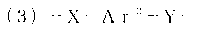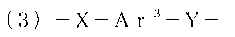Patents
Literature
100 results about "Fiber fabrication" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Holey optical fibres
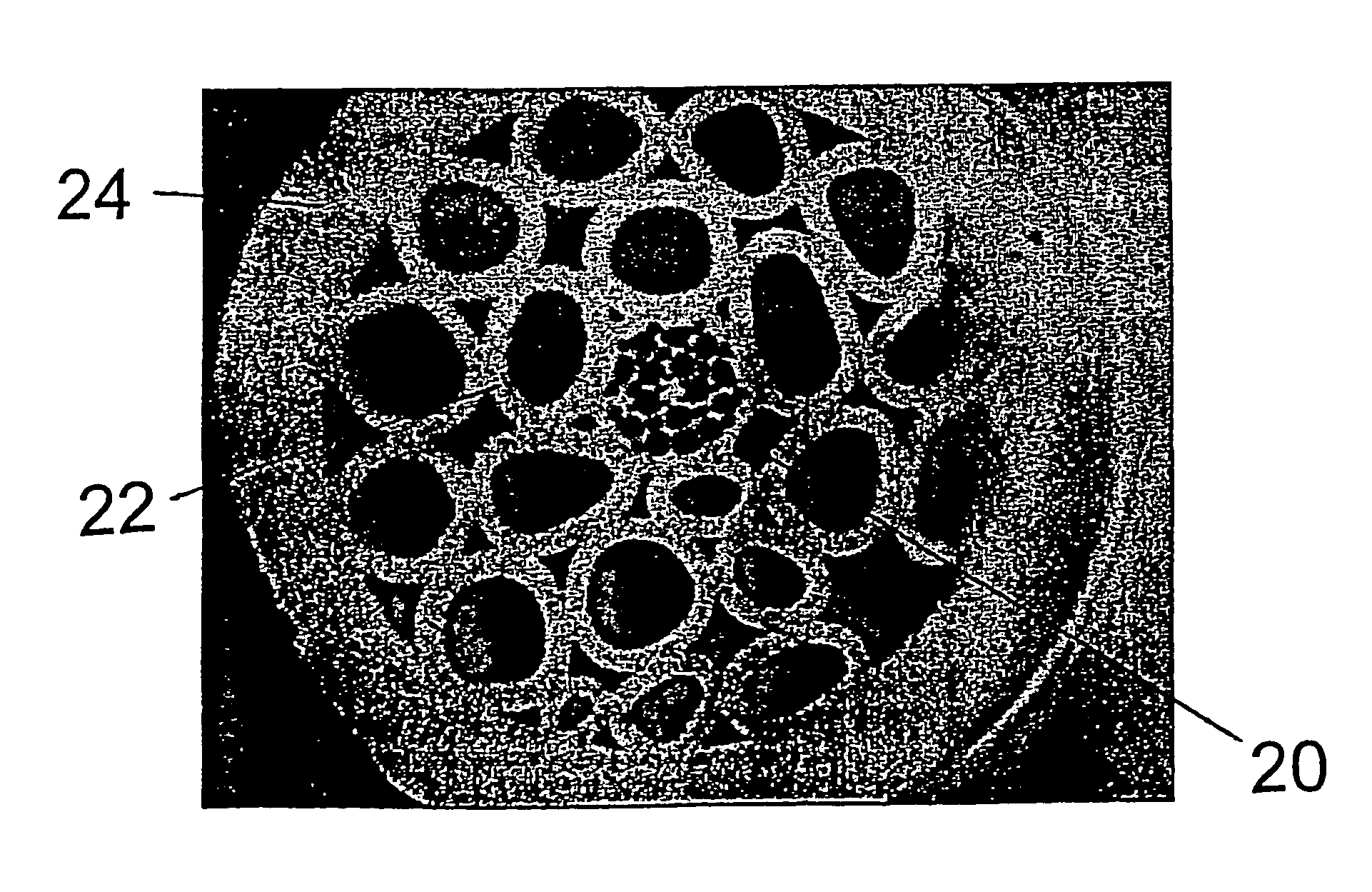
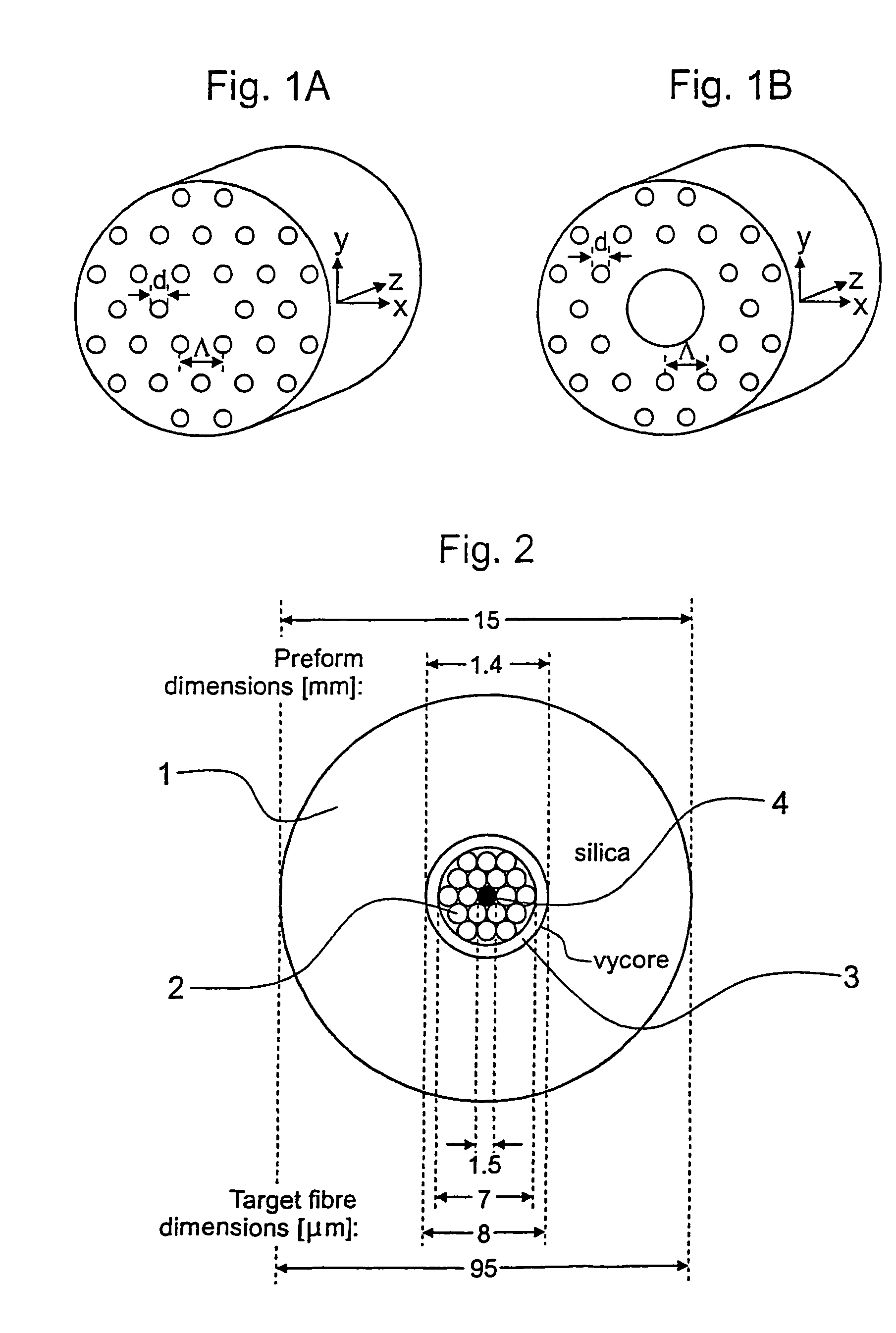
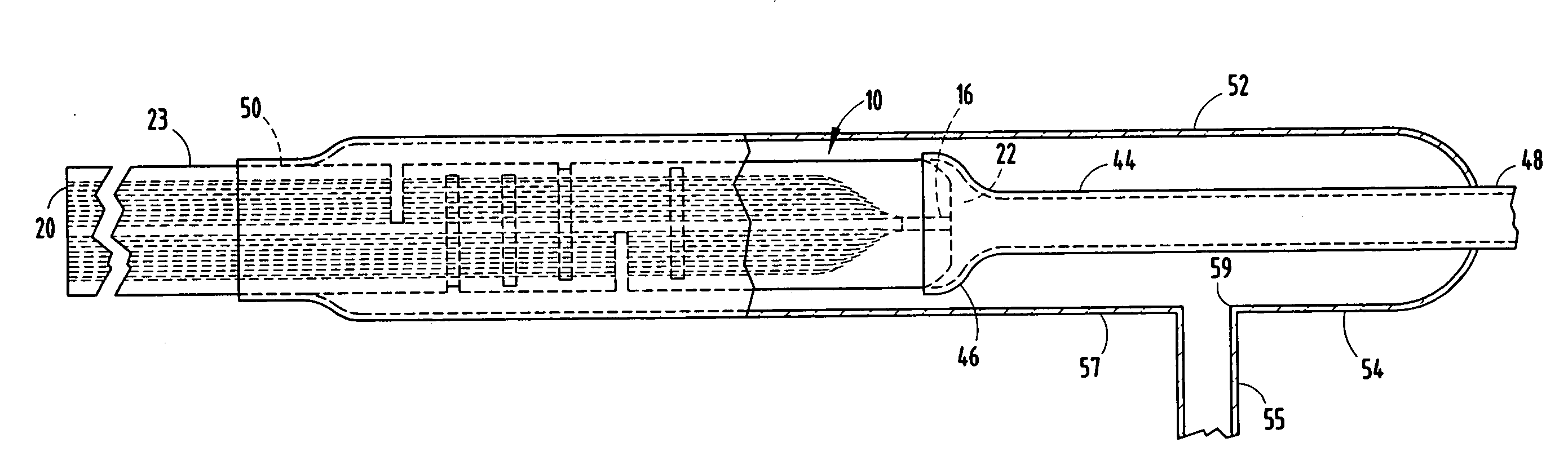
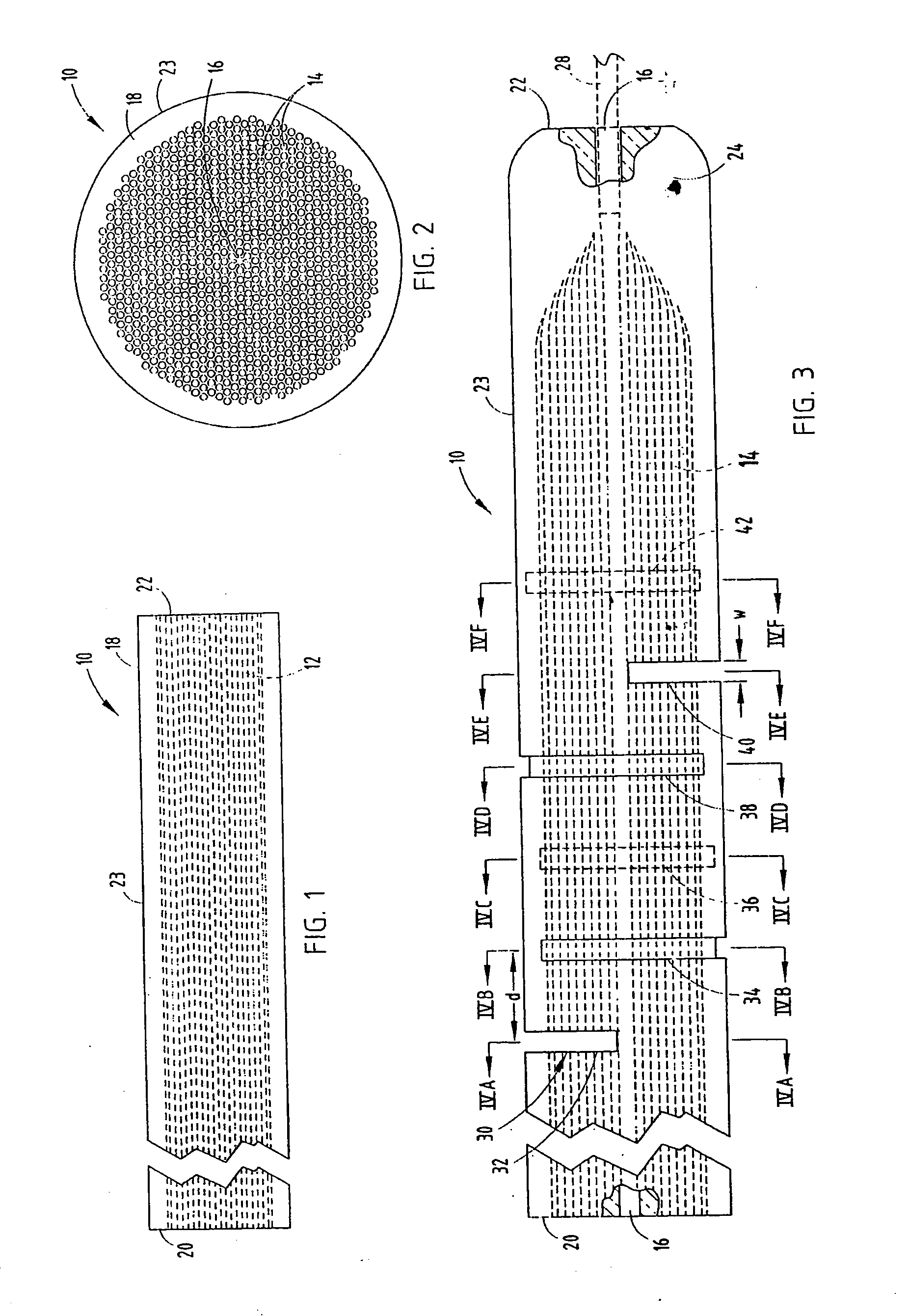
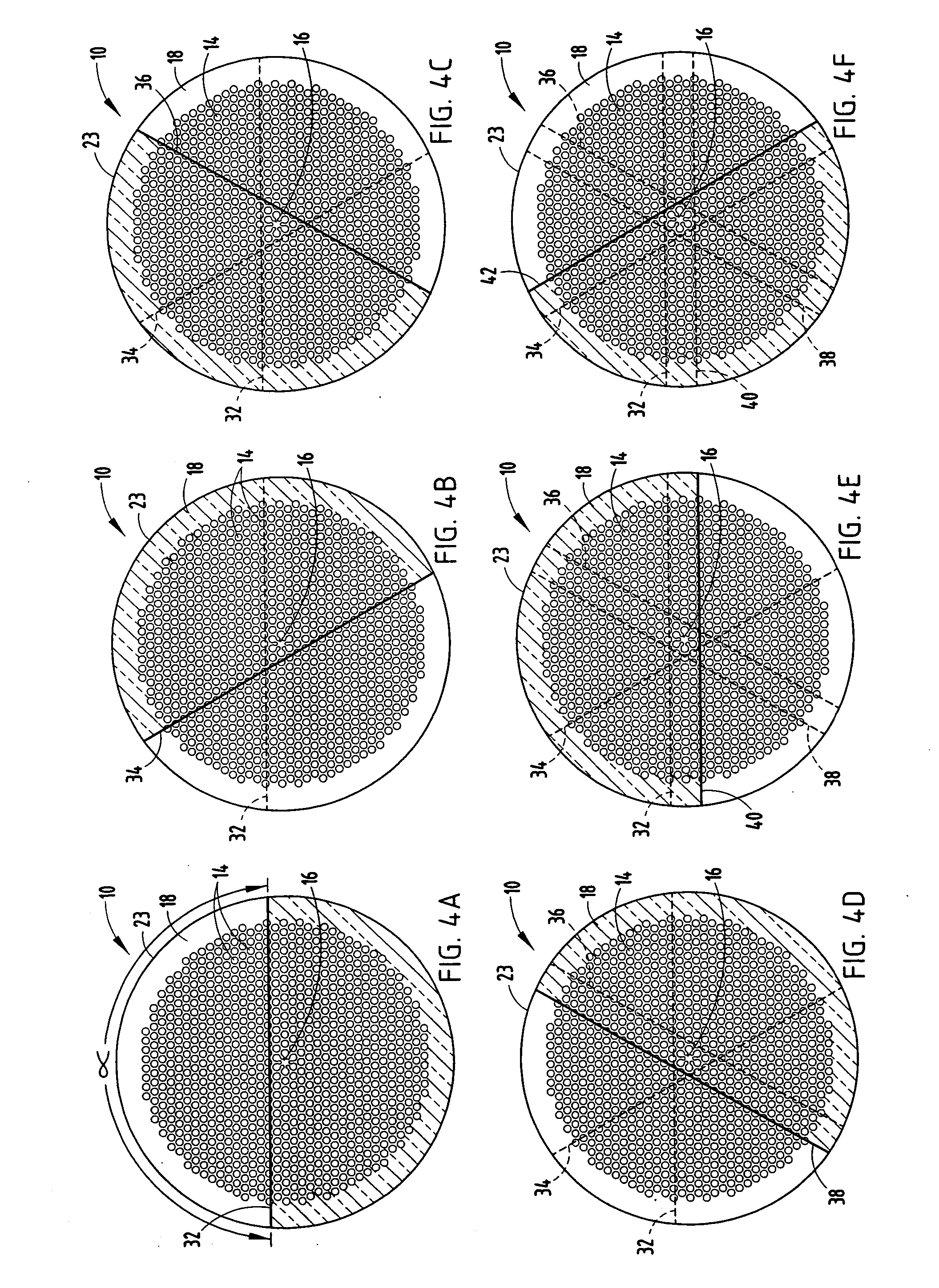
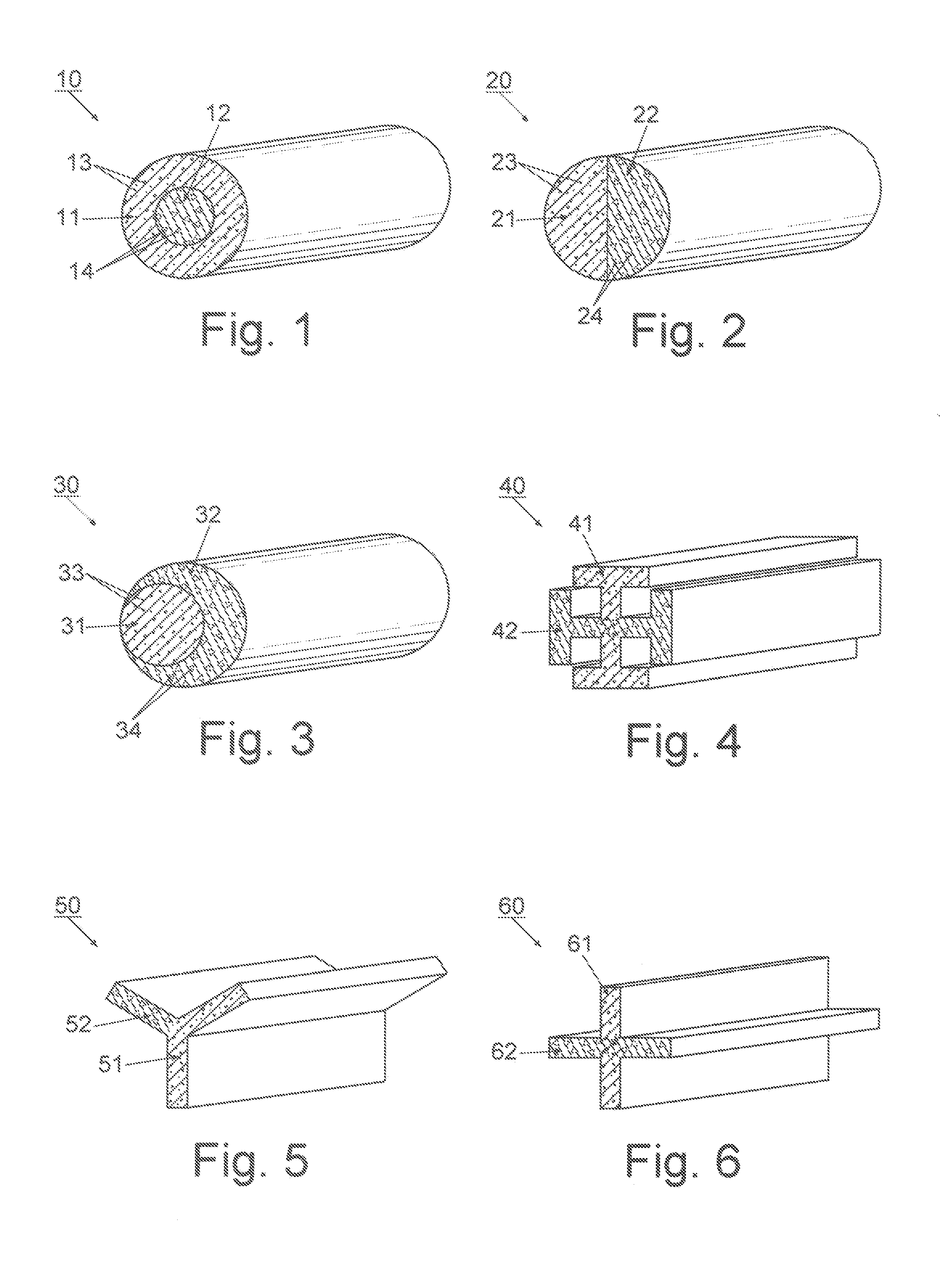
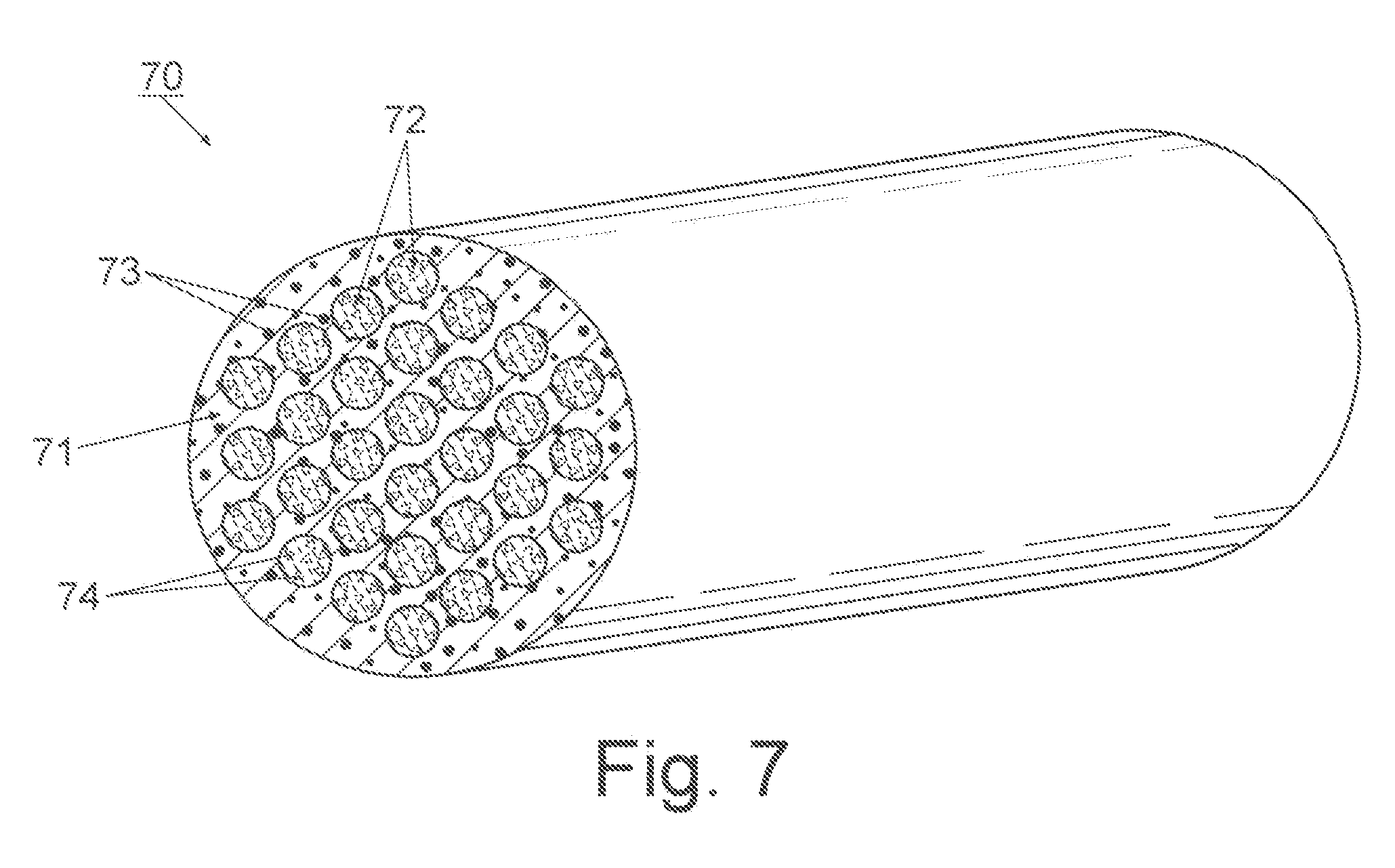
An optical fiber structure having a holey fiber arranged in a holey outer support structure made up of holey tubes encased in a thin walled outer jacket. The holey fiber may have a solid core surrounded by a holey cladding having a plurality of rings of holes. With the invention it is possible to produce robust, coated and jacketed fibers with microstructured core features of micrometer size relatively easily using existing fiber fabrication technology. This improvement is a result of the outer holey structure which reduces the thermal mass of the supporting structure and makes it possible to reliably and controllably retain small hole features during the fiber fabrication process.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHAMPTON
Method for preparing PBT/PET 3-D crimped fiber and use thereof
InactiveCN1962968AIncrease elasticityHigh modulusFilament/thread formingConjugated synthetic polymer artificial filamentsFiberHeat resistance
