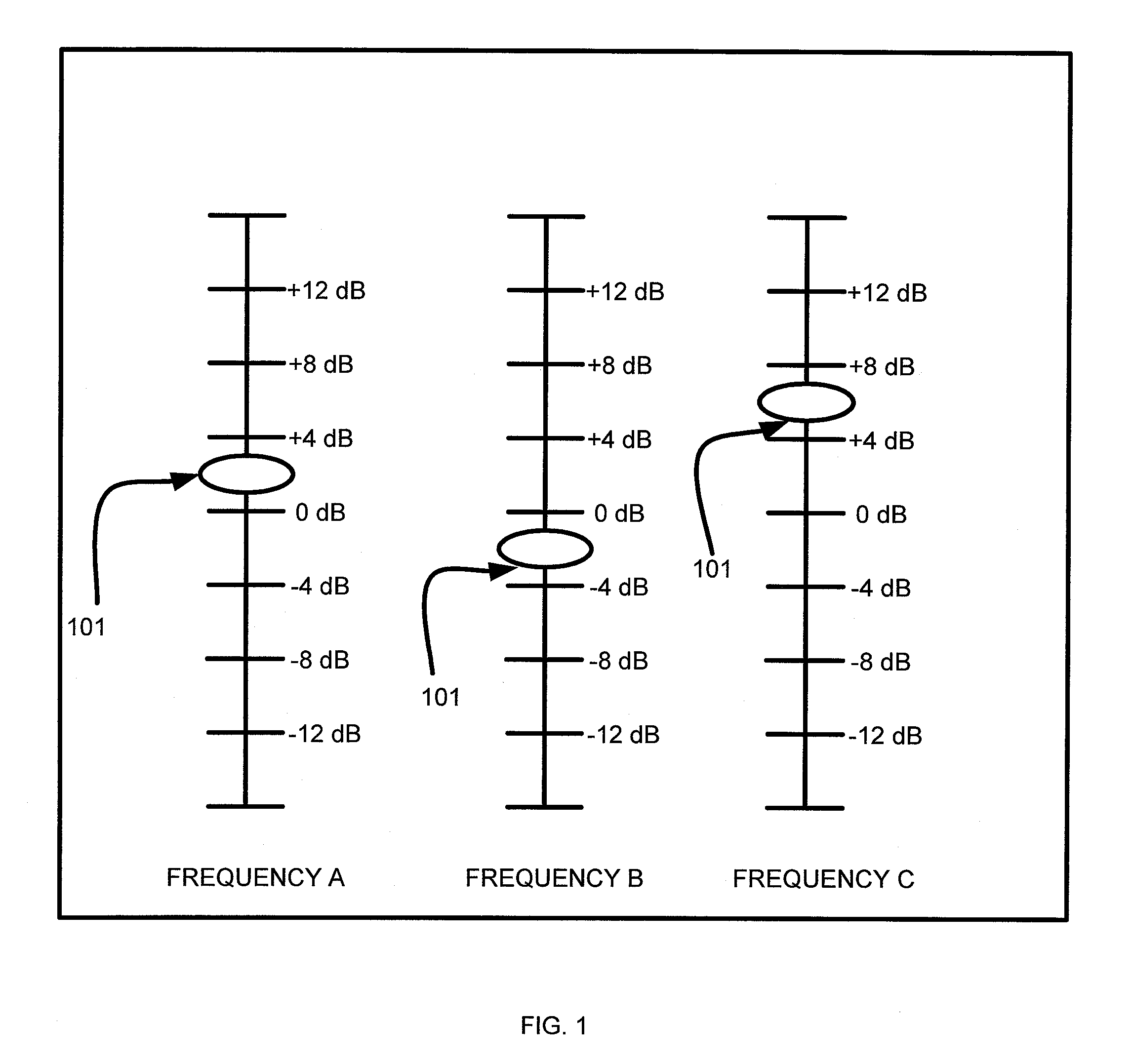
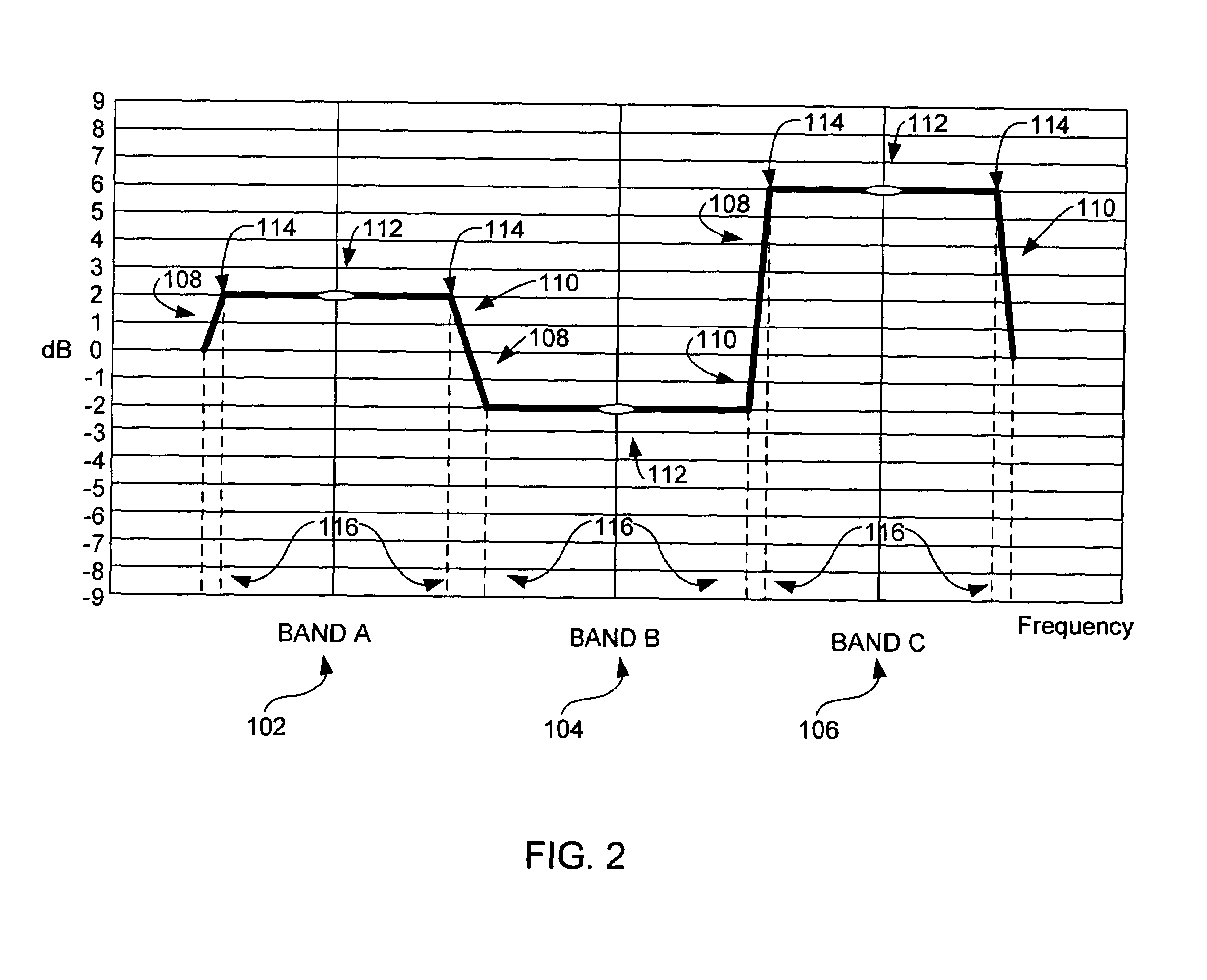
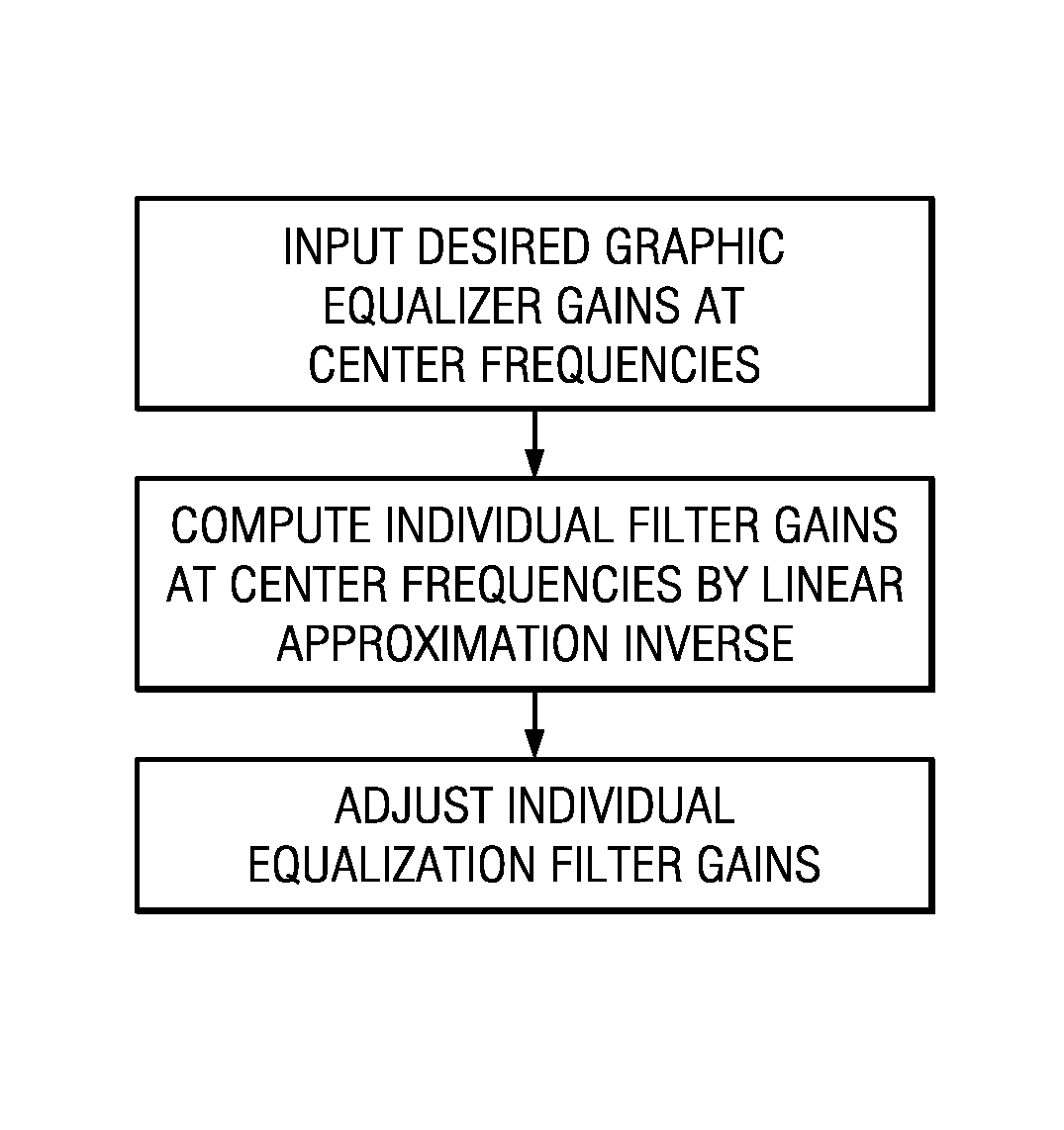
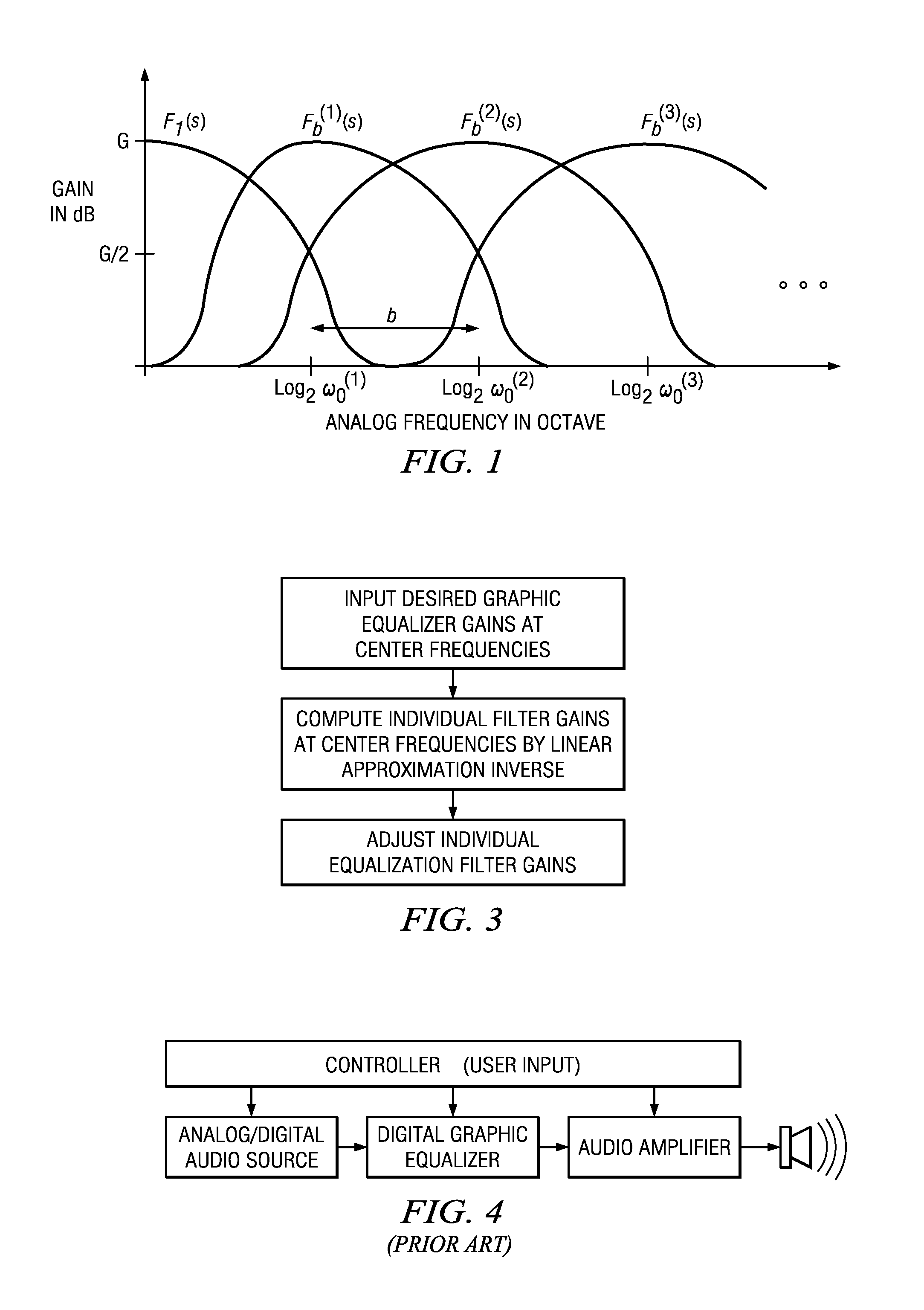
Patents
Literature
165results about "Manually operated tone/bandwidth control" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
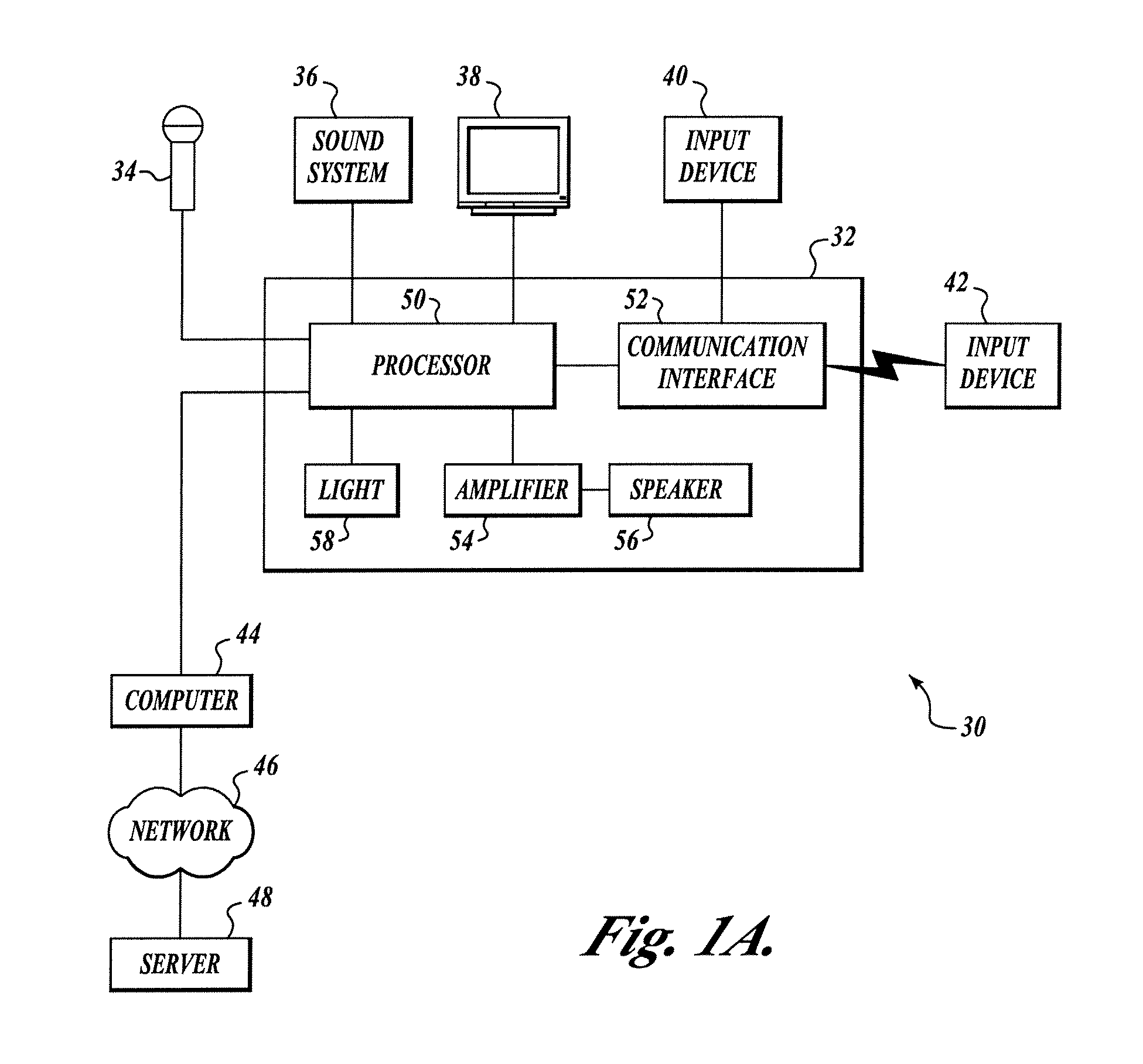
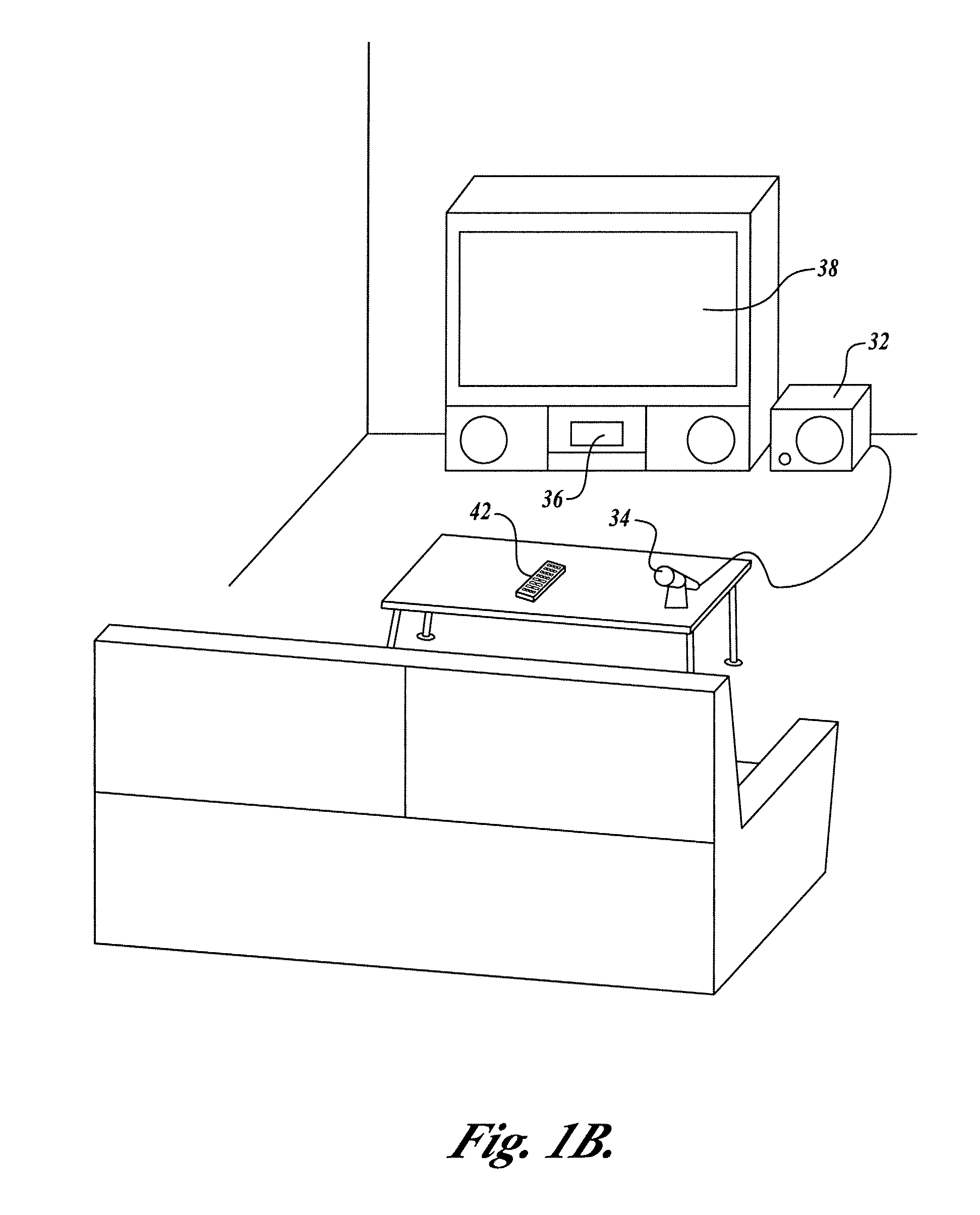
Adjustable speaker systems and methods
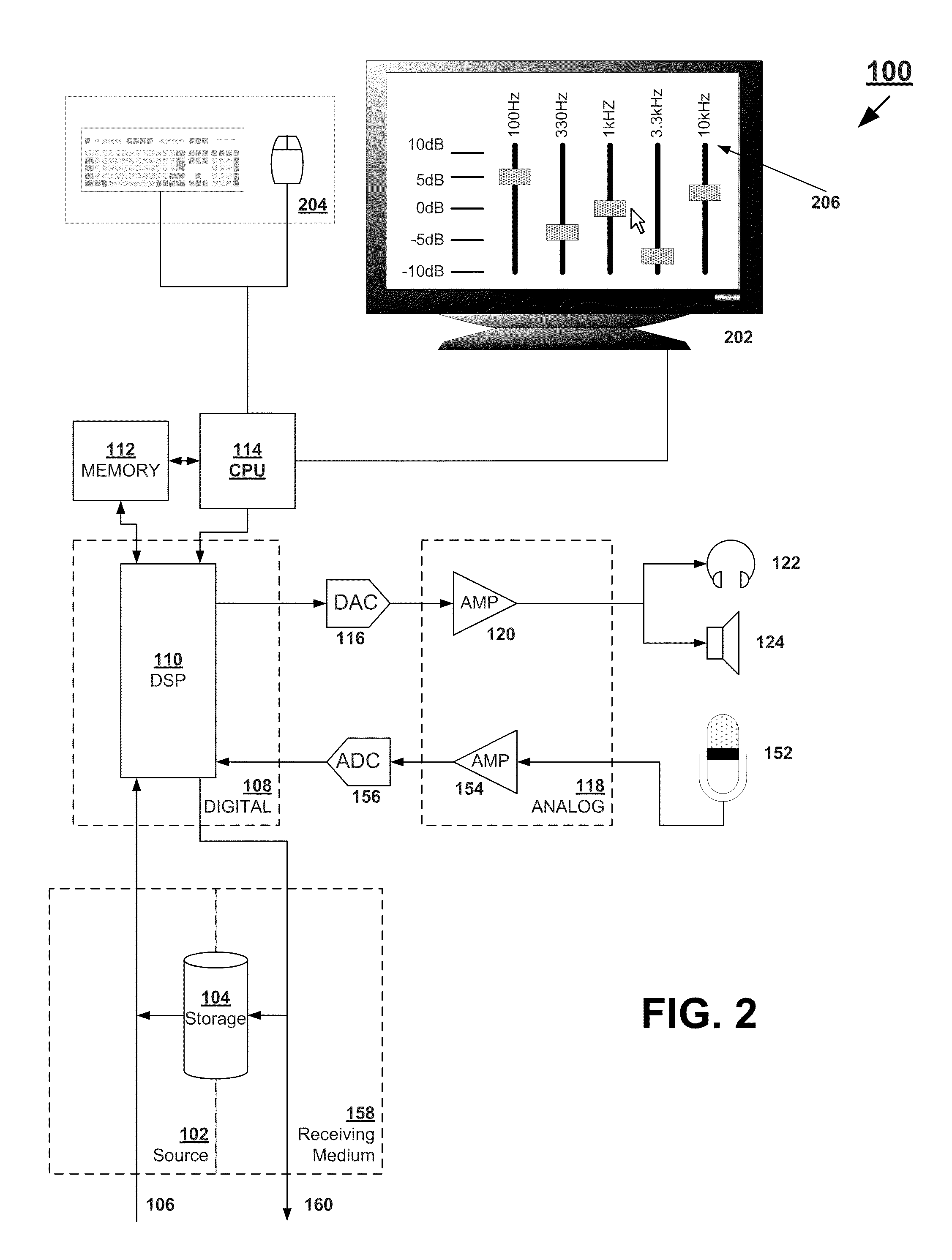
InactiveUS20050069153A1Manually operated tone/bandwidth controlStereophonic systemsAudio power amplifierGraphical user interface
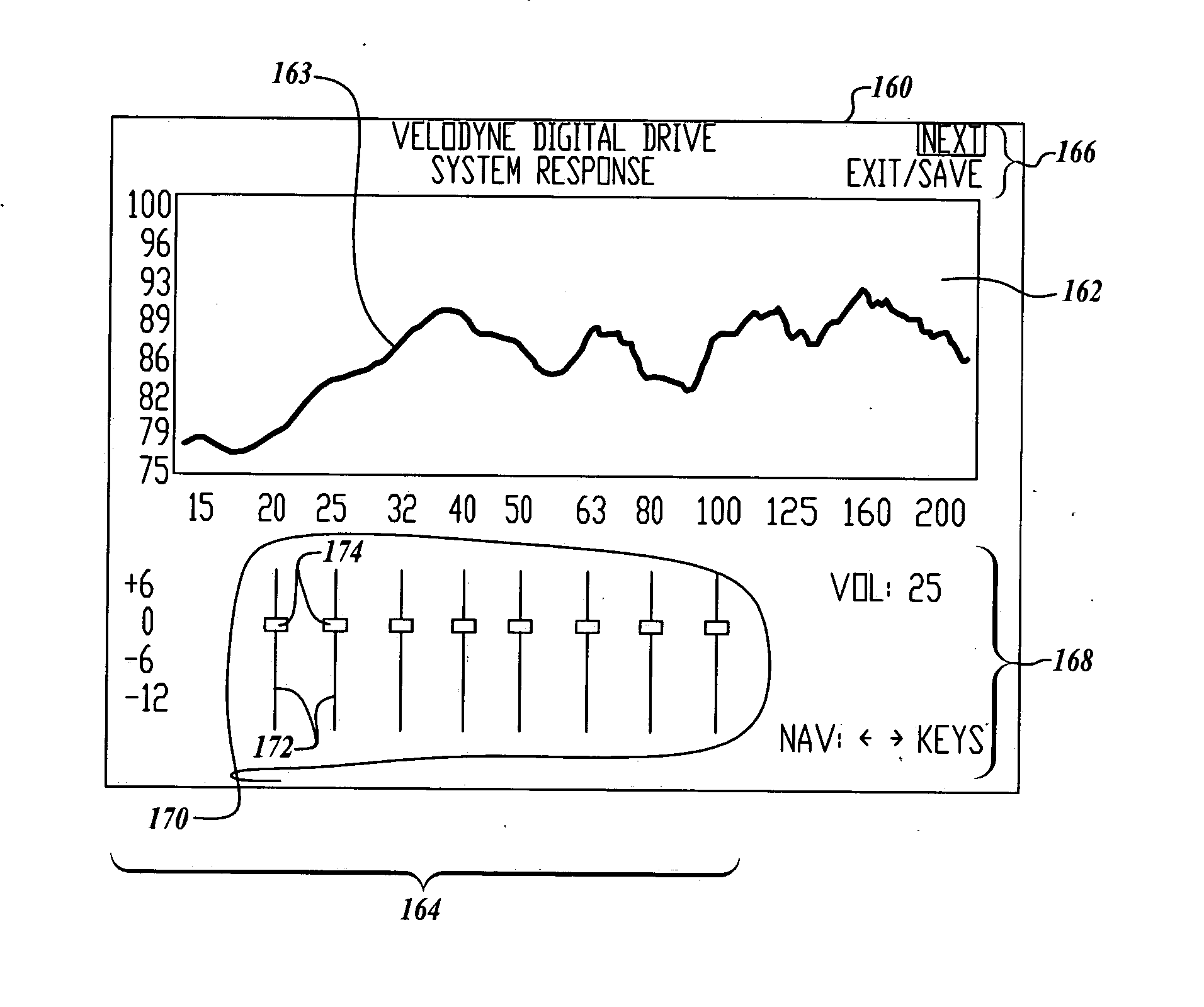
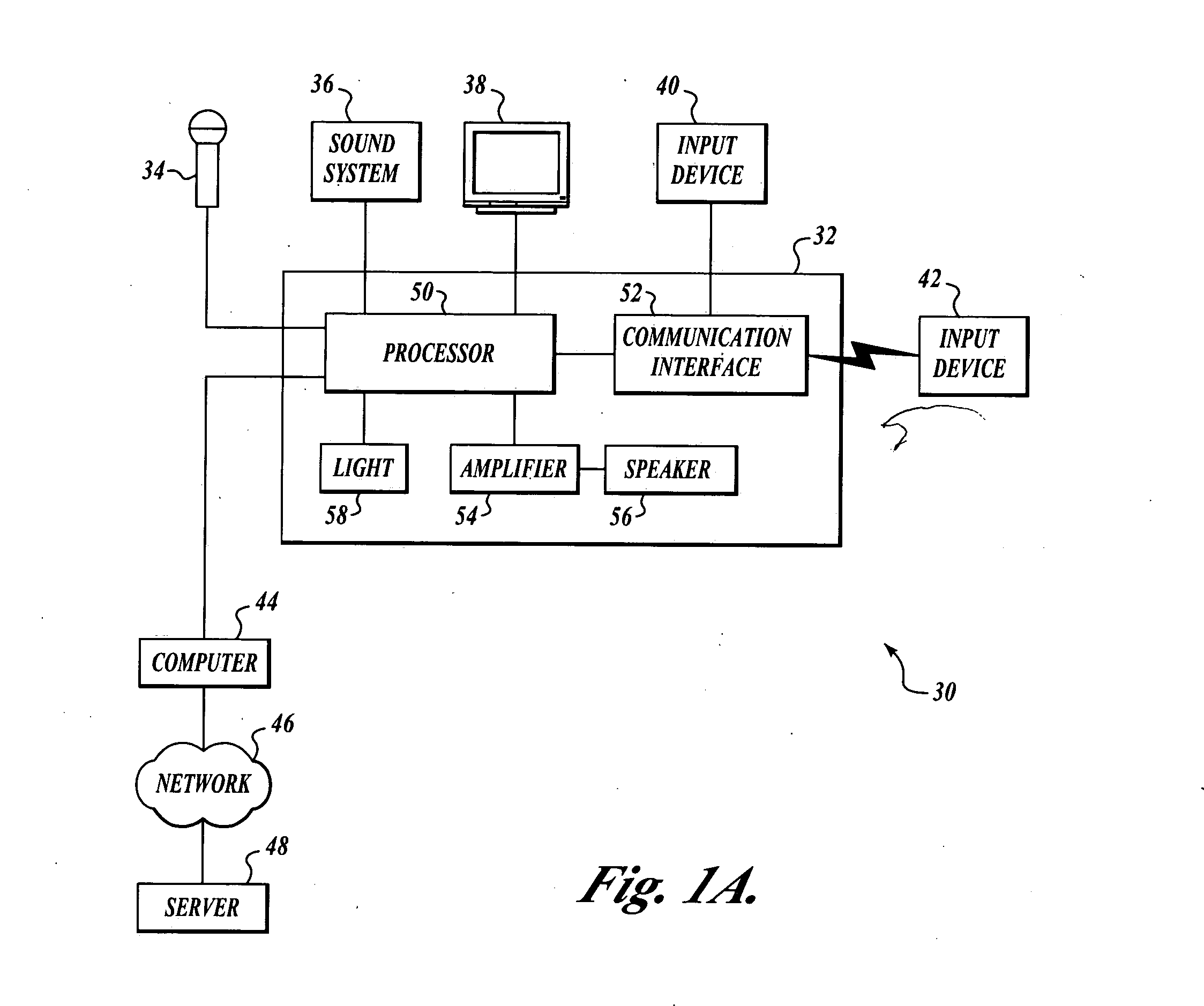
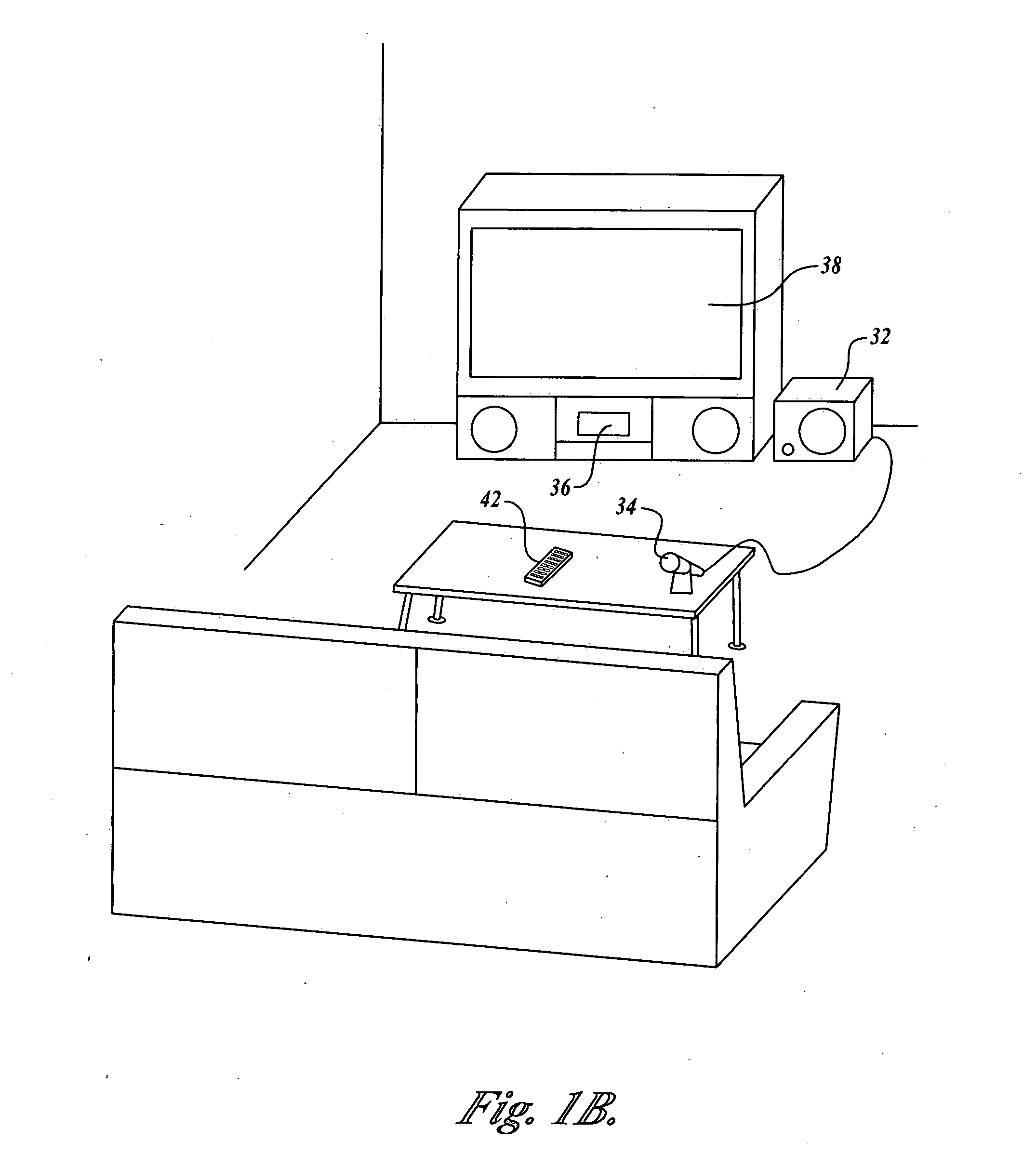
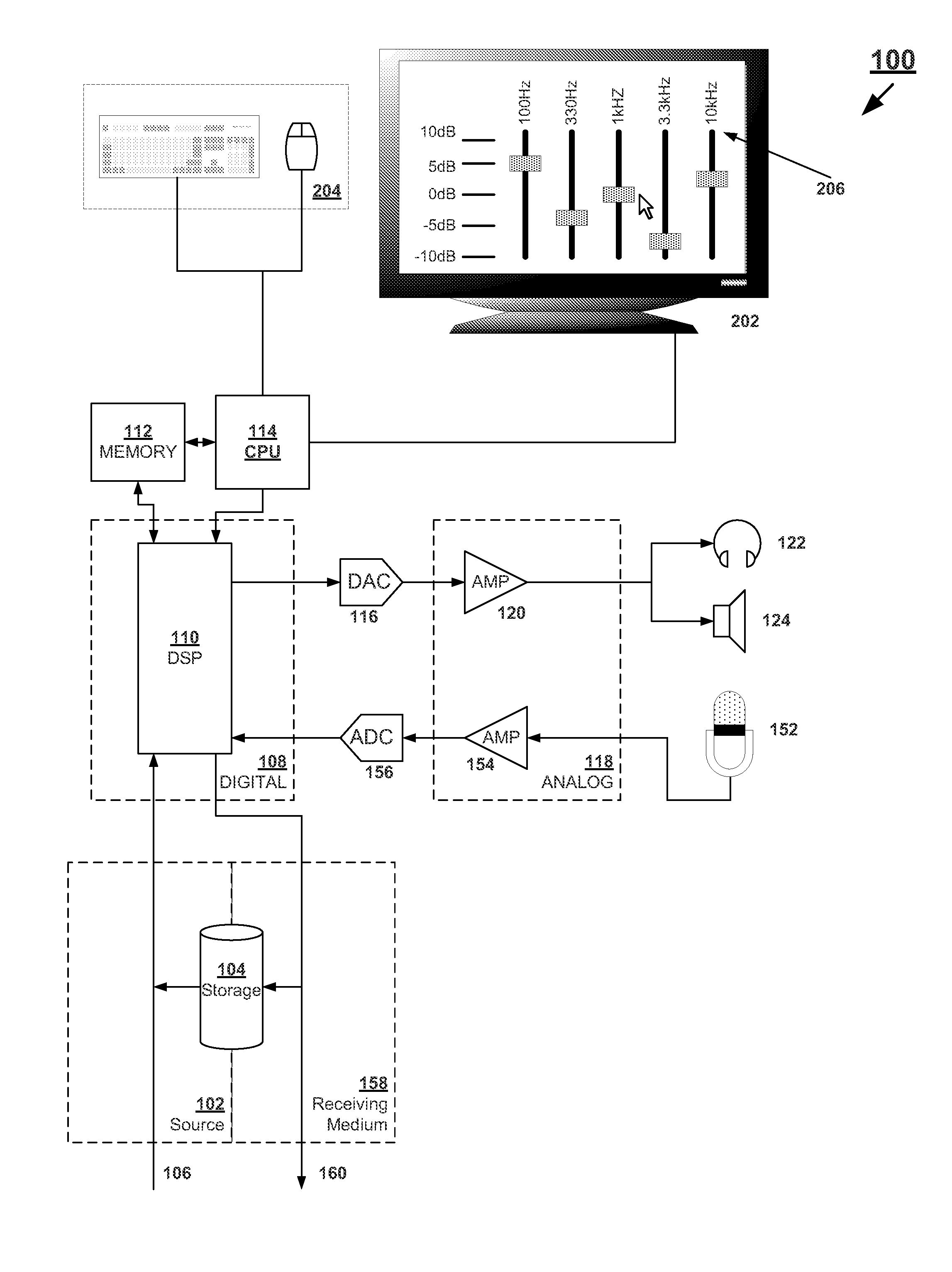
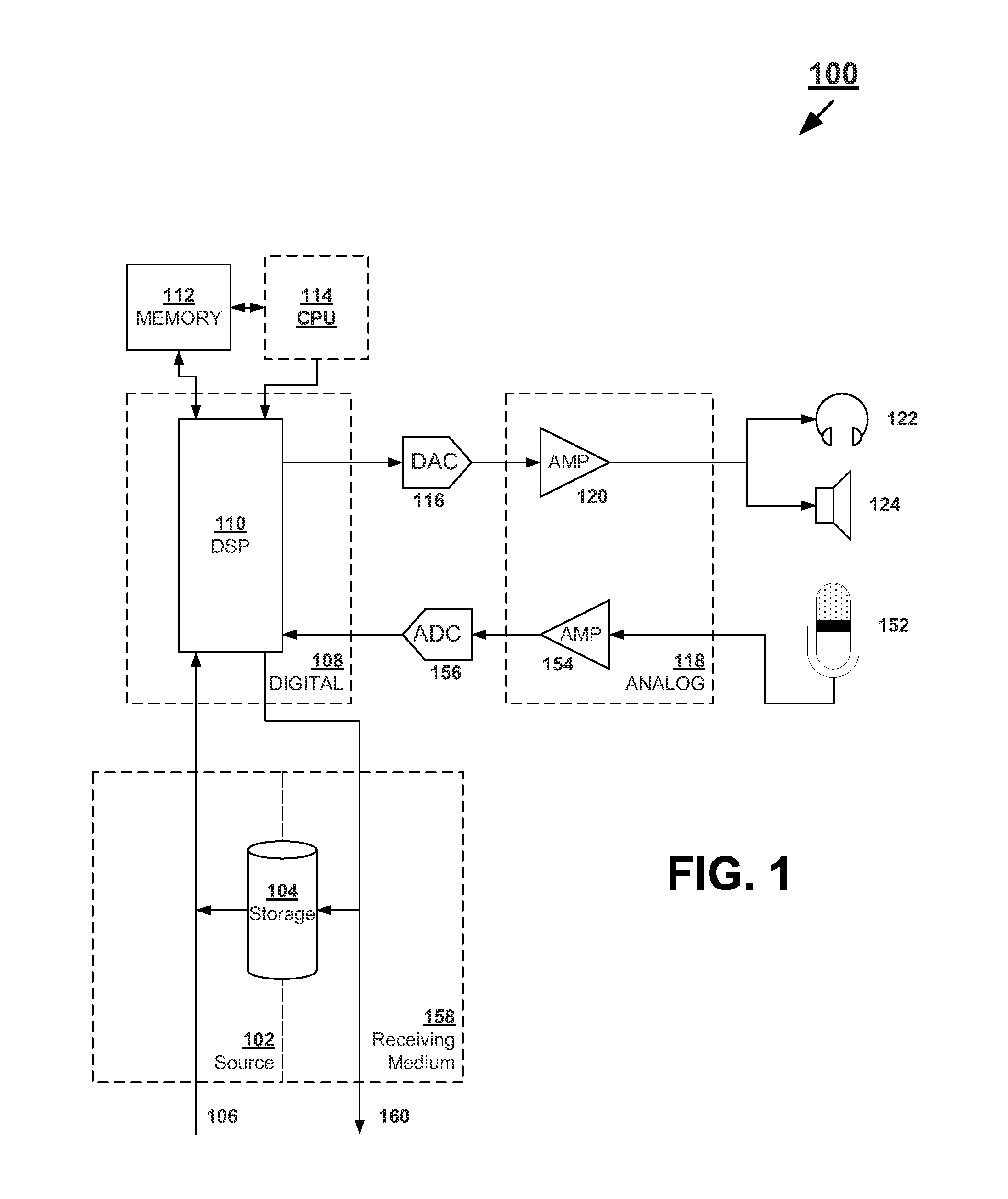
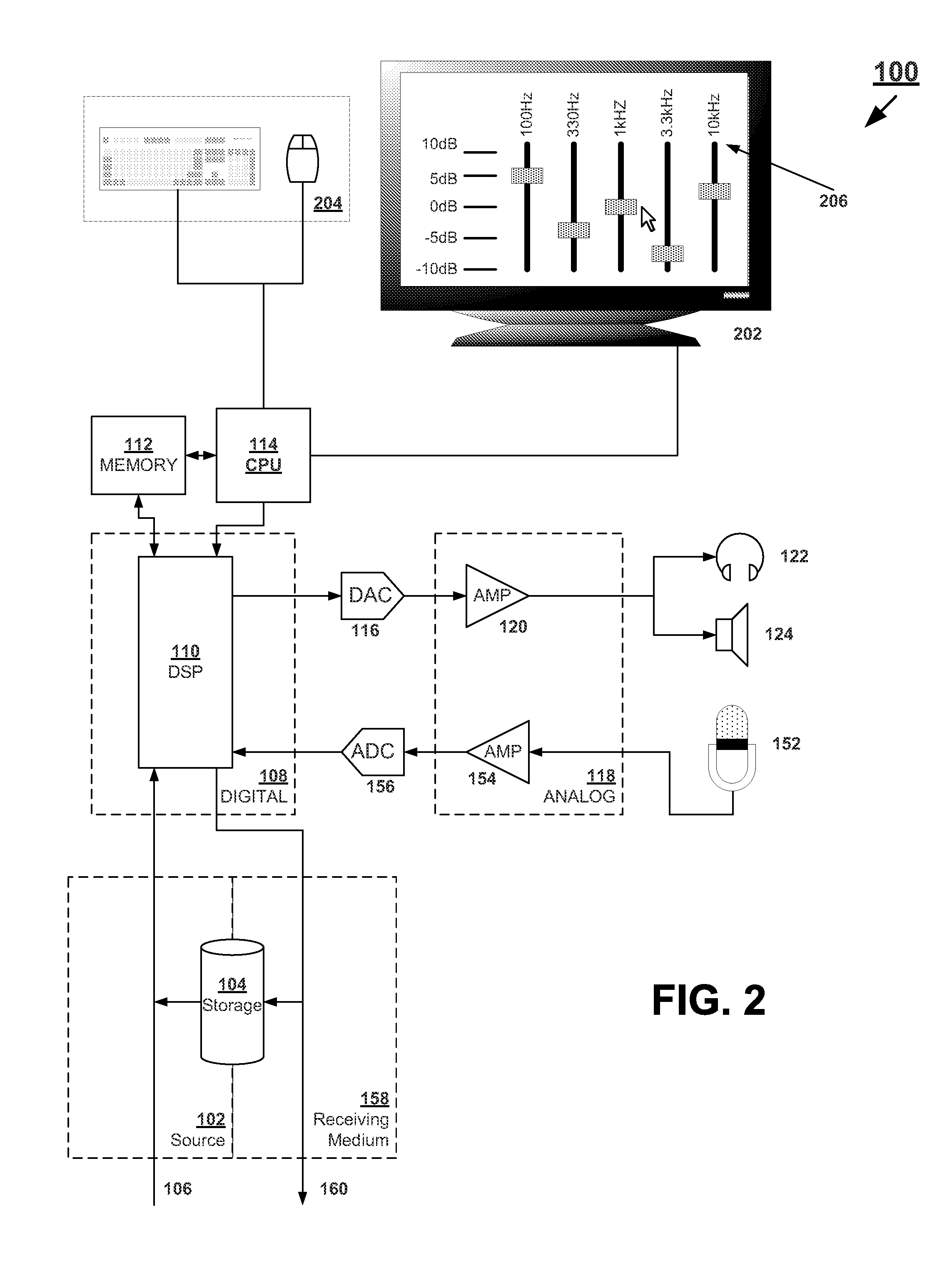
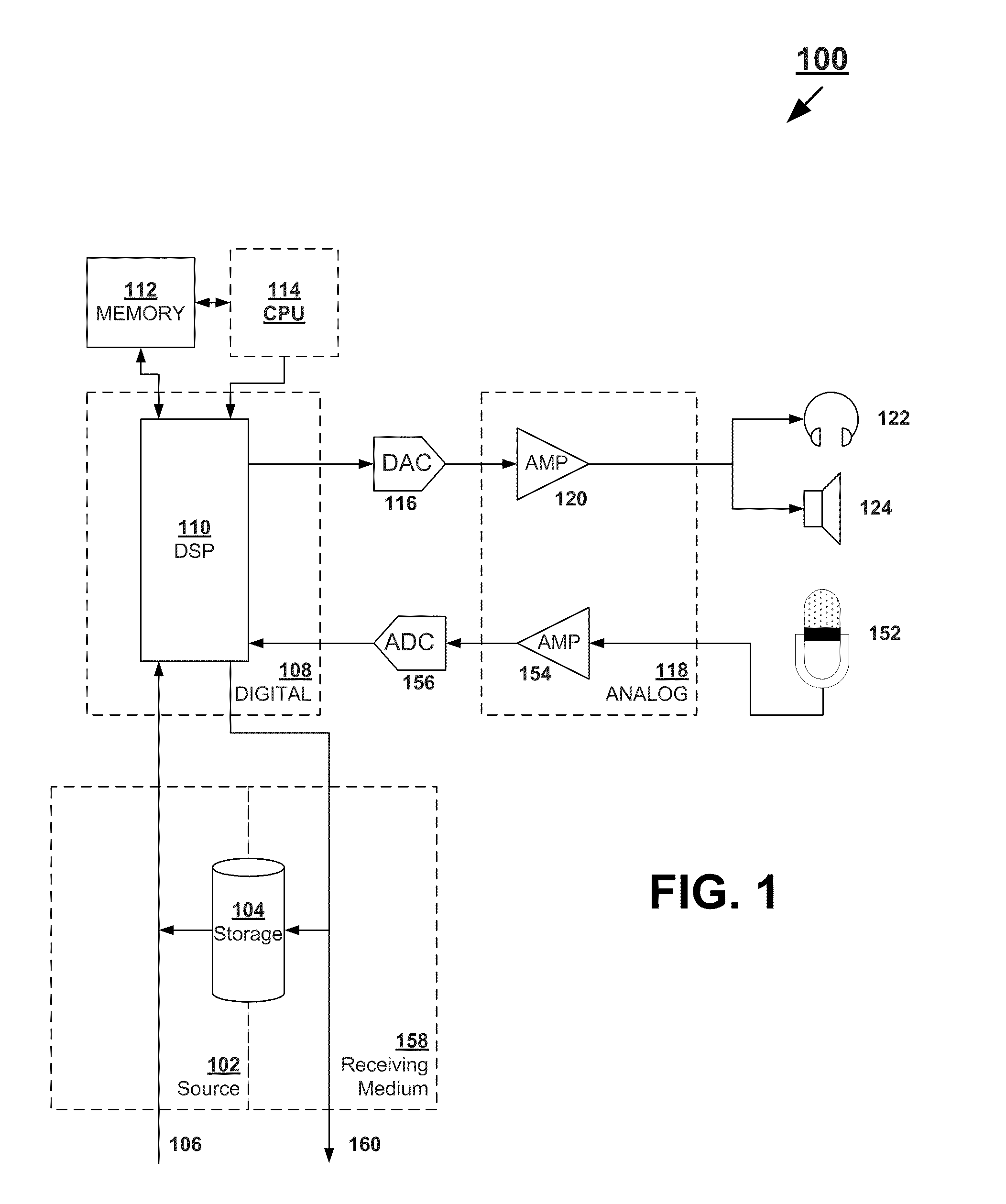
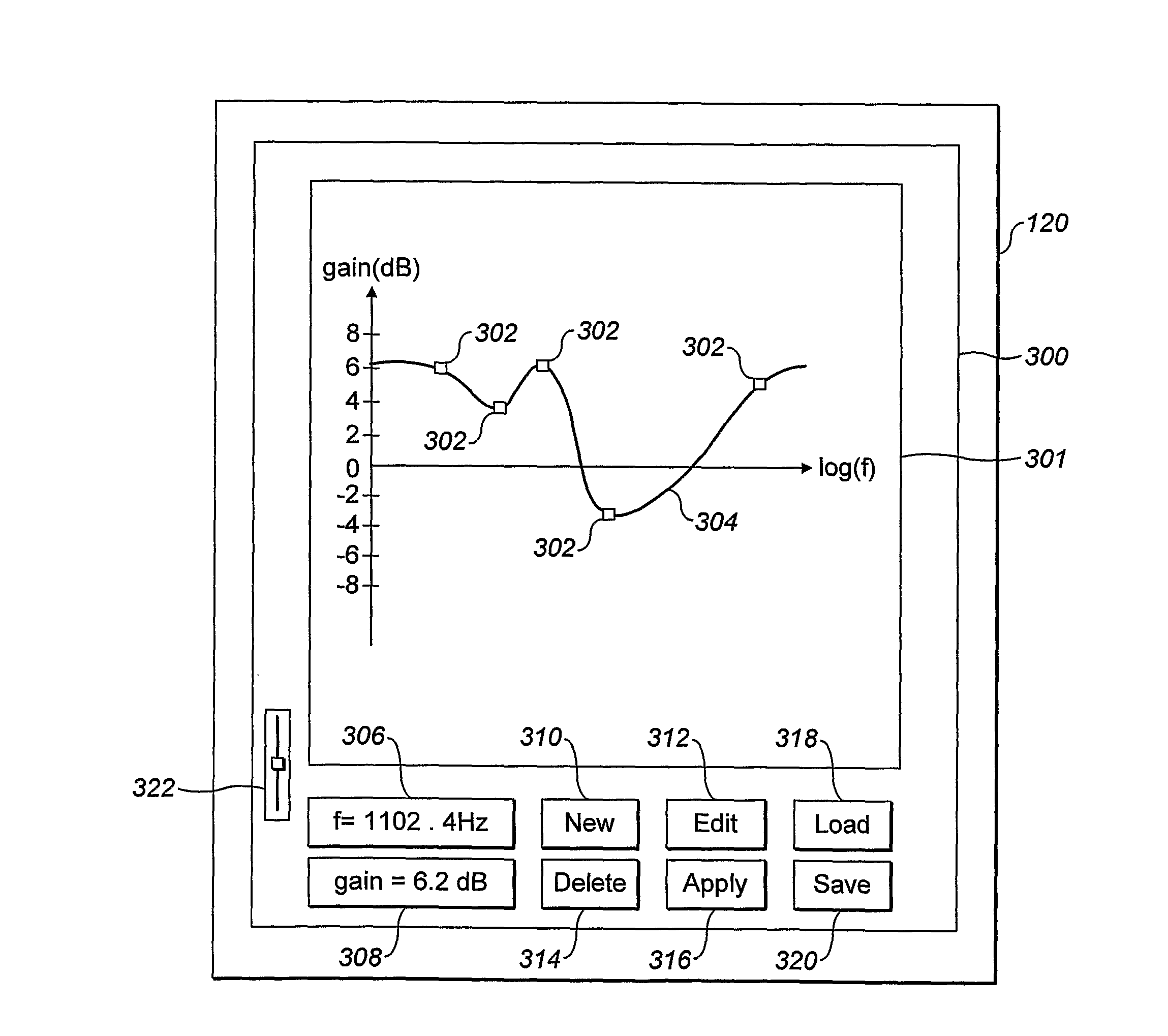
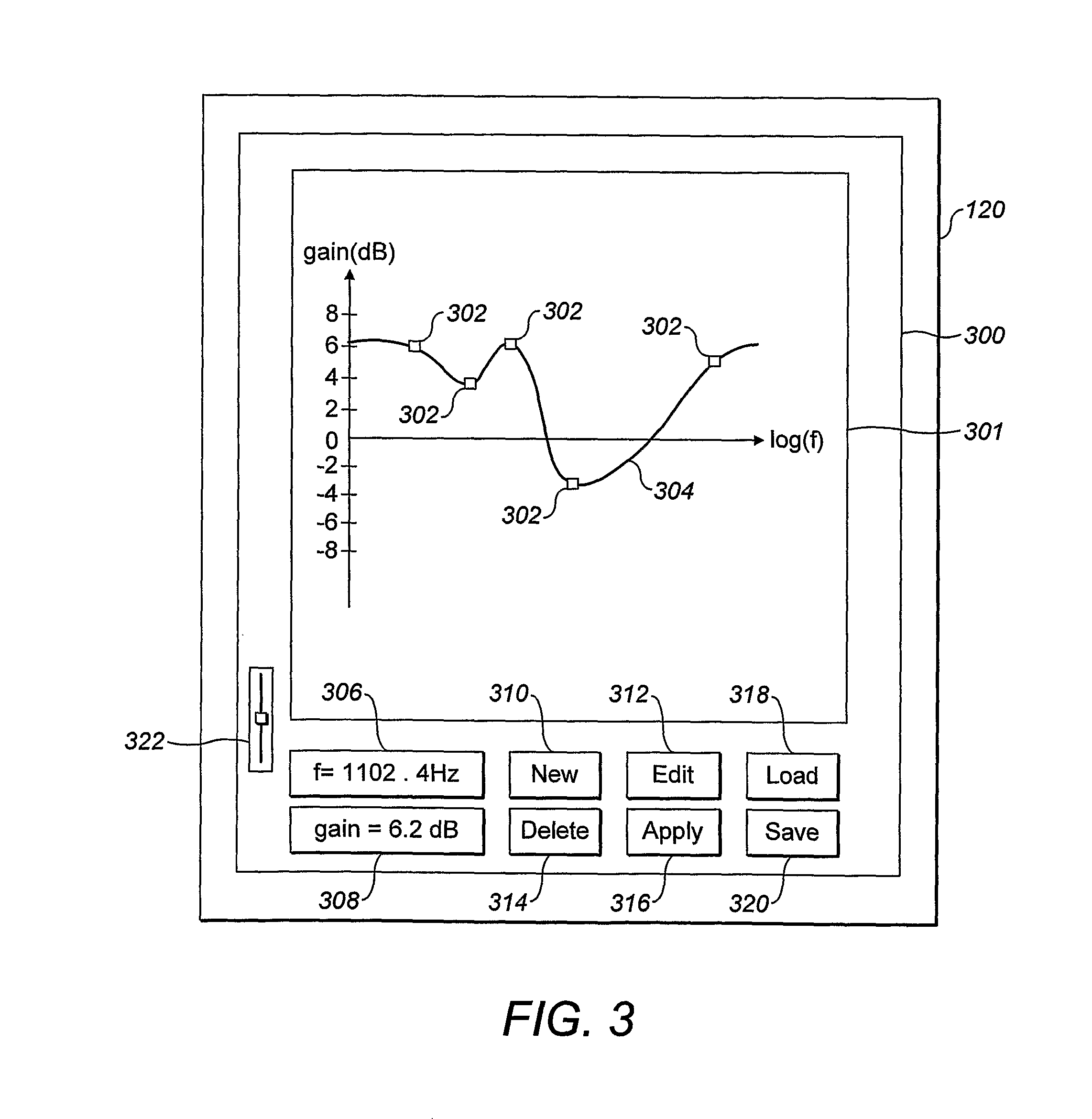
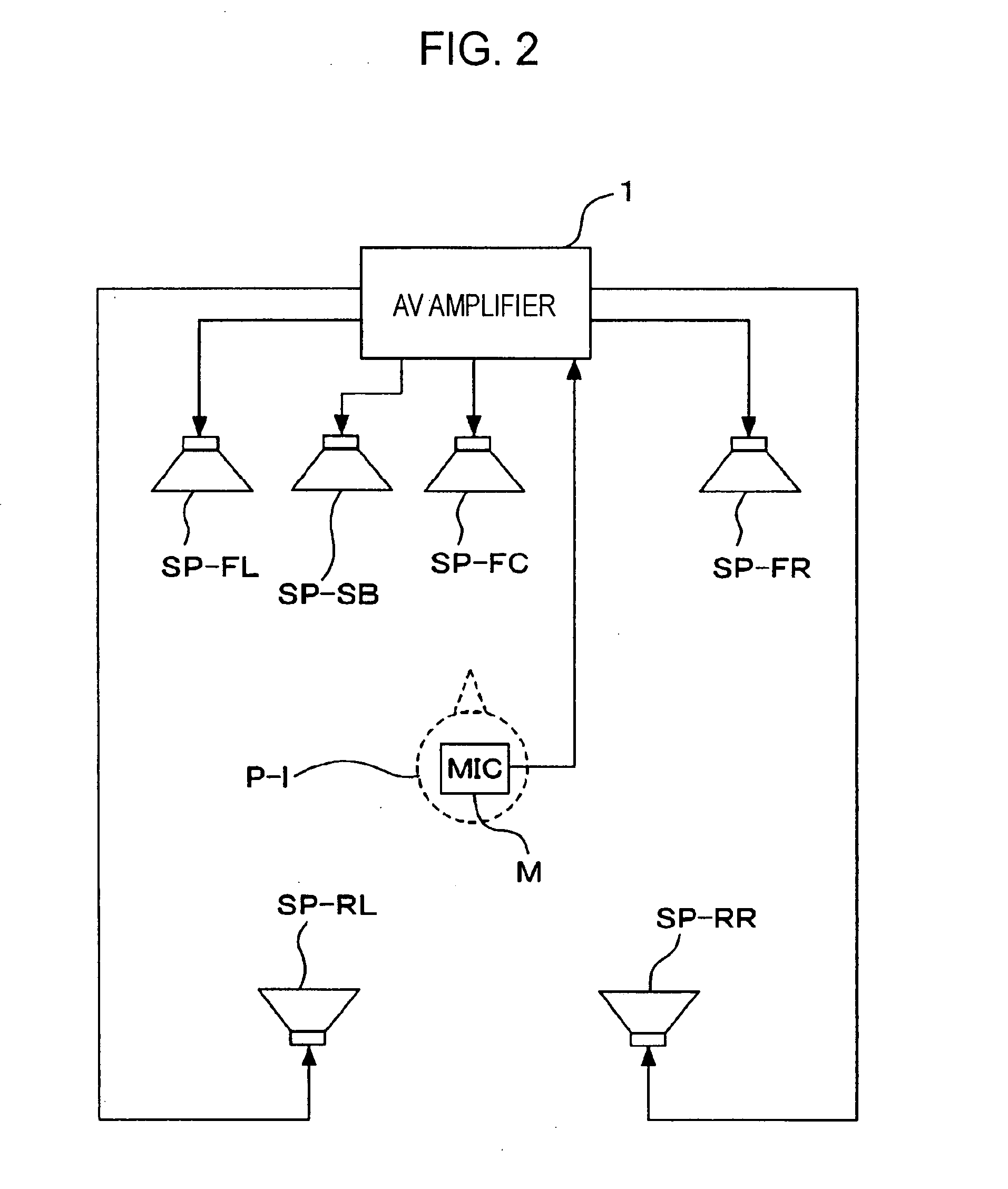
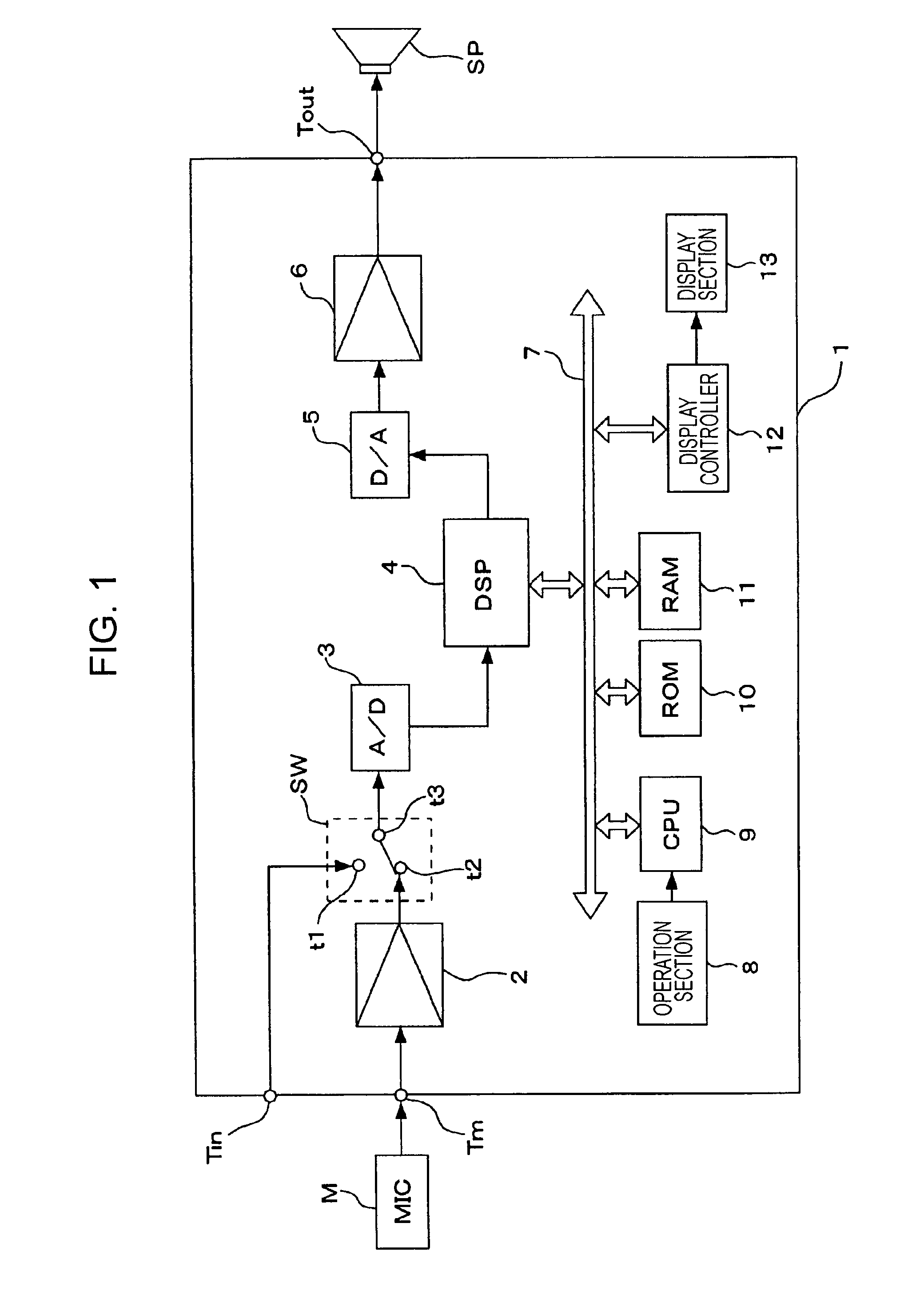
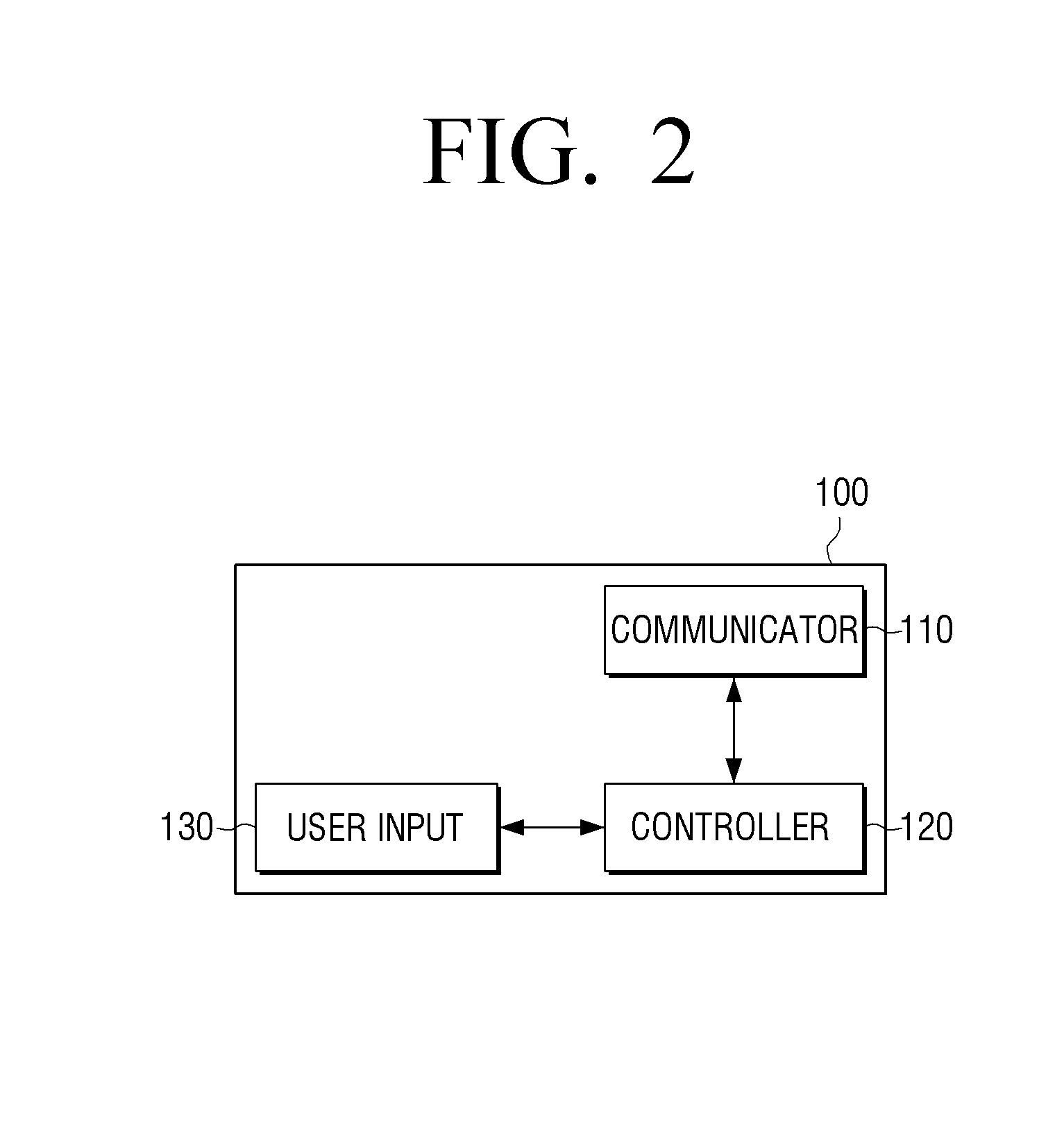
Systems and methods for optimizing speaker performance. The system includes a self-contained speaker unit that includes a speaker, an amplifier coupled to the speaker, and a processor coupled to the amplifier. The processor receives a first sound signal from a receiver and a second sound signal from a microphone, processes the first sound signal based on a plurality of parameters, outputs the processed sound signal to the speaker, and generates a video signal based on the second sound signal. A wireless remote control allows a user to manipulate the parameters. The processor generates a test