Patents
Literature
584 results about "Transistor circuits" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
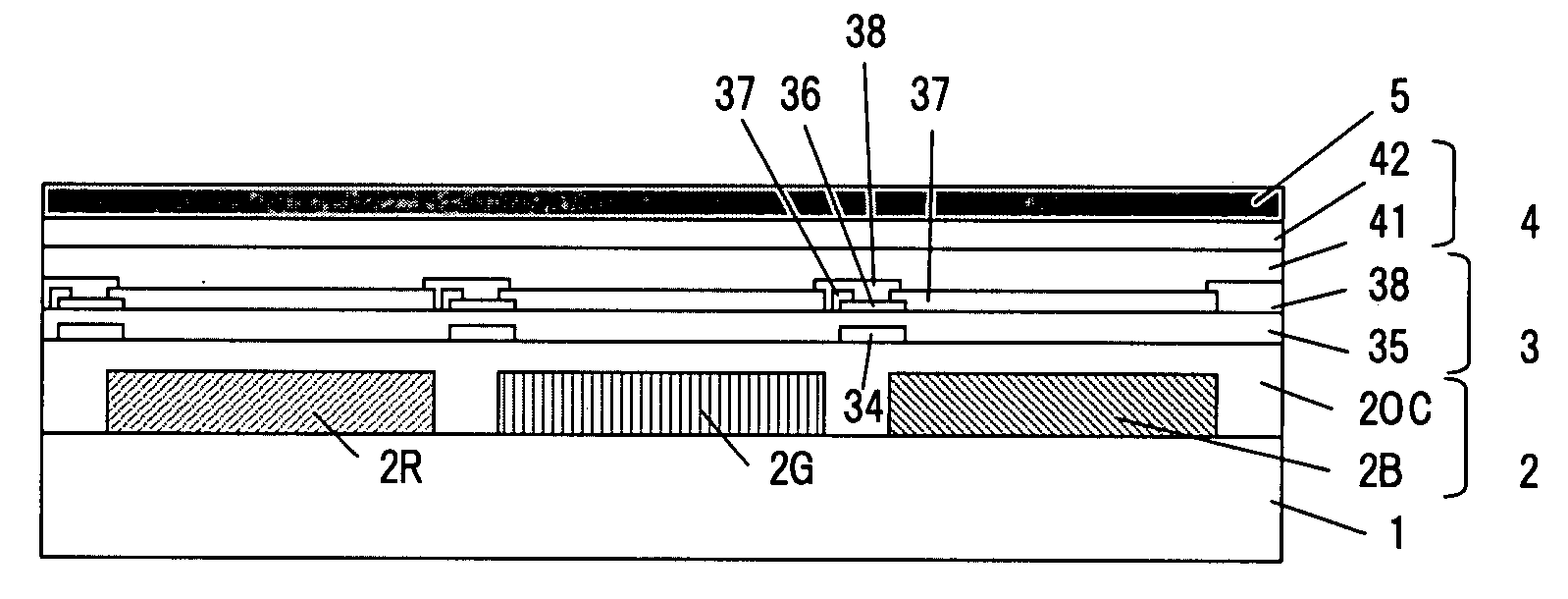
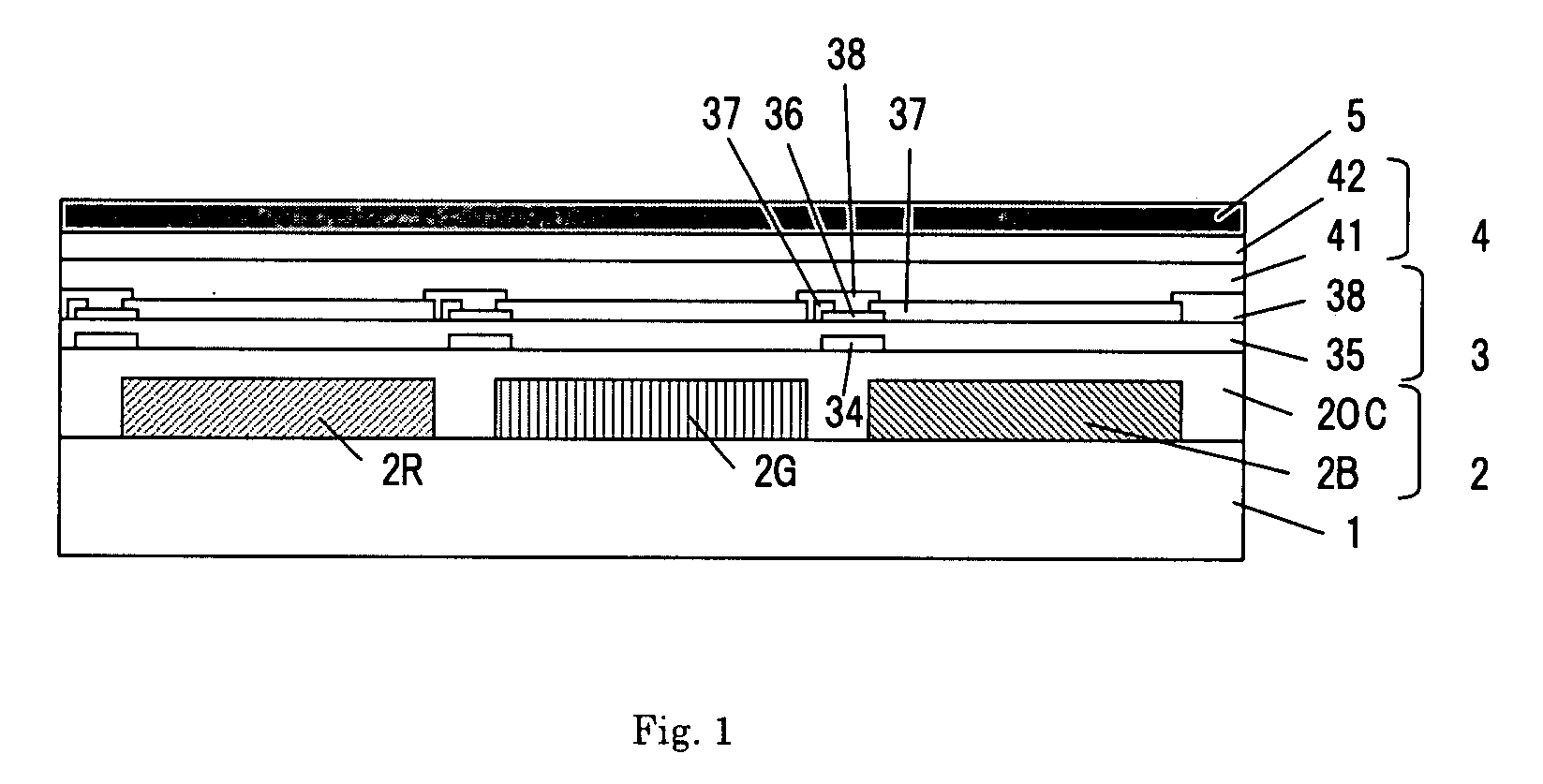
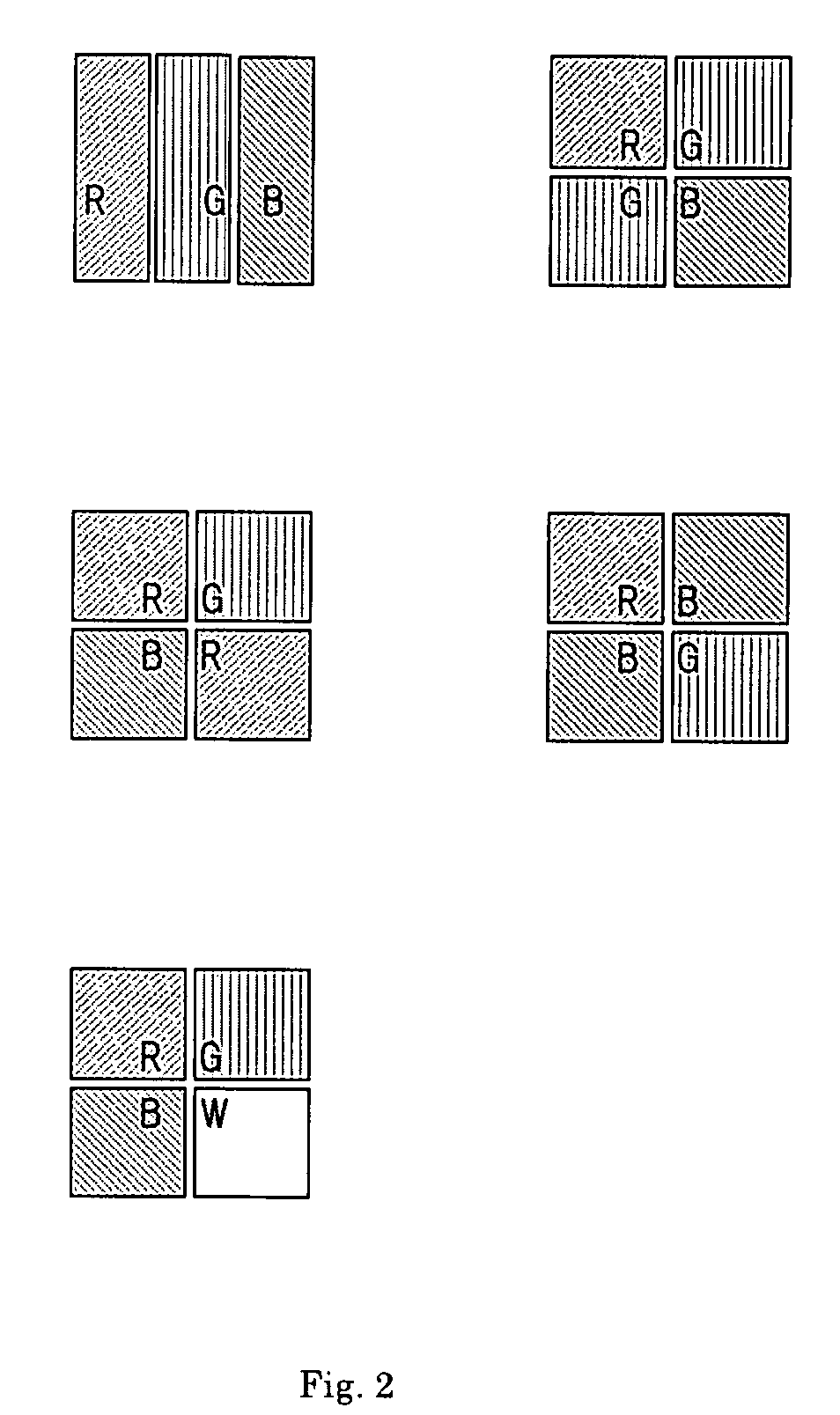
Color el display and method for producing the same
ActiveUS20080129195A1Quality improvementHigh color purityDischarge tube luminescnet screensLamp detailsDisplay deviceEngineering
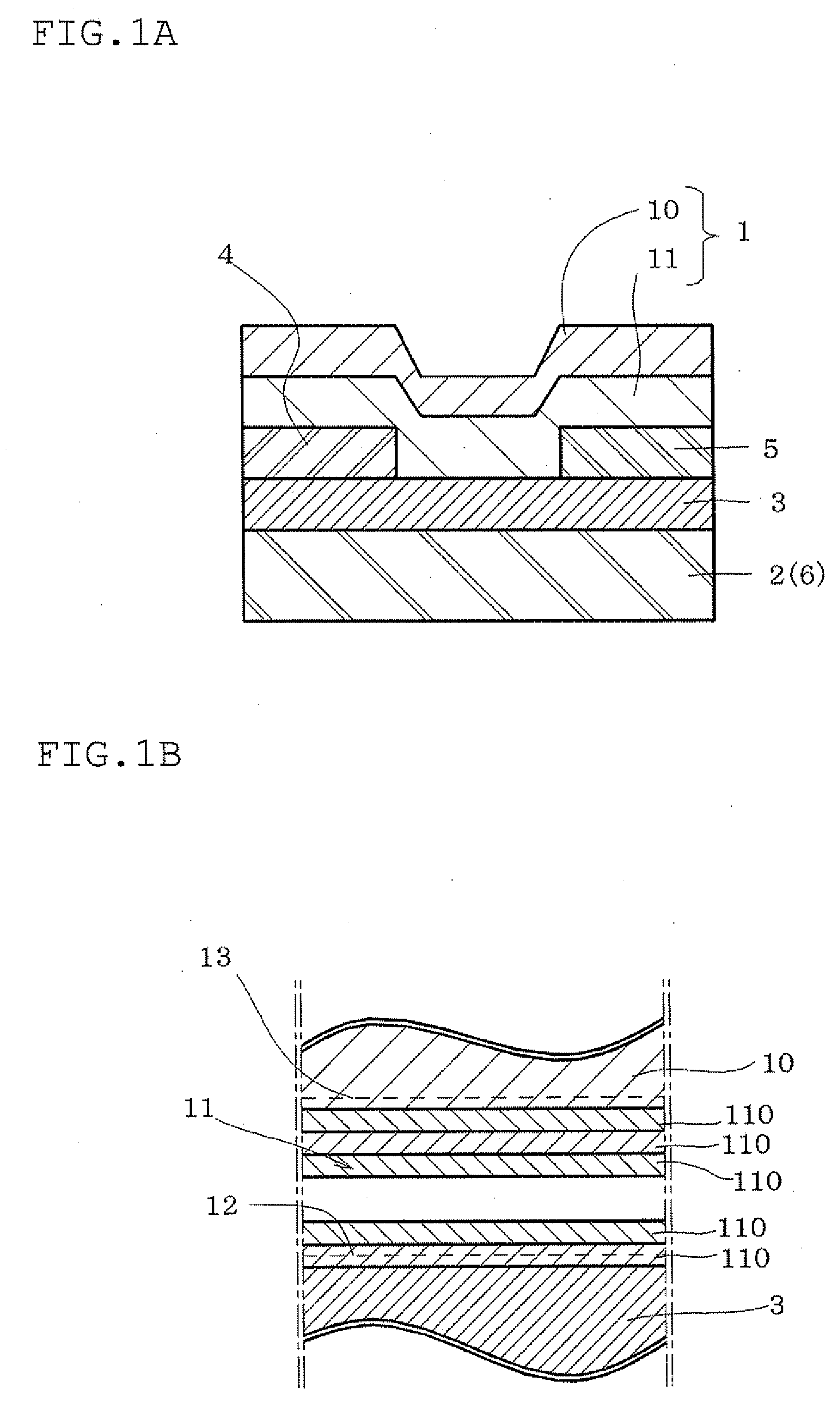
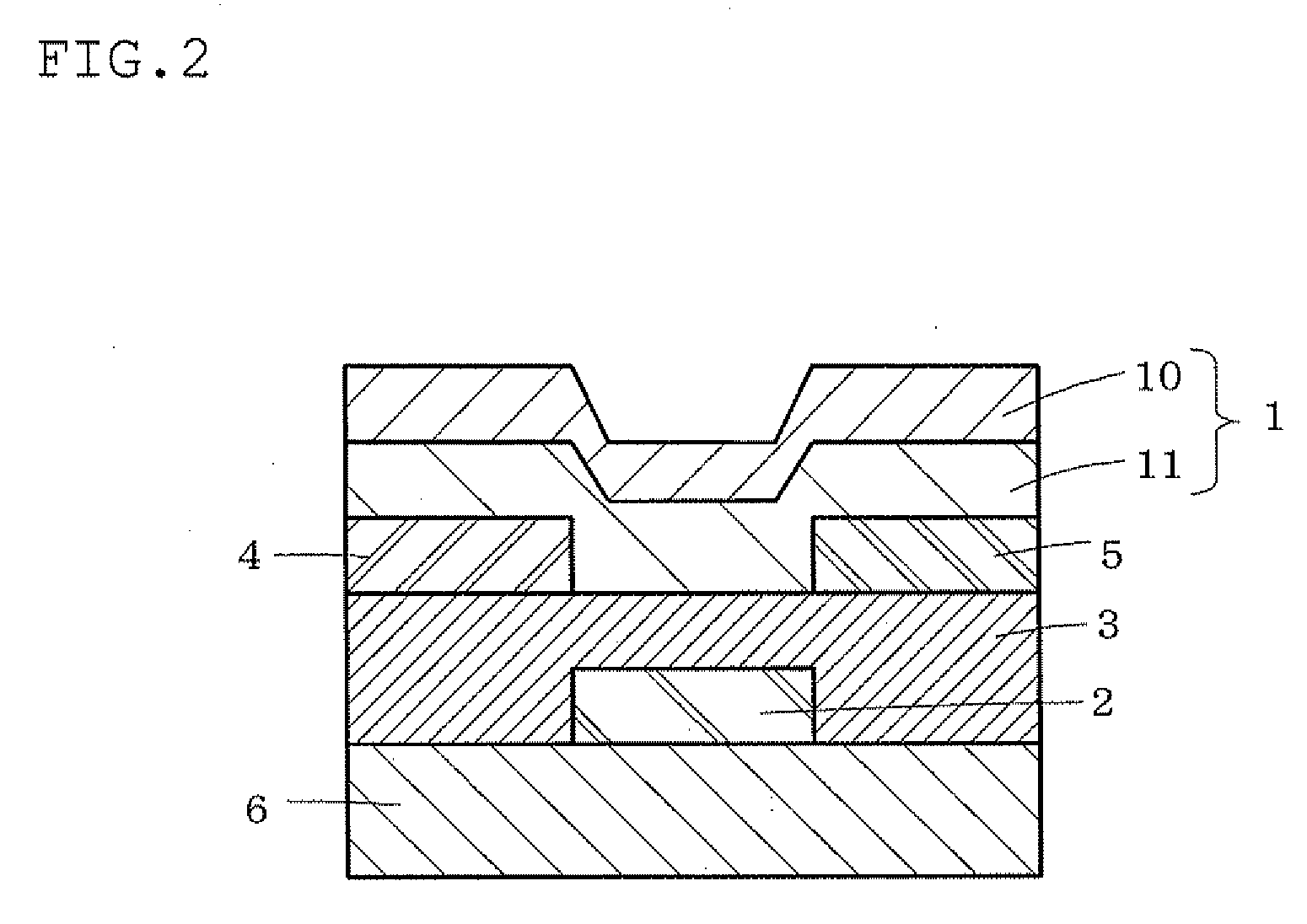
One embodiment of the present invention is a color EL display characterized in that at least color filters, a thin film transistor circuit, an organic EL layer, and a common electrode are laminated in this order on a transparent substrate. Another embodiment of the invention is a method for producing a color EL display comprising the steps of forming color filters or a transparent substrate; forming a thin film transistor circuit; forming an organic EL layer; and forming a common electrode, wherein process temperatures of the steps of forming the thin film transistor circuit and subsequent steps are 200° C. or less.
Owner:TOPPAN PRINTING CO LTD
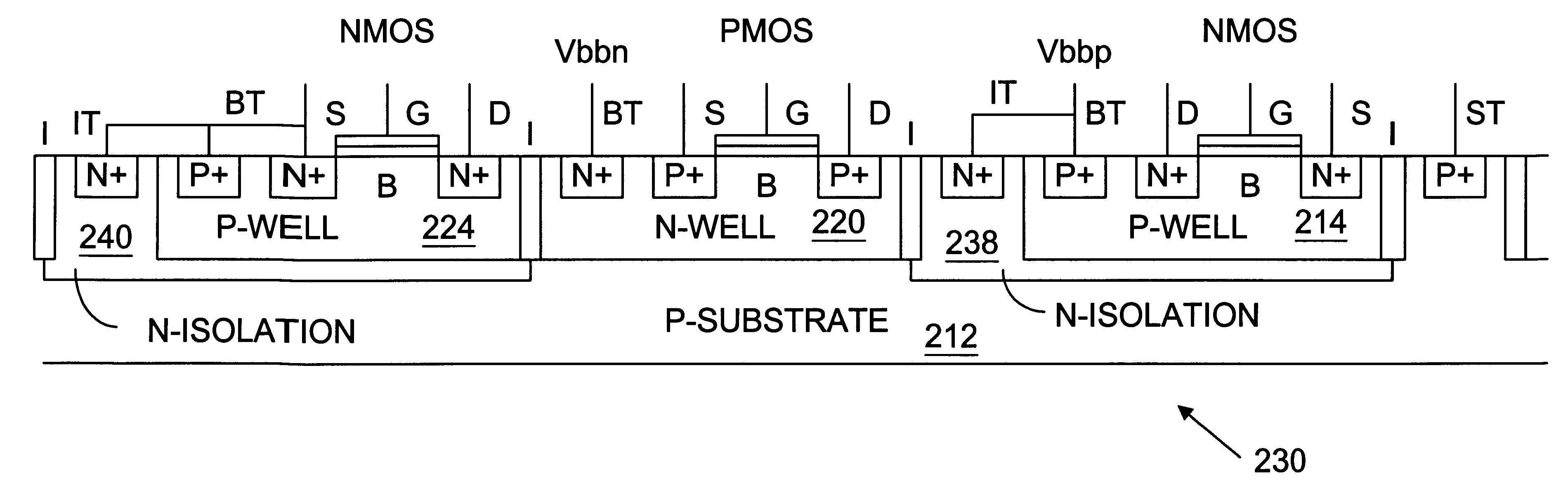
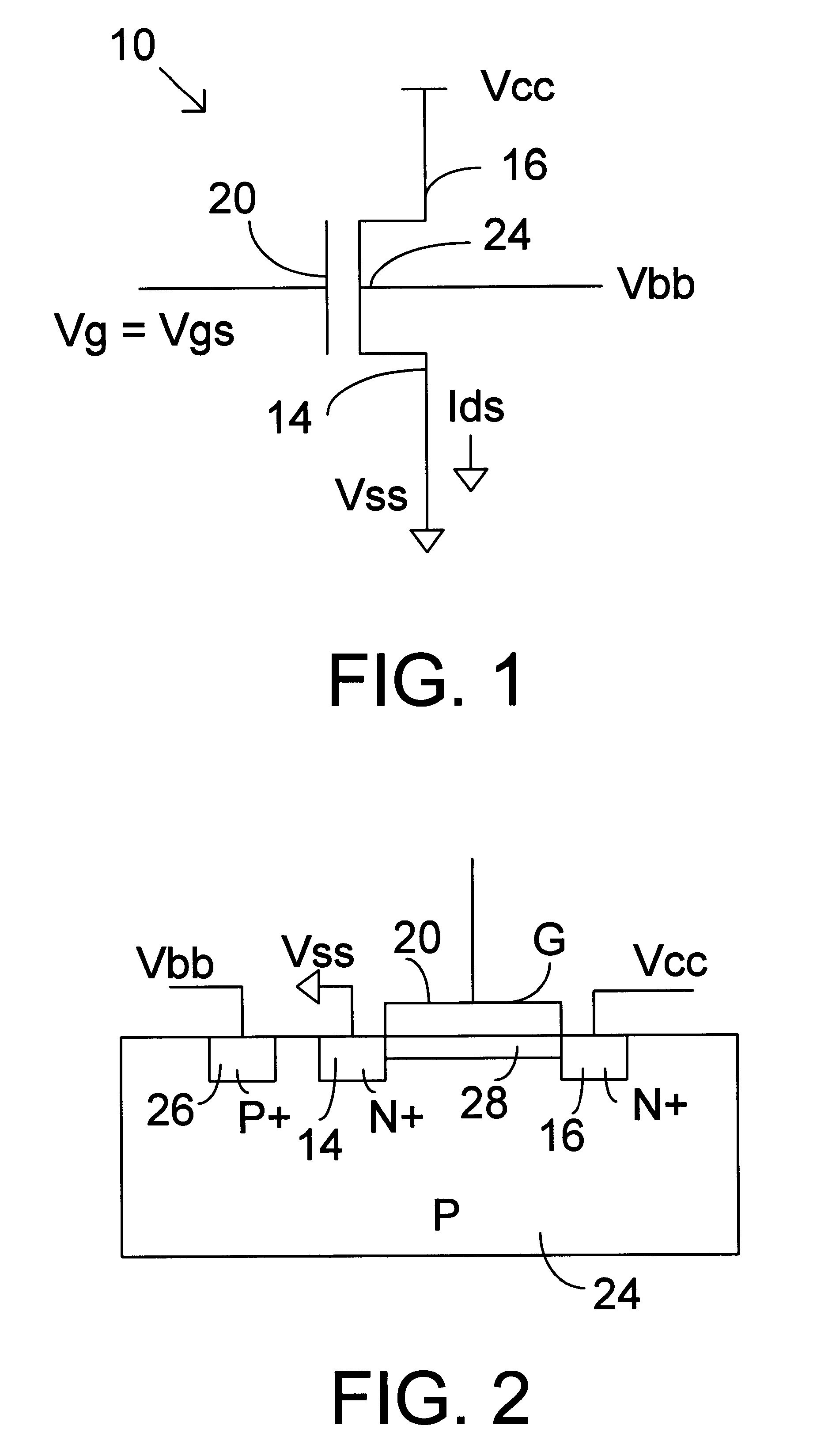
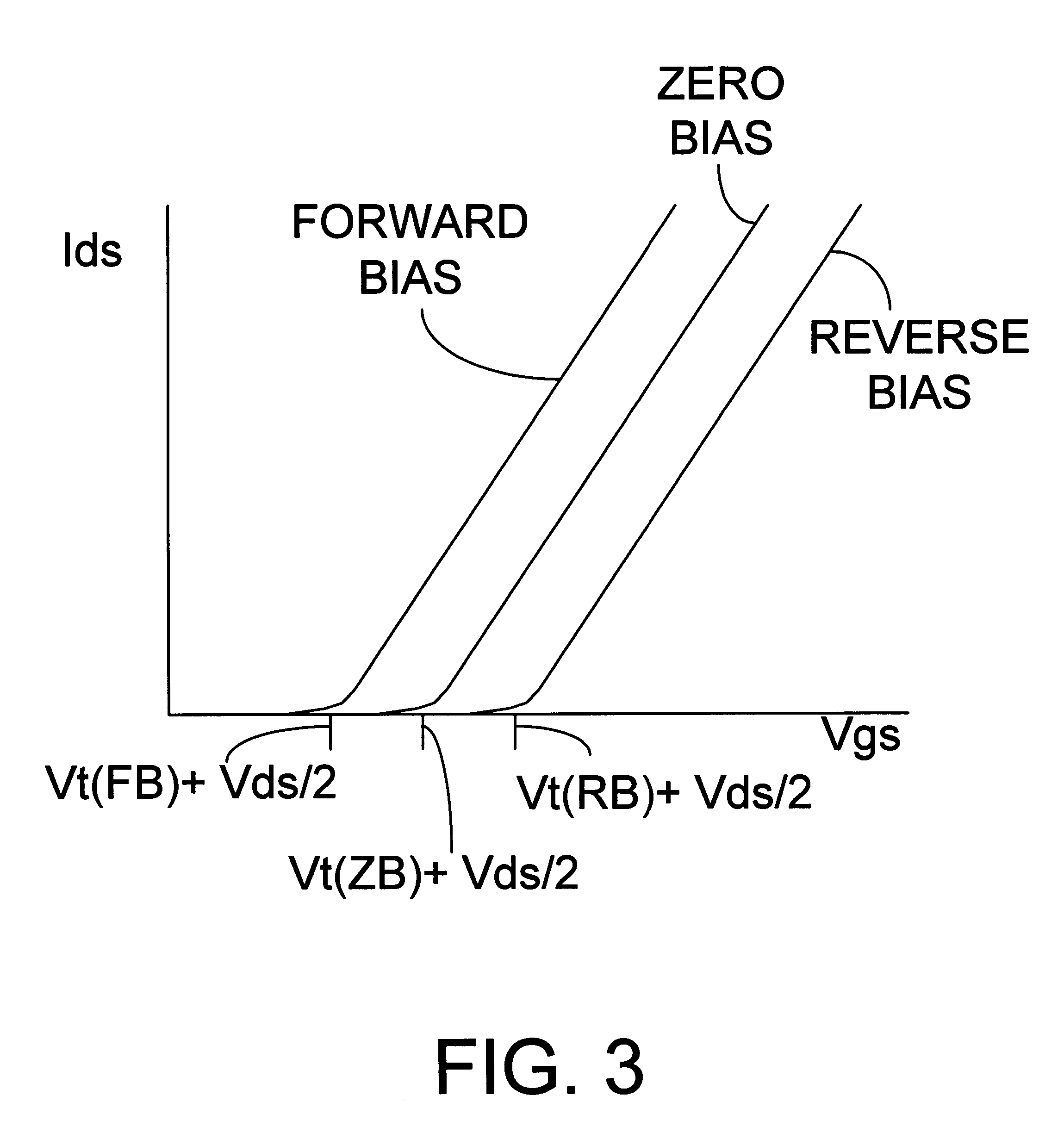
Multiple well transistor circuits having forward body bias
In one embodiment to the invention, a semiconductor circuit includes a substrate and a first well formed in the substrate. A first group of field effect transistors is formed in the first well and has a first body. The circuit includes a first body voltage to the first body to forward body bias the first group of field effect transistors. The circuit includes a first isolation structure to contain the first body voltage in the first well. In another embodiment, the circuit further includes a second group of field effect transistors having a non-forward body bias and the first isolation structure prevents the first body voltage from influencing a voltage of a body of the second group of field effect transistors. In yet another embodiment, a second isolation structure adjacent to the second well contain a second body voltage in a second well holding the second group of field effect transistors.
