Semiconductor device, manufacturing method and transistor circuit
A technology of transistors and semiconductors, which is applied in semiconductor devices, semiconductor/solid-state device components, electric solid-state devices, etc., can solve the problems of thin insulating layers that are easily damaged, and the withstand voltage of GaN-HEMT is not high, so as to improve the withstand voltage Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 Embodiment
[0037] (1) Structure
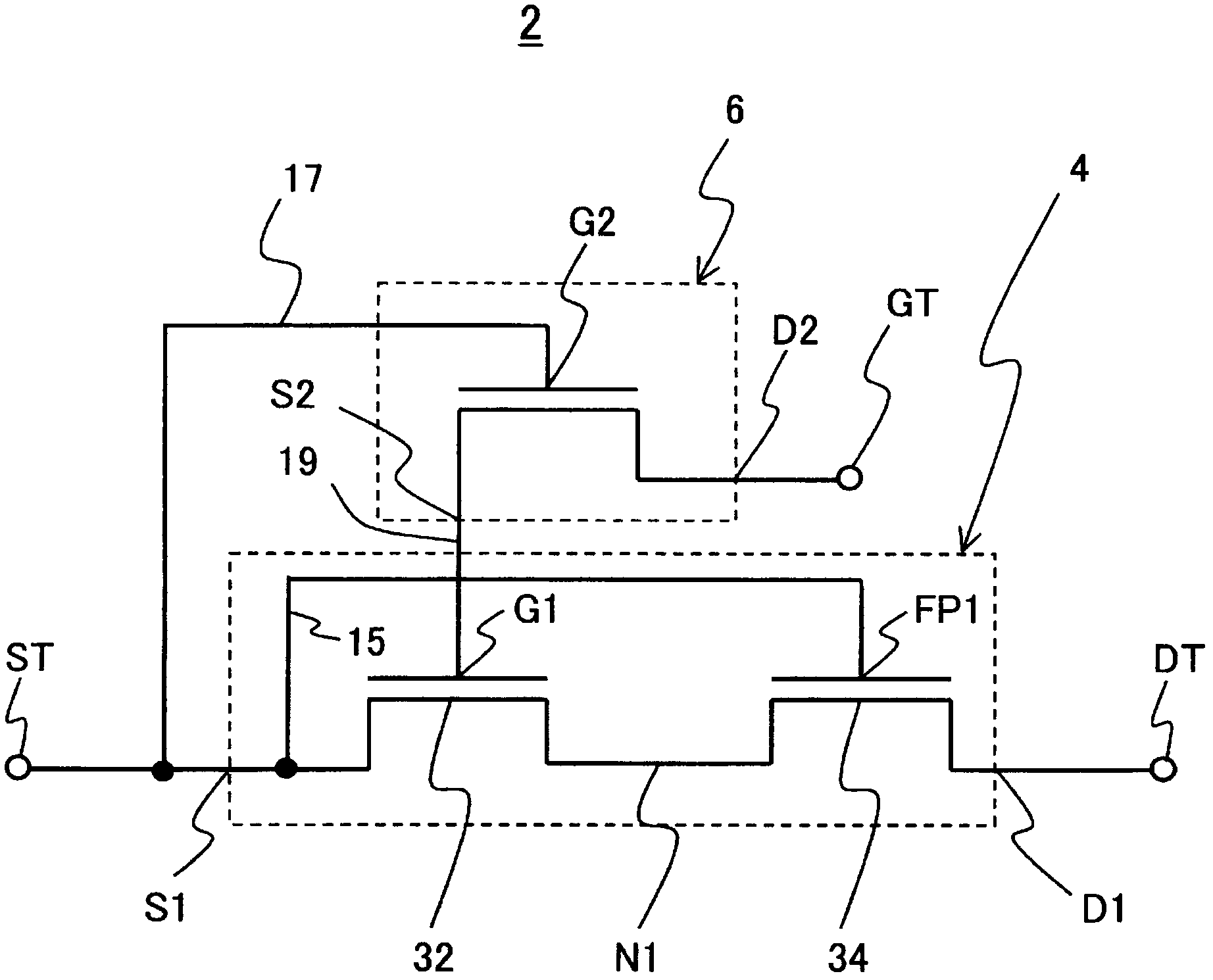
[0038] figure 1 is a circuit diagram of the transistor circuit 2 according to the present embodiment. The transistor circuit 2 comprises a first high electron mobility transistor 4 and a second high electron mobility transistor 6 with a negative threshold voltage. exist figure 1 The equivalent circuits of the first high-electron-mobility transistor 4 and the second high-electron-mobility transistor 6 are shown in boxes drawn with dotted lines in .
[0039] Such as figure 1 As shown, the second source S2 of the second high electron mobility transistor 6 is coupled to the first gate G1 of the first high electron mobility transistor 4 . Moreover, the second gate G2 of the second high electron mobility transistor 6 is coupled to the first source S1 of the first high electron mobility transistor 4 .
