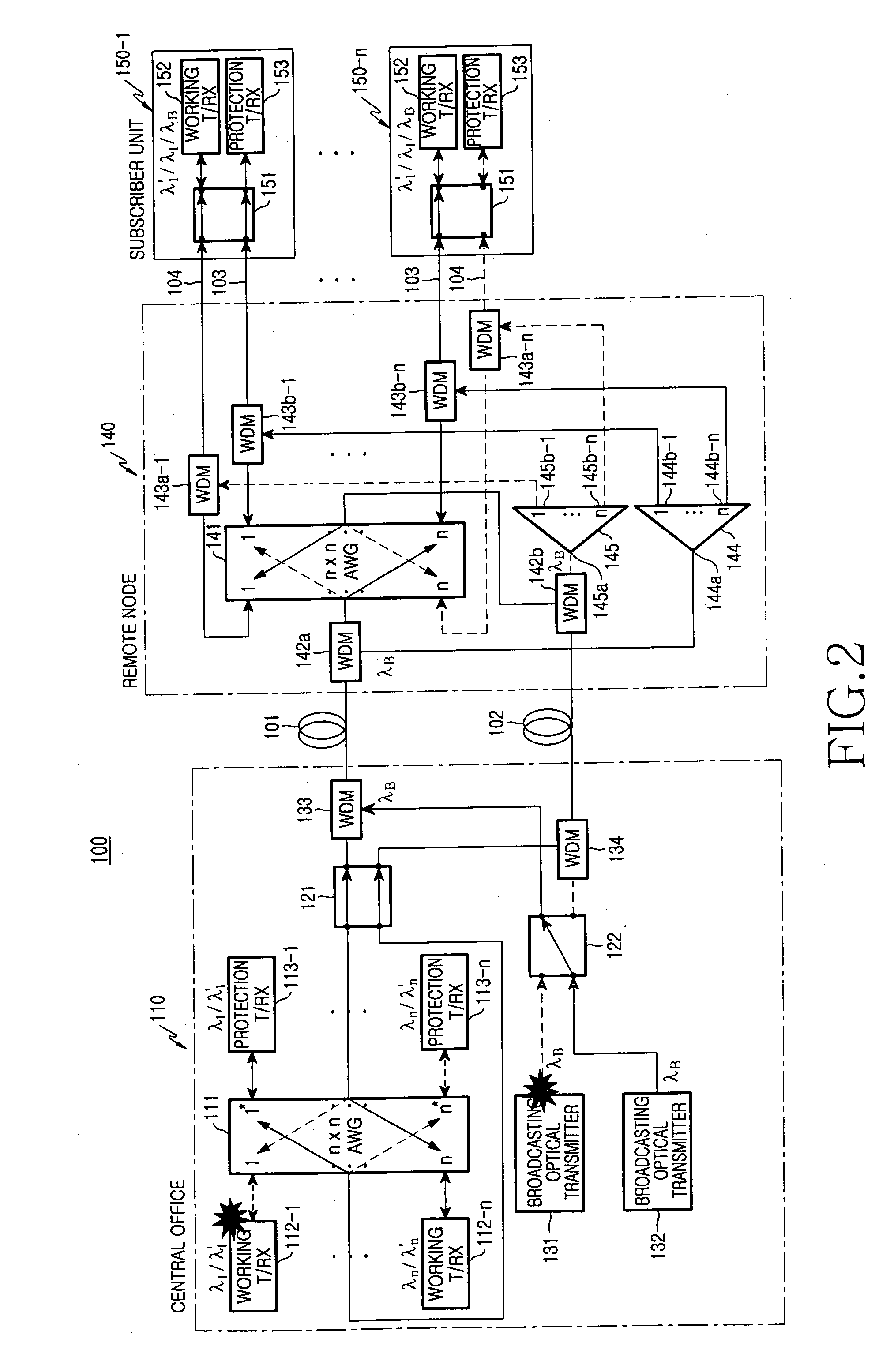
Communication recovering system for wavelength division multiplexed passive optical network
ActiveUS20060104638A1Enhance economical efficiencyMargin is maximizedLaser detailsOptical multiplexTransceiverNetwork structure
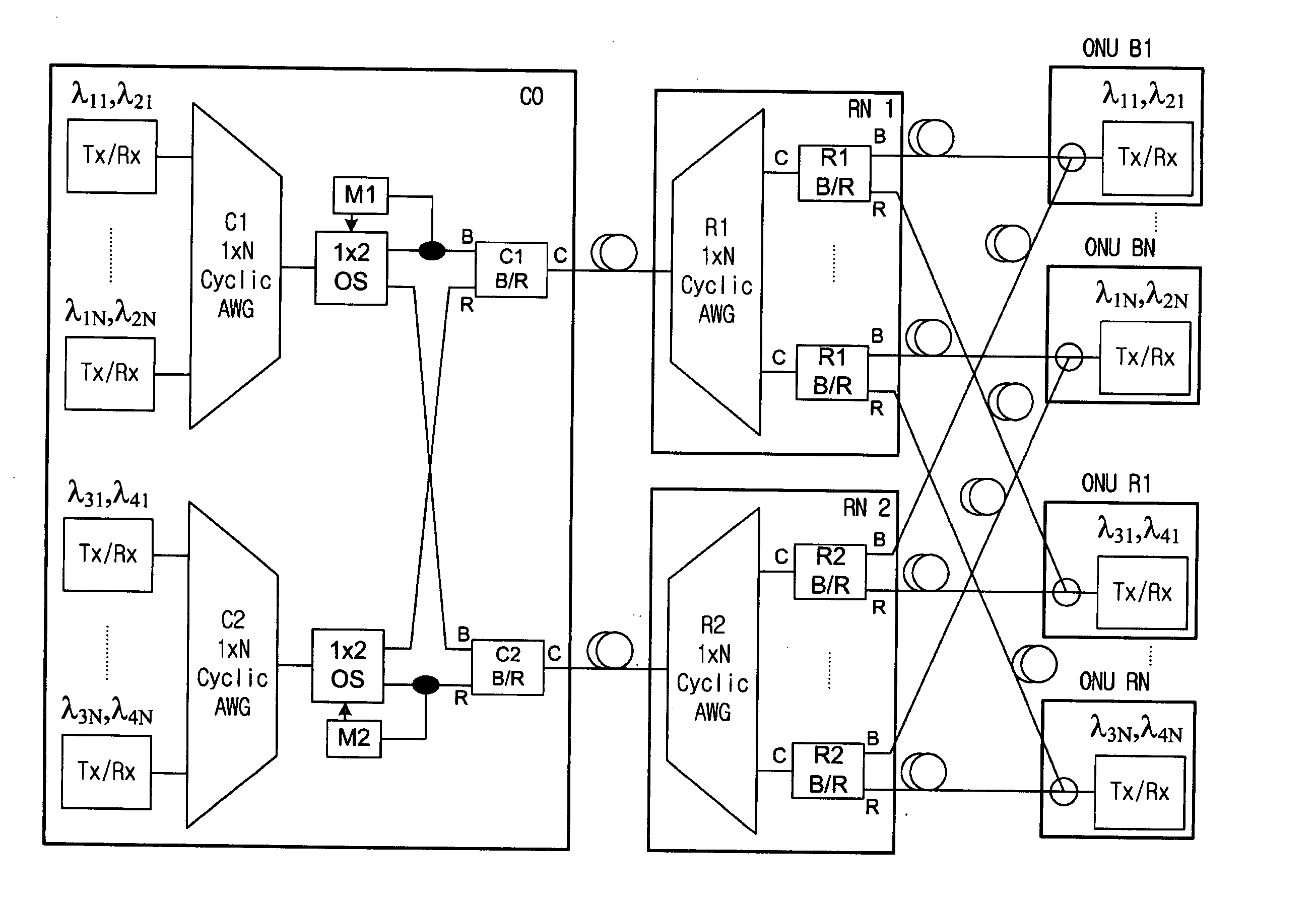
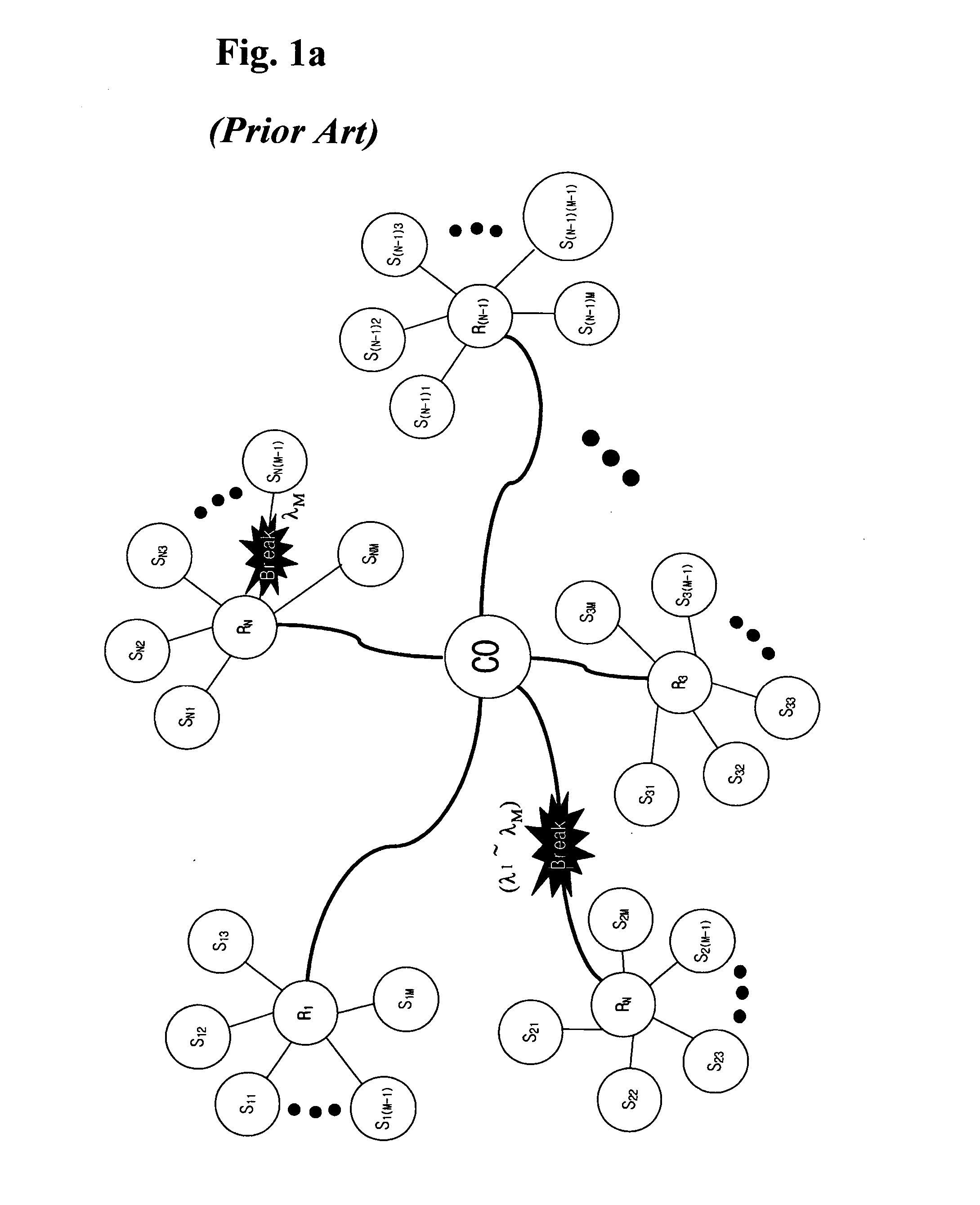
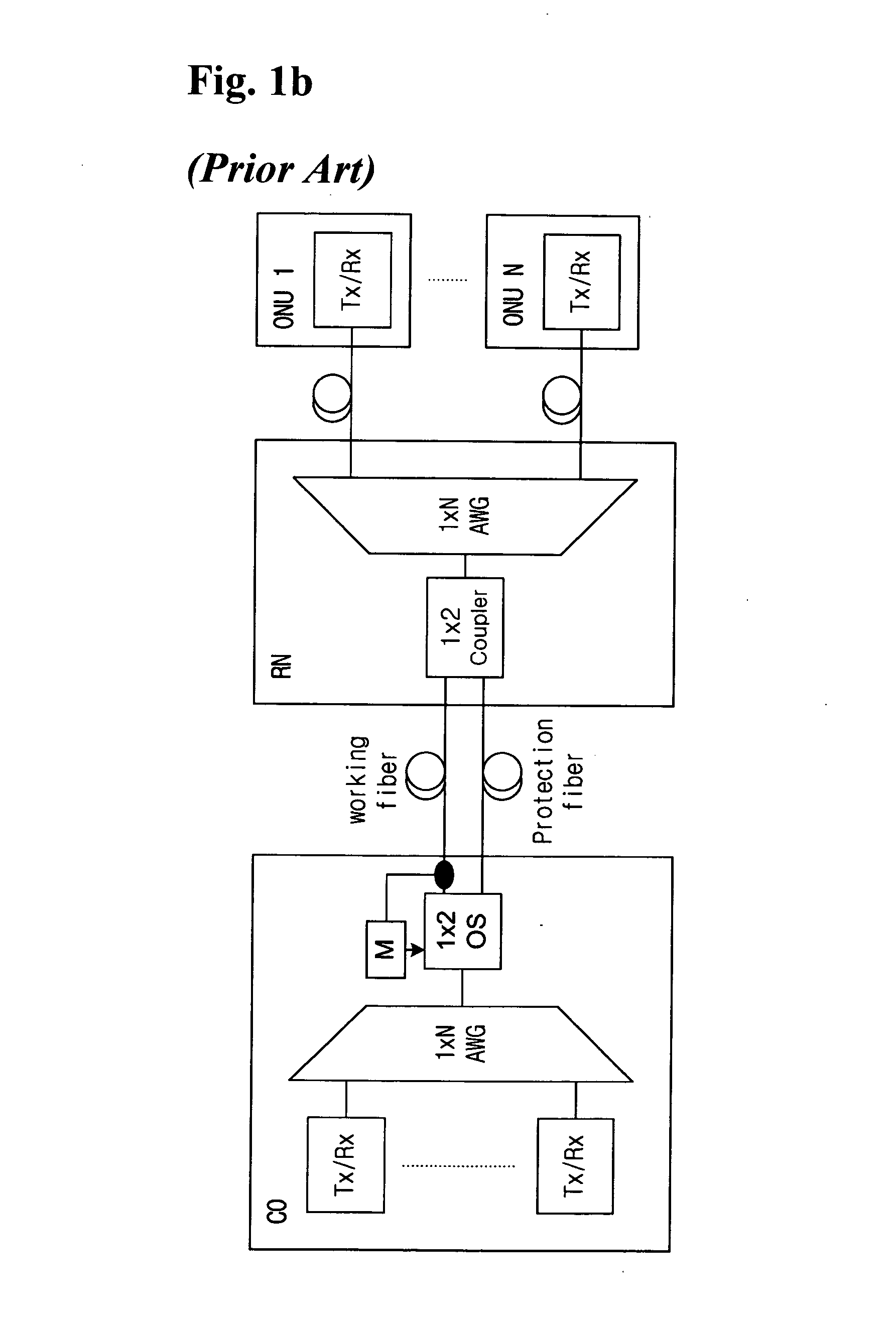
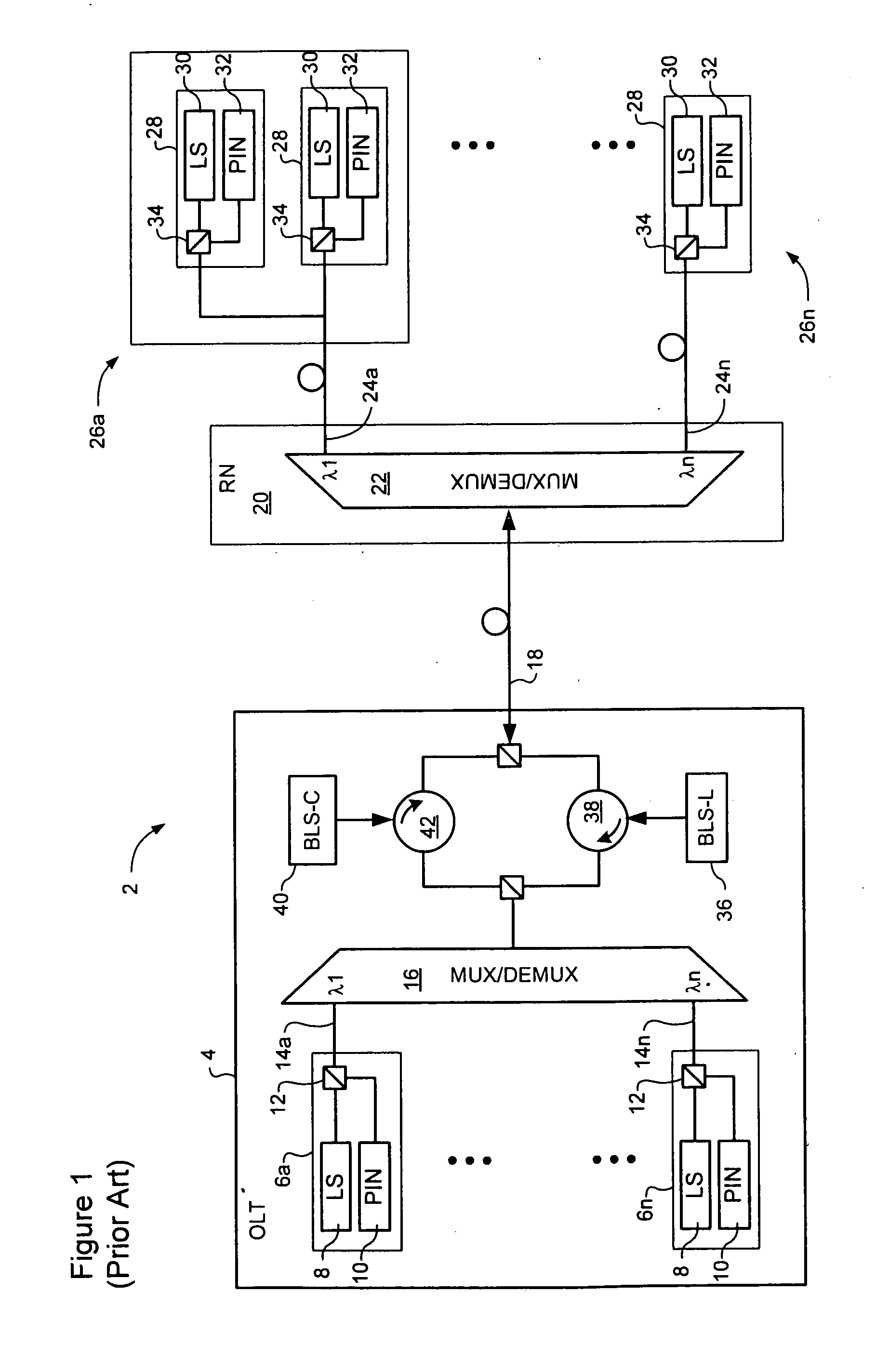
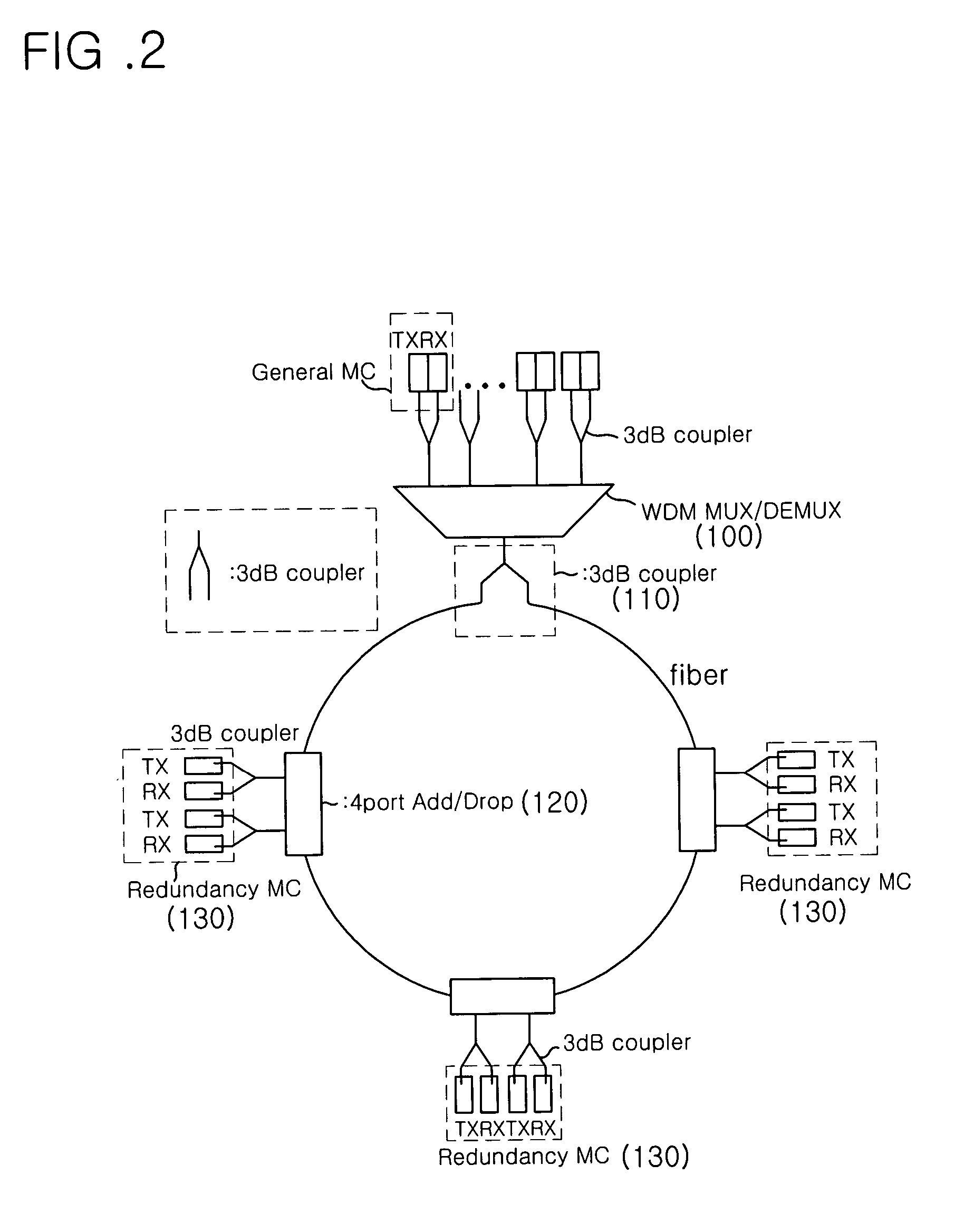
A communication recovering system for a wavelength division multiplexed passive optical network (WDM PON). The communication recovering system can recover fault of optical fibers between the central office and the remote nodes without additional optical fibers by grouping two remote nodes and employing an AWG having periodic transmission characteristics, and can also simply and rapidly recover such a fault with minimal optical loss using an AWG of 2×N structure and an On-Off optical switch, although protection optical fibers are additionally installed therein. The system can rapidly recover fault of optical fibers between a local office and optical network units, 1:N manner, using 2×2 optical switches, which are installed to each of the optical network units, a reserved transmitter and receiver, and a transceiver. The communication recovering system has advantages in that it can simplify network structure, be cost-effectively implemented, reduce optical loss, and rapidly perform protection of optical fiber fault.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
Method for decreasing and compensating the transmission loss at a wavelength-division-multiplexed passive optical network and an apparatus therefor
InactiveUS20030142978A1Decreasing and compensating optical lossLaser detailsWavelength-division multiplex systemsLength waveTransmission loss
The present invention relates to a wavelength-division multiplexed passive optical network. In particular, it relates to a technology for minimizing the optical loss at a wavelength-division multiplexed passive optical network based on wavelength-locked light source Thereby it improves the transmission quality and increases the transmission distance. A 4-port optical path setting device of the present invention increases the amount of light injected into an optical transmitter and thereby improves the wavelength-locking characteristic of a light source. In addition, it can decrease the optical transmission loss in an optical transmission path, and by an optical amplifier being inserted therein; it can also compensate the optical loss in an optical transmission path. In the present invention, a 4-port optical path setting device having the characteristics described above and a method for fault recovery without an additional optical loss are presented.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
