Patents
Literature
47 results about "Carotid artery.common" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
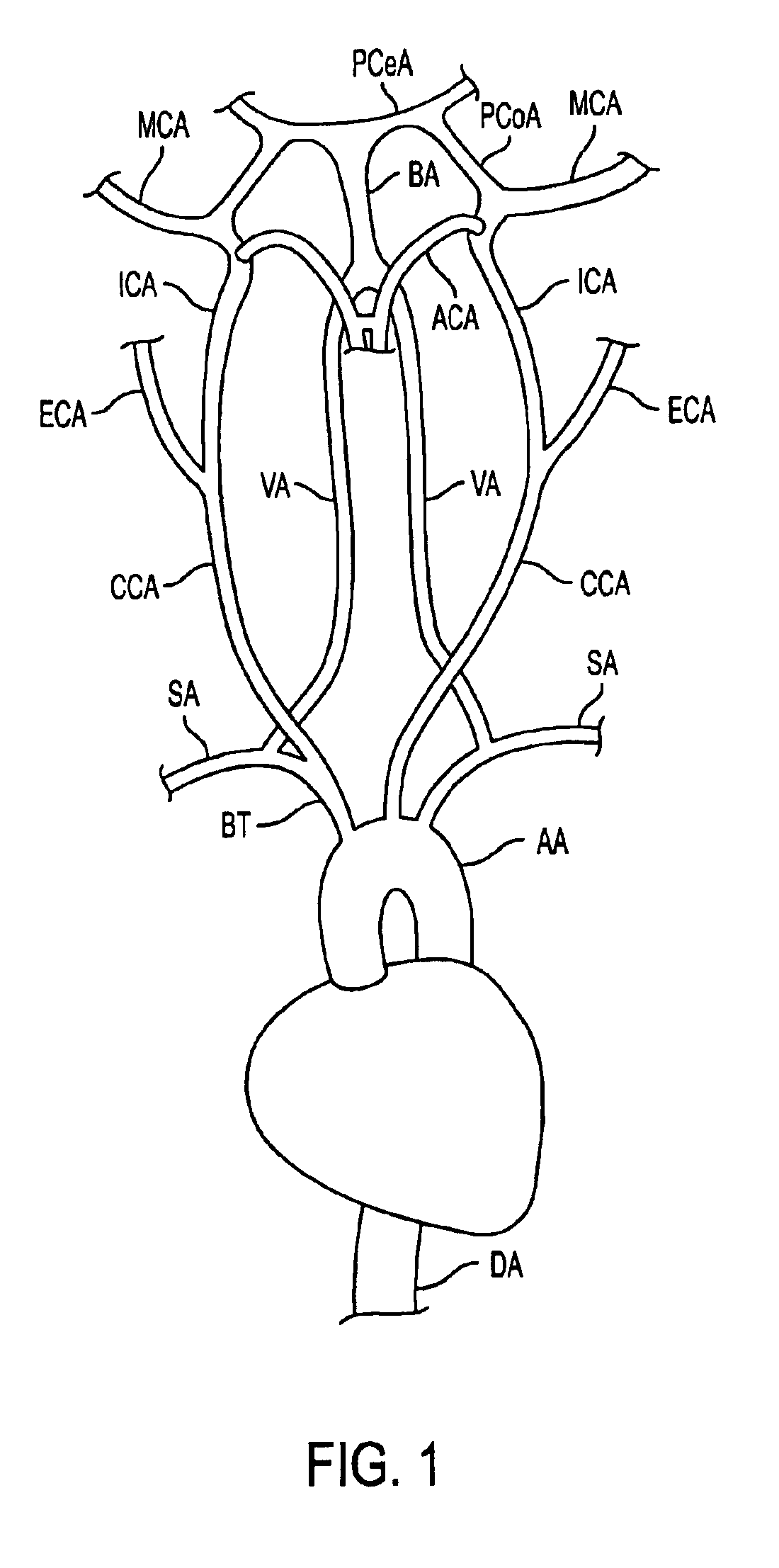
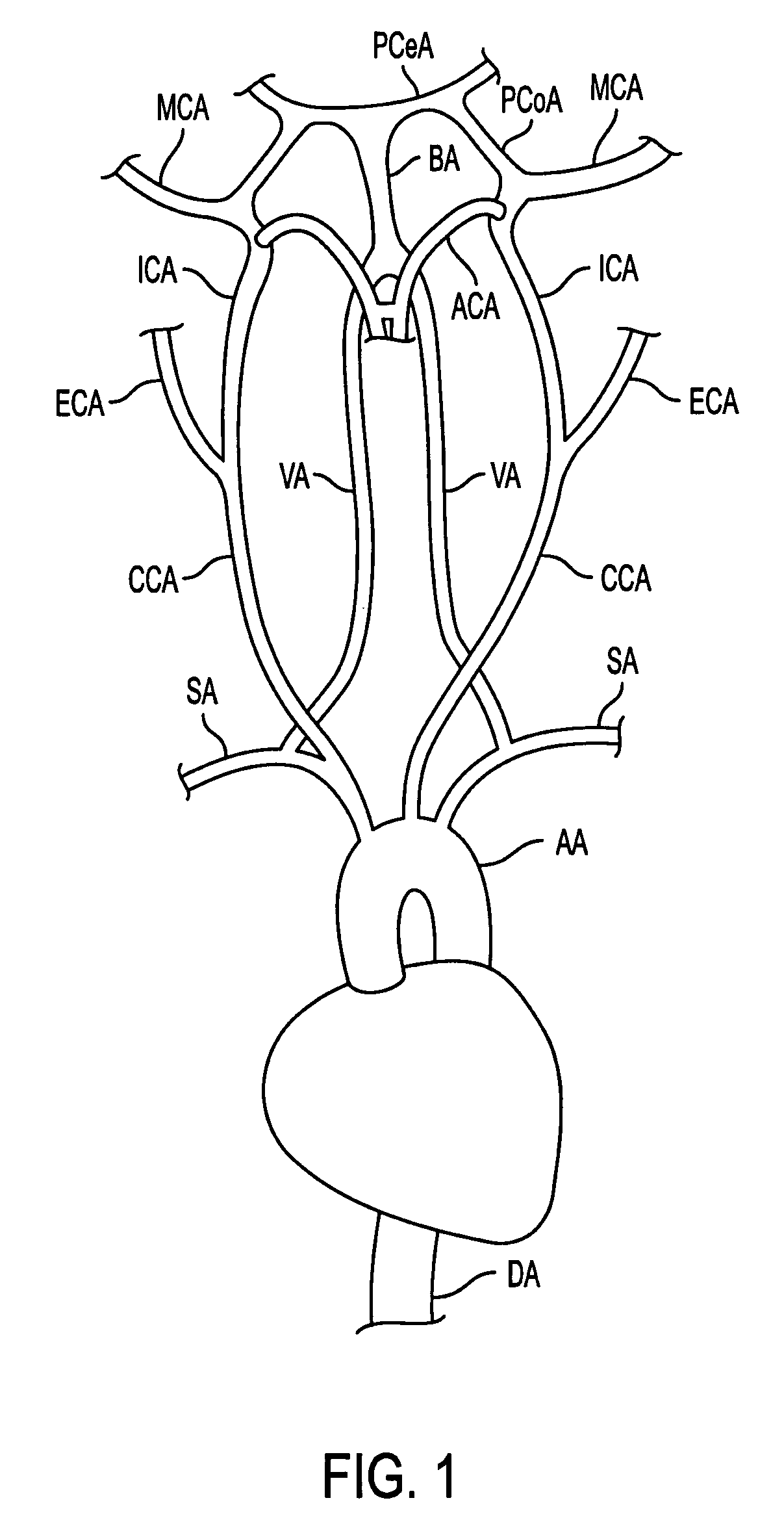
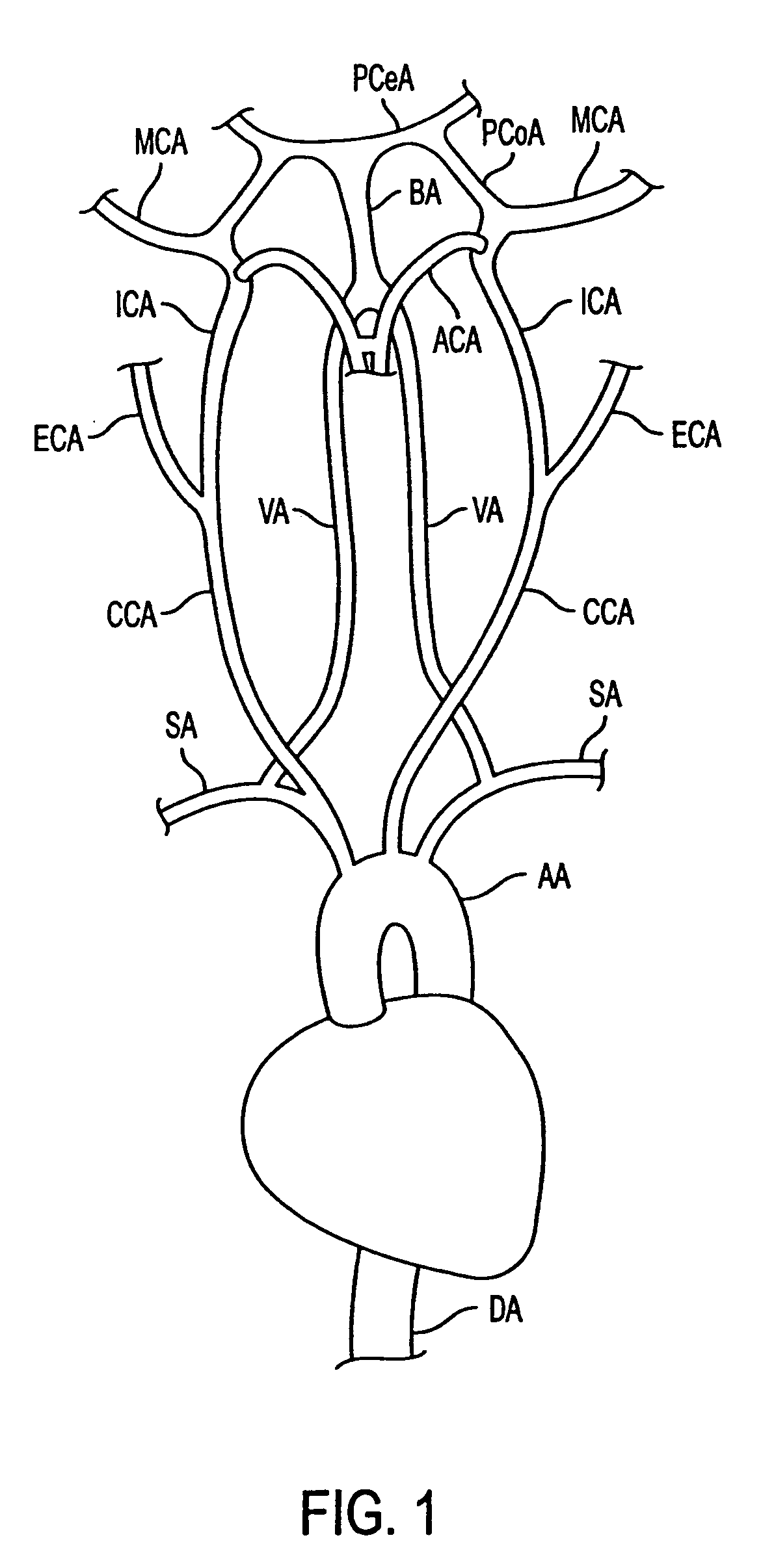
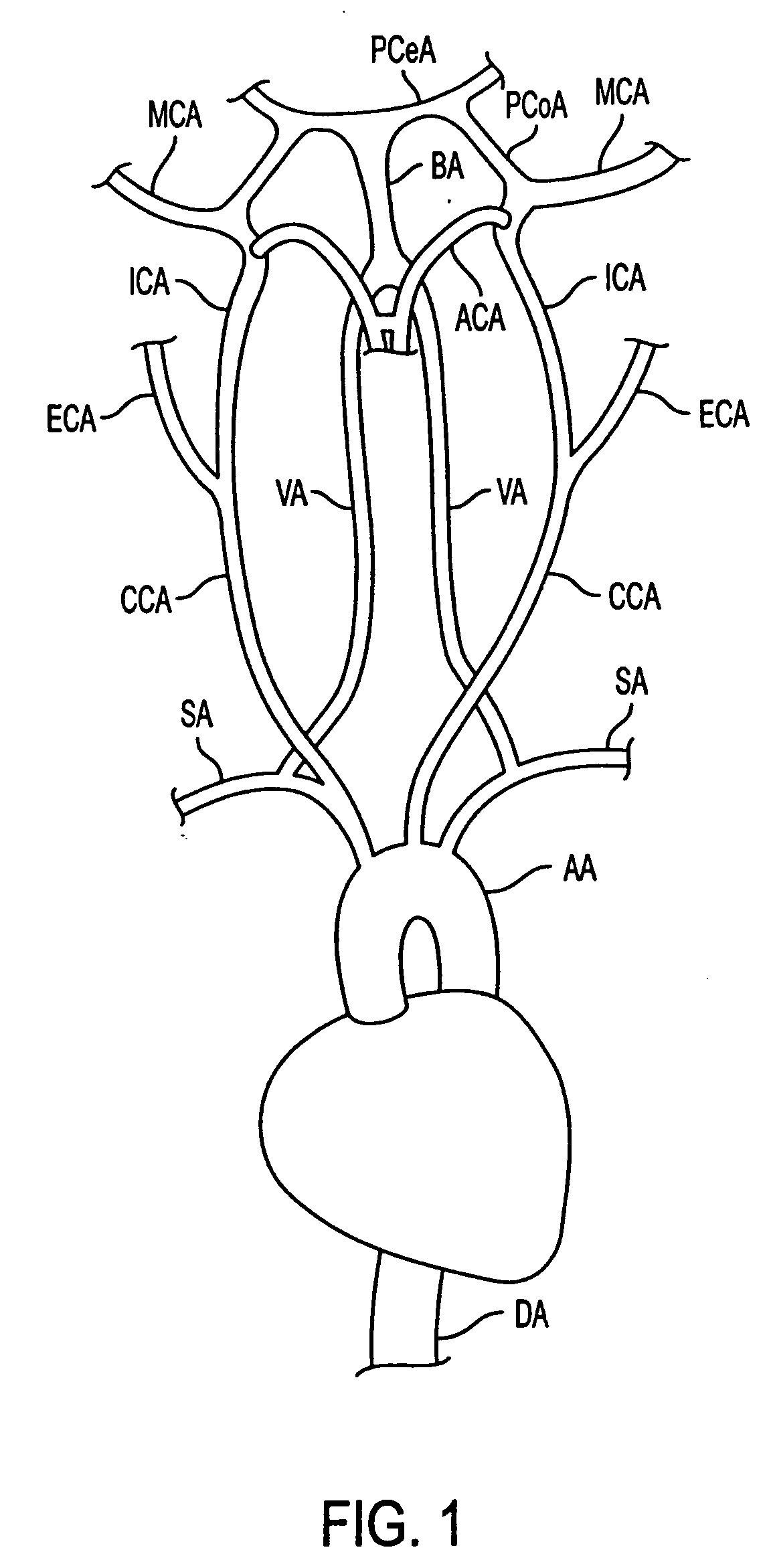
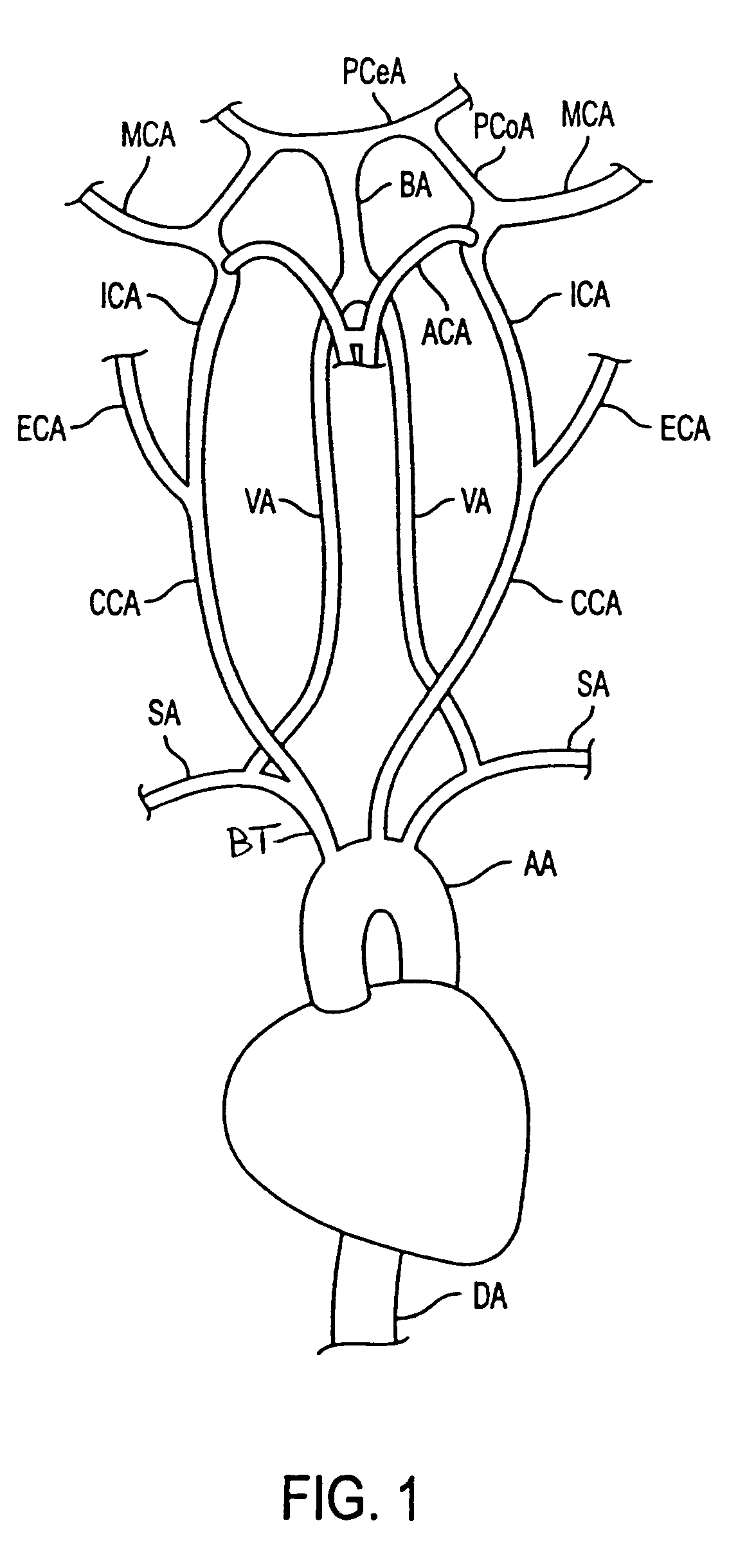
The common carotid artery is a large elastic artery, which provides the main blood supply to the head and neck region. There is one common carotid artery on either side of the body and these arteries differ in their origin.
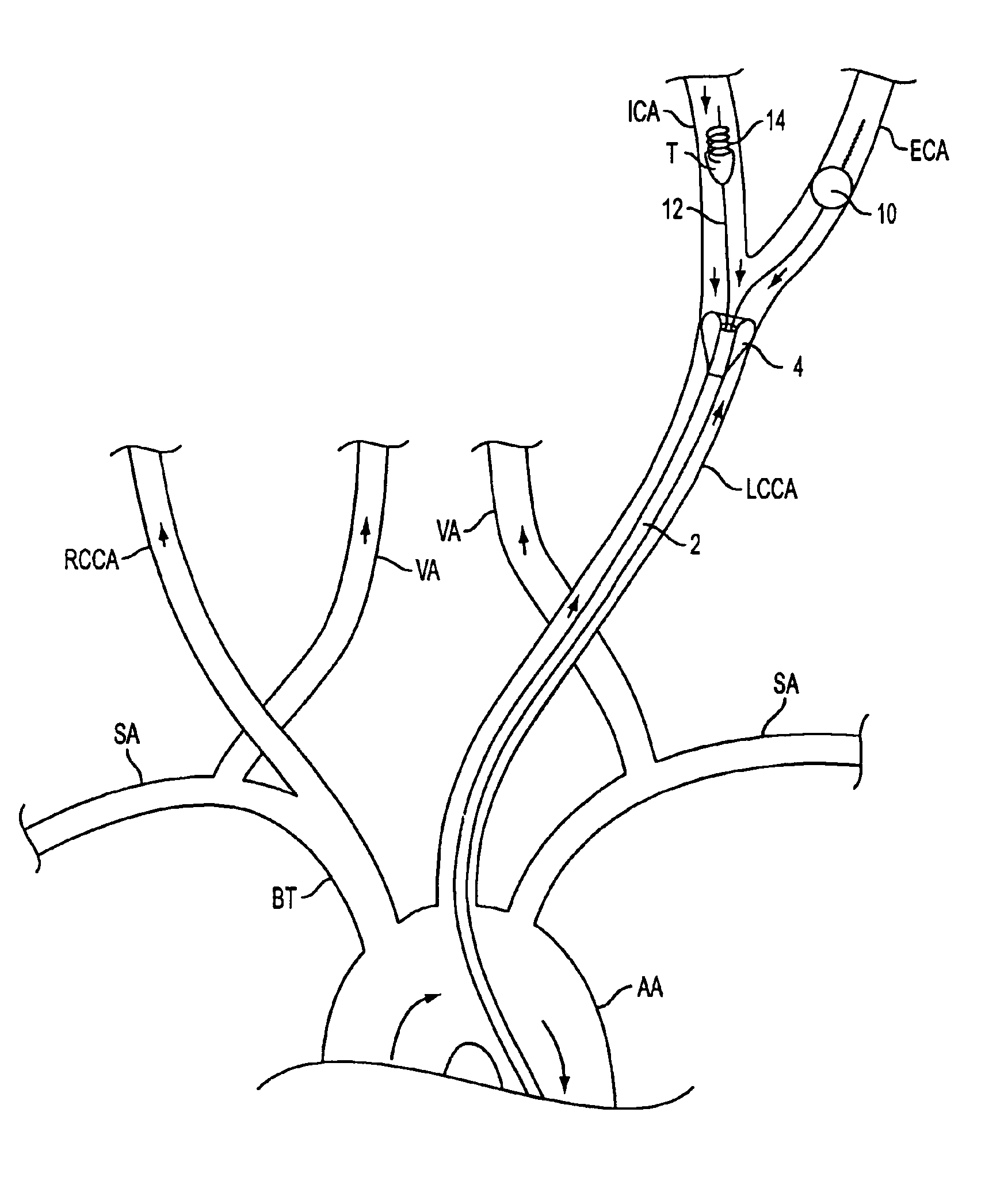
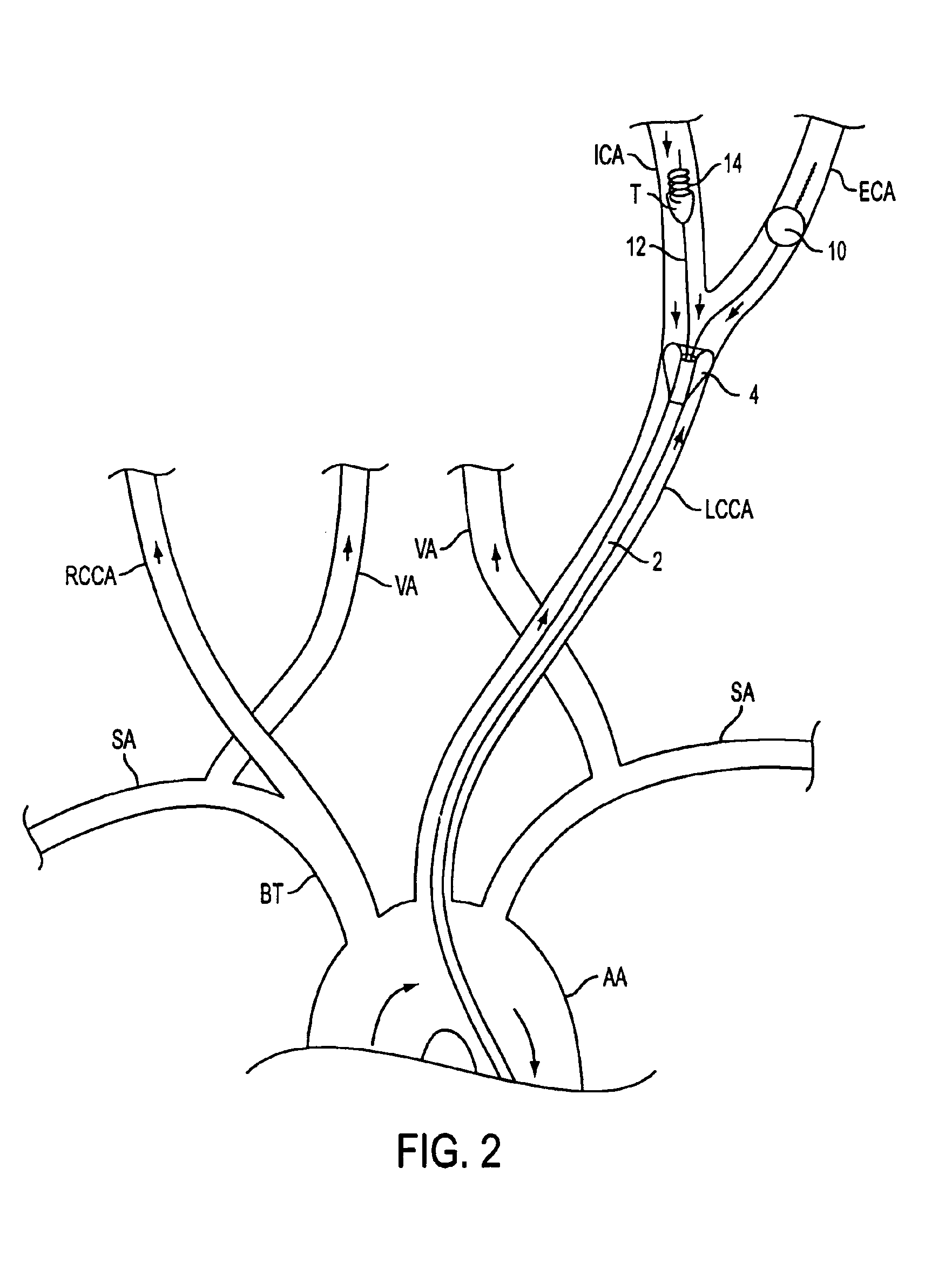
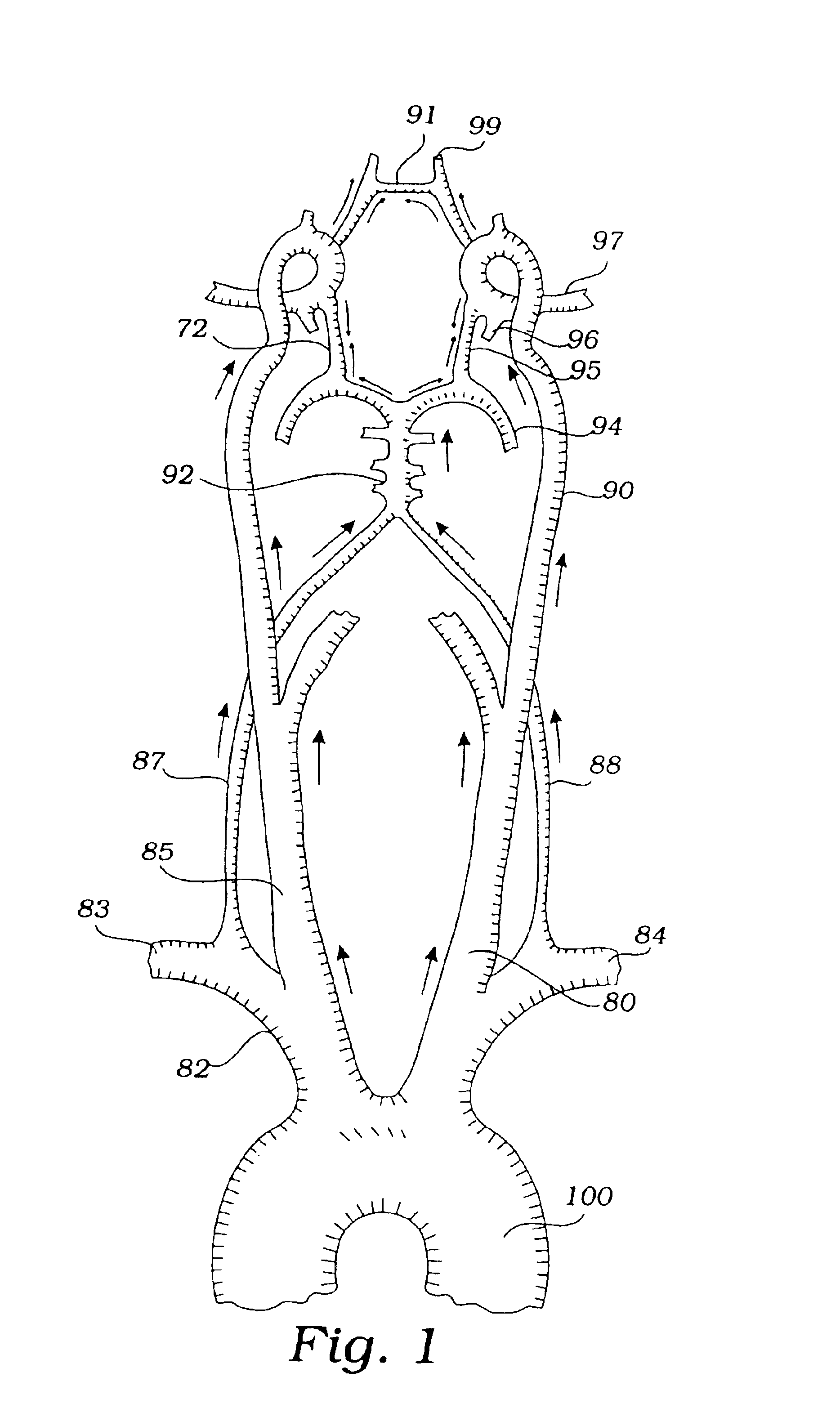
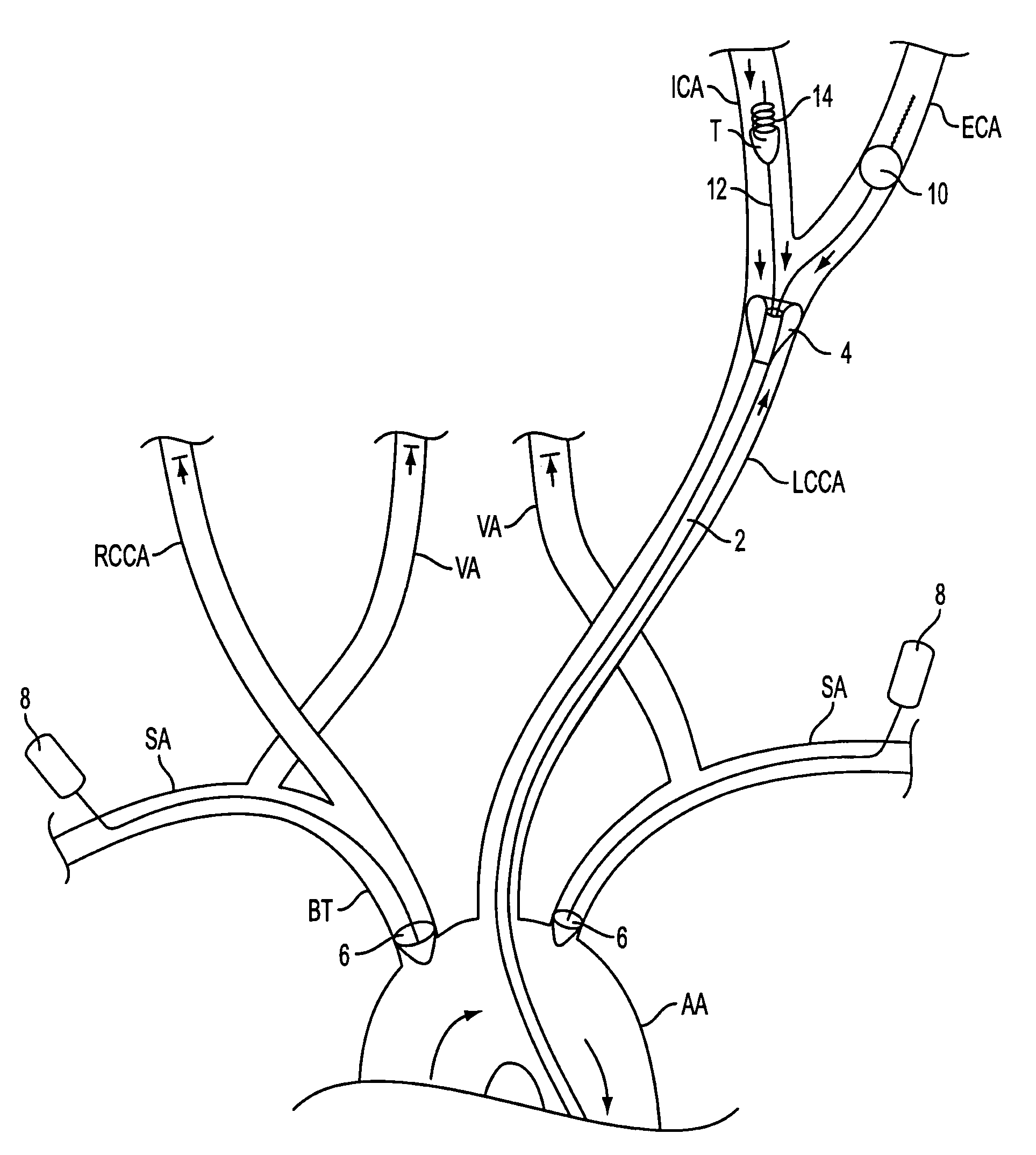
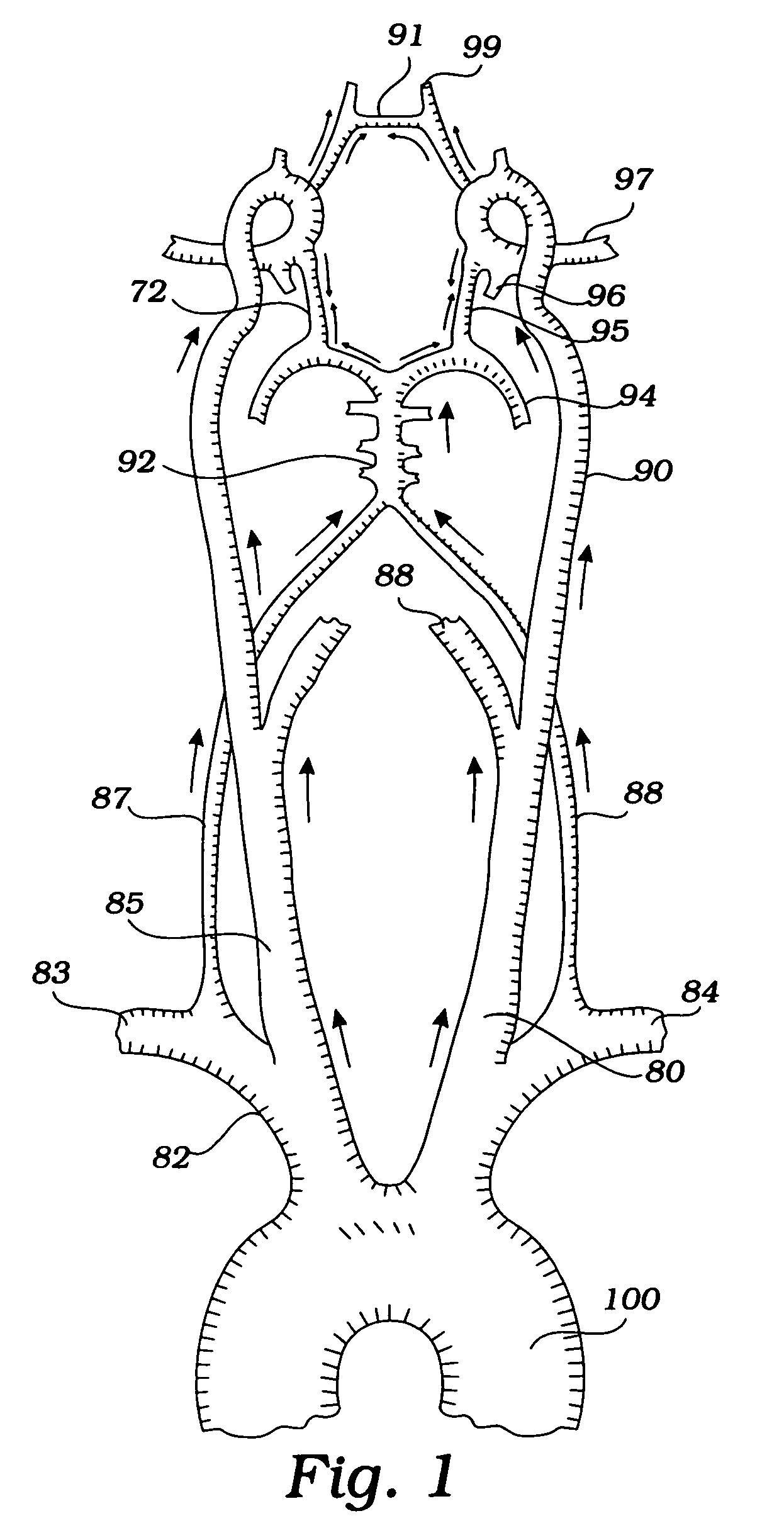
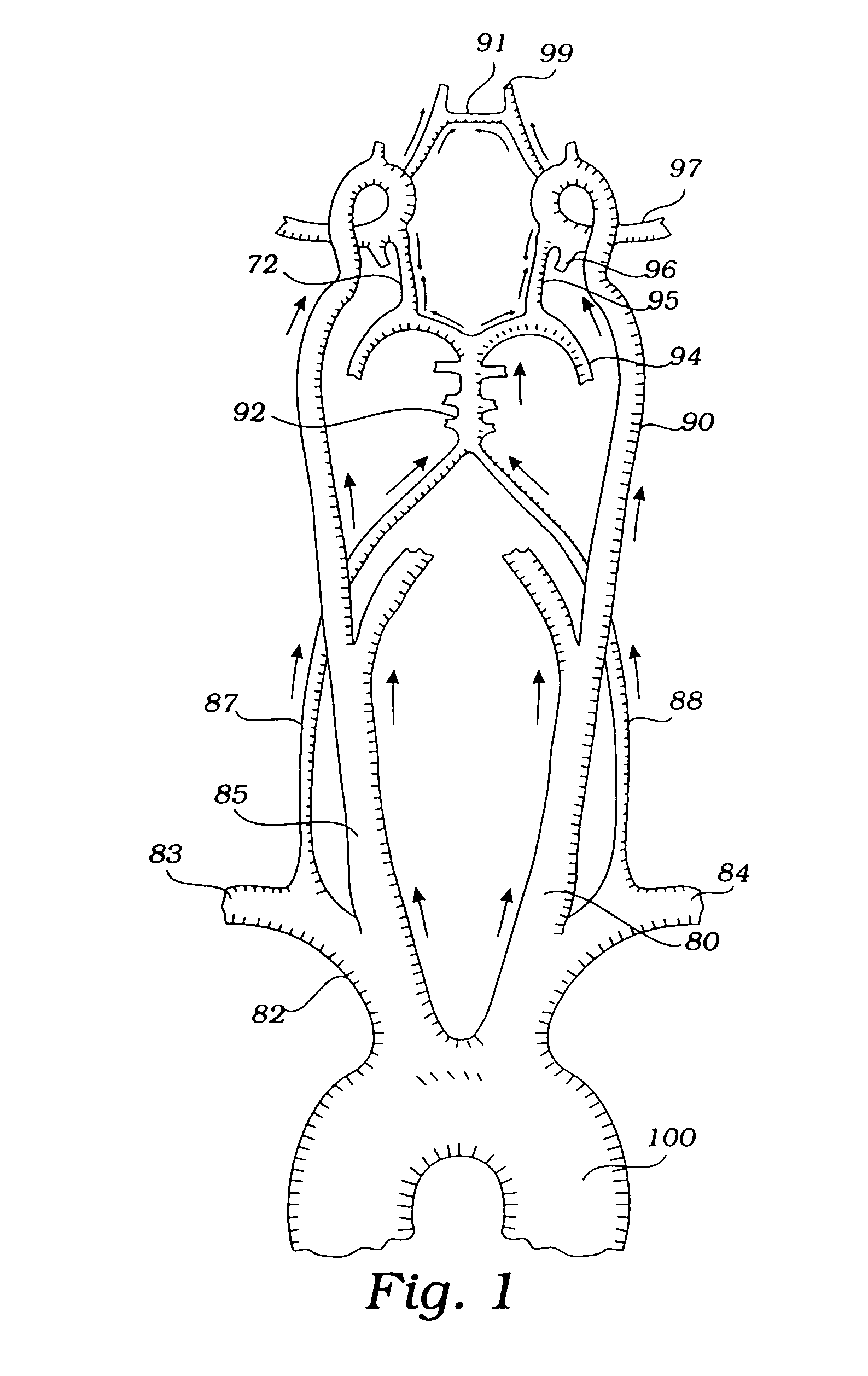
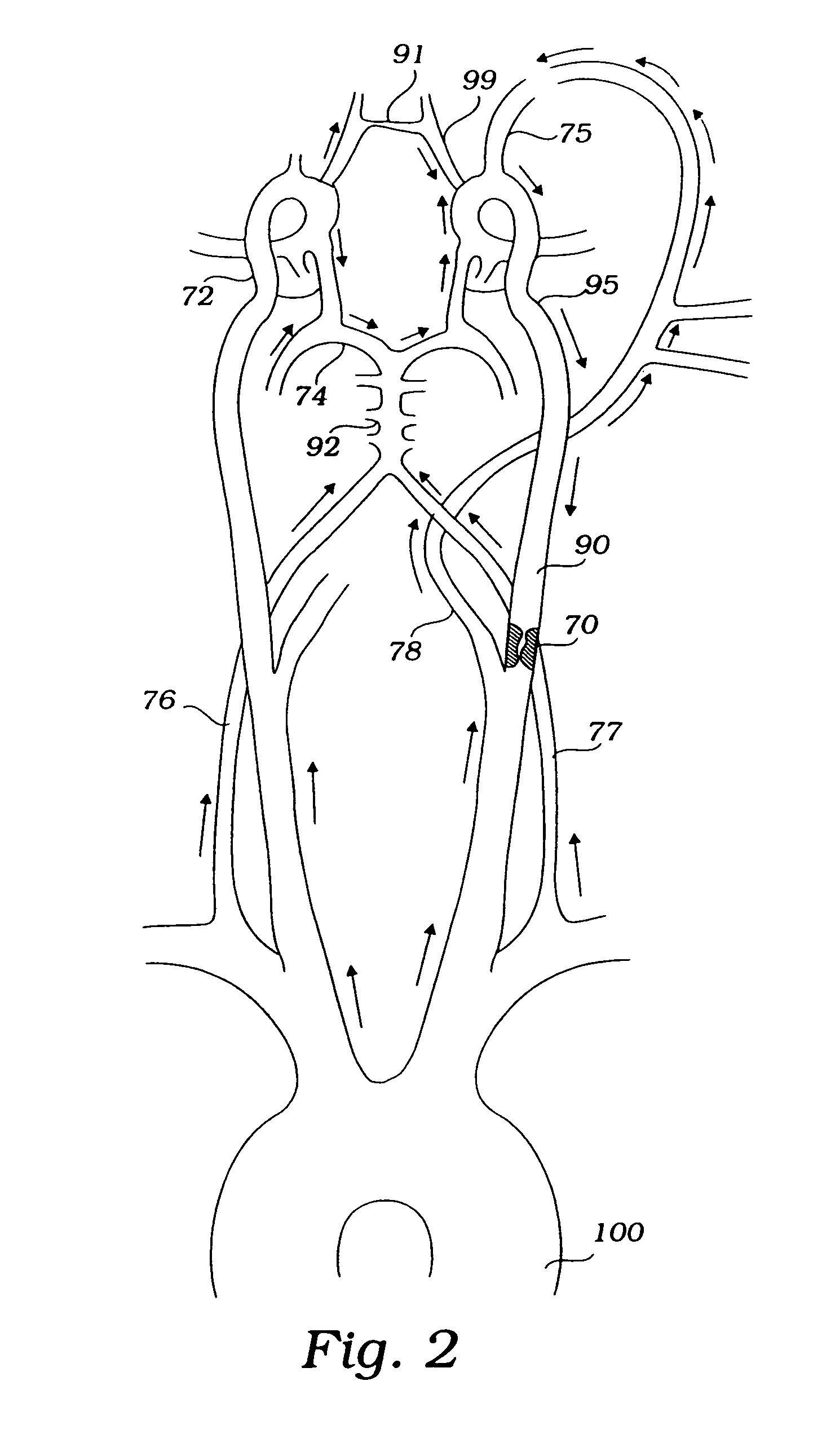
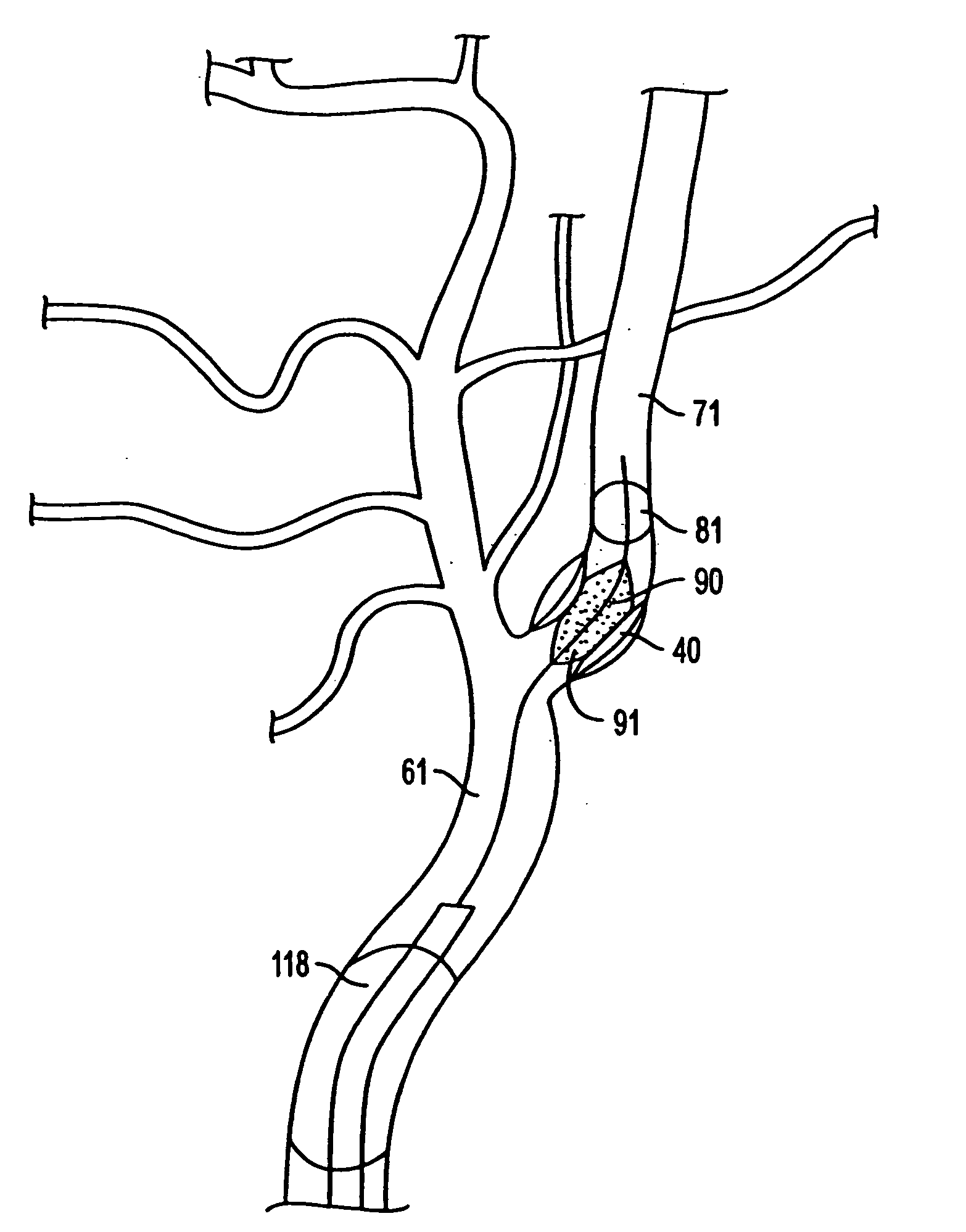
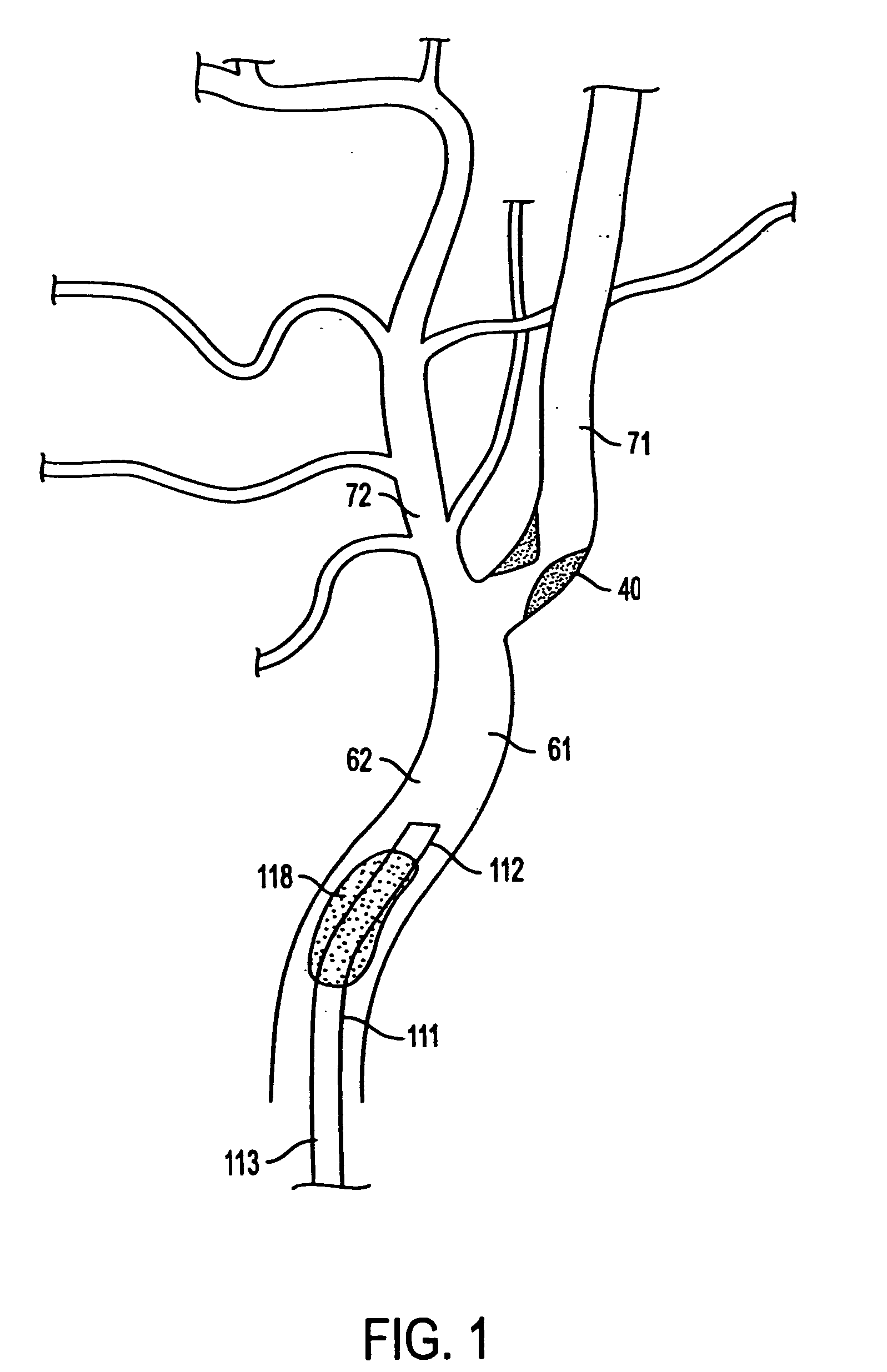
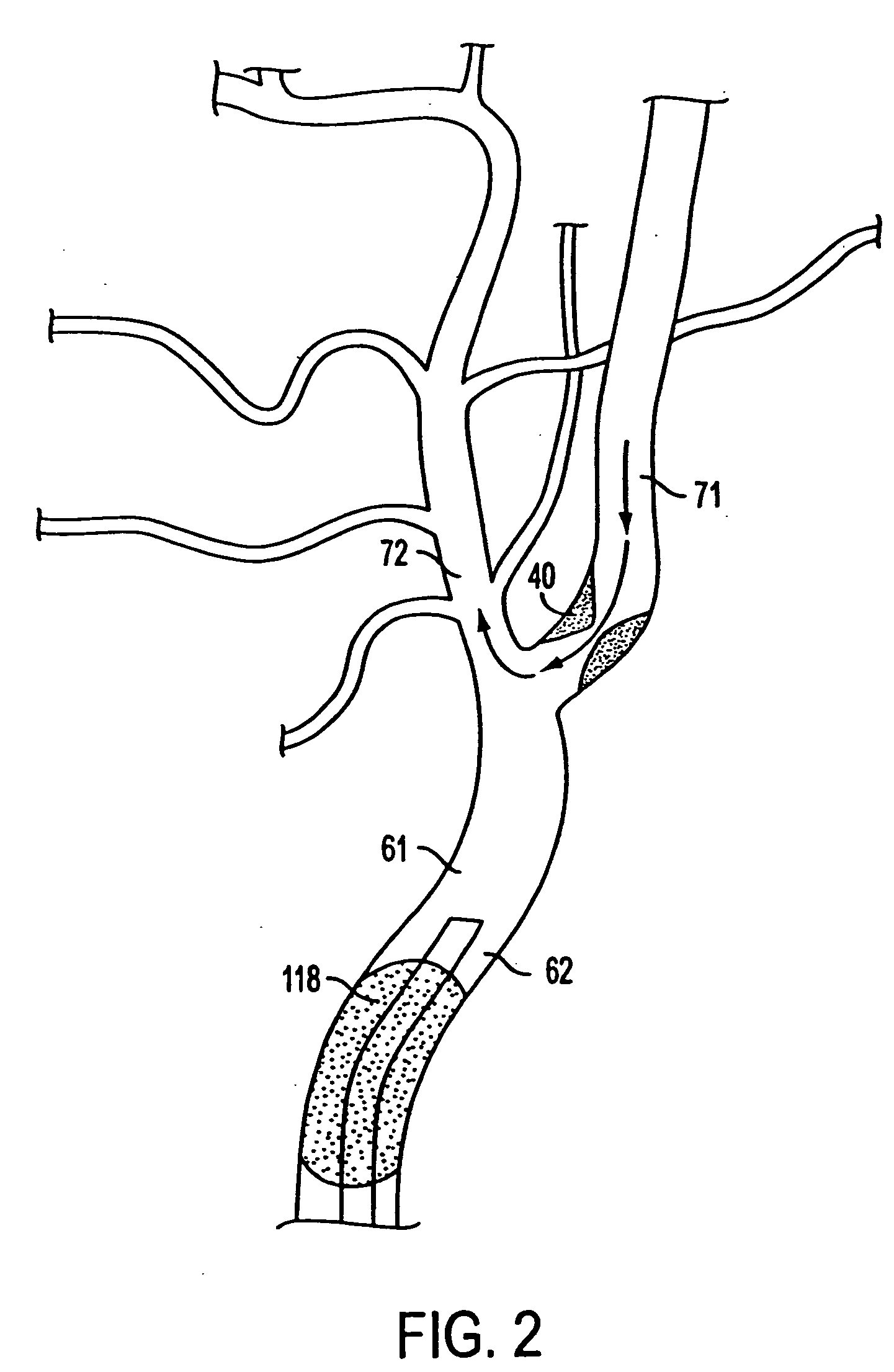
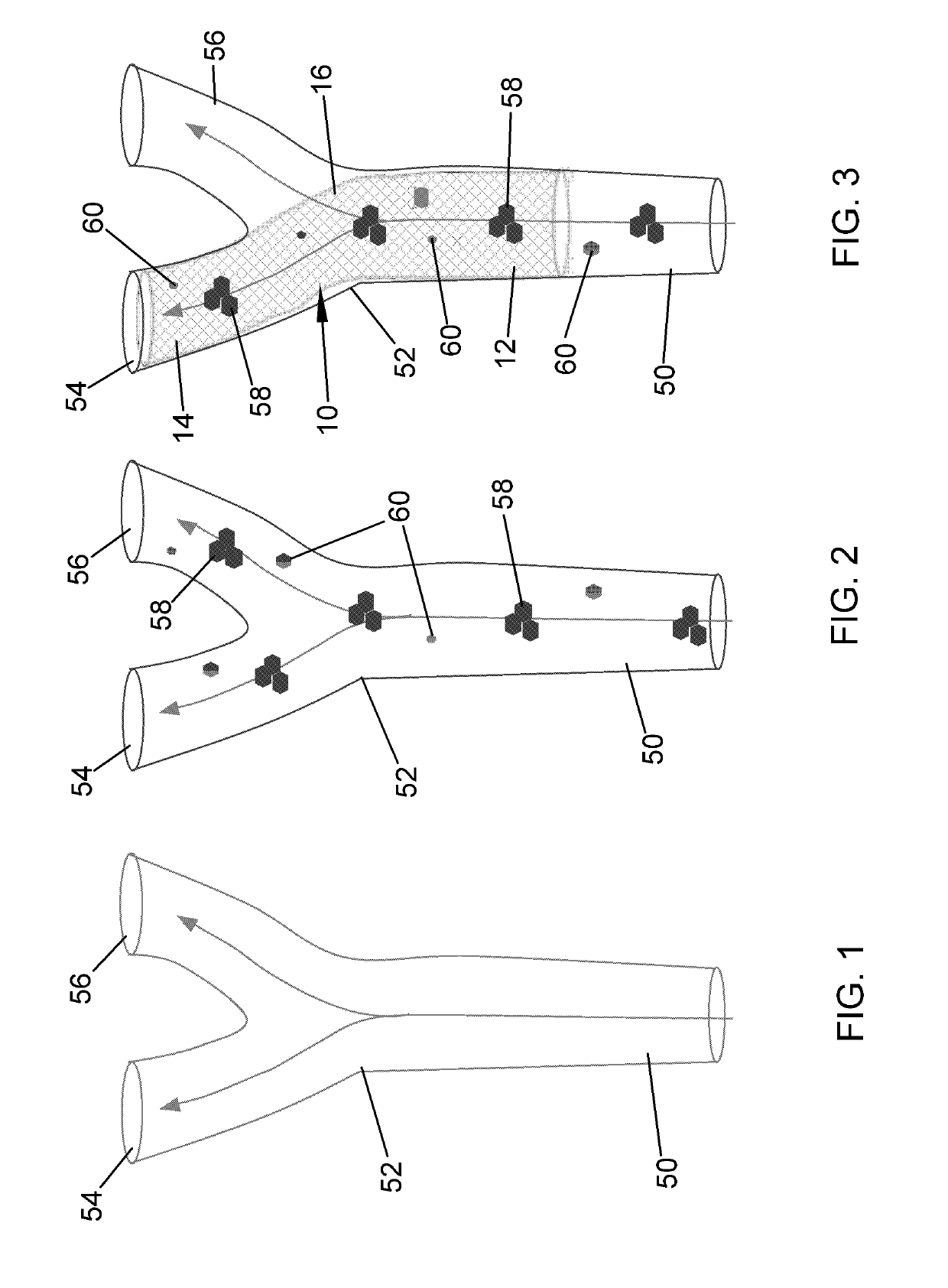
Apparatus and methods for treating stroke and controlling cerebral flow characteristics
InactiveUS6929634B2Quickly and efficiently treat cerebral occlusionConvenient introductionStentsBalloon catheterThrombusRetrograde Flow
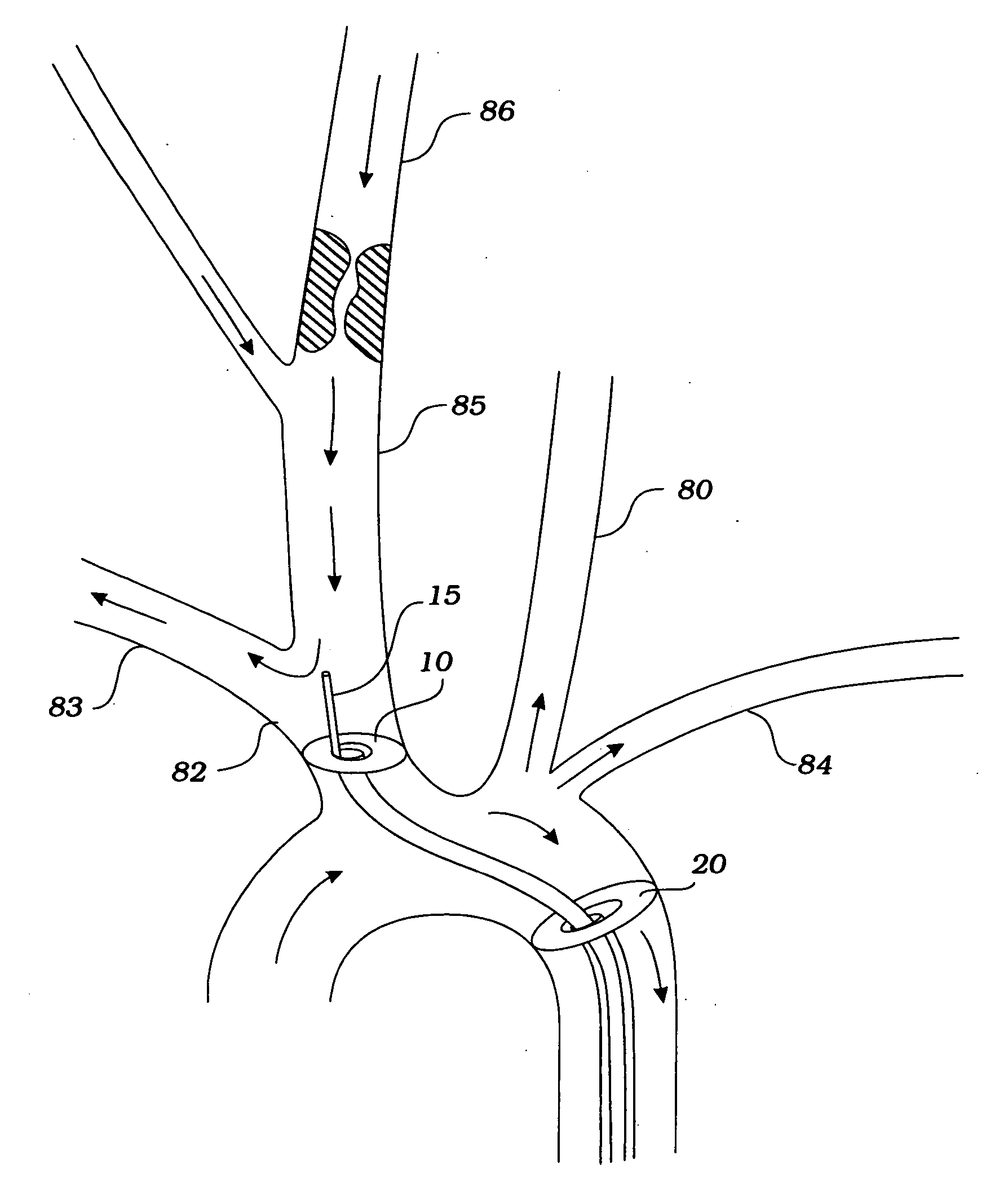
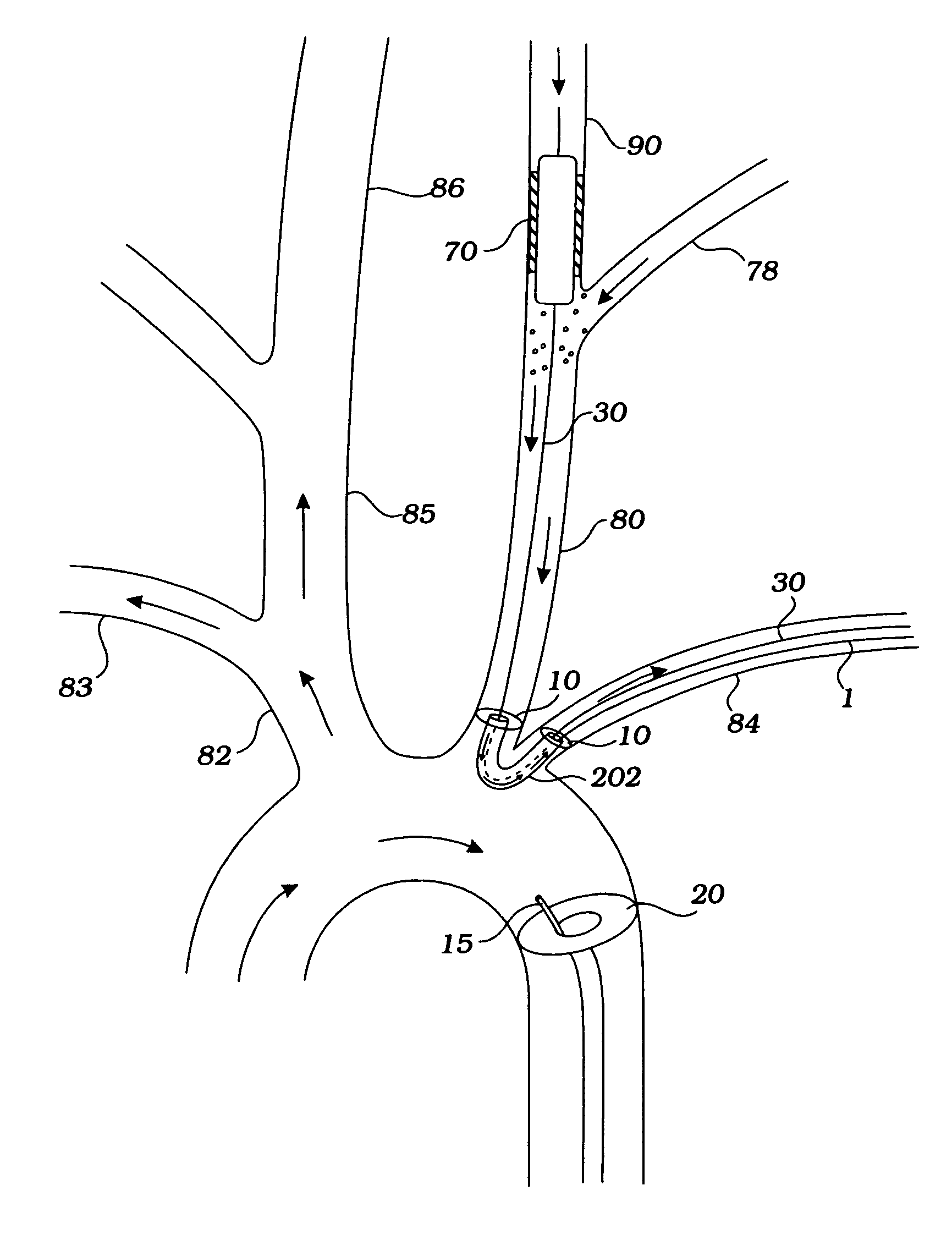
Apparatus and methods for treatment of stroke are provided. In a preferred embodiment, the present invention disposes at least one catheter having a distal occlusive member in the common carotid artery of the hemisphere of the cerebral occlusion. Retrograde flow may be provided through the catheter to effectively control cerebral flow characteristics. Under such controlled flow conditions, a thrombectomy device may be used to treat the occlusion, and any emboli generated are directed into the catheter.
