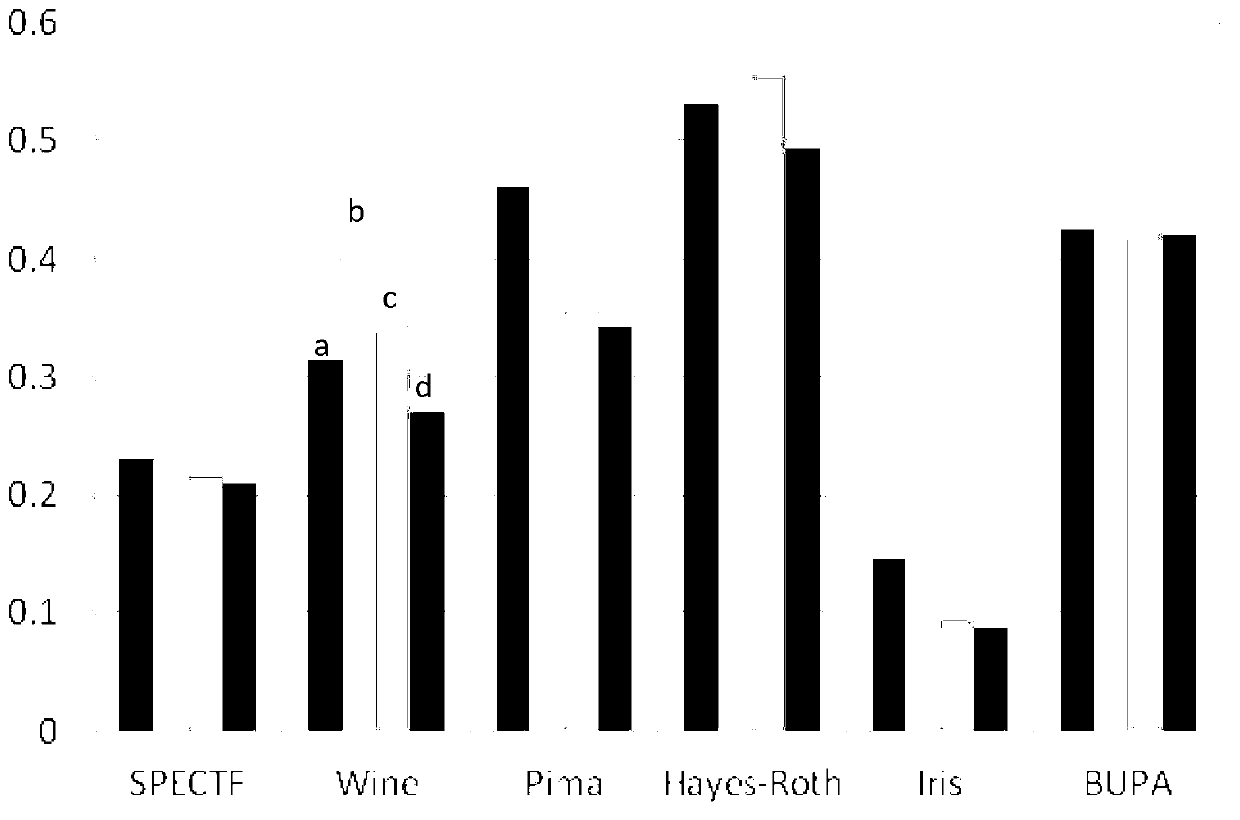
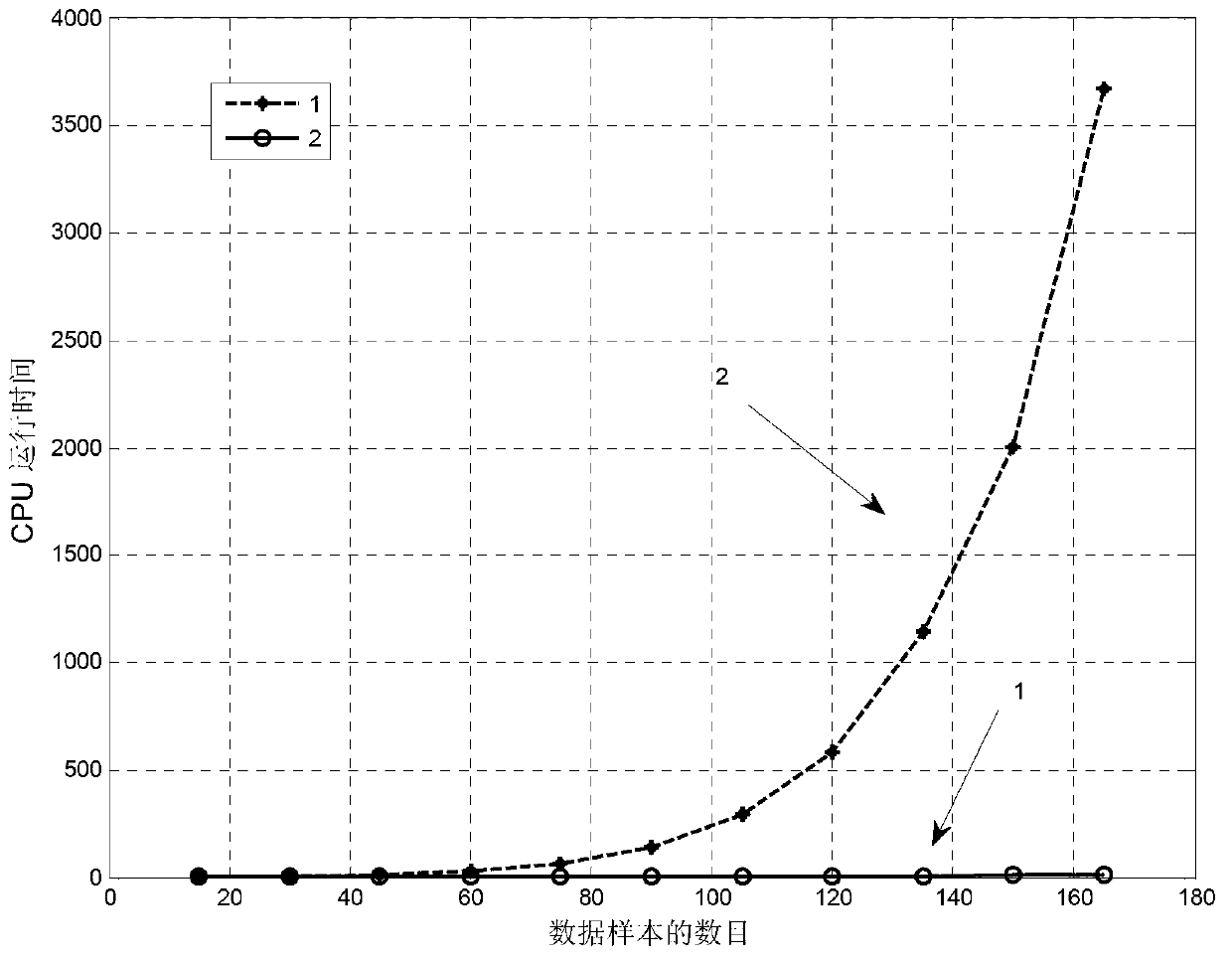
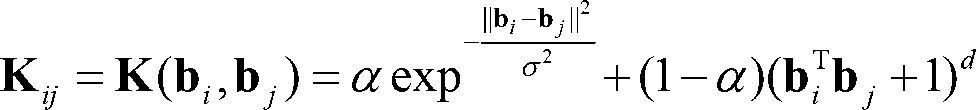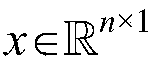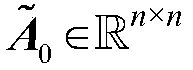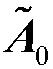Patents
Literature
97 results about "Z eigenvalue" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
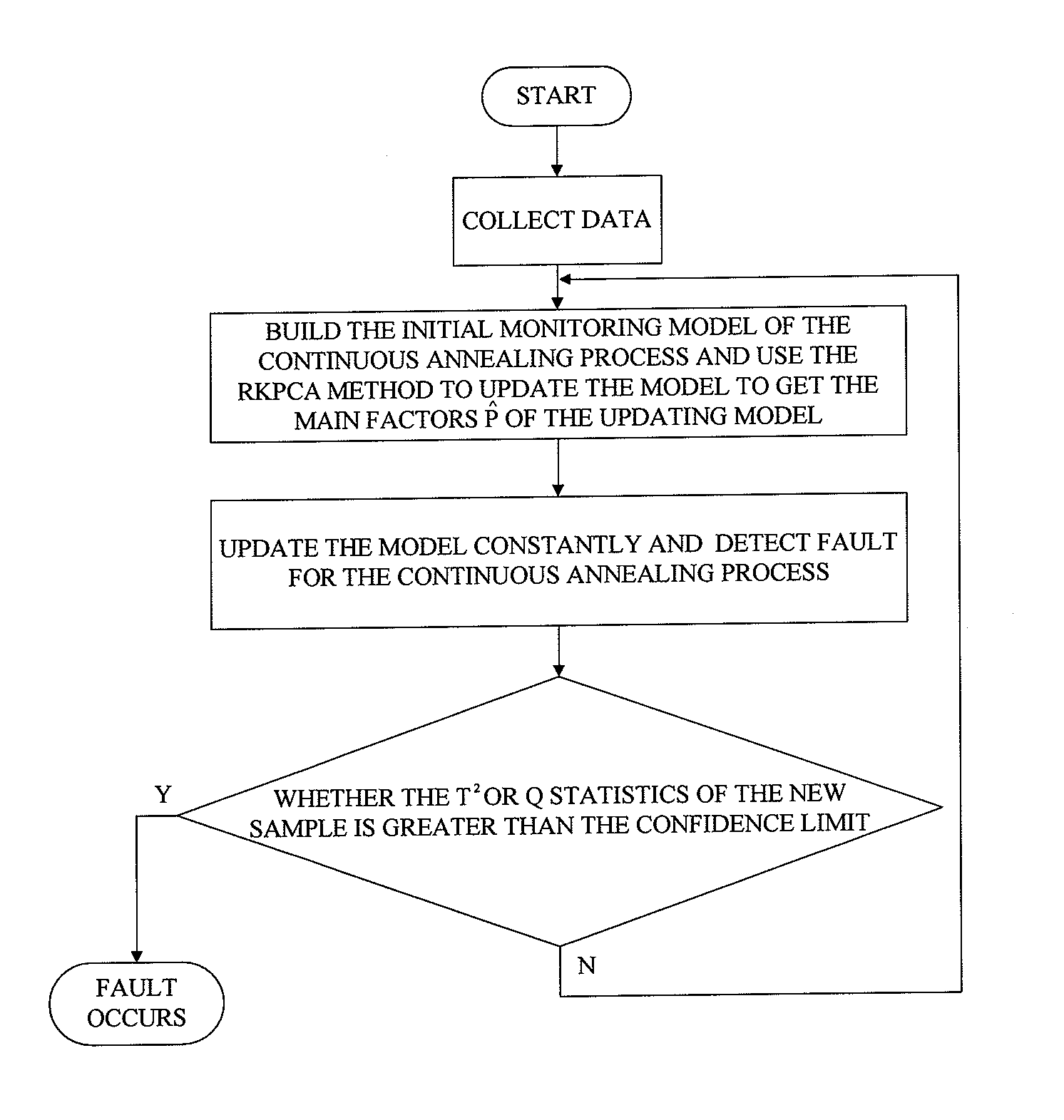
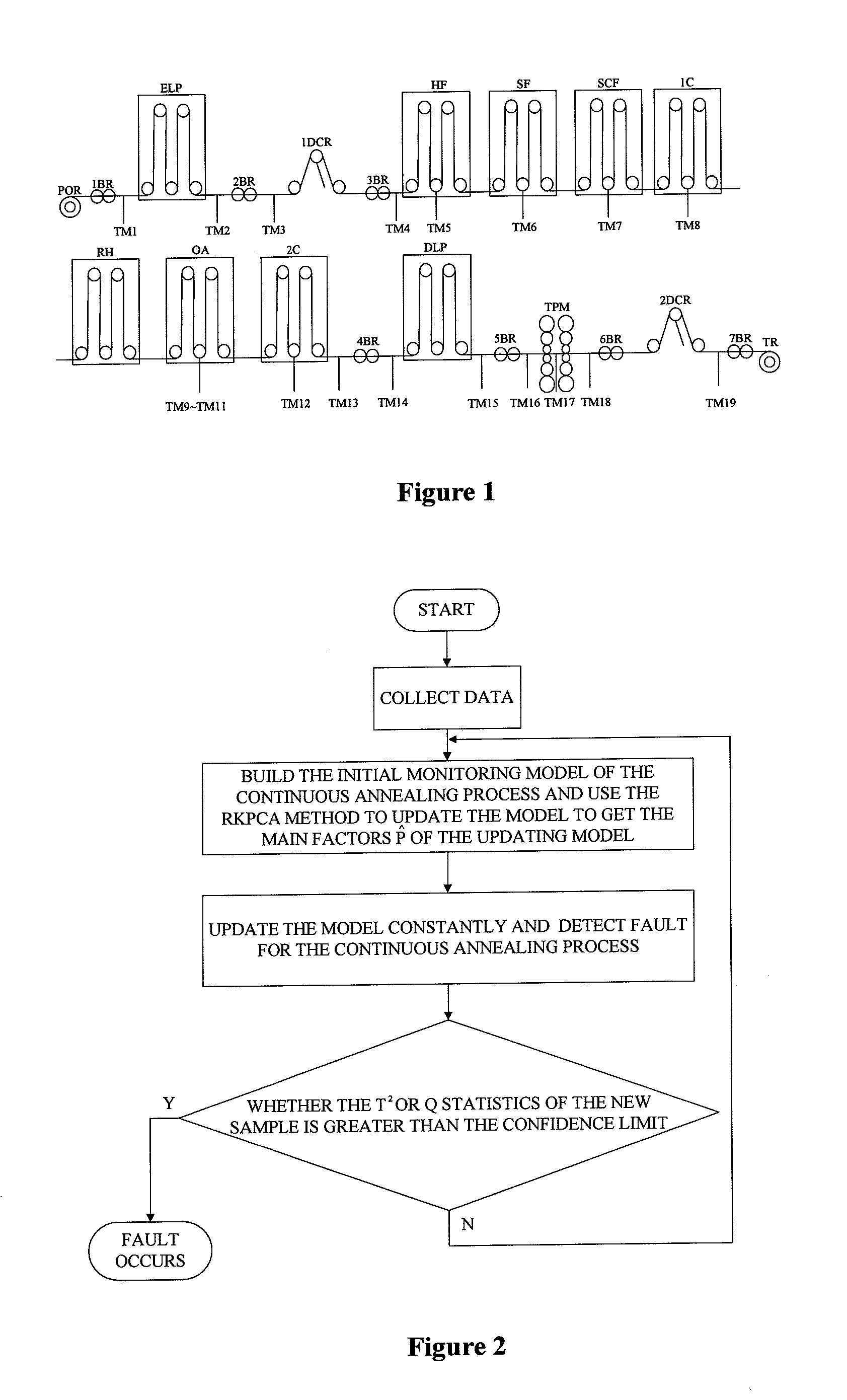
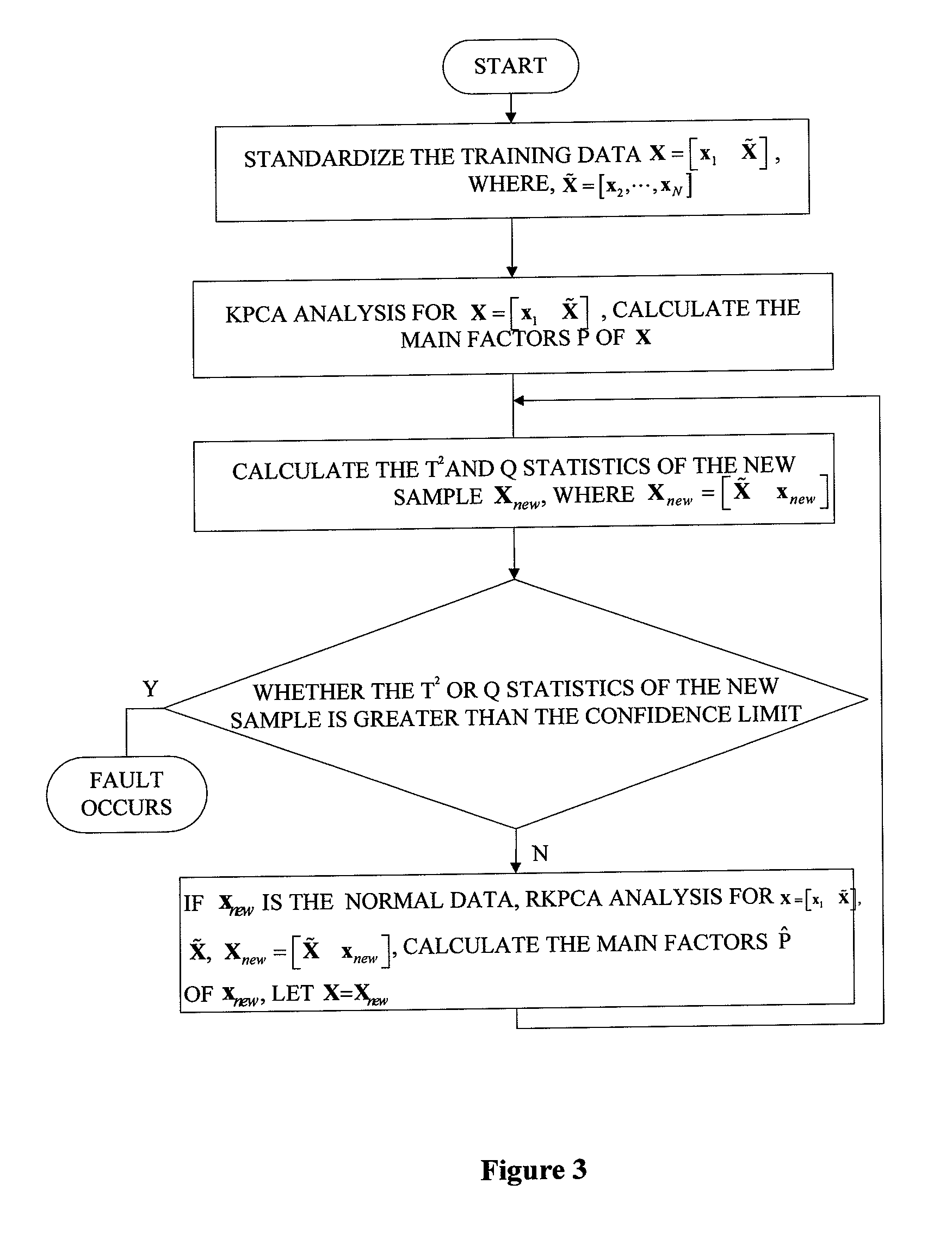
Continuous annealing process fault detection method based on recursive kernel principal component analysis
ActiveUS20130035910A1Reduce false alarm rateImprove accuracyTesting/monitoring control systemsComputation using non-denominational number representationKernel principal component analysisAlgorithm
A fault detection method in a continuous annealing process based on a recursive kernel principal component analysis (RKPCA) is disclosed. The method includes: collecting data of the continuous annealing process including roll speed, current and tension of an entry loop (ELP); building a model using the RKPCA and updating the model, and calculating the eigenvectors {circumflex over (p)}. In the fault detection of the continuous annealing process, when the T2 statistic and SPE statistic are greater than their confidence limit, a fault is identified; on the contrary, the whole process is normal. The method mainly solves the nonlinear and time-varying problems of data, updates the model and calculates recursively the eigenvalues and eigenvectors of the training data covariance by the RKPCA. The results show that the method can not only greatly reduce false alarms, but also improve the accuracy of fault detection.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV +3
Systems and methods for parametric mapping for correction of noise -based systematic bias of DTI metrics, using a DTI mapping phantom
A system and method for minimizing, if not completely eliminating, the systematic bias present in an MR system used for DTI is disclosed. A test object or “phantom” of the present invention is scanned with a desired DTI protocol. The eigenvalues measured with the phantom are compared to the actual values that should have been measured, and a parametric map that links measured eigenvalues to actual eigenvalues is calculated, which is applicable to the desired protocol. Future eigenvalue measurements using this protocol can be recalibrated to actual eigenvalues using this map.