sound signal and outputs it to the receiver. The receiver processes the test sound signal and returns it to the processor for output through the speaker. The video signal includes a graphical user interface having a frequency response graph of the second sound signal and an eight band equalizer.
Owner:VELODYNE ACOUSTICS
Systems and methods for transducer calibration and tuning
ActiveUS20110002471A1Headphones for stereophonic communicationDigital data processing detailsHard disc driveEarcon
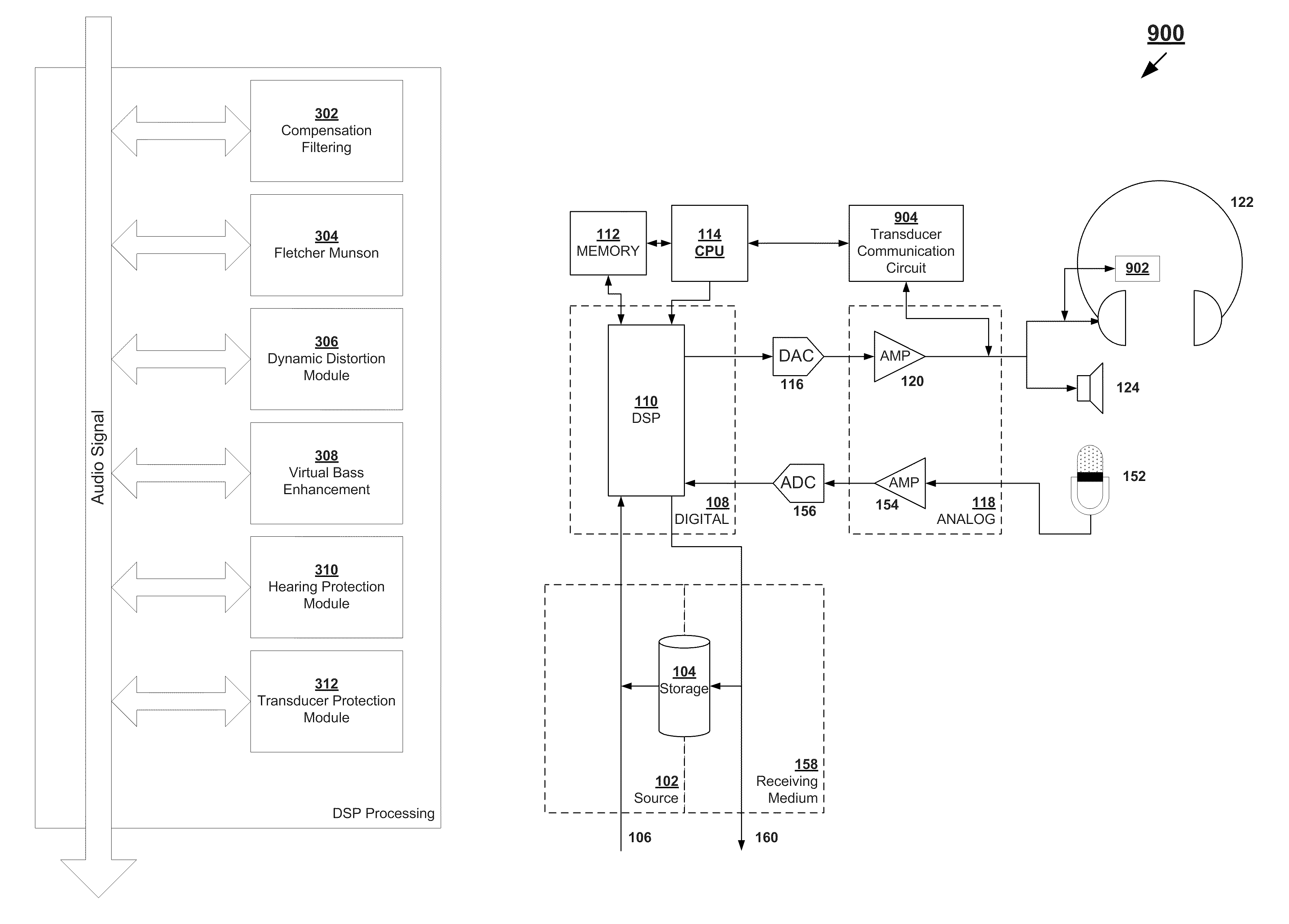
Audio transducers (headphones, speakers, microphones) inherently do not accurately reproduce the signal presented to them at the input. This can be compensated for by taking into account the transducer characteristics and transforming the input signal using a digital signal processor (DSP) to counteract the inaccuracies. However, for the compensation to take place, the DSP needs to know the characteristics of the transducer. For systems with built-in transducers (like laptops with internal speakers) the characteristics of the internal speakers can be stored on the hard-drive of the laptop and the DSP can read this data and make the appropriate compensations. Because a transducer (headphone, speaker, microphone) has its own characteristics that need to be compensated for separately, a profile is supplied to the DSP either by a database lookup based on an identification made by the user or transducer itself or by profile information stored on the transducer. Once the characteristics of a transducer are known, many additional DSP algorithms can be applied in order to improve the audio performance and even safety of the system.
