Patents
Literature
53 results about "Intraoperative imaging" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The intraoperative magnetic resonance imaging (the iMRI) gives neurosurgeons real-time views of the brain during surgery, allowing them to detect abnormal tissues and remove brain tumors safely and effectively. Intraoperative imaging during surgery enables neurosurgeons to operate more precisely.
Videotactic and audiotactic assisted surgical methods and procedures
InactiveUS20080243142A1Medical simulationMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesAnatomical structuresSurgical operation
The present invention provides video and audio assisted surgical techniques and methods. Novel features of the techniques and methods provided by the present invention include presenting a surgeon with a video compilation that displays an endoscopic-camera derived image, a reconstructed view of the surgical field (including fiducial markers indicative of anatomical locations on or in the patient), and / or a real-time video image of the patient. The real-time image can be obtained either with the video camera that is part of the image localized endoscope or with an image localized video camera without an endoscope, or both. In certain other embodiments, the methods of the present invention include the use of anatomical atlases related to pre-operative generated images derived from three-dimensional reconstructed CT, MRI, x-ray, or fluoroscopy. Images can furthermore be obtained from pre-operative imaging and spacial shifting of anatomical structures may be identified by intraoperative imaging and appropriate correction performed.
Owner:GILDENBERG PHILIP L
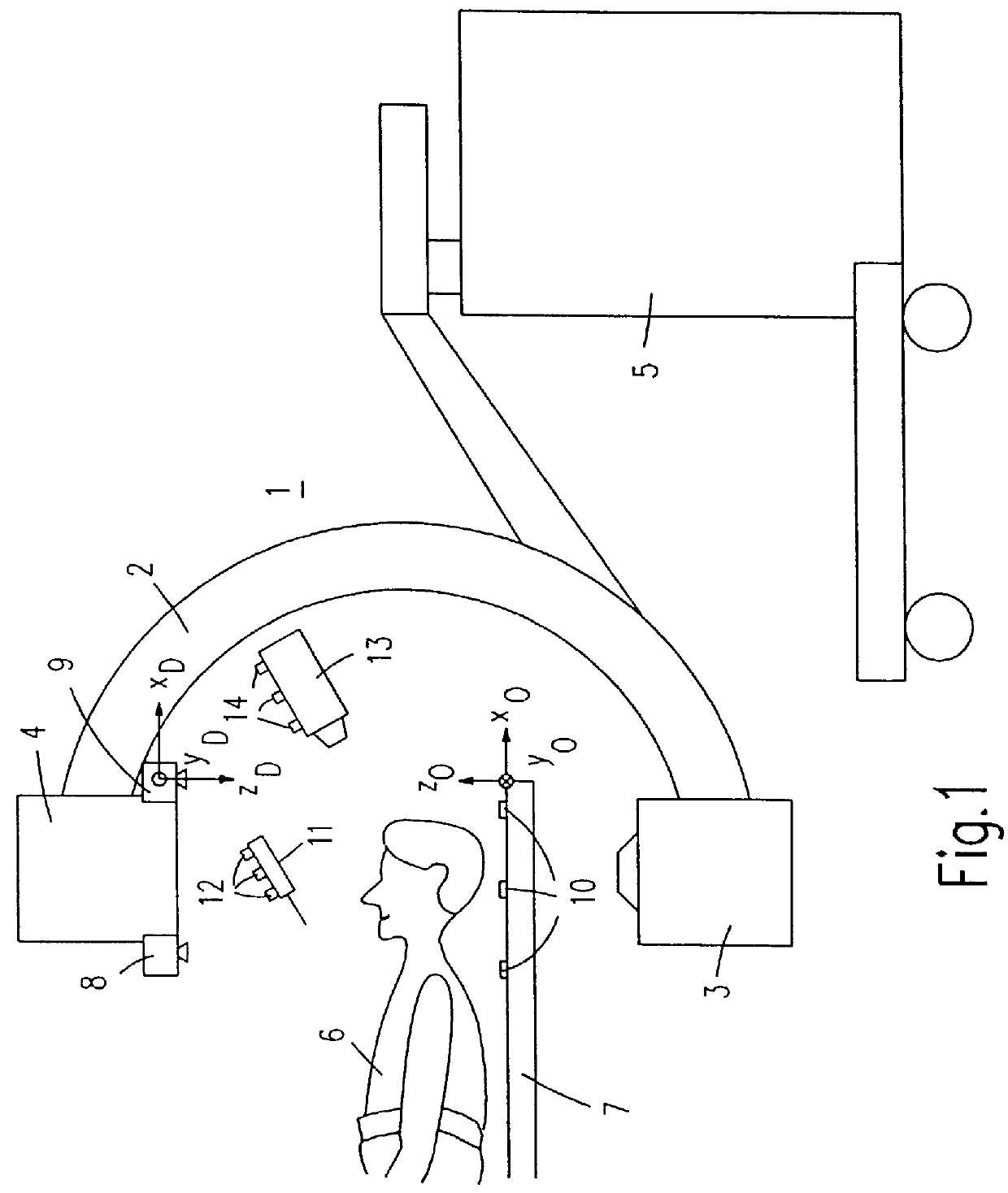
Method of and device for position detection in X-ray imaging
InactiveUS6050724AAccurately determineSimplified determinationSurgical navigation systemsForeign body detectionSoft x rayLocation detection
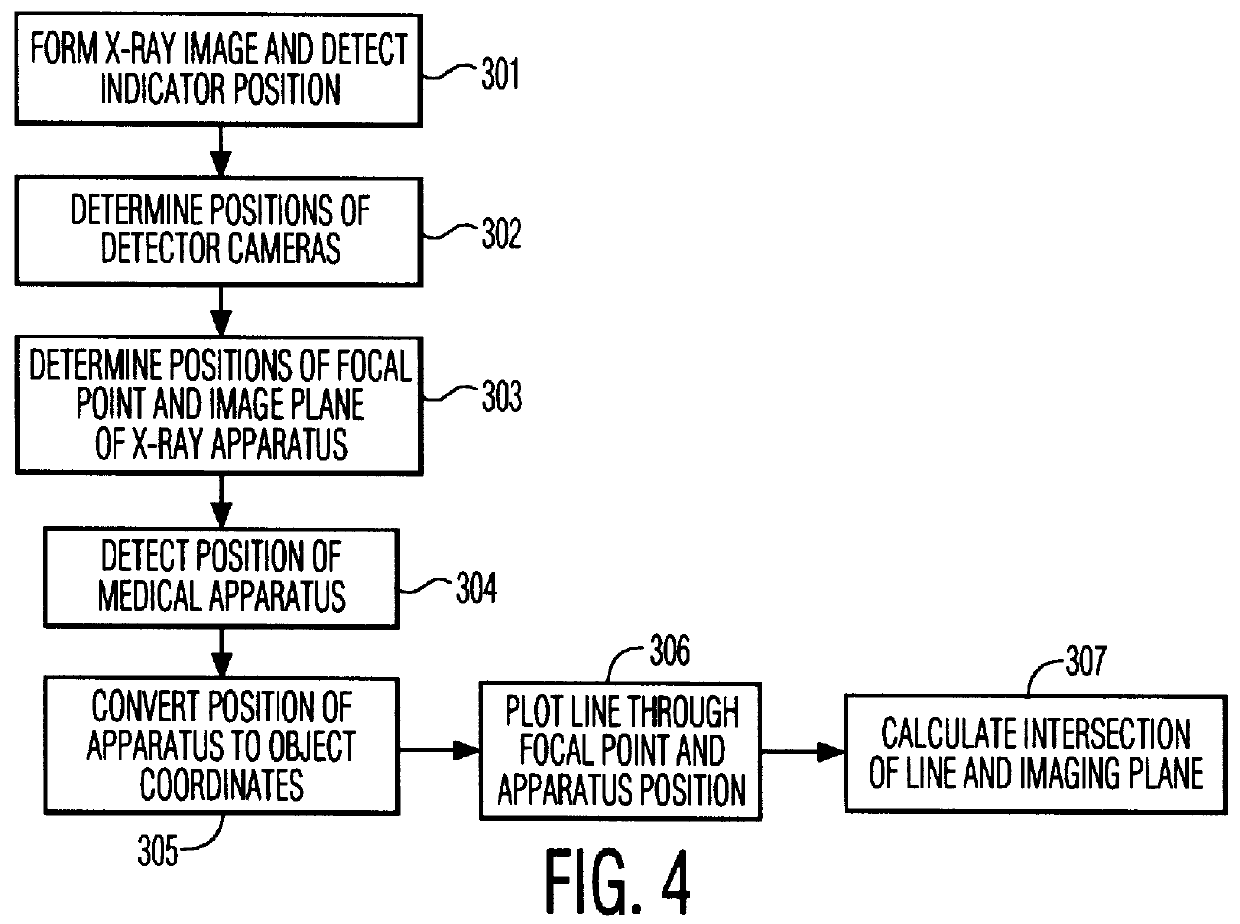
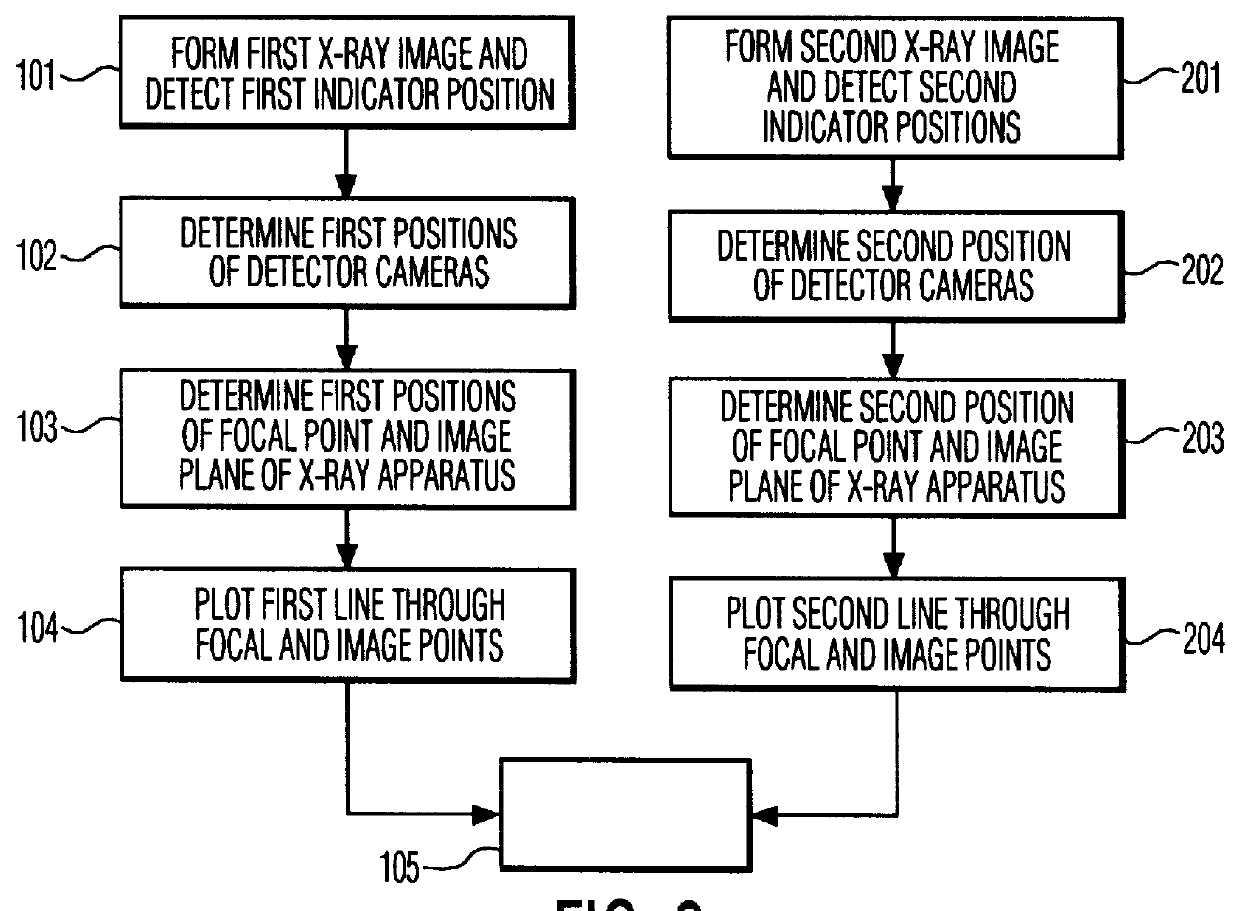
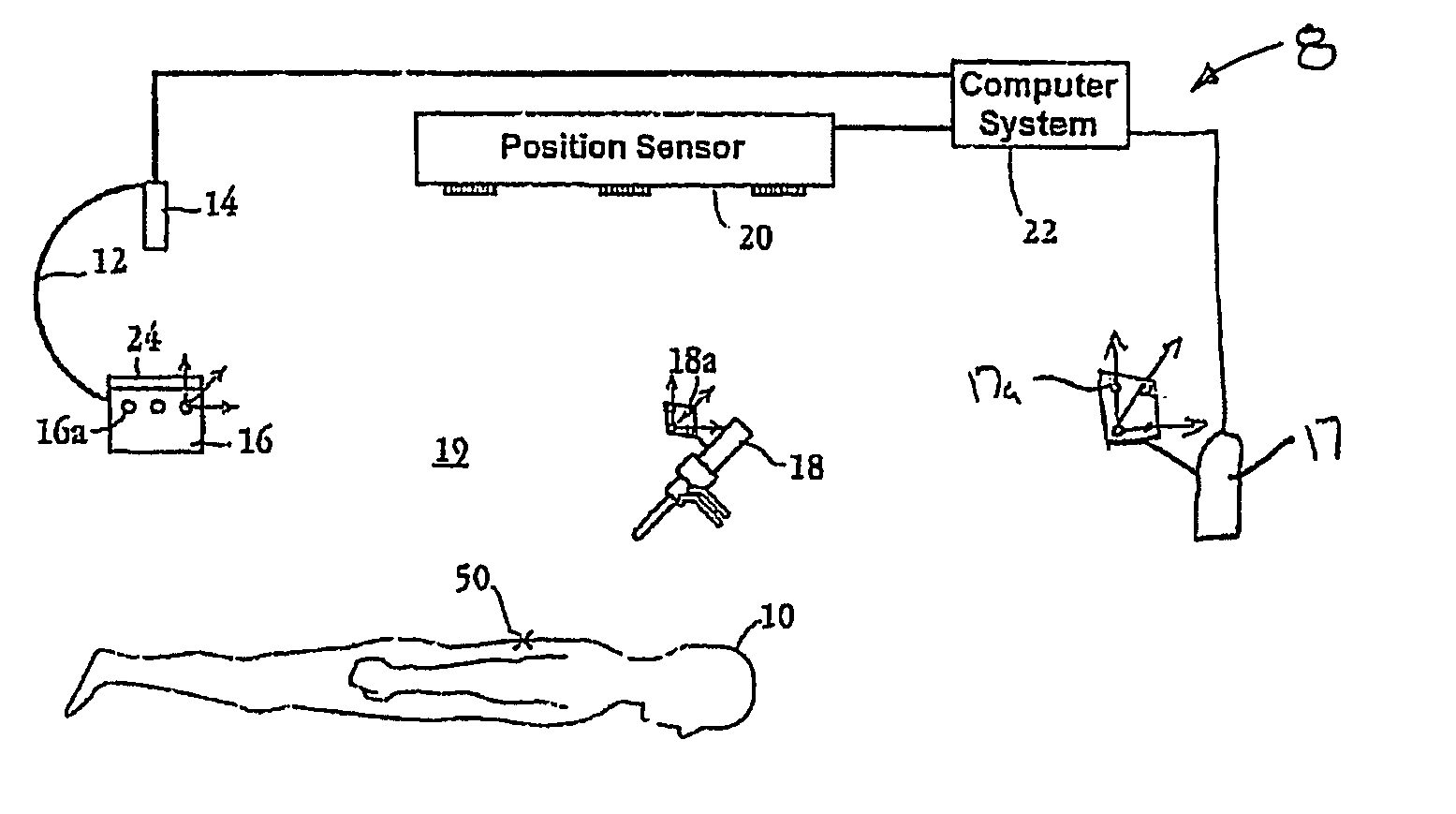
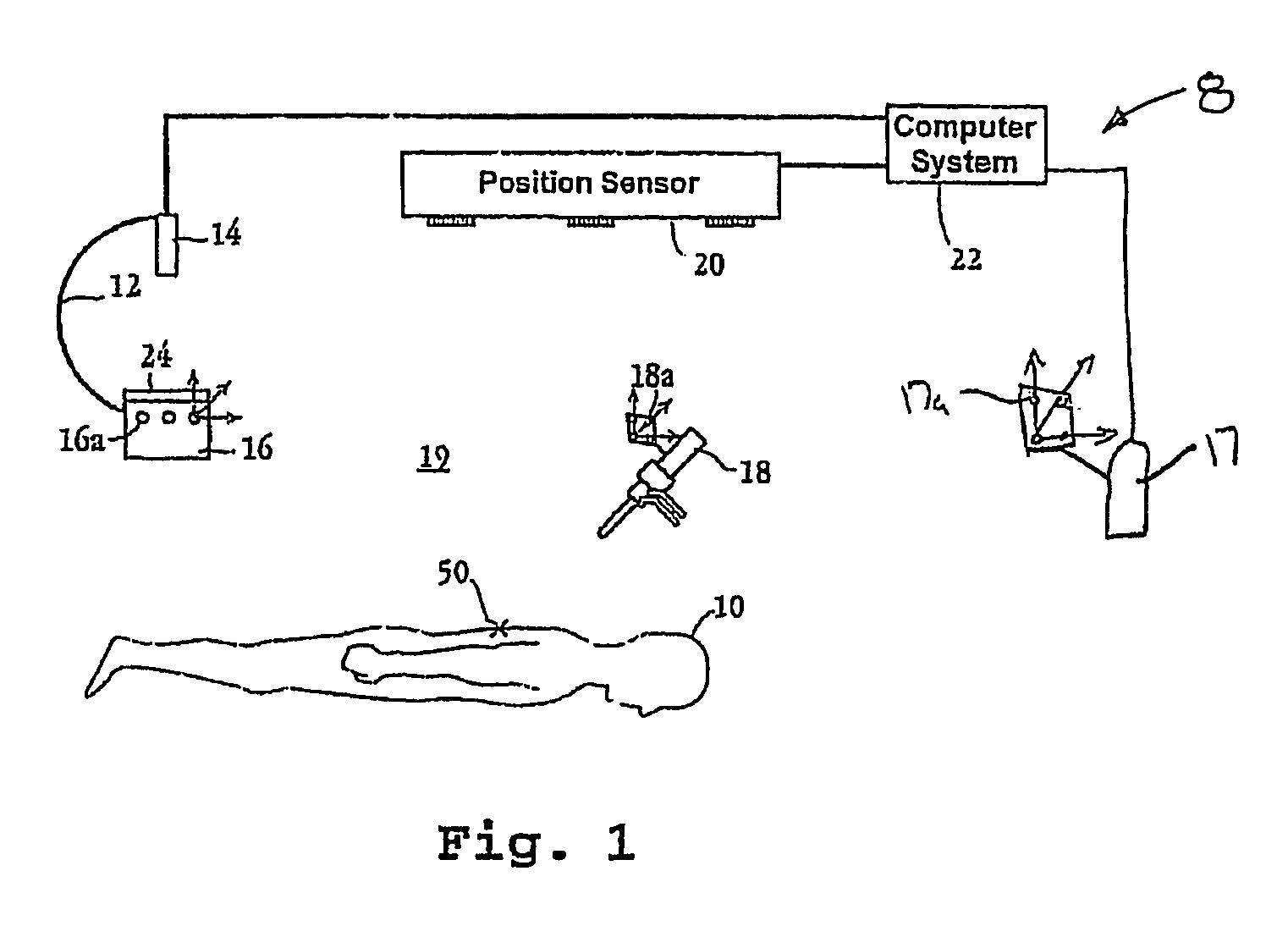
The invention relates to a method of position detection in X-ray imaging, and to a device for carrying out such a method by means of an X-ray apparatus, a detector device, including at least two detector elements, and an indicator device. The exact association of the X-ray image with the object imaged is very important notably for intraoperative imaging. Exact knowledge of the position and orientation of the components of the X-ray apparatus associated with the imaging system is required for this purpose. However, it is often problematic that the lines of sight of the position measuring system are obscured by attending staff or other apparatus. Therefore, in the device according to the invention the detector device is mounted on the X-ray apparatus and the indicator device is provided so as to be stationary on the object to be examined or stationary relative to the object to be examined. Also described is a method of position detection in X-ray imaging by means of such a device.
Owner:U S PHILIPS CORP
Method and apparatus for guiding a medical instrument to a subsurface target site in a patient
Intraoperative image(s) of a patient target site are generated by an intraoperative imaging system (e.g., ultrasound or X-ray). The intraoperative imaging system is tracked with respect to the patient target site and surgical instrument(s) (e.g., a pointer, endoscope or other intraoperative video or optical device). The intraoperative images, surgical instruments, and patient target site are registered into a common coordinate system. Spatial feature(s) of the patient target site are indicated on the images of the patient target site. Indicia relating the position and orientation of the surgical instrument(s) to the spatial feature(s) of the patient target site are projected on the images, with the indicia being used to correlate the position and orientation of the surgical instruments with respect to the target feature.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Intra-operative system for identifying and tracking surgical sharp objects, instruments, and sponges
Intra-operative systems for identifying surgical sharp objects are provided. Aspects of the systems include an intra-operative imaging device for obtaining intra-operative surgical sharp object image data; and a surgical sharp object automated shape recognition module configured to identify a surgical sharp object from intra-operative surgical sharp object image data. Systems of the invention may further include additional components, such as surgical instrument and / or sponge identification and tracking devices. Systems of the invention find use in a variety of methods and applications, including tracking of surgical items during a surgical procedure.
Owner:DEIN JOHN RICHARD
System and method for image guided medical procedures
InactiveUS20140073907A1Correction can be minimizedEasy to useUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgical needlesDiagnostic Radiology ModalitySoft tissue deformation
A system and method combines information from a plurality of medical imaging modalities, such as PET, CT, MRI, MRSI, Ultrasound, Echo Cardiograms, Photoacoustic Imaging and Elastography for a medical image guided procedure, such that a pre-procedure image using one of these imaging modalities, is fused with an intra-procedure imaging modality used for real time image guidance for a medical procedure for any soft tissue organ or gland such as prostate, skin, heart, lung, kidney, liver, bladder, ovaries, and thyroid, wherein the soft tissue deformation and changes between the two imaging instances are modeled and accounted for automatically.
Owner:CONVERGENT LIFE SCI
Intraoperative Imaging of Renal Cortical Tumors and Cysts
ActiveUS20080161662A1Solve the lack of functionEasy to manageDiagnostics using fluorescence emissionCatheterCystRenal tumor
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
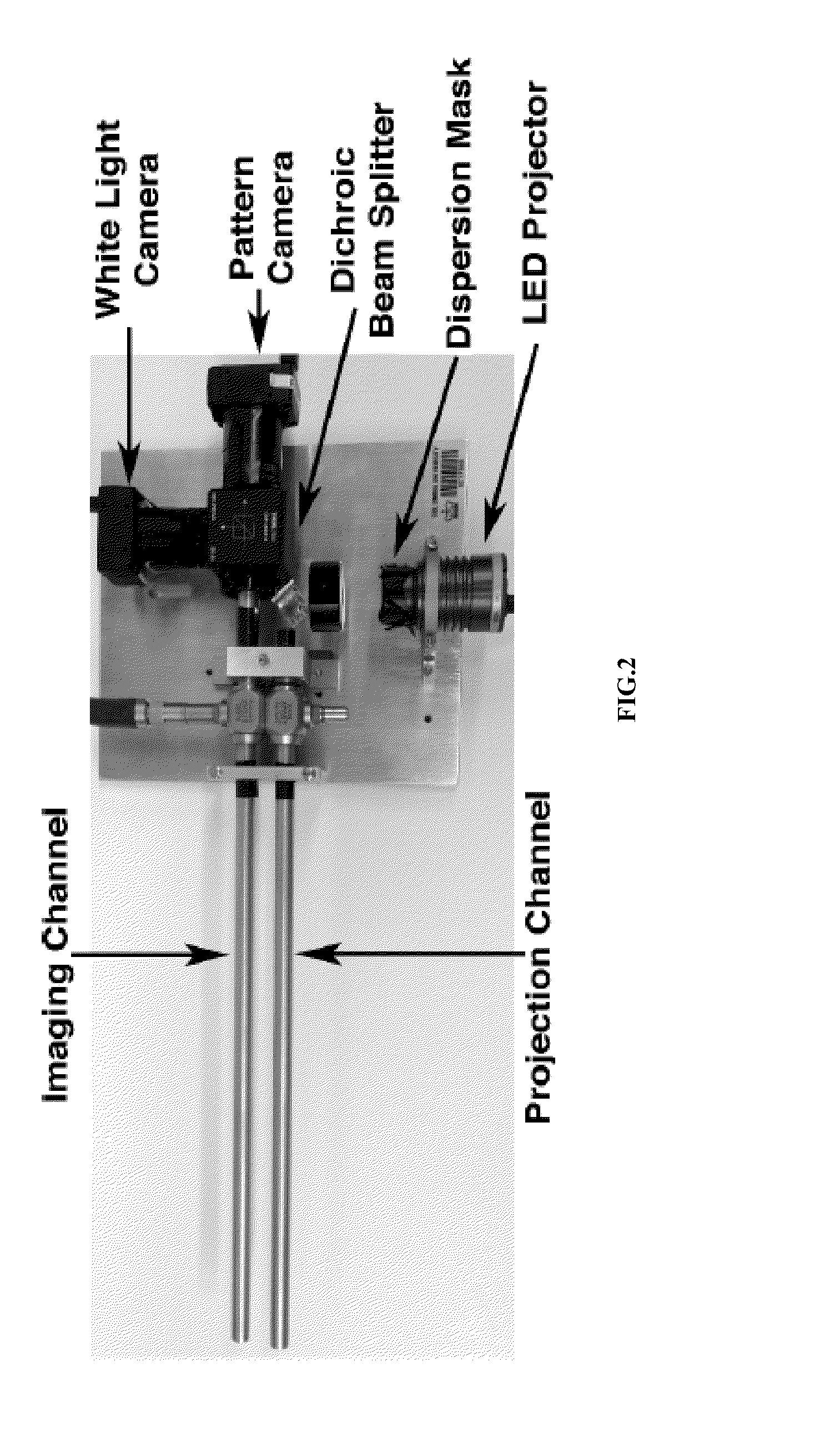
Surgical structured light system
InactiveUS20140336461A1Improved navigation and safetyEasy to learnSurgeryEndoscopesVisual perceptionMarine navigation
A Surgical Structured Light (SSL) system is disclosed that provides real-time, dynamic 3D visual information of the surgical environment, allowing registration of pre- and intra-operative imaging, online metric measurements of tissue, and improved navigation and safety within the surgical field.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Instrument guidance system for sinus surgery
ActiveUS20170231714A1Enhanced D perceptionImage enhancementImage analysisGuidance systemObject based
A method for generating an augmented reality image for supporting the adjustment of the position of a surgical instrument during sinus surgery comprising the steps of: selecting at least one of sinus cells, cavities and orifices of the sinus in a pre-operative image by marking them with at least one geometric primitive or tube shaped object; using real-time intra-operative imaging for displaying the operating field; determining the relative positions at least between the real-time imaging of the patient and the pre-operative image data; computing a virtual image corresponding to a real-time image comprising at least one marked geometric primitive or tube shaped object based on the determined relative positions; combining the virtual image and the real-time intraoperative image for visualization in an augmented reality image.
