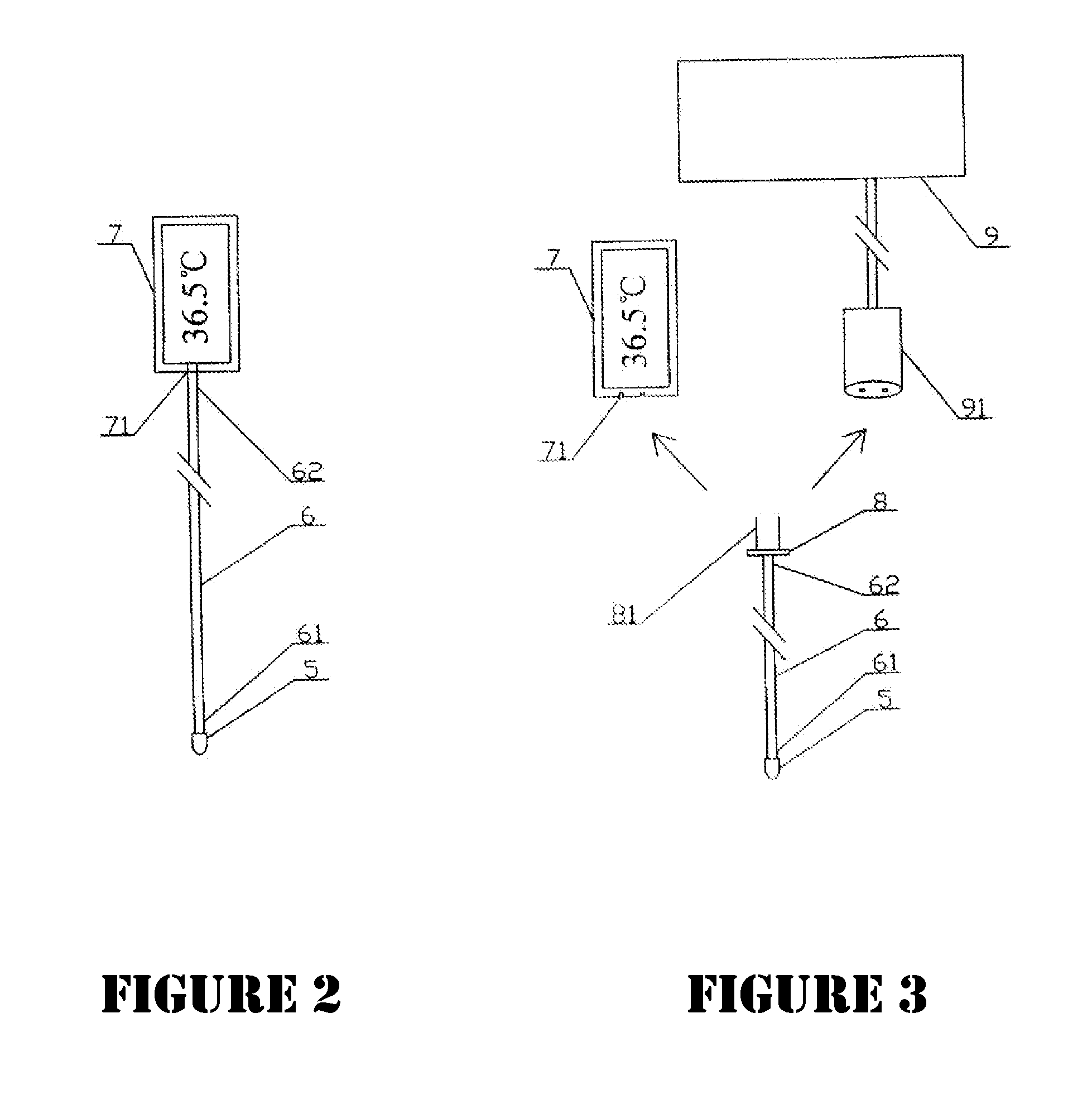
Patents
Literature
251 results about "Artificial respiration" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Artificial ventilation, (also called artificial respiration) is means of assisting or stimulating respiration, a metabolic process referring to the overall exchange of gases in the body by pulmonary ventilation, external respiration, and internal respiration. It may take the form of manually providing air for a person who is not breathing or is not making sufficient respiratory effort on their ...
Optical techniques for the measurement of chest compression depth and other parameters during cpr
ActiveUS20110040217A1Accurate measurementImprove accuracyImage enhancementElectrotherapyChest regionEmergency medicine
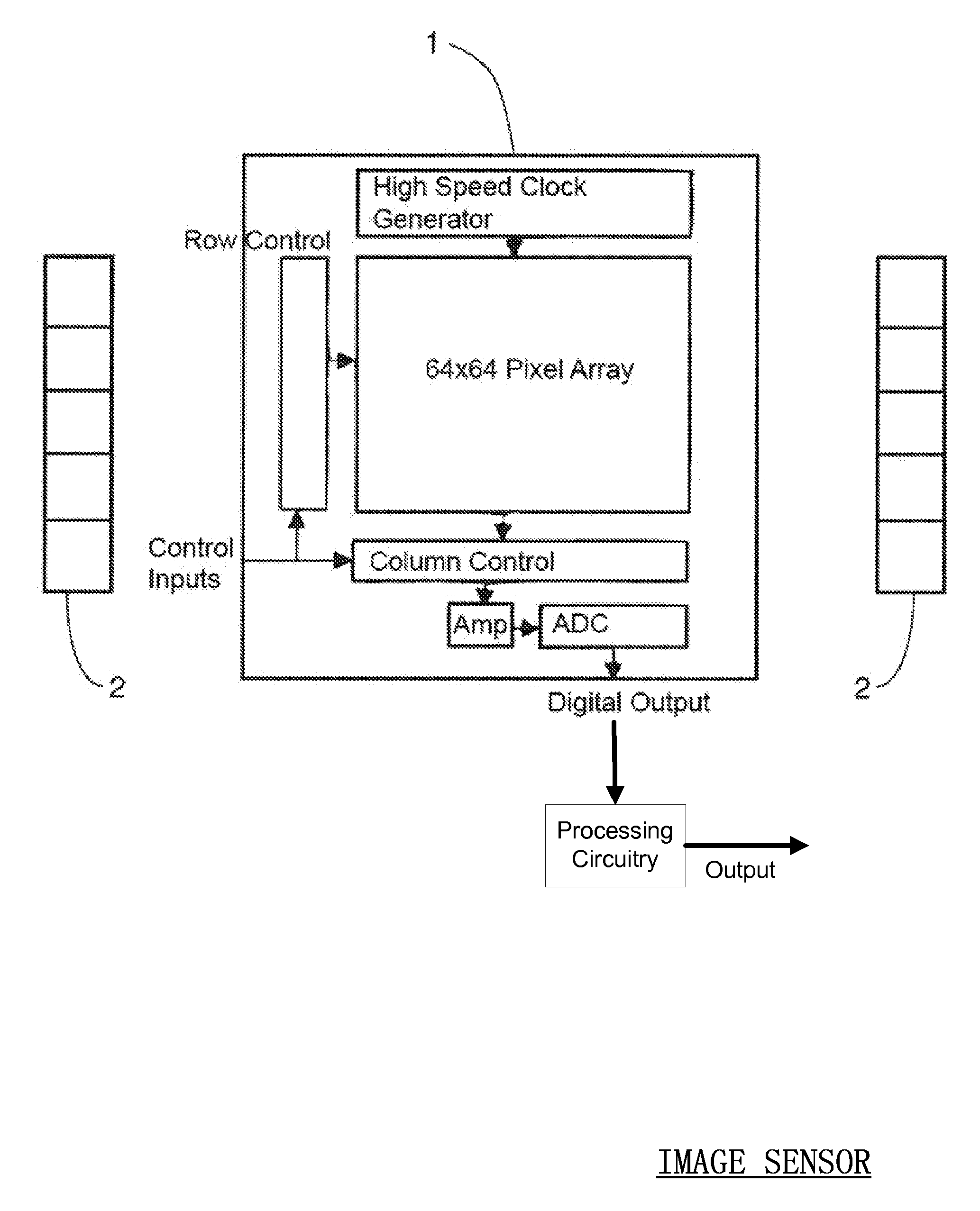
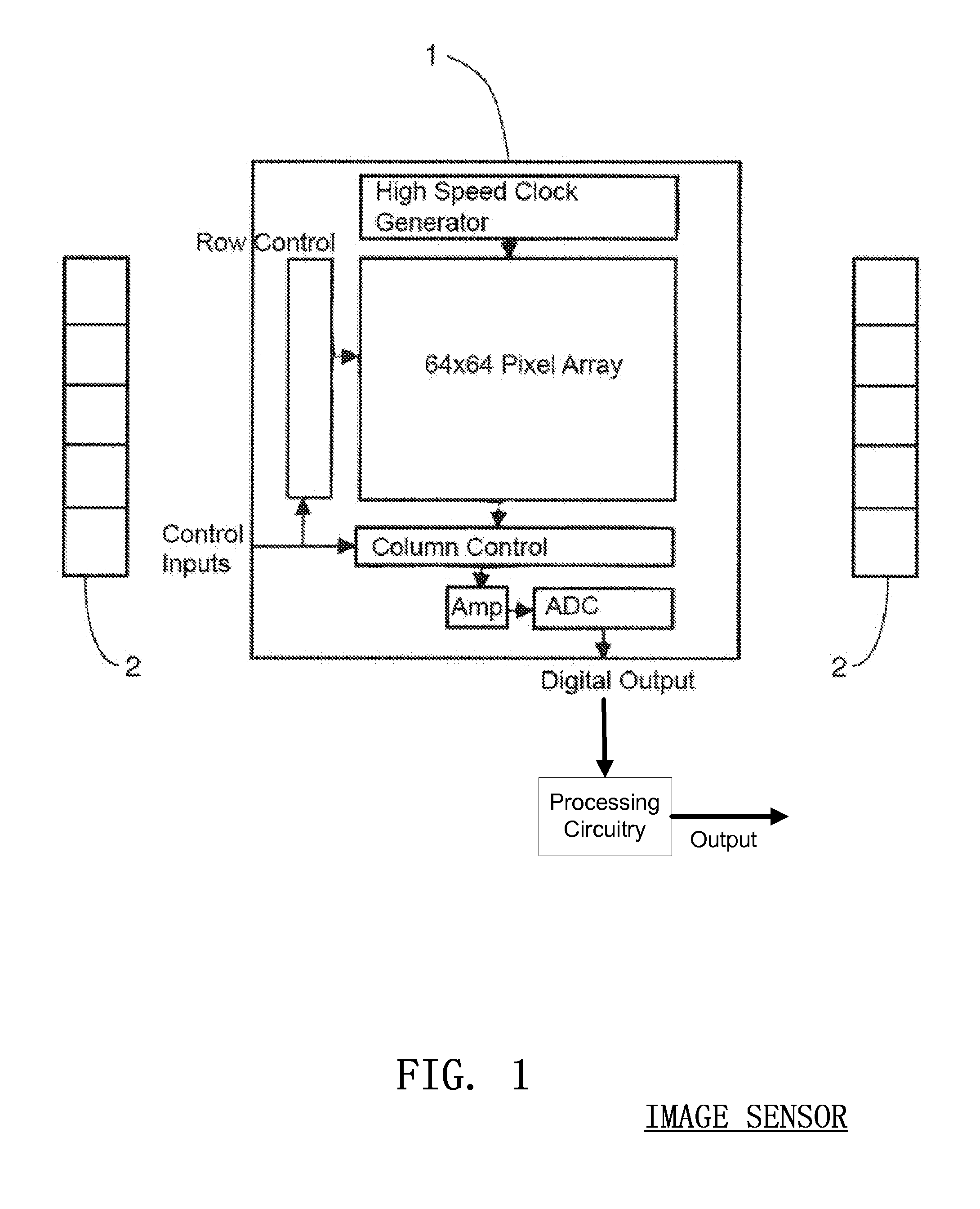
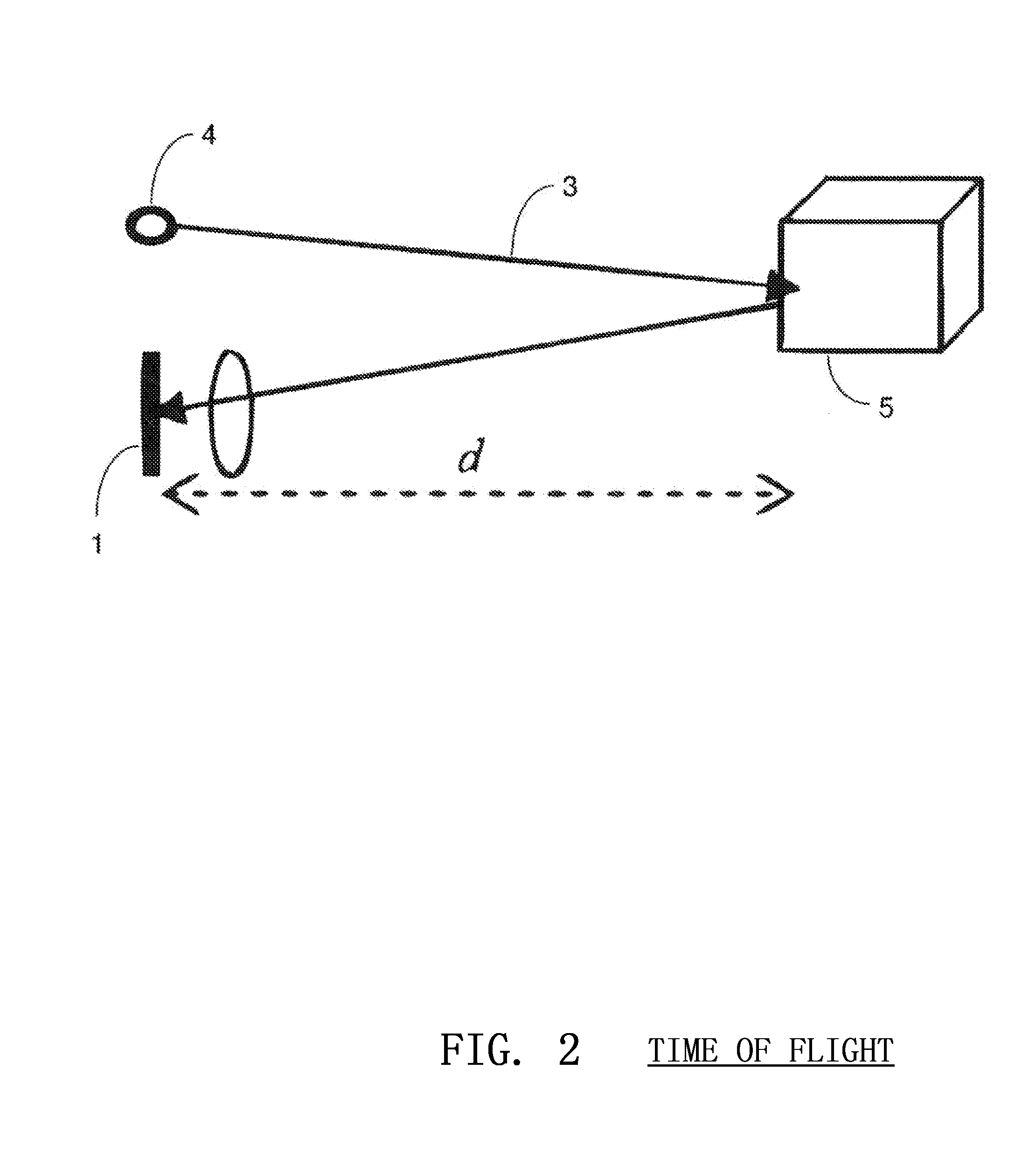
Embodiments of the present invention are related to a method and device for the determination and calculation of the depth of chest compressions during the administration of cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR). Embodiments use an optical sensor to monitor the distance that a victim's chest is displaced during each compression throughout the administration of CPR. The optical sensor is most commonly an image sensor such as a CMOS or CCD sensor, and more specifically a CMOS image sensor capable of three-dimensional imaging based on the time-of-flight principle. An infrared emitter may illuminate the victim's body and any visible piece of ground beside the victim. As the infrared light interacts with any surfaces it encounters, it is reflected and returns to the image sensor where the time of flight of the infrared light is calculated for every pixel in the image sensor. The distance data is used to gauge the effective displacement of the victim's chest. The optical sensors can be used to visualize the size of a patient and immediately gauge the body type and instruct the user accordingly. Furthermore, optical measurement techniques can be used to accurately measure chest rise during artificial respiration and ensure that proper ventilation is being administered in between compressions. In addition, optical measurements of the chest of the victim and the hands of the rescuer can be used to help ensure that the rescuer has positioned his or her hands in the anatomically correct location for effective CPR.
Owner:STRYKER CANADA ULC
Device for artificial respiration with an endotracheal tube
InactiveUS7481222B2Avoid disadvantagesEasy to continueTracheal tubesOperating means/releasing devices for valvesIntratracheal intubationEndotracheal tube
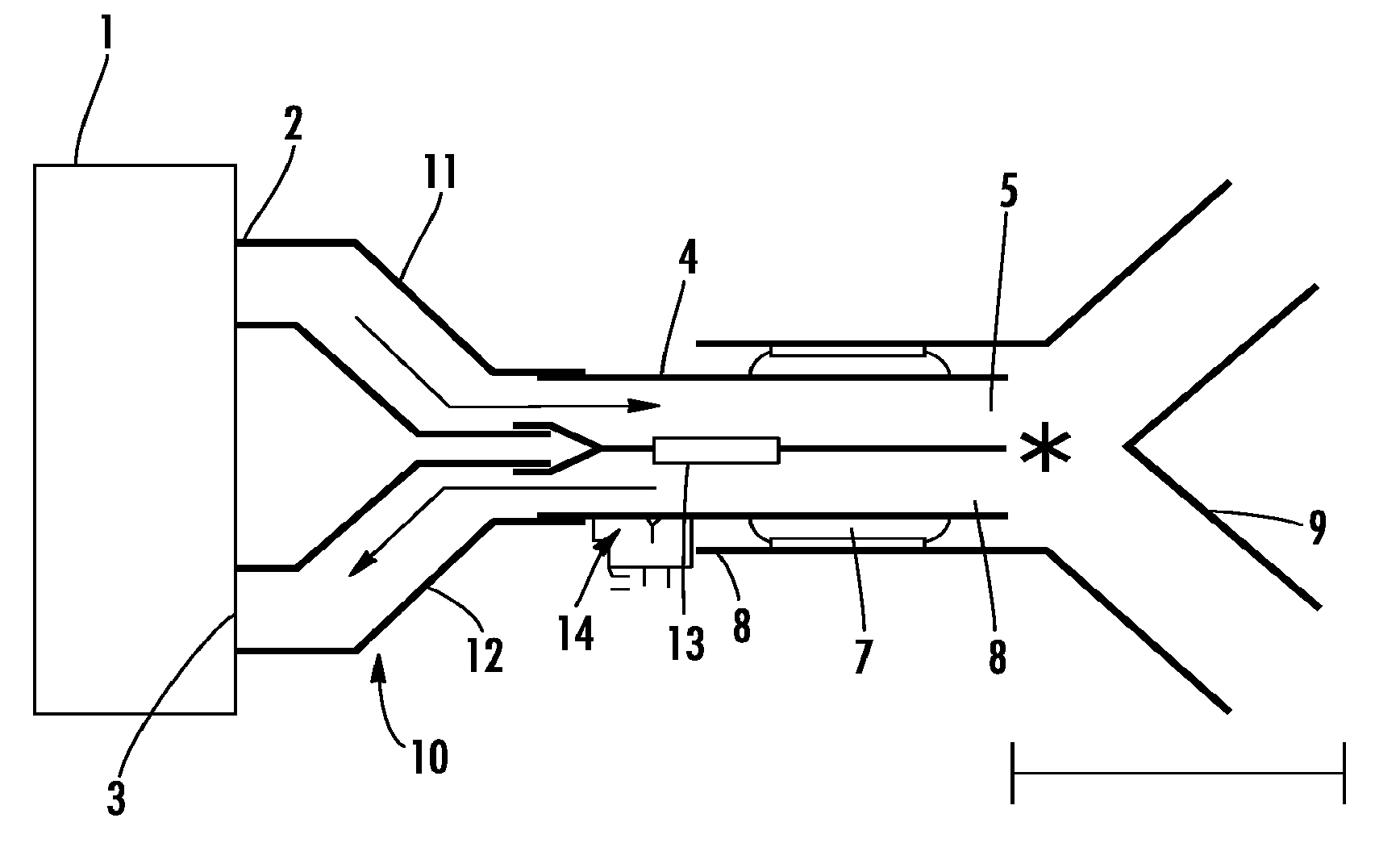
A device for ventilation, comprisinga ventilator for providing a stream of gas for ventilation at an outlet,a hose for inspiration air one end of which is connected to the outlet,a double-lumen endotracheal tube one lumen of which, at its end distal to the patient, is connected to the other end of the hose for inspiration air,flow meters for measuring the streams of gas in the two lumina of the endotracheal tube,pressometers for measuring the pressures at the ends distal to the patient of the two lumina,an evaluation means for determining the flow resistance in a lumen flowed through by gas because of the stream of gas measured therein and the pressures measured, anda means for outputting an information about the flow resistance of the lumina.
Owner:REISSMANN HAJO
Unit for adjusting humidification
InactiveUS6557551B2Readily disposed into patient circuitAvoid passingRespiratorsOther heat production devicesFiberBreathing gas
A humidification unit adapted to be disposed in a patient circuit for humidifying the flow of breathing gas delivered to the patient via the patient circuit by an artificial ventilator system. The humidification unit includes an exothermic member having an outer surface and a plurality of hollow fibers disposed on the outer surface of the exothermic member. Each hollow fiber is defined by a peripheral wall having minute openings large enough to allow a gas to pass therethrough yet small enough to prevent a liquid from passing therethrough. Liquid delivered to the hollow fibers is heated by the exothermic member and the gas vapor resulting from the heating passes through the hollow fiber walls and humidifies the flow of breathing gas delivered to the patient.