Owner:WL GORE & ASSOC INC
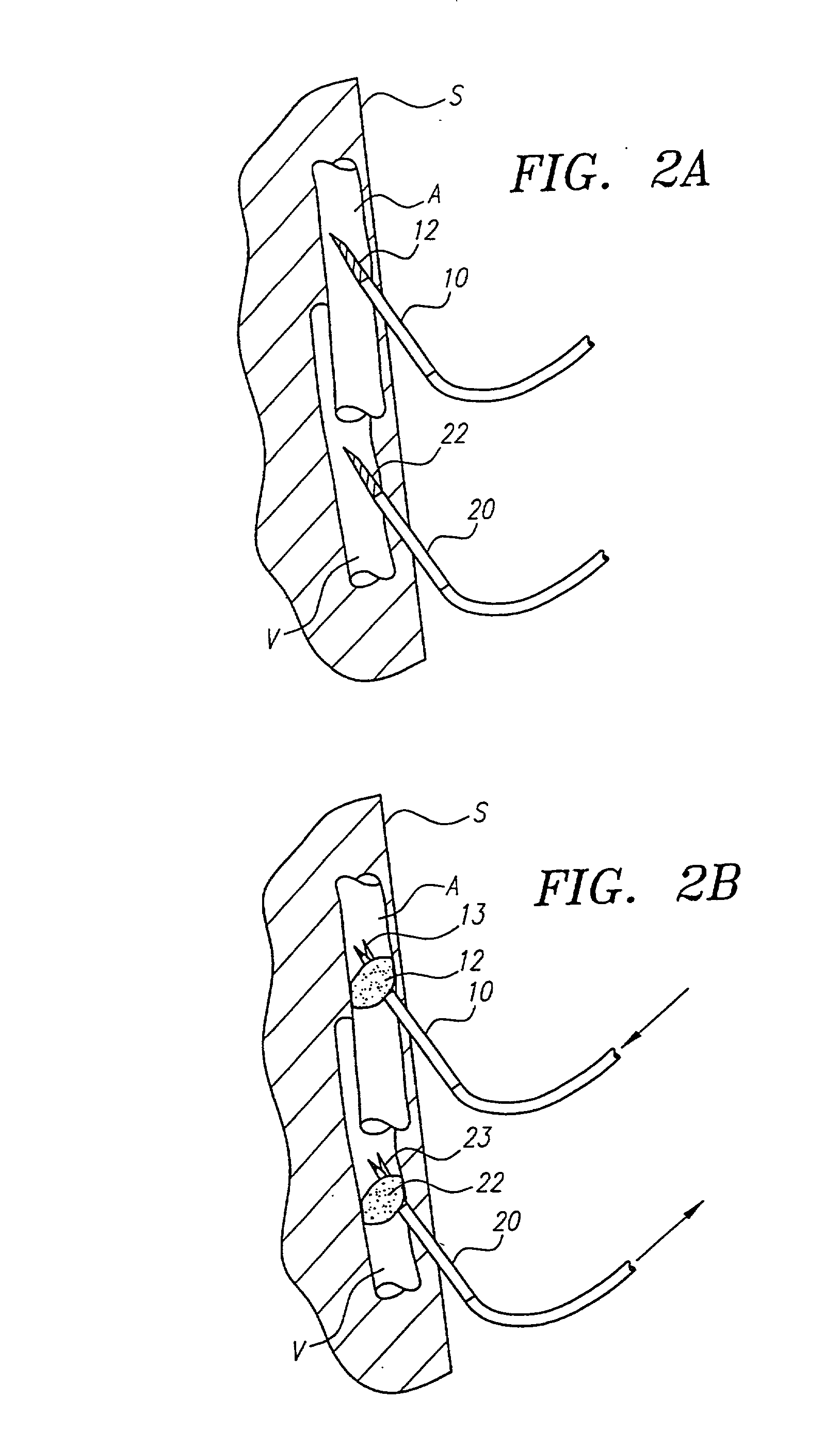
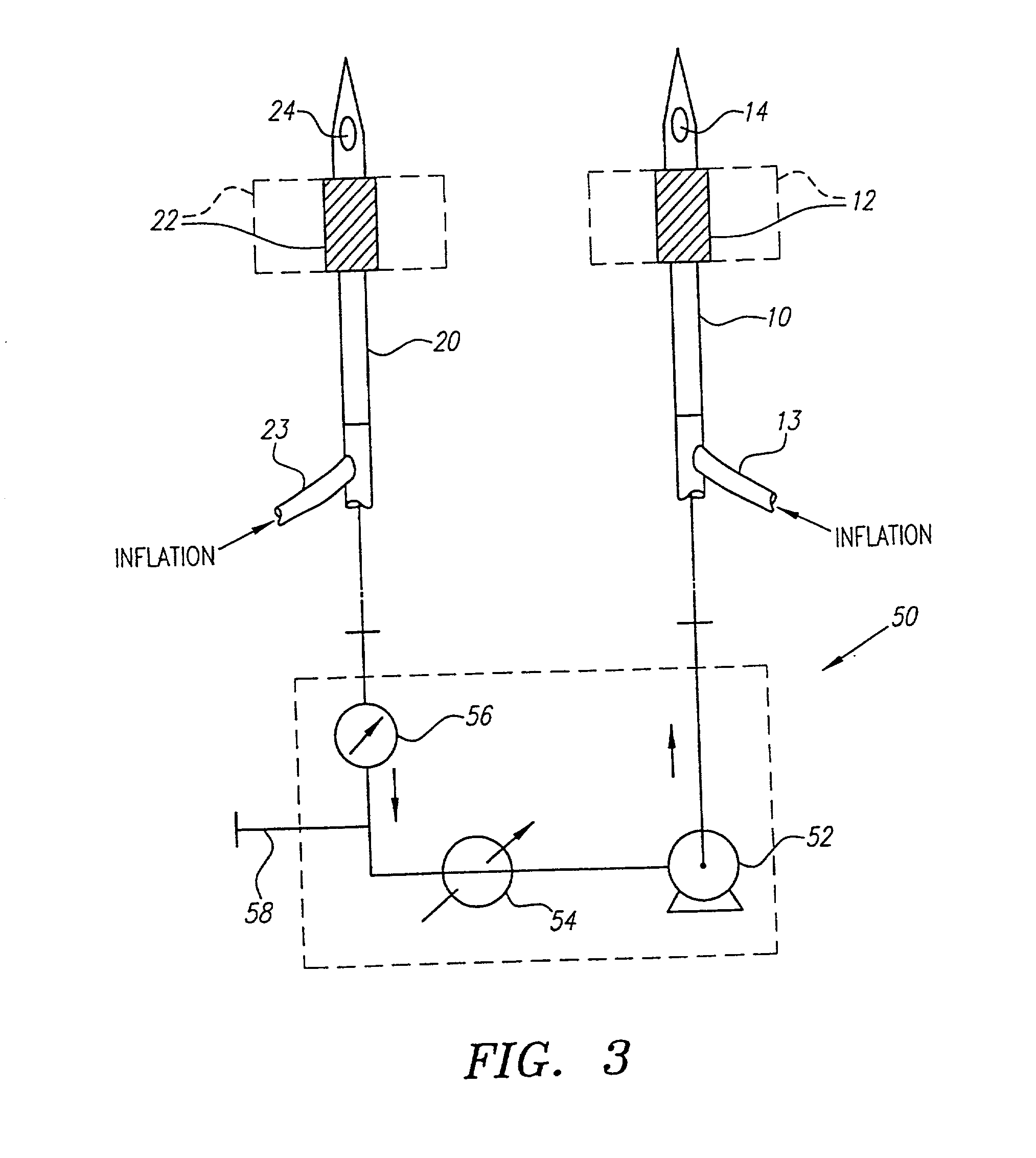
Devices and methods for preventing distal embolization using flow reversal by partial occlusion of the brachiocephalic artery
InactiveUS6837881B1Prevention of distal embolizationMinimizing blood lossStentsBalloon catheterAtherectomyPercutaneous angioplasty
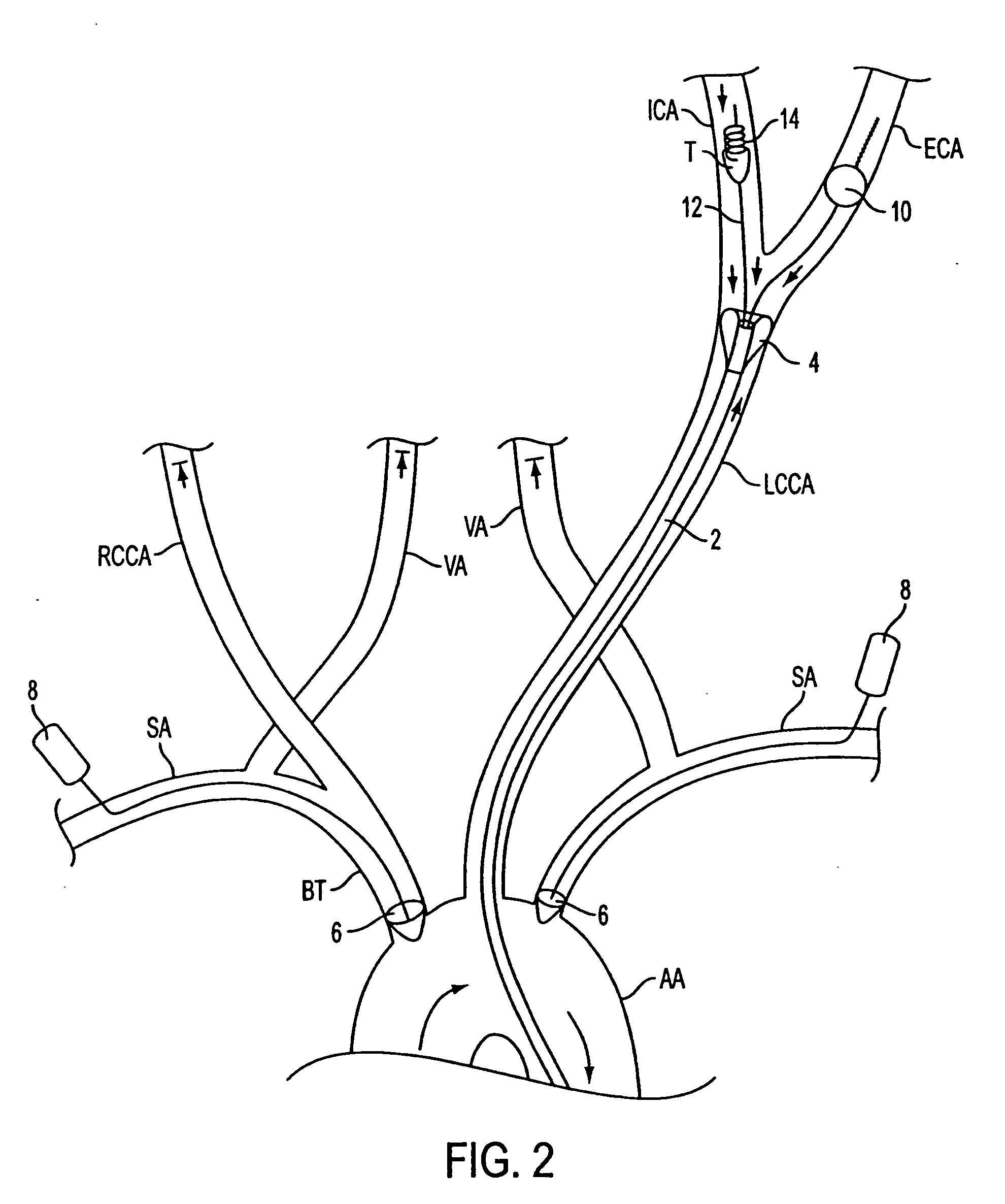
The invention provides a medical device having a catheter and one or more expandable constricting / occluding members. The catheter is adapted for use with therapeutic or diagnostic devices, including an angioplasty / stent catheter and an atherectomy catheter. The constrictor / occluder is mounted at the distal end of the catheter. Manometers may be mounted distal to one or more constrictors for measuring pressure distal to the constrictor(s). Methods of using the devices for preventing distal embolization during extracranial or intracranial carotid procedures or vertebral artery procedures by reversing blood flow in an internal carotid artery, an external carotid artery, and / or a common carotid artery toward the subclavian artery are disclosed.
Owner:ZOLL CIRCULATION
Intravascular methods and apparatus for isolation and selective cooling of the cerebral vasculature during surgical procedures
InactiveUS6555057B1Reduce riskIncrease perfusionOther blood circulation devicesMedical devicesRisk strokeSurgical department
