Patents
Literature
34 results about "Diaphragm muscle" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
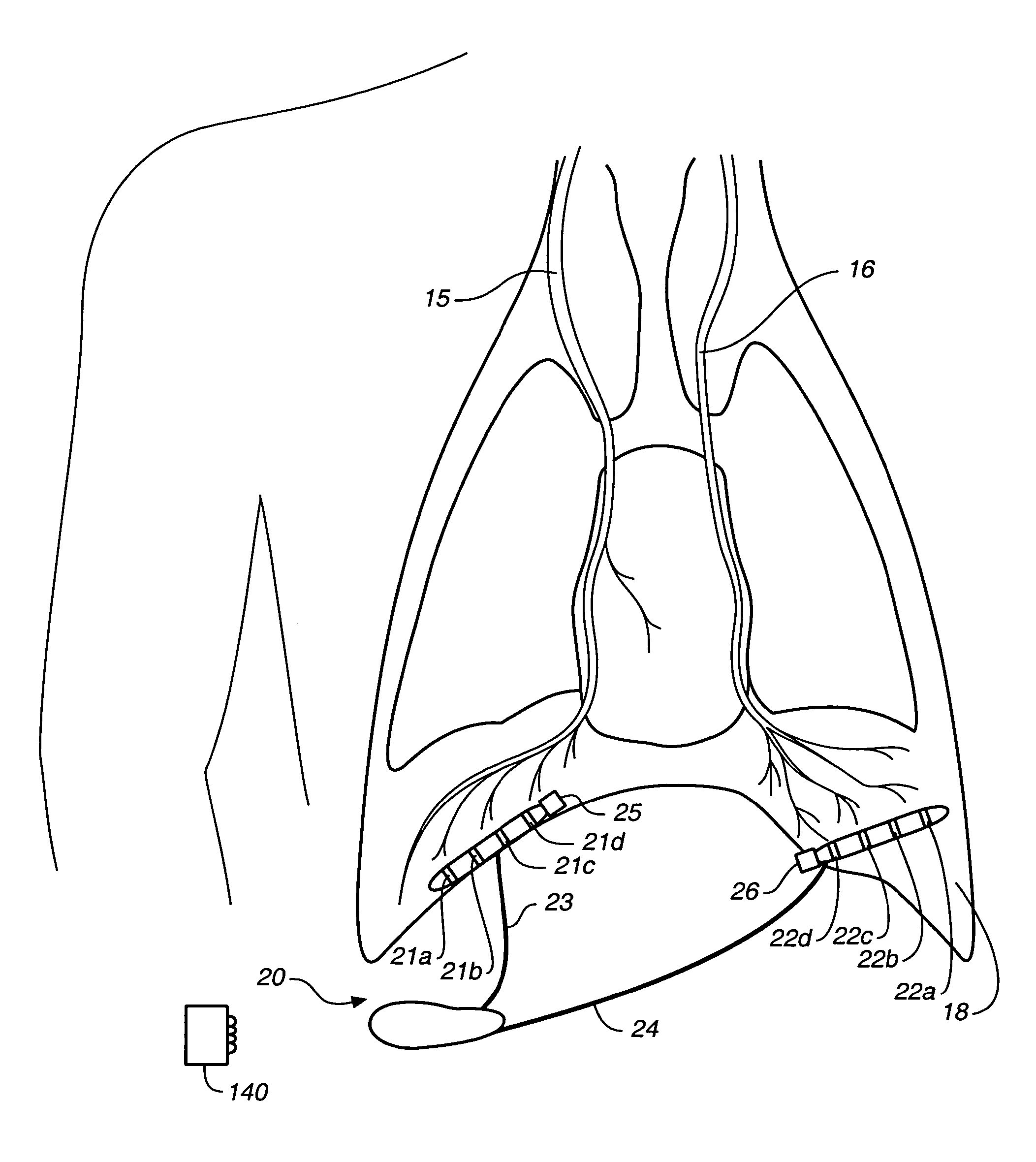
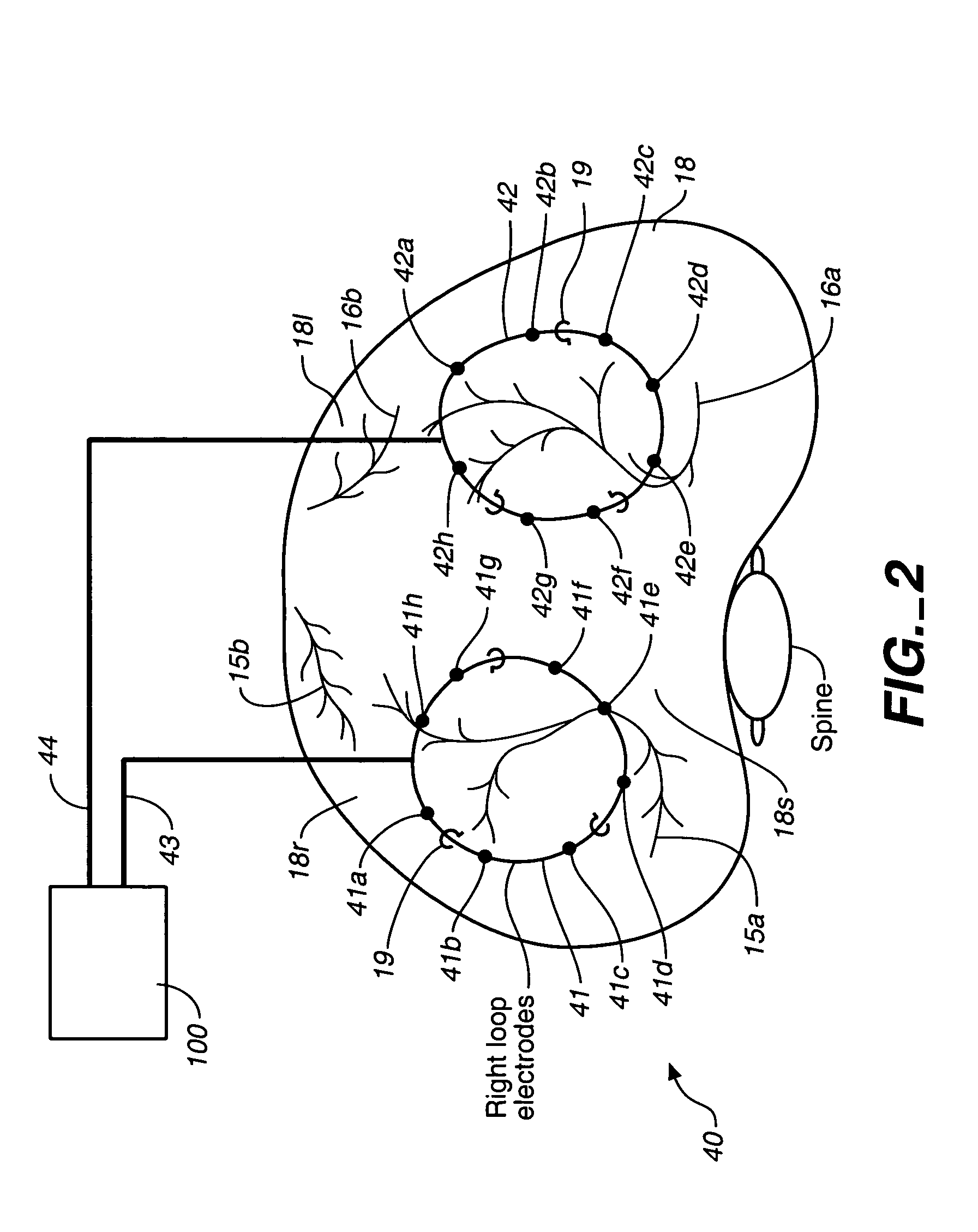
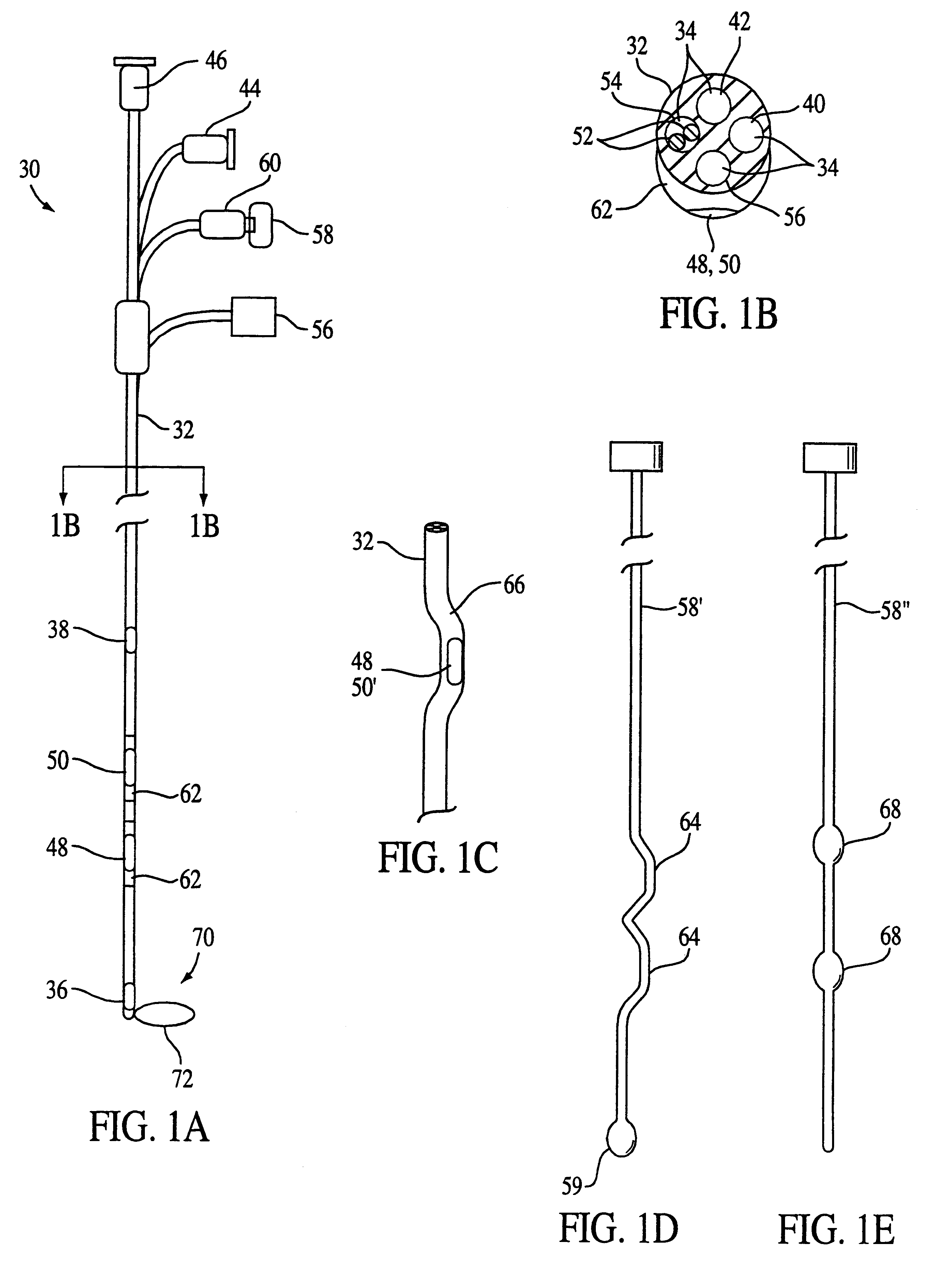
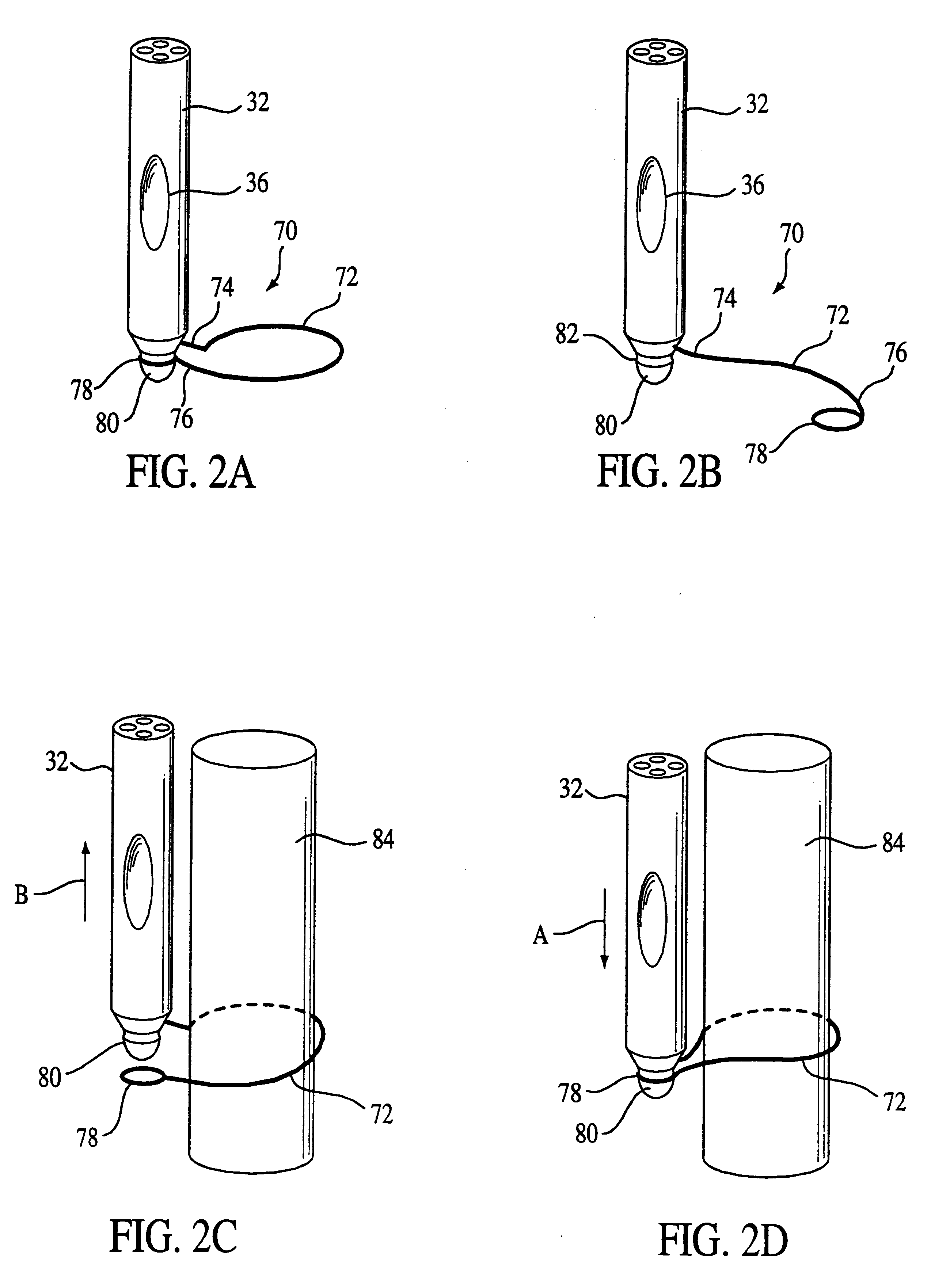
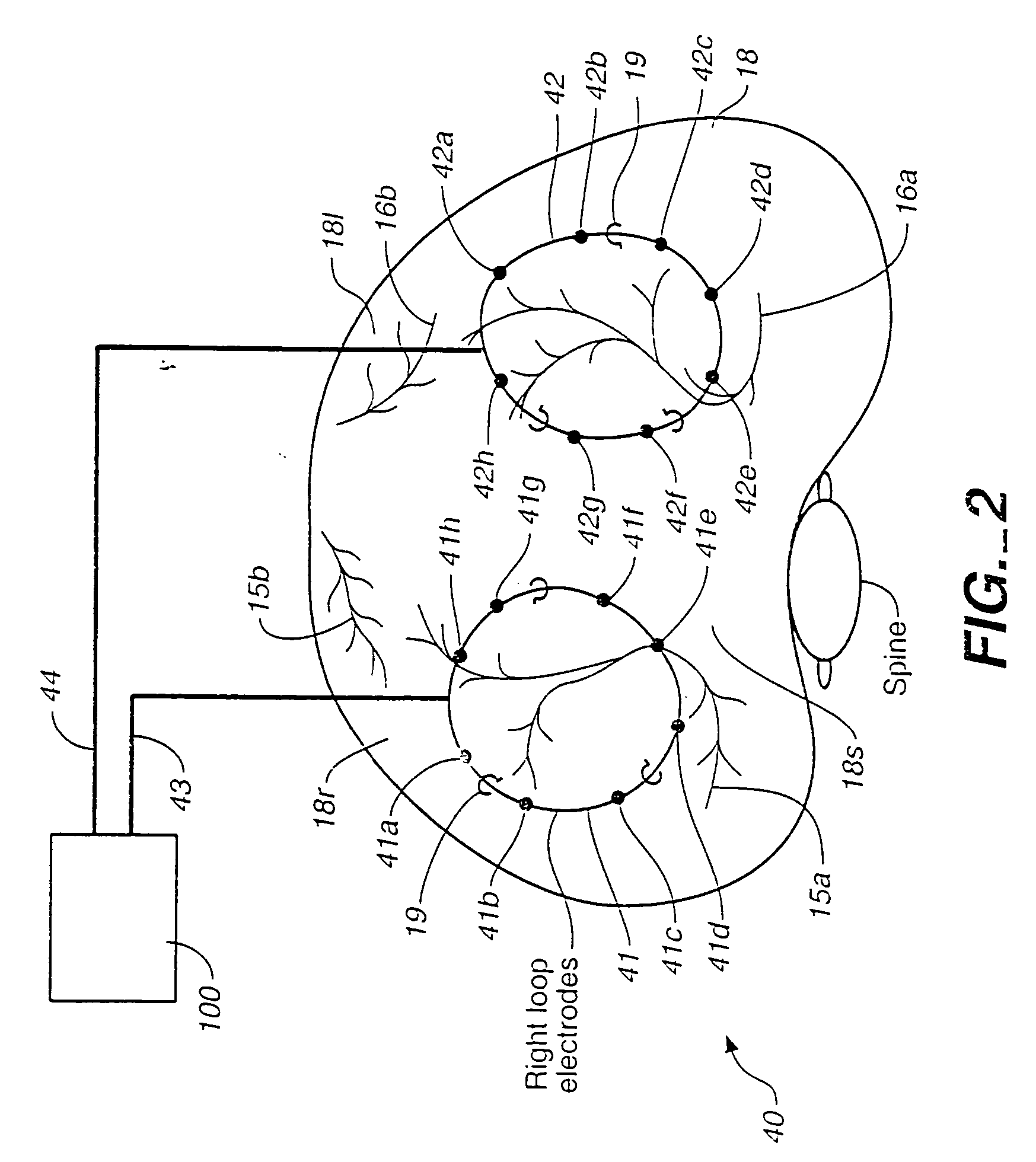
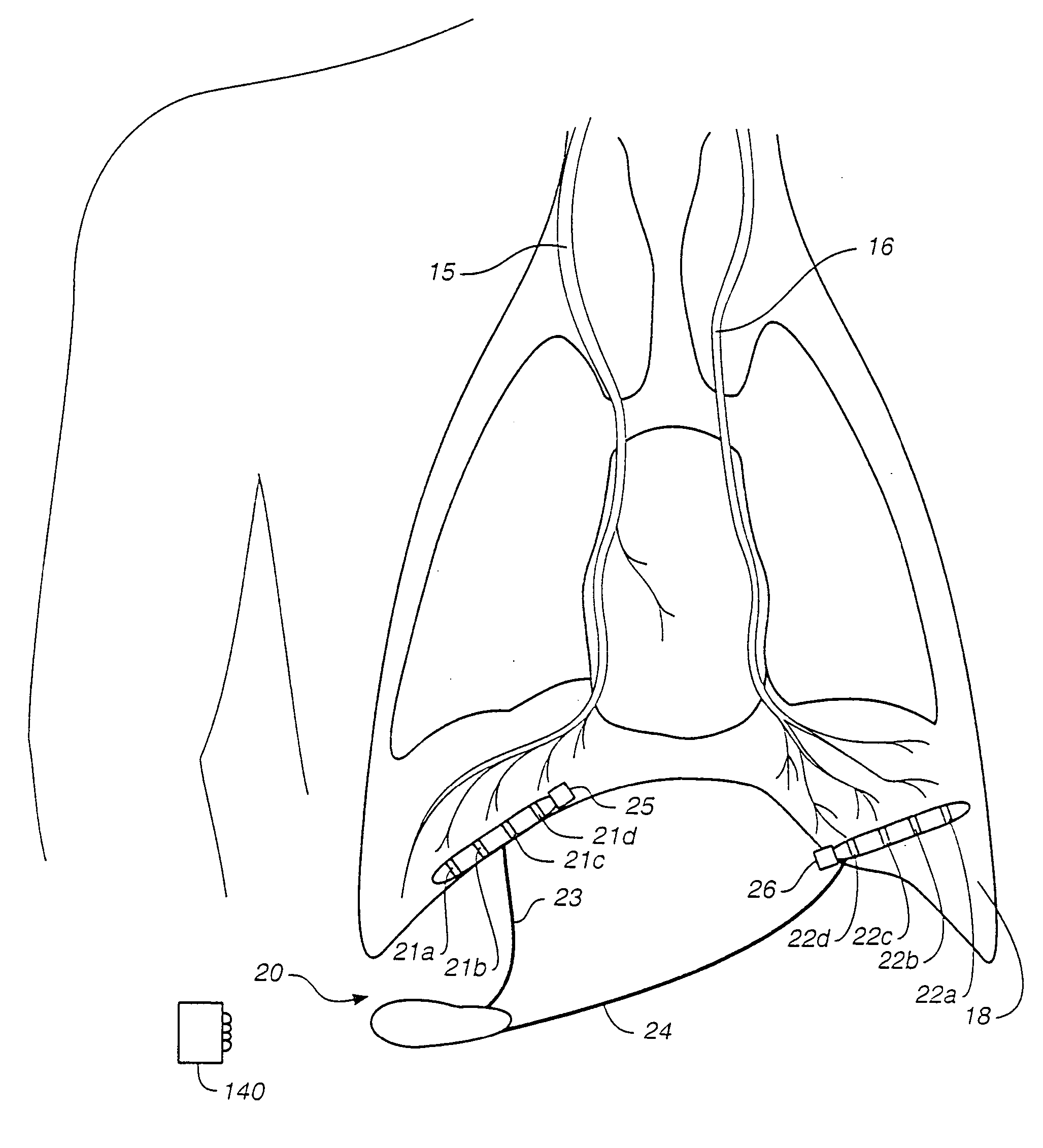
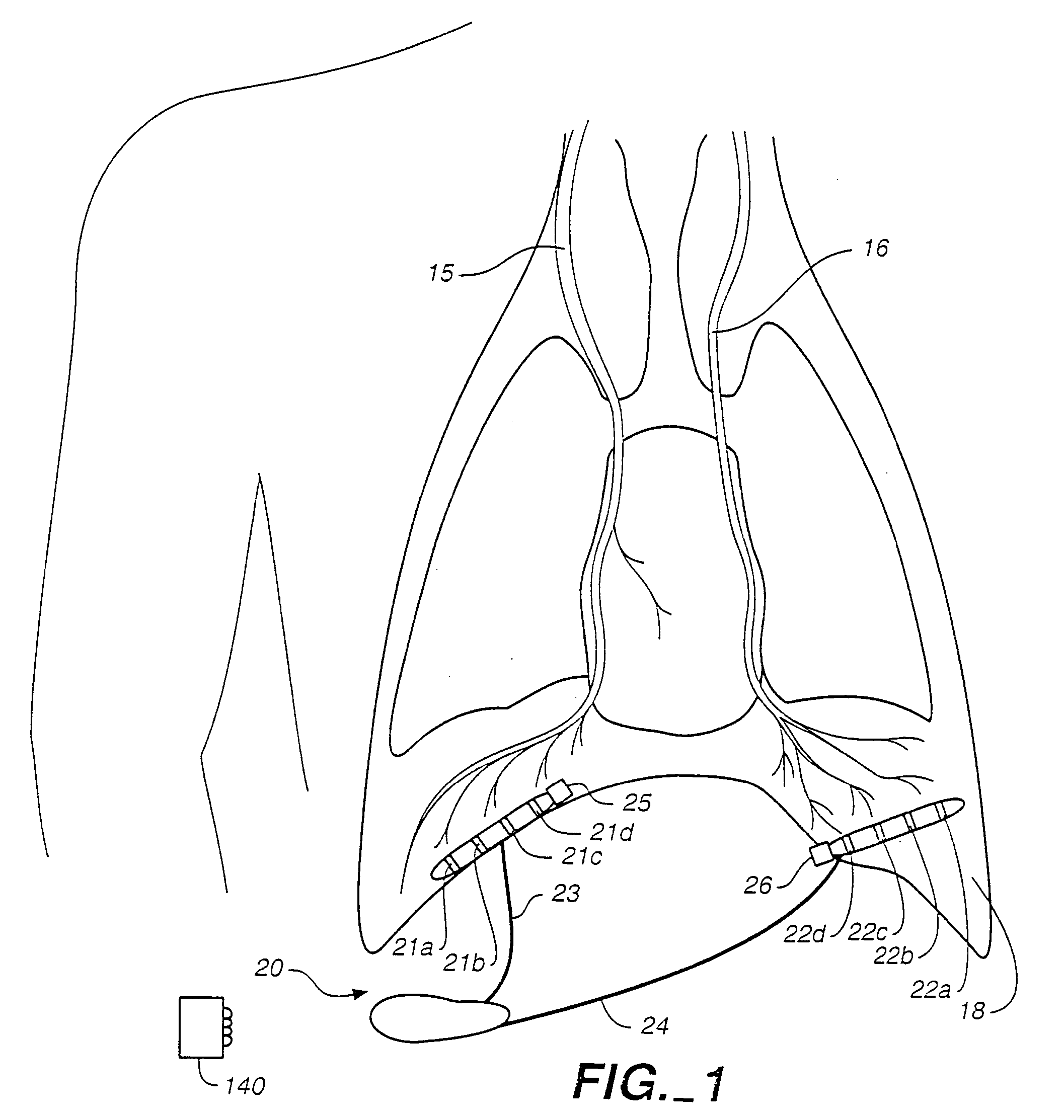
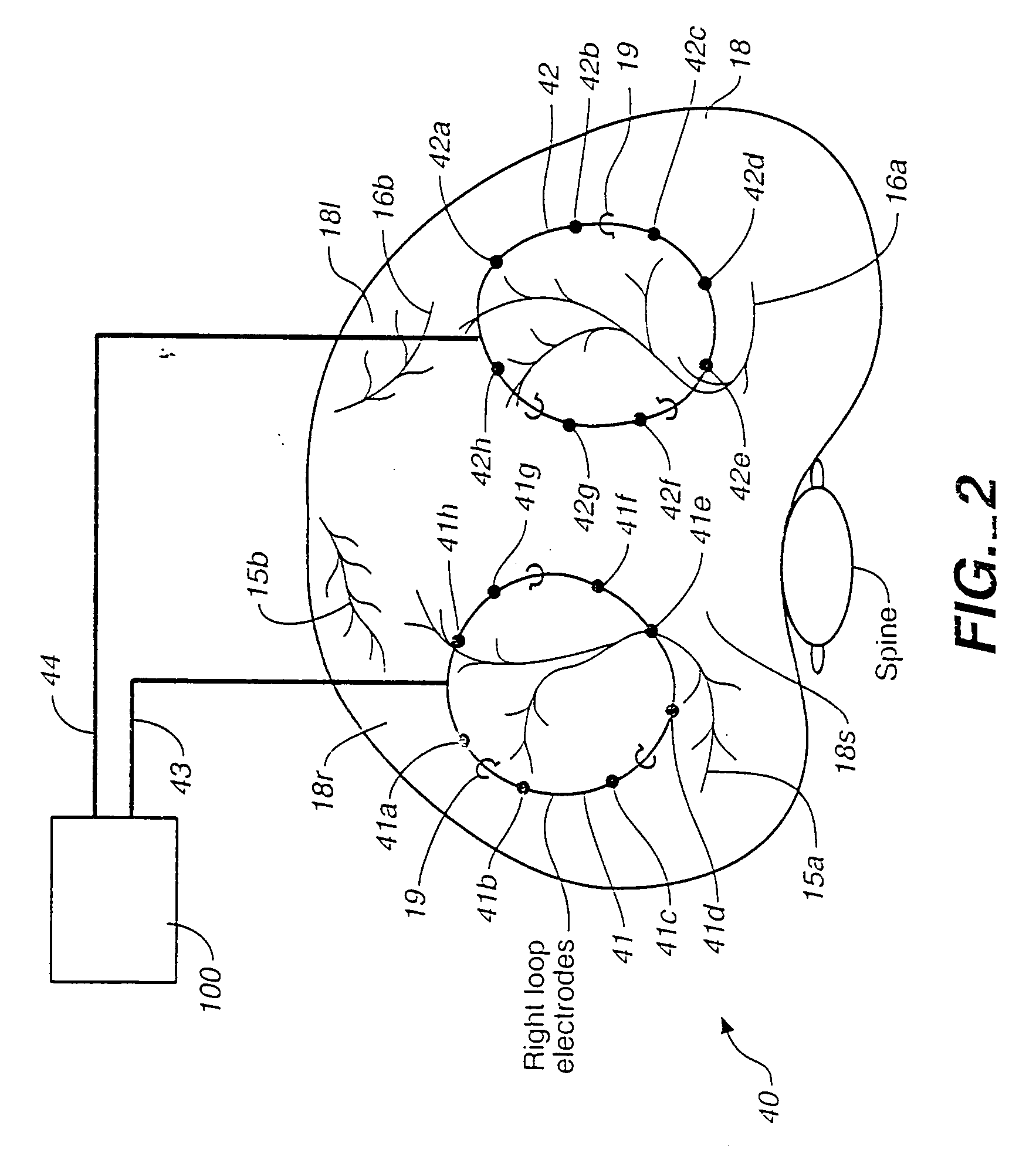
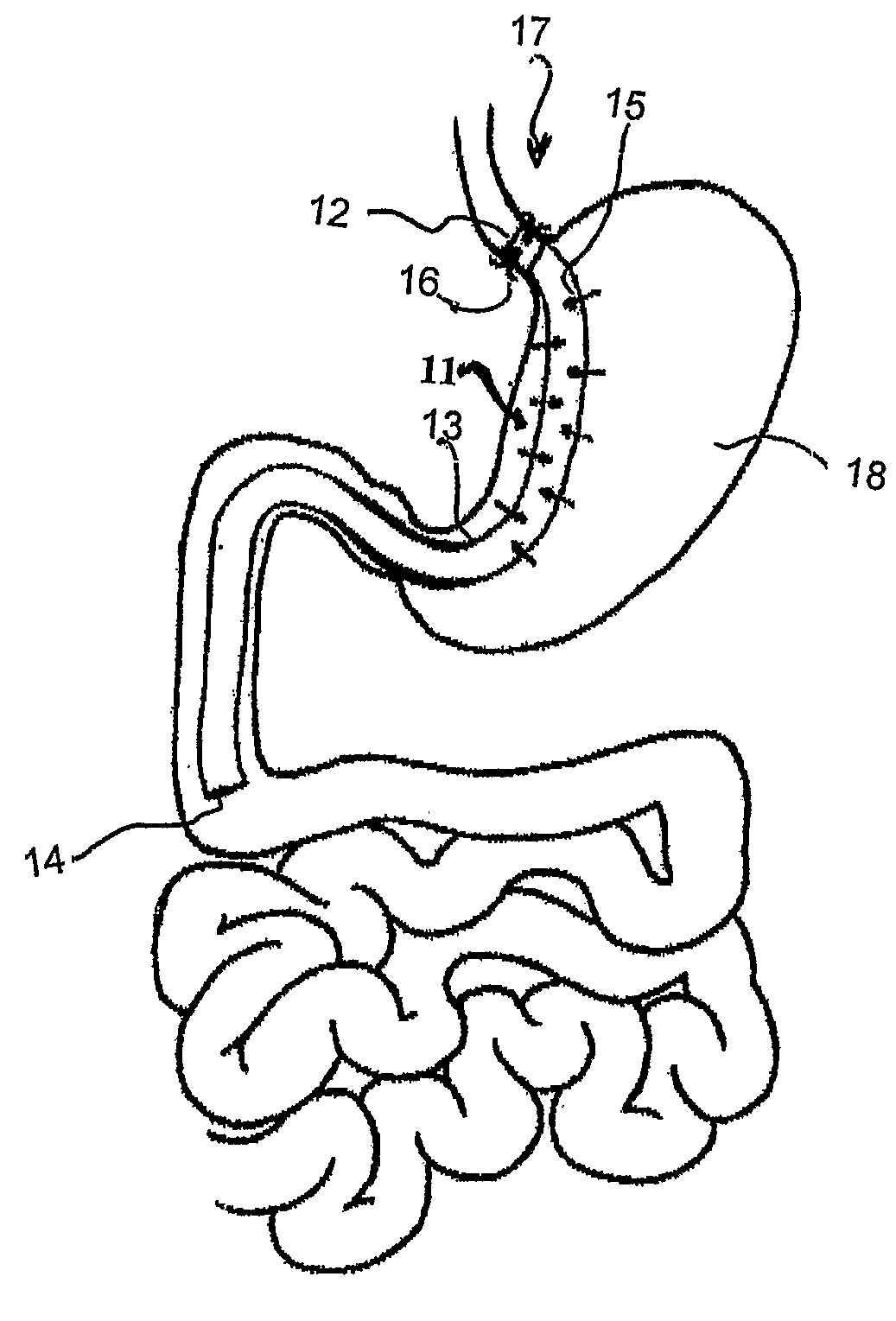
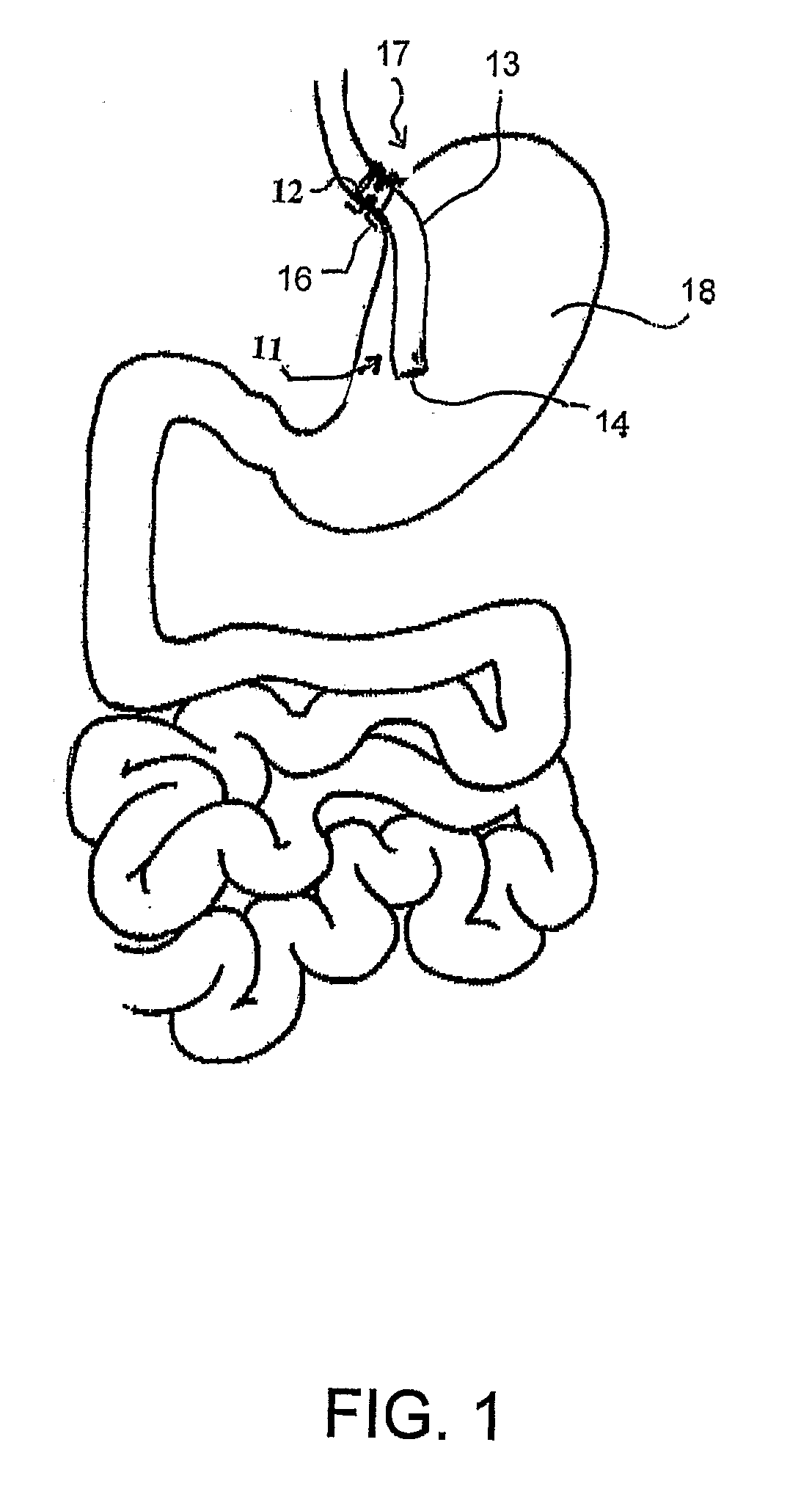
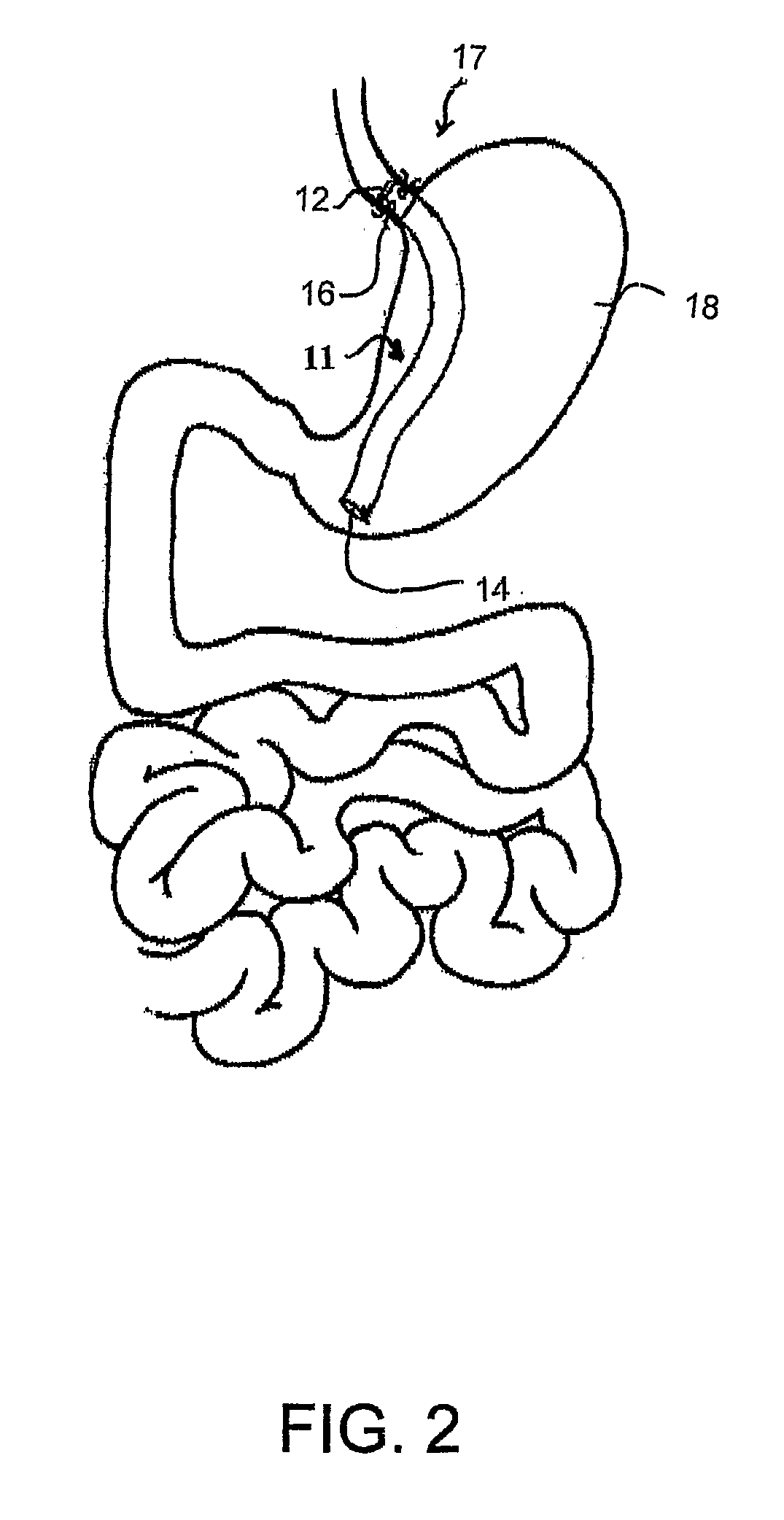
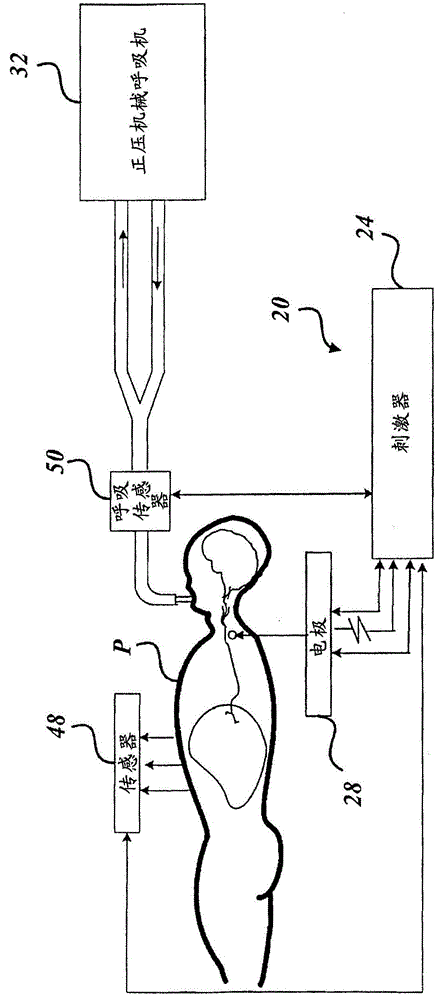
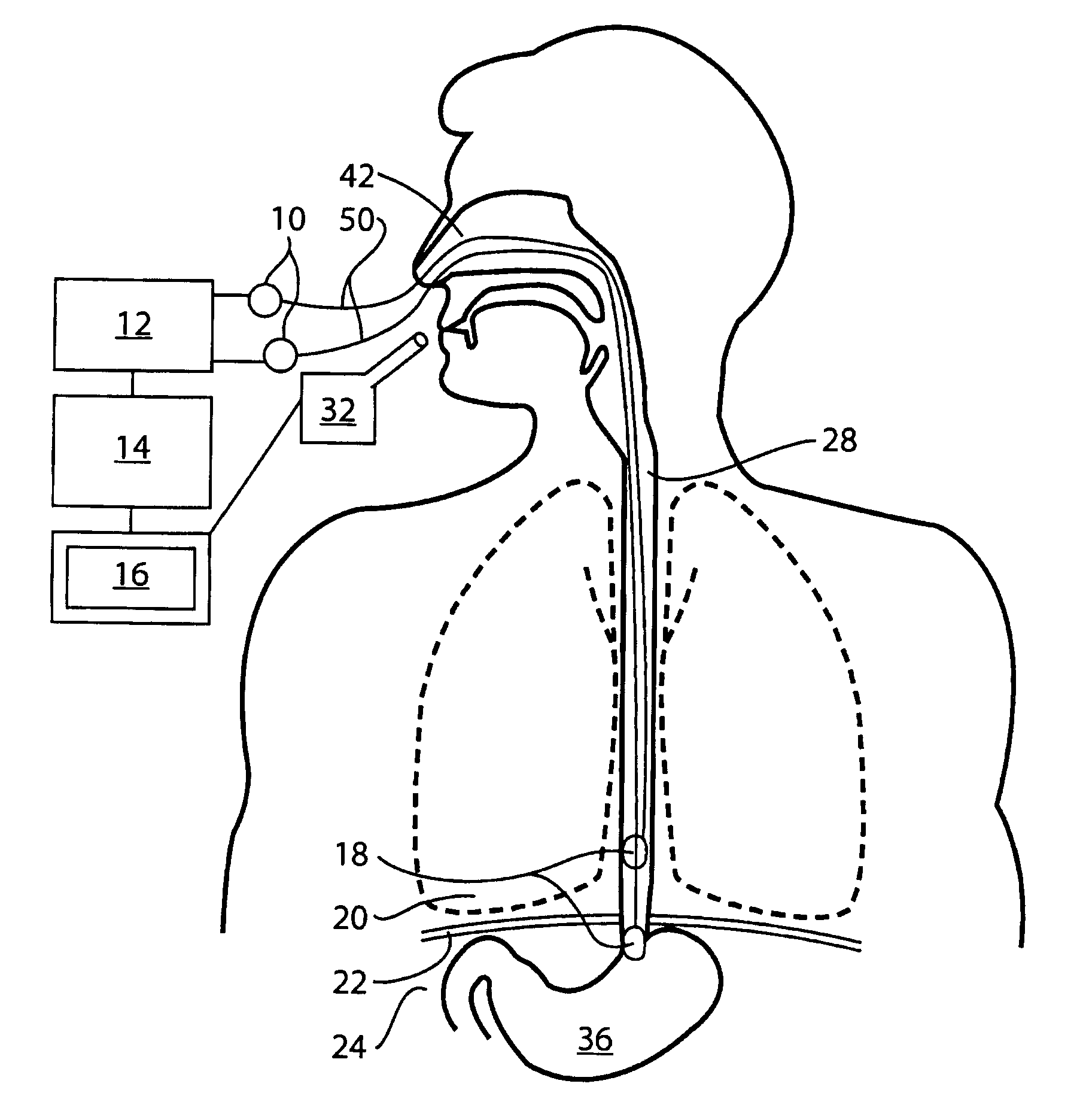