Owner:RIC INVESTMENTS LLC
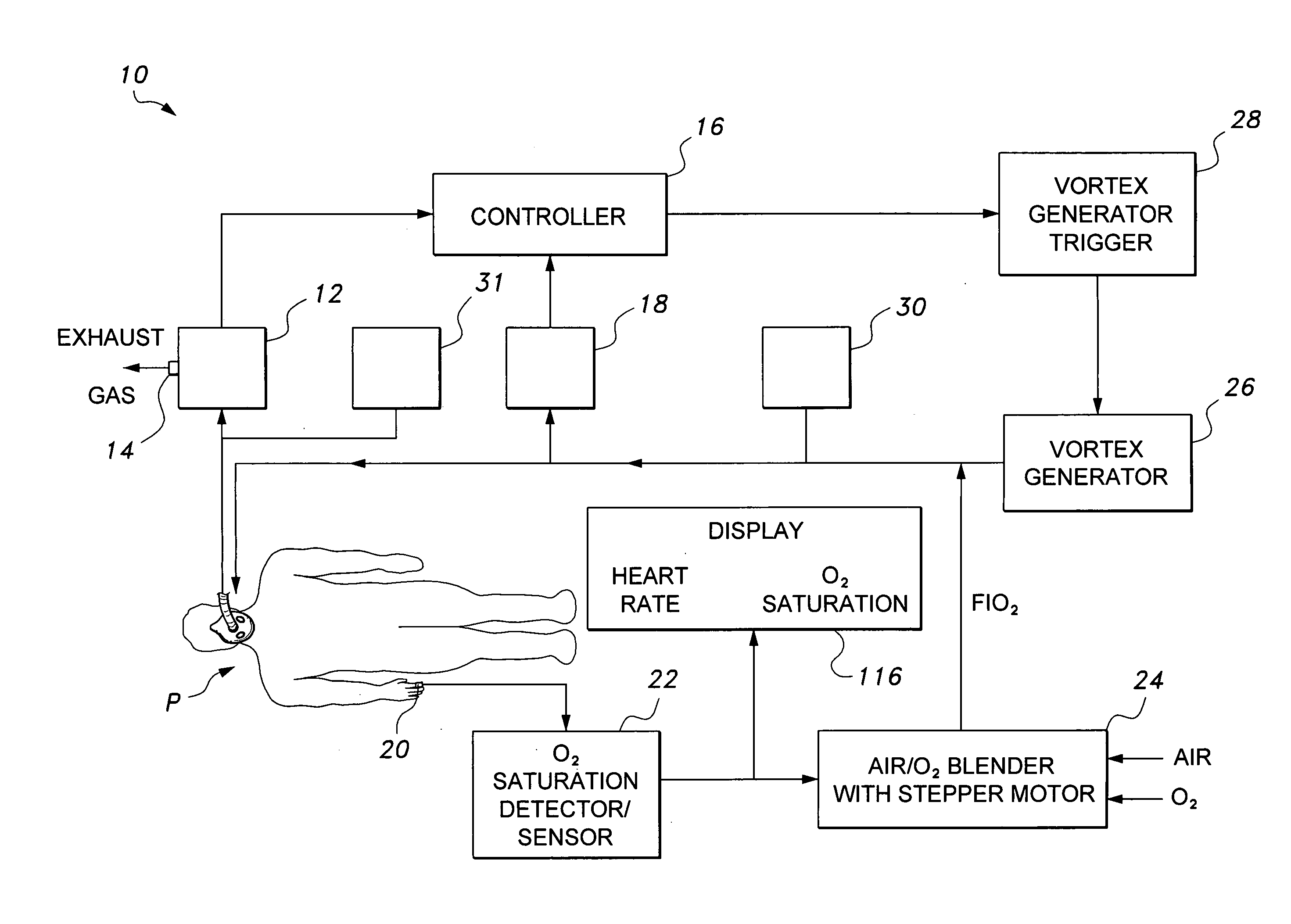
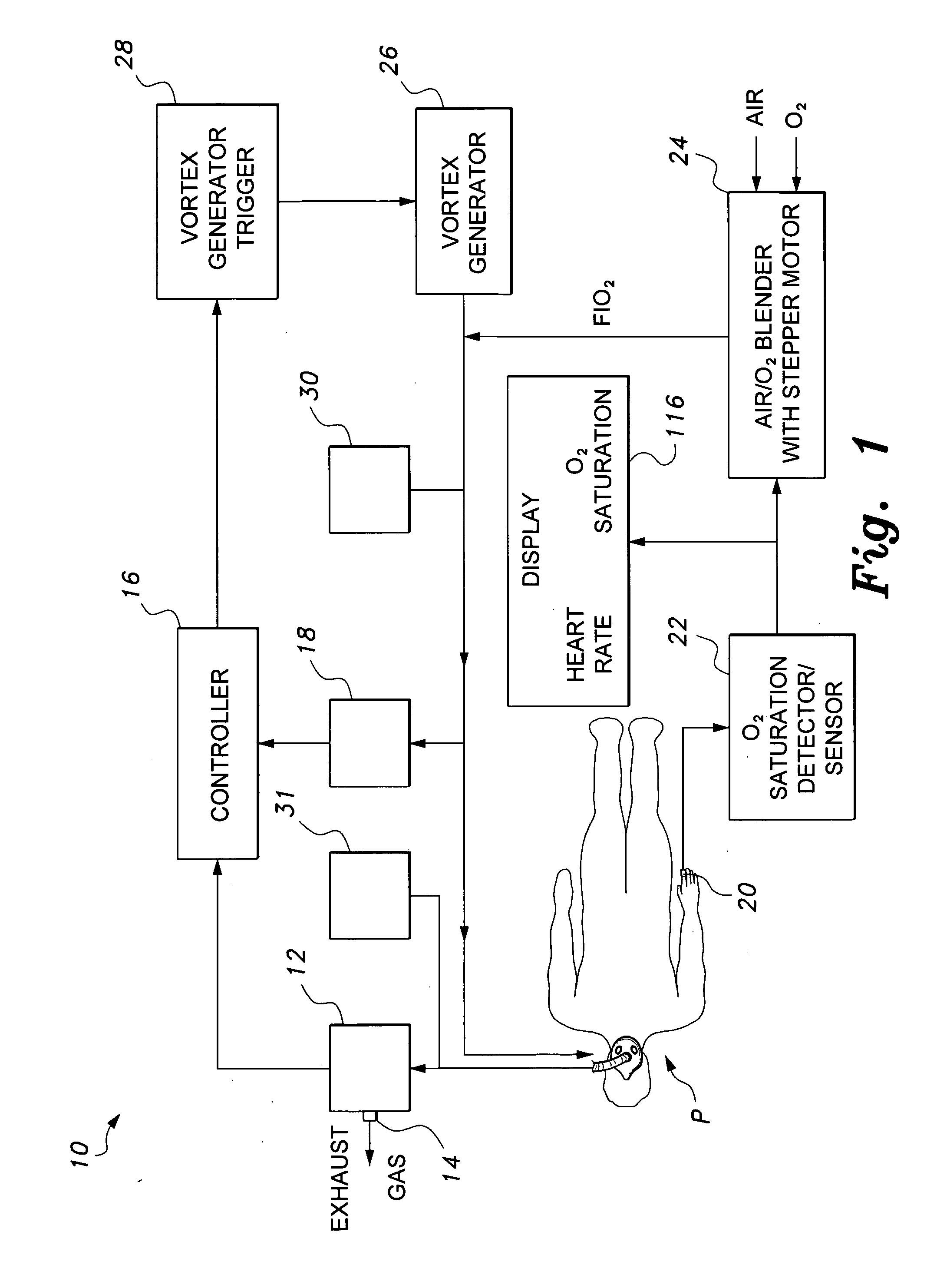
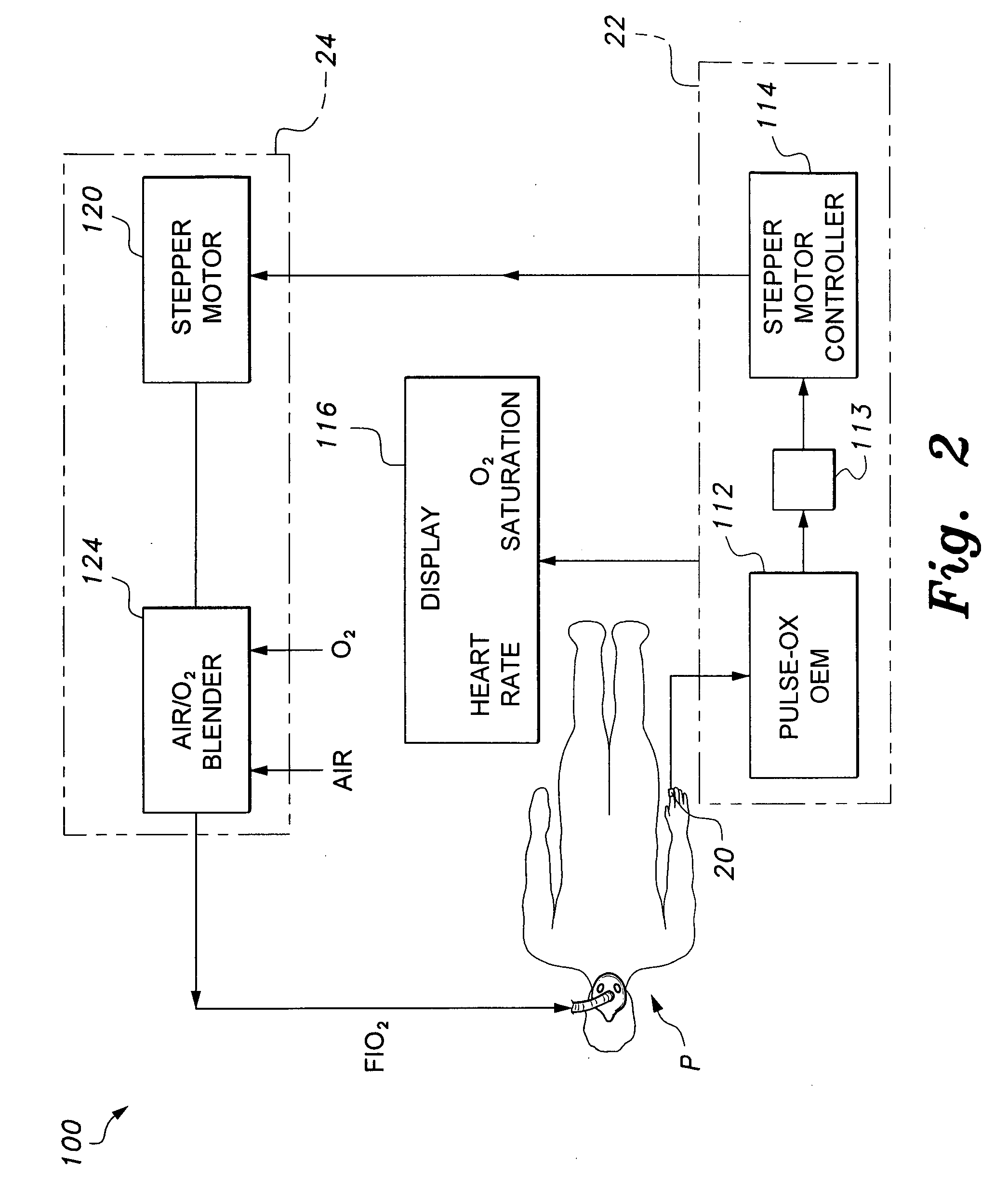
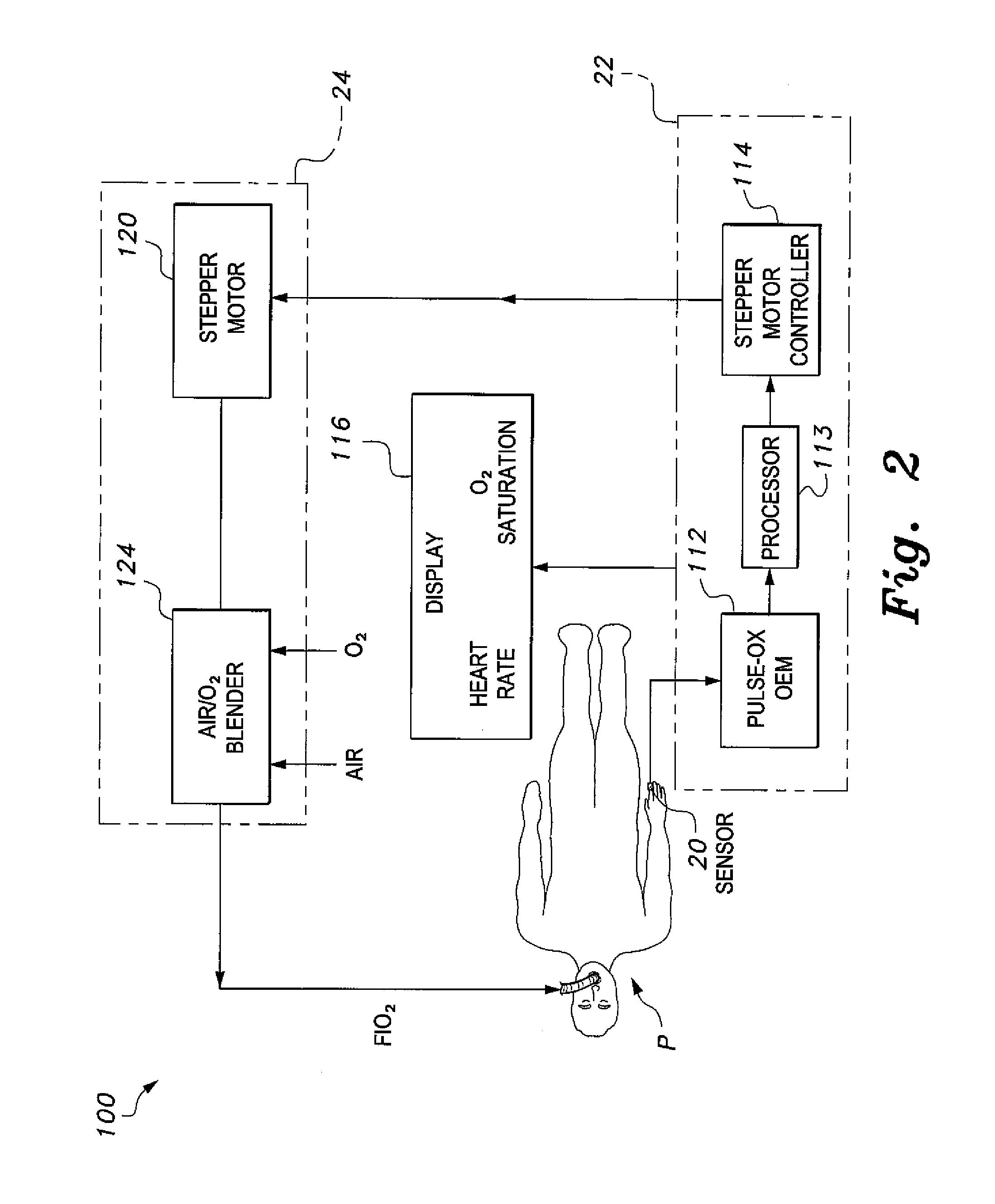
Mechanical ventilator system
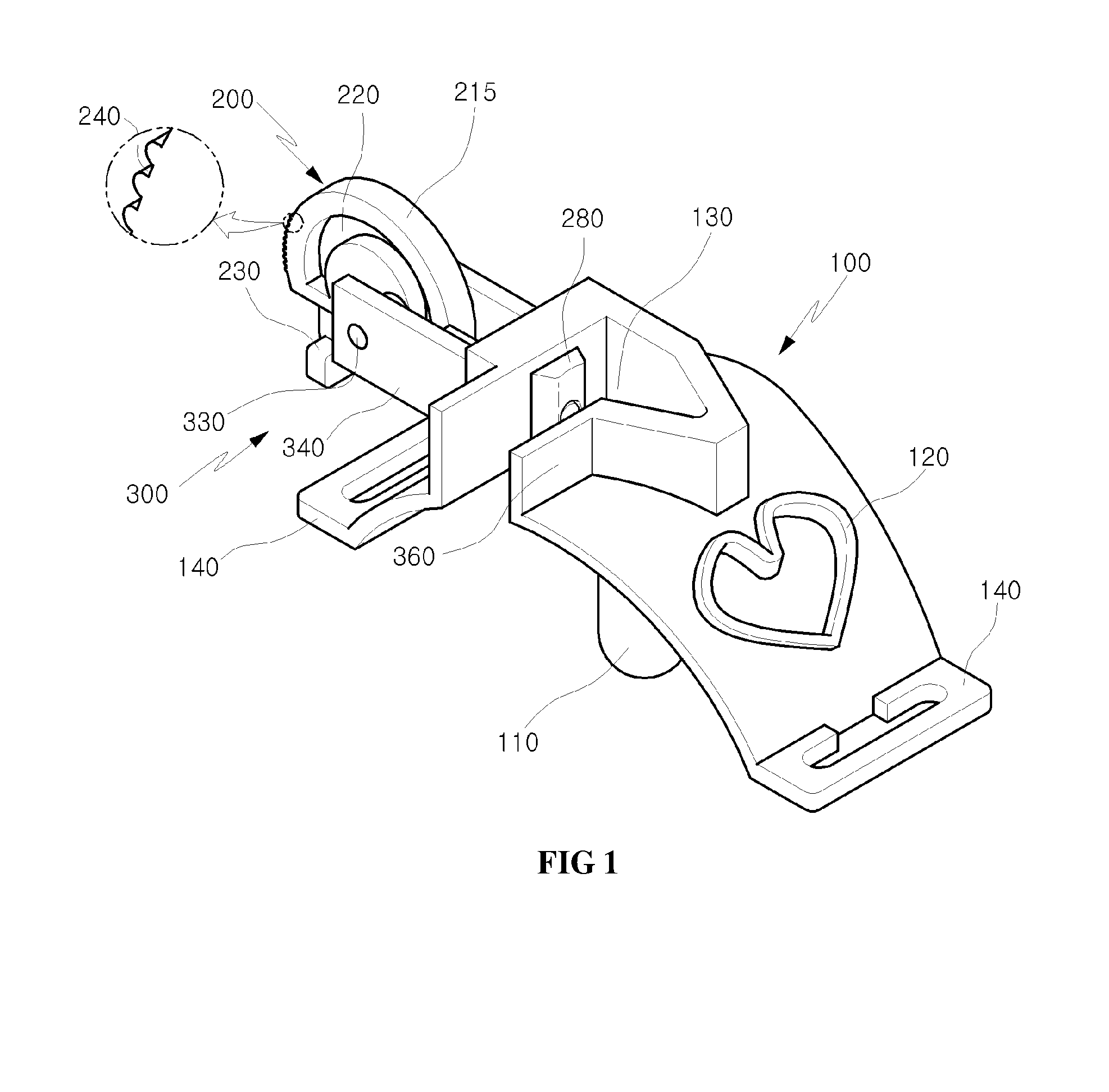
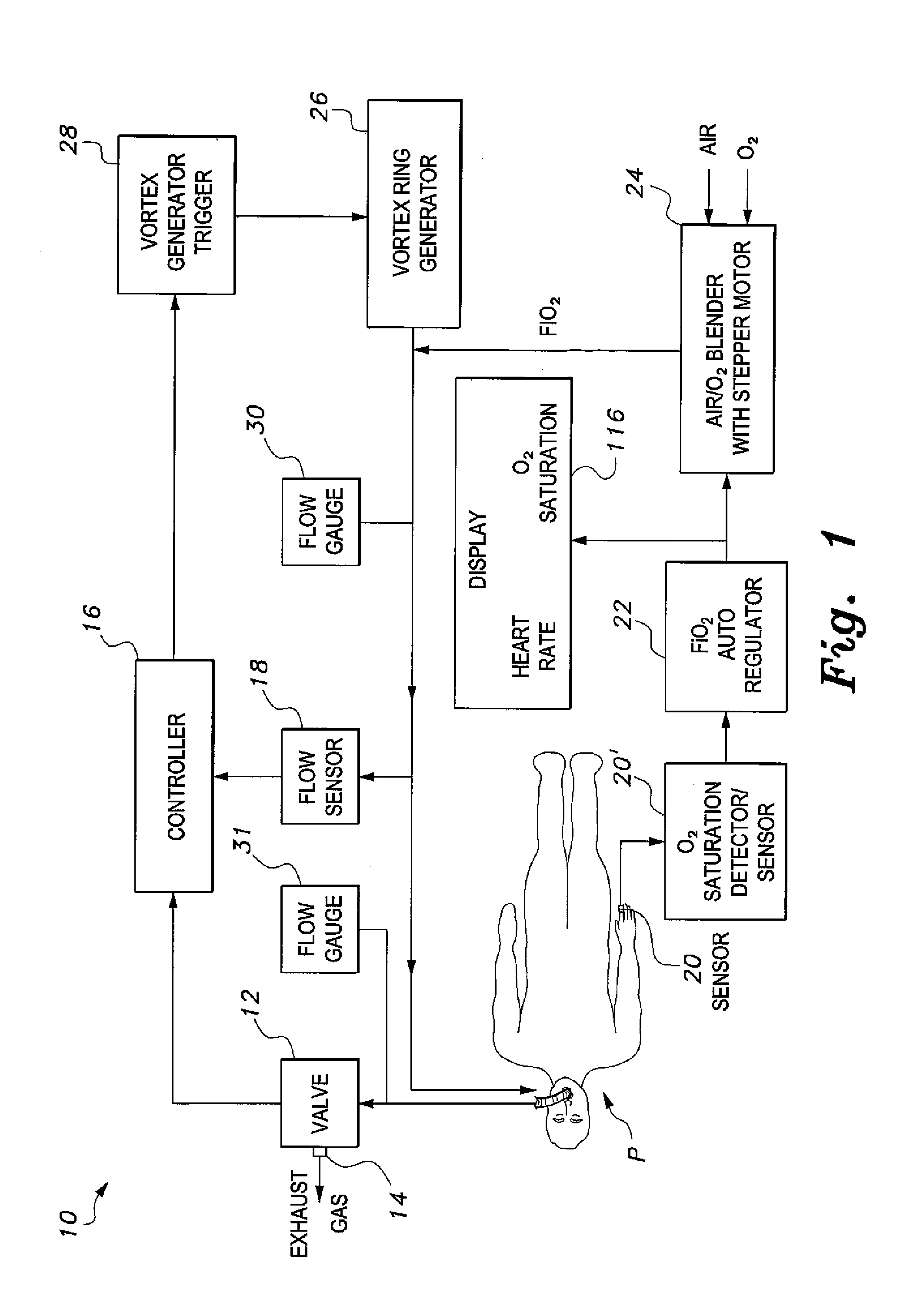
The mechanical ventilator system is a compact and portable artificial respiration system. A negative pressure vortex generator delivers an FiO2 mix from an air-oxygen blender to the patient during the patient's inhalations, but remains idle during the patient's exhalations. Exhaust gases generated by the patient are released through an exhaust gas valve. During operation, the patient's oxygen saturation level is measured by an infrared pulse-oxygen probe, and an FiO2 autoregulator is in communication with the probe to receive oxygen saturation level signals. The FiO2 autoregulator is coupled with the air-oxygen blender to control the oxygen proportion of the FiO2 mix. An automatic pressure flow sensor is fluidly coupled with the patient's airway to control actuation of the negative pressure vortex generator. The automatic flow sensor is coupled with a controller, which actuates a vortex generator trigger circuit in communication with the vortex generator.
Owner:RAO CHAMKURKISHTIAH P +1
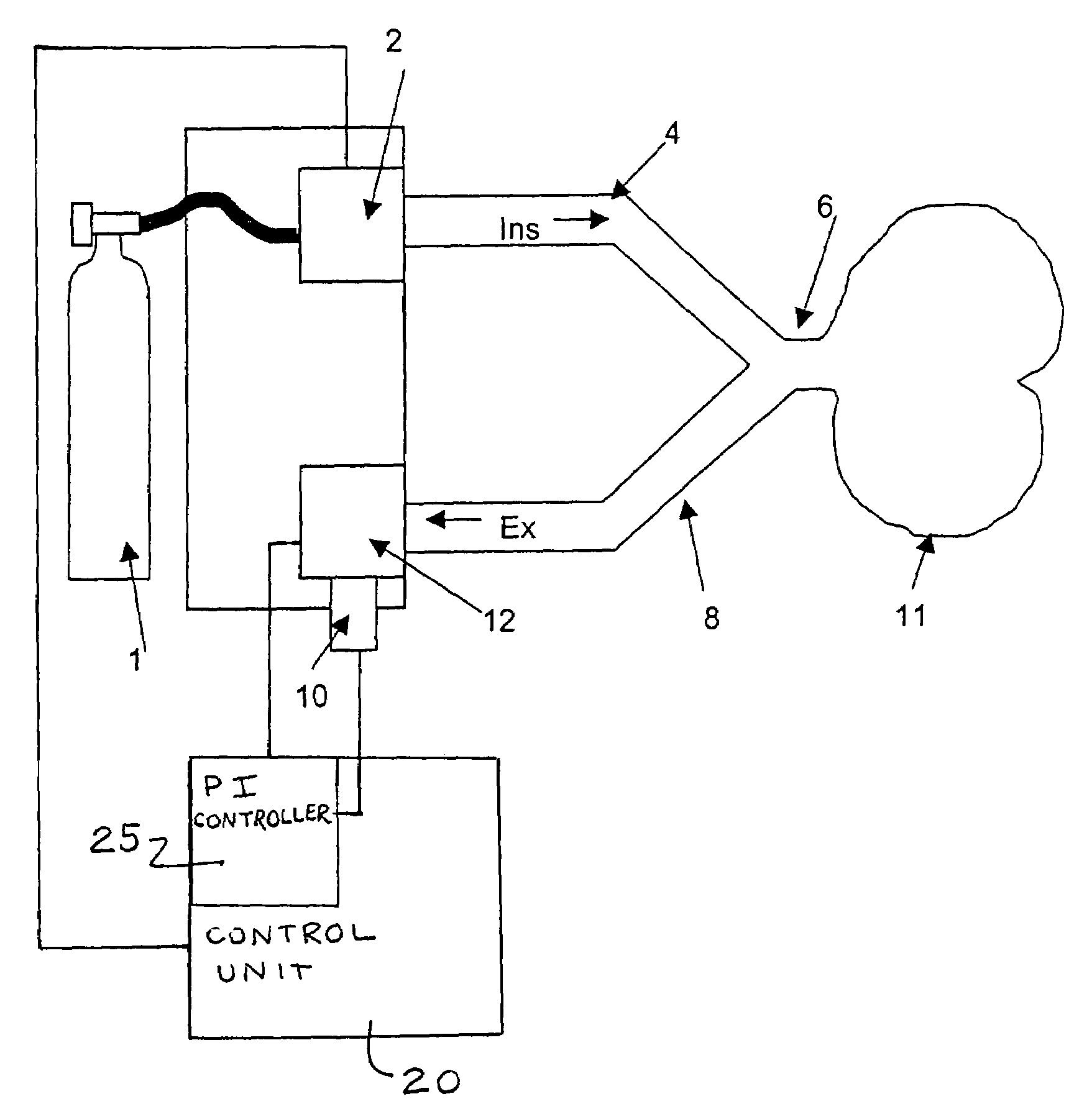
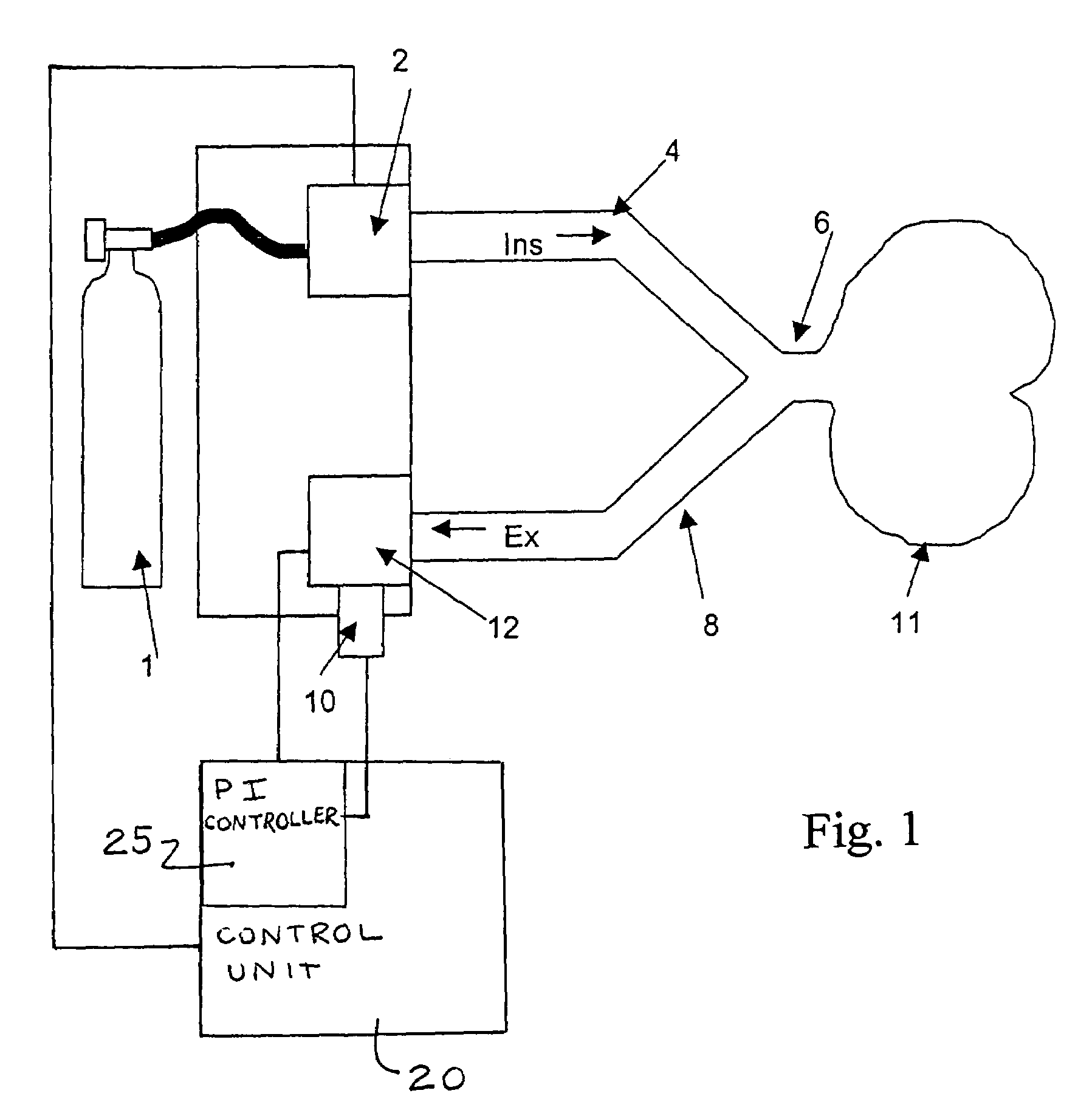
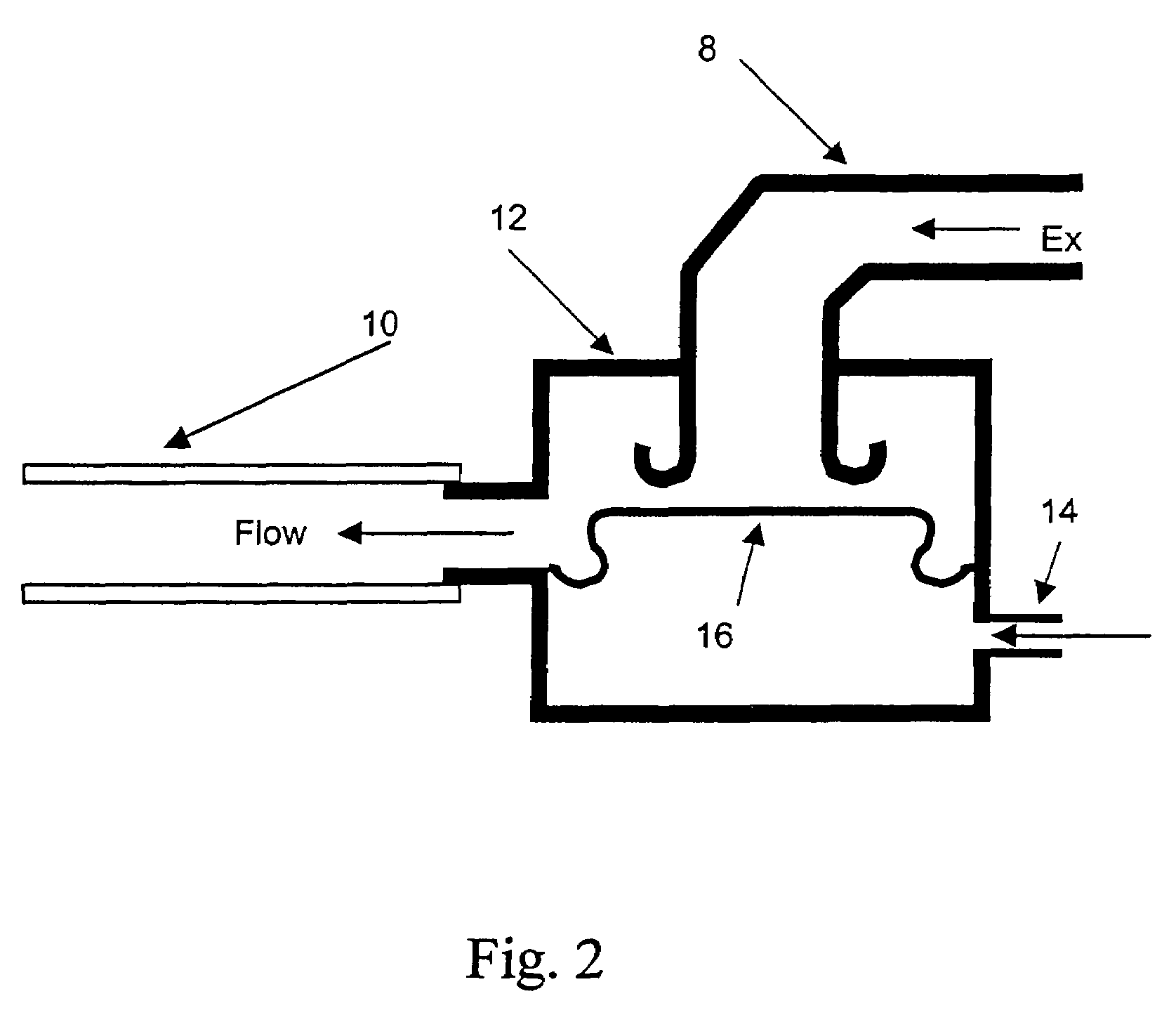
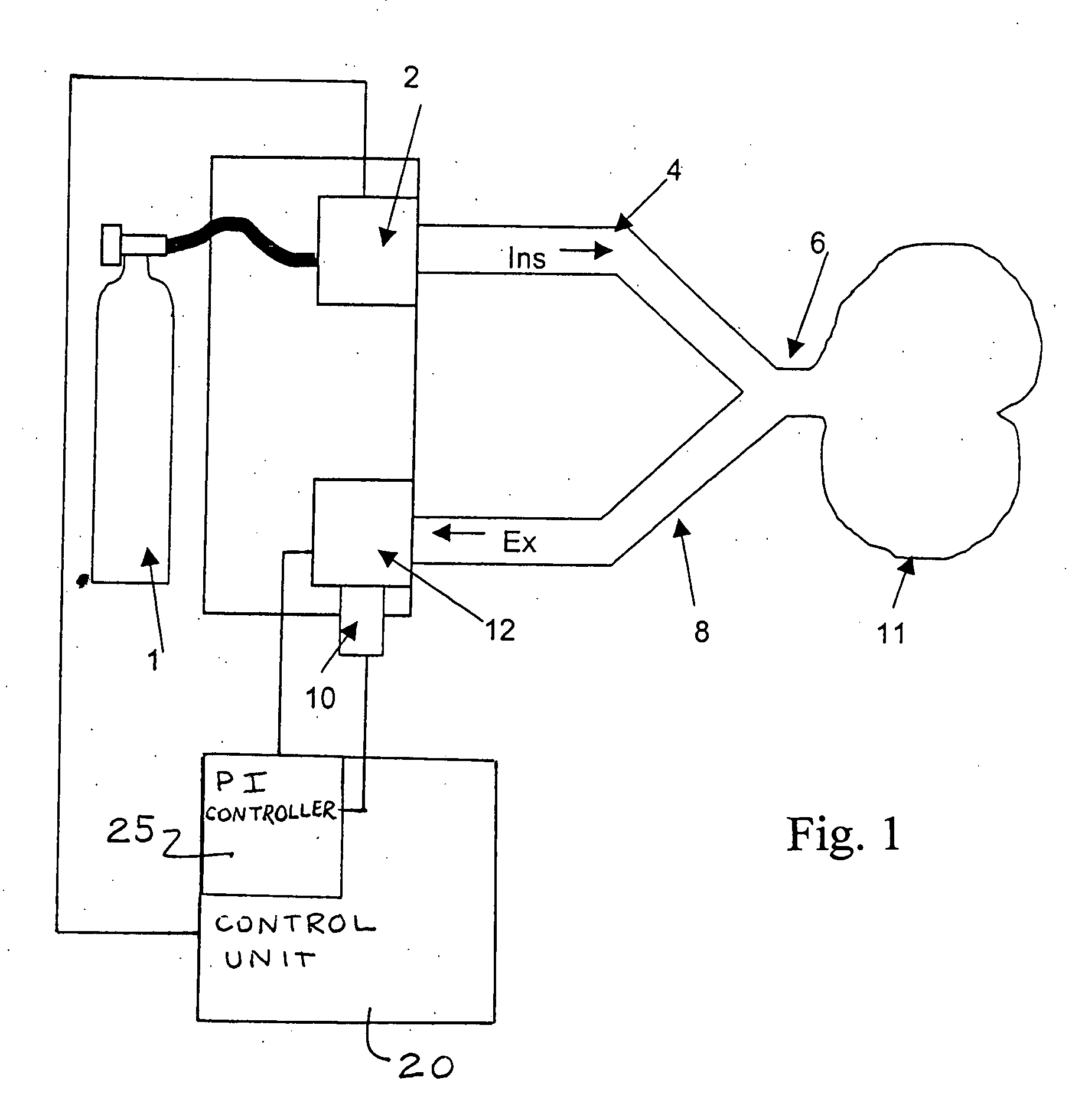
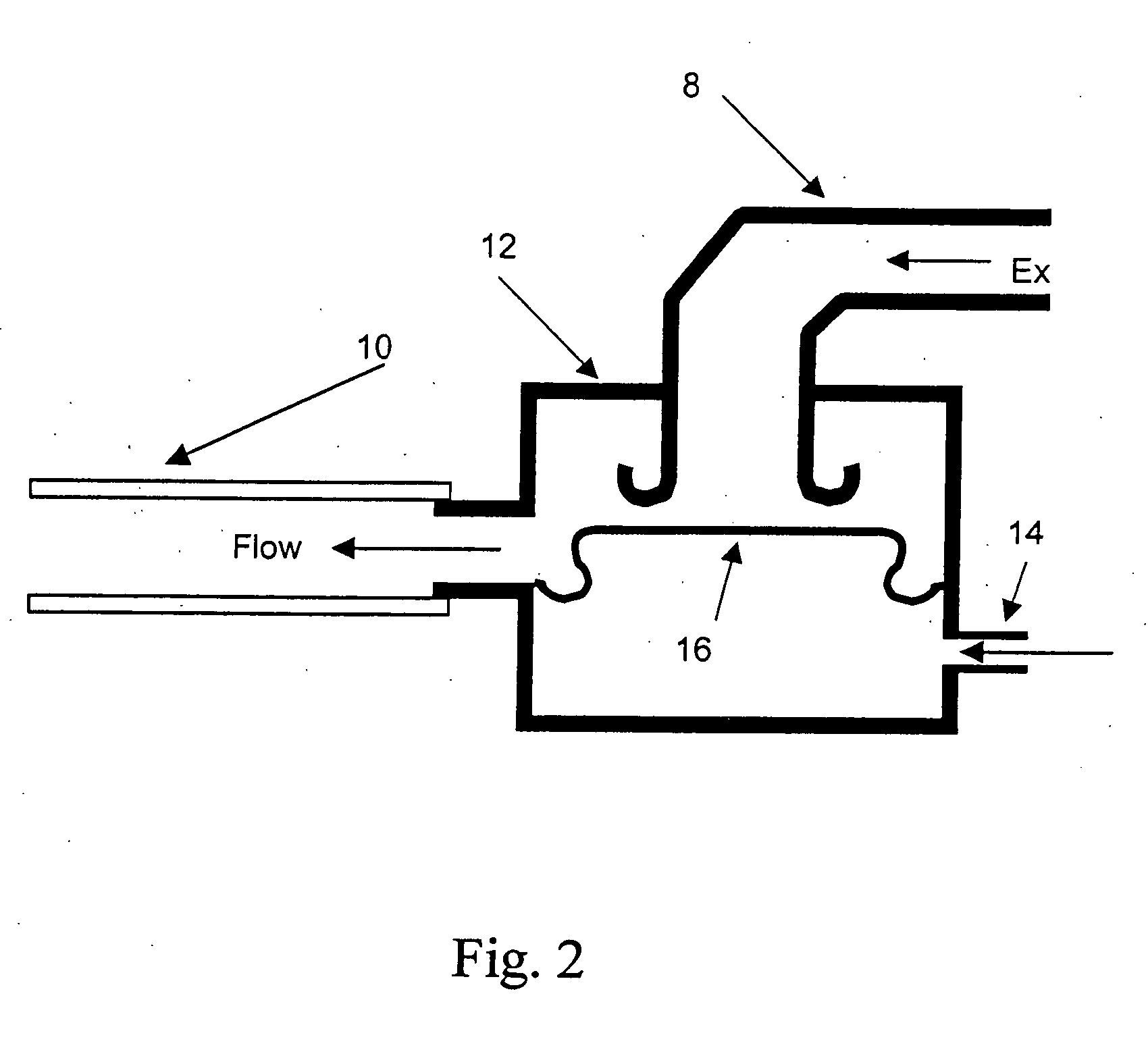
Process for the automatic recording of pressure-vs.-volume curves during artificial respiration
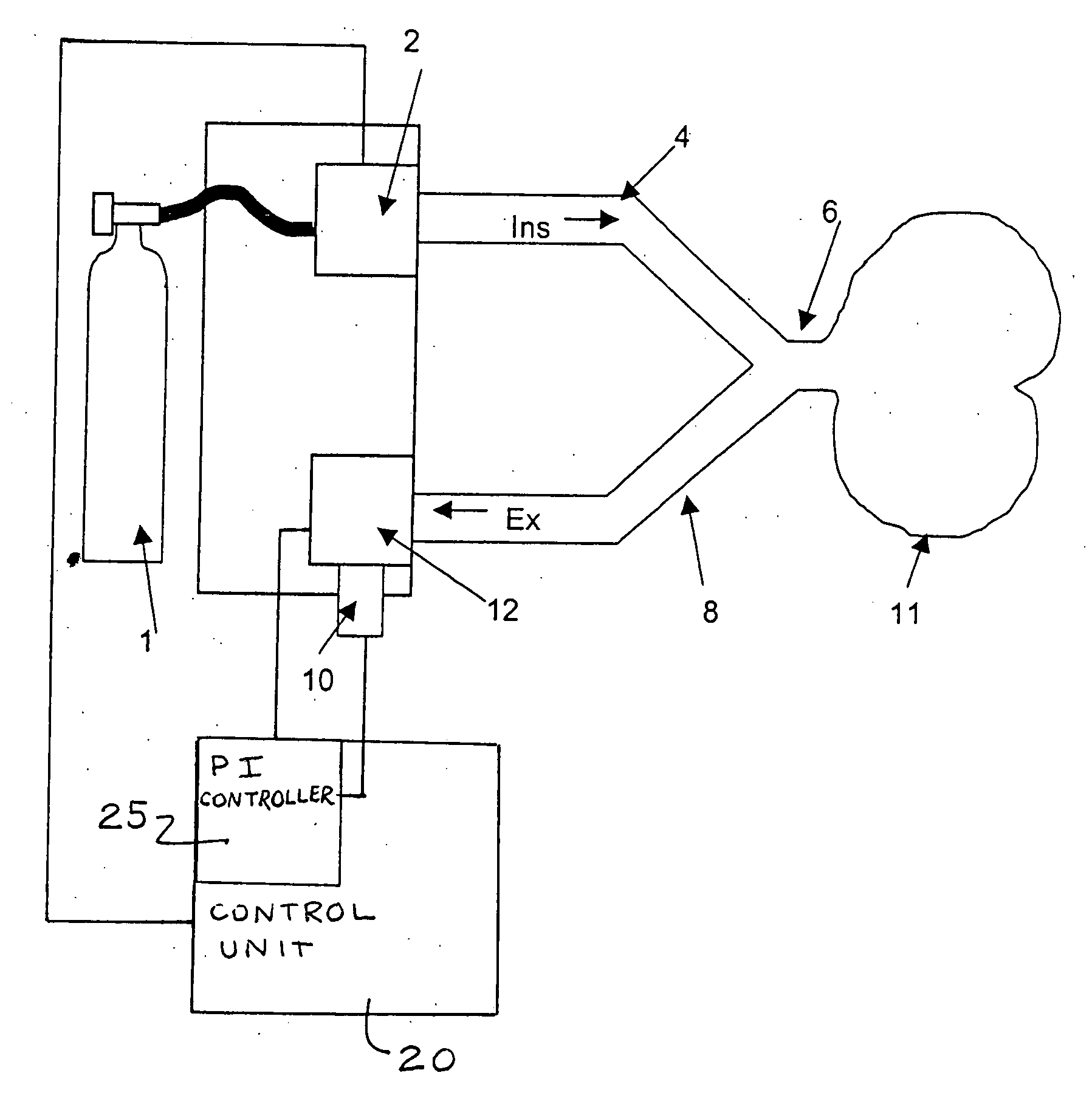
A process, system and device are provided for automatically recording pressure-vs.-volume curves during artificial respiration with a respirator. The inspiration pressure is increased during the supply of a breathing gas volume flow under the control of a control unit. The resulting breathing gas volume flow rate is detected and the volume is determined from the latter by integration. The control unit compares the breathing gas volume flow detected during the phase of expiration with a preselected set point and acts on an expiration valve (12) in the expiration line (8) by means of a controller in case of deviation from the set point in order to return the breathing gas volume flow to the set point.