Wavelength-division multiplexing-passive optical network
InactiveUS20060153567A1Enhanced advantageWavelength-division multiplex systemsStar/tree networksEngineeringTime-division multiplexing
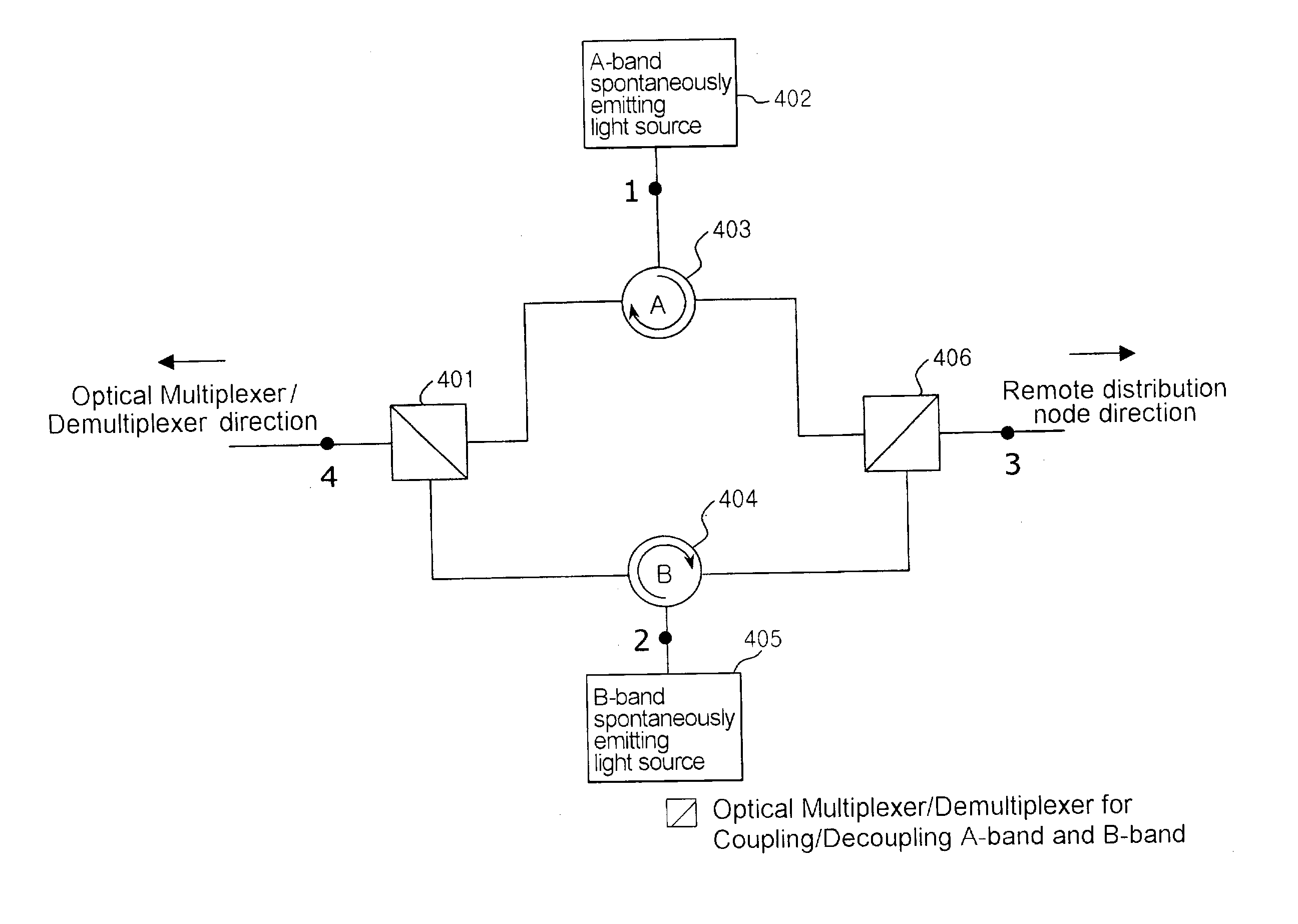
Disclosed is a wavelength-division multiplexing-passive optical network having a central office including a plurality of first working and protection transmit / receive modules, working and protection optical transmitters, and a plurality of first optical switches, the first working and protection transmit / receive modules generating downstream optical signals and detecting upstream optical signals having corresponding wavelengths, the working and protection optical transmitters generating broadcasting optical signals, the first optical switches performing a switching operation when faults occur, a plurality of subscriber units for receiving broadcasting optical signals and downstream optical signals having corresponding wavelengths and generating upstream optical signals, the subscriber units including second optical switches, a remote node including working and protection optical splitters for dividing intensity of the broadcasting optical signals, the remote node being positioned between the subscriber units and the central office, working and protection main optical fibers for linking the central office with the remote node; and a plurality of working and protection branch optical fibers for linking the remote node with the subscriber units, respectively.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Planar lightwave circuit (PLC) device wavelength tunable light source comprising the same device and wavelength division multiplexing-passive optical network (wdm-pon) using the same light source
ActiveUS20100119231A1Improve performanceImprove stabilityWavelength-division multiplex systemsSolid-state devicesExternal cavity laserOptical axis alignment
In the manufacture and application of a PLC-ECL type wavelength tunable light source, provided is a wavelength tunable mechanism with improved performance and stability, a light source with improved packaging performance and mass productivity, and a light source applied to a WDM-PON with initialization and stabilization functions. The wavelength tunable light source having a PLC (planar lightwave circuit)-ECL (external cavity laser) structure includes a first housing in which a semiconductor optical gain medium is mounted, a second housing in which a PLC device is mounted, and a third housing in which an optical fiber is mounted. The first, second, and third housings make an optical axis alignment through an optical coupling lens and combined in a laser welding method.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
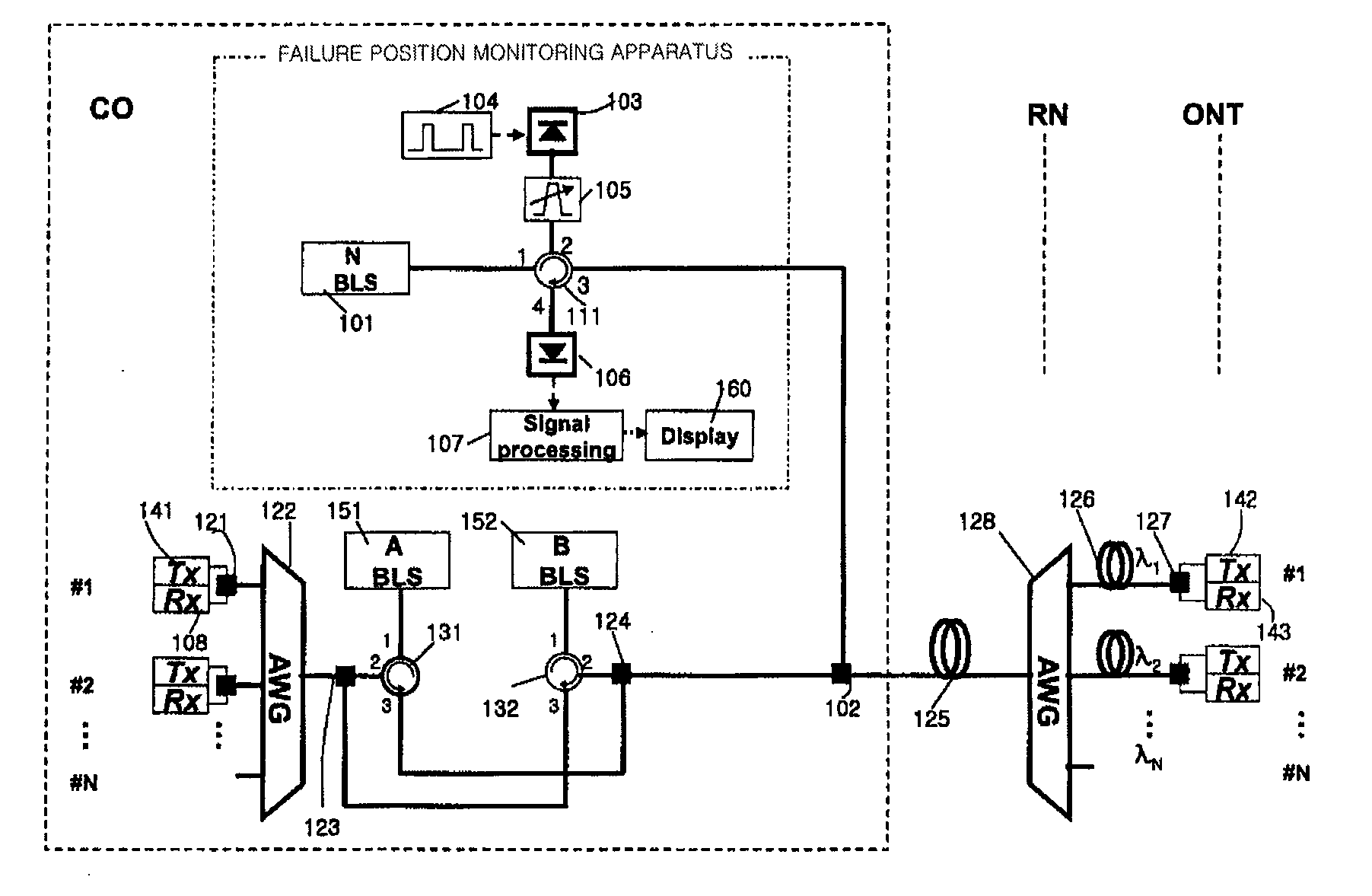
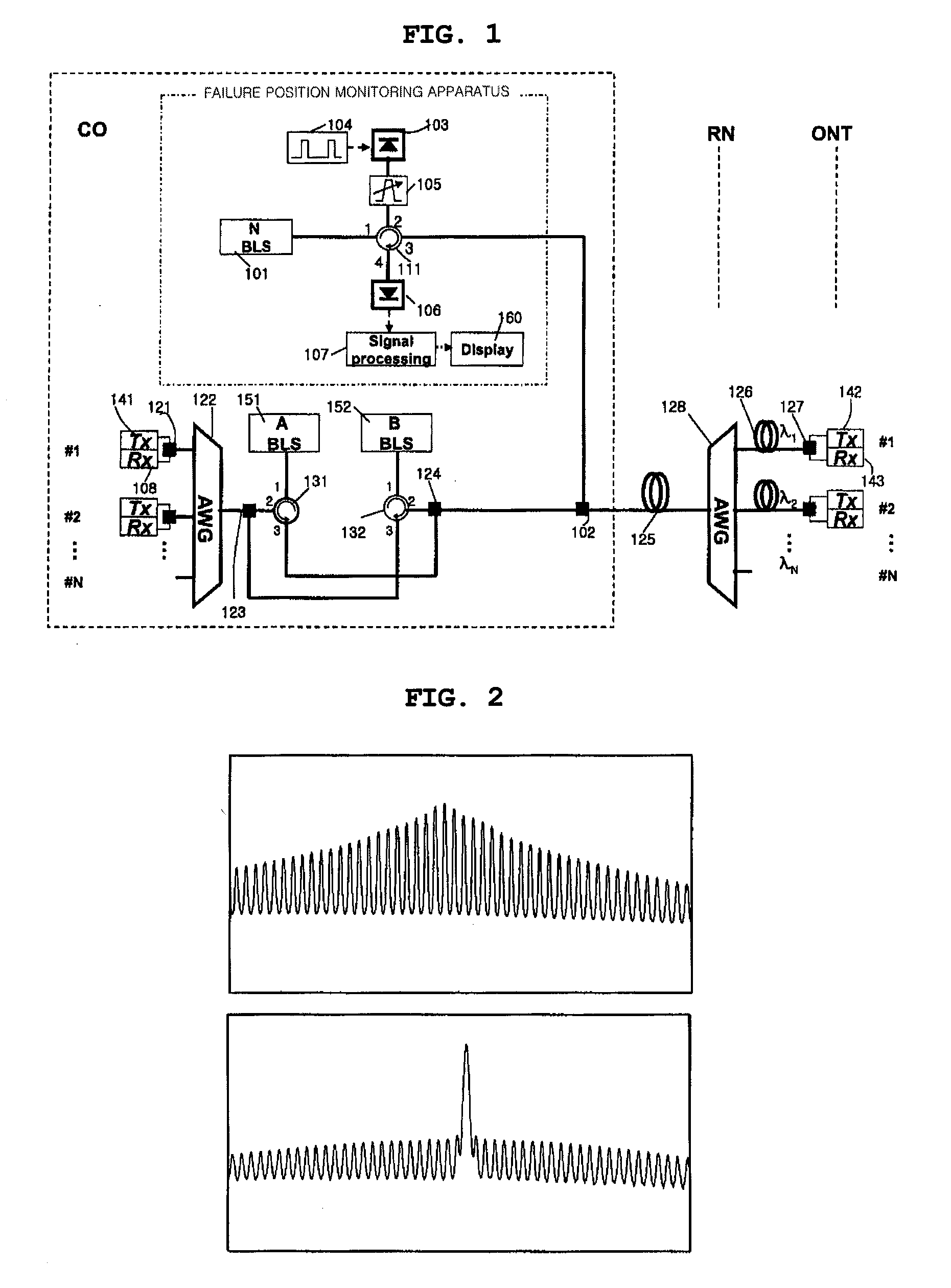
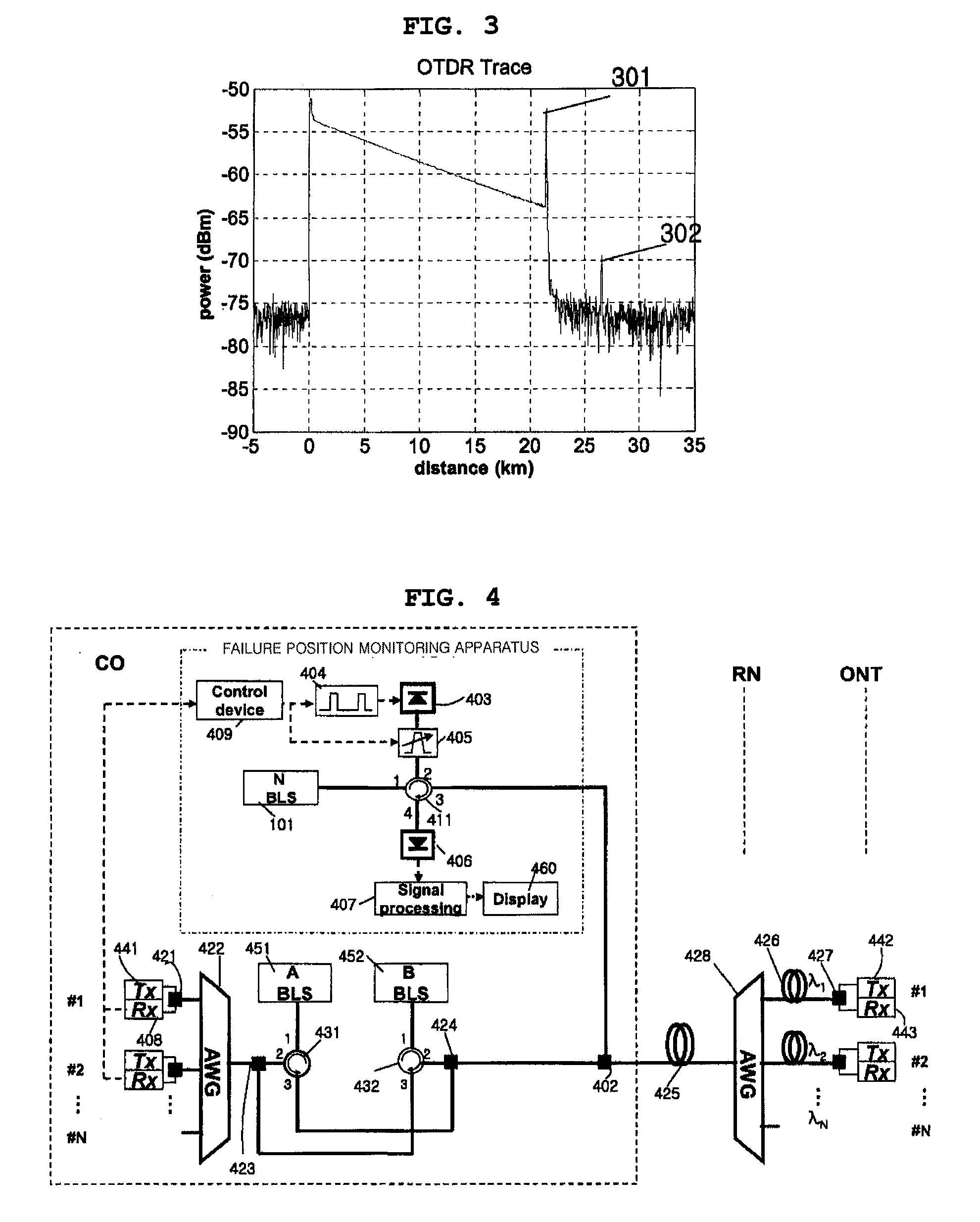
