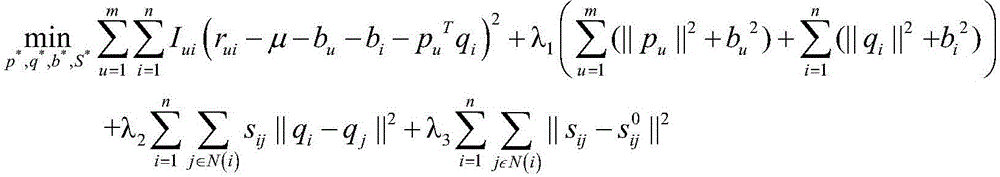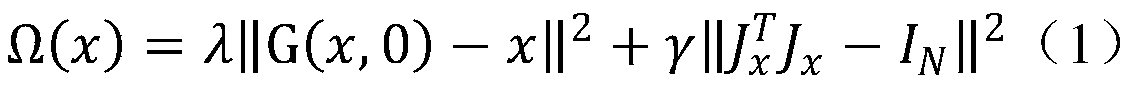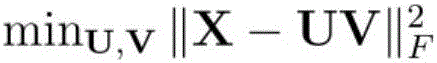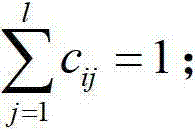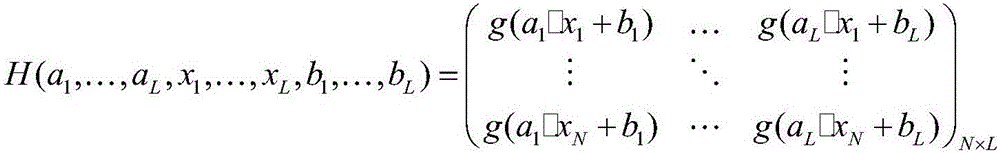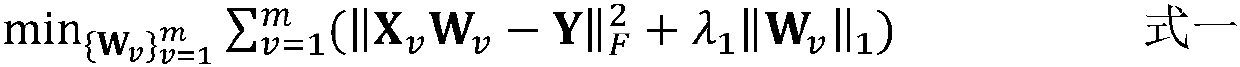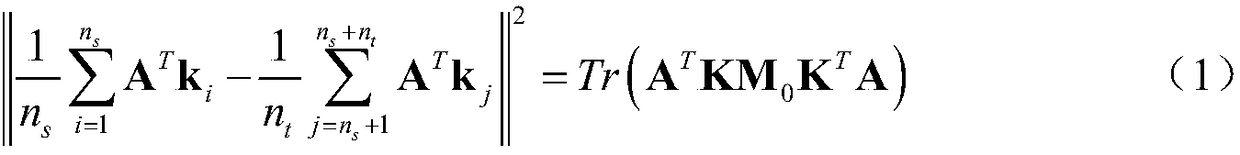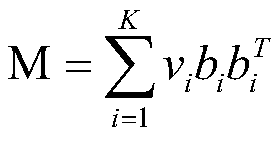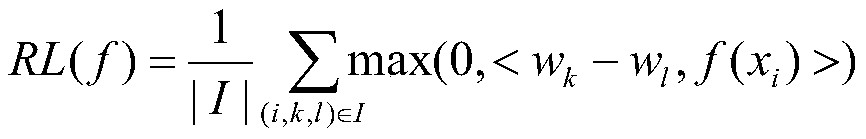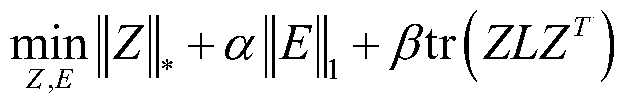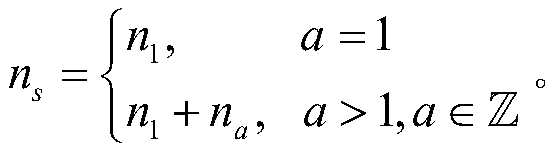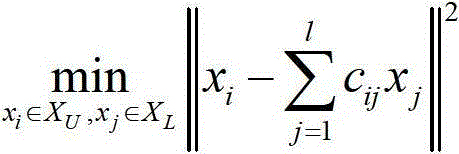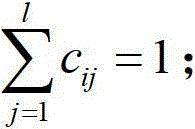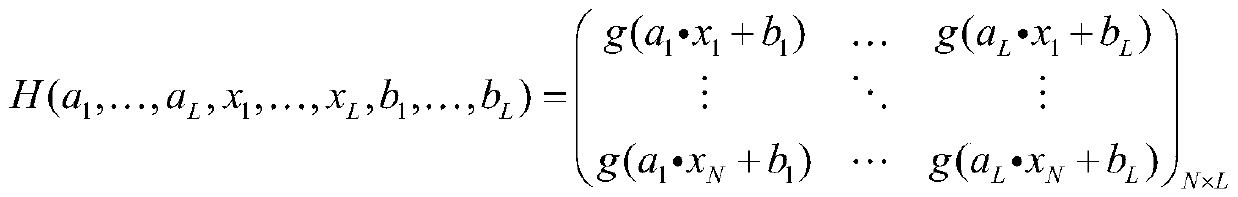Patents
Literature
49 results about "Manifold regularization" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In machine learning, Manifold regularization is a technique for using the shape of a dataset to constrain the functions that should be learned on that dataset. In many machine learning problems, the data to be learned do not cover the entire input space. For example, a facial recognition system may not need to classify any possible image, but only the subset of images that contain faces. The technique of manifold learning assumes that the relevant subset of data comes from a manifold, a mathematical structure with useful properties. The technique also assumes that the function to be learned is smooth: data with different labels are not likely to be close together, and so the labeling function should not change quickly in areas where there are likely to be many data points. Because of this assumption, a manifold regularization algorithm can use unlabeled data to inform where the learned function is allowed to change quickly and where it is not, using an extension of the technique of Tikhonov regularization. Manifold regularization algorithms can extend supervised learning algorithms in semi-supervised learning and transductive learning settings, where unlabeled data are available. The technique has been used for applications including medical imaging, geographical imaging, and object recognition.
Matrix decomposition recommendation method in graph construction framework
InactiveCN106846106AImprove performanceImprove recommendation accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionBuying/selling/leasing transactionsStochastic gradient descentMatrix decomposition
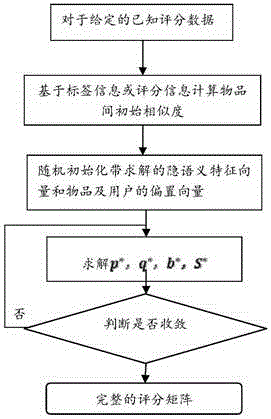
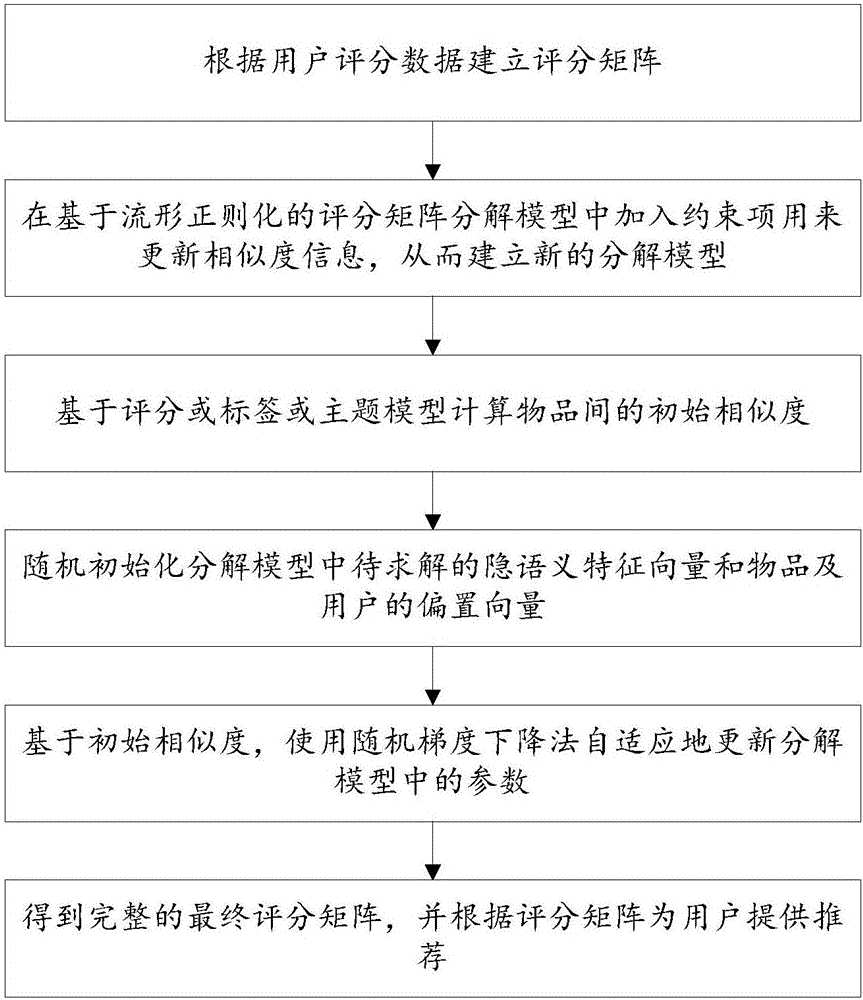
The invention discloses a matrix decomposition recommendation method in a graph construction framework. The method comprises the following steps of (1) establishing a score matrix according to user score data; (2) adding constraint terms to a manifold regularization-based score matrix decomposition model to update similarity information so as to build a new decomposition model; (3) calculating initial similarity between articles based on a score, tag or topic model; (4) randomly initializing to-be-solved latent semantic eigenvectors in the decomposition model and offset vectors of the articles and a user; (5) based on the initial similarity, adaptively updating parameters in the decomposition model by using a stochastic gradient descent method; and (6) obtaining a complete final score matrix, and providing recommendation for the user according to the score matrix. According to the method, the deficiency of a recommendation algorithm depending on similarity in inaccurate similarity calculation can be made up for.
Owner:NANJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
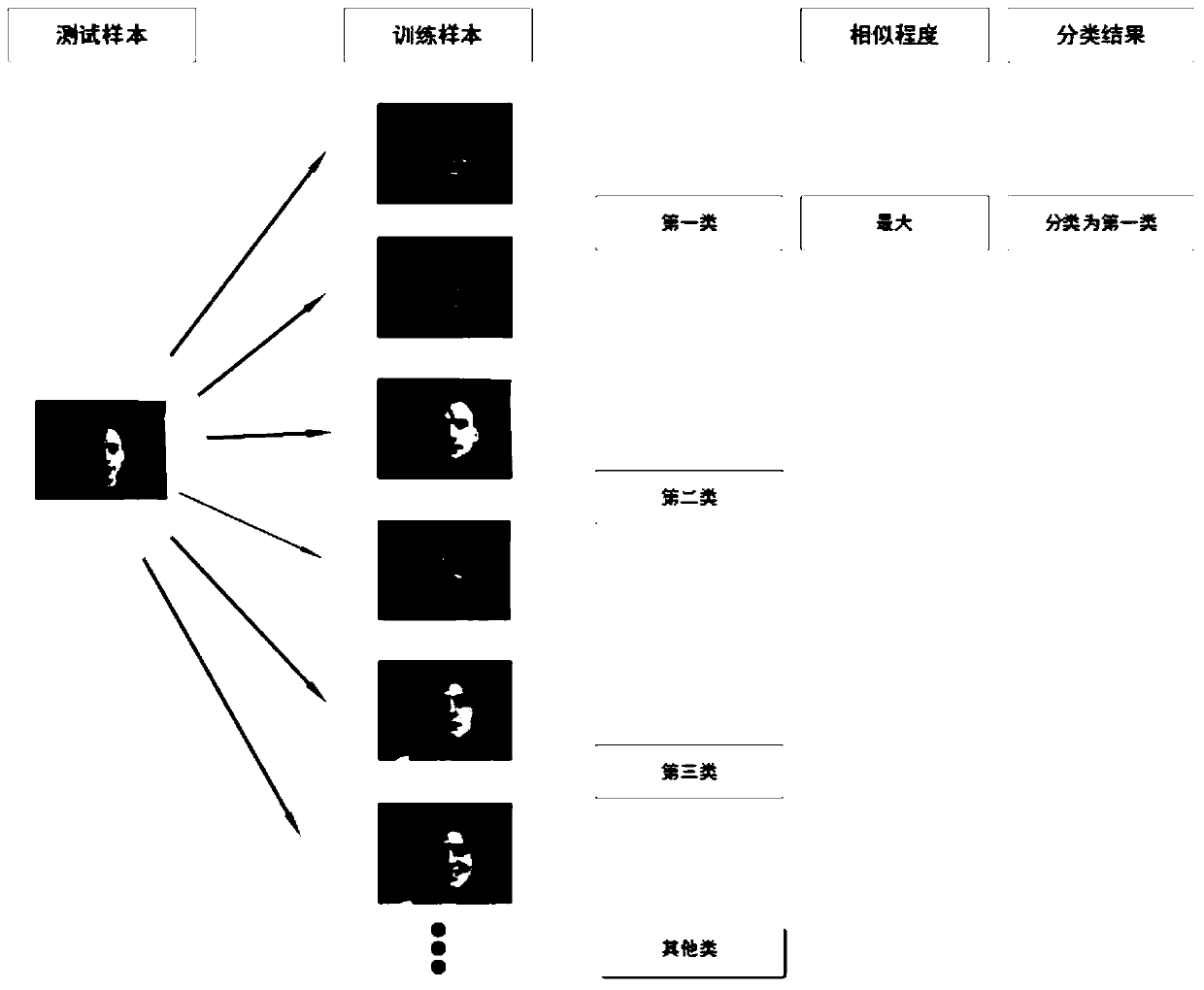
Robust visual image classification method and system
ActiveCN105354595AThe induction process is fast and preciseHigh speedCharacter and pattern recognitionHat matrixClassification methods
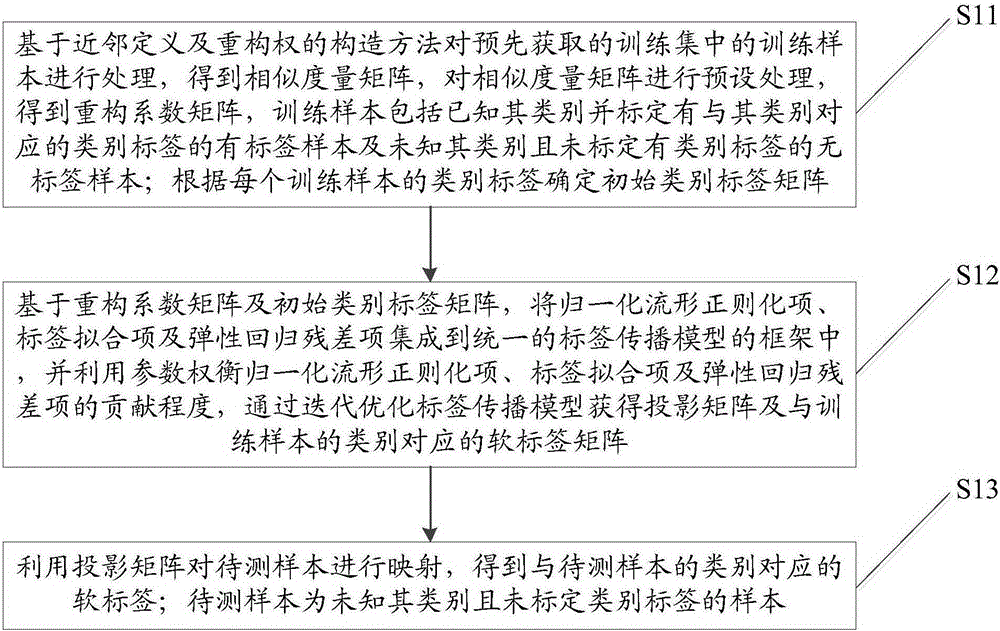
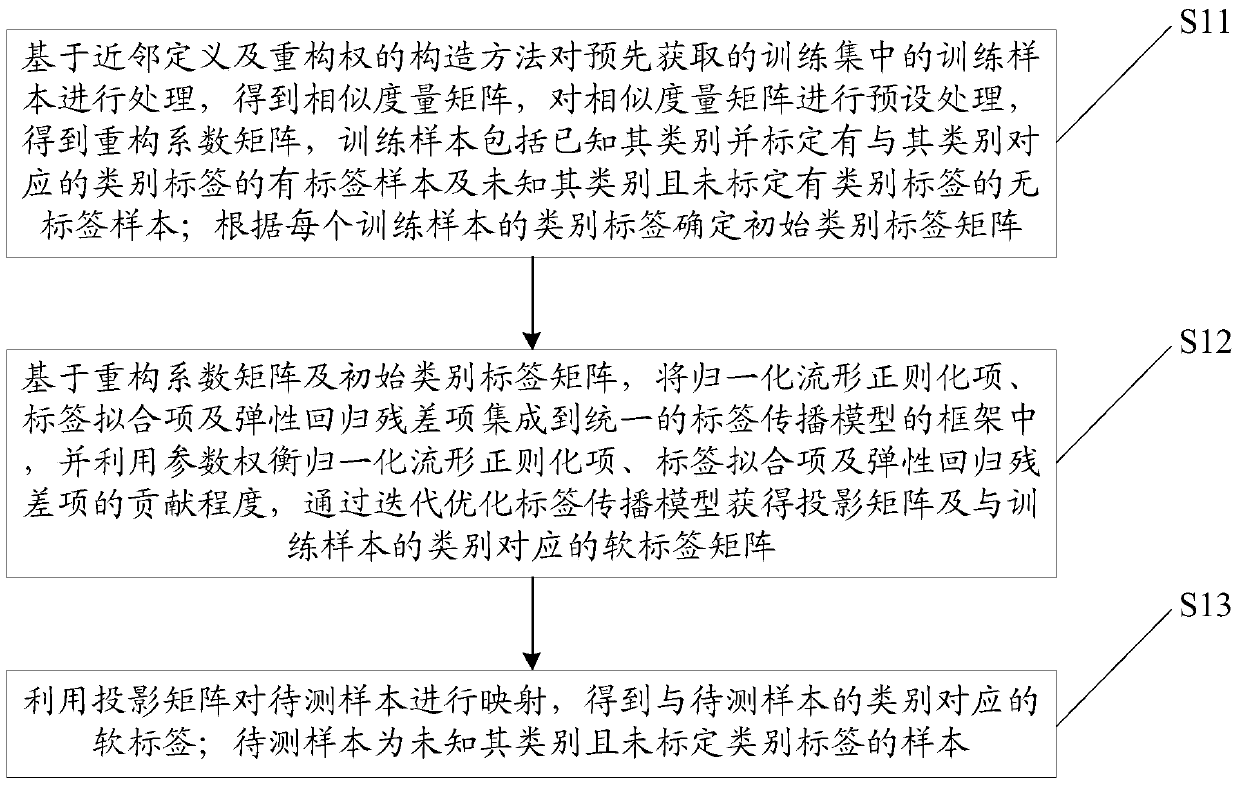
The present invention discloses a robust visual classification method and system and aims to effectively achieve category prediction of a no-label sample in a training sample and rapid induction and reasonable dimension reduction of a to-be-detected sample. The method comprises: integrating an error metric based on elastic regression analysis into a label propagation model outside the training sample; by a parameter, weighing the influence of a normalization manifold regularization term, a label fitting term based on soft label l2, 1 norm regularization and an elastic regression residual term based on l2, 1 norm regularization on sample description and category identification so as to complete establishing a label propagation model; and then, iteratively optimizing the label propagation model to acquire a projection matrix for determining a category of a to-be-detected sample. Therefore, according to the robust visual classification method and system, by introducing a regression error term based on l2, 1 norm regularization and soft label l2, 1 norm regularization, robustness of the system can be effectively improved while the advantages of a label propagation classification method is carried on, so that the induction process of the to-be-detected sample is rapid and accurate.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
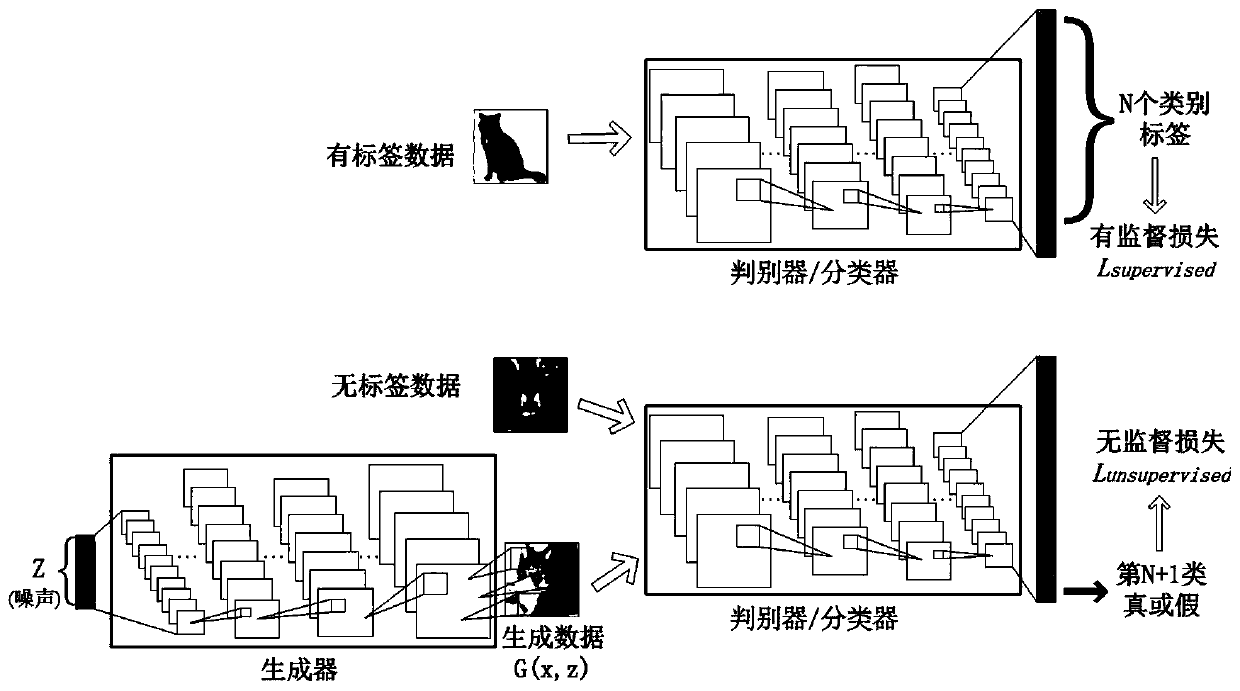
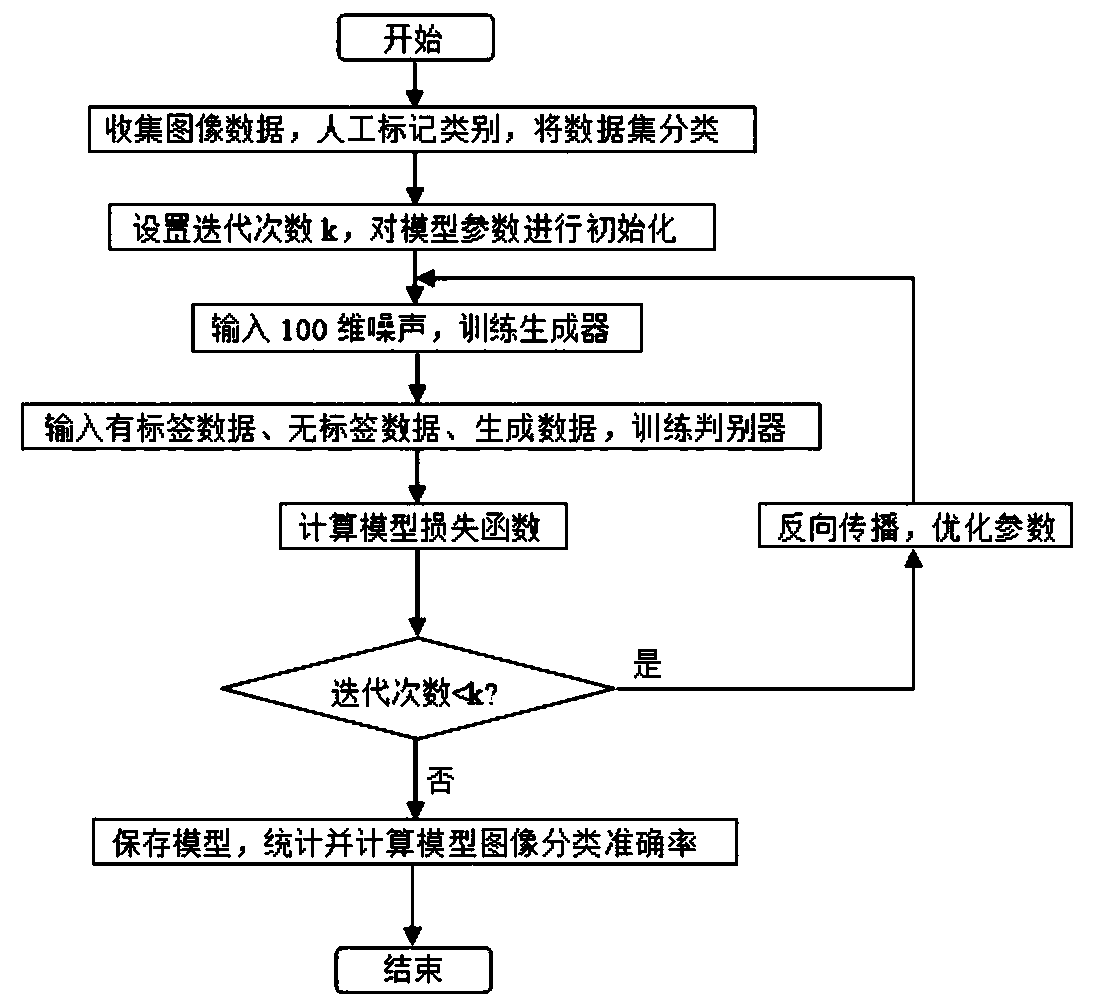
Semi-supervised generative adversarial network image classification method based on local manifold regularization
ActiveCN111046900AStrong construction abilityImprove fitting abilityCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesData streamGenerative adversarial network