Owner:DRAGERWERK AG
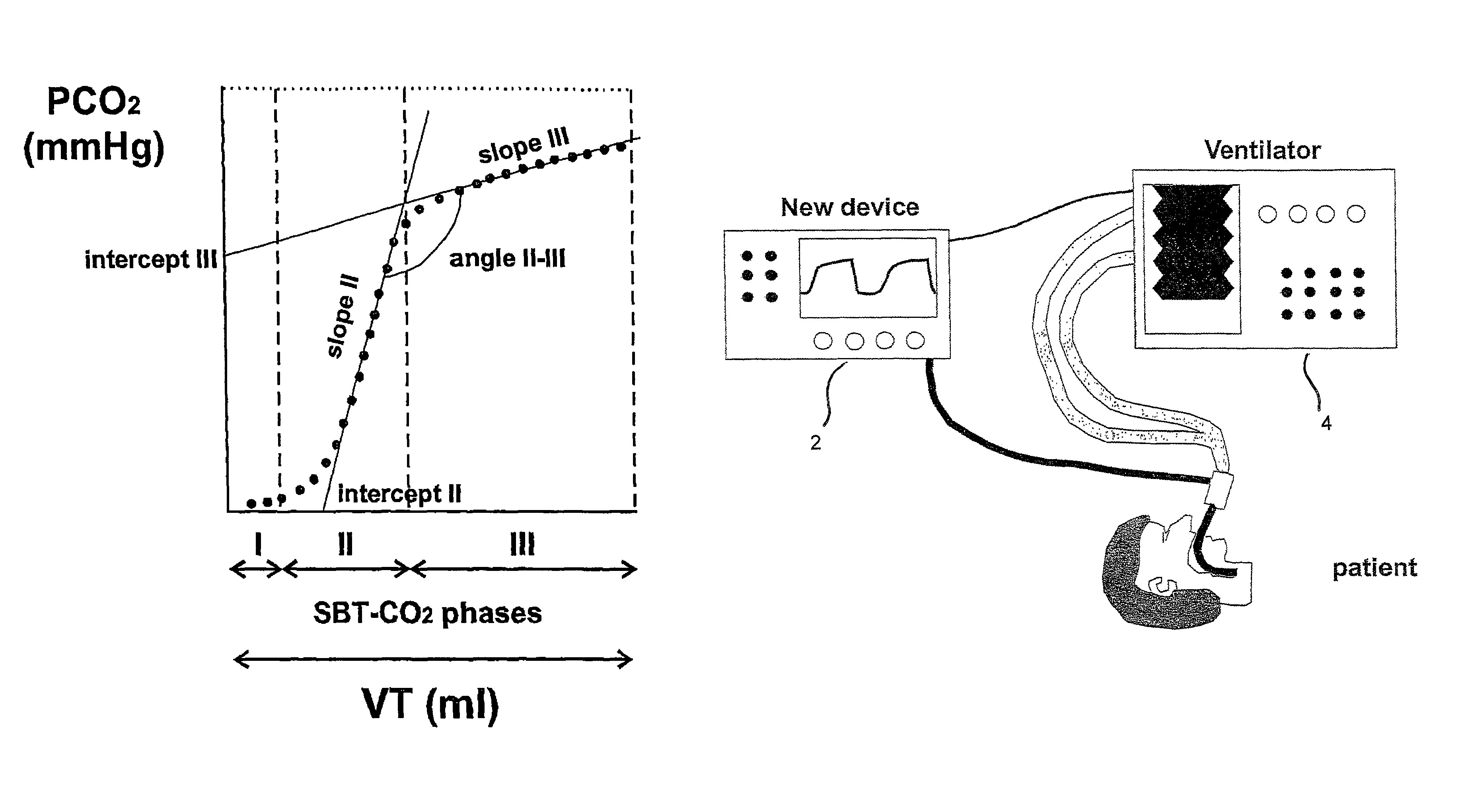
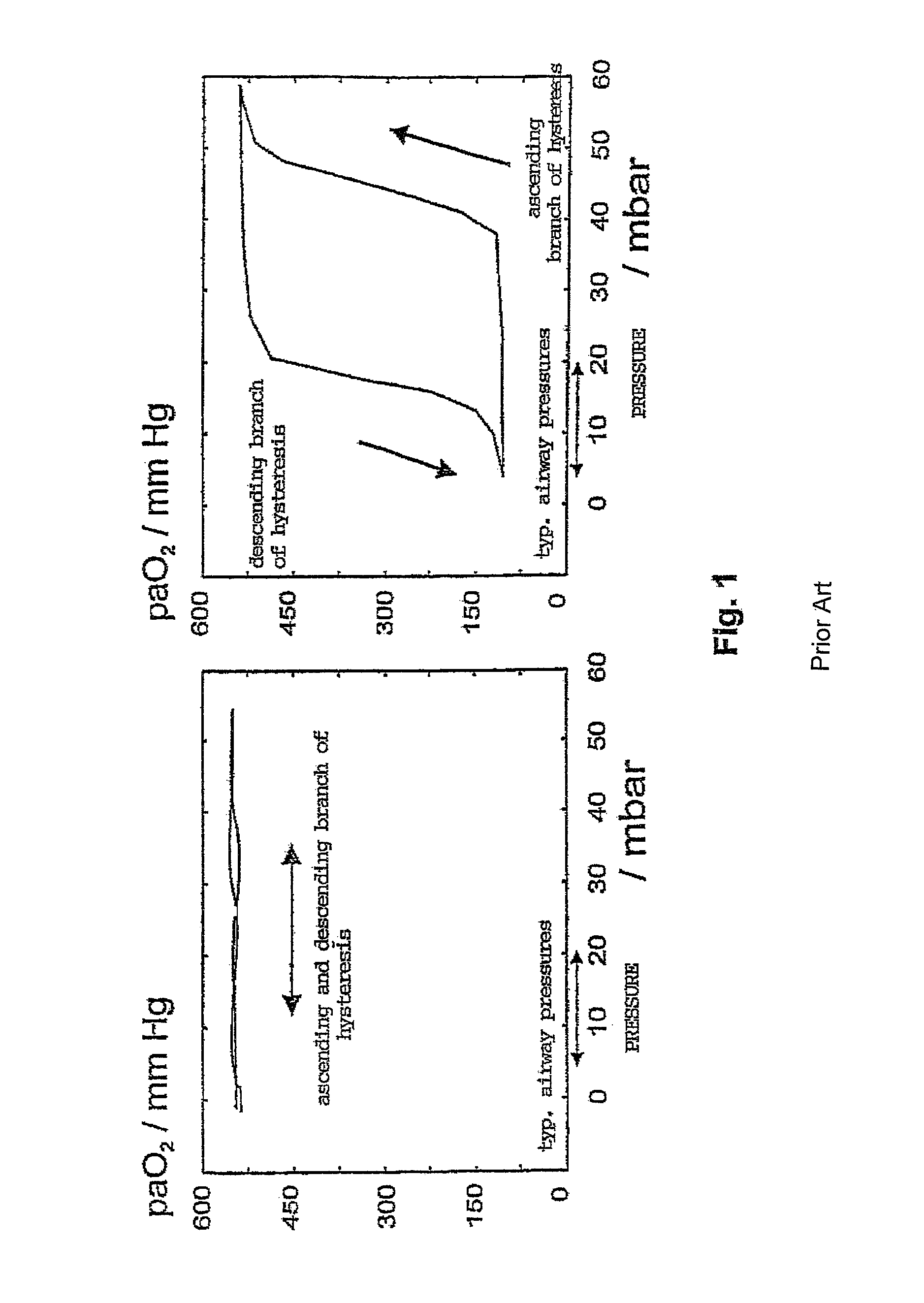
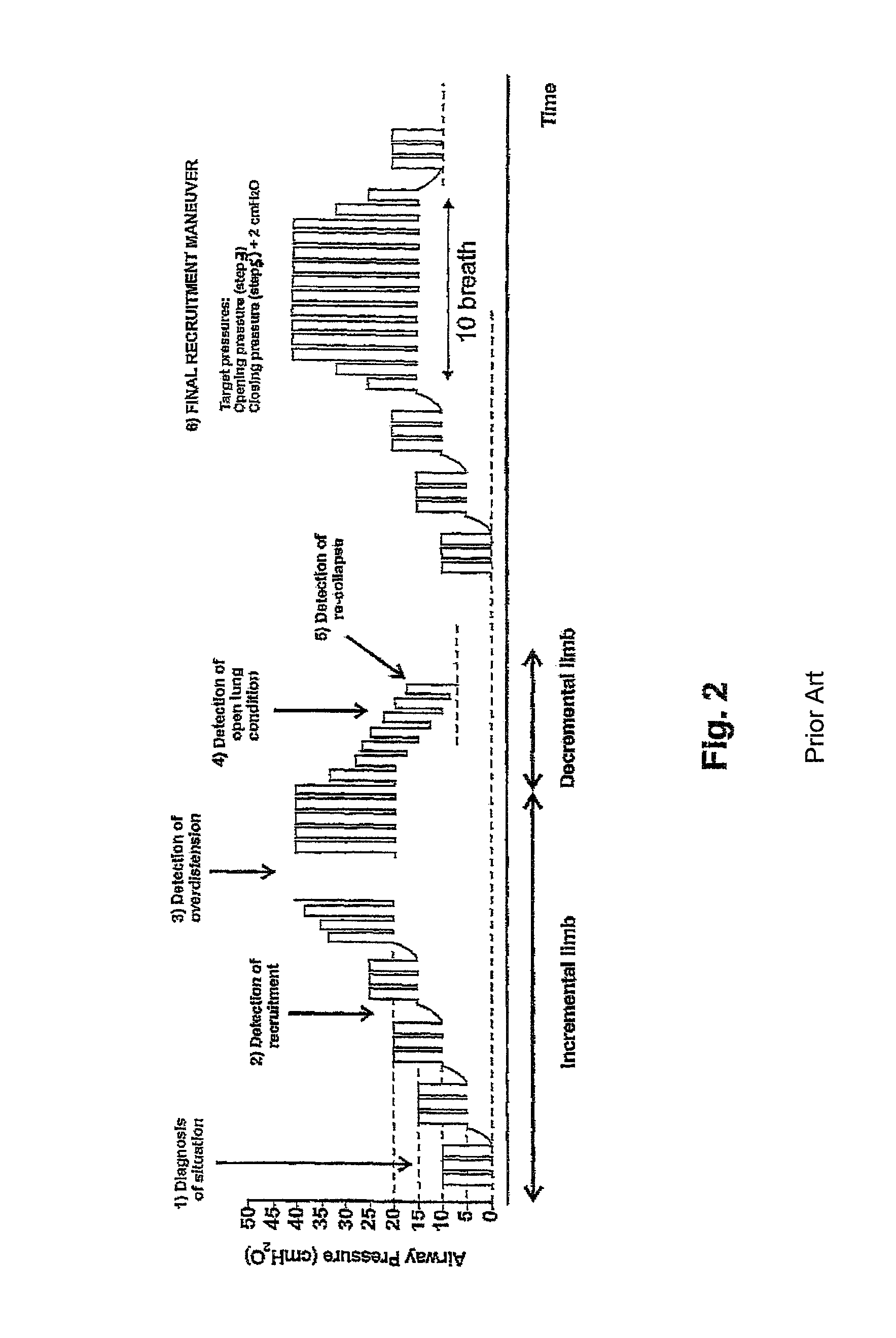
Non-invasive method and apparatus for optimizing the respiration of atelectatic lungs
ActiveUS9173595B2Improve accuracyReduce pressureRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesLung alveolusNon invasive
Method for providing ventilatory settings with regard to the airway pressure levels of an artificial ventilator, the artificial ventilator is connected to a lung, including the steps of obtaining data samples of a gas concentration of the expired gas over a single breath; selecting a plurality of data samples from the obtained data samples; calculating a tracing value being sensitive to changes of alveolar dead space on the basis of the selected data samples; repeating steps a), b) and c) for obtaining a plurality of tracing values; and changing at least one airway pressure level of the artificial ventilator, wherein from an observation of a resulting course of the plurality of calculated tracing values an airway pressure level at which alveolar opening or lung overdistension or lung open condition or alveolar closing occurs is detected. Apparatus for providing ventilatory settings with regard to the airway pressure levels of an artificial ventilator is also disclosed.
Owner:SALVIA MEDICAL
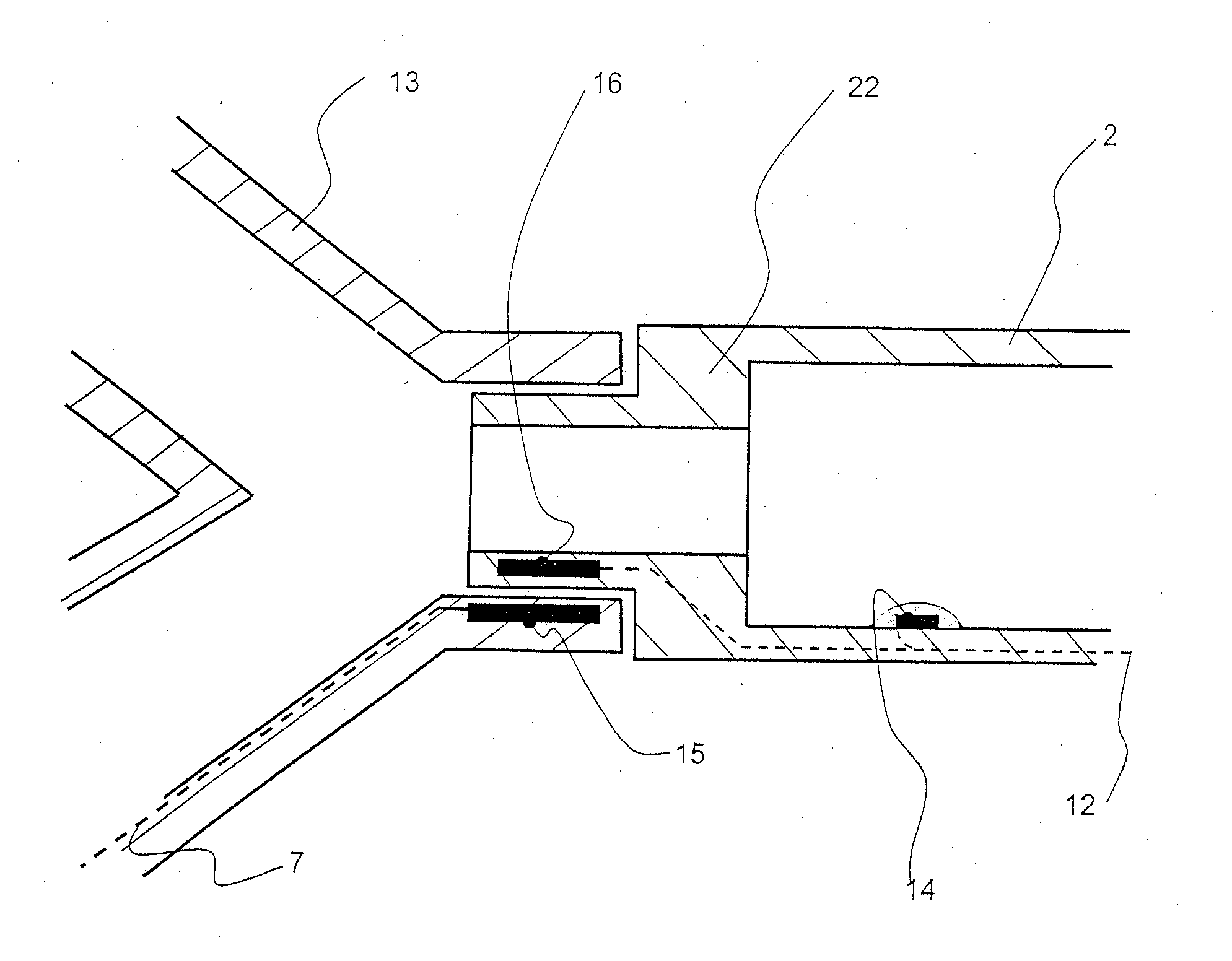
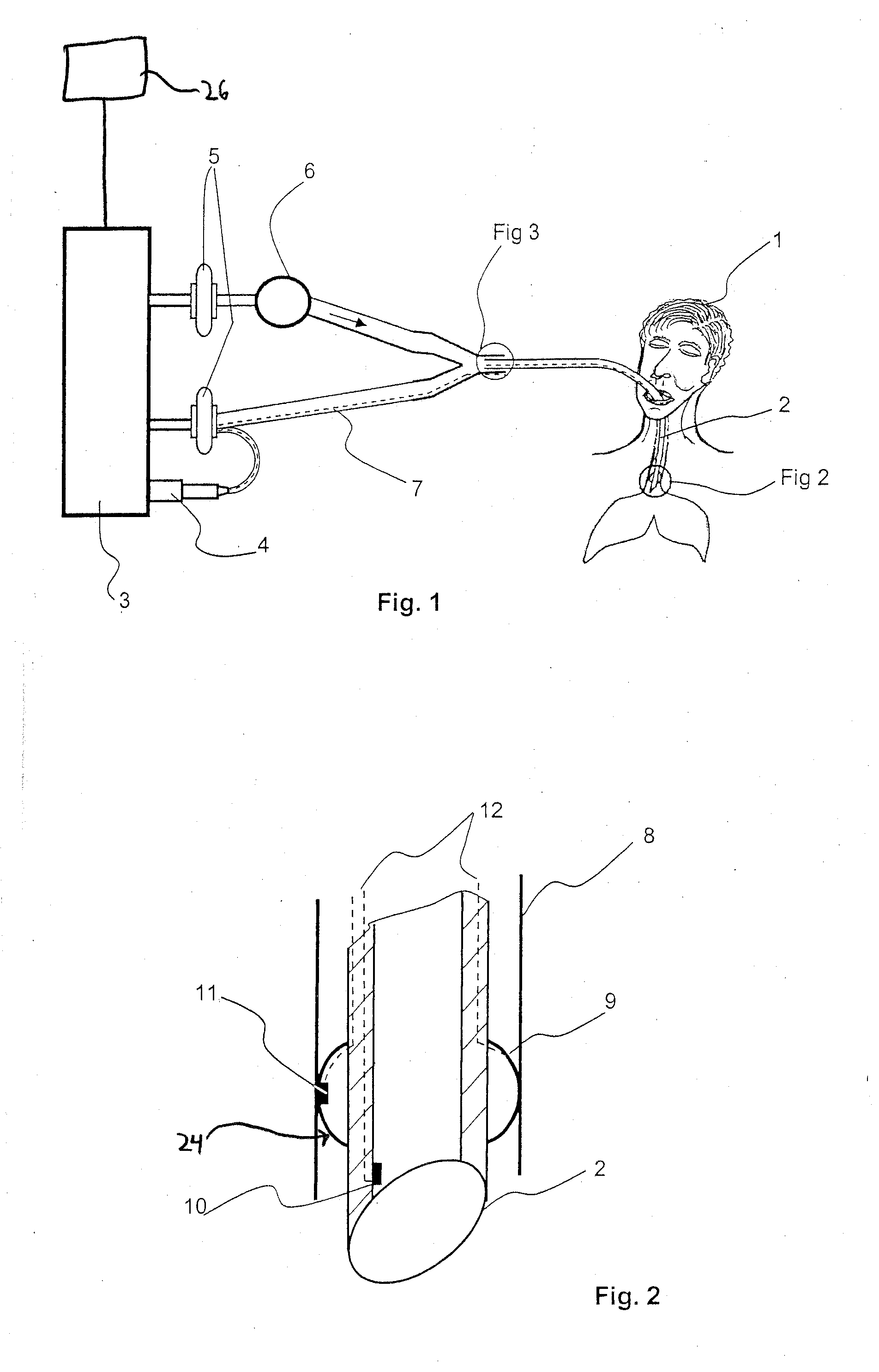
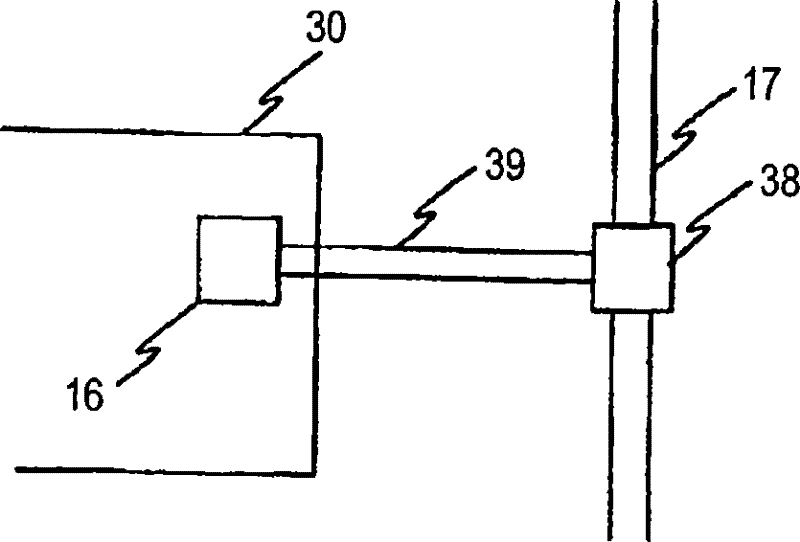
Patient connection for the artificial respiration of a patient
A breathing gas-carrying patient connection (2) for the artificial respiration of a patient (1) by means of an anesthesia apparatus or respirator (3) with one or more sensors (9, 10, 11) for detecting patient-relevant measured variables and with means for the telemetric transmission of the sensor data from the patient connection (2) to a machine-side connection element (13) for the patient connection (2), wherein the means for the telemetric transmission of the sensor data are designed for wireless bidirectional communication between the patient connection (2) and the connection element (13), makes possible the reliable transmission of data into the machine-side connection element (13).