Owner:AUGUSTA UNIV RES INST INC
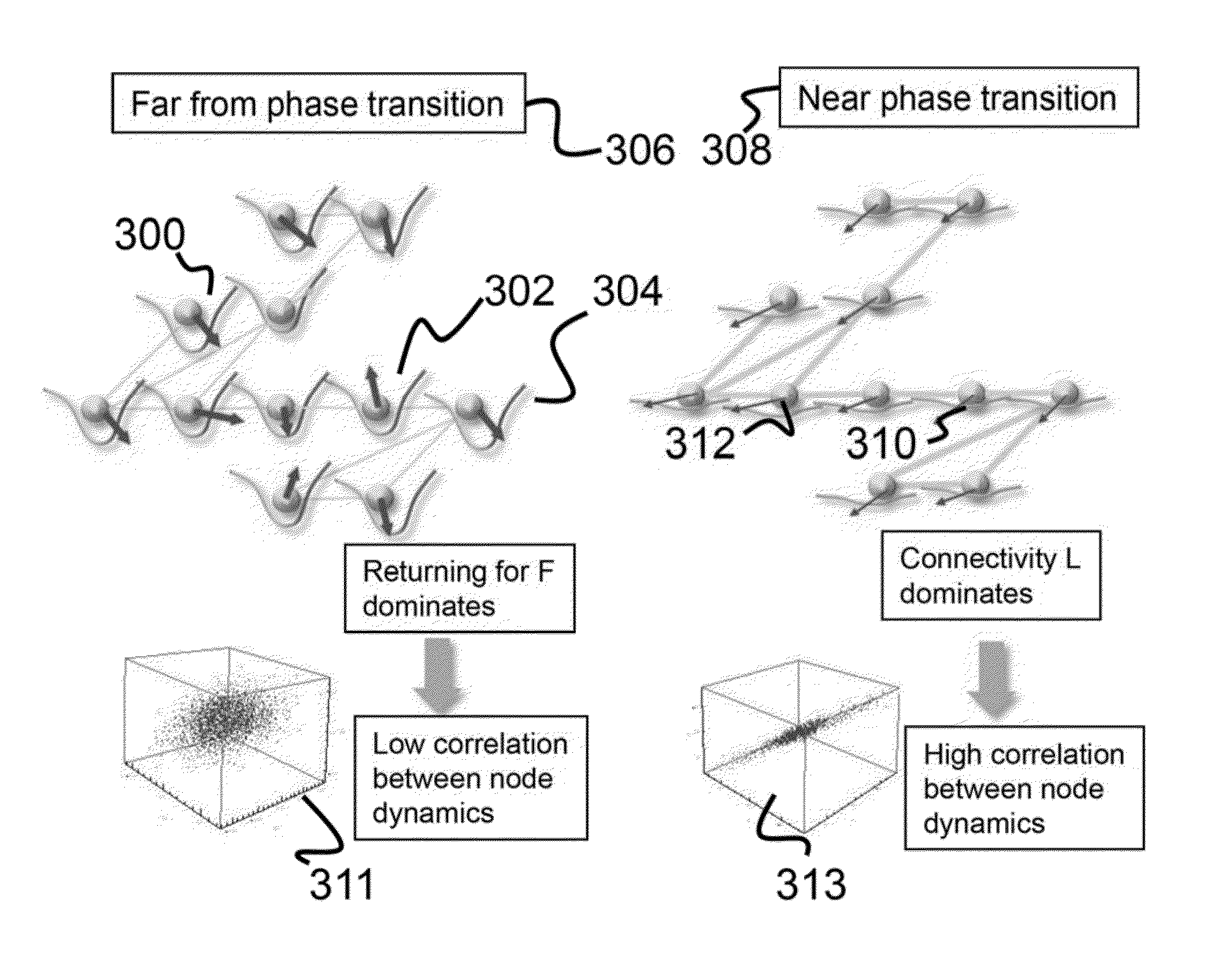
System for instability detection and structure estimation of complex network dynamics
ActiveUS9367804B1Maximize differenceMathematical modelsKnowledge representationCritical transitionInstability
Described is a system for predicting system instability. The system can measure the degree of the network's instability due to critical transitions using the leading eigenvalue of the covariance matrix, where the instability measure is invariant to (1) the changes in network structure in terms of addition / removal of nodes and links, and (2) the feedback of the global system stability to the changes in stability. Based on that, the system is operable for providing an estimation of the network's changing connectivity when the network is near critical transitions.
Owner:HRL LAB
Gas detection method based on KPCA (Kernel Principal Component Analysis)
InactiveCN106841085AAvoid false alarmsGuaranteed leak-proof alarmCharacter and pattern recognitionColor/spectral properties measurementsData setRegression analysis
The invention discloses a gas concentration detection method, which is characterized by adopting a KPCA (Kernel Principal Component Analysis) algorithm for identifying a large number, firstly building two mixed kernel functions, utilizing a vector method for building a kernel matrix, and utilizing kernel principle component analysis for calculating characteristic vectors of the kernel matrix, wherein the algorithm has higher recognition rate and higher arithmetic speed. The algorithm converts a KPCA process on a training set into a PCA process on a data set of coordinates of all kernel training samples under a group of basis through a group of standard orthogonal basis of a subspace expanded by the training samples in a characteristic space, meanwhile, carries out characteristic extraction on the training samples so as to effectively capture nonlinear characteristics of training data, and is widely interested and applied in mode recognition and regression analysis. During a solving process of KPCA, an M*M kernel matrix (M represents the number of the training samples) needs to be subjected to eigenvalue decomposition, so that when sample characteristics are extracted, only a sample and a kernel function for forming the group of Kidd samples need to be calculated, and an experimental result verifies that the algorithm is effective.
Owner:URUMQI VOCATIONAL UNIV
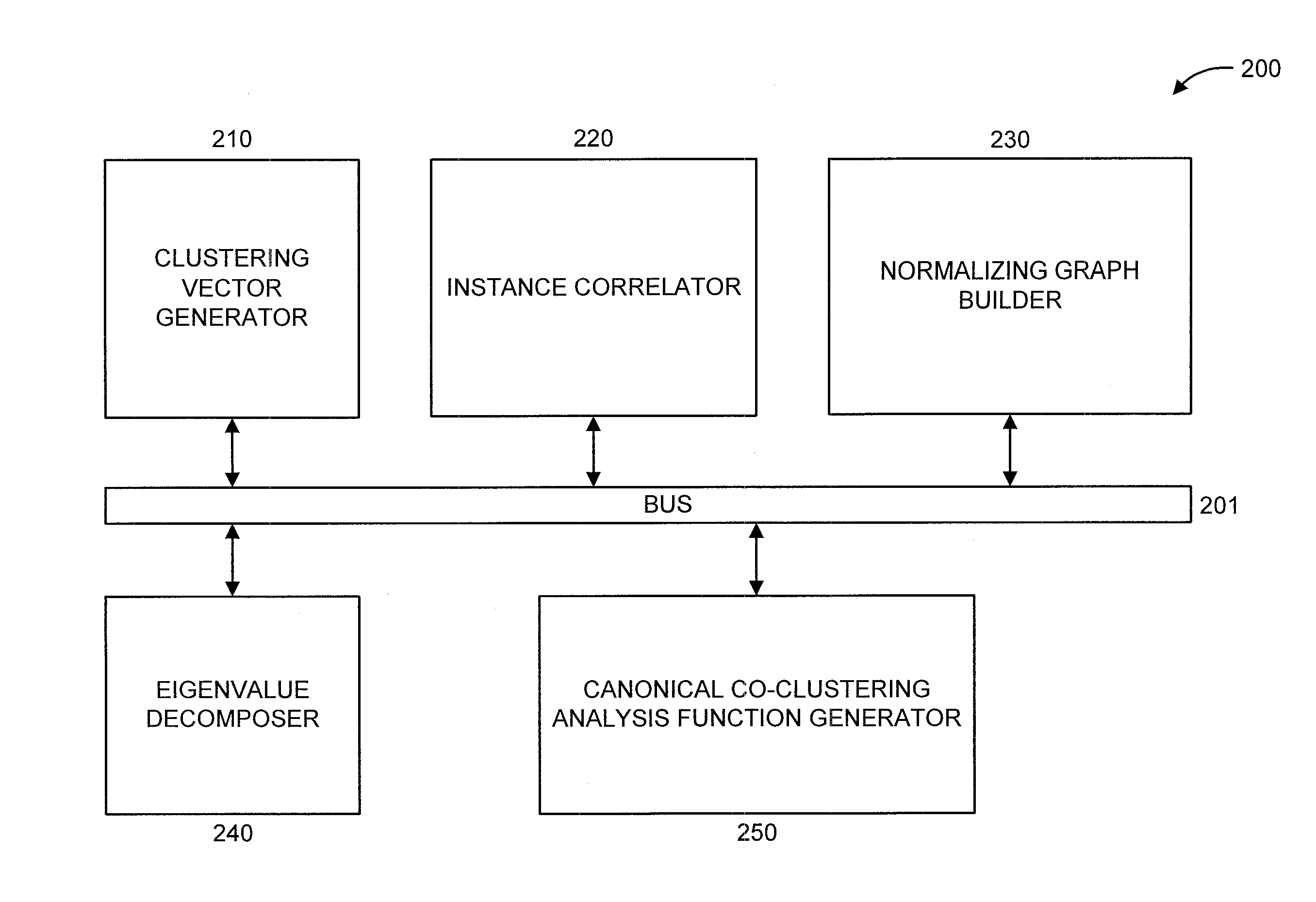
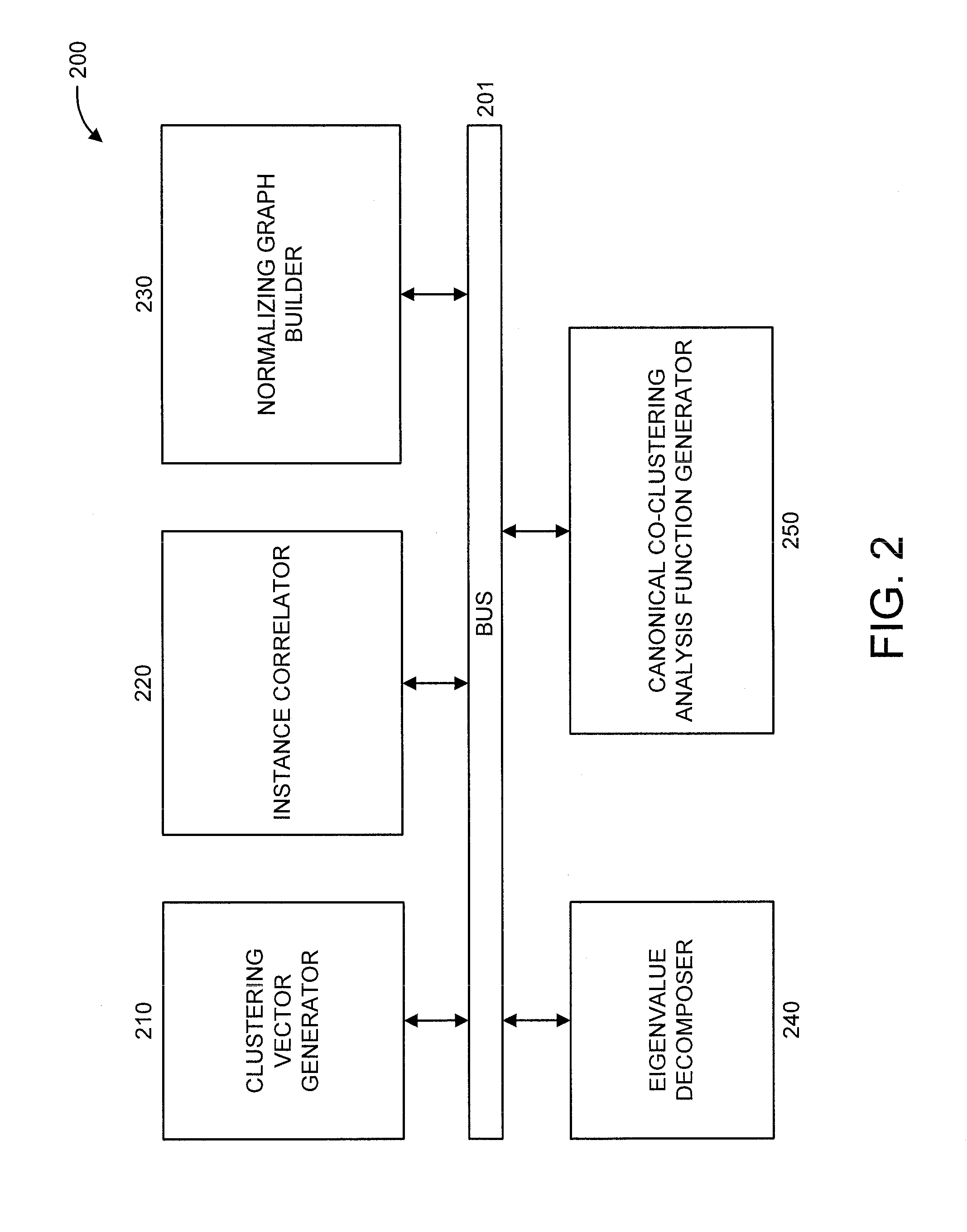
Canonical co-clustering analysis
InactiveUS20150347927A1Digital computer detailsRelational databasesMachine learningManifold regularization
A method and system are provided. The method includes determining from a data matrix having rows and columns, a clustering vector of the rows and a clustering vector of the columns. Each row in the clustering vector of the rows is a row instance and each row in the clustering vector of the columns is a column instance. The method further includes performing correlation of the row and column instances. The method also includes building a normalizing graph using a graph-based manifold regularization that enforces a smooth target function which, in turn, assigns a value on each node of the normalizing graph to obtain a Lapacian matrix. The method additionally includes performing Eigenvalue decomposition on the Lapacian matrix to obtain Eigenvectors. The method further includes providing a canonical co-clustering analysis function by maximizing a coupling between clustering vectors while concurrently enforcing regularization on each clustering vector using the Eigenvectors.
Owner:NEC LAB AMERICA
Method for Design and Optimization of Convolutional Neural Networks
InactiveUS20200143203A1Value maximizationMathematical modelsCharacter and pattern recognitionSingular value decompositionMaximum eigenvalue
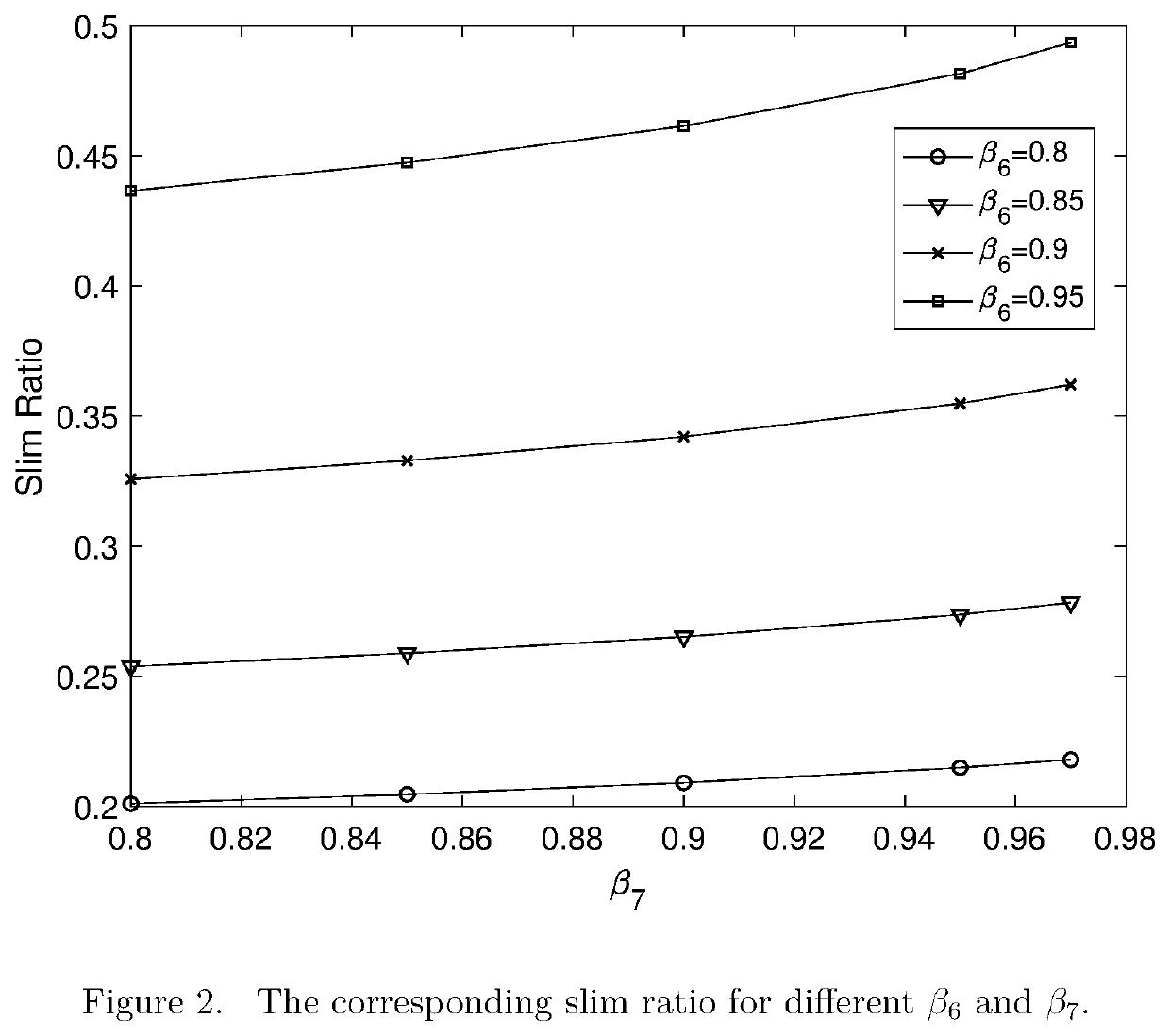
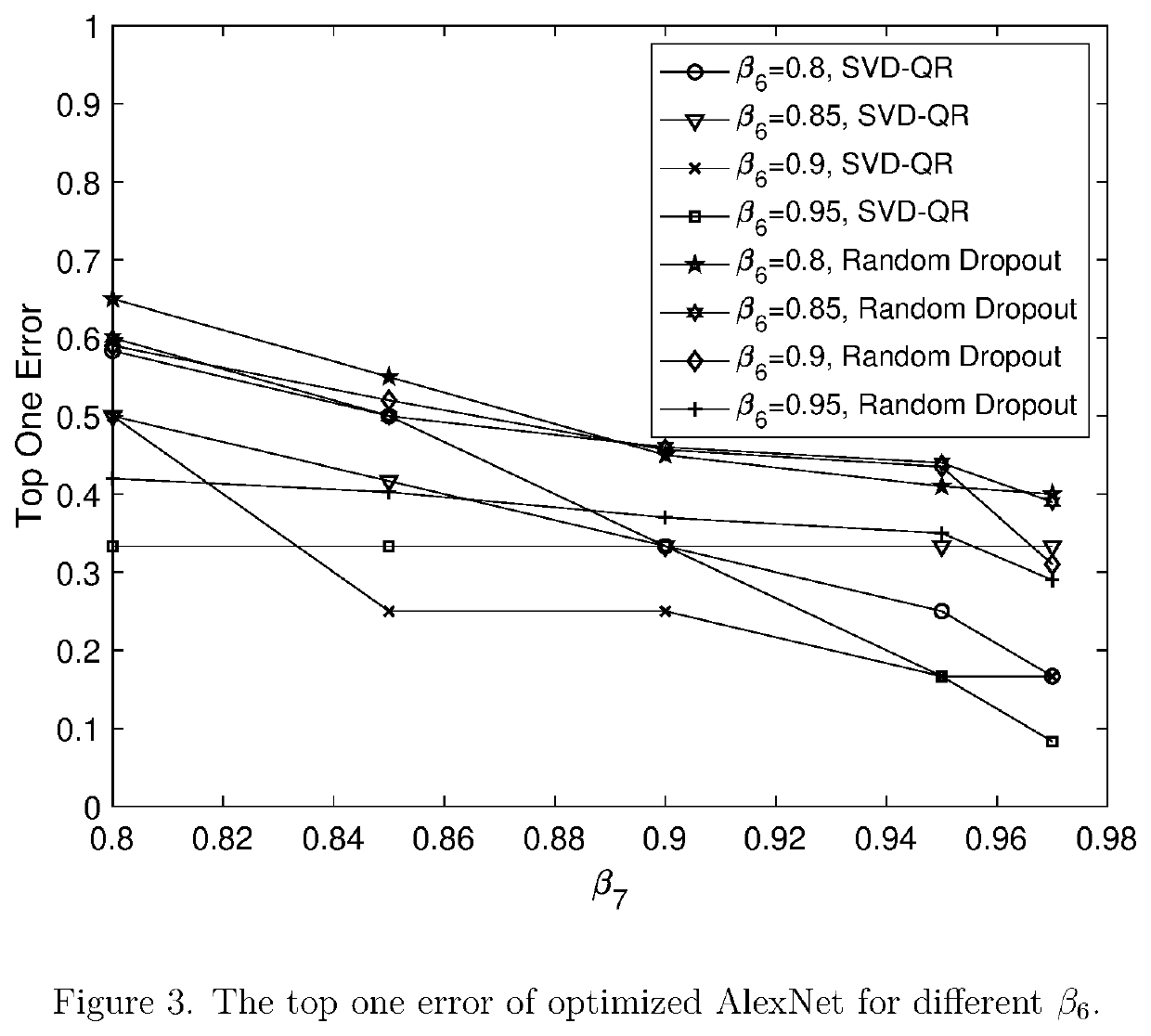
The deep Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) has vast amount of parameters, especially in the Fully Connected (FC) layers, which has become a bottleneck for real-time sensing where processing latency is high due to computational cost. In this invention, we propose to optimize the FC layers in CNN for real-time sensing via making it much slimmer. We derive a CNN Design and Optimization Theorem for FC layers from information theory point of view. The optimization criteria is eigenvalues-based, so we apply Singular Value Decomposition (SVD) to find the maximal eigenvalues and QR to identify the corresponding columns in FC layer. Further, we propose Efficient Weights for CNN Design Theorem, and show that weights with colored Gaussian are much more efficient than those with white Gaussian. We evaluate our optimization approach to AlexNet and apply the slimmer CNN to ImageNet classification. Testing results show our approach performs much better than random dropout.