The invention discloses a semi-supervised generative adversarial network image classification method based on local manifold regularization. According to the method, local manifold regularization is introduced into a semi-supervised generative adversarial network. According to the method, local manifold regularization is introduced based on the excellent fitting capability of the generative adversarial network to the data manifold, so that the problem of excessive training of the discriminator can be well solved. The manifold regularization item is added into the loss functions of the discriminator and the generator to punify the sudden change of the data manifold, so that the model can be prevented from falling into local collapse, the local disturbance of the model to the data manifold is enhanced to keep invariance, and the model has better robustness. The semi-supervised generative adversarial network image classification method combined with local manifold regularization can significantly improve the accuracy of image classification in the aspect of semi-supervised image classification.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Target tracking method based on manifold discriminant non-negative matrix factorization
InactiveCN106097381ADescribe wellImprove interferenceImage enhancementImage analysisPositive sampleFeature extraction
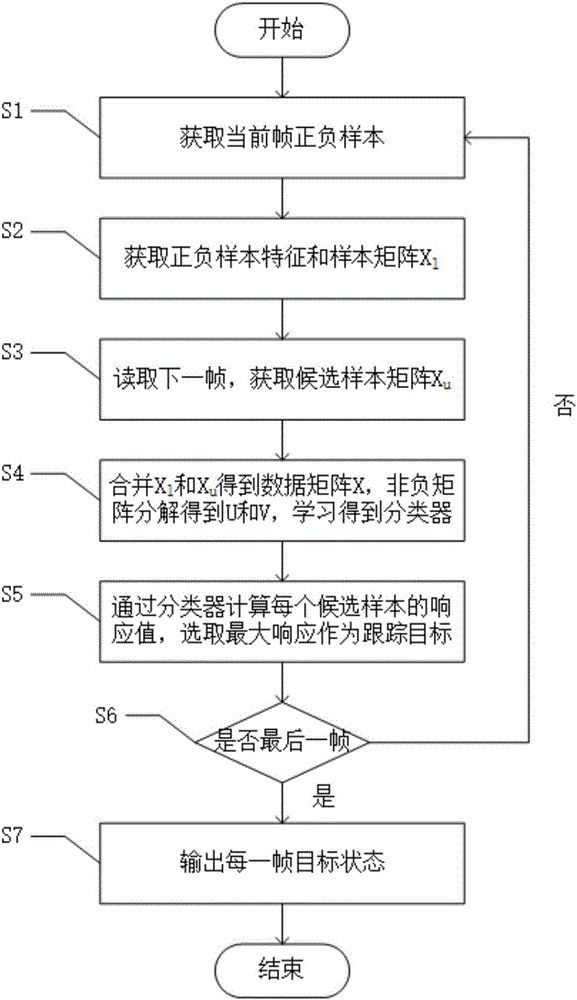
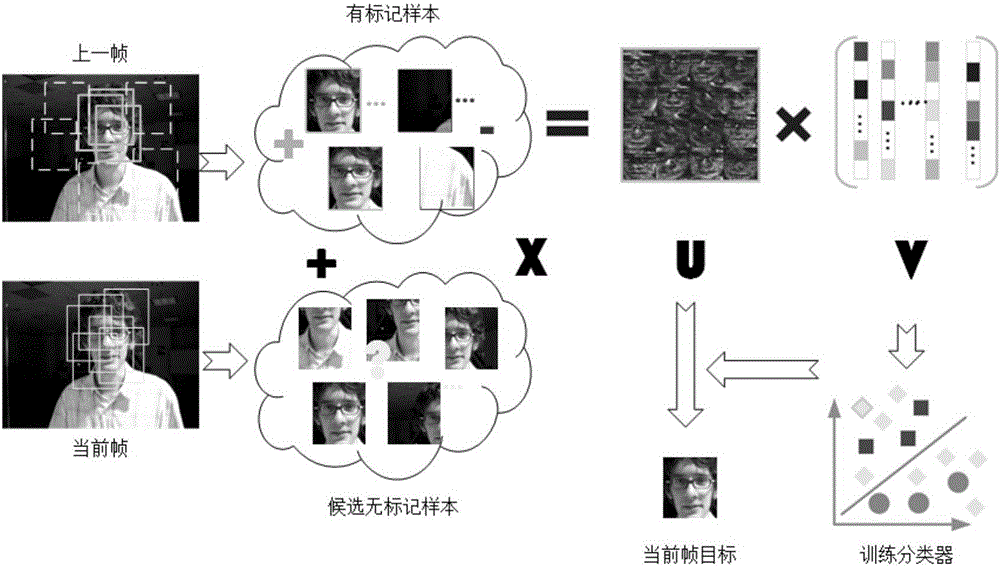
The invention discloses a target tracking method based on manifold discriminant non-negative matrix factorization. The target tracking method comprises the following steps: S1: obtaining a positive sample and a negative sample of a current frame; S2: obtaining the characteristics of the positive sample and the negative sample and a sample matrix X1; S3: reading a next frame, and obtaining a candidate sample matrix Xu; S4: combining X1 with Xu as a data matrix X, decomposing X into a non-negative matrix product, and learning to obtain a classifier; S5: through the classifier, calculating the response value of each candidate sample, and selecting a maximum response as a tracking target; and S6: judging whether the current frame is a last frame or not, entering S7 if the current frame is the last frame to output the state of each frame of target, and otherwise, jumping to S1. By use of the target tracking method, through the non-negative matrix factorization, higher-level image features are obtained, local characteristics can be better described, and shielding and background interference can be eliminated. A semi-supervised manifold regularization method is used and is combined with marked and unmarked samples to train the classer which contains spatial structure information, more discriminant information can be retained, and illumination and target deformation can be effectively coped with. A feature extraction model is trained and updated on line to quickly position an appointed target in a video.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
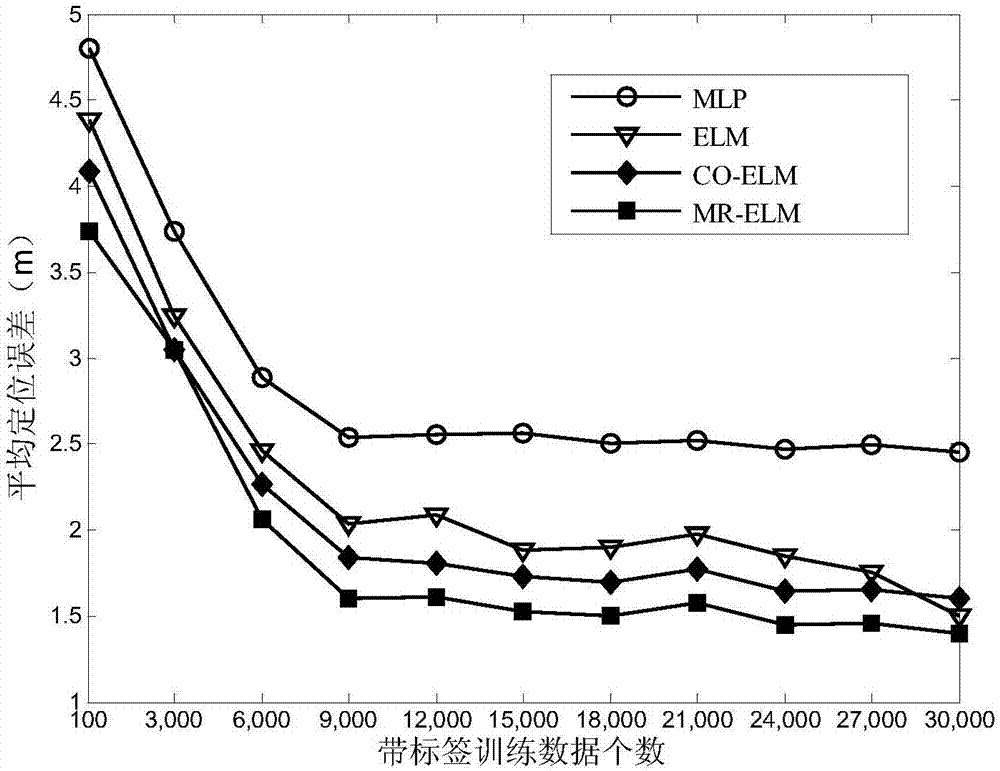
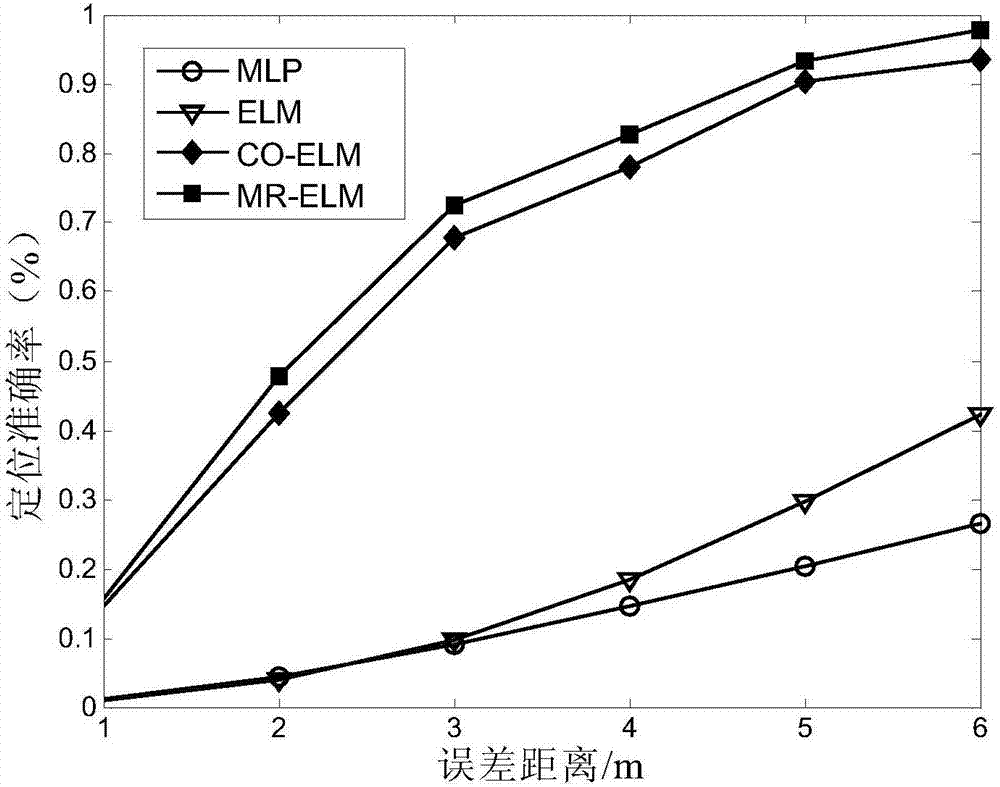
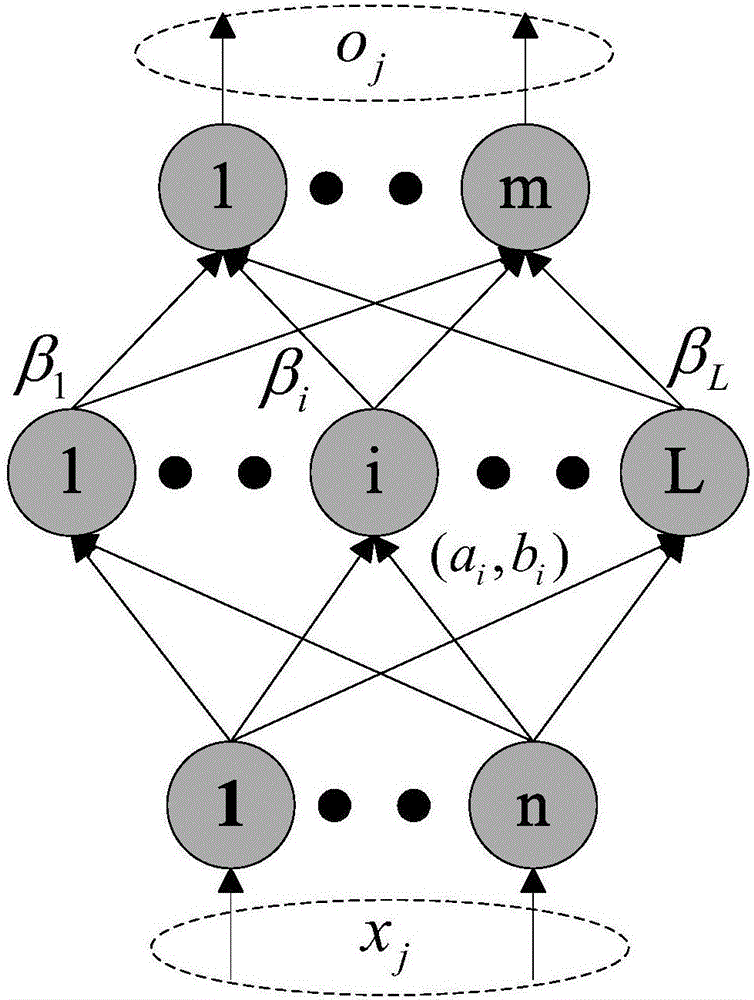
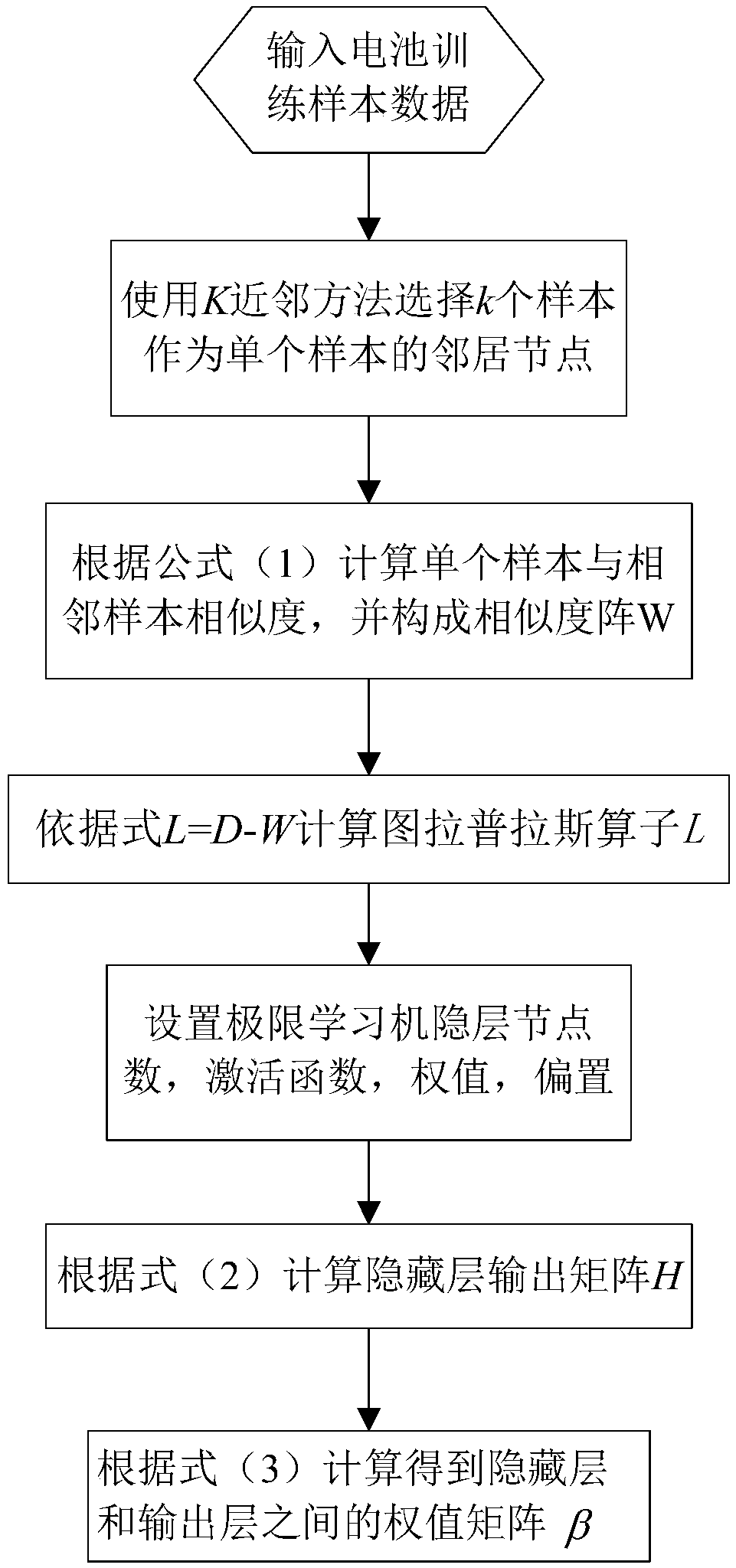
Semi-supervised fingerprint positioning algorithm based on manifold regularization
InactiveCN107423762AReduce positioning costsCharacter and pattern recognitionMachine learningLearning machineHidden layer
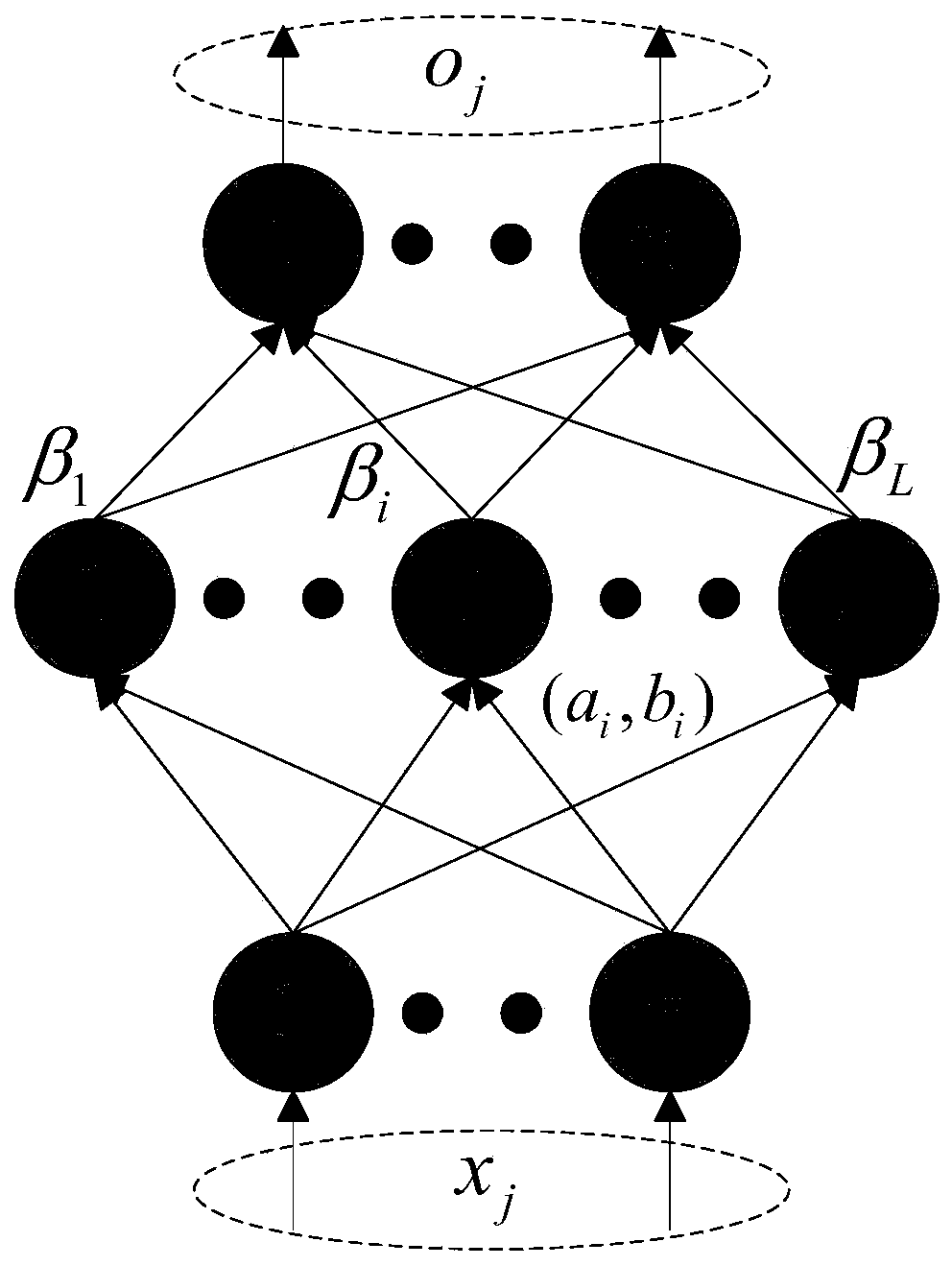
The invention provides a semi-supervised fingerprint positioning algorithm based on manifold regularization. The algorithm comprises the following steps: 1, training data with a tag and training data without a tag acquired from an actual environment together serve as a semi-supervised learning training data set; 2, a graph Laplacian operator is built in input space of the training data with the tag and the training data without the tag; 3, a Gauss kernel function is introduced to calculate the weight matrix of an adjacent graph; and 4, a manifold regularization frame and an extreme learning machine with random feature mapping are combined to solve a hidden layer output weight matrix, and a position estimation model is built. The manifold regularization frame and the extreme learning machine are combined, the easily-acquired training data without the tag are used thoroughly, and the positioning cost is reduced.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
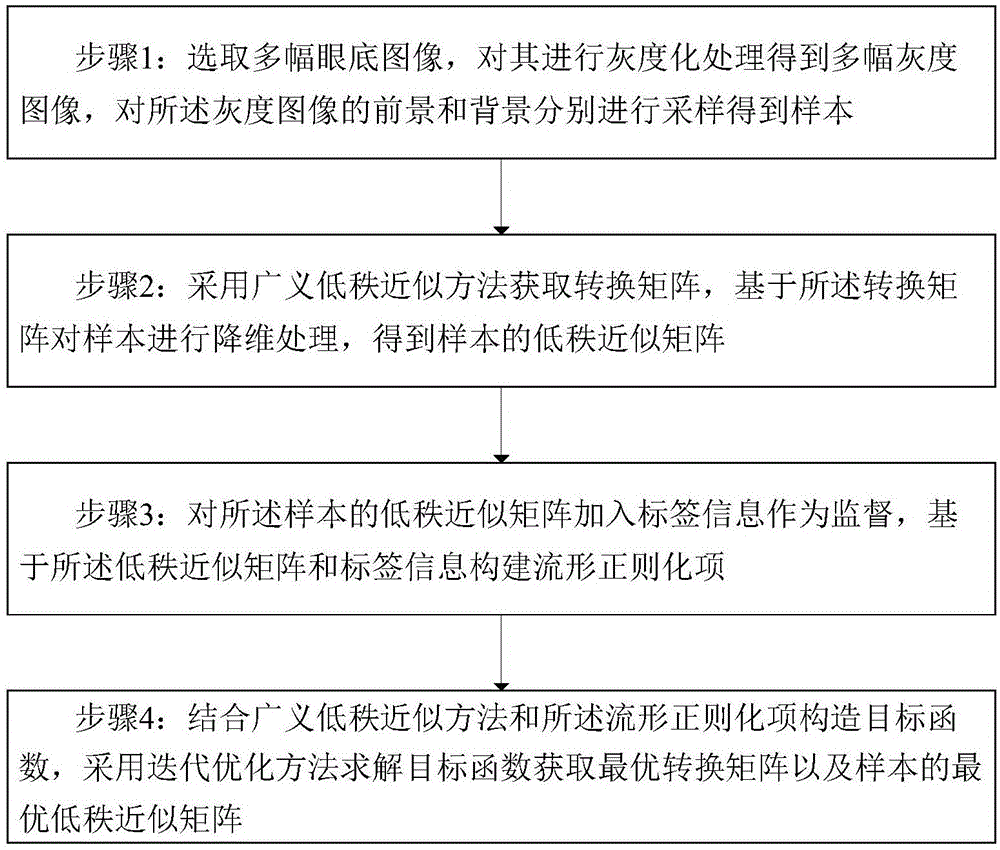
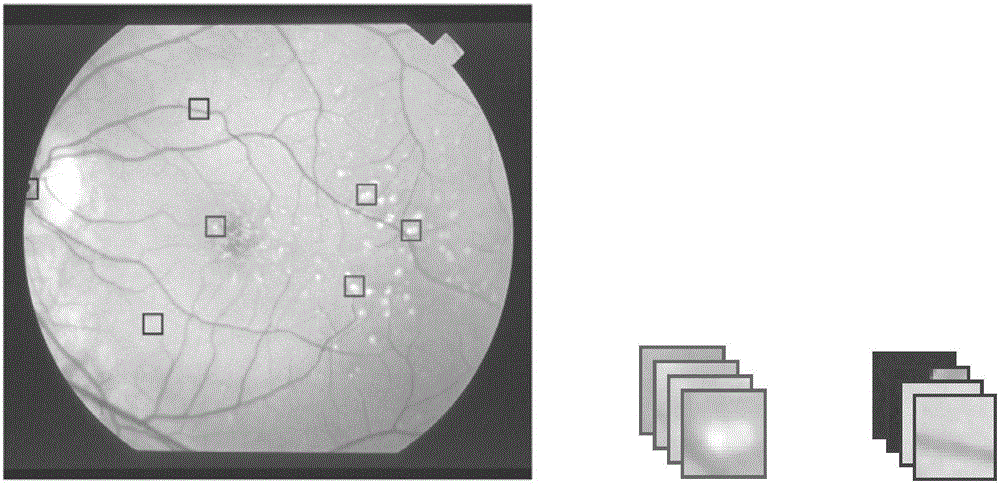
Classification model construction method and device used for macula degeneration region segmentation
ActiveCN107437252AStrong descriptive abilityAccurate diagnosisImage enhancementImage analysisManifold regularizationMachine learning
The invention discloses a classification model construction method used for macula degeneration region segmentation. The method includes the following steps: selecting multiple fundus images, conducting graying processing on the fundus images to obtain multiple gray scale images, and sampling foregrounds and backgrounds of the gray scale images to obtain samples; adopting a generalized low-rank approximate method to obtain a transformation matrix, conducting dimension reduction on the samples on the basis of the transformation matrix, and obtaining a low-rank approximate matrix of the samples; adding label information into the low-rank approximate matrix of the samples to perform a supervision function, and constructing manifold regularization items; establishing a target function through the generalized low-rank approximate method and the manifold regularization items, solving the target function through an iterative optimization method, and obtaining an optimal transformation matrix and an optimal low-rank approximate matrix of the samples; and constructing a classification model on the basis of the optimal low-rank approximate matrix and the label information. The classification model can extract low dimensional and also highly distinguishable feature descriptors, and can improve the segmentation precision.