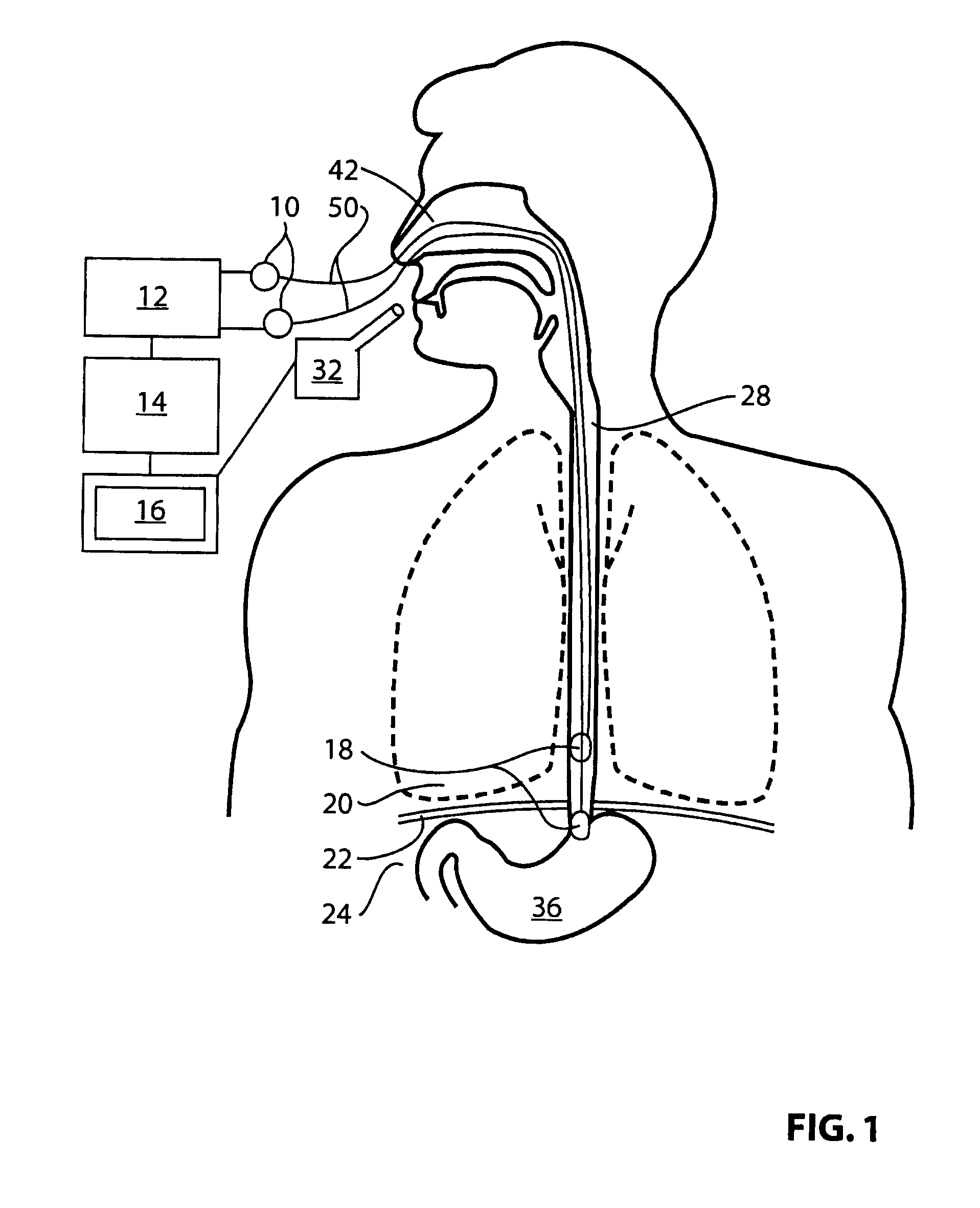
Breathing disorder detection and therapy delivery device and method
A device and method are provided for managing the treatment of a patient with respiratory disorders or symptoms. Respiratory parameters are sensed and recorded and communicated to an external device to provide information to a patient and / or provider for further treatment or diagnosis. Also respiratory disorders such as apnea or hypoventilation may be treated by electrically stimulating the diaphragm muscle or phrenic nerve in response to a sensed respiratory parameter or characteristic.
