Patents
Literature
221 results about "Optical axis alignment" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Planar lightwave circuit (PLC) device wavelength tunable light source comprising the same device and wavelength division multiplexing-passive optical network (wdm-pon) using the same light source
ActiveUS20100119231A1Improve performanceImprove stabilityWavelength-division multiplex systemsSolid-state devicesExternal cavity laserOptical axis alignment
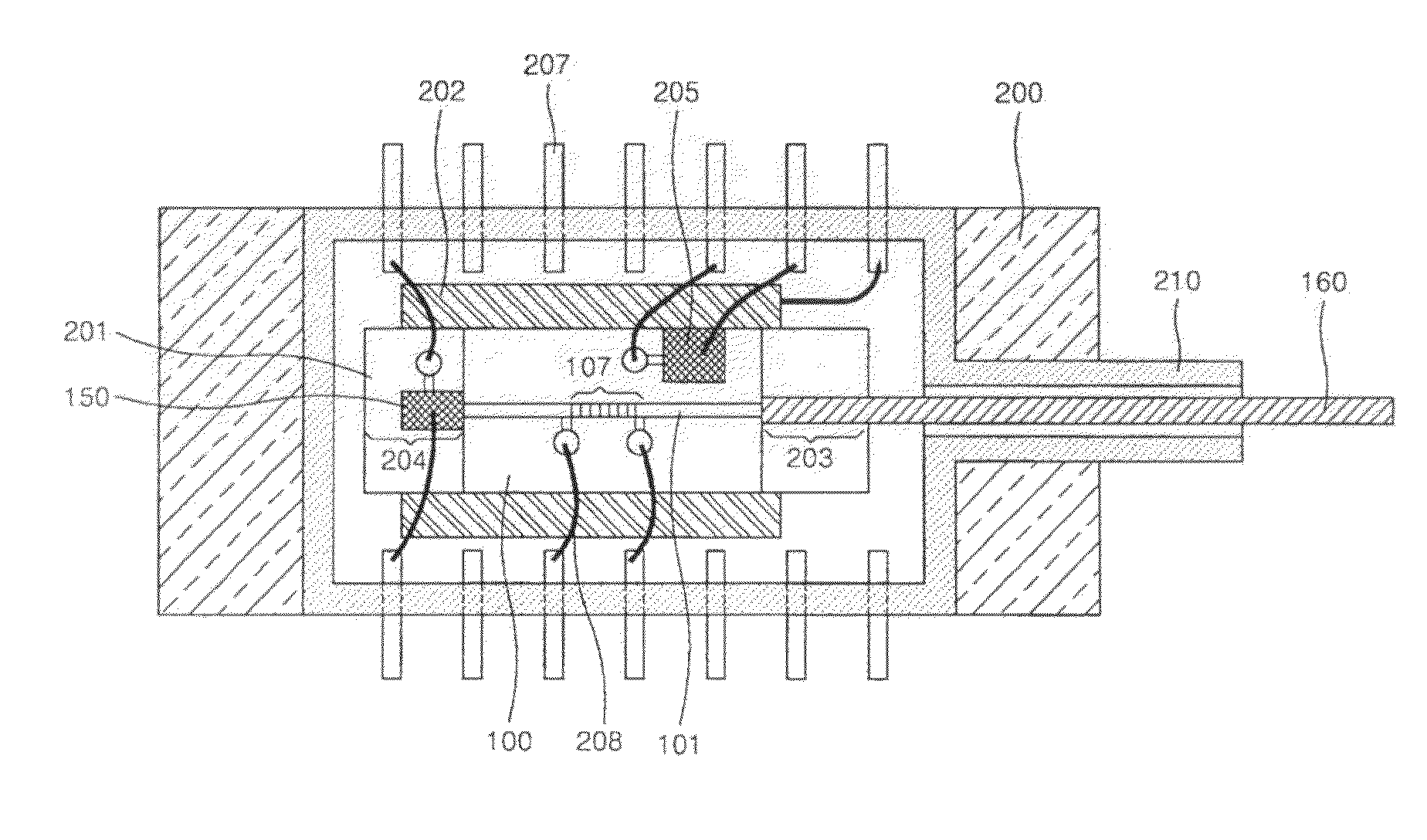
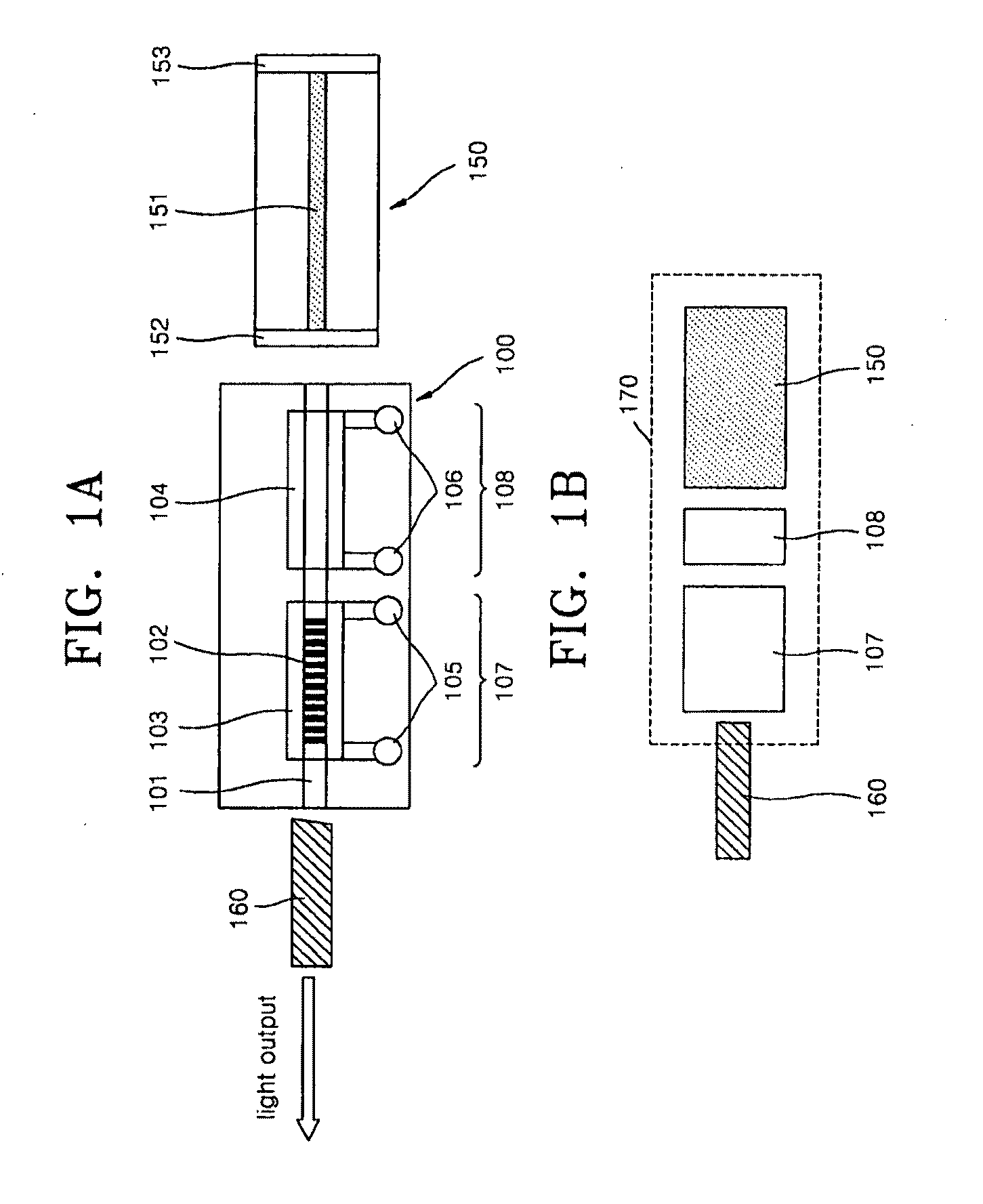
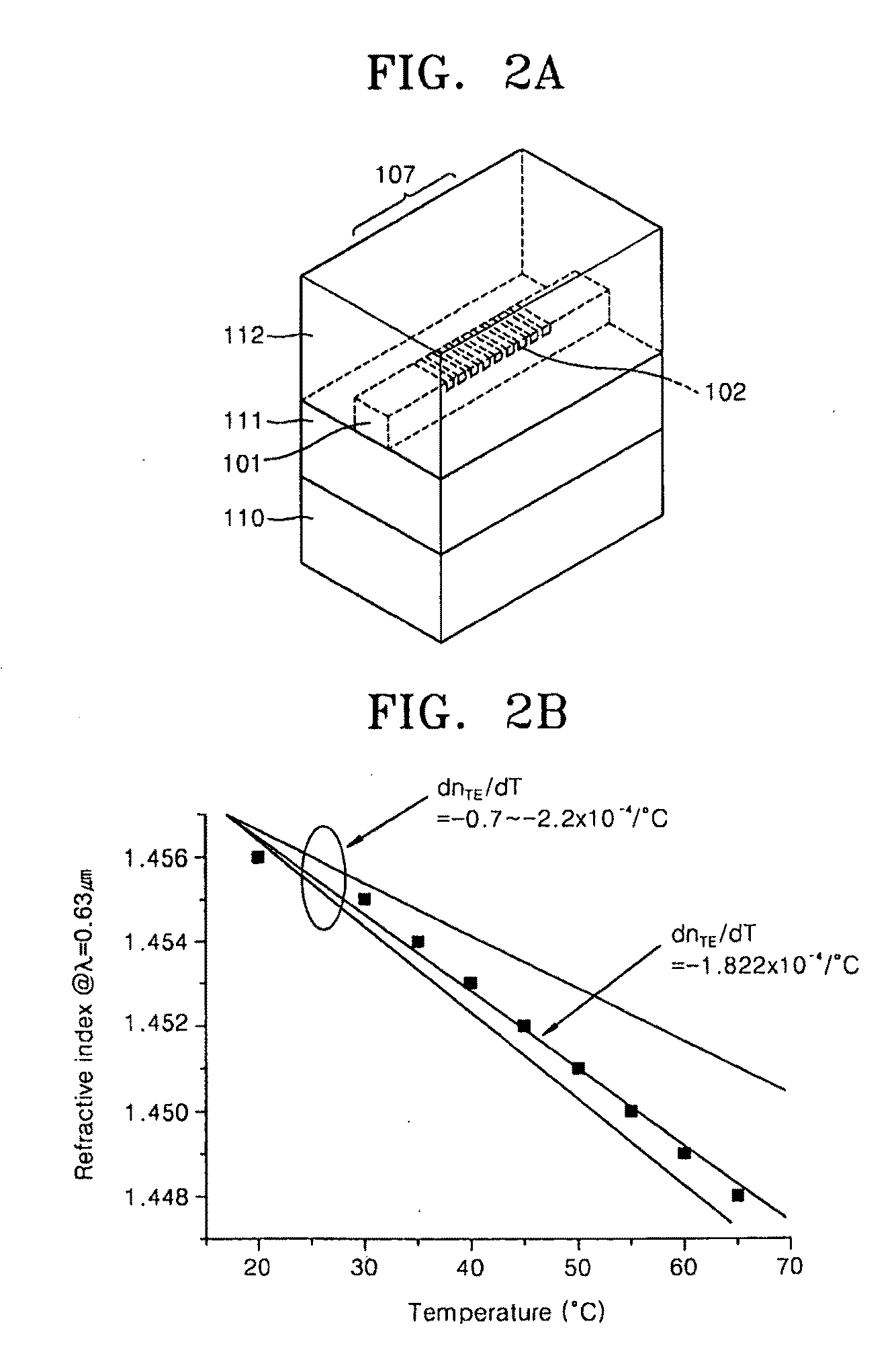
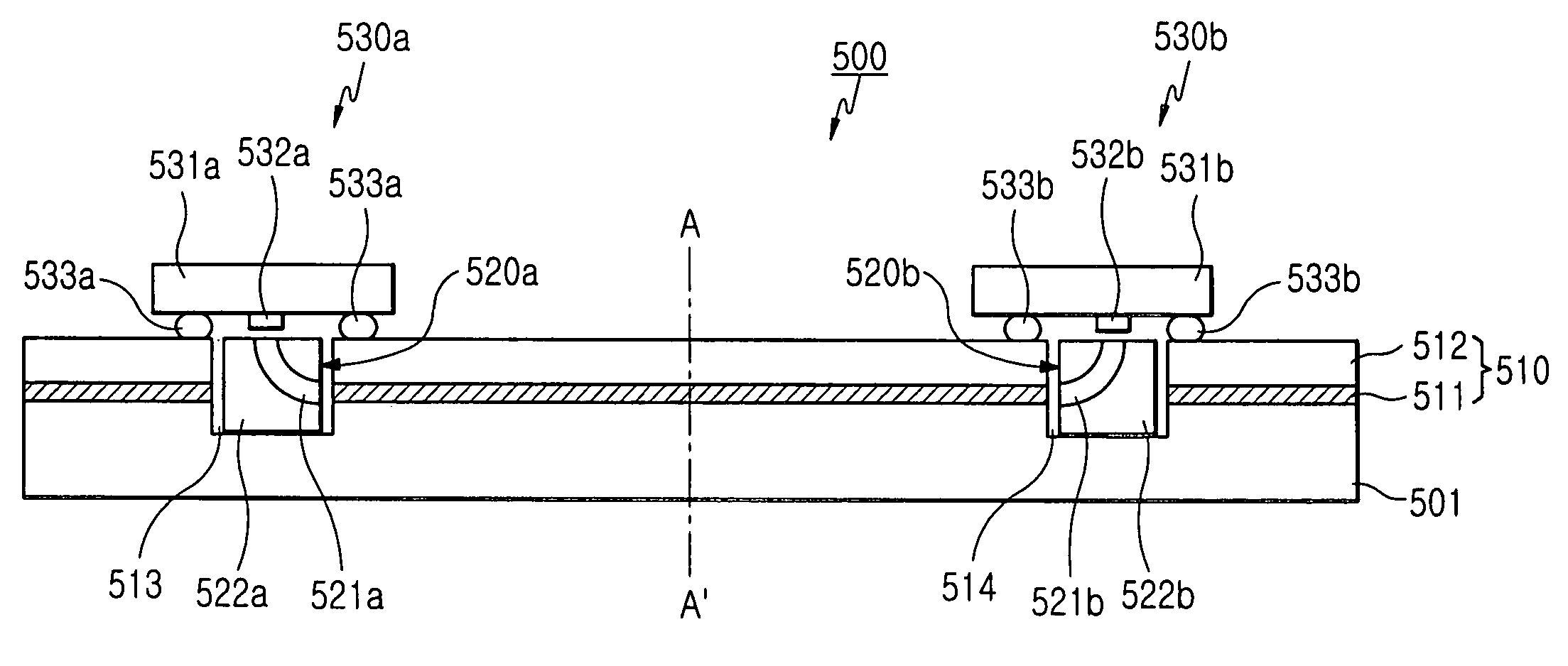
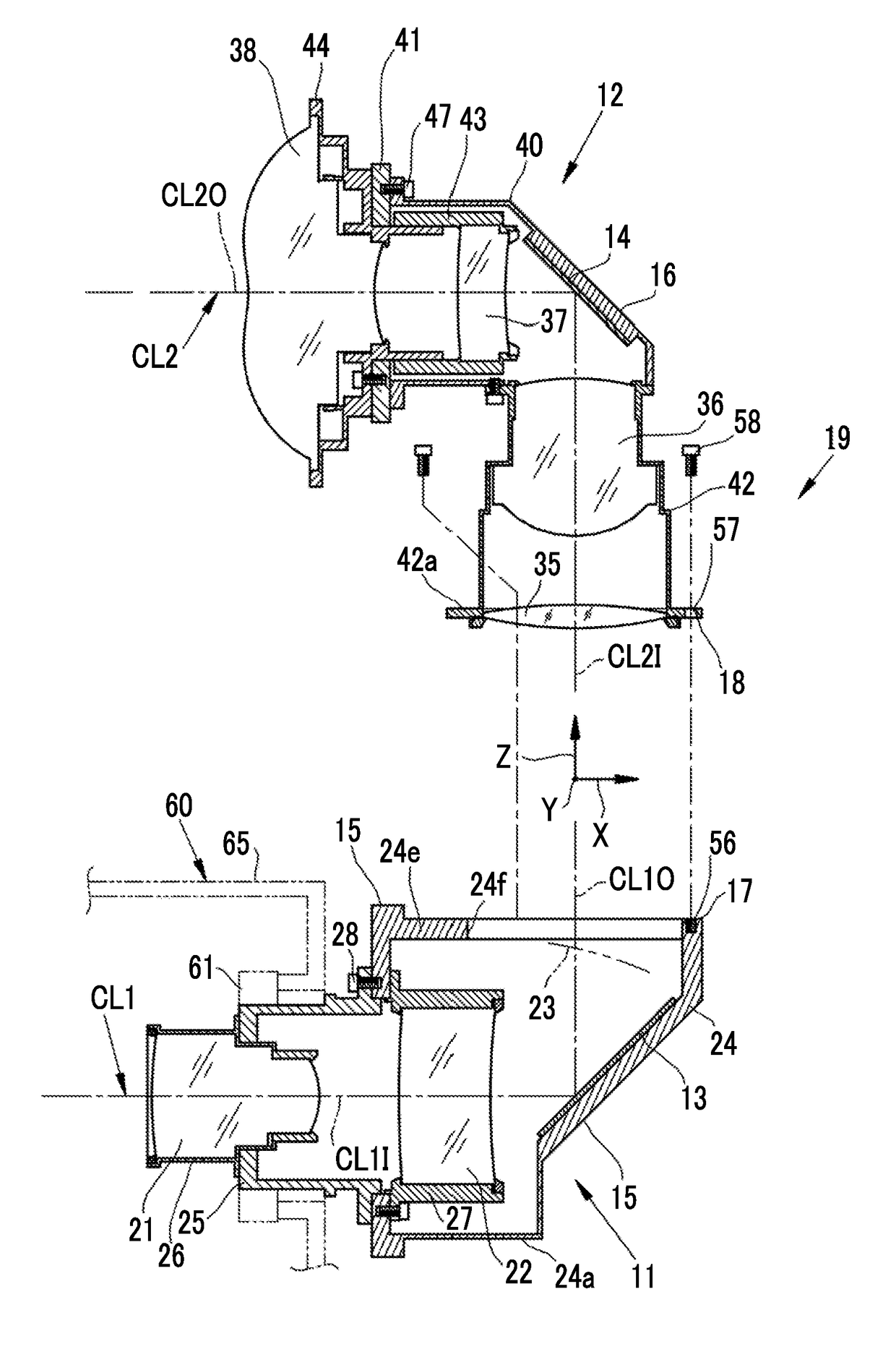
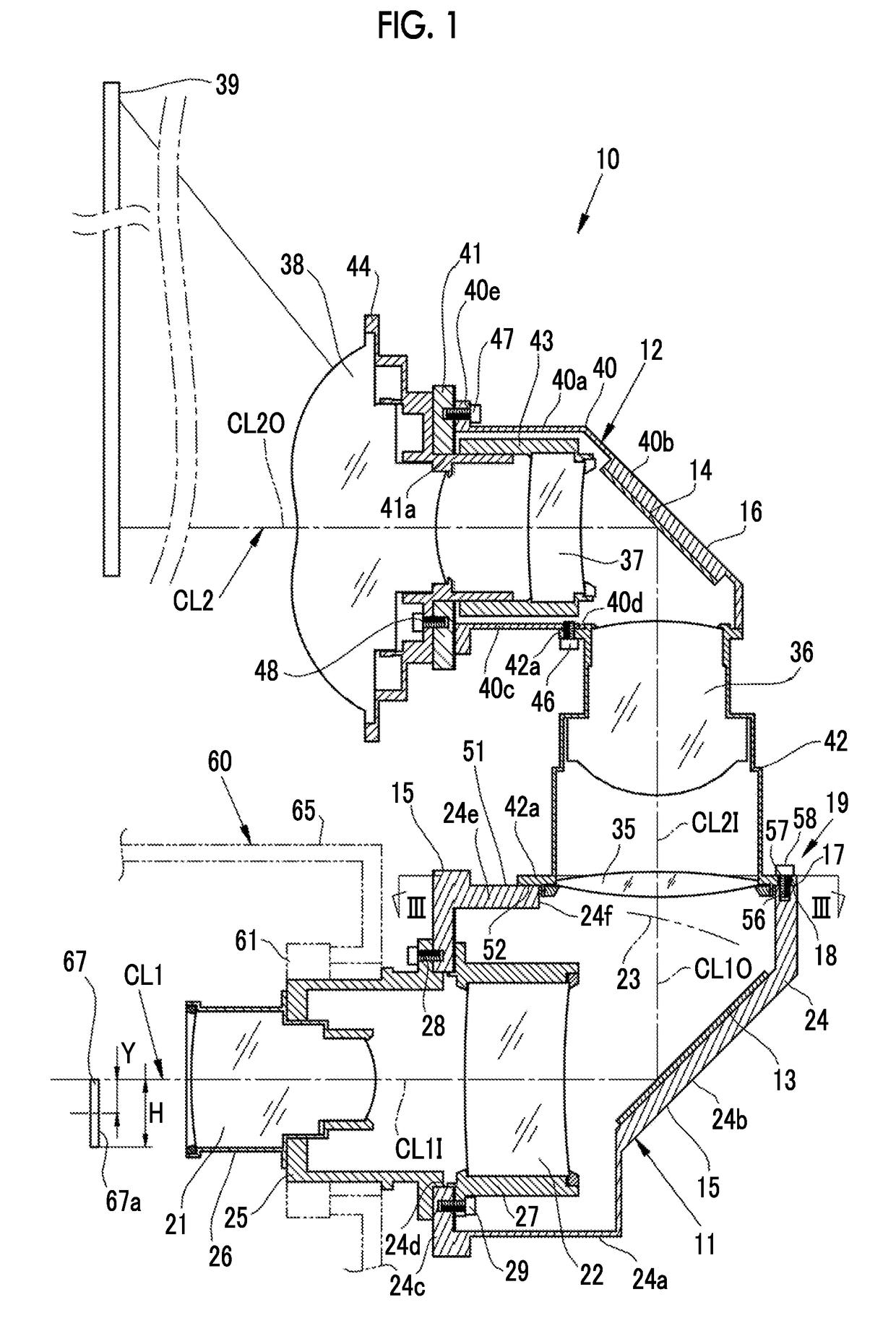
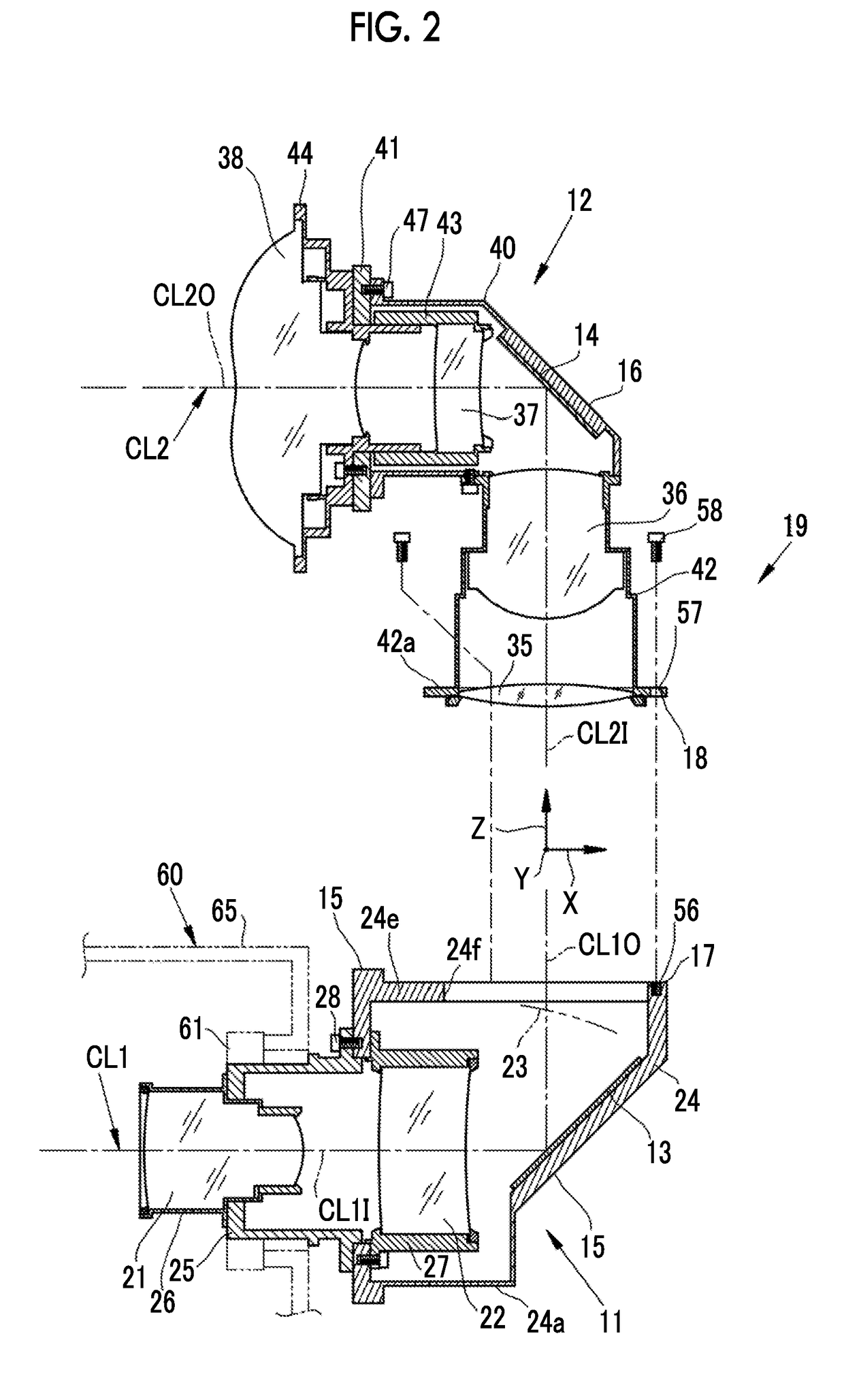
In the manufacture and application of a PLC-ECL type wavelength tunable light source, provided is a wavelength tunable mechanism with improved performance and stability, a light source with improved packaging performance and mass productivity, and a light source applied to a WDM-PON with initialization and stabilization functions. The wavelength tunable light source having a PLC (planar lightwave circuit)-ECL (external cavity laser) structure includes a first housing in which a semiconductor optical gain medium is mounted, a second housing in which a PLC device is mounted, and a third housing in which an optical fiber is mounted. The first, second, and third housings make an optical axis alignment through an optical coupling lens and combined in a laser welding method.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
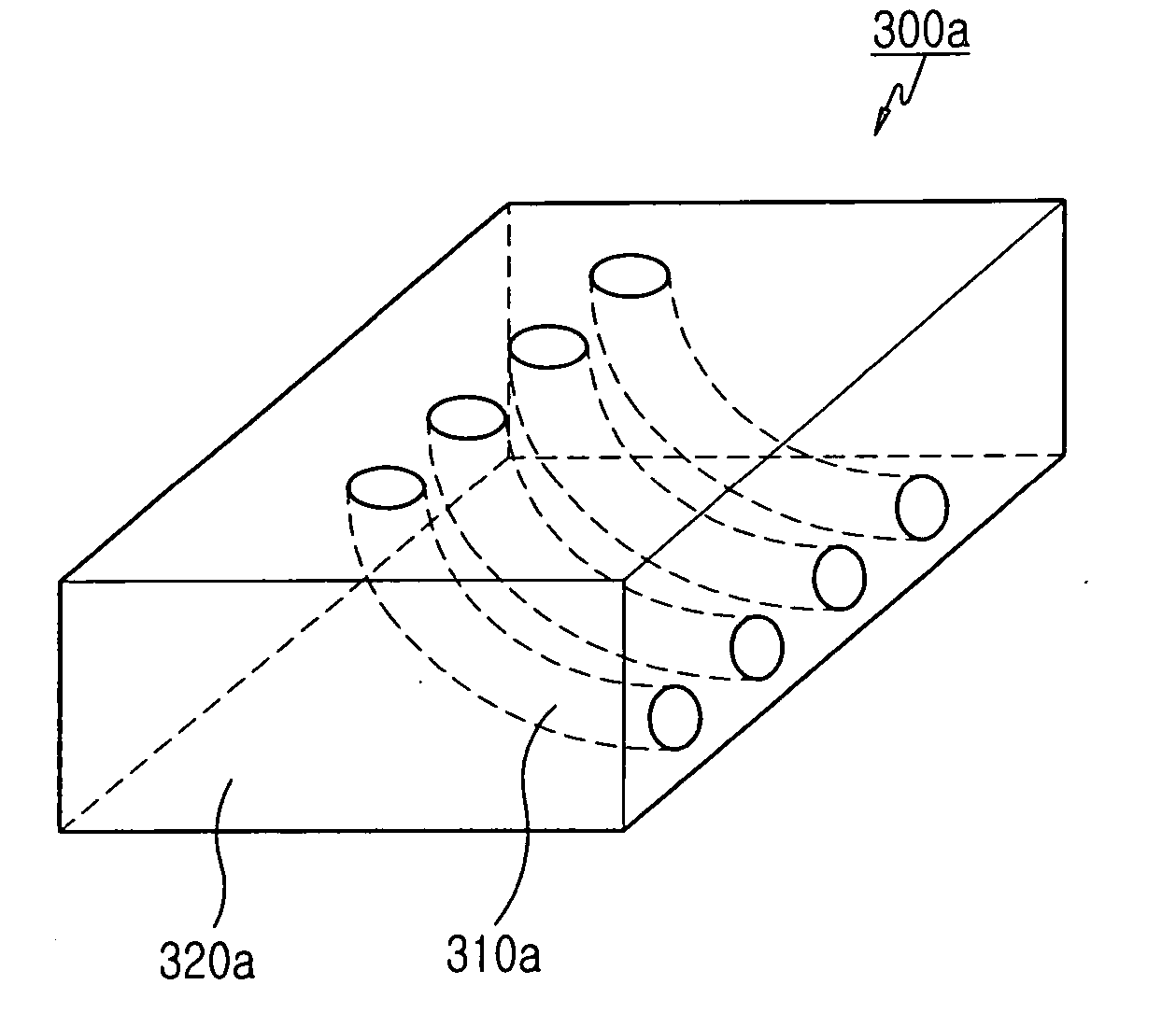
Optical connection block, optical module, and optical axis alignment method using the same