Owner:SHANDONG NORMAL UNIV
Augmented sample-based manifold regularization correlation filtering target tracking method
InactiveCN107067410AImprove classification accuracy performanceImprove discrimination abilityImage enhancementImage analysisCorrelation filterBlock detection
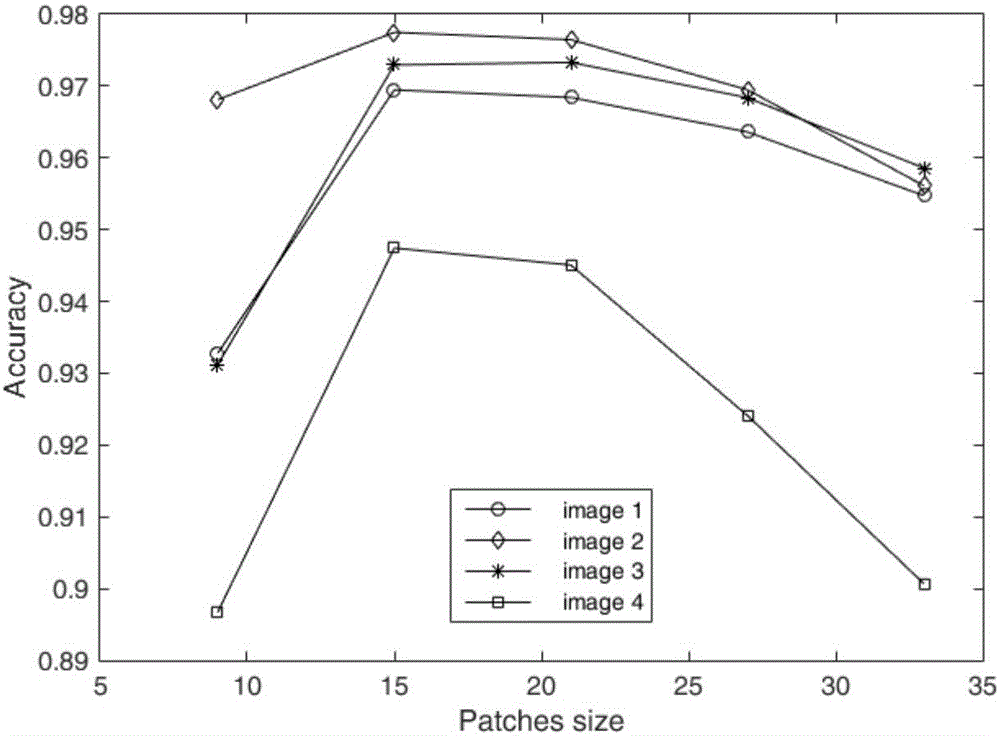
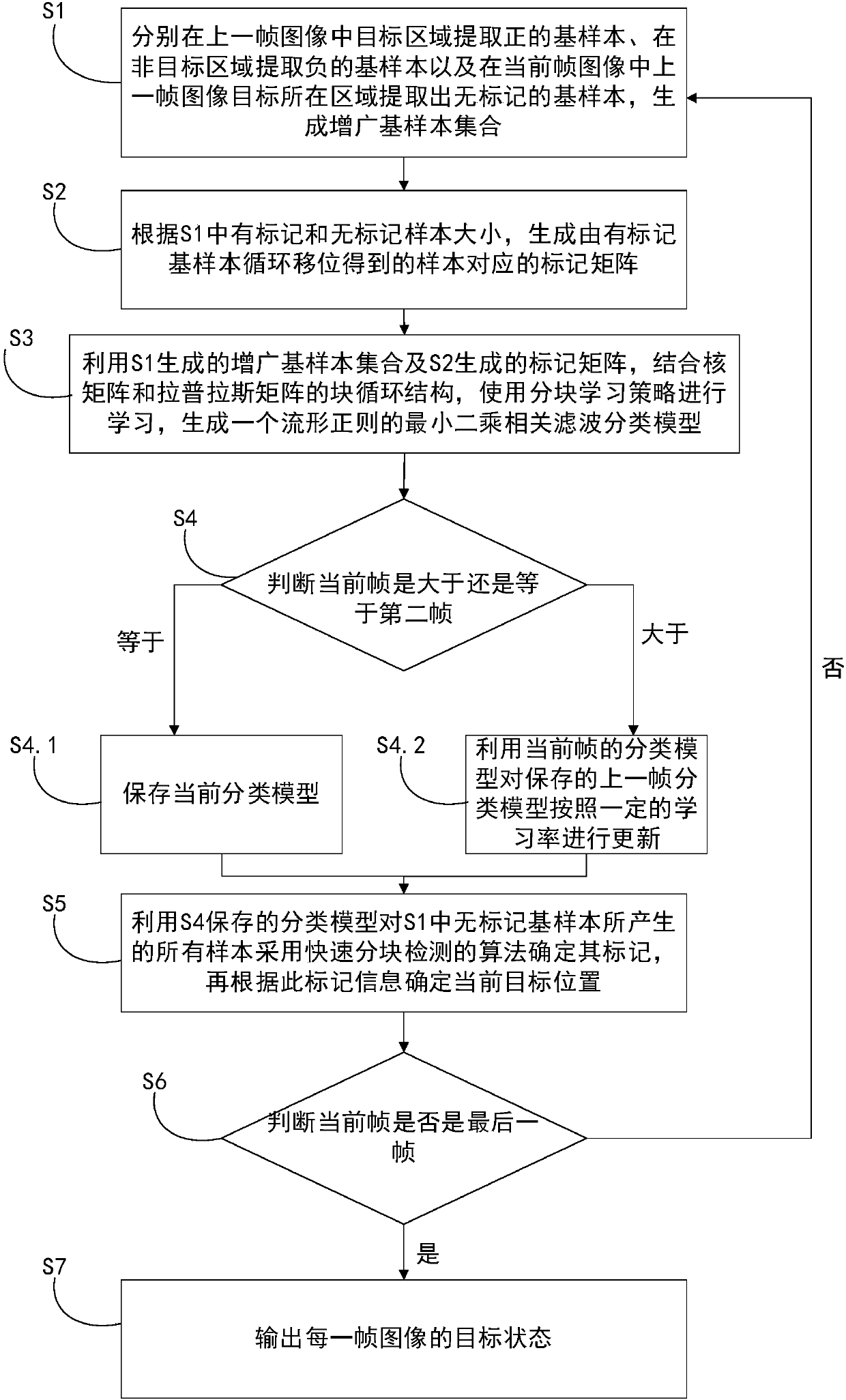
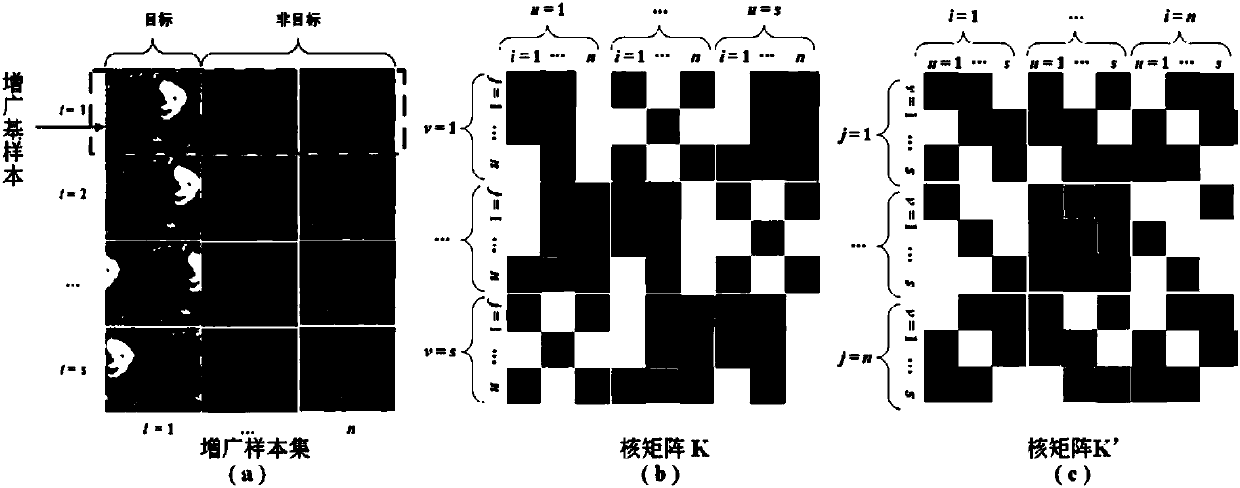
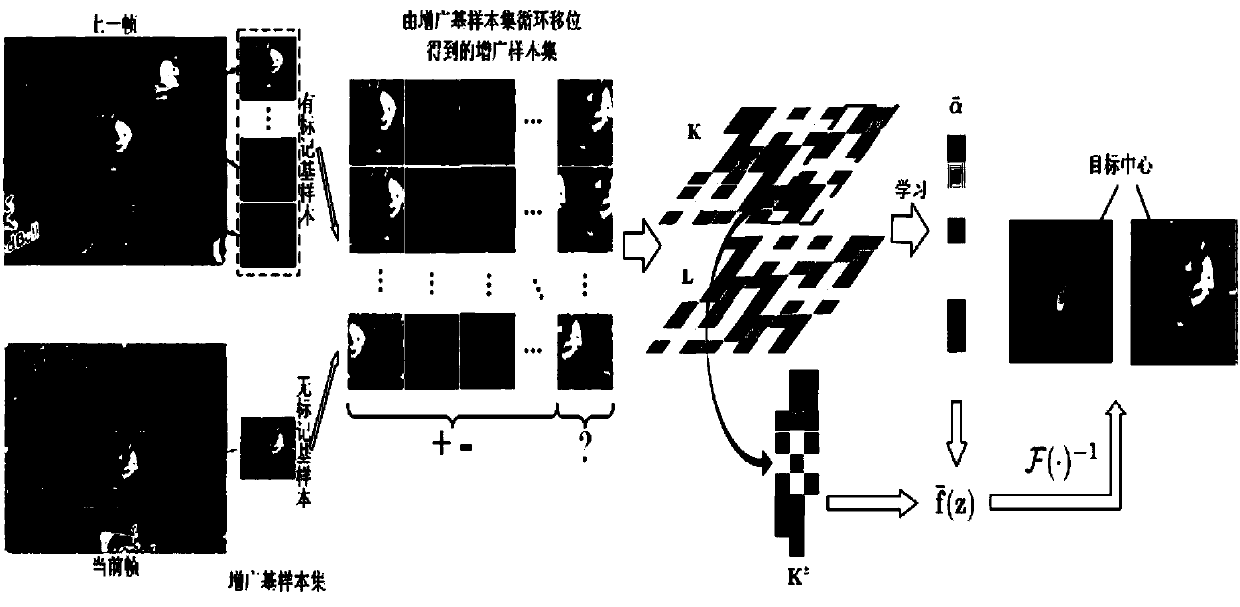
The invention discloses an augmented sample-based manifold regularization correlation filtering target tracking method. The method comprises the steps of S1, extracting a positive basic sample and a negative basic sample in a target region and a non target region of a previous frame respectively and extracting an unmarked basic sample to form an augmented basic sample set; S2, generating a mark matrix according to an output of S1; S3, by utilizing outputs of S1 and S2, in combination with block circulant structures of a kernel matrix and a Laplacian matrix, learning a least square correlation filtering classification model of manifold regularization; S4, judging whether a current frame is a second frame or not and performing corresponding operation; S5, determining marks of all samples, generated by performing operation on the unmarked basic sample in S1 by utilizing S4, by adopting a quick block detection algorithm, and determining a current target position; S6, judging whether the current frame is the last frame or not, deciding to jump to S1 or S7; and S7, outputting a target state of each frame. According to the method, the unmarked sample is predicted in a semi-supervised manner, so that the classification accuracy of the correlation filtering classification model is remarkably improved; and the method can be applied to a real-time system.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Semi-supervised width learning classification method based on manifold regularization and width network
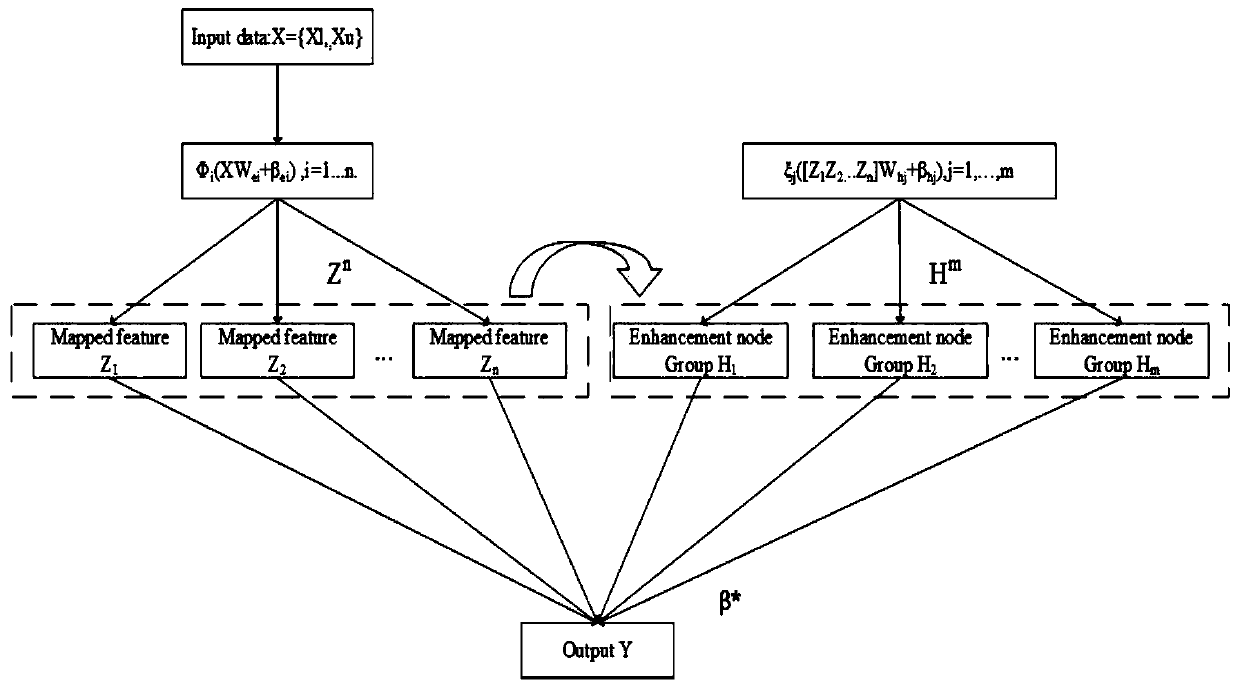
PendingCN110288088AAble to learnComputationally efficientCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural learning methodsNODALData set
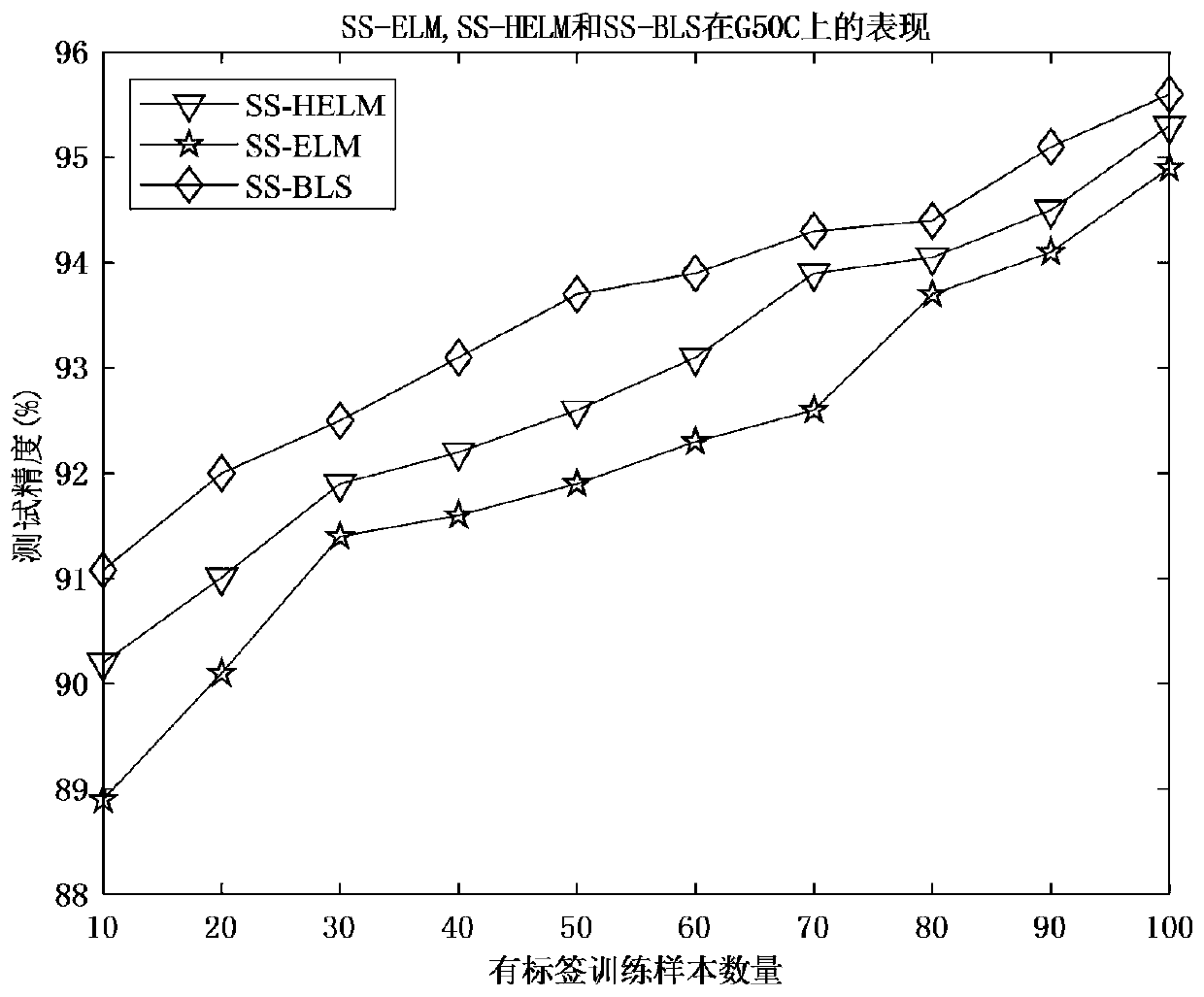
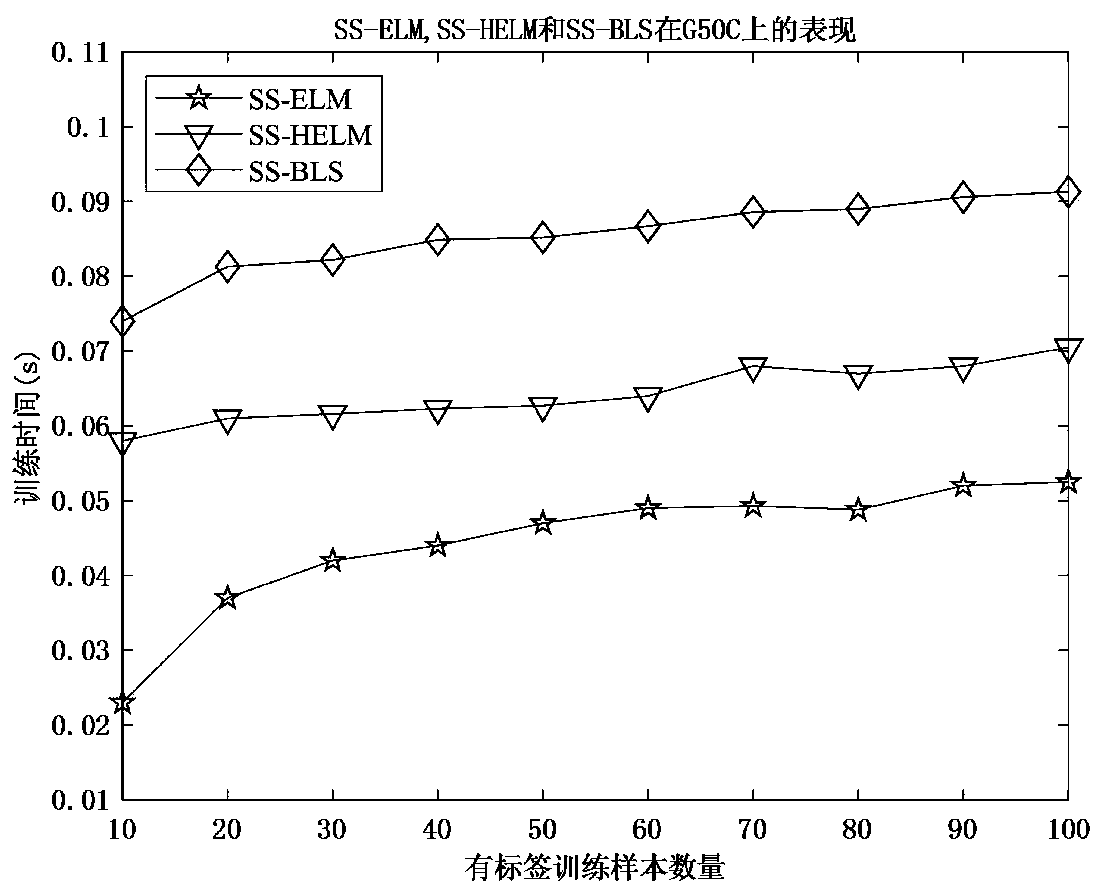
The invention relates to the technical field of width learning systems, in particular to a semi-supervised width learning classification method based on manifold regularization and a width network, which comprises the following steps of: S1, establishing feature nodes by using input data; s2, establishing an enhanced node by using the established feature node; s3, solving an output weight. According to the invention, the manifold regularization framework is introduced into the BLS; a semi-supervised broad learning system (SS-BLS for short) is proposed, according to the method, BLS is expanded through a manifold regularization framework; therefore, the applicability of the BLS is improved; the SS-BLS completely has the learning capability and the calculation efficiency of the BLS; meanwhile, the method can efficiently complete semi-supervised classification tasks under different complex data sets, the experimental results of various data sets show that SS-BLS has extremely high adaptability and relatively high stability, and in addition, the experimental results of the data sets also prove that the provided method has competitiveness compared with the most advanced semi-supervised method.