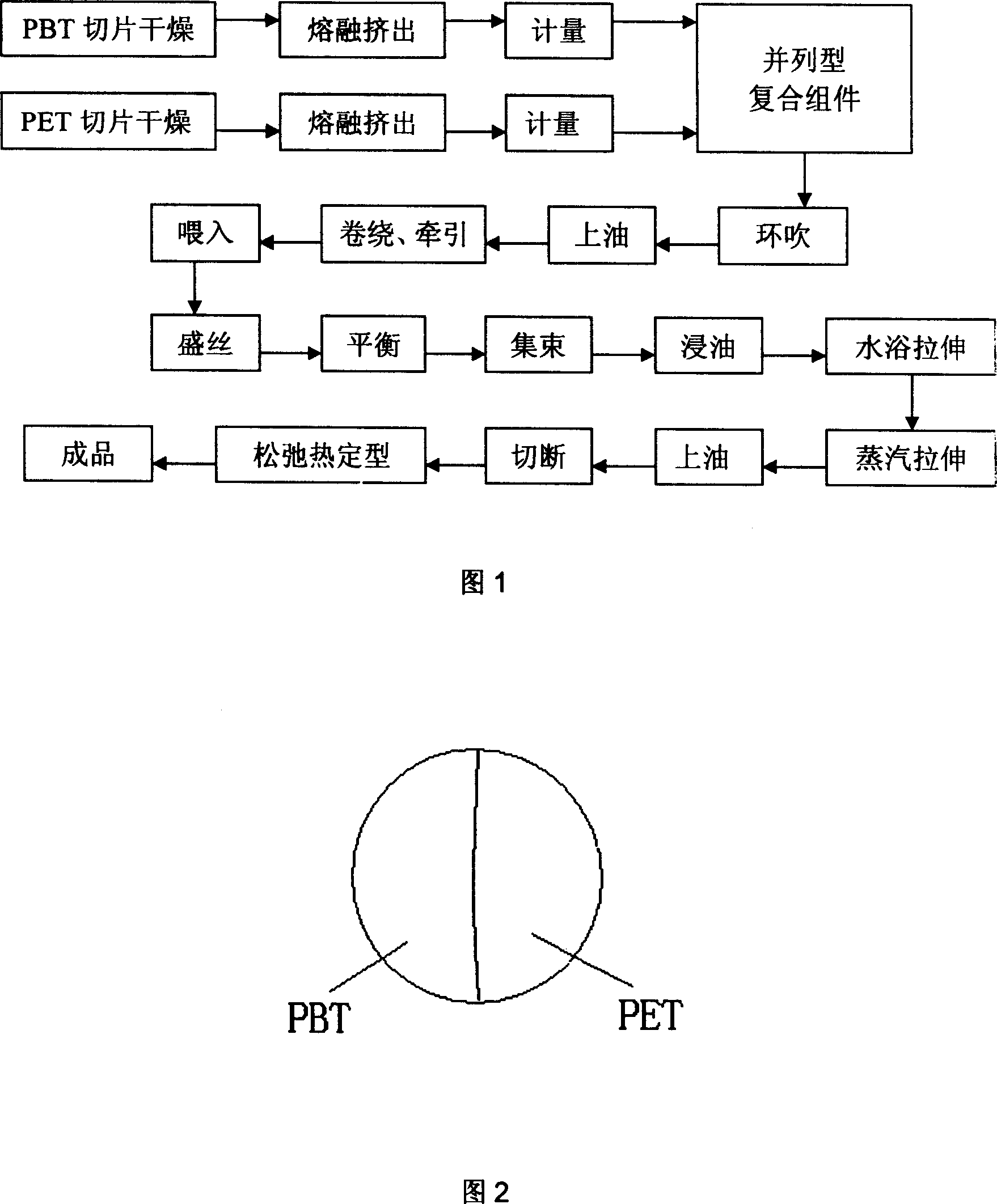
The invention involves a product method of PBT / PET 3D crimp fiber fabrication which includes steps: (1) PBT biopsies are composed with the PET on the after drying; (2) PET slices are after drying, through high-temperature melting e composite; (3) After blowing Central, greasing winding drive, feed, Sheng be parallel wire composite fiber winding wire; After balancing, cluster, the Baptist tensile oil bath, steam tensile, greasing cut off heat and relaxation to be stereotyped PBT / PET 3D curly fibers. The fibers produced through the method are system of the fiber's flexibility, dyeability and heat resistance and used in flexible woven and knitted fabrics such as high-end sportswear, stretch jeans and strait jacket, Nonwovens and filler widely.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Ultra high-power continuous wave planar waveguide amplifiers and lasers
InactiveUS6904219B1Avoid bend lossesLaser detailsOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingWaveguide amplifierHigh power diode laser
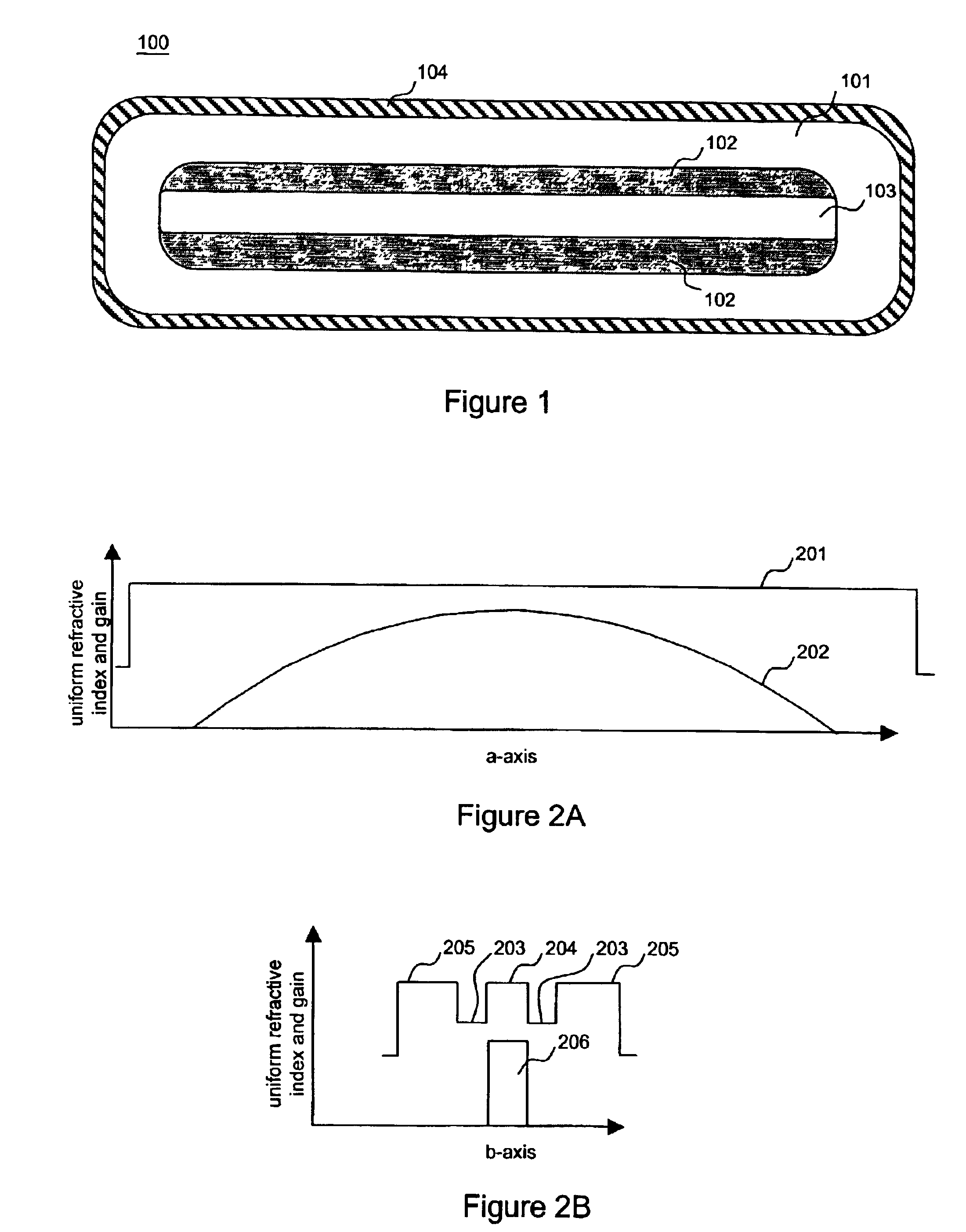
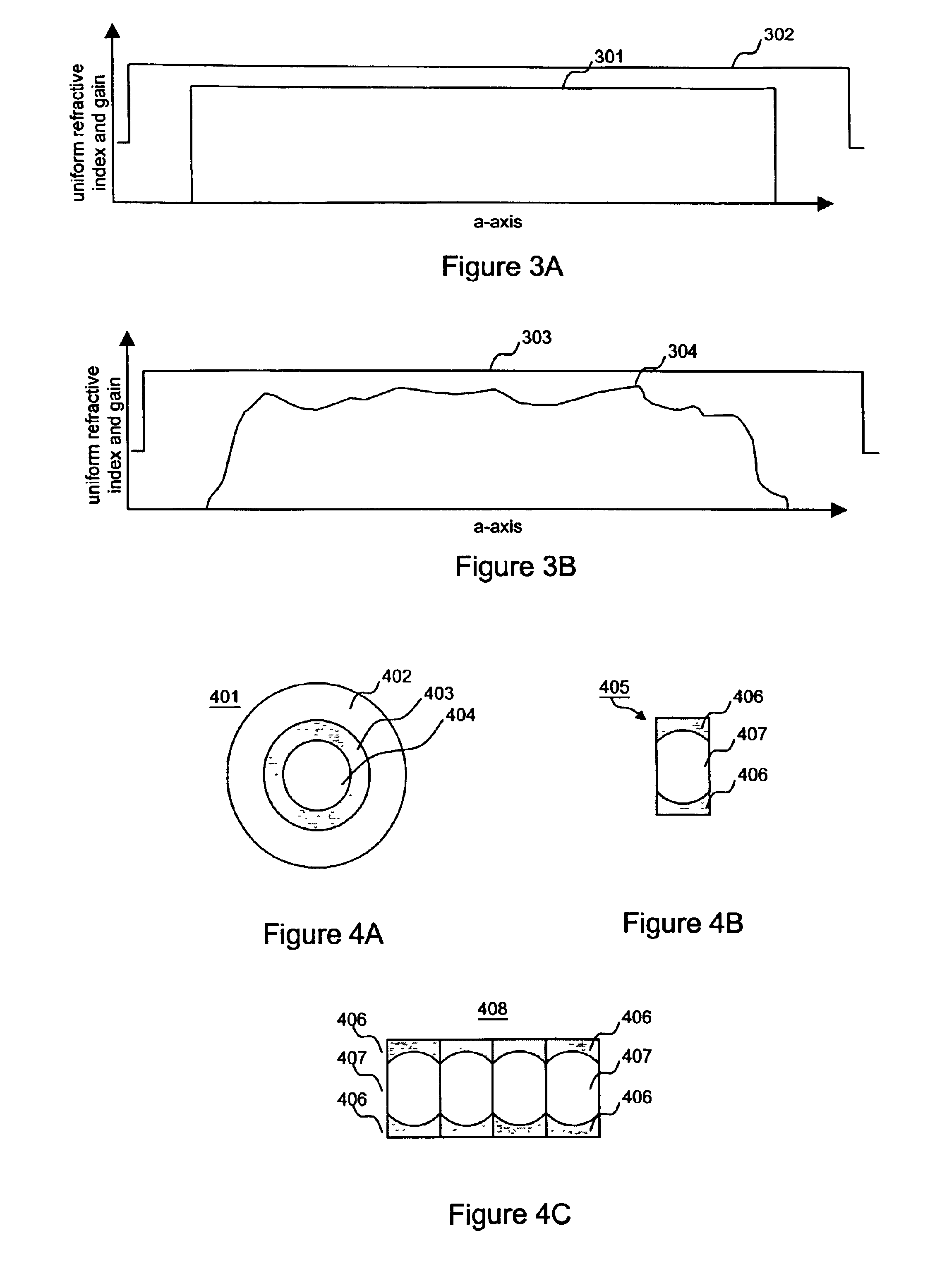
Double clad large mode area planar lasers or amplifiers comprising rare-earth or transition metal doped planar core regions are used to generate near-diffraction-limited optical beams of ultra-high power. The amplified light is guided in the core using different guiding mechanisms in two orthogonal axes inside the core. Waveguiding along a first long core axis is obtained substantially by gain-guiding or thermal lensing. Waveguiding along a second short core axis is obtained by index guiding. This is accomplished by surrounding the planar core region with regions of different refractive index. The long sides of the planar core region are surrounded with a depressed refractive index cladding region. The short sides of the planar core region are surrounded with a cladding region substantially index-matched to the core region. The whole structure is surrounded by an outer cladding region with a low refractive index to enable cladding pumping of the planar waveguide with high-power diode lasers. The rare-earth or transition metal doping level inside the planar core can be constant and can also vary substantially without negatively affecting the waveguiding properties. To avoid bend losses along the long axis of the planar waveguide, the planar core region and the planar waveguide are aligned parallel to each other and the planar waveguide is coiled with the long side of the planar waveguide mounted to a drum. The drum can also be used as a heat sink. A planar waveguide comprising a planar core region can be manufactured using conventional fiber fabrication methods.