Owner:DRAGERWERK AG
Cardiopulmonary resuscitation unit control apparatus
InactiveUS20090187123A1Easy constructionControl pressureRespiratorsElectrotherapyControl signalEmergency medicine
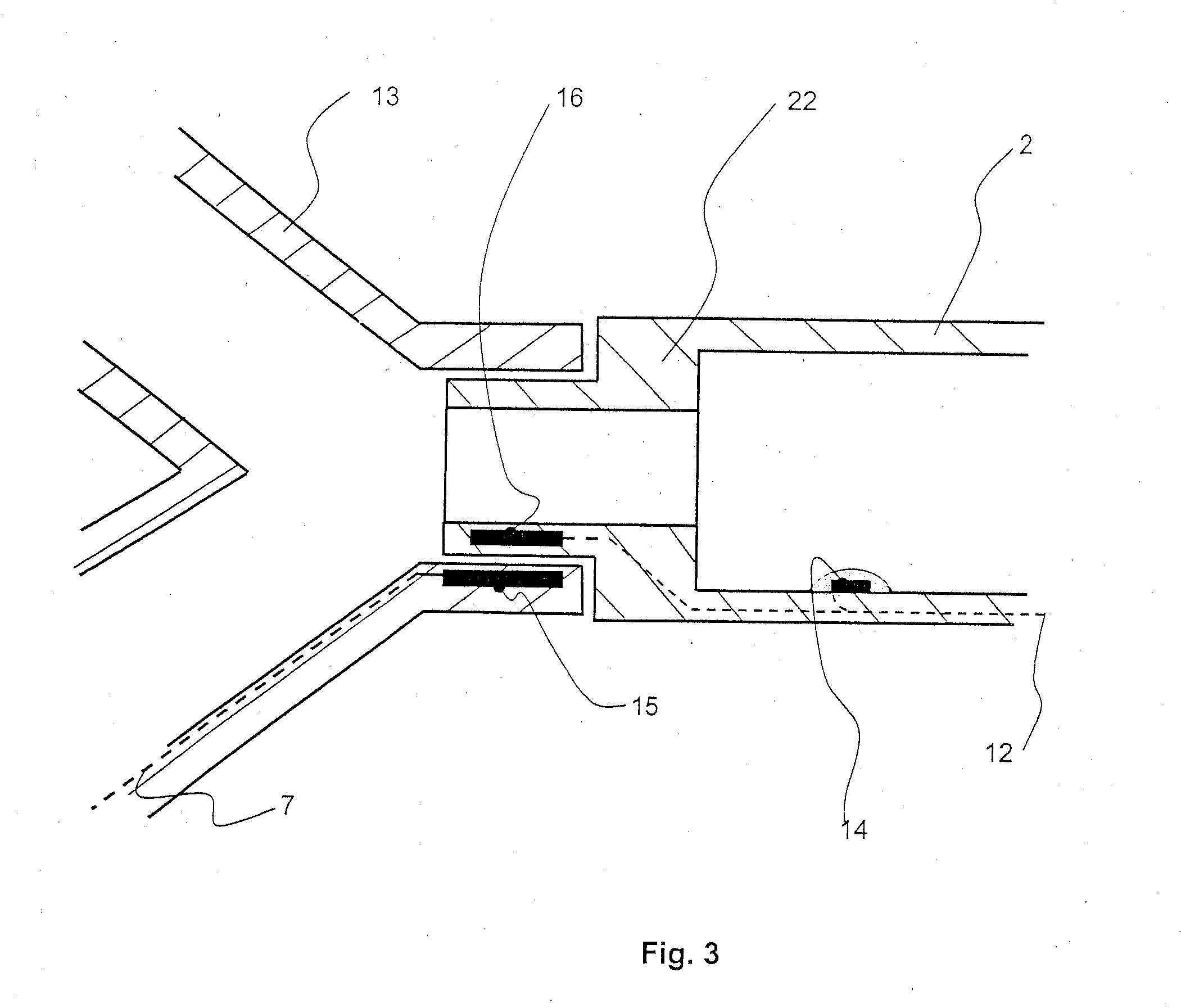
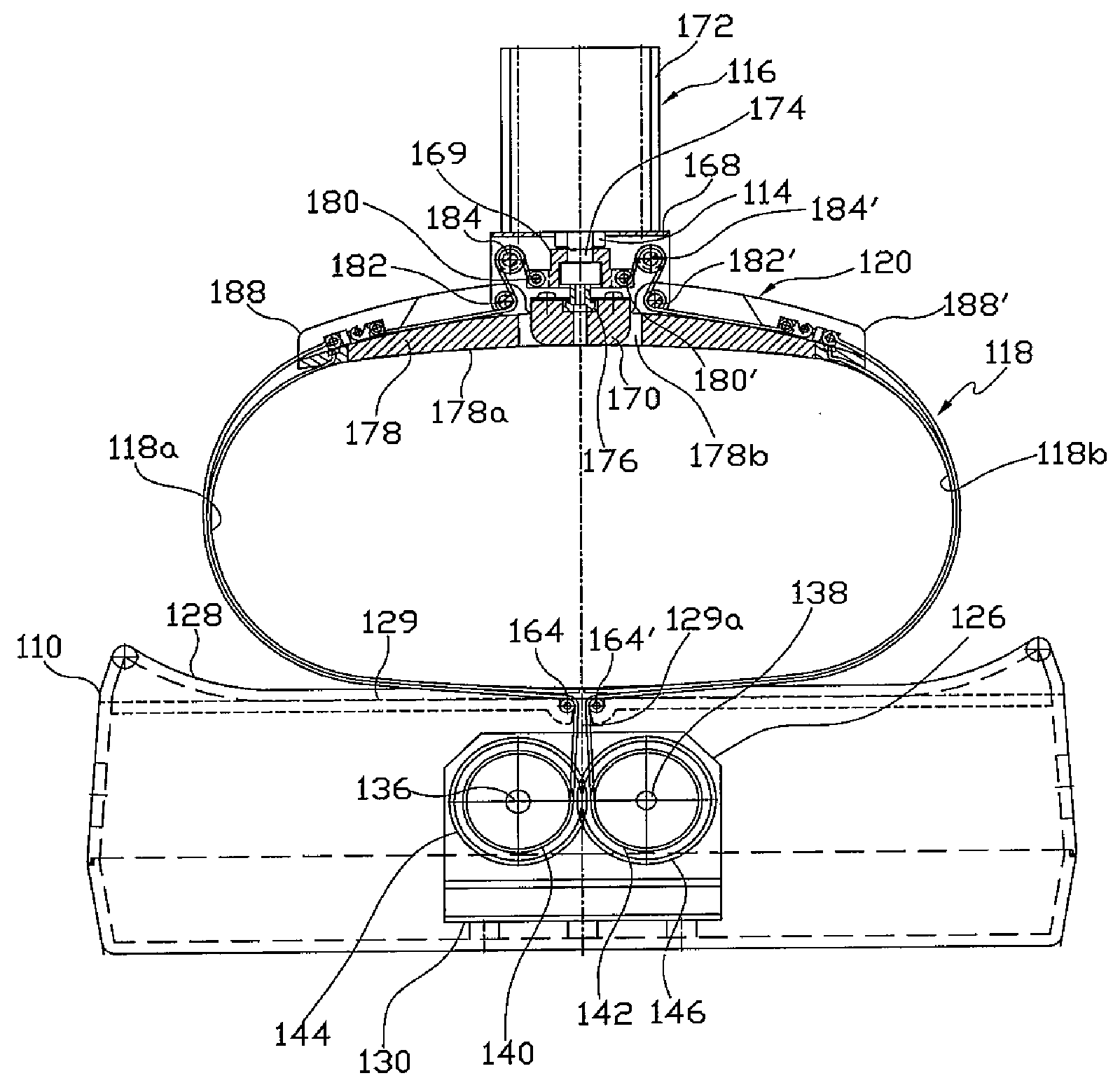
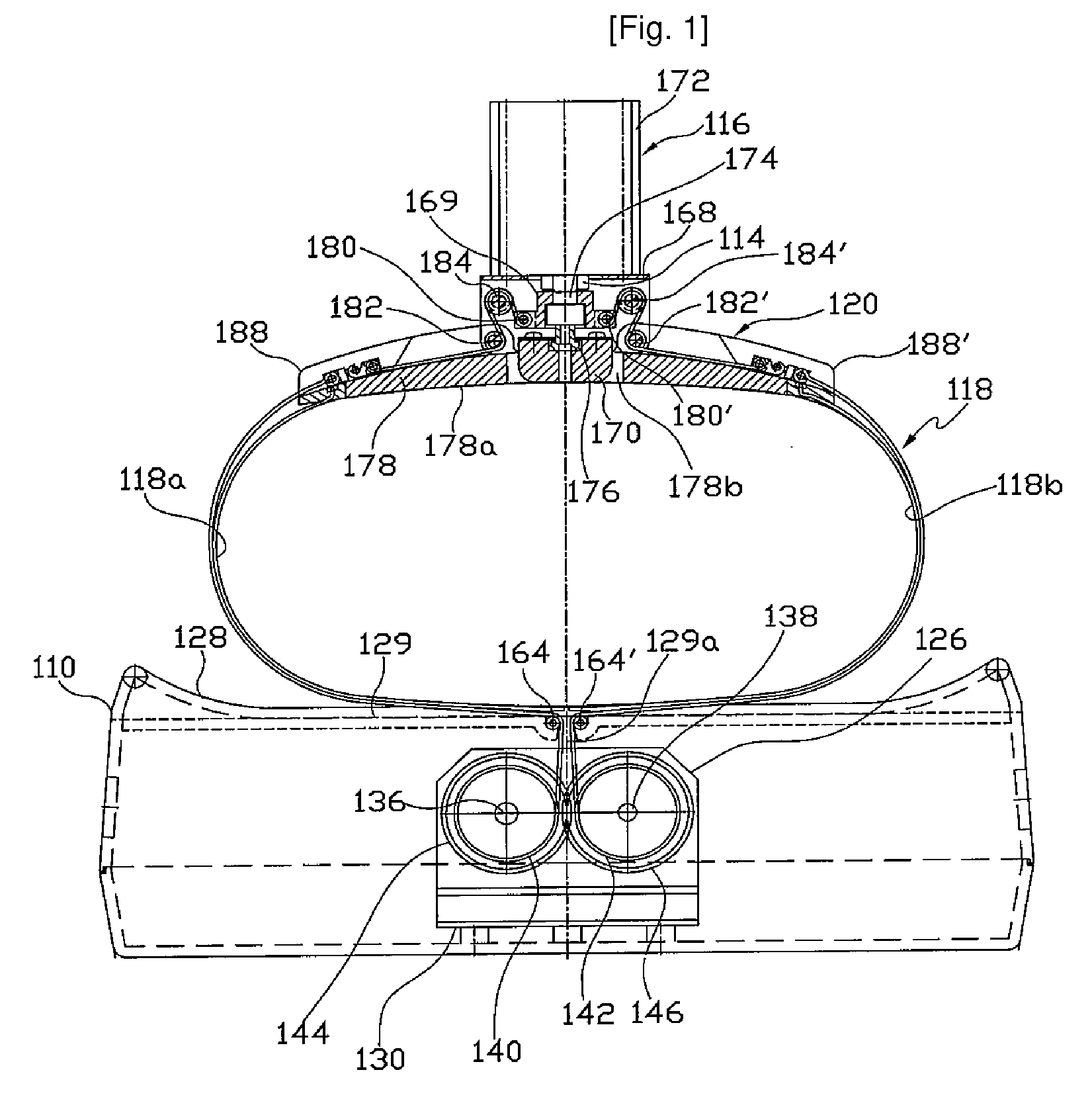
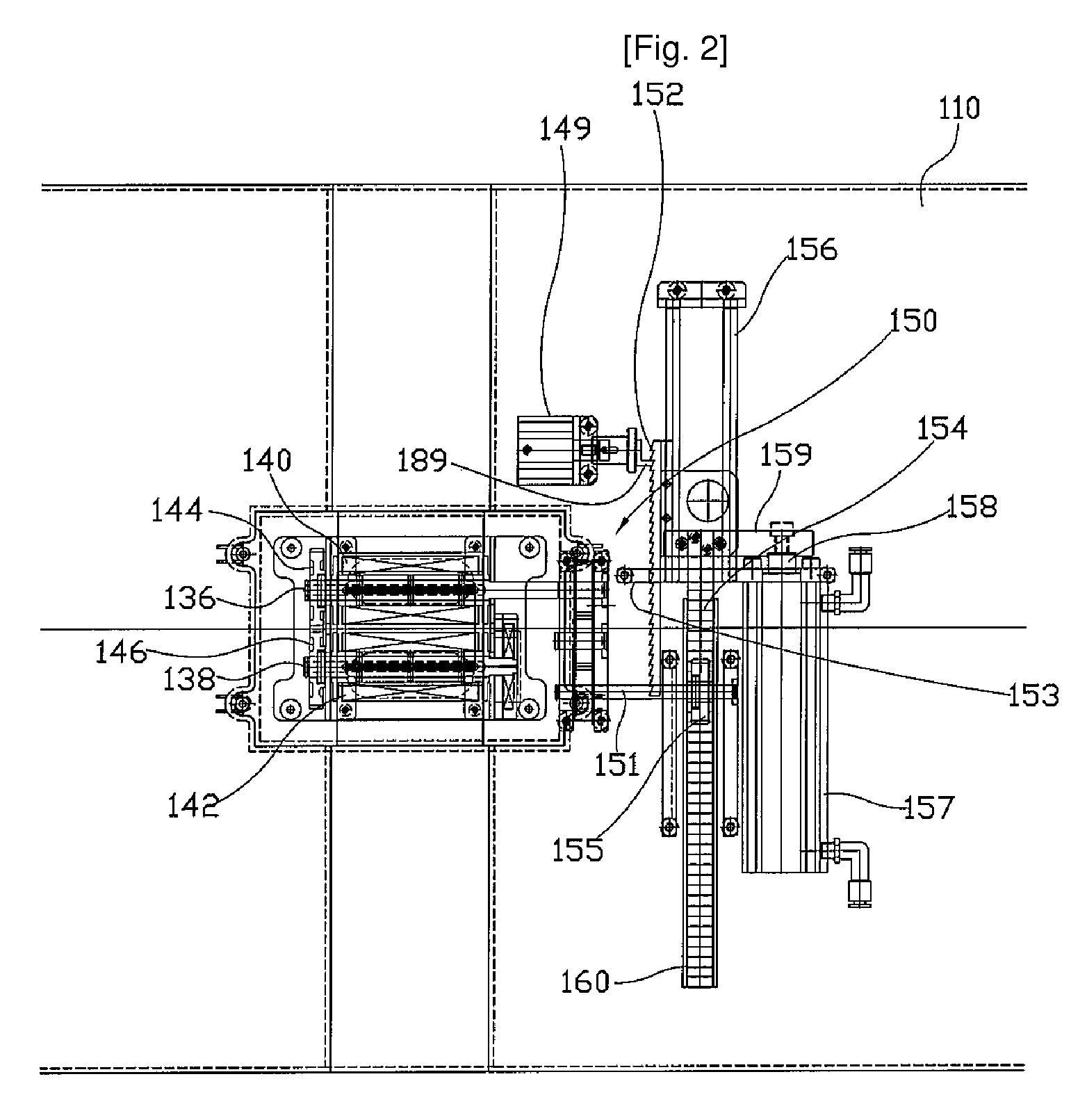
The present invention relates to a controller for a cardiopulmonary resuscitation apparatus. Automation and precise control can be realized in the cardiopulmonary resuscitation apparatus by using a driving unit involving in constricting the chest band of the cardiopulmonary resuscitation apparatus, locking, and pressing the chest by air pressure, and a control unit controlling the driving unit according to a control signal. Further, air pressure used in driving the cardiopulmonary resuscitation apparatus is controlled so as to be also supplied to a line of artificial respiration, such that a simple construction of the cardiopulmonary resuscitation apparatus and automation of artificial respiration are obtained. Thanks to the present invention, the operator does not have to care about the operation of the cardiopulmonary resuscitation apparatus while performing cardiopulmonary resuscitation, which allows the operator pay more attention to taking care of a patient.
Owner:HUMED +1
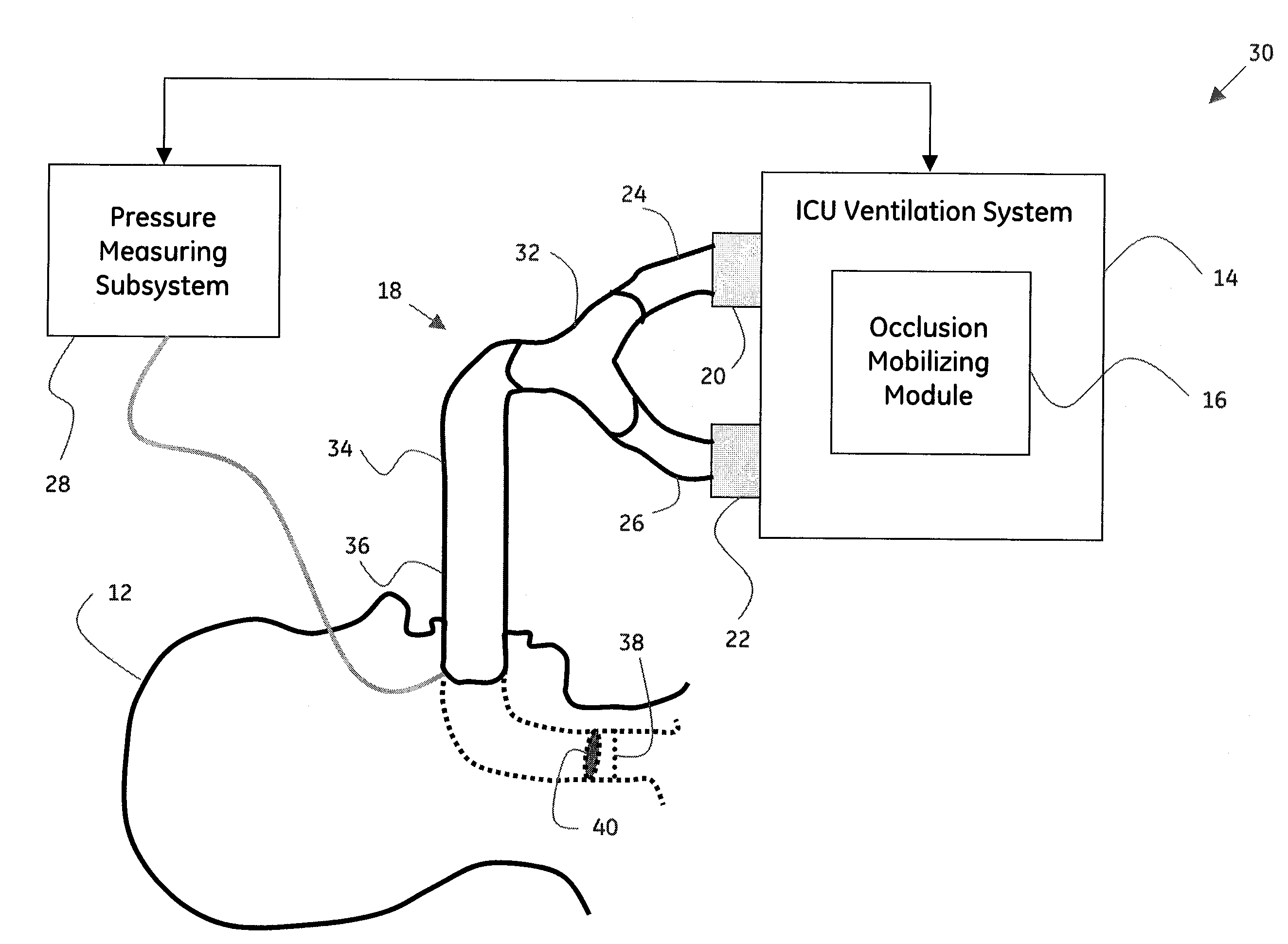
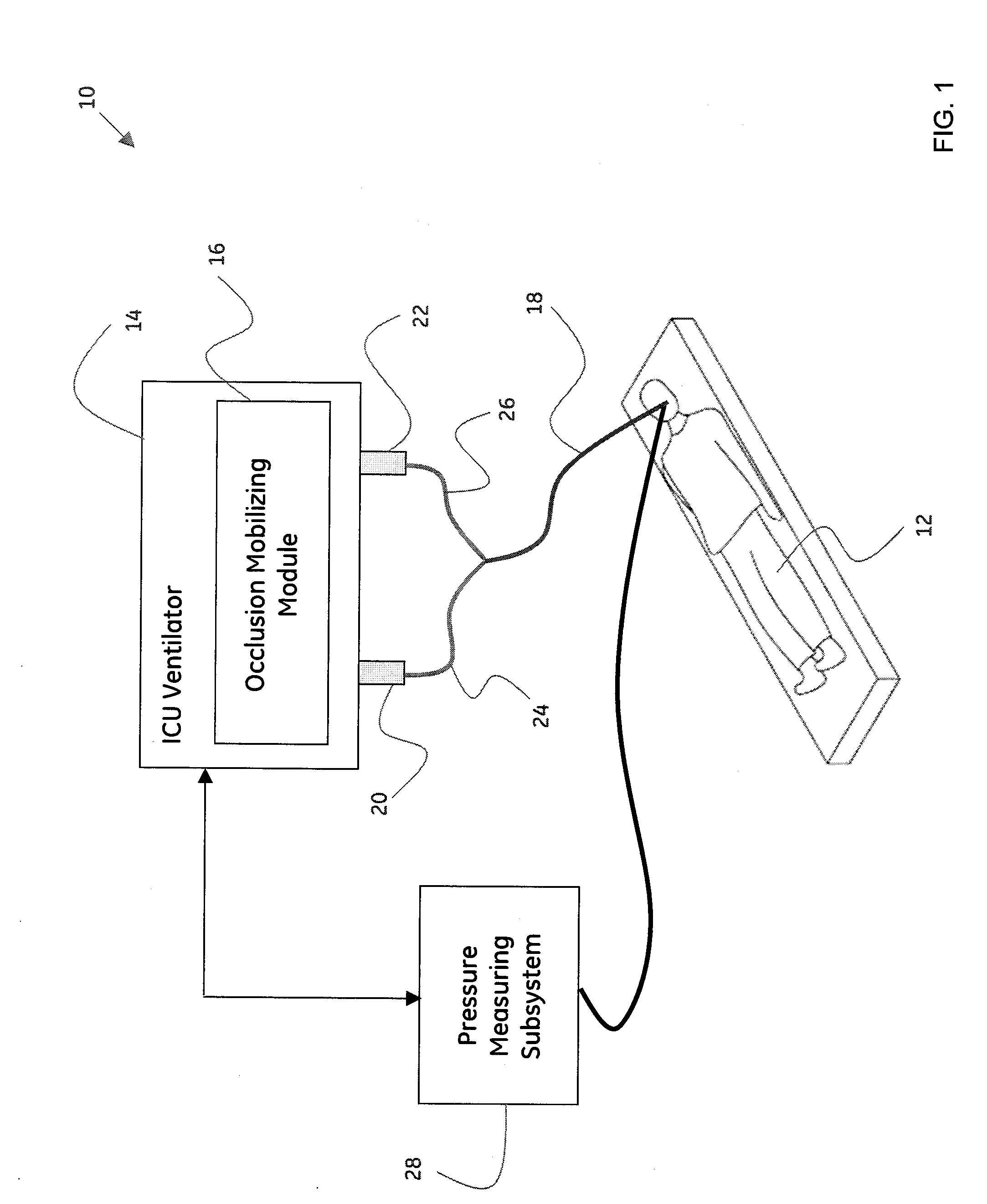
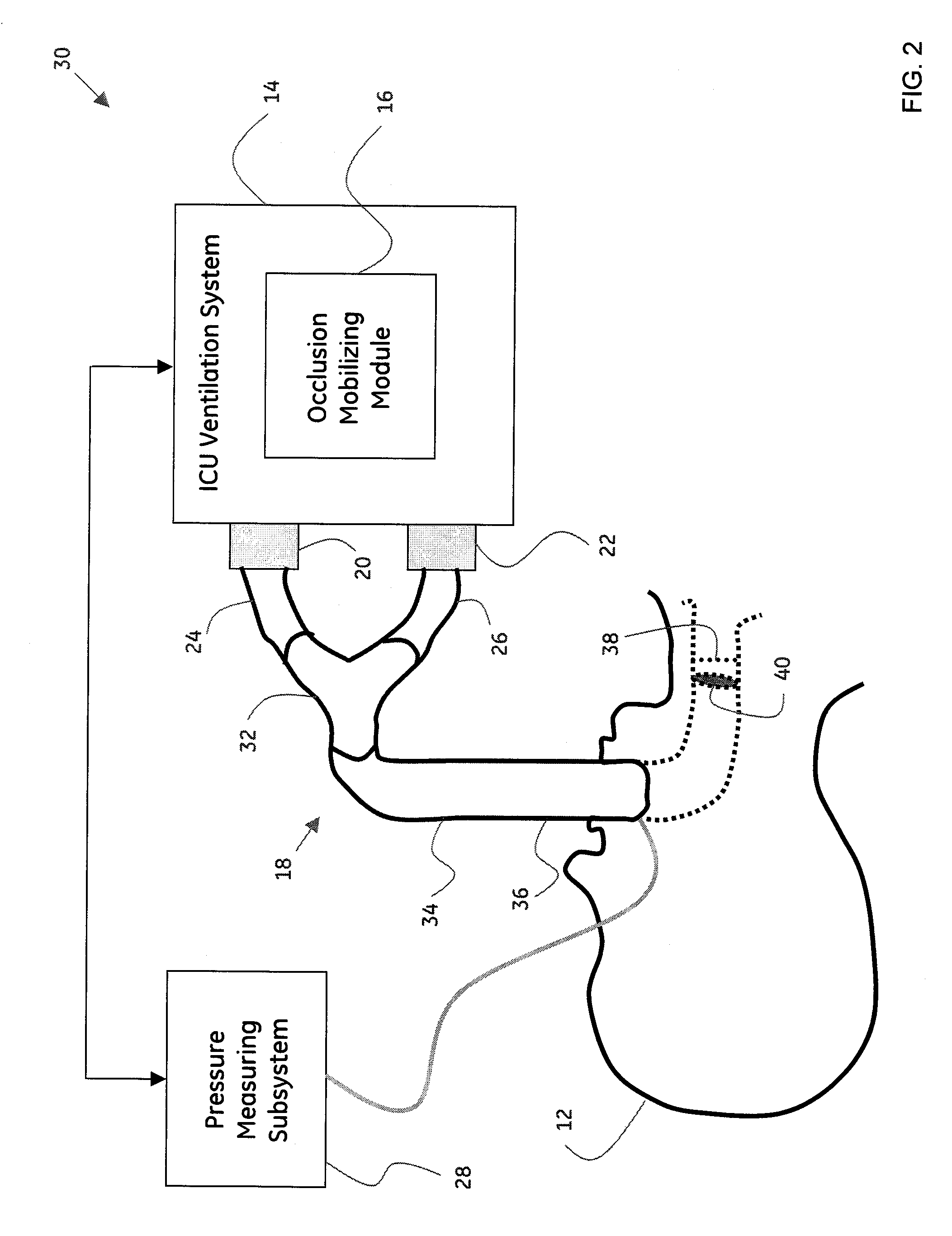
System and method for mobilizing occlusions from a breathing tube
ActiveUS20090266360A1Tracheal tubesOperating means/releasing devices for valvesInspiratory flowIntensive care medicine
A method for mobilizing an occlusion from a breathing tube is presented. The method includes automatically mobilizing the occlusion from the breathing tube by regulating an inspiratory flow, an expiratory flow, or a combination thereof, where the breathing tube is configured to operationally couple a patient to a ventilation system, and where the ventilation system is configured to provide artificial respiration to the patient.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
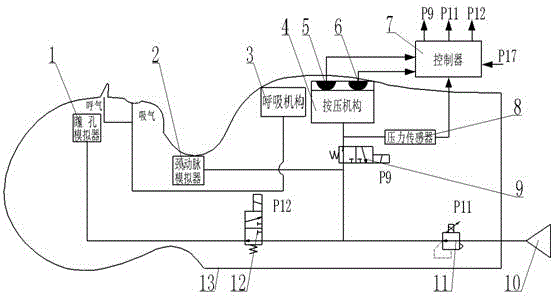
Pneumatic reaction cardiopulmonary resuscitation teaching simulation human model
InactiveCN105608974AQuality improvementHigh experiential teaching effectEducational modelsPupilThoracic cavity
The invention relates to a pneumatic reaction cardiopulmonary resuscitation teaching simulation human model. The pneumatic reaction cardiopulmonary resuscitation teaching simulation human model comprises a breathing mechanism, a pressing mechanism, a force sensor, an acceleration sensor, a controller and a pressure sensor, wherein the breathing mechanism comprises a lung simulator, the pressing mechanism comprises a chest simulator, before resuscitation, the chest simulator is controlled by a proportion pressure-reducing valve to simulate hardness of a human thorax, a pupil simulator realizes air intake to simulate a pupil amplification state, and a carotid simulator realizes air intake to simulate a carotid beating stop state. When a chest portion of an upper human body model is pressed, the carotid simulator beats according to the pressing frequency of the chest simulator to simulate the carotid beating state; when the upper human body model is gassed, the lung simulator simulates an artificial respiration state; after recovery, the pupil simulator exhausts to simulate a normal pupil state, and the carotid simulator is controlled by the proportion pressure-reducing valve to simulate the normal carotid beating state. According to the simulation human model, the simulators are driven through air to simulate symptoms of organs such as the chest, the lung, the eyes and the neck before and after cardiopulmonary resuscitation, and vivid symptom simulation effects and accurate positioning are realized.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
Ventilating element, system, and methods
A manually operated ventilating element such as a bellows for administration of artificial respiration, for example, during anesthesia, has wall sections or pleats of different diameters. When the element is actuated through a small stroke length, the smaller section is actuated. A small volume of gas is delivered and the change in delivered volume per unit stroke length is small, so that the operator can precisely control the delivered volume. When the element is actuated through a larger stroke length, a larger volume per unit stroke length is delivered. The same element can be used to treat children and adults.