Owner:SYNAPTICS INC
Systems and methods for transducer calibration and tuning
Owner:SYNAPTICS INC
Sound processing apparatus, method, and program
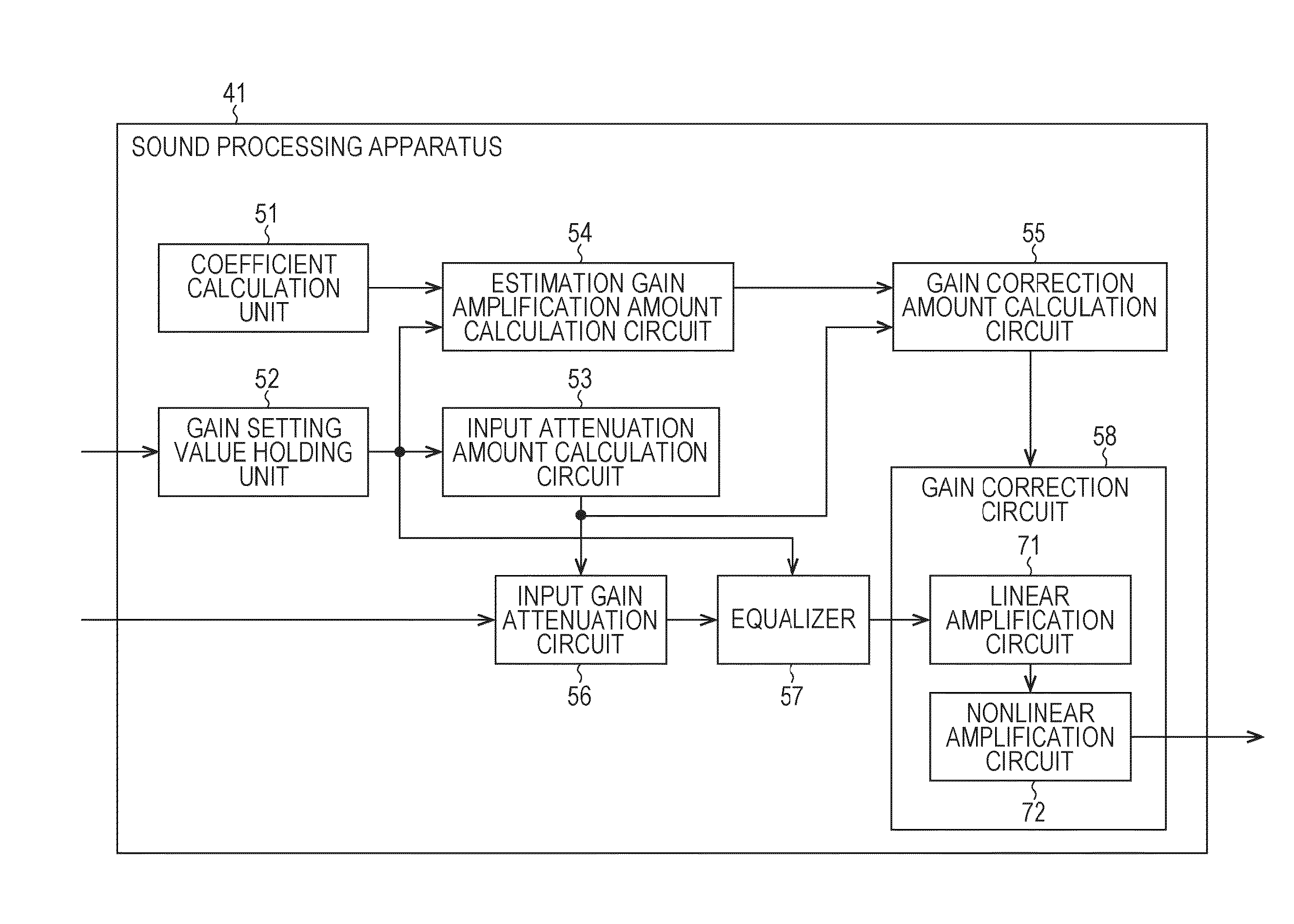
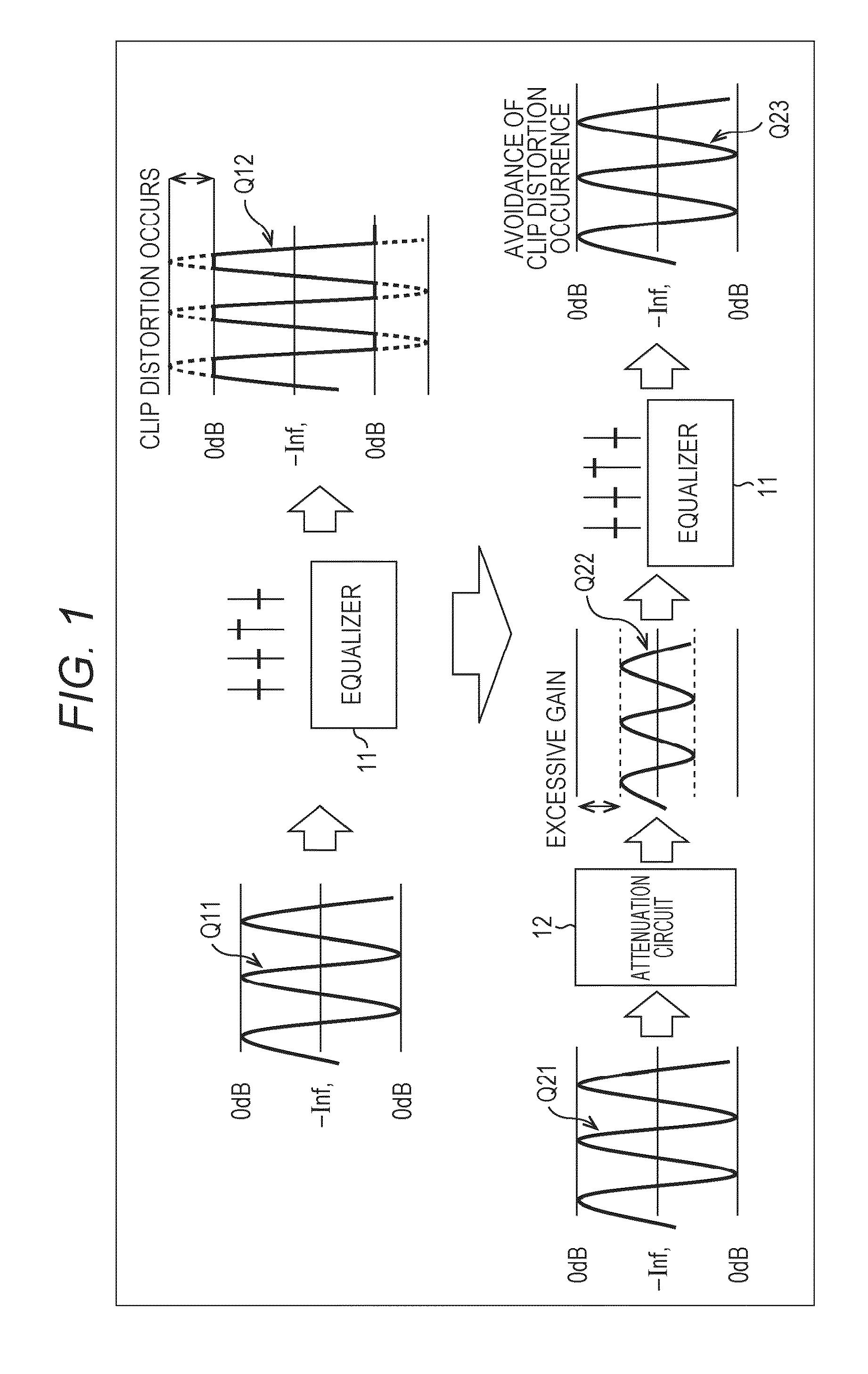
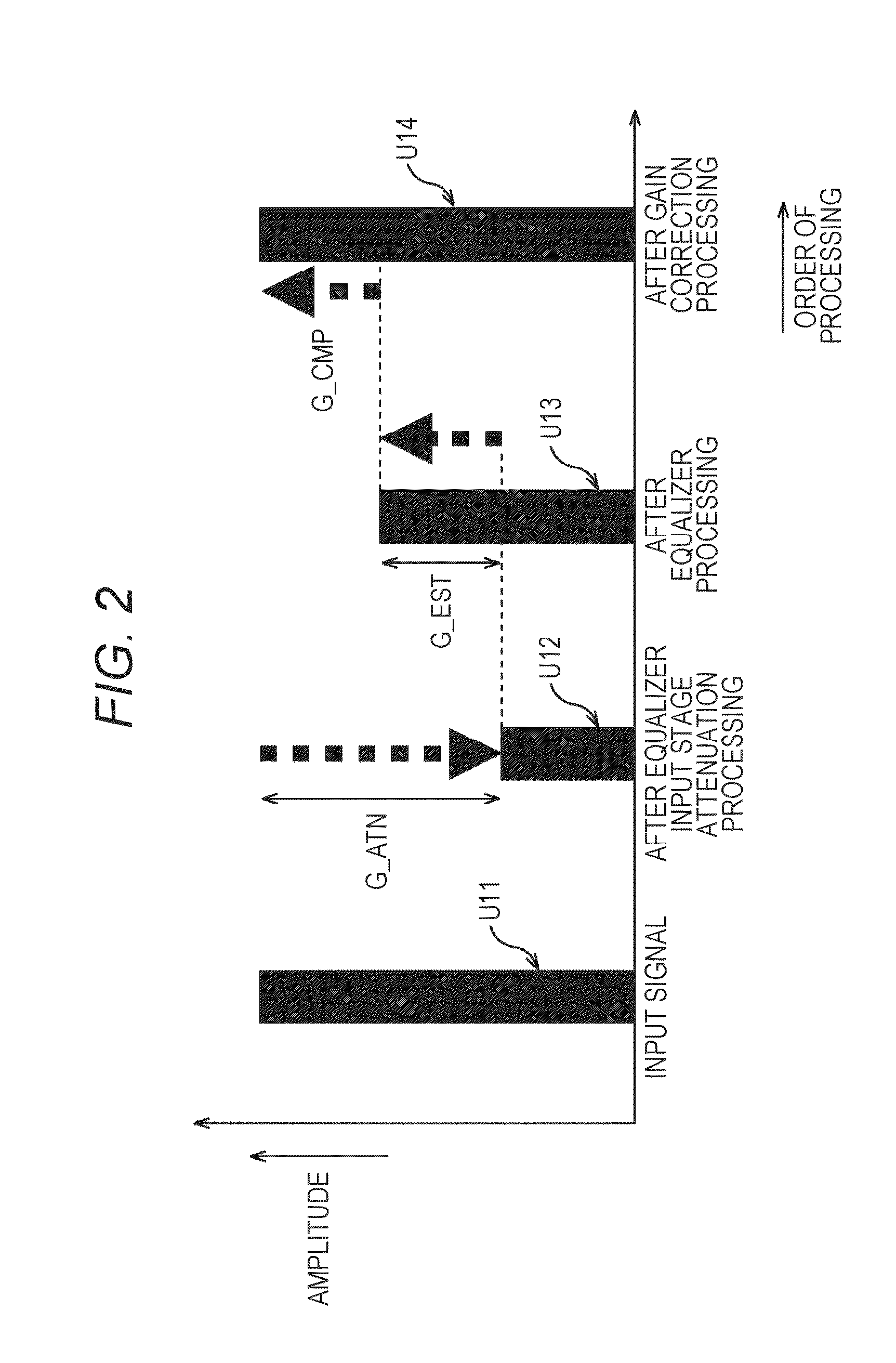
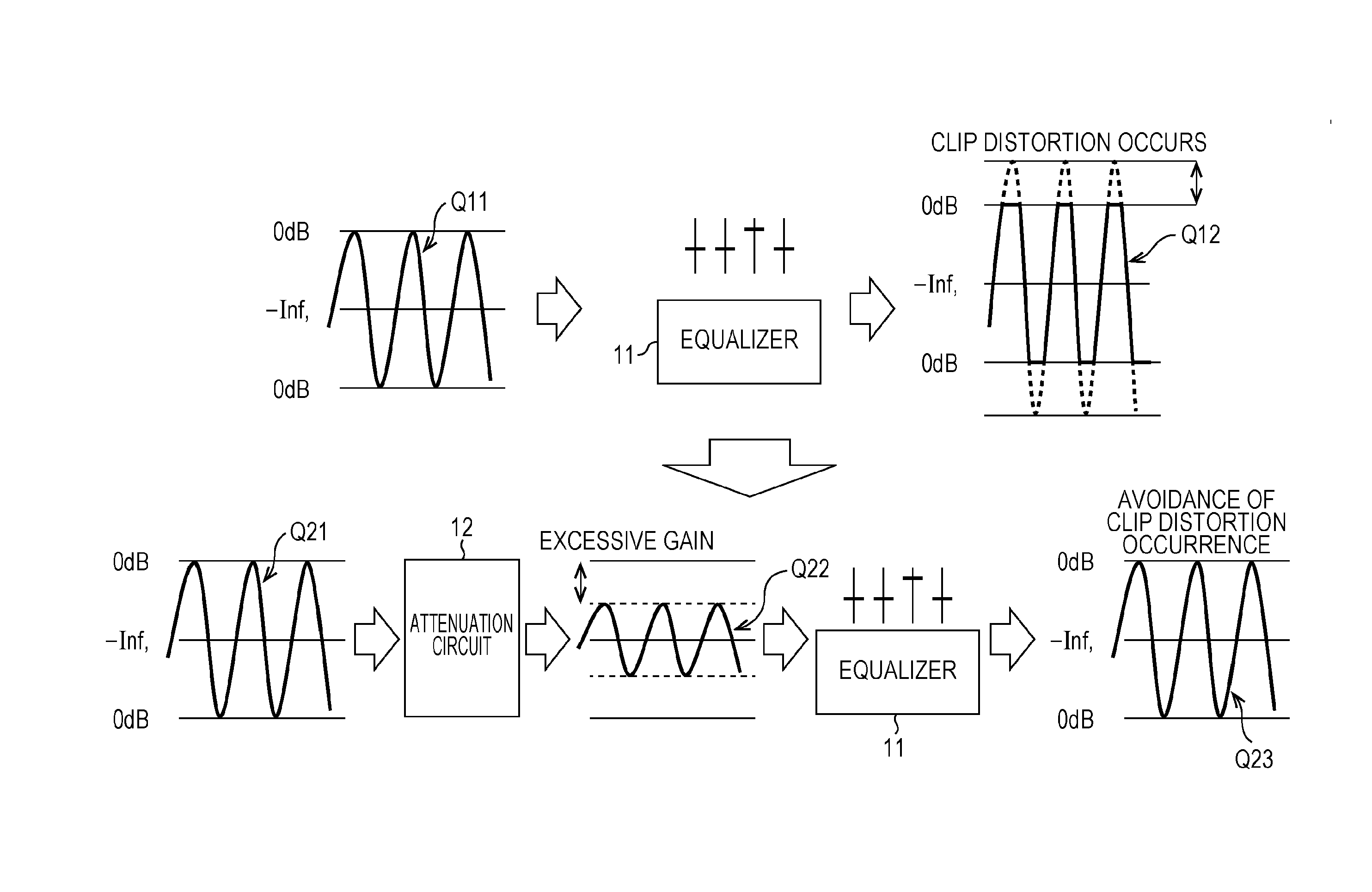
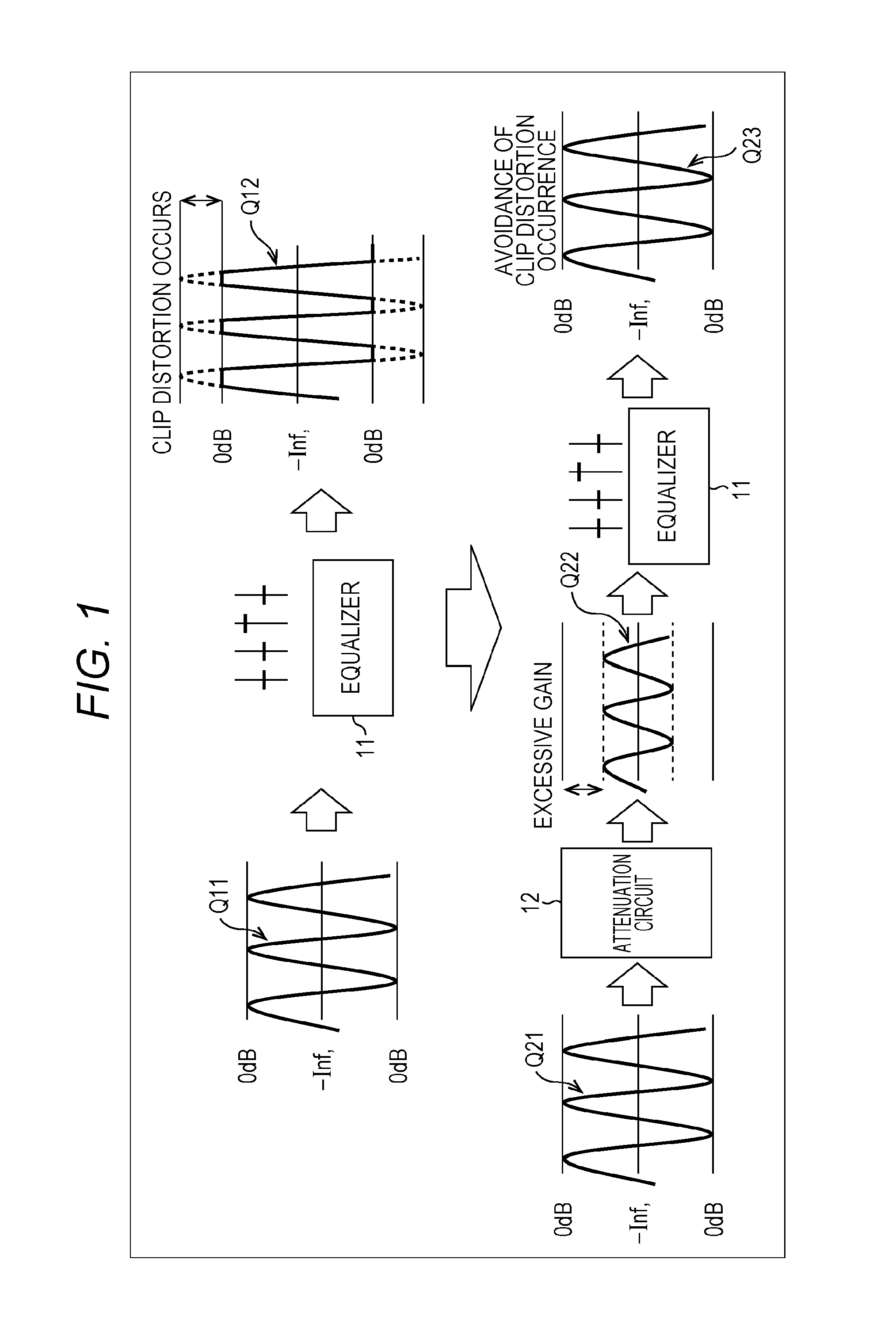
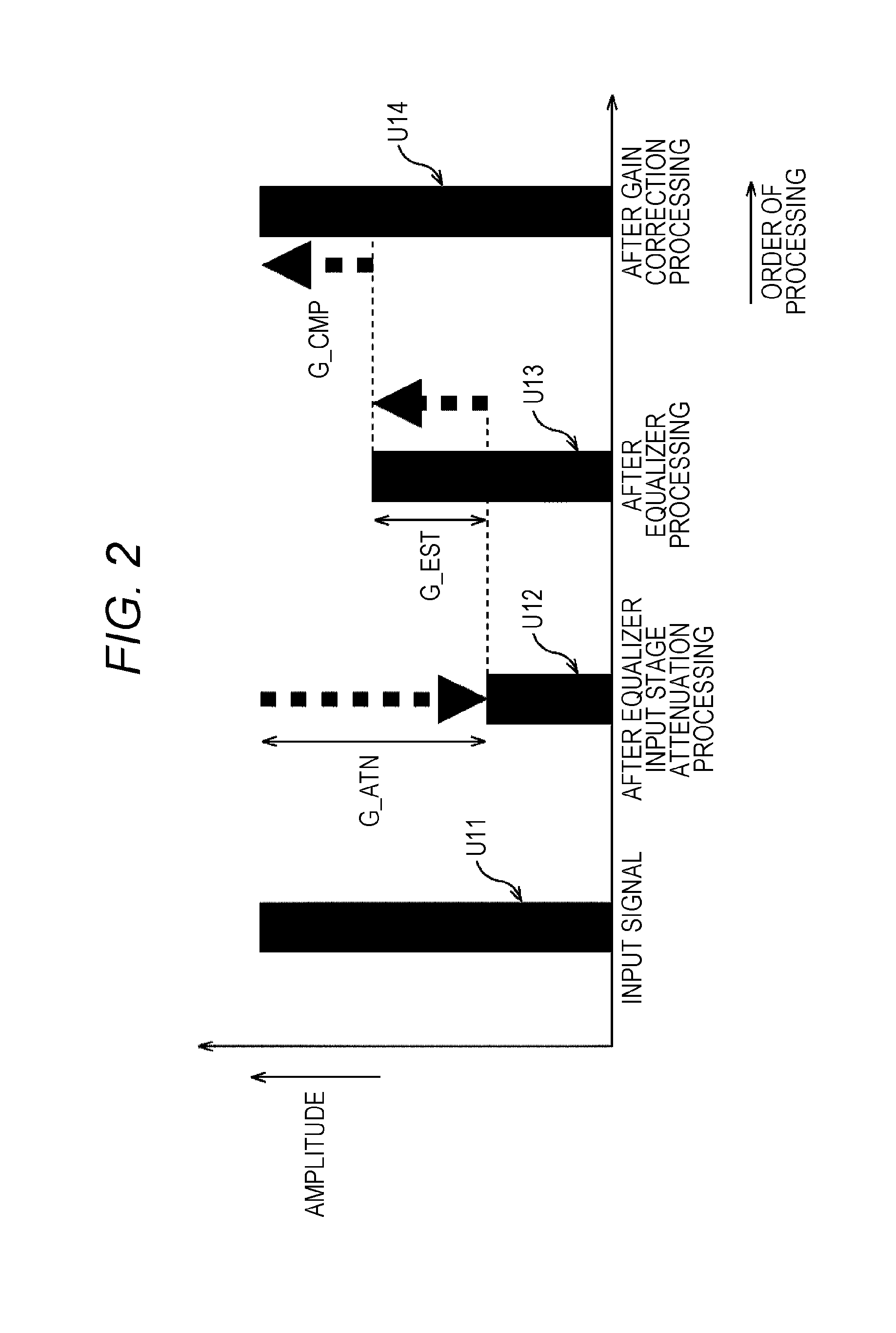
ActiveUS9294062B2Reduce quality degradationQuality improvementAnalog signal digital controlAutomatic tone/bandwidth controlUltrasound attenuationWeight coefficient
The present technique relates to a sound processing apparatus, a method, and a program capable of alleviating degradation of the quality of sound in a case where the gain of a sound signal is amplified.When equalizer processing for adjusting the gain of each frequency band of an input signal on the basis of a gain setting value is performed, an input signal is attenuated by an input attenuation amount derived from the gain setting value, and the equalizer processing is performed on the input signal attenuated. The amount of amplification of the gain of the input signal in the equalizer processing is estimated on the basis of the gain setting value and a weight coefficient of each frequency band derived from a generally-available music signal prepared in advance, and a difference of the estimation value and the input attenuation amount is calculated as a gain correction amount. Further, nonlinear amplification processing is performed on the input signal so as to actually amplify the input signal, which has been subjected to the equalizer processing, by a gain correction amount, and an output signal is obtained. The present technique can be applied to a sound processing apparatus.
Owner:SONY CORP
Audio processing
ActiveUS20110096933A1Quantity minimizationDigital technique networkGain controlEngineeringAudio frequency
A method of generating a desired shelving filter for audio data, the desired shelving filter having a low-corner frequency U and a high-corner frequency f2, wherein the difference between the gain of the frequency response of the desired shelving filter at f2 and the gain of the frequency response of the desired shelving filter at U is substantially equal to a non-zero desired amount, the method comprising: determining an order for a first shelving filter of a first predetermined type, wherein the low-corner frequency of the first shelving filter is U and the high-corner frequency of the first shelving filter is fΣ, determining, for a second shelving filter of a second predetermined type and of a predetermined order m, a frequency fz for the low-corner frequency of the second shelving filter and a frequency Z4 for the high-corner frequency of the second shelving filter, where h is at least fi, f4 is greater than f3, and f4 is at most fi, and forming the desired shelving filter as a filter combination of the first shelving filter and the second shelving filter; wherein fz, f4 and the order of the first shelving filter are determined such that difference between the gain of the frequency response of the filter combination at fe and the gain of the frequency response of the filter combination at fi is substantially equal to the desired amount.
Owner:OXFORD DIGITAL
Linearized filter band equipment and processes
ActiveUS7266205B2Amplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceDigital computer detailsGraphicsSystems design
A method for use with equipment having filters, the method characterized by multiplying a matrix having a specified cut-boost setting of a filter of a graphic equalizer by a correction matrix to create a matrix having a corrected cut-boost setting of the filter of the graphic equalizer; adjusting an actual cut-boost setting of the filter of the graphic equalizer to be substantially equal to the corrected cut-boost setting of the filter of the graphic equalizer; and configuring the filter to have a Q value substantially equal to a linearizing Q value. In addition to the foregoing, other method embodiments are described in the claims, drawings, and text forming a part of the present application. In one or more various embodiments, related systems include but are not limited to circuitry and / or programming for effecting the foregoing-referenced method embodiments; the circuitry and / or programming can be virtually any combination of hardware, software, and / or firmware configured to effect the foregoing-referenced method embodiments depending upon the design choices of the system designer.