Owner:CIVIL AVIATION UNIV OF CHINA
Semi-supervision sequencing study method for image searching based on manifold regularization
ActiveCN102831161AEfficient use ofImprove sorting effectCharacter and pattern recognitionSpecial data processing applicationsSpurious correlationPattern recognition
The invention discloses a semi-supervision sequencing study method for image searching based on manifold regularization. The semi-supervision sequencing study method comprises the following steps of: extracting visual characteristics from a network searching result from a database or an initial text-based network to form an image sample set; dividing the image sample set into three grades including 2, 1, and 0 according to degrees for inquiring subject coherence, wherein 2 represents that the image sample set is very coherent with the inquiry, 1 represents that the image sample set is commonly coherent with the inquiry and 0 represents that the image sample set is incoherent with the inquiry; calculating spurious correlation grade information yi of an unmarked image sample; calculating a distance between two image samples; constructing a Laplace manifold regularization item according to the distance between the two image samples; constructing a target function through the Laplace manifold regularization item; and solving a sequencing score for obtaining each image sample by the target function and feeding a sequenced result back to a user. According to the semi-supervision sequencing study method disclosed by the invention, the searching and sequencing performances are improved, marking information is sufficiently utilized and the searching precision is improved; and less supervision information is effectively utilized to improve the sequencing performance.
Owner:宿州高航知识产权服务有限公司
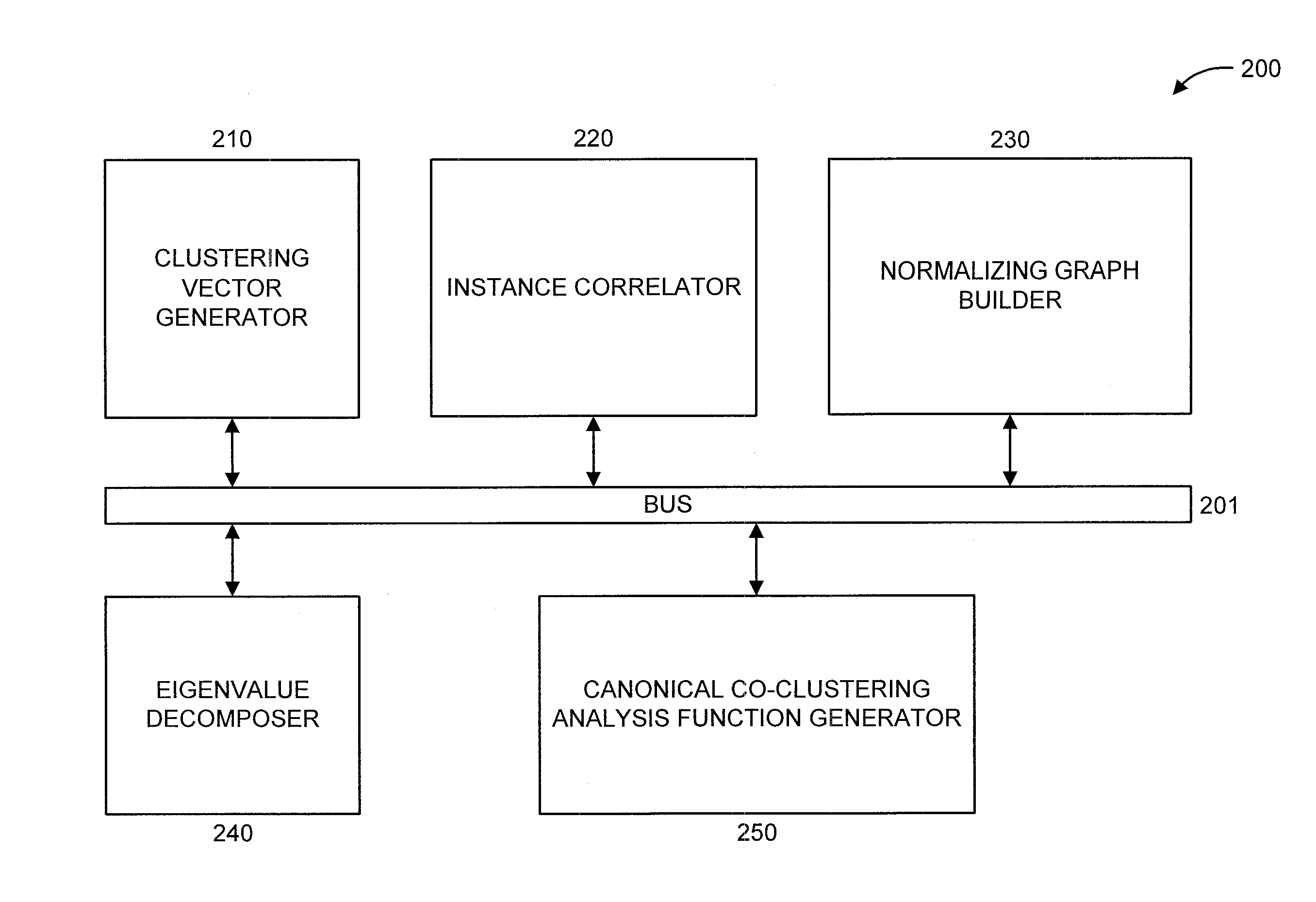
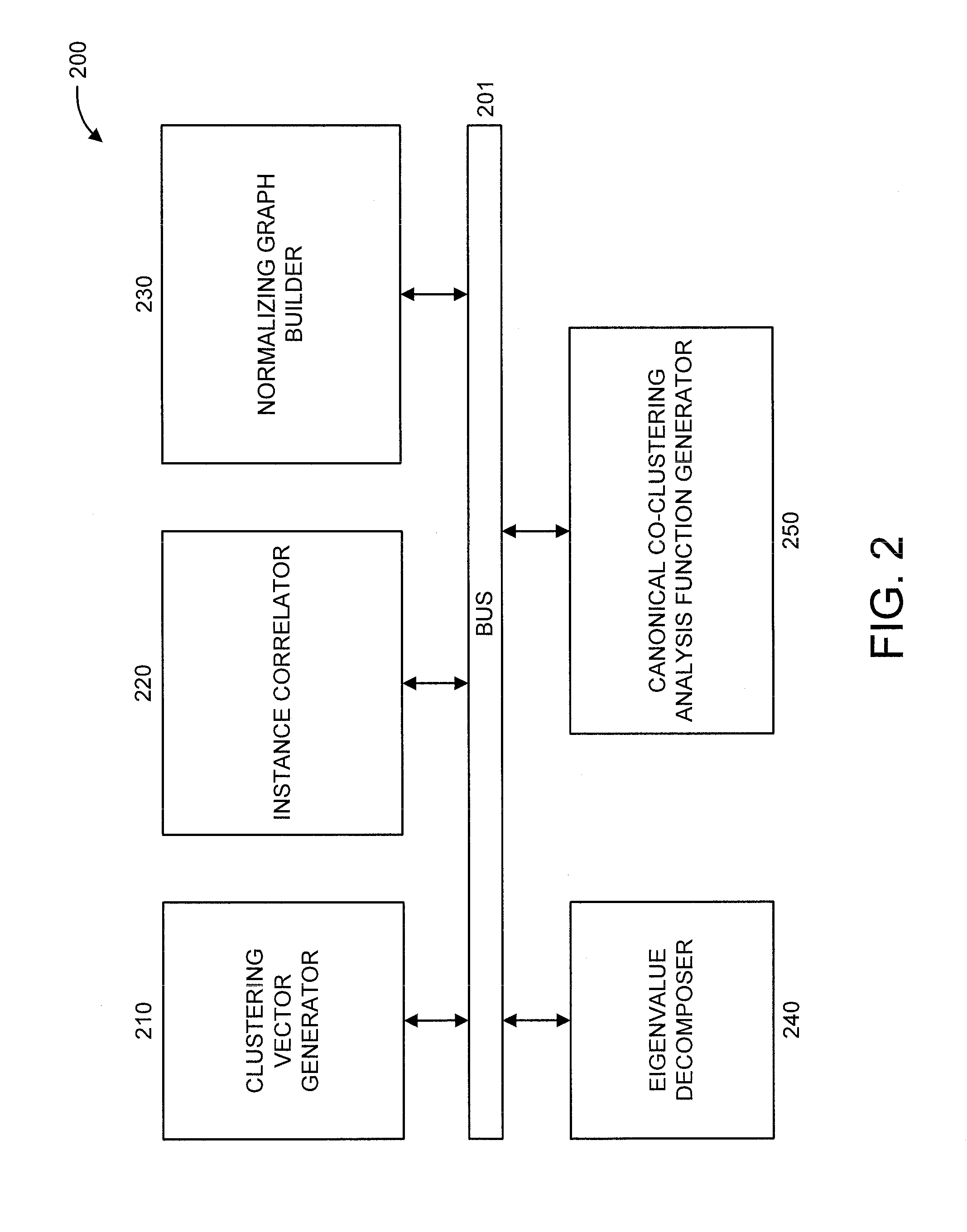
Canonical co-clustering analysis
InactiveUS20150347927A1Digital computer detailsRelational databasesMachine learningManifold regularization
A method and system are provided. The method includes determining from a data matrix having rows and columns, a clustering vector of the rows and a clustering vector of the columns. Each row in the clustering vector of the rows is a row instance and each row in the clustering vector of the columns is a column instance. The method further includes performing correlation of the row and column instances. The method also includes building a normalizing graph using a graph-based manifold regularization that enforces a smooth target function which, in turn, assigns a value on each node of the normalizing graph to obtain a Lapacian matrix. The method additionally includes performing Eigenvalue decomposition on the Lapacian matrix to obtain Eigenvectors. The method further includes providing a canonical co-clustering analysis function by maximizing a coupling between clustering vectors while concurrently enforcing regularization on each clustering vector using the Eigenvectors.
Owner:NEC LAB AMERICA
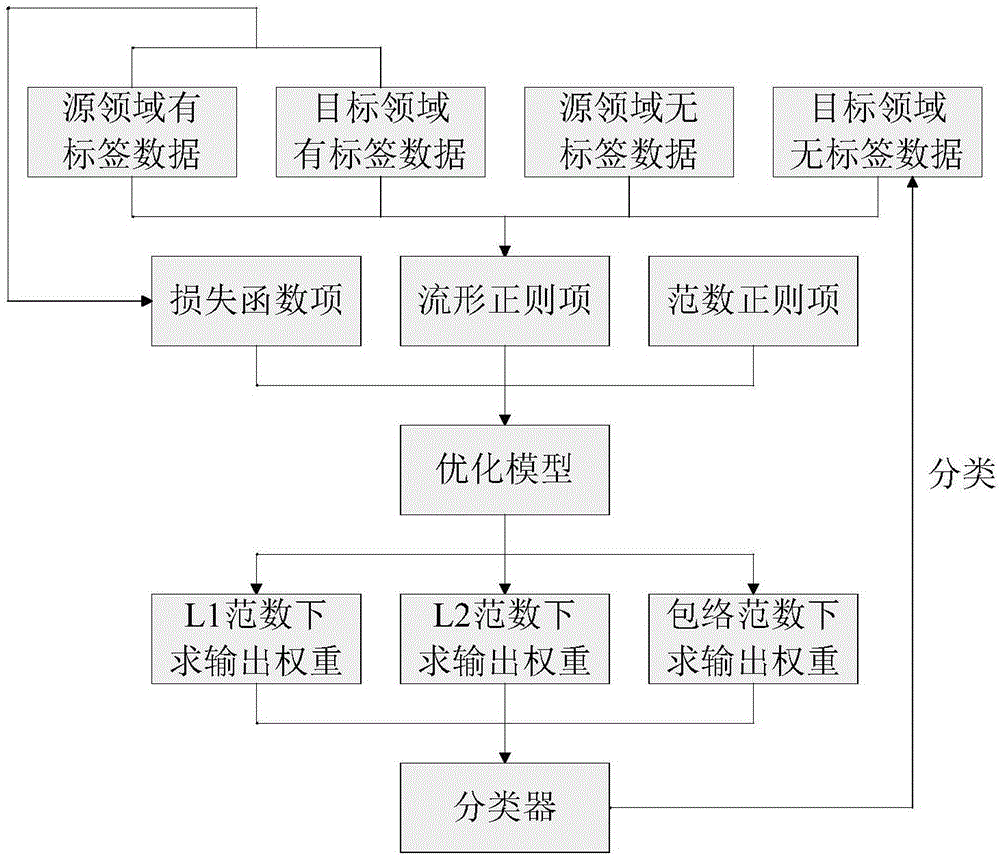
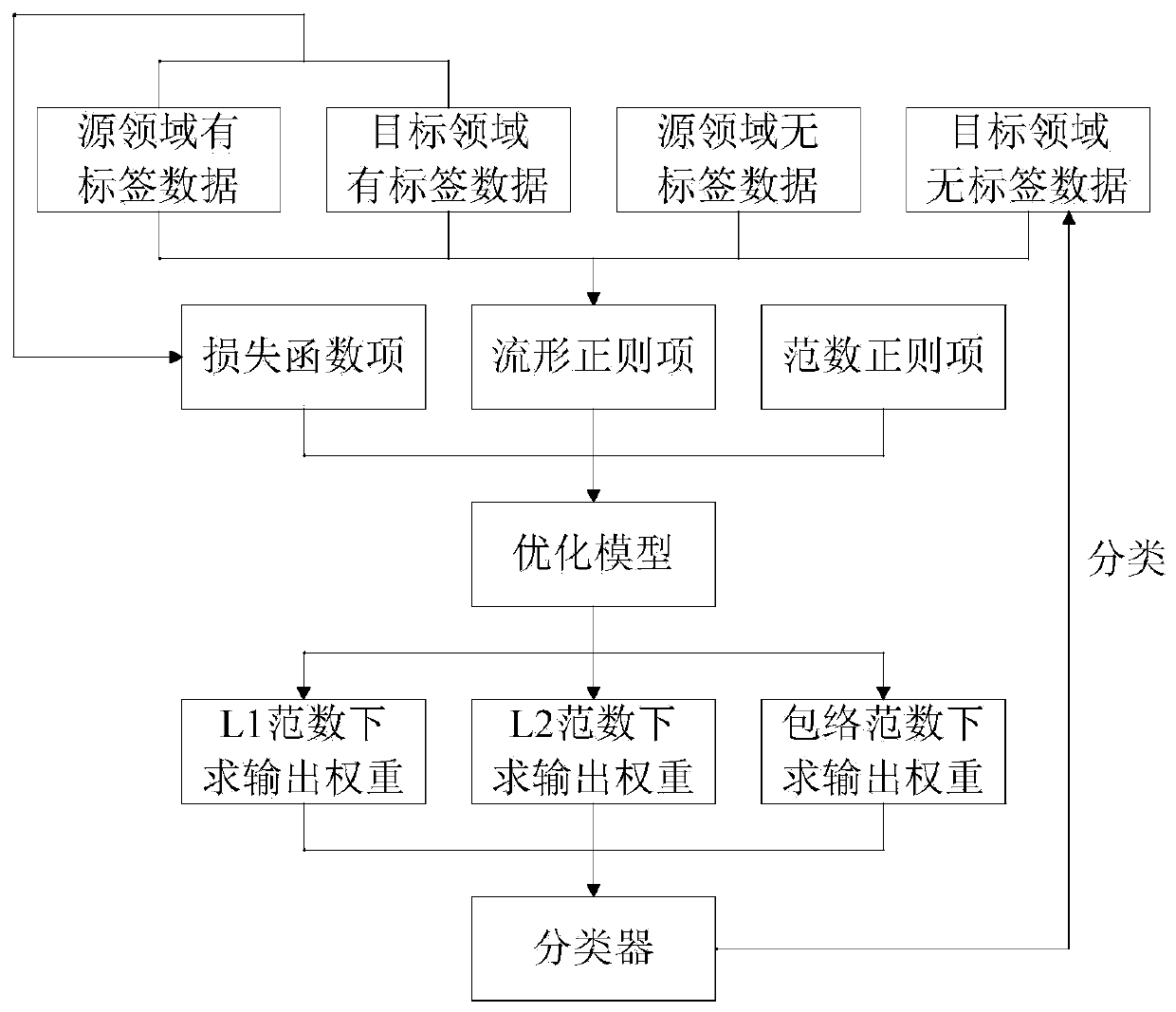
Domain transfer extreme learning machine method based on manifold regularization and norm regularization
ActiveCN106803124AAchieve overfittingPrevent overfittingMachine learningA domainManifold regularization
The invention discloses a domain transfer extreme learning machine method based manifold regularization and norm regularization. On the basis of a traditional extreme learning machine, the thought of semi-supervised learning and transfer learning is introduced, and a novel extreme learning machine model is built and consists of three parts: a manifold regularization term capable of excavating geometric distribution shapes of data samples with tags and without tags to realize semi-supervised learning; a loss function term considering error minimization of source domain data and target domain data to realize transfer learning; and norm regularizers constraining weight space. The domain transfer extreme learning machine method provide by the invention is combined with the source domain to process the problem of prediction of the target domain, thereby increasing the generalization capability and range of application of the extreme learning machine. Introduction of the manifold regularization term also enables the method proposed by the invention to still maintain a relatively good learning effect when data with tags are little, the restriction that a traditional machine learning method requires a large amount of data with tags is overcome, and the accuracy and robustness of prediction are also improved.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
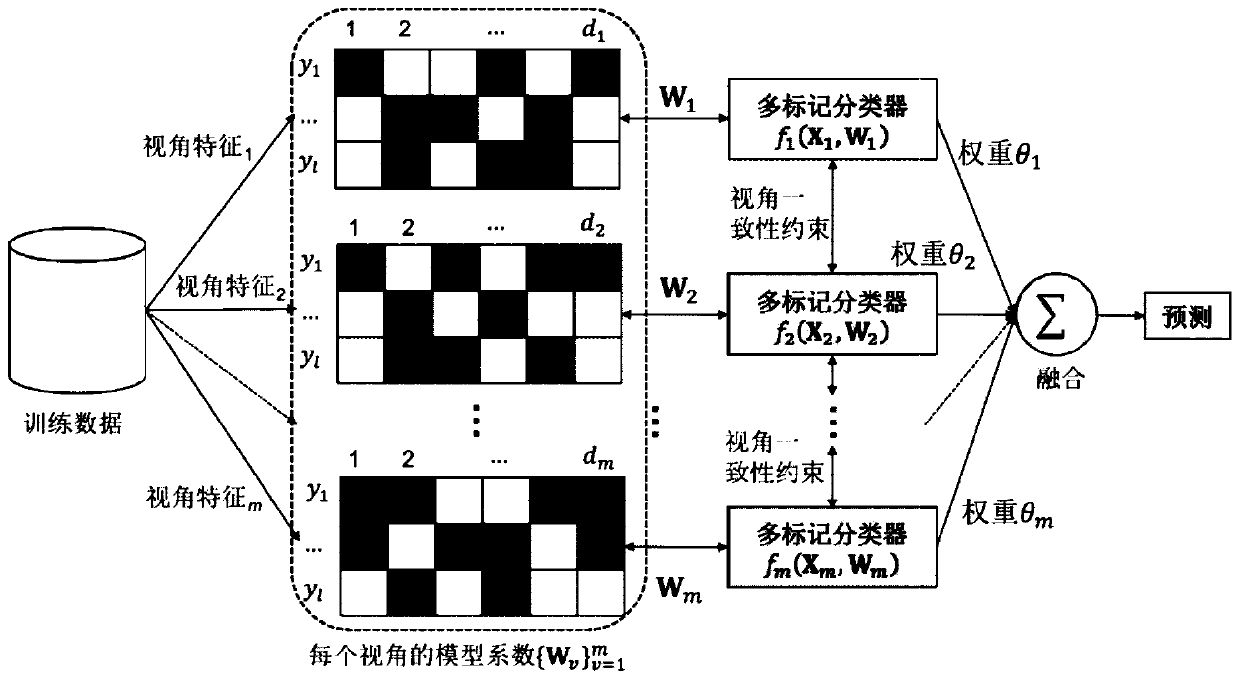
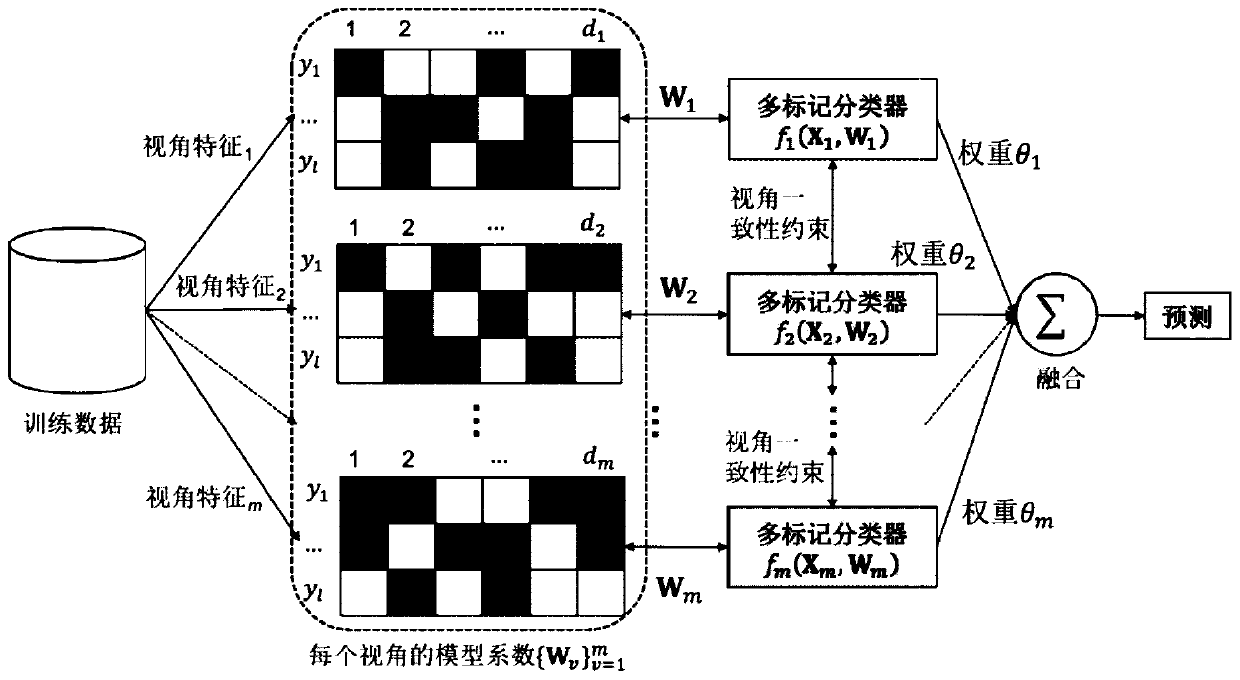
Multi-view multi-mark classification method based on view category characteristic learning
PendingCN110009017ALittle impact on performanceReduce complexityCharacter and pattern recognitionTest sampleClassification methods
The invention relates to a multi-mark learning technology in the field of machine learning, and relates to a multi-view multi-mark classification method based on view category characteristic learning.The method comprises the following steps: S1, acquiring training data, and establishing a class mark matrix; S2, constructing a linear model of mapping the visual angle characteristic data after thecategory marking to a category marking matrix; S3, on the basis of the linear model, establishing contribution degree models of all visual angle characteristics; S4, adopting a regular item to constrain the contribution degree model of the visual angle characteristics, and enabling each visual angle characteristic data to have consistency on a prediction result; S5, adopting manifold regularization to constrain the similarity of the model coefficients corresponding to the related category marks; S6, performing mark prediction, giving a test sample t, and substituting the test sample t into thesteps S1 to S2; and S5, obtaining a fusion prediction value. According to the technical scheme provided by the invention, multi-source information is effectively utilized to learn the discriminationperformance of different features on the category mark in each view angle, and a multi-mark learning task is better carried out.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
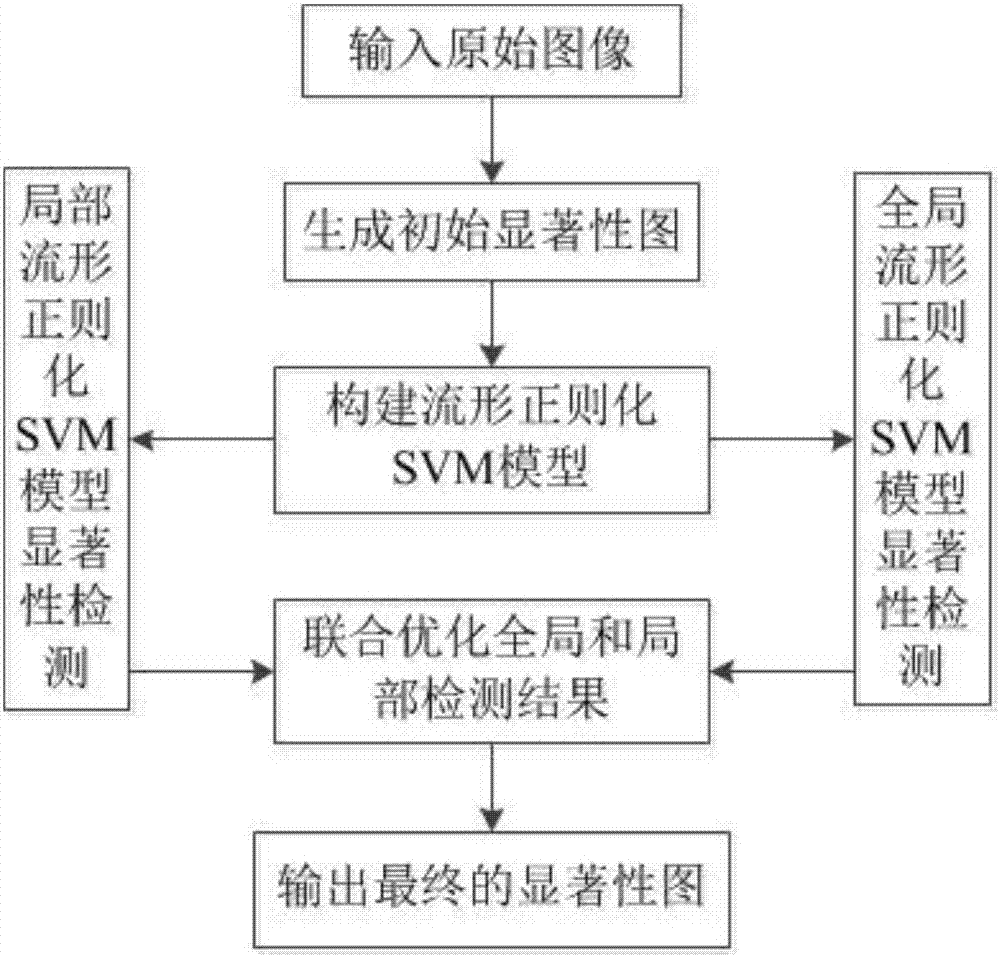
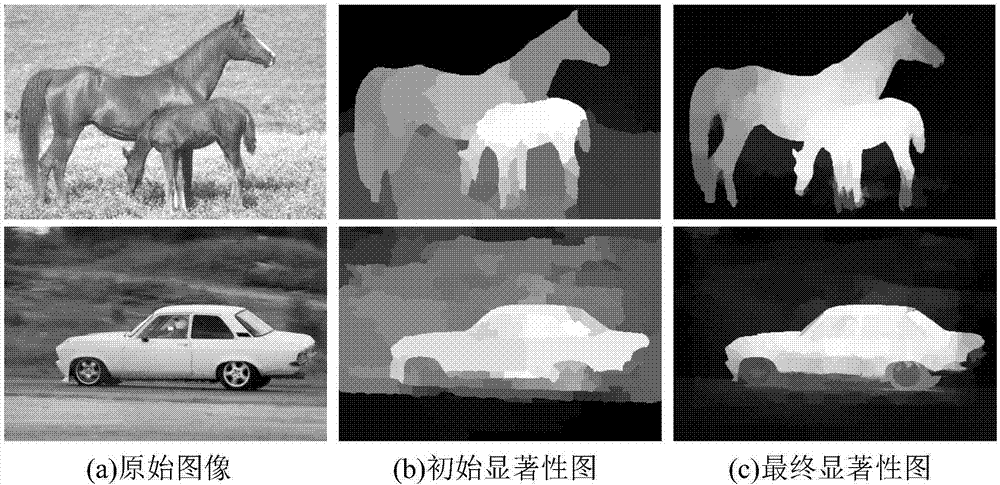
Manifold regularization support vector machine-based image significance detection method
ActiveCN107146219AReduce the cost of trainingIntegrity guaranteedImage enhancementImage analysisSupport vector machineTruth value