Owner:RMX
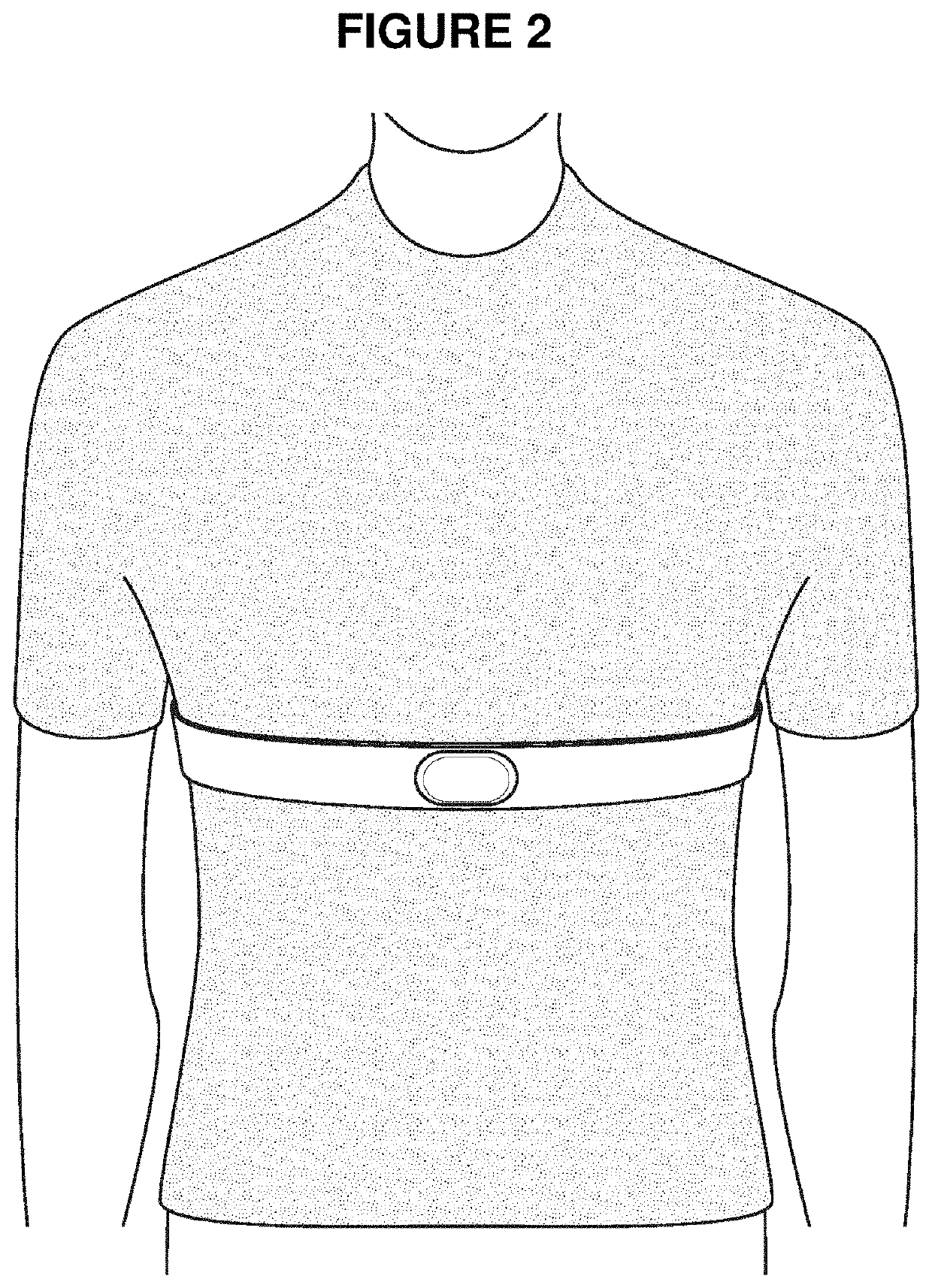
Monitoring catheter and method of using same
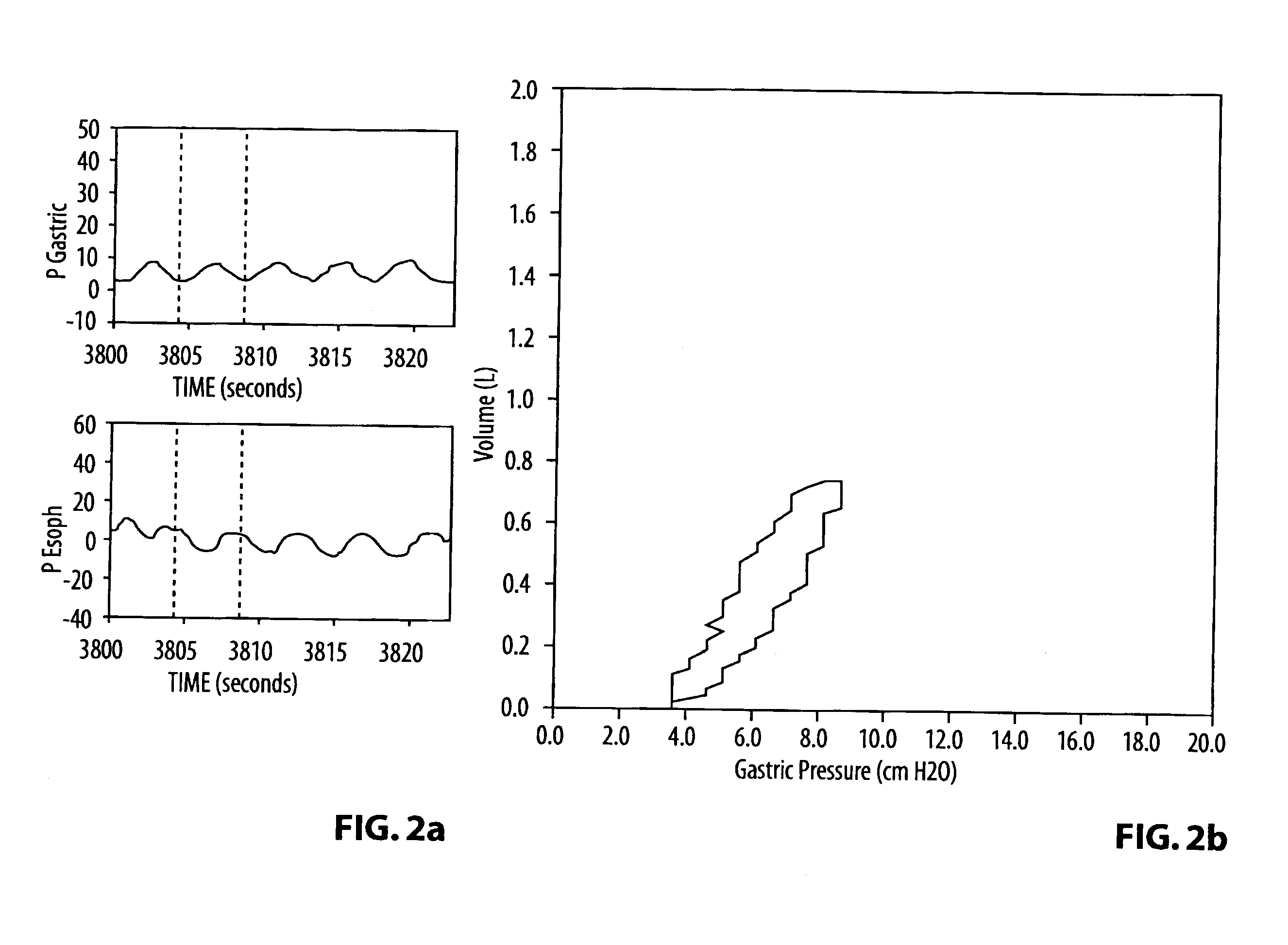
A monitoring catheter that inserts into the patient's esophagus alone or in combination with an existing catheter, such as a feeding or aspiration tube. The monitoring catheter includes a pair of EMG electrodes on an exposed surface that contact the patient's esophageal wall to measure the activity of the diaphragm and / or a pair of pressure detecting mechanisms that measure the pressures within the patient at separate locations. The electrodes are sized and spaced from one another so as to maximize detection of diaphragm muscle activity while minimizing detection of noise. The pressure detecting mechanisms are sized and spaced apart to measure the patient's esophageal and gastric pressures, for example. If necessary, an attaching mechanism secures at least a portion of the monitoring catheter to the existing catheter so that the monitoring catheter uses the existing catheter as a tracking guide.
Owner:RIC INVESTMENTS LLC
Breathing disorder detection and therapy device for providing intrinsic breathing
A device and method are provided for managing the treatment of a patient with respiratory disorders or symptoms. Respiratory parameters are sensed and recorded and communicated to an external device to provide information to a patient and / or provider for further treatment or diagnosis. Also respiratory disorders such as apnea or hypoventilation may be treated by electrically stimulating the diaphragm muscle or phrenic nerve in response to a sensed respiratory parameter or characteristic.
Owner:RMX
Patient compliance management device and method
A device and method are provided for managing the treatment of a patient With respiratory disorders or symptoms. Respiratory parameters are sensed and recorded and communicated to an external device to provide information to a patient and / or provider for further treatment or diagnosis. Also respiratory disorders such as apnea or hypoventilation may be treated by electrically stimulating the diaphragm muscle or phrenic nerve in response to a sensed respiratory parameter or characteristic.
Owner:RMX
Medical Device and Method For Controlling Obesity
InactiveUS20080249533A1Slow down passage of foodEat more slowlyEar treatmentOesophagiPyloric orificeDiaphragm muscle
A method of, and device for, slowing the passage of food through a digestive tract of a patient and thereby treating obesity. The device is an obesity tube comprising (A) an upper ring of a size corresponding to a point under a patient's esophagus and above the patient's diaphragm muscle, and (B) a lower tube having a length and a distal opening. The method comprises stapling the upper ring under the patient's esophagus, above the patient's diaphragm muscle, and placing the lower tube distal to the upper ring. The length of the lower tube depends on whether the tube is to terminate distally in the stomach or terminate past the pylorus, in which case a section can be provided which is thick enough to resist collapsing under pylorus pressure. The lower tube can be entirely or partially non-permeable or semi-permeable. Semi-permeable tubes or sections thereof have walls which permit the passage of gastric hydrochloric acid but not food.
Owner:KS BIOMEDIX LTD
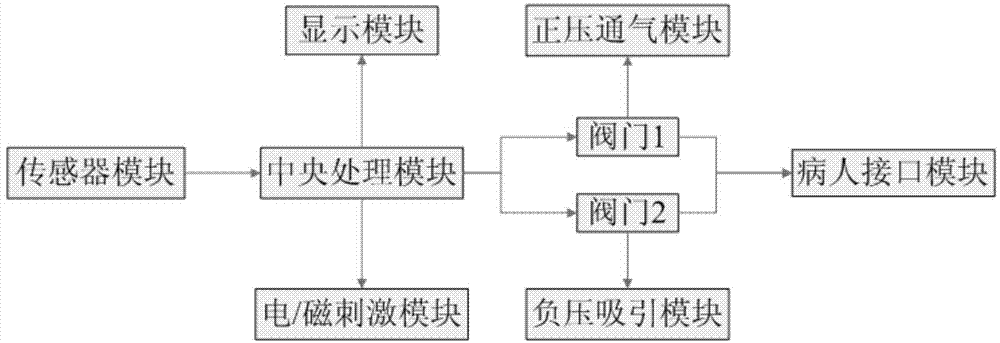
Diaphragm muscle stimulation inspiration and expiration system
ActiveCN103933648AGood man-machine synchronizationReduce man-machine confrontationRespiratorsElectrotherapyElectricityPositive pressure
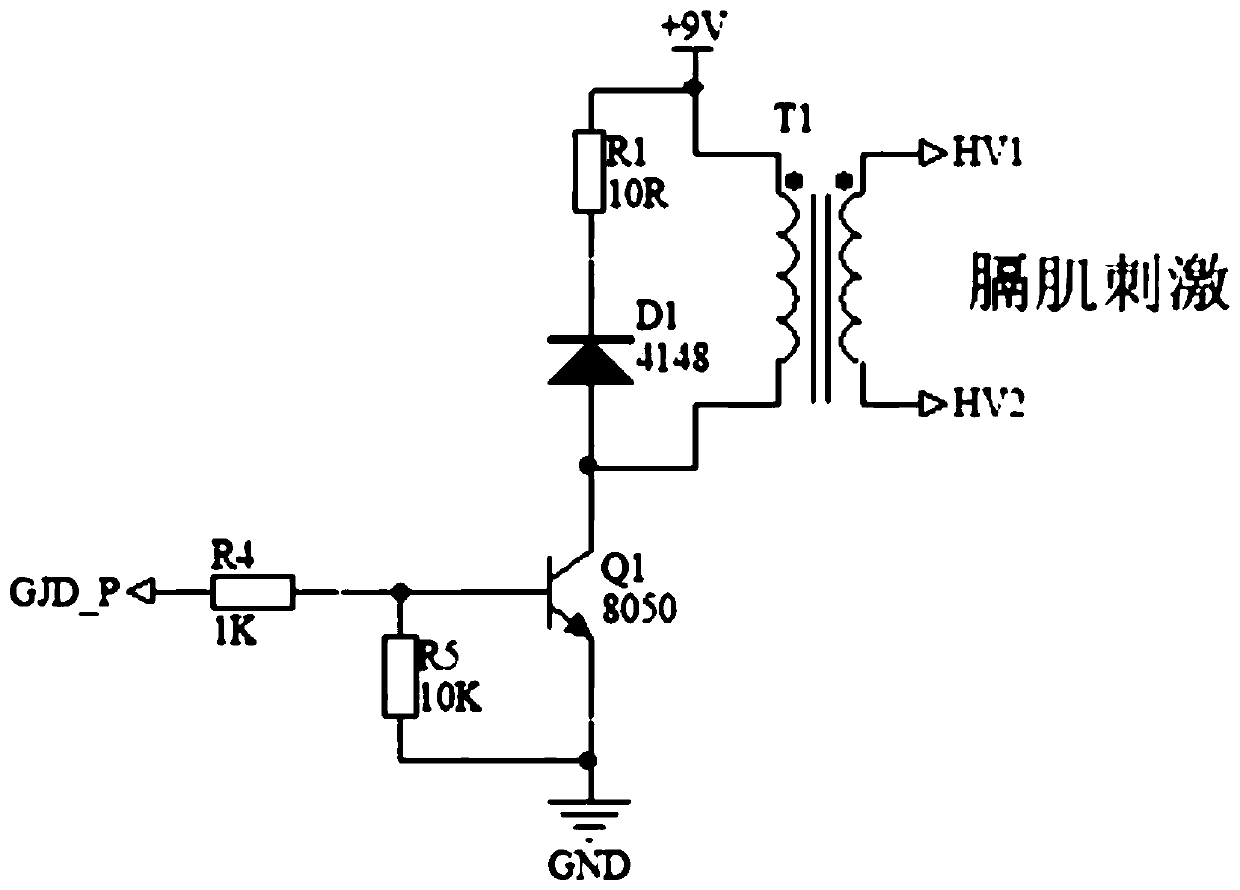
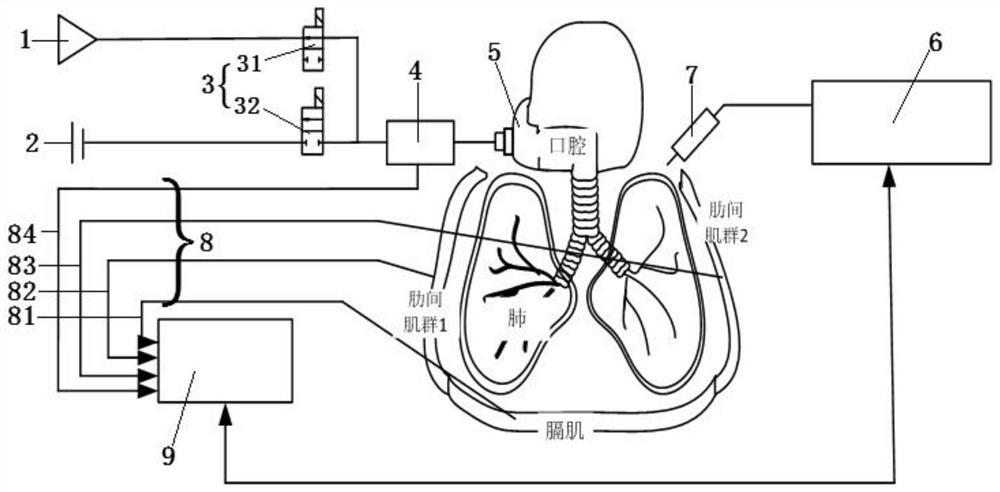
The invention relates to the field of medical health, and provides a diaphragm muscle stimulation inspiration and expiration system. The diaphragm muscle stimulation inspiration and expiration system comprises a positive pressure ventilation module, a negative pressure aspiration module, a patient connector module, a central processing module and an electric / magnetic stimulation module. The positive pressure ventilation module is used for generating positive pressure air flow. The negative pressure aspiration module is used for generating negative pressure air flow. The patient connector module is used for allowing the positive pressure air flow and the negative pressure air flow to pass through. The positive pressure ventilation module, the negative pressure aspiration module and the patient connector module are connected through a tee joint device. The central processing module is connected with the tee joint device and the electric / magnetic stimulation device. The central processing module controls on-off of the positive pressure ventilation module, the negative pressure aspiration module and the patient connector module through the tee joint device and controls whether the electric / magnetic stimulation module works or not.