Owner:BOSTON LASER
Method for manufacturing modal fiber
ActiveCN101545150AHigh strengthBrightly dyedArtificial filaments from viscoseInternational standardDissolution
The invention discloses a method for manufacturing modal fiber, which comprises basification reaction, ageing reaction, yellowing reaction, dissolution of viscose glue, filter of the viscose glue, defoaming of the viscose glue, ripening of the viscose glue, wet spinning, drawing and other related process steps. The method adopts cellulose pulp with alpha cellulose content of less than 95 percent as a raw material, uses common equipment for producing common viscose glue short fiber, and adopts the technology to control a simple and practical special process formulation and a spinning drawing mode to manufacture the modal fiber capable of reaching international standards. The method has the advantages of little investment, easily obtained and low-cost raw materials, high productivity and simple process operation; and the manufactured modal fiber has good quality and stable performance.
Owner:杭州奥通新材料智能科技有限公司
Complex composite structures and method and apparatus for fabricating same from continuous fibers
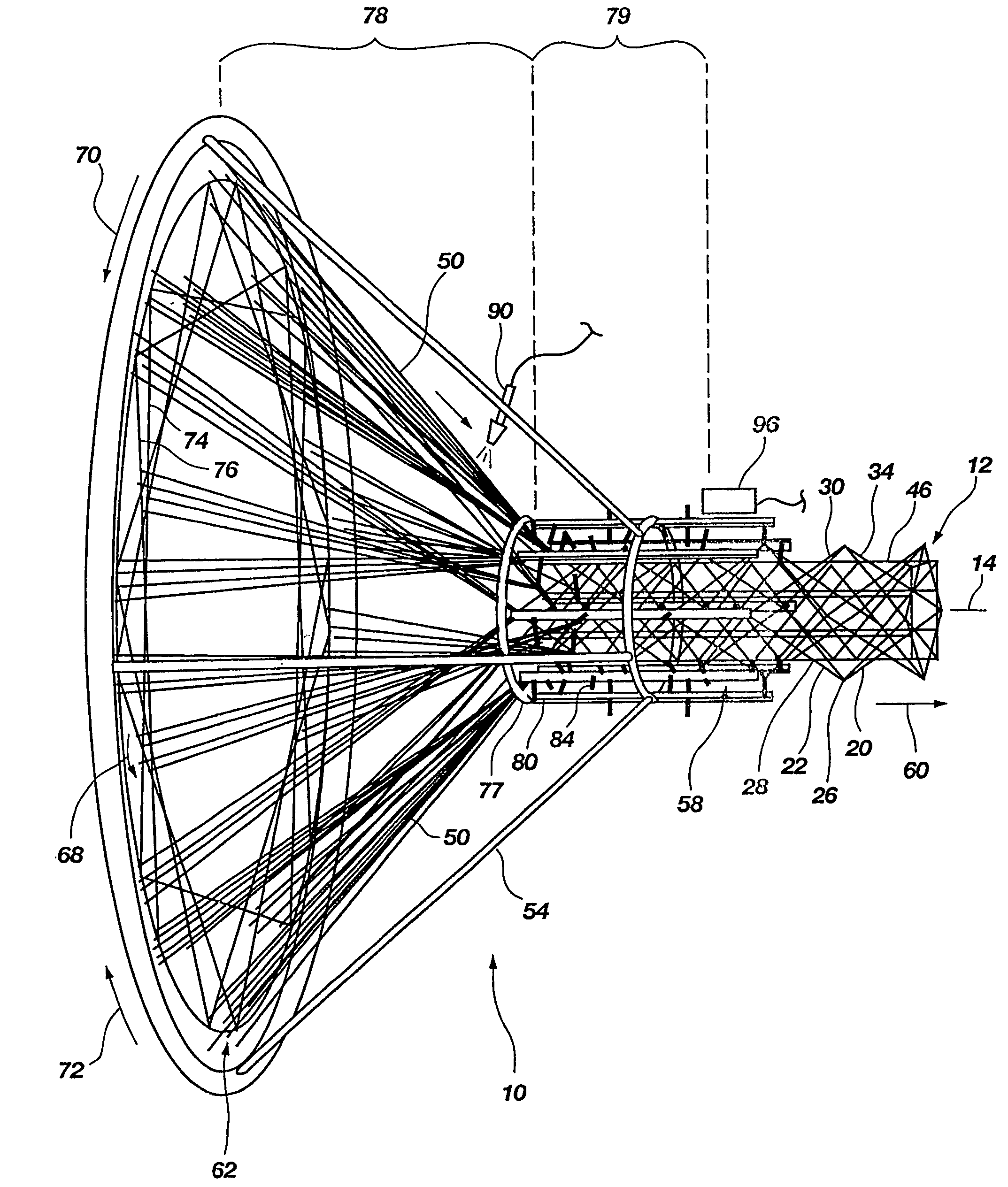
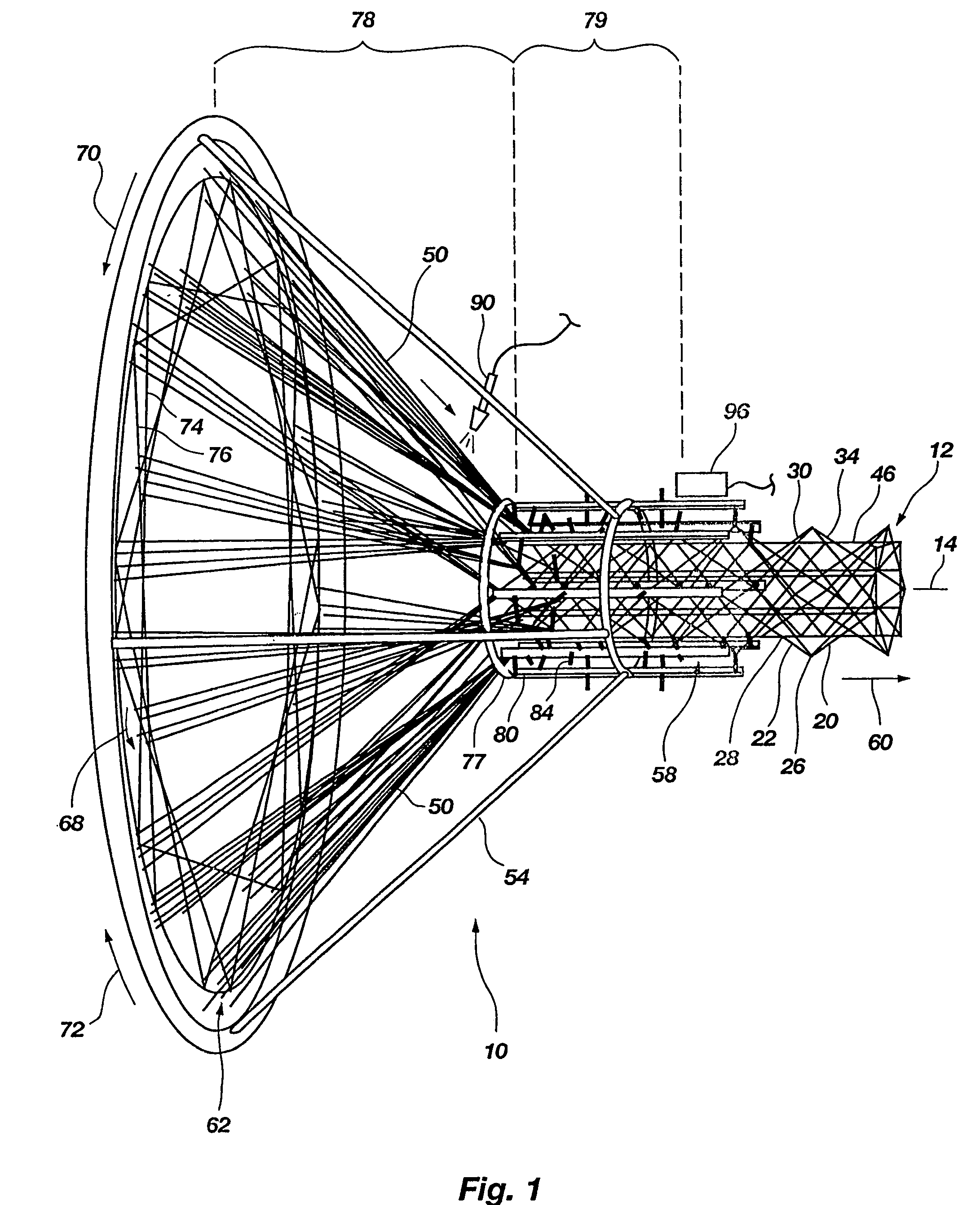
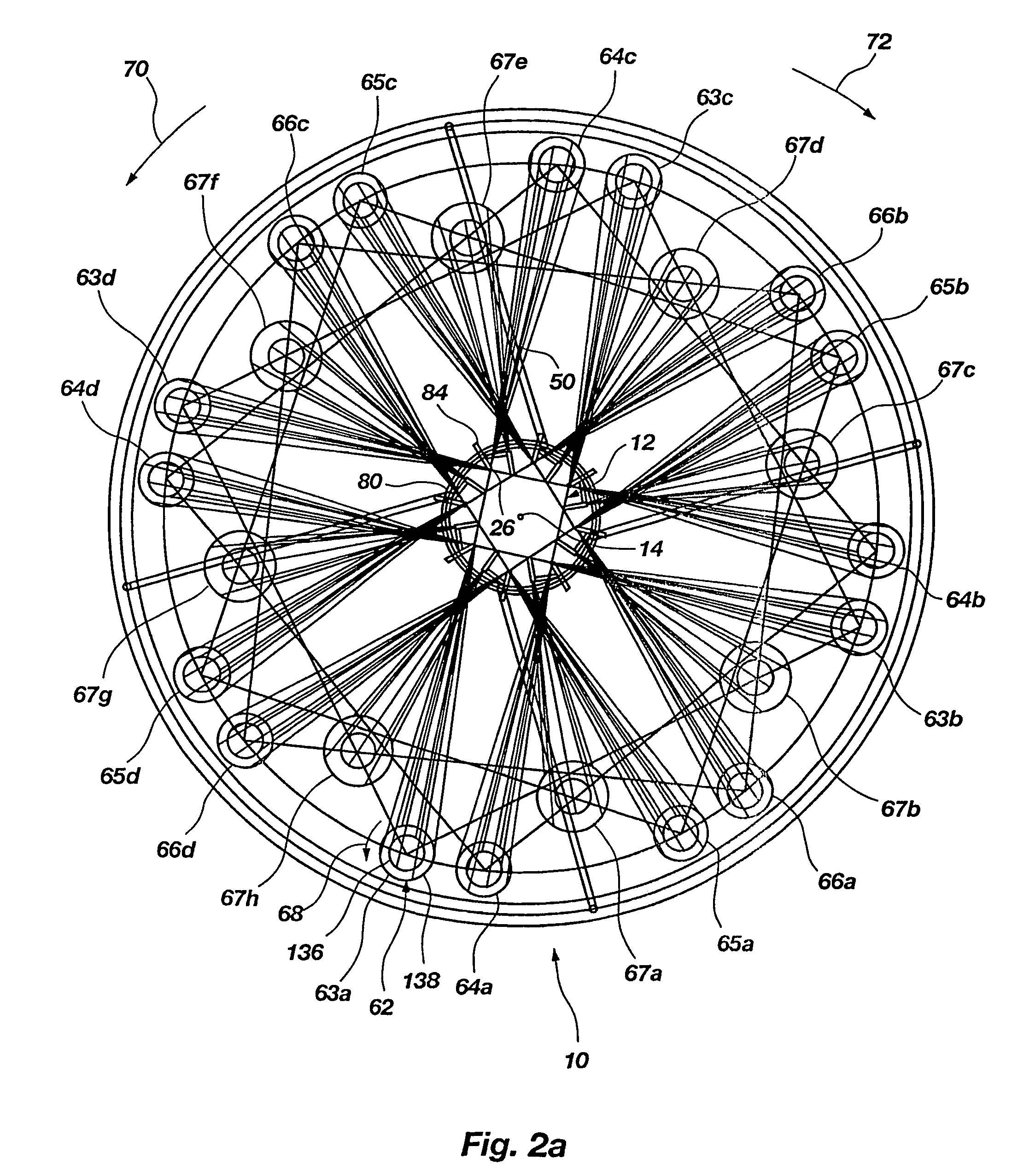
A method and apparatus for fabricating a complex, three-dimensional structure (12), such as a truss, from composite fiber / resin includes pulling a plurality of continuous fibers (50) from a feed source (62) along a processing path (58) about a longitudinal axis (14). At least some of the fibers are wound around the longitudinal axis in opposite directions (70,72) by rotational elements to form helical and reverse helical components (30, 34) that intersect at nodes (26,28). Select nodes are engaged by engagement members (84) and are maintained radially outwardly from the longitudinal axis by a support frame (80) to create sequential discrete segments (22) in the helical and reverse helical components. The select nodes can be engaged and maintained from outside the helical and reverse helical components. Resin can be applied to the fibers by resin applicator (90) and cured. A three-dimensional structure (200) can be formed with one or more continuous fibers forming two or more different components (204, 206) of the structure and transitioning at transition nodes (207). A three-dimensional structure can be formed with the components including a sleeve (162) of braided fibers surrounding a core (163) of elongated fibers to reduce gaps.