An optical module is disclosed. The optical module includes a substrate, and at least one planar optical waveguide that includes a plurality of waveguides and at least one groove vertically penetrating the upper surface of the substrate and which is successively laminated on the substrate. The optical module also includes at least one PCB having at least one integrated photoelectric conversion device that is positioned on the planar optical waveguide facing a corresponding groove, and at least one optical connection block including a body and optical fibers embedded in the body in such a manner that both ends thereof are exposed to the lateral and upper surfaces of the body. The optical connection block is inserted into the corresponding groove of the planar optical waveguide in such a manner that both ends of the optical fibers, which have been exposed, face the waveguides and the PCBs, respectively.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Interferometer system and method for lens column alignment
InactiveUS6160628ASemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingUsing optical meansLight beamOptical axis alignment
A projection exposure apparatus and method aligns a substrate with an optical axis of a lens column using one or more interferometers, mirrors, and a control device. The lens column projects a pattern from a mask onto the substrate. The optical axis of the lens column is perpendicular to the substrate. To ensure precise alignment of the lens column and the substrate, the one or more interferometers use a plurality of beams having respective paths, the lengths of which change in response to movement of the optical axis. In response to the detected changes of the interferometer beams, a control device adjusts the position of the stage so that the substrate is aligned with the optical axis of the lens column.