Owner:YAGUO
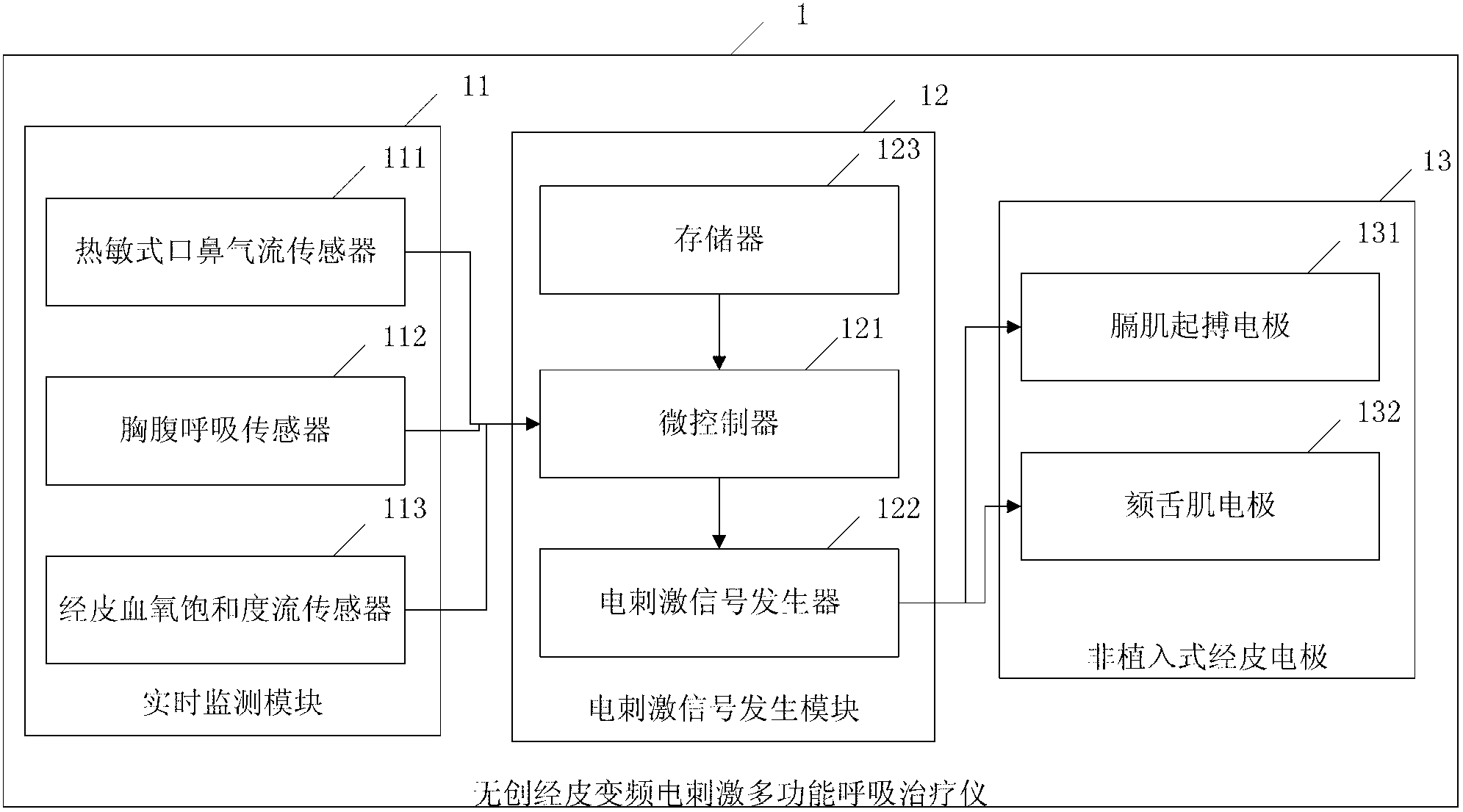
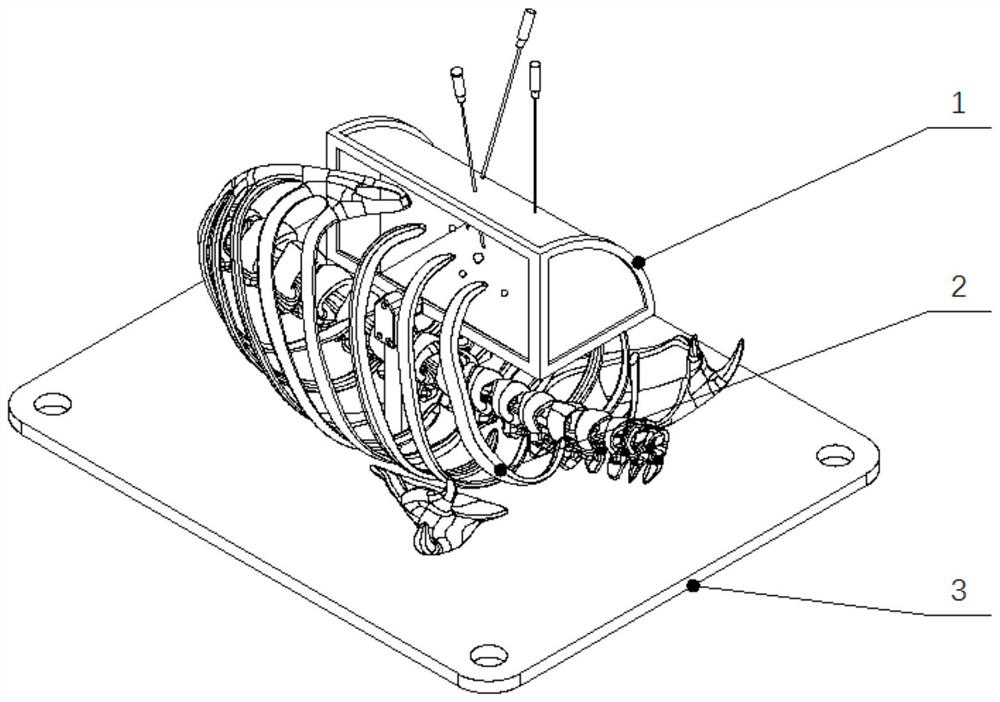
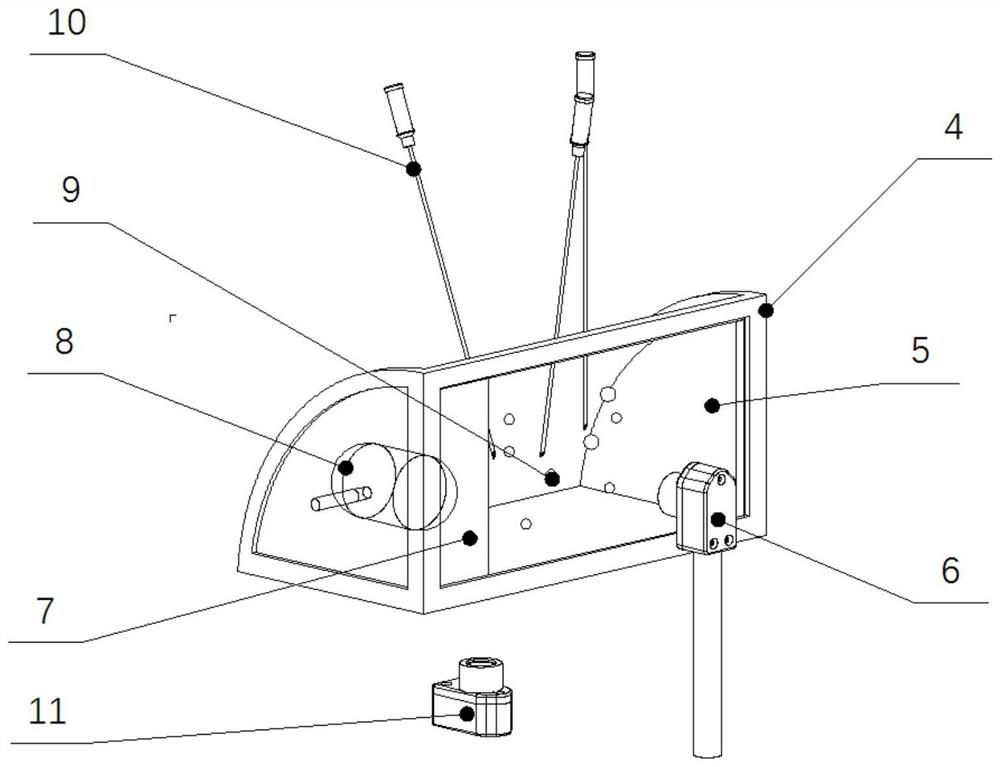
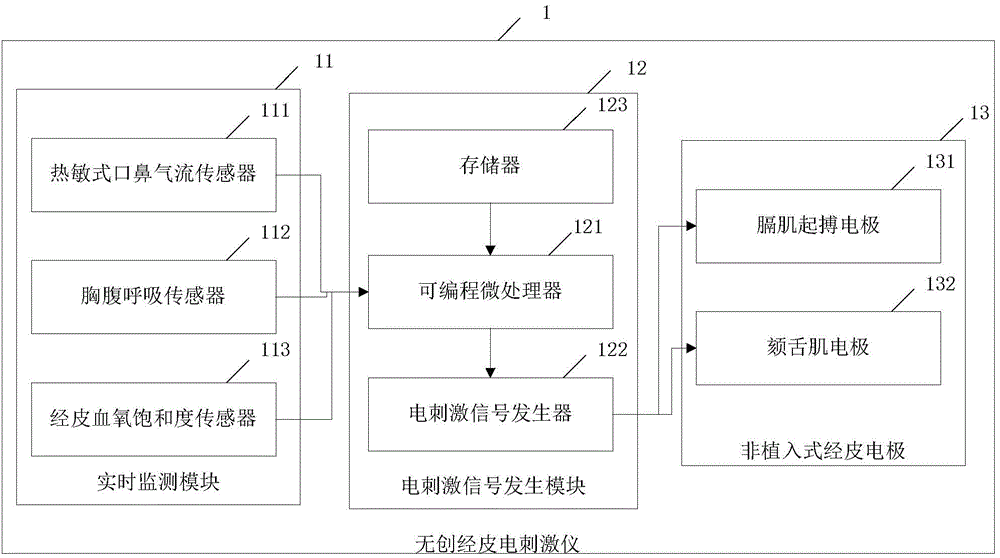
Noninvasive percutaneous frequency-conversion electrical-stimulation breathing therapeutic apparatus with multiple functions
ActiveCN103055417AFacilitate Type ConversionPromote conversionArtificial respirationElectricityFrequency conversion
The invention discloses a noninvasive percutaneous frequency-conversion electrical-stimulation breathing therapeutic apparatus with multiple functions. The percutaneous frequency-conversion electrical-stimulation breathing therapeutic apparatus with the multiple functions comprises a real-time monitoring module for monitoring breathing condition, an electrical-stimulation signal-producing module, and a non-implantable percutaneous electrode. The real-time monitoring module is used for monitoring the breathing condition of a monitored person in real time when the monitored person is in a sleep condition and obtaining sleep parameters. The electrical-stimulation signal-producing module is used for providing more than two electrical-stimulation modes. The non-implantable percutaneous electrode is used for conducting chronic frequency-conversion electrical-stimulation signals to diaphragm muscle or genioglossus of the monitored person or conducting acute frequency-conversion electrical-stimulation signals to the diaphragm muscle or the genioglossus of the monitored person. The percutaneous frequency-conversion electrical-stimulation breathing therapeutic apparatus with the multiple functions combines an acute diaphragm muscle pace-making function, a chronic frequency-conversion diaphragm muscle electrical-stimulation function, an acute genioglossus pace-making function, a chronic frequency-conversion genioglossus electrical-stimulation function, and the like as a whole. The percutaneous frequency-conversion electrical-stimulation breathing therapeutic apparatus with the multiple functions has double functions of treating and preventing.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF THIRD MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY OF PLA
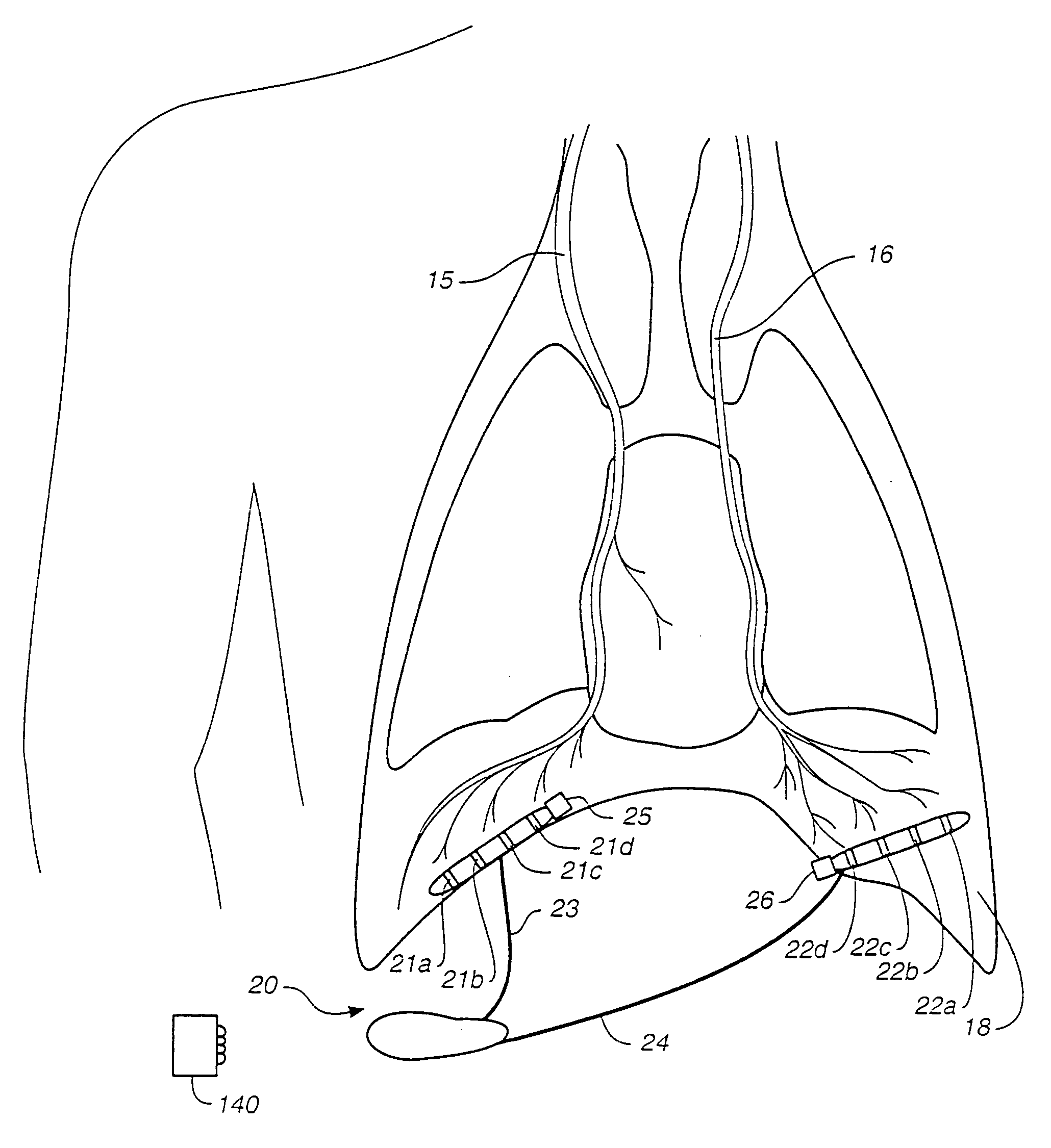
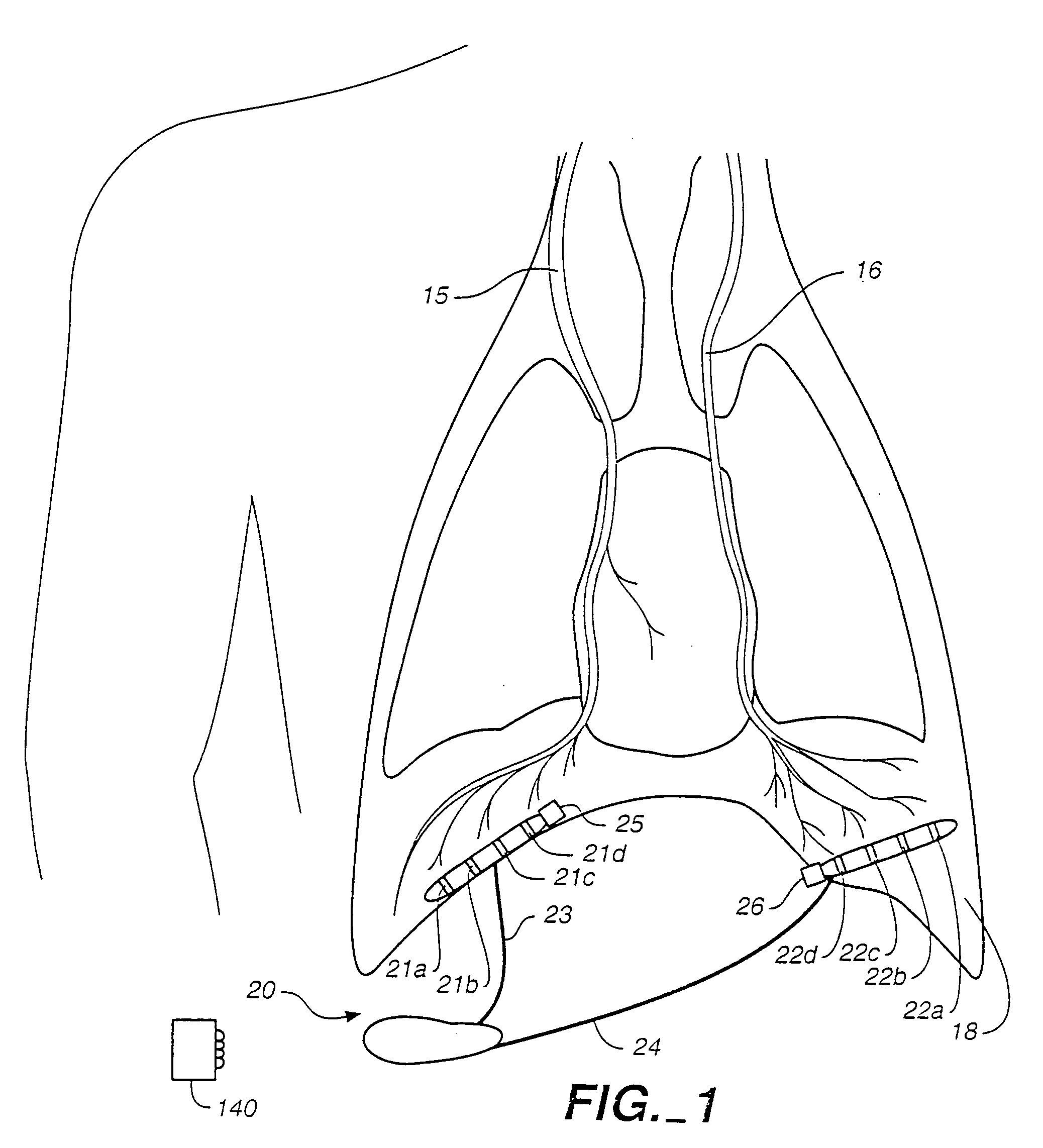
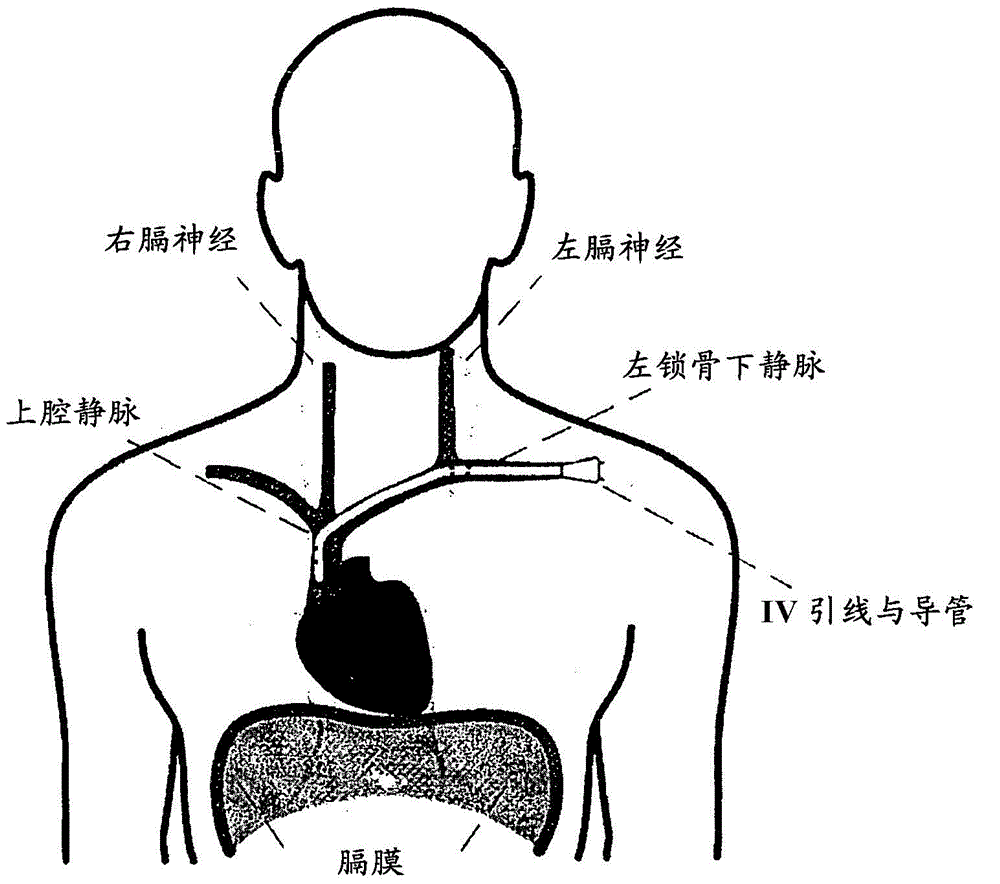
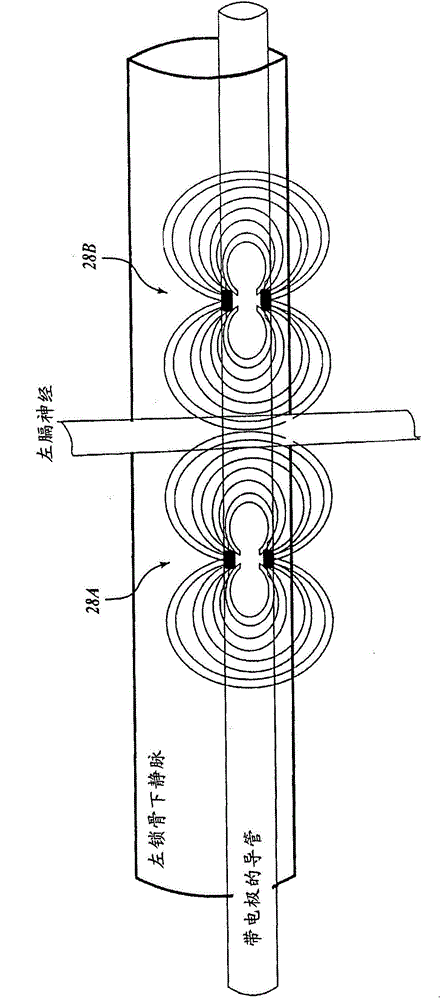
Transvascular diaphragm pacing systems and methods of use
Transvascular diaphragm pacing systems (TDPS) and methods are disclosed for providing respiratory therapy to a patient. The TDPS can provide rapid insertion and deployment of endovascular pacing electrodes in critically ill patients who require intubation and invasive PPMV in order to support the physiological requirements of the human ventilatory system. The systems and methods make best use of the contractile properties of the diaphragm muscle and prevent muscle disuse and muscle atrophy. This can be carried out by engaging the phrenic nerves using patterned functional electrical stimulation applied to endovascular electrodes that are temporarily and reversibly inserted in central veins of the patient, such as the left subclavian vein and the superior vena cava. The TDPS can be designed to seamlessly interface with any commercially available positive-pressure ventilatory assistance / support equipment such as is commonly in use in hospital intensive care units (ICU) for treating critically ill patients with breathing insufficiencies, pain, trauma, sepsis or neurological diseases or deficits.