Owner:LIANG STEPHEN D
Method for computing conformal parameterization
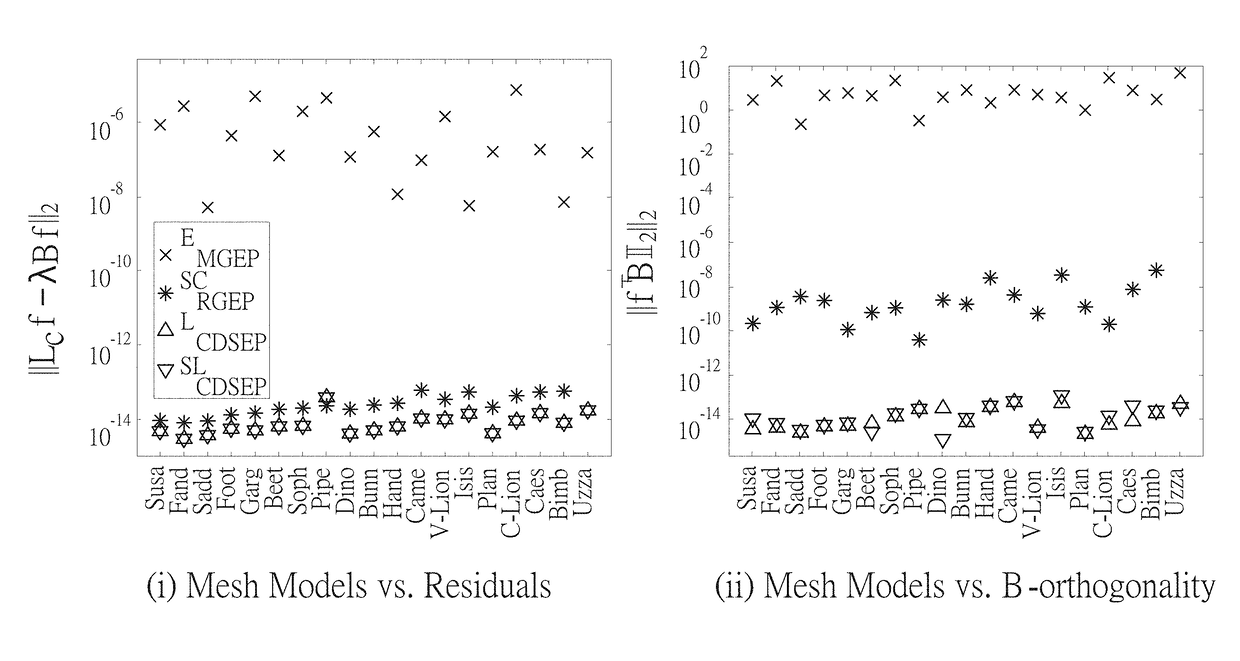
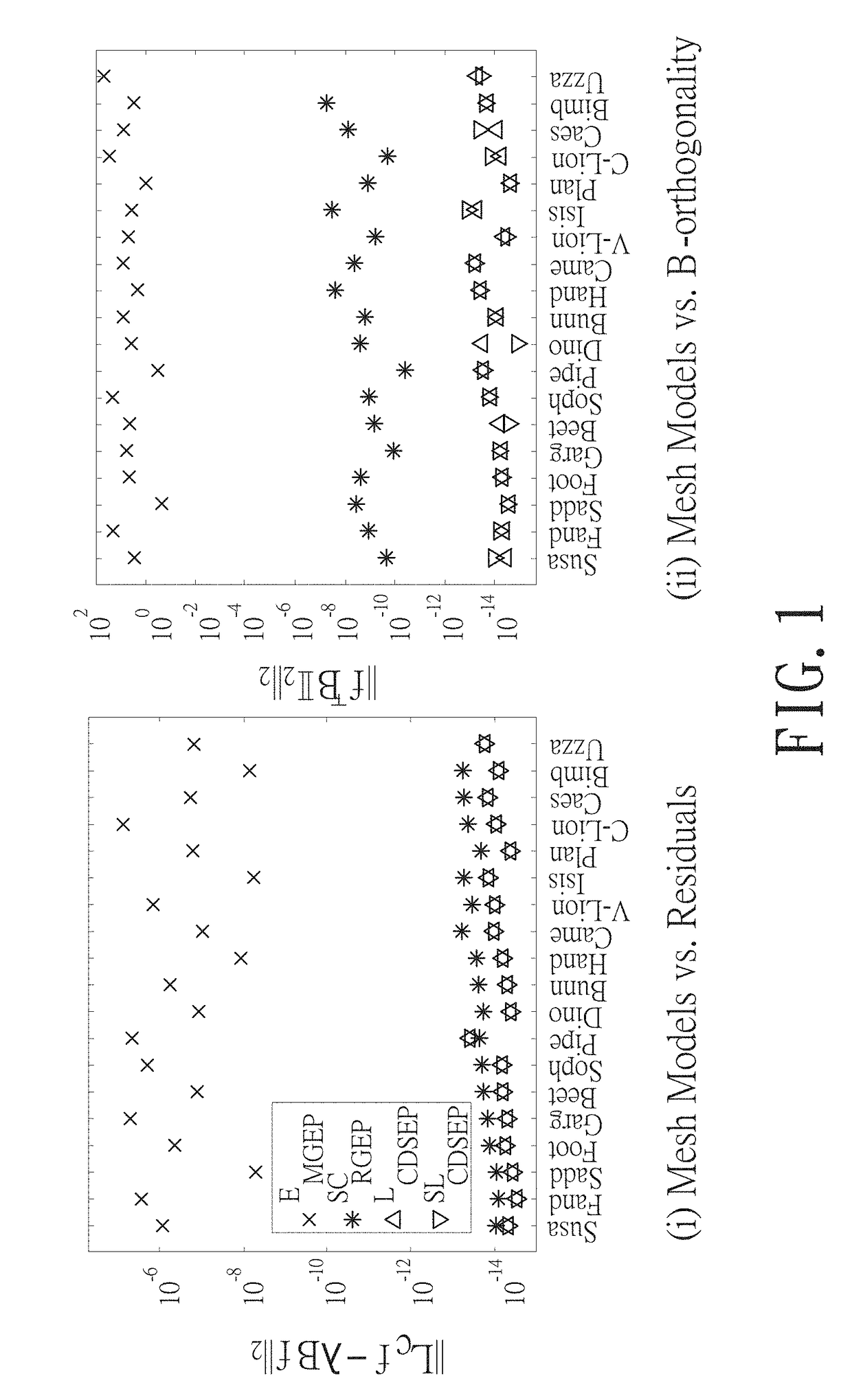
A method for computing conformal parameterizations is revealed. First discrete conformal maps are reviewed for computing a generalized eigenvalue problem (GEP) arising from spectral conformal parameterization. Then nonequivalence deflation and null-space free compression techniques are applied to transform the GEP to a small-scaled compressed and deflated standard eigenvalue problem (CDSEP). Lastly a skew-Hamiltonian isotropic Lanczos algorithm (SHILA) is used to solve the CDSEP. Numerical experiments and comparisons are presented to show that the present method compute the conformal parameterization accurately and efficiently.
Owner:GEOMETRIC INFORMATICS TECH INC
Positive semidefinite spectral clustering method based on Lagrange dual
The invention provides a positive semidefinite spectral clustering method based on a Lagrange dual, and relates to a spectral clustering method. A, principal component analysis in given sample data is adopted to conduct dimensionality reduction. B, similarity matrix forms sample data based on an omnibearing connection diagram, and similarity between the sample data is used based on weighted sum and a method of a Gaussian kernel function and a polynomial kernel function. C, positive semidefinite of similarity matrix is conducted based on Lagrange dual property. D, singular value decomposition of normalization matrix is conducted, and then the matrix which is formed by feature vector corresponding to the front K eigenvalue of maximum is obtained. E, a traditional K mean value cluster or other cluster methods is adopted to conduct clustering analysis on the feature vector matrix and obtain a final clustering result. All data can be effectively clustered, people know by algorithm analysis that compared with a common positive semidefinite spectral clustering method, not only be precision of spectral clustering can improved, but also required time for the spectral clustering can be greatly reduced .
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
SOD-IRK based time-delay power system stability determination method
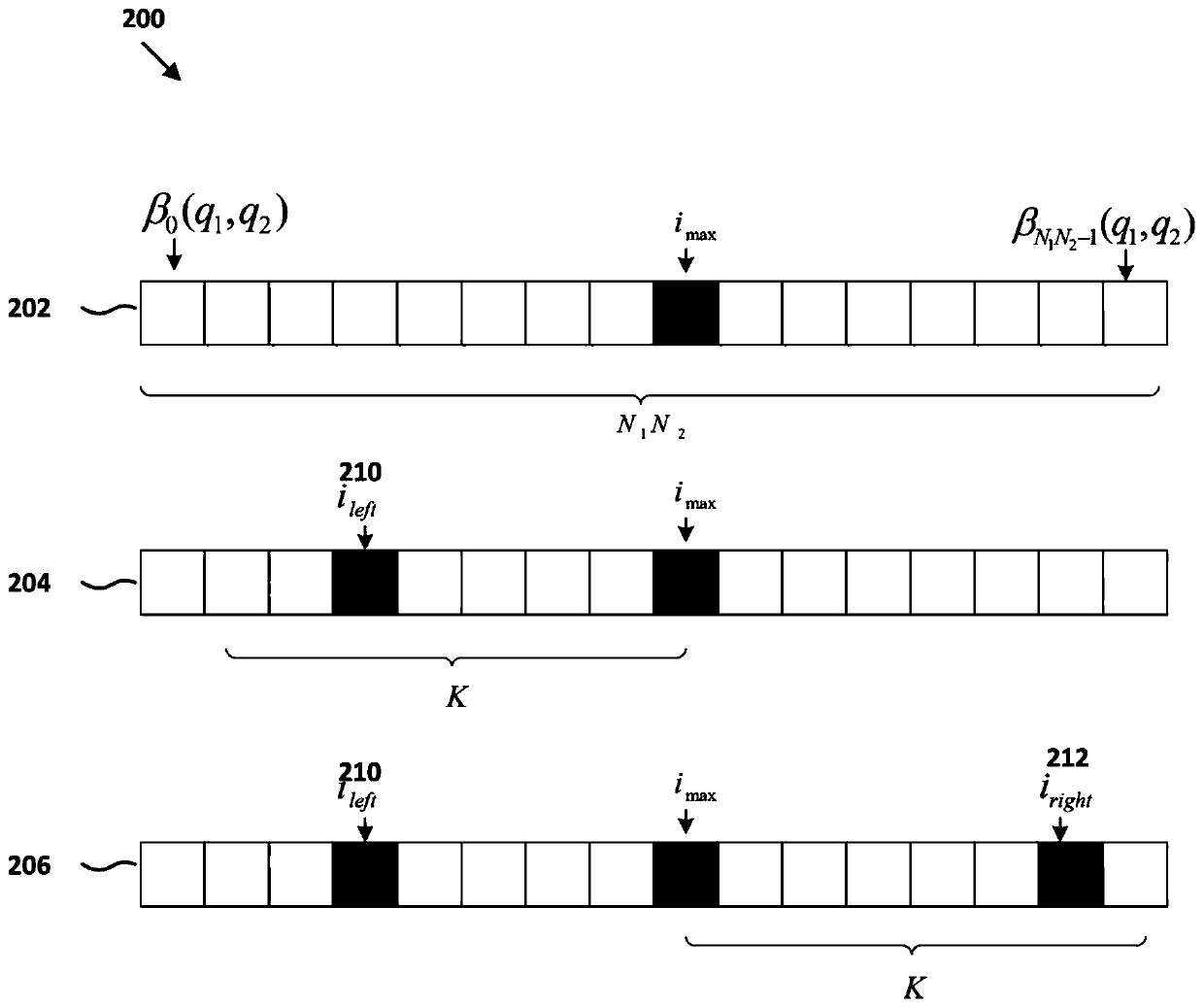
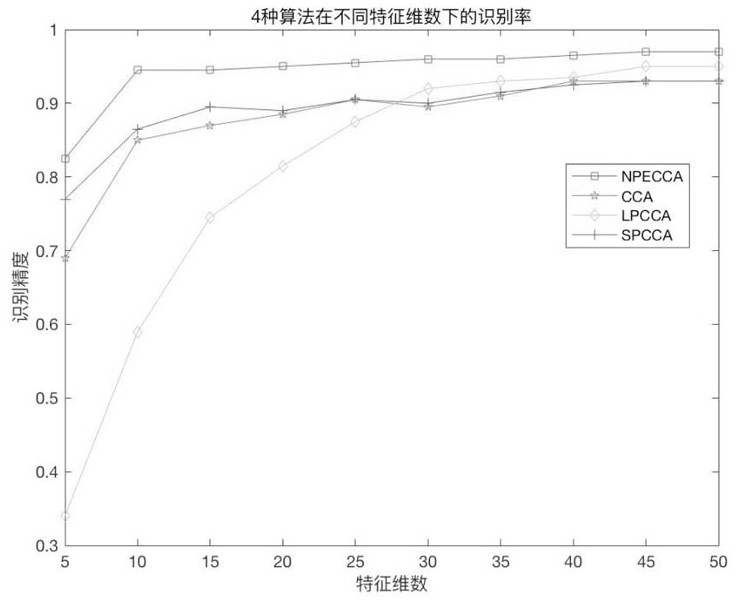
ActiveCN108321821AFully consider the scaleFully consider the impact of communication time lagPower oscillations reduction/preventionZ eigenvalueComputation process
The invention discloses a SOD-IRK based time-delay power system stability determination method. The SOD-IRK based time-delay power system stability determination method comprises: establishing a time-delay power system model; using different implicit Runge-Kutta methods to discretize solution operators to obtain a discretized matrix of the solution operators; transforming an eigenvalue problem ofinfinite dimension into an eigenvalue problem of finite dimension; using an implicit Arnoldi algorithm to calculate an approximate value of the eigenvalue having the maximum modulus, of the discretized matrix of the solution operators; using a rotation-amplifying method to perform preprocessing during calculation, and performing sparse implementation by using the properties of a Kronecker product;transforming the approximate value of the eigenvalue having the maximum modulus, of the discretized matrix into the approximate eigenvalue of the time-delay power system model according to the spectral mapping relationship; using the Newton iteration method to correct the approximate eigenvalues to obtain the exact eigenvalues of the time-delay power system; and determining the stability of the time-delay power system according to the magnitude of the exact eigenvalue damping ratio.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
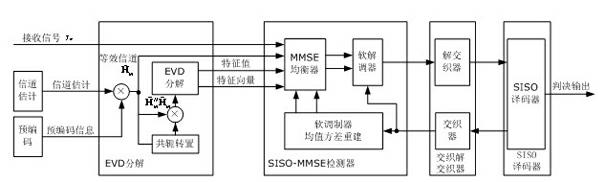
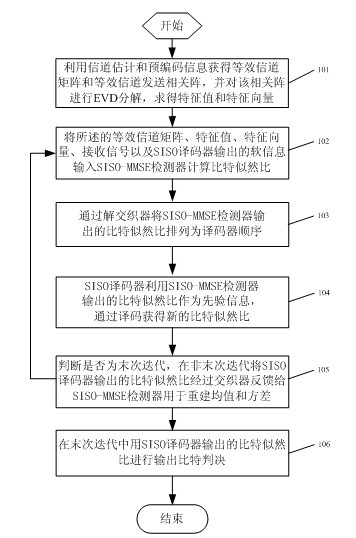
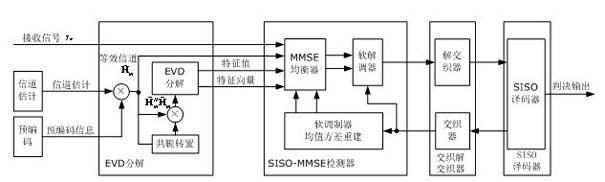
Soft-input soft-out (SISO) minimum mean squared error (MMSE) iteration receiving method based on eigenvalue decomposition
InactiveCN102158313APrevent inversionReduce implementation complexityError preventionBaseband system detailsPrecodingEigenvalues and eigenvectors
The invention relates to a soft-input soft-out (SISO) minimum mean squared error (MMSE) iteration receiving method based on eigenvalue decomposition, which is characterized by comprising the following steps of: first, figuring out an equivalent channel matrix and an equivalent transmission correlation matrix by channel estimation and precoding of codebook information; carrying out eigenvalue decomposition on the equivalent transmission correlation matrix to acquire an eigenvalue and an eigenvector; inputting the equivalent channel matrix, the eigenvalue, the eigenvector and received signals into an SISO-MMSE detector, wherein the detector and an SISO decoder iteratively work by utilizing soft information input from the detector and the SISO detector as priori information; and finally, outputting a bit judgment by the decoder after the predefined iterations are reached. In the method of the invention, eigenvalue decomposition is introduced to transform the matrix inversion operation in each SISO-MMSE iteration process into division operation, thus the implementation complexity of the system is effectively reduced.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
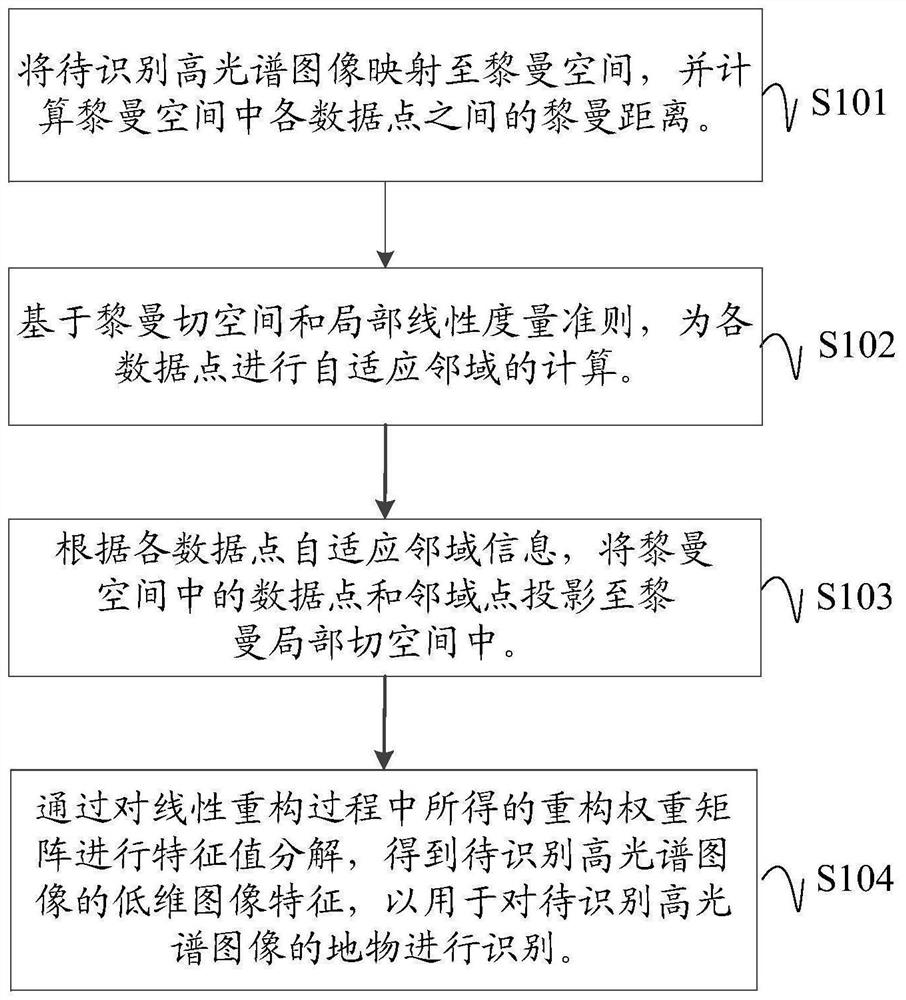
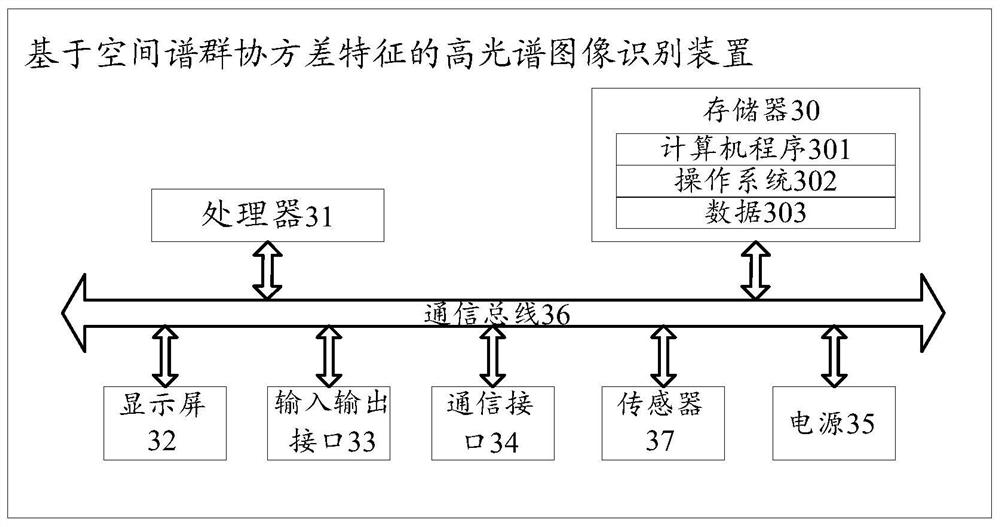
Hyperspectral image recognition method and device based on spatial spectrum group covariance characteristics
ActiveCN113537252AEasy extractionEasy to refactorCharacter and pattern recognitionZ eigenvalueImaging Feature
The invention discloses a hyperspectral image recognition method and device based on spatial spectrum group covariance features and a computer readable storage medium. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring a hyperspectral image to be identified, mapping the hyperspectral image to be identified to a Riemann space, and calculating the Riemann distance between data points in the Riemann space; and on the basis of a Riemann cutting space and a local linear measurement criterion, performing adaptive neighborhood calculation on each data point; projecting the data points in the Riemann space to a Riemann local tangent space according to the self-adaptive neighborhood information of each data point; obtaining the low-dimensional image features of the to-be-recognized hyperspectral image by performing eigenvalue decomposition on the reconstruction weight matrix obtained in the linear reconstruction process, and recognizing the surface features of the hyperspectral image based on the low-dimensional image features, so that the surface feature recognition accuracy of the hyperspectral image is effectively improved.