Owner:INTEL CORP
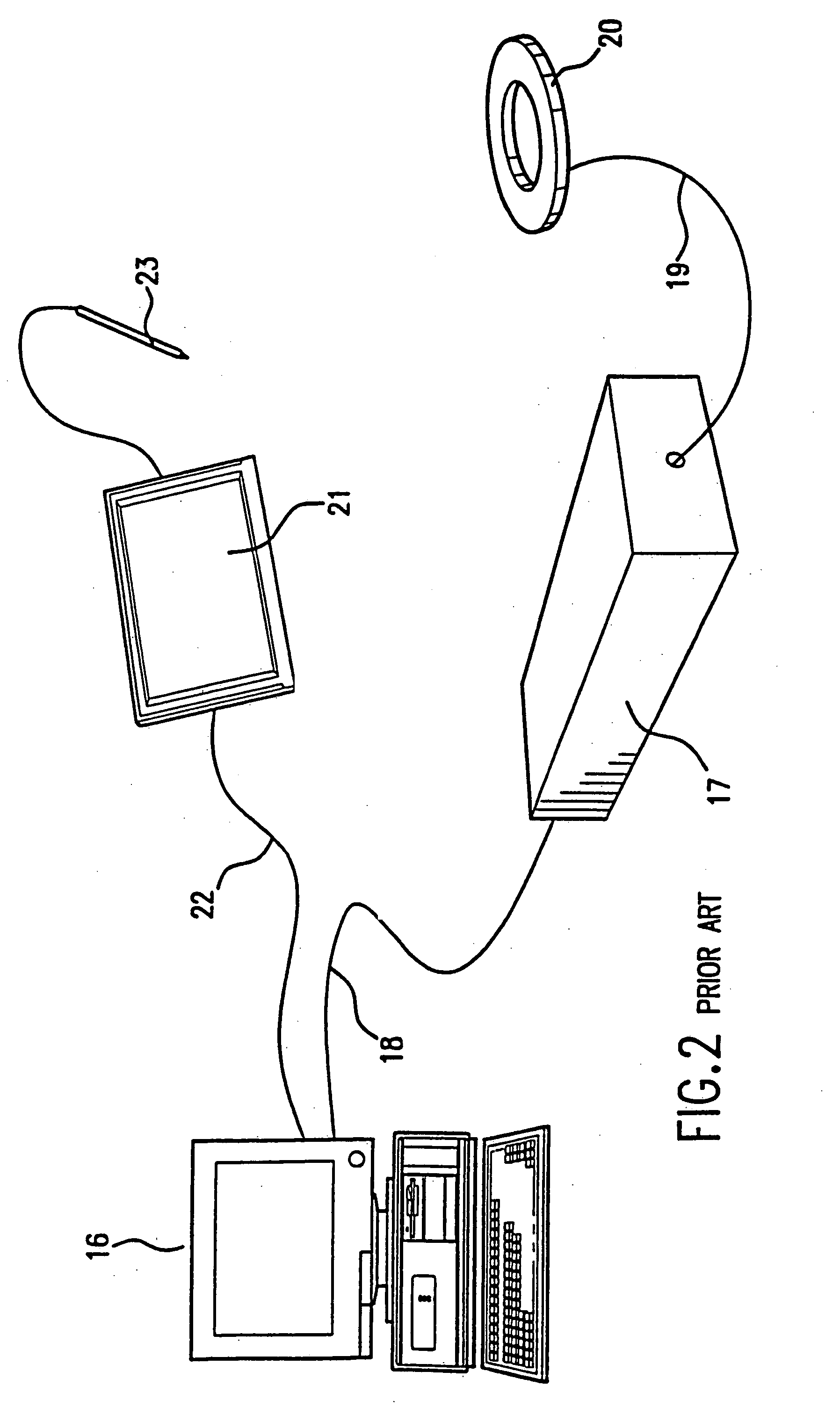
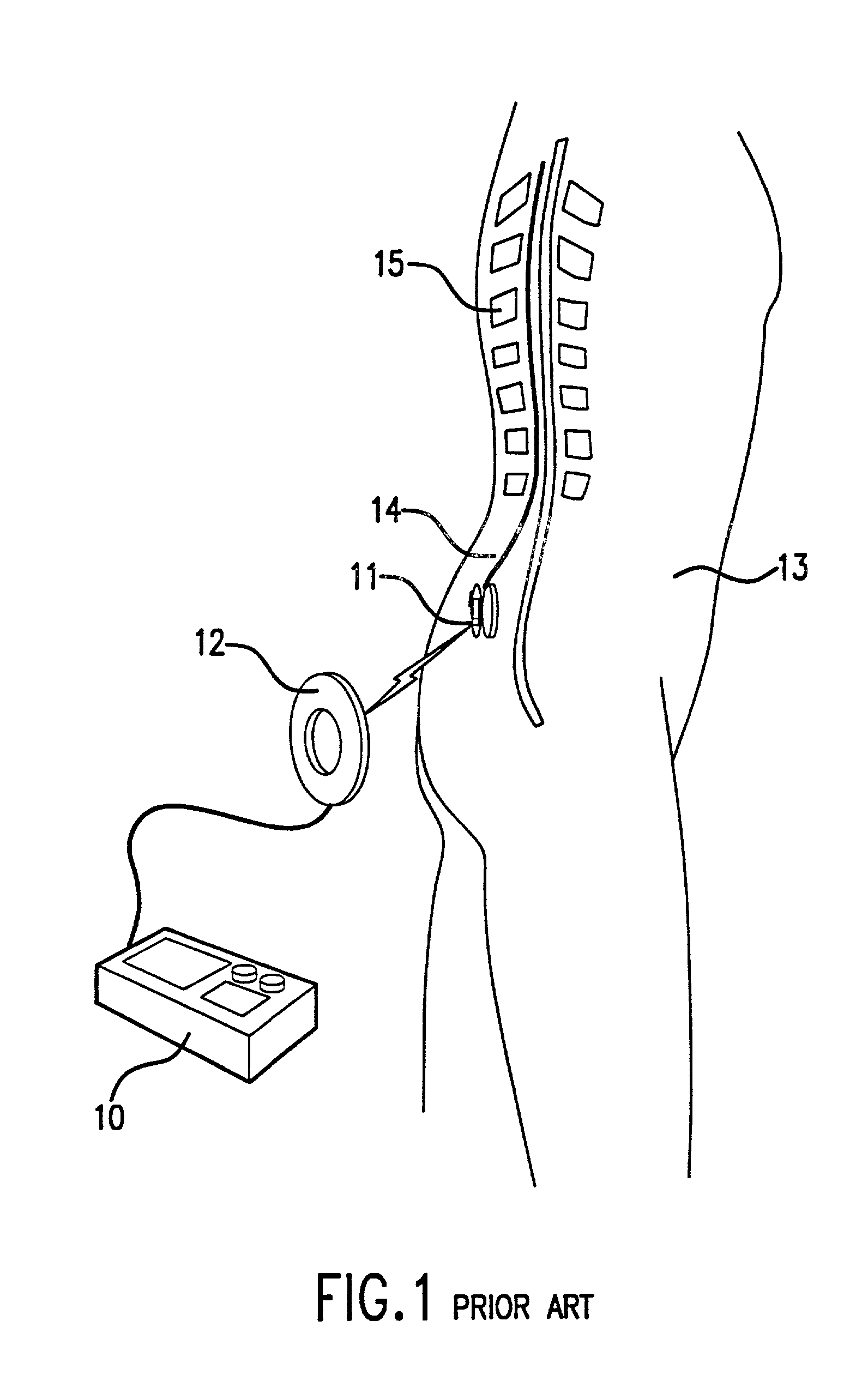
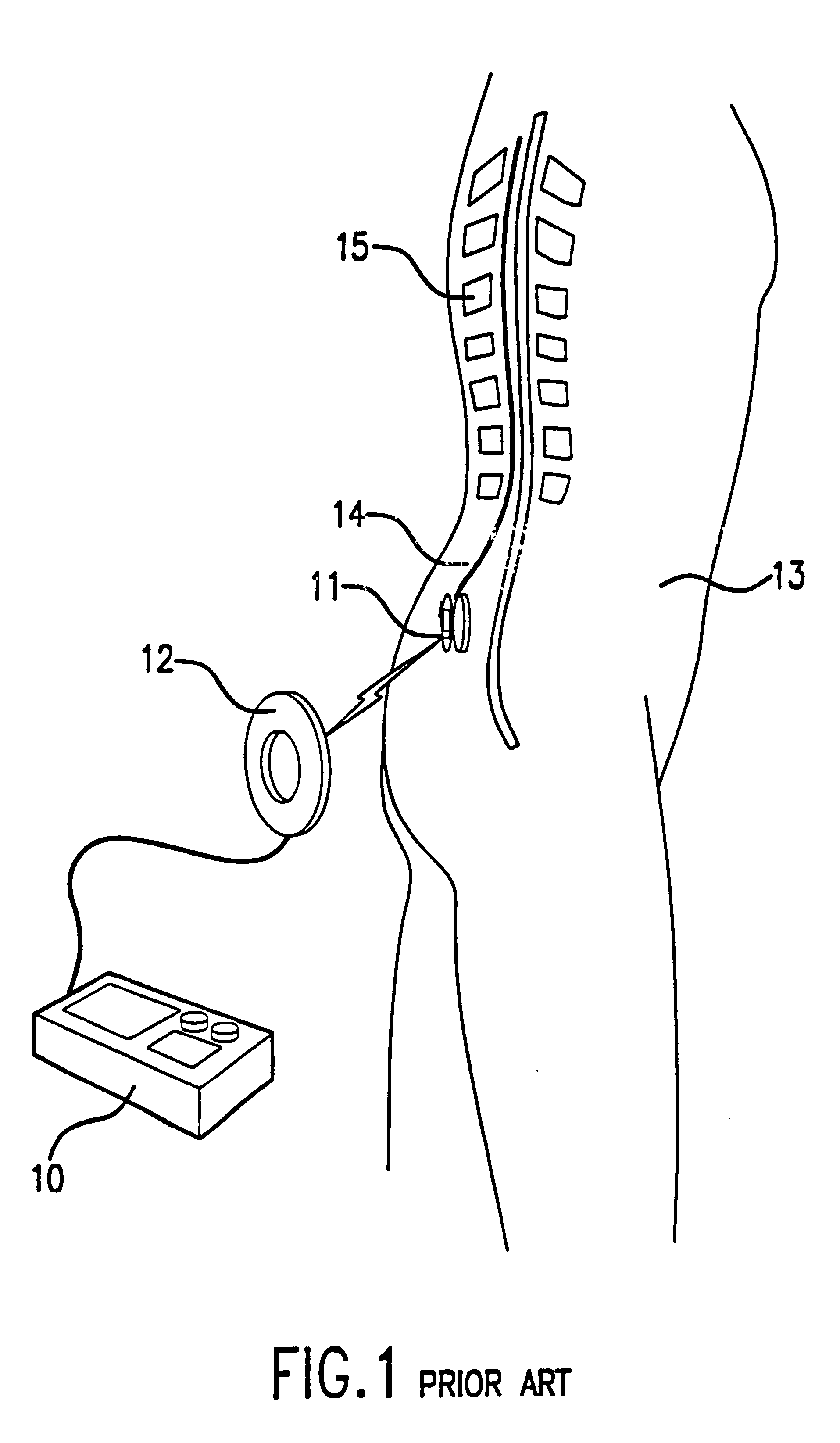
Patient interactive neurostimulation system and method
A fully automated computer controlled system is provided for adjustment of neurostimulation implants used in pain therapy and in treating neurological dysfunction which includes a patient interactive computer, and a universal transmitter interface integrally embedded in the patient interactive computer or built into the antenna which is capable of stimulating any type of implanted neurostimulation devices by imitating programming codes. The patient interacts with the system through the patient interactive computer. The universal transmitter interface includes a direct digital synthesizer, a transistor circuitry driving the antenna in ON-OFF fashion and a gating unit for driving the transistor circuitry under control of the processing means in the patient-interactive computer. Alternatively, the universal transmitting interface includes a balanced modulator for modulation of the carrier signal generated at the direct digital synthesizer.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Patient interactive neurostimulation system and method
A fully automated computer controlled system is provided for adjustment of neurostimulation implants used in pain therapy and in treating neurological dysfunction which includes a patient interactive computer, and a universal transmitter interface integrally embedded in the patient interactive computer or built into the antenna which is capable of stimulating any type of implanted neurostimulation devices by imitating programming codes. The patient interacts with the system through the patient interactive computer. The universal transmitter interface includes a direct digital synthesizer, a transistor circuitry driving the antenna in ON-OFF fashion and a gating unit for driving the transistor circuitry under control of the processing means in the patient-interactive computer. Alternatively, the universal transmitting interface includes a balanced modulator for modulation of the carrier signal generated at the direct digital synthesizer.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
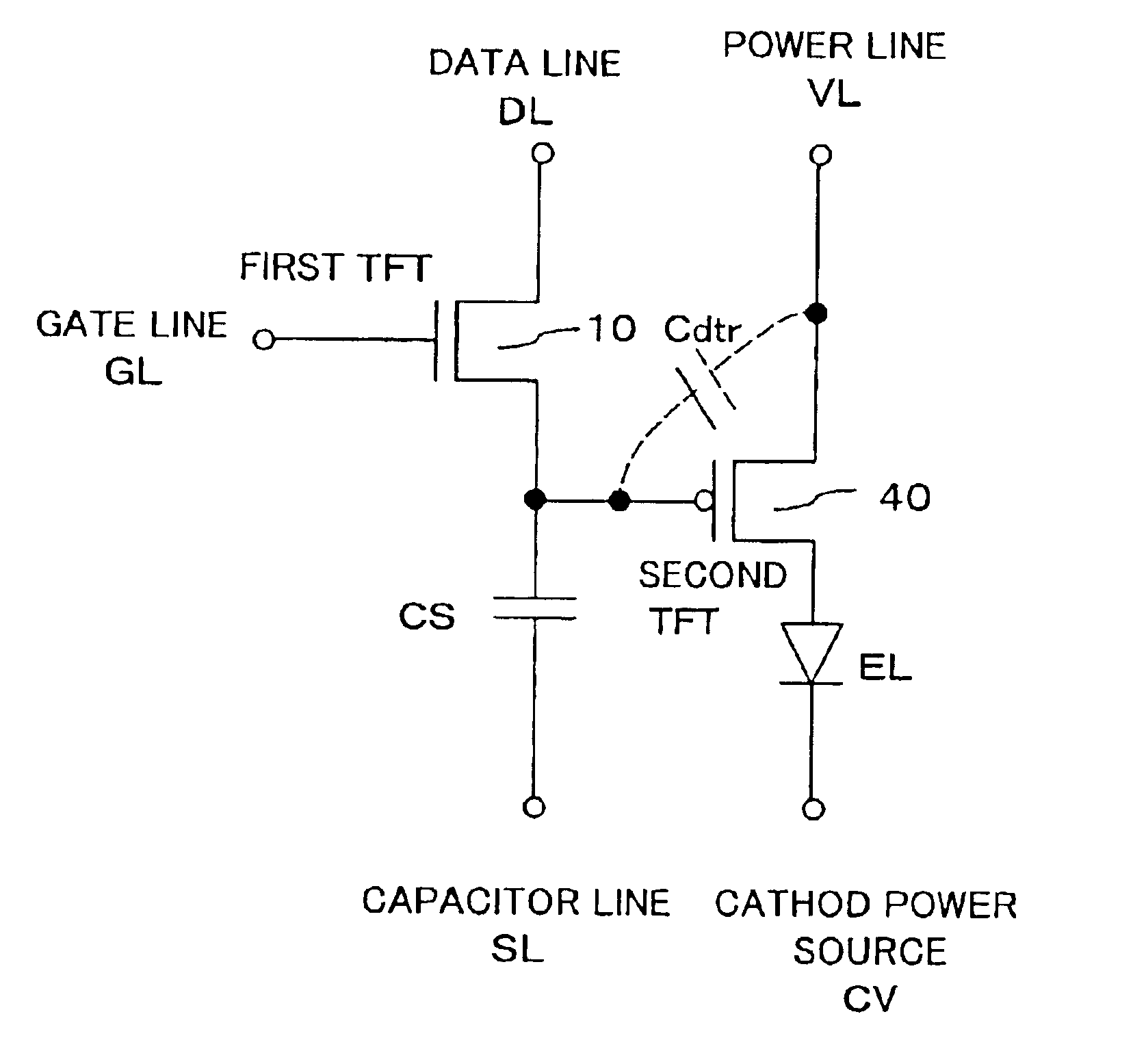
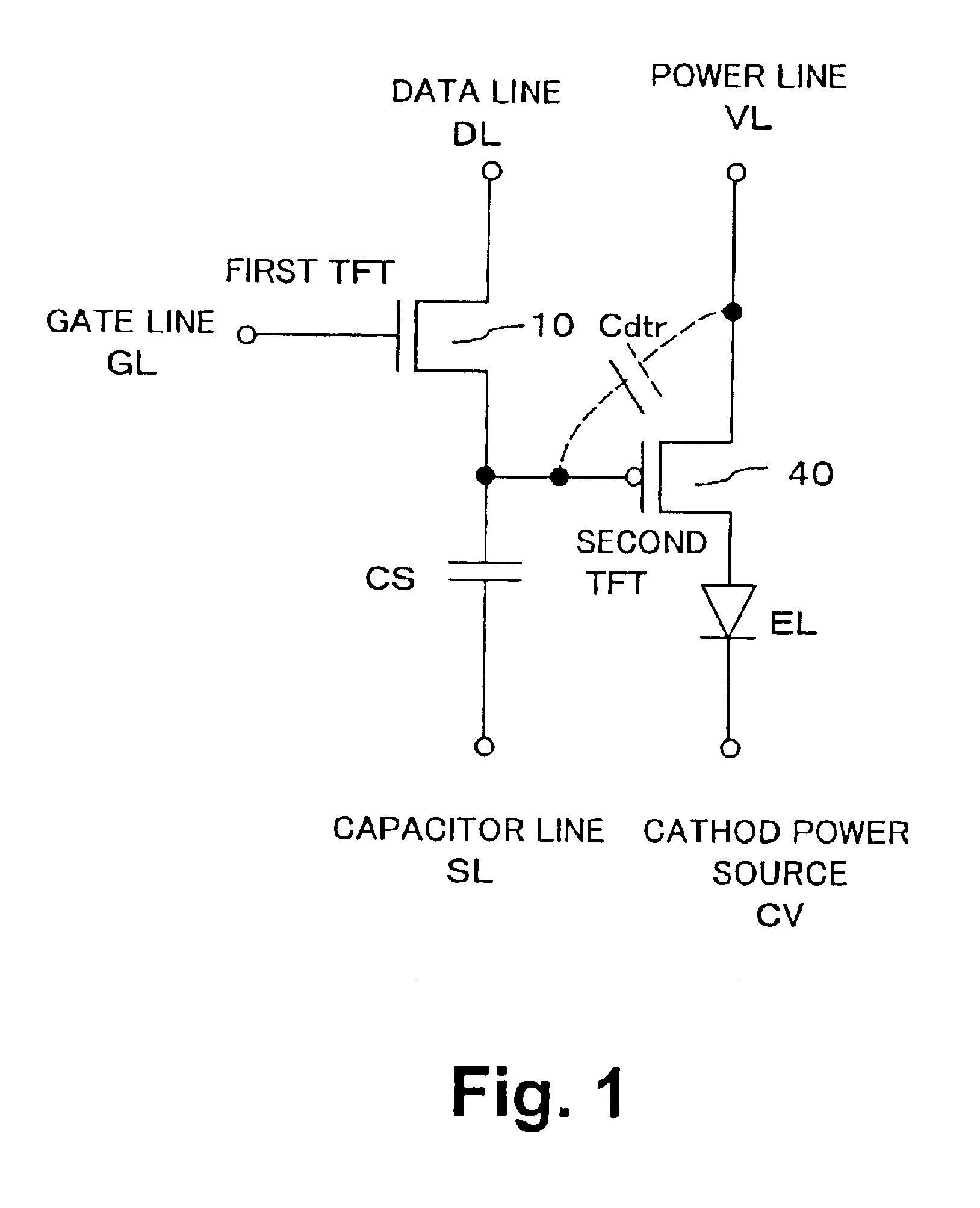
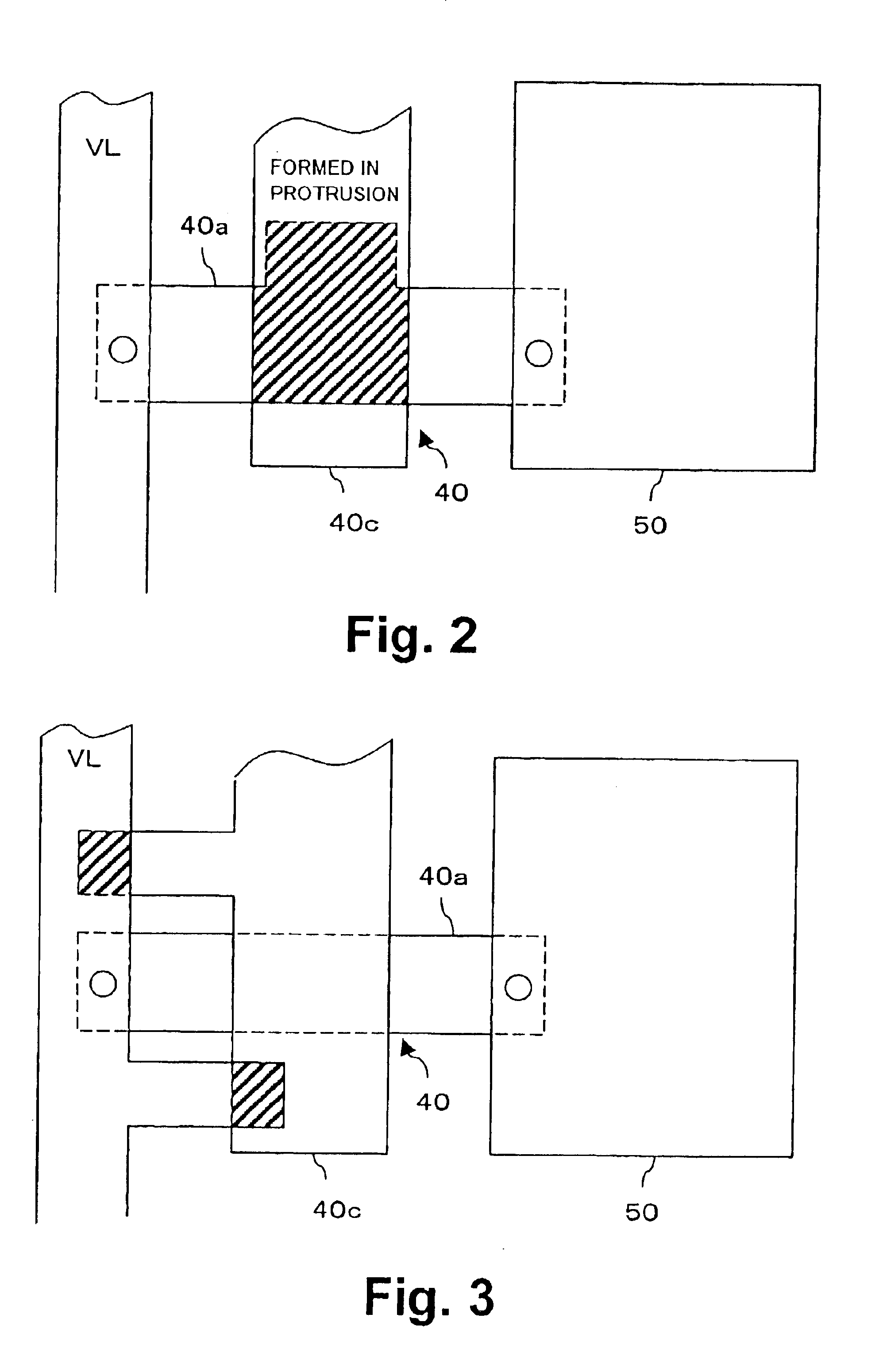
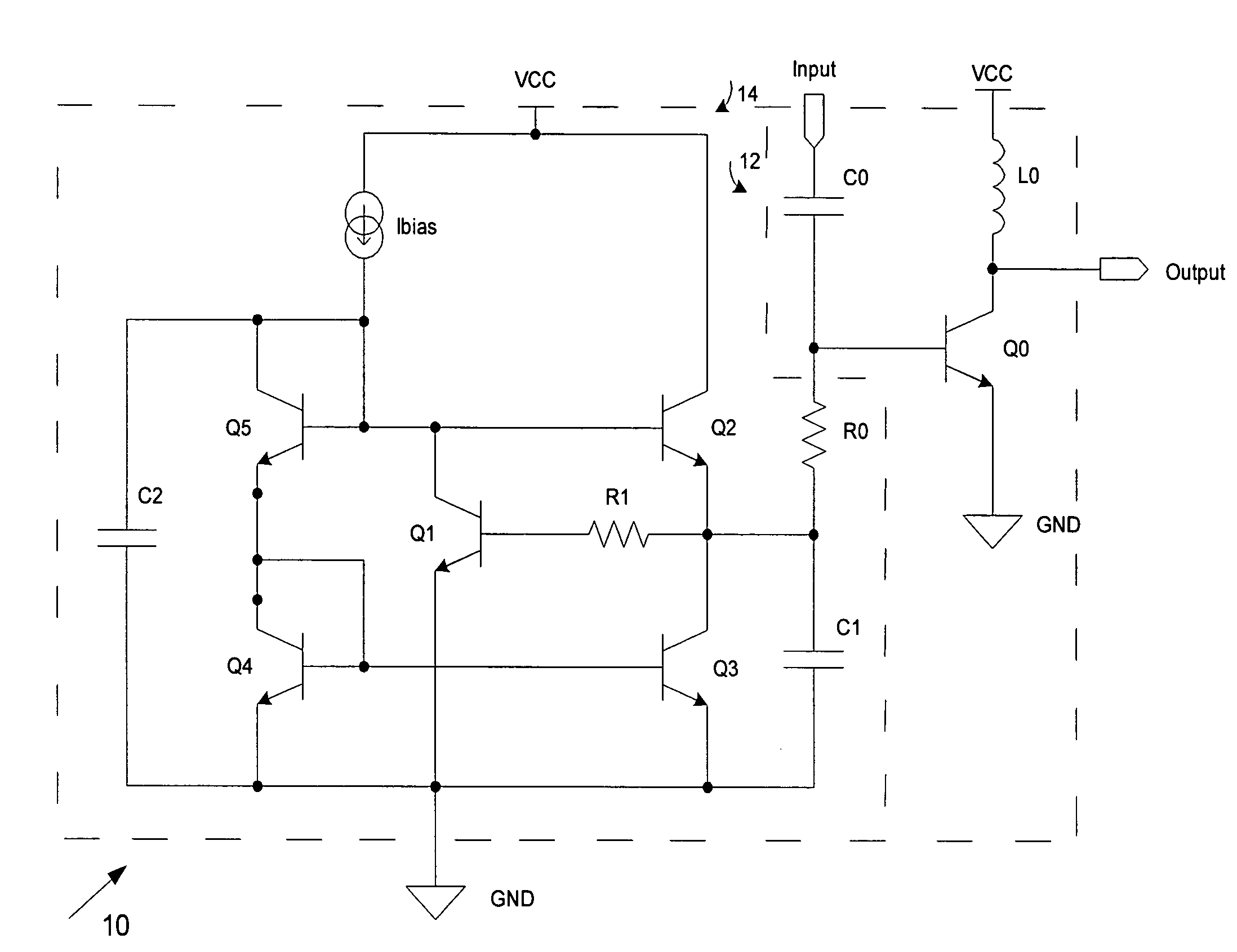
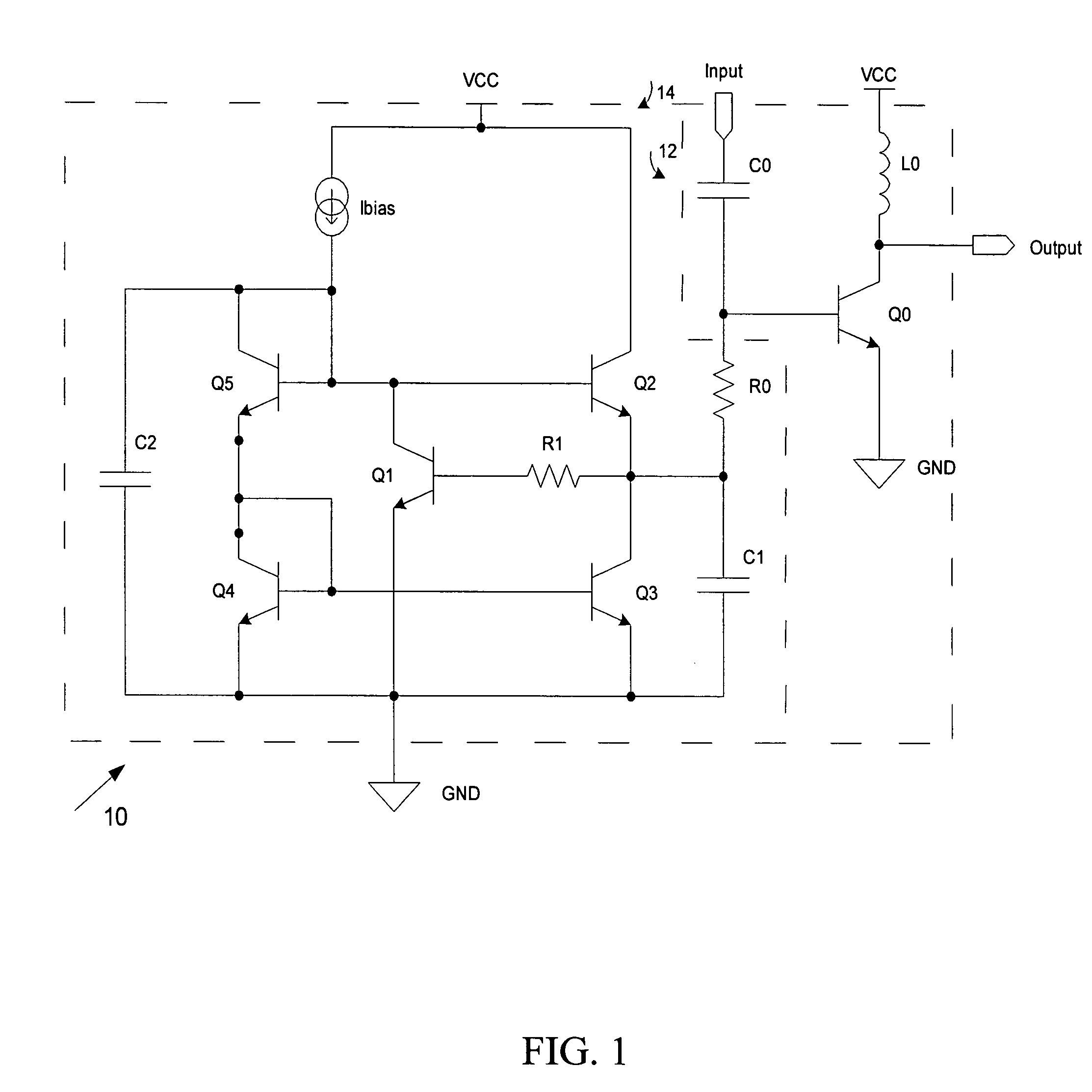
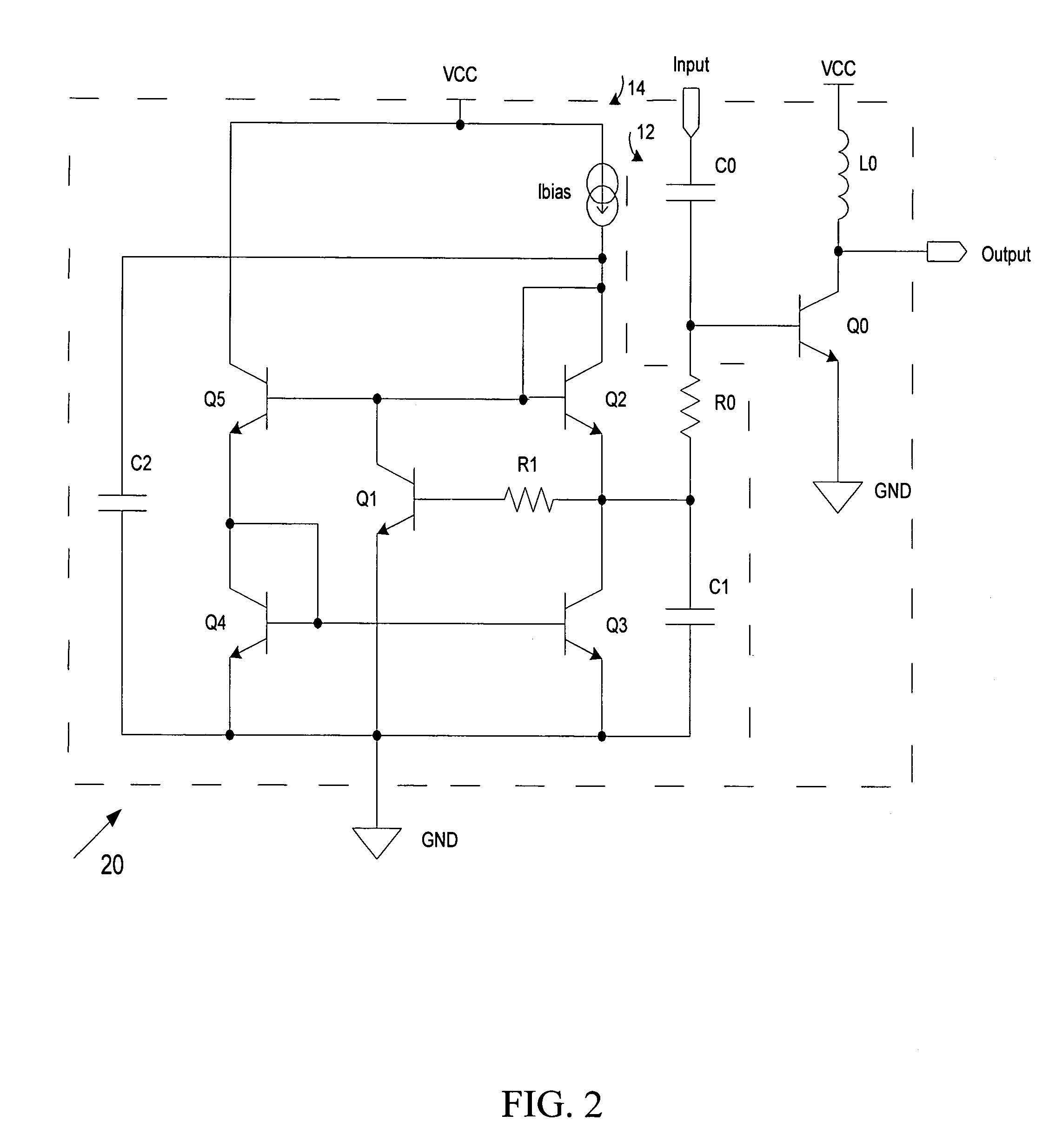
Transistor circuit
InactiveUS6914448B2Increase capacitanceTransistorStatic indicating devicesCapacitanceTransistor circuits
Transistor capacitance Cdtr inevitably generated between the gate and the drain of a second TFT is increased. Accordingly, an operation test of a first TFT and the second TFT can be conducted by turning on the first TFT to charge the transistor capacitance Cdtr and detecting the stored charges.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
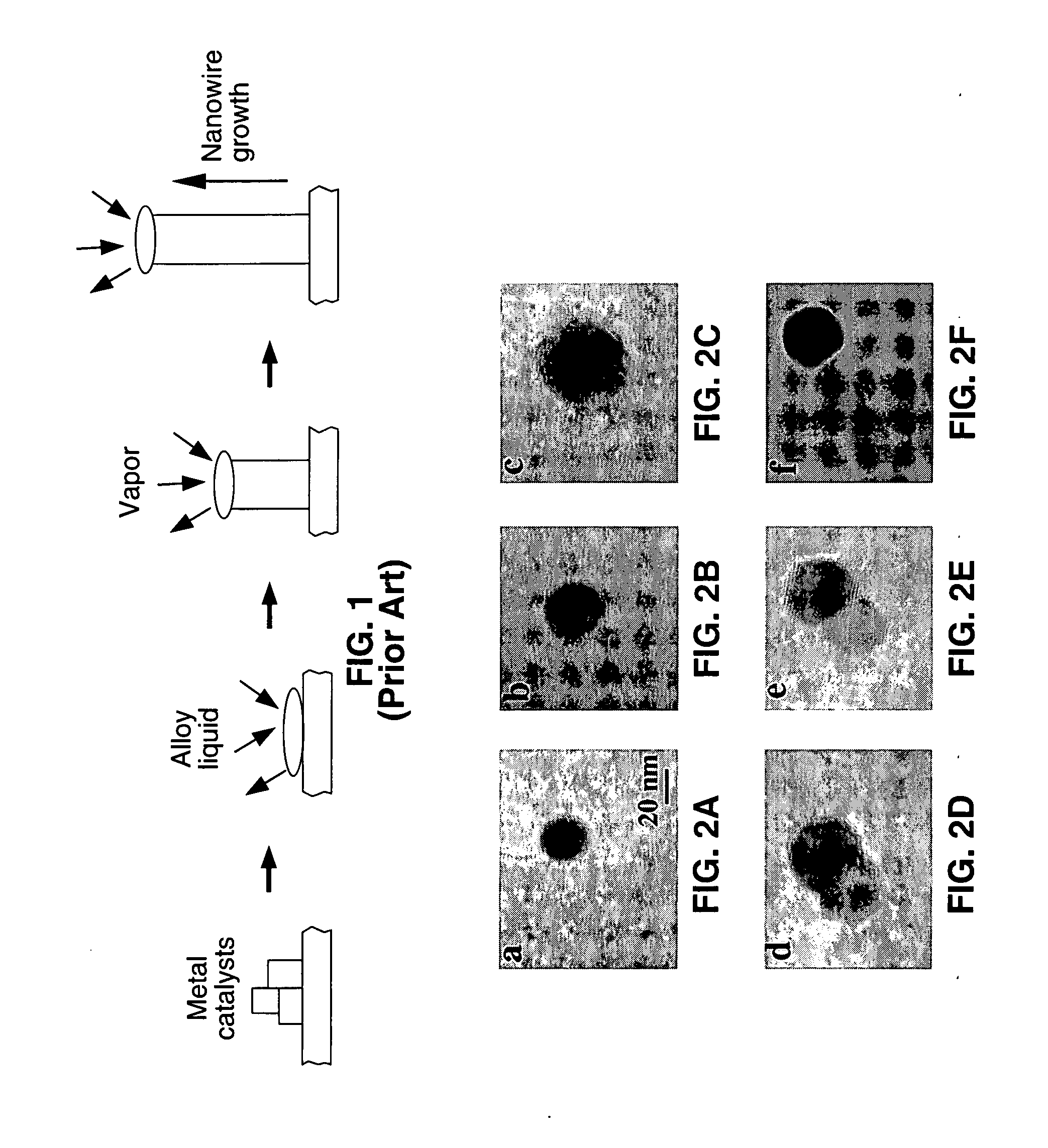
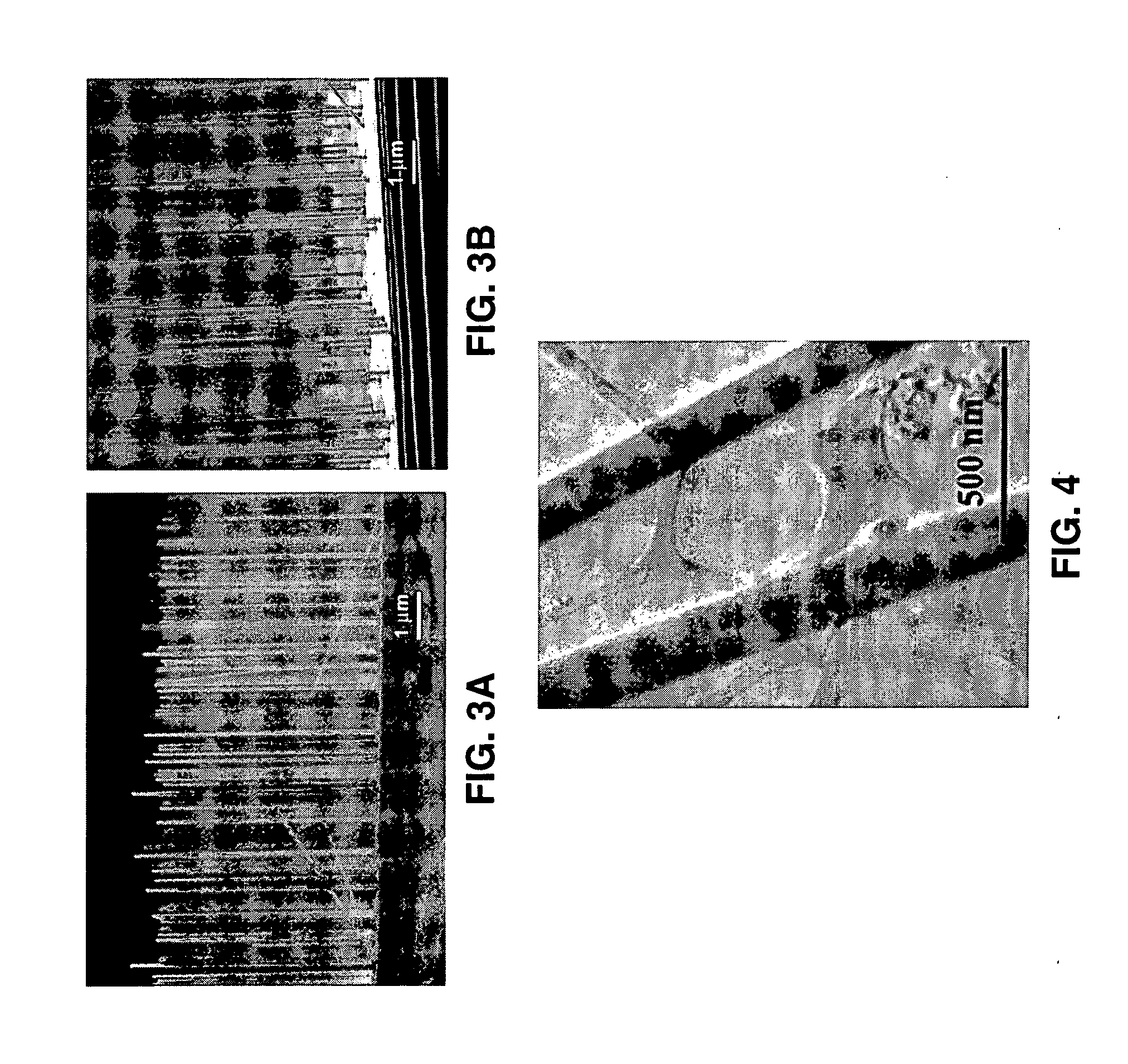
Vertical integrated silicon nanowire field effect transistors and methods of fabrication