Owner:STRYKER EUROPEAN OPERATIONS LIMITED
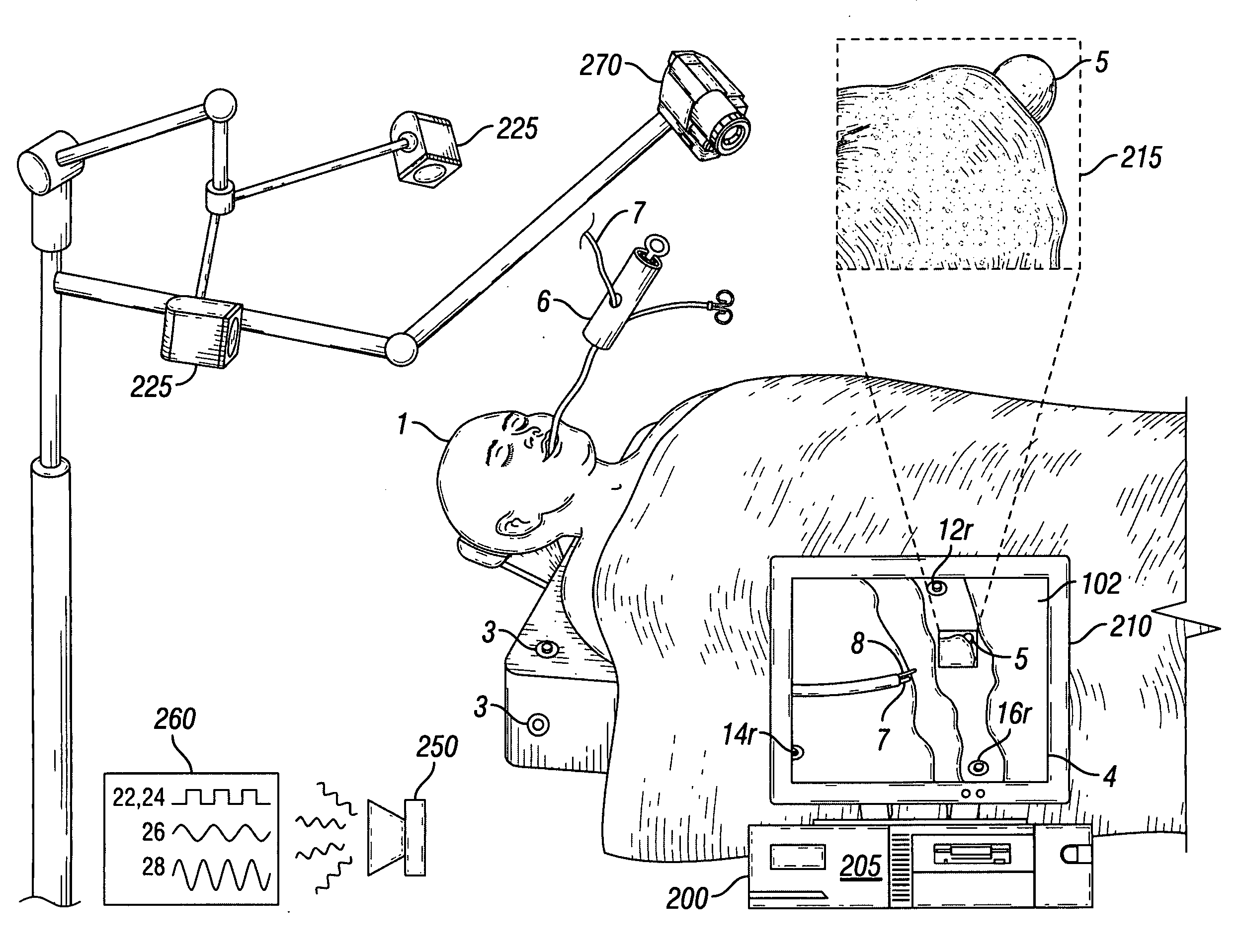
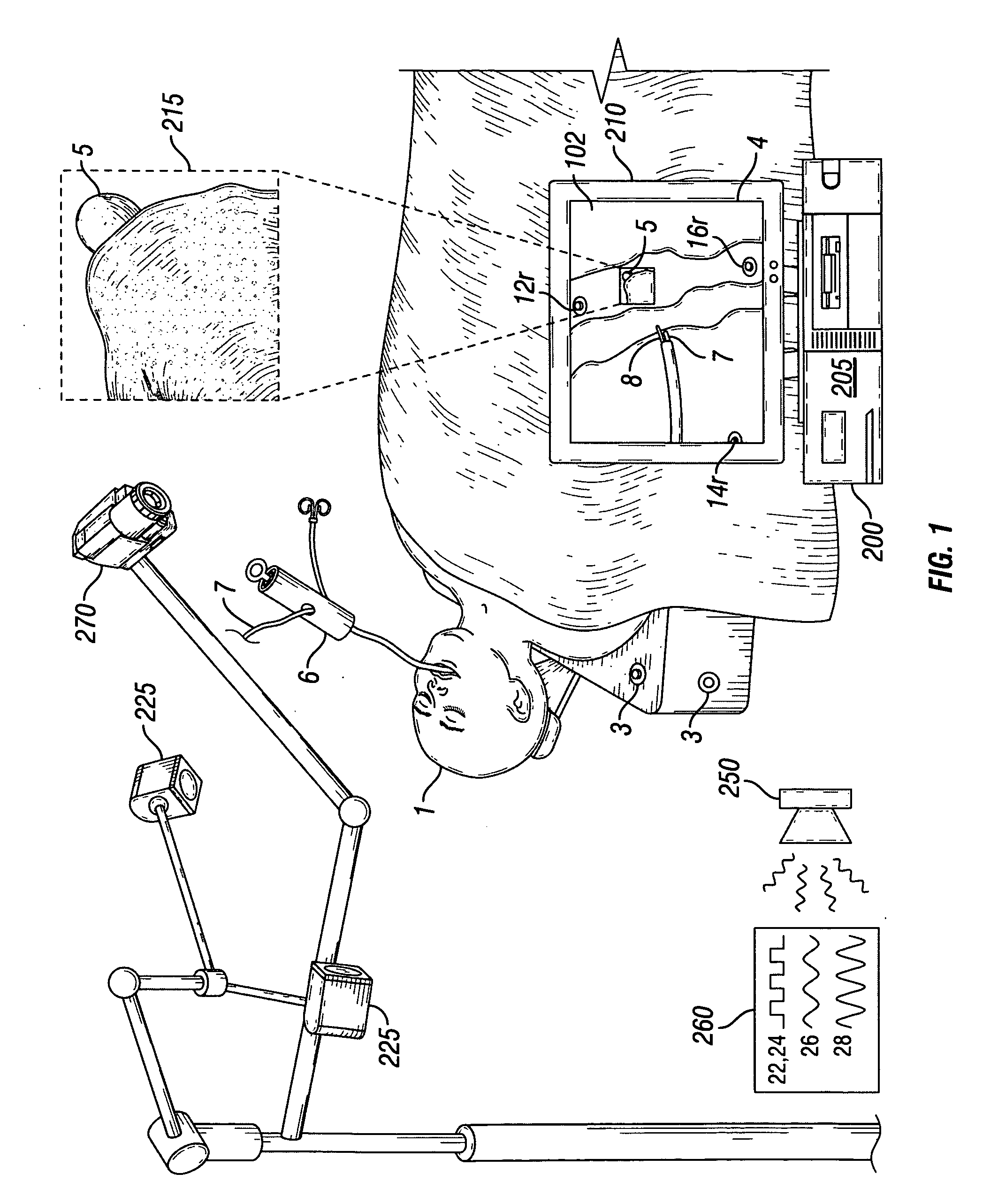
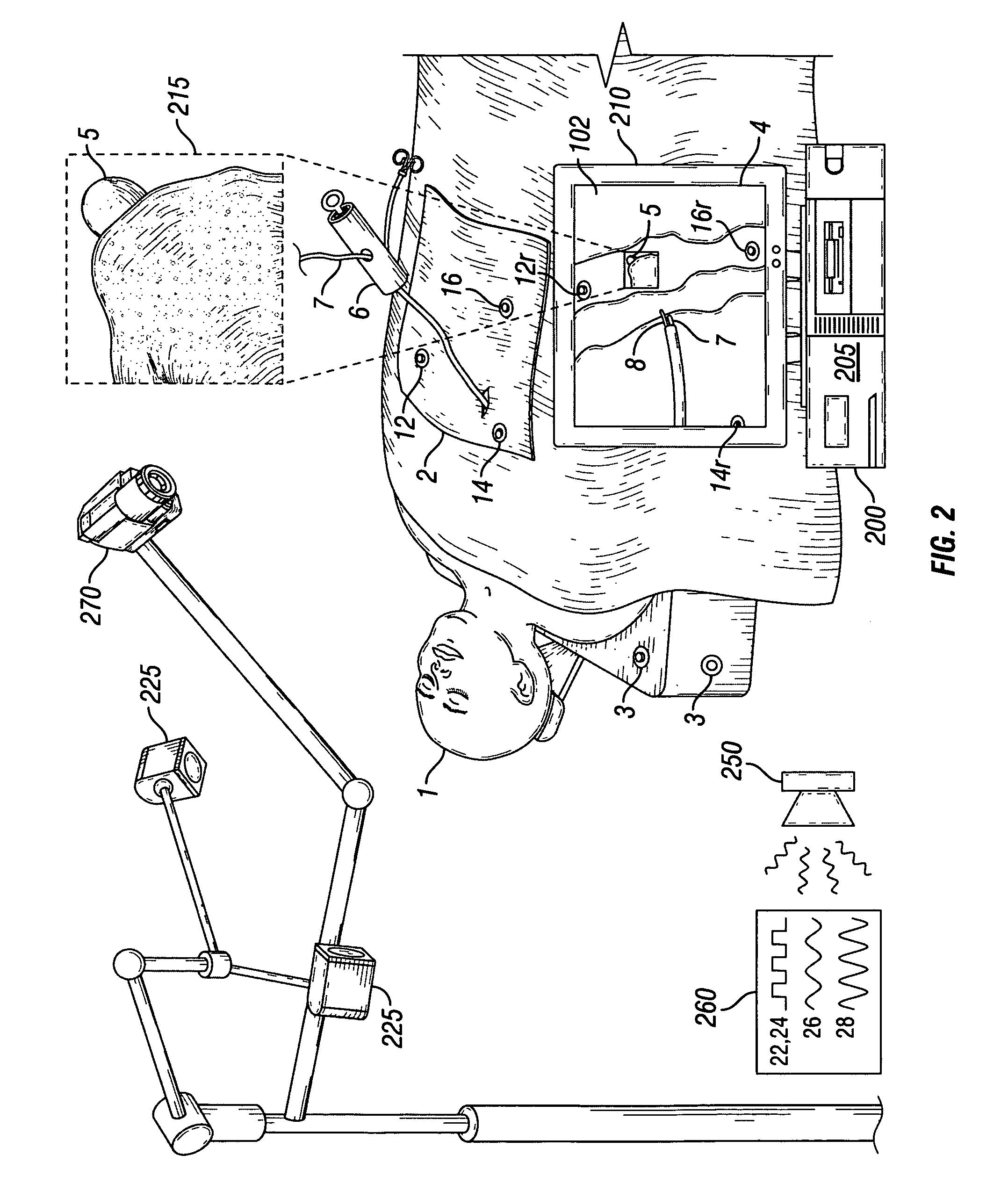
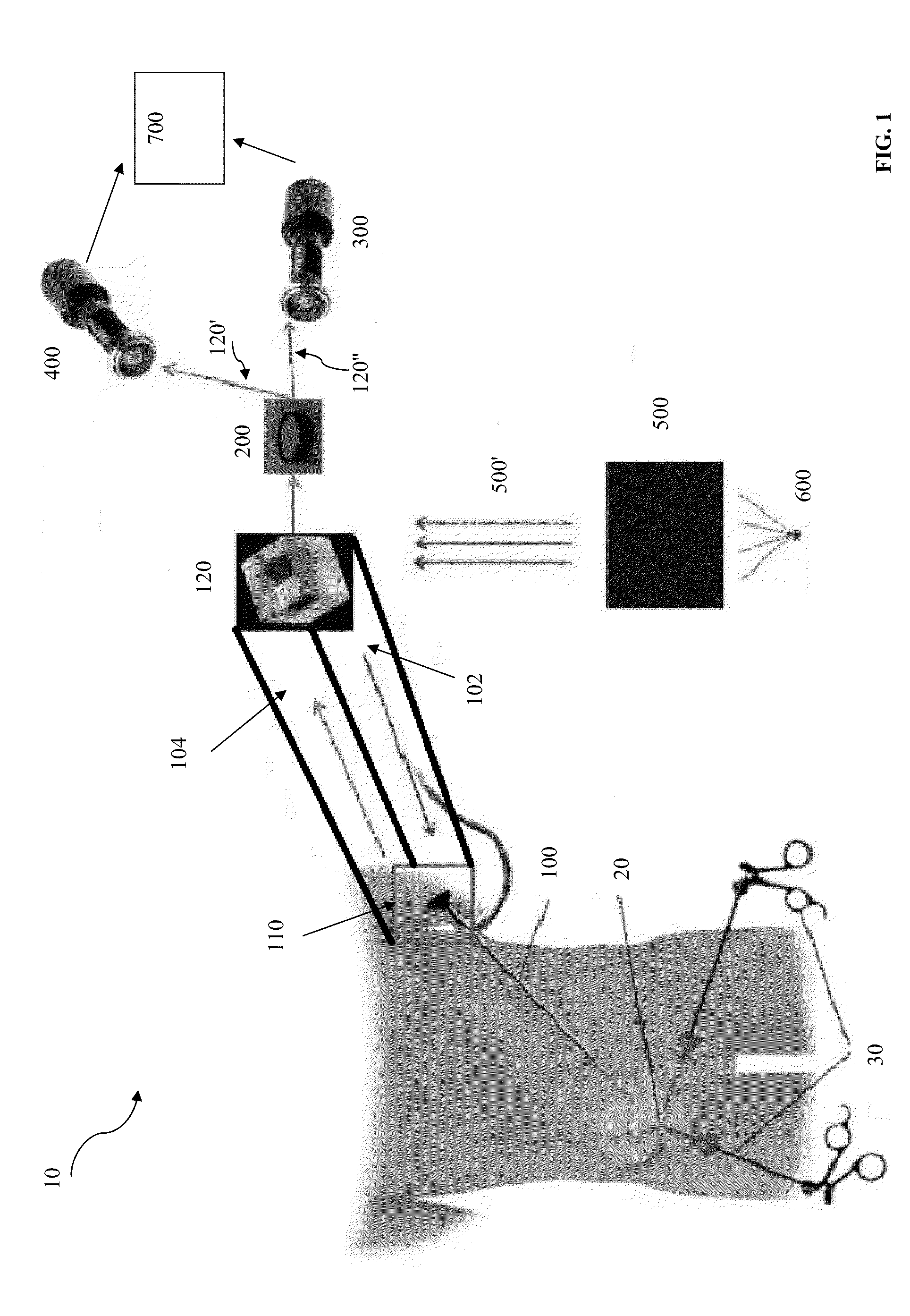
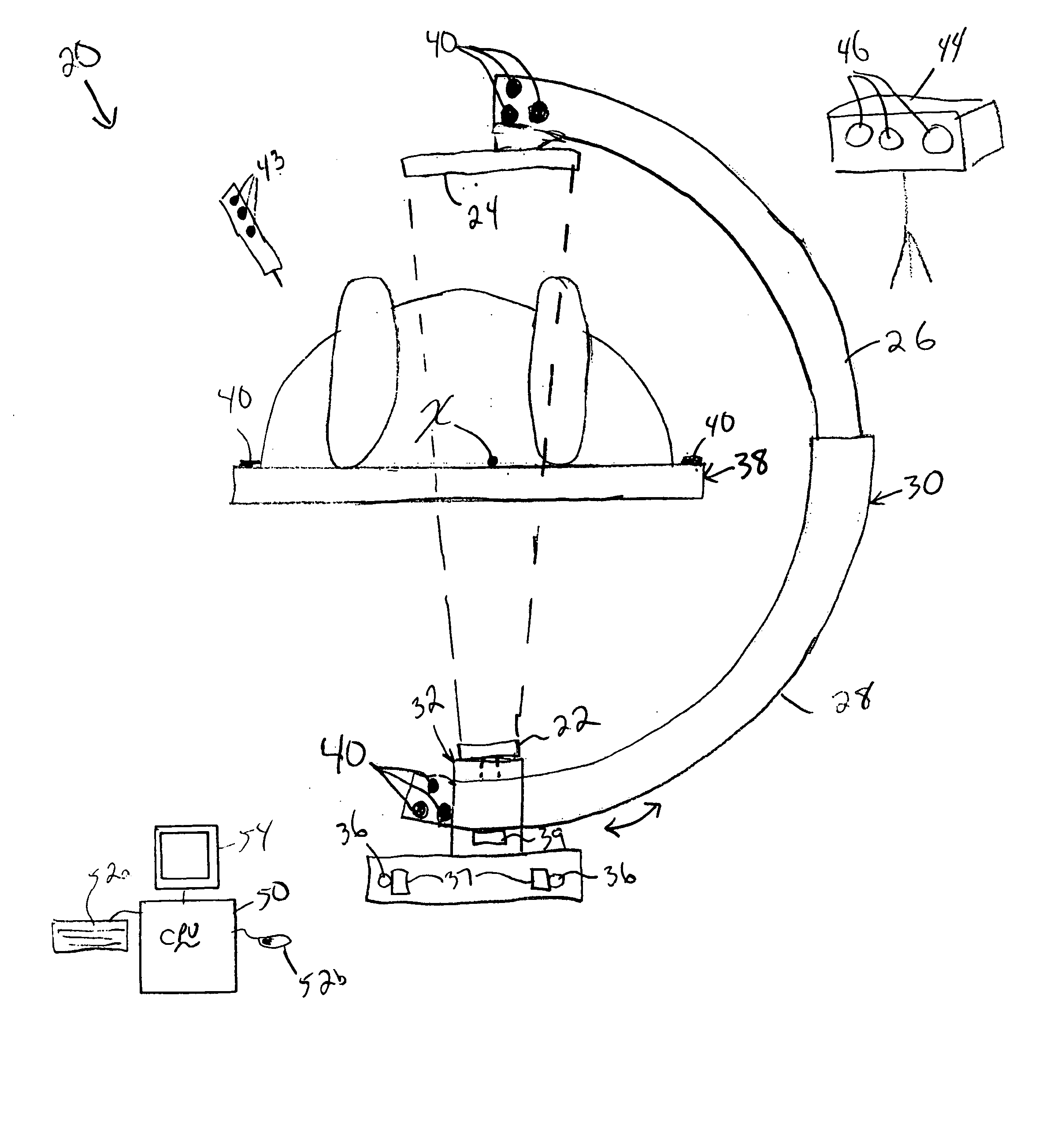
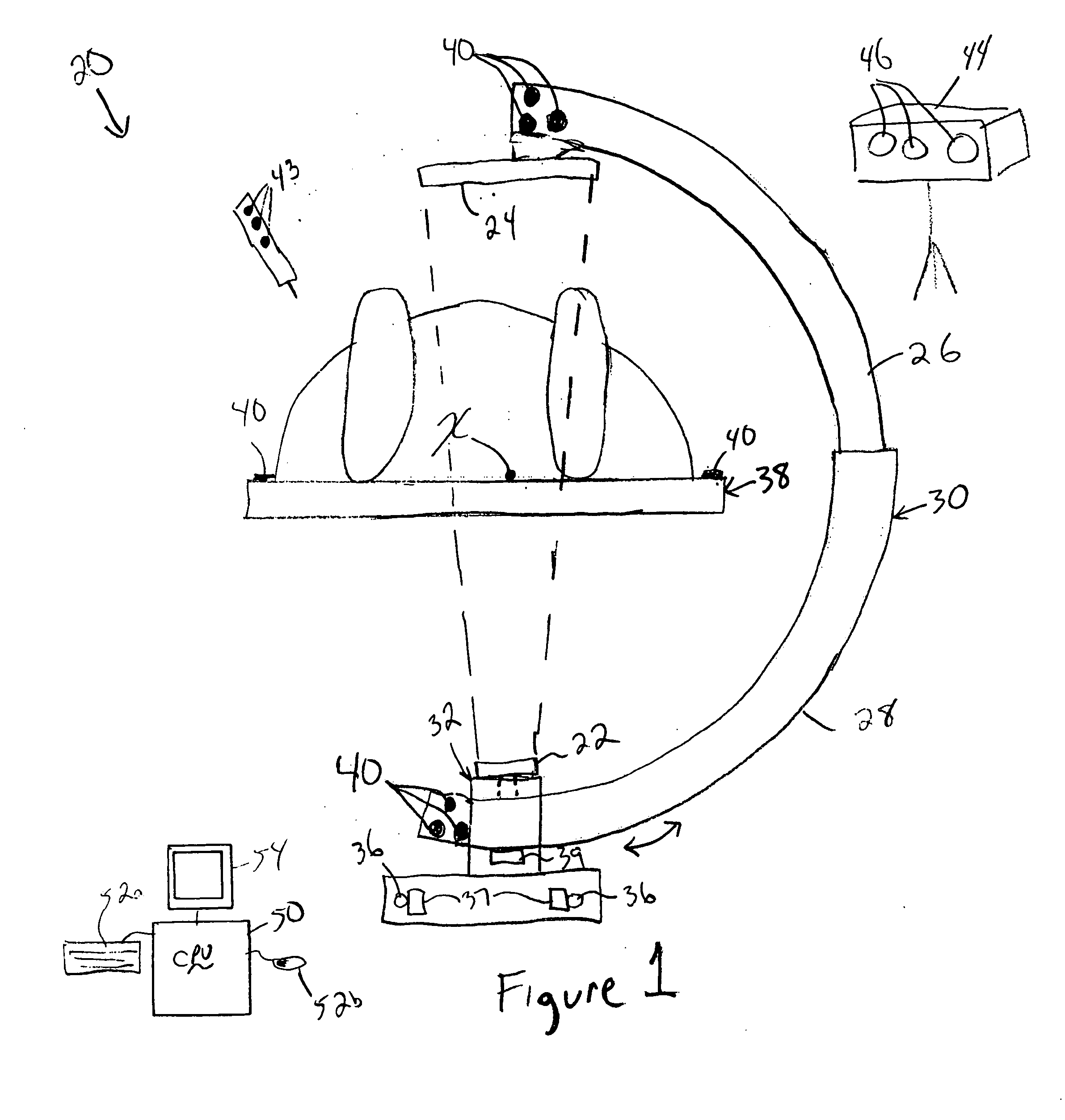
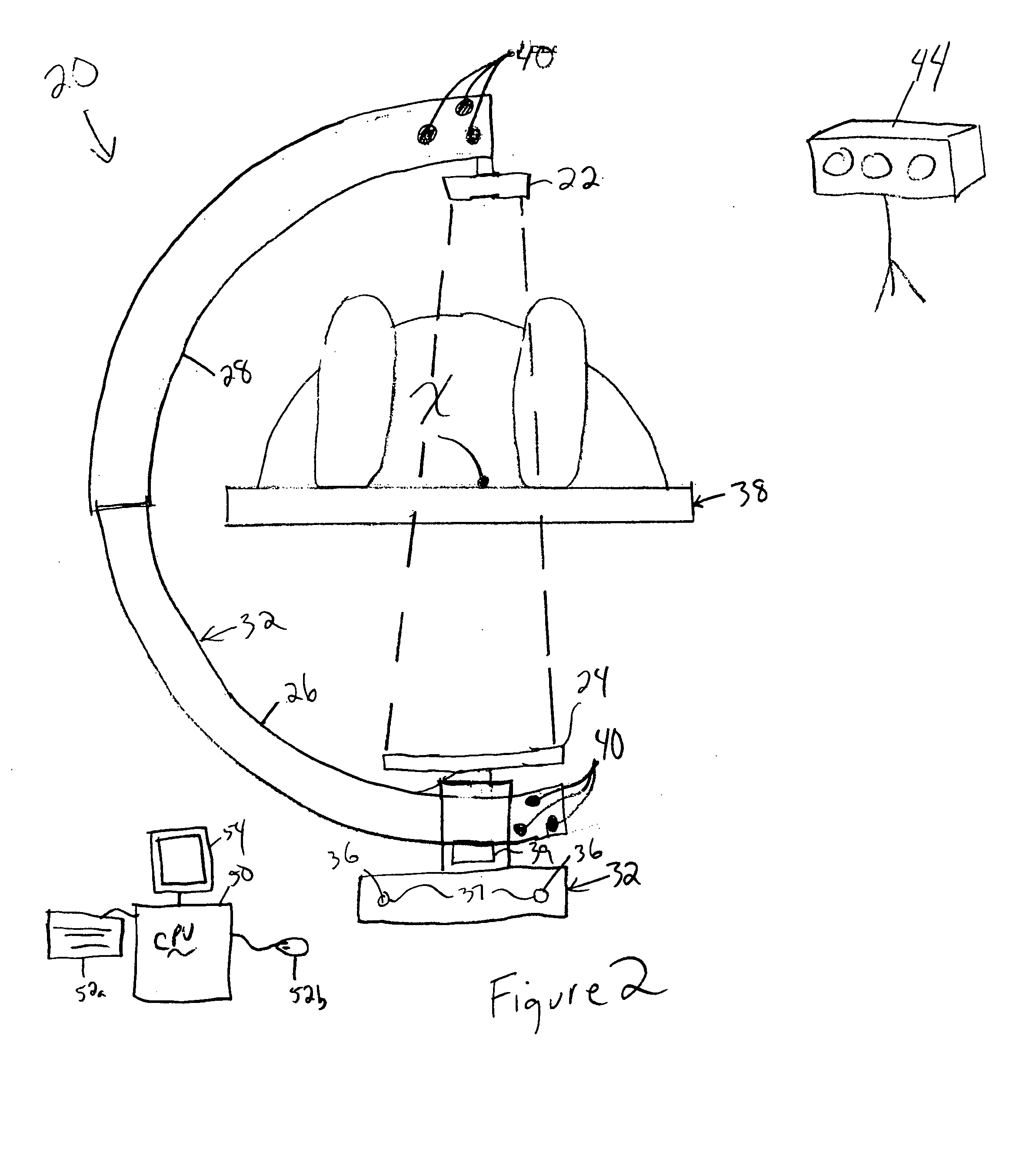
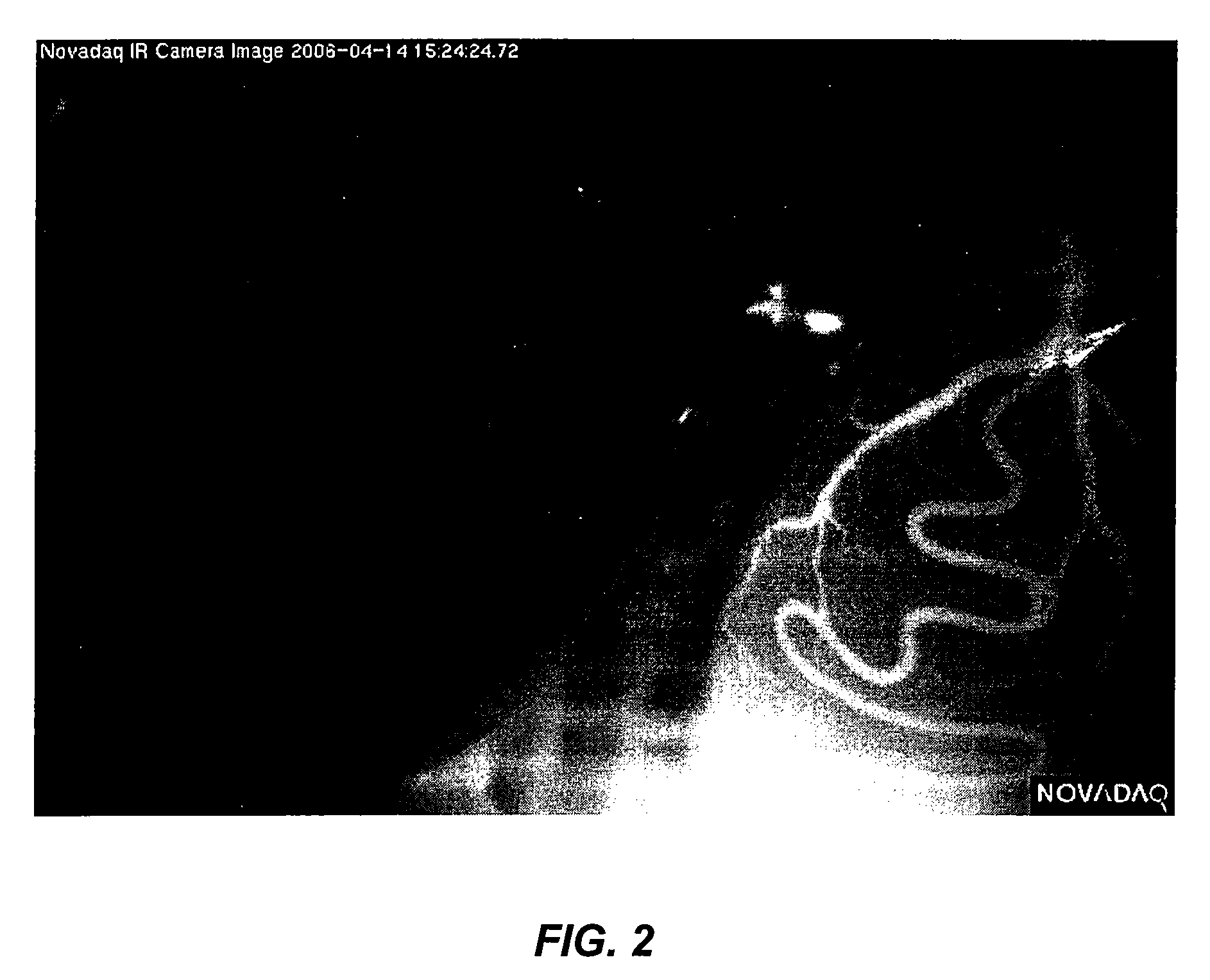
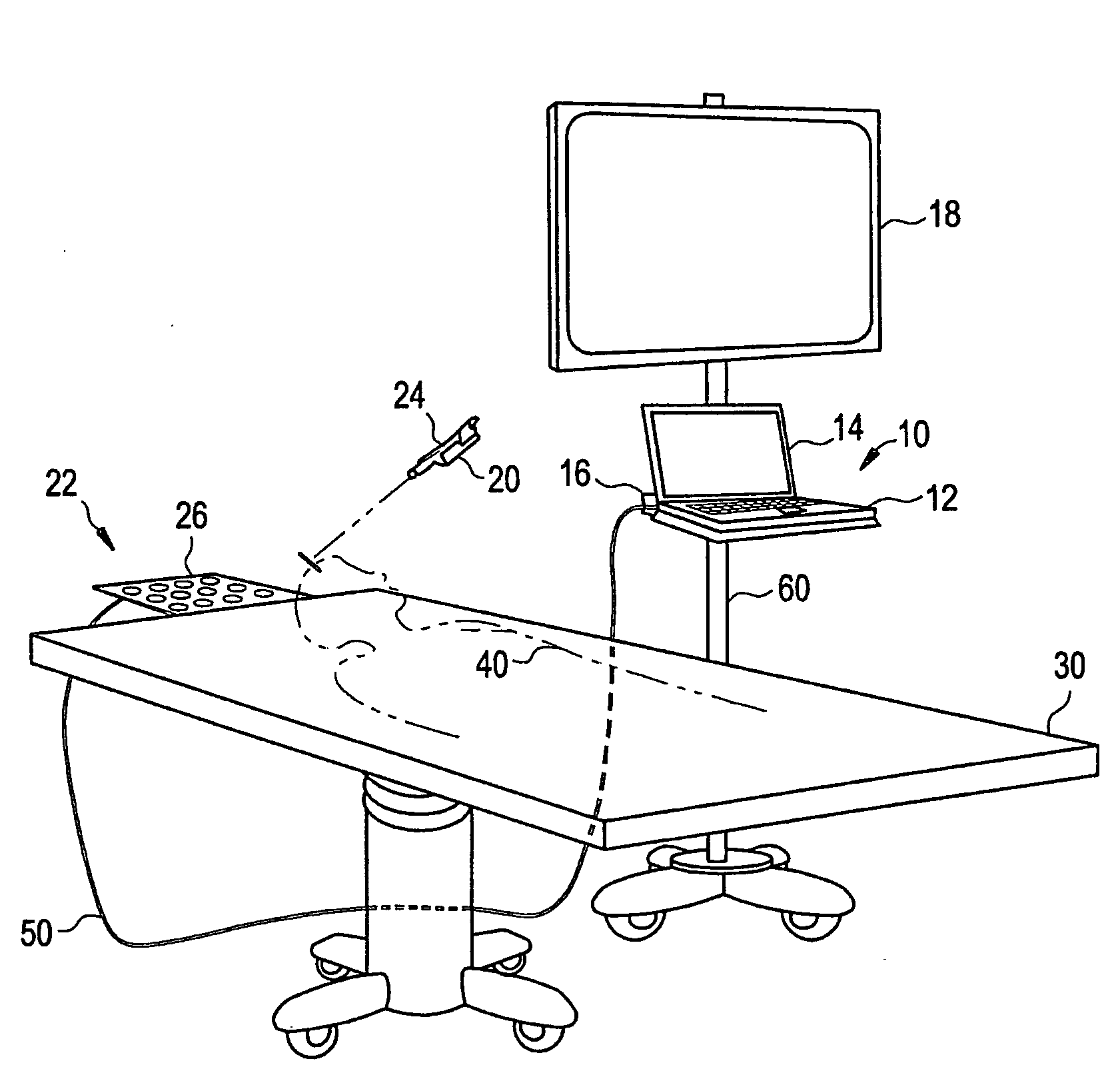
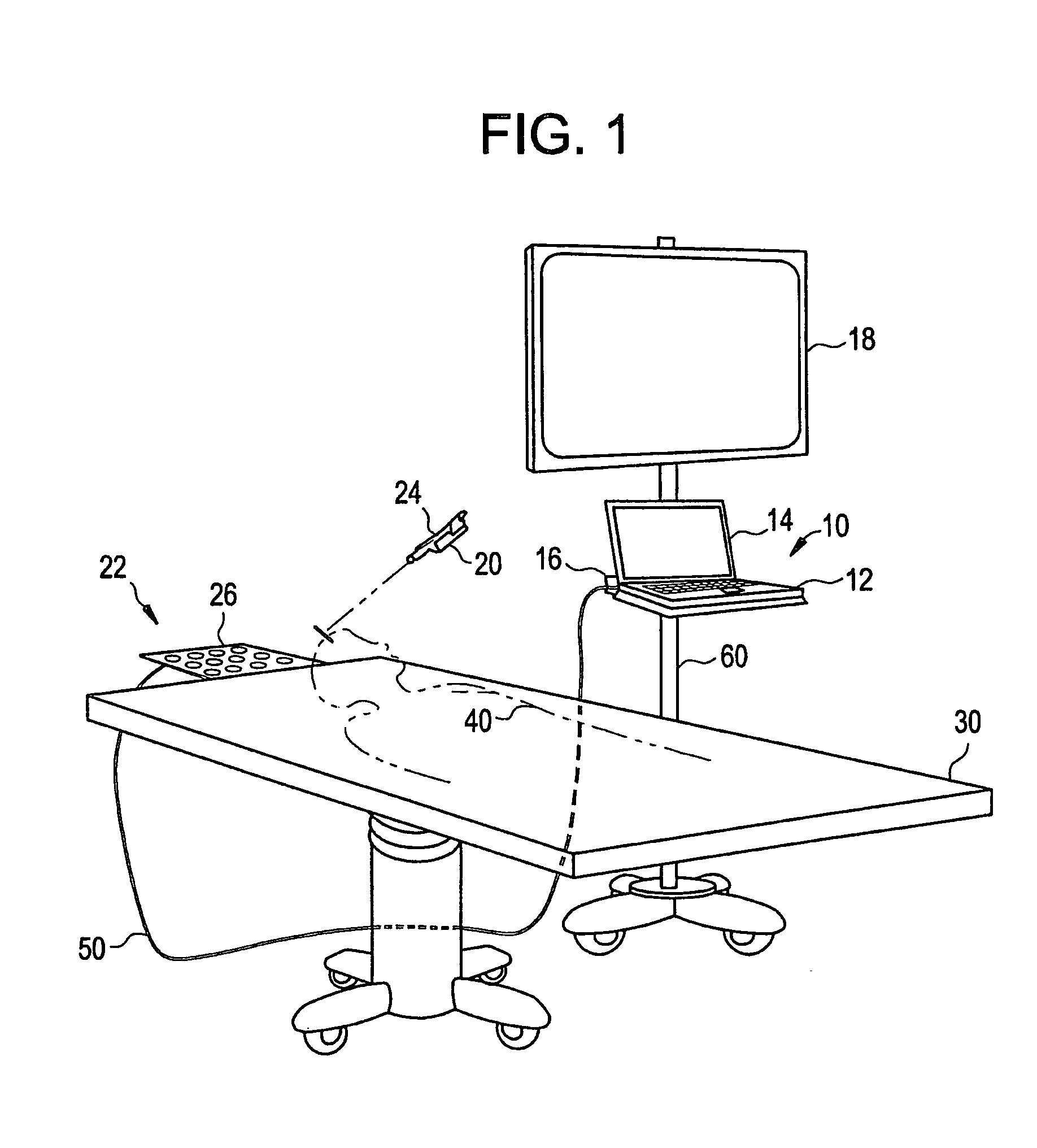
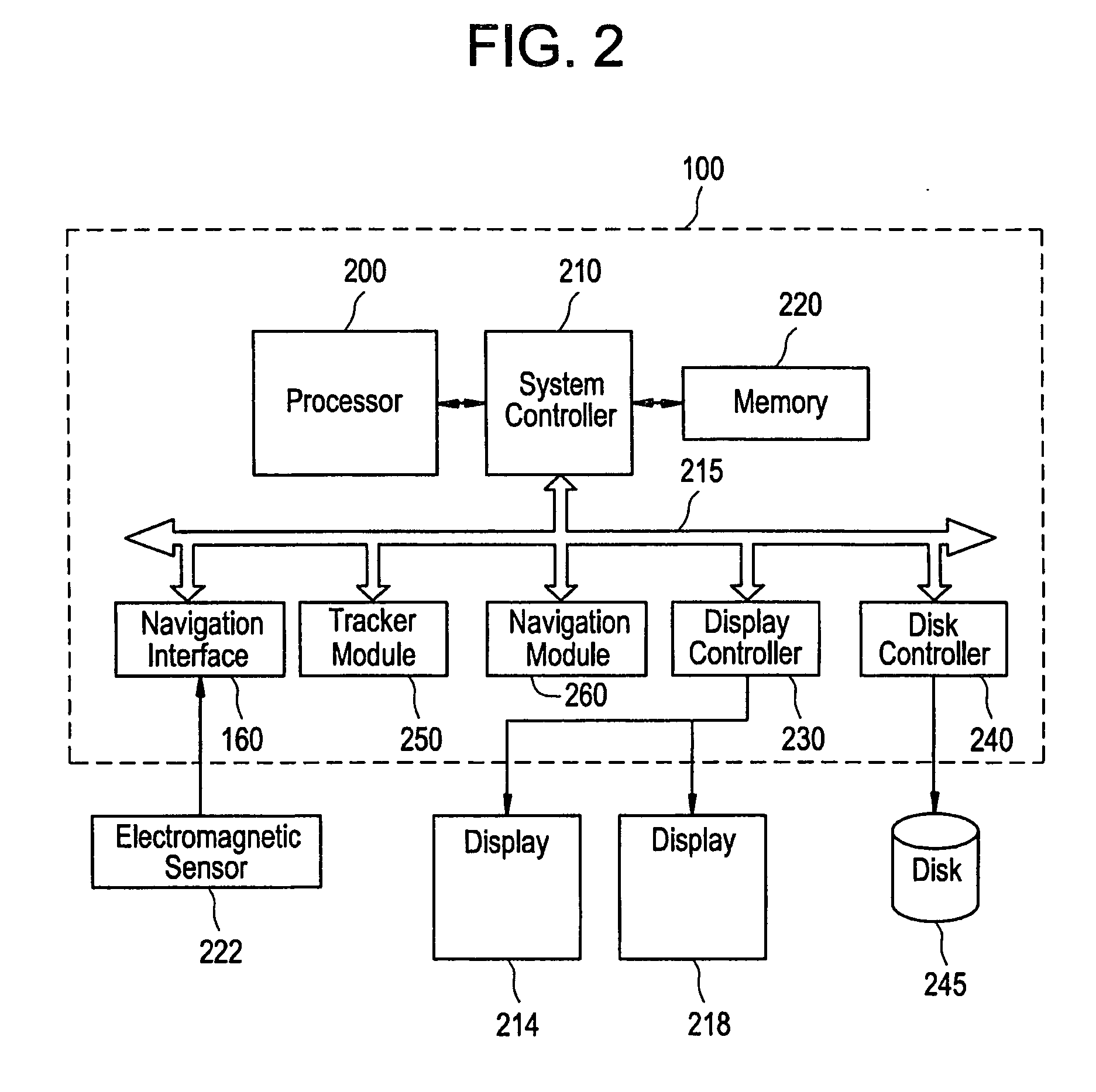
Intraoperative imaging system
ActiveUS20050054915A1Quickly and easily moved out of waySmall sizeMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingProximateNavigation system
An imaging system includes a source and a detector that can be quickly and easily moved out of the way after scanning. During scanning, the actual paths that the source and detector travel are tracked, such as by an associated surgical navigation system tracking system. The actual locations of the source and detector during each x-ray image are used in the image reconstruction algorithm. Since the actual locations are used in the algorithm, the locations do not have to be as precisely controlled. In one embodiment, the source and detector are mounted proximate outer ends of first and second c-arm sections. The first and second c-arm sections are extendable to form a complete c-arm and retractable to a collapsed position when not in use. In the disclosed embodiment, the c-arm sections are mounted to a base or carriage under the patient support surface (such as the surgical table).
Owner:XORAN TECH
Virtual image with optical shape sensing device perspective
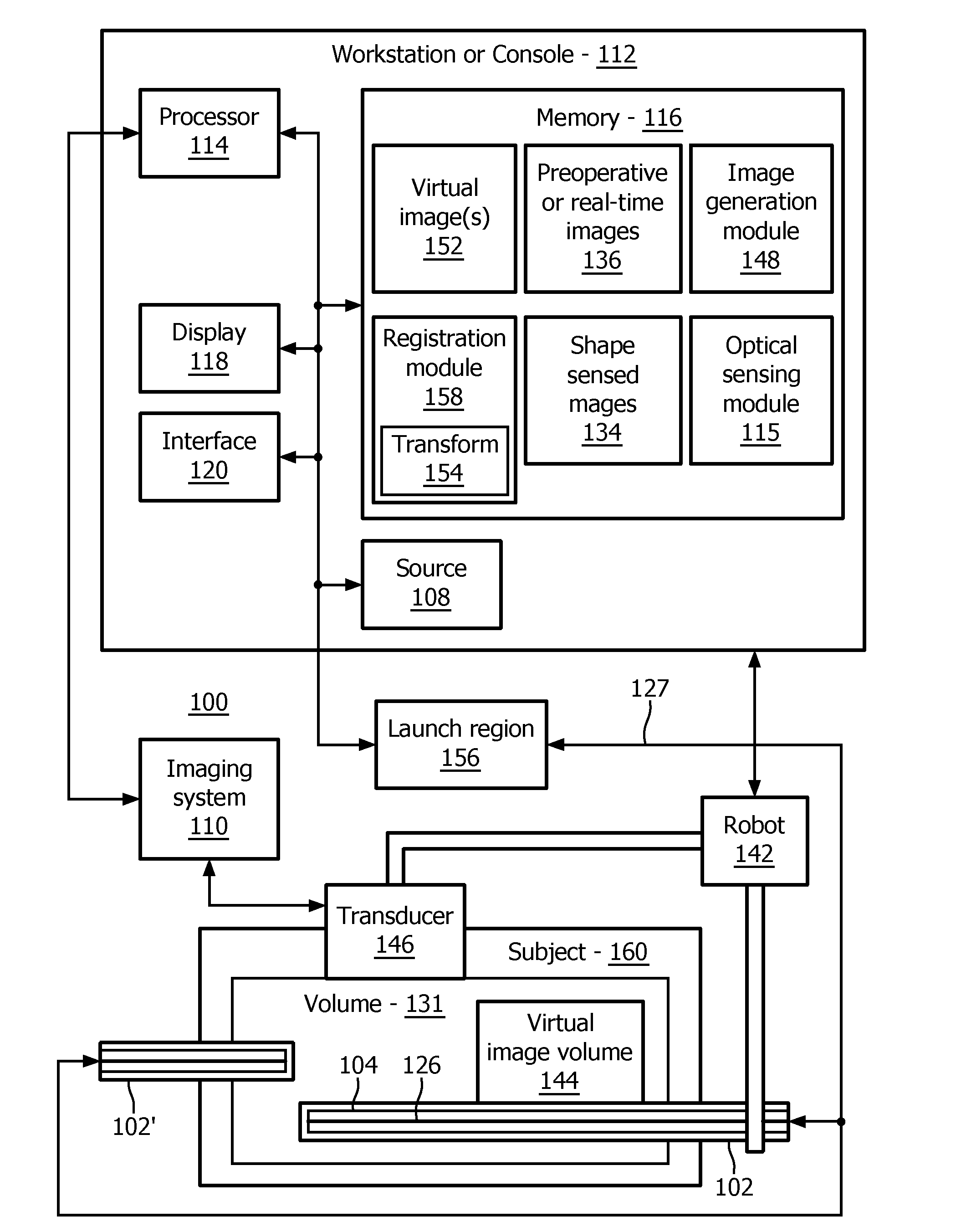
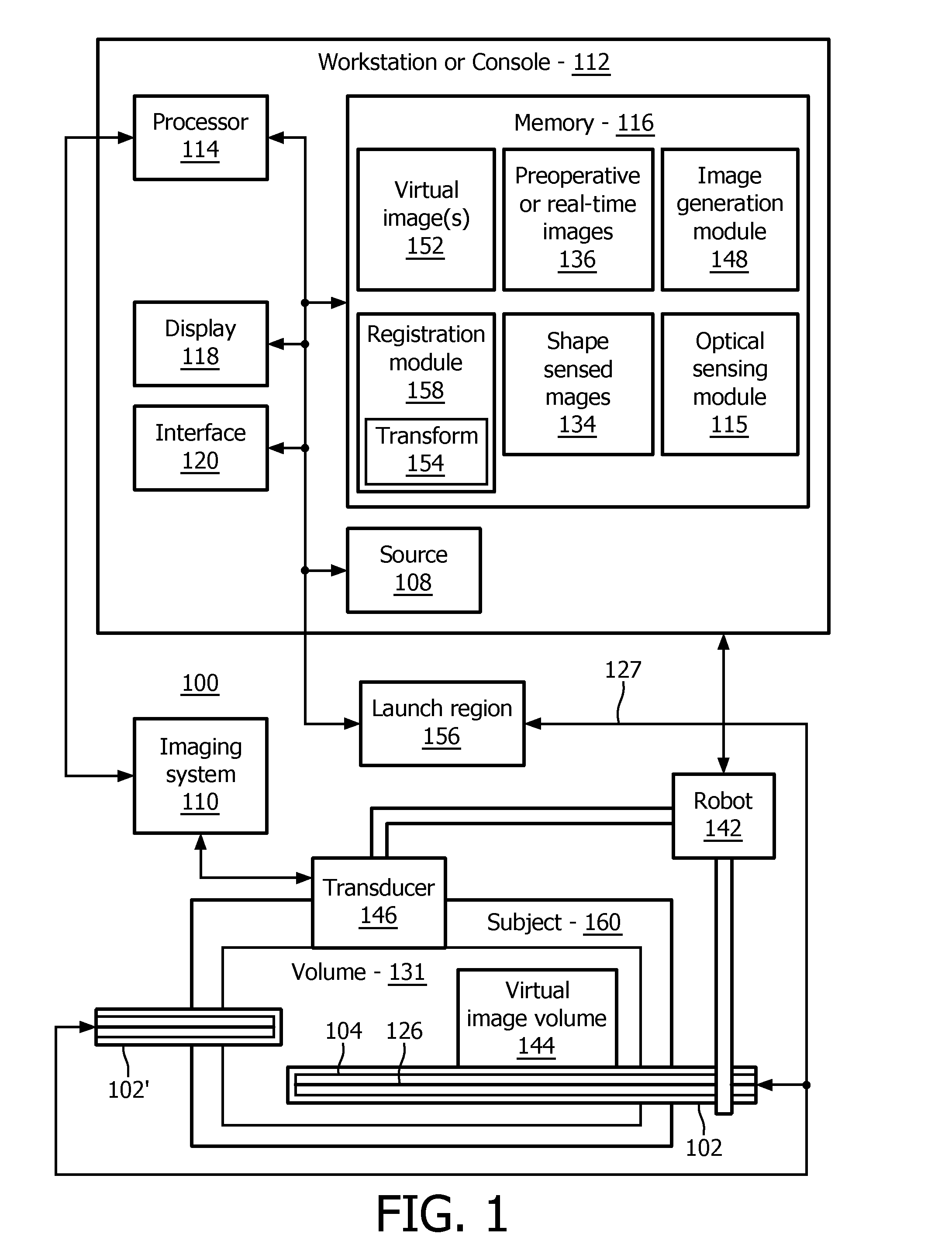
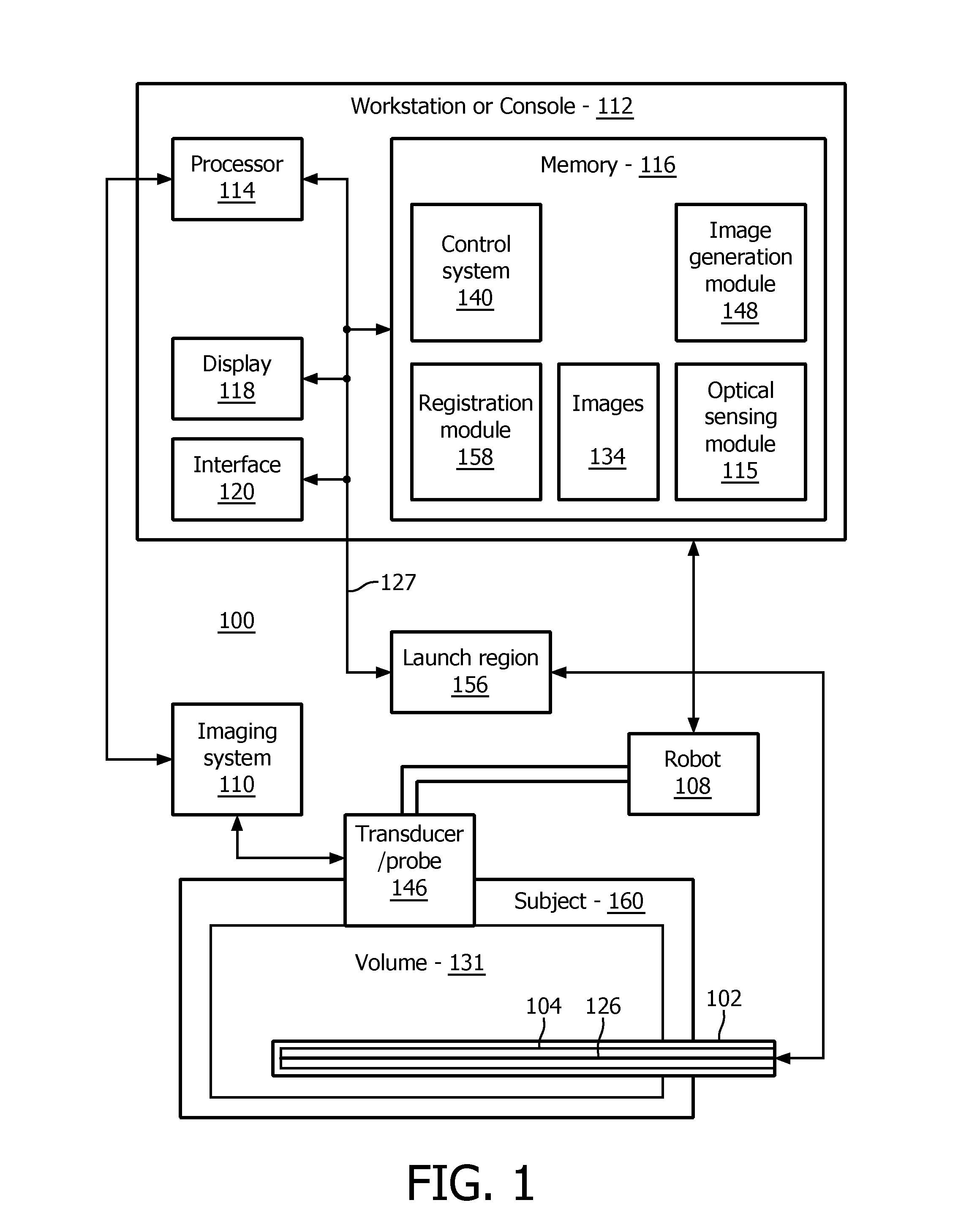
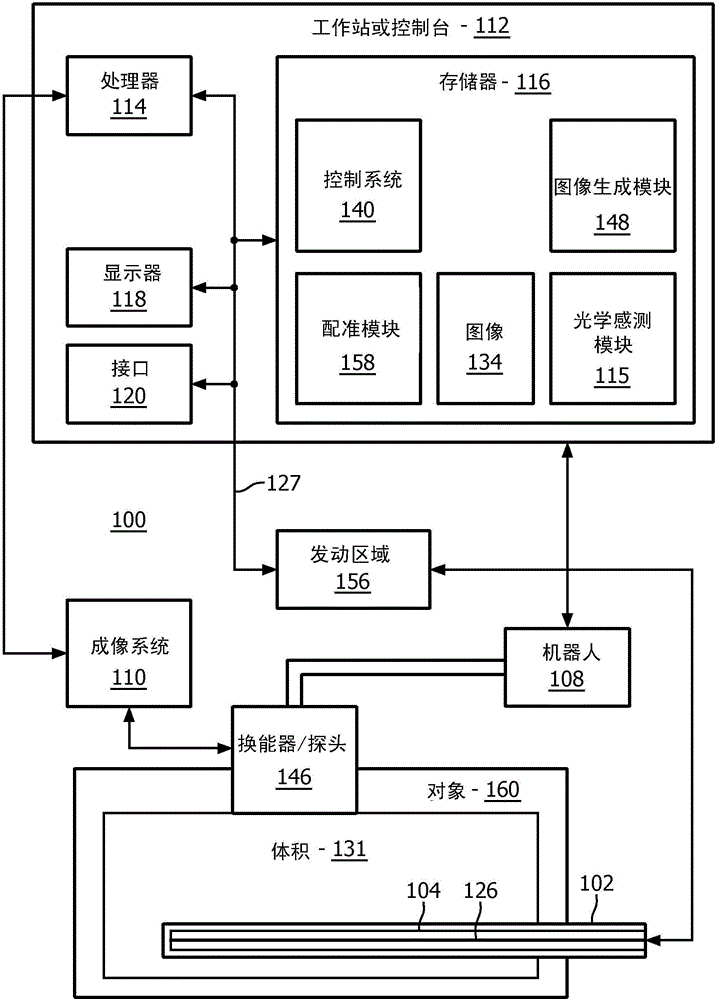
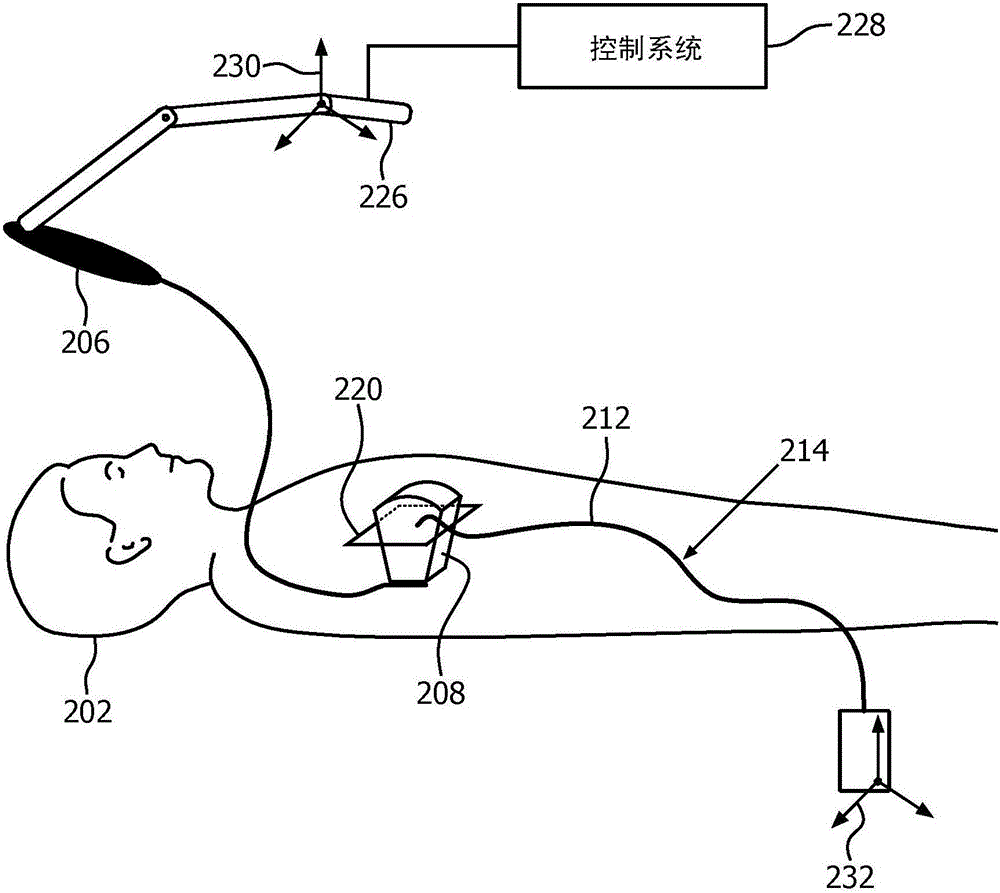
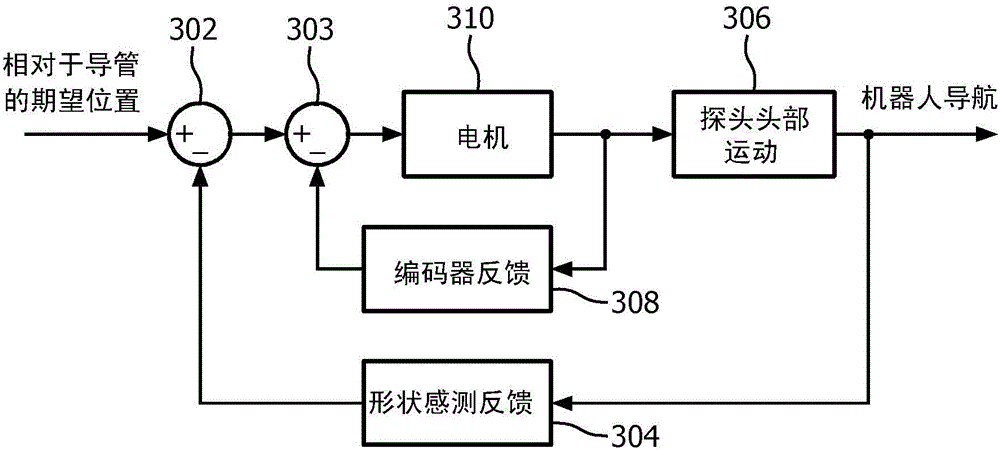