Owner:HAINAN UNIVERSITY +1
Coal-mine gas concentration measurement method
InactiveCN106096633AAvoid false alarmsGuaranteed leak-proof alarmCharacter and pattern recognitionData setAlgorithm
The invention discloses a coal-mine gas concentration measurement method. ''A great number'' is identified by adopting a KPCA (Kernel Principal Components Analysis) algorithm; two mixed kernel functions are constructed firstly; a kernel matrix is constructed by utilizing a vector method; and an eigenvector of the kernel matrix is calculated by utilizing KPCA. The algorithm has relatively high identification rate and relatively high calculation speed. According to the algorithm, a KPCA process on a training set is converted into a PCA process in which coordinates of all kernel training samples under a group of standard orthogonal bases are data sets through the group of the standard orthogonal bases of subspaces formed by the training samples in a characteristic space, and characteristics of the training samples are extracted, so that nonlinear characteristics of training data can be effectively captured; and therefore, the algorithm is widely interested and applied in mode identification and regressive analysis. In a solving process of the KPCA, an eigenvalue is required for decomposing an M*M kernel matrix (M represents the number of training samples), and only a kernel function between the samples and a group of formed Kidd samples needs to be calculated during sample characteristic extraction, and an experimental result verifies that the algorithm is valid.
Owner:丁旭秋
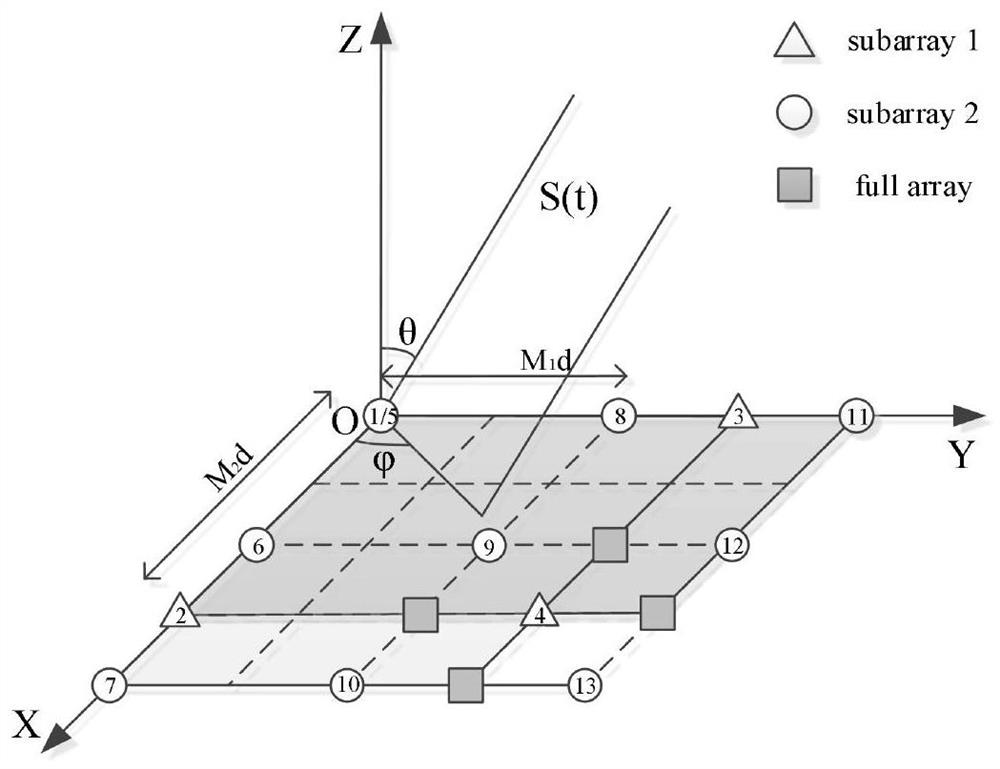
Two-dimensional direction finding estimation method based on polynomial rooting in uniform area array
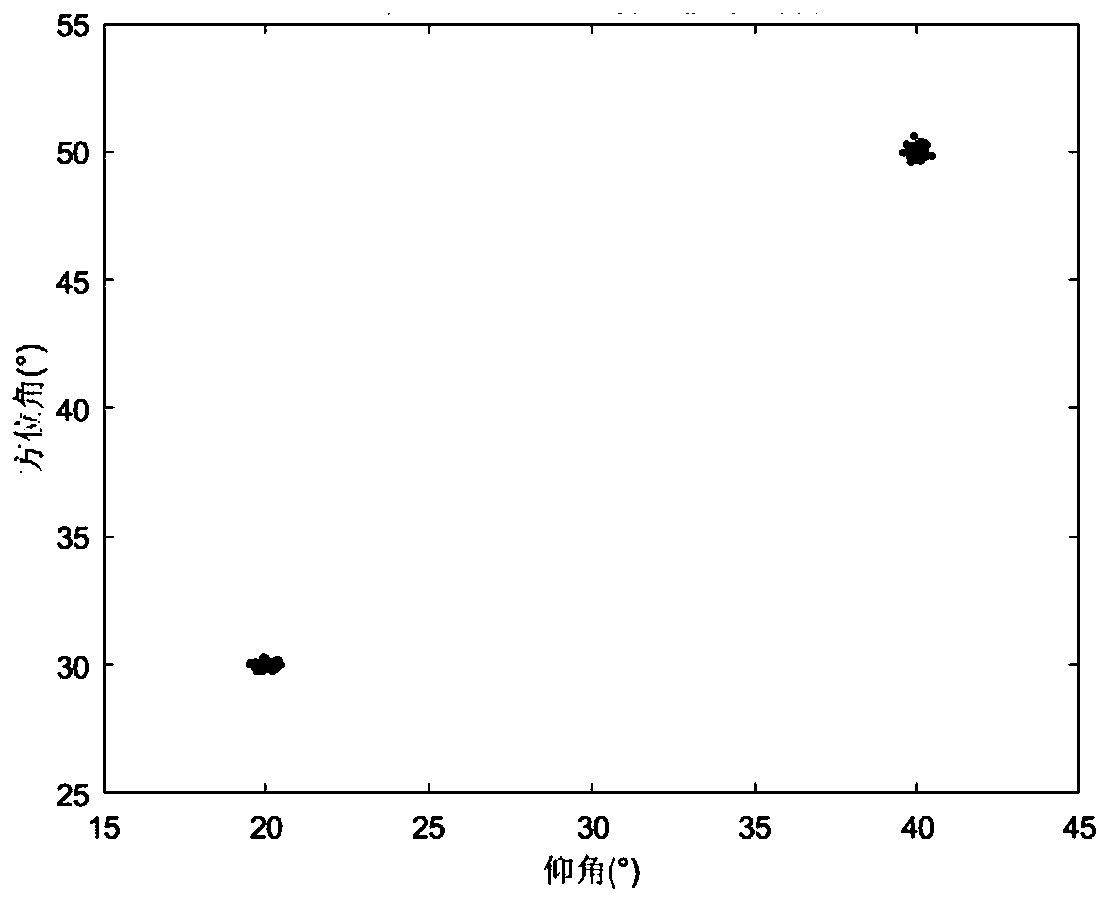
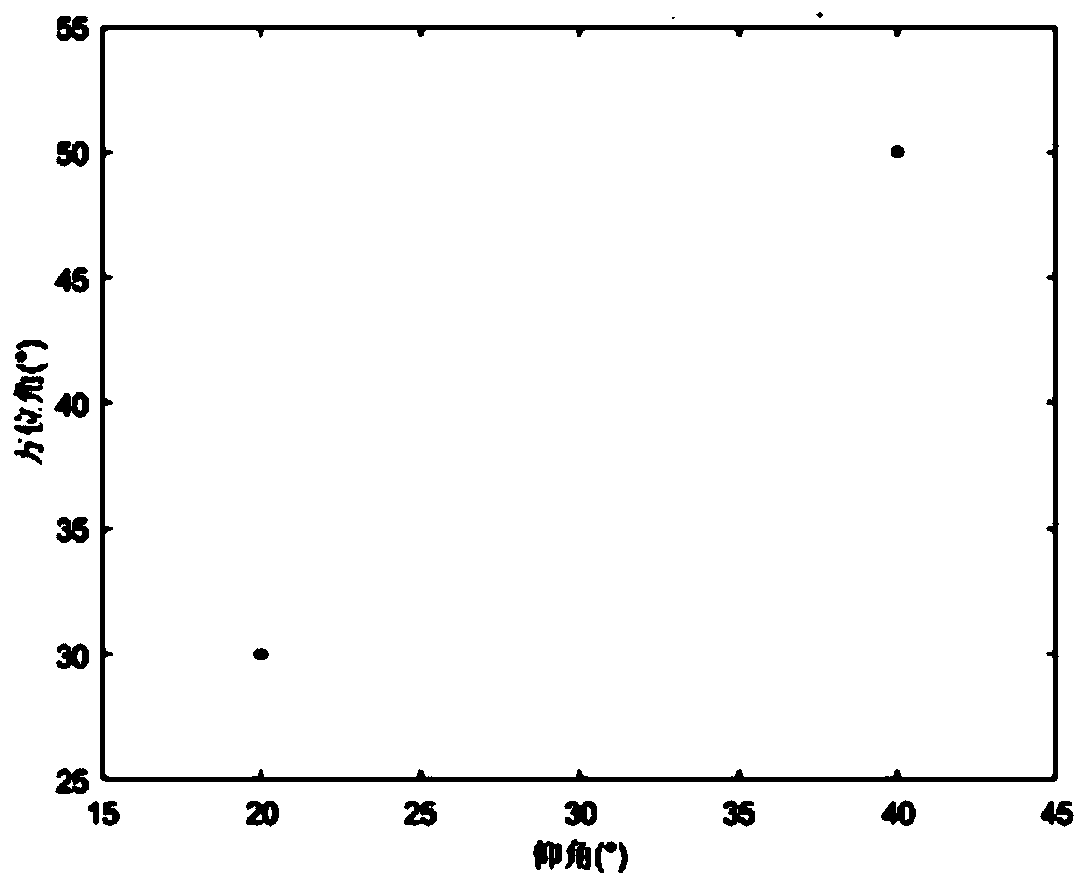
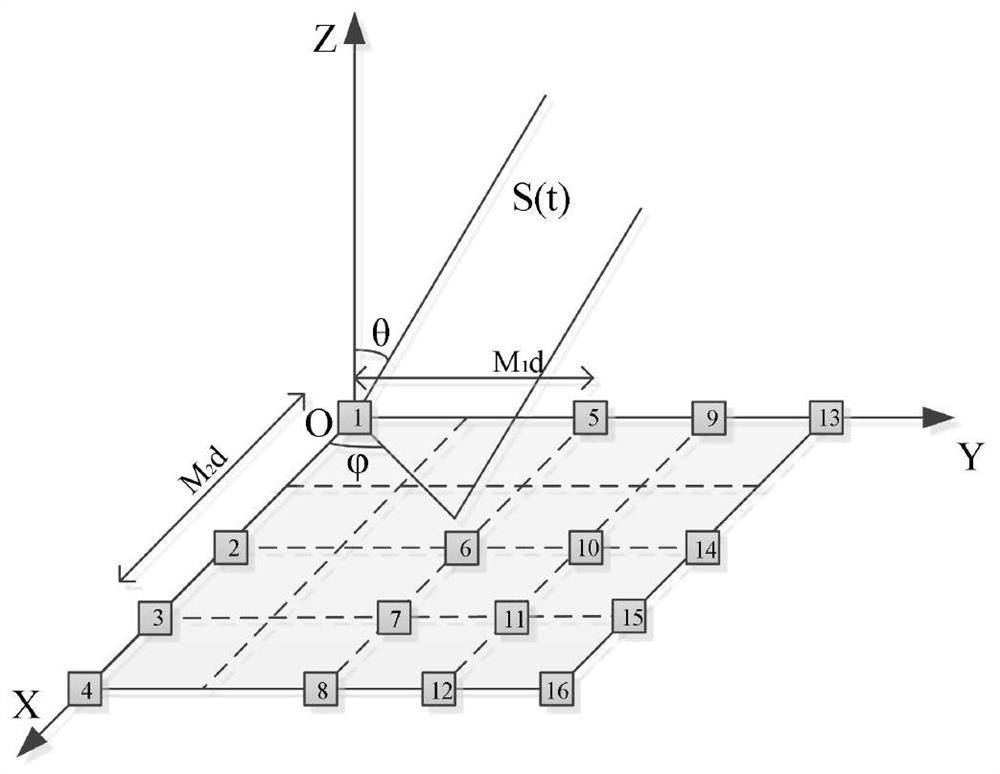
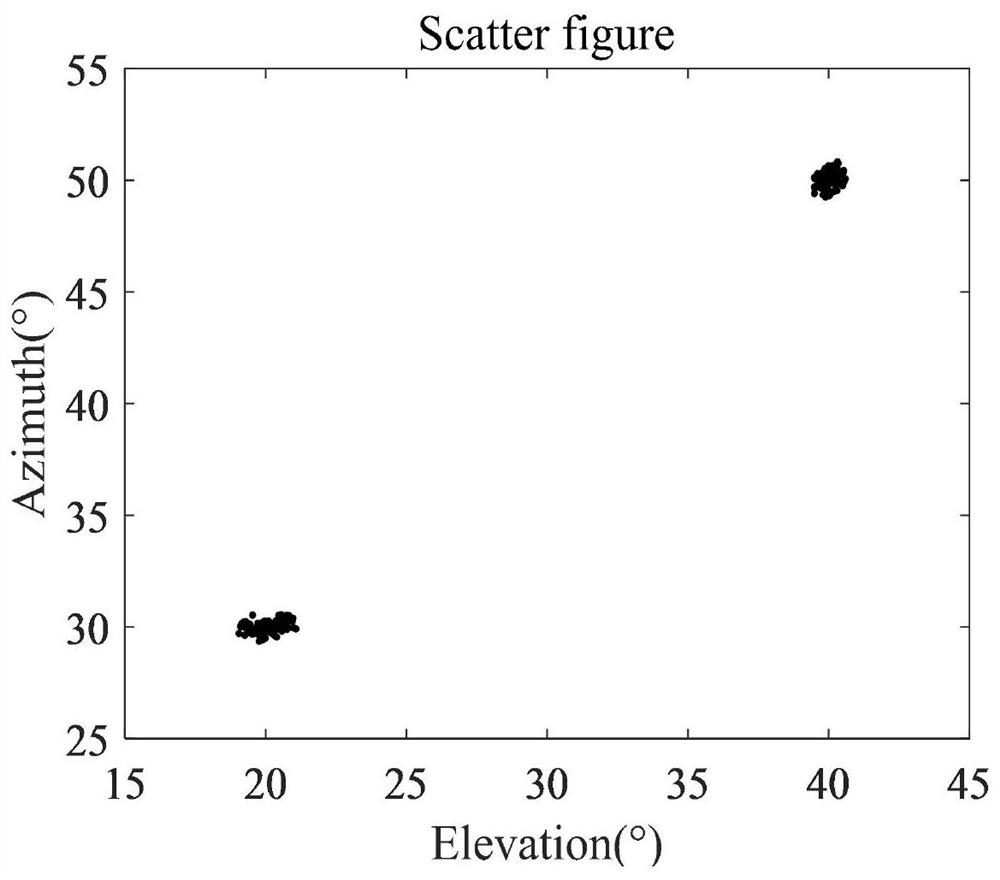
PendingCN111352063AReduce complexityReduce difficultyRadio wave direction/deviation determination systemsMulti-channel direction-finding systems using radio wavesZ eigenvalueRound complexity
The invention discloses a two-dimensional direction-finding estimation method based on polynomial rooting in a uniform area array. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, obtaining a covariance matrix from received signals of the uniform area array; carrying out eigenvalue decomposition on the covariance matrix to obtain a signal subspace and a noise subspace, and determining a rootingpolynomial according to the orthogonal relation between the direction matrix and the noise subspace; finally, solving the root of the polynomial, completing parameter pairing, and completing two-dimensional angle parameter estimation. According to the method, the complexity and the angle estimation performance can be fully balanced, and the limitation that in a traditional two-dimensional angle estimation method, the angle estimation performance is good but the complexity is high or the complexity is low but the angle estimation performance is common is broken through; moreover, high-resolution two-dimensional DOA estimation can be realized, the angle estimation performance is superior to that of a 2D-PM algorithm and a 2D-ESPRIT algorithm, the angle estimation performance is basically consistent with that of a 2D-MUSIC algorithm, and the algorithm complexity is far lower than that of the 2D-MUSIC algorithm.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
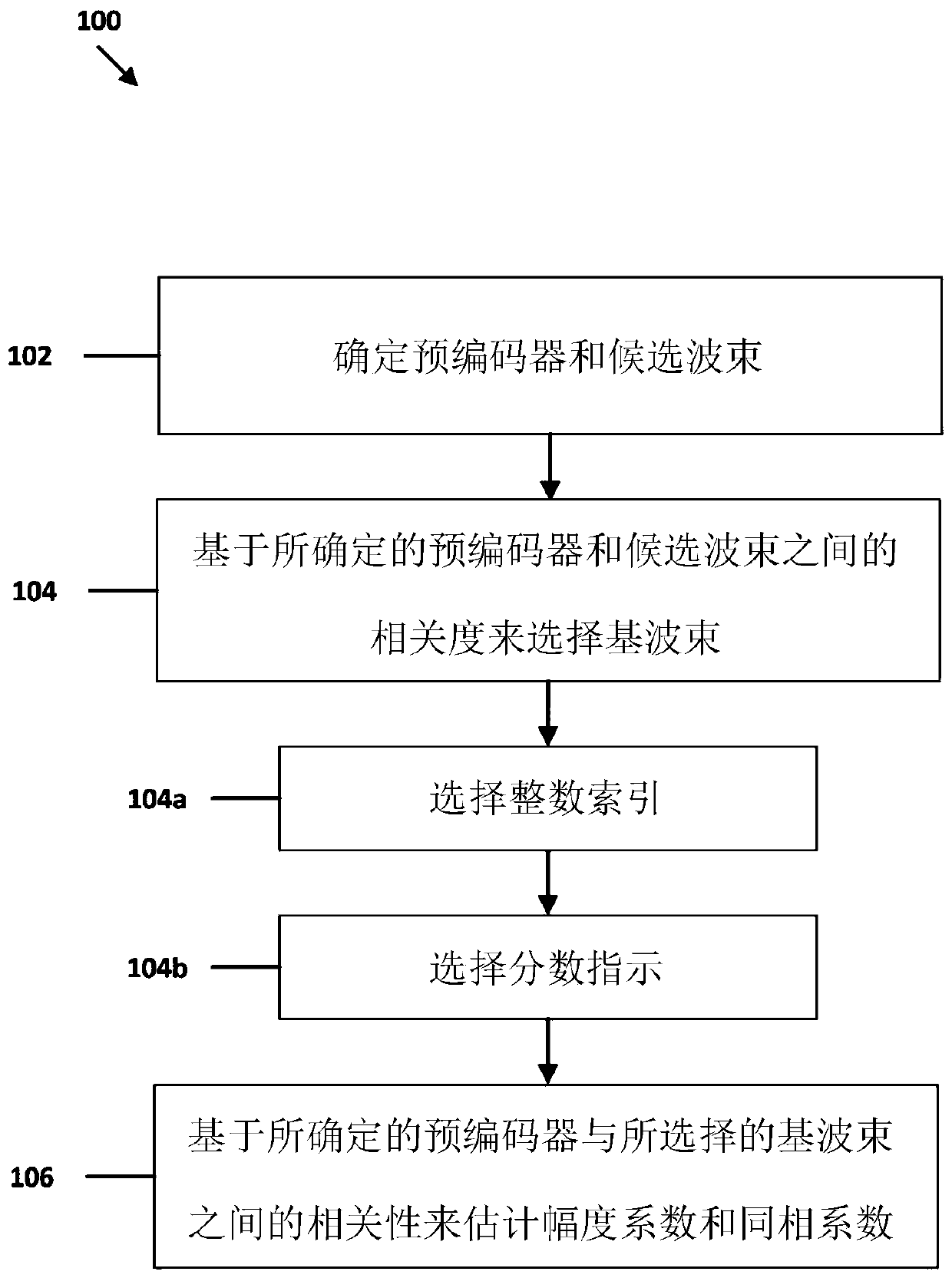
Eigenvalue decomposition precoding matrix index selection
The invention relates to eigenvalue decomposition precoding matrix index selection. A method and system for selecting precoding matrix index are herein disclosed. The method includes determining a precoder and candidate beams, selecting base beams based on a correlation power between the determined precoder and determined candidate beams, and estimating amplitude coefficients and cophase coefficients based on a correlation between the determined precoder and the selected base beams.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Face recognition method based on neighbor preserving canonical correlation analysis
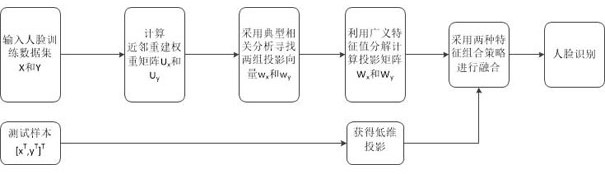
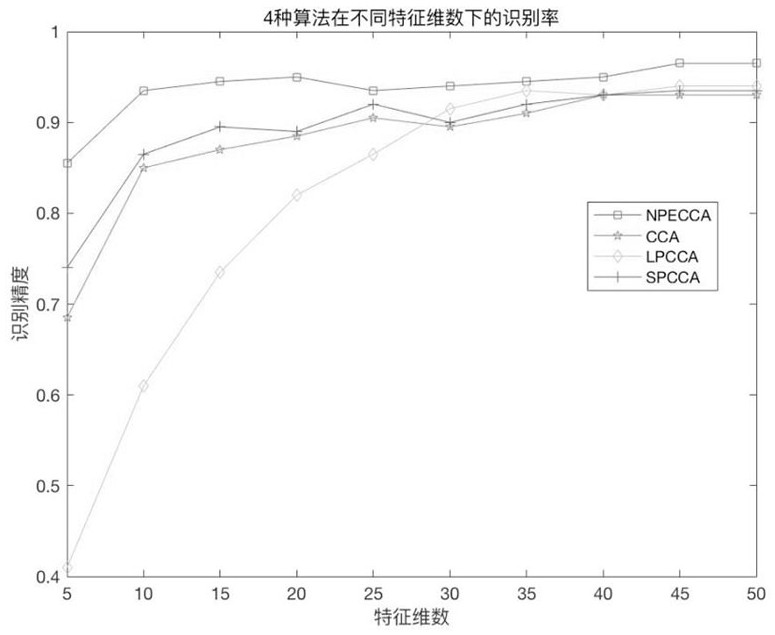
PendingCN111611963AMaintain neighborhood structureEasy to identifyCharacter and pattern recognitionData setGeneralized eigenvalue decomposition