Fault localization apparatus for optical line in wavelength division multiplexed passive optical network
InactiveUS20060222364A1Efficient administrationImprove network reliabilityEar treatmentMedical devicesLength waveOptical network unit
A fault localization apparatus for an optical line in a wavelength division multiplexed passive optical network is disclosed. The apparatus can detect light loss and fault positions as a channel exhibiting an abnormal receiving state of signals received by each of the upstream receivers is checked, and a monitoring optical signal is used, in which the monitoring optical signal is generated as a pulse is inputted to a light source of the downstream transmitter corresponding to the channel showing such an abnormal receiving state. The apparatus according to the present invention can detect fault positions of optical lines between the central office and the remote nodes and between the remote nodes and the optical network units, since the light source of downstream channel in which faults occur is used as a monitoring light source. The apparatus according to the present invention can be cost-effectively implemented.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
Loop-back wavelength division multiplexing passive optical network
InactiveUS20060093360A1Eliminate power lossSimple structureWavelength-division multiplex systemsMultimode transmissionDriving currentAudio power amplifier
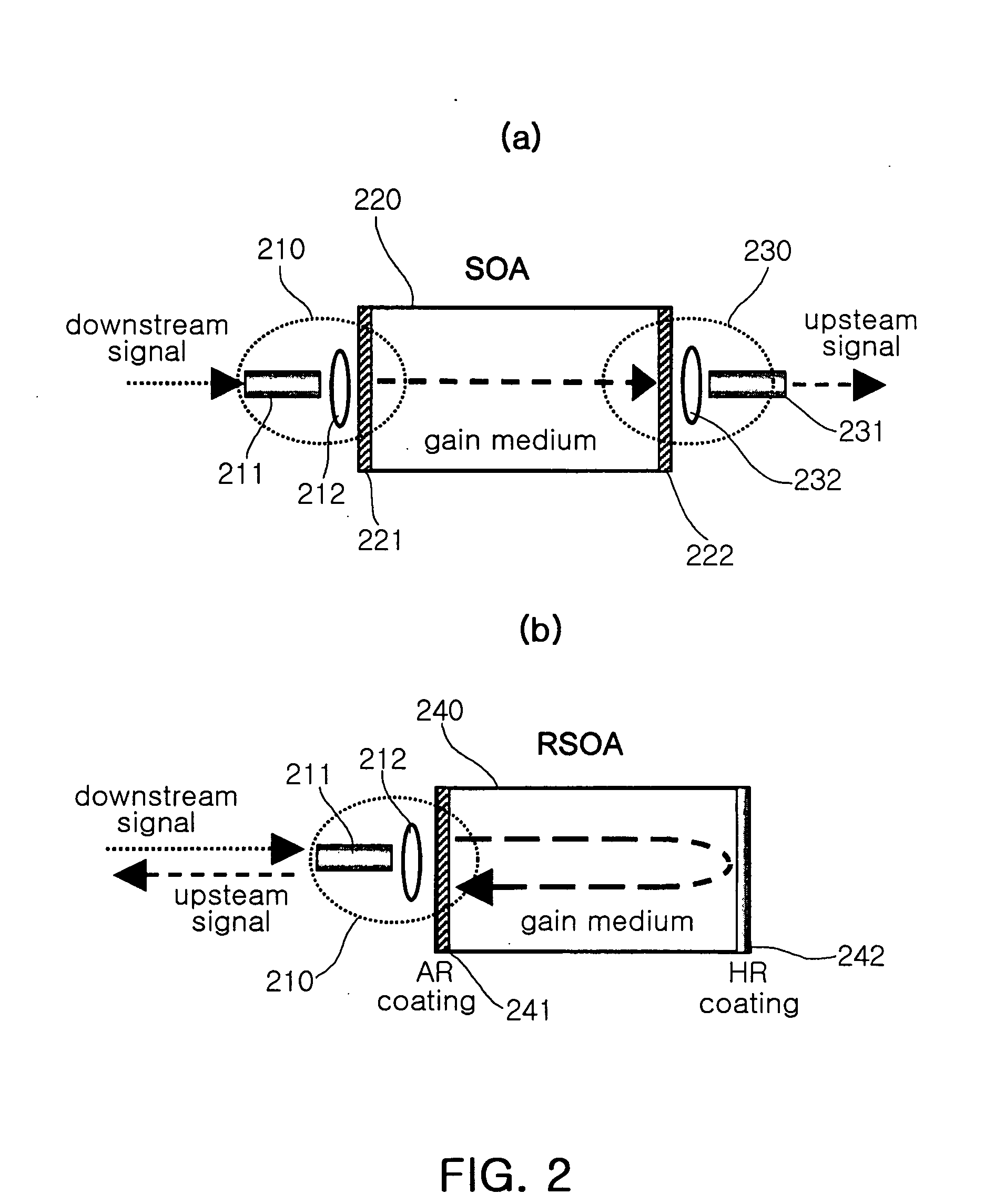
Disclosed herein is a loop-back Wavelength Division Multiplexing Passive Optical network (WDM-PON). The loop-back WDM-PON includes a coupler, a terminal receiver, and a reflective semiconductor amplifier. The coupler branches a downstream signal, which is transmitted from a central office, into first and second downstream signals. The terminal receiver receives and converts the first downstream signal into electrical signal and provides the electrical signal to a subscriber. The reflective semiconductor optical amplifier flattens modulated optical power of the second downstream signal input to the RSOA and re-modulating the flattened signal by changing driving current in response to upstream data.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
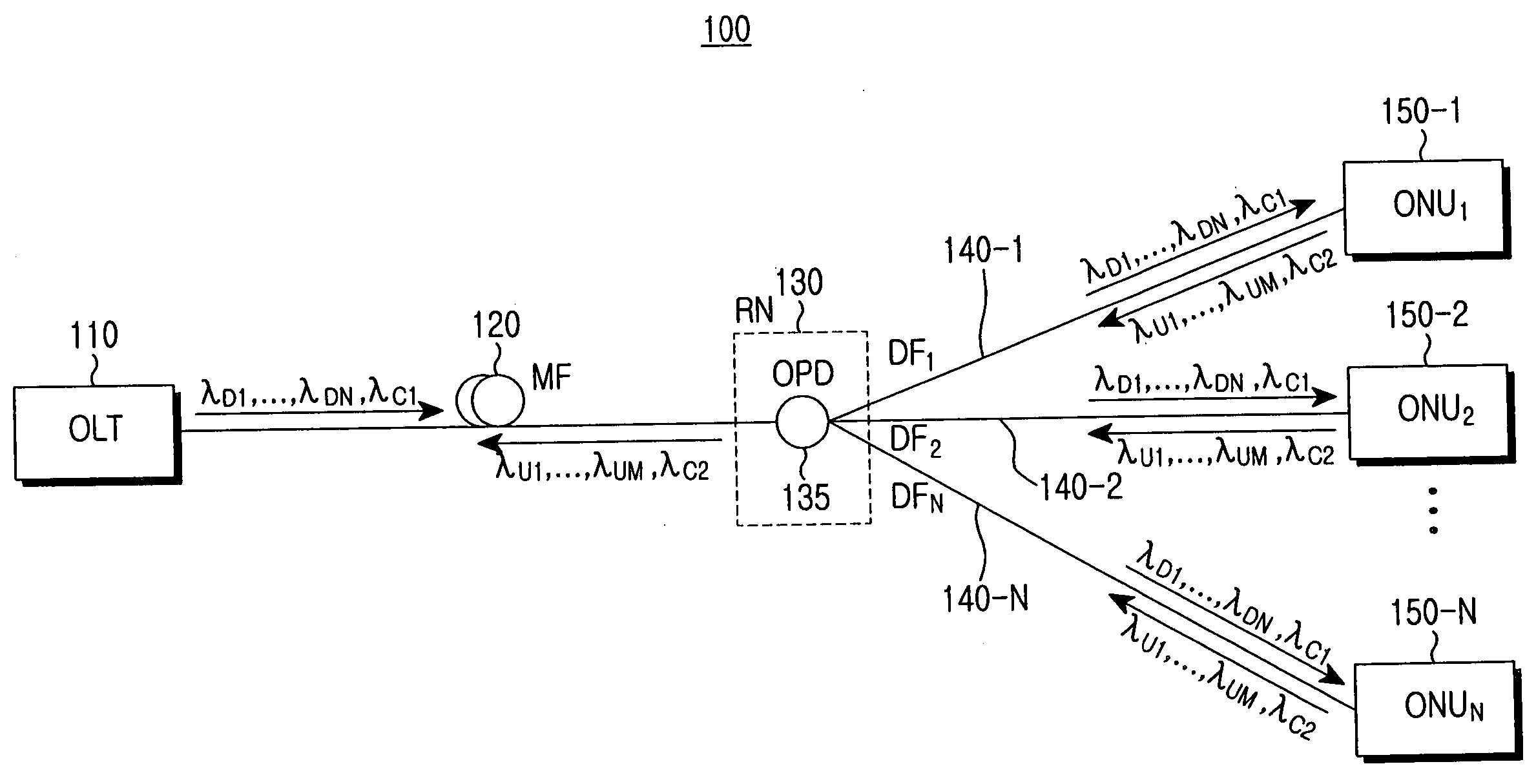
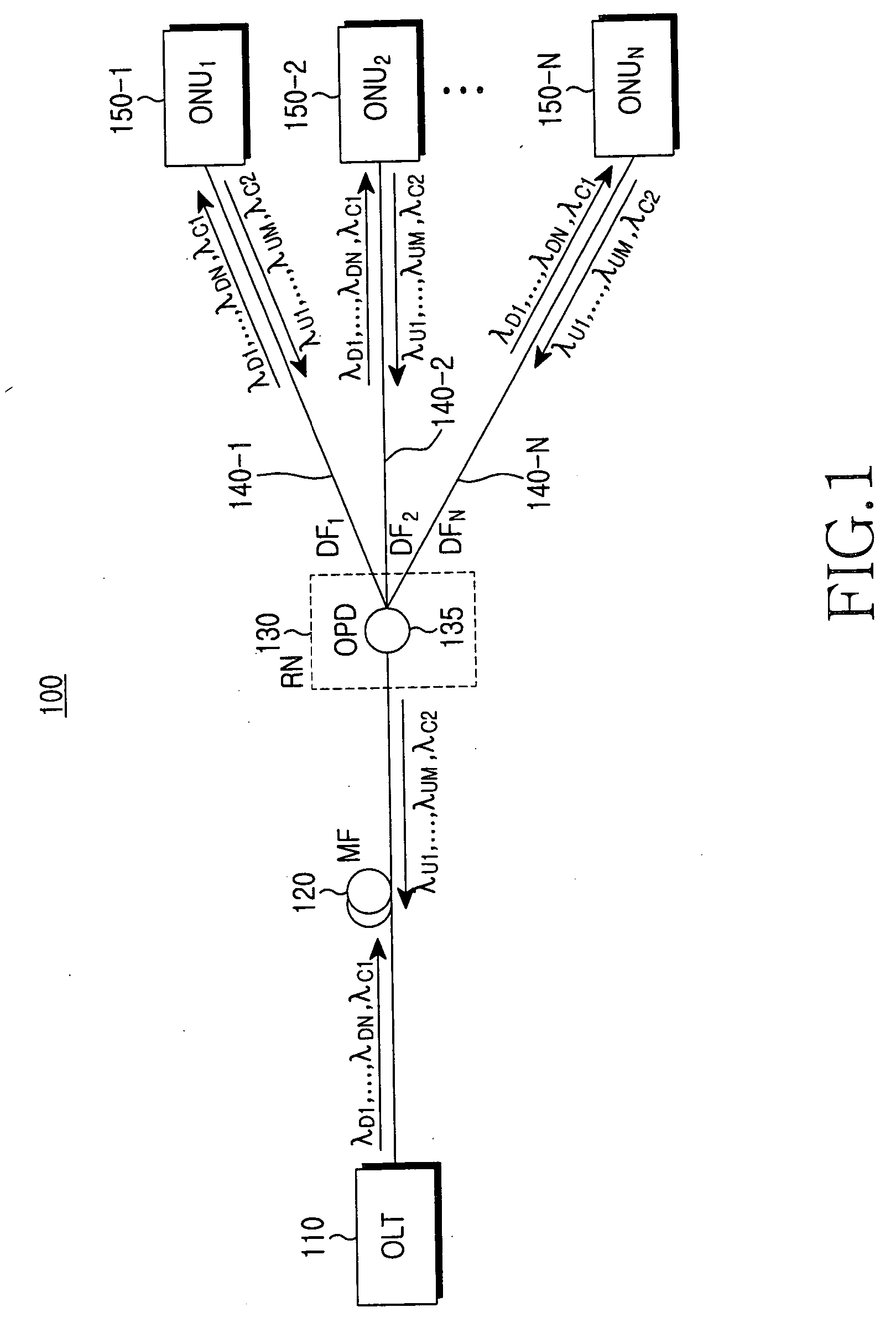
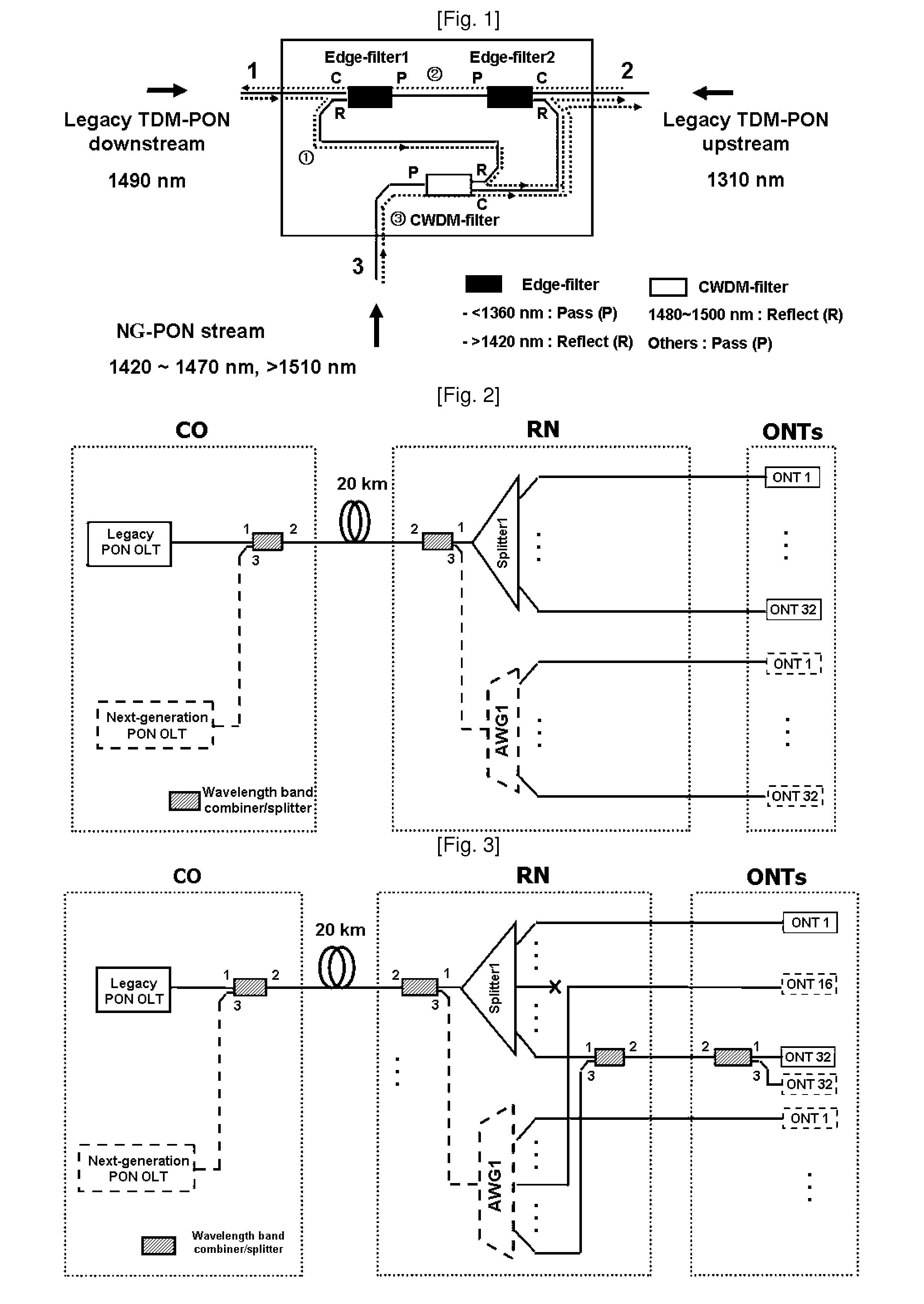
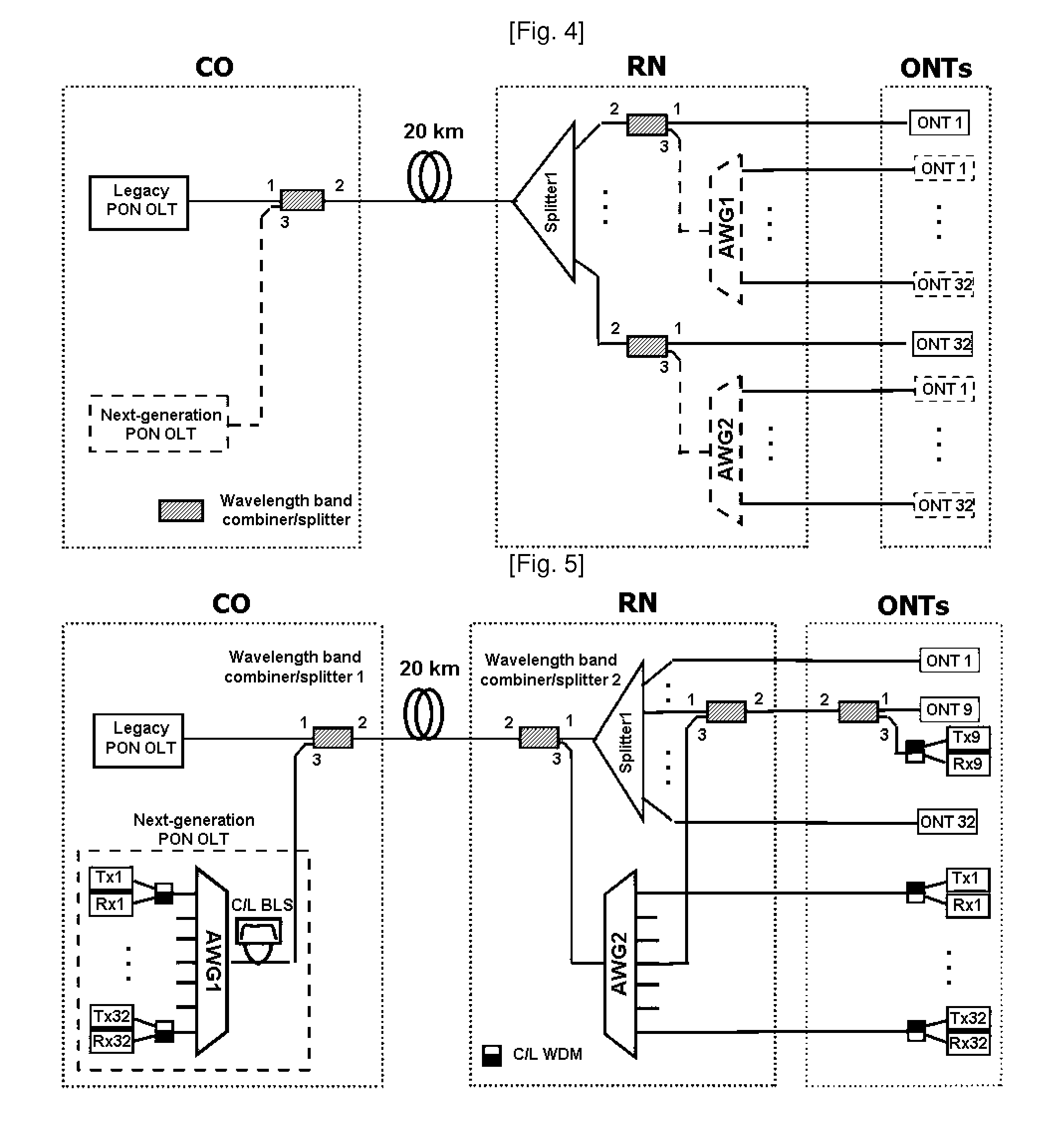
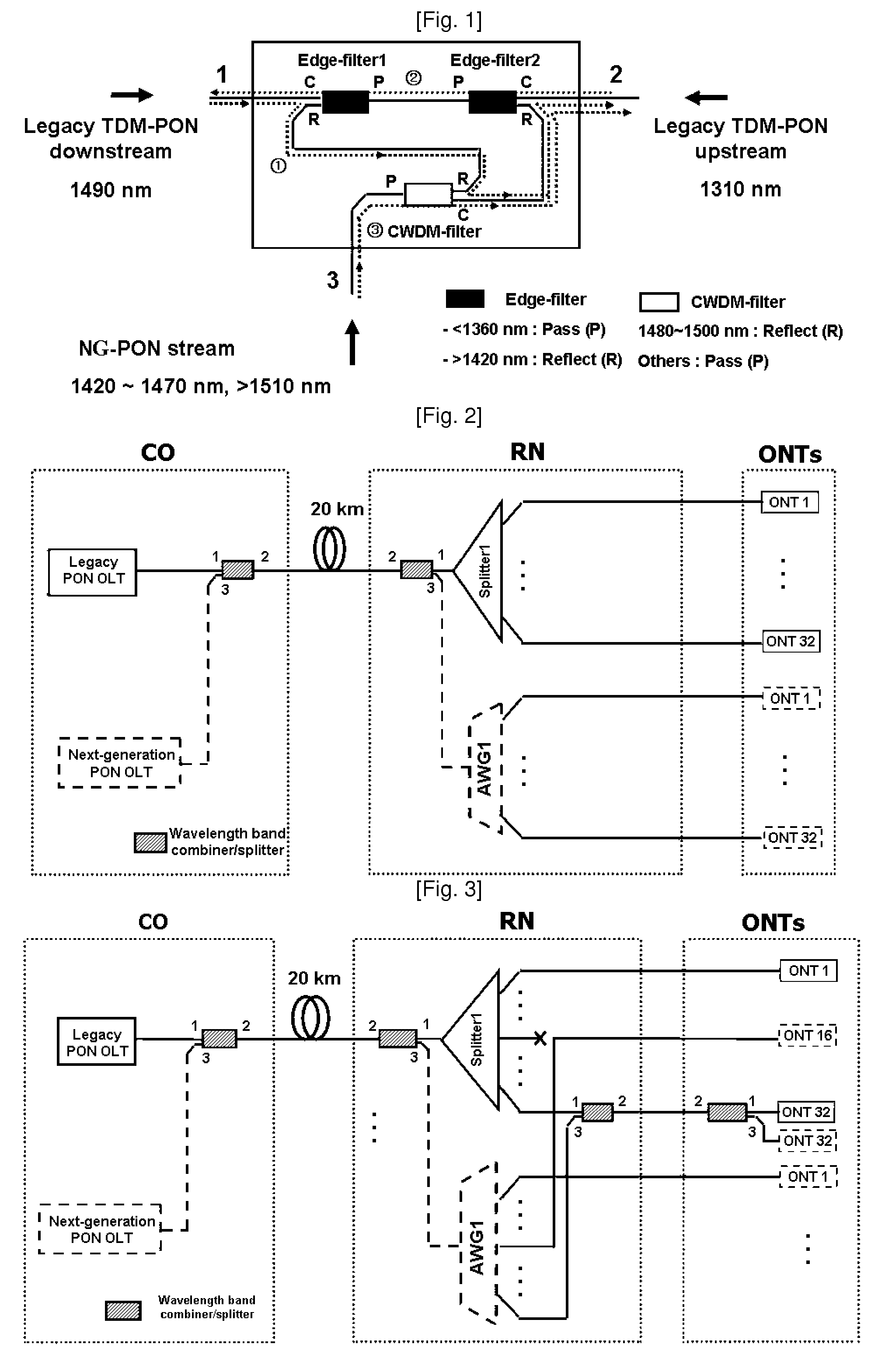
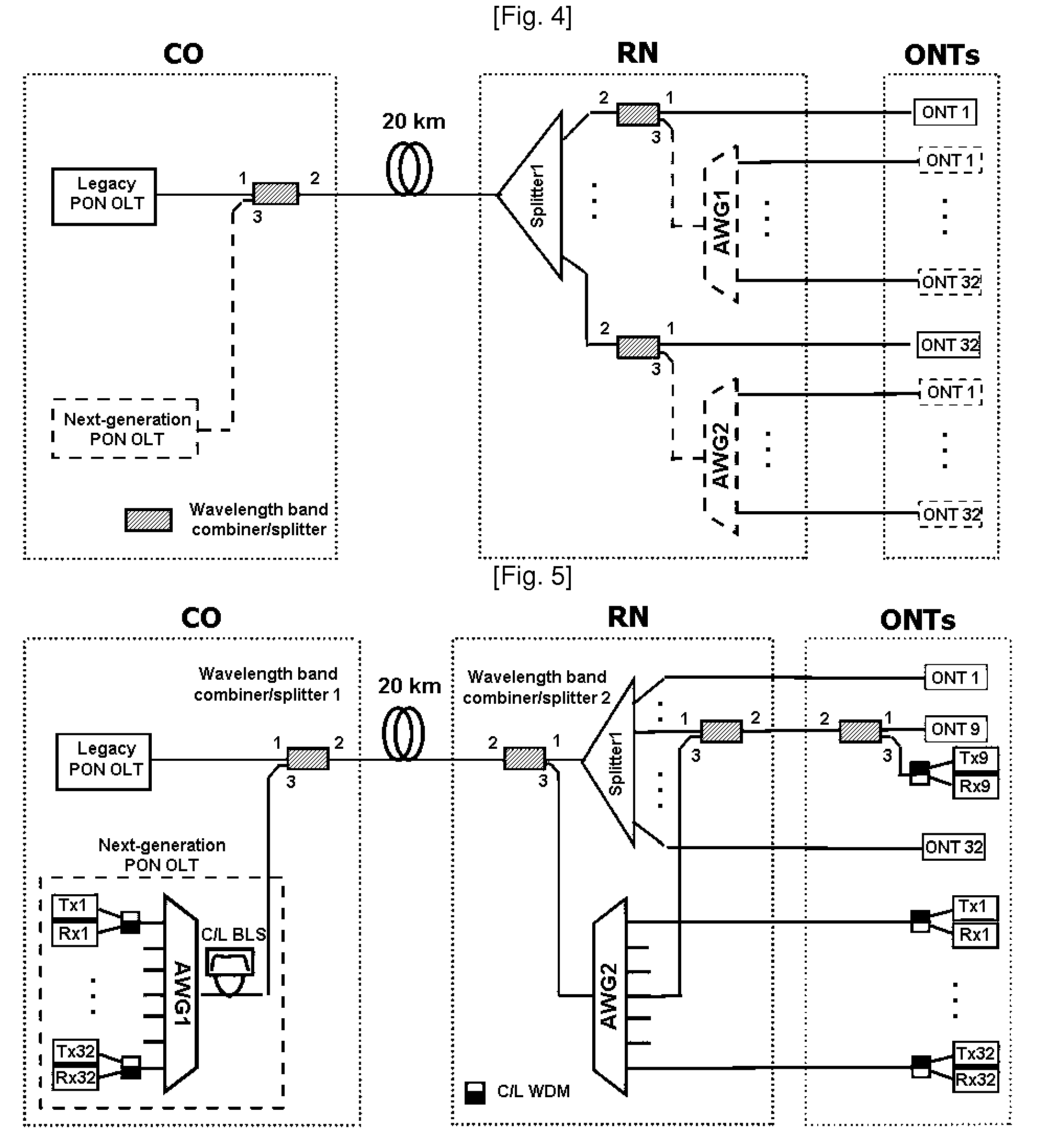
Method and network architecture for upgrading legacy passive optical network to wavelength division multiplexing passive optical network based next-generation passive optical network
InactiveUS20100054740A1Increase the number ofExpansion of bandwidthTime-division optical multiplex systemsWavelength-division multiplex systemsNetwork terminationNetwork architecture
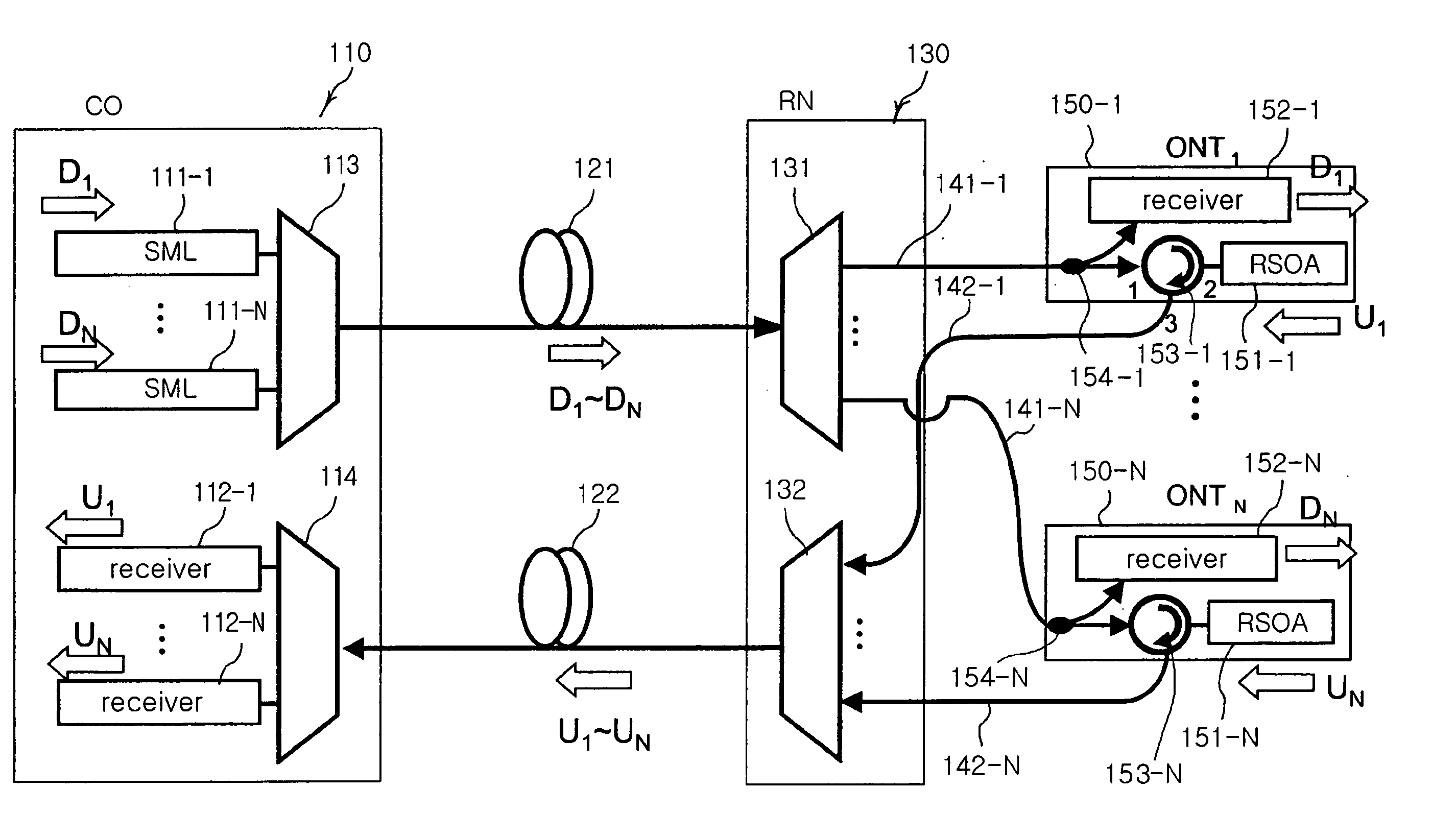