The invention provides a manifold regulation support vector machine-based image significance detection method, and belongs to the technical field of computer vision. The invention provides a semi-supervised manifold regulation support vector machine-based image significance detection method, artificially marked truth values are not needed, only few training samples are needed and significant target detection is respectively carried out from the global and local angles of images. According to the method, few pseudo-marked samples are trained, so that the artificial workload and model training cost are decreased; manifold regularization matrixes are respectively constructed from the global and local angles, so that the highlighting and integrity of the detected significant targets are ensured; an optimization method is combined to furthermore optimize the significance detection results predicted by vector support machine models, so that the detection is corrector and the target areas are more highlighted and smooth; and in special images, the method also can preferably detect the images with oversized or undersized significant targets and the images with a plurality of targets.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
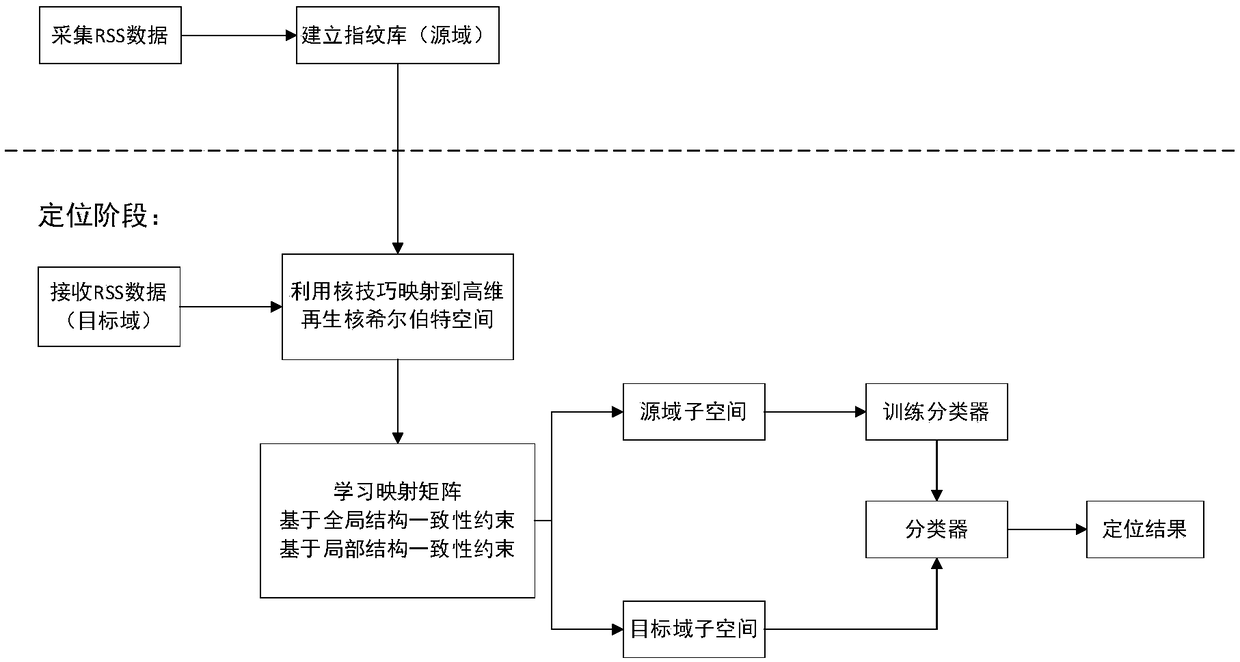
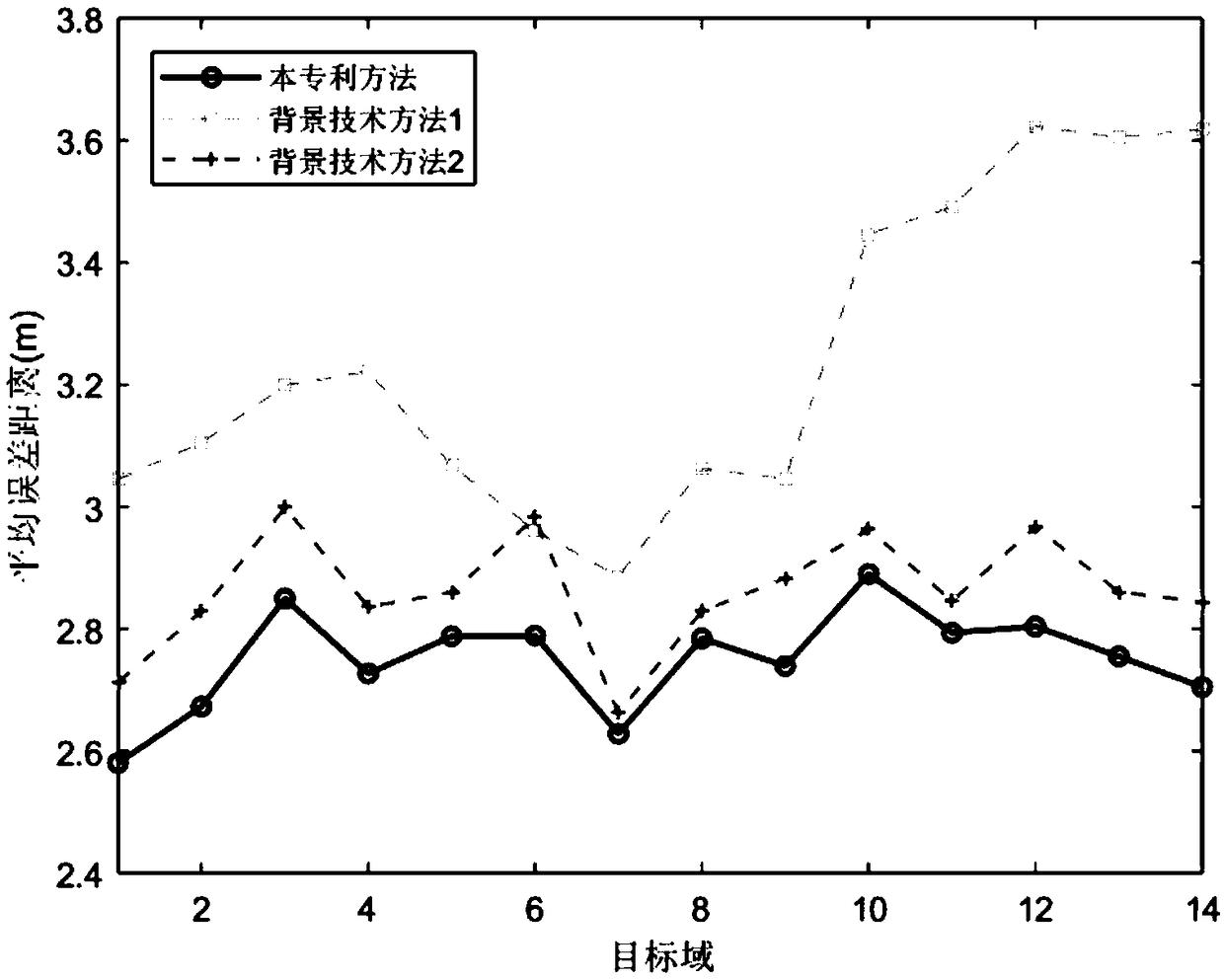
Indoor positioning method based on global and local joint constraint transfer learning
ActiveCN109348410AHigh positioning accuracyAddressing Inadequate MigrationParticular environment based servicesLocation information based serviceAlgorithmStudy methods
The invention belongs to the technical field of indoor positioning, particularly an indoor positioning method based on global and local joint constraint transfer learning. According to the method provided by the invention, through minimization of inter-domain marginal and conditional probability distribution discrepancy and maximization of a sample variance in a potential subspace, consistency ofa global structure is constrained. Through minimization of an intraclass variance and maximization of an interclass variance, dependency of each class and corresponding samples is kept. Through manifold regularization, a local neighborhood relationship is kept. Further, the consistency of local structures is constrained. The problem that an existing transfer learning method is insufficient in knowledge transfer can be solved. According to knowledge obtained from a source domain through transfer, positioning precision of a target domain can be effectively improved. The problem of RSS (ReceivedSignal Strength) fluctuation resulting from environment change is solved. The indoor positioning method based on the global and local joint constraint transfer learning provided by the invention is anew high precision positioning method applicable to a complex indoor environment.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Image segmentation method based on local region homogeneity manifold constrained MRF model
ActiveCN107895373AAvoid interferenceAvoid oversmoothing penaltiesImage analysisPattern recognitionImage segmentation
The invention discloses an image segmentation method based on a local region homogeneity manifold constrained MRF model. On the basis of a PairwiseMRF model, an image segmentation model based on a local region MRF model is constructed on an extended neighborhood of MRF nodes, and the prior distribution of a local region effectively avoids the interference of noise or texture mutations; and meanwhile, on the basis of a manifold learning theory, a manifold regularization term under a probabilistic framework is established, a local region probability distribution is used to effectively describe the local spatial geometric structure prior with complex natural images, and the local spatial geometric structure described by this manifold learning is introduced into the local region MRF segmentation model. Experiments have proved that compared with the prior art, the method of the invention not only avoids the local region prior oversmoothing penalty, but also effectively maintains the local geometric structure information of the image segmentation.
Owner:XI'AN UNIVERSITY OF ARCHITECTURE AND TECHNOLOGY
CS-MRI image reconstruction method based on sparse manifold joint constraint
ActiveCN111047661AImprove refactoring qualityIncrease contrastReconstruction from projectionCharacter and pattern recognitionMri imageGraph model
The invention discloses a CS-MRI image reconstruction method based on sparse manifold joint constraint, and belongs to the technical field of digital image processing. According to the method, the MRIimage reconstruction is realized by simultaneously utilizing norm constraint image sparsity and manifold regular term constraint image inter-block correlation. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, pre-reconstructing undersampled data of an MRI image by adopting a traditional method; finding a similar block set of the target block through a K-nearest neighbor method to obtain a structure group; establishing a graph model for each structure group, calculating an adjacent weight coefficient to construct a corresponding manifold regularization term, converting the manifold regularization term from a spatial domain to a coefficient domain, establishing a sparse manifold joint constraint reconstruction model, and finally solving the model by adopting an alternating direction multiplier method. According to the method, the manifold regularization term constraints are adopted to accurately describe the correlation of different degrees among the image blocks in different structure groups, a large amount of detail information is reserved in the reconstructed image, high reconstruction performance is obtained, and therefore the method can be used for medical image recovery.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
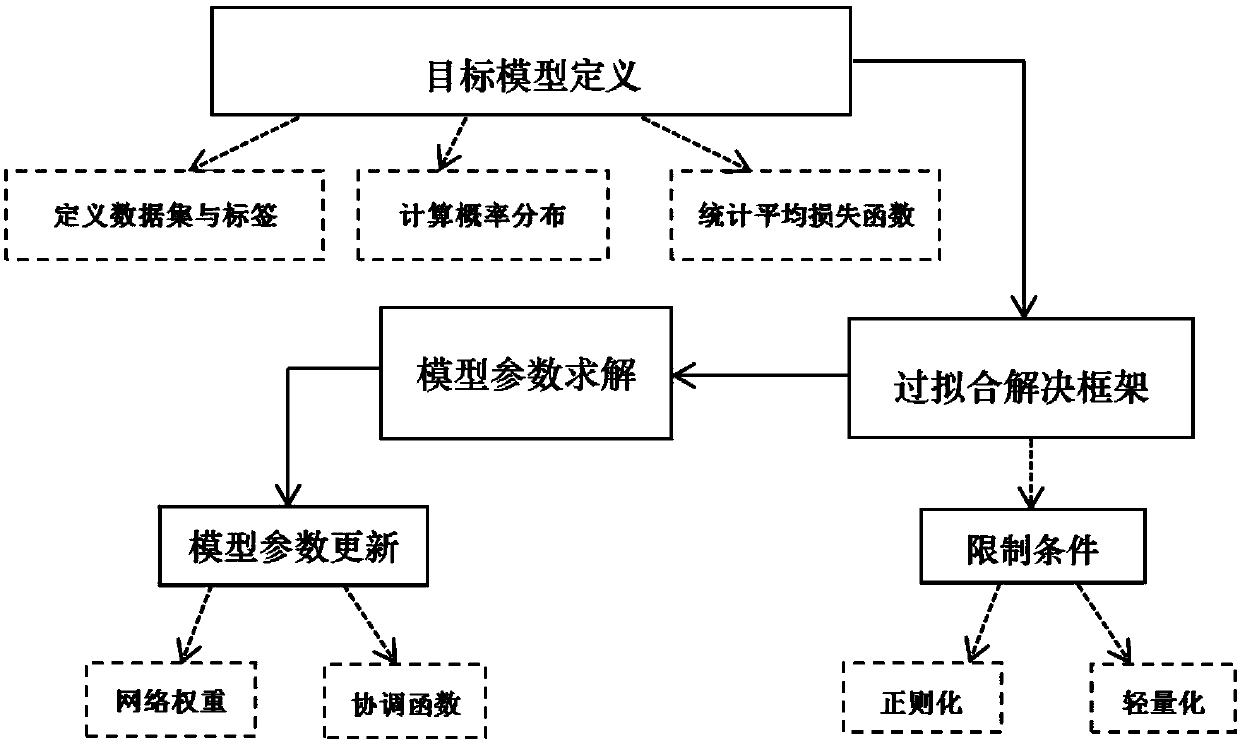
Over-fitting solution based on low-dimensional manifold regularized neural network
The invention discloses an over-fitting solution based on a low-dimensional manifold regularized neural network. Target model definition, over-fitting solution framework, model parametric solution andmodel parameter update are involved in the method. The method comprises the steps that restrictive definition is conducted on a target model, wherein the definition comprises a data set, the label ofthe data set and an average loss function; a framework for solving an over-fitting phenomenon is proposed, network parameters are solved by using a method based on regularization and weight lightening under restrictive conditions, and study capability and robustness are enhanced by proposing a bidirectional noise variable; the training optimum solution is finally obtained by using methods based on counterpropagation and point integration respectively to update a network weight and a coordination function according to the obtained network parameter set. By means of the method, solutions aimingat non solution, locally optimal solution and over-fitting solution of training results of a deep neural network can be provided, and demands on calculation resources are reduced by using an appropriate method to improve the efficiency of actual application calculations.