Owner:NIKON CORP
Otoscope
An otoscope permitting examination of a patient's ear is defined by an instrument head including a proximal end and a distal insertion portion that is insertable into the ear. The otoscope includes an imaging lens train disposed within the instrument head, wherein each of the imaging lens train, an eyepiece and a distal opening of said insertion portion are aligned along an optical axis. The otoscope further includes a focusing mechanism for selectively moving at least one of the imaging lens train and the optics contained within the eyepiece relative to one another along the optical axis. The imaging lens train and the optics in the eyepiece define an optical system such that an entrance pupil is substantially located in the distal insertion portion of the instrument head, thereby enabling the entire tympanic membrane to be viewed at once by the user.
Owner:WELCH ALLYN INC
Medical handpiece with a light guide which can be displaced in an axial direction
InactiveUS6461349B1Little manual effortIncrease the cross-sectional areaSurgical instrument detailsCoupling light guidesFiberLight guide
A medical handpiece for transmitting energy from a laser beam into biological tissue. An optical fiber for conveying the laser beam to the handpiece and a light guide for radiating the laser energy into the tissue are arranged in a base body. Means are provided for aligning the optical axis of the light guide in relation to the optical axis of the fiber and means for aligning the optical axis of the light guide in relation to the base body are also provided. The light guide can be displaced in an axial direction in relation to the base body and the alignment can be set according to the direction of displacement or maintained. The light guide is easy to replace and the device is easy to clean in accordance with all hygiene requirements.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MEDITEC AG
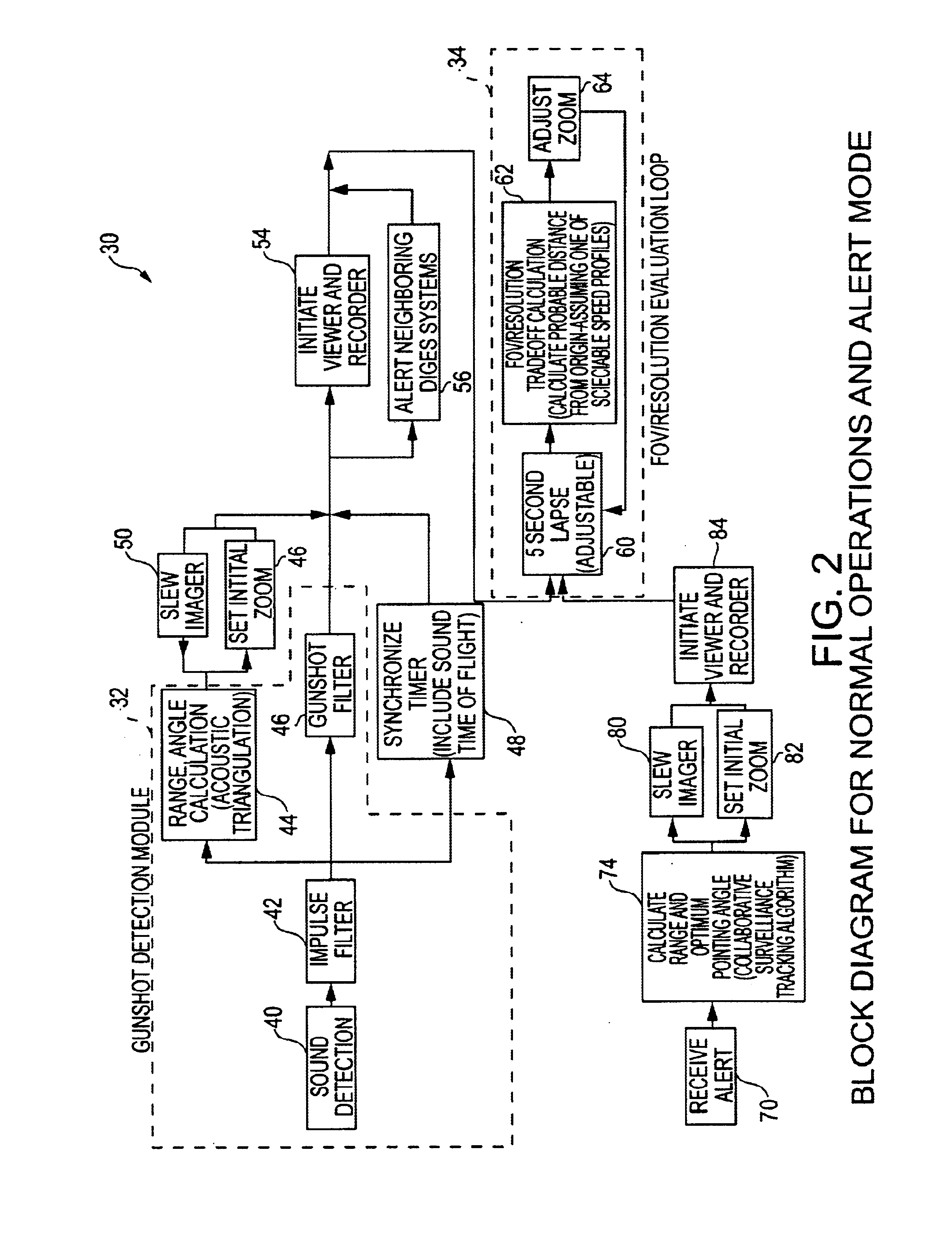
Gun shot digital imaging system
InactiveUS6965541B2Rapid detection and imaging and trackingPosition fixationDiversity direction findingDigital imagingSound sources
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
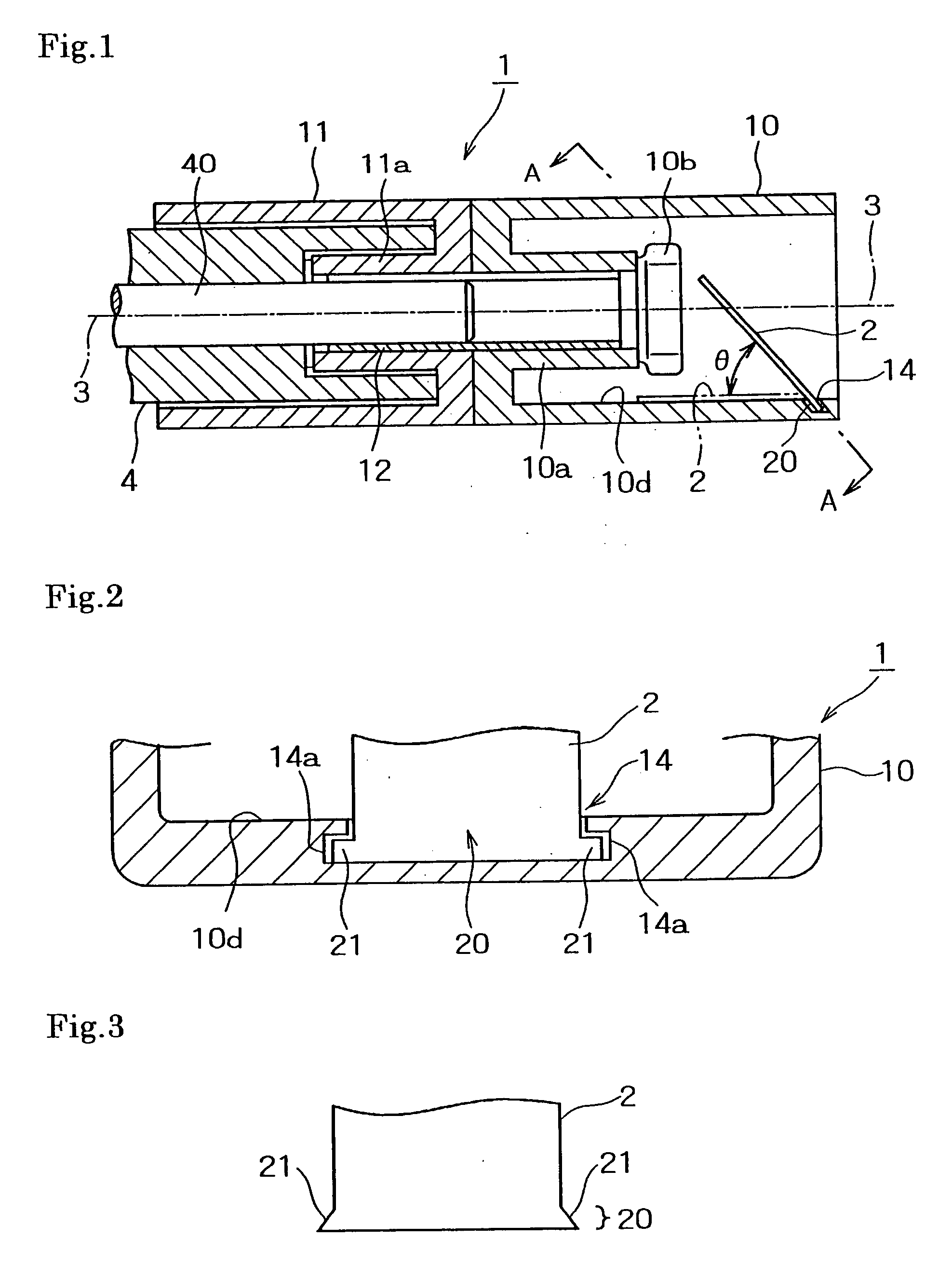
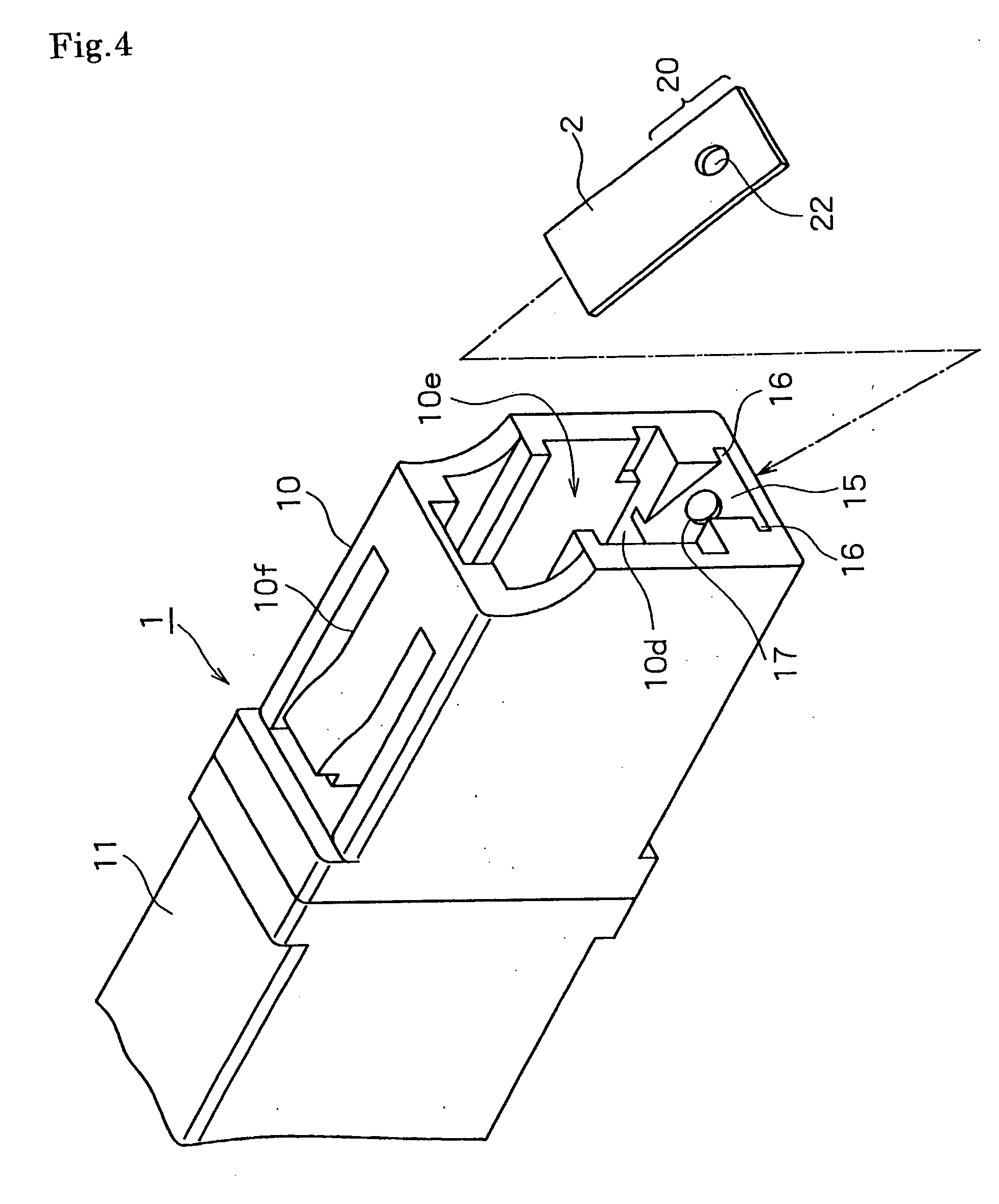
Optical connector
InactiveUS20100329604A1Highly accurate optical axis alignmentEfficient selectionCoupling light guidesSignal lightEngineering
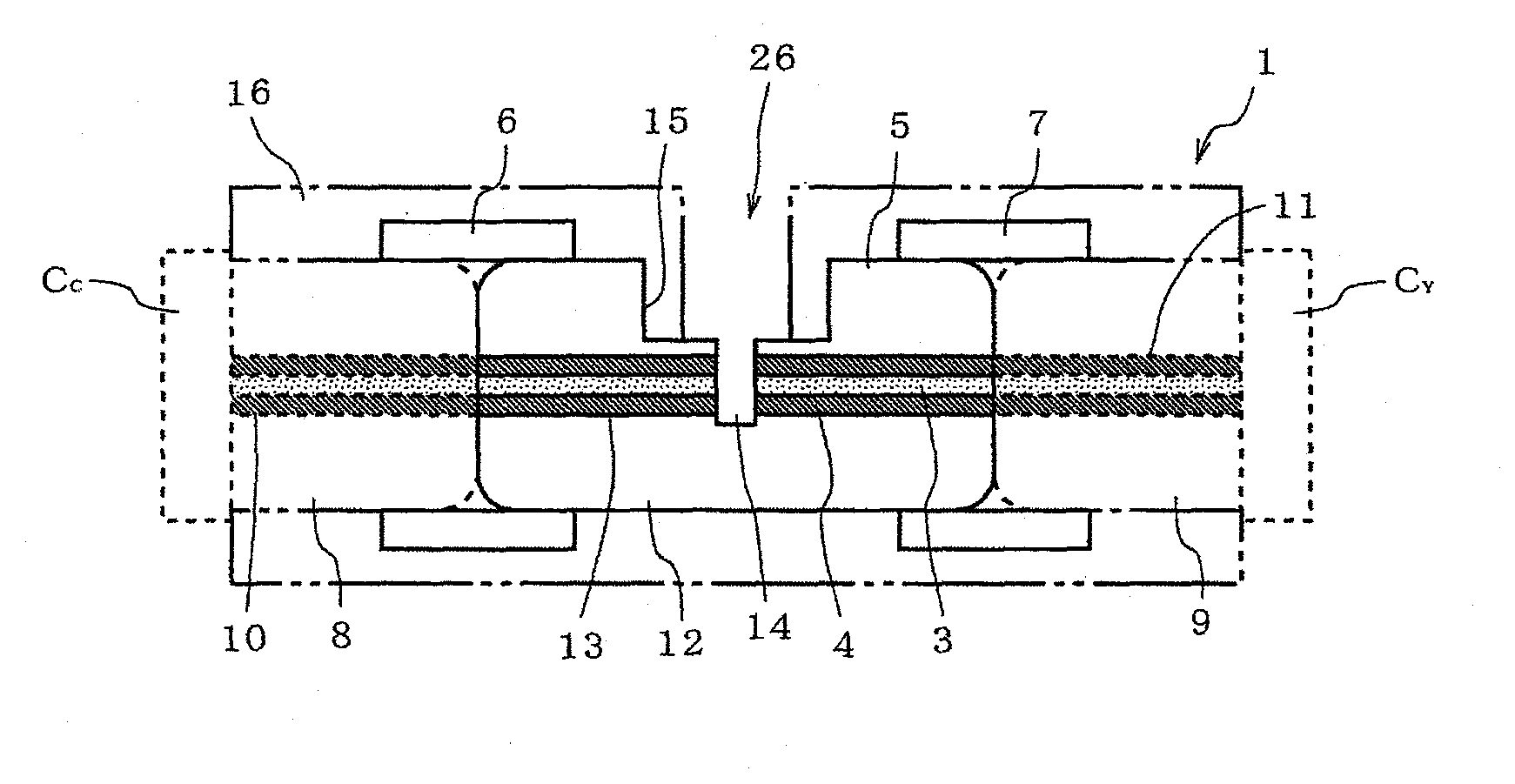
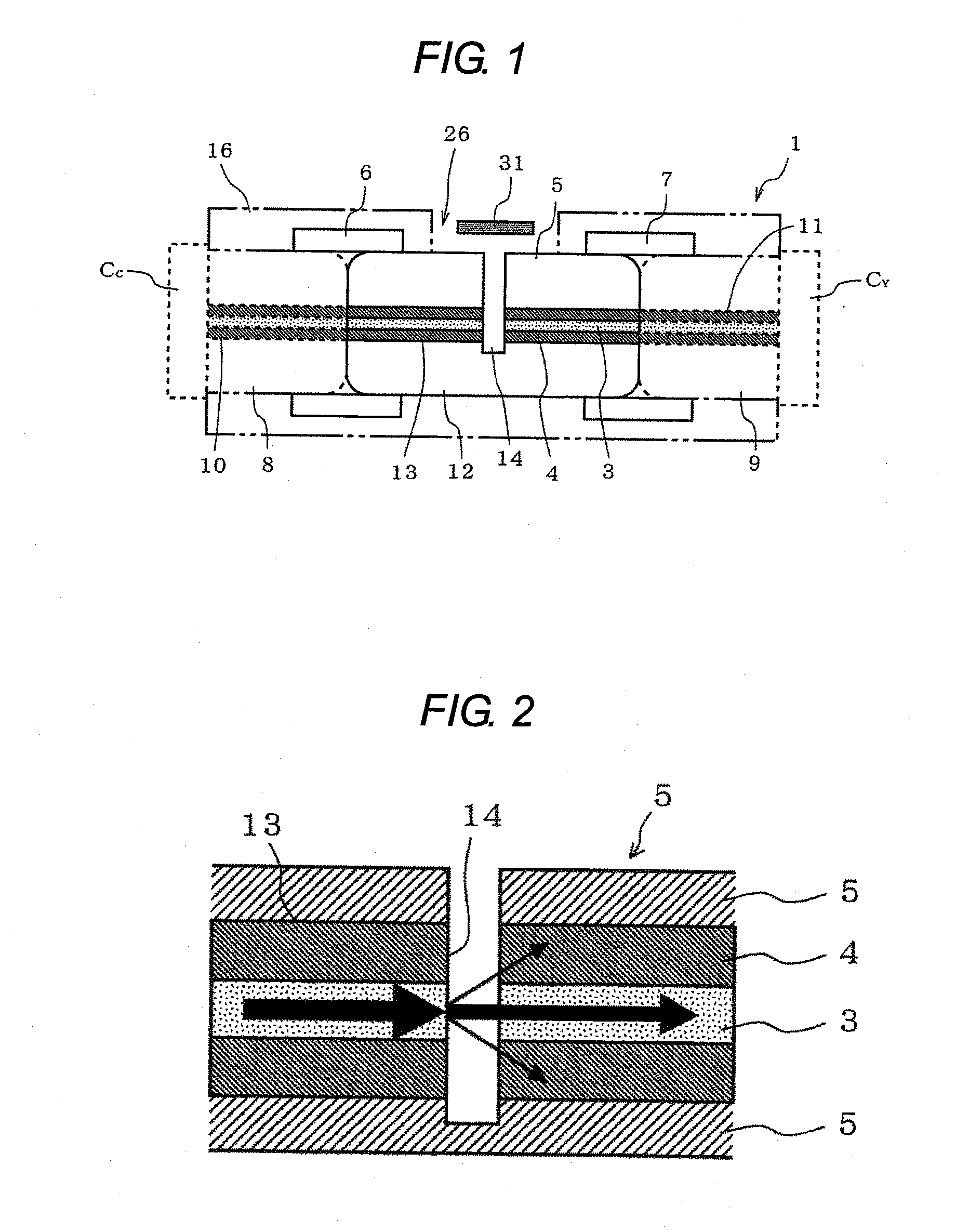
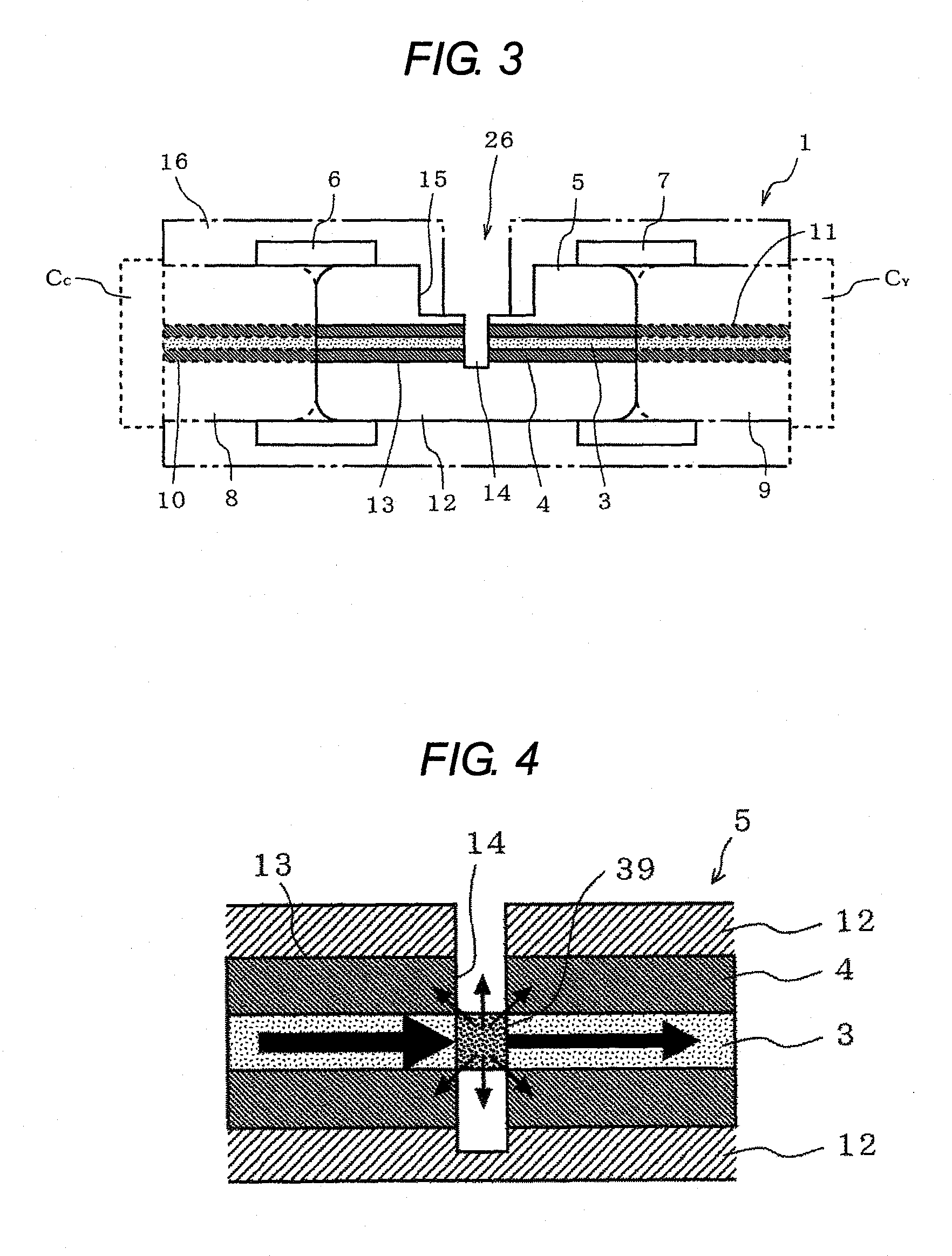
An optical connector that requires no complicated fabrication operation such as highly accurate optical axis alignment and that permits an efficient pick up of part of the communication signal light being on-propagation along an optical transmission line, is provided. The optical connector 1 for connecting optical transmission lines each other is comprised of at least a connector main body 16 and a joining element 5 provided inside the connector main body 16 being interposed between the optical transmission lines and coupled to each end face of the optical transmission lines, wherein the