Owner:LUNGPACER MEDICAL INC
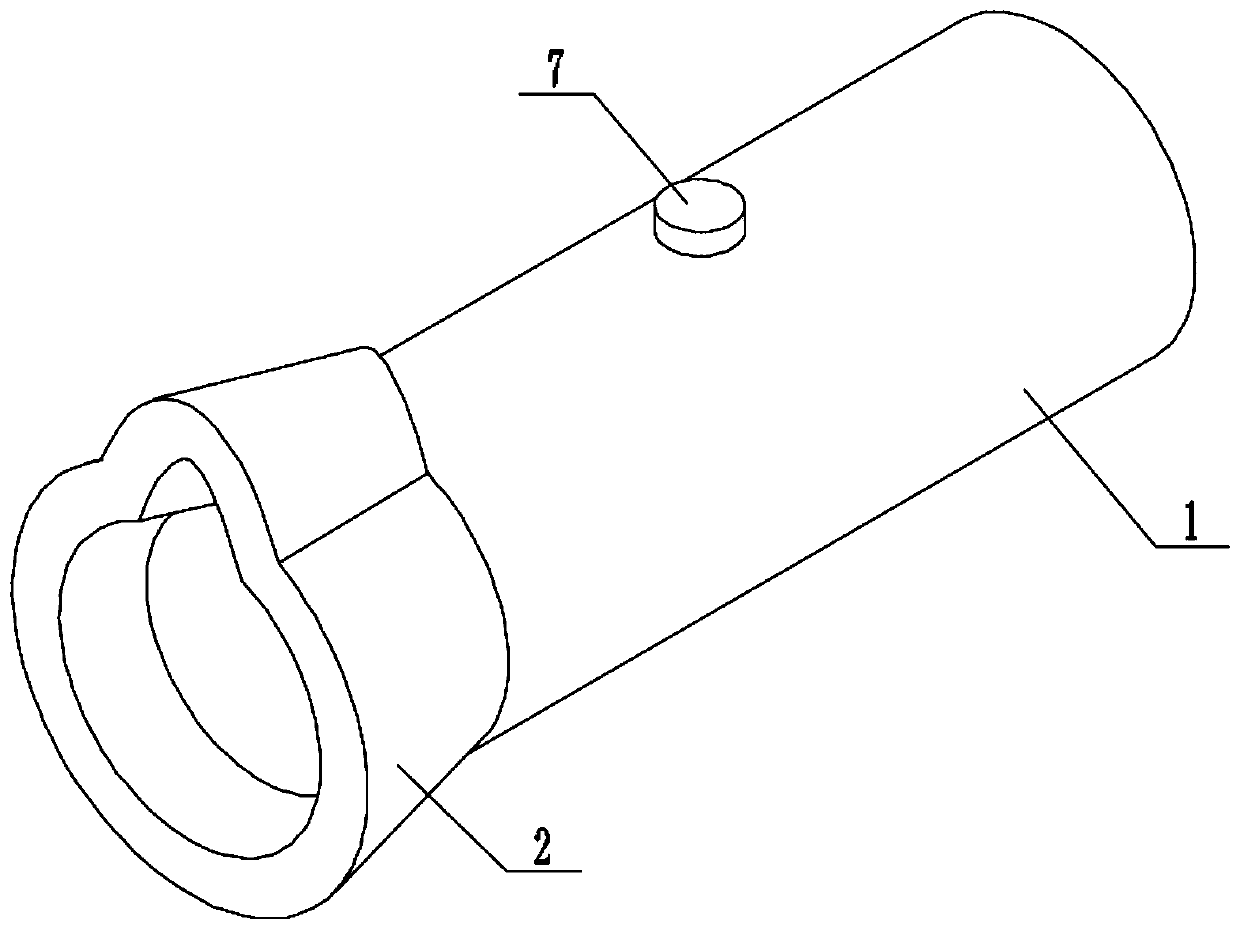
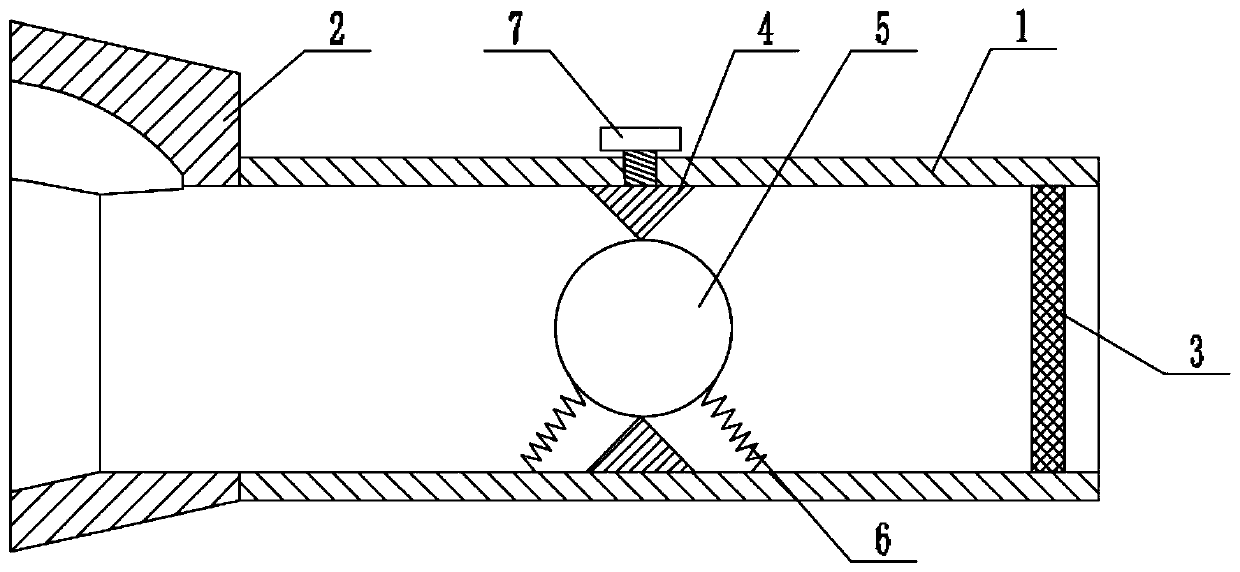
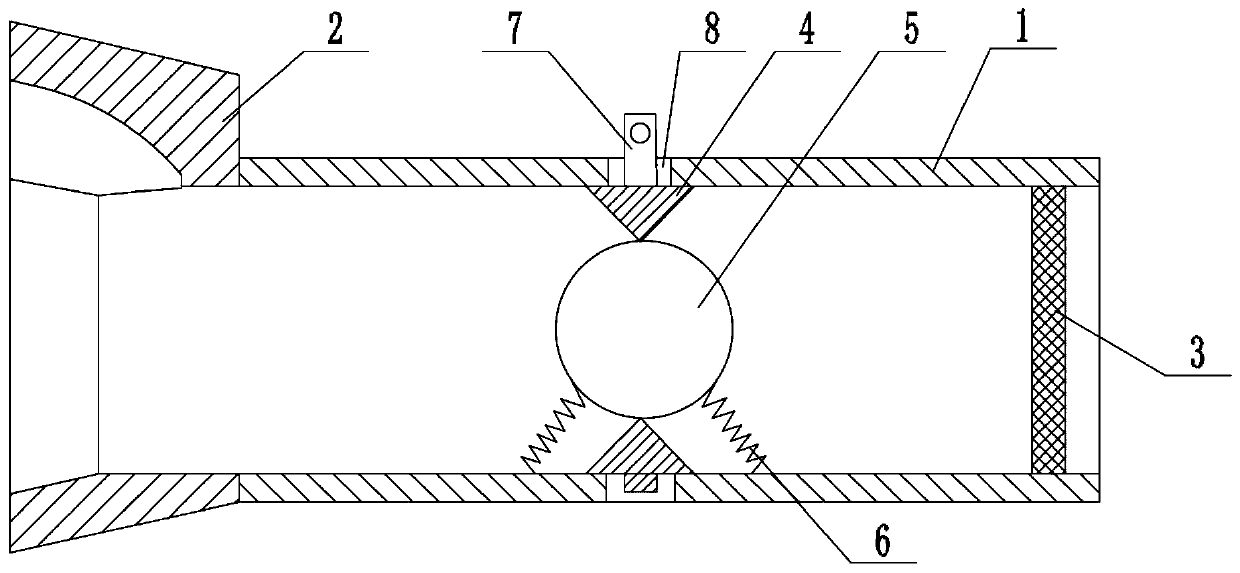
Respiratory function training instrument
ActiveCN110237505AHigh strengthImprove toleranceFrictional force resistorsRespiratory muscleInterference fit
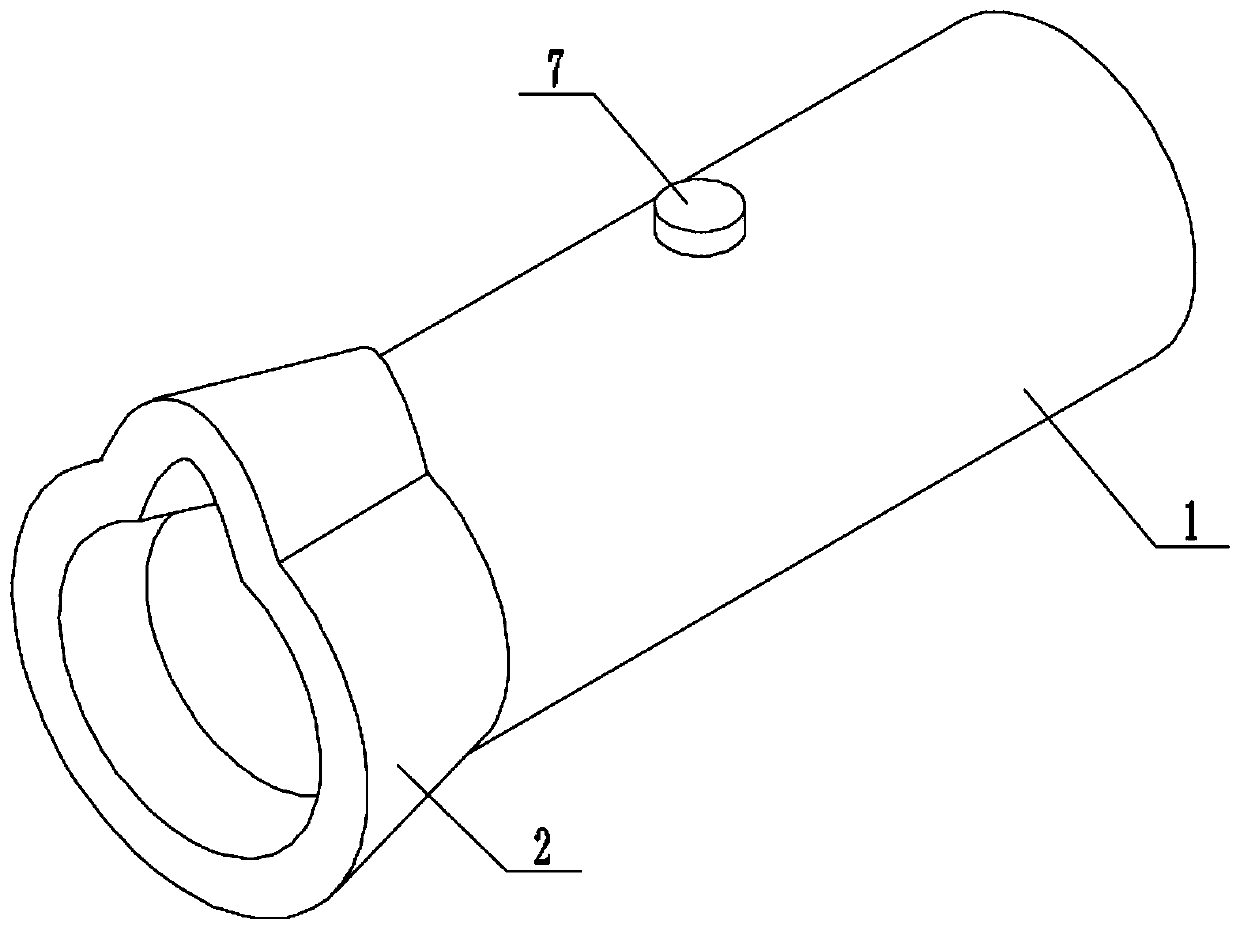
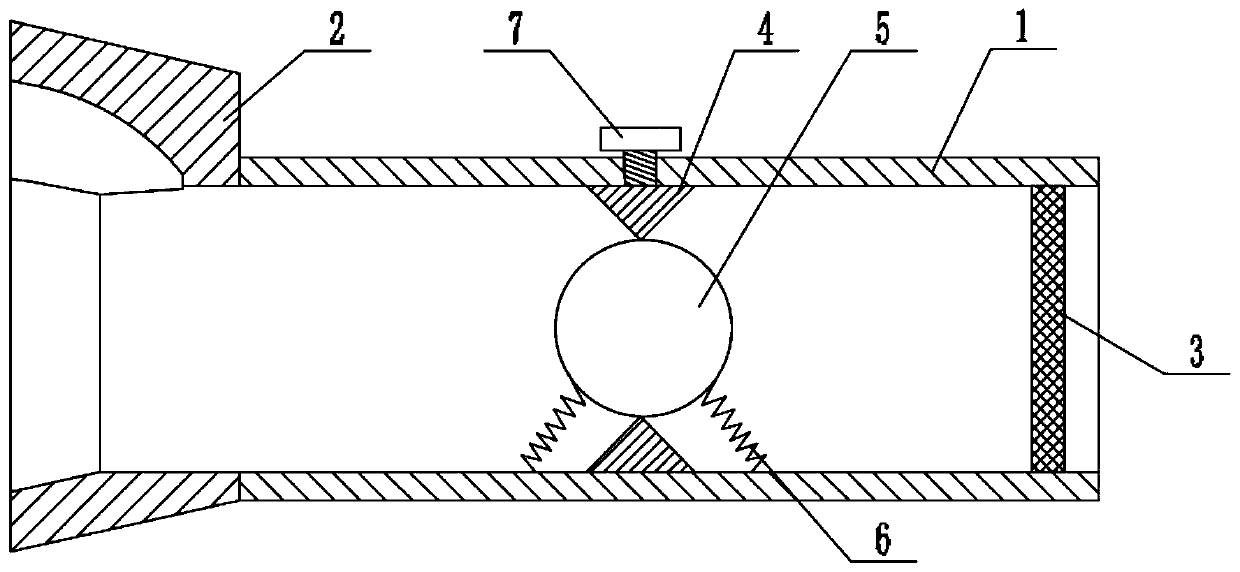
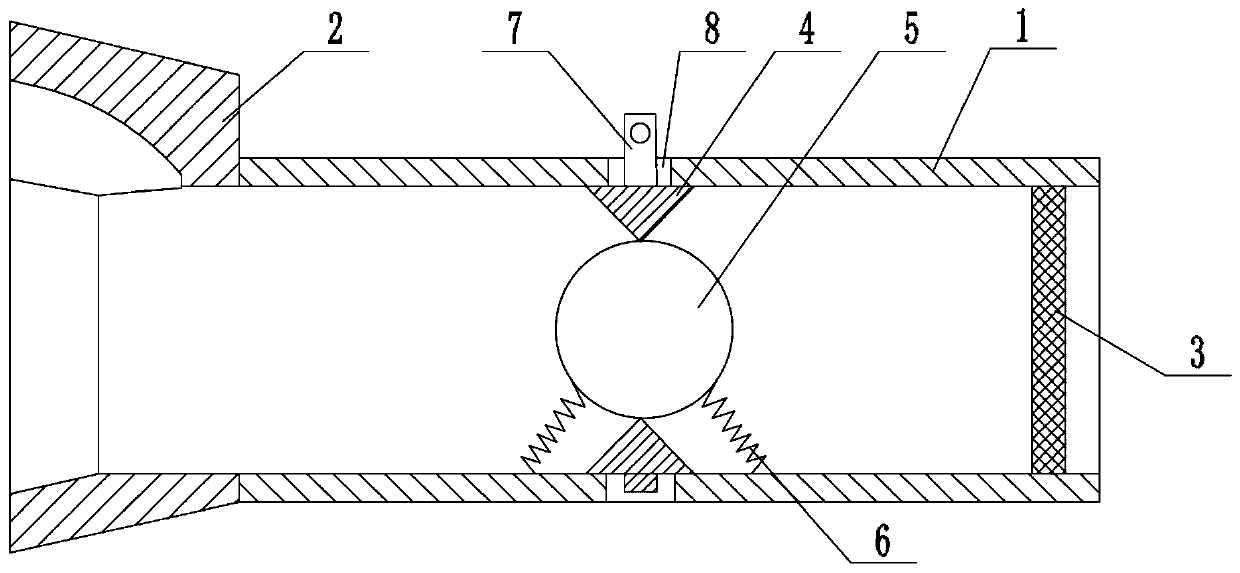
The invention relates to the field of medical apparatus and instruments, and provides a respiratory function training instrument. The respiratory function training instrument comprises a respiratory tube and a respirator mounted at one end of the respiratory tube, wherein the respiratory tube is internally provided with a resistance component which includes a resistance ring, a resistance ball and at least two elastic bodies; the outer circumference of the resistance ring is connected to the inner wall of the respiratory tube, and the inner circumference of the resistance ring is in interference fit with the resistance ball; and the elastic bodies are separately disposed on both sides of the resistance ring, one ends of the elastic bodies are connected to the inner wall of the respiratory tube, and the other ends of the elastic bodies are connected to the resistance ball. The respiratory function training instrument is provided with the resistance component to enable a patient to train the contraction and relaxation of respiratory muscles such as a diaphragm muscle in the inspiration process and the expiration process, thereby improving the strength and tolerance of the respiratory muscles to improve the training effect; and meanwhile, the respiratory function training instrument is simple in structure and convenient to carry.
Owner:山东鸿创科技有限公司
Patch special for esophageal hiatus hernia
The invention relates to a patch special for an esophageal hiatus hernia. The patch special for the esophageal hiatus hernia comprises a polyL-lactide-PLCL absorbable layer and a polypropylene non-absorbable layer bonded to the absorbable layer, wherein the outer surface of the absorbable layer faces the stomach, and the outer surface of the non-absorbable layer faces the diaphragm muscle. The non-absorbable layer and the absorbable layer have the same or similar contour shape and are both of a hollow circle structure, and the distance from the edge of the non-absorbable layer to the edge of the absorbable layer is 2-6 mm. The patch special for the esophageal hiatus hernia does not need to completely wrap the esophagus, and overcomes the defects that peristalsis of the esophagus is limited, so dyskinesia of the esophagus is caused and a swallowing function after an operation is affected. The patch special for the esophageal hiatus hernia can completely make contact with the visceral organ and is good in tissue adaptability.