The invention discloses a face recognition method based on neighbor preserving canonical correlation analysis, and the method comprises the following steps: 1, inputting a face training data set X belonging to Rm*N, Y belonging to Rn*N, and calculating neighbor weight reconstruction matrixes Ux and Uy of an image through neighbor preserving learning; 2, searching two groups of projection vectors wx and wy by adopting canonical correlation analysis, introducing neighbor preserving into a canonical correlation analysis framework by adopting an optimization method, and calculating projection matrixes Wx and Wy by utilizing generalized eigenvalue decomposition; 3, performing low-dimensional projection and fusion on the test face image by adopting two feature fusion strategies; and 4, applyingthe fused features to face recognition by using a nearest neighbor classifier. According to the invention, a face proximity weight reconstruction matrix is learned through neighbor preserving; neighbor preserving is introduced into a typical correlation analysis framework by using an optimization method, and label information of human faces is utilized, so that the extracted human face features not only maximize the correlation between different human faces, but also maintain the neighborhood structure of the human faces as much as possible, and the human face recognition capability and stability are improved.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
Local sensitivity discriminant analysis method for defect thermal image of composite material
PendingCN112489016AAids in defect identificationImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionDiscriminant model
The invention discloses a local sensitivity discriminant analysis method for a defect thermal image of a composite material. The method comprises the following steps: 1) acquiring a defect thermal imaging sequence set; 2) setting initial parameters and calculating a nearest neighbor distance; 3) constructing a nearest neighborhood graph to obtain a weight matrix; 4) calculating a Laplace operatorto construct an optimal target function; 5) decomposing the eigenvalue to obtain low-dimensional embedding; and 6) defect image reconstruction and evaluation. According to the method, the features areextracted from the simulation data, the local sensitivity discrimination model of the defect thermal image of the composite material is established, the training model is evaluated, the LSDT method better processes the information, uneven backgrounds, defect features and measurement noise can be separated to a large extent, and therefore defect recognition is better facilitated.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
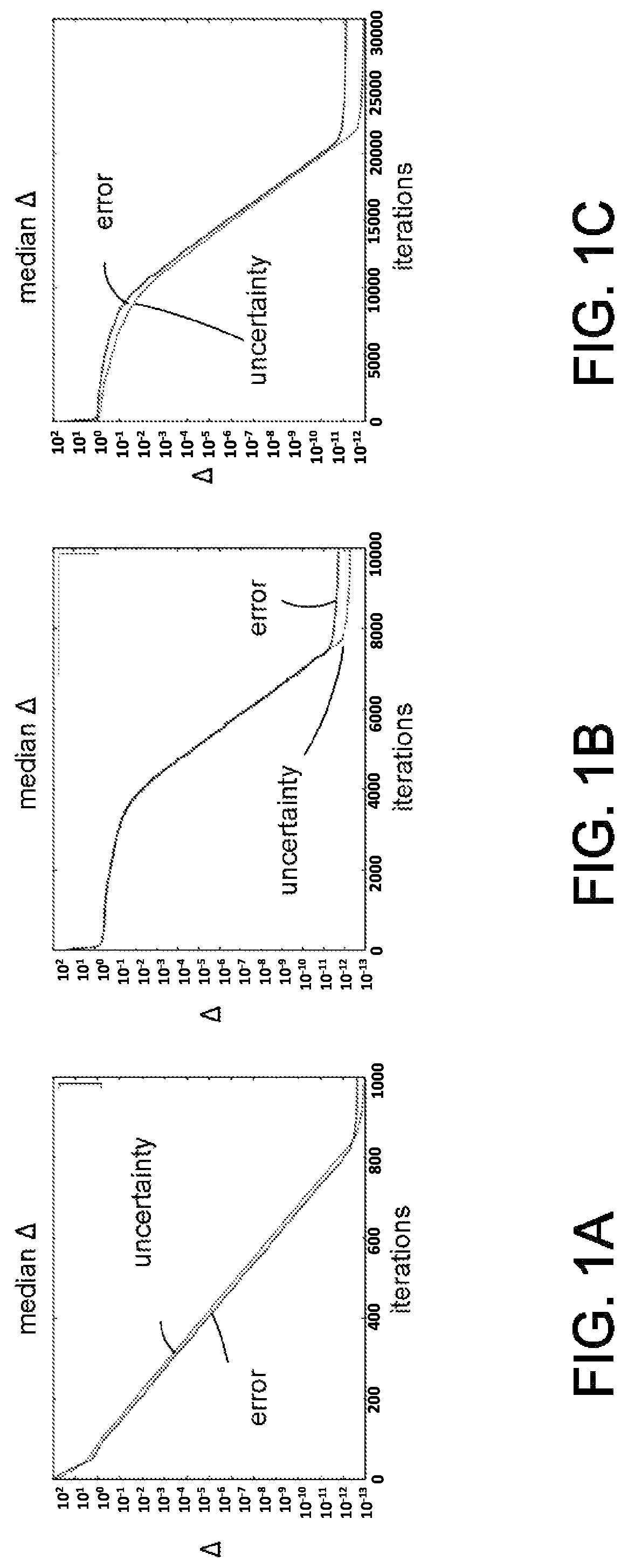
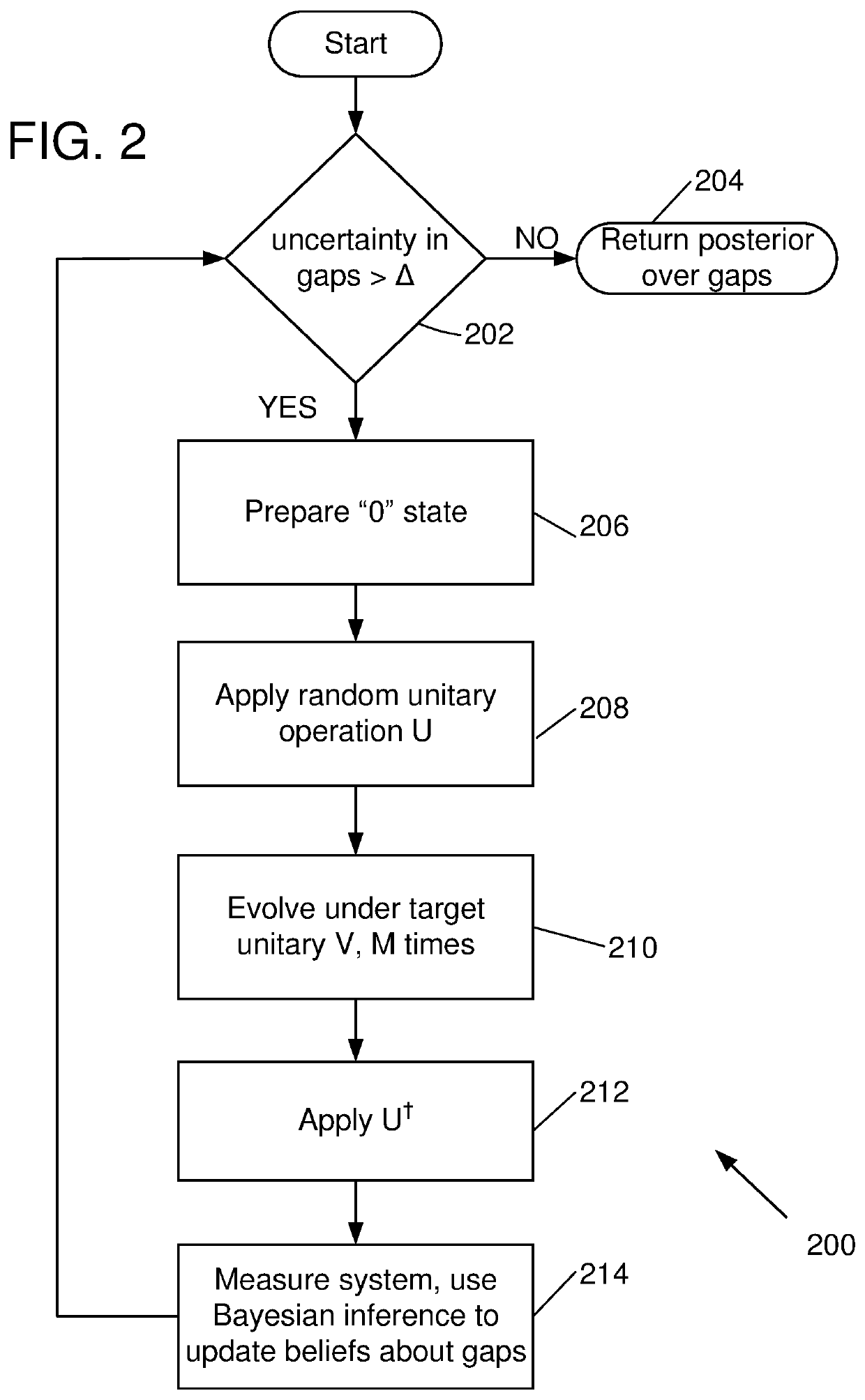
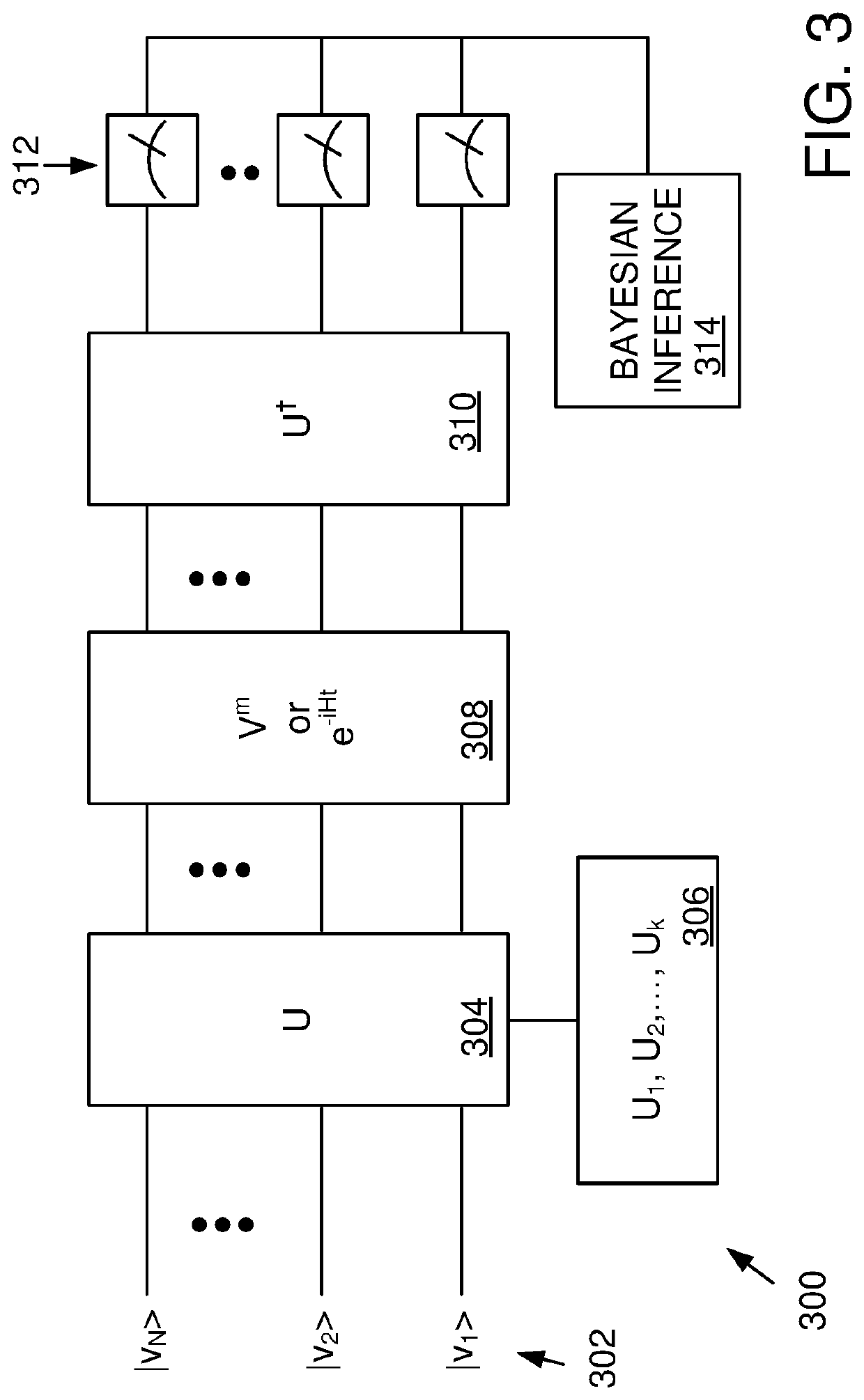
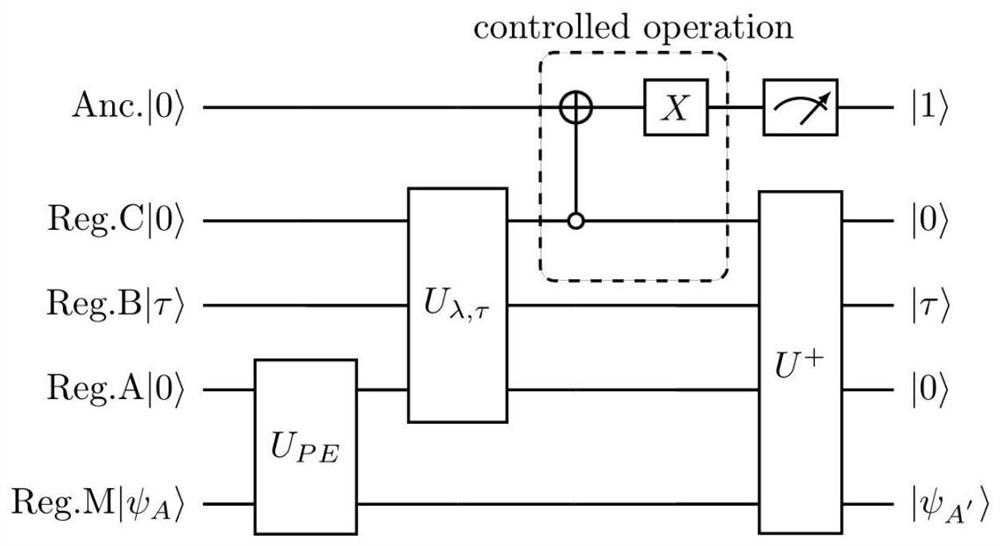
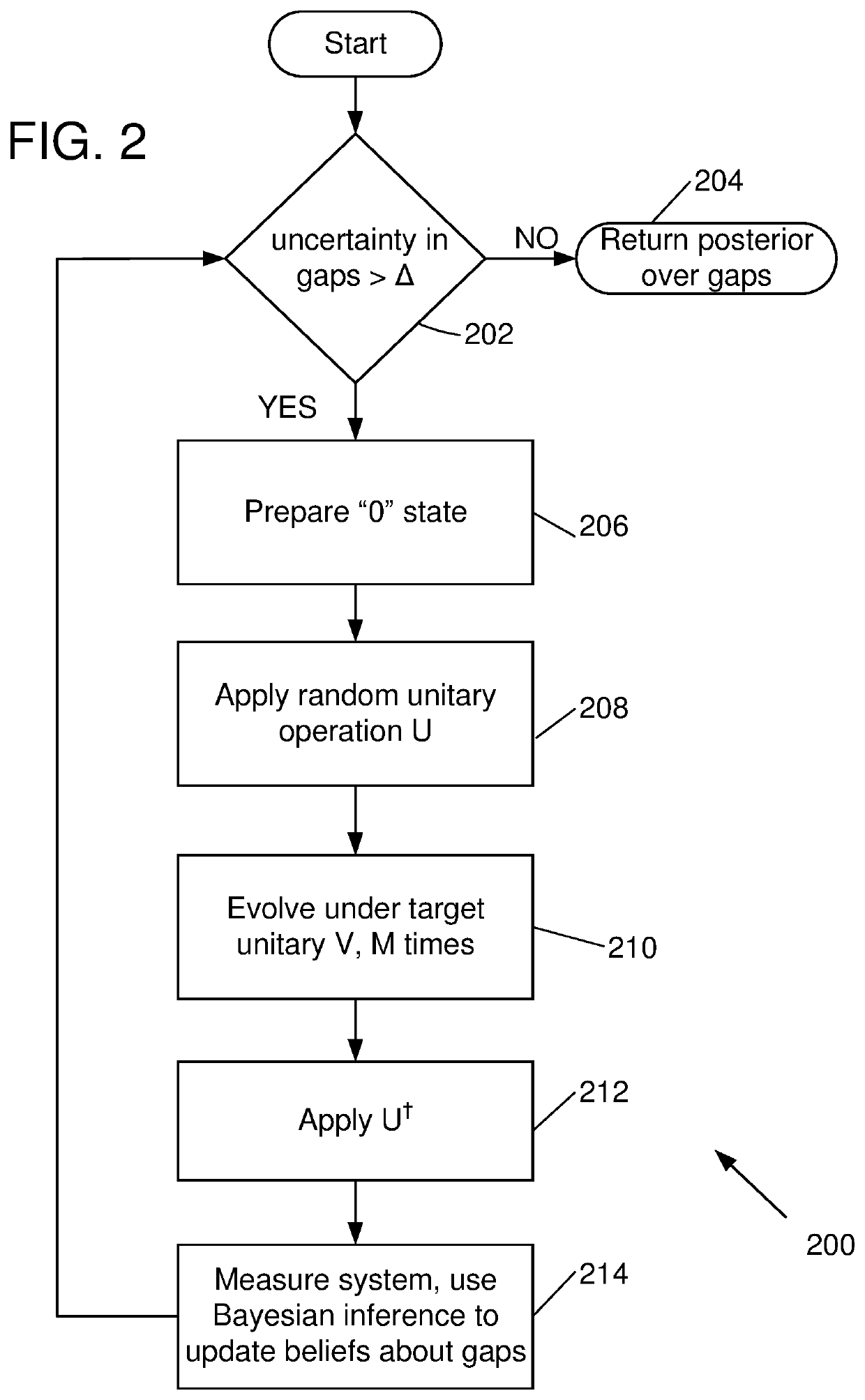
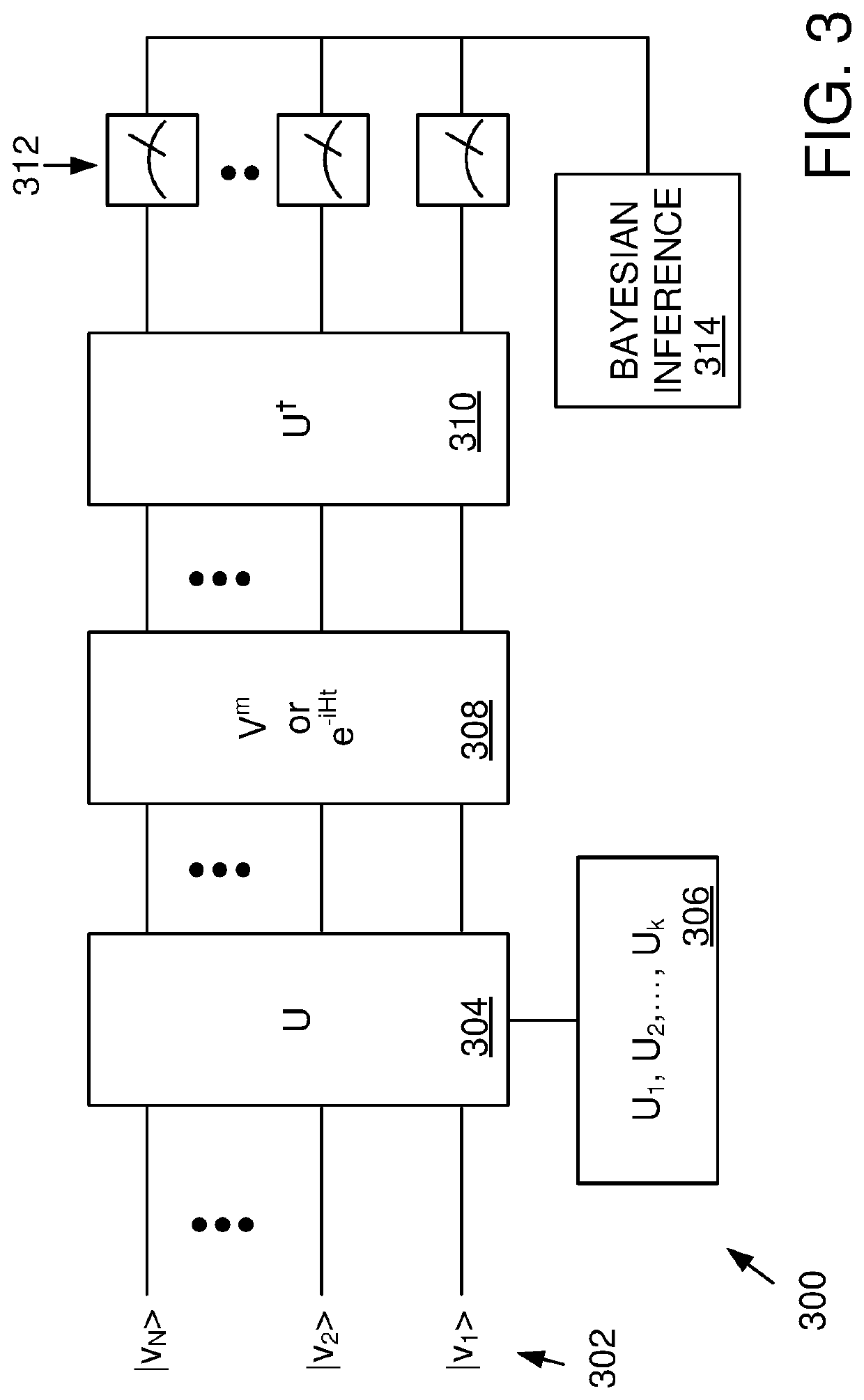
Randomized gap and amplitude estimation
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Two-dimensional direction finding estimation method based on polynomial rooting in co-prime area array
PendingCN112733333AReduce complexityReduce difficultyDesign optimisation/simulationComplex mathematical operationsComputation complexityEstimation methods
The invention discloses a two-dimensional direction-finding estimation method based on polynomial rooting in a co-prime area array, and the method comprises the following steps: firstly, obtaining a covariance matrix through a received signal of the co-prime area array; secondly, performing eigenvalue decomposition on the covariance matrix to obtain a signal subspace and a noise subspace, and rebuilding a spectral function by using the relationship between a co-prime area array and the FCPA; then, determining a rooting polynomial according to the orthogonal relation between the direction matrix and the noise subspace; finally, solving the root of the polynomial, finishing parameter pairing, and finishing two-dimensional angle parameter estimation. The invention has the advantages that the complexity and the angle estimation performance can be fully balanced, and the limitation that in a traditional two-dimensional angle estimation method, the angle estimation performance is good but the complexity is high or the calculation complexity is low but the angle estimation performance is poor is broken through. According to the algorithm, high-resolution two-dimensional DOA estimation can be realized, and the problem of influence of initial estimation precision on subsequent estimation is effectively solved.