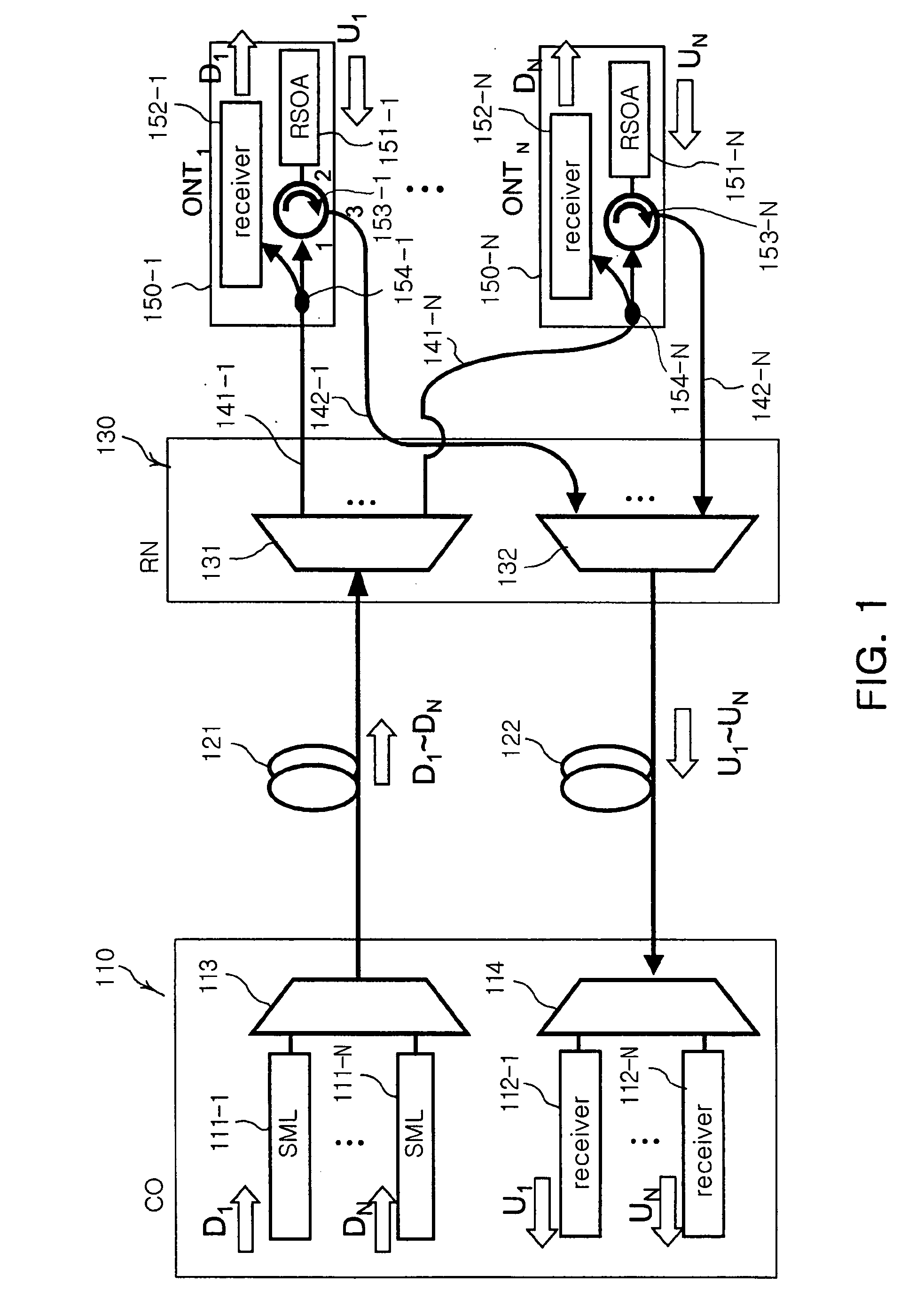
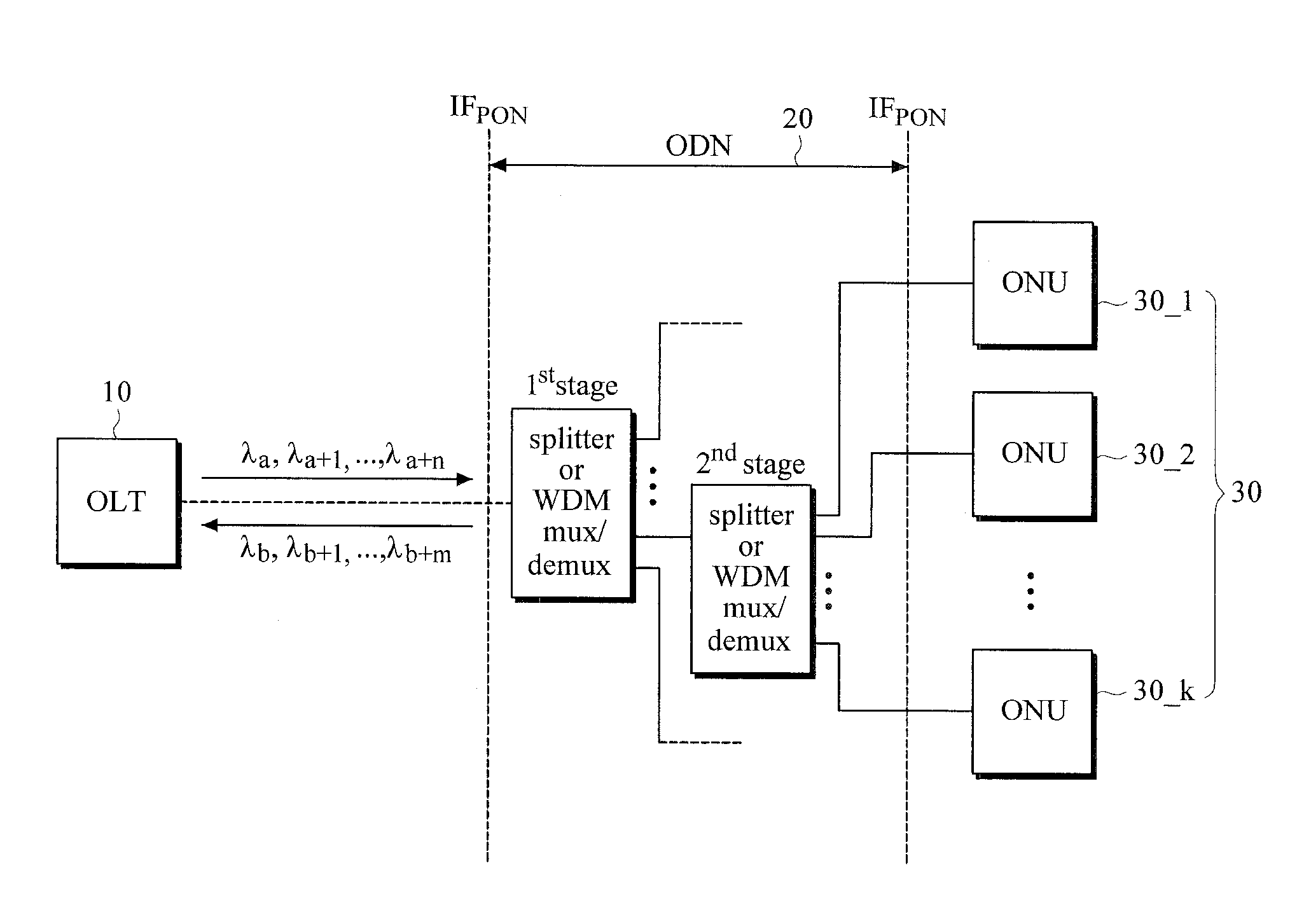
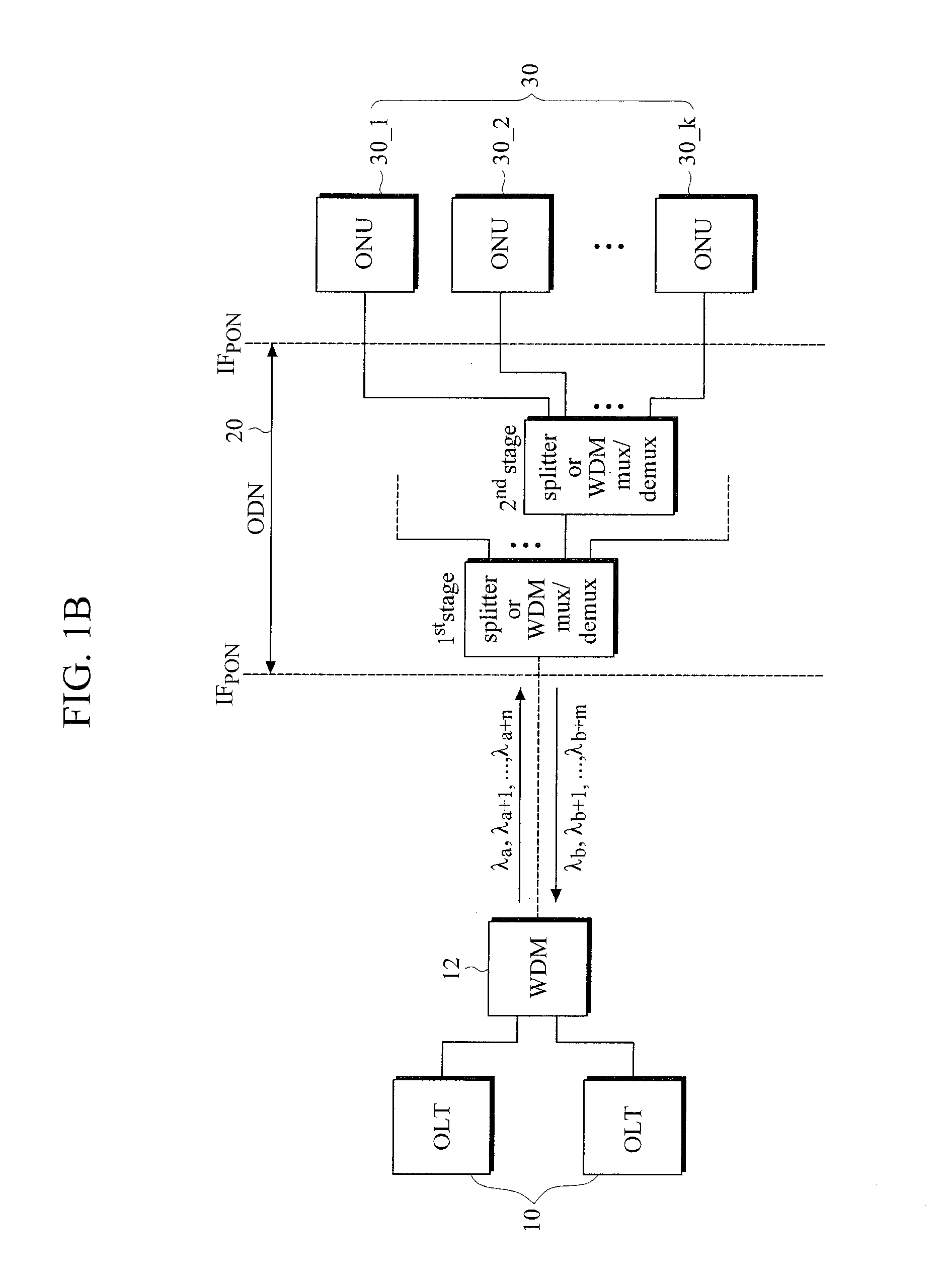
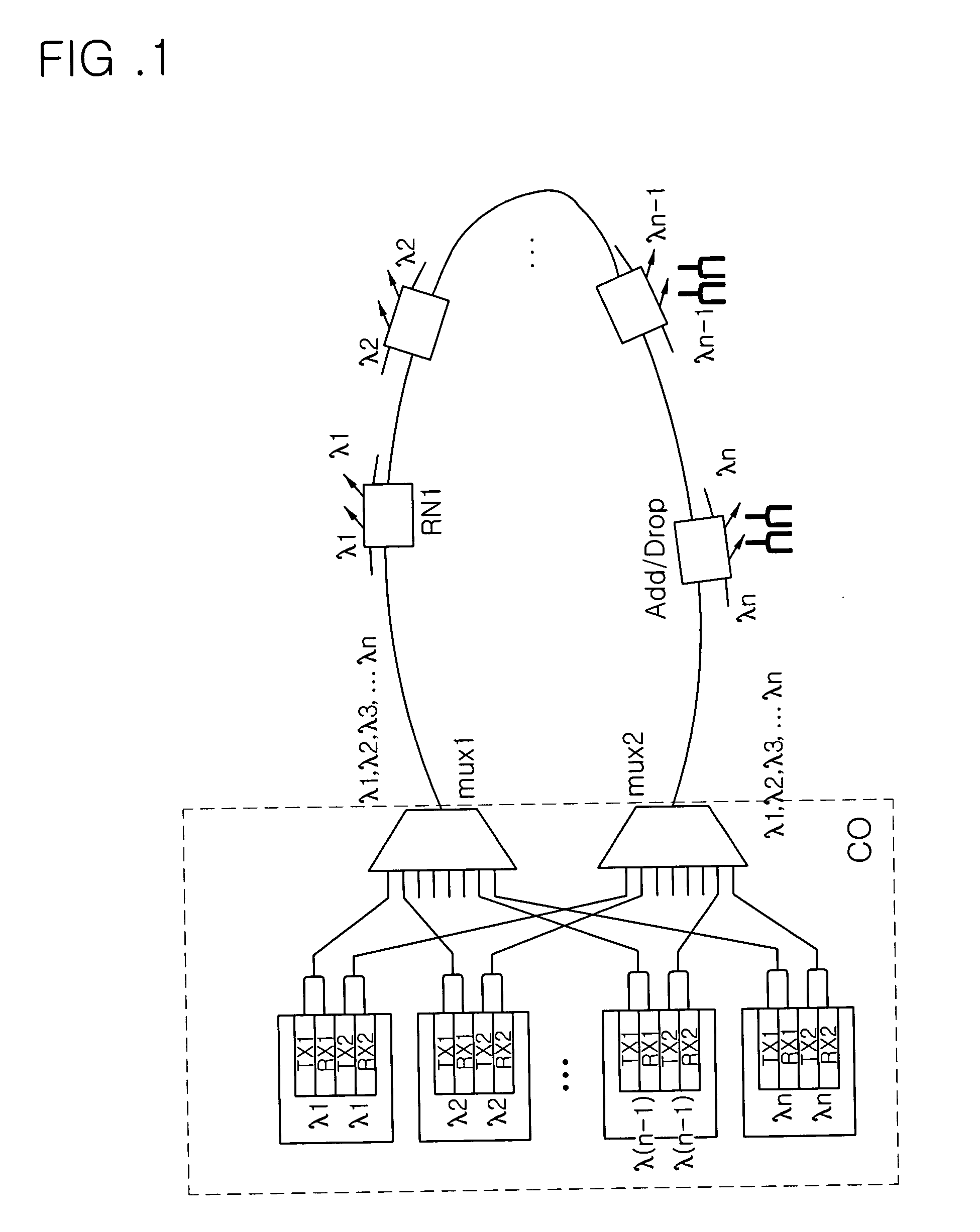
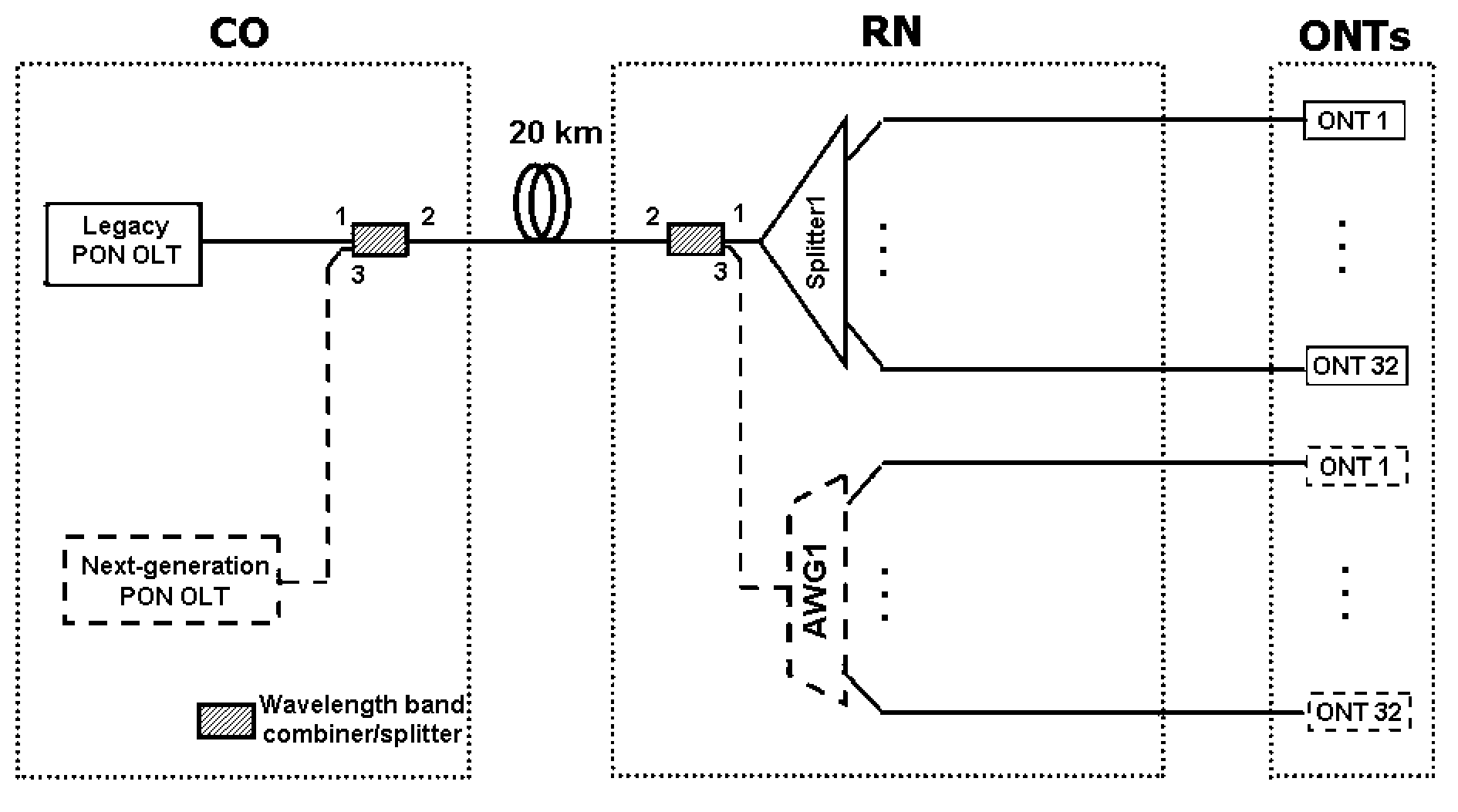
The present invention discloses a network architecture for upgrading a legacy time division multiplexing-passive optical network (TDM-PON) to a wavelength division multiplexing-passive optical network (WDM-PON) based next-generation passive optical network (next-generation PON), wherein the legacy TDM-PON comprises: a central office (CO) having a first optical line termination (OLT); a remote node (RN) having a splitter; a single mode fiber (SMF) connecting the first OLT and the splitter; and a first group of one or more optical network terminations (ONTs) being connected to the splitter by a first group of one or more distribution fibers, and wherein the network architecture further comprises: in case that the next-generation PON is a WDM-PON, a first apparatus for combining and splitting wavelength bands being positioned between the SMF and the first OLT, in order to add a second OLT to be used for the WDM-PON within the CO or within another CO which is located in a position different from the CO, while sharing the SMF; a second apparatus for combining and splitting wavelength bands being positioned at a front terminal of the splitter; and an arrayed waveguide grating (AWG) being connected to the second apparatus for combining and splitting wavelength bands within the RN, and being connected to a second group of one or more ONTs by a second group of one or more distribution fibers within the RN or within another RN which is located in a position different from the RN.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
Apparatus for Monitoring Failure Positions in Wavelength Division Multiplexing-Passive Optical Networks and Wavelength Division Multiplexing-Passive Optical Network Systems Having the Apparatus
InactiveUS20090080880A1Reduce noisePrecise positioningWavelength-division multiplex systemsTransmission monitoringFiberEngineering
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
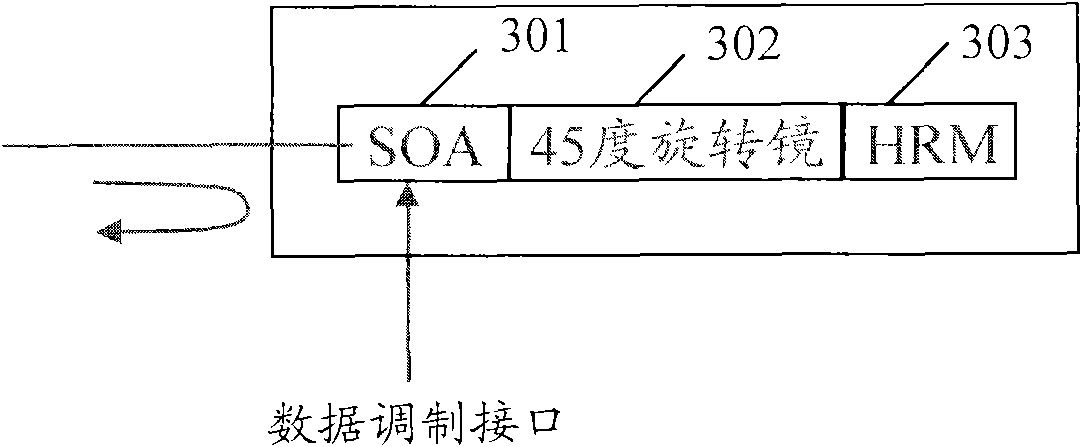
Wdm-pon system using self-injection locking, optical line terminal thereof, and data transmission method
InactiveUS20080279557A1Wavelength-division multiplex systemsTransmission monitoring/testing/fault-measurement systemsTemperature controlMultiplexer
Disclosed are a wavelength division multiplexing-passive optical network (WDM-PON) system using self-injection locking, an optical line terminal thereof, and a data transmission method. A wavelength division multiplexing-passive optical network (WDM-PON) system according to an aspect of the invention includes an optical line terminal. The optical line terminal includes a reflector that is installed at the input side of a multiplexer