Owner:克力木·阿不都热依木 +1
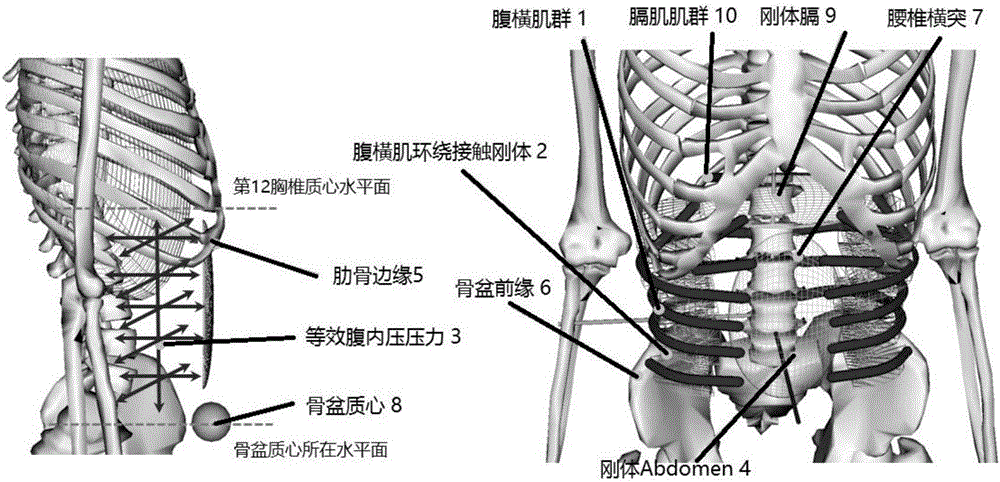
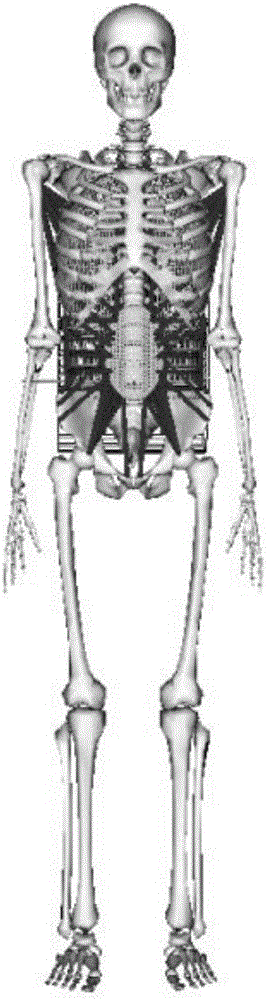
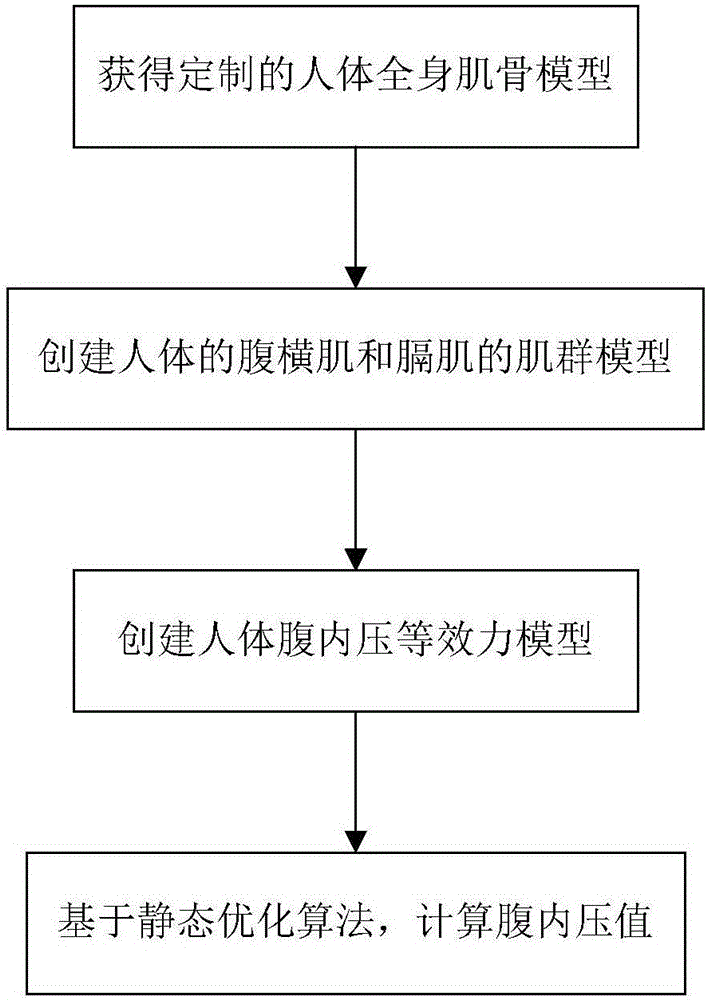
Human intra-abdominal pressure testing method based on musculoskeletal biodynamics
InactiveCN106333697AHigh solution accuracyMedical simulationSpecial data processing applicationsHuman bodyModel composition
The invention relates to a human intra-abdominal pressure testing method based on musculoskeletal biodynamics. The human intra-abdominal pressure testing method comprises the steps of acquiring a human whole body musculoskeletal model customized according to a human body; establishing musculus trasversus abdominis to surround a contact rigid body, representing a musculus trasversus abdominis group and a diaphragm muscle group through a muscle-tendon model, and further creating a muscle group model of musculus trasversus abdominis and diaphragm muscle of the human body; enabling intra-abdominal pressure to be equivalent to equivalent intra-abdominal pressure in the horizontal direction and the vertical direction so as to create a human intra-abdominal pressure equivalent force model; and capturing each posture joint angle of a certain standing posture of a tester, and inputting each posture joint angle into a human musculoskeletal biodynamics model formed by combination of the established models; and calculating the intra-abdominal pressure value under the posture. The method can be used for solving the problems that under different postures or actions, the intra-abdominal pressure is unknown, and is difficult to directly measure, the measuring cost is high, and the like.
Owner:BEIJING MECHANICAL EQUIP INST
Method for capturing diaphragm movement to assist in judging offline of breathing machine by utilizing ultrasonic AI technology
PendingCN110974298AHigh precisionImprove efficiencyRespiratorsOrgan movement/changes detectionTesting ultrasoundUltrasound probe
The invention discloses a method for capturing diaphragm movement to assist in judging offline of a breathing machine by utilizing an ultrasonic AI technology. The method comprises the following steps: step S1, a doctor detects the diaphragm muscle position of a patient through an ultrasonic probe to capture the diaphragm muscle motion states of expiration and inspiration of the patient, and diaphragm muscle thickness images during expiration and inspiration are generated on a display interface of an ultrasonic detection device; step S2, the doctor detects the diaphragm position of the patientby using the ultrasonic probe to capture diaphragm motion states of expiration and inspiration of the patient, and a diaphragm mobility change image from expiration to inspiration is generated on a display interface of the ultrasonic detection device; step S3, an AI diagnosis device respectively scans the images generated in the step S1 and the step S2, after scanning is completed, the content ofthe images is analyzed and processed, and the specific numerical values of the diaphragm thickness change rate and the diaphragm mobility of the user are measured and calculated; and step S4, the doctor compares the calculated specific numerical values of the diaphragm thickness change rate and diaphragm mobility of the user with the diaphragm thickness change rate cutoff value and the diaphragmmobility cutoff value respectively.
Owner:SUZHOU SCI&TECH TOWN HOSPITAL
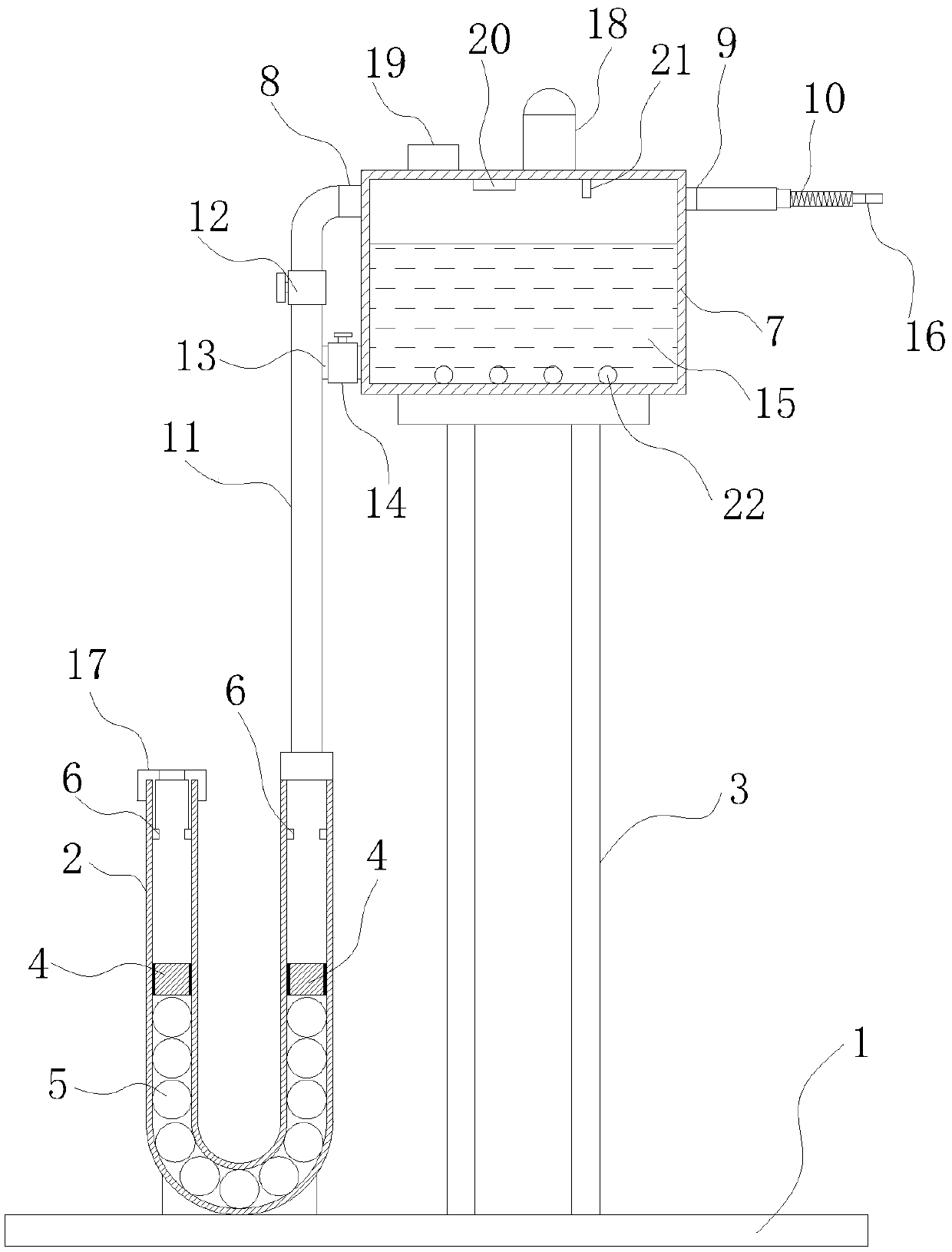
Breath training device
InactiveCN109675260AEasy Breathing TrainingSimple structureGymnastic exercisingMedical devicesEngineeringDiaphragm muscle
The invention relates to the field of breath training devices, and aims at providing a breath training device which can exercise chest diaphragm muscle. According to a technical scheme adopted by theinvention, the breath training device comprises a base, wherein a U-shaped tube with an upward opening is arranged at one side of the upper surface of the base, a vertical mounting rack is arranged atthe other side; a first sliding piston is arranged in the tube body at each of two sides of the U-shaped tube, a plurality of counter weight balls are arranged in the tube bodies between the slidingpistons, and the diameter of the counter weight balls is matched with the diameter of the tube holes of the U-shaped tube; and a standard limiting part is further arranged in the U-shaped tube close to two ends. The breath training device can perform breath training conveniently, and exercise the chest diaphragm muscle, and is simple in structure.
Owner:郭彩霞
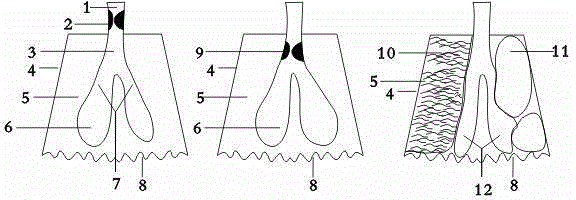
Model for demonstrating pulmonary ventilation disfunction
InactiveCN102750859ASimple structureIntuitive imageEducational modelsLongissimus ThoracisThoracic cavity
The invention discloses a model for demonstrating pulmonary ventilation disfunction and relates to a pathophysiology training aid. The model for demonstrating pulmonary ventilation disfunction comprises a thorax model, a thoracic central airway model, an intrathoracic central airway model, a thoracic cavity model, a pulmonary alveoli model, a diaphragm muscle model, airway foreign body models, a pulmonary atelectasis model, a pleural effusion model, an aerothorax model and a diaphragm muscle model, wherein the thoracic central airway model is positioned outside the thorax model, the intrathoracic central airway model and the pulmonary alveoli model are positioned in the thorax model, the intrathoracic central airway model is downwards divided into a left bronchus and a right bronchus which are respectively communicated with the pulmonary alveoli model, the thoracic central airway model and the intrathoracic central airway model are provided with the airway foreign body models, and the pleural effusion model and the aerothorax model are arranged between the pulmonary atelectasis model and the thorax model. The diaphragm muscle model is an elastic film. The model disclosed by the invention can be used for visually and vividly demonstrating the influence of obstructive hypoventilation and restrictive hypoventilation on respiratory failure.
Owner:关真民
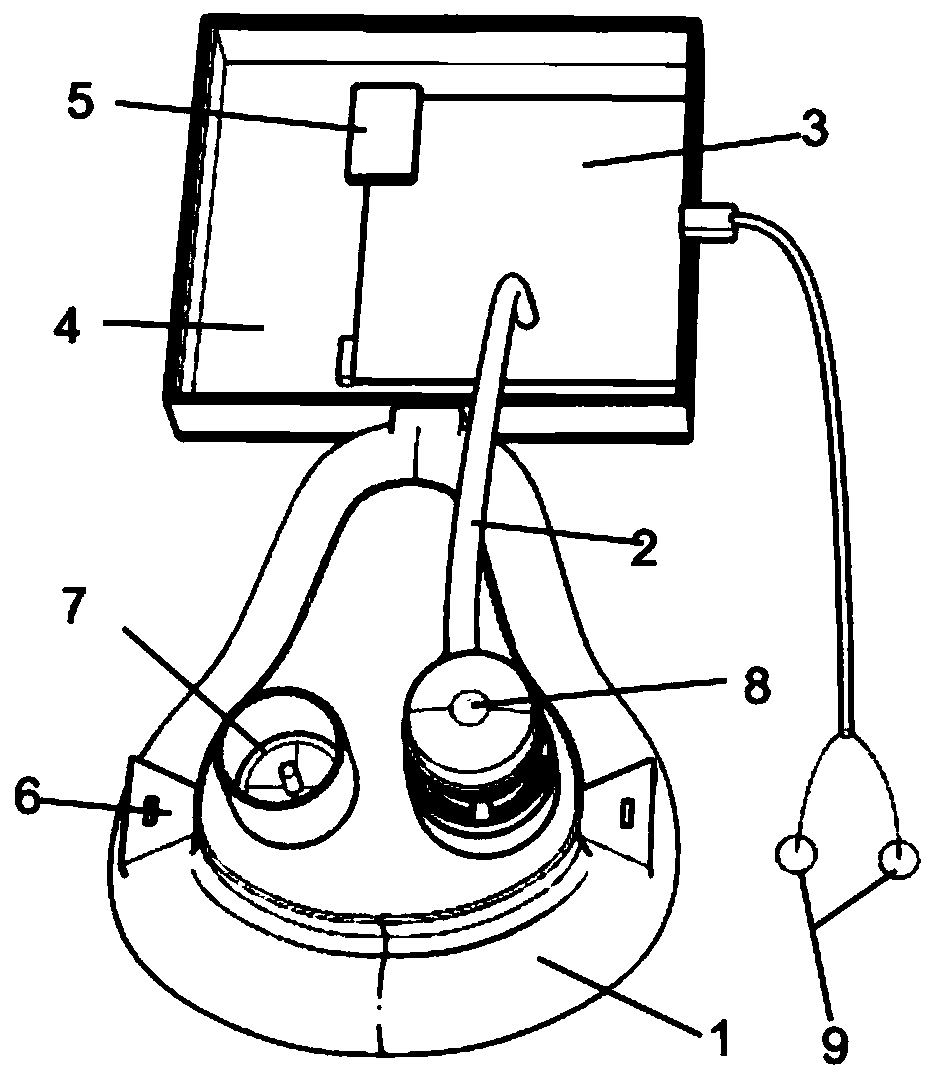
Breathing mask with hypoglossal nerve and diaphragm muscle stimulation functions, and ventilation treatment equipment
PendingCN110585546ADoes not affect sleepGood effectElectrotherapyRespiratory masksObstructive ApneaDiaphragm muscle
The invention discloses a breathing mask with hypoglossal nerve and diaphragm muscle stimulation functions, and ventilation treatment equipment. The breathing mask comprises a mask body, a breathing state monitoring device, a hypoglossal stimulation electrode and a diaphragm muscle stimulation electrode, wherein the breathing state monitoring device is mounted at the bottom of the mask body, and the hypoglossal stimulation electrode and the diaphragm muscle stimulation electrode are connected with the breathing state monitoring device; the mask body communicates with the breathing state monitoring device through a thin tube; the breathing state monitoring device comprises a protection shell, and further comprises a sensor detection circuit, a CPU controller and a stimulation pulse circuitwhich are arranged in the protection shell; the pressure, temperature, blood oxygen saturation degree and heart rate data of a breathing air flow, introduced into the protection shell, of a wearer aredetected by the sensor detection circuit and transmitted to the CPU controller; and the CPU controller judges whether the wearer has obstructive apnea and central apnea or not, and triggers the stimulation pulse circuit to stimulate the hypoglossal nerve to contract the genioglossus muscle and stimulate the diaphragm muscle to contract.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Device and method for detecting and monitoring cough
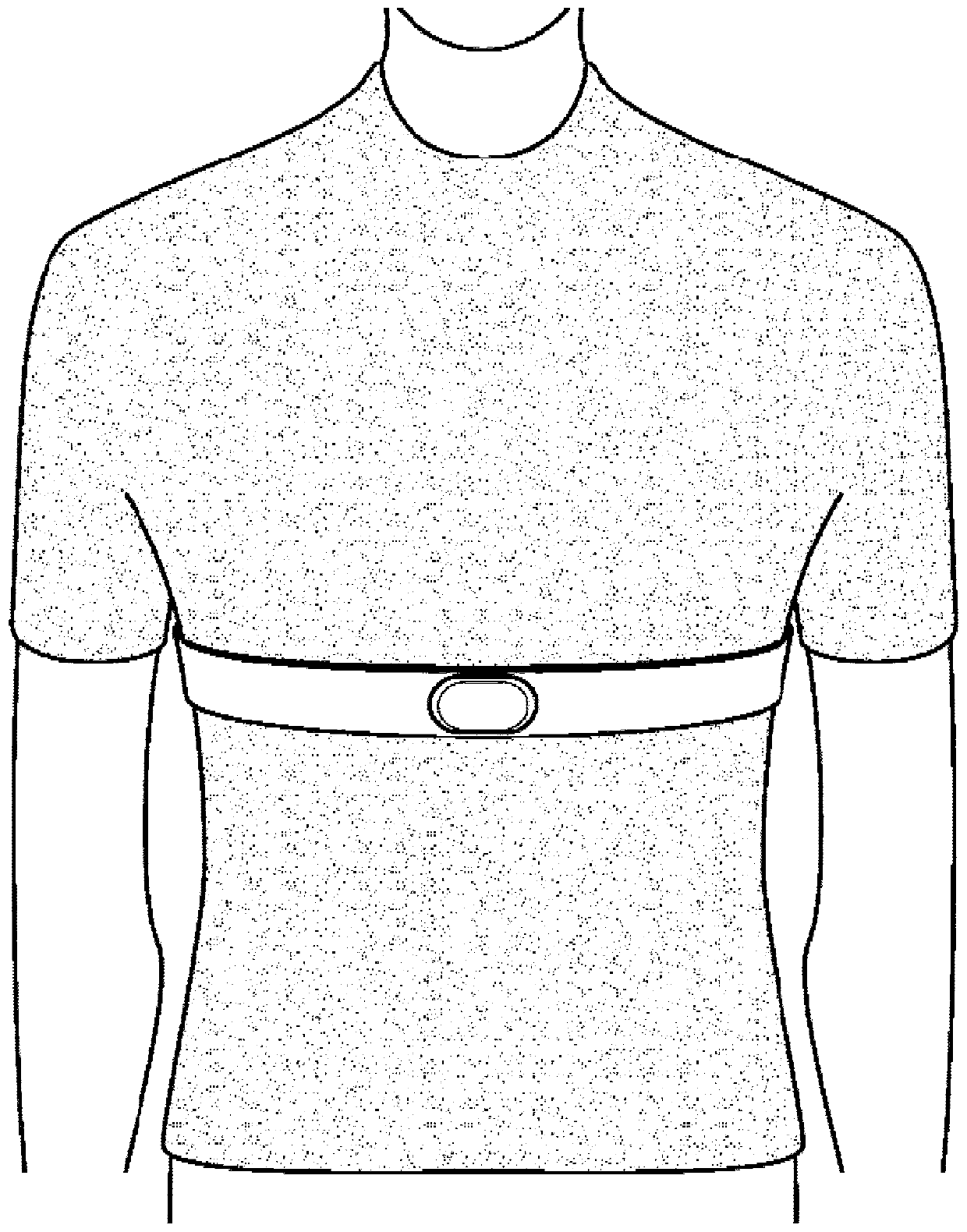
Coughing is a common experience and the most common reason why individuals seek to see a doctor. The incidence of cough is about over 10% of the population. Coughing is a manifestation of many upper respiratory and digestive tract diseases, and especially the consequences of serious lower respiratory tract diseases such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and asthma, because increasedcoughing can lead to emergency treatment and hospitalization. A method is needed to monitor the frequency of coughing in some patients. Traditionally, all automatic cough monitors use cough sound as asignal to measure a cough. In the present invention, the movement of the diaphragm muscle recorded by a motion sensor located above the xiphoid process is configured to count the coughs. A device forsuch recording is described, and data is collected. The method is validated by using a citric acid spray to trigger the cough sound and show that ab excited acoustic signal matches an electronic signal from the motion sensor.