Vertical integrated field effect transistor circuits and methods are described which are fabricated from Silicon, Germanium, or a combination Silicon and Germanium based on nanowires grown in place on the substrate. By way of example, vertical integrated transistors are formed from one or more nanowires which have been insulated, had a gate deposited thereon, and to which a drain is coupled to the exposed tips of one or more of the nanowires. The nanowires are preferably grown over a surface or according to a desired pattern in response to dispersing metal nanoclusters over the desired portions of the substrate. In one preferred implementation, SiCl4 is utilized as a gas phase precursor during the nanowire growth process. In place nanowire growth is also taught in conjunction with structures, such as trenches, while bridging forms of nanowires are also described.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Patient interactive neurostimulation system and method
A fully automated computer controlled system is provided for adjustment of neurostimulation implants used in pain therapy and in treating neurological dysfunction which includes a patient interactive computer, and a universal transmitter interface integrally embedded in the patient interactive computer or built into the antenna which is capable of stimulating any type of implanted neurostimulation devices by imitating programming codes. The patient interacts with the system through the patient interactive computer. The universal transmitter interface includes a direct digital synthesizer, a transistor circuitry driving the antenna in ON-OFF fashion and a gating unit for driving the transistor circuitry under control of the processing means in the patient-interactive computer. Alternatively, the universal transmitting interface includes a balanced modulator for modulation of the carrier signal generated at the direct digital synthesizer.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
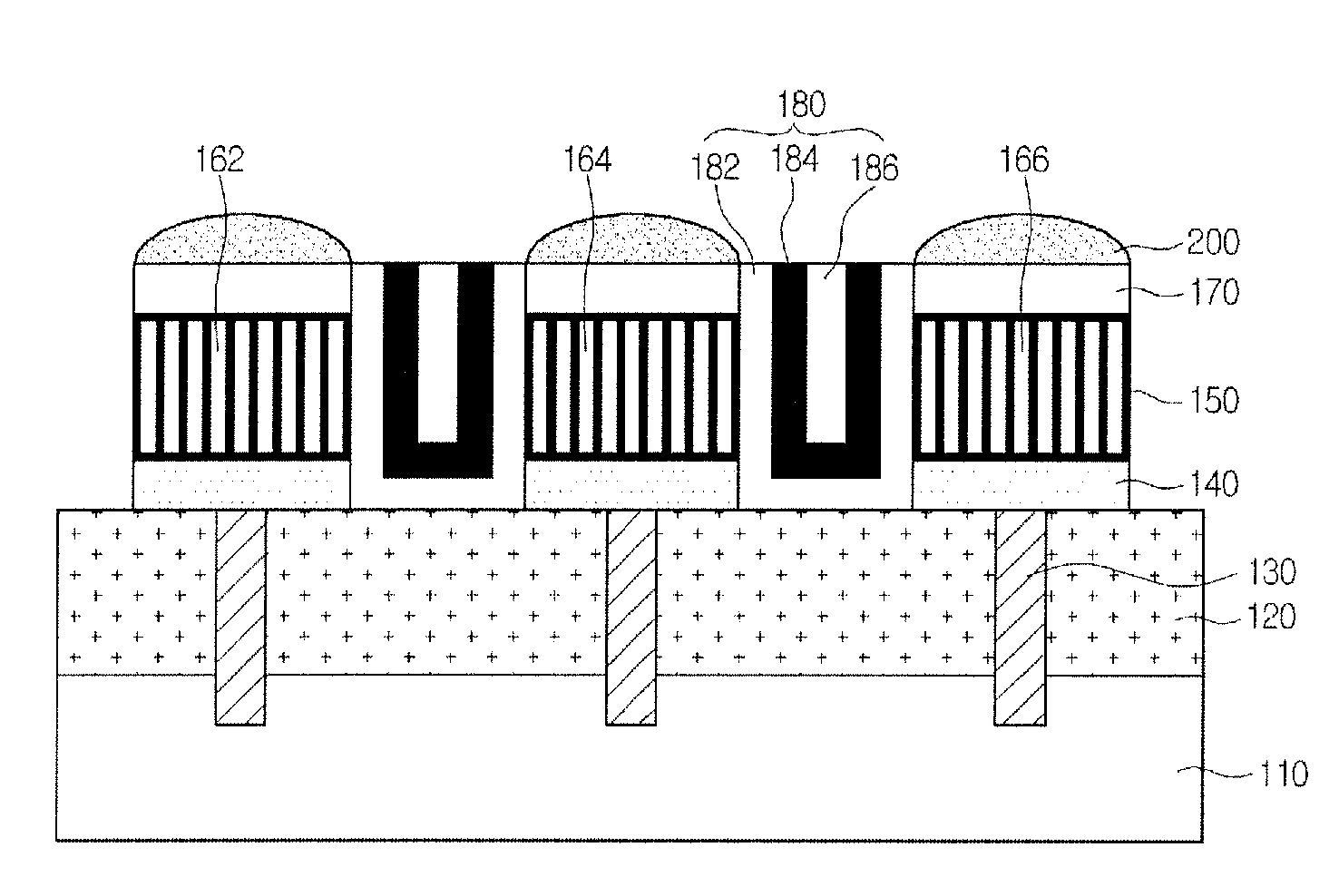
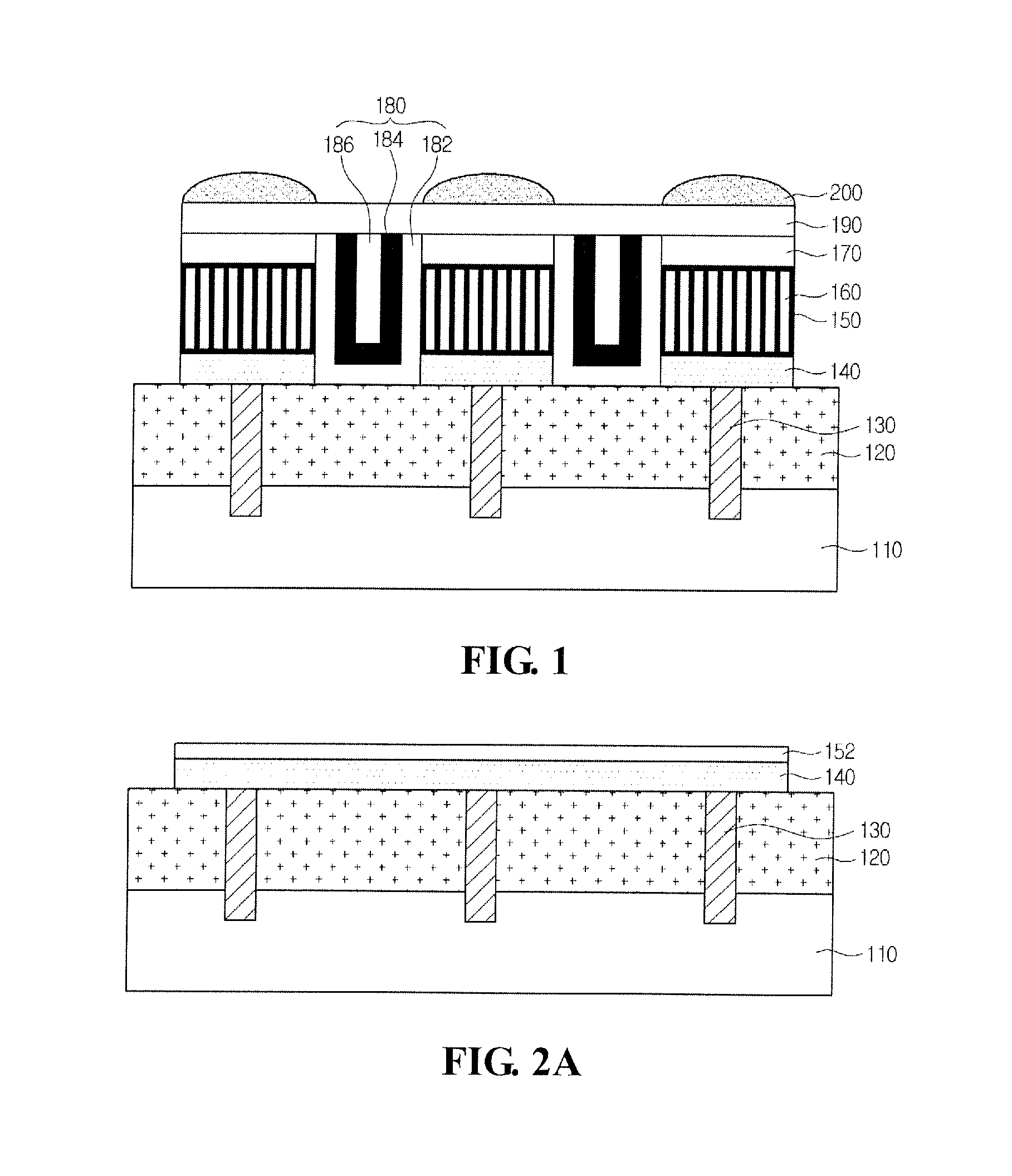
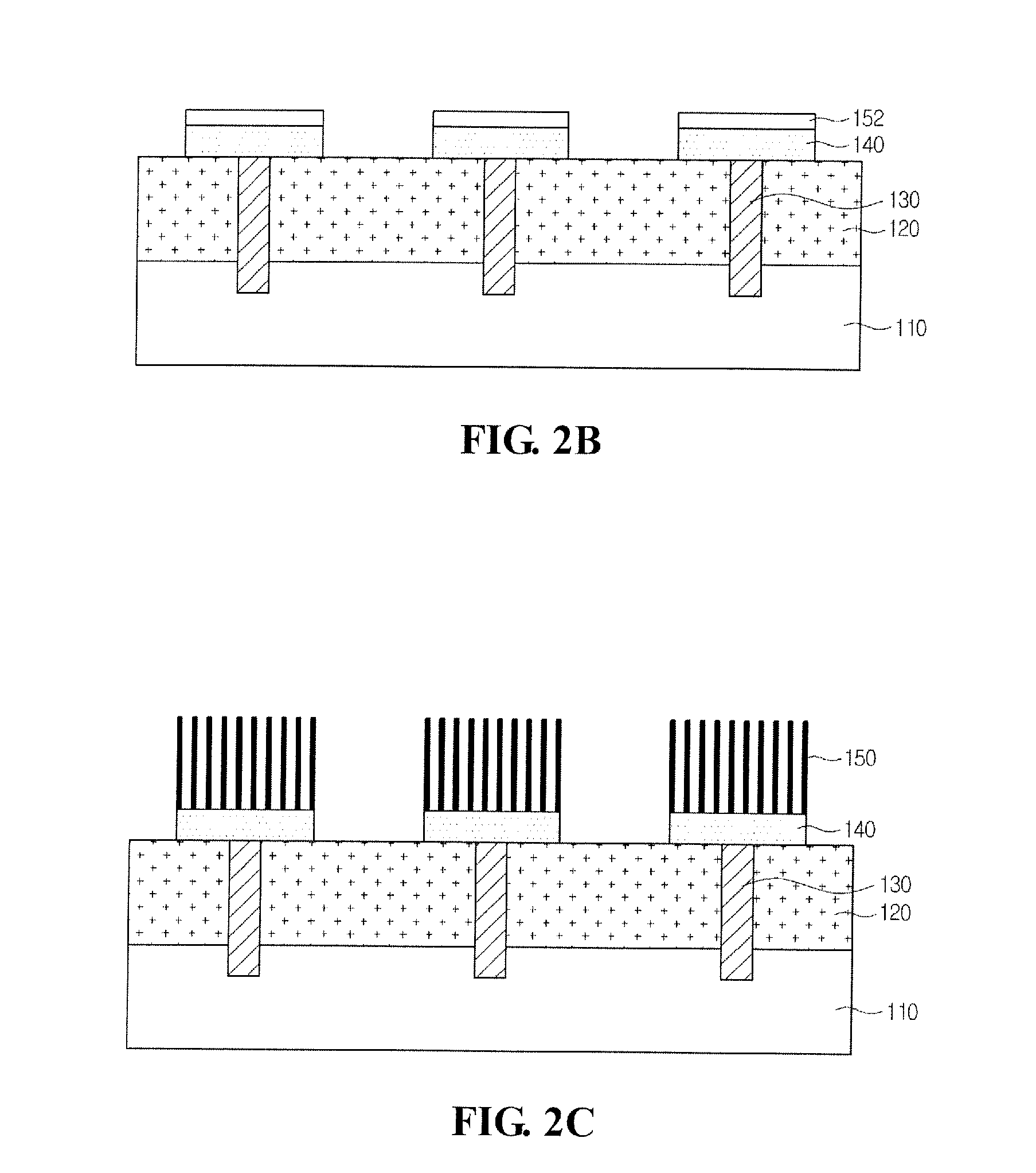
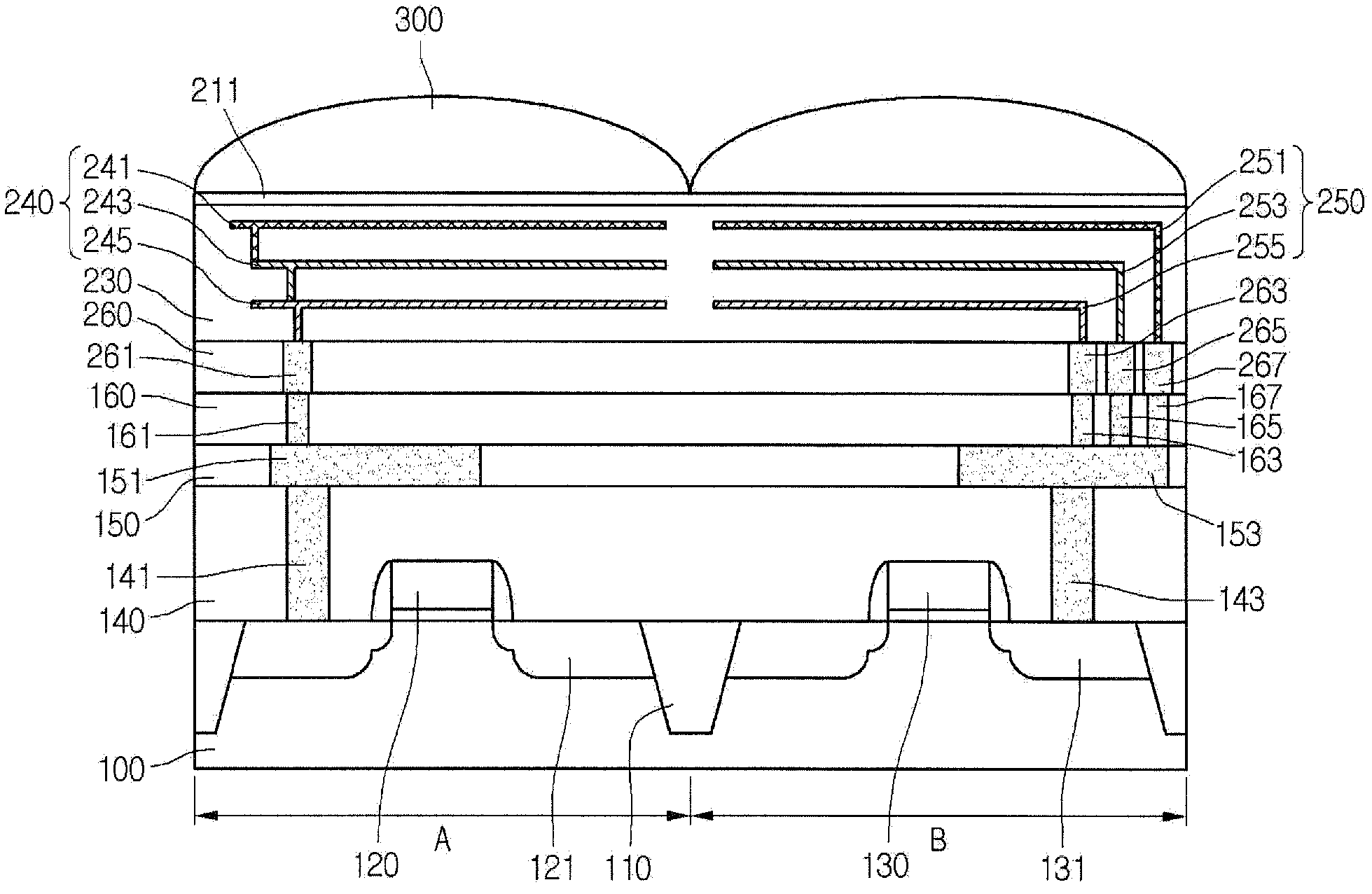
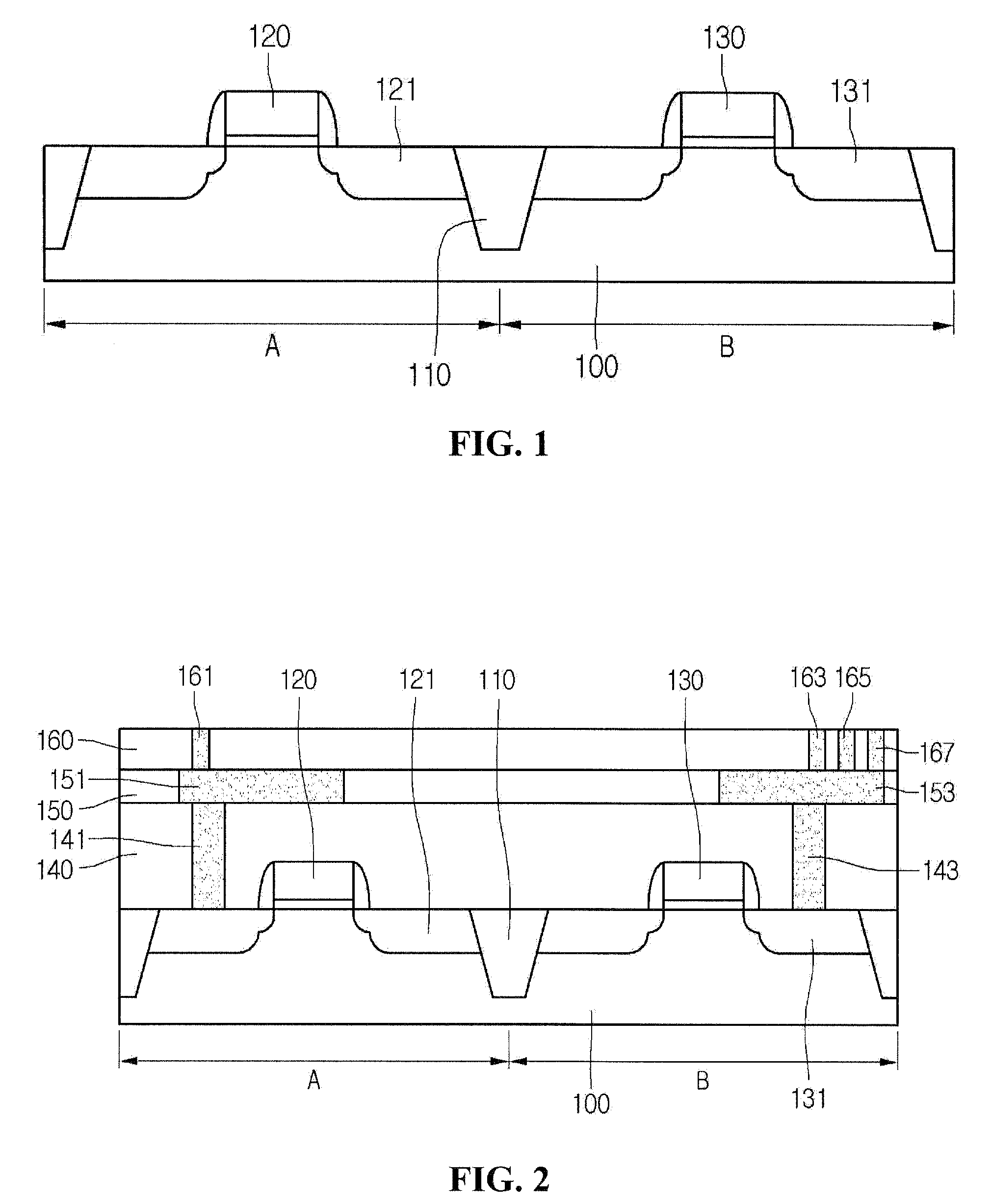
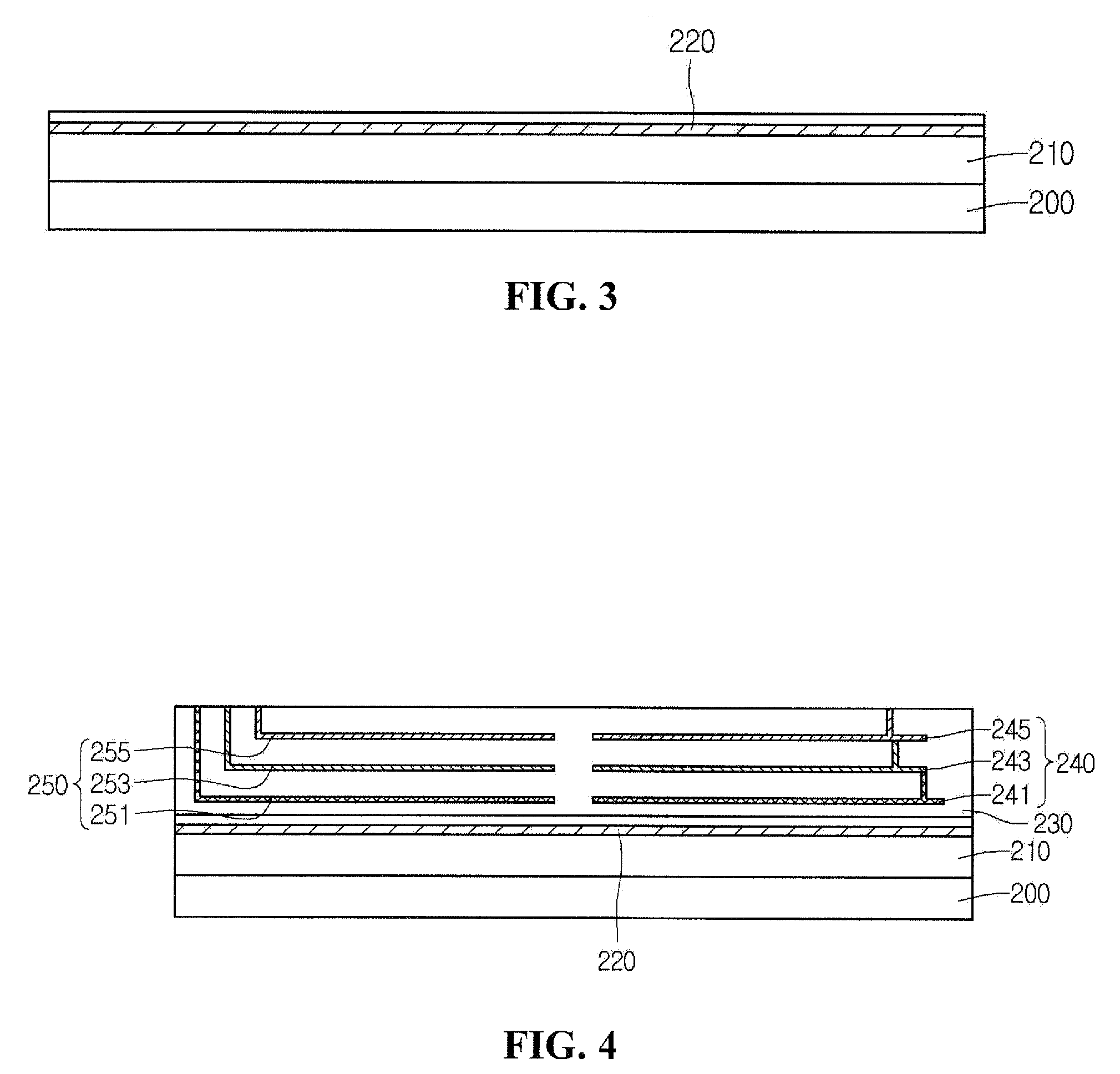
Image sensor and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS8022493B2Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingTransistor circuitsEngineering
Provided are embodiments of an image sensor. The image sensor can comprise a first substrate including a transistor circuit, a lower interconnection layer, an upper interconnection layer, and a second substrate including a vertical stacked photodiode. The lower interconnection layer is disposed on the first substrate and comprises a lower interconnection connected to the transistor circuit. The upper interconnection layer is disposed on the lower interconnection layer and comprises an upper interconnection connected with the lower interconnection. The vertical stacked photodiode can be disposed on the upper interconnection layer and connected with the upper interconnection through, for example, a single plug connecting a blue, green, and red photodiode of the vertical stack or a corresponding plug for each of the blue, green, and red photodiode of the vertical stack.