Owner:INMUSIC BRANDS
Graphic equalizers
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
System and method for digital signal processing
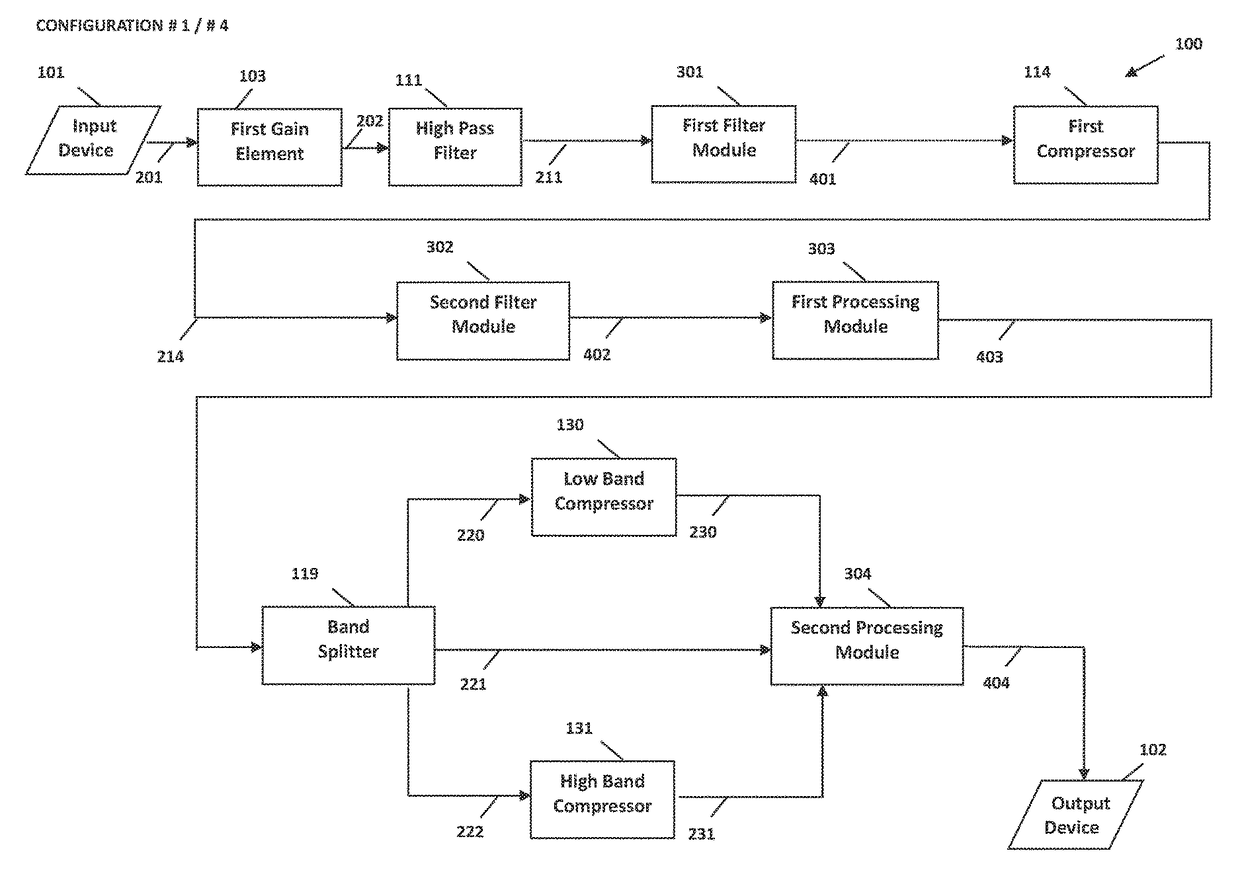
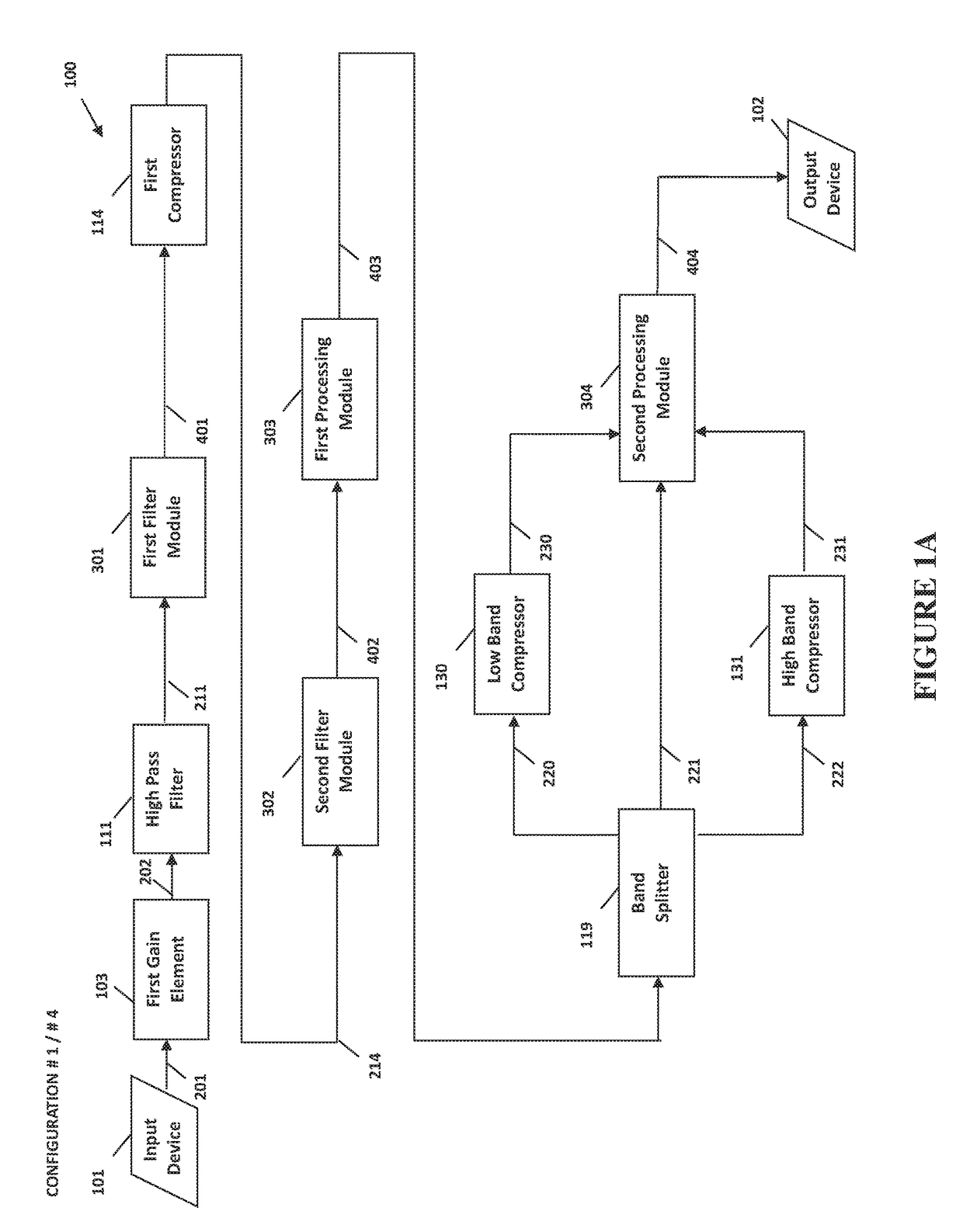
ActiveUS9397629B2Increase or decrease overshoots or undershoots in the signalDigital/coded signal controlSpeech analysisDigital signal processingIntermediate frequency
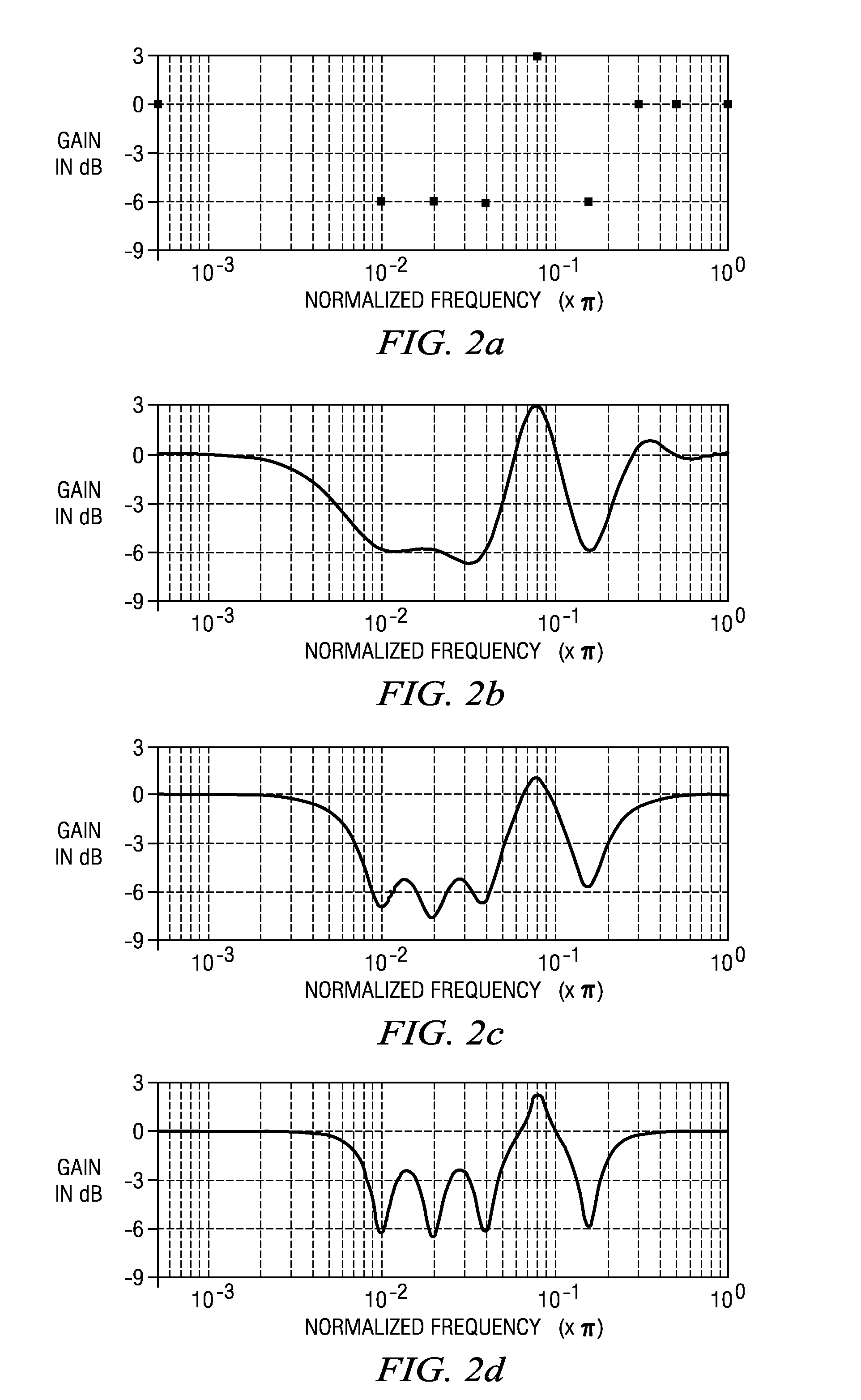
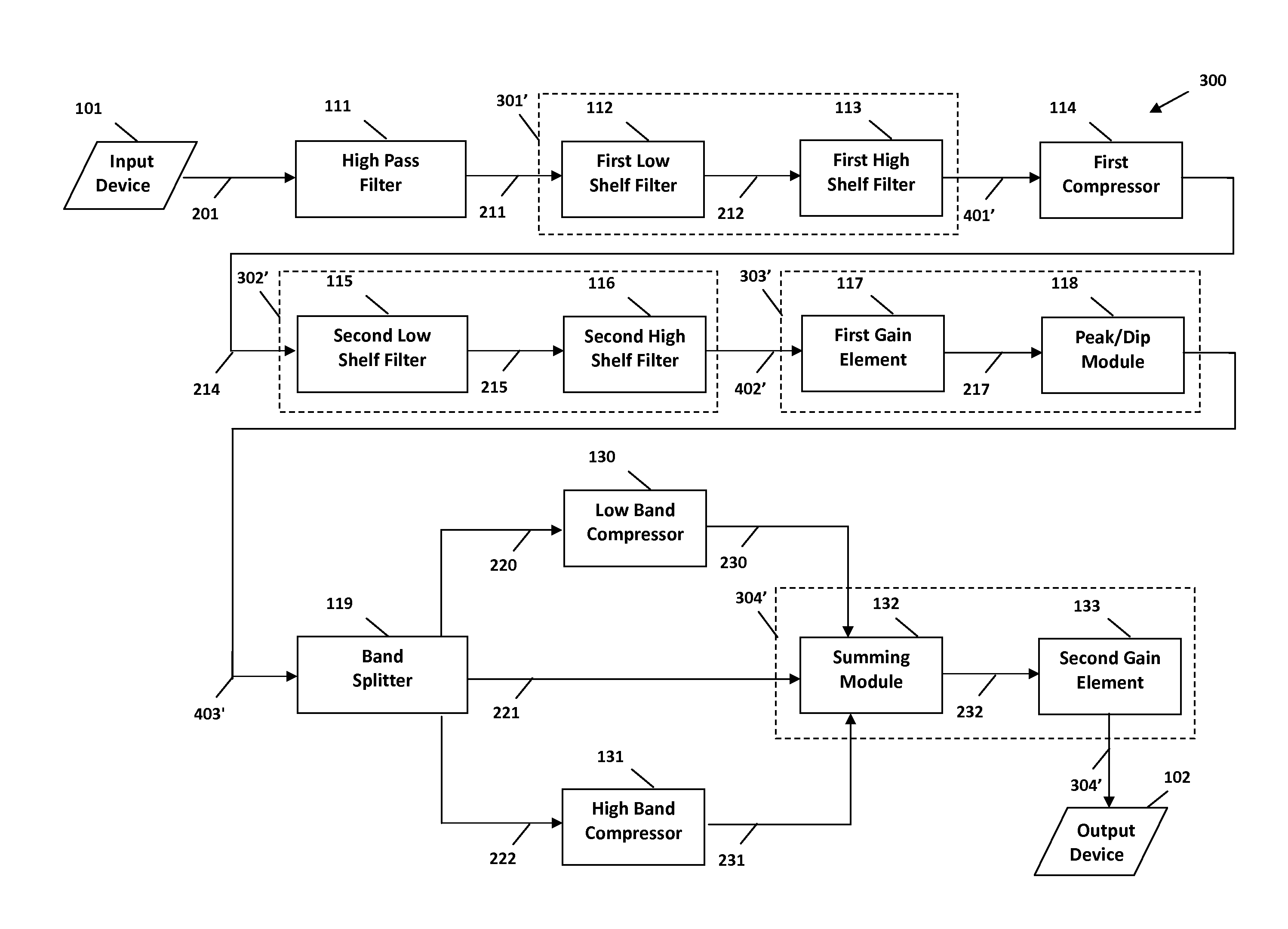
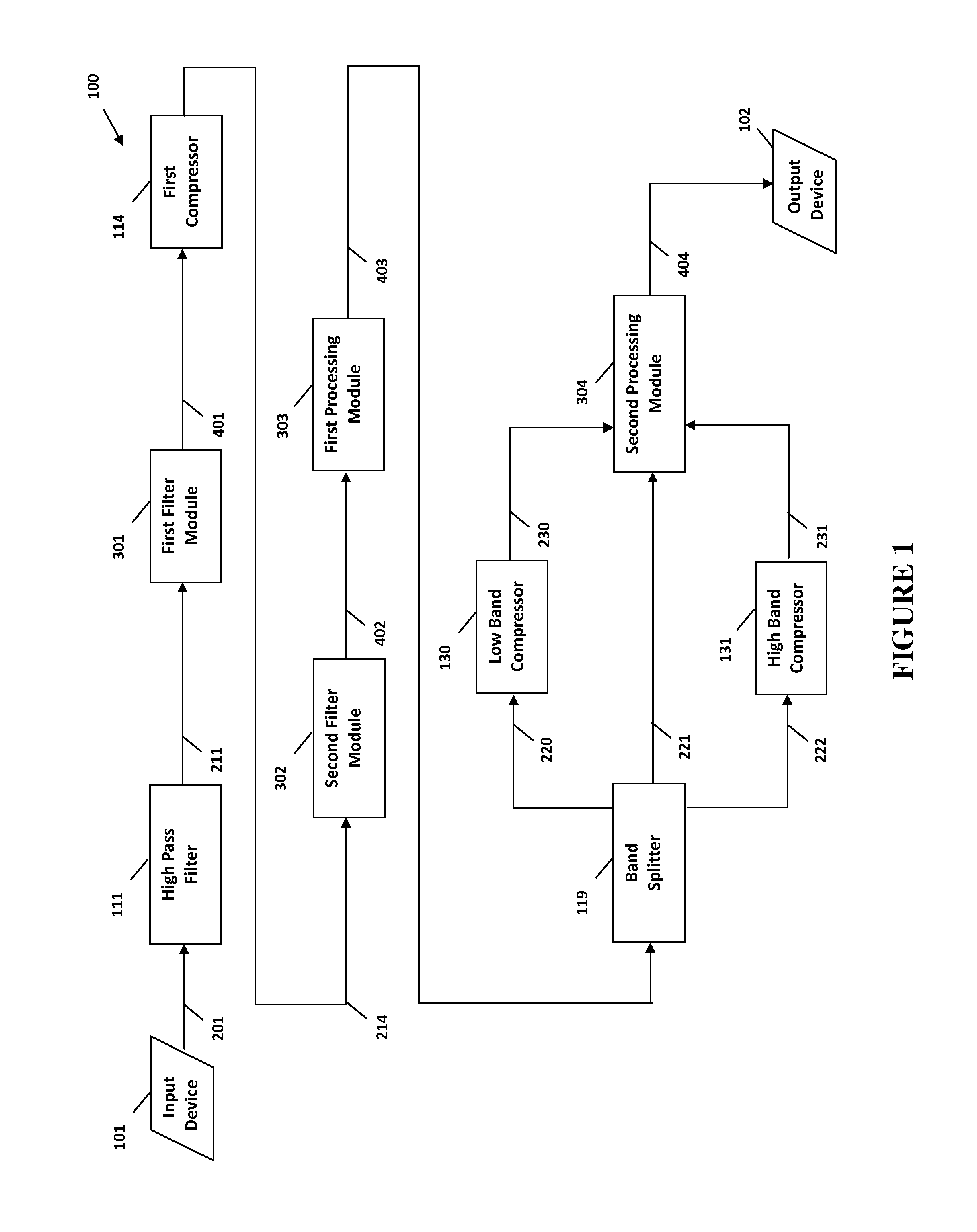
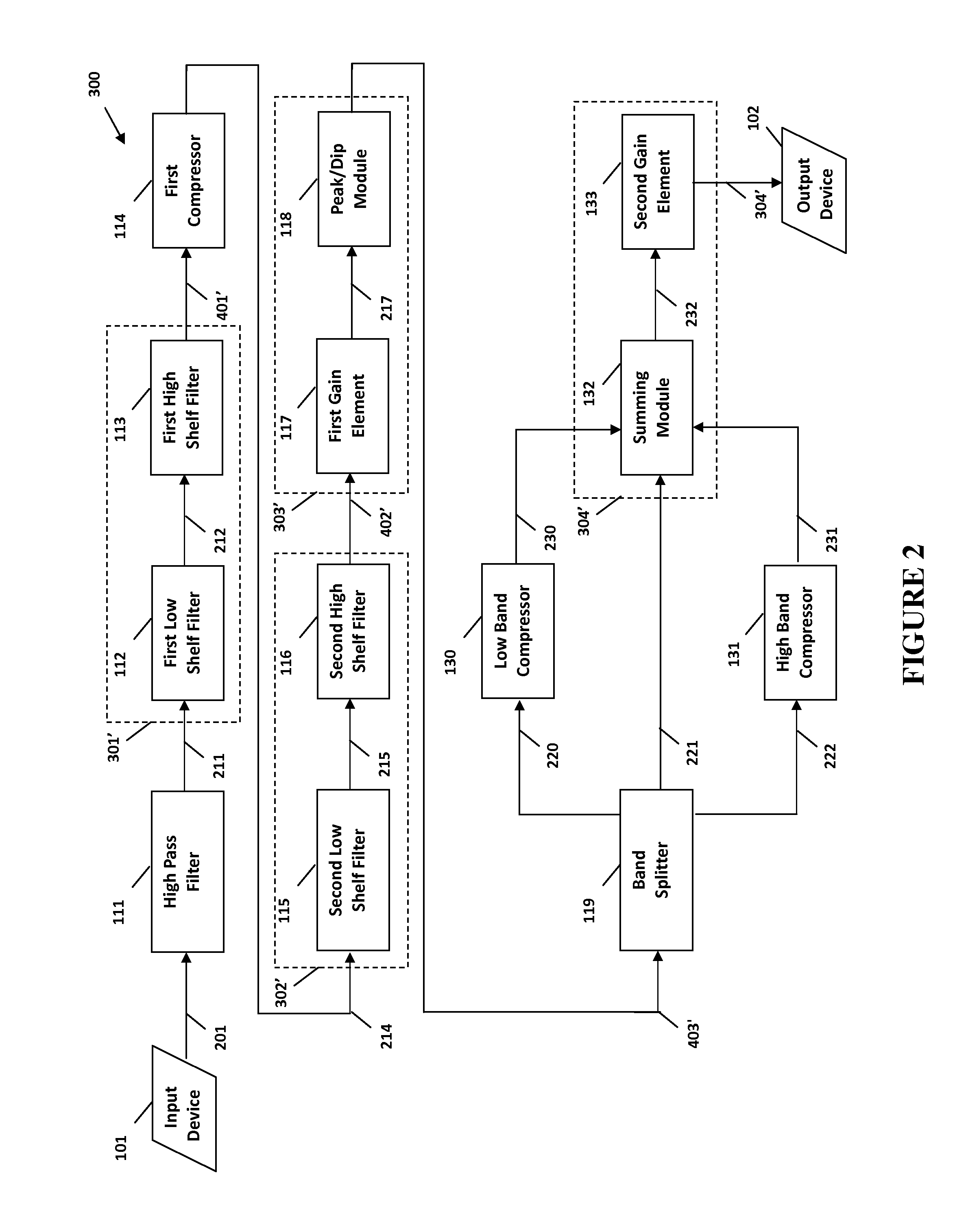
The present invention provides methods and systems for digital processing of an input audio signal. Specifically, the present invention includes a high pass filter configured to filter the input audio signal to create a high pass signal. A first filter module then filters the high pass signal to create a first filtered signal. A first compressor modulates the first filtered signal to create a modulated signal. A second filter module then filters the modulated signal to create a second filtered signal. The second filtered signal is processed by a first processing module. A band splitter splits the processed signal into low band, mid band, and high band signals. The low band and high band signals are modulated by respective compressors. A second processing module further processes the modulated low band, mid band, and modulated high band signals to create an output signal.
Owner:BONGIOVI ACOUSTICS LLC
Sound processing apparatus, method, and program
ActiveUS20140205111A1Reduce quality degradationQuality improvementAnalog signal digital controlAutomatic tone/bandwidth controlUltrasound attenuationSignal on
The present technique relates to a sound processing apparatus, a method, and a program capable of alleviating degradation of the quality of sound in a case where the gain of a sound signal is amplified.When equalizer processing for adjusting the gain of each frequency band of an input signal on the basis of a gain setting value is performed, an input signal is attenuated by an input attenuation amount derived from the gain setting value, and the equalizer processing is performed on the input signal attenuated. The amount of amplification of the gain of the input signal in the equalizer processing is estimated on the basis of the gain setting value and a weight coefficient of each frequency band derived from a generally-available music signal prepared in advance, and a difference of the estimation value and the input attenuation amount is calculated as a gain correction amount. Further, nonlinear amplification processing is performed on the input signal so as to actually amplify the input signal, which has been subjected to the equalizer processing, by a gain correction amount, and an output signal is obtained. The present technique can be applied to a sound processing apparatus.
Owner:SONY CORP
Audio output apparatus
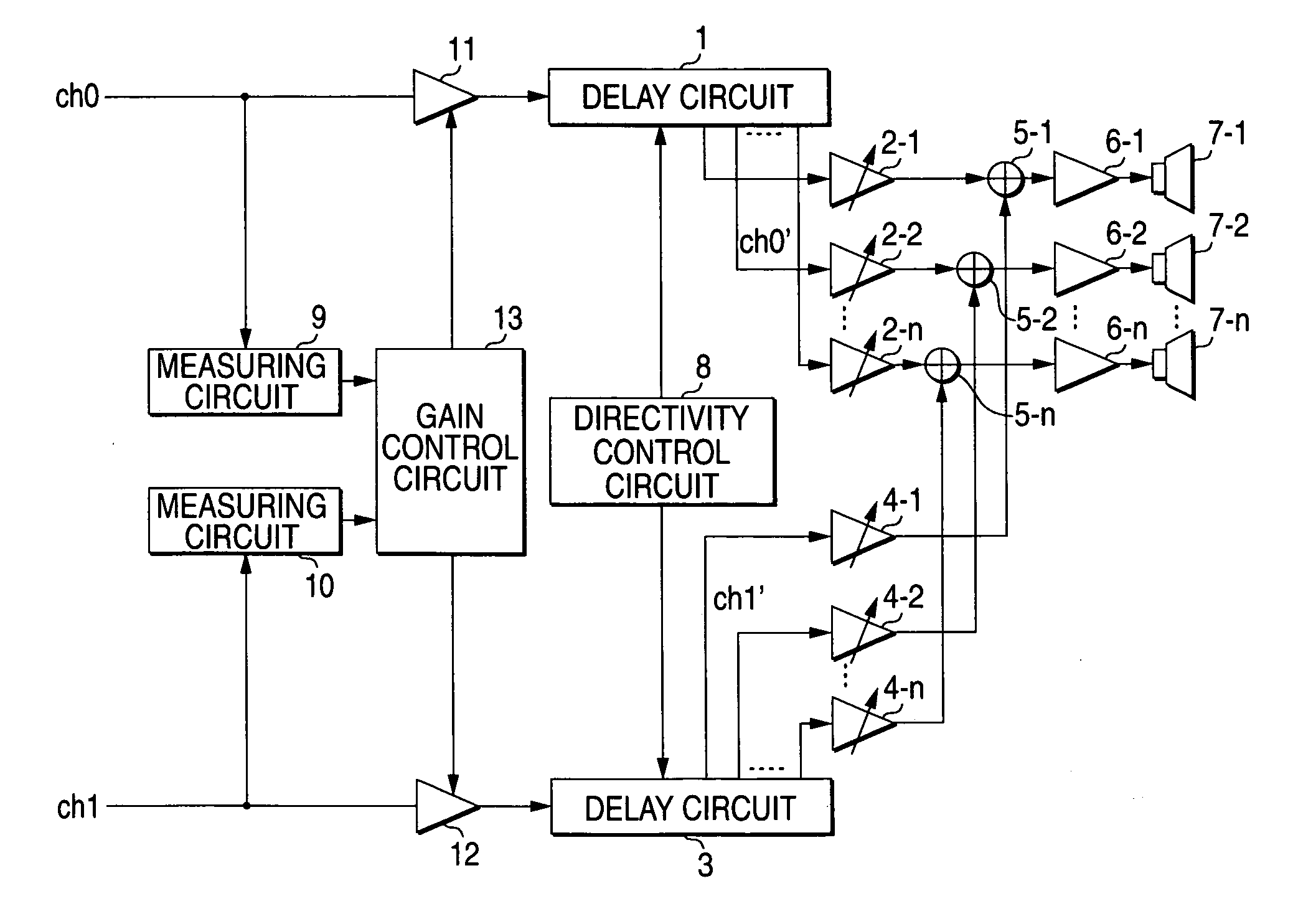
ActiveUS20070076905A1Improve the separation of audibility of a plurality of soundsExcellently listenSignal processingTransducers for sound channels pluralityAudio power amplifierEngineering
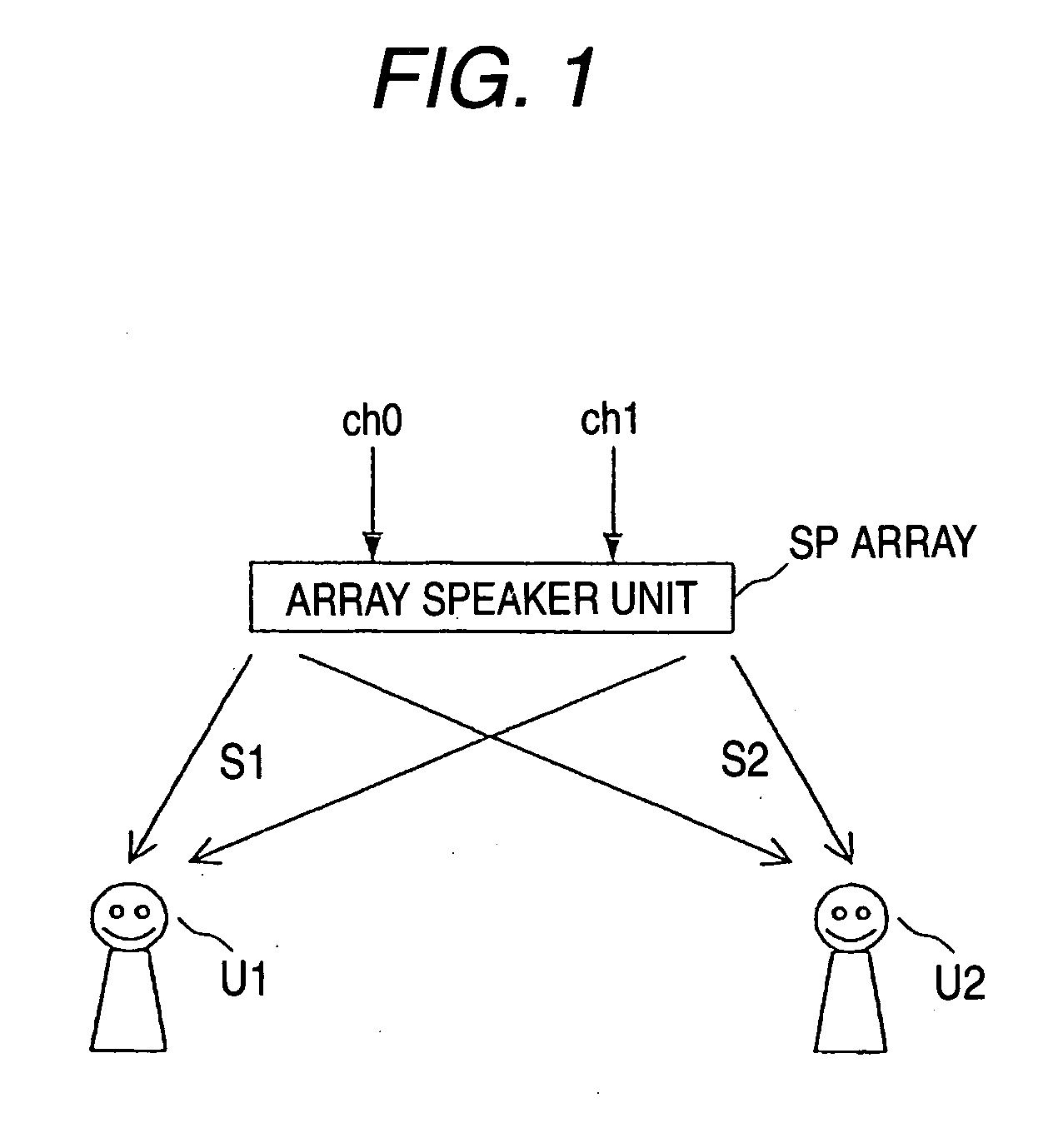
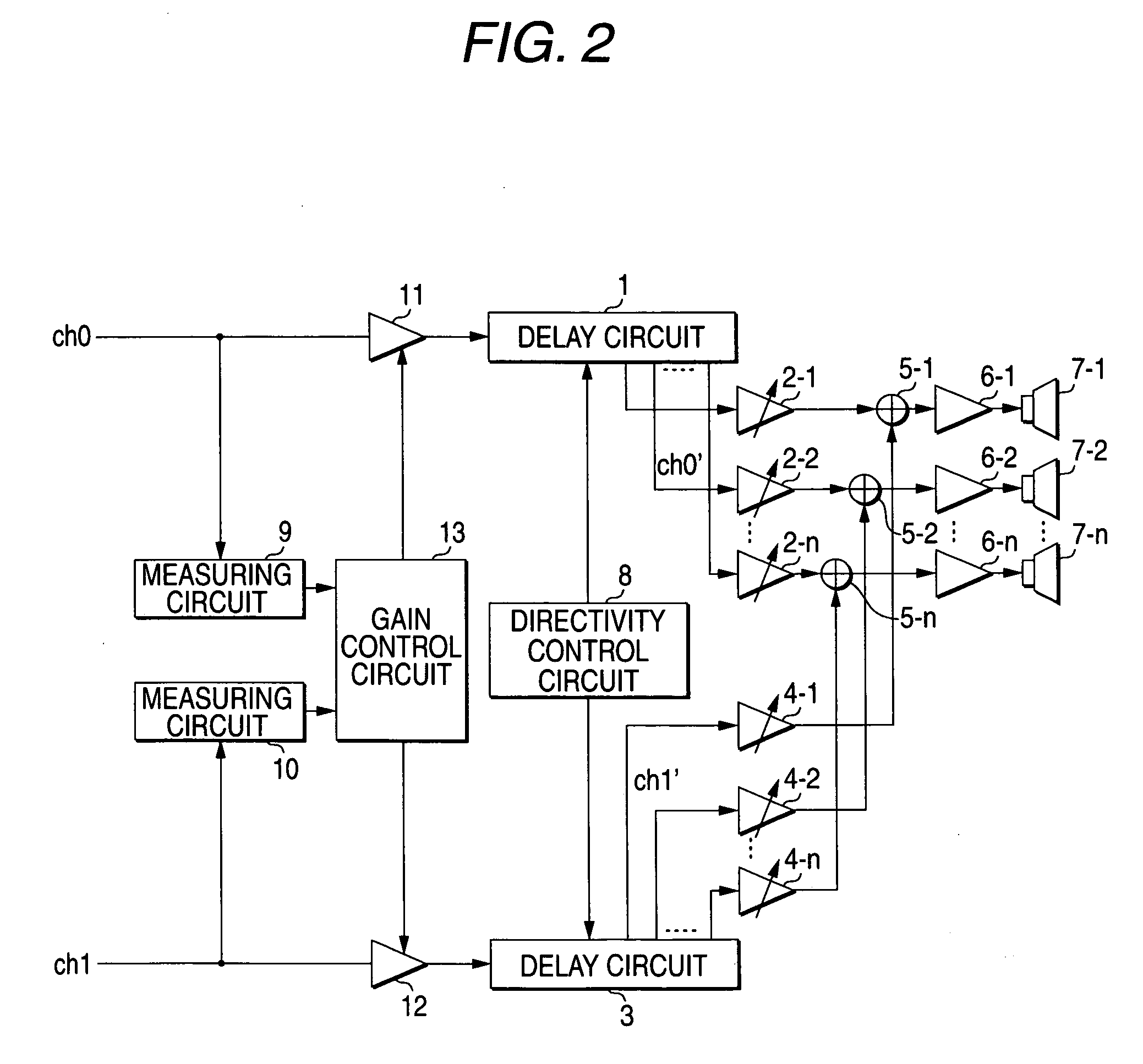
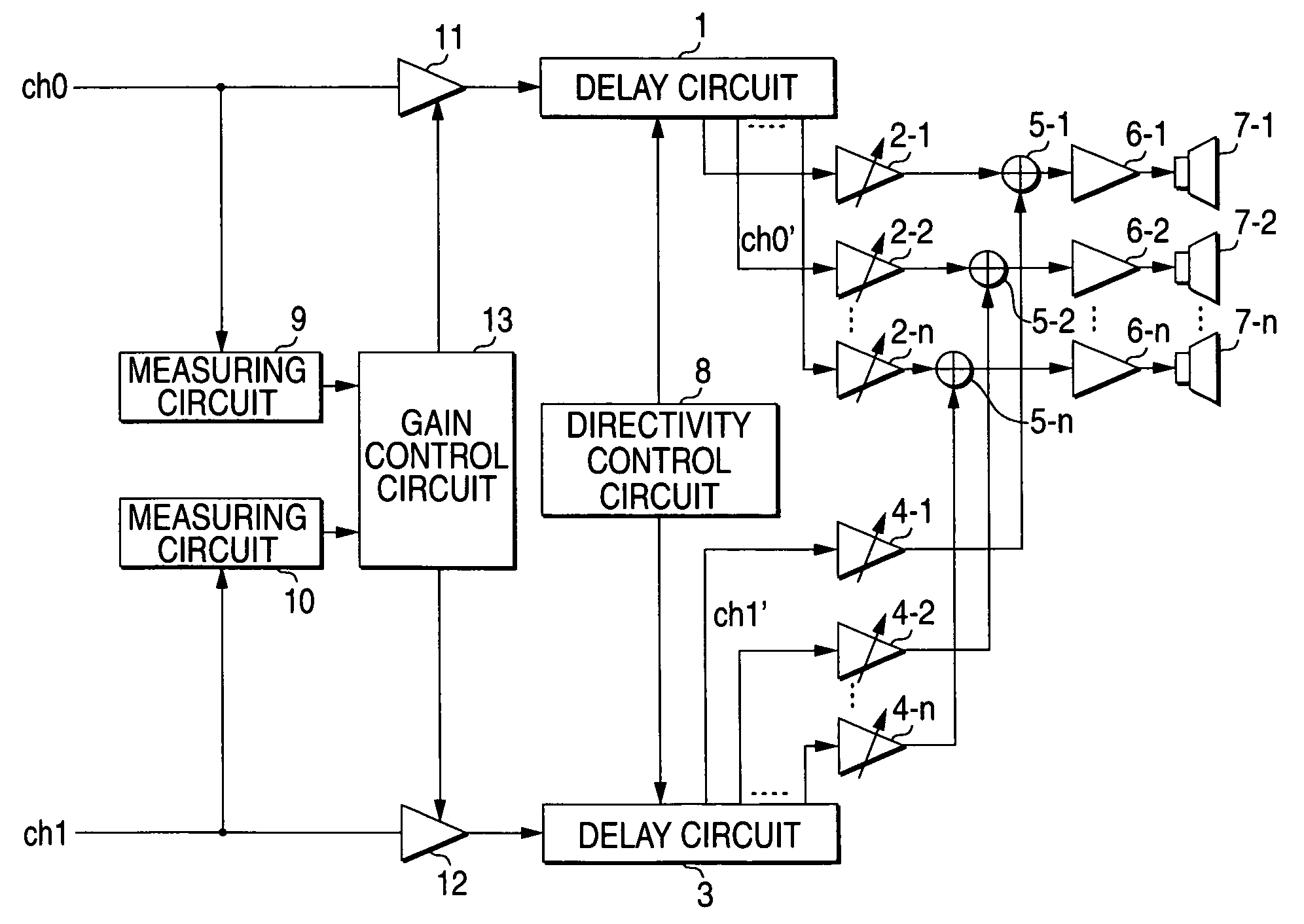
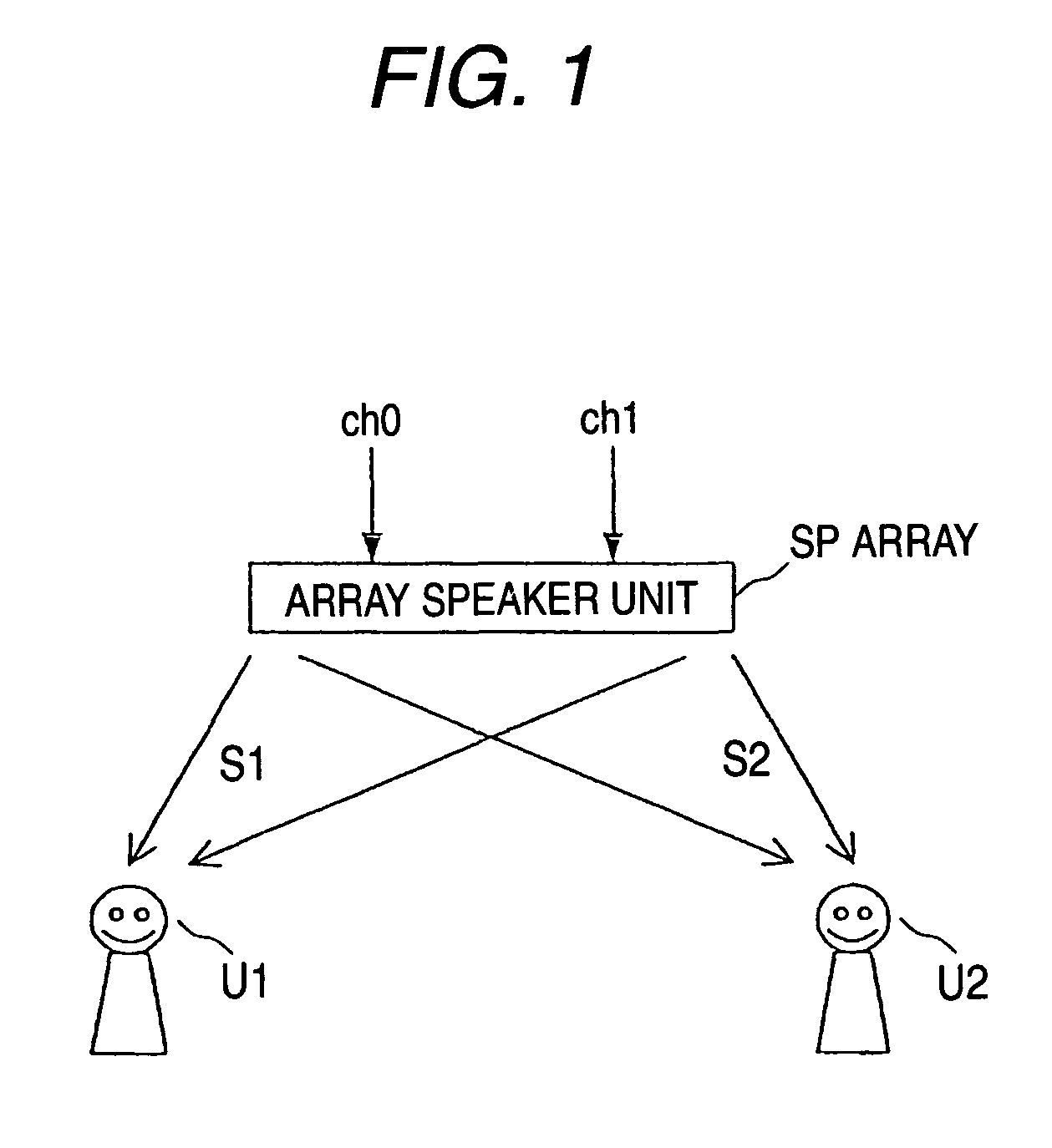
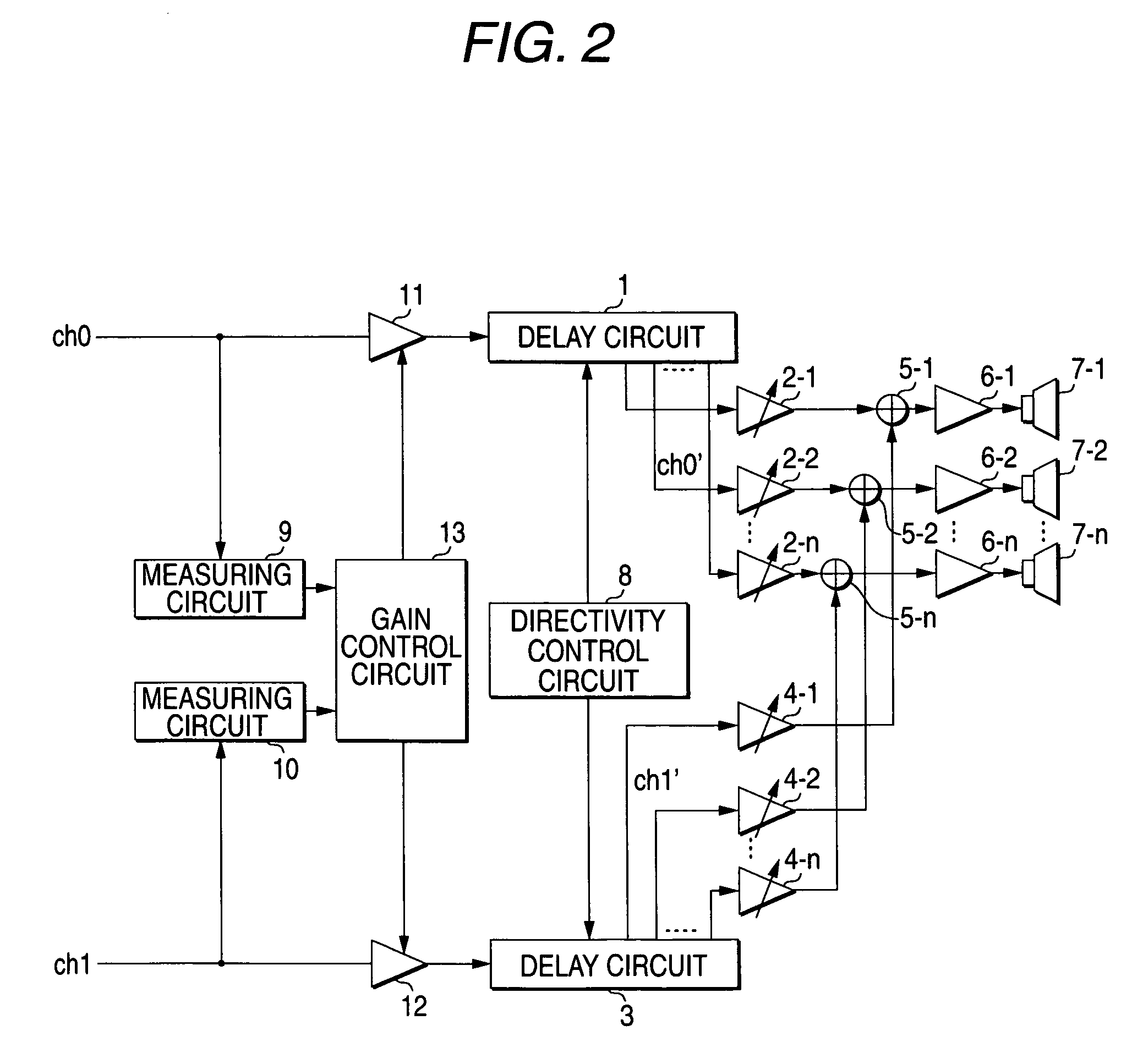
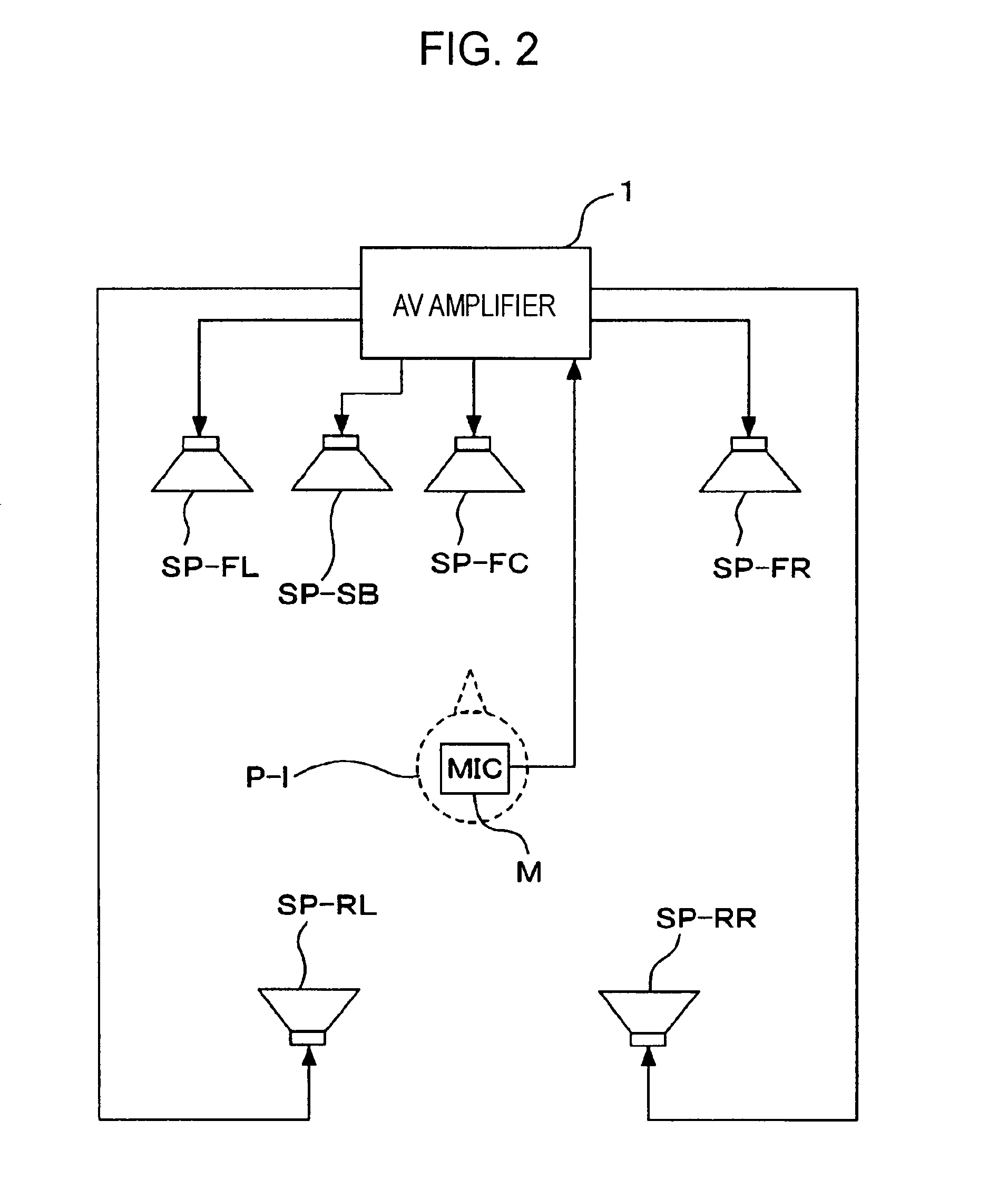
An audio output apparatus has a measuring circuit which measures the levels of at least two sound signals, a sound level adjusting module (a sound level adjusting circuit and a gain control circuit) which adjusts a sound level so as to equal the levels of the sound signals based on the levels measured at the measuring circuit, and an array speaker unit (a delay circuit, a multiplier, an adder, an amplifier and a speaker unit) which emits sounds in accordance with the sound signals outputted from the sound level adjusting module in different directivities respectively.