Owner:FIBRET (SHANGHAI) SMART TECH CO LTD
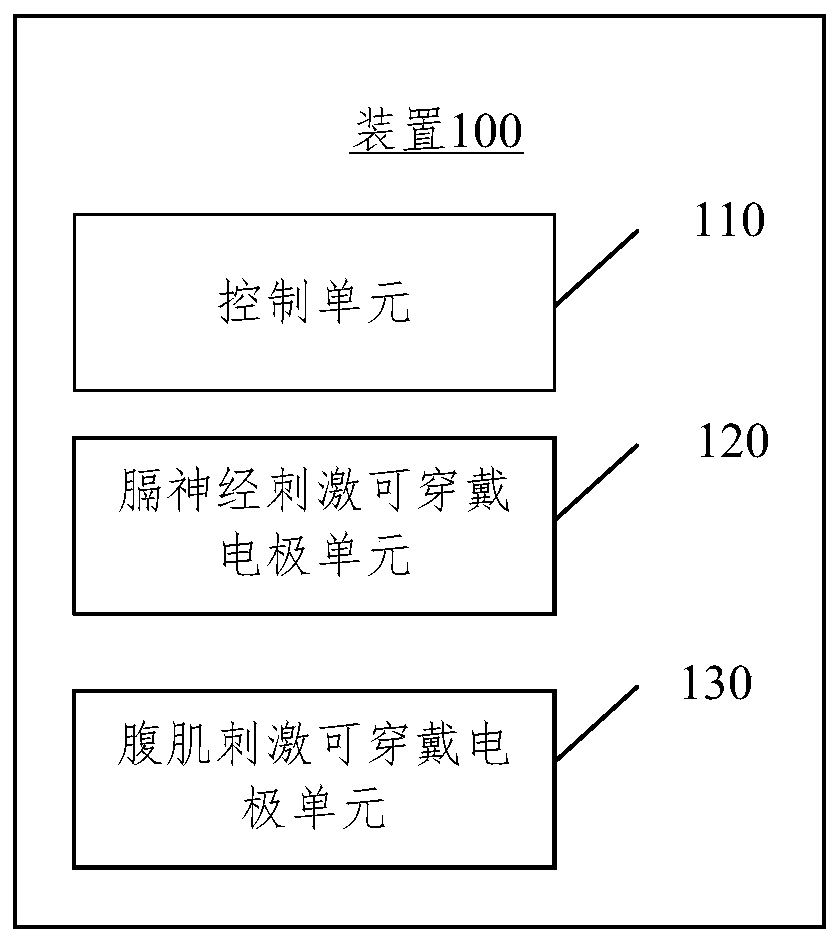
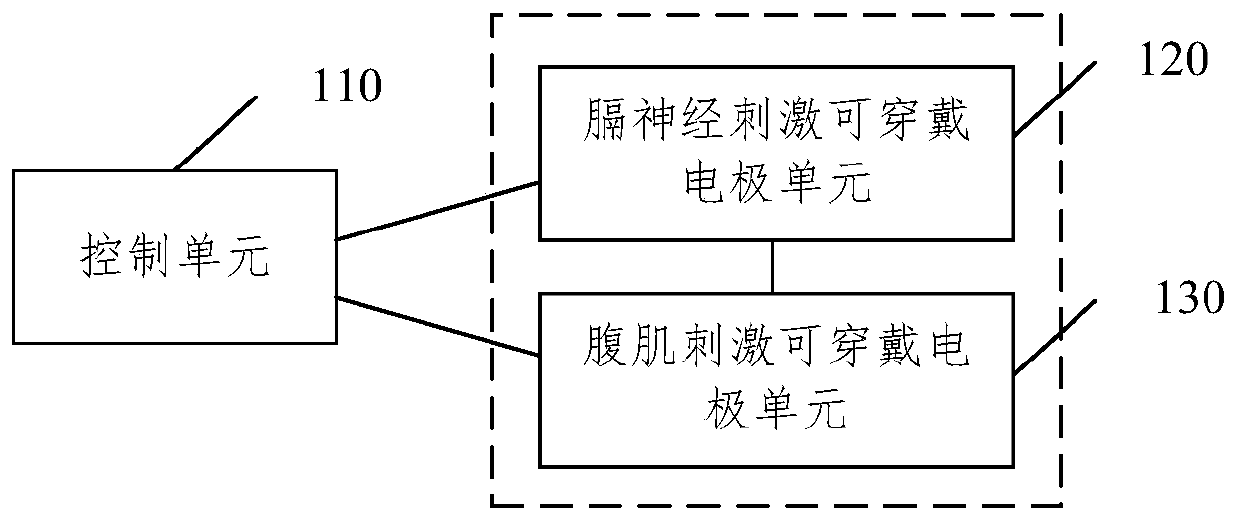
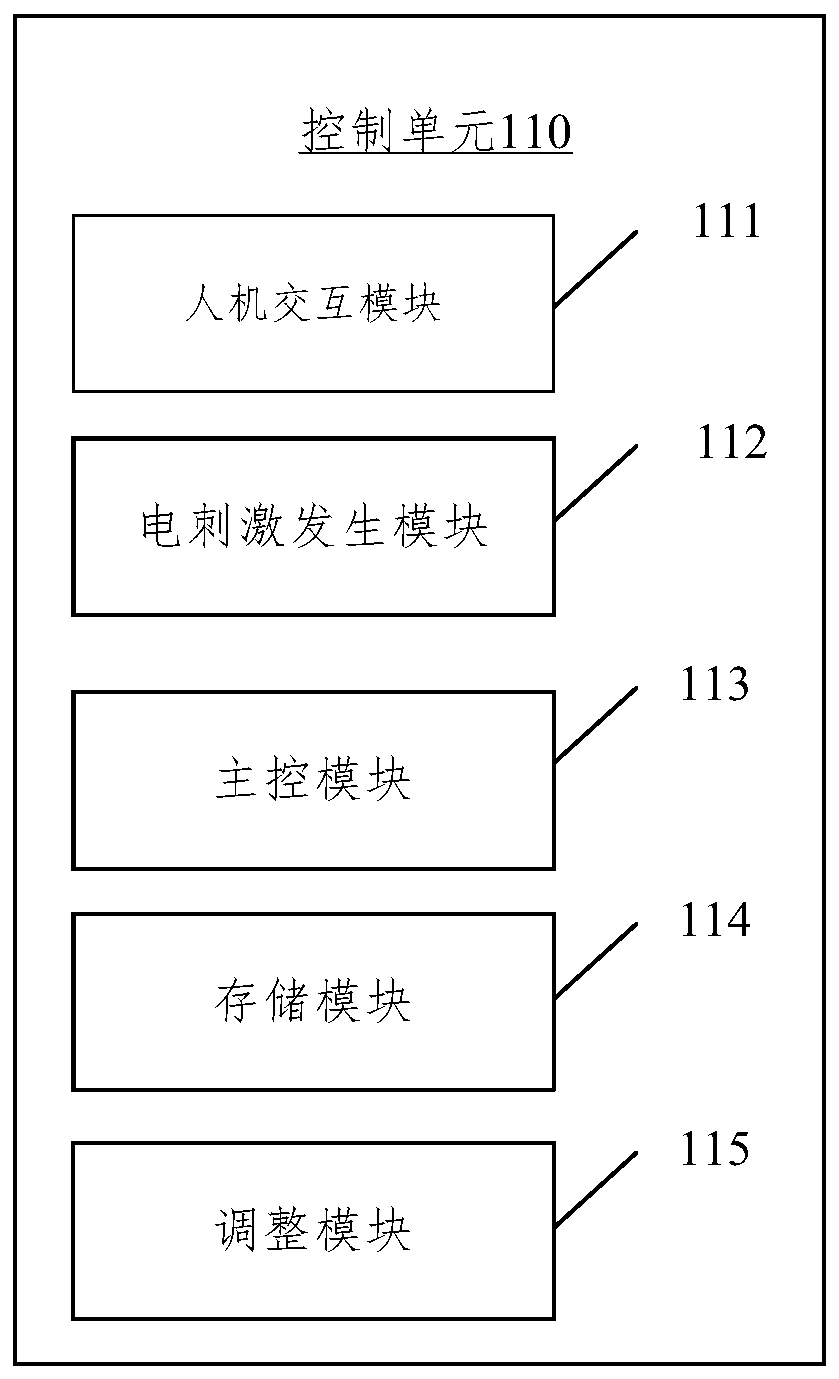
Wearable respiratory myoelectricity stimulation device
ActiveCN110327546AEasy to wearReturn to spontaneous breathingExternal electrodesArtificial respirationMuscle strengthPower flow
The embodiment of the present disclosure relates to a wearable respiratory myoelectricity stimulation device. The device comprises: a control unit which is used for generating corresponding electric stimulation current according to input information; and a phrenic nerve stimulation wearable electrode unit and an abdominal muscle stimulation wearable electrode unit which are both connected to the control unit and used for receiving the current, wherein the current acts on nerves or muscles, wherein the electrode position of the phrenic nerve stimulation wearable electrode unit corresponds to the phrenic nerve after being worn, and the electrode position of the abdominal muscle stimulation wearable electrode unit corresponds to rectus abdominis and obliquus abdominis. The embodiment of the present disclosure provides the wearable device suitable for household, the device is convenient for a user to wear, the electrode is aligned with a part needing electric stimulation after wearing, theoperation is simple, and the user can be helped to recover the spontaneous respiration by training the muscle strength and endurance of the diaphragm muscle and the abdominal muscle.
Owner:YAGUO
Device and method for detection and monitoring of cough
Cough is a common experience and the most frequent reason why an individual seeks a visit to a physician. The prevalence of cough is about 10+% of the population. Cough is a manifestation of many aerodigestive tract disorders and especially consequential for serious lower airway diseases such as respiratory infections, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and asthma because increased coughing leads to emergency room visits and hospitalization. There is a need for methods to oversee coughing frequency in certain patients. Traditionally, all automated cough monitors have used cough sound as the signal for the measurement of cough. In the present invention movements of the diaphragm muscle, recorded by a motion sensor placed above the xiphoid process, are used for counting coughs. A device for such recordings is described and data were collected. This method is validated by using citric acid spray to trigger cough sounds and to show that the provoked acoustic signal is matched by the electronic signals from the movement sensors. The xiphoid process is a unique anatomical landmark for the non-acoustic detection of cough.
Owner:WEI EDWARD T +2
Adeno-associated virus vector delivery of muscle specific micro-dystrophin to treat muscular dystrophy
The invention provides gene therapy vectors, such as adeno-associated virus (AAV) vectors, expressing a miniaturized human micro-dystrophin gene and method of using these vectors to express micro-dystrophin in skeletal muscle s including diaphragm and cardiac muscle and to protect muscle fibers from injury, increase muscle strength and reduce and / or prevent fibrosis in subjects suffering from muscular dystrophy.
Owner:RES INST AT NATIONWIDE CHILDRENS HOSPITAL
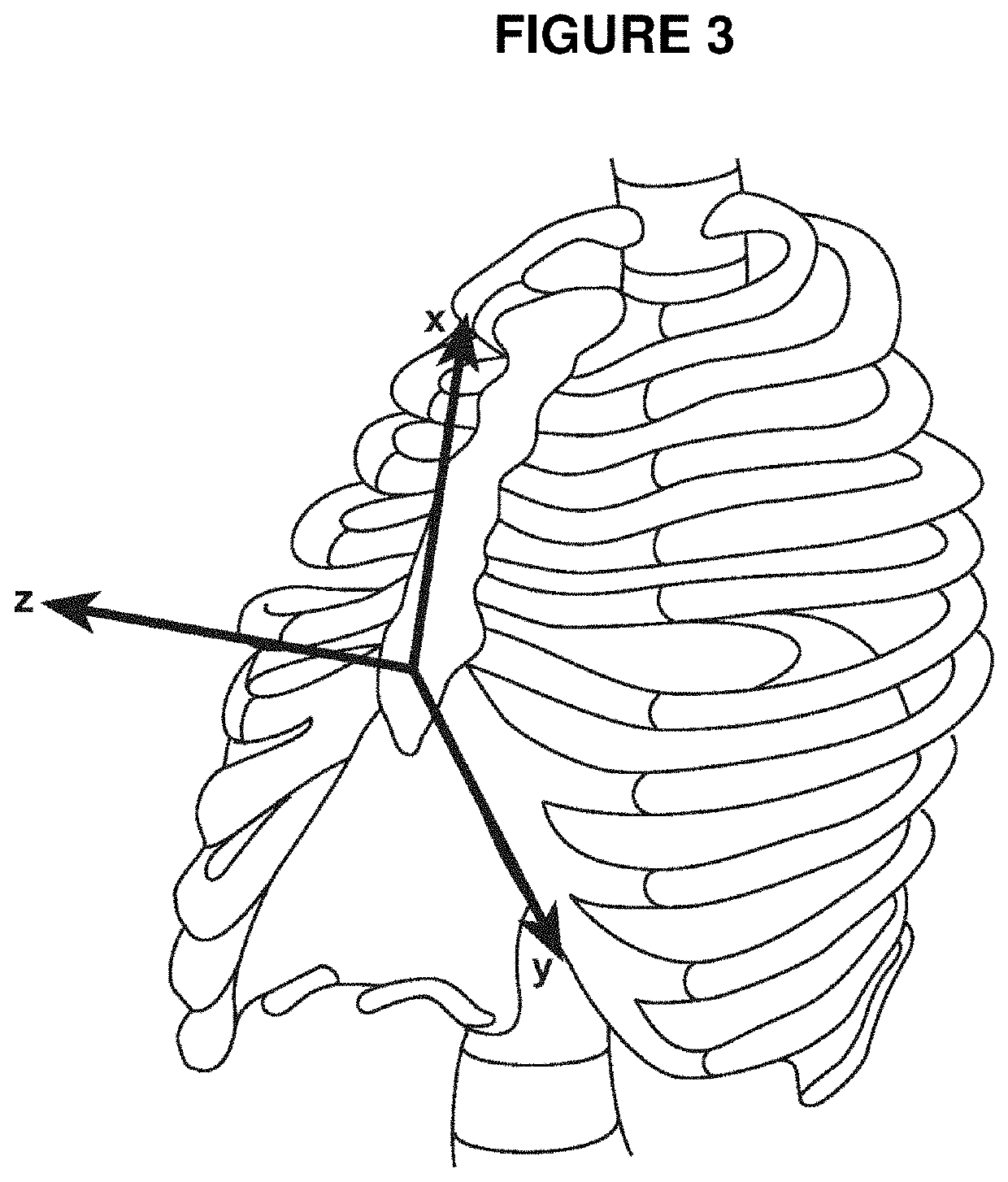
Relative contribution of thoracic muscles to breathing
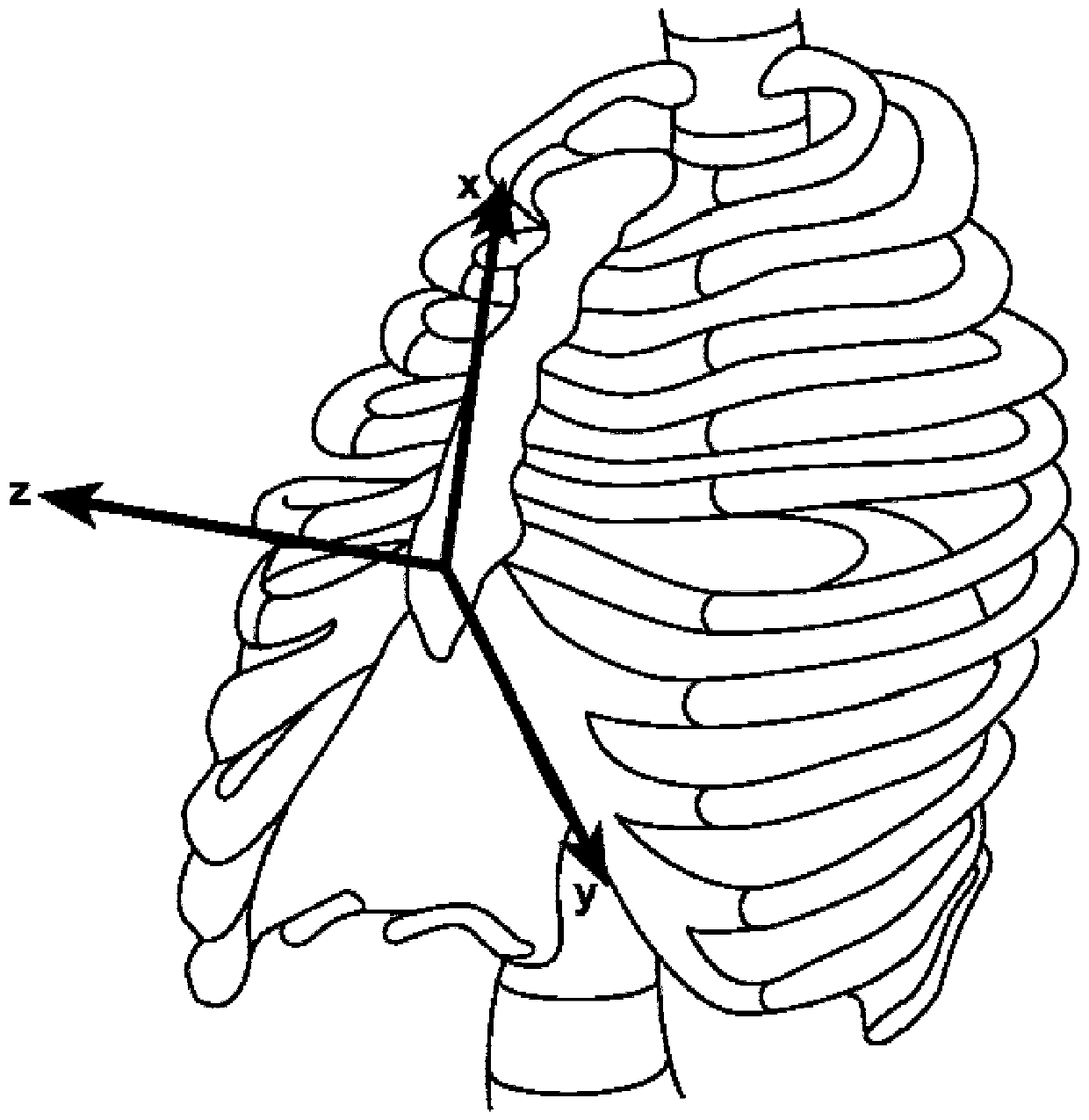
InactiveUS20110144516A1Increase pressureRespiratory organ evaluationSensorsThoracic structureAbdominal cavity
A method and apparatus for evaluating the relative contribution of the diaphragm versus other thoracic muscles to breathing by obtaining measurements of parameters that correlate with changes in thoracic cavity and intra-abdominal cavity pressures over identical time increments and organizing the measurement data in manner that reveals whether the pressures changes are characteristic of the pattern of contemporaneous pressure changes in those cavities that accompany contraction and / or relaxation of the diaphragm muscles or whether the pressure changes are characteristic of the pattern of contemporaneous pressure changes in those cavities that accompany contraction and / or relaxation of the intercostal muscles.
Owner:FISHER JOSEPH +4
Respiratory Function Trainer
ActiveCN110237505BHigh strengthImprove toleranceFrictional force resistorsRespiratory musclePhysical medicine and rehabilitation
The invention relates to the field of medical apparatus and instruments, and provides a respiratory function training instrument. The respiratory function training instrument comprises a respiratory tube and a respirator mounted at one end of the respiratory tube, wherein the respiratory tube is internally provided with a resistance component which includes a resistance ring, a resistance ball and at least two elastic bodies; the outer circumference of the resistance ring is connected to the inner wall of the respiratory tube, and the inner circumference of the resistance ring is in interference fit with the resistance ball; and the elastic bodies are separately disposed on both sides of the resistance ring, one ends of the elastic bodies are connected to the inner wall of the respiratory tube, and the other ends of the elastic bodies are connected to the resistance ball. The respiratory function training instrument is provided with the resistance component to enable a patient to train the contraction and relaxation of respiratory muscles such as a diaphragm muscle in the inspiration process and the expiration process, thereby improving the strength and tolerance of the respiratory muscles to improve the training effect; and meanwhile, the respiratory function training instrument is simple in structure and convenient to carry.
Owner:山东鸿创科技有限公司
Chinese medicinal preparation for treating diaphragm muscle spasm
InactiveCN101690776AGood treatment effectRaw materials are easy to getMuscular disorderNeuromuscular disorderSide effectMuscle spasm
The invention relates to a Chinese medicinal preparation for treating diaphragm muscle spasm, which comprises the following raw material medicines by weight: ophiopogon, persimmon calyx and receptacle, evadia pulp, sea-ear shell, uncaria, raw white peony, red tangerine peel and ginseng rhizome; and the preparation comprises powder, capsule preparation and oral liquid preparation prepared by a conventional preparation process or modern preparation process. The raw material medicines selected by the invention are combined to have the effects of nourishing blood and astringing yin, alleviating asthma and stopping hiccups, eliminating cold and stopping pain, and clearing away lung-heat and reducing fire. The Chinese medicinal preparation has ideal treatment effect on the diaphragm muscle spasm caused by various causes, and has easily available raw materials, low treatment cost, no toxic or side effect, and good treatment effect in clinical application.
Owner:蒲灵珍
Orange peel and bamboo shavings juice capable of regulating functional activities of qi
InactiveCN106267044ALow priceEasy to takeDigestive systemPlant ingredientsFunctional activityDiaphragm muscle
The invention discloses orange peel and bamboo shavings juice capable of regulating functional activities of qi. The juice is prepared by decocting 8-12 orange peel, 6-10 bamboo shavings, 3-6 rhizome of common ginger and 3-6 fructus jujubae with water, wherein the adding amount of water is twice of the total amount of raw materials, filtering to remove residue, canning and sealing. The drink provided by the invention is low in price and convenient to take, and has the effects of regulating functional activities of qi, warming stomach and regulating qi and relaxing diaphragm muscle.
Owner:徐润平
Lung puncture simulation platform
PendingCN114495671ARealistic occlusion problemTelevision system detailsColor television detailsEngineeringLung tissue
The invention provides a lung puncture simulation platform. The lung puncture simulation platform comprises a base; the thoracic cavity skeleton model is arranged on the upper surface of the base; the simulated lung tissue model is arranged in the thoracic cavity skeleton model, a simulated diaphragm muscle is arranged at the position, close to the abdominal cavity, in the simulated lung tissue model, and a cavity is formed in the simulated diaphragm muscle; the simulated breathing unit is connected with the simulated diaphragm muscle gas circuit and is used for controlling inflation and inhalation of the cavity of the simulated diaphragm muscle; and the controller is in communication connection with the simulation respiration unit. The lung puncture simulation platform is provided with the thoracic cavity skeleton model, the problem of skeleton shielding during puncture can be simulated more vividly under CT or X-rays, in addition, the air bag is arranged at the position close to the abdominal cavity to simulate the diaphragm, and the lung puncture simulation platform better conforms to the human body structure.