Owner:DONGBU HITEK CO LTD
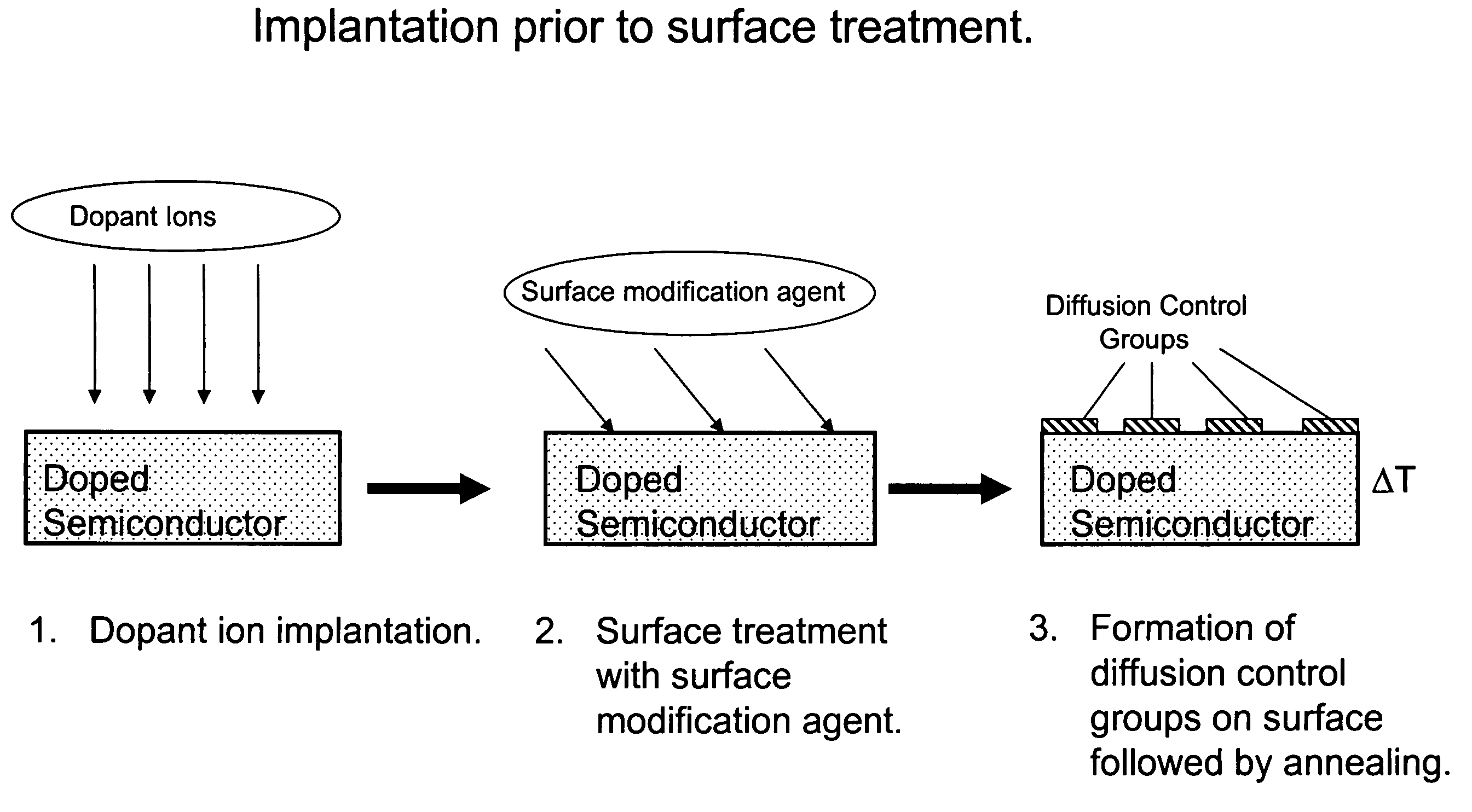
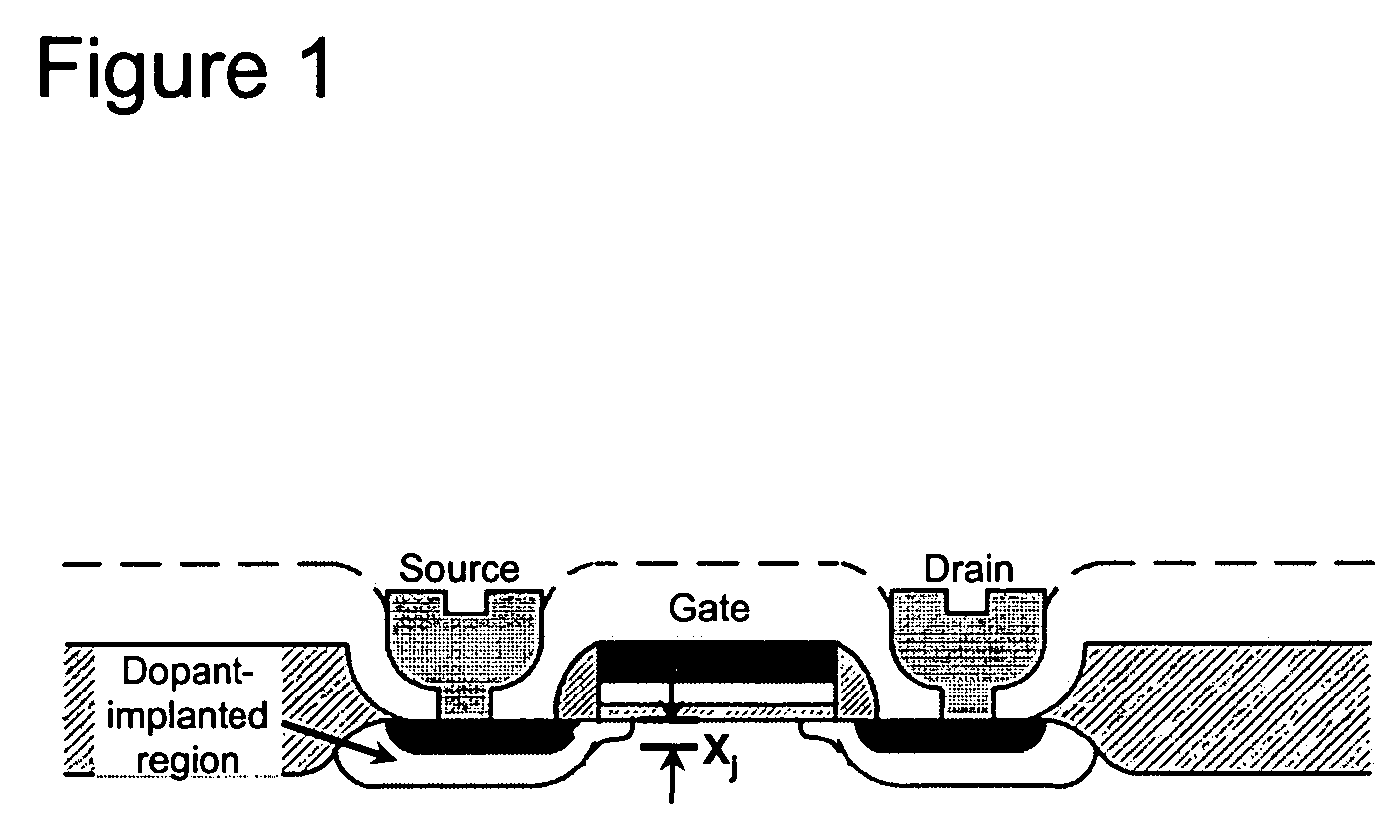
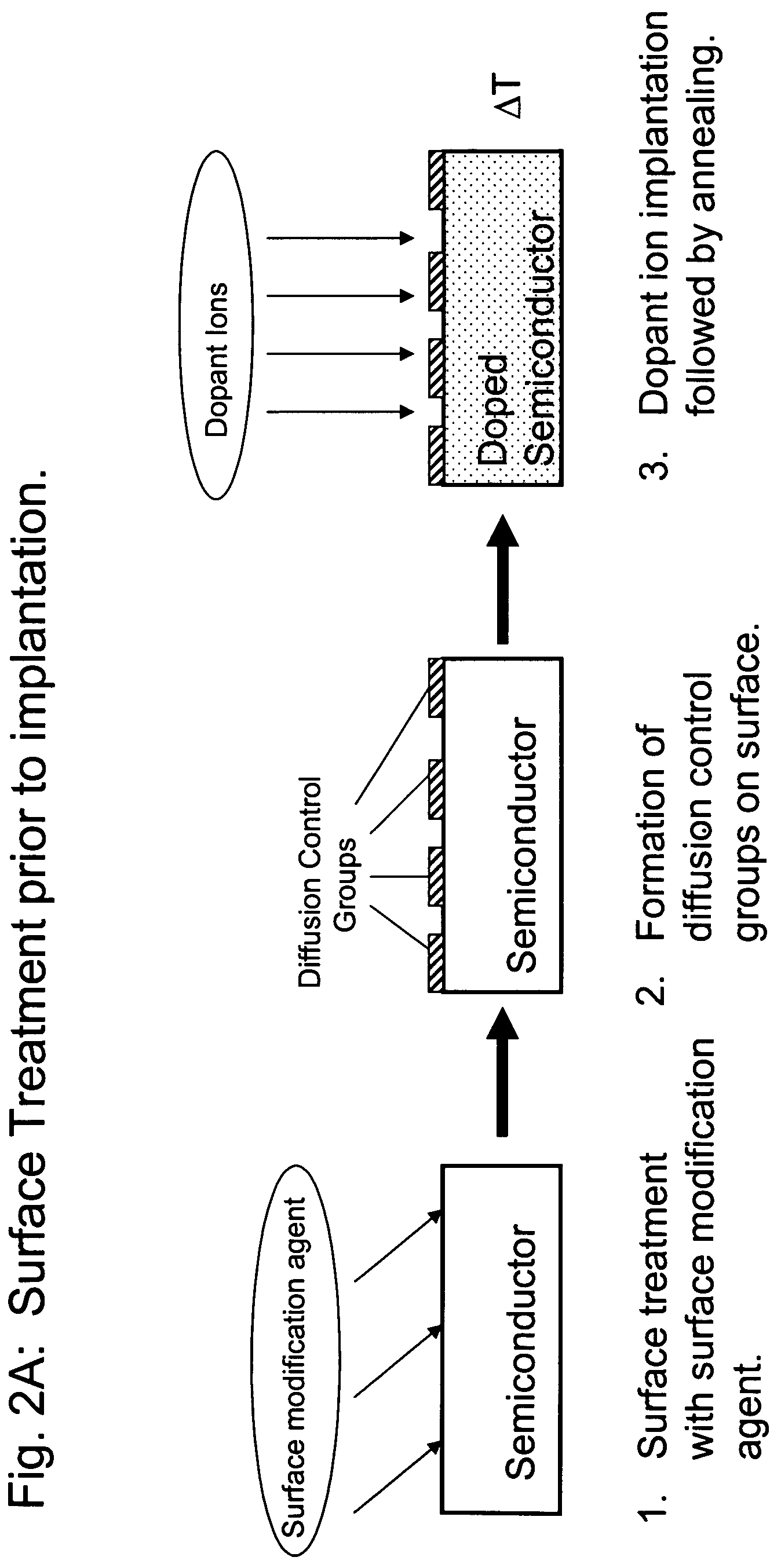
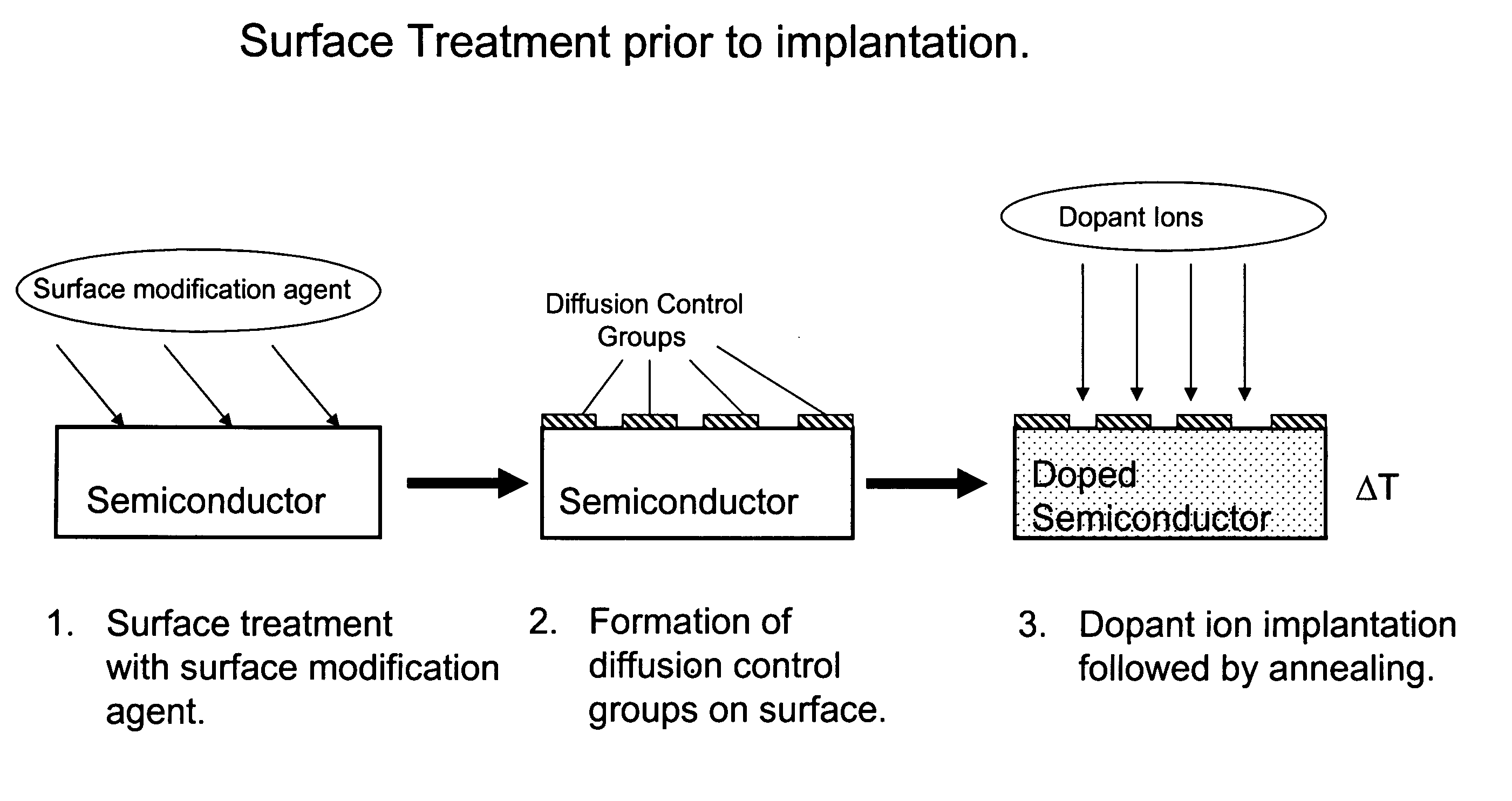
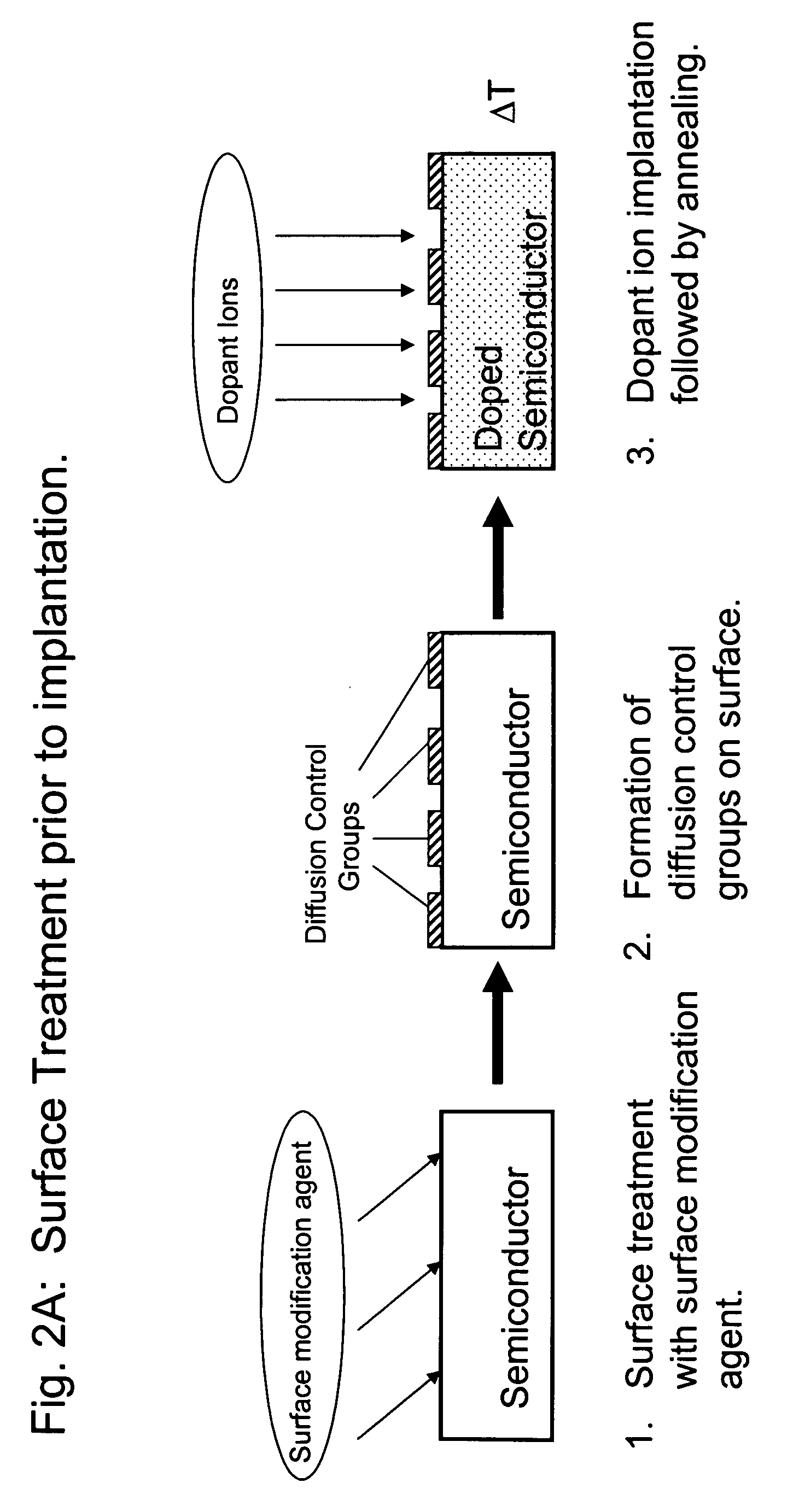
Methods for controlling dopant concentration and activation in semiconductor structures
InactiveUS7846822B2Easy to integrateLower resistanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesDopantSemiconductor materials
The present invention provides methods for fabricating semiconductor structures and devices, particularly ultra-shallow doped semiconductor structures exhibiting low electrical resistance. Methods of the present invention use modification of the composition of semiconductor surfaces to allow fabrication of a doped semiconductor structure having a selected dopant concentration depth profile, which provides useful junctions and other device components in microelectronic and nanoelectronic devices, such as transistors in high density integrated circuits. Surface modification in the present invention also allows for control of the concentration and depth profile of defects, such as interstitials and vacancies, in undersaturated semiconductor materials.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
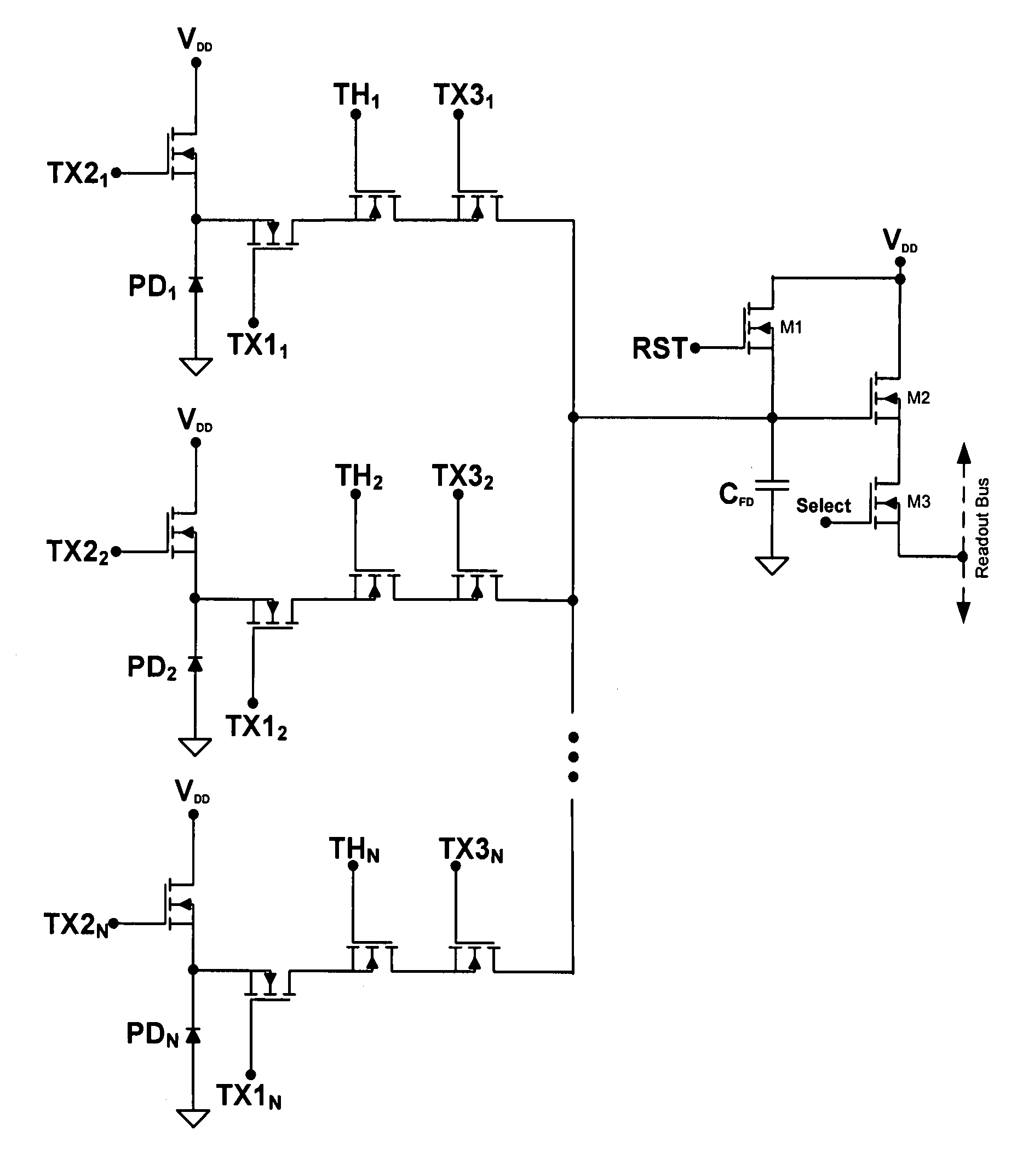
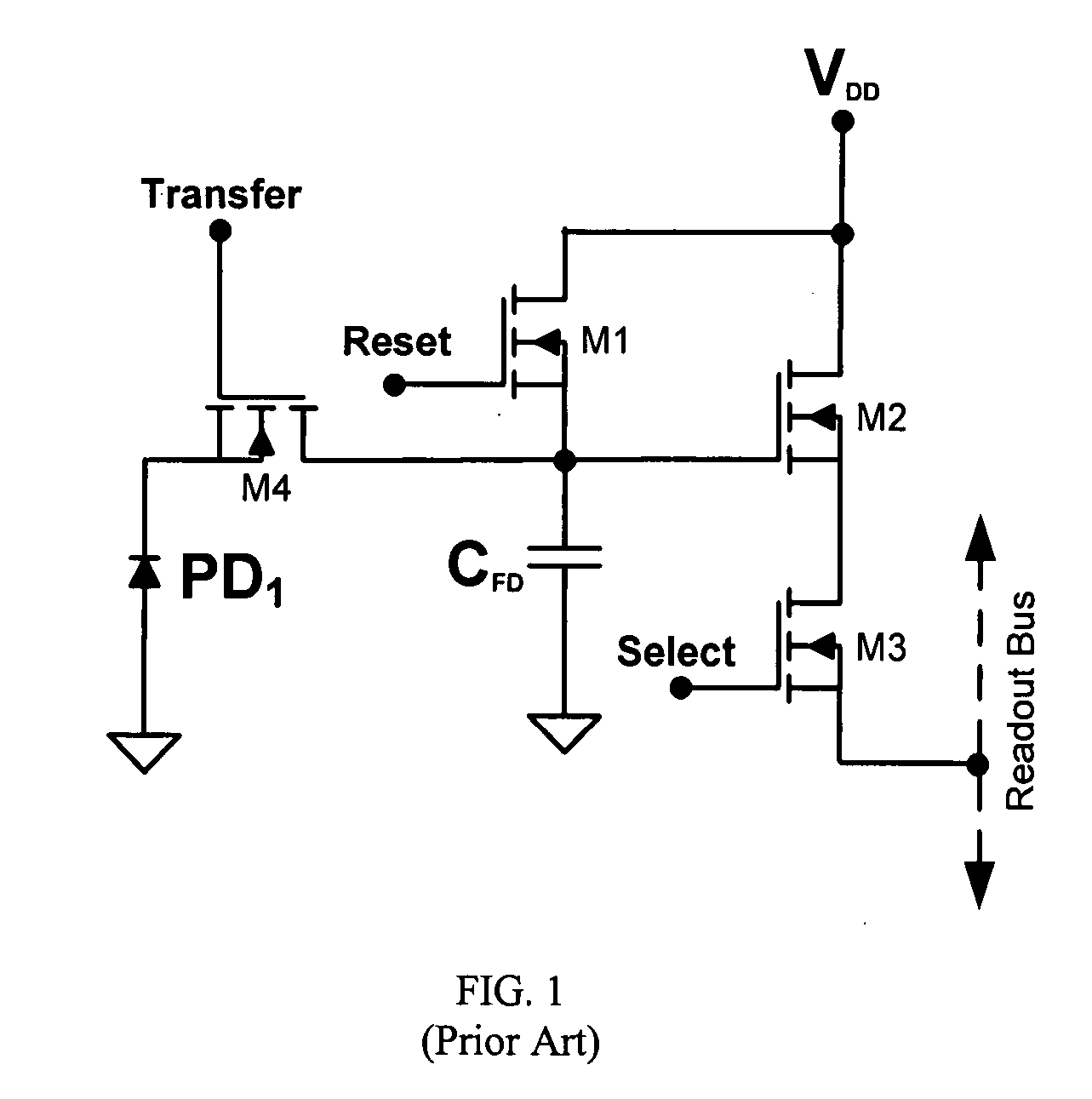
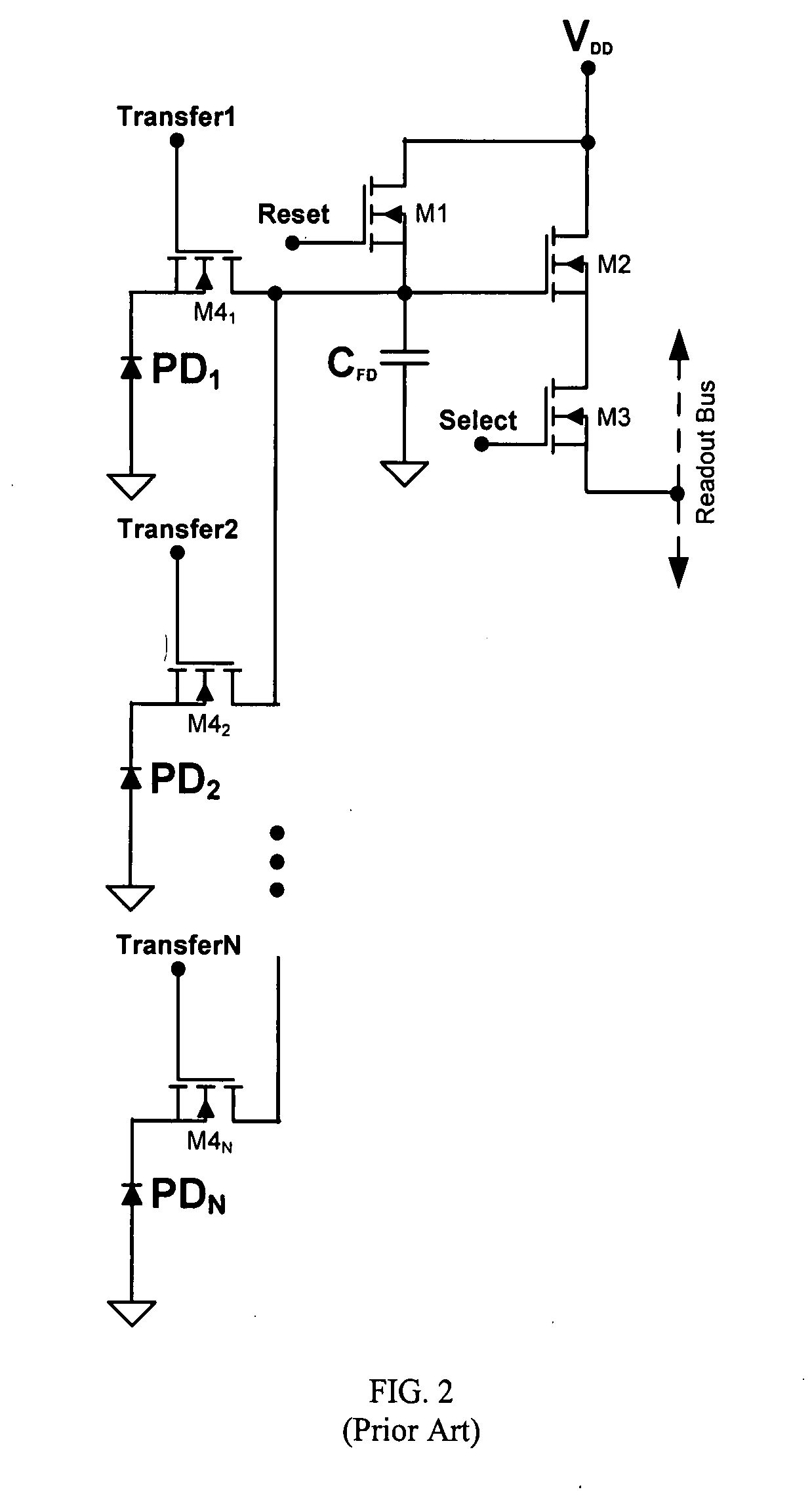
Global shutter pixel circuit with transistor sharing for CMOS image sensors
InactiveUS20090108176A1Reduce average transistor count per pixelTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesCMOSAudio power amplifier
A pixel circuit having a global shutter and transistor circuit sharing for CMOS image sensors. In one embodiment, a shared circuit includes a reset transistor, an amplifier transistor, and a readout transistor. At least two photodiode signal generation circuits share the shared circuit, wherein each signal generation circuit includes a capture transistor, a hold transistor, and a transfer transistor. Each pixel generation circuit may also include a photodiode reset transistor. In an alternate embodiment, each signal generation circuit does not include a separate transfer transistor, instead, the transfer transistor is part of the shared circuit.