A system for providing a perspective for a virtual image includes an intraoperative imaging system (110) having a transducer (146) configured to generate an image data set for a region. A shape sensing enabled device (102) is configured to have at least a portion of the shape sensing enabled device positioned relative to the region. The shape sensing enabled device has a coordinate system registered with a coordinate system of the intraoperative imaging system. An image generation module (148) is configured to render a virtual image (152) of at least a portion of the region using the image data set wherein the virtual image includes a vantage point relative to a position on the shape sensing enabled device.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
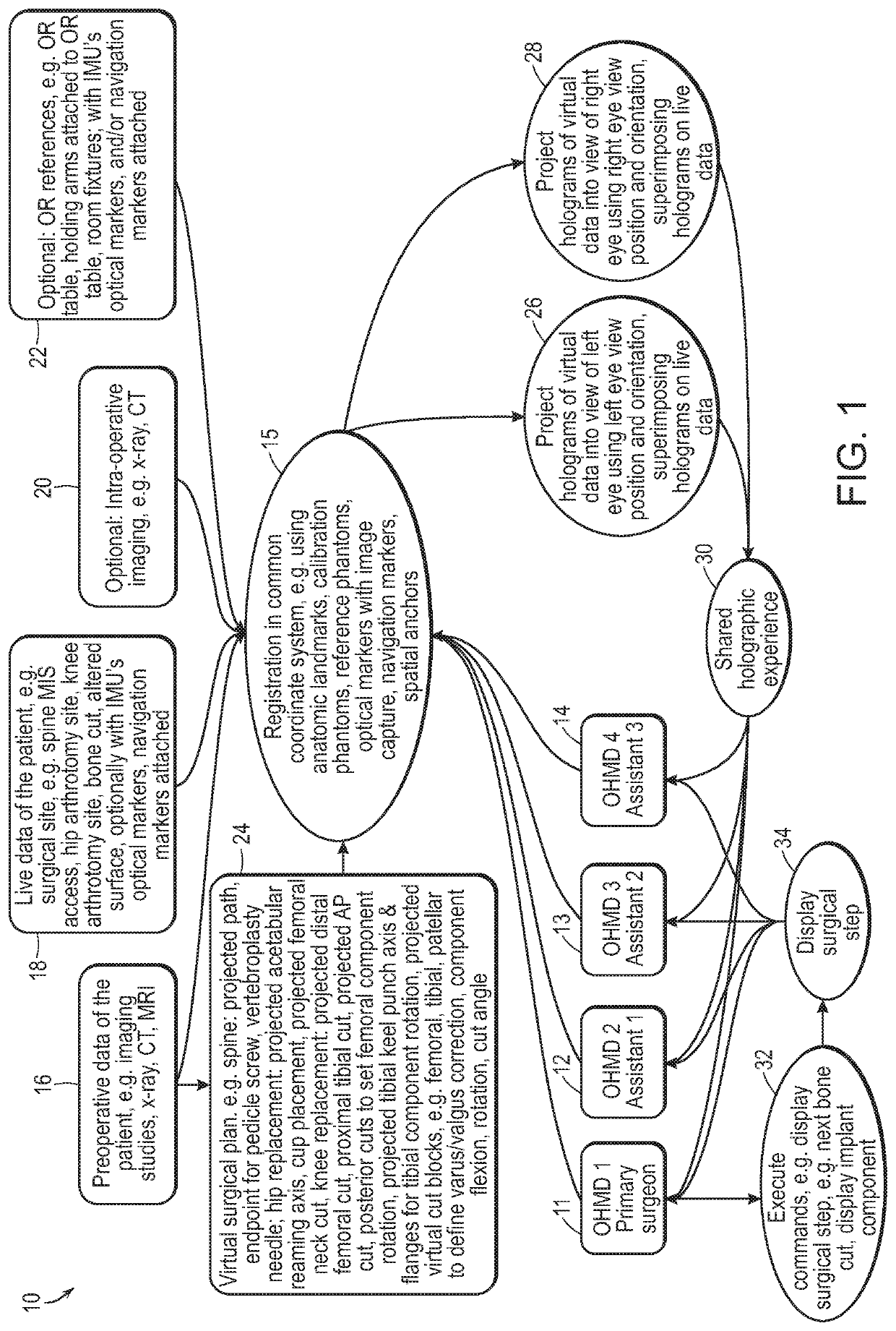
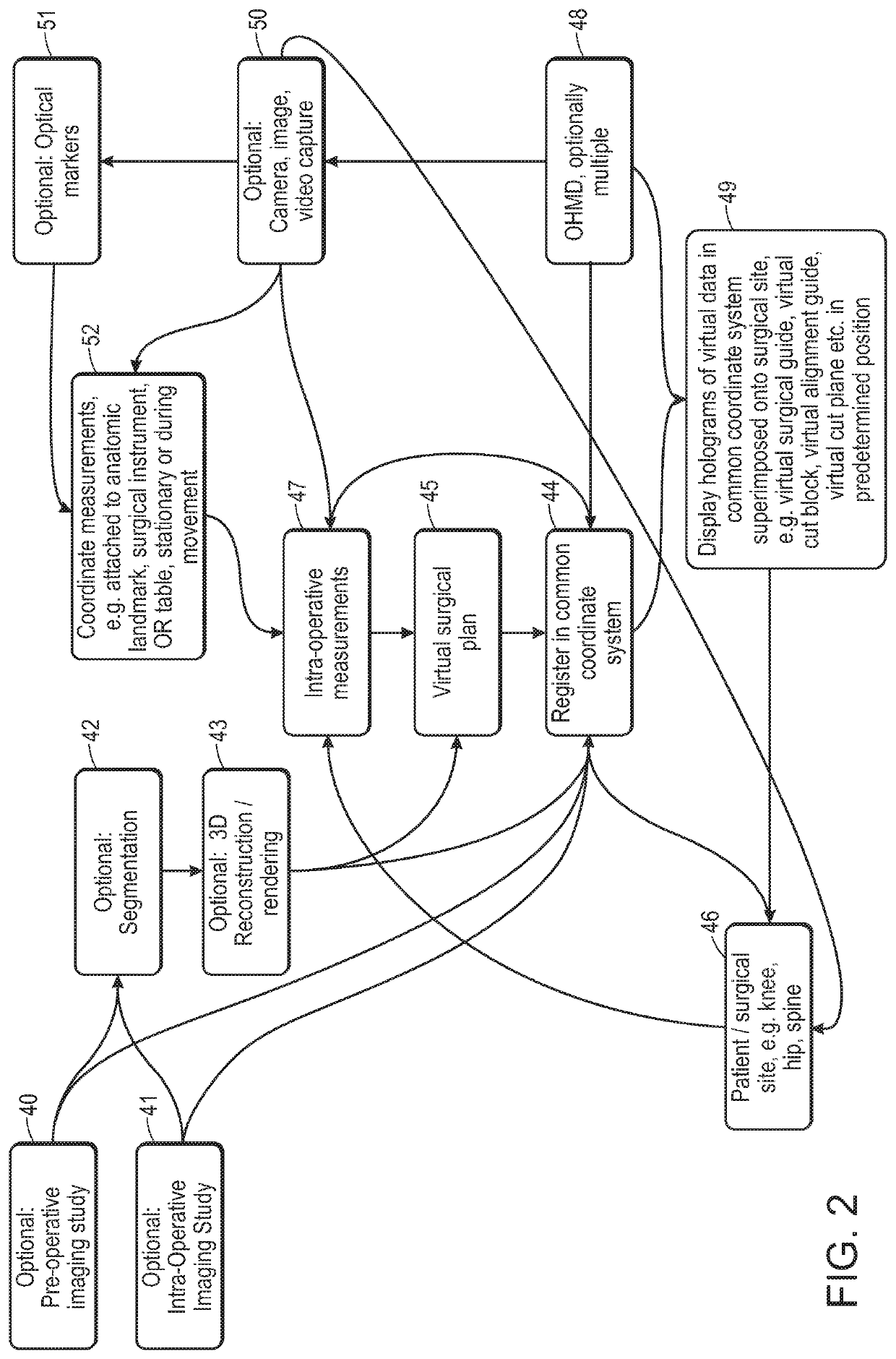
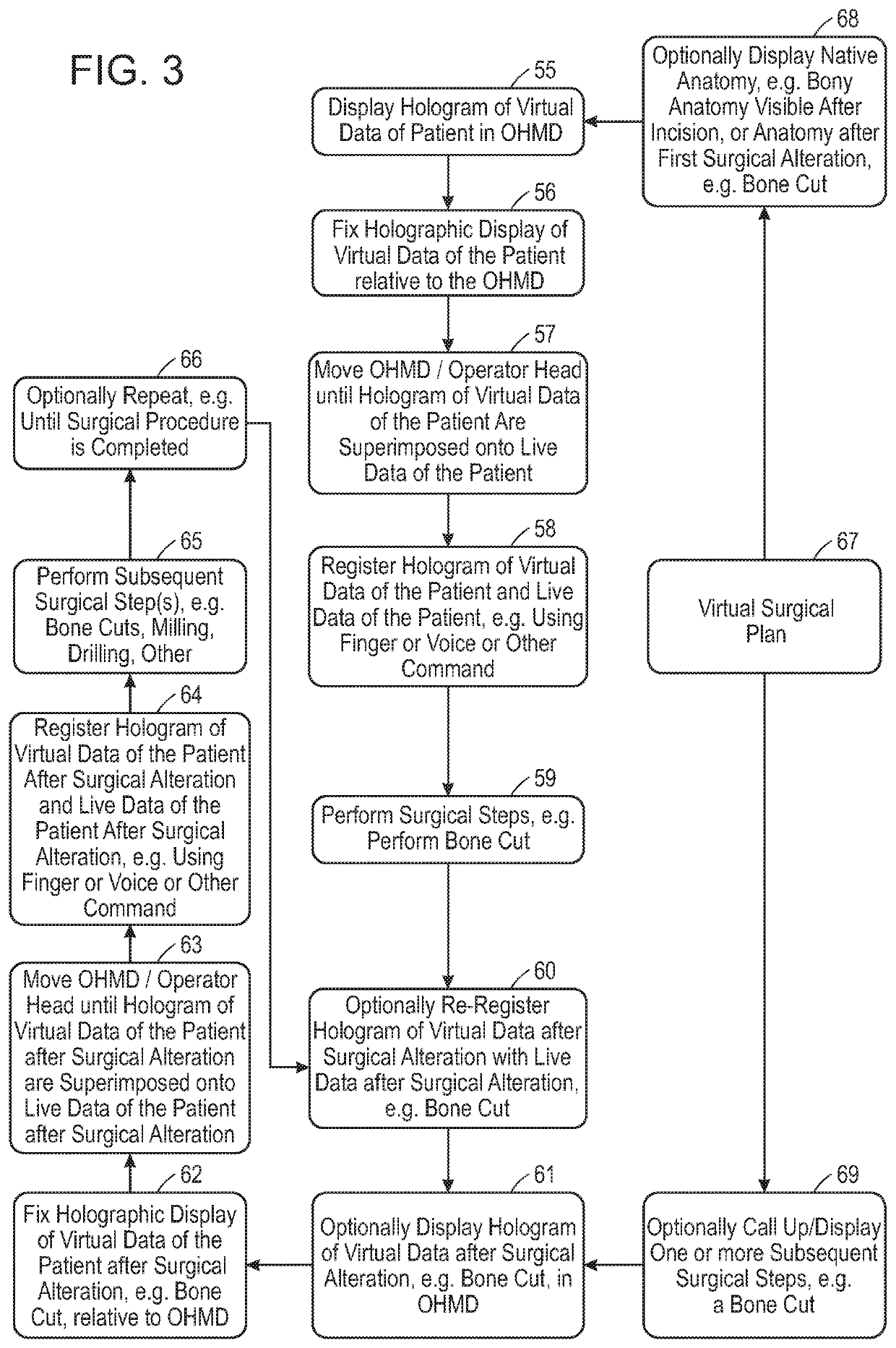
Augmented Reality System Configured for Coordinate Correction or Re-Registration Responsive to Spinal Movement for Spinal Procedures, Including Intraoperative Imaging, CT Scan or Robotics
Devices and methods for performing a surgical step or surgical procedure with visual guidance using an optical head mounted display are disclosed.
Owner:LANG PHILIPP K
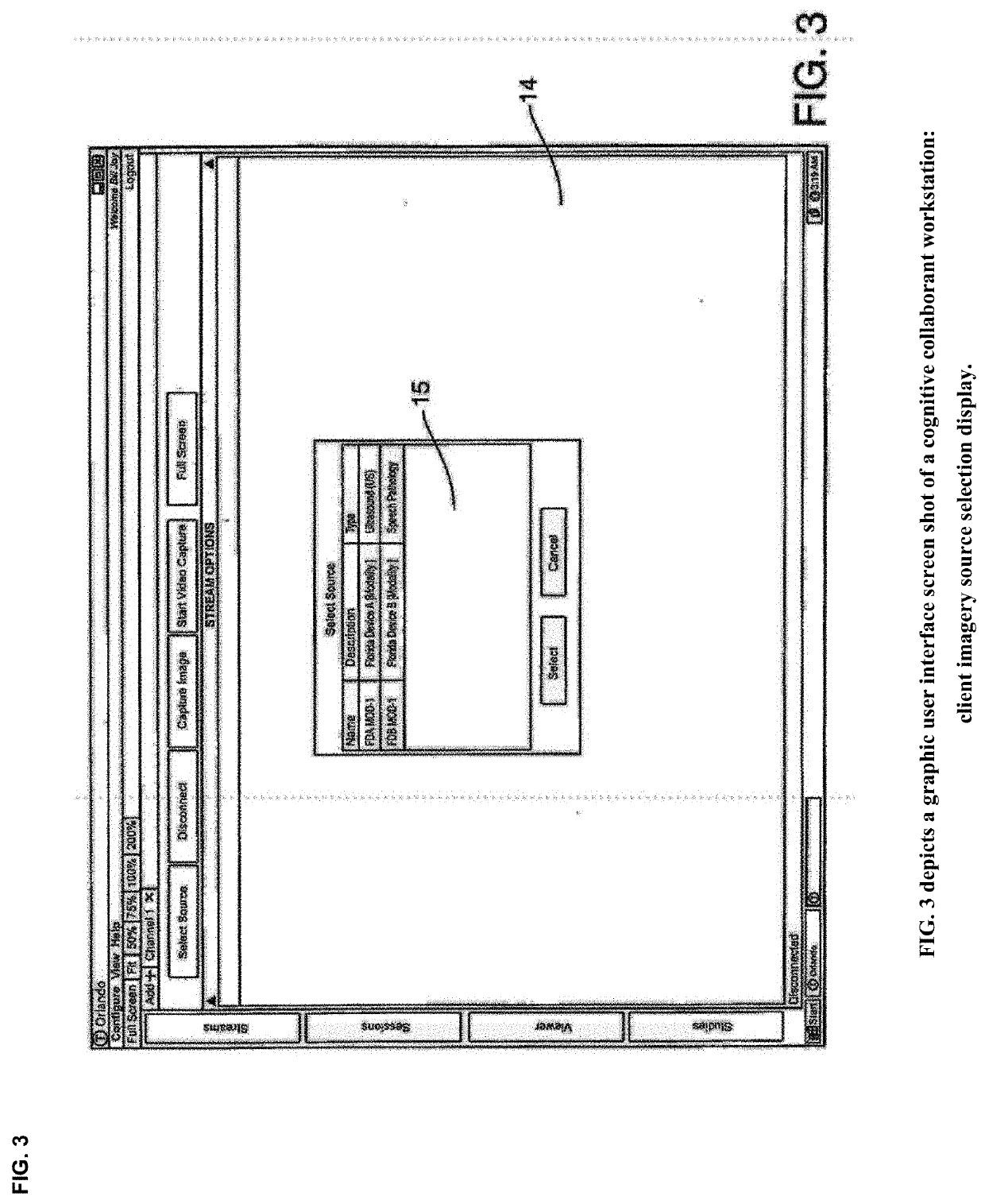
Cognitive Collaboration with Neurosynaptic Imaging Networks, Augmented Medical Intelligence and Cybernetic Workflow Streams
ActiveUS20190355483A1Improve business performanceReduces image latencyTelevision conference systemsTwo-way working systemsDiseaseIntervention measures
The invention integrates emerging applications, tools and techniques for machine learning in medicine with videoconference networking technology in novel business methods that support rapid adaptive learning for medical minds and machines. These methods can leverage domain knowledge and clinical expertise with cognitive collaboration, augmented medical intelligence and cybernetic workflow streams for learning health care systems. The invention enables multimodal cognitive communications, collaboration, consultation and instruction between and among