Owner:YAMAHA CORP
System and method for digital signal processing in deep diving environment
ActiveUS9564146B2Facilitate operational safetyFacilitate communicationGain controlSpeech analysisDigital signal processingComputer module
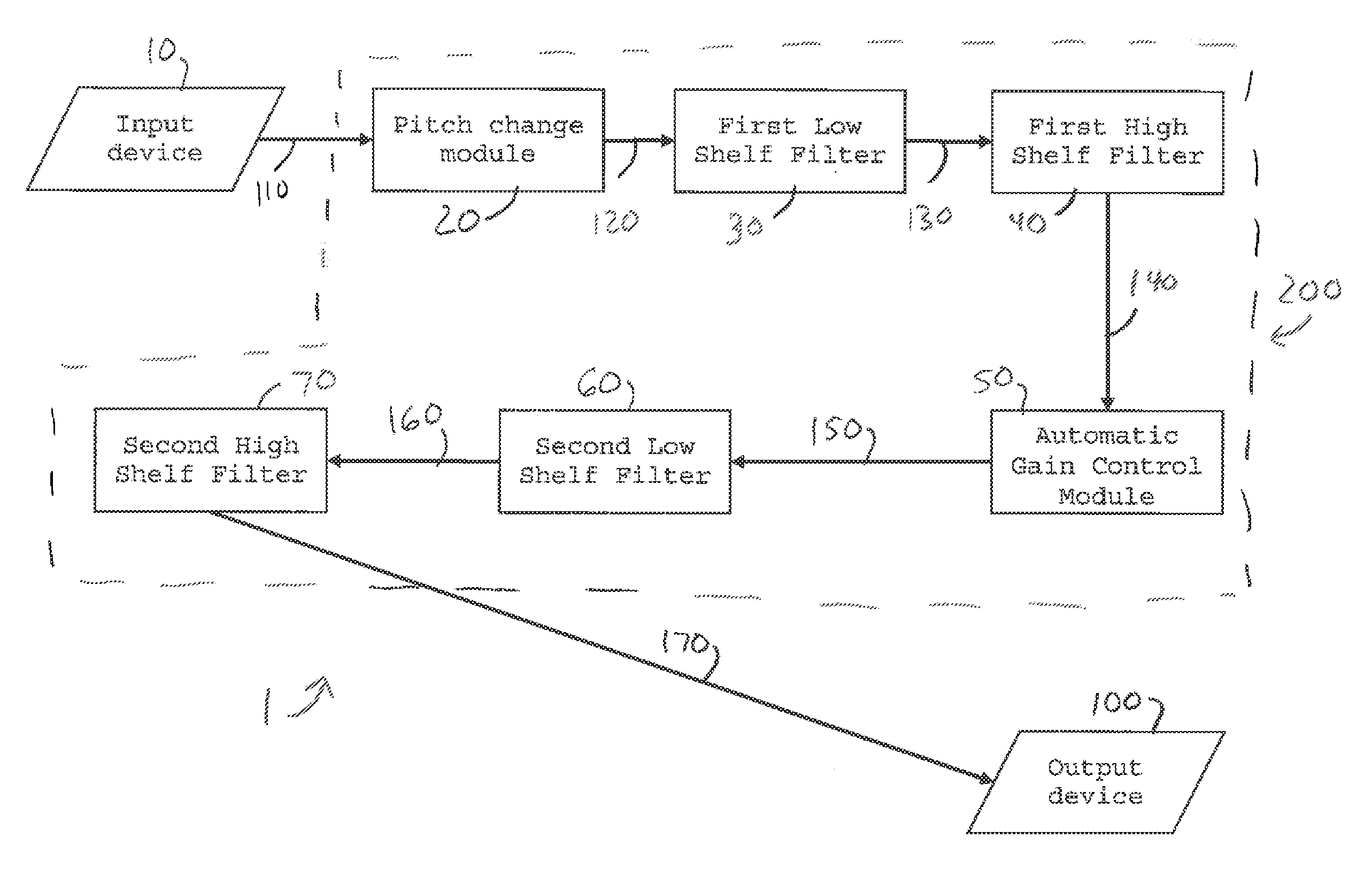
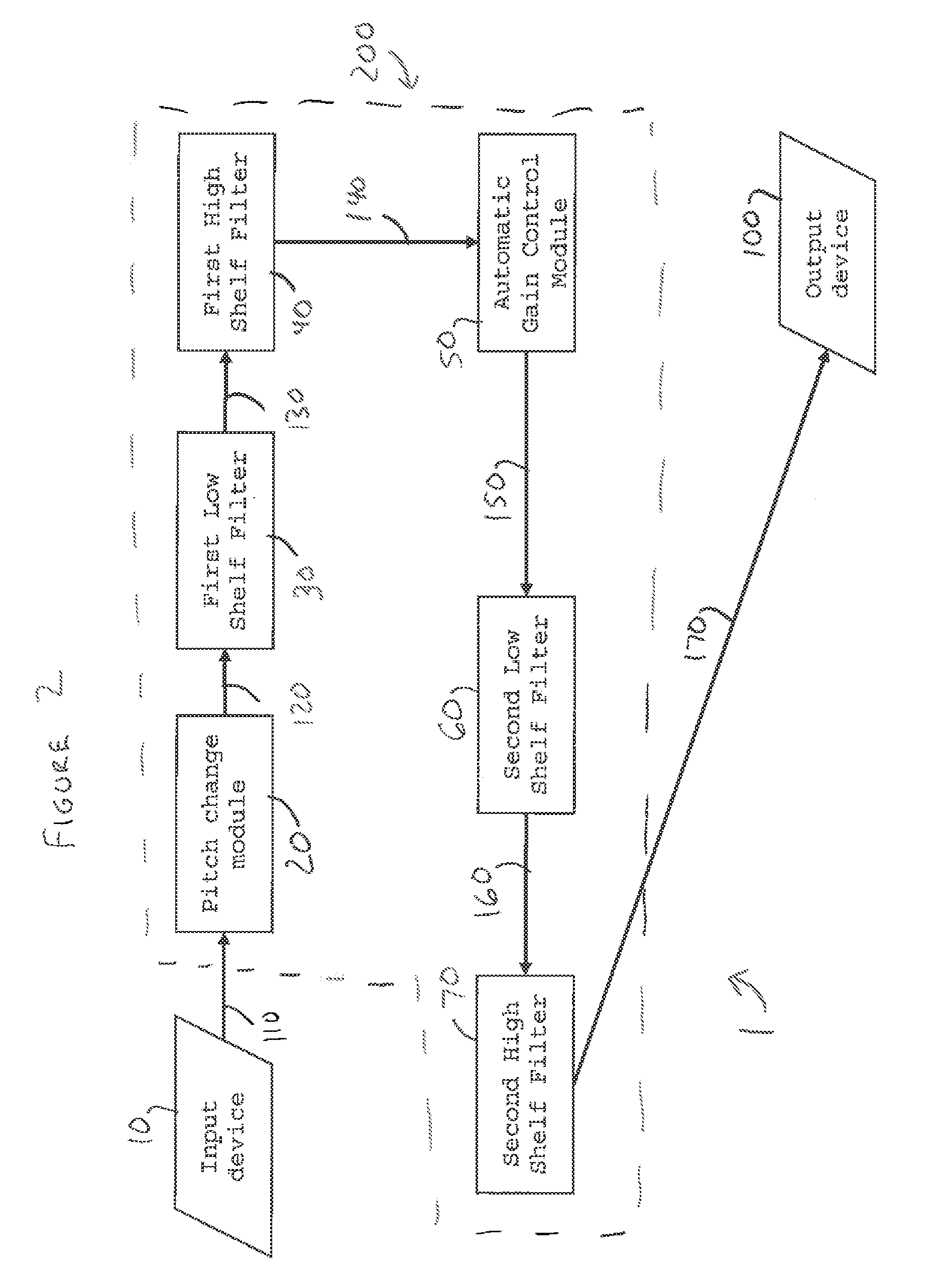
The present invention relates to a system for processing of an audio signal relating to a diver in a deep diving environment. The system comprises an input device structured to receive the signal, a pitch changing module configured to change the pitch of the received signal, a plurality of processing modules collectively configured to process the pitch changed signal and produce a processed signal. The present invention is further directed to a method for processing of an audio signal relating to a diver in a deep diving environment.
Owner:BONGIOVI ACOUSTICS LLC
LNA with Linearized Gain Over Extended Dynamic Range
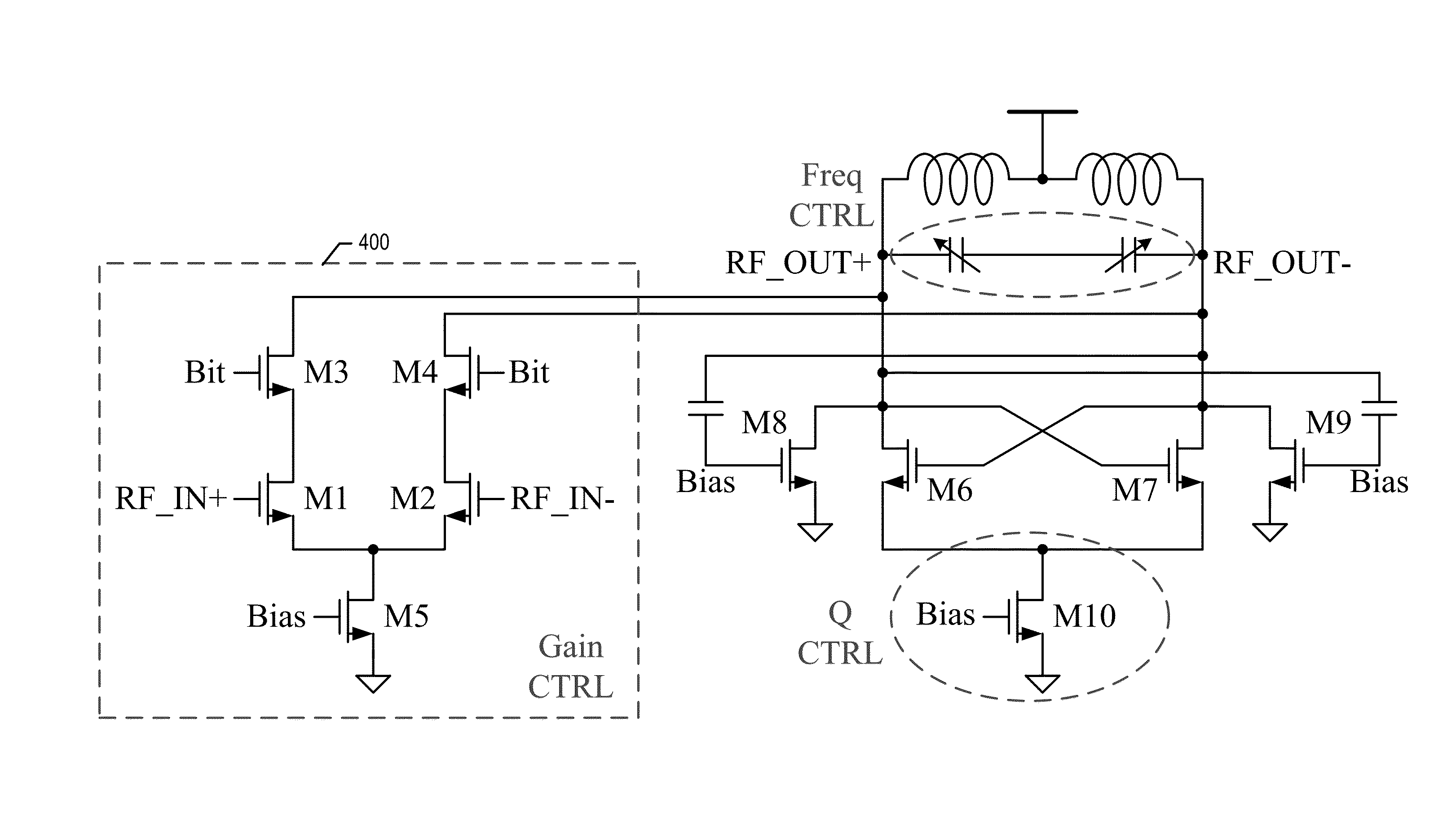
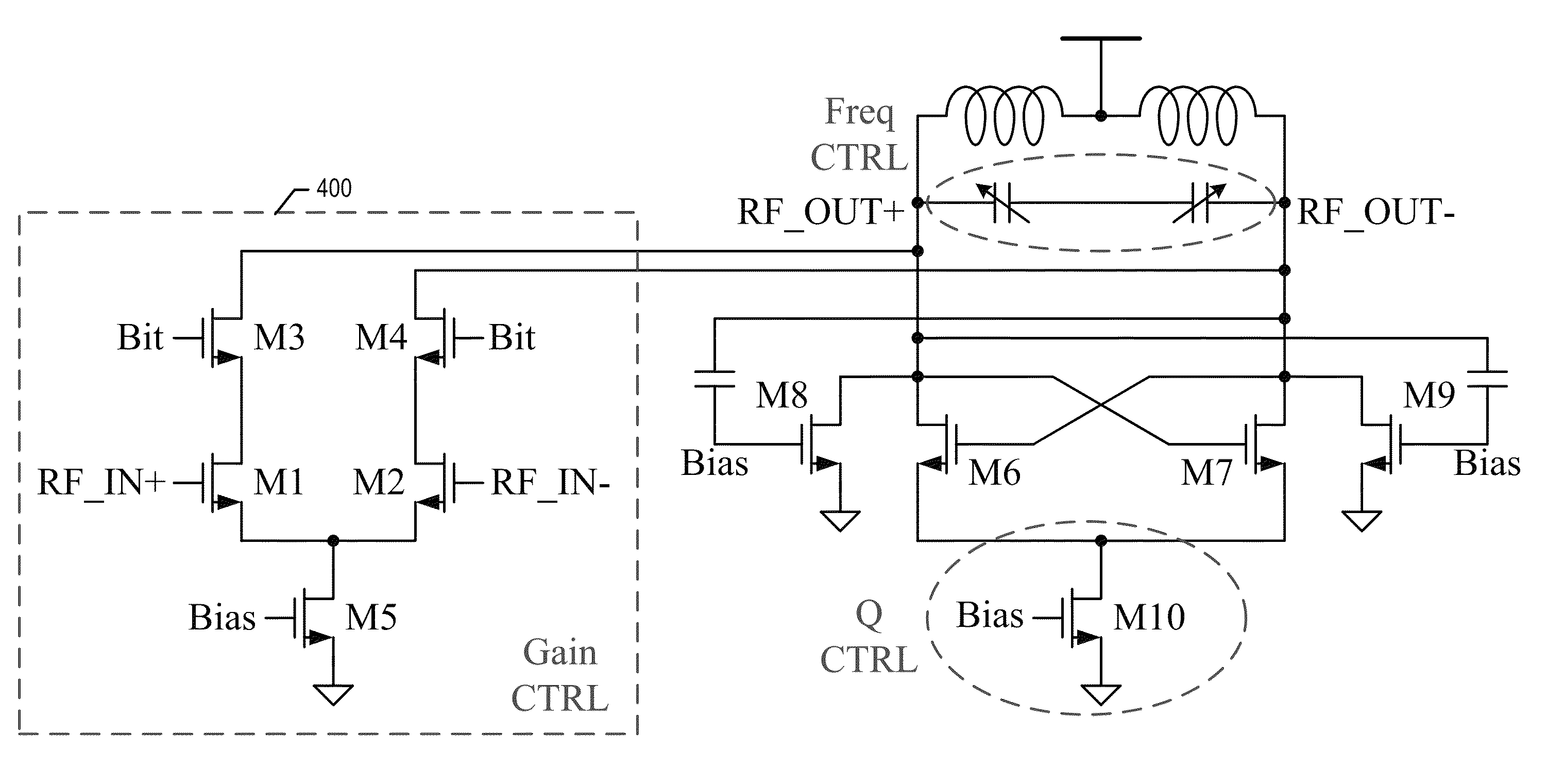
ActiveUS20140266454A1Switched capacitors controlAmplifier with semiconductor-devices/discharge-tubesBandpass filteringVariable-gain amplifier
A low noise amplifier including a variable gain amplifier stage configured to accept an input signal and to provide a load driving signal; a tunable bandpass filter connected as a load to the variable gain amplifier stage, wherein the bandpass filter includes a cross-coupled transistor pair, and at least one cross-coupled compensation transistor pair biased in a subthreshold region configured to add a transconductance component when the load driving signal is of a magnitude large enough to decreases a transconductance of the cross-coupled transistor pair; and, a controller circuit configured to tune the bandpass filter. The filter can be tuned in respect to the frequency and the quality factor Q.
Owner:INNOPHASE
Audio quality adjustment device
InactiveUS20060182290A1InhibitionImprove precision controlDigital technique networkCombination control in untuned amplifierFrequency spectrumProcessing element
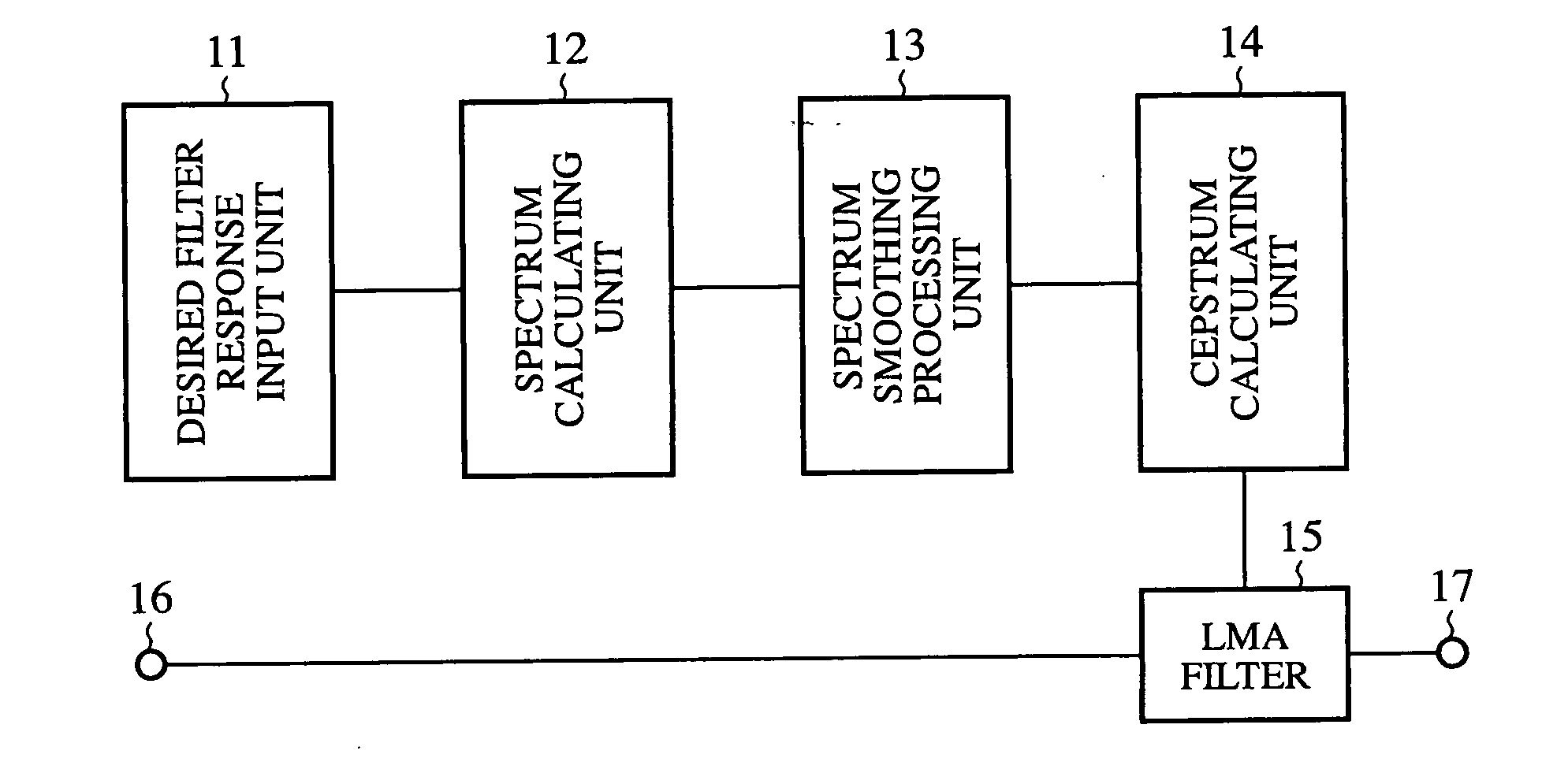
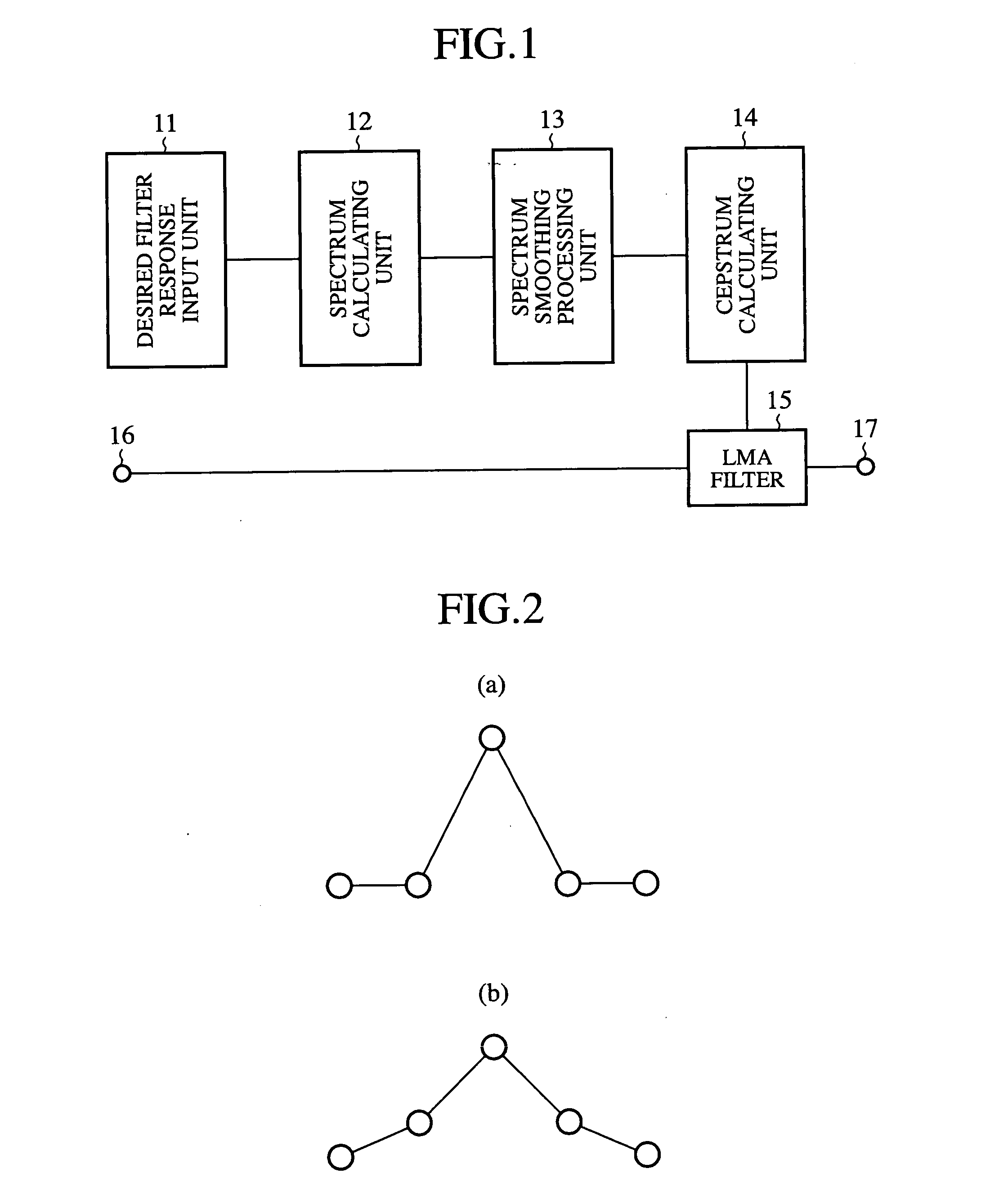
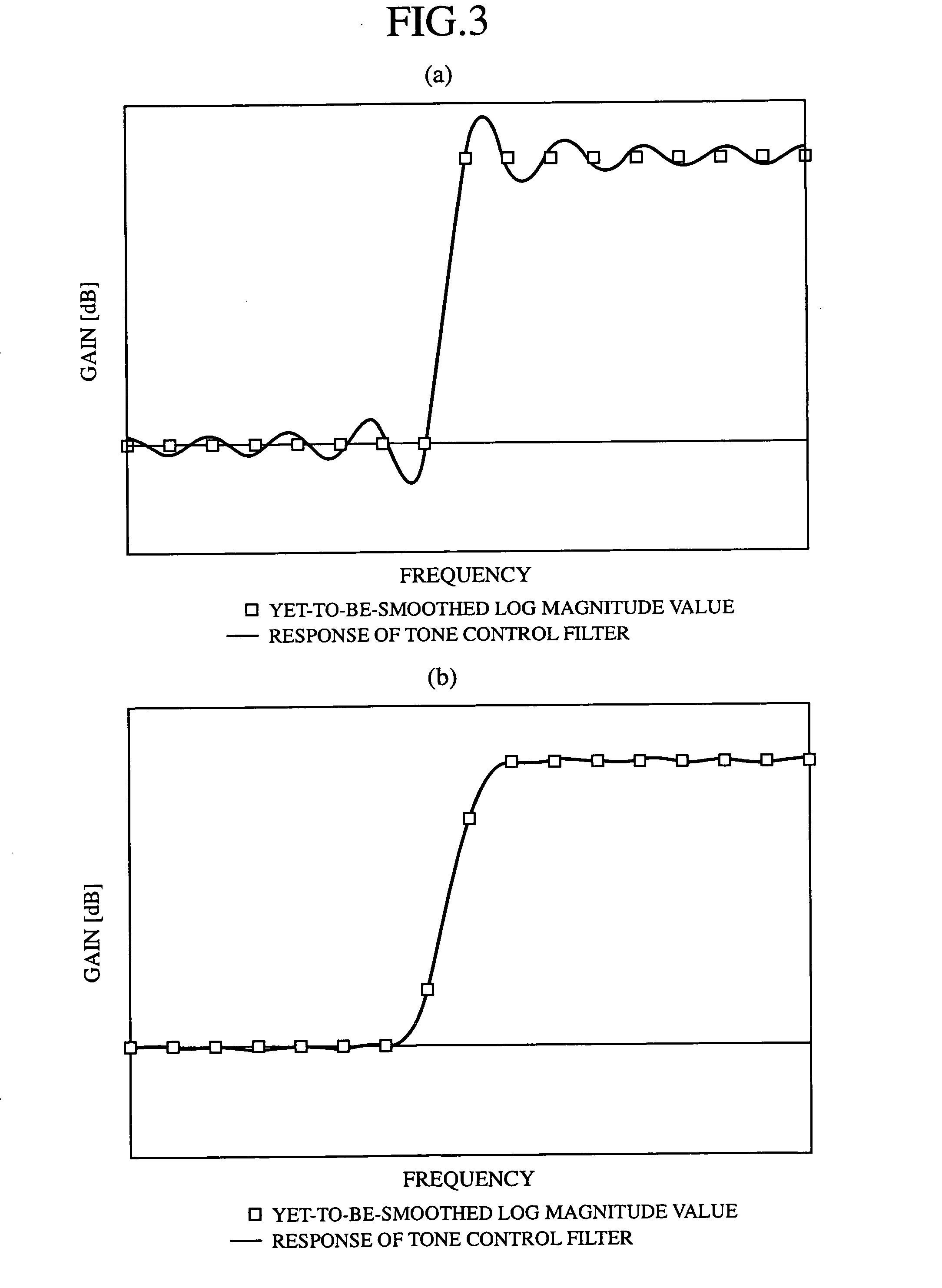
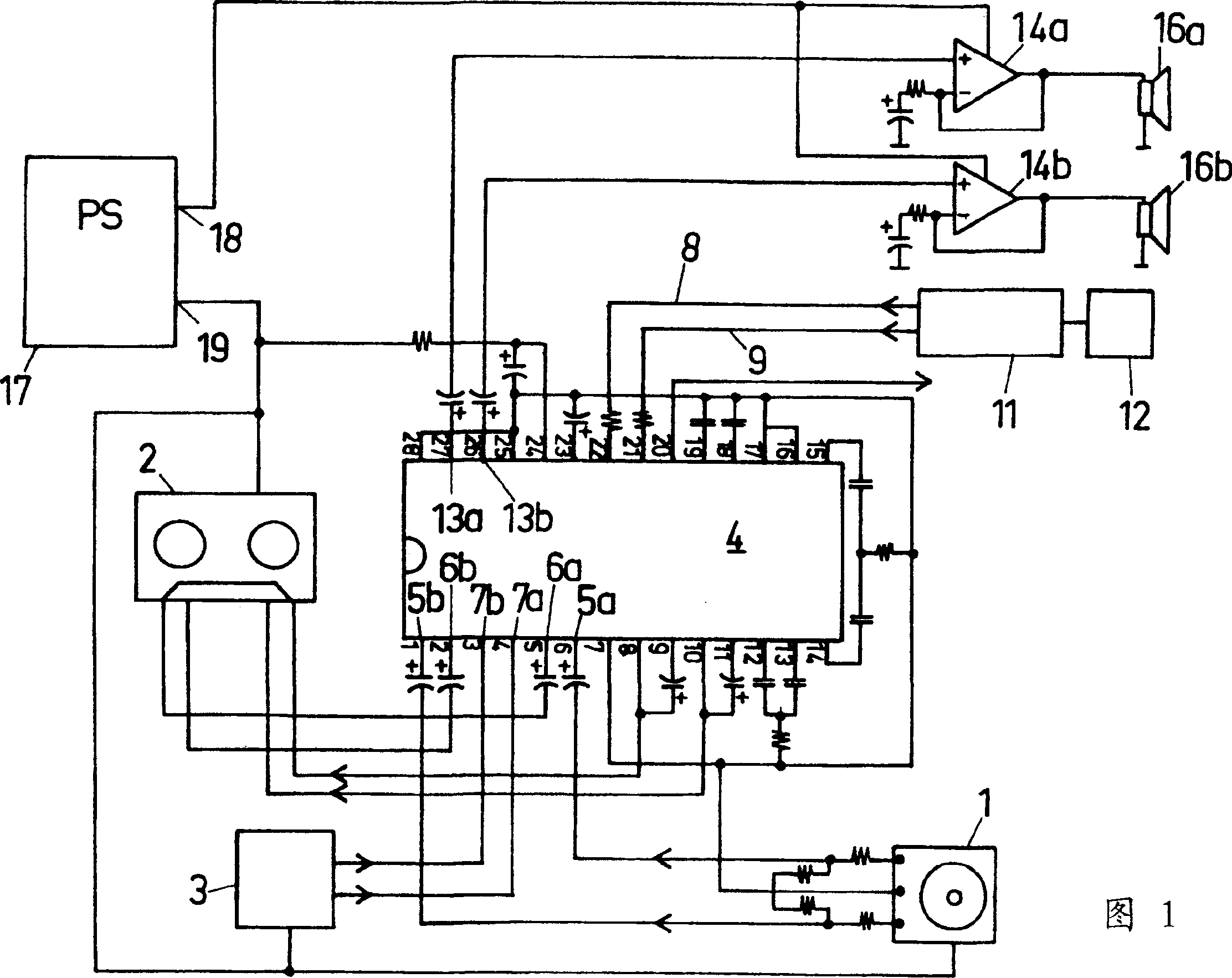
A tone control apparatus is provided with a desired filter response input unit 11 for inputting a desired filter response into the tone control apparatus, a spectrum calculating unit 12 for calculating a Fourier spectrum for the set filter response which is inputted by the desired filter response input unit 11, a spectrum smoothing processing unit 13 for performing smoothing processing on the Fourier spectrum calculated by the spectrum calculating unit 12, a cepstrum calculating unit 14 for converting the Fourier spectrum smoothed by spectrum smoothing processing unit 13 into a cepstrum, and an LMA filter 15 to which the cepstrum calculated by the cepstrum calculating unit 14 is set as the filter factor of the LMA filter. The tone control apparatus also has an input terminal 16 for inputting a sound signal into the LMA filter 15, and an output terminal 17 for outputting a sound signal.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Adjustable speaker systems and methods
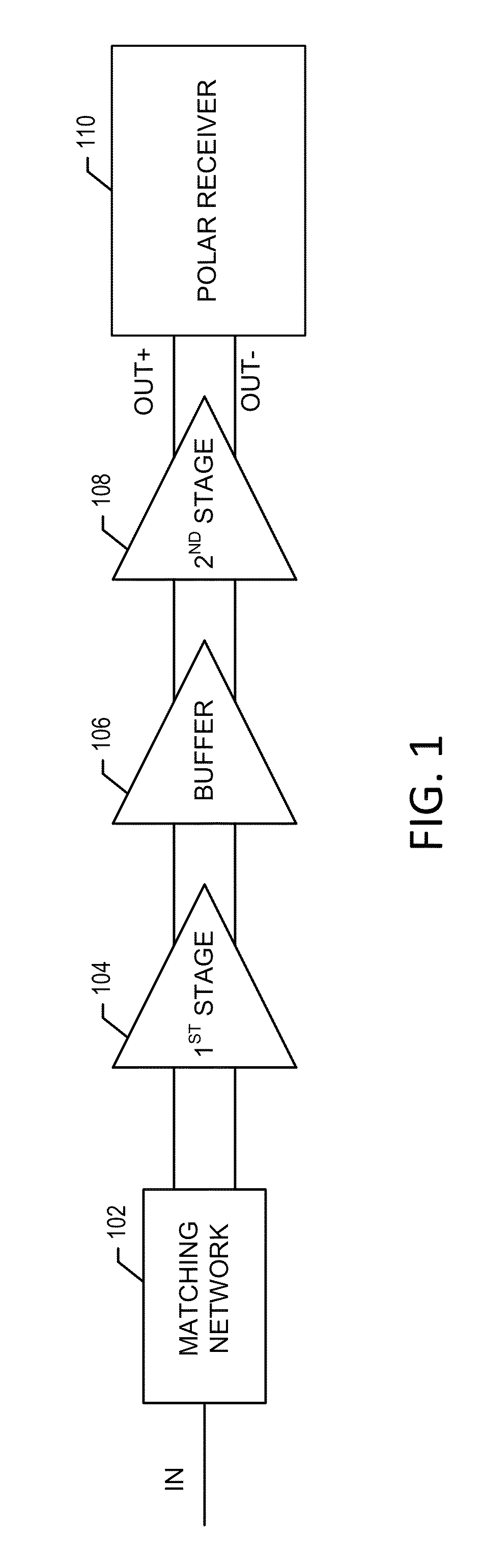
InactiveUS20070217619A1Manually operated tone/bandwidth controlStereophonic systemsAudio power amplifierGraphical user interface
Systems and methods for optimizing speaker performance. The system includes a self-contained speaker unit that includes a speaker, an amplifier coupled to the speaker, and a processor coupled to the amplifier. The processor receives a first sound signal from a receiver and a second sound signal from a microphone, processes the first sound signal based on a plurality of parameters, outputs the processed sound signal to the speaker, and generates a video signal based on the second sound signal. A wireless remote control allows a user to manipulate the parameters. The processor generates a test sound signal and outputs it to the receiver. The receiver processes the test sound signal and returns it to the processor for output through the speaker. The video signal includes a graphical user interface having a frequency response graph of the second sound signal and an eight-band equalizer.