and reflects an optical signal having a predetermined wavelength, and a light source that generates a multimode optical signal to transmit the generated multimode optical signal to the multiplexer through the reflector, receives reflected light by the reflector, and oscillates at a wavelength of the received reflected light. According to the aspect of the invention, it is not necessary to separately control the temperature of a light source for a downstream signal, and stable communication can be performed by collectively controlling wavelengths of downstream channel optical signals for downstream channels through temperature control of the multiplexer.
Owner:LUXPERT TECH
WDM-PON having optical source of self-injection locked fabry-perot laser diode
InactiveUS20060083515A1Wavelength-division multiplex systemsStar-type electromagnetic networksInjection lockingLength wave
A wavelength division multiplexed-passive optical network includes an optical line terminal for generating downstream optical signals of discrete wavelengths and for receiving upstream optical signals of discrete wavelengths, a remote node, coupled to the optical line terminal, a wavelength division unit settled to reflect a predetermined wavelength, and a plurality of optical network units. Each optical network unit has an optical source which is oscillated in a multi-mode and is self-injection locked by the predetermined wavelength provided thereto, thereby to generate the upstream optical signal in a single mode to be provided to the remote node.
Owner:GWANGJU INST OF SCI & TECH
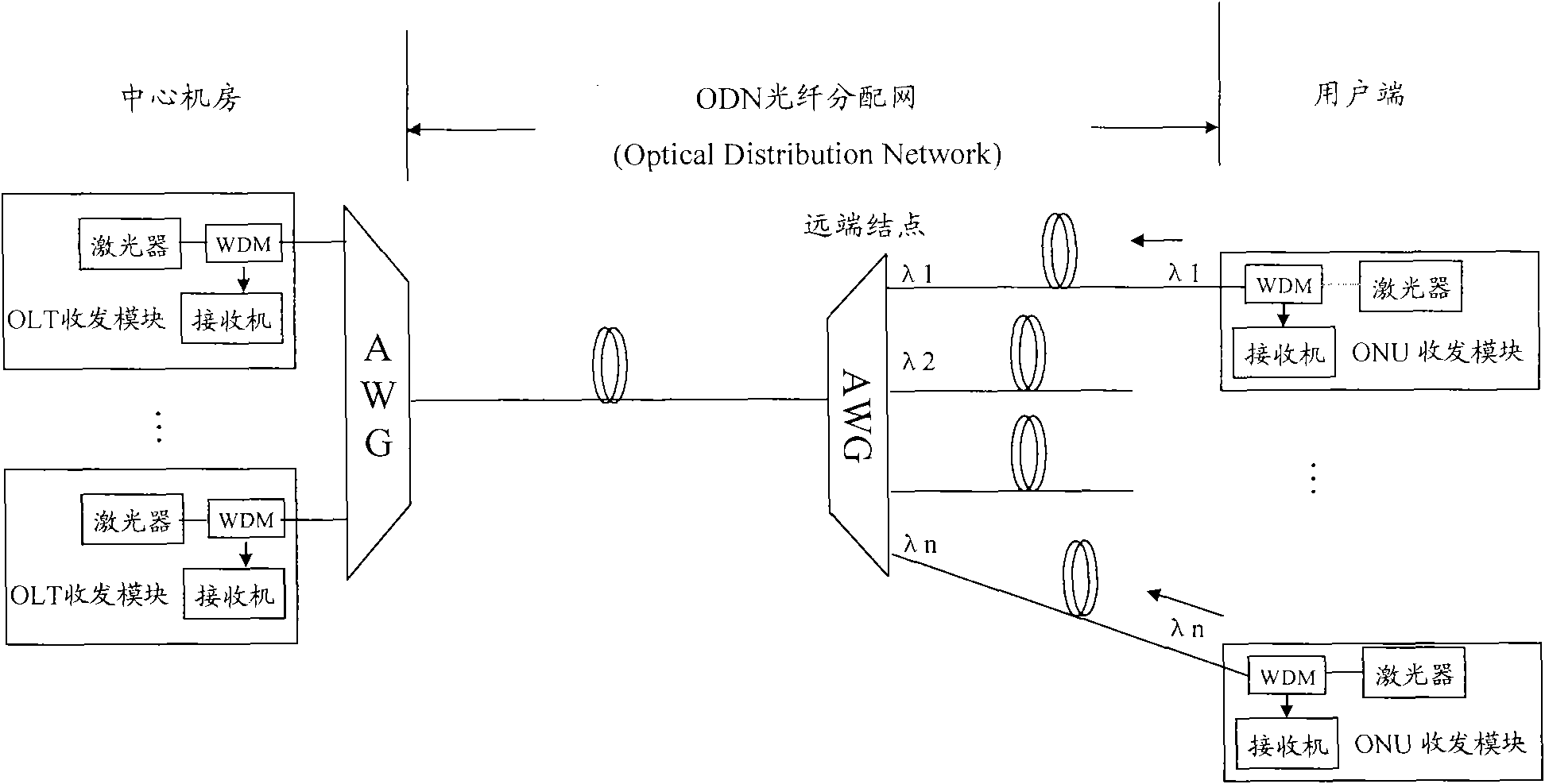
WDM PON with distribution via cyclic array waveguide grating
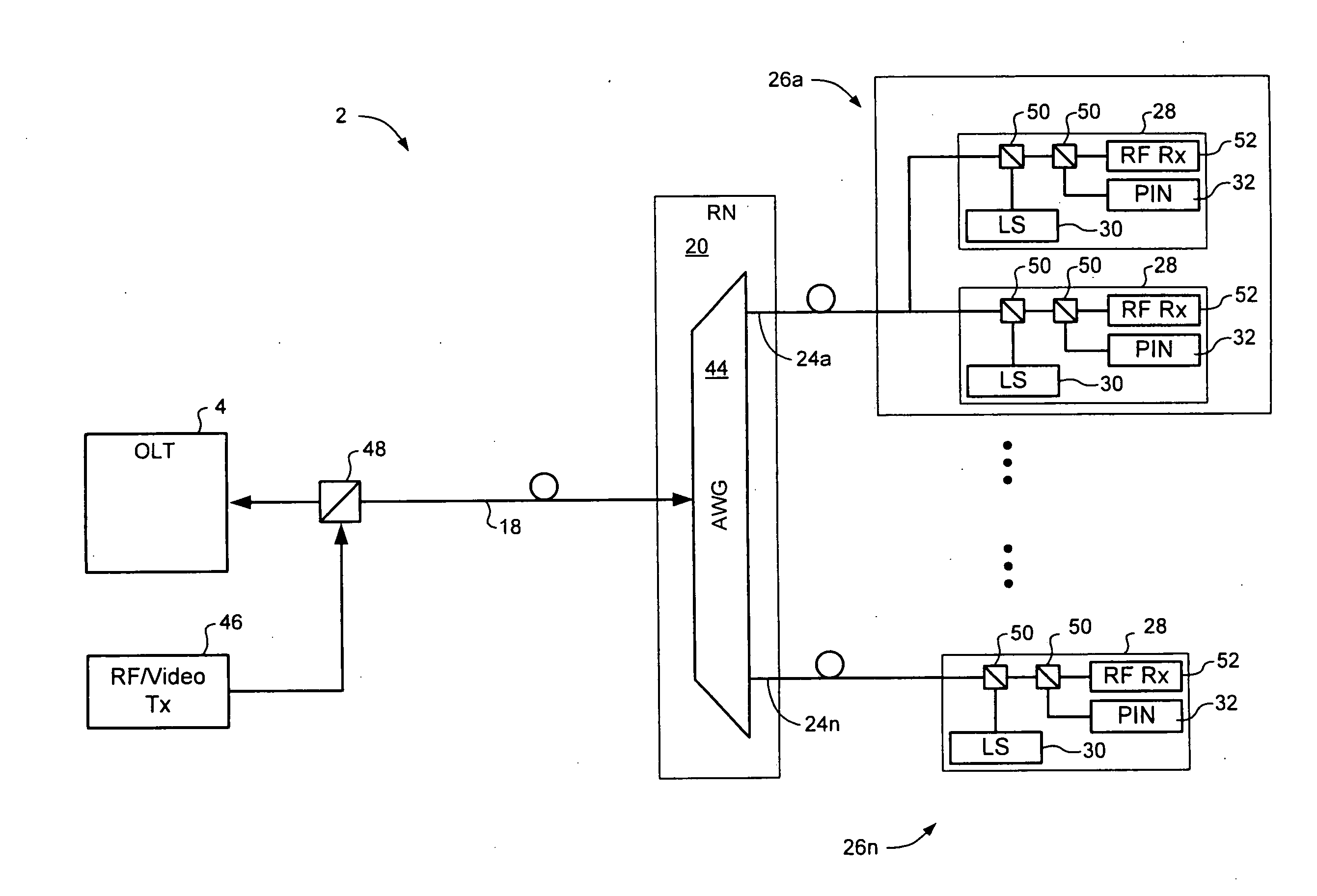
InactiveUS20100266283A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsFiberLength wave
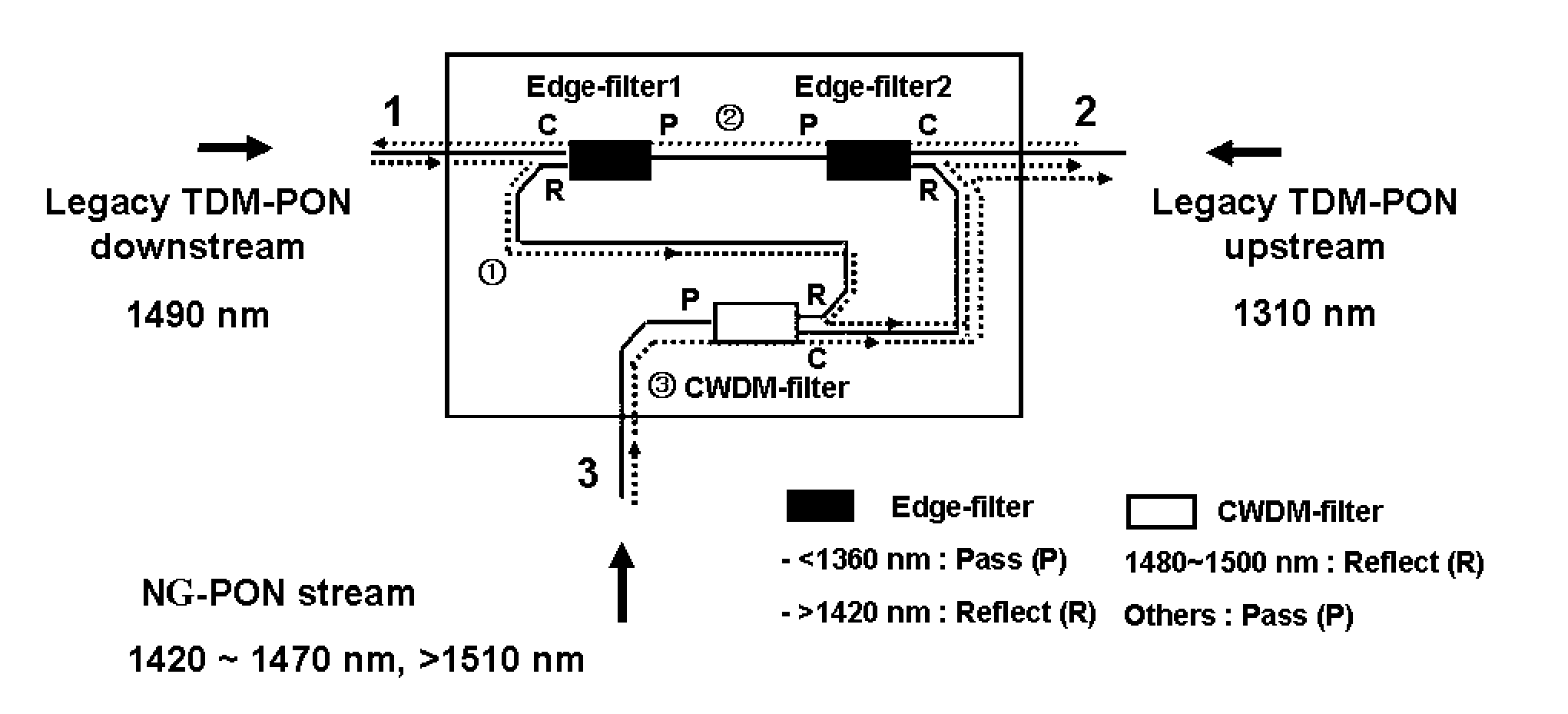
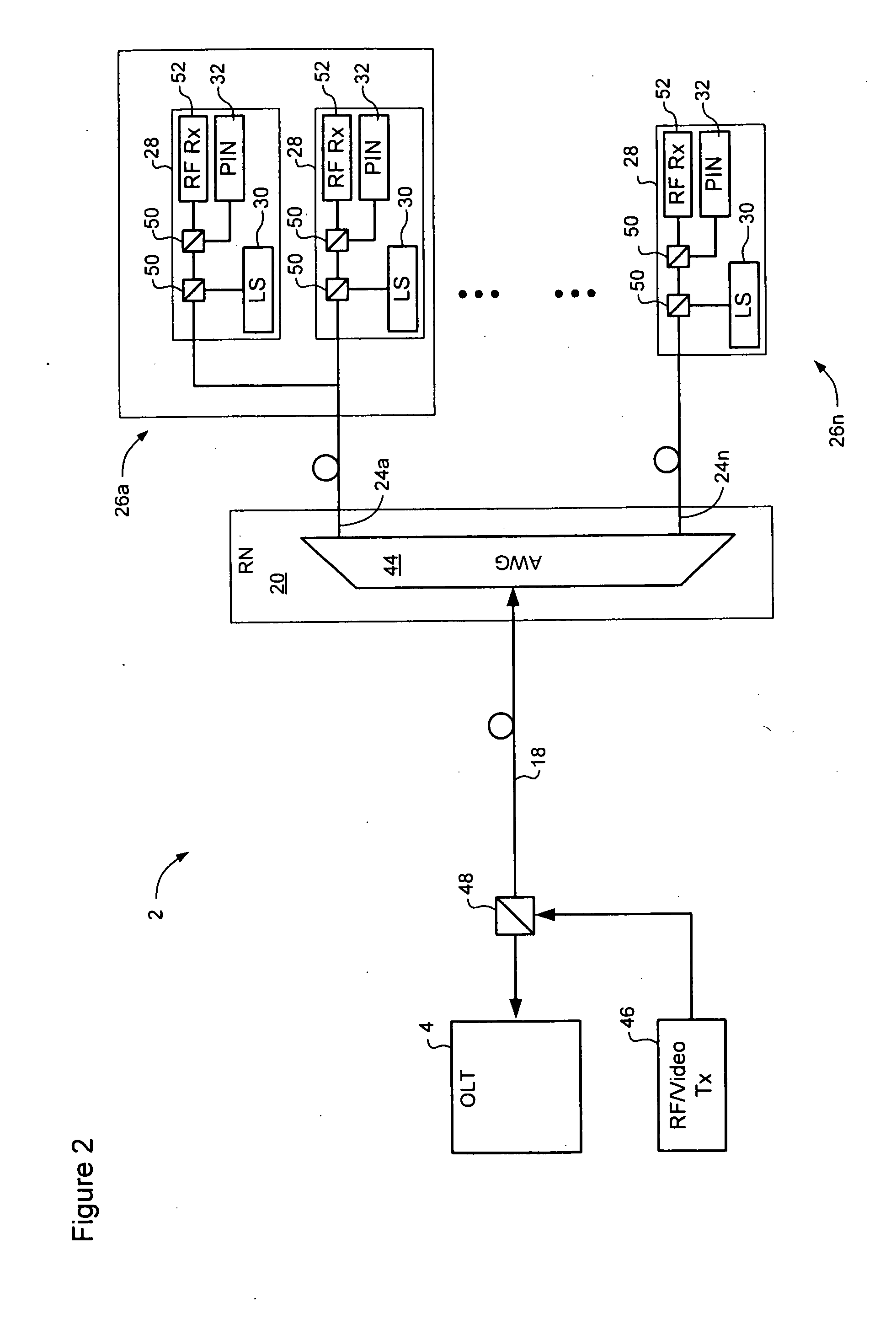
In a Wavelength Division Multiplexed Passive Optical Network (WDM-PON) including, a system for distributing uplink, downlink and RF / Video broadcast signalling. An Array Waveguide Grating (AWG) couples respective wavelength channels between a trunk fibre of the WDM-PON and a plurality of branch fibers of the WDM-PON. The AWG has a predetermined free spectral range and implements a channel plan comprising at least three spectral segments, each segment having a width equal to the free spectral range of the AWG. An Optical Line Terminal of the WDM-PON receives wavelength division multiplexed uplink signals within a first one of the spectral segments, and transmits wavelength division multiplexed downlink signals within a second one of the spectral segments. Respective channel plans within the first and second spectral segments are identical. An RF / Video broadcast transmitter generates an RF / Video broadcast signal within a third one of the spectral segments.