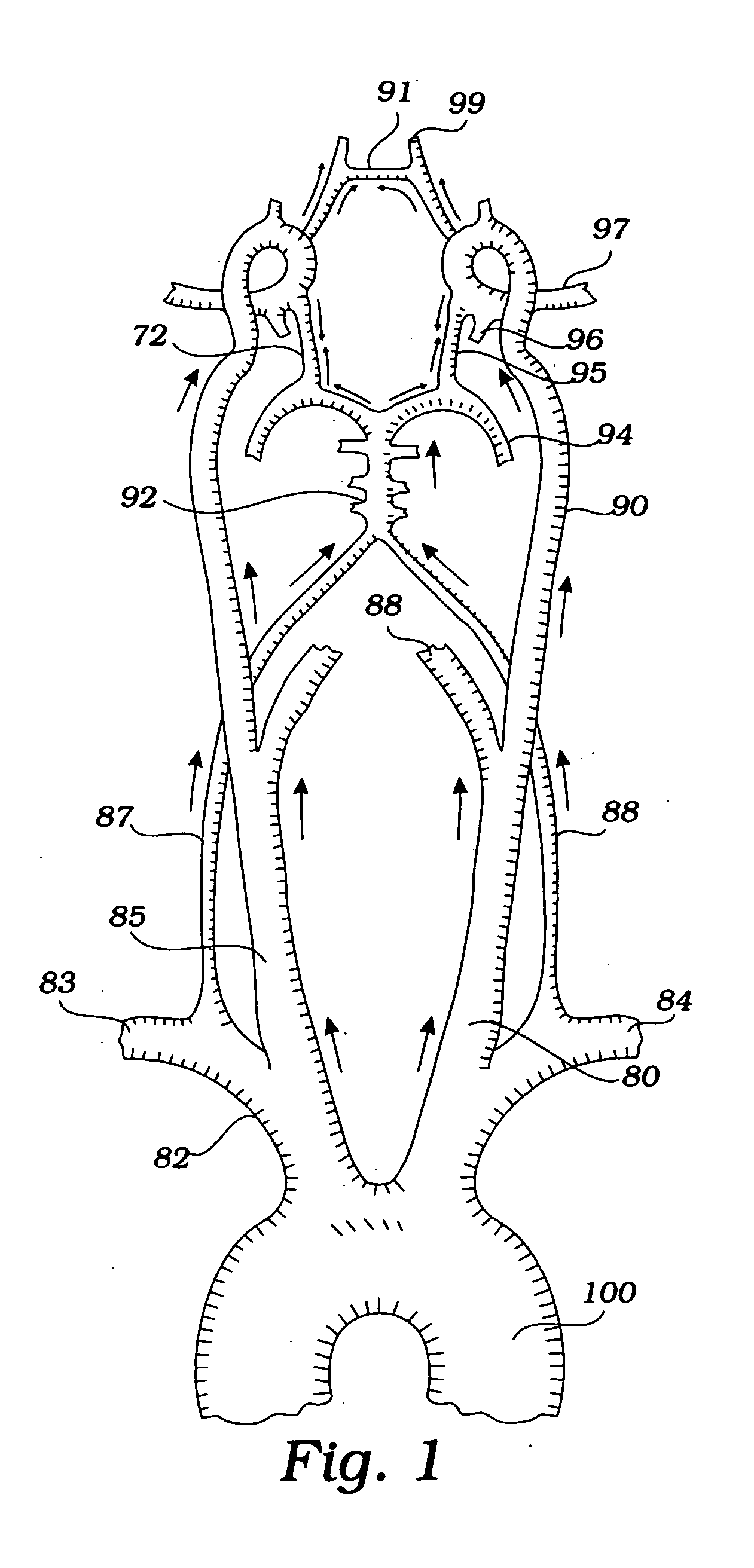
Patients having diminished circulation in the cerebral vasculature as a result of stroke or from other causes such as cardiac arrest, shock or head trauma, or aneurysm surgery or aortic surgery, are treated by flowing an oxygenated medium through an arterial access site into the cerebral vasculature and collecting the medium through an access site in the venous site of the cerebral vasculature. Usually, the cold oxygenated medium will comprise autologous blood, and the blood will be recirculated for a time sufficient to permit treatment of the underlying cause of diminished circulation. In addition to oxygenation, the recirculating blood will also be cooled to hypothermically treat and preserve brain tissue. Isolation and cooling of cerebral vasculature in patients undergoing aortic and other procedures is achieved by internally occluding at least the right common carotid artery above the aortic arch. Blood or other oxygenated medium is perfused through the occluded common carotid artery(ies) and into the arterial cerebral vasculature. Usually, oxygen depleted blood or other medium leaving the cerebral vasculature is collected, oxygenated, and cooled in an extracorporeal circuit so that it may be returned to the patient. Occlusion of the carotid artery(ies) is preferably accomplished using expansible occluders, such as balloon-tipped cannula, catheters, or similar access devices. Access to the occlusion site(s) may be open surgical, percutaneous, or intravascular.