Owner:VELODYNE ACOUSTICS
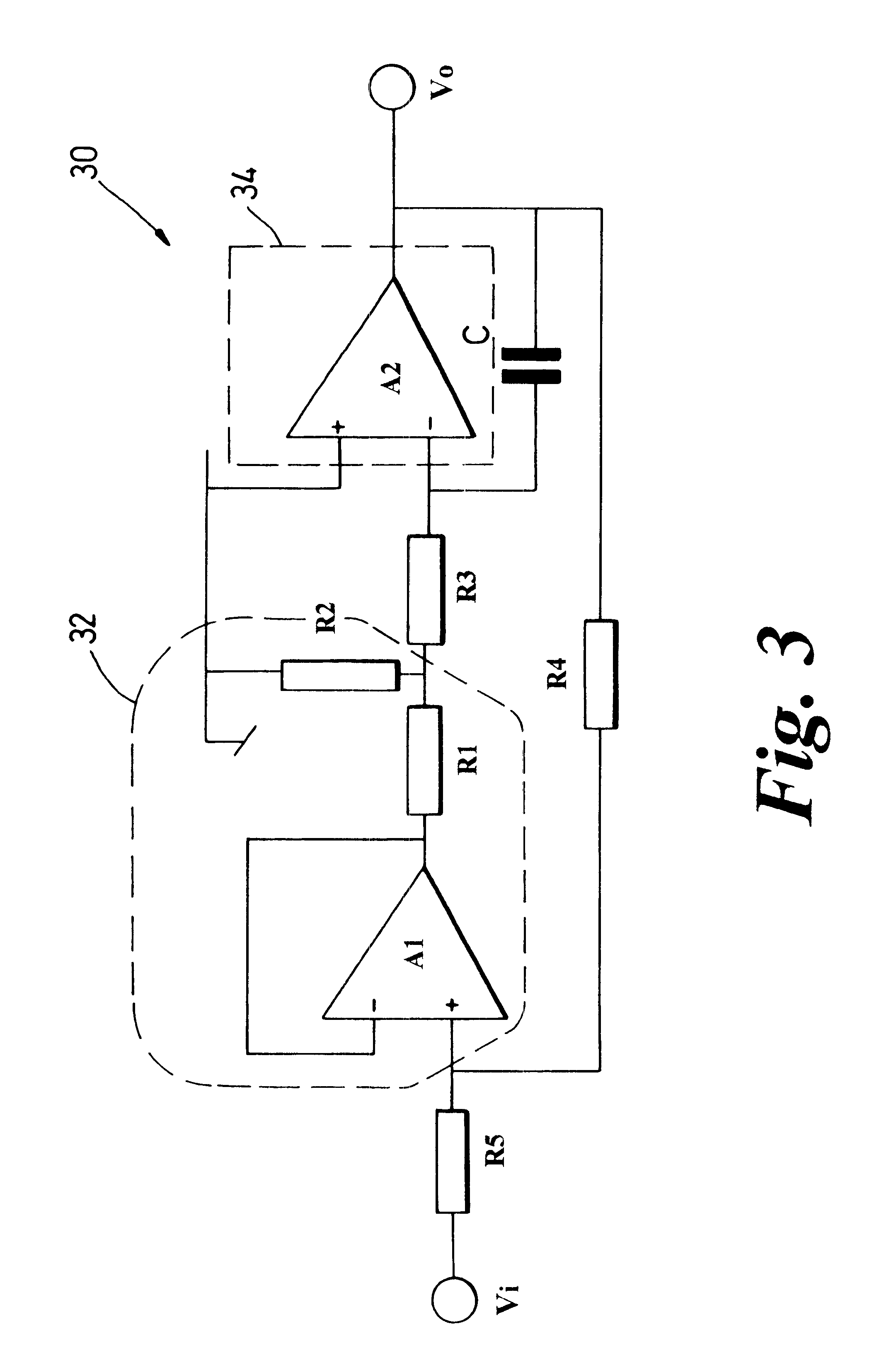
Fully integrated long time constant integrator circuit
InactiveUS6476660B1Extension of timeConstant gainComputing operations for integral formationComputing operations for integration/differentiationCapacitanceIntegrator
The present invention provides a long time constant integrator circuit as part of an integrated circuit. The integrator circuit is fully integrated on chip with no external capacitive or resistive components for enhancing the circuit's time constant. It achieves a -3 dB cut-off frequency of 1.6 Hz. The circuit is realisable on a very small area of silicon being formed by a bipolar process using npn transistors, resistive and capacitive elements. The integrator circuit comprises a transconductance stage as an input to an operational amplifier. The circuit design is fully differential and employs realisable resistors and capacitors.
Owner:NORTEL NETWORKS LTD
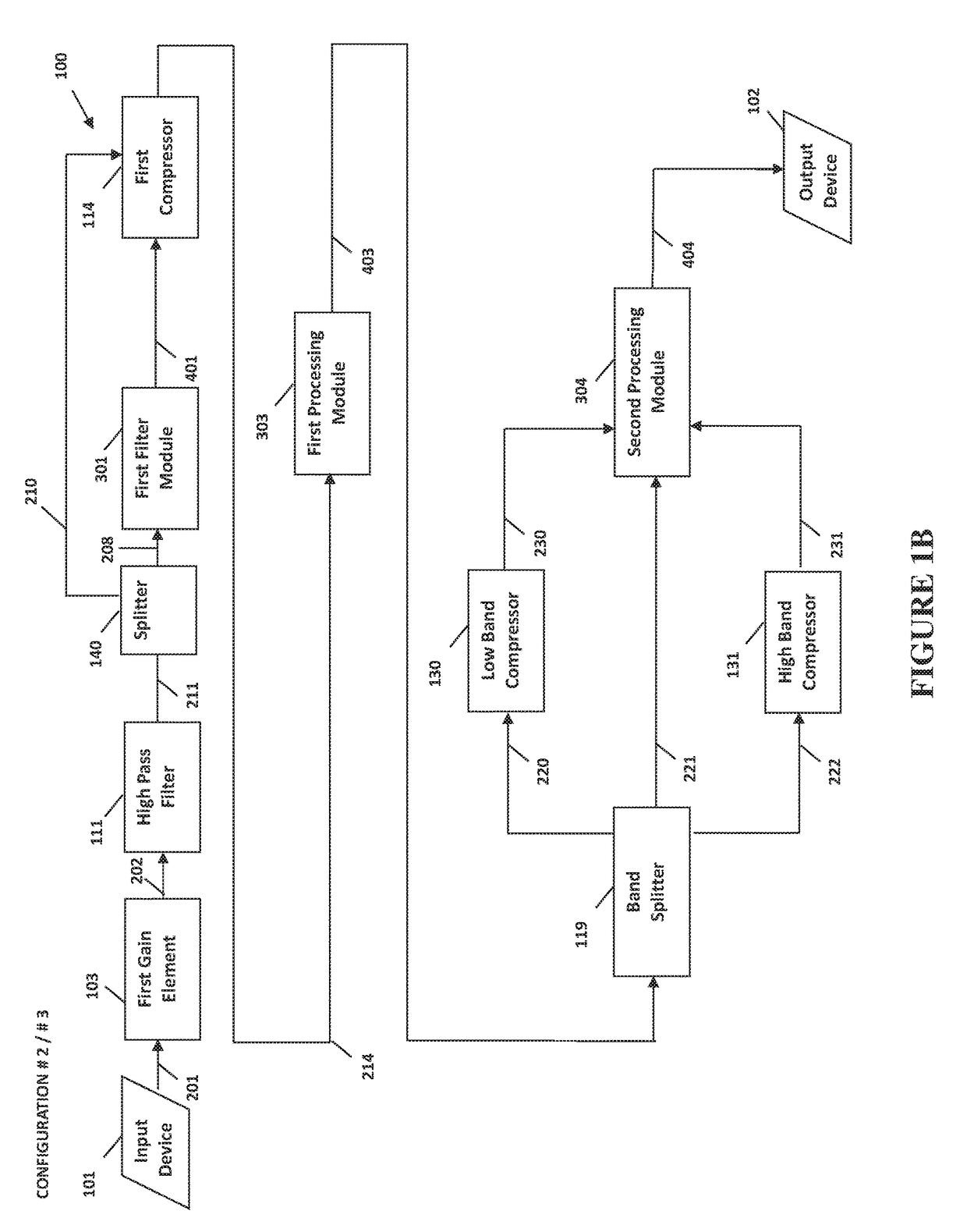
System and method for digital signal processing
ActiveUS9906858B2Increase or decrease overshoots or undershoots in the signalVolume compression/expansion in untuned/low-frequency amplifiersVolume compression/expansion in digital/coded amplifiersDigital signal processingComputer module
A system and method for digital processing including a gain element to process an input audio signal, a high pass filter to then filter the signal and create a high pass signal, a first filter module to filter the high pass signal and create a first filtered signal and a splitter to split the high pass signal into two high pass signals. The first filter module filters one high pass signals before a first compressor modulates the signal or a high pass signal to create a modulated signal. A second filter module filters the modulated signal to create a second filtered signal that is processed by a first processing module including a band splitter that splits the signal into low and high band signals that are then modulated by compressors. A second processing module processes the modulated low and high band signals to create an output signal.
Owner:BONGIOVI ACOUSTICS LLC
Audio output apparatus
ActiveUS7970153B2Improve the separation of audibility of a plurality of soundsExcellently listenSignal processingTransducers for sound channels pluralityComputer moduleEngineering
An audio output apparatus has a measuring circuit which measures the levels of at least two sound signals, a sound level adjusting module (a sound level adjusting circuit and a gain control circuit) which adjusts a sound level so as to equal the levels of the sound signals based on the levels measured at the measuring circuit, and an array speaker unit (a delay circuit, a multiplier, an adder, an amplifier and a speaker unit) which emits sounds in accordance with the sound signals outputted from the sound level adjusting module in different directivities respectively.
Owner:YAMAHA CORP
LNA with linearized gain over extended dynamic range
ActiveUS8941441B2Switched capacitors controlDifferential amplifiersBandpass filteringVariable-gain amplifier
Owner:INNOPHASE
Signal processing apparatus, signal processing method, and sound field correction system
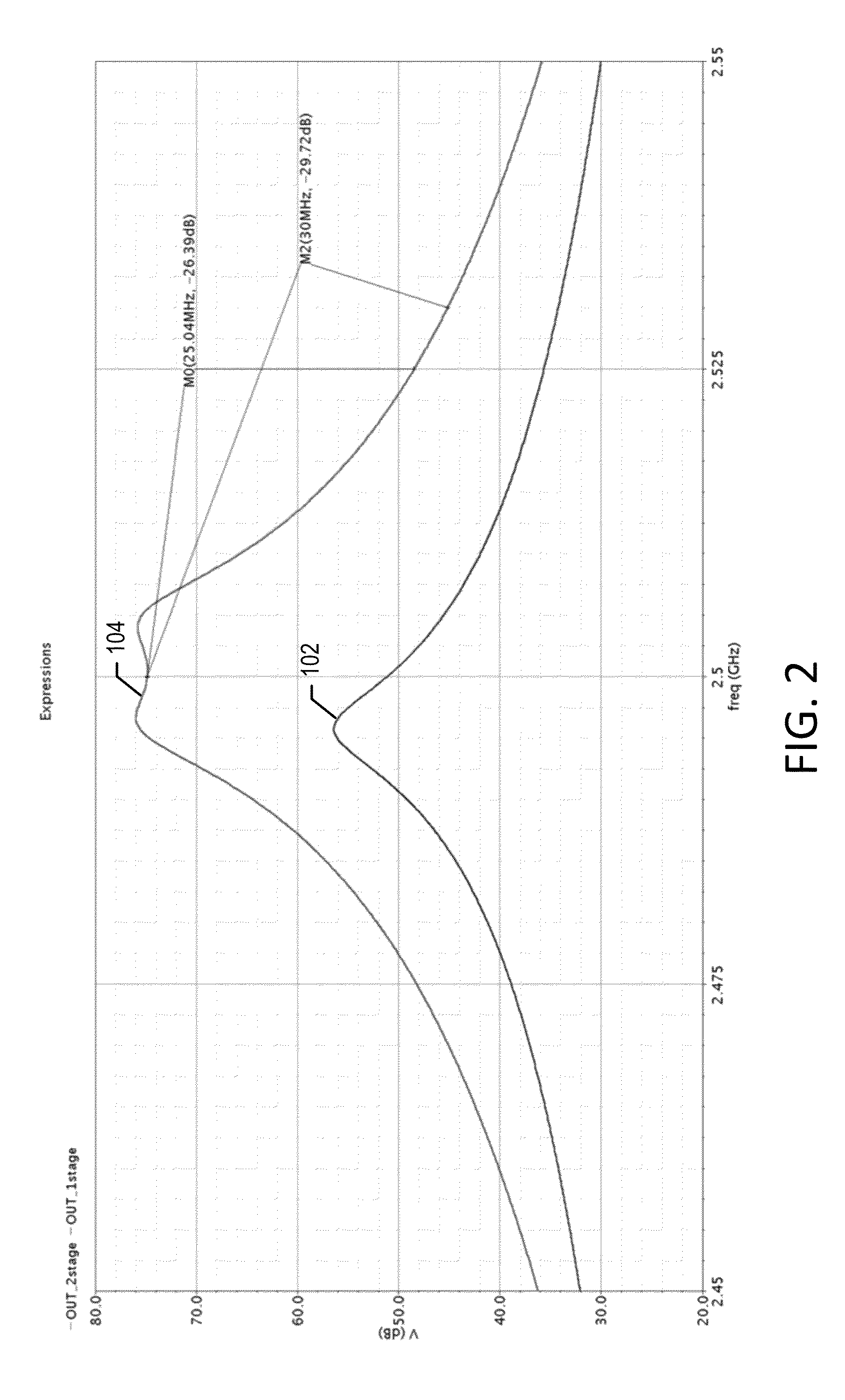
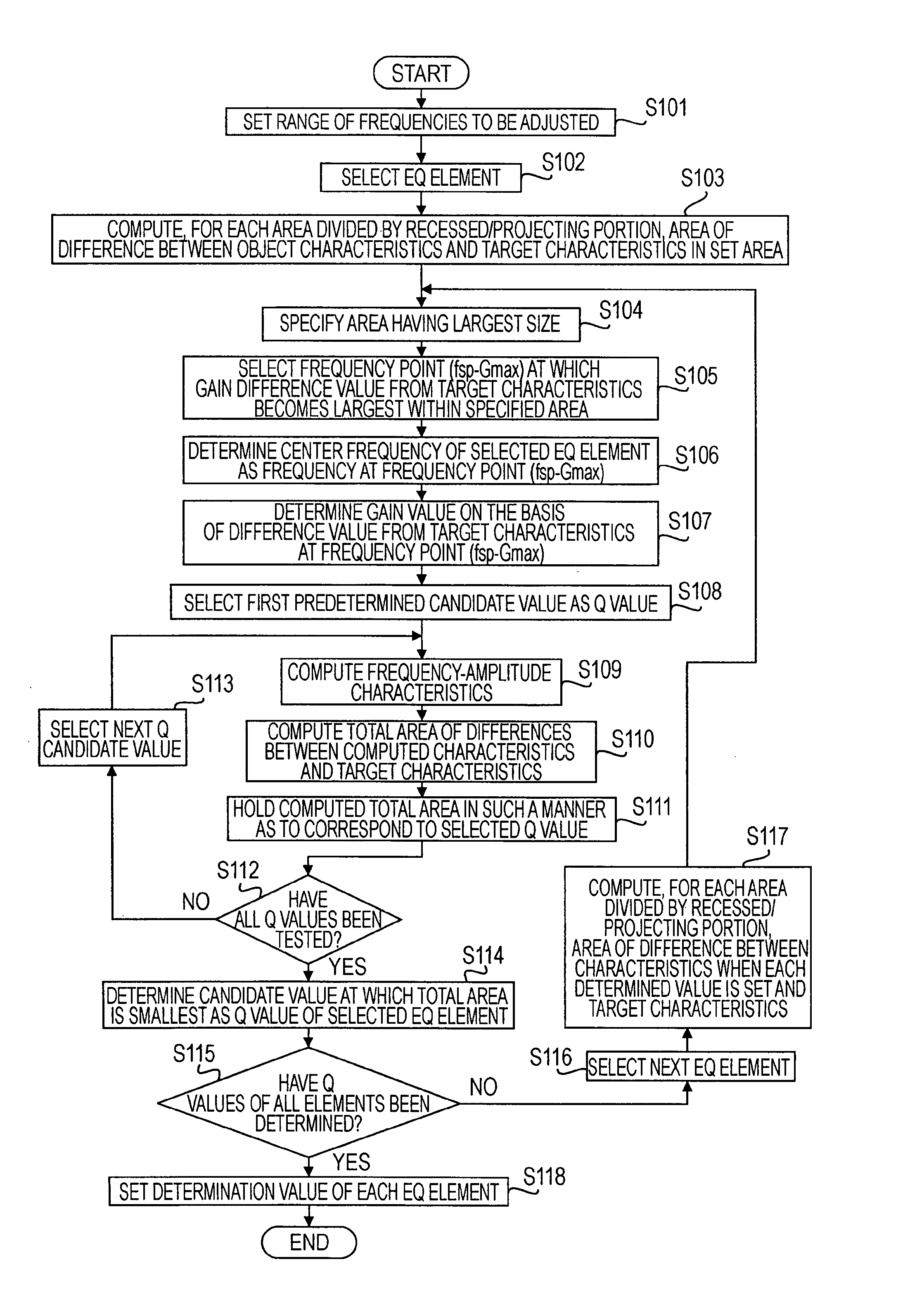
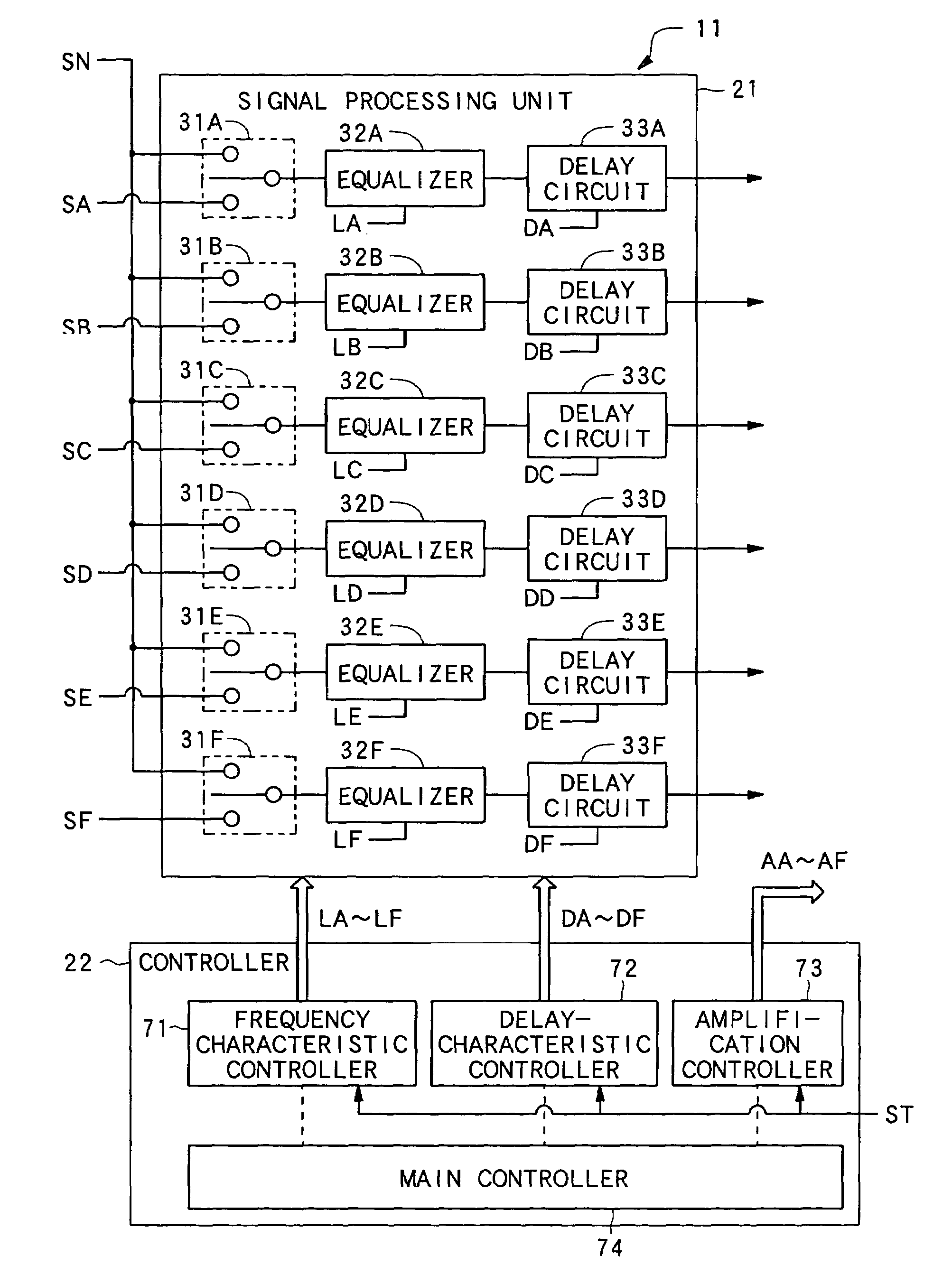
InactiveUS20070230556A1Accurate frequencyMultiple-port networksDelay line applicationsEngineeringEqualization
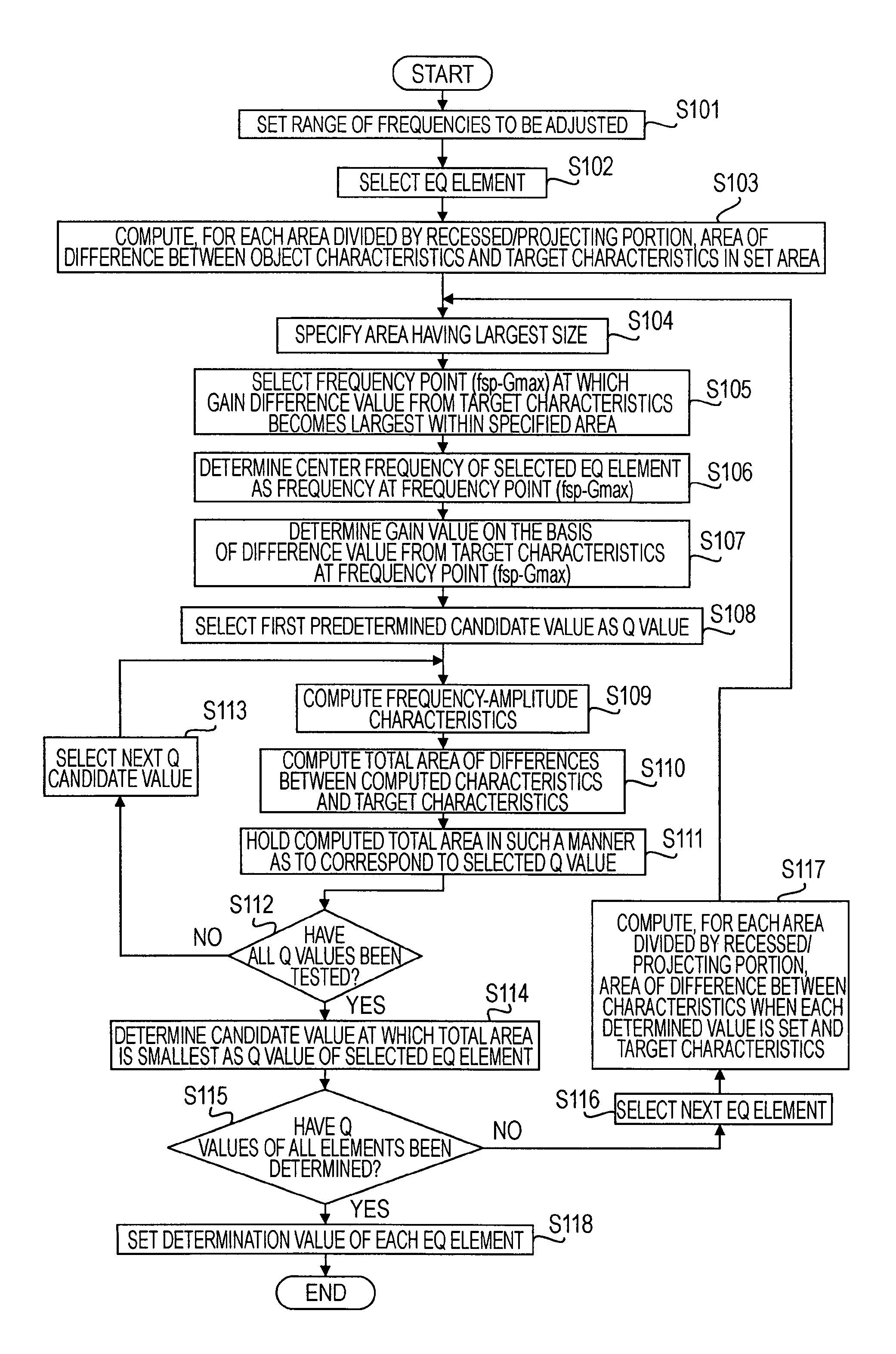
A signal processing apparatus includes at least one equalization section, each of the equalization section being capable of setting a center frequency, a gain value at the center frequency, and a Q value and allowing set frequency-amplitude characteristics to be applied to an input signal; and a computation section. The computation section performs a center frequency determination process for computing, for target characteristics of the equalization section, a difference from the target characteristics for each area divided by a frequency portion where the gain of the characteristics of the equalization section is small and a frequency portion where the gain of the characteristics of the equalization section is large, a gain value determination process for determining the gain value at the center frequency of the equalization section, and a Q value determination process for setting the determined center frequency and the determined gain value.
Owner:SONY CORP
Audio processing apparatus suitable for singing practice
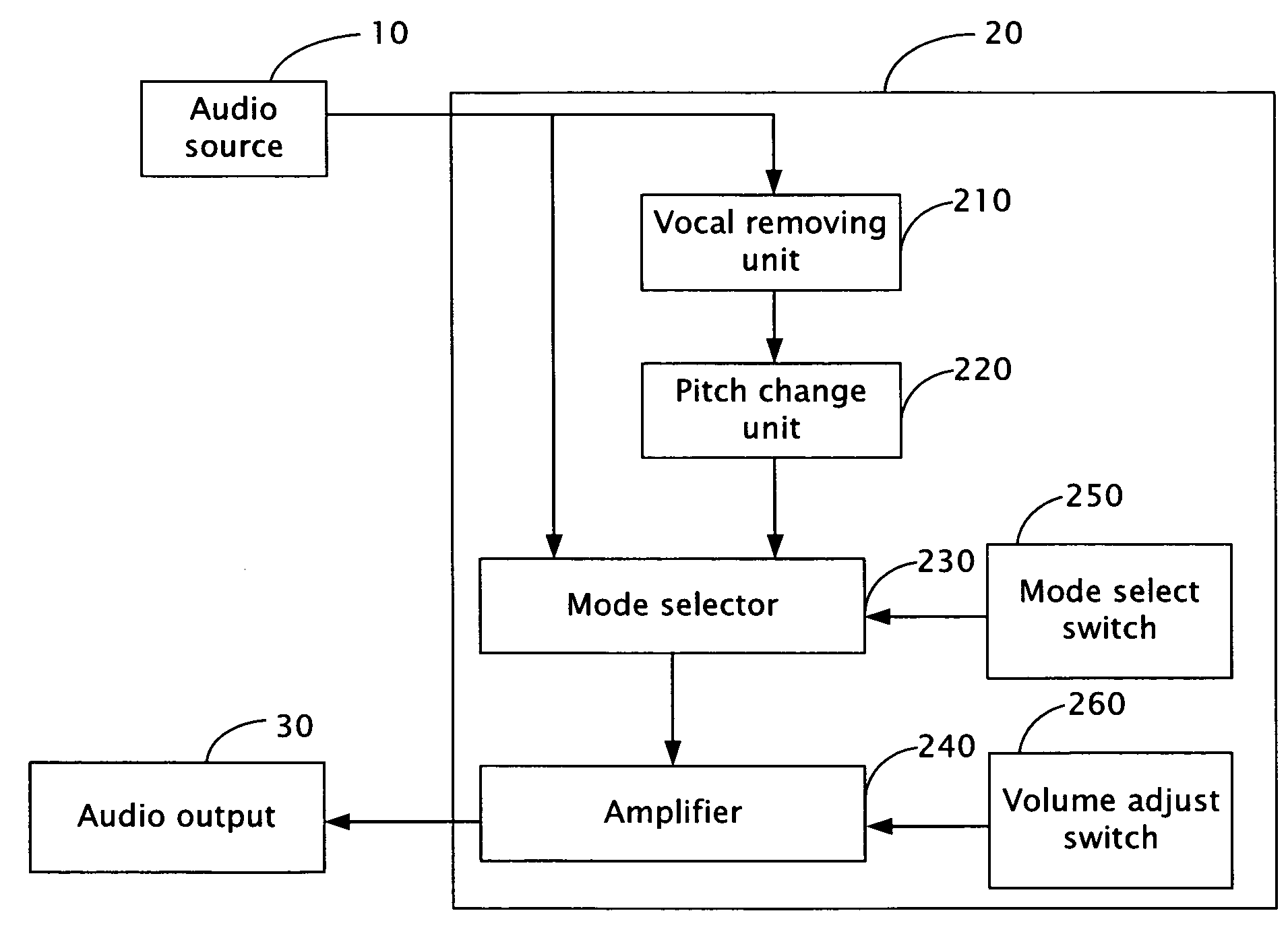
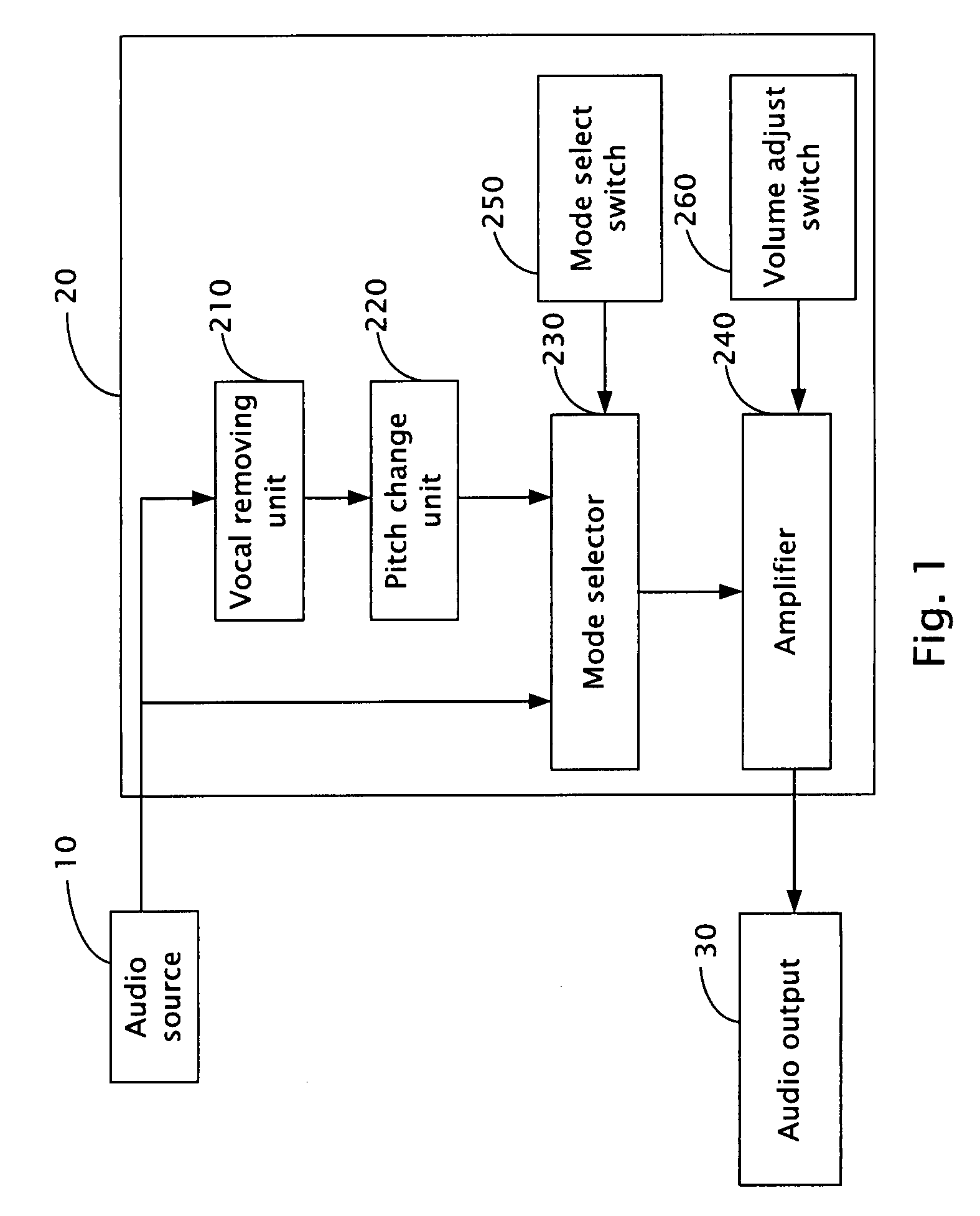
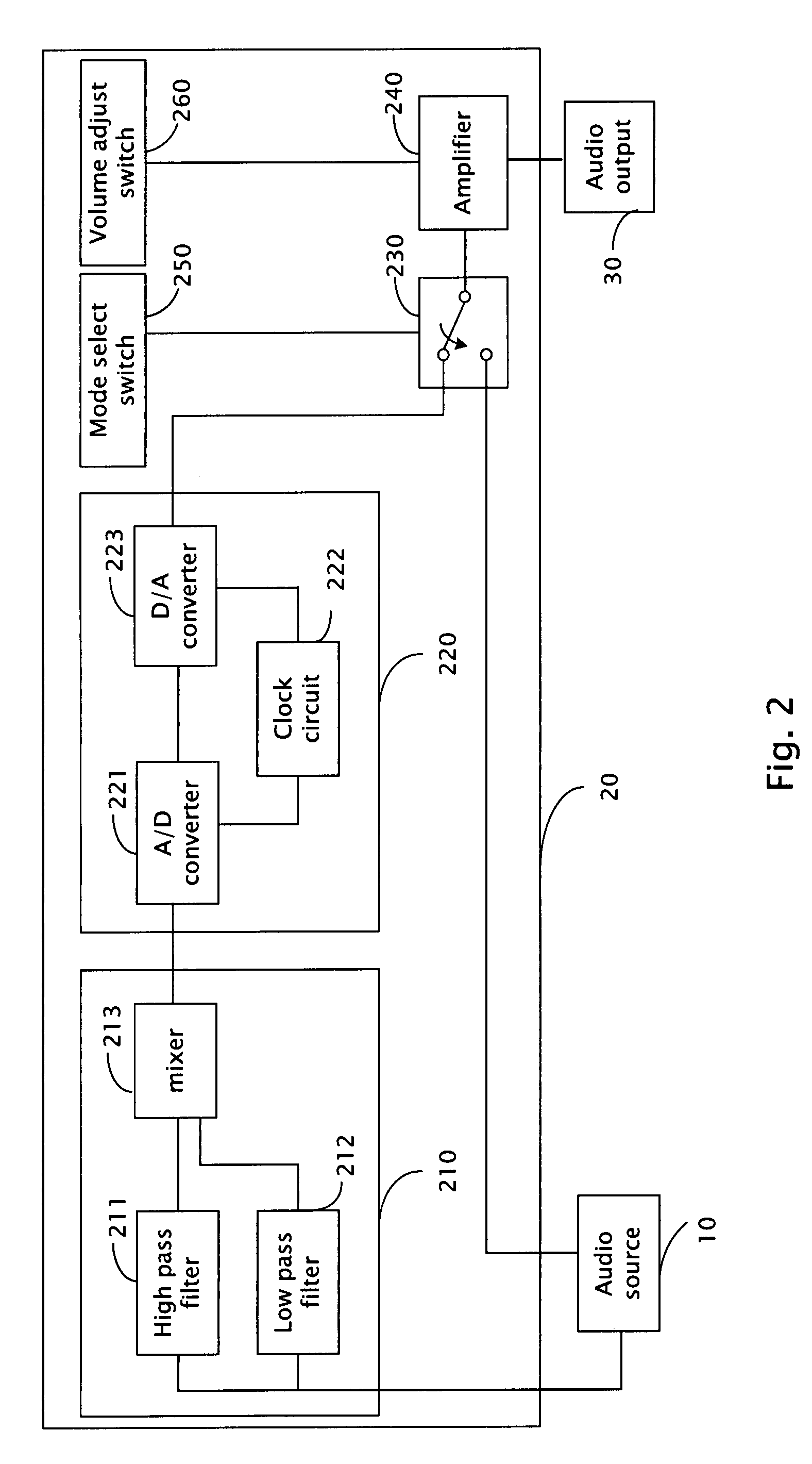
An audio processing apparatus (20) connected between an audio source (10) and an audio output (30) is provided. The audio processing apparatus is suitable for singing practice of users and includes a vocal removing unit (210) and a pitch change unit (220). The vocal removing unit is for removing vocal signals from audio signals of the audio source, and the pitch change unit is for changing pitch of the audio signals and outputting the audio signals to the audio output.