Owner:LG ERICSSON
Link setup method for wavelength division multiplexing wavelength passive optical network(WDM pon) system
ActiveUS20130004174A1Wavelength-division multiplex systemsStar-type electromagnetic networksComputer networkPhysical layer
A link setup method for a wavelength-division-multiplexing passive optical network (WDM PON) system. The system includes a service providing device, a local node, and a plurality of subscriber devices. The link setup method includes assigning an initial wavelength for communication between the service providing device and a new subscriber device to be installed in the local node. The assigning of the initial wavelength may be performed as a part of process for activating the subscriber device, and this procedure may be performed between a physical layer of the service providing device and a physical layer of the new subscriber device.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Loop-back wavelength division multiplexing passive optical network
InactiveUS20060093359A1Sure easyElectromagnetic network arrangementsOptical multiplexMultiplexerEngineering
Disclosed herein is an apparatus and method for managing faults of a loop-back Wavelength Division Multiplexing Passive Optical Network (WDM-PON). The apparatus includes a control light source as well as a plurality of light sources in a central office, a loop-back means for transmitting control light to the central office through a remote node optical demultiplexer or remote node optical multiplexer in a remote node, a control light receiver for receiving looped-back control light, and a control unit for maintaining power of the upstream signals, which are received by central office receivers, and power of the control light, which is received by the control light receiver, at a maximum.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
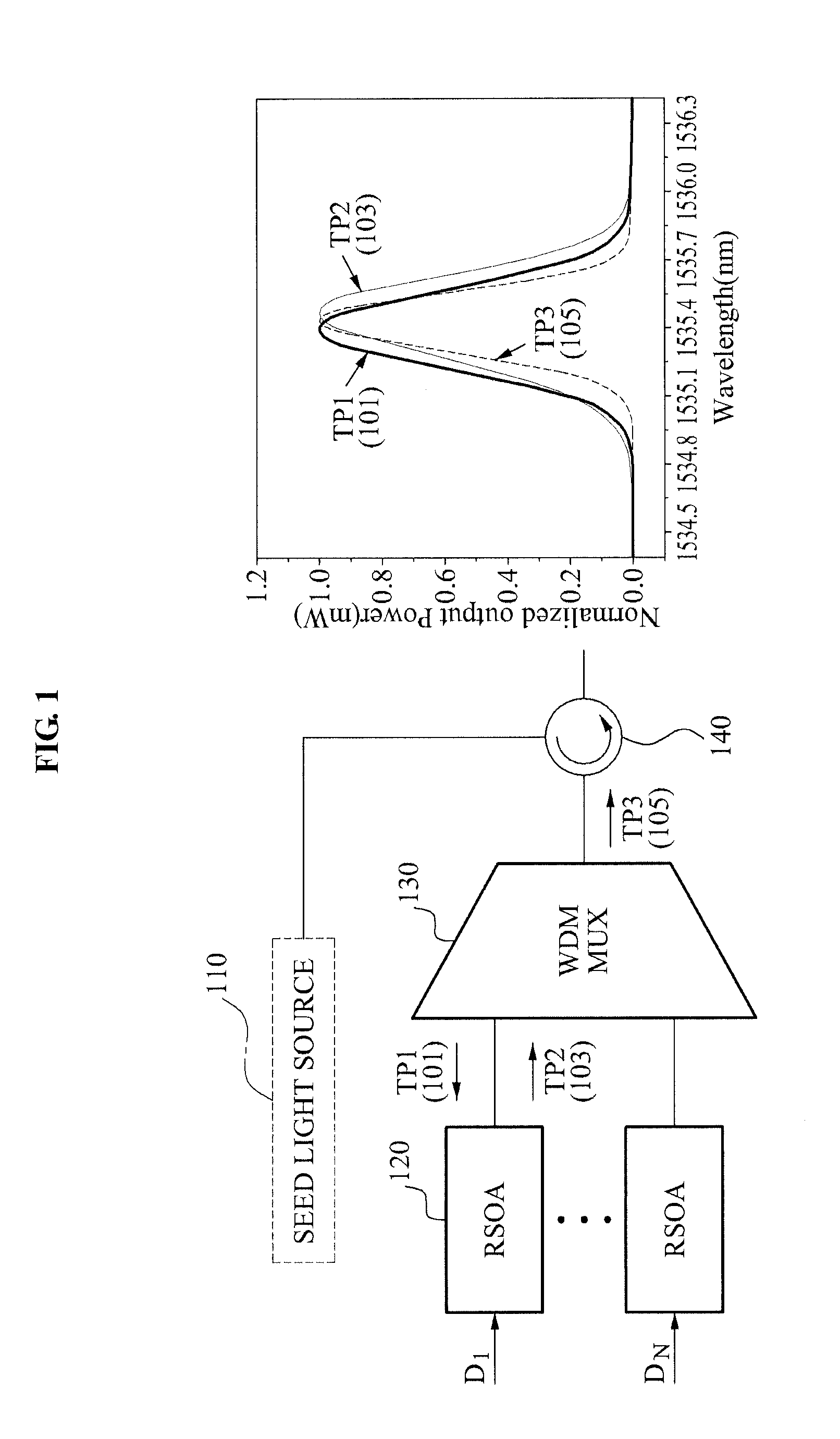
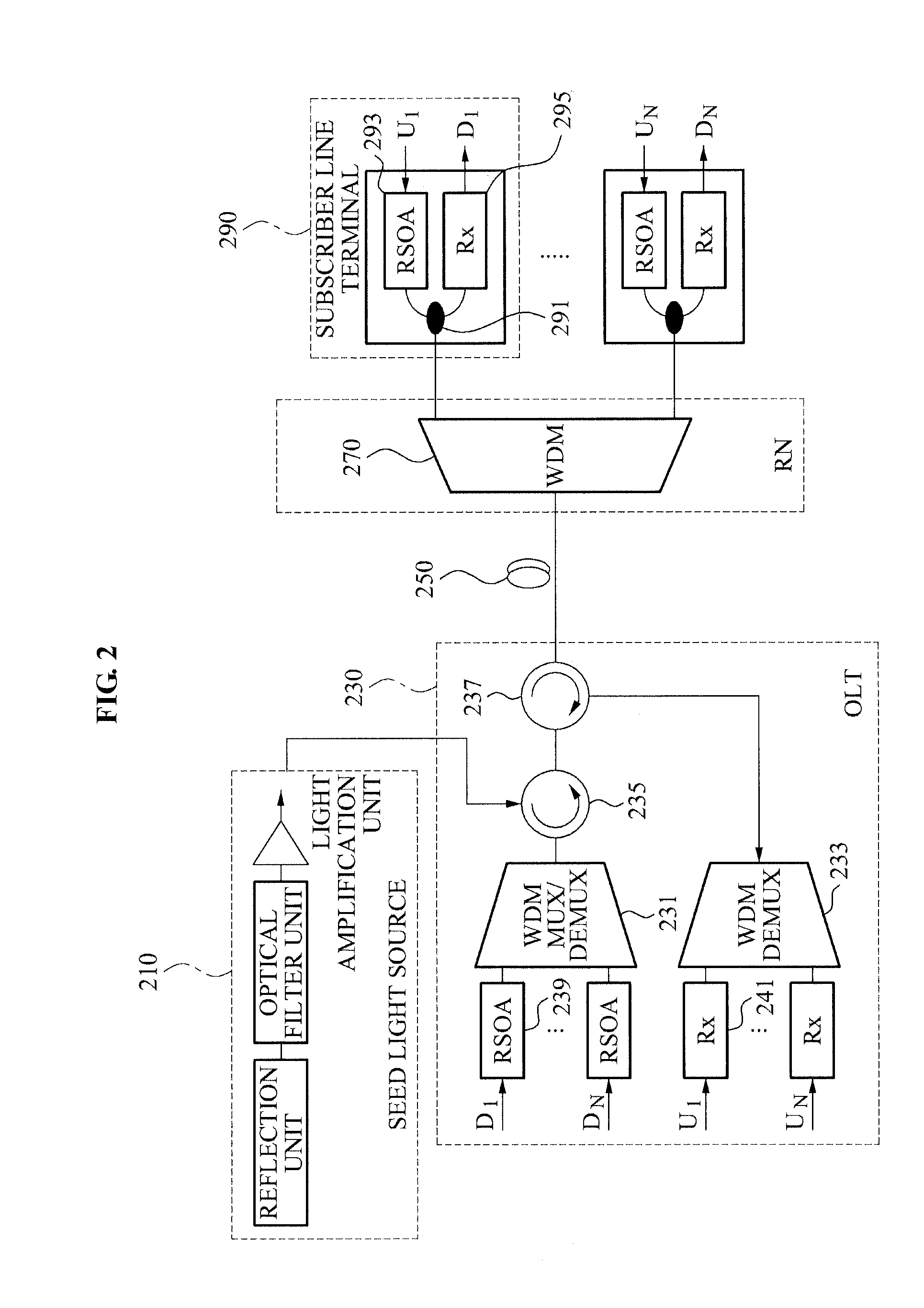
Wavelength division multiplexing-passive optical network using external seed light source
ActiveUS20100278535A1Quality improvementIncrease the number ofWavelength-division multiplex systemsMultimode transmissionFrequency spectrumCode division multiple access
Provided are a wavelength division multiplexing-passive optical network (WDM-PON) in which a reflective semi-conductor optical amplifier (RSOA) is used as each optical transmitter of an optical line termination (OLT) and an optical network unit (ONU) and additional spectrum-sliced light is injected into RSOAs of each of the OLT and the ONU, and a WDM-PON that is combined with time division multiple access (TDMA) technology, by which the number of included ONUs increases and conventional TDMA ONUs can be used.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Wavelength division multiplexing-passive optical network (wdm-pon)
InactiveUS20110135309A1Eliminate lossEfficiently transmitting signalWavelength-division multiplex systemsMultimode transmissionMultiplexerWavelength division multiplexing passive optical networks
Provided is an Optical Line Terminal (OLT). The OLT may include a first Wavelength division multiplexer / demultiplexer (WDM MUX / DeMUX) to perform a wavelength demultiplexing on seed light received from a seed light source, and a second Wavelength division demultiplexer (WDM DeMUX) to receive, from at least one ONU / ONT, an upstream optical signal generated using the seed light having the wavelength demultiplexing performed, and to perform a wavelength multiplexing on the received upstream optical signal.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Wavelength-division-multiplexed light source and wavelength-division-multiplexed passive optical network using the same
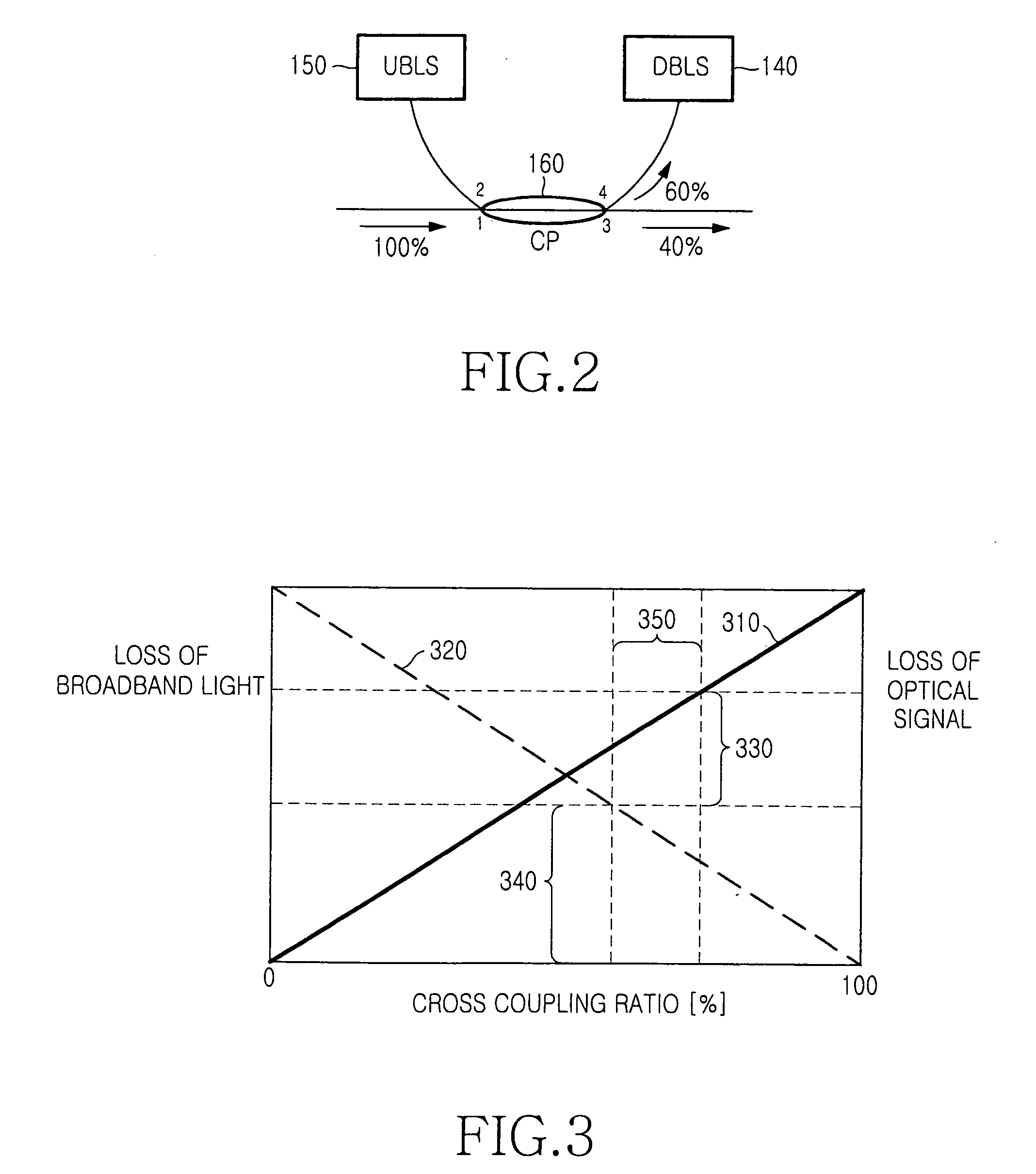
InactiveUS20070036483A1Effective maintenanceWavelength-division multiplex systemsCoupling light guidesFiberCoupling ratio
A wavelength-division-multiplexed light source for transmitting broadband light through a fiber and receiving an optical signal through the fiber is disclosed. The wavelength-division-multiplexed light source includes: a light source for outputting broadband light; and a coupler for outputting the broadband light, which has been input from the light source, to the fiber through cross coupling, and outputting an optical signal, which has been input from the fiber, through bar coupling, based on a predetermined cross coupling ratio, wherein the cross coupling ratio of the coupler is adjusted depending on a power of the optical signal.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
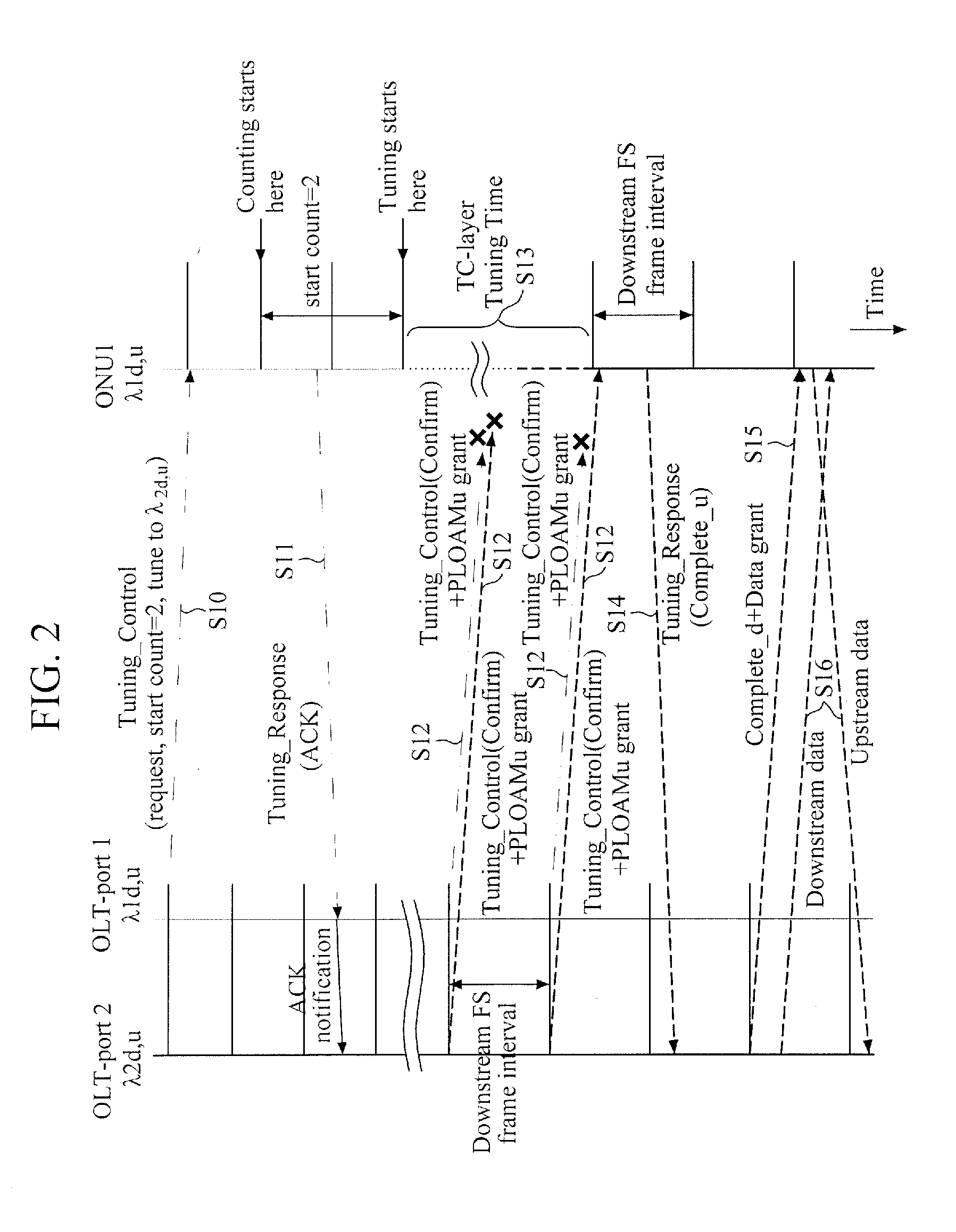
Method of tuning wavelength of tunable optical network unit (ONU) in time and wavelength division multiplexing-passive optical network (TWDM-pon)
InactiveUS20150365192A1Efficient changeMultiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsLength waveOptical network unit
A method of tuning a wavelength of a tunable ONU in a TWDM-PON is provided. The method includes transmitting a wavelength change request message from a source OLT to request the ONU to change a wavelength thereof from a first wavelength to a second wavelength and in response to the wavelength change request message, transmitting a wavelength change response message from the ONU to the source OLT to indicate whether or not the ONU can change a wavelength thereof. The wavelength change request message is ID information for specifying an ONU that is requested to change a wavelength thereof, and the message may comprise one of the following: system ONU ID, channel ONU ID, and individual ONU ID.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Method, system and device for transmitting wavelength division multiplexing passive optical network
ActiveCN102143407AAchieve colorlessSolving Polarization ProblemsMultiplex system selection arrangementsElectromagnetic transmissionTerminal equipmentOptoelectronics