Owner:苏州市冠伽安全科技有限责任公司
Selectable accurate quantum principal component analysis method and application
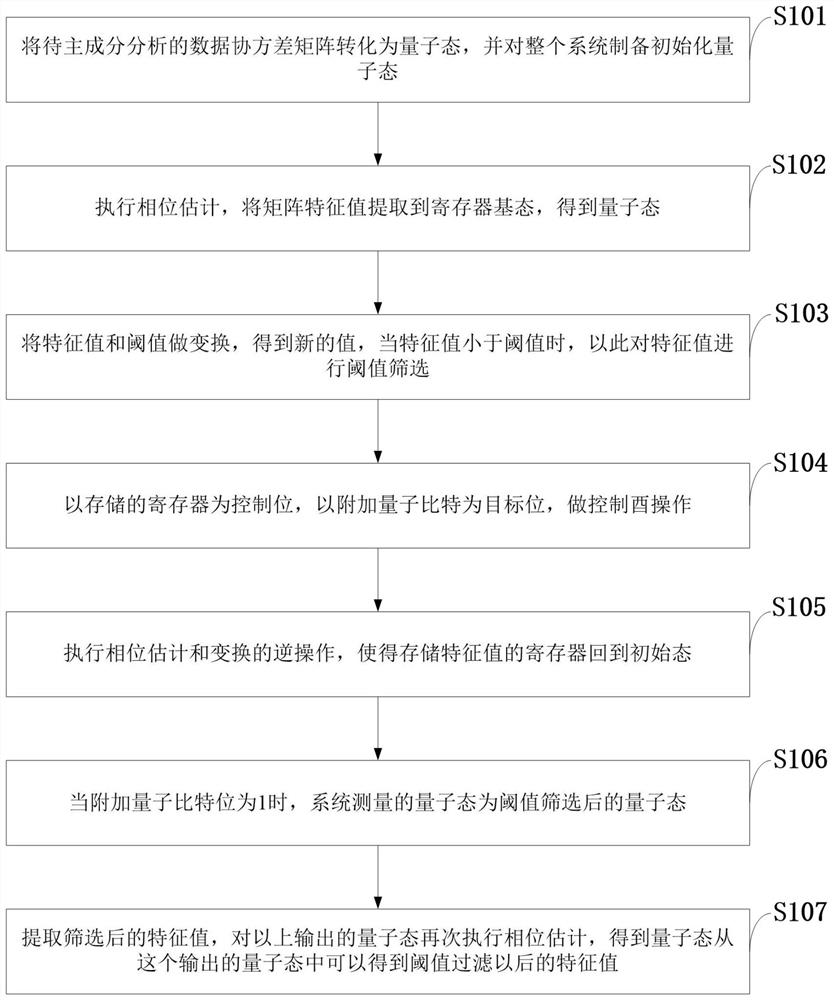
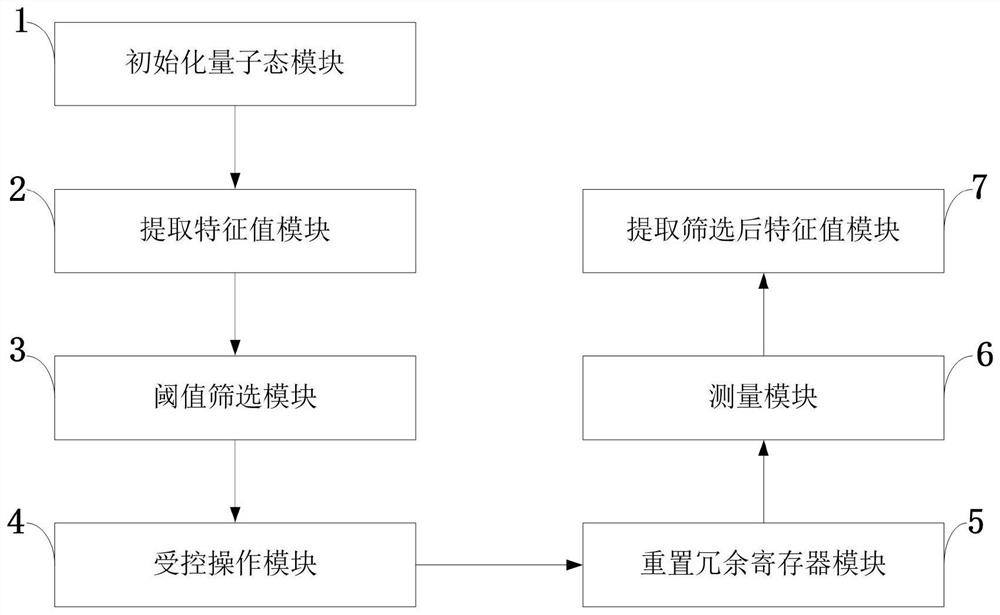
PendingCN112183756AReduce the impactIncrease flexibilityQuantum computersEnergy efficient computingFeature vectorTheoretical computer science
The invention belongs to the technical field of quantum machine learning, and discloses a selectable accurate quantum principal component analysis method and application, wherein based on a quantum singular value threshold decomposition algorithm, compared with traditional quantum principal component analysis, the flexibility is high, main components, namely main characteristic value characteristic vectors, are output by controlling thresholds, and all components, namely all eigenvalue eigenvectors, can be output, and compared with the previous improved algorithm, the algorithm reduces the number of quantum gates in the parallel direction, and the result is more accurate. According to the invention, the accurate quantum principal component analysis algorithm selected by the invention mainly comprises seven steps of inputting a covariance matrix quantum state, extracting a characteristic value through phase estimation, converting the characteristic value, performing controlled overturning, performing inverse transformation, measuring, extracting and screening the characteristic value through phase estimation, and finally outputting the characteristic value greater than a given threshold value and a corresponding characteristic vector; and the method can be used as a subroutine of other algorithms in the field of quantum machine learning, and the execution efficiency of the wholealgorithm is improved.
Owner:NORTHWEST UNIV
Finite element algorithm for decoupling unsteady vibration based on complex domain eigenvalue and application process
ActiveCN112989663AProgrammaticGeometric CADSustainable transportationFinite element algorithmTime domain
The invention relates to a finite element algorithm for decoupling unsteady vibration based on a complex domain eigenvalue and an application process, and the finite element algorithm is characterized in that the finite element algorithm carries out complex domain solution on a time domain vibration differential equation through Laplacian transformation, and the solution becomes matrix calculation with Laplacian variables as eigenvalues. When a calculation result captures a complex domain characteristic value, the complex domain characteristic value is essentially a vibration mode causing an unstable system response to be deduced, and then essential reasons of automobile structure vibration and braking howling are revealed. The finite element algorithm for decoupling the unsteady vibration through the complex domain eigenvalue and the application process of the finite element algorithm are applied to the field of finite element numerical calculation of automobile structure design, good calculation efficiency and precision are achieved, the unsteady vibration mode can be reasonably predicted and decoupled, and the actual application level is achieved.
Owner:中昇易维软件科技(苏州)有限公司
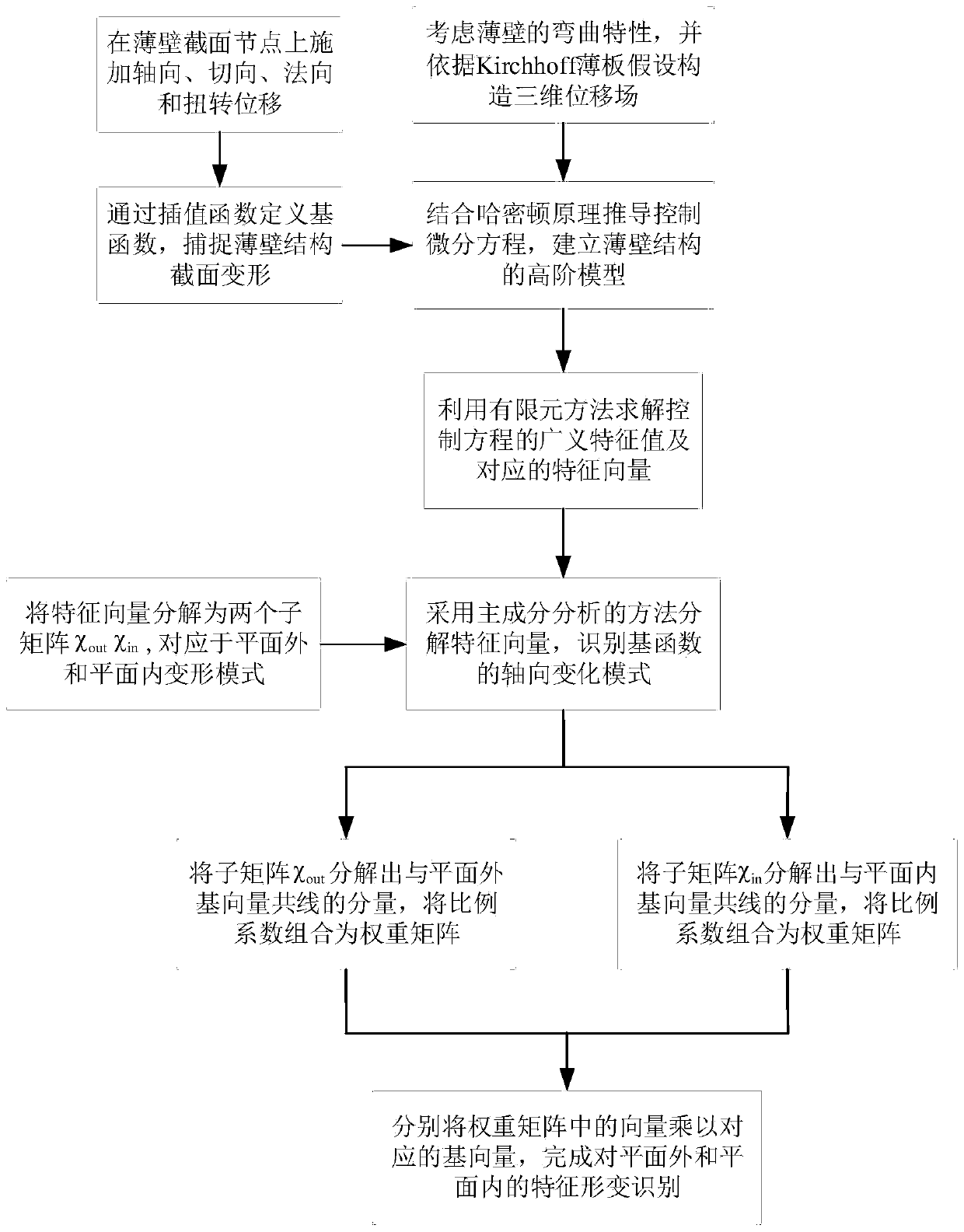
Thin-wall section characteristic deformation identification method
ActiveCN111414714AClear hierarchyExplicit Physical InterpretationGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationEngineeringMechanical engineering