Owner:HON HAI PRECISION IND CO LTD
Dynamic compensation of audio signals for improved perceived spectral imbalances
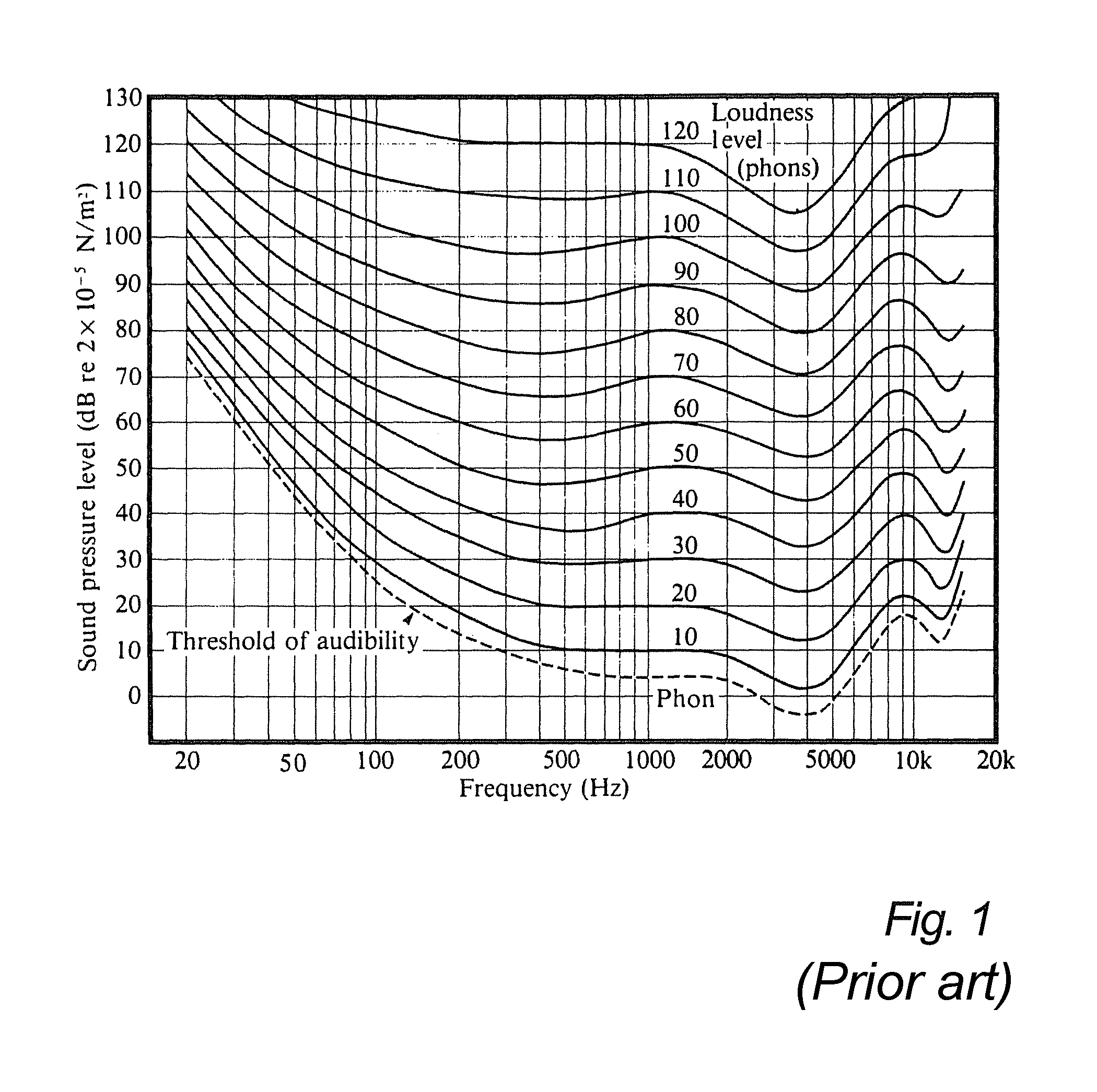
ActiveUS9391579B2Improve hearingGain controlCombination control in untuned amplifierFrequency spectrumElectrophonic hearing
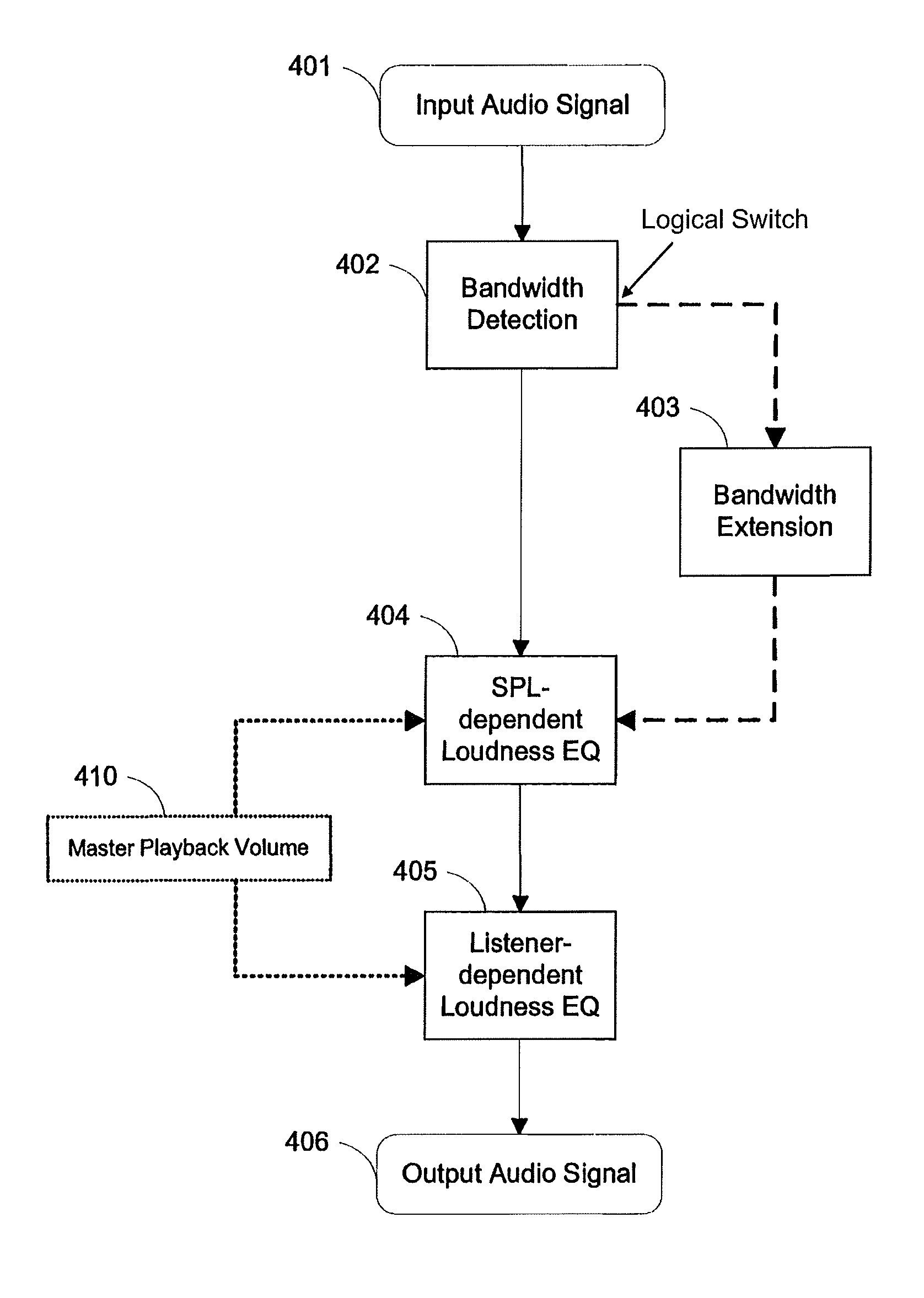
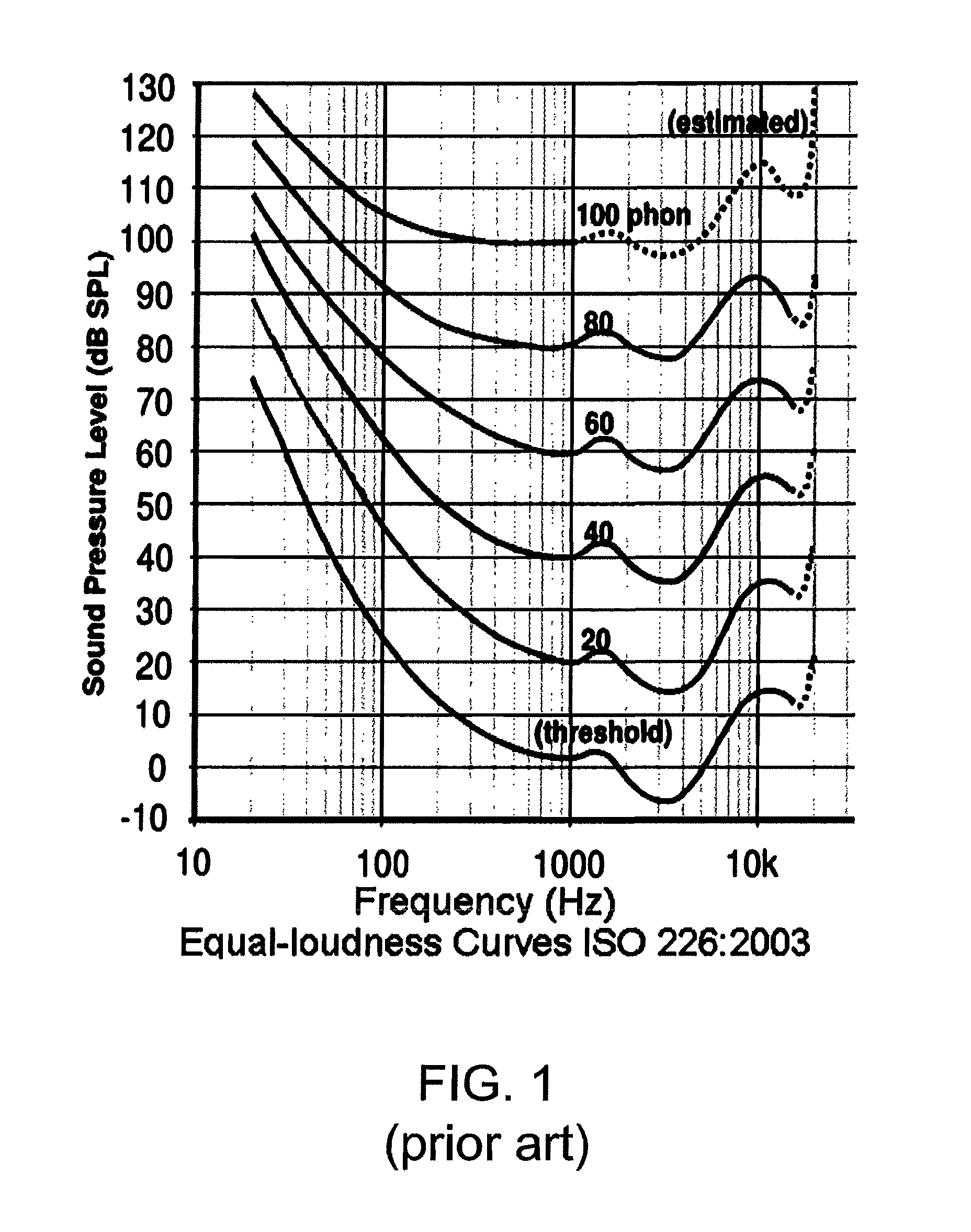
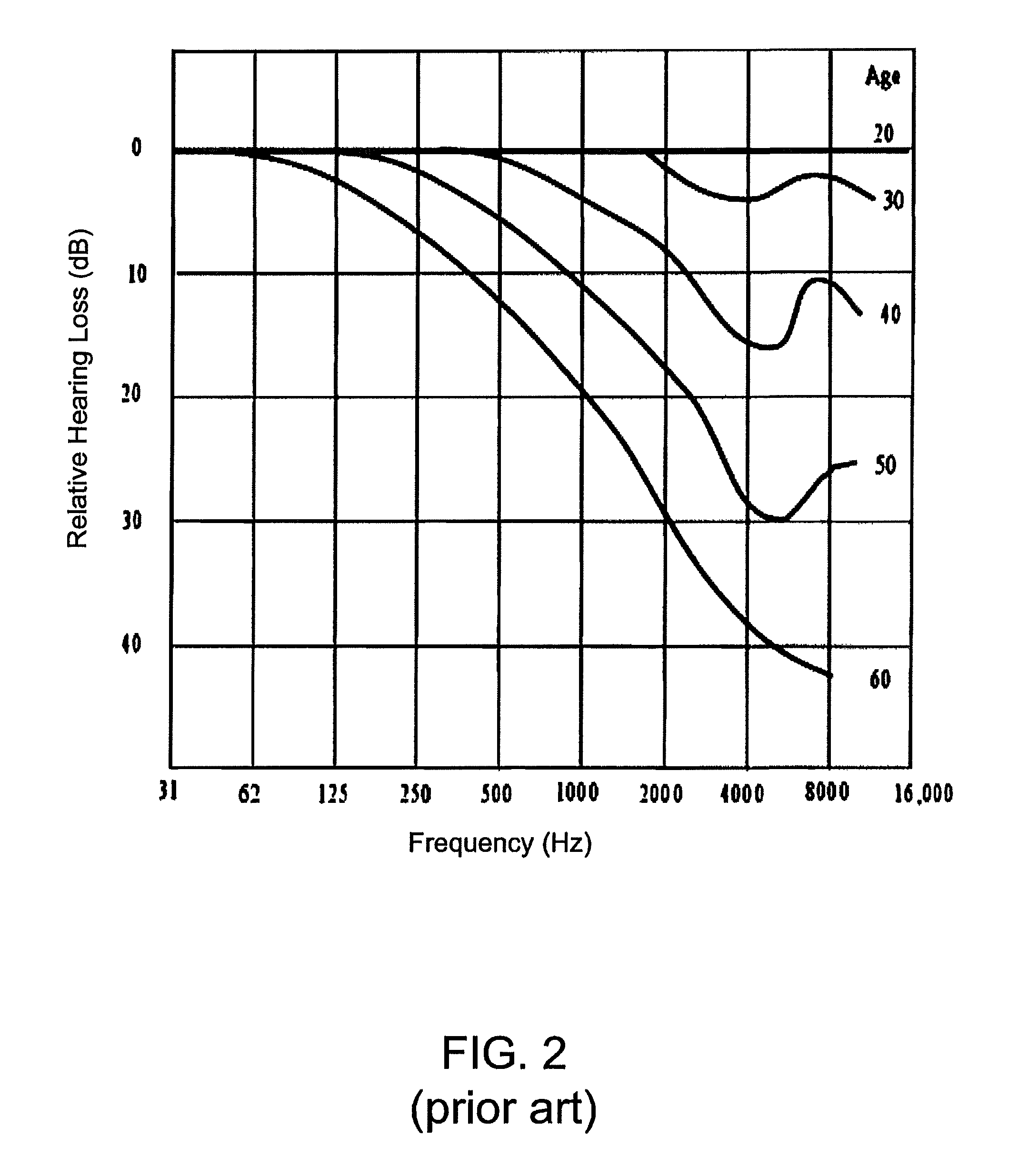
An input audio signal is equalized to form an output audio signal on the basis of an intended listening sound pressure level, the output capabilities of a particular playback device, and unique hearing characteristics of a listener. An intended listening level is first determined based on the properties of the audio signal and a mastering sound level. The intended listening level is used to determine an optimal sound pressure level for the particular playback device based on its capabilities and any master volume gain. These two levels are used to determine how much louder to make individual frequencies based on data pertaining to human auditory perception, either standardized or directly measured. The audio is further compensated on the basis of hearing loss data, again either standardized or directly measured, after optionally extending the signal bandwidth. The final, compensated audio signal is sent to the playback device for playback.
Owner:DTS
Signal processing apparatus, signal processing method, and sound field correction system
InactiveUS8150069B2Accurate frequencyMultiple-port networksDelay line applicationsEngineeringEqualization
A signal processing apparatus includes at least one equalization section, each of the equalization section being capable of setting a center frequency, a gain value at the center frequency, and a Q value and allowing set frequency-amplitude characteristics to be applied to an input signal; and a computation section. The computation section performs a center frequency determination process for computing, for target characteristics of the equalization section, a difference from the target characteristics for each area divided by a frequency portion where the gain of the characteristics of the equalization section is small and a frequency portion where the gain of the characteristics of the equalization section is large, a gain value determination process for determining the gain value at the center frequency of the equalization section, and a Q value determination process for setting the determined center frequency and the determined gain value.
Owner:SONY CORP
Method and apparatus for adjusting frequency characteristic of signal
InactiveUS7409067B2Improve accuracyGain controlCombination control in untuned amplifierLoudspeakerFrequency characteristic
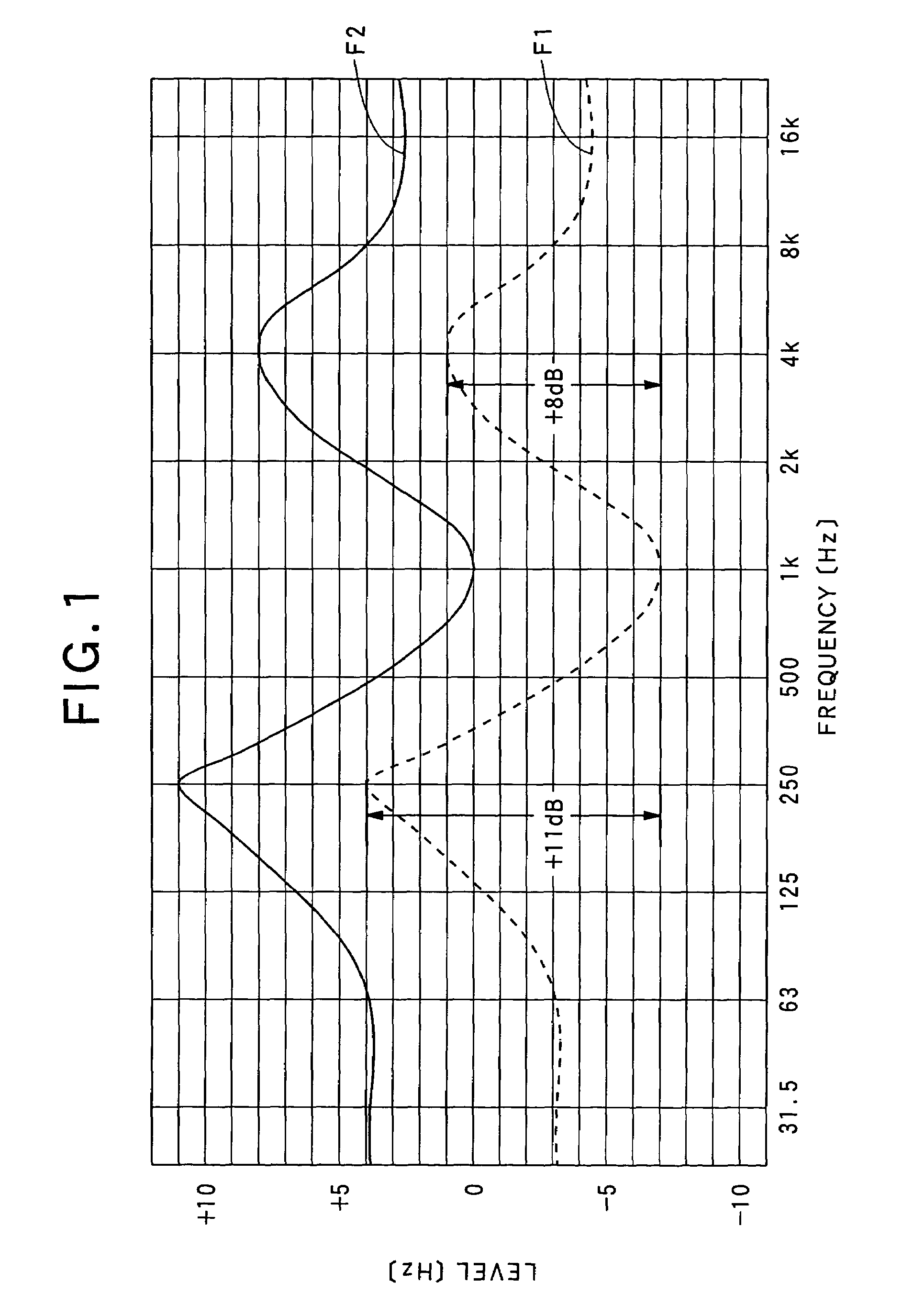
In a frequency characteristic adjustment apparatus incorporated in an audio system, a frequency characteristic of an audio signal is made to agree with a target frequency characteristic, thus providing an equalizing function. In the apparatus, by a frequency characteristic controller, a measurement signal is detected as a sound-collected signal that received by way of speakers / microphone, and the sound-collected signal is divided into a signal component falling into a one fixed-level band and one or more signal components falling into one or more variable-level bands. A relative level of the signal component in each variable-level band is estimated on the basis of a level of the signal component in the fixed-level band in the target frequency characteristic. Based on the estimated relative levels, the levels at equalizers are set, so that the levels of signal components of the signal are adjusted by the equalizers channel by channel.
Owner:ONKYO KK D B A ONKYO CORP
Method for adjusting audio equalizing and audio system for providing equalizing adjustment
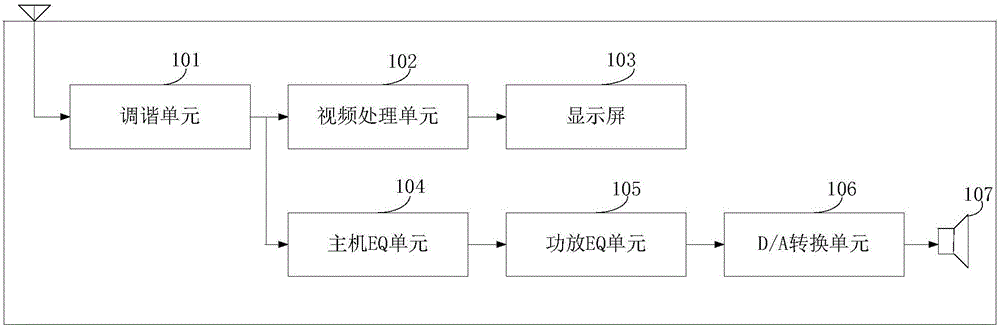
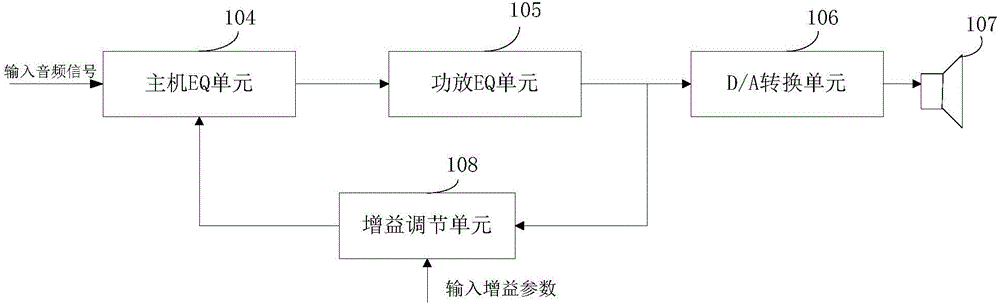
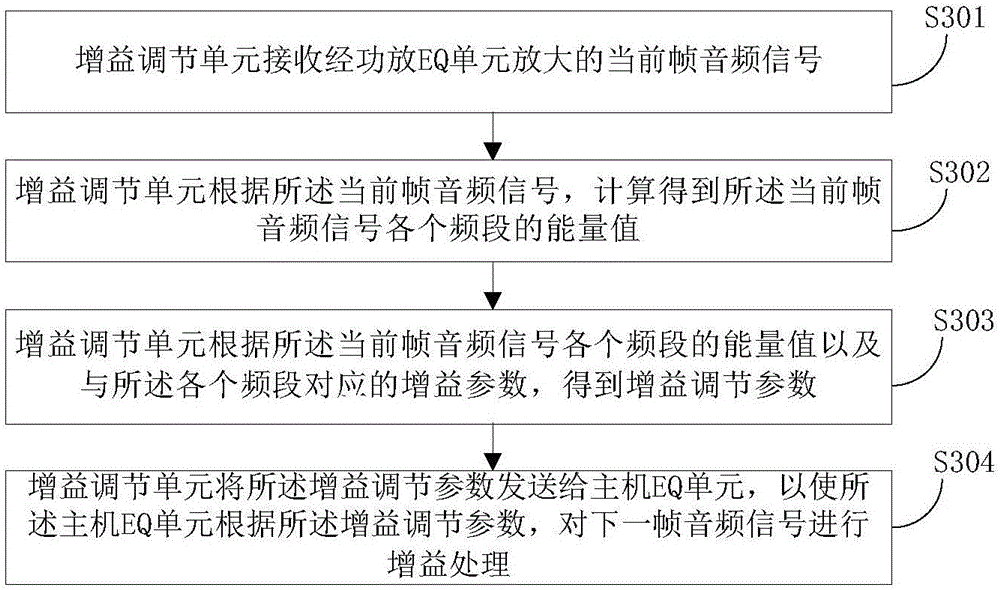
ActiveCN106713794ASatisfy hearing requirementsHigh gainTelevision system detailsColor television detailsQuality adjustmentComputer science
The invention relates to the technical field of audio processing, and particularly relates to a method for adjusting audio equalizing and an audio system for providing equalizing adjustment. The method comprises the steps that a gain adjusting unit receives a current frame audio signal amplified by a power amplifier EQ unit; the gain adjusting unit calculates the energy value of each band of the current frame audio signal according to the current frame audio signal and obtains gain adjusting parameters according to the energy value of each band of the current frame audio signal and the gain parameters corresponding to each band; and the gain adjusting unit transmits the gain adjusting parameters to a host EQ unit so that the host EQ unit is enabled to perform gain processing on the next frame audio signal according to the gain adjusting parameters. According to the method for adjusting audio equalizing and the audio system for providing equalizing adjustment, the problem in the prior art that the auditory requirements of the user cannot be met due to distortion of the audio signal caused by the fact that gain processing is performed on the audio signal through the host EQ unit and then the audio signal is amplified by the power amplifier EQ unit can be solved.
Owner:HISENSE VISUAL TECH CO LTD
Sounder signal processor and its method
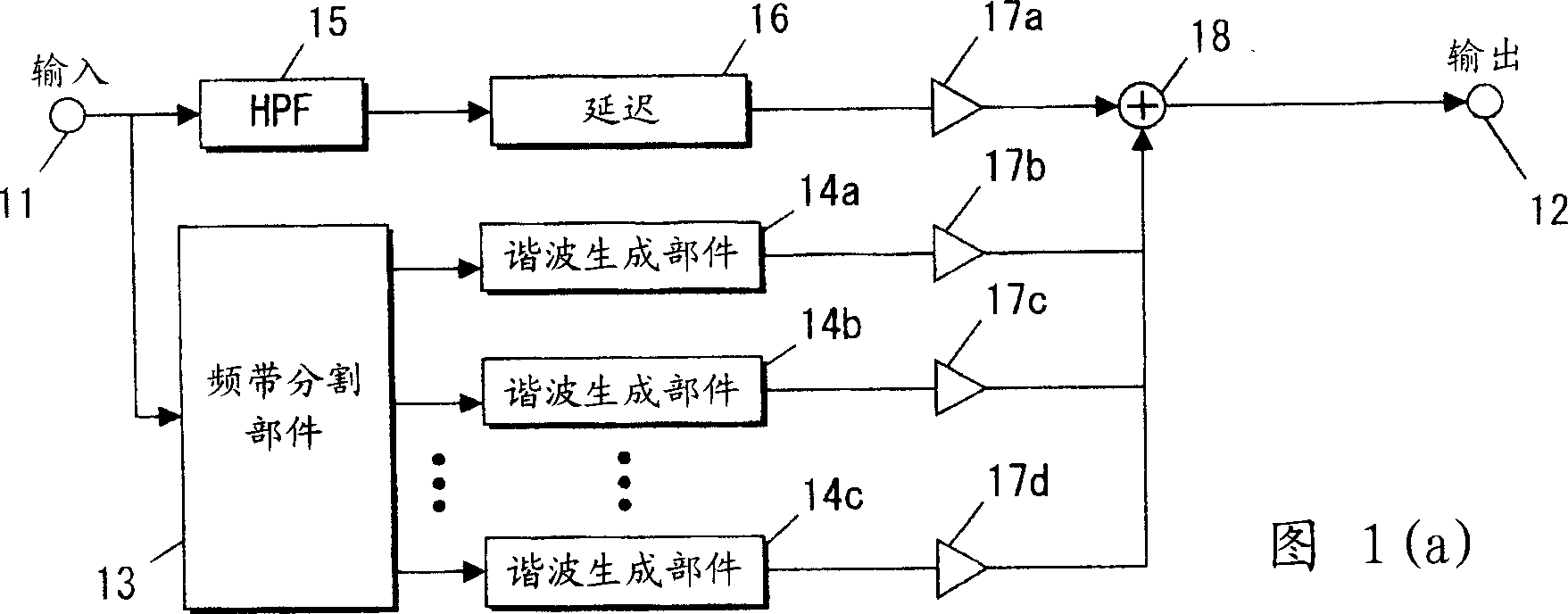
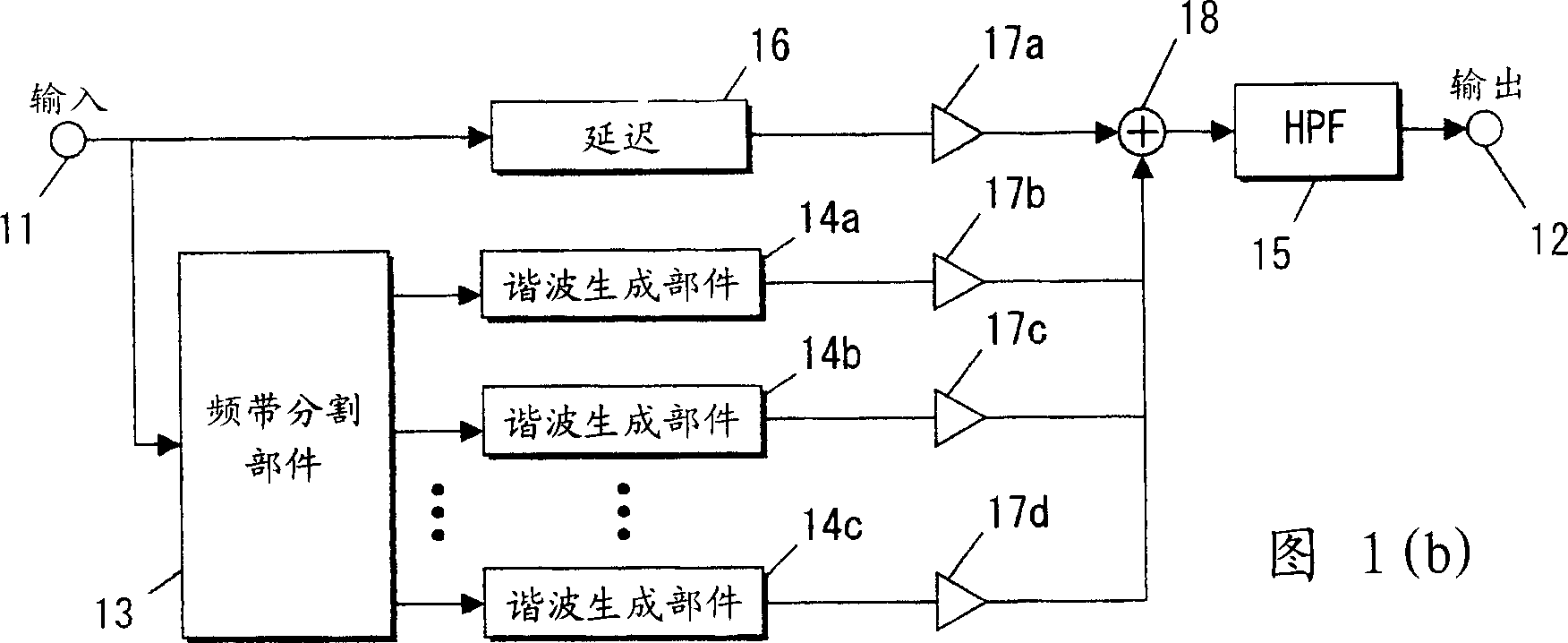
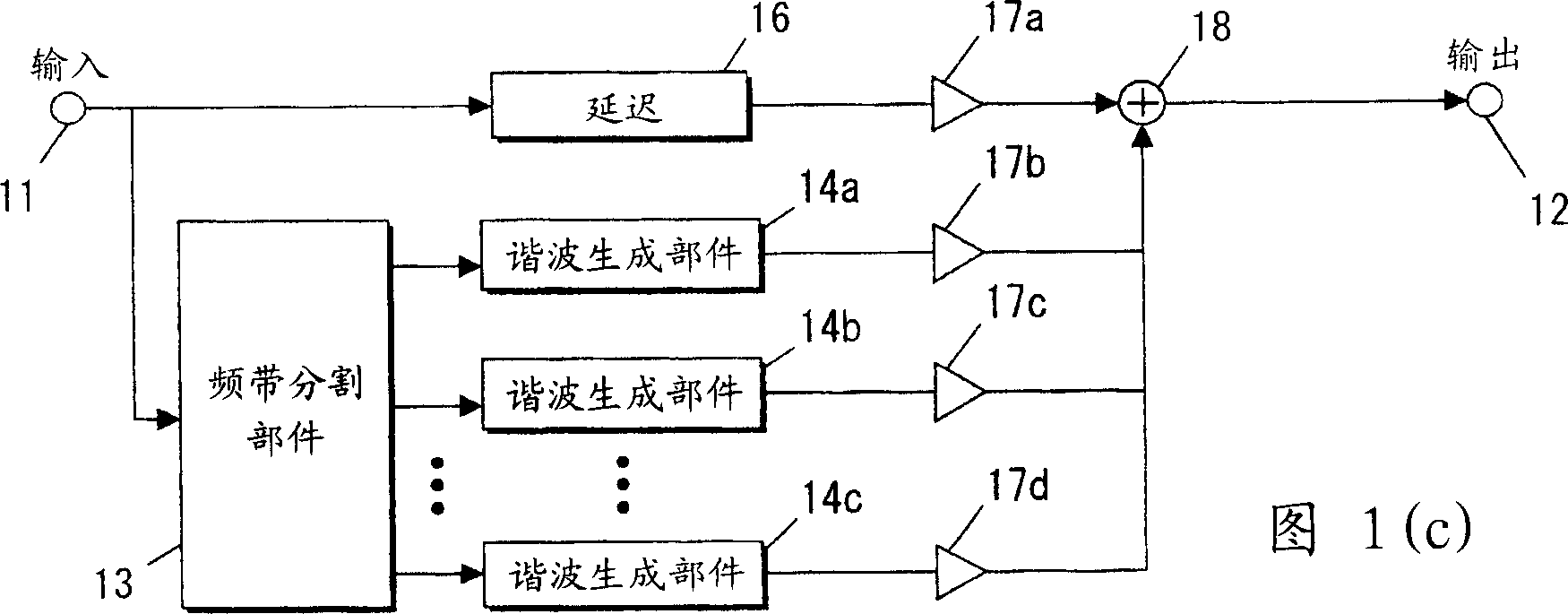
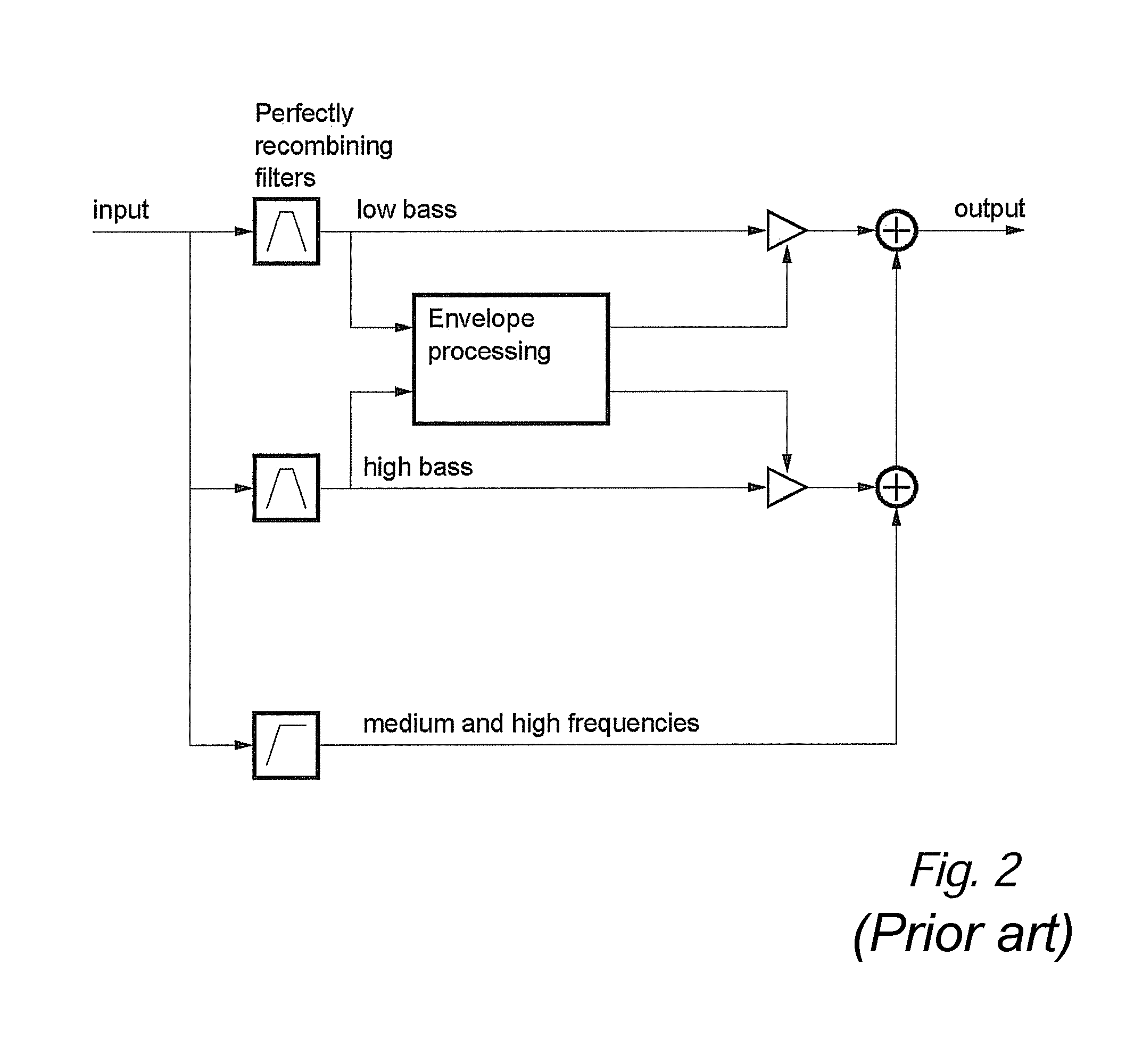
InactiveCN1494353ASuppress sound quality deteriorationElectrophonic musical instrumentsAutomatic tone/bandwidth controlHarmonicEngineering
The sound signal processor and method therefor are characterized in that after a band dividing means having band division characteristics based upon the overtone constitution and low interval limit of a musical instrument divides a lower-register signal to be artificialized into a plurality of band signals, overtone generation is carried out for the respective band signals. Individual overtones can be generated for the individual pure-sound component constituting a composite sound and deterioration in sound quality can be suppressed. An increase in the number of band divisions can be suppressed to decrease a circuit scale.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
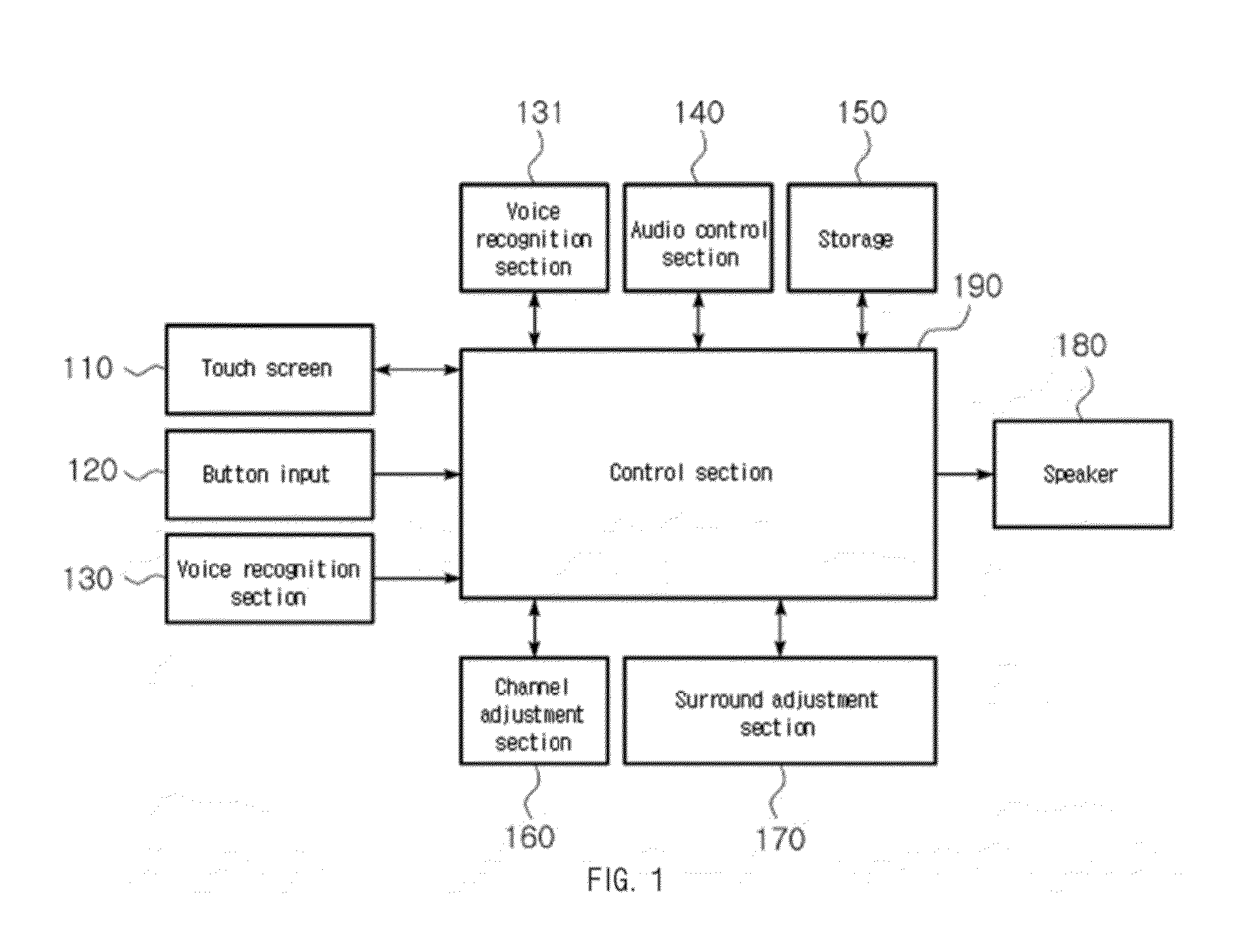
Audio control device using multi-screen and control method thereof
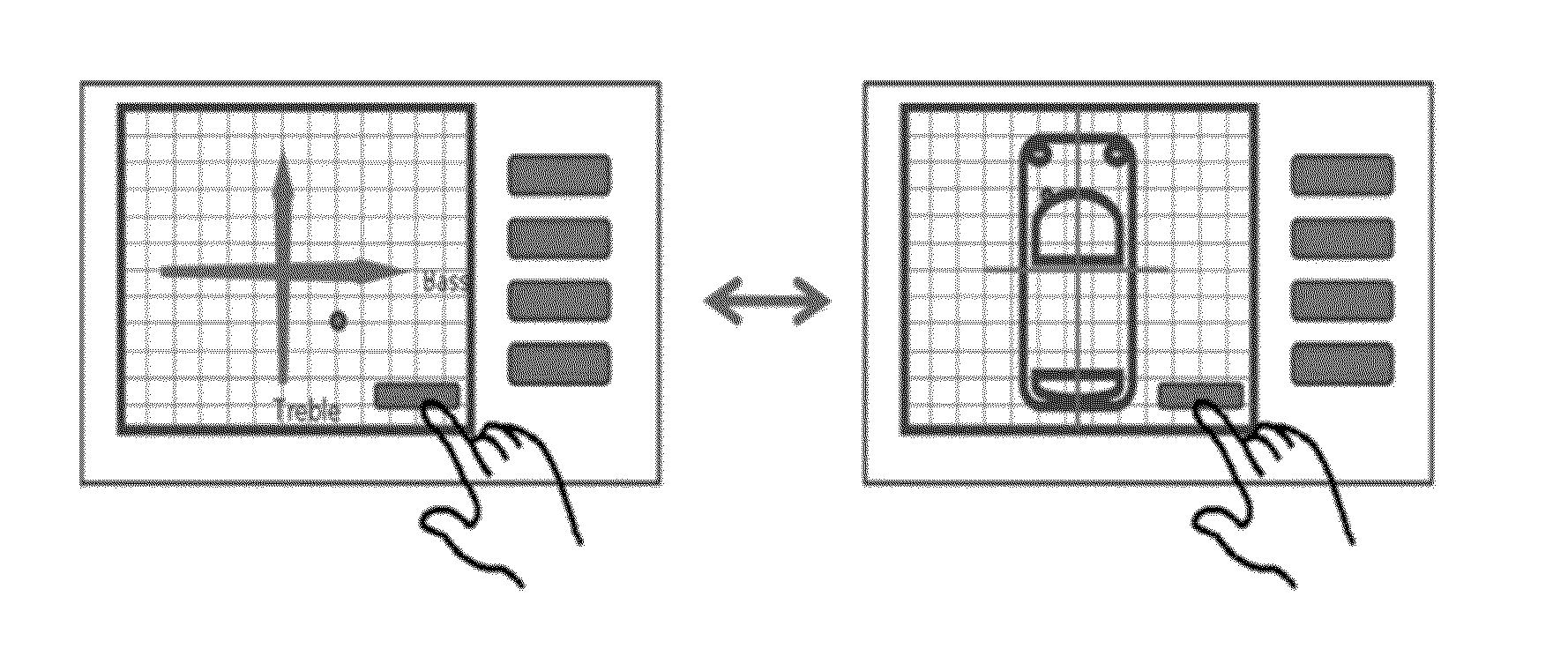
InactiveUS20130305155A1Improve user convenienceSound input/outputDigital signal tone/bandwidth controlEngineeringBass (sound)
The present invention relates to an audio control device using a multi-screen. The audio control device has a touch screen on which a bass axis and a treble axis for the sound of audio equipment are displayed in a multidimensional fashion, and on which a point selected by a user for audio control is inputted. An audio control section collectively calculates a bass value and a treble value corresponding to the point selected for audio control. A control section controls a speaker based on a result calculated by the audio control section.