Owner:GRADIAN HEALTH SYST
Providing automated or manual guidance on dynamic patient positioning based on measured variables for ventilation control
InactiveUS20080202527A1Minimize cost functionConvenient treatmentRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesArtificial ventilationAutomatic control
Methods and systems that incorporate automated or manual control of ventilation and kinetic rotation therapy are provided. In one exemplary embodiment, an artificial ventilator is used to artificially ventilate one of the patient's lungs, the status of the artificially ventilated lung is determined by measuring one or more ventilation status measures, and one or more of the ventilation status measures is used to provide feedback for controlling the positioning of the patient. In some exemplary embodiments, the feedback is used for automated control of the positioning of the patient, while in other exemplary embodiments, the feedback is used as guidance for manual control of the positioning of the patient.
Owner:HUNTLEIGH TECH LTD
Method and apparatus for determining alveolar opening and closing
InactiveUS7122010B2Prevent crashEfficient exchangeRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesElectrical resistance and conductanceRadiology
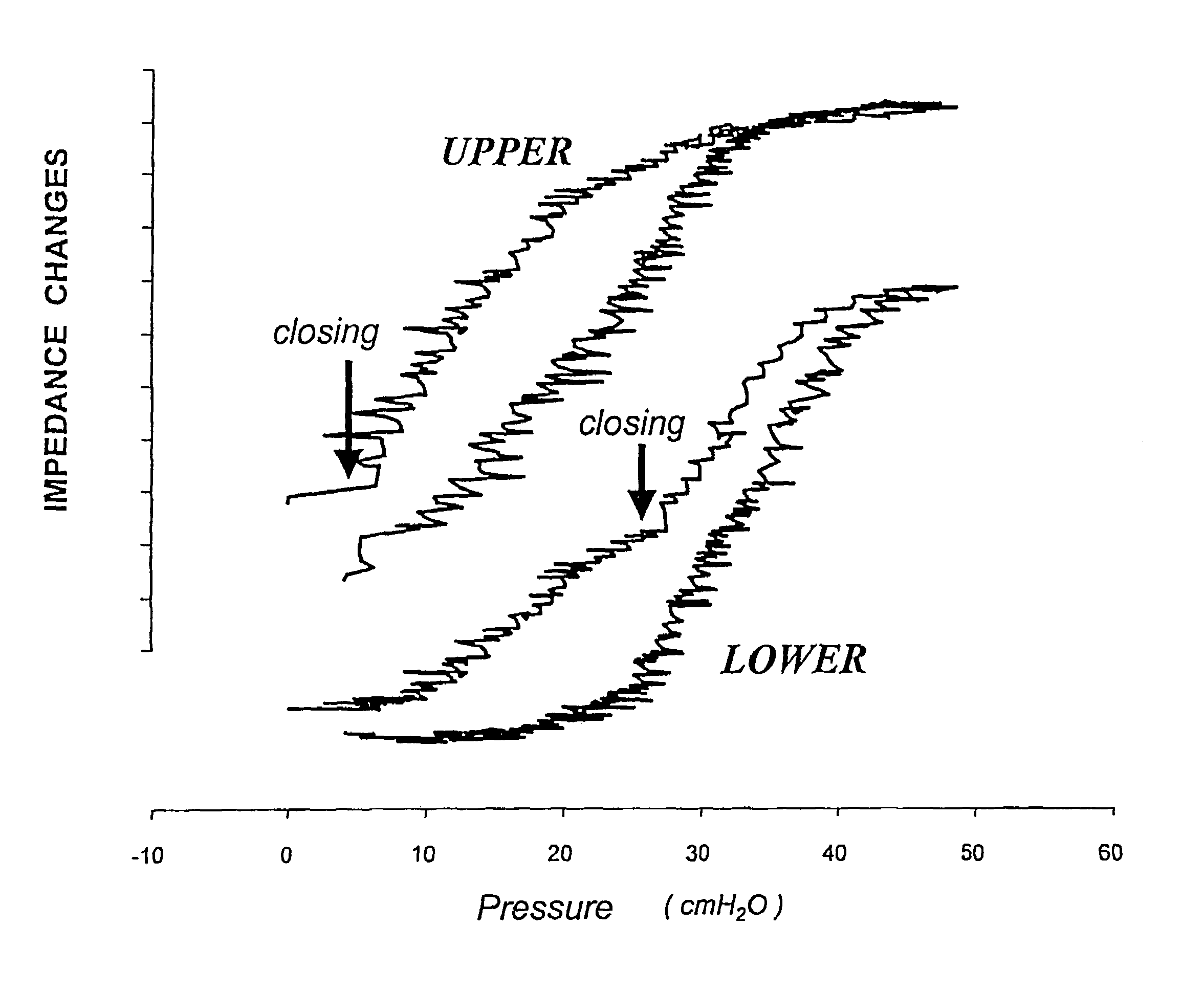
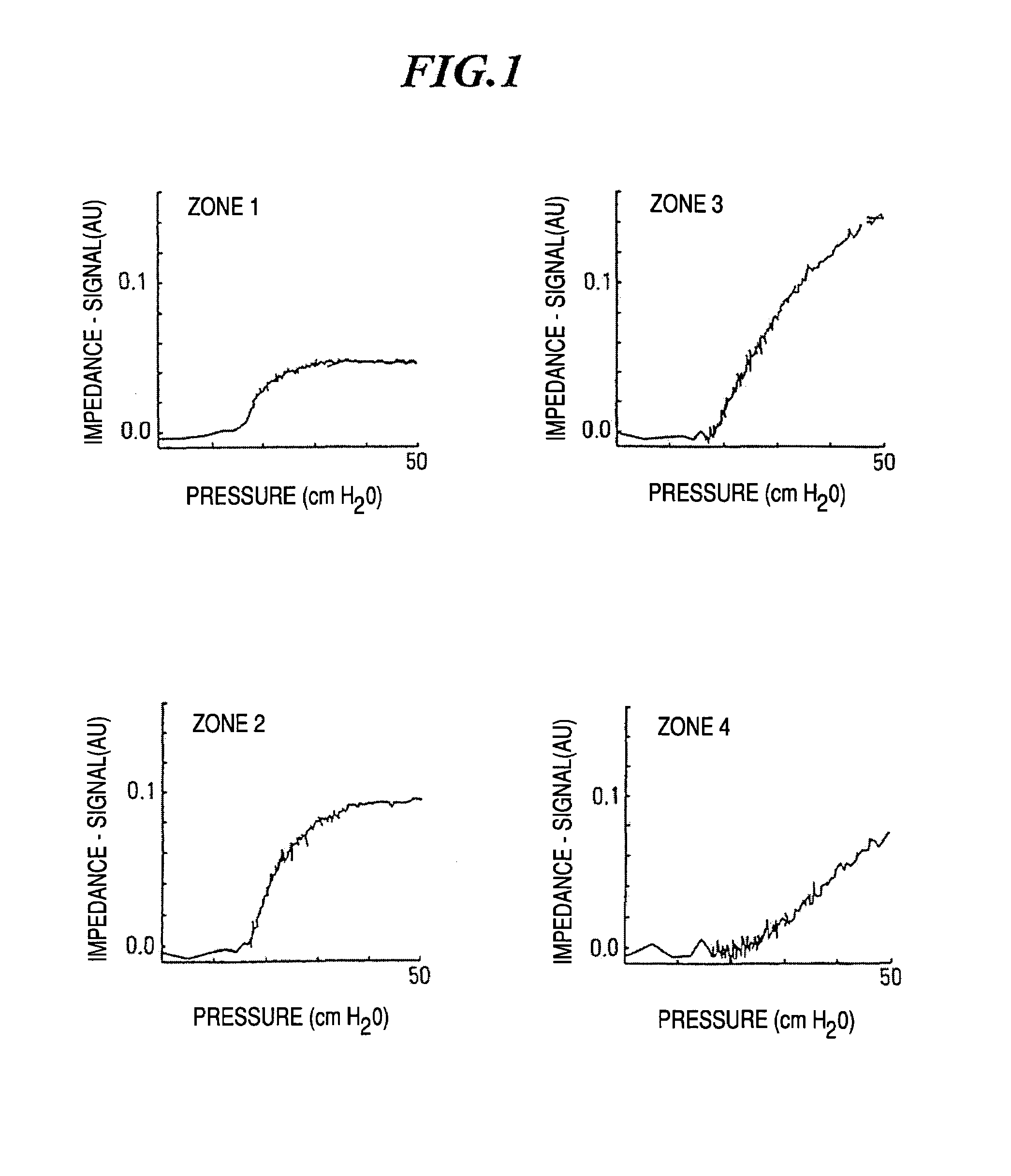
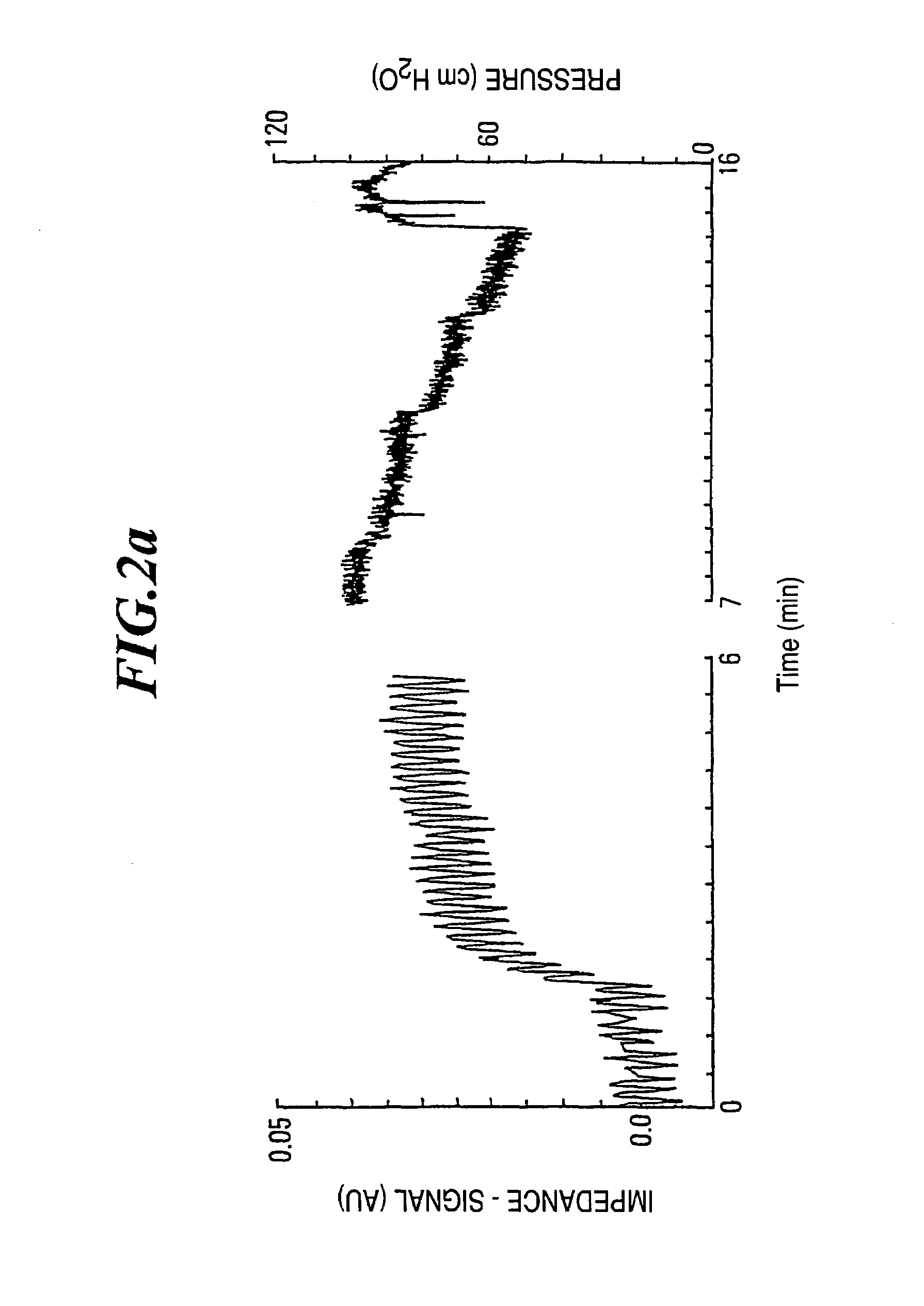
The invention refers to a method for the regional determination of the alveolar opening and alveolar closing of the lung depending on the respiration pressure, wherein according to the method of electrical impedance tomography, an impedance signal is measured in at least one lung zone depending on the respiration pressure. The alveolar opening or closing of a lung zone is determined, in particular to enable an improved artificial respiration.
Owner:TIMPEL MEDICAL BV
Process for the automatic recording of pressure-vs.-volume curves during artificial respiration
ActiveUS20060037616A1Improve accuracyGently for patientRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesRespiratorBreathing gas
A process, system and device are provided for automatically recording pressure-vs.-volume curves during artificial respiration with a respirator. The inspiration pressure is increased during the supply of a breathing gas volume flow under the control of a control unit. The resulting breathing gas volume flow rate is detected and the volume is determined from the latter by integration. The control unit compares the breathing gas volume flow detected during the phase of expiration with a preselected set point and acts on an expiration valve (12) in the expiration line (8) by means of a controller in case of deviation from the set point in order to return the breathing gas volume flow to the set point.
Owner:DRAGERWERK AG
Breathing apparatus for internal medicine
InactiveCN105771048AImprove rehabilitation effectSimple structureRespiratory masksIntravenous devicesGynecologyMedical equipment
The invention relates to a breathing apparatus for the internal medicine, belonging to the technical field of medical equipment. The technical scheme is as follows: the breathing apparatus for the internal medicine comprises a body and a face mask, wherein a combined converter is arranged on the left side of the body; a sputum suction connecting handle is arranged on the upper side of the combined converter; an air supply conversion handle is arranged on the left side of the sputum suction connecting handle; a combined conduit is arranged on the left side of the combined converter; a combined plug is arranged on the right side of the combined conduit; a combined sealing socket is arranged on the right side of the combined plug; and a plug locking buckle is arranged on the outer side of the combined sealing socket. The breathing apparatus provided by the invention is simple in structure and convenient to use and can finish the operations such as oxygen absorption, artificial respiration and sputum suction without changing the face mask; and moreover, the breathing apparatus is simple and convenient to operate, has diversified functions and can effectively improve the rehabilitation effect of patients.
Owner:毕贞水
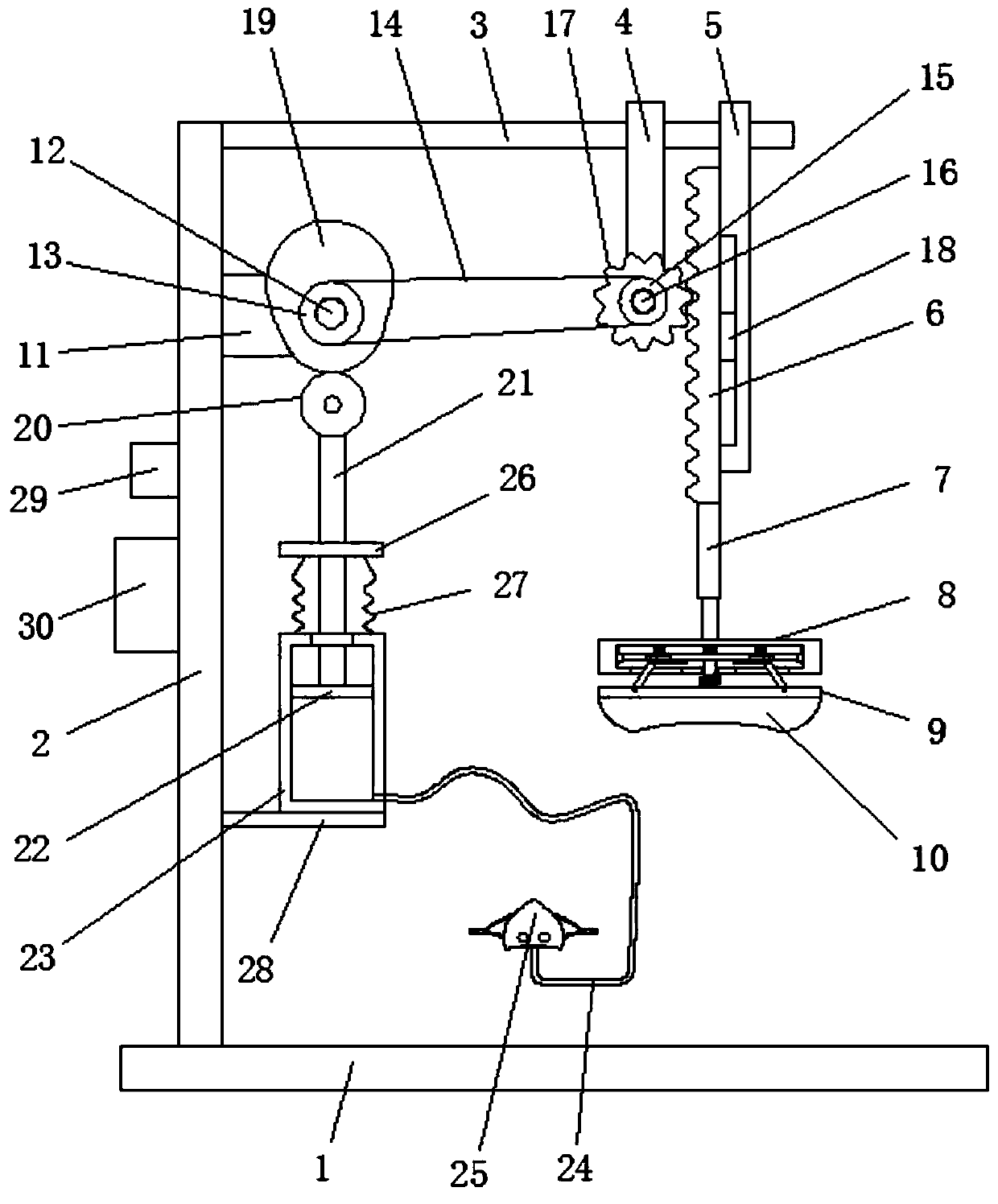
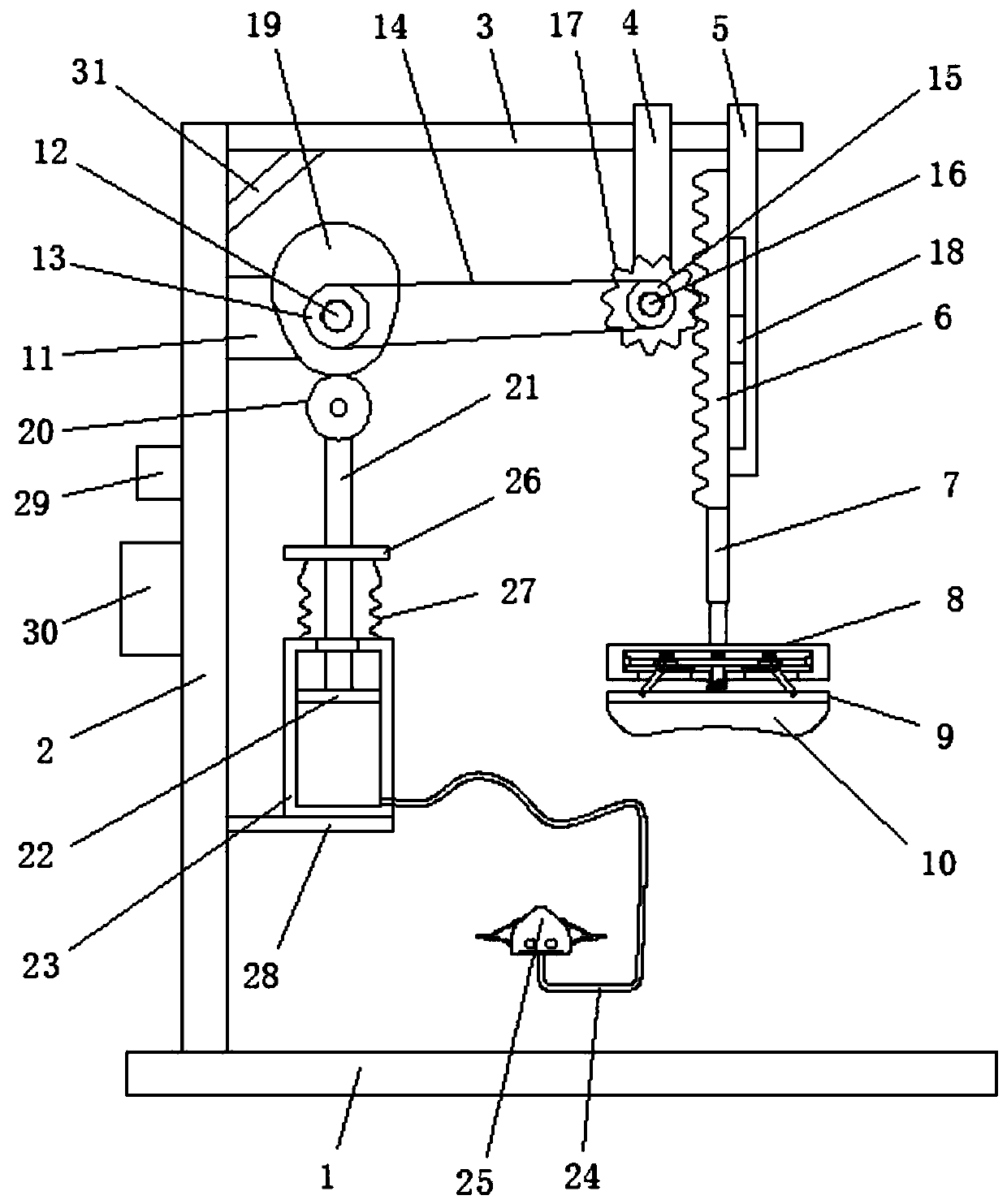
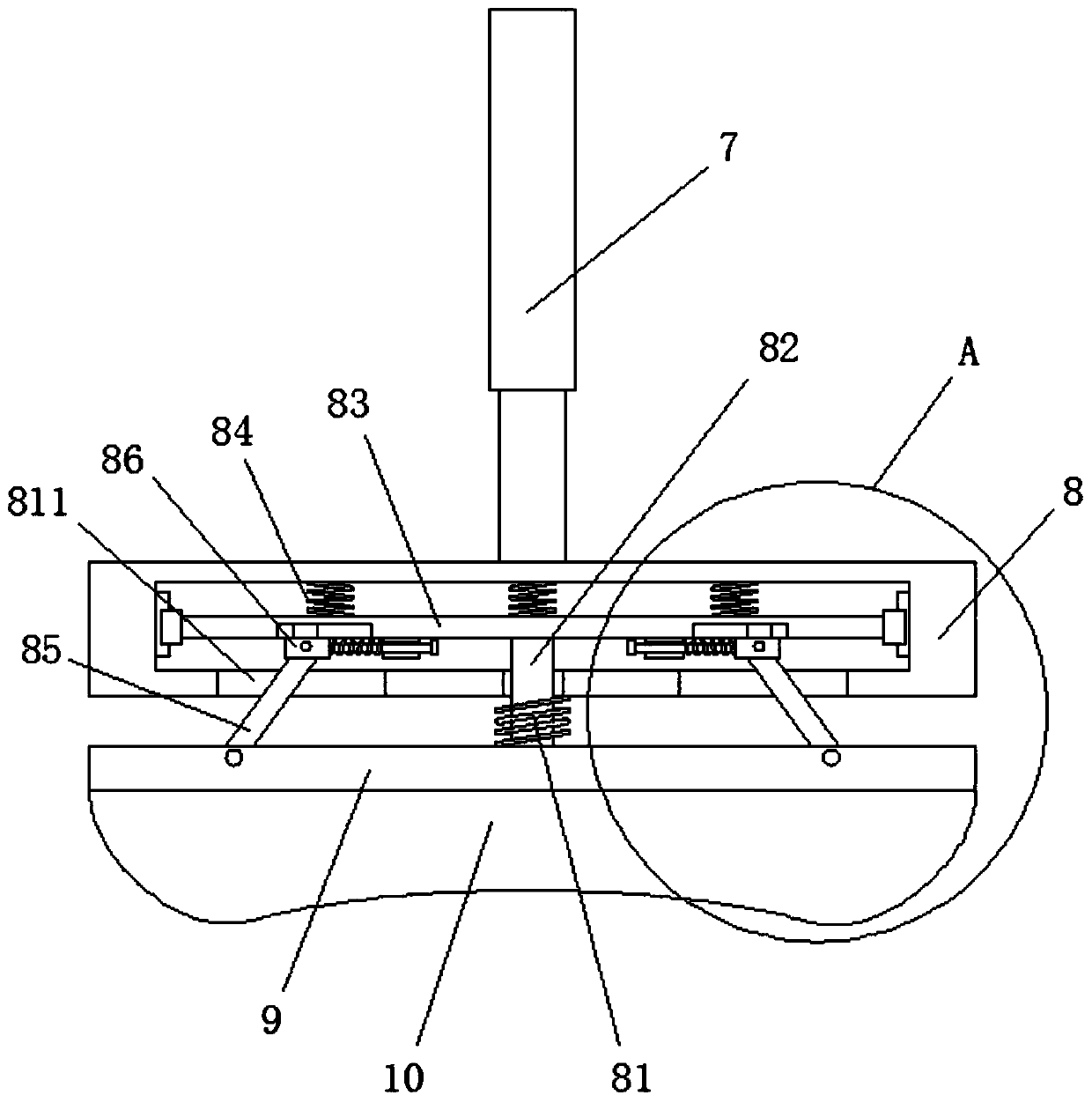
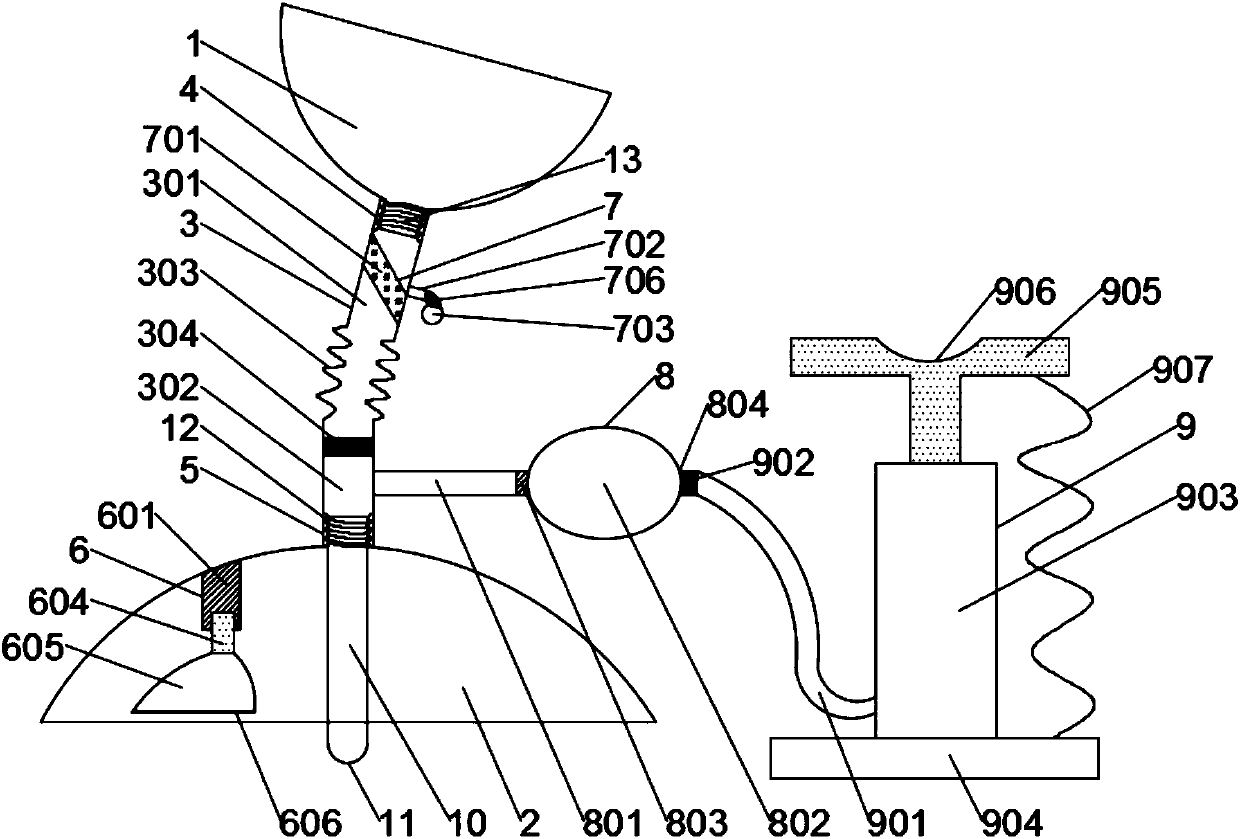
Critical medical patient respiration recovery assisting device
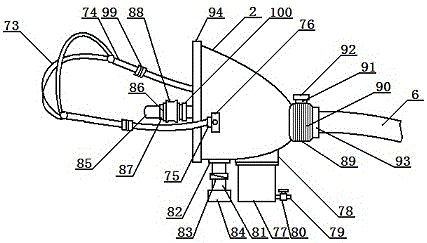
InactiveCN111358688AFast breathingRescue in timeElectrotherapyHeart stimulationEngineeringPreventing injury
The invention discloses a critical medical patient respiration recovery assisting device. The device comprises a bottom plate; the left end of the top of the bottom plate is provided with a support frame; and the top of the right side of the support frame is provided with a transverse frame. In the device, an air bag moves up and down to press the cardiopulmonary part of a patient up and down, sothat the purposes of cardiopulmonary resuscitation and respiration recovery are achieved, the trouble of manual pressing operation is avoided, great convenience is brought, and the critical patient can be timely rescued; in the process of pressing the cardiopulmonary part of the patient up and down, the device has good buffer effect, thereby preventing injury of internal organs of the patient dueto overlarge pressing force; and respiration operation of inhaling and exhaling is performed on the patient to achieve the purpose of artificial respiration, and cardiopulmonary resuscitation rescue and artificial respiration are kept consistent in frequency and are performed at the same time, so that the purposes of fast rescue and respiration recovery of the patient are achieved and the effect is better.