joining element 5 is comprised of a core 3 and a cladding 4 provided on the periphery of the core 3 that are optically coupled to the optical transmission line, and a light pick-up means for picking up part of communication signal light being on-propagation along the optical transmission line, and wherein the connector main body 16 has, in a position that faces the light pick-up means, an optical output port 26 for outputting part of the communication signal light picked up by the light pick-up means to a light detector 2.
Owner:ADVANCED CABLE SYST CORP +1
Collimated optical system
An optical system provides a lens cell having a generally cylindrical lens cell body and an optical lens system therein. The lens cell body has a lens cell central longitudinal axis and a lens cell optical axis, eccentrically offset from the lens cell central longitudinal axis. A sleeve has a generally cylindrical sleeve body, an outer surface with a first longitudinal axis, and an inner surface with a second longitudinal axis, eccentrically offset from the first longitudinal axis. The lens cell is inserted into the sleeve. A housing has a generally cylindrical body into which the sleeve is at least partially inserted. The lens cell and the sleeve are rotated relative to each other and to the housing such that the lens cell optical axis is aligned in a desired location. After the lens cell optical axis is aligned in the desired location, the lens cell is fixedly connected to the sleeve and the sleeve is connected to the housing to prevent rotation of the sleeve relative to the housing.
Owner:ELBIT SYSTEMS OF AMERICA LLC
Stacked optical glass lens array, stacked lens module and manufacturing method thereof
A stacked optical glass lens array, a stacked lens module and a manufacturing method thereof are disclosed. The stacked optical glass lens array includes at least two optical glass lens arrays whose optical axis are aligned and then stacked with each other by cement glue in glue grooves. A stacked optical glass lens element can be singularized by cutting along with the alignment notches of stacked optical glass lens array. The stacked lens module is formed by a single stacked optical glass lens element and related optical element mounted in a lens holder. Thereby the optical axis of the lenses of the stacked lens module are aligned precisely, the manufacturing processes are simplified and the production cost is reduced.
Owner:E PIN OPTICAL IND
Camera Modules With Lens Drive Device
InactiveUS20080211955A1Stabilizing orientation of the platformLimit motionTelevision system detailsProjector focusing arrangementCamera lensComputer module
A camera module has a plurality of lenses aligned along an optic axis that receive and transmit light from a scene being imaged by the camera module. At least one lens is mounted on a platform which is movable along the optic axis and is moved by action of a piezoelectric motor. Optionally, at least one lens is mounted on a second platform which is movable along the optic axis. The second platform may be driven by a second piezoelectric motor or moved by action of the first platform.