Owner:SHENZHEN WEITESHI TECH
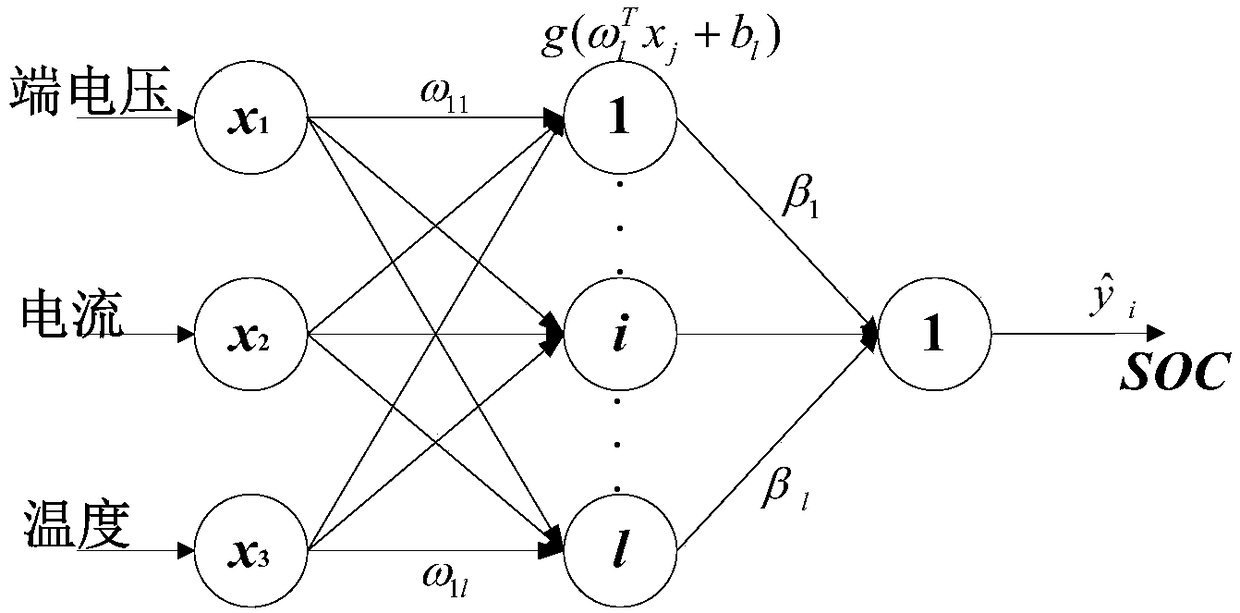
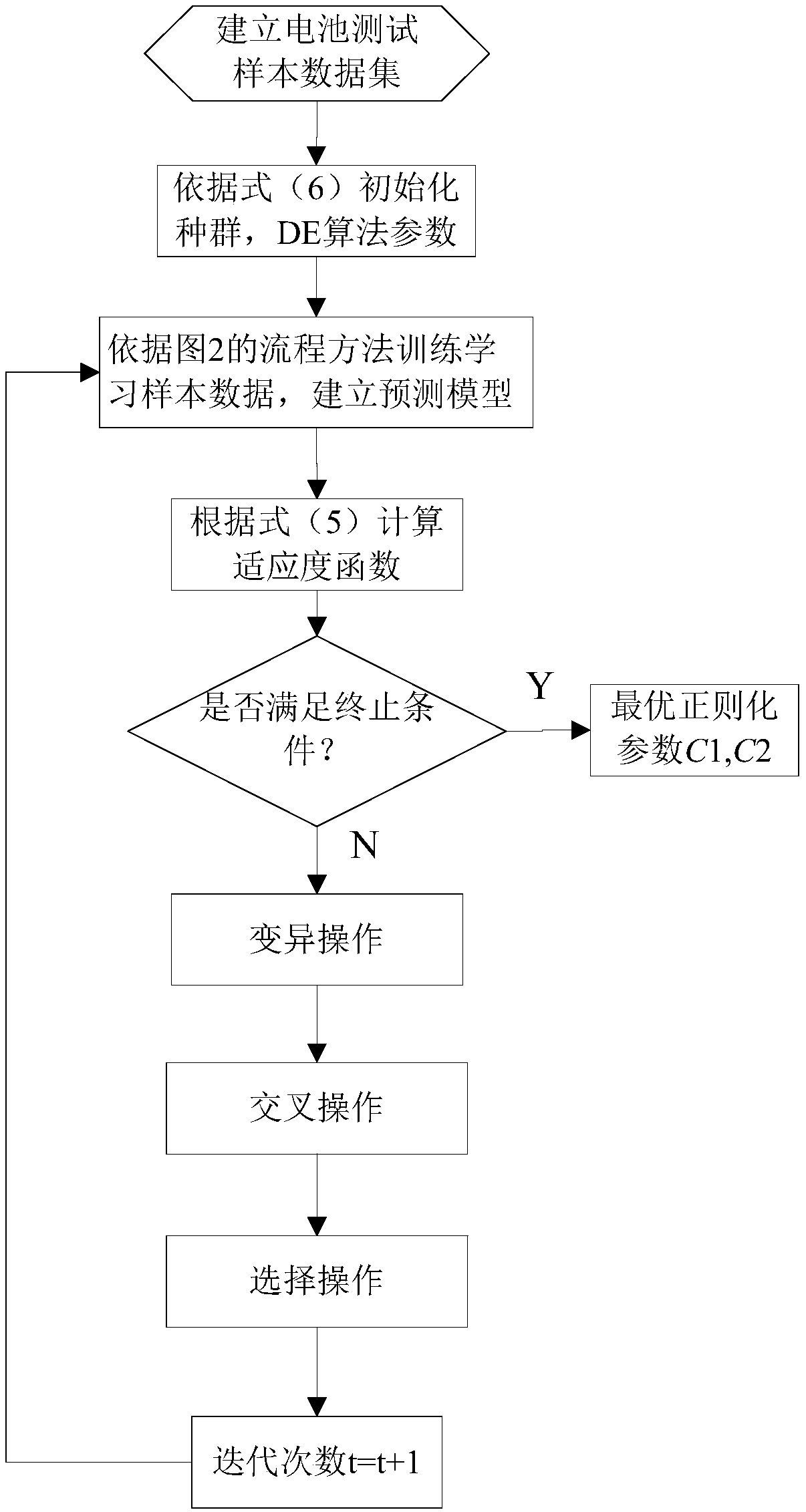
Method for predicting SOC of power battery by using extreme learning machine under manifold regularization framework
InactiveCN109239603AImprove generalization abilityImprove predictive performanceElectrical testingLearning machinePower battery
The invention discloses a method for predicting an SOC of a power battery by using an extreme learning machine under a manifold regularization framework, and belongs to the technical field of batterymanagement systems. The method comprises the following steps: collecting laboratory sample data; establishing a model to obtain sample data normalization; using a z-score normalization method, and selecting a Gaussian kernel function to calculate the similarity between each point and xi; reflecting the manifold of a sample space, and setting a relevant parameter and a function form according toan extreme learning machine prediction SOC model; and under the manifold regularization framework, creating an extreme learning machine SOC prediction model, and using a differential evolution methodto optimize regularization parameters. According to the method for predicting the SOC of the power battery by using the extreme learning machine under the manifold regularization framework provided bythe invention, a manifold regularization theory is introduced to optimize the extreme learning machine, thus the generalization performance of the extreme learning machine is improved; a differentialevolution optimization algorithm is introduced to improve the prediction performance of the extreme learning machine; and a power battery SOC prediction model established by using the extreme learning machine can improve the prediction accuracy, the prediction efficiency and the prediction stability.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV OF TECH
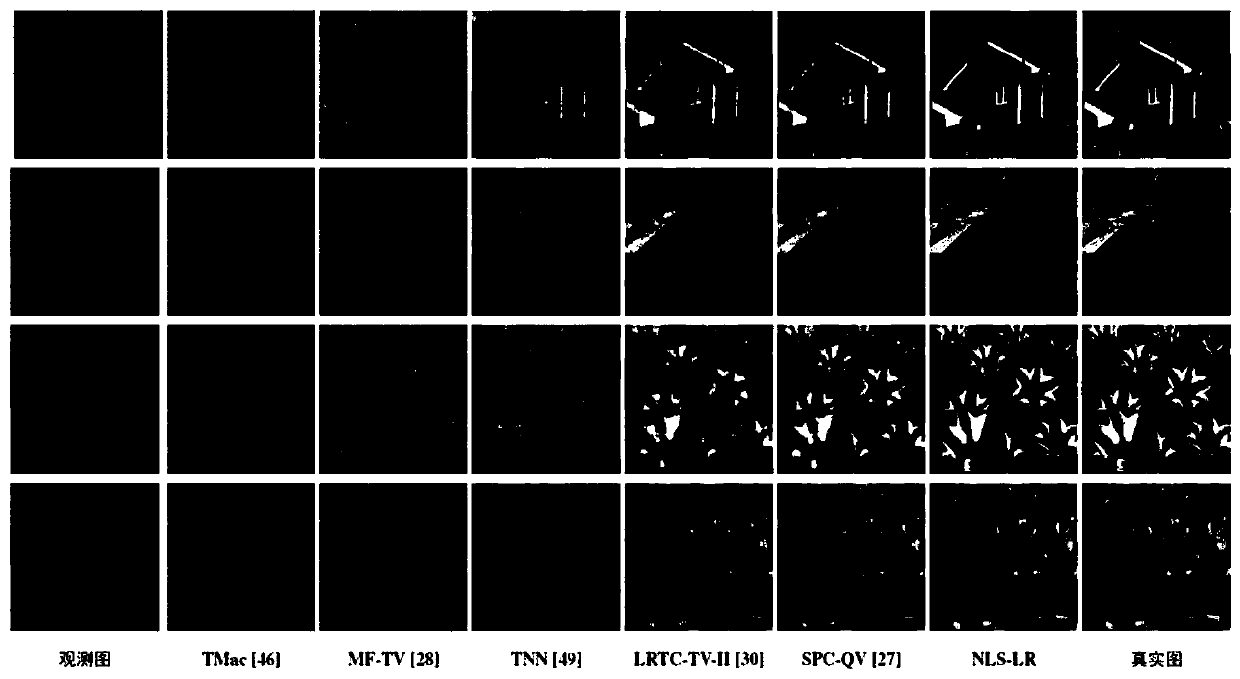
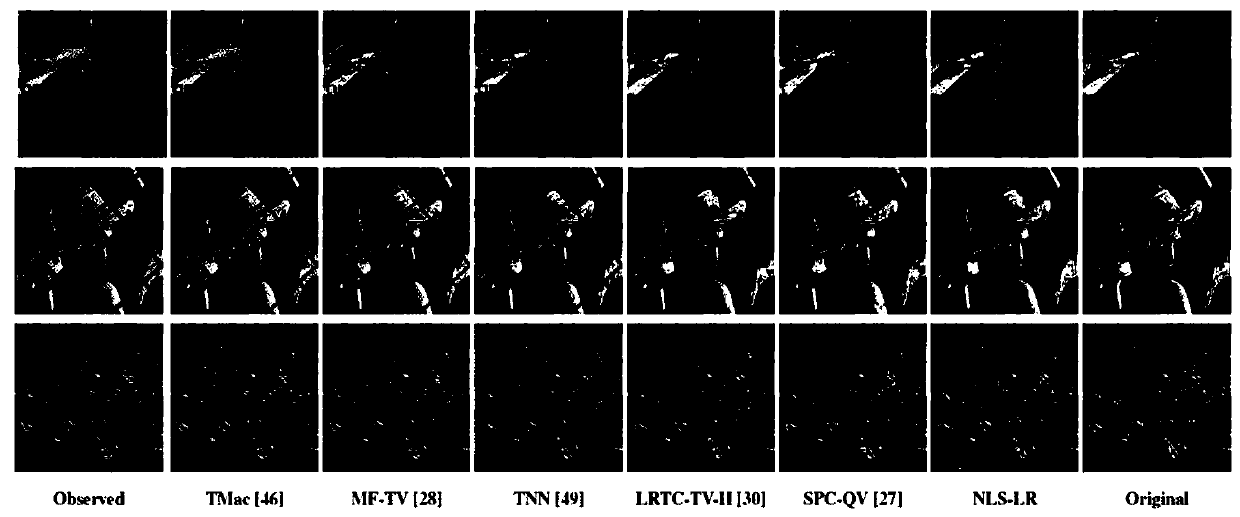
Tensor repairing method based on non-local self-similarity and low-rank regularization of tensors
The invention discloses a tensor repairing method based on non-local self-similarity and low-rank regularization of tensors. The method comprises the following steps: S1, establishing a tensor model;S2, optimizing a target function according to the adjacent operator function, and solving the tensor model; and S3, carrying out iterative solution by utilizing a rank growth strategy. A plug-and-playframework is utilized to design a non-explicit non-local self-similarity rule to promote detail recovery of the tensor, a model solving algorithm based on a block continuous upper bound descent method is designed. Numerical experiment shows that the proposed model NLS-LR has obvious advantages in the aspects of structure, contour, details and the like of the recovery target tensor, and experimental results show that the visual effect and evaluation indexes of the model all exceed those of a plurality of existing mainstream methods.
Owner:李晓彤
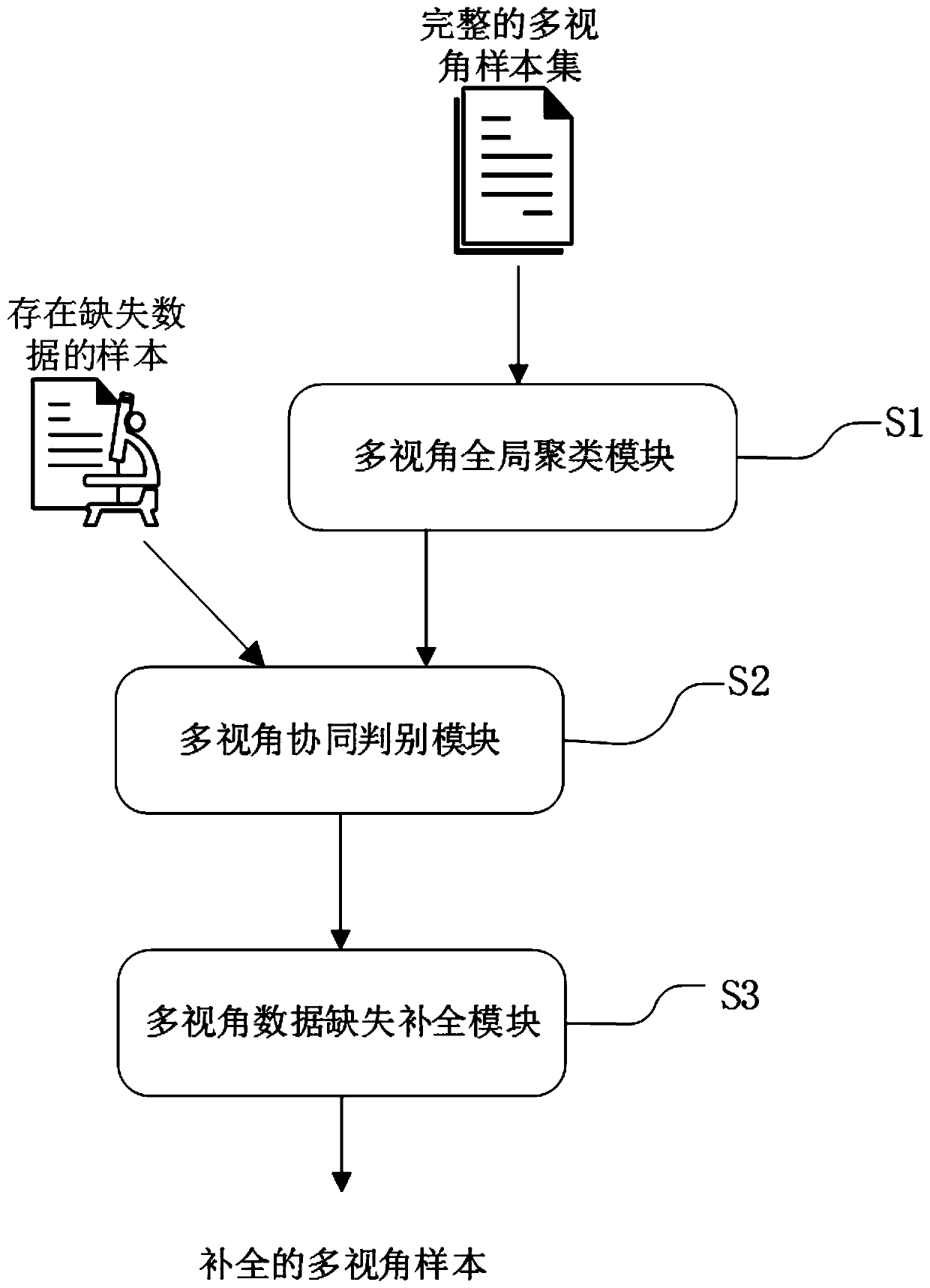
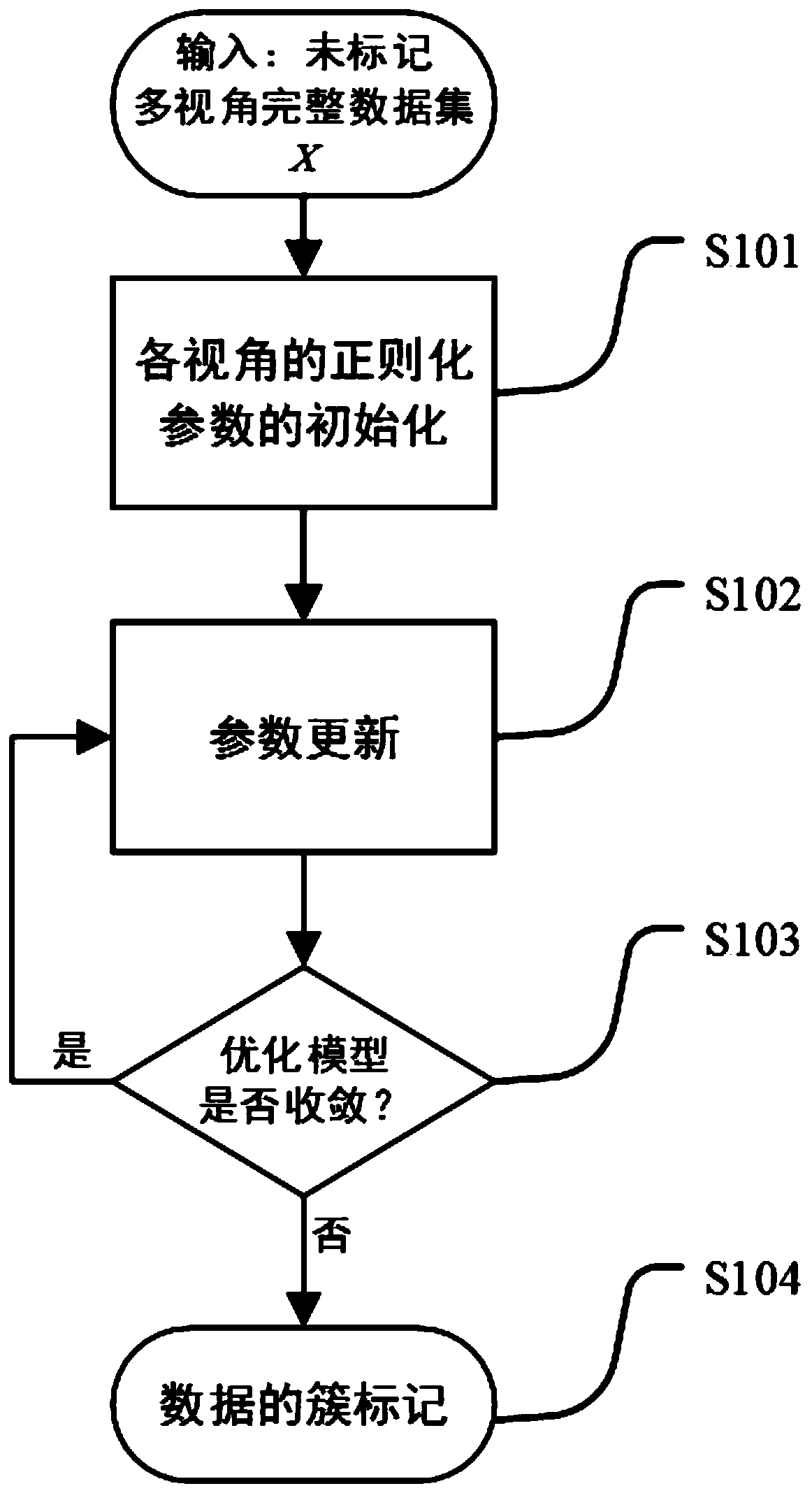
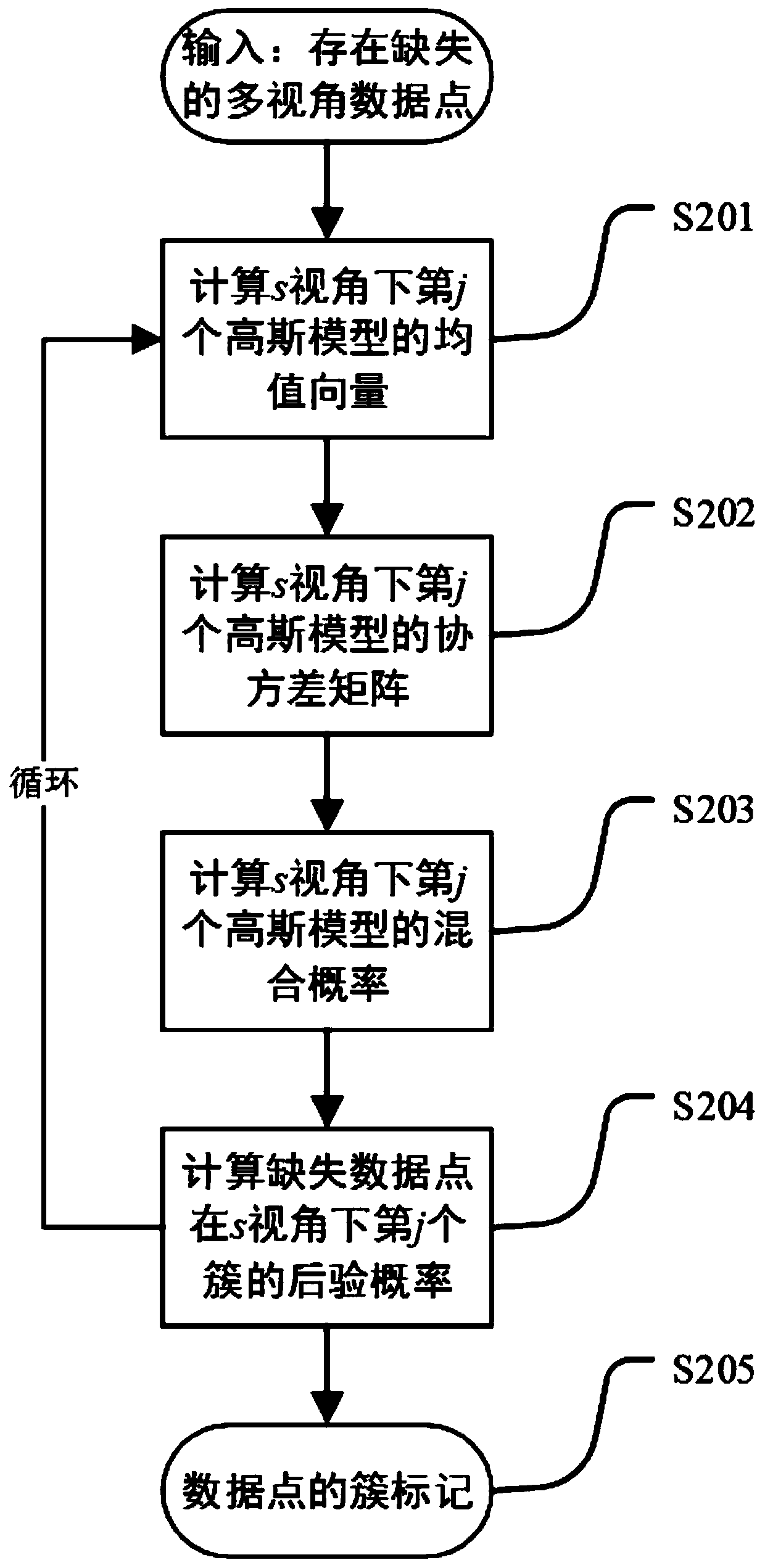
Multi-view data missing completion method for multi-manifold regularization non-negative matrix factorization
ActiveCN111368254ARealize processingImprove the ability to understand and discoverCharacter and pattern recognitionMachine learningMissing dataAlgorithm
The invention discloses a multi-view data missing complementing method for multi-manifold regularization non-negative matrix factorization, which comprises the following steps of: obtaining manifold and global clustering in which unmarked multi-view data tends to be consistent by utilizing a multi-manifold regularization non-negative matrix factorization algorithm through consistency assumption among multiple views; and constructing a multi-view collaborative discrimination model by adopting a view collaborative improved Gaussian mixture method. Pre-calibration of a cluster to which a sample belongs is realized by calculating the cluster relevancy level of the sample with missing data under a non-missing view angle; and establishing a missing data prediction model under a specific view angle by utilizing the consistency of multiple view angles in a low-dimensional space and adopting a multiple linear regression analysis method, thereby realizing accurate data completion under a multi-attribute missing condition. According to the method, large-scale labeled samples are not needed for training, the pre-defined category relation and related characteristics are avoided, and the understanding and discovering capacity of an existing multi-view mining technology for unlabeled multi-source data is improved.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
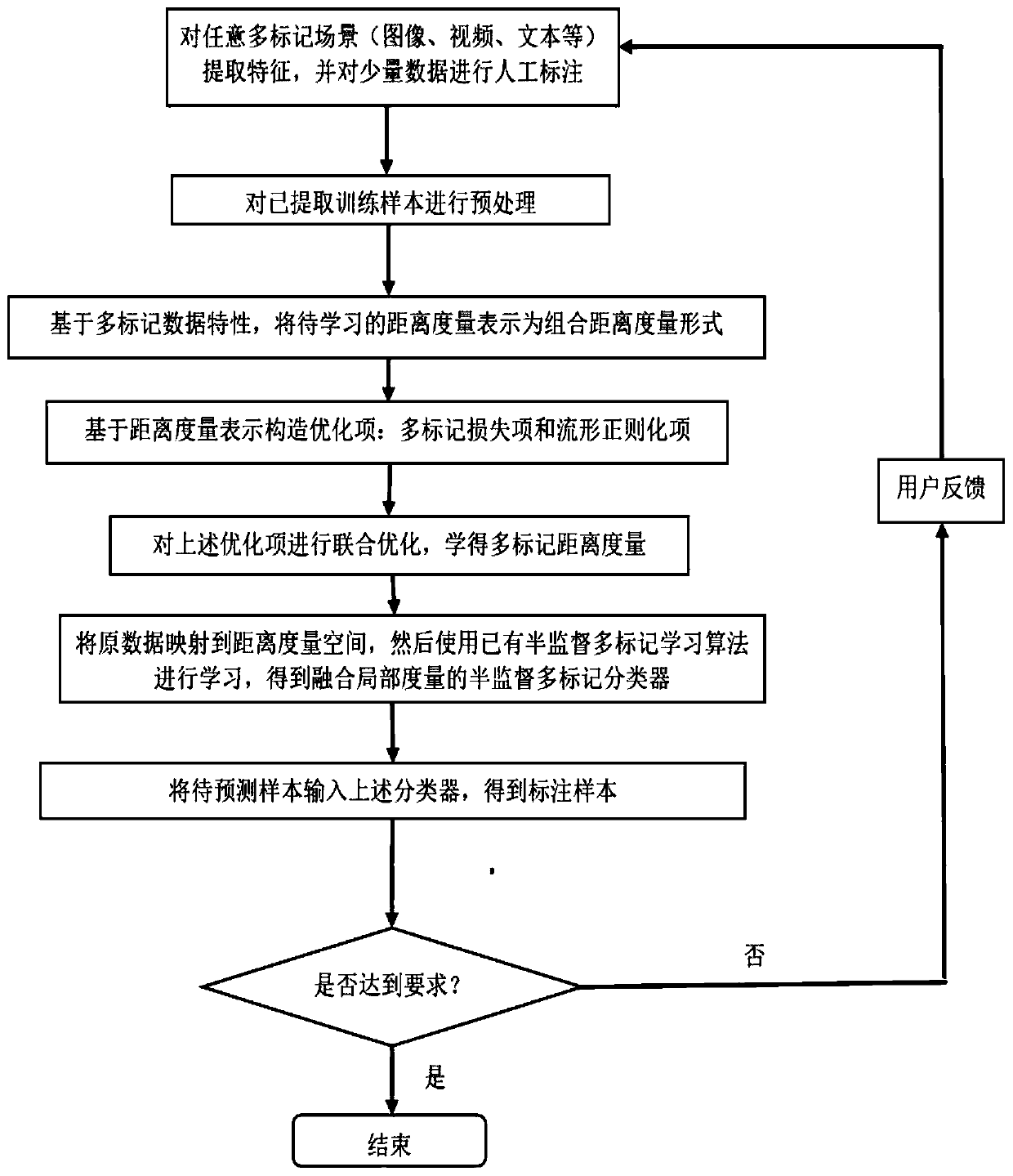
Semi-supervised multi-mark distance metric learning method fusing local metric
PendingCN110414575AEfficient use ofReduce labor labeling costsCharacter and pattern recognitionOriginal dataManifold regularization