heterogeneous networked teams of persons, machines, devices, neural networks, robots and algorithms. It provides for both synchronous and asynchronous cognitive collaboration with multichannel, multiplexed imagery data streams during various stages of medical disease and injury management—detection, diagnosis, prognosis, treatment, measurement, monitoring and reporting, as well as workflow optimization with operational analytics for outcomes, performance, results, resource utilization, resource consumption and costs. The invention enables cognitive curation, annotation and tagging, as well as encapsulation, saving and sharing of collaborated imagery data streams as packetized medical intelligence. It can augment packetized medical intelligence through recursive cognitive enrichment, including multimodal annotation and [semantic] metadata tagging with resources consumed and outcomes delivered. Augmented medical intelligence can be saved and stored in multiple formats, as well as retrieved from standards-based repositories. The invention can incorporate and combine various machine learning techniques [e.g., deep, reinforcement and transfer learning, convolutional and recurrent neural networks, LSTM and NLP] to assist in curating, annotating and tagging diagnostic, procedural and evidentiary medical imaging. It also supports real-time, intraoperative imaging analytics for robotic-assisted surgery, as well as other imagery guided interventions. The invention facilitates collaborative precision medicine, and other clinical initiatives designed to reduce the cost of care, with precision diagnosis and precision targeted treatment. Cybernetic workflow streams—cognitive communications, collaboration, consultation and instruction with augmented medical intelligence—enable care delivery teams of medical minds and machines to ‘deliver the right care, for the right patient, at the right time, in the right place’—and deliver that care faster, smarter, safer, more precisely, cheaper and better.