The invention discloses a thin-wall section characteristic deformation identification method, which comprises the following steps of: 1) constructing a thin-wall structure high-order model by considering section deformation, and deriving a control differential equation of a thin-wall structure by adopting a Hamiltonian principle; 2) solving the generalized eigenvalue of the control differential equation and a corresponding eigenvector by using a finite element method; 3) performing order reduction approximation processing on the feature matrix to identify the axial change mode of the basis function; and 4) orthogonally decomposing the feature vector into a component which is collinear with the axial change mode of the primary function to obtain a proportional relation between the componentand the axial change mode, and multiplying the original deformation mode by the corresponding proportionality coefficient to generate a new deformation mode. According to the method, numerical valueimplementation can be carried out in a simple and visual mode, the derived deformation mode has definite hierarchy and physical interpretability, the dynamic behavior of the thin-wall structure can betruly reflected, the calculation efficiency is greatly improved, and the calculation cost is reduced.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV CHANGZHOU
Time-delay power system characteristic value calculation method based on partial variable discretization
ActiveCN109583065AThere is no case of infinite delay termsPreserve sparsenessSpecial data processing applicationsDifferential algebraic equationAlgorithm
The invention discloses a time delay power system characteristic value calculation method based on partial variable discretization. The method comprises the following steps of firstly establishing a linear model of time-delay power system based on differential-algebraic equations DDAE; discretizing some variables with time-delay by N-order Lagrangian interpolation polynomial, and establishing a single-variable single-delay and multi-variable augmented discretization matrix of two kinds of time-delay cases with multiple delays; obtaining a discretization matrix by eliminating the algebraic variables of the augmented discretization matrix, so as to transform the eigenvalue problem of the time-delay power system into the eigenvalue problem of the discretized matrix; The method greatly reducesthe order of the discretization matrix, and has the characteristics of fast calculation speed and high calculation precision, and is suitable for eigenvalue calculation of large-scale time-delay power systems.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
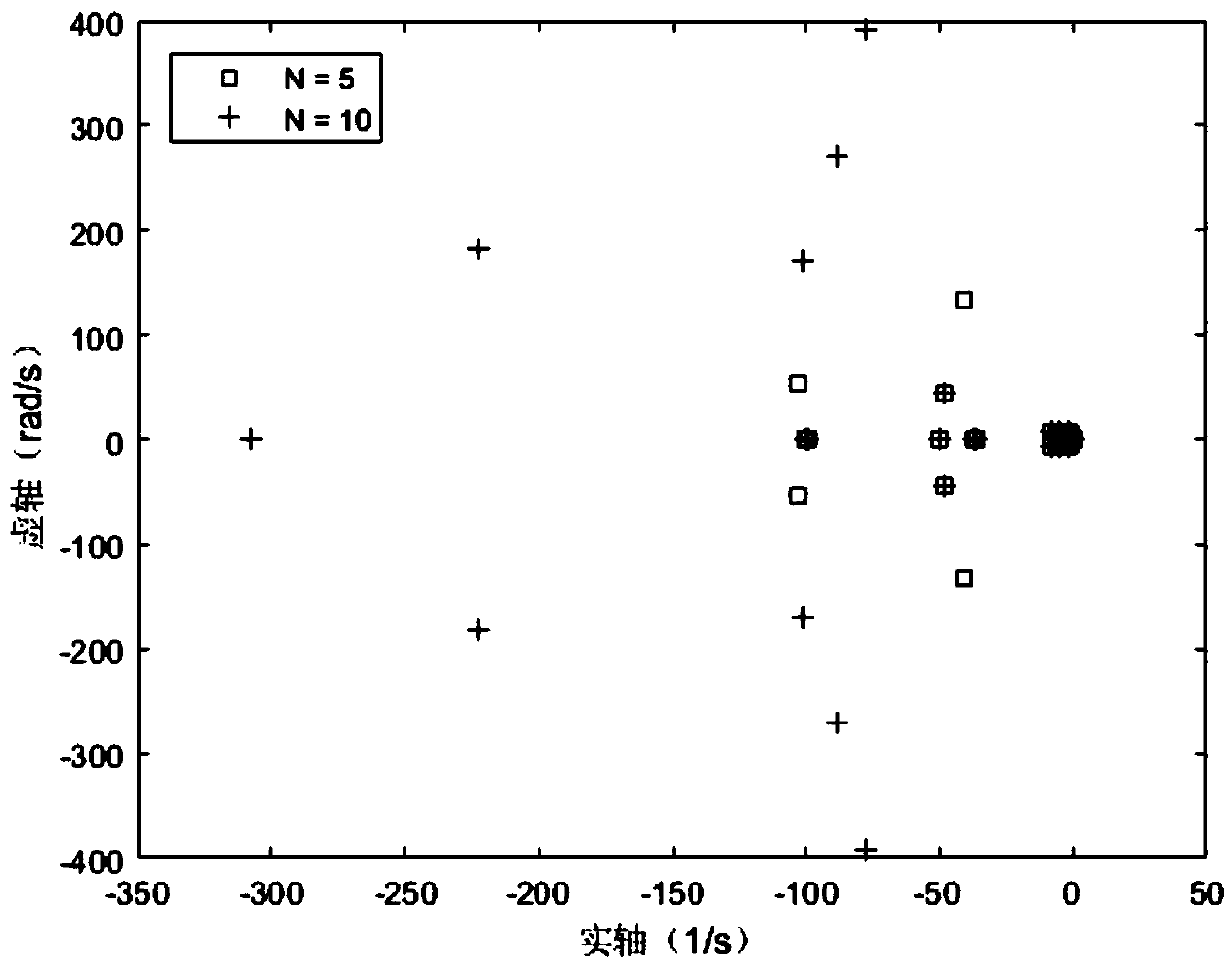
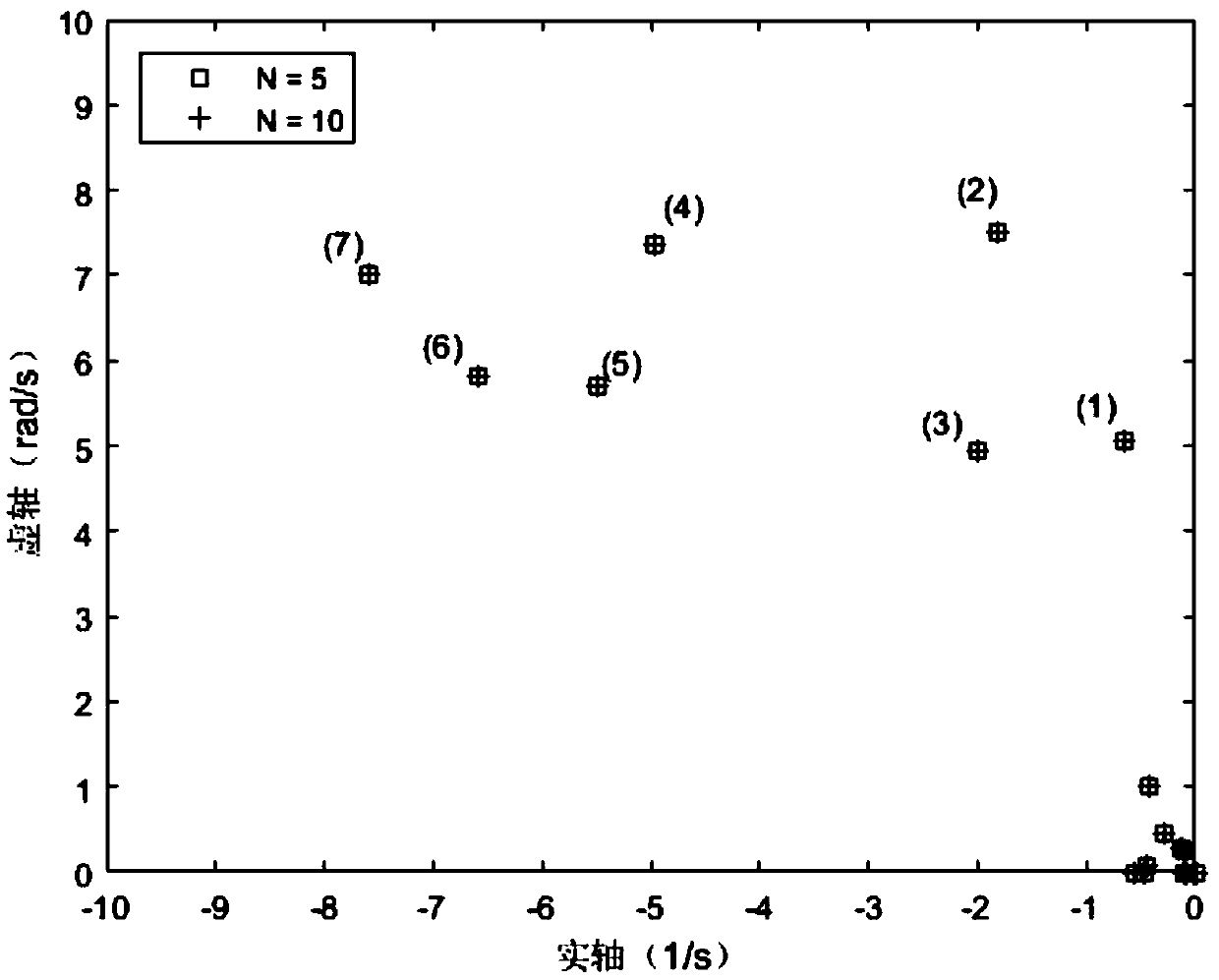
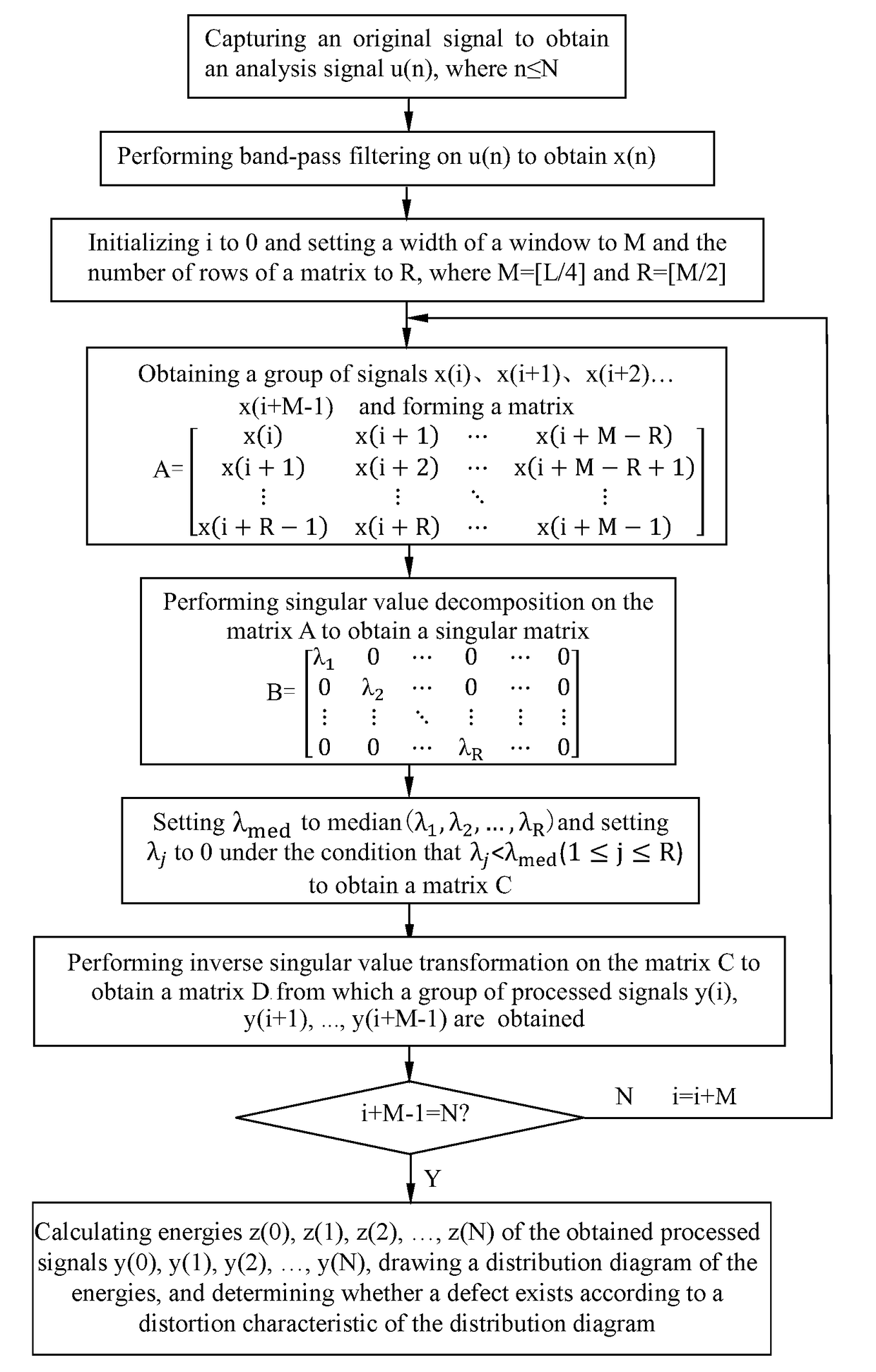
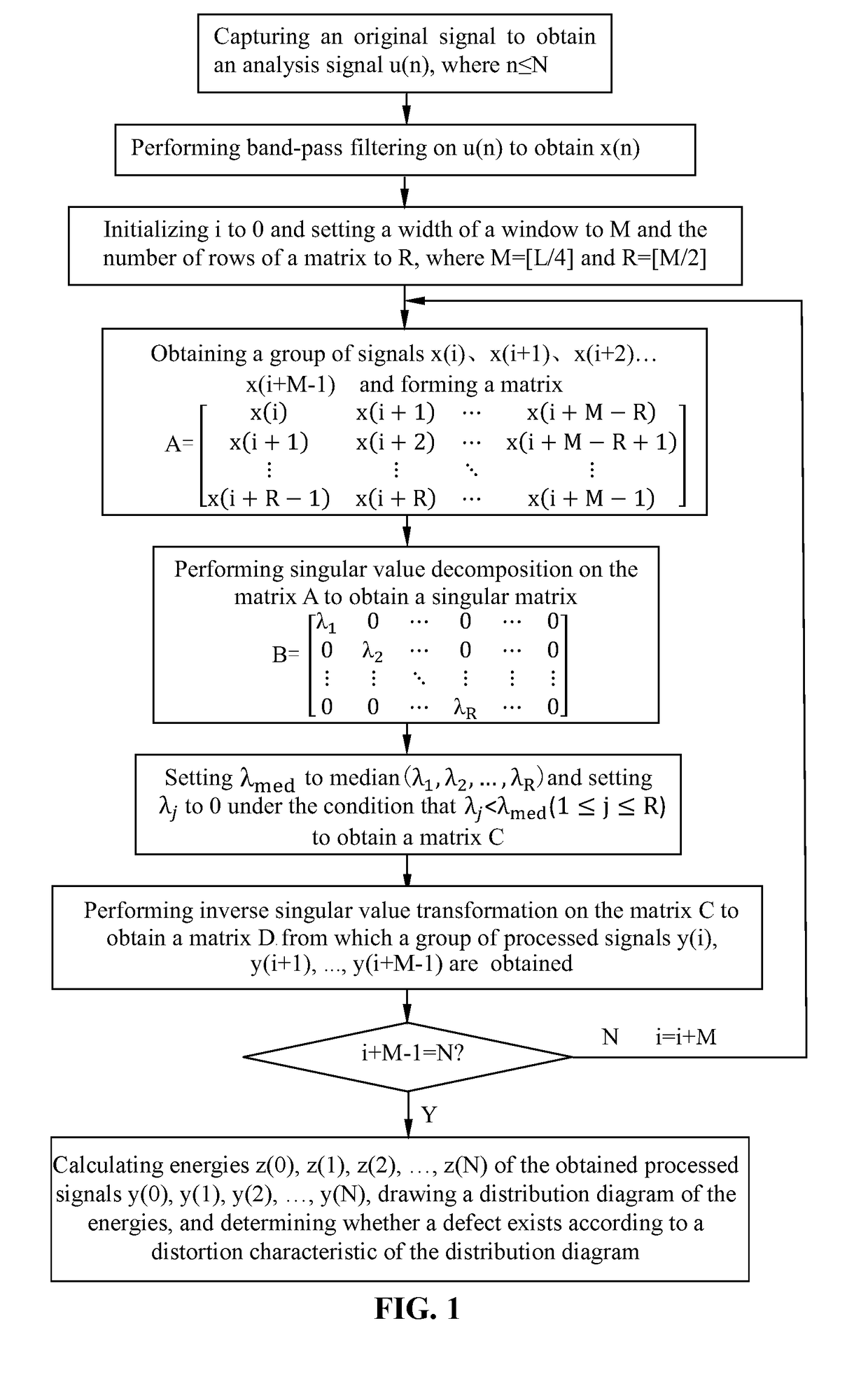
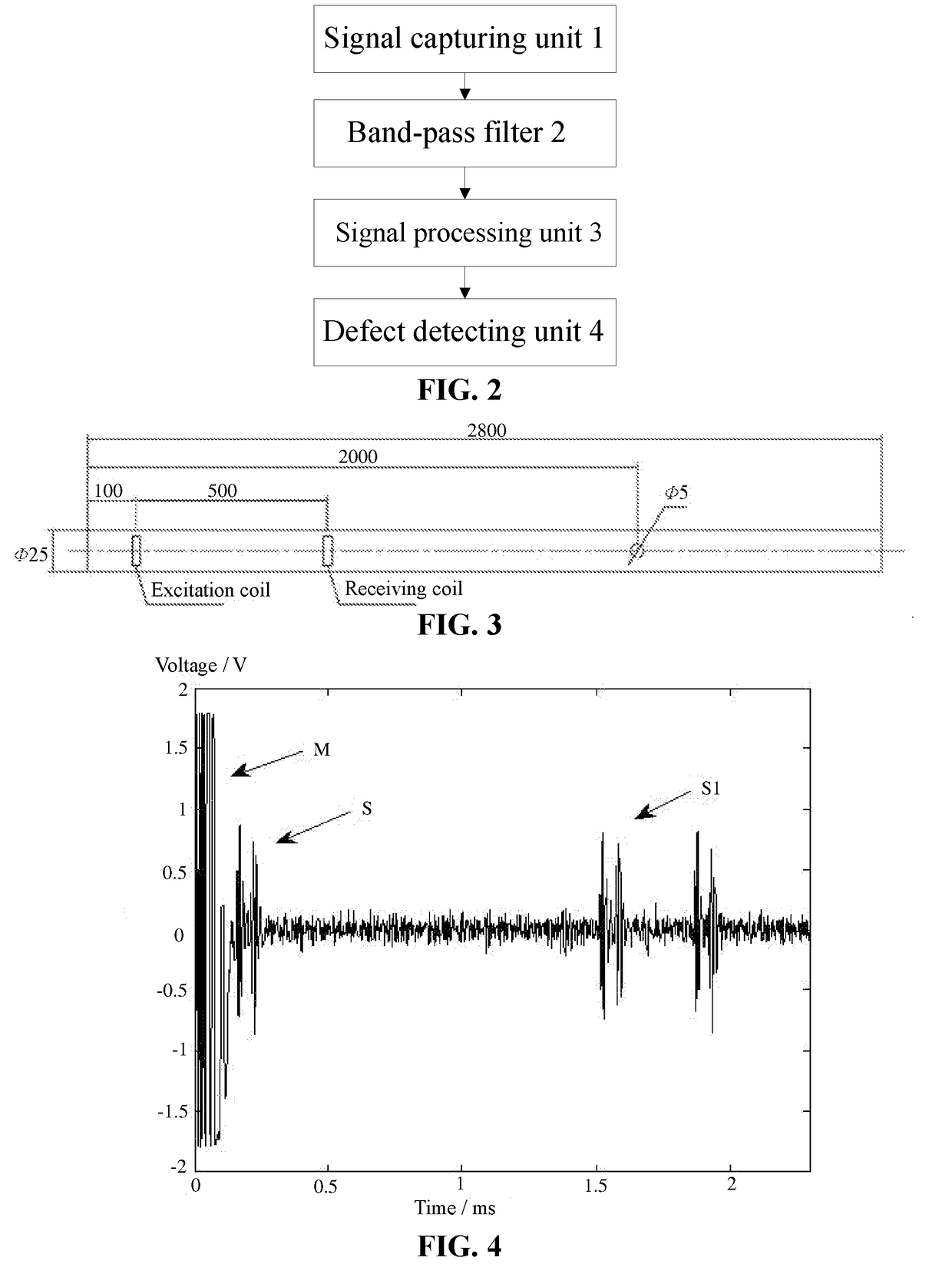
Method and device for processing magnetostrictive guided wave detection signals
InactiveUS20170356881A1Reduce impactImprove accuracyResponse signal detectionProcessing detected response signalSingular value decompositionWave detection
A method for denoising magnetostrictive guided wave detection signals to improve detection accuracy. The method includes forming a matrix A by using the signals; performing a singular value decomposition on the matrix A to obtain a singular matrix B including a plurality of eigenvalues; setting eigenvalues in the singular matrix B that are smaller than the median to zero to obtain a matrix C; performing an inverse transformation of the singular value decomposition on the matrix C to obtain a matrix D; and determining the denoised signals according to the matrix D.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Liveness detection method
The invention provides a living body detection method, which relates to the field of face recognition. The present invention solves the problem that the current face recognition process is vulnerable to video or photo attacks, so that it is impossible to accurately identify real faces and fake faces. The Laplace eigenvalues and Tamura texture eigenvalues of each sample in the training set are stitched together, and then the model is trained using the splicing results, and the initial output range of the model is set, and then the Laplace eigenvalues of each sample in the verification set are calculated separately. Stitch eigenvalues and Tamura texture eigenvalues and stitch them, and transfer the stitching results to the model for calculation, and judge whether the calculation results are within the initial output range, and if so, record the relevant parameters of the model at this time , if not, calculate the loss value of the calculation result and reversely transmit the loss value to the model, and adjust the relevant parameters of the model according to the loss value.