Owner:BARBUT DENISE +3
Implantable stroke preventing device
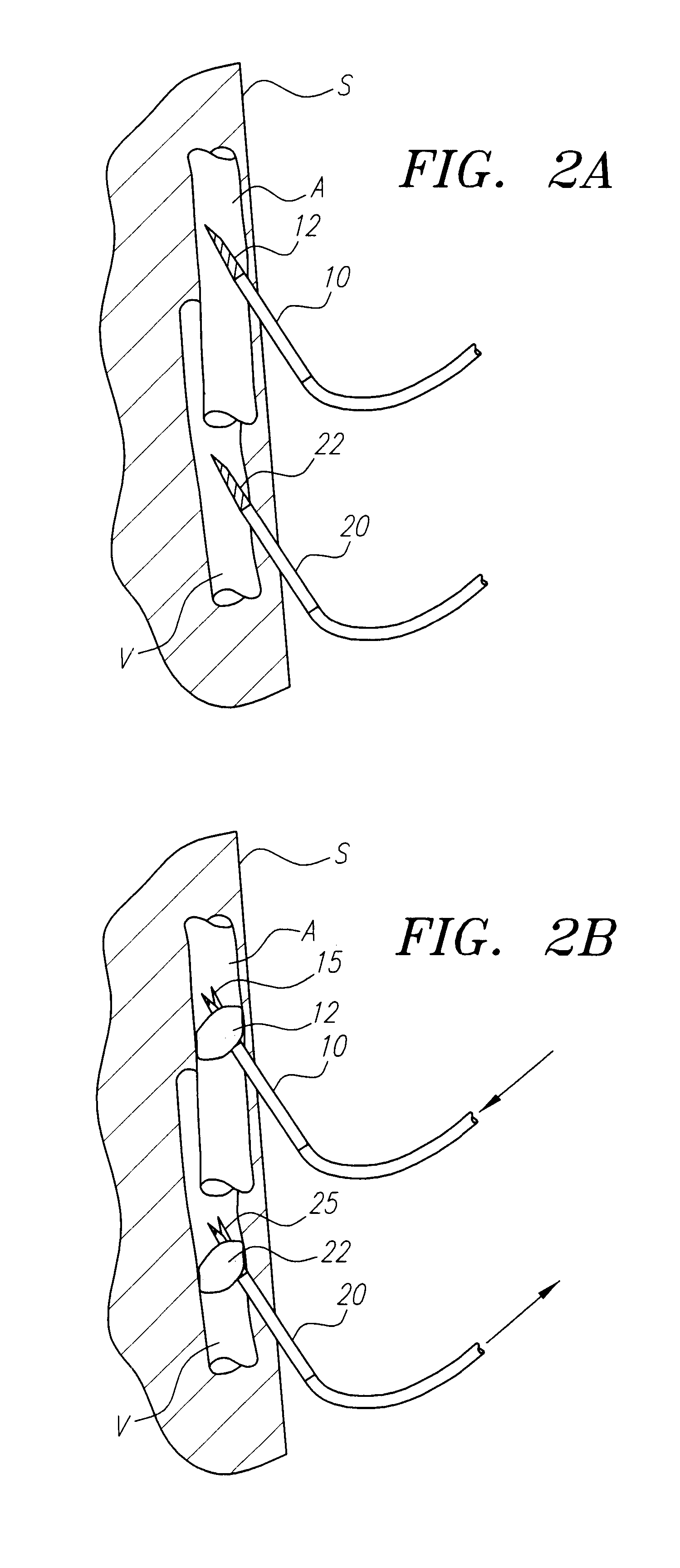
An implantable device for positioning in the vicinity of the bifurcation of the common carotid artery (CCA) into the internal carotid artery (ICA) and the external carotid artery (ECA), comprises a deflecting element suitable to deflect the flow of embolic material flowing in the CCS toward the ICA, into the ECA, without filtering.
Owner:STRYKER EURO OPERATIONS HLDG LLC +1
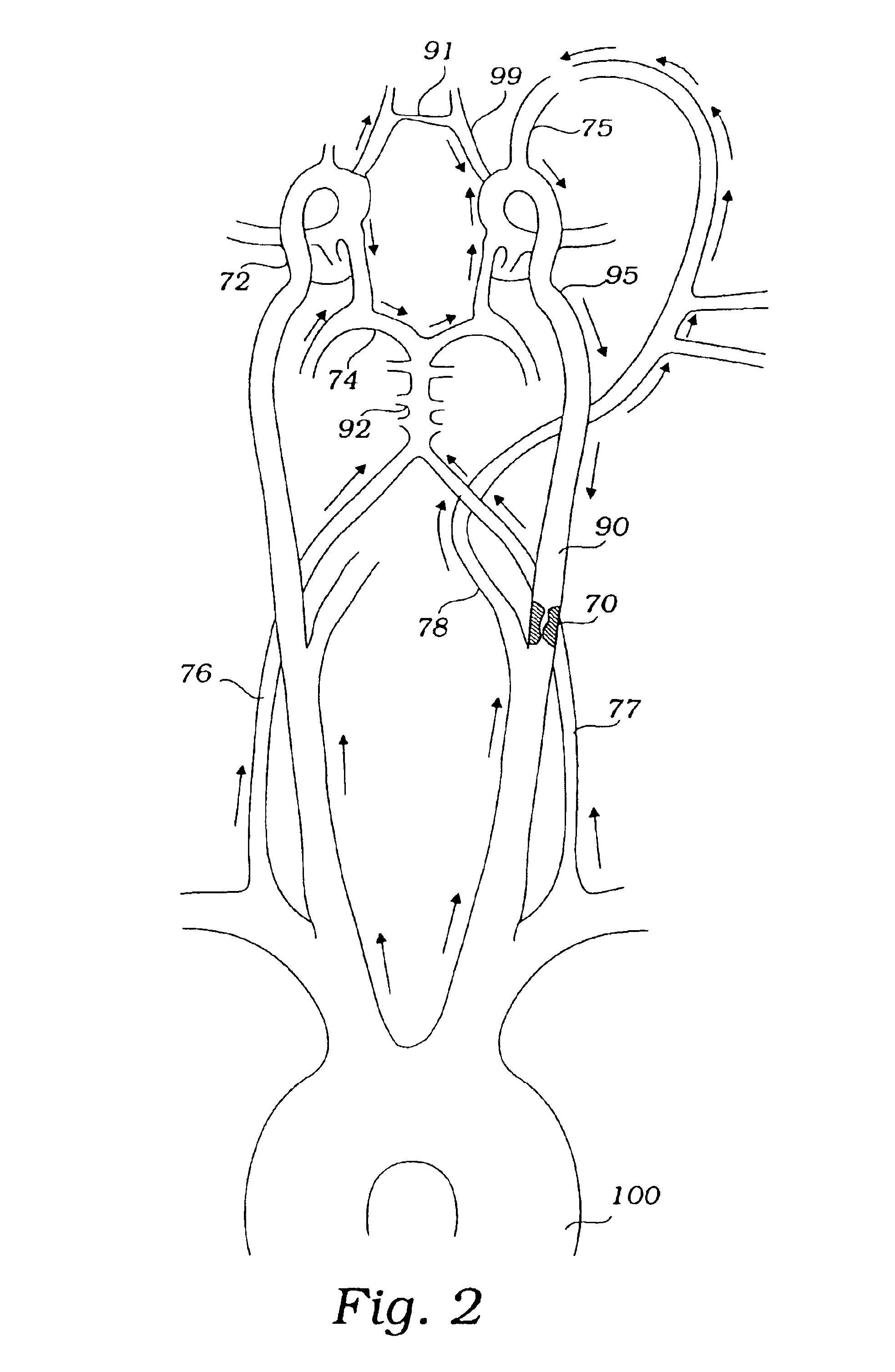
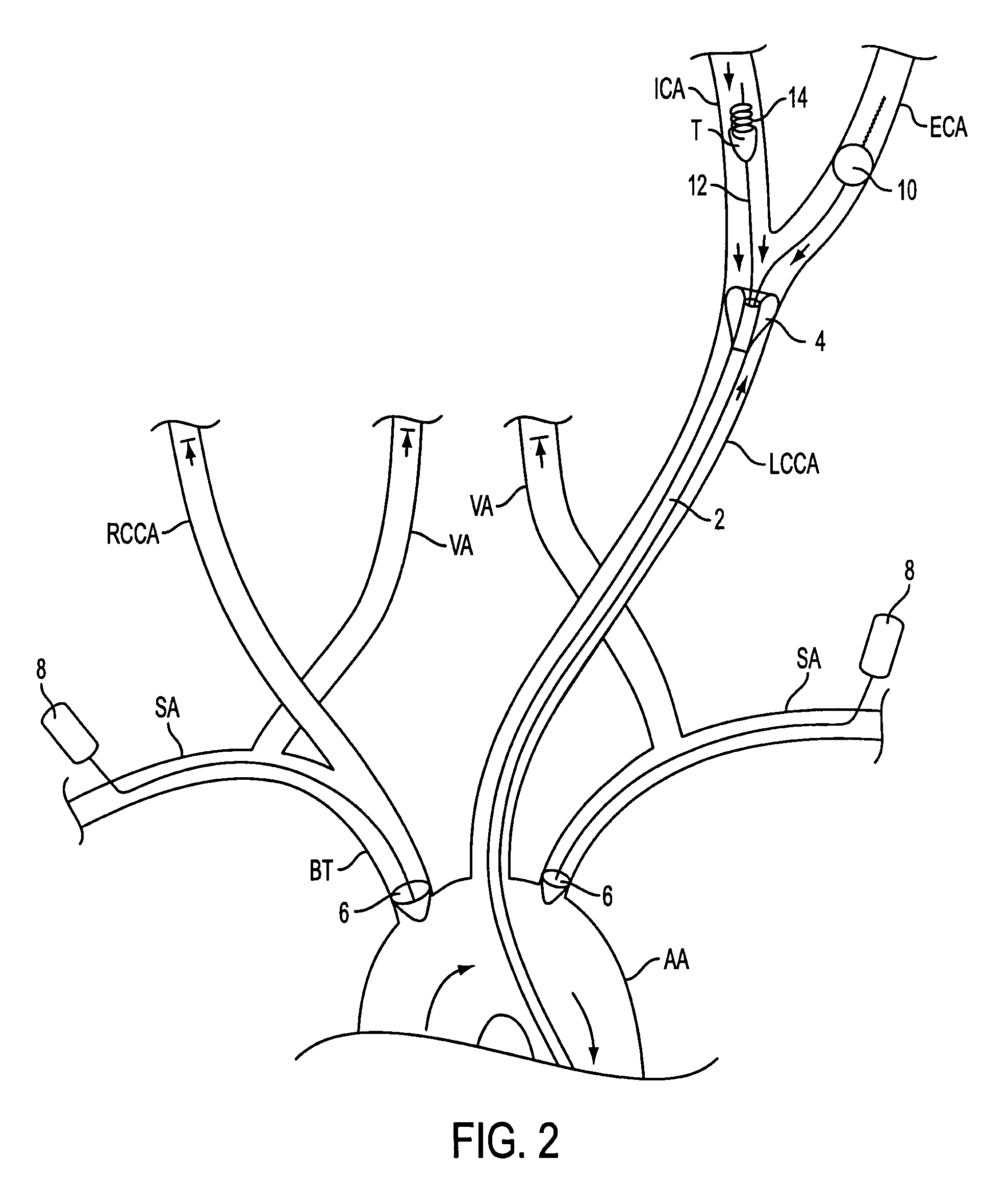
Apparatus and methods for treating stroke and controlling cerebral flow characteristics
InactiveUS7063714B2Quickly and efficiently treat cerebral occlusionEfficient removalStentsBalloon catheterLeft vertebral arteryThrombus
Apparatus and methods for treatment of stroke are provided. In a preferred embodiment, the present invention disposes at least one catheter having a distal occlusive member in either the common carotid artery (CCA) or both the vertebral artery (VA) and the CCA on the hemisphere of the cerebral occlusion. Blood flow in the opposing carotid and / or vertebral arteries may be inhibited. Retrograde or antegrade flow may be provided through either catheter independently to effectively control cerebral flow characteristics. Under such controlled flow conditions, a thrombectomy device may be used to treat the occlusion, and any emboli generated are directed into the catheter(s).
Owner:WL GORE & ASSOC INC
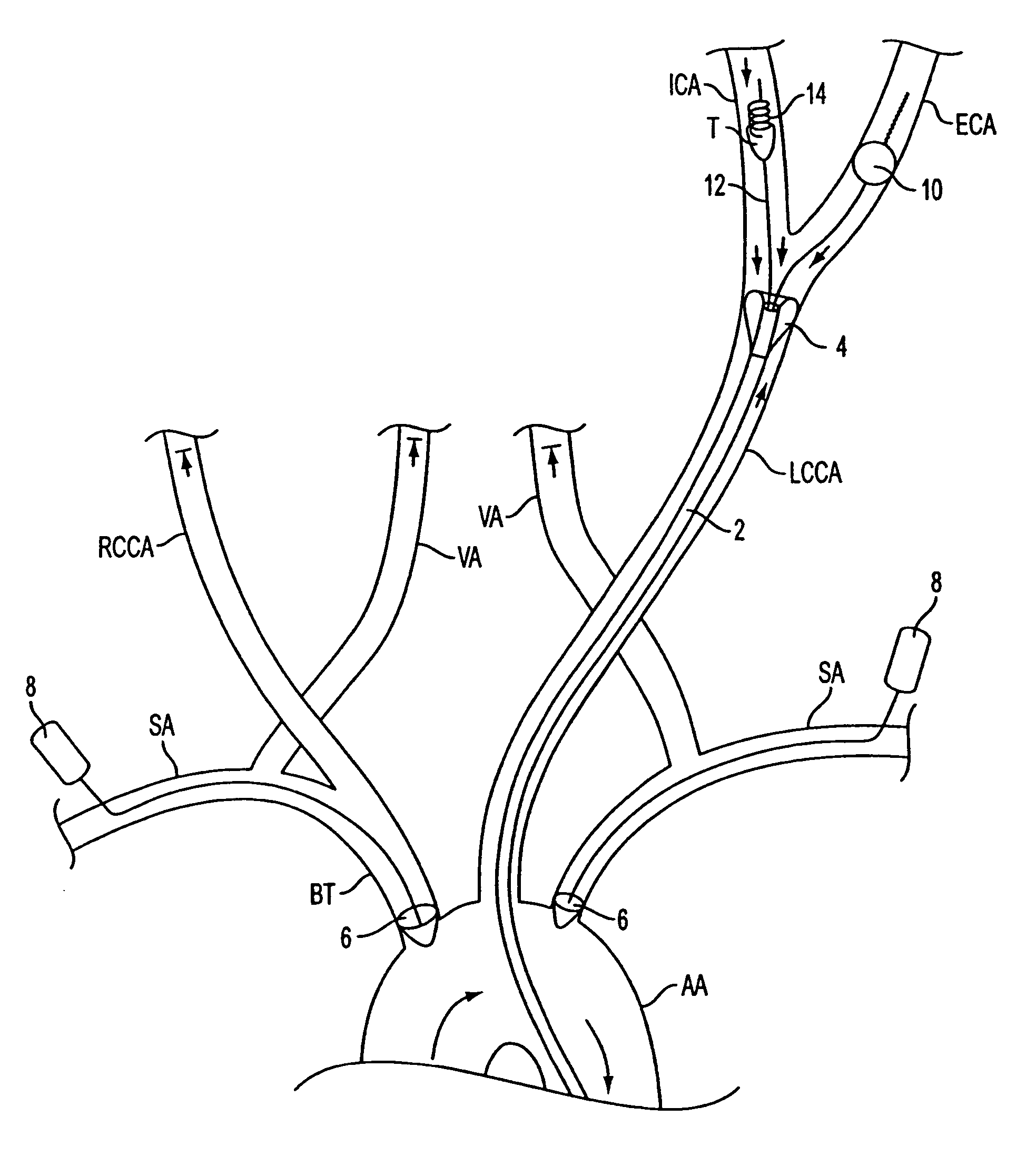
Apparatus and methods for treating stroke and controlling cerebral flow characteristics
InactiveUS20050267323A1Quickly and efficiently treat cerebral occlusionEfficient removalStentsBalloon catheterLeft vertebral arteryThrombus
Apparatus and methods for treatment of stroke are provided. In a preferred embodiment, the present invention disposes at least one catheter having a distal occlusive member in either the common carotid artery (CCA) or both the vertebral artery (VA) and the CCA on the hemisphere of the cerebral occlusion. Blood flow in the opposing carotid and / or vertebral arteries may be inhibited. Retrograde or antegrade flow may be provided through either catheter independently to effectively control cerebral flow characteristics. Under such controlled flow conditions, a thrombectomy device may be used to treat the occlusion, and any emboli generated are directed into the catheter(s).
Owner:WL GORE & ASSOC INC
Method and system for selective or isolated integrate cerebral perfusion and cooling
InactiveUS6736790B2Reduce riskImproving cerebral perfuisionBronchoscopesLaryngoscopesOxygenPerfusion
Patients having diminished circulation in the cerebral vasculature as a result of cardiac arrest or from other causes are treated by flowing an oxygenated medium through an arterial access site into the cerebral vasculature and collecting the medium through an access site in the venous site of the cerebral vasculature. In addition to oxygenation, the recirculating blood may also be cooled to hypothermically treat and preserve brain tissue. Isolation and cooling of cerebral vasculature in patients undergoing aortic and other procedures is achieved by internally occluding at least the right common carotid artery above the aortic arch. Blood or other oxygenated medium is perfused through the occluded common carotid artery(ies) and into the arterial cerebral vasculature. Usually, oxygen depleted blood or other medium leaving the cerebral vasculature is collected, oxygenated, and cooled in an extracorporeal circuit so that it may be returned to the patient.
Owner:BARBUT DENISE & PATTERSON RUSSEL +1
Apparatus and methods for treating stroke and controlling cerebral flow characteristics
InactiveUS20050124973A1Enhance flow manipulationEasy to disassembleStentsBalloon catheterLeft vertebral arteryThrombus
Apparatus and methods for treatment of stroke are provided. In a preferred embodiment, the present invention disposes at least one catheter having a distal occlusive member in either the common carotid artery (CCA) or both the vertebral artery (VA) and the CCA on the hemisphere of the cerebral occlusion. Blood flow in the opposing carotid and / or vertebral arteries may be inhibited. Retrograde or antegrade flow may be provided through either catheter independently to effectively control cerebral flow characteristics. Under such controlled flow conditions, a thrombectomy device may be used to treat the occlusion, and any emboli generated are directed into the catheter(s).
Owner:WL GORE & ASSOC INC
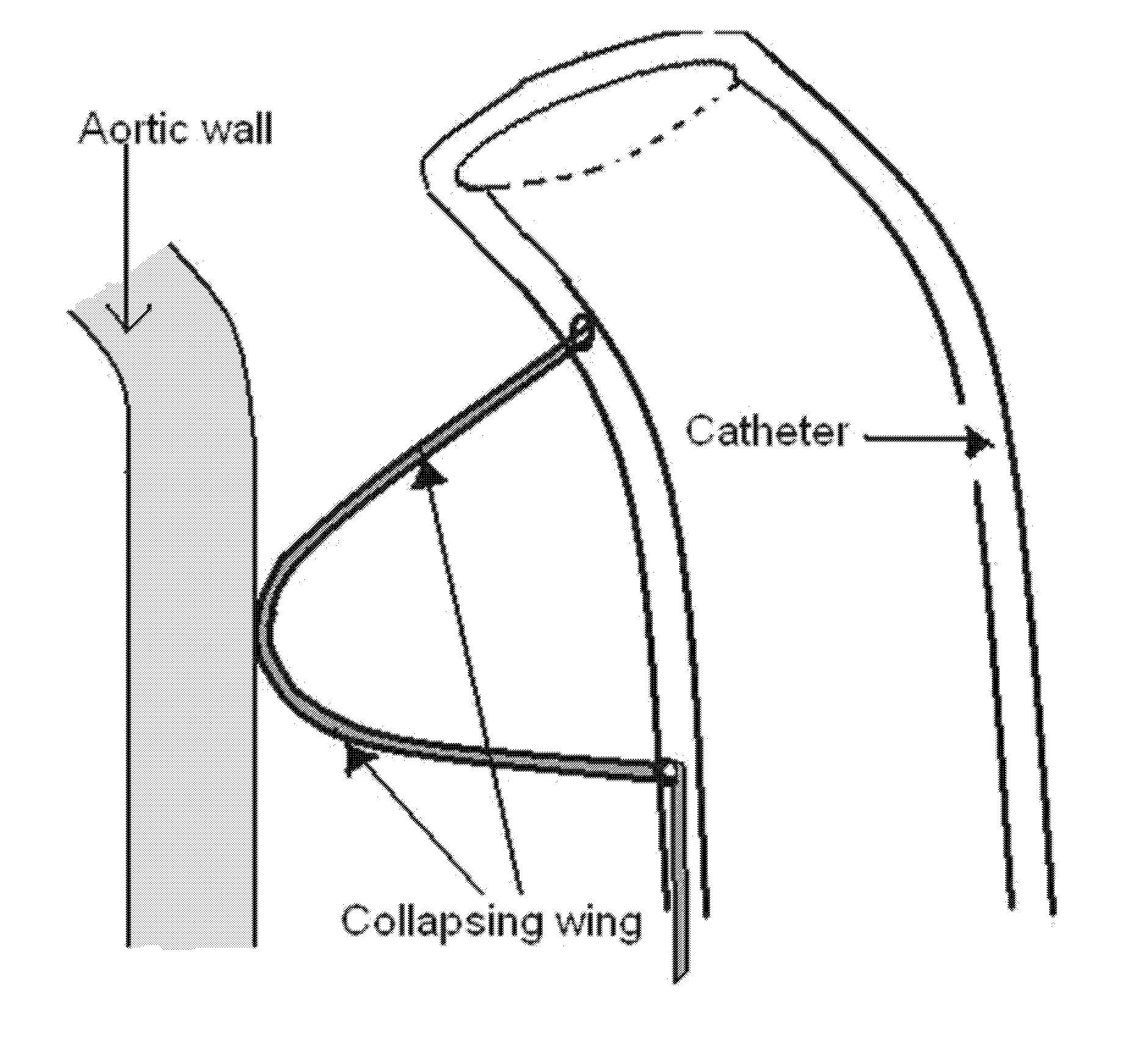
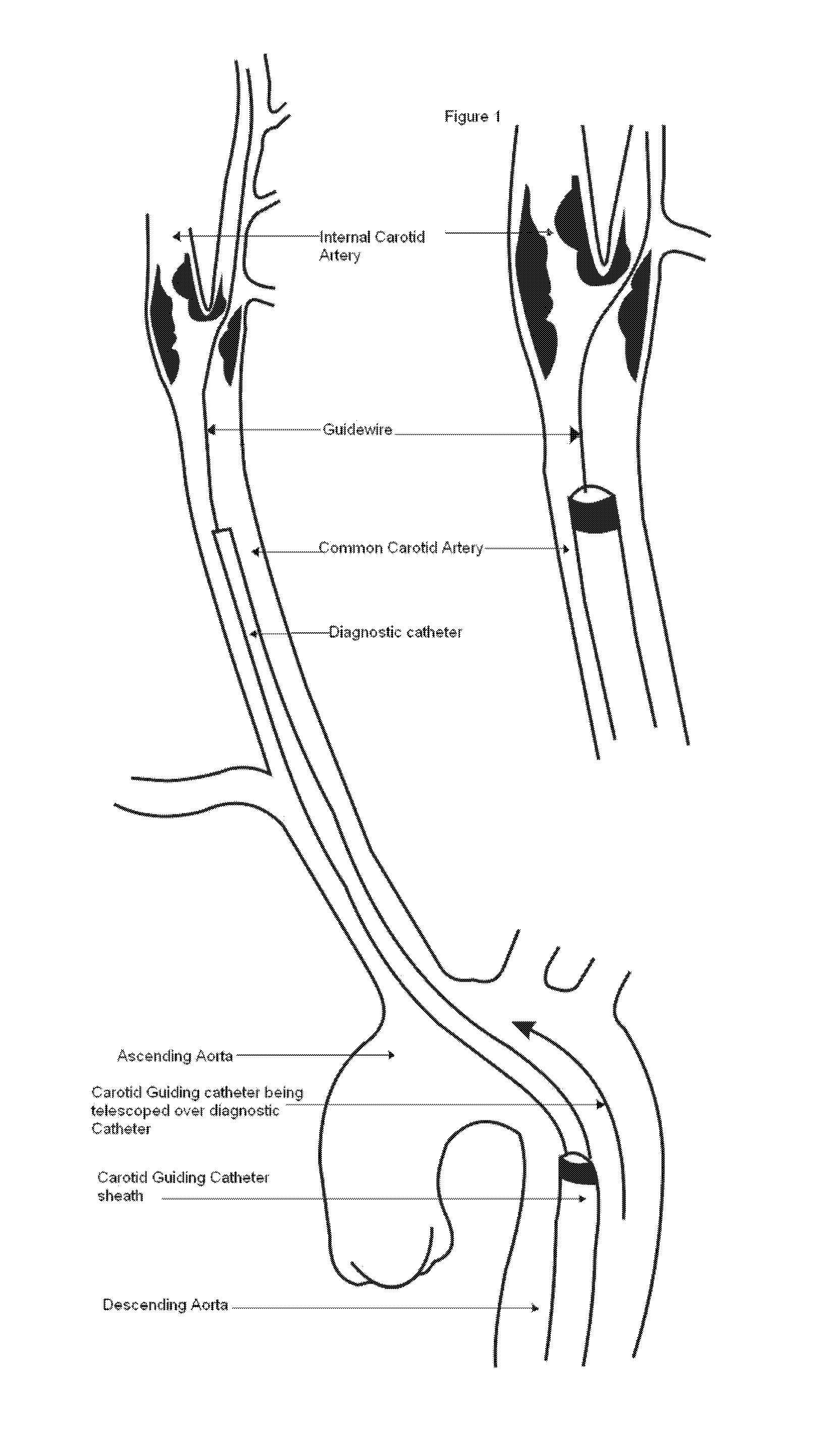
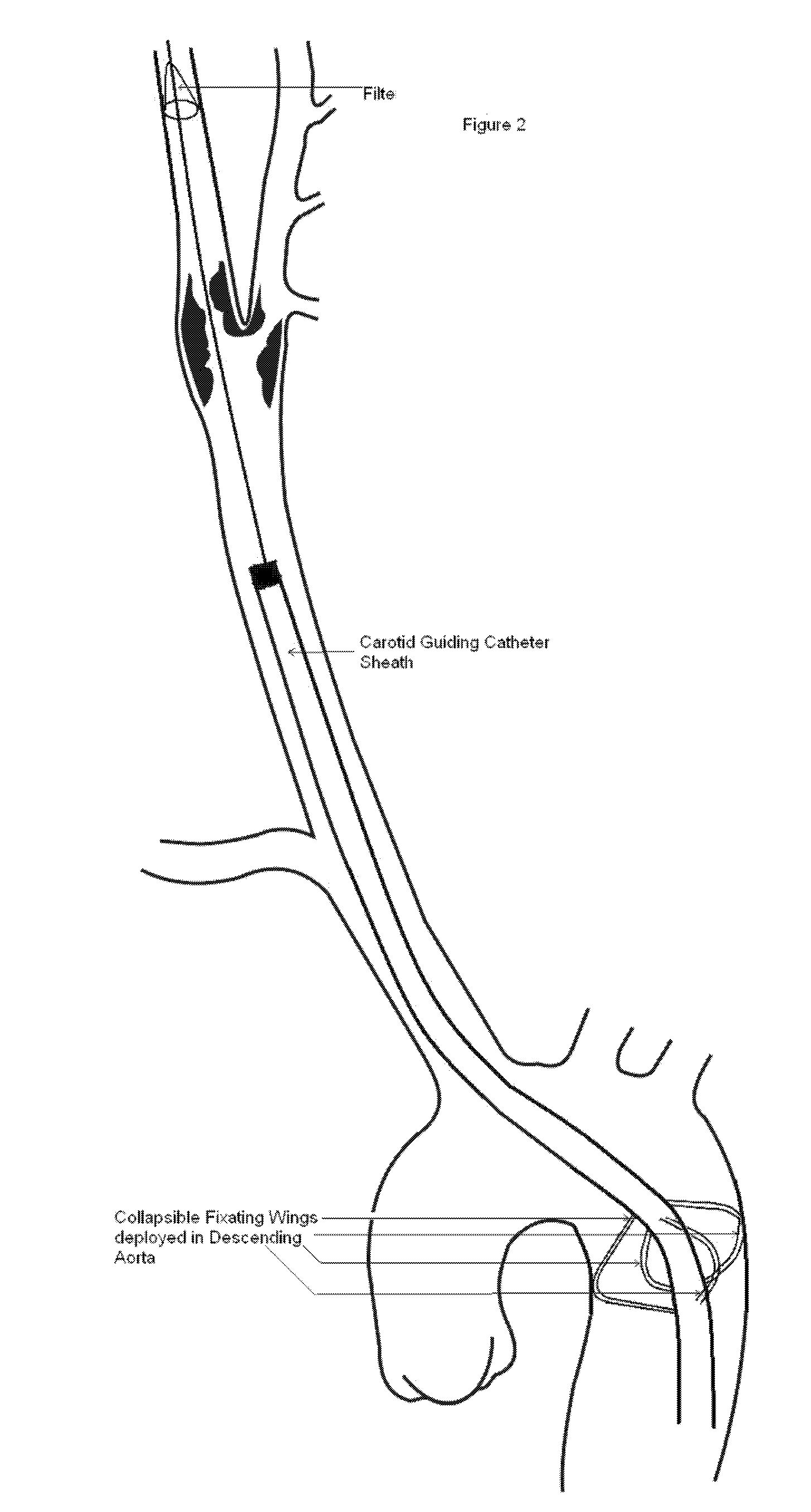
Carotid guiding catheter (sheath) for carotid percutaneous intervention/stenting with internal fixation device to prevent migration of the Carotid guiding catheter (sheath)
InactiveUS20100204708A1Easy accessIncrease friction forceStentsEar treatmentComing outInsertion stent
A carotid intervention guiding catheter (sheath) including a central lumen adapted to receive a therapeutic catheter and stent delivery catheter. The catheter includes a soft tip adapted to lodge in the common carotid artery. The distal body of the guiding catheter includes a mechanism to fixate the catheter to the wall of the aorta to prevent sliding of the guiding catheter in and out of the common carotid artery. The mechanism is a collapsible set of wings that come out of the wall of the catheter using a mechanical switch outside the body that deploys the wings and fixate the catheter to the wall of the descending or transverse aorta. The same mechanical switch allows the wings to collapse into the wall of the guiding catheter and allow the catheter to be retrieved out of the body.