Owner:ALTASENS
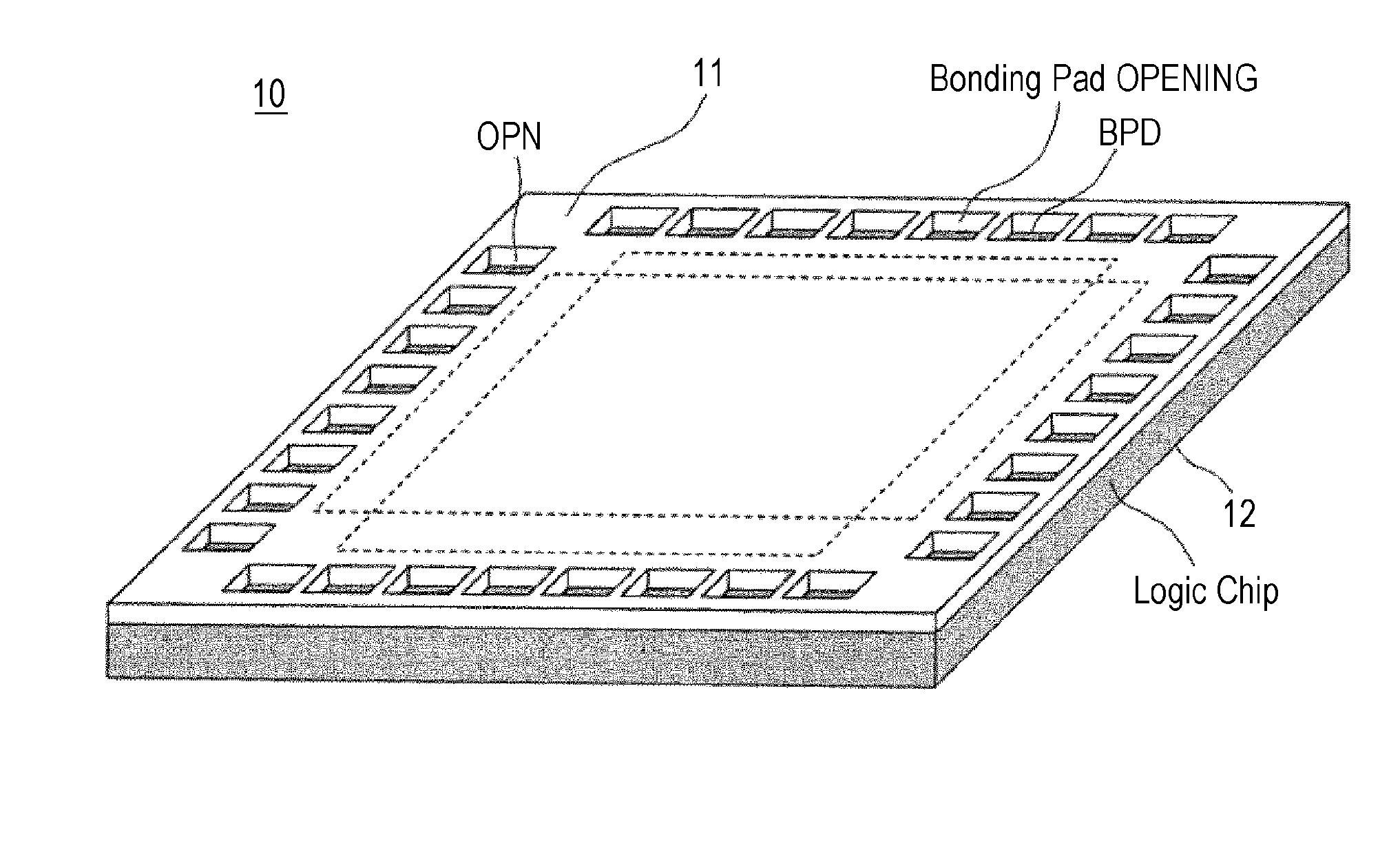
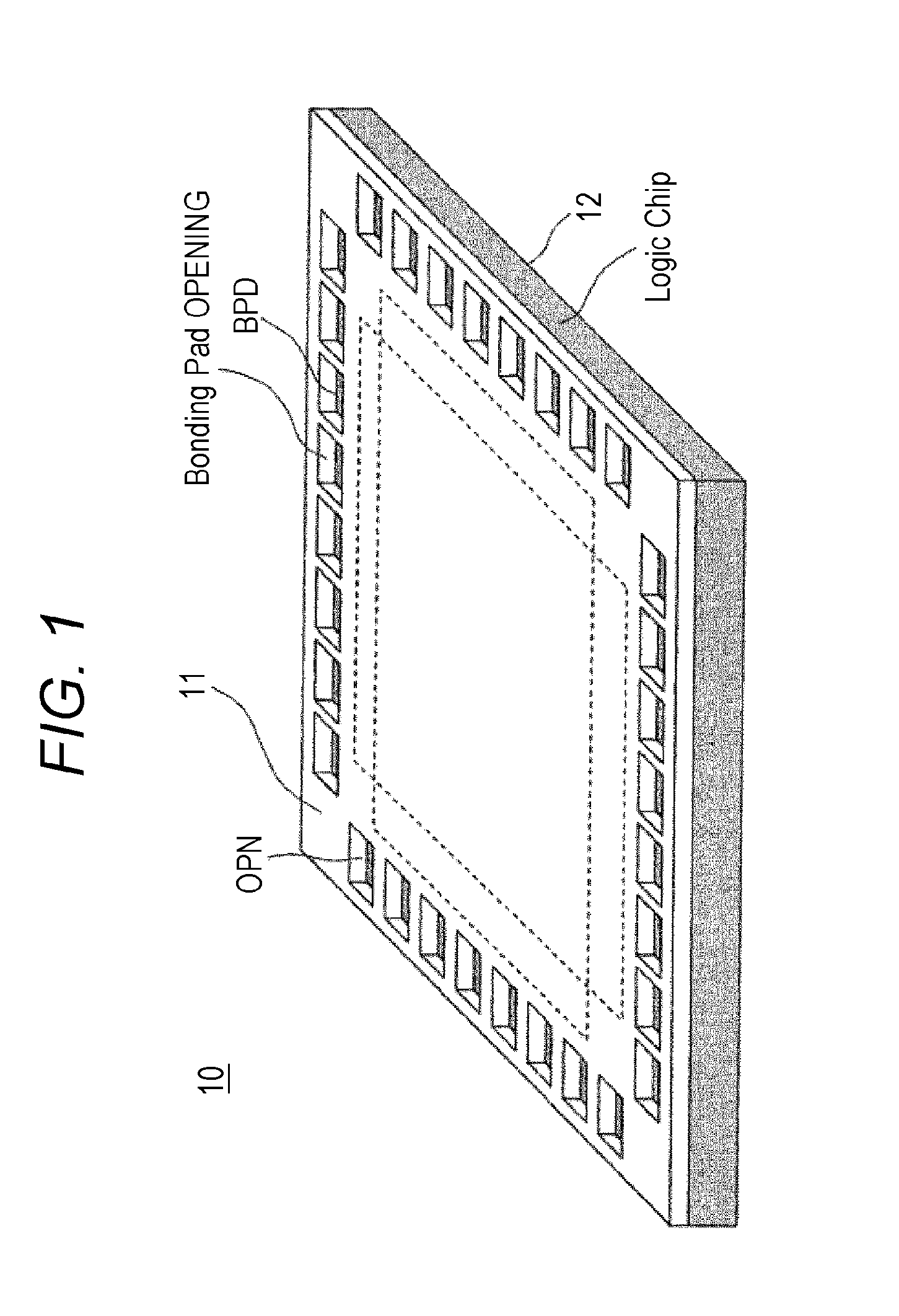
Semiconductor device, solid-state image sensor and camera system
InactiveUS20120293698A1Noise influencingLow costTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsPower semiconductor deviceHigh voltage transistors
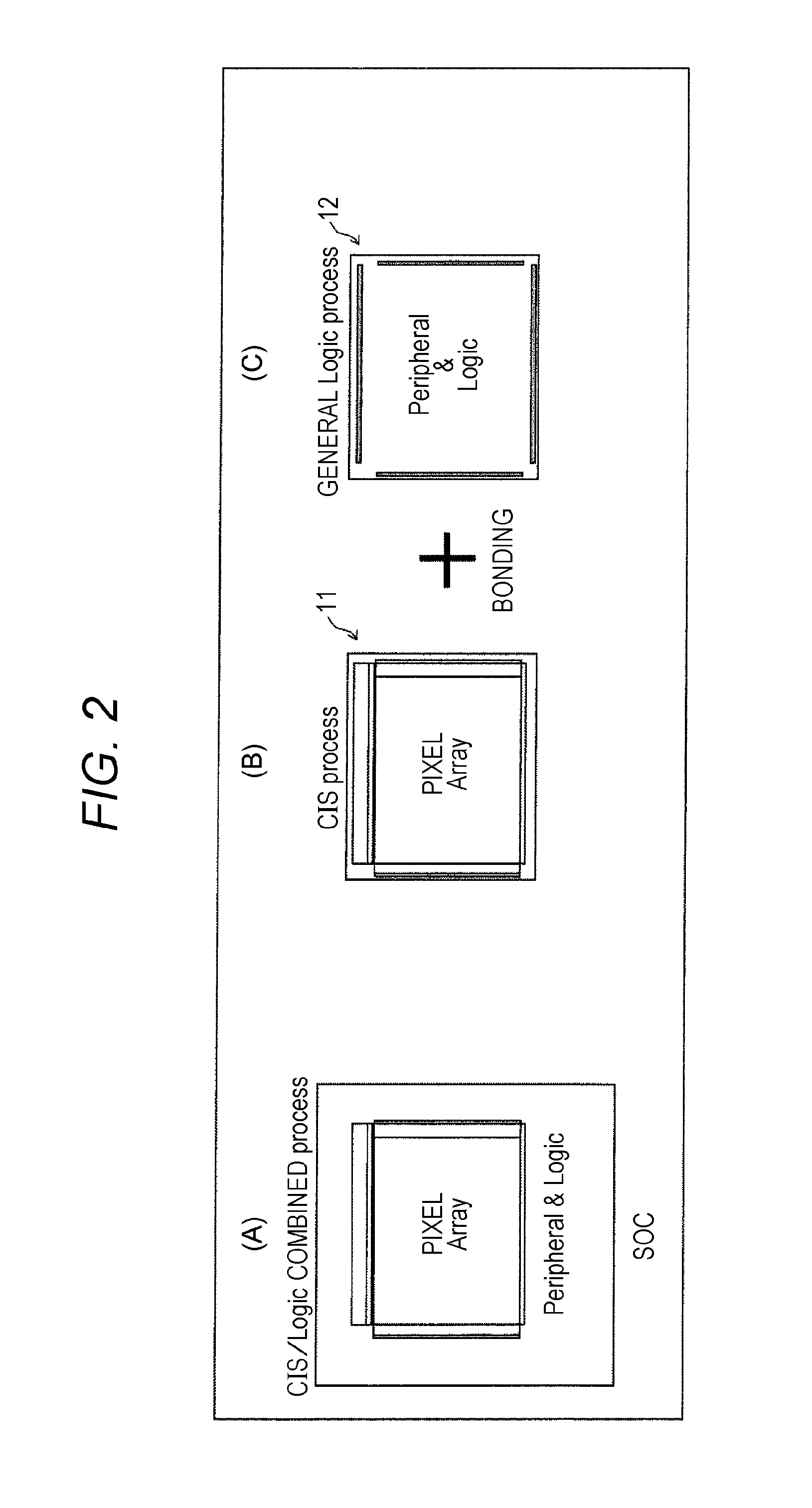
The present invention relates to a semiconductor device, a solid-state image sensor and a camera system capable of reducing the influence of noise at a connection between chips without a special circuit for communication and reducing the cost as a result. The semiconductor device includes: a first chip 11; and a second chip 12, wherein the first chip 11 and the second chip 12 are bonded to have a stacked structure, the first chip 11 has a high-voltage transistor circuit mounted thereon, the second chip 12 has mounted thereon a low-voltage transistor circuit having lower breakdown voltage than the high-voltage transistor circuit, and wiring between the first chip and the second chip is connected through a via formed in the first chip.
Owner:SONY CORP
Touch Screen Border Regions
ActiveUS20110074705A1Light weightMany regionStatic indicating devicesDigital data processing detailsTouch SensesTransistor circuits
Touch screens with more compact border regions can include an active area that includes touch sensing circuitry including drive lines, and a border region around the active area. The border region can include an area of sealant deposited on conductive lines, and transistor circuitry, such as gate drivers, between the active area and the sealant. The conductive lines can extend from the sealant to the active area without electrically connecting to the transistor circuitry. The conductive lines can have equal impedances and can connect the drive lines to a touch controller off of the touch screen. A set of drive signal characteristics for the drive lines can be obtained by determining a transfer function associated with each drive line, obtaining an inverse of each transfer function, and applying a set of individual sense signal characteristics to the inverse transfer functions to obtain the corresponding set of drive signal characteristics.
Owner:APPLE INC
Methods for controlling dopant concentration and activation in semiconductor structures
InactiveUS20060024928A1Easy to integrateLower resistanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesDopantElectrical resistance and conductance
The present invention provides methods for fabricating semiconductor structures and devices, particularly ultra-shallow doped semiconductor structures exhibiting low electrical resistance. Methods of the present invention use modification of the composition of semiconductor surfaces to allow fabrication of a doped semiconductor structure having a selected dopant concentration depth profile, which provides useful junctions and other device components in microelectronic and nanoelectronic devices, such as transistors in high density integrated circuits. Surface modification in the present invention also allows for control of the concentration and depth profile of defects, such as interstitials and vacancies, in undersaturated semiconductor materials.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
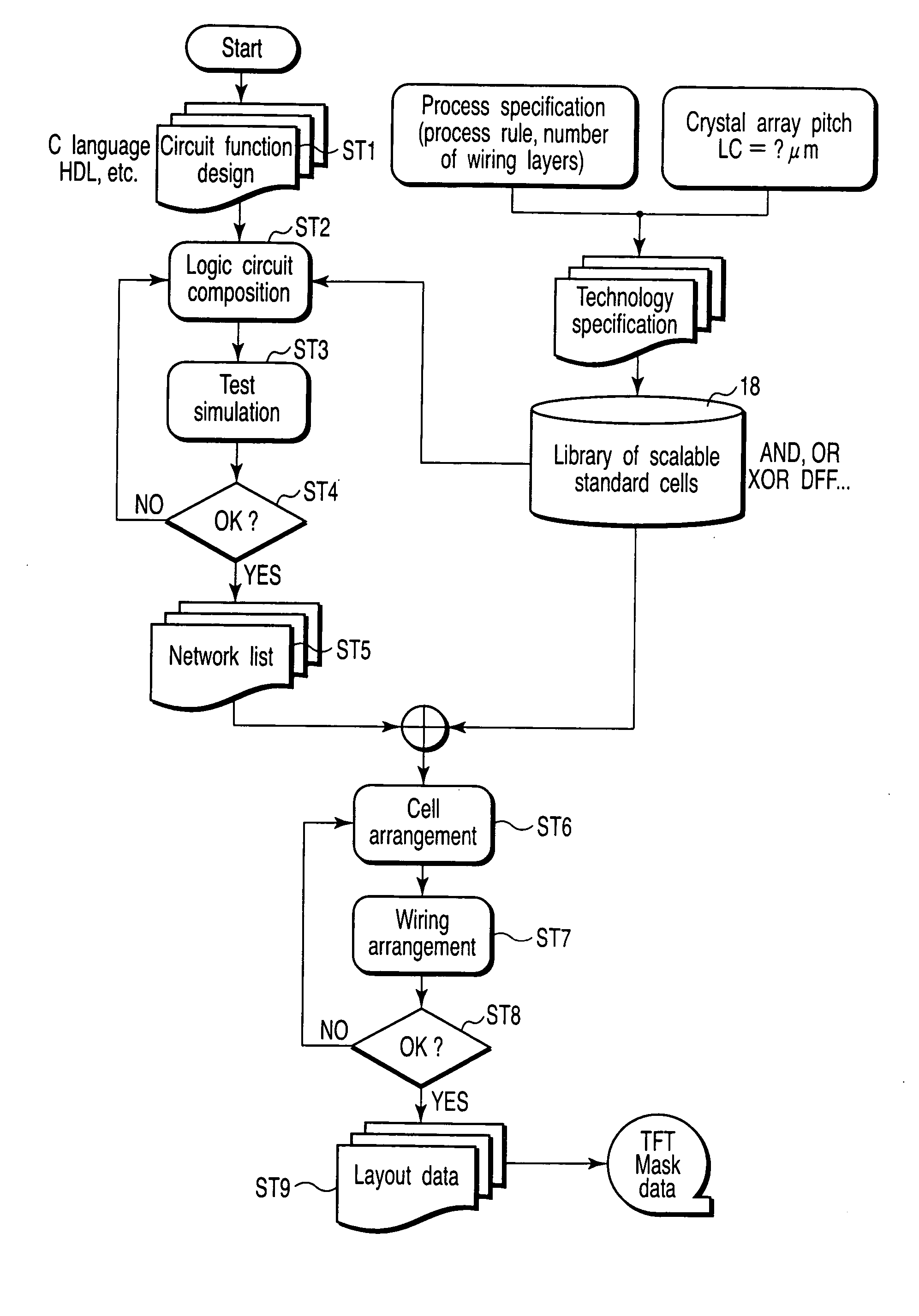
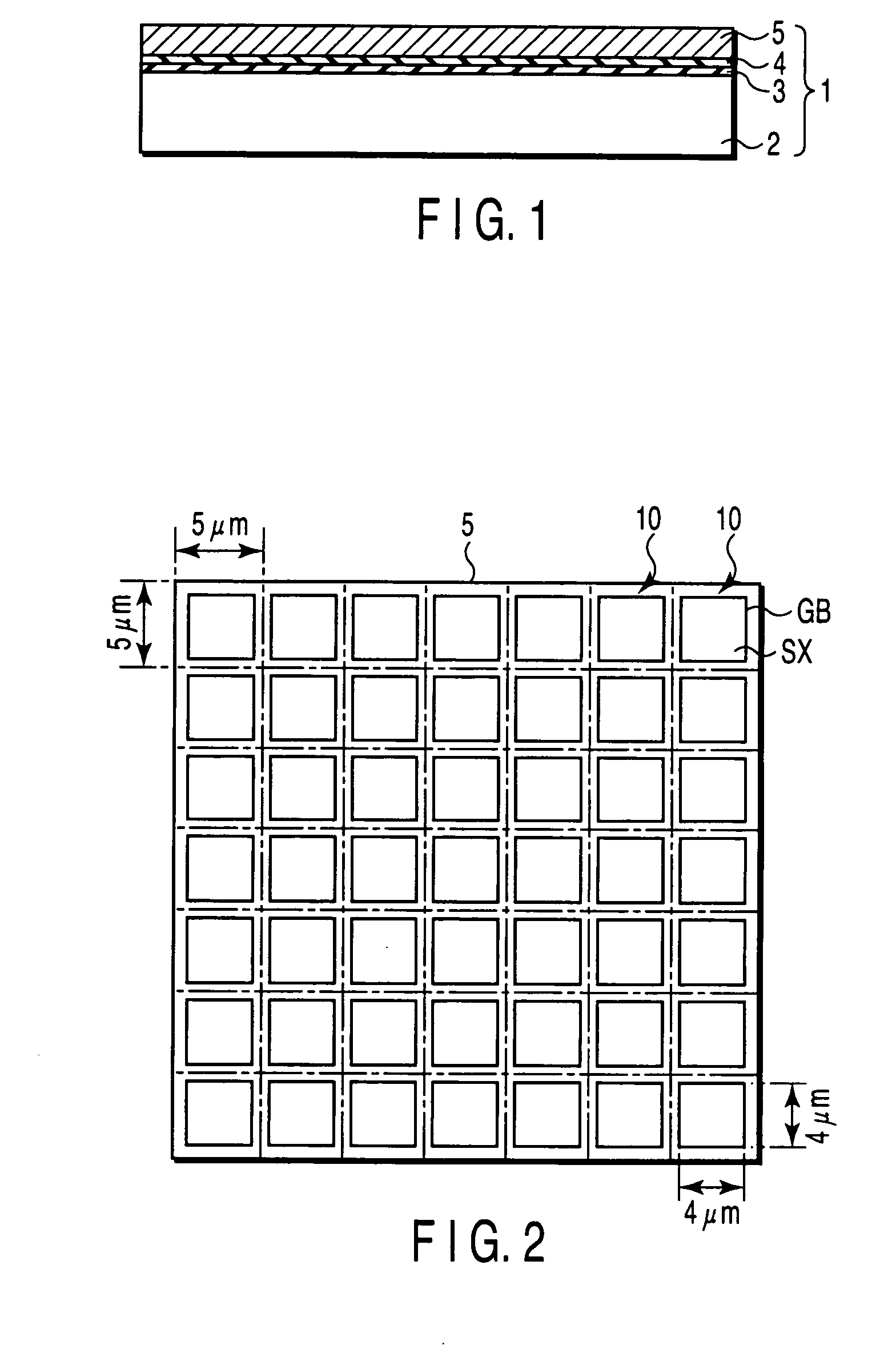
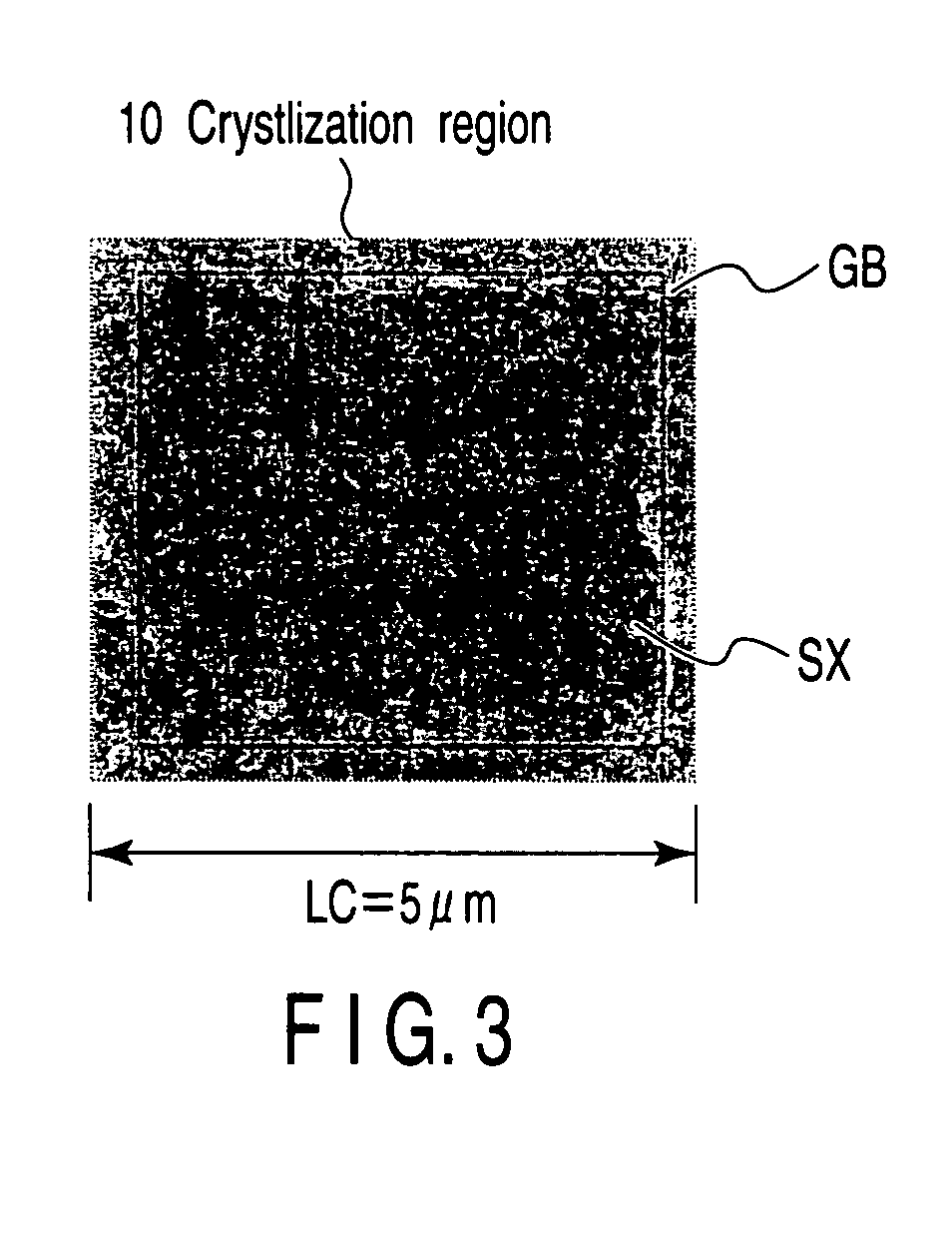
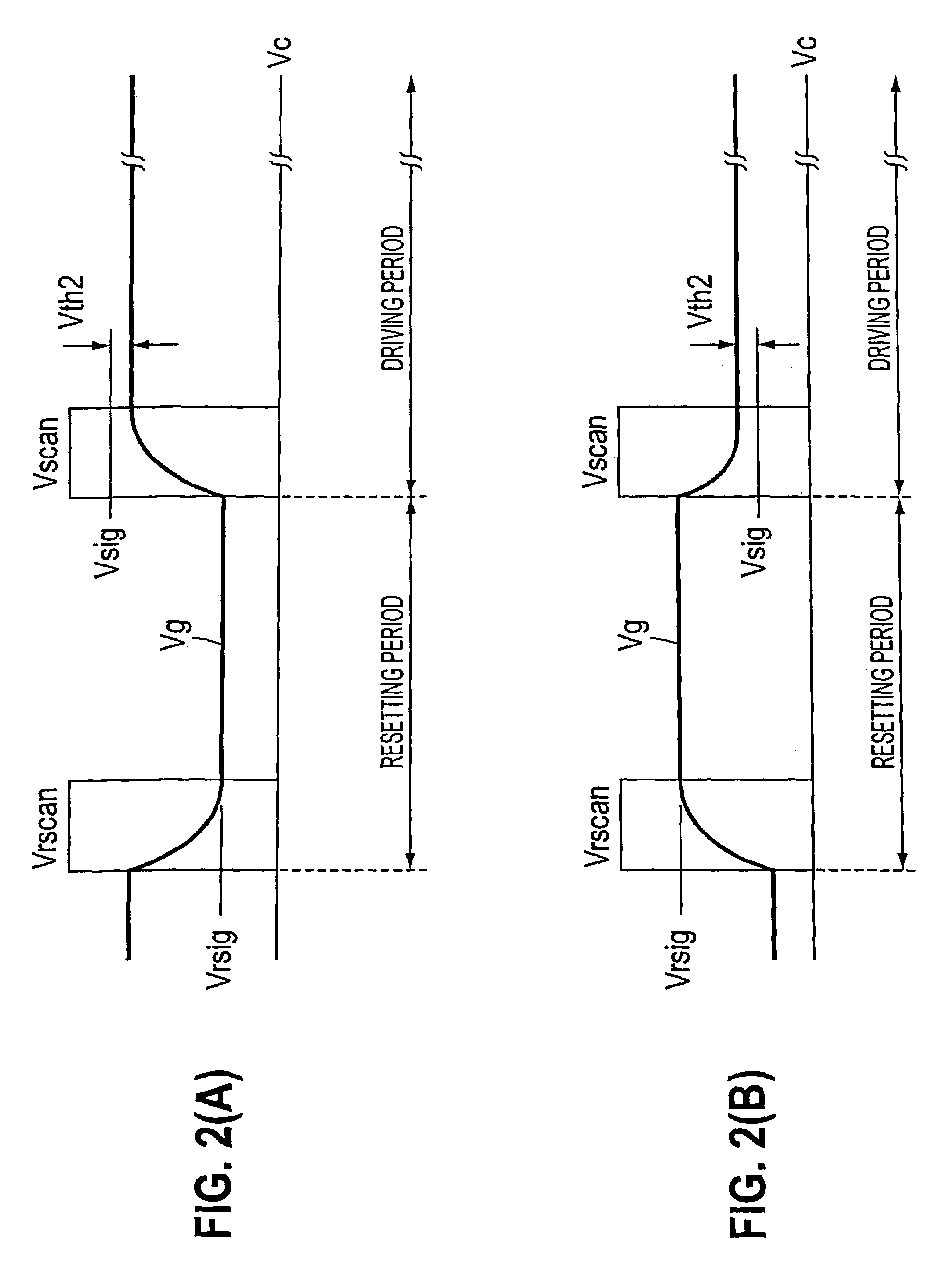
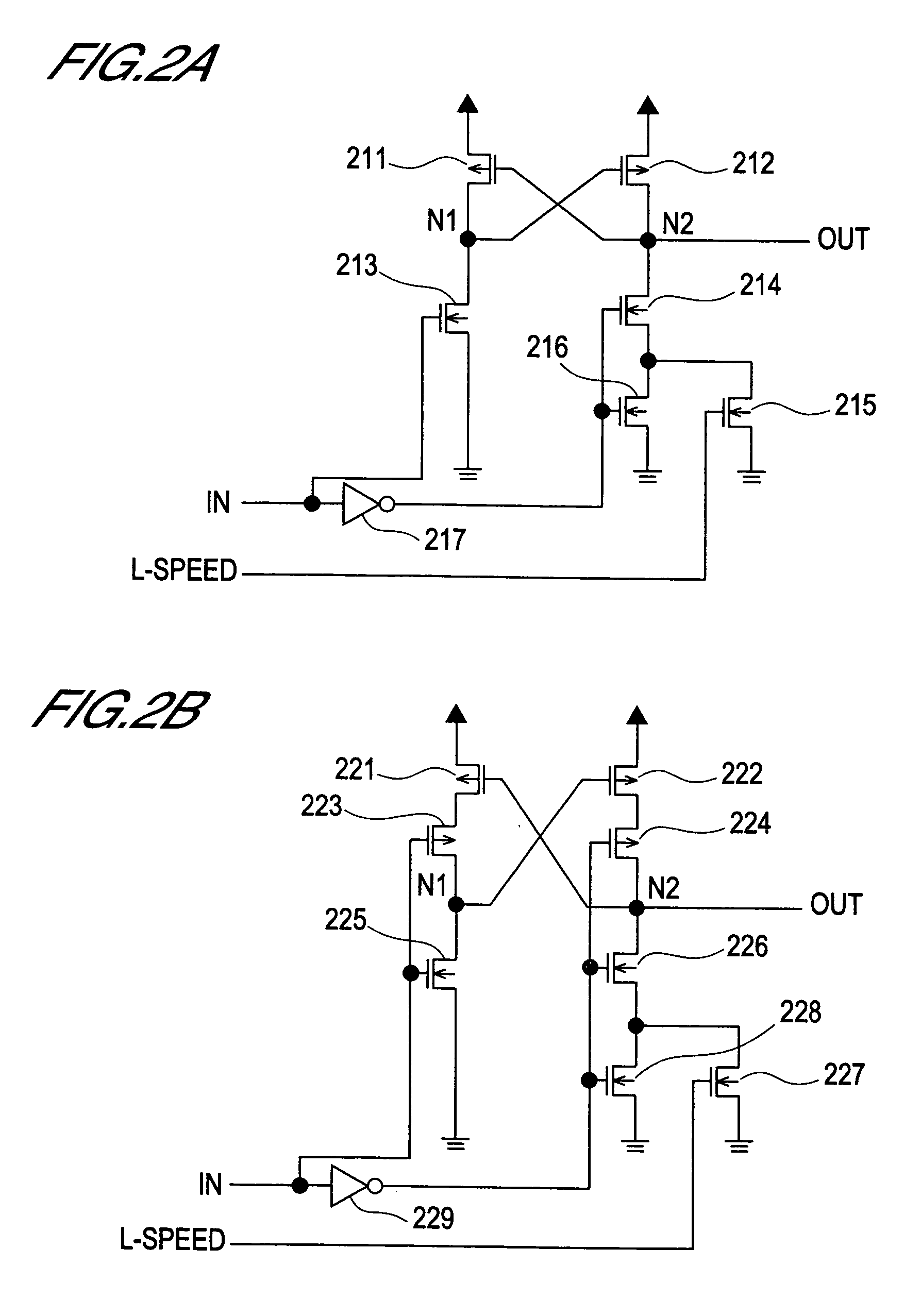
Thin-film transistor circuit, design method for thin-film transistor, design program for thin-film transistor circuit, design program recording medium, design library database, and display device
InactiveUS20050278673A1Improve relationshipShorten the timeMemory architecture accessing/allocationTransistorDisplay deviceEngineering
A thin-film transistor circuit includes a crystallized semiconductor thin film two-dimensionally partitioned into crystal-grain-defining areas each of which accommodates a crystal grain larger than a predetermined size, thin-film transistors each of which has a channel region placed at the center position of a corresponding one of the crystal-grain-defining areas, and wirings which interconnect the thin-film transistors.
