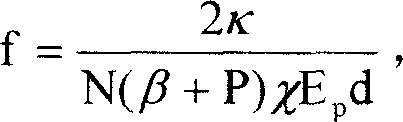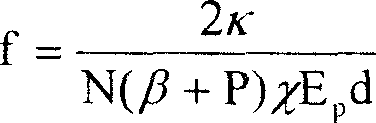A compensation method for laser bar thermal lens effect
A technology of thermal lens effect and compensation method, applied in the field of laser rods, can solve the problems of increased laser loss, difficult laser device adoption, and reduced laser energy conversion efficiency, and achieves the effect of simple structure
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
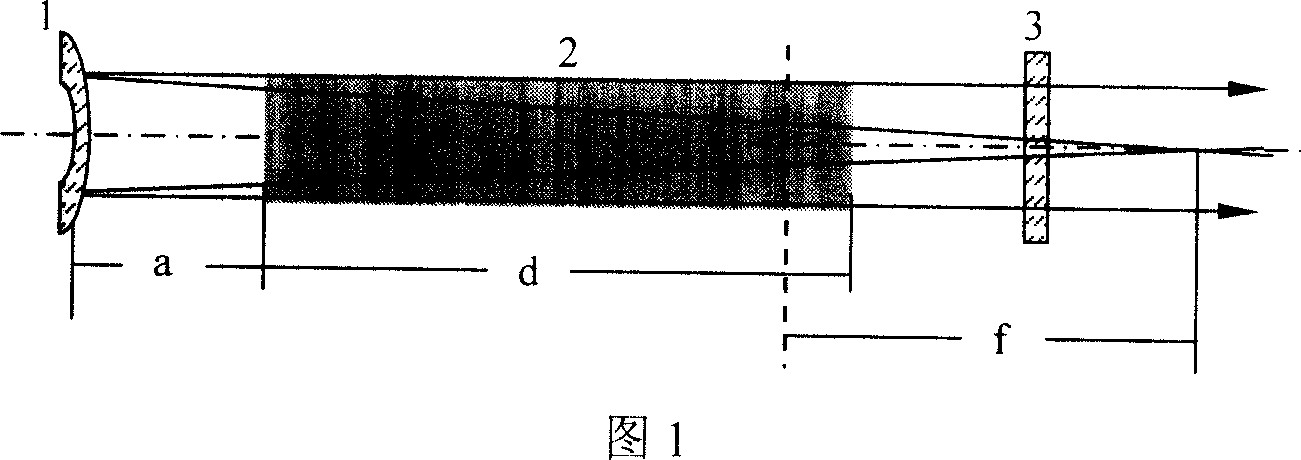
[0009] Embodiment 1: As shown in the figure, 1 is a full-reflection spherical mirror coated with a wavelength of 1053nm, 2 is a φ8×200 N3122 phosphate neodymium glass laser rod, and 3 is a laser output coupling mirror. Glass laser rod volume is 10cm 3 , let the pump energy density E p =20J / cm 3 , the repetition frequency is N=5Hz, the heating efficiency of N3122 glass is χ=0.08, the temperature coefficient of refraction index β=-4.3×10 -6 / °C, stress thermo-optic coefficient P=5.8×10 -6 / °C, thermal conductivity κ=0.0056W / cm°C, rod length d=20cm into the formula f = 2 κ N ( β + P ) χ E p d get glass rod 2 The focal length of the thermal lens is f=47...
Embodiment 2
[0010] Embodiment 2: As shown in the figure, 1 is a spherical mirror coated with a 1064nm total reflection film, 2 is a φ6×100 YAG laser rod, and 3 is a laser output coupling mirror. Set pump energy density E p =15J / cm 3 , the repetition frequency is N=10Hz, the YAG heating efficiency χ=0.05, the temperature coefficient of refraction index β=7.3×10 -6 / °C, stress thermo-optic coefficient P=8×10 -6 / °C, thermal conductivity κ=0.13W / cm°C, rod length d=10cm into the formula f = 2 κ N ( β + P ) χ E p d get the glass rod The focal length of the thermal lens is f=227cm, the radius of curvature R=1.8 f=409cm of the spherical mirror 1 is taken, and f, d valu...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Refractive index temperature coefficient | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com