The embodiment of the invention discloses a method for transmitting a wavelength division multiplexing passive optical network. The method comprises the following steps of: receiving a downlink optical signal from local terminal equipment, and dividing the downlink optical signal into a first optical signal and a second optical signal; demodulating the first optical signal so as to restore downlink data carried in the first optical signal; performing reflection irrelevant to polarization on the second optical signal so as to obtain a reflected light of which the polarization direction is orthogonal to the second optical signal, and loading uplink data to the reflected light corresponding to the second optical signal by a modulation method so as to generate an uplink optical signal carrying the uplink data; and transmitting the uplink optical signal to the local terminal equipment. By the embodiment of the invention, the decoloring of a light source can be realized, the cost is reduced effectively, and the transmission performance after reflection and modulation is guaranteed. The embodiment of the invention also discloses a system and a device for transmitting the wavelength division multiplexing passive optical network.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
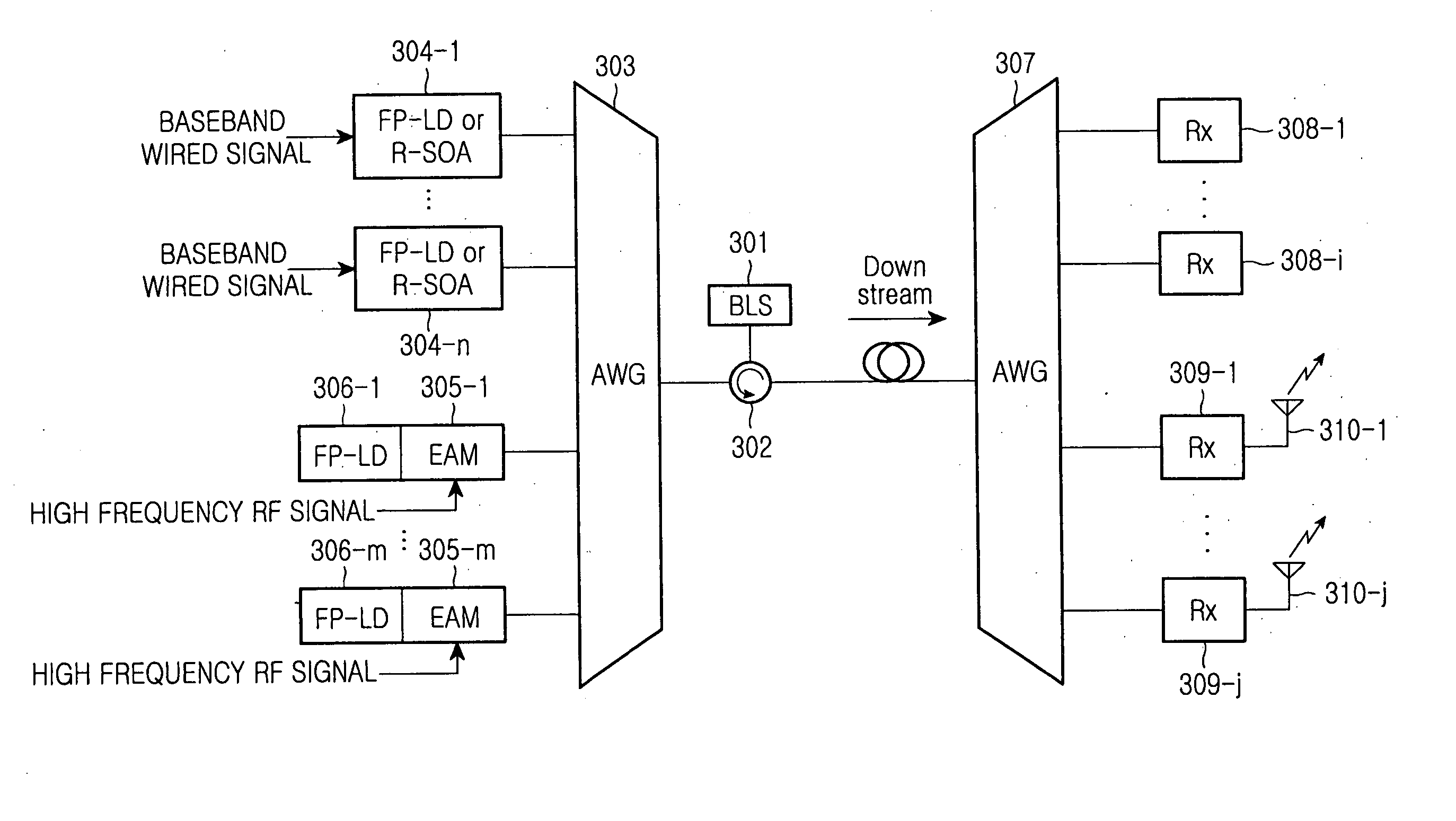
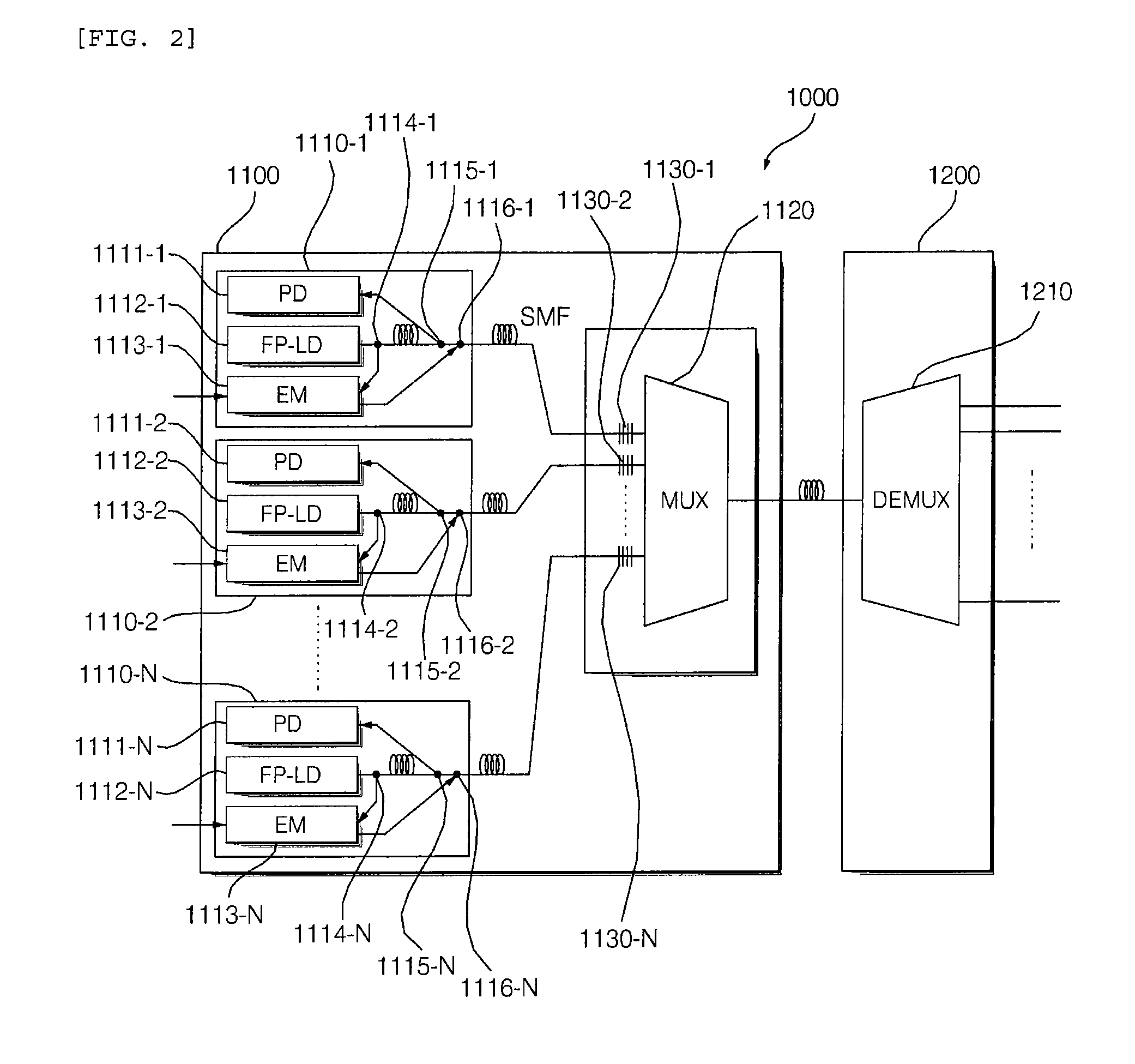
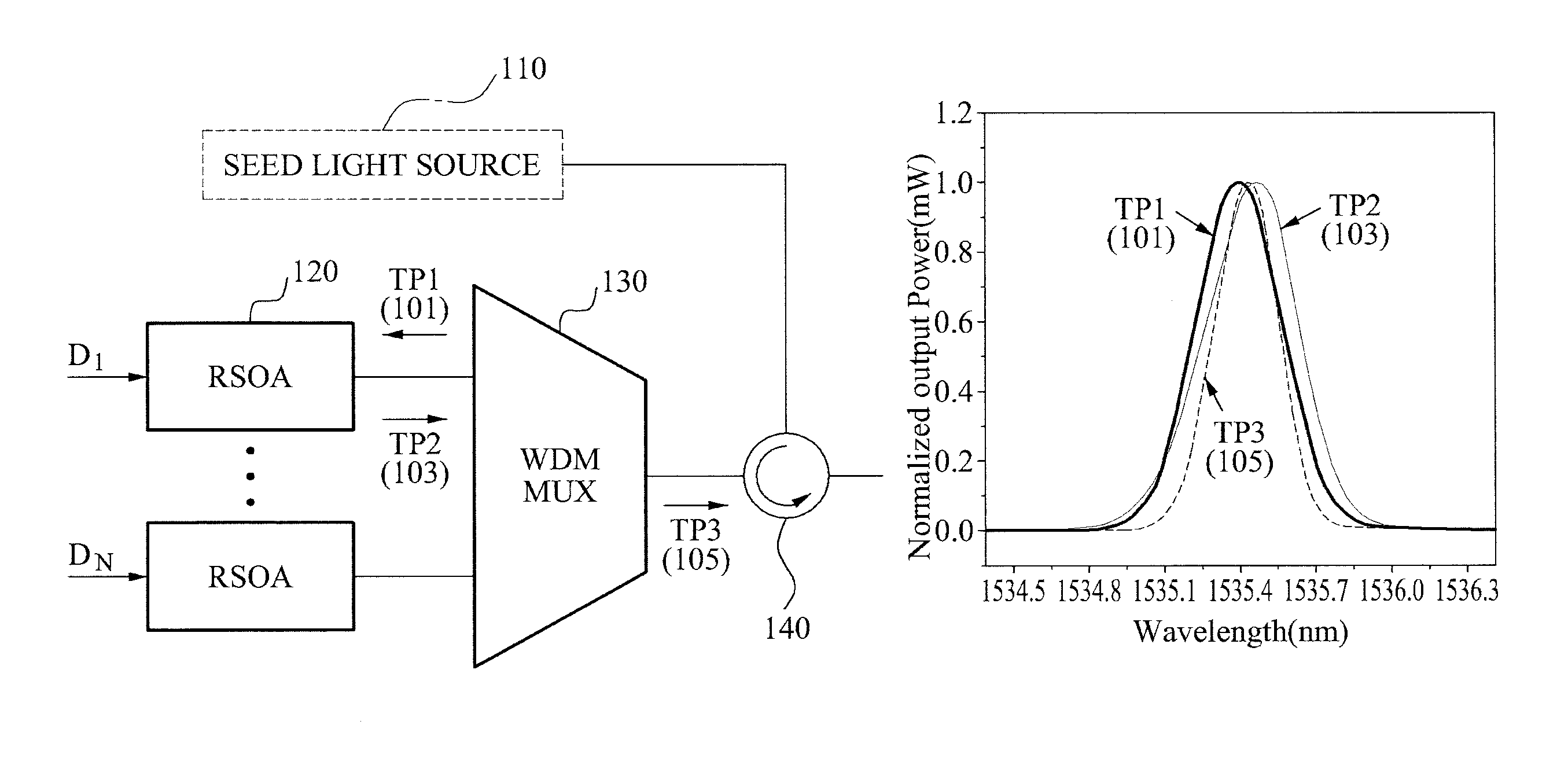
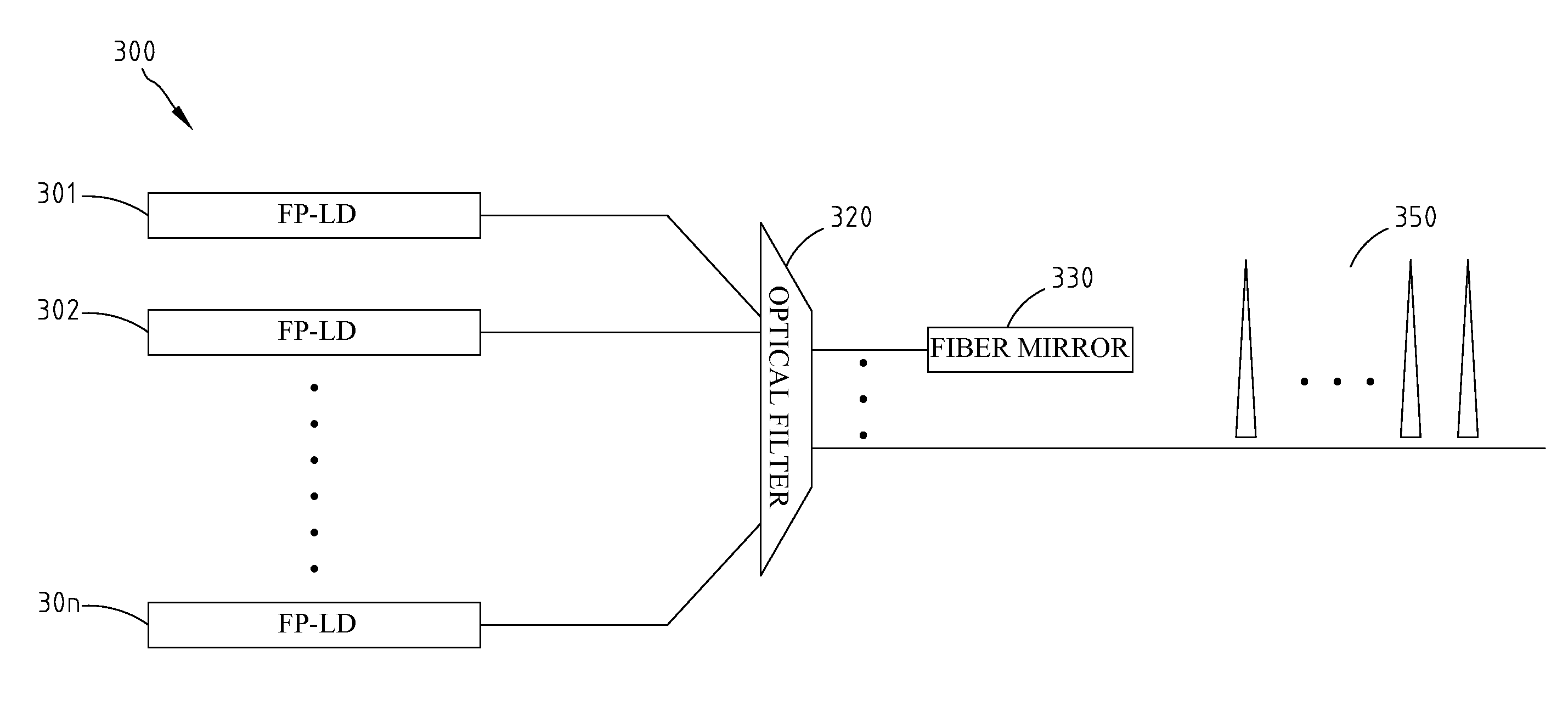
Laser Source Based On Fabry-Perot Laser Diodes And Seeding Method Using The Same
Disclosed is directed to a laser source based on Fabry-Perot laser diodes (FP-LDs) and seeding method using the same. The laser source comprises a plurality of FP-LDs, an optical filter, and at least a fiber mirror. The FP-LDs are aligned to their corresponding filter modes of the optical filter, and output their optical spectrums. The optical spectrums are filtered via the optical filter then reflected into the FP-LDs. Each of the FP-LDs further outputs its optical spectrum with a form of continuous wave (CW) of single longitudinal mode (SLM). The outputted CWs may be treated as injected laser light sources. They may also be applied to the transmission architecture in wavelength-division-multiplexed passive optical networks.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Apparatus and method for olt and onu for wavelength agnostic wavelength-division multiplexed passive optical networks
ActiveUS20110026923A1Lowering in extinction ratioPossible to transmitLaser detailsWavelength-division multiplex systemsComputer terminalLength wave
In a Wavelength-Division-Multiplexed Passive Optical Network (WDM-PON) utilizing a conventional downstream optical signal reusing method, there is an inventory problem that different optical transmitter types need to be provided for the operation, management, replacement, etc. of a system. A WDM-PON system according to the present invention, includes: a seed light (SL) unit generating a seed light whose wavelength intervals and center wavelengths are adjusted using at least one seed light source; an optical line terminal (OLT) receiving the wavelength-multiplexed seed light from the seed light unit, transmitting a downstream optical signal to a subscriber of the WDM-PON, and receiving a upstream optical signal from the subscriber; and an optical network unit (ONU) receiving the downstream optical signal from the OLT, flattening and modulating the downstream optical signal with upstream data so that the downstream optical signal is reused for carrying upstream data. It is possible to improve the quality and reliability of downstream transmission by sufficiently increasing an extinction ratio, and improve the quality and reliability of upstream transmission by sufficiently flattening an input downstream optical signal in a semiconductor optical amplifier.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Centrally Managed, Self-Survivable Wavelength Division Multiplexed Passive Optical Network
InactiveUS20100158512A1Multiple failureSimple designLaser detailsWavelength-division multiplex systemsFiberEngineering
A centrally-managed, colorless, bi-directional wavelength division multiplexed passive optical network (WDM-PON) architecture. The WDM-PON architecture is self-survivable, and can protect network failures in, for example, distribution / feeder fiber, remote node and laser failure. The WDM-PON architecture requires only N-wavelength channels for N optical network units.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
Method for decreasing and compensating the transmission loss at a wavelength-division-multiplexed passive optical network and an apparatus therefor
InactiveUS7171123B2Light loss is minimizedImprove transmission qualityLaser detailsWavelength-division multiplex systemsLength waveTransmission loss
The present invention relates to a wavelength-division multiplexed passive optical network. In particular, it relates to a technology for minimizing the optical loss at a wavelength-division multiplexed passive optical network based on wavelength-locked light source Thereby it improves the transmission quality and increases the transmission distance.A 4-port optical path setting device of the present invention increases the amount of light injected into an optical transmitter and thereby improves the wavelength-locking characteristic of a light source. In addition, it can decrease the optical transmission loss in an optical transmission path, and by an optical amplifier being inserted therein; it can also compensate the optical loss in an optical transmission path.In the present invention, a 4-port optical path setting device having the characteristics described above and a method for fault recovery without an additional optical loss are presented.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
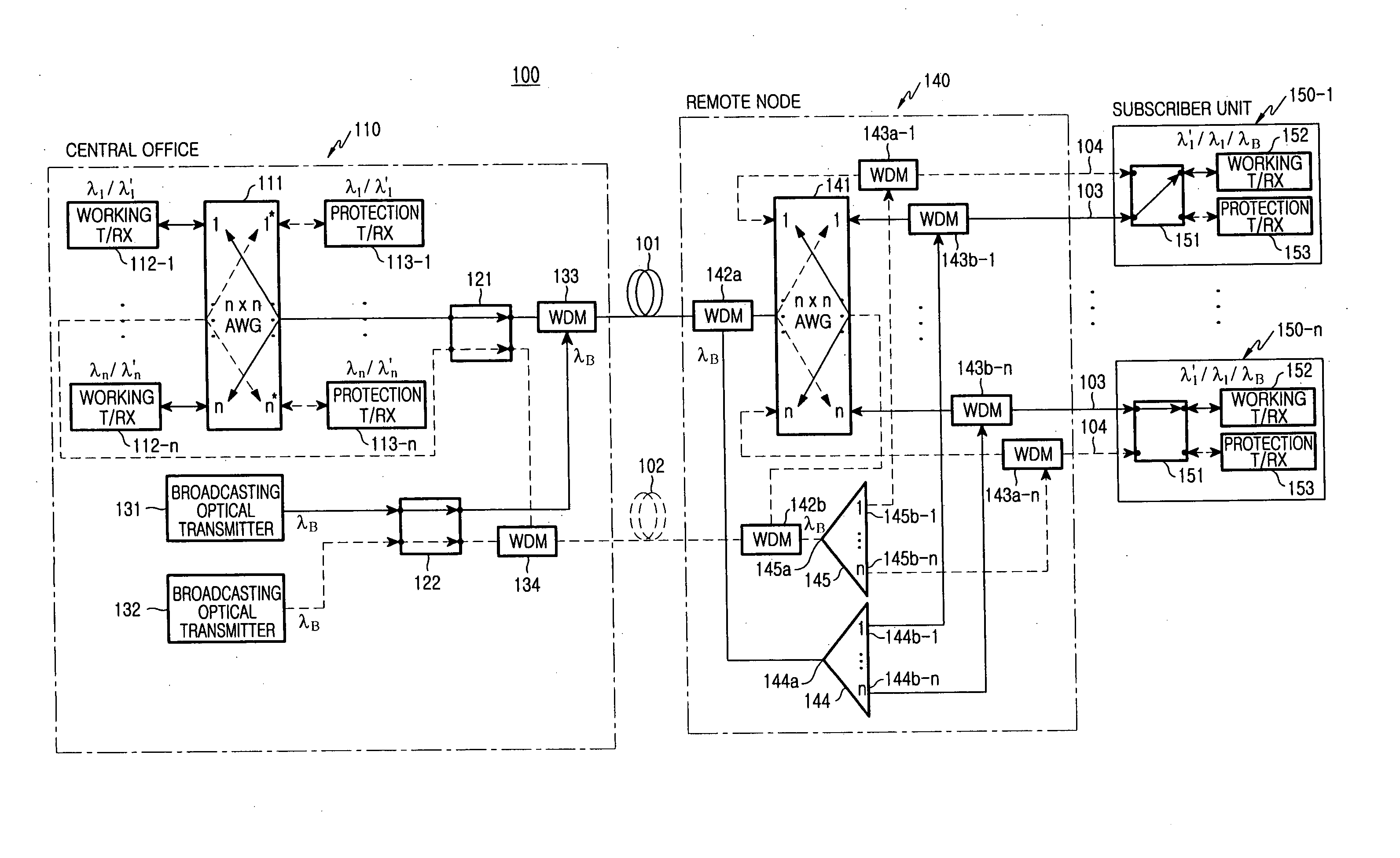
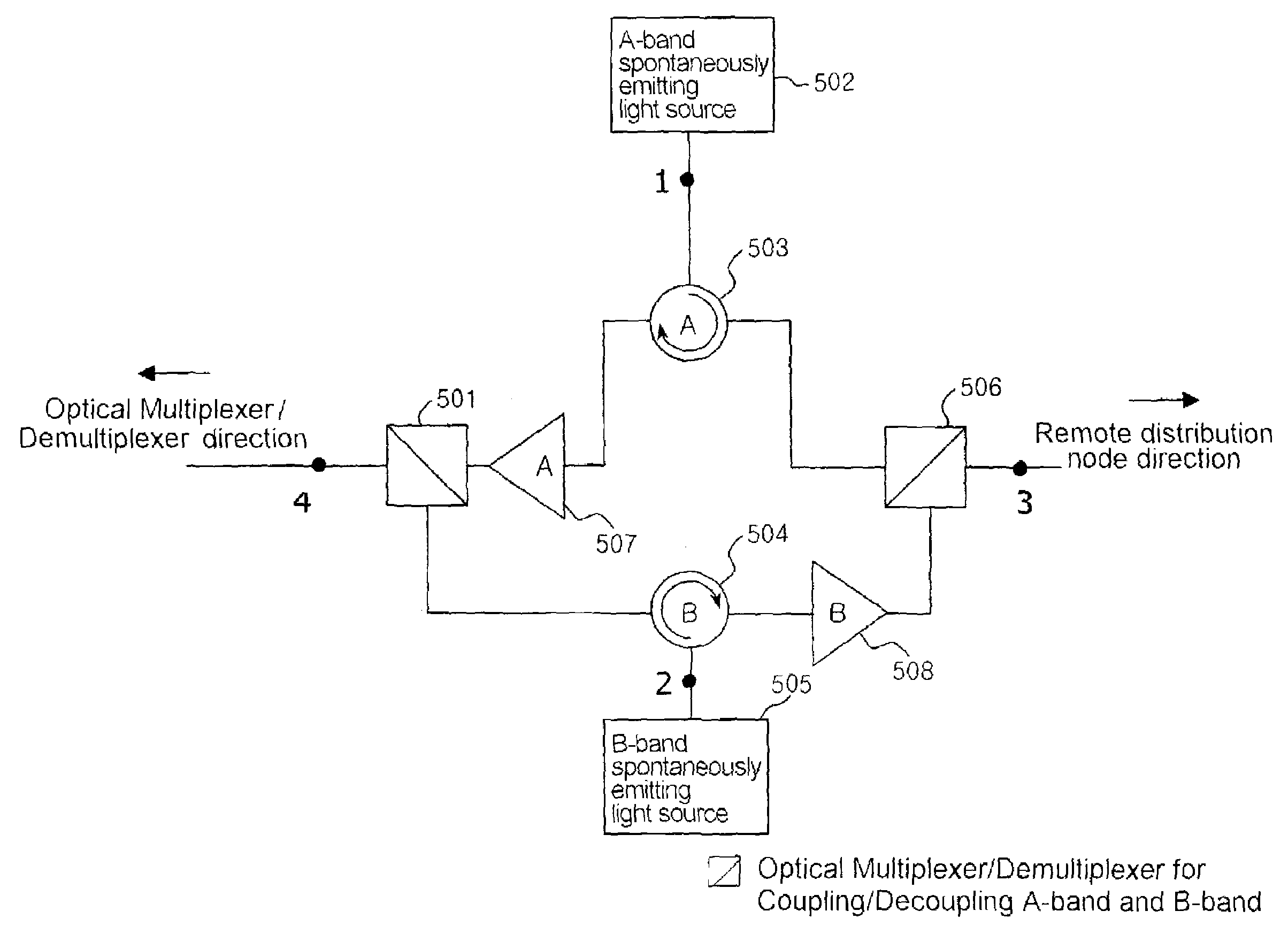
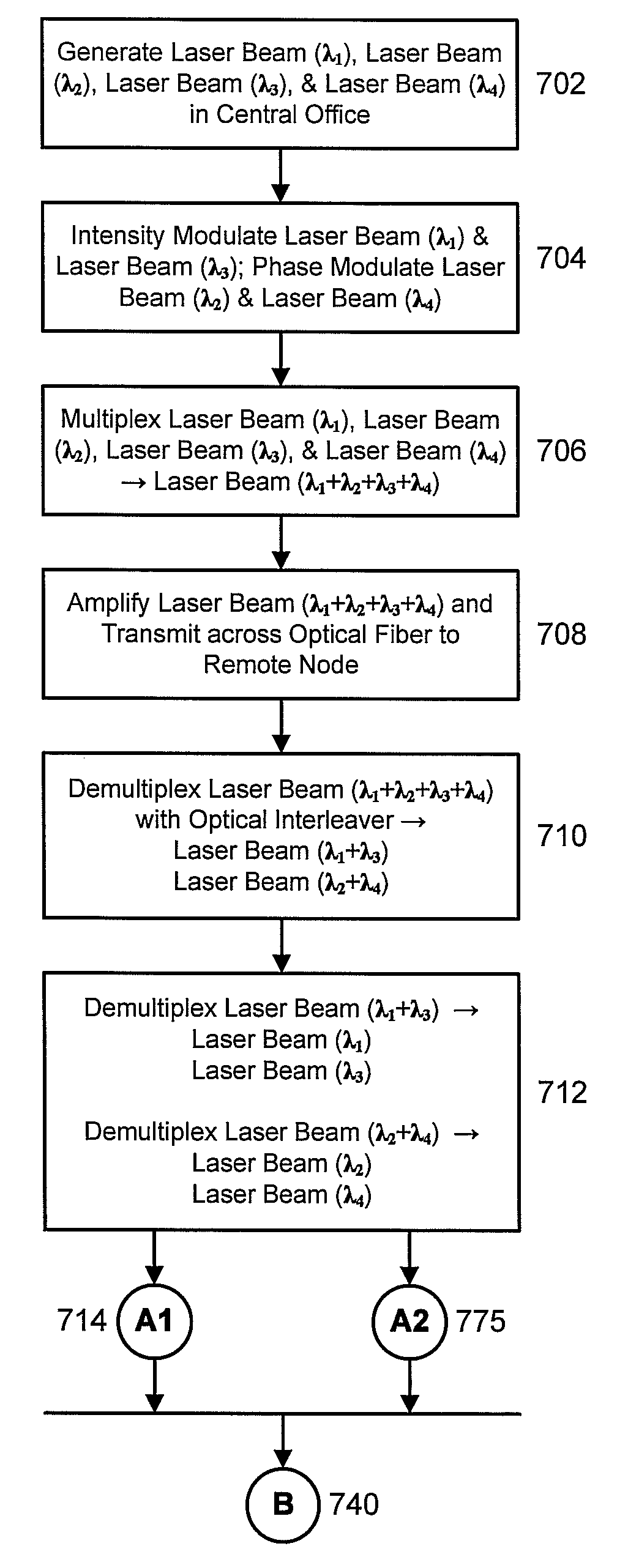
Wavelength Division Multiplexed Passive Optical Network
ActiveUS20080279556A1Wavelength-division multiplex systemsMultimode transmissionIntensity modulationLaser beams