Owner:NANOMOTION
Optical connection block, optical module, and optical axis alignment method using the same
InactiveUS20050220437A1Improves optical axis alignmentEasy to manufactureCoupling light guidesOptical ModuleEngineering
An optical module is disclosed. The optical module includes a substrate, and at least one planar optical waveguide that includes a plurality of waveguides and at least one groove vertically penetrating the upper surface of the substrate and which is successively laminated on the substrate. The optical module also includes at least one PCB having at least one integrated photoelectric conversion device that is positioned on the planar optical waveguide facing a corresponding groove, and at least one optical connection block including a body and optical fibers embedded in the body in such a manner that both ends thereof are exposed to the lateral and upper surfaces of the body. The optical connection block is inserted into the corresponding groove of the planar optical waveguide in such a manner that both ends of the optical fibers, which have been exposed, face the waveguides and the PCBs, respectively.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
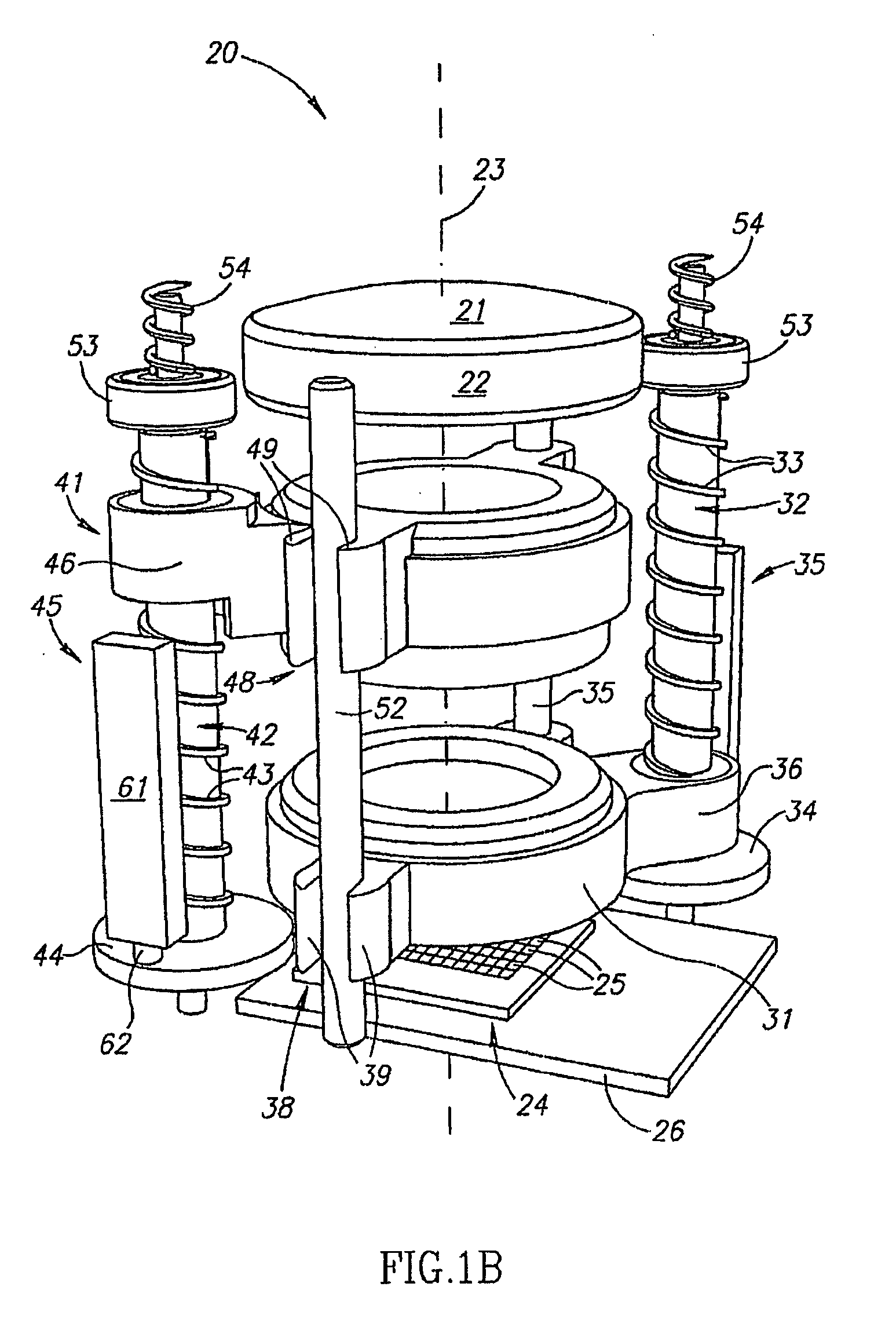
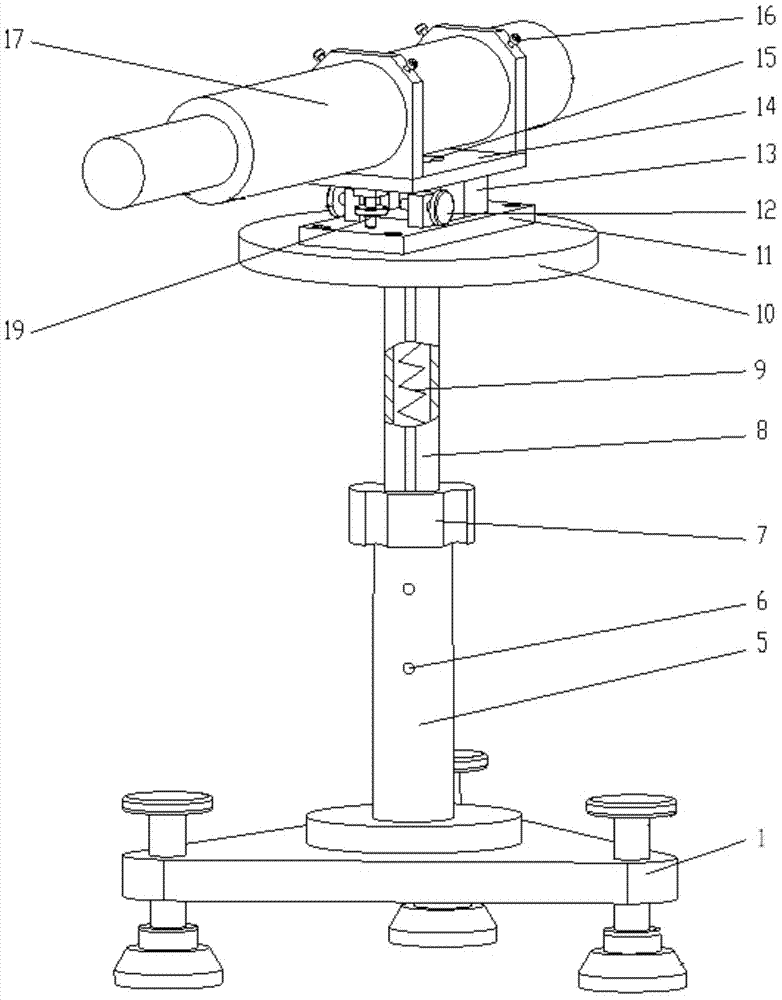
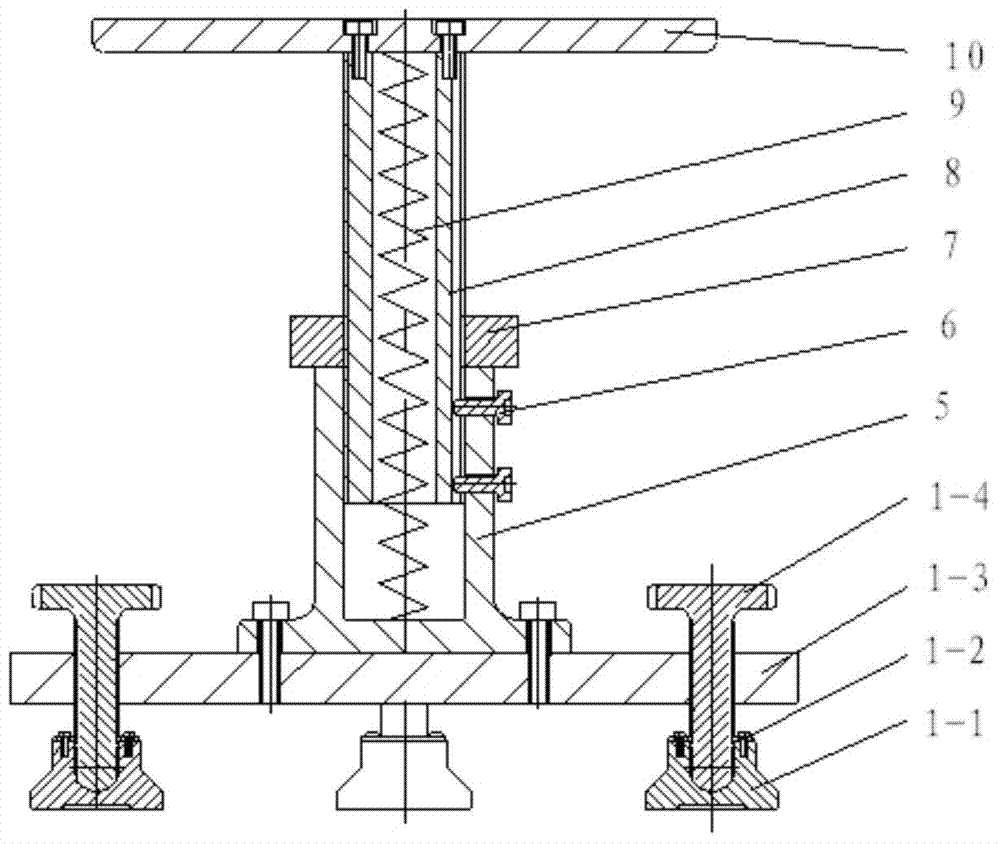
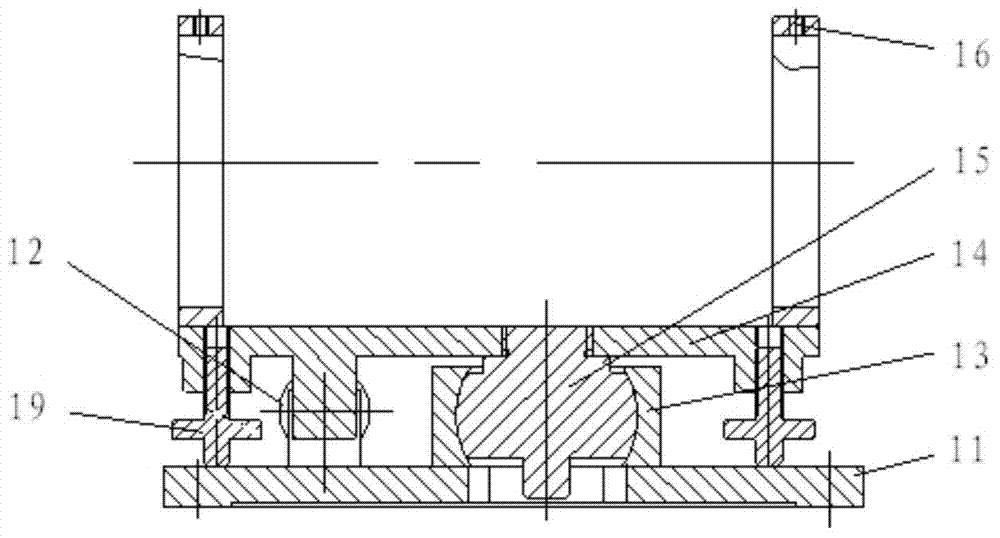
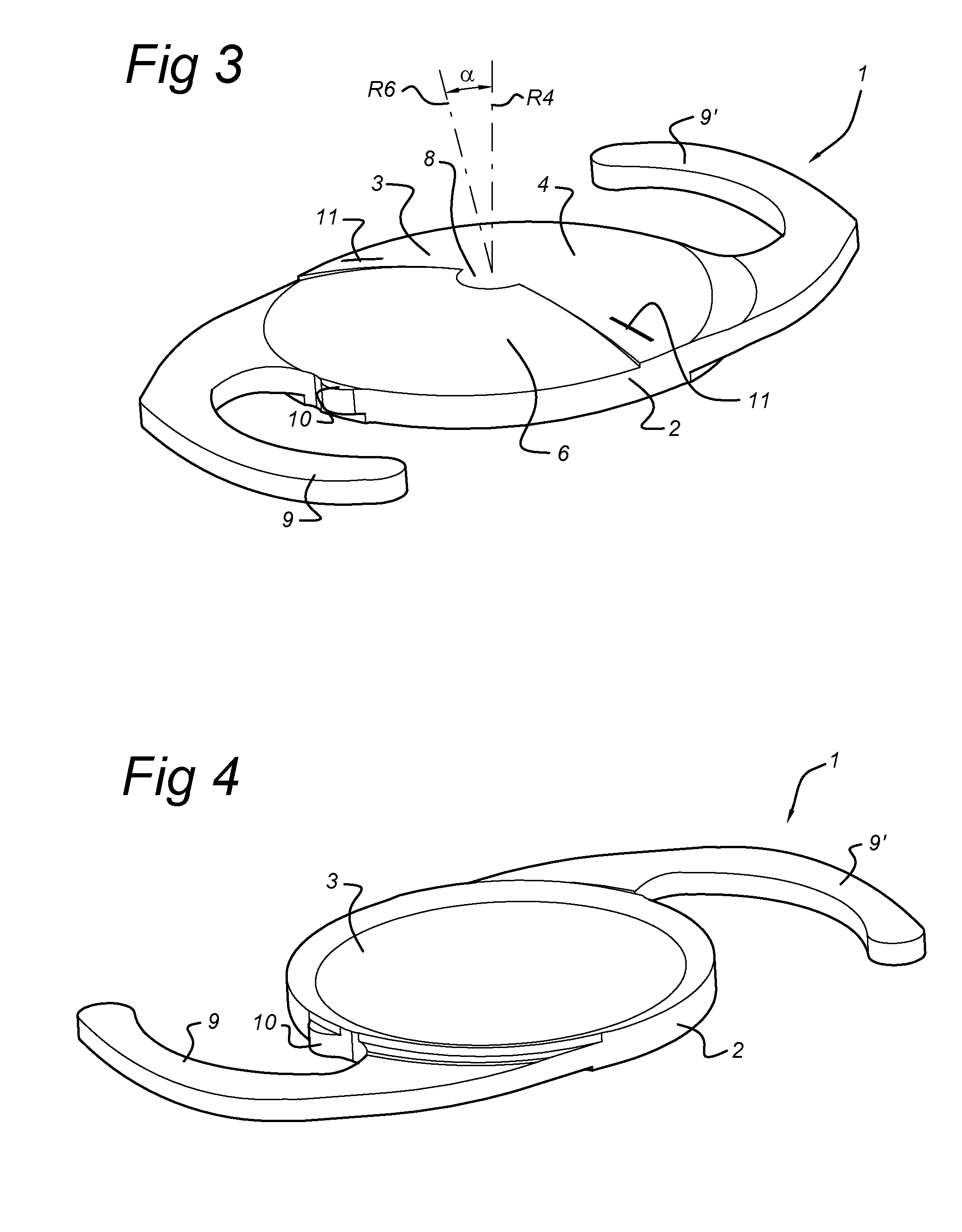
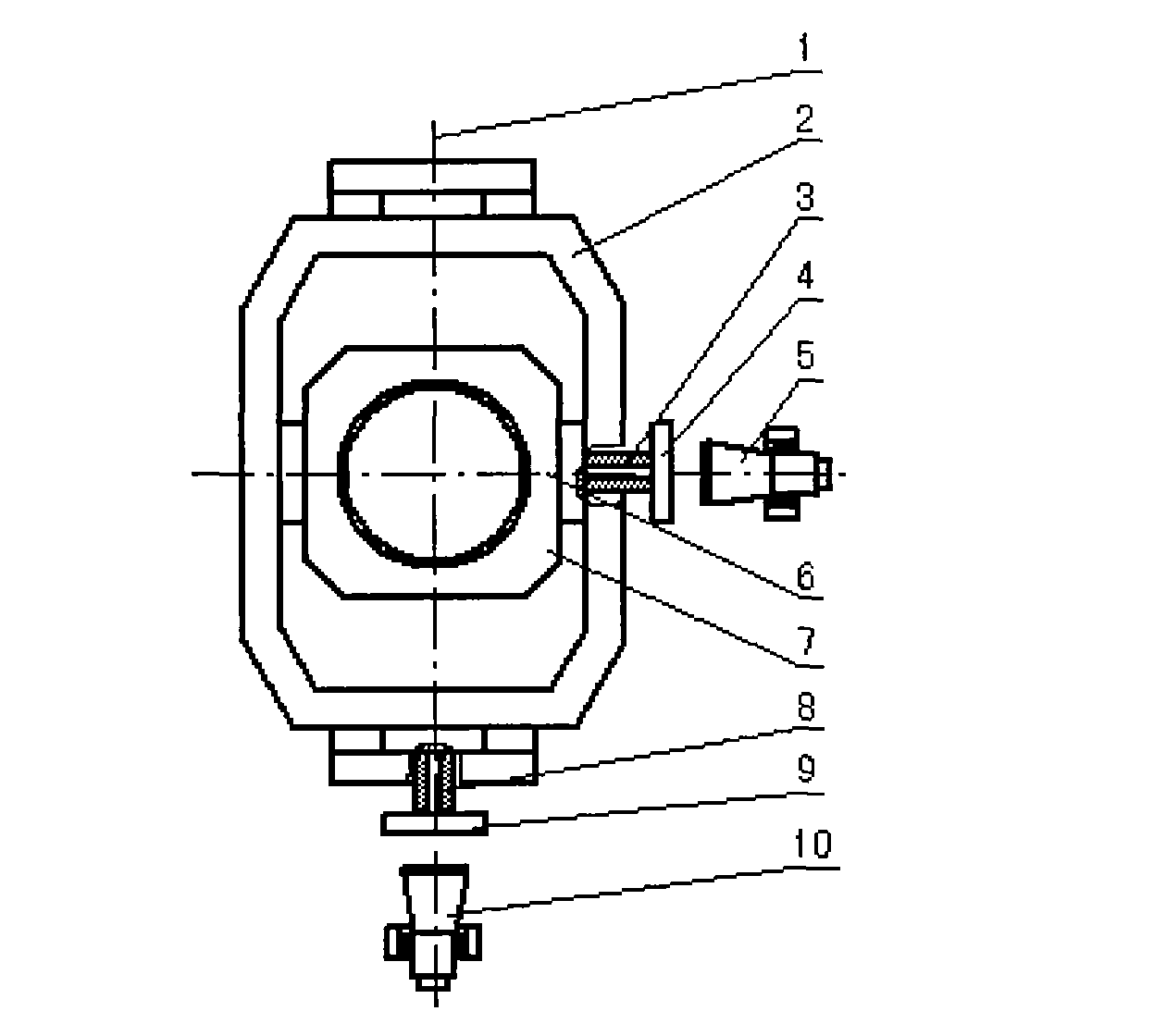
Support fine-tuning device applied to pre lens optical axis alignment
ActiveCN103777301AFast levelThe continuous lifting process is stableMountingsEngineeringMechanical engineering
The invention discloses a support fine-tuning device applied to pre lens optical axis alignment. The device is formed by fixedly connecting a leveling platform, a lifting component and an angle fine-tuning component from bottom to top. The leveling platform uses a three point leveling principle to realize rapid leveling. The lifting component uses a nut screw mechanism with limiting and a tension spring to realize smooth and continuous lifting. A pipe seat in the angle fine-tuning component is fixedly connected with a ball pin. A base is fixedly connected with a ball pin seat. The ball pin and the ball pin seat form a spherical pair. A limiting shaft on the ball pin and a rectangular groove on the base form a sliding pair. When in use, a pre lens is arranged in the pipe seat. By rotating a pitch wheel on the pipe seat, fine-tuning and locking can be carried out on the pitch angle of the pre lens. By rotating an orientation wheel on the base, the pipe seat is pushed to realize fine-tuning and locking of the orientation angle of the pre lens, thus a pre lens optical axis is accurately aligned with a tested product. According to the invention, the problems of support and fine-tuning of the pre lens are solved, and the device has the characteristics of simple structure, convenient erection, small occupied space, convenient adjusting and the like.