Owner:SMURRO JAMES PAUL
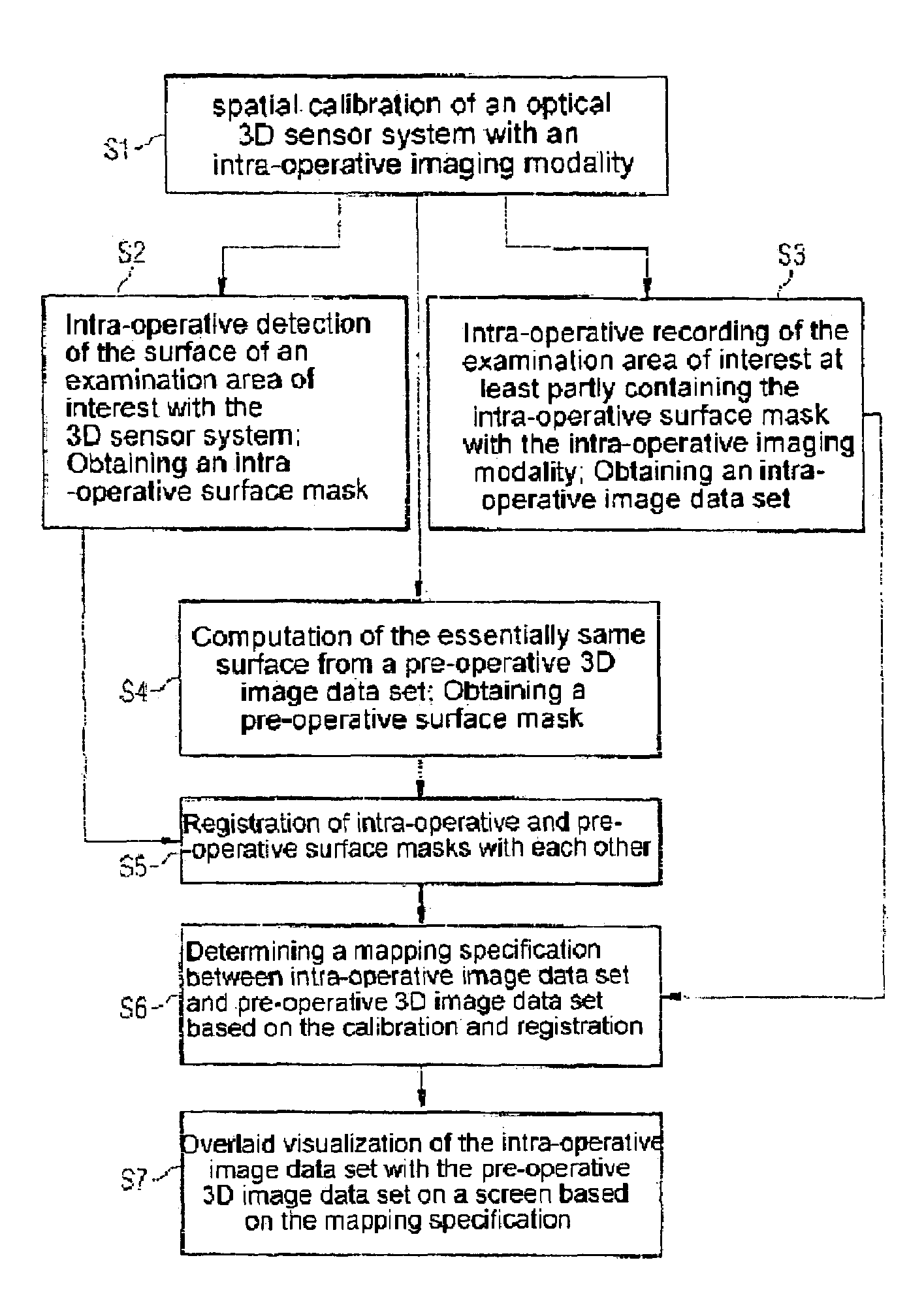
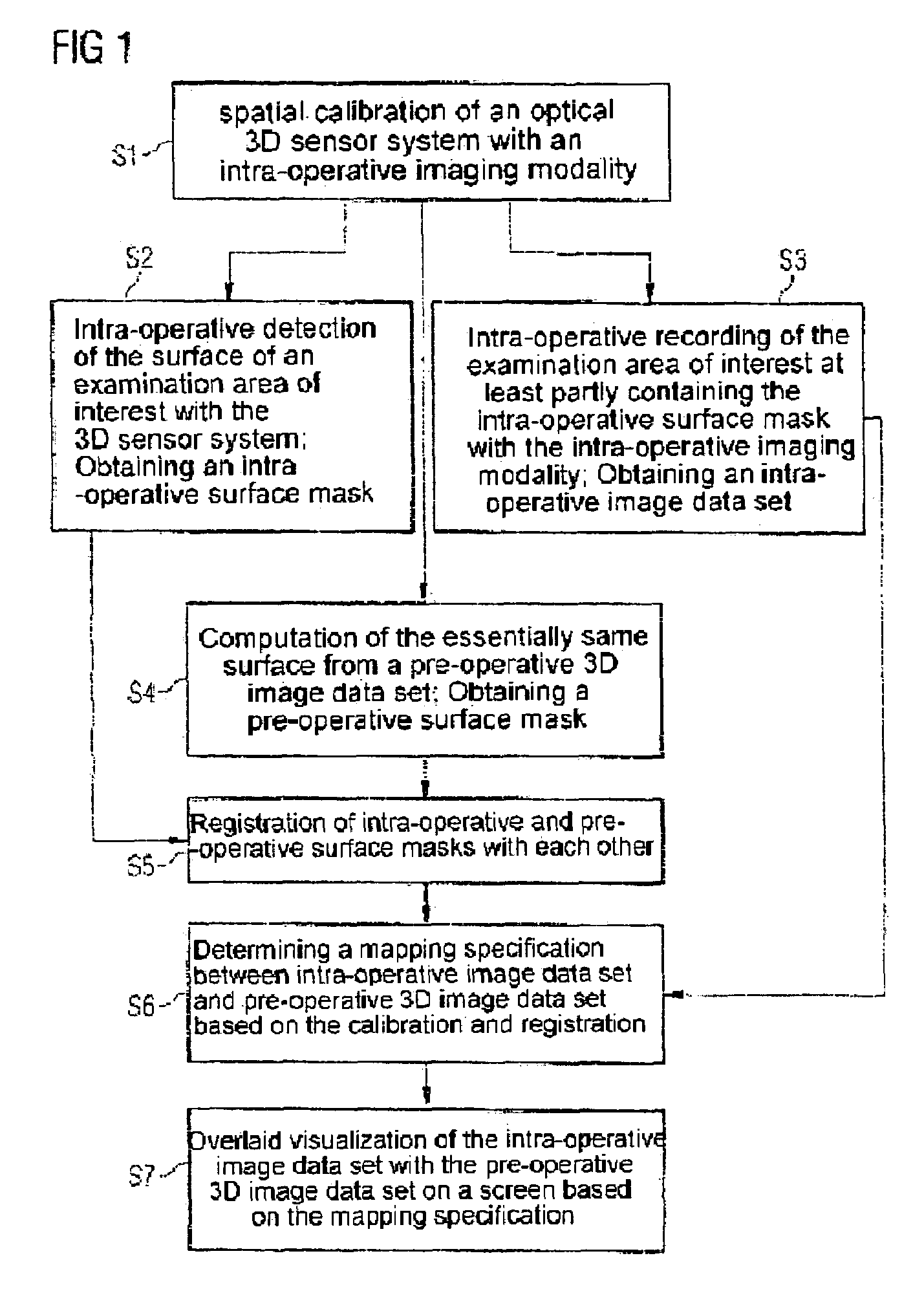
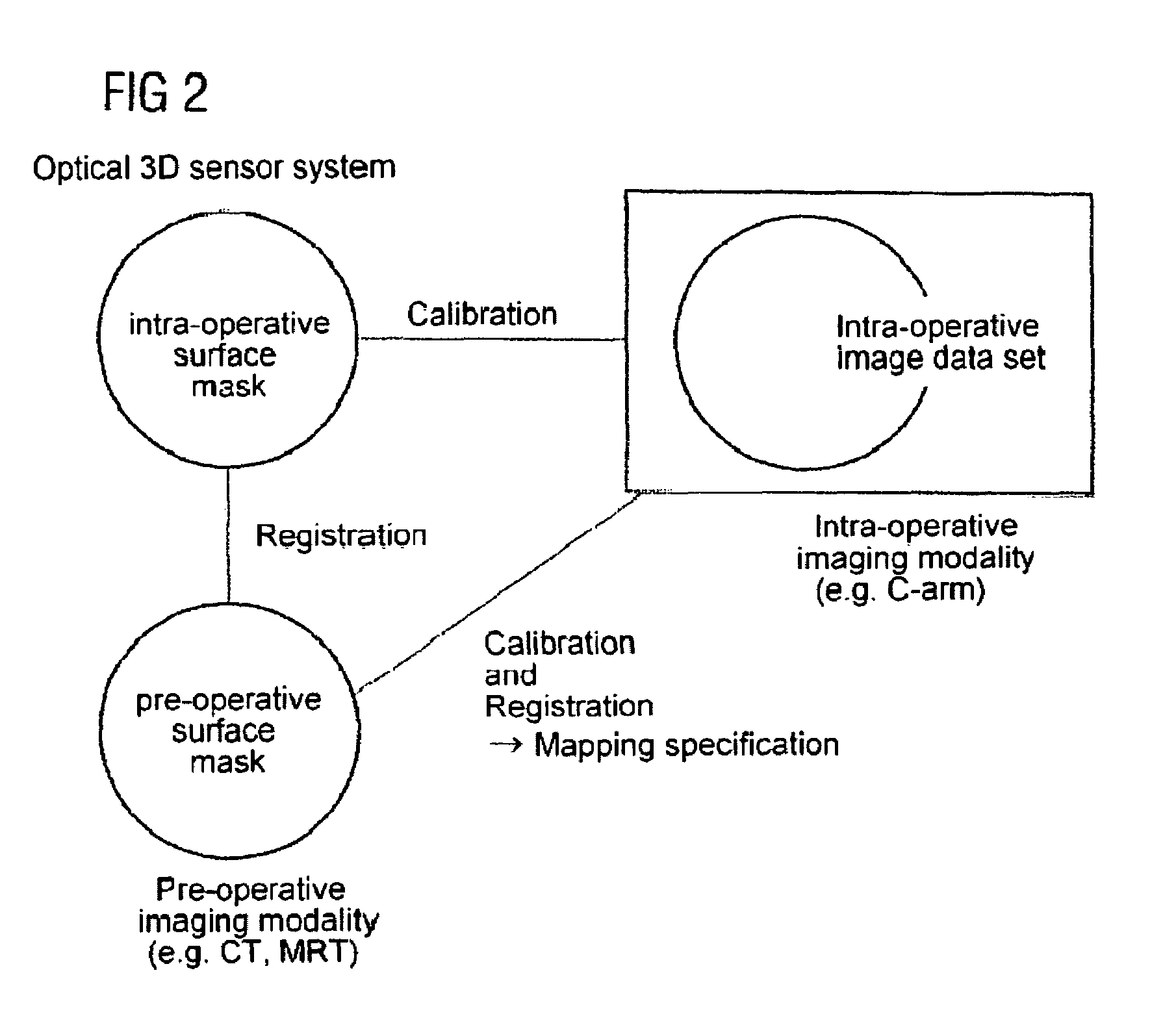
Registering intra-operative image data sets with pre-operative 3D image data sets on the basis of optical surface extraction
InactiveUS7664542B2Convenient registrationReduce Motion ArtifactsImage enhancementImage analysis3d sensorData set
The invention relates to a method for registering intra-operative image data set with pre-operative 3D image data set, including:spatially calibrating an optical 3D sensor system with an intra-operative imaging modality,intra-operatively detecting the surface of an examination area of interest with the 3D sensor system to produce an intra-operative surface mask,intra-operatively recording the area of interest for examination with the intra-operative modality at least partly containing the intra-operative surface mask to obtain an intra-operative image data set,computing the same surface from the pre-operative 3D image data set containing the detected surface to obtain a pre-operative surface mask,registering the intra-operative and pre-operative surface mask with each other,determining a mapping specification between pre-operative 3D image data set and intra-operative image data set based on the calibration and the registration, andoverlaying the intra-operative image data set with the pre-operative 3D data set based on the mapping specification.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Systems and methods for inferred patient annotation
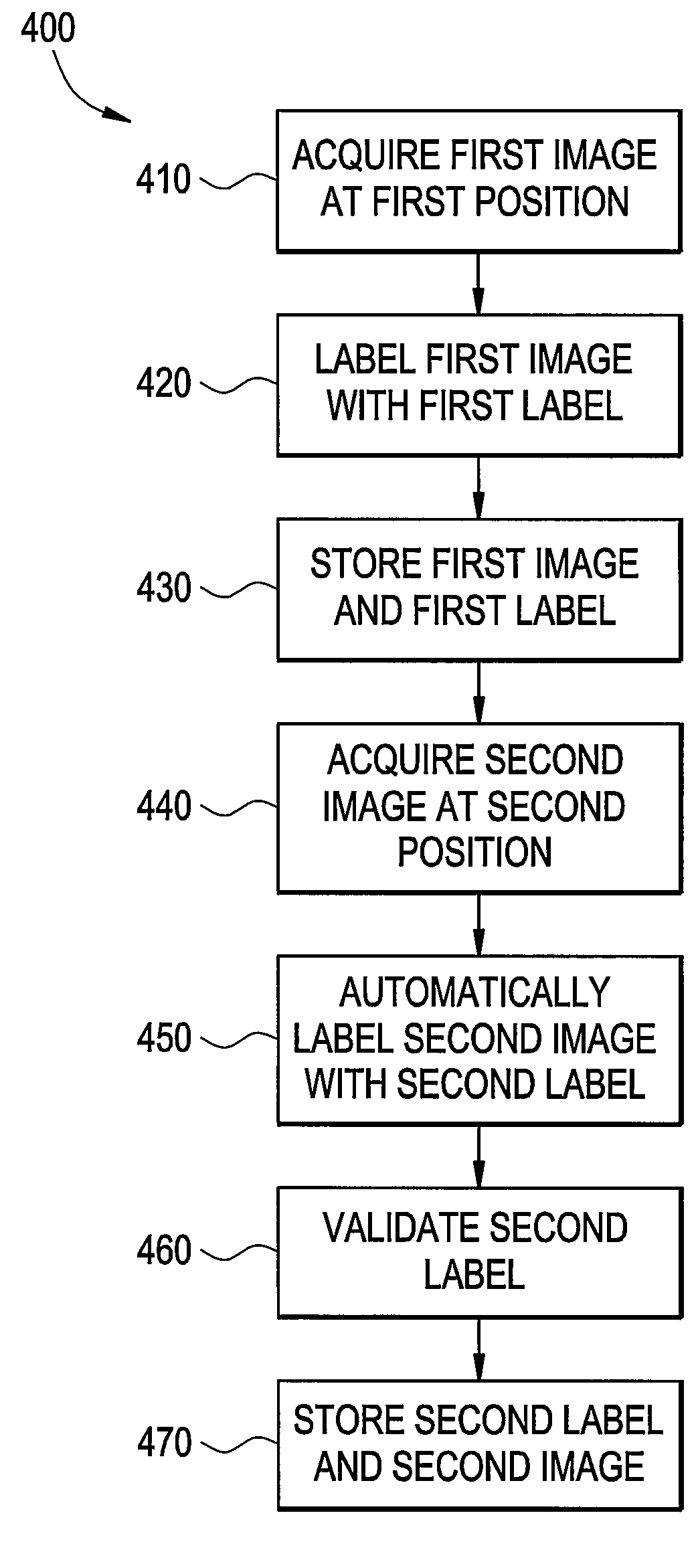
Certain embodiments of the present invention provide an improved method for automatically labeling an image using an intraoperative imaging system. The method includes acquiring a first image at a first position, labeling the first image with a first label, acquiring a second image at a second position, automatically labeling the second image with a second label based at least in part on the first label, the first position, and the second position.
Owner:STRYKER EURO OPERATIONS HLDG LLC
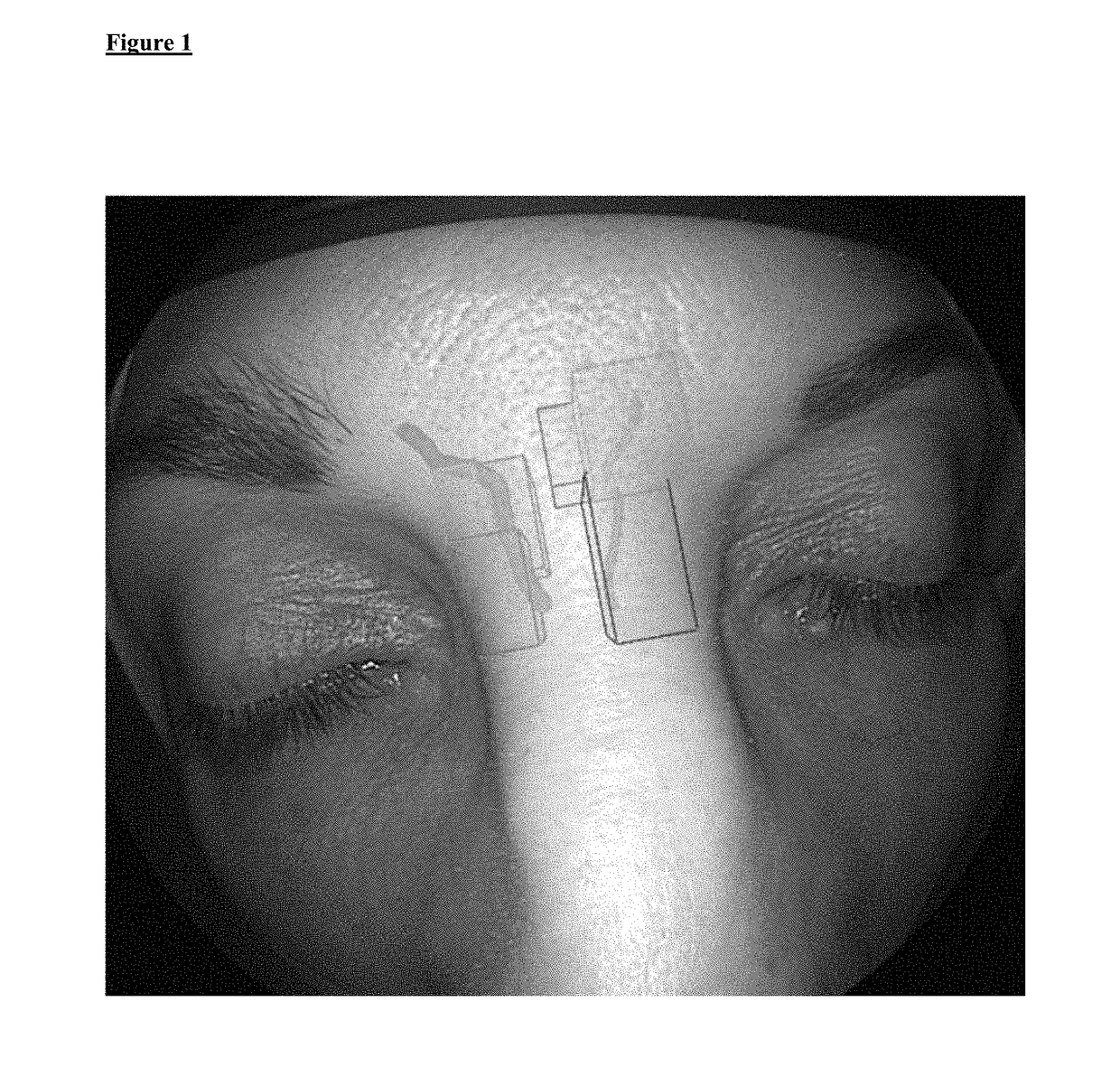
Image registration and augmented reality system and method augmented reality thereof
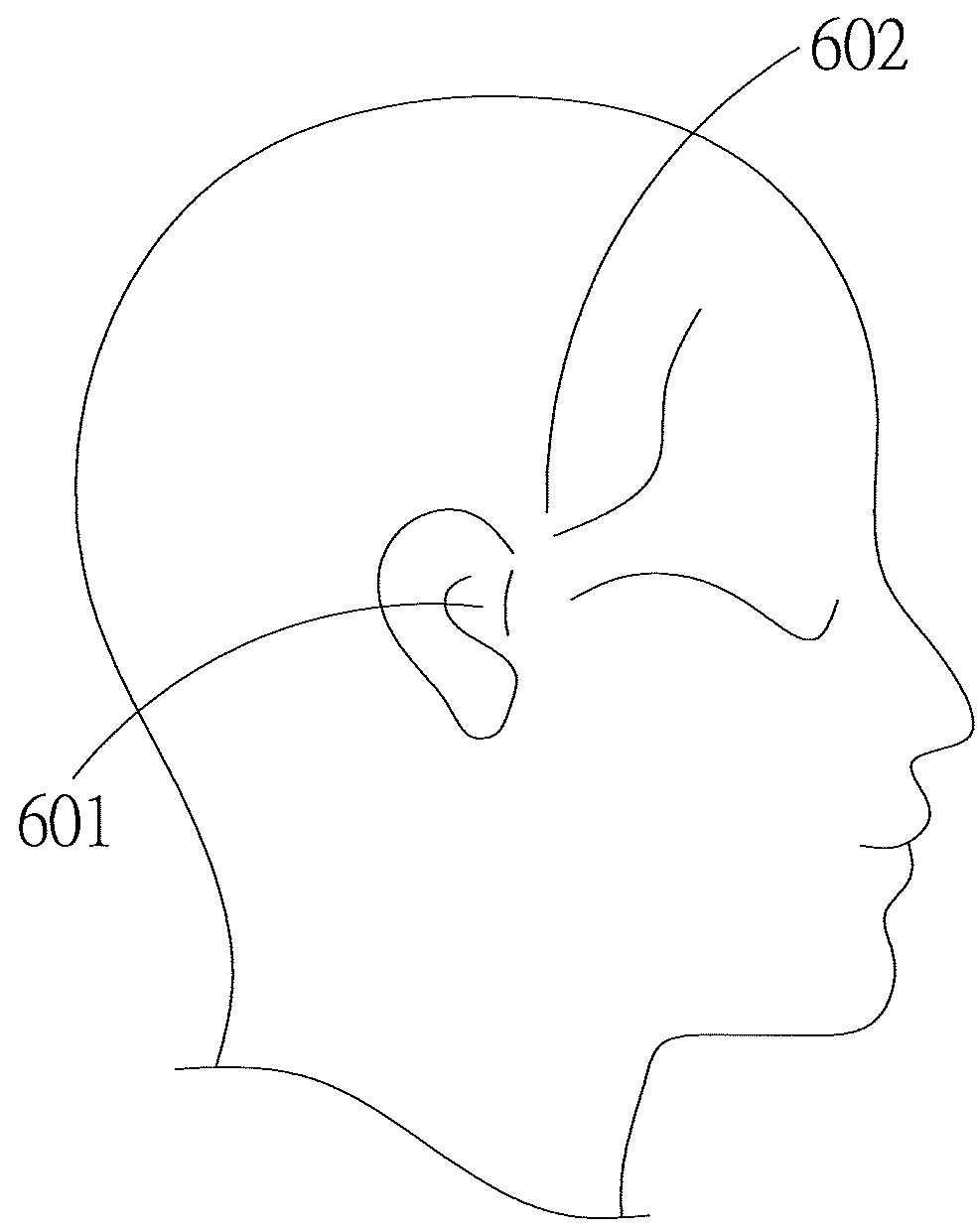
ActiveUS20180263698A1Details involving processing stepsImage enhancementArthroscopic procedureTemporomandibular joint
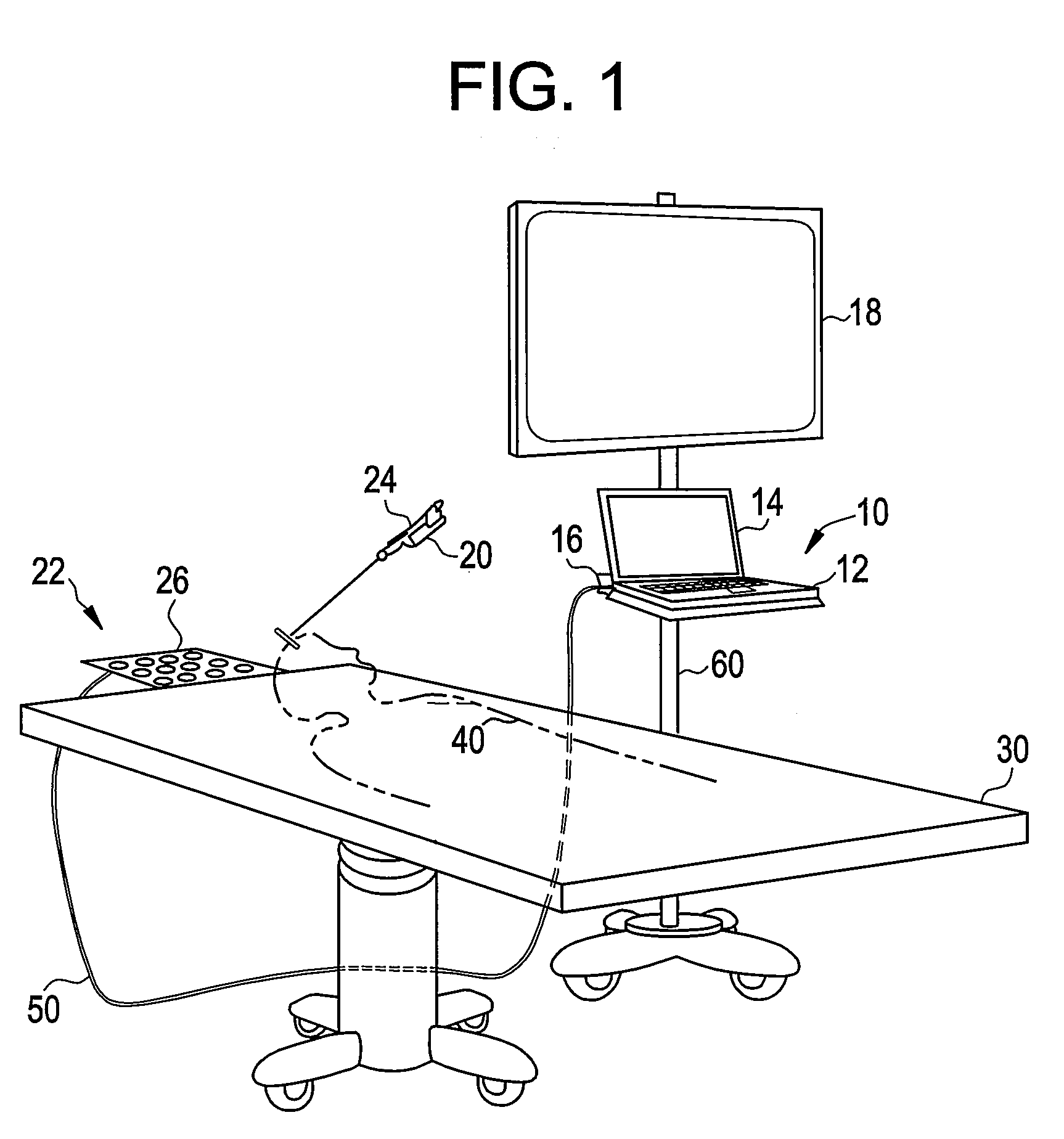
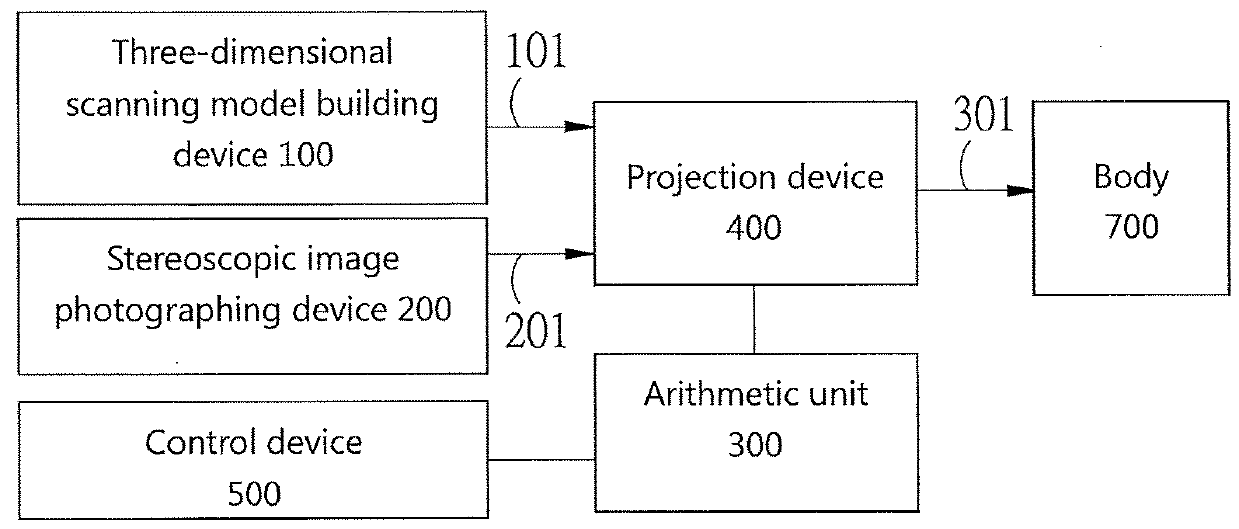
Disclosed is an image registration and an augmented reality system and an augmented reality method thereof which is suitable for solving the problem of spatial localization of the temporomandibular joint (TMJ) in arthroscopic surgery. The system comprises a three-dimensional scanning model building device, a stereoscopic image photographing device, a projection device and an arithmetic unit. The three-dimensional scanning model was constructed by preoperative or intraoperative imaging of the patient, and the surface three-dimensional model constructed by the stereoscopic image photographing device was spatially aligned to remove the surface (skin layer) of the three-dimensional image to display the TMJ image. Through the calibration of the stereoscopic image photographing device and the projection device, accurate, three-dimensional TMJ image location information is projected onto the patient's body to achieve the purpose.
Owner:MEDICALTEK CO LTD
Light-emitting dye for intraoperative imaging or sentinel lymph node biopsy
The present invention relates generally to the field of fluorescent dyes as a system useful for surgery imaging. More particularly, the present invention relates to systems, methods and kits for exciting fluorescent, phosphorescent or luminescent molecules with light from a light source and detecting the relative fluorescent, phosphorescent, or luminescent light intensity emitted from the fluorescent, phosphorescent, or luminescent molecule. Such systems may be applied as mapping agents for various surgical techniques, such as for cancer surgeries and biopsies.