Owner:ISOTRUSS IND LLC
Method for making environment-friendly artificial leather from ultra micro fiber without solvent treatment
InactiveUS20060218729A1Not consuming much energyPre-tanning chemical treatmentTextiles and paperSolventNonwoven fabric
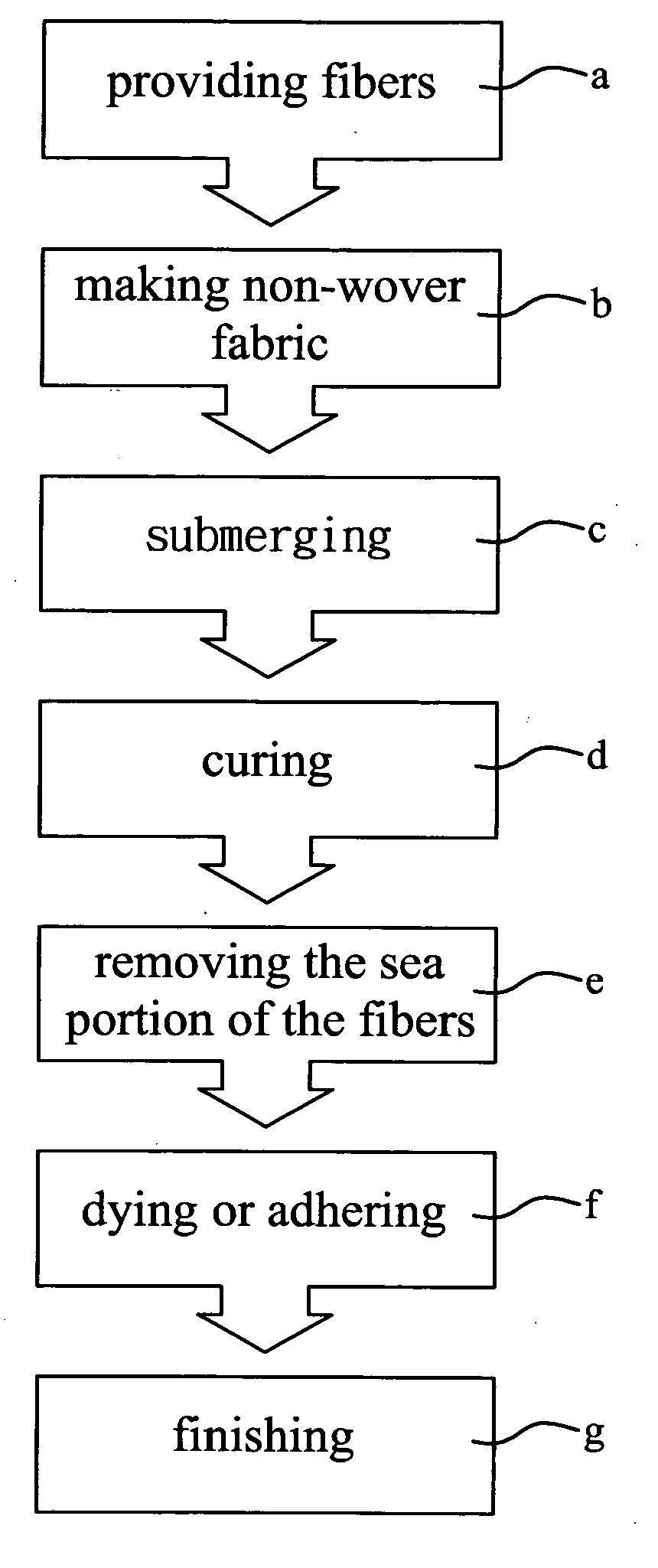
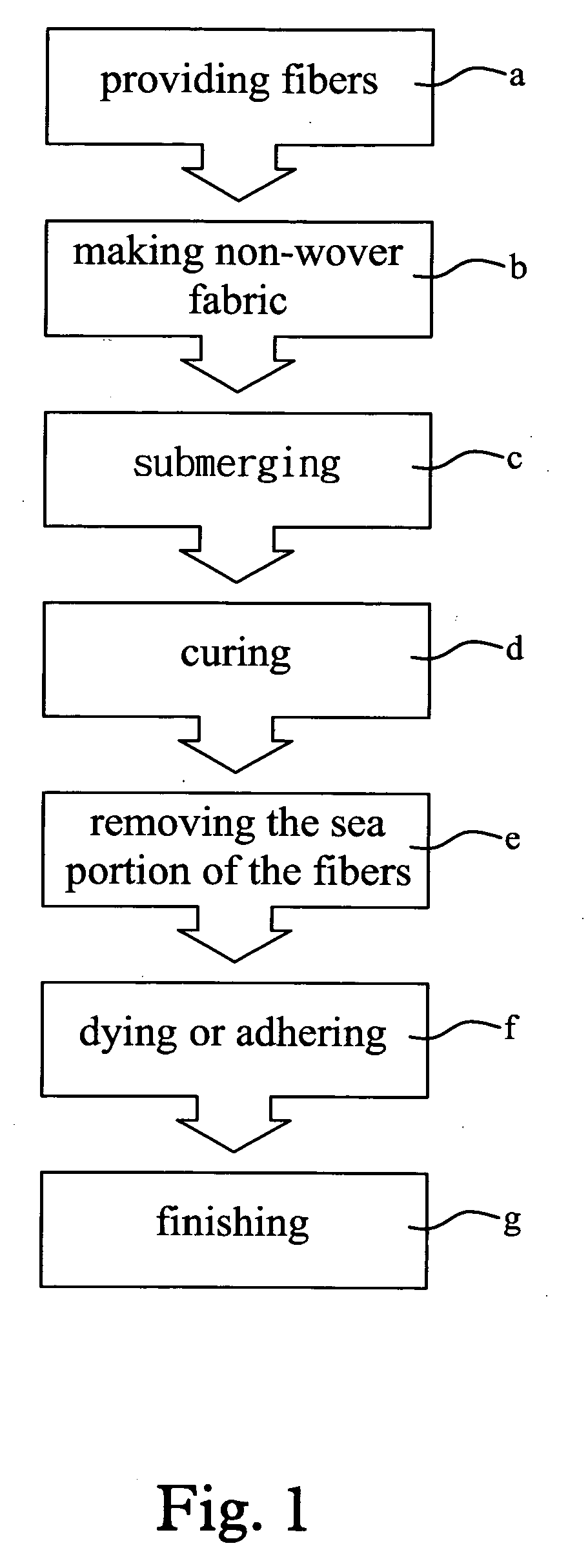
There is disclosed a method for making environment-friendly artificial leather from ultra micro fiber without solvent treatment. The method includes the step of making at least two components into ultra micro fibers, as raw materials, by means of conjugate spinning. By means of spun lacing or water lacing, three-dimensional interlacing is conducted on the ultra micro fibers in order to provide non-woven fabric, as a substrate. After the substrate is impregnated with water-borne resin solution, salt solution is used to solidify the water-borne resin solution in the substrate. The sea component of the ultra micro fibers is removed by means of alkaline. Abrading and finishing are conducted in order to obtain a semi-product of the environment-friendly artificial leather. The semi-product is dyed or water-borne resin is adhered to the semi-product in order to provide the environment-friendly artificial leather made from the ultra micro fibers without solvent treatment, providing a leather-like feel and excellent softness and physical properties.
Owner:SAN FANG CHEM IND
Method enabling dual pressure control within fiber preform during fiber fabrication
ActiveUS20070204656A1Facilitates close controlShorten the timeGlass fibre drawing apparatusCoupling light guidesPhotonic bandgapPhotonics
A method of fabricating a photonic crystal or photonic band gap optical fiber comprises providing a preform that includes a plurality of holes in an outer diameter, wherein the holes extend from a first end of a preform to a second end of the preform, and forming at least one radially inwardly-extending slot within the preform such that the slot intersects at least some of the holes, wherein the slot does not intersect at least one hole. The method also includes establishing a first pressure in the holes intersected by the slot by introducing the first pressure to the slot, and establishing a second pressure in the at least one hole not intersected by the slot by introducing the second pressure to an end of the at least one hole not intersected by the slot. The method further includes drawing the preform into a fiber while independently controlling the first and second pressures.