Owner:SHARMA SANJIV
Apparatus and methods for treating stroke and controlling cerebral flow characteristics
InactiveUS20050277979A1Quickly and efficiently treat cerebral occlusionConvenient introductionStentsBalloon catheterThrombusRetrograde Flow
Apparatus and methods for treatment of stroke are provided. In a preferred embodiment, the present invention disposes at least one catheter having a distal occlusive member in the common carotid artery of the hemisphere of the cerebral occlusion. Retrograde flow may be provided through the catheter to effectively control cerebral flow characteristics. Under such controlled flow conditions, a thrombectomy device may be used to treat the occlusion, and any emboli generated are directed into the catheter.
Owner:WL GORE & ASSOC INC
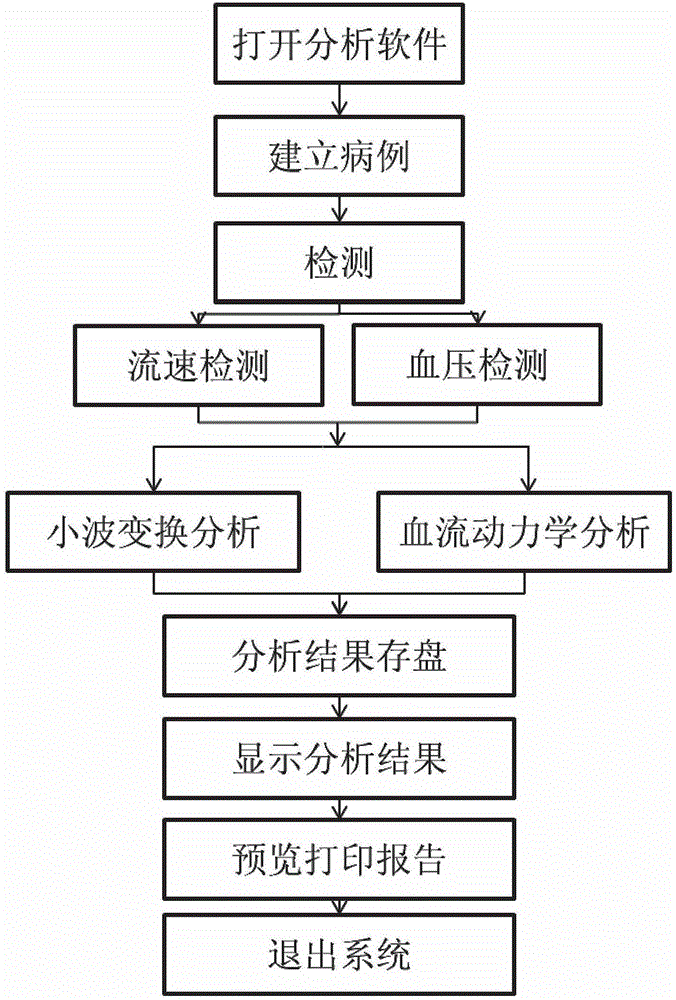
Hemodynamics and signal analysis system and method of carotid arterial system
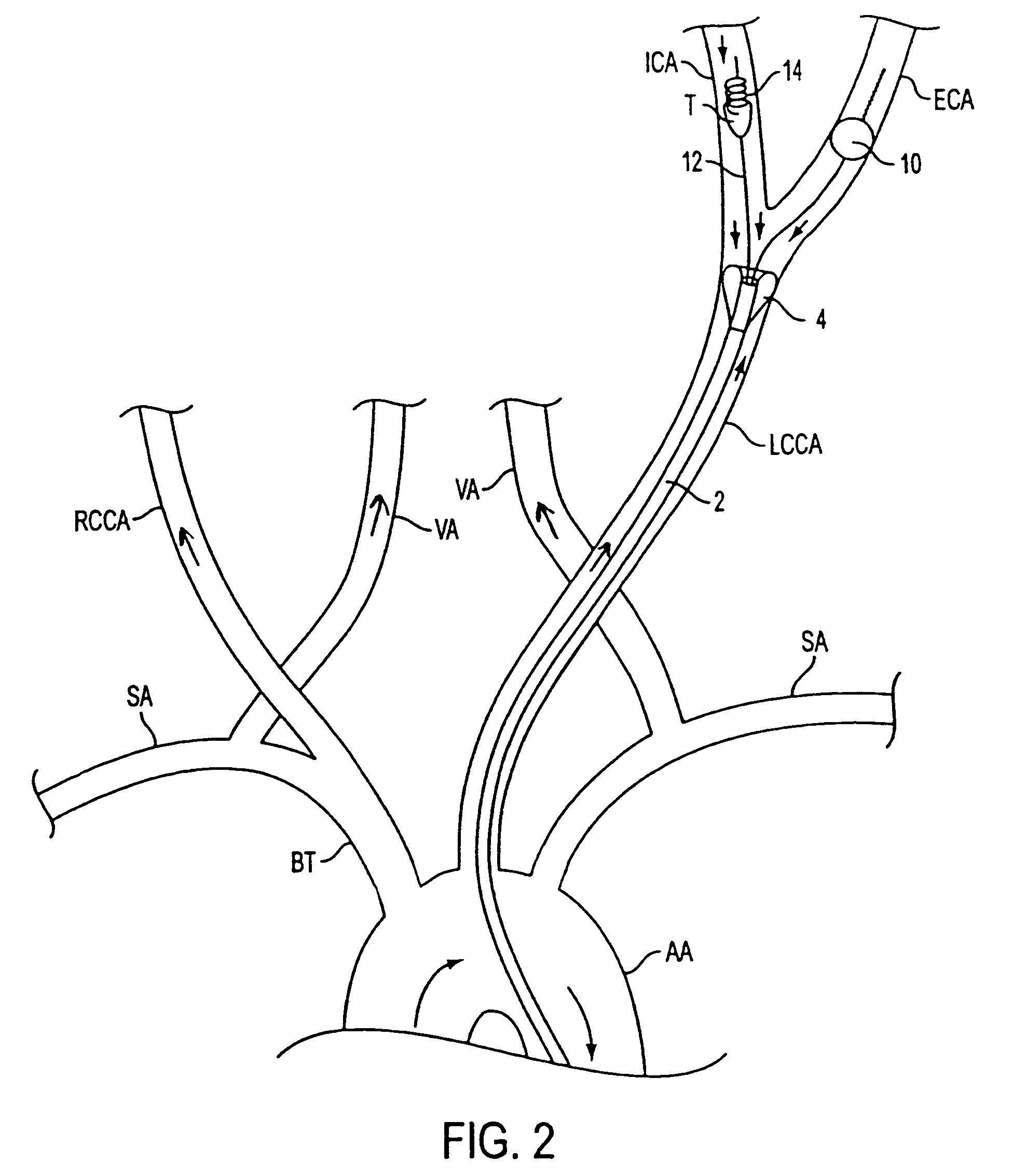
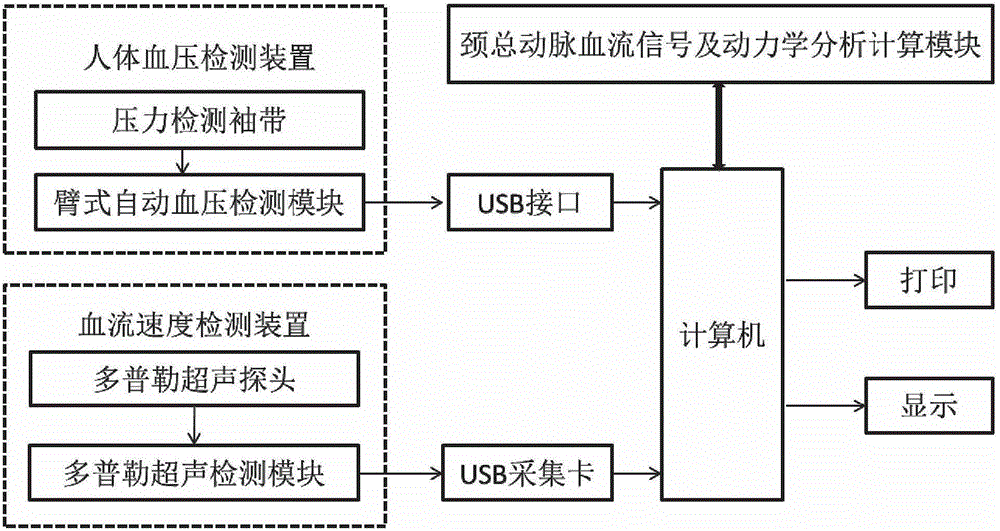
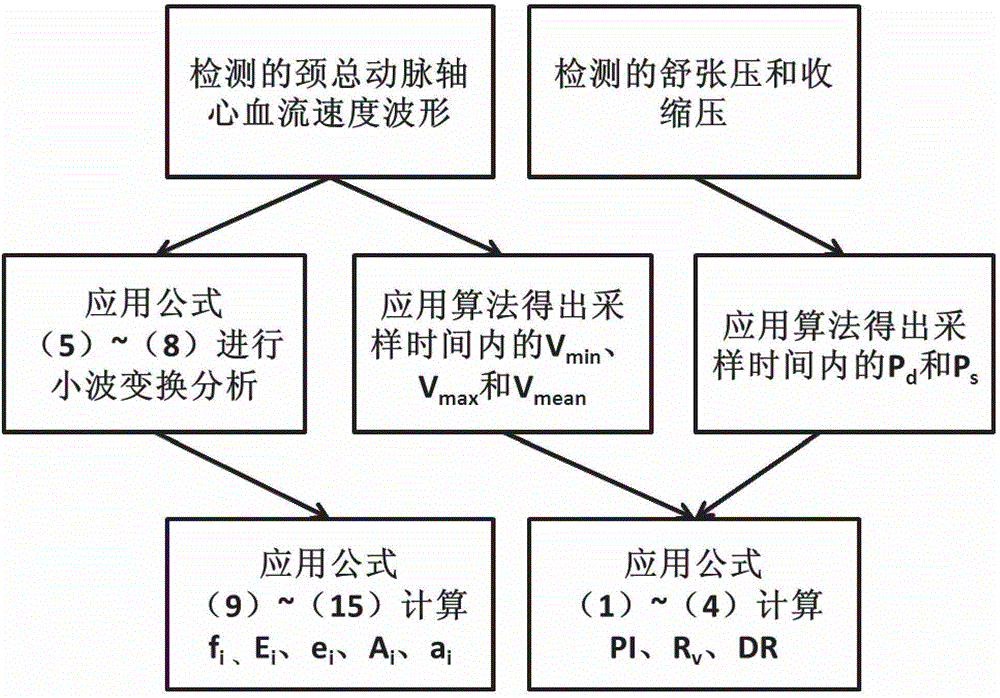
The invention provides a simple and convenient method and a simple and convenient system for evaluating hemodynamic indexes and characteristic parameters of a blood signal of a carotid arterial system through non-invasive detection on blood pressure of brachial arteries and an axial blood velocity signal of a common carotid artery. The method comprises the following steps: detecting the waveform and a numerical value of an axial blood velocity of the common carotid artery by using a continuous Doppler blood velocity waveform detecting module, detecting diastolic pressure and systolic pressure of a human body by using an arm-type electronic blood pressure detecting module, and then calculating hemodynamic parameters of the carotid arterial system by a simplified method; and selecting Morlet mother wavelet for wavelet analysis on the waveform of the blood velocity of the common carotid artery, and calculating the characteristic parameters of the blood signal. The method is an analysis method which combines the hemodynamic principle and wavelet transformation; compared with the method adopted by the conventional cerebral hemodynamic analysis device, the signal acquisition and analysis method is simpler; and to a great extent, the defects that the conventional analysis device is complicated in structure, huge in volume, complex in operation, high in price and the like are overcome.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH +1
Method and system for selective or isolated integrate cerebral perfusion and cooling
InactiveUS20010038807A1Reduce riskImproving cerebral perfuisionBronchoscopesLaryngoscopesOxygenPerfusion
Patients having diminished circulation in the cerebral vasculature as a result of cardiac arrest or from other causes are treated by flowing an oxygenated medium through an arterial access site into the cerebral vasculature and collecting the medium through an access site in the venous site of the cerebral vasculature. In addition to oxygenation, the recirculating blood may also be cooled to hypothermically treat and preserve brain tissue. Isolation and cooling of cerebral vasculature in patients undergoing aortic and other procedures is achieved by internally occluding at least the right common carotid artery above the aortic arch. Blood or other oxygenated medium is perfused through the occluded common carotid artery(ies) and into the arterial cerebral vasculature. Usually, oxygen depleted blood or other medium leaving the cerebral vasculature is collected, oxygenated, and cooled in an extracorporeal circuit so that it may be returned to the patient.
Owner:BARBUT DENISE & PATTERSON RUSSEL +1
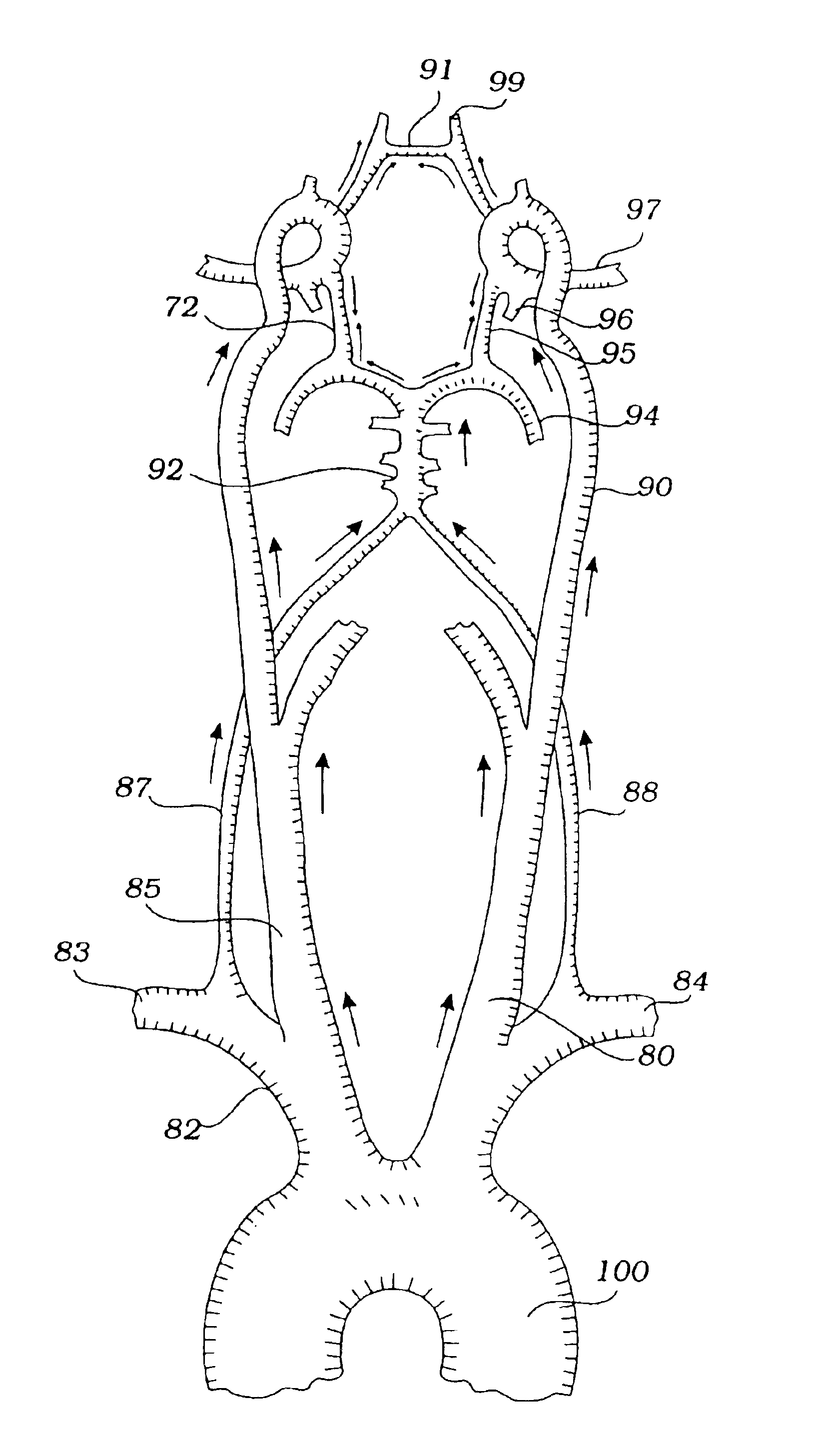
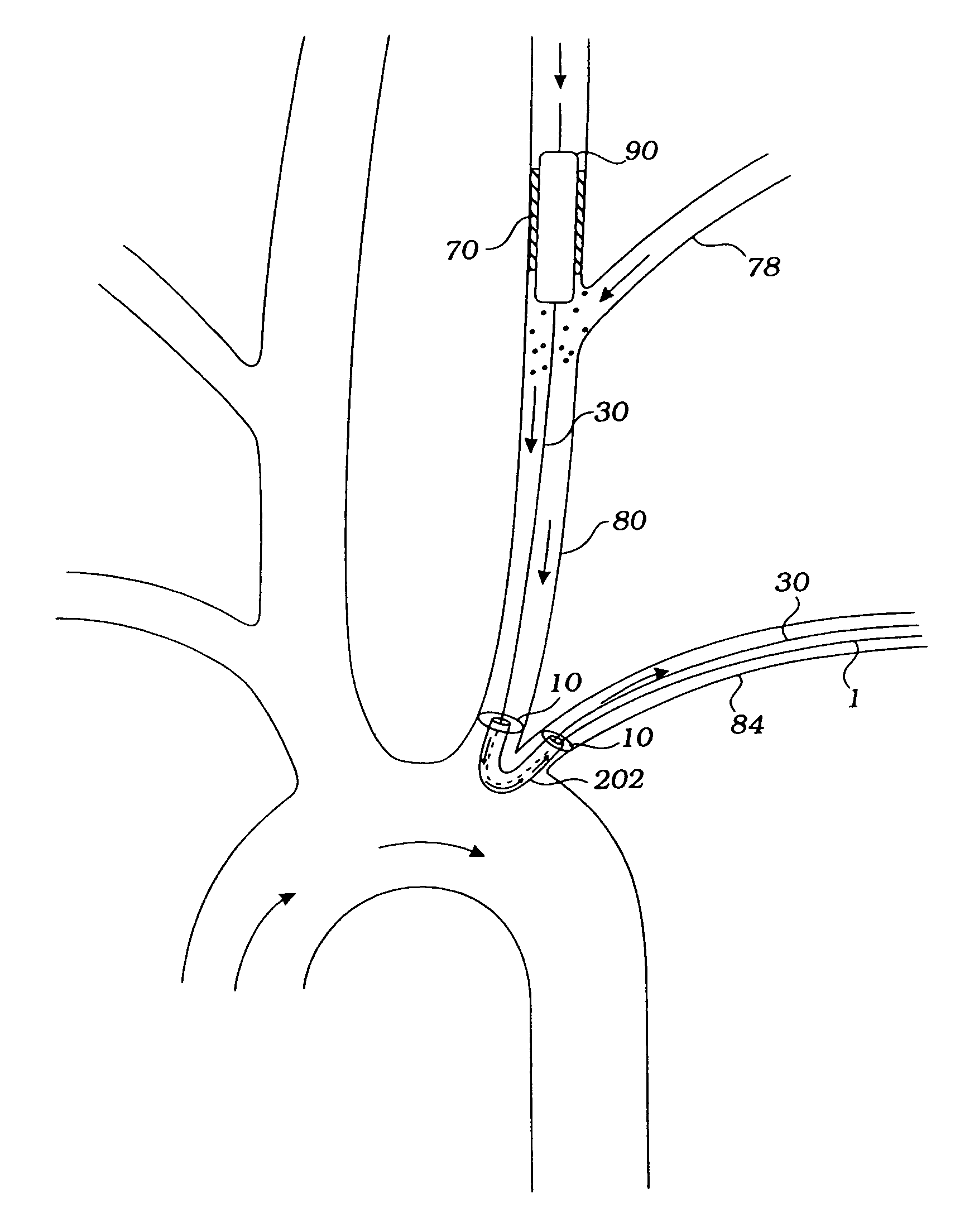
Devices and methods for preventing distal embolization using flow reversal and perfusion augmentation within the cerebral vasculature
InactiveUS20050090854A1Prevention of distal embolizationMinimizing blood lossBalloon catheterSurgeryAtherectomyBlood flow
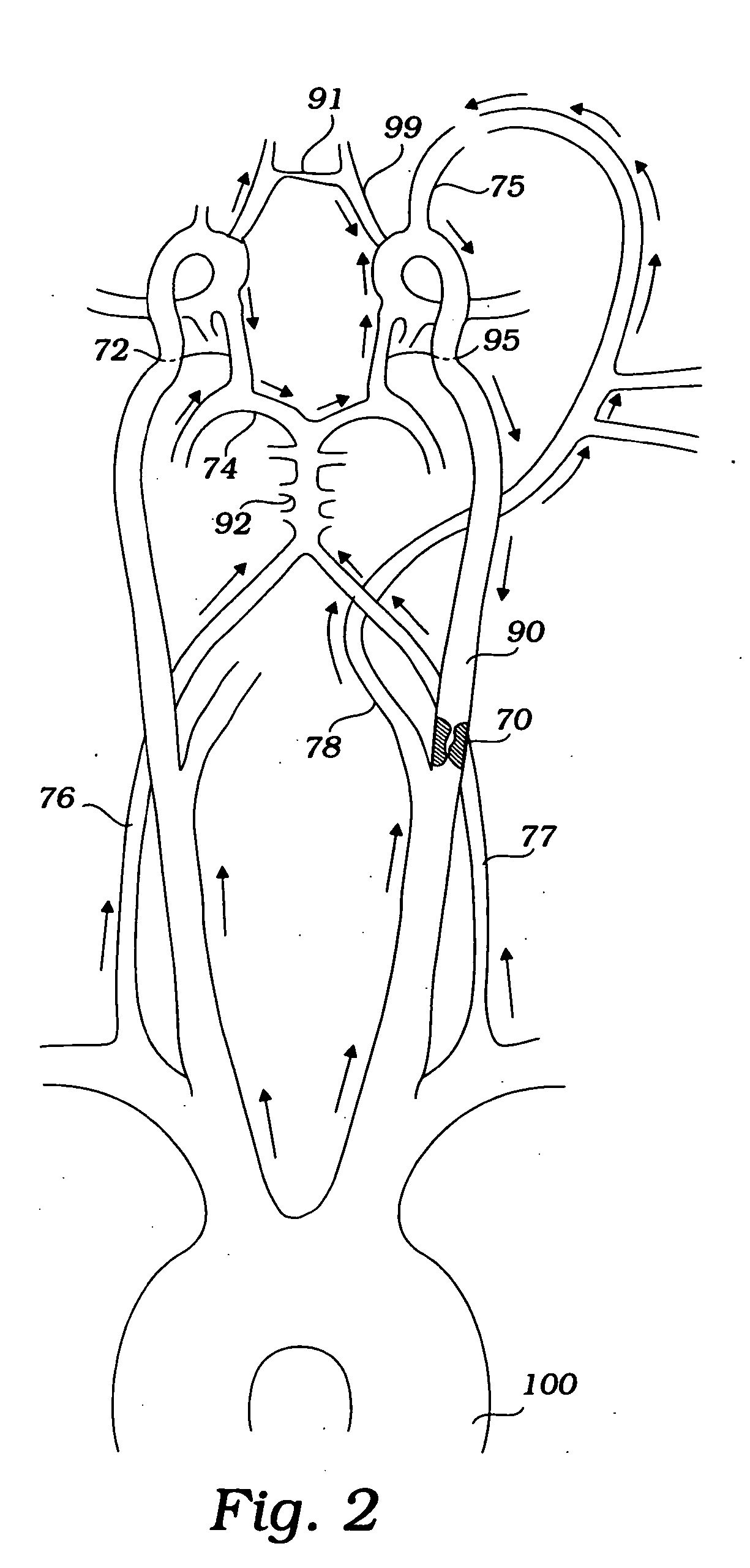
A medical device having a catheter and one or more expandable constricting / occluding members. The catheter is adapted for use with therapeutic or diagnostic devices, including an angioplasty / stent catheter and an atherectomy catheter. A first constrictor / occluder mounted at the distal end of the catheter is adapted for placement in a brachiocephalic or subclavian artery. A second constrictor mounted proximal to the first constrictor / occluder is adapted for placement in the descending aorta. Pressure measuring devices may be included, and filters may be used to capture embolic debris. Methods of using the devices for preventing distal embolization during extracranial or intracranial carotid procedures or vertebral artery procedures by augmenting collateral cerebral circulation by coarctation of the aorta to enhance reversal of blood flow in an internal carotid artery, an external carotid artery, and / or a common carotid artery toward the subclavian artery are disclosed.