Owner:SHARP KK
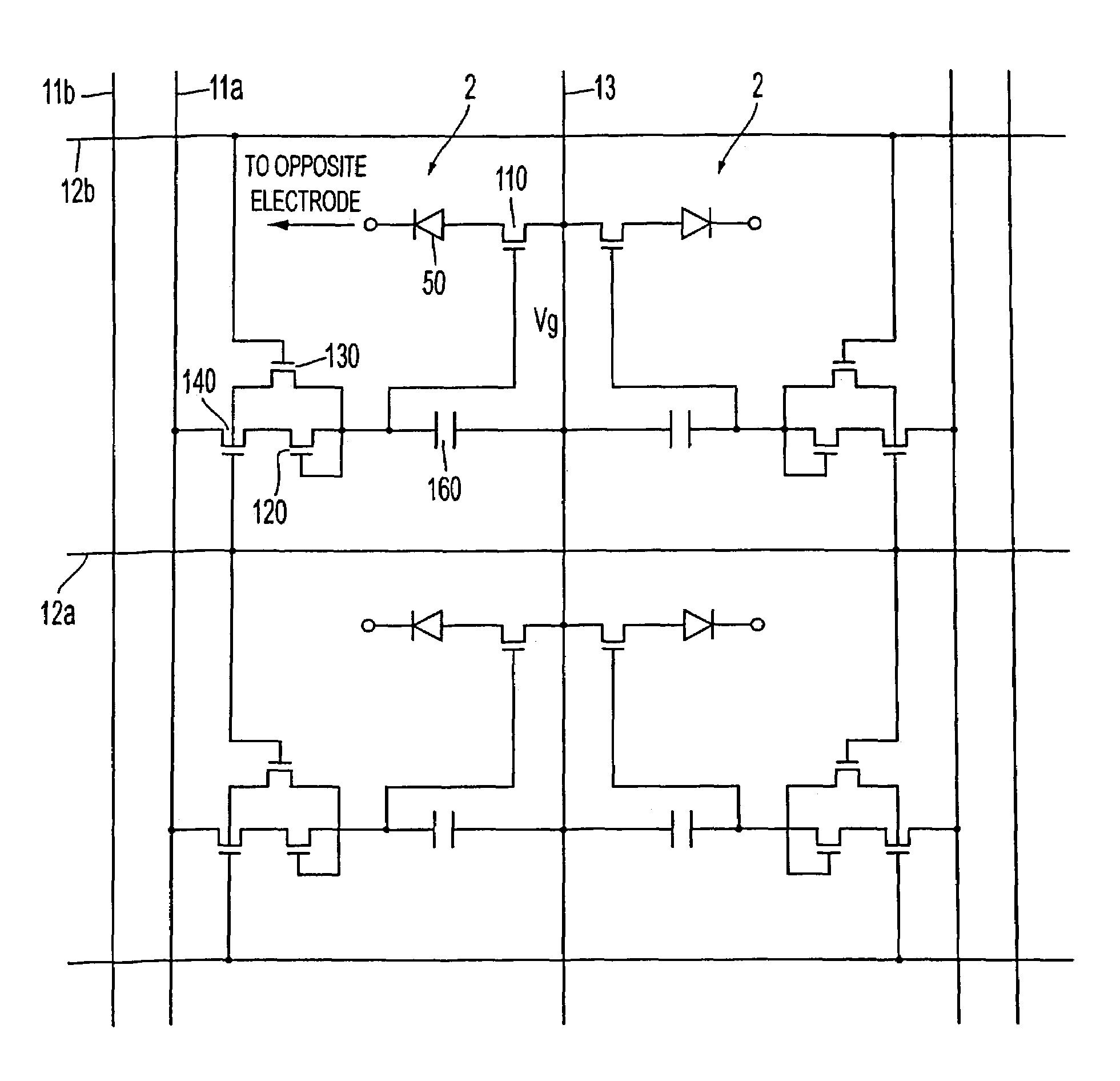
Transistor circuit, display panel and electronic apparatus
InactiveUS7173584B2Good precisionReduce brightness unevennessTransistorStatic indicating devicesLow voltageTransistor circuits
A transistor circuit is provided including a driving transistor where conductance between the source and the drain is controlled in response to a supplied voltage, and a compensating transistor where the gate is connected to one of the source and the drain, the compensating transistor being connected so as to supply input signals to the gate of the driving transistor through the source and drain. In a transistor circuit where conductance control in a driving transistor is carried out in response to the voltage of input signals, it is possible to control the conductance by using input signals of a relatively low voltage and a variance in threshold characteristics of driving transistors is compensated. With this transistor circuit, a display panel that can display picture images with reduced uneven brightness is achieved.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Image Sensor and Method for Manufacturing the Same
InactiveUS20080283883A1Improve quantum efficiencyImprove resolutionFinal product manufactureNanoinformaticsConductive polymerCarbon nanotube
An image sensor and a method for manufacturing the same are provided. The image sensor can include transistor circuitry on a substrate, and a photodiode arranged above the transistor circuitry. The photodiode can include carbon nanotubes and a conductive polymer layer on the carbon nanotubes. A transparent conducting electrode can be provided on the carbon nanotubes.
Owner:DONGBU HITEK CO LTD
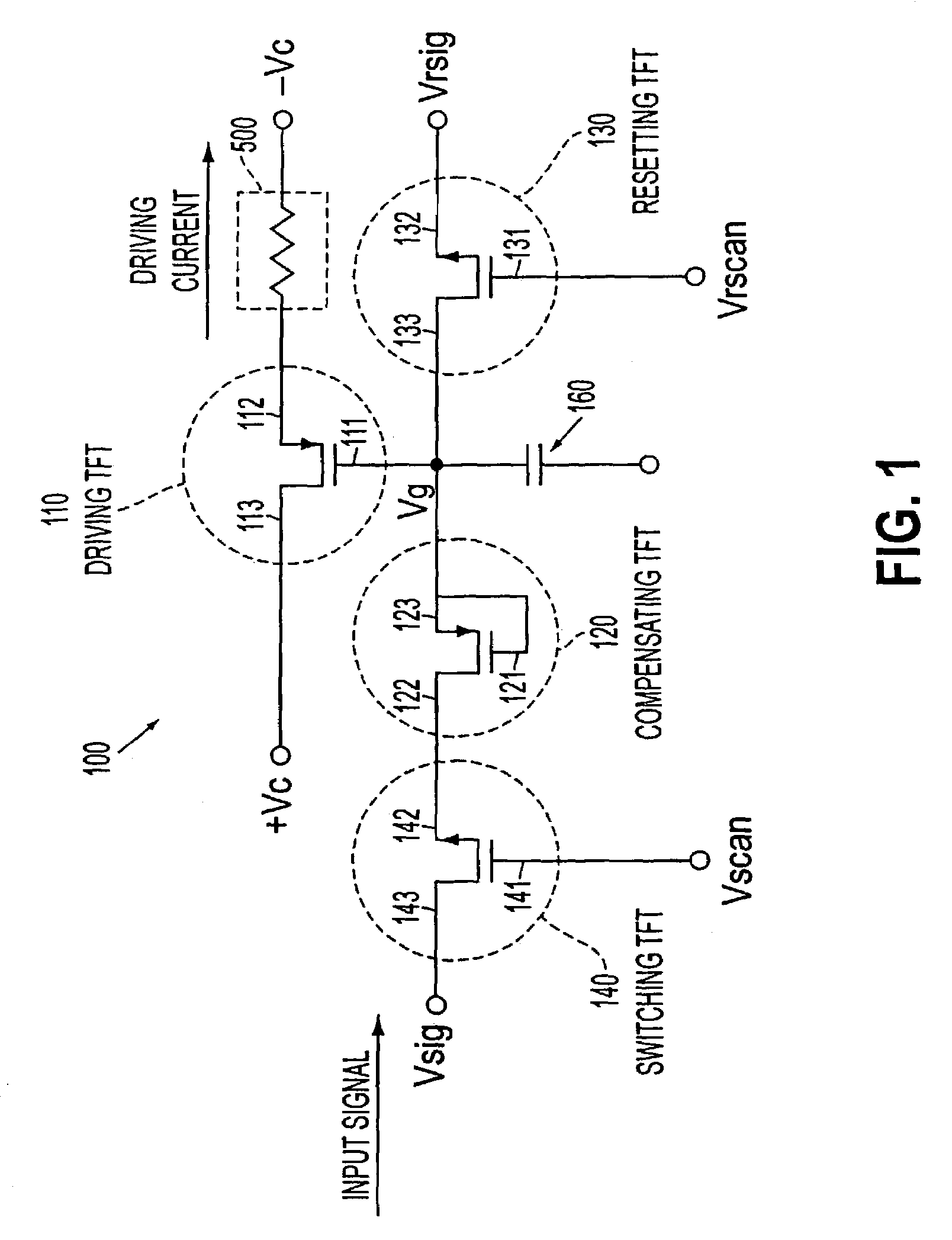
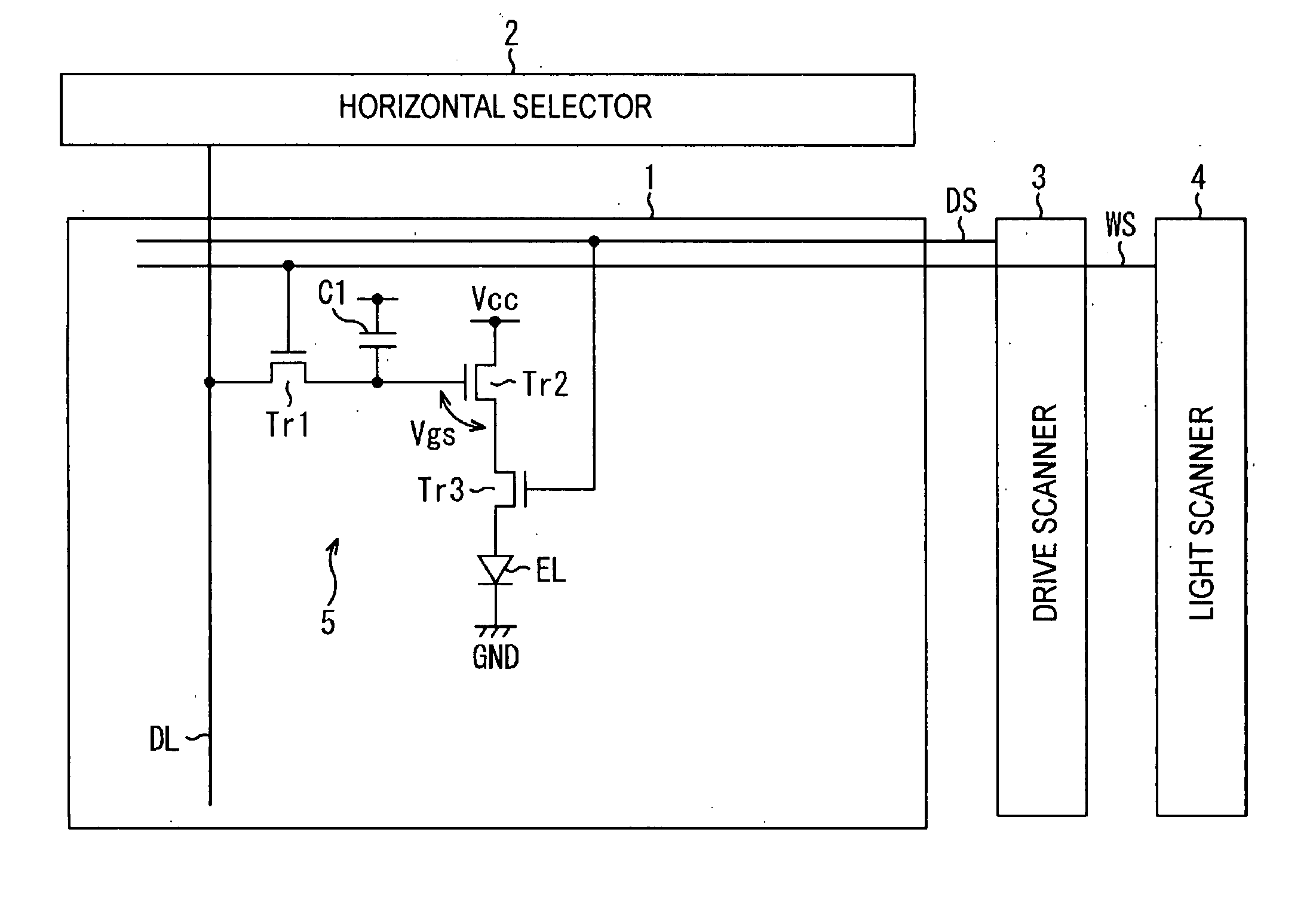
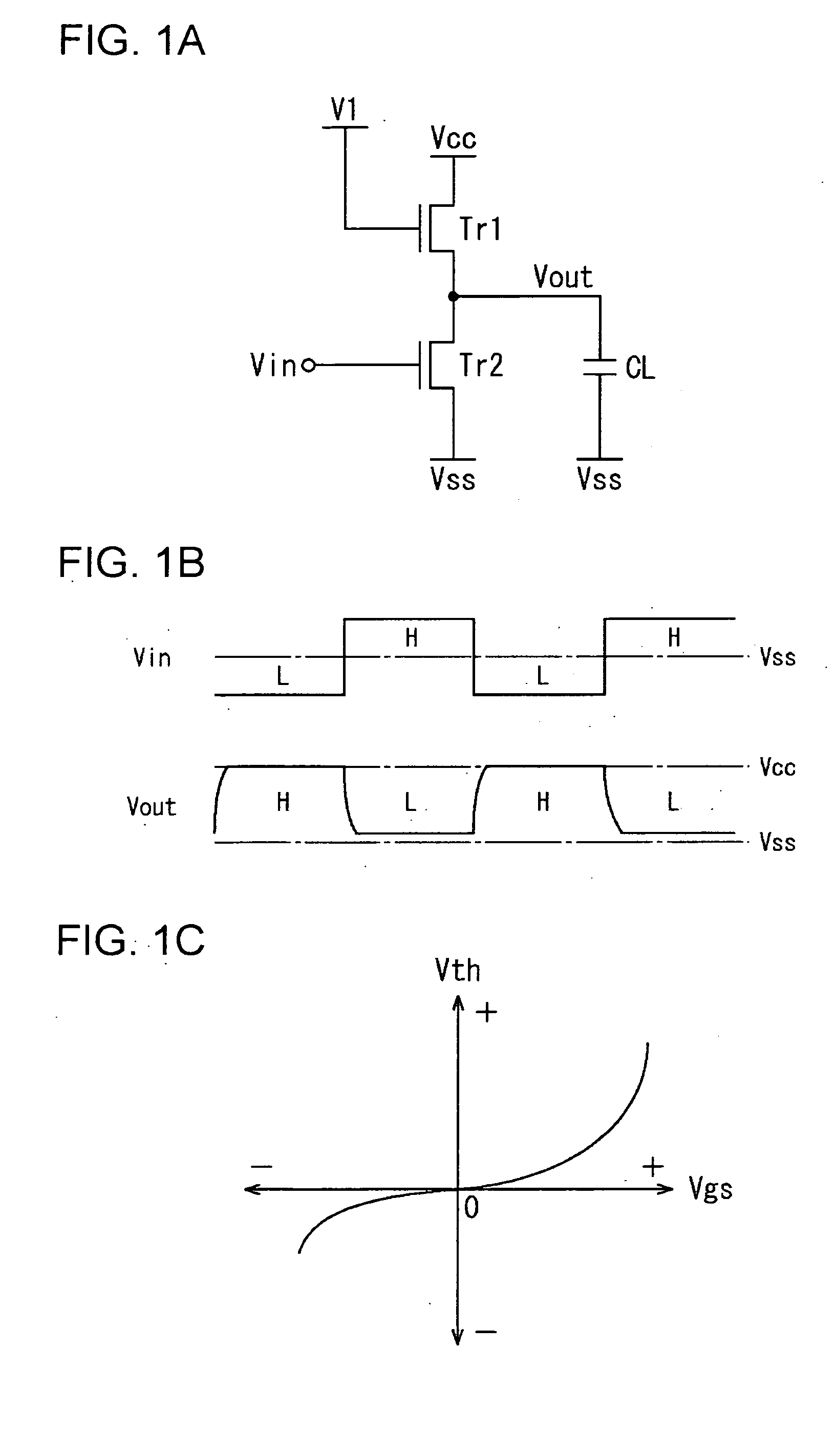
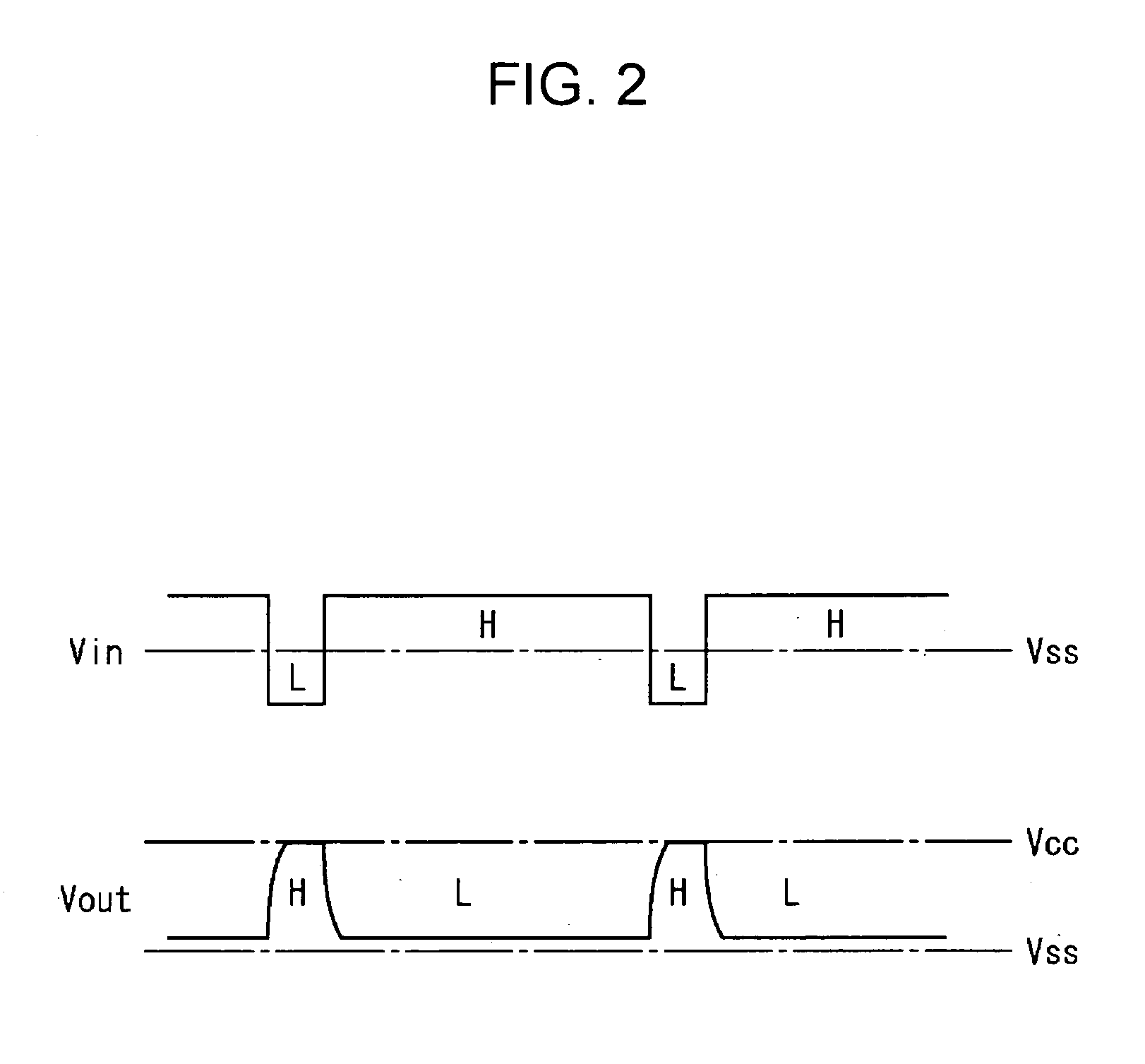
Transistor circuit, pixel circuit, display device, and driving method therefor
ActiveUS20070091029A1Correction for variationReliability increasing modificationsStatic indicating devicesDisplay deviceTransistor circuits
A transistor circuit having the function of correcting variations in the threshold voltage of a thin-film transistor is provided. The transistor circuit includes a plurality of thin-film transistors (Tr1 to Tr3) formed on a substrate and wiring which connects the gate, source, and / or drain of each of the transistors, so as to perform a predetermined operation. During the operation, a forward bias is applied between the gate and source of the thin-film transistor (Tr2) via the wiring repeatedly and / or continuously. A reverse bias is applied between the gate and source of the transistor (Tr2) in such timing that the operation is not disturbed so that the variations in the threshold voltage are suppressed. More specifically, an additional transistor (Tr3) connected in parallel to the transistor (Tr2) is driven complementarily, so as to generate the above-described timing where the operation is not disturbed, and the reverse bias is applied to the transistor (Tr2) in the generated timing.
Owner:JOLED INC
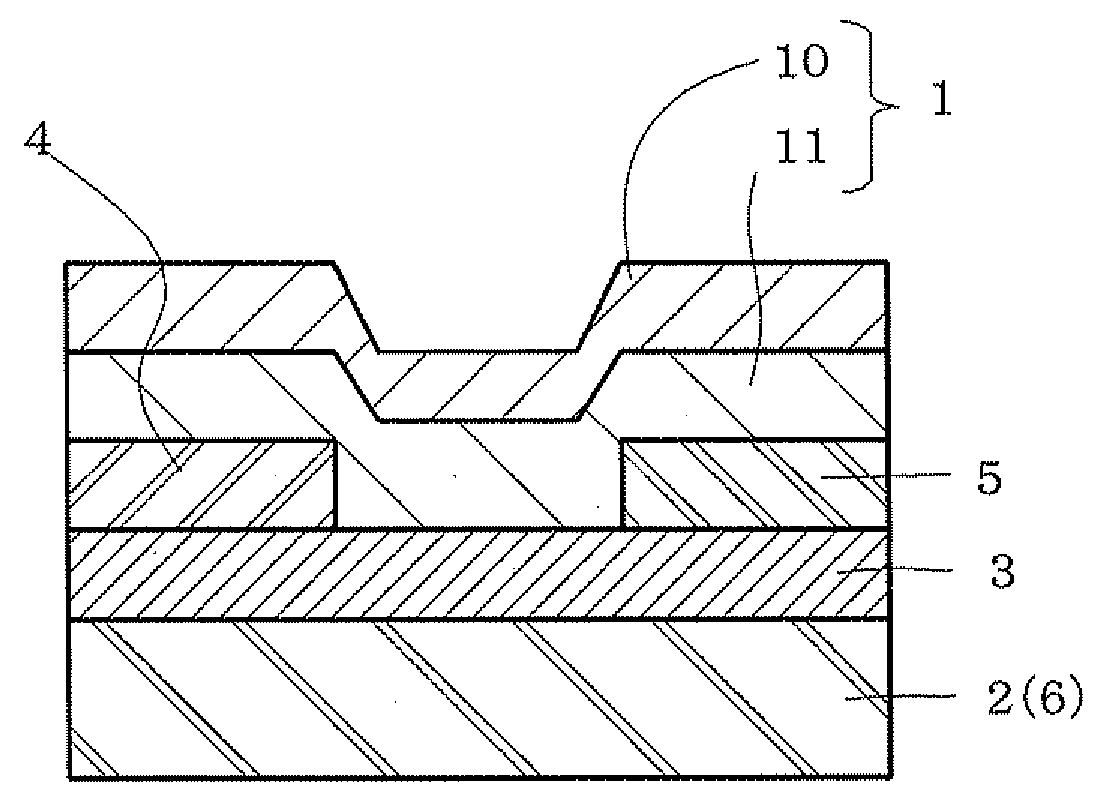
Semiconductor, semiconductor device, complementary transistor circuit device
InactiveUS20080197344A1Guaranteed uptimeImprove featuresSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingTransistor circuitsOrganic semiconductor
A semiconductor device including a semiconductor 1, a first electrode 2, an insulating layer 3 interposed between the semiconductor 1 and the first electrode 2, the second electrode 4 which is in contact with the semiconductor 1 and is detached from the first electrode 2, and the third electrode 5 which is in contact with the semiconductor 1 and is detached from the first electrode 2 and the second electrode 4, wherein the semiconductor 1 is provided with the organic semiconductor layer 10 and the oxide semiconductor layer 11.