Owner:THE AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF QINGDAO UNIV
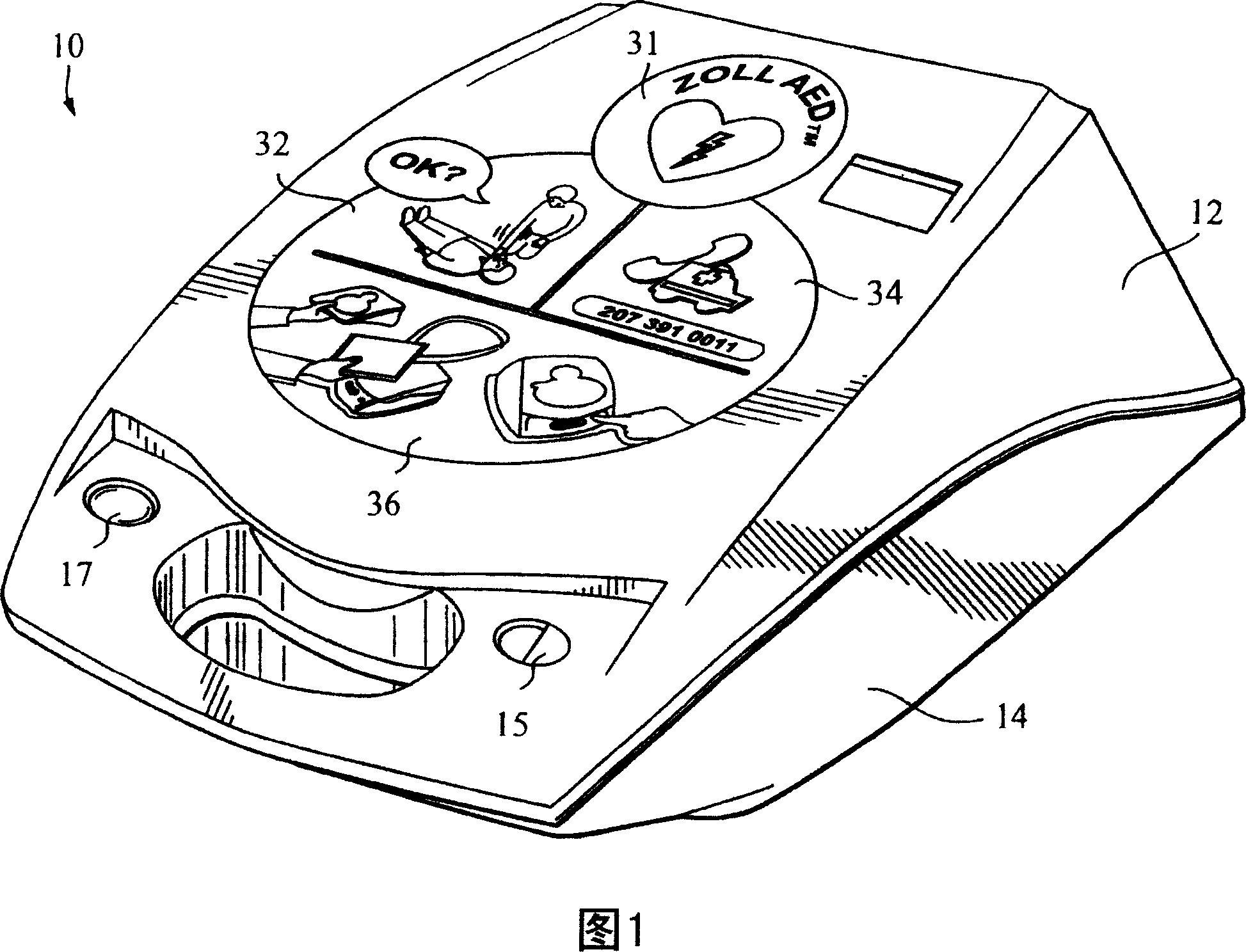
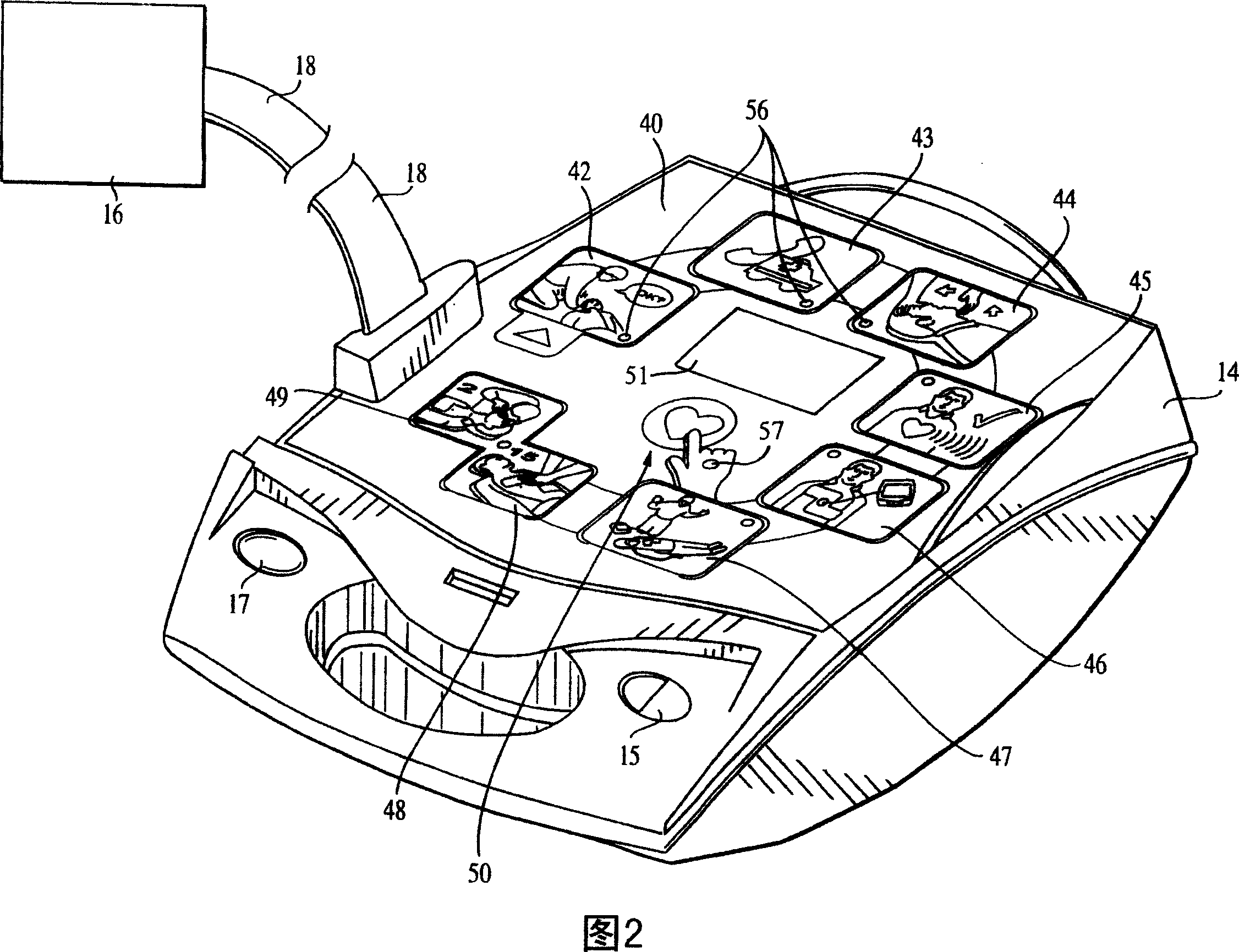
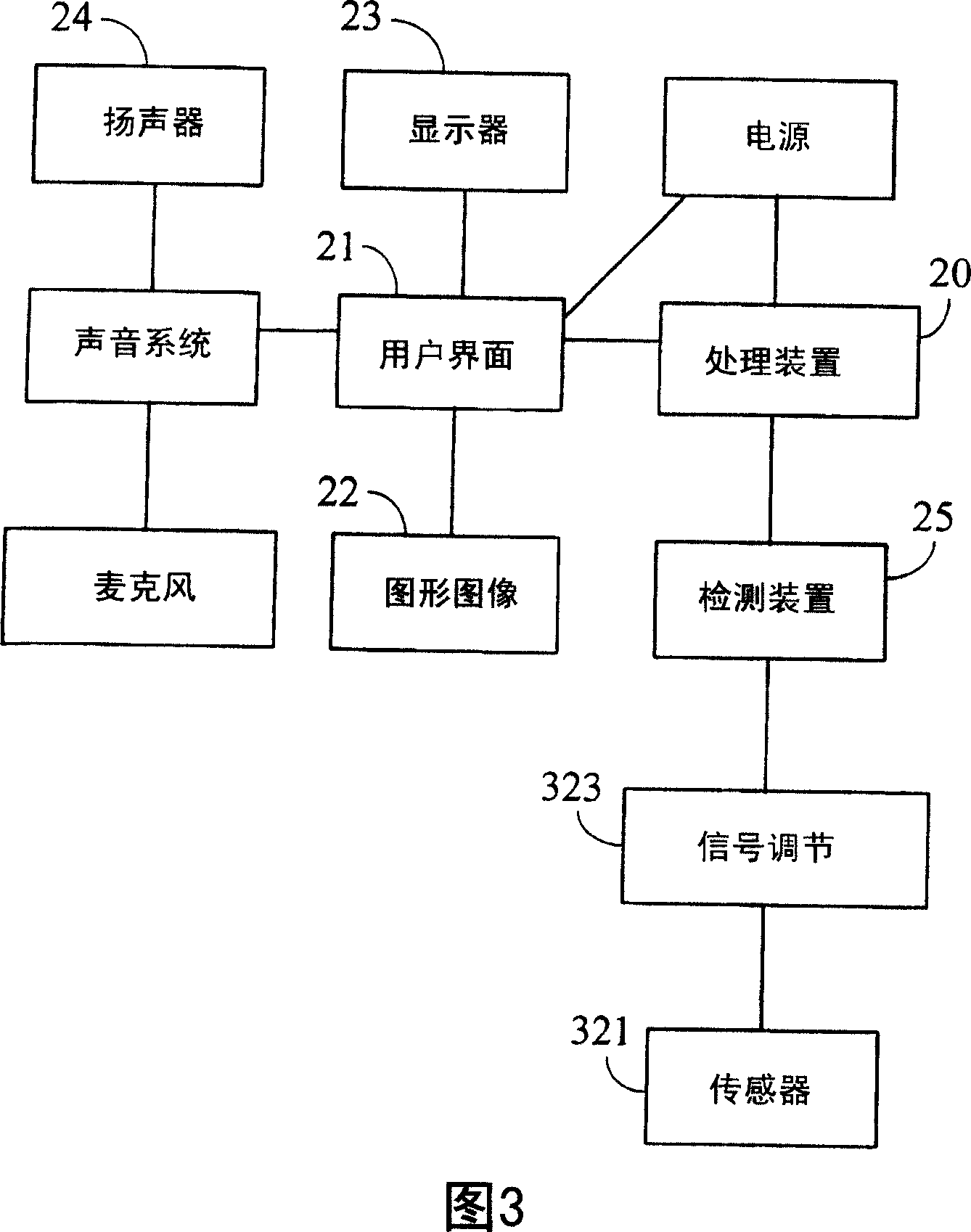
Automated resuscitation device sensing and promoting artificial respiration
InactiveCN101061985AEfficient measurementEasy to measureTracheal tubesDiagnosticsTidal volumeCardiac resuscitation
A device for assisting a caregiver in delivering cardiac resuscitation to a patient, the device comprising a user interface configured to deliver prompts to a caregiver to assist the caregiver in delivering cardiac resuscitation to a patient; at least one sensor configured to detect the caregiver's progress in delivering the cardiac resuscitation, wherein the sensor is configured to provide a signal containing information indicative of ventilation; a memory in which a plurality of different prompts are stored, including at least one ventilation progress prompt to guide the rescuer's performance of ventilation; a processor configured to process the output of the sensor to determine a parameter descriptive of ventilation progress and to determine whether the ventilation progress prompt should be selected for delivery. Possible parameters descriptive of ventilation progress include ventilation rate, delivered tidal volume, and flow rate.
Owner:ZOLL MEDICAL CORPORATION
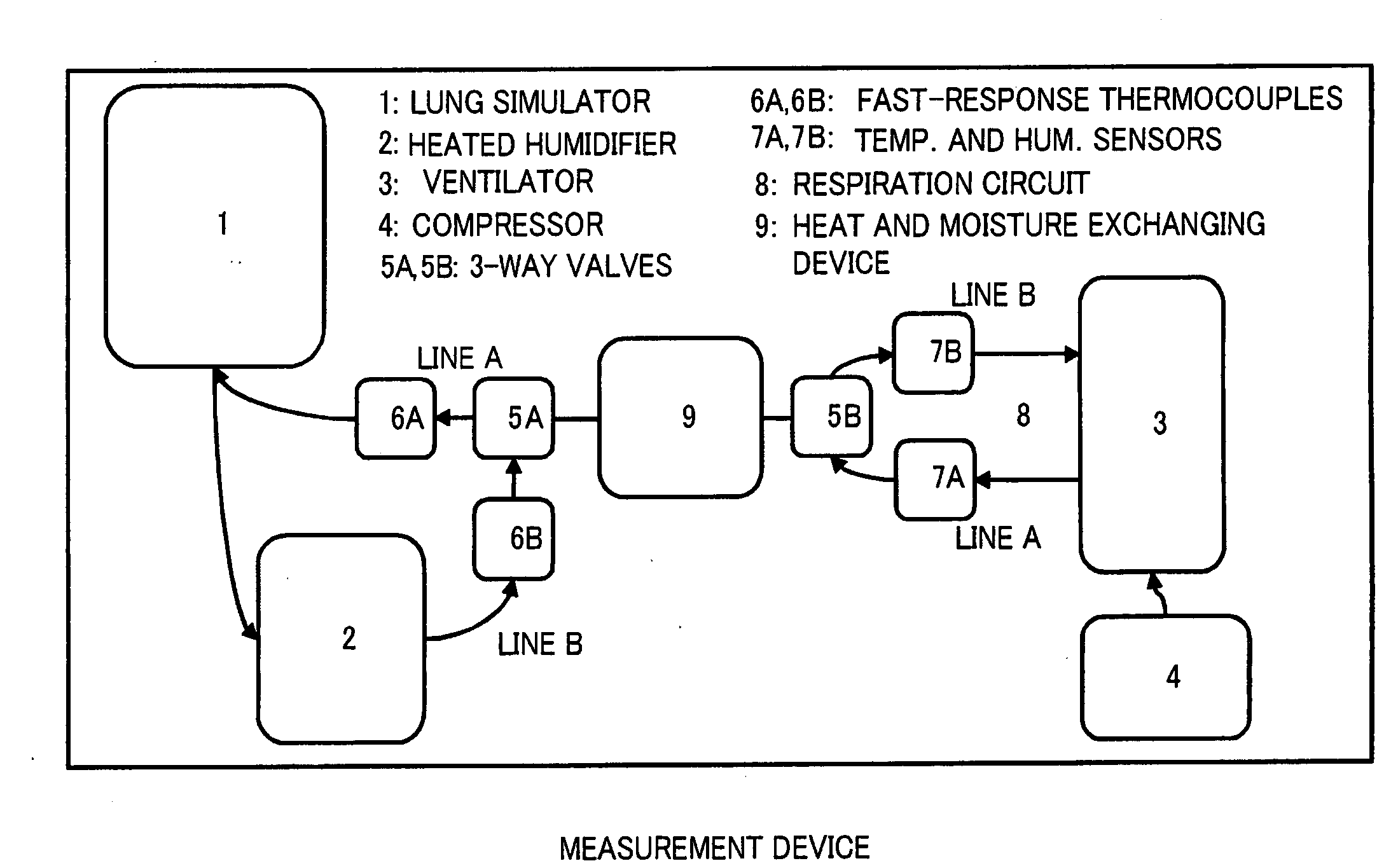
Heat and moisture exchanger, heat and moisture exchanging device, and mask
ActiveUS20090301478A1Easy to adjustOther heat production devicesBreathing masksRespiratorHeat and moisture exchanger
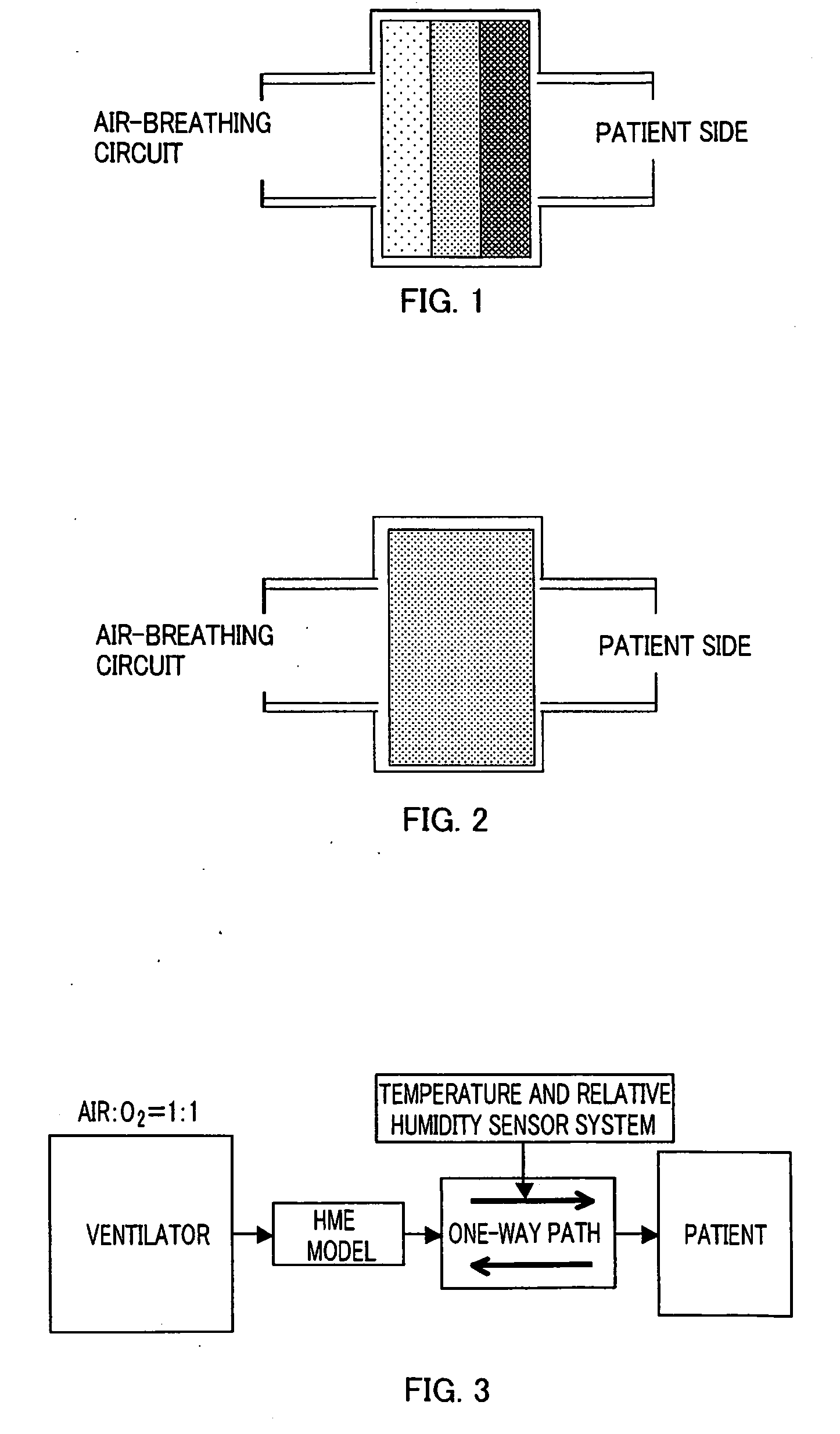
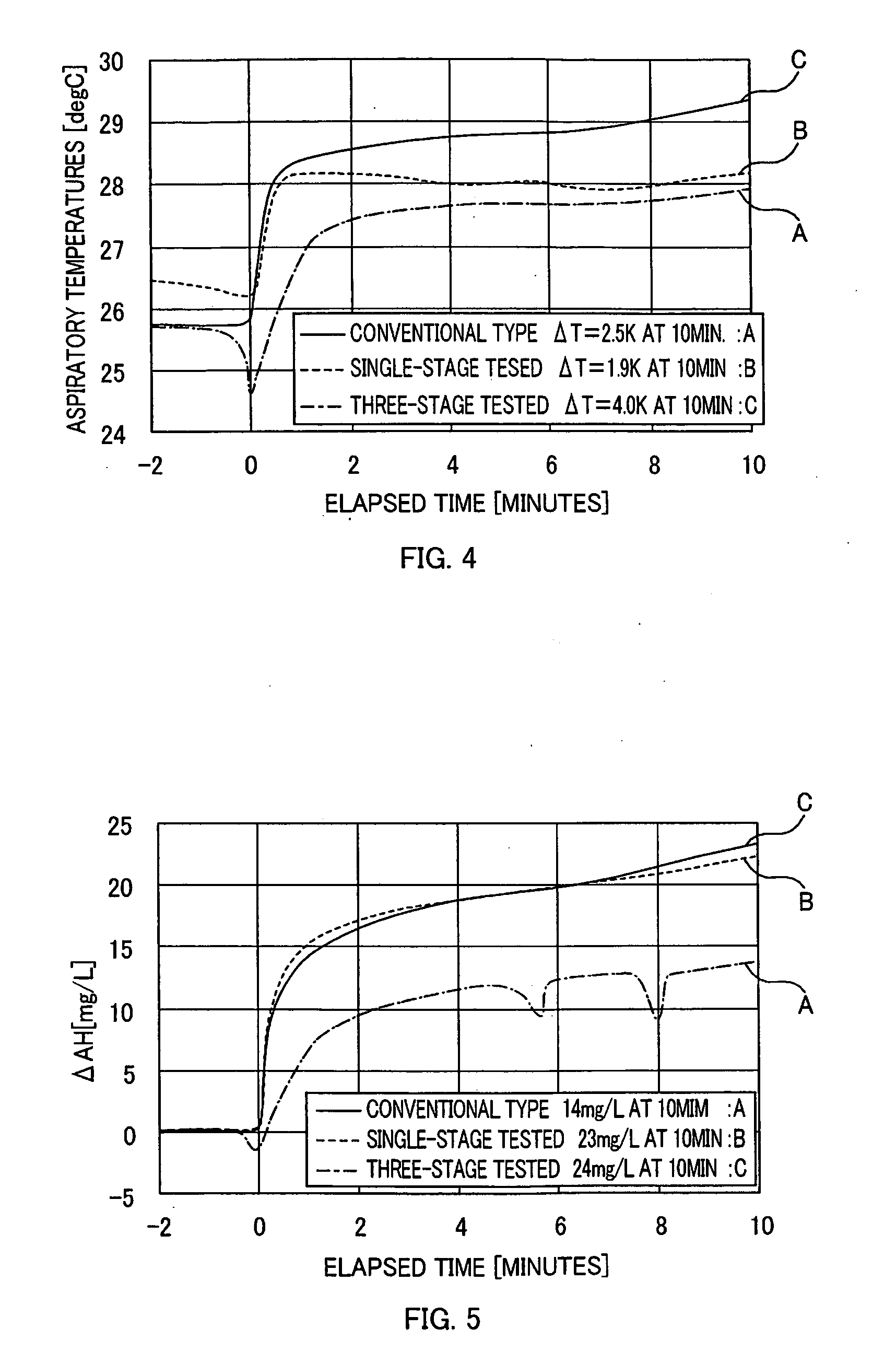
A heat and moisture exchanger configured to be located between a respiratory system of a patient and an anesthesia circuit connected to an anesthesia apparatus, or a respiratory circuit connected to a respirator for maintaining a temperature and humidity of an aspired gas required to a patient under anesthesia or artificial respiration comprises a heat storage carrier material, and a moisture absorption and release material added to the heat storage carrier material. In the heat and moisture exchanger, at least one of density of the heat storage carrier material, number of cells of the heat storage carrier material, and an added amount of the moisture absorption and release material in the heat storage carrier material is set to decrease from the patient side to the side of the anesthesia apparatus or the respirator, along a flow direction of a respiratory gas in the heat storage carrier material.