Owner:成都智汇脸卡科技有限公司
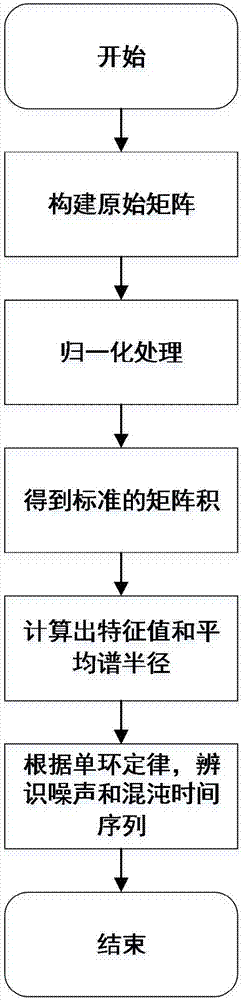
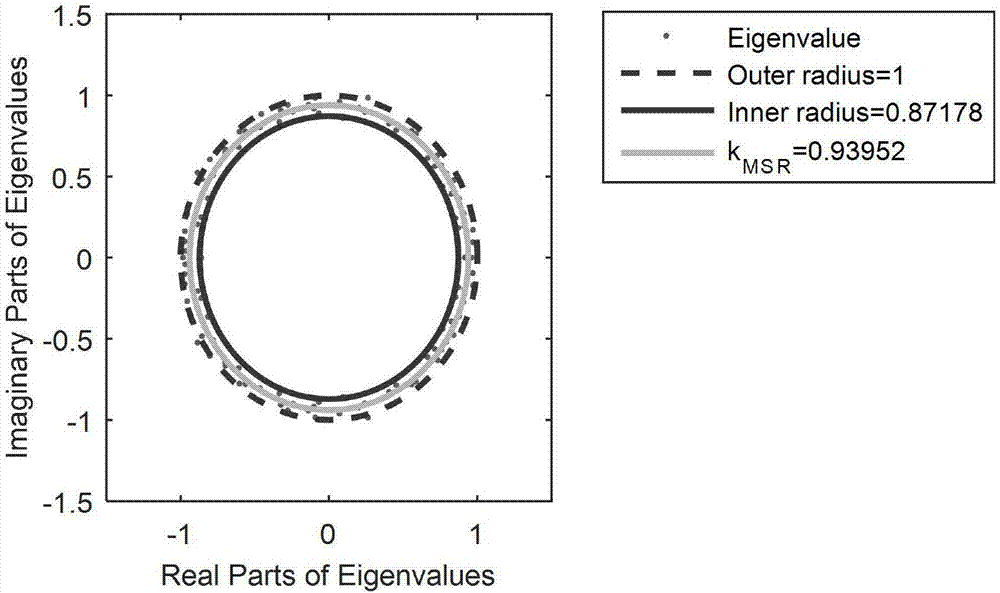
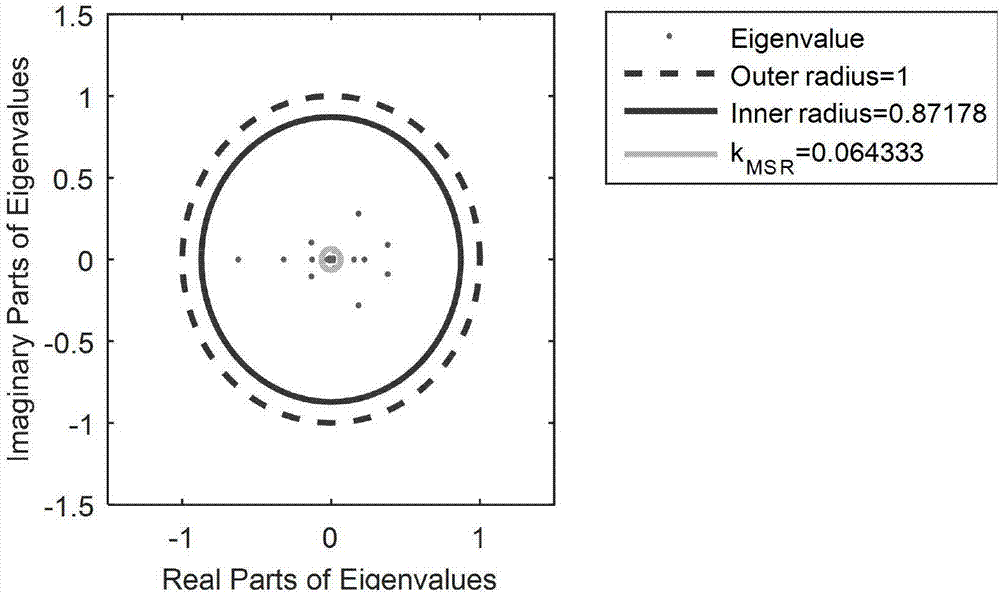
Method for recognizing chaotic time series based on random matrix theory
PendingCN107391448AEasy to identifyConvenient researchComplex mathematical operationsS-matrix theoryLaws of thermodynamics
The invention discloses a method for recognizing chaotic time series based on the random matrix theory. The method comprises the specific steps of A, randomly selecting a time series to be recognized, and constructing original matrix X according to the time series; B, normalizing the matrix X, converting it into a non-Hermite matrix, shown in the description, having a row vector average of 0 and a variance of 1; C, calculating the non-Hermite matrix to obtain its singular value equivalent matrix X, and calculating the singular value equivalent matrix X to obtain a standard matrix product shown in the description; D, calculating according to the standard matrix product to obtain its characteristic values, and calculating an average spectral radius of the characteristic values; E, recognizing the time series as a noise time series or a chaotic time series according to the single ring law in the random matrix theory. Short chaotic time series or noise-containing chaotic time series can be recognized through the method, and subsequent research is thus facilitated; the method has a simple processing procedure and is good in universality and robustness.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH
Method and device for determining hydrocarbon production for a reservoir
The present invention relates to a method for determining hydrocarbon production for a reservoir. The method comprisesdetermining a projector matrix based on a Jacobian matrix function of the gridded model, then splitting the Jacobian matrix into subsets of consecutive lines.For each subset of consecutive lines, creating a respective square matrix based on said subset.A determining eigenvectors and respective eigenvalues associated with the respective square matrix and then determining relevant eigenvectors having respective eigenvalues below a predetermined threshold.The projector is determined as a concatenation of the extended eigenvectors ordered according to multiple criteria: the respective order value of the subset; and the respective eigenvalue of the relevant eigenvector.
Owner:ARDYNE HLDG LTD +1
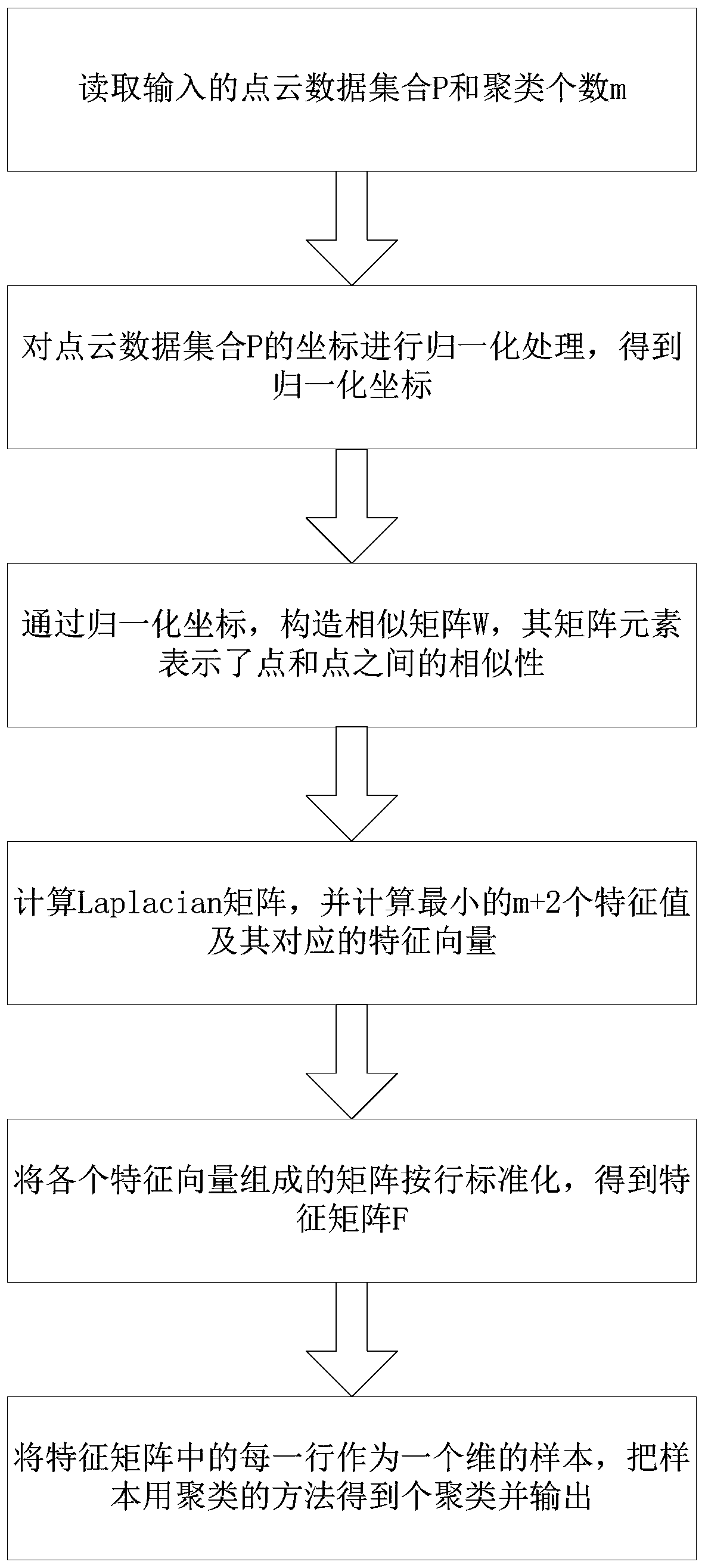
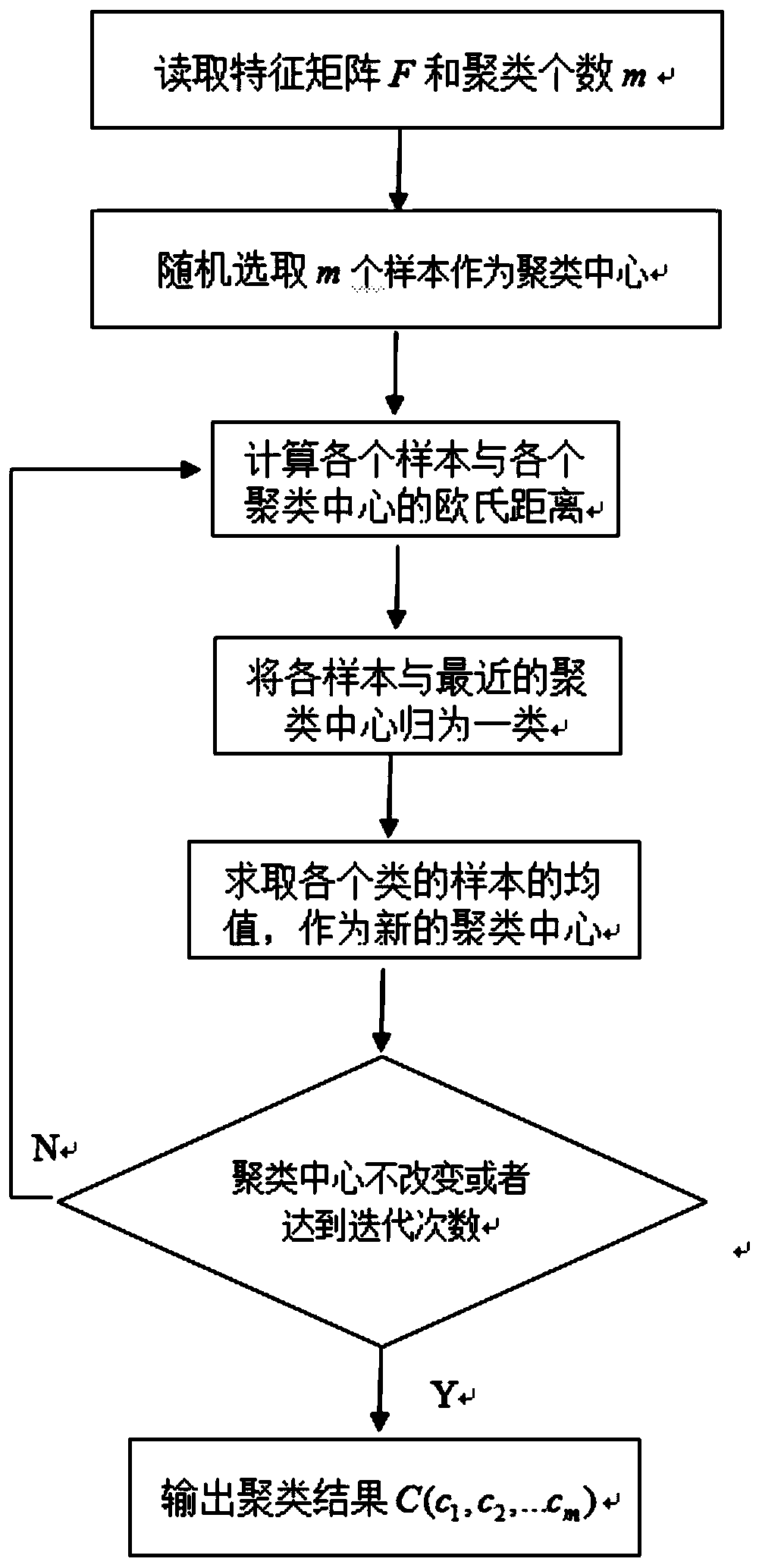
Point cloud data segmentation method based on spectral clustering
ActiveCN111462123AAvoid redundant informationProcessing speedImage enhancementImage analysisFeature vectorData set
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Two-way wave pre-stack depth migration method based on matrix multiplication
ActiveCN111077567ASolve problemsImprove imaging effectSeismic signal processingZ eigenvalueWave field
The invention discloses a two-way wave pre-stack depth migration method based on matrix multiplication. The method comprises the following steps: S1, constructing a first-order equation system about adepth variable; S2, performing calculation to obtain eigenvalue decomposition or spectral decomposition of a matrix H; S3, performing calculation to obtain a recursive two-way wave field depth continuation equation from z to z+delta z; S4, calculating a vertical wave number and a trigonometric function of the vertical wave number according to matrix multiplication; S5, bringing the vertical wavenumber and the trigonometric function thereof back to the S3, and calculating a recursive two-way wave field depth continuation equation in a general form; S6, after calculation a continuation wave field of the next depth, calculating an offset result by utilizing a cross-correlation imaging principle; S7, judging whether the offset program is calculated to the maximum model depth or not, and if so, ending the algorithm; otherwise, repeating the steps from S3 to S6; and S8, verifying the stability and accuracy of structure imaging under the salt mounds in the steps from S1 to S7 based on the salt mound model.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
An eddy current hardness sorting method based on ls-svm
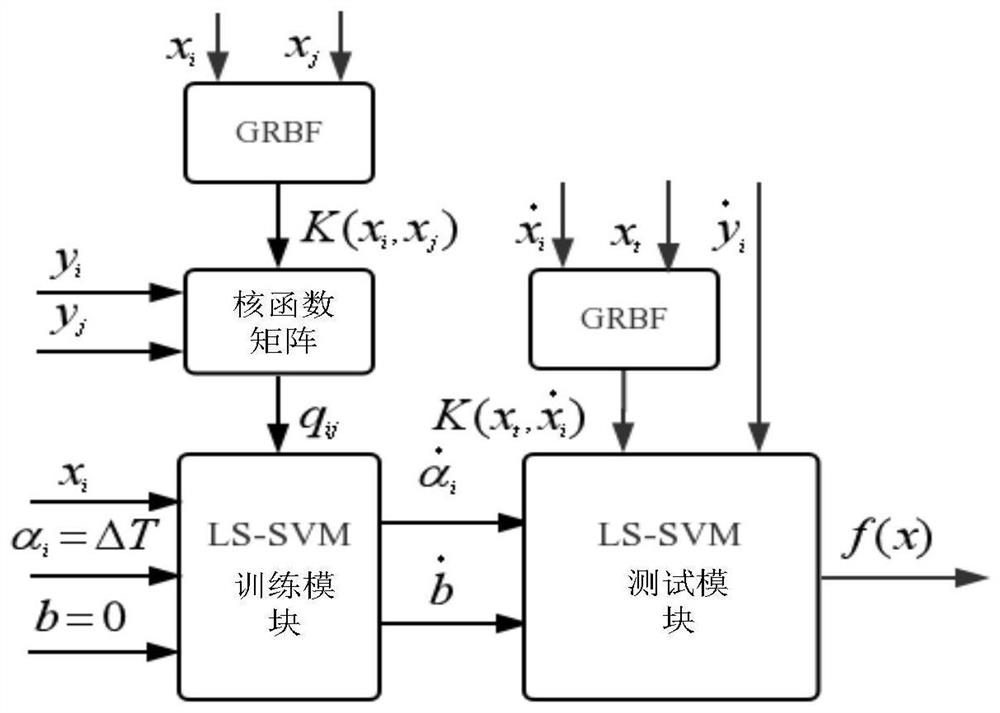
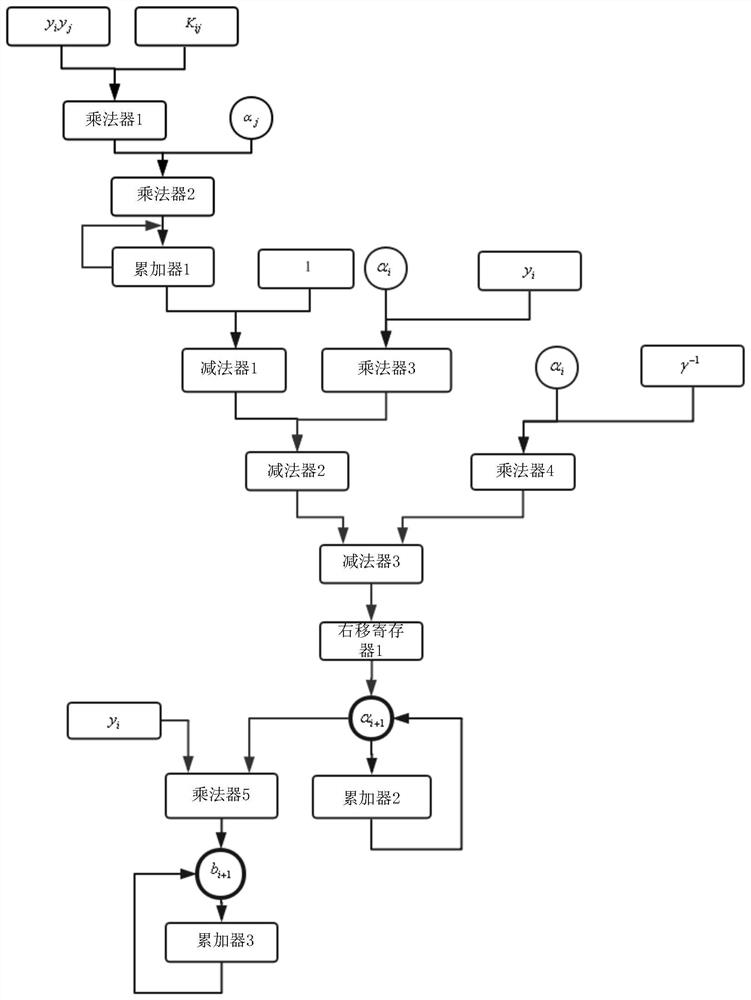
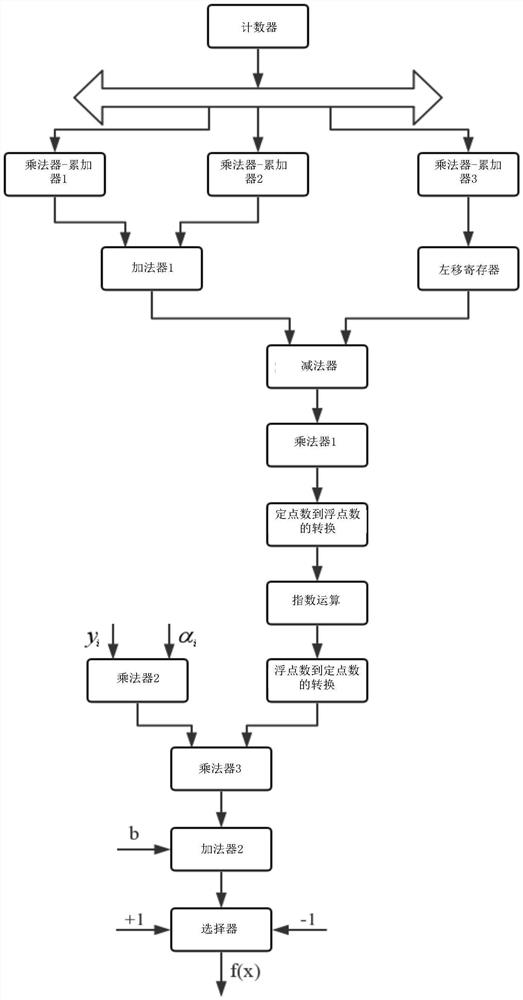
ActiveCN110490243BCharacter and pattern recognitionComplex mathematical operationsProduction lineAlgorithm
The invention discloses an eddy current hardness sorting method based on LS-SVM, which replaces the inverse operation of a large matrix in a conventional SVM algorithm by a finite number of iterative operations of a Lagrangian operator, and the solution process is a purely linear process, and more Easy to implement in hardware. The pure hardware algorithm has more advantages than the software algorithm in terms of speed due to the characteristics of processing parallelism, which provides the basis for the online sorting technology with high speed requirements on the production line; the acquisition of the training sample support vector coefficients The key is to determine the decisive parameters of the sorting hyperplane. The sorting method based on LS‑SVM can sort out qualified parts surrounded by unqualified parts. Its algorithm has strong practical value in the case that its eigenvalues are quite different from those of other qualified products under the same furnace number, resulting in wrong sorting.
Owner:REACH PRECISION MEASUREMENT GUIYANG COMPANY +1
Randomized gap and amplitude estimation
Methods and apparatus are provided that permit estimation of eigenphase or eigenvalue gaps in which random or pseudo-random unitaries are applied to a selected initial quantum state to produce a random quantum state. A target unitary is then applied to the random quantum state one or more times, or an evolution time is allowed to elapse after application of the target unitary. An inverse of the pseudo-random unitary used to produce the random quantum state is applied, and the resultant state is measured with respect to the initial quantum state. Measured values are used to produce Bayesian updates, and eigenvalue / eigenvector gaps are estimated. In some examples, the disclosed methods are used in amplitude estimate and control map determinations. Eigenvalue gaps for time-dependent Hamiltonians can be evaluated by adiabatic evolution of the Hamiltonian from an initial Hamiltonian to a final Hamiltonian.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com