The invention discloses a semi-supervised multi-mark distance measurement learning method fusing local measurement, and the method comprises the steps: extracting training data of any multi-mark application scene, and marking a small amount of data; for labeled data, filtering out samples with the labeling occupancy smaller than a set threshold value, removing abnormal points of unlabeled data through clustering and other operations, and improving the sample quality; expressing the distance metric to be learned as a combined distance metric form; constructing an optimization item based on thedistance metric representation; constructing a multi-mark loss item and manifold regularization item joint optimization model, and learning distance measurement; mapping the original data to a distance measurement space, and then performing learning by using an existing semi-supervised multi-mark learning algorithm to obtain a semi-supervised multi-mark classifier fused with local measurement; andinputting a to-be-predicted sample into the classifier to obtain a labeled sample. By adopting the method, the manual labeling cost can be reduced, and the practical application of the multi-label learning framework is promoted.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Deep migration semi-supervised domain adaptive classification method for histopathology images
PendingCN112733859AReduce time consumptionImplement deep transfer learningImage enhancementImage analysisThresholdingSelf adaptive
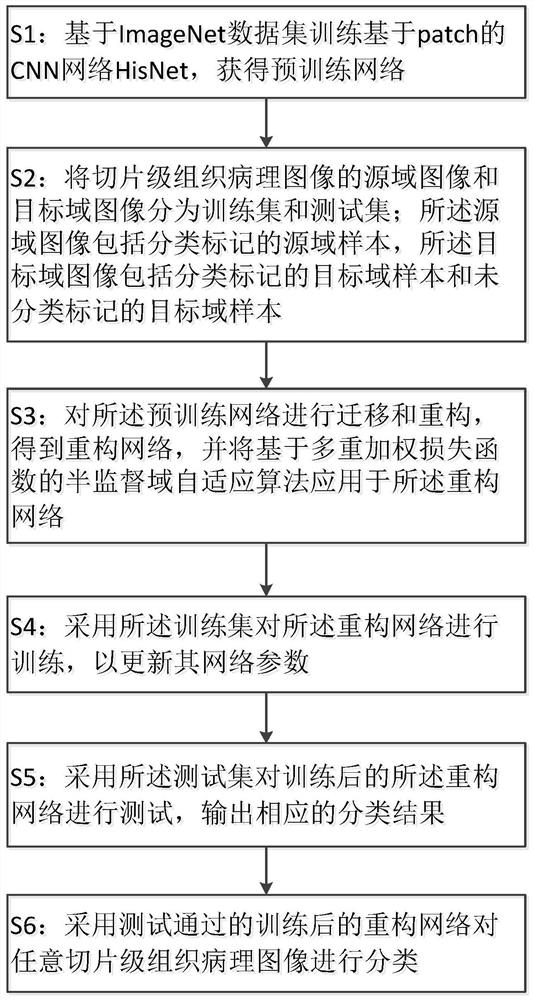
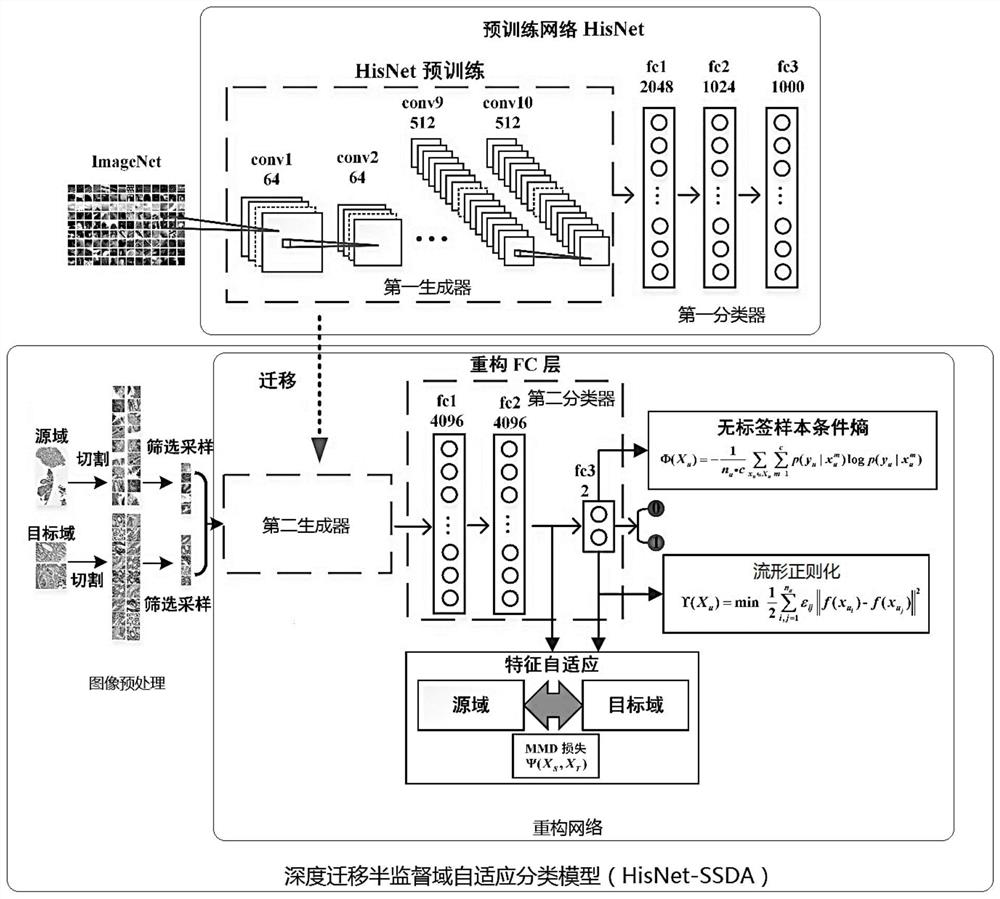
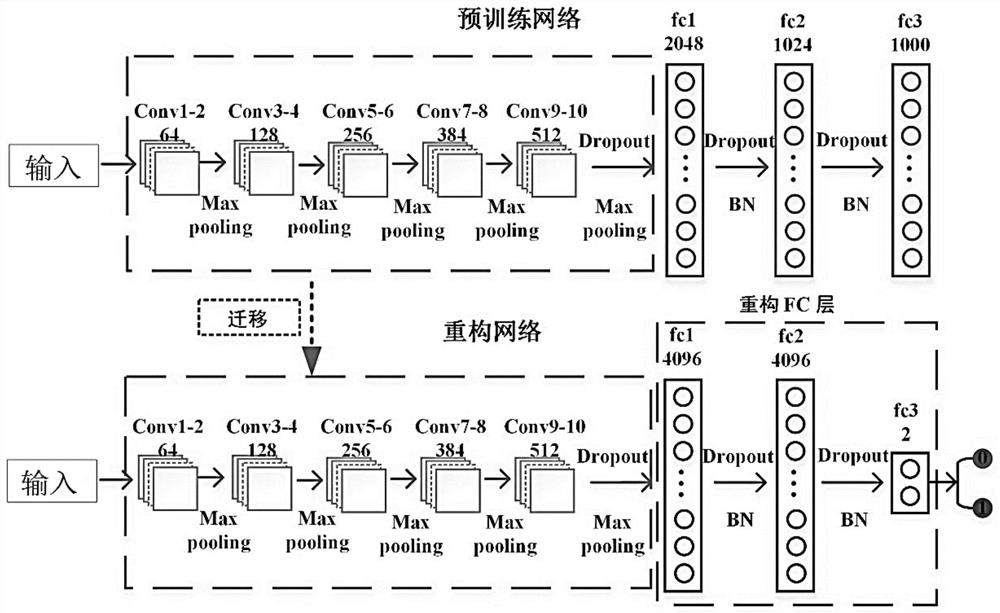
The invention relates to the technical field of histopathological image classification, in particular to a depth migration semi-supervised domain self-adaptive classification method for histopathological images, which adopts a self-adaptive threshold filtering and sampling strategy to be used for patch dicing so as to reduce time consumption. According to the method, deep migration learning can be realized by migrating a patch-based CNN network HisNet; according to the method, high-order features of a source domain and a target domain are extracted through a reconstruction network, and alignment is carried out in a self-adaptive mode through a semi-supervised domain with multiple weighted loss function criteria; a novel manifold regularization loss function is introduced to fully utilize the characteristics of a target domain sample and obtain a better classification result. Experimental results show that the method provided by the invention has high accuracy, efficiency and stability in histopathology image classification, and has great clinical application value.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
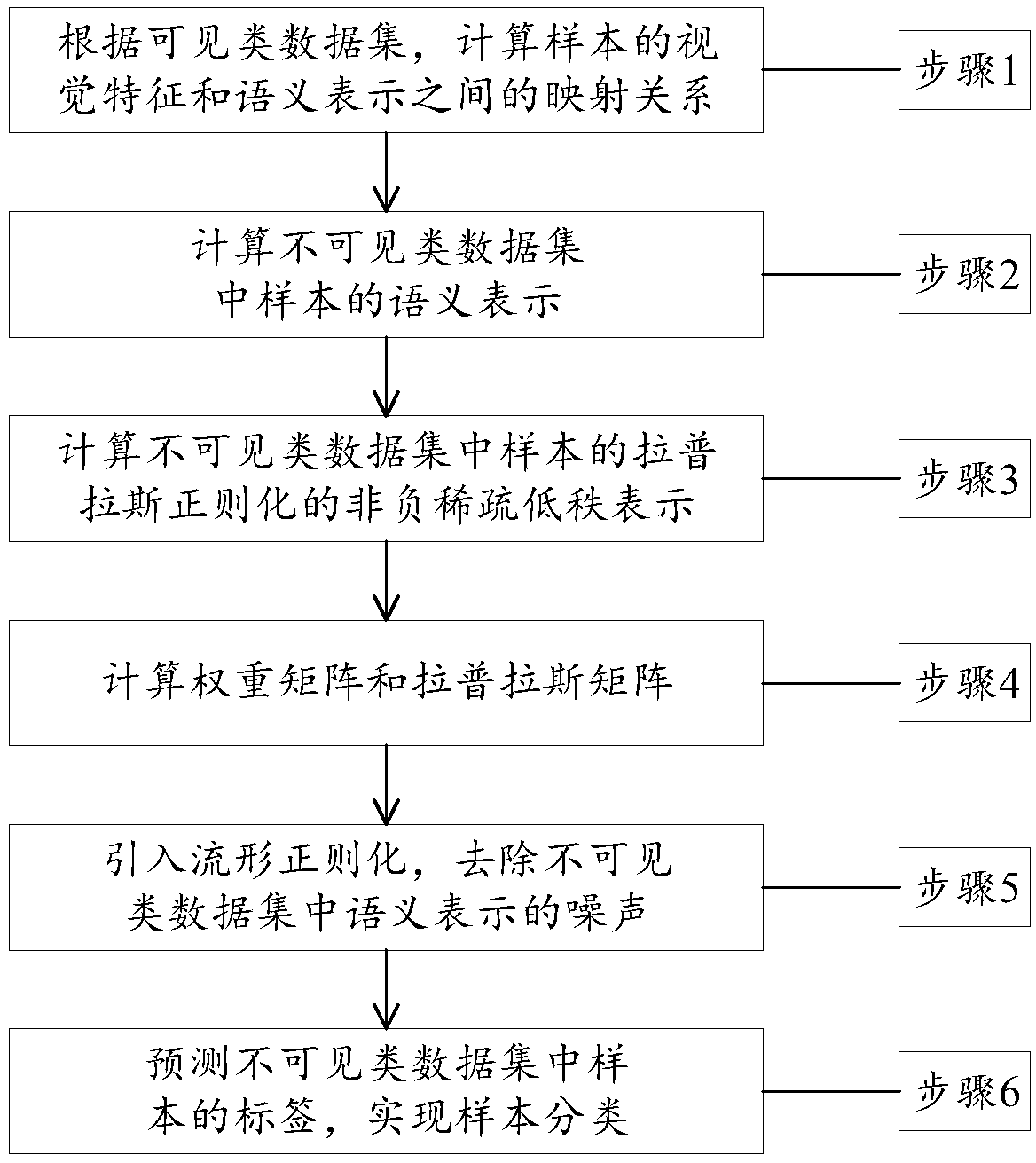
Zero-sample classification method based on low-rank representation and manifold regularization
ActiveCN108921226AEnhanced description abilityHigh precisionCharacter and pattern recognitionComplex mathematical operationsData setClassification methods
The invention discloses a zero-sample classification method based on low-rank representation and manifold regularization. The method comprises the steps of calculating a mapping relation between visual features and semantic features of samples in a visible data set; calculating semantic representations of samples in an invisible data set; introducing sparse constraints and in combination with Laplacian regularization constraints, calculating low-rank representations of the samples in the invisible data set; calculating a weight matrix and a Laplacian matrix; introducing the manifold regularization, and removing noises of the semantic representations in the invisible data set; and predicting labels of the samples in the invisible data set, thereby realizing sample classification. Accordingto the zero-sample classification method based on the low-rank expression and the manifold regularization, the classification method effectively overcomes the limitation of low classification precision under the conditions of few samples, sample label information loss and the like in a traditional classification method; the more accurate semantic representations in the invisible data set are obtained; the description capability of data features is enhanced; and the precision of zero-sample classification can be effectively improved.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
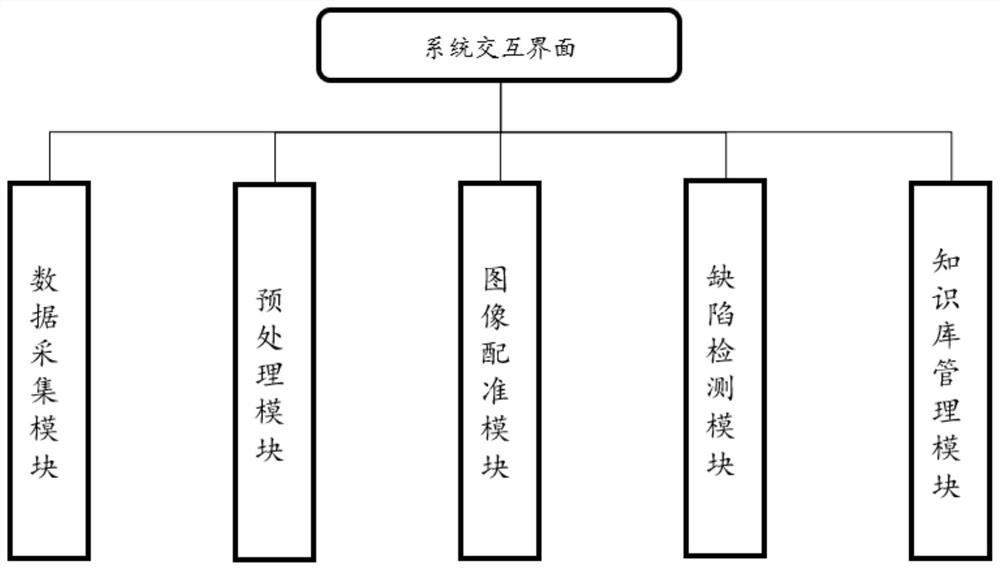
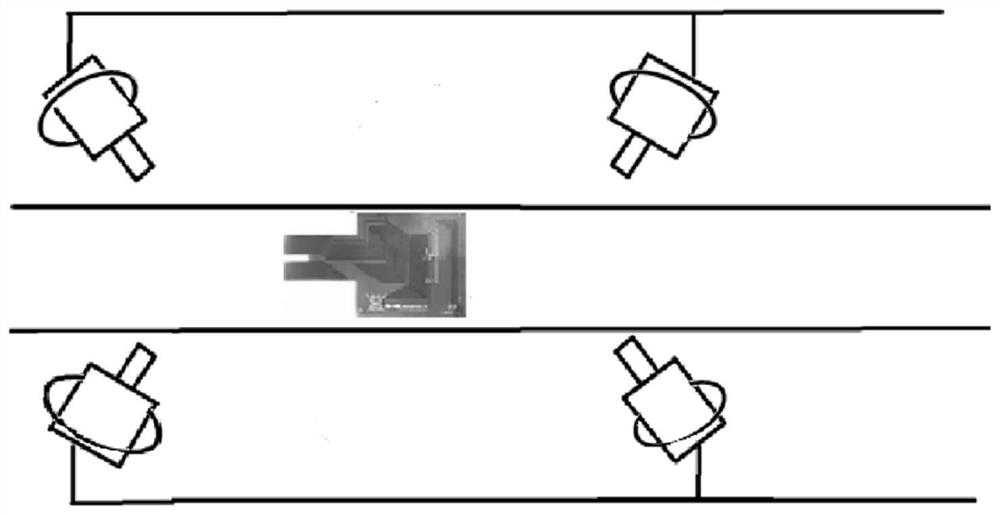
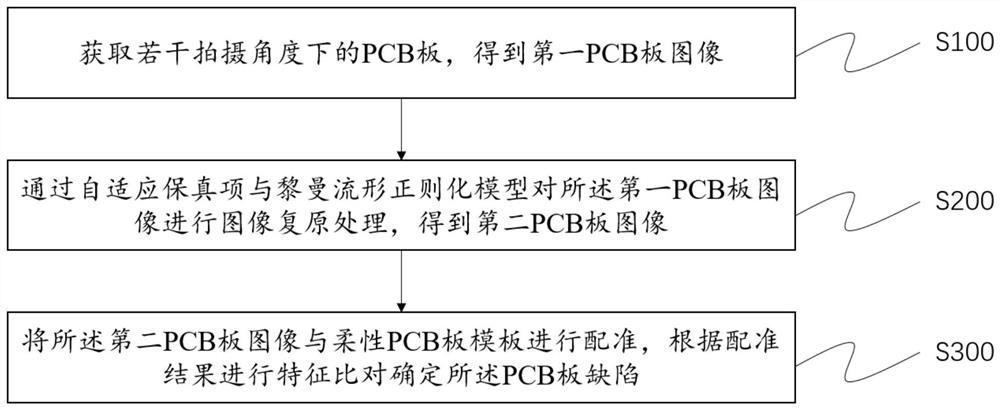
Flexible PCB defect detection method, visual system, device and medium
PendingCN113781419AAccurate descriptionOvercoming the disadvantages of obeying the uniform priorImage enhancementImage analysisImaging processingEngineering
The invention provides a flexible PCB defect detection method, a visual system, a device and a medium, and the method comprises the steps: obtaining a PCB at a plurality of shooting angles, and obtaining a first PCB image; performing image restoration processing on the first PCB image through an adaptive fidelity term and a Riemannian manifold regularization model to obtain a second PCB image; and performing registration on the second PCB image and the flexible PCB template, and performing feature comparison according to a registration result to determine PCB defects. The method can accurately describe geometric deformation under the condition that the speed and the acceleration are not zero in the image acquisition process, overcomes the defect that all parts of the image obey unified prior, realizes maintenance of detail structure characteristics of the image, and further realizes high-progress and high-speed defect sample identification; and the intelligent process can save certain labor cost, so that the method can be widely applied to the technical field of image processing.