Data is transmitted between a central office and customer premises by a wavelength division multiplex passive optical network. Two laser beams with separate wavelengths are transmitted from the central office to an optical network unit in the customer premises. Both laser beams carry downstream data. One laser beam is intensity modulated by on / off keying. The other laser beam is phase modulated by differential phase shift keying, which maintains a constant optical intensity. The first laser beam is received by a first optical receiver, which demodulates the first downstream data. The second laser beam is split in two. One laser beam is sent to a second optical receiver, which demodulates the second downstream data. The other laser beam is sent to a reflective semiconductor amplifier, which modulates the beam with upstream data and transmits the beam back to a receiver in the central optical system.
Owner:NEC CORP
Optical transceiver apparatus and wavelength division multiplexing passive optical network system
InactiveUS20120269516A1Improve signal transmission performanceImprove signal qualityWavelength-division multiplex systemsElectromagnetic transmittersTransceiverLength wave
An optical transceiver apparatus includes a gain medium, a photoelectric converter, at least one AWG, and a partial reflection mirror. The at least one AWG includes two common ports and multiple branch ports. One of the two common ports functions as a signal sending port, and the other functions as a signal receiving port, where bandwidth of the signal sending port is less than that of the signal receiving port. The gain medium and the photoelectric converter are connected to one of the branch ports of the AWG. The AWG and the partial reflection mirror are configured to cooperatively perform wavelength self-injection locking on an optical signal provided by the gain medium, and output the optical signal through the signal sending port. The AWG is further configured to demultiplex an optical signal received by the signal receiving port to a branch port. A WDM-PON system is also provided.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Dense wave division multiplex passive optical network system for self-implant locked Fabry-Perot laser diode
InactiveCN1497894AWavelength-division multiplex systemsMultimode transmissionInjection lockedLength wave
Disclosed is a dense wavelength division multiplexing-passive optical network (DWDM-PON) system utilizing self-injection locking of Fabry-Perot laser diodes, in which output optical signals of different wavelengths are partially fed back by a partial mirror, so as to injection-lock the Fabry-Perot laser diodes, respectively. In accordance with this system, inexpensive Fabry-Perot laser diodes can be used as respective light sources of a central office and optical network units (ONUs). Accordingly, it is possible to minimize the system construction costs, as compared to conventional optical networks.
Owner:崔埈国
Switching media converter and ring type wavelength division multiplexing passive optical network system using the same
InactiveUS20050031348A1Simplifying the architecture of its central officeLow costMultiplex system selection arrangementsRing-type electromagnetic networksLength waveBackward channel
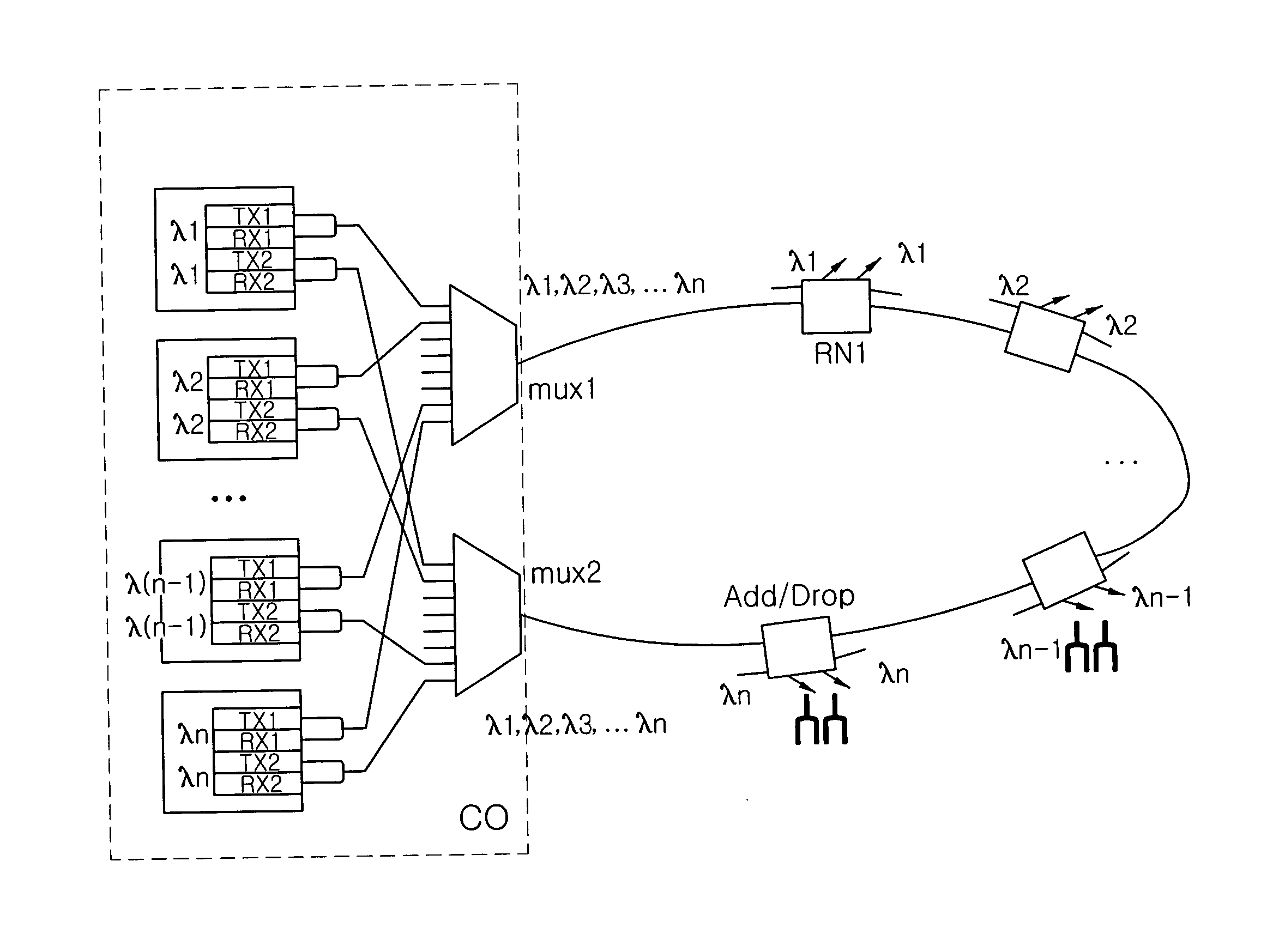
Disclosed is a ring type wavelength division multiplexing (WDM) passive optical network (PON) system using the same wavelength for forward and backward channels while inexpensively implementing a redundancy function, and a switching media converter usable in the ring type WDM PON system. The WDM PON system provided a redundancy function to each node, so that the central office of the system can have a simplified architecture. Accordingly, there is an advantage in that the construction costs of the central office can be reduced. And, the network construction costs can be minimized because it is possible to provide a desired redundancy to a part of the nodes, taking into consideration the significance of each node.
Owner:JUN KOOK CHOI
Method and network architecture for upgrading legacy passive optical network to wavelength division multiplexing passive optical network based next-generation passive optical network
InactiveUS7773838B2Increase the number ofExpansion of bandwidthWavelength-division multiplex systemsCoupling light guidesNetwork terminationNetwork architecture
The present invention discloses a network architecture for upgrading a legacy time division multiplexing-passive optical network (TDM-PON) to a wavelength division multiplexing-passive optical network (WDM-PON) based next-generation passive optical network (next-generation PON), wherein the legacy TDM-PON comprises: a central office (CO) having a first optical line termination (OLT); a remote node (RN) having a splitter; a single mode fiber (SMF) connecting the first OLT and the splitter; and a first group of one or more optical network terminations (ONTs) being connected to the splitter by a first group of one or more distribution fibers, and wherein the network architecture further comprises: in case that the next-generation PON is a WDM-PON, a first apparatus for combining and splitting wavelength bands being positioned between the SMF and the first OLT, in order to add a second OLT to be used for the WDM-PON within the CO or within another CO which is located in a position different from the CO, while sharing the SMF; a second apparatus for combining and splitting wavelength bands being positioned at a front terminal of the splitter; and an arrayed waveguide grating (AWG) being connected to the second apparatus for combining and splitting wavelength bands within the RN, and being connected to a second group of one or more ONTs by a second group of one or more distribution fibers within the RN or within another RN which is located in a position different from the RN.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com