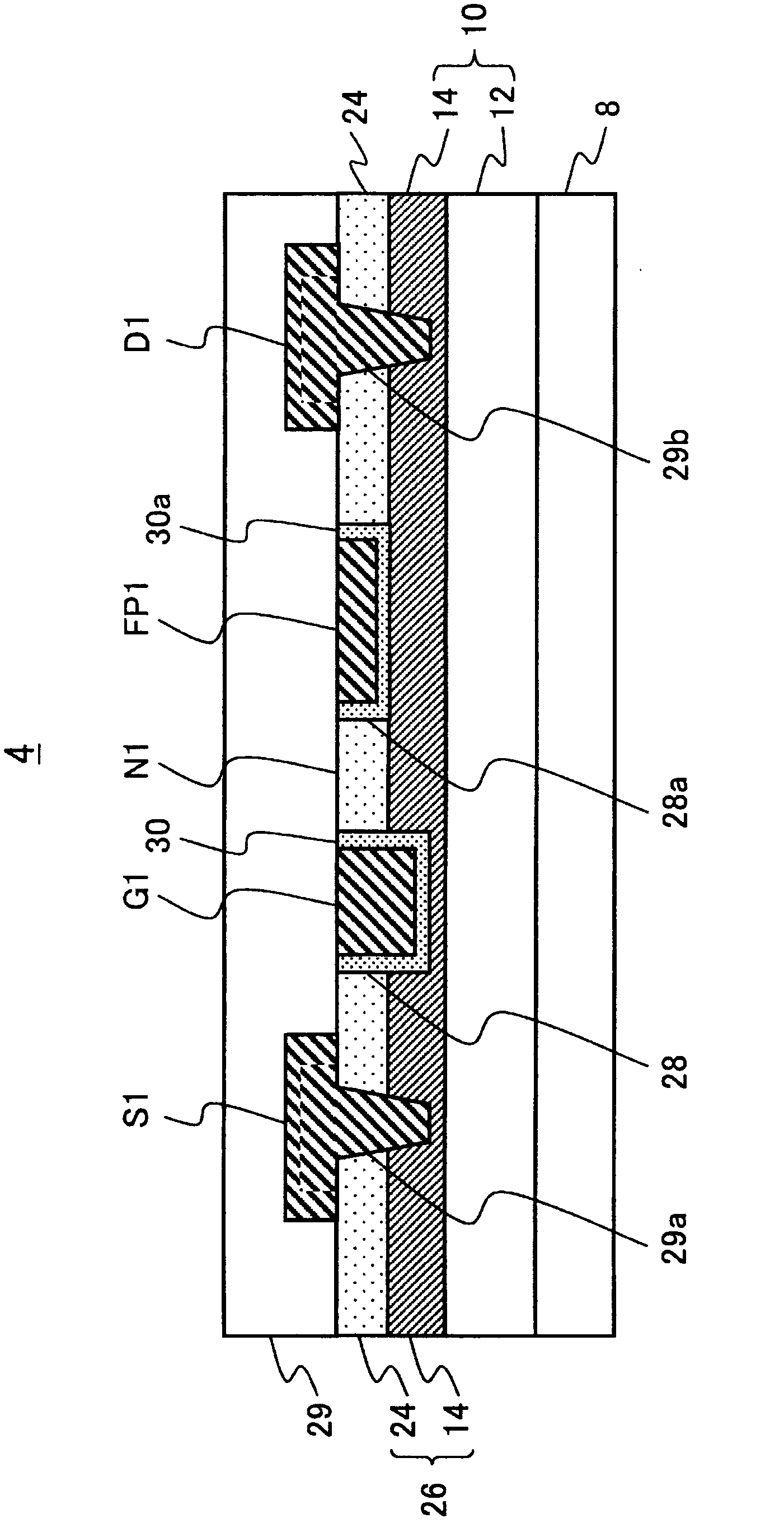
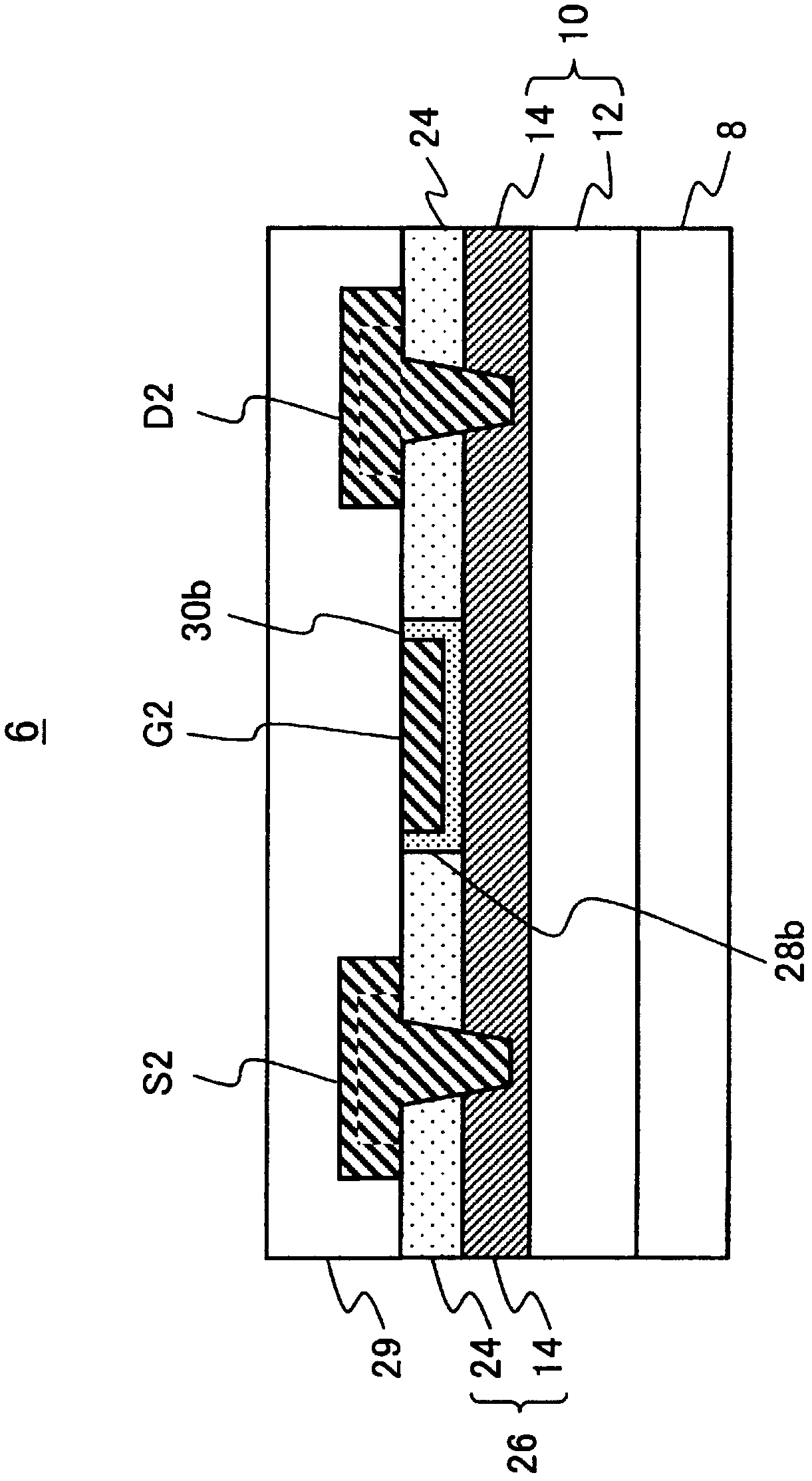
[0040] figure 2 is the cross section of the first high electron mobility transistor 4 . Such as figure 2 As shown, the first high electron mobility tr...
no. 2 Embodiment
[0119] Image 6 is a plan view of the transistor circuit 2b according to the present embodiment. In the first embodiment, a first high electron mobility transistor 4 is coupled to a second high electron mobility transistor 6 . On the other hand, if Image 6 As shown, in the transistor circuit 2 b according to this embodiment, a plurality of first high electron mobility transistors 4 are coupled to one second high electron mobility transistor 6 . Here, the first high electron mobility transistor 4 and the second high electron mobility transistor 6 are devices formed on the same substrate.
[0120] The structures of the first high electron mobility transistor 4 and the second high electron mobility transistor 6 are the same as those according to the first embodiment (refer to figure 2 , image 3 The structures of the first high electron mobility transistor and the second high electron mobility transistor described above are substantially the same. For example, a region bet...
no. 3 Embodiment
[0130] Figure 8 is a circuit diagram of the transistor circuit 2d according to the present embodiment. Such as Figure 8 As shown, the transistor circuit 2d is similar to the transistor circuit 2 of the first embodiment. Therefore, descriptions of parts common to the transistor circuit 2 of the first embodiment will be omitted.
[0131] Such as Figure 8 As shown, the transistor circuit 2d includes a first high electron mobility transistor 4a and a second high electron mobility transistor 6a.
[0132] (1) The first high electron mobility transistor
[0133] The first high electron mobility transistor 4 a includes a first gate G1 , a first field plate FP1 a and a second field plate FP2 .
[0134] Similar to the first field plate FP1 in the first embodiment, the first field plate FP1a is a field plate provided between the first gate G1 and the first drain D1. The first field plate FP1a may be a field plate of which a portion extends between the first gate G1 and the first...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com