Owner:西安应用光学研究所
Intraocular lens
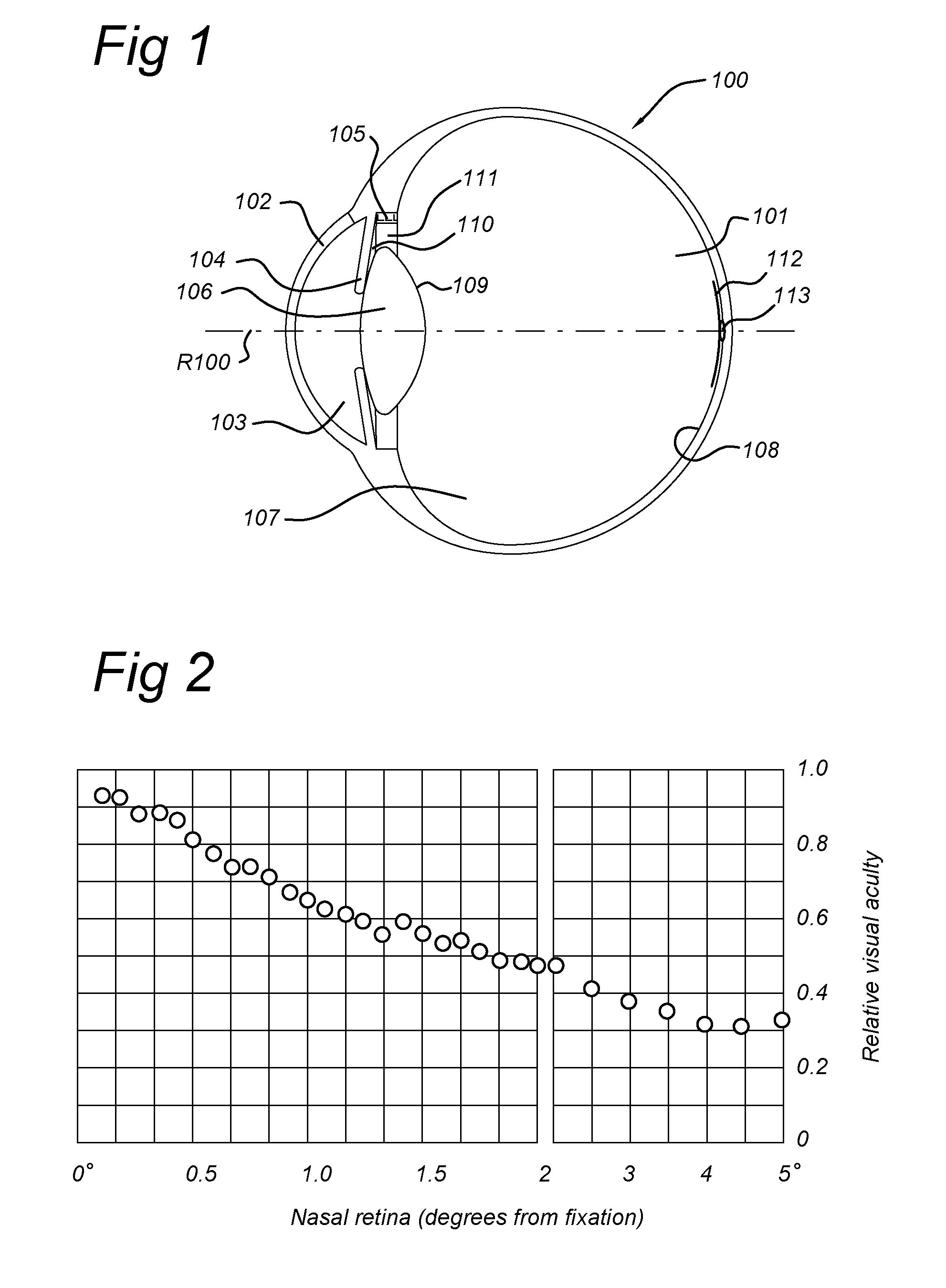
ActiveUS20150005877A1Negative impactUndesirable appearanceIntraocular lensIntraocular lensOptical axis
An intraocular lens includes an optic, which includes a first lens having a first optical axis for alignment with an optical axis of the human eye having a macula; and a second lens having a second optical axis. The second optical axis and the first optical axis enclose an angle between 0.5 and 10 degrees. The first and second lens are arranged next to one another in a direction transverse to the first optical axis to provide no overlap in a direction along the first optical axis such that the first lens and the second lens each, independent from one another, image onto the macula of the eye. The angle and a direction of the second optical axis are chosen such that the second lens images onto a functional part of the macula of the human eye, which functional part is not compromised by a defect, such as a scotoma.
Owner:TELEON HLDG BV
Lens array, light source device, projector and light source device fabrication method
ActiveUS20130057834A1Easy alignmentNon-electric lightingPoint-like light sourceOptoelectronicsOptical axis alignment
A lens array which facilitates the alignment of optical axes of light source elements with optical axes of lenses, a light source device that employs this lens array, a projector that employs this light source device and a light source device fabrication method are provided. A lens array 73 is an integrated assembly of a plurality of lens portions 73b which collect individually light from a plurality of light source elements and has cylindrical portions 73c for positioning the plurality of light source elements on a light entrance side of the individual lens portions 73b.
Owner:CASIO COMPUTER CO LTD
Microlens array, method of fabricating microlens array, and liquid crystal display apparatus with microlens array
InactiveCN1749829AEasy alignmentImprove production efficiencyPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusProduction rateLiquid-crystal display
The invention provides a microlens array and a liquid crystal display apparatus that allow easy optical axis alignment of a microlens array and is superior in productivity. A method of fabricating a microlens array has a step of forming a photosensitive resin layer 210 on the surface of a transparent substrate 102 opposite from the surface having an aperture portion 161a; a step of placing an exposure substrate and the transparent substrate 102 so that a parallel light, having an intensity distribution corresponding to a shape of an exposure microlens array 403, is focused by the exposure microlens array 403 and enters the transparent substrate 102 through the aperture portion 161a, with respect to the parallel light; a step of exposing the photosensitive resin layer 210, by applying the parallel light to the photosensitive resin layer 210 via the exposure substrate, and a step of developing the exposed photosensitive resin layer 210.
Owner:HITACHT MAXELL LTD
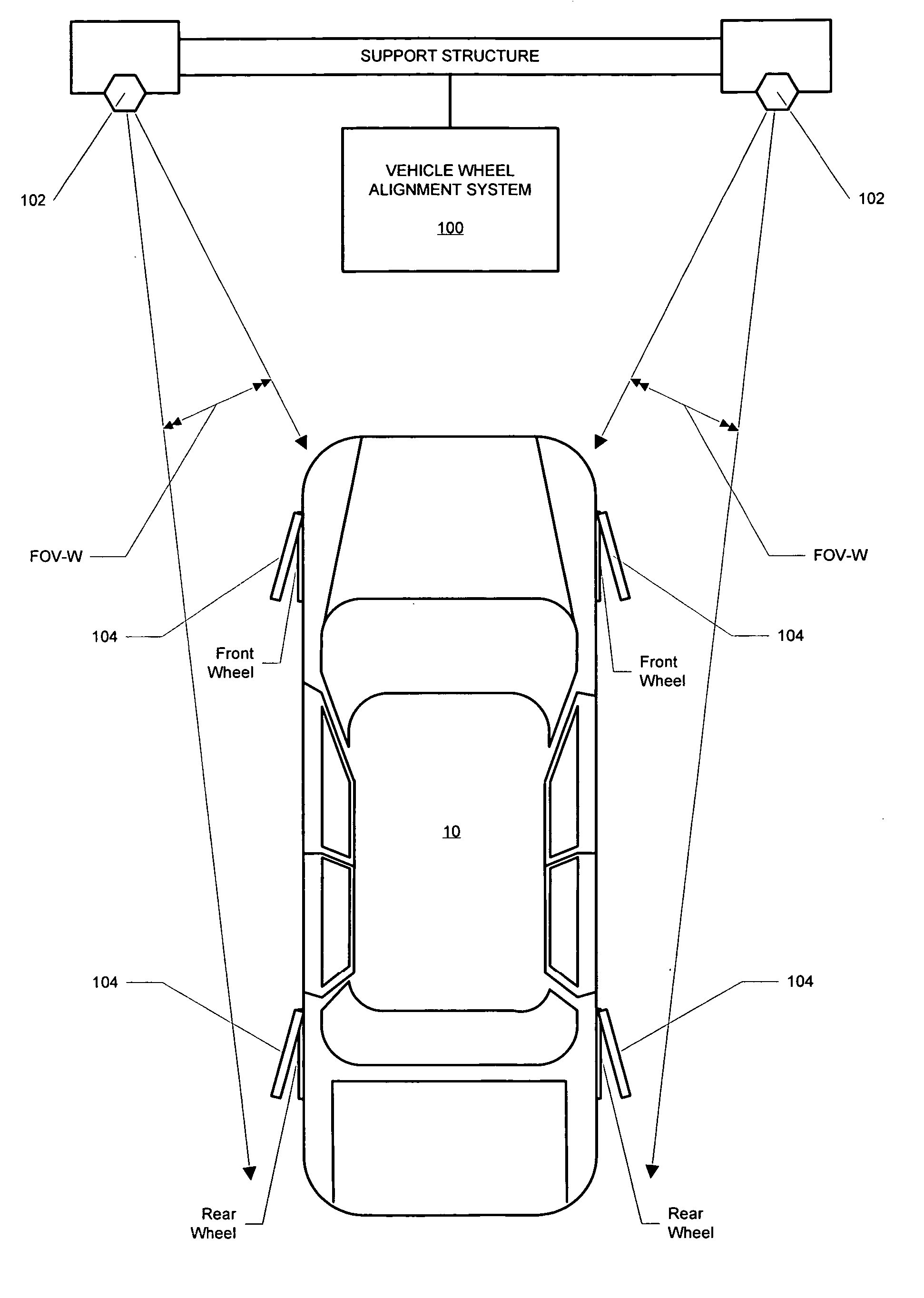
Vehicle service system with variable-lens imaging sensors
A optical imaging sensor assembly for a machine-vision vehicle service system comprising a variable lens optical assembly. The variable lens optical assembly is controlled in response to direction from a vehicle service software application to alter an optical characteristic such as a field of view, a lens focal length, or an optical axis alignment to acquire images for use in a vehicle service procedure such as a vehicle wheel alignment procedure, vehicle tire balancing procedure, or tire changing procedure.
Owner:HUNTER ENG
Underwater housing with offset domes for dual lens spherical camera
ActiveUS10536615B2Television system detailsColor television detailsMechanical engineeringField of view
An underwater housing comprises a laterally offset back-to-back dome configuration. A dual-lens camera having laterally offset back-to-back lenses is mounted within the housing such that the optical axes of the camera lenses align with the optical axes of the domes. This configuration beneficially minimizes effects introduced by the dome on field of view and focus.
Owner:GOPRO
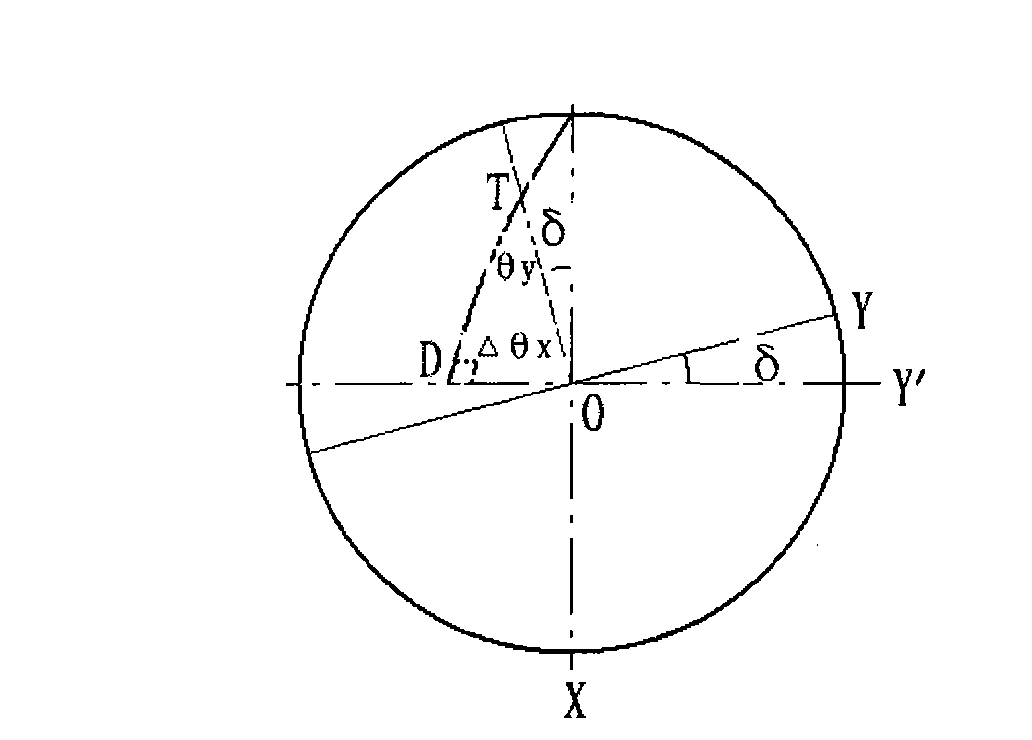
Optical detection method of verticality error of longitudinal axis and latitudinal axis of horizontal type telescope
InactiveCN101650165AThe principle of the method is simpleEasy to operateUsing optical meansFixed starsTheodolite
The invention relates to an optical detection method of the verticality error of a longitudinal axis and a latitudinal axis of a horizontal type telescope, comprising the following steps: respectivelyinstalling an optical planar mirrors on axis heads of the longitudinal axis and the latitudinal axis of the horizontal type telescope; also correspondingly installing a theodolites on the outer sideof each optical planar mirror, and enabling optical axes of the two theodolites to respectively coincide with turning axes of the longitudinal axis and the latitudinal axis of the horizontal type telescope; rotating azimuth axes and pitch axes of the two theodolites, enabling the optical axes of the two theodolites to be aligned, and recording rotating azimuth angles (A1 and A2) of the two theodolites so that the verticality error of the longitudinal axis and the latitudinal axis of the horizontal type telescope is that delta=90 DEG-(A1+A2). The detection method has simple principle, is easy to operate compared with a star comparison method, does not need to know the position of a fixed star, is not limited by weather and fields, does not need to carry out complicated mathematical calculation and is easy to realize.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Compatible optical pickup and method of aligning optical axes therein
InactiveUS20030053394A1Optical beam sourcesRecord information storageOptical pickupPhotovoltaic detectors
An optical pickup includes a light source which emits first and second lights having different wavelengths for a first recording medium and a second recording medium having a relatively large thickness, respectively, an optical path changer which alters a traveling path of incident light, and an objective lens which focuses the first and second lights on the recording medium. While the light source emits the first light, a photodetector is adjusted to be aligned with the optical axis for the first recording medium. The light source and / or a sensing lens are adjusted in the direction of the optical axis, and the tilt of the objective lens is adjusted. Next, while the light source is operated to emit the second light, the light source is adjusted in a rotating direction. As such, an optical axis alignment is completed for the first and second recording media.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Veterinary otoscope
A veterinary otoscope permitting examination of an ear is defined by an instrument head including a proximal end and a distal insertion portion that is insertable into the ear. The veterinary otoscope includes an imaging lens train disposed within the instrument head, wherein each of the imagine lens train, an eyepiece and a distal opening of said insertion portion are aligned along an optical axis. The veterinary otoscope further includes a focusing mechanism for selectively moving at least one of the imagine lens train and the optics contained within the eyepiece relative to one another along the optical axis. The imagine lens train and the optics in the eyepiece define an optical system such that an entrance pipil is substantially located in the distal insertion portion of the instrument head, thereby enabling the entire tympanic membrane to be viewed at once by the user.
Owner:WELCH ALLYN INC
Camera module, electronic equipment and optical anti-shake method thereof
PendingCN112073600AAchieve Optical Image StabilizationReduce the impactTelevision system detailsColor television detailsEngineeringChipset
The invention provides a camera module. The camera module comprises a lens assembly which is used for receiving an optical signal; the chip assembly is arranged opposite to the lens assembly, and thechip assembly is used for converting the optical signal into an image signal; the driving assembly is connected with the chip assembly, and the driving assembly can drive the chip assembly to return to the position aligned with the optical axis of the lens assembly when the chip assembly deviates relative to the lens assembly. The invention further provides electronic equipment and an optical anti-shake method thereof. By arranging the driving assembly connected with the chip assembly, the driving assembly can drive the chip assembly to return to the position aligned with the optical axis of the lens assembly when the chip assembly and the lens assembly relatively deviate, and therefore the influence of shaking of the camera module in the photographing process on the quality of a generatedimage is compensated; therefore, optical anti-shake during shooting of the camera module is realized, and the shooting quality of the electronic equipment is improved.