Owner:GUANGZHOU UNIVERSITY
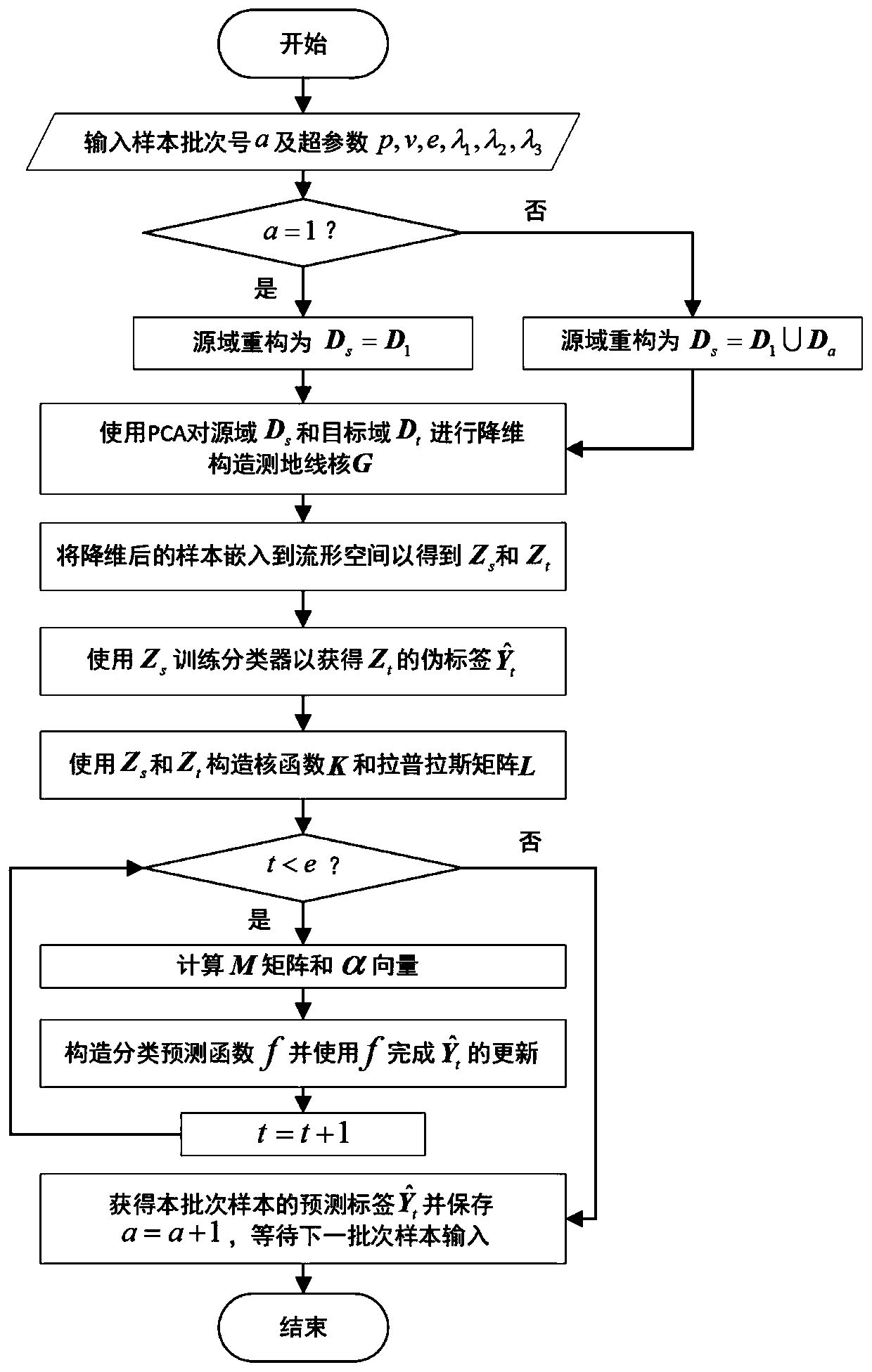
Online drift compensation method for sensor in bionic olfaction system
ActiveCN111474297AExtended service lifeCharacter and pattern recognitionGas analyser calibrationAlgorithmSelf adaptive
The invention relates to an online drift compensation method for a sensor in a bionic olfaction system, and belongs to the technical field of sensors. The method comprises the following steps: 1) performing source domain reconstruction according to an input sample batch number; and 2) constructing a classification model by using the reconstructed source domain and target domain samples, and storing a prediction result; using output response samples of sensors in two successive batches of bionic olfaction systems; performing source domain reconstruction on a previous batch of samples predictedby a classification model and an initial batch of manually labeled samples, and establishing the classification model through conditional distribution adaptation and manifold regularization to realizeonline drift compensation of the sensor in the bionic olfaction system. According to the invention, the gas identification model can be continuously updated along with the drifting of the sensor, theactual production and use scenes of the bionic olfaction system in a real scene are better met, and the service life of equipment can be prolonged.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
A Semi-Supervised Ranking Learning Method Based on Manifold Regularization for Image Retrieval
ActiveCN102831161BEfficient use ofImprove sorting effectCharacter and pattern recognitionSpecial data processing applicationsSpurious correlationImage retrieval
The invention discloses a semi-supervision sequencing study method for image searching based on manifold regularization. The semi-supervision sequencing study method comprises the following steps of: extracting visual characteristics from a network searching result from a database or an initial text-based network to form an image sample set; dividing the image sample set into three grades including 2, 1, and 0 according to degrees for inquiring subject coherence, wherein 2 represents that the image sample set is very coherent with the inquiry, 1 represents that the image sample set is commonly coherent with the inquiry and 0 represents that the image sample set is incoherent with the inquiry; calculating spurious correlation grade information yi of an unmarked image sample; calculating a distance between two image samples; constructing a Laplace manifold regularization item according to the distance between the two image samples; constructing a target function through the Laplace manifold regularization item; and solving a sequencing score for obtaining each image sample by the target function and feeding a sequenced result back to a user. According to the semi-supervision sequencing study method disclosed by the invention, the searching and sequencing performances are improved, marking information is sufficiently utilized and the searching precision is improved; and less supervision information is effectively utilized to improve the sequencing performance.
Owner:宿州高航知识产权服务有限公司
A robust visual image classification method and system
ActiveCN105354595BThe induction process is fast and preciseHigh speedCharacter and pattern recognitionHat matrixClassification methods
The invention discloses a robust visual image classification method and system. In order to effectively realize the category prediction of unlabeled samples in training samples and the rapid induction and reasonable dimensionality reduction of samples to be tested, the error measurement based on elastic regression analysis is integrated into Train an out-of-sample label propagation model, and normalize the manifold regularization term through parameter trade-offs, based on soft labels l 2,1 Norm regularized label fitting term and based on l 2,1 The impact of the norm regularized elastic regression residual term on the sample description and category identification completes the establishment of the label propagation model; and then obtains the projection matrix used to determine the category of the sample to be tested through the iterative optimization of the label propagation model. Therefore, in this application by introducing based on l 2,1 Norm regularized regression error term and soft label l 2,1 Norm regularization can effectively improve the robustness of the system while inheriting the advantages of the label propagation classification method, making the induction process of the samples to be tested fast and accurate.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Domain Transfer Extreme Learning Machine Method Based on Manifold Regularization and Norm Regularization
ActiveCN106803124BAchieve overfittingPrevent overfittingMachine learningLearning machineSupervised learning
The invention discloses a domain transfer extreme learning machine method based manifold regularization and norm regularization. On the basis of a traditional extreme learning machine, the thought of semi-supervised learning and transfer learning is introduced, and a novel extreme learning machine model is built and consists of three parts: a manifold regularization term capable of excavating geometric distribution shapes of data samples with tags and without tags to realize semi-supervised learning; a loss function term considering error minimization of source domain data and target domain data to realize transfer learning; and norm regularizers constraining weight space. The domain transfer extreme learning machine method provide by the invention is combined with the source domain to process the problem of prediction of the target domain, thereby increasing the generalization capability and range of application of the extreme learning machine. Introduction of the manifold regularization term also enables the method proposed by the invention to still maintain a relatively good learning effect when data with tags are little, the restriction that a traditional machine learning method requires a large amount of data with tags is overcome, and the accuracy and robustness of prediction are also improved.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
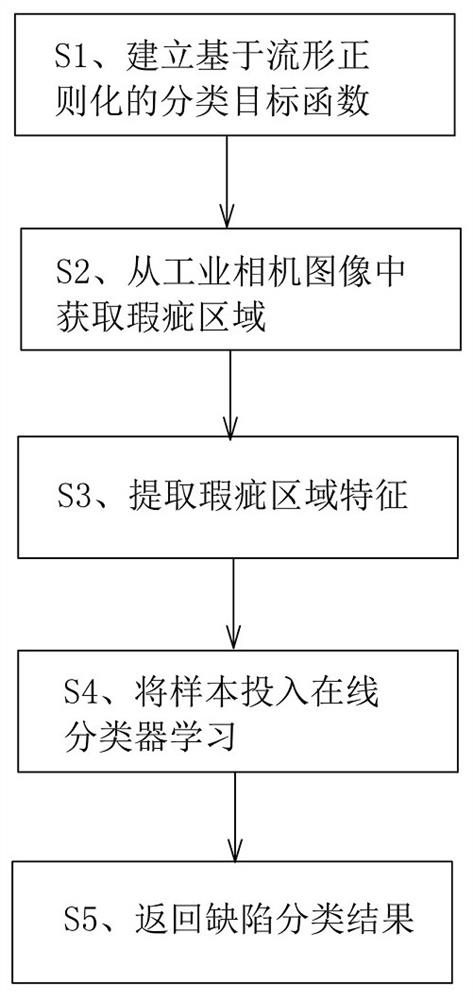
Product defect online classification method in industrial visual inspection
PendingCN112098422AImprove detection efficiencyReduce computational complexityOptically investigating flaws/contaminationCamera imageData information
The invention discloses a product defect online classification method in industrial visual inspection. The method comprises the following process steps: S1, establishing a classification target function based on manifold regularization: establishing the classification target function by adopting an one vs the rest strategy; S2, acquiring a defect area from the industrial camera image: acquiring the defect area from the industrial camera image by adopting Blob analysis; S3, extracting defect area features: extracting the defect area features by adopting Blob analysis; S4, putting the samples into an online classifier for learning: putting the defect area features as the samples into the online classifier for learning; S5, returning a defect classification result: classifying the samples through an online classifier to obtain a defect classification return result. According to the method, the flaw area characteristics of the defective products are obtained through the Blob analysis, andthe data information of the defective products can be counted in real time; defected products are classified through an online learning method based on manifold regularization, so that the algorithm complexity can be reduced, the algorithm error rate can be reduced, and the classification efficiency can be effectively improved.
Owner:深圳市睿阳精视科技有限公司
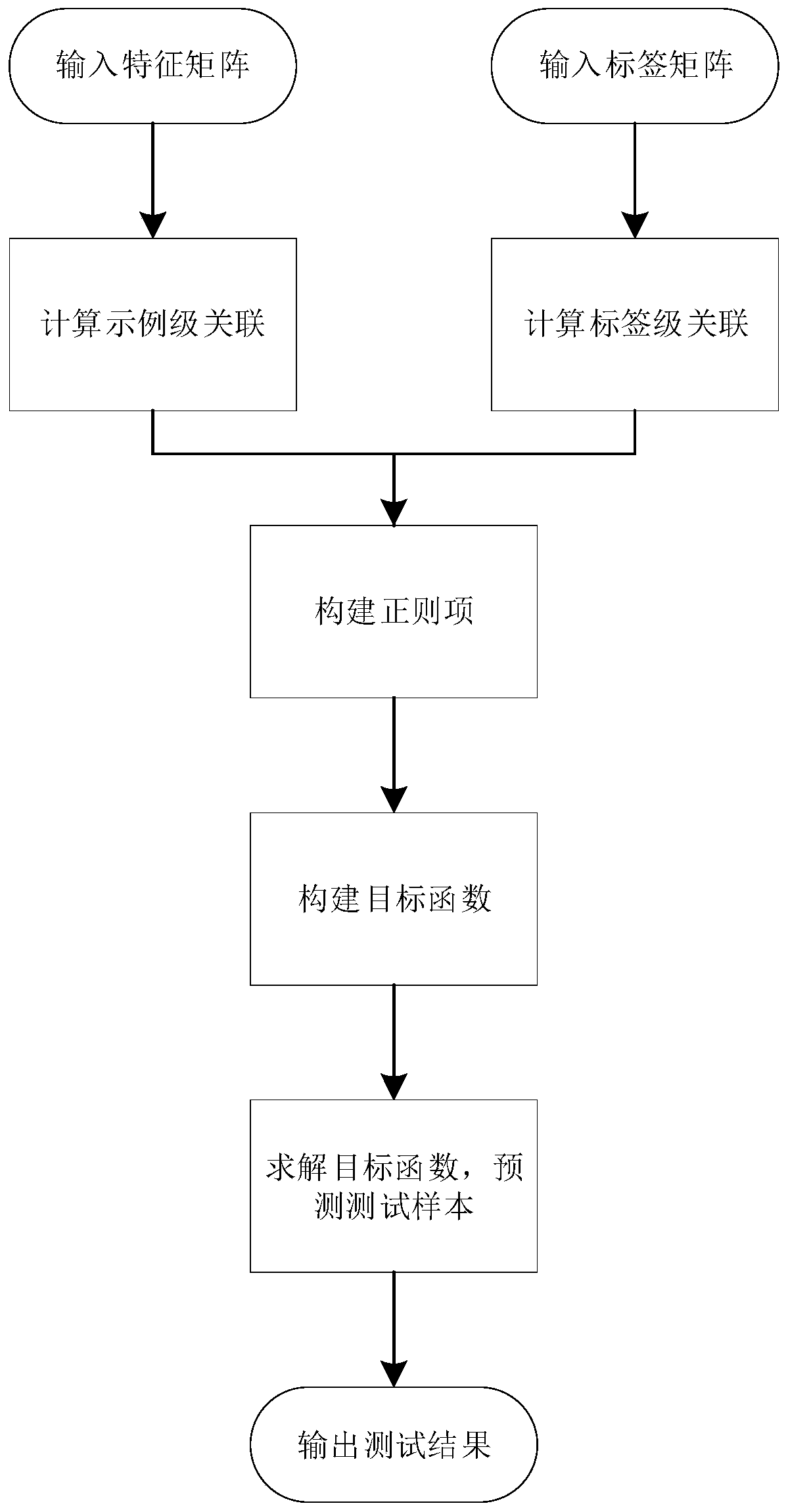
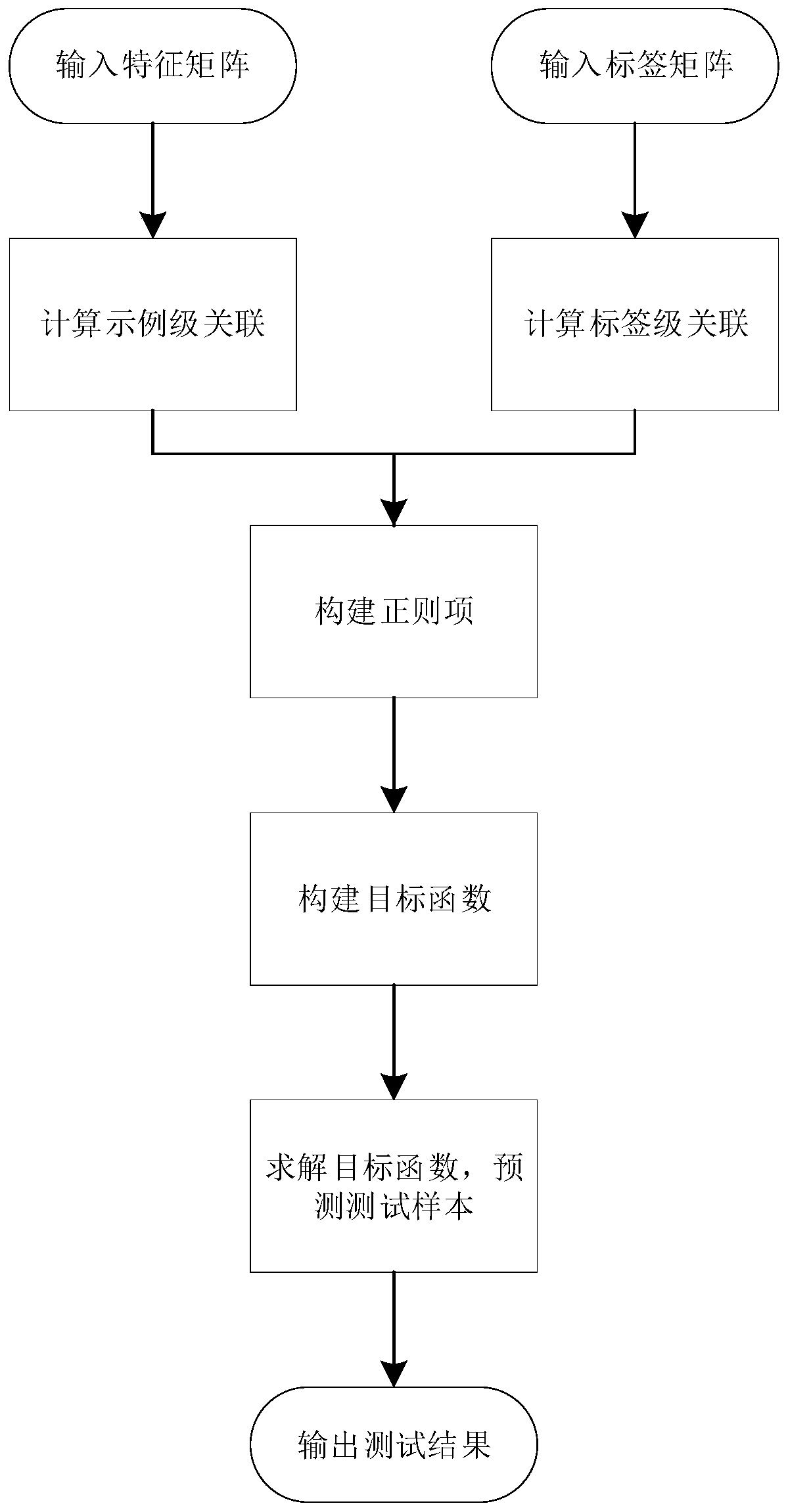
Missing label multi-label classification method based on example-level and label-level association
ActiveCN111160398AAccurate associationImprove classification performanceCharacter and pattern recognitionMulti-label classificationClassification methods
The invention requests to protect a missing label multi-label classification method based on example-level and label-level association, and the method comprises the steps: S1, inputting a feature matrix of a training sample, constructing a feature-based sample neighbor graph through a linear recombination strategy, mining the geometric structure information of the sample, and obtaining an example-level association matrix; S2, inputting a label matrix of a training sample, and constructing a label-based semantic association graph through a low-rank representation method to mine semantic association information of labels to obtain a label-level association matrix; S3, utilizing Laplace manifold regularization to associate and construct the two labels into two regularization items; and S4, constructing an objective function and solving the objective function. According to the multi-label classification method, the relevance of the example level and the label level is combined, and the classification effect of the multi-label classification method can be effectively improved under the condition that the labels are partially lost.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com