Owner:ZOLL CIRCULATION
Devices and methods for preventing distal embolization using flow reversal and perfusion augmentation within the cerebral vasculature
InactiveUS7635376B2Preventing ischemic strokeStroke preventionBalloon catheterSurgeryAtherectomyCoarctation of the aorta
Owner:ZOLL CIRCULATION
Devices and methods for preventing distal embolization using flow reversal by partial occlusion of the brachiocephalic artery
InactiveUS8034043B1Preventing ischemic strokeStroke preventionStentsBalloon catheterAtherectomyPercutaneous angioplasty
Owner:ZOLL CIRCULATION
Collection device dedicated for arterial blood sample of mouse
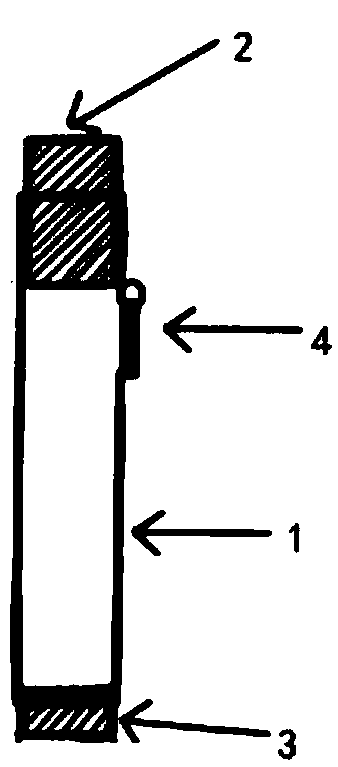
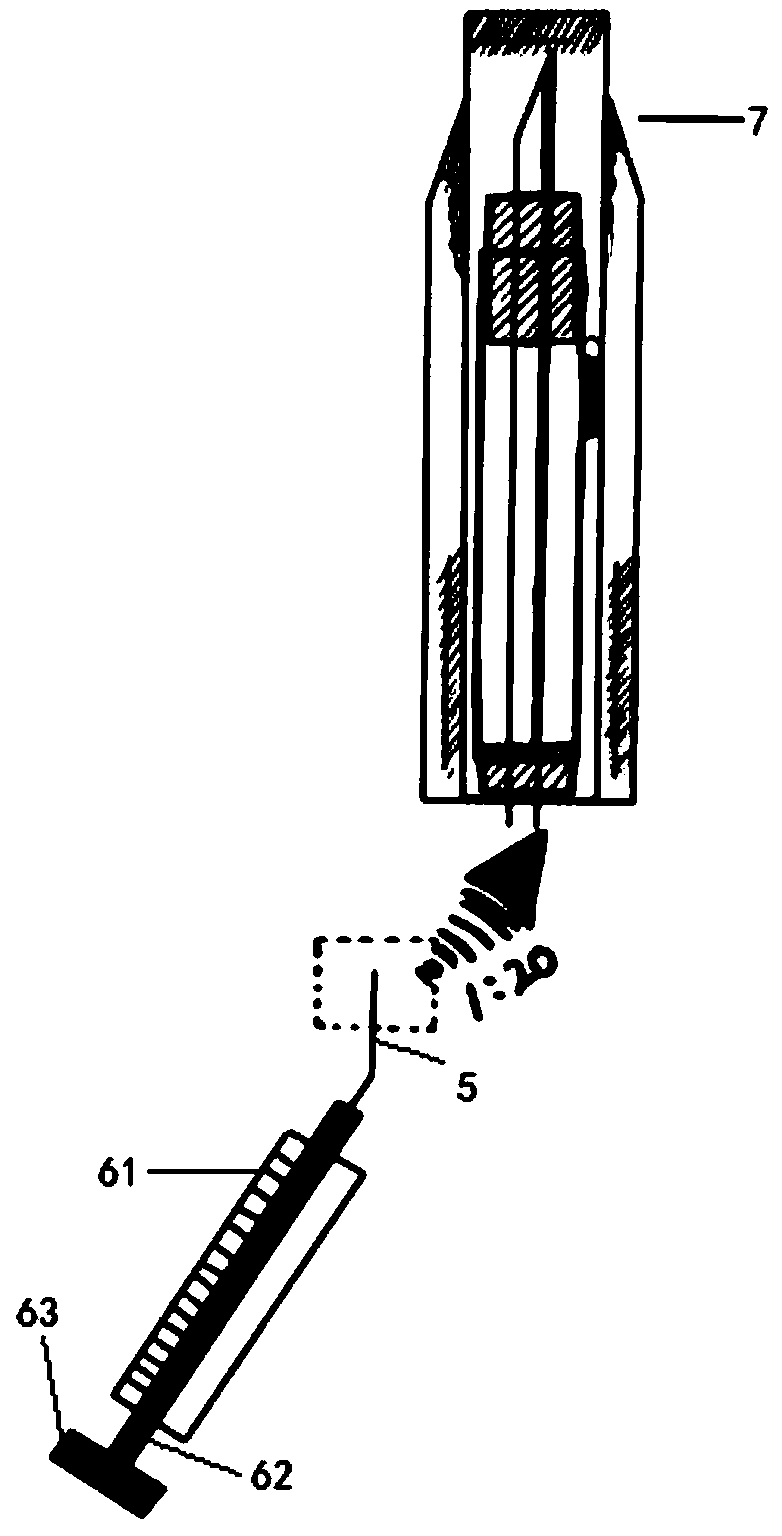
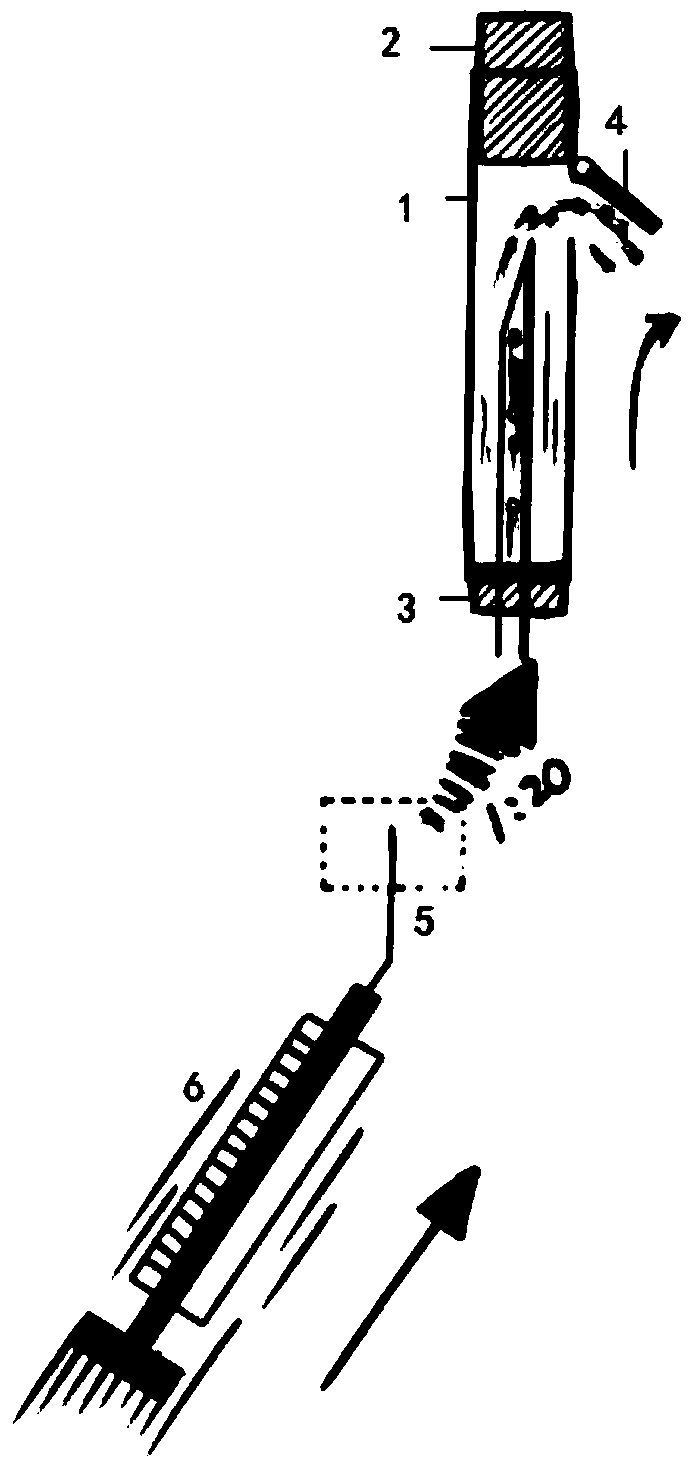
ActiveCN105662439AGuaranteed stabilityAvoid deathDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsWhole bodyGeneral anaesthesia
The invention relates to a collection device dedicated for an arterial blood sample of a mouse. The collection device comprises a blood sample drawing device, a puncturing component and a needle stand cover; the puncturing component is arranged on the needle stand cover; the needle stand cover is connected with the blood sample drawing device; the puncturing component is a thin and soft catheter. When the collection device is used, after being subjected to general anesthesia, the mouse is fixed on a mouse board; a common carotid artery is separated and exposed; the common carotid artery is cut to form a centripetal incision forming an angle of 30 to 45 degrees relative to a blood vessel; the thin and soft catheter is inserted into the artery from the incision to a cardiac direction to draw arterial blood of required amount. As the thin and soft catheter is adopted to puncture the blood vessel, the collection device cannot penetrate through an arterial wall; the collection device is safe, simple and convenient to operate; moreover, the thin and soft catheter can be conveniently retained and fixed in the body of a laboratory animal, so that the arterial blood can be conveniently collected repeatedly.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF WENZHOU MEDICAL UNIV
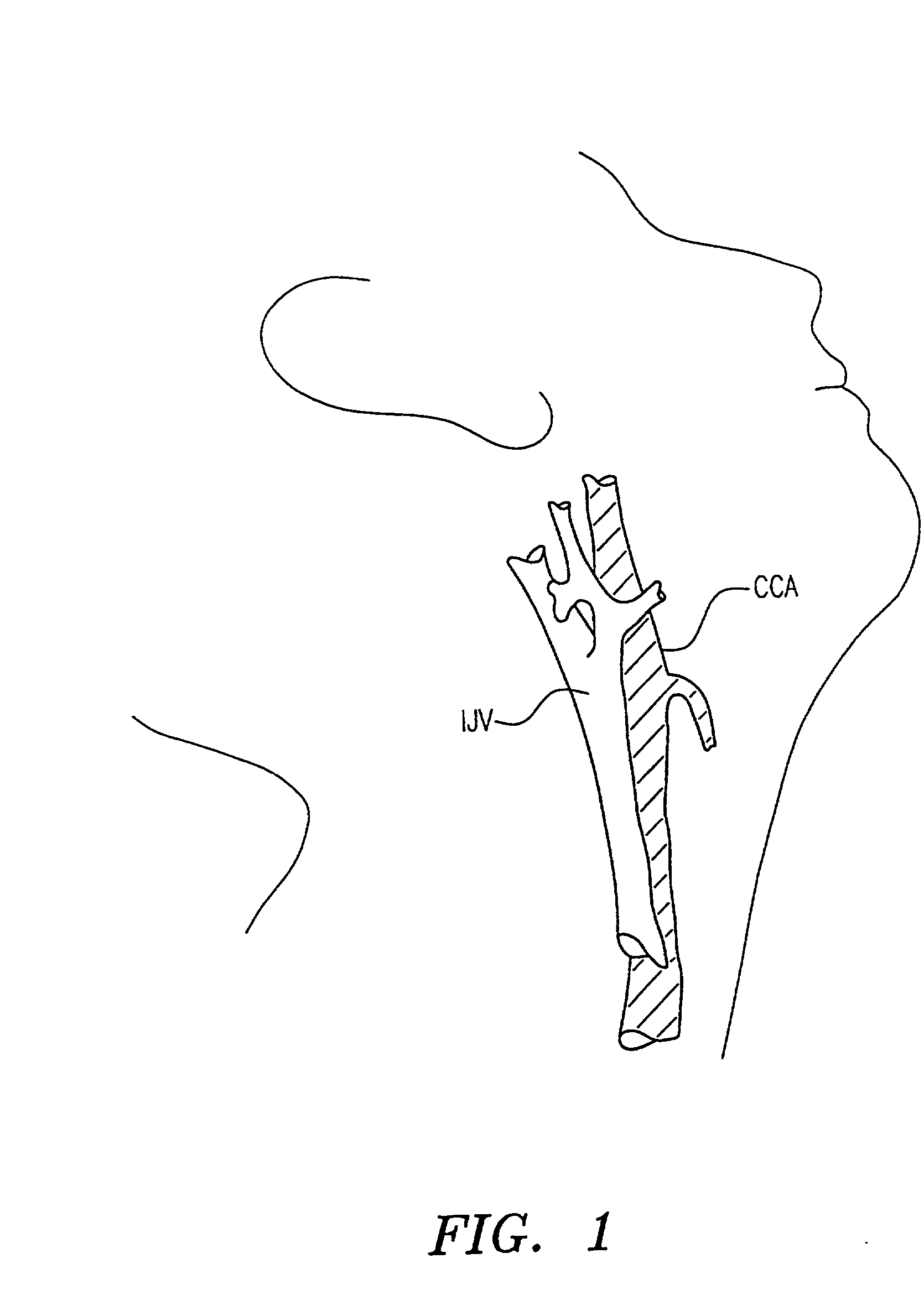
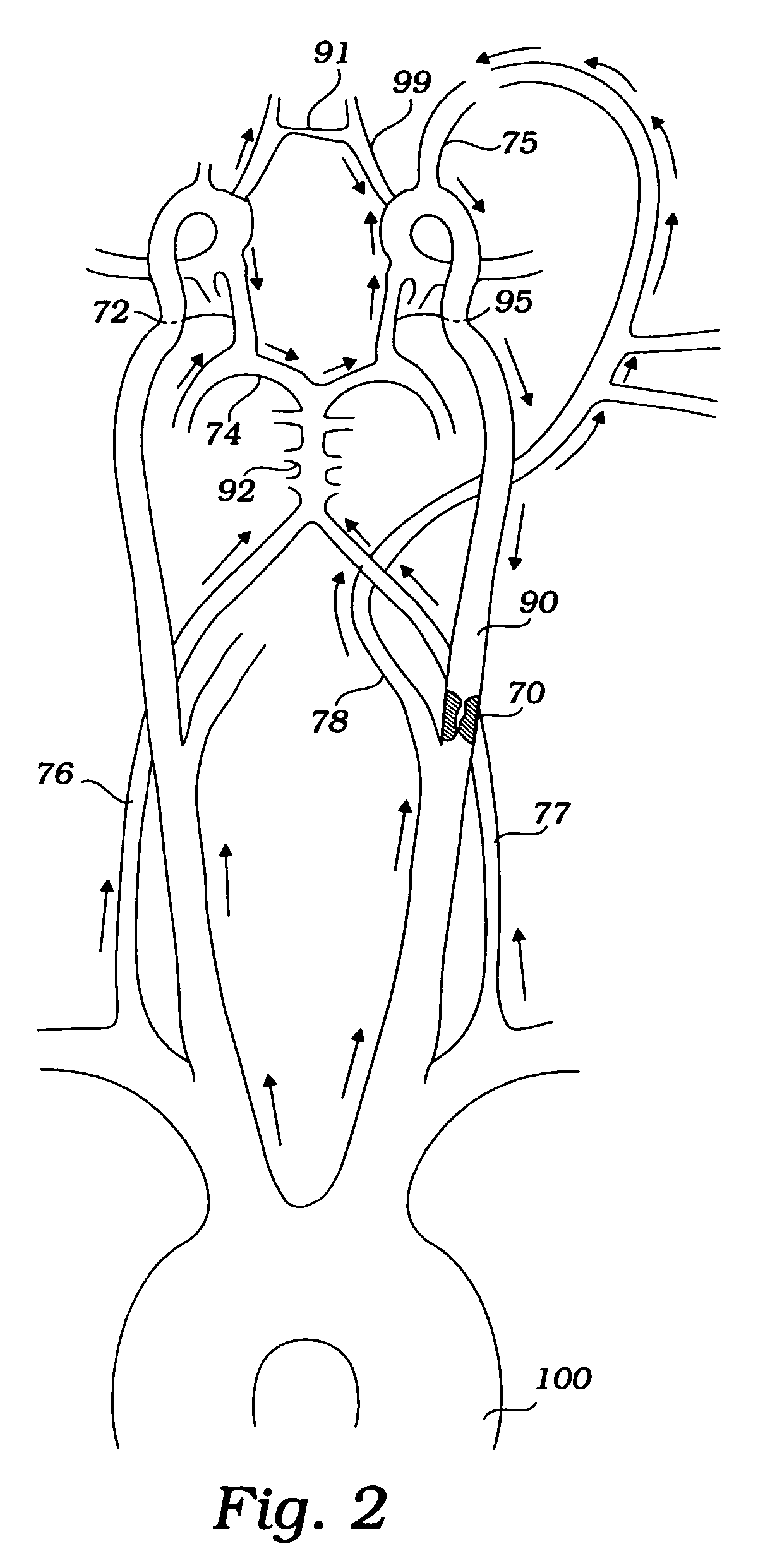
ICA angioplasty with cerebral protection
The present invention provides a method and device for preventing cerebral embolization during endovascular procedures in the carotid arteries. The invention comprises a guide catheter and balloon, which may selectively occlude the common carotid artery, and further comprises a wire and balloon, which may selectively occlude the internal carotid artery. Occlusion of the common carotid artery will induce retrograde flow at the site, redirecting emboli to the external carotid artery. Occlusion of the internal carotid artery reduces the risk of emboli migrating to the brain, and allows clearance of the site by antegrade blood flow from the common carotid artery. Occlusion of both the common and internal carotid arteries induces a quiescent state at the site during the procedure. Control of blood flow by selective inflation and deflation of either or both balloons, in concert with the procedures, will reduce the risk of emboli migrating to the brain.
Owner:WL GORE & ASSOC INC
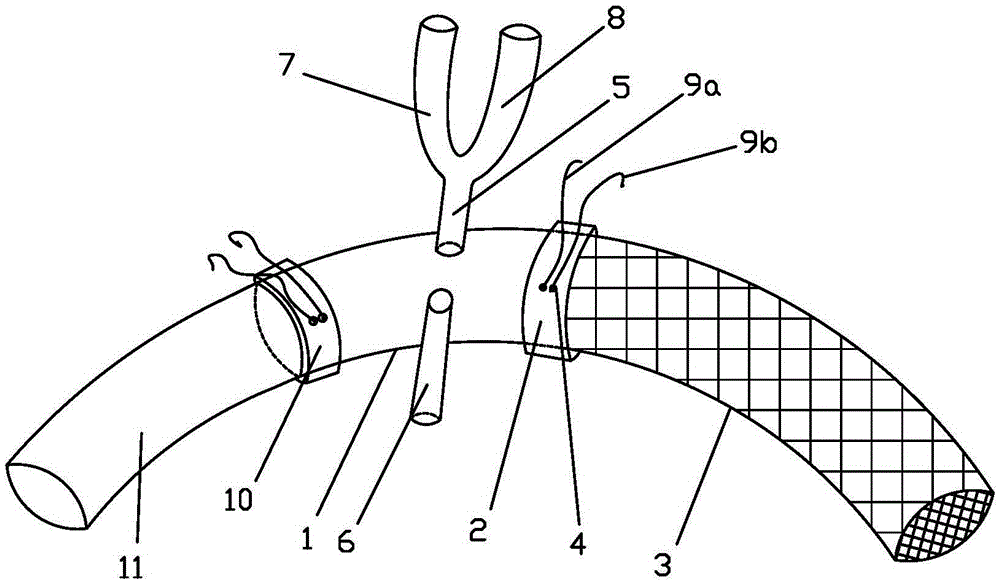
Arcus aortae stent graft vascular structure for department of surgery and application
The invention discloses an arcus aortae stent graft vascular structure for the department of surgery. The structure comprises a first artificial blood vessel, a connecting ring and a second artificial blood vessel. The connecting ring is embedded into the exterior of one side of the first artificial blood vessel. A reflection portion is reserved at the connecting ring and the end of the first artificial blood vessel. The reflection portion is turned outwards to wrap the connecting ring to form the compound end. One end of the second artificial blood vessel is embedded at the compound end to form a connecting portion. A threading hole is formed in the peripheral side wall of the connecting ring. A first branch and a second branch are arranged on the periphery of the first artificial blood vessel. The first branch comprises a first forked portion for being connected with an innominate artery and a second forked portion for being connected with the left common carotid artery. The second branch is connected with a pump blood vessel and then disconnected with the left subclavian artery. The second artificial blood vessel is the stent graft artificial blood vessel, and the far end of the second artificial blood vessel is used for being connected with the thoracic descending aorta.
Owner:JIANGSU PROVINCE HOSPITAL
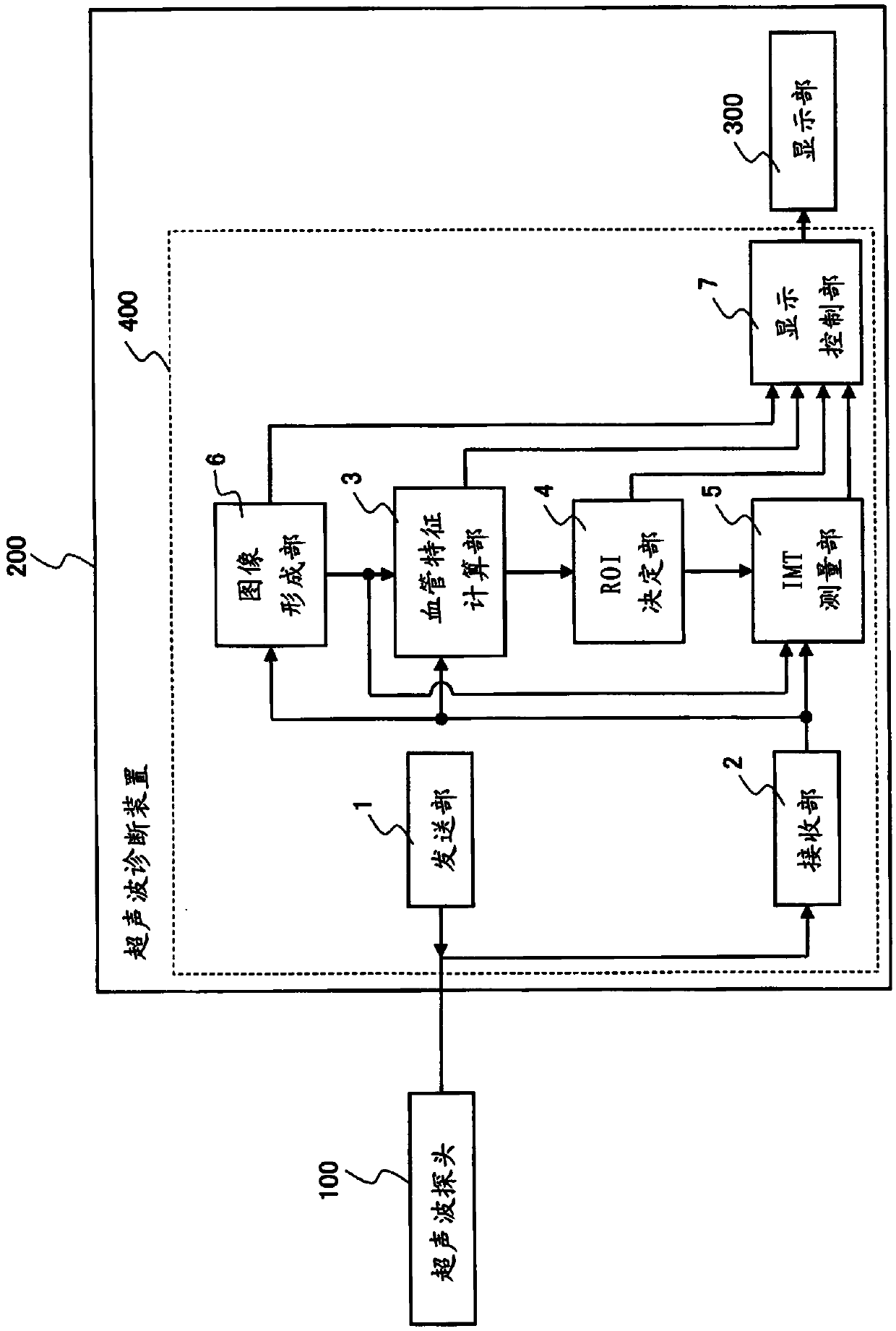
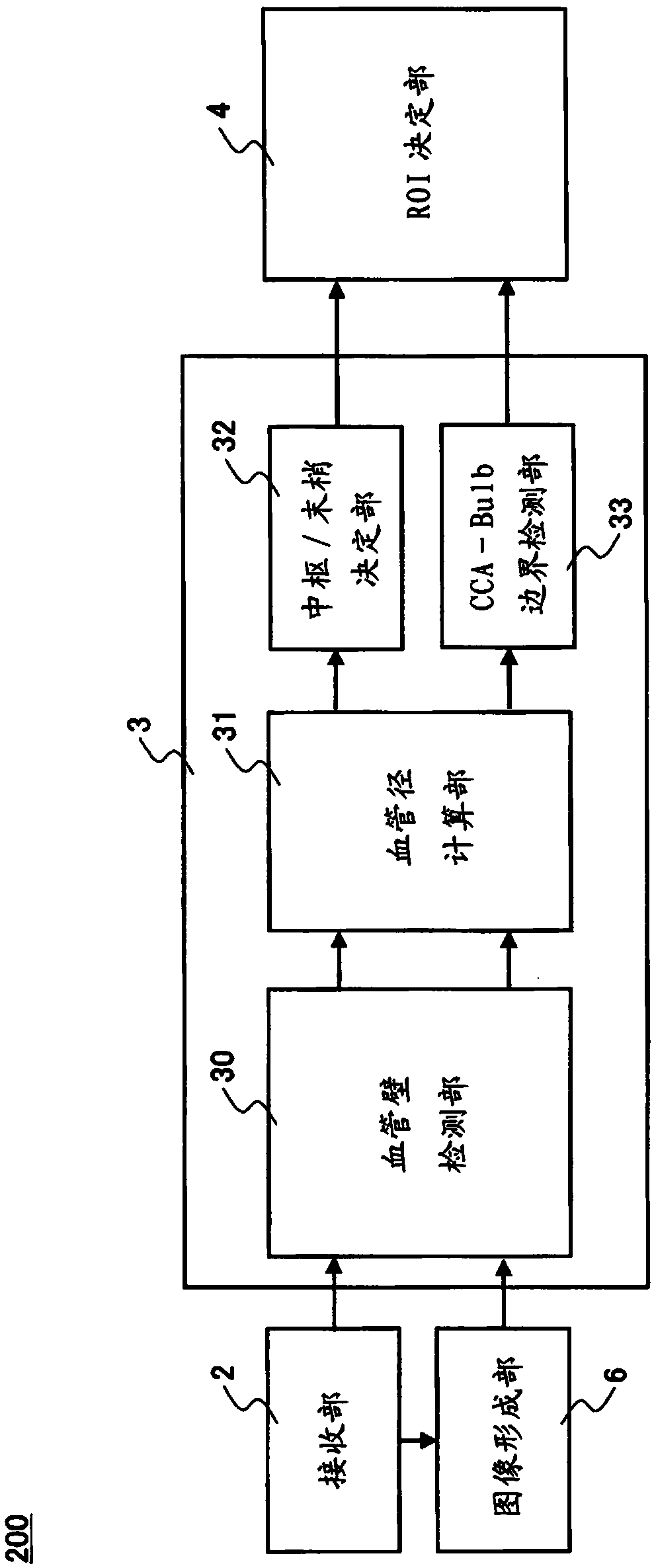
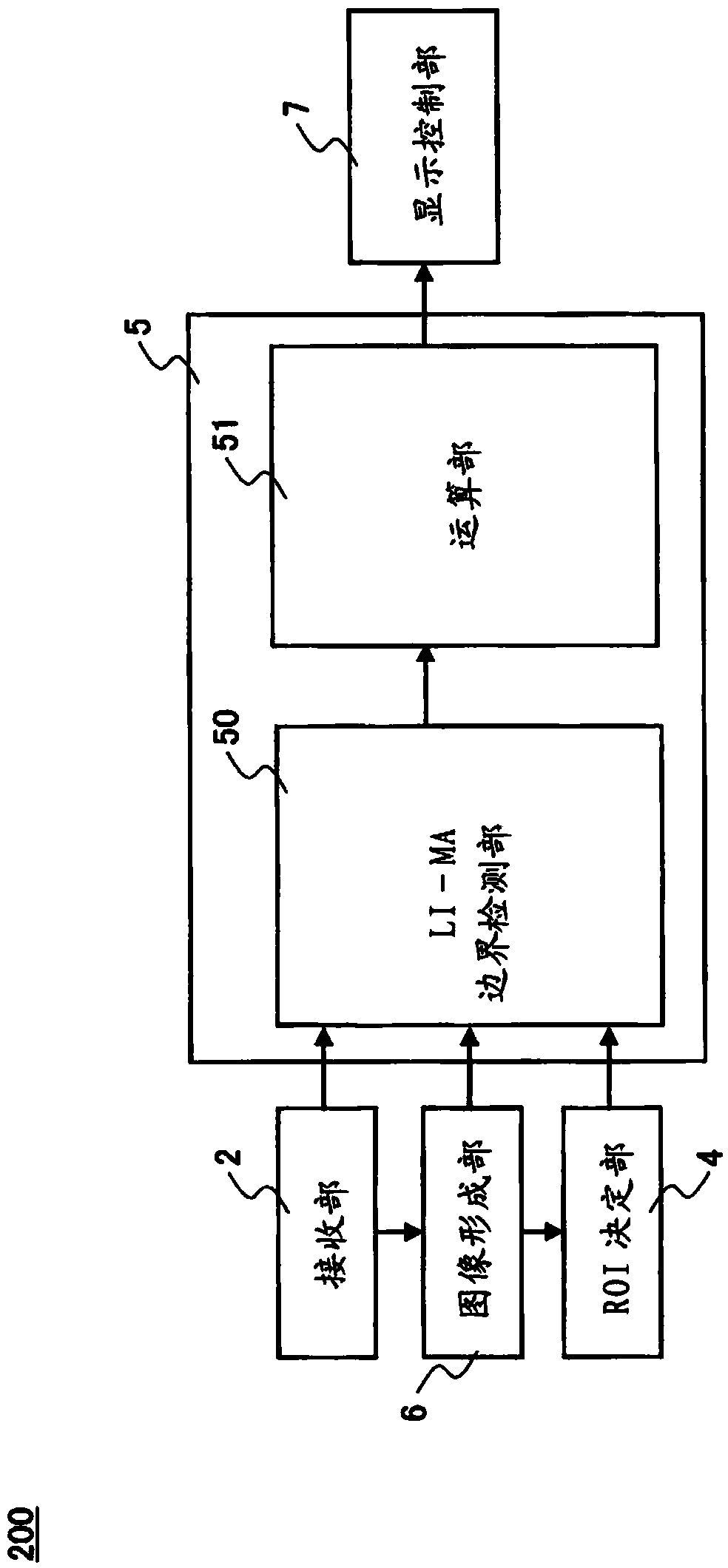
Ultrasound diagnostic device and ultrasound diagnostic device control method
InactiveCN103874464AQuick measurementHealth-index calculationInfrasonic diagnosticsIliac arteryBlood vessel
Provided is an ultrasound diagnostic device which is configured to be connectable to an ultrasound probe, and with which IMT of a carotid artery wall is measured, comprising: a transmission unit which supplies to an ultrasound probe a transmission signal for causing the ultrasound probe to transmit ultrasound along a longitudinal cross-section of a carotid artery; a receiving unit which receives a signal based on the reflected ultrasound which the ultrasound probe receives from the carotid artery and generates a received signal; a blood vessel characteristic computation unit which, on the basis of the received signal, extracts location information which includes a location of each part which configures the carotid artery wall and / or a relative relation between the locations, and detects a boundary location between the common carotid artery and the bulb of the carotid artery on the basis of the longitudinal change of the carotid artery of the location information; an ROI establishment unit which, using the boundary location as a reference, establishes an ROI which defines the measurement range for measuring the IMT; and an IMT measurement unit which measures the IMT of the blood vessel wall which is included in the ROI.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA INC