Owner:FURREX
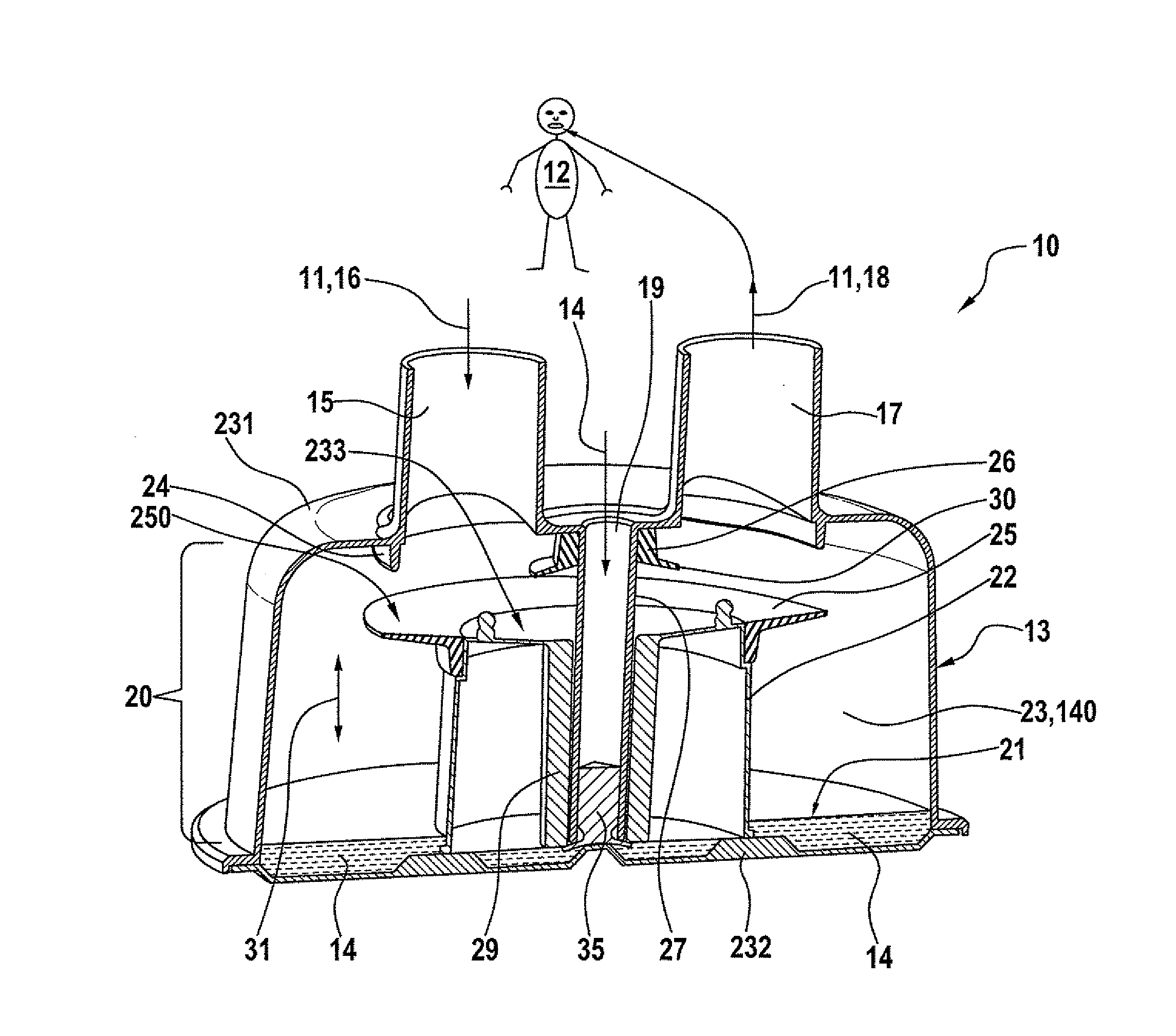
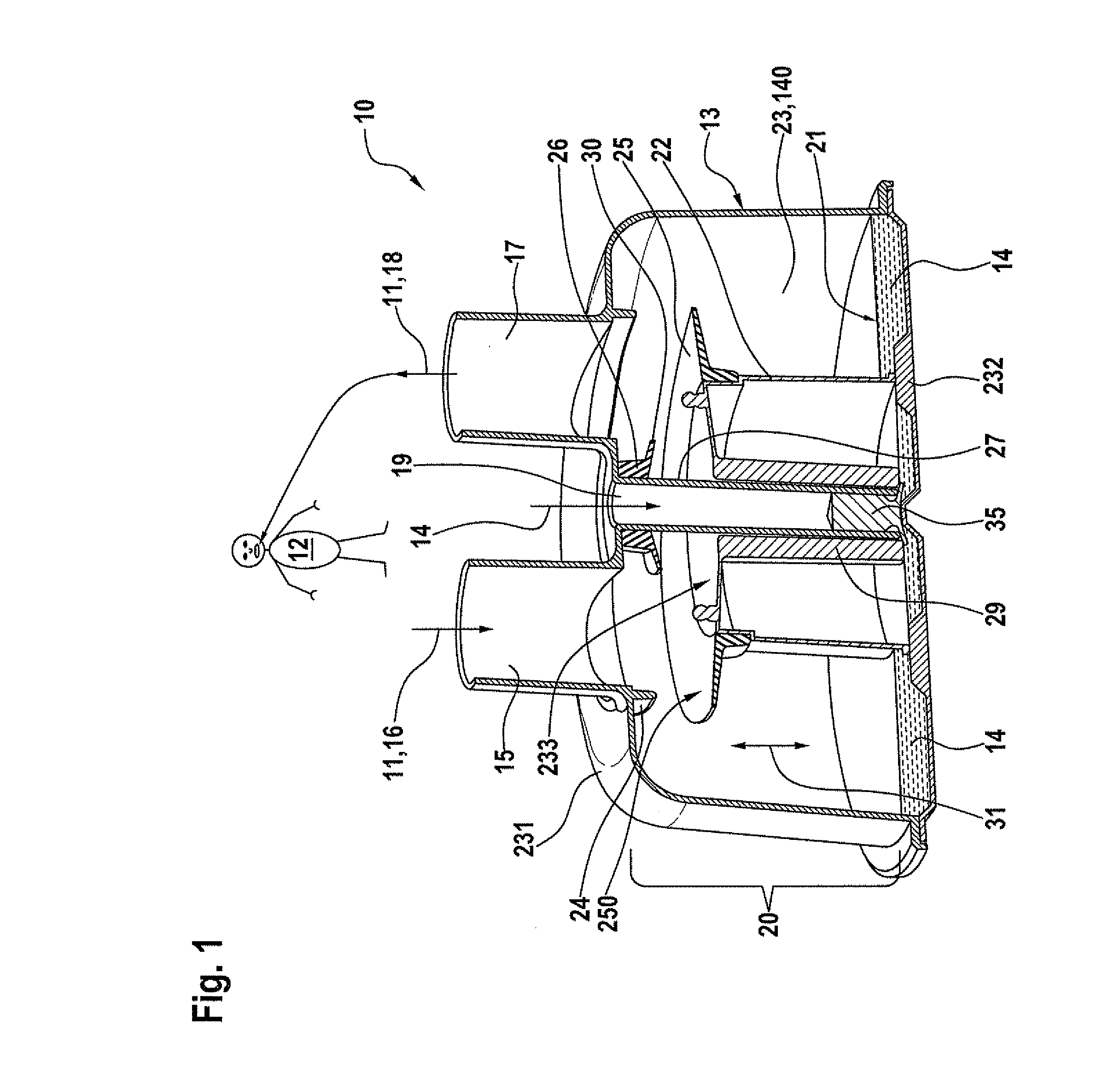
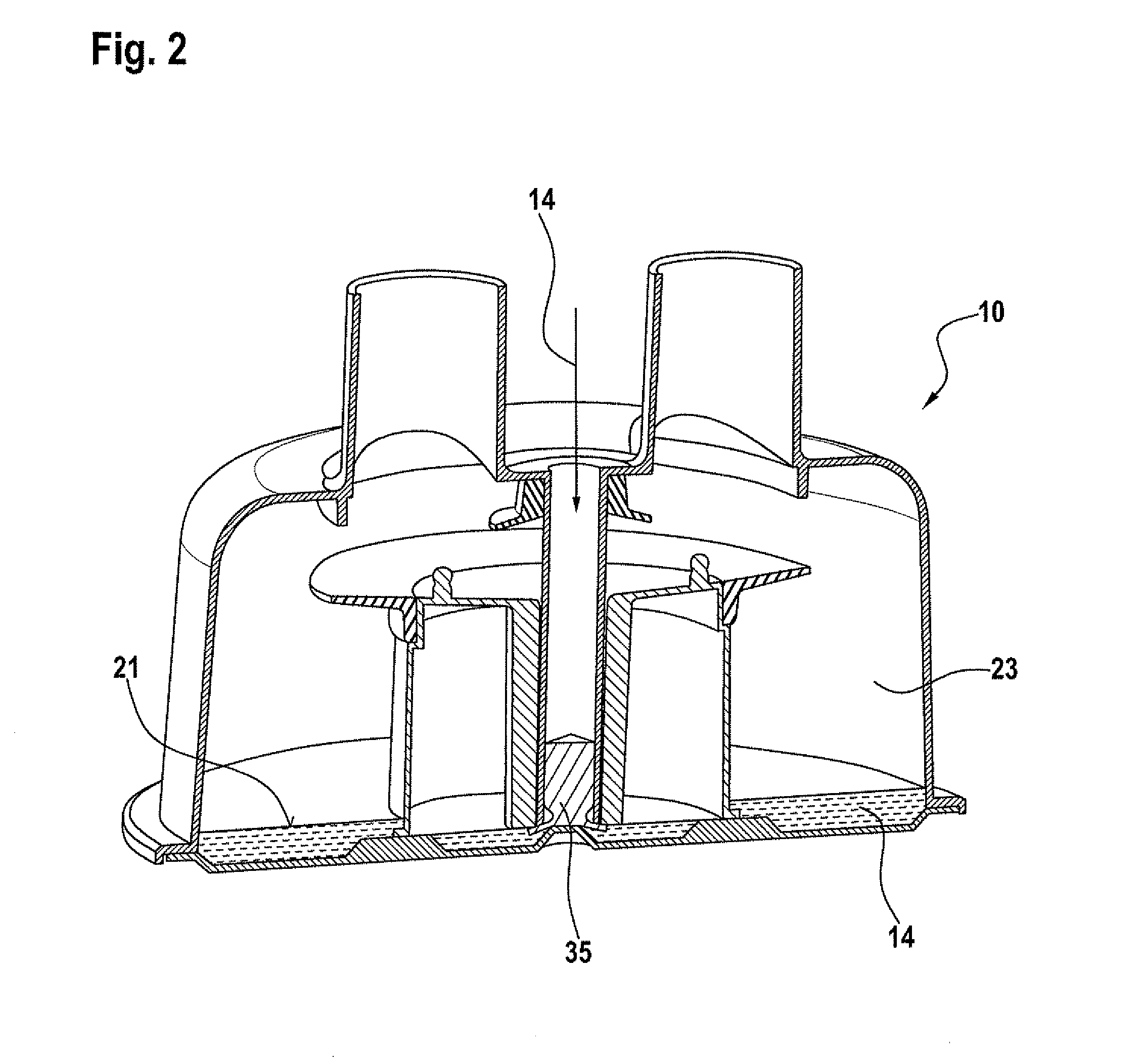
Artificial ventilation apparatus
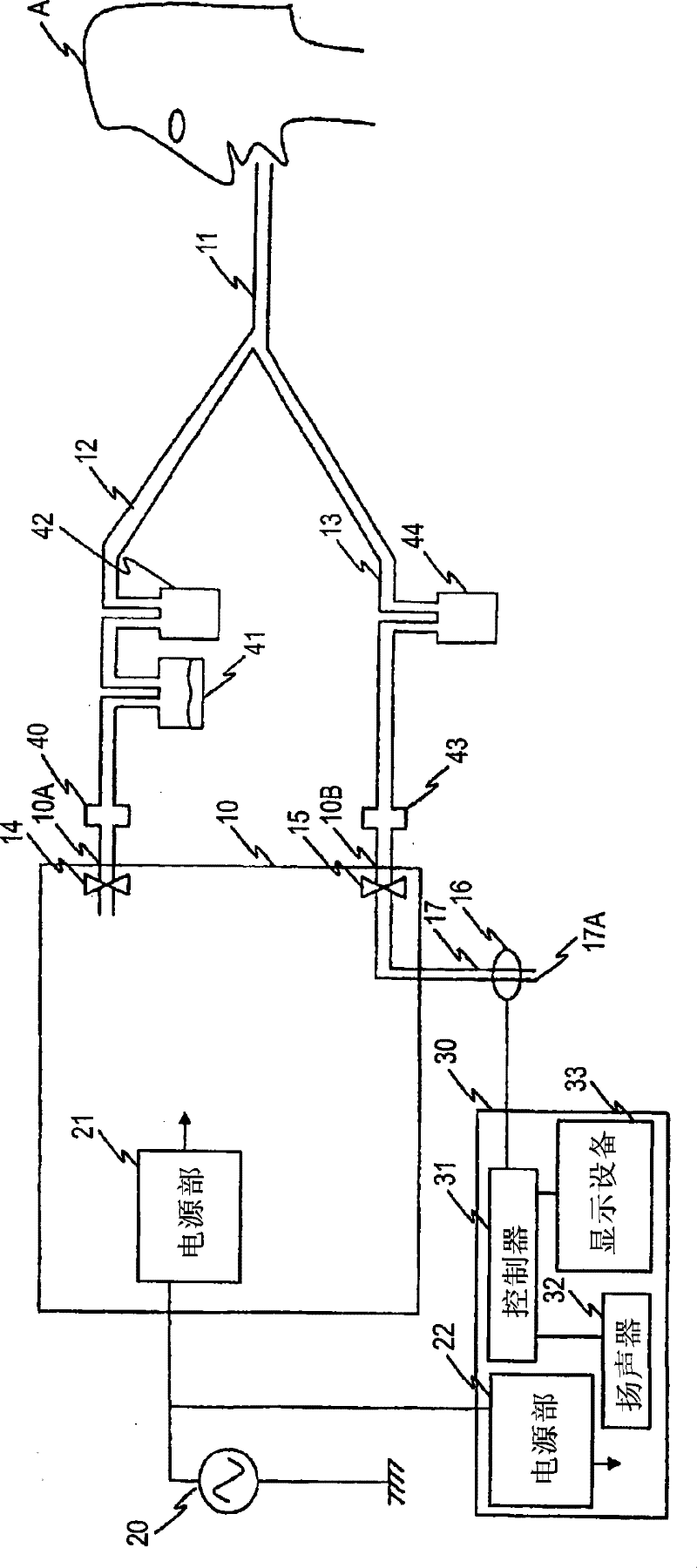
InactiveCN102302817AShorten the time periodReduce in quantityRespiratorsArtificial ventilationExpiratory valve
An artificial ventilation apparatus includes: a connecting portion which is connected to a respiratory system of a patient; an inspiratory circuit which is a flow path for flowing a gas from a ventilator to the connecting portion; an expiratory circuit which is a flow path for guiding a gas exhausted from the connecting portion to an exhaust portion of the ventilator; an expiratory valve which blocks a flow of a gas from the exhaust portion toward the connecting portion; a carbon dioxide concentration sensor which is disposed in a circuit that is arranged at a downstream side of the expiratory valve and which detects a carbon dioxide concentration; and an alarm outputting unit which outputs an alarm based on an output of the carbon dioxide concentration sensor.
Owner:NIHON KOHDEN CORP
Device for humidifying breathing air for artificial respiration
A device for humidifying breathing air for artificial respiration of mammals, in particular human beings, includes at least one essentially closed container for receiving water, a first opening for letting in the non-humidified air and a second opening for letting out humidified air, and an inlet for supplying the water to the container. The inlet is located in the upper part of the container, which is adjoined by a tube essentially crossing through the container interior, and on the free end of the tube, a valve is disposed, which limits the level of the water supplied via the tube in such a way that the container bottom in the container interior is essentially covered with water.
Owner:ARTA PLAST
Efficient artificial ventilator for cardiological nursing
ActiveCN108030989AConvenient treatmentAvoid direct contactRespiratory masksArtificial ventilationNasal cavity
The invention discloses an efficient artificial ventilator for cardiological nursing, comprising a medical mask and a patient mask connected with each other through a gas conducting tube; the gas conducting tube comprises an upper gas conducting tube and a lower gas conducting tube; the connection of the upper gas conducting tube and the medical mask is provided with a first intake port, the connection of the lower gas conducting tube and the patient mask is provided with a second intake port, the patient mask is provided with a nasal auto-blocking structure, the upper gas conducting tube is provided with a liquid blocking preventive structure, and the lower gas conducting tube is connected with an auxiliary artificial ventilation structure. The efficient artificial ventilator for cardiological nursing allows the nasal cavity of a patient to be automatically blocked during artificial ventilation so that artificial ventilation is more effective; it can be prevented that liquid exhaled by medical staff blocks a line; artificial ventilation and auxiliary artificial ventilation can be carried out alternately; therefore, artificial ventilation frequency can be kept constantly normal during long-term treatment of a patient, and therapy of the patient is benefited.
Owner:李玉玲
Artificial respiration system with timing control and automatic mask detection
ActiveUS20170143932A1Reduce the amount requiredRespiratory masksMedical devicesDifferential pressureBiological activation
A ventilator system and method can deliver artificial respirations to a person receiving cardiopulmonary resuscitation. The system and method may provide intermittent breath delivery (e.g., with interruptions), so that activation of the device gives a specific predetermined number of breaths, interspersed with a set time period of no breath. This pattern may be by default, manually triggered where one activation gives a set number of breaths followed by a pause until the next activation for breath (one activation gives one breath cycle), or one activation results in continuous cycle of intermittent breaths). In some embodiments, a signaling mechanism may deliver signals to a rescuer relating to timing of chest compressions of the person. The timing of the chest compressions for the signals may be based on a time of delivery of the artificial respirations. In certain embodiments, different sized masks each include a gas flow restrictor which is unique for the size of mask. The ventilator system may assess the size of the mask based on a pressure differential created by the unique gas flow restrictor.
Owner:MCCARTHY DANIEL A
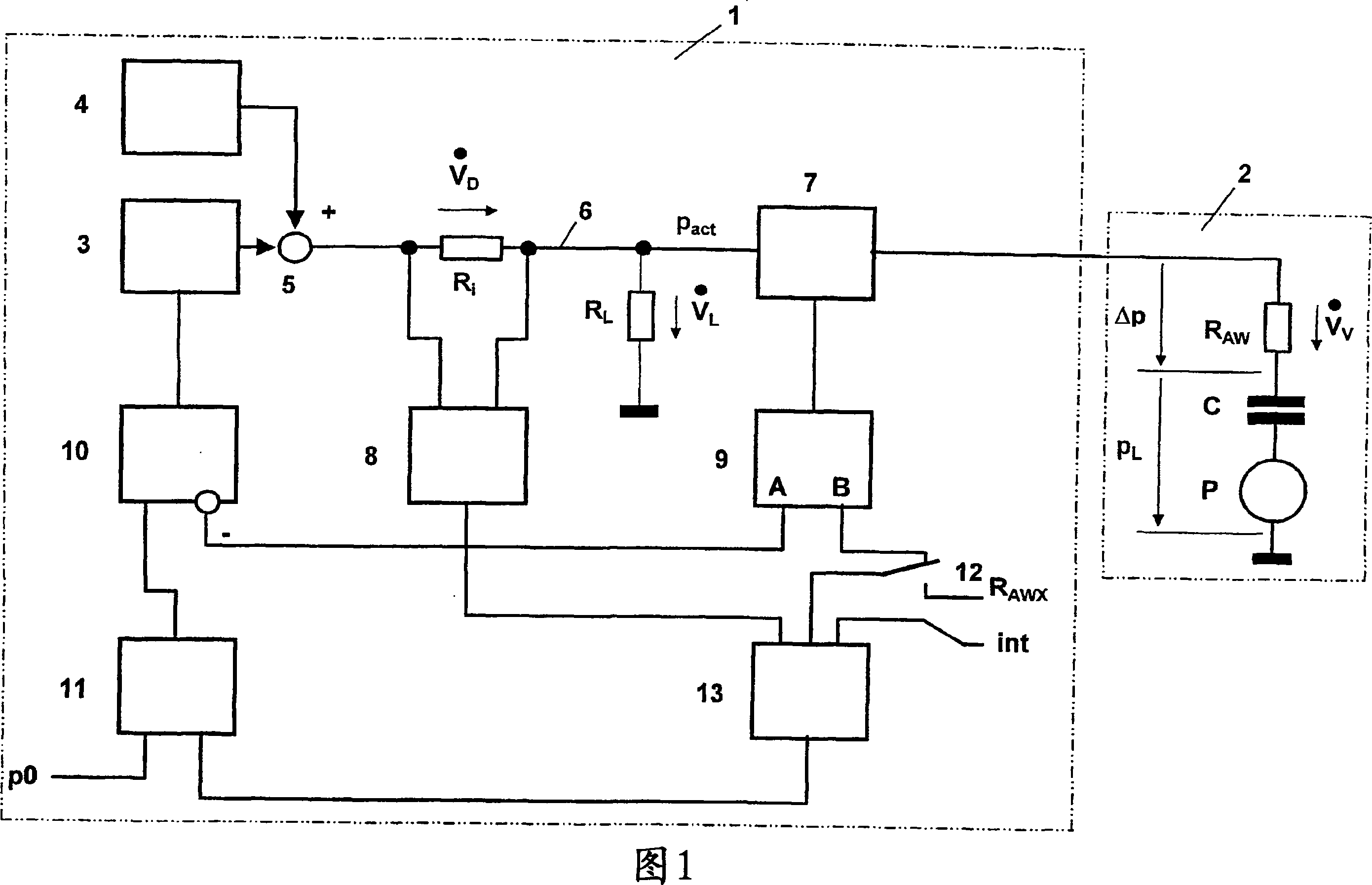
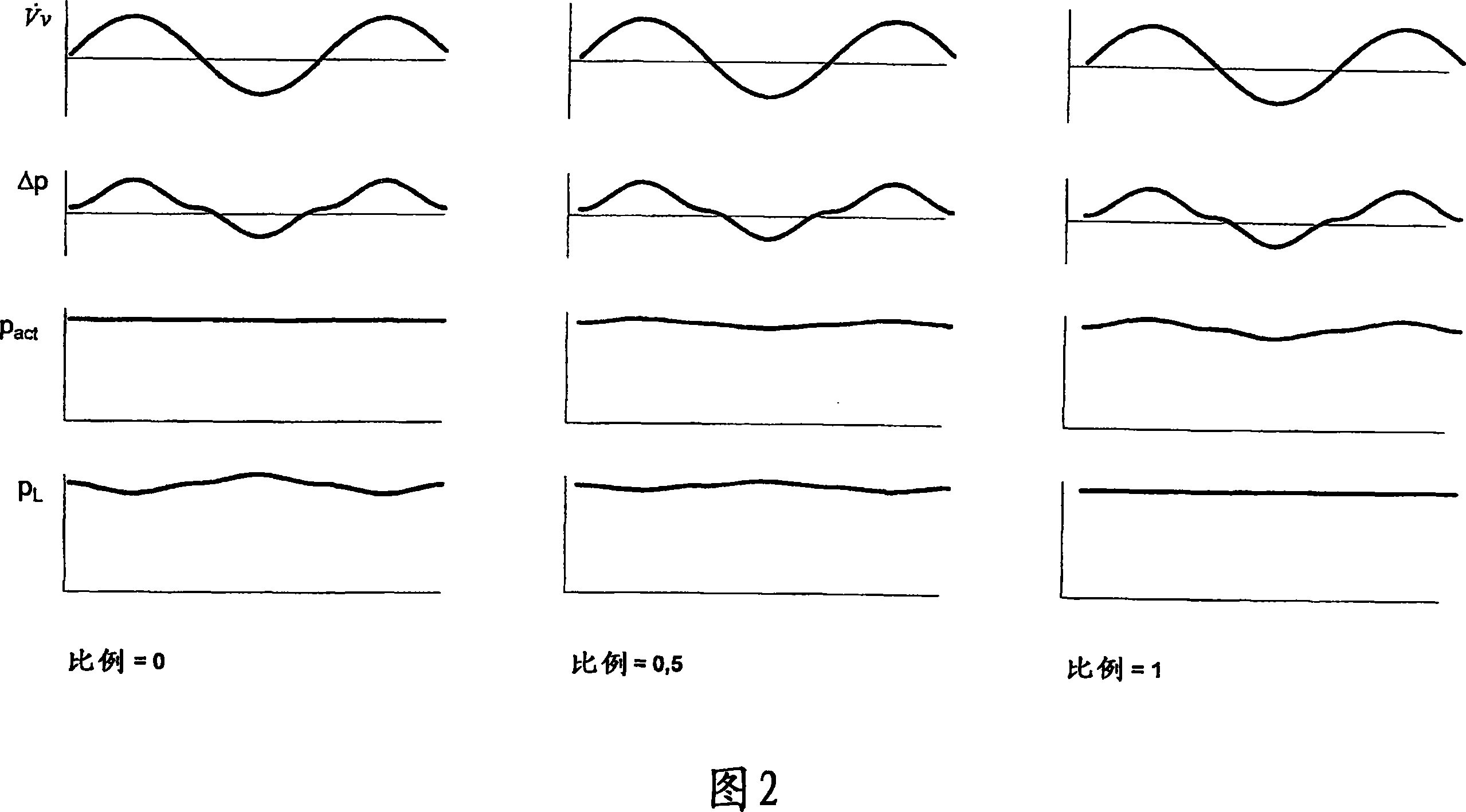
Ventilator device for treating obstructive sleep apnea and method for its control
InactiveCN101104092AAuto-continuationAutomatic intermittent measurementRespiratorsRespiratory muscleTreatment sleep
The present invention relates to a manpower respirator for treatment of obstructive sleep apnea, which comprises a pressure generator (3) for generating an artificial atmosphere with a therapy pressure (pact), a pressure regulating device (10) for controlling the pressure generator, and a respiration soft tube (6) as well as a respiratory mask (7) for supplying the artificial atmosphere to a patient (2). The manpower respirator is characterized in that it has a controller (13), which is used for continuously determining a loss pressure (Delta p) resulting over a respiratory tract resistance (RAW) of a respiratory tract of the patient, and for proportional adjustment of the therapy pressure progress in the process of the determined loss pressure. The manpower respirator reduces the burden of the patient breathing muscle distinctly and the result of delay treatment, and makes the treatment process be more comfortable.
Owner:HOFFRICHTER
Condensing well for breathing tube
InactiveCN101856533AReduce manufacturing costOperational securityRespiratorsEngineeringBreathing system
The invention relates to a condensing well for a breathing tube, a breathing system and a manufacturing method thereof. The well is characterized in that the manufacturing cost is low and the mounting position can be the lowest position on the breathing tube so as to reliably discharge the condensate water generated in the breathing tube when the artificial respiration is performed on the patients.
Owner:德尔格医疗控股有限责任公司
Trachael Intubation Tube Fixing Device With Suction Tube Insertion Opening
ActiveUS20080087281A1Improve survivabilityQuickly securedTracheal tubesRespiratory apparatusWhole bodyCoupling
Disclosed is a tracheal intubation tube fixing device for securing an airway in the patient's respiratory tract and inducing the artificial respiration of a patient in the intensive care unit or under a general anesthesia operation. The device includes a body to surround the patient's face and mouth and including an airway securing block, a suction tube insertion opening, an intubation tube insertion hole and band fixing holes, a pivotal fixing member to fix an inserted intubation tube, a coupling structure to assure free entrance and exit of the pivotal fixing member into and out of the intubation insertion hole, a padding member attached to Velcro tapes of the body, and a holding member configured to closely surround the patient's rear neck and coupled to the body via the band fixing holes to prevent the body from being moved from a wearing position thereof.
Owner:UNIMEDICS
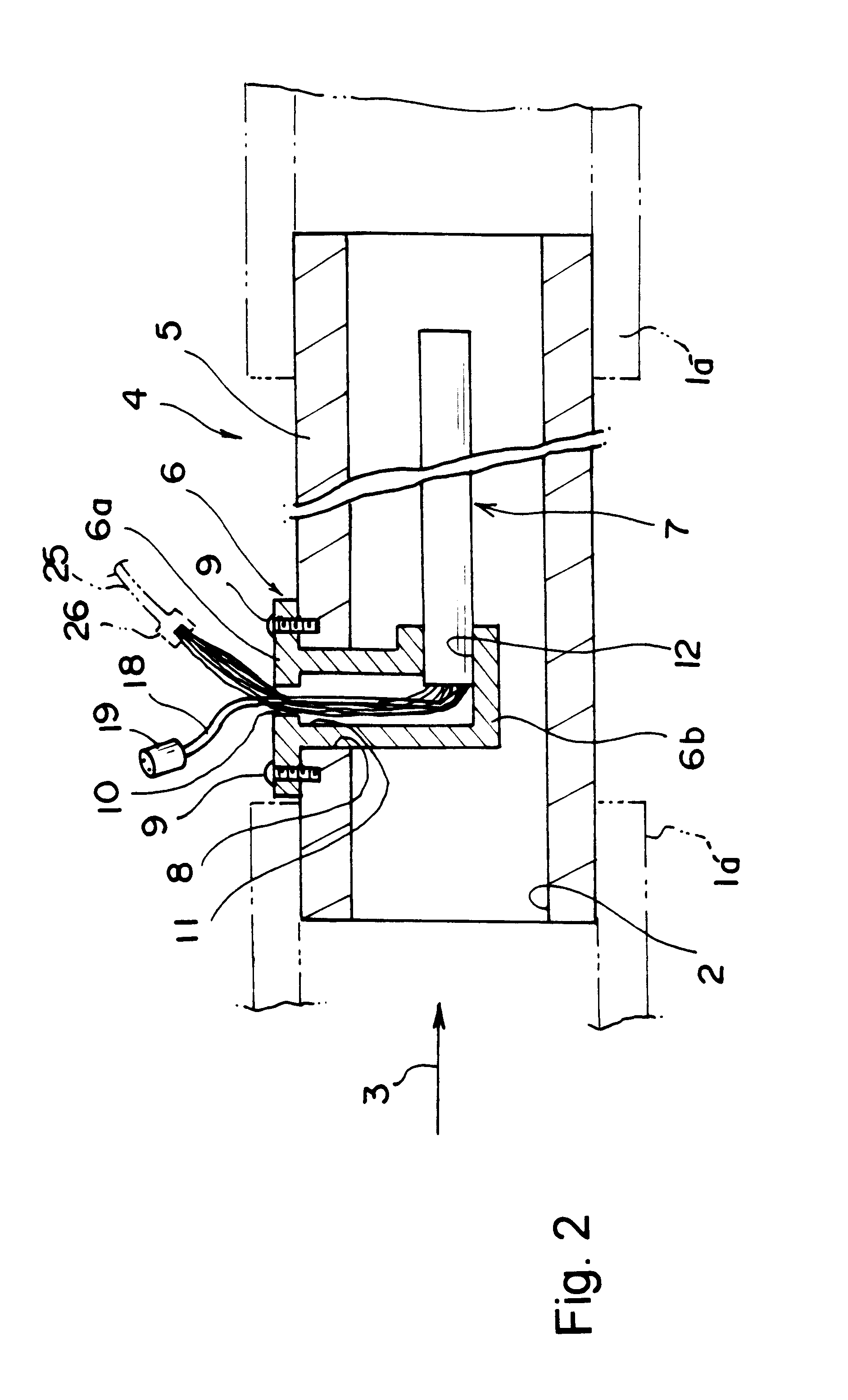
Toroidal ring ventilator
InactiveUS20160045696A1Augmenting negative intrapulmonary pressureNegative pressureTracheal tubesElectrocardiographyOxygenEndotracheal tube
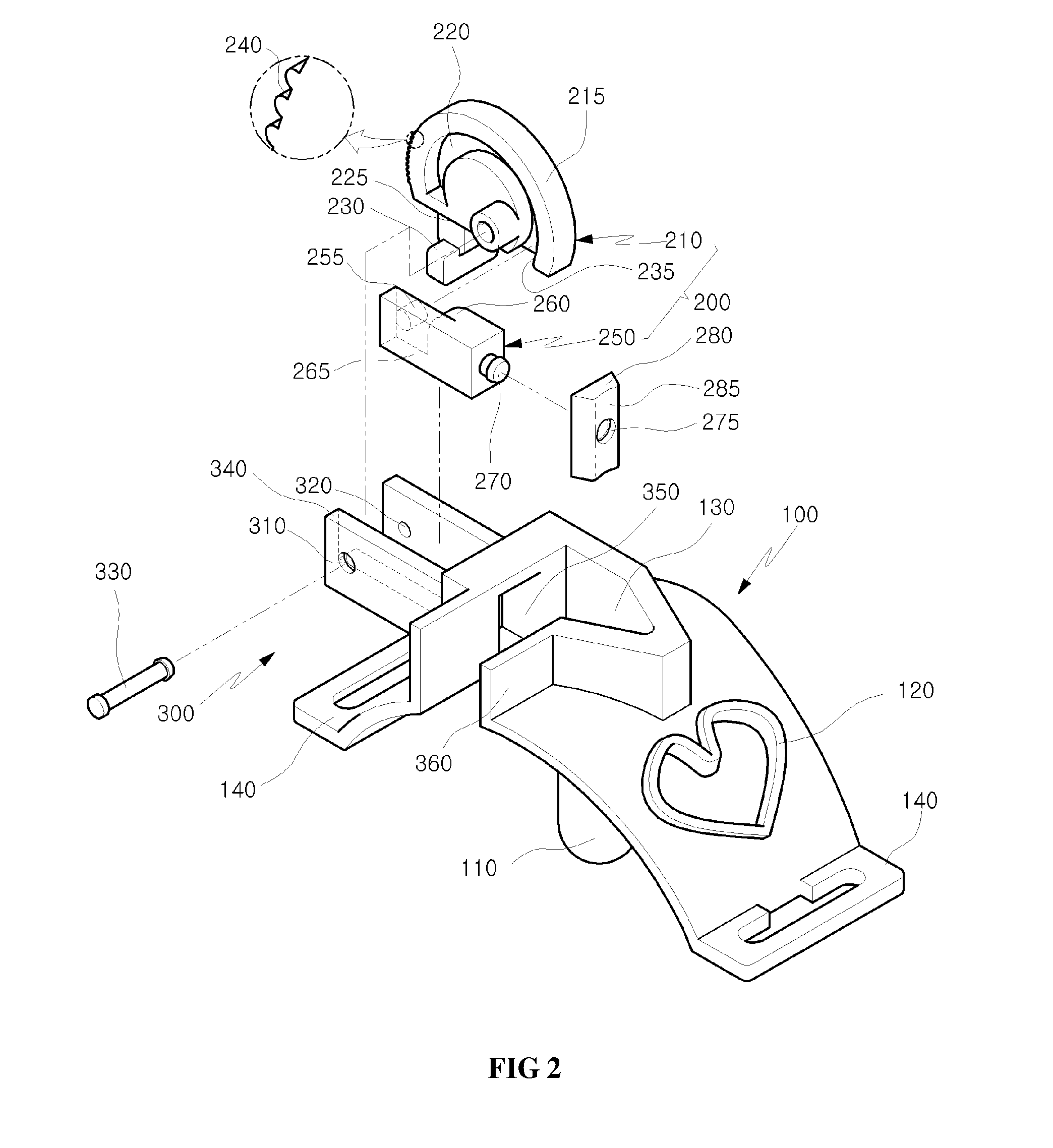
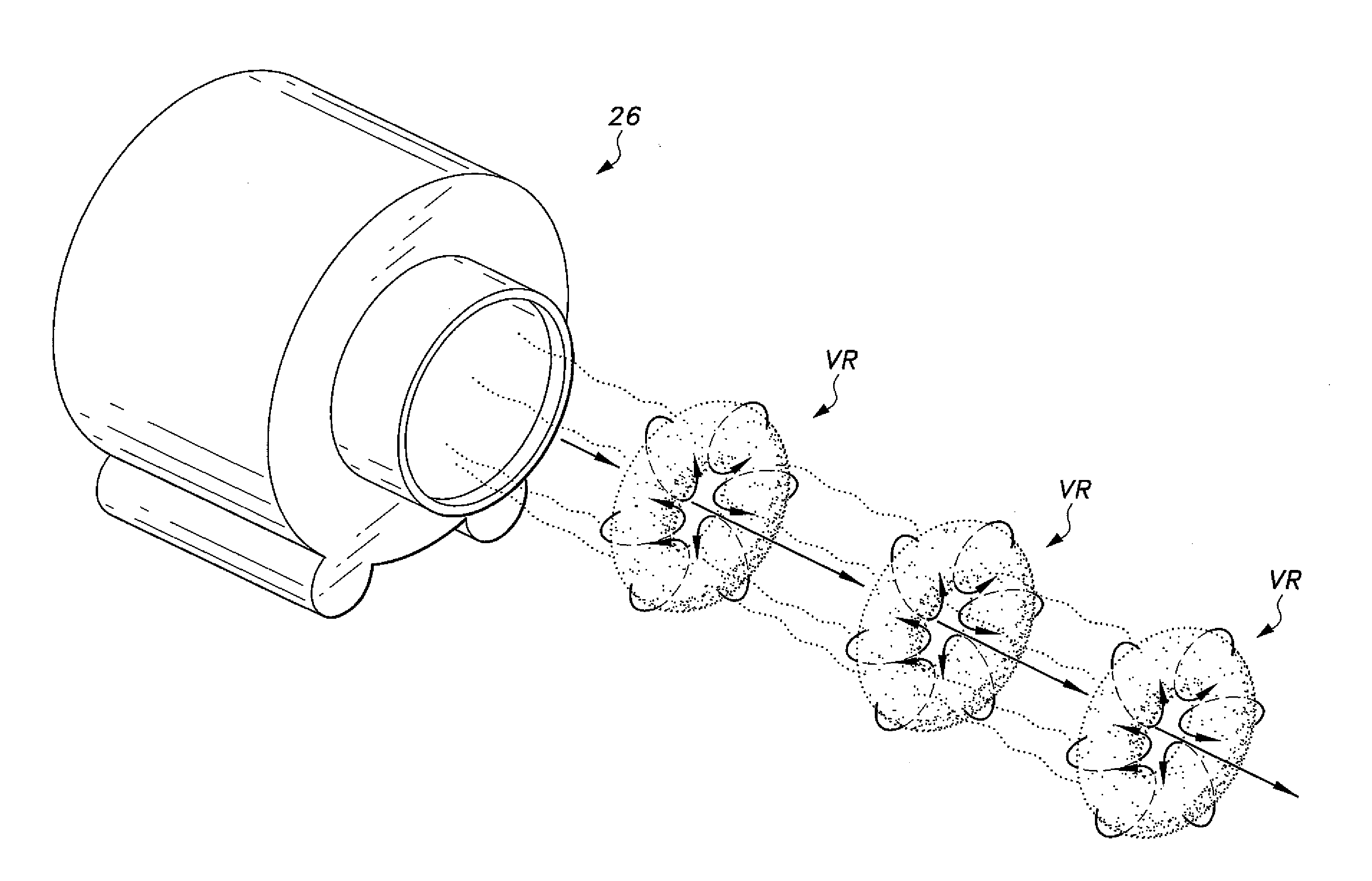
The mechanical ventilator system is a compact and portable artificial respiration system. A vortex ring generator delivers a FiO2 mix from an air-oxygen blender to a patient's alveoli via an endotracheal tube during the s patient's inhalations, but remains idle during the patient's exhalations. Exhaust gases generated by the patient are released through an exhaust gas valve. During operation, the patient's oxygen saturation level is measured and kept in communication to receive oxygen saturation level signals and to control the oxygen proportion of the FiO2 mix. A pressure flow sensor is fluidly coupled with the patient's airway to control actuation of the vortex generator. The flow sensor is coupled with a controller, which actuates a vortex generator trigger circuit in communication with the vortex ring generator.