Owner:UNIV OF UTAH RES FOUND
Intraoperative imaging of renal cortical tumors and cysts
ActiveUS8725225B2Solve the lack of functionEasy to manageDiagnostics using fluorescence emissionCatheterCystAnatomy
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
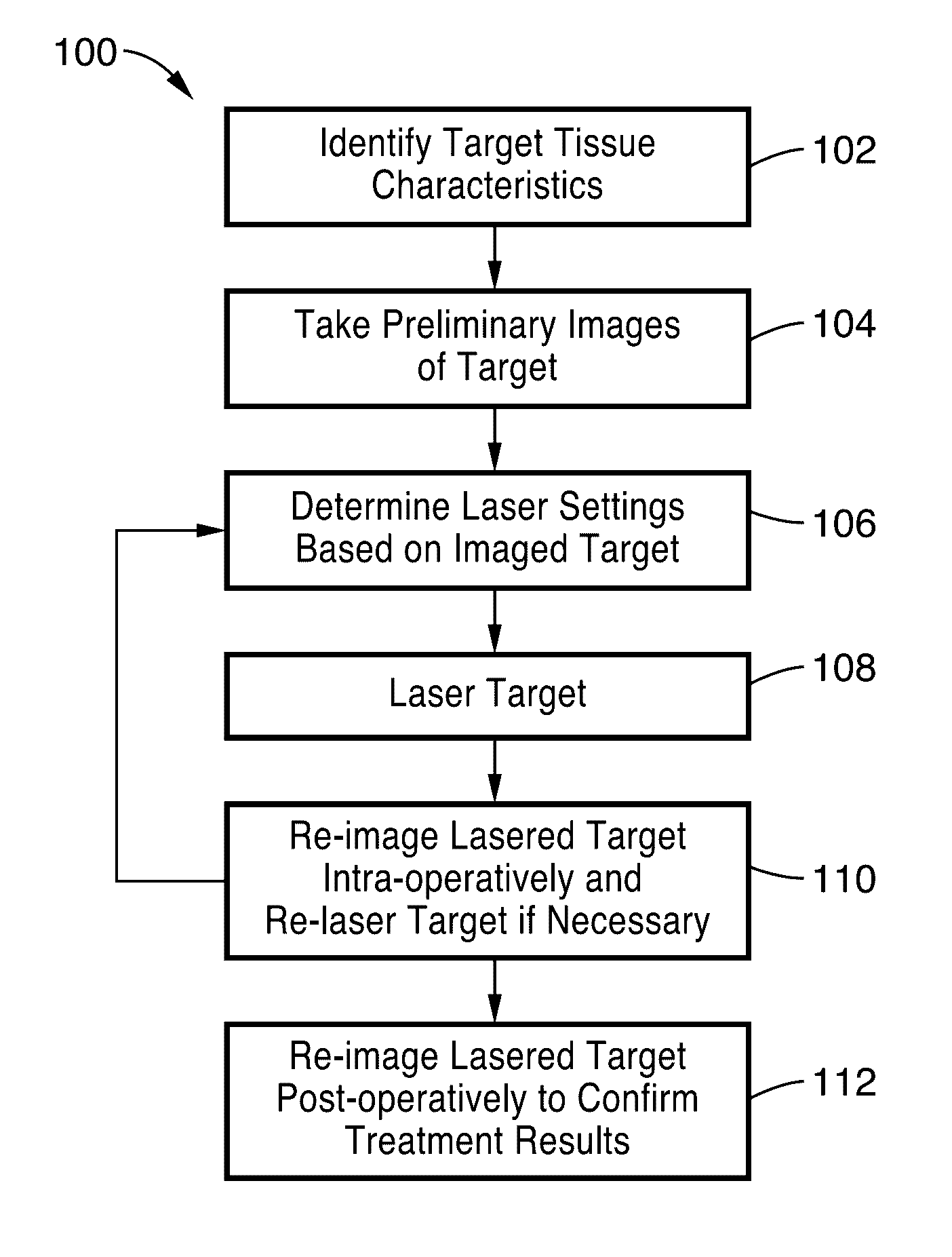
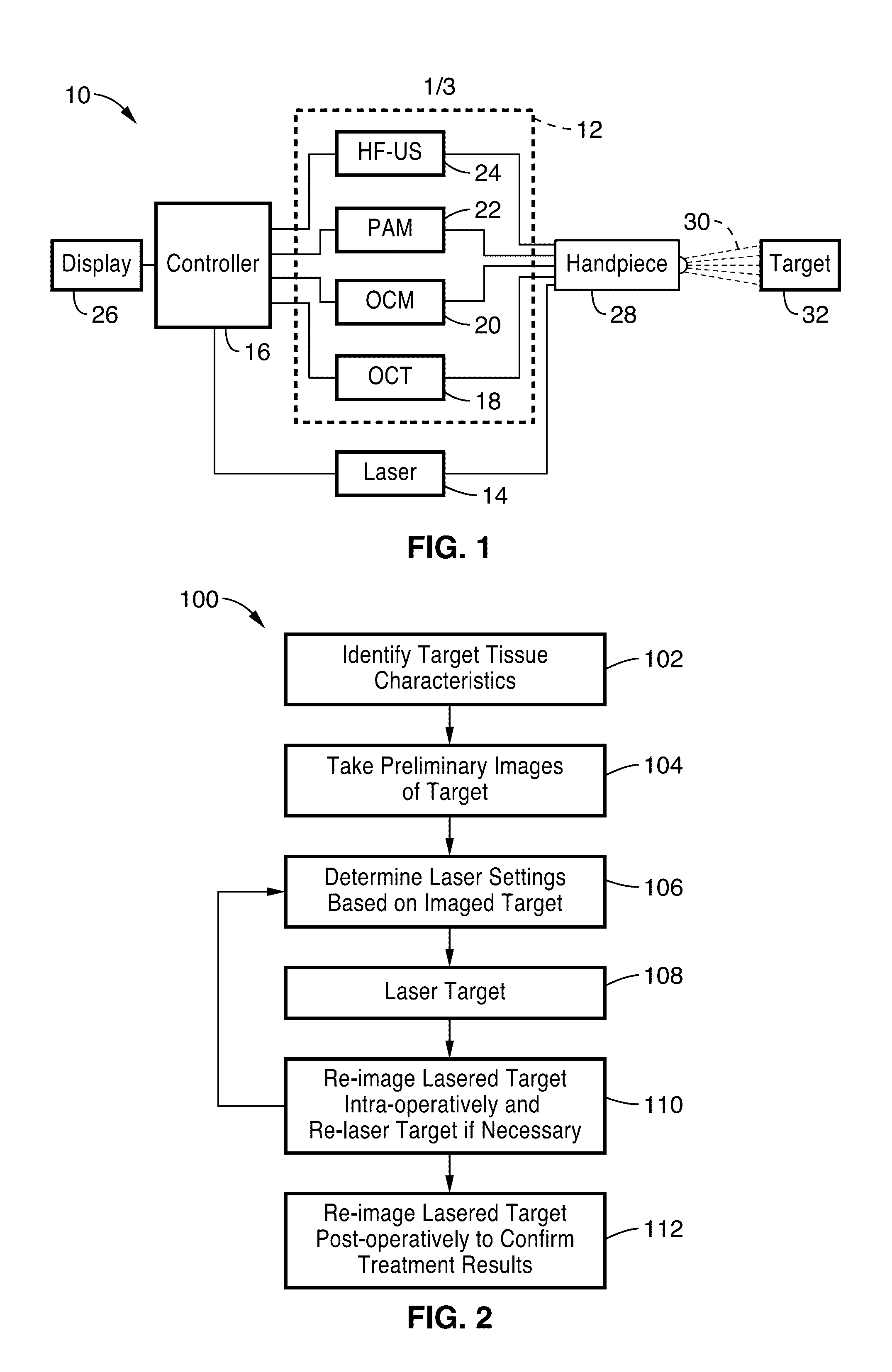
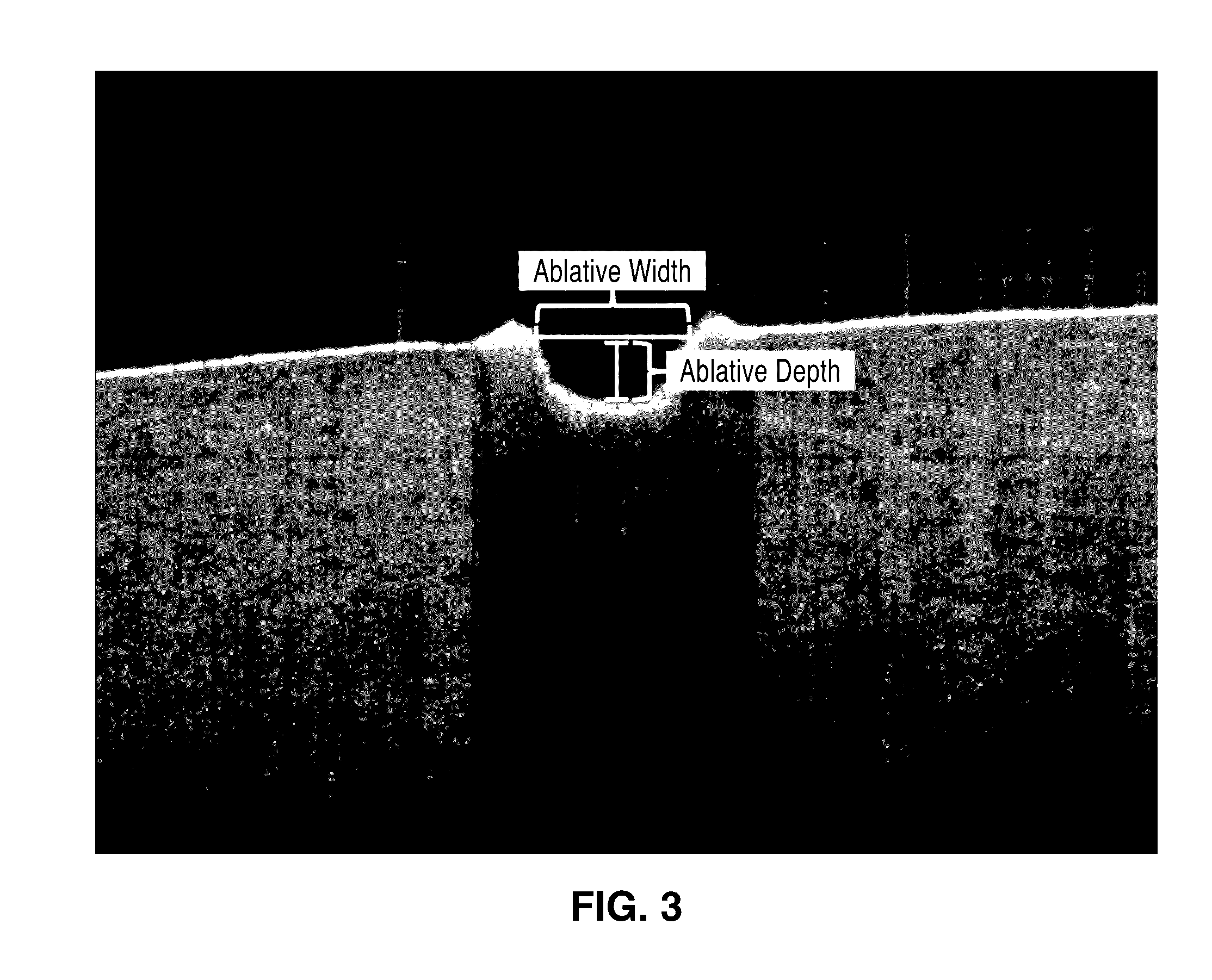
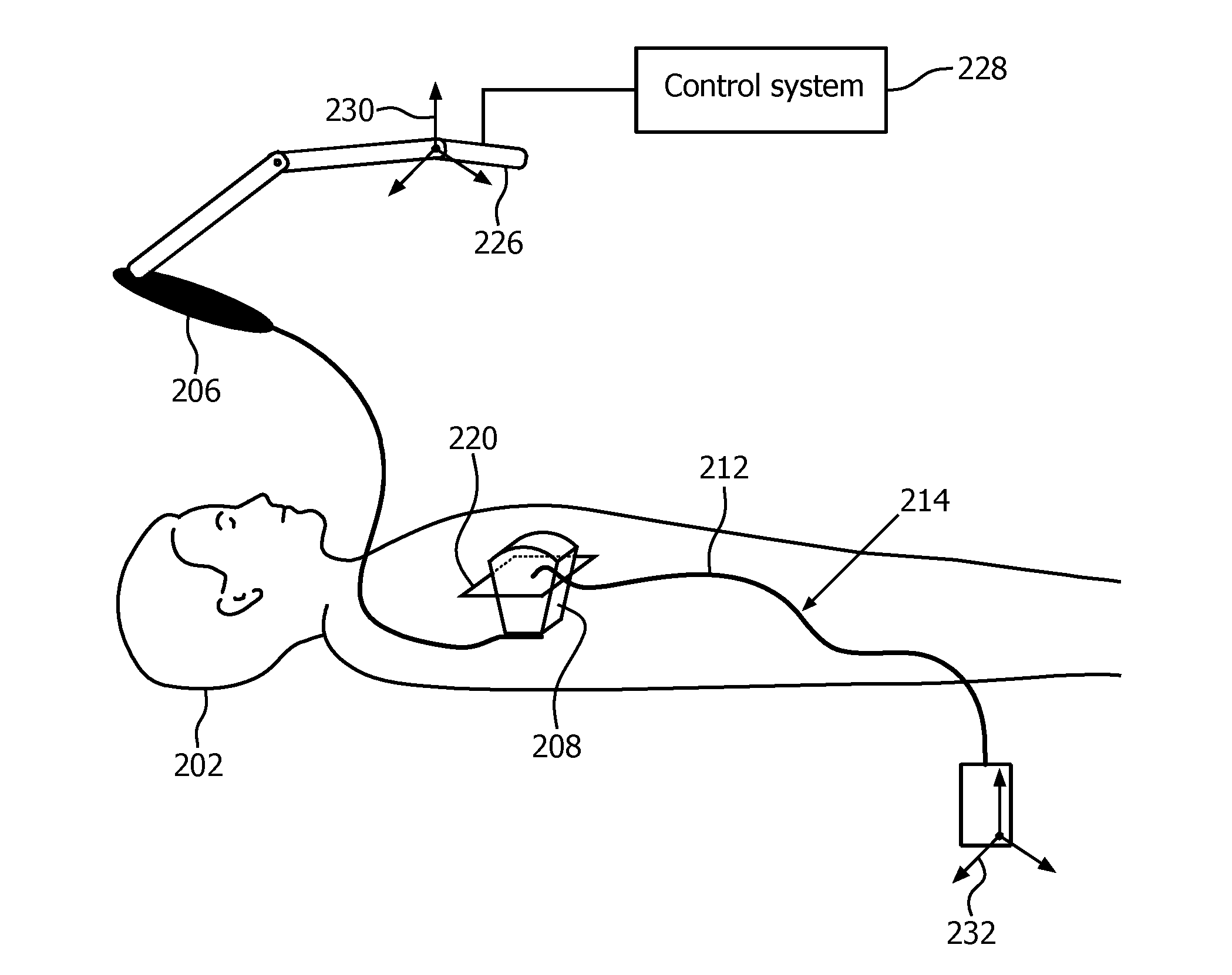
System and method of combined tissue imaging and image-guided laser therapy
InactiveUS20160317226A1High energyControlling energy of instrumentTomographyDiagnostic Radiology ModalityImaging modalities
A system and method for combined tissue imaging and image-guided laser therapy is provided. The apparatus has one or more imaging modalities and lasers that are controlled by a controller. The setting configuration of the laser is determined by the location of designated boundaries and the structures of the target tissue that have been imaged. Intra-operative imaging of the target tissue allows a real time evaluation of the laser administration and determines the laser configuration if the contemporary images indicate a re-treatment is necessary. Over treatment and under treatment by the laser is avoided by image-directed laser ablation or non-ablative laser therapy.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Intraoperative Imaging Of Hepatobiliary Structures
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
Robotic control of imaging devices with optical shape sensing
A system for tracking a device image includes an intraoperative imaging system (110) having a probe (146) configured to generate an image for a region. A shape sensing enabled instrument (102) is configured to have a portion of the shape sensing enabled instrument positionable relative to the region. The shape sensing enabled instrument has a coordinate system registered with a coordinate system of the intraoperative imaging system. A robot is configured to coordinate movement between the probe and the shape sensing enabled instrument such that movement of the shape sensing enabled instrument relative to the region causes the probe to be moved to maintain the shape sensing enabled instrument within the image.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Intra-operative 3-D reconstruction of bone cement boli using X-rays
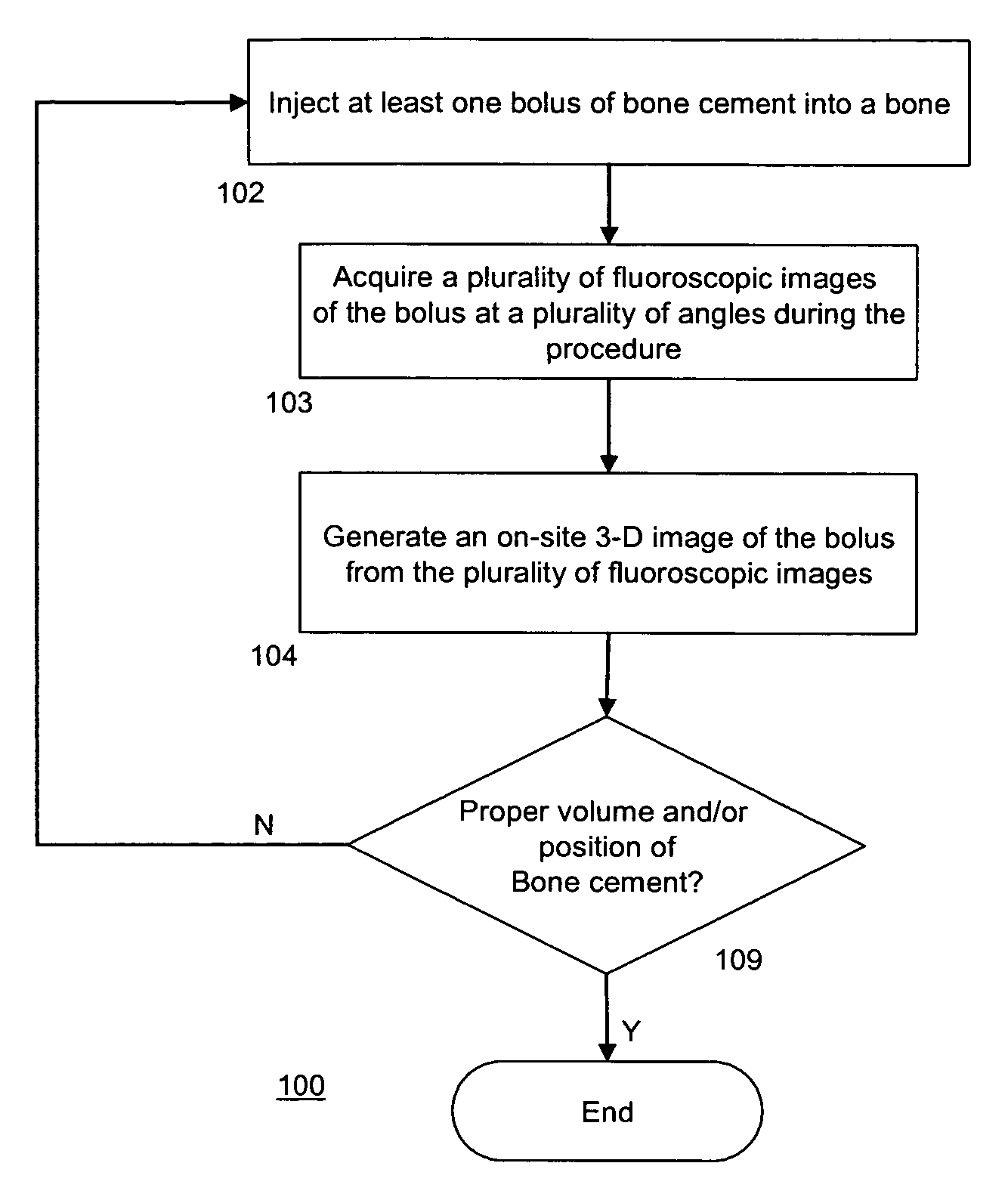
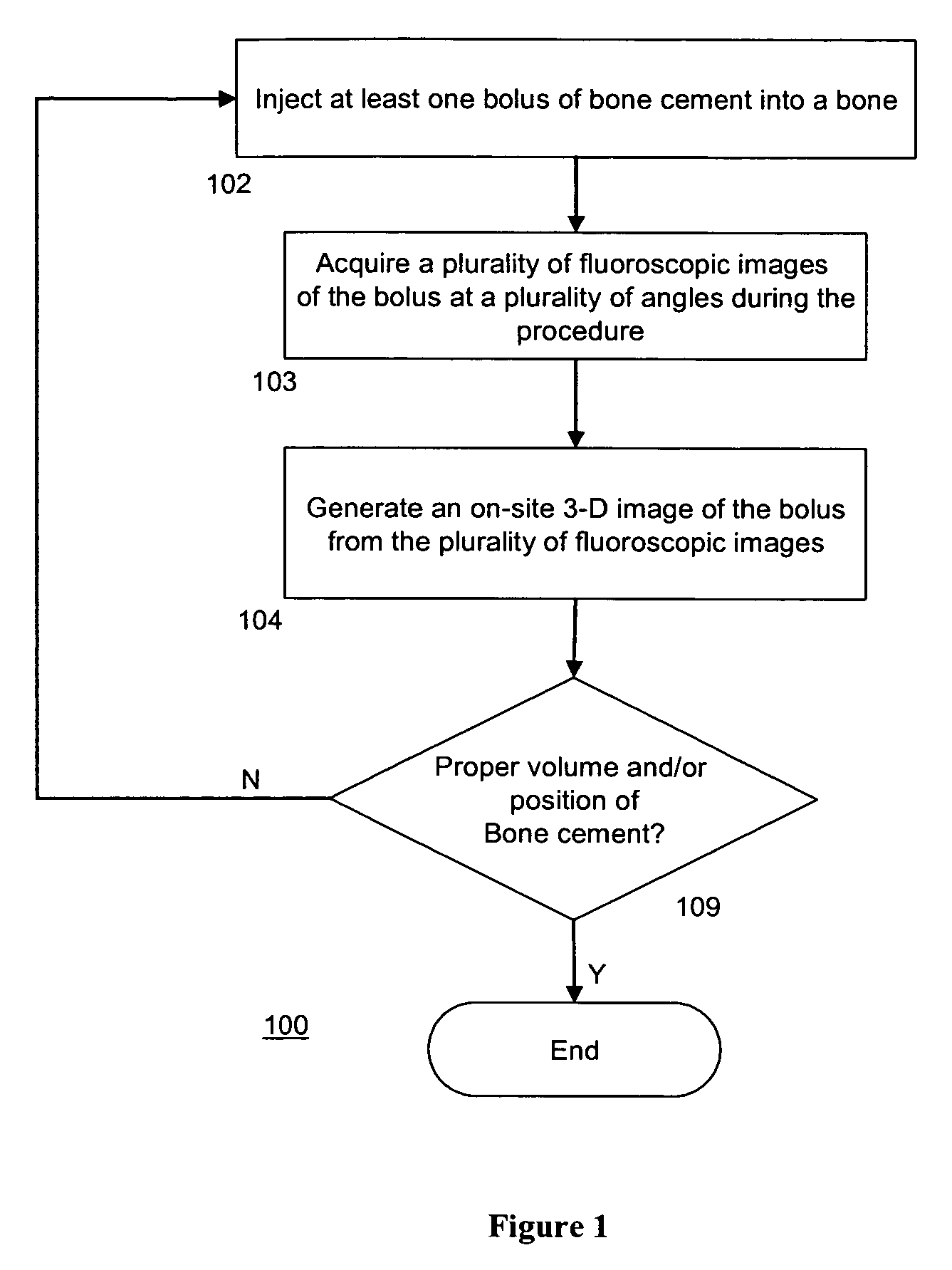
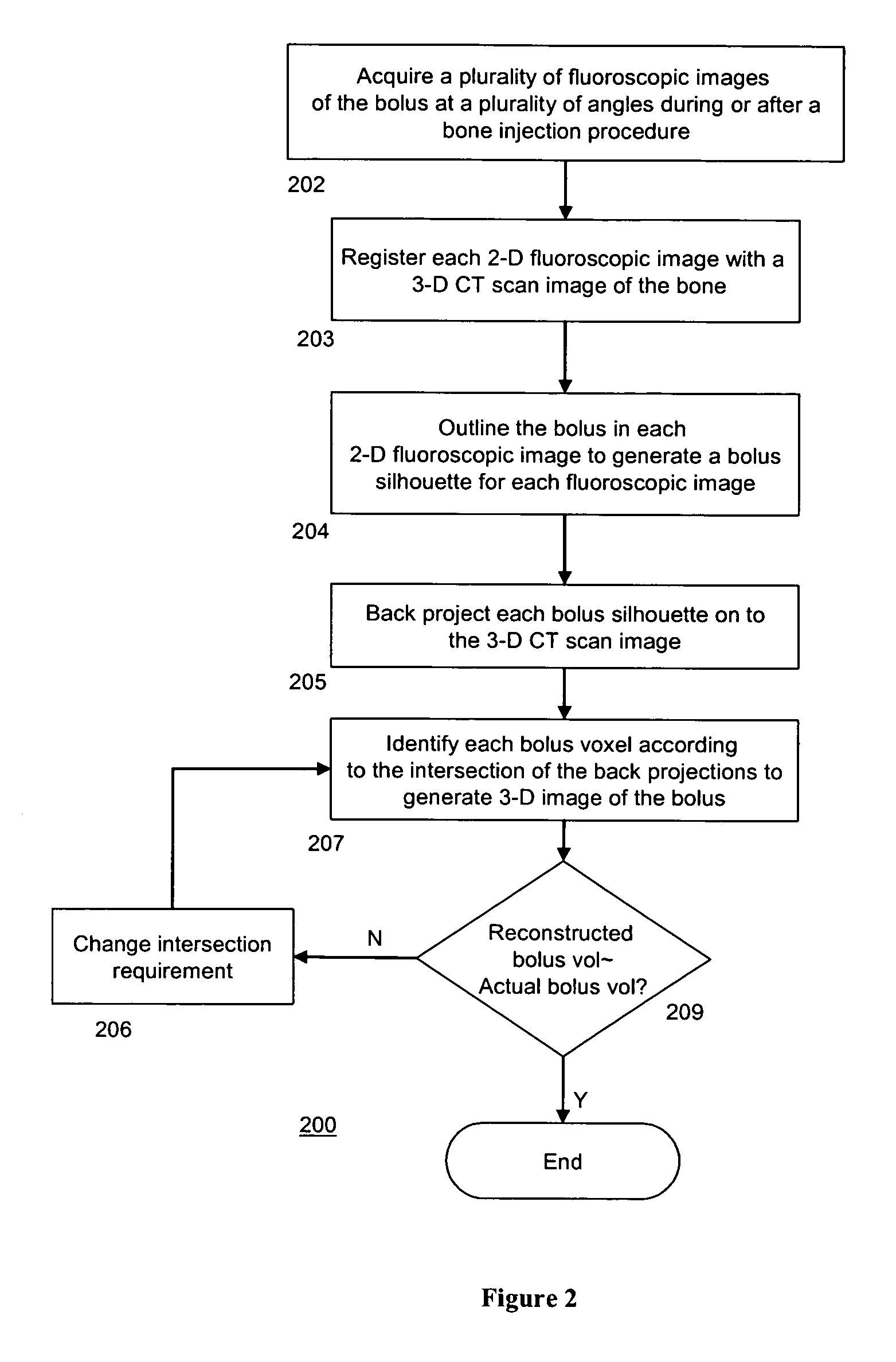
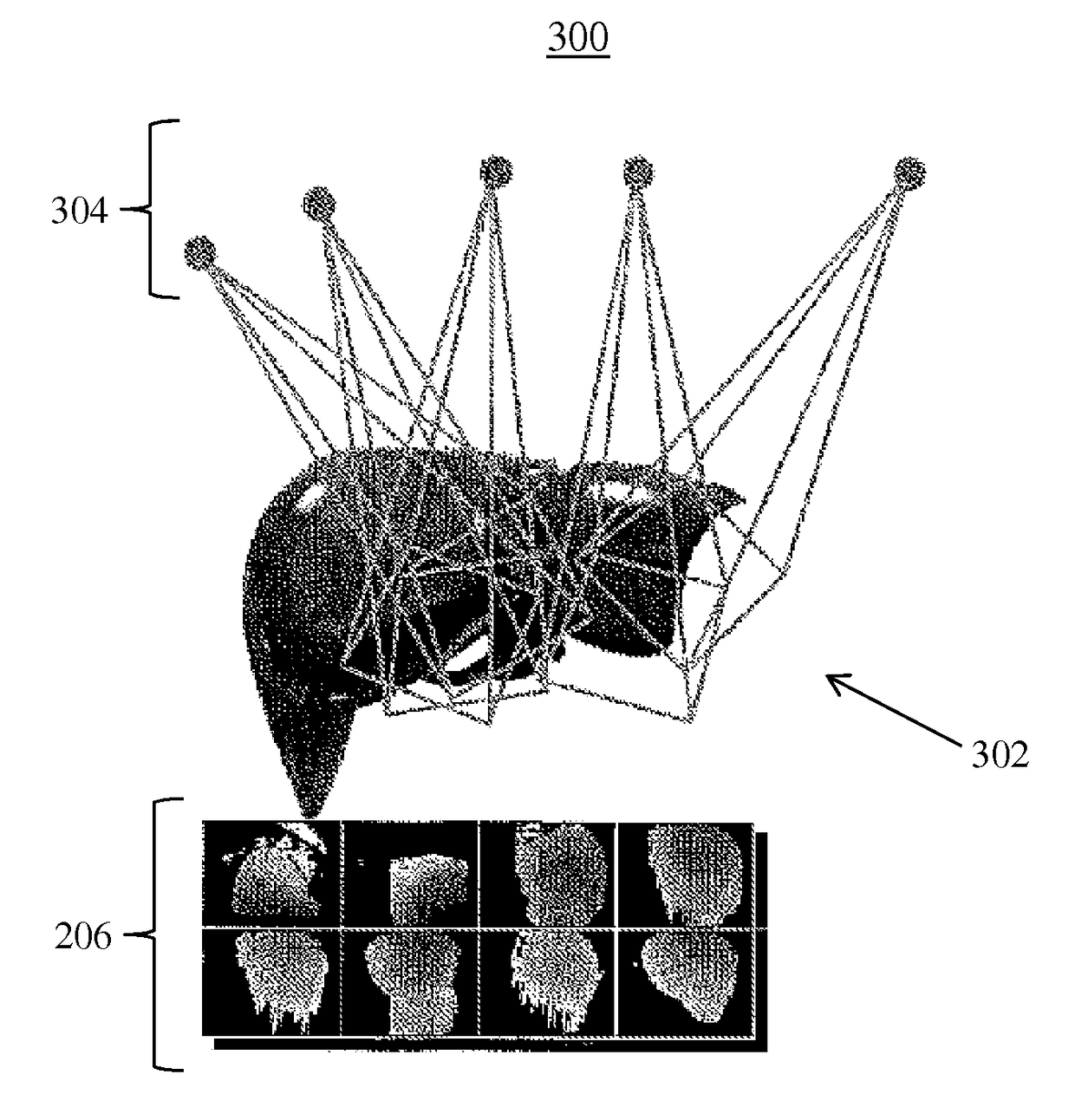
InactiveUS7596254B2Avoid secondary damageEasy assessment processPerson identificationCharacter and pattern recognitionVoxelFluoroscopic image
The present invention provides method of generating a 3-D image of at least one cement bolus in relation to a bone comprising acquiring a plurality of fluoroscopic images of the bolus during or after a bone cement injection procedure. The method further comprises registering each fluoroscopic image with a CT scan image of the bone. Additionally, the method comprises outlining the bolus in each fluoroscopic image to generate a plurality of silhouettes of the bolus. The method also comprises projecting the silhouettes on to the CT scan image to generate a plurality of back-projections. Moreover, the method comprises identifying a plurality of bolus voxels to generate the 3-D image of the bolus, wherein each bolus voxel comprises an intersection of at least two back-projections. Furthermore, a method for intra-operative imaging of at least one bolus of bone cement during a bone cement injection procedure is disclosed.