Owner:CORNING INC
Fiber composite and process of manufacture
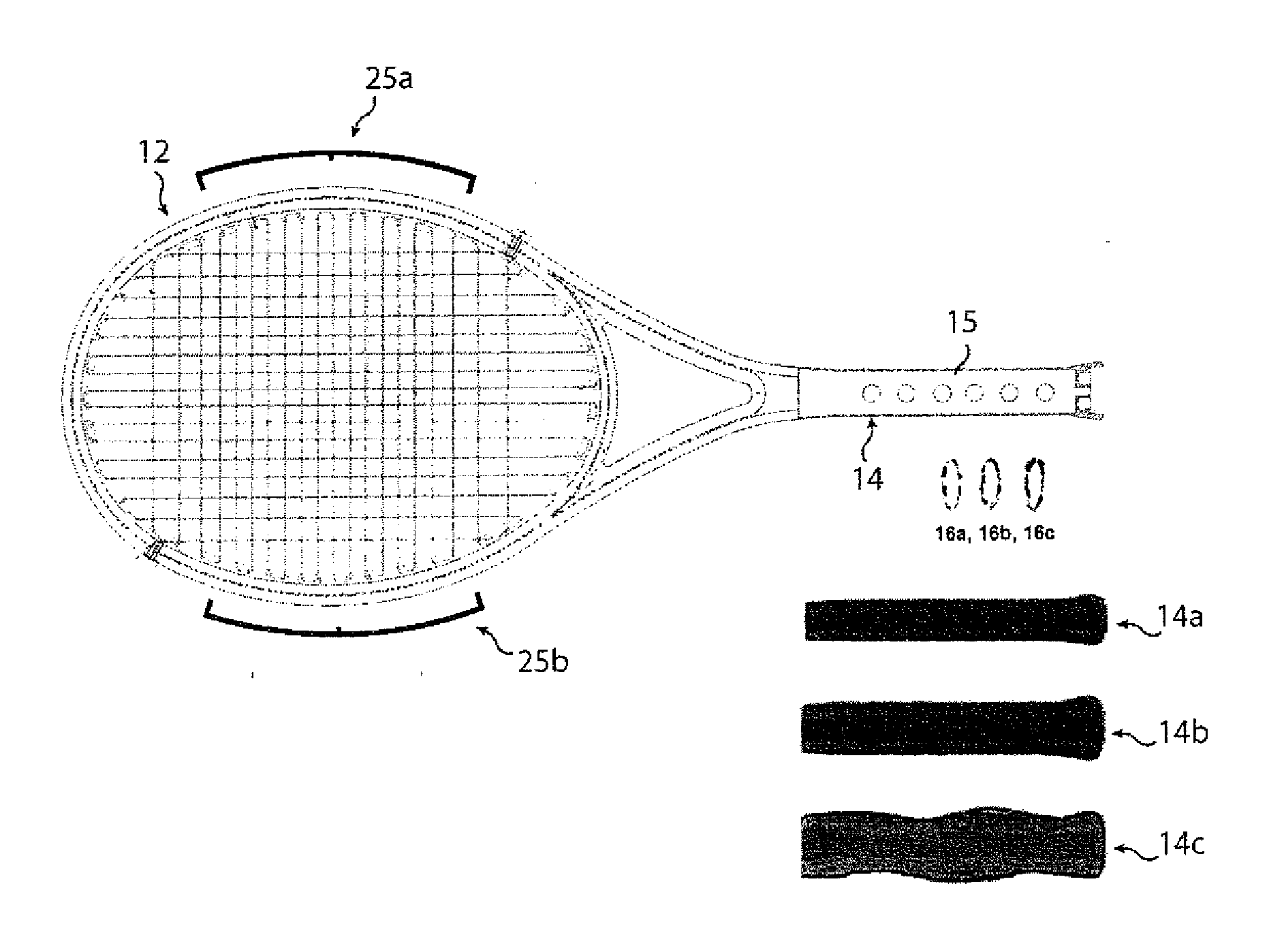
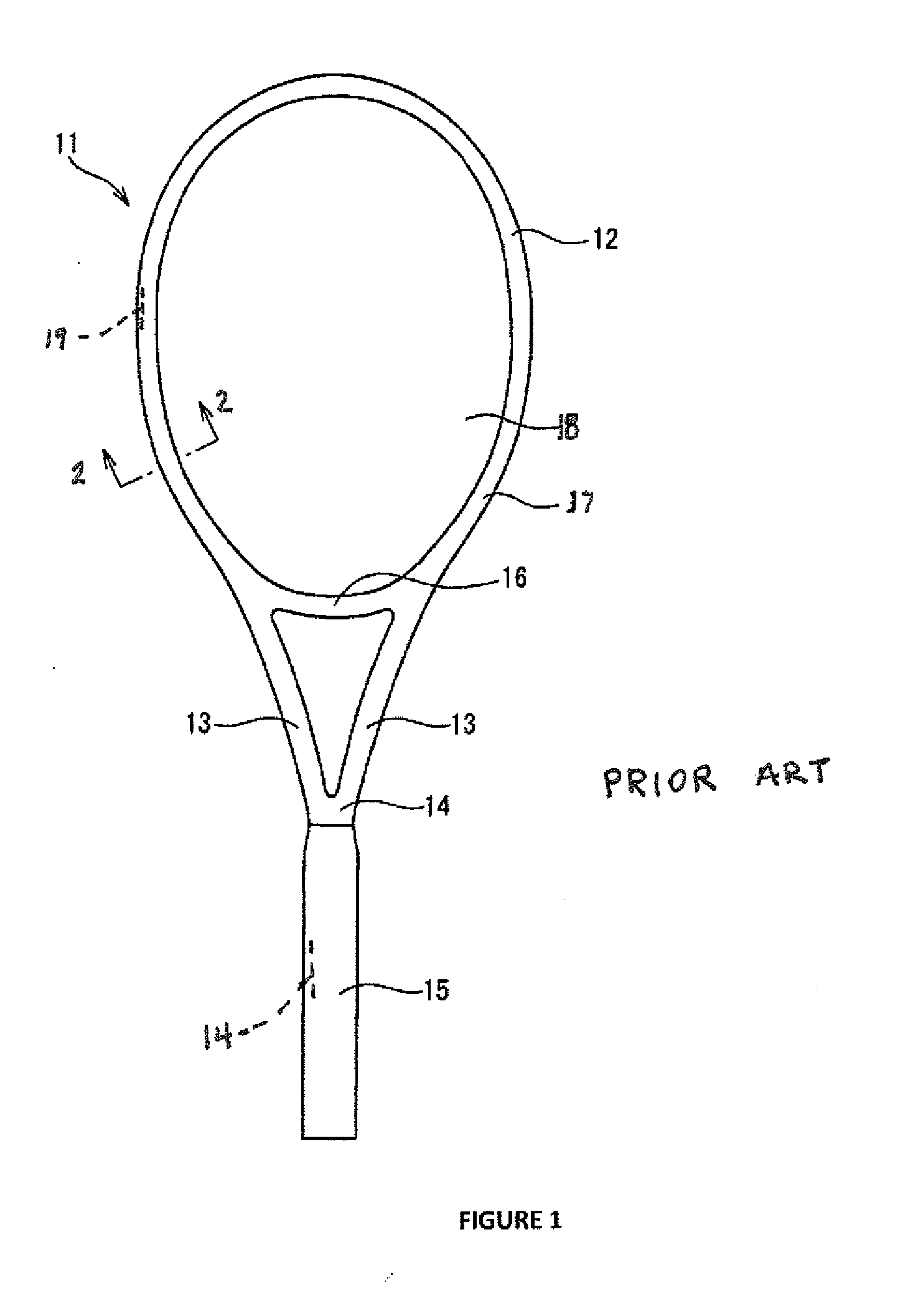
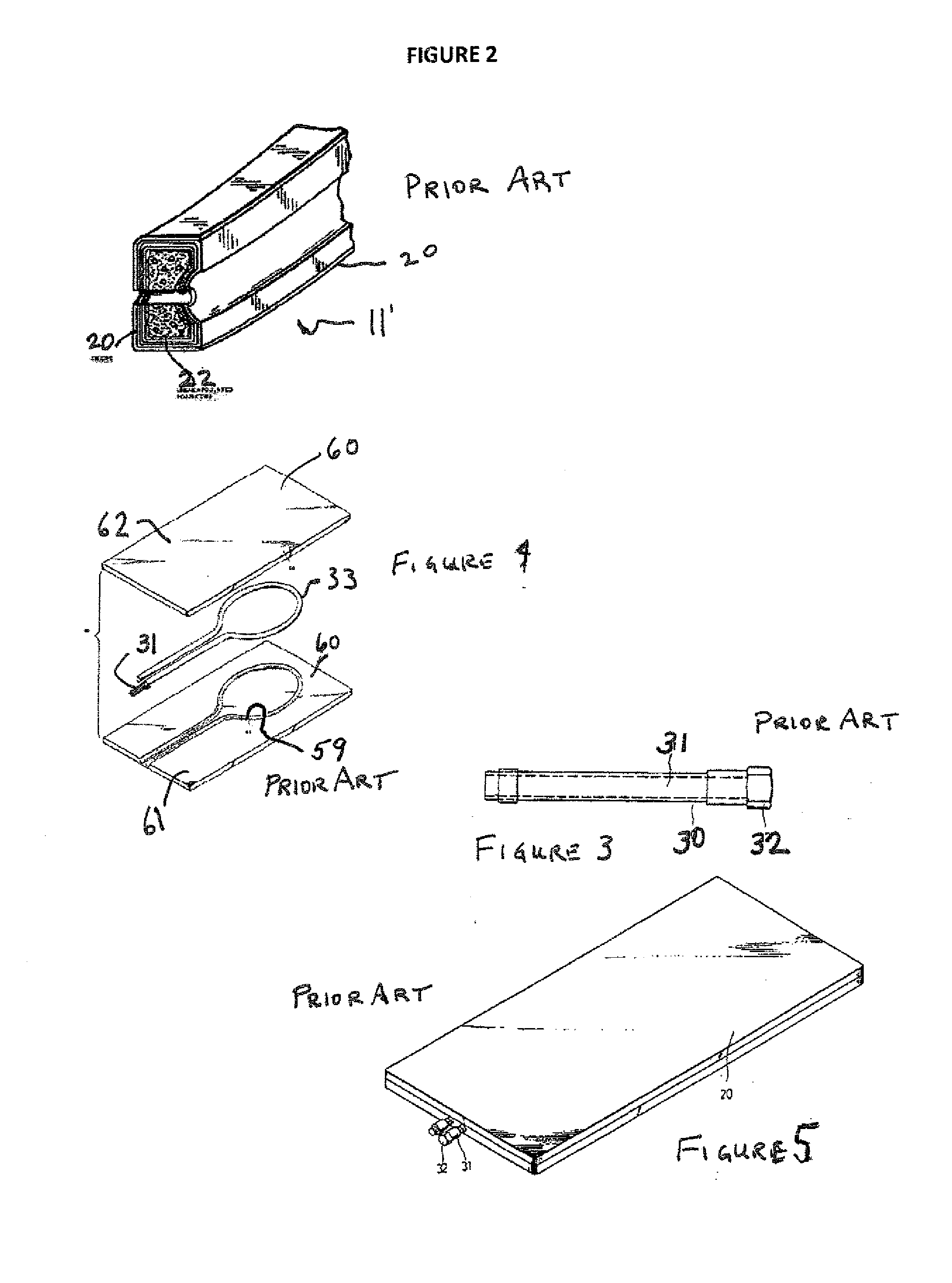
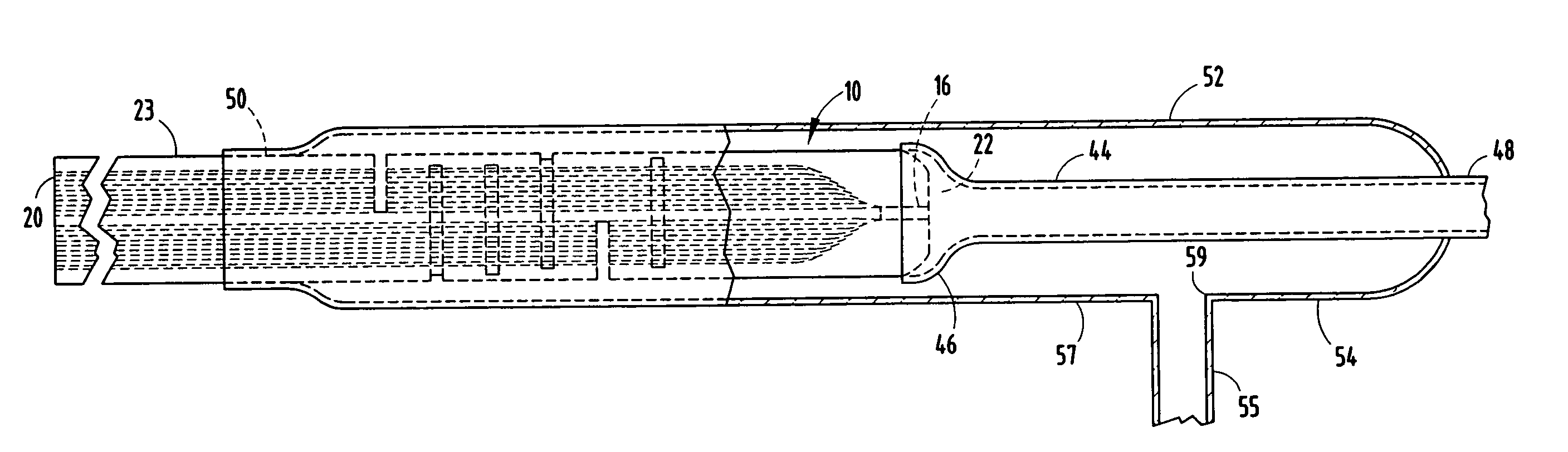
InactiveUS20110136602A1Additional injuryShock can worsenLayered product treatmentDomestic articlesEngineeringFibrous composites
The inventive fiber manufacturing process is particularly adapted for demanding applications such as sports racquets, including tennis racquets, badminton racquets and other sports applications. Because of the improved strength to weight ratio of components formed using the inventive method, a wide range of flexibility is achieved, allowing use of the inventive process to manufacture, for example, a fiber reinforced (for example, graphite) modular sports racquet, optionally provided with user-selectable weights and / or handle replacements. From the standpoint of the player, this allows a racquet frame featuring self customization. From the standpoint of a retailer, the benefit provided is reduction of inventory. The inventive fiber, for example graphite fiber) racquet frame is filled with a plastic foam and is formed using, for example, microencapsulation technology to time, generate and apply the pressure used to form the graphite composite material of which the racquet is comprised. Advantageously, inner and outer tubular members may be used to form the racquet frame, with the inner tubular member extending around the head of the racquet frame. This compares to the standard industry technique of air injection. The racquet is thus not hollow like conventional graphite racquets, and the walls therefore can be made thinner than those of existing graphite racquets still being of the same strength or being stronger, which gives the racquet exceptional performance. In addition, the overall dimensions of, for example the cross-section, of the racquet can also be reduced while still maintaining performance characteristics.
Owner:XENE CORP
Far infrared magnetic fiber and its production process
The present invention relates to one kind of far infrared magnetic fiber and fits production process. The fiber features its coating-core structure includes a coating layer comprising polymer, far infrared powder and coupling agent, and the core material includes polymer, magnetic powder and modifier. It is produced through the steps of producing coating material including mixing, extruding and pelletizing; producing core material including mixing, extruding and pelletizing; prdoucing composite fiber including spinning with the coating material and the core material in certain proportion and drawing; and magnetizing of the composite fiber to obtain far infrared magnetic fiber. The fiber of the present invention has excellent far infrared and magnetic health performance.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Method enabling dual pressure control within fiber preform during fiber fabrication
ActiveUS7793521B2Facilitates close controlReduce time and expense and complexityGlass fibre drawing apparatusGlass fibre productsPhotonic bandgapPhotonics
Owner:CORNING INC
Sheet material, block-like sheet material, method of manufacturing sheet material and method of separating fiber-formed layer unit and backing layer from tile carpet and recovering the unit and the layer
InactiveUS20060147669A1Efficient separationReduce noiseAdhesivesThin material handlingFiberRecovery method
The present invention provides a effective recycling method for a fiber fabrication layer unit which has been separated and retrieved from a tile carpet and which comprising a fiber assembled layer to which a part of a backing layer being integrally contacted and also provide a method for producing a product to be recycled. And the method for effectively recycling the fiber fabrication layer unit comprises the steps of; applying a pressured shearing force to a surface of a backing layer of a tile carpet collected from the market before it is broken, so that at least a part of the backing layer is separated from a fiber assembled layer or from a rest of portion of the backing layer; separating the backing layer and the fiber fabrication layer unit including the fiber assembled layer from the tile carpet from each other; after that, gathering and connecting the tile carpets or the fiber fabrication layer units to each other with utilizing heat energy or suitable adhesive, to form a tile shaped block like sheet material or a longitudinal sheet material; and forming various kinds of industrial materials from these sheets.