Owner:NANCHANG O FILM OPTICAL ELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
Alignment method for optical axis of compound wave plate and device for same
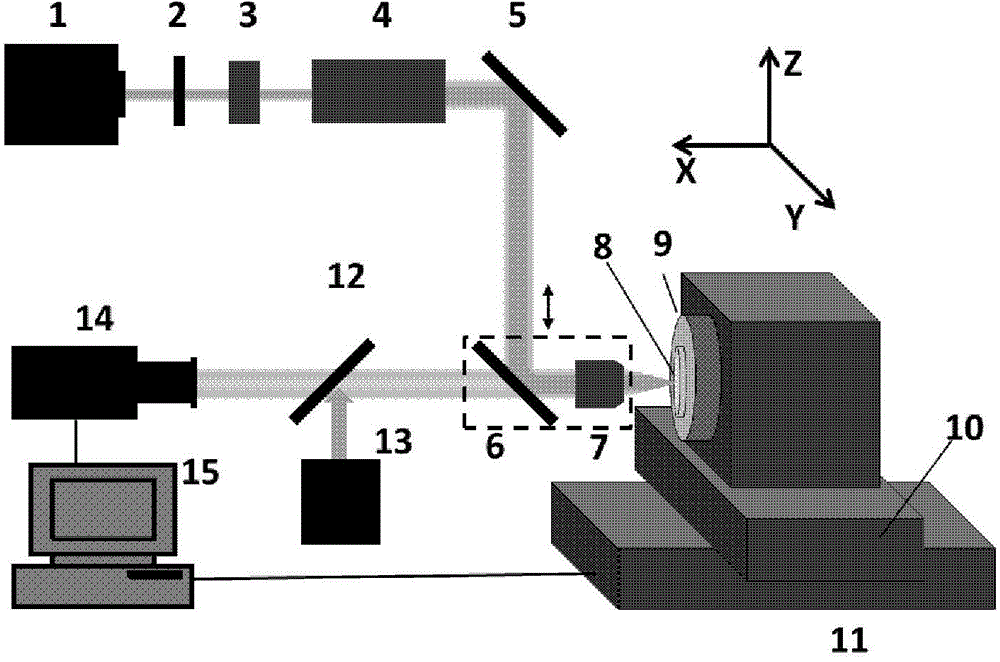
The present invention discloses an alignment method for the optical axis of a compound wave plate and a device for the same. Two wafers of a compound wave plate to be aligned are arranged on a bracket, and then are mounted on a fixed wave plate chuck and a rotary wave plate chuck respectively; light emitted from a light source forms linearly polarized light after passing through a polarizer; after passing through the compound wave plate to be aligned, the linearly polarized light become changed in the polarization state; according to the intensity signal of transmitted beam detected by a detector, the variation amplitude of the phase delay fluctuation quantity of the compound wave plate to be aligned can be obtained further; the relative magnitude of the variation amplitude of the phase delay fluctuation quantity is compared; and the rotary wave plate chuck is controlled to rotate through an electric control rotary table until the optical axis of the compound wave plate is aligned to be in the required precision range. The device comprises the light source, the polarizer, the fixed wave plate chuck, the rotary wave plate chuck, a rotary polarization analyzer, the detector, the electric control rotary table, a computer, a stepping motor and an electric control rotary table controller. The method can align the optical axis of a compound wave plate with high precision, the deviceis simply equipped, and the operation is simple.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Charge neutralizer for glass substrate
InactiveUS20070188970A1Accurate irradiationReliably neutralizeConveyorsElectrostatic discharge protectionSoft x rayOptoelectronics
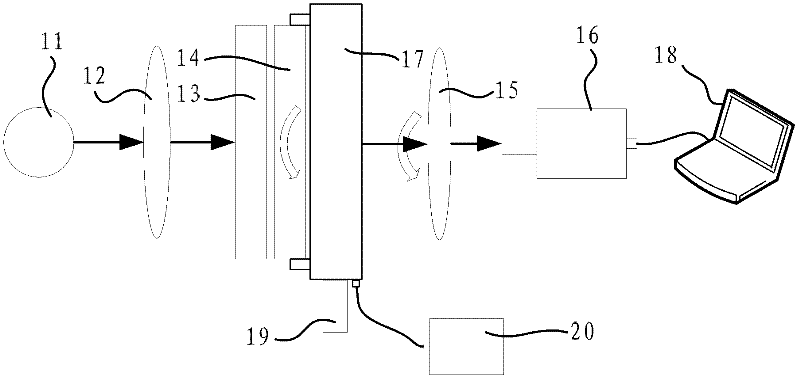
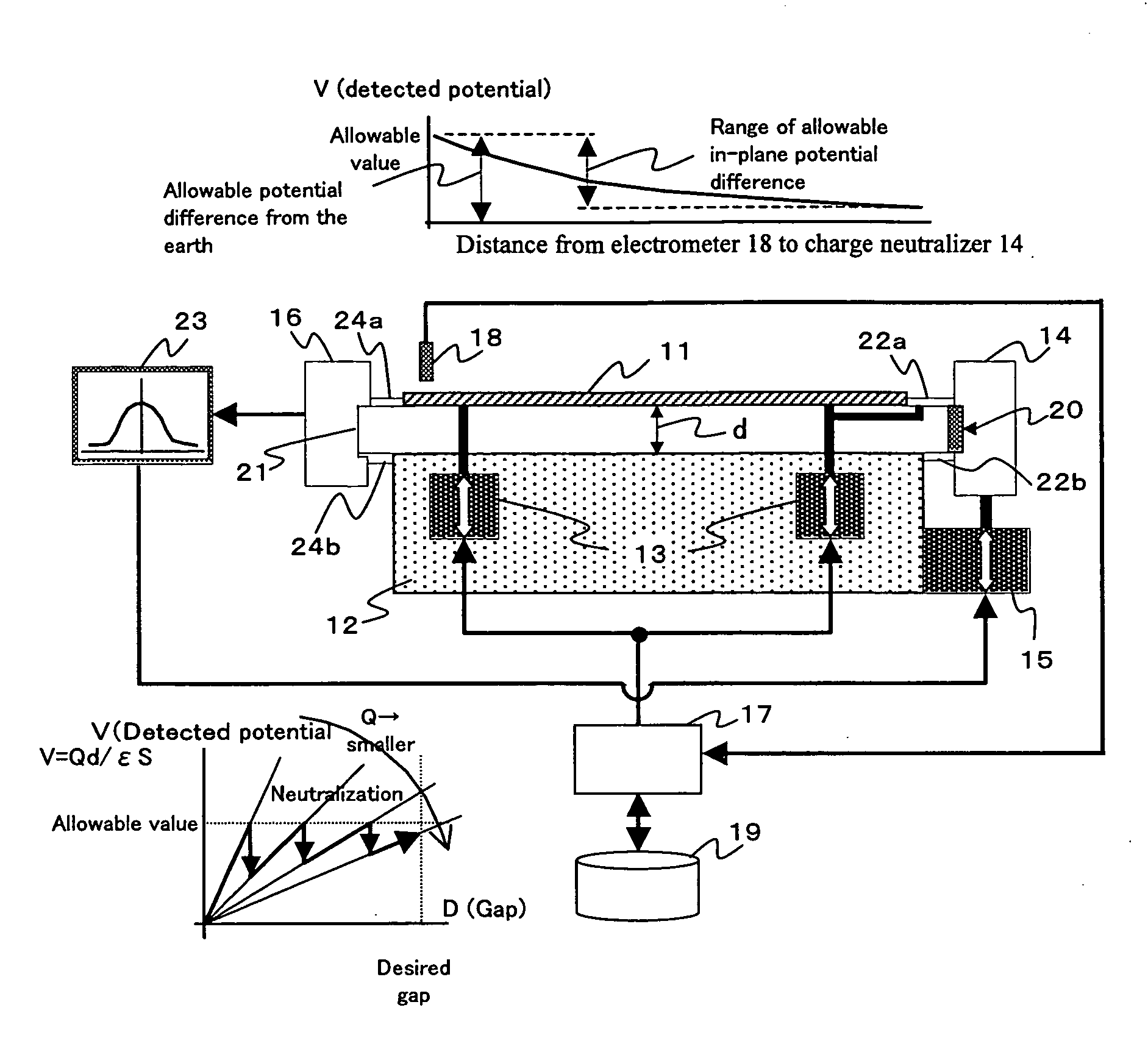
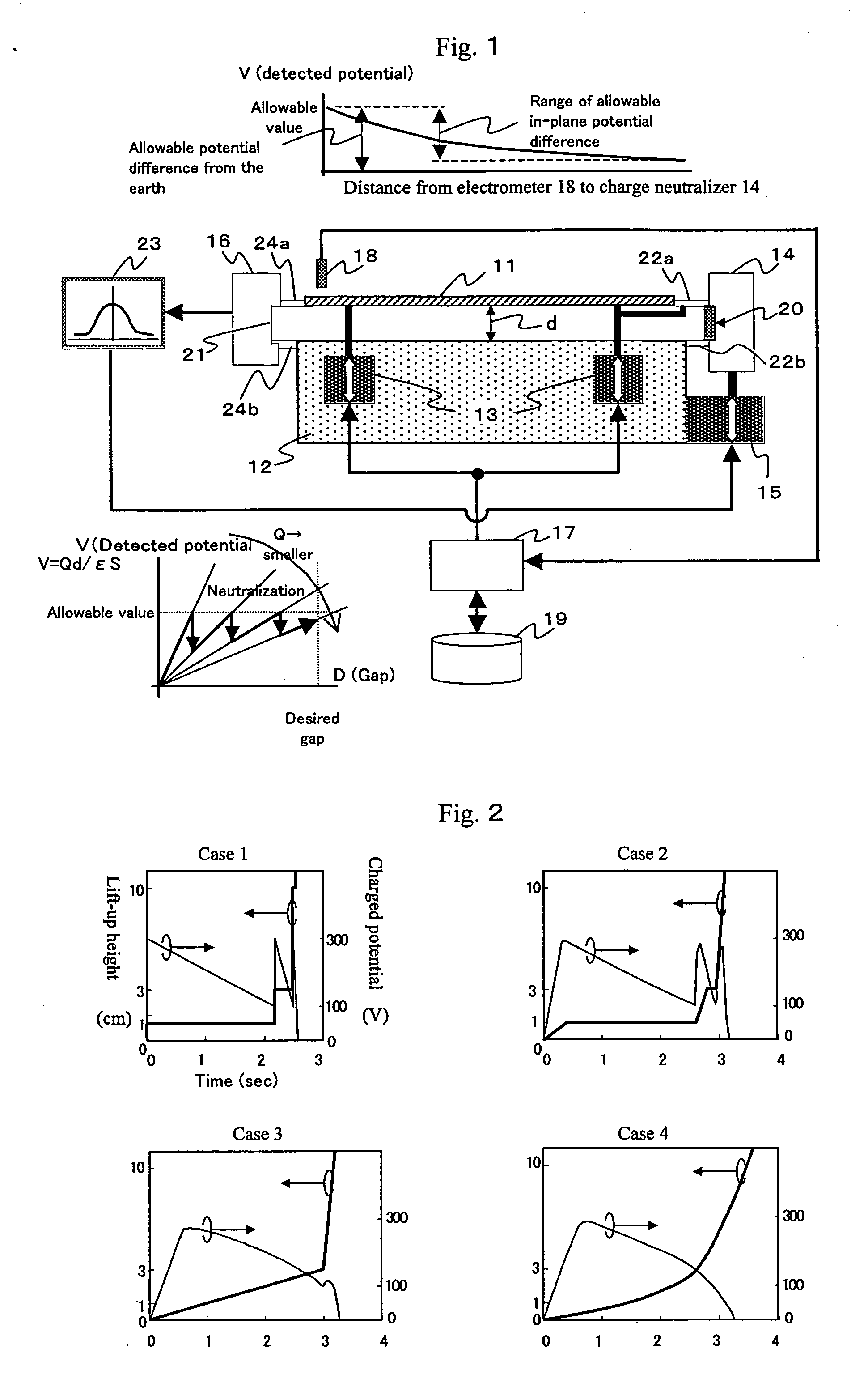
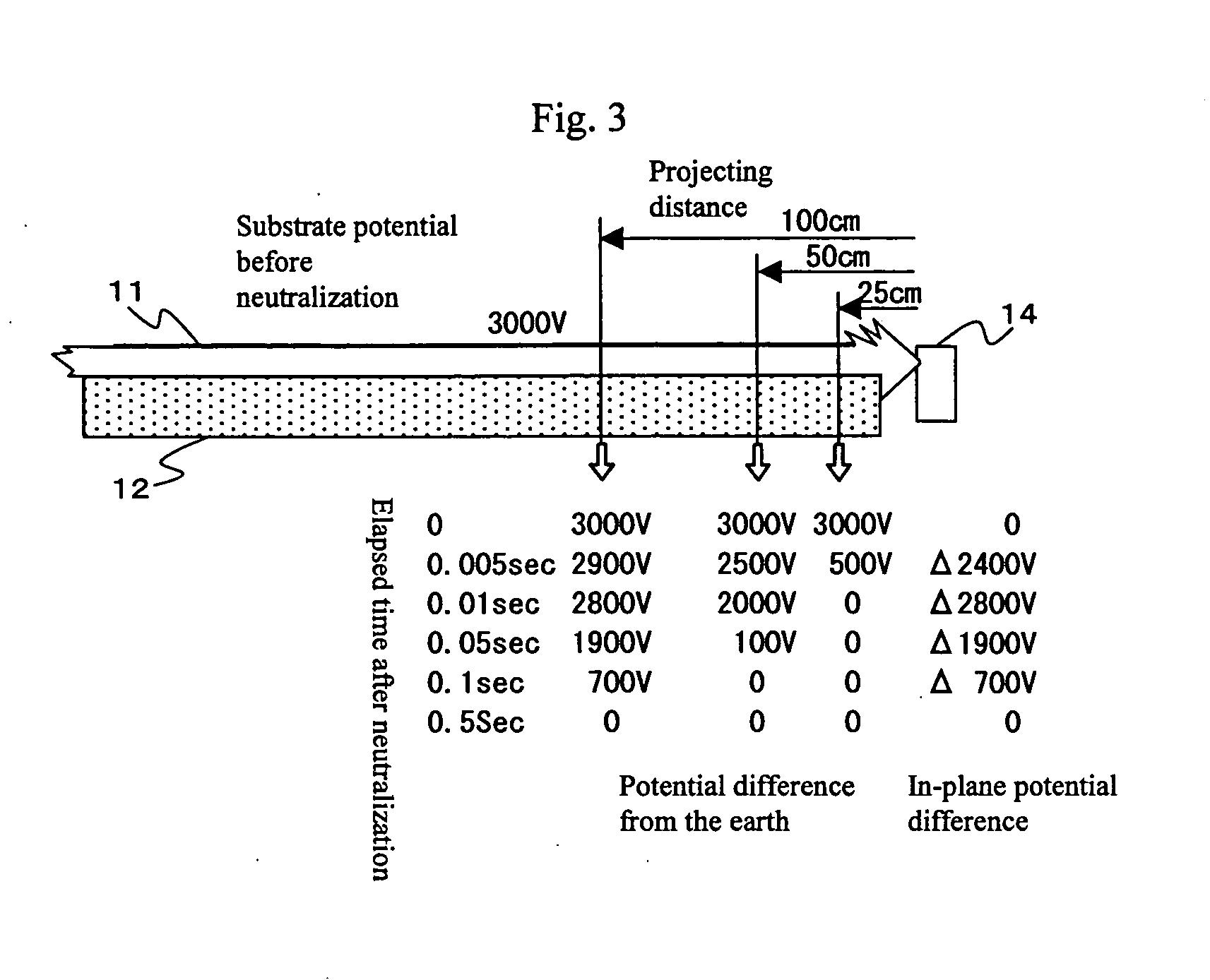
The present invention provides a charge neutralizer for accurately irradiating a soft X ray into a narrow gap after a glass substrate is lifted up. A soft X ray is introduced into a gap “d” from a soft X ray charge neutralizer 14, and the soft X ray is detected by a soft X ray optical axis monitor 16. Mounting position adjusting means 15 is adjusted by a detection output from said soft X ray optical axis monitor, and optical axis alignment is performed. Next, according to information from a database 19, a control unit 17 controls gap adjusting means 13, and charge neutralization is performed. Charge neutralization can also be performed by controlling the gap “d” by the gap adjusting means 13 while judging neutralizing conditions as to whether a charged potential measured by an electrometer 18 is within an allowable value by the control unit 17 or not.