Owner:SIRIWARDENA MAPATUNAGE A +1
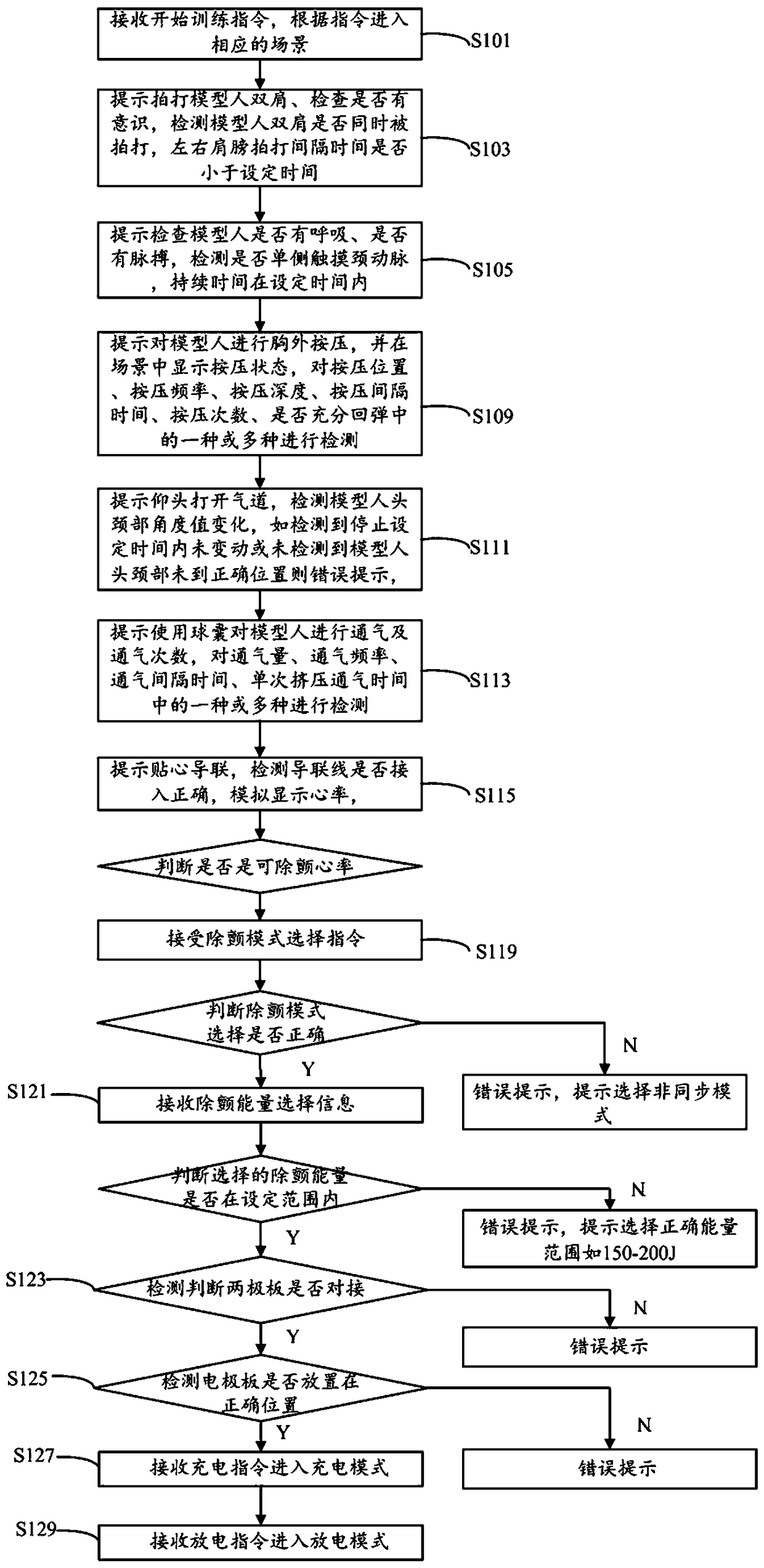
First aid simulation training method and virtual simulation first aid training system
InactiveCN108694873AImprove first aid operation abilityCosmonautic condition simulationsEducational modelsConductive pasteArtificial respiration
The invention discloses a first aid simulation training method and system. The method comprises steps of scene entering, consciousness judgment, emergency first aid and CPR simulation. The CPR simulation comprises external chest compression, airway opening and artificial respiration. In the case of the CPR simulation or after the CPR simulation, simulated electrocardiogram monitor connection is entered, whether to be a defibrillation heart rate is judged, and if yes, simulated defibrillation is entered. Simulated defibrillation comprises defibrillation mode selection, defibrillation energy selection, conductive paste coating, electrode plate placement, charging and discharging. According to the above first aid simulation training method and the virtual simulation first aid training system,an operator is guided by a prompt to perform the first aid, the operation is judged and evaluated timely, the judgment and the evaluation are timely fed back to the operator, the operator is guided for operation, guidance is timely given, how to perform CPR is guided, how to operate on a defibrillator for defibrillation is guided, the operation is guided step by step, the operation is judged andevaluated timely, and the first aid operation ability of the operator is improved.
Owner:苏州敏行医学信息技术有限公司
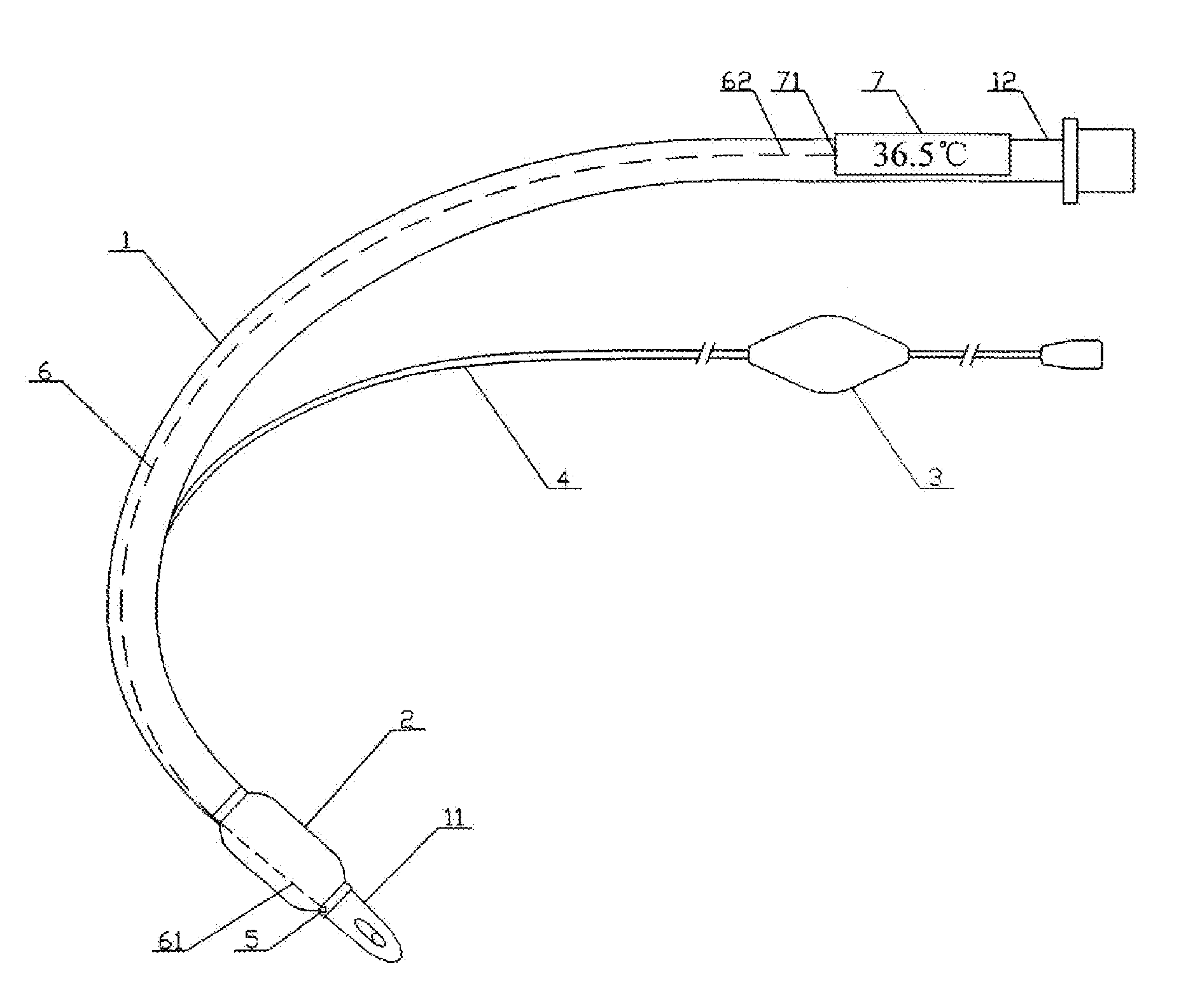
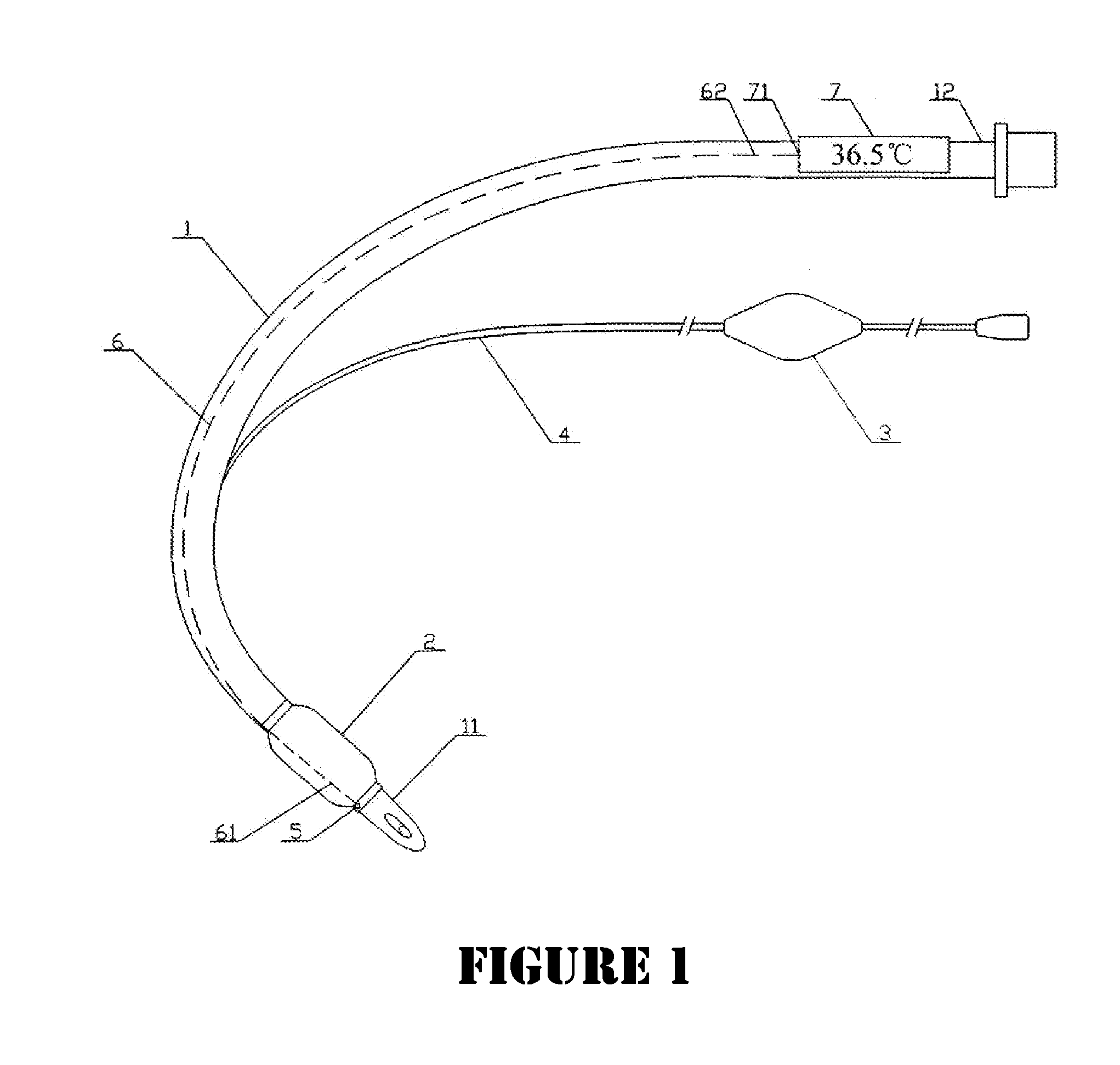
Artificial Airway with Integrated Core Temperature Monitor
This is a device for use in clinical, surgical intro- and post-operative patient core temperature monitoring, which utilizes an artificial airway to integrate a temperature probe, removing the need for an external cord for connecting to an external display unit, or the traditional way of an esophageal tube that necessitates more medical procedures. Consequently, for patients under general anesthesia with ET Tube or LMA, accurate monitoring of core temperature becomes feasible. As a result, the overall cost for surgical operation, including that of anesthesia, is reduced and the with reduced risk of complication associated with extra oral procedural for inserting an esophageal tube to measure temperature.
Owner:HE KONGYUAN +1
Respirator
The invention discloses a respirator, which comprises an oxygen therapy system and a breathing mask, wherein the breathing mask is connected with the oxygen therapy system, and can press over a face respiratory organ of a rescue receiver through being driven by a press-down mechanism. During CPR (cardiopulmonary resuscitation), the artificial respiration and the external chest cardiac compression are cooperated; after each external chest compression period is completed, the breathing mask presses over the face of the rescue receiver; oxygen gas is conveyed to the mouth and the nose of the rescue receiver through the breathing mask; the oxygen quantity of oxygen therapy to the rescue receiver is increased; and meanwhile, the workload of a rescuer can be reduced. In addition, the respirator also has the following two functions: 1, the respirator can replace a common-use artificially opened airway; and 2, a chest compression counting mechanism can accurately record the number of thoracic compression times, can report the number after each time of thoracic compression to control the external chest compression frequency, can automatically press down the breathing mask after the completion of each chest compression period, and can automatically extruding a breathing bag twice, so that the cooperation of the chest compression and the oxygen intake is accurate.
Owner:THE THIRD AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF THIRD MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF PLA
Device for cardio-pulmonary resuscitation training
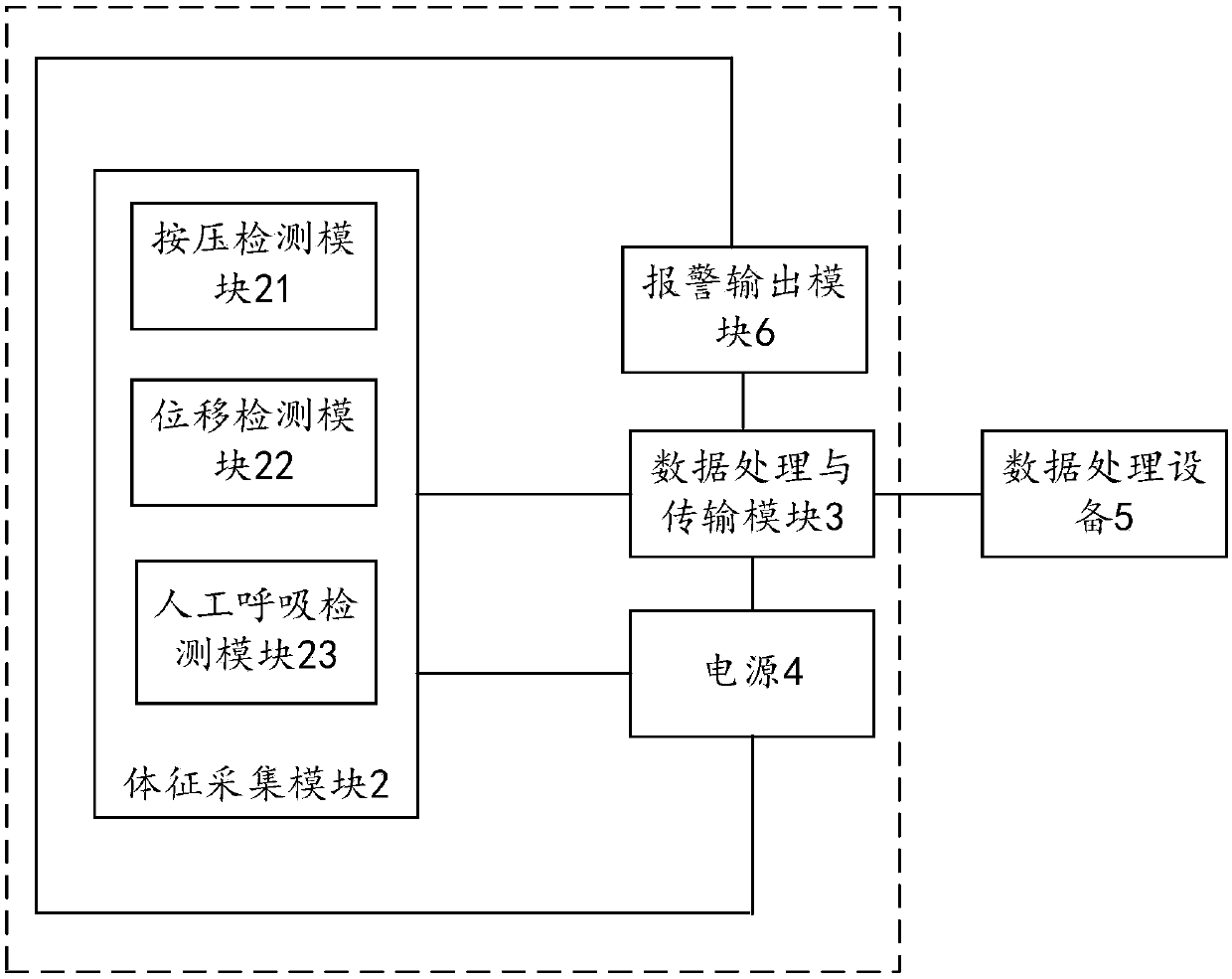
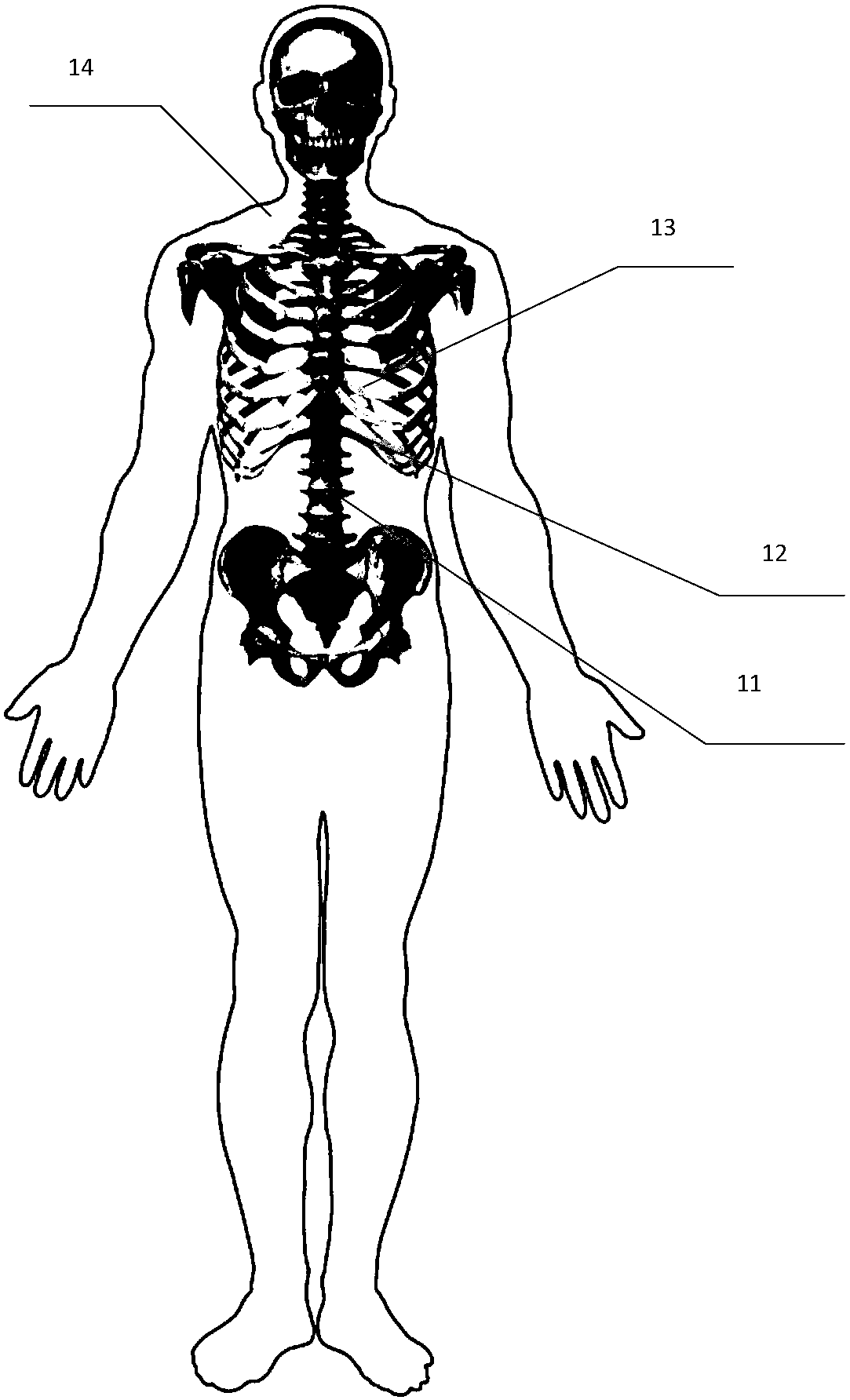
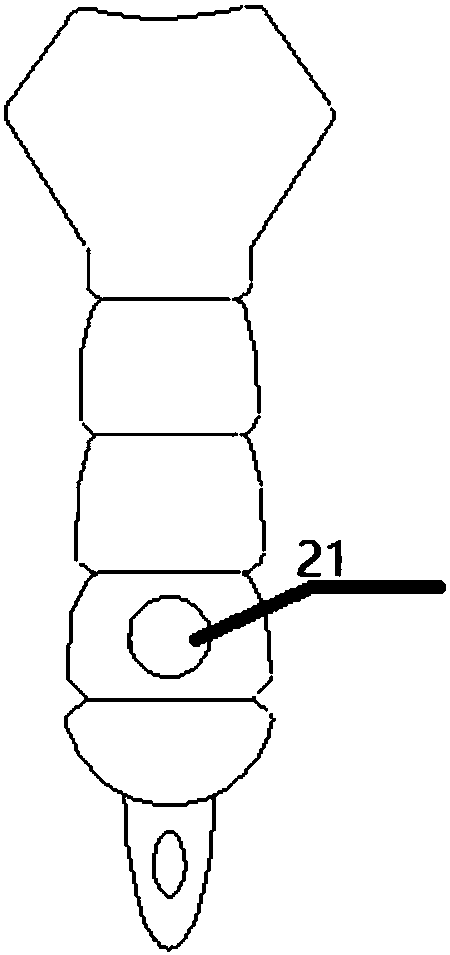
The invention relates to a device for cardio-pulmonary resuscitation training. The device comprises a training model, a physical sign acquisition module and a data processing and transmission module,a sternum model in the training module is made of stainless steel elastic plate strips; the physical sign acquisition module comprises a pressing detection module, a displacement detection module, andan artificial respiration detection module, wherein the pressing detection module is arranged on the sternum model, a pressing pressure stressed on the sternum model is induced to generate a pressingdetection signal, the displacement detection module is arranged on a spinal model and corresponds to the position of the pressing detection module, the change of the distance between the sternum model and the spinal model is detected to generate a displacement detection signal; the artificial respiration detection module is arranged in a simulated chest cavity, and the gas flow in the simulated chest cavity is detected to generate a gas flow detection signal; the data processing and transmission module receives the pressing detection signal, the displacement detection signal and / or the gas flow detection signal and sends to a data processing device for analyzing and processing, cardio-pulmonary resuscitation training monitoring data and / or result data is generated and output.
Owner:ANYANG NORMAL UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com