Owner:IDEMITSU KOSAN CO LTD
Methods of forming field effect transistors and field effect transistor circuitry
InactiveUS6958519B2Logic circuits characterised by logic functionSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsVoltage referenceTransistor circuits
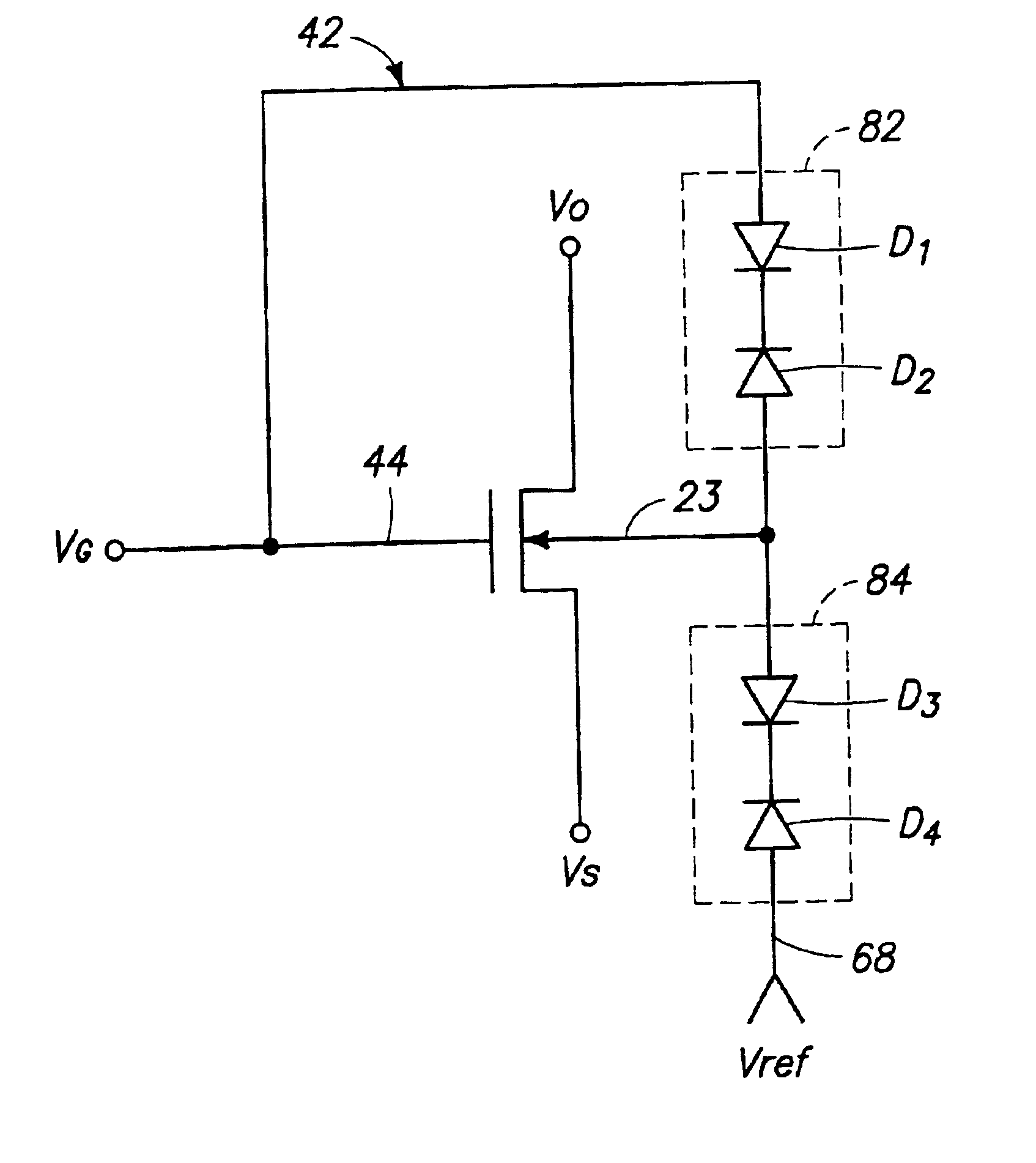
Methods of forming field effect transistors and resultant field effect transistor circuitry are described. In one embodiment, a semiconductive substrate includes a field effect transistor having a body. A first resistive element is received by the substrate and connected between the transistor's gate and the body. A second resistive element is received by the substrate and connected between the body and a reference voltage node. The first and second resistive elements form a voltage divider which is configured to selectively change threshold voltages of the field effect transistor with state changes in the gate voltage. In a preferred embodiment, first and second diode assemblies are positioned over the substrate and connected between the gate and body, and the body and a reference voltage node to provide the voltage divider.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
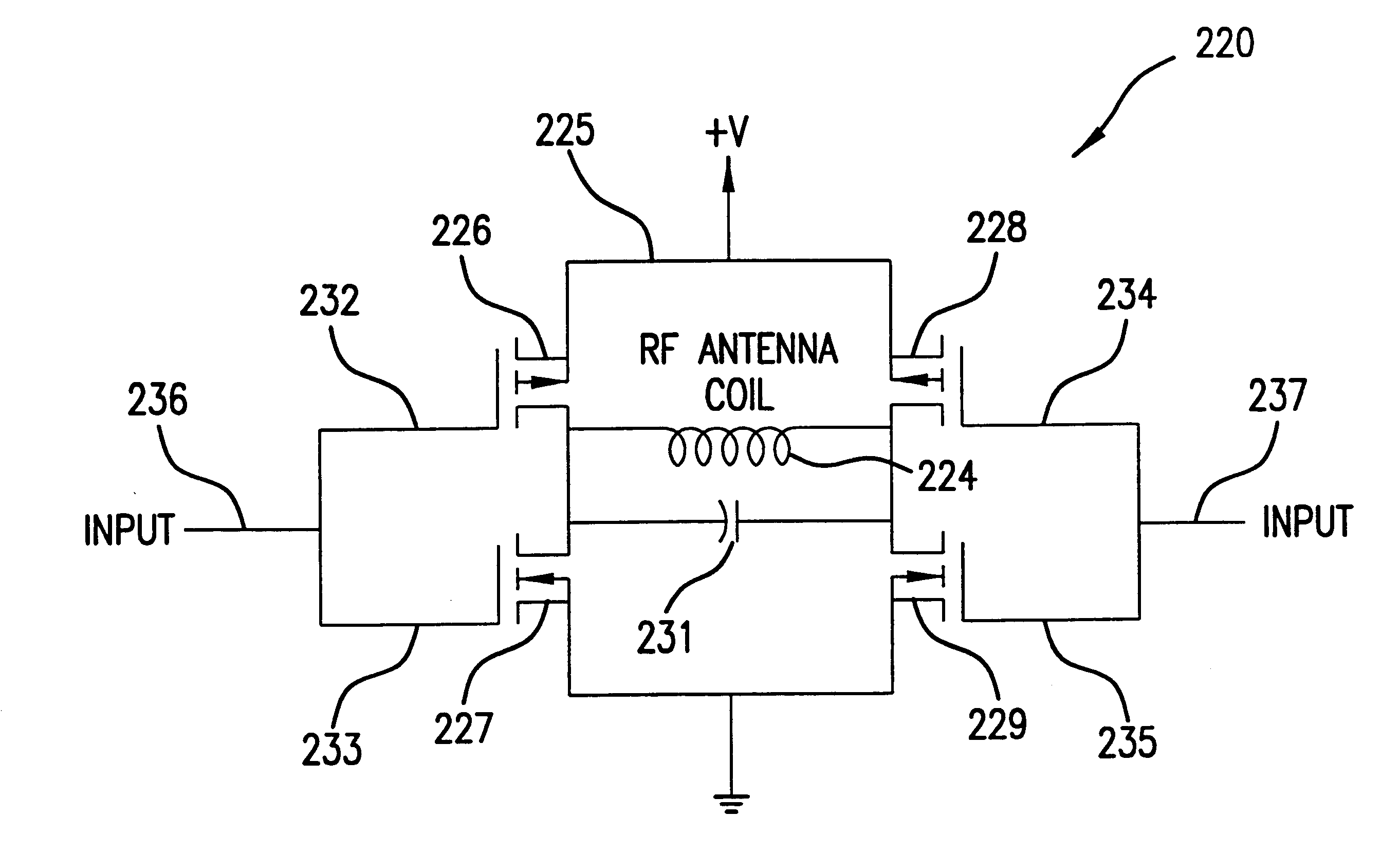
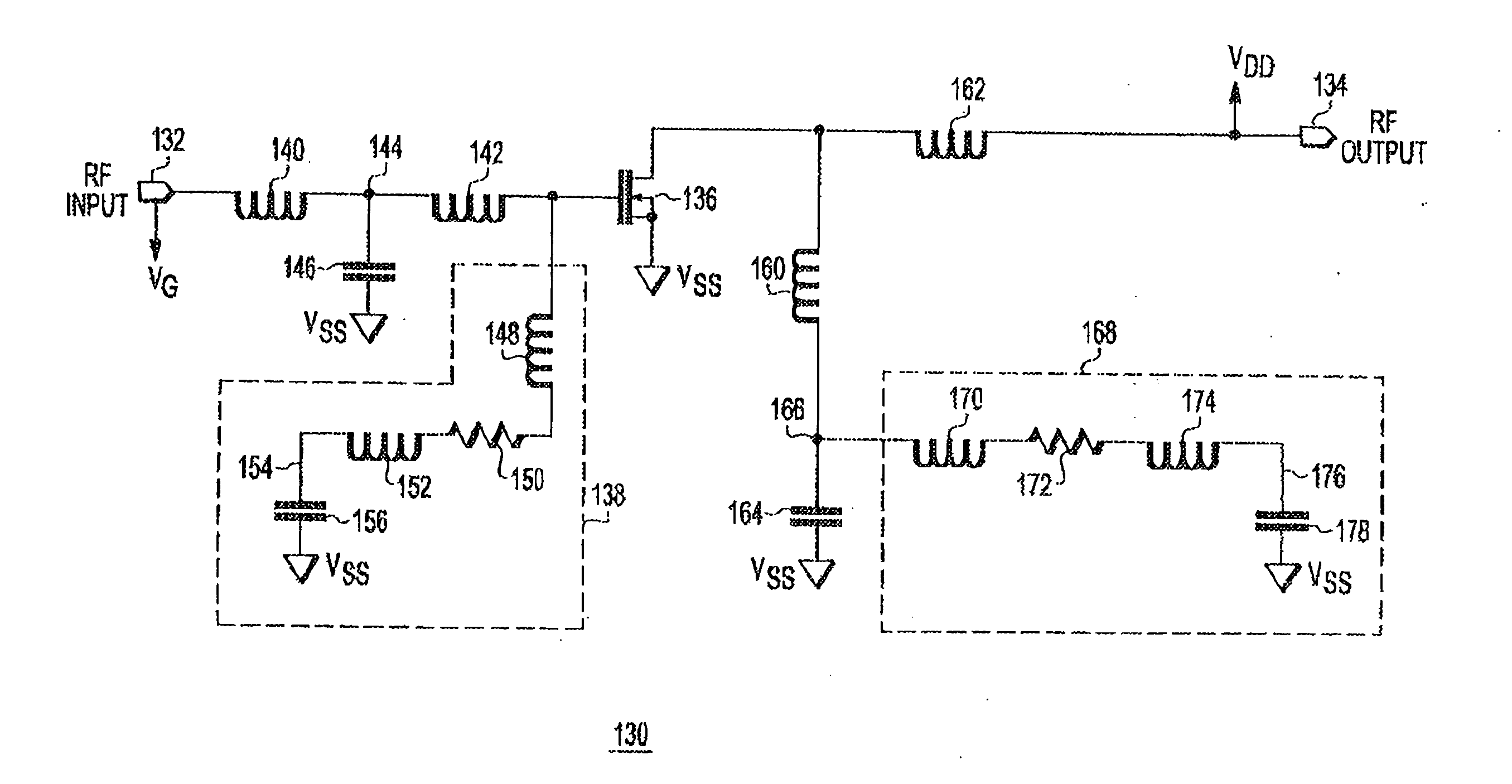
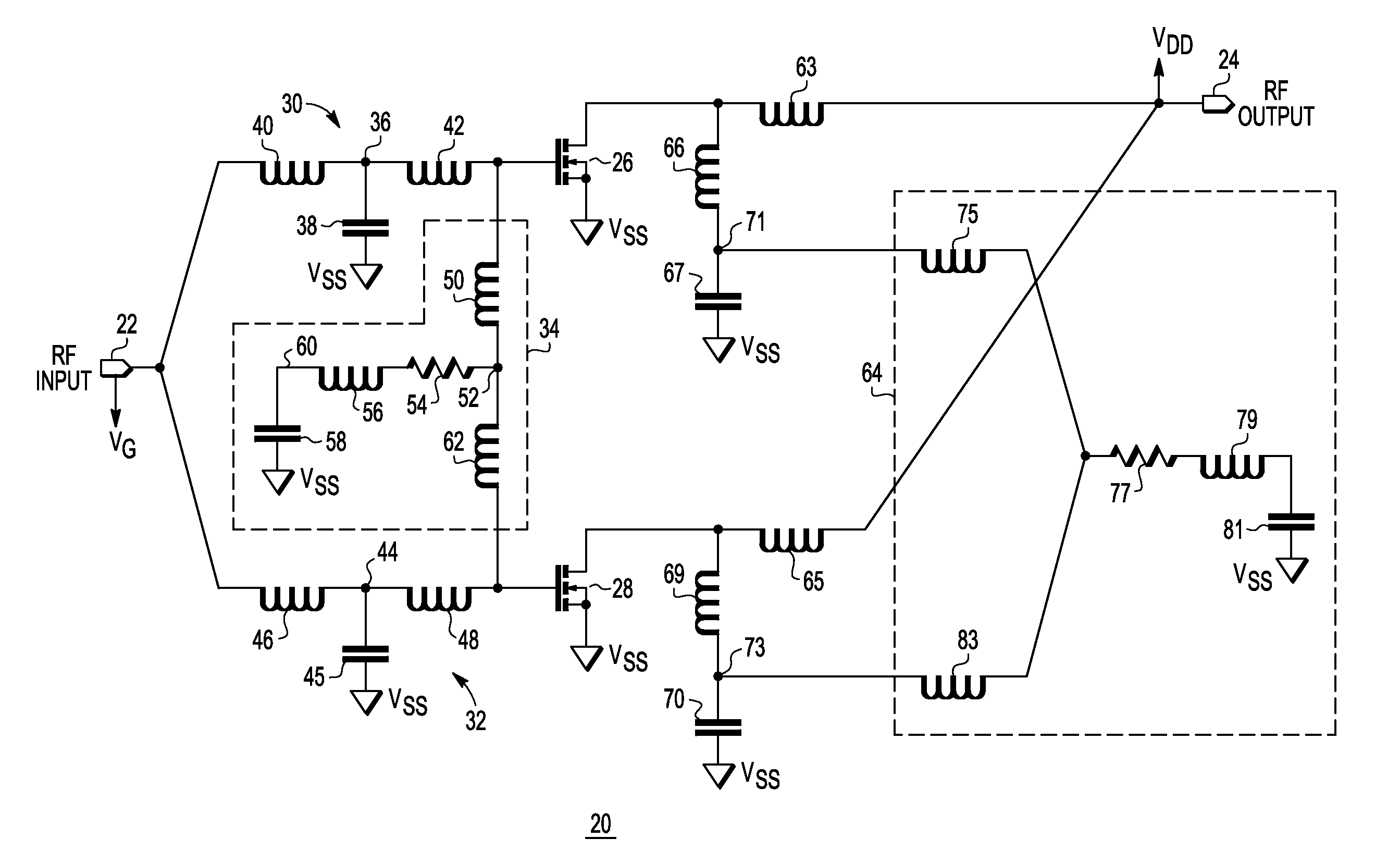
RF power transistor circuit
A radio frequency (RF) power transistor circuit includes a power transistor and a decoupling circuit. The power transistor has a control electrode coupled to an input terminal for receiving an RF input signal, a first current electrode for providing an RF output signal at an output terminal, and a second current electrode coupled to a power supply voltage terminal. The decoupling circuit includes a first inductive element, a first resistor, and a first capacitor coupled together in series between the control electrode of the first power transistor and the power supply voltage terminal. The first decoupling circuit is for dampening a resonance at a frequency lower than an RF frequency.
Owner:NXP USA INC
RF amplifier with a bias boosting scheme
The present invention provides methods and apparatuses for an amplifier circuit for amplifying an input signal. An amplifier circuit for amplifying an input signal comprises an amplifying transistor circuit having a power transistor and a dc bias circuit having a plurality of current mirror circuits and a discharge transistor wherein the discharge transistor and the power transistor form a combined current mirror circuit to control quiescent current in the power transistor.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
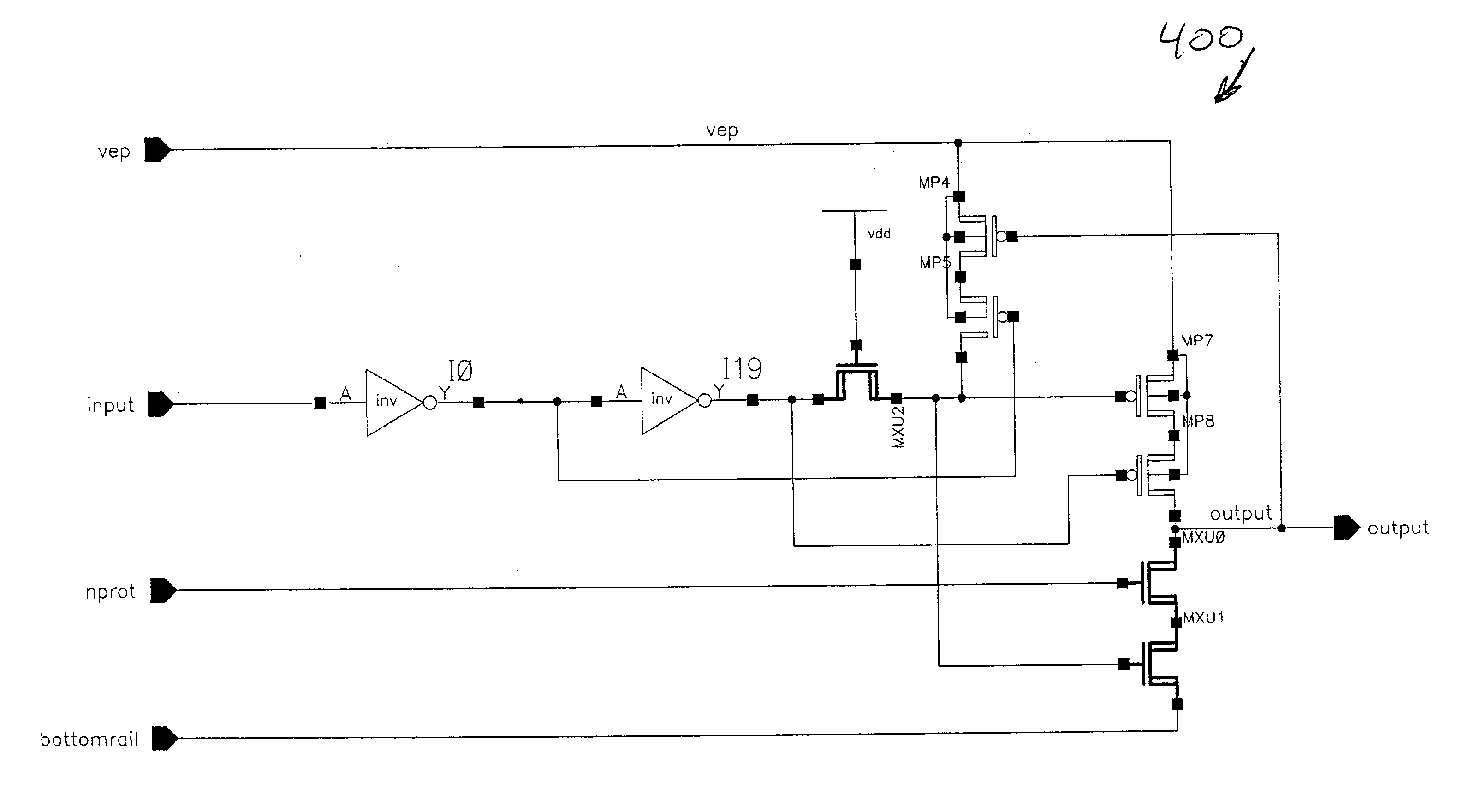
Method and apparatus for avoiding gated diode breakdown in transistor circuits
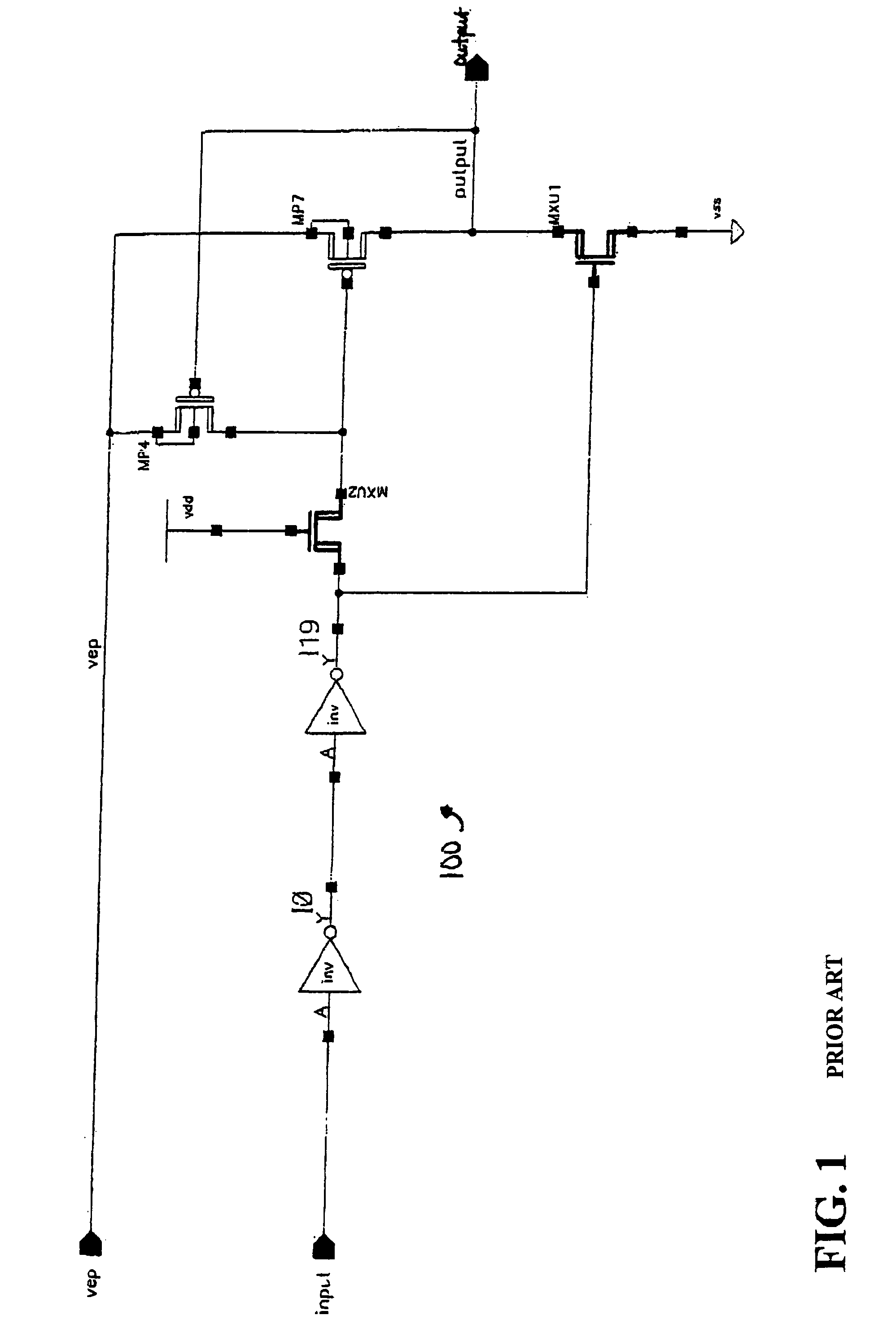
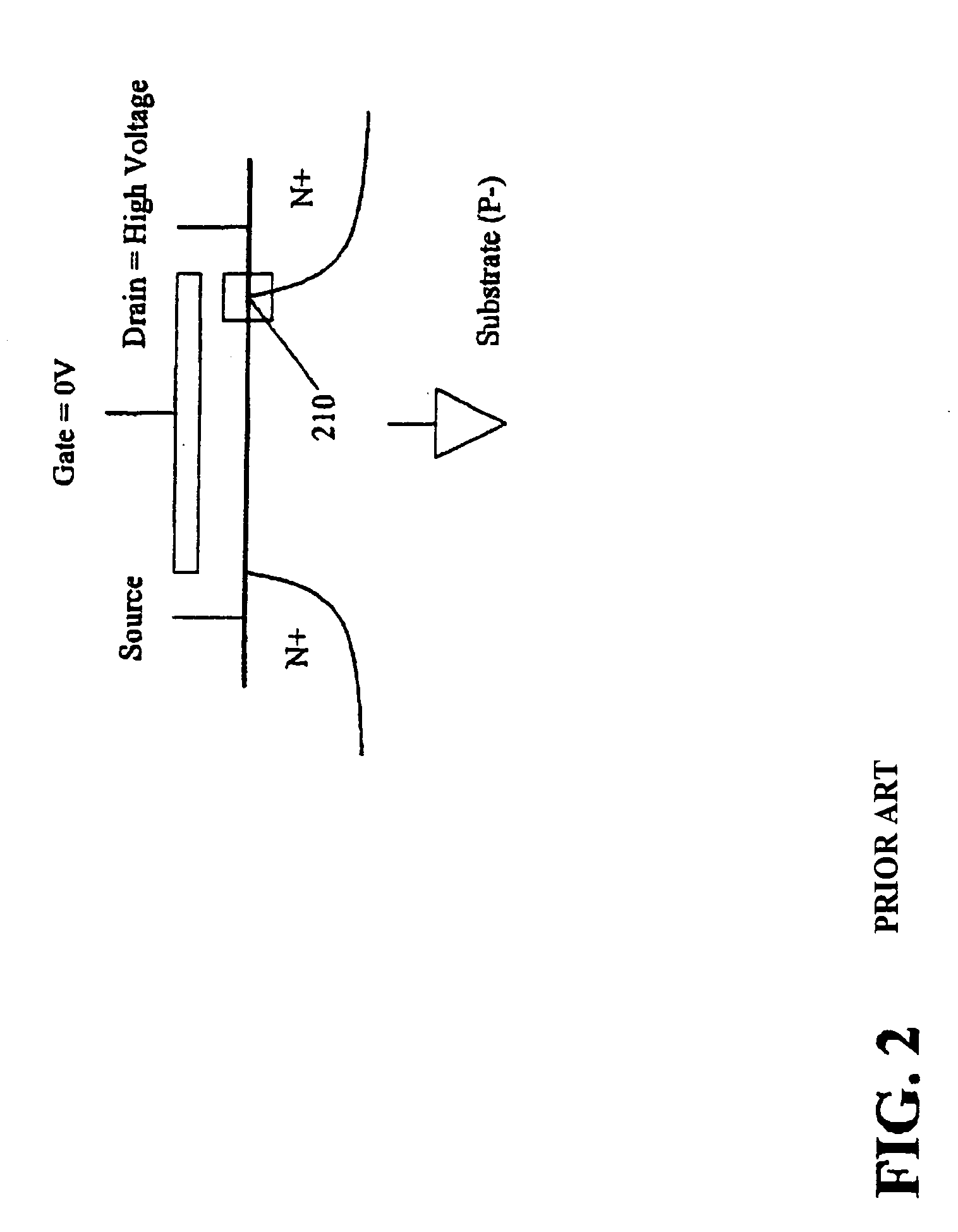
InactiveUS7132873B2Prevents gated diode breakdownAvoid failureTransistorPulse automatic controlTransistor circuitsHigh pressure
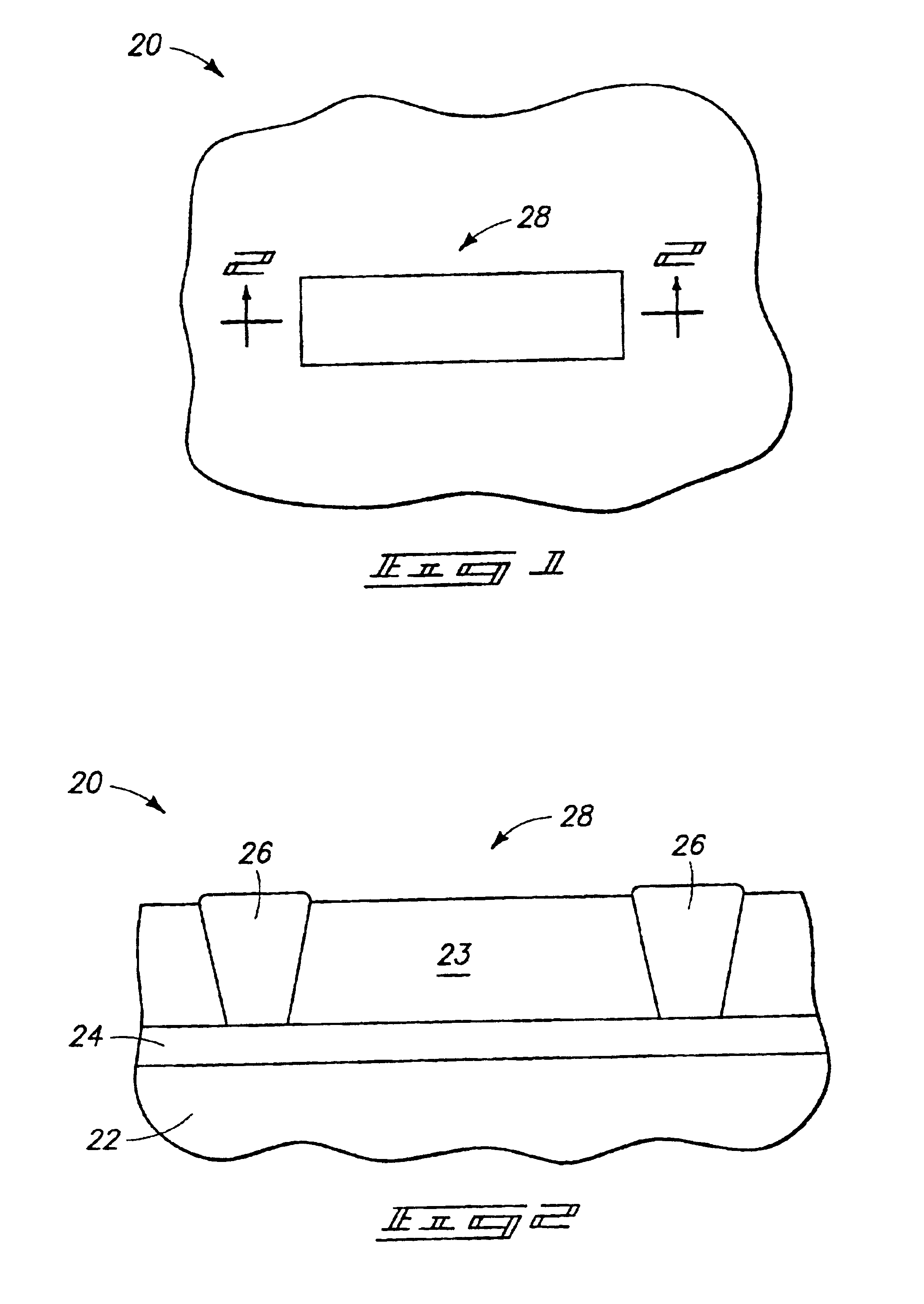
An N-channel transistor protection circuit and method are disclosed that prevent gated diode breakdown in N-channel transistors that have a high voltage on their drain. The disclosed N-channel protection circuit may be switched in a high voltage mode between a high voltage level and a lower rail voltage. A high voltage conversion circuit prevents gated diode breakdown in N-channel transistors by dividing the high voltage across two N-channel transistors, MXU0 and MXU1, such that no transistor exceeds the breakdown voltage, Vbreakdown. An intermediate voltage drives the top N-channel transistor, MXU0. The top N-channel transistor, MXU0, is gated with a voltage level that is at least one N-channel threshold, Vtn, below the high voltage level, Vep, using the intermediate voltage level, nprot. The drain voltage of MXU0 will be at least one N-channel threshold, Vtn, lower than the input voltage level, nprot, and the drain voltage Vd of the bottom N-channel transistor, MXU1, is limited to less than the breakdown voltage, Vbreakdown.
Owner:EMOSYN AMERICA
Level shift circuit
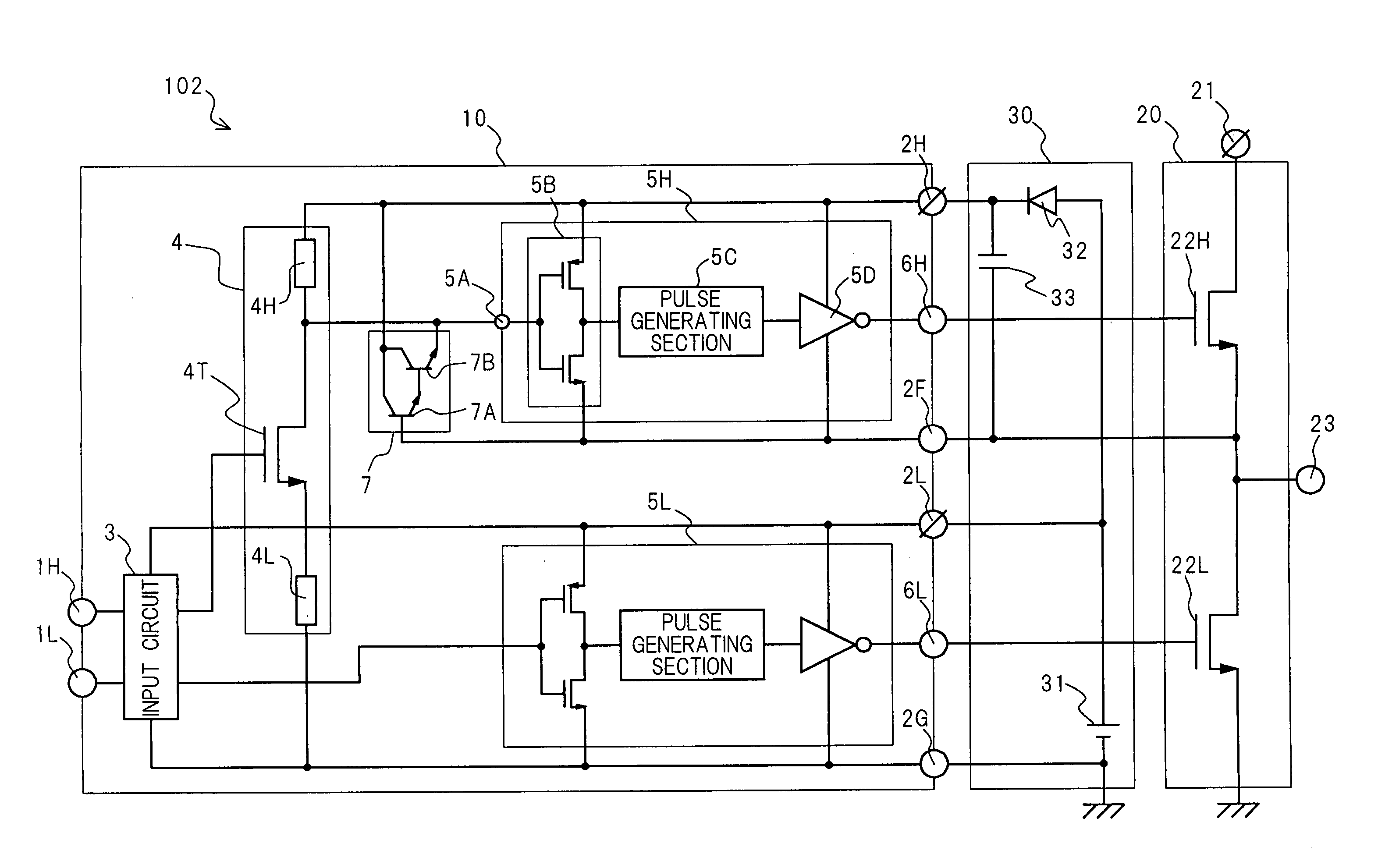
InactiveUS7019559B2High speedAmount of shift is increasedPulse automatic controlLogic circuits coupling/interface using field-effect transistorsControl signalTransistor circuits
A level shift circuit including a first transistor circuit connected between a power supply line and a first node, a second transistor circuit connected between the power supply line and a second node, a first transistor connected between the ground line and the first node, and a second transistor connected between the ground line and the second node. A gate of the first transistor circuit is connected to the second node, and a gate of the second transistor circuit is connected to the first node. An input signal is supplied to a gate of the first transistor and an inverted value of the input signal is supplied to a gate of the second transistor. Additionally, control transistors switch a ratio of inflow current and emission current of the first node or the second node according to a control signal.
Owner:LAPIS SEMICON CO LTD
Image Sensor and Manufacturing Method Thereof
InactiveUS20090085135A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingTransistor circuitsEngineering
Provided are embodiments of an image sensor. The image sensor can comprise a first substrate including a transistor circuit, a lower interconnection layer, an upper interconnection layer, and a second substrate including a vertical stacked photodiode. The lower interconnection layer is disposed on the first substrate and comprises a lower interconnection connected to the transistor circuit. The upper interconnection layer is disposed on the lower interconnection layer and comprises an upper interconnection connected with the lower interconnection. The vertical stacked photodiode can be disposed on the upper interconnection layer and connected with the upper interconnection through, for example, a single plug connecting a blue, green, and red photodiode of the vertical stack or a corresponding plug for each of the blue, green, and red photodiode of the vertical stack.