Owner:YOON KEEJUNG
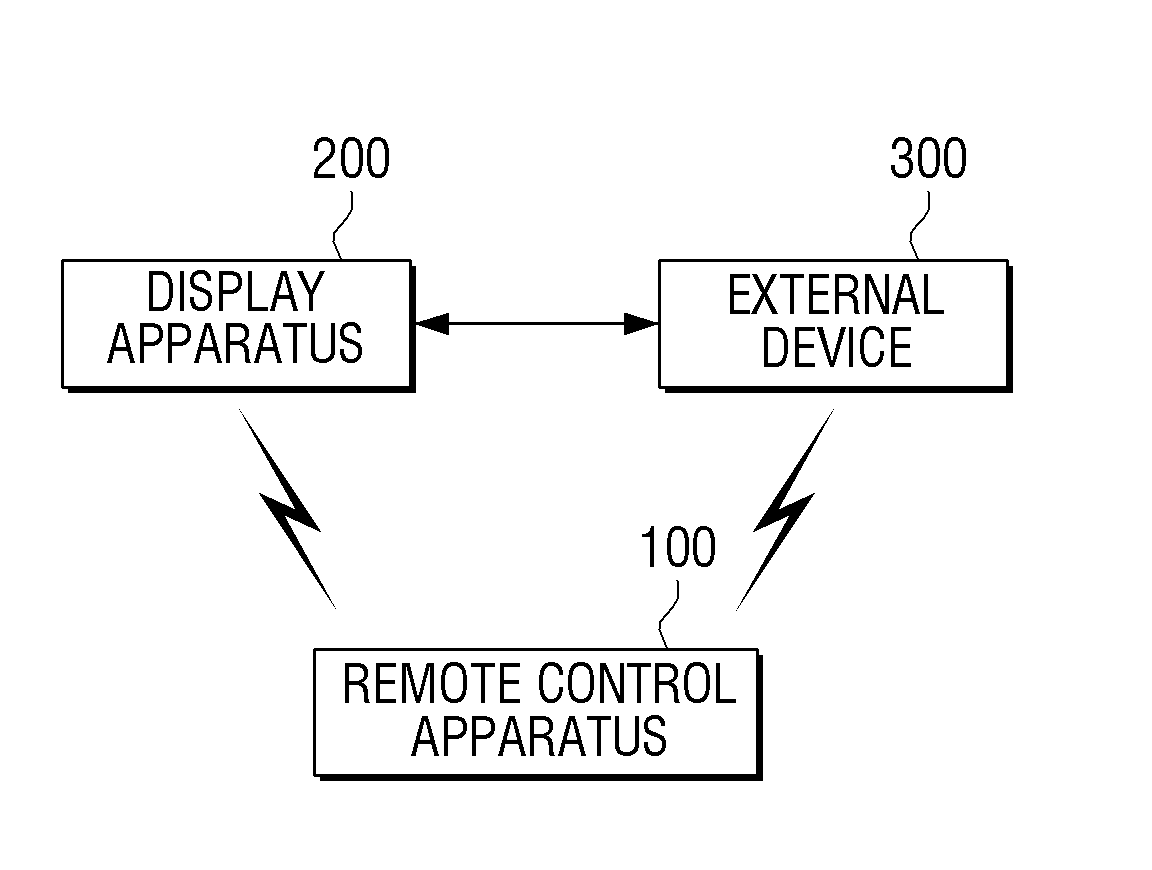
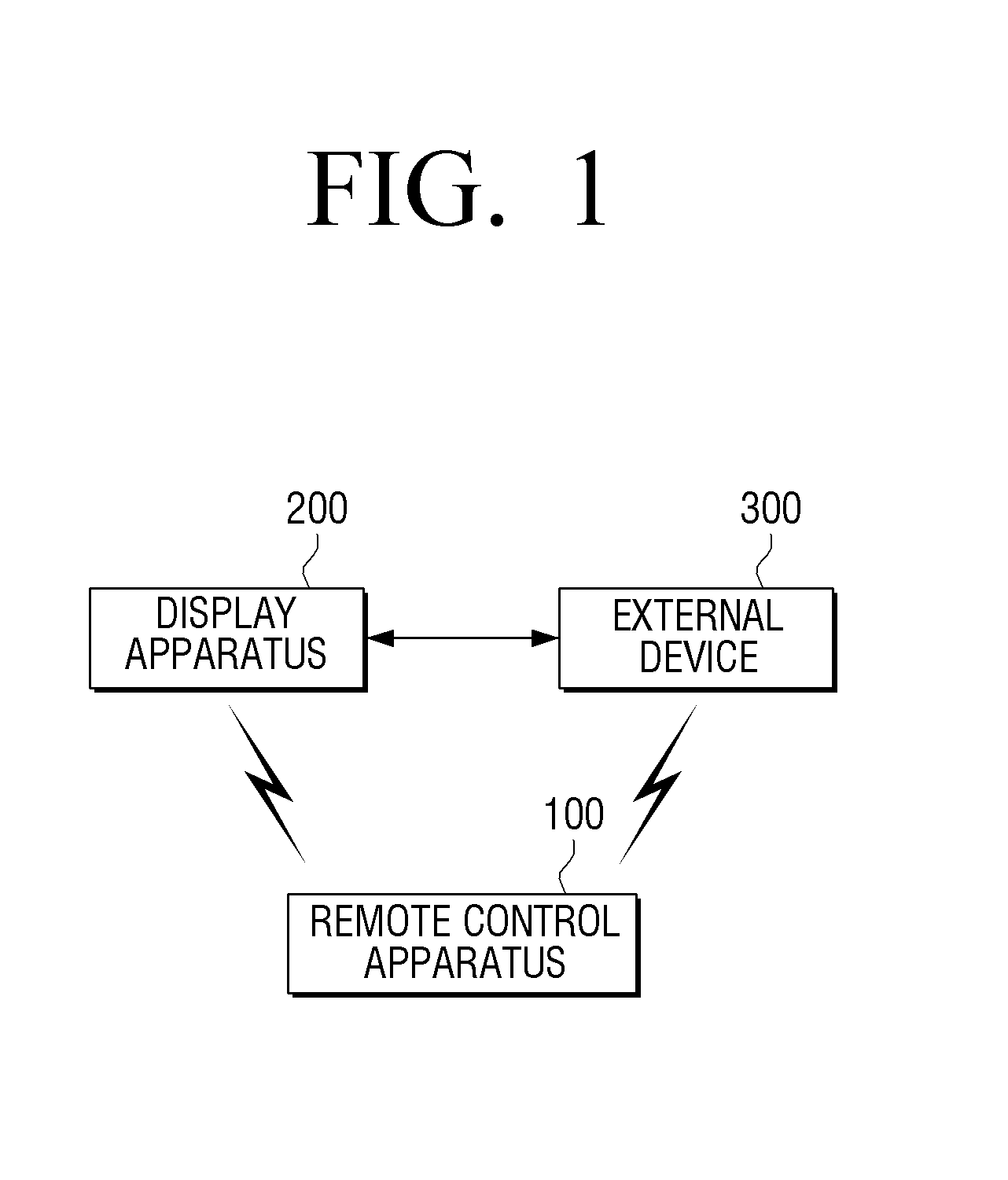
Remote control apparatus, method and multimedia system for volume control
Apparatuses, methods and systems are provided for controlling volume of a media system. A remote control is configured to control volume of a media unit and an external device simultaneously or consecutively.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Digital audio processor
InactiveCN1491480AMake sure not to workGain controlDigital signal tone/bandwidth controlFrequency characteristicComputer science
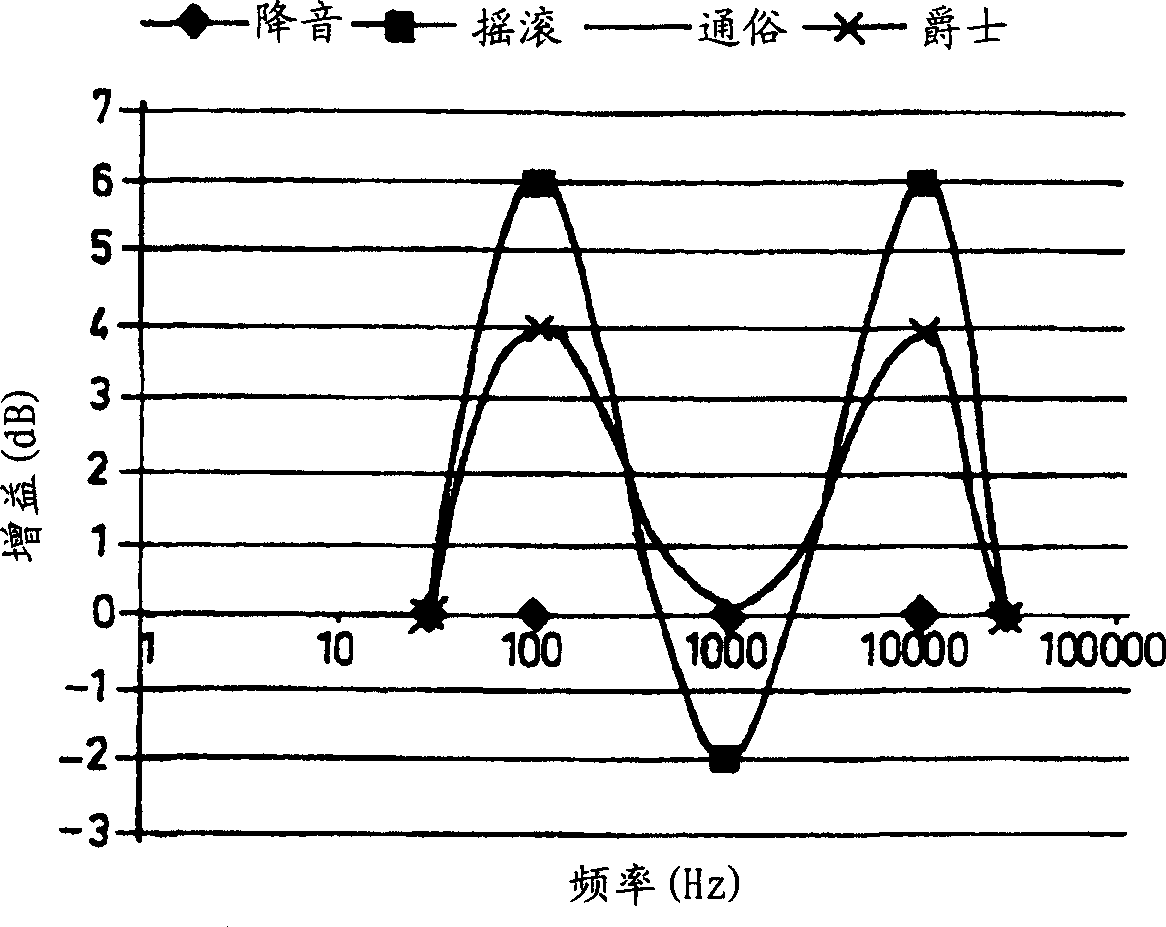
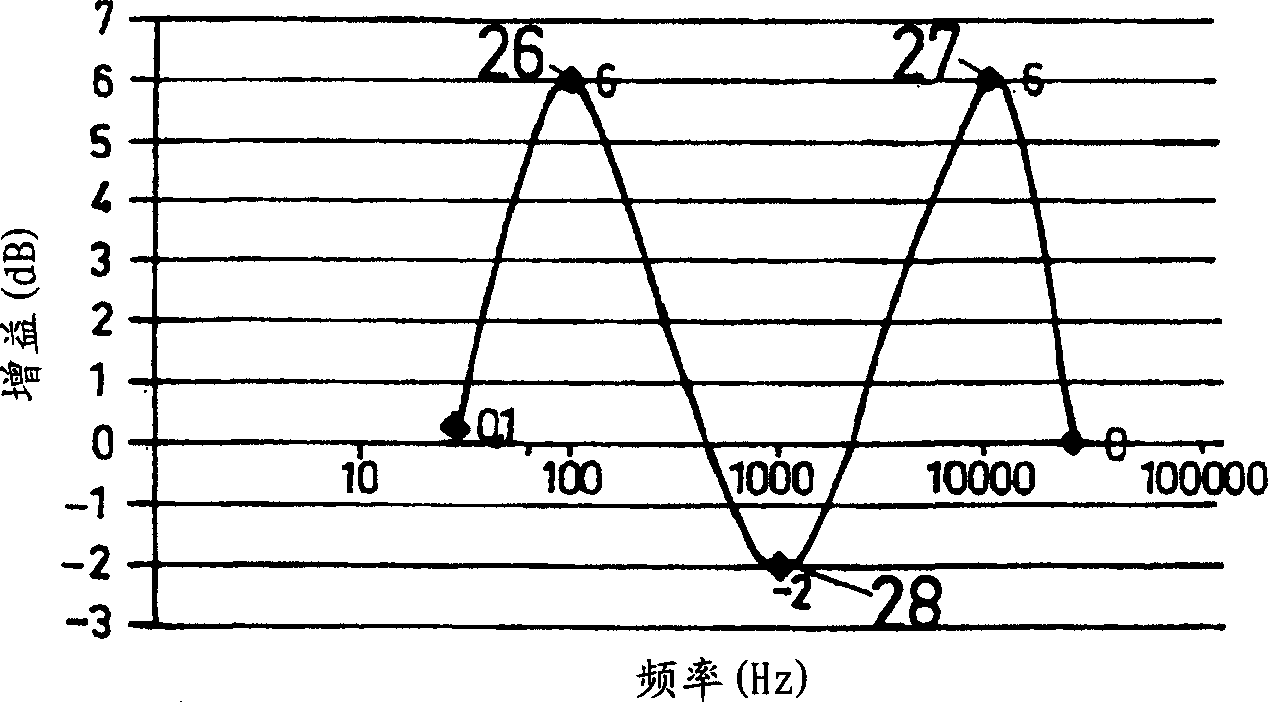
The present invention is related to a method for adjusting the frequency characteristic of a digital audio processor having adjustable parameters including at least low frequency gain, high frequency gain and volume gain. The invention is also related to an audio device executing the inventive method every time the characteristic frequency response curve is adjusted. Today's audio devices frequently offer the feature that the user can select among a group of different sound characteristics. Typically the user may want to adapt the sound characteristic of the device to the kind of music he is listening, e.g. rock, jazz, or classic music. In technical terms the sound characteristic is widely determined by the characteristic frequency response curve of the audio signal processing. Those characteristic curves are essentially defined by a gain value in the low, middle and high frequency range. Normally, a 3-band audio processor, which allows adjusting these three parameters independently is used for this purpose. However, 3-band audio processors are relatively more expensive than 2-band audio processors, which allows only adjusting the gain value at the low frequency range and high frequency range. The invention suggests a method how to adjust the volume gain, the low and high frequency gain of a 2-band audio processor to achieve the same features a 3-band audio processor offers.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL CE PATENT HLDG
Bass enhancement
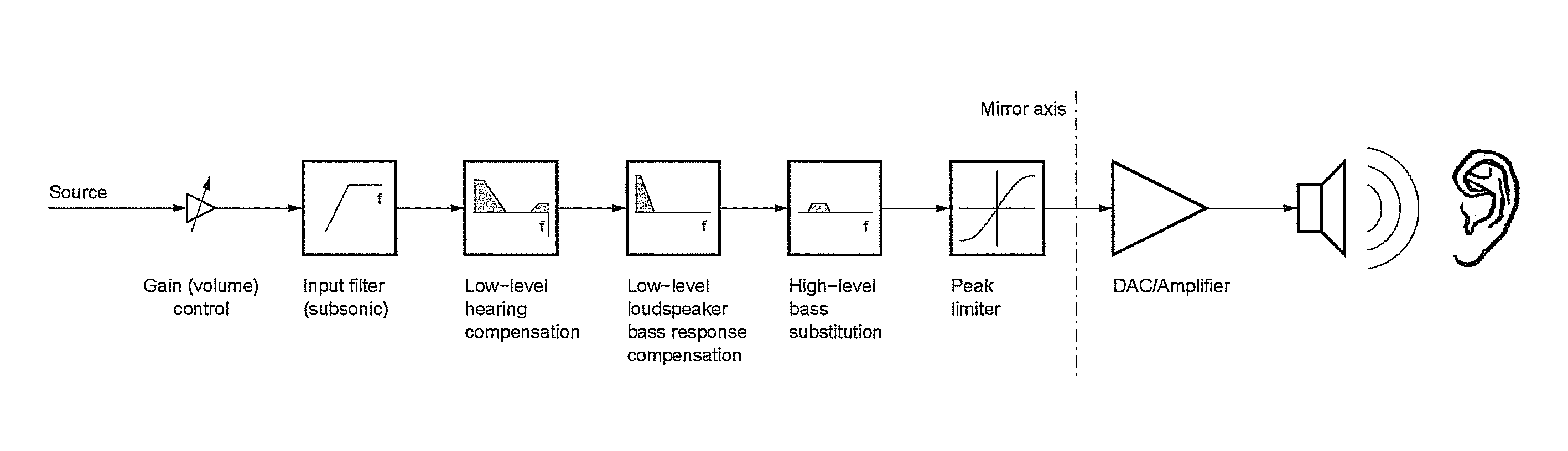
ActiveUS9319789B1Low frequency gainAutomatic tone/bandwidth controlTransducer protection circuitsLoudspeakerBand width
The present invention relates to a bass enhancement system comprising a bass substitution filter with variable gain and variable band width, wherein said variable gain and variable bandwidth at least partly depends on characteristics of an input signal.The present invention further relates to a bass enhancement system according to the above, further comprising a hearing compensation filter and a loudspeaker bass response compensation filter, wherein said input signal is coupled to said hearing compensation filter, the output of which is coupled to said loudspeaker bass response filter, the output of which is coupled to said bass substitution filter.The present invention further relates to a method of enhancing bass perception comprising boosting a reproducible bass frequency band in accordance with characteristics of signal content in a substantially non-reproducible bass frequency band.
Owner:MUSIC TRIBE INNOVATION DK AS
Methods and apparatus for audio signal equalization
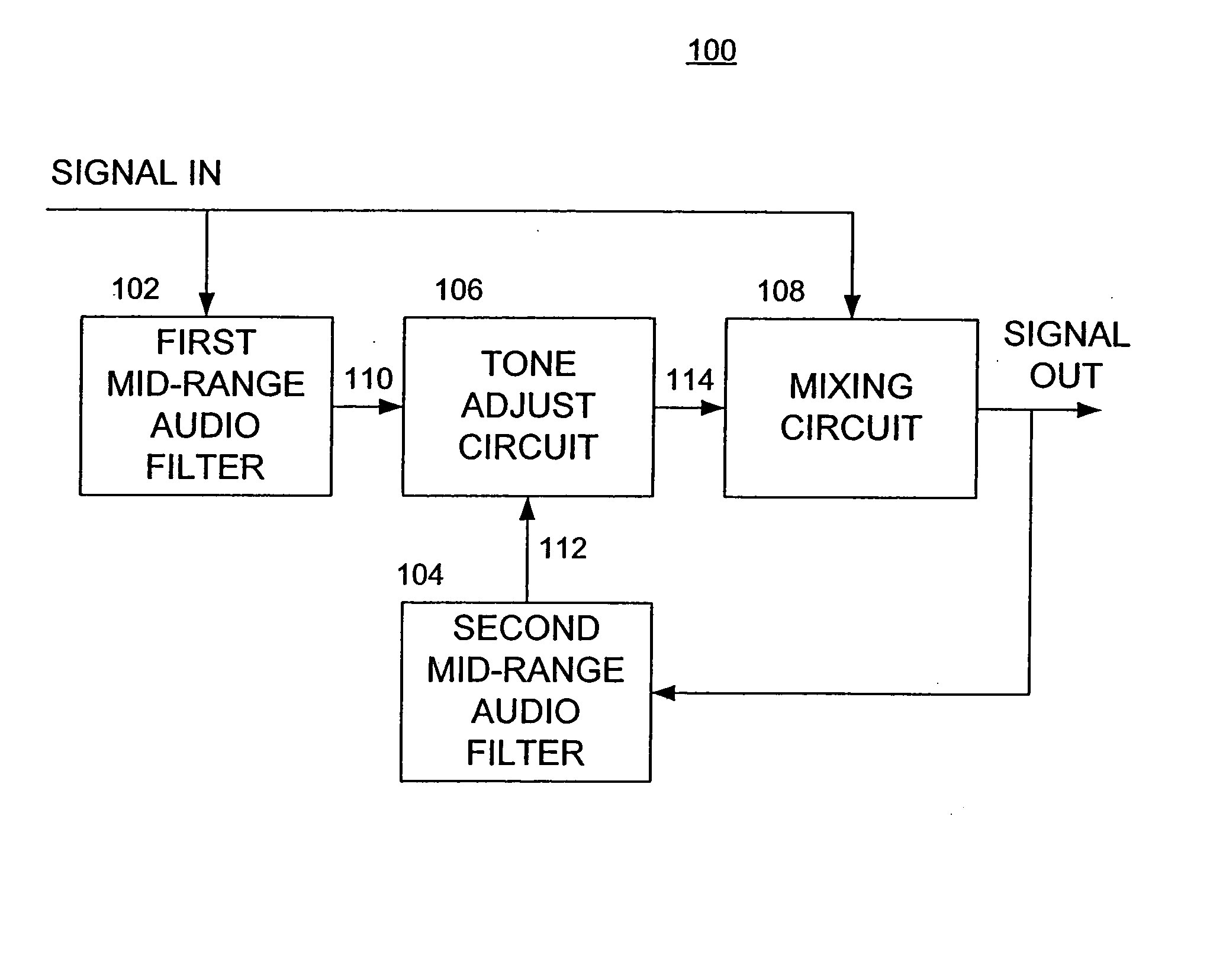
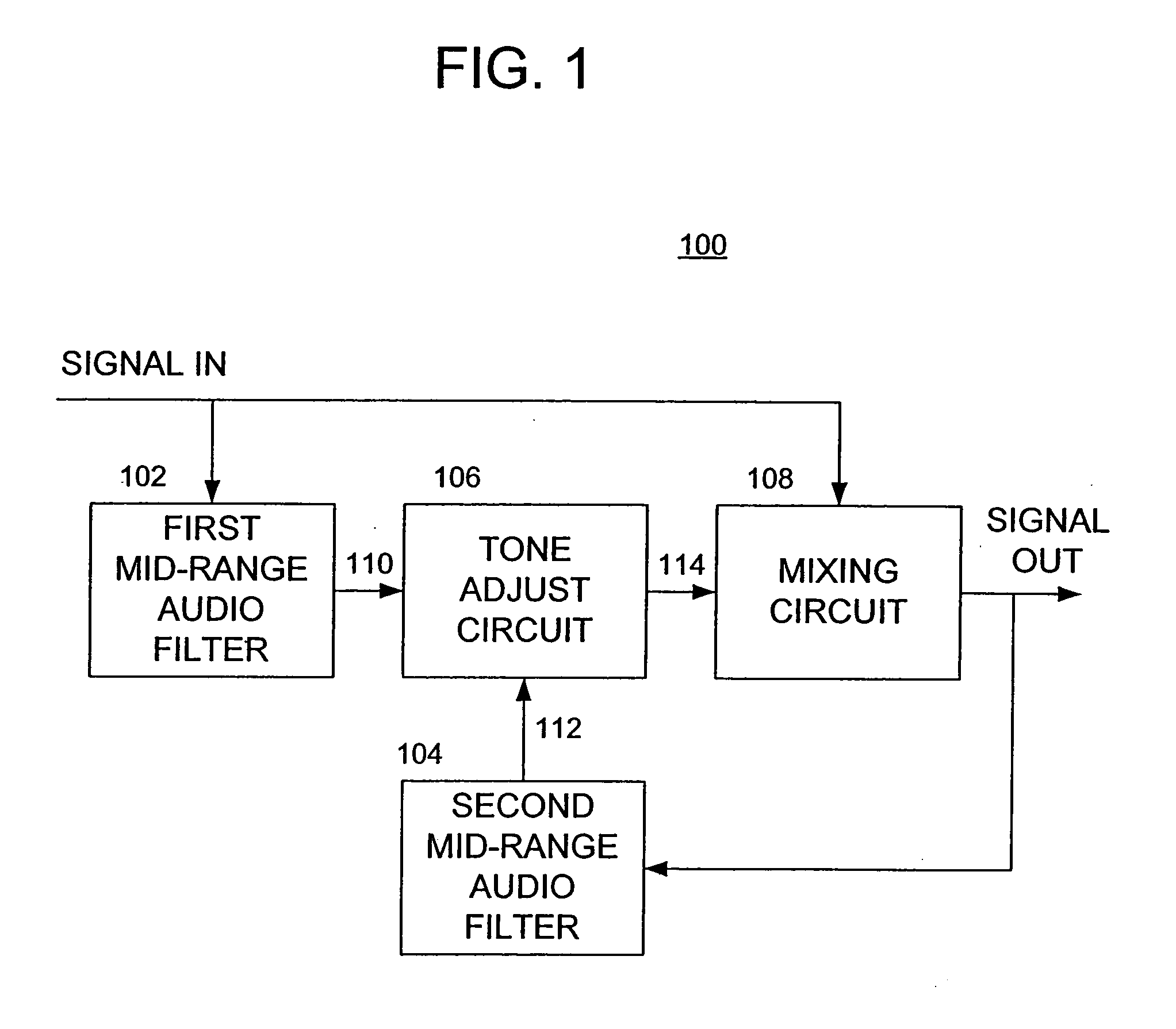
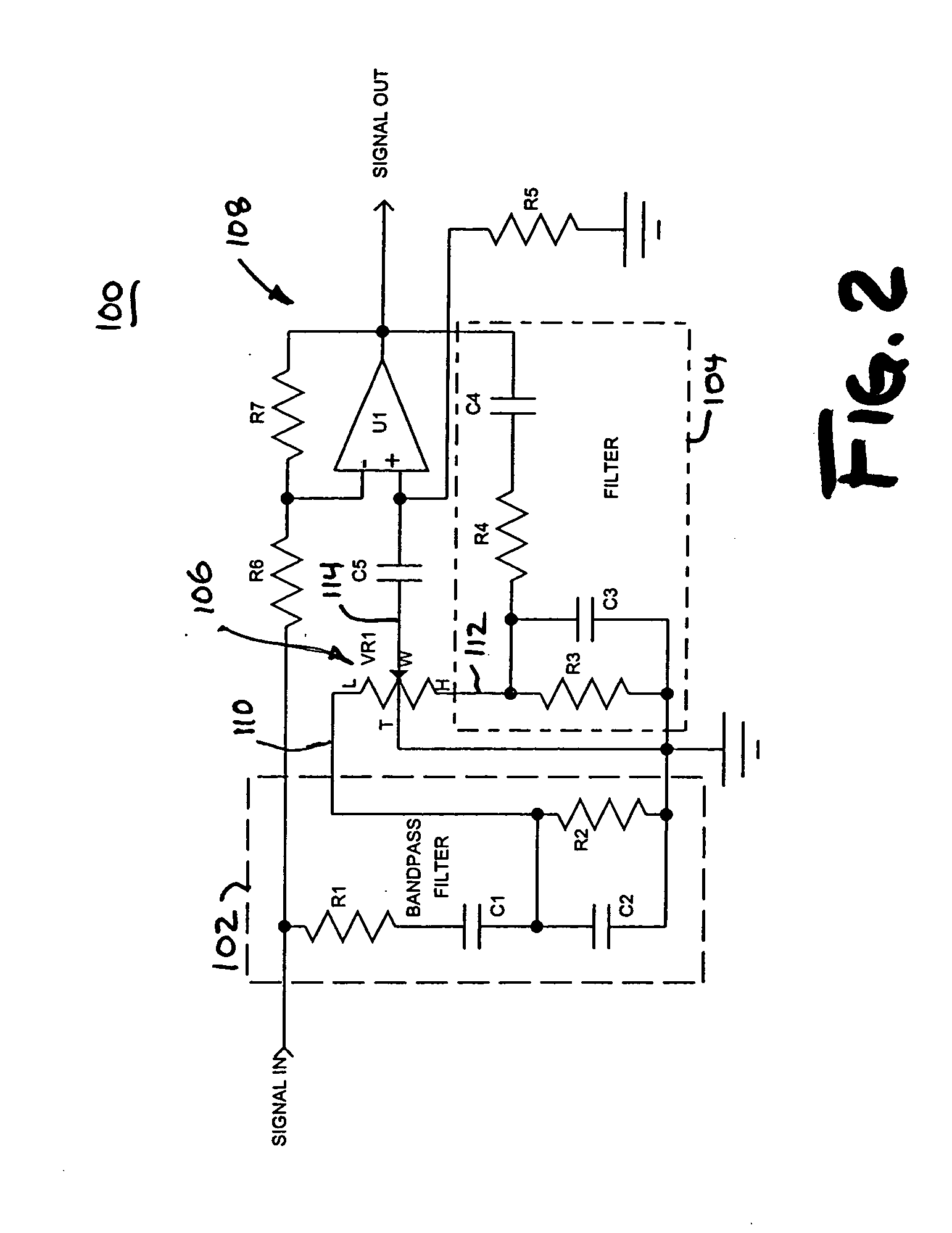
InactiveUS20050213779A1Tone qualityEasy to removeTransmissionManually operated tone/bandwidth controlSound qualityEqualization
Methods and apparatus for adjusting a tonal quality of an audio signal include functional elements and / or steps, comprising producing a first intermediate signal containing a band of frequencies at a lower mid-range of the audio signal; producing a second intermediate signal containing a band of frequencies at an upper mid-range of the audio signal; combining the first intermediate signal, the second intermediate signal and the audio signal to produce a tonally adjusted version of the audio signal; and adjusting respective gains of the first and second intermediate signals to affect the tonal quality of the audio signal without substantially altering the tonal quality of the audio signal at frequencies between the lower mid-range and the upper mid-range.
Owner:PEAVEY ELECTRONICS
Popular searches
Transducer casings/cabinets/supports Special data processing applications Combination controls Transmission noise suppression Electric digital data processing Transmitter/receiver shaping networks Delay lines Frequency response correction Digital/coded signal combination control Volume compression/expansion
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com