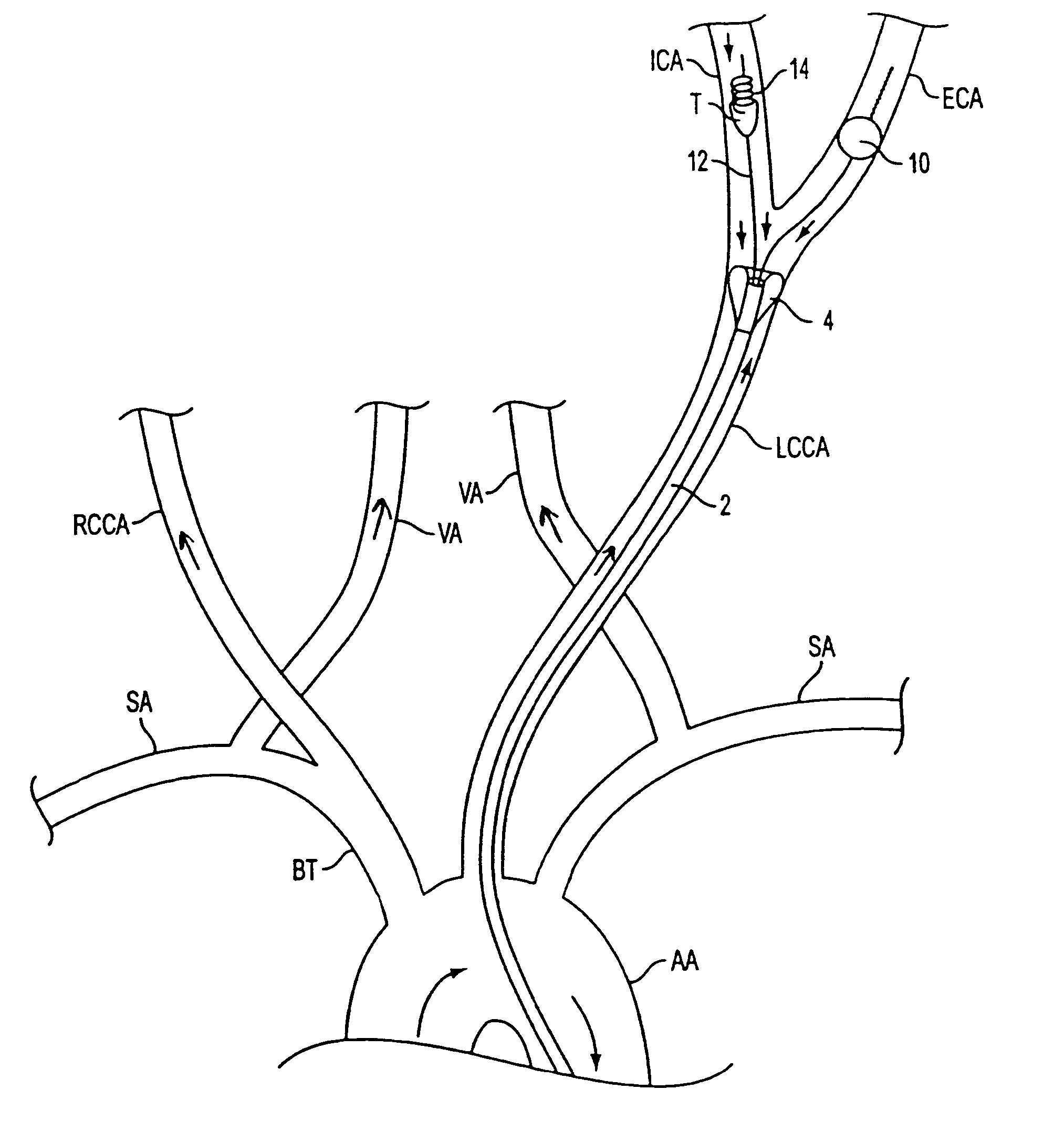
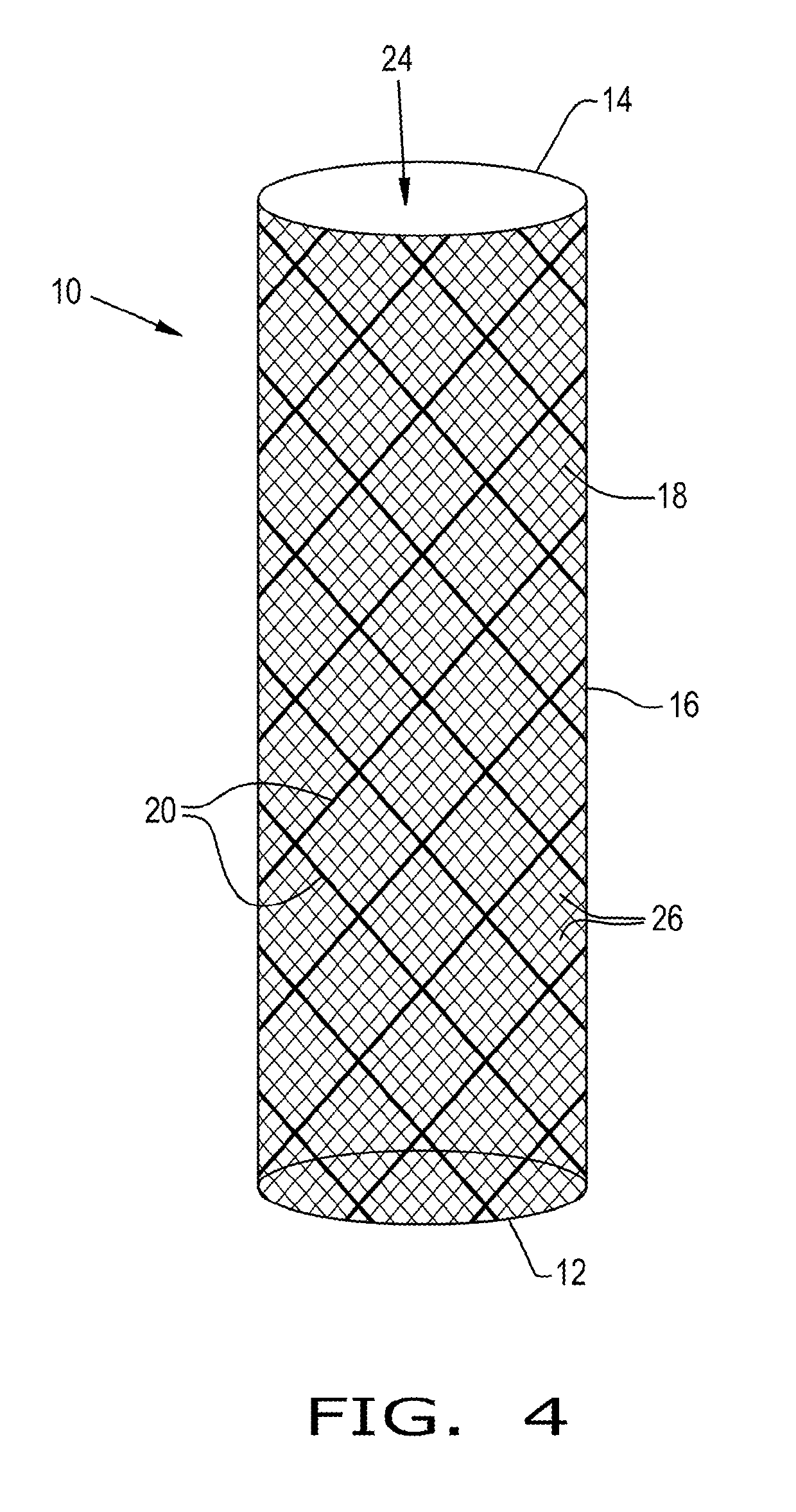
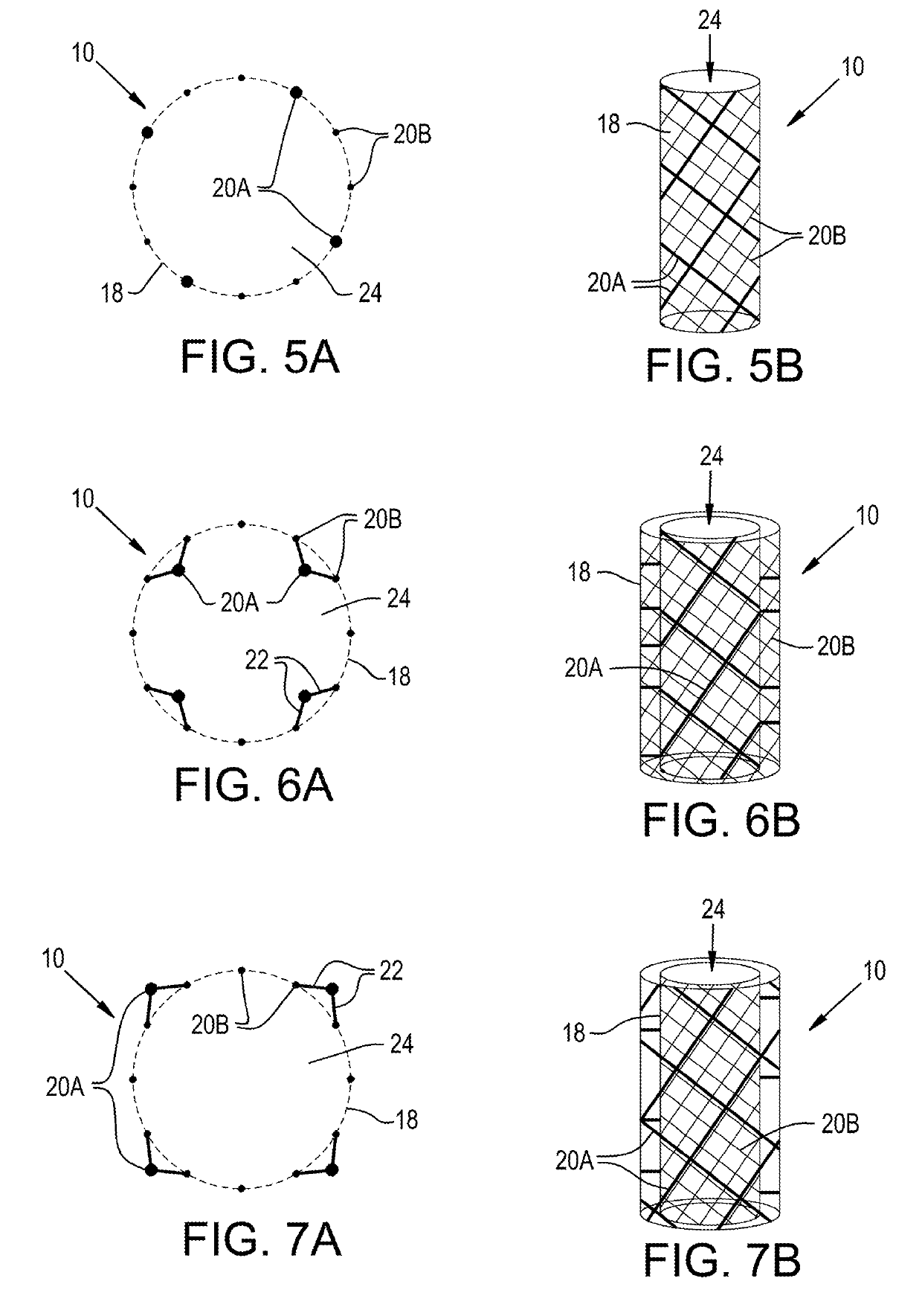
Thromboembolic protective flow-diverting, common carotid to external carotid intravascular stent
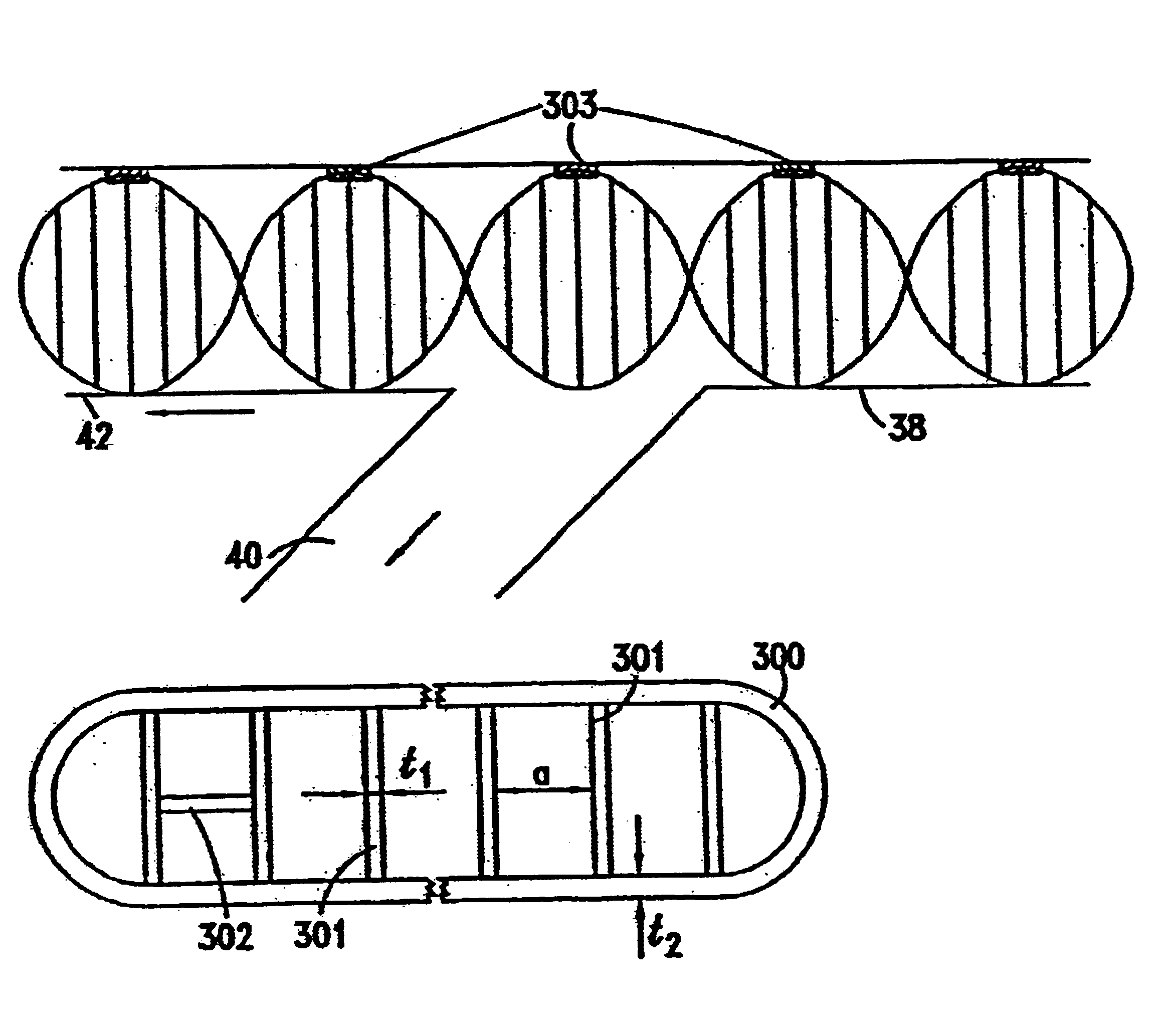
Medical procedures and devices suitable for reducing the risk of embolic cerebrovascular events, including but not limited to cardioembolic stroke, that result from emboli entering the right or left common carotid artery. The invention uses a combination of intracranial flow diverting stent technologies and carotid stent technologies to achieve clinical objectives of embolic stroke prevention without thromboembolic and / or vascular stenosis complication. Such a stent has struts that generate high radial forces for endothelial apposition, and a mesh with interstices sufficiently small to prevent clinically significant-sized embolic material from passing therethrough from the common carotid artery into the internal carotid artery, but sufficiently large to enable blood and small clinically insignificant-sized embolic material to pass therethrough from the common carotid artery into the internal carotid artery.
Owner:LOYOLA UNIV OF CHICAGO
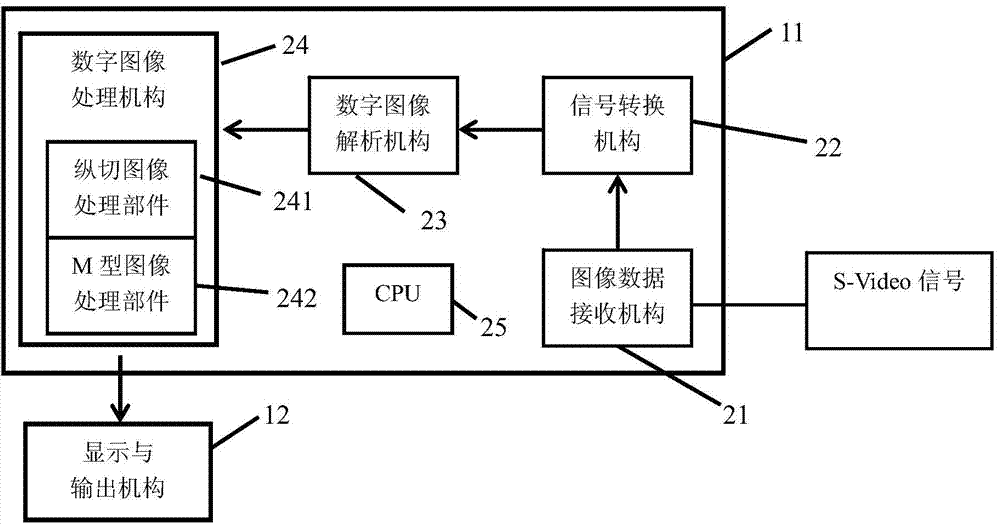
Post treatment device and method of M-shaped ultrasound image of common carotid artery
InactiveCN104510494AHigh precisionImprove transmission efficiencyHeart/pulse rate measurement devicesInfrasonic diagnosticsCardiac cycleDiameter measurement
The invention discloses a post treatment method of an M-shaped ultrasound image of a common carotid artery. The post treatment method comprises the following steps: after an ultrasonic wave is longitudinally cut and imaged, M-shaped ultrasound imaging is executed by selecting a sample line to obtain the M-shaped ultrasound image, an artery lumen region in the image is judged, and a row of pixel points transversely passing through the entire lumen region is used as a canal diameter measurement reference row; a mask mtehod is adopted to search in the near-field and far-field directions of each pixel point in the canal diameter measurement reference row, the demarcation point of the intima and the canal diameter is confirmed, the canal diameter change data of the common carotid artery positioned at the sample lines in several cardiac cycles and pulsed along the heart is obtained through calculation and the pulse wave velocity is estimated. The invention discloses a device for realizing the method. According to the post treatment method, the pulse wave velocity in the common carotid artery can be measured by a computer, the precision is obviously improved and the transfer efficiency is greatly promoted.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
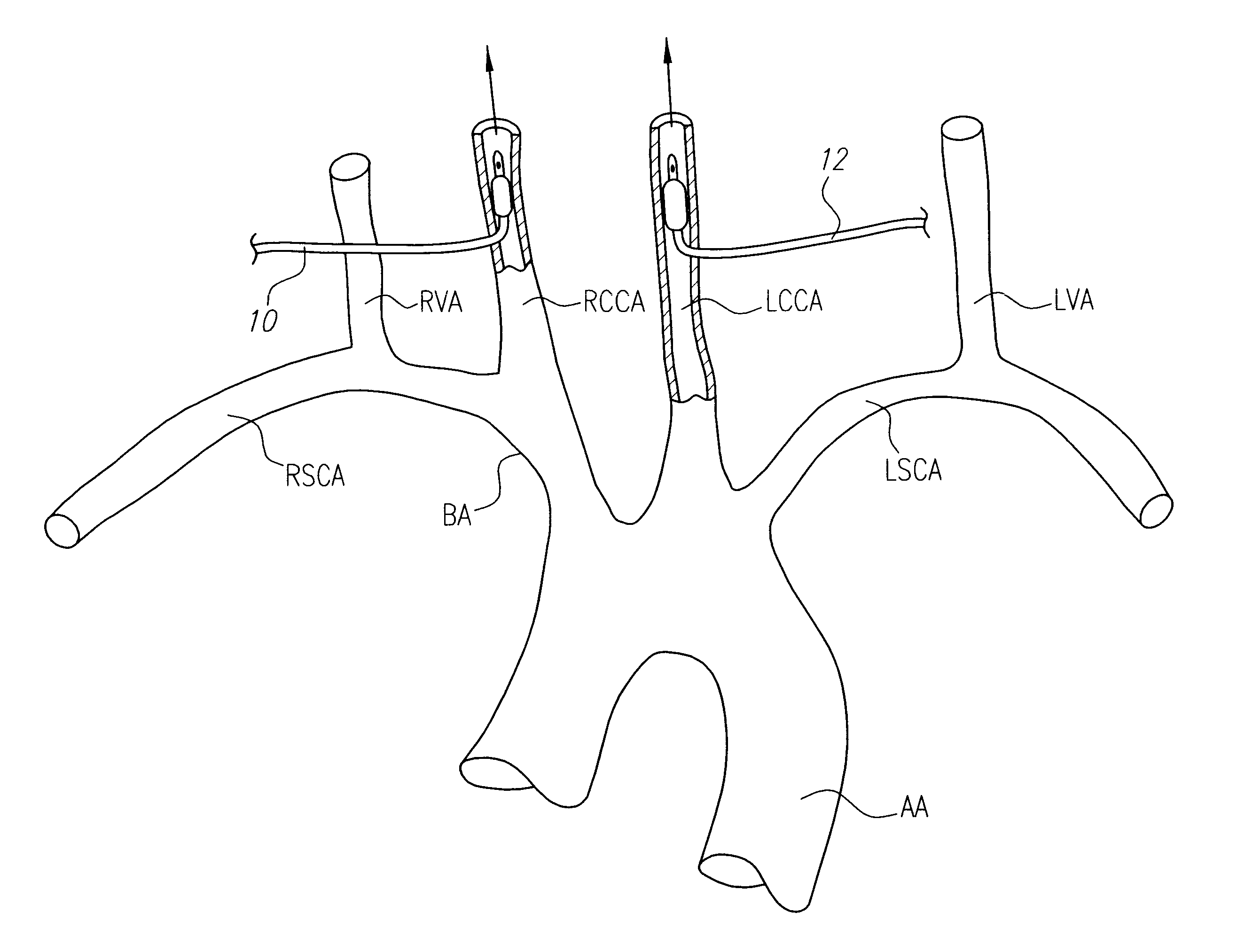
Methods and devices for transcarotid access
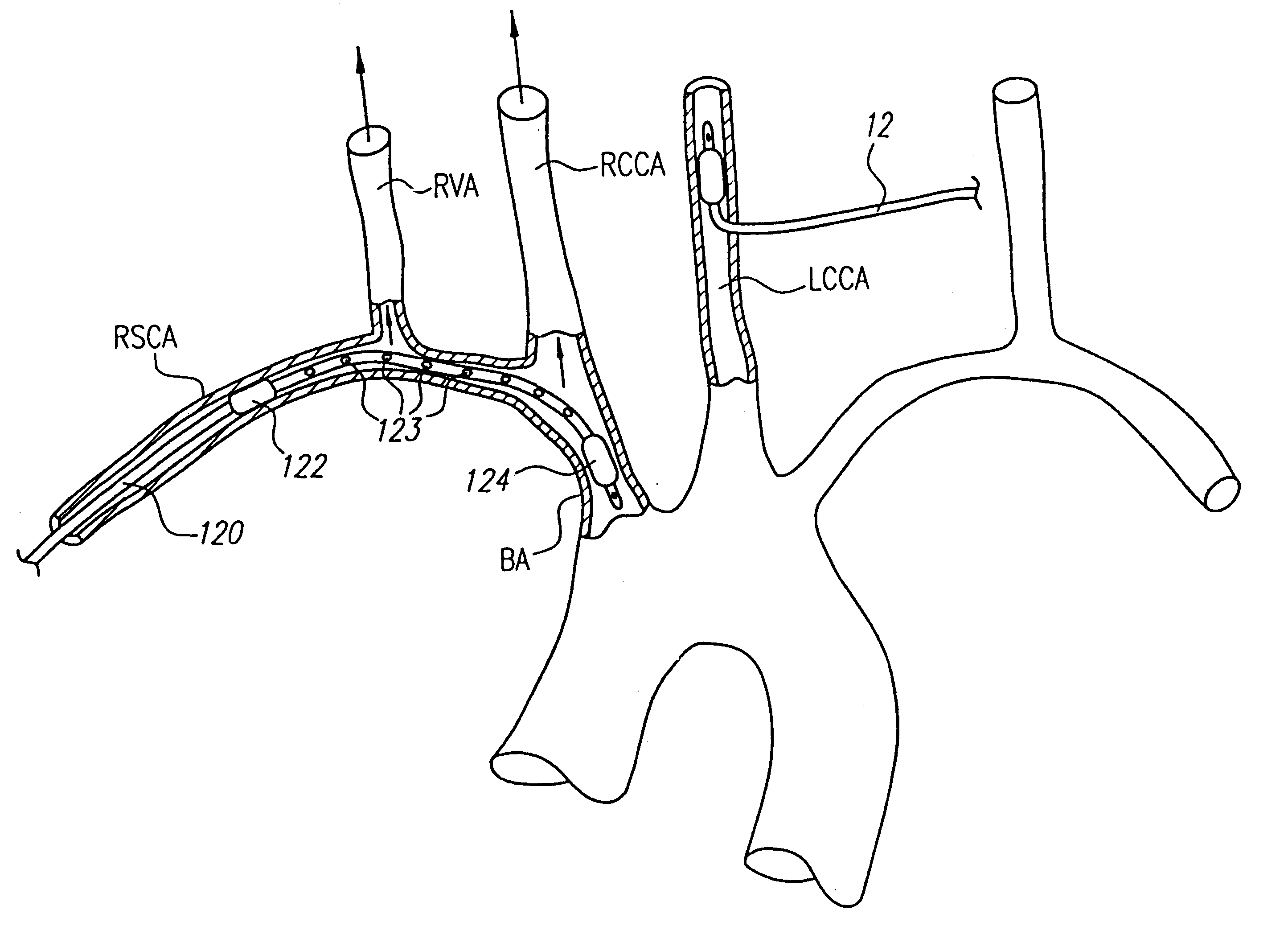
Disclosed is an arterial access sheath for introducing an interventional device into an artery. The arterial access sheath includes an elongated body sized and shaped to be transcervically introduced into a common carotid artery at an access location in the neck and an internal lumen in the elongated body having a proximal opening in a proximal region of the elongated body and a distal opening in a distal region of the elongated body. The internal lumen provides a passageway for introducing an interventional device into the common carotid artery when the elongated body is positioned in the common carotid artery. The elongated body has a proximal section and a distalmost section that is more flexible than the proximal section. A ratio of an entire length of the distalmost section to an overall length of the sheath body is one tenth to one half the overall length of the sheath body.
Owner:SILK ROAD MEDICAL
Method for making guinea pig MCAO (middle cerebral artery occlusion) model
InactiveCN110612941AGuaranteed reperfusion effectAvoid damageAnimal husbandryMuscle tissueCervical fascia
The invention discloses a method for making a guinea pig MCAO (middle cerebral artery occlusion) model, which comprises the steps of preparing an anesthetic, weighing a guinea pig, and injecting a certain amount of the anesthetic into the abdominal cavity according to the weight of the guinea pig, so that the guinea pig is anesthetized; placing the guinea pig on a temperature control blanket, fixing the guinea pig on an operating table with the body of the guinea pig straight and free of tension, scraping the neck hair of the guinea pig with a hair clipper, and locally sterilizing with entoiodine; cutting the skin along the paracervical median of the guinea pig to open the anterior cervical fascia and expose the sternocleidomastoid muscle on the right side, then separating the anterior cervical muscle group and sternocleidomastoid muscle, and drawing with a fine silk thread to separate the muscle tissues until a complete CCA (common carotid artery) is observed. Compared with the traditional common carotid artery plug-in method, the method has the advantages that blood is directly supplied from the common carotid artery through the internal carotid artery after reperfusion, the common carotid artery is directly ligated after reperfusion, the reperfusion blood supply can only be circulated through lateral branches, the reperfusion effect similar to the clinical effect can be achieved, and the success rate of model preparation is high.
Owner:昆明医科大学第二附属医院
Methods and systems for establishing retrograde carotid arterial blood flow
Devices and methods establish and facilitate retrograde or reverse flow blood circulation in the region of the carotid artery bifurcation in order to limit or prevent the release of emboli into the cerebral vasculature such as into the internal carotid artery. The methods are particularly useful for interventional procedures performed through a transcarotid approach or transfemoral into the common carotid artery.