Owner:FUTURE VISION
Adapting camera systems to accessory lenses
ActiveUS20180048793A1Improve alignment of optical axisMaximize imagingTelevision system detailsPrintersCamera lensImaging processing
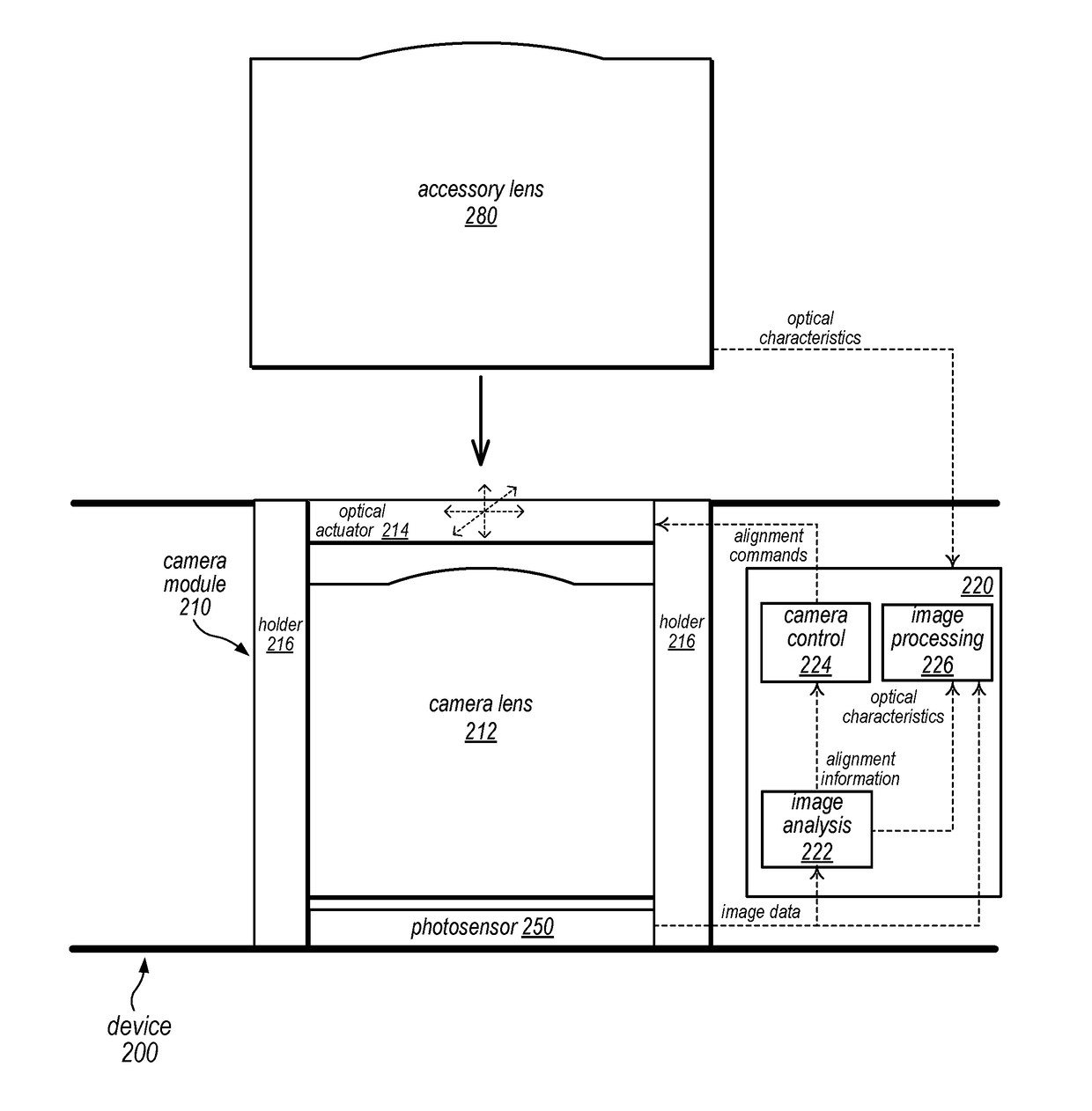
A small format factor camera system for mobile devices that provides improved image quality when using accessory lenses. The system may detect an accessory lens attached to the camera, either via sensing technology or by analyzing captured images. The system may analyze image data to determine current alignment (e.g., optical axis alignment, spacing, and / or tilt) of the accessory lens relative to the camera lens, and may shift the camera lens on one or more axes using a mechanical or optical actuator, for example to align the camera lens optical axis with the accessory lens optical axis. The system may also determine optical characteristics of the accessory lens, either via sensing technology or by analyzing captured images, and may apply one or more image processing functions to images captured using the accessory lens according to the determined optical characteristics of the accessory lens.
Owner:APPLE INC
Lens tube and mounting base thereof
ActiveUS7311453B2Avoid dust pollutionReduce swingTelevision system detailsNon-electric lightingEngineeringOptical axis alignment
A lens tube and a mounting base thereof comprise a lens tube for reception of a lens array and a mounting base for accommodation of an image sensor. On an outer periphery of the lens tube is formed a first conical surface, and in the mounting base is formed a concave portion. A second conical surface is formed in the concave portion for mating with the first conical surface of the lens tube. The first conical surface of the lens tube and the second conical surface of the mounting base can cooperate with each other, so as to prevent dust contamination and to make the central axis aligned with the optical axis.
Owner:LARGAN PRECISION
Projection lens and projector
A first holding member holds a first optical system and a first mirror, and has a first junction surface. A second holding member holds a second optical system and a second mirror, and has a second junction surface. A junction portion is configured such that, in a state where the first junction surface and the second junction surface are aligned with each other, the second holding member is capable of being shifted in a direction of both the junction surfaces and rotated around an optical axis, and makes it possible to perform optical axis alignment. An emission-side optical axis of the first optical system and an incidence-side optical axis of the second optical system are aligned with each other, and thus a U-shaped optical path is formed by the first and second optical systems.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Alignment assembly and method for aligning rotating shaft of rotating table type laser direct writing device to direct writing optical axis
ActiveCN104972232ASimplify Alignment OperationsLaser beam welding apparatusRotary stageDigital imaging
Disclosed is an assembly for aligning a rotating shaft of a rotating table type laser direct writing device to the direct writing optical axis. The direct writing device comprises a laser source, a laser path and a rotating table, wherein a laser modulator, a first reflector, a second reflector and a microscope objective are sequentially arranged on the laser path, laser beams are modulated by the laser modulator and then reflected by the first and second reflectors to be incident onto the microscope objective, and the tabletop of the rotating table is perpendicular to the direct writing optical axis. The alignment assembly comprises a panel piece and a digital imaging system, wherein a metal film is arranged on one side of the panel piece, the panel piece is fixed to the tabletop of the rotating table, the metal film faces the microscope objective, and the digital imaging system comprises a lighting source, a visible light splitter, an image sensor and a displayer. Visible light from the lighting source is reflected by the light splitting piece and then passes through the second reflector to be incident onto the metal film through the microscope objective, visible light reflected by the metal film passes through the microscope objective, the second reflector and the visible light splitter to enter the image sensor, and the displayer displays images from the image sensor.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
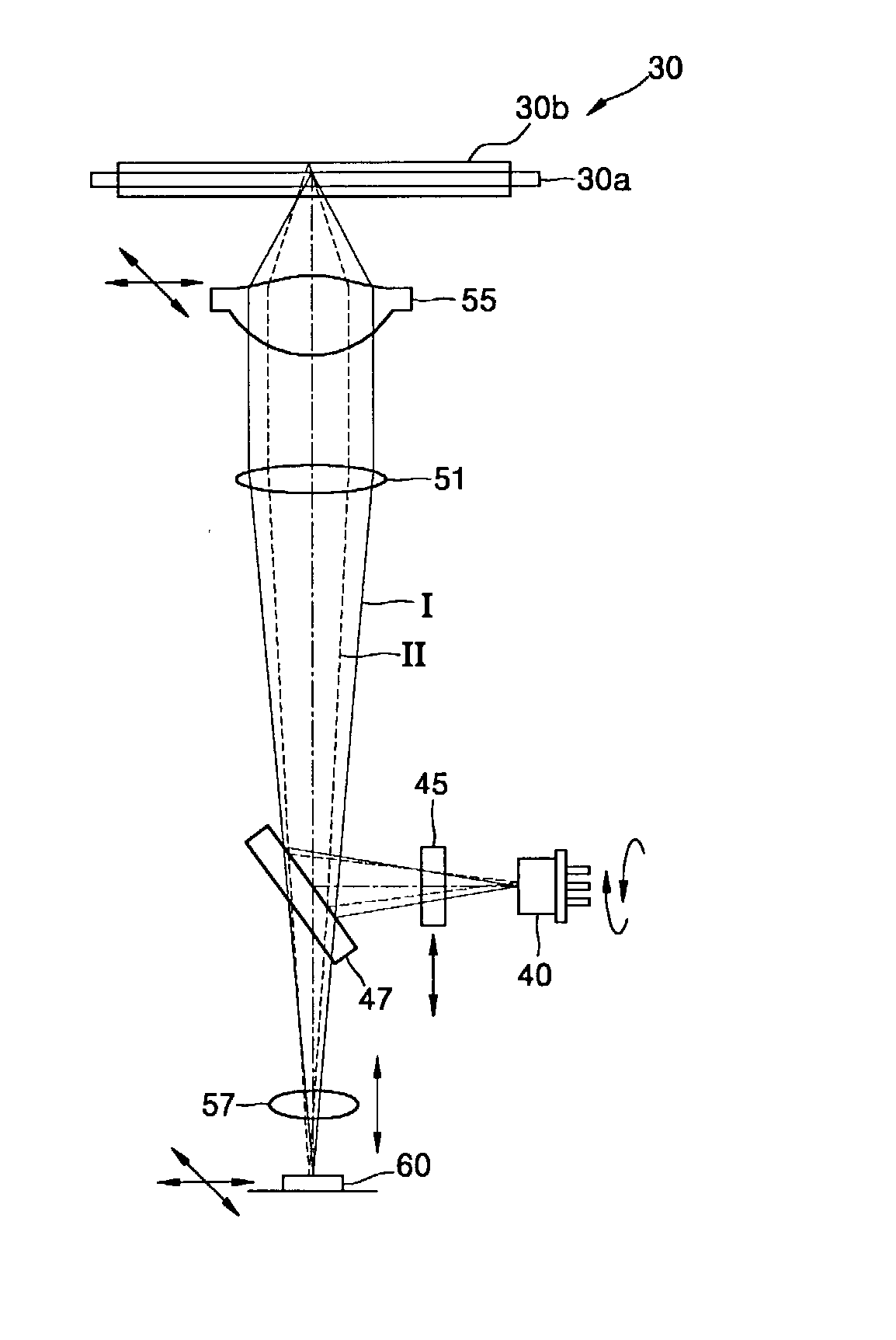
Laser beam focusing arrangement and method
ActiveUS20060119805A1Precise alignmentHigh resolutionCosmonautic condition simulationsLaser using scattering effectsLight beamOptoelectronics
A lightweight, compact image projection module, especially for mounting in a housing having a light-transmissive window, is operative for causing selected pixels in a raster pattern to be illuminated to produce an image of high resolution of VGA quality or higher in color. A laser beam focusing arrangement aligns a mechanical axis of a focusing lens with an optical axis along which a laser beam is directed to reduce pointing errors.
Owner:MICROVISION
Optical connector-use adaptor and optical connector use shutter component
InactiveUS20070019913A1Reduce manufacturing costReduce material costsCoupling light guidesAdaptor/connectorEngineering
The present invention relates to an optical connector adapter that is so configured as to prevent a laser beam from leaking outwards to do harm to a person at the time of insertion or removal of an optical connector plug for optical connection, and, specifically, an optical connector adapter having, at one end side, a housing part with a tip end being open, and at the other end side, a coupling part adapted to provide coupling with an optical component, and serving to couple an optical connector plug coupled with the housing part by insertion with the optical component such that an optical axis is aligned, wherein a super-elastic alloy shutter plate having been subjected to a plate-shape memory heat-treatment without providing any bent part is so mounted at an inner position close to an opening end of the housing part as to stand upward from one wall surface to a position adapted to shield the optical axis.
Owner:FURUKAWA TECHNO MATERIAL
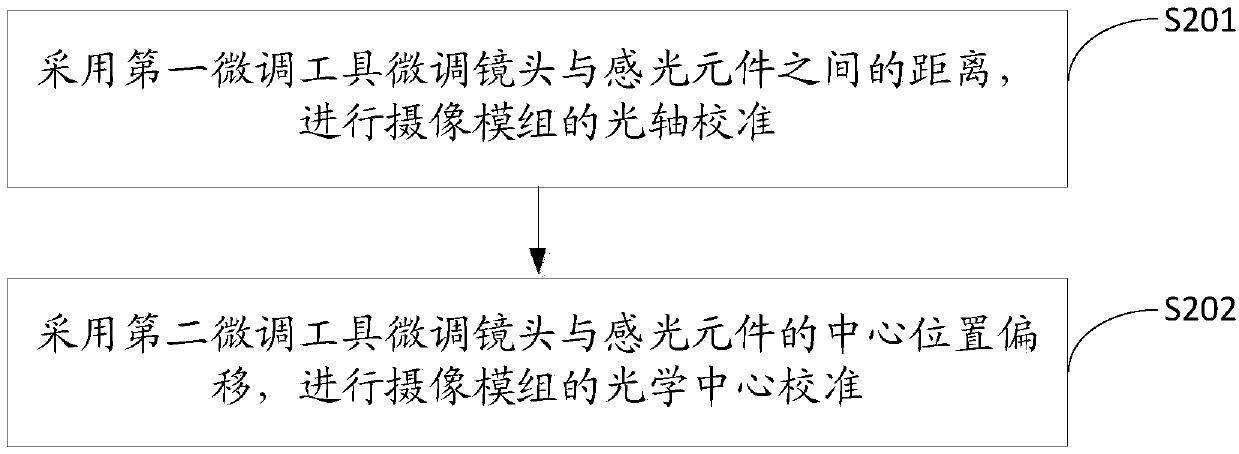
Camera module active alignment device and alignment method thereof
The invention discloses a camera module active alignment device and an alignment method thereof. The camera module active alignment device comprises a lower base, a photosensitive element assembled with the lower base, an upper base, a lens assembled with the upper base, and a clamp for clamping the upper base. First fine adjustment tools of which extension directions are a vertical direction areset at four corners of the clamp and are used for finely adjusting the distance between the lens and the photosensitive element and carrying out optical axis alignment of a camera module. A second fine adjustment tool of which extension direction is a horizontal direction is set in the middle of the clamp and is used for finely adjusting central position offset between the lens and the photosensitive element and carrying out optical central alignment of the camera module. According to the device and the method, through setting of the first fine adjustment tool and the second fine adjustment tool, the angle and optical central position offset between the lens and the photosensitive element in the camera module can be adjusted, thereby finishing aligning, the operation is simple and the accuracy is high.
Owner:TRULY OPTO ELECTRONICS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com