Owner:HUZHOU INST OF ZHEJIANG UNIV
A non-invasive transcutaneous electrical stimulator
ActiveCN103055417BFacilitate Type ConversionPromote conversionArtificial respirationElectricitySleep state
The invention discloses a noninvasive percutaneous frequency-conversion electrical-stimulation breathing therapeutic apparatus with multiple functions. The percutaneous frequency-conversion electrical-stimulation breathing therapeutic apparatus with the multiple functions comprises a real-time monitoring module for monitoring breathing condition, an electrical-stimulation signal-producing module, and a non-implantable percutaneous electrode. The real-time monitoring module is used for monitoring the breathing condition of a monitored person in real time when the monitored person is in a sleep condition and obtaining sleep parameters. The electrical-stimulation signal-producing module is used for providing more than two electrical-stimulation modes. The non-implantable percutaneous electrode is used for conducting chronic frequency-conversion electrical-stimulation signals to diaphragm muscle or genioglossus of the monitored person or conducting acute frequency-conversion electrical-stimulation signals to the diaphragm muscle or the genioglossus of the monitored person. The percutaneous frequency-conversion electrical-stimulation breathing therapeutic apparatus with the multiple functions combines an acute diaphragm muscle pace-making function, a chronic frequency-conversion diaphragm muscle electrical-stimulation function, an acute genioglossus pace-making function, a chronic frequency-conversion genioglossus electrical-stimulation function, and the like as a whole. The percutaneous frequency-conversion electrical-stimulation breathing therapeutic apparatus with the multiple functions has double functions of treating and preventing.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF THIRD MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY OF PLA
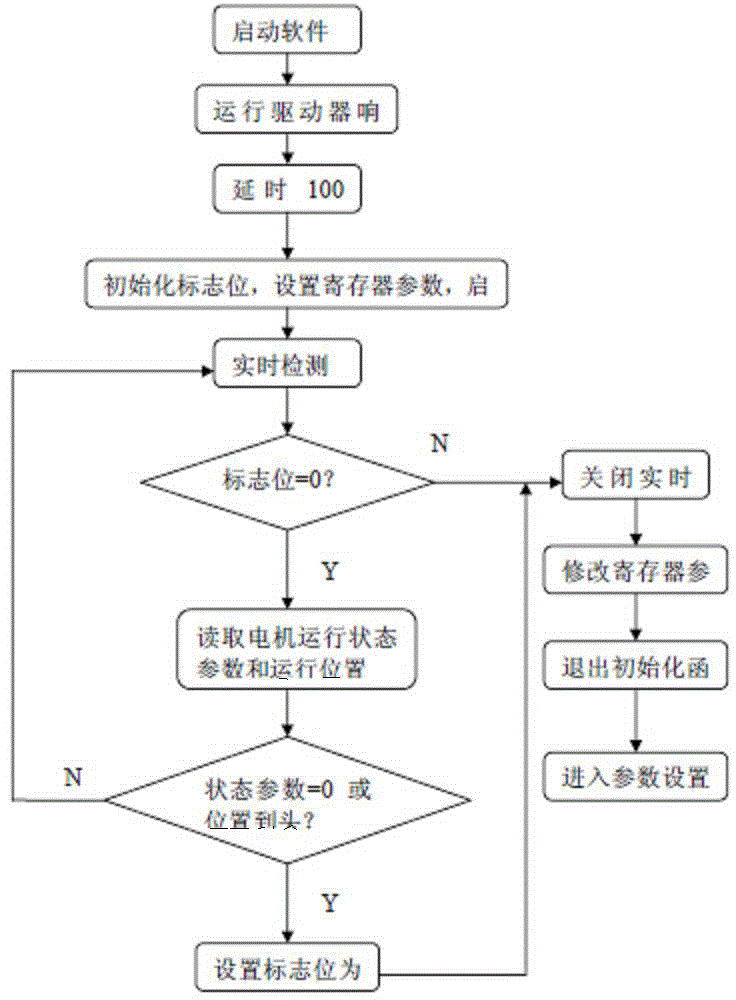
Novel pressure-changing and position-changing mechanical ventilation system
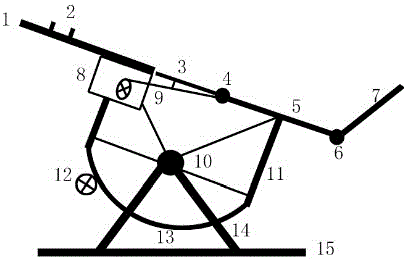
The invention discloses a novel pressure-changing and position-changing mechanical ventilation system. The novel pressure-changing and position-changing mechanical ventilation system comprises a rotation bed body, a rotation support, a floor stand and a circuit control and driving unit, wherein the rotation bed body comprises a head and chest supporting board (1), a head and face supporting pillow (2), an abdomen supporting board (3), an abdomen supporting board rotating shaft (4), an abdomen and leg supporting board (5), a shank supporting board rotating shaft (6) and a shank supporting board (7); the rotation support comprises a fixing support rotating shaft (10), a bed body fixing support (11) and an arc-shaped wheel (13); the floor stand comprises a supporting foot stool (14) and a supporting bottom support (15); and the circuit control and driving unit comprises a circuit control cabinet (8), a rocking bar driving unit (9) and a motor driving wheel (12). The mechanical ventilation system is simple in structure and low in cost; and a method for changing the position along with breathing synchronously and conducting inclined prone position suspended abdomen pressure changing is ingeniously used, and the breathing potential of the diaphragm muscle is sufficiently aroused and realized under the effects of gravity and inertia force, so that the effectiveness of a transverse diaphragm in the breathing process is sufficiently used, and the breathing tidal volume is improved.
Owner:贾洁
An auxiliary device for diaphragmatic pacing and expectoration
ActiveCN111298293BRealize the simulation of coughingEasy to controlRespiratorsElectrotherapyDiaphragm musclePhysical therapy
The invention discloses an auxiliary device for diaphragmatic muscle pacing and expectoration, comprising: a gas source, an exhaust port, a pneumatic reversing valve, a gas flow meter, an oxygen mask, a nerve electrical stimulation system, a probe and an acquisition card. The meter is connected with the oxygen mask, the acquisition card is respectively connected with the electrical nerve stimulation system and the gas flow meter, and the electrical nerve stimulation system is connected with the probe. The diaphragm pacing and expectoration auxiliary device provided by the present invention adopts the way of external electric stimulation of the diaphragm nerve to cause the diaphragm muscle to produce contraction and relaxation pacing movements, thereby achieving the effect of simulating human cough and stimulating expectoration.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Special mesh for hiatal hernia
Owner:克力木·阿不都热依木 +1
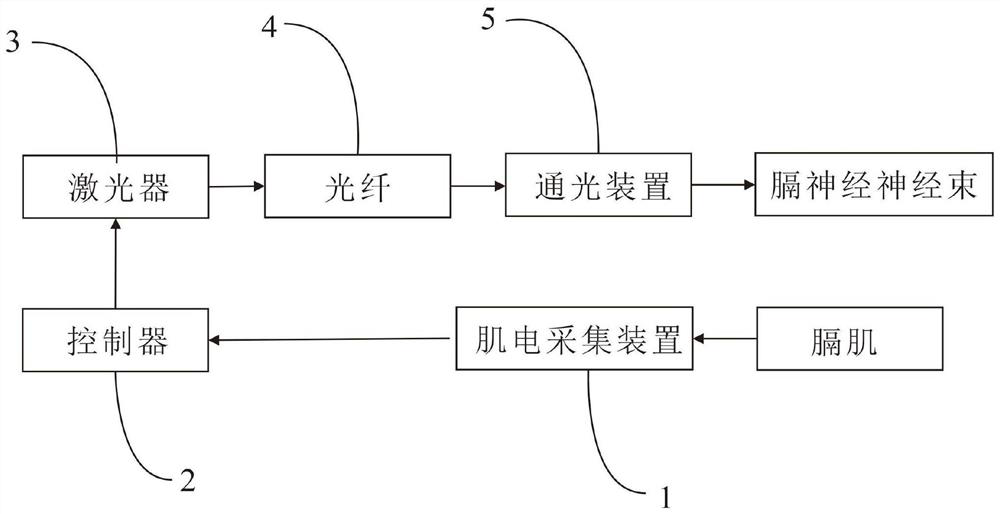
A Phrenic Nerve Light Stimulation System with Variable Light Intensity
ActiveCN111298304BEasy to fixEasy to installDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsOptical stimulationMaterials science
The invention discloses a phrenic nerve optical stimulation system with variable light intensity, which comprises a myoelectric collection device, a controller, a laser, an optical fiber and a light transmission device; Pass it to the controller; the controller is used to receive the diaphragm contraction signal transmitted by the myoelectric collection device, and send an instruction to the laser to emit a specific intensity infrared pulse laser according to the diaphragm contraction signal; the laser is used to emit a specific intensity infrared pulse according to the instruction issued by the controller Laser; the optical fiber is connected between the laser and the light-passing device; the light-passing device is provided with an optical path reflection mirror for changing the optical path of the infrared pulse laser. Using the system of the present invention can directly irradiate nerve tissue with infrared pulsed laser, causing instantaneous energy accumulation in the tissue, thereby establishing a temperature gradient, causing light and heat to be generated in the tissue, thereby inducing nerve activity, and improving the safety and accuracy of use.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
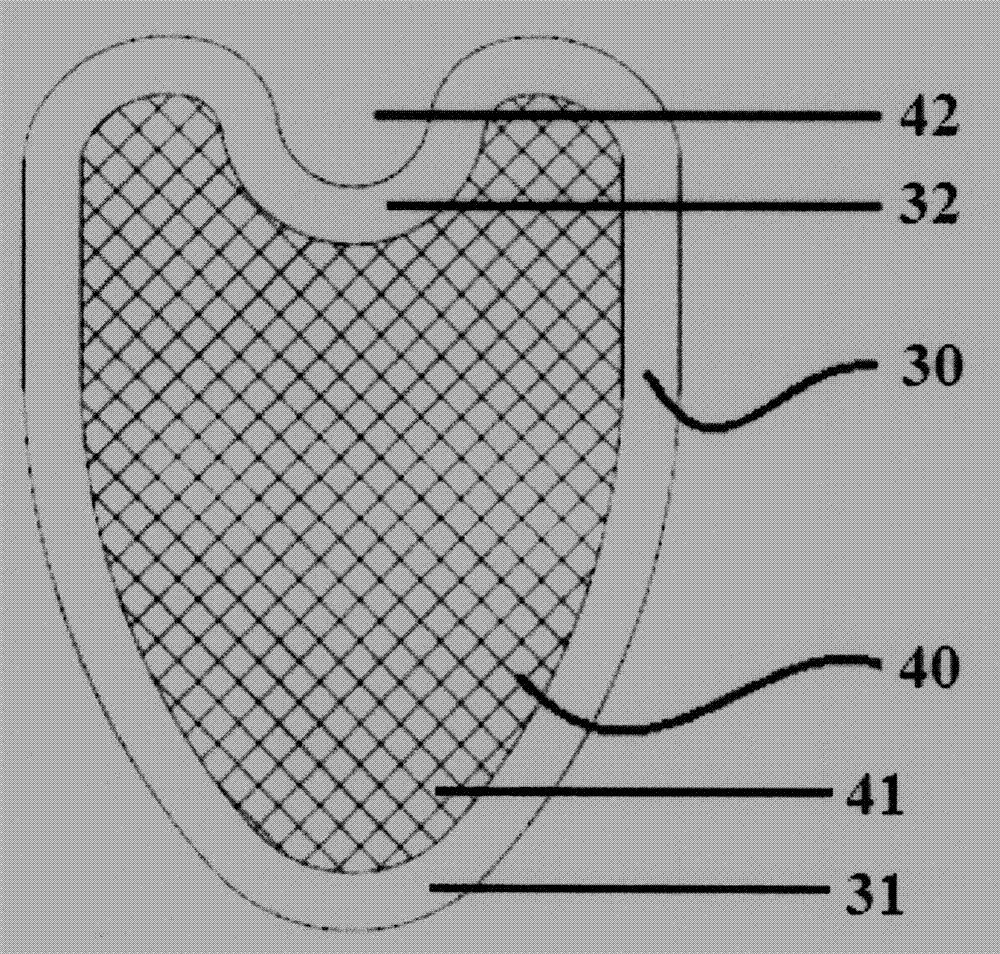
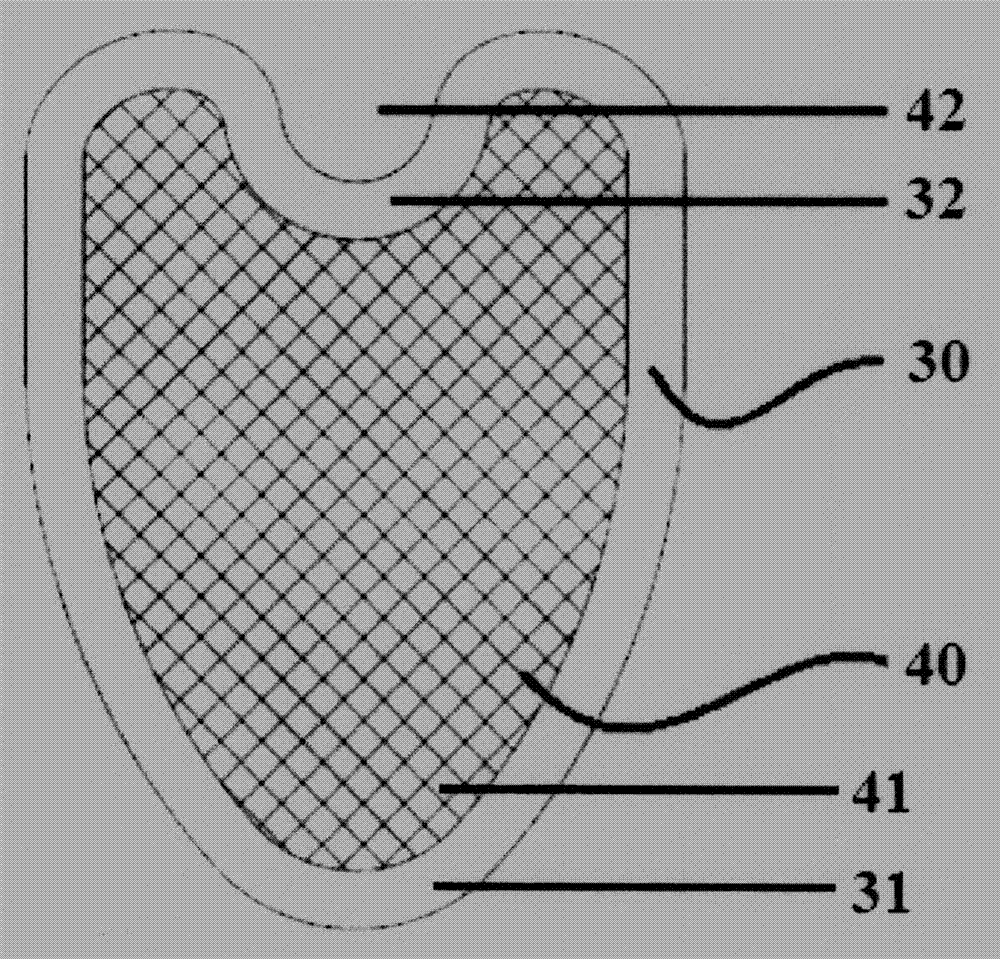
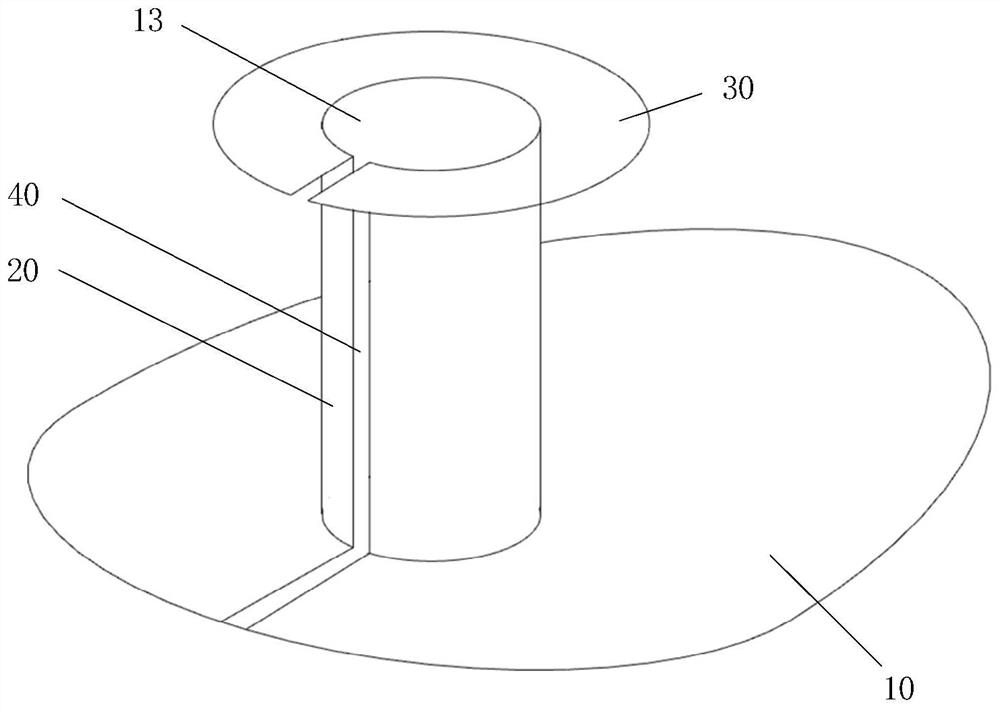
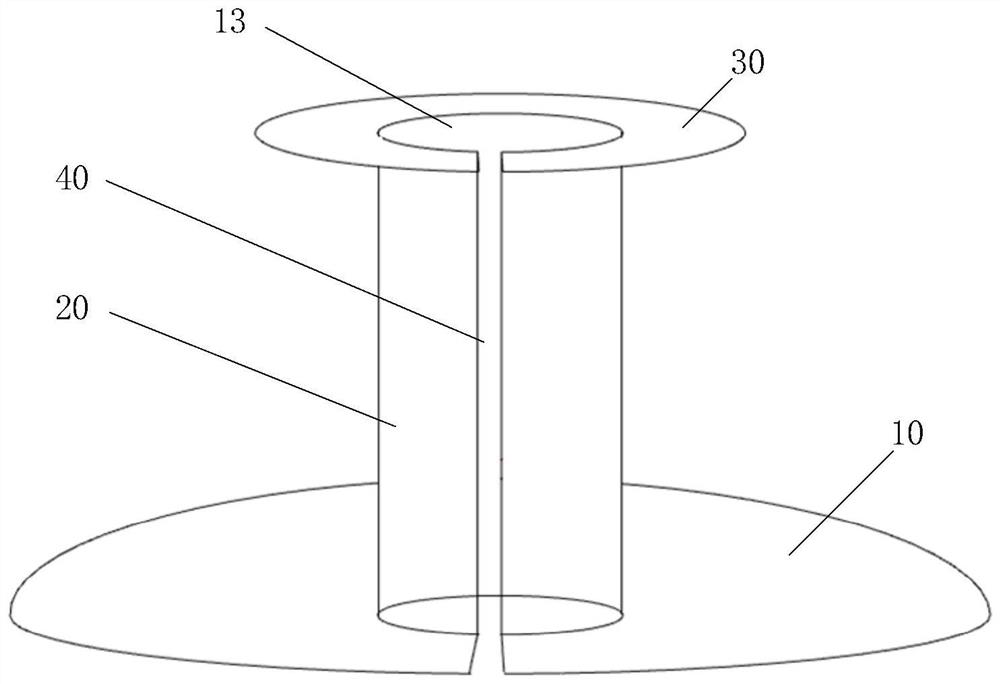
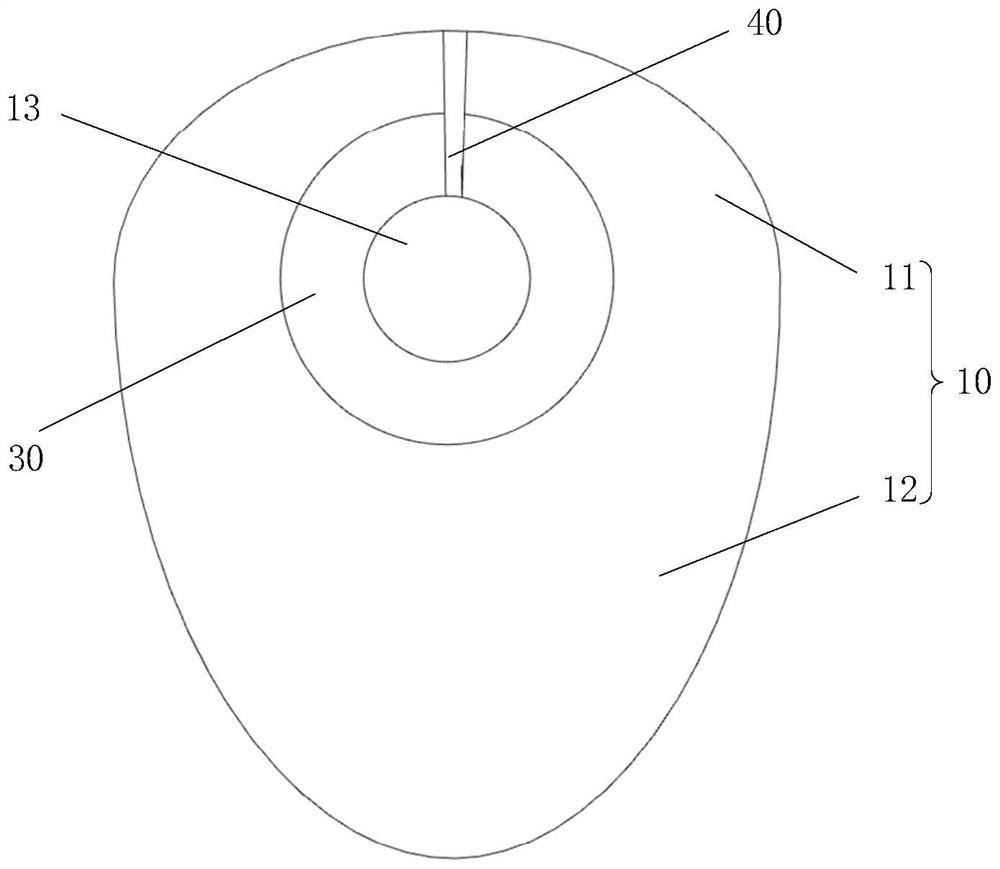
Anti-reflux hiatus hernia patch
The invention provides an anti-reflux hiatus hernia patch which comprises a substrate, a chimney body and a base plate, the substrate is used for being attached to the diaphragm muscle, the chimney body is used for wrapping the lower section of the esophagus, and the base plate is used for being attached to the cardia; the substrate is arranged at the lower end of the chimney body, and the base plate is arranged at the upper end of the chimney body. By means of the hiatus hernia treatment device, the technical problems that the hiatus hernia operation difficulty is large, the normal anatomical structure of the human body needs to be changed, and the postoperative recurrence rate is high are solved.
Owner:BEIJING CHAOYANG HOSPITAL CAPITAL MEDICAL UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com