Owner:TAJIMA
Multicomponent taggant fibers and method
InactiveUS20100062251A1Prevent and mitigate adverse chemical reactionImprove stealth and securityNon-fibrous pulp additionSynthetic resin layered productsFiberWavelength
Taggant fibers and methods of use provide for enhanced protection and security when the fibers are used in documents such as land titles, currency, passports and other documents of value. The taggant fibers consist of a minimum of two separate zones with each zone containing a different taggant to emit different wave lengths when excited. The taggants may consist of organic or inorganic compounds as are conventionally known and can be manufactured using for example polymeric materials which can be extruded during the fiber manufacturing process. A first zone may comprise a fiber sheath which includes a taggant and a second or inner zone or core which may be formed into a company logo having letters with different or the same taggants. Authentication of the fibers or documents containing such fibers can be readily viewed using conventional techniques.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL PROD PROTECTION +1
Multicomponent Taggant Fibers and Method
ActiveUS20100063208A1Prevent and mitigate adverse chemical reactionImprove stealth and securityConjugated synthetic polymer artificial filamentsYarnFiberWavelength
Taggant fibers and methods of use provide for enhanced protection and security when the fibers are used in documents such as land titles, currency, passports and other documents of value. The taggant fibers consist of a minimum of two separate zones with each zone containing a different taggant to emit different wave lengths when excited. The taggants may consist of organic or inorganic compounds as are conventionally known and can be manufactured using for example polymeric materials which can be extruded during the fiber manufacturing process. Authentication of the fibers or documents containing such fibers can be readily viewed using conventional techniques.
Owner:YPB GRP +1
Sheet material, a block like sheet material, a method for producing a sheet material, a method for separating and retrieving a fiber fabrication layer unit and a backing layer from a tile carpet
InactiveUS7517426B2Efficient separationReduce noiseMechanical working/deformationAdhesivesFiberAdhesive
Owner:TAJIMA
Manufacturing method of polyethylene colored fibers with ultrahigh molecular weight
ActiveCN106544747ALightweight and softConsider comfortArtificial filament heat treatmentDry spinning methodsYarnColour fastness
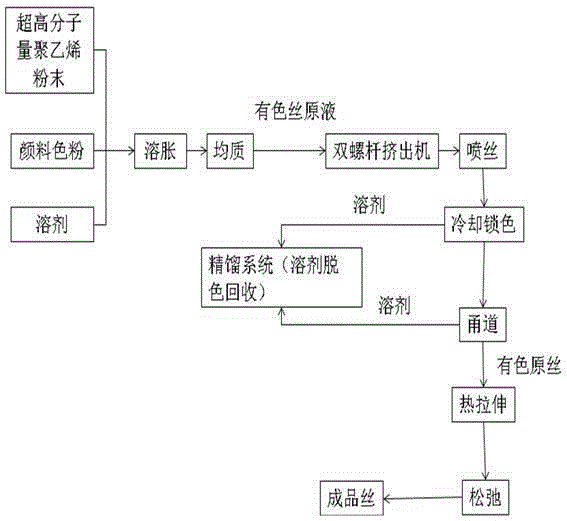
The invention discloses a manufacturing method of polyethylene colored fibers with ultrahigh molecular weight. According to the manufacturing method, colored fibers with the filament number of 0.33dtex-2.0dtex, the bundle fiber fineness of 22dtex-1776dtex, the fiber strength of 10cN / dT-40cN / dT, the modulus of 1000cN / dT-1600cN / dT and the elongation at break of 2%-4% are prepared through steps of preparing a colored spinning stock liquid, preparing colored proto-filaments and preparing the colored fibers. The polyethylene colored fibers have fine monofilament fineness and have thin and soft textures; the prepared colored fibers have good color uniformity and rich color varieties; the depth of color is adjustable, and the color fastness is high; the wear-resisting color fastness reaches the grade 4 or more, and the sunlight-resisting color fastness reaches the grade 4 or more; the soaping-resisting color fastness reaches the grade 4 or more, and the weather-resisting color fastness reaches the grade 4 or more; in a production process, a process is simple, and continuous and stable production is realized; one hundred thousand meters of a product can have no connectors, and a solvent is easy to volatilize; and after purification and separation are carried out by a rectification system, the solvent does not contain any pigment, and each bath of yarns have no color difference. The recycling rate is more than or equal to 99.5%, waste emission is reduced, and low carbon and environment friendliness are realized.
Owner:SINOPEC YIZHENG CHEM FIBER +1
Method for manufacturing plates from waste fibers
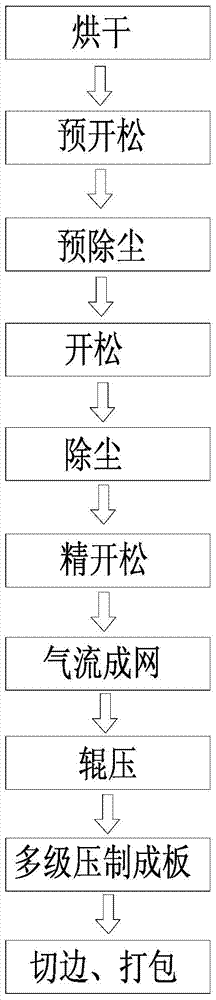
The invention provides a method for manufacturing plates from waste fibers of waste filtering bags, waste textiles and the like. The method comprises the steps of drying, loosening, dedusting, air laying, rolling, multi-stage compressing to form plates, trimming and packaging. An air laying technology is selected, so that fibers are arranged in a fiber net without directivity, and the horizontal and longitudinal ratio of the plates is approximate to 1:1, and the method is suitable for various fibers with different lengths and wide varieties, requires less on raw materials, and is suitable for a wide range of fibers; compared with a scheme that the required thickness of plates is reached by laying for multiple layers in a traditional carding method, the air-laying can obtain the required thickness of plates by directly controlling the output speed.
Owner:福建鑫华股份有限公司 +2
Apparatus for processing fiber-reinforced composites using fiber mat and its manufacture
InactiveCN1622872AUniform thicknessNeedling machinesFlat articlesFiber-reinforced compositeFiber fabrication
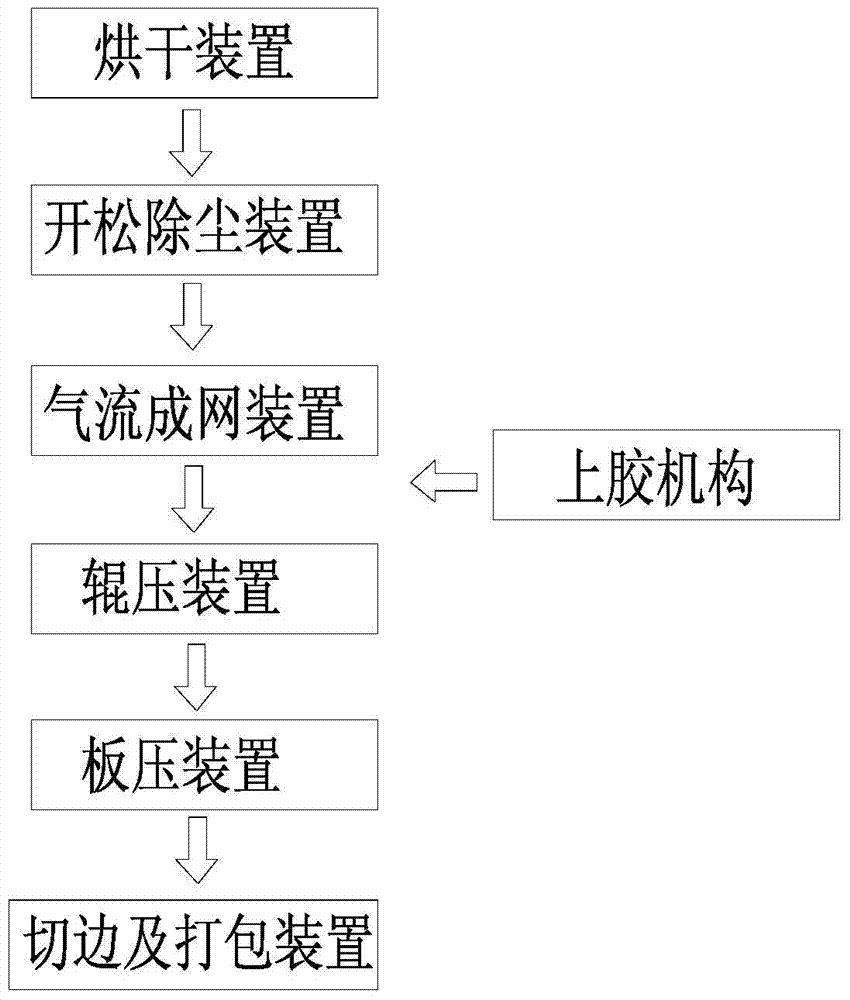
Disclosed is a method of manufacturing a multifunctional fiber-reinforced composite using a composite fiber mat and an apparatus for manufacturing the same, in which at least two types of thermoplastic fiber and reinforcing fiber are used to manufacture a composite mat or a composite sheet, as well as a light adiabatic sheet having cells foamed due to inherent resilience of the reinforcing fiber while the composite sheet is compressed by rollers. The method includes fibrillating and combining the thermoplastic fiber and the reinforcing fiber to form the composite mat, dispersing and volatilizing the composite mat, and needle-punching the dispersed and volatilized composite mat. Then, the composite mat is subjected to preheating in a preheating zone, melting, compressing and molding in a compressing zone, and cooling in a cooling zone, to yield the composite sheet. Selectively, the composite sheet is re-heated to obtain a pseudo-foamed composite sheet by inherent resilience of the fiber.
Owner:普莱科斯普可利亚有限会社
Novel glass compositions for fiber formation
Provided is a range of glass compositions and glass fiber products made therefrom that show a unique combination of properties for both discontinuous fiber manufacturing and end use service. The glass compositions are particularly useful in high volume, high throughput, economical processes such as rotary spinning.
Owner:JOHNS MANVILLE CORP
Low temperature dyeable flexible bright polyester fiber and production method thereof
InactiveCN101498062ASpecial alkali hydrolysis propertiesEasy to processFibre treatmentDyeing processChemistrySynthetic fiber
The invention relates to a lower-temperature, dyeable and soft-glossy lanon and a preparation method thereof, belonging to the manufacture field of synthetic fibers. The preparation method is characterized in that conventional polyester slices and ionic co-polyester slices are singly dried or mixed and dried under a vacuum condition and the dried mixture is spinned at a temperature ranging from 280 DEG C to 320 DEG C under the conditions of a hot tray temperature of 65 DEG C to 95 DEG C, a hot plate temperature of 140 DEG C to 190 DEG C, a drawing ratio of 3.0 to 4.5 and a winding speed of 800-1200m / min; then the mixture is treated in a treatment solution which comprises fibers and 10 percent to 20 percent of sodium hydroxide by weight and has a bath ratio of 1:20 to 1:50 at a temperature of 80 DEG C to 100 DEG C for 30min to 60min, and the fibers with the alkali mass loss rate of 7 percent to 20 percent after alkali treatment is dyed in a disperse dye solution at a temperature of 90 DEG C to 102 DEG C for 45min to 60min. The lower-temperature, dyeable and soft-glossy lanon can achieve a dyeing rate of 90 percent to 98 percent under a low-temperature condition and has bright texture color and soft luster.