Owner:RICE UNIV
System and method for guidance of laparoscopic surgical procedures through anatomical model augmentation
InactiveUS20180189966A1Medical simulationDetails involving processing stepsPERITONEOSCOPEBiomechanical model
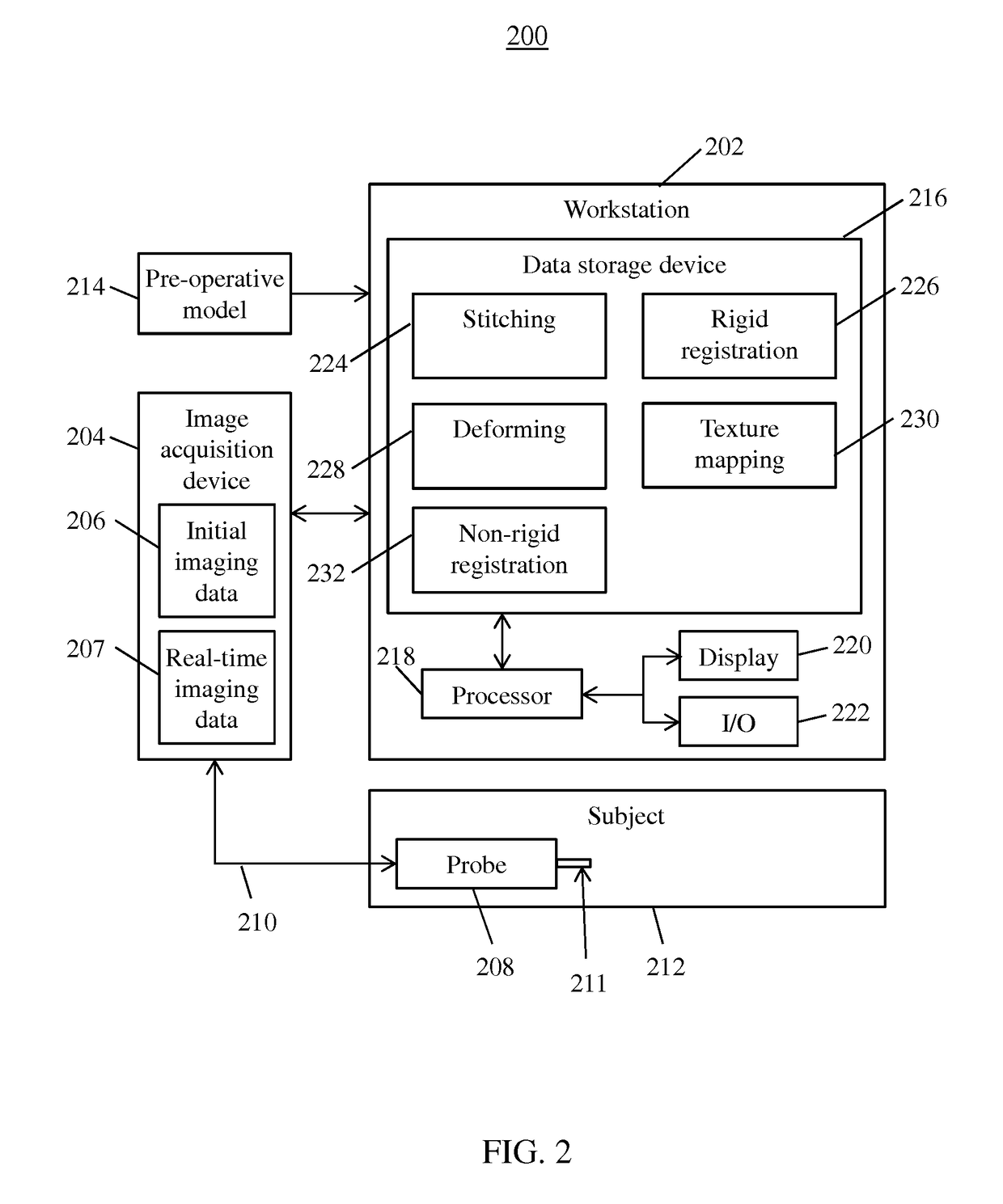
Systems and methods for model augmentation include receiving intra-operative imaging data of an anatomical object of interest at a deformed state. The intra-operative imaging data is stitched into an intra-operative model of the anatomical object of interest at the deformed state. The intra-operative model of the anatomical object of interest at the deformed state is registered with a pre-operative model of the anatomical object of interest at an initial state by deforming the pre-operative model of the anatomical object of interest at the initial state based on a biomechanical model. Texture information from the intra-operative model of the anatomical object of interest at the deformed state is mapped to the deformed pre-operative model to generate a deformed, texture-mapped pre-operative model of the anatomical object of interest.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
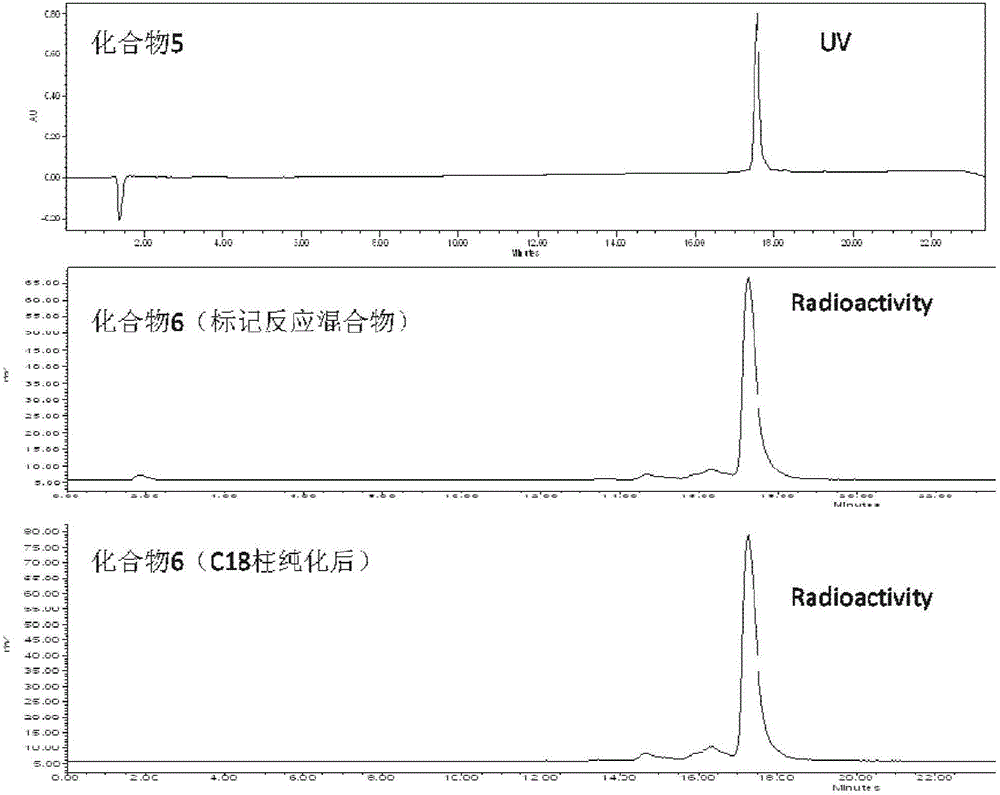
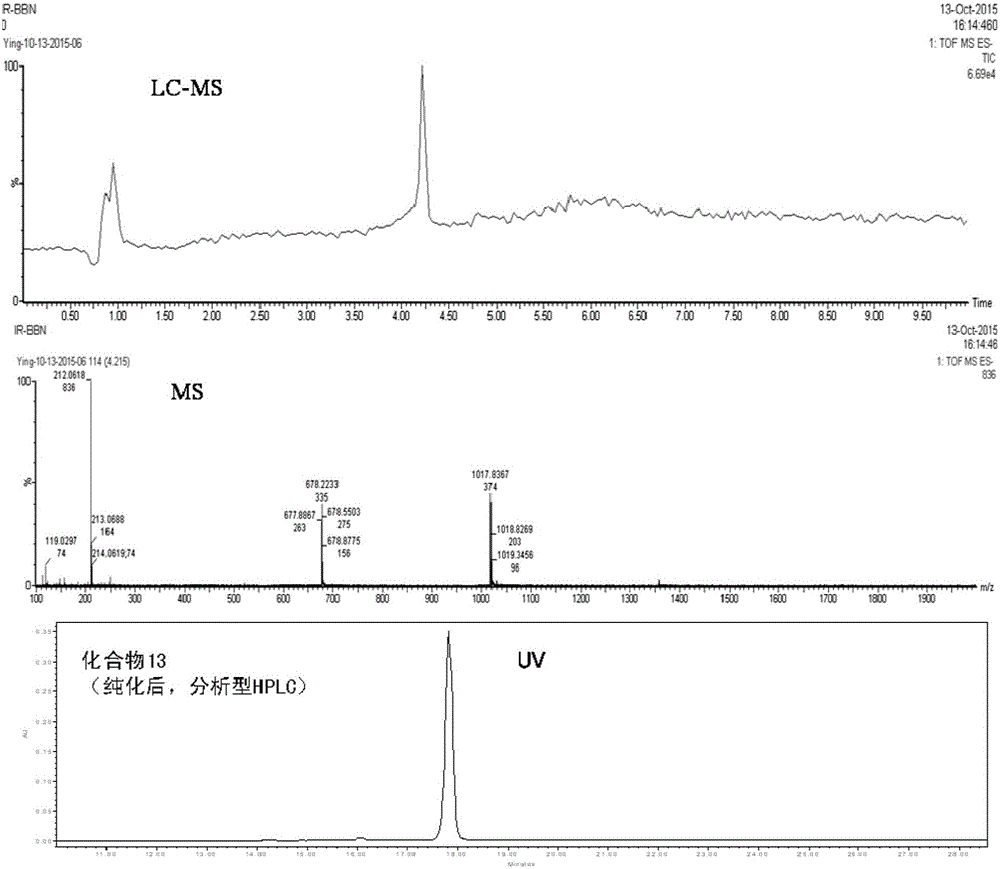
Multifunctional imaging probe and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN106543268ASimple methodEasy to makeX-ray constrast preparationsPeptide preparation methodsTumor targetTumor targeting
The invention provides a multifunctional imaging probe. The multifunctional imaging probe is a radionuclide labelled peptide complex and takes a peptide compound which has the structure as shown in the formula (I) defined in the description and has the tumor targeting fluorescence imaging function, wherein X is a NOTA radical group or-CH2-, R is targeting peptide BBN with the structure as shown in the formula (II) defined in the description or targeting peptide RM26 with the structure as shown in the formula (III). The multifunctional imaging probe can be used for positron emission computer tomography (PET) and optical imaging simultaneously. The invention further provides a preparation method of the functional probe and application in preparation of a human or animal organ or tissue imaging agent, precise positioning on the tumor boundary can be achieved through application, and the advantages of real-time performance, high precision, high specificity, high sensitivity and high resolution are brought to preoperative and intraoperative imaging navigation.
Owner:NANTONG SHIMEIKANG PHARMA CHEM
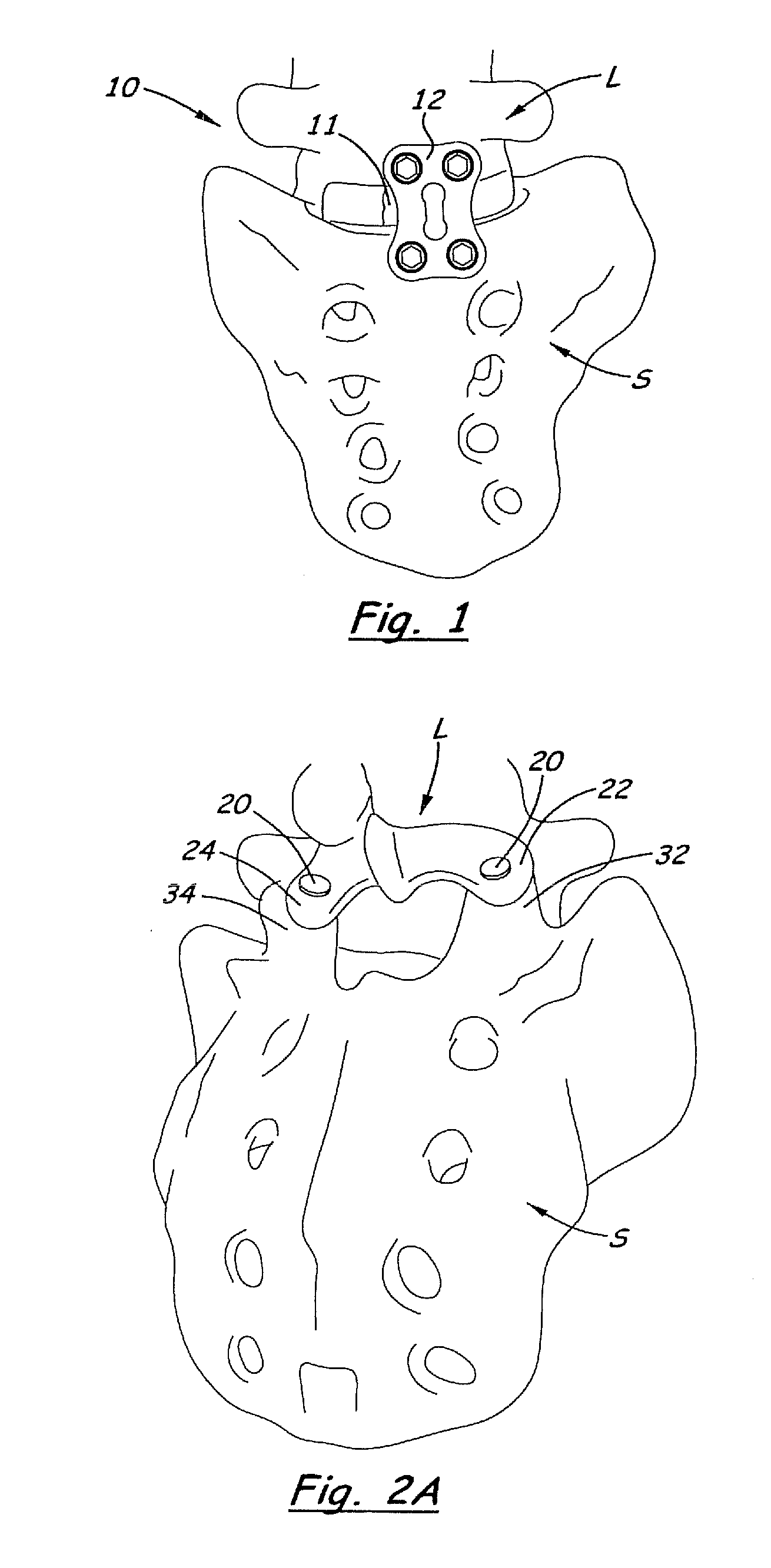
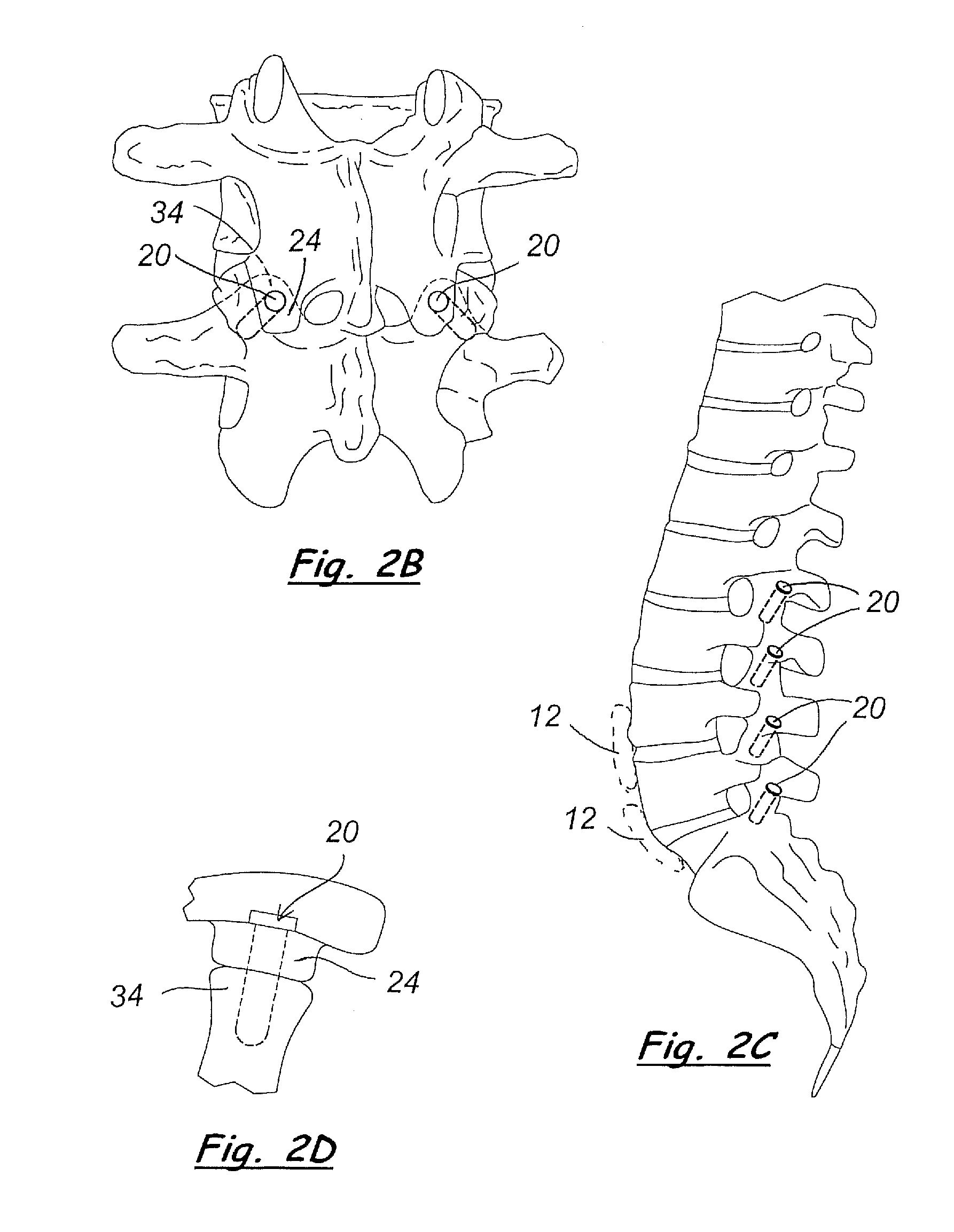
Tack for spine fixation
InactiveUS20110106170A1Extremely non-invasive apparatus and surgery methodsSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisBone growthTarsal Joint
A tack for insertion into facets joints of the human spine includes one or more bioactive materials. The tack is preferably pushed / impacted axially into a hole in the facets, rather than rotated or screwed into the hole / facets. For example, the bioactive material may be outer sidewall(s) made of porous material that receives and / or encourages bone growth into its pores. Or, for example, the bioactive material may be osteobiologic material, demineralized bone matrix (DBM), sponge holding bone morphogenic protein (BMP), allograft bone, or other bioactive material inside an interior space of the tack. Apertures may be provided in the outer wall of a hollow tack to allow bone growth into the interior space of the tack. The tack may have a longitudinal passage, so that the tack may be installed on and slid along a guide-wire in percutaneous surgery that is guided by intraoperative imaging navigation. Preferably, the tack is not threaded, and is installed with little, and preferably no, rotation of the tack on its longitudinal axis.