Owner:SILK ROAD MEDICAL
Portable blood pressure automatic adjustment system based on carotid baroreceptor ultrasonic stimulation
InactiveCN110025332ATo achieve the purpose of reducing blood pressureInfrasonic diagnosticsSonic diagnosticsFocus ultrasoundSonification
The invention relates to a portable blood pressure automatic adjustment system based on carotid baroreceptor ultrasonic stimulation, which is a non-invasive, wearable and fully automatic intelligent blood pressure regulation technology. The system uses a patch-type ultrasound probe and a fast ultrasound imaging technology to measure the carotid blood pressure pulse waveform in real time, Accordingto the measurement results, an appropriate low-power ultrasound focusing pulse is emitted to illuminate a baroreceptor on the carotid sinus to adjust blood pressure. The system consists of three parts: a wearable ultrasound imaging and control panel for intelligent deployment and driving of two flexible ultrasound probes; two flexible ultrasound probes can transmit and receive ultrasonic signals,the probe No. 1 is attached to a carotid baroreceptor, and emits low-power focused ultrasound to illuminate the baroreceptor, the No. 2 probe is attached to the common carotid artery to image and detect the pulsation process of the common carotid artery, and calculates the continuous beat waveform of the common carotid artery blood pressure; and a plugging flexible cable is capable of connectingthe ultrasonic probe and a host.
Owner:徐婷嬿 +2
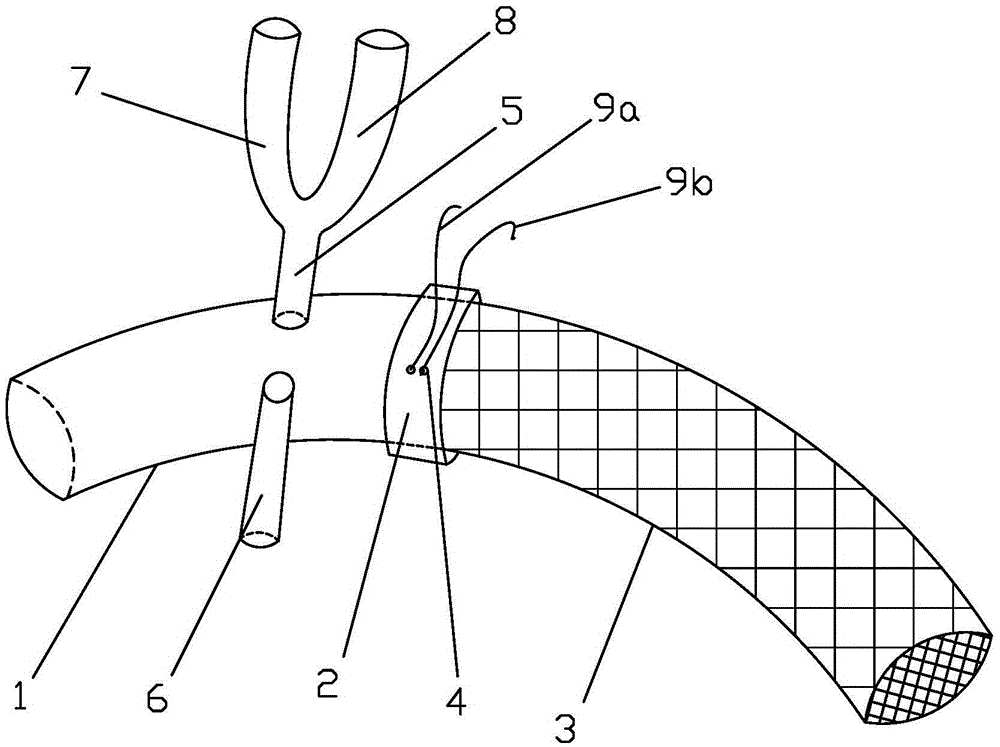
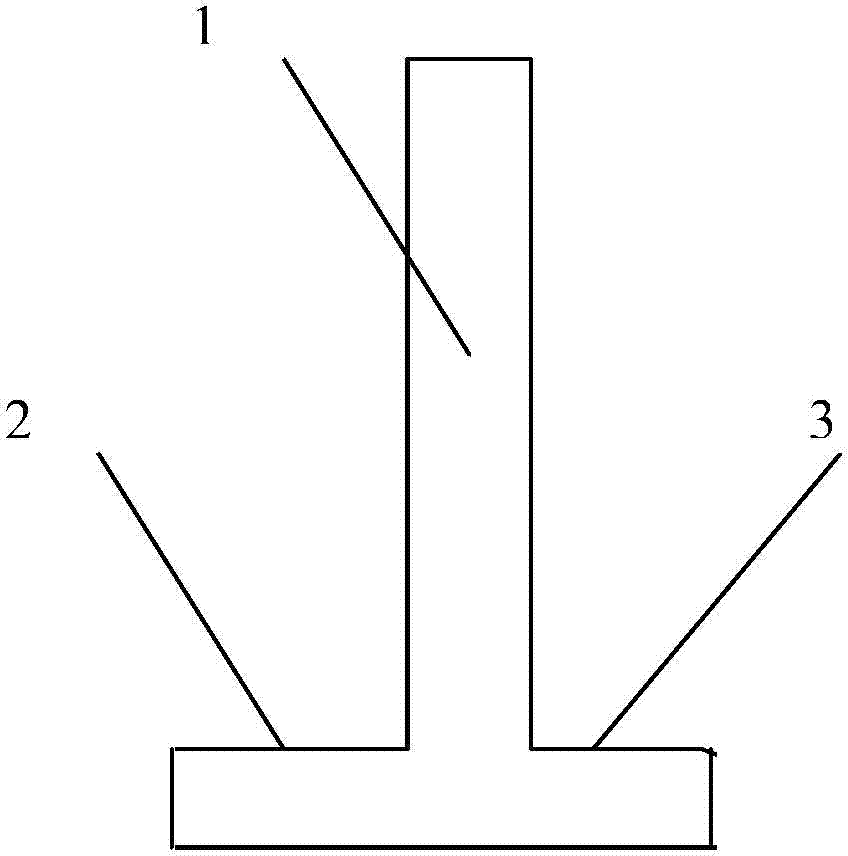
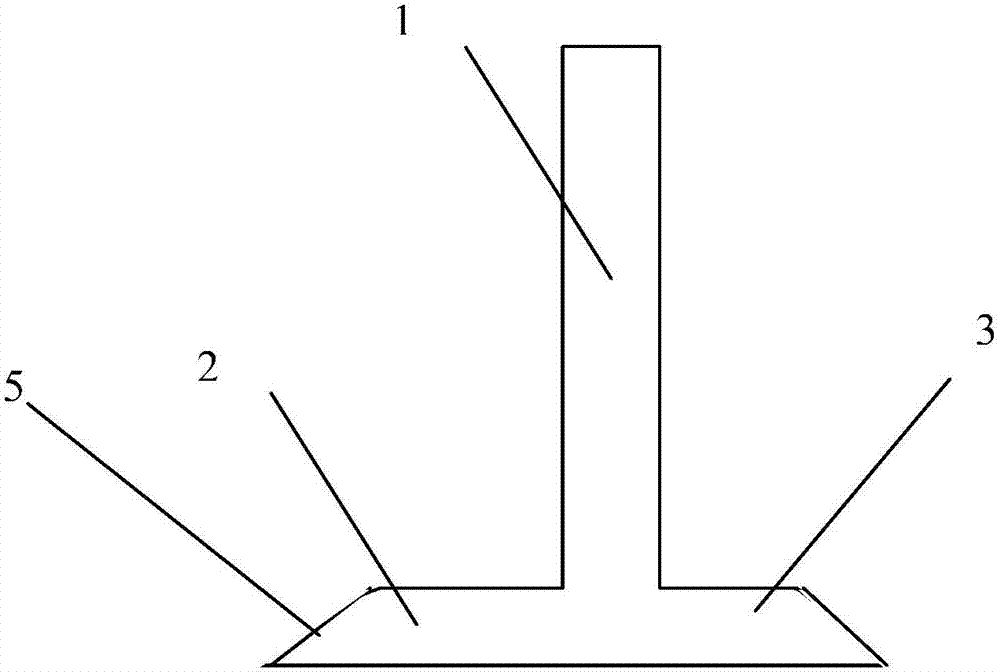
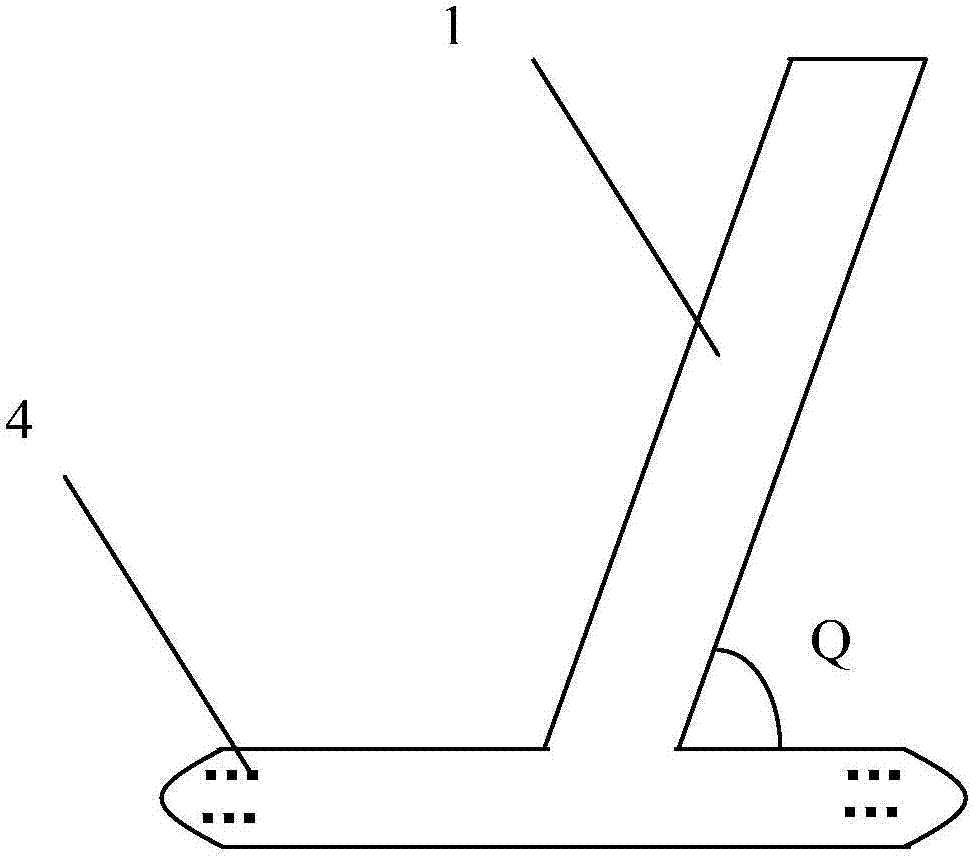
Common carotid artery cannula for adjusting and distributing blood perfusion flow and application
InactiveCN104208799AShorten the timeShorten ischemic timeCatheterExtracorporeal circulationWhole body
The invention relates to a common carotid artery cannula for adjusting and distributing blood perfusion flow and application. The common carotid artery cannula comprises a cannula body at a blood supply end and is characterized by further comprising a T-shaped or Y-shaped structured extracorporeal circulation perfusion plastic tube with a proximal end tube and a distal end tube for dividing flow and pressure, wherein the extracorporeal circulation perfusion plastic tube is communicated with the cannula body and formed on an overall structure. An included angle is formed between the proximal end tube of the Y-shaped structured perfusion tube and the cannula body at the blood supply end to distribute or adjust the blood perfusion flow. The common carotid artery cannula is applied to whole-body arterial perfusion and deep hypothermic circulatory arrest selective cerebral perfusion during extracorporeal circulation of a common carotid artery, and overcomes the shortcomings of an existing artery cannula and method. Carotid artery occlusion time is short during intubation and extubation, and cerebral blood supply is almost not affected, so that cerebral complications and the pain of patients are decreased. Obviously, the common carotid artery cannula is convenient to operate, surgical time is greatly shortened, so that cerebral ischemic time is shortened, the success rate of an aortic arch surgery is increased, and the common carotid artery cannula has a wide clinical application value.
Owner:THE AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF QINGDAO UNIV
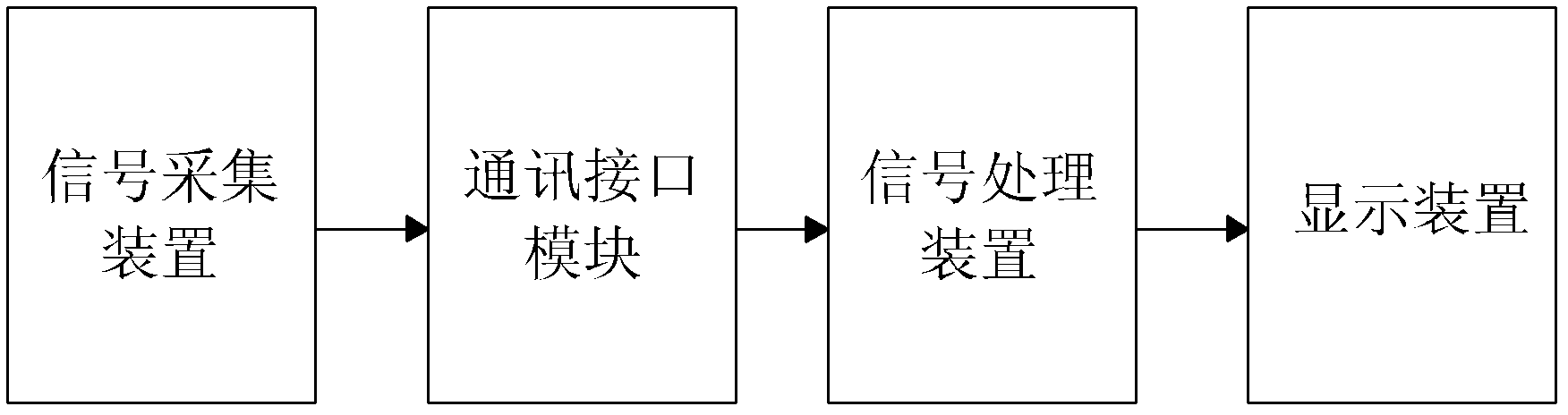
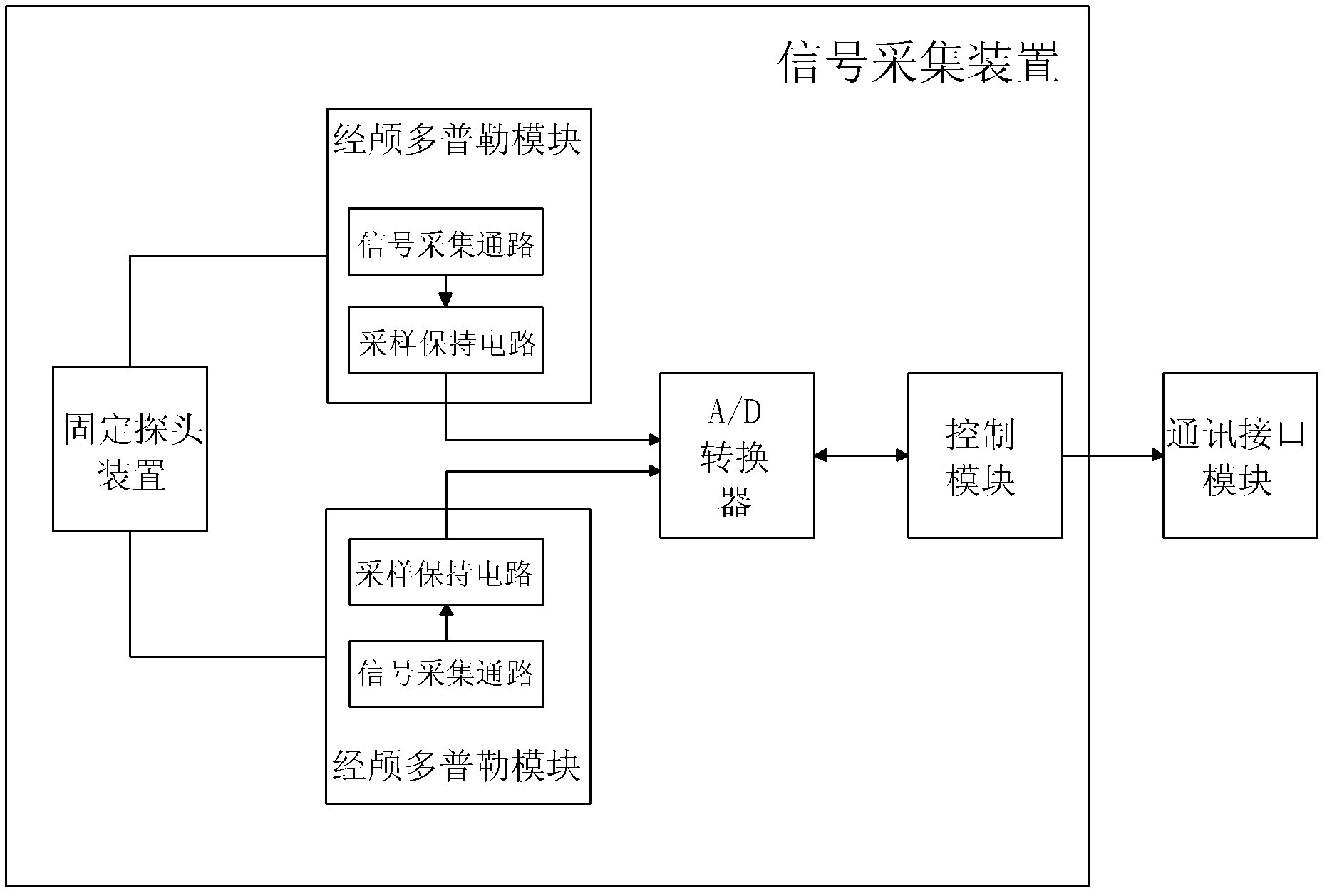
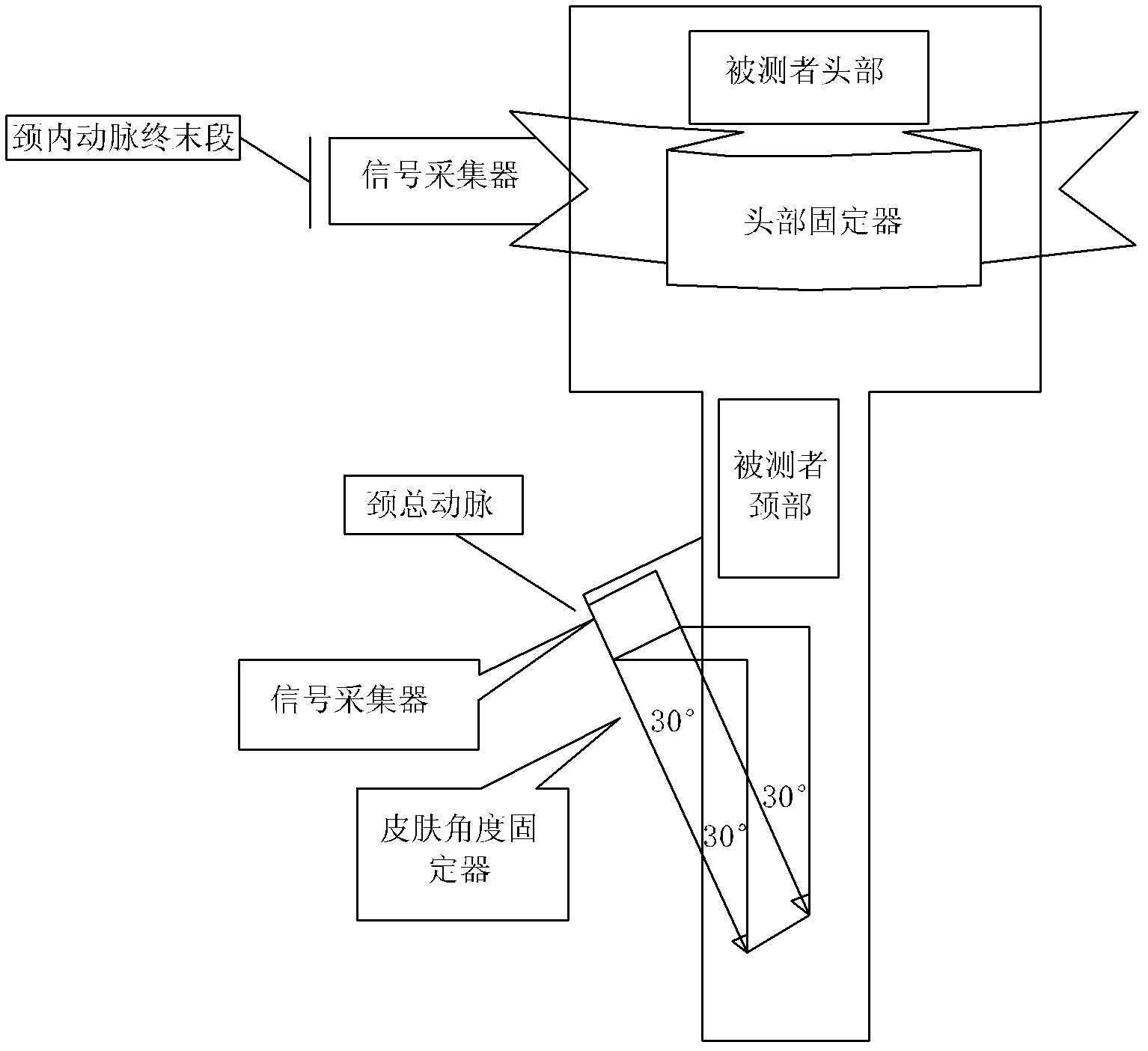
Neck and brain arterial pulse wave speed measurement system
ActiveCN102551698ARealize non-invasive testingAid in early detectionDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsBlood flowDisplay device
The invention relates to a neck and brain arterial pulse wave speed measurement system, which is characterized by comprising a signal collection device, a signal processing device, a display device and a communication interface module, wherein the signal collection device is connected with the signal processing device through the communication interface module, the output end of the signal processing device is connected with the display device, the signal collection device is used for synchronously sampling blood flow signals at the tail sections of a common carotid artery and an internal carotid artery and converting the blood flow signals to corresponding digital signals, the signal processing device is used for processing synchronously obtained brain blood flow signals to obtain time difference among the signals, and the display device is used for displaying parameters of the blood flow signals and parameters of the time difference among the signals. The neck and brain arterial pulse wave speed measurement system achieves noninvasive detection on neck-brain arterial pulse wave speed, is accurate and reliable in results and strong in clinical practicality, reflects stiffness conditions of the cerebral artery more accurately and directly, estimates apoplexy risks, and is beneficial to early discovery and precaution of apoplexy.
Owner:THE SECOND AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF GUANGZHOU MEDICAL UNIV
Method for building stenosis model after rat carotid artery balloon injuries
The invention discloses a method for building a stenosis model after rat carotid artery balloon injuries. The method includes the steps of injecting pentobarbital sodium to the abdominal cavity of a rat to anesthetize the rat, removing furs to prepare the skin, enabling the rat to be fixed on an operation table in a supination mode, cutting the rat along the right middle line of the neck, exposing the left common carotid artery, disinfecting the skin at the position of the groin on the right side of the rat, separating the femoral artery, conducting ligation on the far-heart end at the position 1cm below the branch of the femoral artery, using a needle of a 1m1 injection syringe to puncture the femoral artery, feeding a super-smooth guide wire through the needle of the injection syringe into the carotid artery on the left side, feeding a balloon into the carotid artery on the left side along the super-smooth guide wire, feeding a balloon catheter into the bifurcated position of the internal carotid and external carotid artery of the left side of the neck, enabling the pressure in the balloon to be 1.0 barometric pressure to enable the balloon to right be capable of being pulled in the blood vessel, expanding the balloon to drag the balloon back and forth three times to strip the inner skin to enable the carotid artery to be damaged, withdrawing the balloon catheter, conducting ligation on the near-heart end of a notch of the artery, sewing the skin, and injecting penicillin into the muscle for continuous three days after an operation to avoid infections. According to the method, the operative difficulty in the prior art is reduced, the modeling success rate is improved, and the complication is reduced.
Owner:THE SECOND AFFILIATED HOSPITAL ARMY MEDICAL UNIV
Implantable internal carotid artery constant-speed injection device and operation method thereof
The invention discloses an implantable internal carotid artery constant-speed injection device and an operation method thereof. A sealing cover and a sealing plug which not only have a sealing effect,but also can be pierced by a needle are separately arranged at the top end and the rear end of a common carotid artery implanting guide tube, an injection opening which is covered by a one-way circulating door is formed in the front end of the common carotid artery implanting guide tube, flow speed and time are controlled through a controller, a constant-speed injection micro-pump is driven to push an injection syringe, and cancer cells or injection drugs flow into common carotid artery blood vessels through an injection opening of the common carotid artery implanting guide tube. By the implantable internal carotid artery constant-speed injection device, a surgical method can be simple and convenient, surgical steps are simplified, and surgery time is shortened; and meanwhile, a surgery mode of for an animal model of mouse internal carotid artery injection will be changed completely, the external carotid artery of a mouse does not need to be sutured, pneumogastric nerves and blood vessels cannot be damaged, and the success rate of the surgery is greatly increased.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
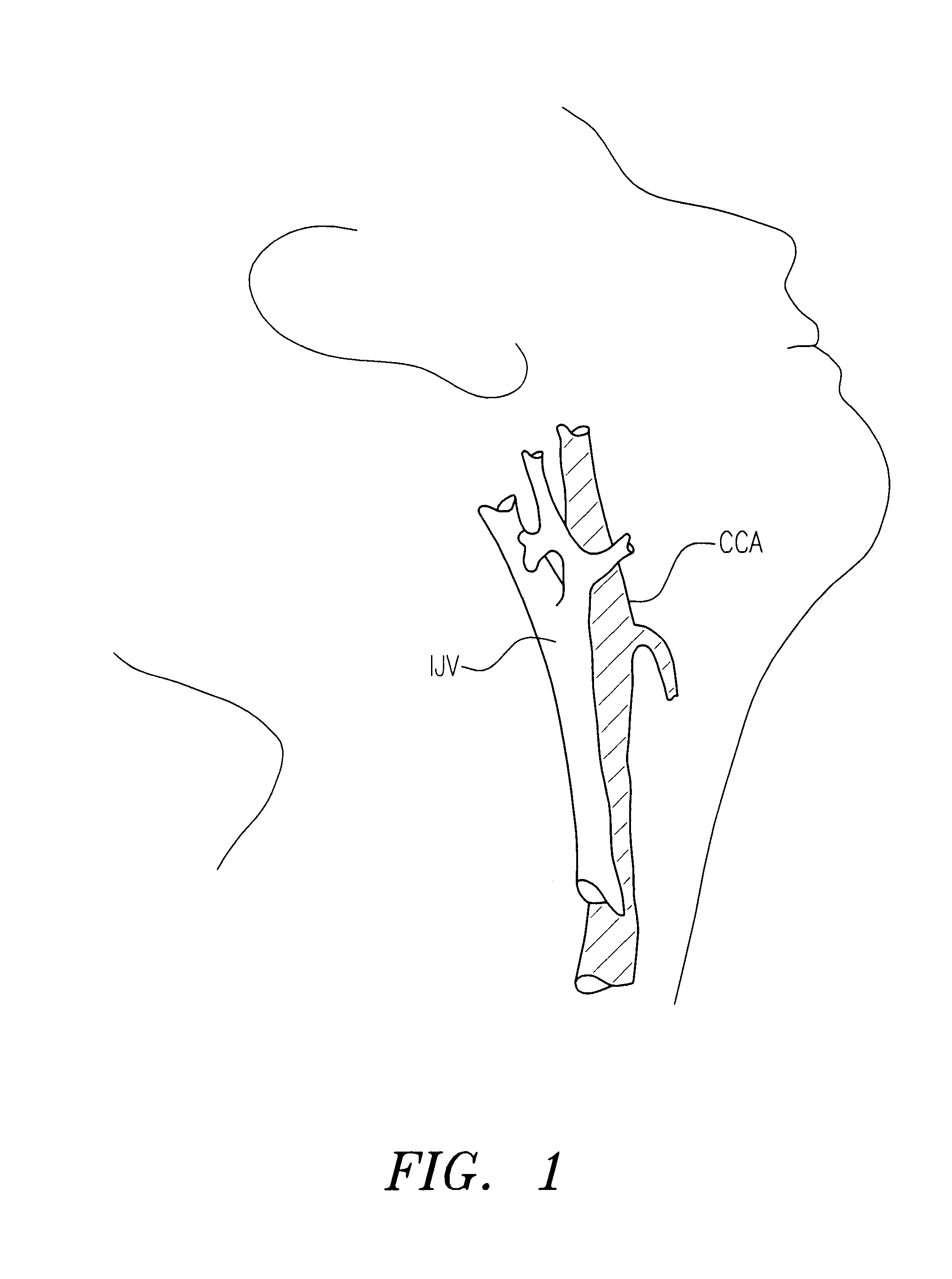
Transcarotid neurovascular catheter
An interventional catheter for treating an artery includes an elongated body sized and shaped to be transcervically introduced into a common carotid artery at an access location in the neck. The elongated body has an overall length such that the distal most section can be positioned in an intracranial artery and at least a portion of the proximal most section is positioned in the common carotid artery during use.
Owner:NEUROCO INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com