Owner:SHAOXING UNIVERSITY
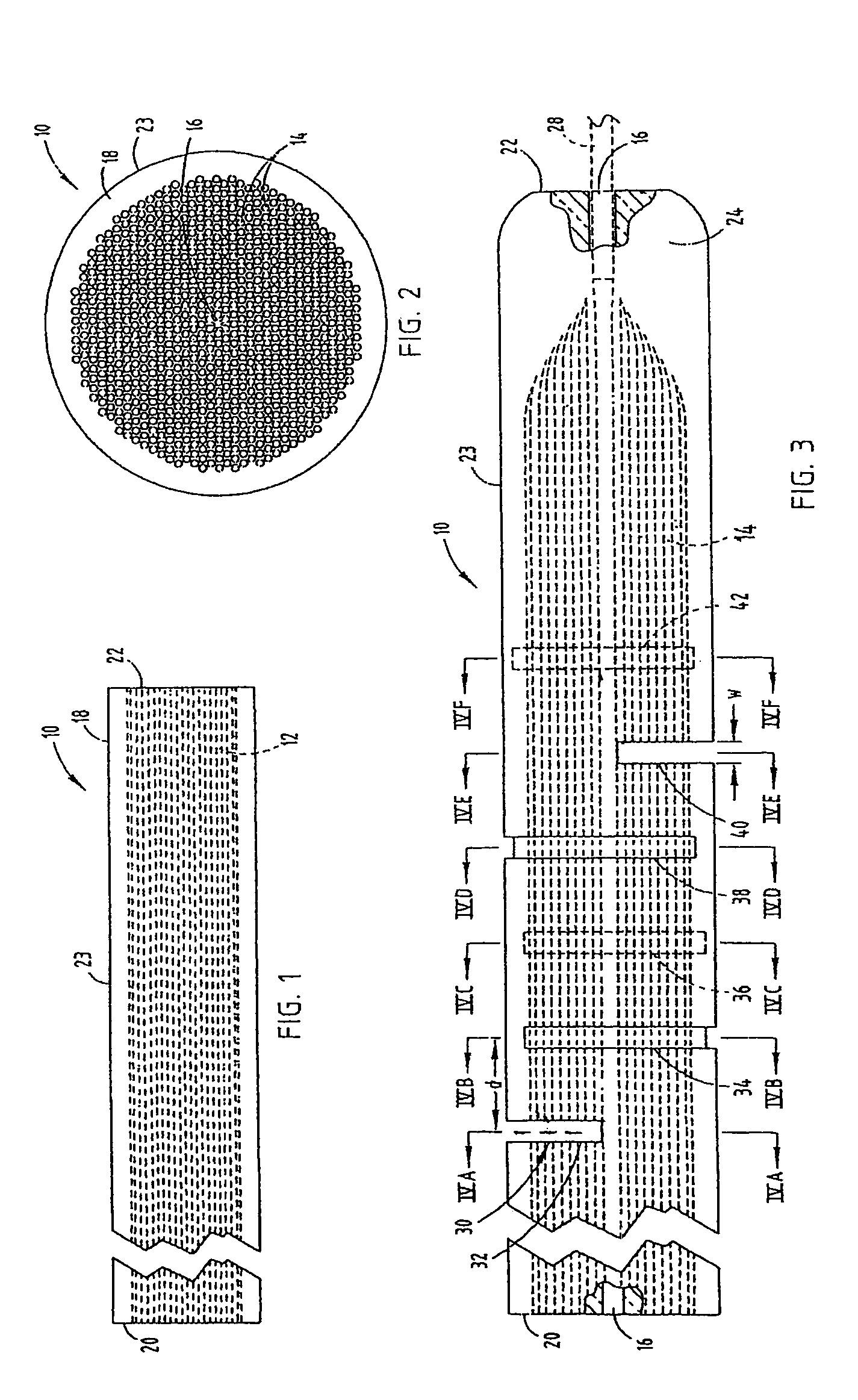
Fiber constructs and process of fiber fabrication
Described herein are fiber compositions, methods of generating the fiber compositions, and methods of using the fiber compositions in various applications utilizing fiber constructs, including for example, tissue engineering.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Novel fibers, methods for their preparation and use in the manufacture of reinforced elements
ActiveUS20160194245A1Improve mechanical stabilitySolid waste managementGrip property fibresFiberPre treatment
Fibers with crystallization seeds attached to its surface, method of making such composite fibers by surface treatment of fibers followed by either treating such fibers with premade crystallization seeds or by precipitation and direct crystallization of seeds onto pretreated fibers. Controlling and tuning the properties of inorganic binder compositions with fiber-bound crystallization seeds and thereby generating inorganic binder compositions with tailor-made characteristics.
Owner:CONSTR RES & TECH GMBH
Preparation method of natural spinnable fiber and okra fiber prepared by the same
InactiveCN1924121ASimple equipment requirementsProcess conditions are easy to achieveBleaching apparatusFibre treatment to obtain bast fibreCelluloseFiber
This invention relates to one method to process fabric fiber by fiber plant stem or plant peel part, which comprises the steps of analyzing, thread out, bleaching, softening and extending, wherein, the bleaching adopts several sections of bleaching as optimization and then for thread process. This invention also relates to one method to extract fabric fiber from Abelmoschus esculentus stem.
Owner:赵子群
Method for making light building board from recovered textile fiber
InactiveCN105670041ASolve processing problemsReduce construction costsTextile disintegration and recoveryFibre disintegrationTextile fiberEngineering
The invention discloses a method for manufacturing light-weight building boards by using recovered textile fibers, which comprises the following steps: using the mixture of cotton fibers and various synthetic fibers obtained through the process of crushing and opening waste textiles as raw materials, and then passing The raw material of waste spinning felt is made by non-woven process; the raw material of waste spinning felt is cut into blanks of certain specifications, and then the blanks are made into lightweight and high-strength building boards through vacuum infiltration and high temperature fixing process with modifiers . To sum up, the present invention collects and processes various waste daily-use textiles to make light-weight and high-strength building boards, which not only solves the problem of waste textile disposal, but also reduces construction costs and energy consumption.
Owner:王正 +1
Multi-clad Optical Fiber
ActiveUS20190025502A1Low propagation lossHigh beam qualityOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingDopantHigh numerical aperture
A multi-clad optical fiber design is described in order to provide low optical loss, a high numerical aperture (NA), and high optical gain for the fundamental propagating mode, the linearly polarized (LP) 01 mode in the UV and visible portion of the optical spectrum. The optical fiber design may contain dopants in order to simultaneously increase the optical gain in the core region while avoiding additional losses during the fiber fabrication process. The optical fiber design may incorporate rare-earth dopants for efficient lasing. Additionally, the modal characteristics of the propagating modes in the optical core promote highly efficient nonlinear mixing, providing for a high beam quality (M2<1.5) output of the emitted light.
Owner:NUBURU INC
Acrylic-fiber finish, acrylic fiber for carbon-fiber production, and carbon-fiber production method
ActiveUS20120021125A1Minimum fiber separationMinimal broken fiberSesquicarbonate preparationFibre typesEpoxyPolymer science
An acrylic-fiber finish for use in carbon-fiber production contributes to high tenacity of resultant carbon fiber. The acrylic-fiber finish for carbon-fiber production includes an epoxy-polyether-modified silicone and a surfactant. The weight ratios of the epoxy-polyether-modified silicone and the surfactant in the total of the non-volatile components of the finish respectively range from 1 to 95 wt % and from 5 to 50 wt %. The carbon fiber production method includes a fiber production process for producing an acrylic fiber for carbon-fiber production by applying the finish to an acrylic fiber which is a basic material for the acrylic fiber for carbon-fiber production; an oxidative stabilization process for converting the acrylic fiber produced in the fiber production process into oxidized fiber in an oxidative atmosphere at 200 to 300 deg.C.; and a carbonization process for carbonizing the oxidized fiber in an inert atmosphere at 300 to 2,000 deg.C.
Owner:MATSUMOTO YUSHI SEIYAKU
Speaker vibration film made of non-wood fibers and manufacture process thereof
ActiveCN101720053AImprove performanceDifferent characteristicsTransducer diaphragmsFiberEcological environment
The invention relates to a speaker vibration film made of non-wood fibers. The vibration film is prepared from the following raw materials in percentage by weight: 15-40% of grass fiber, 20-45% of cotton fiber and 15-65% of bast fiber. The speaker vibration film made of the non-wood fibers has short production period, great yield, relatively low price and high economic benefits, can not cause obvious adverse effect on the ecological environment by extensive use and have rich performance presentations.
Owner:GUOGUANG ELECTRIC +2
Material for fiber manufacturing and fiber
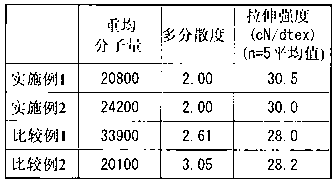
ActiveCN103130995AHigh fiber strengthFilament forming substance formingMonocomponent copolyesters artificial filamentFiberPolyester
Disclosed is a material for fiber manufacturing comprising a liquid crystal polyester satisfying the following requirements (a) and (b), wherein (a) the weight-average molecular weight is equal to or less than 30000 and the polydispersity is equal to or less than 2.5; and (b) the melt viscosity measured at 360 DEG C. with conditions of a nozzle pore diameter of 0.5 mm and a shear velocity of 1000 s-1 using a flow feature testing machine is equal to or less than 70 Pas.
Owner:SUMITOMO CHEM CO LTD
Method and equipment for manufacturing composite fiber containing continuous glass fiber
The invention relates to a method for manufacturing a composite fiber containing a continuous glass fiber. The composite fiber is formed by mutually mixing offline terylene and an online continuous glass fiber; the glass fiber is drawn on line, and the terylene is finished yarn; a plurality of bundles of terylene with different yarn feed angles are drawn to be converged into sheet shapes after being subjected to tension adjustment; and the converged terylene yarn bundles are separated and then compounded with the glass fiber processed with an impregnating compound. The invention has the advantages of simplified process equipment and improved production smoothness; and meanwhile, the introduction of chemical fiber yarn-feed tension adjustment ensures that better practicability and better effect on the baked yarn clew moulding effect are achieved.
Owner:JUSHI GRP CO
Basalt fiber manufacturing process
The invention relates to a basalt fiber manufacturing process. The process comprises the following steps: crushing the basalt raw ore, and then placing the crushed ore into mixing equipment to be mixed; grinding parts of materials in the mixing equipment according to a multi-draw manner, and then mixing the ground parts; preparing the uniformly mixed material powder into specimens, and detecting the phase of the specimens; if the detection result is in accordance with the standard of the basalt fiber, directly adding the materials into a tank furnace; otherwise, according to the difference between the detection result and the standard, adding corresponding components, uniformly mixing the materials added with the corresponding components, and feeding the mixture into the tank furnace; utilizing a heating electrode to heat the materials in the tank furnace, enabling the materials to be molten, and when the liquid level of the melt is raised to be coincident with a liquid level base plate at the front end of a monitoring rod, performing delayed heating; opening a discharge hole at the bottom of the tank furnace to enable the melt to flow out through a bushing plate, and then using a bushing blower to cool the melt, so as to form the fiber. The basalt fiber manufacturing process disclosed by the invention can improve the stability of the product quality and reduce waste of the product resources.
Owner:JILIN JIUXIN BASALT IND
Simulation method of electro-spinning fiber closed-ring control based on finite element and system discrimination
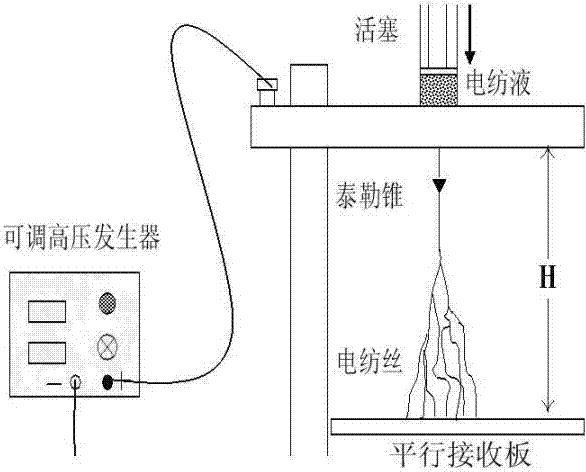
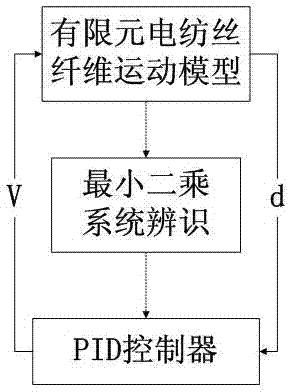
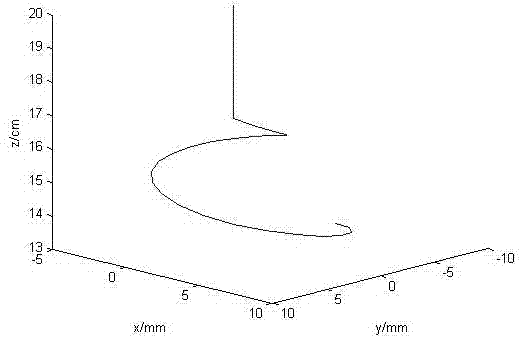
InactiveCN102393648AAvoid controlEliminate limitationsSimulator controlProportion integration differentiationClassical mechanics
The invention discloses a simulation method of electro-spinning fiber closed-ring control based on the finite element and system discrimination. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) solving and establishing a finite element electro-spinning fiber motion model by adopting matlab software, and simulating the electro-spinning fiber moving process to obtain a virtual test system; (2) acquiring input and output values based on the virtual test system, and processing the input and output values by adopting a least square system discrimination method to acquire a procedure transfer function of the system; (3) setting a procedure transfer function controller; and (4) leading the controller to act on the finite element electro-spinning fiber motion model to realize simulation to the electro-spinning fiber closed-ring control. According to the method, time-based PID (proportion integration differentiation) control action is directly reflected into the finite element motion model to perform closed-ring control simulation, the limitation of respectively and independently performing electro-spinning fiber motion analysis and the limitation of a controller are eliminated, cost is reduced, the problem of controlling fiber diameters in the existing device is solved, and support is provided to automation of electro-spinning fiber manufacture devices.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com