Owner:DOERR TIMOTHY E
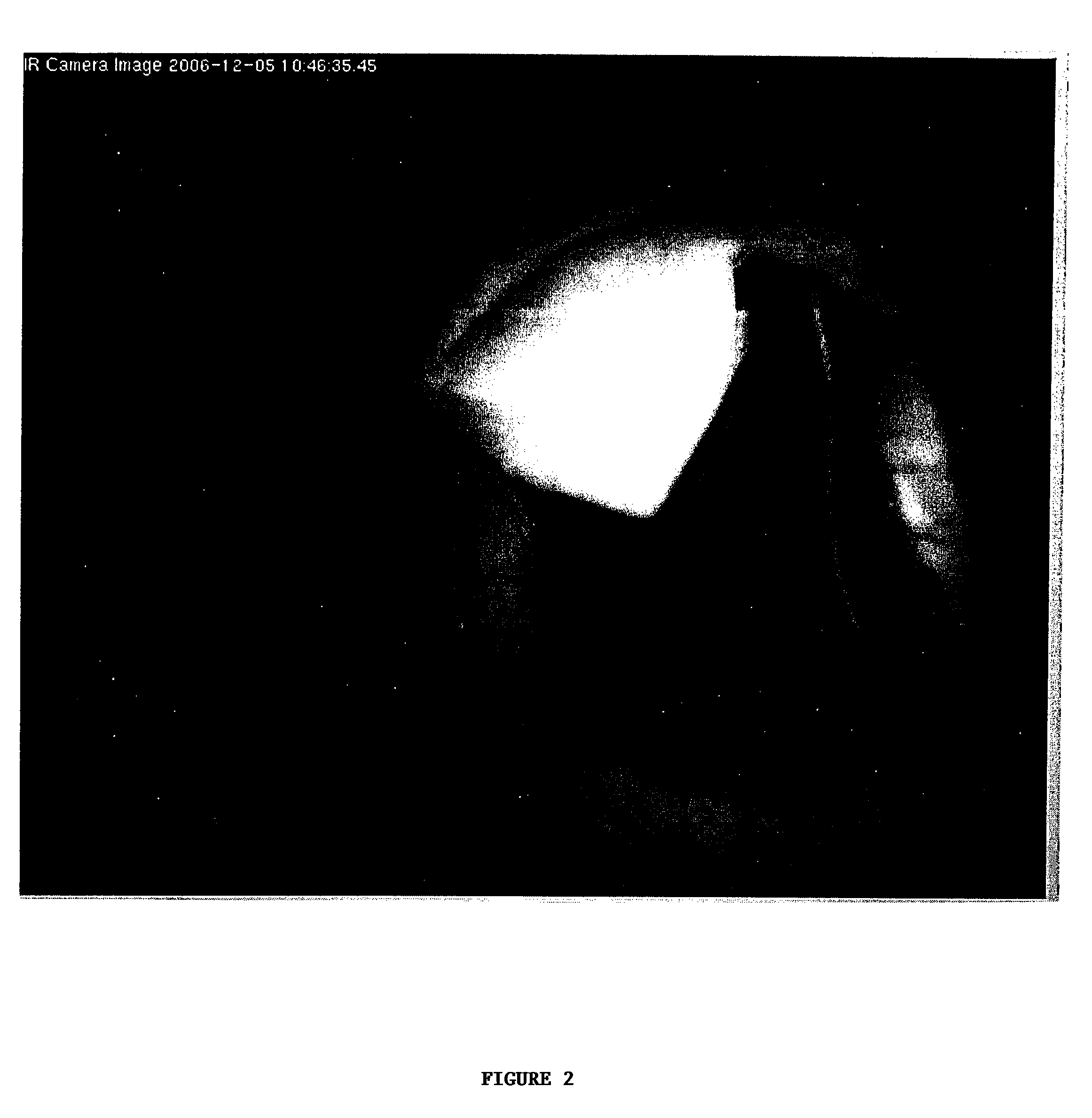
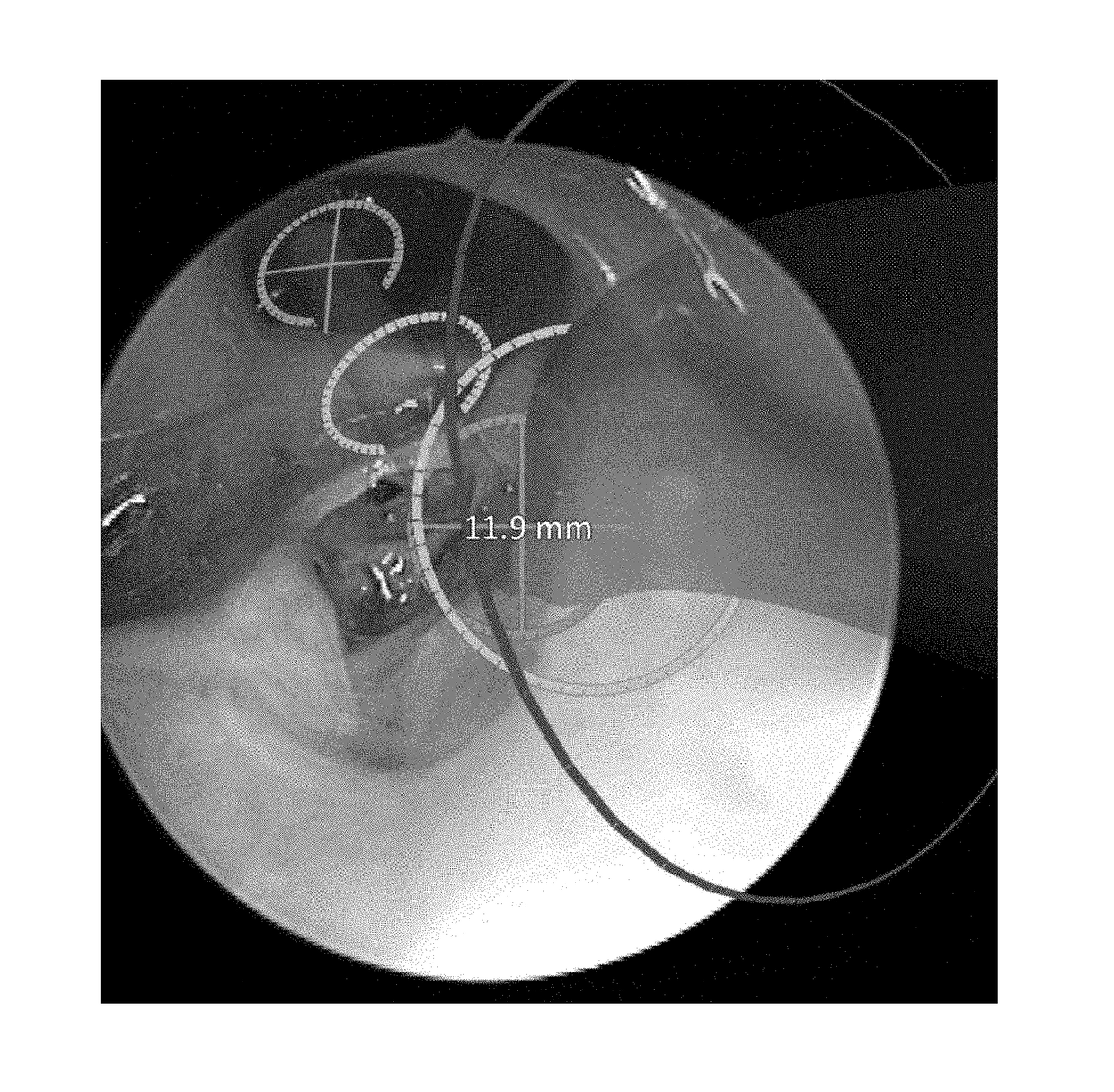
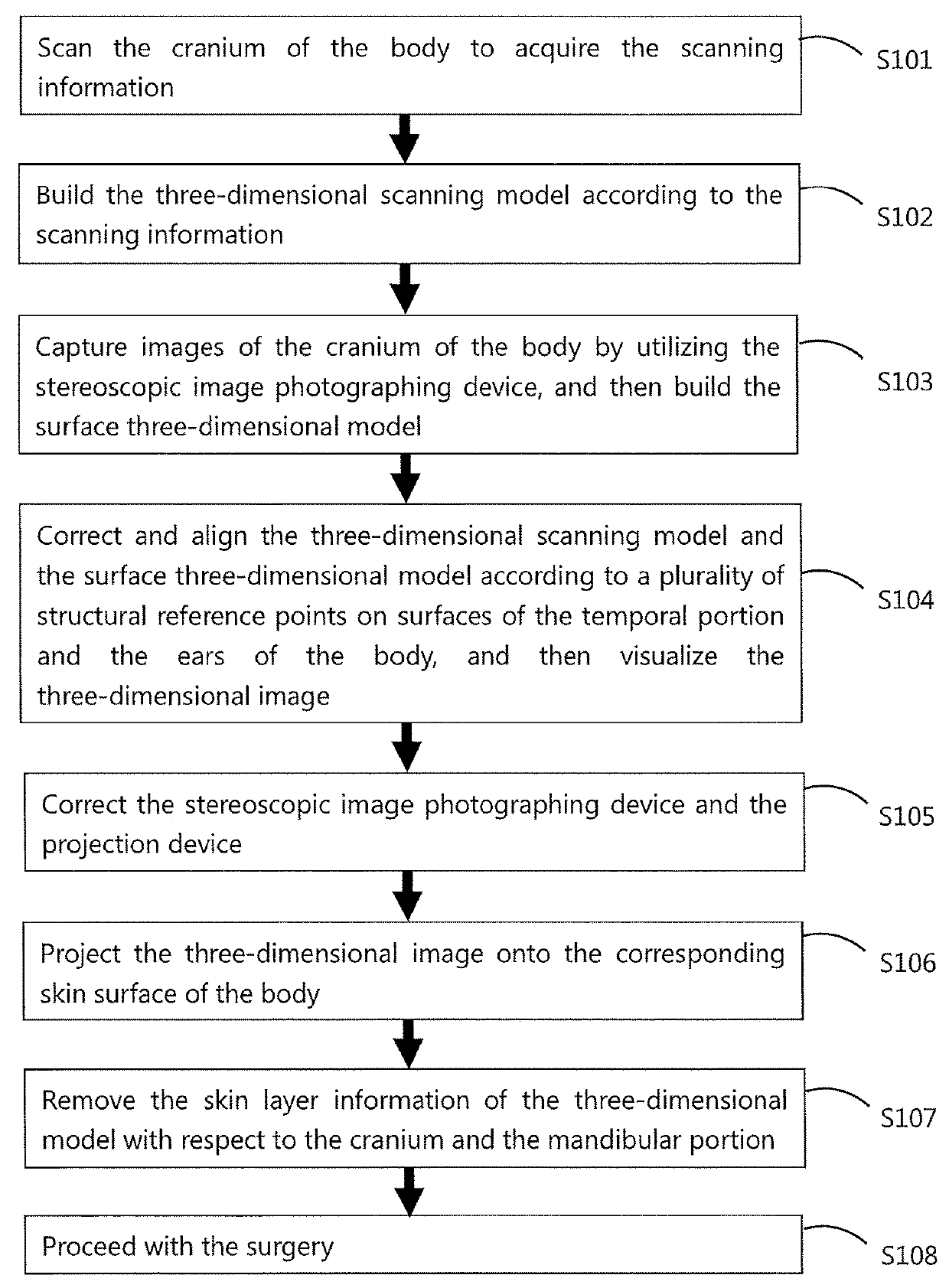
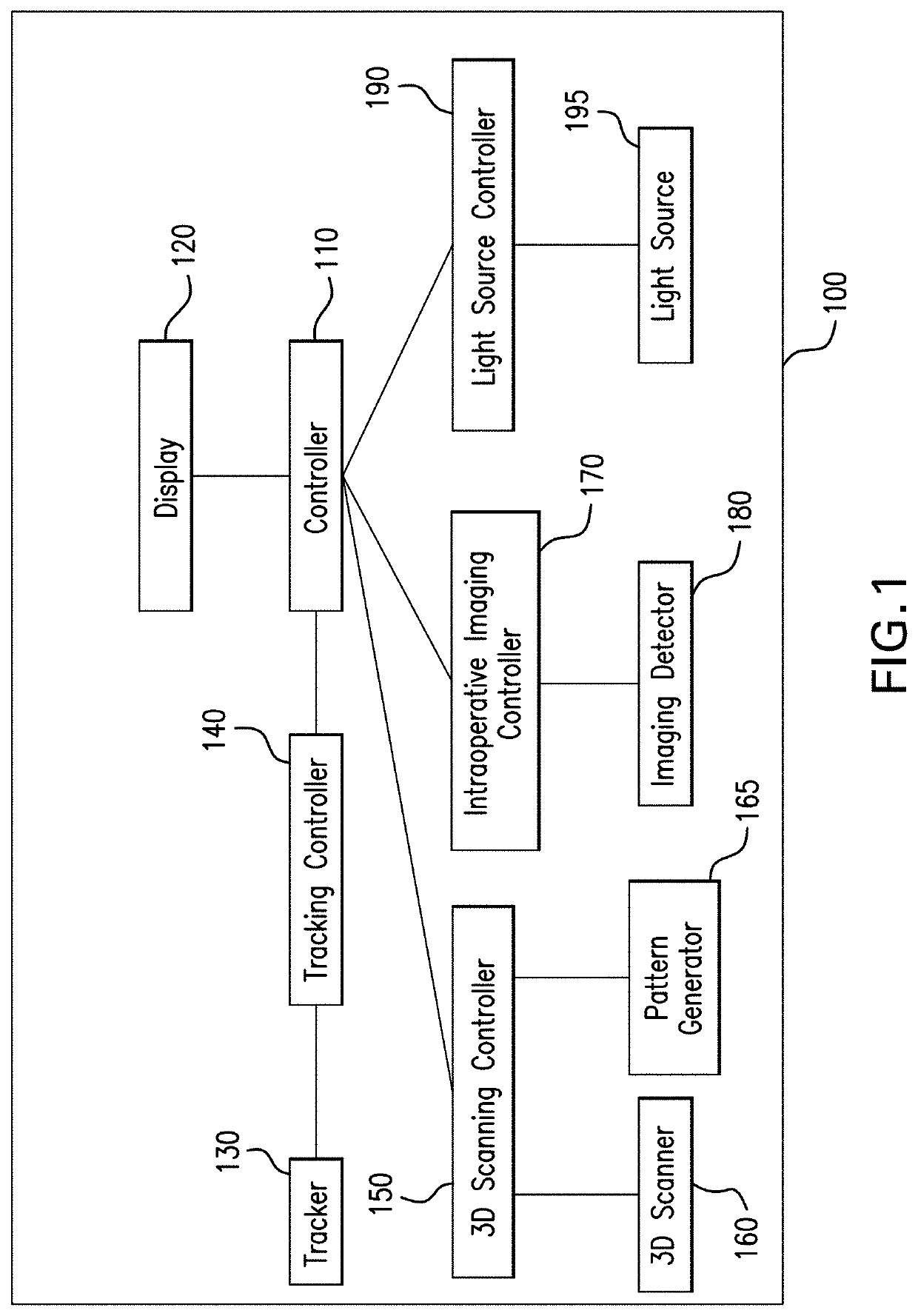
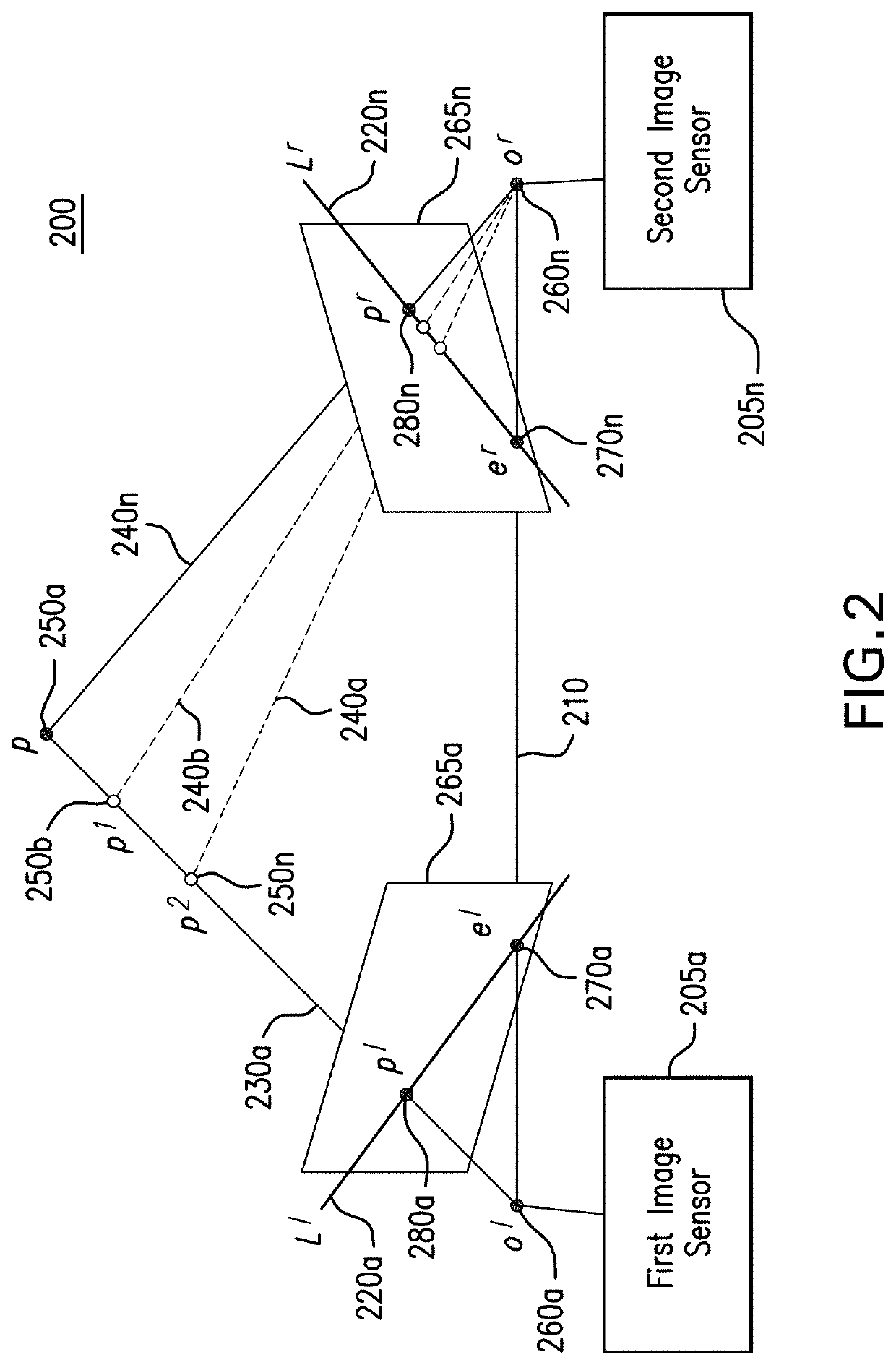
Generation of three-dimensional scans for intraoperative imaging
A system for executing a three-dimensional (3D) intraoperative scan of a patient is disclosed. A 3D scanner controller projects the object points included onto a first image plane and the object points onto a second image plane. The 3D scanner controller determines first epipolar lines associated with the first image plane and second epipolar lines associated with the second image plane based on an epipolar plane that triangulates the object points included in the first 2D intraoperative image to the object points included in the second 2D intraoperative image. Each epipolar lines provides a depth of each object as projected onto the first image plane and the second image plane. The 3D scanner controller converts the first 2D intraoperative image and the second 2D intraoperative image to the 3D intraoperative scan of the patient based on the depth of each object point provided by each corresponding epipolar line.
Owner:UNIFY MEDICAL
Instrument guidance system for sinus surgery
A method for generating an augmented reality image for supporting the adjustment of the position of a surgical instrument during sinus surgery comprising the steps of: selecting at least one of sinus cells, cavities and orifices of the sinus in a pre-operative image by marking them with at least one geometric primitive or tube shaped object; using real-time intra-operative imaging for displaying the operating field; determining the relative positions at least between the real-time imaging of the patient and the pre-operative image data; computing a virtual image corresponding to a real-time image comprising at least one marked geometric primitive or tube shaped object based on the determined relative positions; combining the virtual image and the real-time intraoperative image for visualization in an augmented reality image.
Owner:STRYKER EUROPEAN OPERATIONS LIMITED
Robotic control of imaging devices with optical shape sensing
A system for tracking a device image includes an intraoperative imaging system (110) having a probe (146) configured to generate an image for a region. A shape sensing enabled instrument (102) is configured to have a portion of the shape sensing enabled instrument positionable relative to the region. The shape sensing enabled instrument has a coordinate system registered with a coordinate system of the intraoperative imaging system. A robot is configured to coordinate movement between the probe and the shape sensing enabled instrument such that movement of the shape sensing enabled instrument relative to the region causes the probe to be moved to maintain the shape sensing enabled instrument within the image.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Robotic catheter system for mri-guided cardiovascular interventions
PendingCN109715103AFacilitate communicationSmooth surgical workflowSurgical navigation systemsSurgical instrument detailsTele operationVisually guided
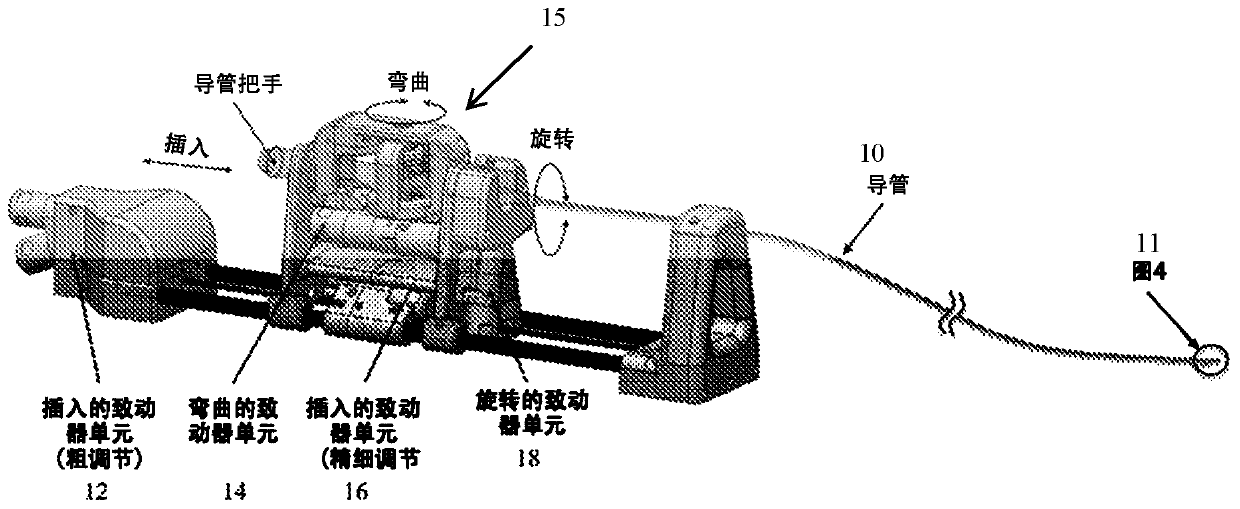
MRI-guided robotics offers possibility for physicians to perform interventions remotely on confined anatomy. While the pathological and physiological changes could be visualized by high-contrast volumetric MRI scan during the procedure, robots promise improved navigation with added dexterity and precision. In cardiac catheterization, however, maneuvering a long catheter (1-2 meters) to the desiredlocation and performing the therapy are still challenging. To meet this challenge, the robot presents an MRI-conditional catheter robotic system that integrates intra-operative MRI, MR-based trackingunits and enhanced visual guidance with catheter manipulation. This system differs fundamentally from existing master / slave catheter manipulation systems, of which the robotic manipulation is still challenging due to the very limited image guidance. This system provides a means of integrating intra-operative MR imaging and tracking to improve the performance of tele-operated robotic catheterization.
Owner:VERSITECH LTD
Pre-And Intra-Operative Imaging of Testicular Torsion
InactiveUS20080125663A1Easy to determineDiagnostics using lightCatheterTesticular torsionSpermatic cord
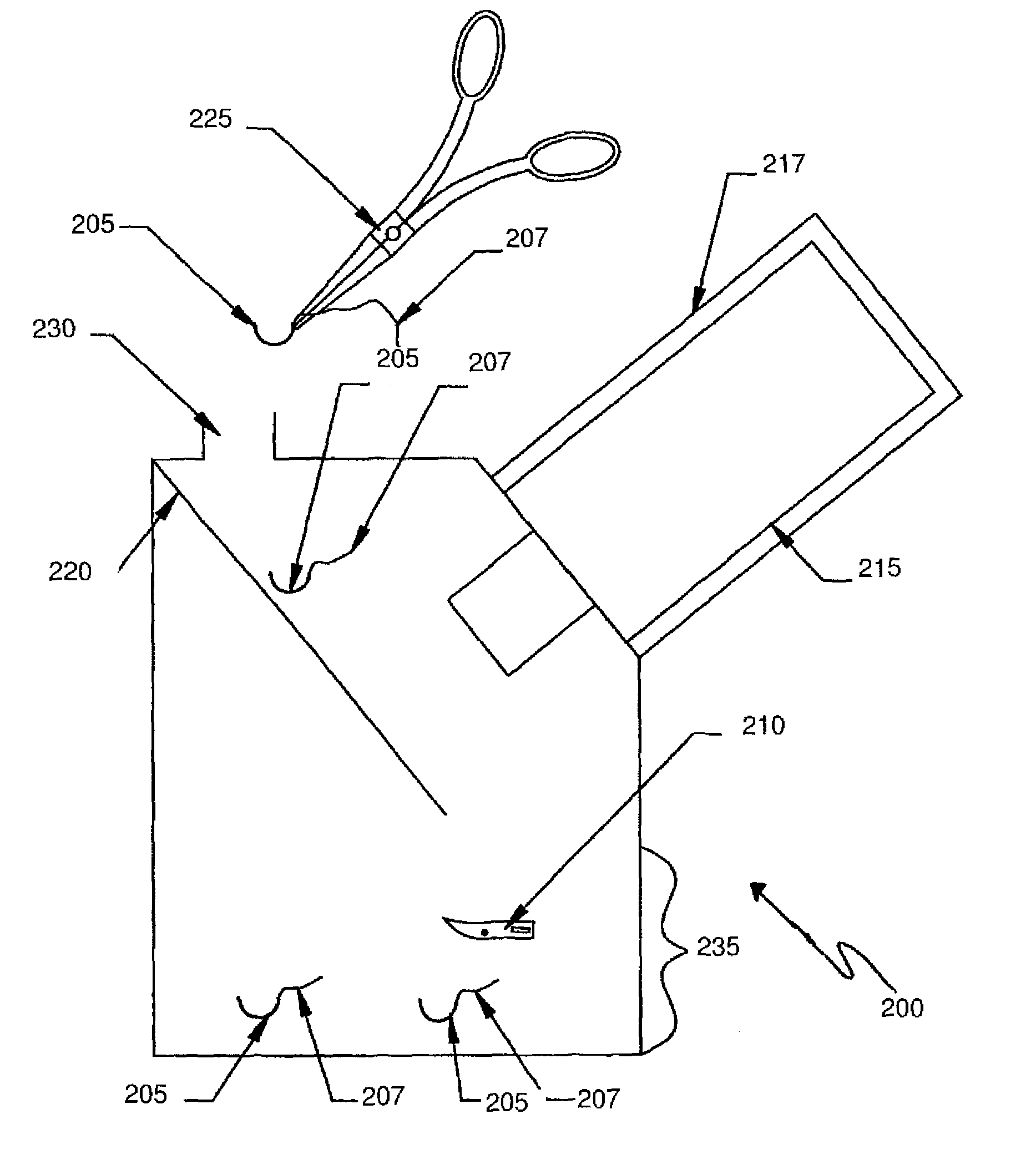
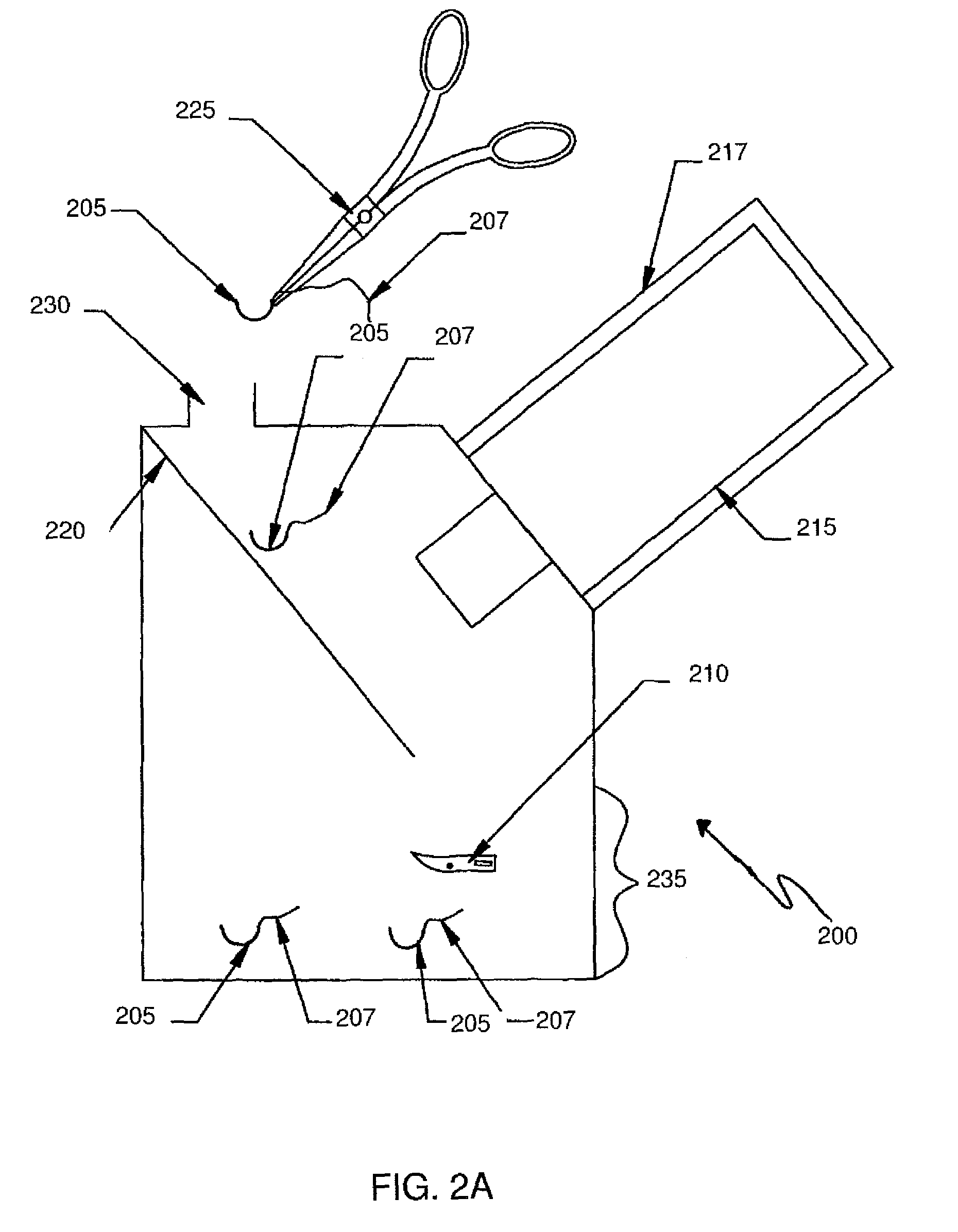
The invention provides methods for visualizing perfusion or lack thereof in the spermatic cord and testicle, as well as for detecting testicular trauma. A surgical forceps adapted to facilitate such visualization is also provided.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
Systems and methods for annotation and sorting of surgical images
ActiveUS20080172383A1Good user interfaceStill image data indexingMetadata still image retrievalImproved methodComputer science
Certain embodiments of the present invention provide an improved method for using an intraoperative imaging system. The method includes acquiring an image using an intraoperative imaging system, labeling the image by associating the image with a label, and storing the image and the label.
Owner:STRYKER EURO OPERATIONS HLDG LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com