Owner:DONGBU HITEK CO LTD
System and method for detecting a reversed battery cell in a battery pack
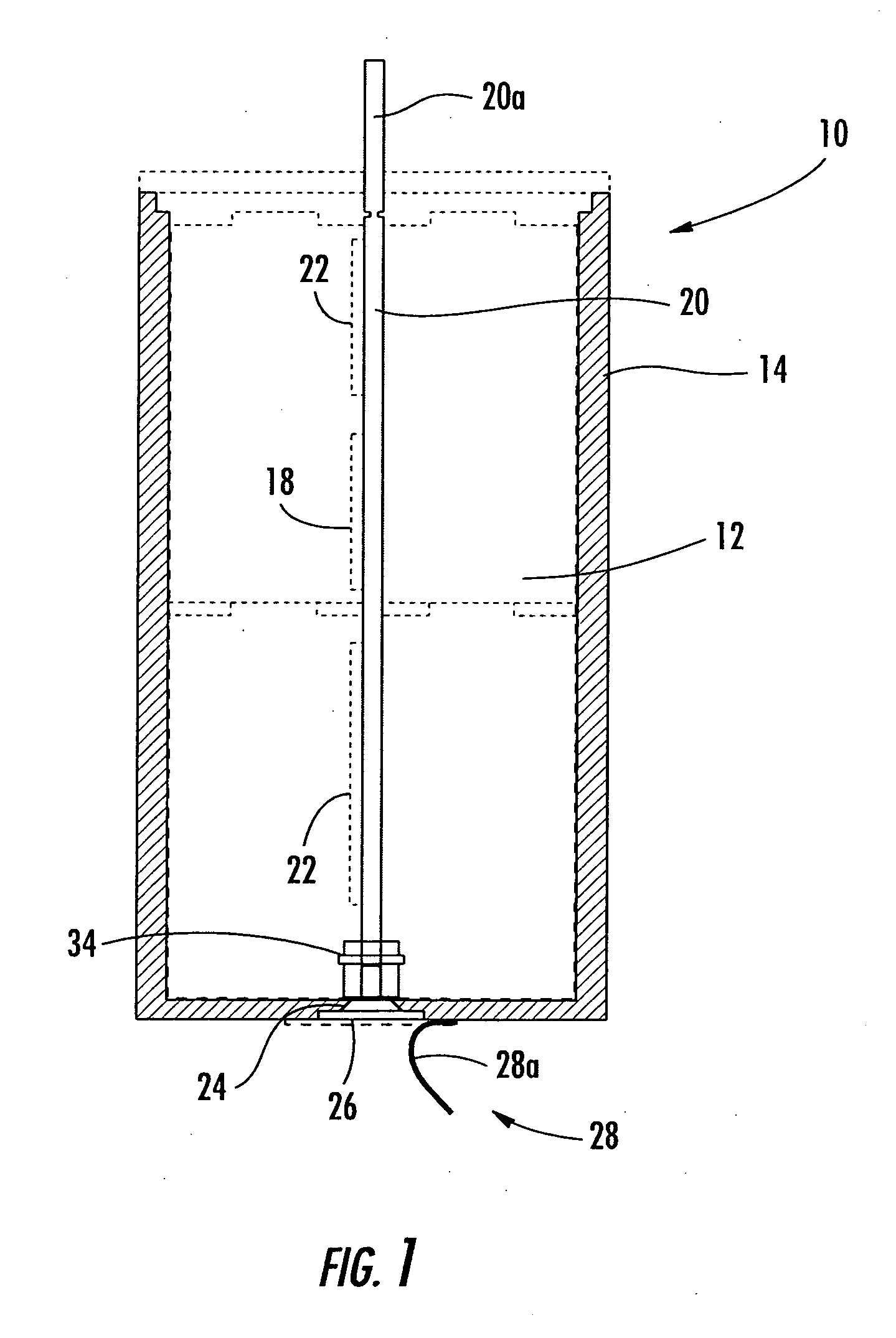
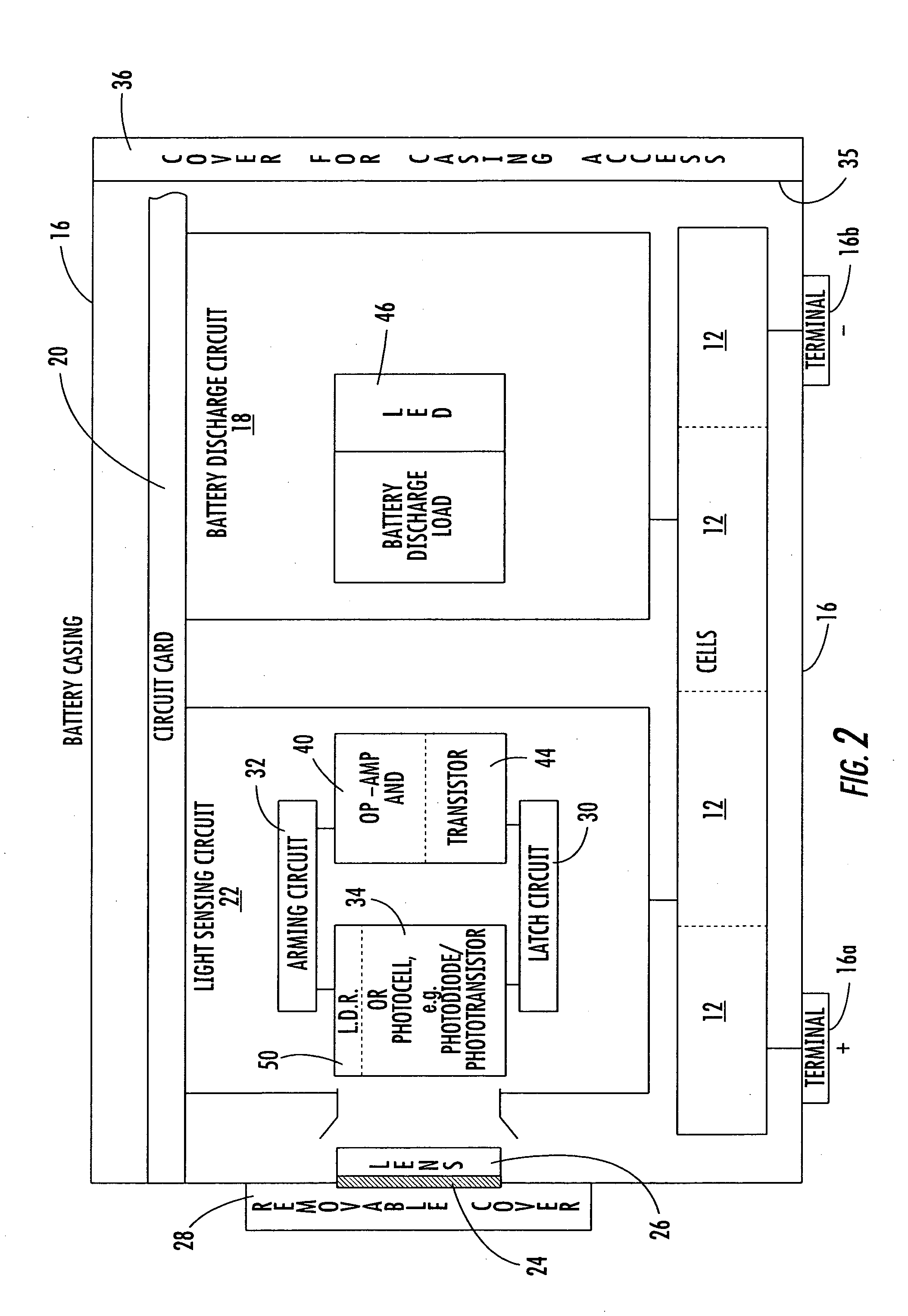
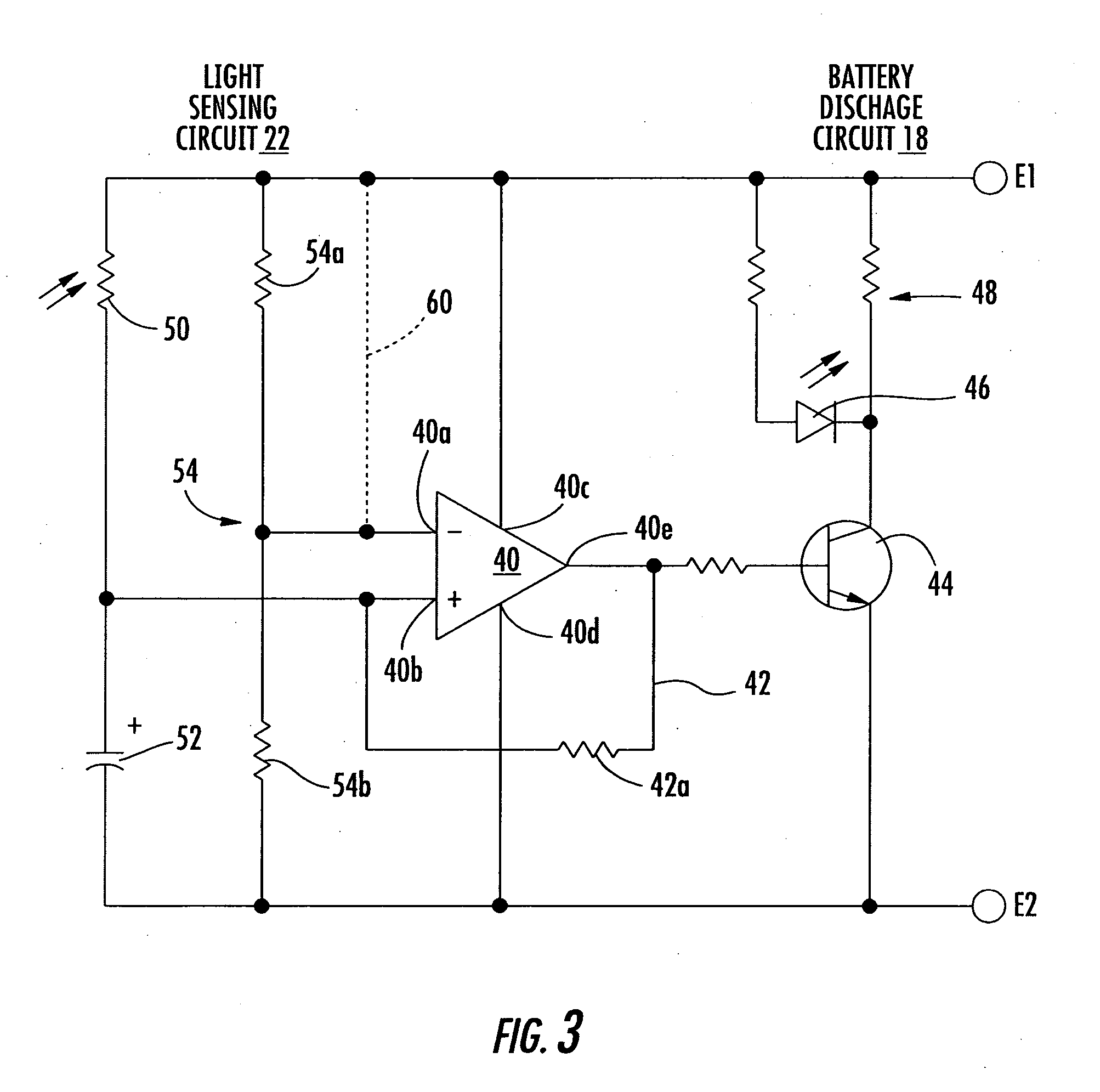
InactiveUS20050156578A1Avoid chargingCircuit monitoring/indicationIndicating/monitoring circuitsEngineeringTransistor circuits
A system and method for detecting a reversed battery cell within a battery pack includes battery cells connected together and forming a battery pack and battery output. A transistor circuit is operatively connected to the battery cells and operative for determining when a voltage condition occurs indicative of a reversed battery cell within the battery pack. An indication circuit is operatively connected to the transistor circuit for indicating a reversed battery cell in the battery pack.
Owner:MATHEWS ASSOCS
Sustain driver, sustain control system, and plasma display
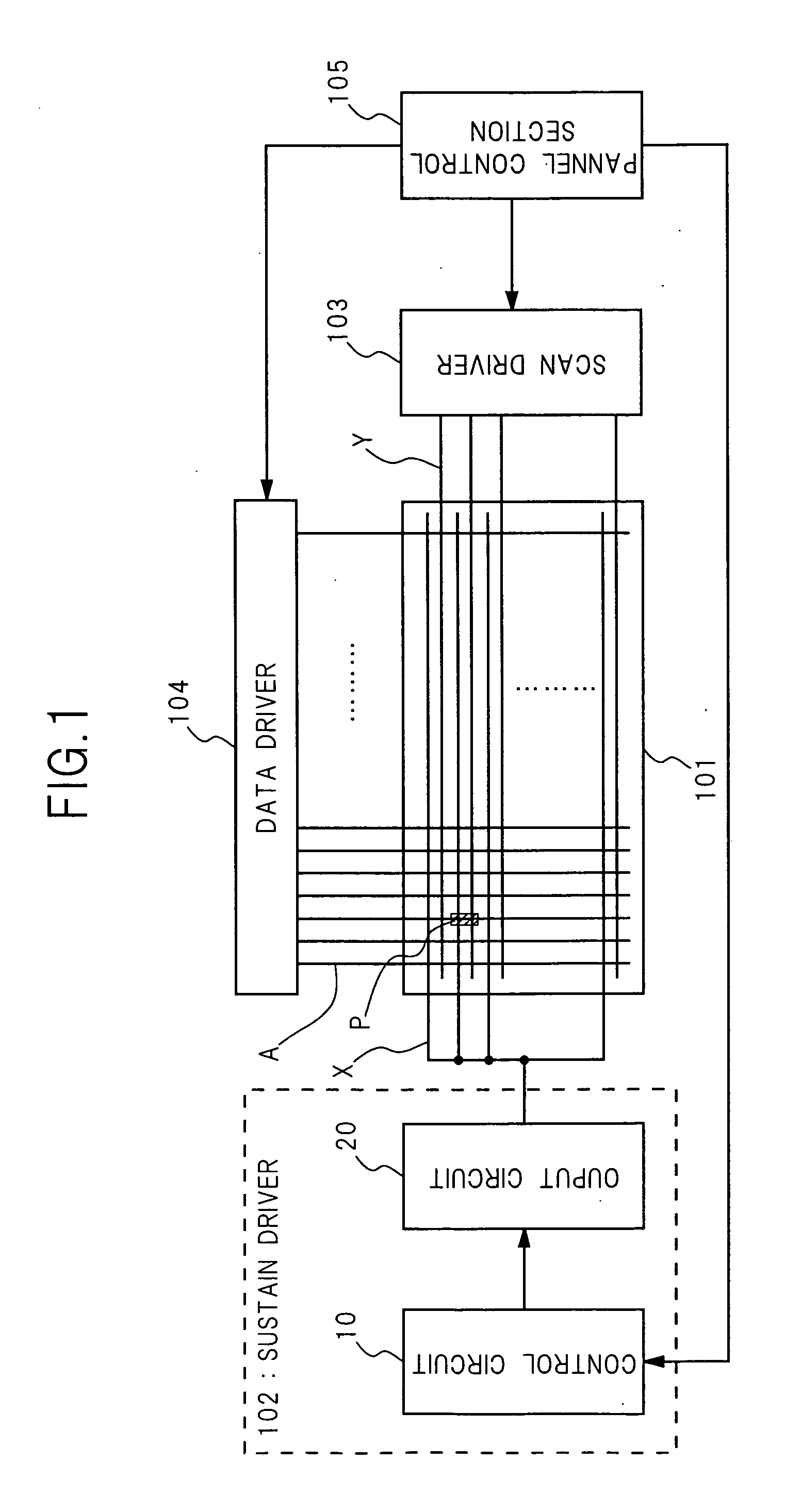
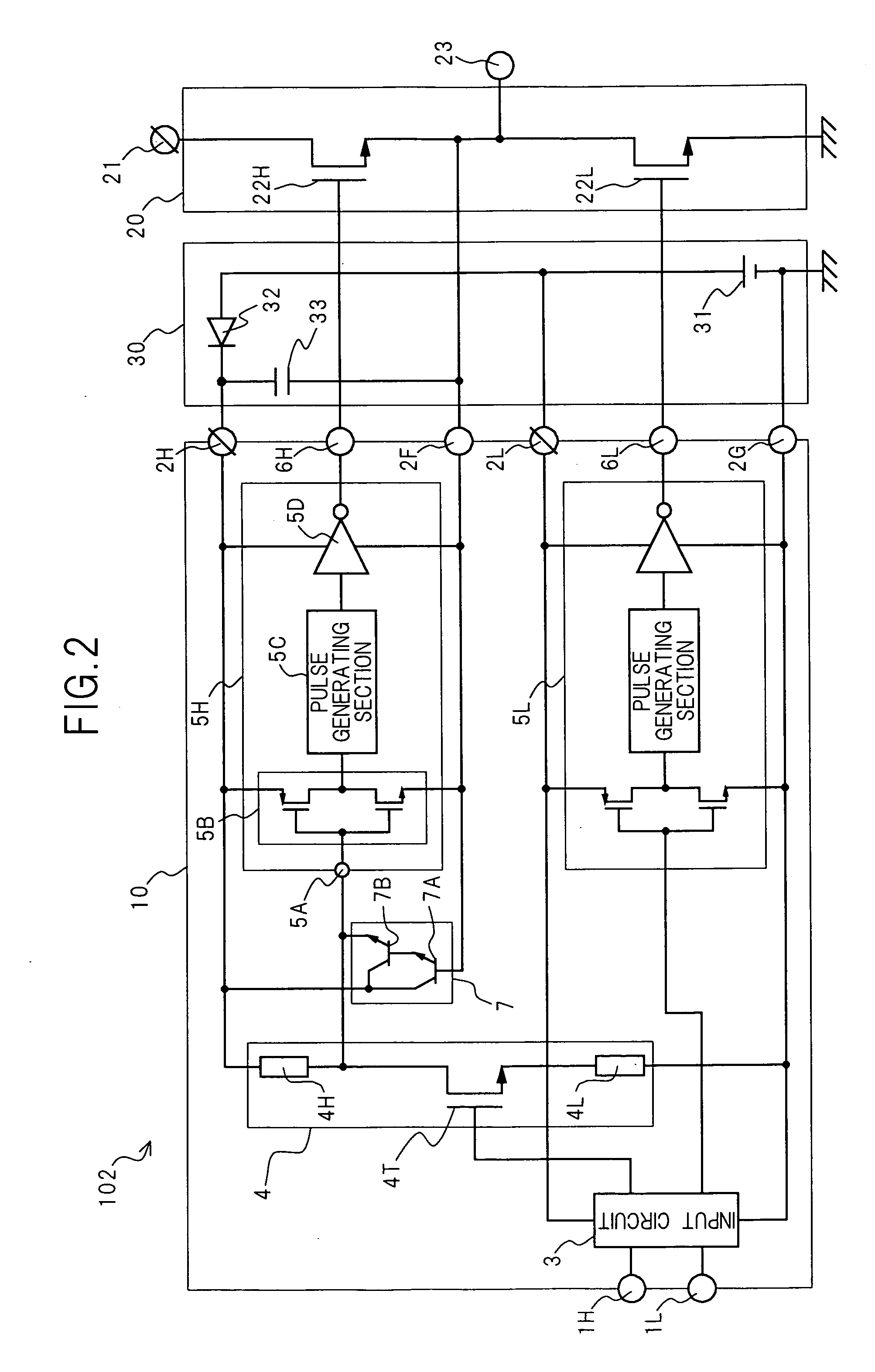
InactiveUS20050134533A1Highly integratedImprove reliabilityTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsControl systemTransistor circuits
The collector, emitter, and base of a bipolar transistor circuit are connected to a high side power supply terminal, the drain of a level shift transistor, and a floating power supply terminal, respectively. When a high side output transistor is on, the floating power supply terminal is at the potential of a high potential power supply terminal. The high side power supply terminal is at a potential higher than the potential of the floating power supply terminal by a constant voltage. Turning the level shift transistor on, its drain potential drops below the potential of the floating power supply terminal; The base current flows through the bipolar transistor circuit and the drain potential of the level shift transistor is clamped near the potential of the floating power supply terminal; The bipolar transistor circuit is turned on and its collector current supplies the drain current of the level shift transistor.
Owner:COLLABO INNOVATIONS INC
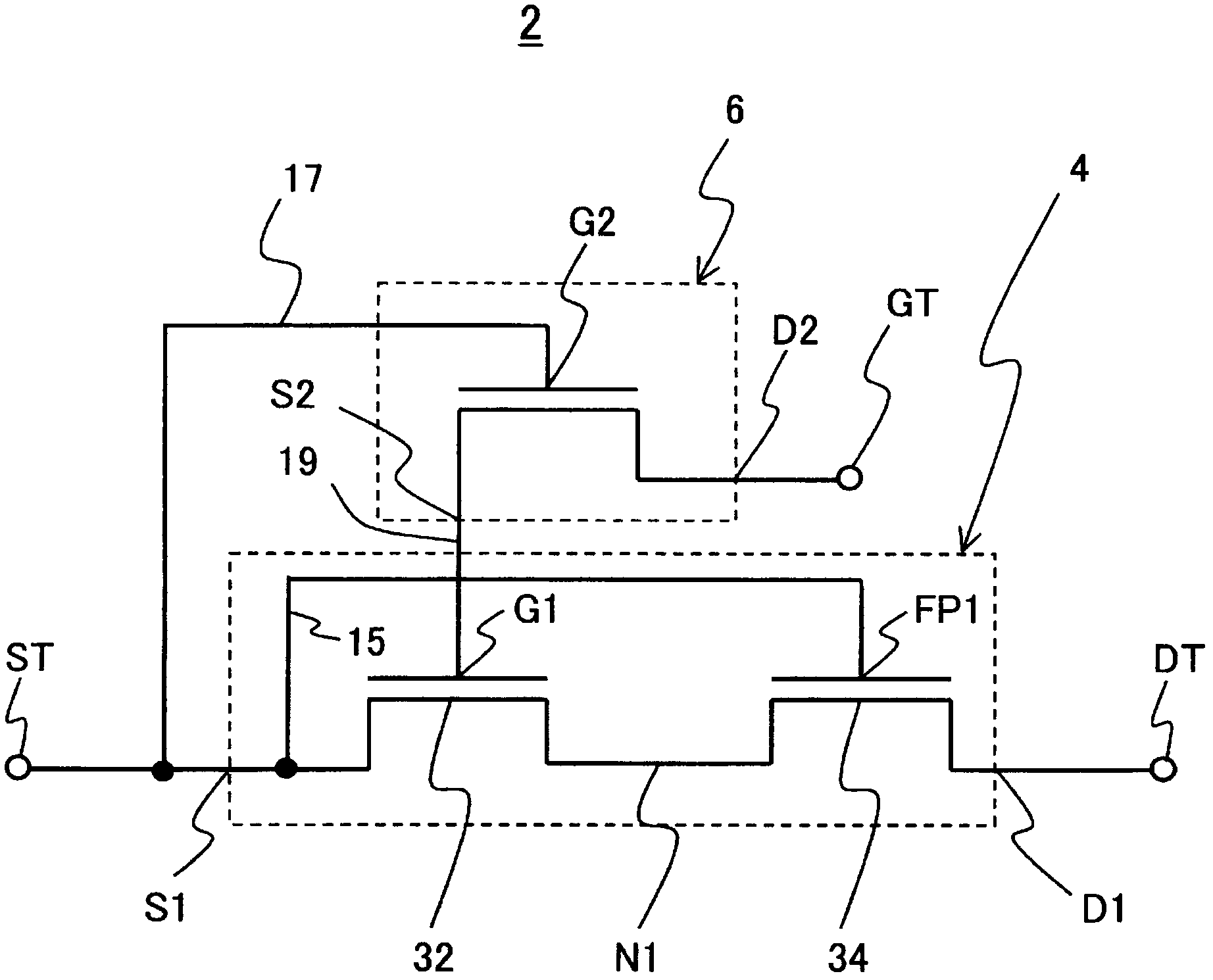
Semiconductor device, manufacturing method and transistor circuit
InactiveCN102683405AImprove withstand voltageSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesPower semiconductor deviceTransistor circuits
A transistor circuit includes a first high electron mobility transistor and a second high electron mobility transistor having a negative threshold voltage, wherein a source of the second high electron mobility transistor is coupled to a gate of the first high electron mobility transistor, and a gate of the second high electron mobility transistor is coupled to a source of the first high electron mobility transistor. The invention enables the withstand voltages of the high electron mobility transistors to be improved.
Owner:TRANSPHORM JAPAN
RF power transistor circuit
A radio frequency (RF) power transistor circuit includes a power transistor and a decoupling circuit. The power transistor has a control electrode coupled to an input terminal for receiving an RF input signal, a first current electrode for providing an RF output signal at an output terminal, and a second current electrode coupled to a power supply voltage terminal. The decoupling circuit includes a first inductive element, a first resistor, and a first capacitor coupled together in series between the control electrode of the first power transistor and the power supply voltage terminal. The first decoupling circuit is for dampening a resonance at a frequency lower than an RF frequency.
Owner:NXP USA INC
Circuits providing ESD protection to high voltage laterally diffused metal oxide semiconductor (LDMOS) transistors
ActiveUS7838937B1TransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSilicon-controlled rectifierLow voltage
Circuits including a laterally diffused output driver transistor and a distinct device configured to provide electrostatic discharge (ESD) protection for the laterally diffused output driver transistor are presented. In general, the device configured to provide ESD protection includes a drain extended metal oxide semiconductor transistor (DEMOS) transistor configured to breakdown at a lower voltage than a breakdown voltage of the laterally diffused output driver transistor. The laterally diffused output driver transistor may be a pull-down or a pull-up output driver transistor. The device also includes a silicon controlled rectifier (SCR) configured to inject charge within a semiconductor layer of the circuit upon breakdown of the DEMOS transistor. Moreover, the device includes a region configured to collect the charge injected from the SCR and further includes an ohmic contact region configured to at least partially affect the holding voltage of the SCR.
Owner:MONTEREY RES LLC
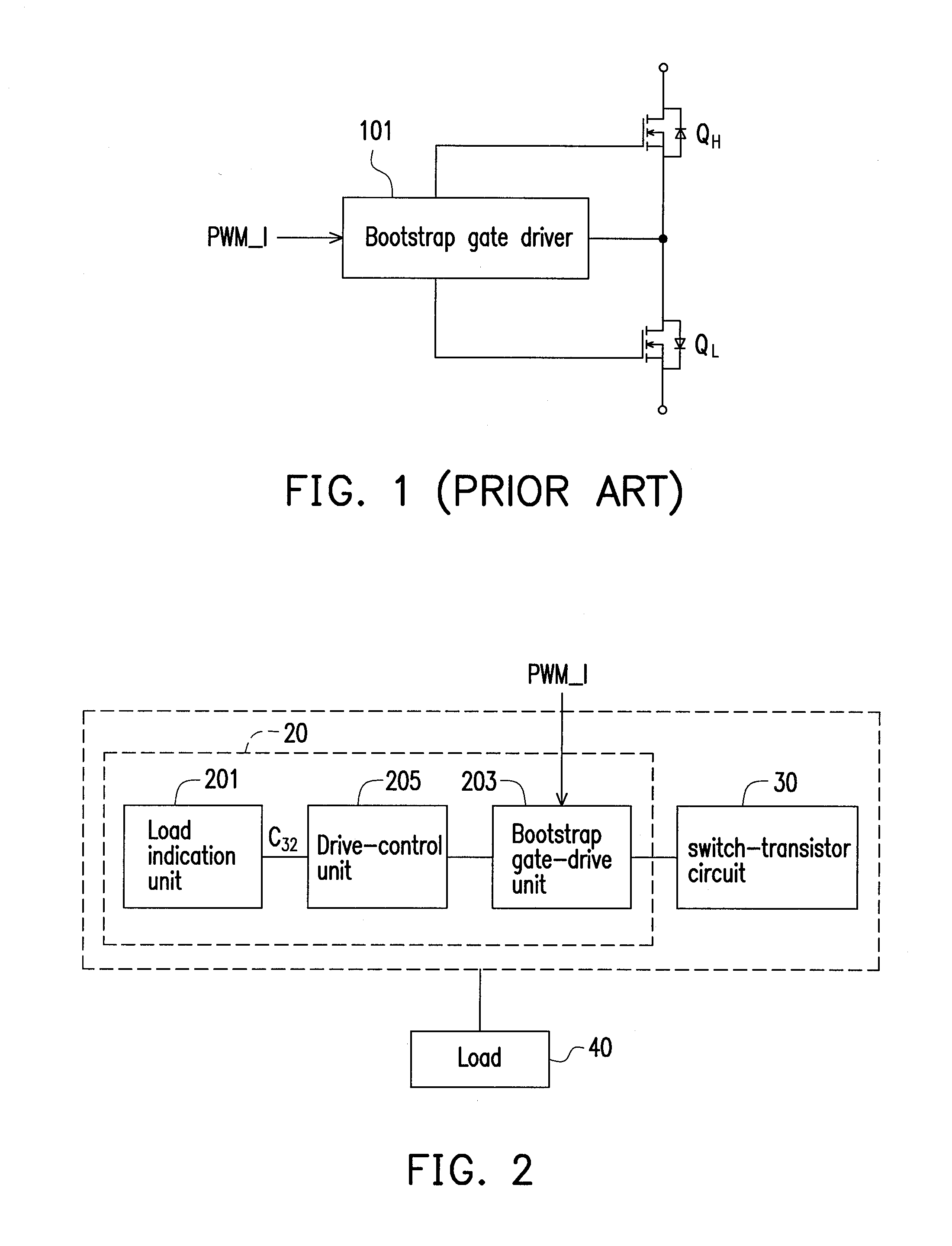
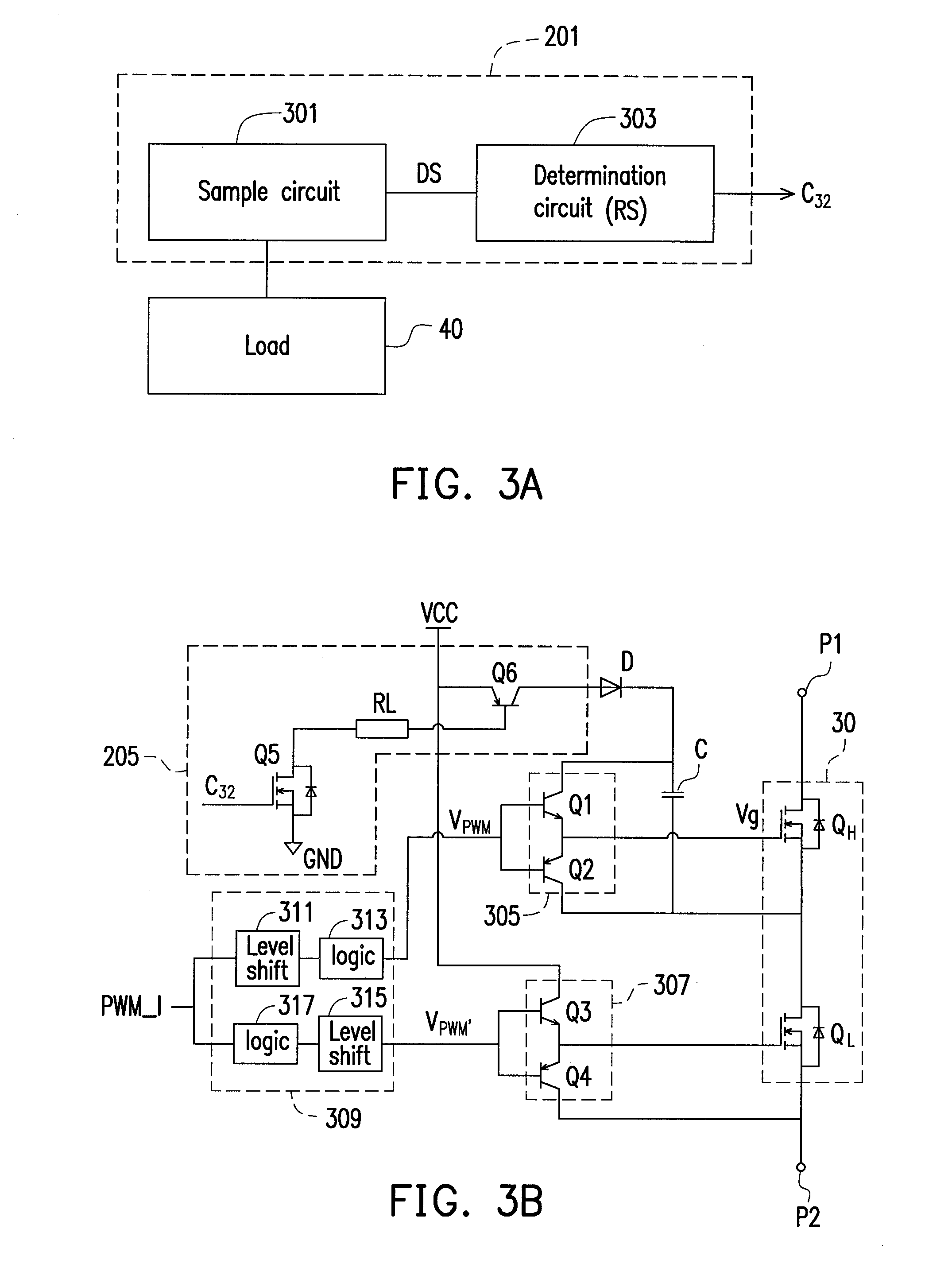
Bootstrap gate driver
ActiveUS20120293219A1Improve efficiencyEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionTransistor circuitsEngineering
A bootstrap gate driver including a load indication unit, a bootstrap gate-drive unit and a drive-control unit is provided. The load indication unit is configured to generate a load indication signal in response to a state of a load. The bootstrap gate-drive unit is configured to drive a switch-transistor circuit in response to an inputted pulse-width-modulation (PWM) signal, wherein the switch-transistor circuit has a high-side driving path and a low-side driving path. The drive-control unit is coupled to the load indication unit and the bootstrap gate-drive unit, and configured to enable or disable the high-side driving path in response to the load indication signal. In the invention, the operation of the low-side driving path is not affected by enabling or disabling the high-side driving path.
Owner:SPI ELECTRONICS +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com